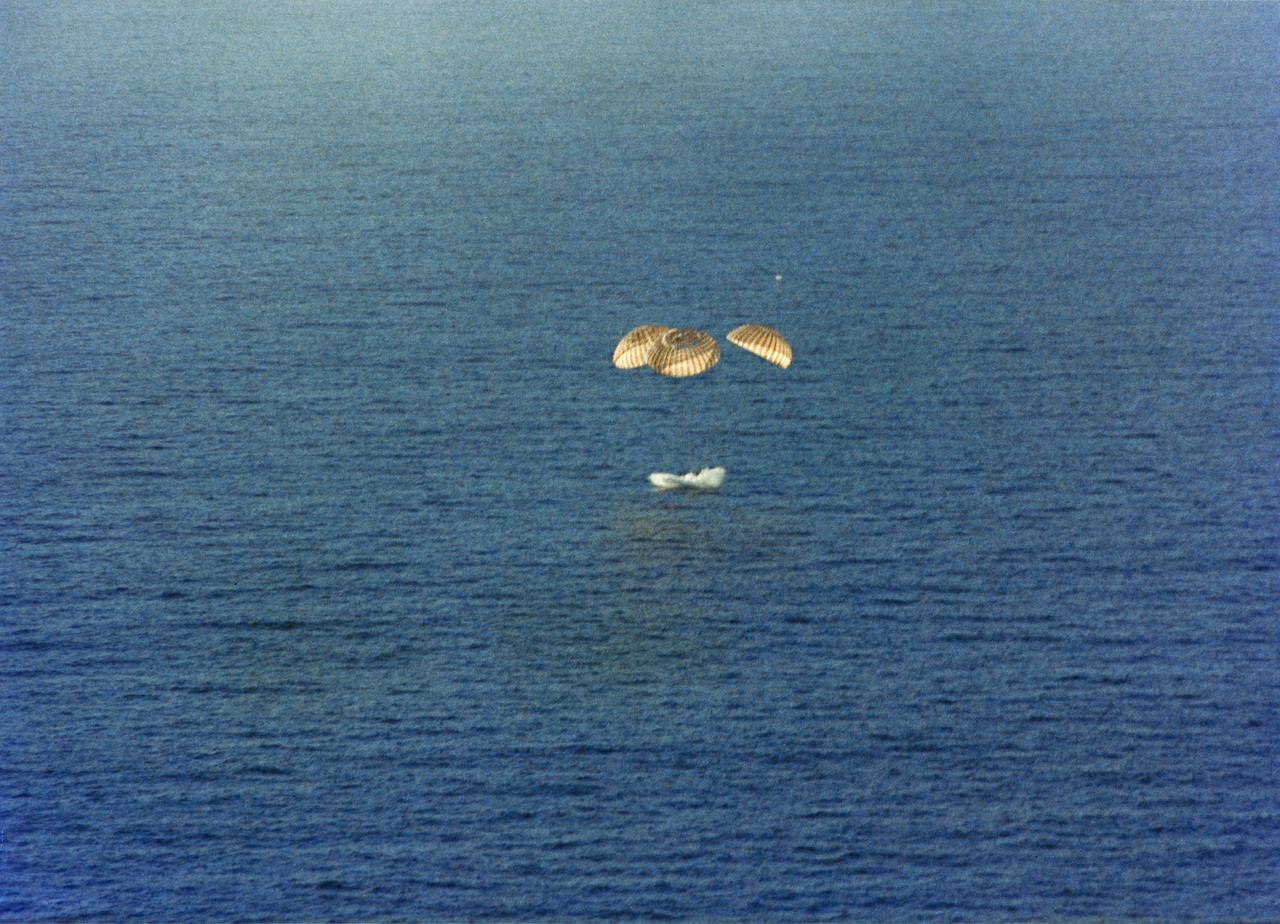

S74-17741 (8 Feb. 1974) --- The Skylab 4 Command Module splashes down in the Pacific Ocean southwest of San Diego, California at 10:17 a.m., Feb. 8, 1974. Photo credit: NASA

On July 3, 1974 NASA commemorated the 5th anniversary of the Apollo 11, first lunar landing mission, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Launch Pad 39, from which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin, and Michael Collins first embarked on their historic journey to the Moon, was dedicated as a national landmark. Apollo 11 was launched at 9:32 am on July 16, 1969 and made the first successful lunar landing July 20th. During the 45 minute ceremony, the three Apollo 11 astronauts unveiled this plaque which was placed at the launch site. Other participating dignitaries included Dr. James Fletcher and Dr. George H. Low, NASA Administrator and Deputy Administrator respectively; Florida Governor Rubin Askew; Senator frank E. Moss; Congressman Olin E. Teague, and Kurt Debus, KSC Director. Apollo 11 launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via a Saturn V launch which was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun.
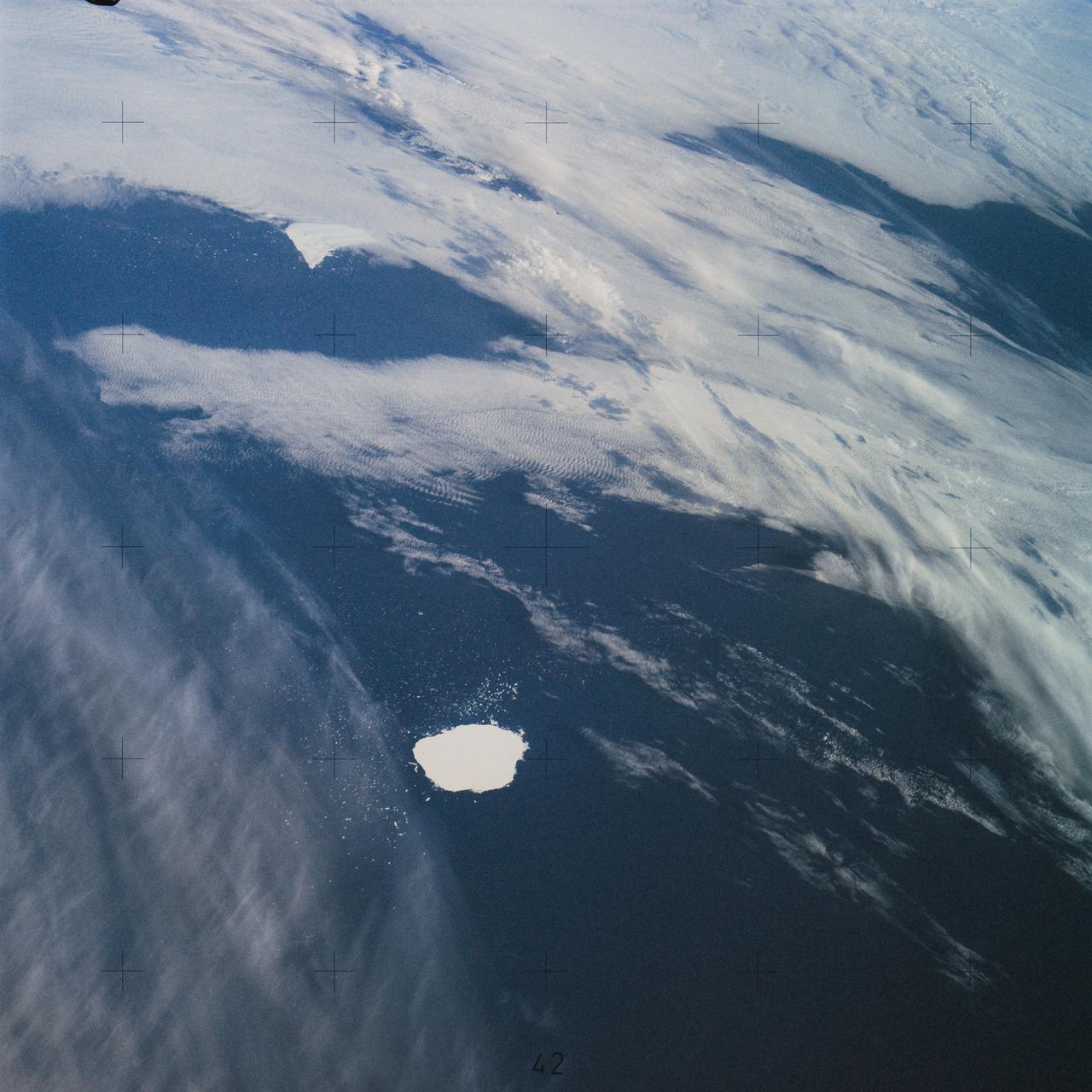

SL4-142-4577 (28 Jan. 1974) --- Two large ice islands in the vicinity of South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic Ocean, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen. The camera used was a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad, with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome. One of the ice islands is partially obscured by clouds. Ice islands were observed as large as 45 by 60 kilometers (27 x 37 miles) and as far north as 45 degrees south latitude. The size and distribution of the "small" icebergs (to a ship they would look very large) can be used to study the local winds and currents. Recent research has suggested the possibility of towing such Antarctic icebergs to selected areas and using them as water supplies. One such iceberg would contain many times the water as in Lake Powell. Photo credit: NASA
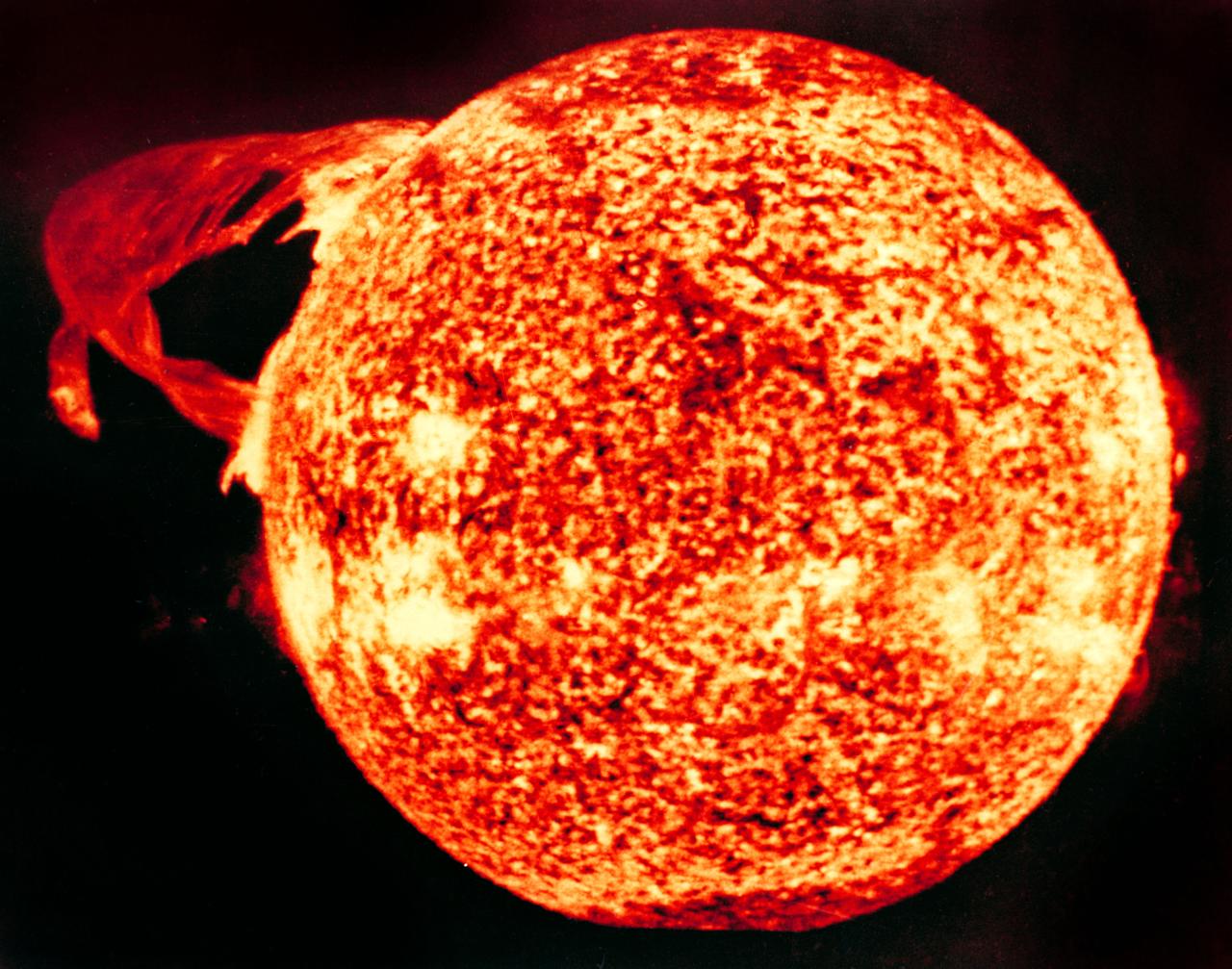
S74-23458 (19 Dec. 1973) --- This photograph of the sun, taken on Dec. 19, 1973, during the third and final manned Skylab mission (Skylab 4), shows one of the most spectacular solar flares ever recorded, spanning more than 588,000 kilometers (365,000 miles) across the solar surface. The last picture, taken some 17 hours earlier, showed this feature as a large quiescent prominence on the eastern side of the sun. The flare gives the distinct impression of a twisted sheet of gas in the process of unwinding itself. Skylab photographs such quiescent features erupt from the sun. In this photograph the solar poles are distinguished by a relative absence of supergranulation network, and a much darker tone than the central portions of the disk. Several active regions are seen on the eastern side of the disk. The photograph was taken in the light of ionized helium by the extreme ultraviolet spectroheliograph instrument of the United States Naval Research Laboratory. Photo credit: NASA
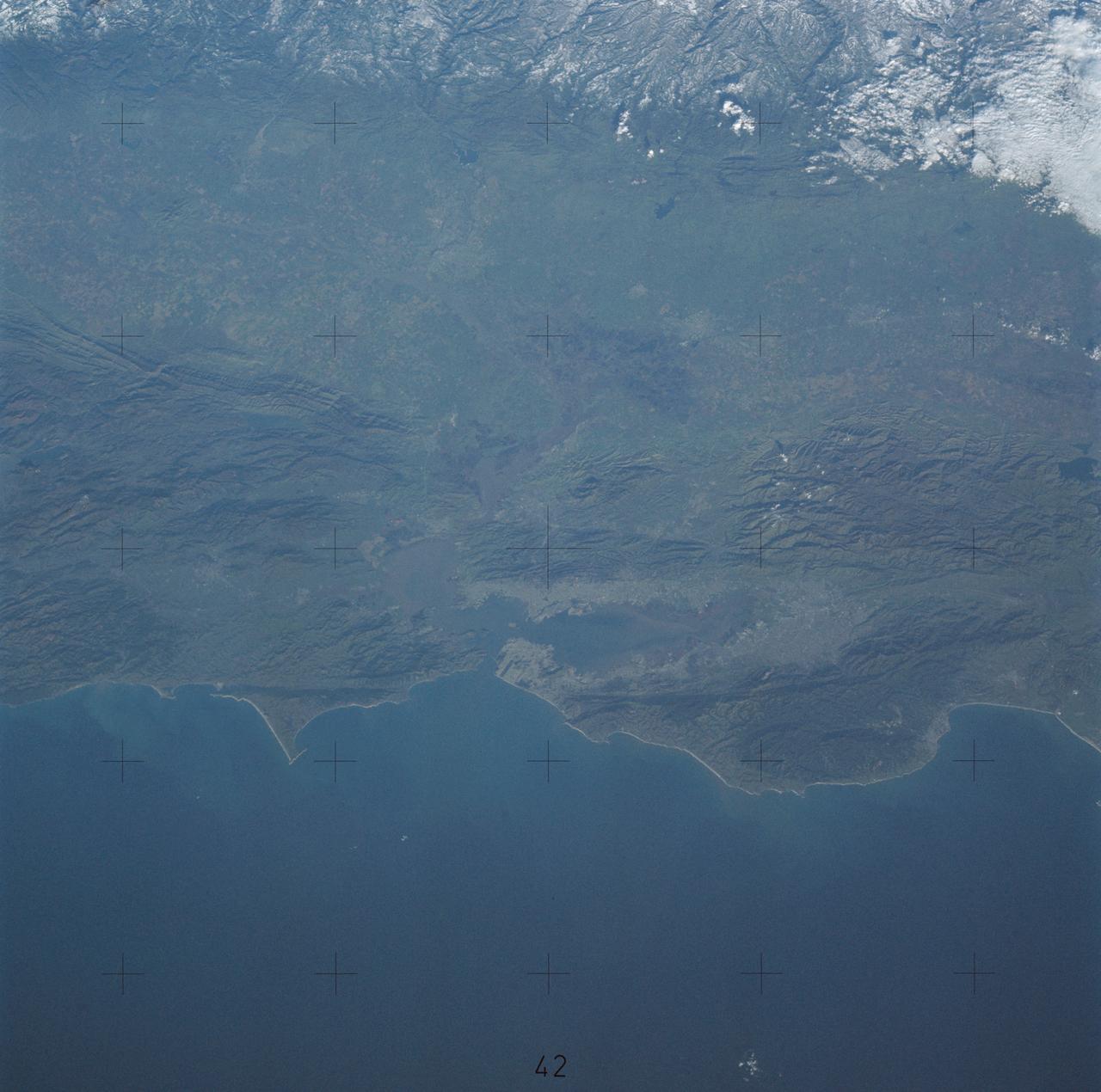

SL4-138-3843 (1 Jan. 1974) --- A part of northern California centered near San Francisco Bay photographed at 3 p.m. Jan. 2, 1974, from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This near vertical view encompasses the coastline from Monterey Bay (right) to about 50 miles north of Point Reyes (left) and includes, from bottom to top, San Francisco Bay (center), Sacramento Valley (left center), San Joaquin Valley (right center), and the snow-covered Sierra Nevada. Afternoon shadows sharply delineate a valley which parallels San Francisco Bay, crosses Point Reyes, and lies between the Bay and the Pacific coastline. This valley marks the location of the San Andreas Fault, a major break in the Earth's crust. Forces acting on the crust are causing the land west (bottom) of the fault line to move north relative to land on the east side. The Skylab 4 astronauts photographed major fault zones in South America, New Zealand, Japan and Africa for use in the study of worldwide tectonic system. Agricultural areas in the Sacramento and San Joaquin Valleys are indicated by the tan areas which are easily discerned in contrast to the green-gray background. Photo credit: NASA
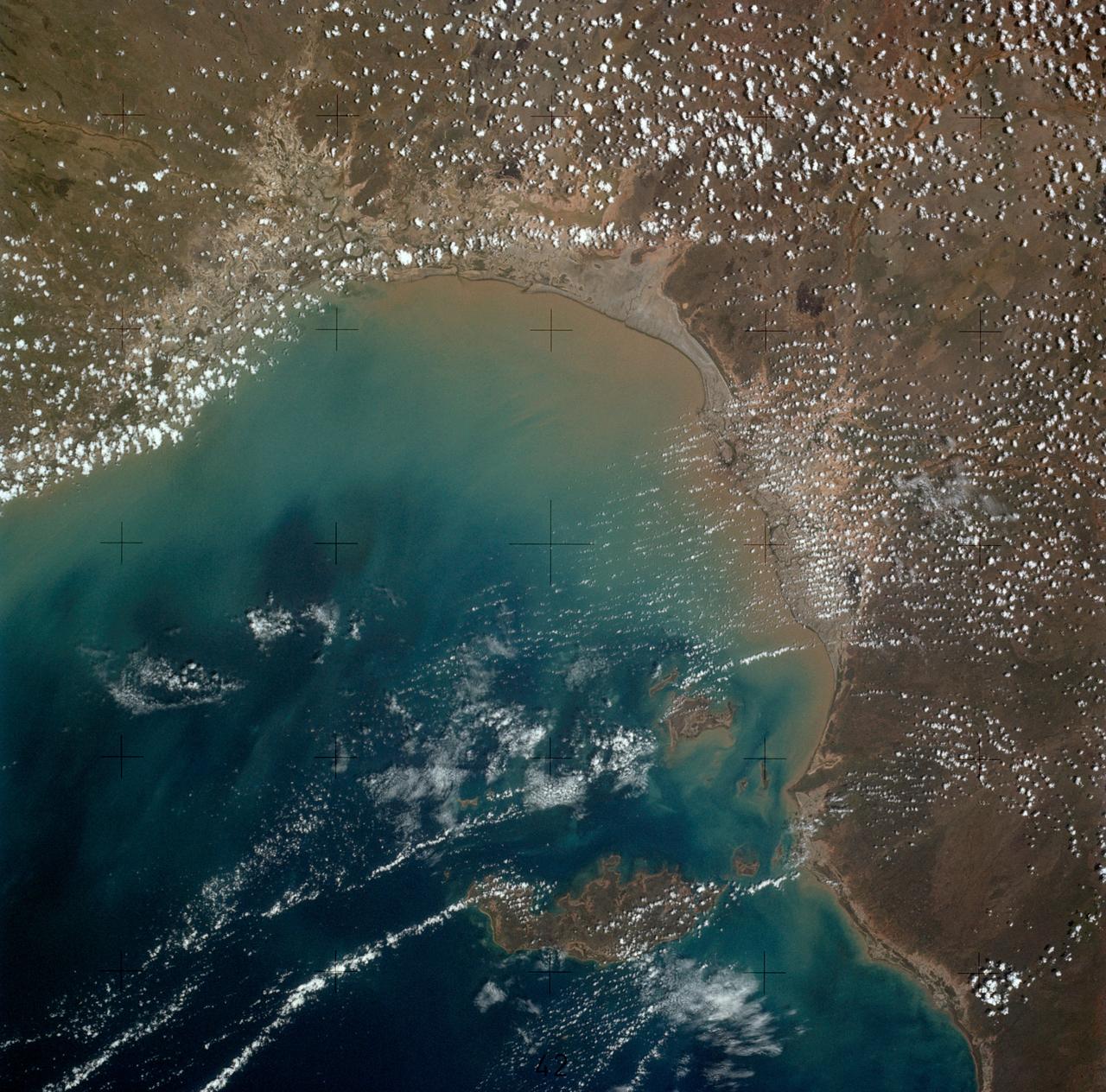

SL4-136-3501 (6 Dec. 1973) --- A vertical view of a portion of the State of Queensland, Australia, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen. The camera used was a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad, with SO-368 medium speed Ektachrome film. The body of water is the southeastern part of the Gulf of Carpentaria. This picture was taken in support studies of the north Australian drought region. The largest island seen is Mornington. The town of Normanton can also be seen. Of interest here is the sediment-laden waters at the perimeter of the Gulf showing how rains at the end of the drought are washing the top soil into the sea after the drought killed the covering vegetation. Also noted is that the vegetation patterns tend more toward those of other arid regions (i.e. they follow topographic and hydrographic patterns) rather than those in other parts of Australia (i.e. more convenient and easier to see, rectilinear patterns which are prevalent in less arid areas). Photo credit: NASA
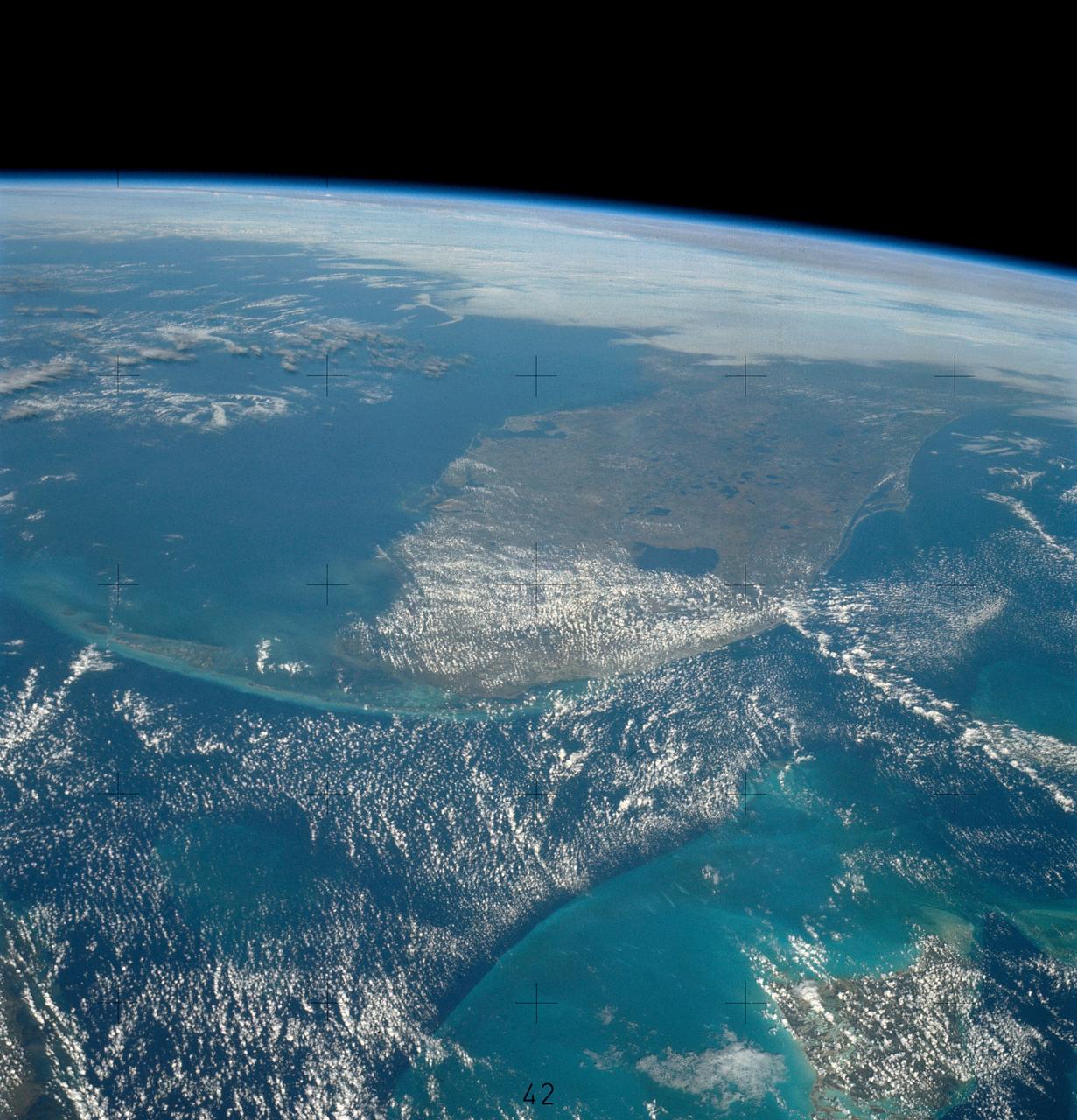

SL4-139-4029 (10 Jan. 1974) --- An oblique view of the State of Florida, looking northward up the peninsula, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crewman. The camera used was a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad, with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome. This view shows almost the entire state, except the panhandle region. The Bahama Banks area appears in the southeast part of the picture as the light blue water. Andros Island in the Bahamas group is the island in the lower right corner. The Gulfstream flows between Florida and the Bahama Banks. This fast-moving, warm-water current transports energy from the tropics to the northern latitudes. The effect of the warmer Gulfstream waters on the atmosphere is seen as increased convection (caused by the warmer water heating the air from below) resulting in the fair weather cumulus seen confined primarily over the Gulfstream. A portion of Cuba is seen in the lower left corner of the picture. Photo credit: NASA
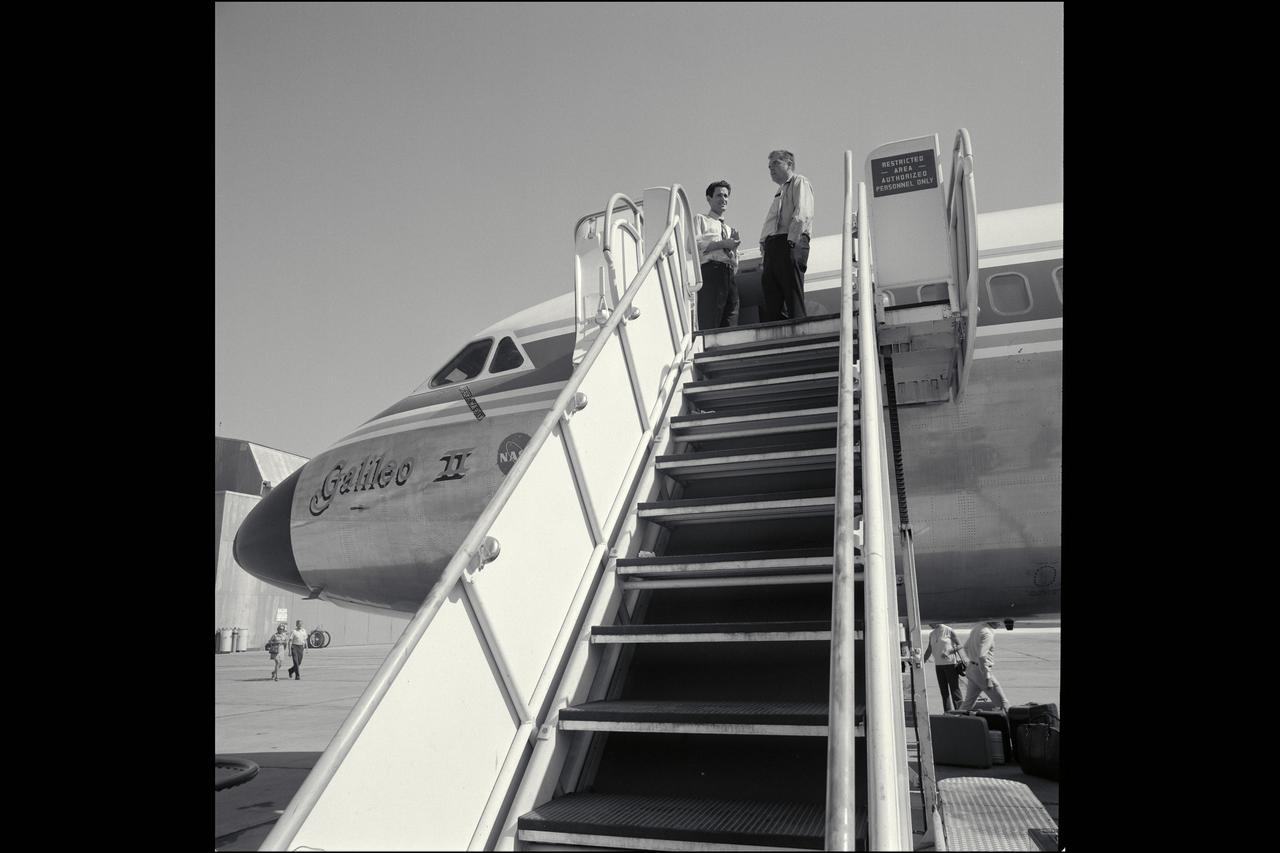

CV-990 Galileo II arrival at Ames after first expedition - decending ramp are from top Don Anderson, Mike Bader, Hans Mark

Minority Professionals at NASA Langley Research Center Samuel J. Scott on the right.
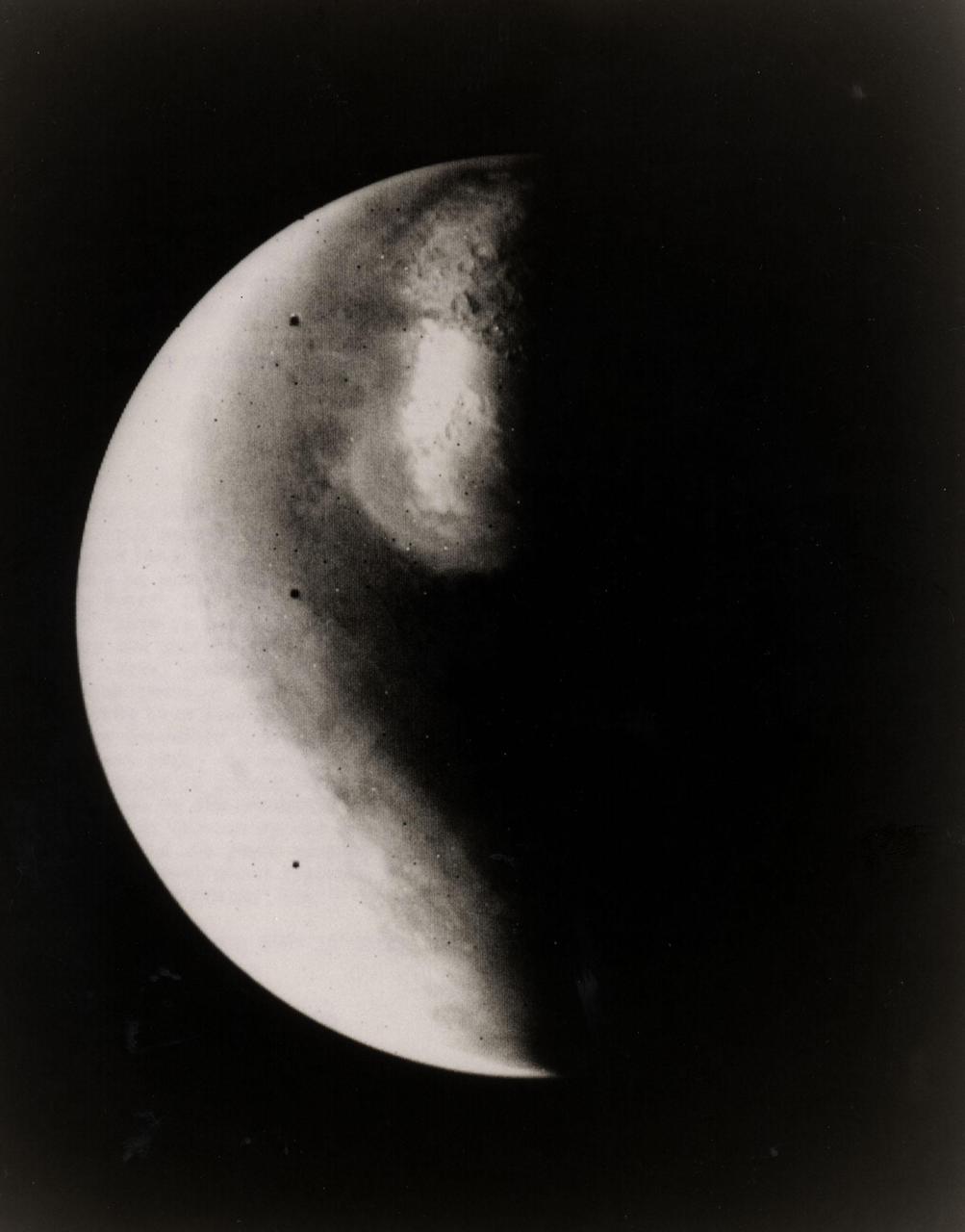

Half-Mars hangs in space 685,000 kilometers (425,000 miles) above Viking 1 as the spacecraft approaches the planet. This picture was taken at 6:40 p.m. PDT on June 16 by one of two telescope-equipped TV cameras aboard the Viking 1 Orbiter. A violet filter was used. Resolution is approximately 17 kilometers (10.5 miles) at center of disk. North is toward upper right and the south pole is in the dark to the lower left. We are looking at the morning side of the planet; that is, the planet is rotating from left to right. Toward the bottom of the image is a very bright irregular feature within a somewhat less bright circular feature. The circular feature is Hellas, a 2,000-kilometer(1,250-mile) diameter impact basin. Numerous craters are just visible within the frost-covered region. To the south of Hellas is another brighter area. This is probably an area of discontinuous frost cover around the south pole. The image is very bright toward the edge of the planet because of atmospheric scattering in the violet. Viking 1 will begin orbiting Mars on Saturday, June 19, with the landing planned for July 4. The Viking Project is managed by the NASA Langley Reseach Center, Hampton, Va.
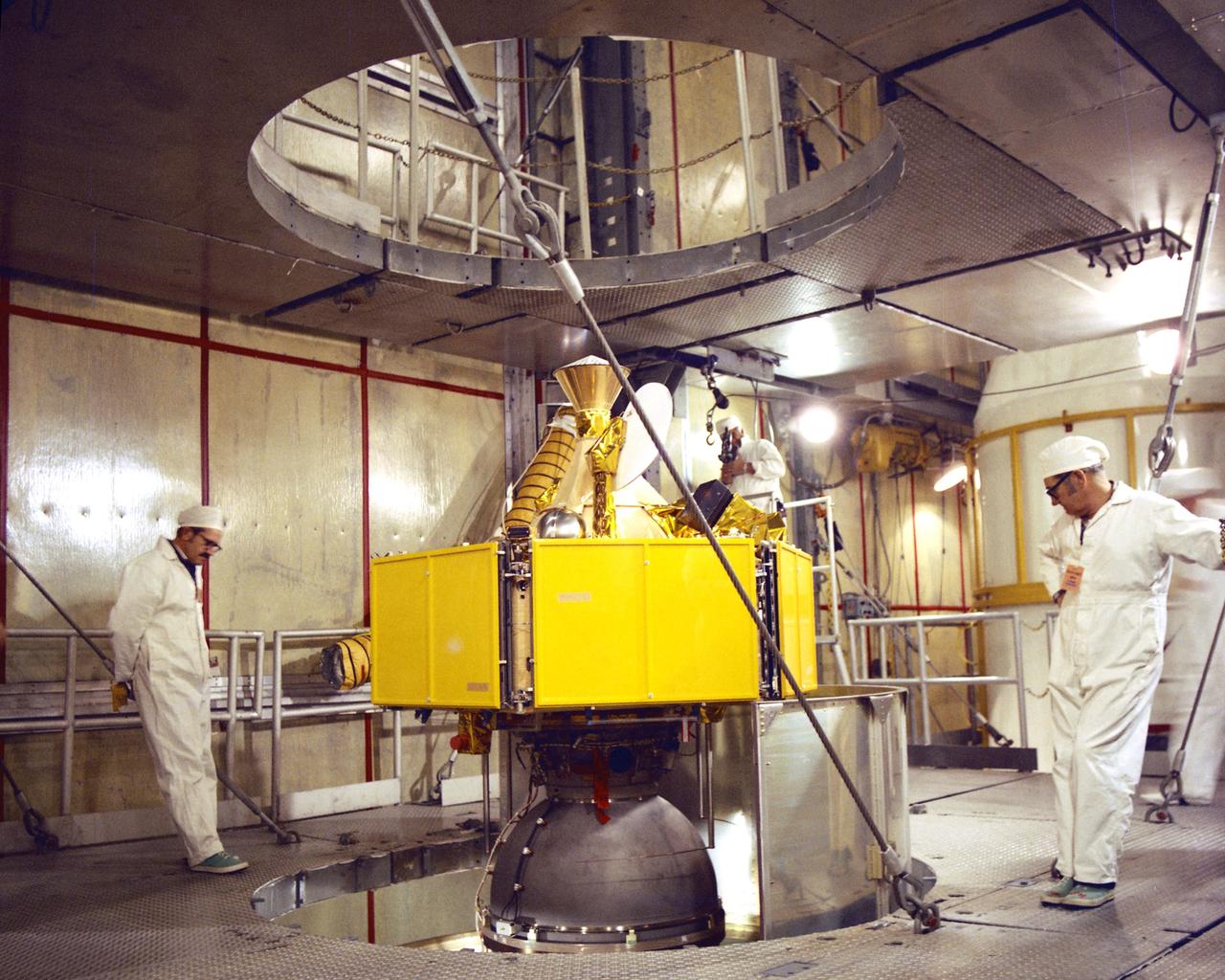

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mating of the Symphonie spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA

C-141 KAO in early morning flight home to Ames Research Center
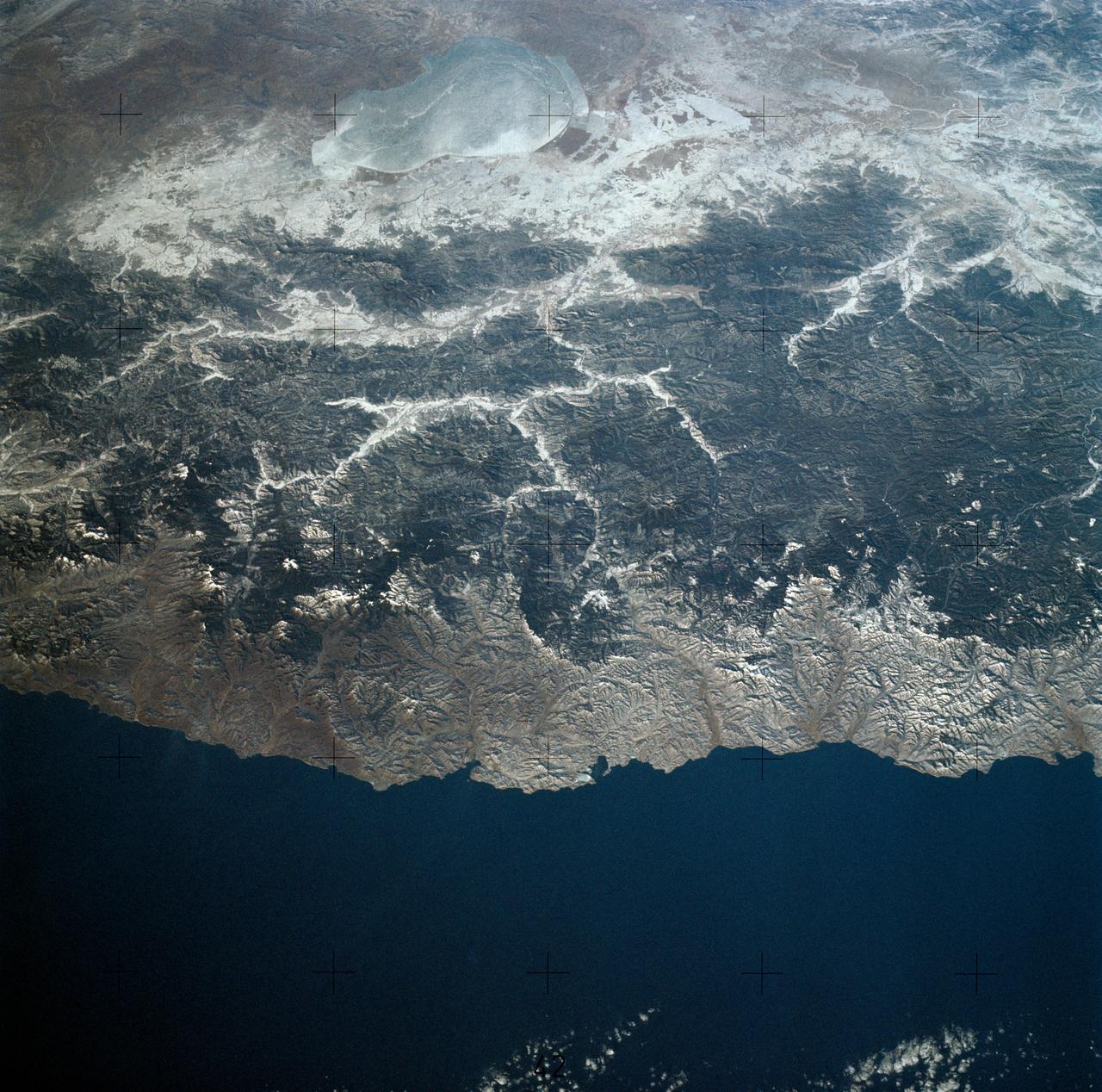

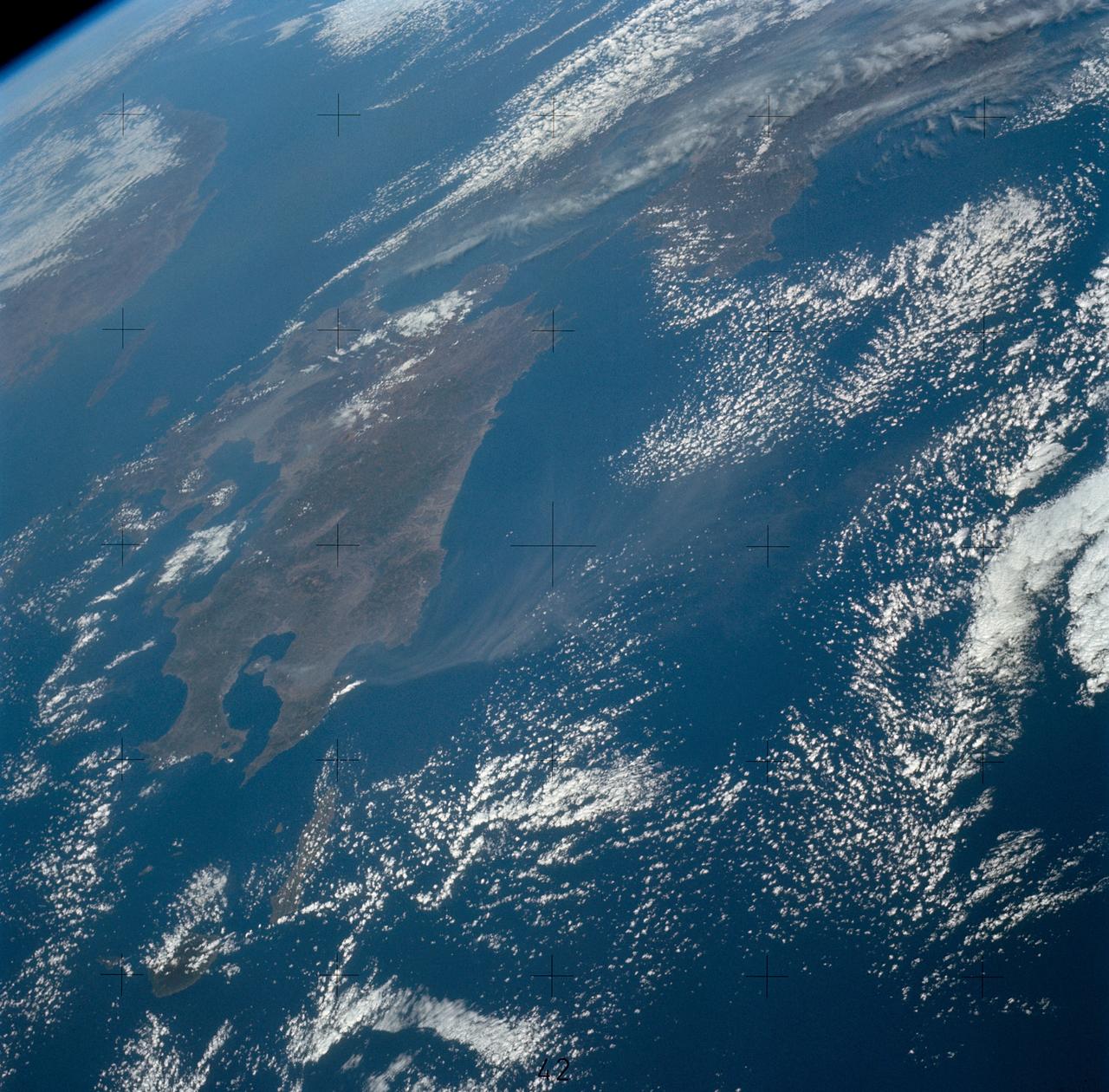
SL4-140-4110 (January 1974) --- View of the USSR, Siberia area from Skylab 4. Other areas seen are Ozero, Kanka, Ussiriysk, the Sea of Japan and Kavalerovo (45.5N, 135.5E). Photo credit: NASA
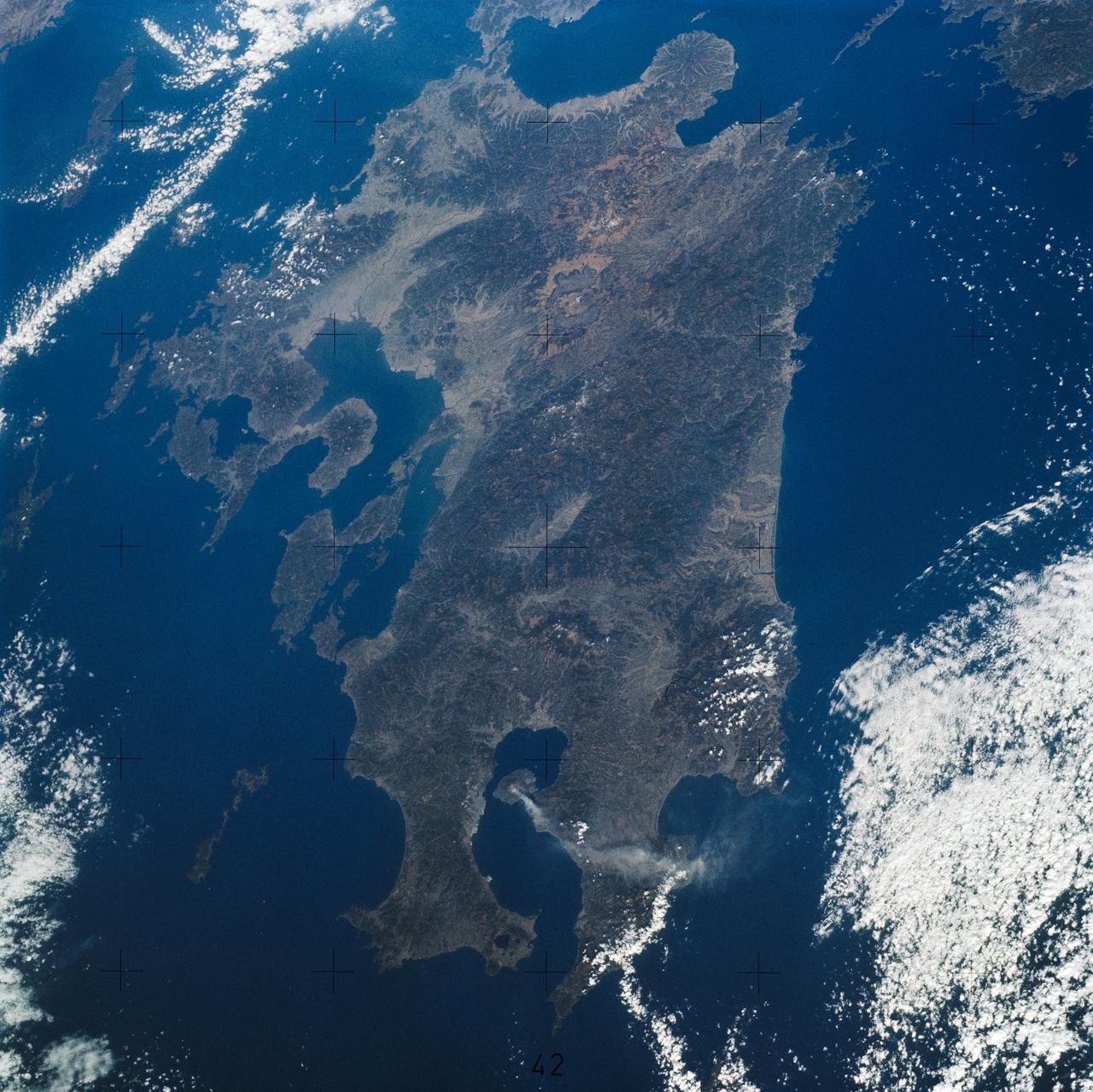

SL4-139-3942 (7 Jan. 1974) --- This oblique view of the Island of Kyushu, Japan, was taken from the Earth-orbiting Skylab space station on Jan. 8, 1974 during its third manning. A plume from the volcano Sakurajima (bottom center) is clearly seen as it extends about 80 kilometers (50 miles) east from the volcano. (EDITOR'S NOTE: On Jan. 10, 2013, a little over 39 years after this 1974 photo was made from the Skylab space station, Expedition 34 crew members aboard the International Space Station took a similar picture (frame no. ISS034-E-027139) featuring smoke rising from the same volcano, with much of the island of Kyushu visible. Interesting comparisons can be made between the two photos, at least as far as the devices used to record them. The Skylab image was made by one of the three Skylab 4 crew members with a hand-held camera using a 100-mm lens and 70-mm color film, whereas the station photo was taken with 180-mm lens on a digital still camera, hand-held by one of the six crew members). Photo credit: NASA

Minority Professionals at NASA Langley Research Center Christine Darden
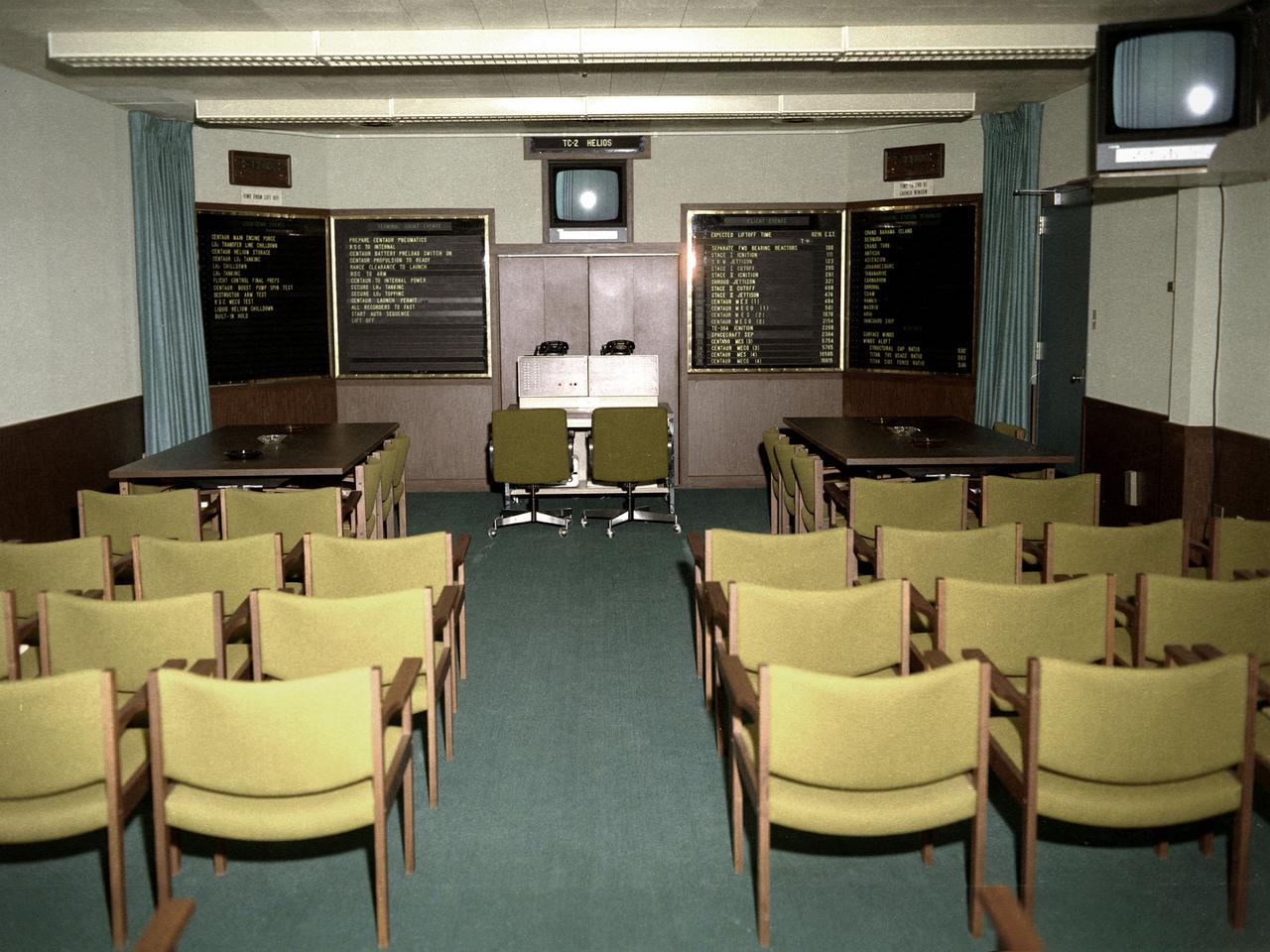

A Centaur rocket control room in the Development Engineering Building (DEB) at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. The DEB, completed in the mid-1960s, provided office space for several hundred development engineers outside the center’s main gate. The location of the DEB emphasized the development staff’s separation from the research side of the laboratory. This control room at Lewis was directly linked to Cape Kennedy. The Lewis staff in Cleveland could monitor and back up the Lewis launch team in the actual control room at the Cape. This photograph was taken during the preparations for the Titan-Centaur-Helios launch on December 10, 1974. The panels to the left listed the countdown events for the Centaur rocket. The launch countdown clock can be seen above these panels. The two panels on the right listed events predicted to occur during the flight and the availability of the tracking stations. The clock above the panels indicated the time remaining before the launch window expired. The Launch Vehicles Division was created in 1969 to manage the launches of all Centaur and Agena rockets. The Launch Vehicles Division worked with the engineers to design the payload in a manner that ensured that its size and weight were within Centaur’s parameters. They also developed the proper trajectory analysis for the launch. These trajectories often had to be adjusted if the launch did not occur on the planned date.
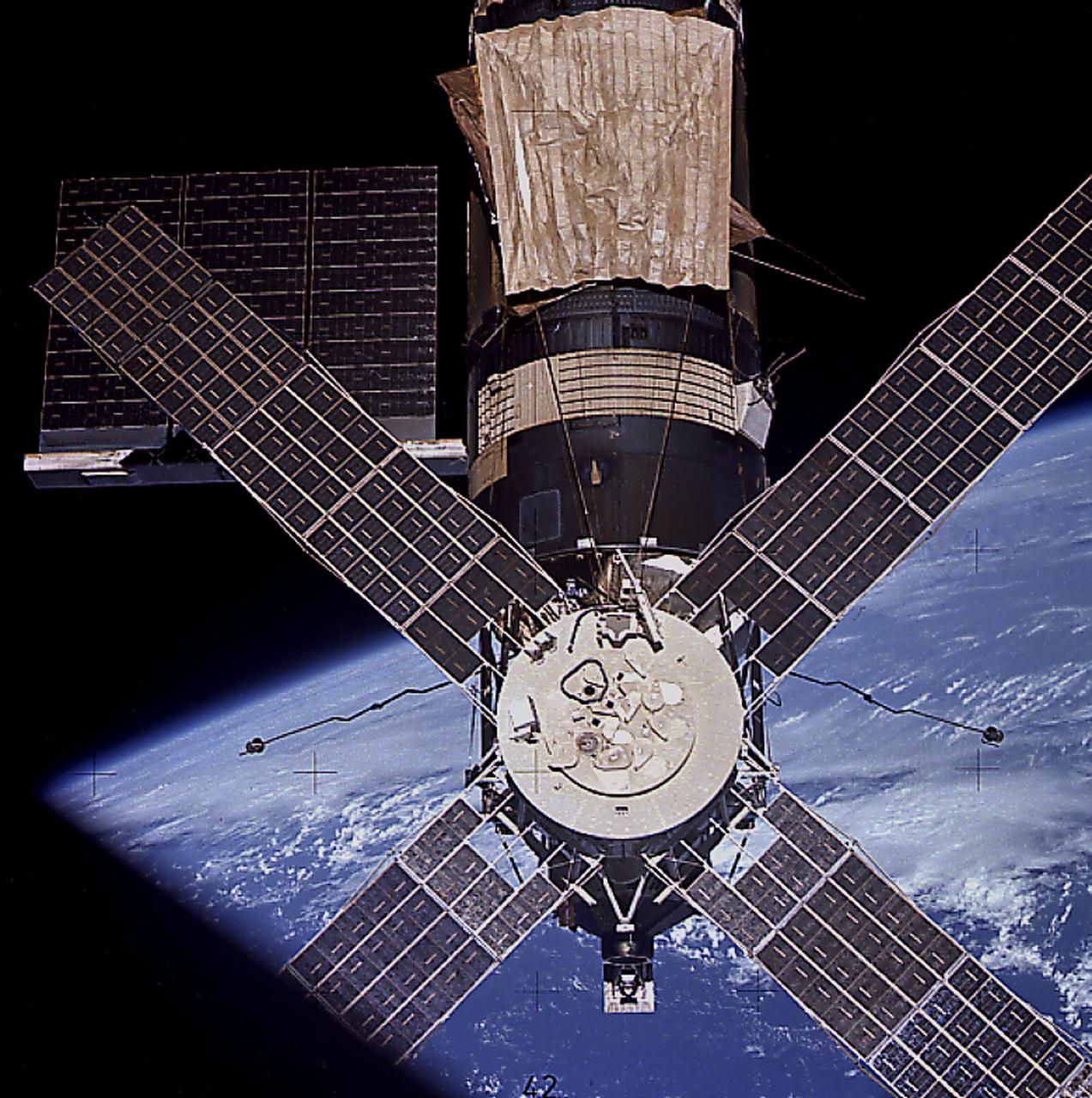

This image of Skylab in orbit was taken as the third crew (Skylab-4) departed the space station after 84 days in the orbiting laboratory. A smiling Skylab seemed to wink good-bye for the job well done.
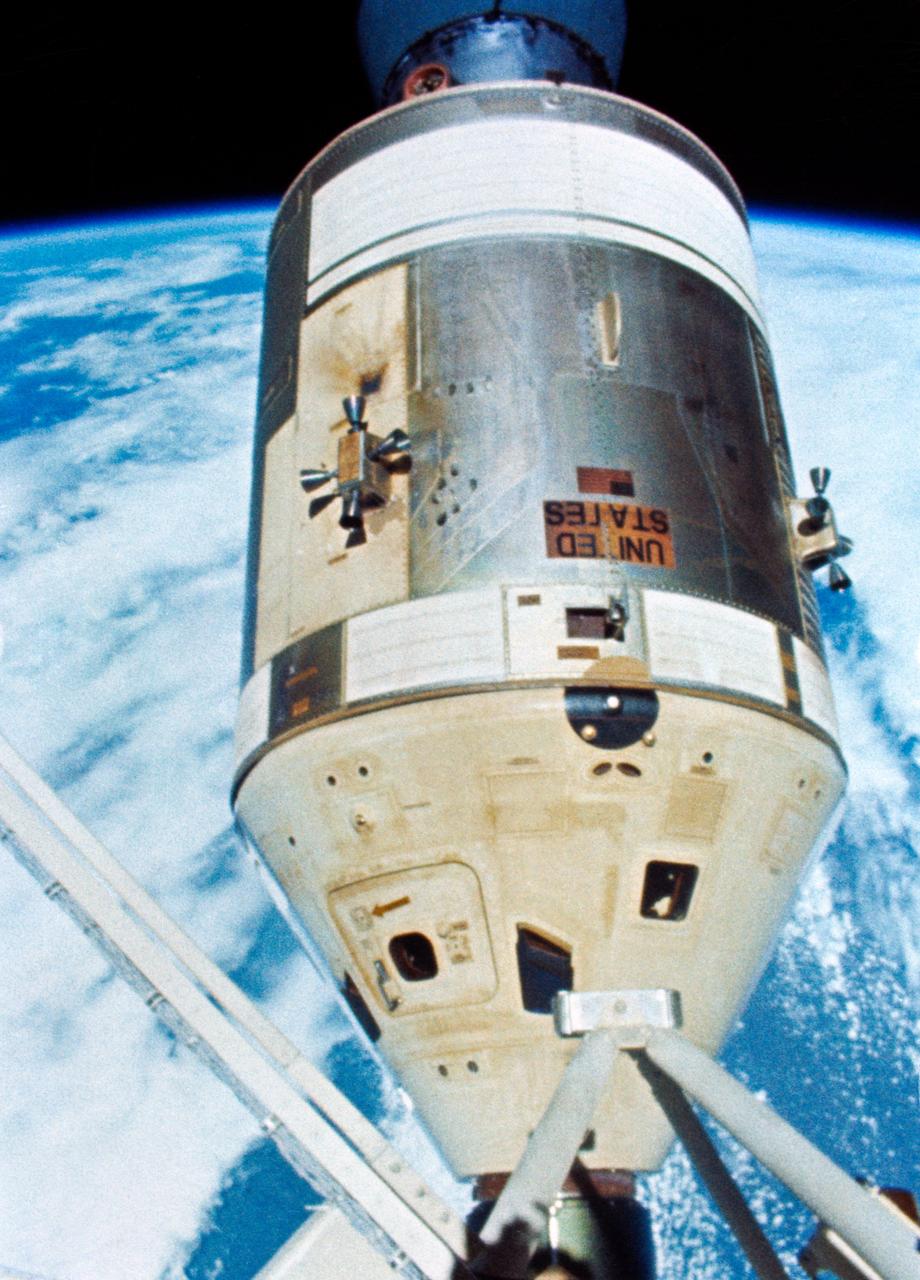
S74-17457 (3 Feb. 1974) --- This view of the Skylab 4 Command/Service Module in a docked configuration is a frame from a roll of movie film exposed by a 16mm Maurer camera. The other four components of the Skylab space station in Earth orbit are out of view to the right. This picture was taken by astronaut Gerald P. Carr, Skylab 4 commander, during the final Skylab extravehicular activity (EVA) which took place on Feb. 3, 1974. The crew members -- Gerald Carr, Edward Gibson and William Pogue -- were the first NASA astronauts to spend New Year's in space. A week earlier, they became the first crew to perform an EVA on Christmas day. Photo credit: NASA
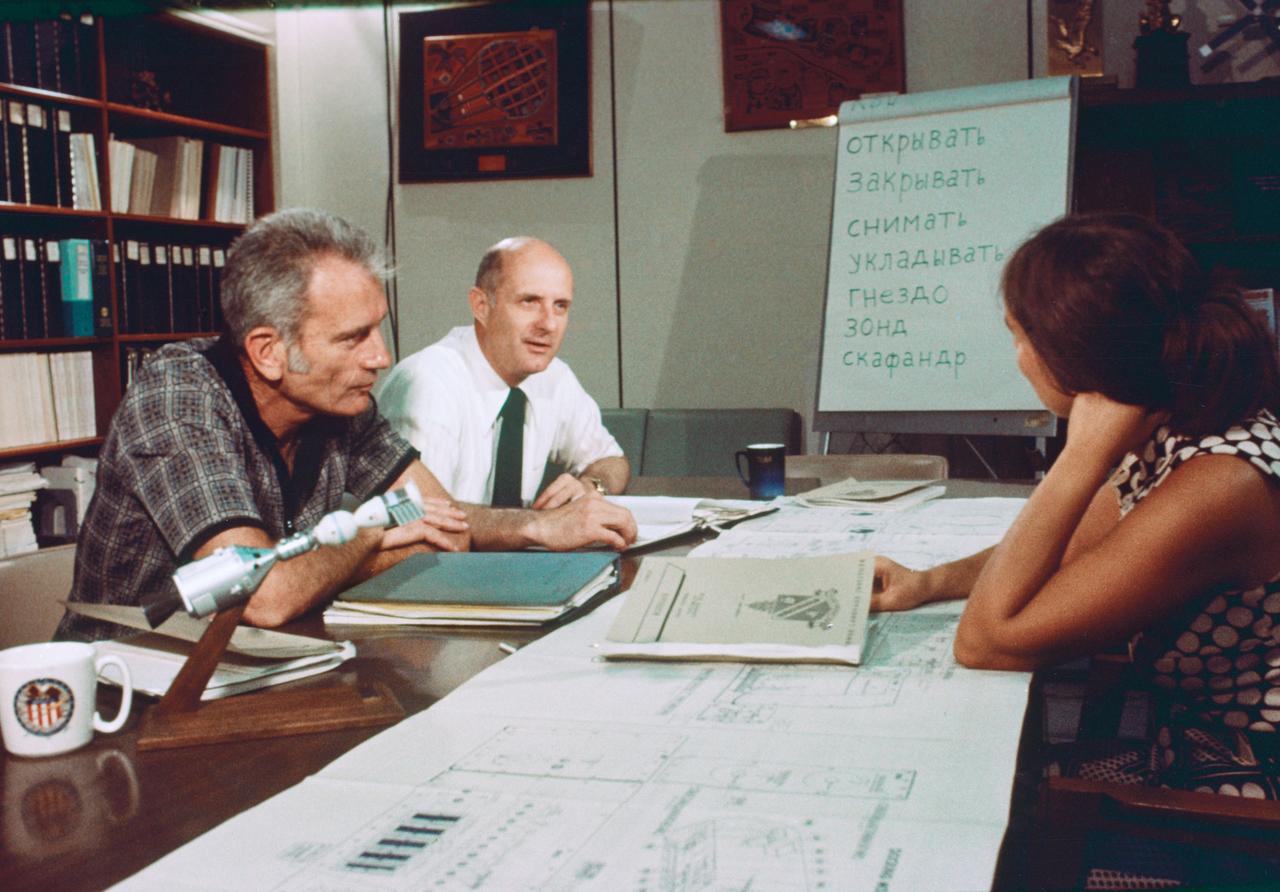

Apollo Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) astronauts Donald K. Slayton, docking module pilot; and Thomas P. Stafford, commander are photographed during ASTP Russian language class.
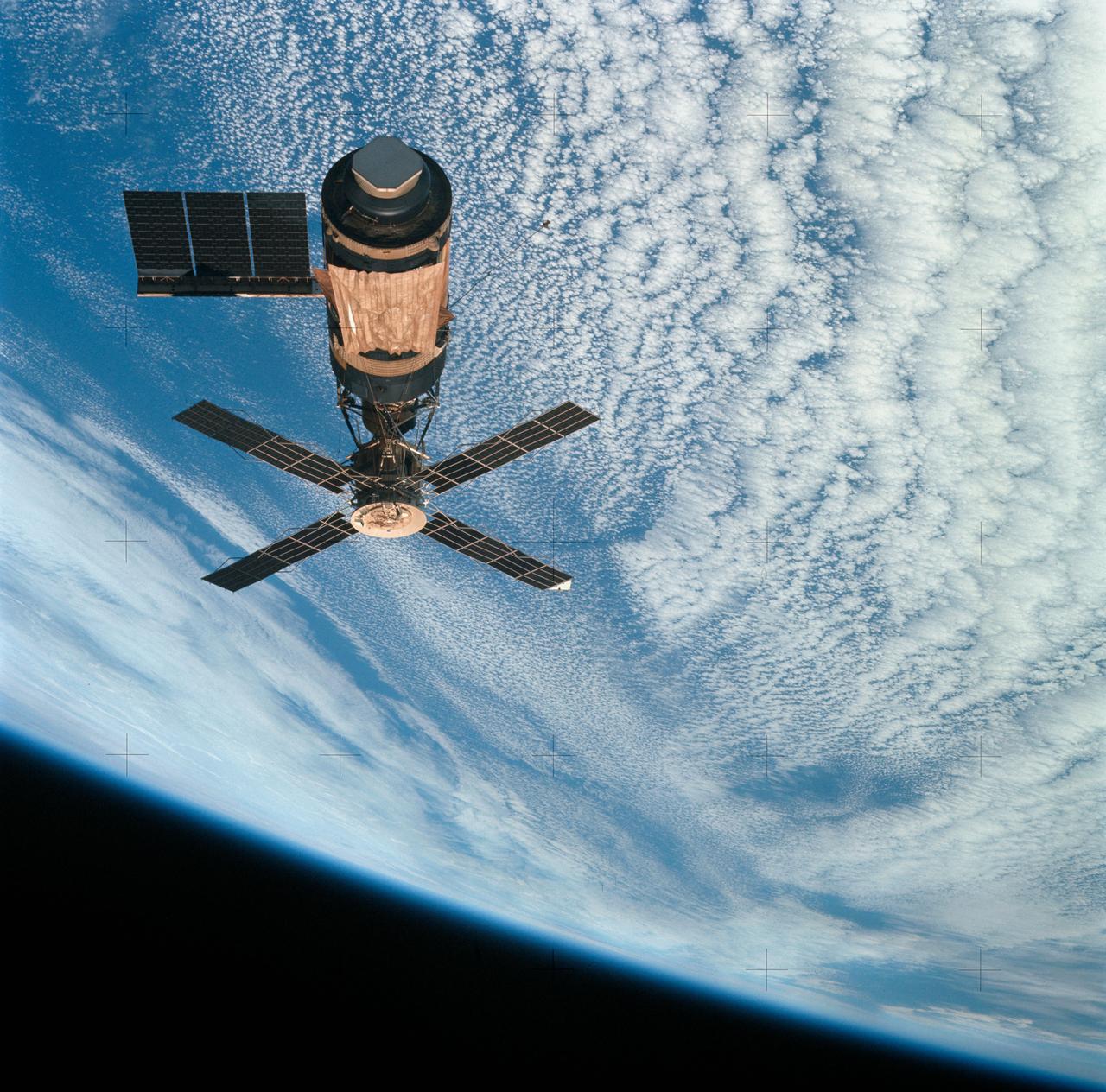

SL4-143-4707 (8 Feb. 1974) --- An overhead view of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit as photographed from the Skylab 4 Command and Service Modules (CSM) during the final fly-around by the CSM before returning home. The space station is contrasted against a cloud-covered Earth. Note the solar shield which was deployed by the second crew of Skylab and from which a micrometeoroid shield has been missing since the cluster was launched on May 14, 1973. The OWS solar panel on the left side was also lost on workshop launch day. Photo credit: NASA
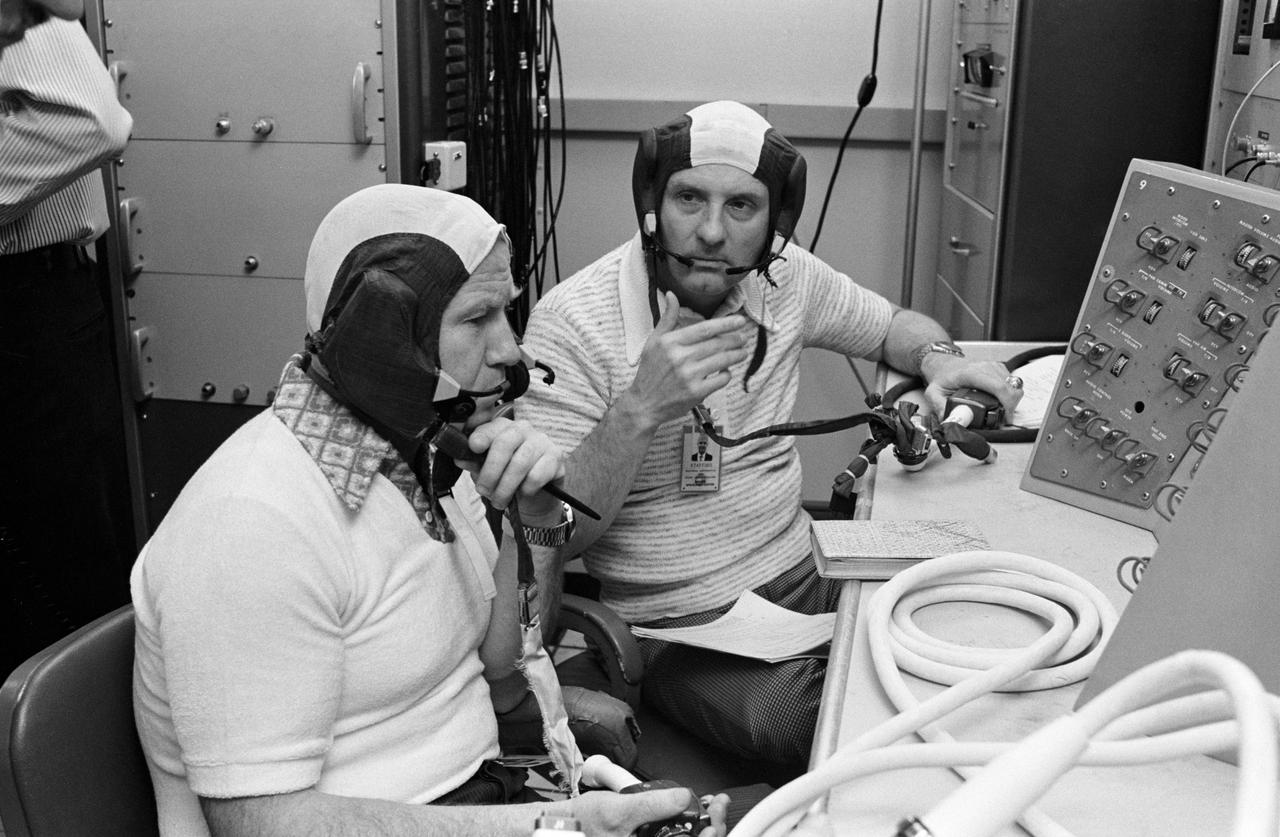

S74-20807 (23 April 1974) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov (foreground) is briefed on the Apollo communications test system console in the Building 440 laboratory during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project training activity at the Johnson Space Center. Leonov is the commander of the Soviet ASTP crew. Leonov is being briefed by astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, commander of the American ASTP crew.
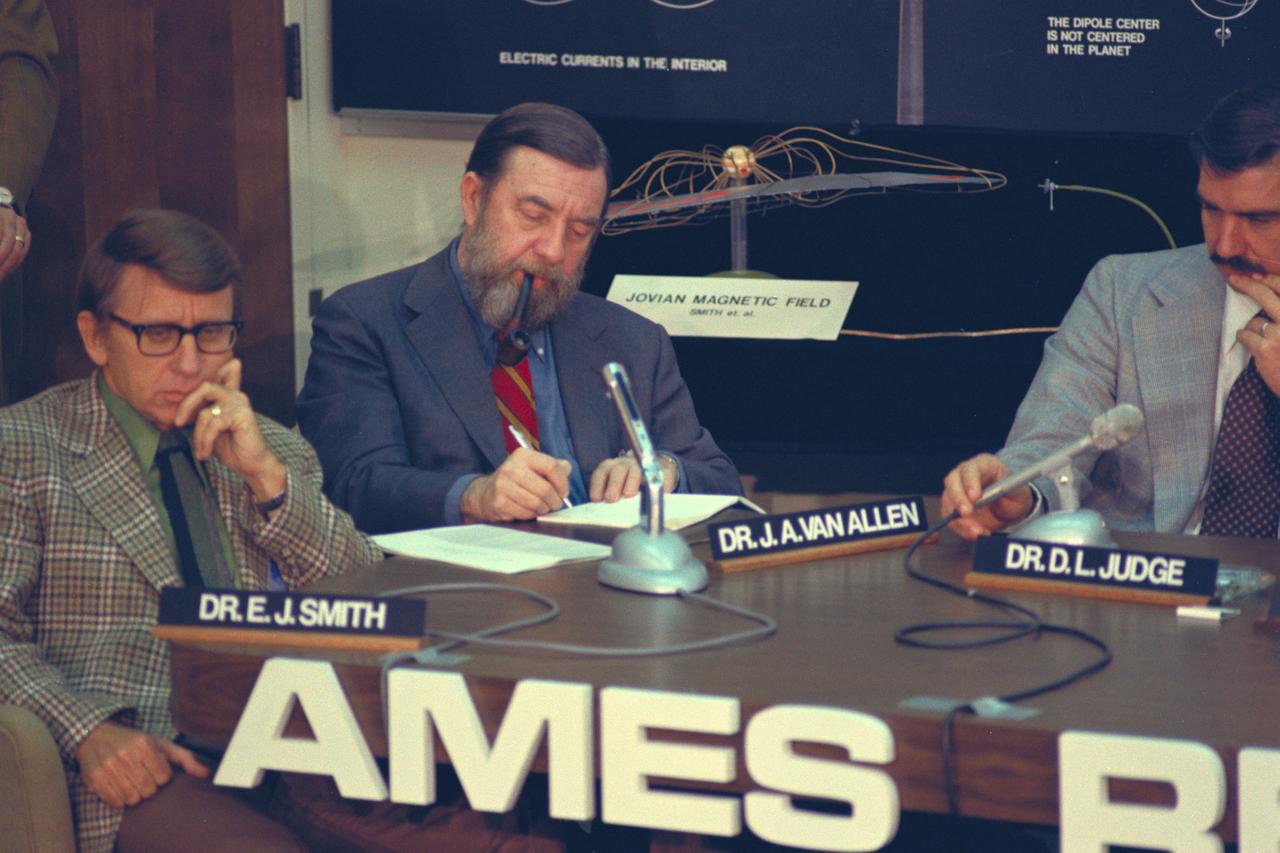

Pioneer 11 Mission to Jupiter: encounter briefing with (L-R) Dr. E. J. Smith, Dr J. A. Van Allen, and Dr D. L. Judge

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The solar panels of Symphonie-A, a Franco-German communications satellite to be launched by KSC aboard a Delta rocket in December, undergo checkout in Hangar S at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Symphonie-A is to be placed in a synchronous orbit 22,300 miles above the equator in the Atlantic Ocean due south of Monrovia, Liberia. Launch by KSC's Unmanned Launch Operations Directorate is scheduled for no earlier than Dec. 17. Photo credit: NASA

N-238 Ames 60mw Arc Heater
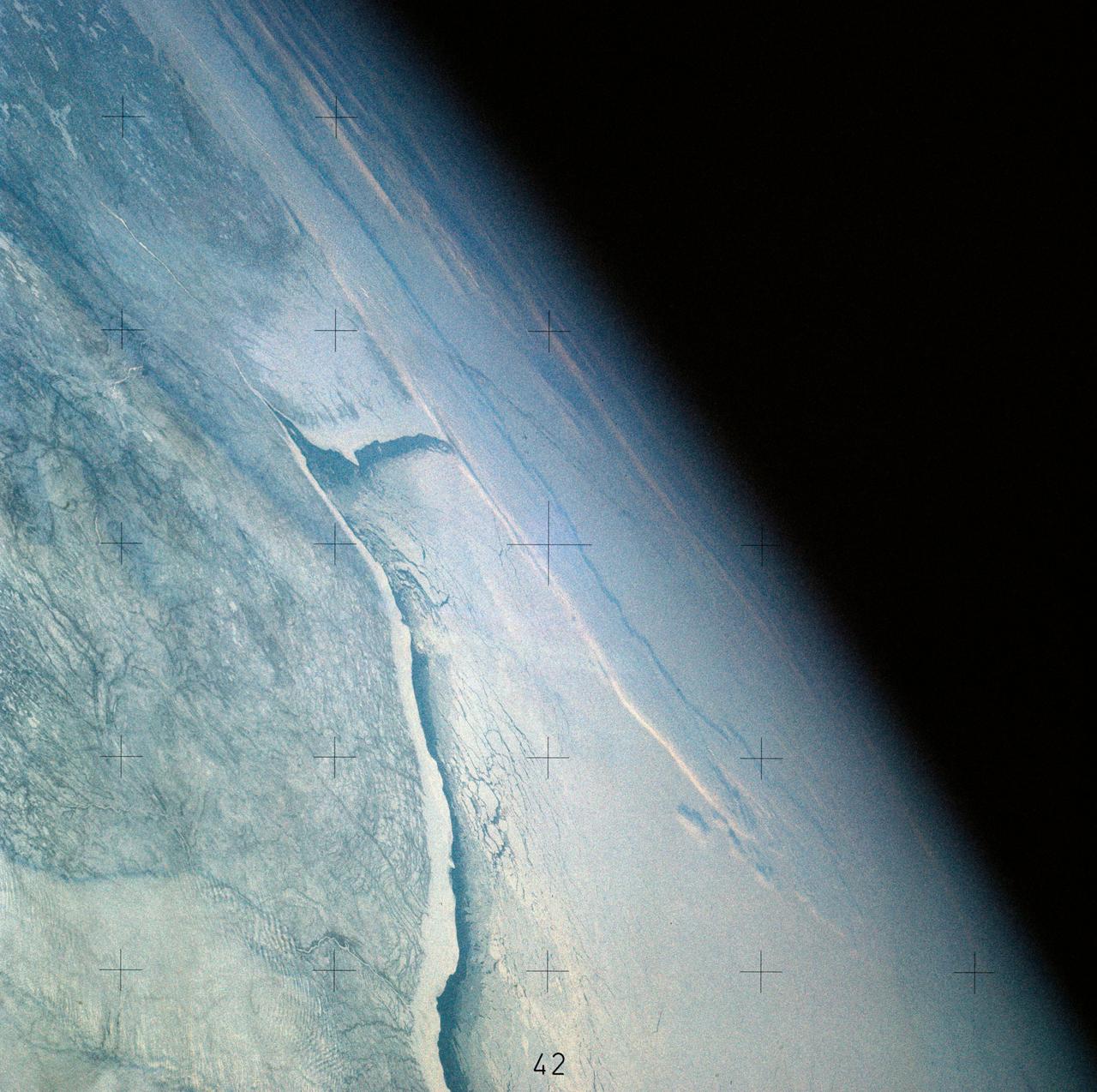

SL4-141-4316 (20 Jan. 1974) --- An oblique view of ice formations in Canada's Hudson Bay, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen. The camera used was a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad, with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome film. The southwestern part of the bay is prominent with the Nelson River in Manitoba flowing into it. Skylab never flew this far north in latitude. However, its orbital vantage point allowed observations and photography while over a point some 600 miles away as in the case of this picture. The ice formation along the southwest portion of Hudson Bay can be studied from photographs such as this one. The buildup of ice along the windward shore (very white) followed by the clear water gap (dark) caused by the wind blowing the newly formed ice toward the opposite shore, and finally the patterns in the ice structure itself are studied to learn more of the nature of the "winterization" of this area. Photo credit: NASA
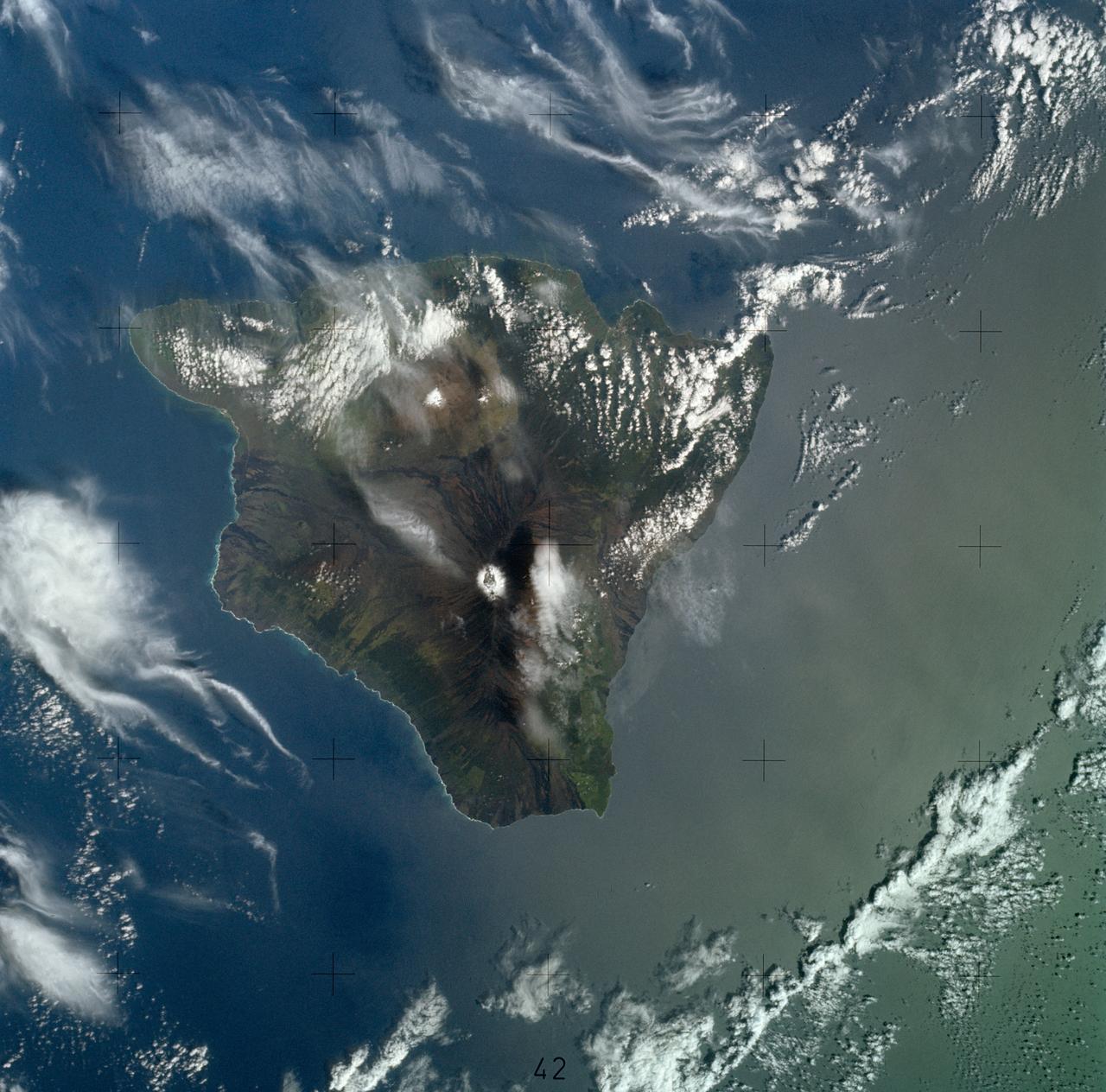

SL4-139-3997 (8 Jan. 1974) --- A vertical view of the Island of Hawaii, State of Hawaii, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by a Skylab 4 crewman. The camera used was a hand-held Hasselblad camera, with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome film. This photograph, taken on Jan. 8, 1974, is very useful in studies of volcanic areas. Prominent volcanic features such as the summit caldera on Mauna Loa, the extinct volcano Mauna Kea, the Kilauea caldera, and the pit crater at Halo mau mau within the caldera are easily identified. (Kilauea was undergoing frequent eruption during the mission). Detailed features such as the extent and delineation of historic lava flows on Mauna Loa can be determined and are important parameters in volcanic studies. Photo credit: NASA
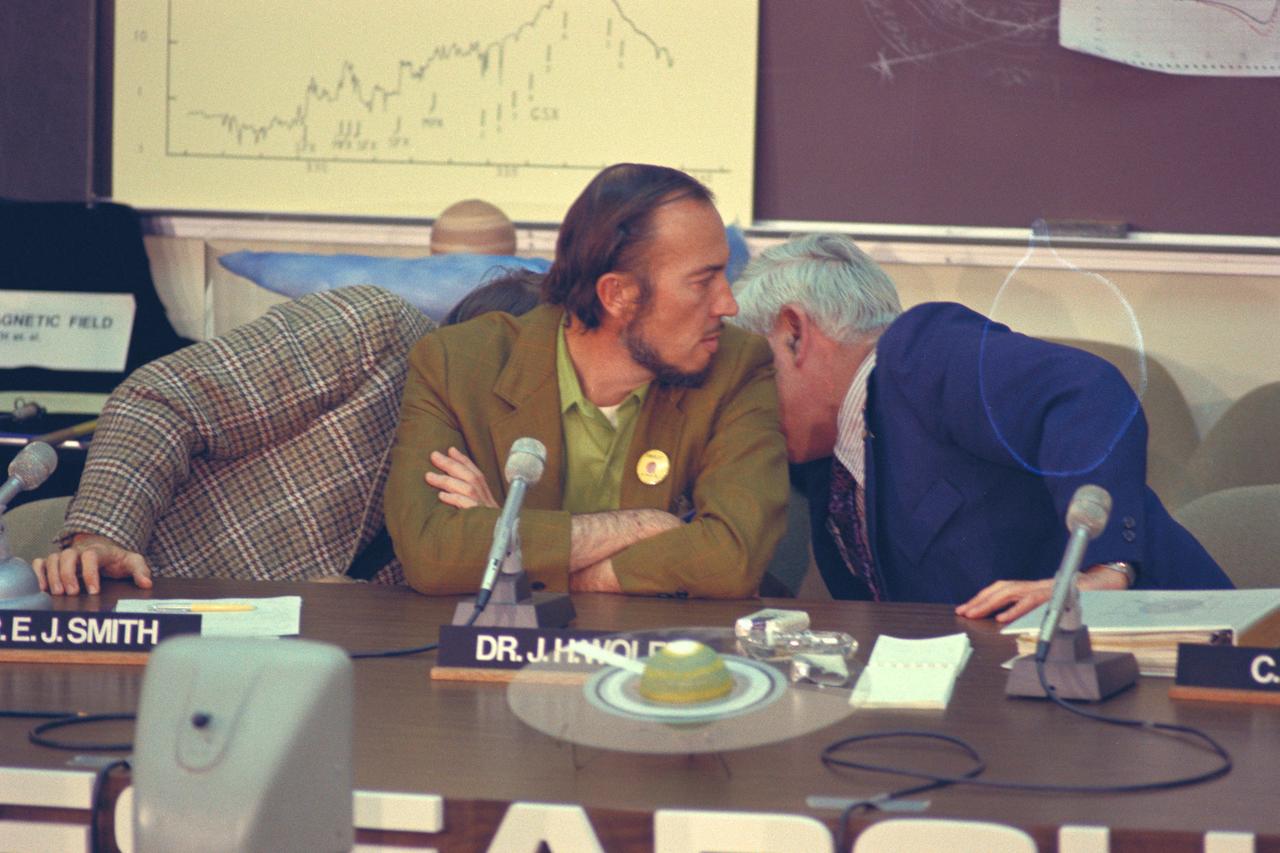

Dr E. J.Smith, John Wolf (Ames) and Charles Hall (Ames) confer during press conference for Pioneer 11 Jupiter encounter
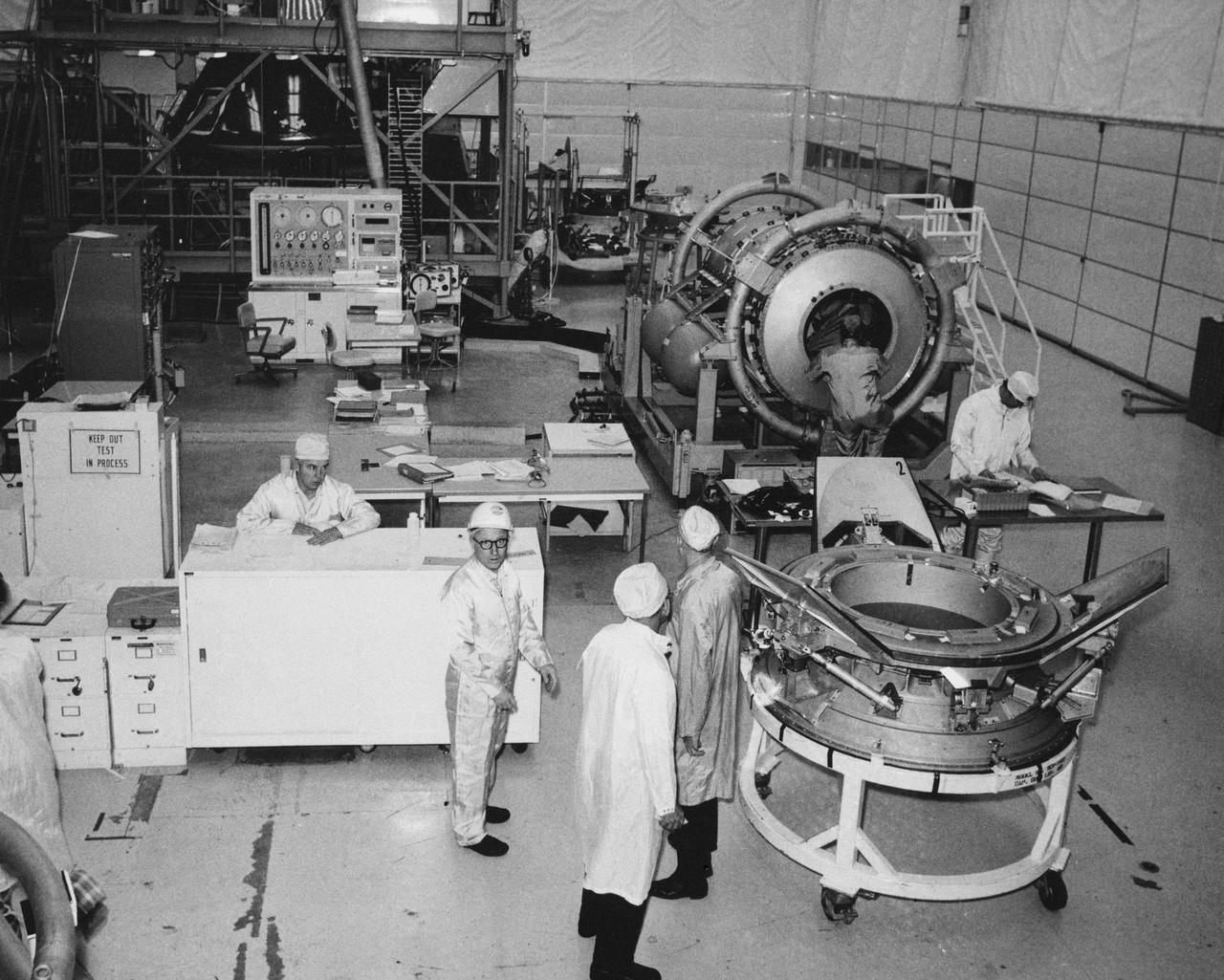
S74-28295 (September 1974) --- American-built hardware for the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission undergoes pre-delivery preparations in the giant clean room at Rockwell International Corporation?s Space Division at Downey, California. The U.S. portion of the ASTP docking system is in the right foreground. In the right background is the cylindrical-shaped docking module, which is designed to link the Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft when they dock in Earth orbit next summer. In the left background is the Apollo Command Module which they will carry the three American astronauts into Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
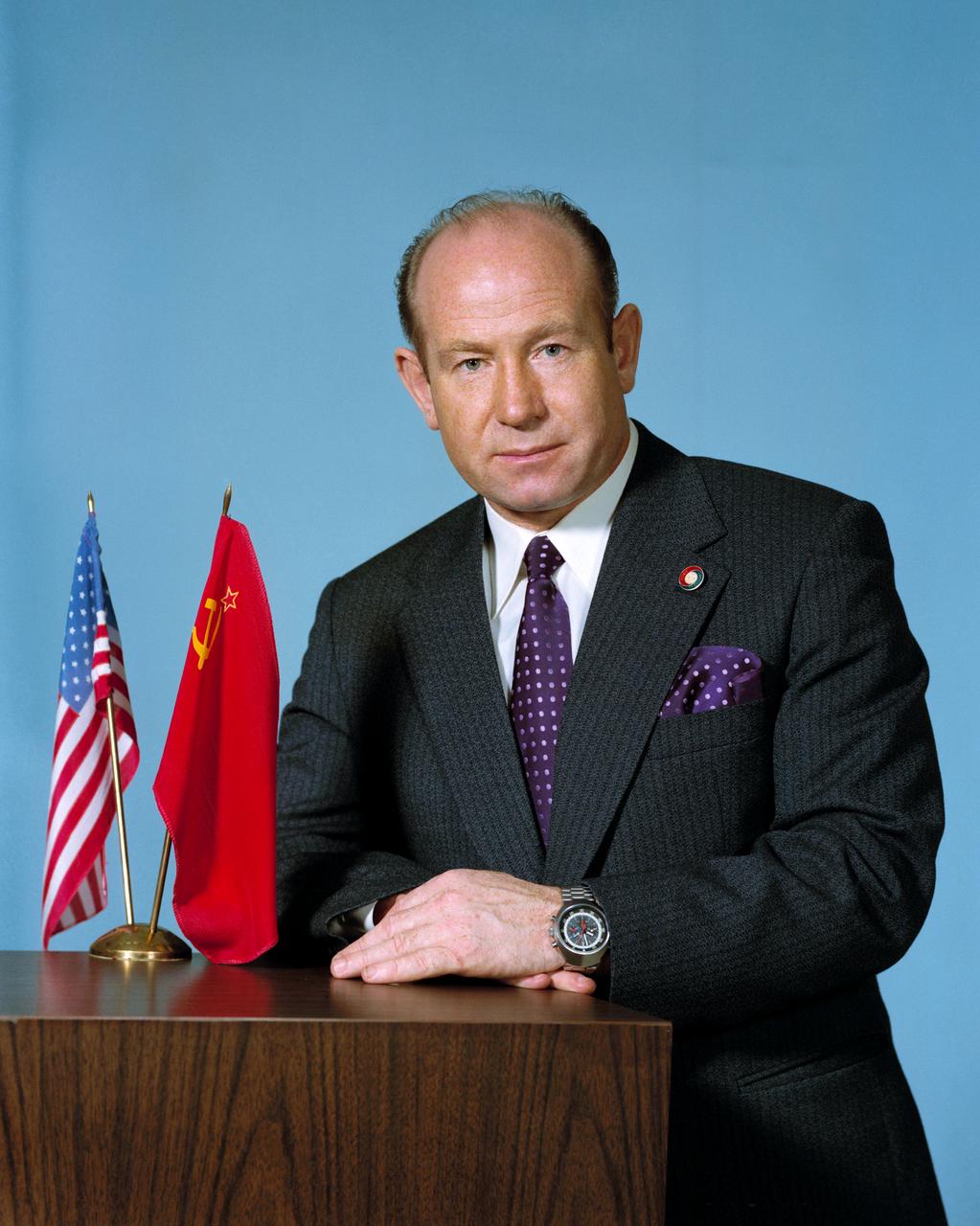

S74-20824 (April 1974) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov

Huntsville’s Jack Giles, Alabama State Senator (left), and Dr. Rocco Petrone, Marshall Space Flight Center Director (Middle), speak with Astronaut Owen Garriott who is inside the Apollo 16 Command Module on display at the Alabama Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The successful Apollo 16 manned lunar landing mission took place April 16, 1972 through April 27, 1972. (Photograph courtesy of Huntsville/Madison County Public Library)
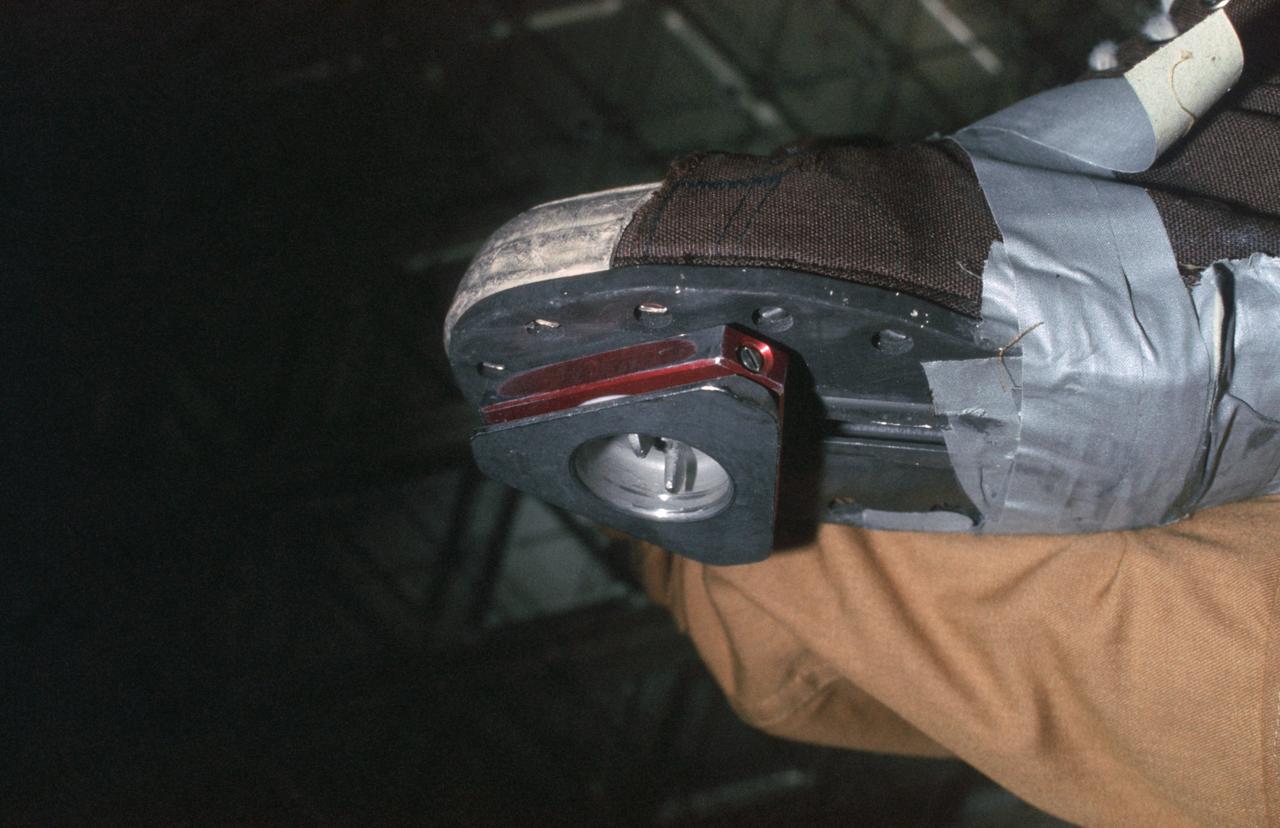

SL4-149-5036 (February 1974) --- View of triangle-shaped cleat taped on the bottom of a shoe of a Skylab 4 crew member. Photo credit: NASA
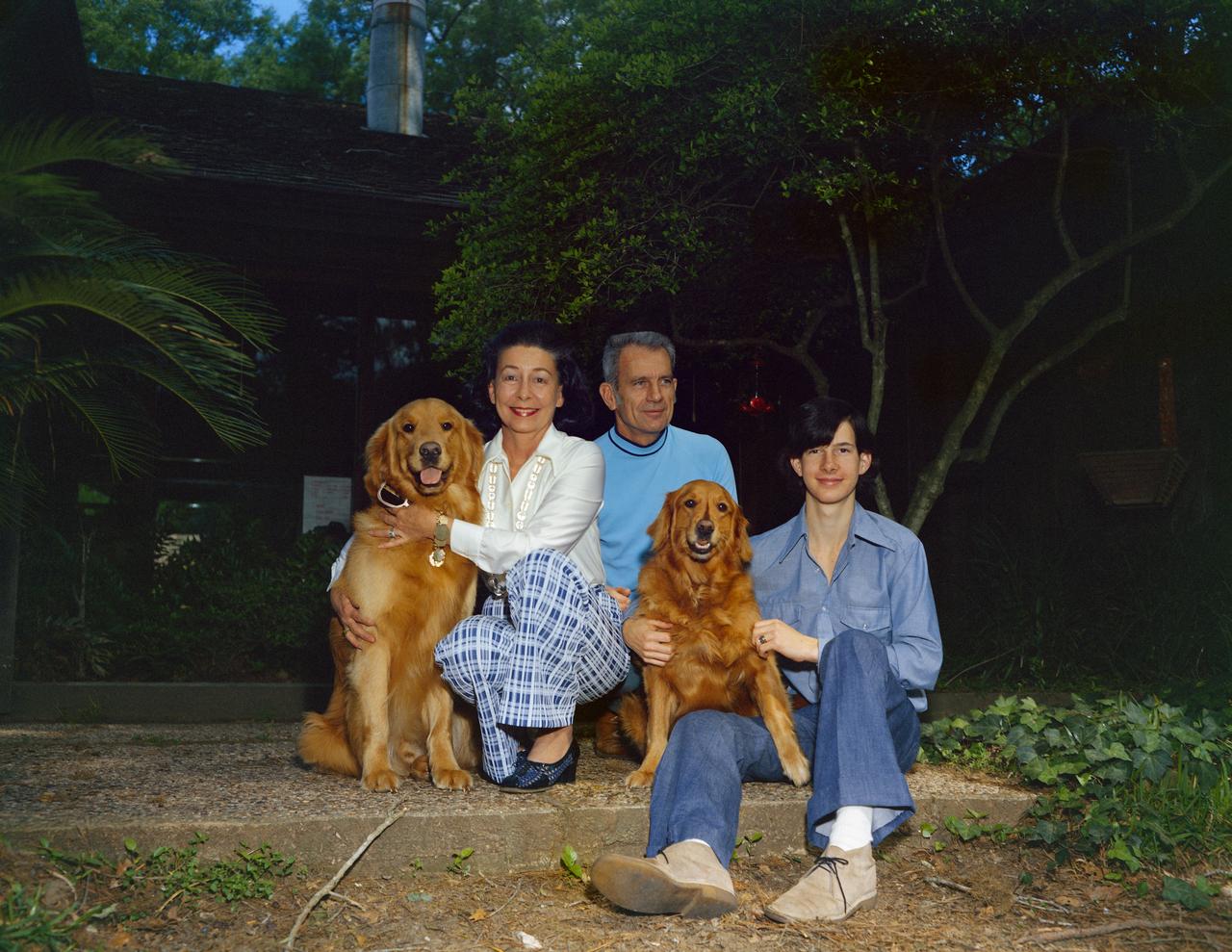

S74-19495 (January 1974) --- Astronaut Donald K. Slayton is shown with his wife, Marjorie, and their son, Kent, 17, at their home in Friendswood, Texas. Slayton is the Director of Flight Crew Operations at NASA's Johnson Space Center. He will be the Docking Module Pilot of the American Crew of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) mission. This portrait includes two family pets.
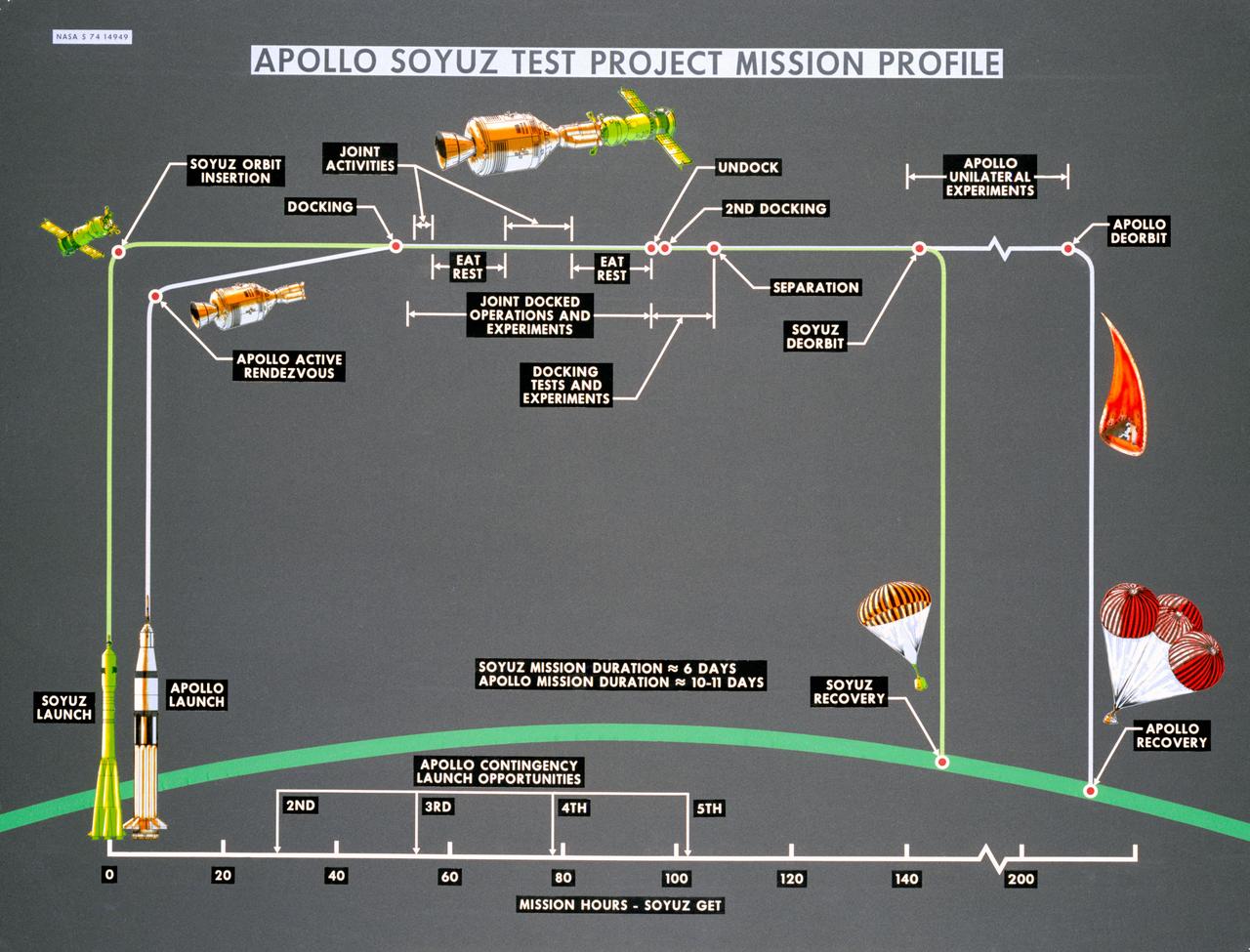
S74-14949 (October 1974) --- Artist?s drawings and call-outs depict phases of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, an Earth-orbital mission which will feature rendezvous and docking of the respective spacecraft of the two nations. ASTP crewmen for the USSR include Aleksey A. Leonov and Valeriy N. Kubasov. The astronaut team includes astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton. The mission is scheduled to take place in summer 1975.
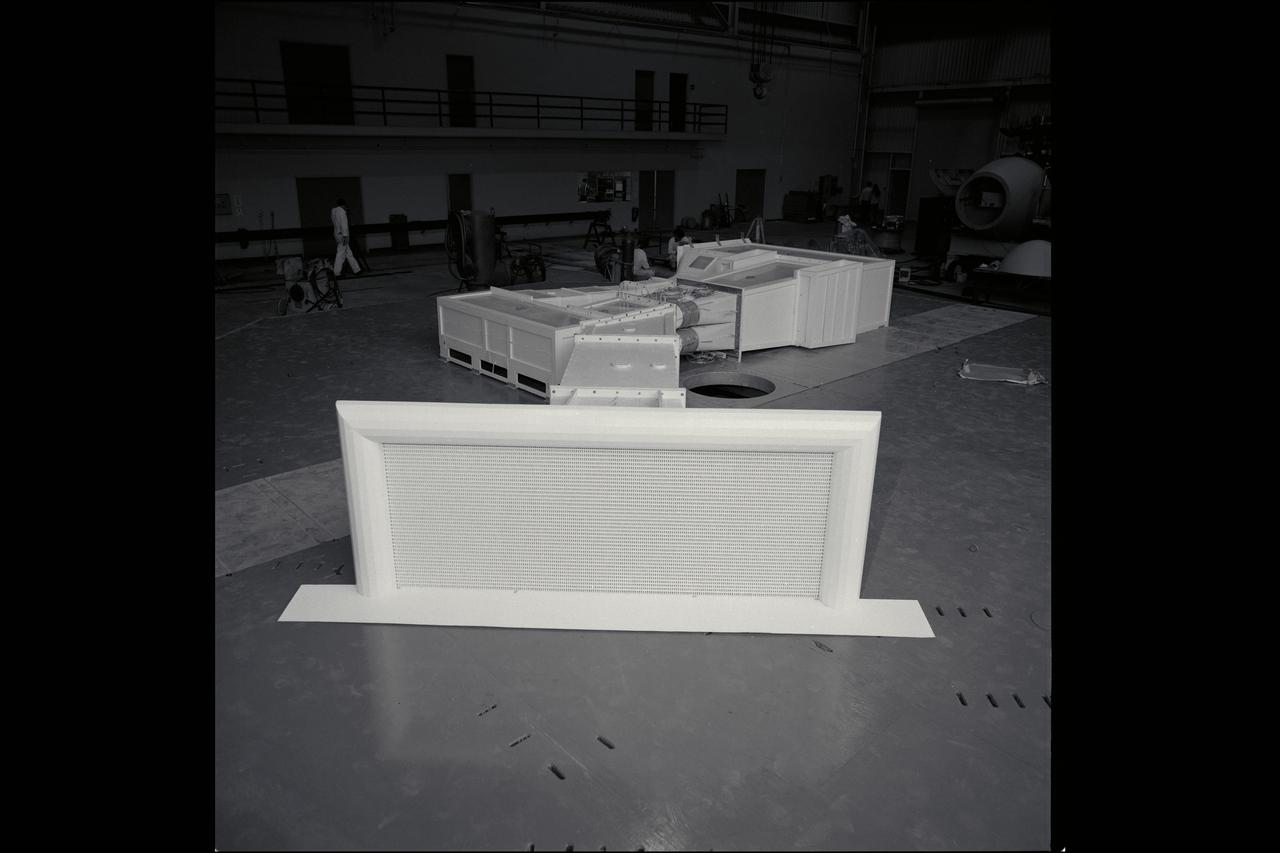

1/5th scale model of the 80x120ft w.t. in N-246

SL4-140-4111 (14 Jan. 1974) --- The Aleutian Islands area of Alaska, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen. The camera used was a hand-held Hasselblad, with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome. Here is another macro scale phenomenon which is difficult to observe except from a space platform. The Aleutian Islands and clouds with very elaborate van Karman vortices was photographed on Jan. 14, 1974. In addition to the vortices the waves in the clouds due to the mountains on the islands are very evident. In fact, the easiest way to find the mountains is to start with their atmospheric disturbance and work back to the mountain. Photo credit: NASA

SL4-139-3971 (8 Jan. 1974) --- An oblique view of Japan as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The Island of Kyushu is at center left. The Island of Honshu is in the right background. The Korean Peninsula is in the left background. This picture was taken by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen using a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera with a 100mm lens. The plume form Kyushu's volcano Sakurajima is clearly seen in this photograph. Volcanic activity at Sakurajima is known to have occurred for over 1,200 years (first recorded in the year 708 A.D.) but for the first time the entire volcanic plume can be documented at one time. Skylab photographs and crew descriptions are much more detailed then information available from other satellites. The volcano and its plume were observed at least seven times during Skylab 4, and photographed and documented with television. In repeated observations the plume was seen to stream out to the south or southeast and become increasingly diffuse away from the volcano. As the plume reached the open ocean cast of Kyushu it changed direction, sometimes abruptly, and fanned out to the northeast. In this photograph it extends about 80 kilometers (50 miles) east from the volcano; the distribution and dispersion of particulate materials and volcanic gasses will be studied in this and similar Skylab photographs. Although the plume is primarily water vapor, it contains significant quantities of oxides of carbon, sulphur and nitrogen. These gases are considered pollutants, and understanding their abundance and distribution will help to evaluate the relative effect and significance of man-made atmospheric pollutants. Photo credit: NASA
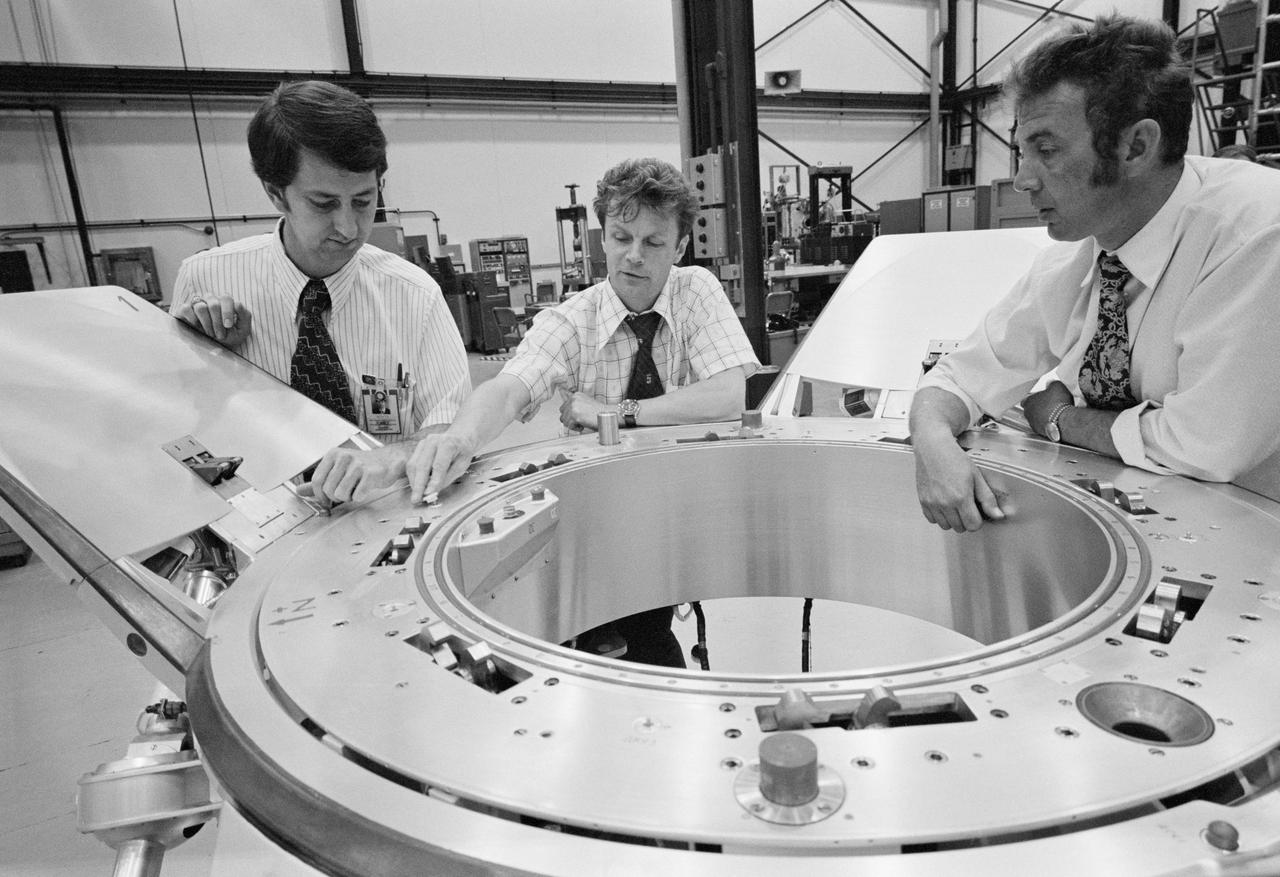

S74-24671 (10 July 1974) --- Three Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) engineers look over a Soyuz spacecraft docking system prior to an ASTP docking mechanism fitness test conducted in Building 13 at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). They are (left to right) Robert White, Vladimir Syromyatnikov and Yevgeniy Bobrov. White is the American chairman of ASTP Working Group Number 3, and Syromyatnikov is his Soviet counterpart. This working group is concerned with ASTP docking problems and procedures. White is with JSC's Spacecraft Design Division. Syromyatnikov is senior researcher of the Soviet State Research Institute of Machine Building. Bobrov is a junior researcher with the Institute of Machine Building. The joint United States - USSR ASTP docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for the summer of 1975.
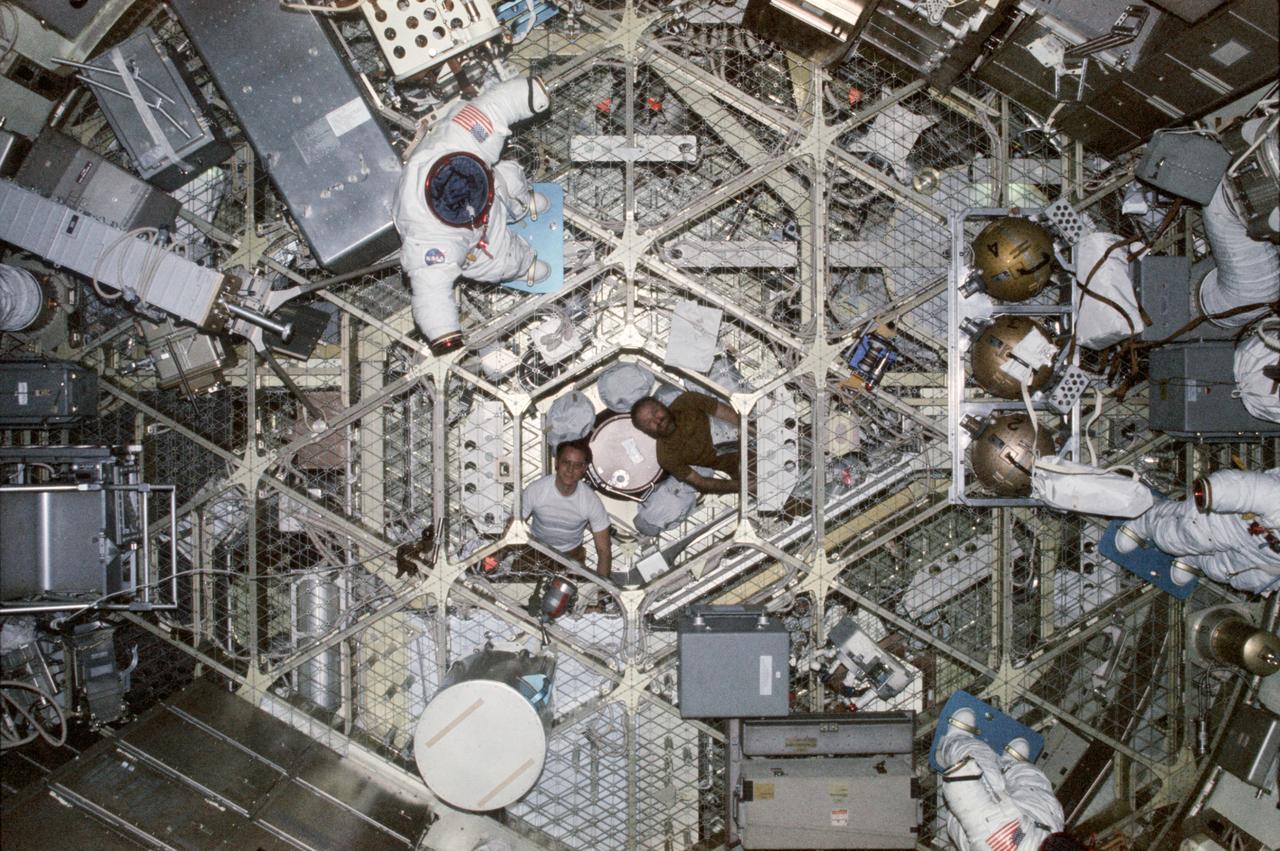
SL4-150-5062 (January 1974) --- A 35mm camera, operated by astronaut William R. Pogue, Skylab 4 pilot, recorded this wide scene of his Skylab 4 crewmates on the other end of the orbital workshop. Astronauts Jerry P. Carr (right), commander, and Edward G. Gibson, science pilot, pose for the snapshot. Also in the frame are parts of three Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuits, used on several EVA sessions during the third manning of the Skylab space station. Photo credit: NASA
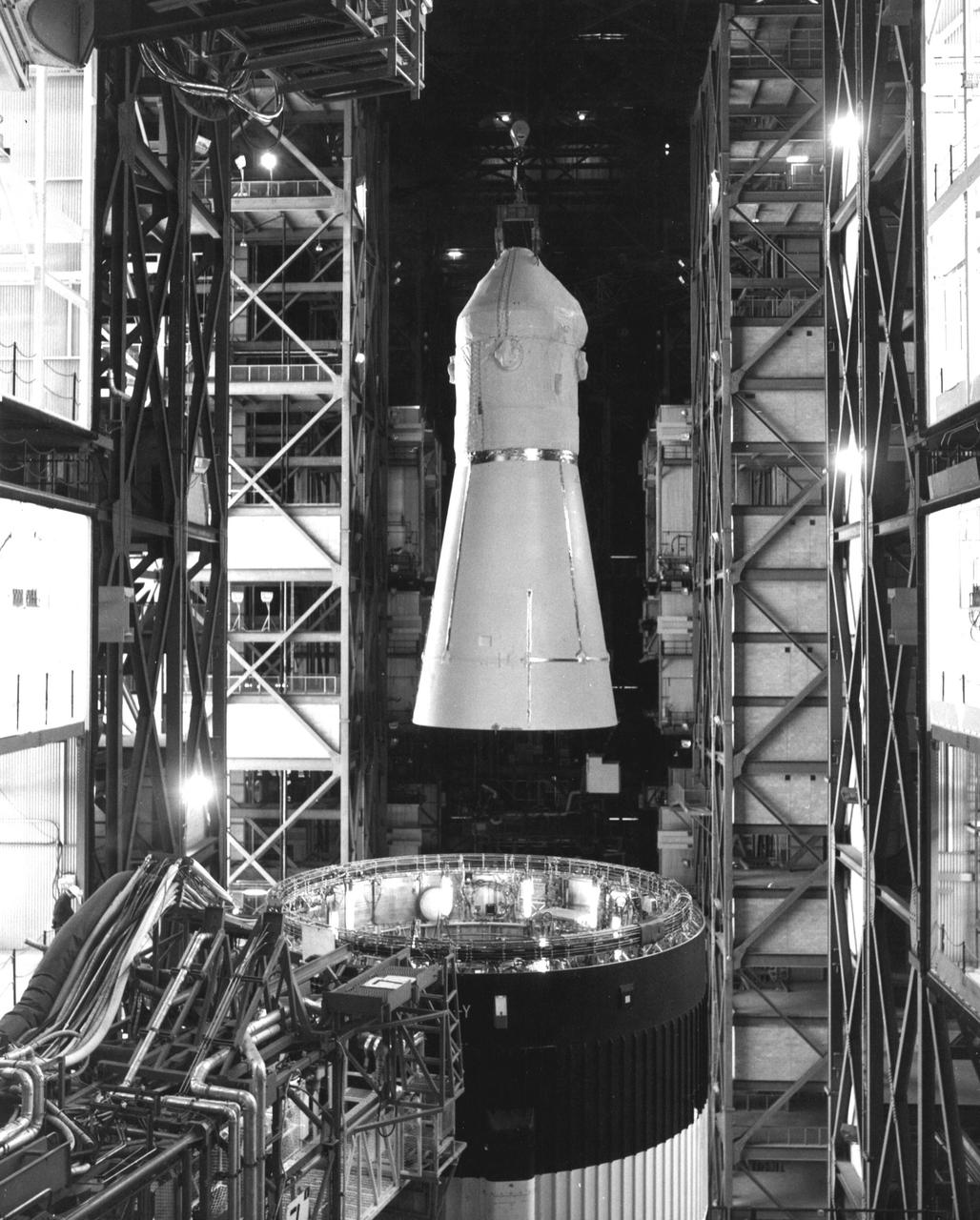

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The command_service module for the Skylab Rescue Vehicle was removed from its Saturn IB rocket in the Vehicle Assembly Building here today. The Skylab Program ended with splashdown of the Skylab 4 crew in the Pacific Ocean Feb. 8, ending the need for the rescue vehicle on Complex 39's Pad B since early December. The SaturnIB_Apollo was returned to the VAB last week and is now being dismantled. The spacecraft is to be taken to the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building in the KSC Industrial Area Feb. 20. Both the spacecraft and rocket will be stored at KSC as backup flight hardware for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975.
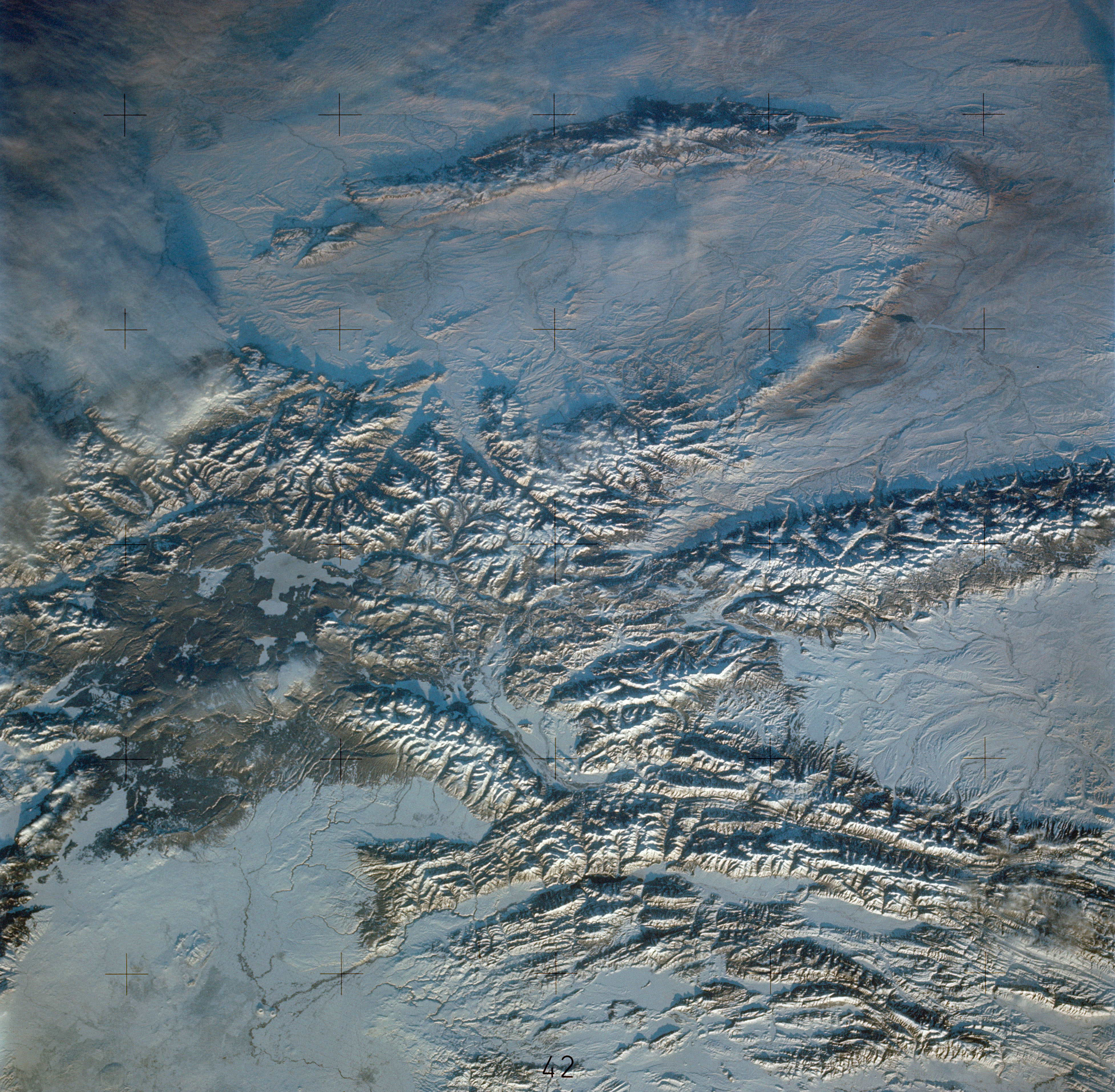

SL4-138-3846 (February 1974) --- A near vertical view of the snow-covered northwest corner of Wyoming as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. A Skylab 4 crewman used a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera to take this picture. A small portion of Montana and Idaho is seen in this photograph also. The dark area is Yellowstone National Park. The largest body of water is Yellowstone Lake. The Absaroka Range is immediately east and northeast of Yellowstone Lake. The elongated range in the eastern part of the picture is the Big Horn Mountain range. The Wind River Range is at bottom center. The Grand Teton National Park area is almost straight south of Yellowstone Lake. Approximately 30 per cent of the state of Wyoming can be seen in this photograph. Photo credit: NASA

This montage is an artist's conception of progressive views of the Comet Kohoutek based on sketches and a description by Skylab-4 astronaut Edward Gibson. An early discovery of a large comet in an orbit that would reach close to the Sun at the end of 1973 prompted NASA to initiate Operation Kohoutek, a program to coordinate widespread observations of the comet from ground observatories, aircraft, balloons, rockets, unmarned satellites, and Skylab.
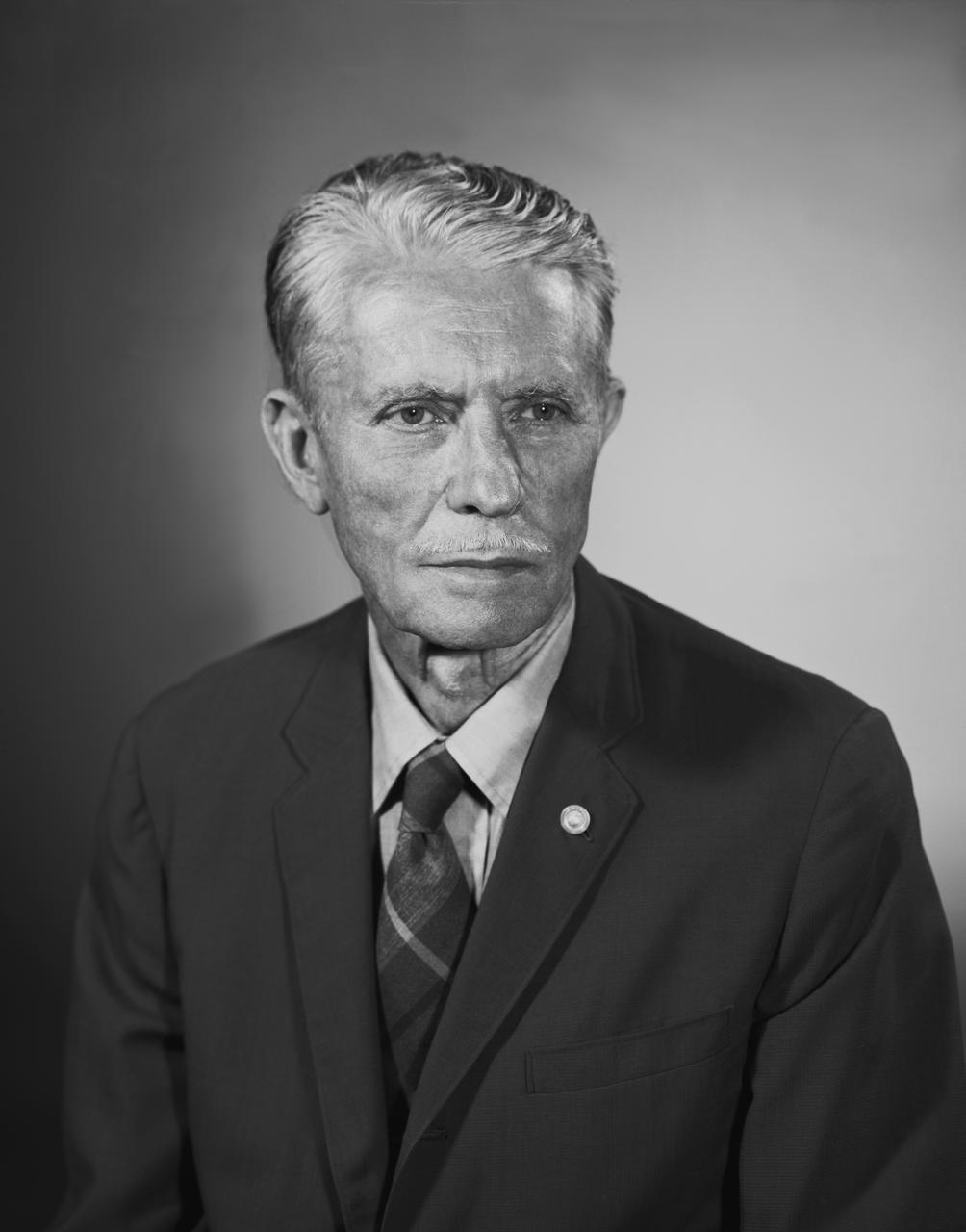

Portrait of Floyd L. Thompson NASA Langley Center Director
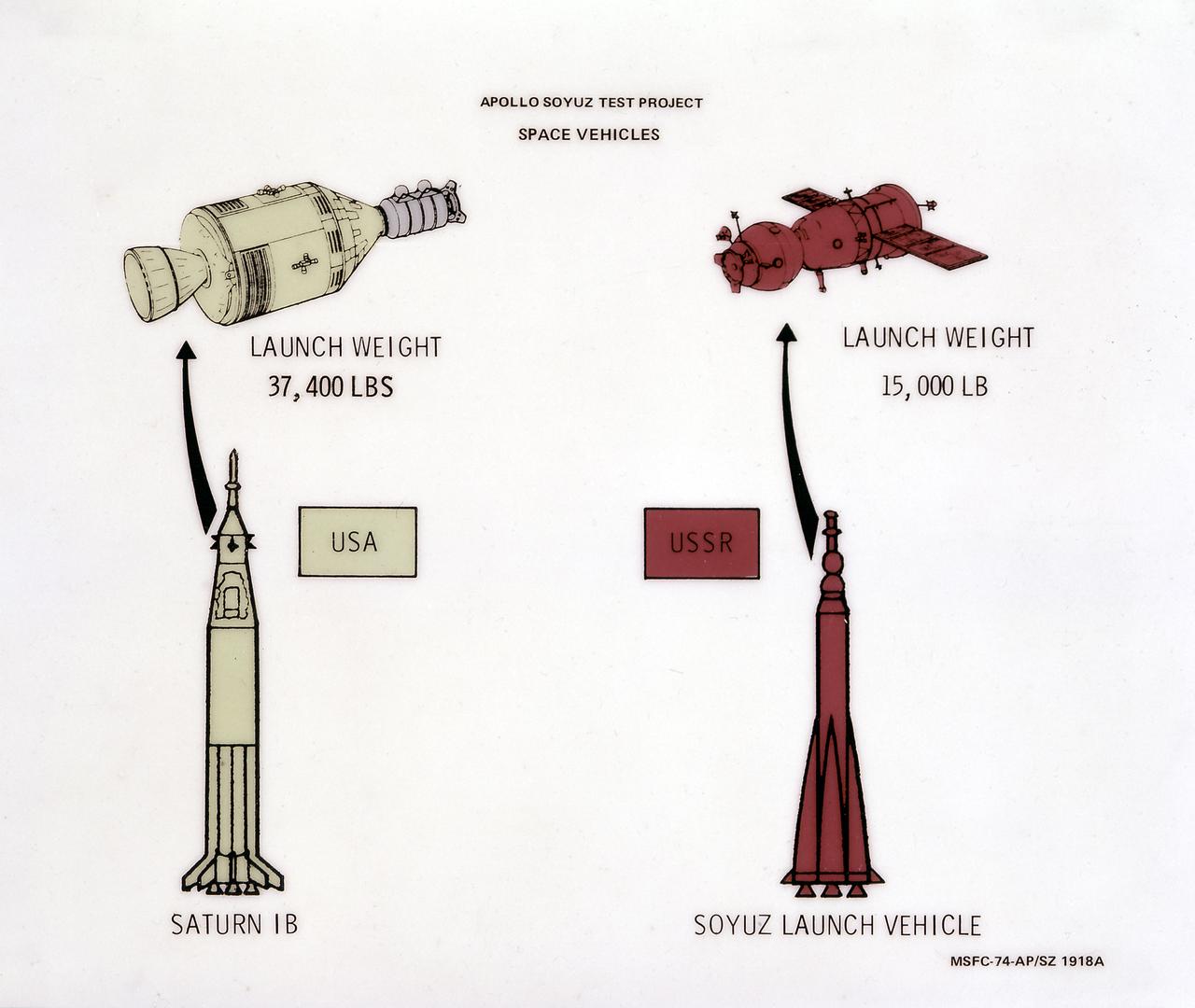
This illustration depicts a comparison of two space vehicles, the U.S.'s Saturn IB launch vehicle and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz launch vehicle, for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The ASTP was the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. A joint engineering team from the two countries met to develop a docking system that permitted the two spacecraft to link in space and allowed the two crews to travel from one spacecraft to the other. This system entailed developing a large habitable Docking Module (DM) to be carried on the Apollo spacecraft to facilitate the joining of two dissimilar spacecraft. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission.

S74-17456 (3 Feb. 1974) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson has just egressed the Skylab EVA hatchway in this frame taken from a roll of movie film exposed by a 16mm Maurer camera. Astronaut Gerald P. Carr, Skylab 4 commander, took this picture during the final Skylab extravehicular activity (EVA) which took place on Feb. 3, 1974. Carr was above on the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) when he shot this frame of Gibson. Note Carr's umbilical/tether line extending from inside the space station up toward the camera. Astronaut William R. Pogue, Skylab 4 pilot, remained inside the space station during the EVA by Carr and Gibson. Photo credit: NASA
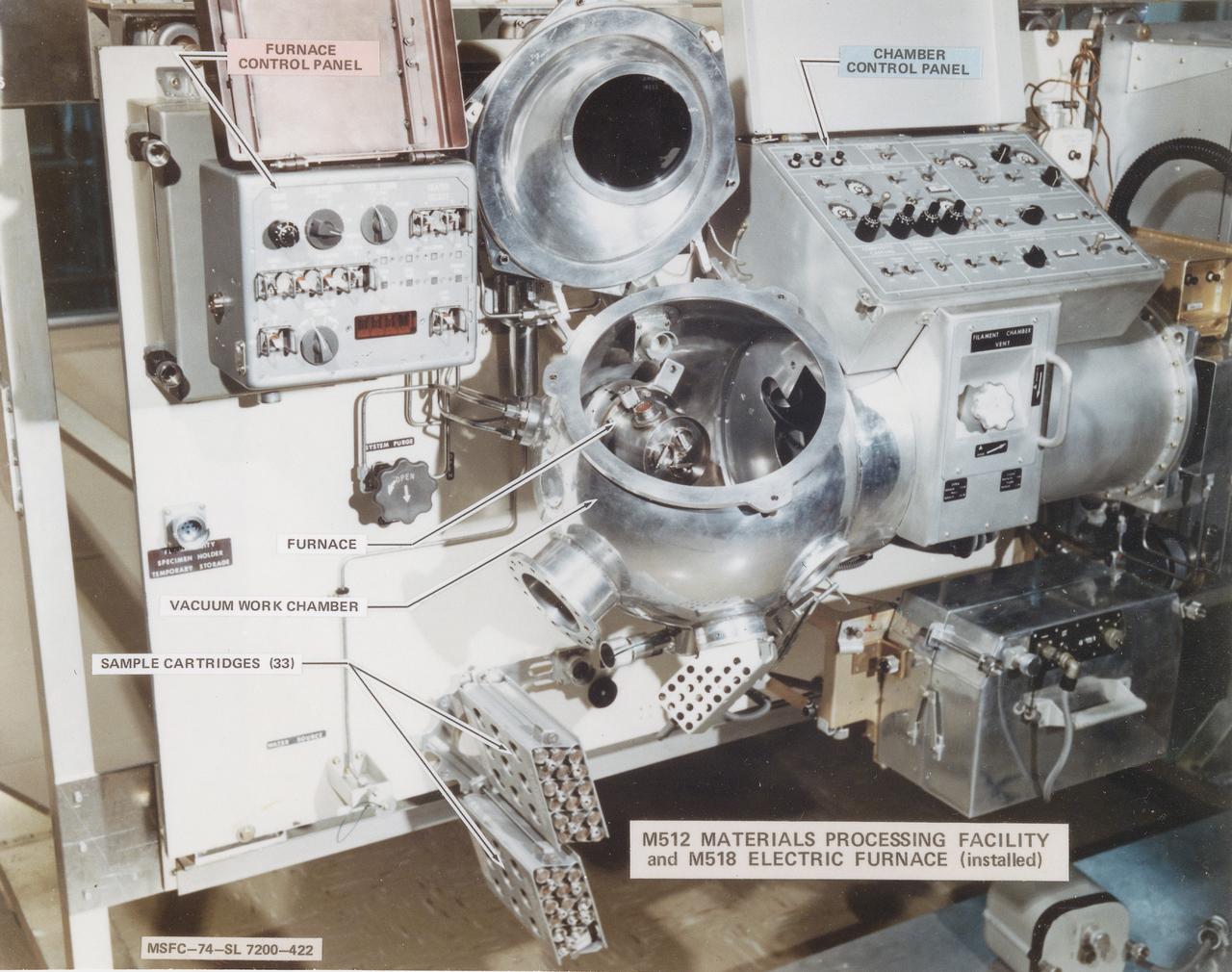
This photograph shows the Skylab Materials Processing Facility (M512) and the Multipurpose Furnace System (M518). This facility, located in the Multiple Docking Adapter, was developed for Skylab,and accommodated 14 different experiments that were carried out during the three marned missions. The abilities to melt and mix without the contaminating effects of containers, to suppress thermal convection and buoyancy in fluids, and to take advantage of electrostatic and magnetic forces and otherwise masked by gravitation opened the way to new knowledge of material properties and processes. This beginning would ultimately lead to the production of valuable new materials for use on Earth.

CV-990 Galileo II arrival at Ames after first expedition - decending ramp are from top Don Anderson, Mike Bader, Dean Chapman (?), Hans Mark and unknown
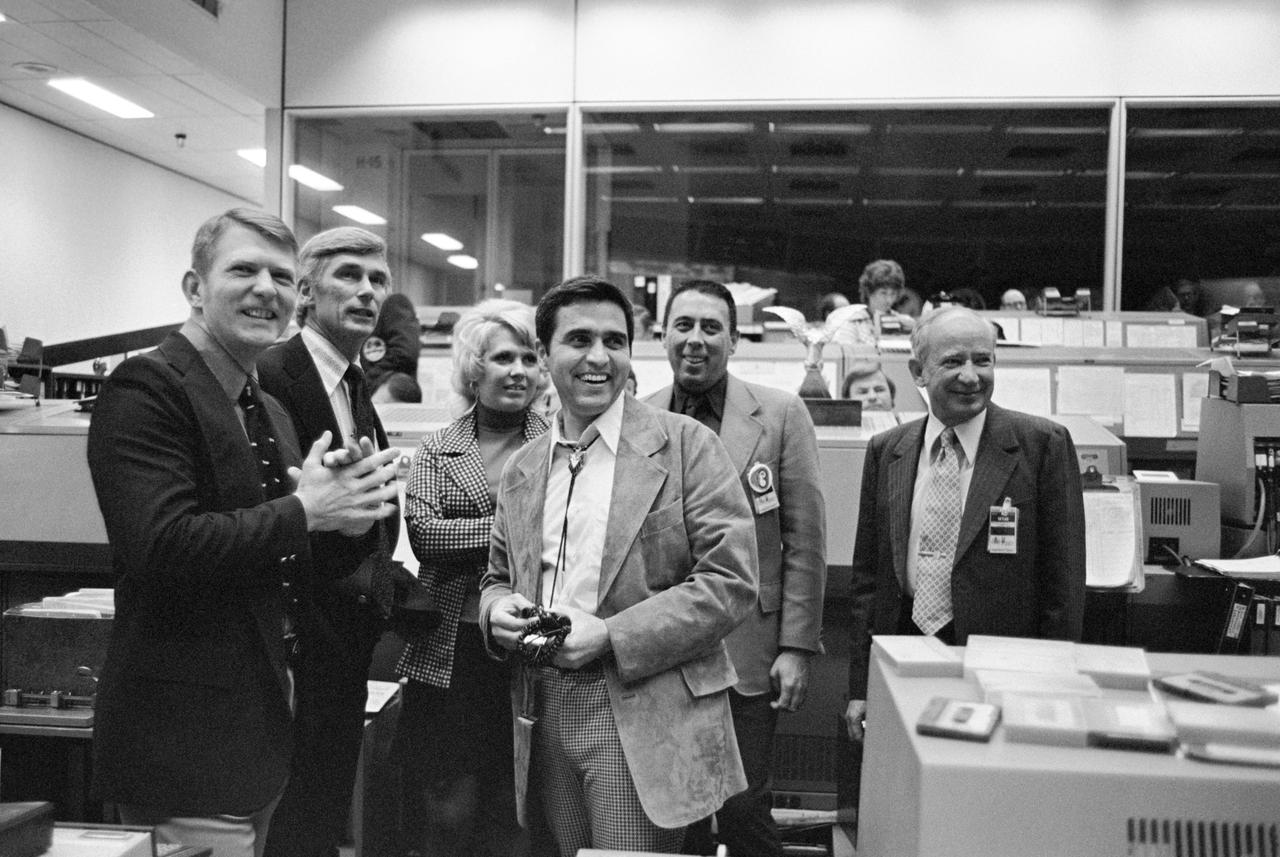

S74-15520 --- Left to right Gene Kranz, Gene Cernan, Karla Garnuch, Harrison Schmitt, George Abbey, and Sigurd A. Sjoberg watching the dedication of the Apollo 17 flag to the Mission Control Center. Photo credit: NASA
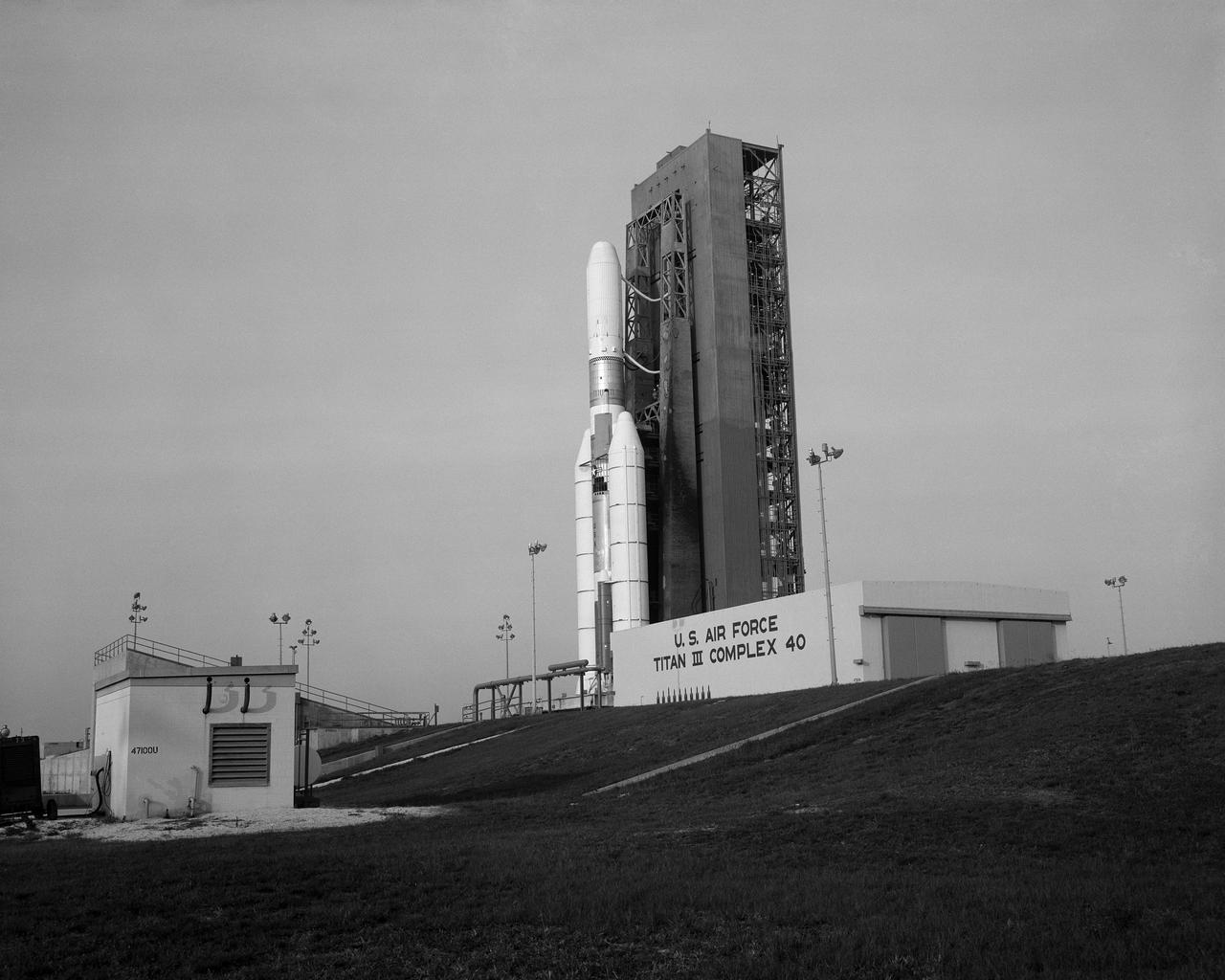

A Titan III-C stands poised on Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for the launch of Application Technology Satellite-F, first in a new generation of NASA communications satellites. (1.3-2)
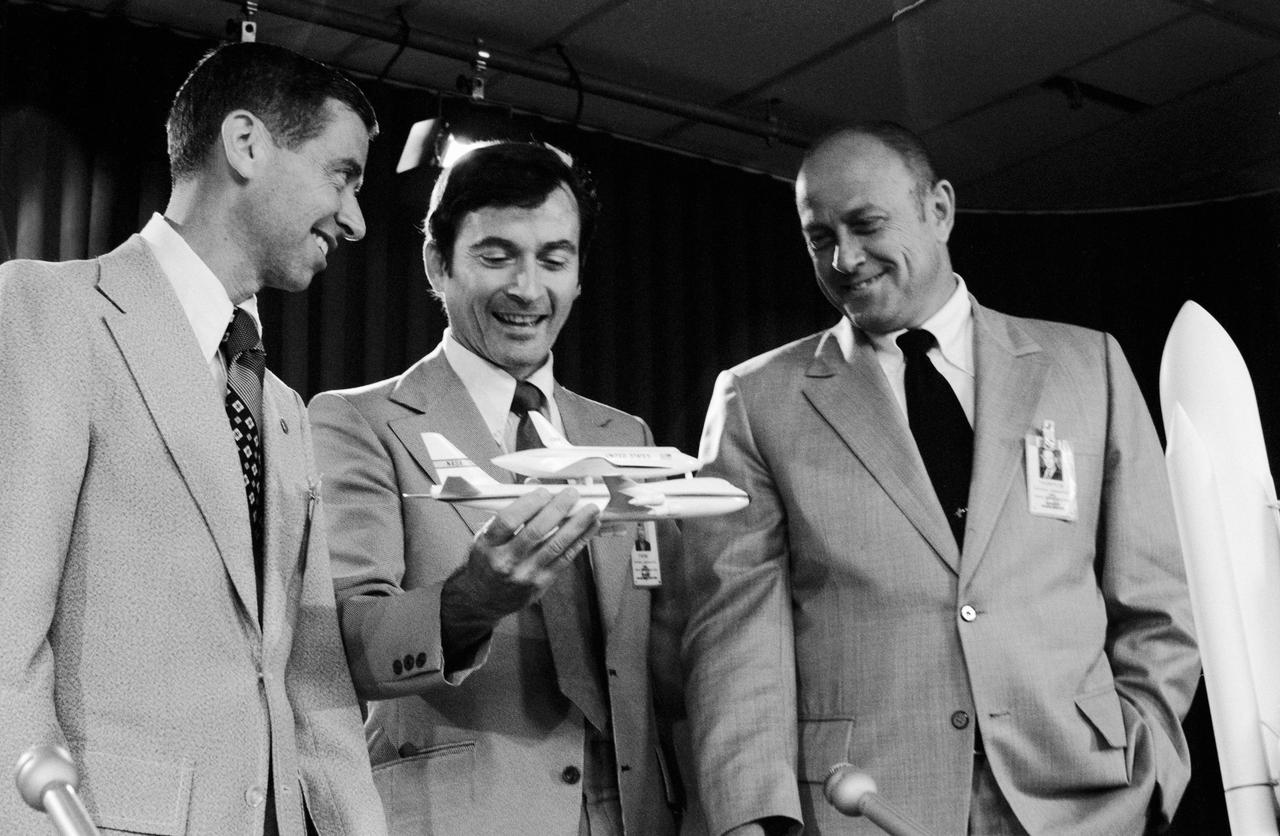

View taken in Building 2, Room 135, during a Shuttle briefing. Shuttle officials Robert Thompson and Aaron Cohen and Astronaut John Young are seen as panel for the Shuttle briefing with various models of the Space Shuttle Program display in front of them. 1. Robert Thompson 2. Aaron Cohen 3. Astronaut John Young JSC, HOUSTON, TX

S74-25259 (June 1974) --- Four crewmen of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are photographed beside a Soyuz spacecraft trainer during ASTP crew training activity at the Cosmonaut Training Center (Star City) near Moscow. They are, left to right, astronaut Donald K. Slayton, docking module pilot of the American ASTP prime crew; cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov, engineer of the Soviet ASTP first (prime) crew; cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, commander of the Soviet ASTP first (prime) crew; and astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, commander of the American ASTP prime crew.

S74-15240 (December 1973) --- Astronaut Donald K. Slayton
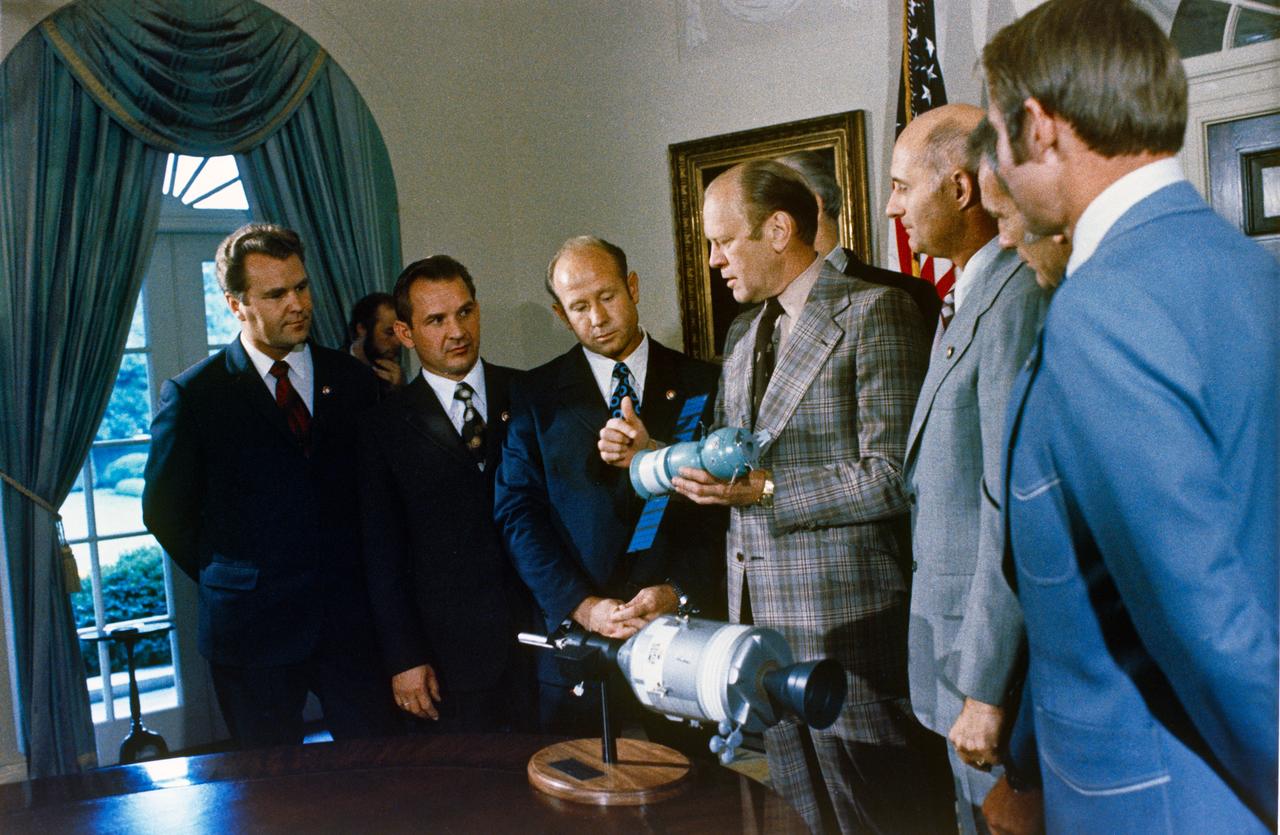

S74-29892 (7 Sept. 1974) --- President Gerald R. Ford removes the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft model from a model set depicting the 1975 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, an Earth orbital docking and rendezvous mission involving crewmen from the U.S. and USSR, who visited Mr. Ford at the White House. The cosmonauts and astronauts are, left to right, Vladimir A. Shatalov, Chief, Cosmonaut Training; Valeriy N. Kubasov, ASTP Soviet engineer; Aleksey A. Leonov, ASTP Soviet crew commander; Thomas P. Stafford, ASTP American crew commander; Donald K. Slayton, American crew?s docking module pilot; and Vance D. Brand, command module pilot for the U.S. team. Dr. George M. Low, Deputy Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, is partially obscured behind Mr. Ford.
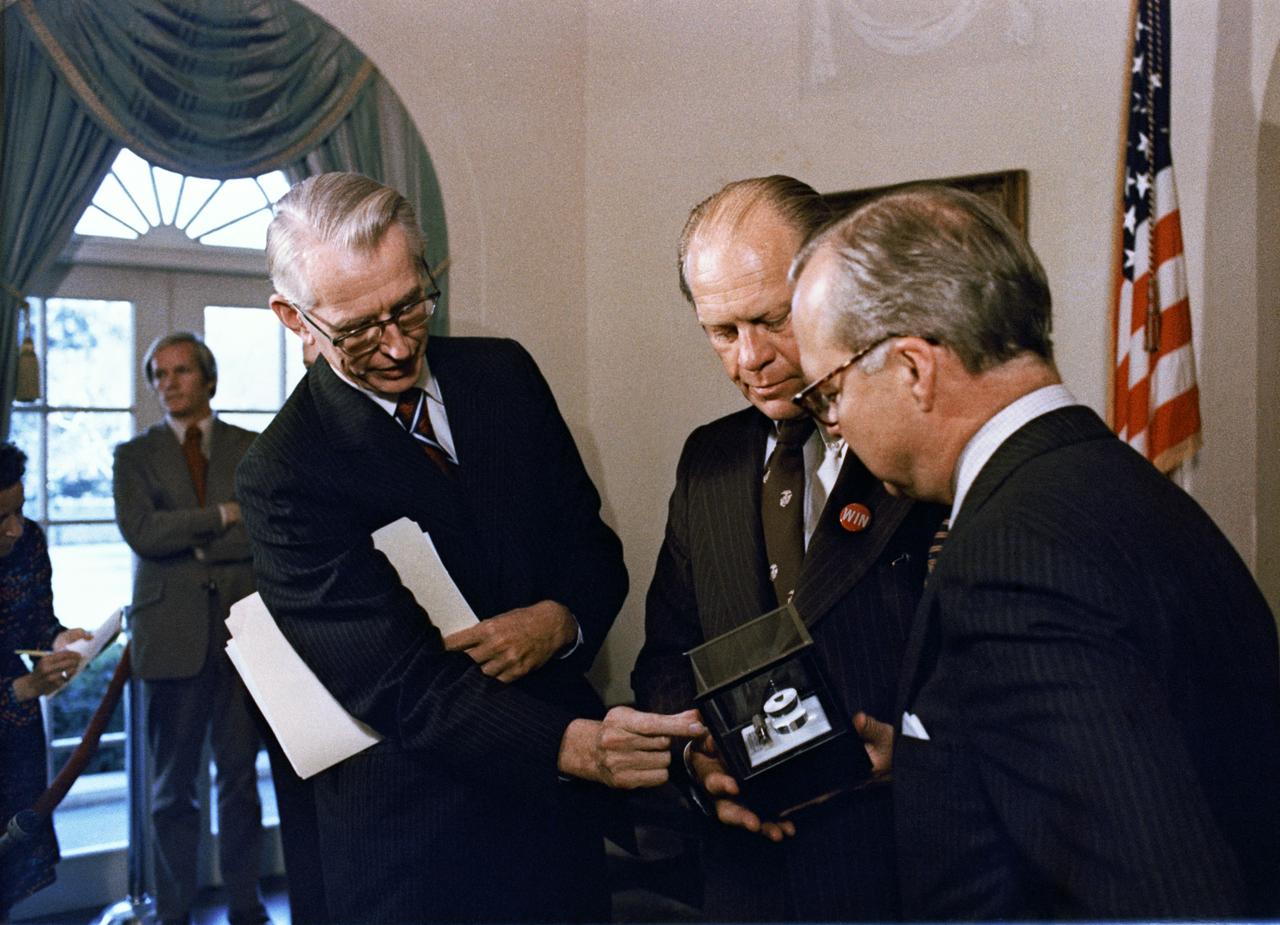

S74-34046 (October 1974) --- Dr. James C. Fletcher, left, NASA Administrator, explains the formation of the indium-antimonide crystal, manufactured in space, to President Gerald R. Ford at the White House. Standing at right is Harold Johnson, Chairman of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The segment of indium-antimonide is cut from a cylindrical single crystal that was partially melted and resolidified aboard the Skylab space station on Jan. 6, 1974, during the third and final manned flight. This segment is approximately one by one centimeters and about three millimeters thick. The sequence of heating and cooling was started and supervised by the members of the third Skylab crew, astronauts Gerald P. Carr, Edward G. Gibson and William R. Pogue. The crystal forming was accomplished in a special multipurpose furnace, known as the Materials Processing Facility (Skylab Technology Experiment M512). Photo credit: NASA
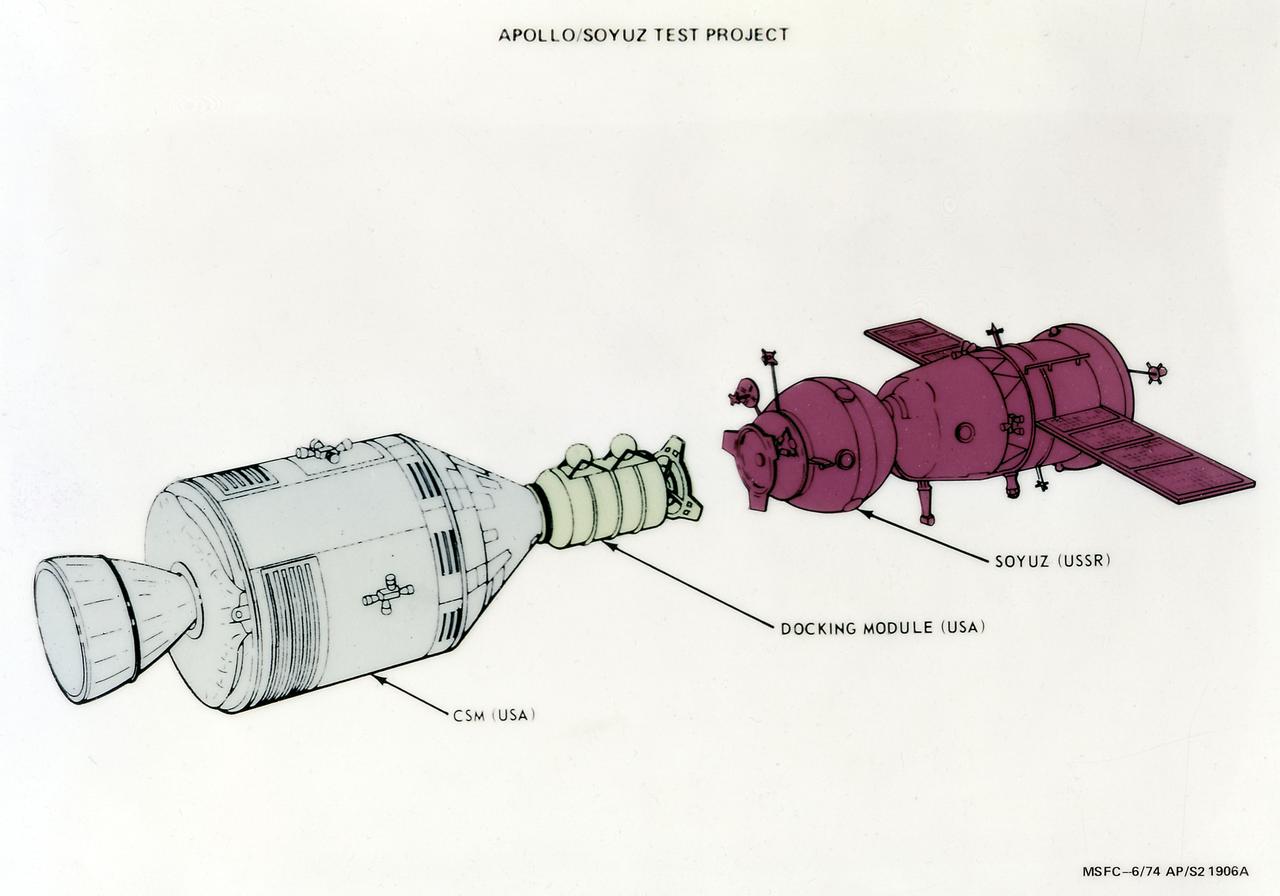
This illustration shows the docking configuration of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP). The ASTP was the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. A joint engineering team from the two countries met to develop a docking system that permitted the two spacecraft to link in space and allowed the two crews to travel from one spacecraft to the other. This system entailed developing a large habitable Docking Module (DM) to be carried on the Apollo spacecraft to facilitate the joining of two dissimilar spacecraft. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission. The ASTP marked the last use of the Saturn Launch Vehicle.
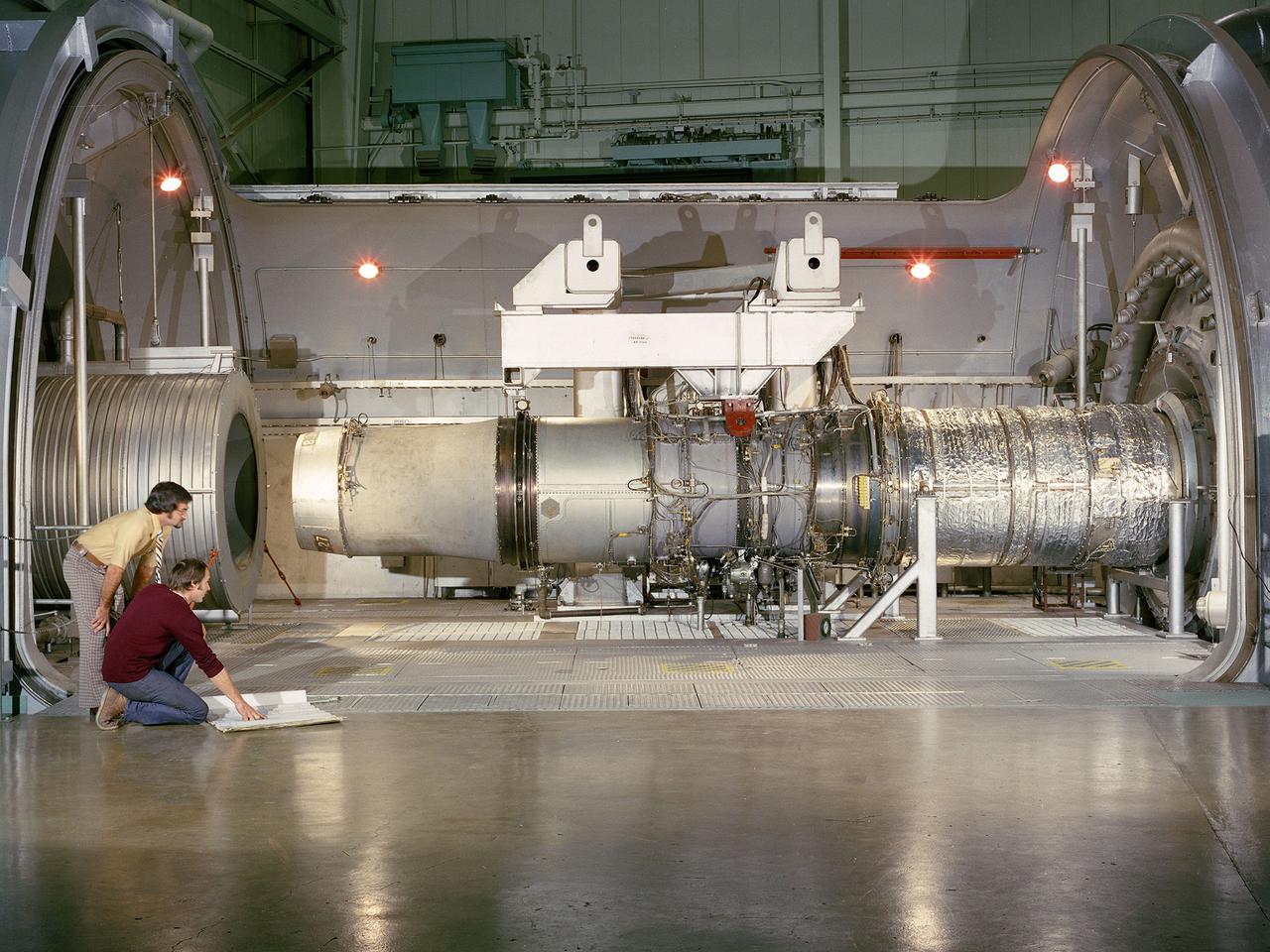
A refanned Pratt and Whitney JT-8D-109 turbofan engine installed in Cell 4 of the Propulsion Systems Laboratory at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. NASA Lewis’ Refan Program sought to demonstrate that noise reduction modifications could be applied to existing aircraft engines with minimal costs and without diminishing the engine’s performance or integrity. At the time, Pratt and Whitney’s JT-8D turbofans were one of the most widely used engines in the commercial airline industry. The engines powered Boeing’s 727 and 737 and McDonnell Douglas’ DC-9 aircraft. Pratt and Whitney worked with the airline manufacturers on a preliminary study that verified feasibility of replacing the JT-8D’s two-stage fan with a larger single-stage fan. The new fan slowed the engine’s exhaust, which significantly reduced the amount of noise it generated. Booster stages were added to maintain the proper level of airflow through the engine. Pratt and Whitney produced six of the modified engines, designated JT-8D-109, and performed the initial testing. One of the JT-8D-109 engines, seen here, was tested in simulated altitude conditions in NASA Lewis’ Propulsion Systems Laboratory. The Refan engine was ground-tested on an actual aircraft before making a series of flight tests on 727 and DC-9 aircraft in early 1976. The Refan Program reduced the JT-8D’s noise by 50 percent while increasing the fuel efficiency. The retro-fit kits were estimated to cost between $1 million and $1.7 million per aircraft.
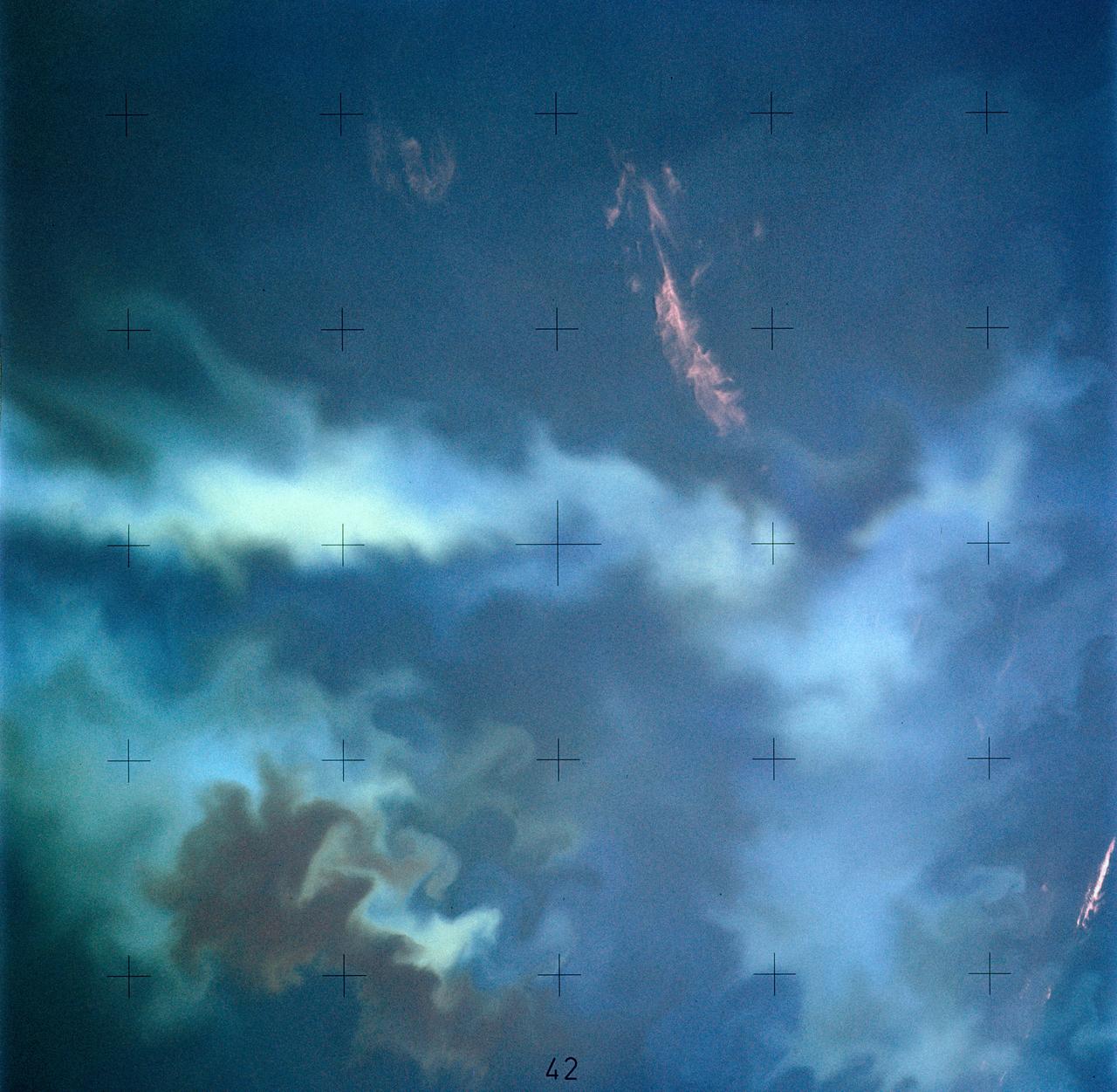

SL4-137-3721 (February 1974) --- Plankton blooms and color variations in the Falkland Current east of the Argentina coast in the South Atlantic Ocean as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This picture was taken by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen using a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera. The Skylab 4 crew made many observations of the Falkland Current and related phenomena. This current flows north and northeastward along the Argentine coast near 40 degree south latitude where it meets the Brazil Current and the two swing eastward. The study of such photographs as this one can add significantly to our knowledge and understanding of the oceans. Photo credit: NASA

Ames Pilot George Cooper and Randy VAn Dyke
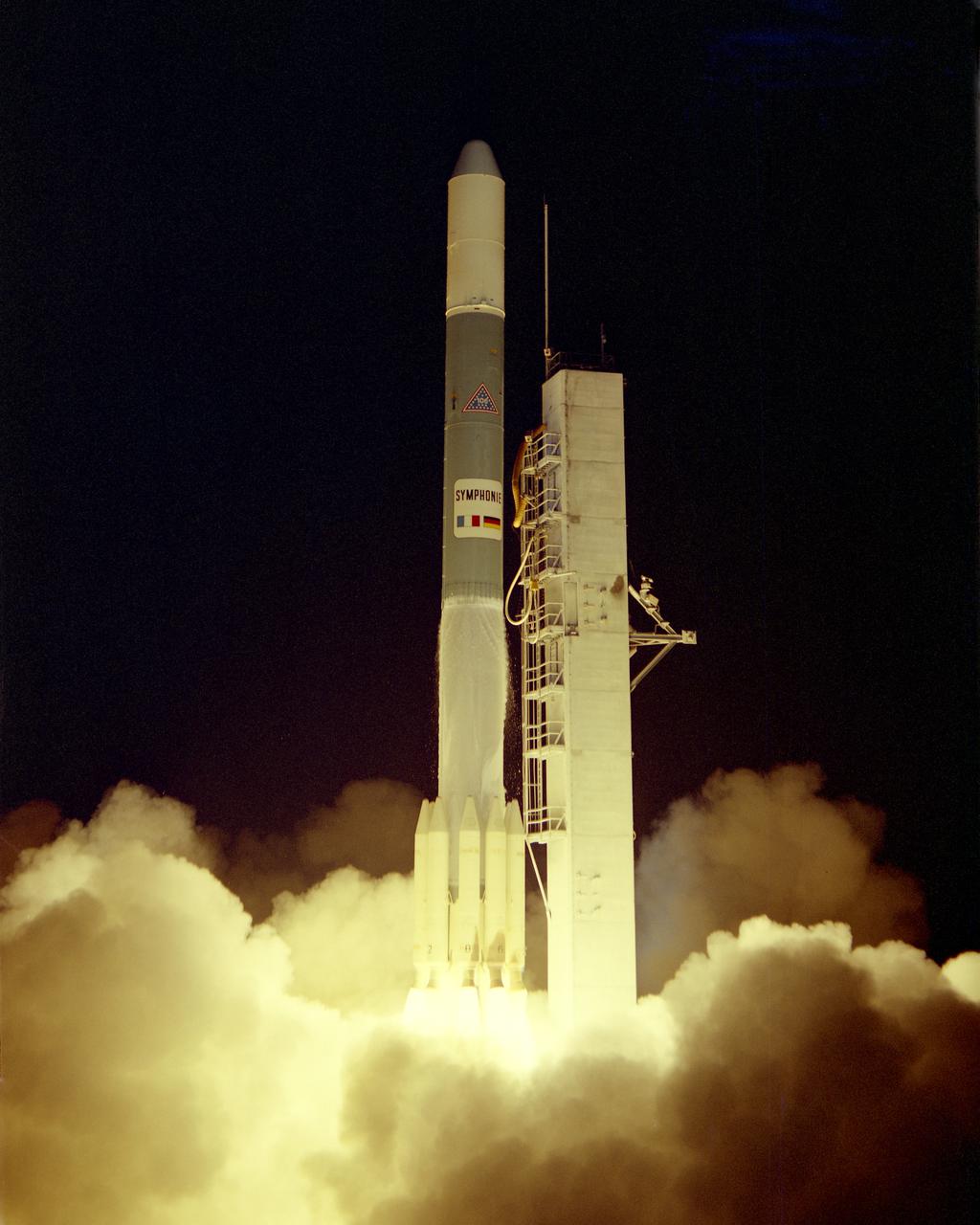

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Launch of Symphonie-A on Complex 17-B at 9:39 p.m. EST. Symphonie-A is a communications satellite for a Franco-German industrial consortium. Photo credit: NASA

S74-17843 (March 1974) --- This is the official emblem of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project chosen by NASA and the Soviet Academy of Sciences. The joint U.S.-USSR space mission is scheduled to be flown in July 1975. Of circular design, the emblem has the words Apollo in English and Soyuz in Russian around a center disc which depicts the two spacecraft docked together in Earth orbit. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project will be carried out by a Soviet Soyuz spacecraft and a U.S. Apollo spacecraft which will rendezvous and dock in orbit. Soyuz and Apollo will remain docked for as long as two days in which period, the three Apollo astronauts will enter Soyuz and the two Soyuz cosmonauts will visit Apollo via a docking module. The Russian word "soyuz" means "union" in English.
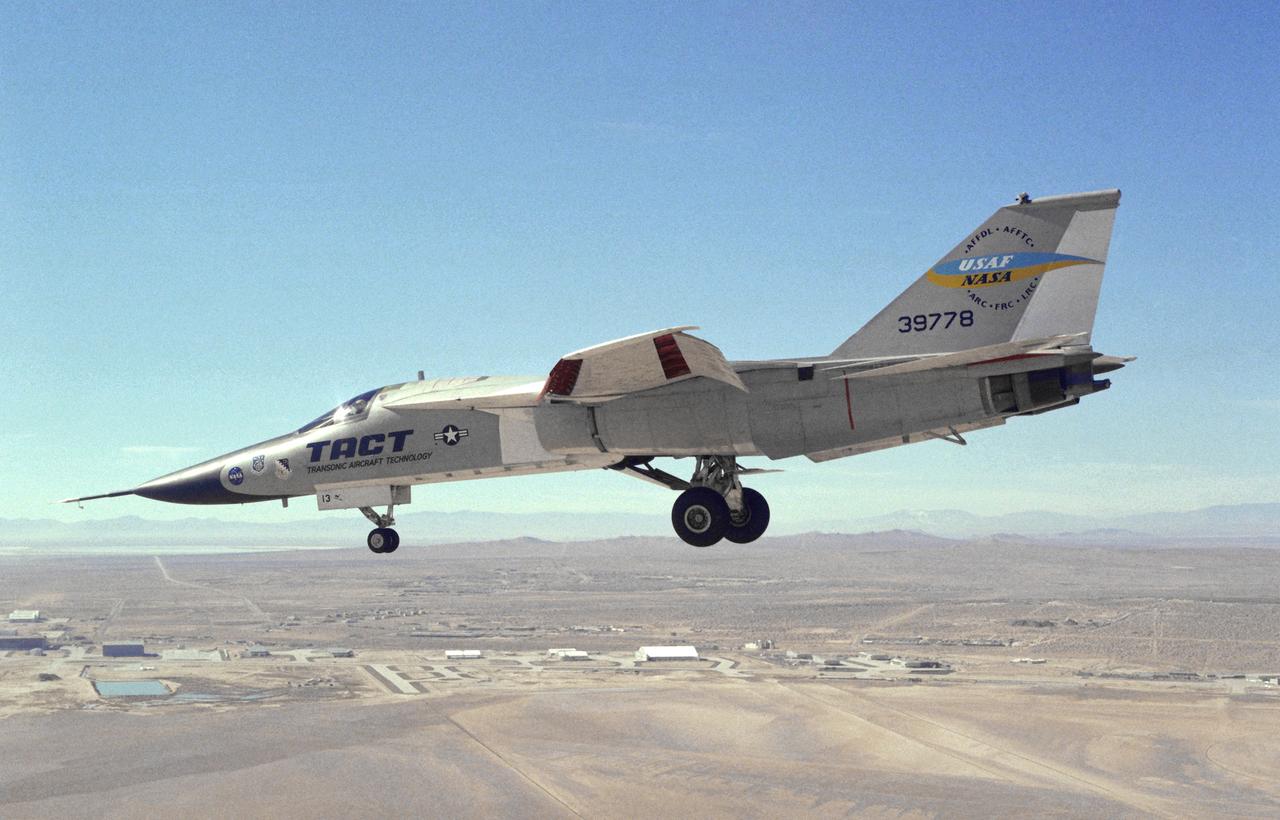

This photograph shows a modified General Dynamics TACT/F-111A Aardvaark with supercritical wings installed. The aircraft, with flaps and landing gear down, is in a decending turn over Rogers Dry Lakebed at Edwards Air Force Base. Starting in 1971 the NASA Flight Research Center and the Air Force undertook a major research and flight testing program, using F-111A (#63-9778), which would span almost 20 years before completion. Intense interest over the results coming from the NASA F-8 supercritical wing program spurred NASA and the Air Force to modify the General Dynamics-Convair F-111A to explore the application of supercritical wing technology to maneuverable military aircraft. This flight program was called Transonic Aircraft Technology (TACT).
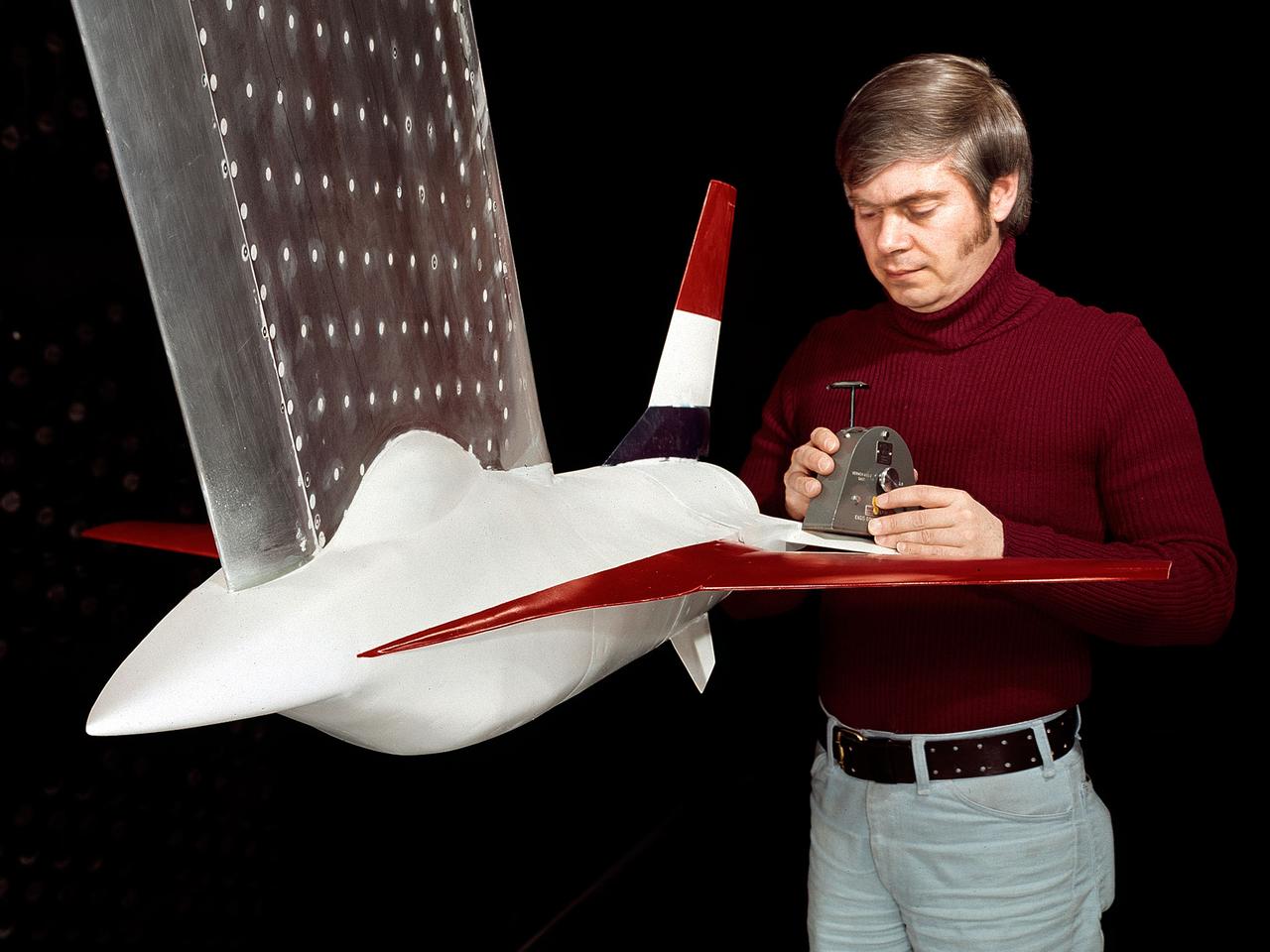

A model of the General Dynamics YF-16 Fighting Falcon in the test section of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The YF-16 was General Dynamics response to the military’s 1972 request for proposals to design a new 20,000-pound fighter jet with exceptional acceleration, turn rate, and range. The aircraft included innovative design elements to help pilots survive turns up to 9Gs, a new frameless bubble canopy, and a Pratt and Whitney 24,000-pound thrust F-100 engine. The YF-16 made its initial flight in February 1974, just six weeks before this photograph, at Edwards Air Force Base. Less than a year later, the Air Force ordered 650 of the aircraft, designated as F-16 Fighting Falcons. The March and April 1974 tests in the 8- by 6-foot tunnel analyzed the aircraft’s fixed-shroud ejector nozzle. The fixed-nozzle area limited drag, but also limited the nozzle’s internal performance. NASA researchers identified and assessed aerodynamic and aerodynamic-propulsion interaction uncertainties associated the prototype concept. YF-16 models were also tested extensively in the 11- by 11-Foot Transonic Wind Tunnel and 9- by 7-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at Ames Research Center and the 12-Foot Pressure Wind Tunnel at Langley Research Center.

C-141 KAO returning home to Ames at sunrise
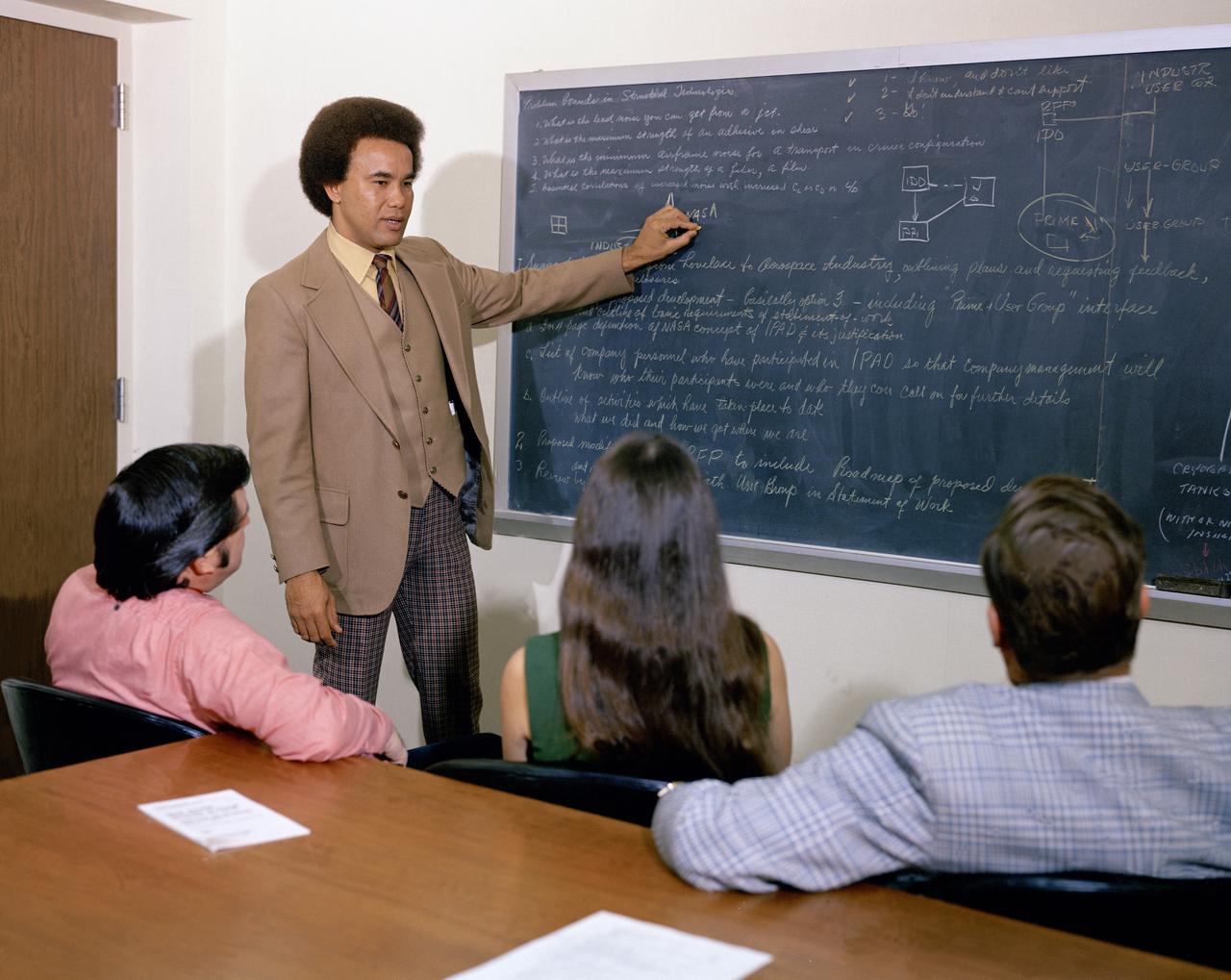

Minority Professionals at NASA Langley Research Center. Samuel J. Scott working in the Office of Director for Structures, Staff Assistant is at the board.

Space Shuttle Tile Thermal Protection System testing in Ames Arc Jet facilities
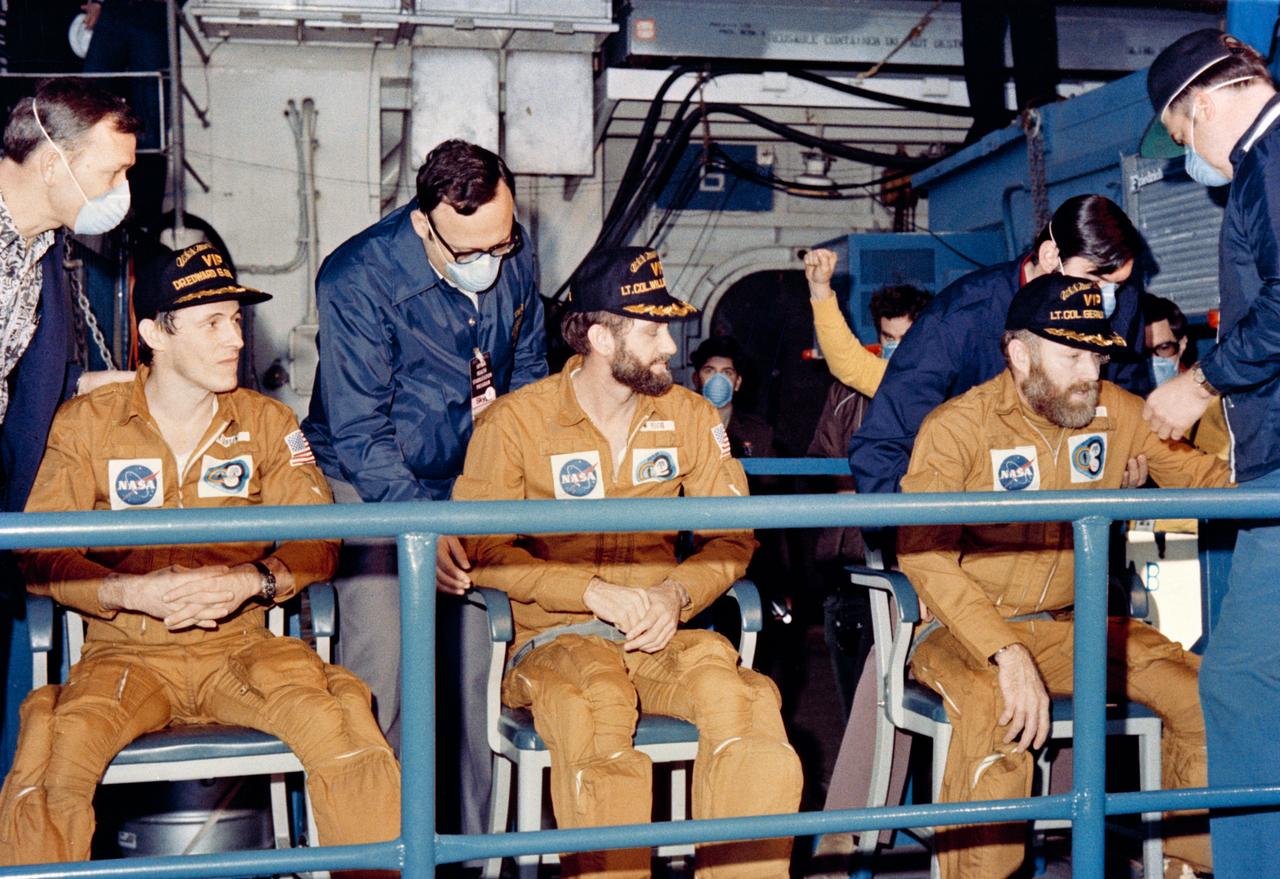

S74-17744 (8 Feb. 1974) --- The crewmen of the third and final manned Skylab mission relax on the USS New Orleans, prime recovery ship for their mission, about an hour after their Command Module splashed down at 10:17 a.m. (CDT), Feb. 8, 1974. The splashdown, which occurred 176 statute miles from San Diego, ended 84 record-setting days of flight activity aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

Space Shuttle Tile Thermal Protection System testing in Ames Arc Jet facilities
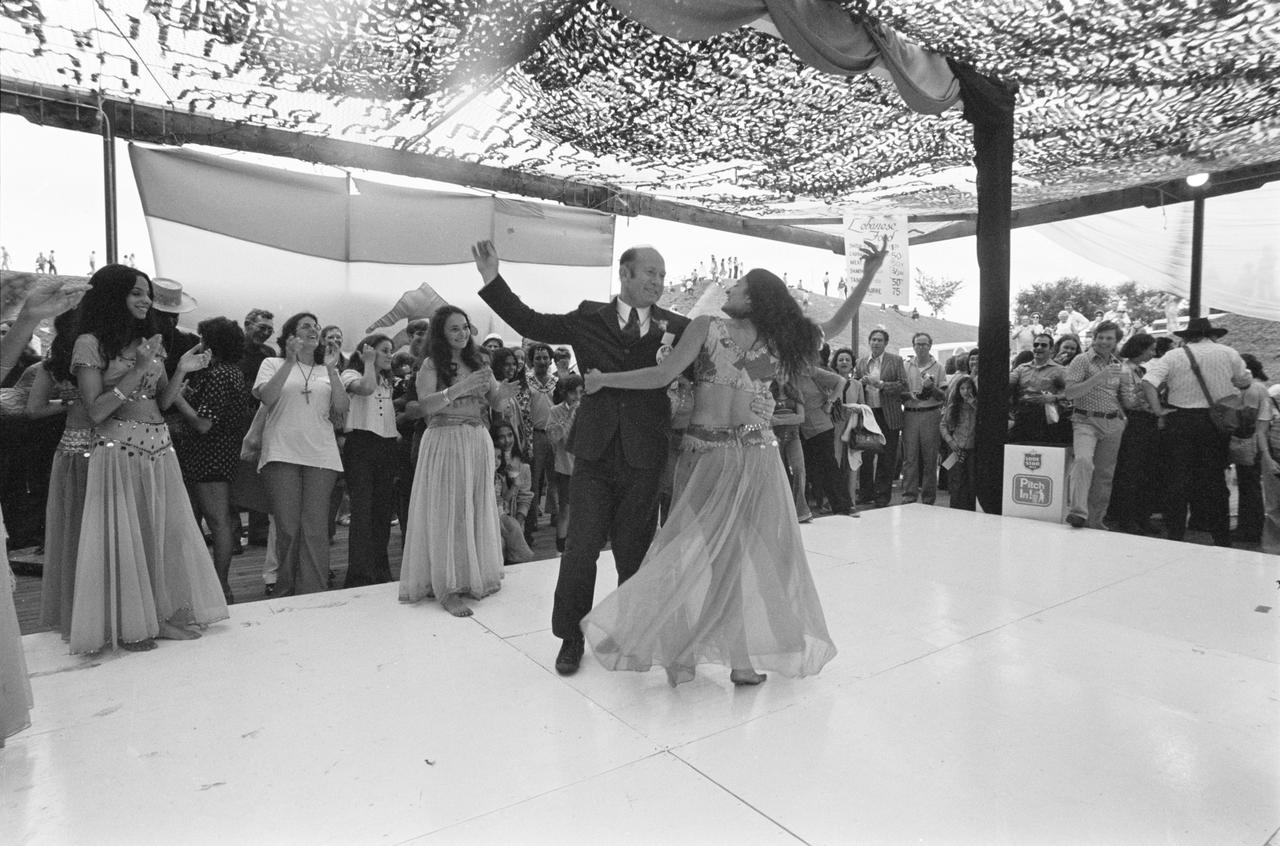

S74-28666 (14 Sept. 1974) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, in one of the lighter moments of activity involving Soviet cosmonauts and American astronauts, joins a belly dancer on stage as several visitors to weekend activity at the site of San Antonio?s HemisFair look on. Leonov is commander of the Soviet Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) crew. A group of cosmonauts is in this country training with American astronauts for the joint U.S.-USSR ASTP rendezvous and docking mission scheduled for the summer of 1975. The Lebanese dancing was just one feature among many during the Texas Folklife Festival, in which members of 26 ethnic groups participated.
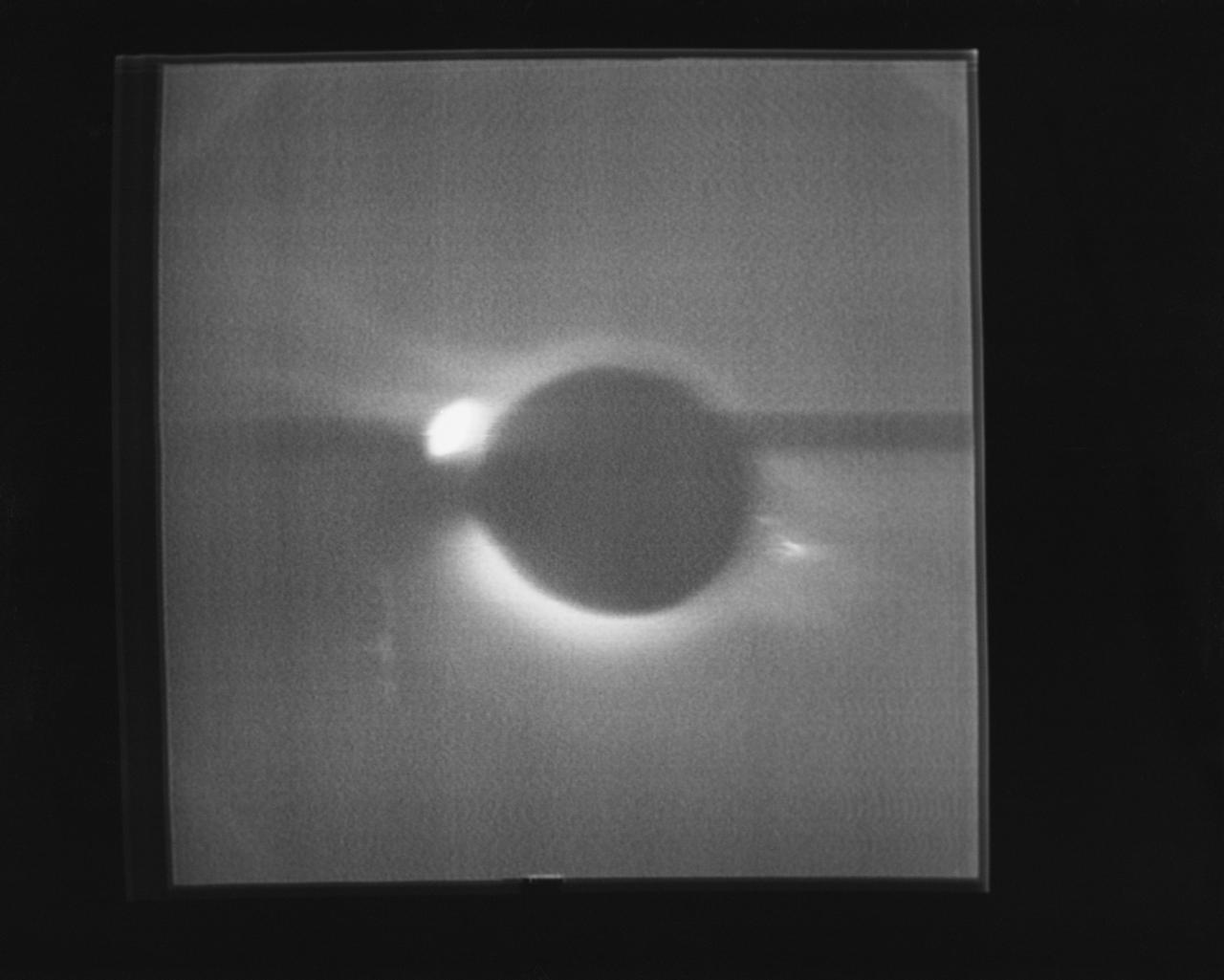

S74-15697 (17 Jan. 1974) --- The solar corona and a solar prominence as seen through the White Light Coronograph, Skylab Experiment S052, on Jan. 17, 1974. This view was reproduced from a television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The bright spot is a burn in the vidicon. The solar corona is the halo around the sun which is normally visible only at the time of solar eclipse by the moon. The Skylab coronography uses an externally-mounted disk system which occults the brilliant solar surface while allowing the fainter radiation of the corona to enter an annulus and be photographed. A mirror system allows either TV viewing of the corona or photographic recording of the image. Photo credit: NASA
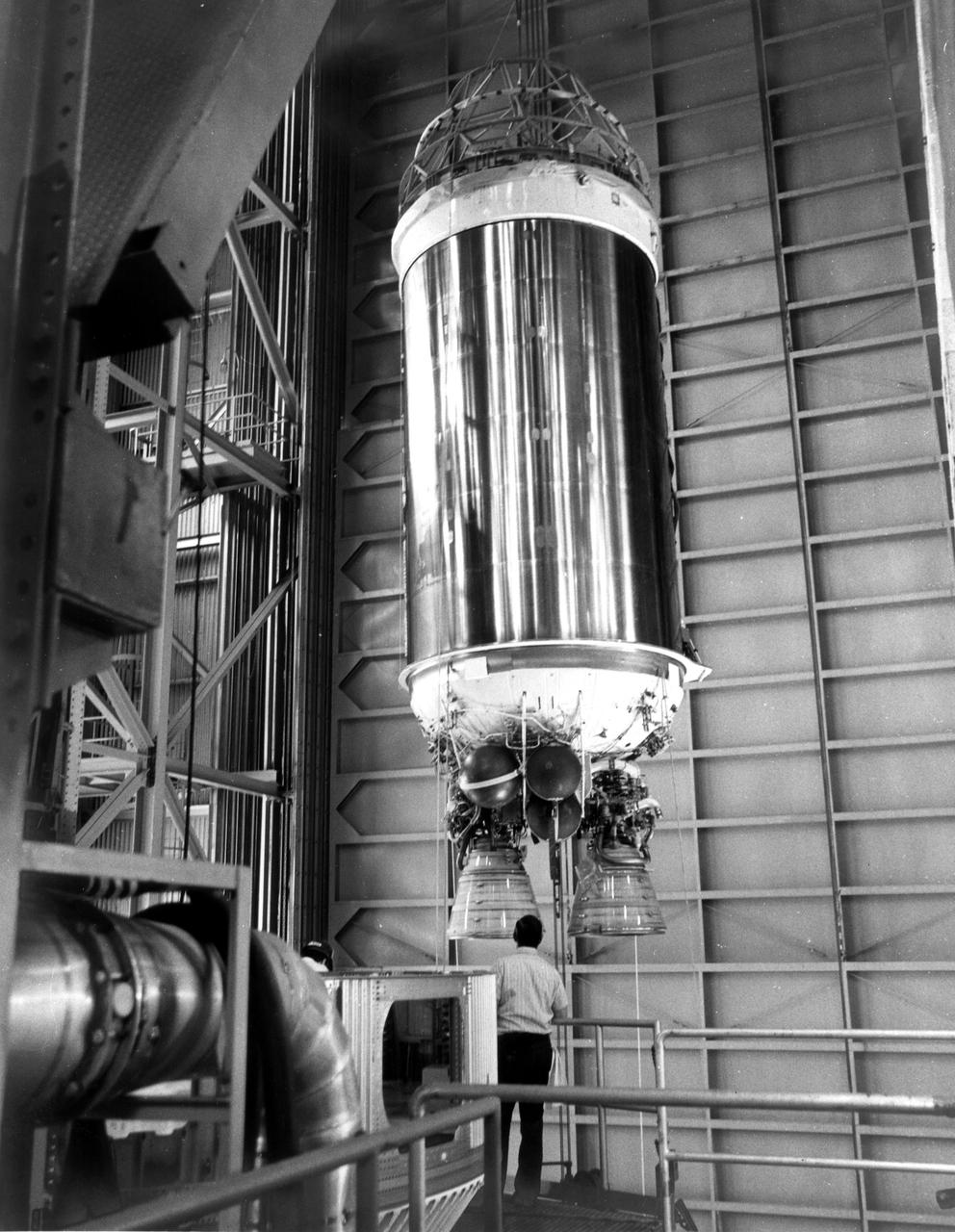

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Centaur high-energy third stage for Titan_Centaur 3 is mated with its Titan rocket in the Vehicle Integration Building in the Titan III complex at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Titan_Centaur 3 and Titan_Centaur 4 will launch twin Viking spacecraft to Mars in the late summer of 1975. Launch will be by KSC's Unmanned Launch Operations Directorate from Complex 41.
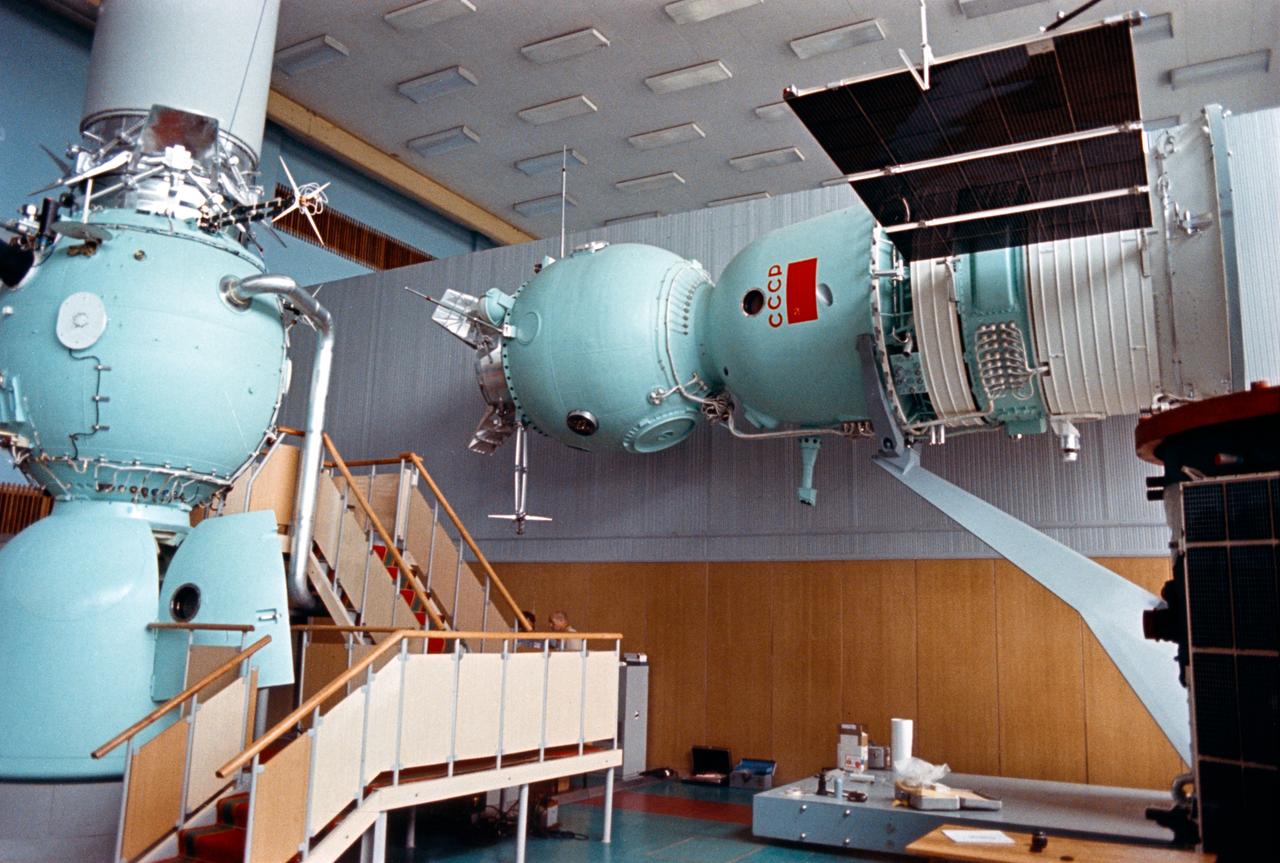
S74-24675 (June 1974) --- Two mock-ups of the USSR Soyuz spacecraft which are on display at the Cosmonaut Training Center (Star City) near Moscow. The Soyuz spacecraft mounted vertically on the left is a training mock-up. The Soyuz mounted horizontally on the right was exhibited at the Paris air show in May-June 1973 in a docked configuration with an Apollo spacecraft. The spherical-shaped section of the Soyuz is called the orbital module. The middle section with the lettering ?CCCP? (USSR) on it called the descent vehicle. Two solar panels extend out from the instrument-assembly module. The joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for the summer of 1975. A docking module mock-up is atop the Soyuz training mock-up on the left.

CV-990 (NASA 711) on Ames ramp at sunrise
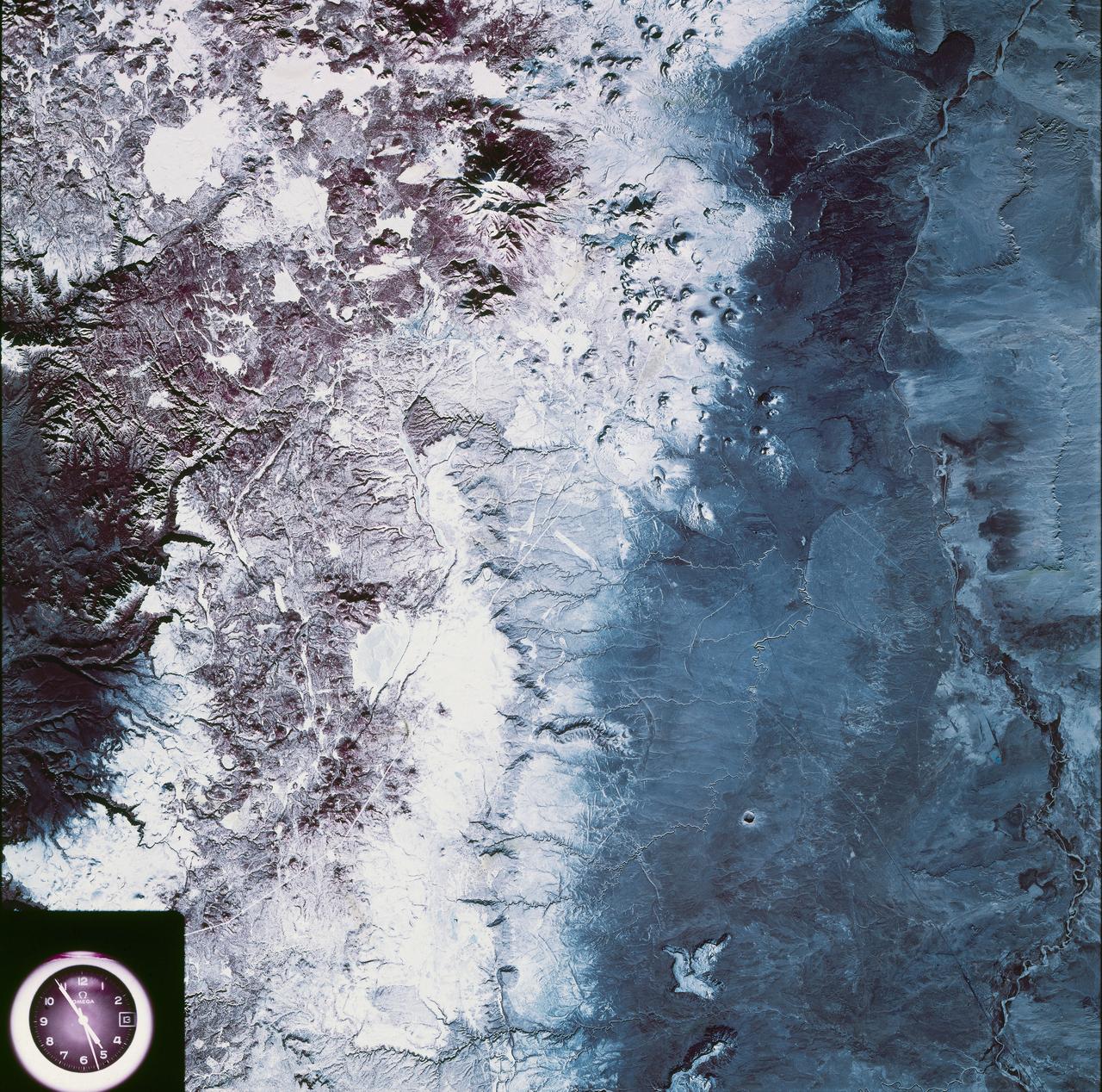

SL4-93-067 (16 Nov. 1973-8 Feb. 1974) --- A spectacular winter view of the Flagstaff, Arizona area is seen in this Skylab 4 Earth Resources Experiments package S190-B (five-inch earth terrain camera) infrared photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Included in the scene are the San Francisco Mountains, Oak Creek Canyon, Painted Desert and Meteor Crater. The infrared picture depicts in red living vegetation, in white the snow, and in bright blue the water. Major features identified in this photograph are Humphrey's peak, top center, Flagstaff at foot of the peak, Sunset Crater volcanic field with numerous vents and craters right of Flagstaff and Meteor Crater (right center). Within the mountainous areas several clear areas generally rectangular are visible and represent the areas where lumbering has removed the forest. The thin white line extending from left corner to Sunset Crater fields is the power transmission line cleared area. Roads are subdued and are not easily visible. Photo credit: NASA

Artist: Rick Guidice Pioneer 10 Crosses the Asteriod Belt: If spacecraft are to visit the outer Solar System, they must cross the asteroid belt between Mars and Jpiter. The Pioneer mission was faced with the question of just how dangerous this astroid belt would be to a spacecraft passing throught it. Note: used in NASA SP-349 'Pioneer Odyssey - Encounter with a Giant' fig. 1-24 and SP-446 ' Pioneer - First to Jupiter, Saturn, and Beyond' fig 1-24
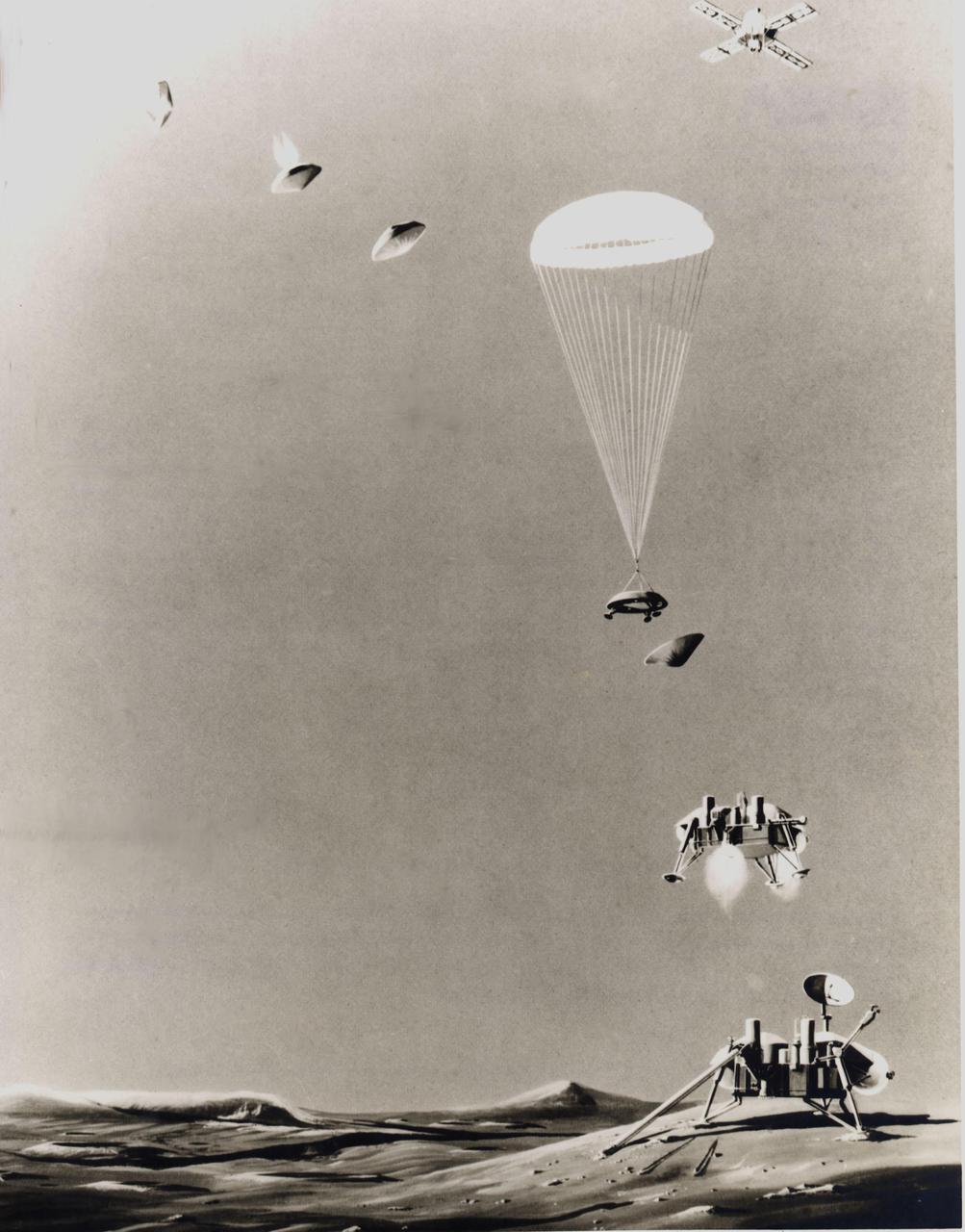

This is an artist's conception of the sequence of events that will take place just prior to landing a life-detection laboratory on the surface of Mars on July 4, 1976. Above right, the Viking spacecraft, composed of an orbiter and a lander, has been in orbit around the Red Planet since June 19, 1976, taking pictures of the planned landing site to ascertain its safety before releasing the lander (top, left) for its threeto five-hour descent. Protected by aeroshells, the heat-sterilized lander hurtles into the thin Martian atmosphere at a speed of about 10,000 mph, to be slowed first by aerodynamic drag until the shell is discarded, then by parachute (center) and finally by retrorockets to assure a gentle landing. Instruments will study the structure and composition of the Martian atmosphere as the lander drifts down. Viking 2 is scheduled to arrive at Mars on Aug. 7 and touch down on the surface on Sept. 4.
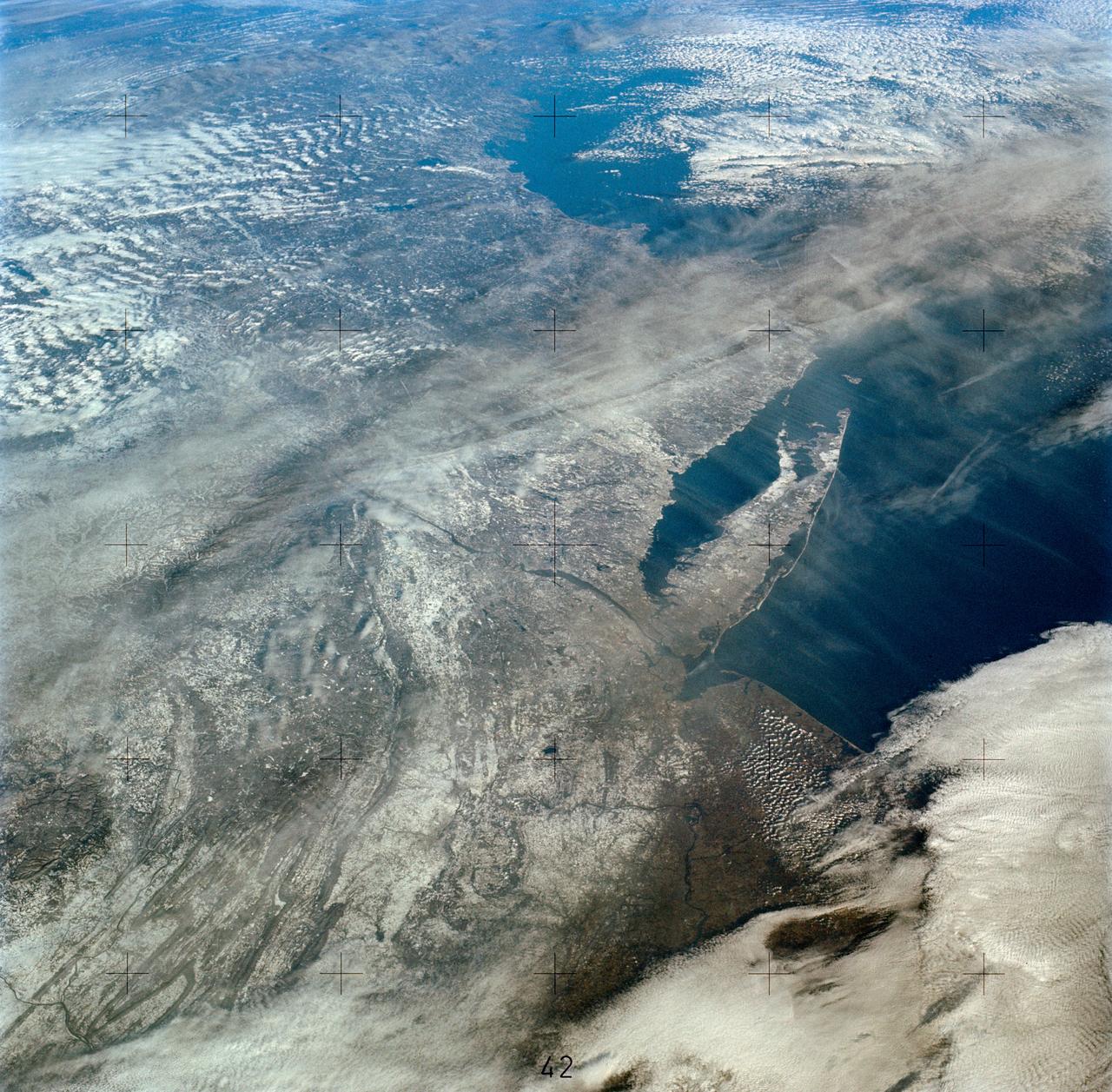

SL4-138-3894 (5 Jan. 1974) --- An oblique view of a portion of the northeastern part of the United States, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen. The camera used was a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad, and with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome film. This is an excellent example of the regional view which is available from space. The entire area of New Jersey, eastern Pennsylvania, southeastern New York, and southern New England can be examined in one view. Long Island, New York City and the lower Hudson River Valley are readily seen in their regional framework. The Boston area, although blurred by clouds, is also included. The spackling of the snow enhances the contrast, especially of terrain and cultural features. Different levels of clouds can be studies, especially the crossing layers of cirrus in the center of the photograph, with the lower cirrus trending north-south and the upper (probably associated with a jet stream) trending east-west. Photo credit: NASA
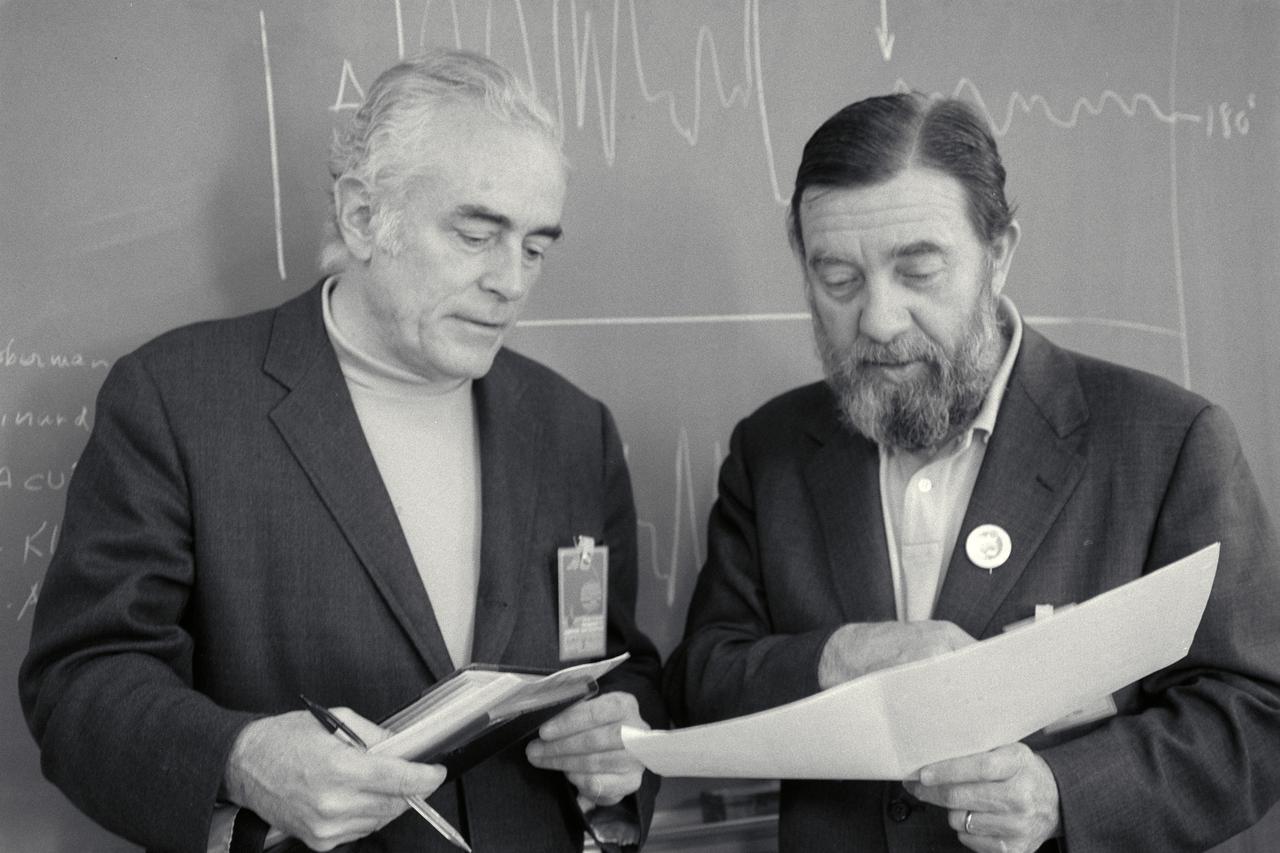

Dr. John A. Simpson and Dr James Van Allen discuss Pioneer 11 Mission to Juiter and Saturn during morning briefing.
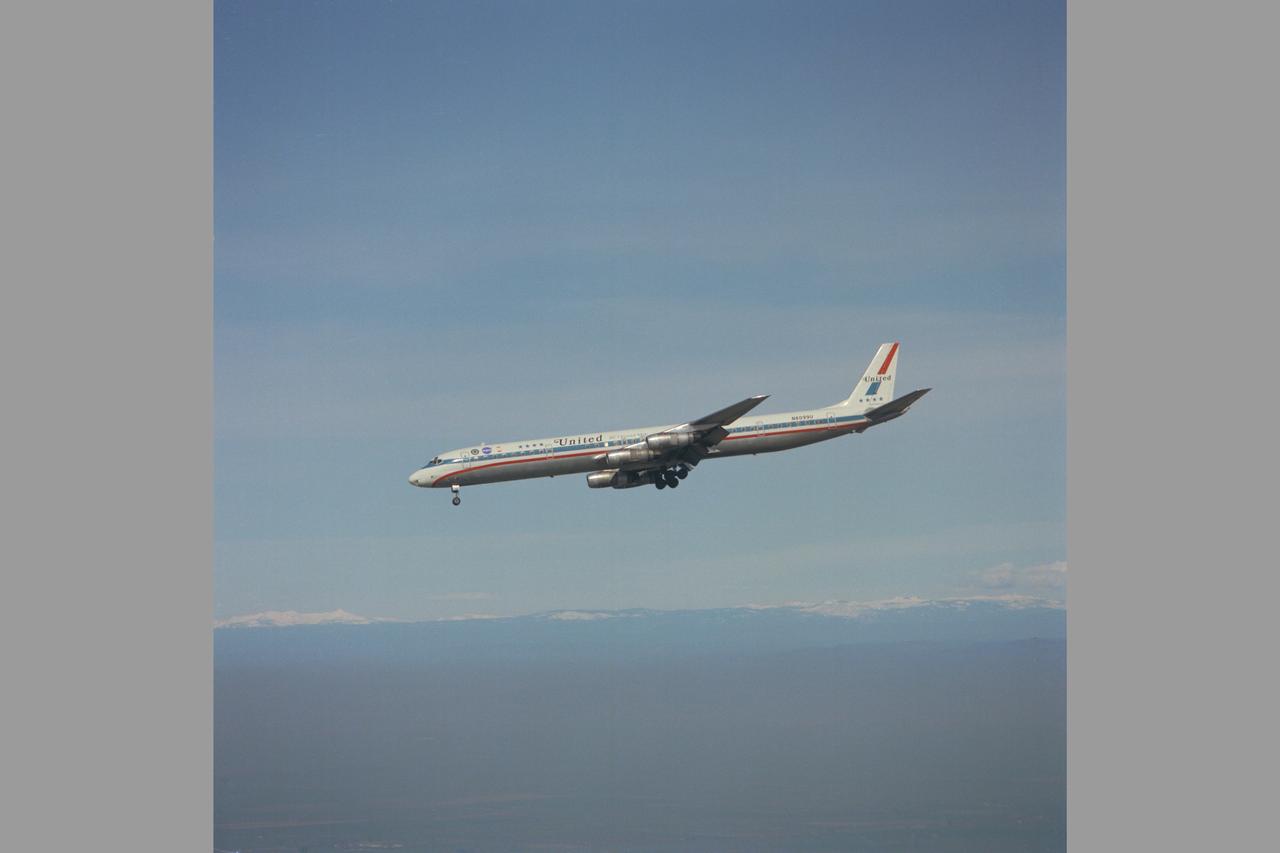

United Airlines DC-8 (N8099U) Two Segment Evaluation. In-Flight Thrust Reversing, Steep Approach Research. The thrust reversing concept was applied to the DC-8 Commercial transport to achieve the rapid descent capability required for FAA certificaiton. Note: Used in publication in Flight Research at Ames; 57 Years of Development and Validation of Aeronautical Technology NASA SP-1998-3300 fig 96
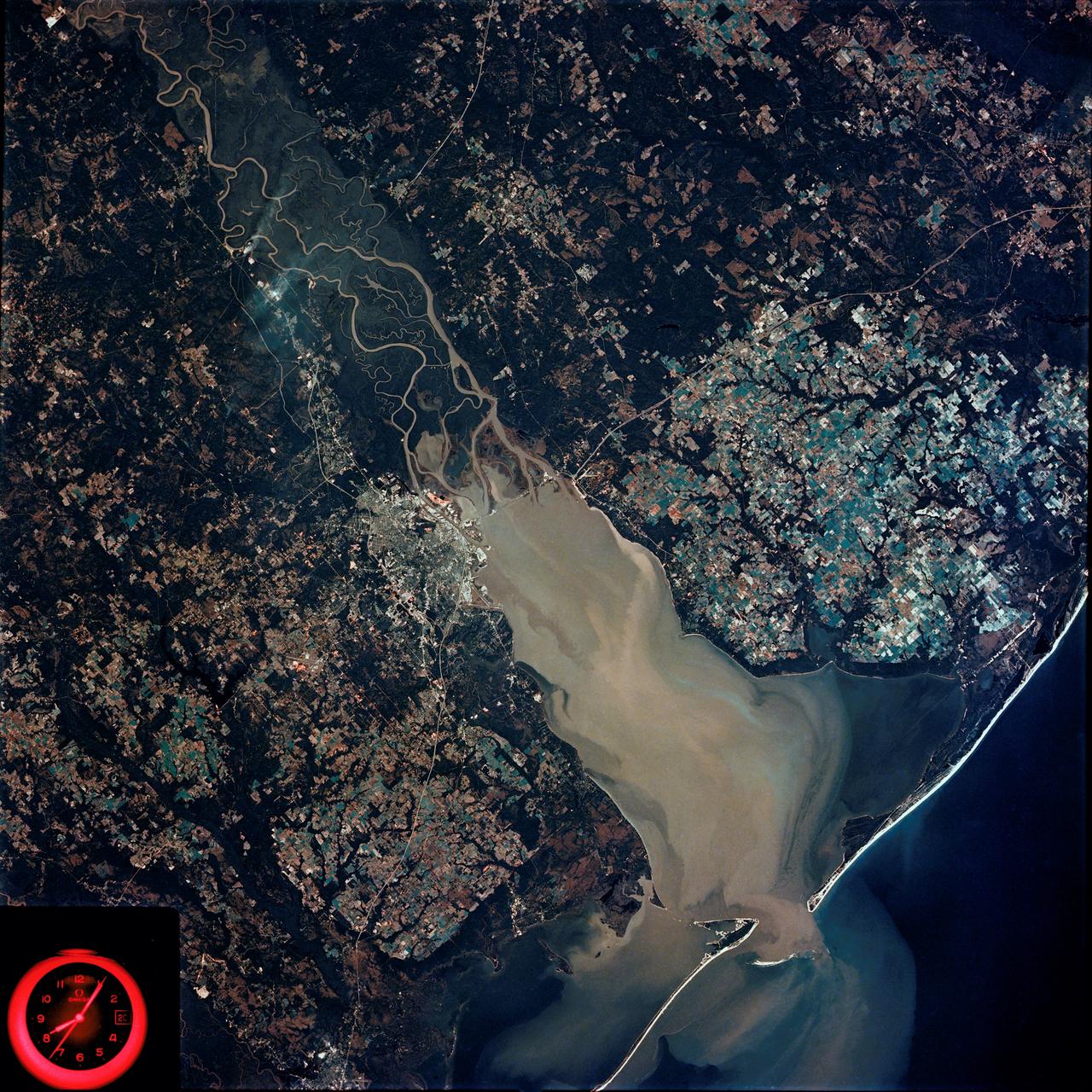

SL4-92-300 (February 1974) --- A near vertical view of the Mobile Bay, Alabama area is seen in this Skylab 4 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. North of Mobile the Tombigbee and Alabama Rivers join to form the Mobile River. Detailed configuration of the individual stream channels and boundaries can be defined as the Mobile River flows into Mobile Bay, and thence into the Gulf of Mexico. The Mobile River Valley with its numerous stream channels is a distinct light shade in contrast to the dark green shade of the adjacent areas. The red coloration of Mobile Bay reflects the sediment load carried into the Bay by the rivers. Variations in red color indicate sediment load and the current paths within Mobile Bay. The waterly movement of the along shore currents at the mouth of Mobile Bay is shown by the contrasting light blue of the sediment-laden current and the blue of the Gulf predominately. Agricultural areas east and west of Mobile Bay are characterized by a rectangular pattern in green to white shades. Color variations may reflect the type and growth cycle of crops. Agricultural areas (light gray-greens) are also clearly visible in other parts of the photograph. Interstate 10 extends from near Pascagoula, Mississippi eastward through Mobile to the outskirts of Pensacola, Florida. Analysis of the EREP photographic data will be undertaken by the U.S. Corps of Engineers to determine bay dynamic processes. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior's Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota. 57198 Photo credit: NASA
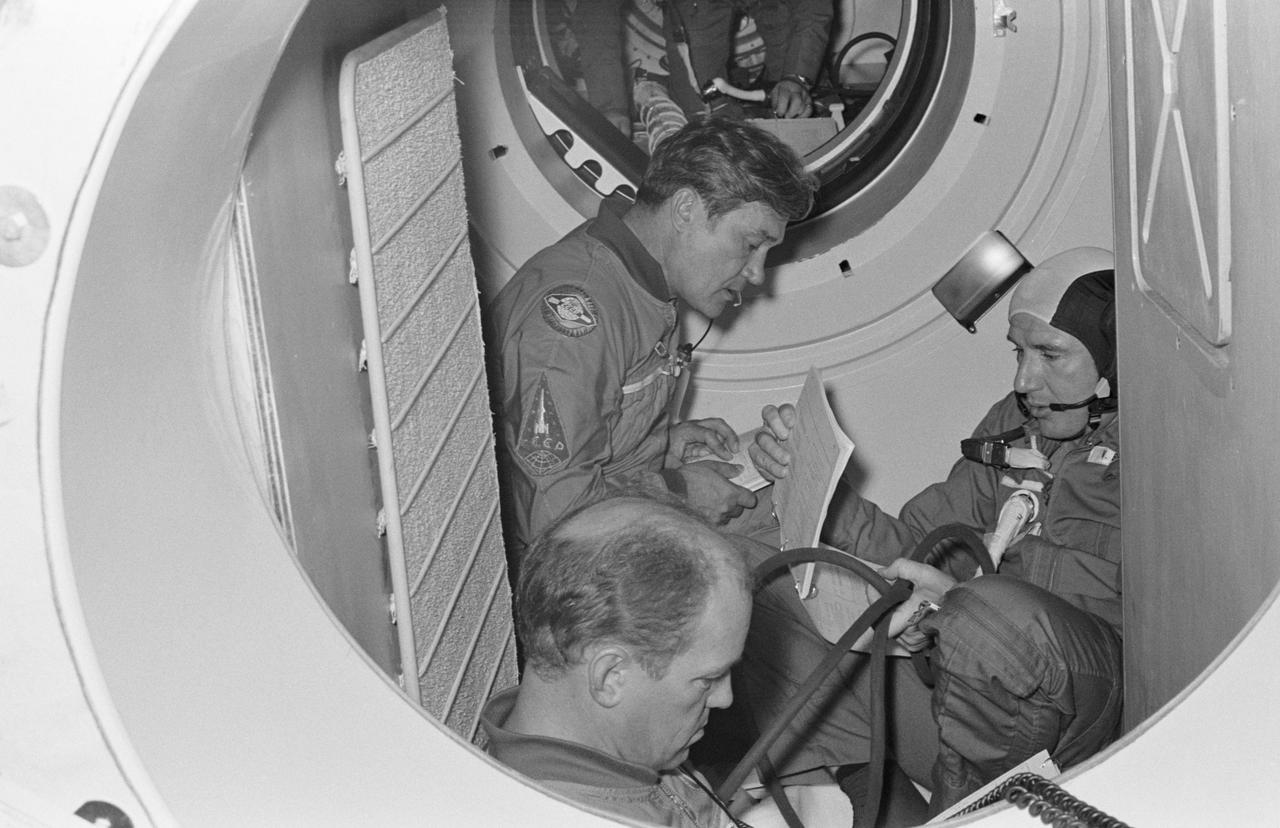

S74-28649 (16 Sept. 1974) --- Three crewmen of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project are seated in a Soviet Soyuz spacecraft orbital module mock-up in Building 35 during ASTP simulation training at the Johnson Space Center. They are cosmonaut Anatoliy V. Filipchenko (left background), commander of the Soviet ASTP second (backup) crew; cosmonaut Nikolay N. Rukavishnikov (left foreground), engineer on the crew; and astronaut Vance D. Brand (right), command module pilot of the American ASTP prime crew. The hatch in the background leads to the Docking Module. During the exercise the American ASTP crew and the Soviet ASTP crew simulated docking the Apollo and Soyuz in Earth orbit and transferring to each other?s spacecraft. Here, Brand is visiting the Soyuz spacecraft. The crewmen are training in both the U.S. and the USSR for the joint mission scheduled for the summer of 1975.

Dr. James Pollack (Ames) and Dr Tom Gehrels during press conference for Pioneer 11 Jupiter encounter
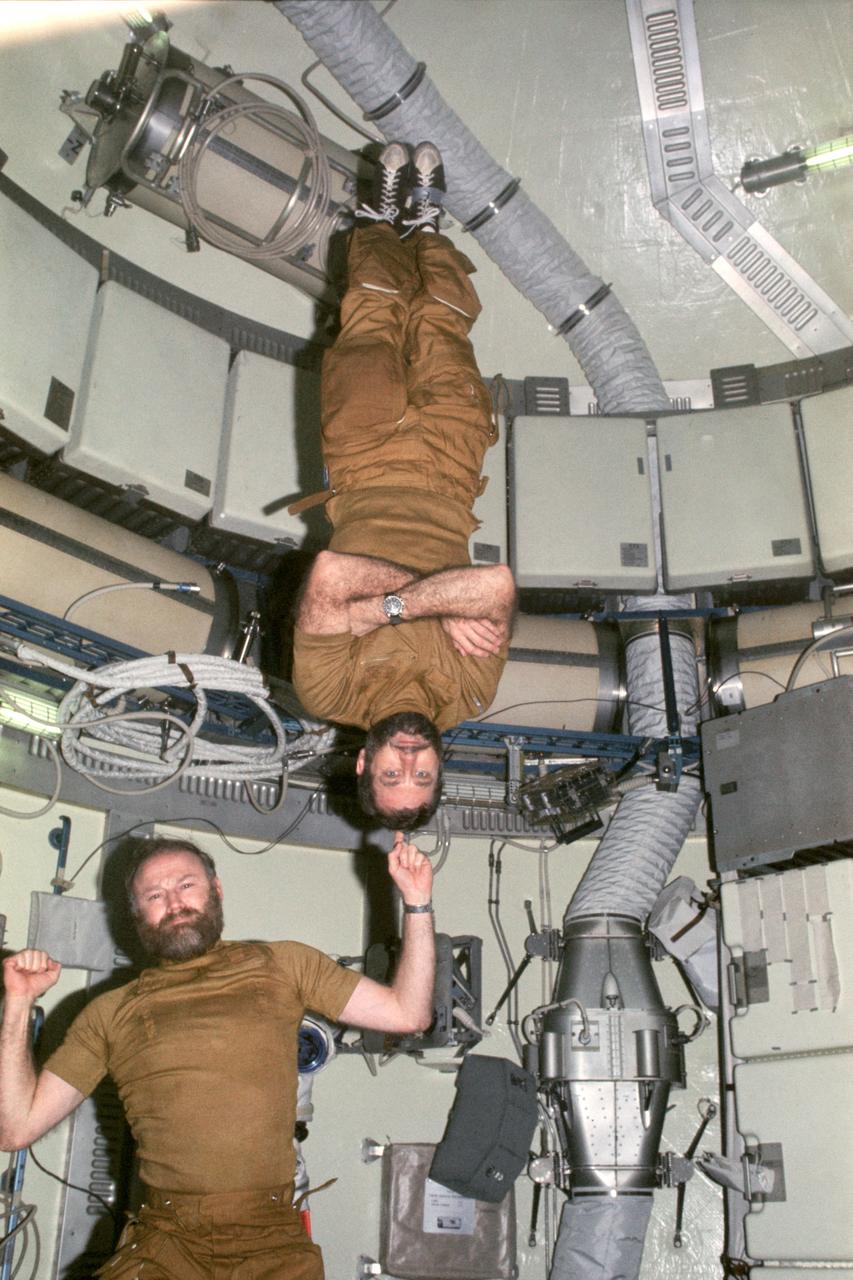

SL4-150-5080 (16 Nov. 1973-8 Feb. 1974) --- Two of the three Skylab 4 (third manning) astronauts exhibit the "magic" that can be accomplished in the weightlessness of space. Astronaut Gerald D. Carr, mission commander, uses his index finger to suspend astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot, in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The two "wizards" completed almost three months aboard the Earth-orbiting Skylab space station, plenty of time to grow these full beards. The photograph was taken with a 35mm camera by astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot. Photo credit: NASA

Portrait: Harold P. 'Chuck' Klein

CV-990 Galileo II arrival at Ames after first expedition

An Air Force Titan III-C lifted off from Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 9:00 A.M. EDT today to launch Application Technology Satellite 6, first in a new generation of NASA Communications satellites. (1.3-13)(Test 7670)
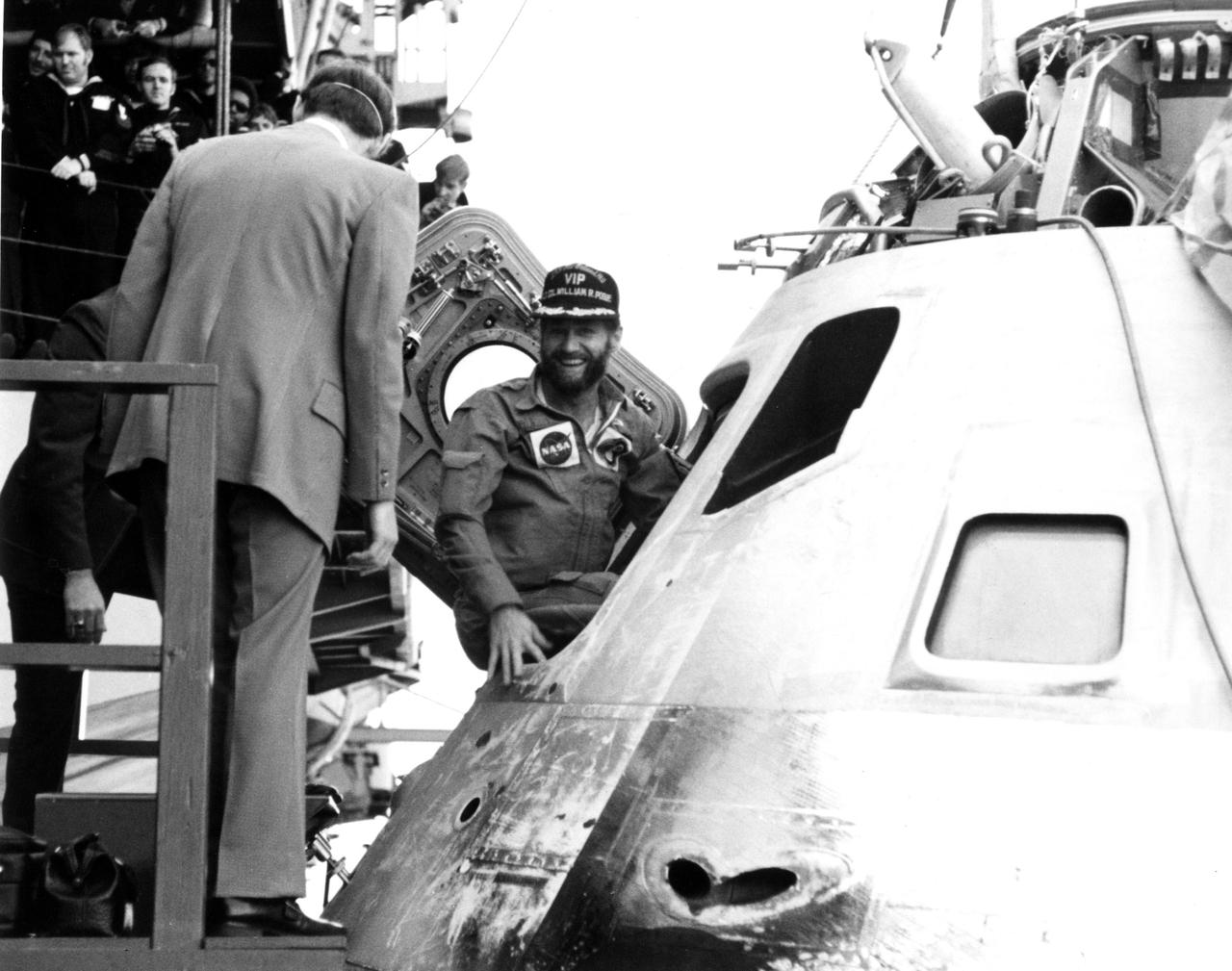

SKYLAB 4 PACIFIC RECOVERY AREA -- A smiling William R. Pogue pauses in hatchway of Skylab 4 command module during recovery activities today aboard the USS New Orleans at the completion of man's longest space journey to date. Pogue splashed down with astronauts Gerald P. Carr and Dr. Edward G. Gibson at 11:17 a.m. EDT Feb. 8, 1974, 84 days after the trio was launched by a Saturn IB rocket from Kennedy Space Center. Circling the globe 1, 214 times aboard the sophisticated Skklab space station during the nearly three-month flight, the astronauts demonstrated man's ability to live and work in space for extended periods.
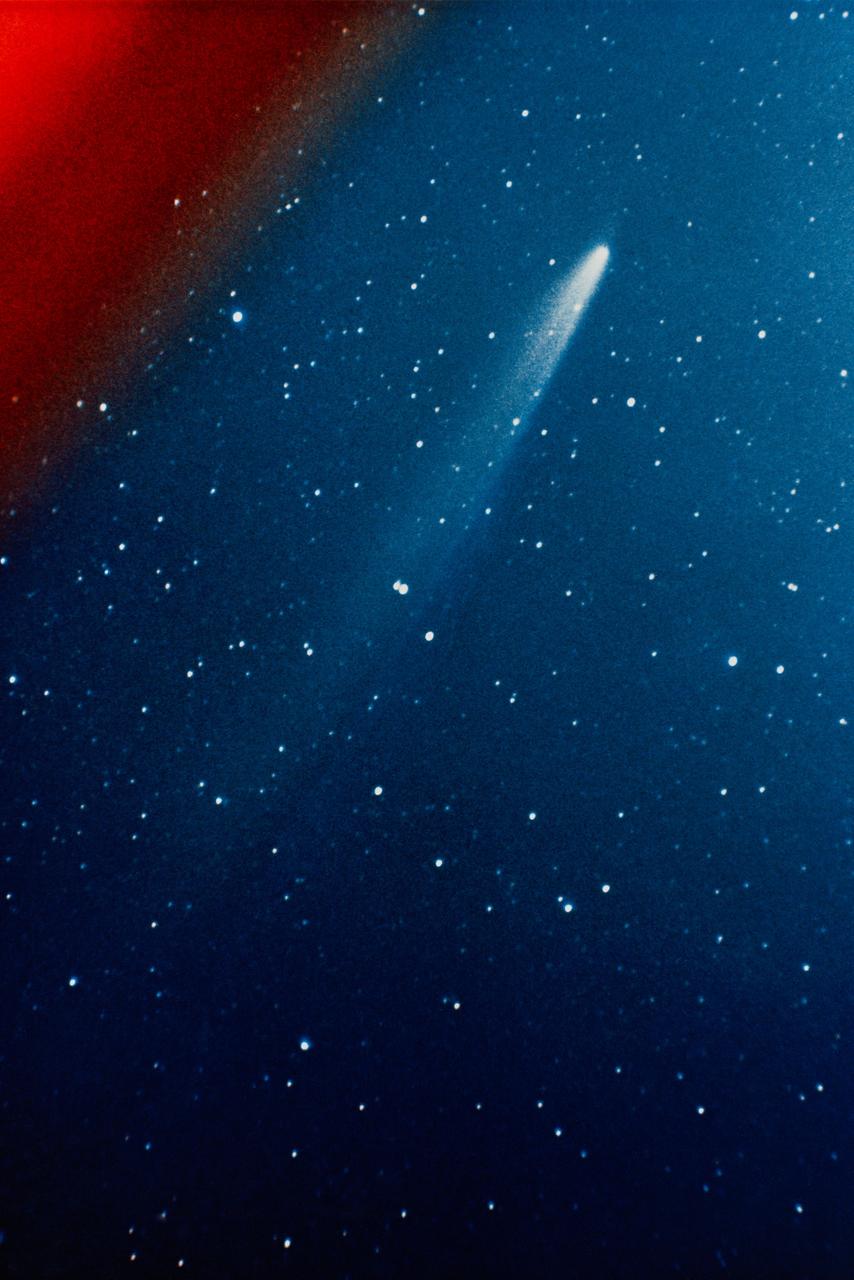

S74-17688 (11 Jan. 1974) --- This color photograph of the comet Kohoutek was taken by members of the lunar and planetary laboratory photographic team from the University of Arizona, at the Catalina Observatory with a 35mm camera on Jan. 11, 1974. Photo credit: NASA
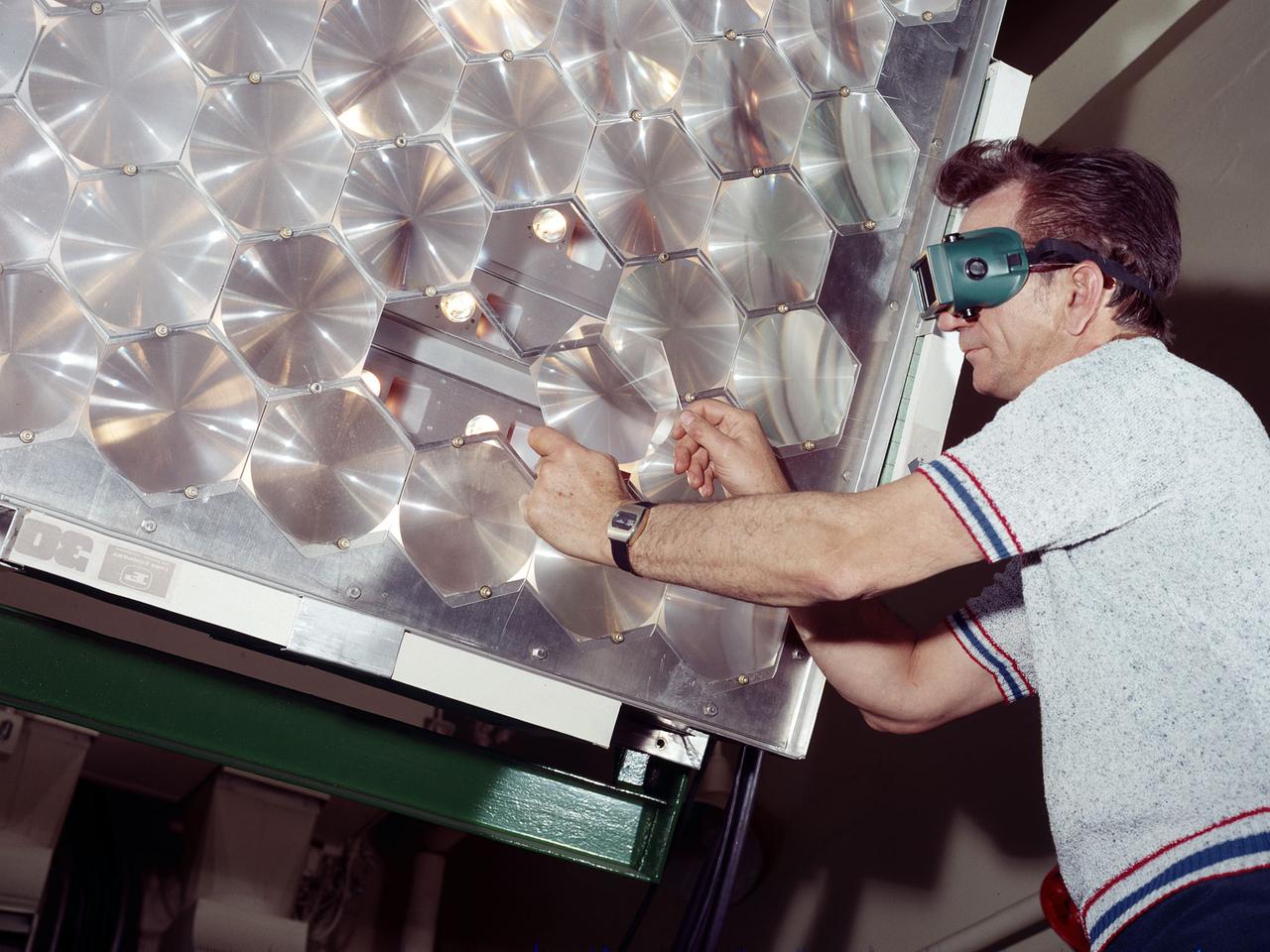

A NASA engineer installs a solar cell into a large array of solar cells.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center’s Convair F-106B Delta Dart equipped with air sampling equipment in the mid-1970s. NASA Lewis created and managed the Global Air Sampling Program (GASP) in 1972 in partnership with several airline companies. NASA researchers used the airliners’ Boeing 747 aircraft to gather air samples to determine the amount of pollution present in the stratosphere. Private companies developed the air sampling equipment for the GASP program, and Lewis created a particle collector. The collector was flight tested on NASA Lewis’ F-106B in the summer of 1973. The sampling equipment was automatically operated once the proper altitude was achieved. The sampling instruments collected dust particles in the air so their chemical composition could be analyzed. The equipment analyzed one second’s worth of data at a time. The researchers also monitored carbon monoxide, monozide, ozone, and water vapor. The 747 flights began in December 1974 and soon included four airlines flying routes all over the globe. The F-106B augmented the airline data with sampling of its own, seen here. It gathered samples throughout this period from locations such as New Mexico, Texas, Michigan, and Ohio. In July 1977 the F-106B flew eight GASP flights in nine days over Alaska to supplement the earlier data gathered by the airlines.
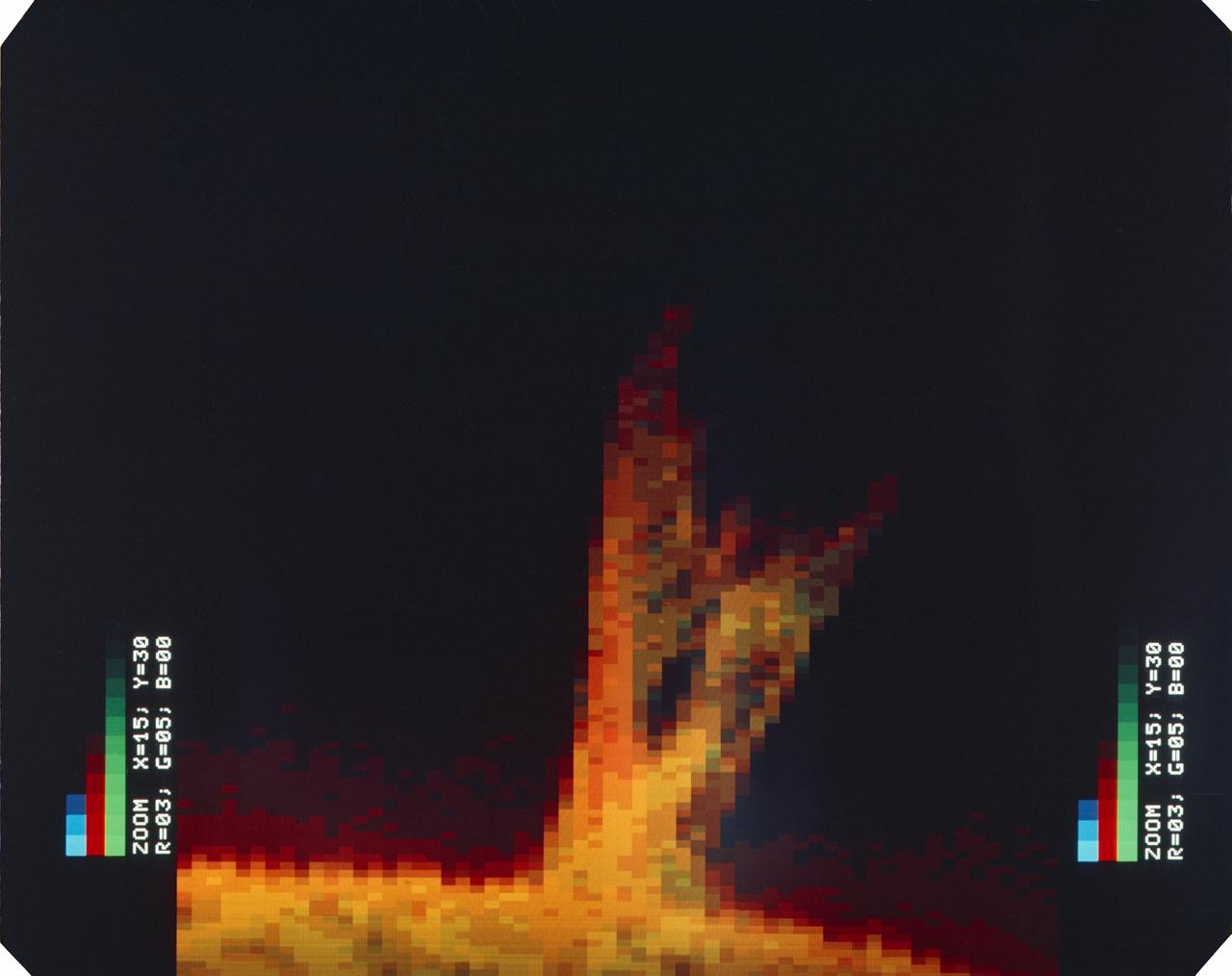

S74-18098 (1974) --- Graphical representation of an ultraviolet photograph depicting a solar flare, using the Skylab 4 Earth Observation Experiment equipment. Photo credit: NASA
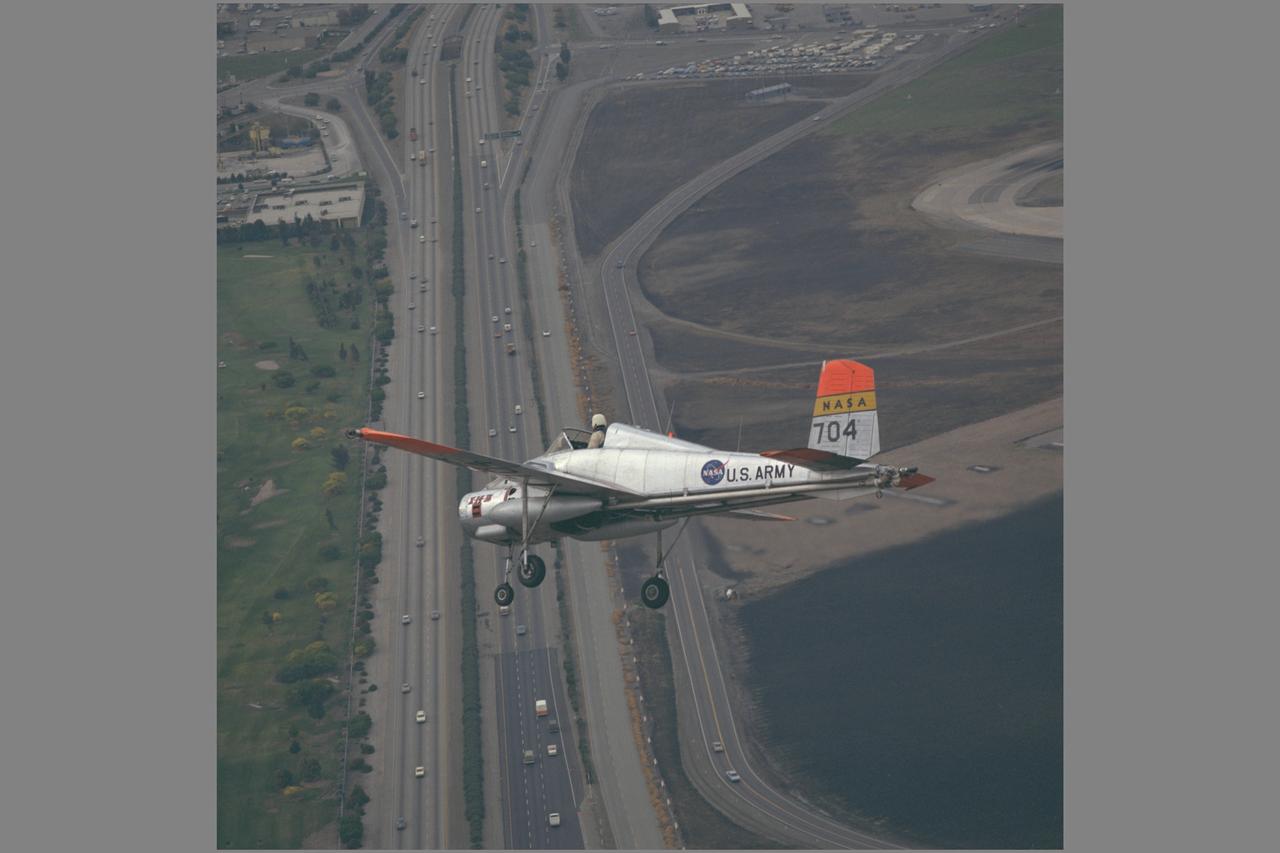

X-14B NASA-704: A Bell single-place, open cockpit, twin-engine, jet-lift VTOL aircraft over Highway 101 in approach to Moffett Field, California. The X-14 was used by NASA Ames Research Center to advance state-of-the-art jet-powered VTOL aircraft.
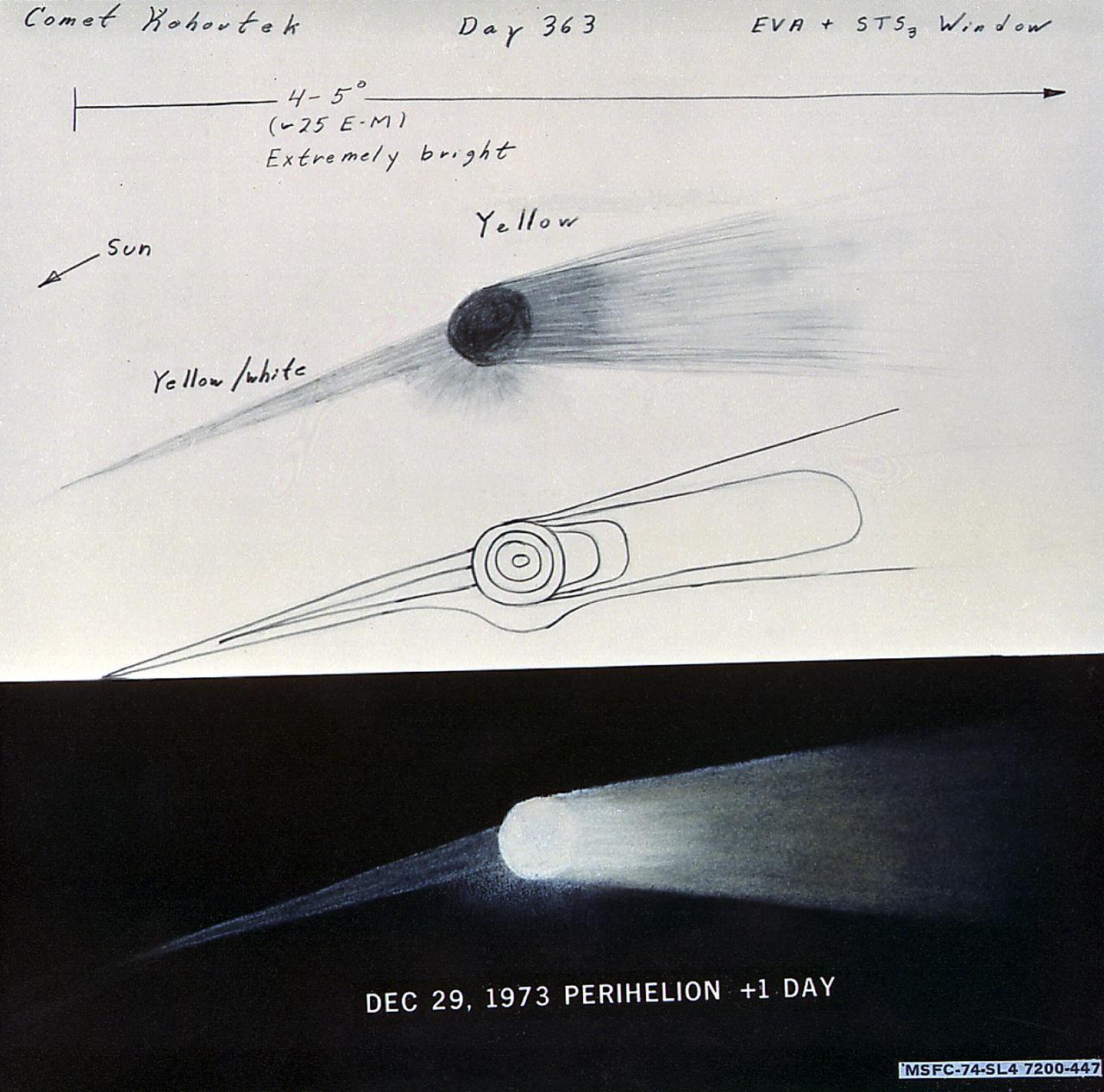
This pencil sketch of the Comet Kohoutek made by Skylab-4 astronaut Edward Gibson illustrates the crew's collective impressions of the comet's appearance on December 29, 1973. An early discovery of a large comet in an orbit that would reach close to the Sun at the end of 1973 prompted NASA to initiate Operation Kohoutek, a program to coordinate widespread observations of the comet from ground observatories, aircraft, balloons, rockets, unmarned satellites, and Skylab.

S74-23654 (22 June 1973) --- This mosaic of Baja and the Sea of Cortez in Mexico (28.0N, 112.0W) is a composite of six 70mm photos carefully pieced together to appear as one. Mosaics such as this one are useful to portray a large area in a single format instead of many photos covering only partial images. In this mosaic, almost the entire area of the Sea of Cortez, the adjacent Baja Peninsula and part of the Sonoran Desert of northwest Mexico can be seen. Photo credit: NASA

SL4-139-4072 (February 1974) --- A high oblique view of the North Atlantic coast of Canada as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. A Skylab 4 crewman used a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera to take this picture. The Strait of Belle Isle, near the center of the picture, separates the Island of Newfoundland from the Canadian mainland. The Strait also connects the Gulf of St. Lawrence with North Atlantic Ocean. The elongated land mass (lower center) is the northern-most peninsula of the Island of Newfoundland. The large land mass at left center is mainland Newfoundland and Quebec. Note the sea ice in the Atlantic. Snow and some ice intermittently cover the land masses, and ice plumes of brash ice or pancake ice can be seen in various shapes and formations. General terrain and ice conditions can be distinguished and evaluated up to at least 55 degrees north latitude in this north looking view. Dr. William Campbell, sea and ice expert with the U.S. Geological Survey, will use this photograph in the study of ice dynamics. Photo credit: NASA

Boeing 747 wake vortex test-440 in thr 40x80ft. w.t. with Rufiange, Vern Rossow, Eloy Martinez
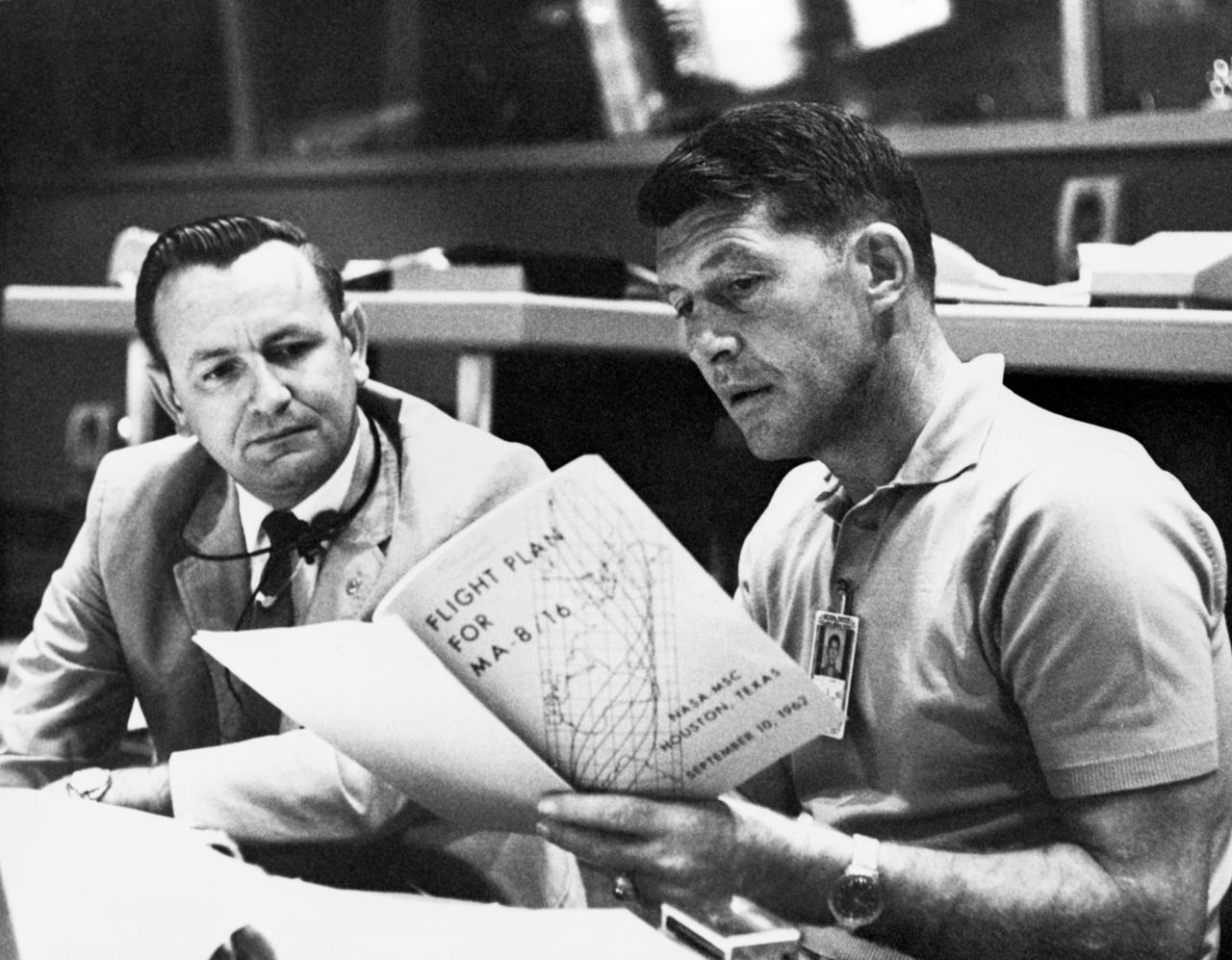

S74-33004 (19 Sept. 1962) --- Astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr, (right), Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) pilot, discusses the MA-8 flight plan with flight director Christopher C. Kraft Jr., Chief of the Flight Operations Division at the Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, during MA-8 preflight preparations at Cape Canaveral, Florida. They are seated at a console in the Mercury Control Center. Photo credit: NASA
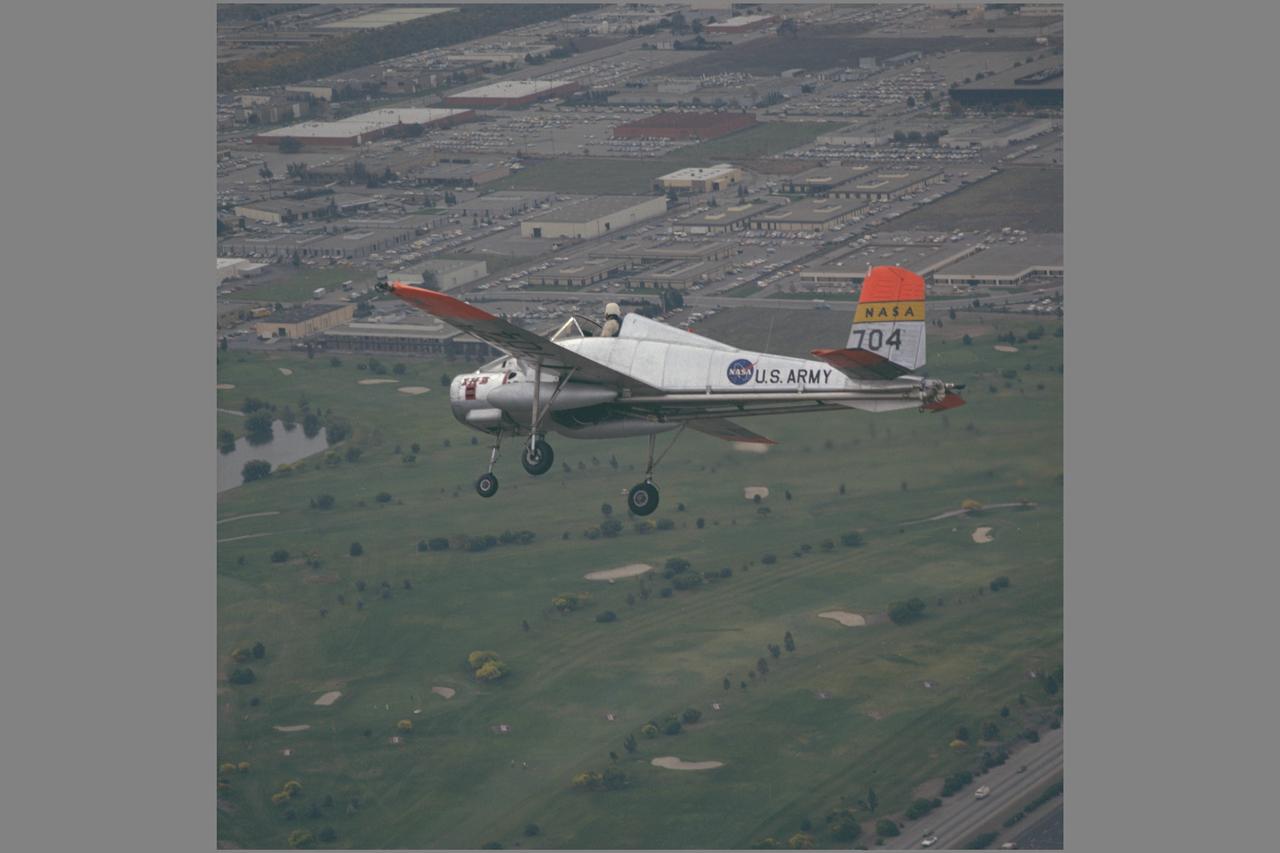

X-14B NASA-704: A Bell single-place, open cockpit, twin-engine, jet-lift VTOL aircraft in flight over Sunnyvale golf course. The X-14 was used by NASA Ames Research Center to advance state-of-the-art jet-powered VTOL aircraft.
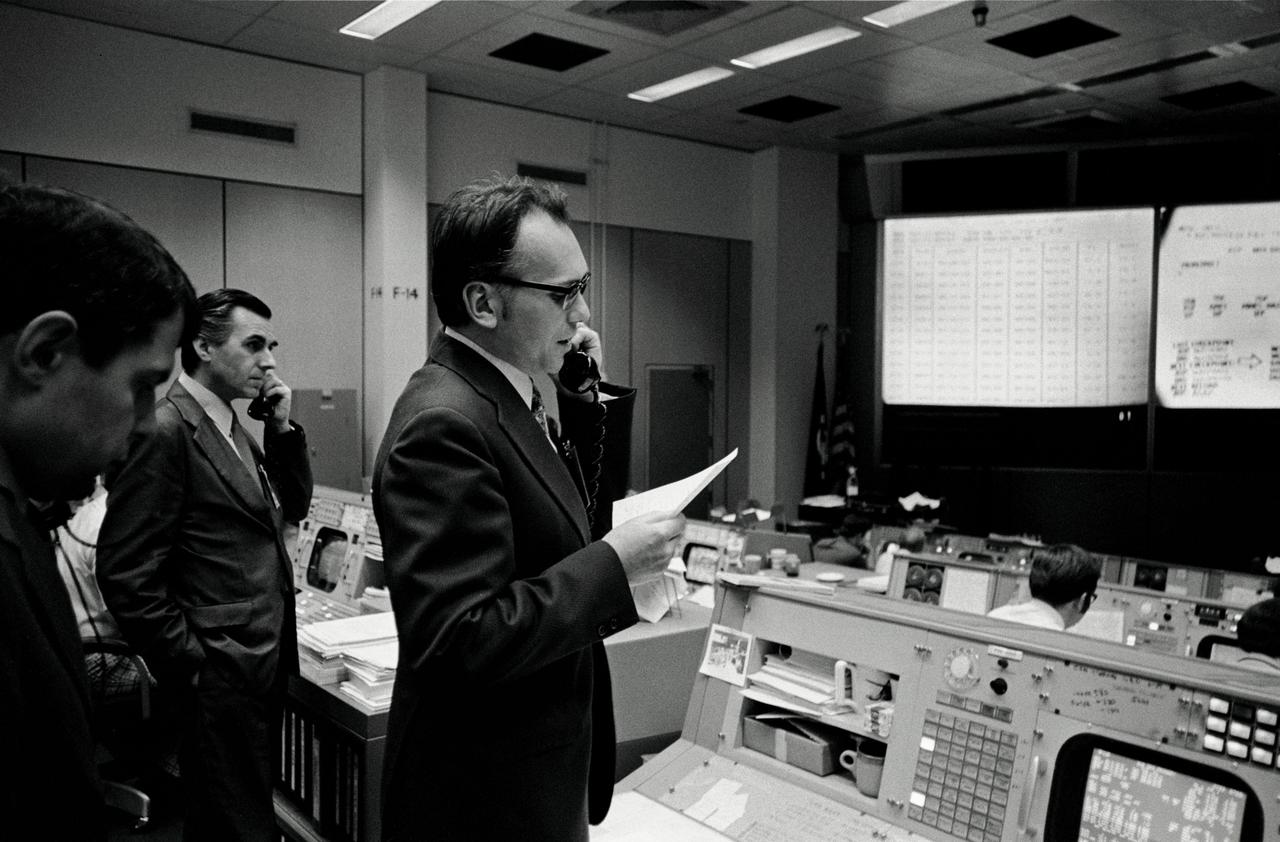

S74-15064 (28 Dec. 1973) --- Dr. Lubos Kohoutek, discoverer of the Comet Kohoutek, is seen in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center during a visit to the Johnson Space Center. He is talking over a radio-telephone with the Skylab 4 crewmen in the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Professor Kohoutek, a well-known Czechoslovakian astronomer who works at the Hamburg Observatory in West Germany, discussed the comet with astronauts Gerald P. Carr, Edward G. Gibson and William R. Pogue. One of the major objectives of the Skylab 4 mission is to monitor the passing of the Comet Kohoutek. Dr. Zdenek Sekania, who accompanied Dr. Kohoutek on the visit to JSC, is on the telephone in the left background. Dr. Sekania is with the Smithsonian Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Photo credit: NASA
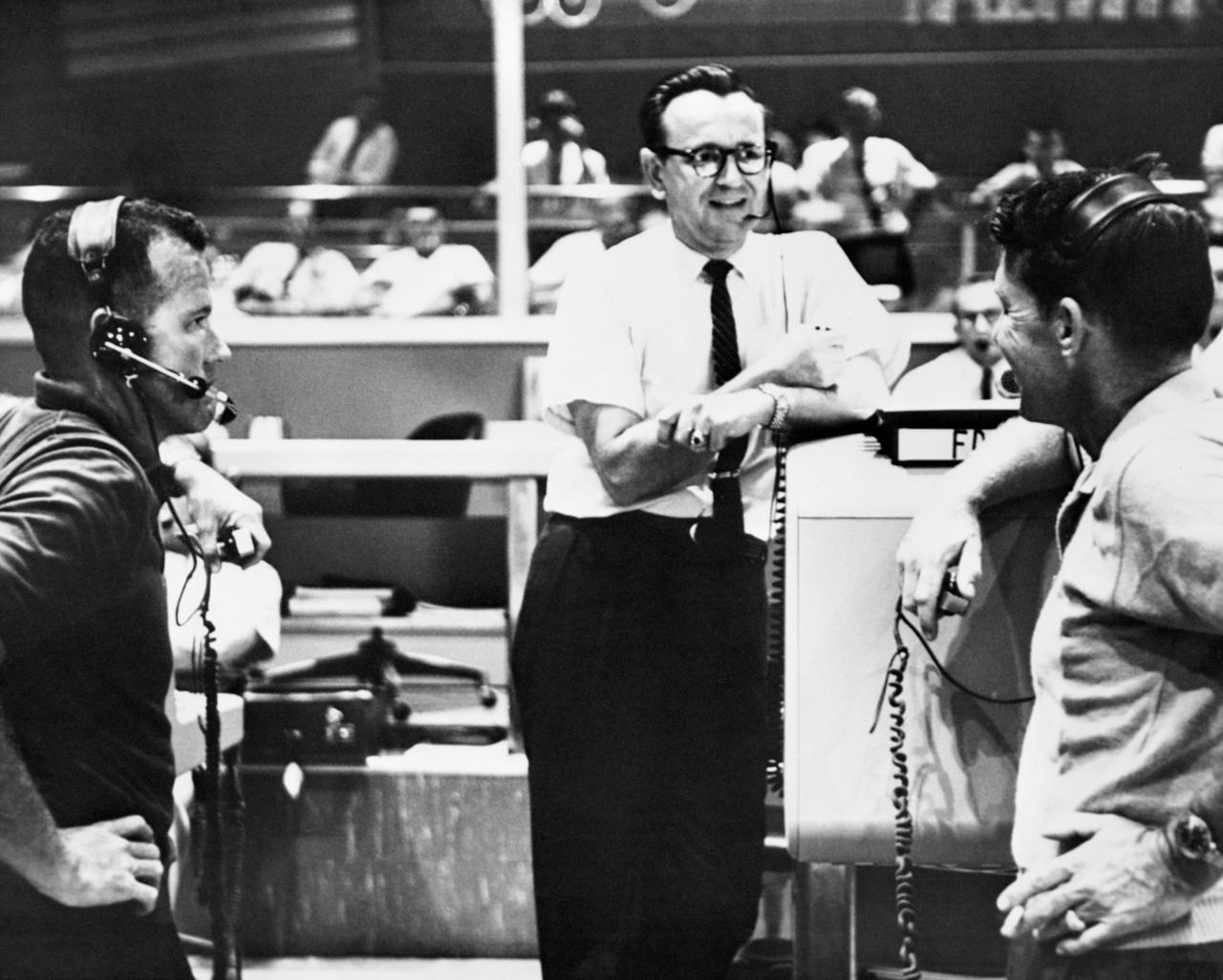

S74-33006 (19 Sept. 1962) --- Flight director Christopher C. Kraft Jr. (center), Chief of the Flight Operations Division at the Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, discusses the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) flight plan with astronauts L. Gordon Cooper Jr. (left) and Walter M. Schirra Jr., on Sept. 19, 1962. They are standing in the Mercury Control Center at Cape Canaveral, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
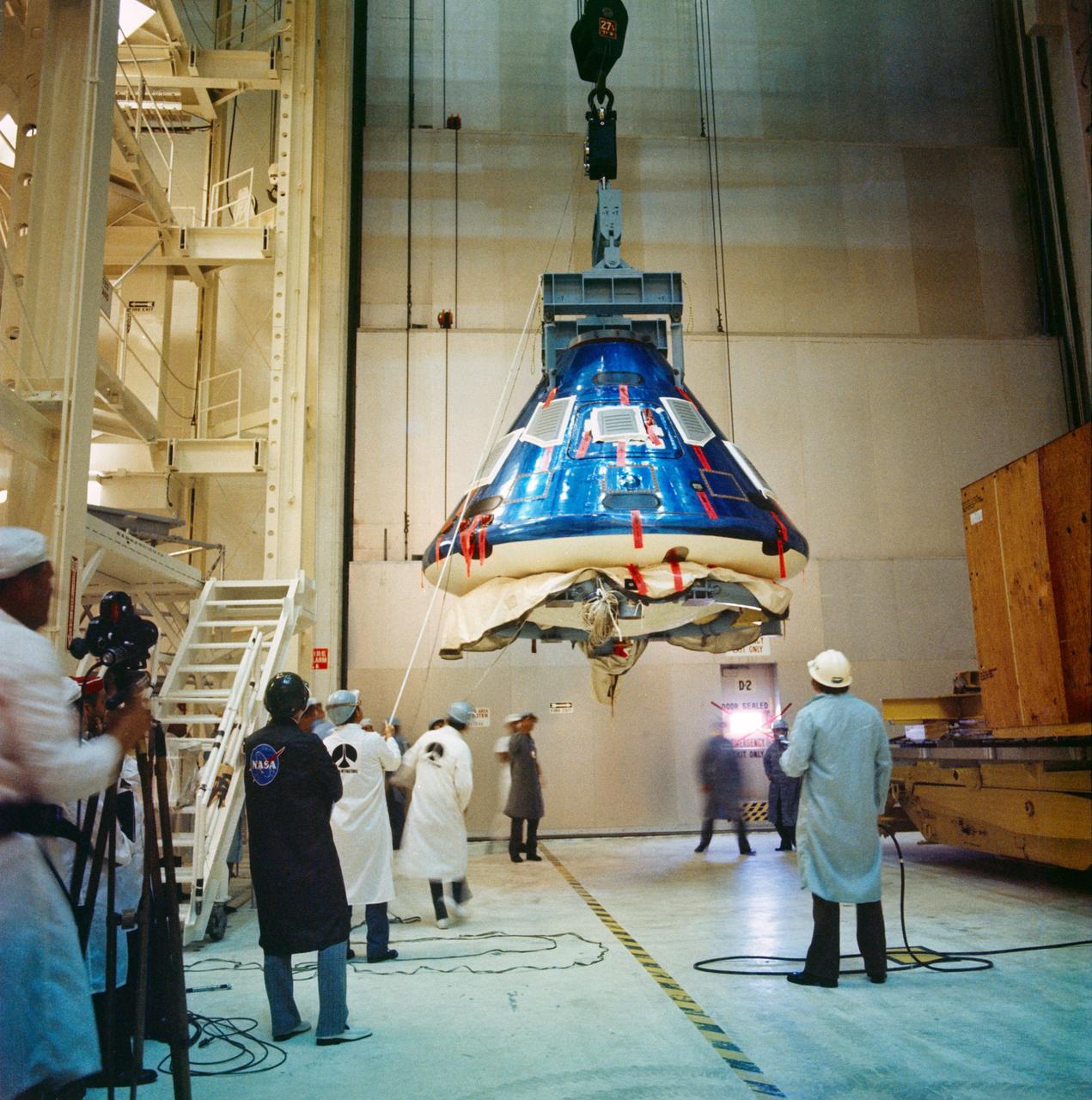

S74-32049 (8 Sept. 1974) --- The Apollo Command Module for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission goes through receiving, inspection and checkout procedures in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building at the Kennedy Space Center. The spacecraft had just arrived by air from the Rockwell International plant at Downey, California. The Apollo spacecraft (Command Module, Service Module and Docking Module), with astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton aboard, will dock in Earth orbit with a Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR ASTP flight scheduled for July 1975. The Soviet and American crews will visit one another?s spacecraft.
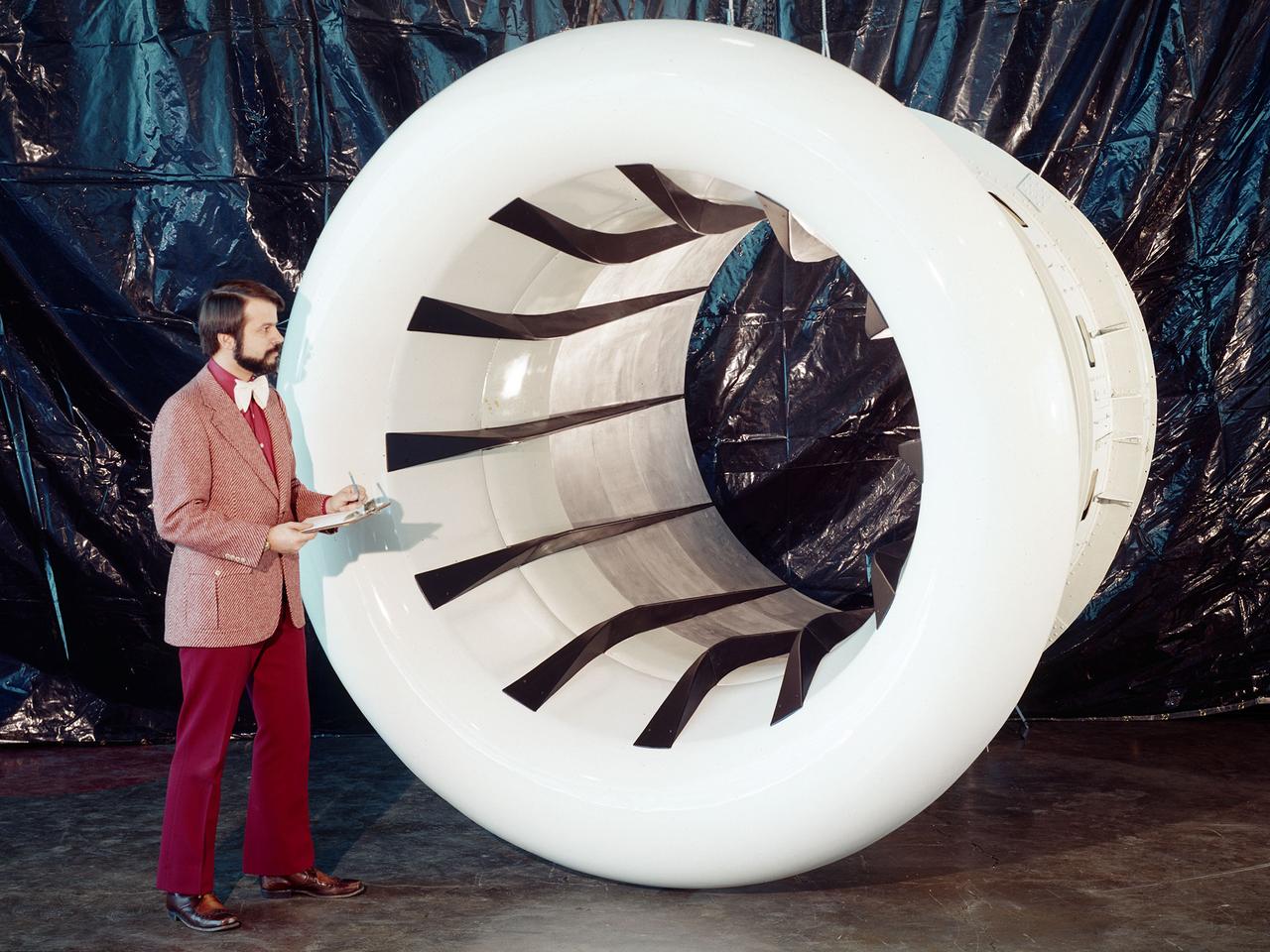

Brent Miller, of the V/STOL and Noise Division at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center, poses with a sonic inlet for the NASA Quiet Engine Program. NASA Lewis had first investigated methods for reducing aircraft engine noise in the mid-1950s. Those efforts were resurrected and expanded in the late 1960s. The researchers found that the use of a sonic, or high-throat-Mach-number, inlet was effective at reducing the noise from the engine inlet. The device accelerated the inlet air to near-sonic speeds which kept the forward moving sound waves away from the inlet. The device also deflected the sound waves into the wall to further reduce the noise. NASA Lewis researchers tested models of the sonic inlet in their 9- by 15-Foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel. They found that the general level of aerodynamic performance was good. The tests during simulated takeoff and landing conditions demonstrated the sonic inlet’s ability to provide good aerodynamic and acoustic performance The researchers then successfully tested two full-scale sonic inlet designs, one from Pratt and Whitney and one from General Electric, with fans. A full-scale engine was installed on a thrust stand to determine the sonic inlet’s effect on the engine’s performance. The amount of noise reduction increased as the inlet flow velocity increased, but the full-scale tests did not produce as great a decrease in noise as the earlier small-scale tests.