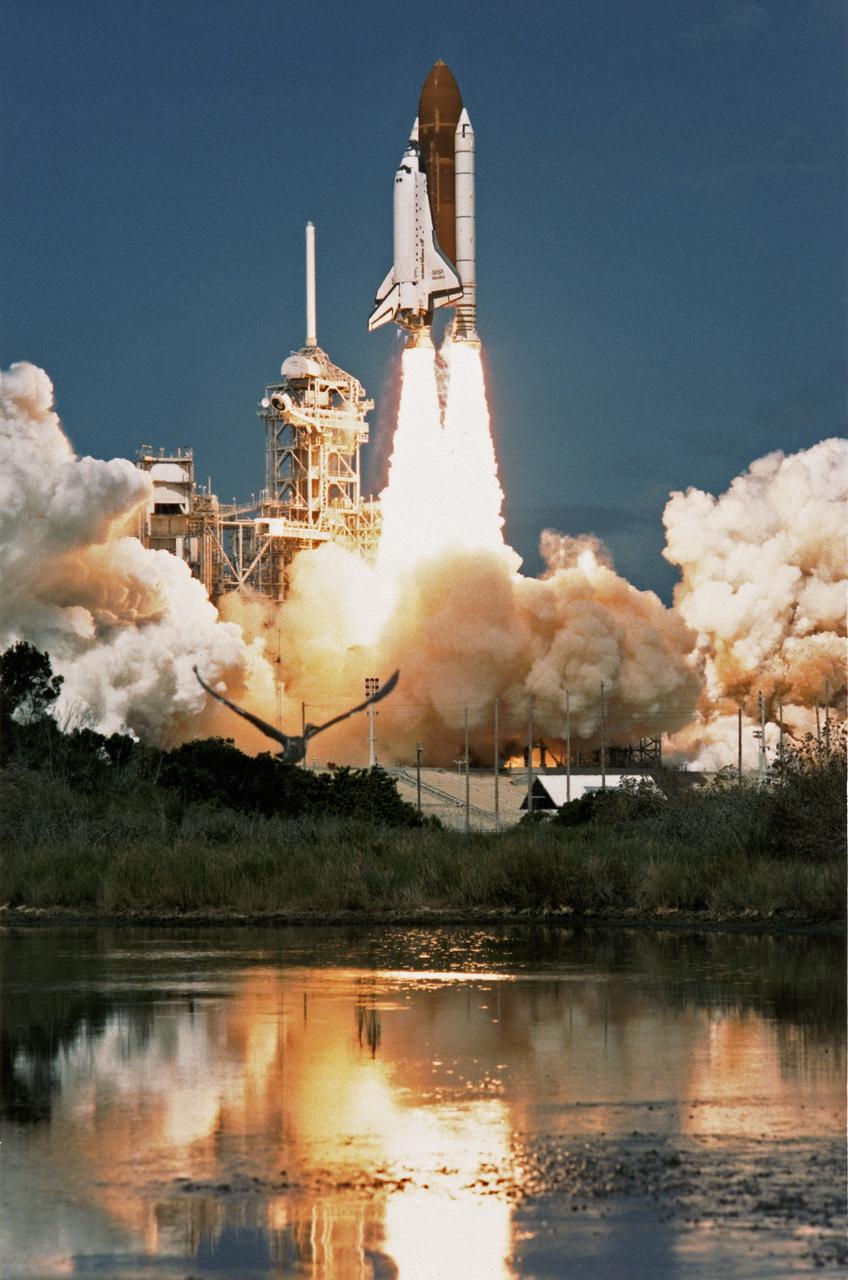

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The space shuttle Discovery and its five-man crew is launched from pad 39B at 11:37 a.m. as STS-26 embarks on a four-day mission marking America's return to space. On the first day of orbit, the crew will deploy from the orbiter's payload bay the primary payload, the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-C. The inertial upper stage, or IUS, will boost the satellite to a geosynchronous altitude from low Earth orbit. When it place, TDRS-C will relay date from low Earth orbiting spacecraft and air-to-ground voice communications sand television from shape shuttle orbiters during missions. The crew members of STST-26 are Commander Rick Hauck, Pilot Richard Covey, and mission specialists Dave Hilmers, Mike Lounge and George "Pinky" Nelson. Photo Credit: NASA
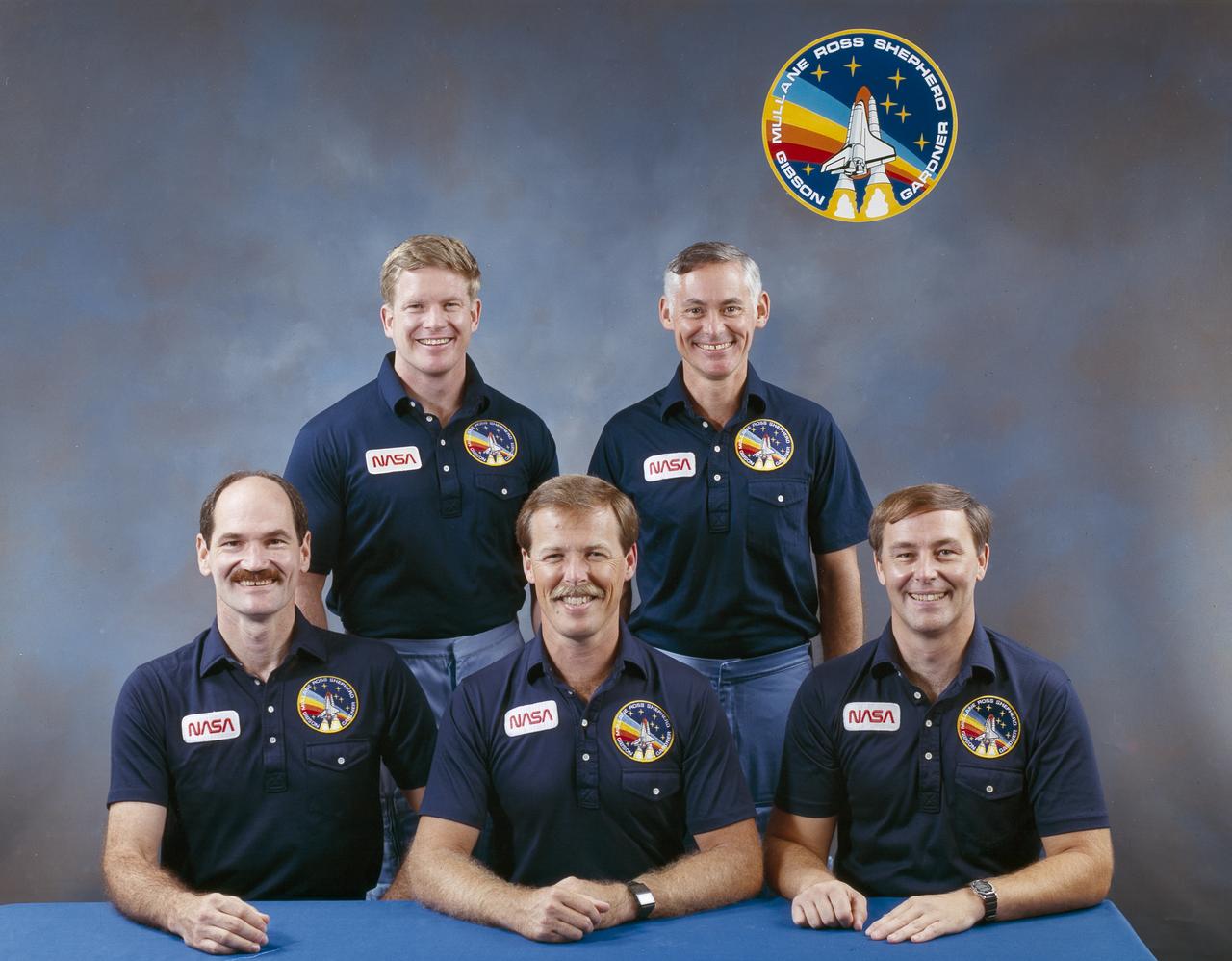

The STS-27 crew portrait features 5 astronauts. Seated, left to right, are Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist; Guy S. Gardner, pilot; and Robert L. Gibson, commander. On the back row, left to right, are mission specialists Richard M. Mullane, and William M. Shepherd. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on December 2, 1988 at 9:30:34 am (EST), the STS-27 mission was the third mission dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD).

Crows Landing runway approach

XV-15 PROJECT TEAM. AEROSPACE SYSTEM DIVISION (CODE F) & FLIGHT OPERATIONS & RESEARCH (CODE O) PERSONNEL Front row: Mike Bondi, Dan Dugan. Shorty Schroers, Wally Deckert, Marty Maisel, Violet Lamica, Robby Robinson, Demo Giulianetti. Back row: Jerry Bree, Gary Churchill, Dave Few, Jerry Barrack, Kip Edenborough, Jim Lane, Mike Carness, Dave Chappel, Duane Allen, Not pictured: Woody Cook, Jim Weiberg, Dean Borgman, Jim Brown, John Hemiup, Al Gahler, Ron Gerdes, Cliff Mckiethan, Bill Snyder, Rick Simmons Note: Used in publication in Flight Research at Ames; 57 Years of Development and Validation of Aeronautical Technology NASA SP-1998-3300 fig 123
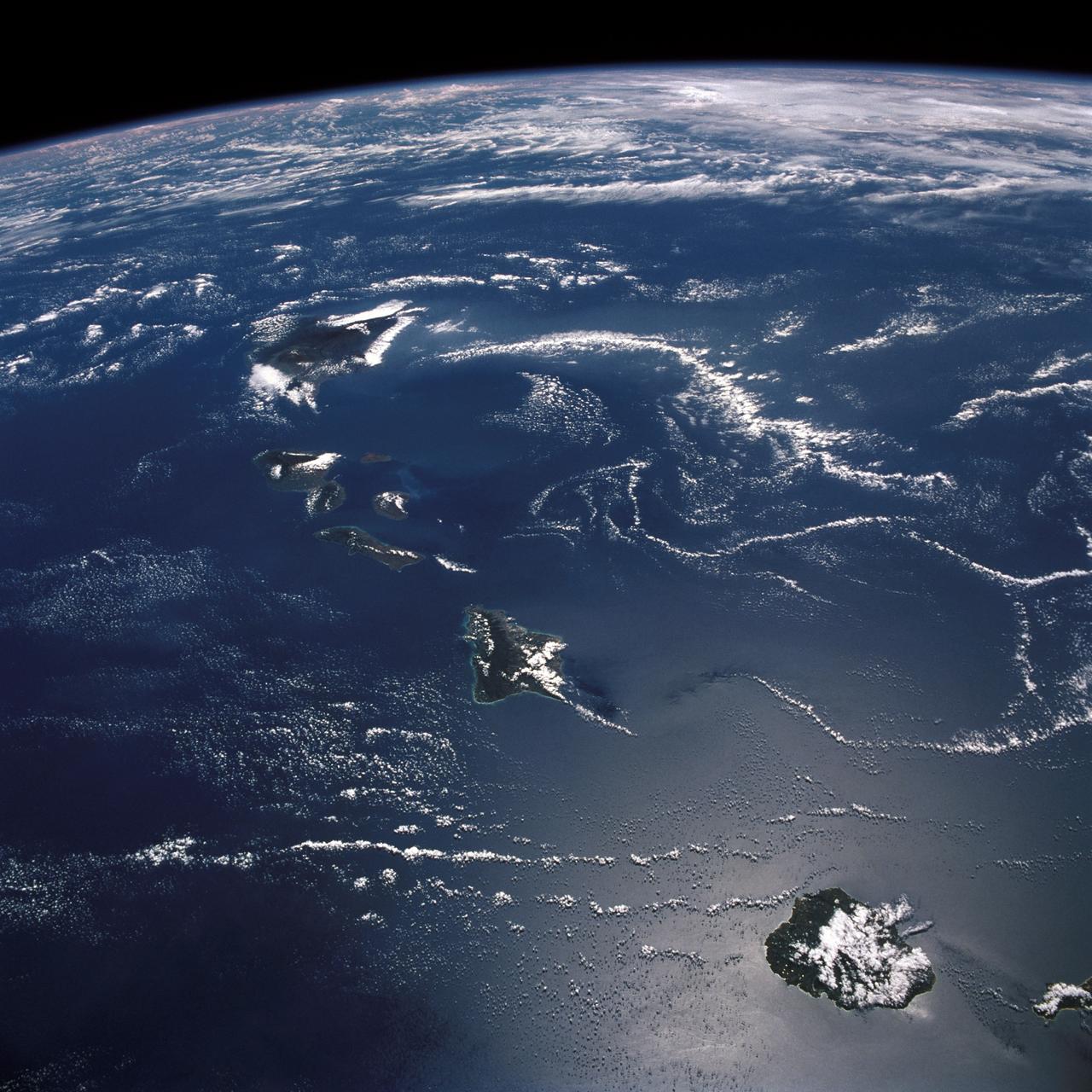

STS026-43-082 (29 Sept. - 3 Oct. 1988) --- This 70mm northerly oriented frame over the Pacific Ocean features the Hawaiian Islands chain. The islands perturb the prevailing northeasterly winds producing extensive cloud wakes in the lee of the islands. Photo experts feel that atmospheric haze in the Hawaii wake is probably a result of the continuing eruptions of Kilauea volcano on the southeast coast. From the lower right corner in a diagonal directed upward to the north are the islands of Nihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lanai, Maui, Kahoolawe, and Hawaii. This photo was shown during the post-flight press conference on October 11, 1988 by the STS-26 astronauts, who at one time during the flight wore Hawaiian attire to pay tribute to the working staff of the Hawaii tracking station.
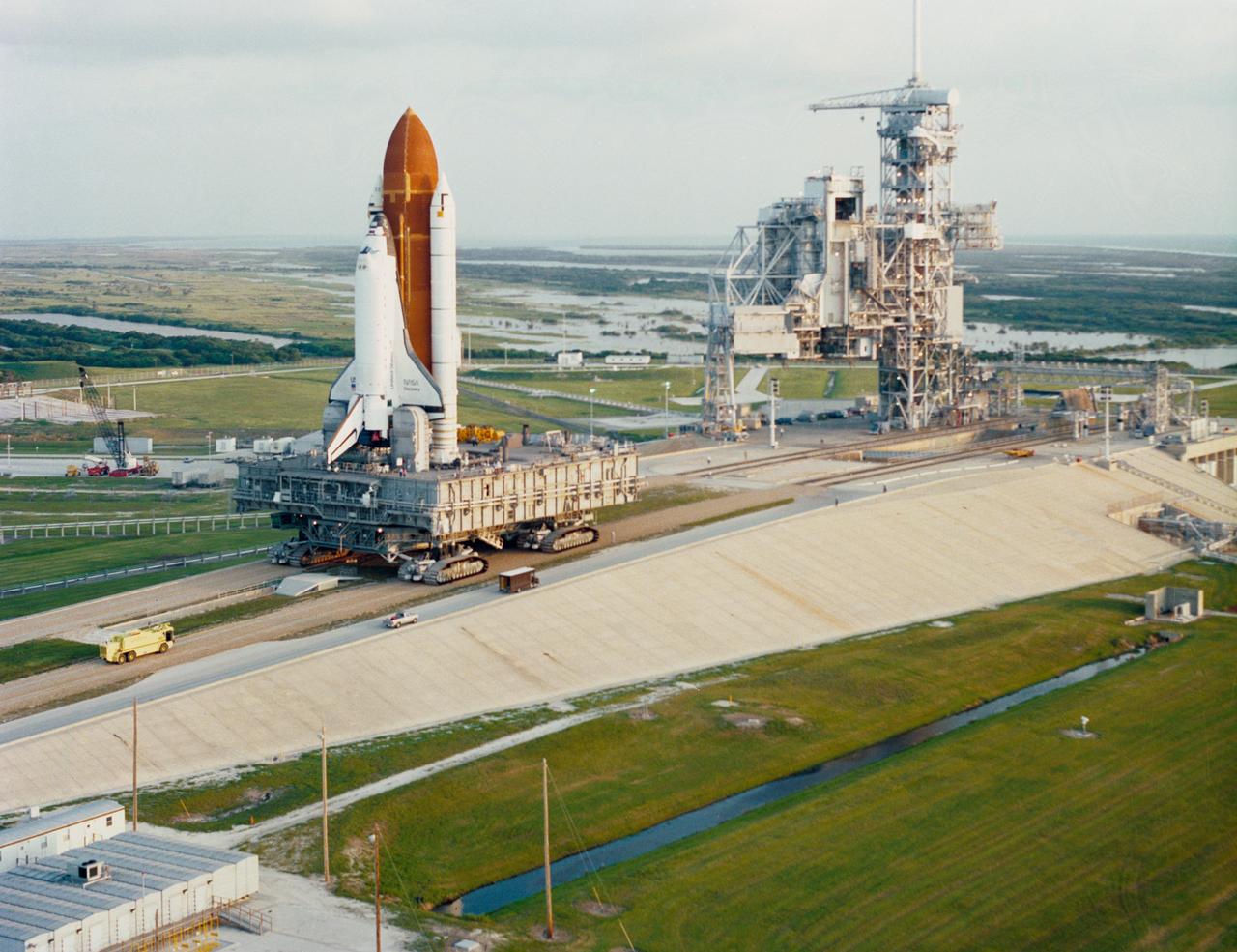

STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, rolls out to Kennedy Space Center (KSC) launch complex (LC) pad 39B on top of the crawler transporter. OV-103 nears LC pad 39B after a six-hour journey from the vehicle assembly building (VAB). When locked onto the nearby rotating service structure (RSS), work will continue to ready the vehicle for the STS-26 launch later in the summer.
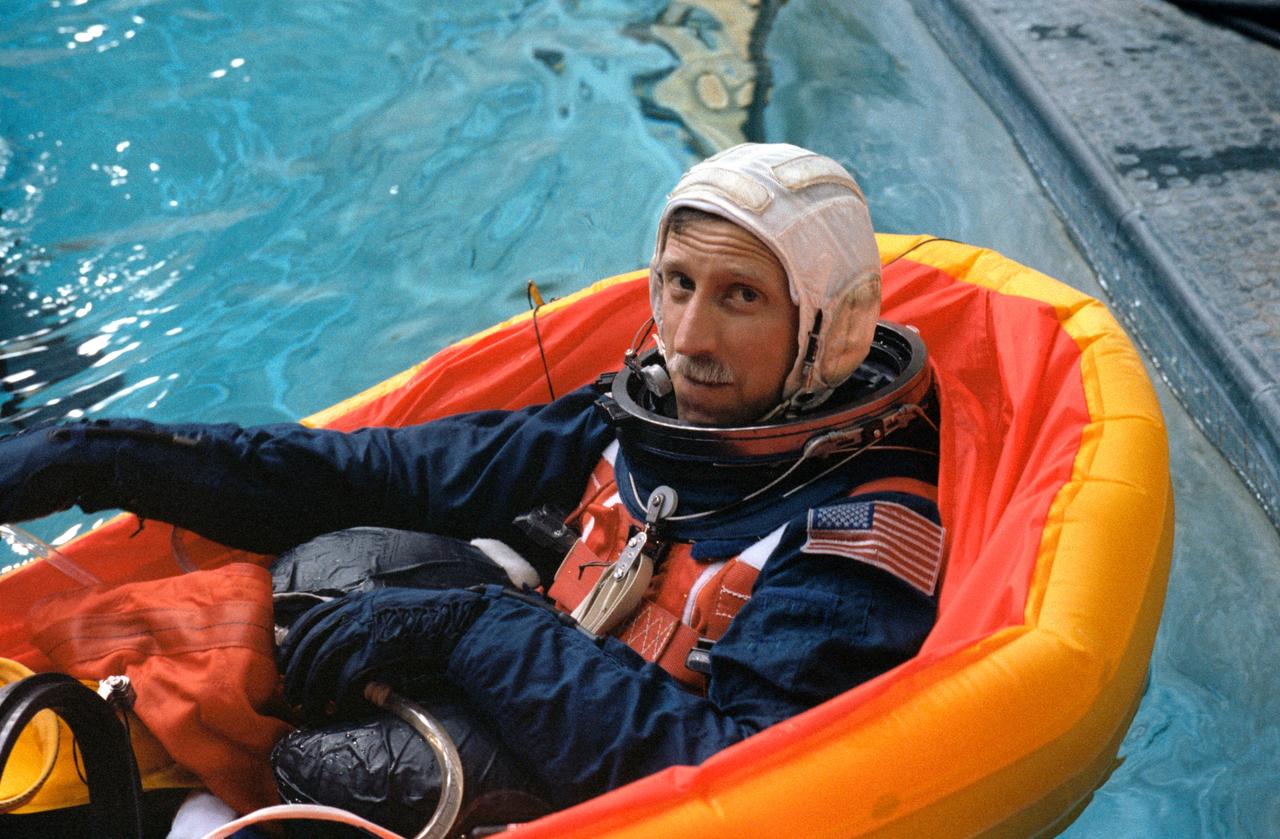

S88-42425 (20 July 1988) --- STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Pilot Richard O. Covey, wearing the newly designed launch and entry suit (LES), floats in single-occupant life raft in JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. The simulation of the escape and rescue operations utilized the crew escape system (CES) pole method of egress from the Space Shuttle.

ASRF - Automated Sciences into the future of spaceflight and planetary research. Artwork
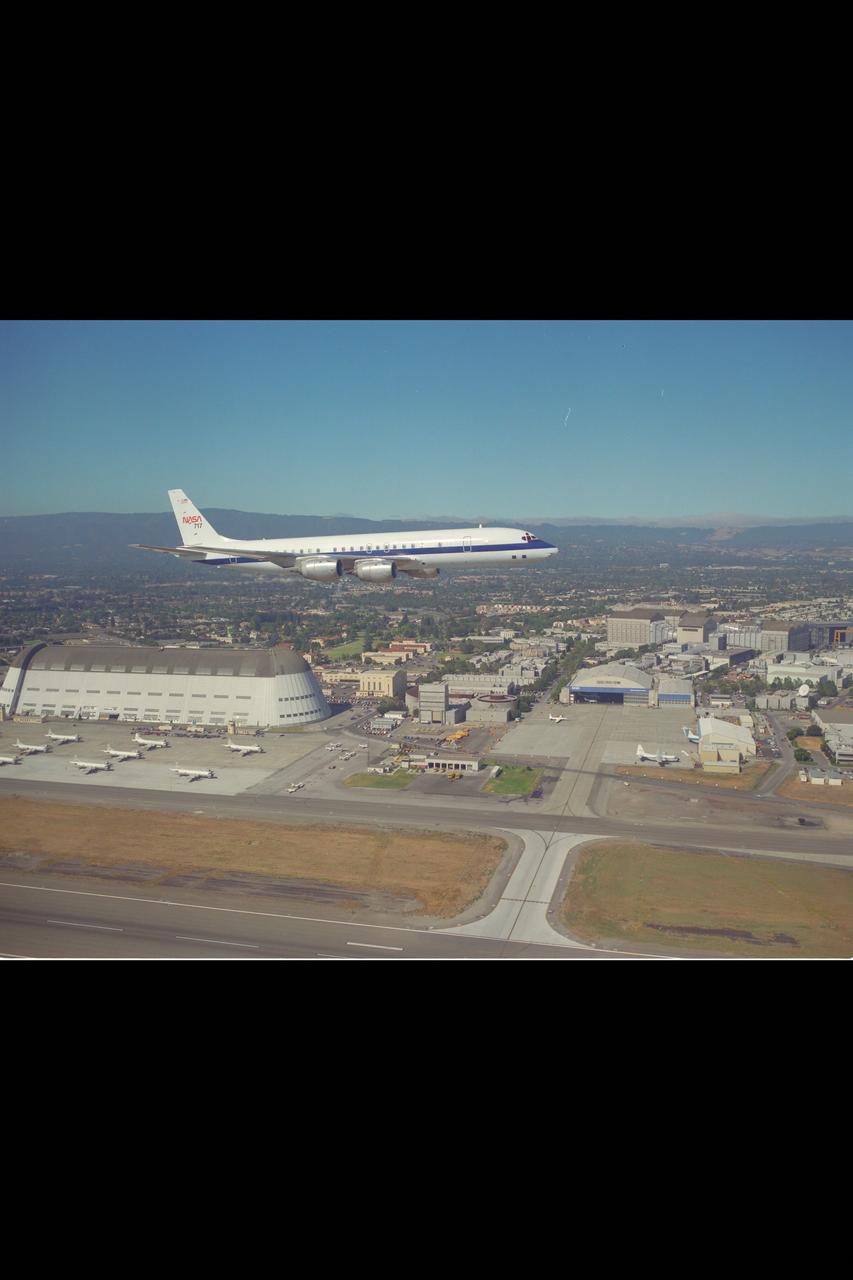

Newly arrived DC-8 (NASA-717) in flight over Ames
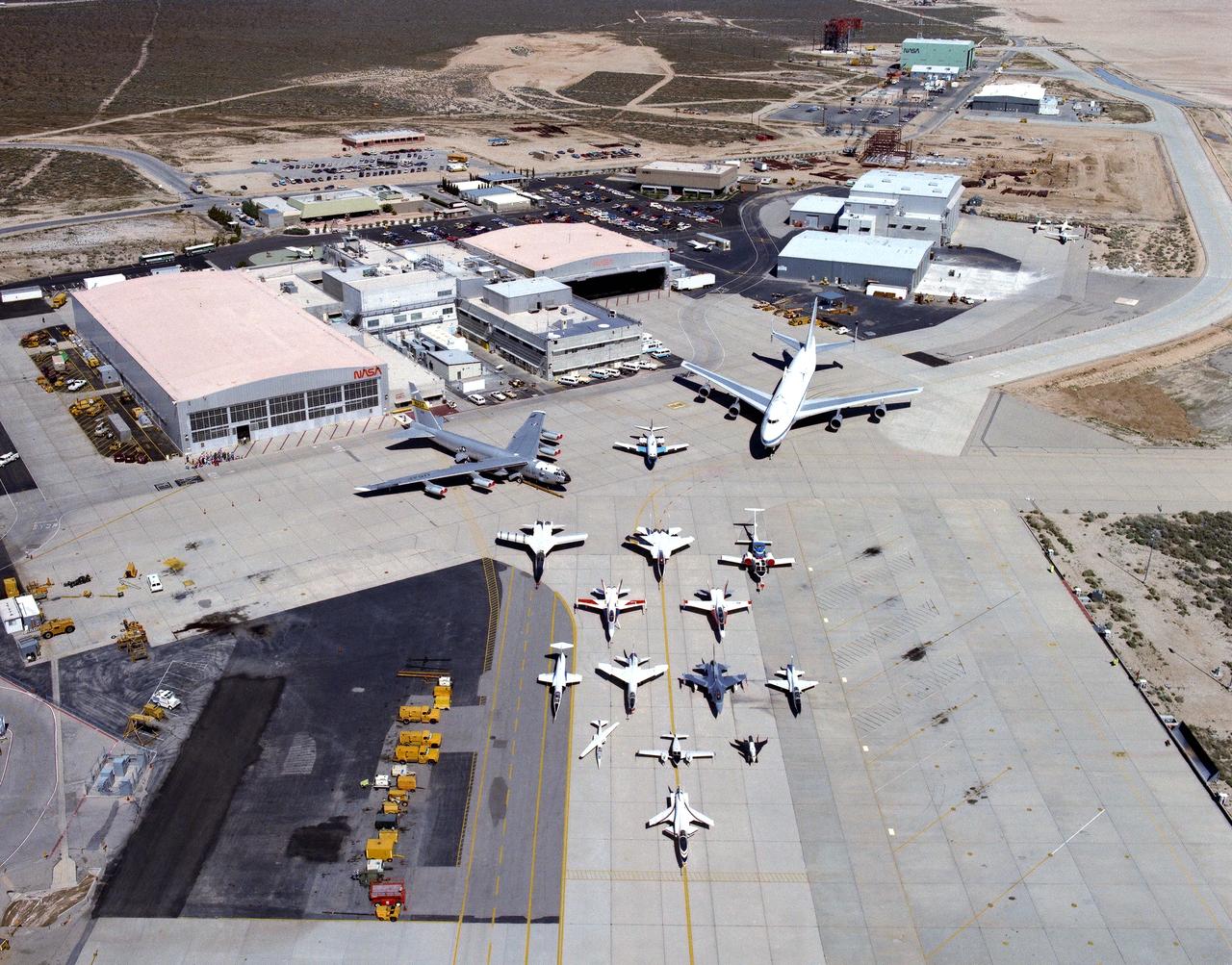

Dryden Aircraft Fleet on ramp and facility - 1988
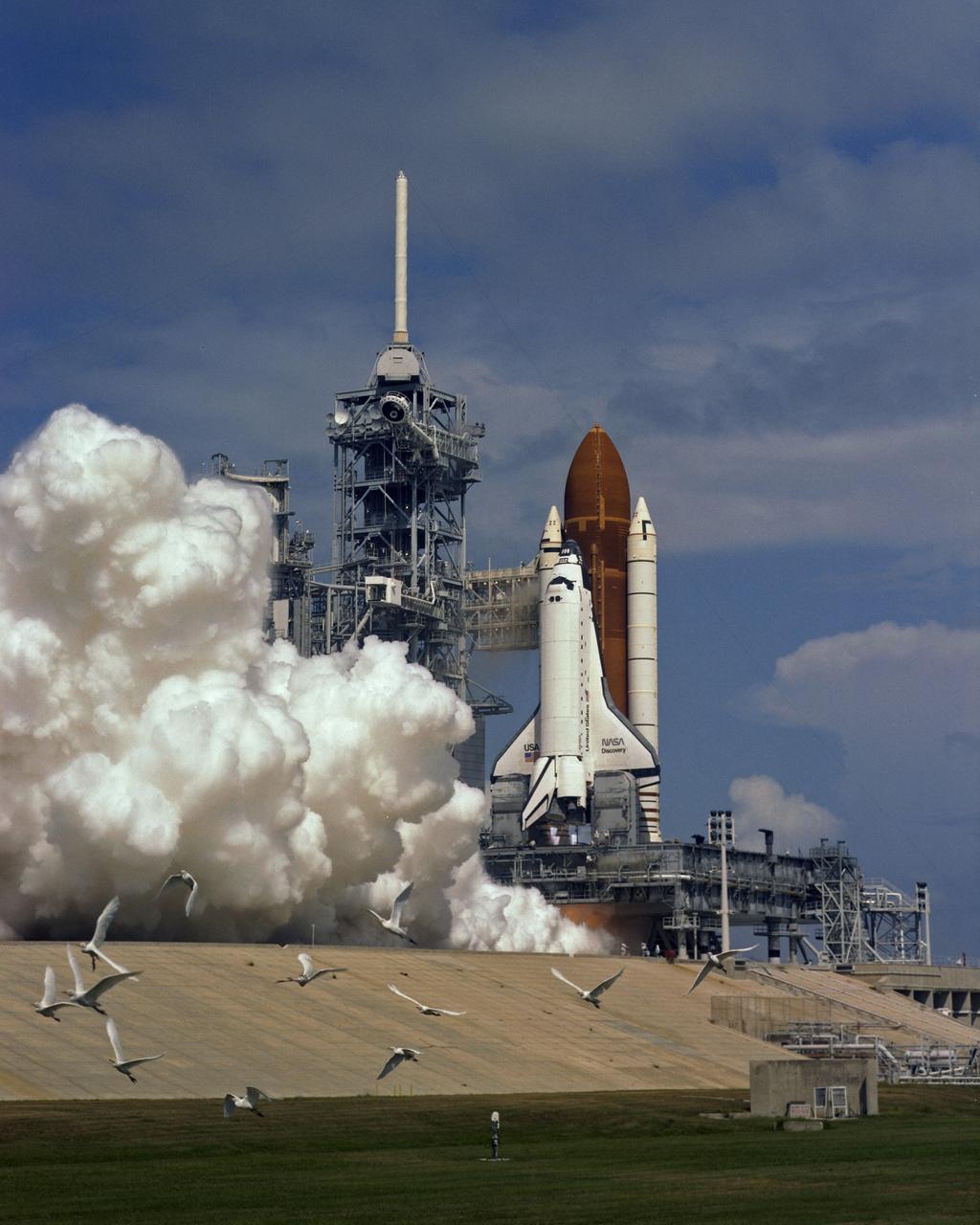

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The space shuttle Discovery and its five-man crew is launched from pad 39B at 11:37 a.m. as STS-26 embarks on a four-day mission marking America's return to space. On the first day of orbit, the crew will deploy from the orbiter's payload bay the primary payload, the Tracking and Date Relay Satellite, or TDRS-C. The inertial upper stage, or IUS, will boost the satellite to a geosynchronous altitude from low Earth orbit. When it place, TDRS-C will relay date from low Earth orbiting spacecraft and air-to-ground voice communications sand television from shape shuttle orbiters during missions. The crew members of STST-26 are Commander Rick Hauck, Pilot Richard Covey, and Mission Specialists Dave Hilmers, Mike Lounge and George "Pinky" Nelson. Photo Credit: NASA
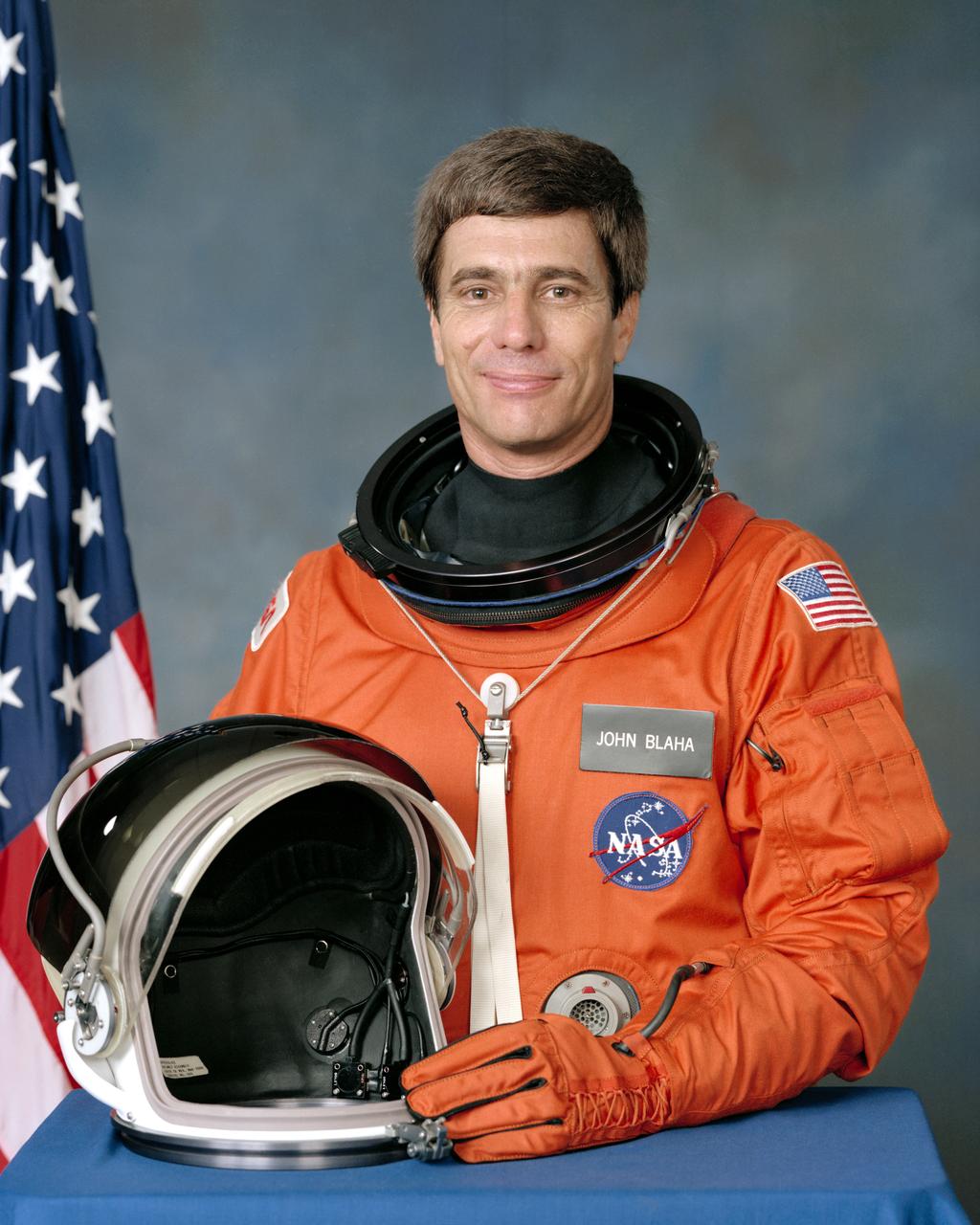

S88-45293 (November 1988) --- Astronaut John E. Blaha, pilot.
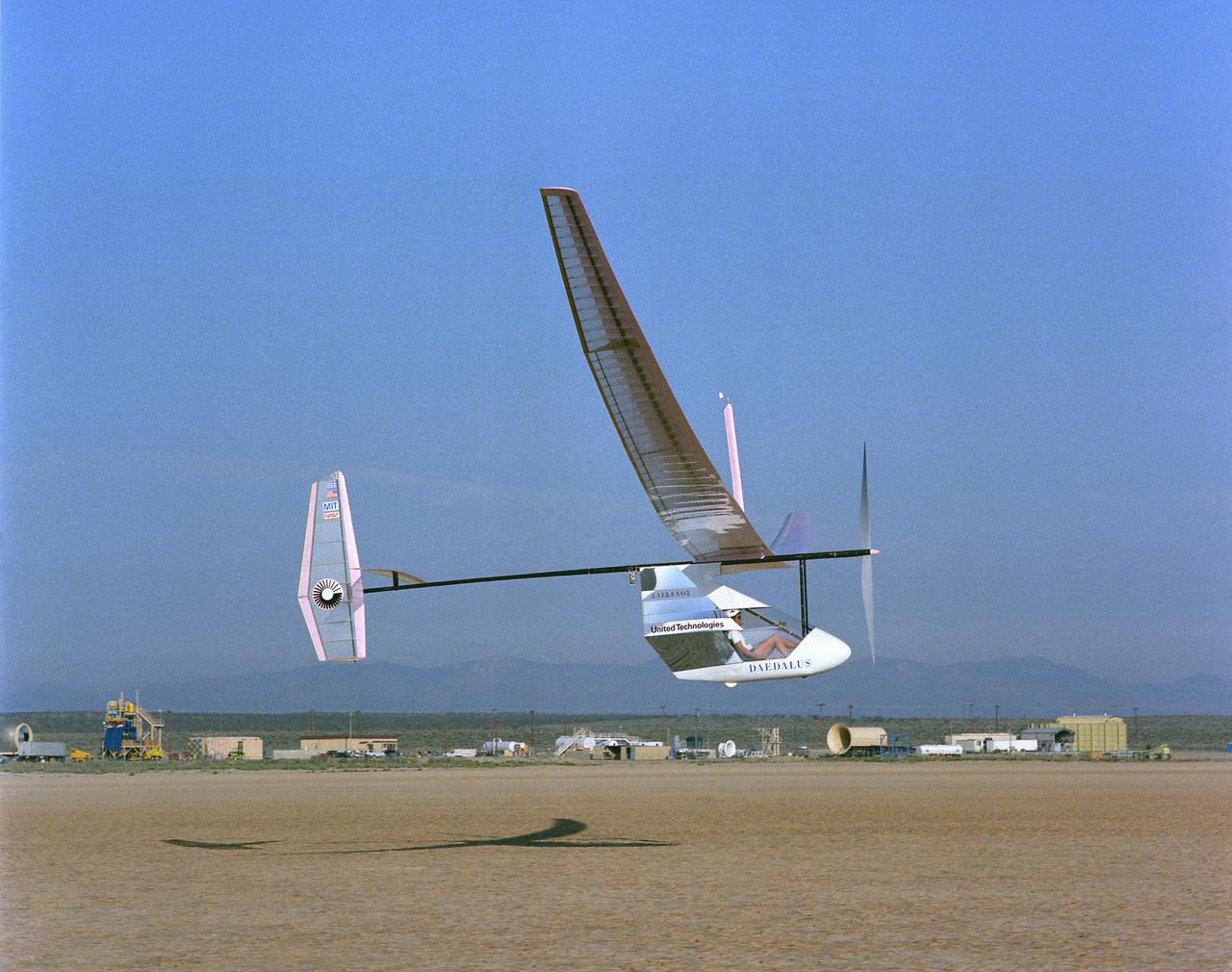

Daedalus - Last Dryden flight with Glenn Tremml
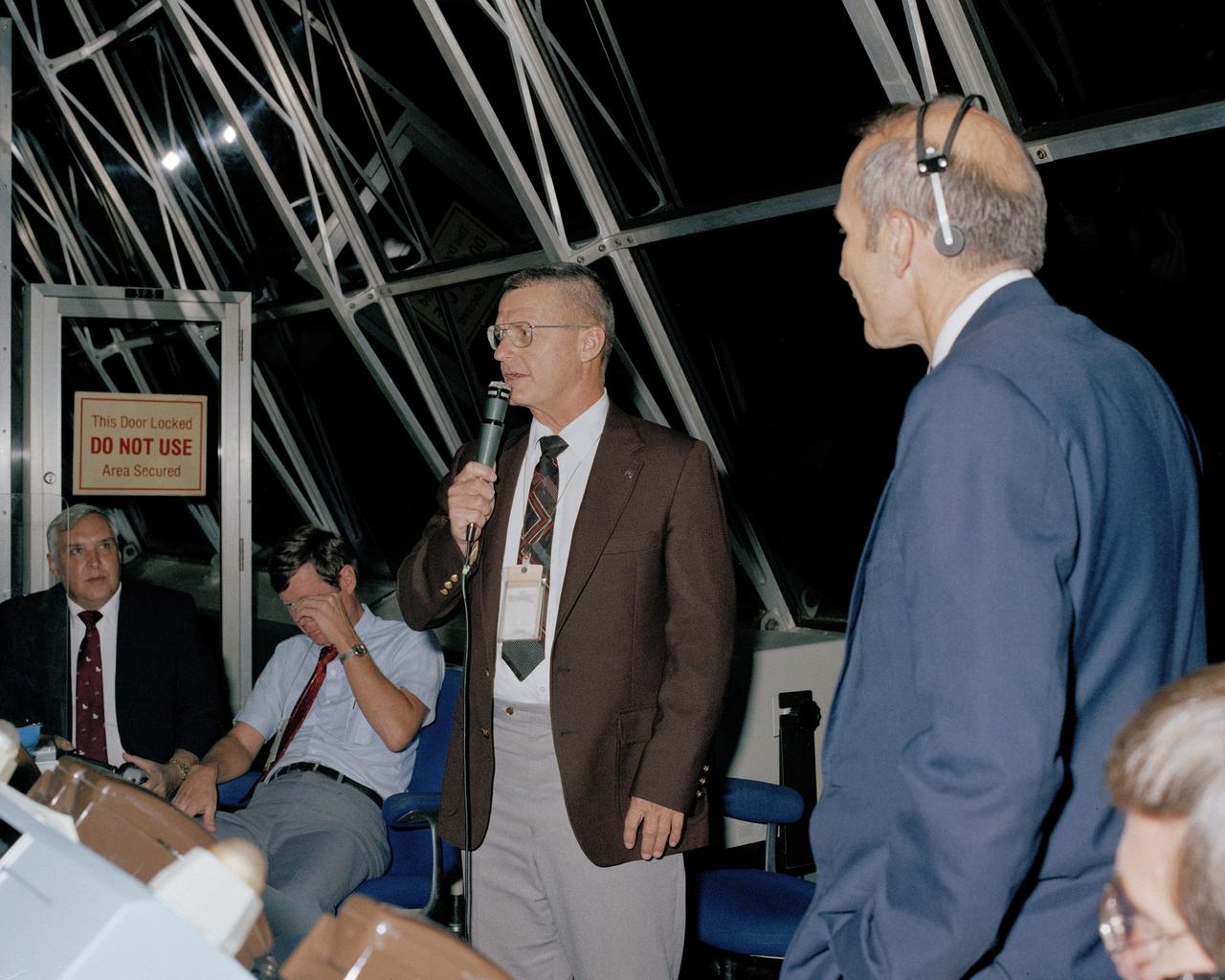

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - After the successful Flight Readiness Firing of the space shuttle Discovery's three main engines, Kennedy Space Center Director Forrest McCartney congratulates members of the launch team in the firing room. The approximate 22-second firing was conducted to evaluate the performance of various components of the shuttle, external tank and solid rocket boosters, as well as the launch facilities and support equipment which will be used during the launch of STS-26. Looking on is Bob Sieck, KSC launch director, right, Hugh Harris, deputy director of KSC Public Affairs, left, and John Conway, director of Payload Management and Operations, second from left. Photo credit: NASA
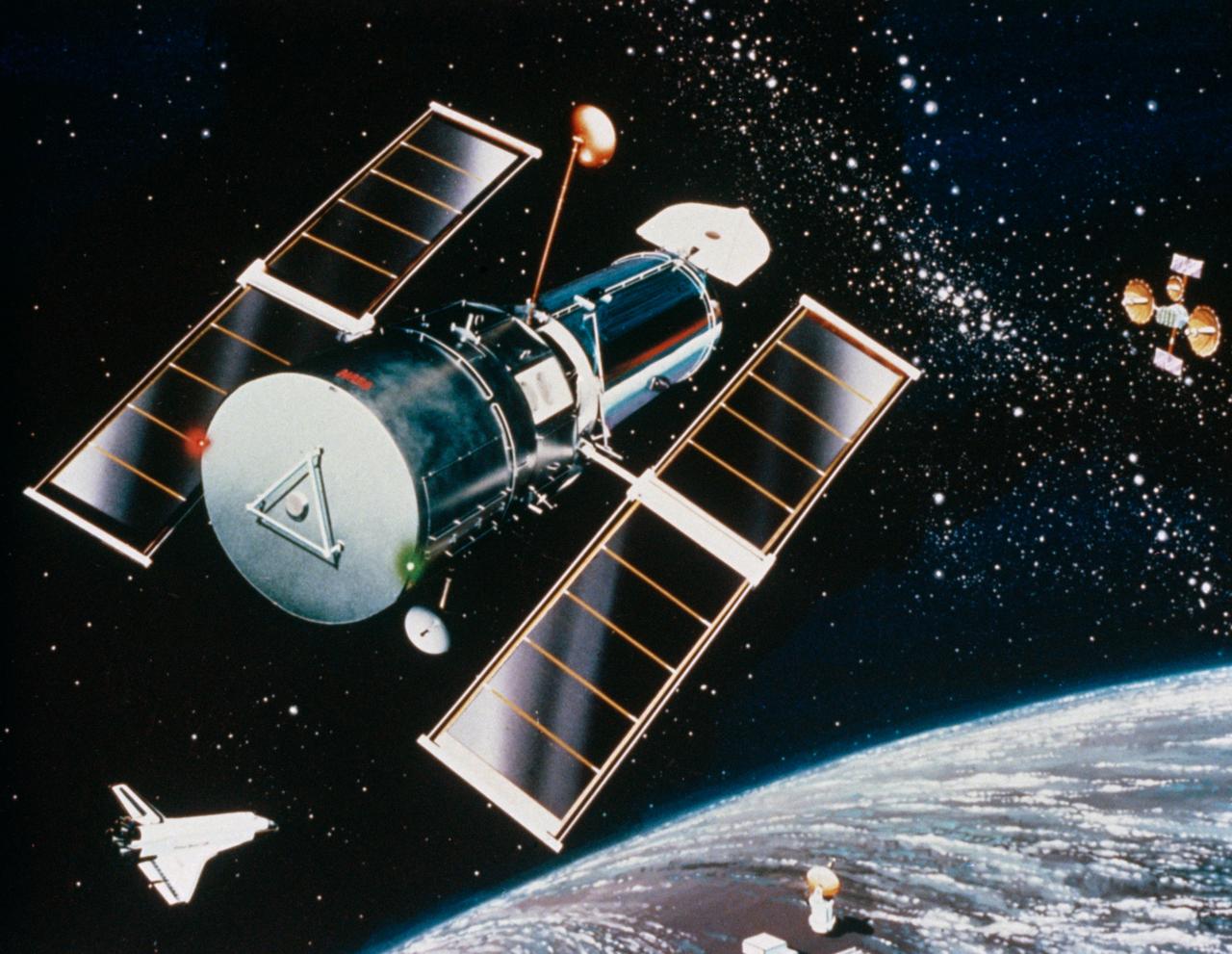

Artist concept shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) placed in orbit above the Earth's distorting layer of atmosphere by Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, during mission STS-31. Tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is visible in the background and ground station is visible below on the Earth's surface. HST is the first of the great observatories to go into service and one of NASA's highest priority scientific spacecraft. Capable of observing in both visible and ultraviolet wavelengths, HST has been termed the most important scientific instrument ever designed for use on orbit. It will literally be able to look back in time, observing the universe as it existed early in its lifetime and providing information on how matter has evolved over the eons. The largest scientific payload ever built, the 12 1/2-ton, 43-foot HST was developed by Lockheed Missiles & Space Company, spacecraft prime contractor, and Perkin-Elmer Corporation, prime contractor for the optical assembly. The European Space Agency (ESA) furnished the power generating solar array and one of the system's five major instruments. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) manages the HST project; Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) will be responsible, when the spacecraft is in orbit, for controlling the telescope and processing the images and instrument data returns.
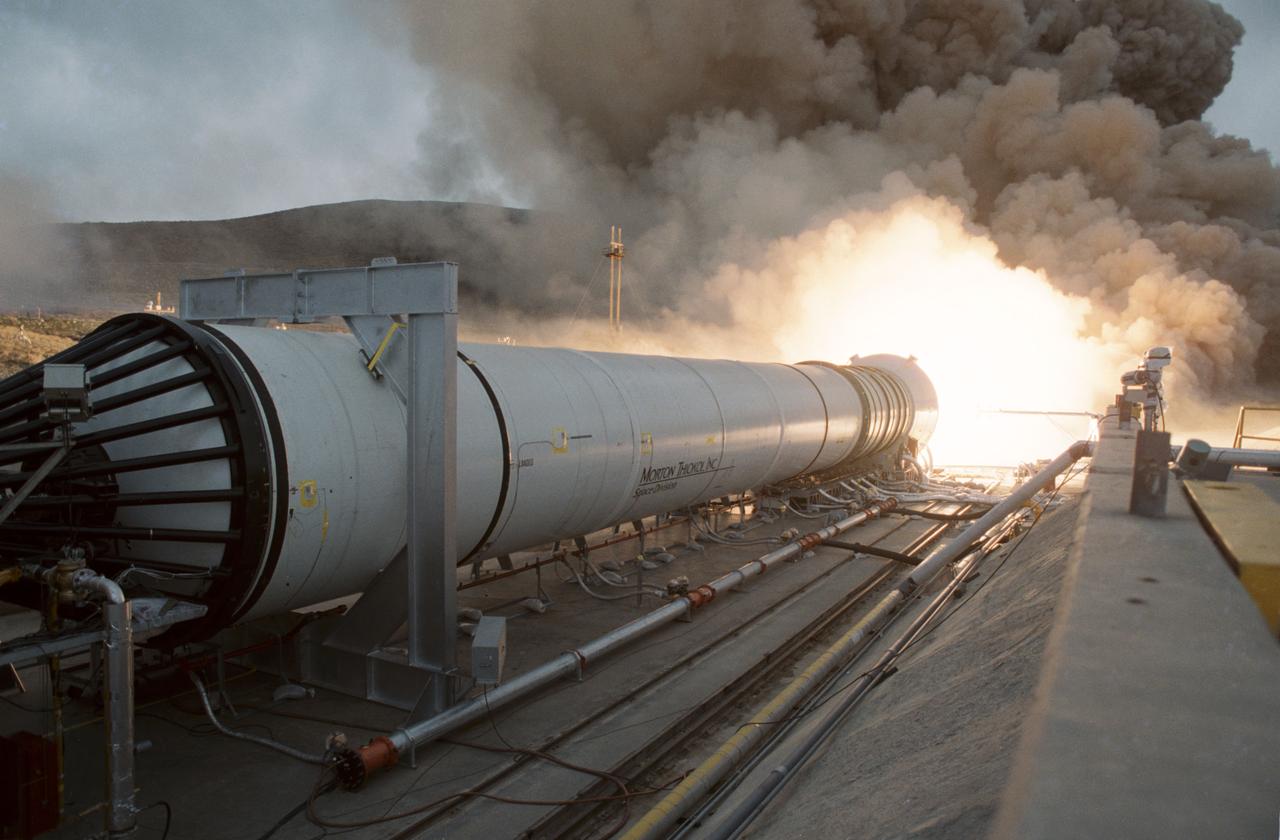

Solid Rocket Qualification Motor Firing at the Morton Thiokol facility at Brigham City, Utah on 20 April 1988.

Origin and Evolution of life Original Art by Robert Bausch UPDATE of AC85-0621
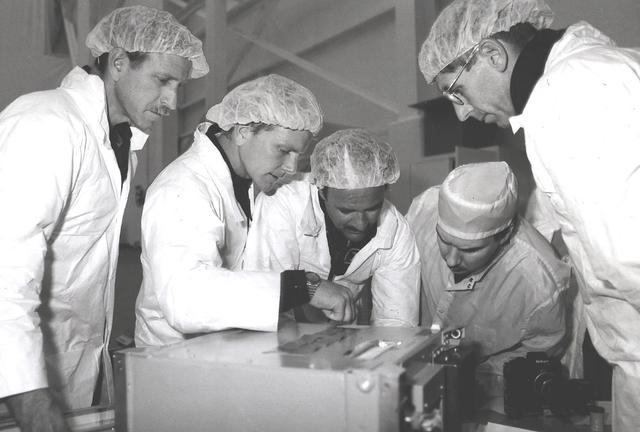

Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-26) astronauts George Nelson, John Lounge, and Richard Covey are pictured training on protein crystal growth (PCG) experiment in Marshall's Building 4708's clean room.
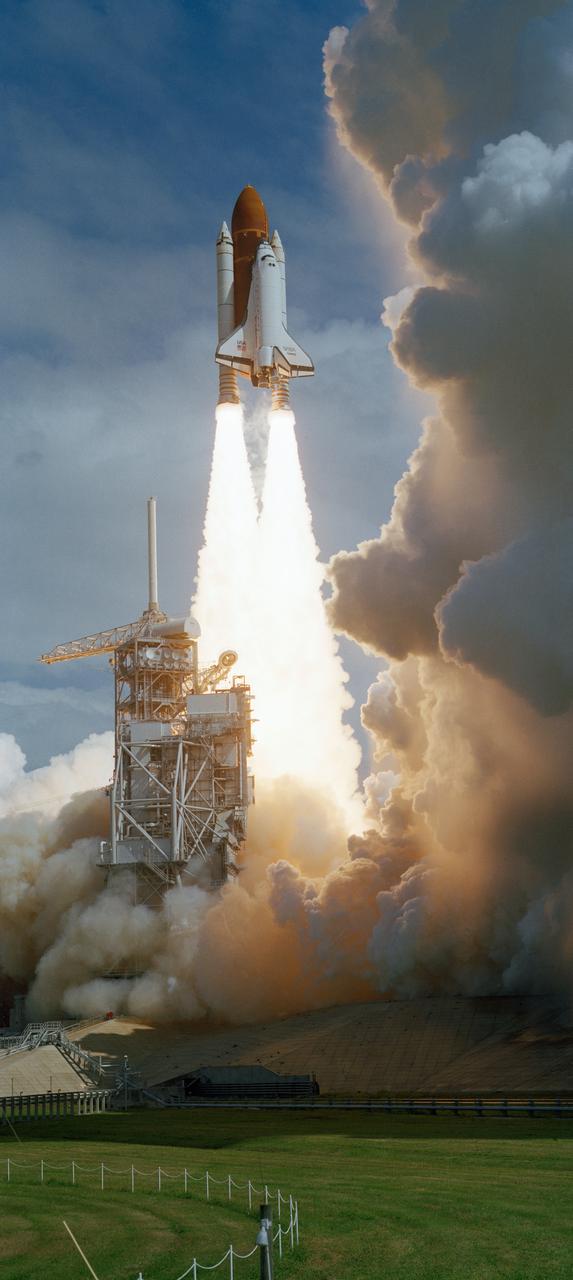

S26-S-032 (29 Sept. 1988) --- The STS-26 launch of space shuttle Discovery begins the first flight to be flown after the Challenger accident. The flight crew included astronauts Rick Hauck, commander; Dick Covey, pilot; and three mission specialists, Dave Hilmers, Mike Lounge, and George (Pinky) Nelson. During the four-day mission, the crew deployed the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-C) and operated eleven mid-deck experiments. Discovery completed 64 orbits of the earth before landing at Edwards Air Force Base, California, on October 3, 1988. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
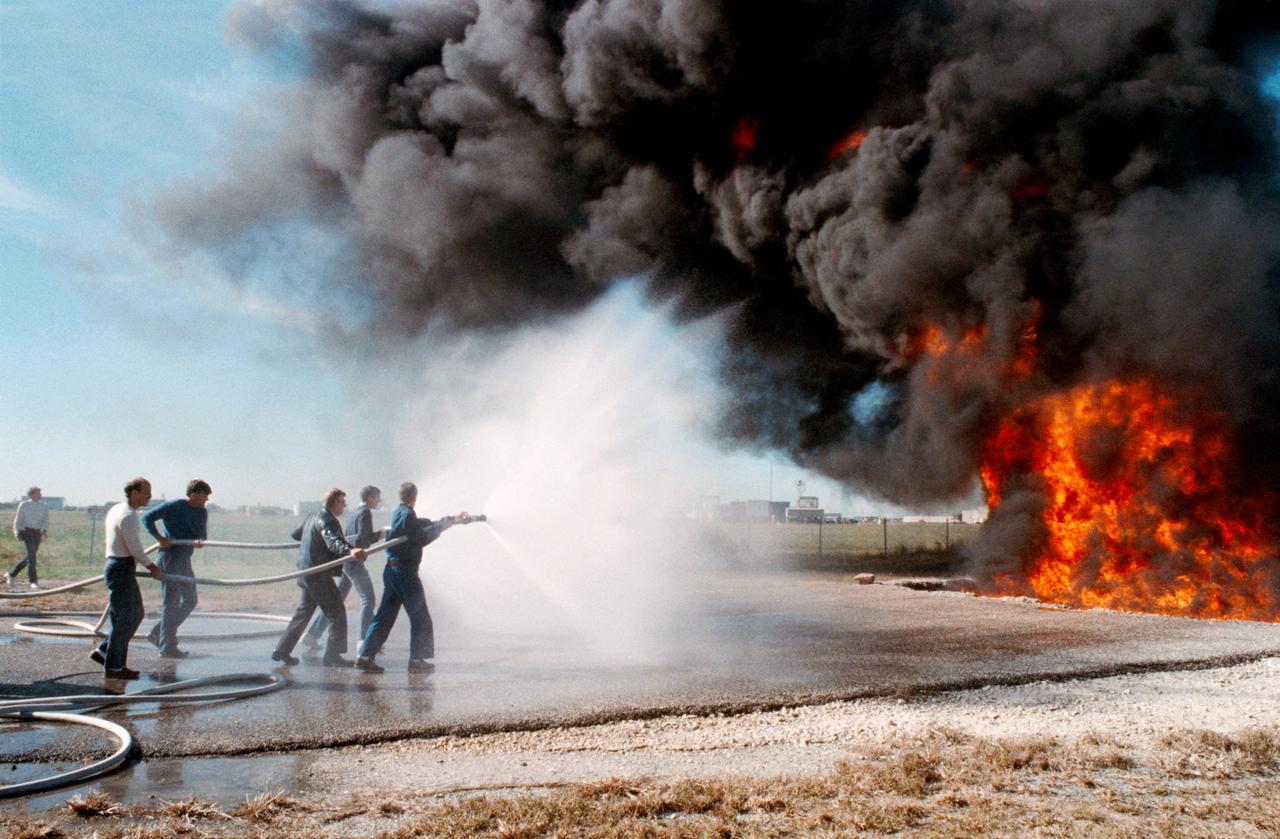

S88-54945 (6 Dec 1988) --- The STS-29 crewmembers are trained in procedures to follow in the event of a fire with their spacecraft. Here, Astronauts Michael L. Coats (far left), mission commander, and James P. Bagian, mission specialist, follow the lead of two fellow crewmembers as they extinguish a fire. The astronauts in front of the action are Robert C. Springer, mission specialist, and John E. Blaha, pilot. Not pictured is James F. Buchli, mission specialist. Their instructor, center, is Robert Fife of NASA's security staff. The training took place on the northern end of the 1625-acre JSC facility.
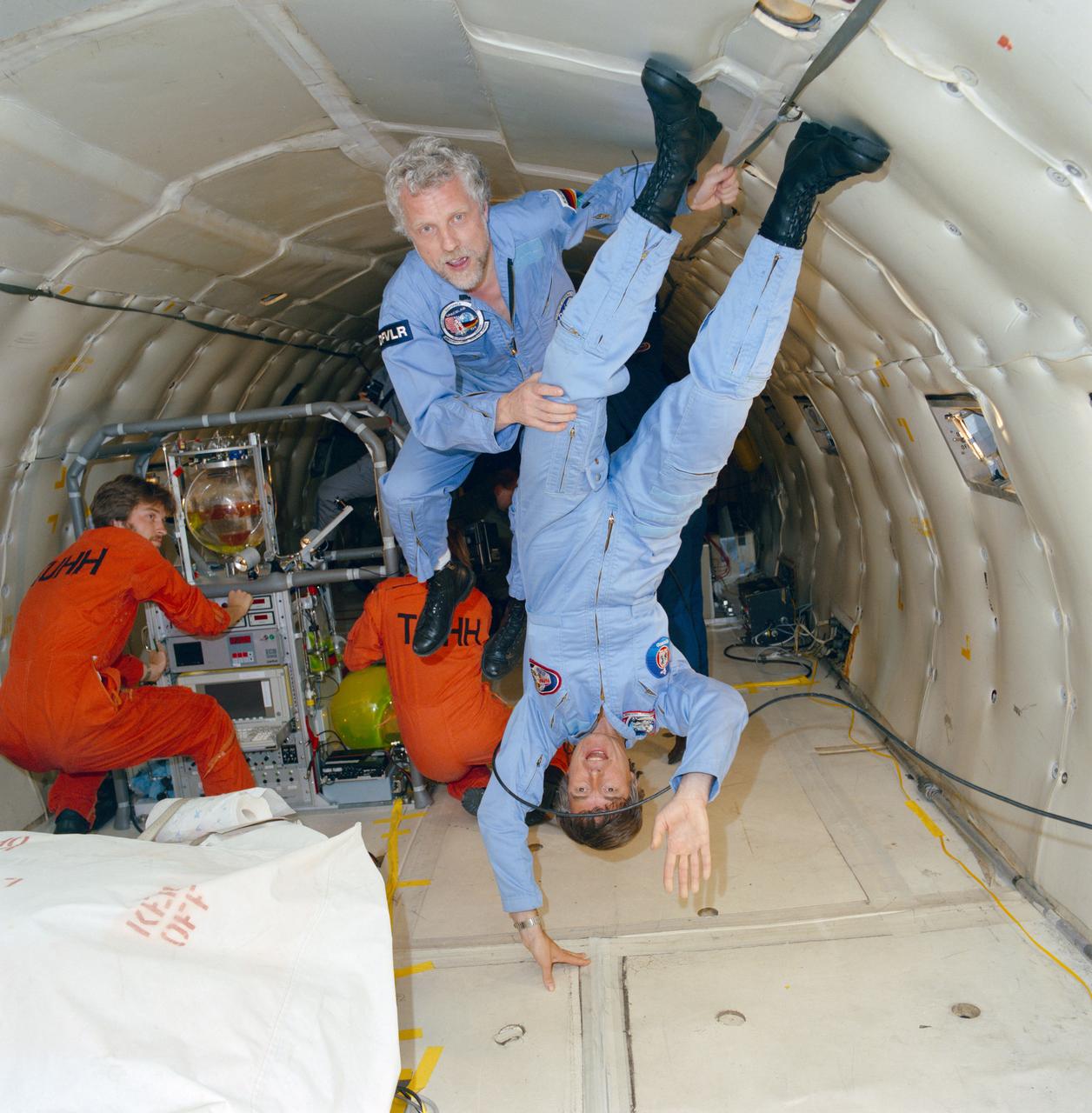

S88-37966 (2 Oct 1988) --- European Space Agency payload specialists Ulf Merbold (STS-42, right) and Reinhold Furrer (STS 61-A) get the "feel" of zero-gravity aboard NASA's KC-135 aircraft over the Gulf of Mexico.
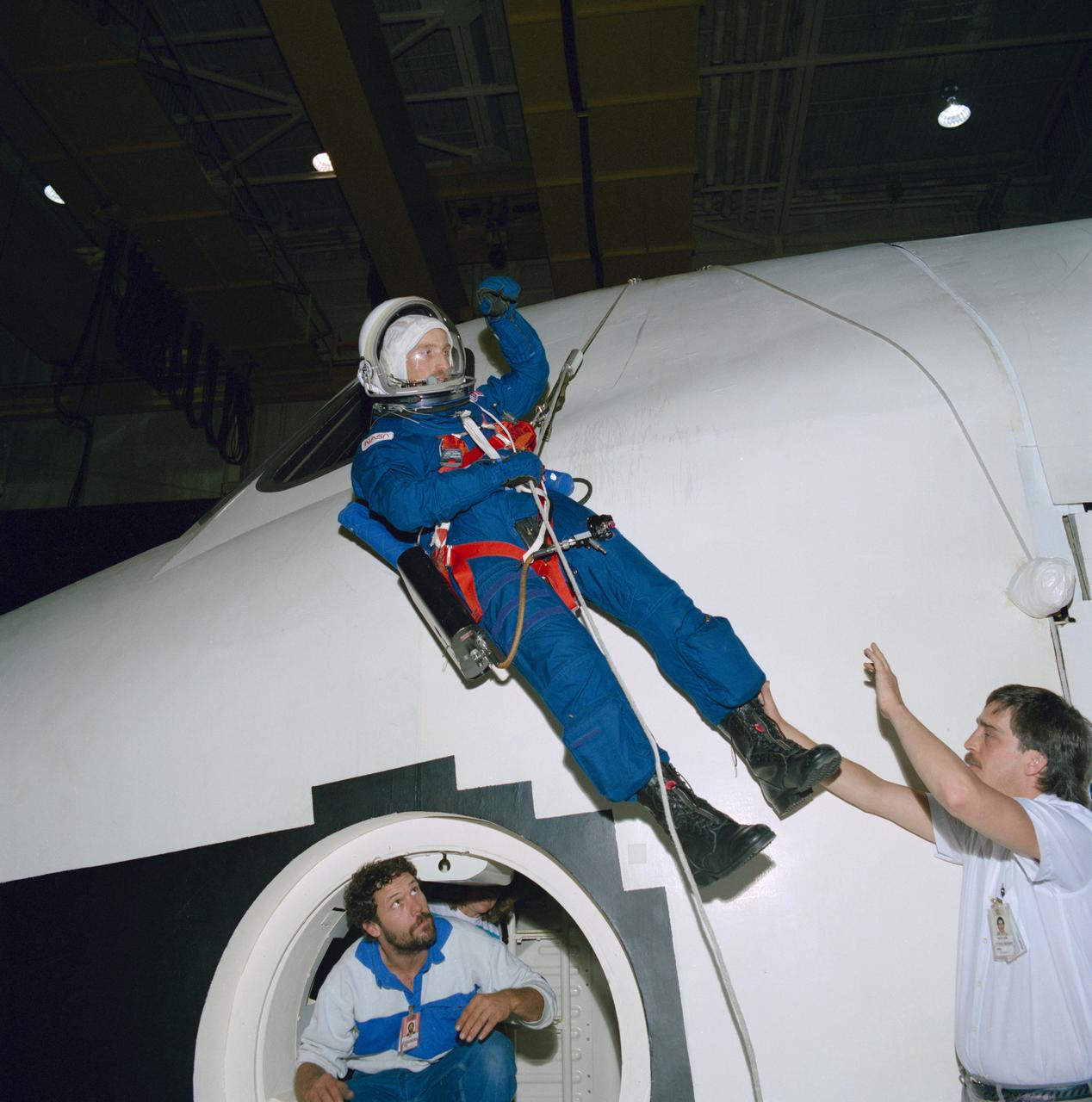

S88-38355 (27 May 1988) --- Astronaut James P. Bagian lowers himself from the top of one of the full-fuselage trainer in JSC's Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory during a post-landing, over-the-top emergency egress test. Bagian, a M.D., and one of three mission specialists assigned to NASA STS-29 flight of the Discovery, is working with engineers evaluating egress using the new crew escape equipment that includes a parachute harness.
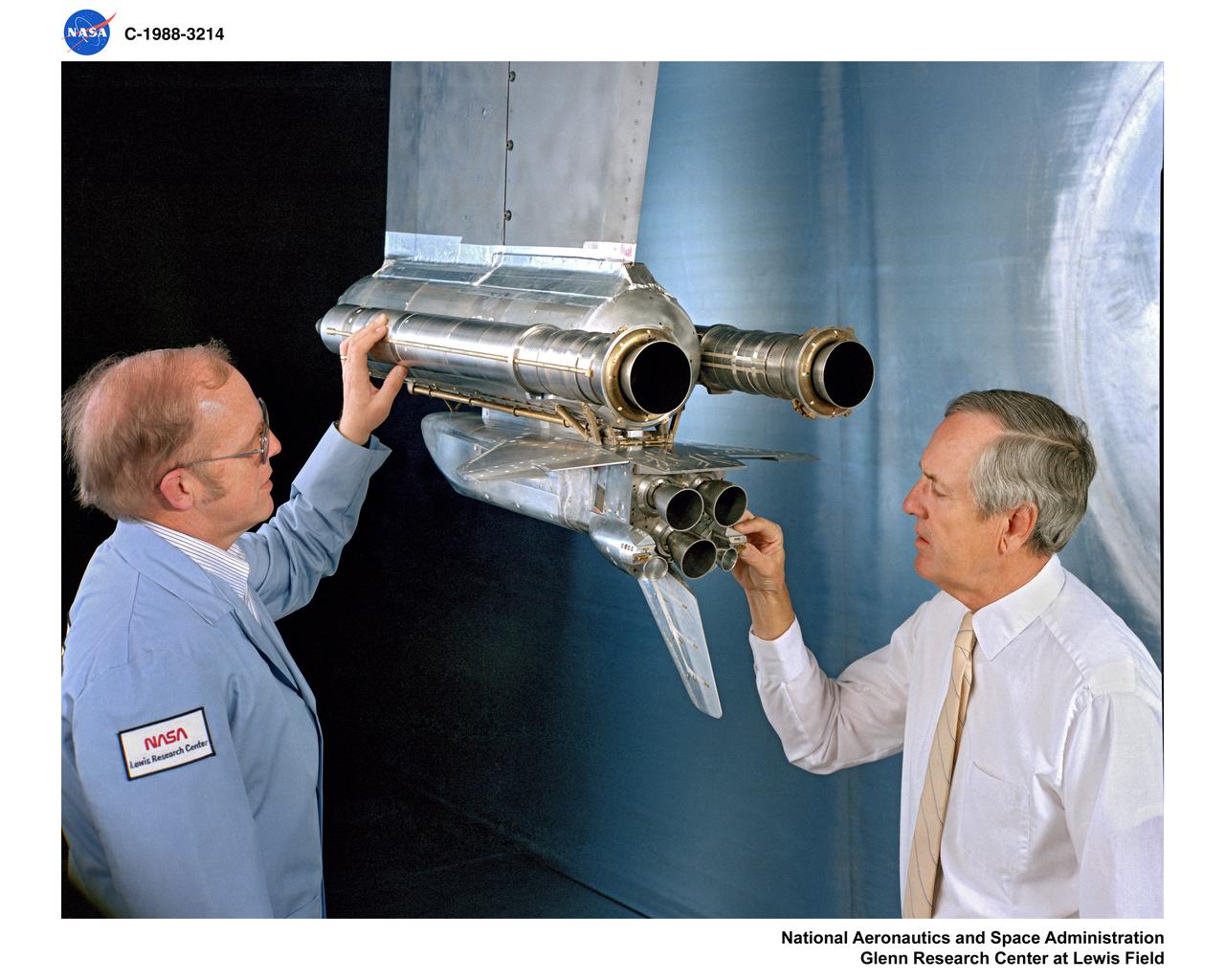

This test conducted in May 1988 shows what happens during launch if a space shuttle main engine fails. The test was conducted in the 10X10 supersonic wind tunnel at the John H. Glenn Research Center.
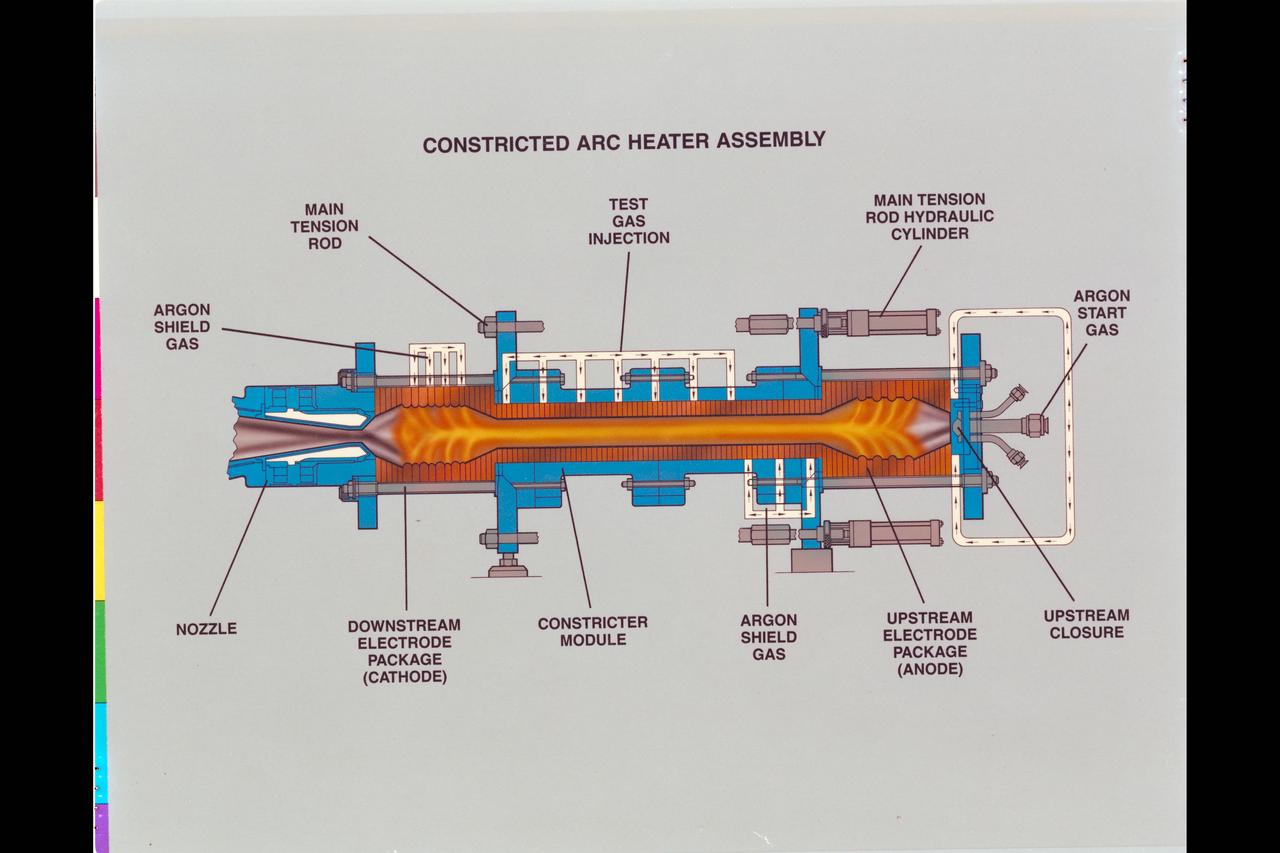
Artwork Constricted Arc Heater Assembly
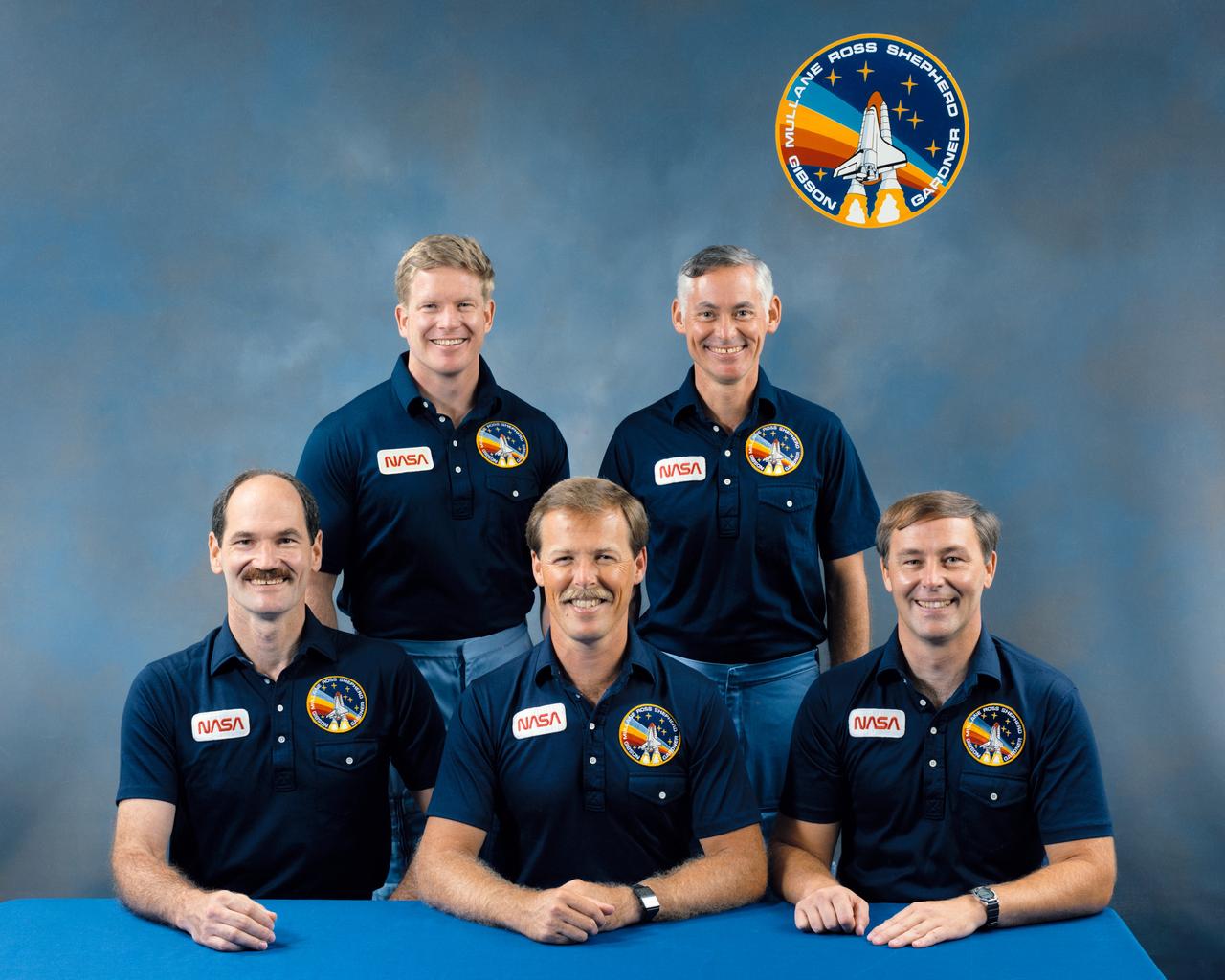

S88-45002 (August 1988) --- These five astronauts will fly aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis for the STS-27 mission. They are (seated left to right) astronauts Guy S. Gardner, Robert L. Gibson and Jerry L. Ross; and (standing, left to right) William M. Shepherd and Richard M. (Mike) Mullane. Gibson is commander; Gardner, pilot; and the other three will serve as mission specialists.

S88-50997 (20 Feb. 1962) --- View of Earth taken by astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. during his Mercury Atlas 6 (MA-6) spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA

Newly arrived DC-8 (NASA-717) in flight over Sierra mountains
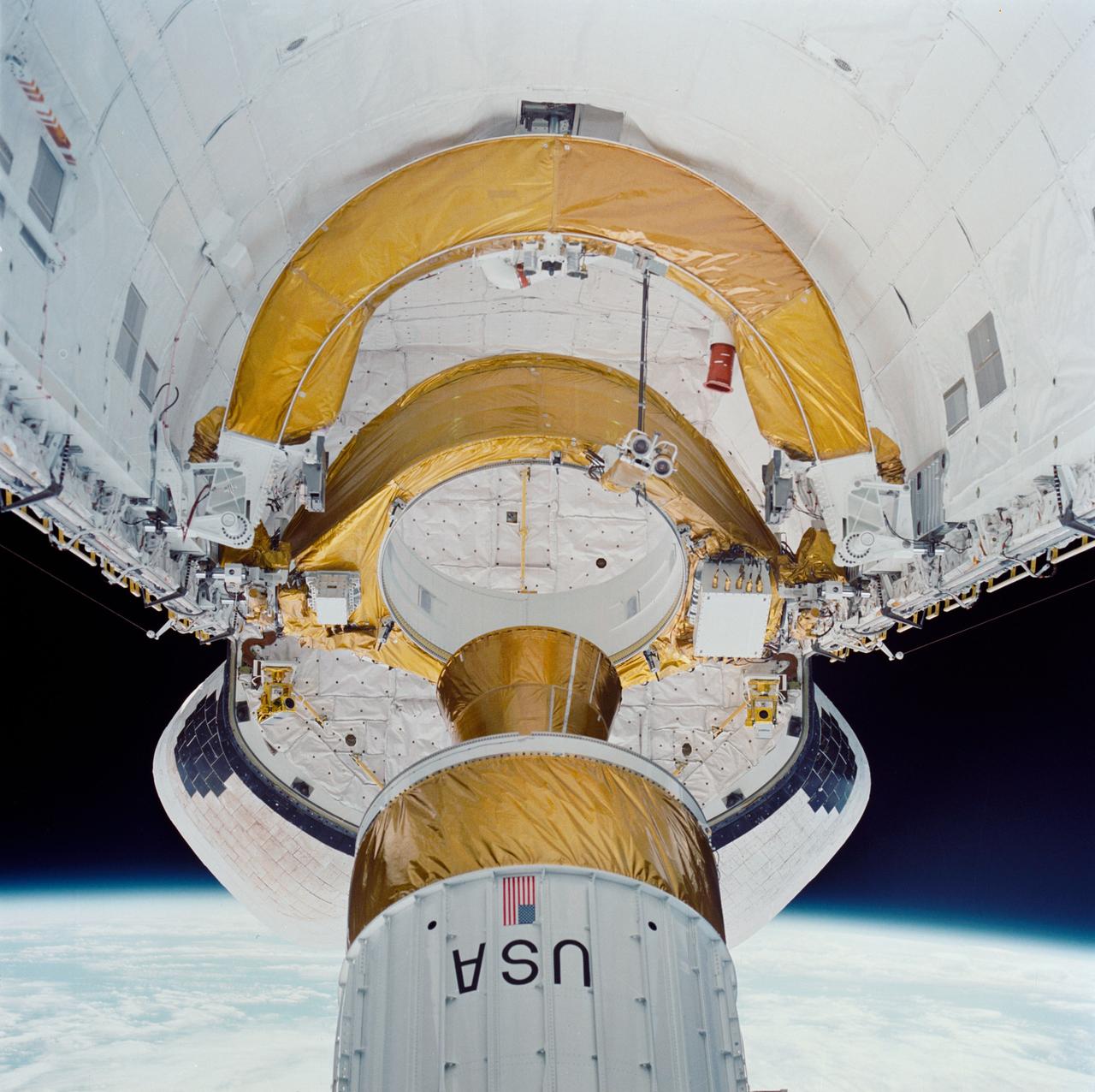

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with the tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) drifts above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, payload bay (PLB) after being positioned in deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). IUS vacates the ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table in the PLB while the disconnected ASE umbilical boom floats above ASE forward cradle. IUS first stage rocket motor and nozzle and the interstage are visible as the IUS is deployed. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's limb.

SH-3G (NASA-735) Helicopter on roll out from Ames ramp

Crows Landing runway approach
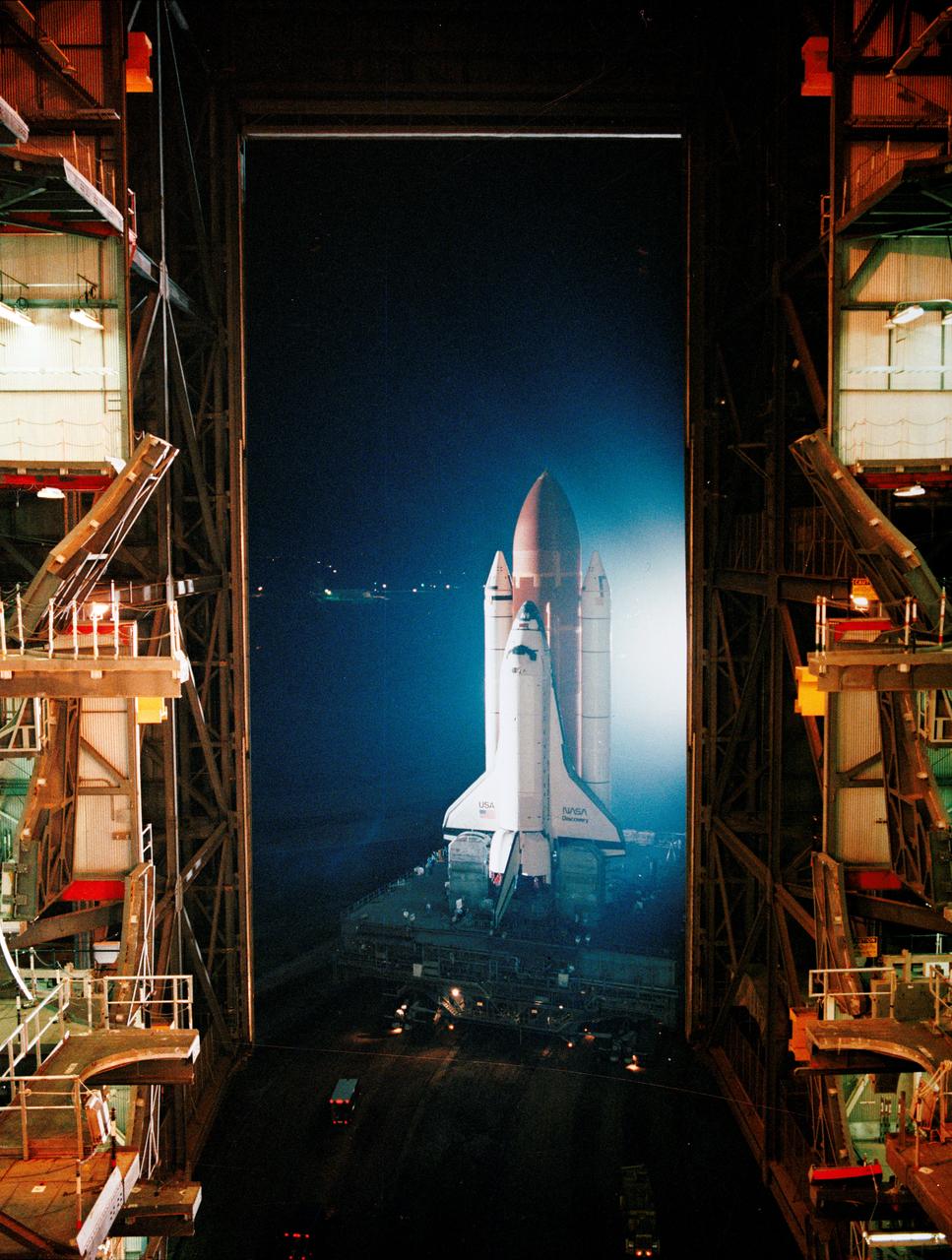
STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, mated with the external tank (ET) and solid rocket boosters (SRBs), is framed by Kennedy Space Center's (KSC's) vehicle assembly building (VAB) doorway as it rolled out. This high angle view shows OV-103 atop the mobile launch pad and crawler transporter as it begins its slow exit from VAB en route to launch complex (LC) pad 39B. The move began shortly after midnight on the nation's 212th birthday. Ceremonies marking the event were held later during daylight hours.
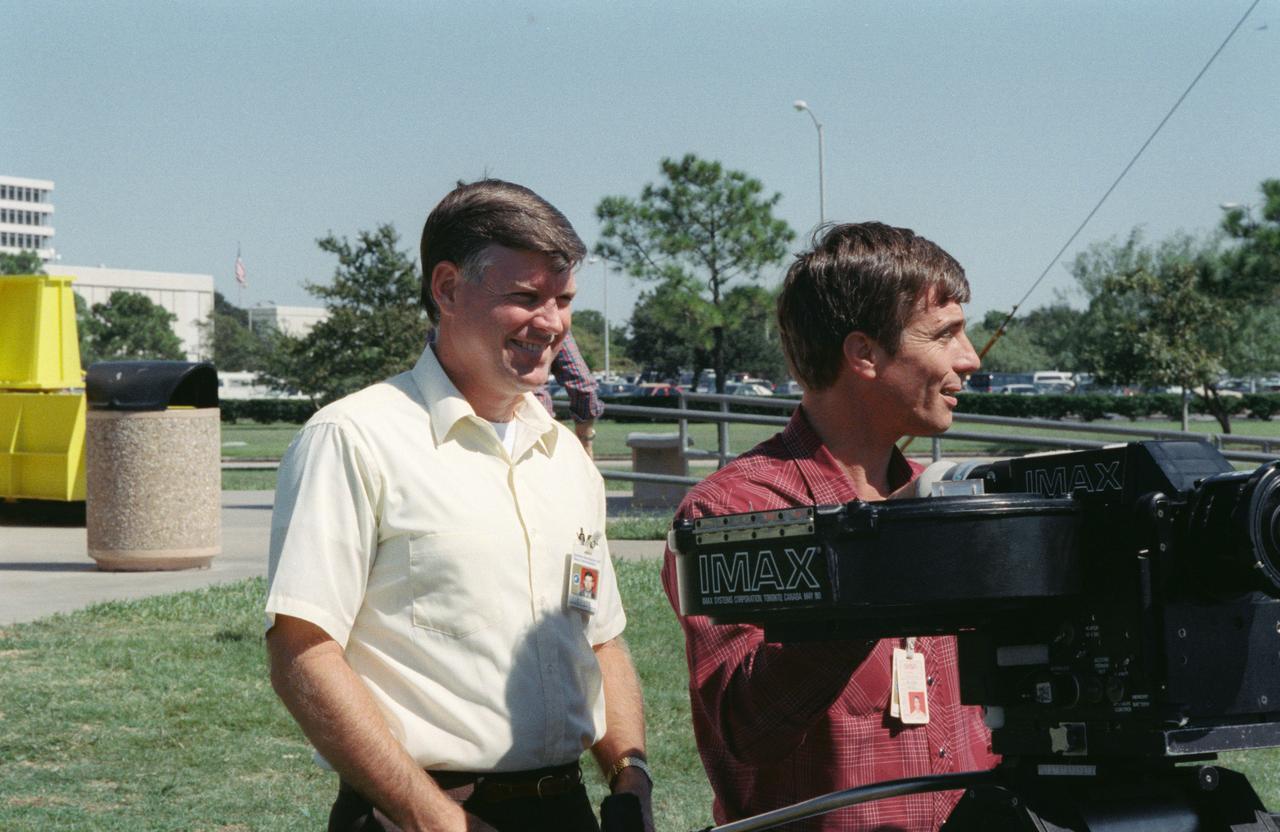

S88-52473 (8 Nov 1988) --- The commander and pilot of NASA's STS-29 mission get some training on the operation of one of the payloads for their upcoming spaceflight aboard Discovery. Astronauts Michael L. Coats, left, and John E. Blaha, along with the three other members of the crew, met with Imax personnel on the JSC grounds to practice using the motion-picture camera, making its first post-Challenger trip into space. The payload flew on a number of earlier STS flights.
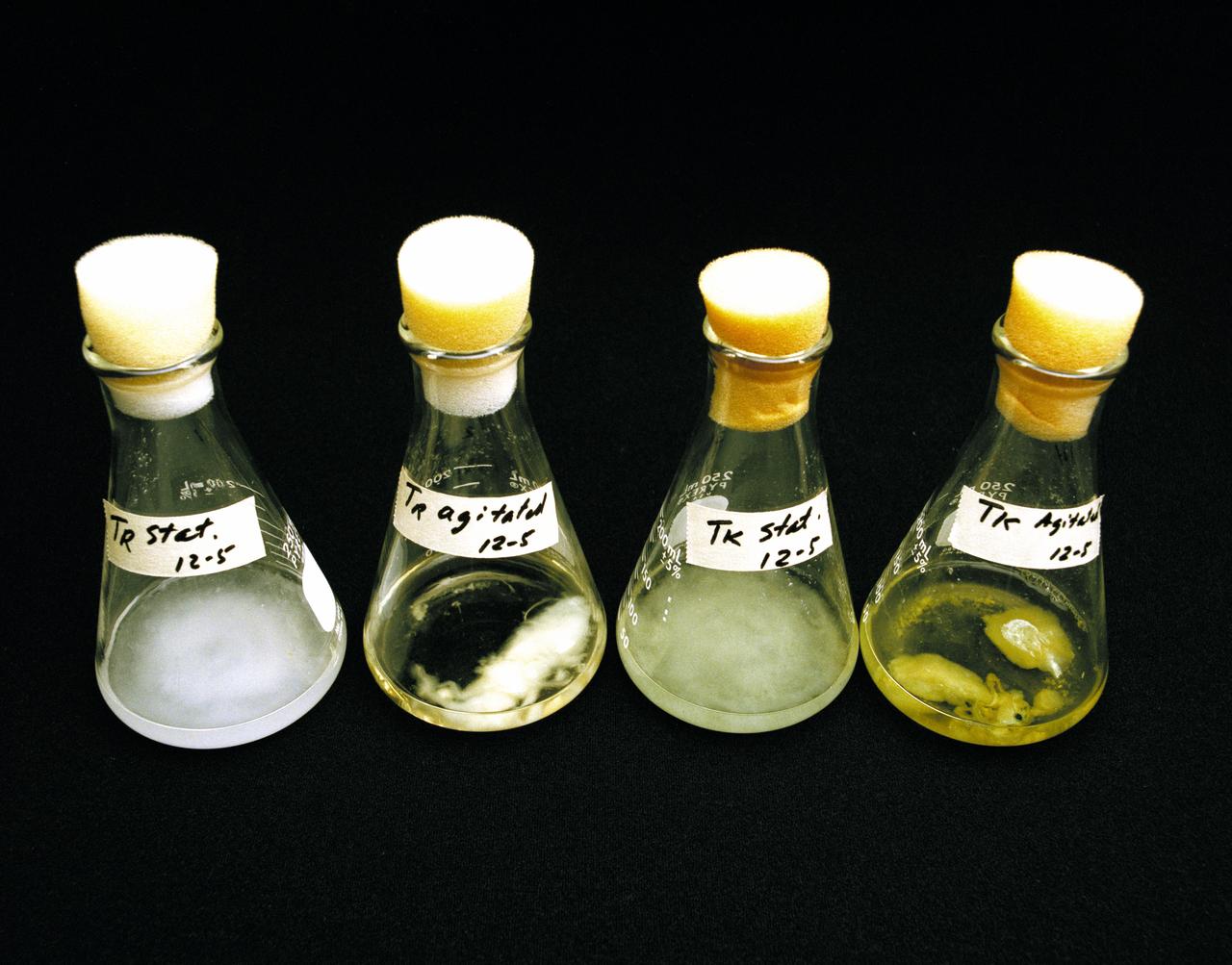

Celloulose Digesting bacteria
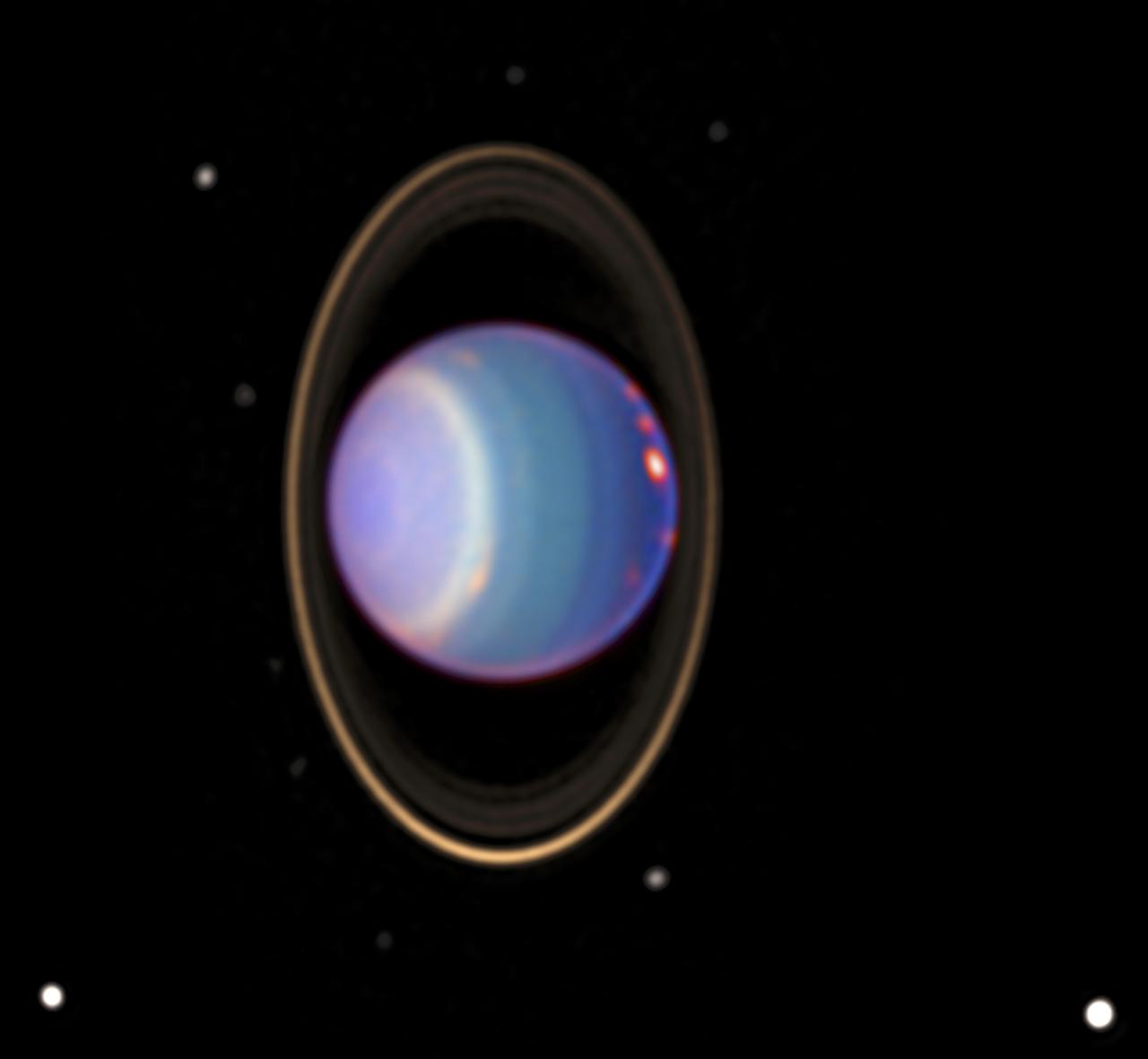

A recent Hubble Space Telescope (HST) view reveals Uranus surrounded by its 4 major rings and 10 of its 17 known satellites. This false color image was generated by Erich Karoschka using data taken with Hubble's Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer. The HST recently found about 20 clouds. The colors in the image indicate altitude. The green and blue regions show where the atmosphere is clear and can be penetrated by sunlight. In yellow and grey regions, the sunlight reflects from a higher haze or cloud layer. The orange and red colors indicate very high clouds, such as cirrus clouds on Earth.
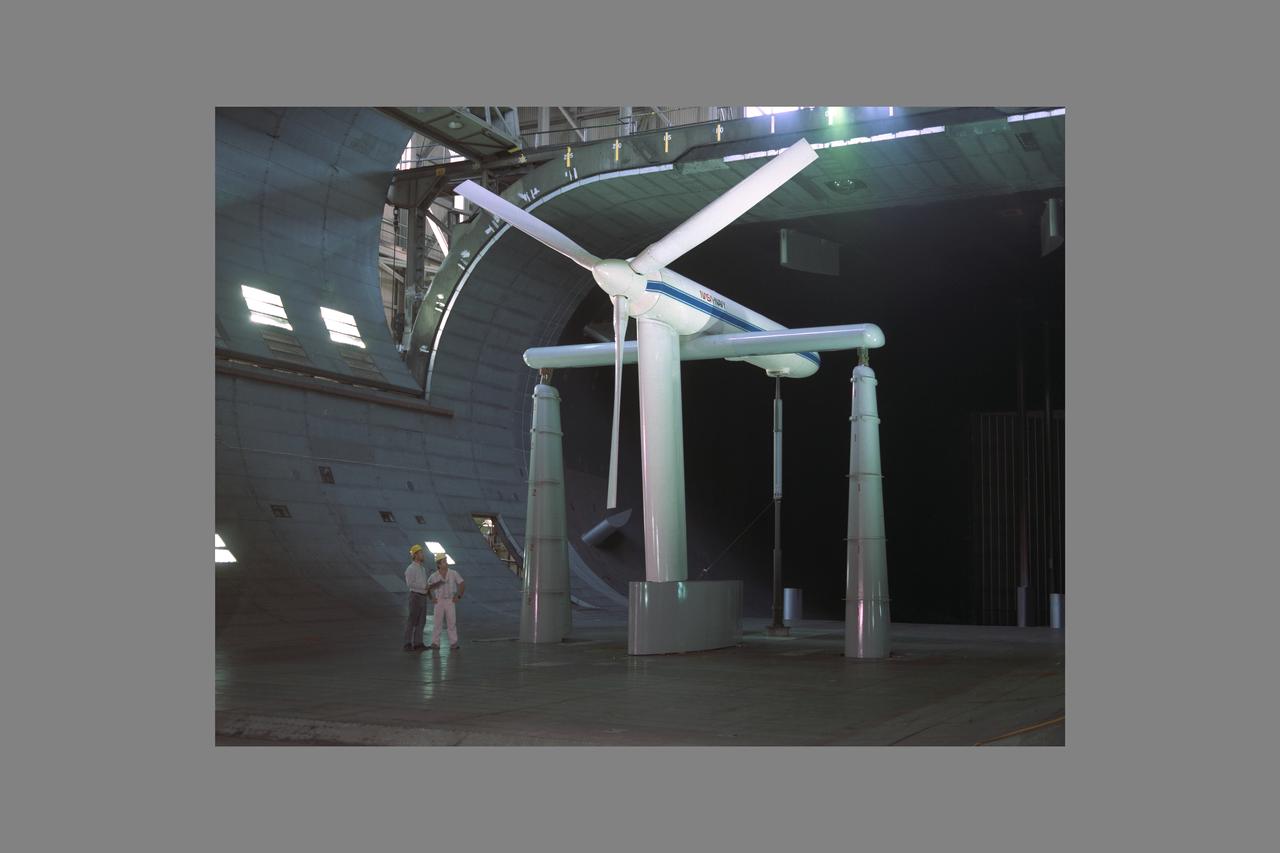

NASA/Navy V-22 Rotor testing in the NASA Ames 40x80ft. Subsonic Wind.Tunnel. Test-568 with Fort Felker and Engenio DeVargas.

JSC Mission Control Center (MCC) Bldg 30 flight control room (FCR) personnel monitor STS-26 post landing activities and ceremonies at Edwards Air Force Base (EAFB) via their monitors. Displayed on front screens are approach and landing diagrams, data, the space shuttle program insignia, the STS-26 mission insignia, the Mission Operations Directorate insignia, and the STS-26 crew standing in front of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103.
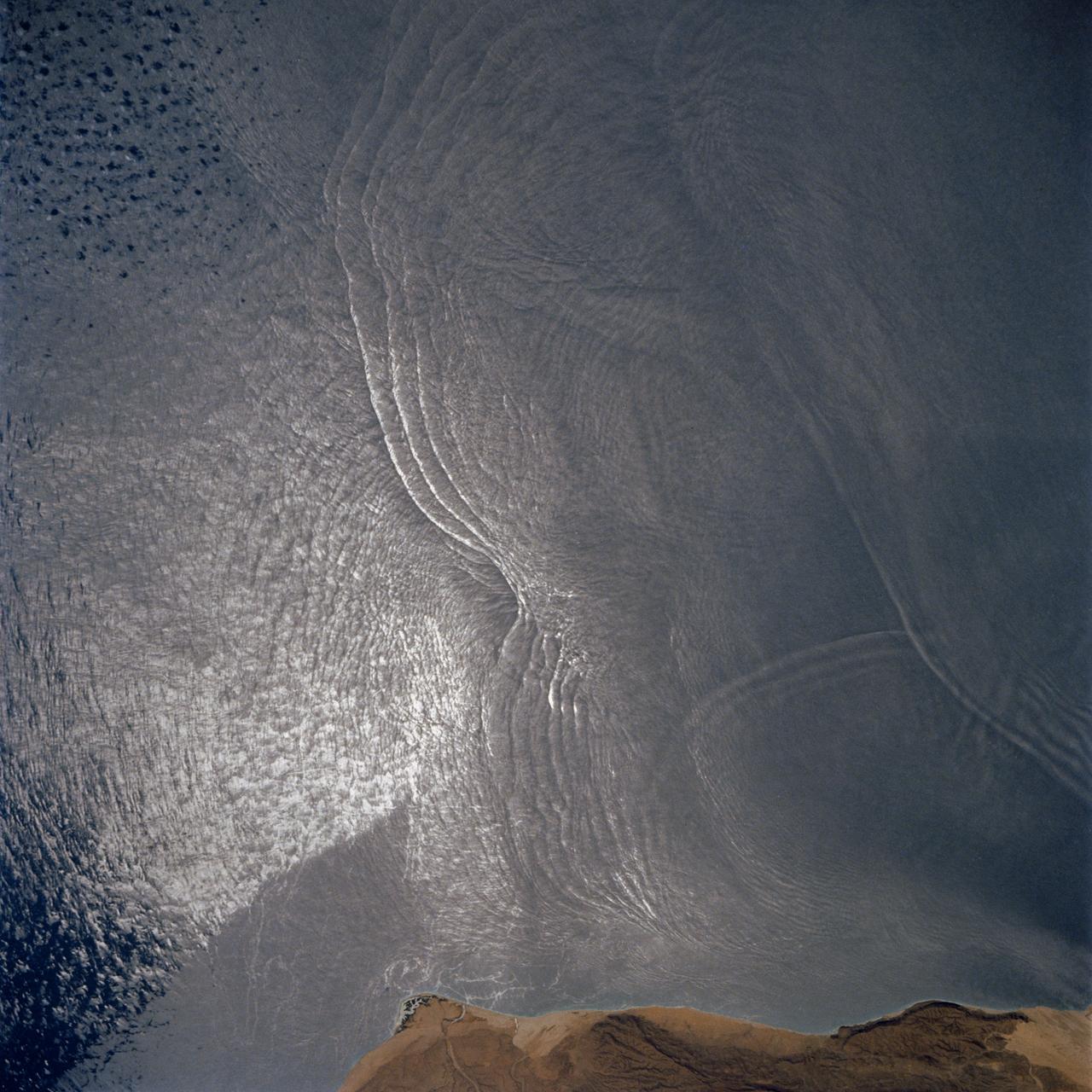

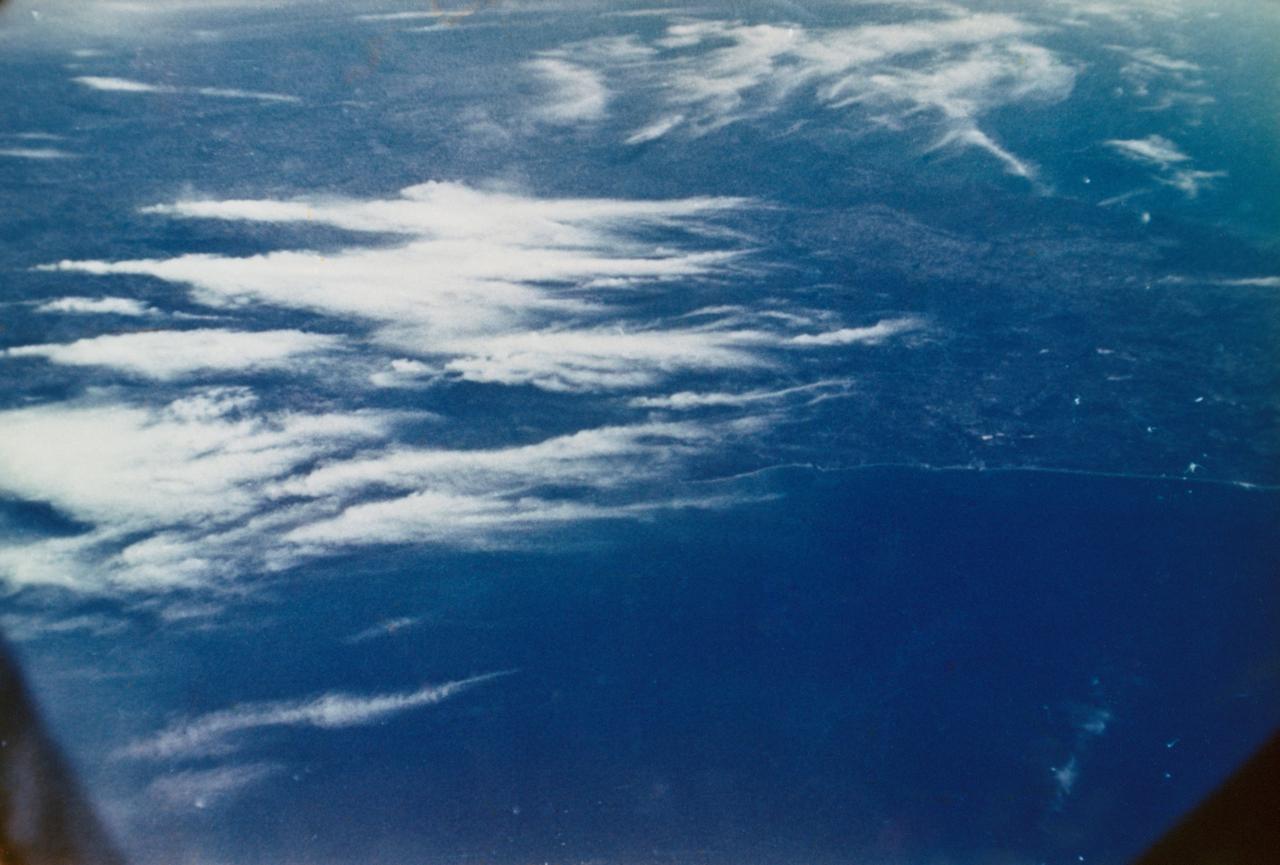
The arculate fronts of these apparently converging internal waves off the northeast coast of Somalia (11.5N, 51.5E) probably were produced by interaction with two parallel submarine canyons off the Horn of Africa. Internal waves are packets of tidally generated waves traveling within the ocean at varying depths and are not detectable by any surface disturbance.
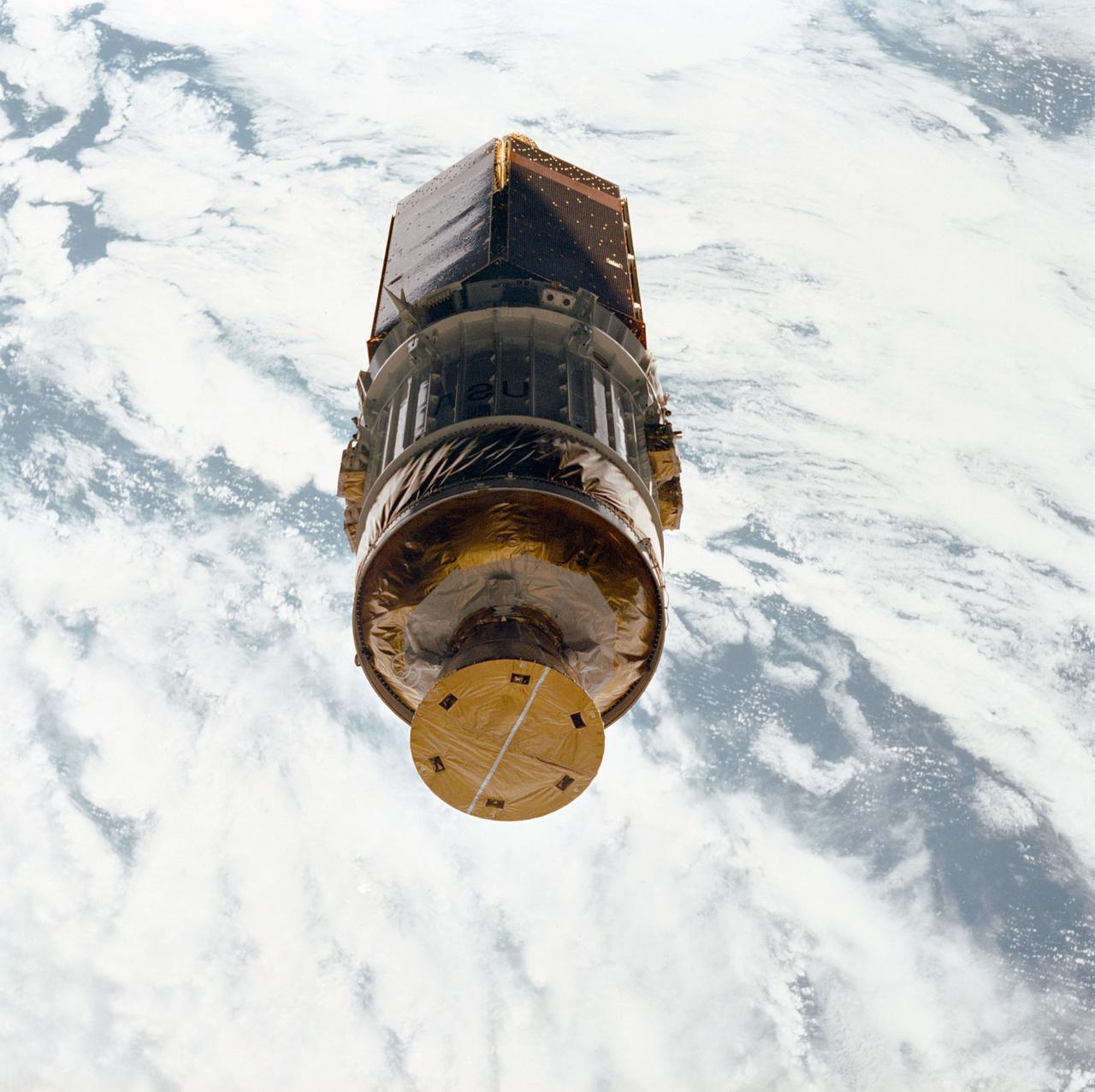

STS026-31-071 (3 Oct 1988) --- After deployment from Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, the inertial upper stage (IUS) with the tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) drifts above the cloud-covered Earth surface. TDRS-C, in stowed configuration (solar array panels visible), is mounted atop the IUS with the interstage and solid rocket motor and nozzle seen in the foreground.

S88-41481 (15 July 1988) --- This is the official insignia of the NASA STS-27 mission. The patch depicts the space shuttle lifting off against the multi-colored backdrop of a rainbow, symbolizing the triumphal return to flight of our nation's manned space program. The design also commemorates the memory of the crew of Challenger mission STS51-L, represented by the seven stars. The names of the flight crew members of STS-27 are located along the border of the patch. They are astronauts Robert L. Gibson, commander; Guy S. Gardner, pilot; Jerry L. Ross, Richard M. (Mike) Mullane and William M. Shepherd, mission specialists. Each crew member contributed to the design of the insignia. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
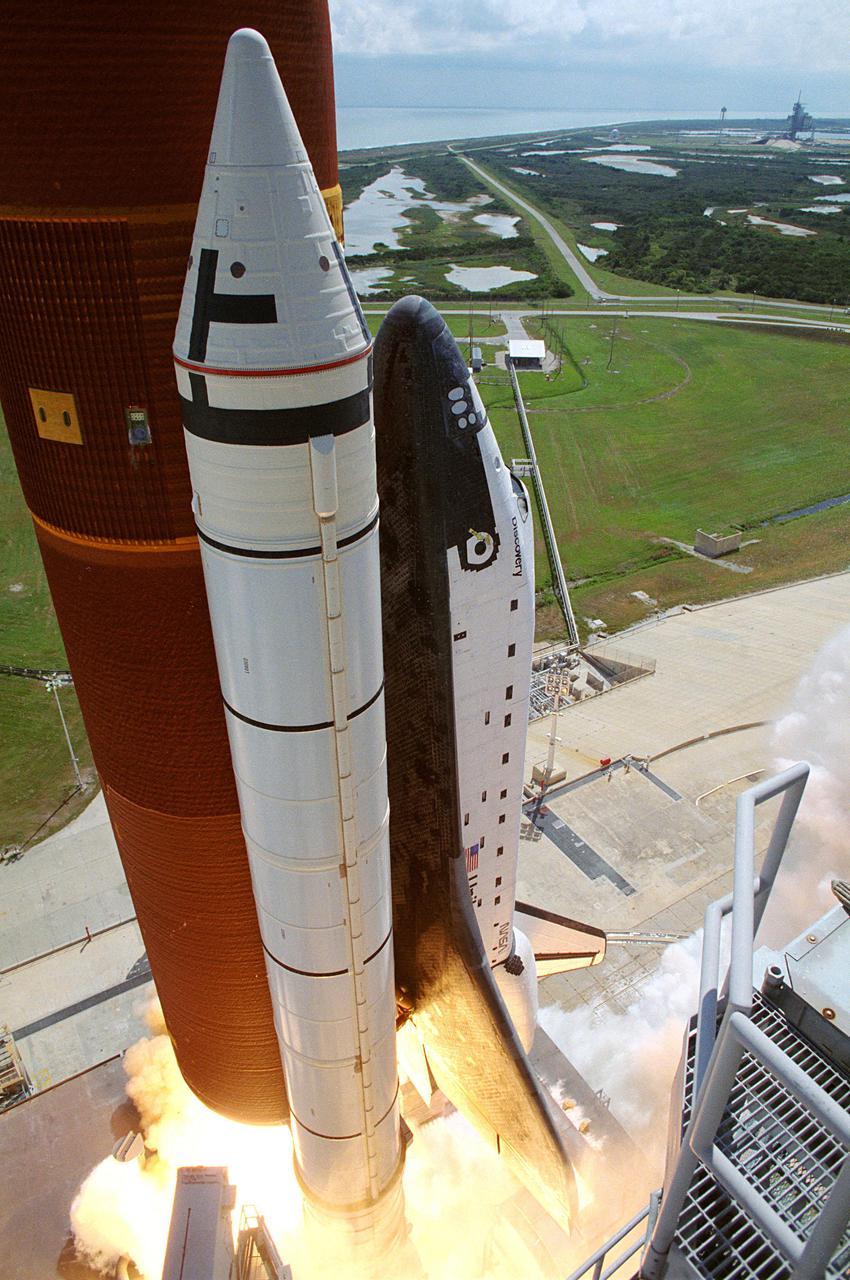

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Discovery and its five-man crew is launched from pad 39B at 11:37 a.m. as STS-26 embarks on a four-day mission, marking America's return to space. On the first day of orbit, the crew will deploy from the orbiter's payload bay the primary payload, the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-C). The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) will boost the satellite to a geosynchronous altitude from low-Earth orbit. When in place, TDRS-C will relay data from low-Earth orbiting spacecraft, and air-to-ground voice communications and television from Space Shuttle orbiters during missions. The crew members of STS-26 are Commander Rick Hauck, Pilot Richard Covey, and Mission Specialists Dave Hilmers, Mike Lounge, and George 'Pinky' Nelson.
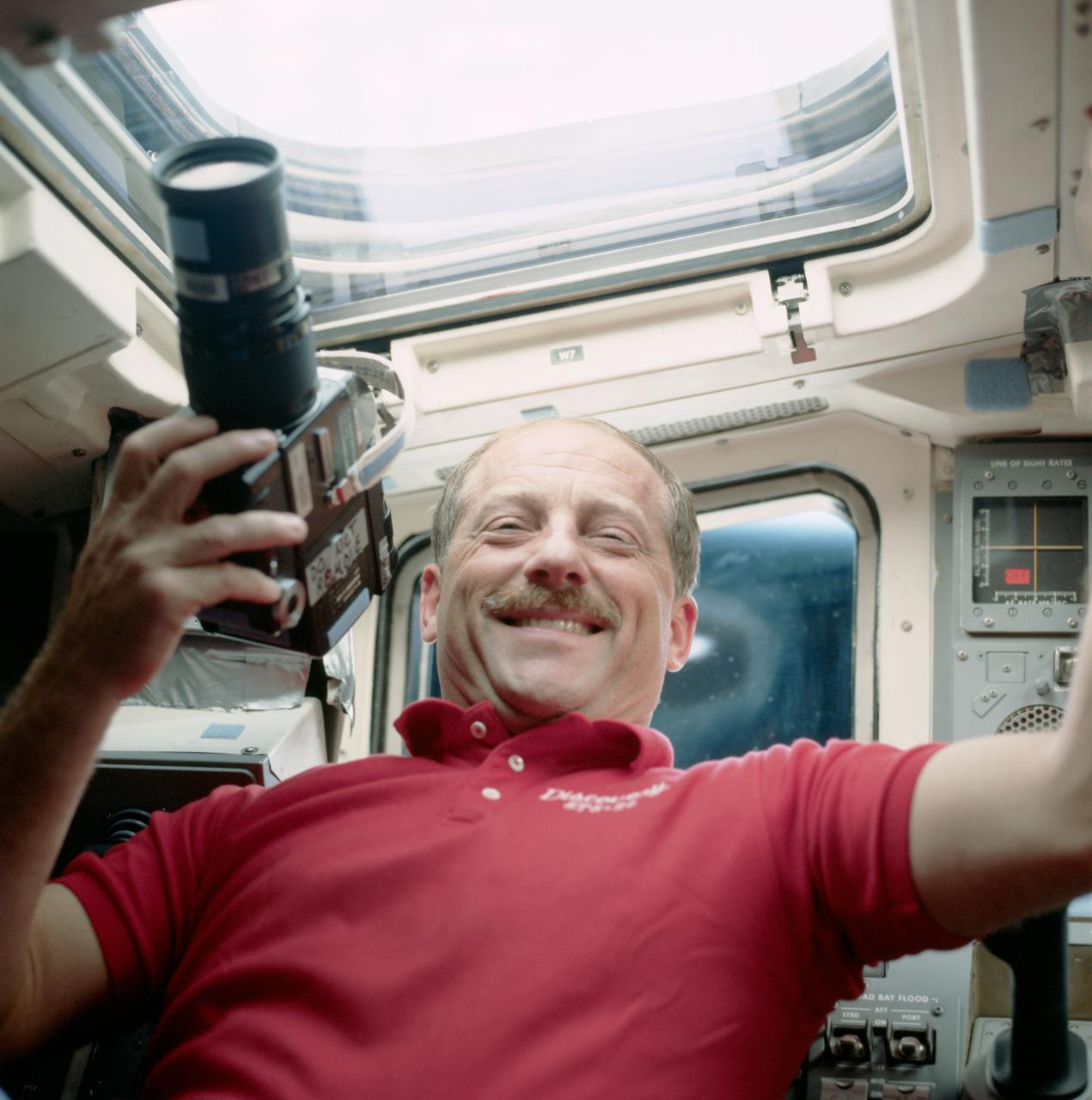

STS026-47-013 (5 Oct 1988) --- Astronaut Frederick H. (Rick) Hauck, commander, on the flight deck, with one of the many cameras carried onboard Discovery to renew documentation of planet Earth. This particular camera is a 70mm handheld Hasselblad.

Photograph by Pioneer Venus OCPP imagery 0900 collected 5-14-88 10th anniversary release Venus image 7540
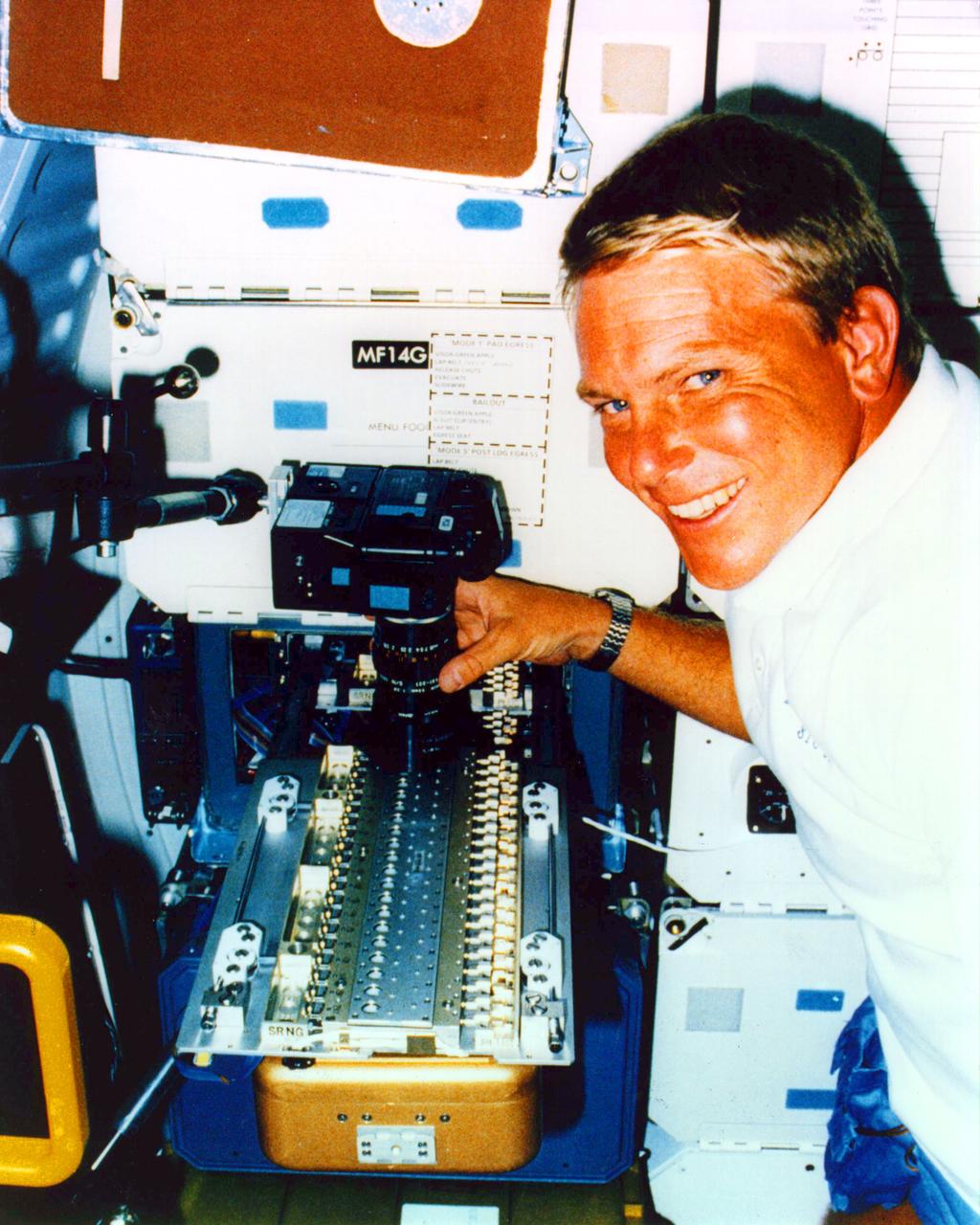
Mission Specialist George (Pinky) D. Nelson uses a 35 mm camera to photograph a protein crystal grown during the STS-26 Protein Crystal Growth (PCG-II-01) experiment. The protein crystal growth (PCG) carrier is shown deployed from the PCG Refrigerator/Incubator Mocule (R/IM) located in the middeck forward locker. The R/IM contained three Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDS) trays (one of which is shown). A total of sixty protein crystal samples were processed during the STS-26 mission.
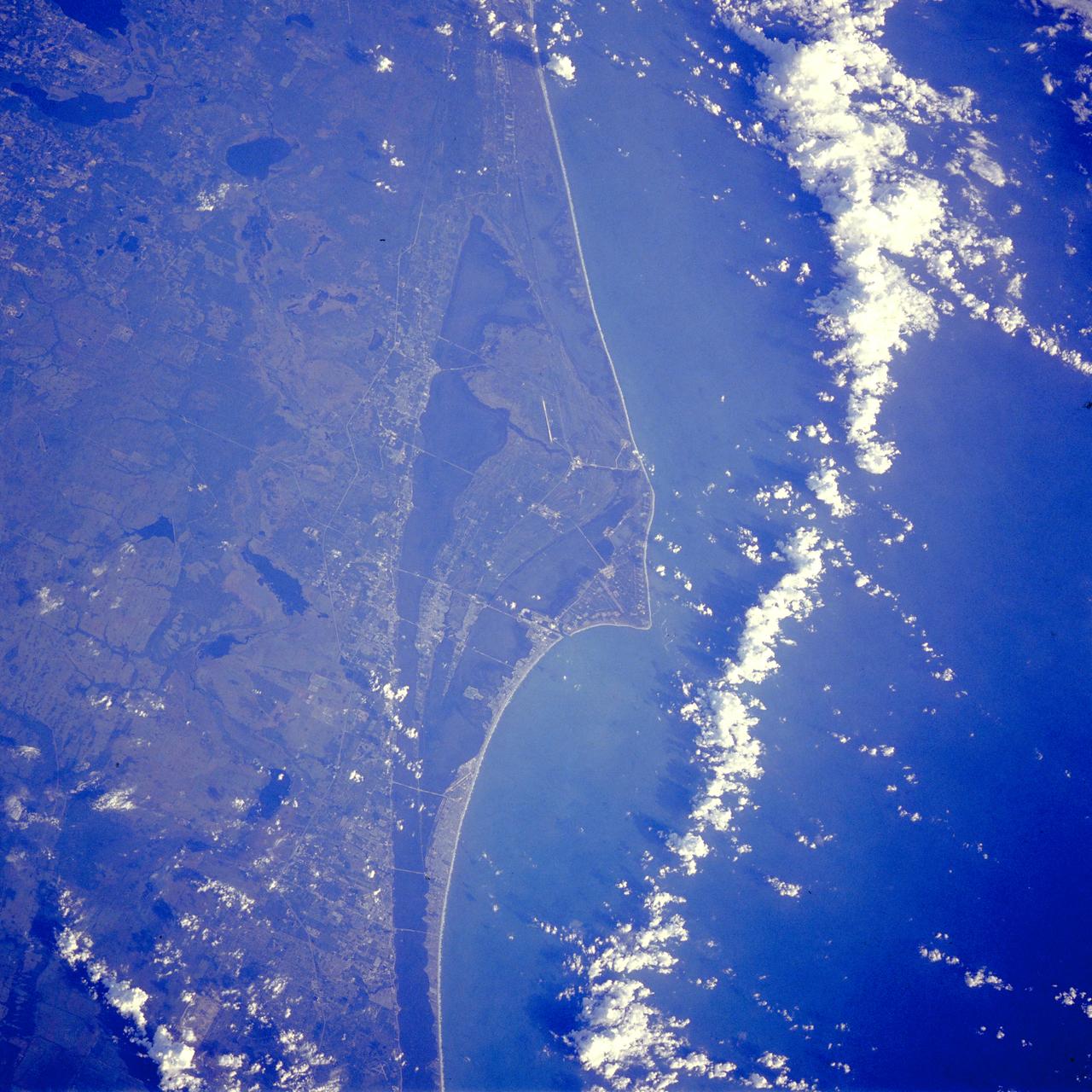

STS-26 ONBOARD - The Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral, and most of Brevard County, Florida, are clearly visible in this photo taken by the crew of the orbiter Discovery while in orbit during space shuttle mission STS-26.
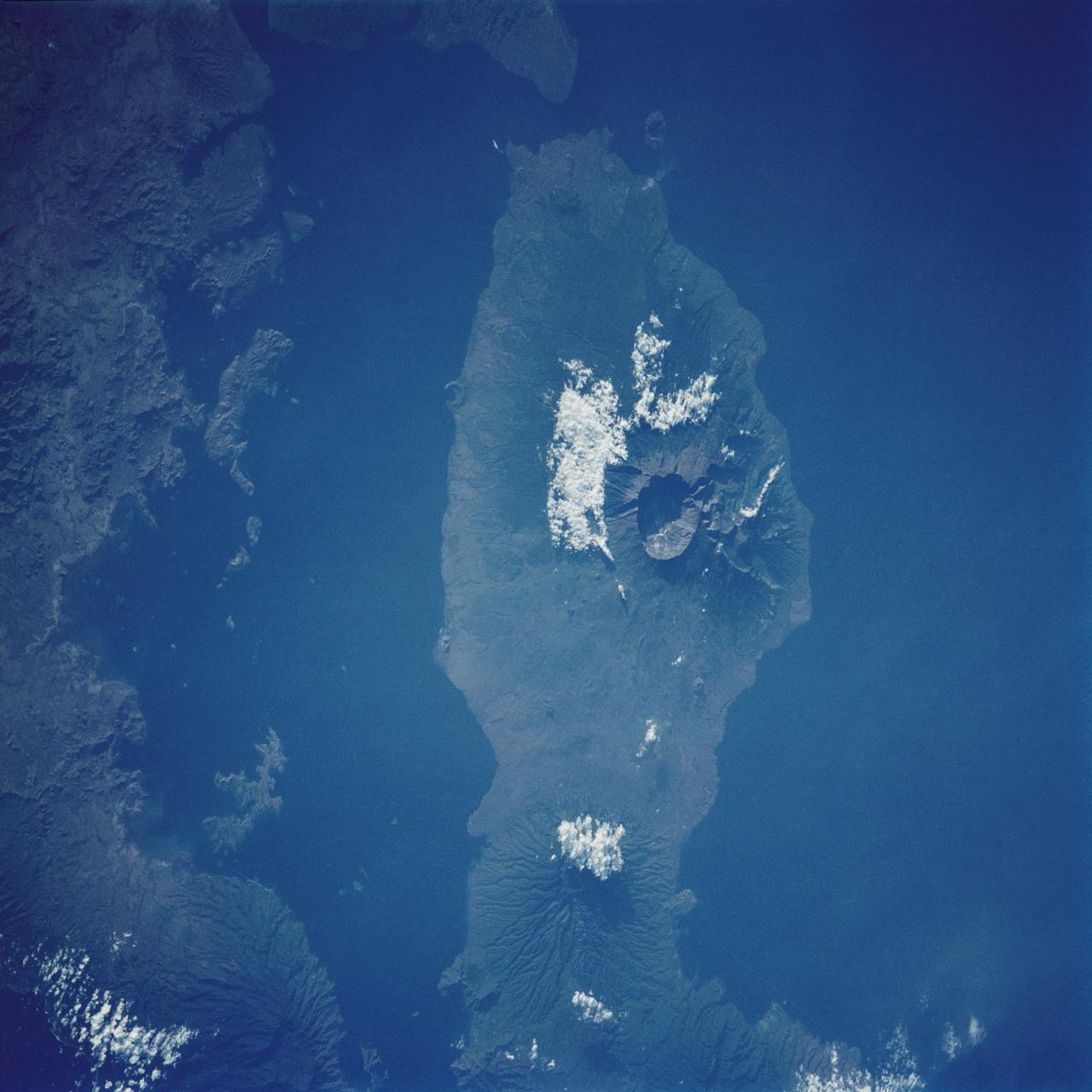

STS026-038-056 (29 Sept. - 3 Oct. 1988) --- Tambora Caldera, Sumbawa Island, Indonesia as photographed with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera. Tambora is a 6-kilometer-wide and 650-meter-deep Caldera formed in 1815 as a result of a huge volcanic eruption. Gases from the eruption were ejected high into Earth's atmosphere and transported around the globe. The atmospheric gases trapped part of the incoming sunglint, resulting in extremely cold weather. In New England, snow fell in June, and freezes occurred throughout the summer of 1816, which became known as "the year without a summer." This photo was shown by the STS-26 astronaut crew during its Oct. 11, l988 post-flight press conference.
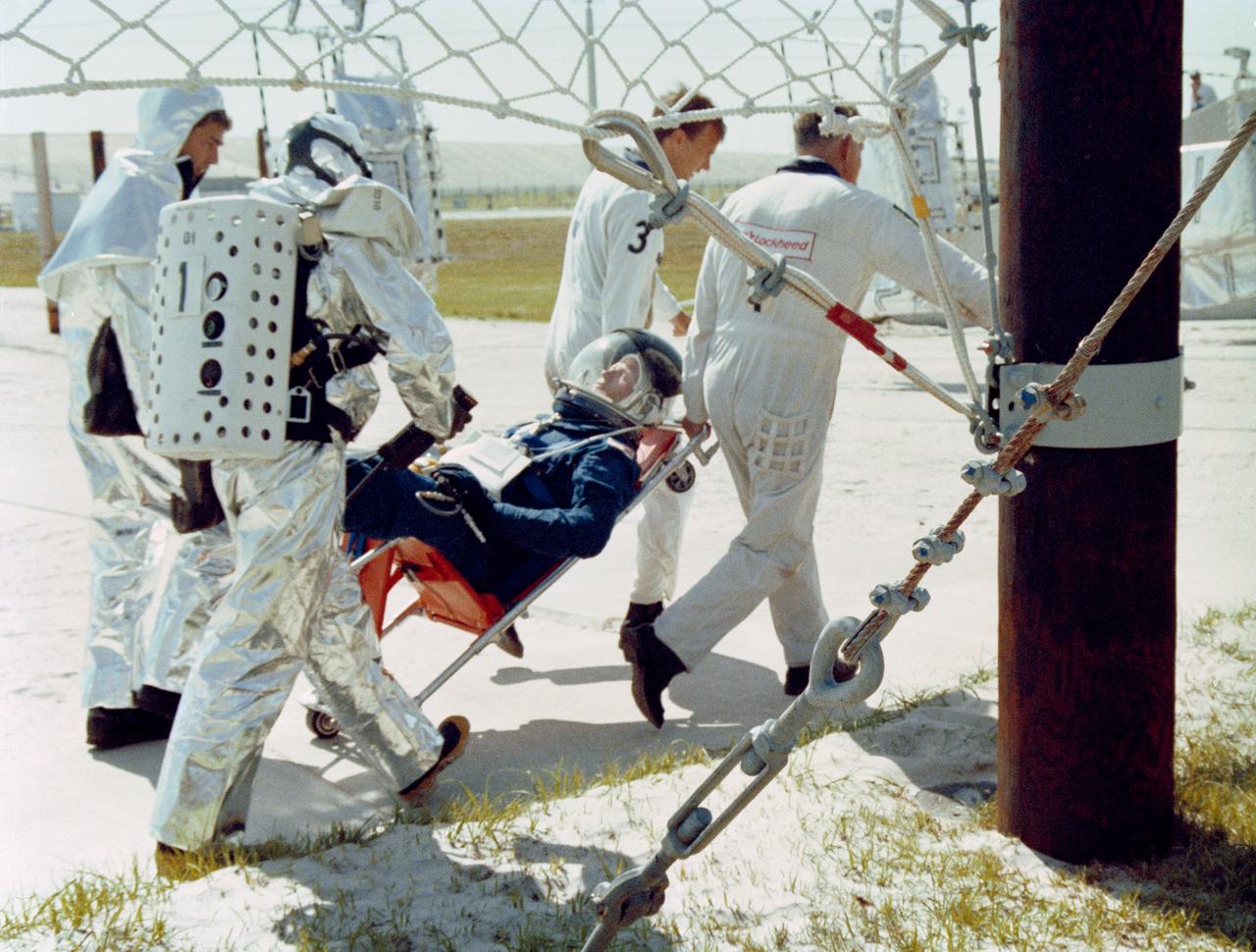

S88-40898 (4 May 1988) --- Astronauts, members of the orbiter close-out crew and fire and rescue personnel participate in a simulated emergency egress exercise near the slide wire termination point bunker at Launch Pad 39B. The simulated exercise was performed to familiarize personnel with evacuation routes as well as emergency equipment and procedures. Reasons for conducting the emergency exercises include the need to validate recent post-Challenger upgrades to the launch pad's emergency escape system and the new procedures developed in preparation for STS-26. (NOTE: The astronaut pictured and many of the others who participated in the exercises are not members of STS-26 prime crew).
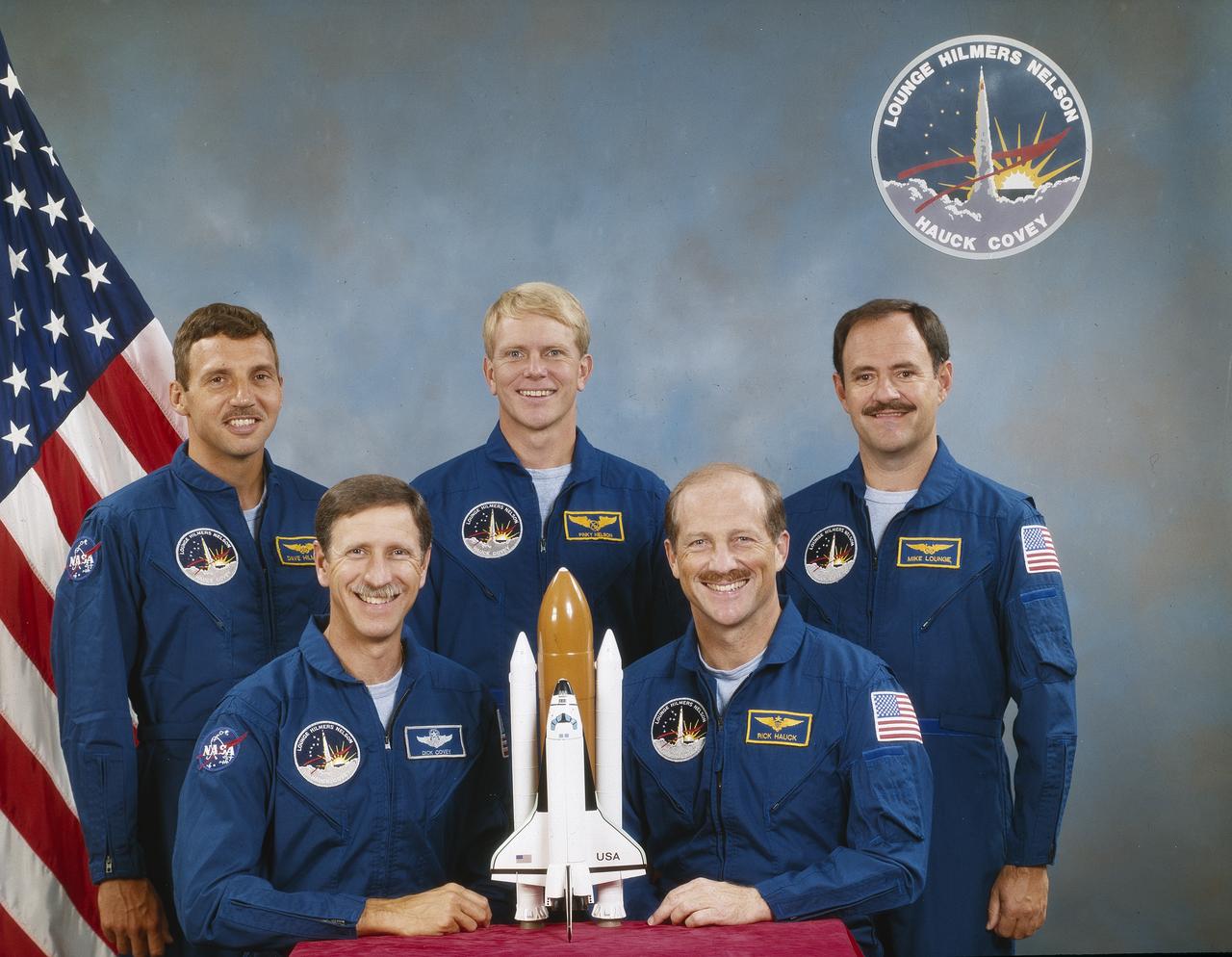

Five astronauts composed the crew of the STS-26 mission. Pictured in the portrait (left to right) are David C. Hilmer, mission specialist; Richard O. Covey, pilot; George D. Nelson, mission specialist; Frederick H. Hauck, Jr., commander; and John, M. Lounge, mission specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery, liftoff occurred on September 29, 1988 at 11:37am (EDT). This was the 7th flight of the Orbiter Discovery, and the return to flight after the STS-51L mission accident. The primary payload was the NASA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-3 (TDRS-3).

Crows Landing runway approach (scanning the horizon)
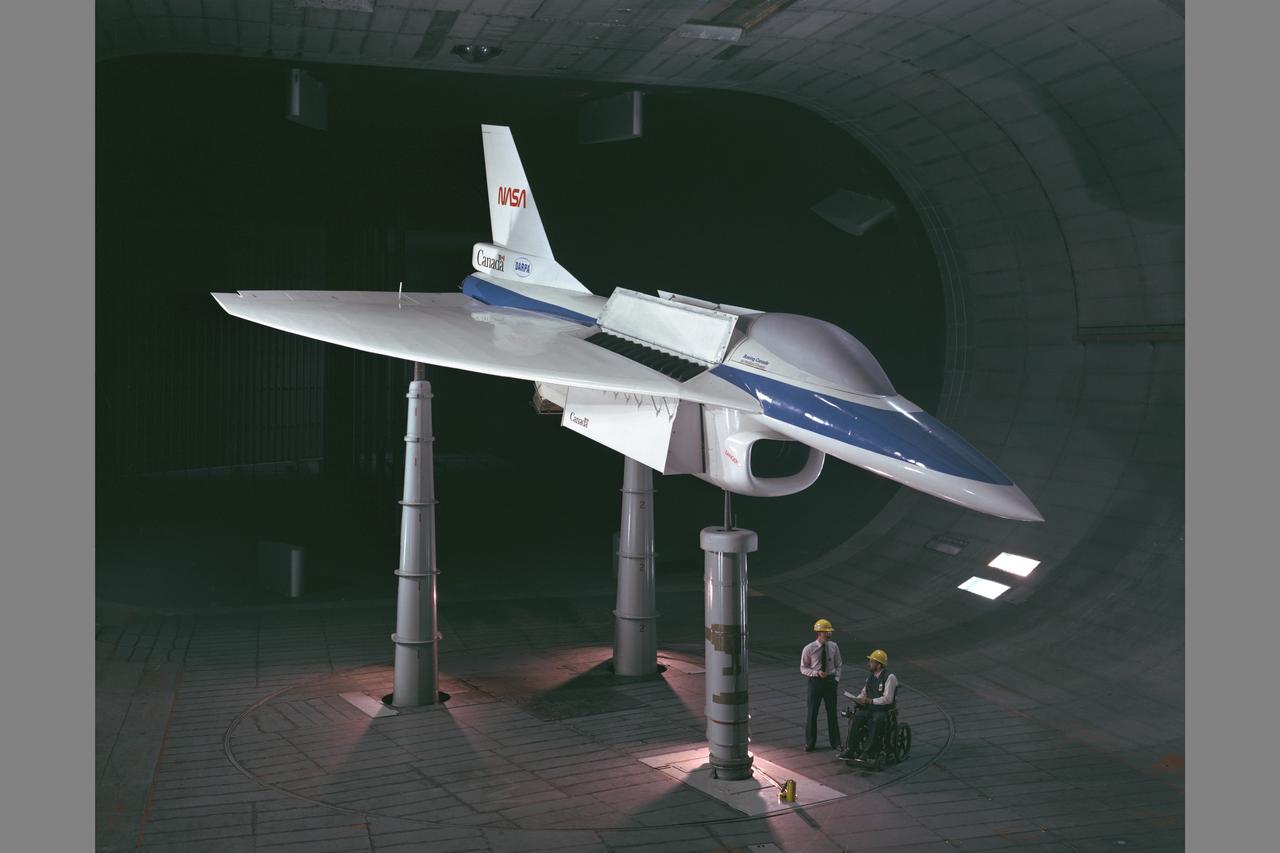

E-7 STOVL fighter model testing in Ames 40x80ft Subsonic wind tunnel. Investigating Supersonic Short Take-off and Vertical Landing (STOVL) technology.
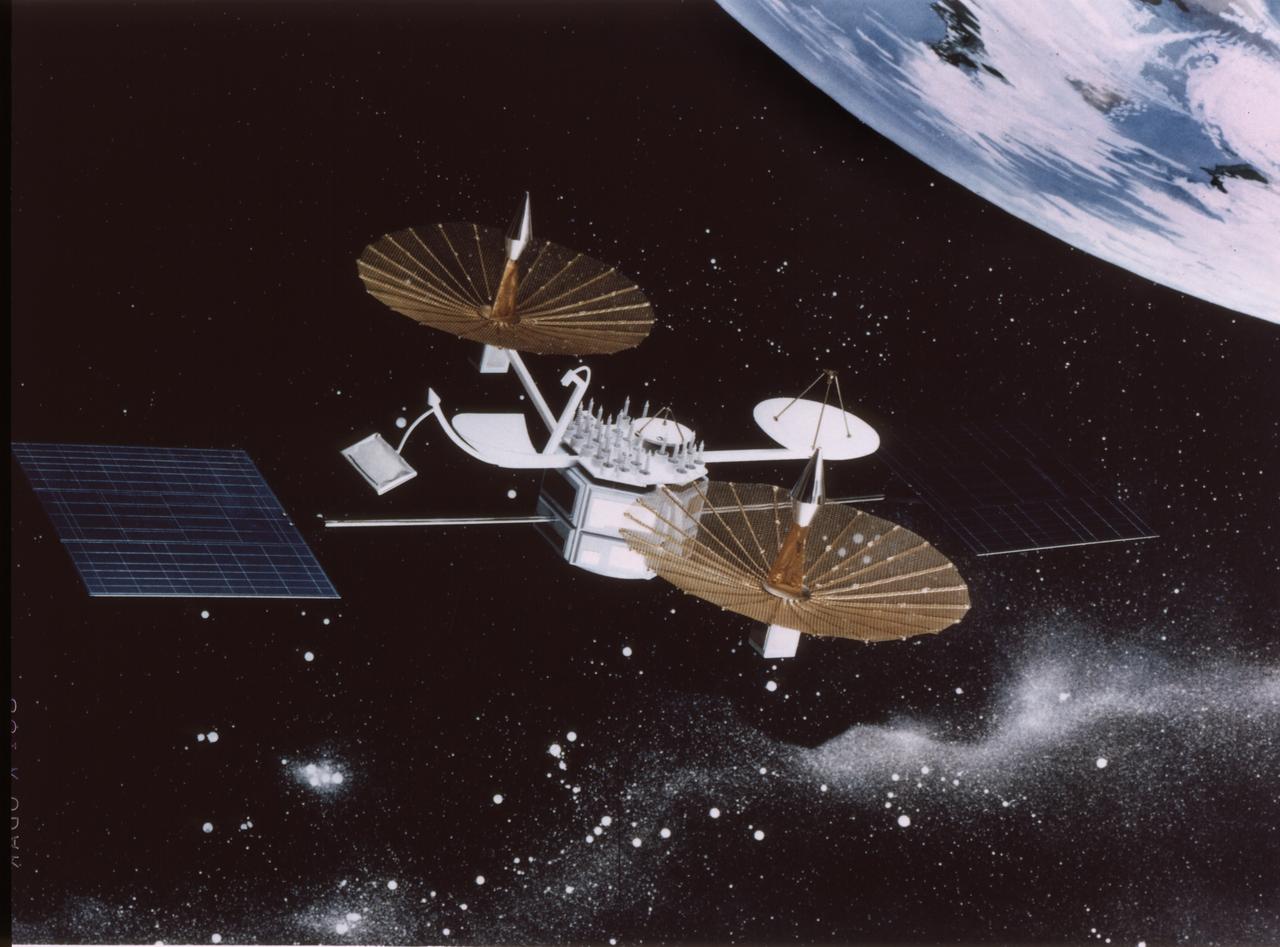

This artist's concept drawing depicts the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-C (TDRS-C), which was the primary payload of the Space Shuttle Discovery on the STS-26 mission, launched on September 29, 1988. The TDRS system provides almost uninterrupted communications with Earth-orbiting Shuttles and satellites, and had replaced the intermittent coverage provided by globe-encircling ground tracking stations used during the early space program. The TDRS can transmit and receive data, and track a user spacecraft in a low Earth orbit. The deployment of TDRS-G on the STS-70 mission being the latest in the series, NASA has successfully launched six TDRSs.
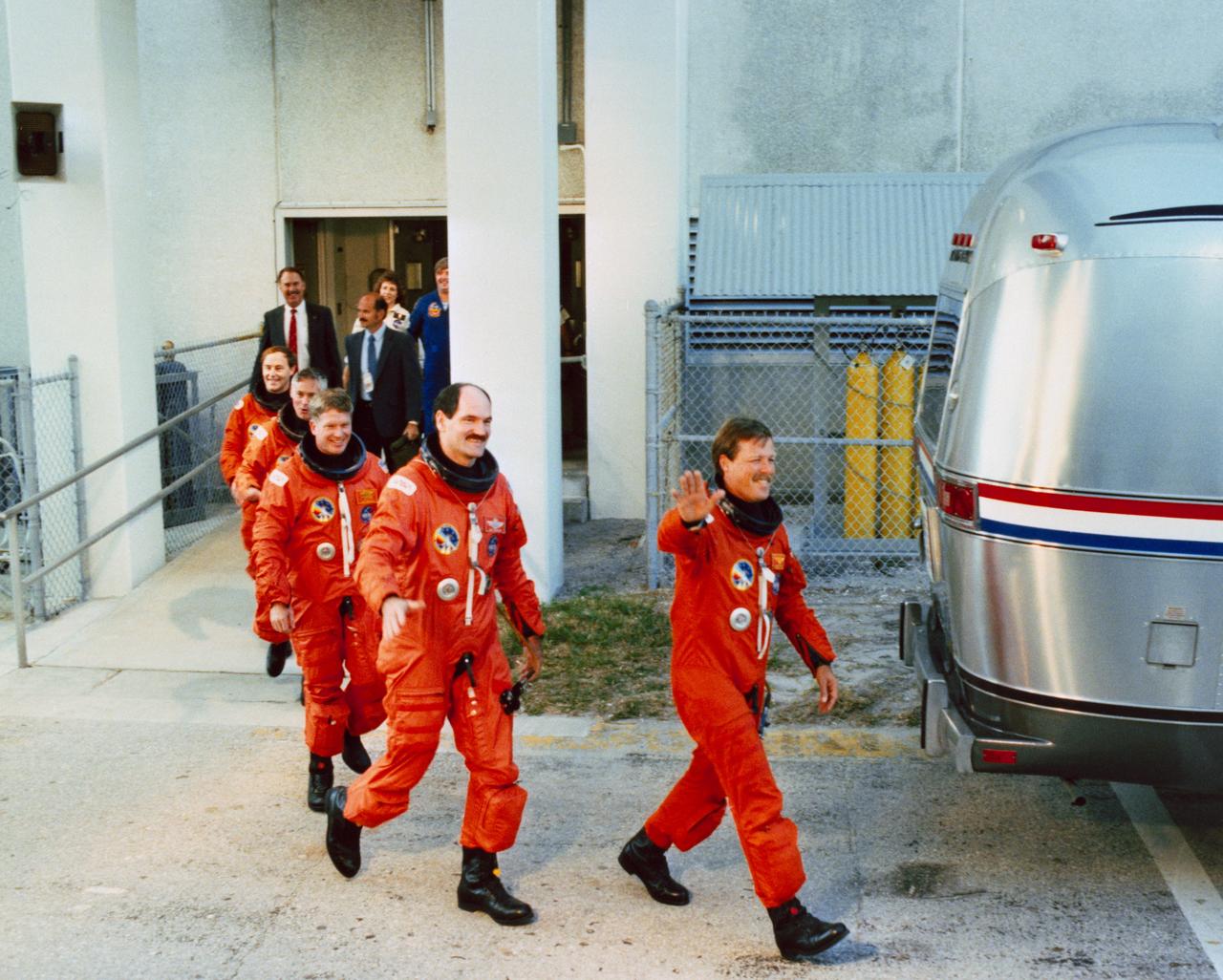

S88-53244 (14 Nov 1988) --- The crewmembers for STS-27 leave the operations and checkout (O&C) building en route to a transfer van that will take them to Launch Pad 39B for their terminal countdown demonstration test. From the front to the rear are astronauts Robert L. Gibson, Guy S. Gardner, William M. Shepherd, Richard M. (Mike) Mullane and Jerry L. Ross.

Crows Landing runway approach
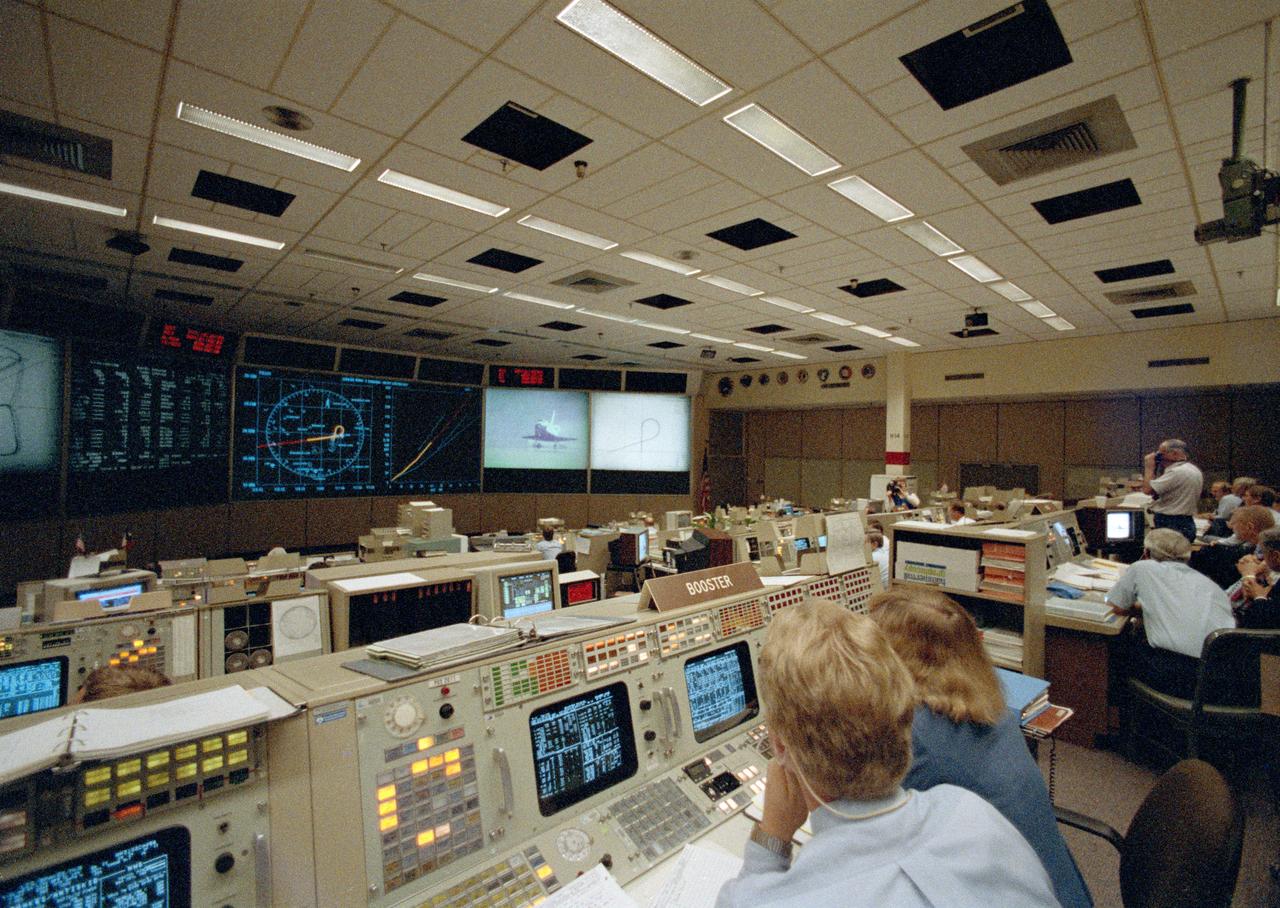

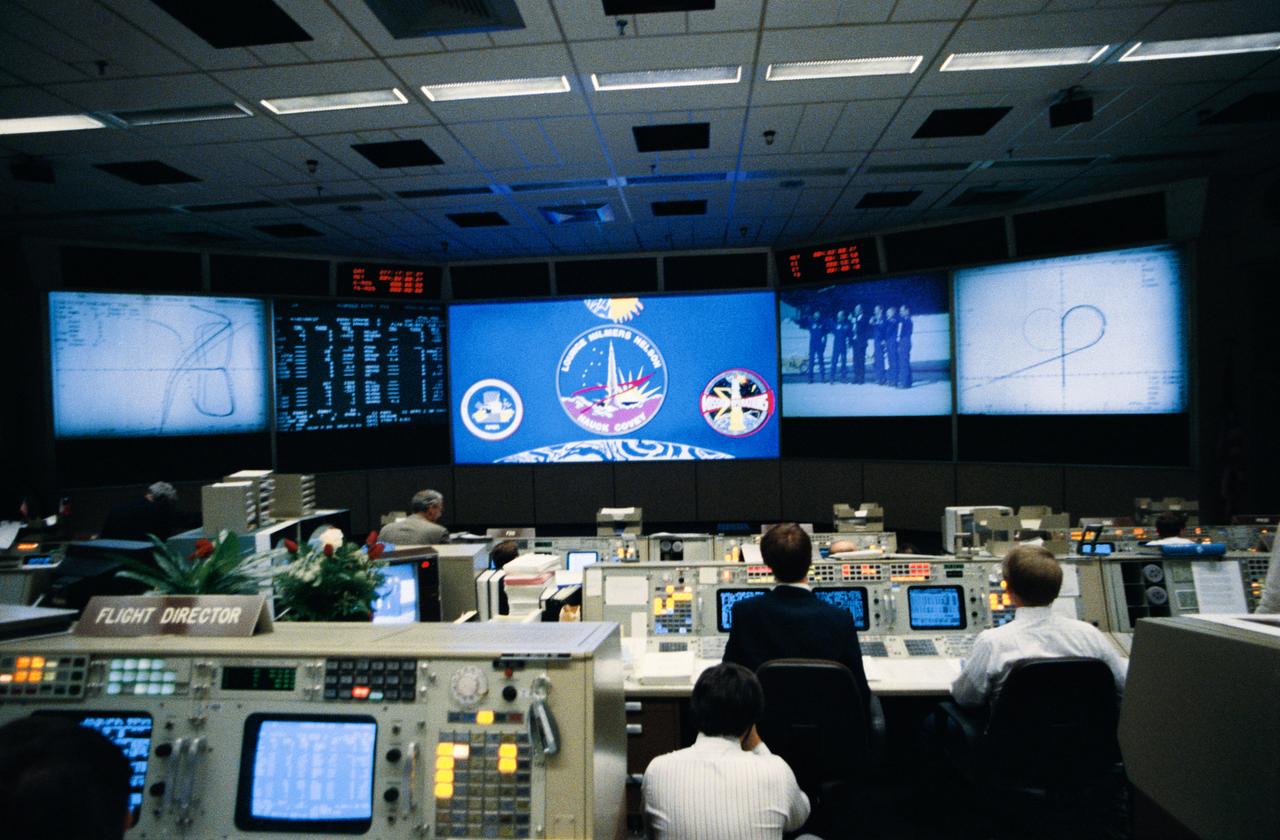
STS026-S-117 (3 Oct 1988) --- Flight controllers in Houston witness the landing of the Space Shuttle Discovery on a dry lake bed at NASA?s Dryden Flight Research Facility. The orbiter is seen on the giant screen in front of the flight control room just as the landing gear touches down.
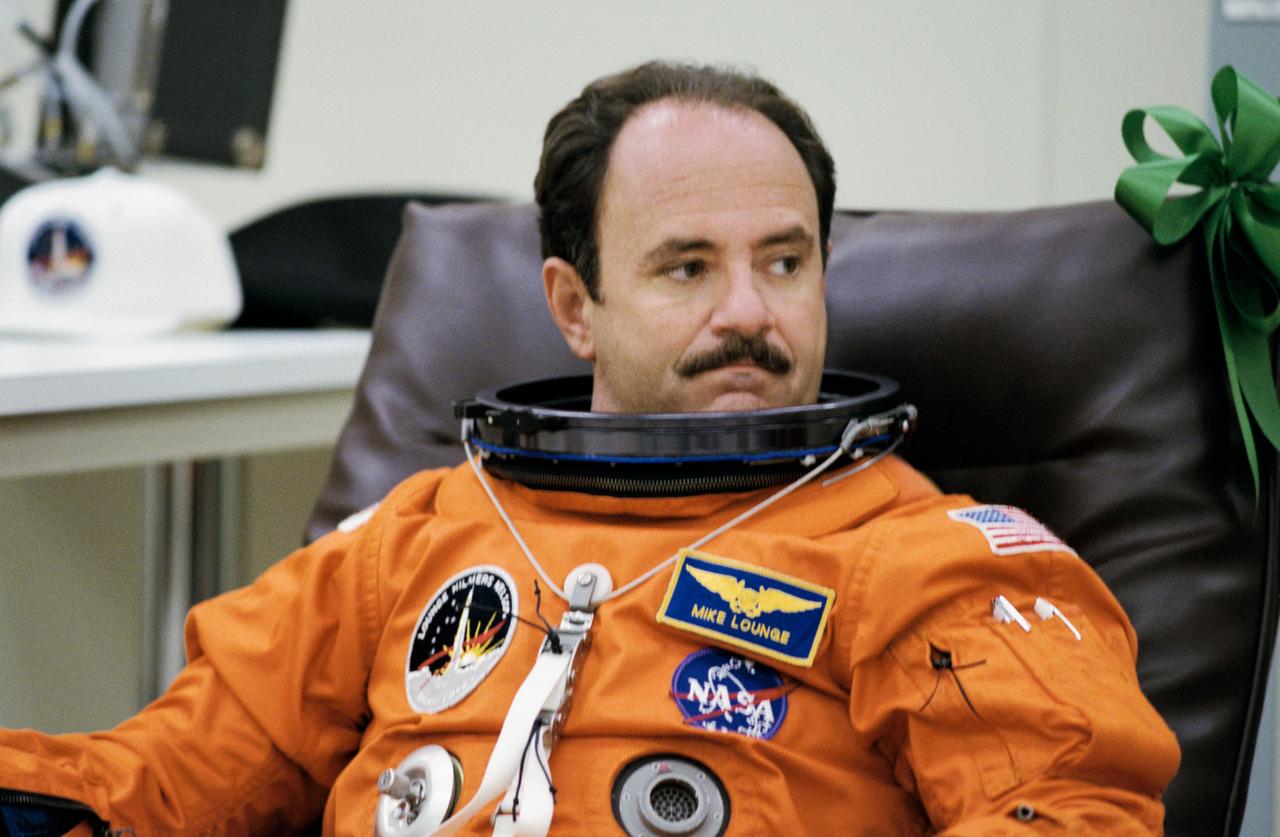

STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Mission Specialist (MS) John M. Lounge relaxes in reclining chair after donning his orange launch and entry suit (LES) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building. Upon completion of preflight suit tests, crewmembers will head to the launch pad.

Artist: Rick Guidice SIRTF Artwork update - cutaway Space Infrared Telescope Facility's will orbit at 900 kilometers aboard a platform-type spacecraft, providing power, pointing, and communications to Earth. The telescope and its infrared instruments, will reside within a cylindrical cryogen tank. The hollow walls of the tank will contain the superfluid helium that cools the telescope to its operating temperature, a few degrees above absolute zero. SIRTF will carry three versatile instruments to analyze the radiation it collects, the Multiband Imaging Photometer, the Infrared Array Camera, and the Infrared Spectrograph. SIRTF long lifetime - 5 years or more - will permit astronomers of all disciplines to use the facililty to carry out a wide variety of astrophysical programs. It will provide ongoing coverage of variable objects, such as quasars, as well as the capability to study rare and transient events such as comets and supernovae. SIRTF's long lifetime will also allow it to distinguish nearby objects by detecting their gradual motions relative to the more distant background stars.
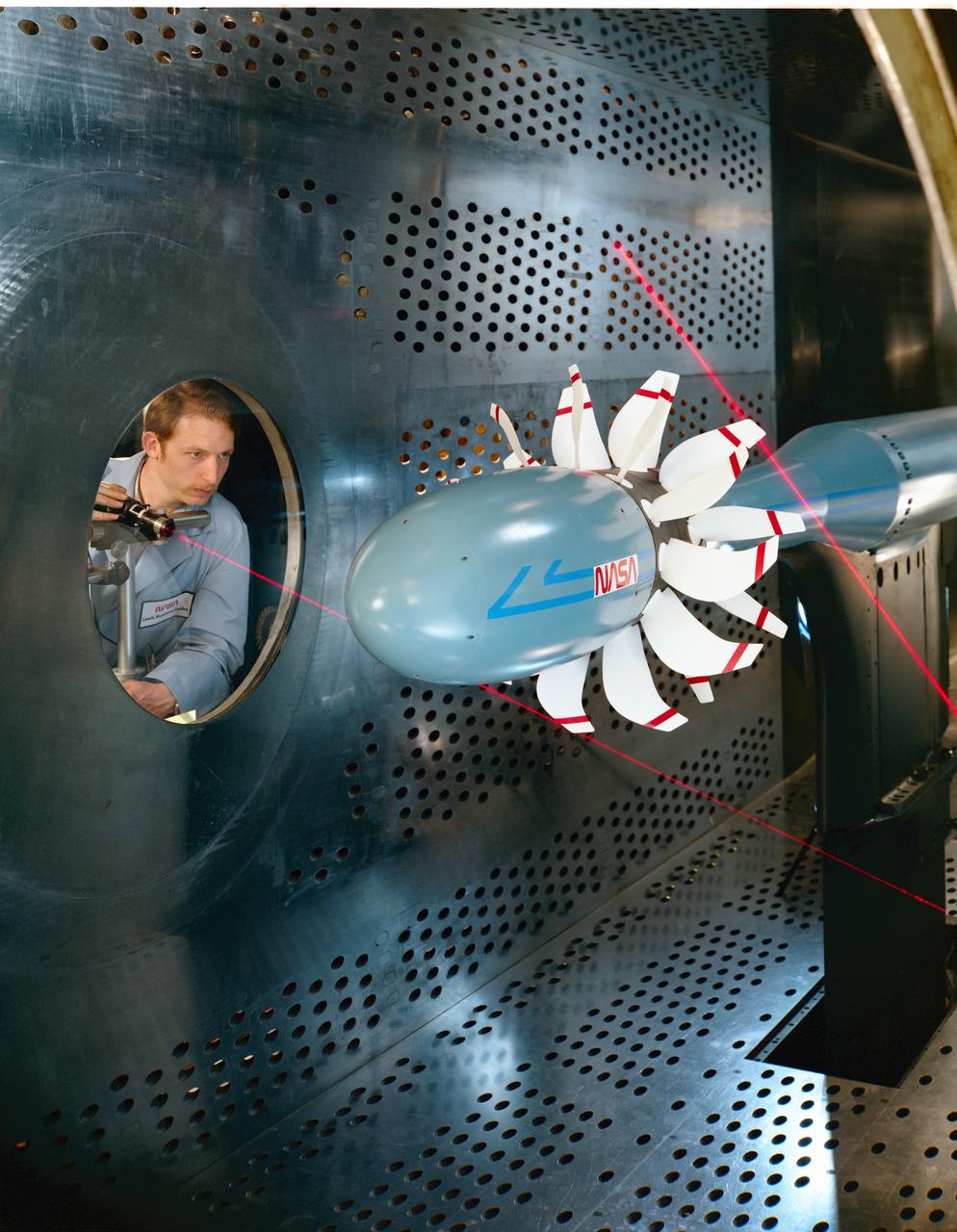
Laser based blade deflection measurement system on Counter Rotation Pusher Propeller model in 8x6 SWT (Supersonic Wind Tunnel)
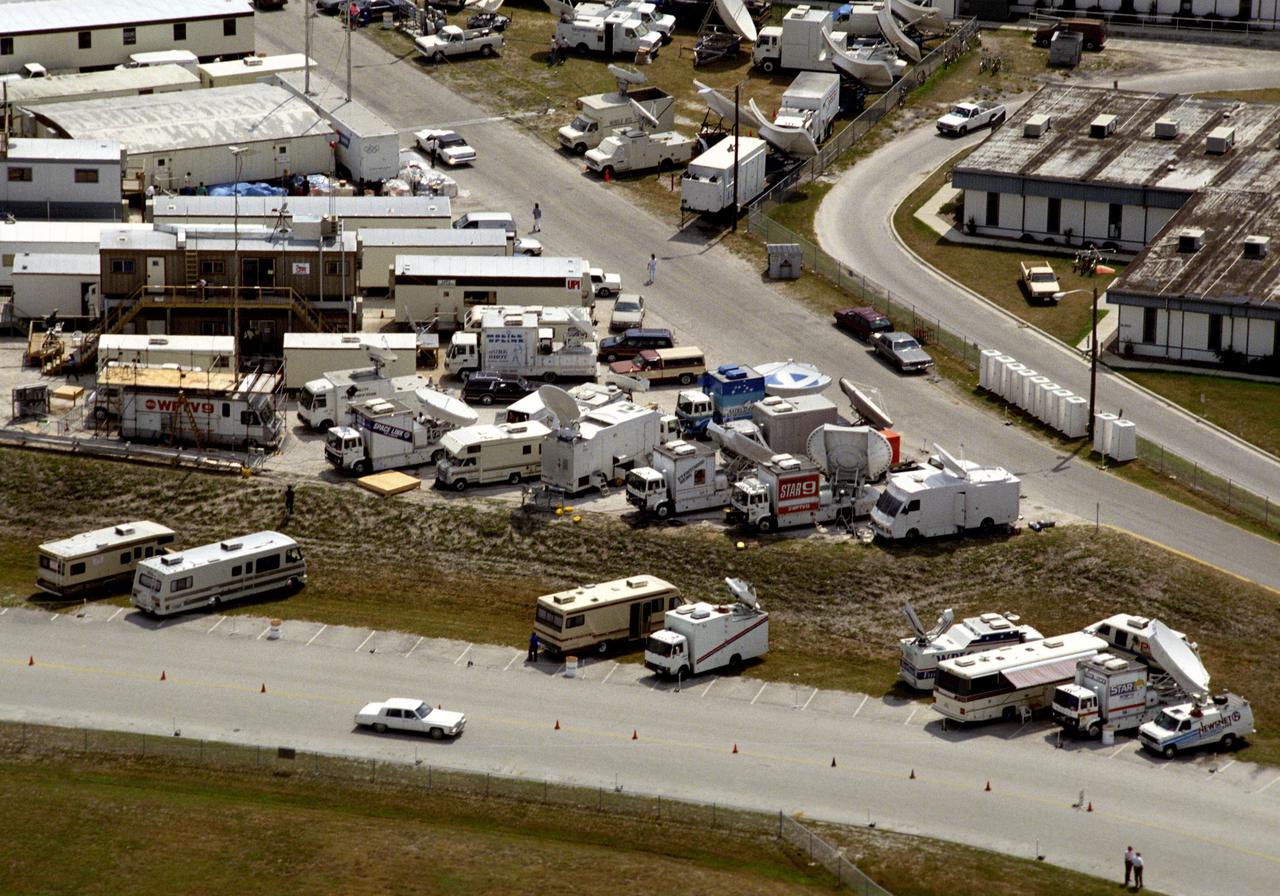

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-26 PRE-LAUNCH ACTIVITIES – PRESS SITE AREA. Photo credit: NASA

SR-3 Advanced Turboprop (Propfan) in 8x6 foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel

This test conducted in May 1988 shows what happens during launch if a space shuttle main engine fails. The test was conducted in the 10X10 supersonic wind tunnel at the John H. Glenn Research Center.
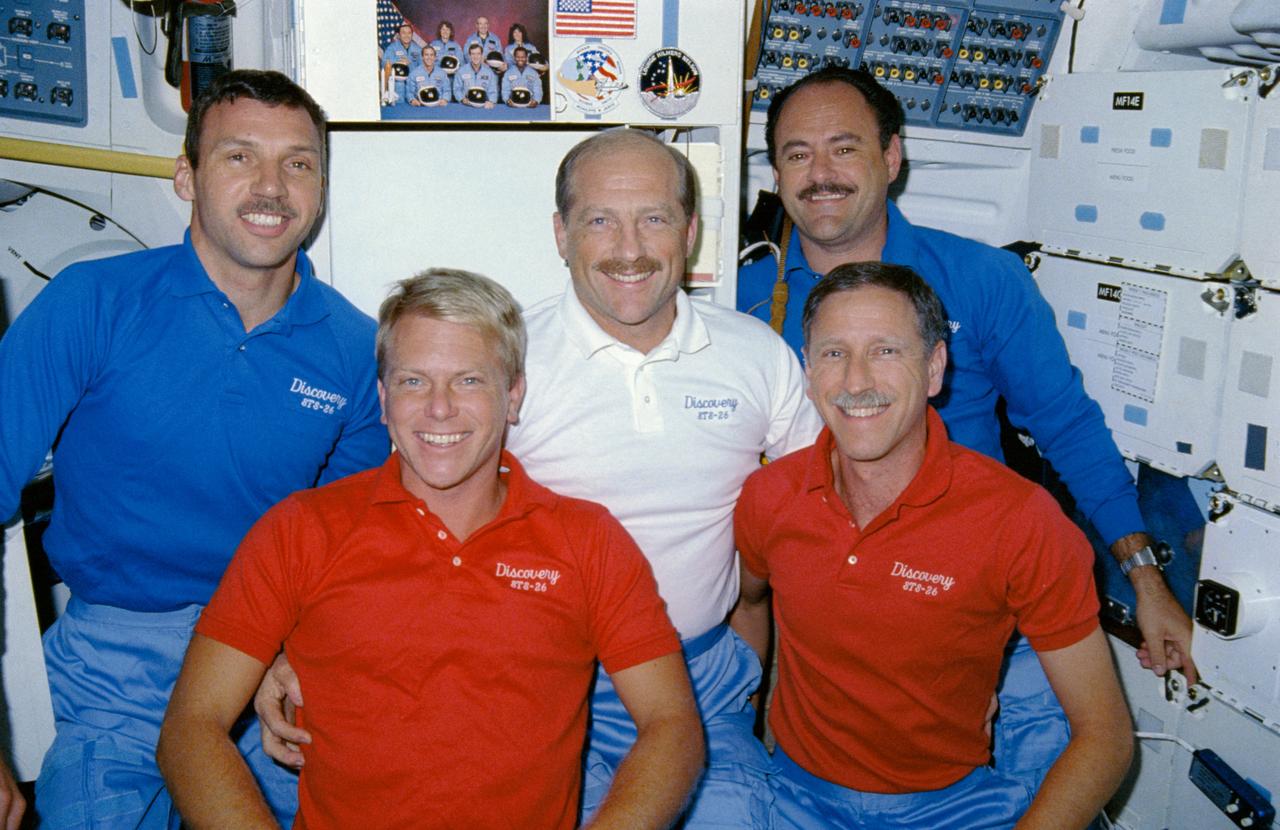

STS026-08-007 (29 Sept-3 Oct 1988) --- An in-space crew portrait on the middeck of Discovery. Left to right are Astronauts David C. Hilmers, George D. Nelson, Frederick H. (Rick) Hauck, John M. (Mike) Lounge and Richard O. Covey (front). The crew portrait for STS 51-L, its flight insignia and the STS 26 flight insignia are at top edge of the frame. This photo was shown by the STS 26 astronaut crew during its Oct. 11, l988 post-flight press conference.
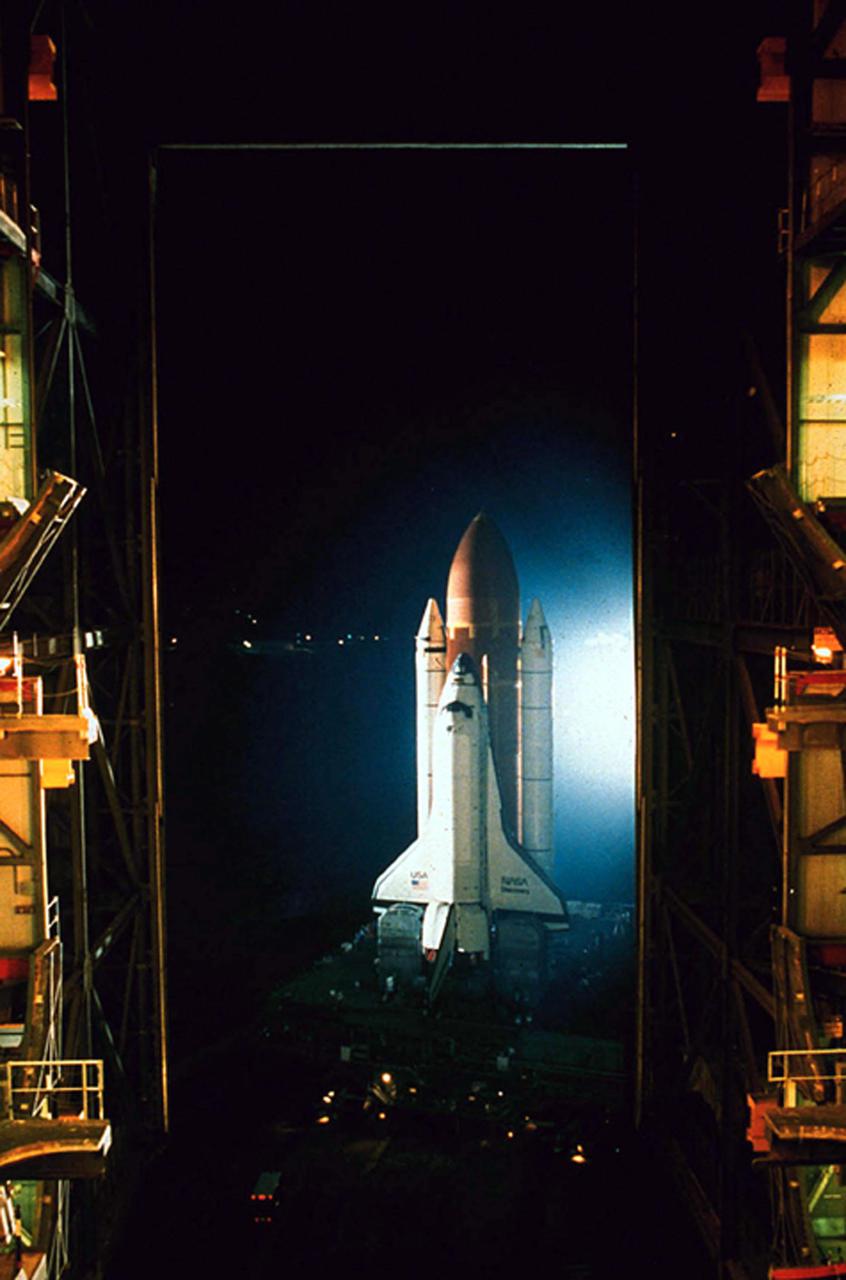

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A view from inside bay three of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) shows the Space Shuttle Discovery washed in white xenon light as it makes a nighttime departure from the VAB on its way to pad 39B. Discovery will fly for mission STS-26 now scheduled for launch in earlly September with its five-man crew and the TDRS-C payload. First motion in the Shuttle's move from the VAB toward the pad came at 12:50 a.m. July 4, 1988.
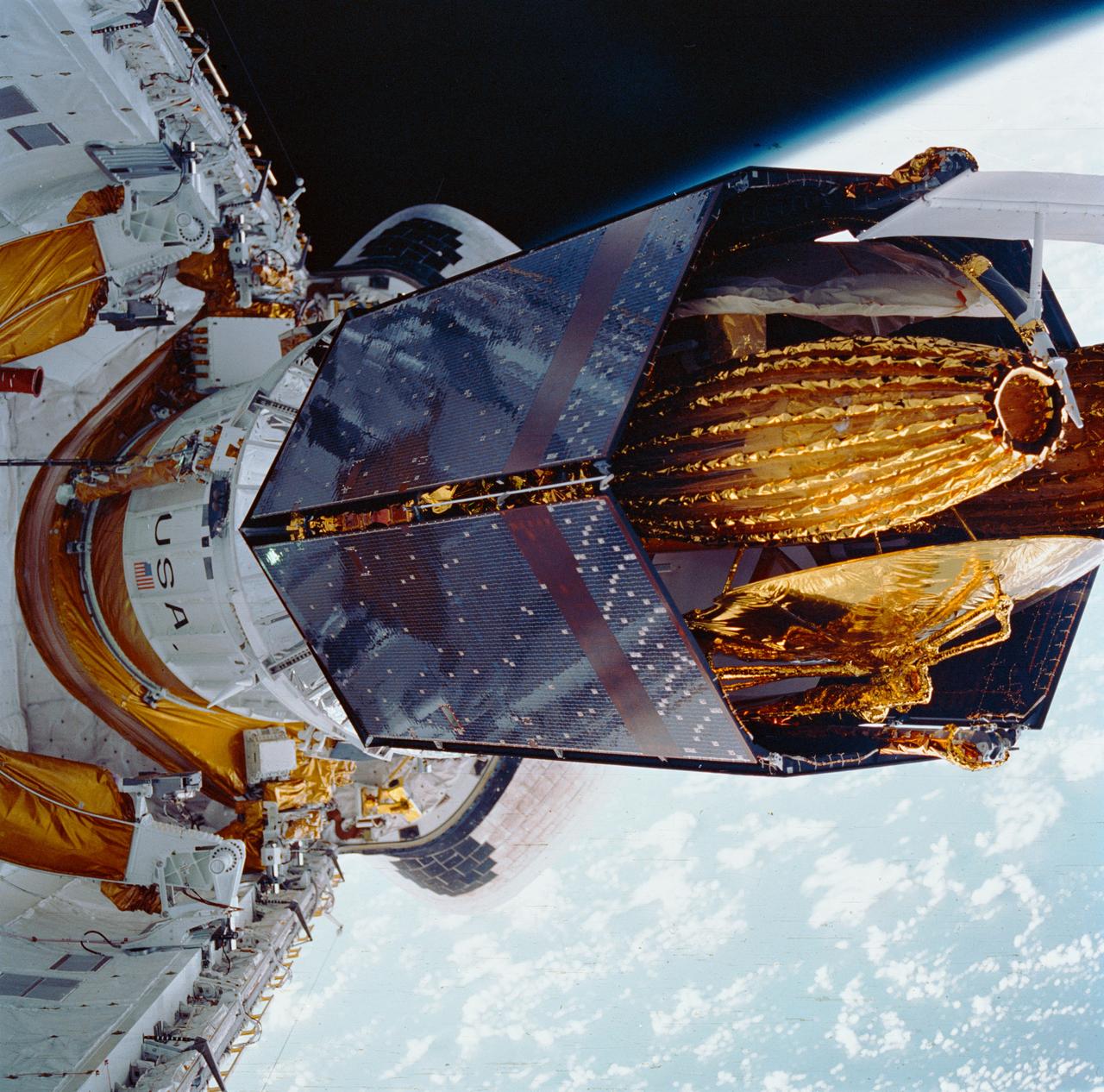

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) located in the payload bay (PLB) of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is positioned into its proper deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). In the foreground, the ASE forward cradle is visible. The IUS is mounted in the ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table. TDRS-C components in stowed configuration include solar array panels, TDRS single access #1 and #2, TDRS SGL, and S-Band omni antenna. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, the Earth's cloud-covered surface, and the Earth's limb.
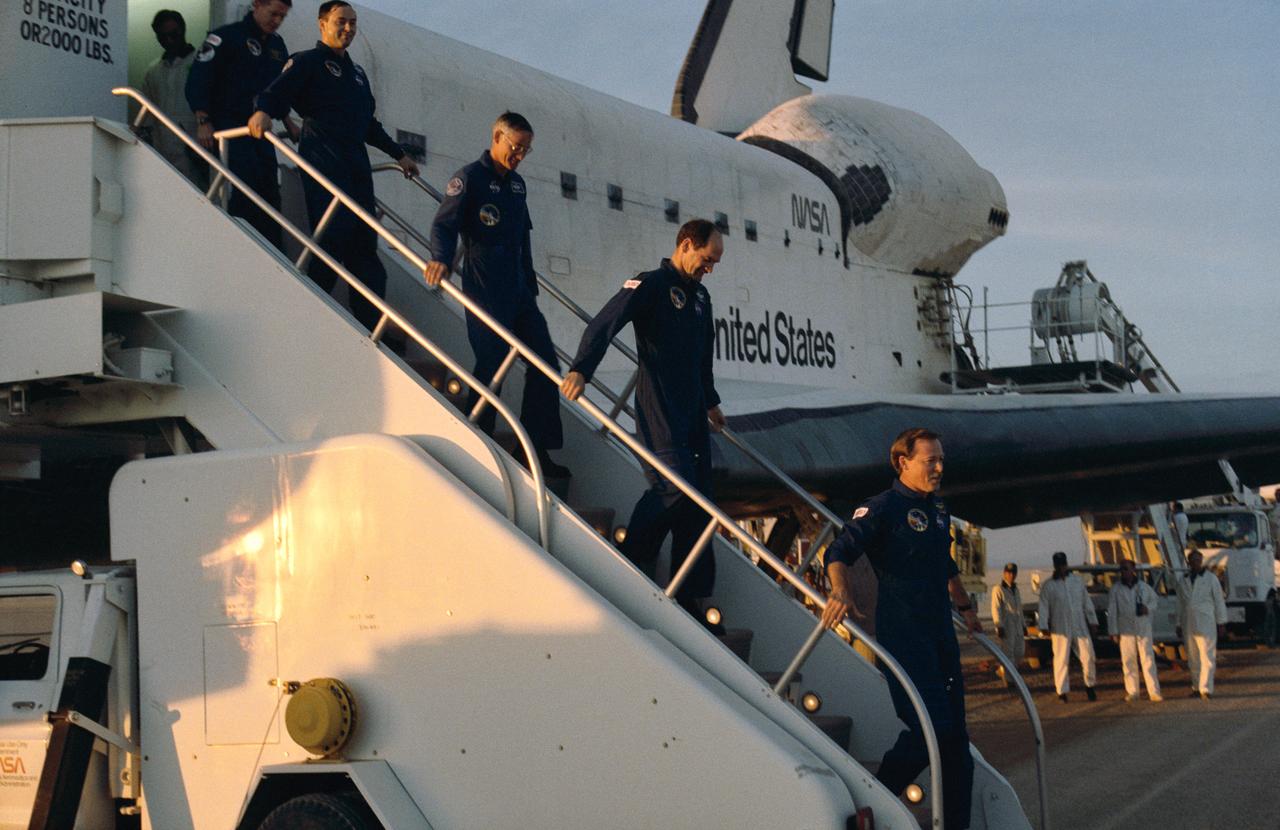

STS027-S-020 (6 Dec 1988) --- The five astronauts who were aboard Atlantis for its return to flight leave their spacecraft after almost 4 1/2 days in space. From bottom to top are Astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Guy S. Gardner, pilot; and Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, Jerry L. Ross and William M. Shepherd, mission specialists. Atlantis touched down on Rogers Dry Lake Bed at 3:36 p.m. (PST), Dec. 6, 1988.
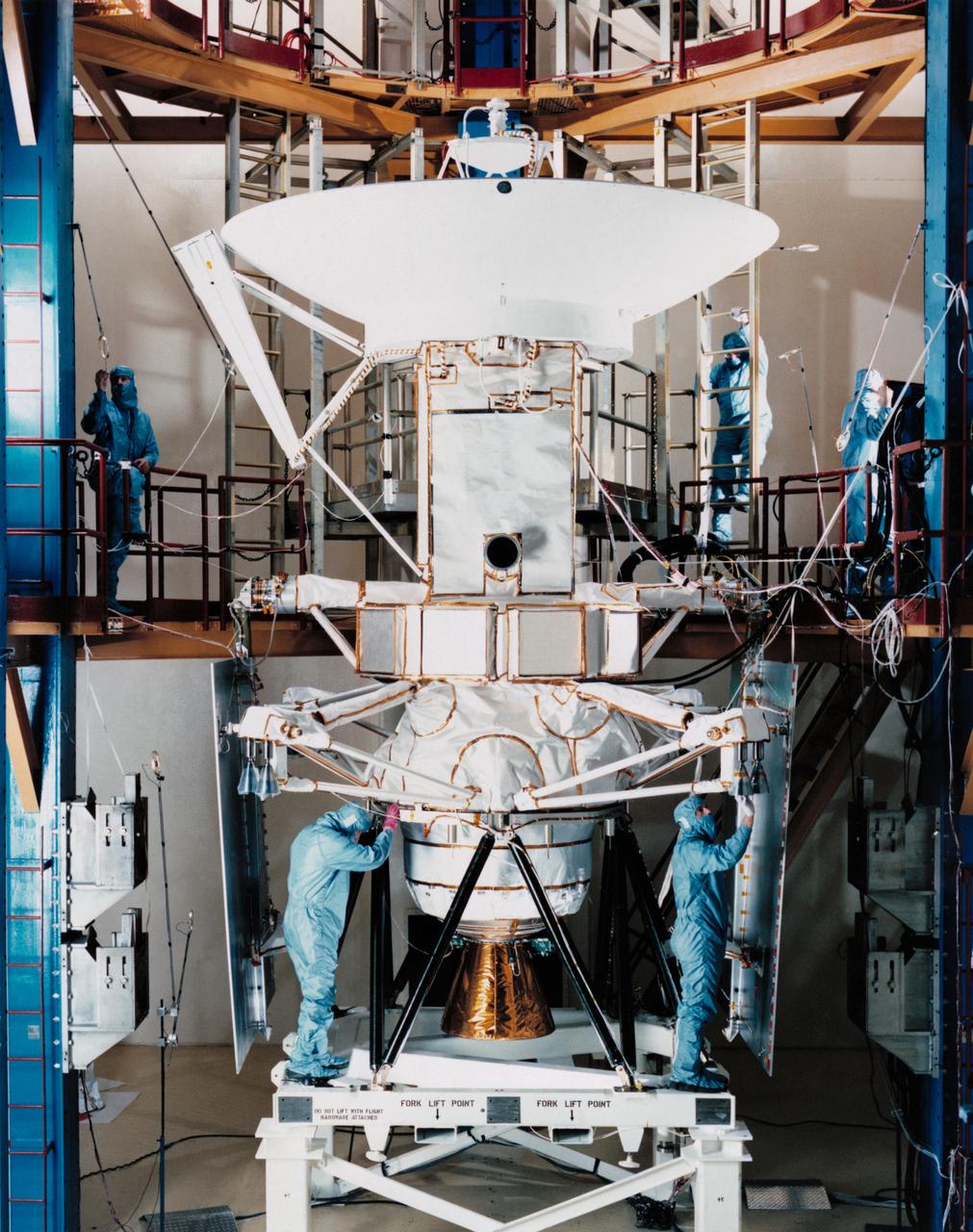
S88-50418 (August 1988) --- Engineers and technicians at the Martin Marietta plant in Denver, Colorado, prepare the spacecraft for its six-week long trip to the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The spacecraft, destined for unprecedented studies of Venusian topographic features, will be mated to its upper stage while at KSC and later onloaded to Atlantis and eventually will be deployed by the crew of NASA's STS-30 mission in April 1989.
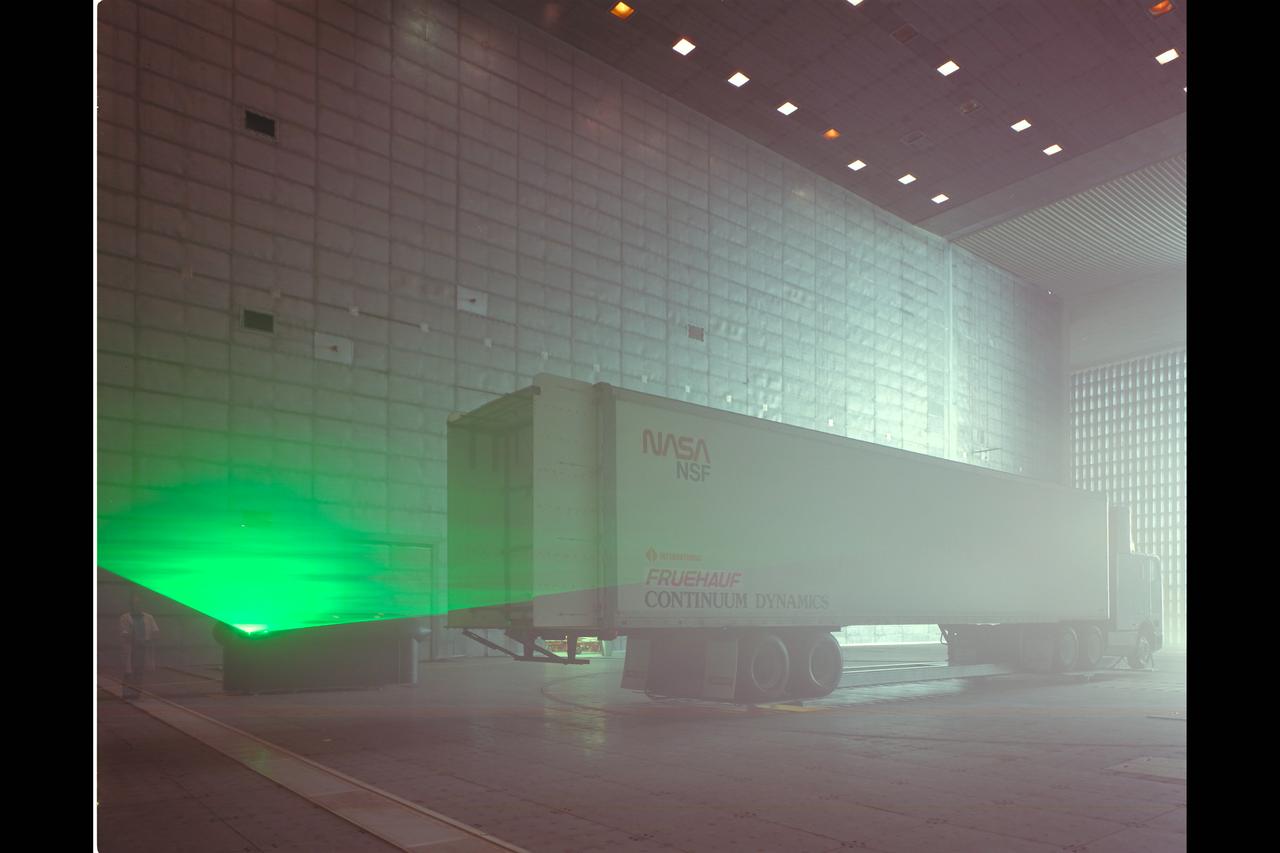

Fruehauf Truck and Trailer Test in 80x120ft W.T. with LRLDV (looking at drag and fuel efficiency)
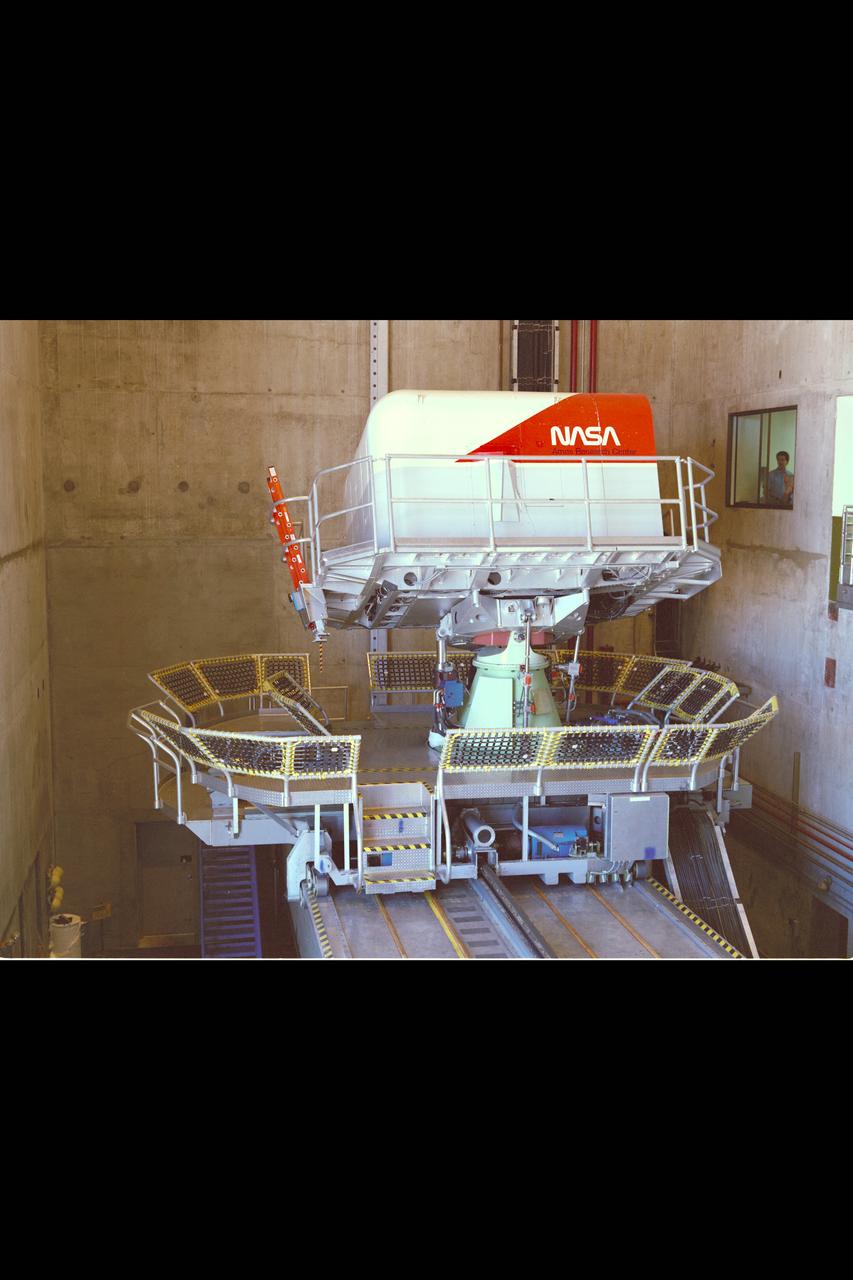

Vertical Motion Simulator (VMS) showing a Space Shuttle configuration
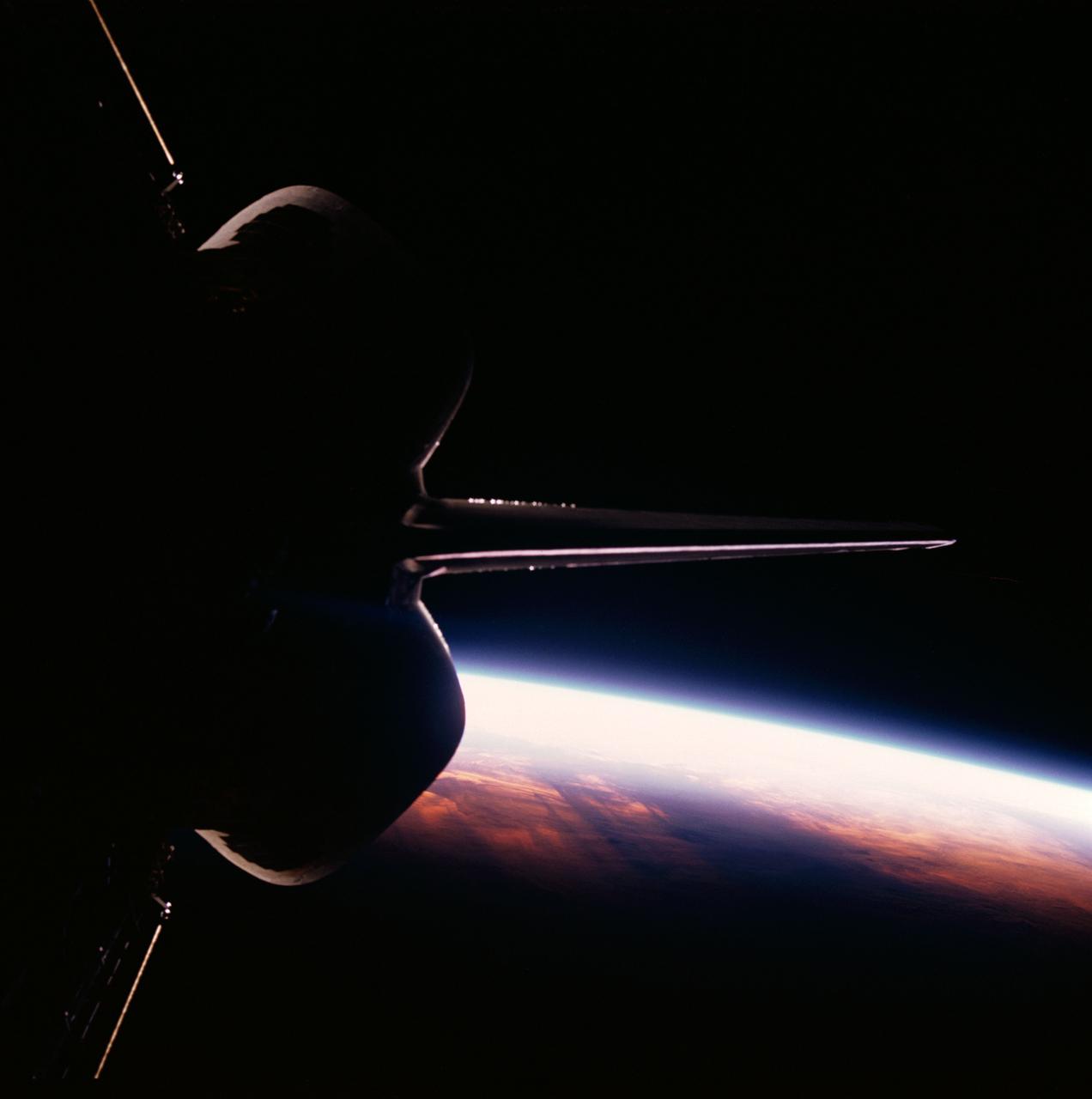

Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods are backdropped against the contrasted blackness of space illuminated by a colorful Earth / sunrise panorama. View was taken through the aft flight deck viewing windows during STS-26.
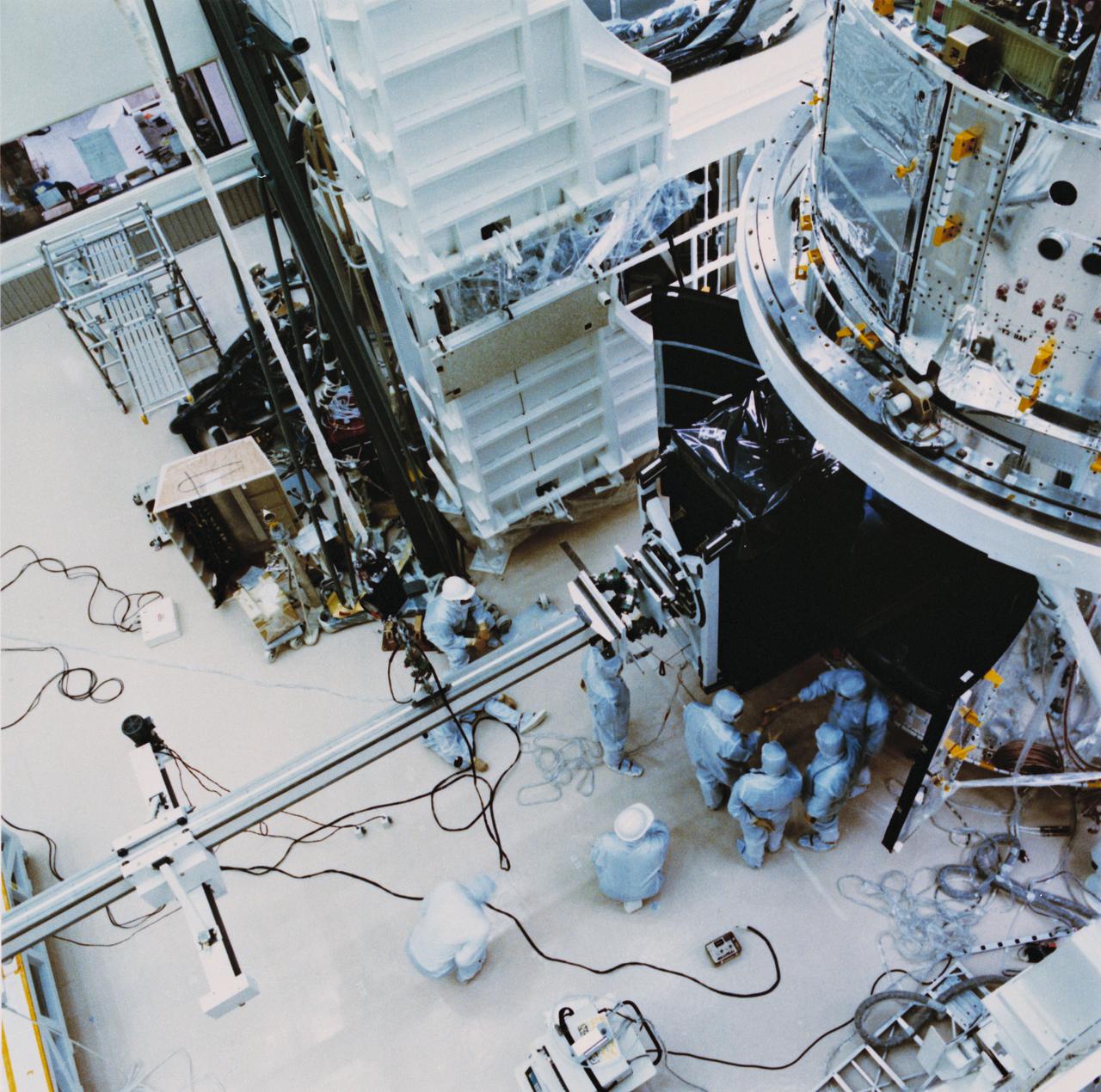

A mechanical arm positions the axial scientific instrument (SI) module (orbital replacement unit (ORU)) just outside the open doors of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Support System Module (SSM) as clean-suited technicians oversee the process. HST assembly is being completed at the Lockheed Facility in Sunnyvale, California.
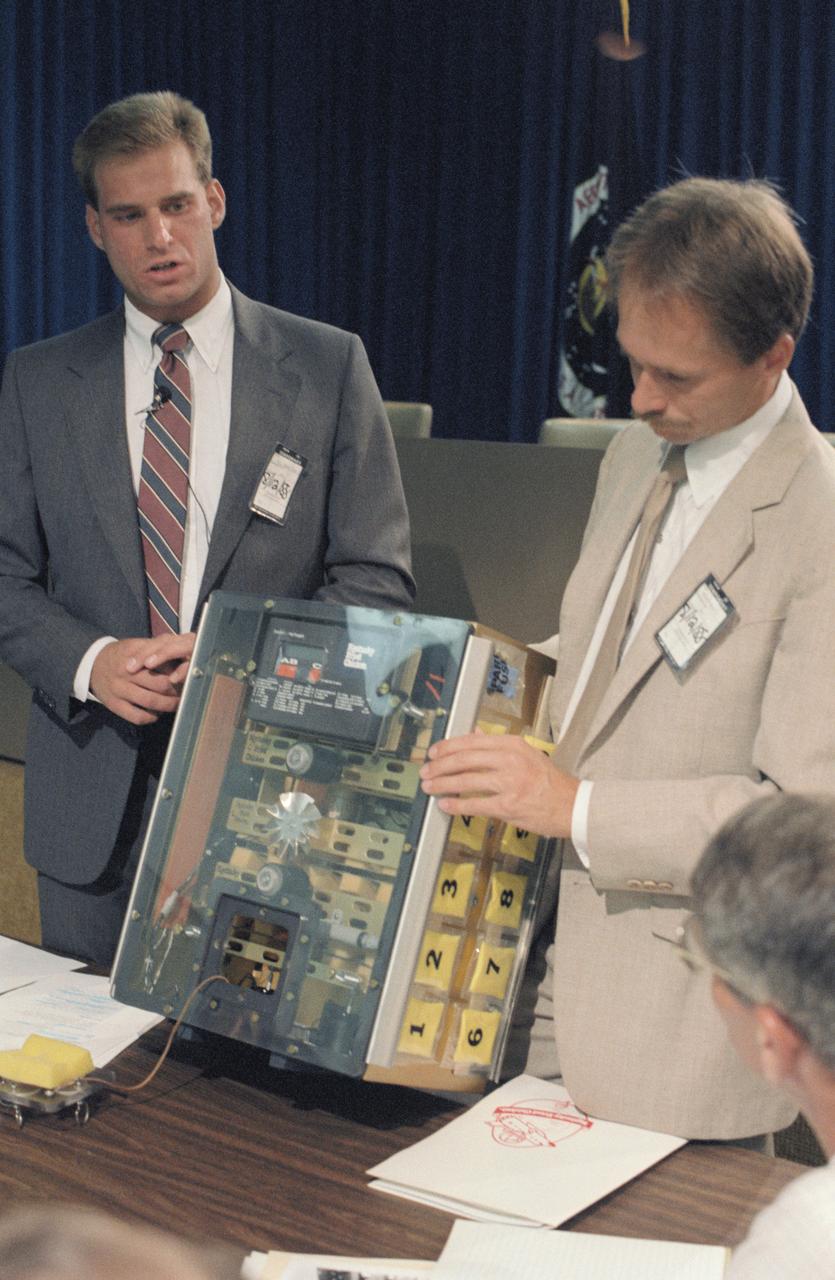

S88-44514 (13 Aug 1988) --- Student experimenter John C. Vellinger, left, explains components of an incubator used in his experiment to be carried onboard the Discovery for NASA's STS-29 mission next year. Mark S. Deusser, representing the sponsoring organization, holds up the incubator for inspection by members of the STS-29 crew who will monitor in-space operation of the experiment, titled "Chicken Embryo Development in Space." Astronaut Robert C. Springer is partially visible in lower right foreground. The student's sponsor is Kentucky Fried Chicken.
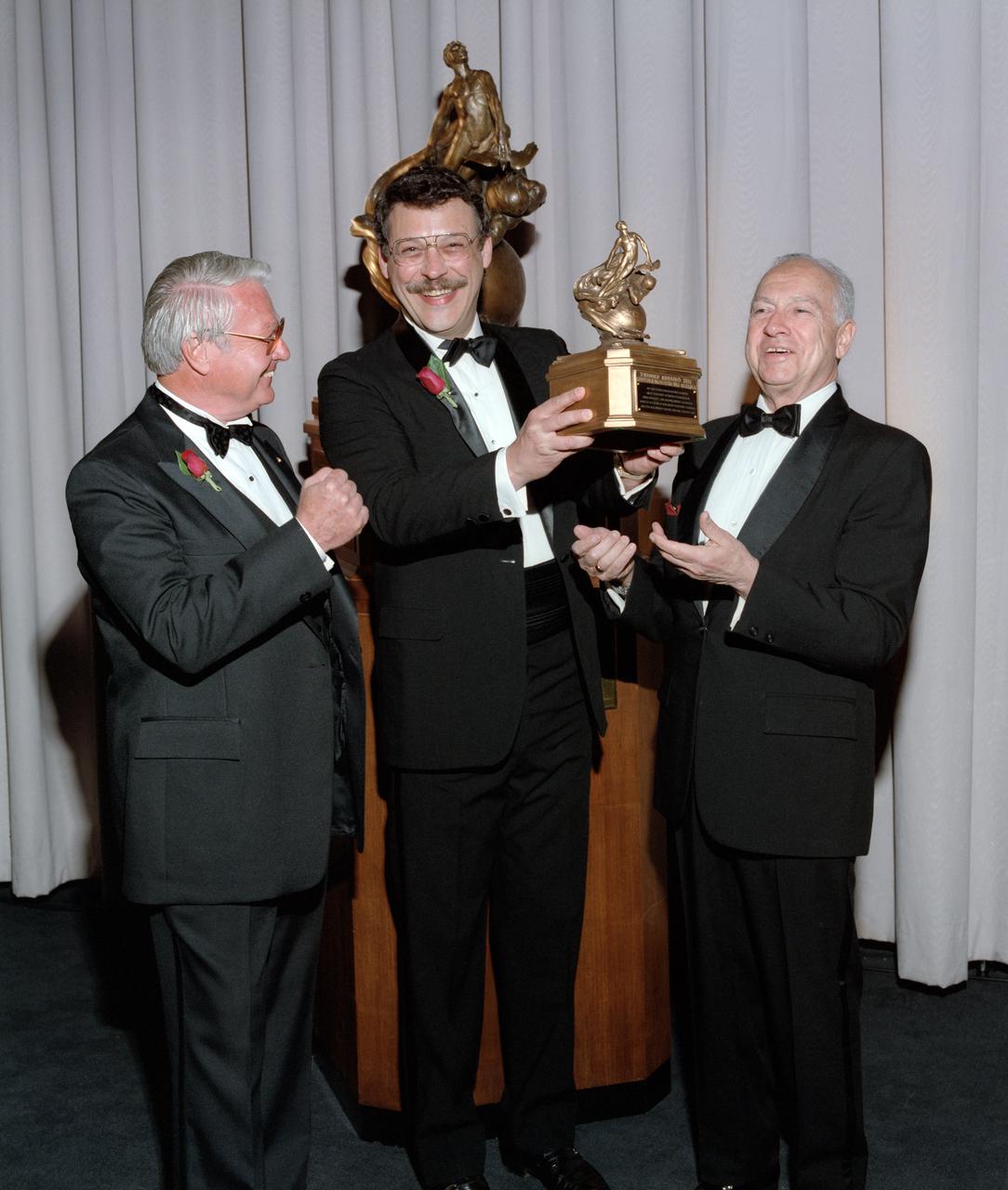

Dr. John Klineberg accepts the Collier Trophy for NASA
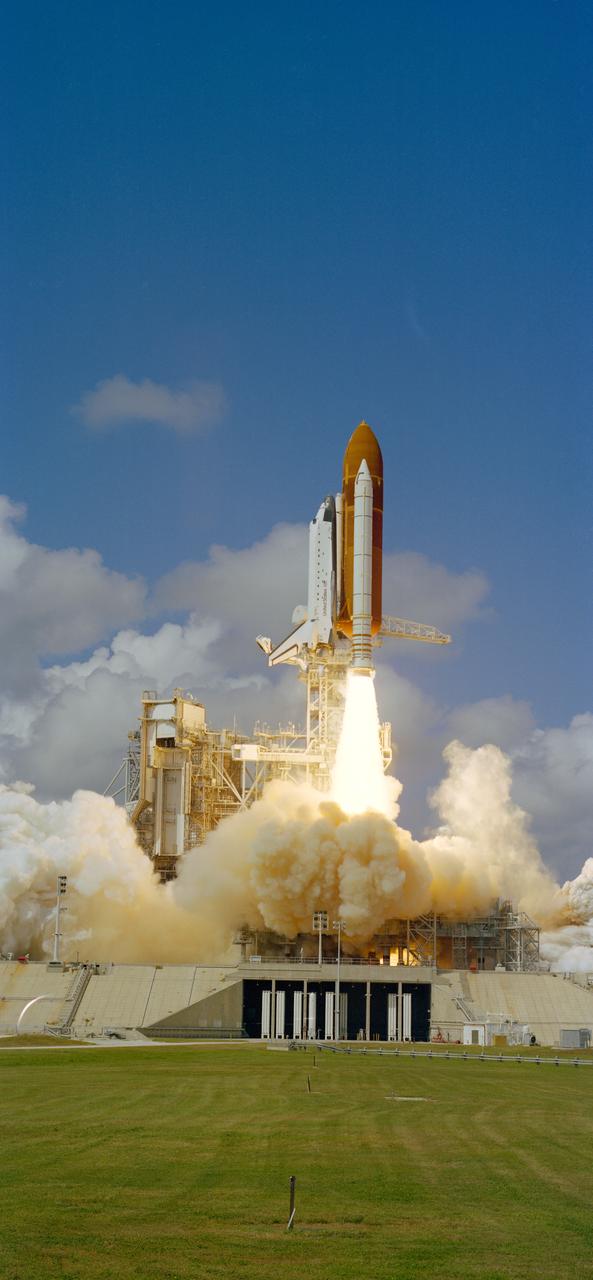

STS026-S-031 (29 Sept 1988) --- Just moments after ignition, the Space Shuttle Discovery, mated to two solid rocket boosters and an external fuel tank, heads, toward Earth orbit. The mission marks Discovery?s first flight since September of 1985 and NASA?s first manned mission since September of 1985 and NASA?s first manned mission since the 51L Challenger accident of January 28, 1986. Onboard the spacecraft are Astronauts Frederick H. (Rick) Hauck, commander; Richard O. Covey, pilot; and George D. Nelson, John M. (Mike) Lounge and David C. Hilmers, mission specialists. Discovery?s dry weight is 171,419 pounds. The tracking and data relay satellite and its inertial upper stage total about 37,000 pounds.

Portrait of Christine M. Darden
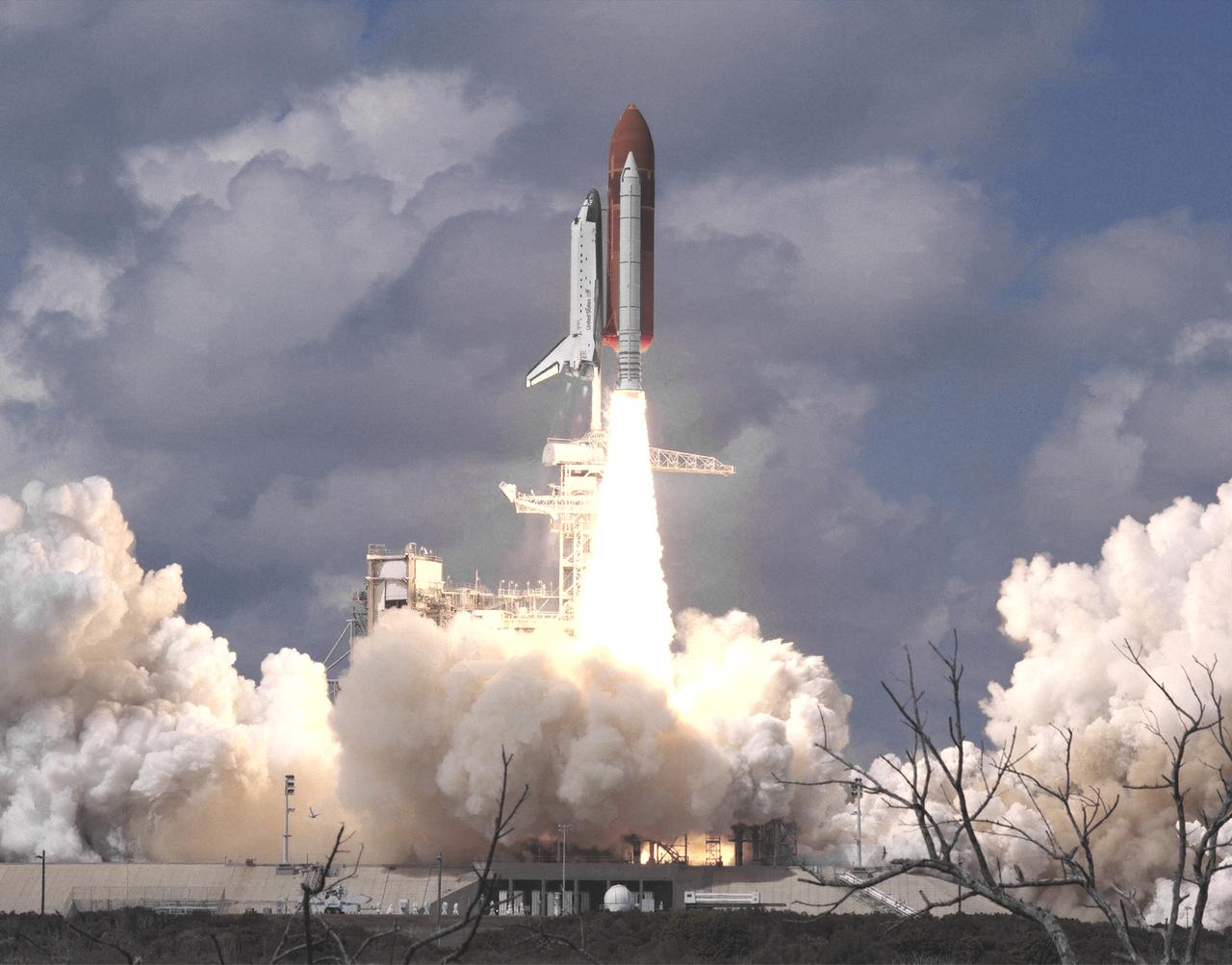

The Space Shuttle Discovery takes off from Launch Pad 39B at the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, to being Mission STS-26 on 29 September 1988,11:37:00 a.m. EDT. The 26th shuttle mission lasted four days, one hour, zero minutes, and 11 seconds. Discovery landed 3 October 1988, 9:37:11 a.m. PDT, on Runway 17 at Edwards Air Force Base, California. Its primary payload, NASA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-3 (TDRS-3) attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), became the second TDRS deployed. After deployment, IUS propelled the satellite to a geosynchronous orbit. The crew consisted of Frederick H. Hauck, Commander; Richard O. Covey, Pilot; John M. Lounge, Mission Specialist 1; George D. Nelson, Mission Specialist 2; and David C. Hilmers, Mission Specialist 3.
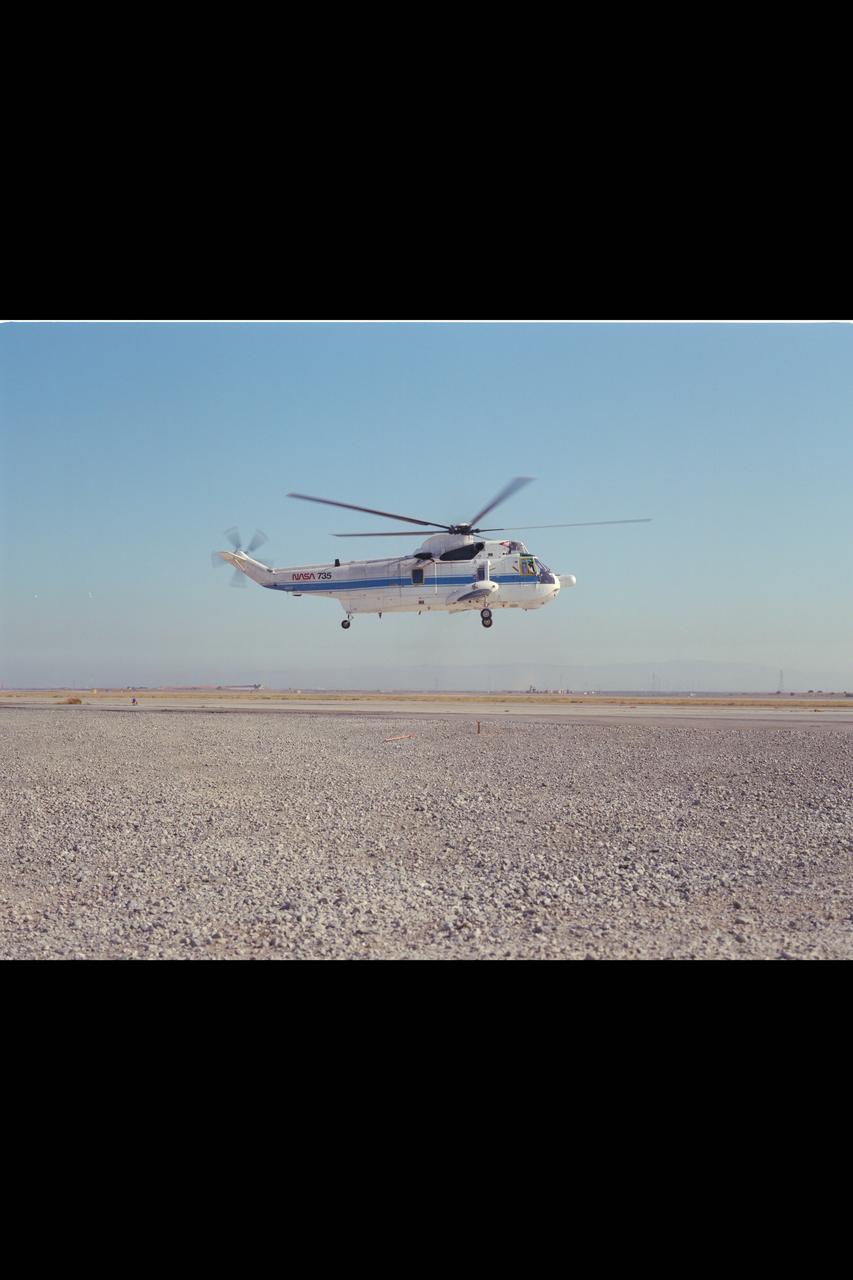

SH-3G (NASA-735) Helicopter in flight.
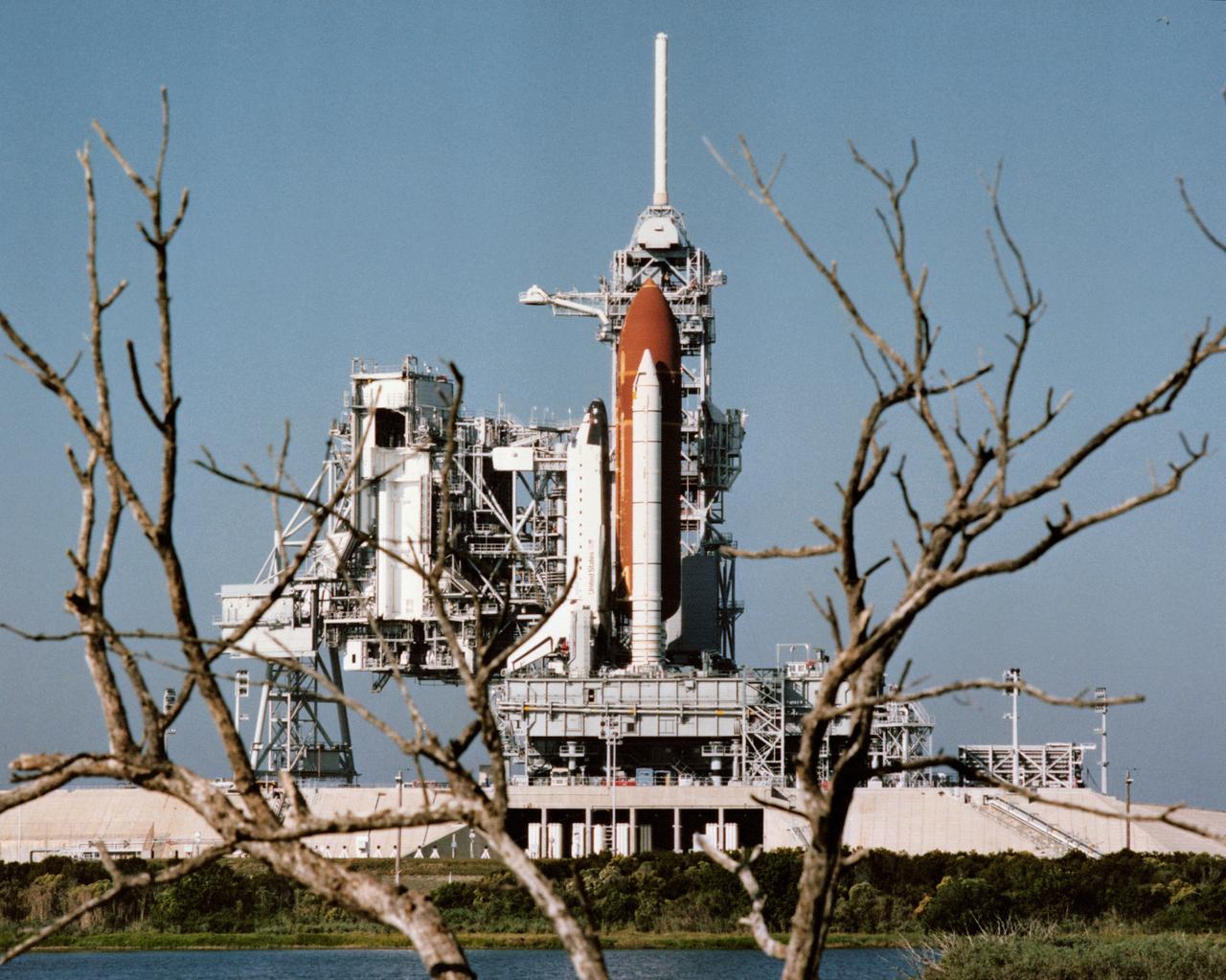

S88-52659 (2 Nov 1988) --- The Space Shuttle Atlantis on Launch Pad 39B at KSC following the roll-out process from the vehicle assembly building. It will undergo final checkouts and evaluations prior to its launch for the STS 27 mission late this month.
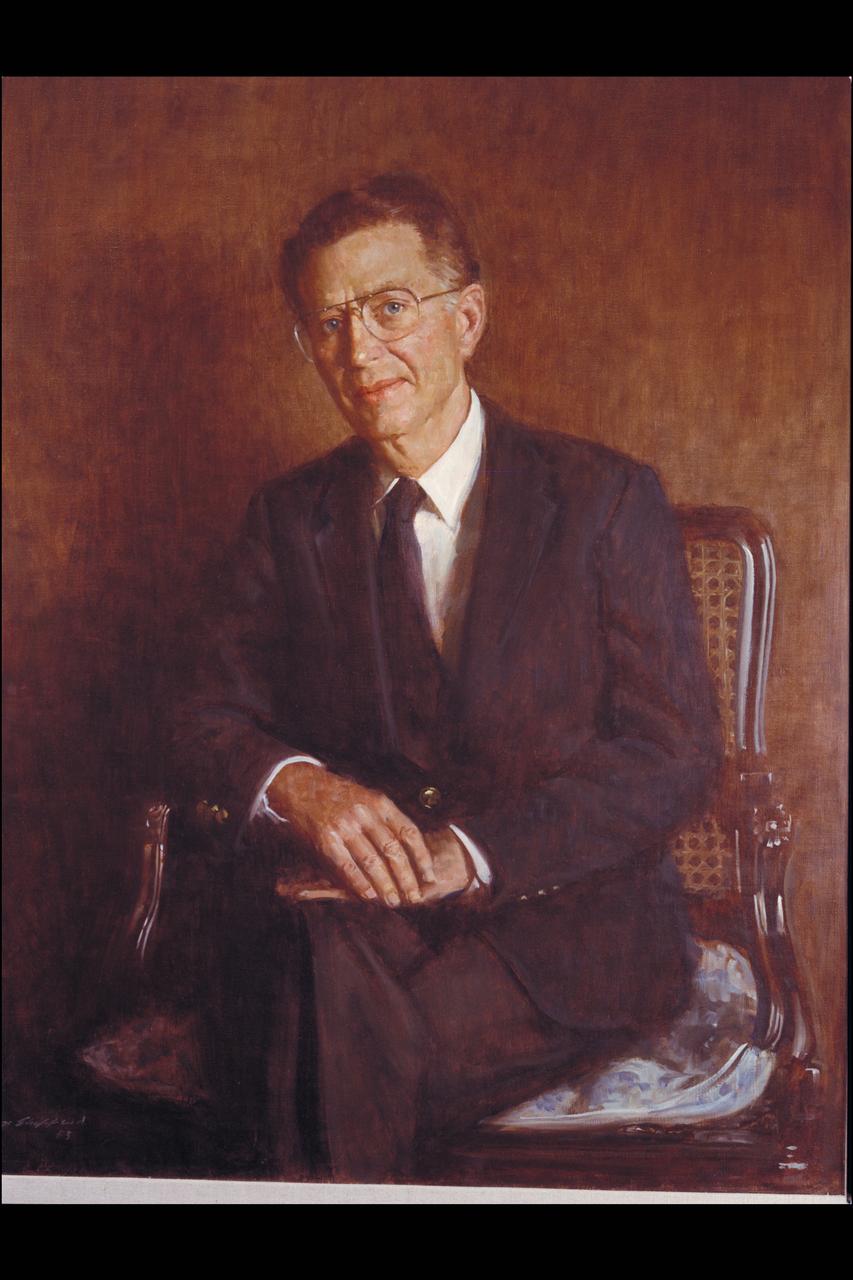

Oil Portrait of Ames Fellow R. T. Jones
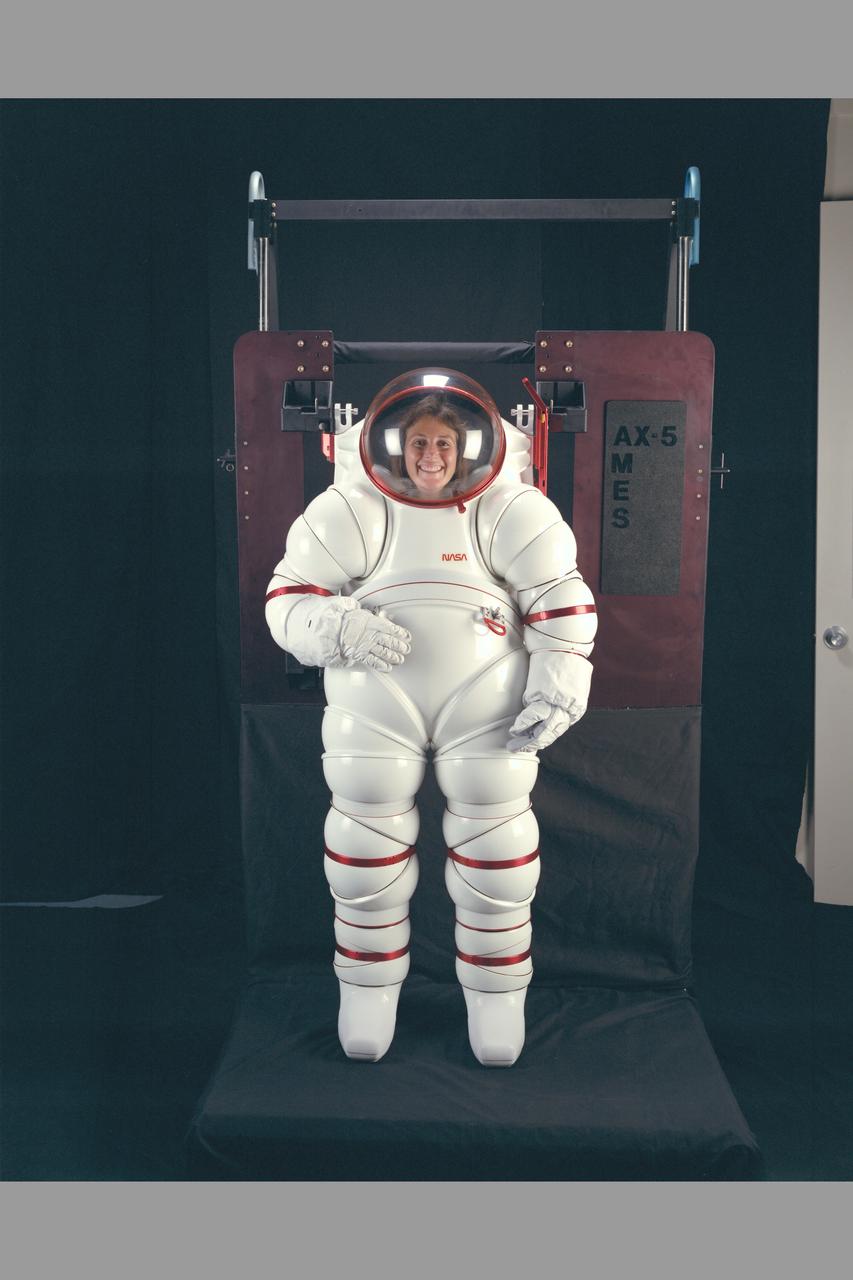

AX-5 Space Suit (Hardsuit) attached to donning stand: This demonstration of new sizing techniques shows the suit adjusted to accommodate the Astronaut's small size. The hardsuit while maintaining mobility offers the astronaut greater protection from debris, micrometerorite penetration, radiation and thermal loads during EVA operations. Developed by NASA Ames. Designer/engineer Hubert 'Vic' Vykukal
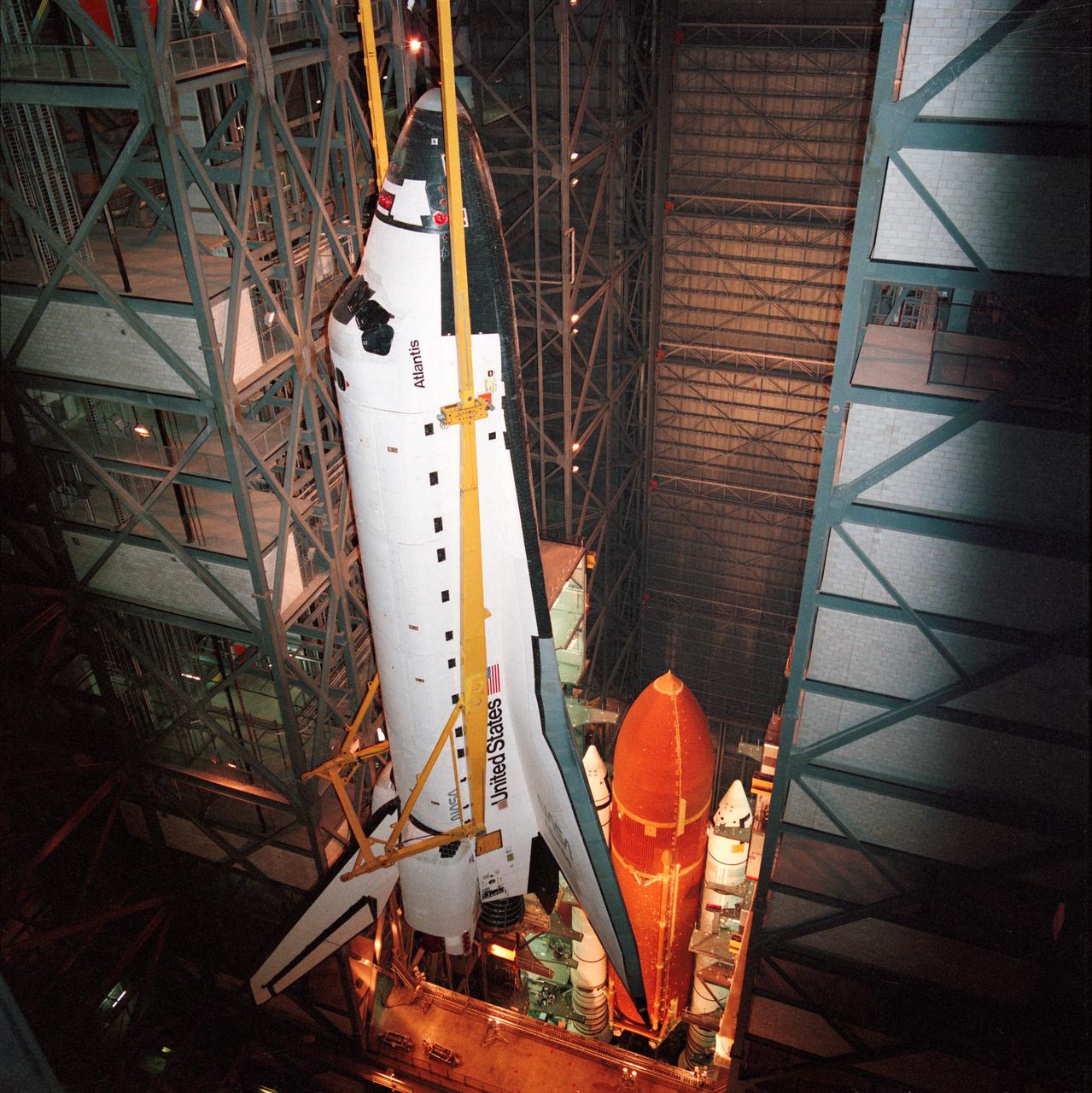

STS-27 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, is suspended via overhead crane, attached at four points, in the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). Below OV-104 on the mobile launcher platform are the external tank (ET) and solid rocket boosters (SRBs). During ET/SRB mating operations, OV-104 will be mounted atop the ET.
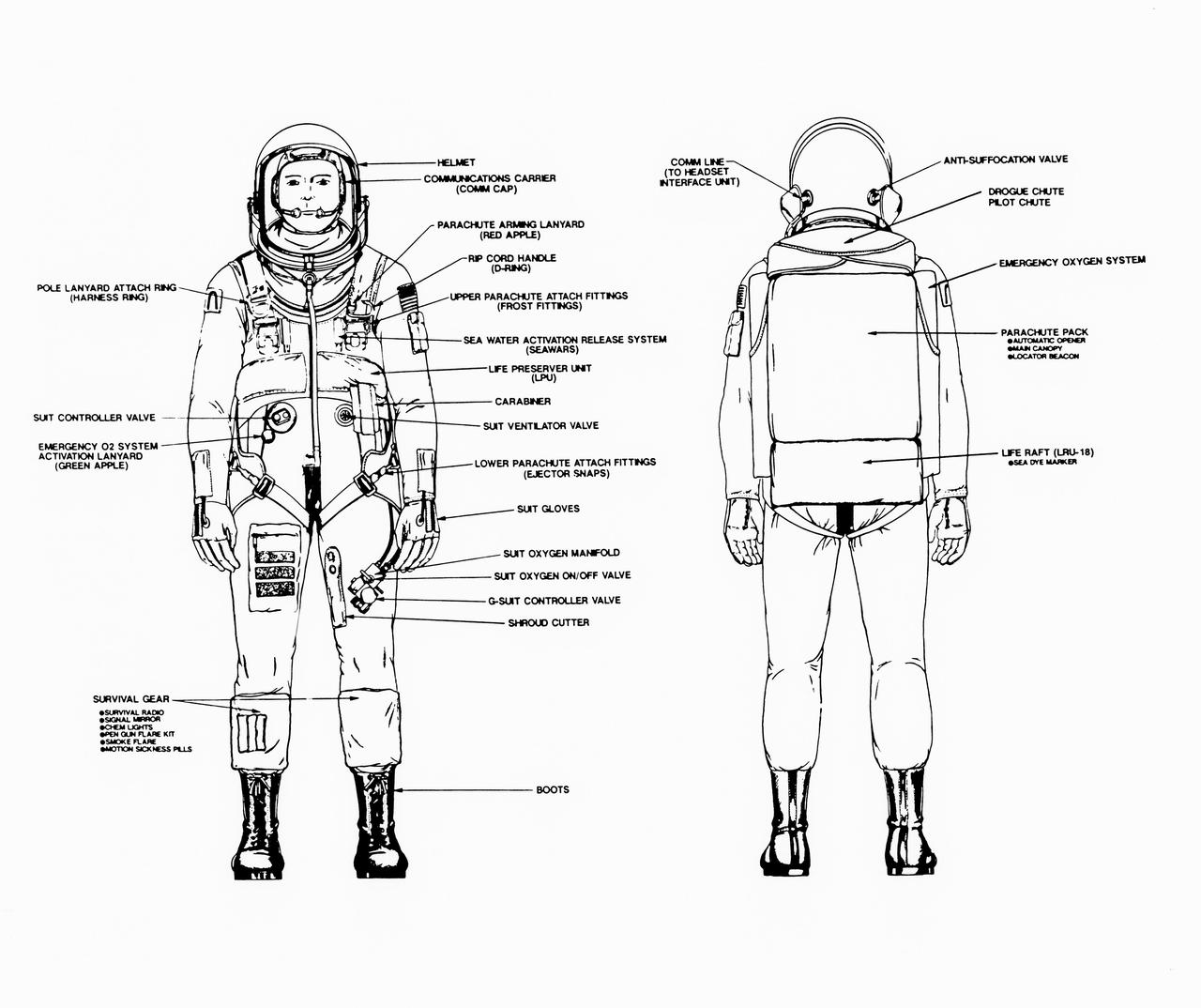
Line drawings illustrate the front and back of the space shuttle launch and entry suit (LES) and labels identify various components. LES was designed for STS-26, the return to flight mission, and subsequent missions. Included in the crew escape system (CES) package are launch and entry helmet (LEH) with communications carrier (COMM CAP), parachute pack and harness, life preserver unit (LPU), life raft unit (LRU), LES gloves, suit oxygen manifold and valves, boots, and survival gear. Details of larger components are also identified.
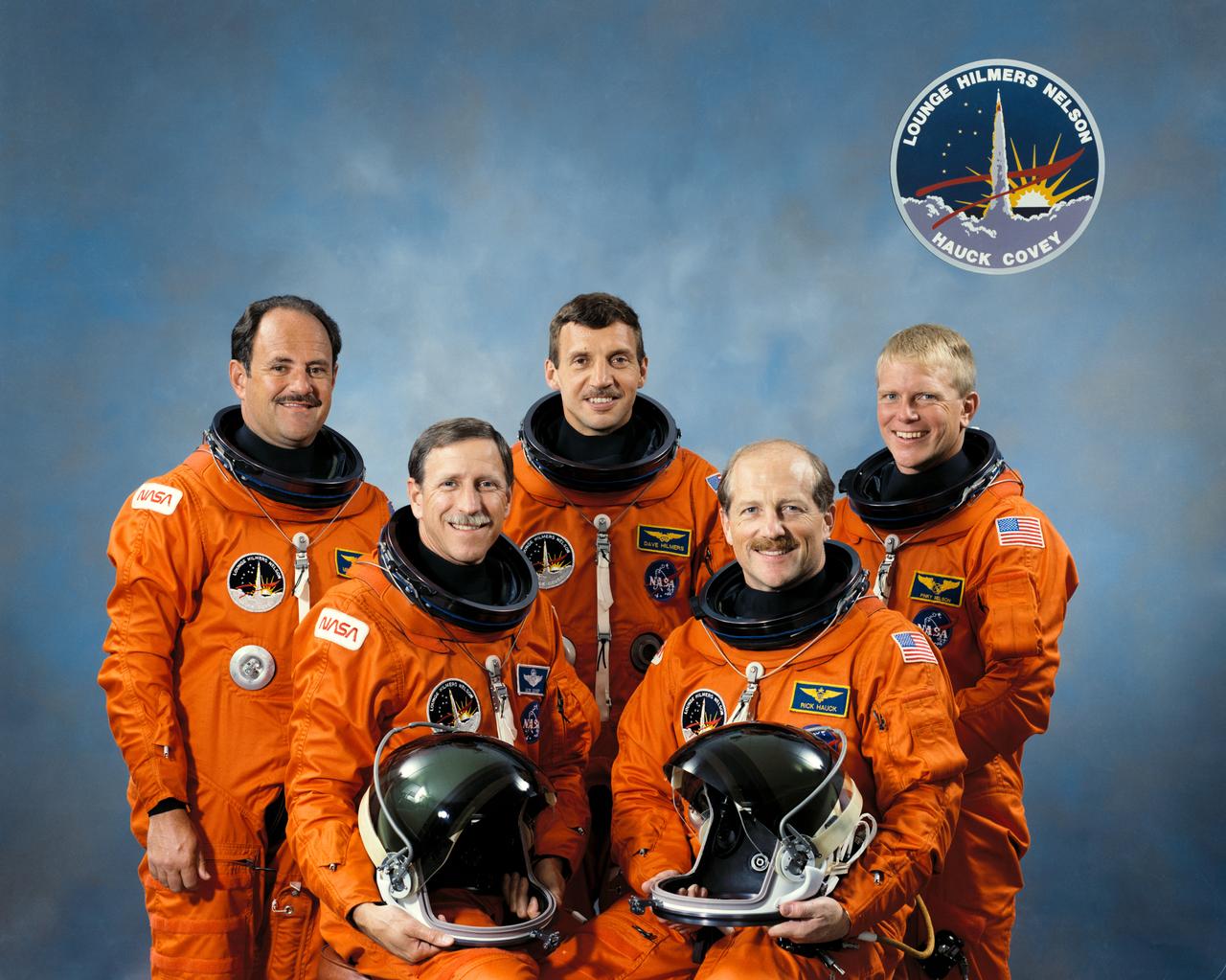

S88-47522 (10 Sept 1988) --- These five veteran astronauts have been training for over a year to serve as NASA's crew aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery for STS-26. On the front row are Astronauts Frederick H. (Rick) Hauck (right), commander; and Richard O. Covey, pilot. On the back row are Astronauts John M. (Mike) Lounge, David C. Hilmers and George D. Nelson -- all mission specialists. The crewmembers are wearing the orange partial pressure garments that they will be wearing on the launch and entry phases of the flight, scheduled for launch later this month.
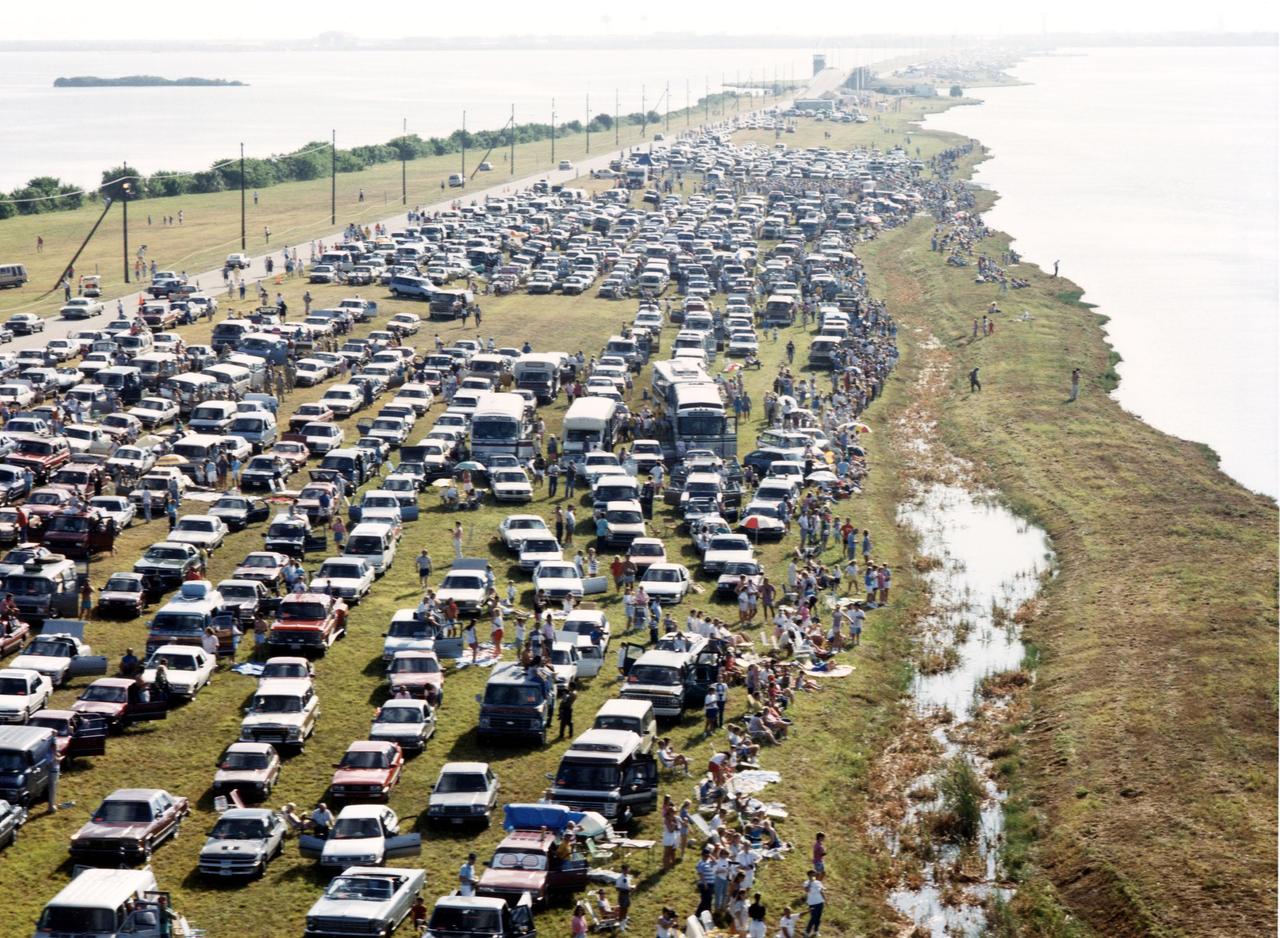

NASA employees, their family and friends gather on the NASA causeway over the Banana River, south of Kennedy Space Center, the morning of the launch of STS-26 and the Space Shuttle Discovery. An estimated 1 million people were expected to view the 11:37 a.m. launch from various locations in Central Florida
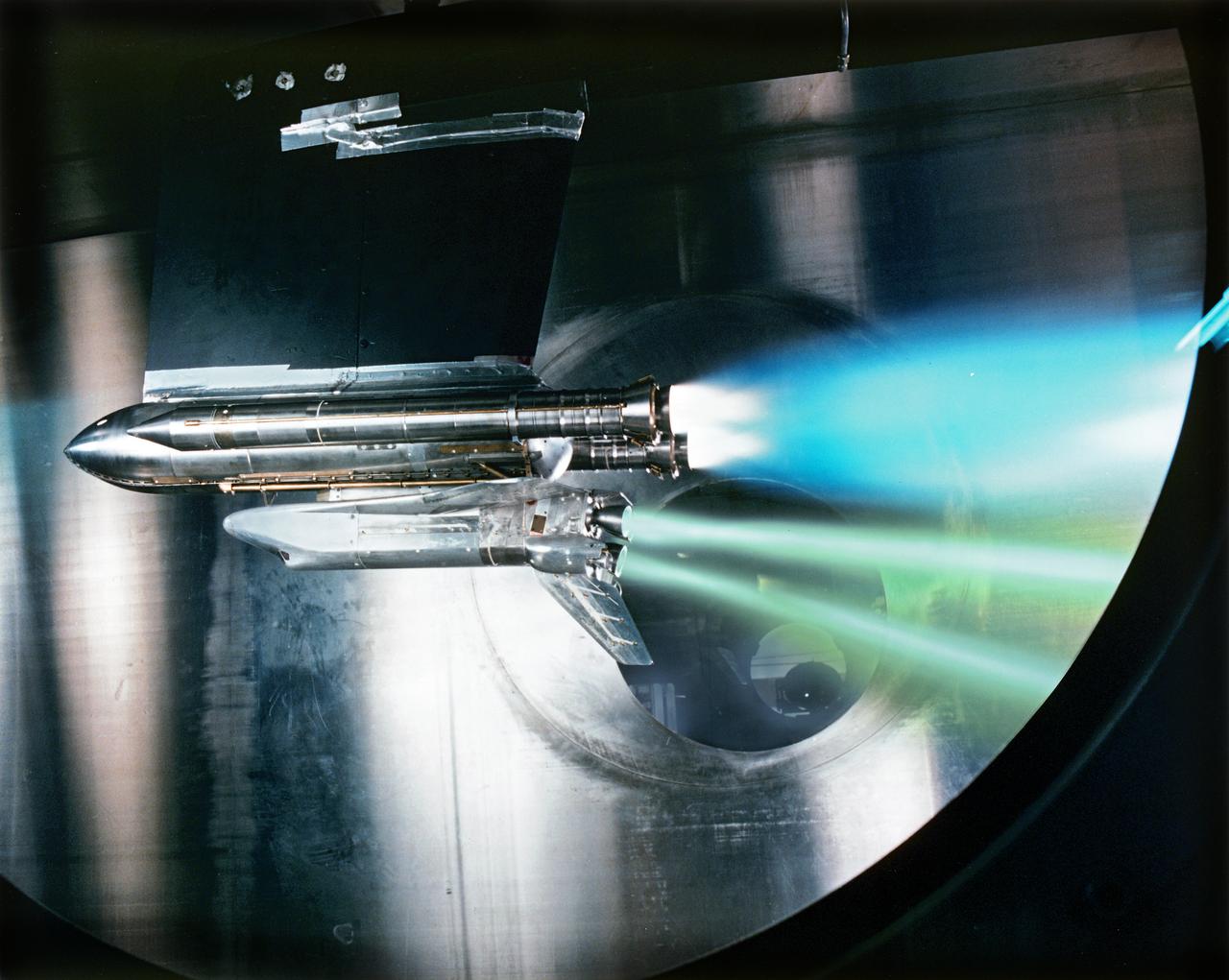

SHUTTLE ENGINE OUT TEST done after the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster. This was part of the investigation after the Challenger accident
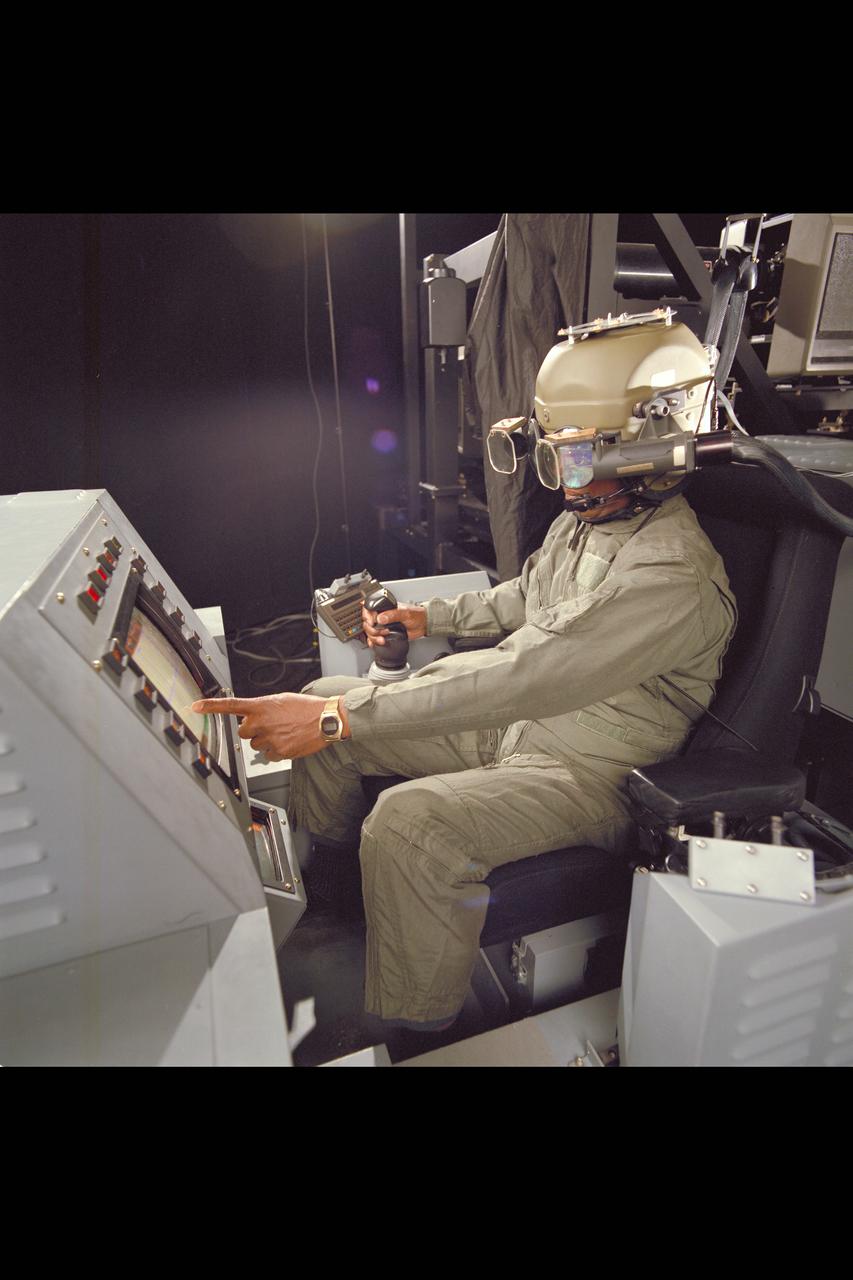

Crew Station Research and Developement Facility (CSRDF) A NASA Army simulator to design and evaluate advanced rotorcraft showing fiber optic helmet & workstation

Newly arrived DC-8 (NASA-717) in flight over Sierra mountains
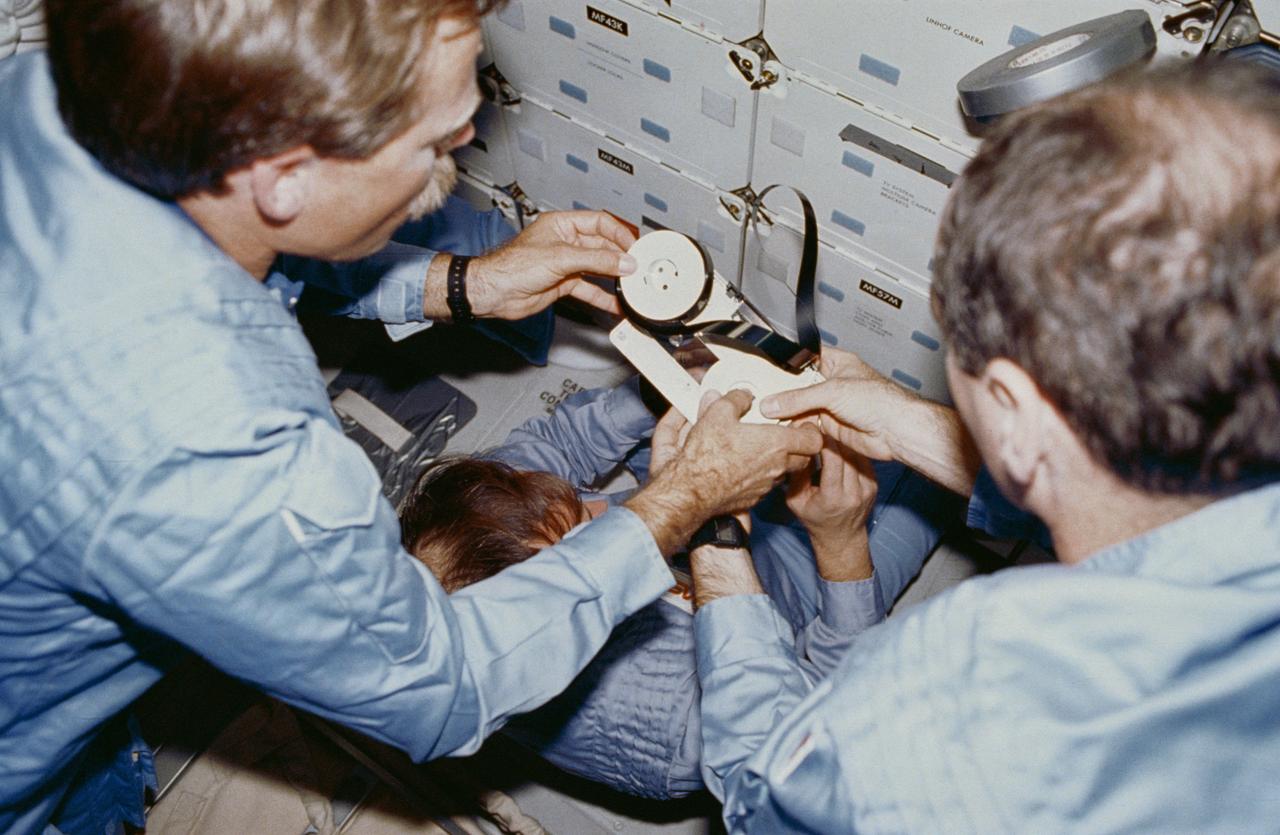

STS027-05-020 (2-6 Dec. 1988) --- In the foreground, astronauts Robert L. Gibson (left) and Guy S. Gardner, commander and pilot, respectively, for the STS-27 mission, repair a 3/4-inch video reel on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Atlantis. Photo credit: NASA
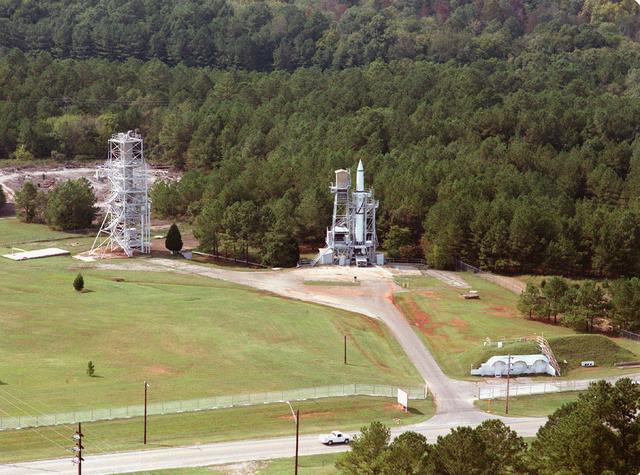

The Redstone Test Stand, shown here, was used throughout the 1950s to test the Redstone missionile, including the modified Redstone that launched America's first astronaut, Alan Shepard. The U. S. Department of the Interior's Park Services designated the Test Stand as a National Historic Landmark January 22, 1986.
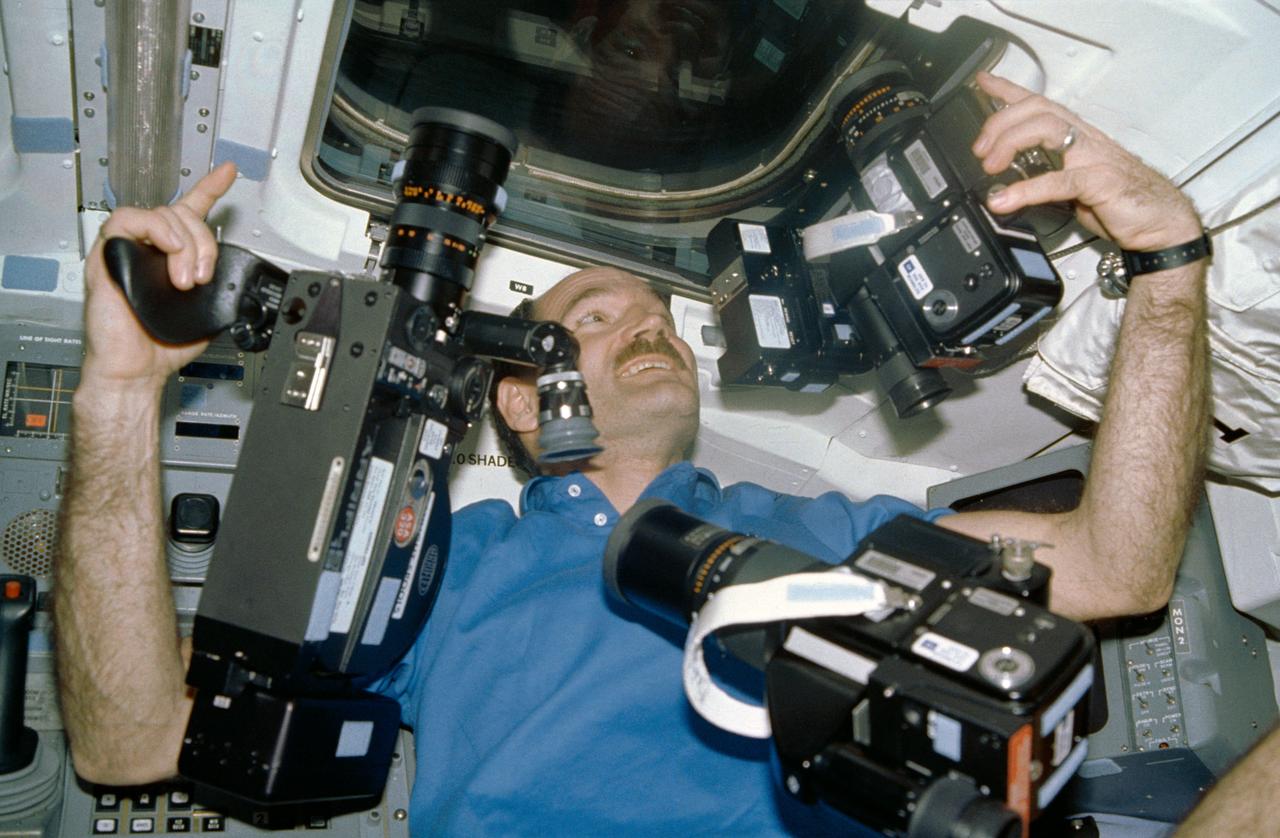

STS027-14-021 (2-6 Dec. 1988) --- Astronaut Guy S. Gardner, STS-27 pilot, appears to have enough cameras as he prepares to take photographs onboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Atlantis. Photo credit: NASA
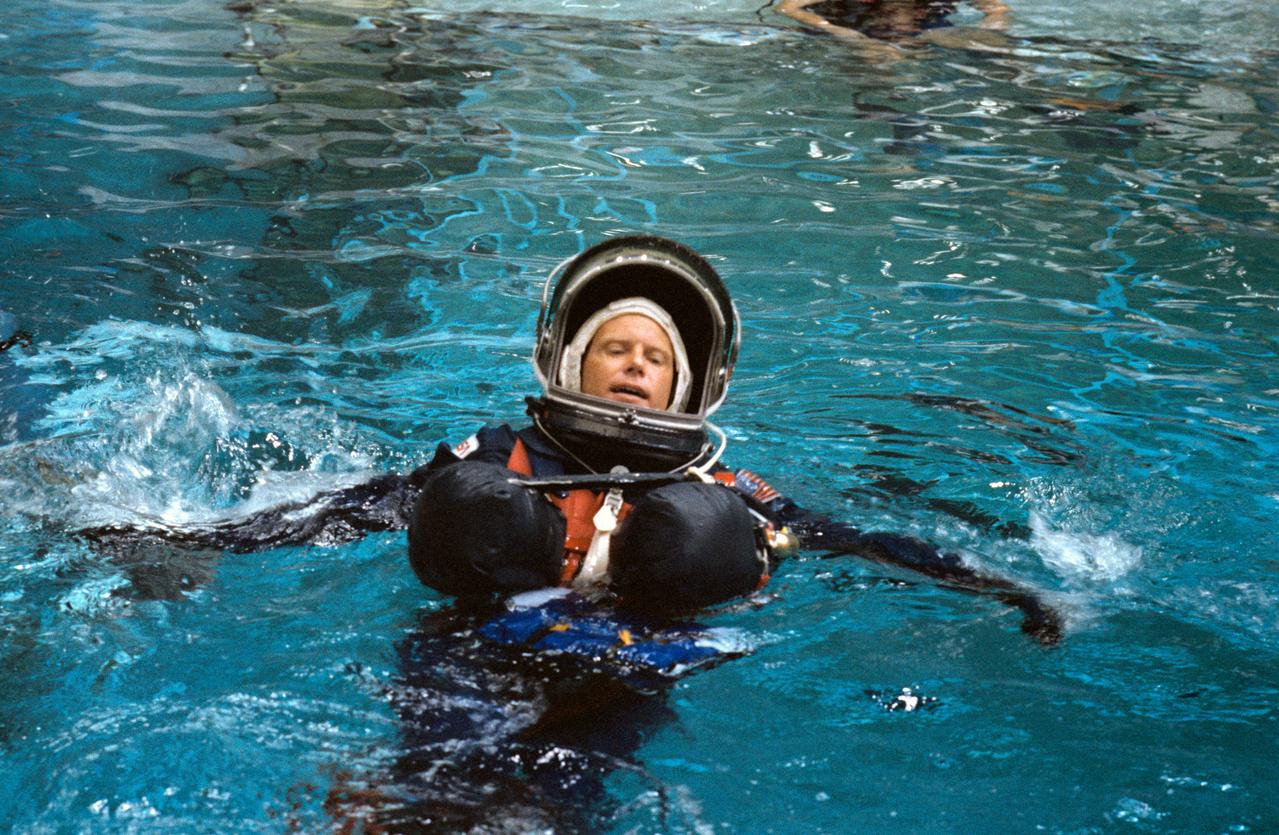

S88-42409 (20 July 1988) --- STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Mission Specialist (MS) George D. Nelson participates in crew escape system (CES) testing in JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. Nelson, wearing the newly designed (navy blue) launch and entry suit (LES), floats in WETF pool with the aid of an underarm flotation device (modern version of Mas West floats). He awaits the assistance of SCUBA-equipped divers during a simulation of escape and rescue operations utilizing a new CES pole for emergency exit from the Space Shuttle.
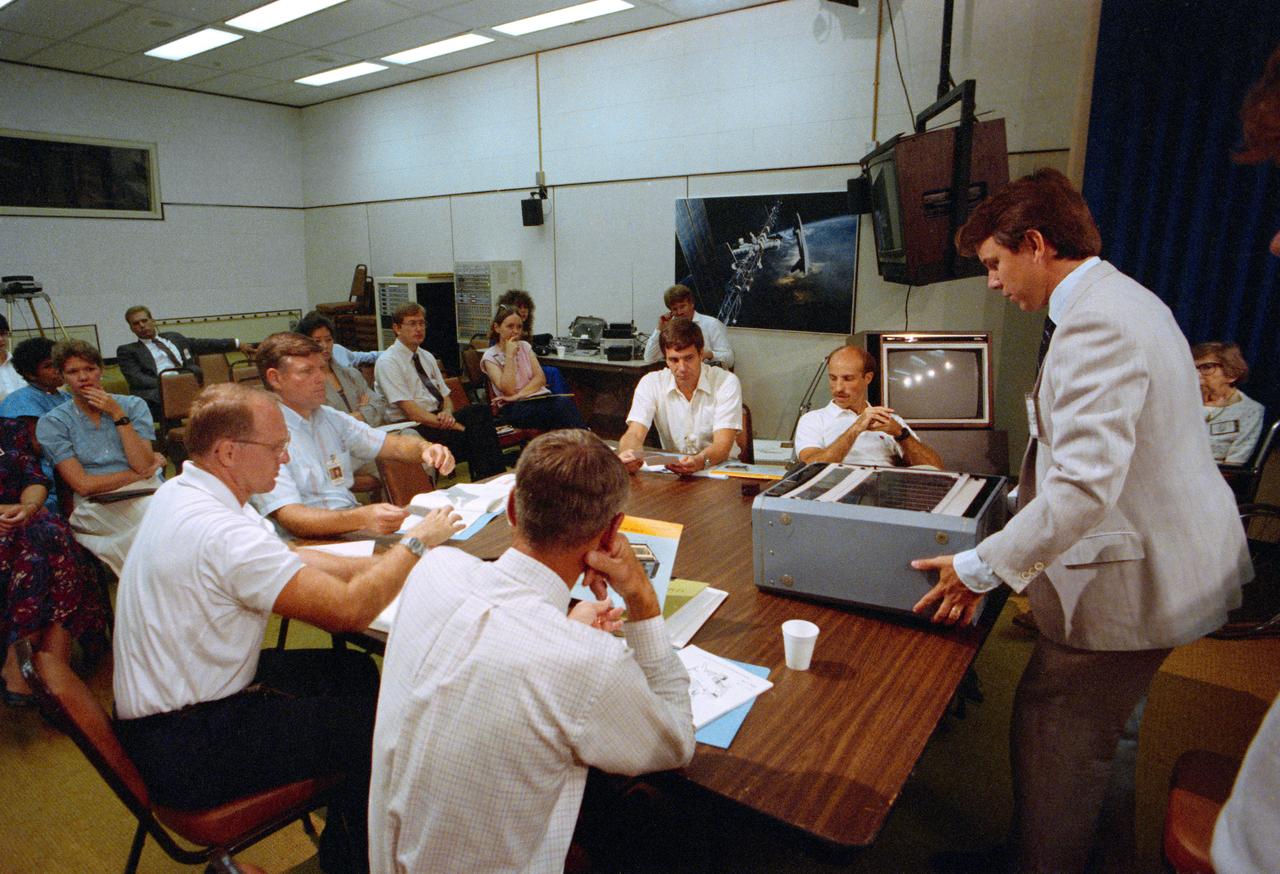

S88-44661 (13 Aug 1988) --- Tom Kestler, with Orthopaedic Hospital, USC, one of the sponsor representatives for student experimenter Andrew Fras explains components of Fras' experiment. It will be carried onboard theDiscovery for NASA's STS-29 mission next year. His primary audience is made up of members of the STS-29 crew who will monitor in-space operation of the experiment, titled "Effects of Weightlessness on Bone Healing." Crewmembers, clockwise around the table from the left, are Astronauts Robert C. Springer, James F. Buchli, Michael L. Coats, John E. Blaha and James P. Bagian. Seated in far right background is Dr. June Marshall of the University of Southern California School of Medicine, the student's sponsoring organization.

Artist concept of the Johnson Space Center Amateur Radio Club logo.
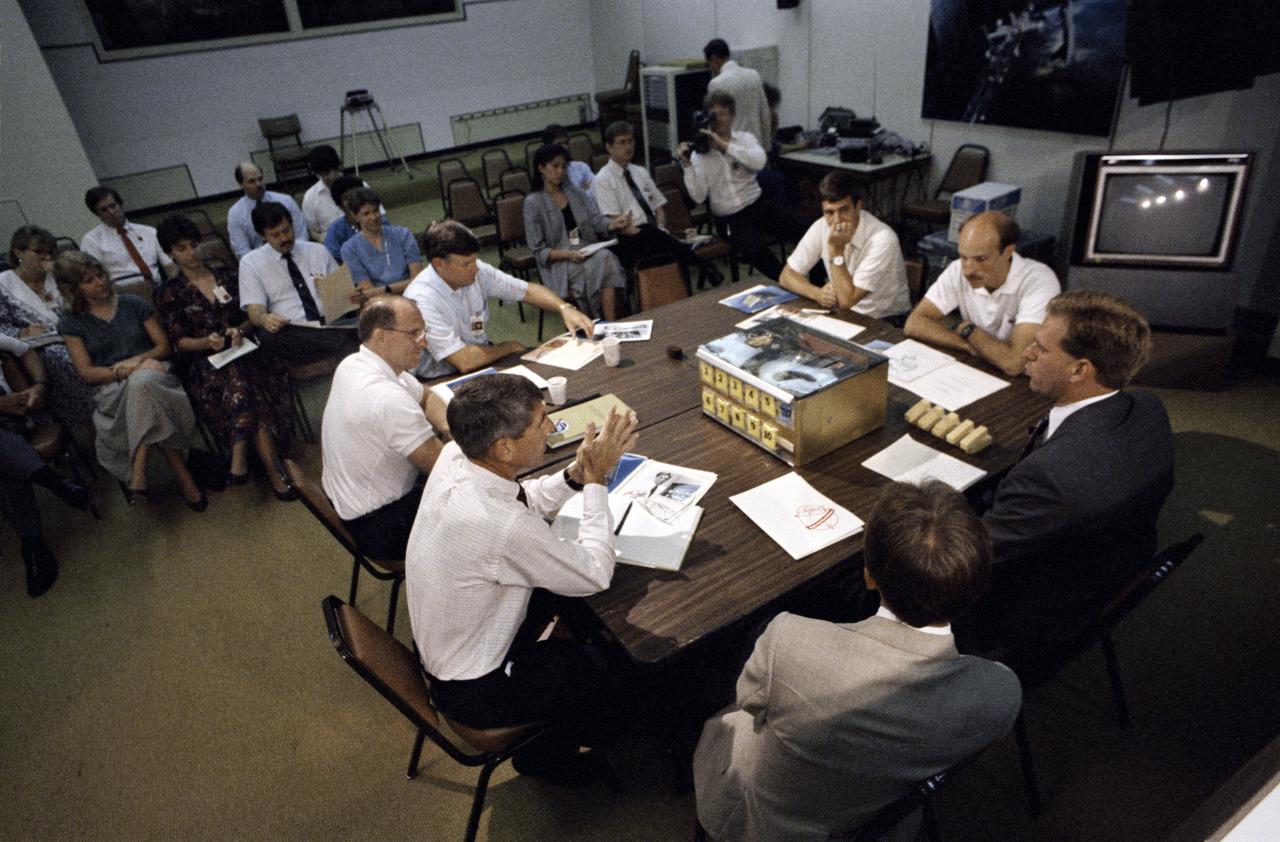

S88-44517 (13 Aug 1988) --- Student experimenter John C. Vellinger, right, explains operation of an incubator used in his experiment to be carried onboard the Discovery for NASA's STS-29 mission next year. His primary audience is made up of STS-29's five-man crew, who will monitor in-space operation of the experiment, titled "Chicken Embryo Development in Space." Kentucky Fried Chicken.
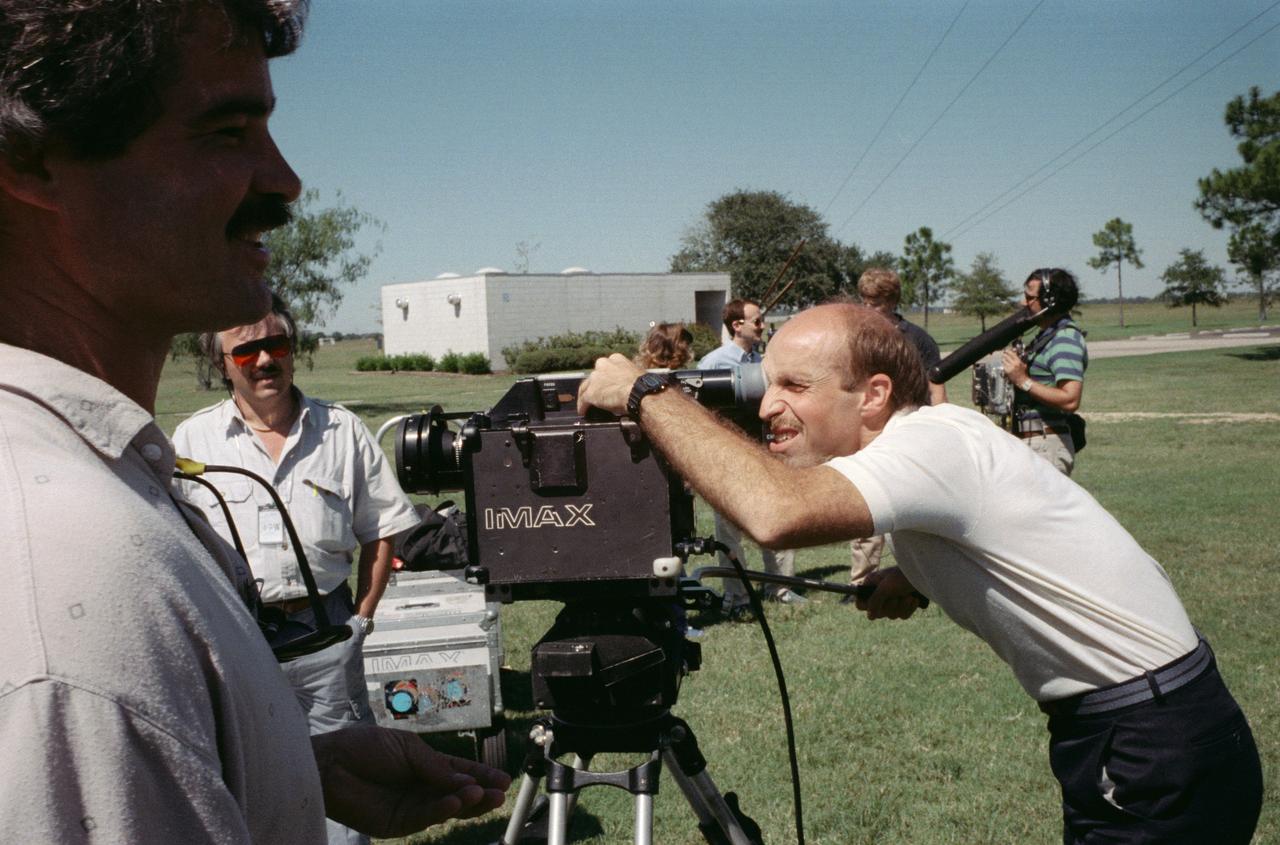

S88-52470 (8 Nov 1988) --- James P. Bagian, STS-29 mission specialist, gets in some training on the operation of one of the payloads for his upcoming spaceflight aboard Discovery. The crew met with Imax personnel, some of whom are pictured here, on the JSC grounds to practice using the motion- picture camera, making its first post-Challenger trip into space. The payload flew on a number of earlier STS flights.

Crows Landing runway approach
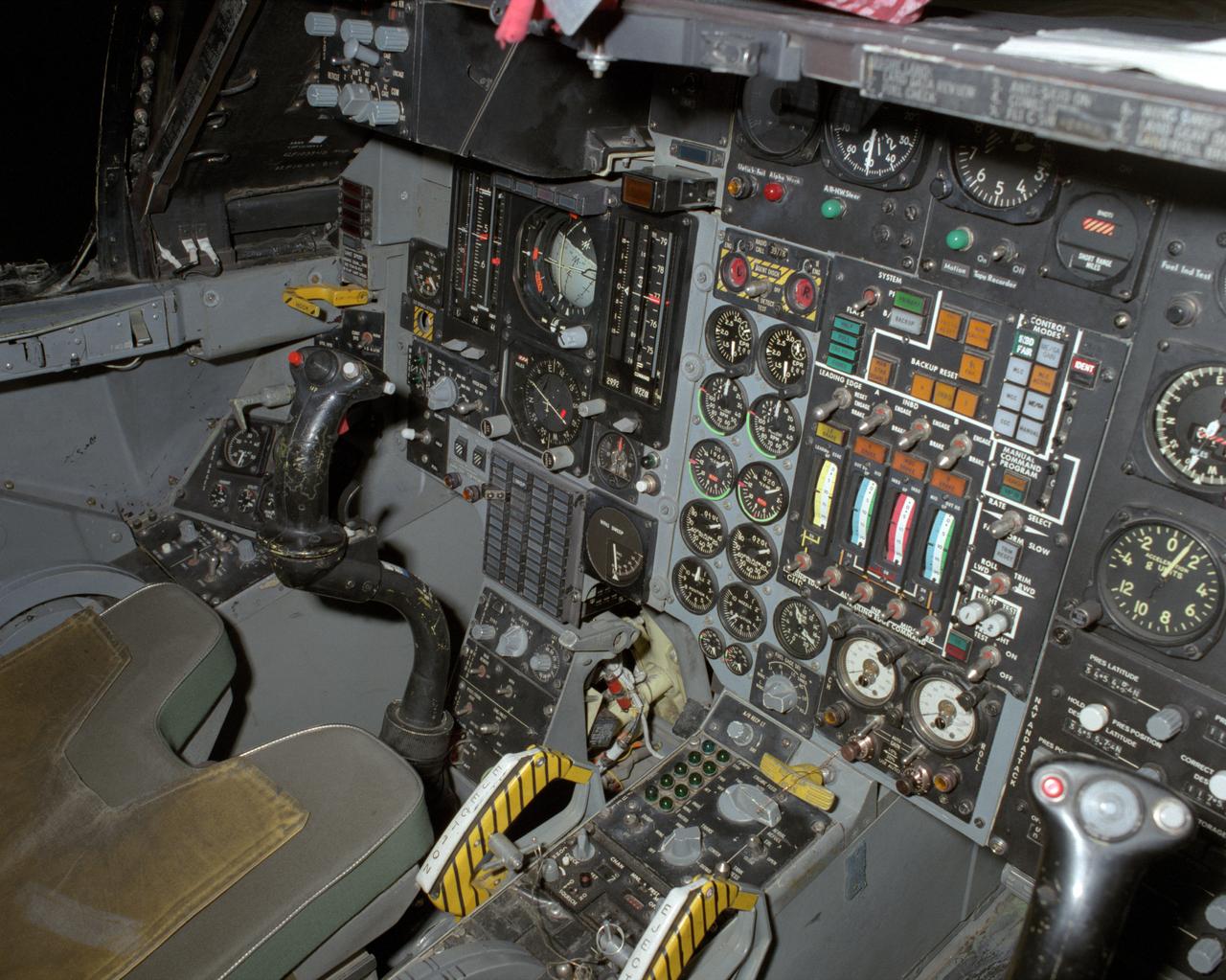

View of the left cockpit and pilot's seat of the F-111 MAW aircraft. Unlike most fighter aircraft of the time, the F-111 had side-by-side seating. The pilot sat on the left side, and the weapons systems officer on the right. Both had control sticks to fly the aircraft. The two yellow and black striped handles would be used in an emergency to eject the entire F-111 cockpit. The F-111 also did not have ejection seats, but used a capsule.

Oil Portrait of Ames Fellow James Pollack
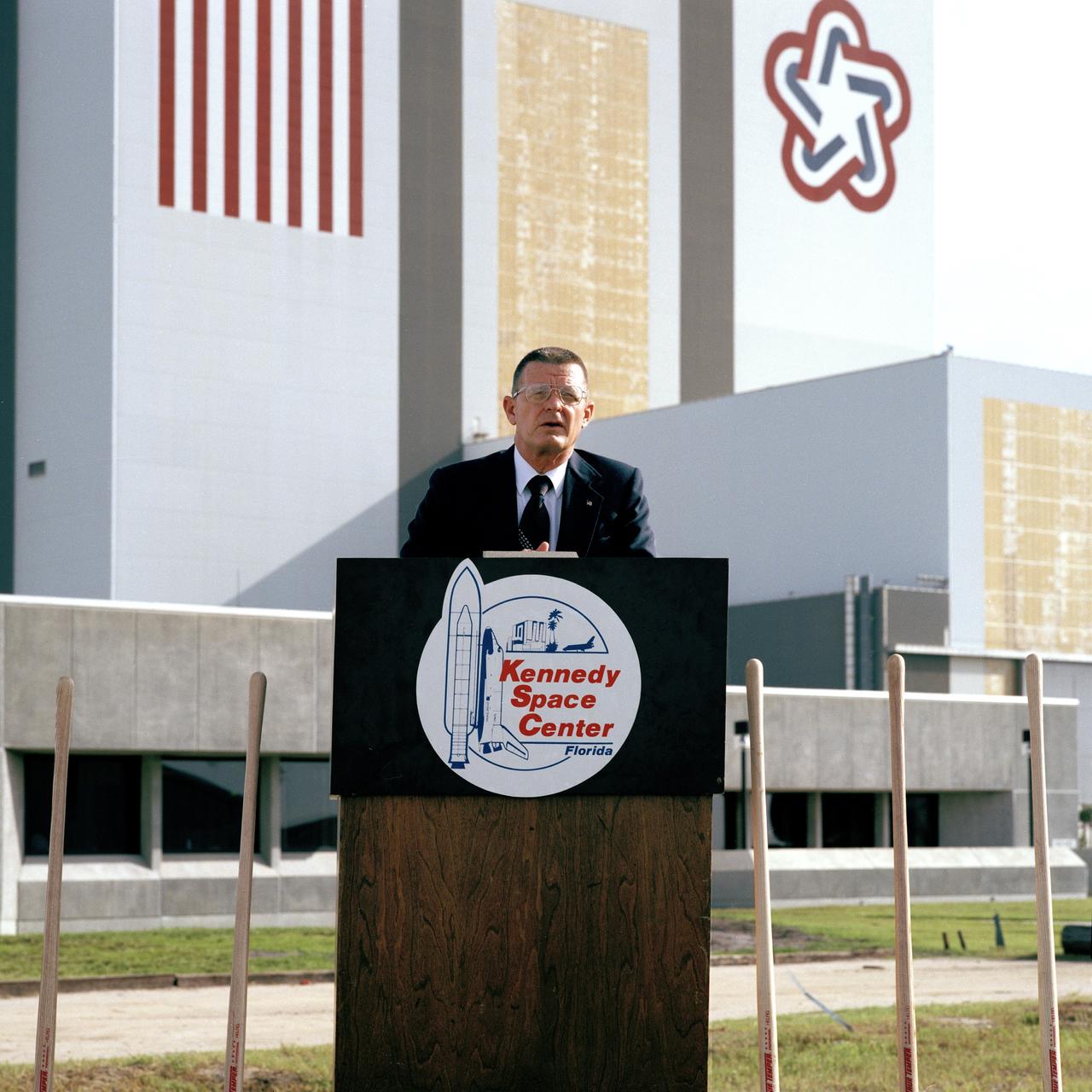

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Kennedy Space Center Director Forrest McCartney speaks at the ground-breaking ceremonies for the new Operations Support Building. This new facility will provide office accommodations for 1,700 NASA and contractor personnel. The $20,695,000, six-story, 300,000-square-foot building is located southwest of the Multi-Function Facility near the corner of the Saturn Causeway and Kennedy Parkway Roads. Construction is due to be completed by June 1990. Photo credit: NASA
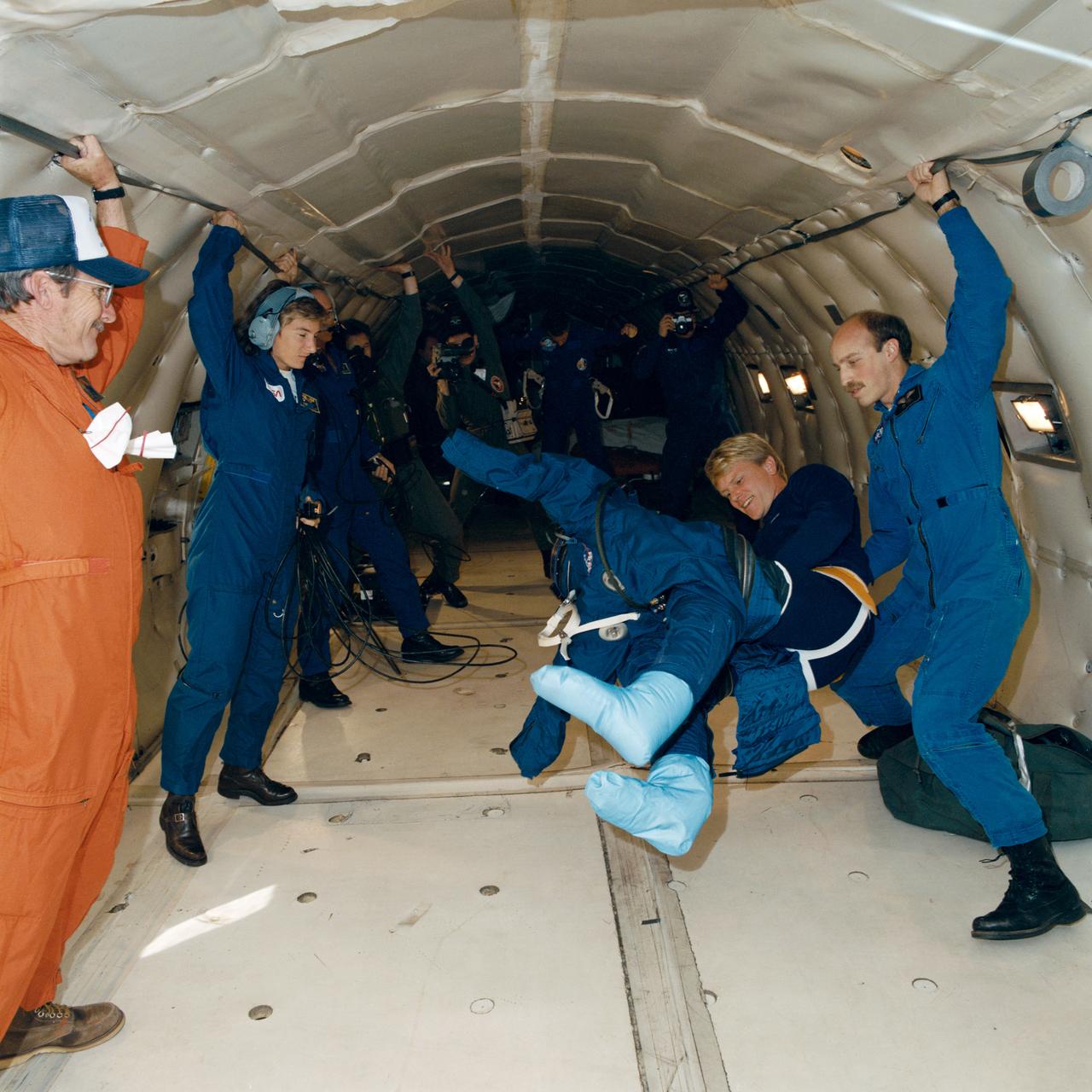
STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Mission Specialist (MS) George D. Nelson practices donning and doffing new (navy blue) partial pressure suit (launch and entry suit (LES)) aboard KC-135 NASA 930 during zero gravity testing. Nelson is assisted by astronaut James P. Bagian as KC-135 flight crew (including Stephanie A. Wells) looks on and photographers document activities.
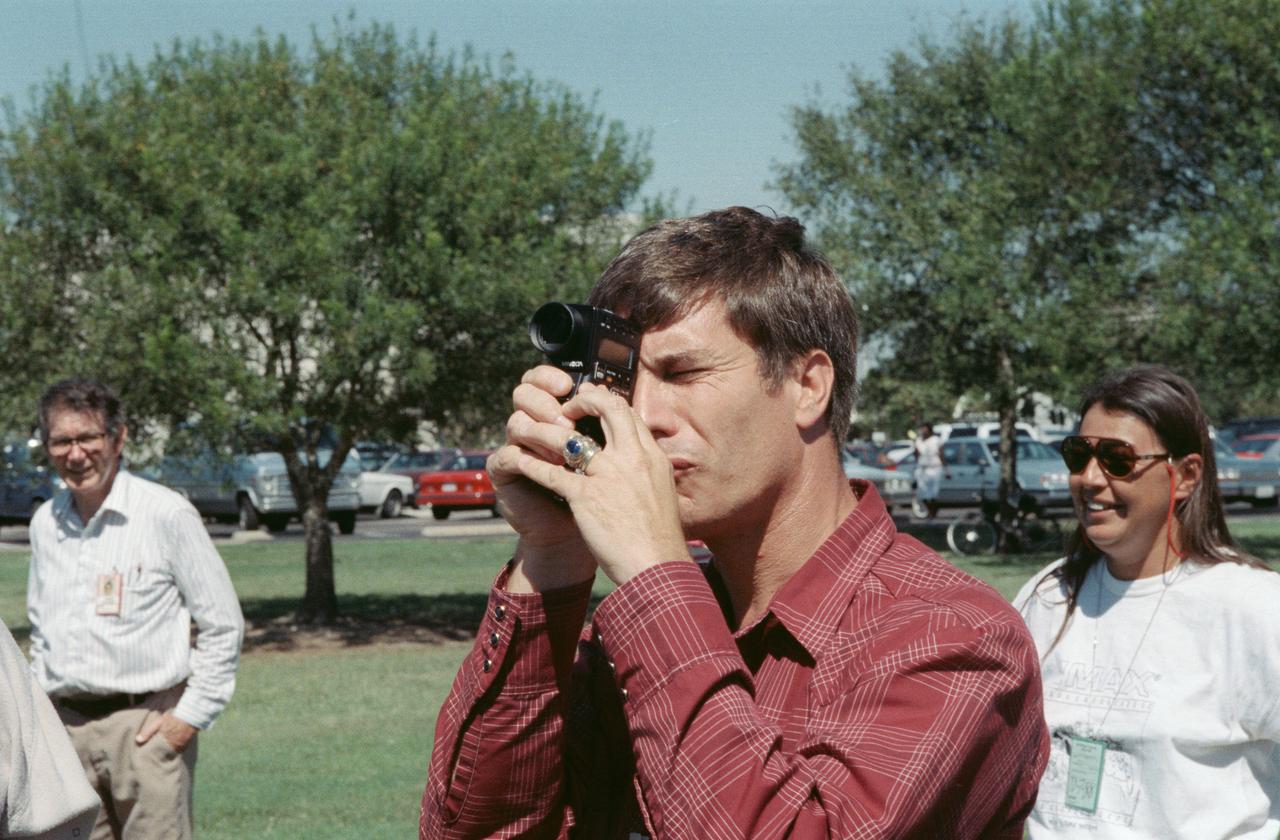

S88-52476 (8 Nov 1988) --- John E. Blaha, STS-29 pilot, gets in some training on the operation of one of the payloads for his upcoming spaceflight aboard Discovery. The payload is an Imax motion-picture camera, hardware of which is out of frame here. Blaha uses a light meter to get a reading before operating the camera in a practice run. The crew met with Imax personnel on the JSC grounds to practice using the motion-picture camera, making its first post-Challenger trip into space. Phyllis Wilson with Imax is at far right. The payload flew on a number of earlier STS flights.
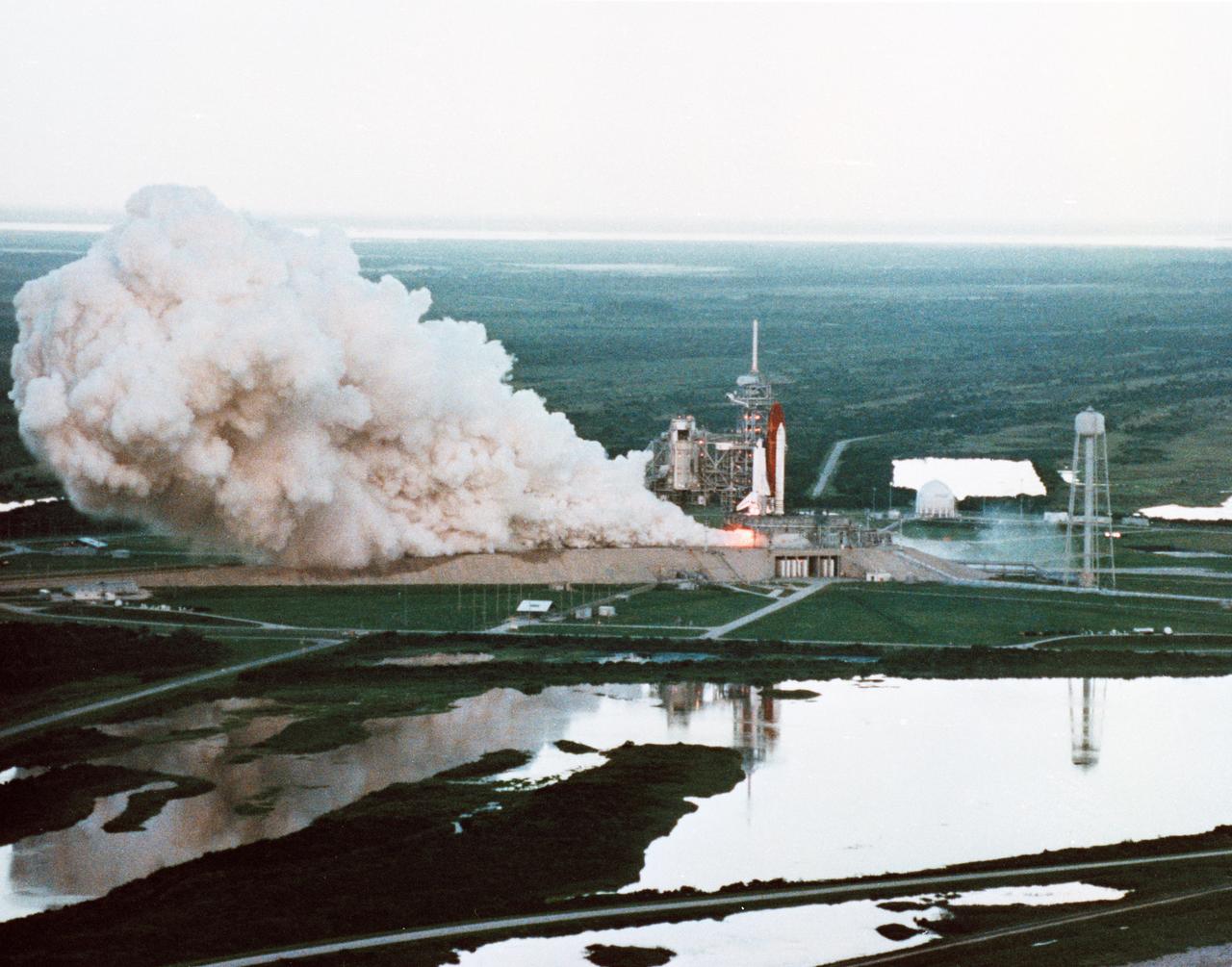

Documentary views of the STS-26 Flight Readiness Firing at KSC, Pad 39B, on 10 Aug 1988. (KSC-88PC-752 closer) (KSC-88PC-752, 753)
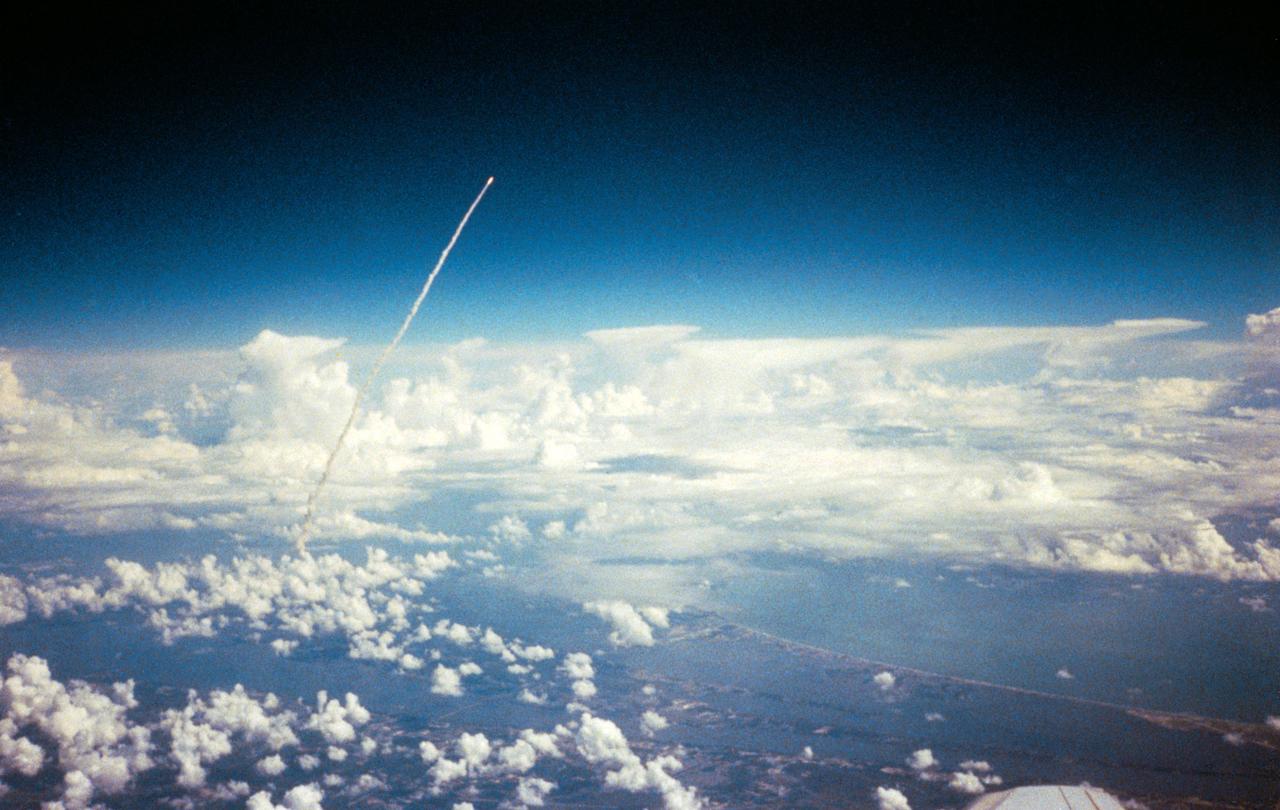

Long range view of an unidentified space shuttle lift off taken from an unidentified high flying aircraft.