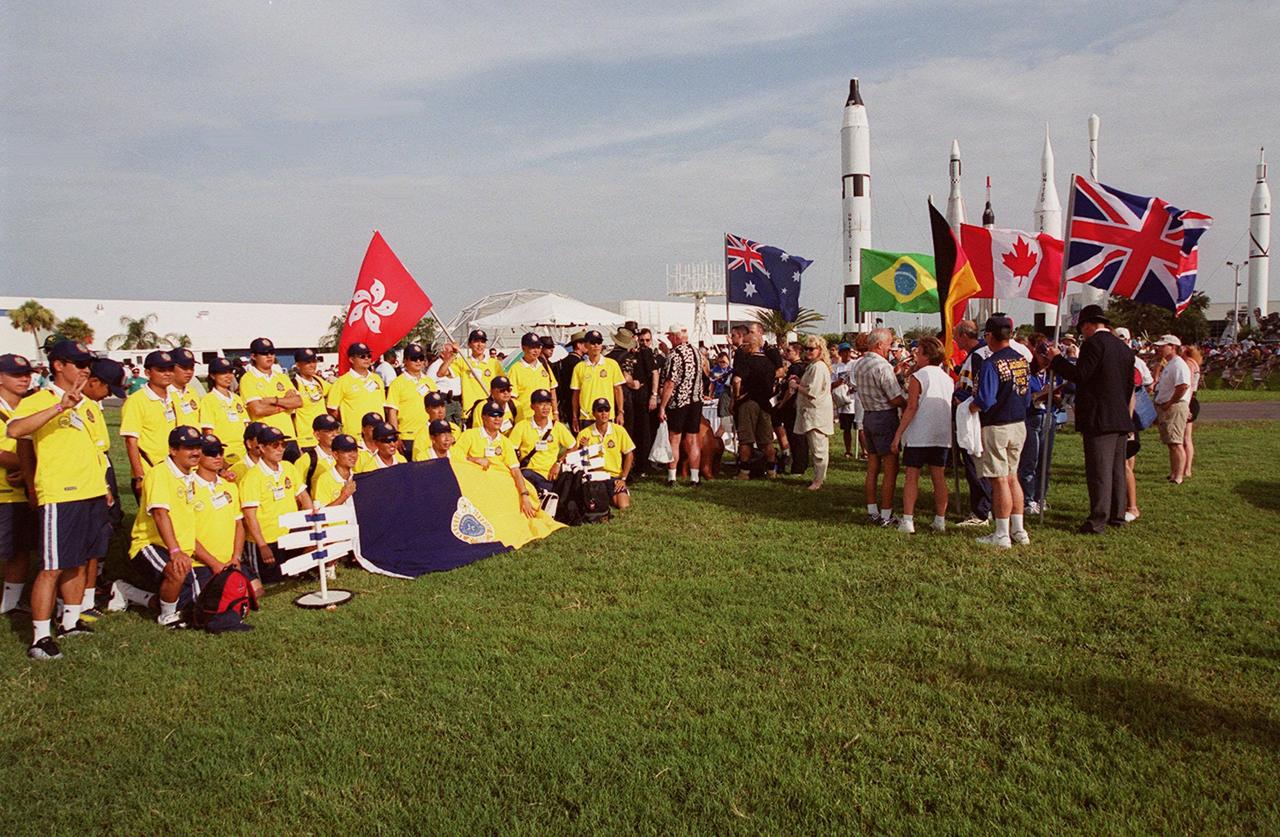

Hong Kong police officers gather in the KSC Visitor Complex Rocket Garden during opening ceremonies of the 2000 International Law Enforcement Games. More than 1,850 participants and their families took part in the opening, held in the Rocket Garden. The ceremony included parades, torch lighting and a tug of war. The games feature officers from 15 countries and 37 United States in competitions around Brevard County, Fla
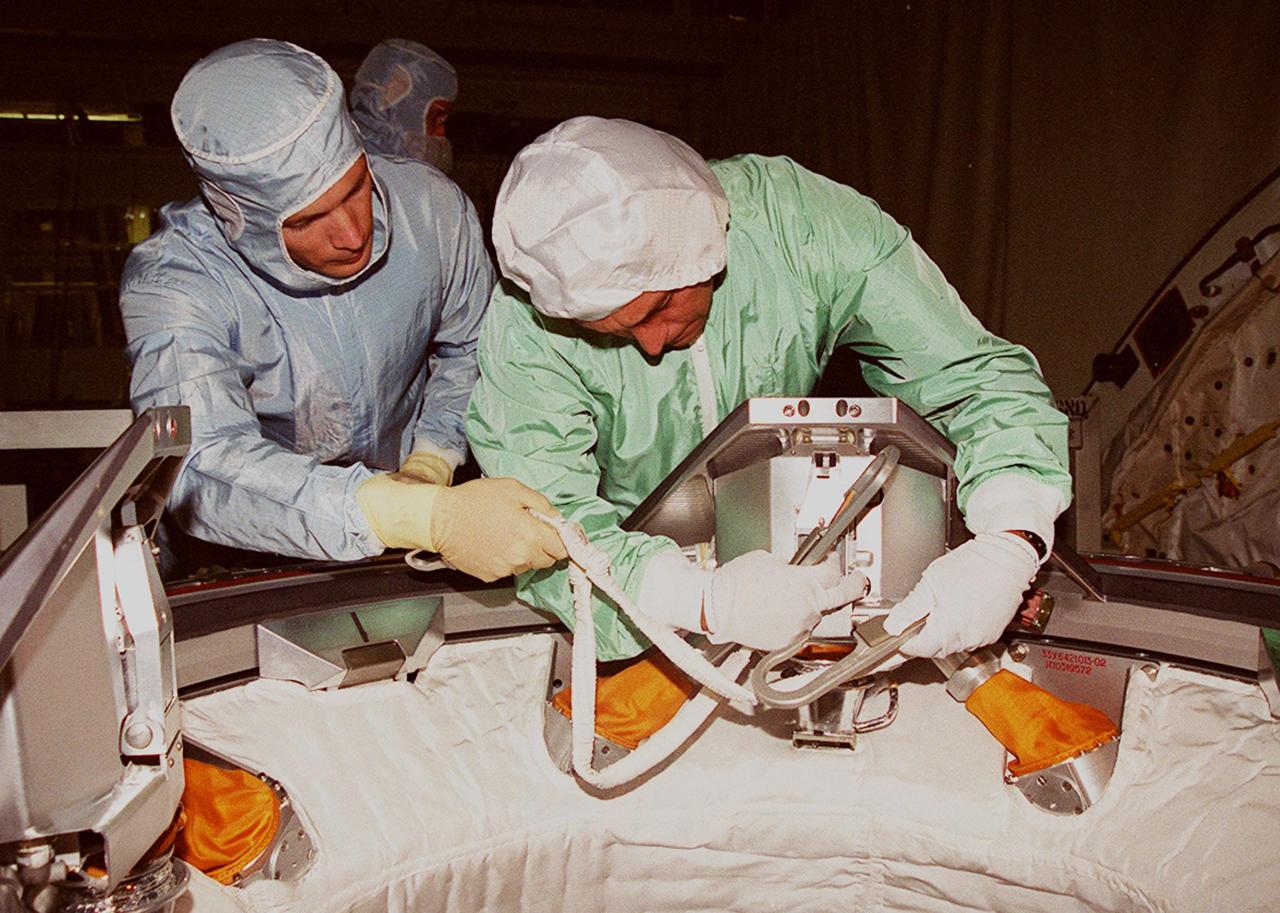
During the STS-97 Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT), Mission Specialist Carlos Noriega (right) gets hands-on experience with parts of the Orbital Docking System in Endeavour’s payload bay. The CEIT provides an opportunity for crew members to check equipment and facilities that will be on board the orbiter during their mission. The STS-97 mission will be the sixth construction flight to the International Space Station. The payload includes a photovoltaic (PV) module, providing solar power to the Station. STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 from KSC for the 10-day mission
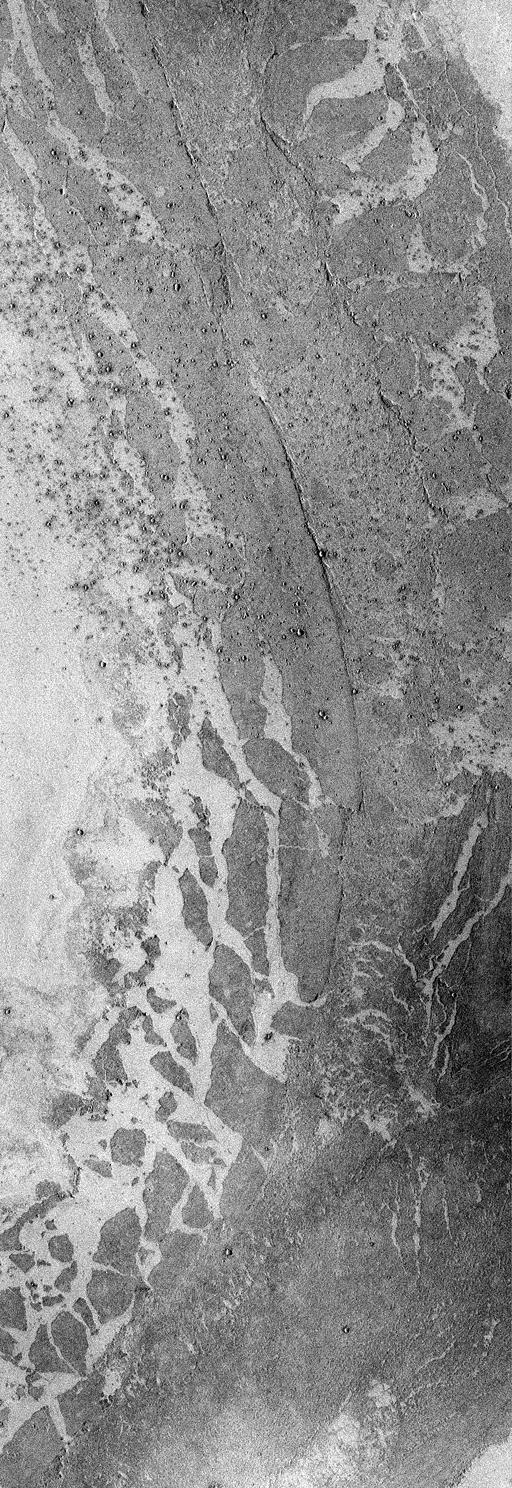
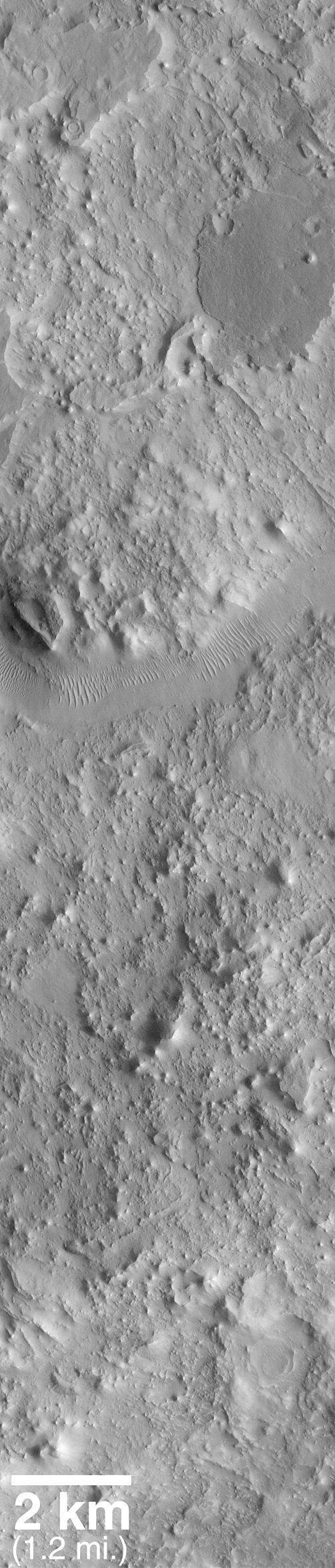
Mars Volcanism: Large, Fluid Lava Flows
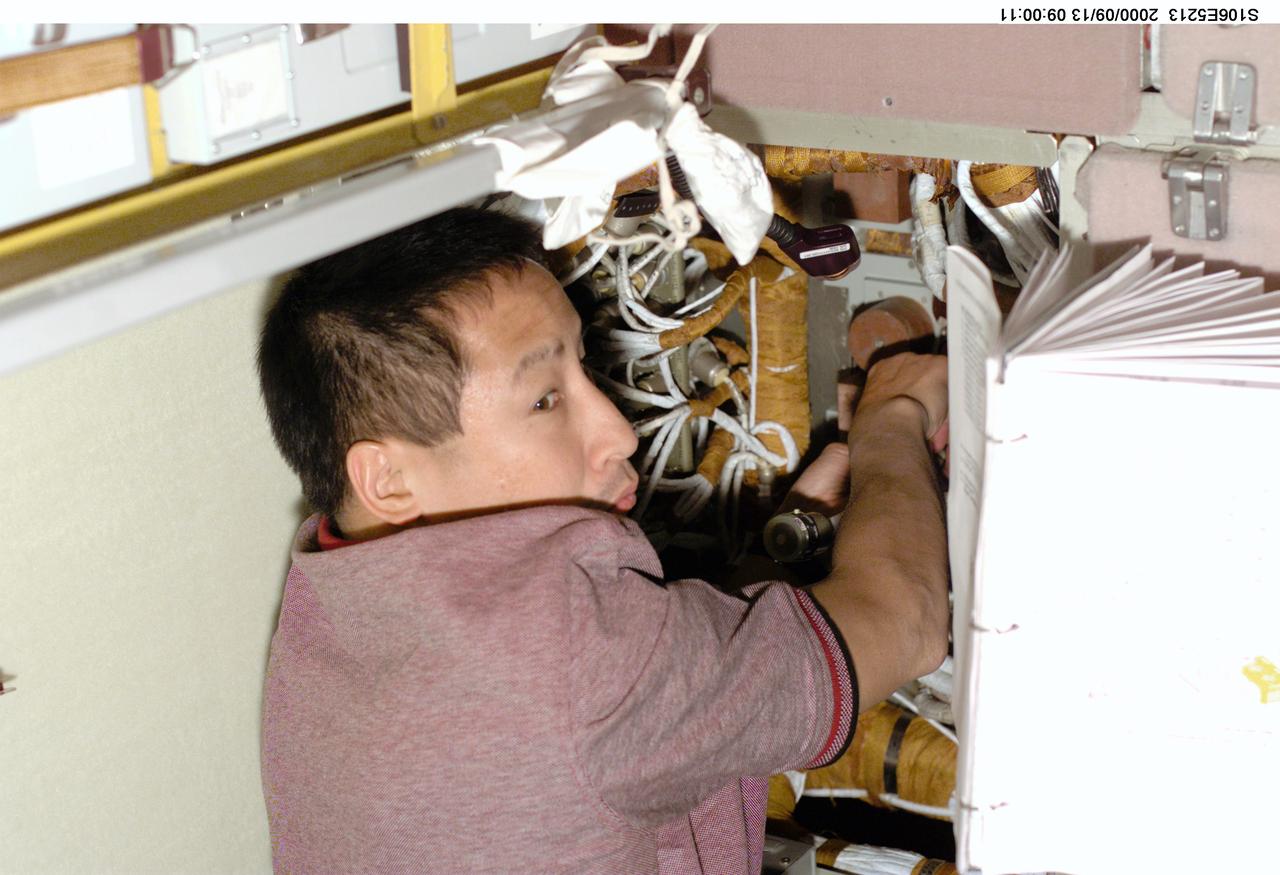

S106-E-5213 (13 September 2000) --- Astronaut Edward T. Lu follows printed guidelines as he assumes the role of an electrician onboard the Zvezda service module on the International Space Station (ISS). Electrical work was the hallmark of the day as four of the mission specialists aboard ISS (temporarily docked with the Space Shuttle Atlantis) replaced batteries inside the Zarya and Zvezda modules while supply transfer continued around them.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-101 Mission Specialist James Voss takes his seat inside Space Shuttle Atlantis for a simulated launch countdown. The countdown is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that also include emergency egress training and familiarization with the payload. Other crew members taking part are Commander James D. Halsell Jr., Pilot Scott J. "Doc" Horowitz and Mission Specialists Mary Ellen Weber, Jeffrey N. Williams, Susan J. Helms, and Yury Usachev of Russia. During their mission to the International Space Station, the STS-101 crew will be delivering logistics and supplies, plus preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. Also, the crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station. This will be the third assembly flight for the Space Station. STS-101 is scheduled to launch April 24 at 4:15 p.m. from Launch Pad 39A

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility control room monitor computers during a Multi-Equipment Interface Test (MEIT) in the U.S. Lab Destiny. Members of the STS-98 crew are taking part in the MEIT checking out some of the equipment in the Lab. During the STS-98 mission, the crew will install the Lab on the station during a series of three space walks. The crew comprises five members: Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell, Pilot Mark L. Polansky, and Mission Specialists Robert L. Curbeam Jr., Thomas D. Jones (Ph.D.) and Marsha S. Ivins. The mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Laboratory Module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. The Lab is planned for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on the sixth ISS flight, currently targeted no earlier than Aug. 19, 2000
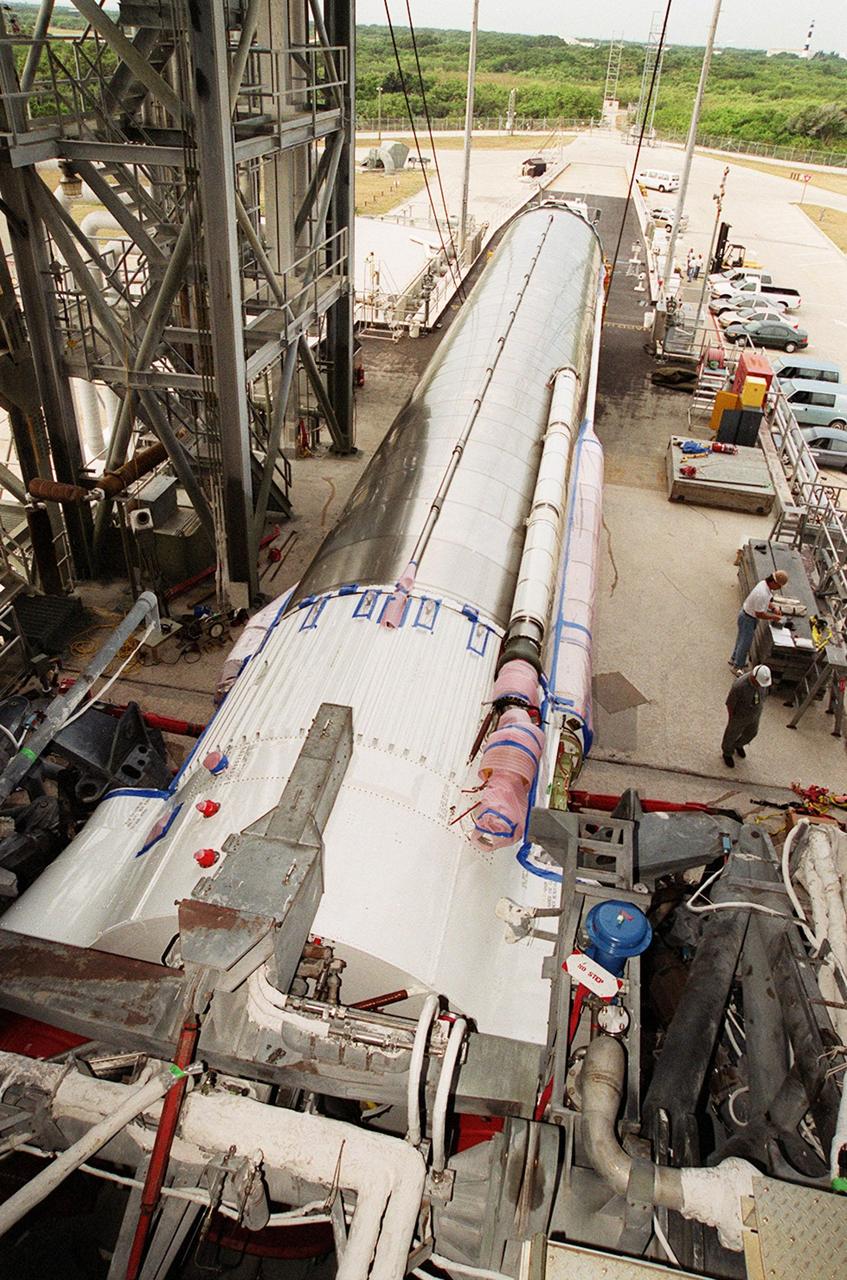

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket is ready to be lifted to vertical in the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
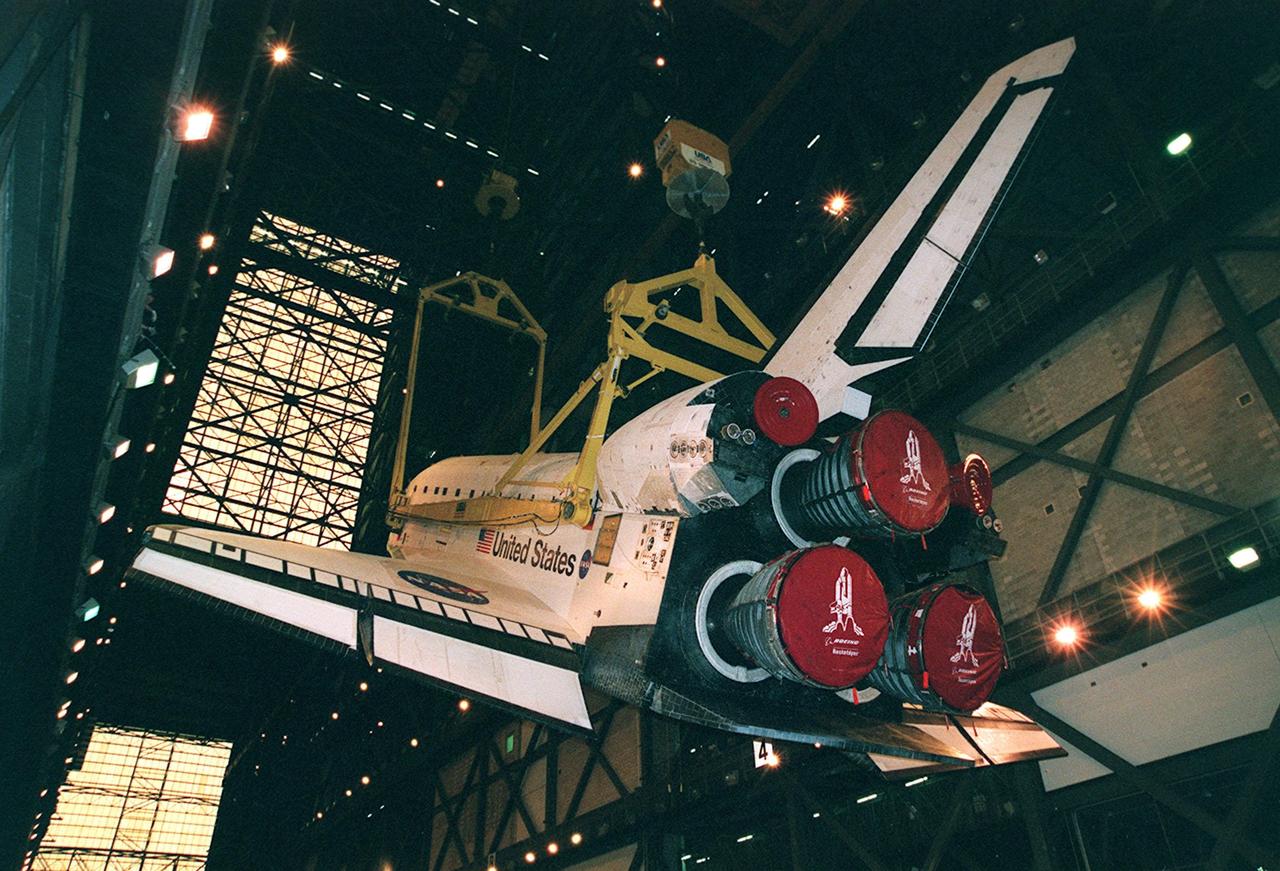

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, orbiter Atlantis is lifted toward a vertical position in the transfer aisle. The 122-foot long orbiter is easily accommodated inside the 525-foot-tall, 518-foot-wide VAB. Once in position, Atlantis will be mated with its external tank and solid rocket boosters before being transported to Launch Pad 39A. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-101 to the International Space Station, where its crew of seven will prepare the Station for the arrival of the next pressurized module, the Russian-built Zvezda. Atlantis is expected to launch no earlier than April 17, 2000
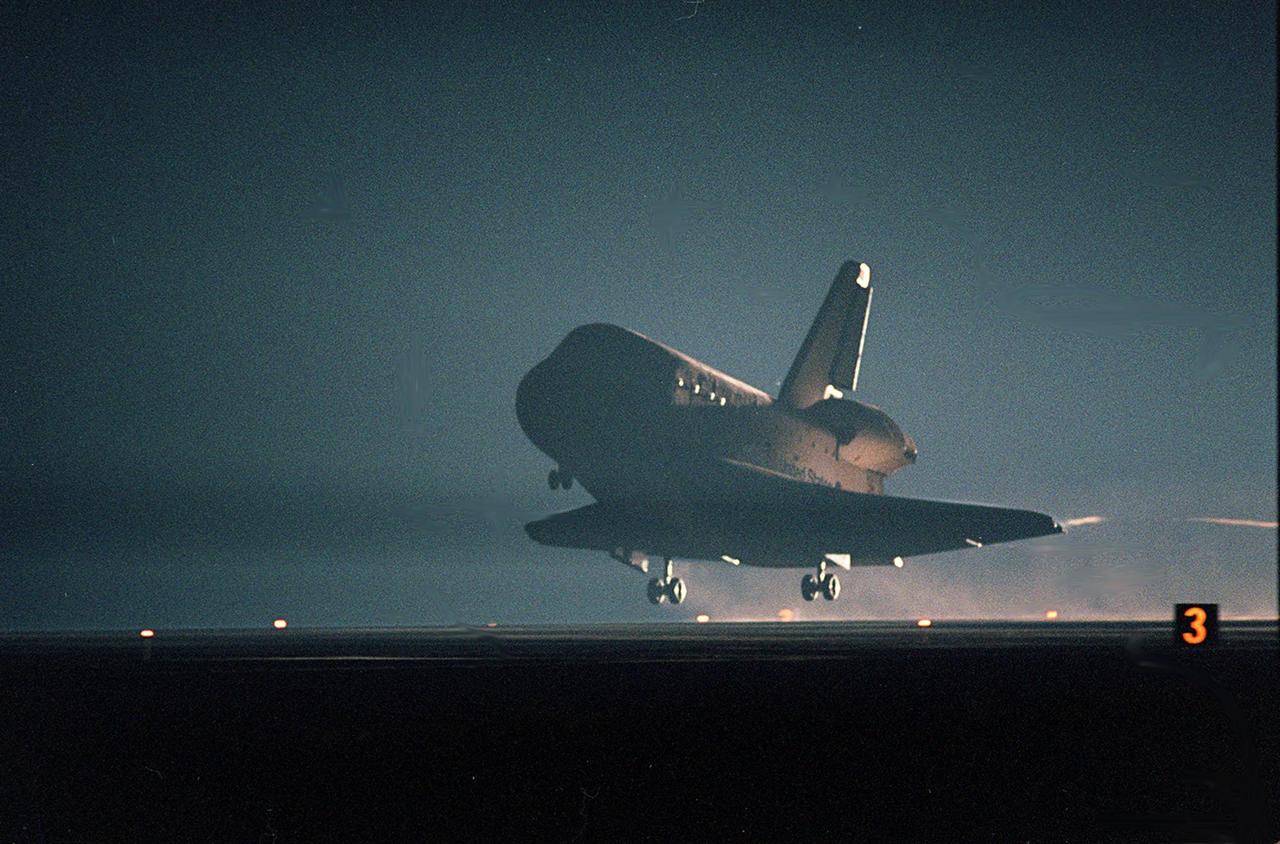

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Seen in the landing lights, an illuminated Space Shuttle Atlantis approaches touchdown on KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility Runway 15 to complete the 9-day, 20-hour, 9-minute-long STS-101 mission. At the controls are Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Scott “Doc” Horowitz. Also onboard the orbiter are Mission Specialists Mary Ellen Weber, James S. Voss, Jeffrey N. Williams, Susan J. Helms and Yury Usachev of Russia. The crew is returning from the third flight to the International Space Station. This was the 98th flight in the Space Shuttle program and the 21st for Atlantis, also marking the 51st landing at KSC, the 22nd consecutive landing at KSC, the 14th nighttime landing in Shuttle history and the 29th in the last 30 Shuttle flights. Main gear touchdown was at 2:20:17 a.m. EDT May 29 , landing on orbit 155 of the mission. Nose gear touchdown was at 2:20:30 a.m. EDT, and wheel stop at 2:21:19 a.m. EDT
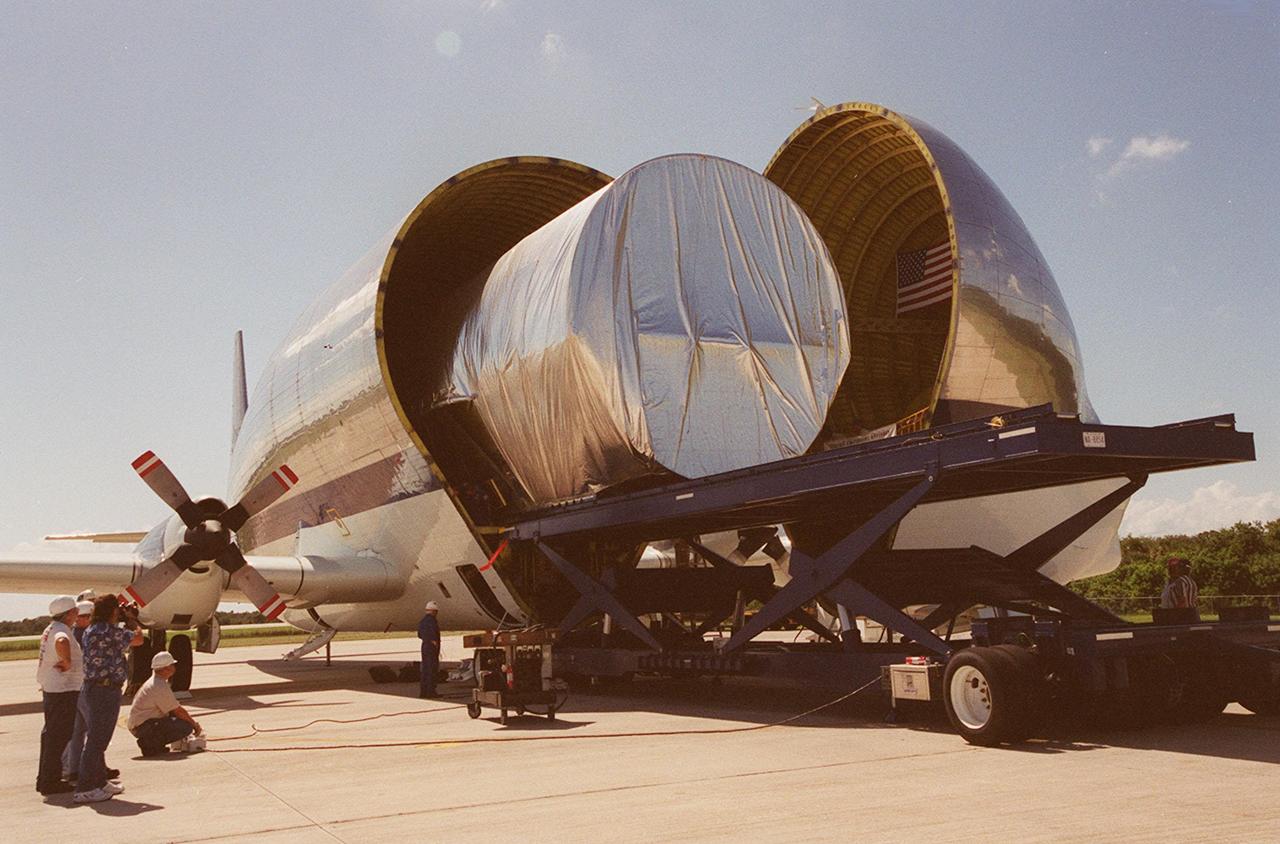

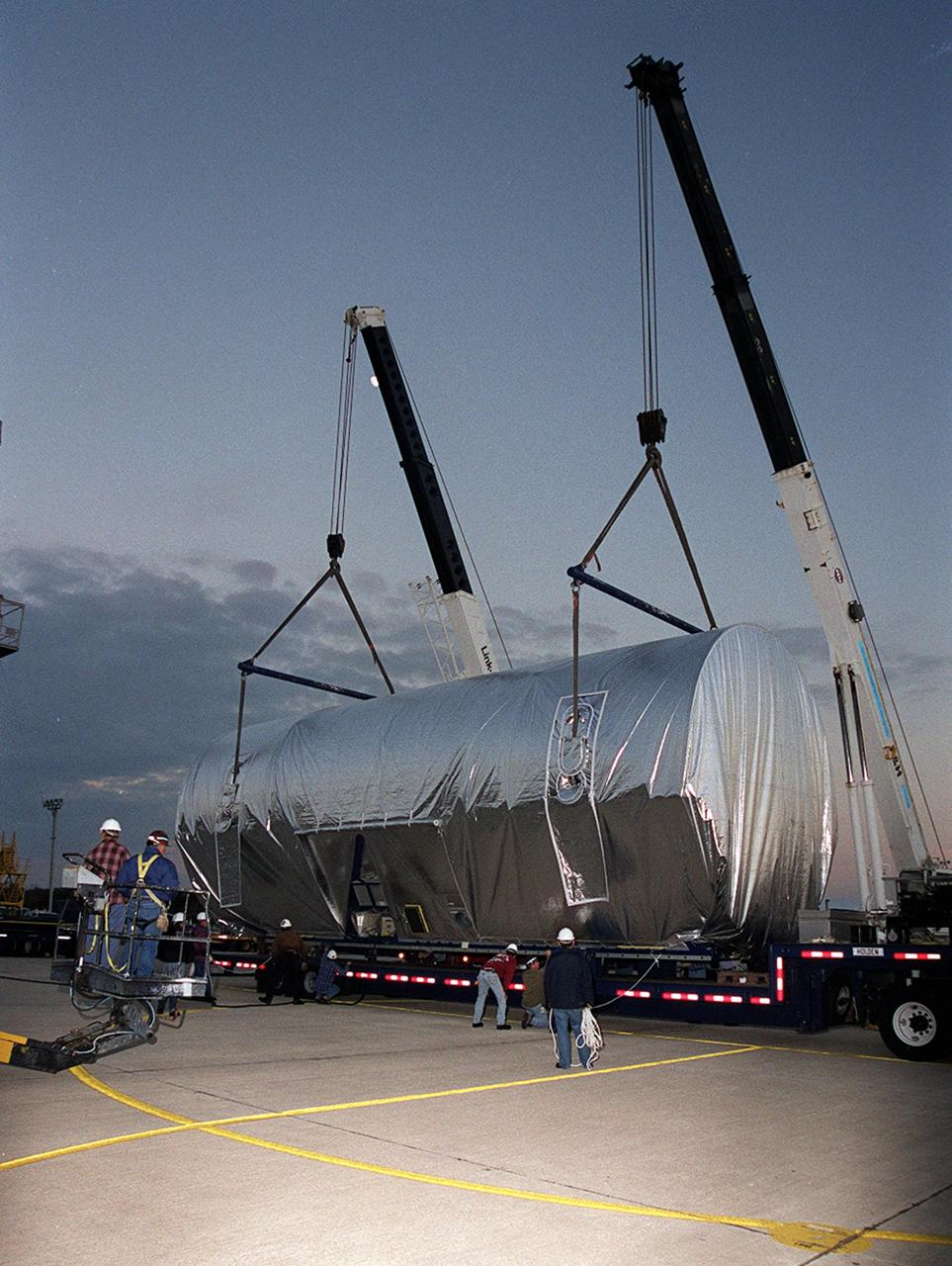
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, rolls out of NASA's Super Guppy aircraft. It will be transferred to the Operations and Checkout Building in the KSC industrial area where it will undergo vacuum chamber testing. It will then be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for further prelaunch preparation and checkout. The massive, spindle-shaped airlock is 20 feet long, has a diameter of 13 feet at its widest point, and weighs six and a half tons. It was manufactured at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center by the Huntsville division of The Boeing Company. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the tenth International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astronaut John Herrington (right) helps Norm Abram try on a tool carrier used in space. Abram is the master carpenter on television’s "This Old House." He is at KSC to film an episode of the series

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy climbs into a T-38 jet aircraft at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility for a flight back to Houston. He and other crew members were at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities, looking over their mission payload and related equipment. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 on Shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. Discovery will carry the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, the PMA-3, Ku-band Communications System, and Control Moment Gyros (CMGs)
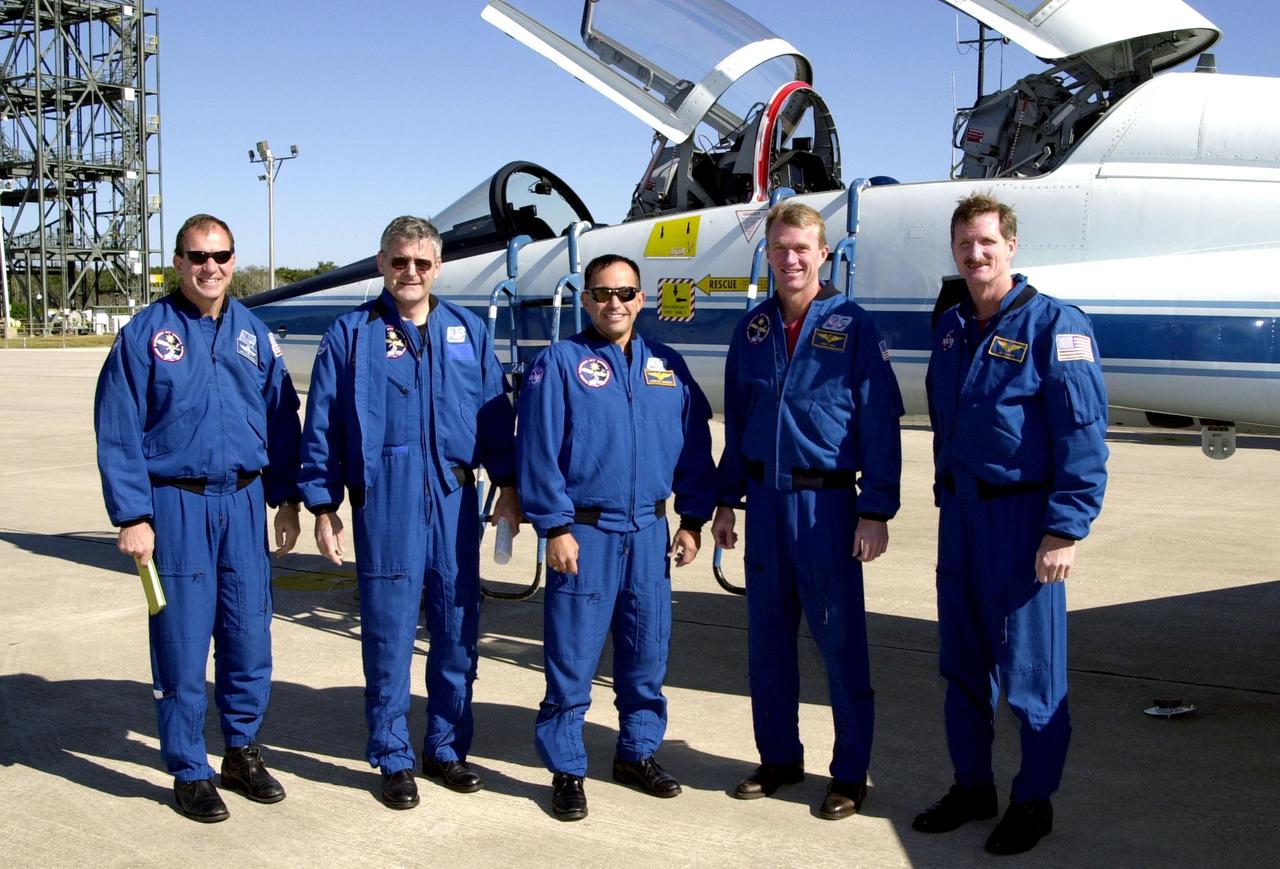

The STS-97 crew poses for a photo after landing at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Standing, left to right, are Pilot Mike Bloomfield, Mission Specialists Marc Garneau and Carlos Noriega, Commander Brent Jett and Mission Specialist Joe Tanner. They are at KSC for a mini-CEIT (Crew Equipment Interface Test). STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. The sixth flight to the International Space Station, the mission is expected to last 11 days, with a planned KSC landing at about 5:58 p.m. Dec. 11
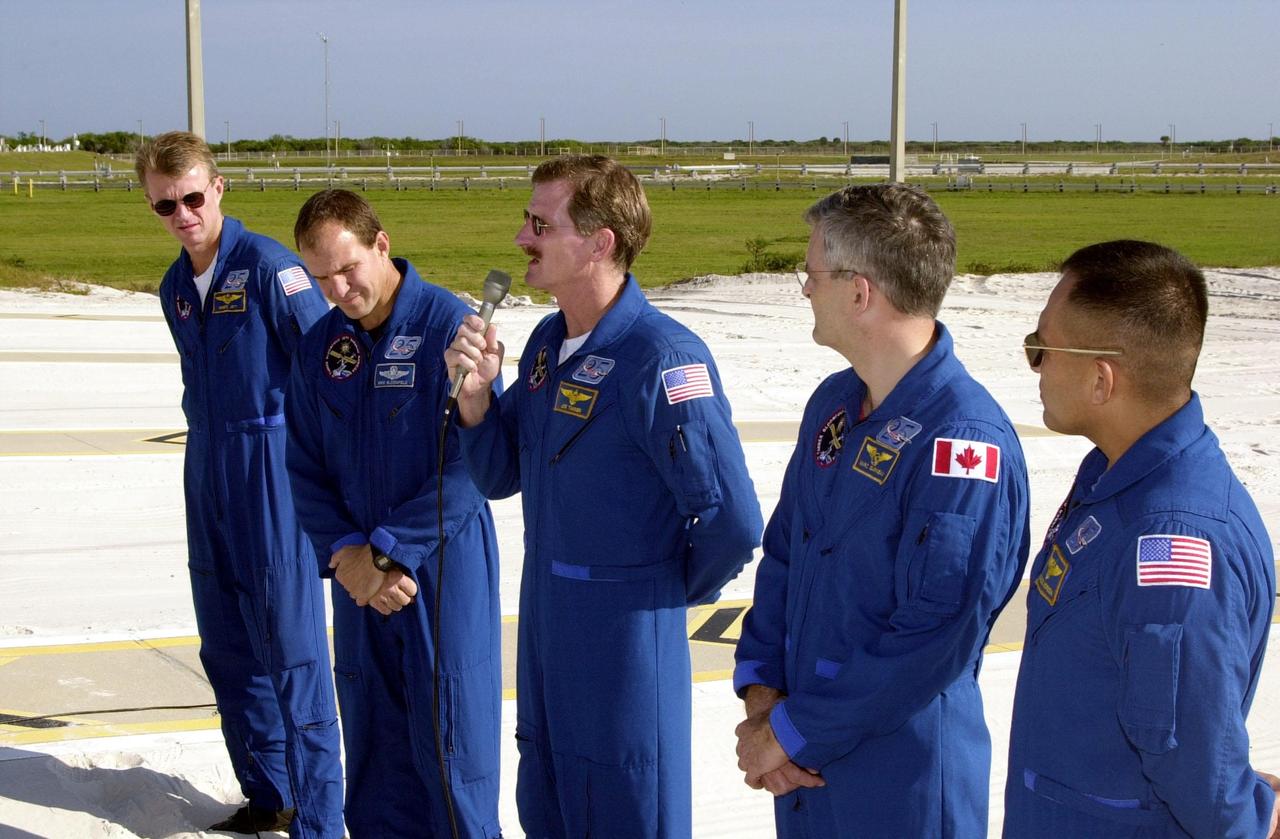

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- From the slidewire landing zone at Launch Pad 39B, STS-97 Mission Specialist Joe Tanner (center, with microphone) speaks to the press about his extravehicular activity (EVA) during the mission. With him are the rest of the crew, Commander Brent Jett and Pilot Mike Bloomfield on the left and Mission Specialists Marc Garneau and Carlos Noriega on the right. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency egress training, familiarization with the payload, and a simulated launch countdown. Visible in the background are the solid rocket booster and external tank on Space Shuttle Endeavour. Mission STS-97is the sixth construction flight to the International Space Station. Its payload includes the P6 Integrated Truss Structure and a photovoltaic (PV) module, with giant solar arrays that will provide power to the Station. The mission includes two spacewalks to complete the solar array connections. STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at about 10:05 p.m. EST
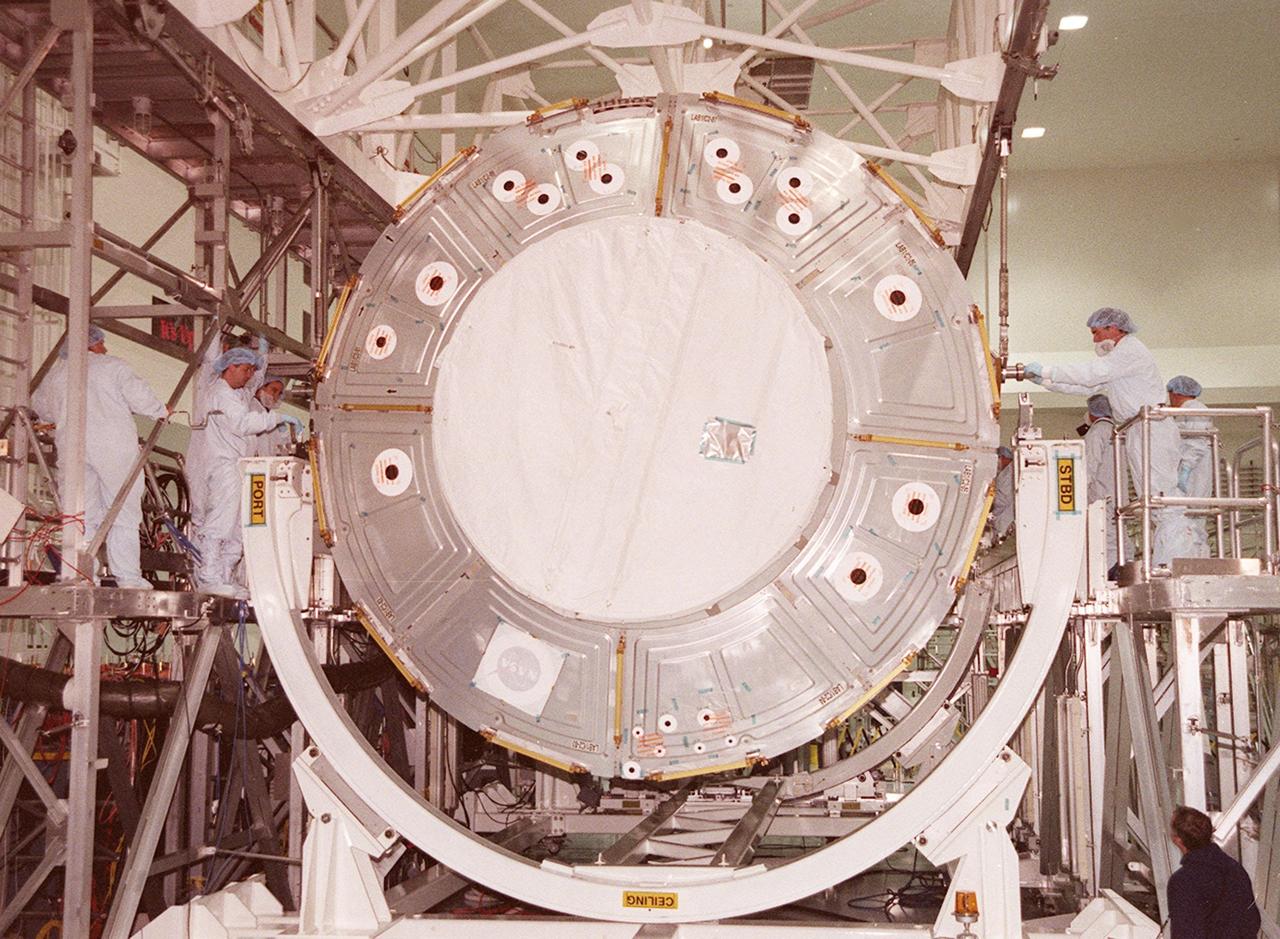
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers attach an overhead crane to the U.S. Lab Destiny. The lab is being moved from its test and integration stand to the Launch Package Integration Stand (LPIS) for a weight and center of gravity determination. Destiny is the payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-98 to the International Space Station. The lab is fitted with five system racks and will already have experiments installed inside for the flight. The launch is scheduled for January 2001
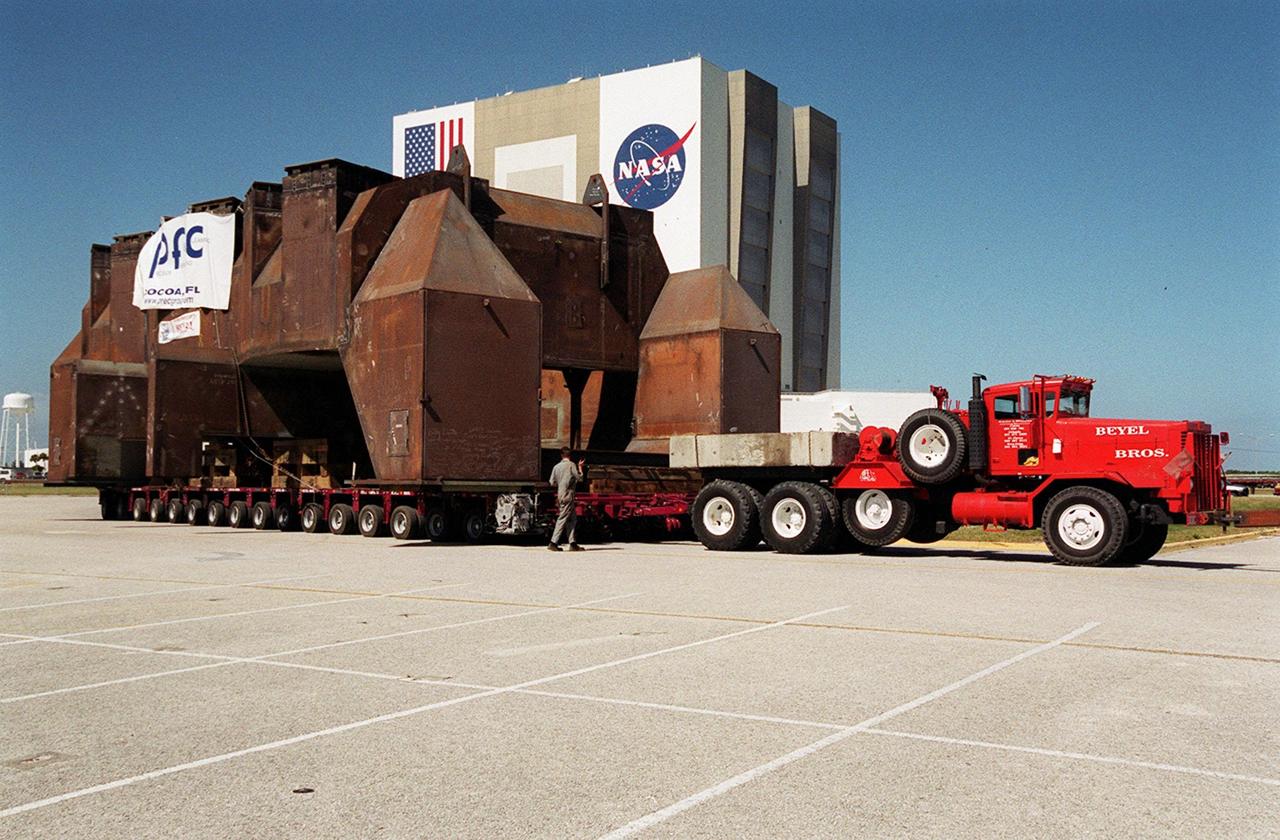

Looking somewhat like a medieval building, this launch table was built in support of the Delta Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program, known as Delta IV. Fabricated by Jered Industries in Georgia, it was floated on a barge down the Intercoastal Waterway, through the Barge Canal to the turn basin in the Launch Complex 39 Area. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The table is approximately 70 feet long, 40 feet wide and 50 feet high, and weighs about 600,000 pounds. It is being transferred to Launch Complex 37B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the site of the Delta IV launch complex under construction. Accompanying the launch table on the barge are flame deflectors, which are also to be erected on pad 37B

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, cranes position the Integrated Truss Structure S3 onto a flatbed trailer for transport to the Operations and Checkout Building. The S3 arrived aboard a Super Guppy aircraft. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
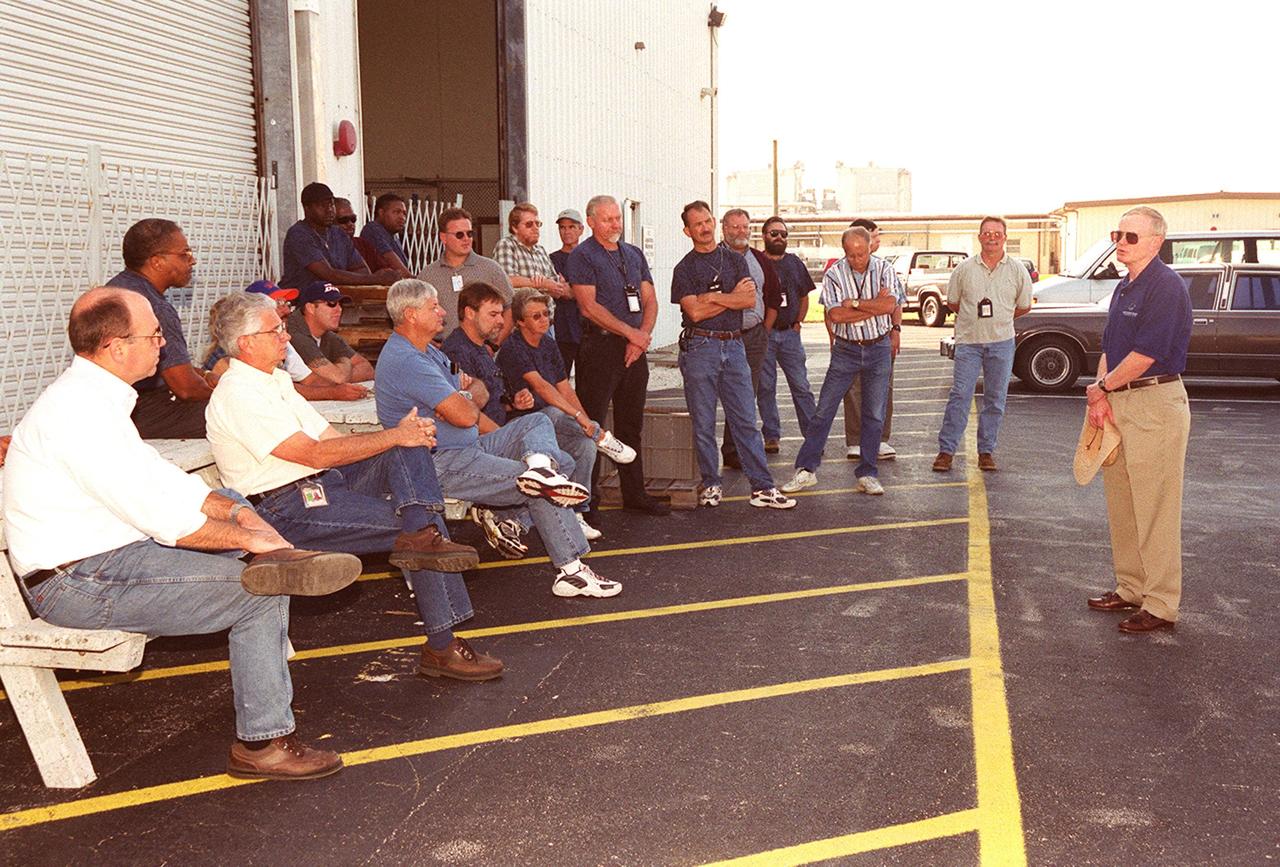

Center Director Roy Bridges talks to workers outside the Hazardous Maintenance Facility during Super Safety and Health Day at KSC. Safety Day is a full day of NASA-sponsored, KSC and 45th Space Wing events involving a number of health and safety related activities: Displays, vendors, technical paper sessions, panel discussions, a keynote speaker, etc. The entire Center and Wing stand down to participate in the planned events. Safety Day is held annually to proactively increase awareness in safety and health among the government and contractor workforce population. The first guiding principle at KSC is “Safety and Health First.” KSC’s number one goal is to “Assure sound, safe and efficient practices and processes are in place for privatized/commercialized launch site processing.
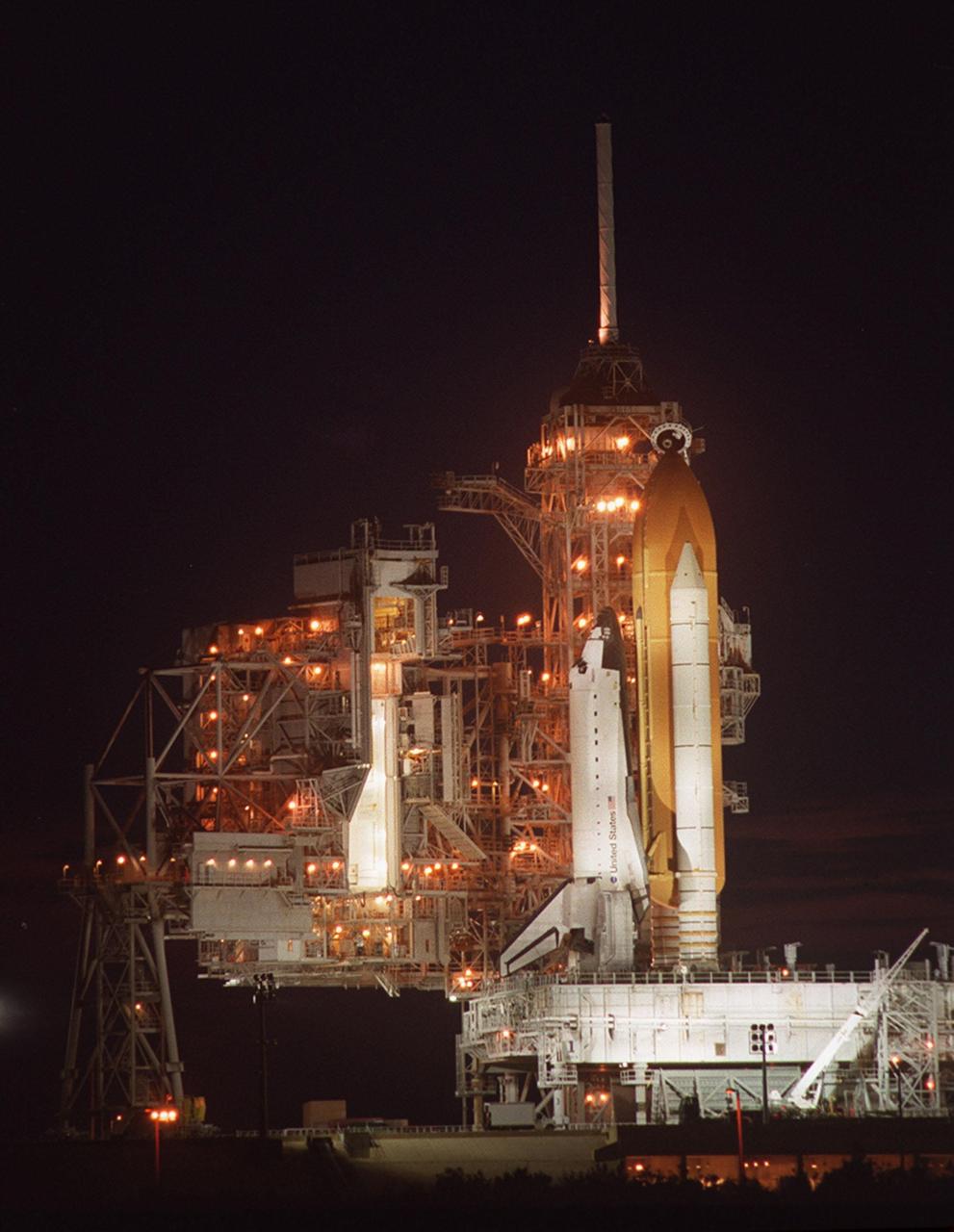

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Rotating Service Structure (left) begins rolling back from Space Shuttle Atlantis on Launch Pad 39A. Atlantis is targeted for liftoff at 4:15 p.m. EDT April 24 on mission STS-101. The mission will take the crew of seven to the International Space Station to deliver logistics and supplies and prepare the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. Also, the crew will conduct one space walk. This will be the third assembly flight to the Space Station

In the early morning skies, flocks of birds soar over KSC wetlands. Kennedy Space Center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge that encompasses 92,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. The marshes and open water of the refuge provide wintering areas for 23 species of migratory waterfowl, as well as a year-round home for great blue herons, great egrets, wood storks, cormorants, brown pelicans and other species of marsh and shore birds, as well as a variety of insects
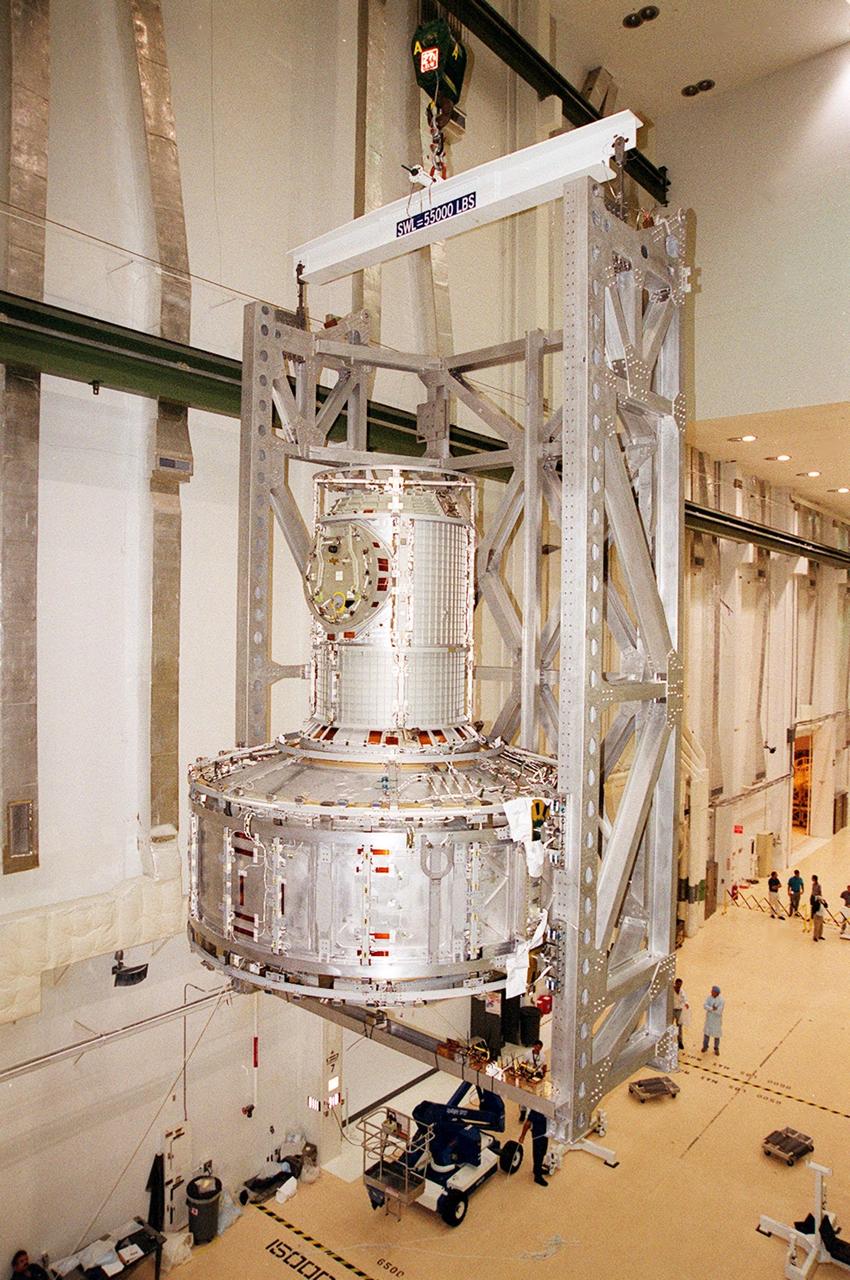
In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the Joint Airlock Module to move it to a vacuum chamber for testing. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module is specially designed to accommodate both suits, providing a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
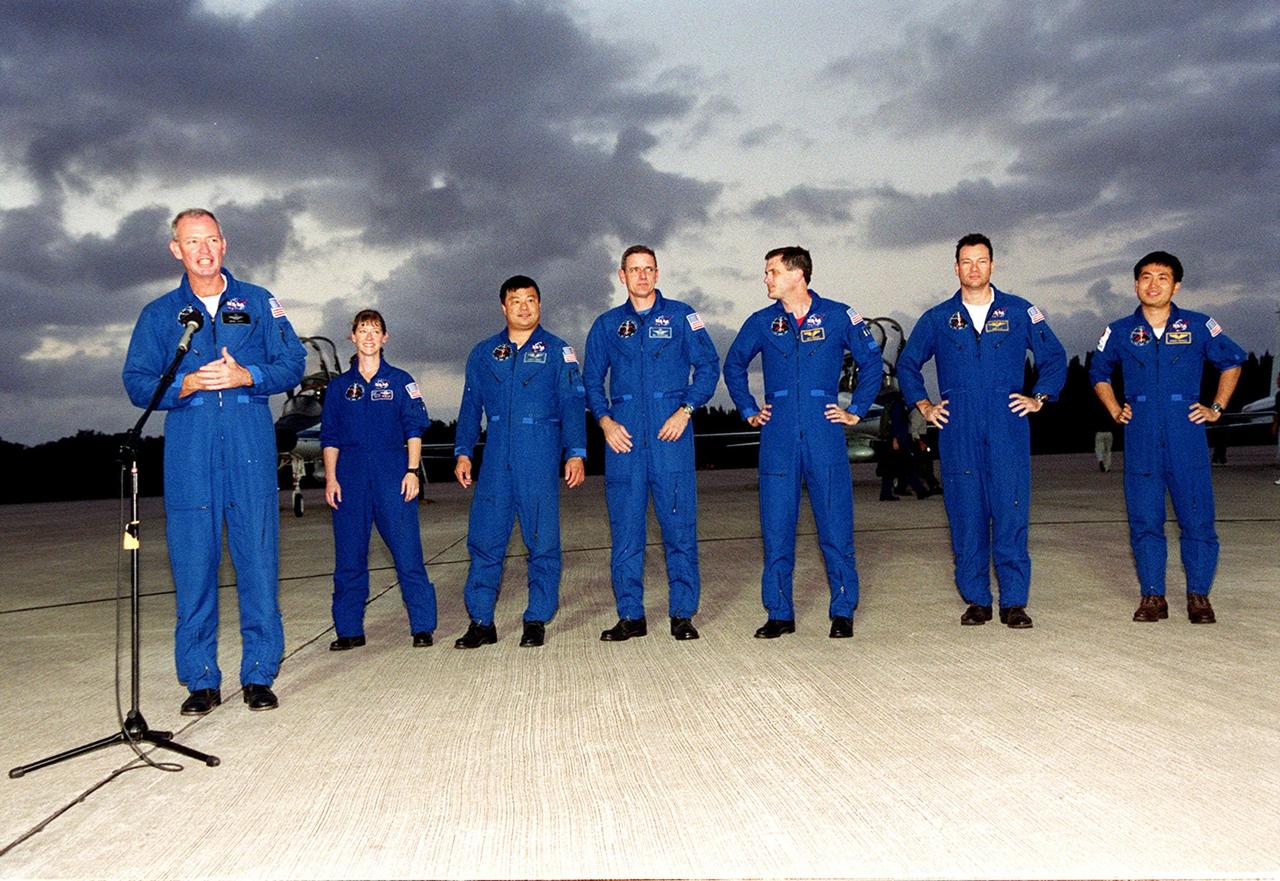

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After their arrival at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, the STS-92 crew paused to talk to the media, who were waiting nearby. At the microphone is Commander Brian Duffy. Standing behind him, left to right, are Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
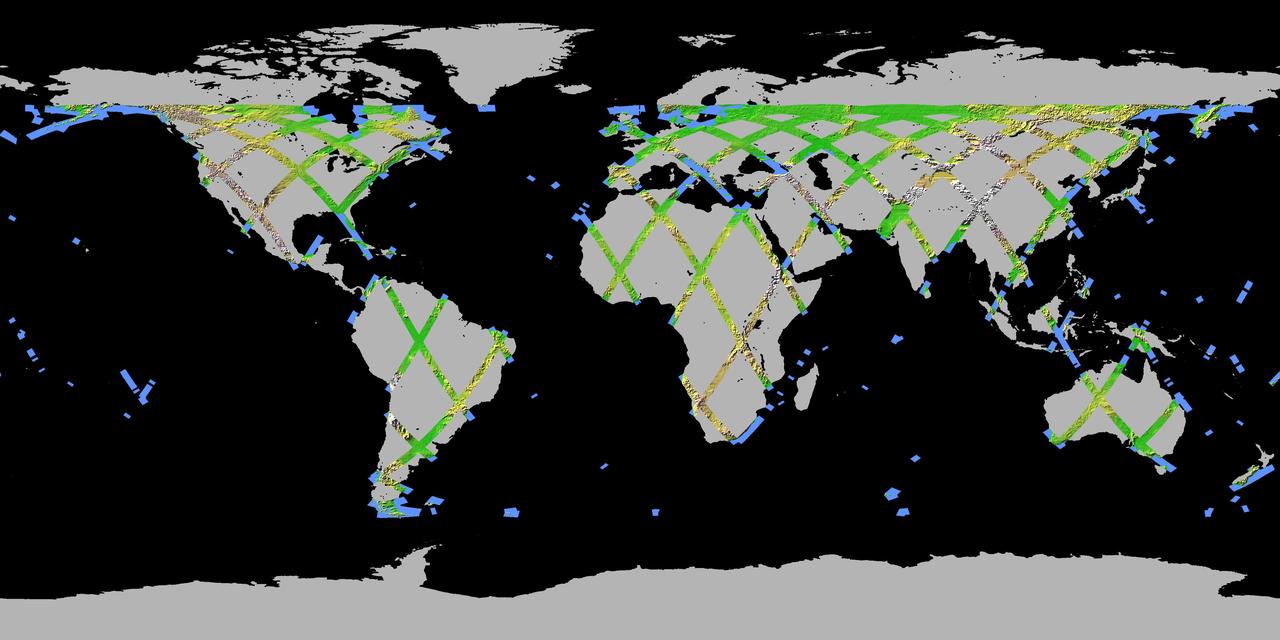
JSC2000E01555 (January 2000) --- A one-dimensional representation of Earth indicates only a portion of the total anticipated coverage area for the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). The primary objective of SRTM is to acquire a high-resolution topographic map of the Earth's land mass (between 60 degrees north and 56 degrees south latitude) and to test new technologies for deployment of large rigid structures and measurement of their distortions to extremely high precision.
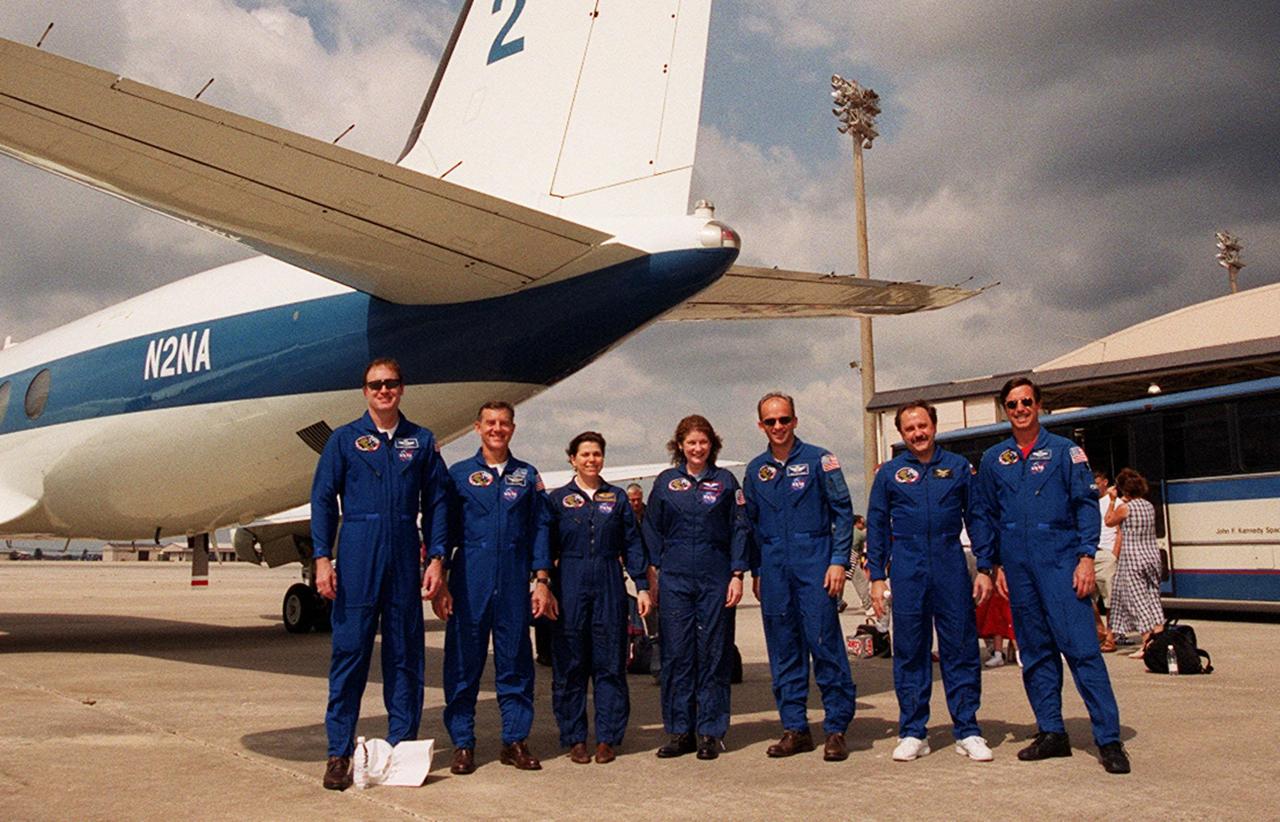

The STS-101 crew pose one more time before departing for Houston from Patrick Air Force Base. From left are Commander James D. Halsell Jr., Mission Specialists James S. Voss, Mary Ellen Weber, Susan J. Helms, Jeffrey N. Williams, Yury Usachev of Russia, and Pilot Scott “Doc” Horowitz. After landing at 2:20 a.m. EDT May 29, the crew and their families enjoyed the Memorial Day holiday in Florida. The crew returned from the third flight to the International Space Station where they made repairs, transferred cargo and completed a space walk to install and connect several pieces of equipment on the outside of the Space Station
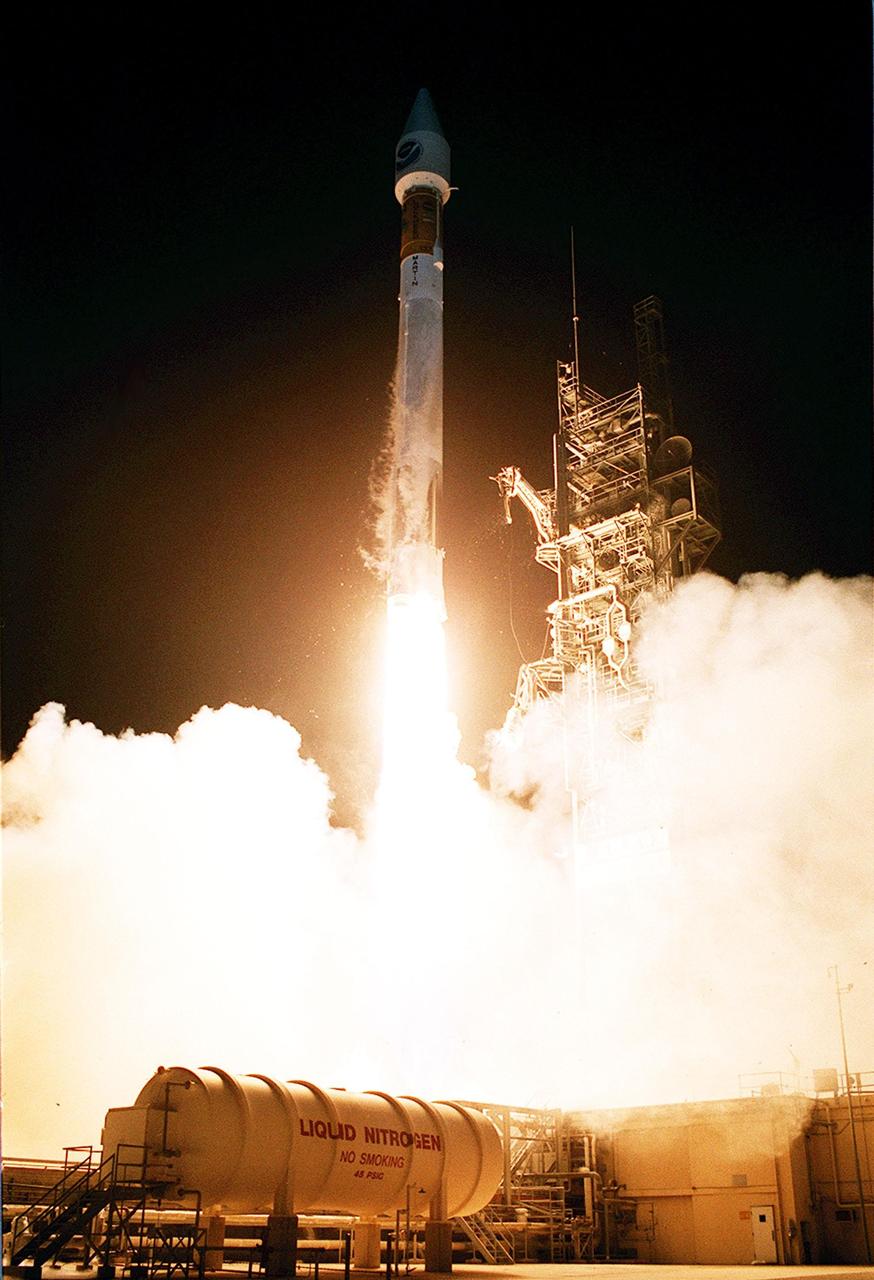

The night sky is briefly turned bright as day with the launch of the Atlas II/Centaur rocket carrying the NASA/NOAA weather satellite GOES-L. Liftoff occurred at 3:07 a.m. EDT. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, in order to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Once in orbit, the spacecraft is to be designated GOES-11 and will complete its 90-day checkout in time for availability during the 2000 hurricane season
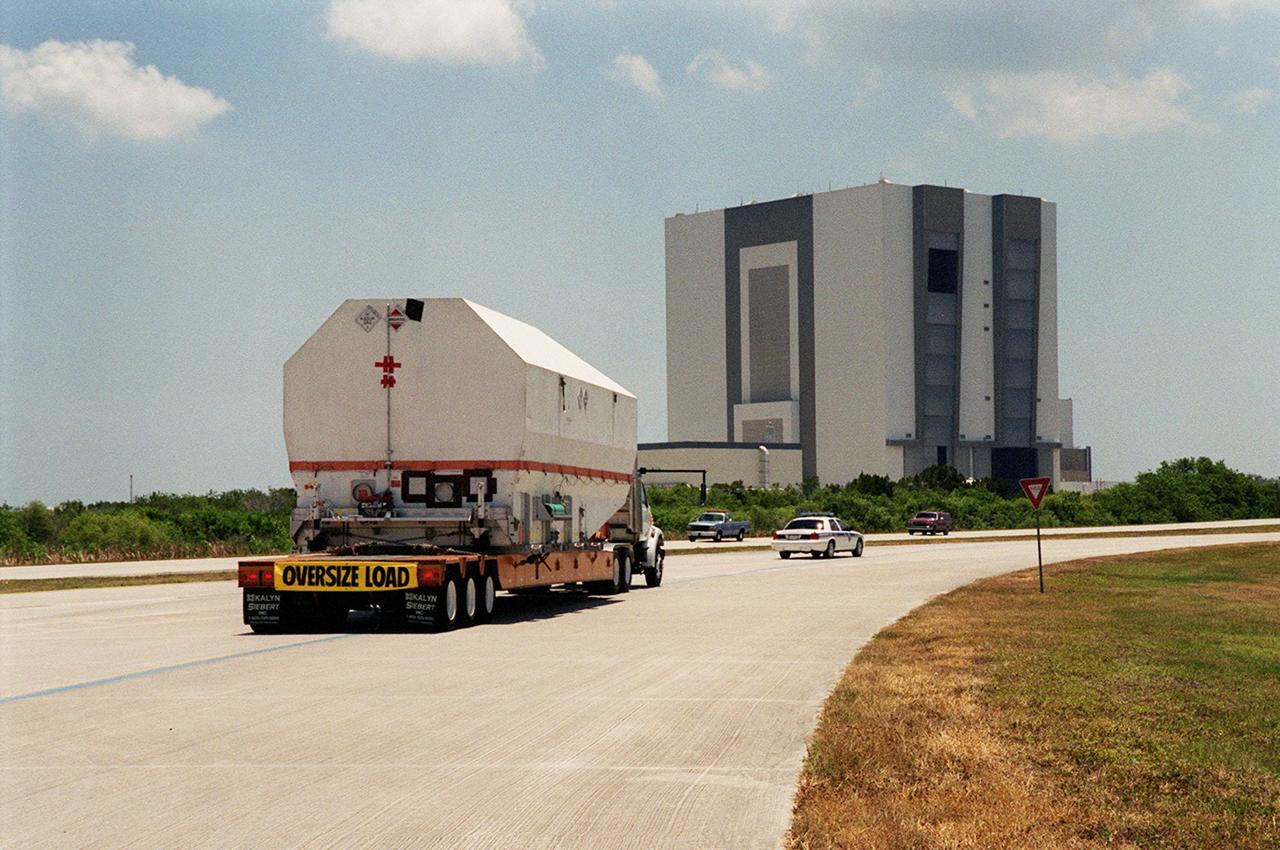

After its arrival at the Shuttle Landing Facility, the crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is transported past the Vehicle Assembly Building (in the background) to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) for testing. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket
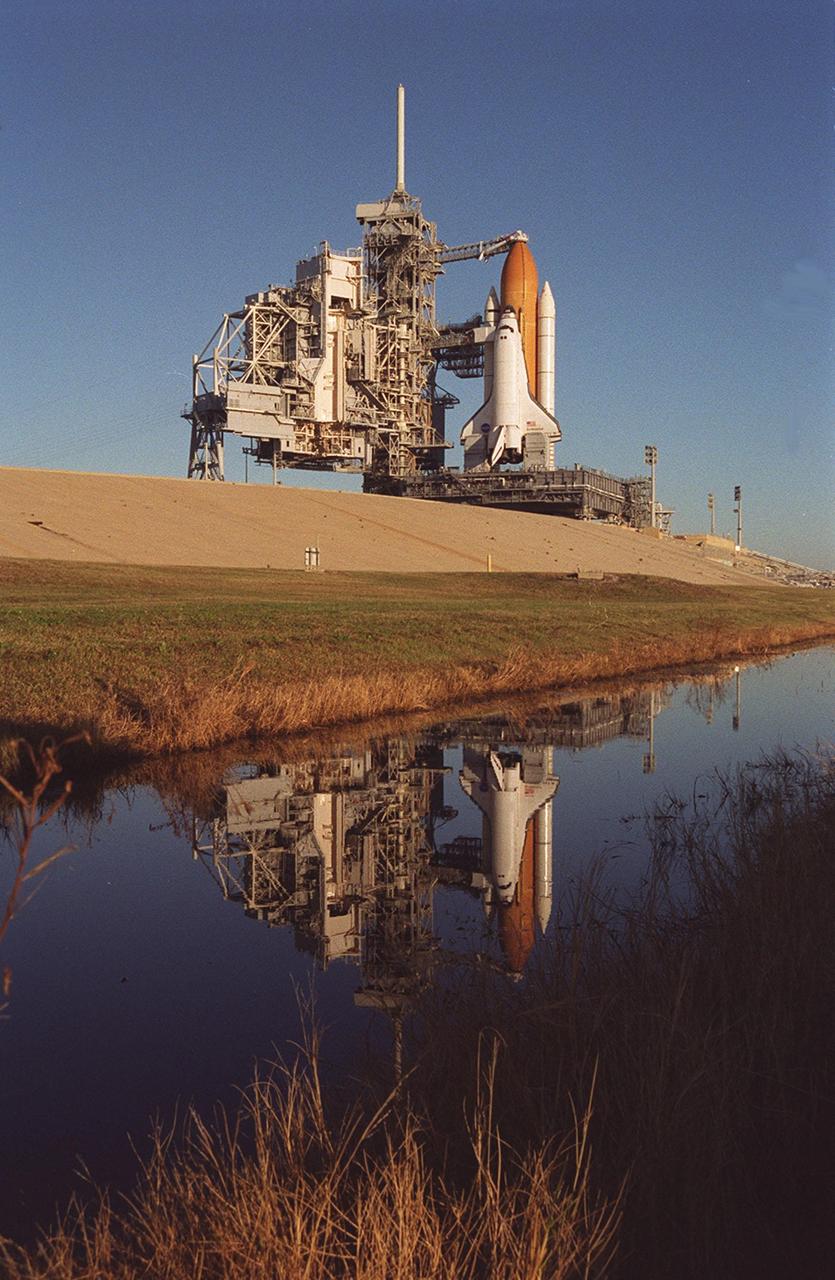

After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure (at left), Space Shuttle Endeavour stands ready for launch targeted for 10:06 p.m. EST tonight on mission STS-97 to the International Space Station. The orbiter carries the P6 Integrated Truss Segment containing solar arrays that will be temporarily installed to the Unity connecting module by the Z1 truss, recently delivered to and installed on the Station on mission STS-92. The two solar arrays are each more than 100 feet long. They will capture energy from the sun and convert it to power for the Station. Two spacewalks will be required to install the solar array connections
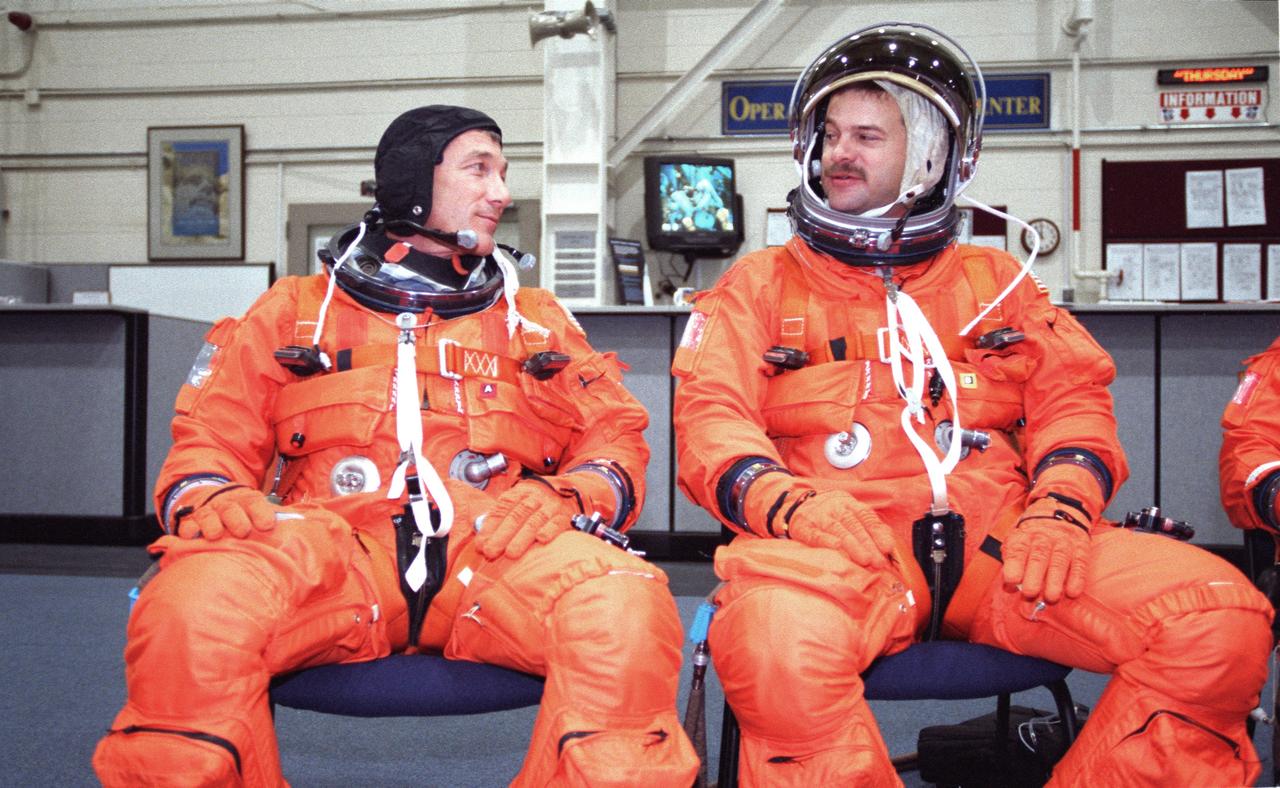

JSC2000-02933 (5 April 2000) --- Astronauts Terrence W. (Terry) Wilcutt (left), mission commander, and Scott D. Altman, pilot, await ingress of a crew training mockup to begin an emergency egress training session at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The two will join three other NASA astronauts and two cosmonauts representing the Russian Aviation and Space Agency for a late summer visit to the International Space Station (ISS).
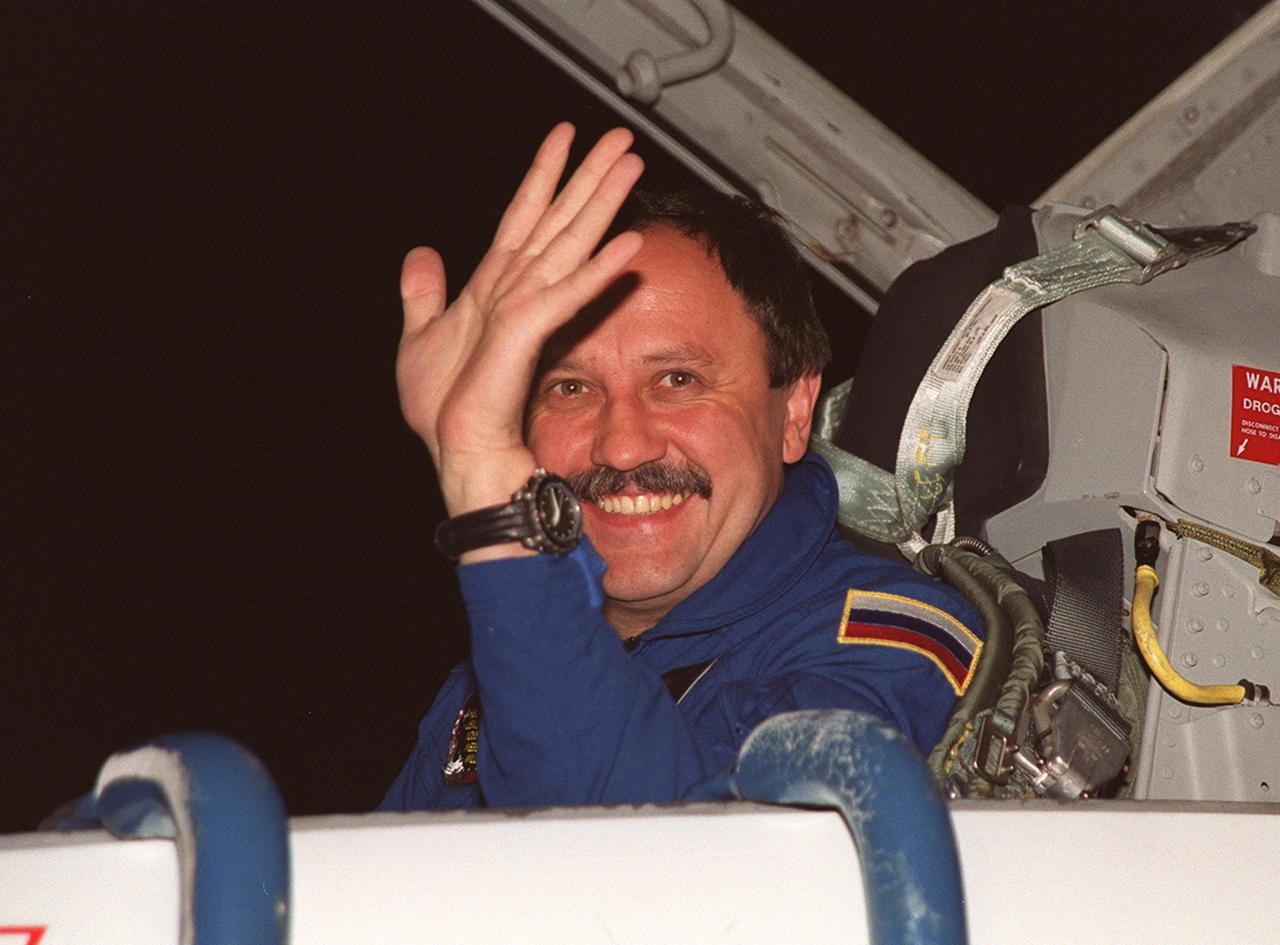

STS-101 Mission Specialist Yuri Usachev waves on his arrival KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet aircraft to prepare for the launch on May 18. The mission will take the crew of seven to the International Space Station, delivering logistics and supplies, plus preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. Also, the crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station. This will be the third assembly flight for the Space Station. STS-101 is targeted for liftoff at 6:38 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
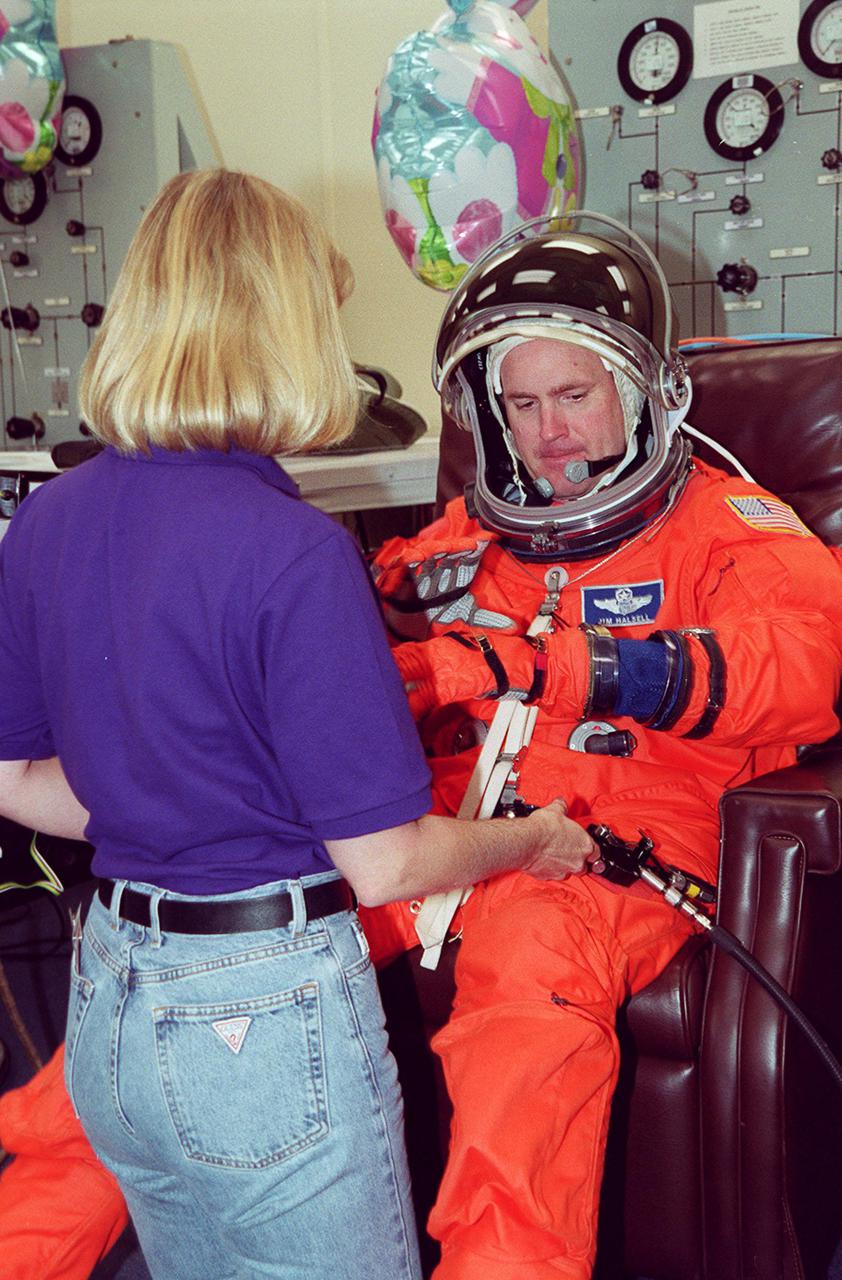

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-101 Commander James D. Halsell Jr. gets final check on his launch and entry suit before heading a second time to Launch Pad 39A and launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The previous day's launch attempt was scrubbed due to high cross winds at the Shuttle Landing Facility. The mission will take the crew to the International Space Station to deliver logistics and supplies and to prepare the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. Also, the crew will conduct one space walk. This will be the third assembly flight to the Space Station. Liftoff is targeted for 3:52 p.m. EDT. The mission is expected to last about 10 days, with Atlantis landing at KSC Saturday, May 6, about 11:53 a.m. EDT
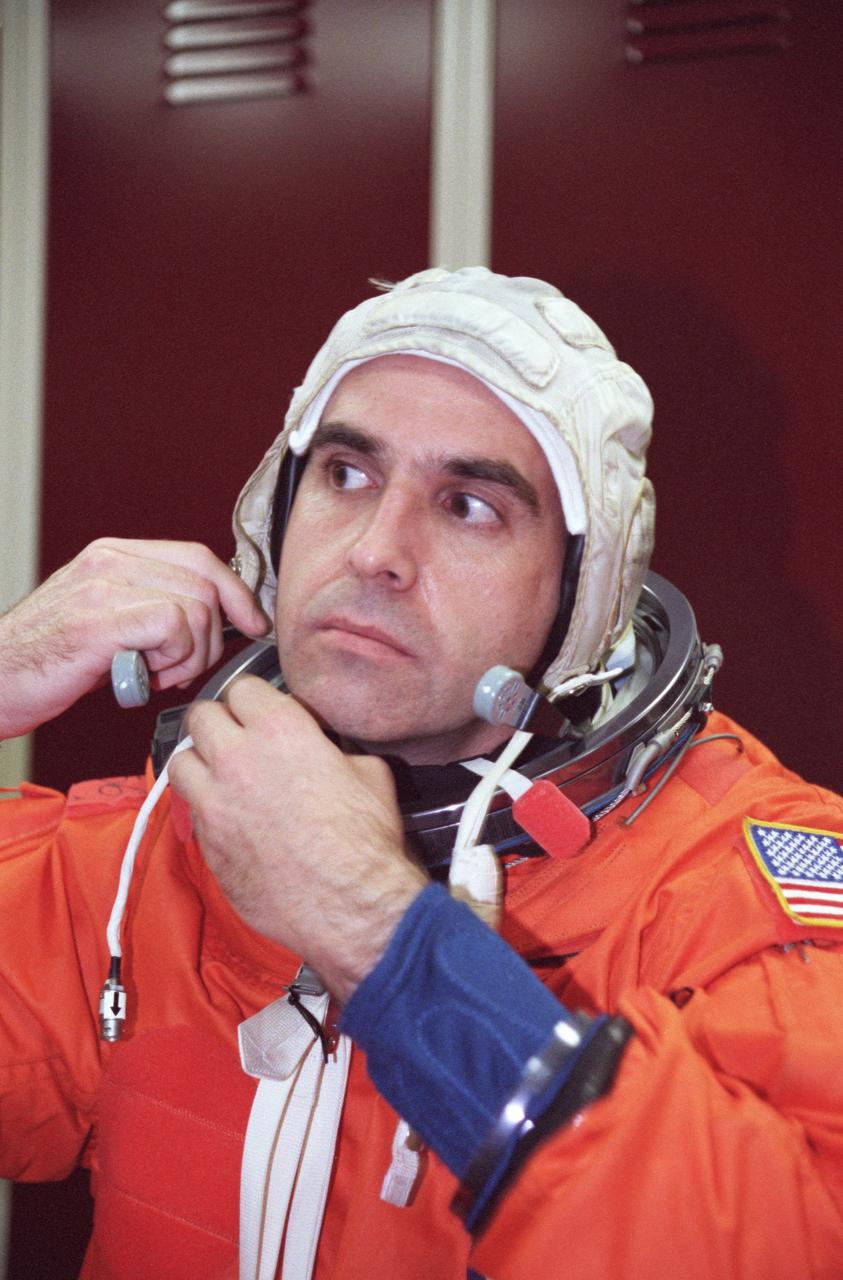

JSC2000-02219 (March 2000) --- Astronaut Richard A. Mastracchio, mission specialist, fastens his communications carrier assembly (CCA), part of the launch and entry suit (LES), during a training session at the Johnson Space Center's Systems Integration Facility.

Eroded, Layered Cratered Highlands of Eastern Arabia Terra
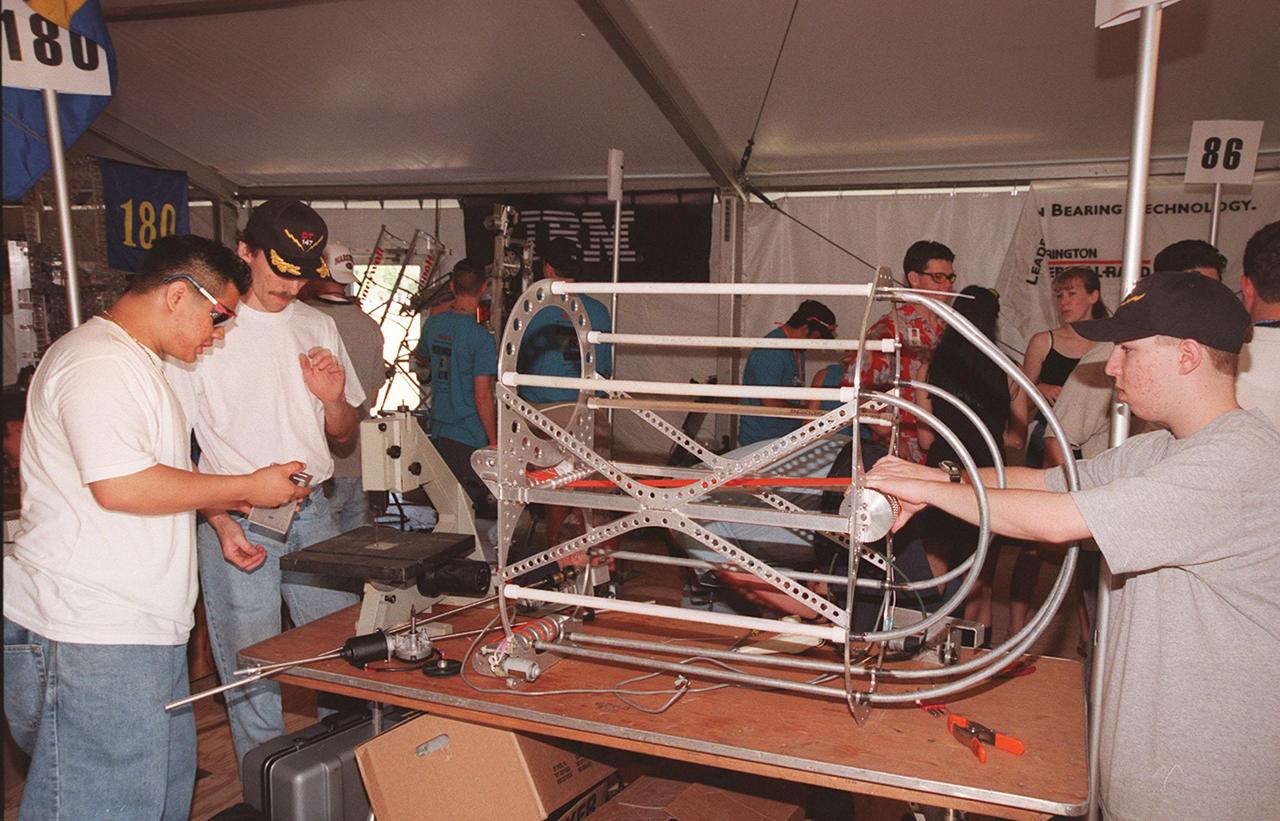
Students from high schools around the United States busily prepare their robots for the FIRST (For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Southeast Regional competition March 9-11 at the KSC Visitor Complex. Teams of high school students are testing the limits of their imagination using robots they have designed, with the support of business and engineering professionals and corporate sponsors, to compete in a technological battle against other schools' robots. Of the 30 high school teams competing at KSC, 16 are Florida teams co-sponsored by NASA and KSC contractors. Local high schools participating are Astronaut, Bayside, Cocoa Beach, Eau Gallie, Melbourne, Melbourne Central Catholic, Palm Bay, Rockledge, Satellite, and Titusville
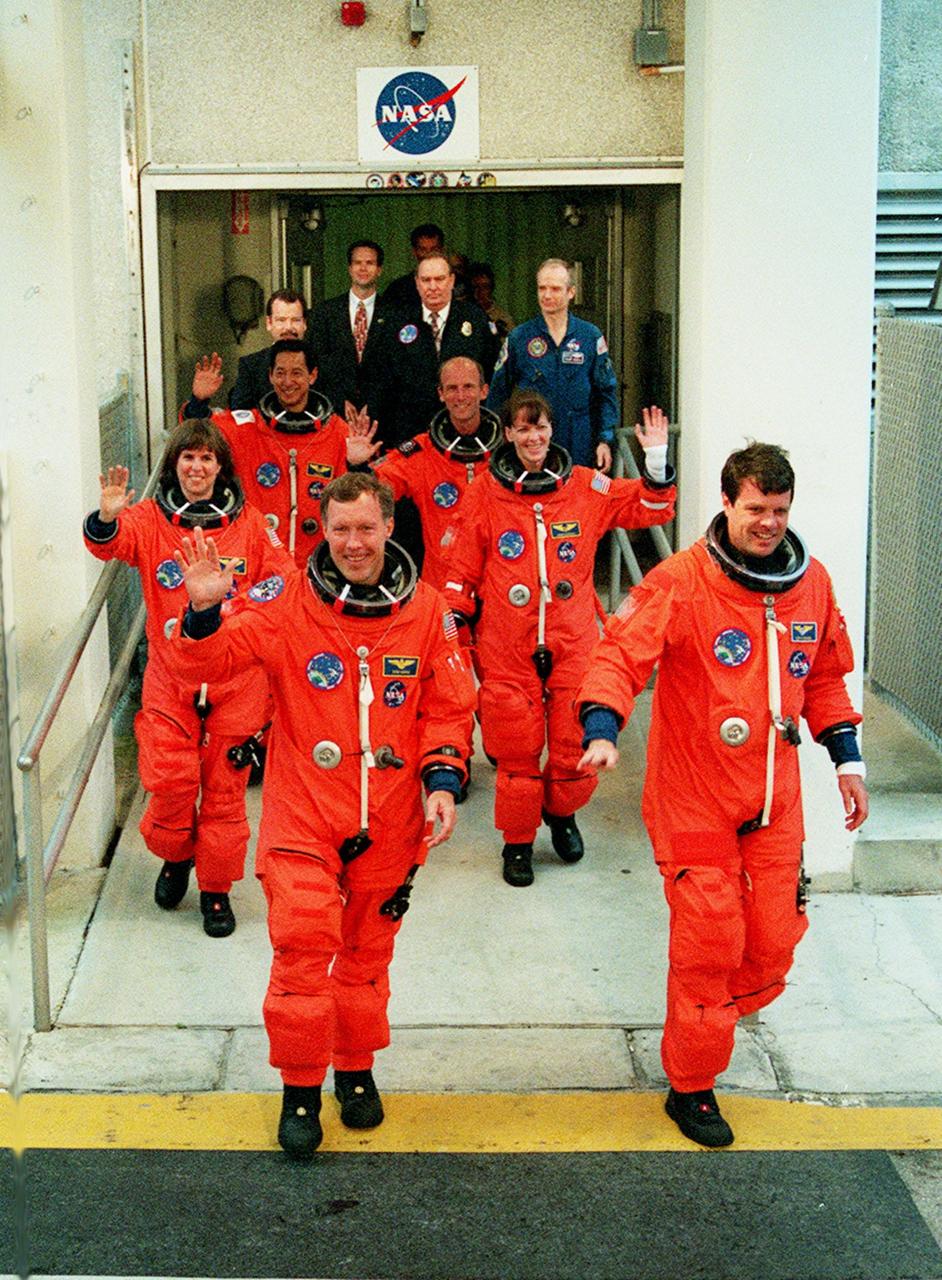

The STS-99 crew wave to onlookers as they leave the Operations and Checkout Building enroute to Launch Pad 39A and liftoff of Space Shuttle Endeavour, targeted for 12:47 p.m. EST. In their orange launch and entry suits, they are (foreground) Pilot Dominic Gorie and Commander Kevin Kregel. Behind them (left to right) are Mission Specialists Janice Voss (Ph.D.), Mamoru Mohri (Ph.D.), Gerhard Thiele and Janet Lynn Kavandi (Ph.D.). Mohri is with the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan, and Thiele is with the European Space Agency. The SRTM will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. The mission is expected to last about 11days, with Endeavour landing at KSC Friday, Feb. 11, at 4:55 p.m. EST
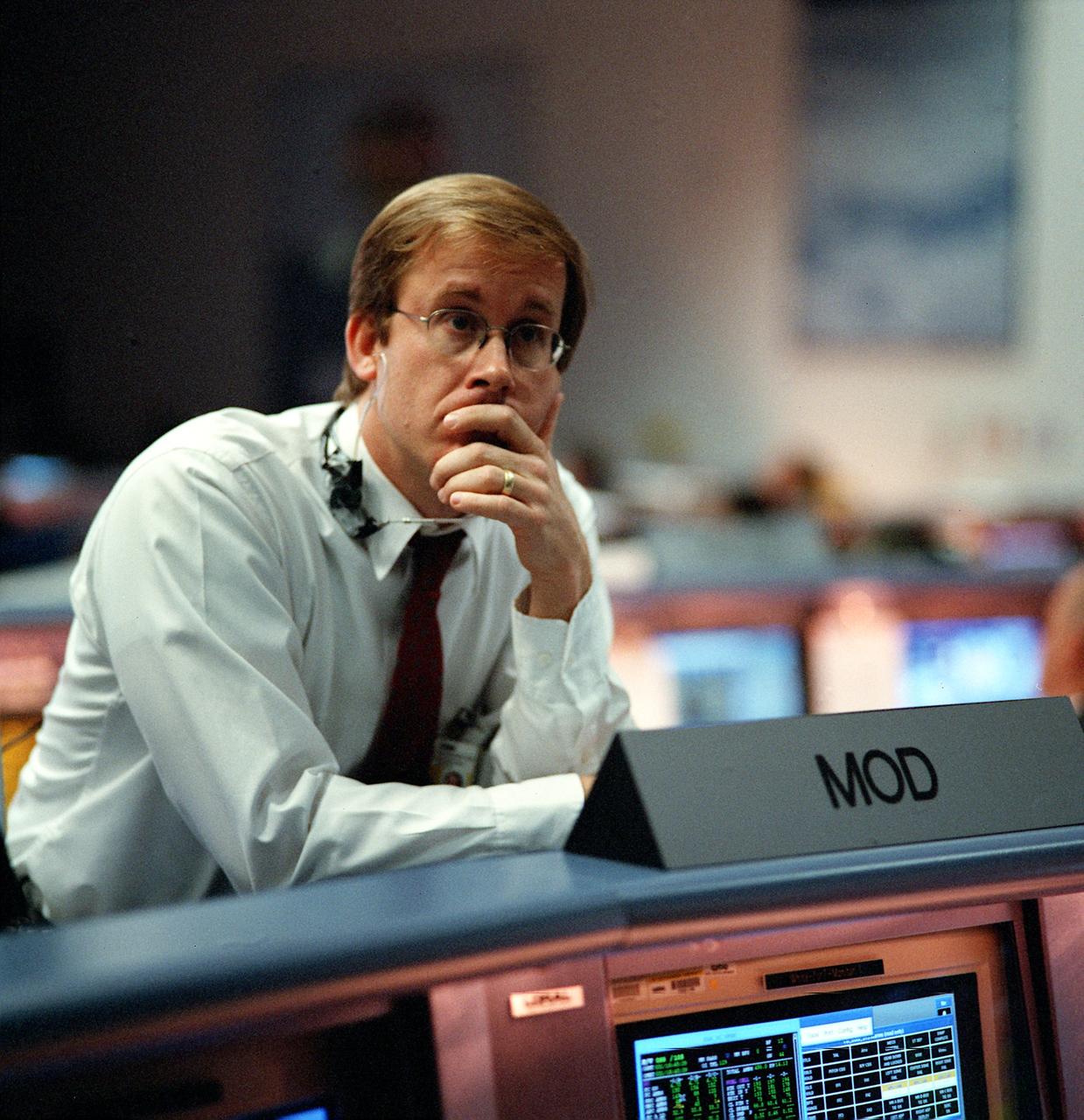

JSC2000-01065 (31 January 2000) --- Flight Director John Shannon, with his back to the FD console, waits patiently for the "go" or "no go" decision from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). This attempt of the STS-99 Endeavour launch was eventually scrubbed, and managers quickly huddled to decide options for the next opportunity.
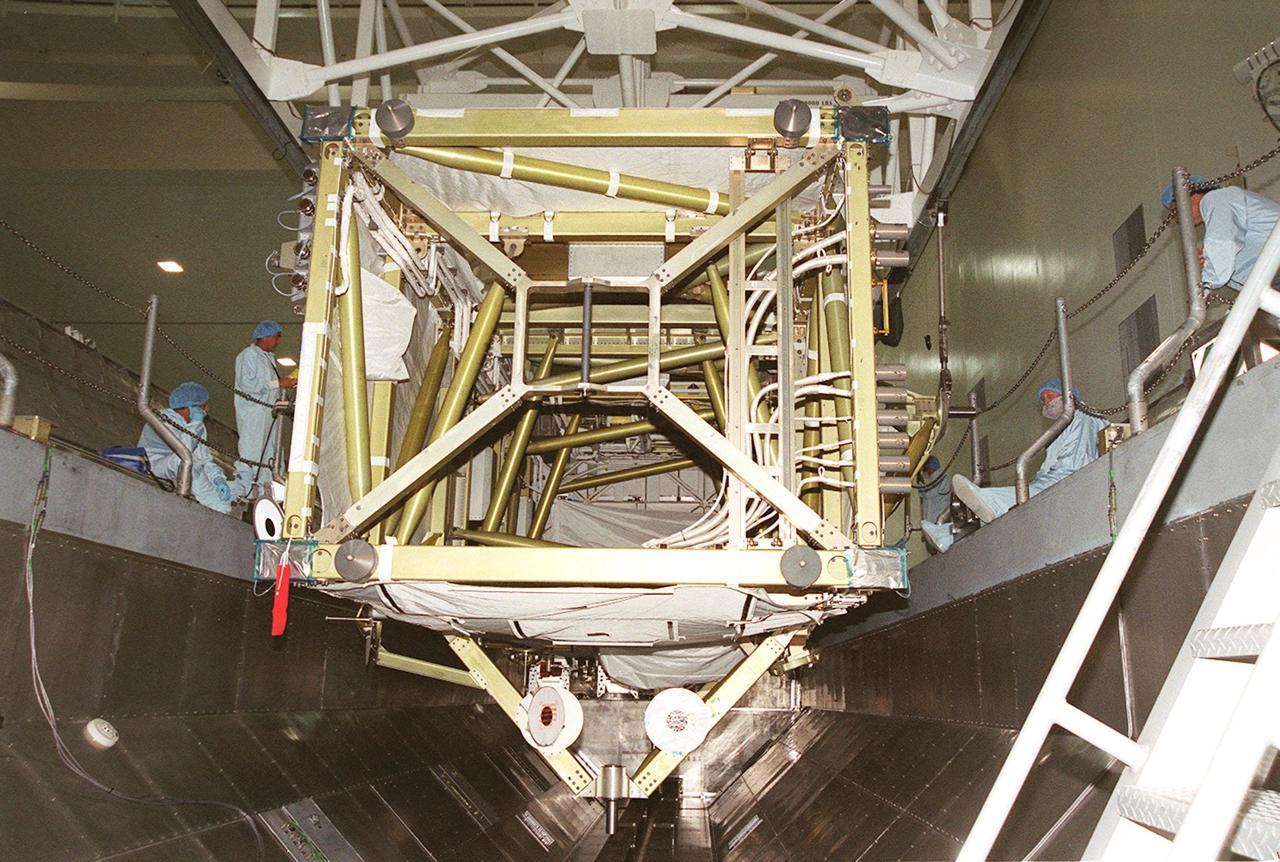

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the P6 integrated truss segment is placed in the payload transport canister while workers watch its progress. After being secured in the canister, the truss will be transported to Launch Pad 39B and the payload changeout room. Then it will be moved into Space Shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay for mission STS-97. The P6 comprises Solar Array Wing-3 and the Integrated Electronic Assembly, to be installed on the Space Station. The Station’s electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays, each 112 feet long by 39 feet wide, to convert sunlight to electricity. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. Gimbals will be used to rotate the arrays so that they will face the Sun to provide maximum power to the Space Station. The STS-97 launch is scheduled Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST

JSC2000-07447 (6 December 2000) --- Cosmonaut Yury V. Usachev, Expedition Two mission commander, checks out his communications gear during a joint Expedition Two/STS-102 training session in the Systems Integration Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The Russian Aviation and Space Agency representative, along with two astronauts on his crew and the four STS-102 crew members, later simulated procedures for a nominal countdown in the crew compartment trainer (CCT-2) in the high bay area of this facility.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-107 crew check out equipment at SPACEHAB. Beginning in the center are Mission Specialists Michael Anderson and Laurel Clark; at far right are Ilan Ramon, from Israel, and Kalpana Chawla. Identified as a research mission, STS-107 is scheduled for launch July 19, 2001
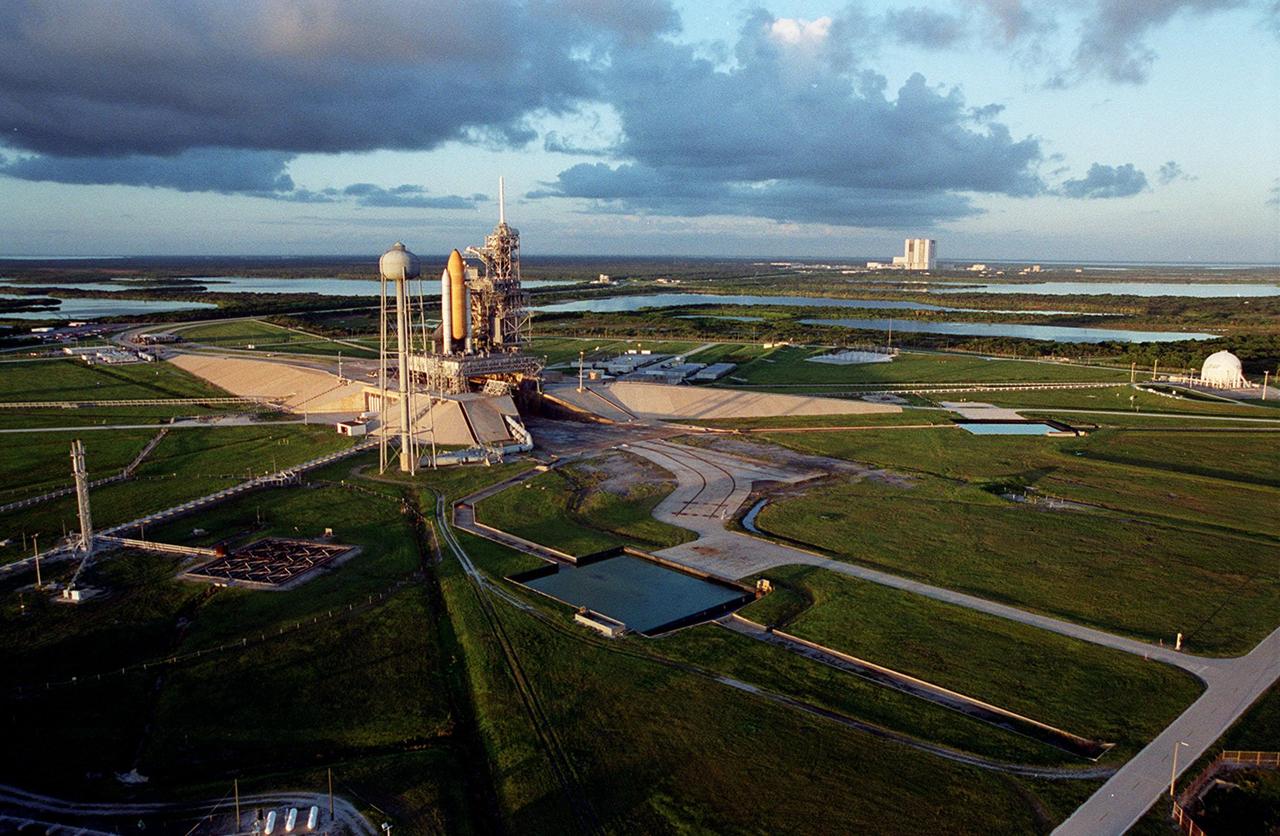

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- A long view of Launch Complex 39 is caught by the early morning sun. Left of center is Launch Pad 39A with Space Shuttle Discovery. At its left is the 300,000-gallon water tank that is part of the sound suppression system. Hoses from the tank can be seen coiling under the pad, next to the opening of the flame trench, part of the flame detector system. In the foreground is a retention pond; another is at right center. At far right, the ball-shaped structure is a 850,000-gallon storage tank for the cryogenic liquid oxygen, one of the propellants of the orbiter’s main engines. On the horizon can be seen the 525-foot tall Vehicle Assembly Building
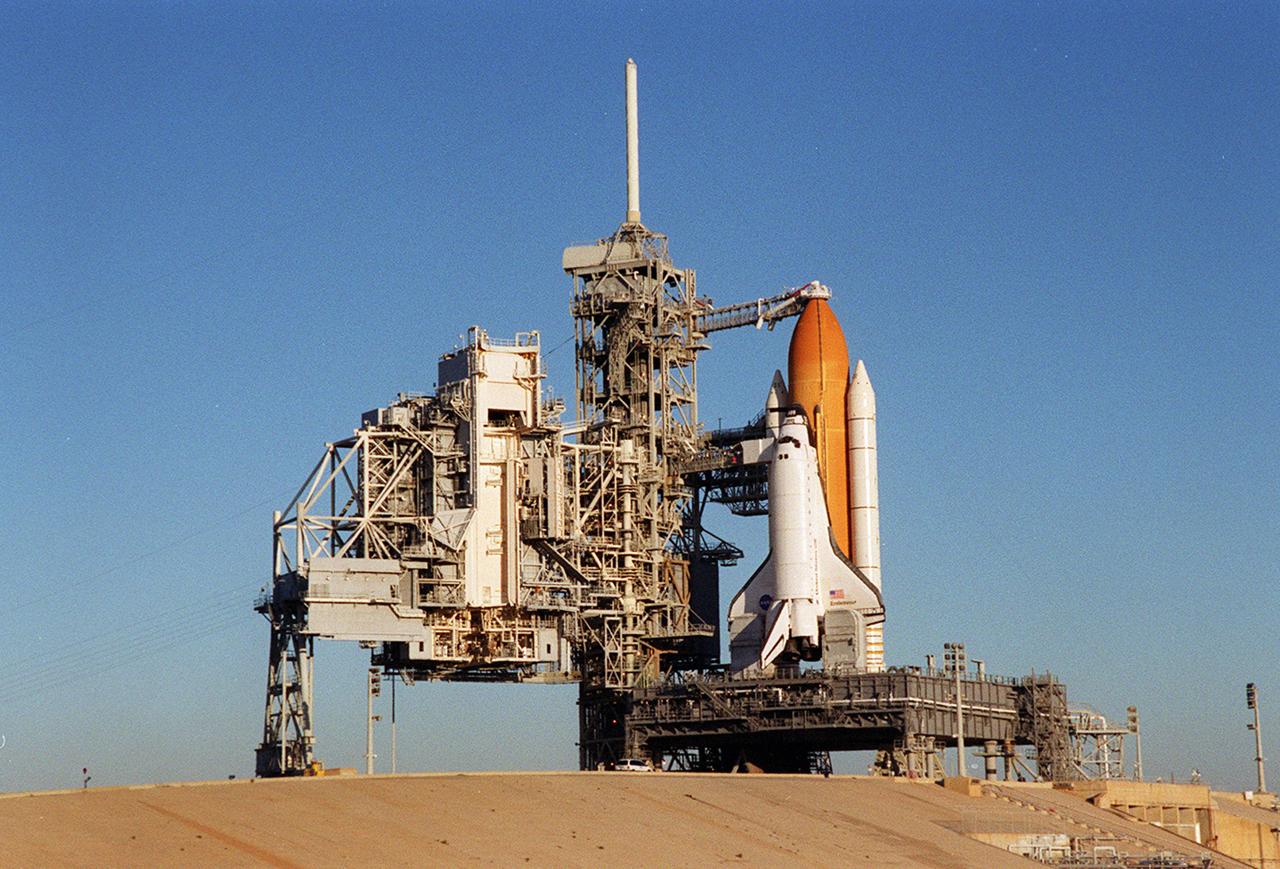
Back dropped by a cloudless blue sky, Space Shuttle Endeavor stands ready for launch after the rollback of the Rotating Service Structure, at left. The orbiter launched that night carrying the STS-97 crew of five. The STS-97 mission's primary objective was the delivery, assembly, and activation of the U.S. electrical power system onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The electrical power system, which is built into a 73-meter (240-foot) long solar array structure, consists of solar arrays, radiators, batteries, and electronics. The entire 15.4-metric ton (17-ton) package is called the P6 Integrated Truss Segment, and is the heaviest and largest element yet delivered to the station aboard a space shuttle. The electric system will eventually provide the power necessary for the first ISS crews to live and work in the U.S. segment.
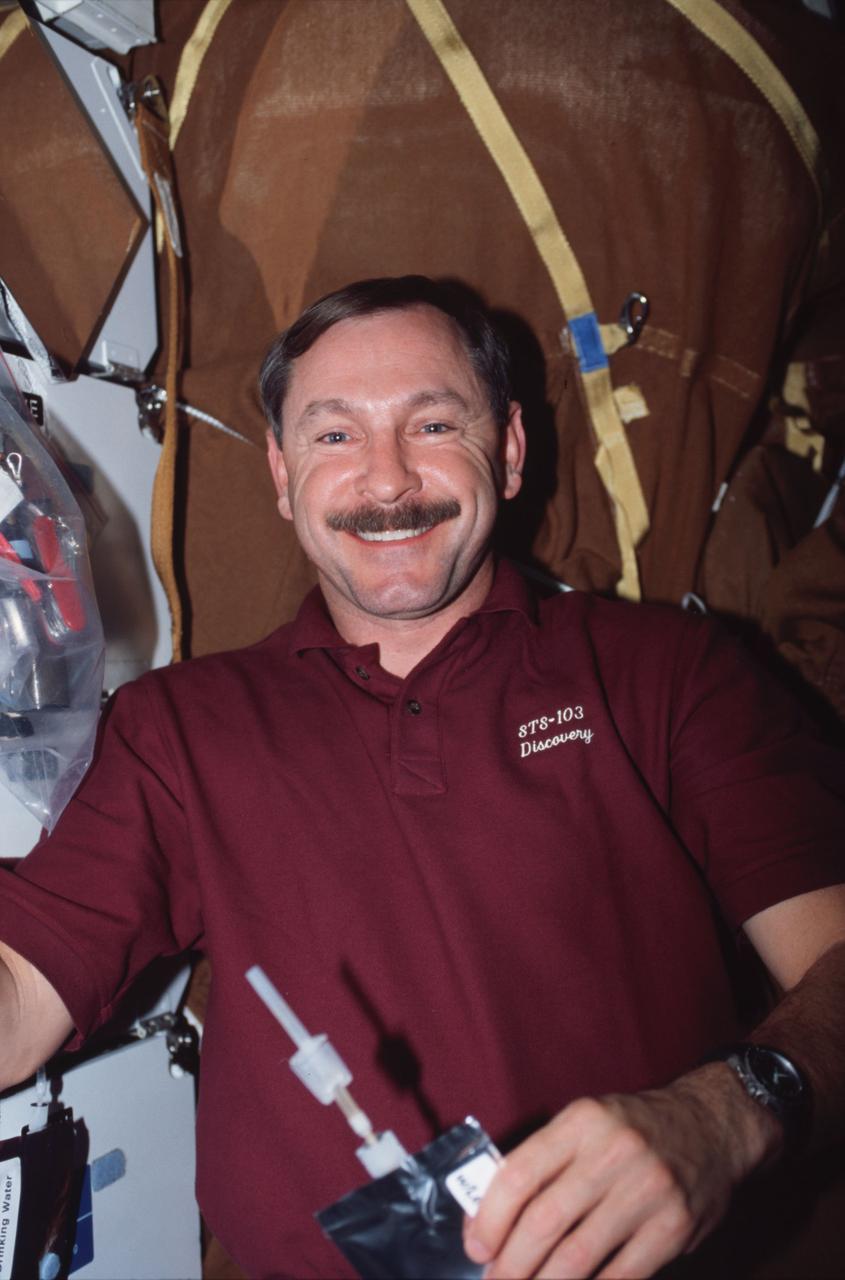

STS103-329-018 (19-27 December 1999) --- Astronaut Curtis L. Brown Jr., mission commander, on Discovery's mid deck holding a drink bag.
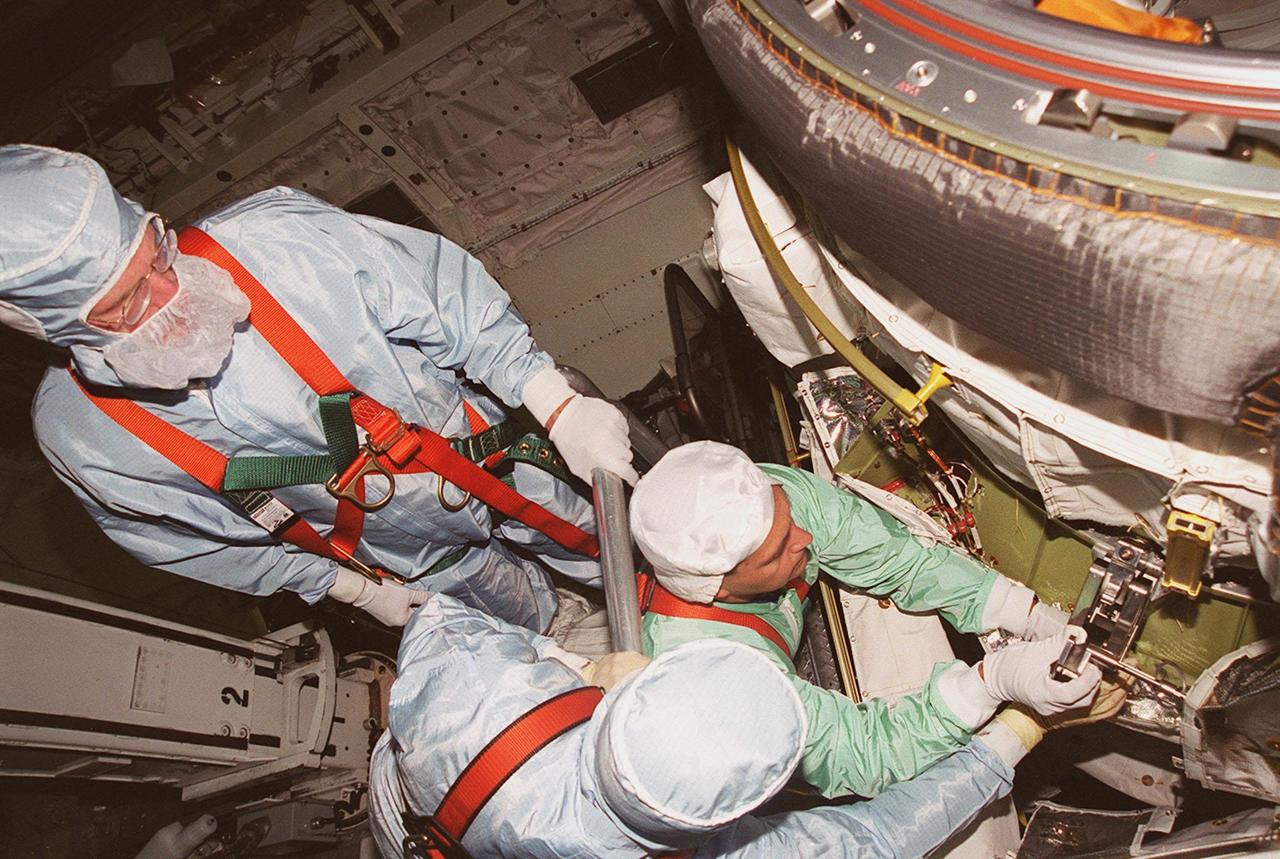

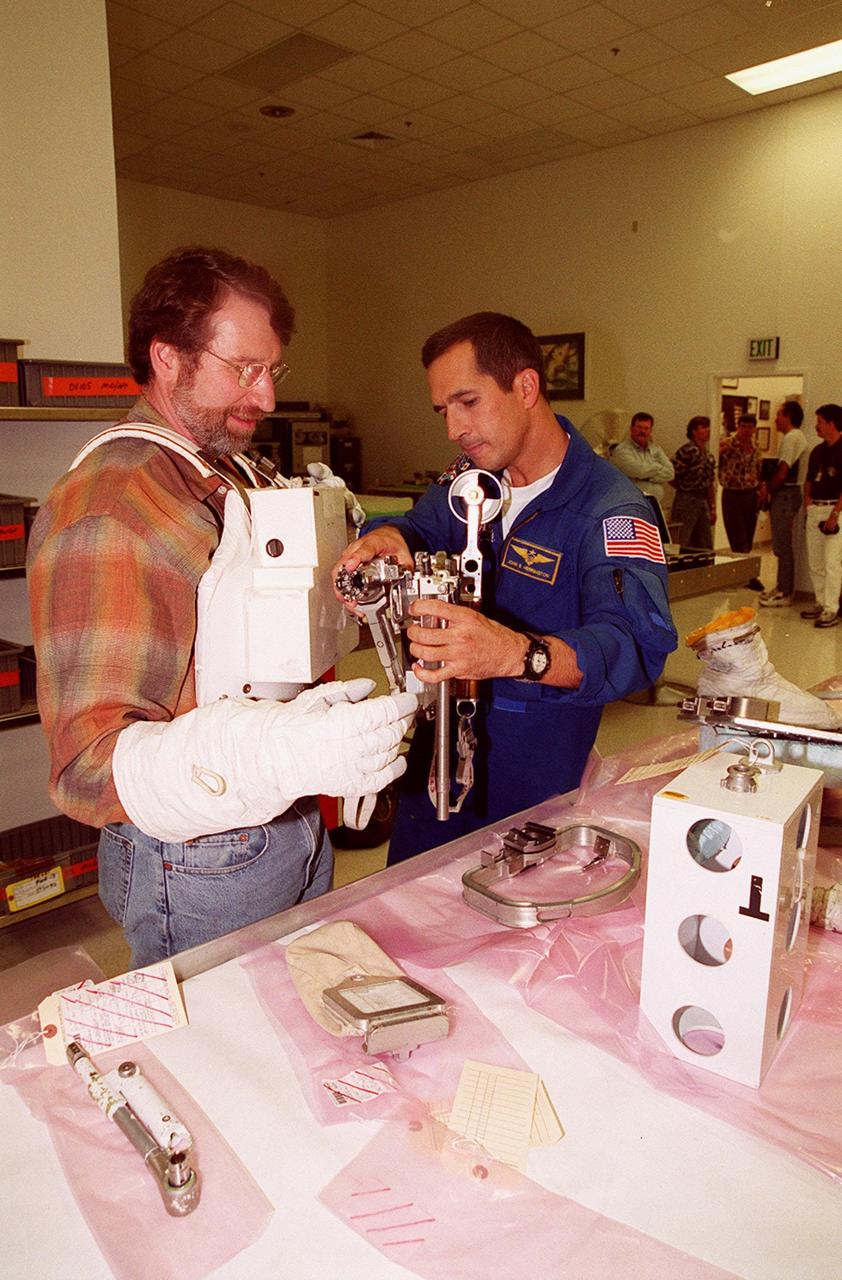
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) bay 2 during Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT), members of the STS-97 crew look over the Orbital Docking System (ODS) in Endeavour’s payload bay. At left, standing, is Mission Specialist Joe Tanner. At right is Mission Specialist Carlos Noriega, with his hands on the ODS. The others are workers in the OPF. The CEIT provides an opportunity for crew members to check equipment and facilities that will be on board the orbiter during their mission. The STS-97 mission will be the sixth construction flight to the International Space Station. The payload includes a photovoltaic (PV) module, providing solar power to the Station. STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 from KSC for the 10-day mission
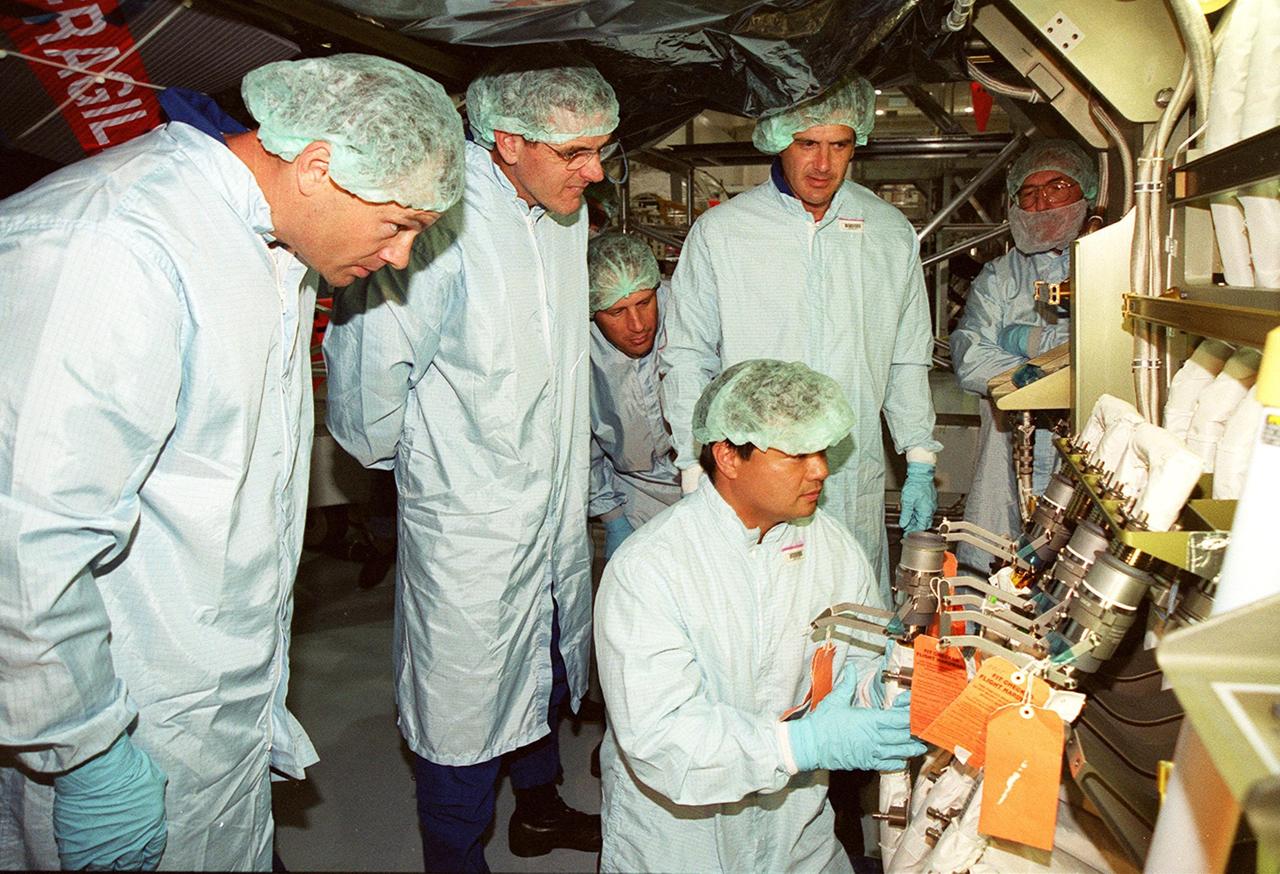

Members of the STS-92 crew check out the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the International Space Station and payload on their mission. From left are Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria, Bill McArthur, Jeff Wisoff and (kneeling) Leroy Chiao. They and other crew members are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities while at KSC. The Z1 truss is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
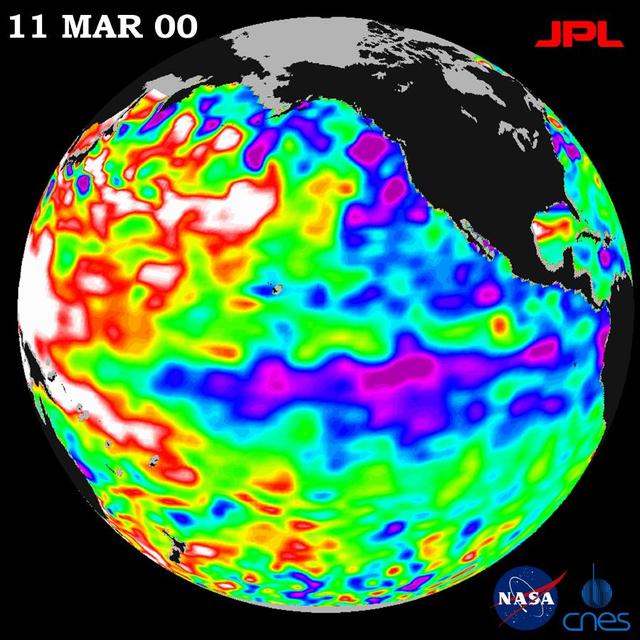
NASA TOPEX/Poseidon data, collected over a 10-day sampling cycle from March 1 to 11, 2000, showed a La Niña condition.
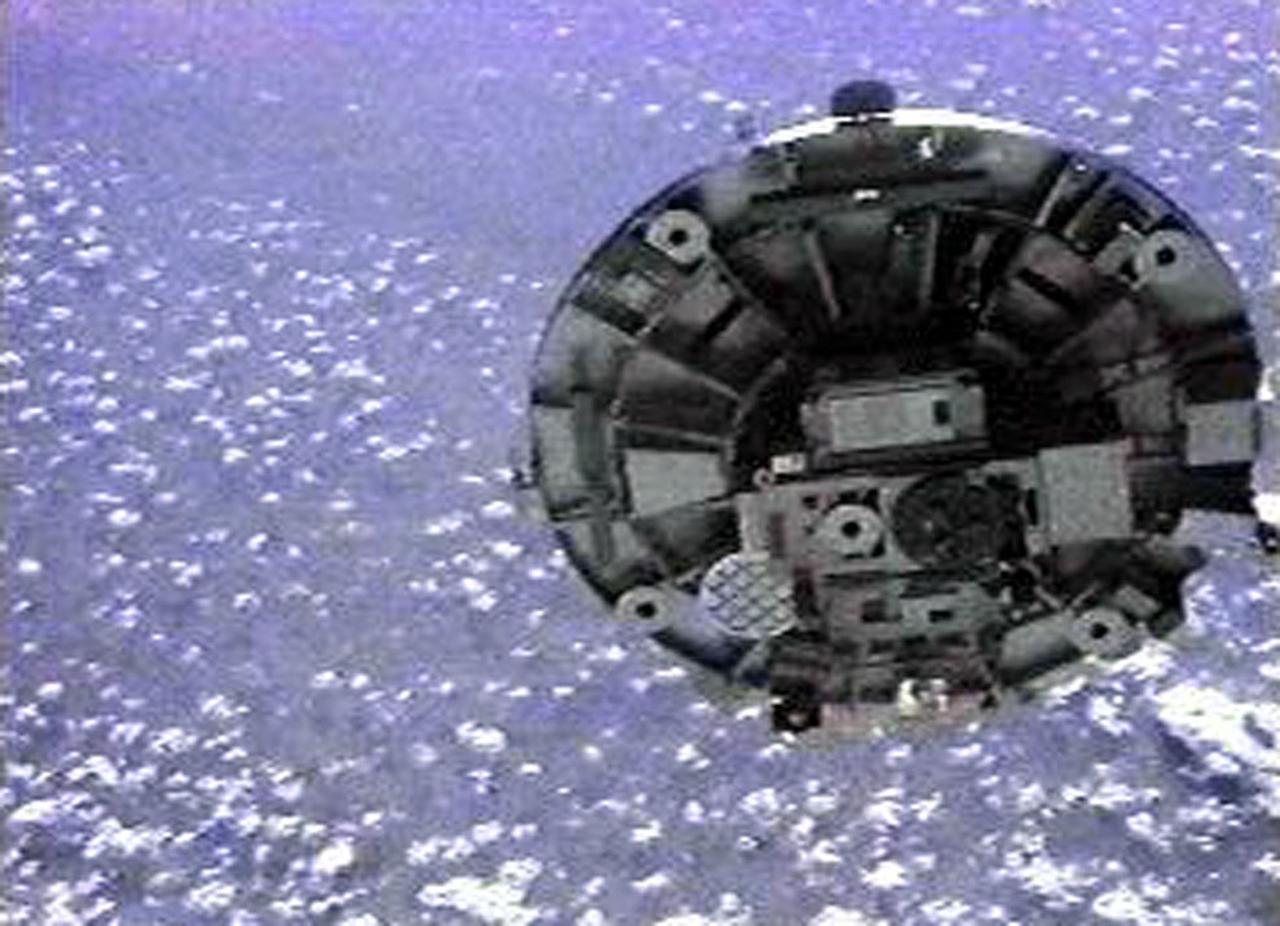
Space Vacuum Epitaxy Center works with industry and government laboratories to develop advanced thin film materials and devices by utilizing the most abundant free resource in orbit: the vacuum of space. SVEC, along with its affiliates, is developing semiconductor mid-IR lasers for environmental sensing and defense applications, high efficiency solar cells for space satellite applications, oxide thin films for computer memory applications, and ultra-hard thin film coatings for wear resistance in micro devices. Performance of these vacuum deposited thin film materials and devices can be enhanced by using the ultra-vacuum of space for which SVEC has developed the Wake Shield Facility---a free flying research platform dedicated to thin film materials development in space.
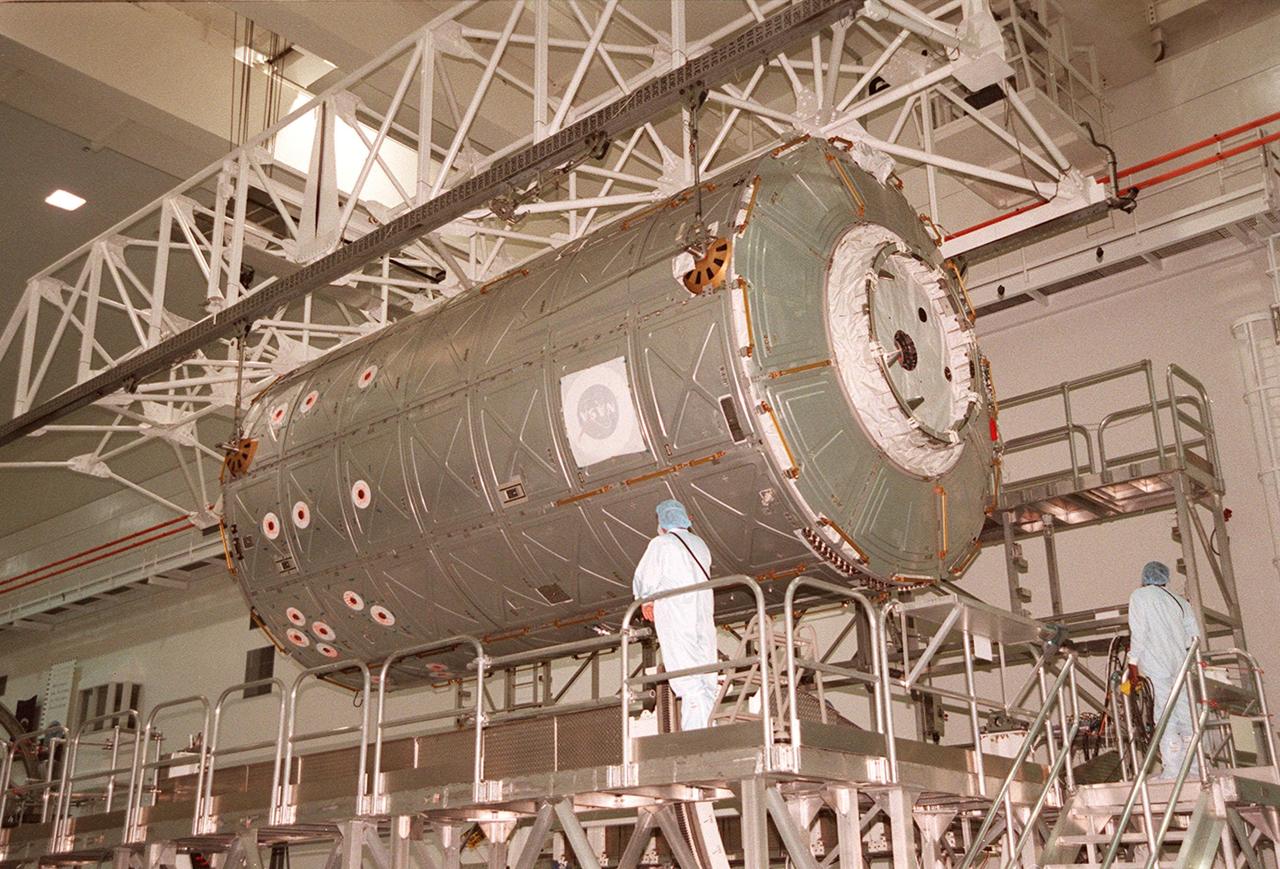
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane begins lifting the U.S. Lab Destiny from its test and integration stand. It will be carried to the Launch Package Integration Stand (LPIS) for a weight and center of gravity determination. Destiny is the payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-98 to the International Space Station. The lab is fitted with five system racks and will already have experiments installed inside for the flight. The launch is scheduled for January 2001

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A firefighter waits for his companions before tackling the flames on a simulated aircraft. Firefighters with Fire and Emergency Services at the Naval Station Mayport, Fla., are taking part in training exercises at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Pad 30.
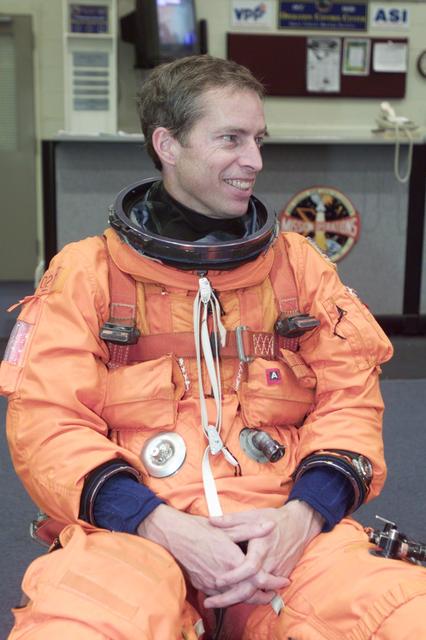

JSC2000-E-23713 (September 2000) --- Attired in a training version of his full-pressure launch and entry garment, astronaut James D. Wetherbee, mission commander for STS-102, is pictured prior to participating in an emergency bailout training exercise in the Crew Compartment Trainer (CCT-2) of the Systems Integration Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC).

Members of KSC’s Native America International Tribal Council and the Space Coast Indian Association (Brevard County) gather in the KSC Visitor Complex during opening ceremonies of the 2000 International Law Enforcement Games. More than 1,850 participants and their families took part in the opening, held in the Rocket Garden. The ceremony included parades, torch lighting and a tug of war. The games feature officers from 15 countries and 37 United States in competitions around Brevard County, Fla
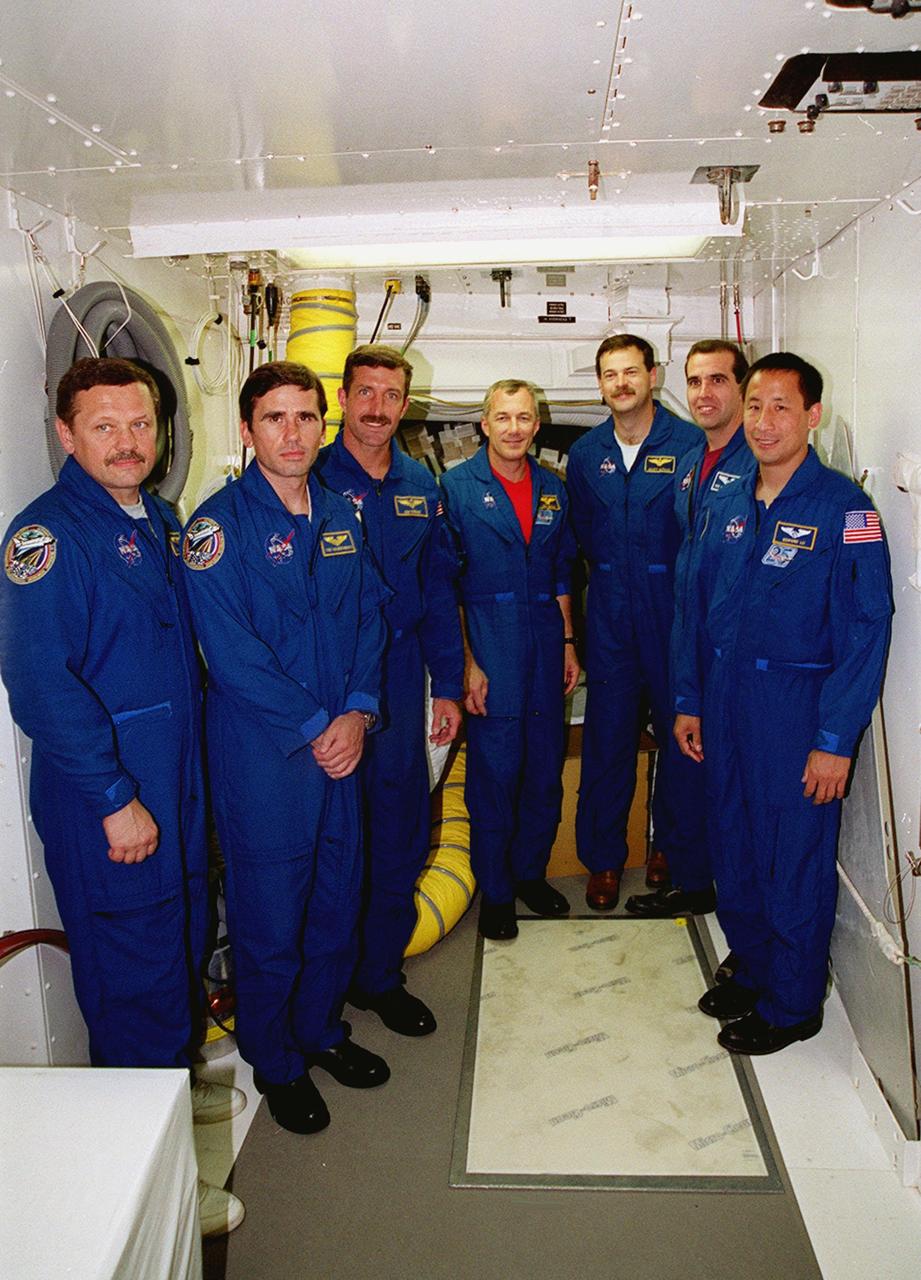

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-106 flight crew gather in the white room of Launch Pad 39-B. Crew members pictured are, from left, Mission Specialists Boris V. Morukov, Yuri I. Malenchenko, Daniel C. Burbank, Commander Terrence W. Wilcutt, Pilot Scott D. Altman, Mission Specialists Richard A. Mastracchio and Edward T. Lu. Malenchenko and Morukov are with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The flight crew were at Kennedy Space Center to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT provides the crew with emergency egress training and opportunities to inspect their mission payload in the orbiter’s payload bay. STS-106 is scheduled to launch Sept. 8, 2000, at 8:31 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B. On the 11-day mission, the seven-member crew will perform support tasks on orbit, transfer supplies and prepare the living quarters in the newly arrived Zvezda Service Module. The first long-duration crew, dubbed “Expedition One,” is due to arrive at the Station in late fall
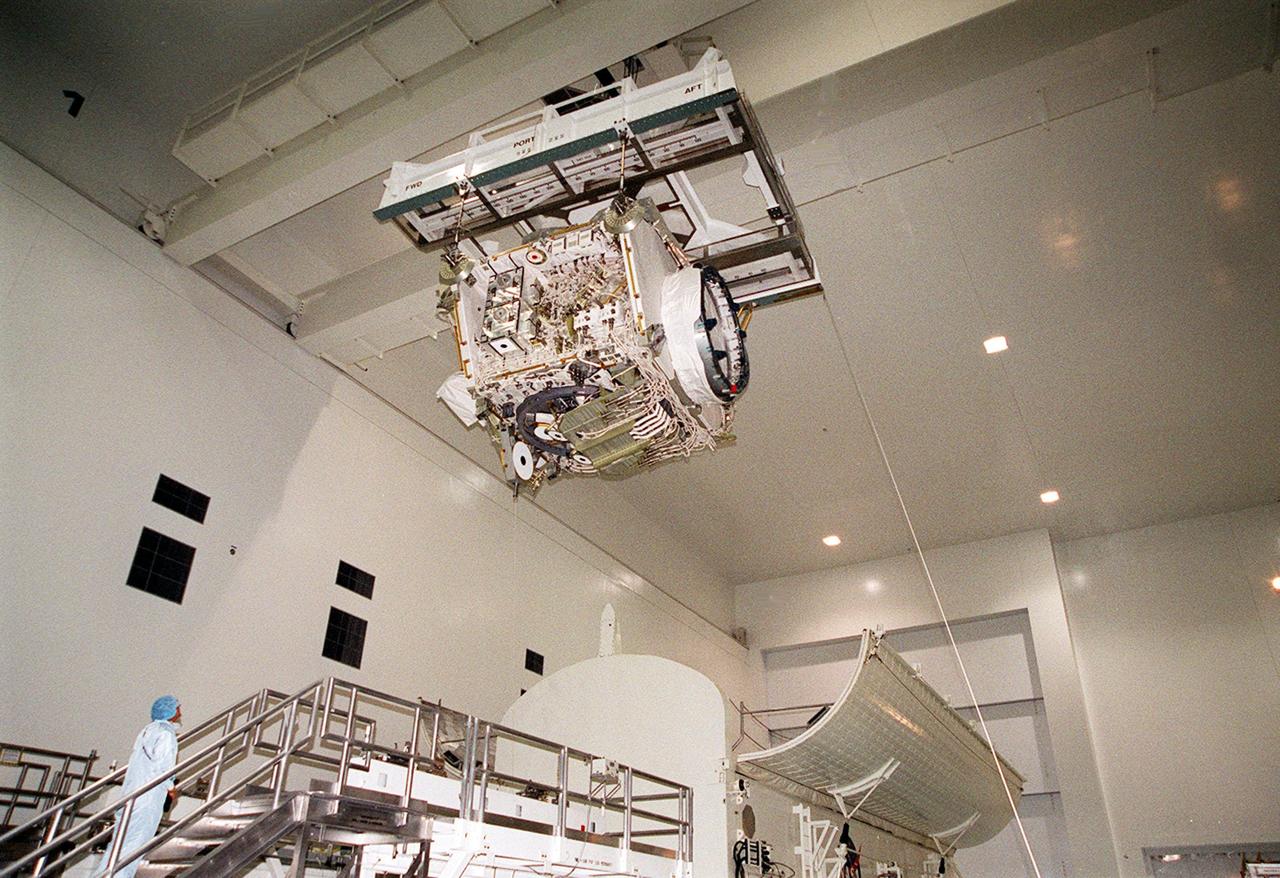

In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, suspended from an overhead crane, is rotated before being placed inside the payload canister below it. The truss will then be transported to Launch Pad 39A. It is part of the payload on mission STS-92 scheduled to lift off Oct. 5, 2000
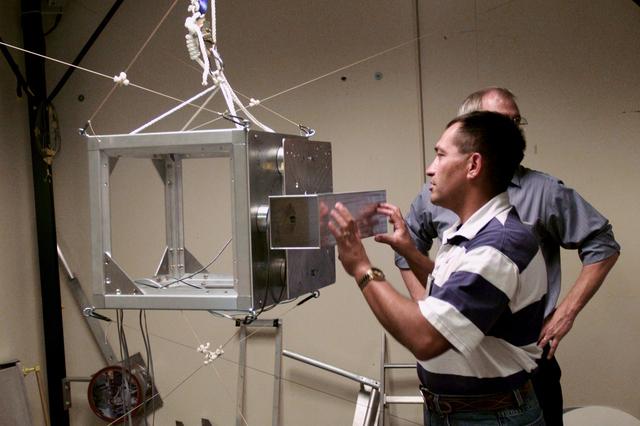

JSC2000-E-26591 (October 2000) --- Astronaut Carlos I. Noriega, one of two STS-97 astronauts assigned to extravehicular activity (EVA) duty, participates in training for the upcoming mission. Noriega and four other astronauts will visit the International Space Station (ISS) via the Space Shuttle Endeavour.
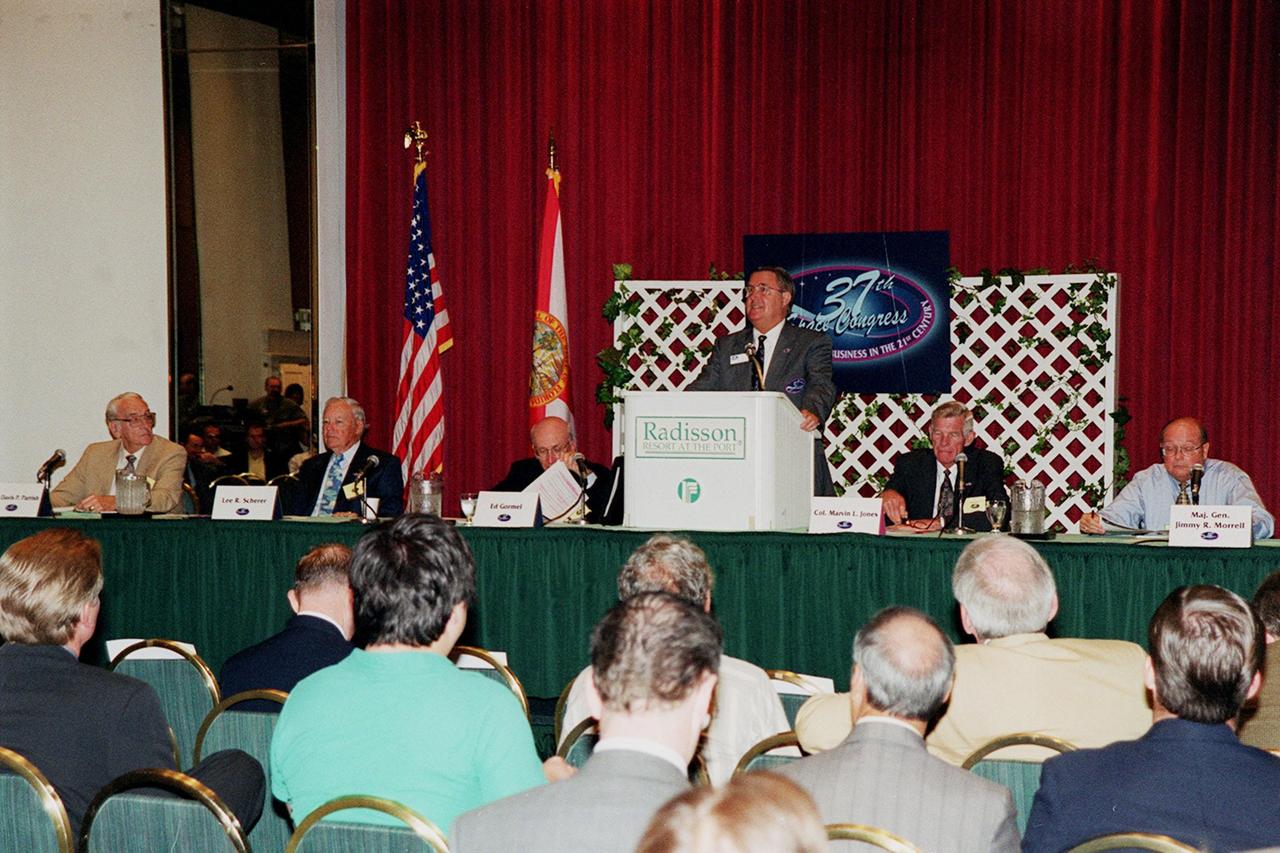

A panel session on the first day of the 37th Space Congress presents "50 Years of Space Exploration." Seated from left are Davis P. Parrish, Col., USAF (ret.); Lee R. Scherer, a senior executive with General Dynamics Commercial Services Group, San Diego, Calif., and former director, KSC; Edmond F. Gormel, executive director of Joint Performance Management Office, KSC; Marvin L. Jones, Col. USAF (ret.)and director of Installation Operations, KSC; and Jimmy R. Morrell, Maj. Gen., USAF (ret.). At the podium is Charles Murphy, Space Congress general chairman. Sponsored by the Canaveral Council of Technical Societies, the 37th Space Congress featured the theme "Space Means Business in the 21st Century." The event was held at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral
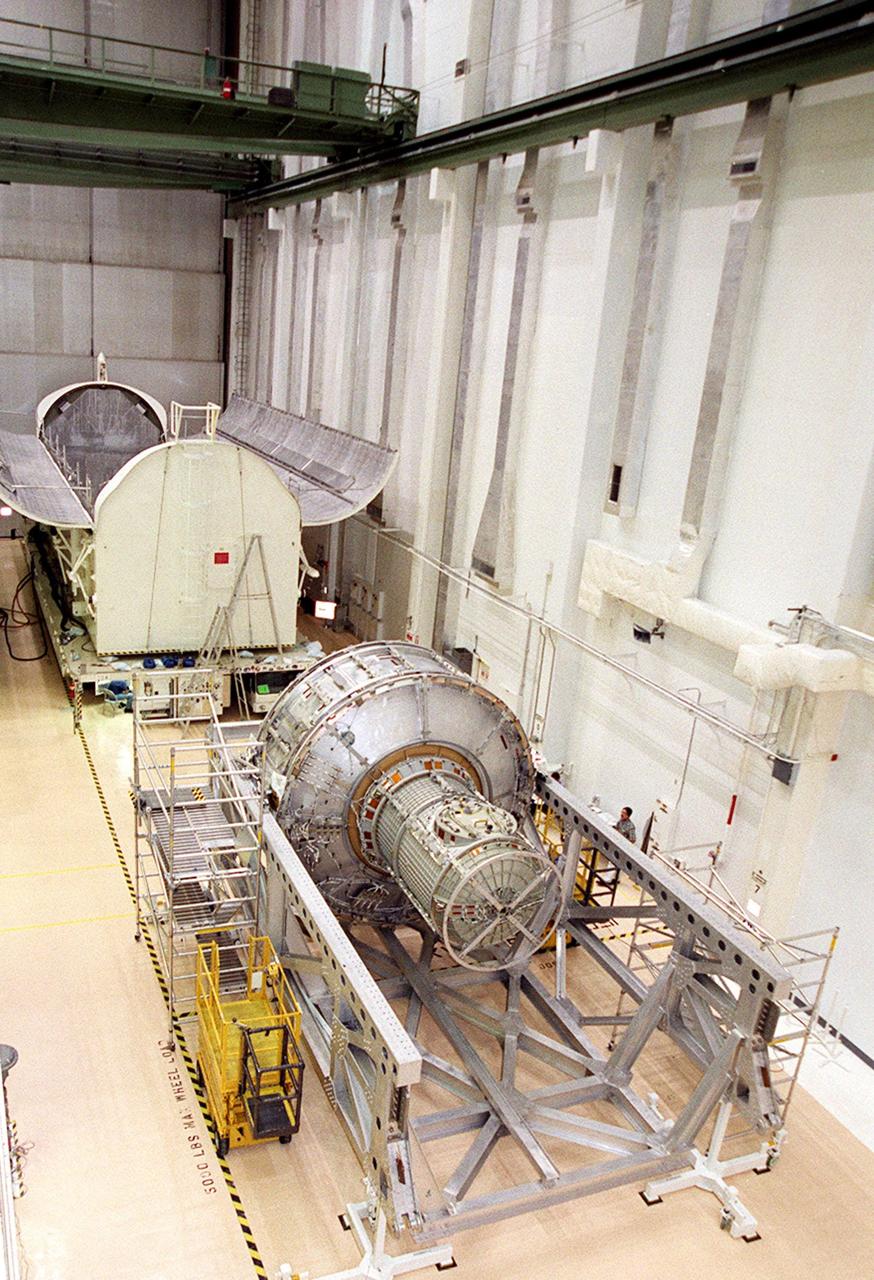

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module waits for transfer to the payload canister behind it after which it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
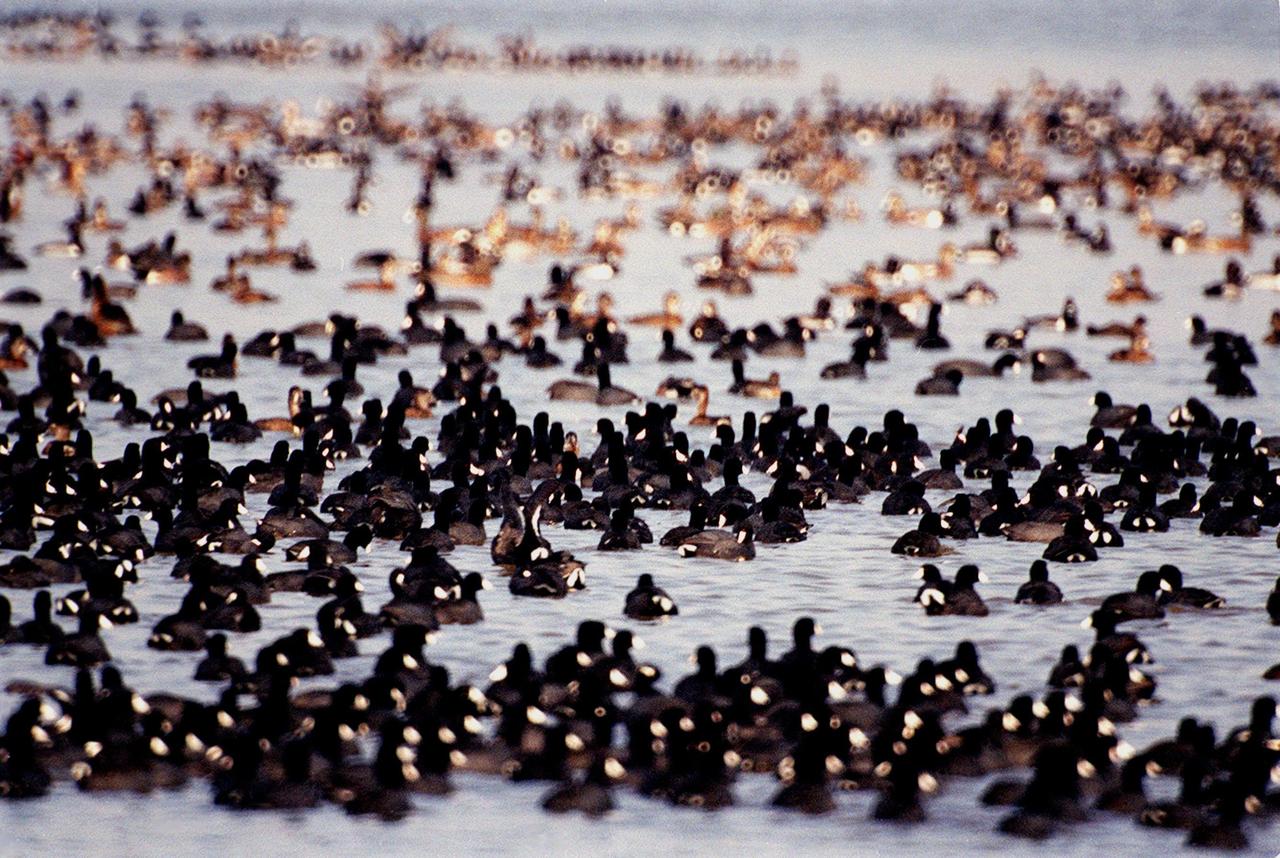

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Coots draw together (foreground) in the waters of the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which shares a boundary with Kennedy Space Center. They are often seen in the Indian River and Banana Creek swimming together in large groups such as these. Other birds, mainly ducks, swim nearby. Coots are readily identified by their slate-gray bodies and conspicuous white bill. They inhabit open ponds and marshes from southern Canada to northern South America. Excellent swimmers and divers, they eat various aquatic plants, but also feed on seeds grass and waste grain on land. The 92,000-acre refuge is a habitat for more than 330 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles. The marshes and open water of the refuge provide wintering areas for 23 species of migratory waterfowl, as well as a year-round home for great blue herons, great egrets, wood storks, cormorants, brown pelicans and other species of marsh and shore birds

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, two Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules, Italian-built Raffaello and Leonardo, undergo testing. Italy's major contributions to the International Space Station program, Raffaello and Leonardo are reusable logistics carriers to resupply and return Space Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. They are slated as payloads on missions STS-102 and STS-100, respectively. Dates have not yet been determined for the two missions
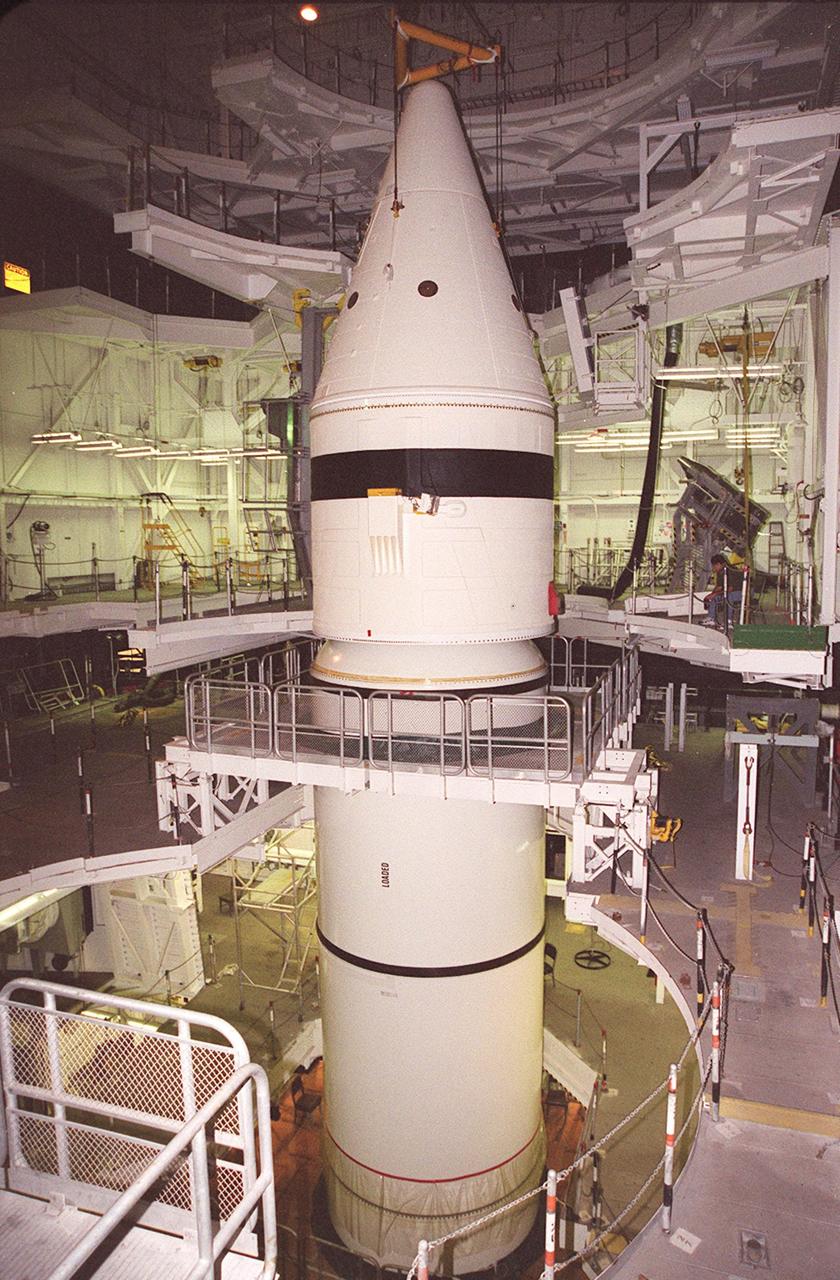
Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, the forward section of a solid rocket booster (SRB) is lowered onto the rest of the stack for mating. The forward section of each booster, from nose cap to forward skirt contains avionics, a sequencer, forward separation motors, a nose cone separation system, drogue and main parachutes, a recovery beacon, a recovery light, a parachute camera on selected flights and a range safety system. Each SRB weighs approximately 1.3 million pounds at launch. The SRB is part of the stack for Space Shuttle Discovery and the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5, from Launch Pad 39A, on the fifth flight to the International Space Station
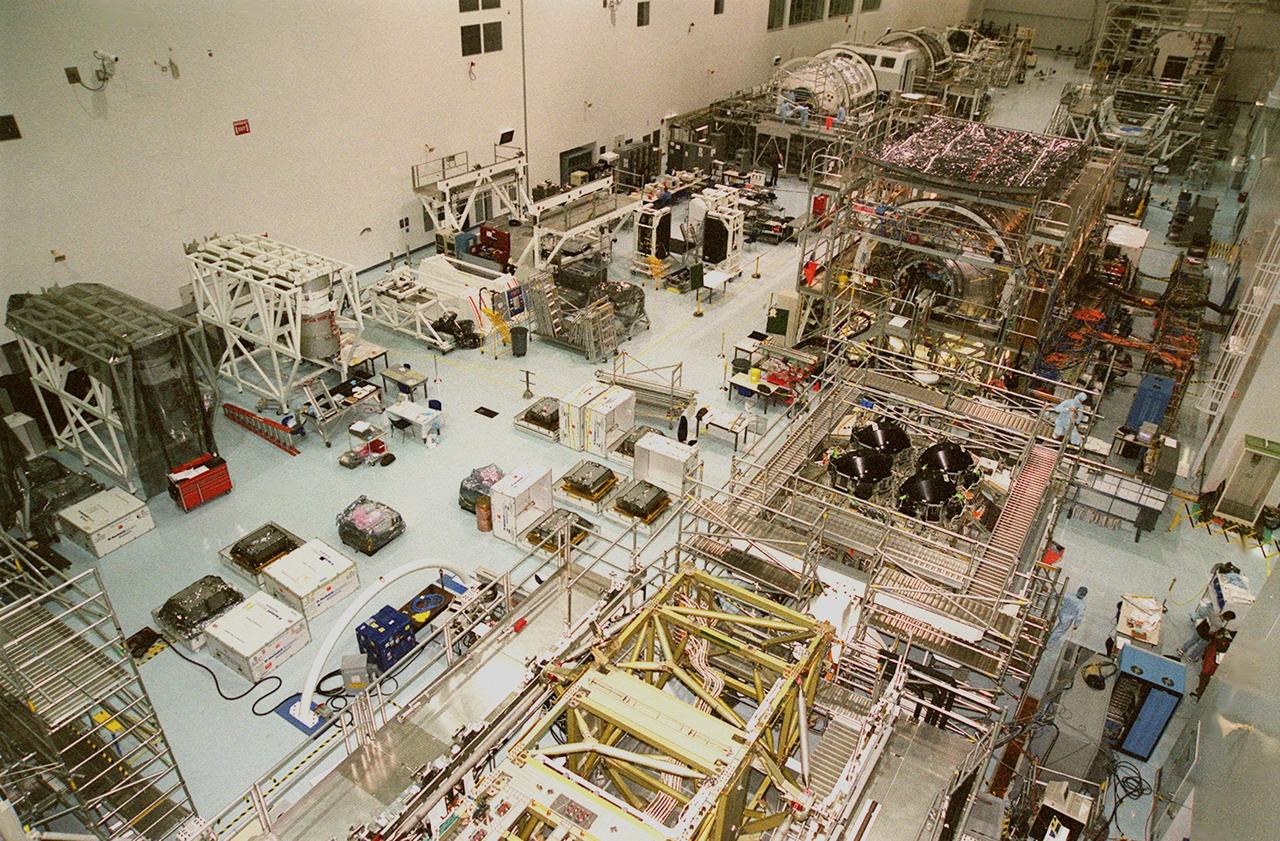
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The floor of the Space Station Processing Facility is filled with racks and hardware for testing the various components of the International Space Station (ISS). The large module in the center of the floor (top) is the U.S. Lab, Destiny. Expected to be a major feature in future research, Destiny will provide facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. It is scheduled to be launched on mission STS-98 (no date determined yet for launch). At top left are the Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules Raffaello and Leonardo and the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3 (PMA-3). Italy's major contributions to the ISS program, Raffaello and Leonardo are reusable logistics carriers to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. They are slated as payloads on missions STS-102 and STS-100, respectively. Dates have not yet been determined for the two missions. The PMA-3, once launched, will be mated to Node 1, a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the Space Station. The primary purpose of PMA-3 is to serve as a Shuttle docking port through which crew members and equipment will transfer to the Space Station during later assembly missions. PMA-3 is scheduled as payload on mission STS-92, whose date for launch is not yet determined
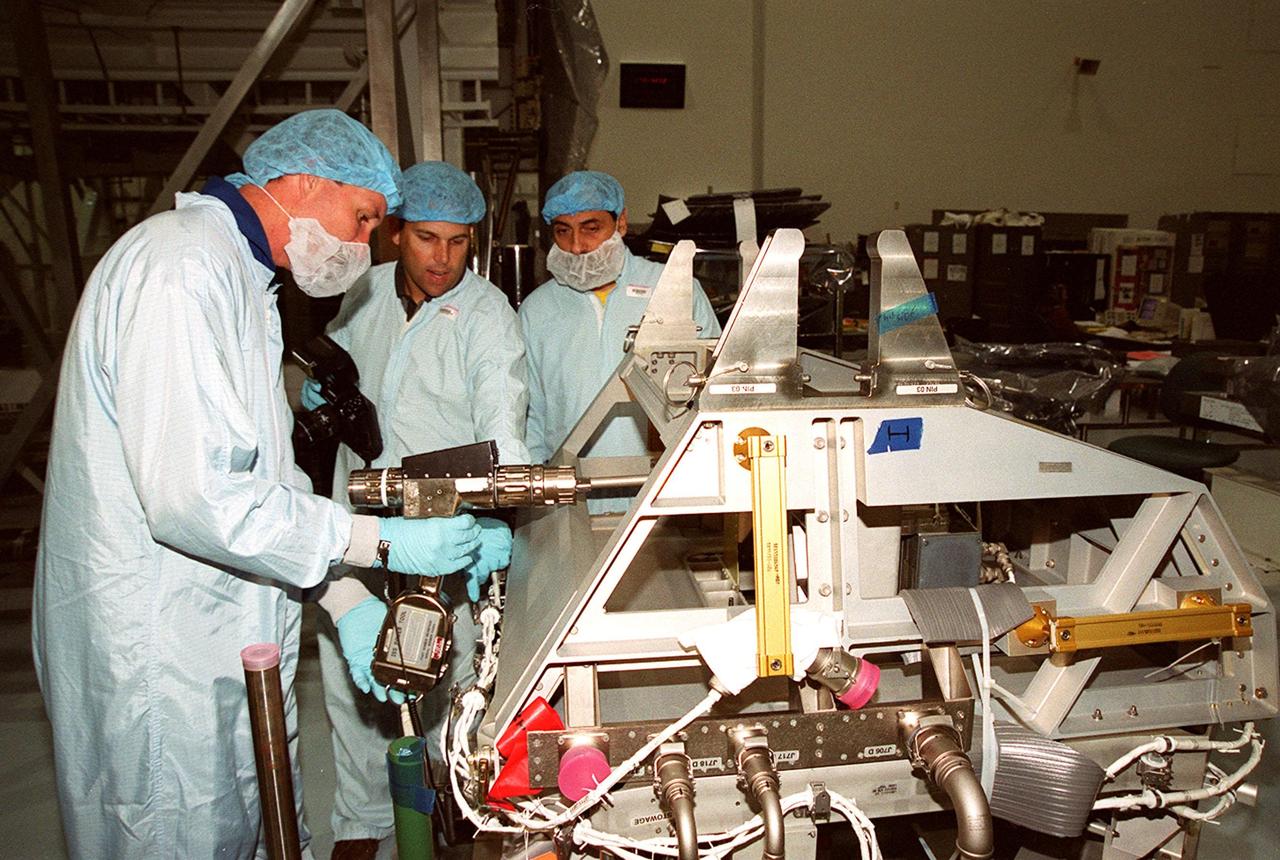

In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-100 Commander Kent Rominger (left) tries out a piece of equipment while a worker (center) gives directions. Looking on at right is Mission Specialist Umberto Guidoni, with the European Space Agency. Mission STS-100, scheduled to launch April 19, 2001, will include Raffaello as well as the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) as its payload. MPLMs are pressurized modules that will serve as the International Space Station's “moving vans,” carrying laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the station aboard the Space Shuttle. The SSRMS is the primary means of transferring payloads between the orbiter payload bay and the International Space Station for assembly
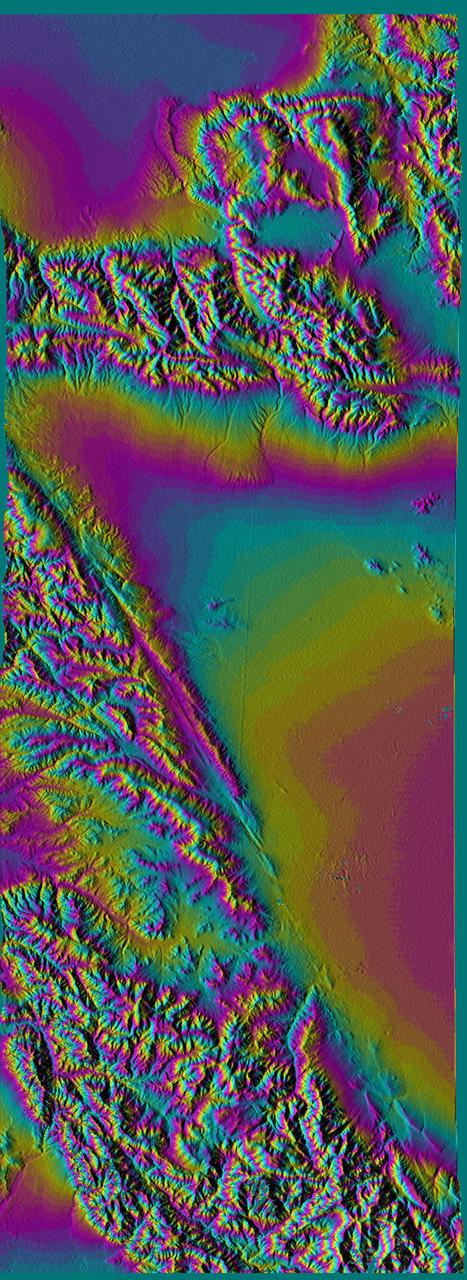
This topographic map acquired by NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM from data collected on February 16, 2000 vividly displays California famous San Andreas Fault along the southwestern edge of the Mojave Desert, Calif.

JSC2000-06750 (October 2000) --- Astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, mission specialist.
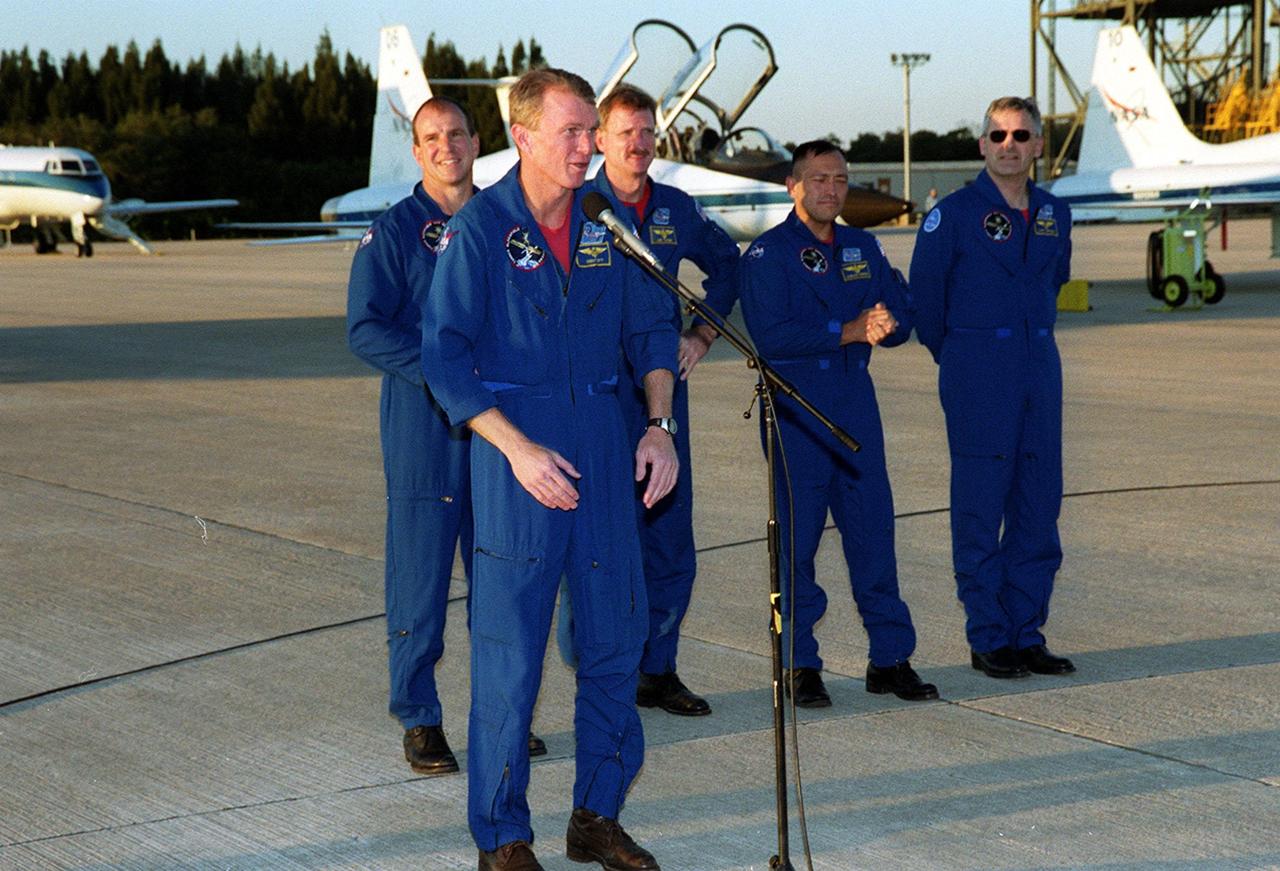

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility, the STS-97 crew gather to address the media. At the microphone, Commander Brent Jett praises the efforts of the KSC workers to get ready for the launch. Behind Jett are Pilot Michael Bloomfield and Mission Specialists Joseph Tanner, Carlos Noriega and Marc Garneau, who is with the Canadian Space Agency. Mission STS-97 is the sixth construction flight to the International Space Station. Its payload includes the P6 Integrated Truss Structure and a photovoltaic (PV) module, with giant solar arrays that will provide power to the Station. The mission includes two spacewalks to complete the solar array connections. STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at about 10:06 p.m. EST
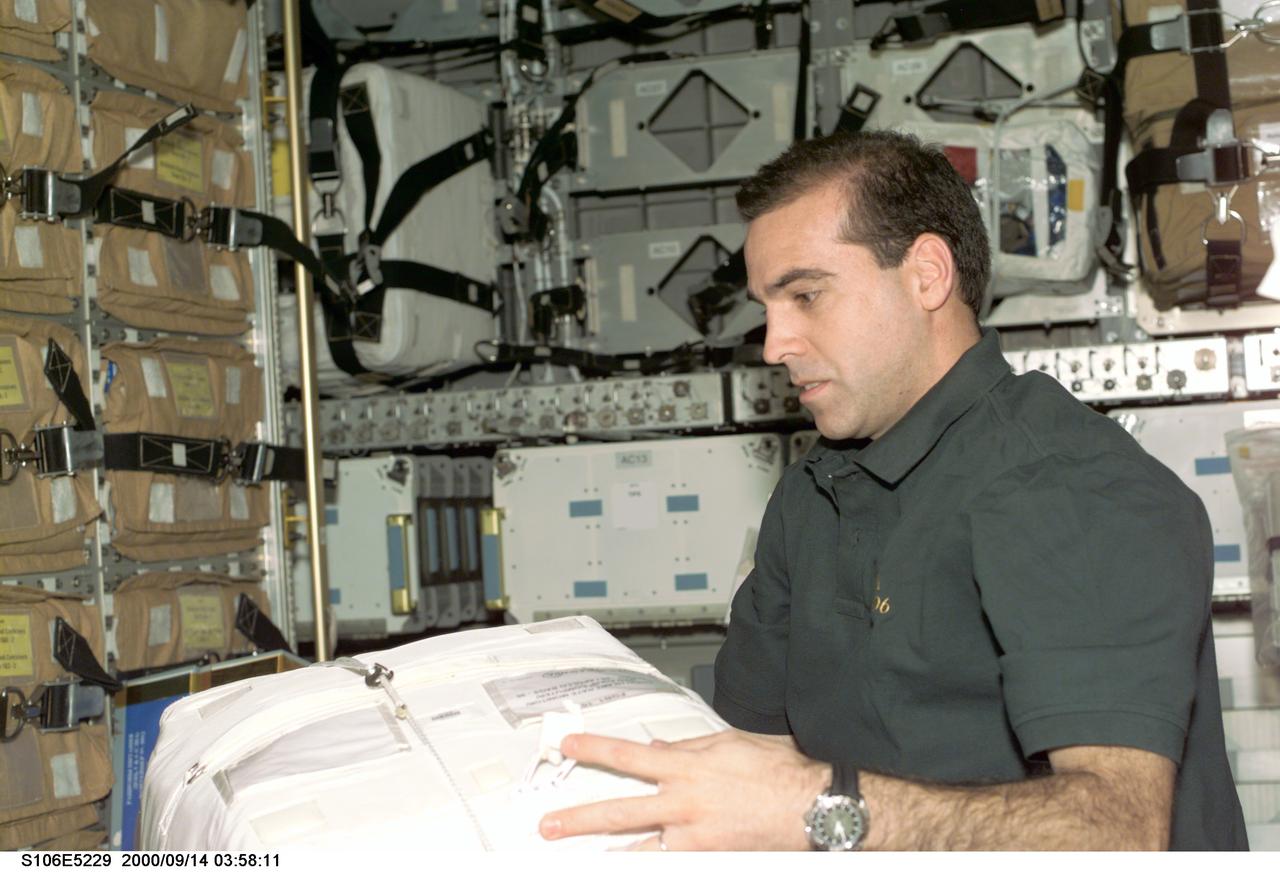

S106-E-5229 (14 September 2000) --- Astronaut Richard A. Mastracchio, mission specialist, works with packages of supplies in the Spacehab double module in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis.
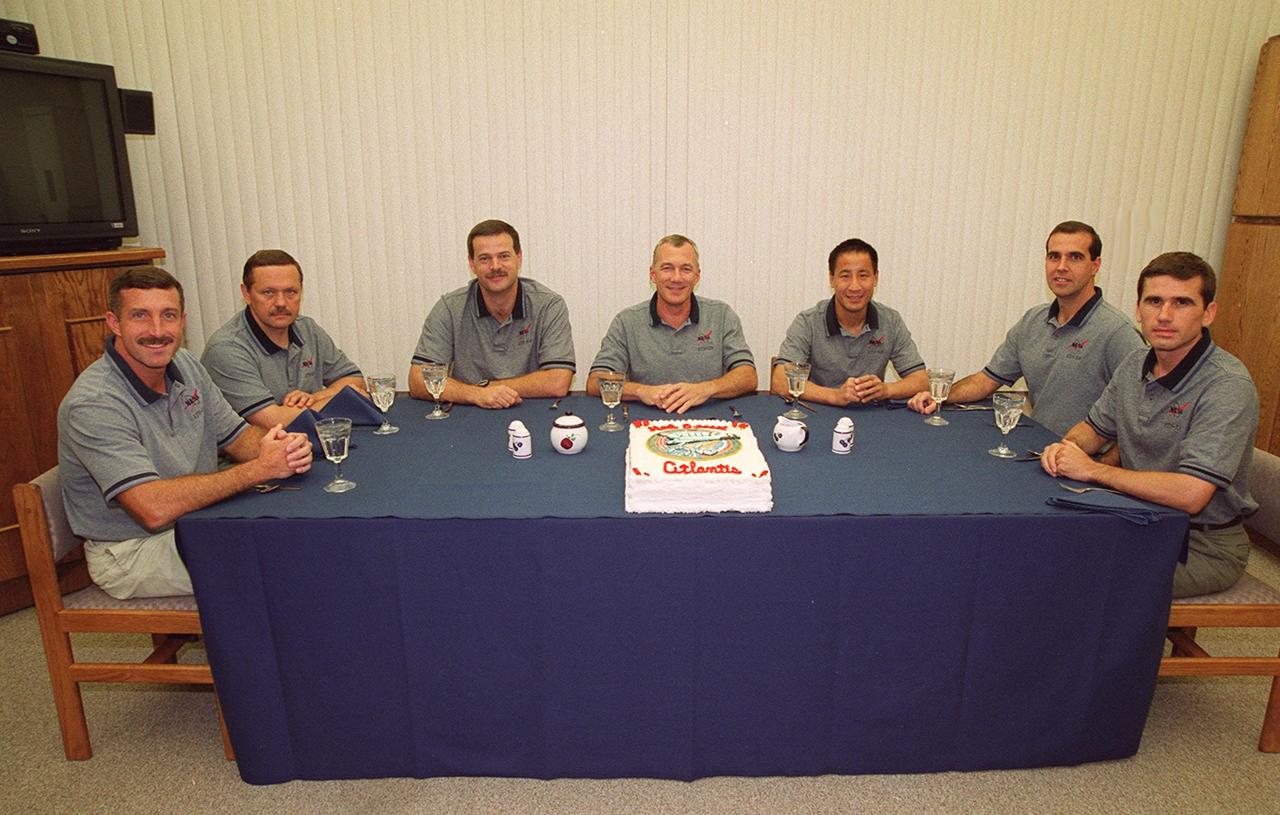

The STS-106 crew relax after breakfast and before suitup for launch. Seated (left to right) are Mission Specialists Daniel C. Burbank and Boris V. Morukov; Pilot Scott D. Altman; Commander Terrence W. Wilcutt; and Mission Specialists Edward T. Lu, Richard A. Mastracchio and Yuri I. Malenchenko. Morukov and Malenchenko are with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis is set for 8:45 a.m. EDT on the fourth flight to the International Space Station. On the 11-day mission, the seven-member crew will perform support tasks on orbit, transfer supplies and prepare the living quarters in the newly arrived Zvezda Service Module. The first long-duration crew, dubbed “Expedition One,” is due to arrive at the Station in late fall
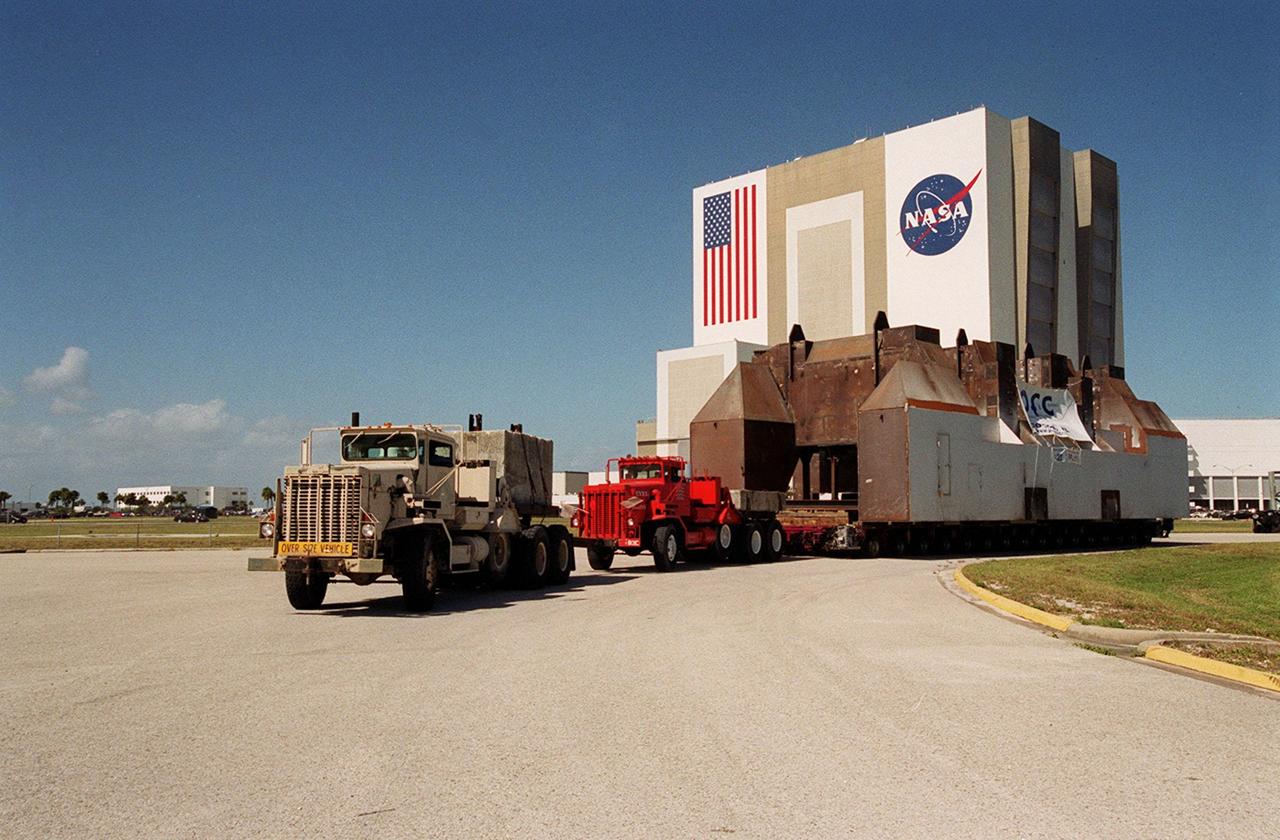

A launch table, fabricated by Jered Industries in Georgia for Boeing, turns the corner away from the barge that brought it to the turn basin in KSC’s Launch Complex 39 Area. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The table was built in support of the Delta Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program, known as Delta IV. It was floated on the barge down the Intercoastal Waterway, through the Barge Canal to the turn basin. The table, whcih is approximately 70 feet long, 40 feet wide and 50 feet high, weighing about 600,000 pounds, is being transferred to Launch Complex 37B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Accompanying the launch table on the barge are flame deflectors, which are also to be erected on pad 37B
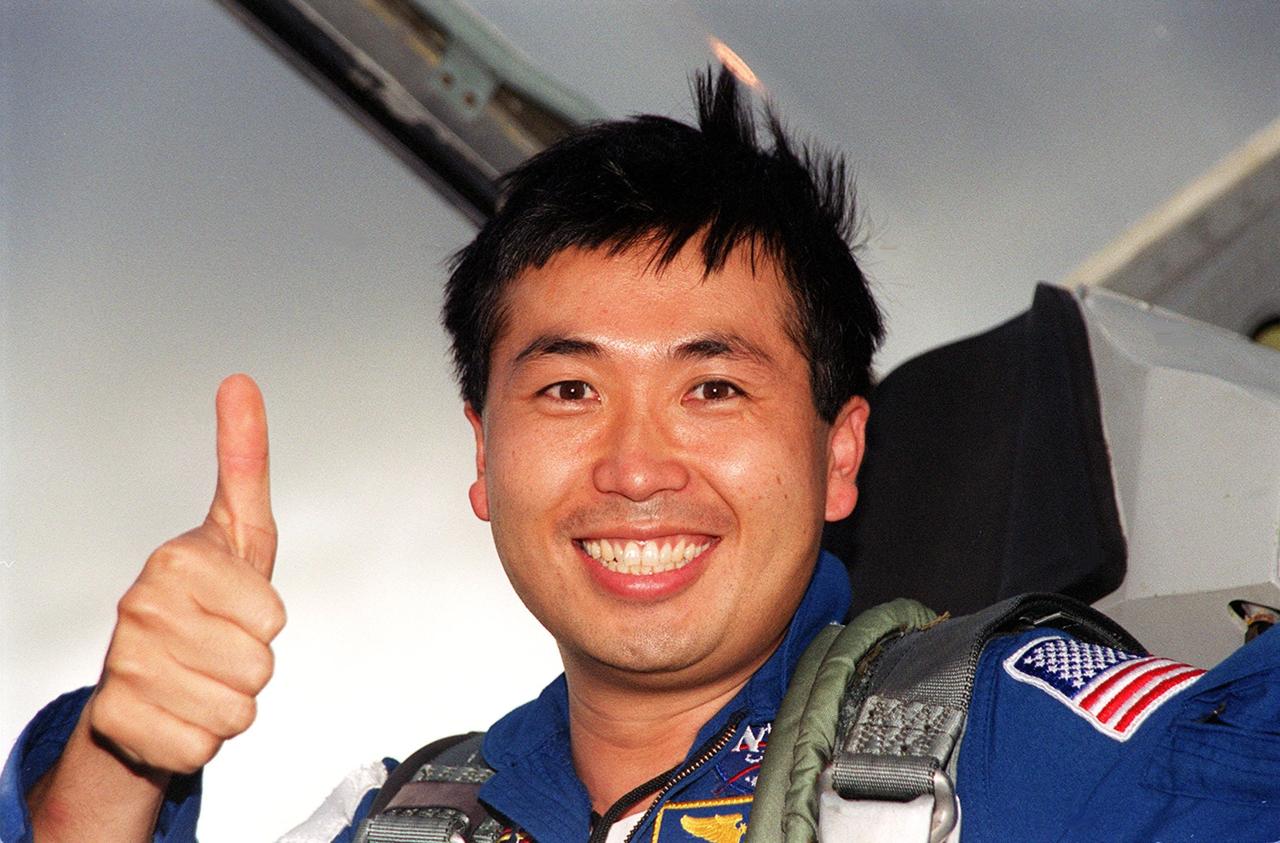

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- For STS-92 Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata of Japan, arrival at KSC for launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Oct. 5 is a thumbs-up experience. He and other crew members Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William S. McArthur Jr. expressed their eagerness to launch to a waiting group of media at the Shuttle Landing Facility. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
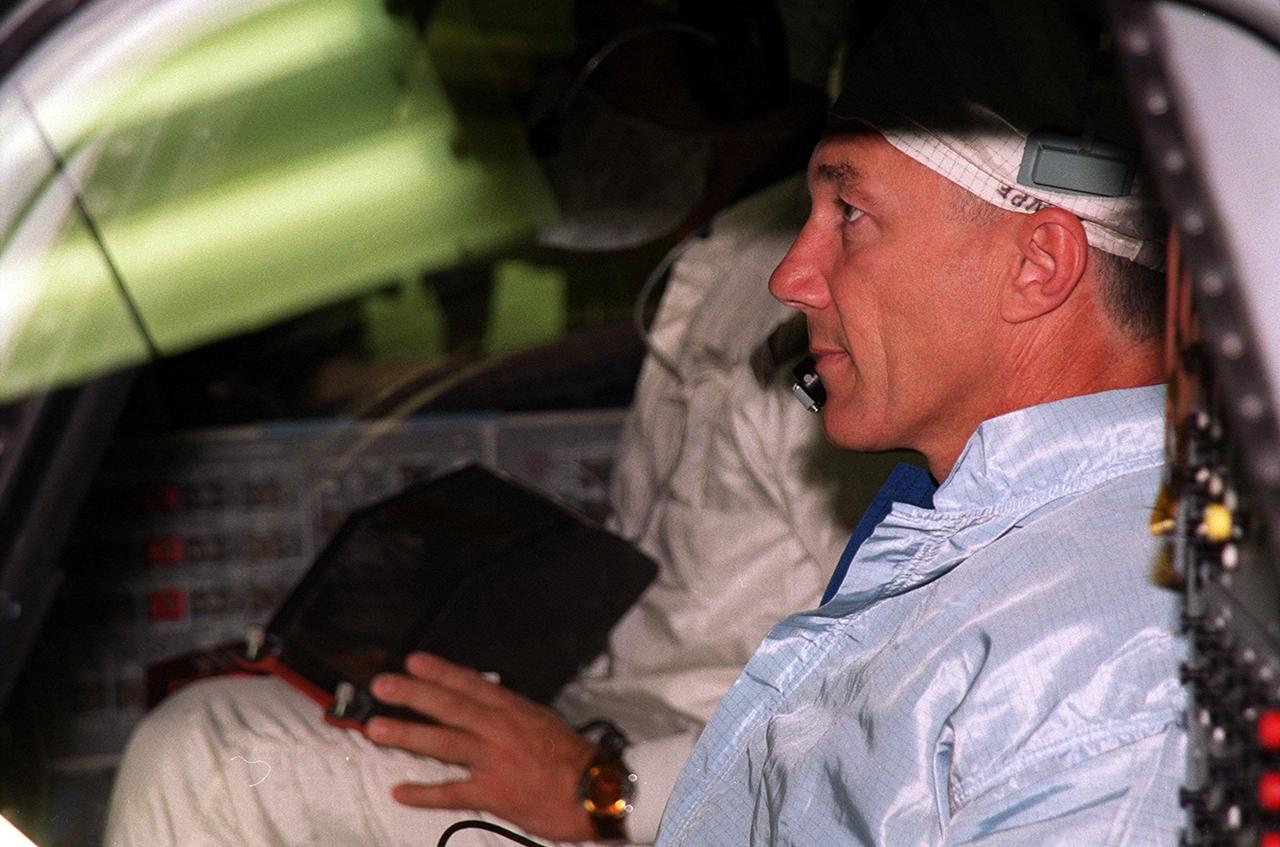

STS-106 Mission Commander Terrence W. Wilcutt checks out the windows in Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis in Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3. He and the other crew members Pilot Scott D. Altman and Mission Specialists Edward T. Lu, Daniel C. Burbank, Yuri I. Malenchenko, Boris V. Morukov and Richard A. Mastracchio are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities. Malenchenko and Morukov represent the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. On the 11-day mission, the seven-member crew will perform support tasks on orbit, transfer supplies and prepare the living quarters in the newly arrived Zvezda Service Module for the first long-duration crew, dubbed "Expedition One," which is due to arrive at the Station in late fall. STS-106 is scheduled to launch Sept. 8, 2000, at 8:31 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B

Cydonia: Two Years Later
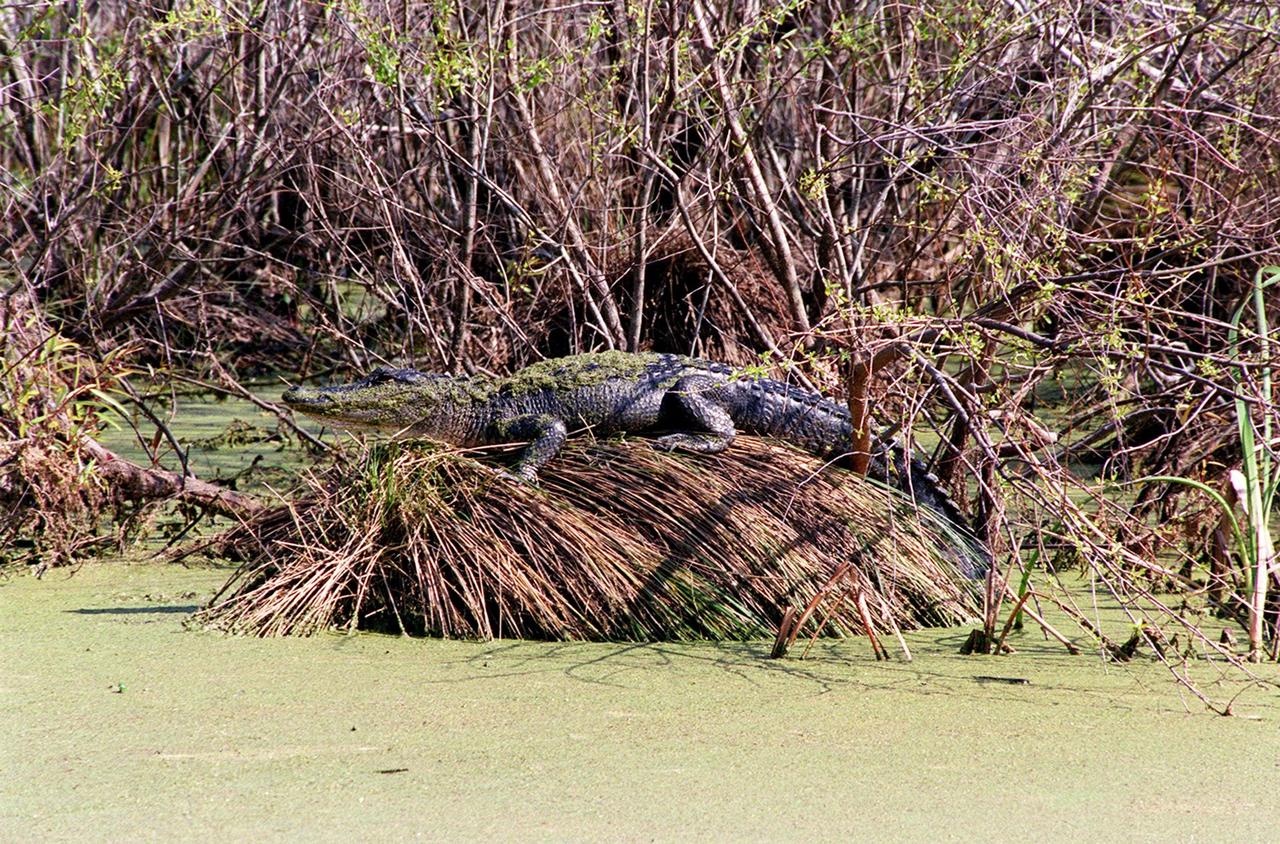

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On top of what may be a nest on the edge of an algae-coated canal near Schwartz Rd. at Kennedy Space Center, a moss-covered alligator rests while keeping a wary eye open for trespassers. Nearly 5,000 alligators can be found in canals, ponds, and waterways throughout the Center and the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which shares a boundary with the Center. American alligators feed and rest in the water, and usually lay their eggs in dens they dig into the banks. The young alligators spend their first several weeks in these dens. The Wildlife Refuge encompasses 92,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. The marshes and open water of the refuge provide wintering areas for 23 species of migratory waterfowl, as well as a year-round home for great blue herons, great egrets, wood storks, cormorants, brown pelicans and other species of marsh and shore birds, as well as a variety of insects
In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check the lower segment of a solid rocket booster (SRB) to be mated to the one above. The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
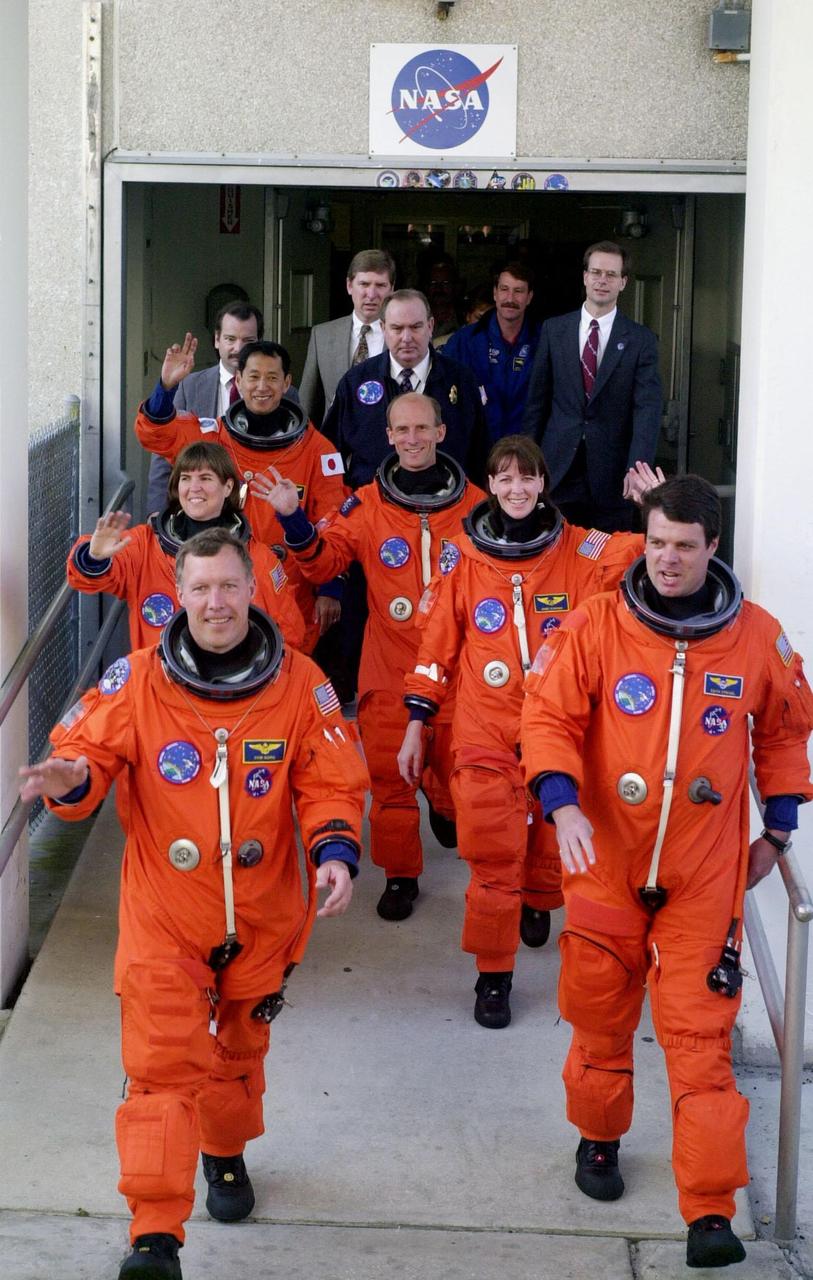

The STS-99 crew wave to onlookers as they step eagerly from the Operations and Checkout Building enroute to Launch Pad 39A for liftoff of Space Shuttle Endeavour. In their orange launch and entry suits, they are (foreground) Pilot Dominic Gorie and Commander Kevin Kregel. Behind them (left to right) are Mission Specialists Janice Voss, Mamoru Mohri of Japan, Gerhard Thiele of Germany and Janet Lynn Kavandi. Mohri is with the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan, and Thiele is with the European Space Agency. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), STS-99 is scheduled for liftoff at 12:30 p.m. EST. The SRTM will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. The mission is expected to last 11days, with Endeavour landing at KSC Tuesday, Feb. 22, at 4:36 p.m. EST. This is the 97th Shuttle flight and 14th for Shuttle Endeavour
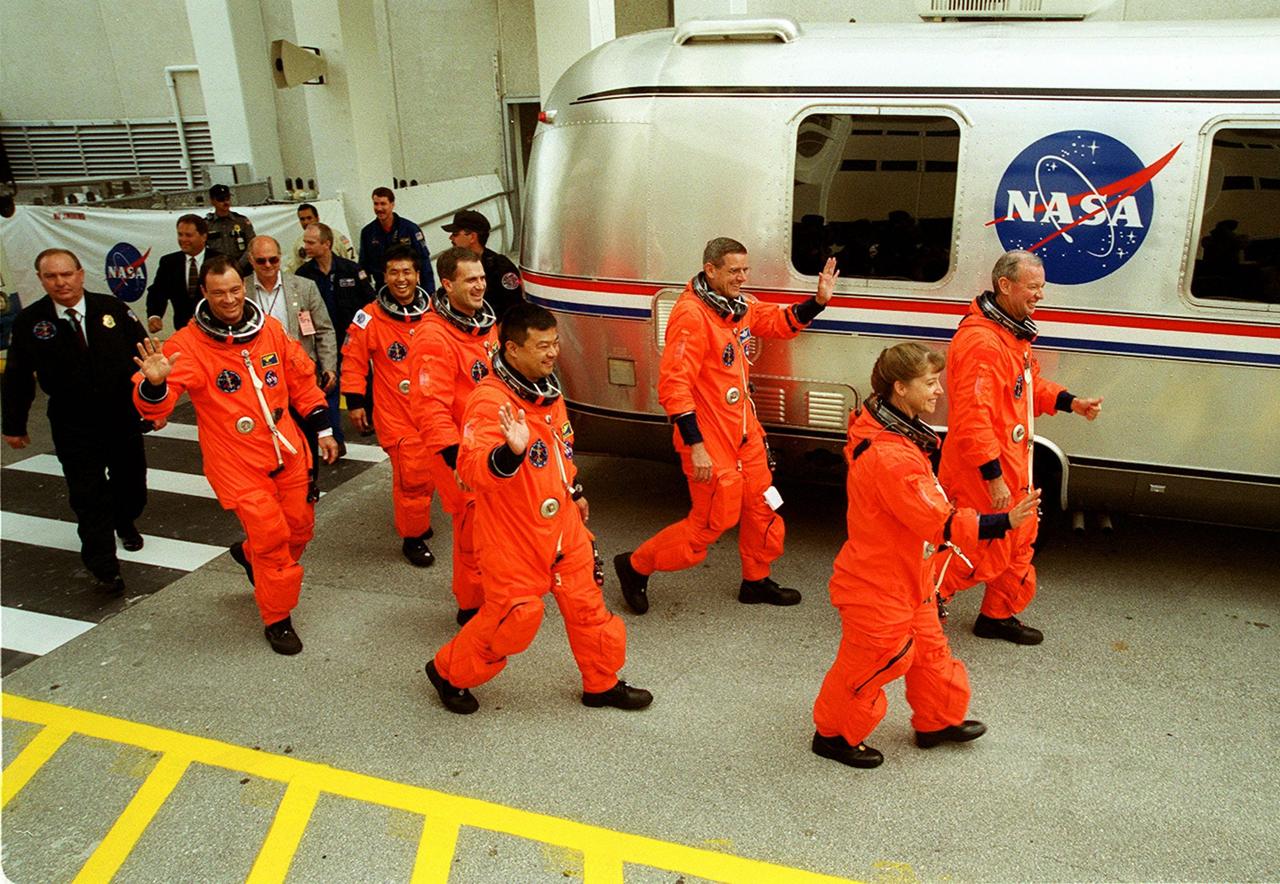

Striding happily to the waiting Astrovan for the trip to Launch Pad 39A are (left to right) STS-92 Mission Specialists Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, Koichi Wakata of Japan, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Leroy Chiao and William S. McArthur; Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy; and Commander Brian Duffy. STS-92 is scheduled for liftoff to the International Space Station (ISS) at 8:05 p.m. EDT. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the ISS. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or spacewalks, are planned. The Z-1 truss is the first of 10 that will become the backbone of the International Space Station, eventually stretching the length of a football field. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Landing is expected Oct. 21 at 3:55 p.m. EDT
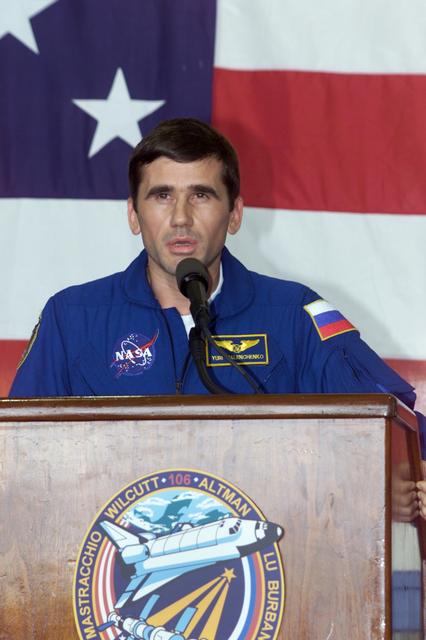

JSC2000-E-23459 (21 September 2000) --- Cosmonaut Yuri I. Malenchenko, STS-106 mission specialist representing the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, addresses the crowd that visited Ellington Field's Hangar 990 to welcome home the STS-106 astronauts and cosmonauts. The seven-man crew landed approximately 24 hours earlier in Florida, wrapping up a 4.9 million-mile mission in which more than three tons of equipment were delivered to the international outpost.
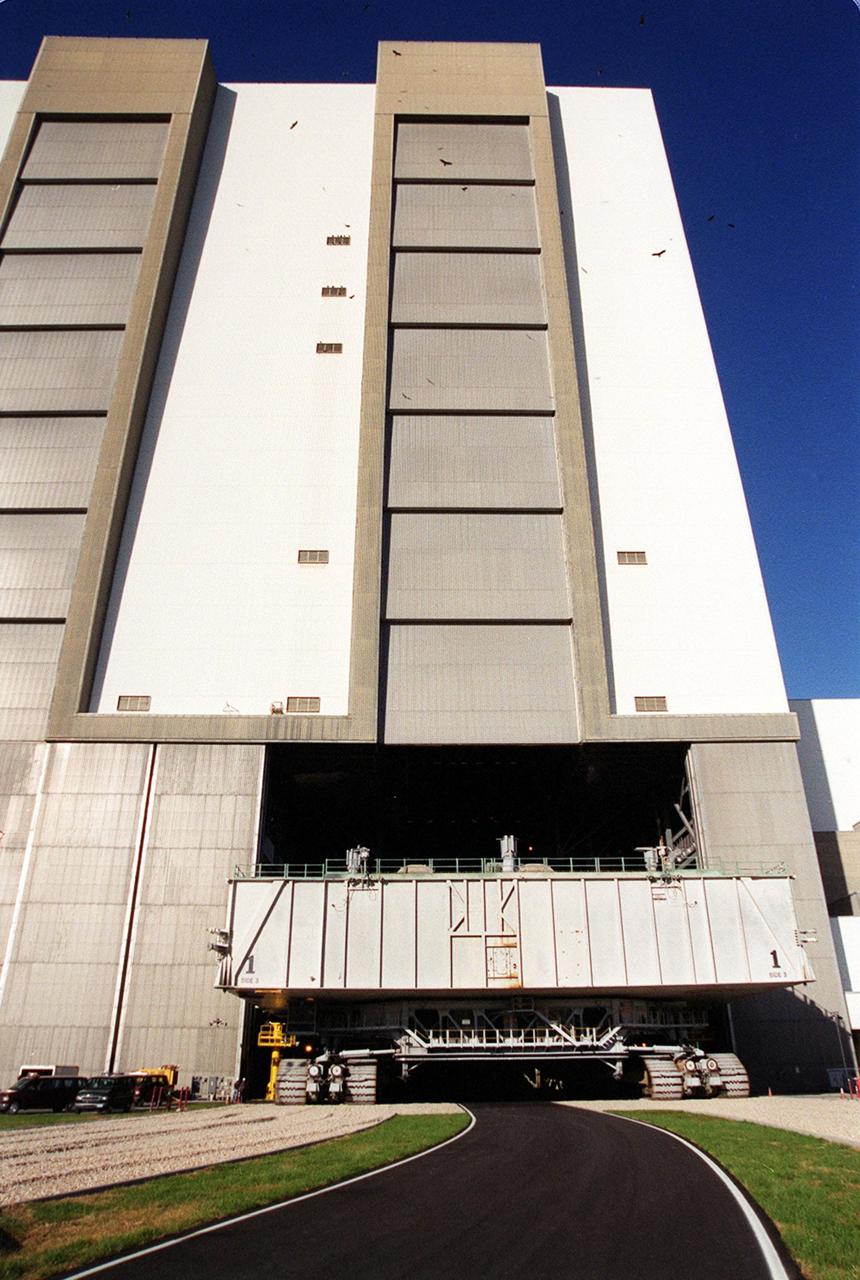

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A mobile launcher platform atop a crawler-transporter, heads through the open door of the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 2. As part of the Safe Haven project, a once-buried portion of the crawlerway was restored to enable rollout of a Shuttle from this third stacking area. The primary goal of the Safe Haven construction project was to strengthen readiness for hurricane season by expanding the VAB’s storage capacity. The new area, in high bay 2, will allow NASA to preassemble stacks and still have room in the VAB to pull a Shuttle back from the pad if severe weather threatens. Potential rollouts of the Space Shuttle to the launch pad from high bay 2 will involve making a turn around the north side of the VAB in contrast to the straight rollouts from high bays 1 and 3, on the east side of the VAB facing the launch pads
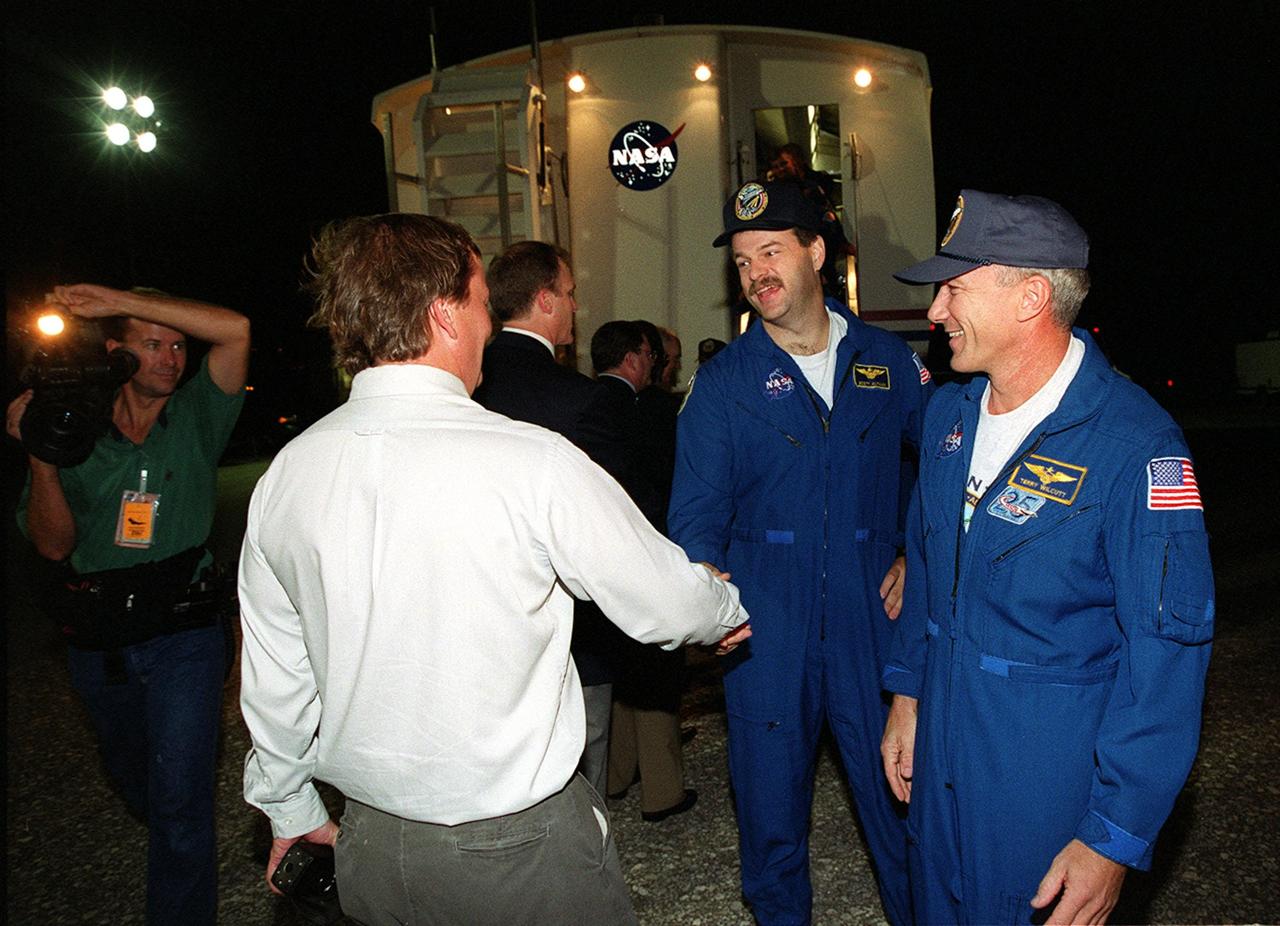

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, KSC Launch Director Michael Leinbach (shaking hands) greets STS-106 Pilot Scott D. Altman and Commander Terrence W. Wilcutt after their successful mission and landing. Just behind Leinbach is Jim Halsell, manager of Space Shuttle Launch Integration and former Shuttle Commander, plus other dignitaries on hand to welcome the crew home. Landing occurred on-time at 3:56:48 a.m. EDT. Atlantis and crew traveled 4.9 million miles on the 11-day, 19-hour, 11-minute STS-106 mission. During the mission to the International Space Station, the crew transferred nearly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies for use by the first resident crew expected to arrive in November. STs-106 was the 99th flight in the Shuttle program and the 22nd for Atlantis. STS-106 also marked the 15th nighttime landing in Shuttle history and the 23rd consecutive landing at KSC
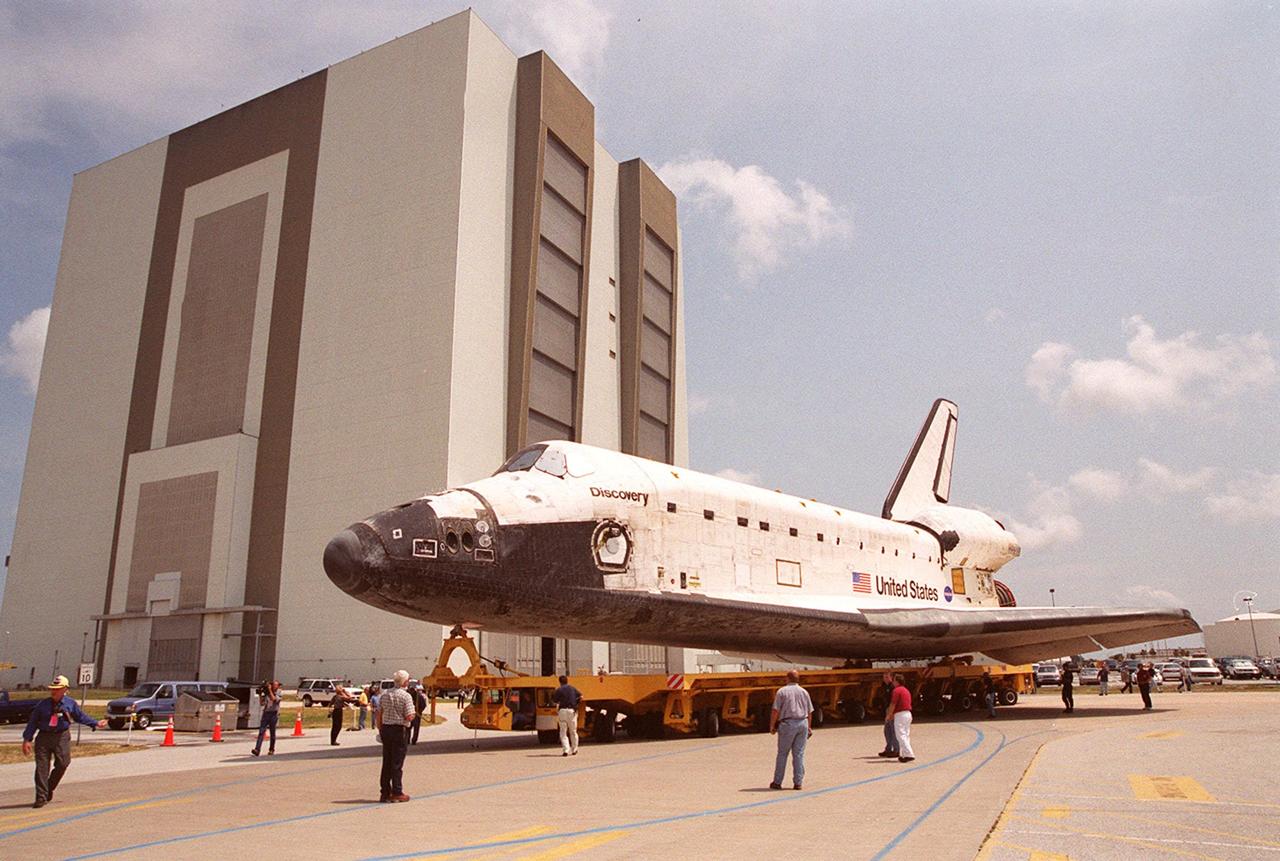

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- KSC workers watch as the orbiter Discovery makes the turn around the Vehicle Assembly Building on its move from Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) bay 1 to OPF bay 3. Ongoing payload and ground processing assessments will be completed in bay 3. Managers will then determine when to roll the orbiter to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking with the external tank and solid rocket boosters, and when to roll out to Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:30 p.m. EDT on mission STS-92, which will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
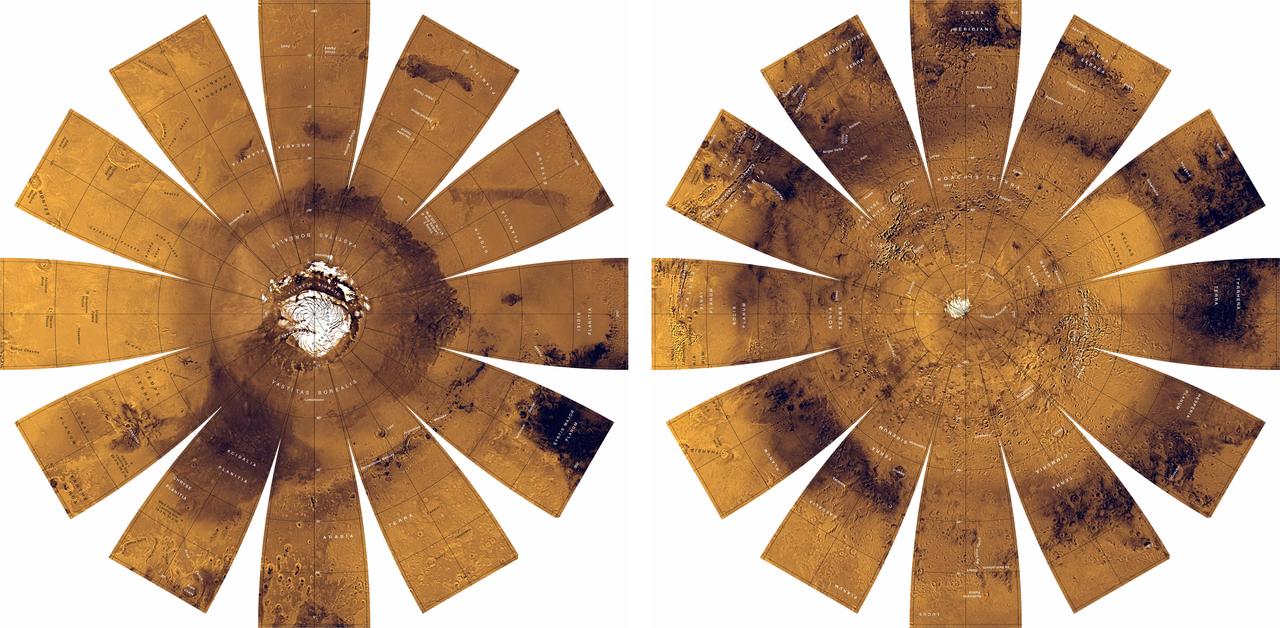

Mars Digital Image Mosaic Globe
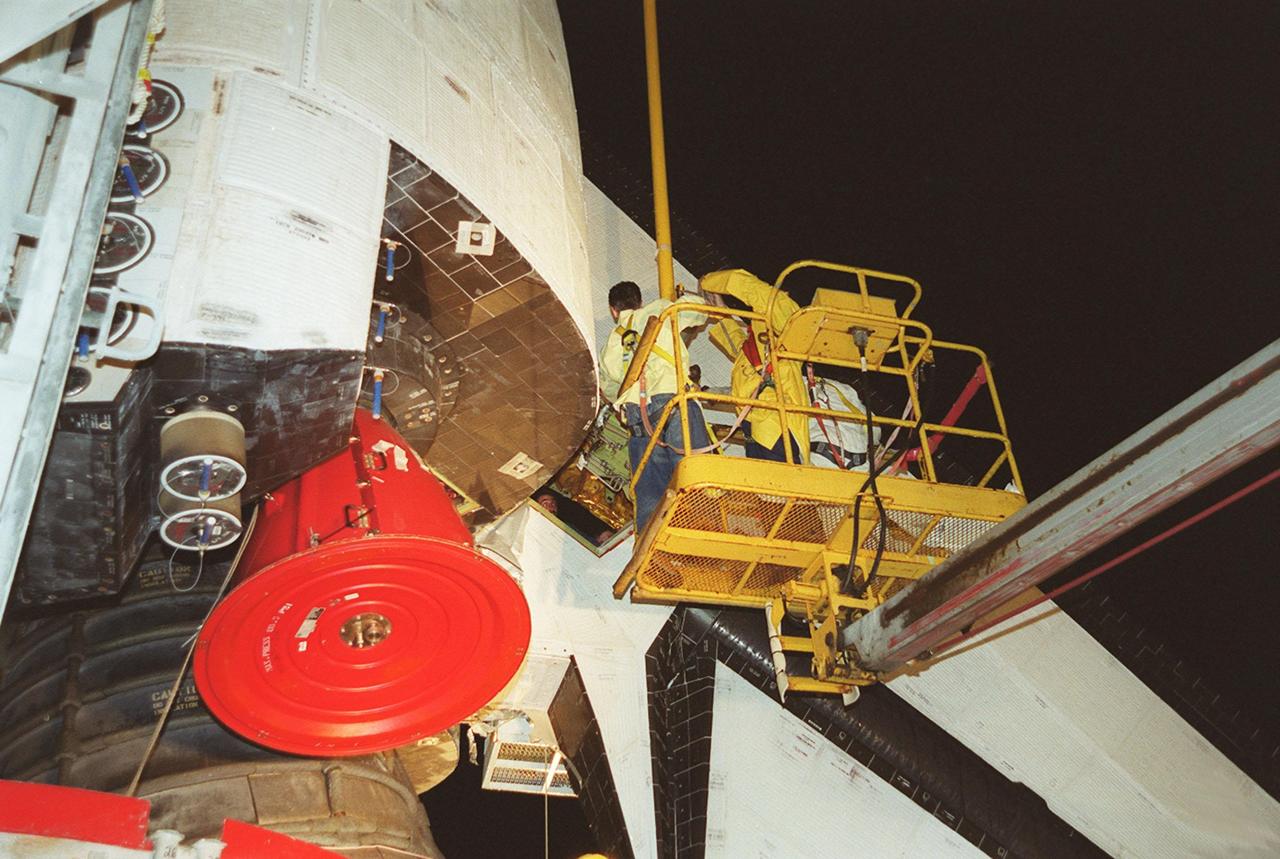

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers help guide the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis into place. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
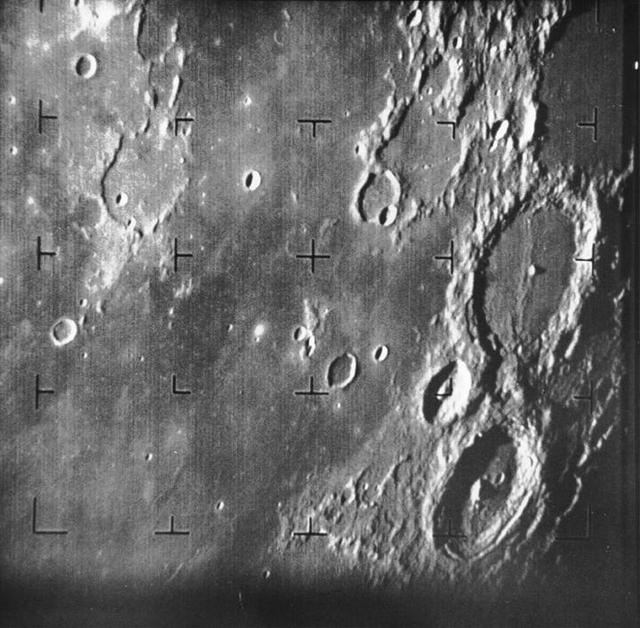

Ranger 7 took this image, the first picture of the Moon by aU.S. spacecraft, on 31 July 1964 at 13:09 UT 9:09 AM EDT about 17 minutes before impacting the lunar surface.
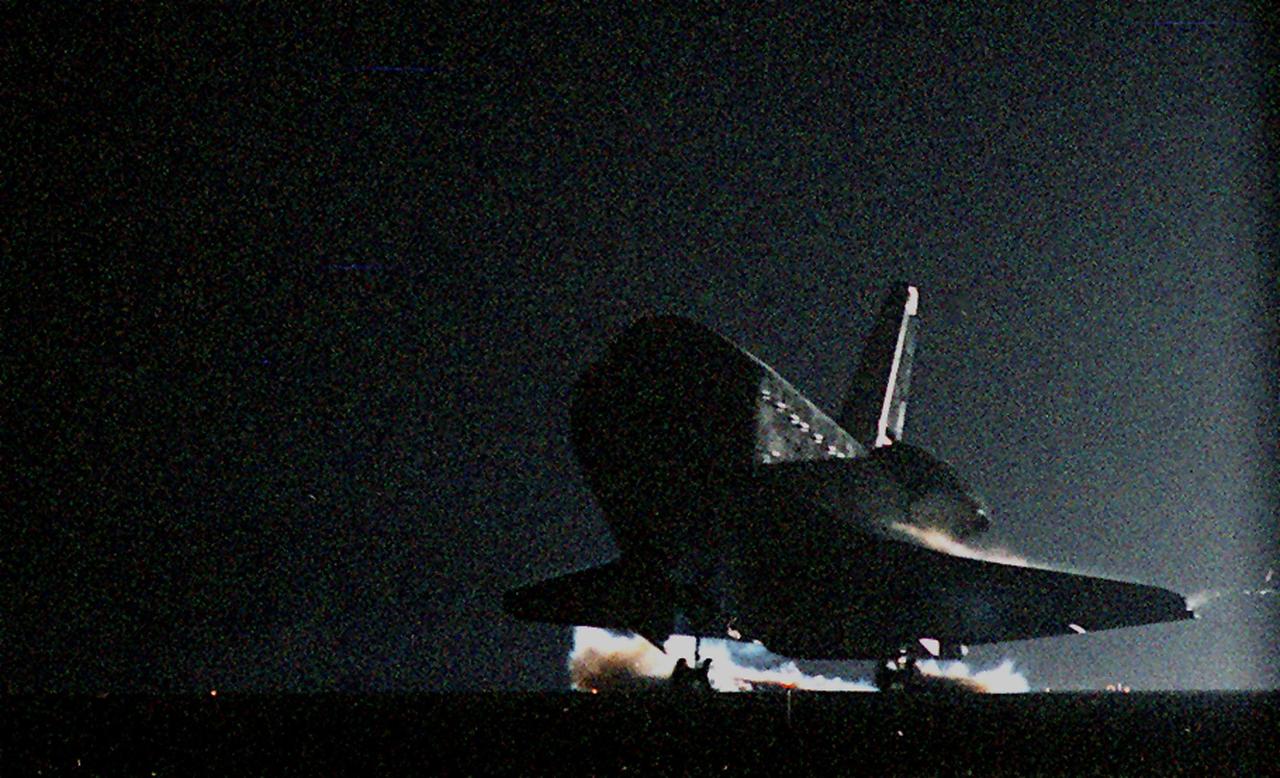

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atlantis’ main gear touchdown on Runway 15 of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility kicks up swirls of dust reflected in the runway lights. Atlantis and crew traveled 4.9 million miles on the 11-day, 19-hour, 11-minute mission STS-106. Main gear touchdown occurred on-time at 3:56:48 a.m. EDT. During the mission to the International Space Station, the crew transferred nearly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies for use by the first resident crew expected to arrive in November. STS-106 was the 99th flight in the Shuttle program and the 22nd for Atlantis. STS-106 also marked the 15th nighttime landing in Shuttle history and the 23rd consecutive landing at KSC
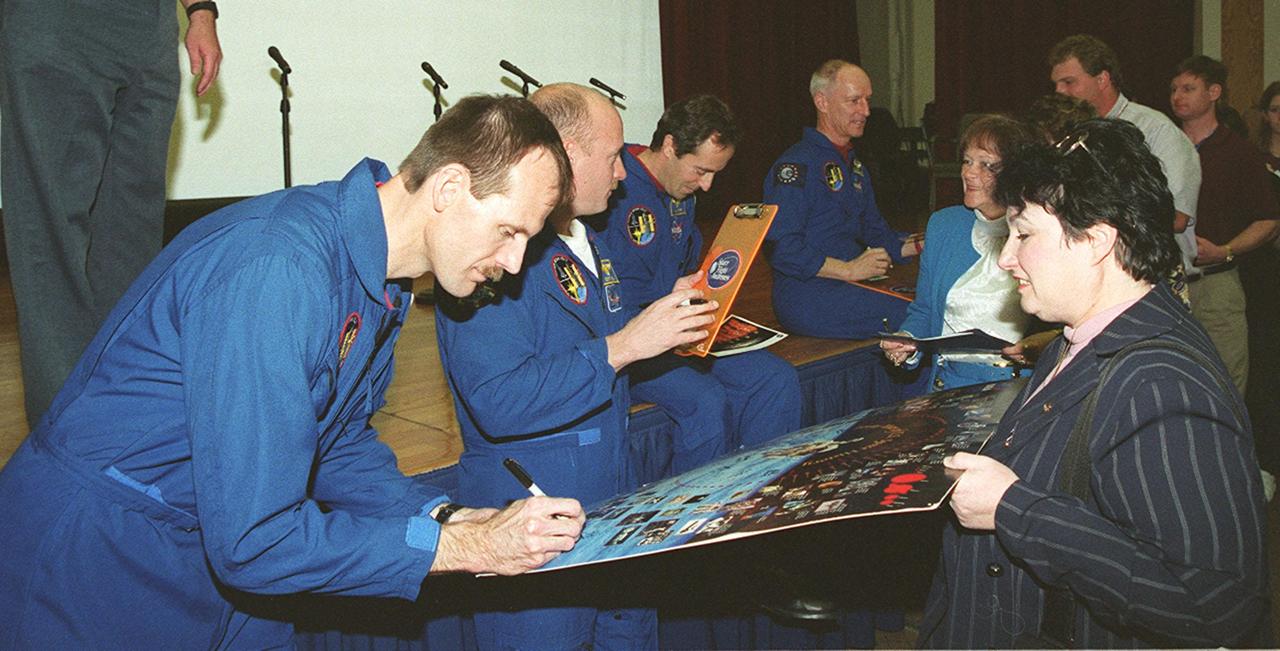

After a presentation at KSC for employees and VIPs about their mission, STS-103 crew members sign autographs. From left are Mission Specialist Steven Smith, Pilot Scott Kelly, and Mission Specialists Jean-Francois Clervoy and Claude Nicollier. The STS-103 mission, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, included three space walks. STS-103 launched Dec. 19, 1999, and landed Dec. 27, 1999
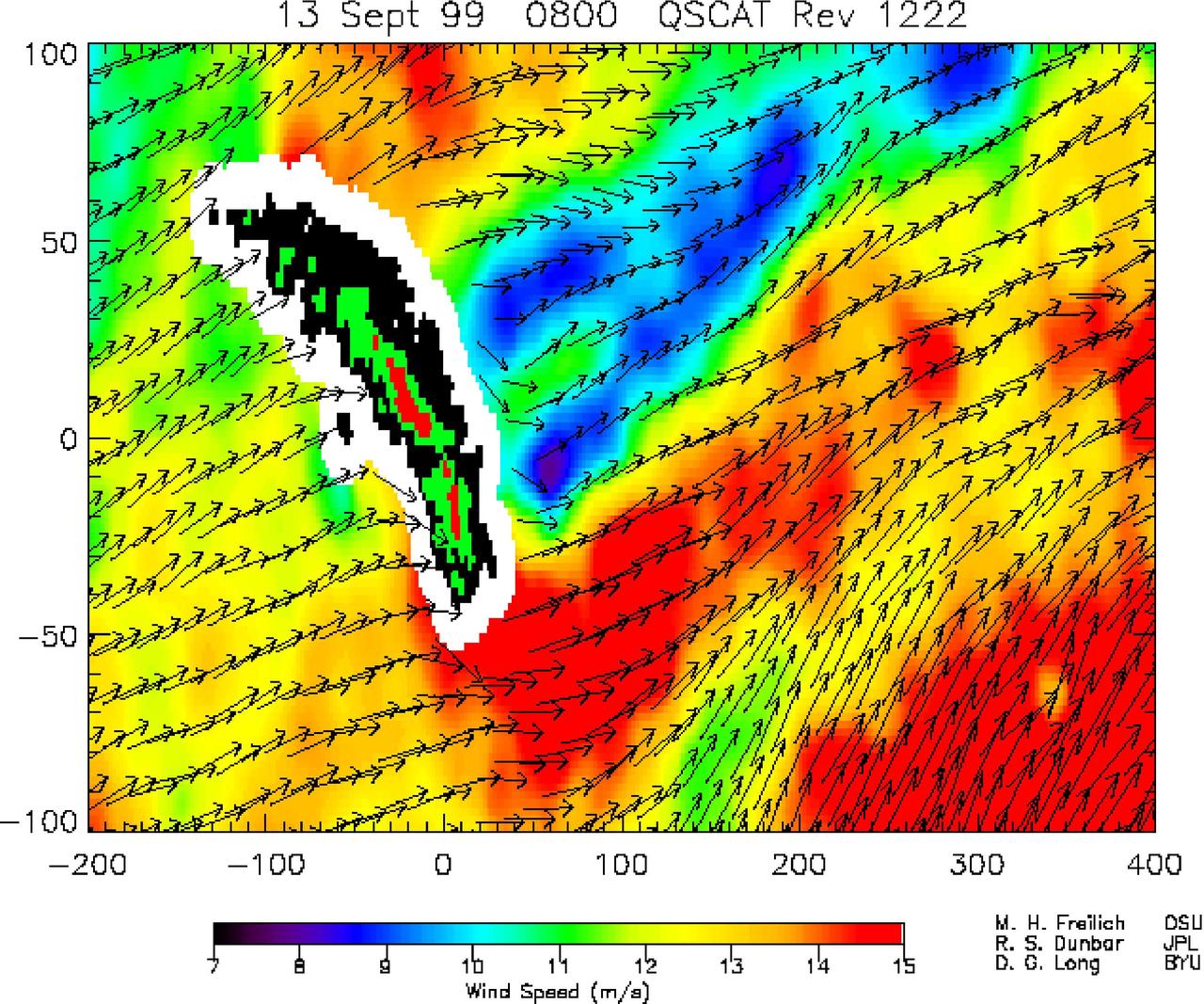
NASA SeaWinds instrument on the QuikScat satellite shows winds are blocked by an island mountain barrier on South Georgia Island, in the South Atlantic Ocean in the year 2000.
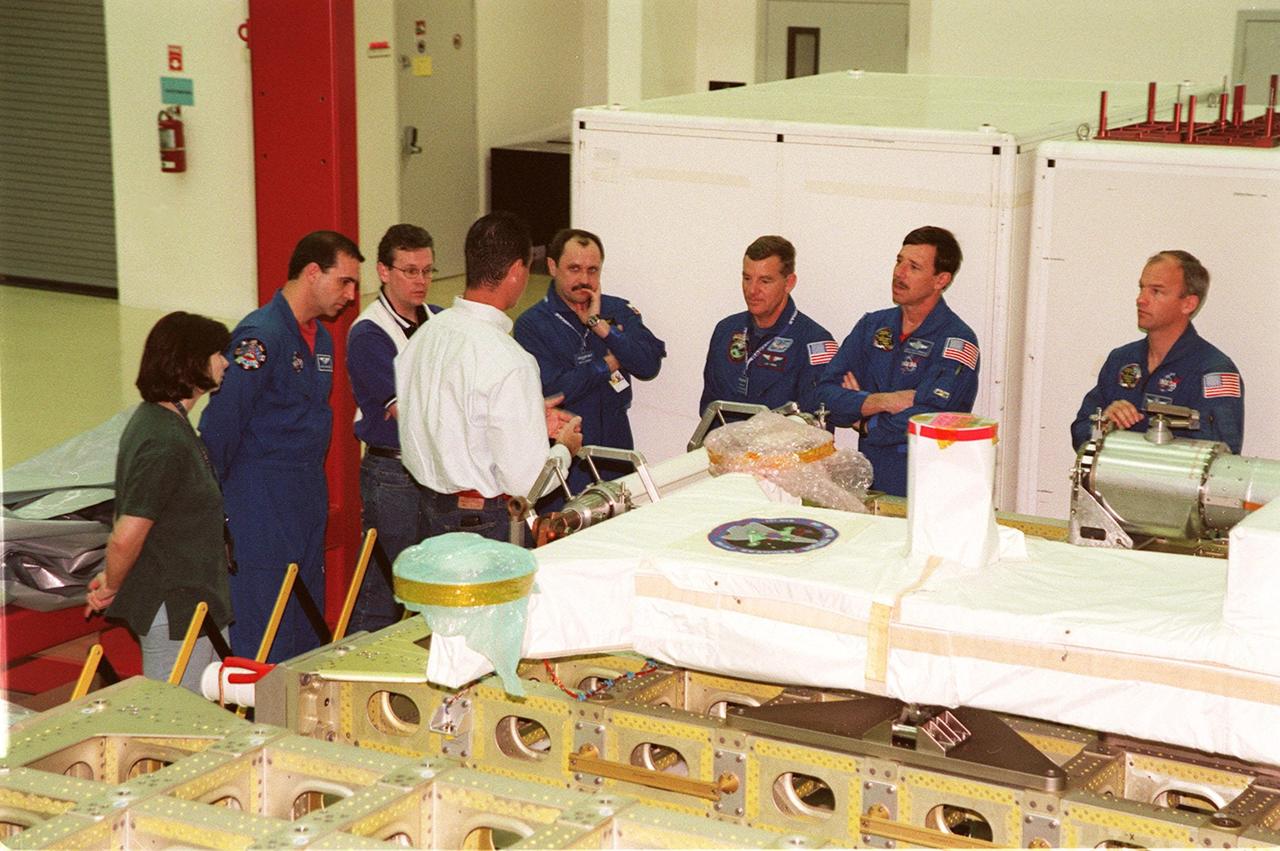

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, in Cape Canaveral, Fla., members of the STS-101 crew and STS-106 crew take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, learning from technicians in the facility about some of the equipment they will be working with on their mission to the International Space Station. From left are Claudia Melchiorre, who is with DASA, Daimler-Chrysler Aerospace; STS-106 Mission Specialist Richard Mastracchio; a SPACEHAB worker; Marty McLellan, director of ground operations; Mission Specialists Yuri Usachev of Russia and James Voss; Pilot Scott Horowitz; and Mission Specialist Jeffrey Williams. Other members of the STS-101 crew (not shown) are Mission Specialists Mary Ellen Weber and Susan Helms. The ST-101 crew will be responsible for preparing the Space Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. Also, the crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station and deliver logistics and supplies. This will be the third assembly flight for the Space Station. STS-101 is scheduled to launch no earlier than April 13 from Launch Pad 39A
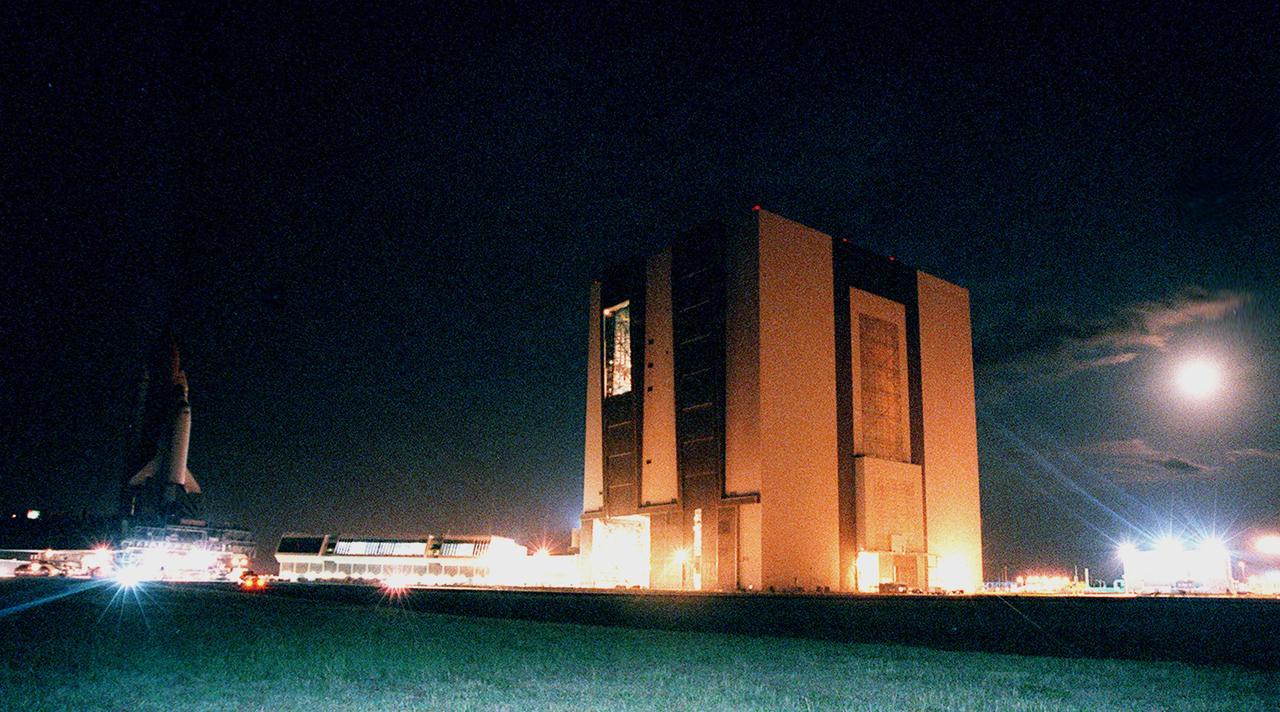

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This 30-second timed exposure captures the bright lights around the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) plus the equally bright moon (upper right) as Space Shuttle Atlantis (far left) rolls out of the east side bay 1. The Launch Control Center sits between the Shuttle and the VAB. The full stack of Shuttle, solid rocket boosters and external tank are taking part in a fit check for the newly renovated crawlerway and high bay 2, which is on the west side. The major modifications to the crawlerway and VAB provide Shuttle flight hardware more storage space and protection - "Safe Haven" - from hurricanes or tropical storms. Atlantis began moving out of VAB high bay 1 at 2:59 a.m. EDT. After the successful Safe Haven fit check, Shuttle Atlantis is scheduled to roll out to Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the STS-106 launch on Sept. 8.
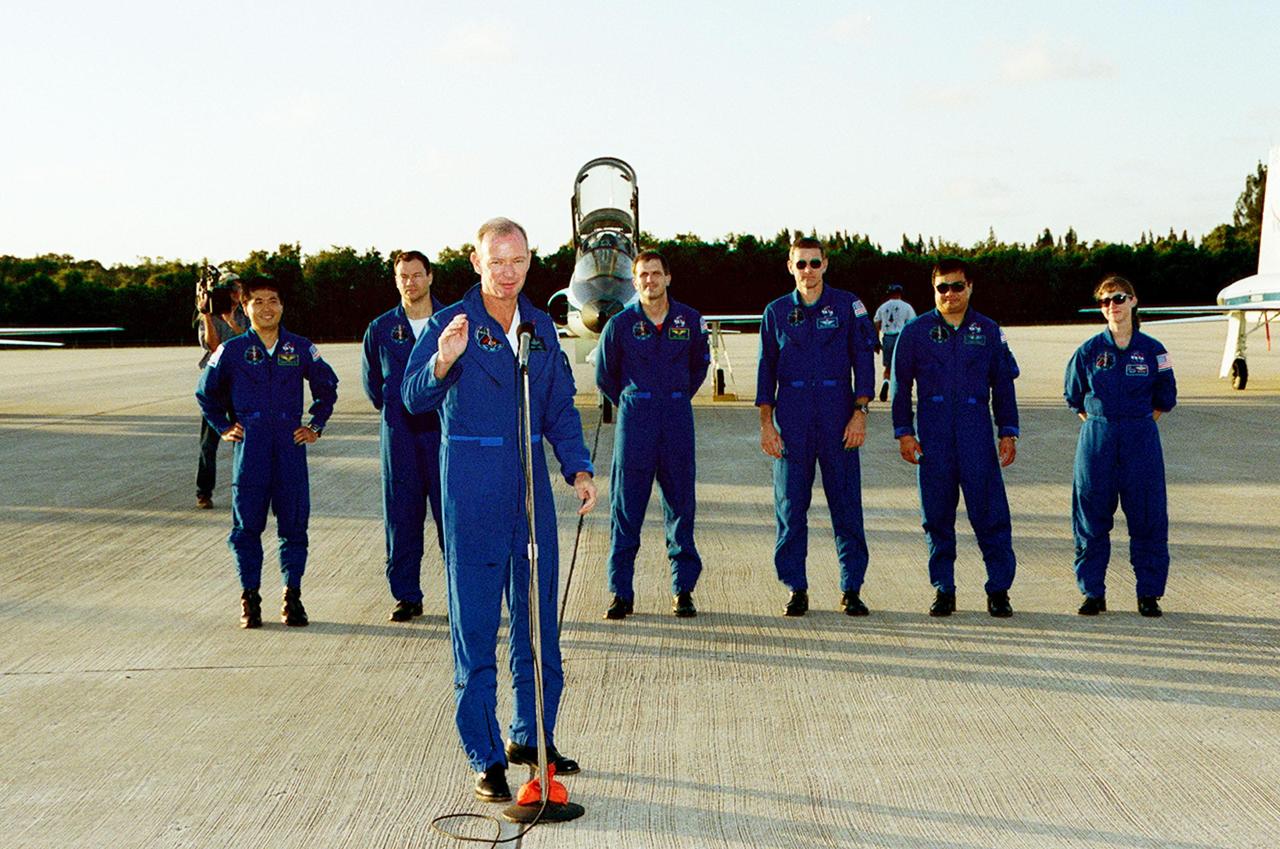

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy, at the microphone, waves to the media after introducing the crew. Standing behind him are Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Michael Lopez-Alegria, Jeff Wisoff, Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao; and Pilot Pam Melroy. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT includes emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, plus a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
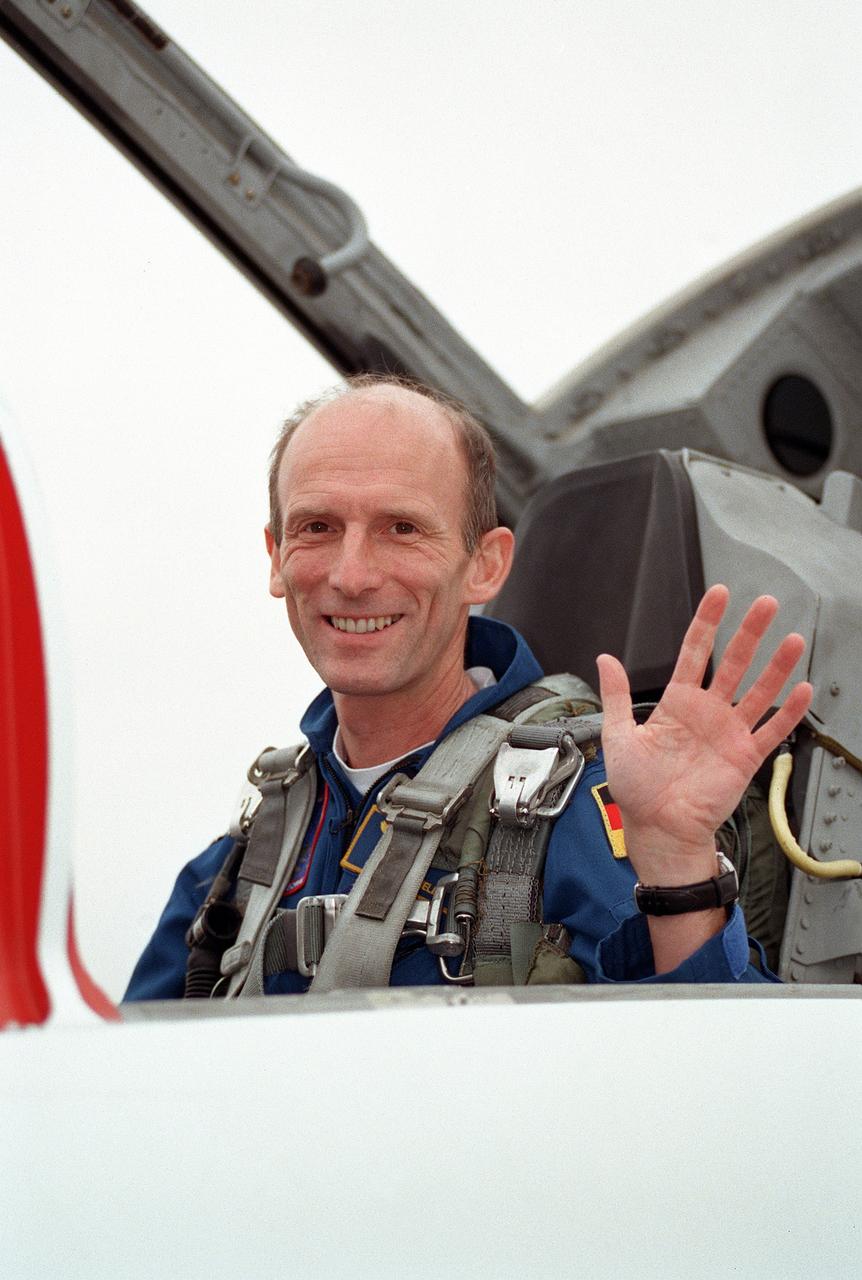

JSC2000-00921 (27 January 2000) --- Astronaut Gerhard P.J. Thiele, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), waves at colleagues from a T-38 jet trainer prior to departure from Ellington Field en route to Florida. Thiele, along with four American astronauts and one representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA), are scheduled for launch aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in a little less than a week.
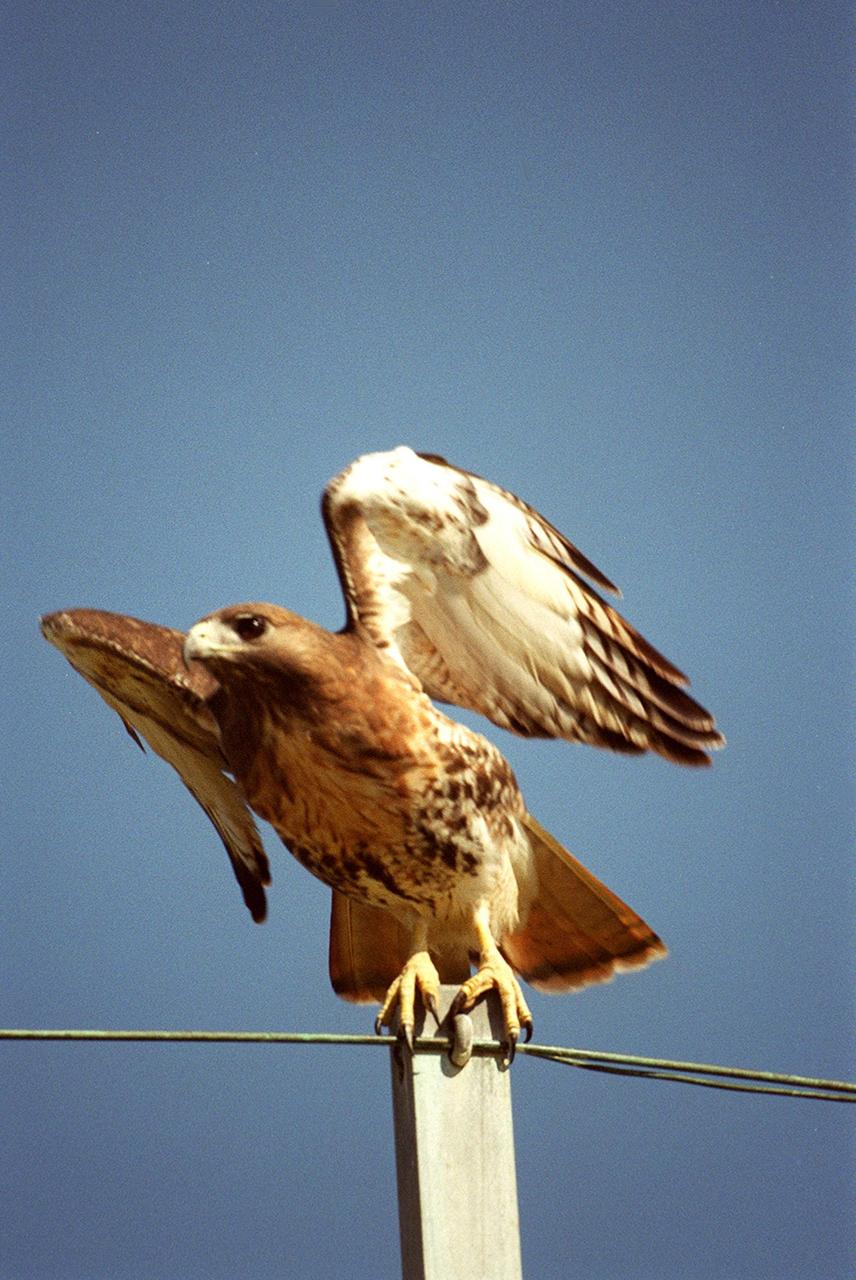

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- From the top of a utility pole, a red-tailed hawk launches into flight, perhaps after spotting prey, typically a small rodent. Ranging in height from 18 inches to 25 inches, the species has a stocky build with a whitish breast and rust-colored tail. It has a high-pitched descending scream with a hoarse quality. The hawk inhabits mainly deciduous forest and adjacent open country from Alaska and Nova Scotia south to Panama. KSC shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which encompasses 92,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. The marshes and open water of the refuge provide wintering areas for 23 species of migratory waterfowl, as well as a year-round home for great blue herons, great egrets, wood storks, cormorants, brown pelicans and other species of marsh and shore birds, as well as a variety of insects
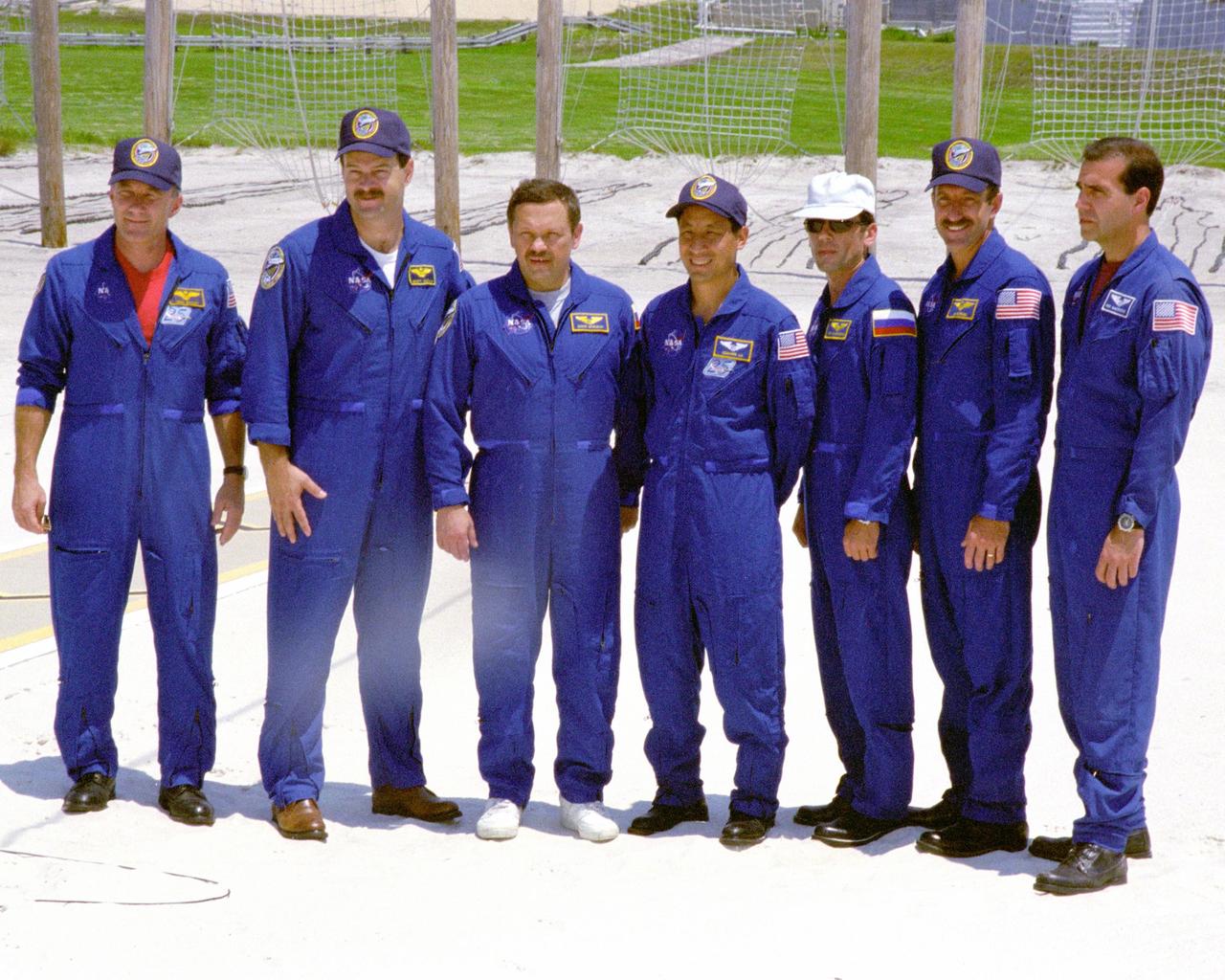

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-106 flight crew participate in a question and answer session for the media at the slide wire basket area of Launch Pad 39-B. Crew members pictured are, from left, Commander Terrence W. Wilcutt, Pilot Scott D. Altman, Mission Specialists Boris V. Morukov, Edward T. Lu, Yuri I. Malenchenko, Daniel C. Burbank and Richard A. Mastracchio. Malenchenko and Morukov are with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The flight crew were at Kennedy Space Center to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT provides the crew with emergency egress training and opportunities to inspect their mission payload in the orbiter’s payload bay. STS-106 is scheduled to launch Sept. 8, 2000, at 8:31 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B. On the 11-day mission, the seven-member crew will perform support tasks on orbit, transfer supplies and prepare the living quarters in the newly arrived Zvezda Service Module. The first long-duration crew, dubbed “Expedition One,” is due to arrive at the Station in late fall.
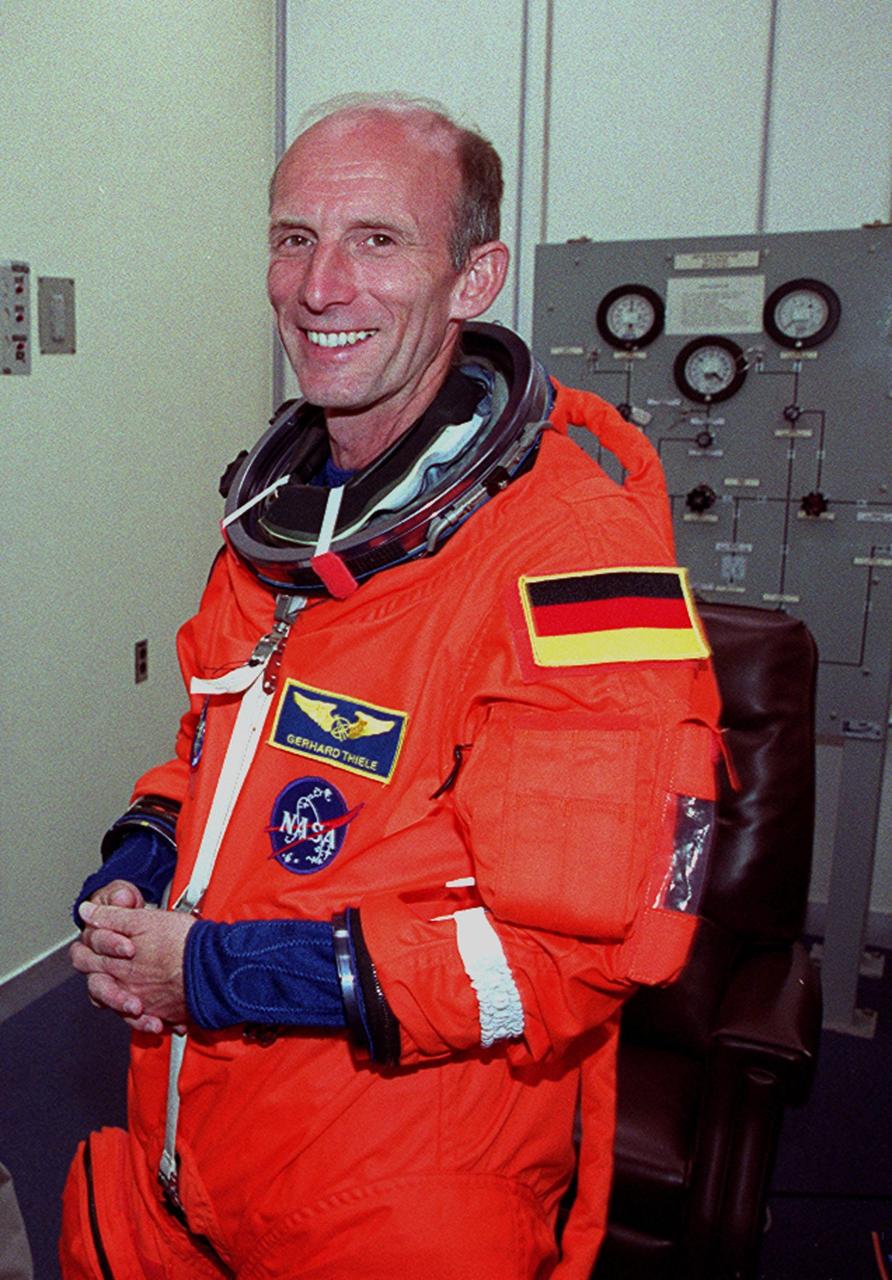

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-99 Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele, who is with the European Space Agency, smiles as he dons his launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. Liftoff of STS-99, known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), is scheduled for 12:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39A. The SRTM will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. The mission is expected to last about 11days. Endeavour is expected to land at KSC Friday, Feb. 11, at 4:55 p.m. EST
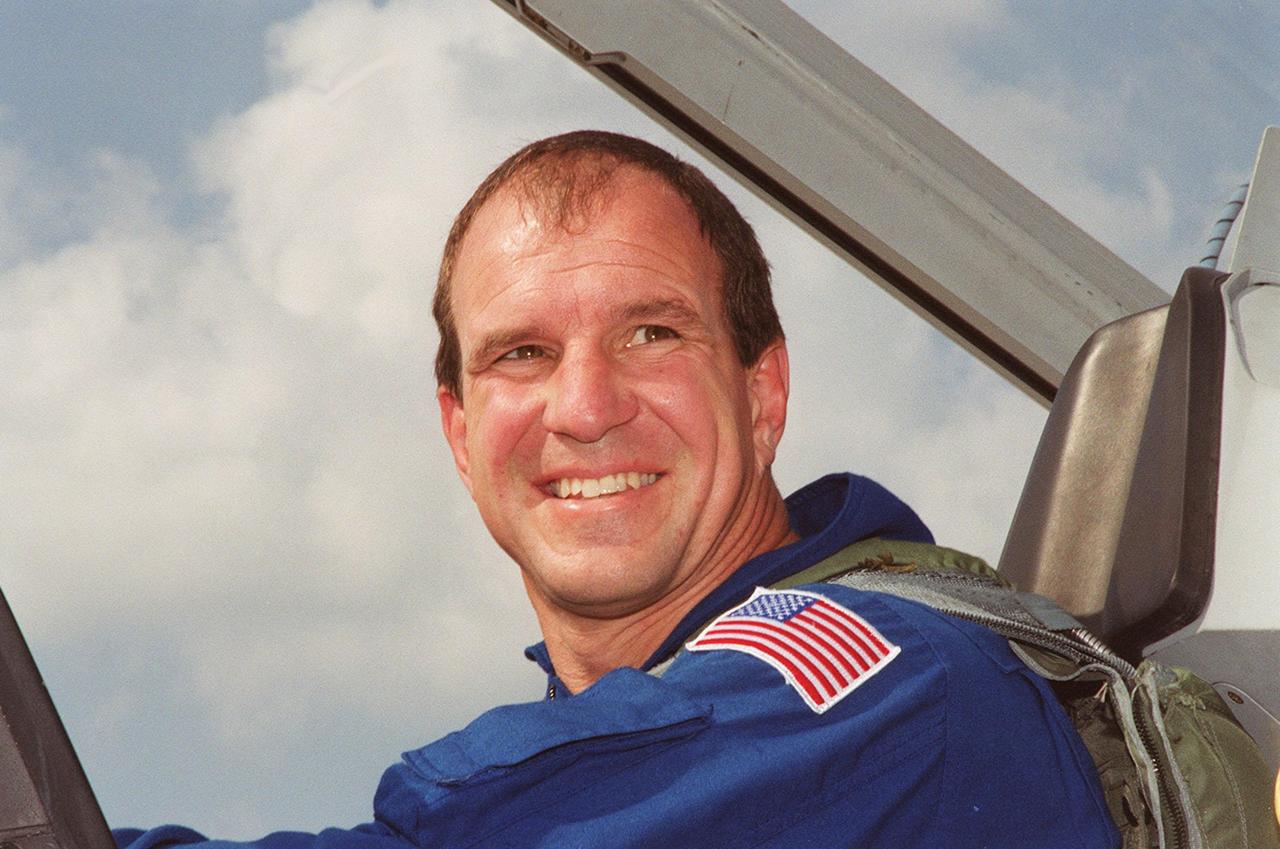

STS-97 Pilot Mike Bloomfield arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He and the rest of the crew are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency egress training, familiarization with the payload, and a simulated launch countdown. The other crew members are Commander Brent Jett, and Mission Specialists Joe Tanner, Carlos Noriega and Marc Garneau, who is with the Canadian Space Agency. Mission STS-97is the sixth construction flight to the International Space Station. Its payload includes the P6 Integrated Truss Structure and a photovoltaic (PV) module, with giant solar arrays that will provide power to the Station. The mission includes two spacewalks to complete the solar array connections. STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at 10:05 p.m. EST
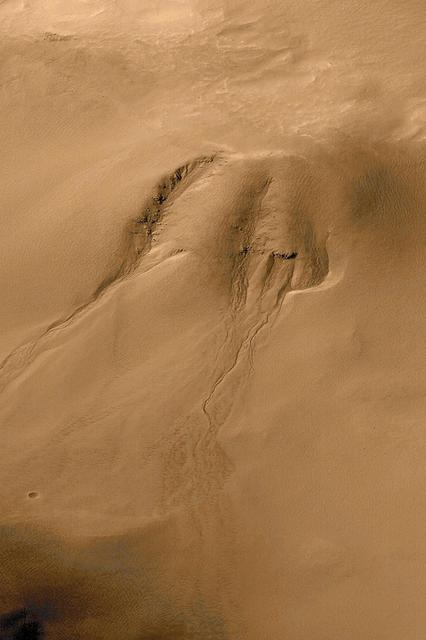

Evidence for Recent Liquid Water on Mars: Gullies in Crater Wall, Noachis Terra
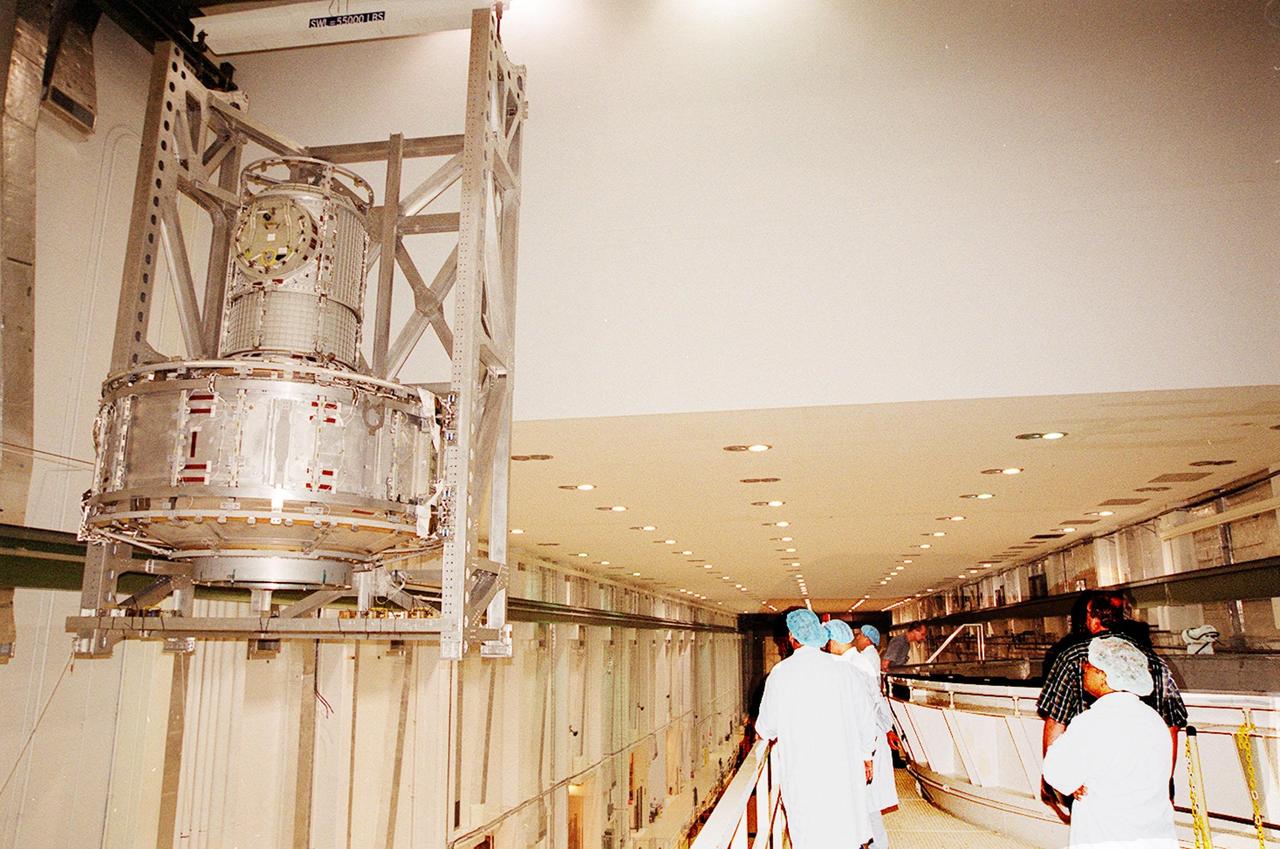

The Joint Airlock Module swings into position near the top of the Operations and Checkout Building to move toward the vacuum chamber at right. Workers alongside the chamber watch the airlock’s progress. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
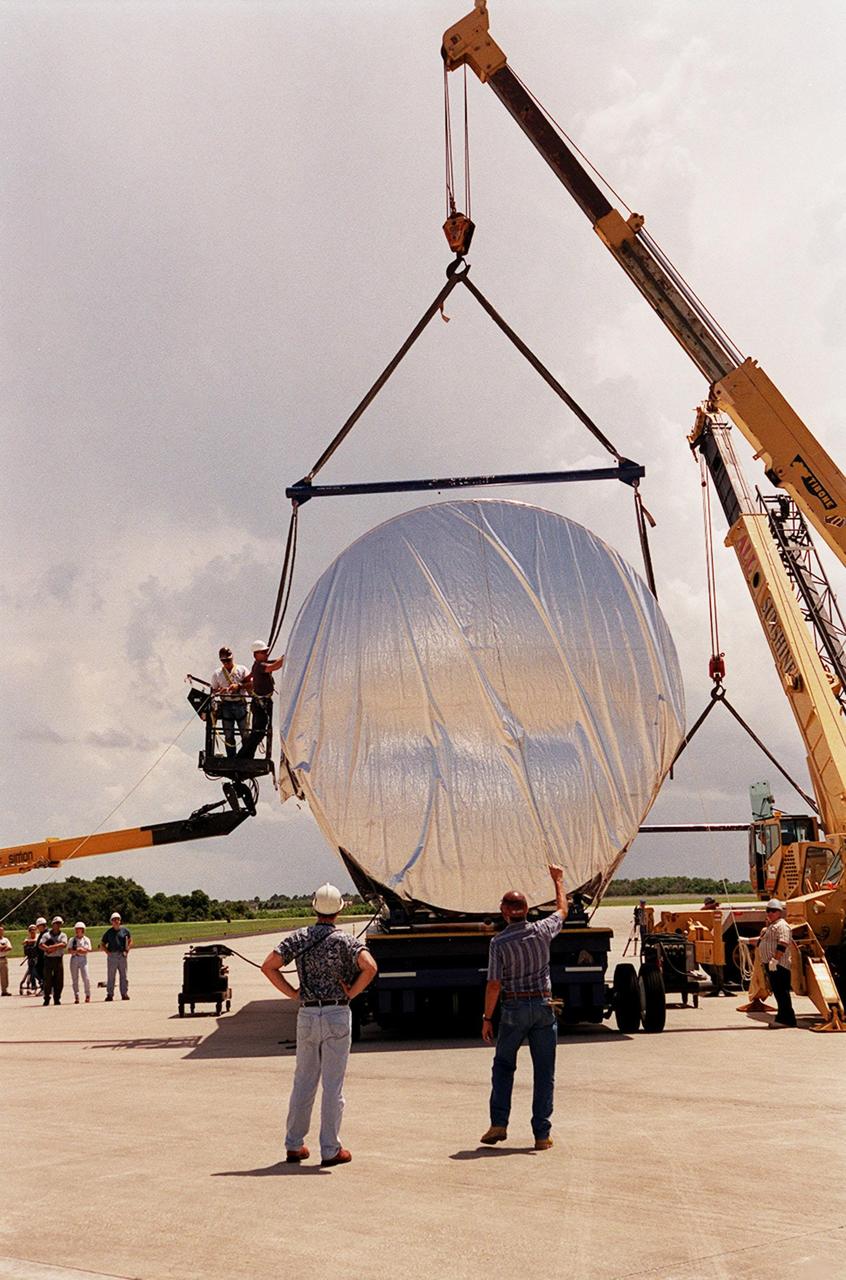

Workers oversee the placement of the P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, onto a flatbed truck that will move it to the Operations and Checkout Building for processing. The P-1 truss, scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
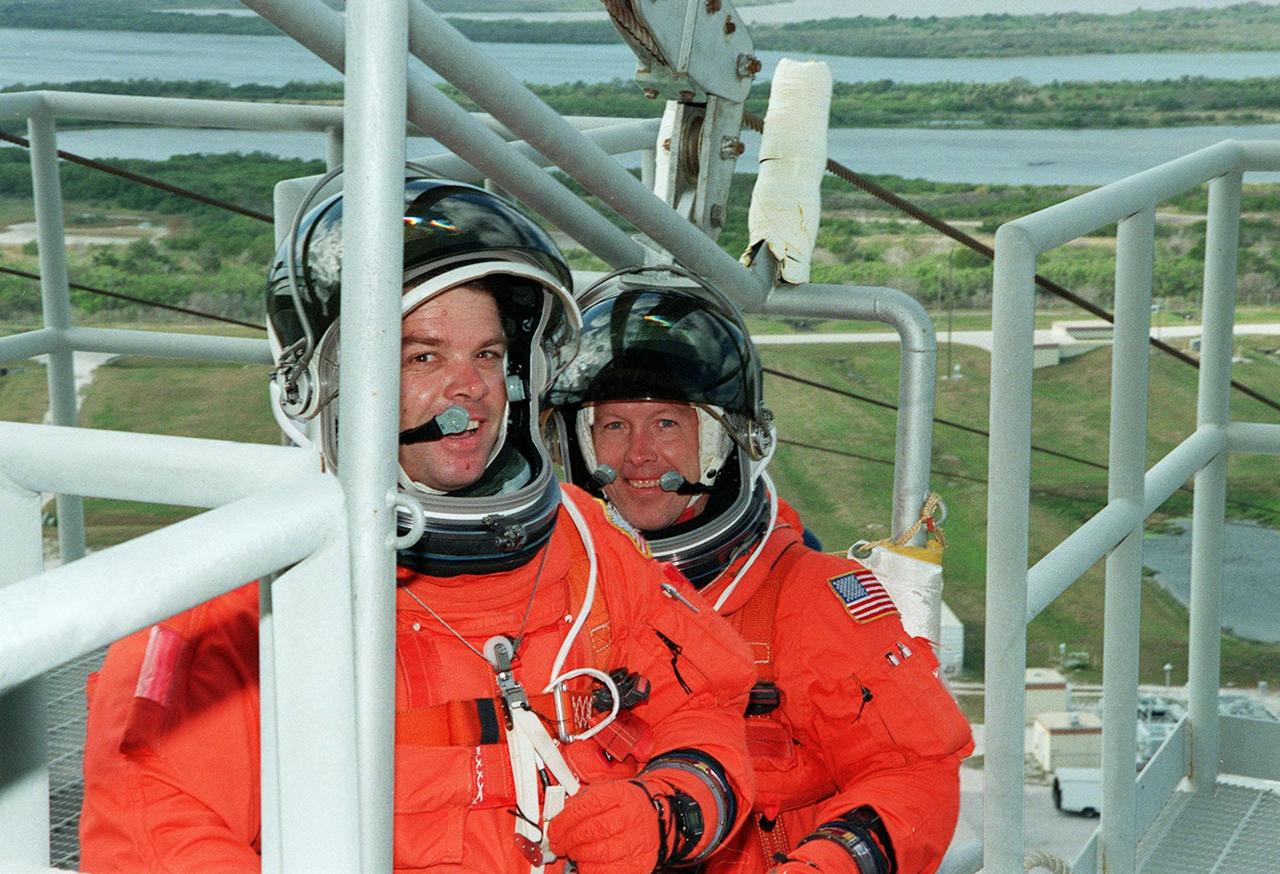

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Pad 39A, STS-99 Mission Specialists Gerhard Thiele (Ph.D.), of the European Space Agency (in front), and Janet Kavandi (Ph.D.) prepare to practice emergency egress procedures with a slidewire basket. Seven slidewires, with flatbottom baskets suspended from each wire, extend from the Fixed Service Structure at the orbiter access arm level. These baskets could provide an escape route for the astronauts until the final 30 seconds of the countdown in case of an emergency. The crew is taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that provide the crew with simulated countdown exercises, emergency egress training, and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-99 is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, which will chart a new course, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. Launch of Endeavour on the 11-day mission is scheduled for Jan. 31 at 12:47 p.m. EST.
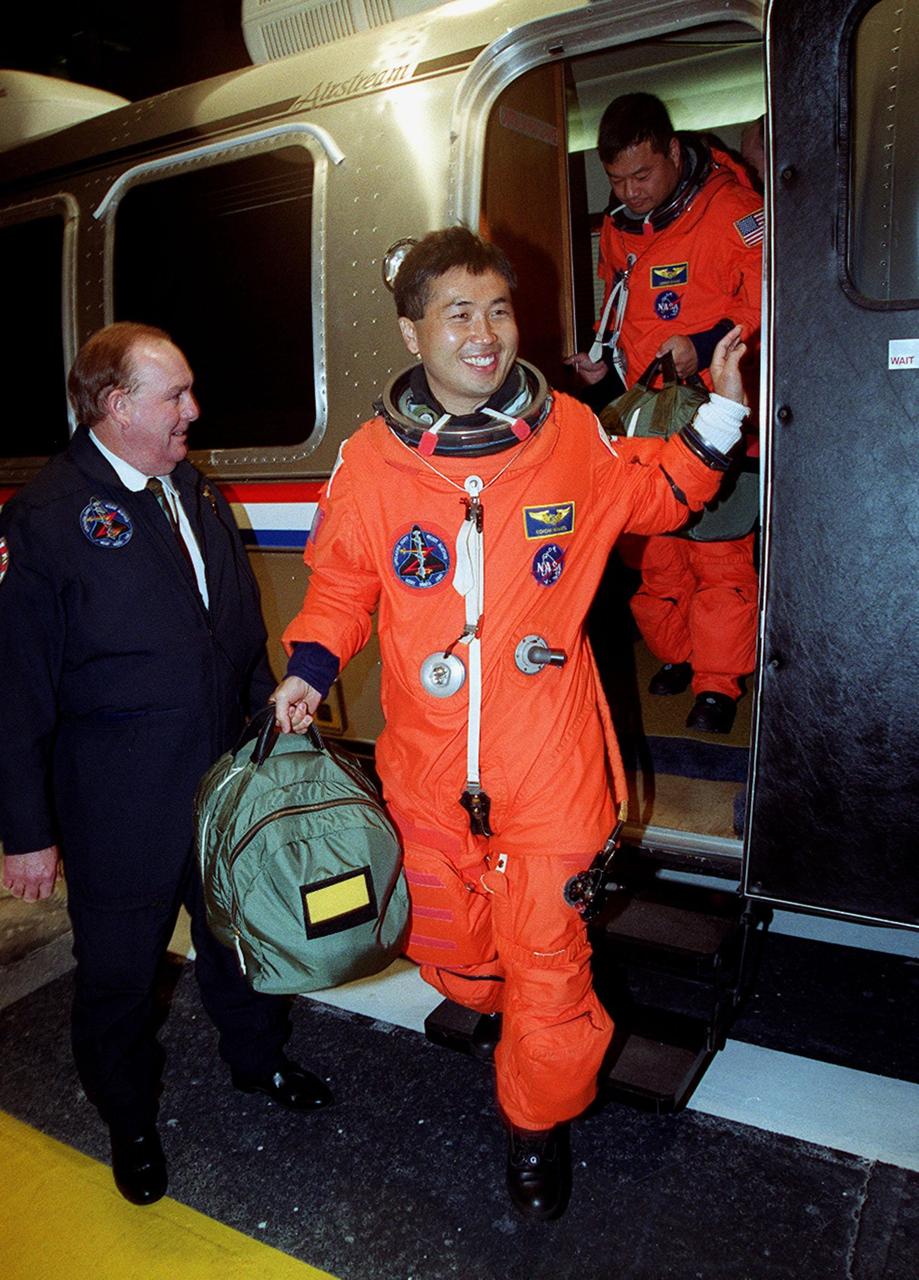

STS-92 Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata of Japan exits the Astrovan on its return to the Operations and Checkout Building. Behind him is Mission Specialist Leroy Chiao. The scheduled launch to the International Space Station (ISS) was scrubbed about 90 minutes before liftoff. The mission will be the fifth flight for the construction of the ISS. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or spacewalks, are planned. The Z-1 truss is the first of 10 that will become the backbone of the International Space Station, eventually stretching the length of a football field. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The launch has been rescheduled for liftoff Oct. 11 at 7:17 p.m
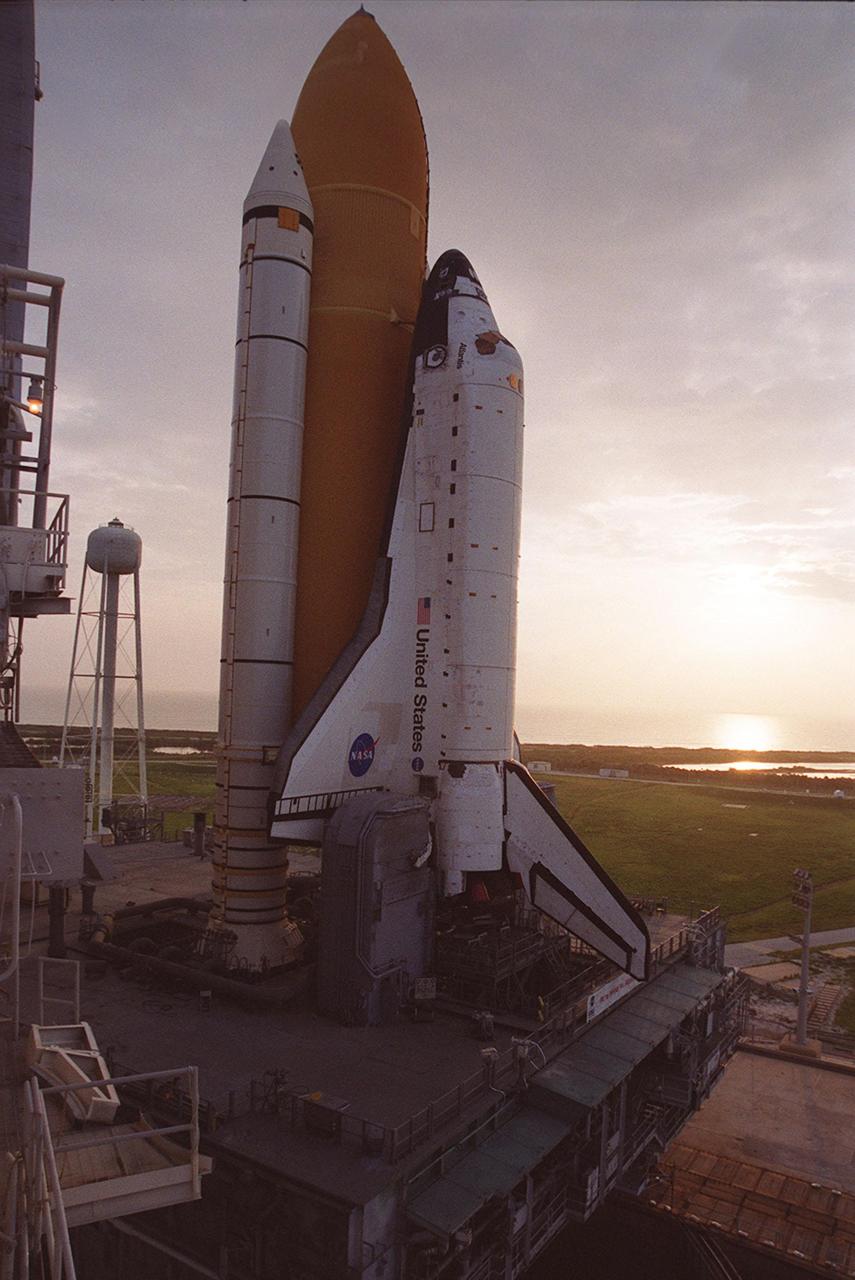

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The sun lights the early morning sky, revealing Space Shuttle Atlantis, atop the Mobile Launcher Platform and Crawler-Transporter, at Launch Pad 39B. It started its 8-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 2 (Safe Haven) at 11:20 p.m., Aug. 13, arriving shortly after 7 a.m. Aug. 14. At its immediate left is the 290-foot high water tank that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system at the pad. At the edge of the photo can be seen part of the Rotating Service Structure. Atlantis is scheduled for launch Sept. 8 at 8:31 a.m. EDT on mission STS-106.
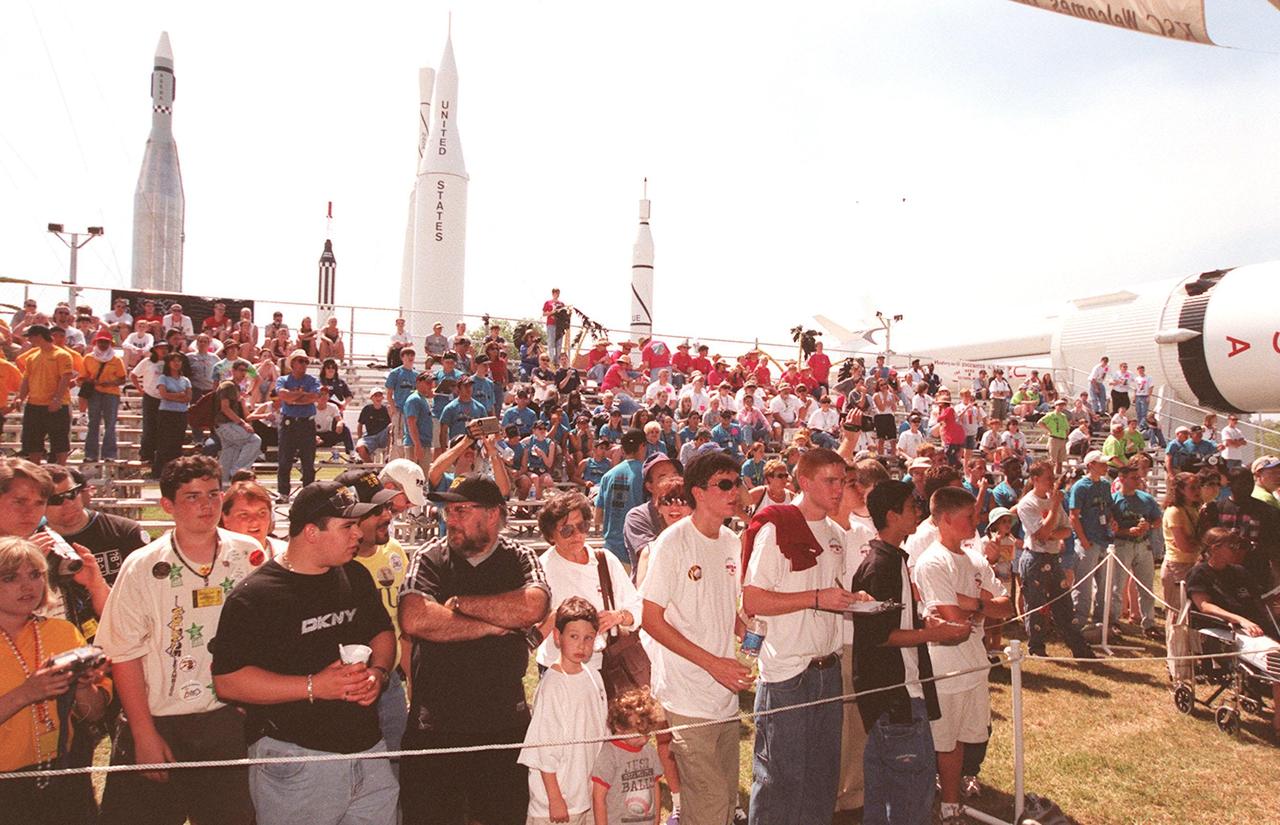

Visitors to Kennedy Space Center, team members and their families fill the stands during practice sessions of the FIRST (For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Southeast Regional competition March 9-11 at the KSC Visitor Complex. Teams of high school students are testing the limits of their imagination using robots they have designed, with the support of business and engineering professionals and corporate sponsors, to compete in a technological battle against other schools' robots. Of the 30 high school teams competing at KSC, 16 are Florida teams co-sponsored by NASA and KSC contractors. Local high schools participating are Astronaut, Bayside, Cocoa Beach, Eau Gallie, Melbourne, Melbourne Central Catholic, Palm Bay, Rockledge, Satellite, and Titusville
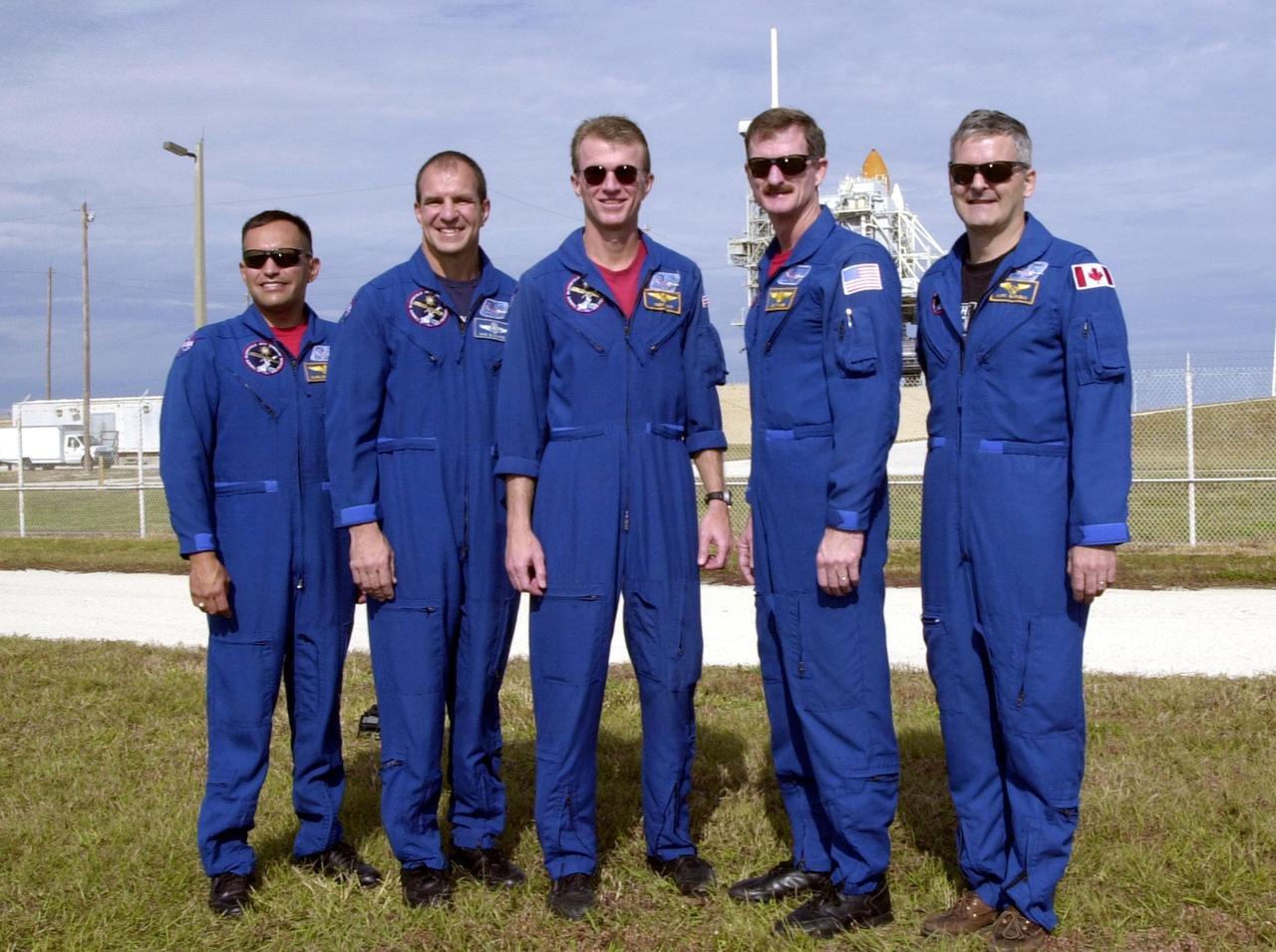

Gathered at Launch Pad 39B, the STS-97 crew pause for a photo. Standing left to right are Mission Specialist Carlos Noriega, Pilot Michael Bloomfield, Commander Brent Jett and Mission Specialists Joseph Tanner and Marc Garneau, who is with the Canadian Space Agency. The mission to the International Space Station carries the P6 Integrated Truss Segment containing solar arrays and batteries that will be temporarily installed to the Unity connecting module by the Z1 truss, recently delivered to and installed on the Station on mission STS-92. The two solar arrays are each more than 100 feet long. They will capture energy from the sun and convert it to power for the Station. Two spacewalks will be required to install the solar array connections. STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at about 10:06 p.m. EST
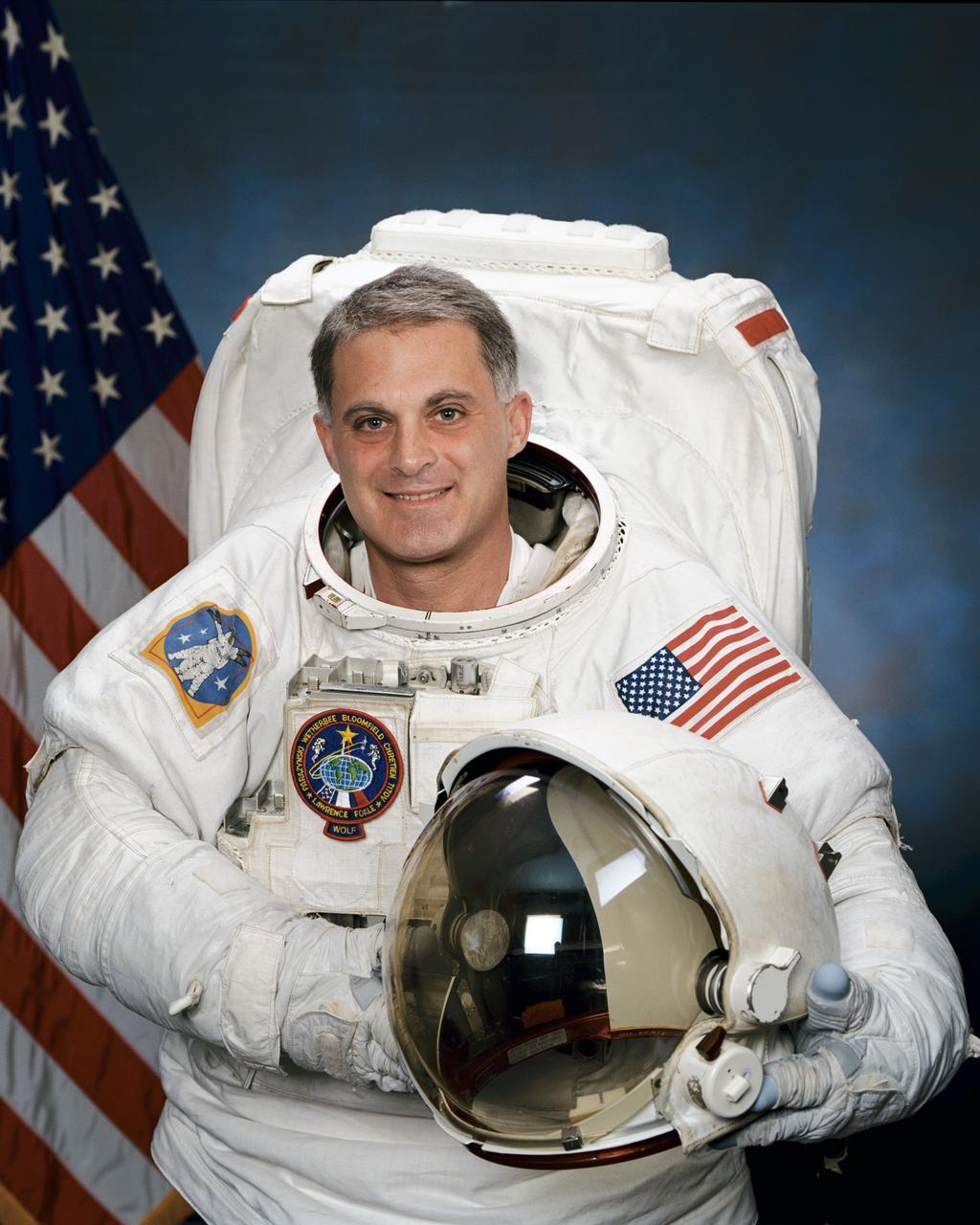

JSC2000-03056 (12 April 2000) --- Astronaut David A. Wolf, mission specialist.
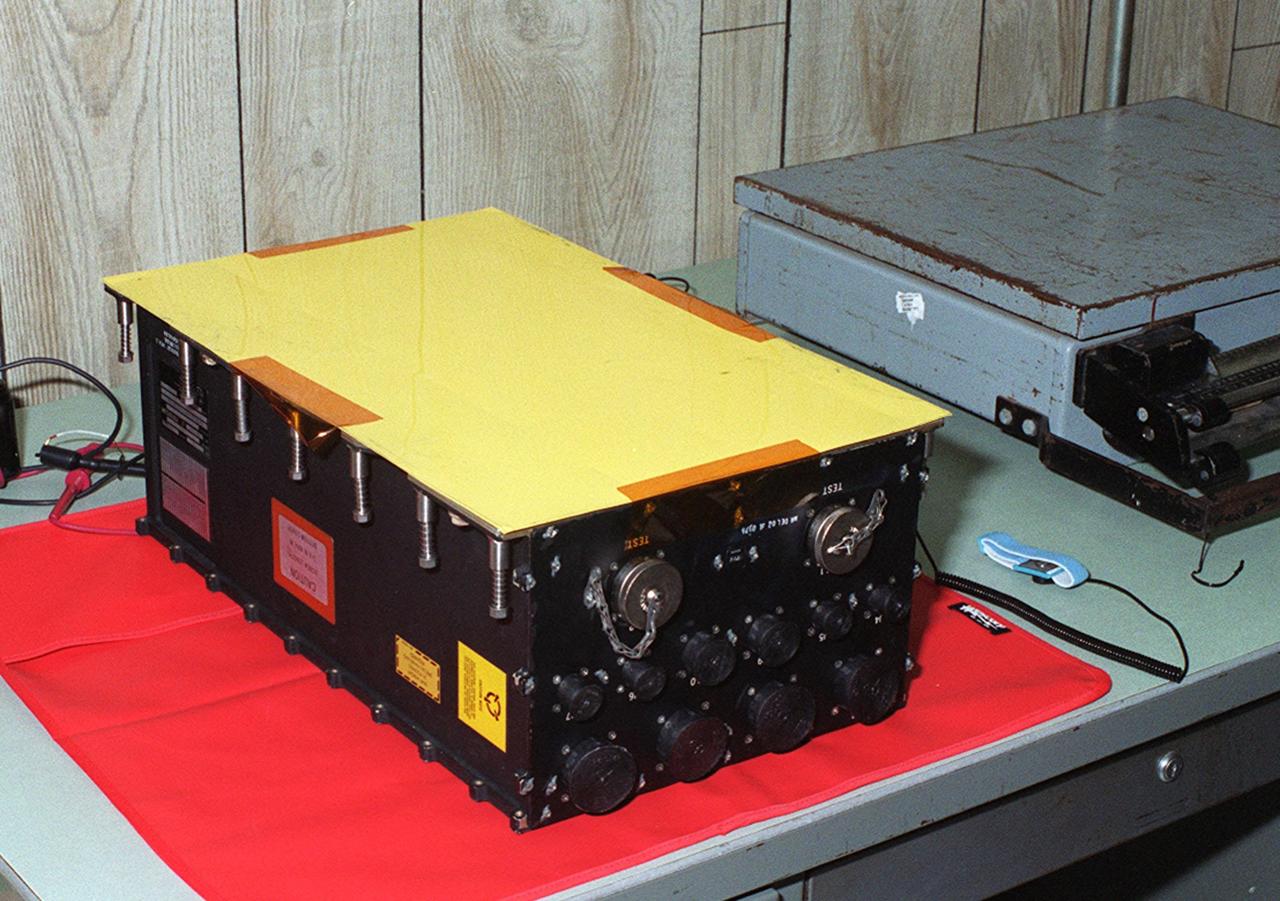

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A new Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) for Shuttle Endeavour sits on a table in a Quality trailer in the Launch Pad 39B area. The original E-MEC in Endeavour became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. The E-MECs are located in the orbiter's aft compartment and both are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. Before workers can begin E-MEC replacement efforts at the launch pad, cryogenic reactants must be offloaded from the orbiter and Space Shuttle ordnance disconnected. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST