
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module (MPLM) for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, arrives at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The canister will be lifted to the payload changeout room. The payload ground-handling mechanism then will be used to transfer Raffaello out of the canister into Atlantis' payload bay. Next, the rotating service structure that protects the shuttle from the elements and provides access will be rotated back into place. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
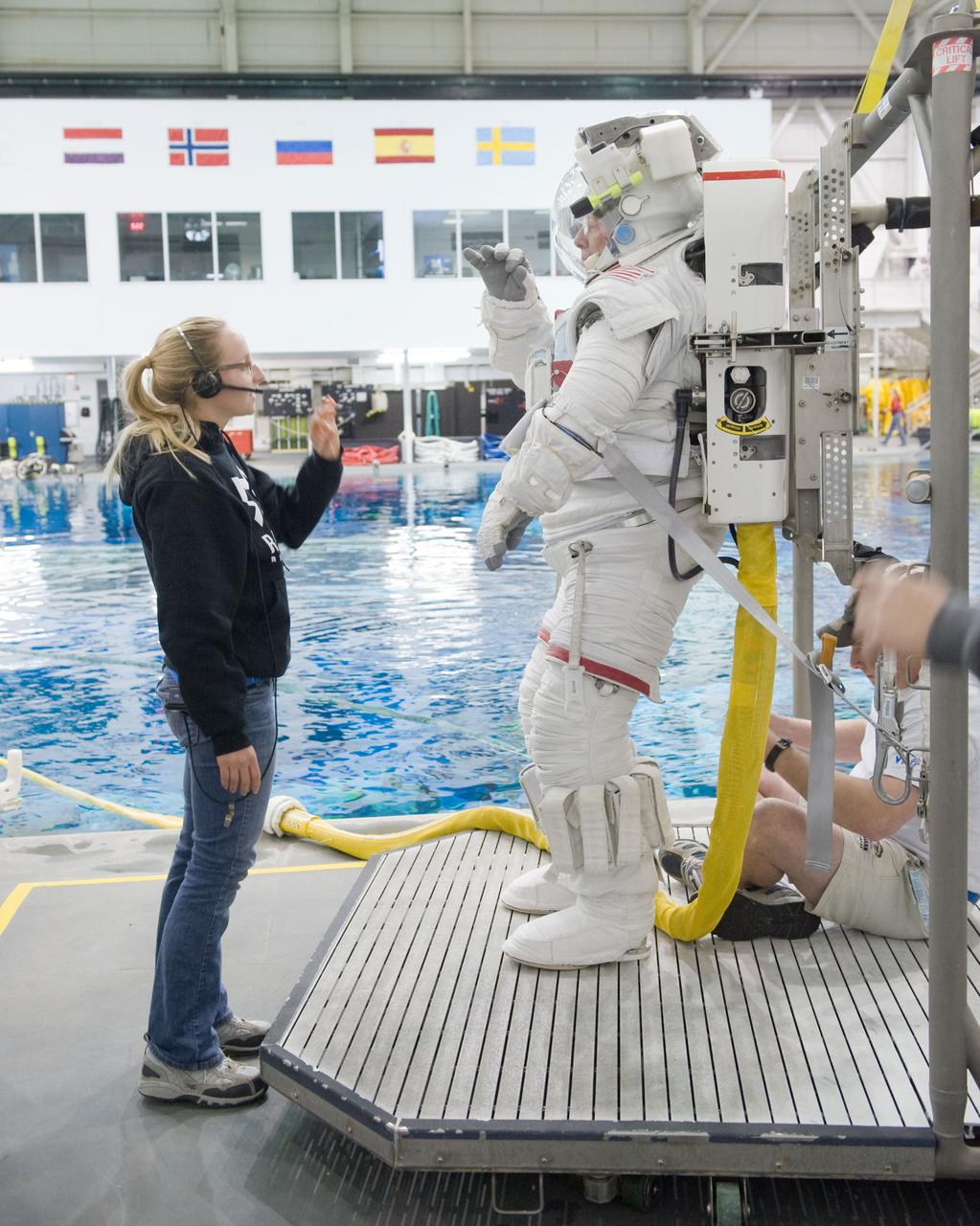

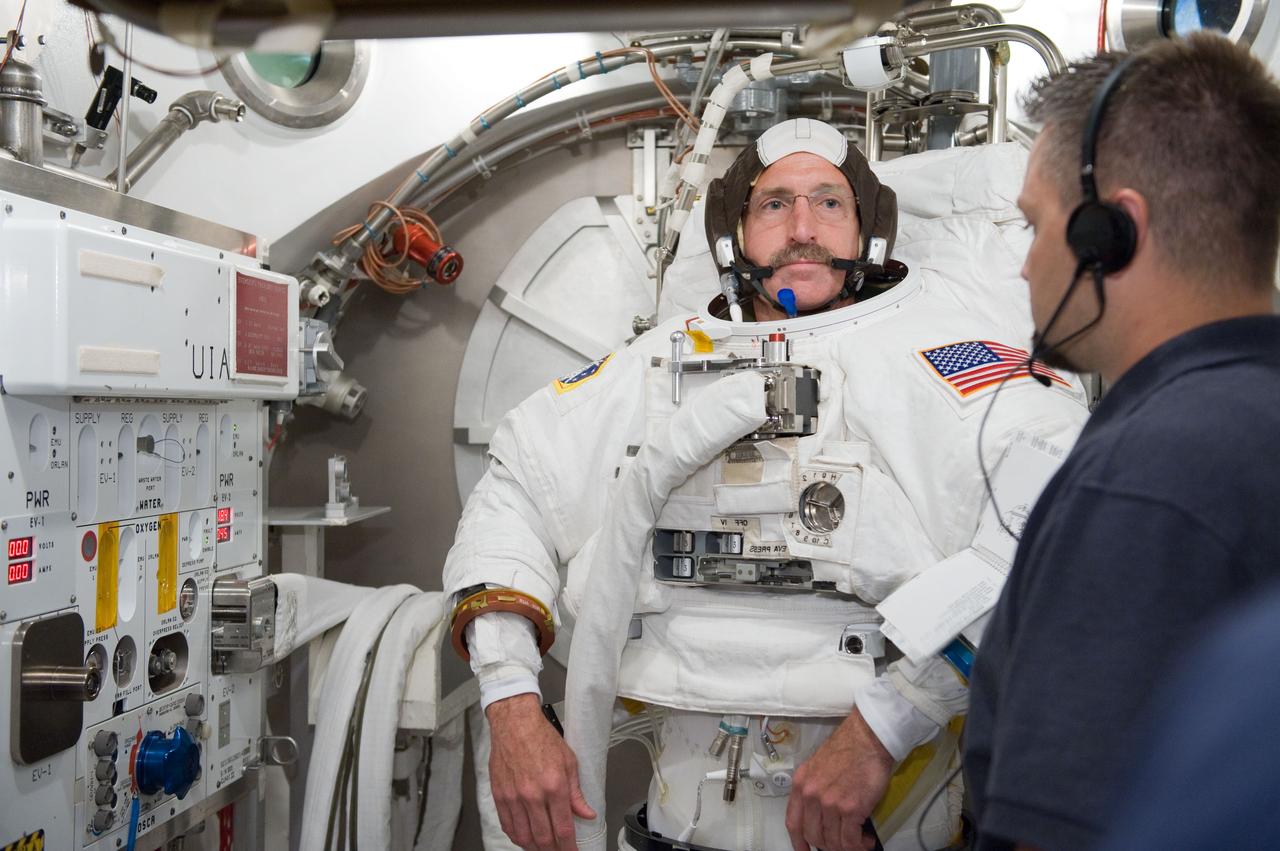
PHOTO DATE: 02-03-11 LOCATION: NBL - Pool Topside SUBJECT: Expedition 28/29 crew members Ron Garan and Mike Fossum during NBL EVA training WORK ORDER: 00281-BS__EXPNBL_02-03-11 PHOTOGRAPHER: BILL STAFFORD

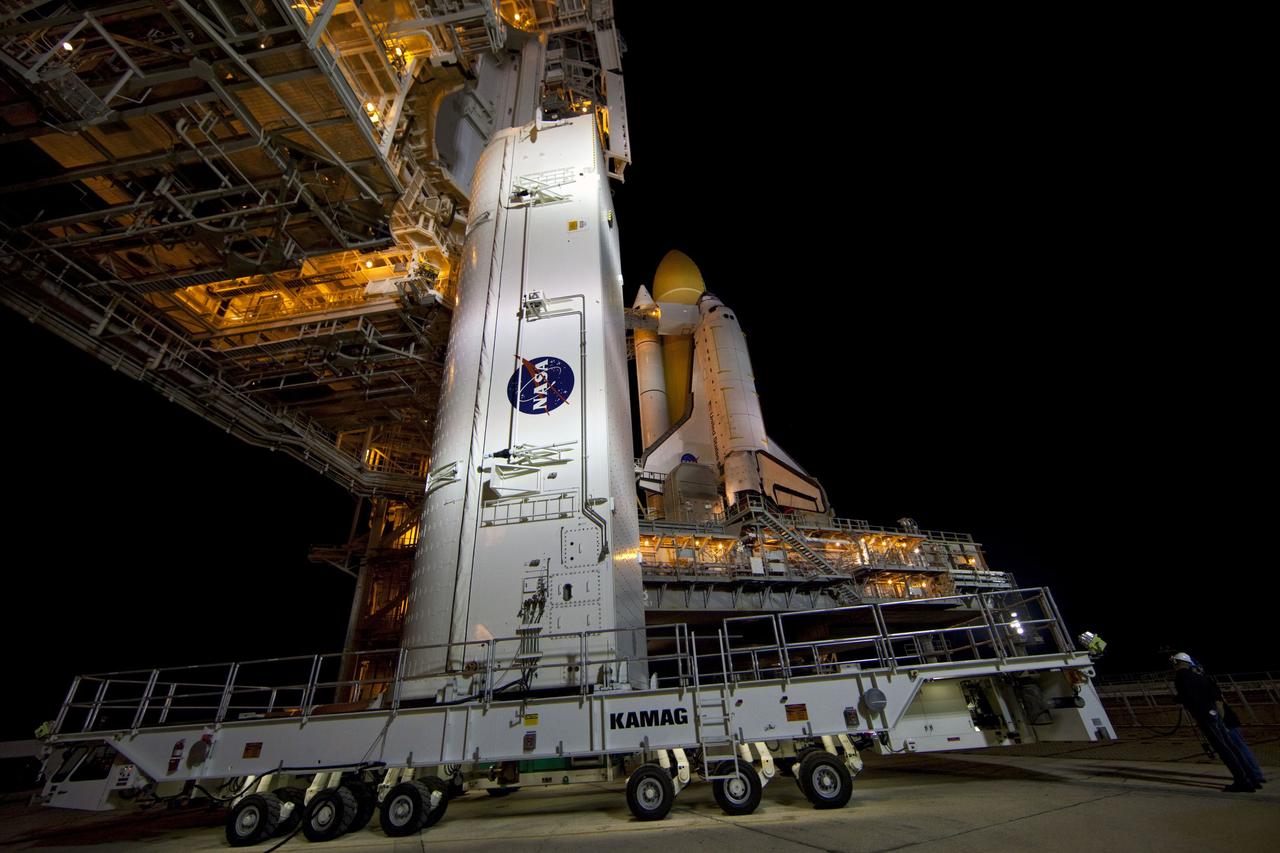
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis, attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters atop a mobile launcher platform, awaits its final journey from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. "Rollout," as it's called, began at 8:42 p.m. EDT. It will take the crawler-transporter about six hours to carry the shuttle stack to its seaside launch pad. The milestone move paves the way for the launch of the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, targeted for July 8. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

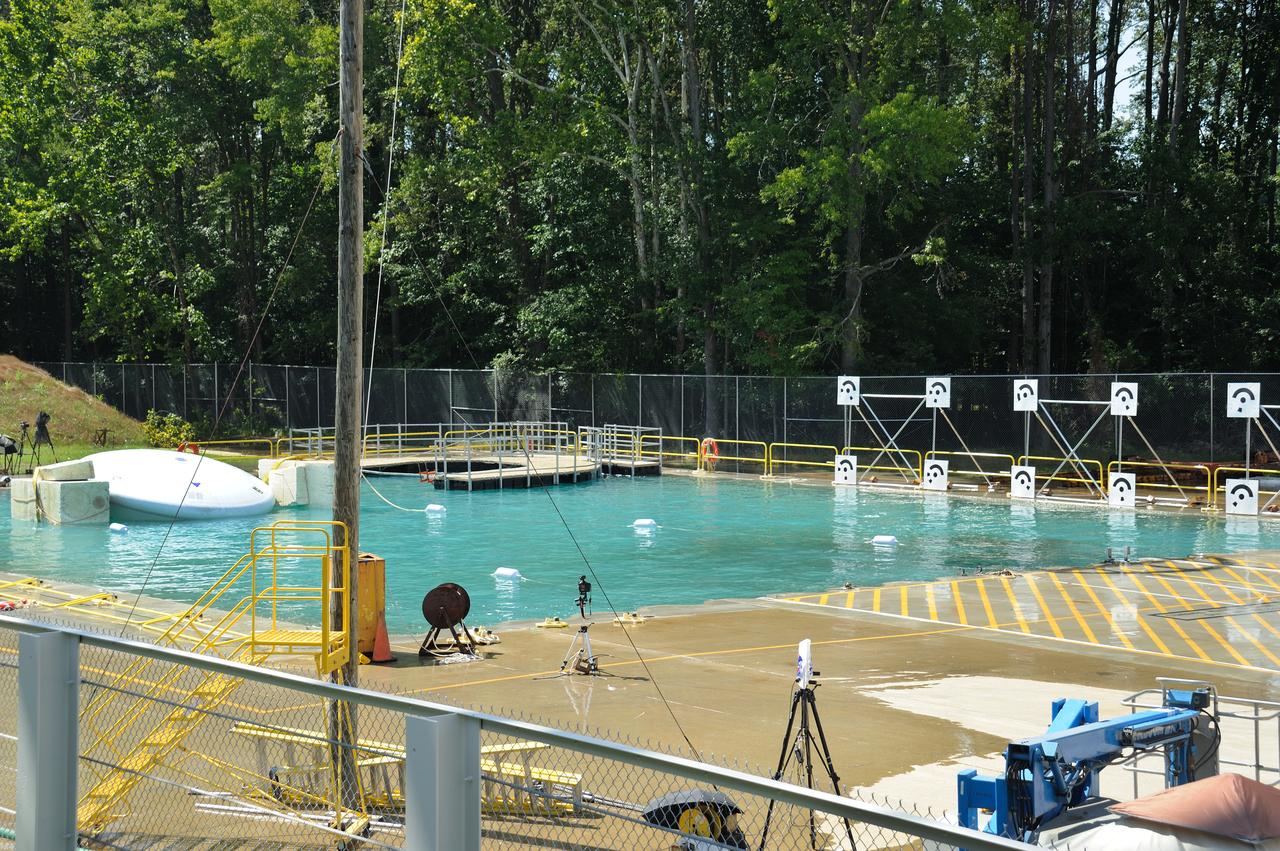
Crew Module Water Landing Model Assessment (CMWLMA) Test site photos at Aberdeen Test Center Aberdeen Maryland
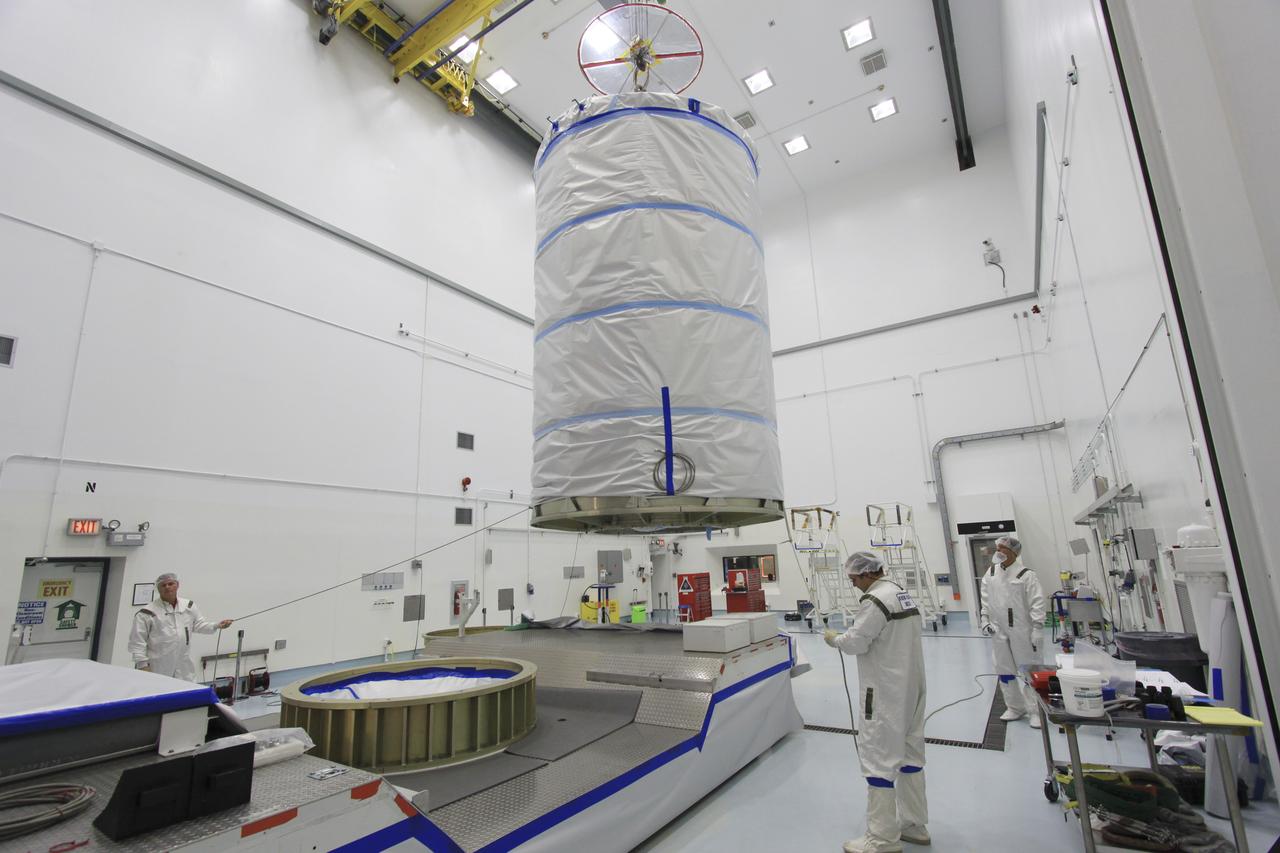

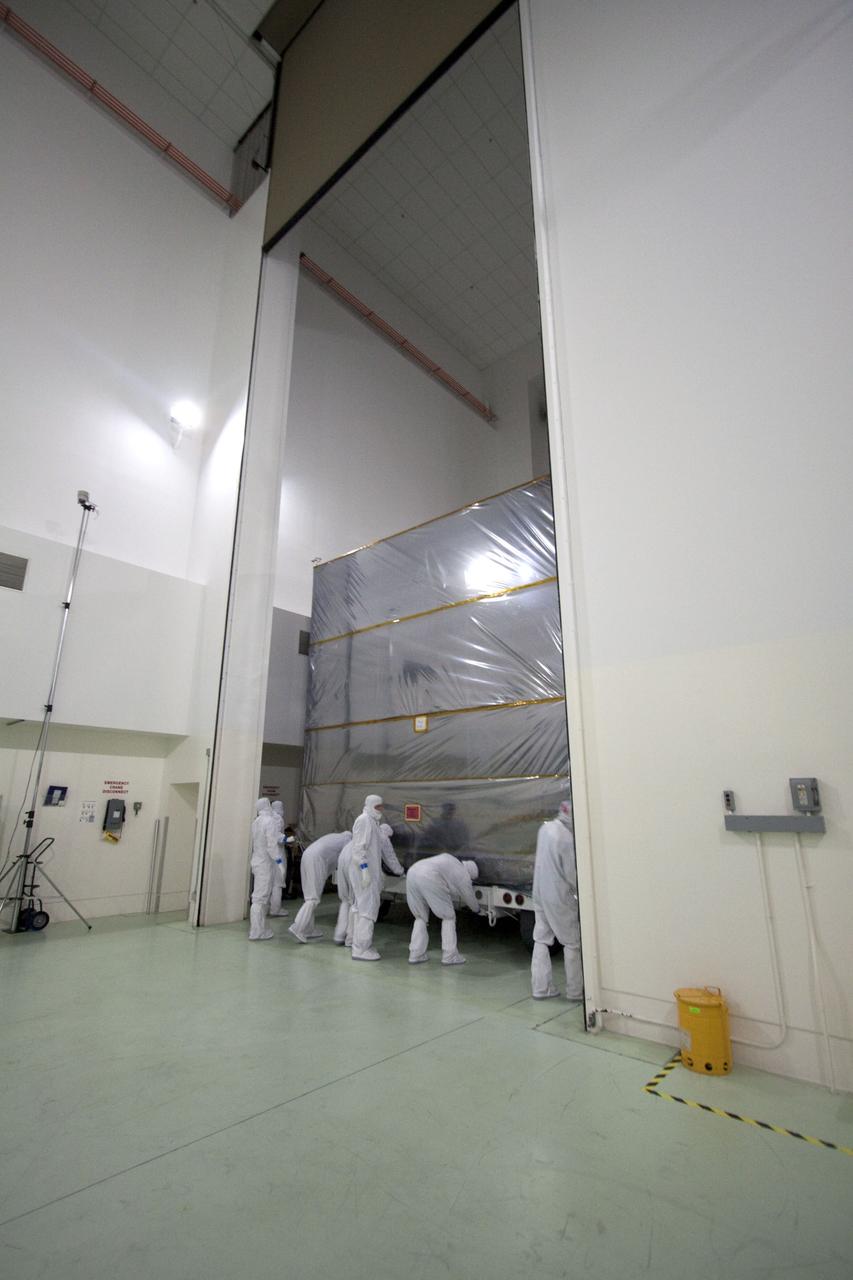
GRAIL put into Canister and Canister lifted onto Transporter
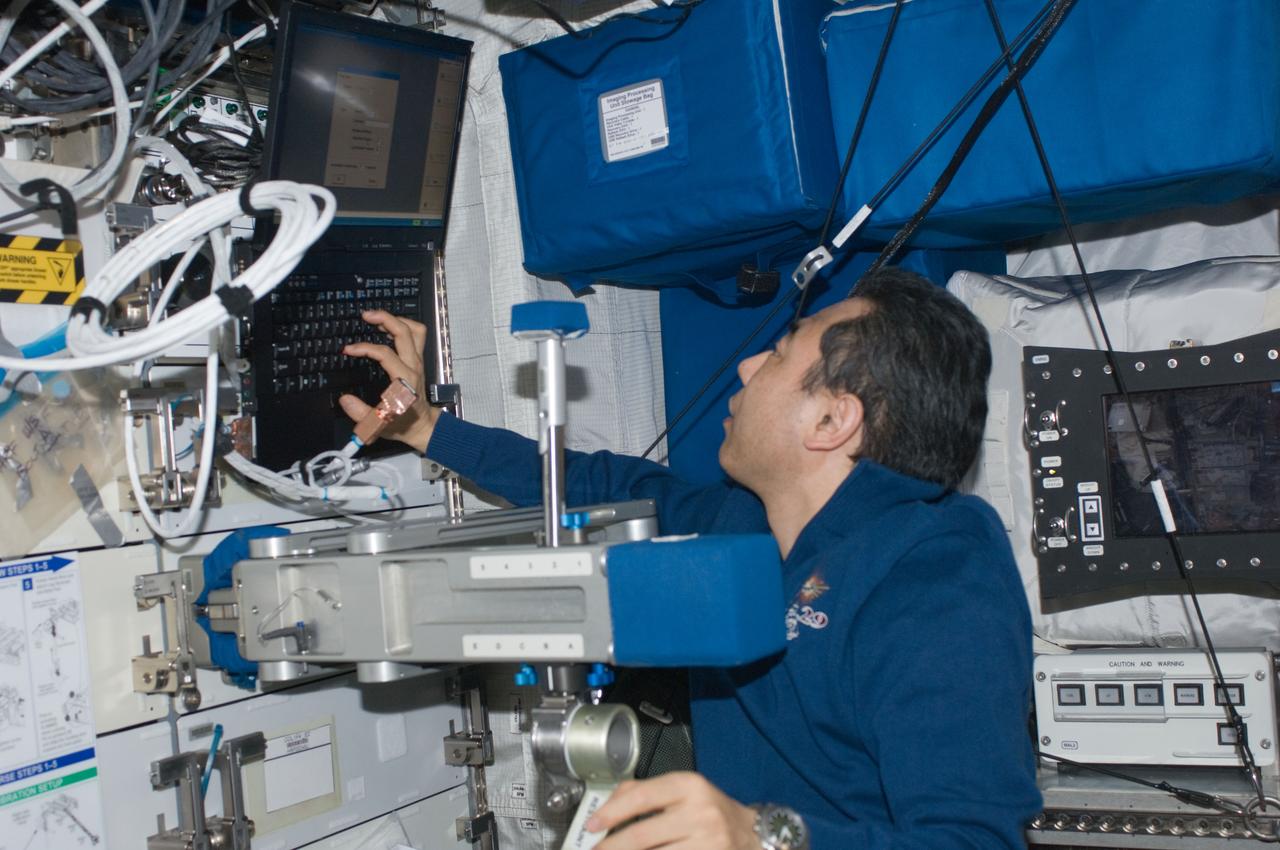

ISS029-E-017474 (5 Oct. 2011) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, Expedition 29 flight engineer, prepares to use the Space Linear Acceleration Mass Measurement Device (SLAMMD) in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station.
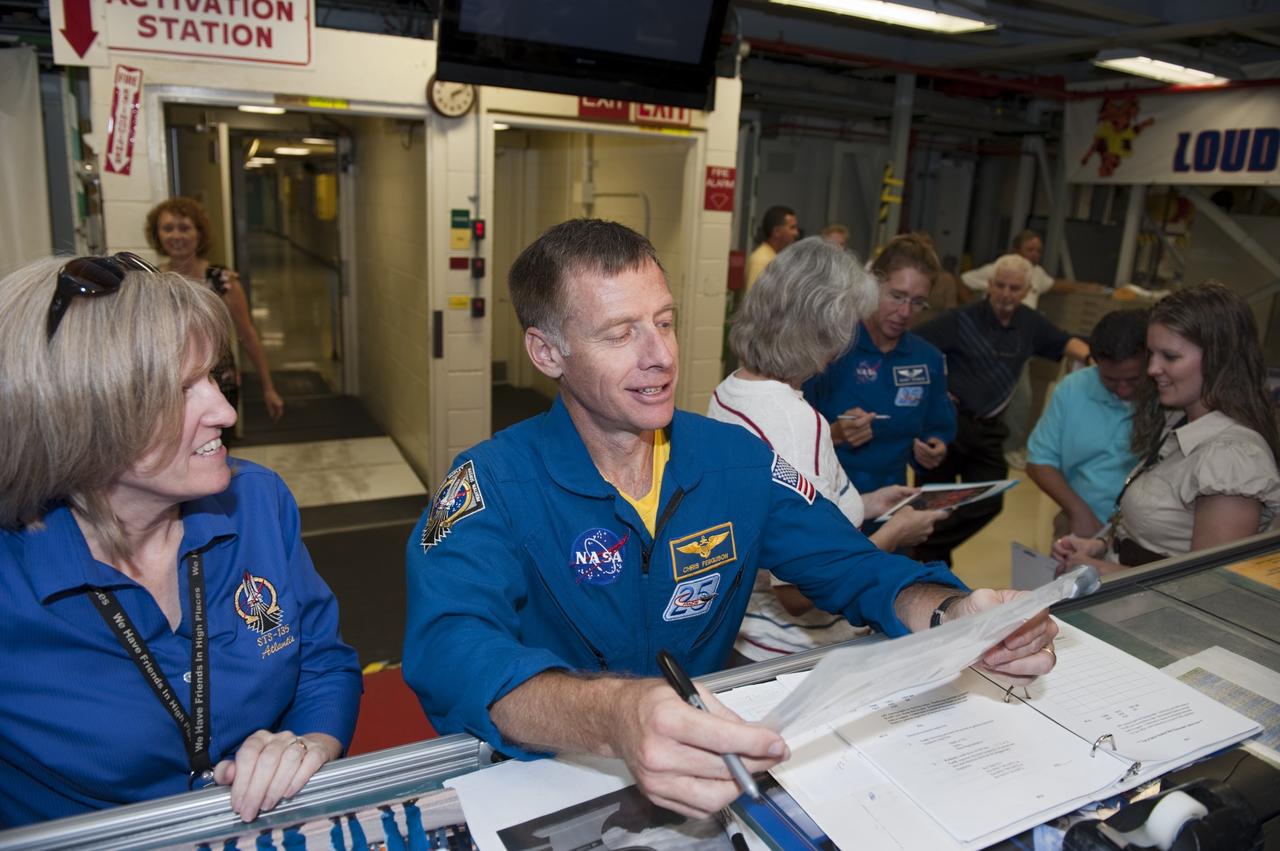

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson talks with Atlantis Flow Director Angie Brewer, while Mission Specialist Sandra Magnus sign autographs for employees inside Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility-2, where space shuttle Atlantis is being prepared for eventual display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The astronauts, along with Pilot Doug Hurley, were at the center for the traditional post-flight crew return presentation. STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim was unable to attend the Kennedy event. In July 2011, Atlantis and its crew delivered to the International Space Station the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis and the final mission of the Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
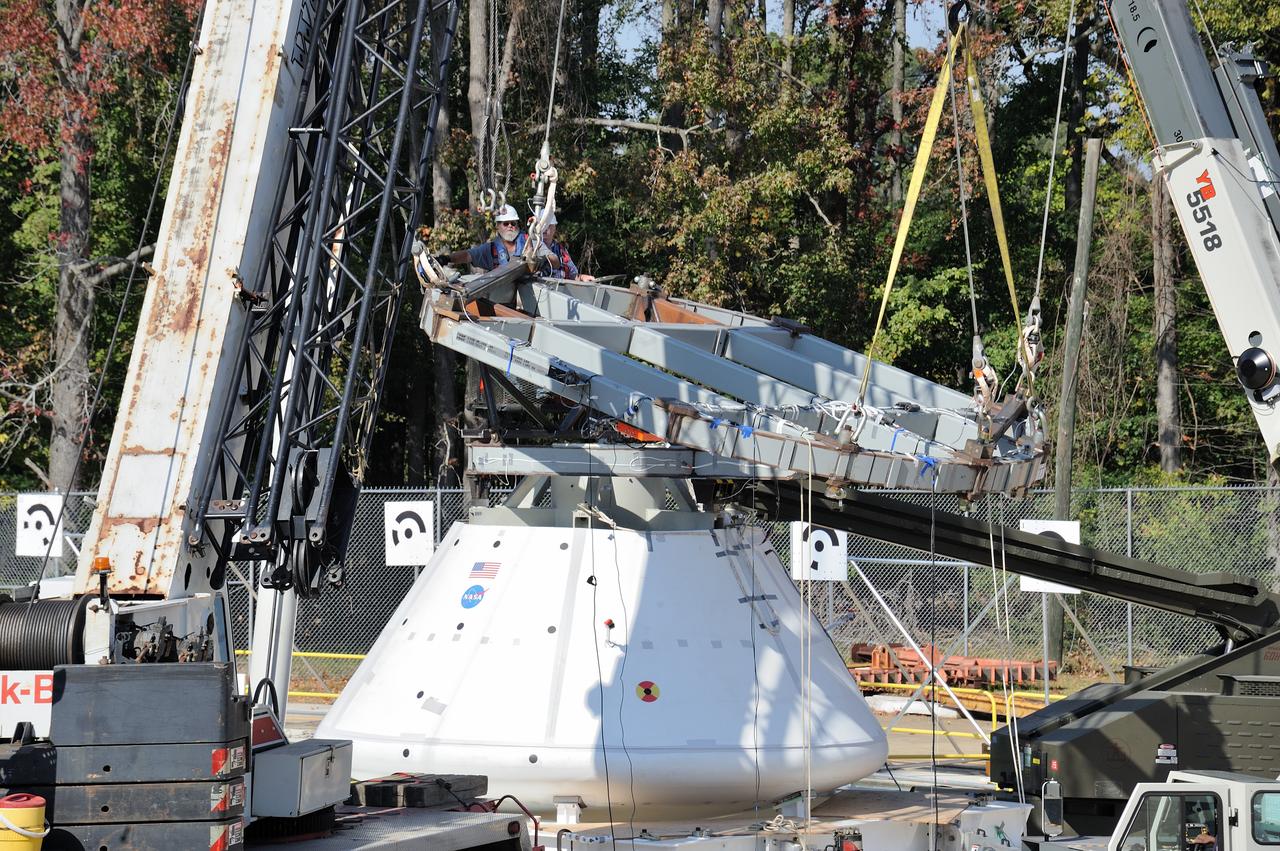

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-P1T#2 Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
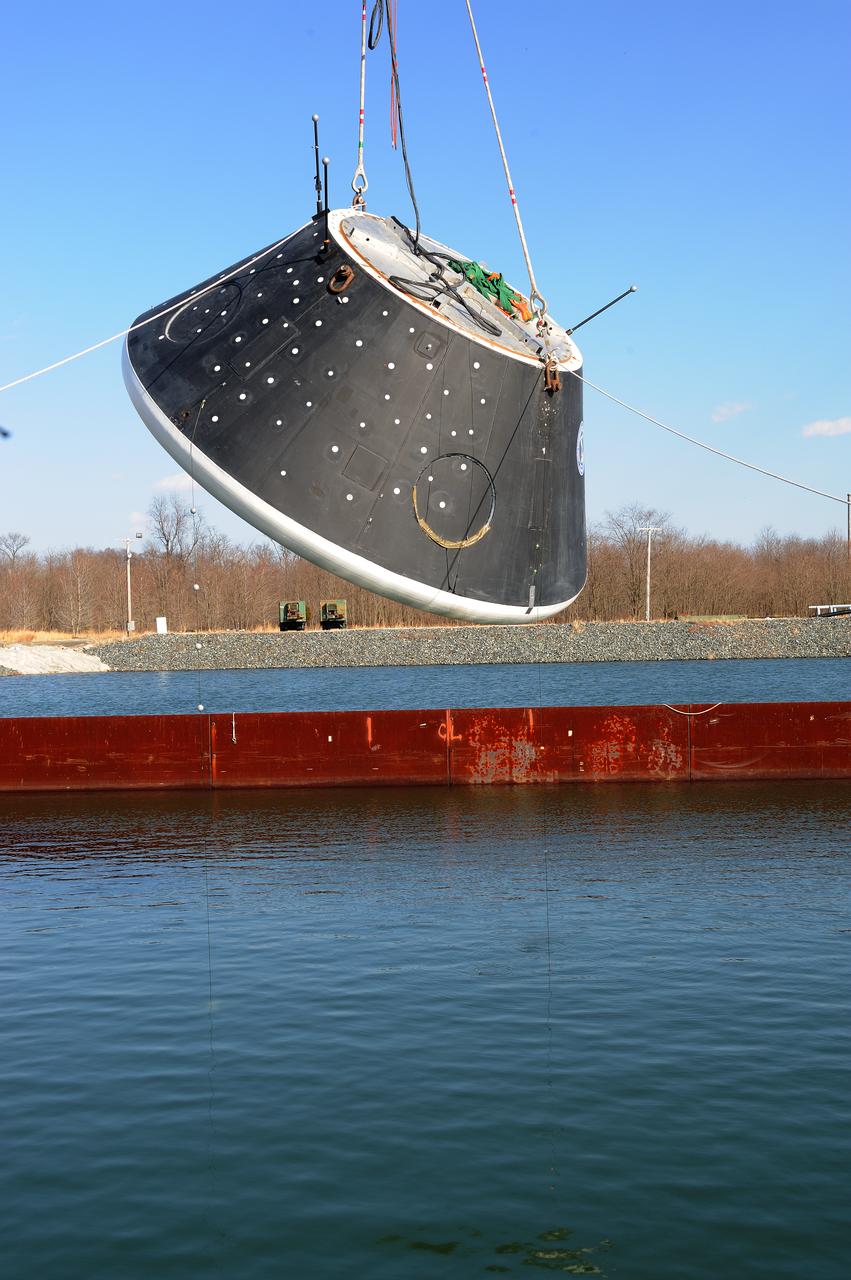

Crew Model Water Landing Module Assessment Photographs taken at Aberdeen Test Facility Aberdeen MD.
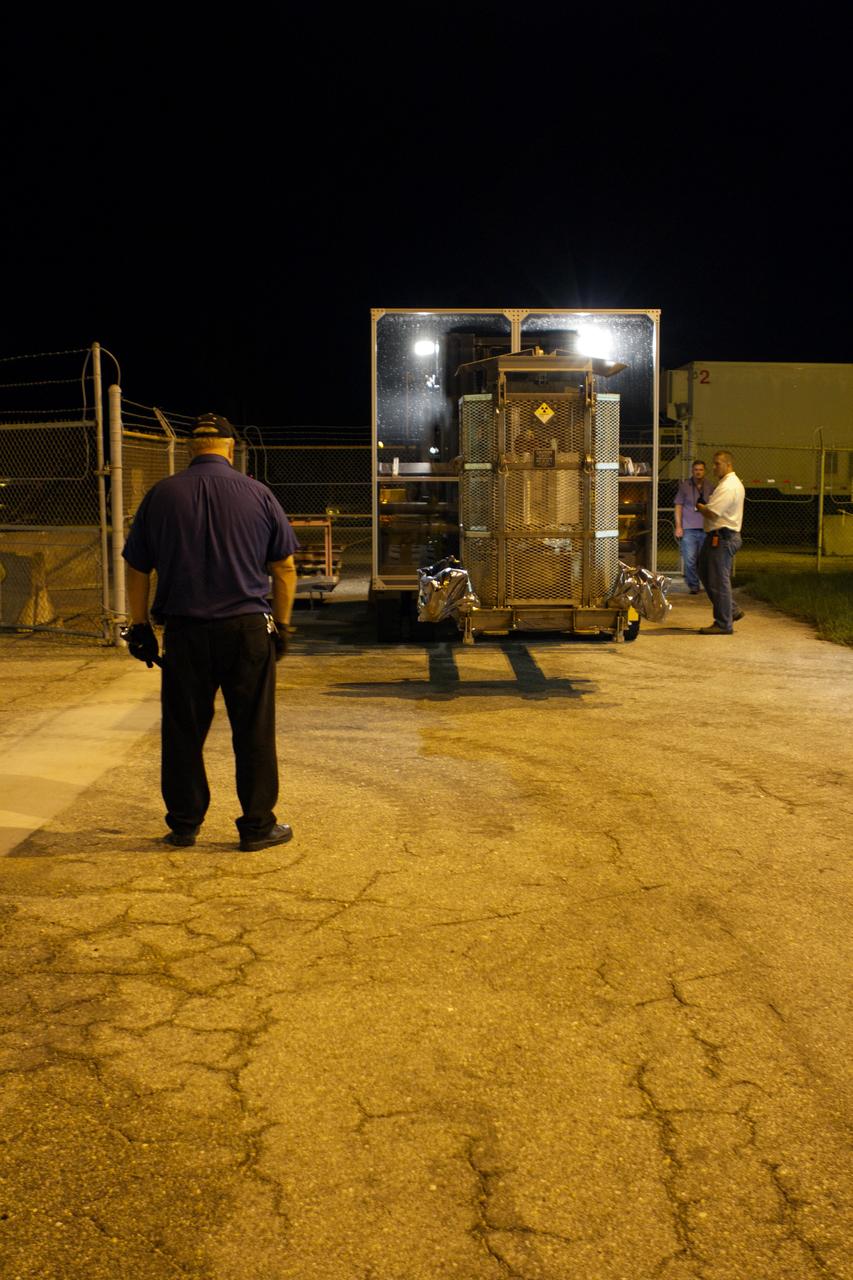

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Outside the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a plexiglass shield has been installed on the forklift enlisted to move the protective mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The shield minimizes the amount of debris dispersed by the wheels of the forklift that can contact the gorilla cage. The cage protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG is being moved to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) where it temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
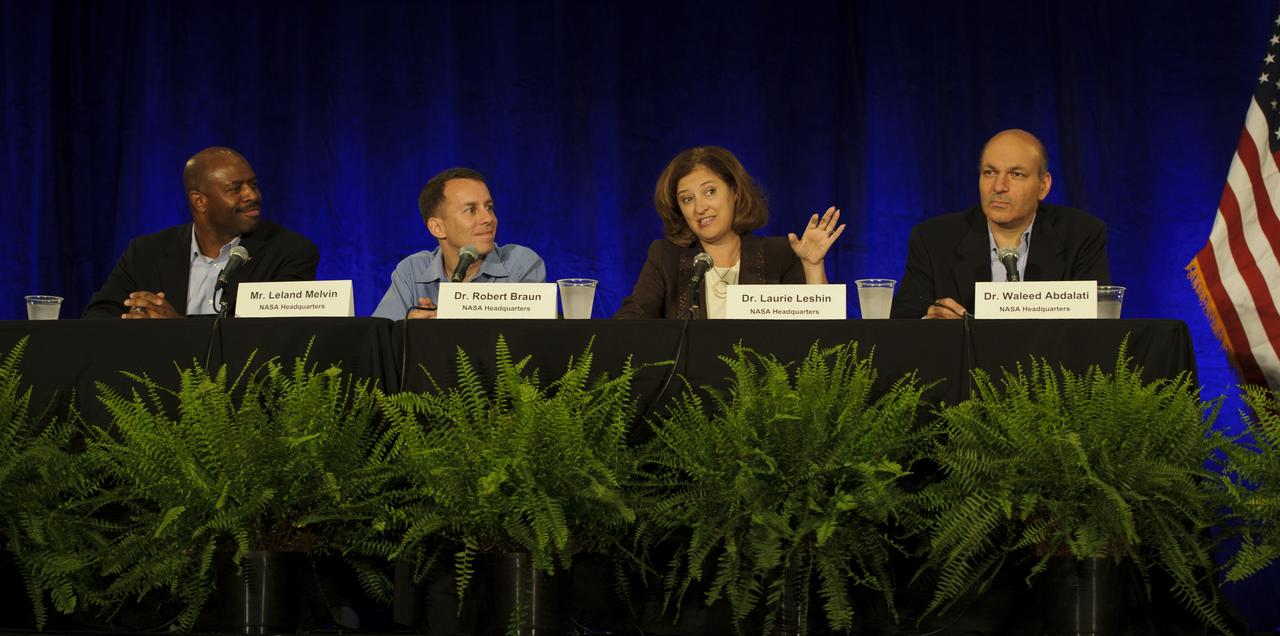

Dr. Laurie Leshin, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator Exploration Systems Mission Directortorate, second from right, speaks as Dr. Waleed Abdalati, NASA Chief Scientist, right, Dr. Robert Braun, NASA Chief Technologist, and Leland Melvin, Assoicate Administrator for NASA Education, far left, at the NASA Future Forum held at the Riggs Alumni Center on the campus of the University of Maryland, Thursday, Aug. 11, 2011 in College Park, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
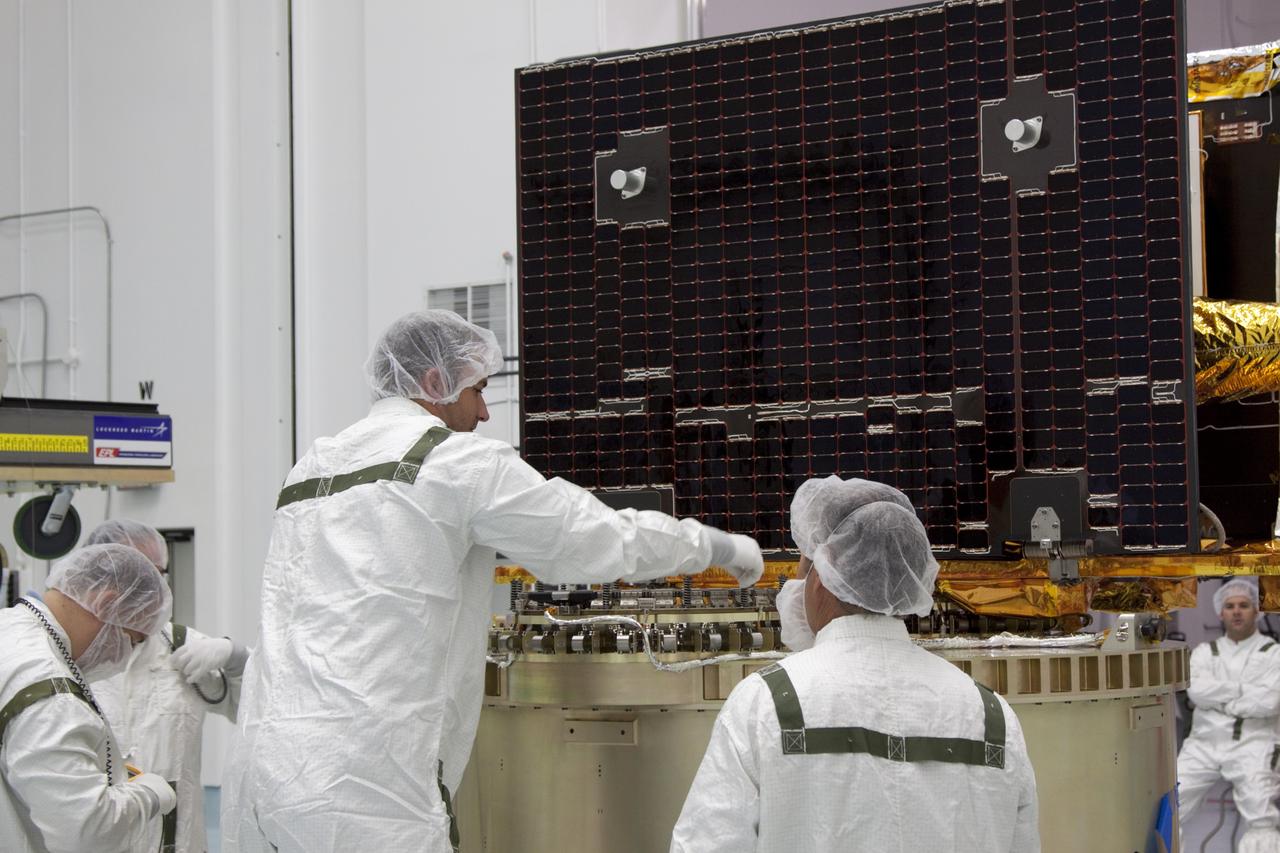

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Lockheed Martin technician secures NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
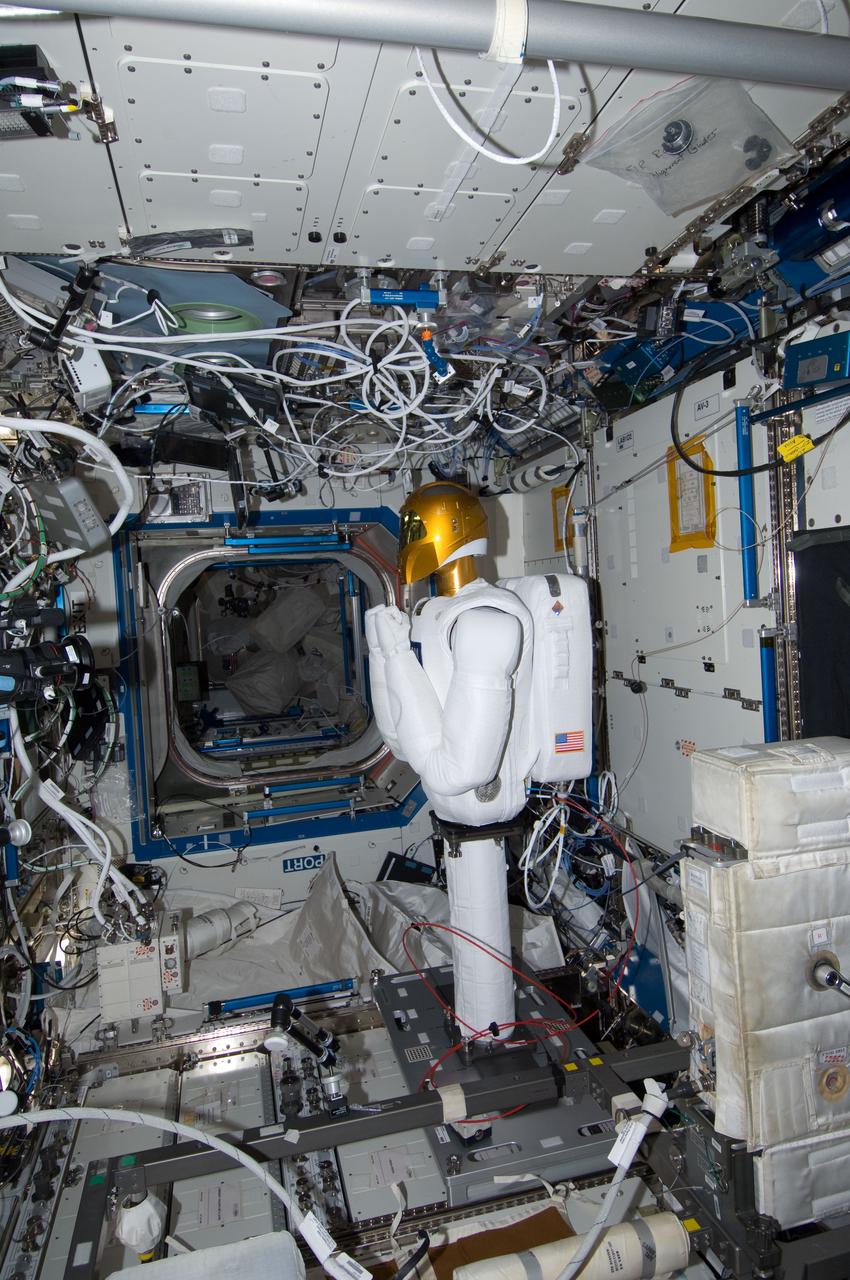

ISS029-E-025806 (13 Oct. 2011) --- Robonaut 2 -- the first dexterous humanoid robot in space – is pictured in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. NASA astronaut Mike Fossum, Expedition 29 commander; and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, flight engineer, (both out of frame) joined forces to conduct the second onboard tests of R2, which was put in motion for the first time in orbit. After performing a coordinated power-up with the ground, the crew maneuvered each arm joint to determine the differences of the microgravity environment by setting control gains through repetitive motions. They also performed an initial vision checkout of the high-def cameras to verify they are working and in focus. The ground then commanded R2 to move to the stow-position while monitoring the motion.
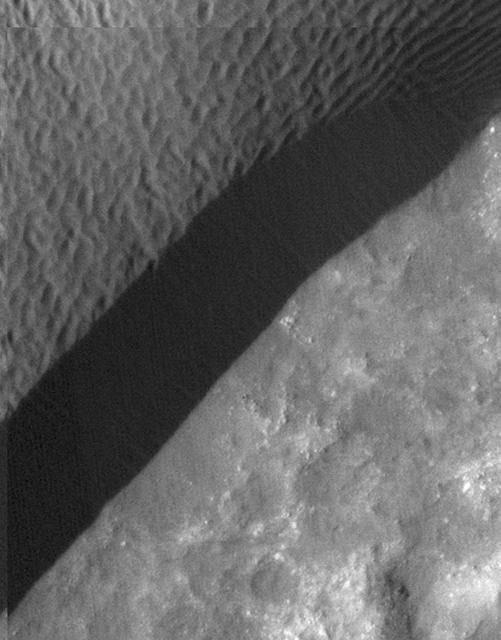

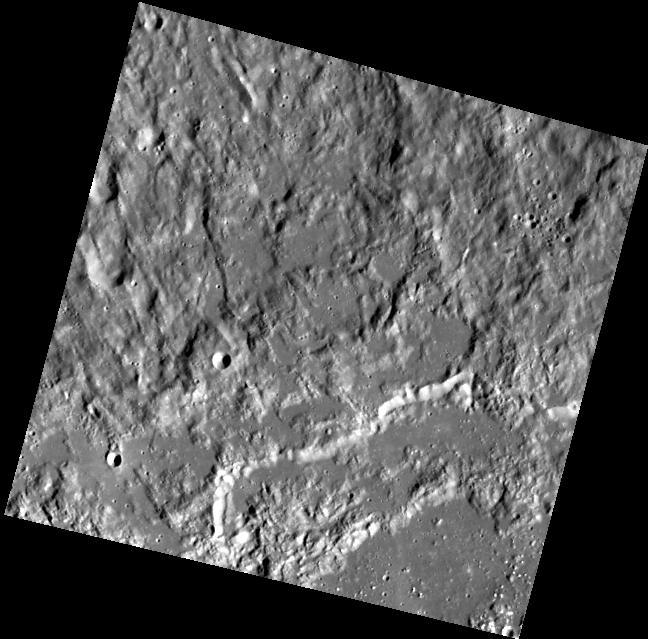
A rippled dune front in Herschel Crater on Mars moved an average of about one meter about one yard between March 3, 2007 and December 1, 2010, as seen in one of two images from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
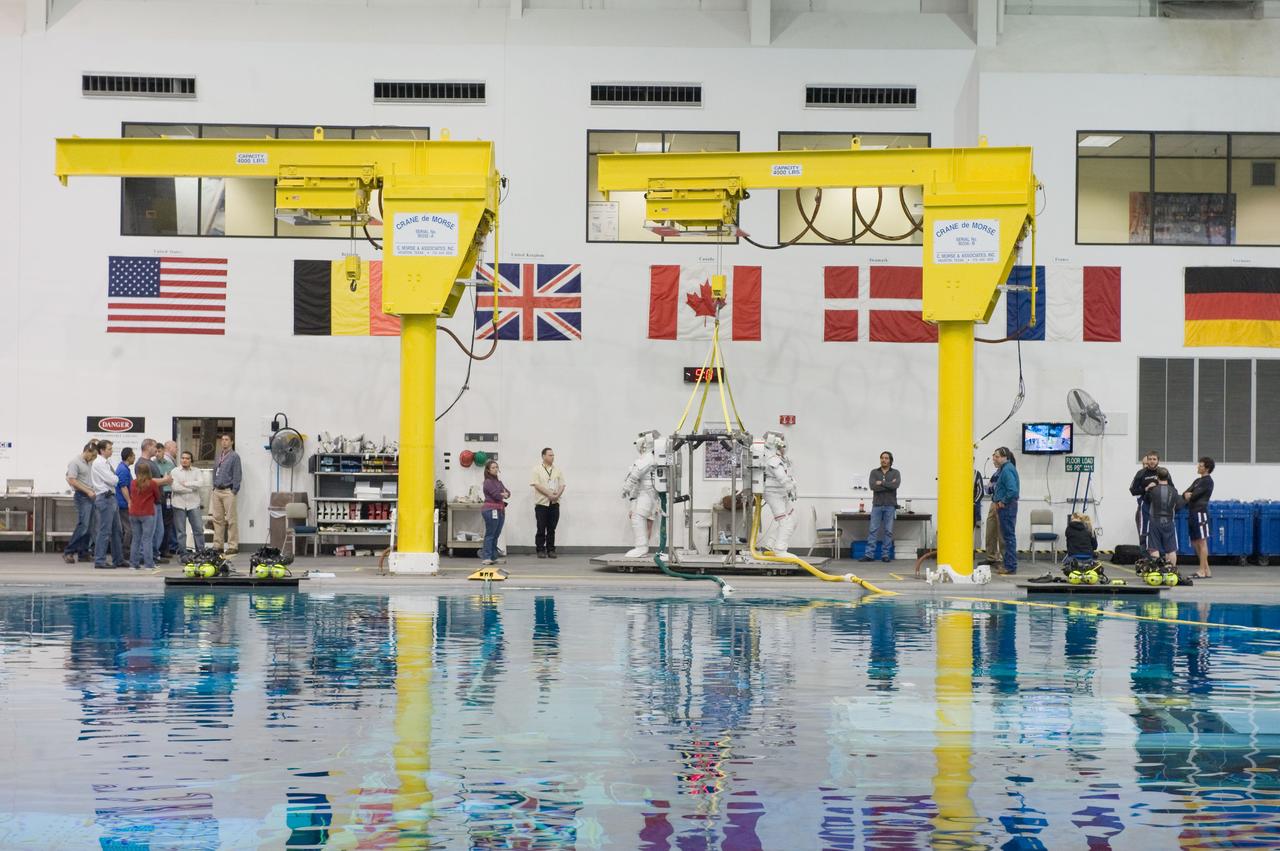
PHOTO DATE: 02-03-11 LOCATION: NBL - Pool Topside SUBJECT: Expedition 28/29 crew members Ron Garan and Mike Fossum during NBL EVA training WORK ORDER: 00281-BS__EXPNBL_02-03-11 PHOTOGRAPHER: BILL STAFFORD
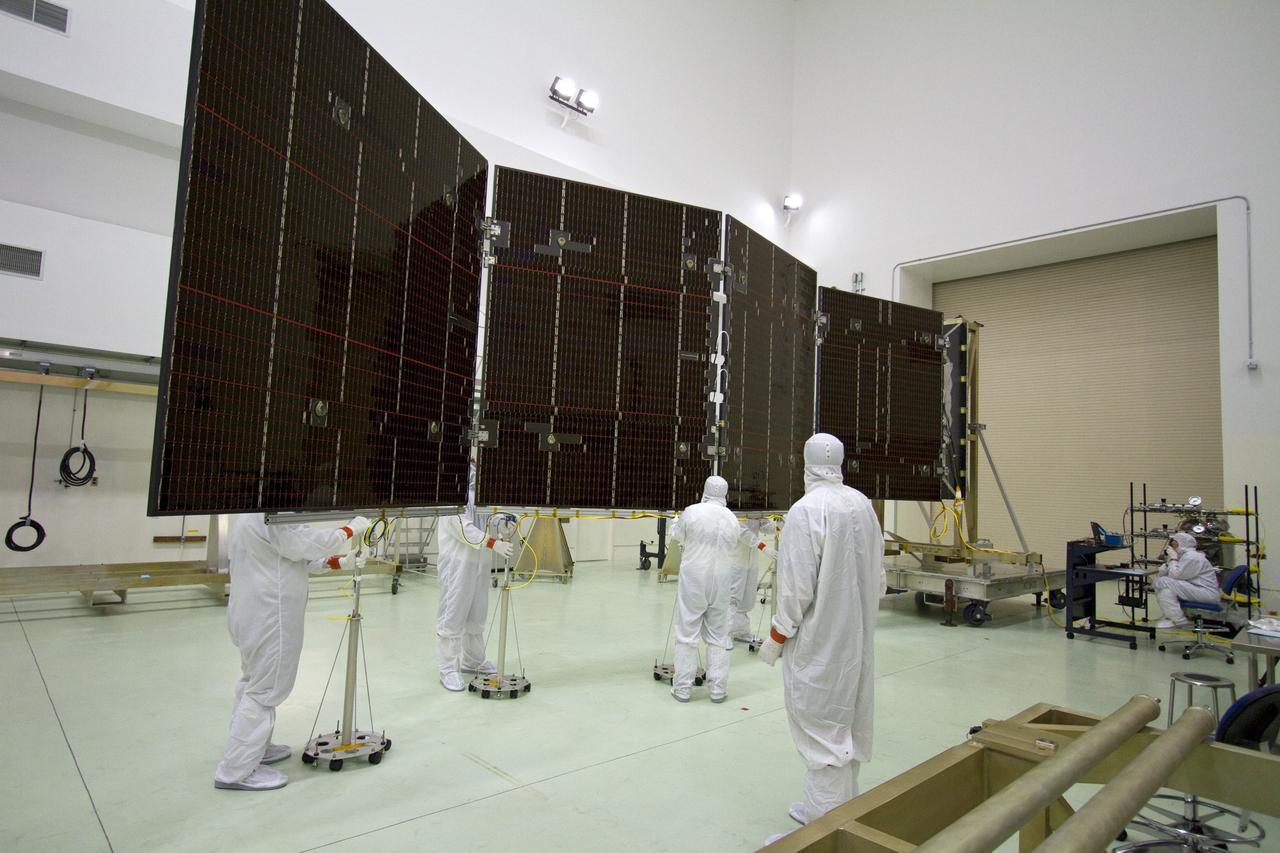

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
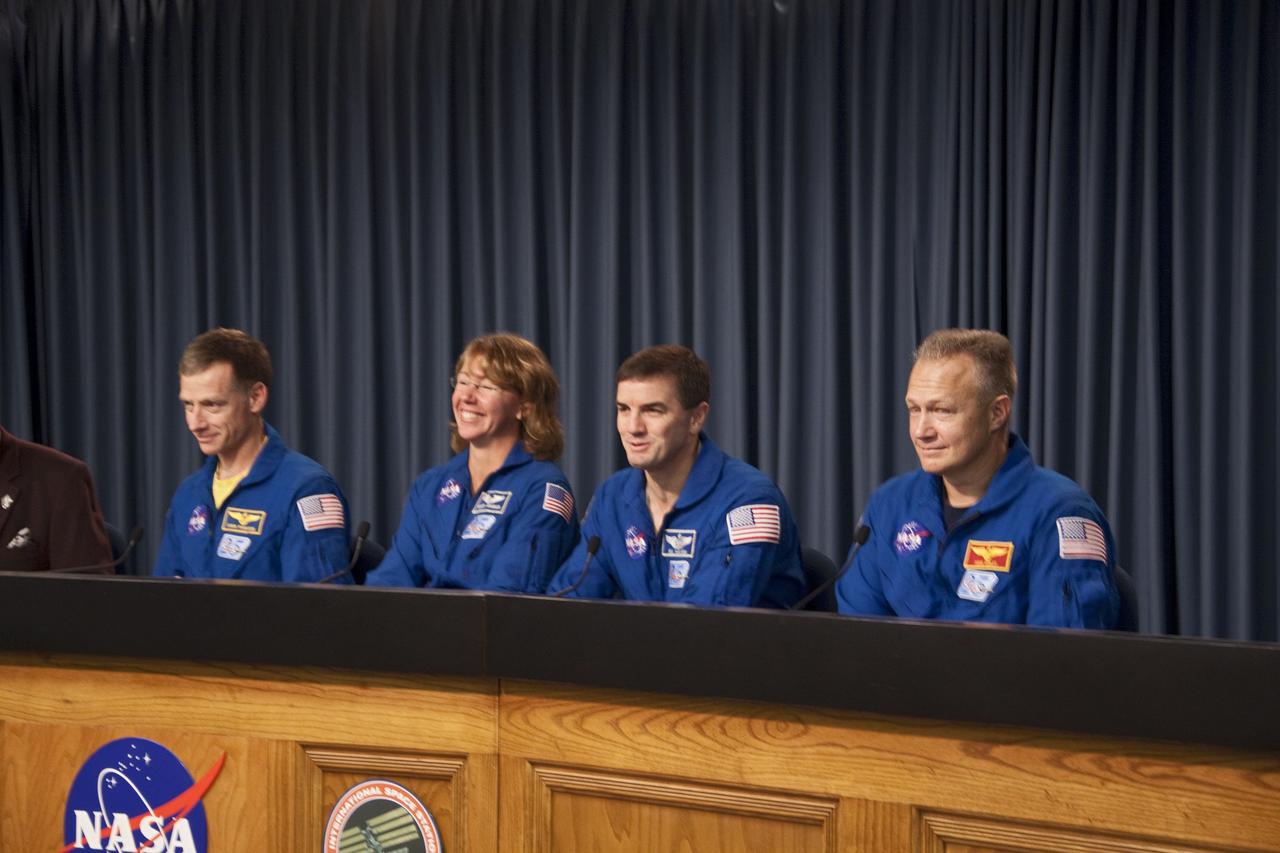

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The crew of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 and final Space Shuttle Program Flight, participates in a news conference in the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on landing day. Seen here are STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson (left), Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim and Pilot Doug Hurley. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. Atlantis and its crew delivered to the International Space Station the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
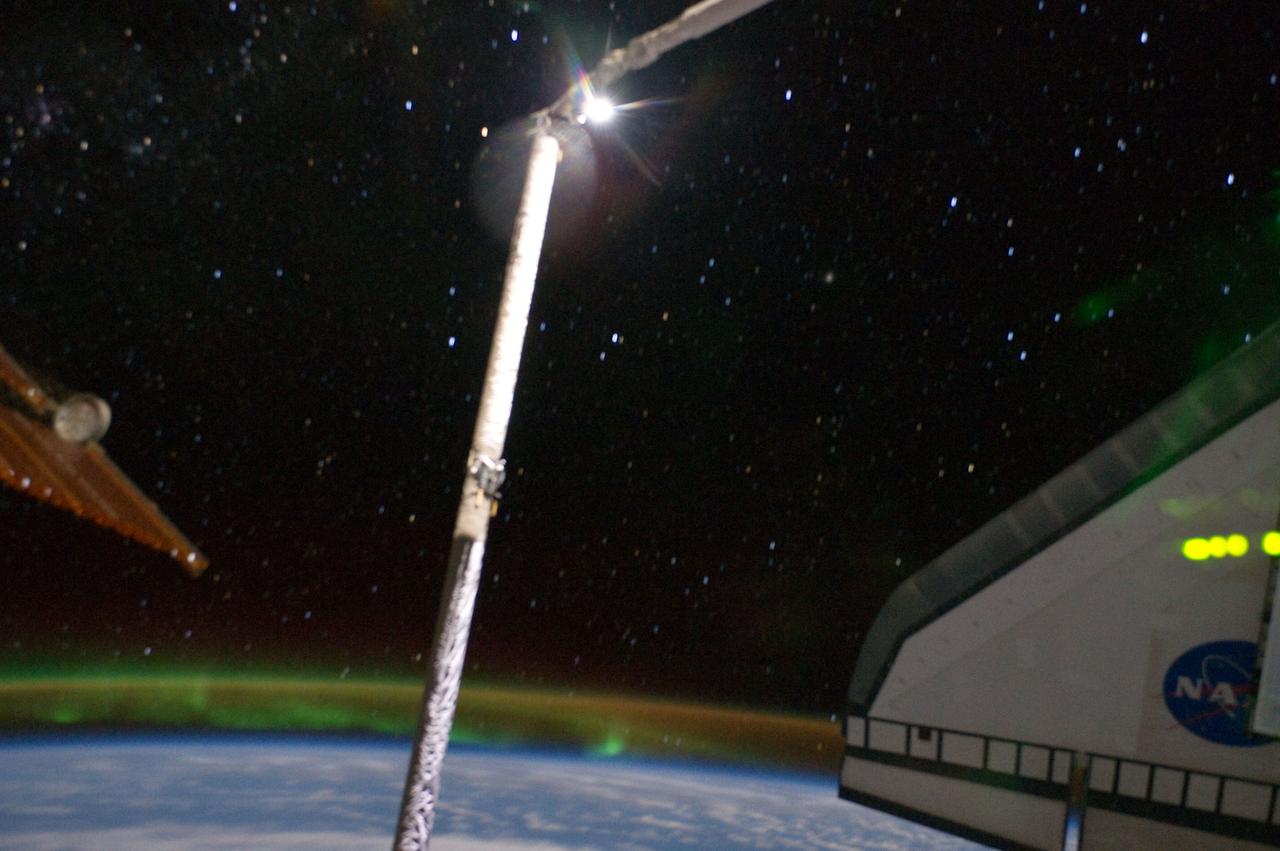

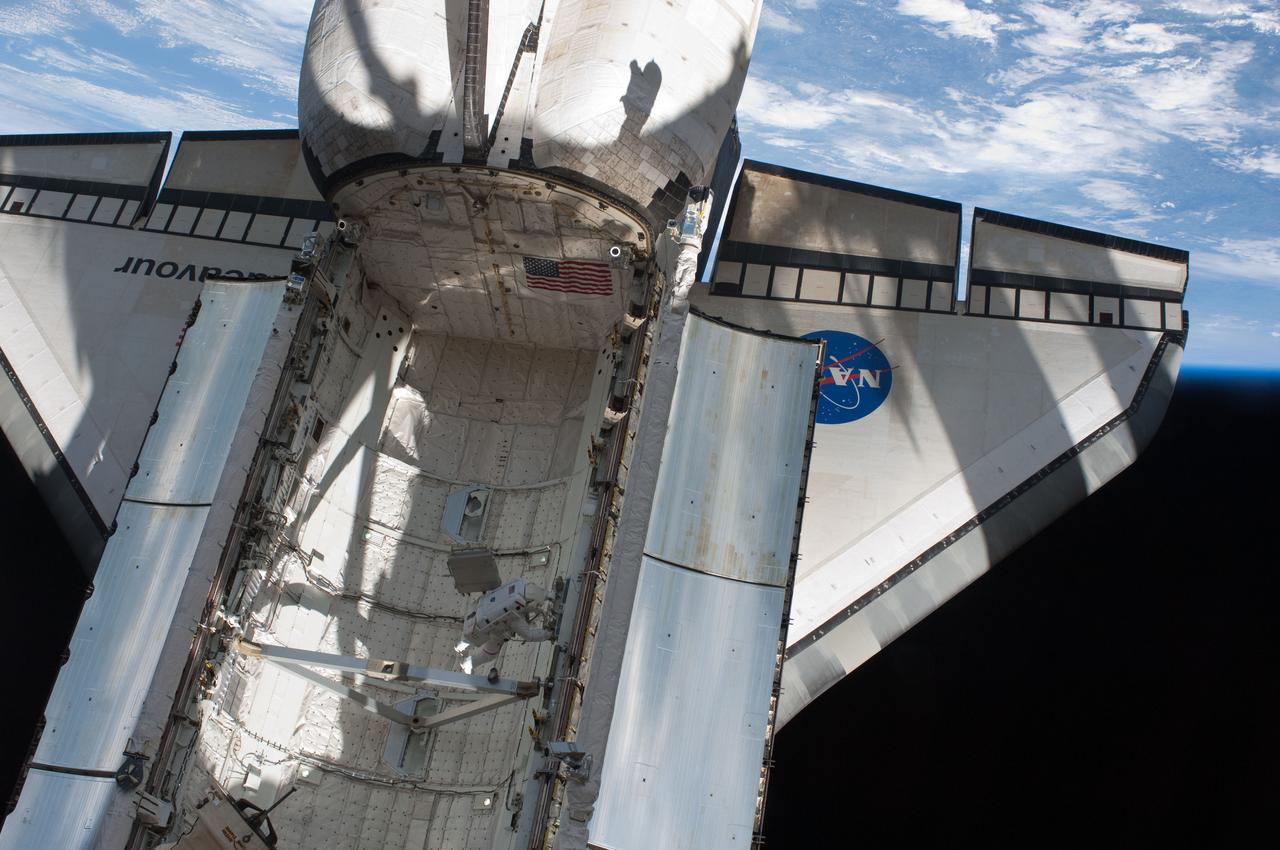
ISS028-E-017393 (17 July 2011) --- This is one of a series of photographs recorded from the International Space Station showing the docked space shuttle Atlantis' port side wing backdropped against the blackness of space. At the bottom of the frame can be seen airglow over Earth, intermingled with auroral activity. A solar wing connected to the station and part of the Orbiter Boom Sensor System are on the left side of the frame.

I Melt With You

This view of the North America nebula combines both visible and infrared light observations, taken by the Digitized Sky Survey and NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Clusters of young stars about one million years old can be found throughout the image.
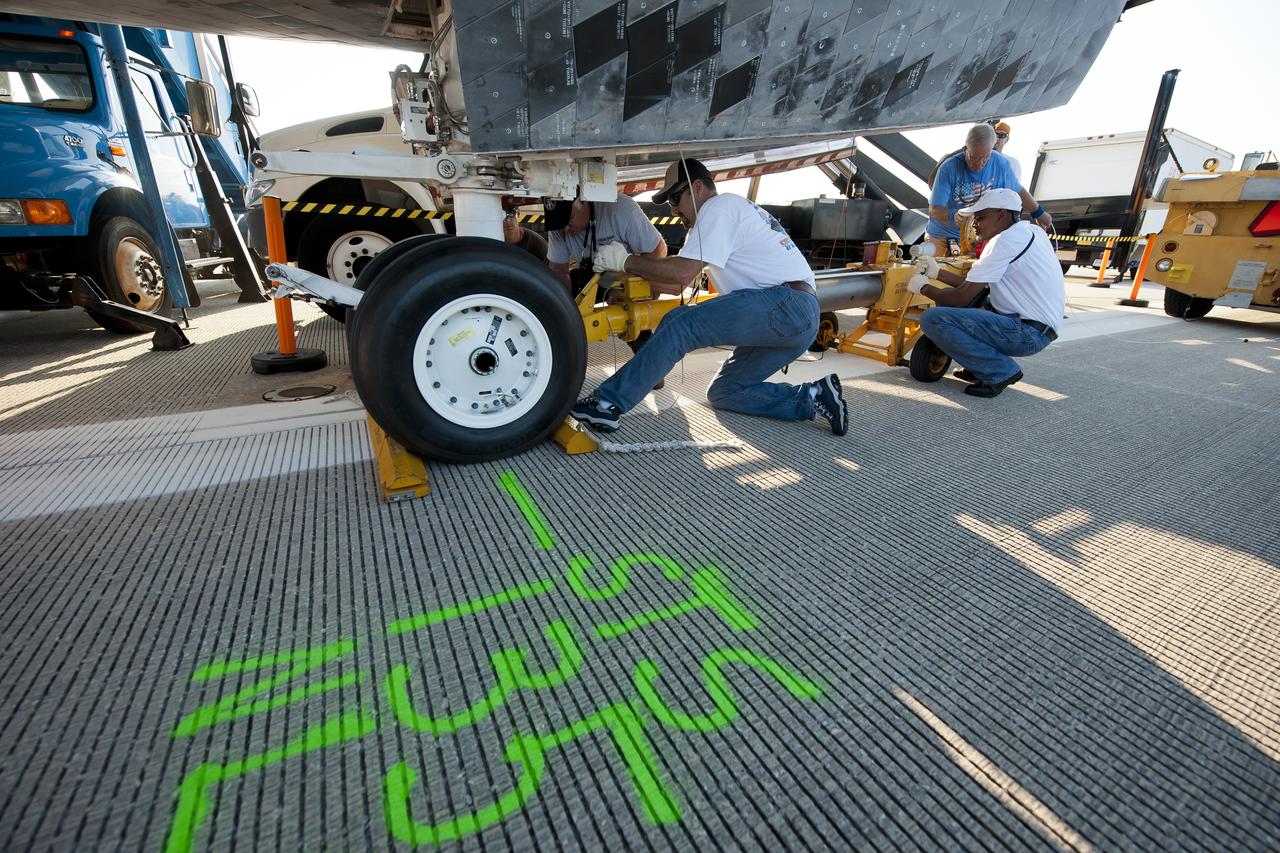

NASA and contractor personnel work to secure the tow bar onto the space shuttle Atlantis at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) shortly after Atlantis (STS-135) landed early Thursday morning, July 21, 2011, in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The runway is marked to show where the nose landing gear wheels stopped. Overall, Atlantis spent 307 days in space and traveled nearly 126 million miles during its 33 flights. Atlantis, the fourth orbiter built, launched on its first mission on Oct. 3, 1985. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
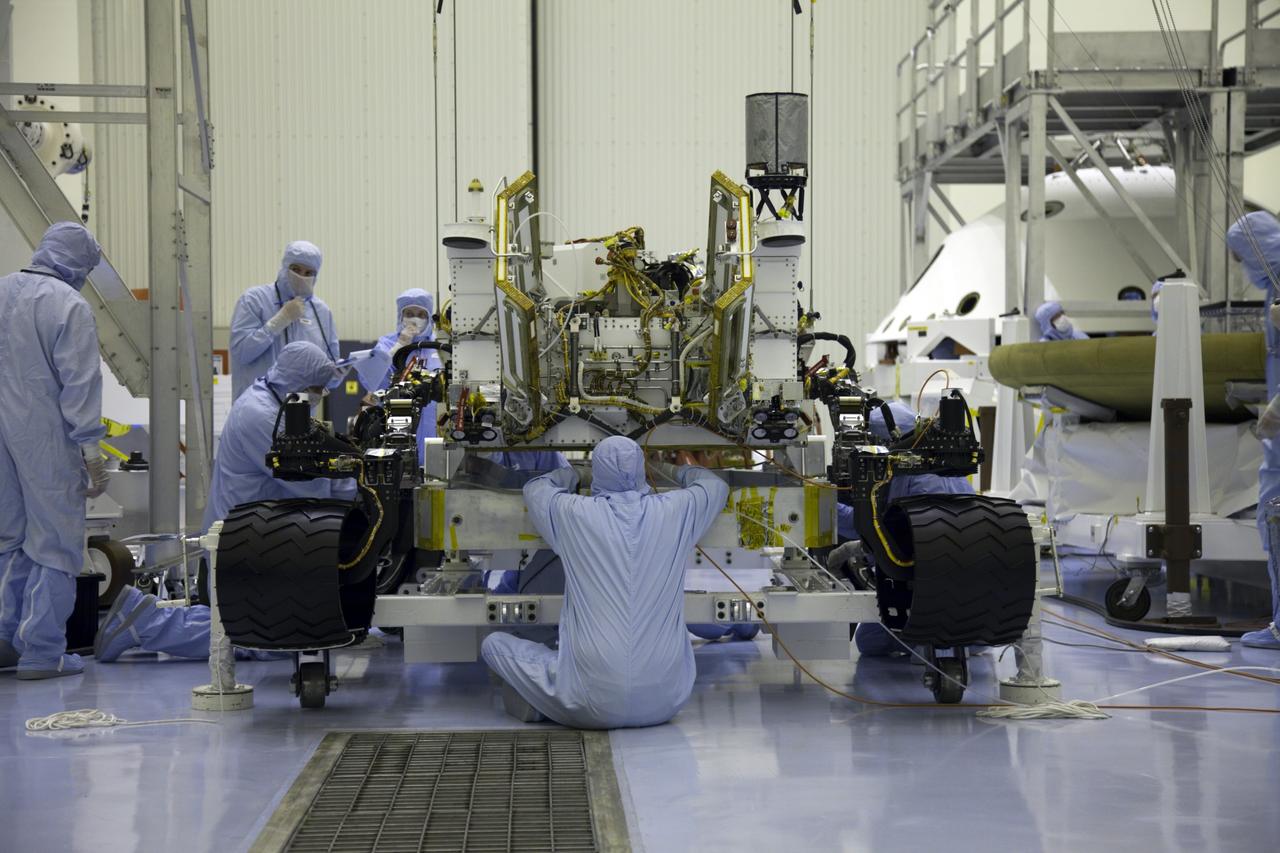

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- Technicians at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepare to move NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, known as Curiosity, to the high bay floor where the instrument mast and science boom will undergo deployment testing. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
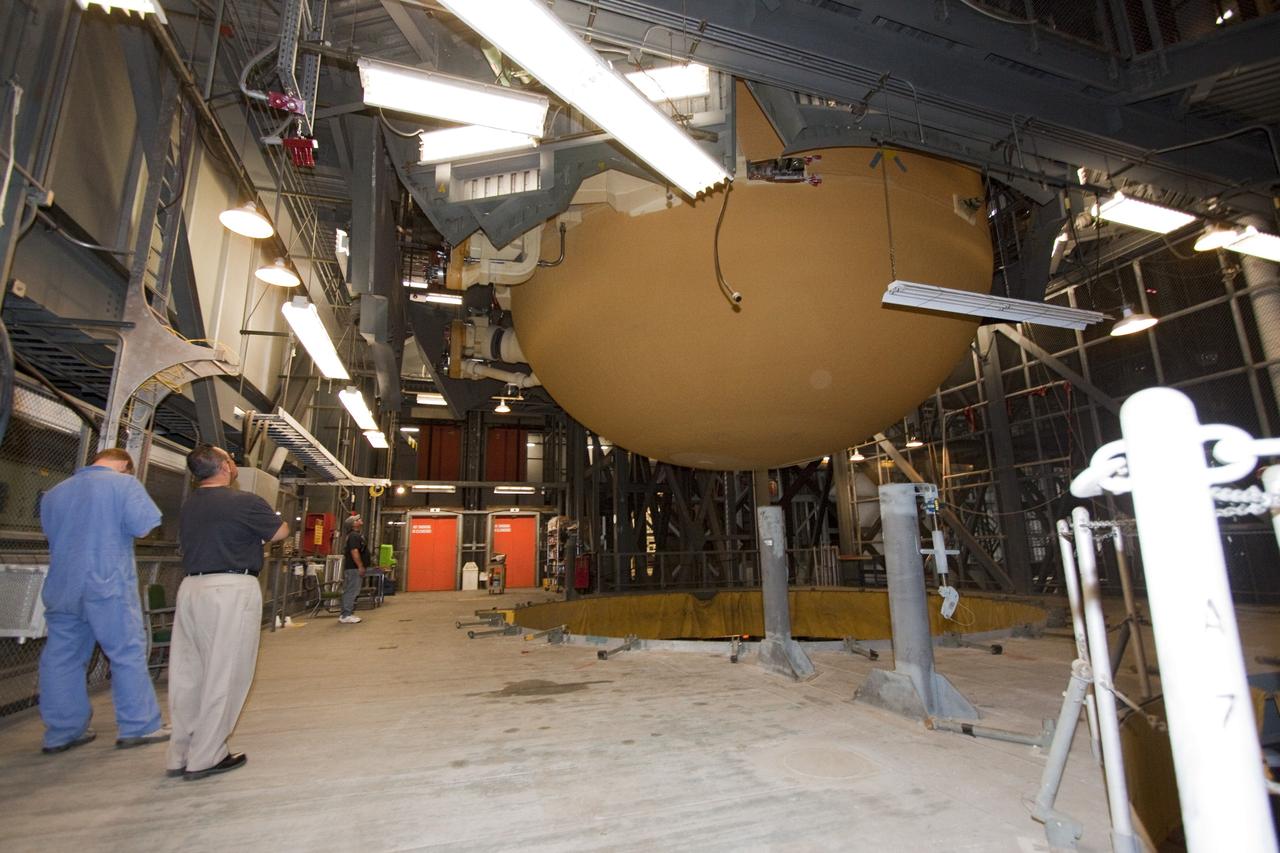

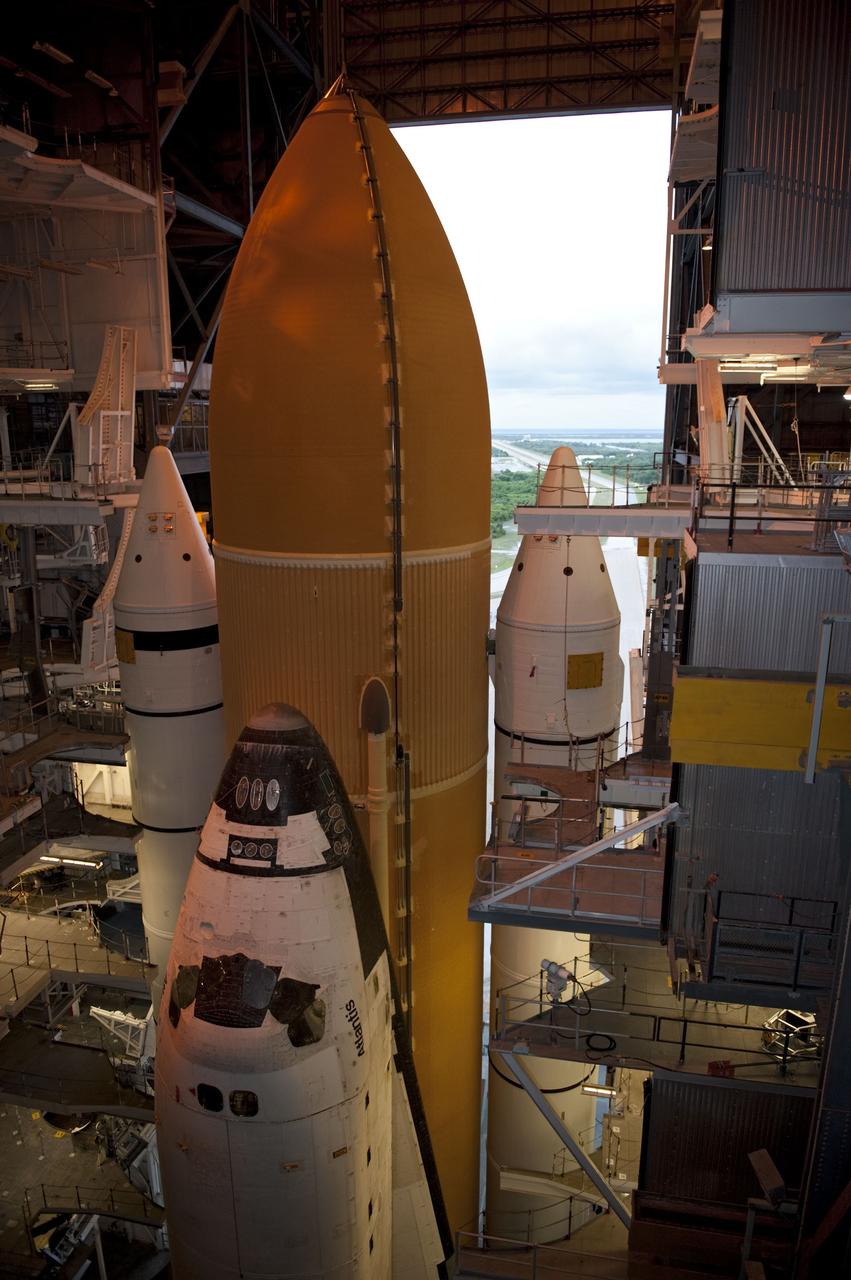
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress of external fuel tank, ET-138, for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission, as it is lifted from its test cell for transfer to high bay-1 for joining with the twin solid rocket boosters on the mobile launcher platform. Shuttle Atlantis' move, or "rollover," from Orbiter Processing Facility-1 to the VAB is targeted for May 10. Once there it will be mated with the external tank and boosters. Atlantis and its crew of four will deliver the Raffaello multipurpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Swarms of people are at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida to watch space shuttle Discovery lift off on its final scheduled mission from Launch Pad 39A. Liftoff is set for 4:50 p.m. EST on Feb. 24. Discovery and its six-member STS-133 crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather at the Press Site bull pen at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

Interior View of ARF Manufacturing Building

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla., -- At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians stretch a protective cover over NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is being prepared for its move to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. The spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the name of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, Curiosity, is emblazoned on its framework. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
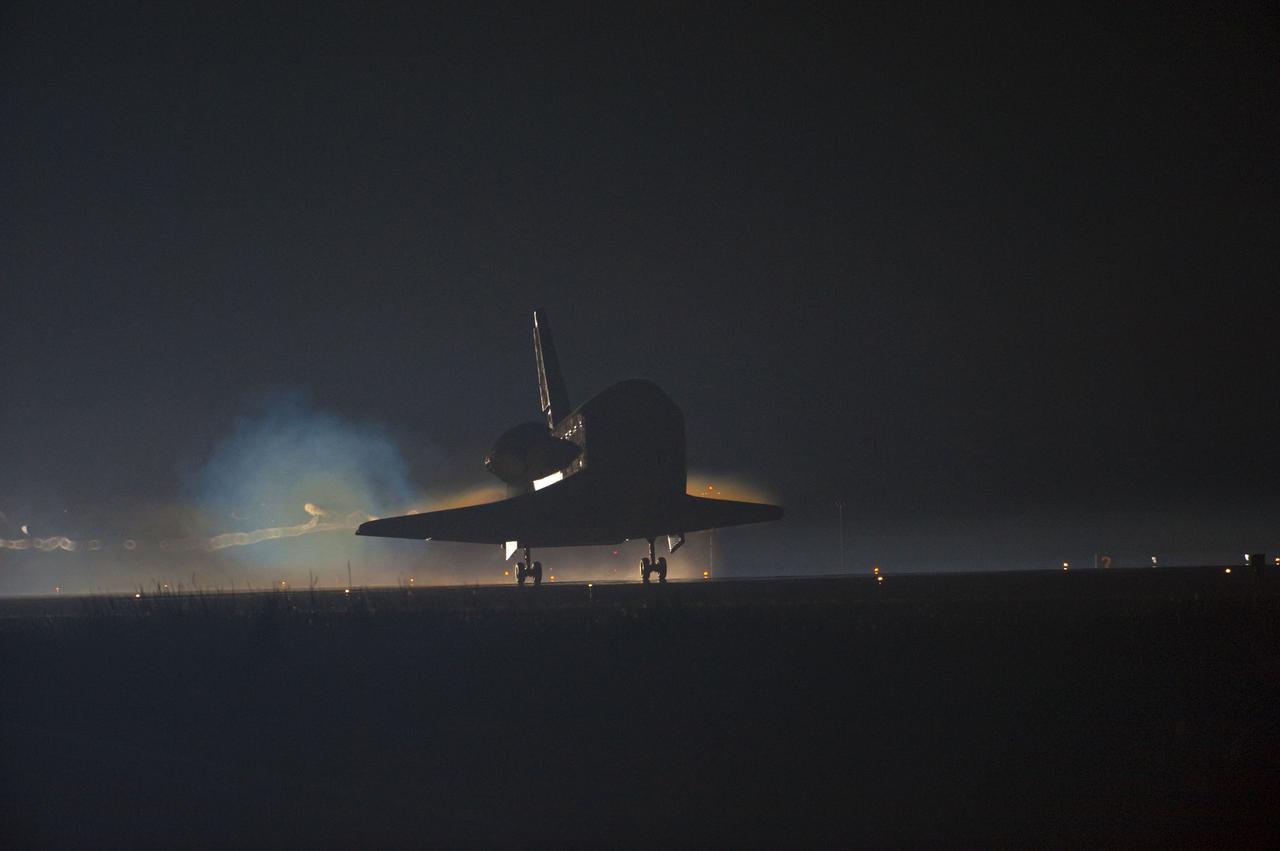

STS135-S-188 (21 July 2011) --- Ribbons of steam and smoke trail space shuttle Atlantis as it touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. (EDT) on July 21, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, STS-135 commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies in the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. Photo credit: NASA
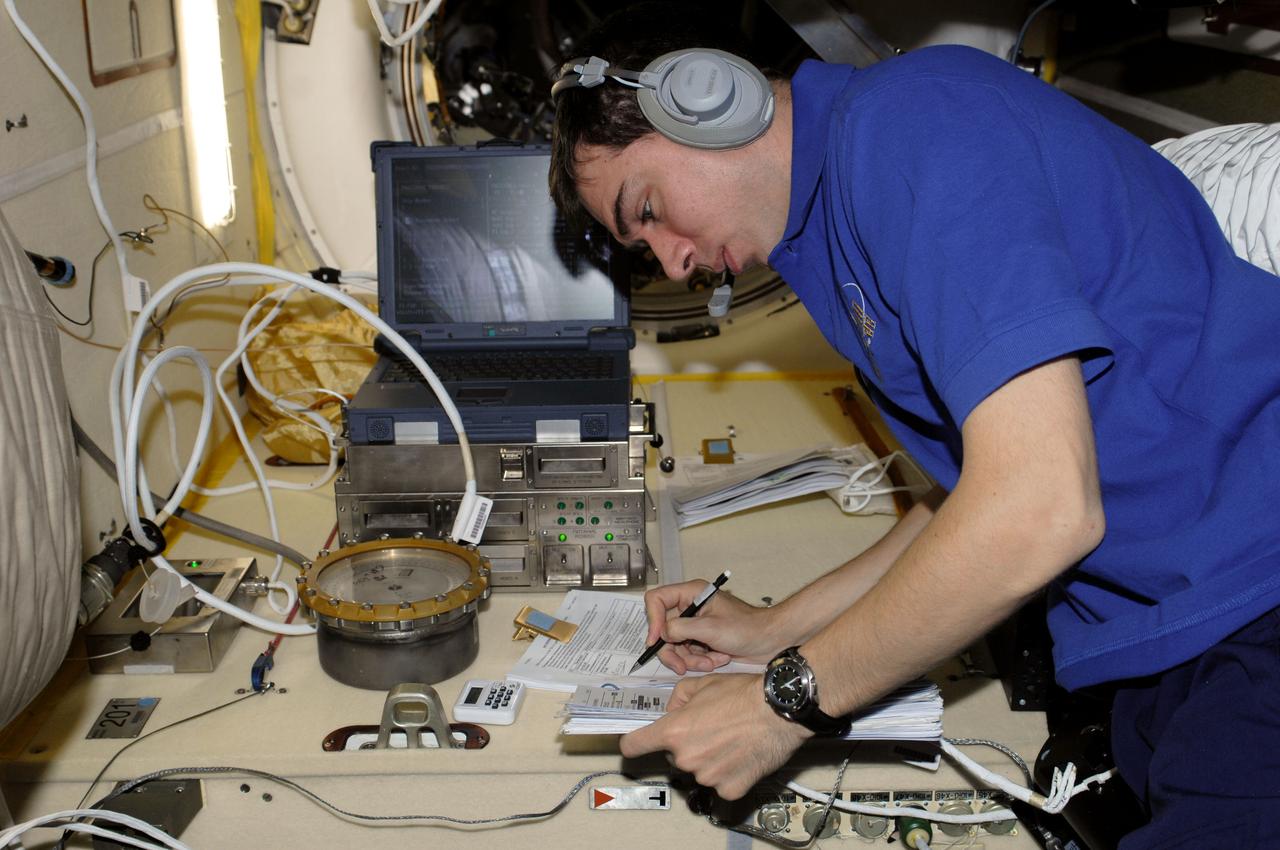

ISS028-E-009754 (27 June 2011) --- Russian cosmonaut Sergei Volkov, Expedition 28 flight engineer, works with the new KPT-21 PK-3+ Plasma Crystal-3+ (Plazmennyi-Kristall-3 plus) Telescience payload in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
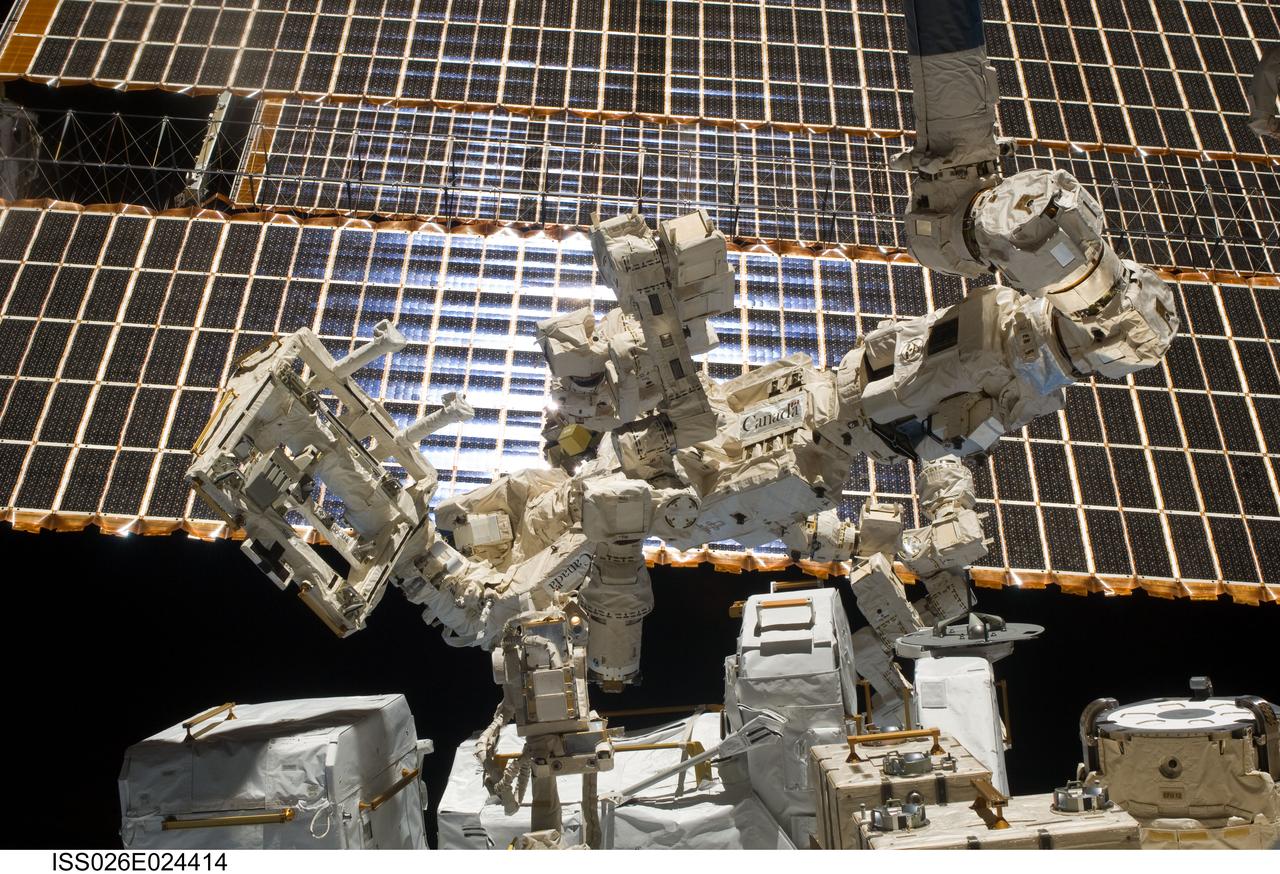

ISS026-E-024414 (3 Feb. 2011) --- While attached on the end of the Canadarm2, Dextre, the Canadian Space Agency’s robotic “handyman”, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member aboard the International Space Station. During the activities, Dextre unpacked two critical pieces of equipment delivered by Japan’s Kounotori2 spacecraft.

Portaits; Kepler Science Group - Chris Burke
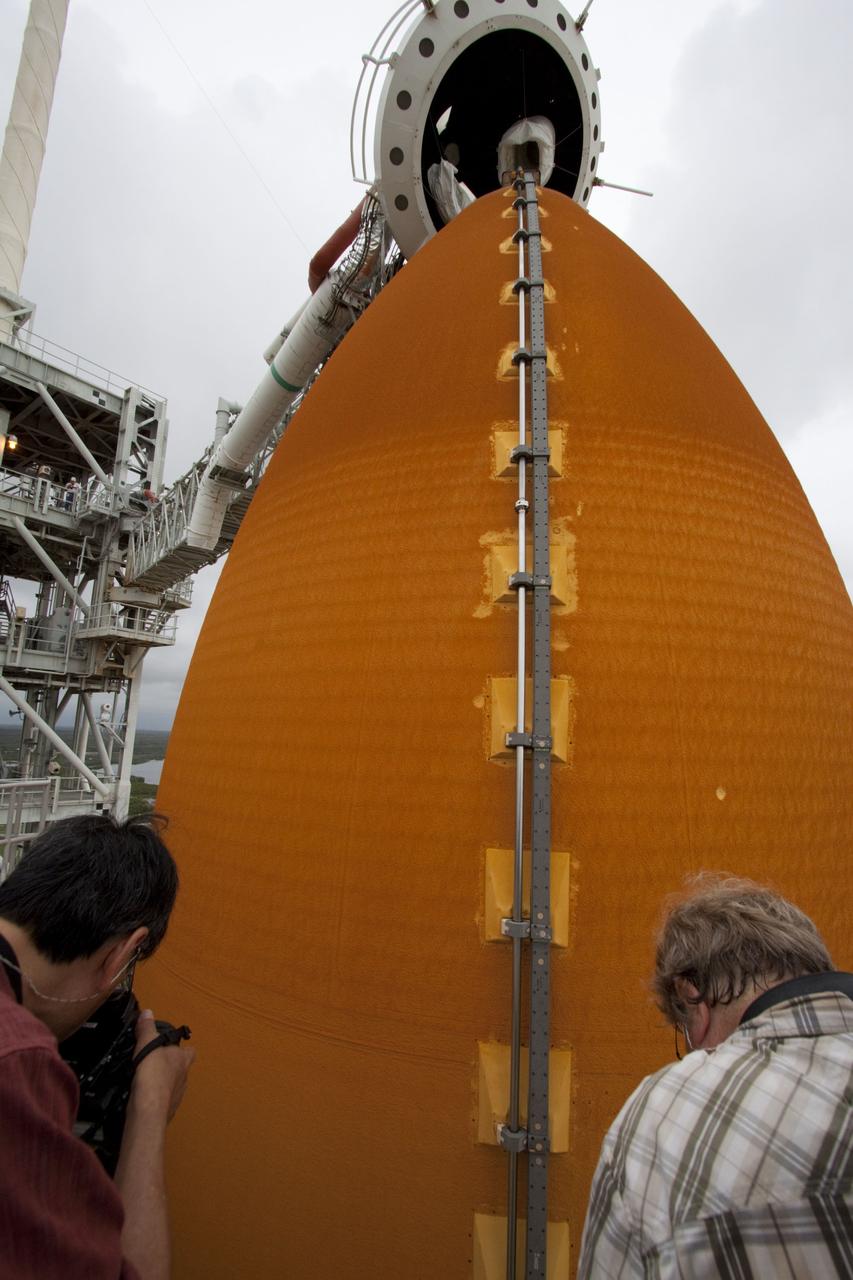

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Photographers Stan Hernda of AFP News, left, and Scott Andrews of Canon record space shuttle Atlantis as it is revealed on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the move of the rotating service structure (RSS). The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
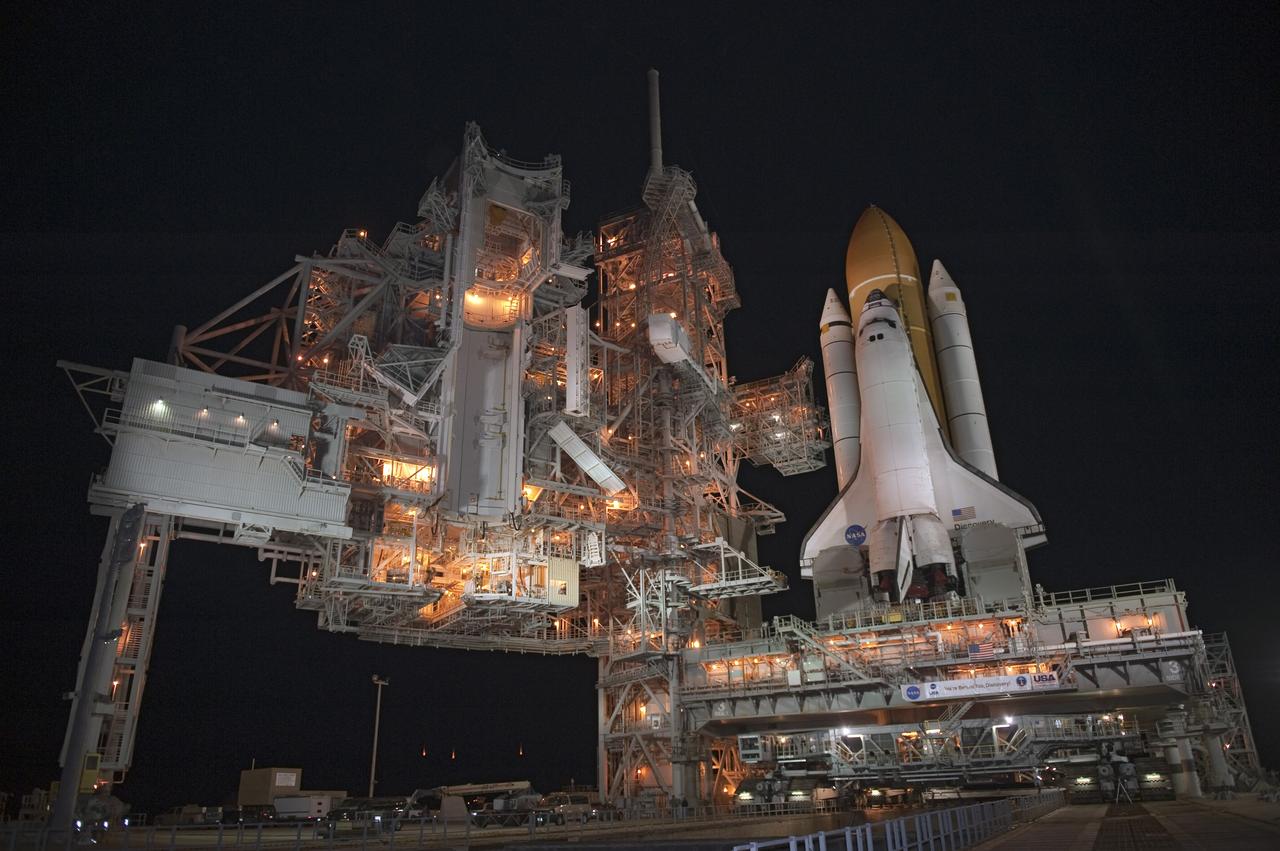

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery arrives at Launch Pad 39A from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It took the shuttle, attached to its external fuel tank, twin solid rocket boosters and mobile launcher platform, about seven hours to complete the move atop a crawler-transporter. This is the second time Discovery has rolled out to the pad for the STS-133 mission, and comes after a thorough check and modifications to the shuttle's external tank. Targeted to liftoff Feb. 24, Discovery will take the Permanent Multipurpose Module (PMM) packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2 (R2) to the International Space Station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
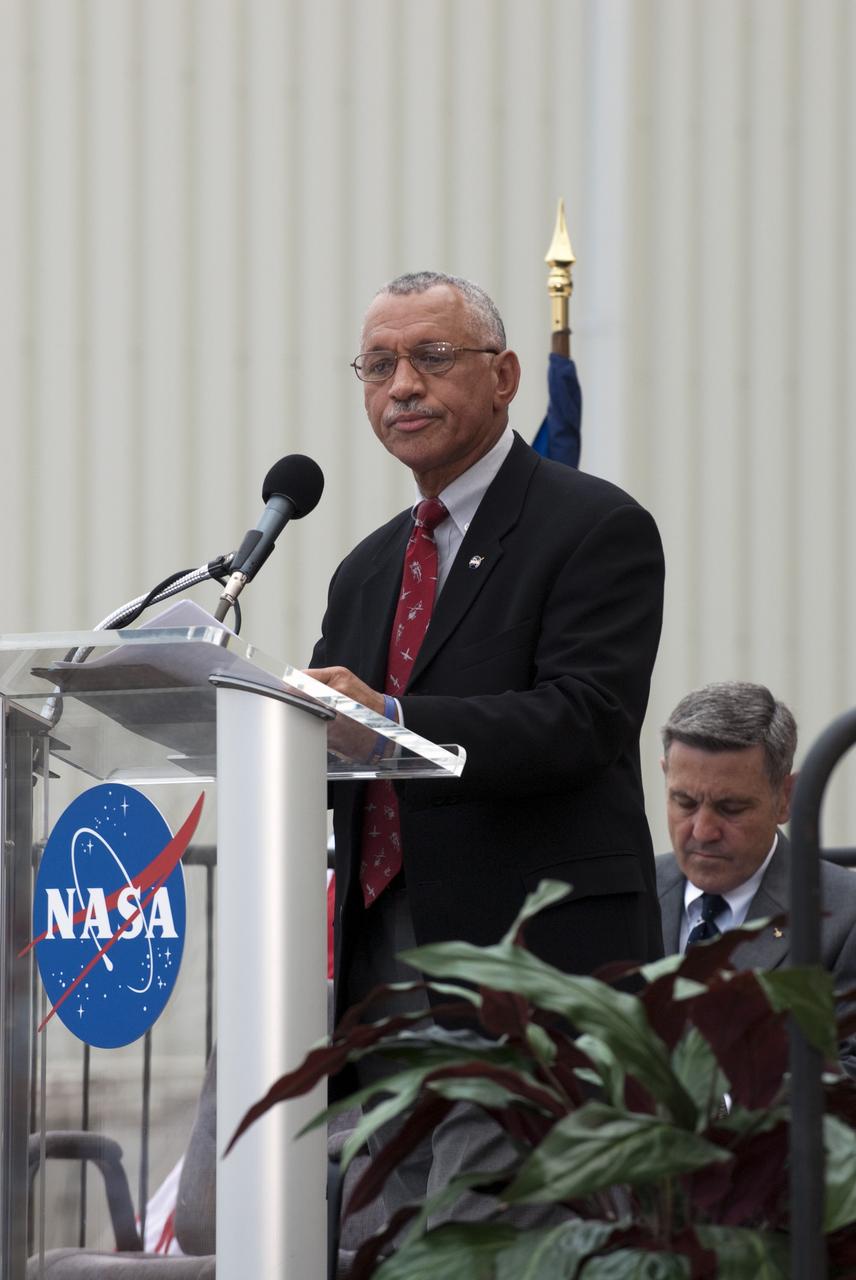

In a ceremony held in front of Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden announced the facilities where four shuttle orbiters will be displayed permanently at the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program. Shuttle Enterprise, the first orbiter built, will move from the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Virginia to the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York. The Udvar-Hazy Center will become the new home for shuttle Discovery, which retired after completing its 39th mission in March. Shuttle Endeavour, which is preparing for its final flight at the end of the month, will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Atlantis, which will fly the last planned shuttle mission in June, will be displayed at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The event also commemorated the 30th anniversary of the first space shuttle launch with the launch of shuttle Columbia. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
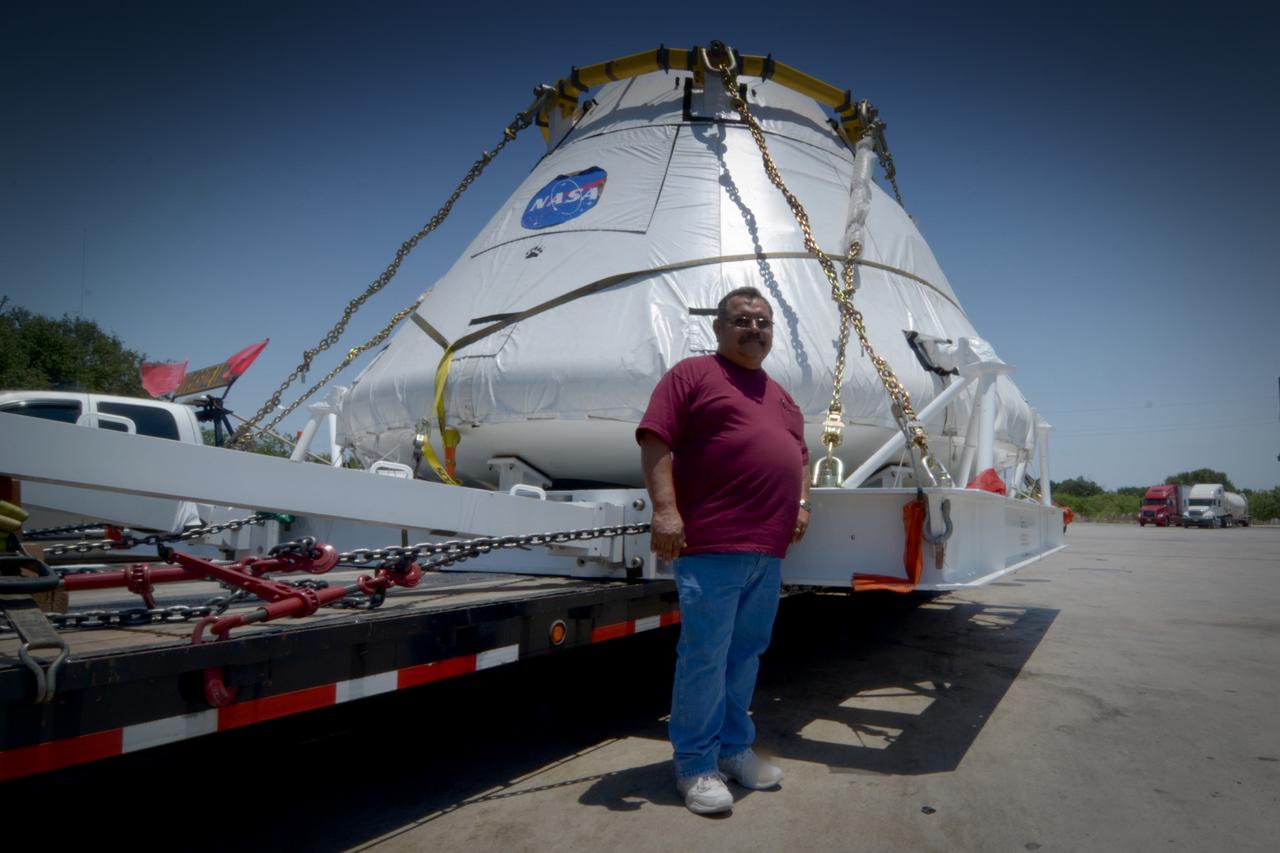

Travelers take a photo with the Orion crew module flown on NASA’s Pad Abort-1 (PA-1) flight test on the road on June 15, 2011. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

JSC2011-E-068761 (22 July 2011) --- A small portion of a large Ellington Field crowd is seen on July 22, 2011 through a door bearing a STS-135 sticker on its window. A short while later the crew of the space shuttle Atlantis' mission used this door for its entrance during a welcome home ceremony. STS-135 is the final mission of the NASA Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA Photo/Houston Chronicle, Smiley N. Pool
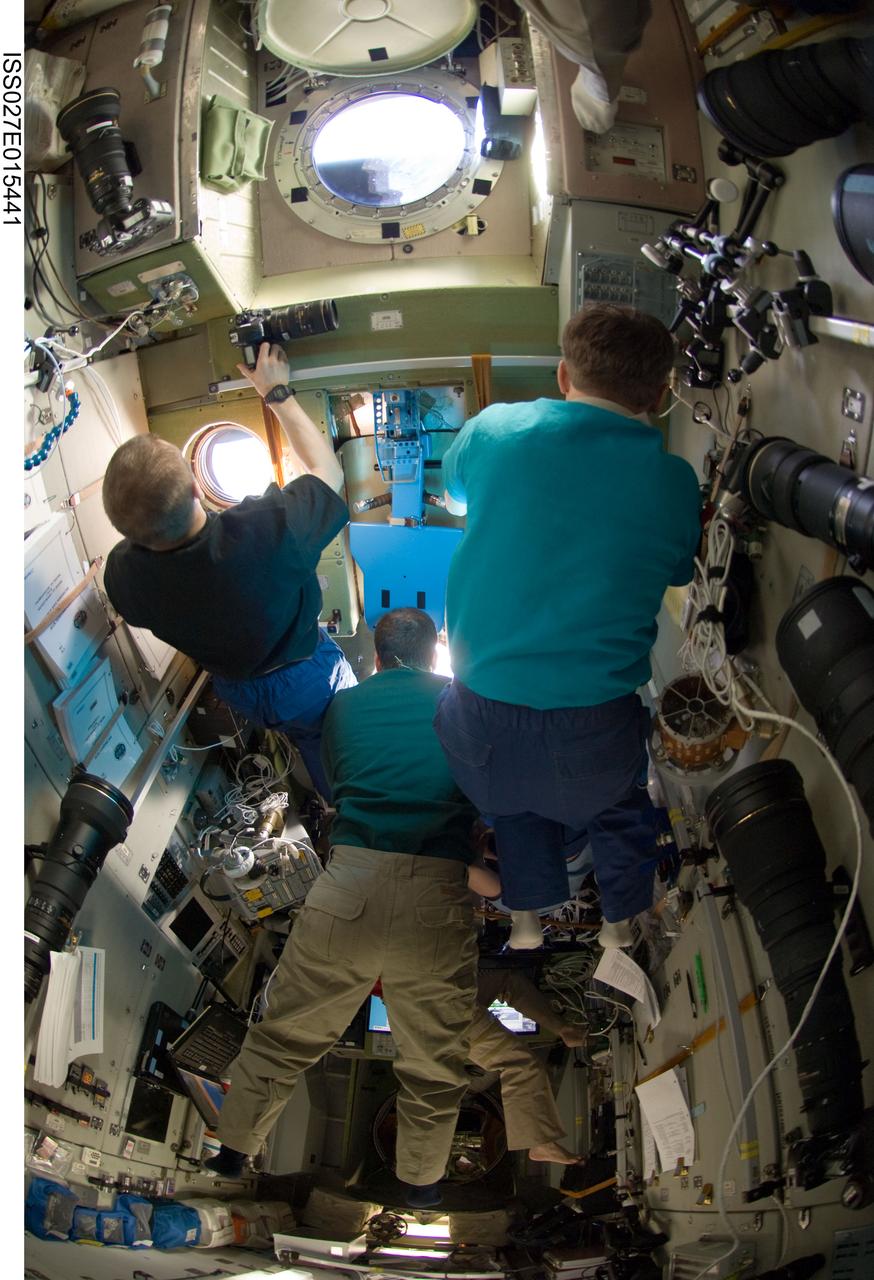

ISS027-E-015441 (22 April 2011) --- Russian cosmonaut Dmitry Kondratyev (left), Expedition 27 commander; along with NASA astronaut Ron Garan (center) and Russian cosmonaut Andrey Borisenko, both flight engineers, watch the departure of the unpiloted ISS Progress 41 supply vehicle through windows in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
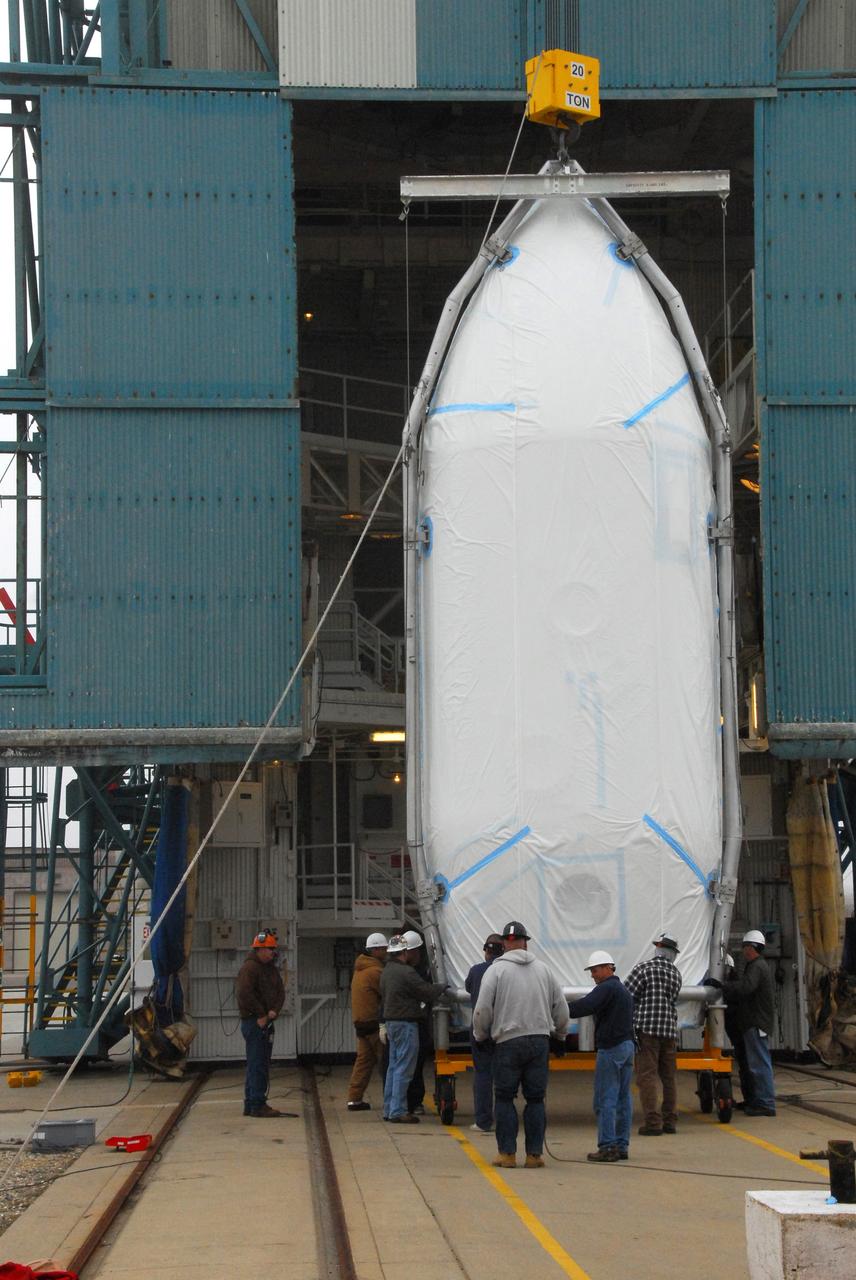

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The payload fairing that will protect NASA's National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) satellite as it launches aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II begins its lift to Level 5 of Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NPP will be positioned 512 miles above the Earth's surface and will orbit about 16 times each day to observe nearly the entire globe. The NPP mission for NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is to measure Earth's atmospheric and sea surface temperatures, humidity sounding, land and ocean biological activity, and cloud and aerosol properties. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/NPP. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB, Roy Allison
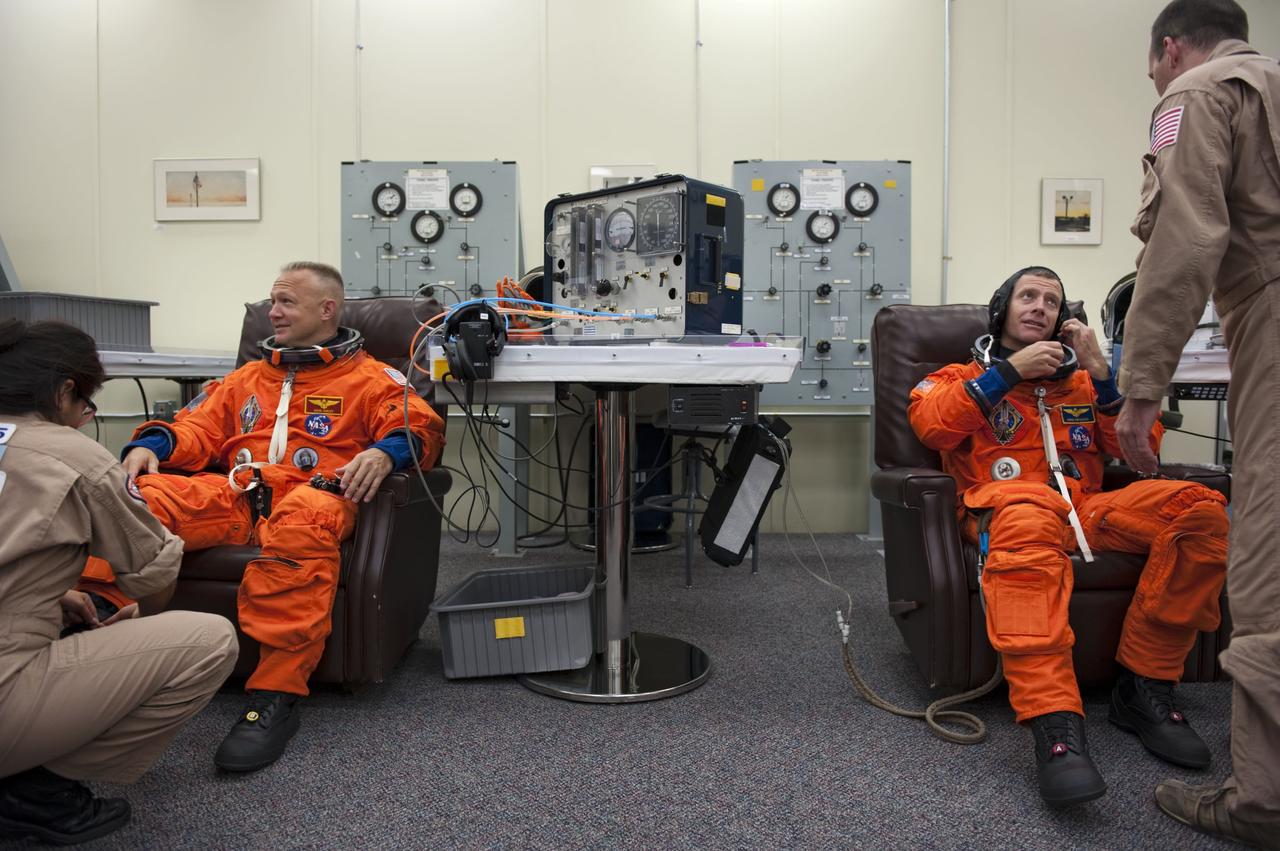

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-135 Pilot Doug Hurley, left, and Commander Chris Ferguson put on the finishing touches of their launch-and-entry suits with the help of United Space Alliance suit technicians in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Hurley and Ferguson are two of the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle. STS-135 is scheduled to lift off aboard space shuttle Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for a mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
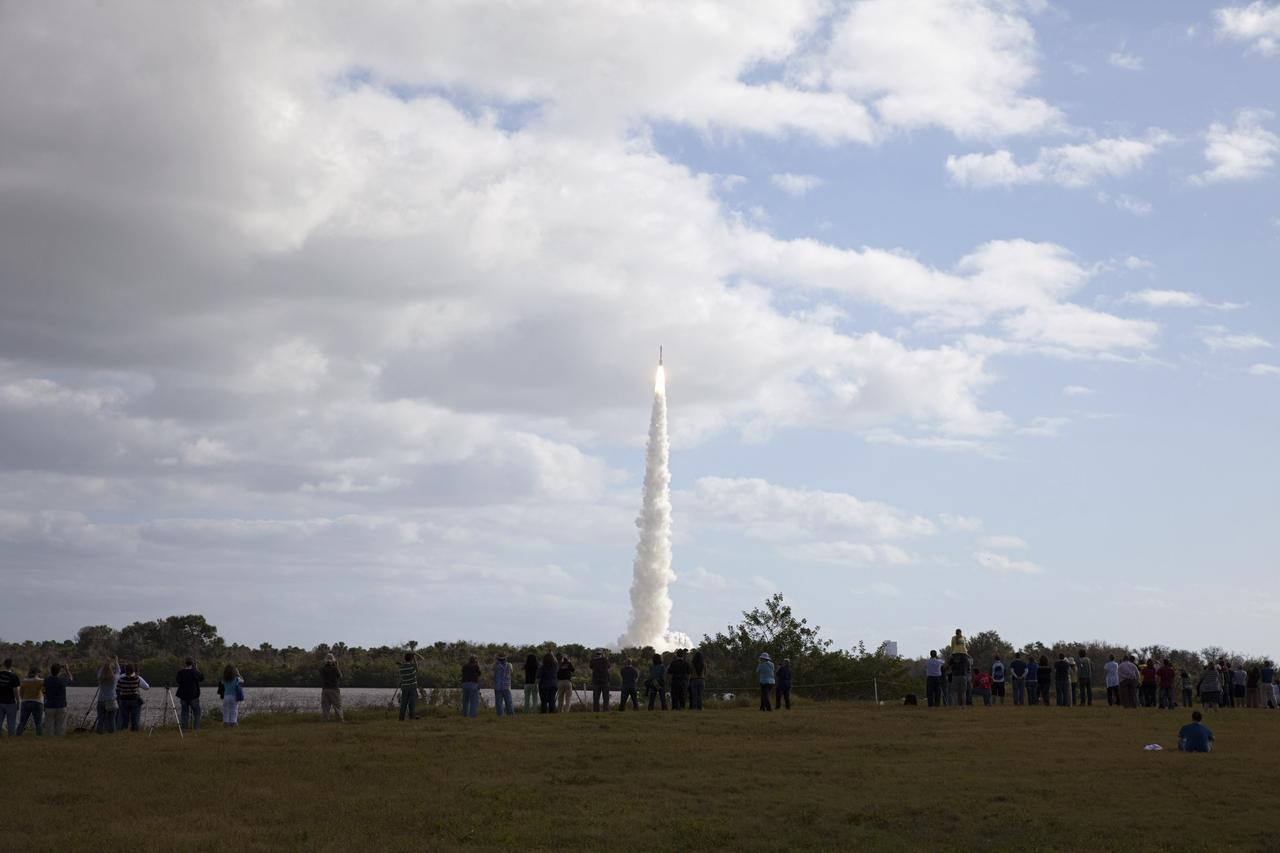

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Press Site in Florida, participants in NASA's Tweetup photograph the launch of the agency's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) from the turn basin. The tweeters will share their experiences with followers through the social networking site Twitter. The 197-foot-tall United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifted off Space Launch Complex-41 on neighboring Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 10:02 a.m. EST at the opening of the launch window. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
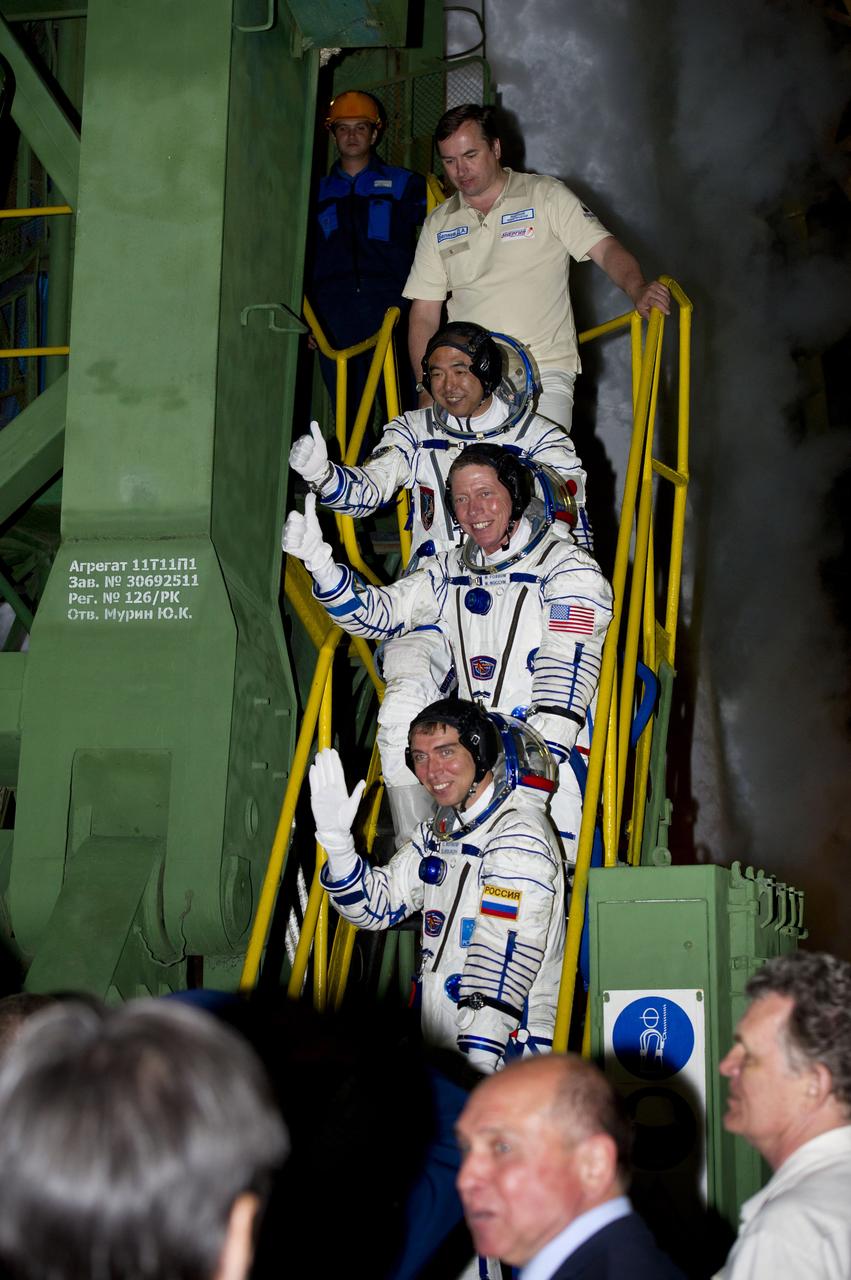

Expedition 28 crew members from bottom, Soyuz Commander Sergei Volkov of Russia, NASA Flight Engineer Mike Fossum and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Flight Engineer Satoshi Furukawa wave from the bottom of the Soyuz rocket prior to their launch to the International Space Station from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, on Tuesday, June 7, 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
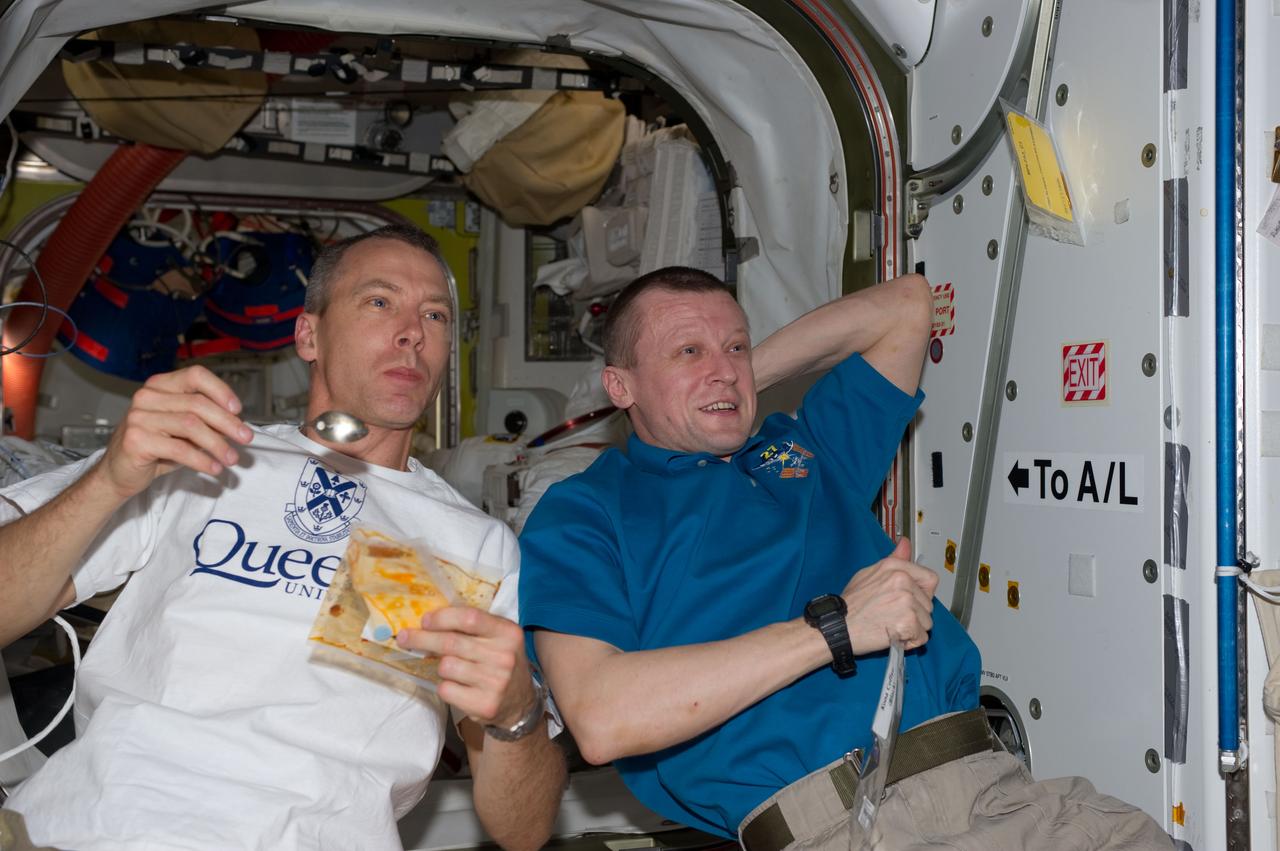

S134-E-008391(21 May 2011) --- Onboard the International Space Station, this snack time snap shot catches two of the twelve joint Expedition 27/STS-134 crew members during a break in a very busy schedule. NASA astronaut Andrew Feustel, STS-134 mission specialist, is at left, and he is joined Russian cosmonaut Dmitry Kondratyev, Expedition 27 commander. Photo credit: NASA
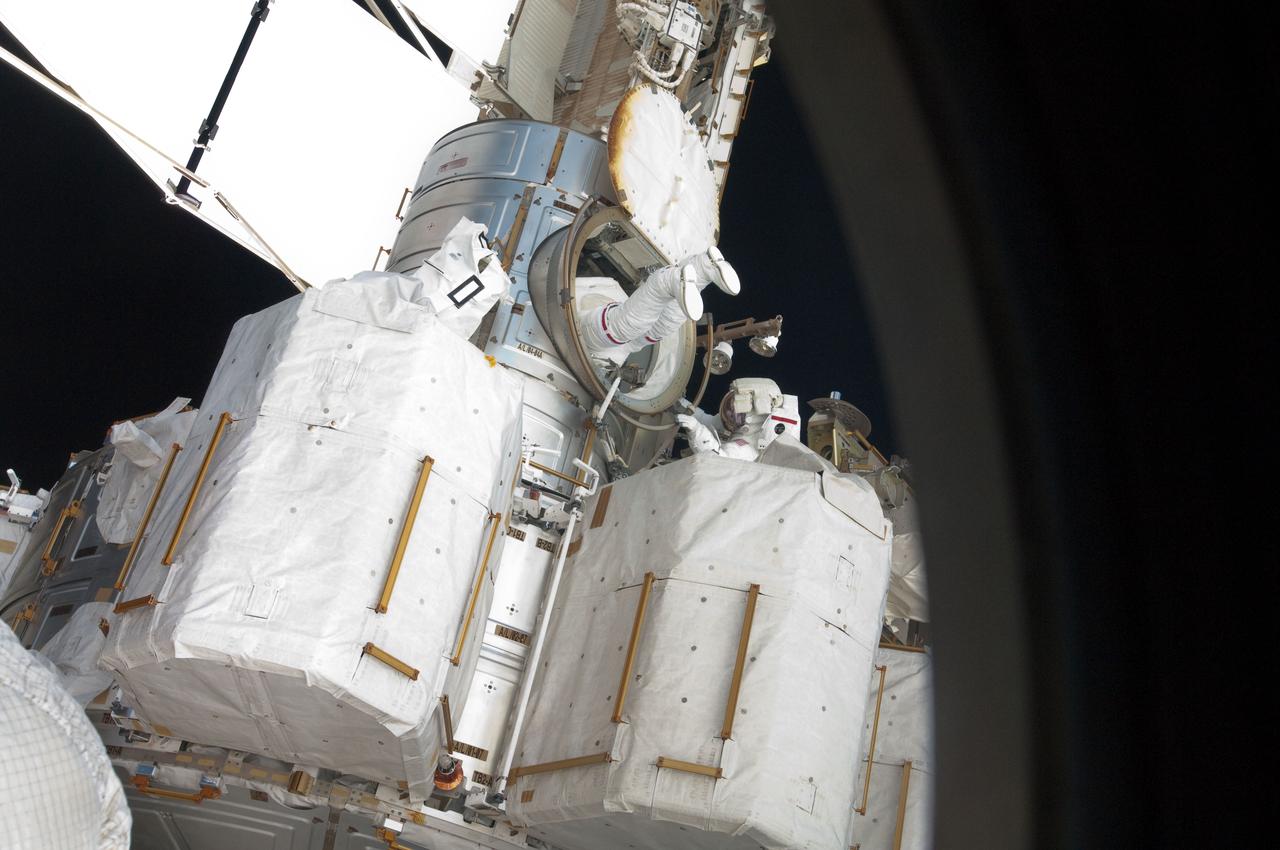

S134-E-009310 (20 May 2011) --- NASA astronaut Greg Chamitoff, STS-134 mission specialist, enters the Quest airlock of the International Space Station as the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) draws to a close. During the six-hour, 19-minute spacewalk, Chamitoff and astronaut Andrew Feustel (out of frame) retrieved long-duration materials exposure experiments and installed another, installed a light on one of the station?s rail line handcarts, made preparations for adding ammonia to a cooling loop and installed an antenna for the External Wireless Communication system. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A wreath is displayed at the foot of the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida during a ceremony to honor space shuttle Challenger's STS-51L crew members who gave their lives for while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. NASA/Jack Pfaller

American Geophysical Union 'AGU' Fall Meeting in San Francisco Moscone Center, California.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket has arrived at Launch Complex 41. NASA's Juno spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
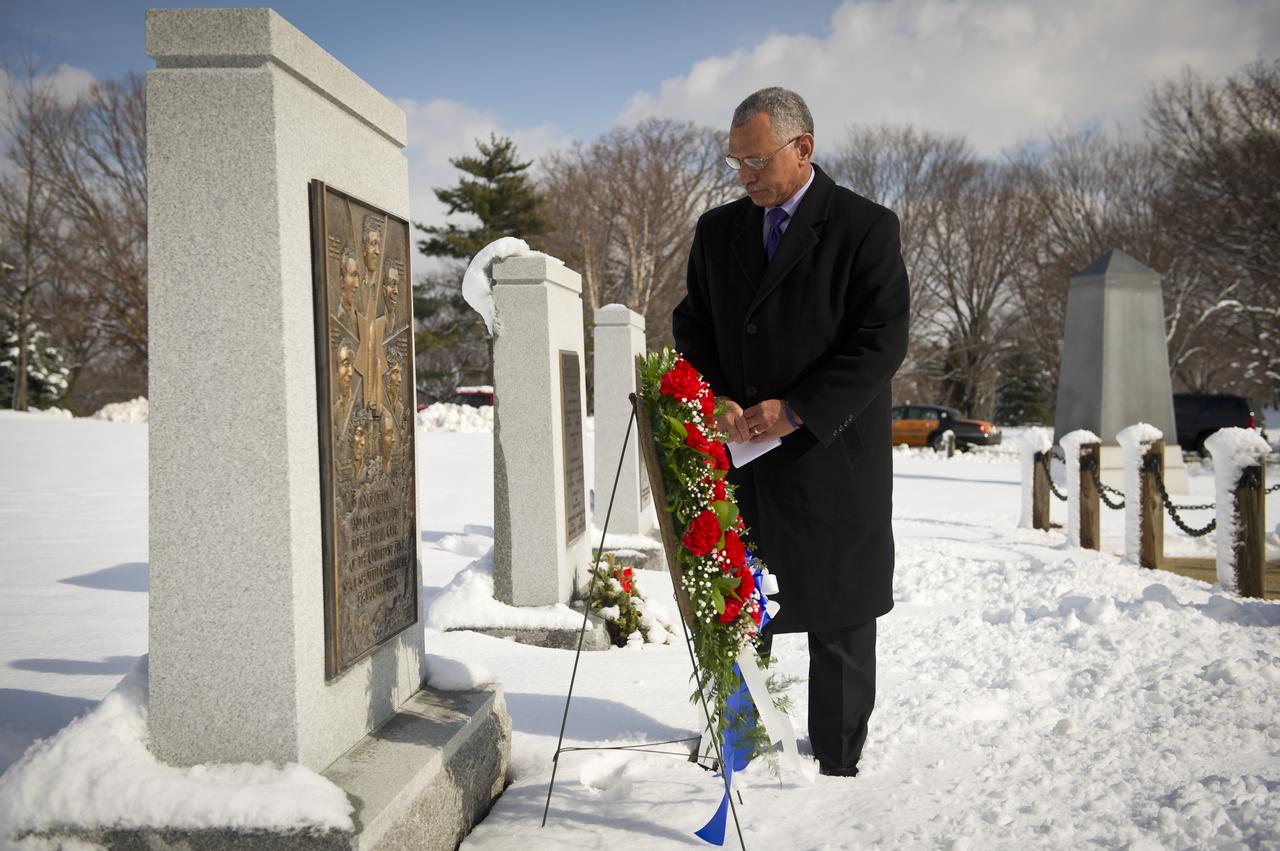

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden participates in a wreath laying ceremony as part of NASA's Day of Remembrance, Thursday, Jan. 27, 2011, at Arlington National Cemetery. Wreathes were laid in memory of those men and women who lost their lives in the quest for space exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
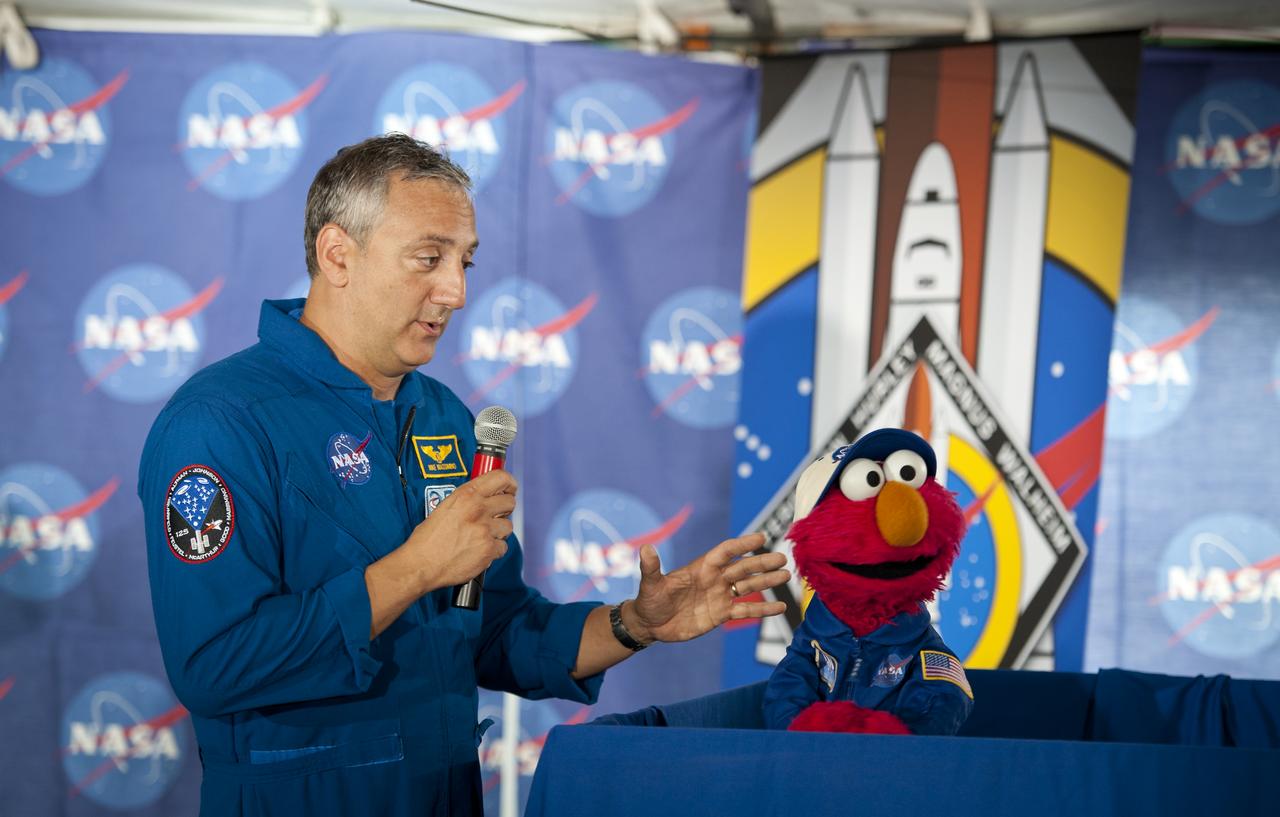

NASA astronaut Mike Massimino, left, and Sesame Street's Elmo speak at the STS-135 Tweetup, Thursday, July 7, 2011, at Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Elmo asked the astronauts questions about living and working in space. About 150 NASA Twitter followers attended the event. The STS-135 mission will be NASA's last space shuttle launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)

ISS027-E-034430 (20 May 2011) --- NASA astronauts Andrew Feustel and Greg Chamitoff (out of frame), both STS-134 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 19-minute spacewalk, Feustel and Chamitoff retrieved long-duration materials exposure experiments and installed another, installed a light on one of the station?s rail line handcarts, made preparations for adding ammonia to a cooling loop and installed an antenna for the External Wireless Communication system.
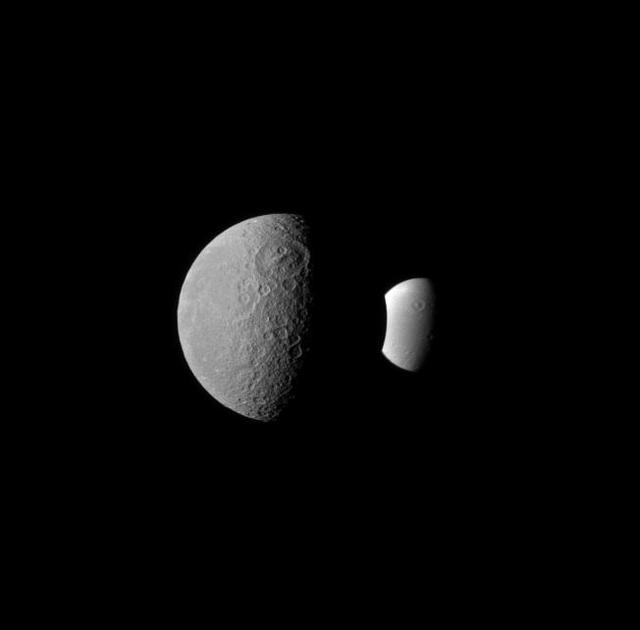

Rhea and Dione seem like dark and light fraternal twins in this image from NASA Cassini spacecraft, with each of these two Saturnian moons displaying a large crater oriented similarly in the northern hemisphere.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences workers monitor NASA's Glory upper stack as a crane lifts it from a stationary rail for attachment to the Taurus XL rocket's Stage 0. The upper stack consists of Stages 1, 2 and 3 of the Taurus as well as the encapsulated Glory spacecraft. Workers put the non-flight environmental shield over the fairing prior to assembly. The Orbital Sciences Taurus XL rocket will launch Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

Expedition 29 crew member Dan Burbank during SSATA Crew Training. Photo Date: May 18, 2011. Location: Building 7 - SSATA Chamber. Photographer: Robert Markowitz.
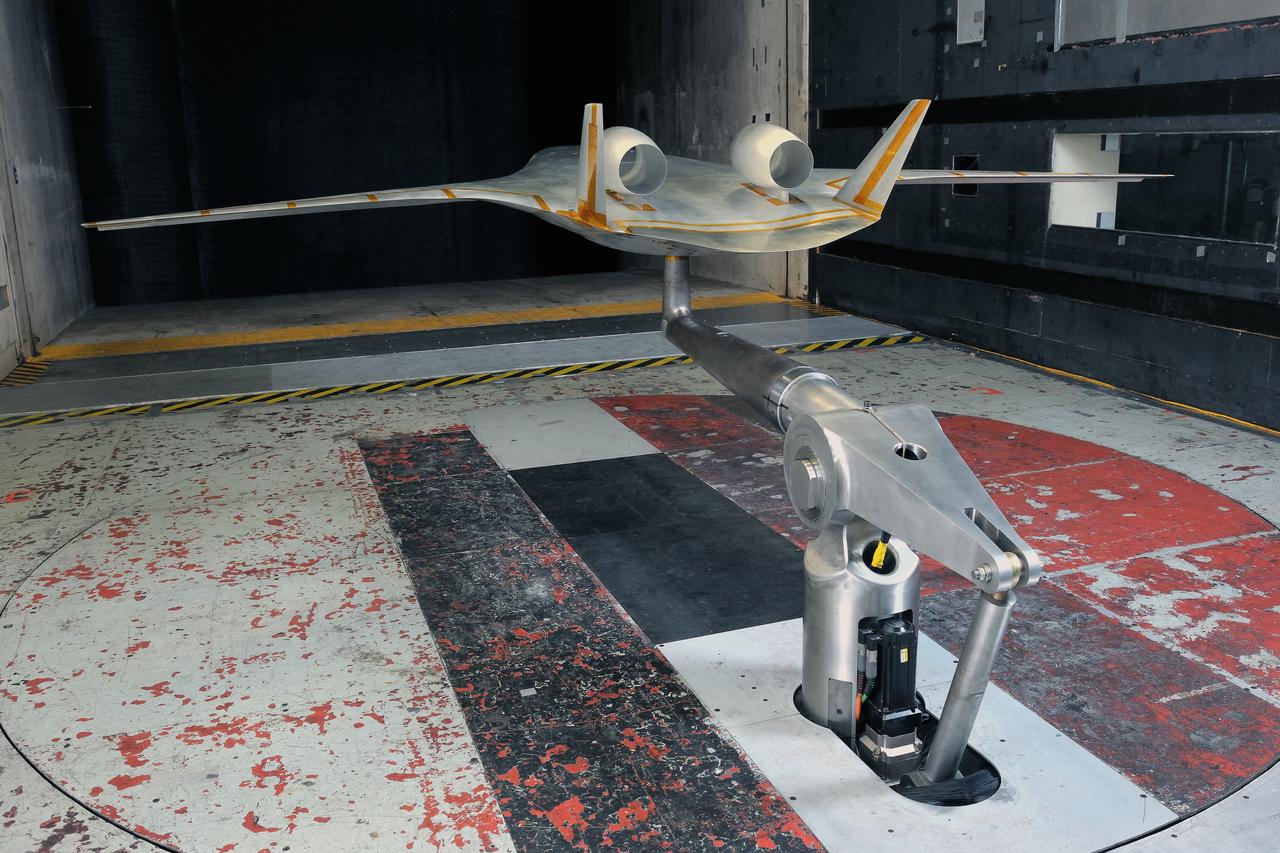

(HWB) Hybrid Wing Body Aerodynamic Test in 14x22 12.3 Foot Span HWB Model as tested in the 14x22 Foot Subsonic Tennel Aerodynamic Test
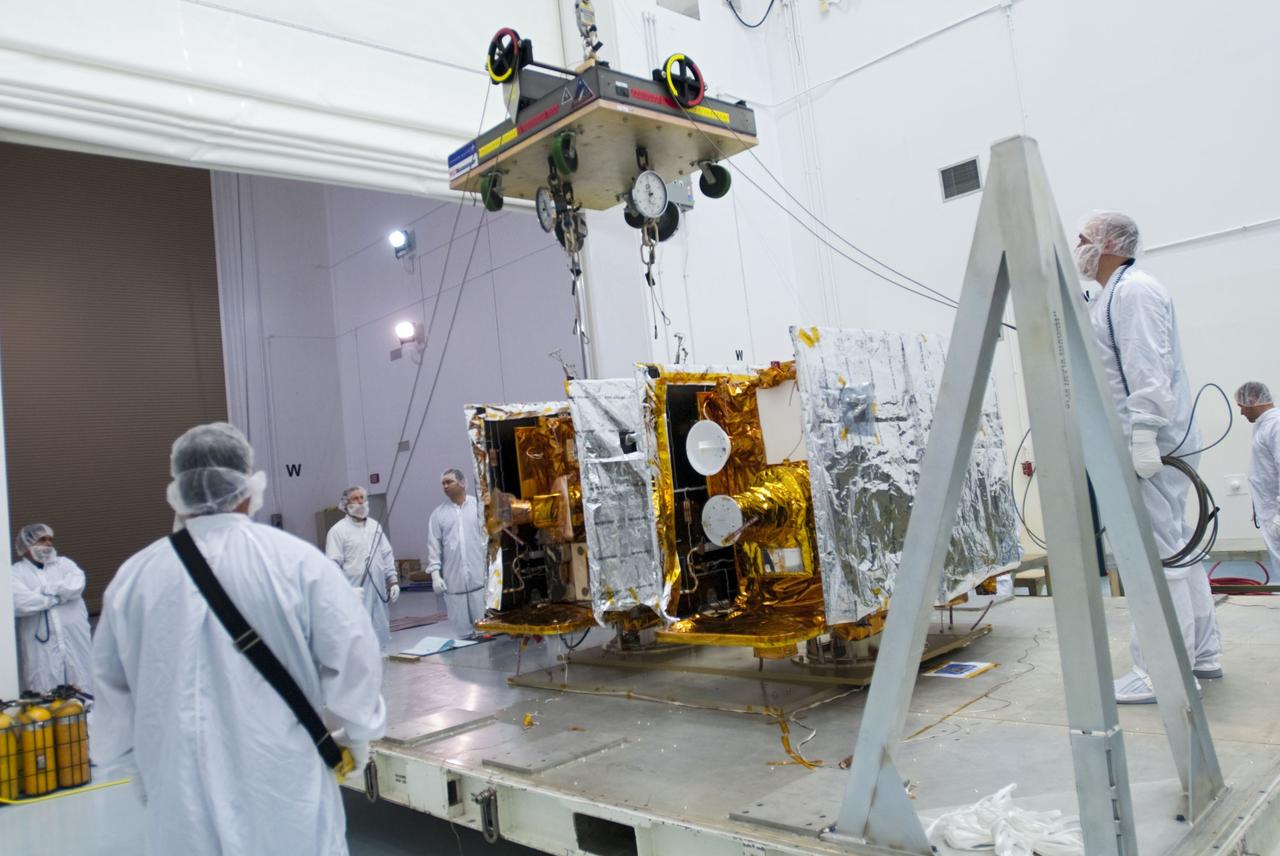

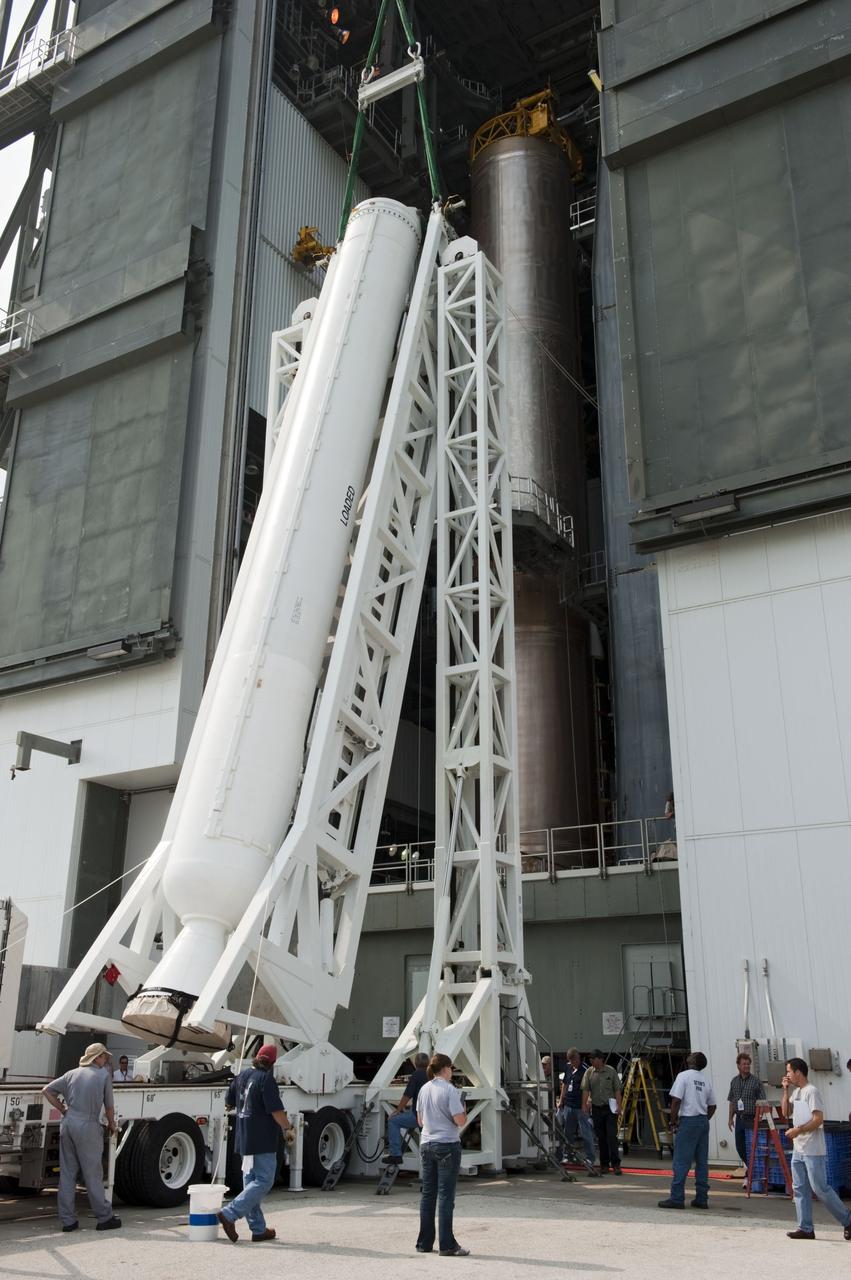
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are under way to lift one of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft onto a workstand in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
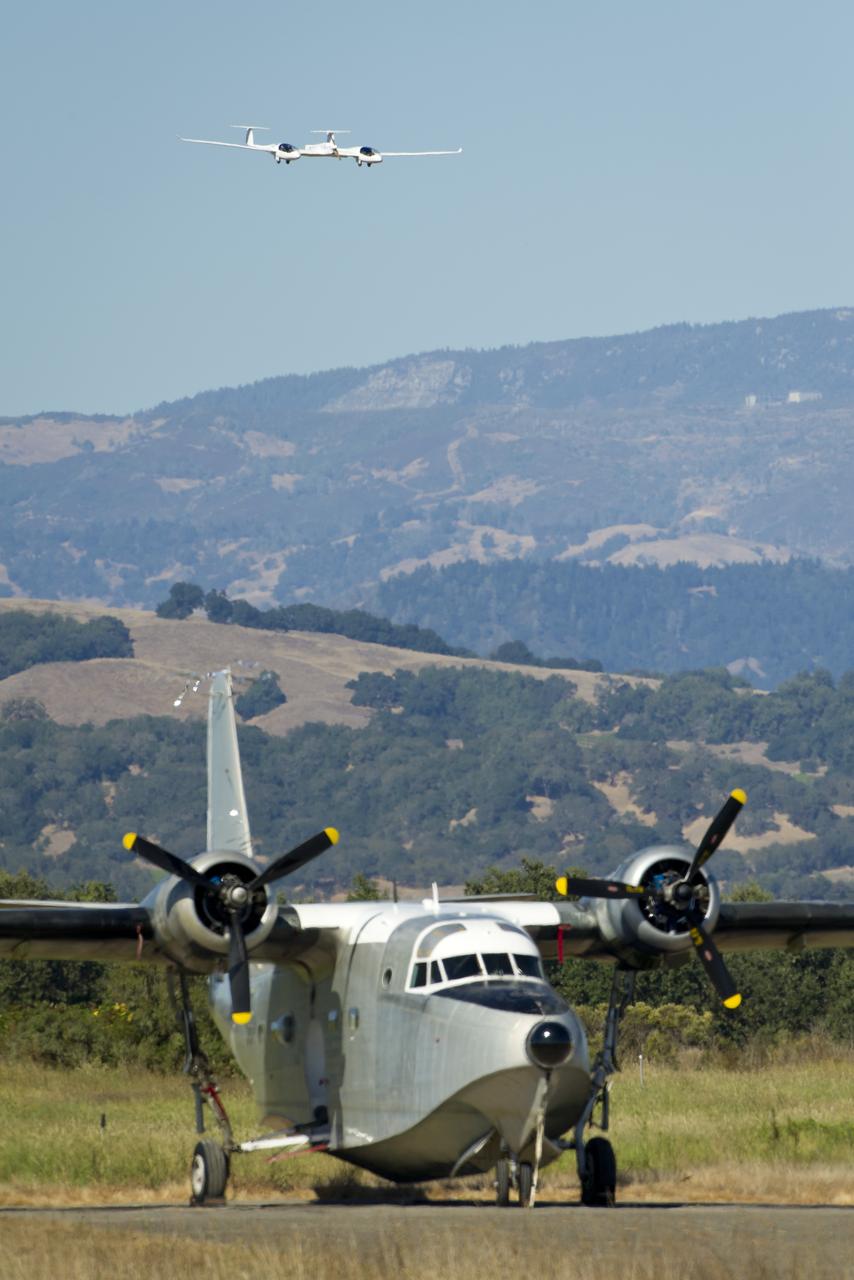

The Pipistrel-USA, Taurus G4 aircraft approaches for landing as a Grumman Albatross plane is seen in the forground during the 2011 Green Flight Challenge, sponsored by Google, at the Charles M. Schulz Sonoma County Airport in Santa Rosa, Calif. on Monday, Sept. 26, 2011. NASA and the Comparative Aircraft Flight Efficiency (CAFE) Foundation are having the challenge with the goal to advance technologies in fuel efficiency and reduced emissions with cleaner renewable fuels and electric aircraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
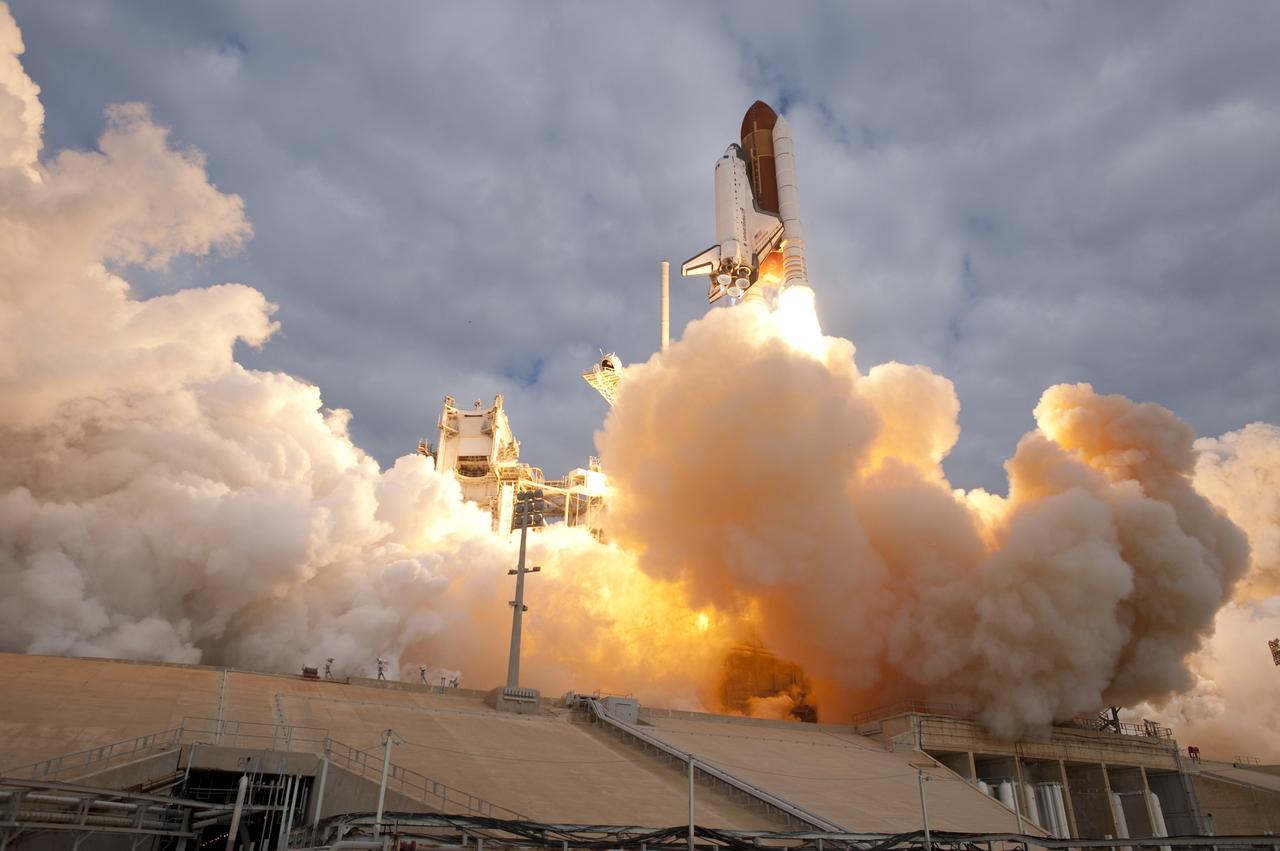

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour rises through clouds of smoke and steam from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
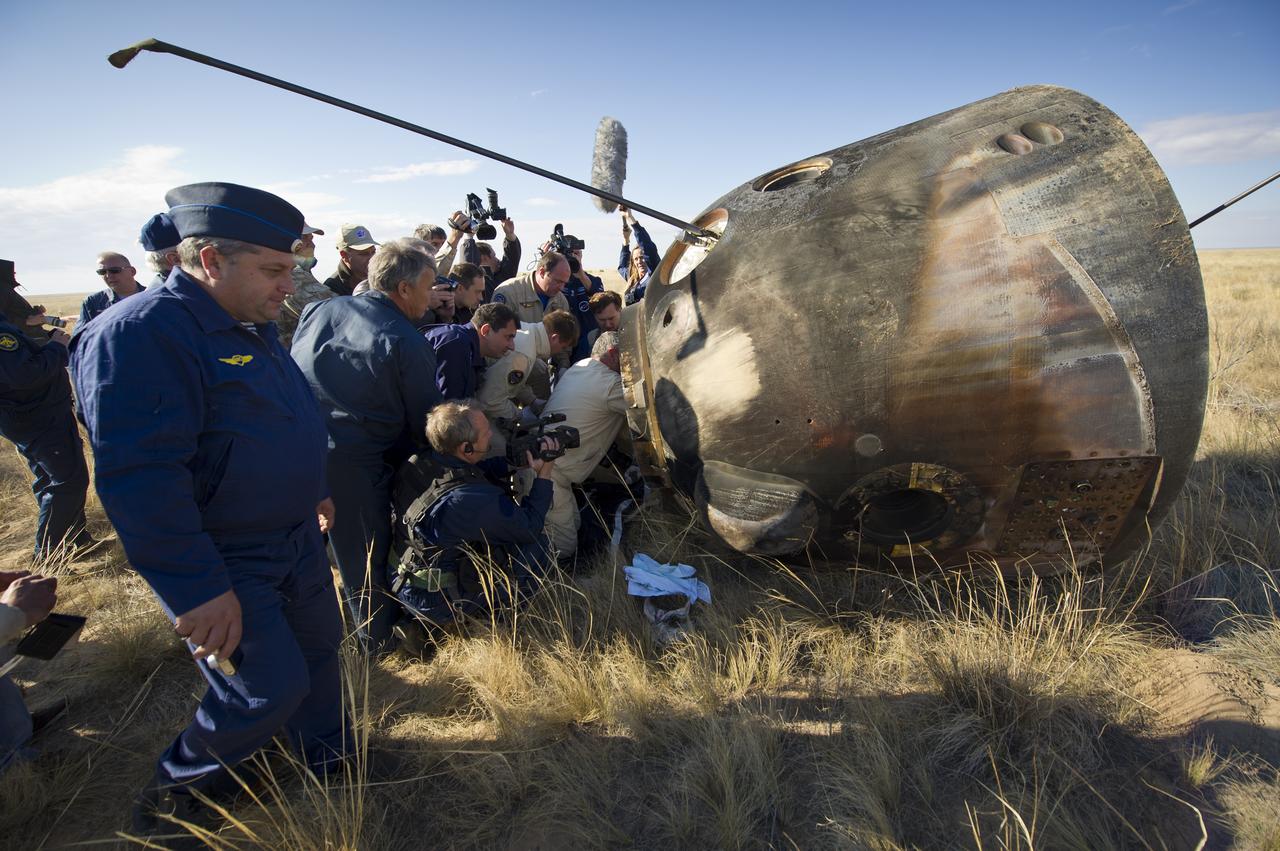

Russian support personnel work to help get crew members out of the Soyuz TMA-21 spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 28 Commander Andrey Borisenko, and Flight Engineers Ron Garan, and Alexander Samokutyaev in a remote area outside of the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan, on Friday, Sept. 16, 2011. NASA Astronaut Garan, Russian Cosmonauts Borisenko and Samokutyaev are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 27 and 28 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
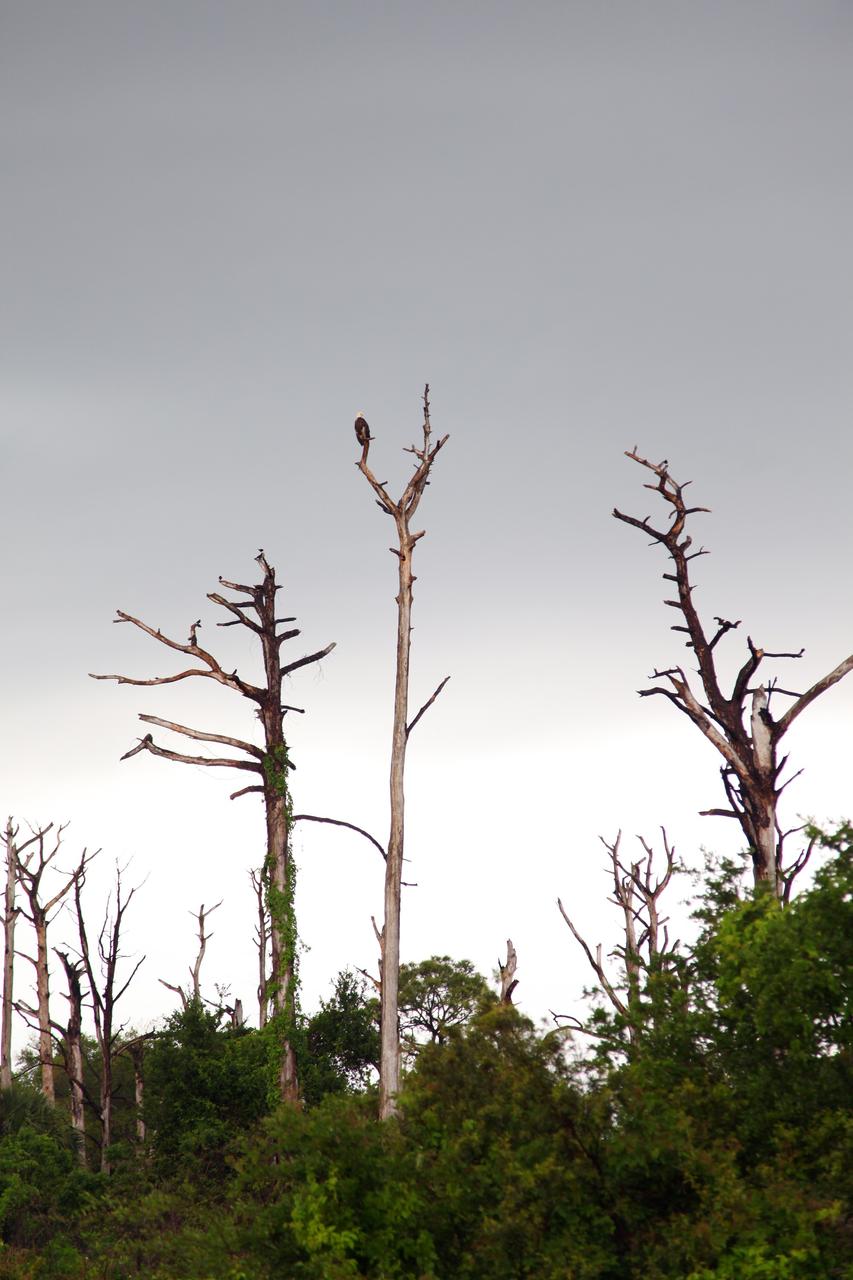

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A Bald Eagle takes advantage of a break in rain and perches on a tree at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Severe storms associated with a frontal system are moving through Central Florida, producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
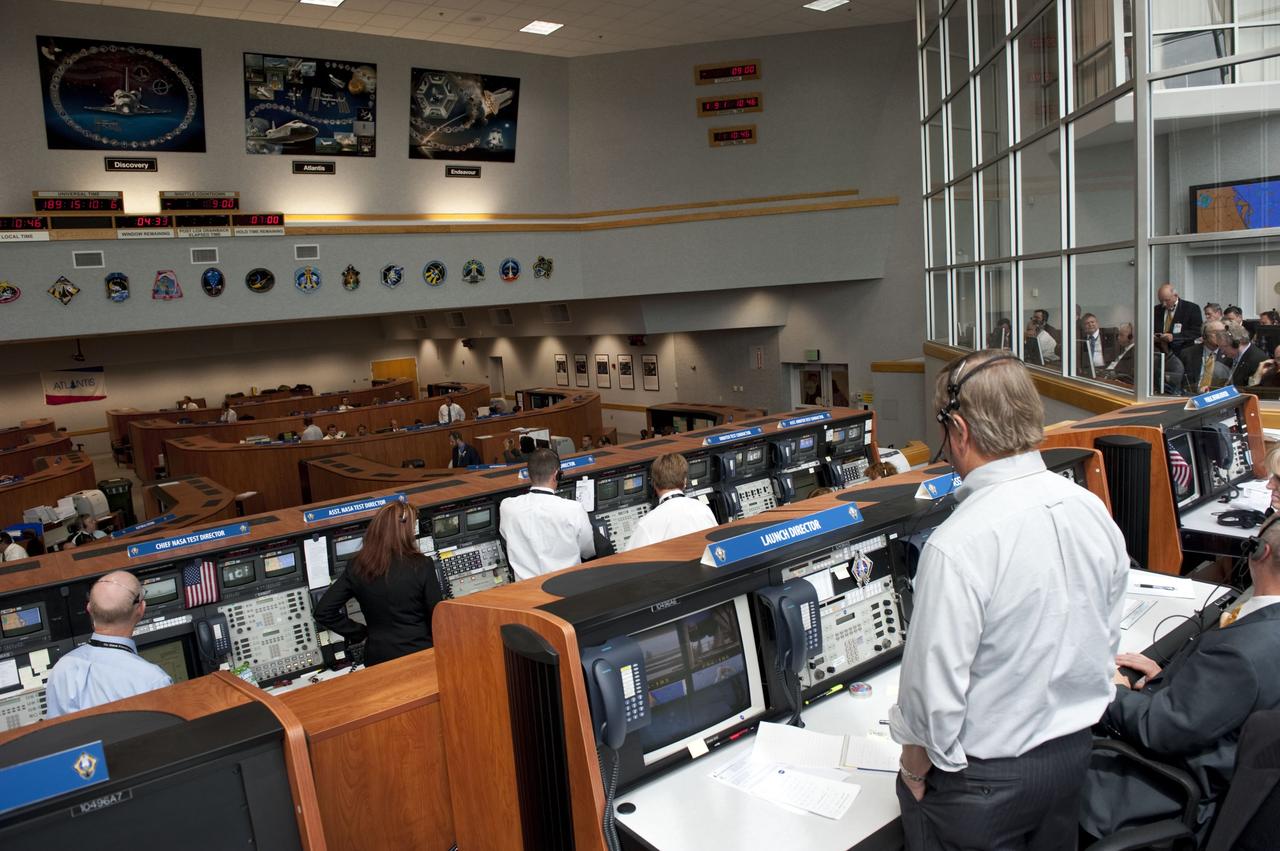

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach oversees the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
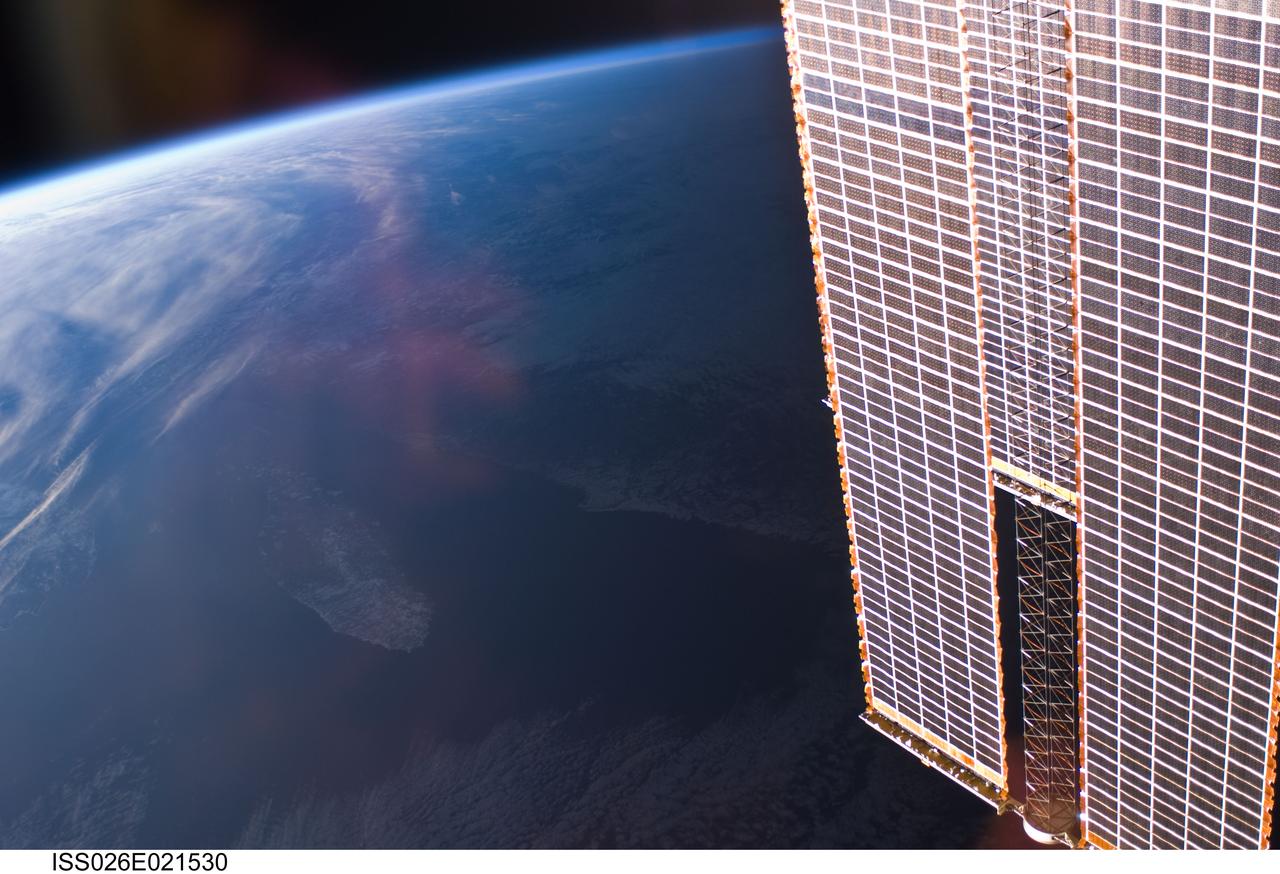

ISS026-E-021530 (1 Jan. 2011) --- Backdropped by Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space, International Space Station solar array panels are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member aboard the station.

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- Priscilla Moore, NASA Education Programs Specialist, speaks to students from across the nation gathered for the closing events of the NASA Explorer Schools (NES) symposium. During the NES gathering, students presented their investigation project to their peers, scientists, engineers and education specialists. About 60 fourth- through 12-grade students nationwide are at the center May 4-7 participating in tours of processing and launch facilities and the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, as well as several educational activities and a career panel question-and-answer session. About 30 teachers will receive professional development opportunities during the symposium. The participants were competitively selected after they completed an original investigation focused on existing NASA missions or research interests. Photo Credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor for the United Launch Alliance Delta II that will carry NASA's National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) satellite is hoisted up at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2. NPP represents a critical first step in building the next-generation of Earth-observing satellites. NPP will carry the first of the new sensors developed for this satellite fleet, now known as the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) to be launched in 2016. NPP is the bridge between NASA's Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites and the forthcoming series of JPSS satellites. The mission will test key technologies and instruments for the JPSS missions. NPP is targeted to launch Oct. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/NPP. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB, Dan Liberotti
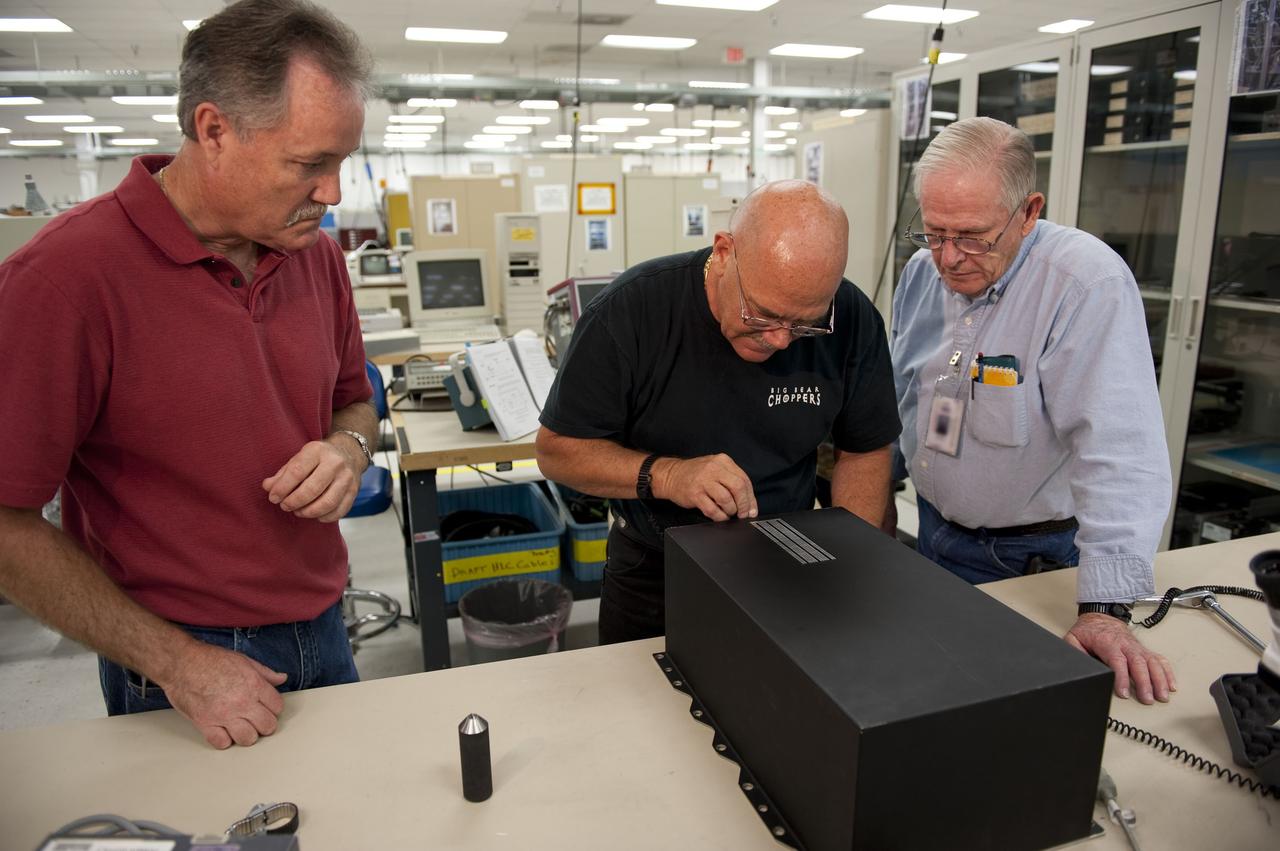

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, technicians remove the cover on the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) to begin the testing process. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

DATE: 9-1-11 LOCATION: Bldg. 5south, SSTF SUBJECT: Expedition 30 crew member and ESA astronaut Andre Kuipers training in SSTF near Columbia module on laptops with trainer Michaela Benda. PHOTOGRAPHER: Lauren Harnett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, workers using an overhead crane lift a solid rocket motor into the Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41. It then will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster stage, already at the pad. NASA's Juno spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
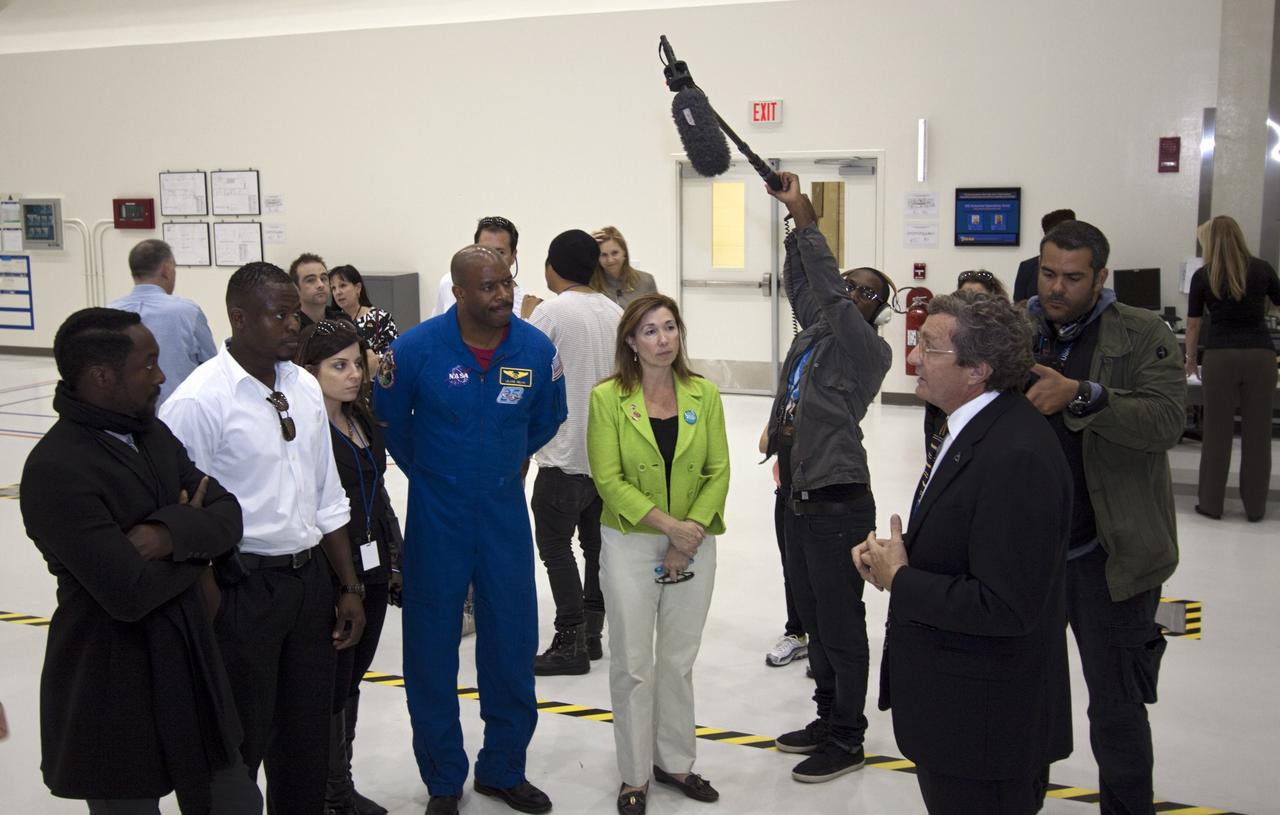

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Will.i.am (left), entertainer and member of The Black Eyed Peas, accompanied by Yves Lamothe, lead systems engineer for the 21st Century Ground Systems Program at Kennedy; former astronaut Leland Melvin, NASA associate administrator for Education (blue flight suit), and NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver (green jacket), receives a tour of the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) from Larry Price, Lockheed Martin deputy program manager. The visit to the O&C followed their participation in a NASA Tweetup. The Tweetup is part of prelaunch activities for the agency’s Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) launch and provides the opportunity for tweeters will share their experiences with followers through the social networking site Twitter. The MSL mission will pioneer precision landing technology and a sky-crane touchdown to place a car-sized rover, Curiosity, near the foot of a mountain inside Gale Crater on Aug. 6, 2012. During a nearly two-year prime mission after landing, the rover will investigate whether the region has ever offered conditions favorable for microbial life, including the chemical ingredients for life. Liftoff of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 10:02 a.m. EST on Nov. 26. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
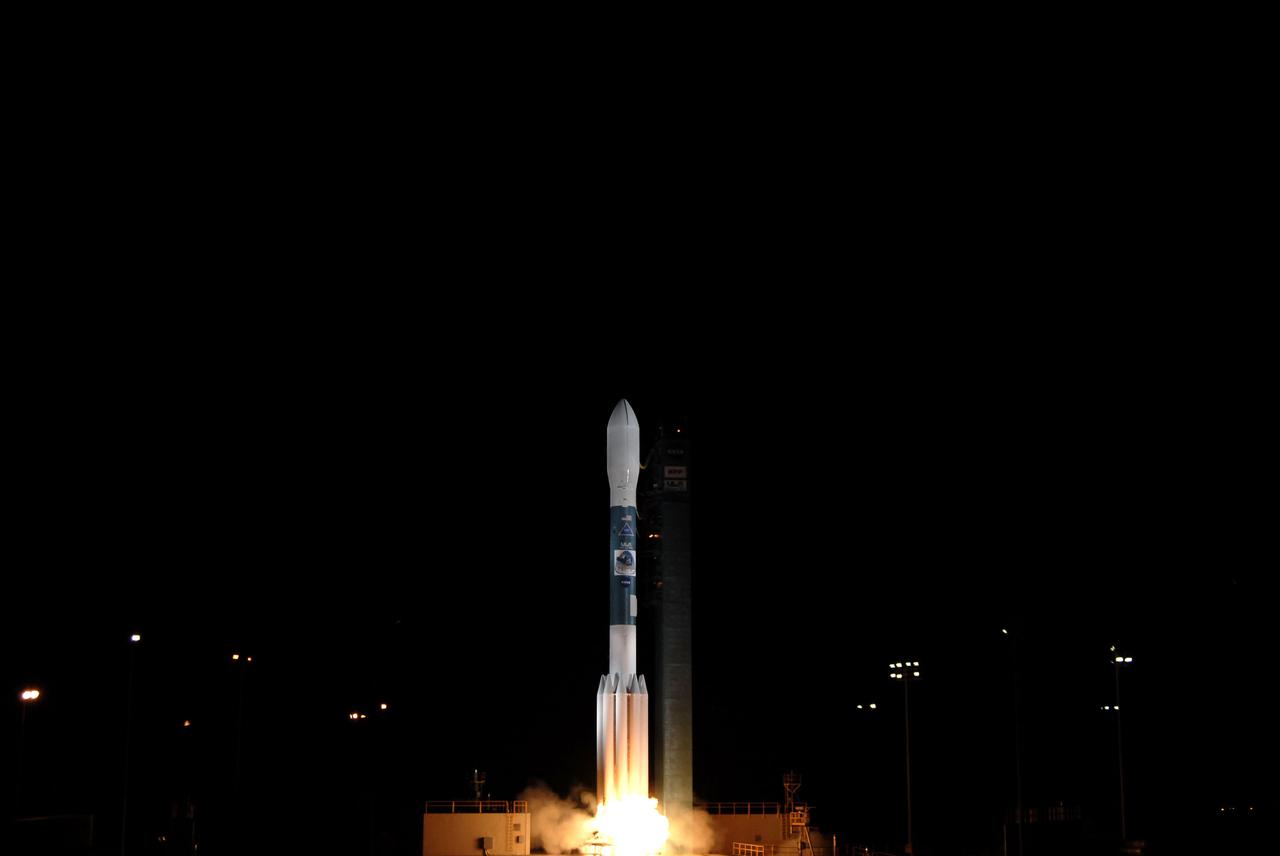

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex-2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the engines ignite beneath the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket carrying NASA's National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) into space. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. PDT. NPP represents a critical first step in building the next-generation of Earth-observing satellites. NPP will carry the first of the new sensors developed for this satellite fleet, now known as the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) to be launched in 2016. NPP is the bridge between NASA's Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites and the forthcoming series of JPSS satellites. The mission will test key technologies and instruments for the JPSS missions. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_NPP. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
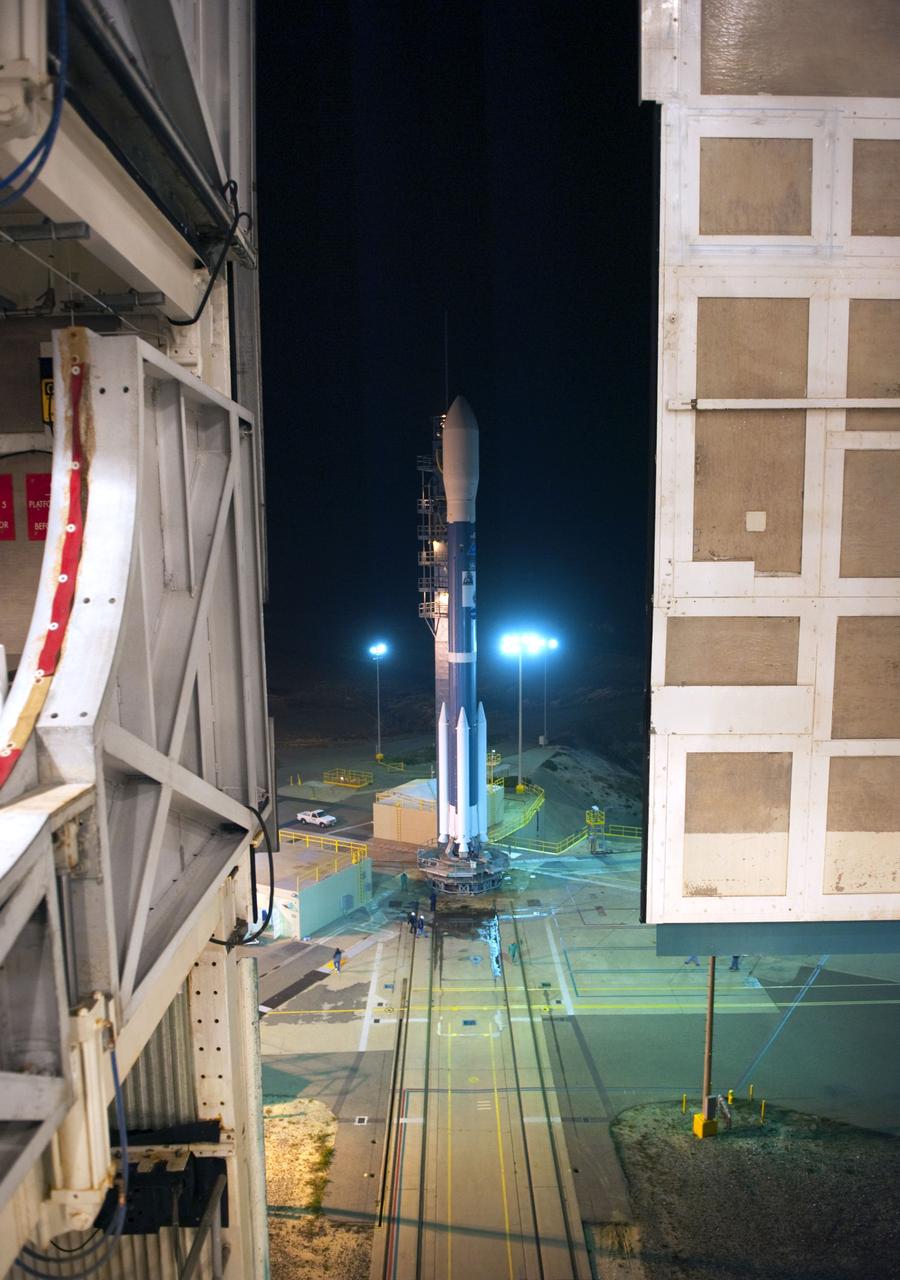

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At NASA's Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft atop is prepared for launch. Liftoff is slated for 7:20 PDT/10:20 EDT today. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/aquarius. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
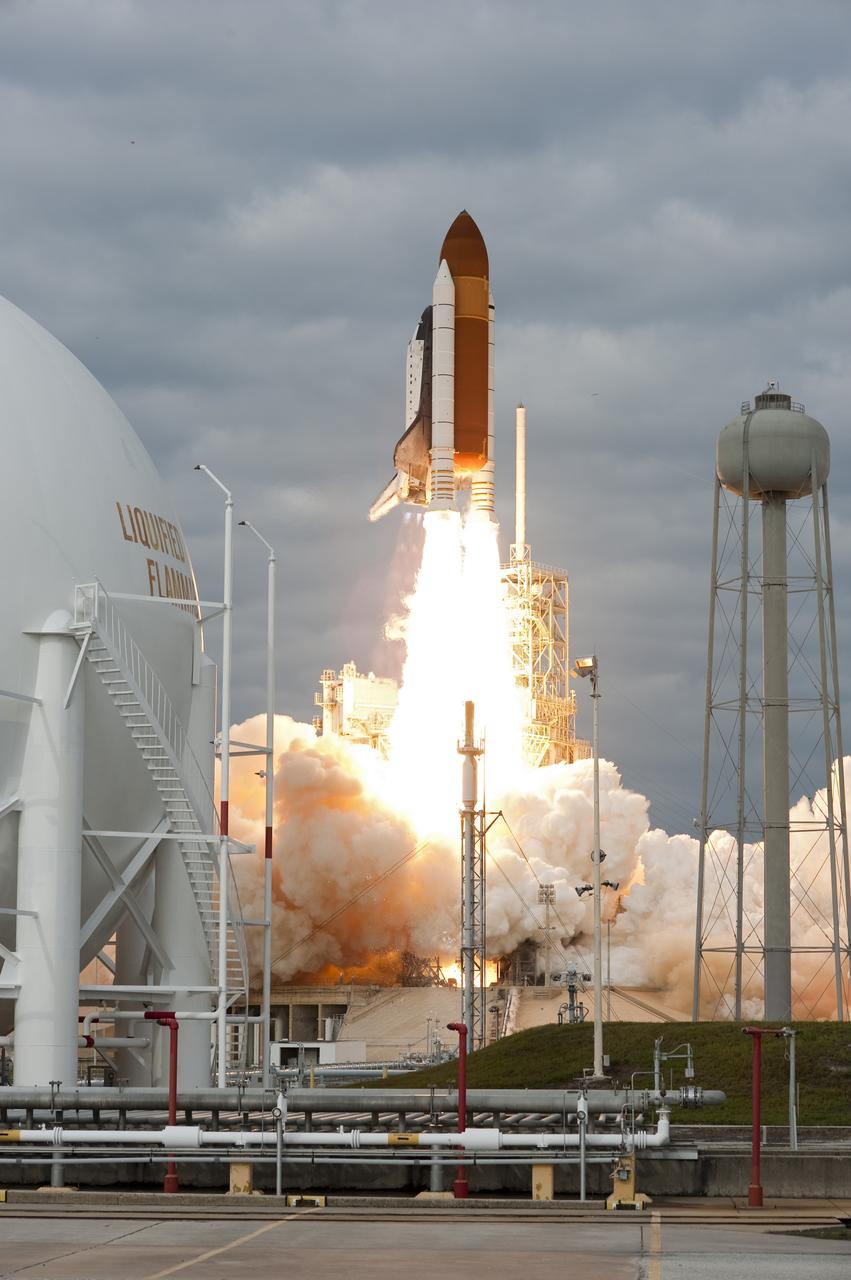

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour rises on twin columns of flame from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
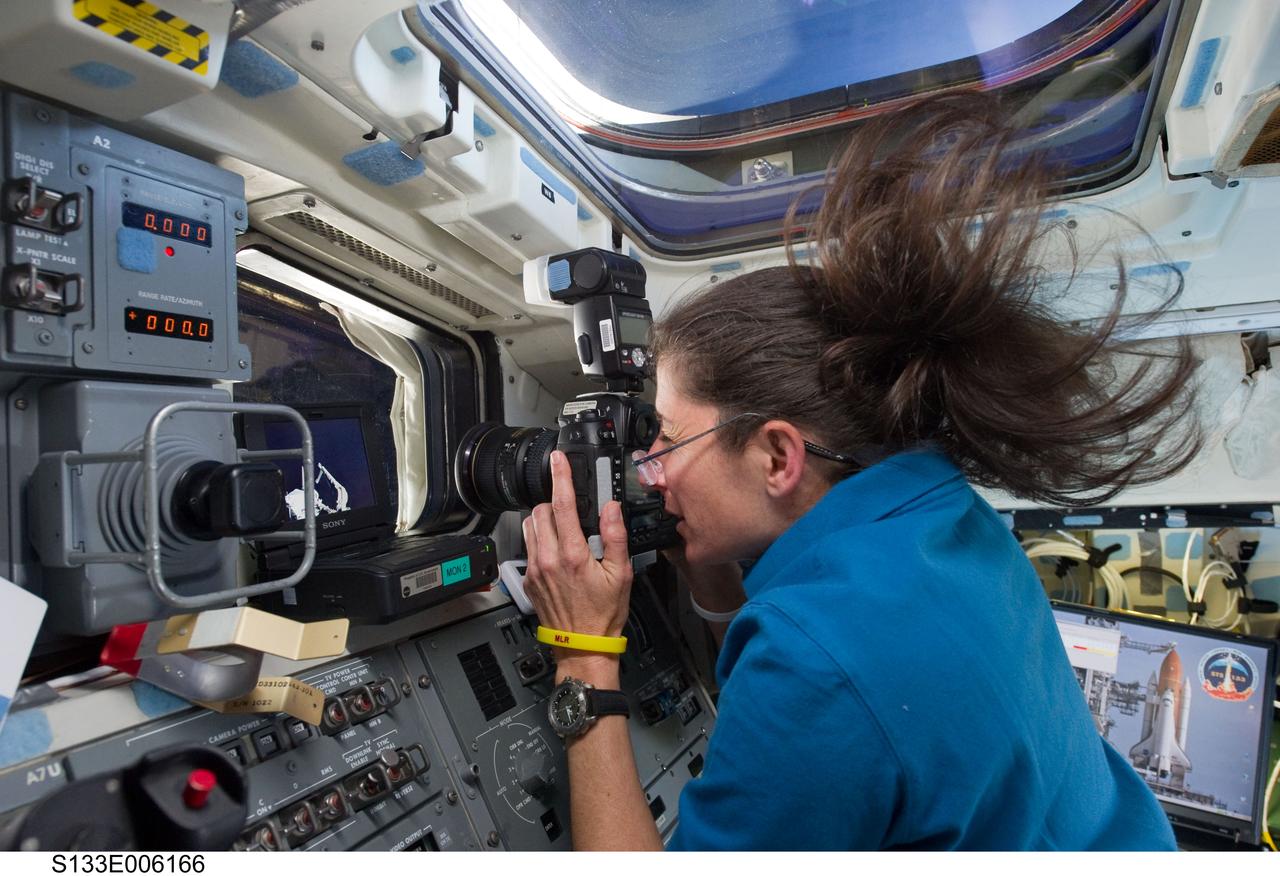

S133-E-006166 (25 Feb. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Nicole Stott, STS-133 mission specialist, uses a still camera at a window on the aft flight deck of space shuttle Discovery during flight day two activities. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
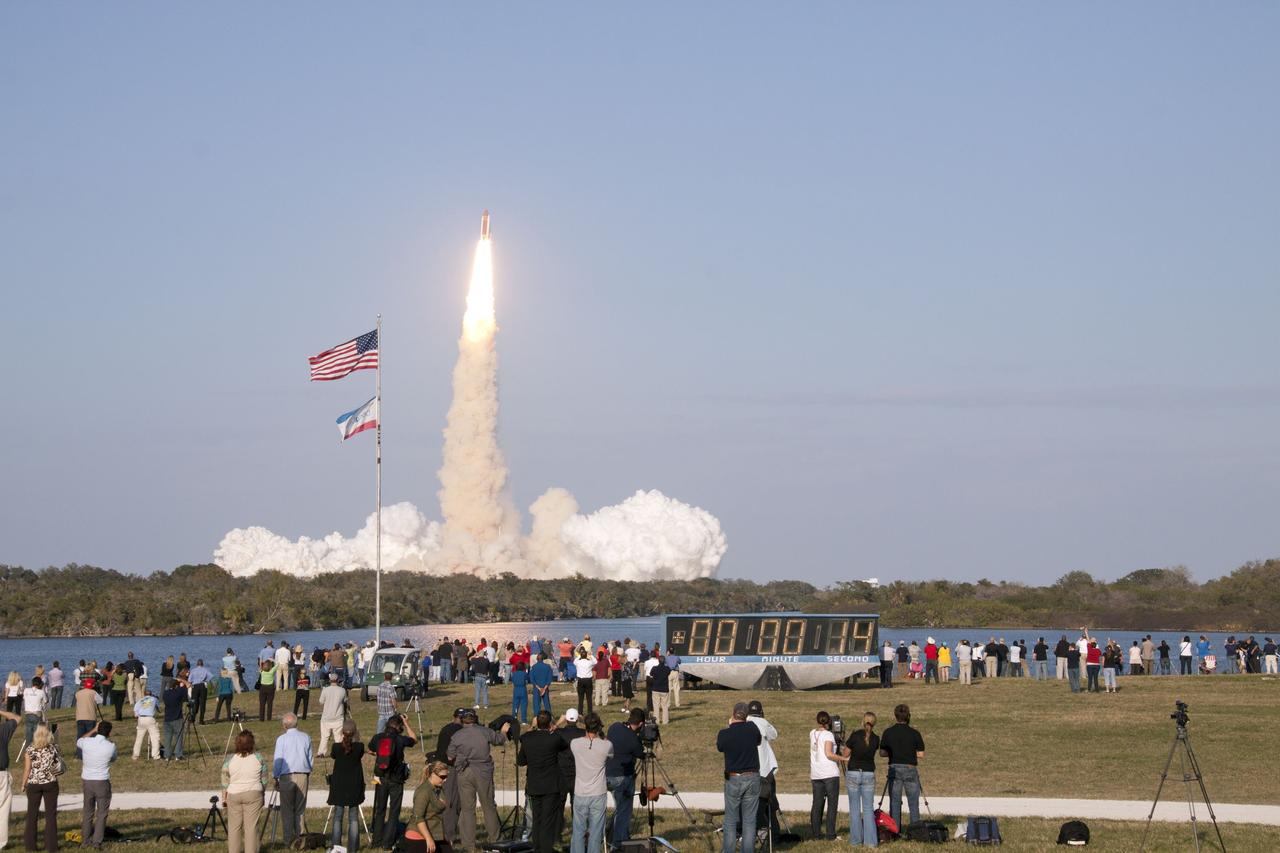

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Discovery's liftoff from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on a picturesque, warm, late February afternoon is witnessed by news media representatives near the countdown clock at the Press Site. Launch of the STS-133 mission was at 4:53 p.m. EST on Feb. 24. Discovery and its six-member crew are on a mission to deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Discovery is making its 39th mission and is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This is the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

JSC2011-E-065977 (10 July 2011) --- STS-135 lead flight director Kwatsi Alibaruho (right) and Public Affairs Office moderator Rob Navias are pictured during a flight day three mission status briefing at NASA's Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
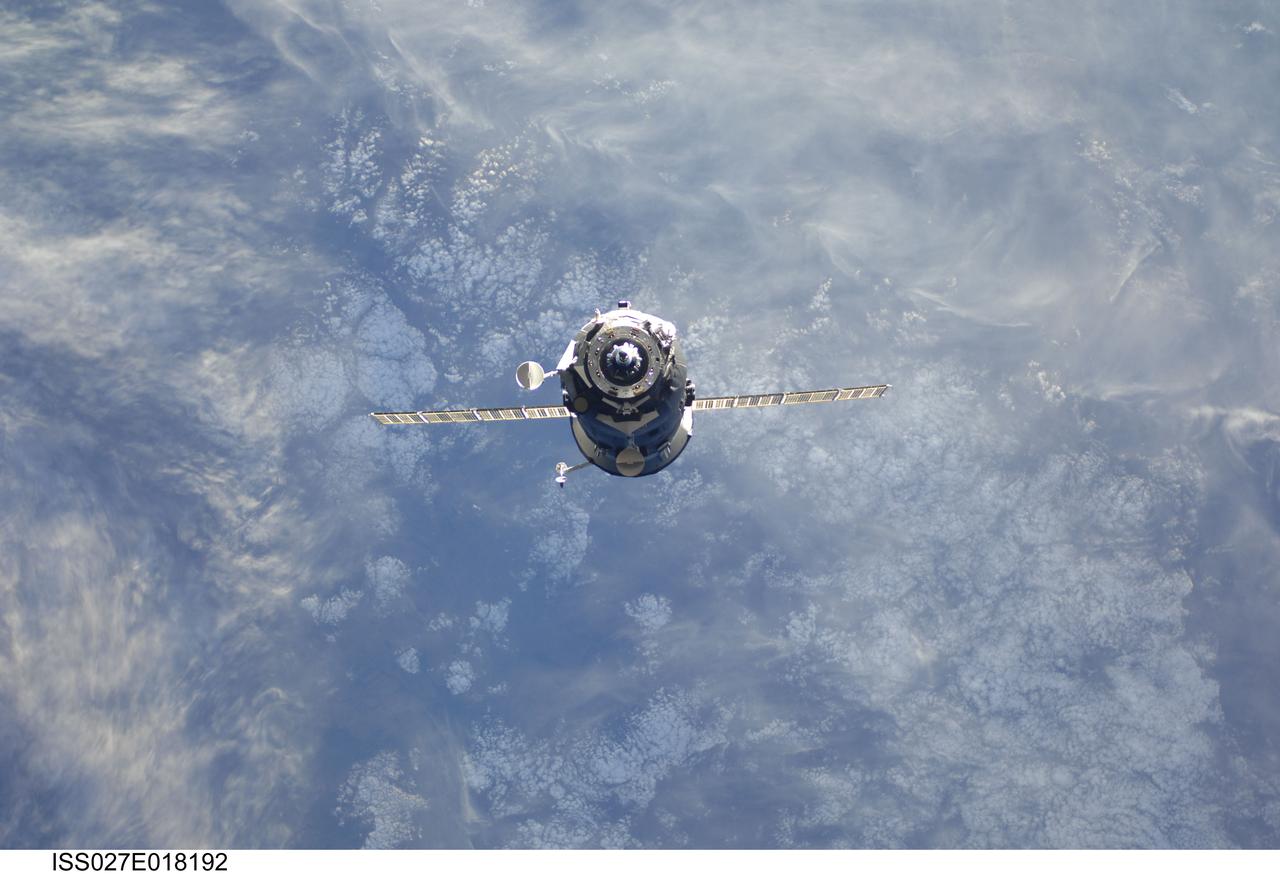

ISS027-E-018192 (29 April 2011) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress resupply vehicle approaches the International Space Station, carrying 1,940 pounds of propellant, 110 pounds of oxygen and air, 926 pounds of water and 2,976 pounds of maintenance hardware, experiment equipment and resupply items for the Expedition 27/28 crew. Progress 42 docked to the station’s Pirs docking compartment at 10:28 a.m. (EDT) on April 29, 2011.
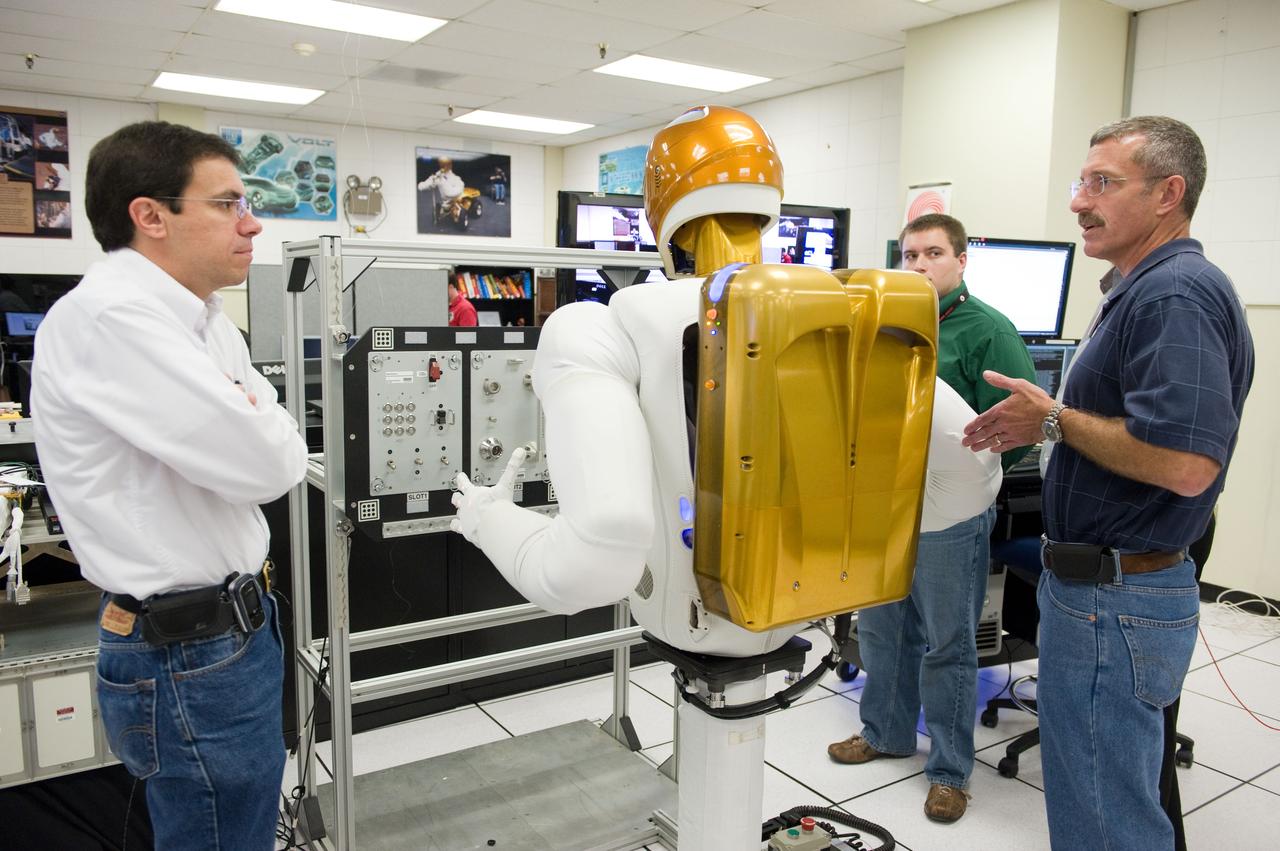

Expedition 29/30 crew training with astronaut Dan Burbank working with Robonaut (overview, skills, taskboard). Photo Date: June 17, 2011. Location: Building 32A, Room 2009. Photographer: Robert Markowitz

Orion Project SPLASH BTA Water Impact POT Boiler Plate Test Article (BTA) (SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew. (POT) Phase "0" Test Water Impact Test #3
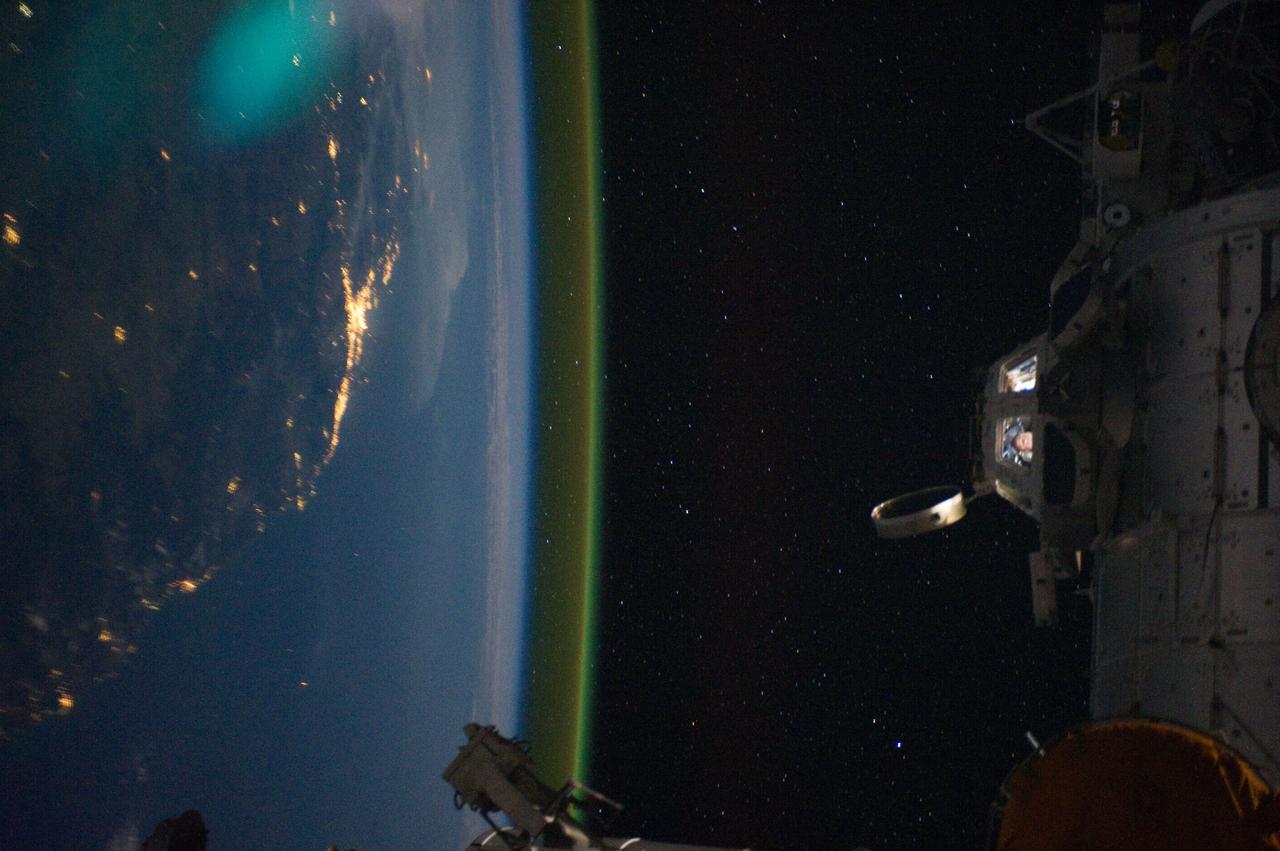

ISS028-E-050186 (15 Sept. 2011) --- This unique photographic angle, featuring the International Space Station?s Cupola and crew activity inside it, other hardware belonging to the station, city lights on Earth and airglow, was captured by one of the Expedition 28 crew members. The major urban area on the coast is Brisbane, Australia. The station was passing over an area southwest of Canberra.
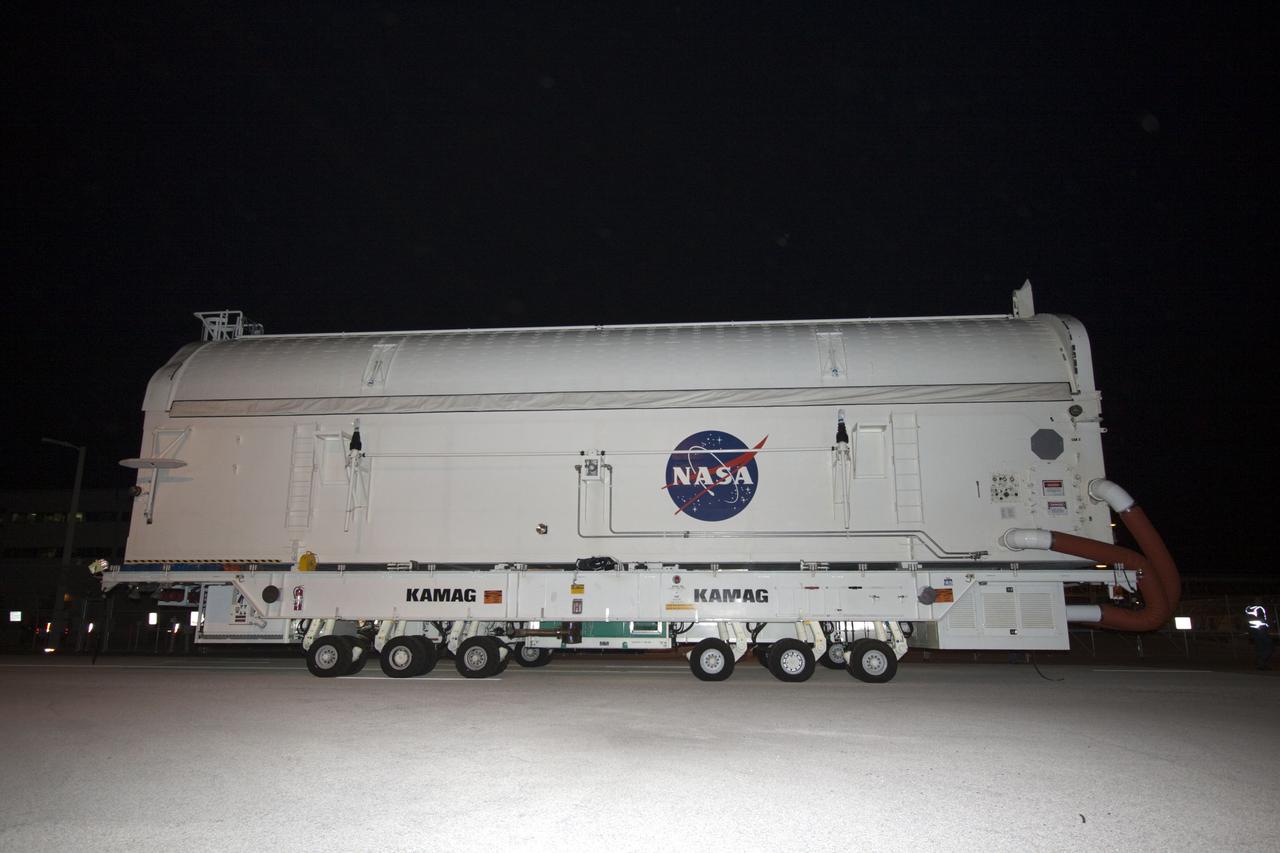

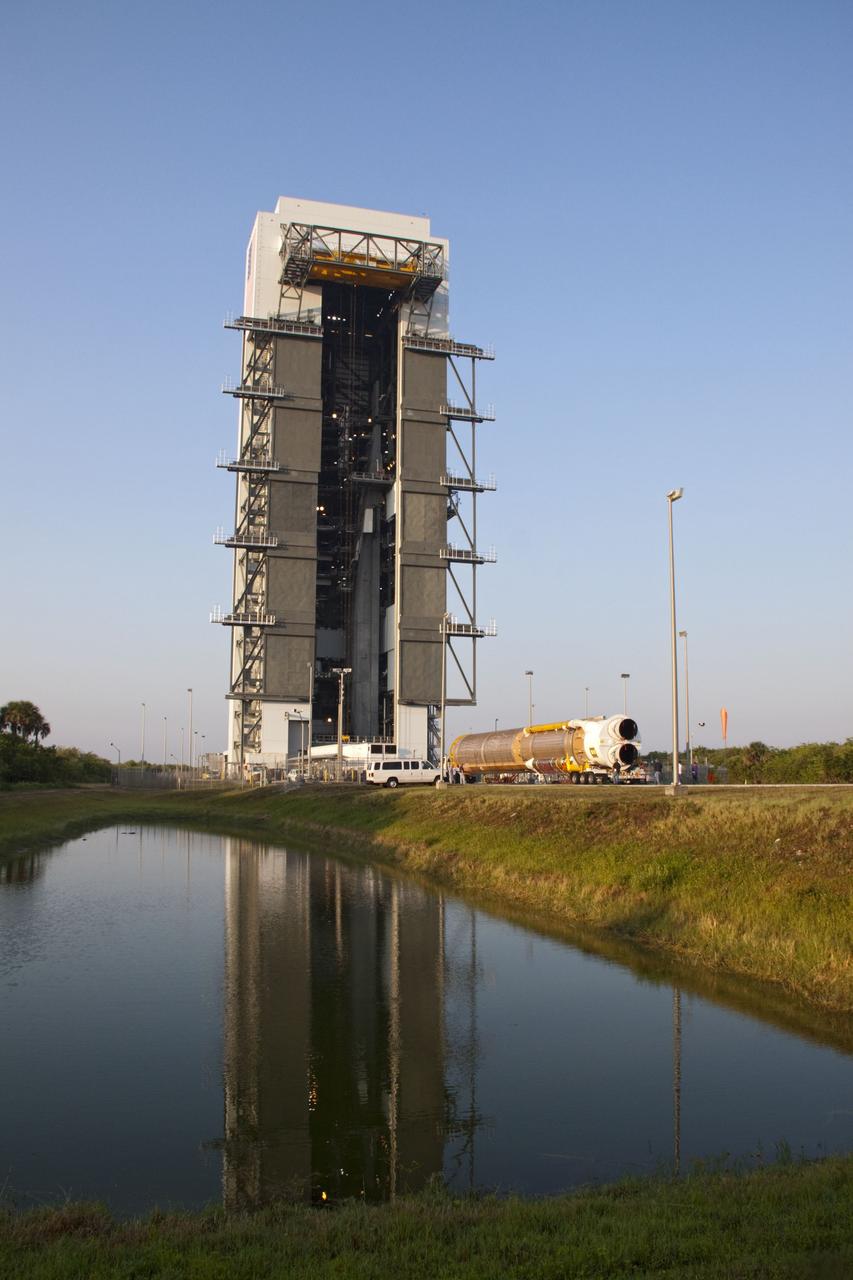
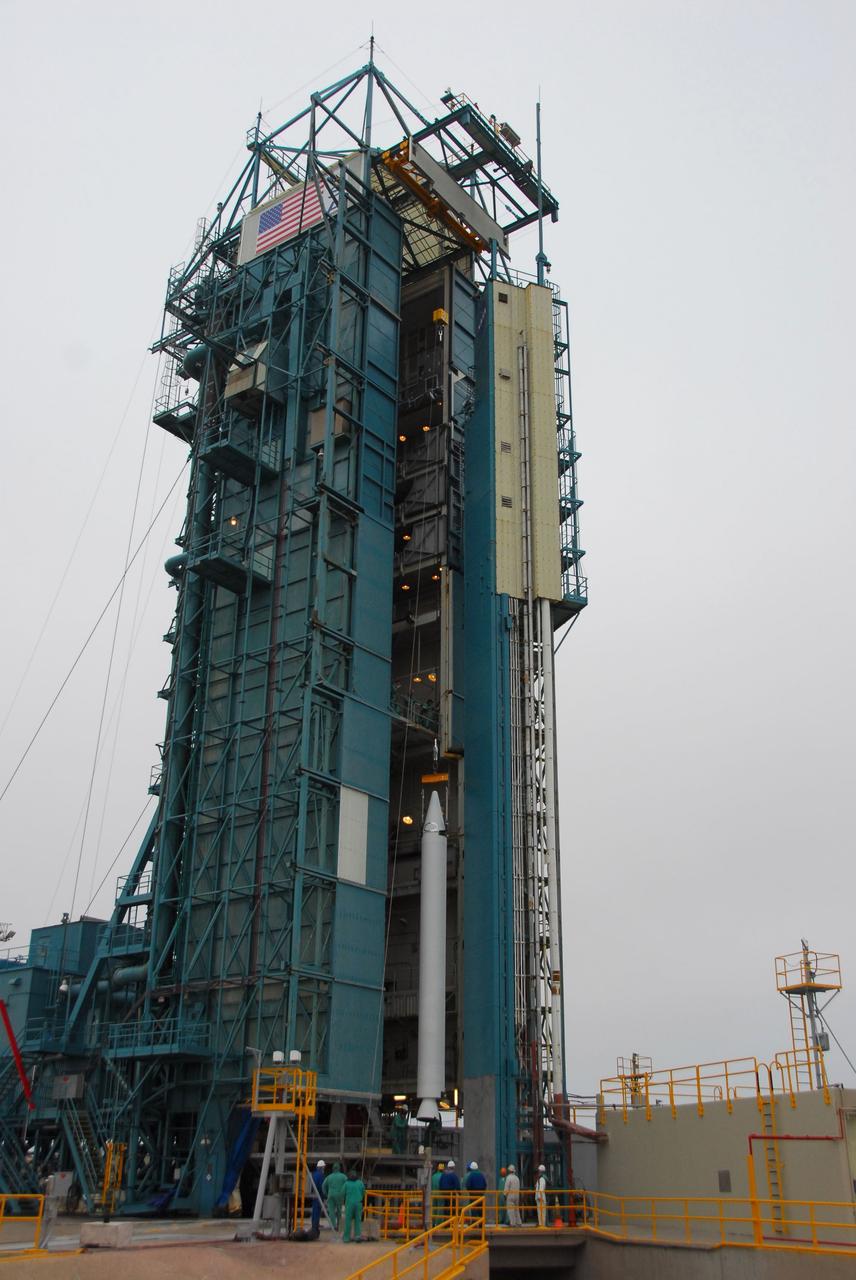
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers move the payload canister, atop its transporter with the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, secured inside, from the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the Canister Rotation Facility. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
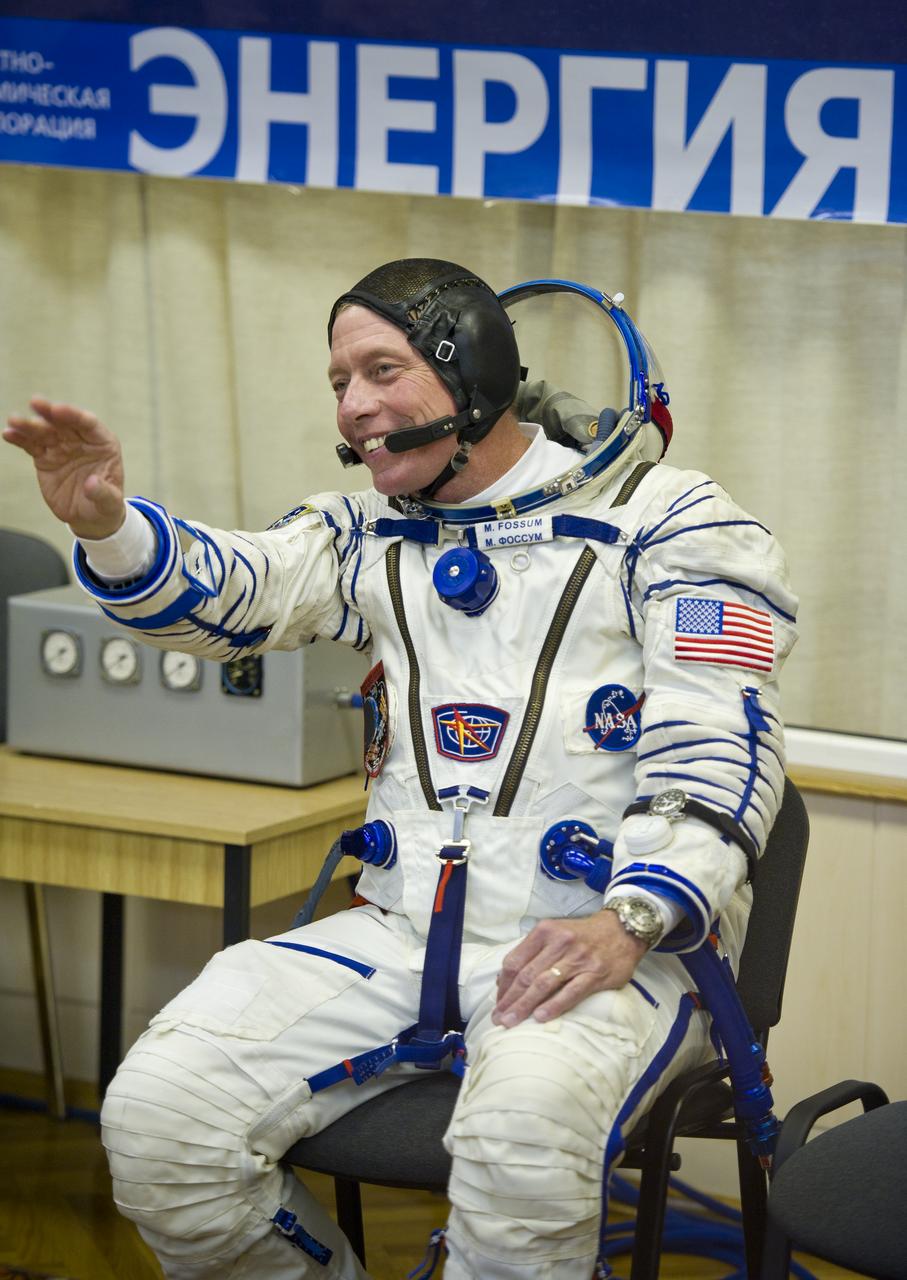

NASA astronaut and Expedition 28 Flight Engineer Mike Fossum waves to friends and family while he waits to have his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch onboard the Soyuz TMA-02M on Tuesday, June 7, 2011 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz spacecraft will carry Expedition 28 Soyuz Commander Sergei Volkov, JAXA (Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency) Flight Engineer Satoshi Furukawa and Fossum to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
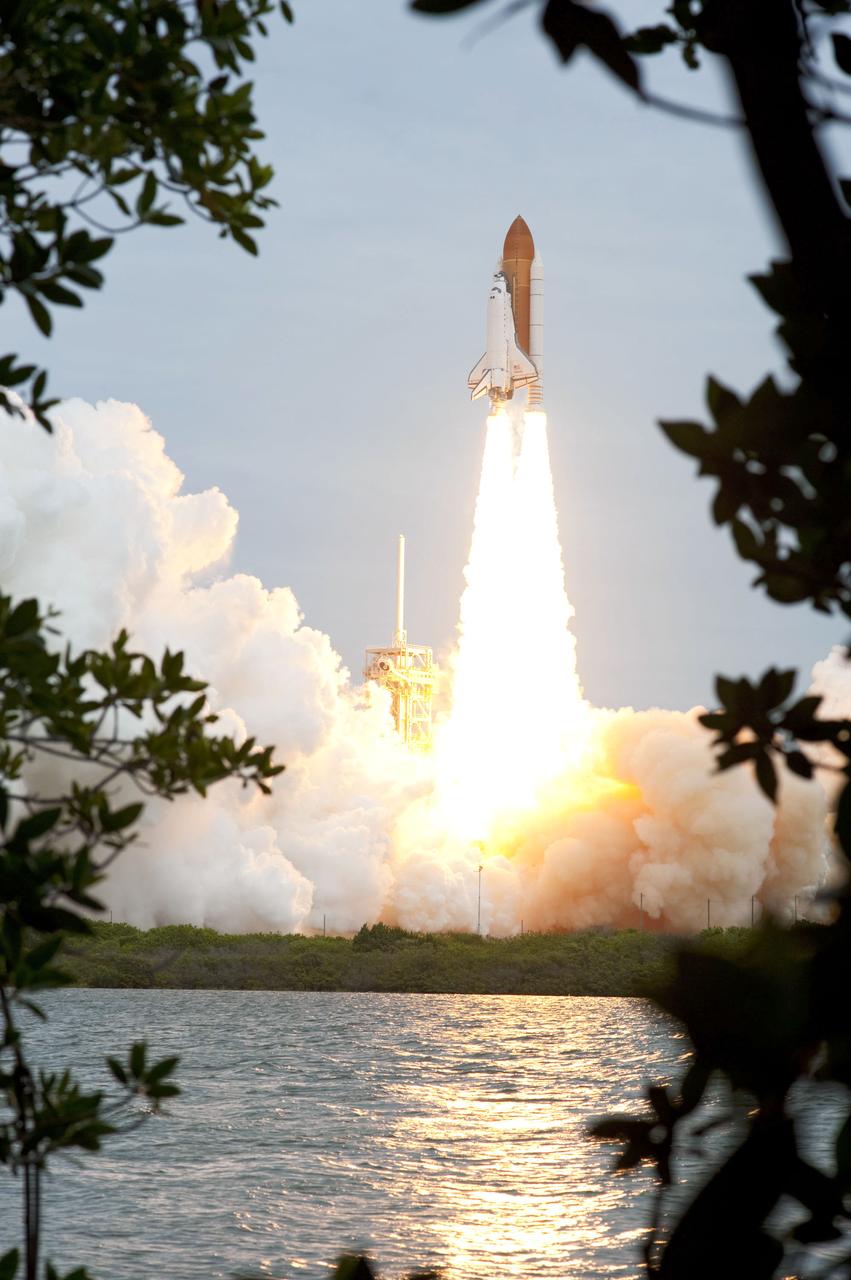

STS135-S-148 (8 July 2011) --- Space shuttle Atlantis and its four-member STS-135 crew head toward Earth orbit and rendezvous with the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:29 a.m. (EDT) on July 8, 2011 from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Onboard are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the space station. Atlantis also carries the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
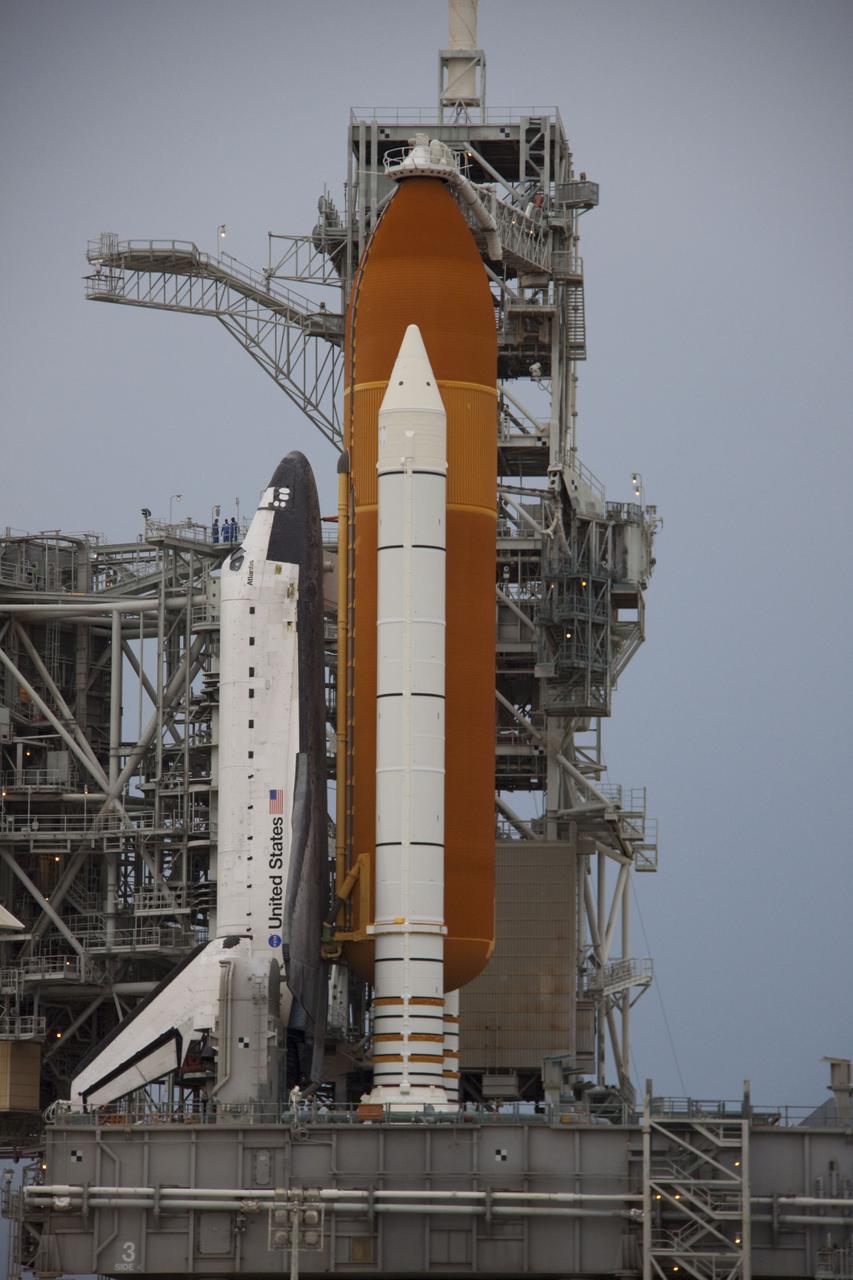

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is revealed on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the move of the rotating service structure (RSS). The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
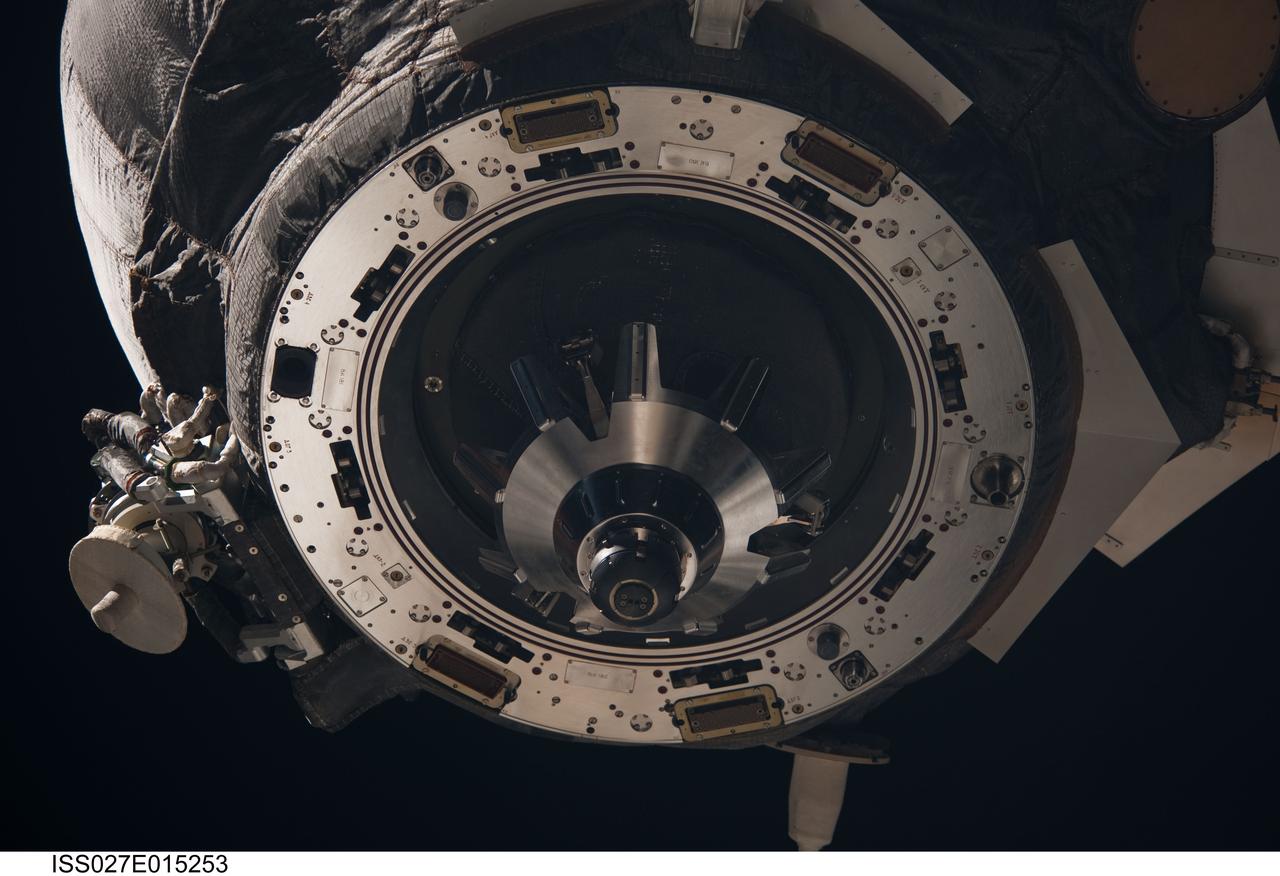

ISS027-E-015253 (22 April 2011) --- A close-up view of the unpiloted ISS Progress 41 supply vehicle is photographed by an Expedition 27 crew member as it departs from the International Space Station at 7:41 a.m. (EDT) on April 22, 2011. Filled with trash and discarded items, Progress 41 will remain in orbit a safe distance from the station for engineering tests before being commanded by flight controllers to descend to a destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The departure of Progress 41 clears the way for the next unpiloted supply ship, ISS Progress 42, which is set to launch April 27 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, delivering three tons of food, fuel and supplies for the Expedition 27 crew.
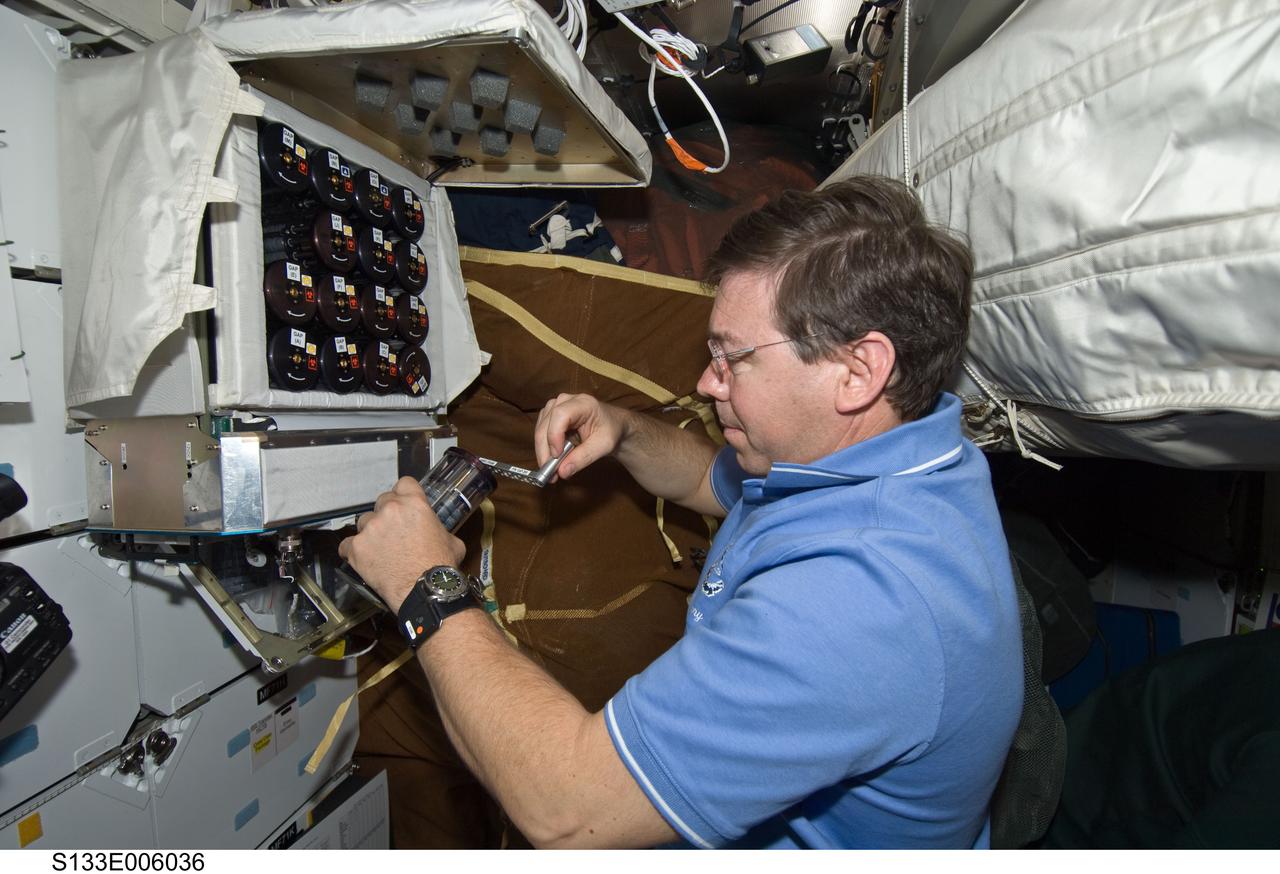

S133-E-006036 (25 Feb. 2011) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, STS-133 mission specialist, works with the Microbe Group Activation Pack containing eight Fluid Processing Apparatuses on the middeck of space shuttle Discovery while en route to a rendezvous with the International Space Station. A previous set of similar tests made a key discovery about the mechanism that makes salmonella more infectious, aiding the fight against food poisoning on Earth. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
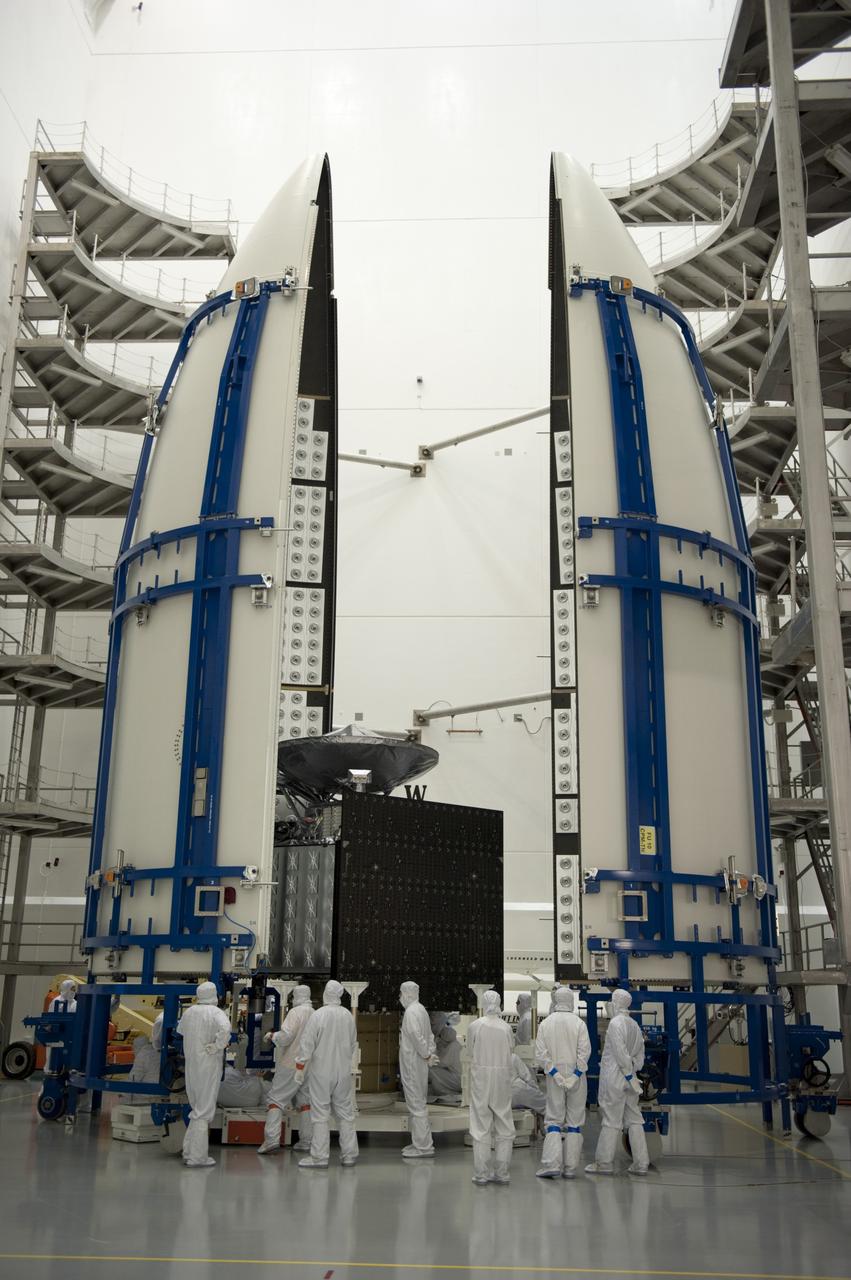

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Astrotech payload processing facility near Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Juno spacecraft is carefully positioned into half of the Atlas payload fairing during work to enclose the spacecraft for launch. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
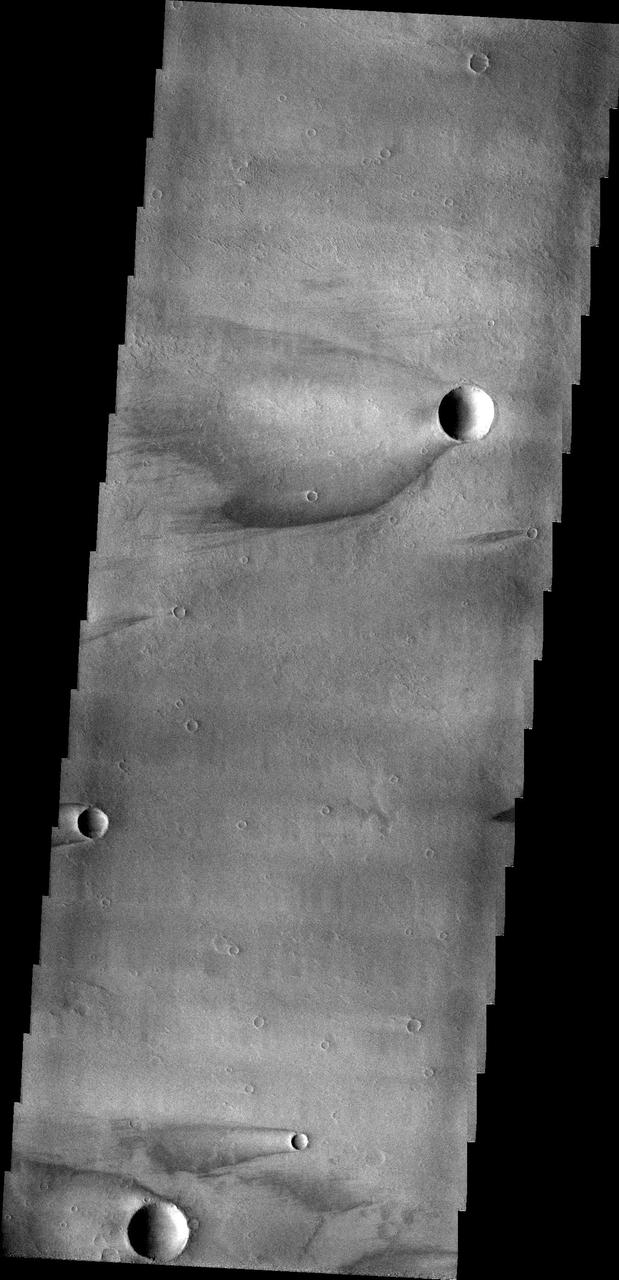
This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft show windstreaks found on Daedalia Planum.
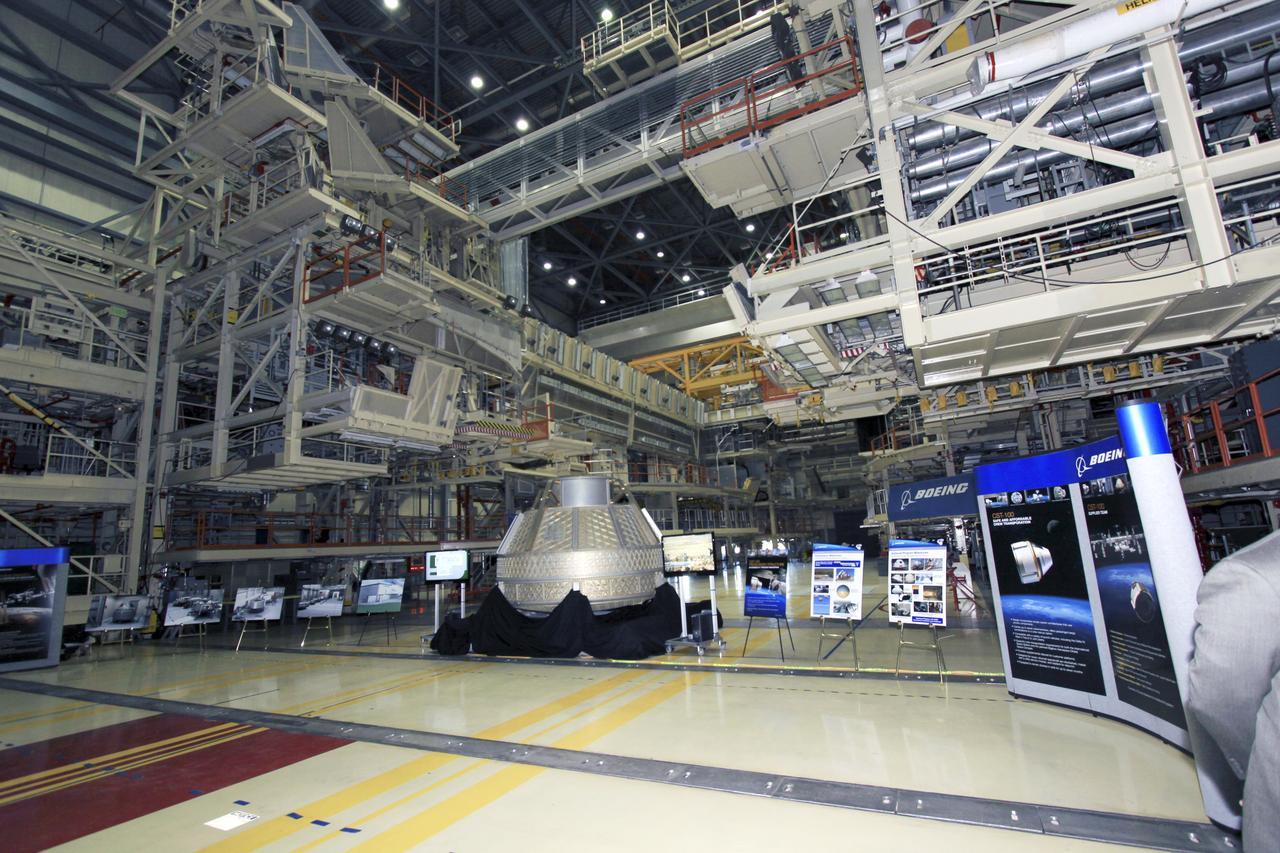

Commercial Crew Program Briefing and Press Tour
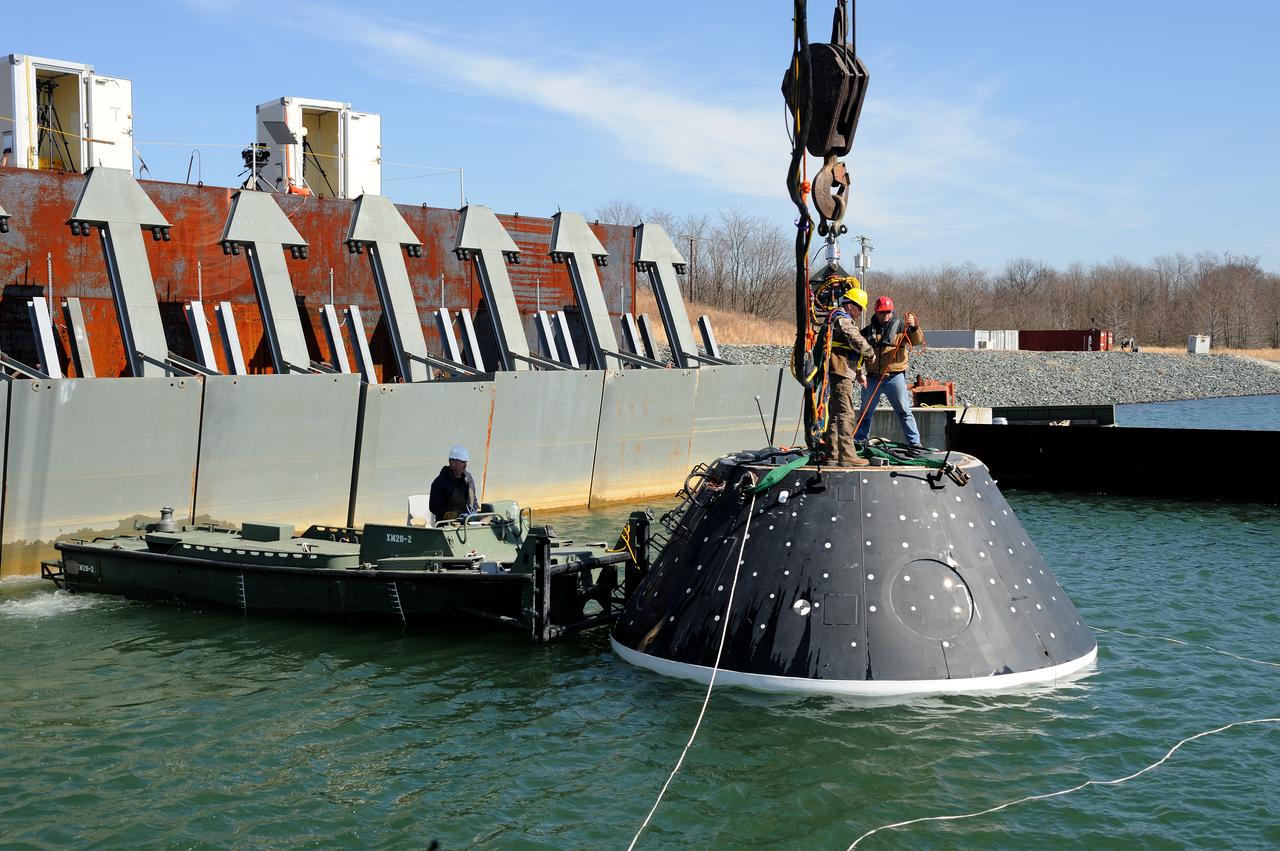

Crew Model Water Landing Module Assessment Photographs taken at Aberdeen Test Facility Aberdeen MD.
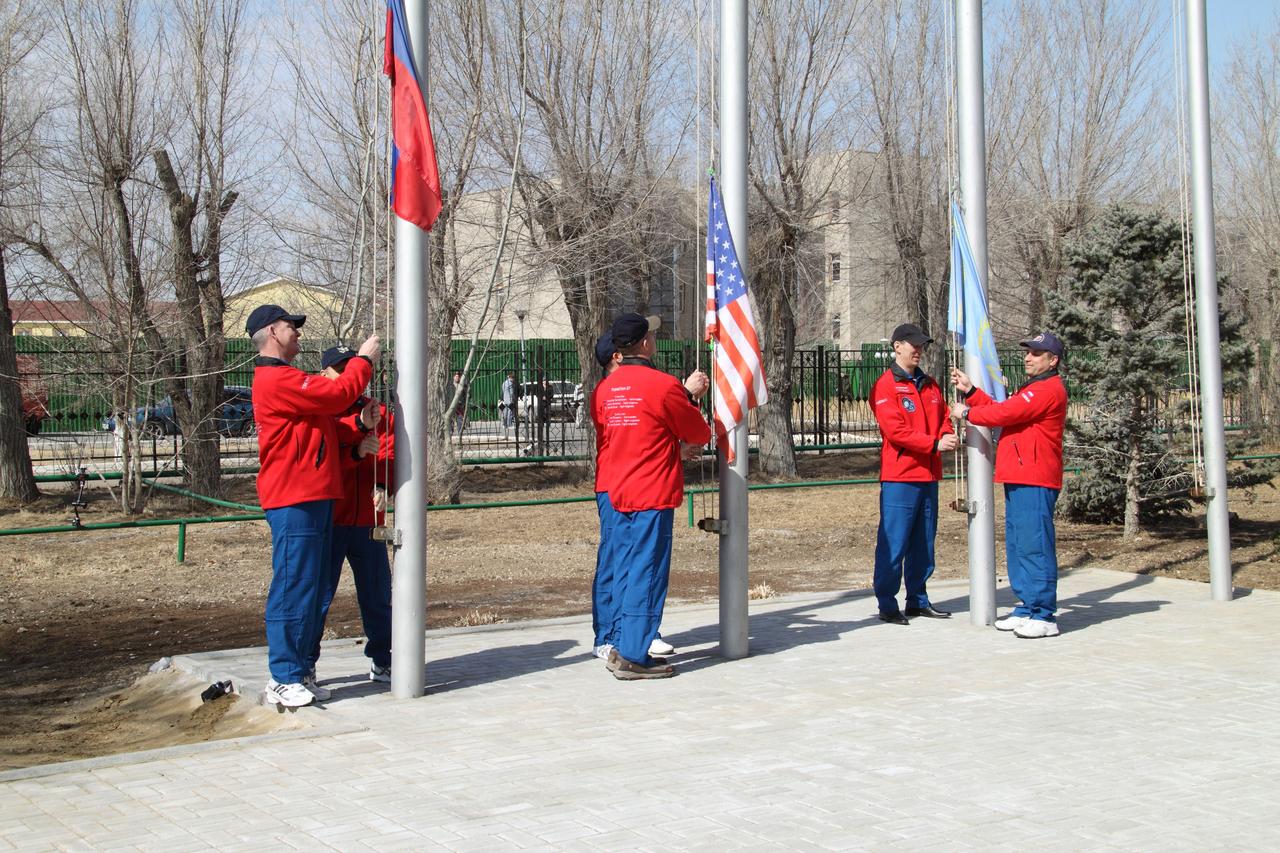

Outside their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, the Expedition 27 prime and backup crewmembers conducted the ceremonial raising of the Russian, U.S. and Kazakh flags on March 23, 2011 as part of their traditional pre-launch activities. Seen from left to right are prime Russian crewmembers Alexander Samokutyaev and Andrey Borisenko, prime NASA Flight Engineer Ron Garan (center) and his backup, Dan Burbank and backup Russian crewmembers Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin. Garan, Samokutyaev and Borisenko are scheduled to launch on April 5 (April 4, U.S. time) from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan to the International Space Station on the Soyuz TMA-21 spacecraft that has been dubbed “Gagarin”, in honor of the 50th anniversary of the launch of Yuri Gagarin on April 12, 1961 to become the first human to fly in space. Credit: NASA/Victor Zelentsov
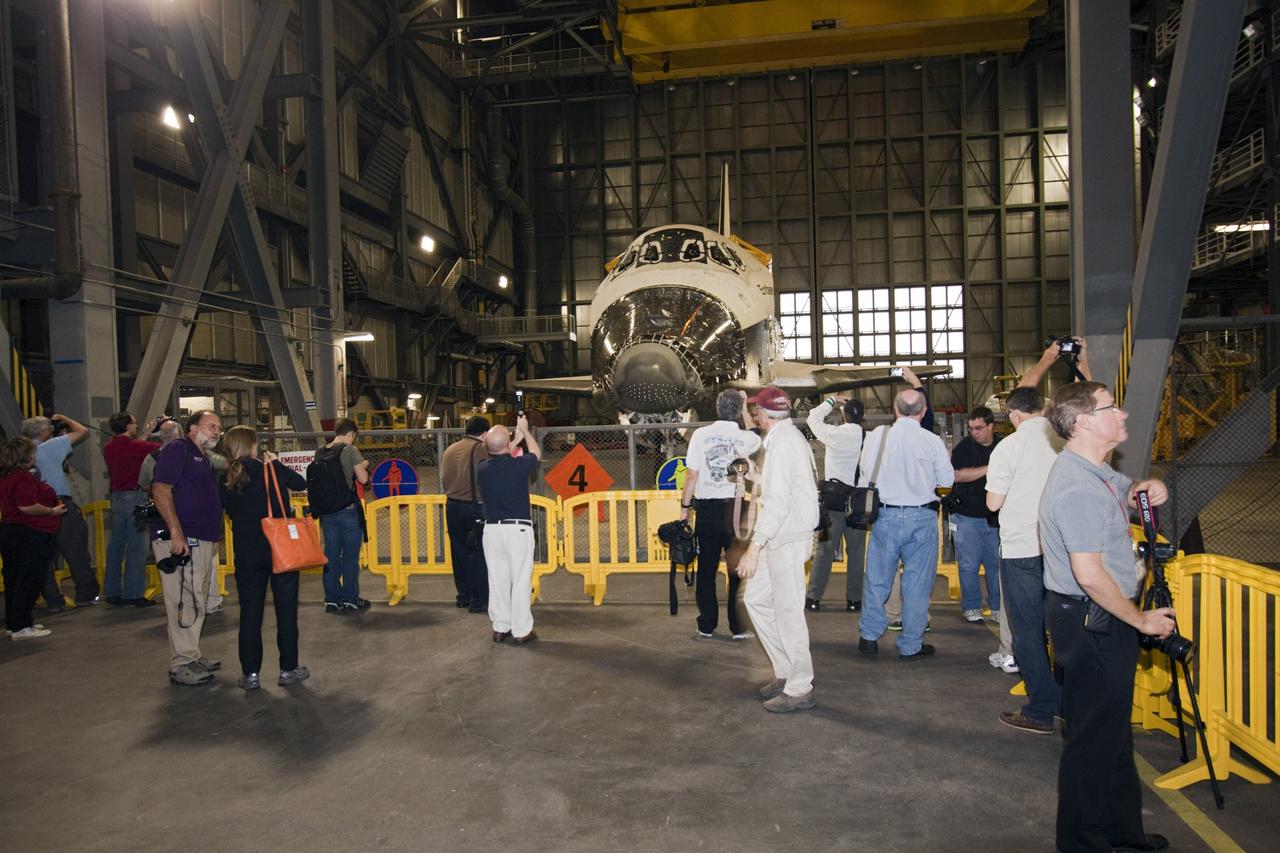

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media representatives taking the 21st Century Ground Systems tour get a close-up look at space shuttle Endeavour which is being stored in the Vehicle Assembly Building. Other stops on the tour include a crawler-transporter parked on the crawlerway, the new mobile launcher on Launch Pad 39B, and the Launch Control Center's Firing Room 1. These facilities and equipment will be used to prepare and launch NASA's new Orion spacecraft on the Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket. The tour was arranged as part of prelaunch media activities for the agency's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) launch. Liftoff of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is planned during a launch window which extends from 10:02 a.m. to 11:45 a.m. EST on Nov. 26. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
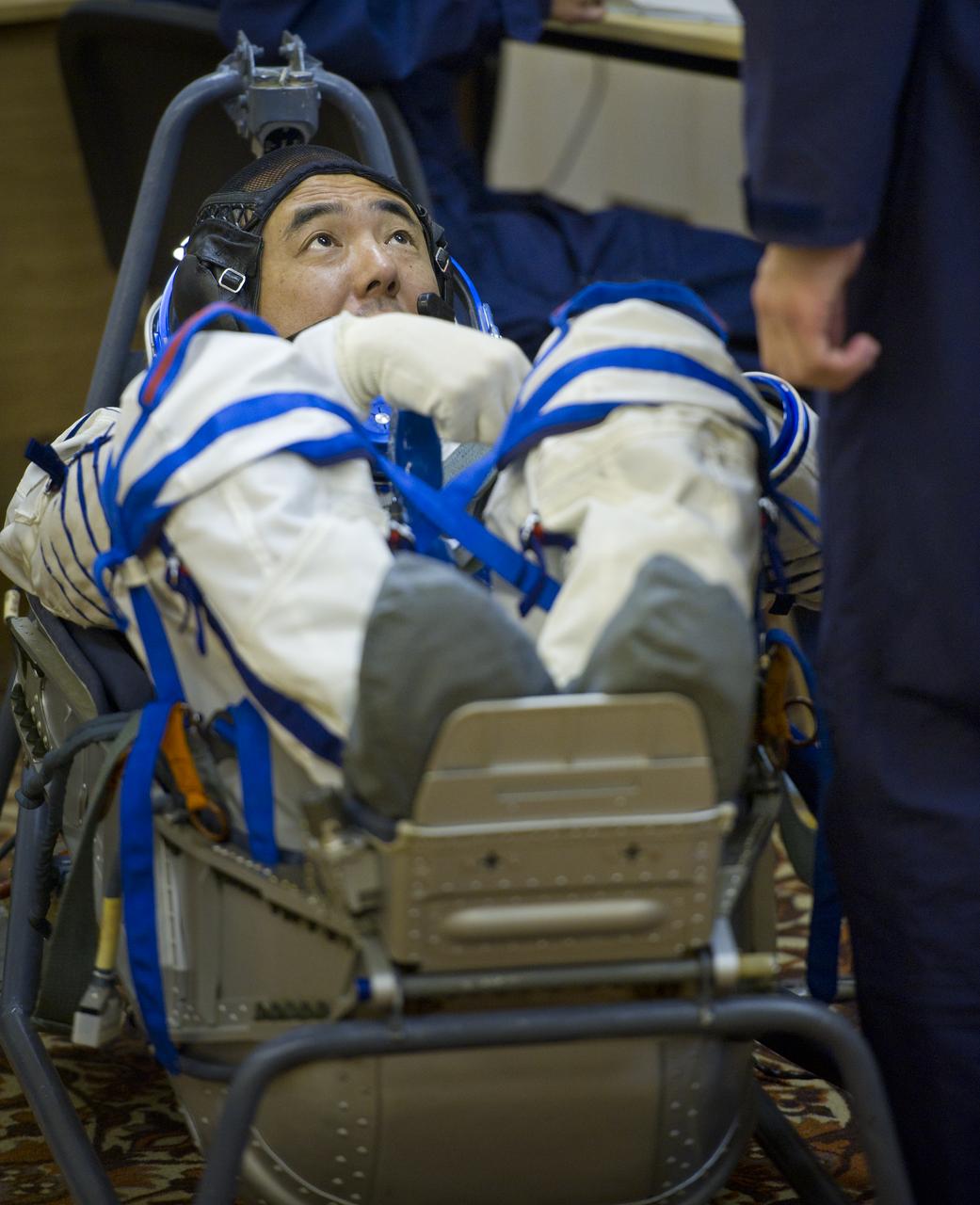
JAXA (Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 28 Flight Engineer Satoshi Furukawa has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch to the International Space Station, Tuesday, June 7, 2011 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz spacecraft will launch the following morning on June 8 carrying Expedition 28 Soyuz Commander Sergei Volkov, NASA Flight Engineer Mike Fossum and Furukawa. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
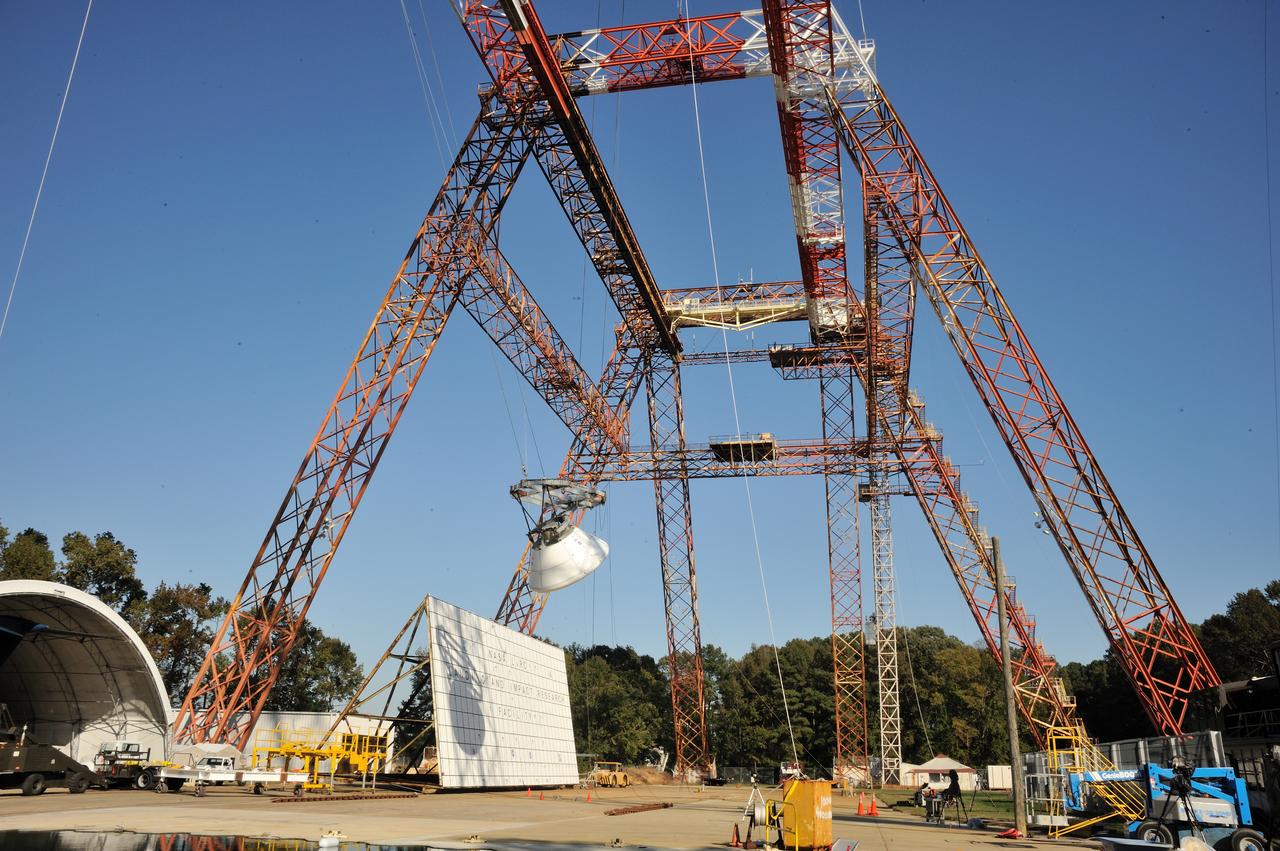

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
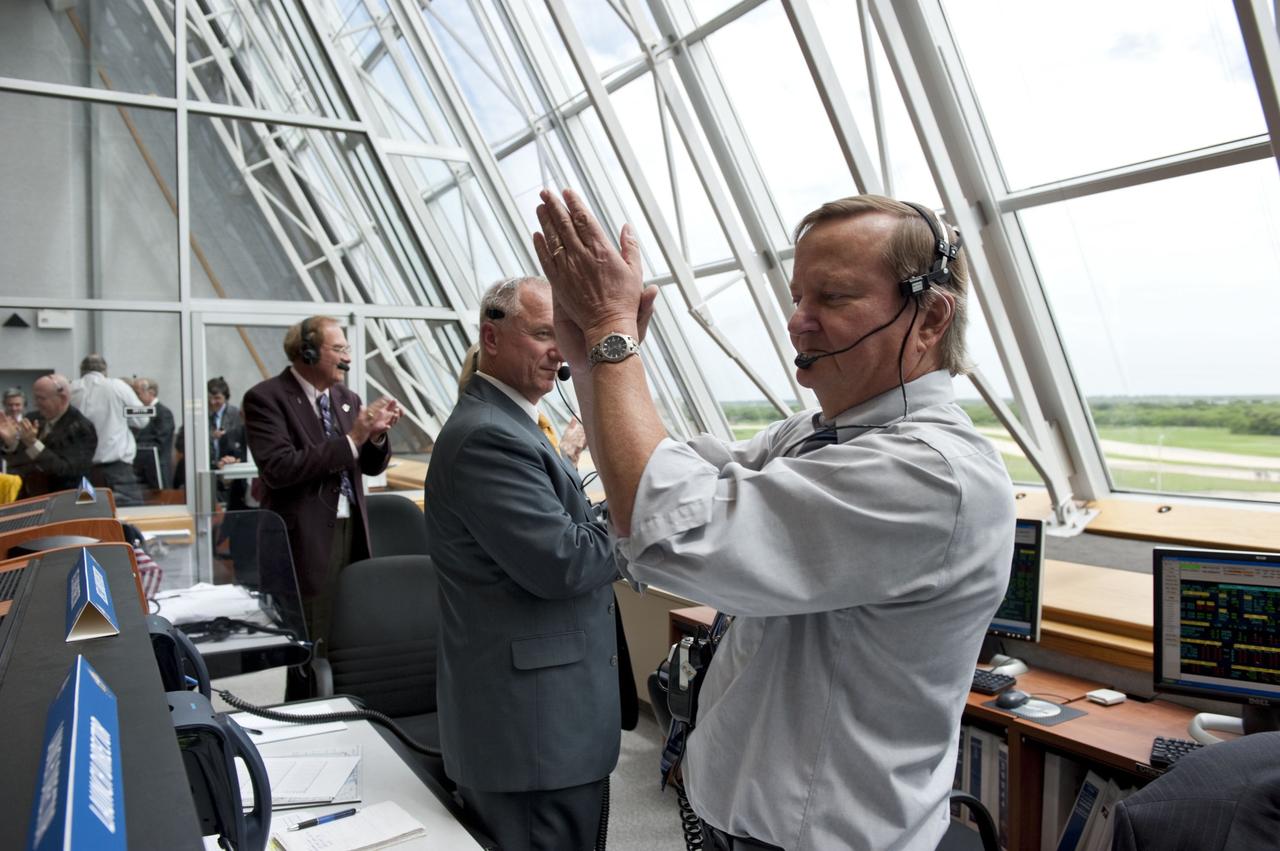

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach (right), Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko and NASA Commentator and Public Affairs Officer George Diller applaud the successful launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
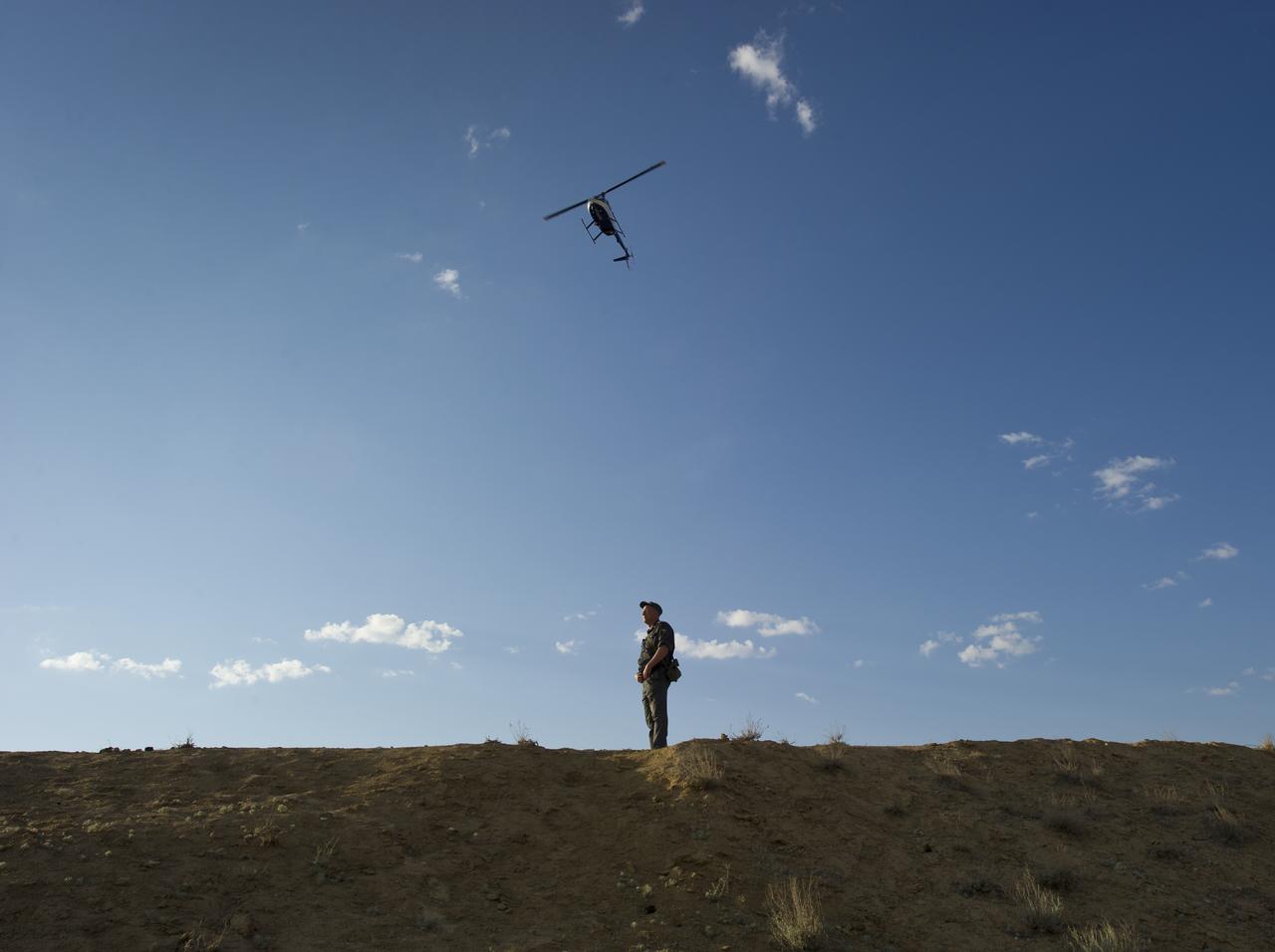

A Russian security guard stands watch as a Russian military helicopter flies overhead during the rollout of the Soyuz TMA-02M rocket to the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on Sunday, June 5, 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
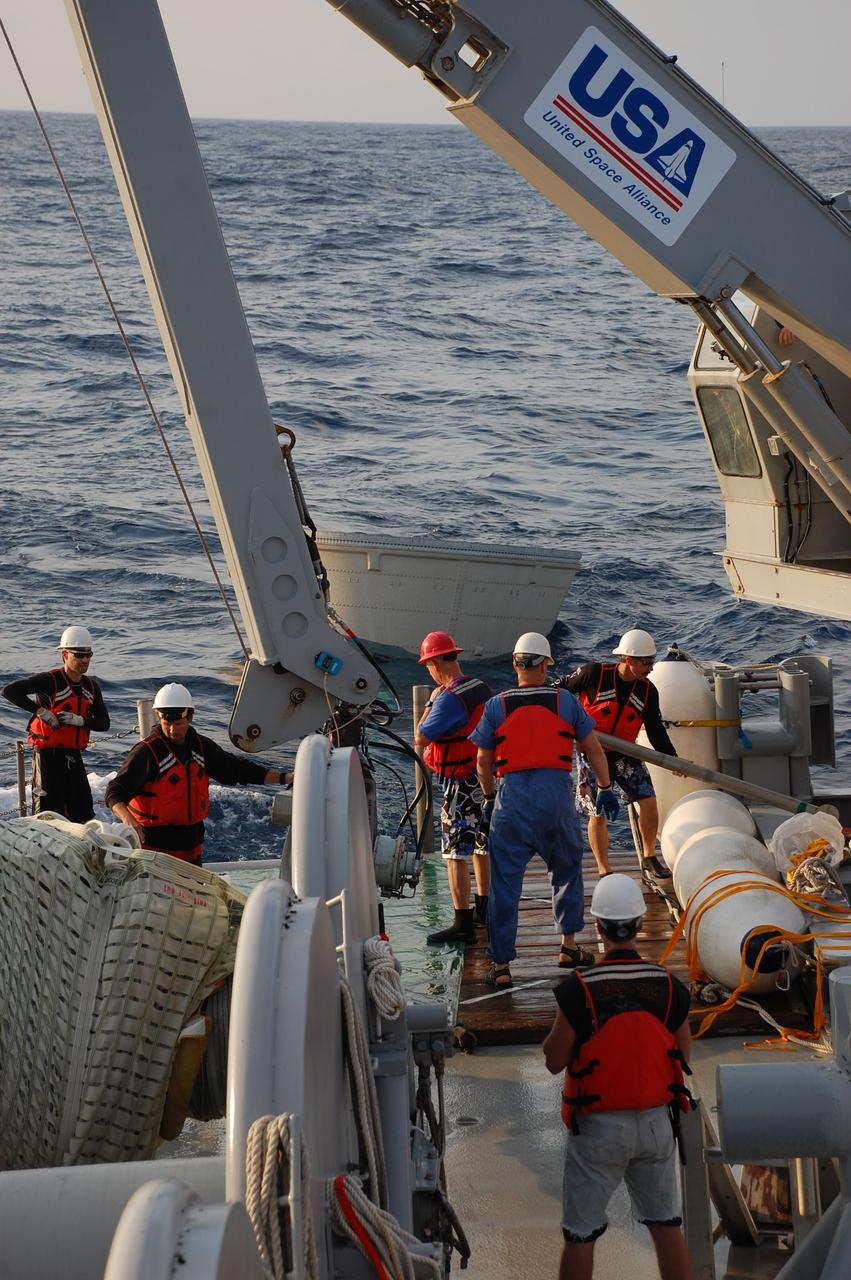

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members from Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, recover the left spent booster nose cap from the Atlantic Ocean after space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Liberty Star and Freedom Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
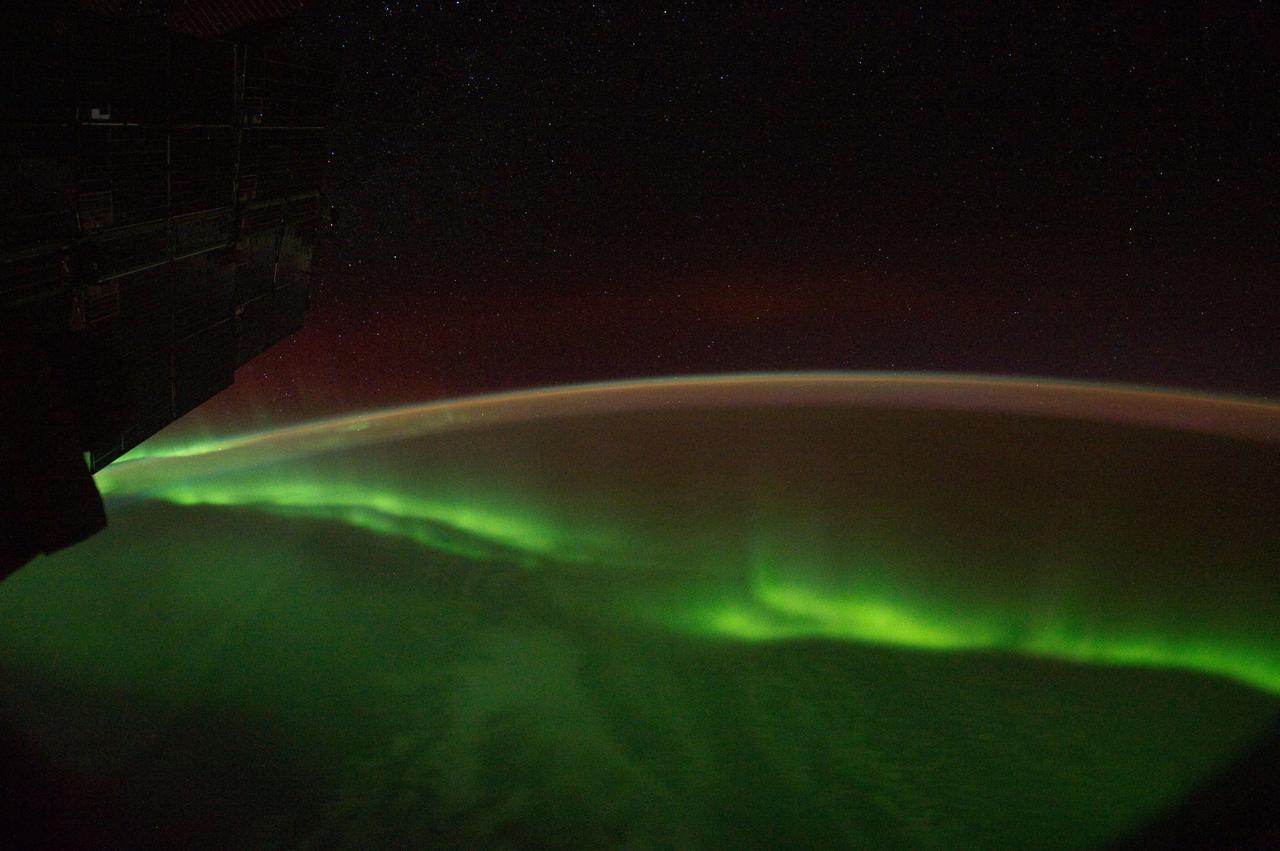

ISS029-E-006404 (18 Sept. 2011) --- This is one of a series of night time images photographed by one of the Expedition 29 crew members from the International Space Station. It features Aurora Australis and parts of the southeastern Indian Ocean. Nadir coordinates are 49.42 degrees south latitude and 121.01 degrees east longitude.
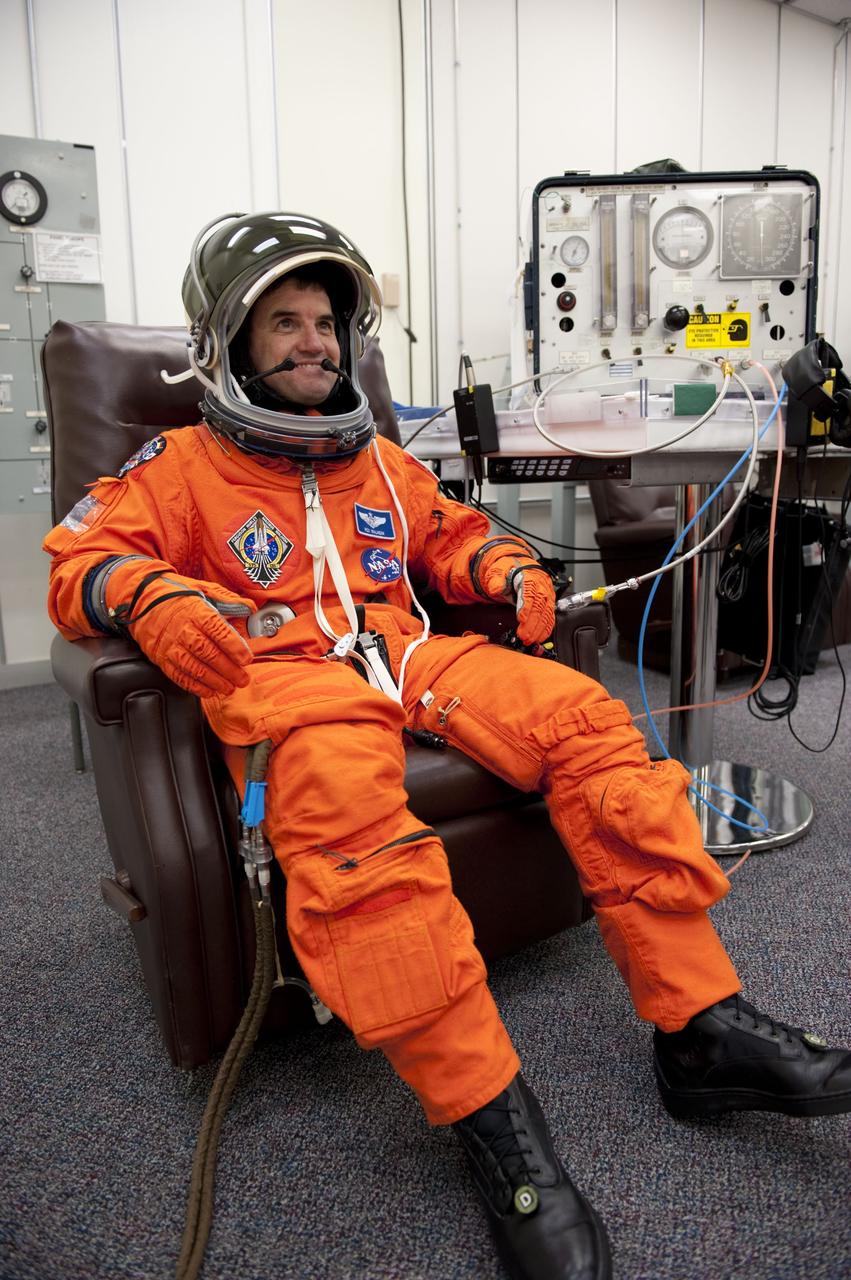

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mission Specialist Rex Walheim checks the fit of his launch and landing suit, helmet and gloves. The STS-135 crew is at Kennedy to participate in a launch countdown dress rehearsal called the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) and related training in preparation for the upcoming STS-135 mission. Atlantis and its crew are targeted to lift off July 8, taking with them the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
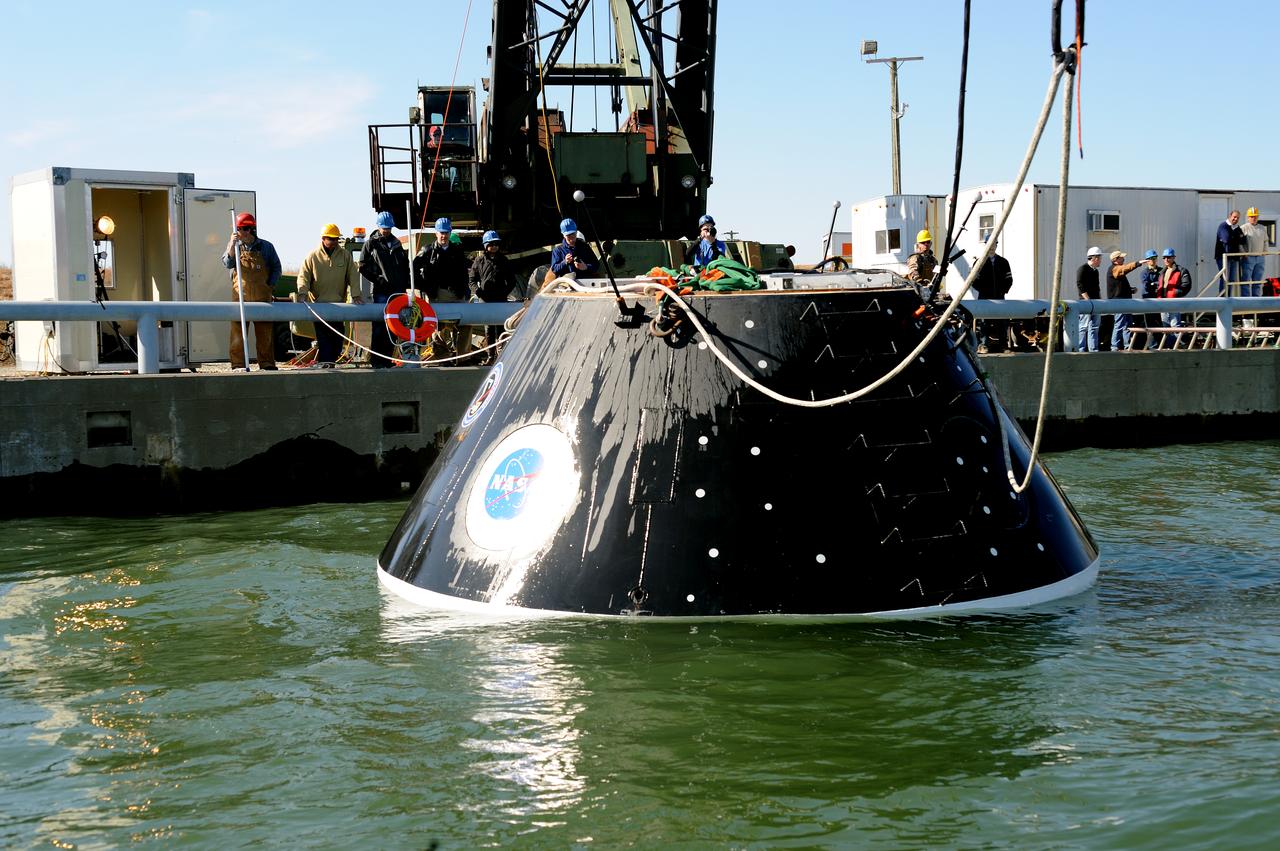

Crew Model Water Landing Module Assessment Photographs taken at Aberdeen Test Facility Aberdeen MD.
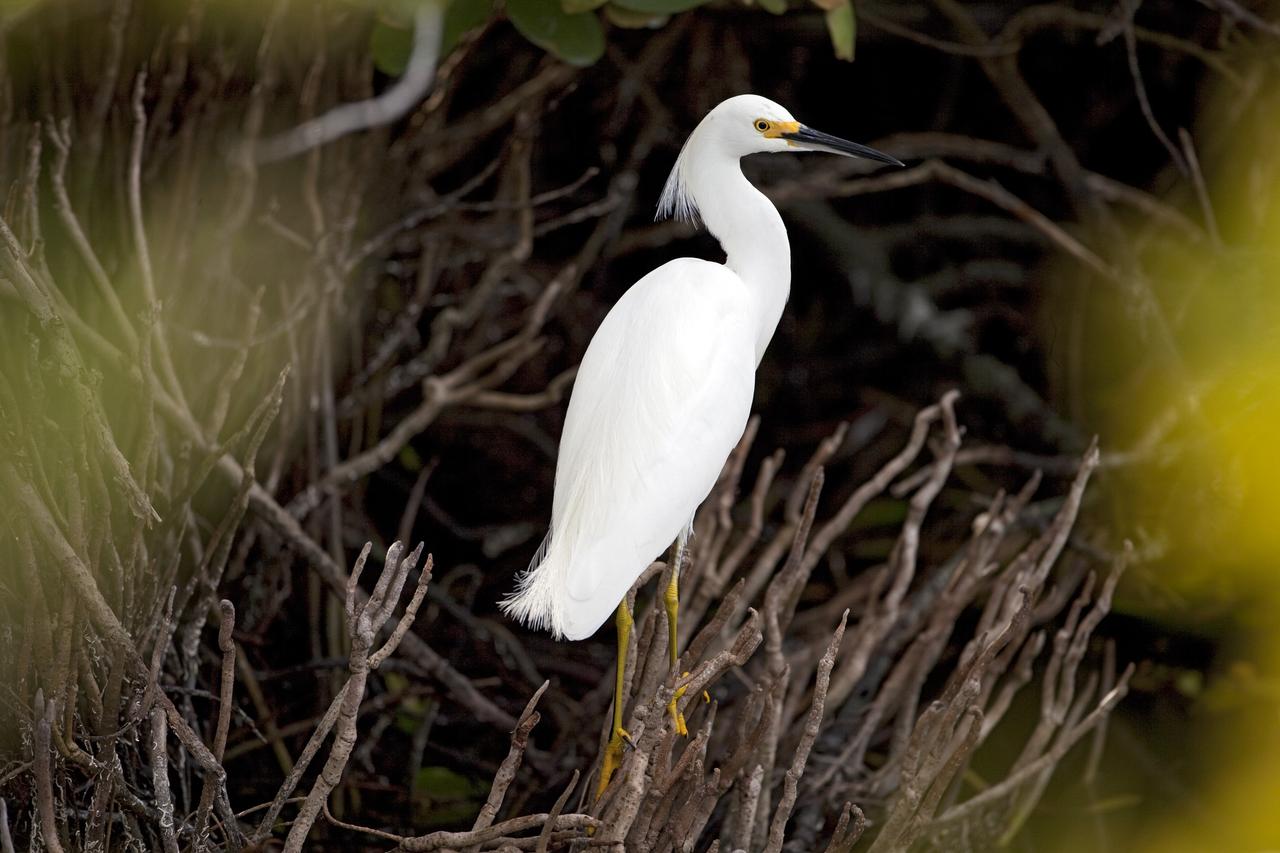

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A great white egret is perched in some brush just north of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Kennedy coexists with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, habitat to more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fish and 65 amphibians and reptiles. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
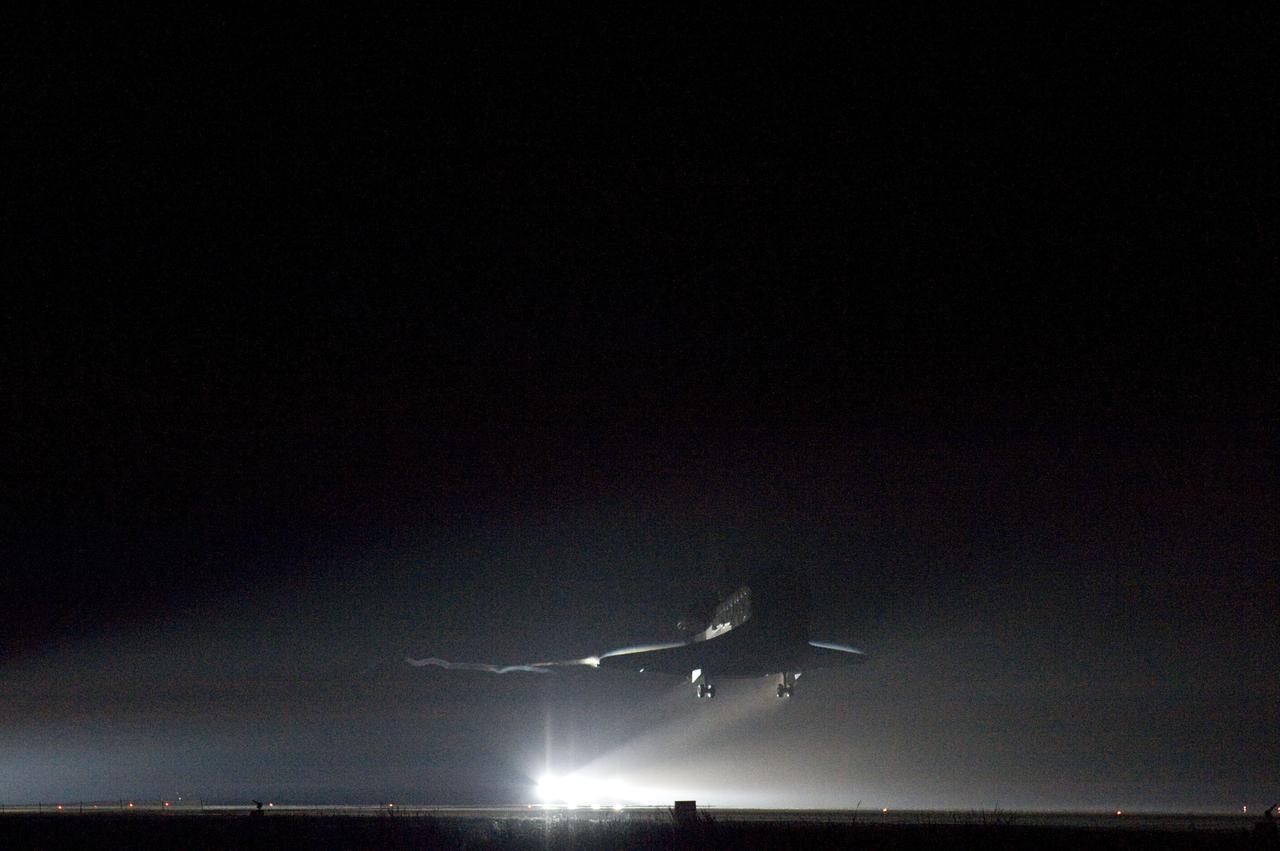

STS134-S-089 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA