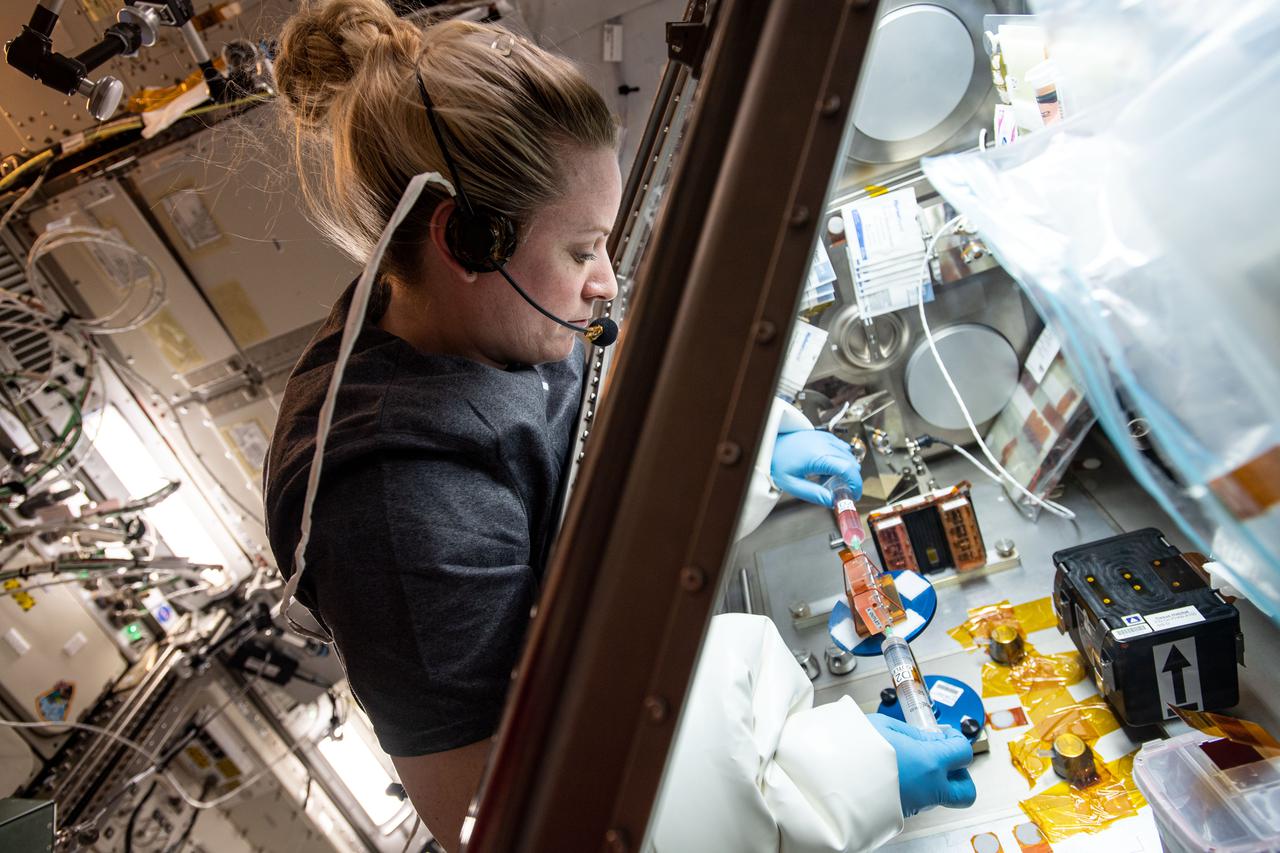

iss064e015256 (12/24/2020) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins works inside the Life Sciences Glovebox conducting research for the Cardinal Heart study. The biomedical research seeks to help scientists understand the aging and weakening of heart muscles to provide new treatments for humans on Earth and astronauts in space.
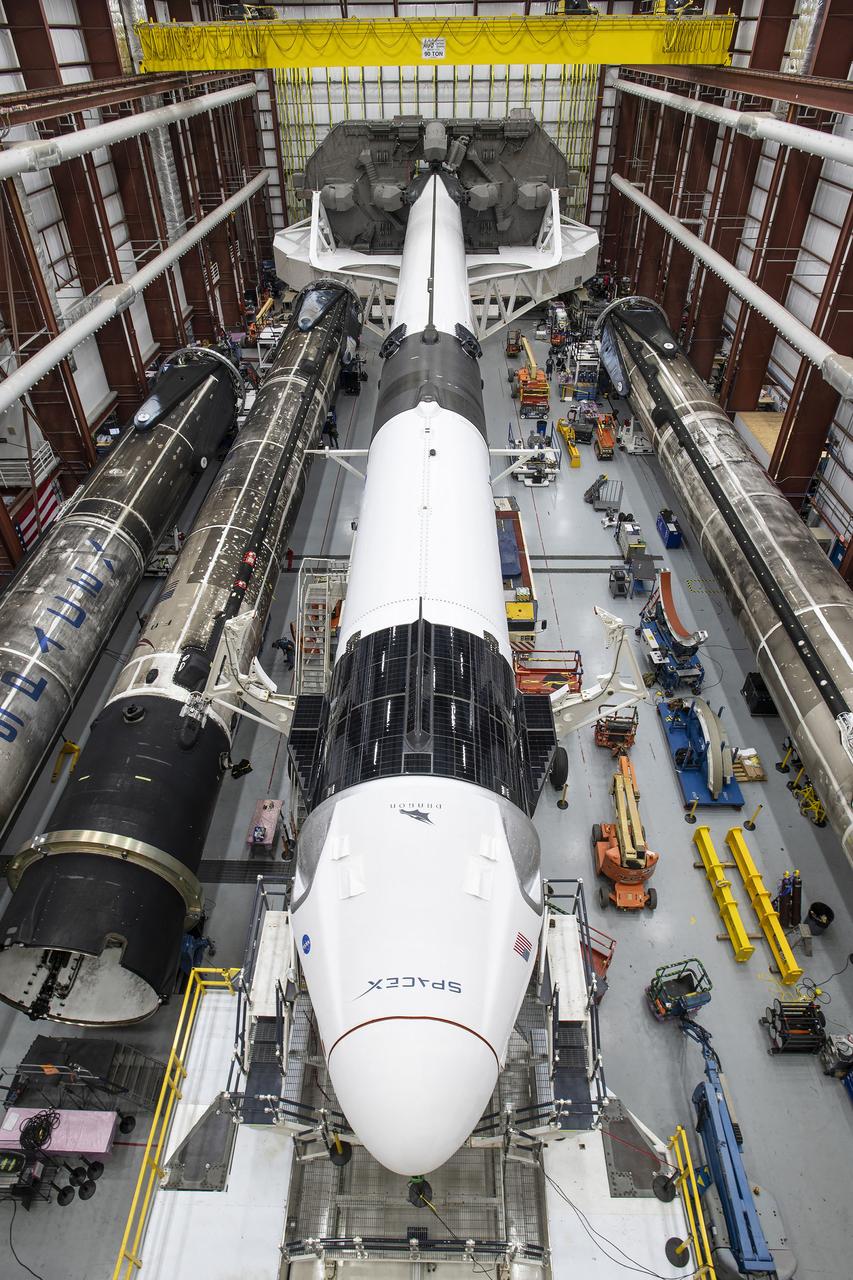

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon Resilience for NASA SpaceX’s Crew-1 mission are seen inside the SpaceX Hangar at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 9, 2020, before rollout to Launch Pad 39A. Crew-1 is the first regular crew mission of a U.S. commercial spacecraft with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew Dragon capsule will launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A carrying NASA astronauts Michael Hopkins, Victor Glover, Shannon Walker and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi to the space station for a six-month science mission.
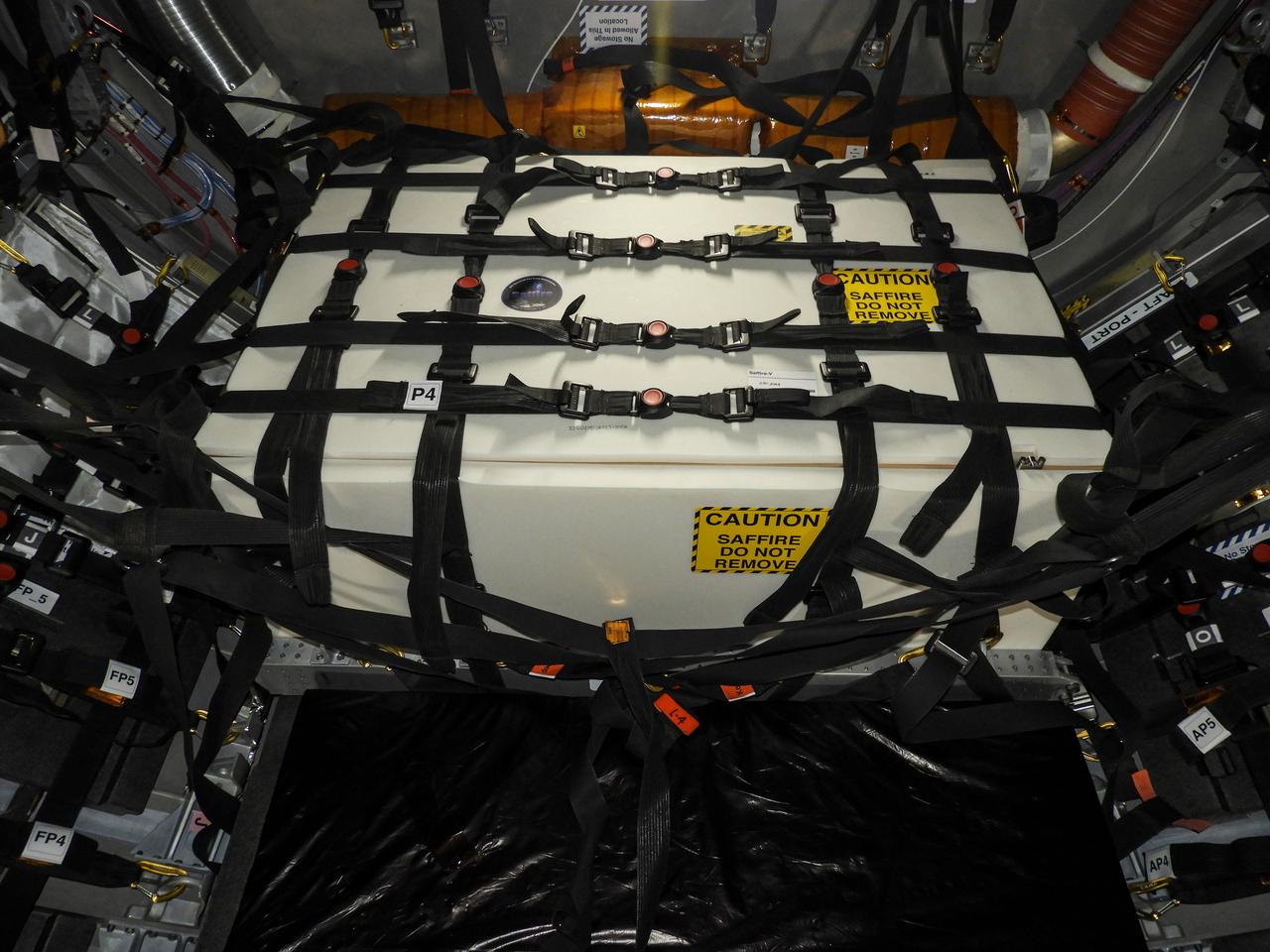

jsc2020e043815 (Sept. 10, 2020) --- A view of the Spacecraft Fire Safety Experiments (Saffire) V experiment hardware, loaded inside the Northrop Grumman(NG) Cygnus cargo vehicle for the 14th NG resupply mission to the International Space Station. Saffire is a series of experiments to investigate how fire spreads on a variety of combustible materials in the microgravity environment. The experiments are ignited in Cygnus cargo spacecraft after it departs the space station and before it reenters the Earth's atmosphere. Studying the development and growth of fire in a re-supply cargo vehicle eliminates the risk of exposure to humans in an occupied spacecraft. Understanding how fire behaves in microgravity, and how different materials propagate flames in space is immensely important for the development of future crew spacecraft.
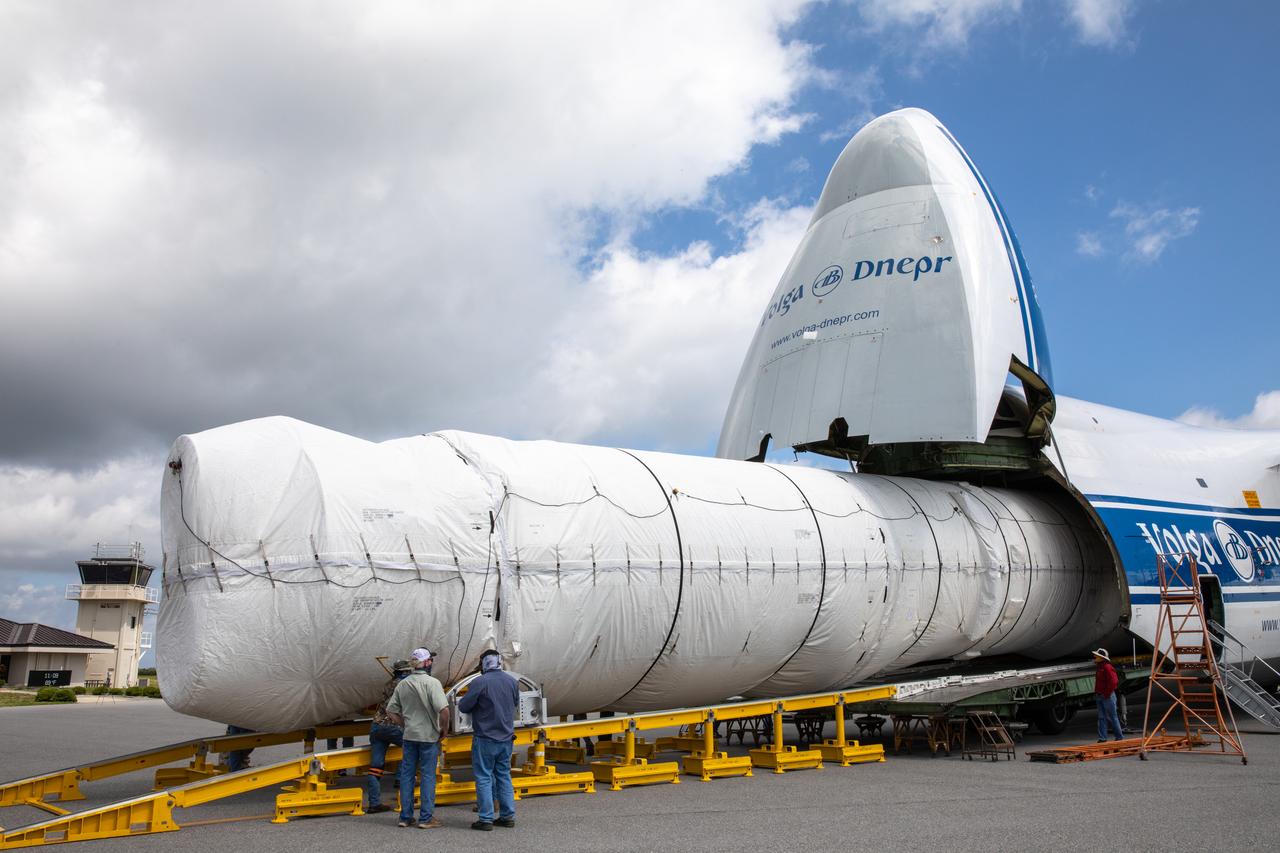

The United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
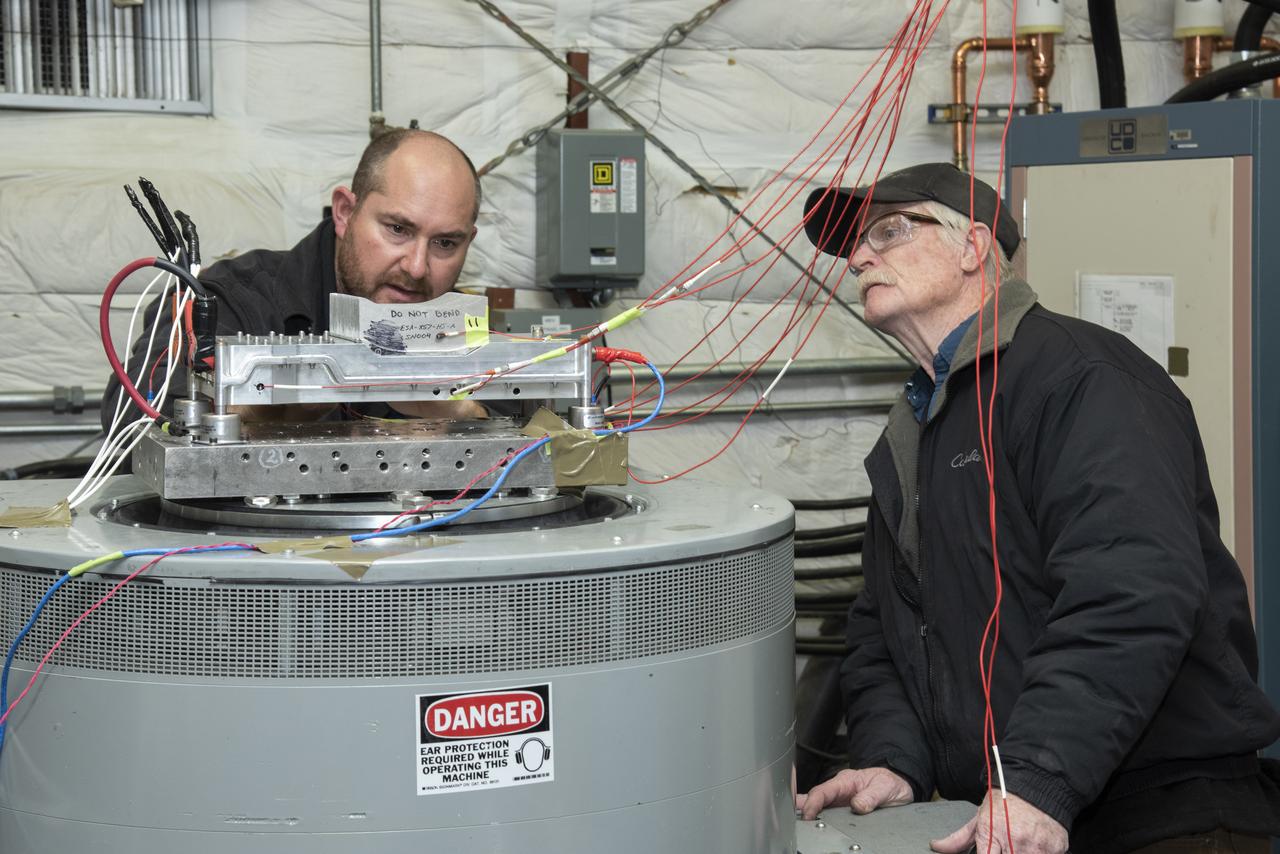

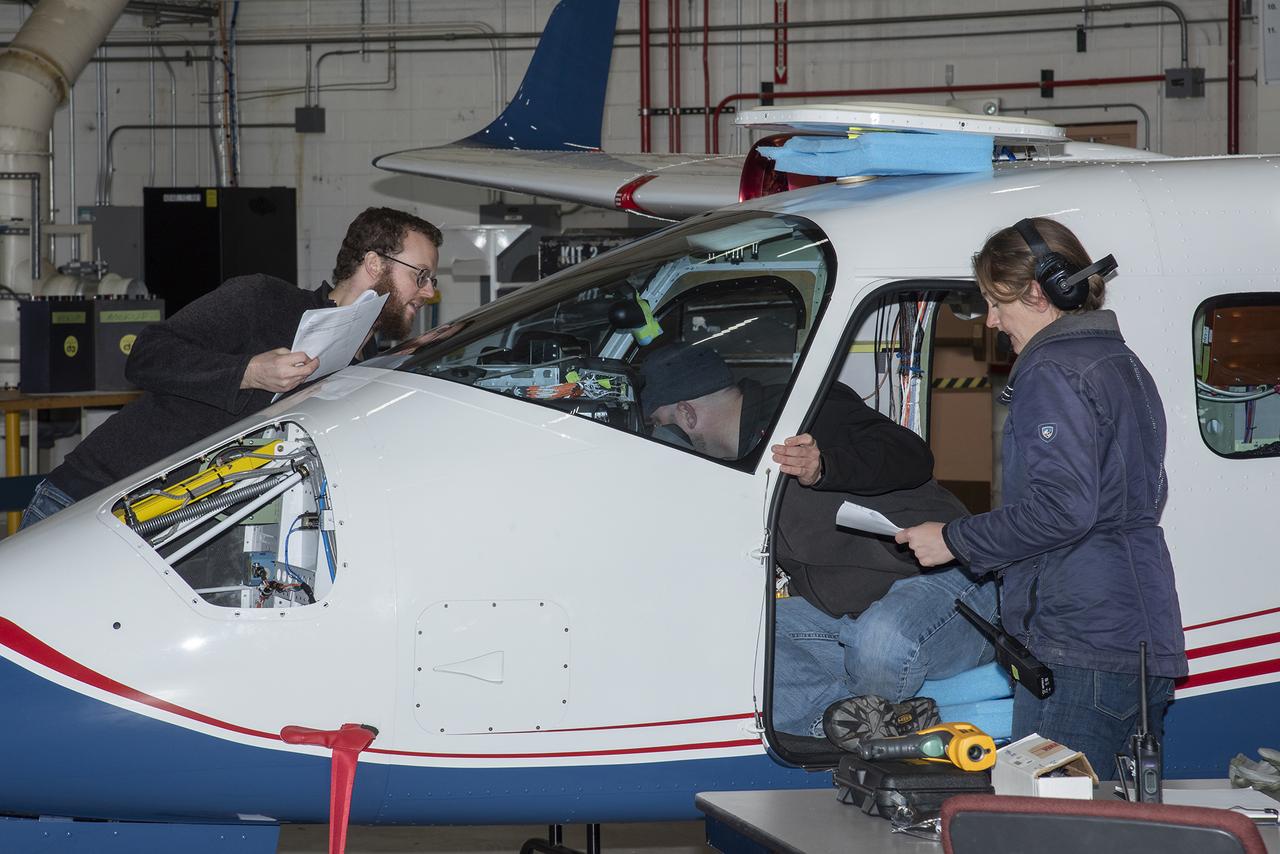
Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASAs first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
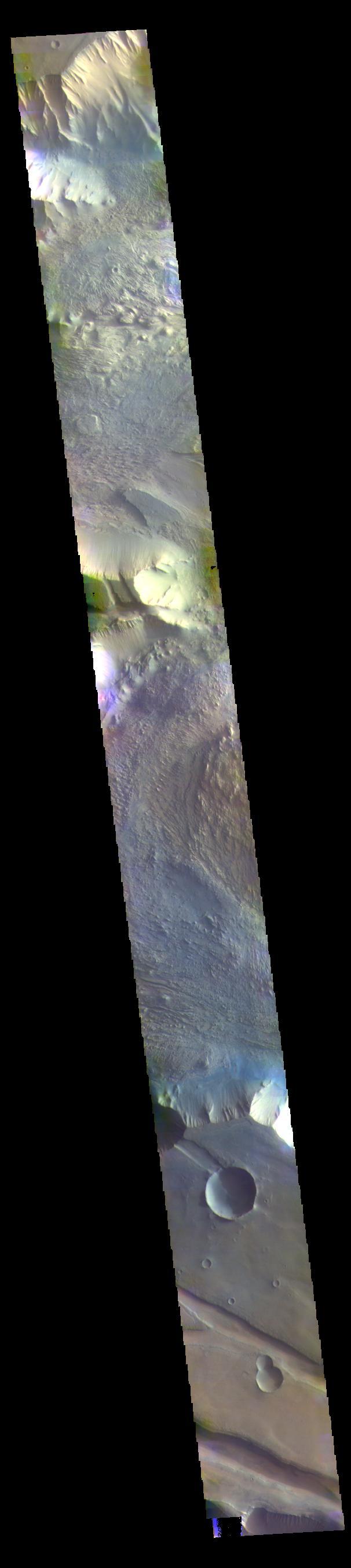

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of western Candor Chasma. Candor Chasma is one of the largest canyons that make up Valles Marineris. It is approximately 810 km long (503 miles) and has is divided into two regions — eastern and western Candor. Candor is located south of Ophir Chasma and north of Melas Chasma. The border with Melas Chasma contains many large landslide deposits. The floor of Candor Chasma includes a variety of landforms, including layered deposits, dunes, landslide deposits and steep sided cliffs and mesas. Many forms of erosion have shaped Candor Chasma. There is evidence of wind and water erosion, as well as significant gravity driven mass wasting (landslides). Orbit Number: 69411 Latitude: -5.95186 Longitude: 283.147 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-08-07 08:33 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24081
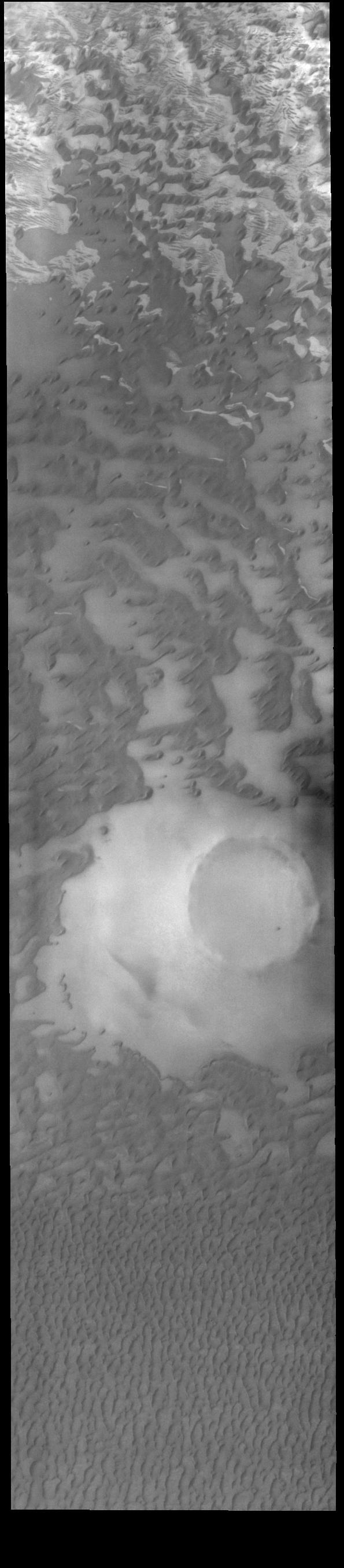
This VIS image shows part of Olympia Undae, a vast sand sea near the north pole. In regions with limited sand abundance, individual dunes form and the surface below the dunes are visible. This is the case at the top of the image. When sand abundances grow, the individual dunes coalesce into a sheet of sand hiding the underlaying surface. This is the case at the bottom of the image. Orbit Number: 80393 Latitude: 80.0028 Longitude: 143.285 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-01-28 21:30 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23835
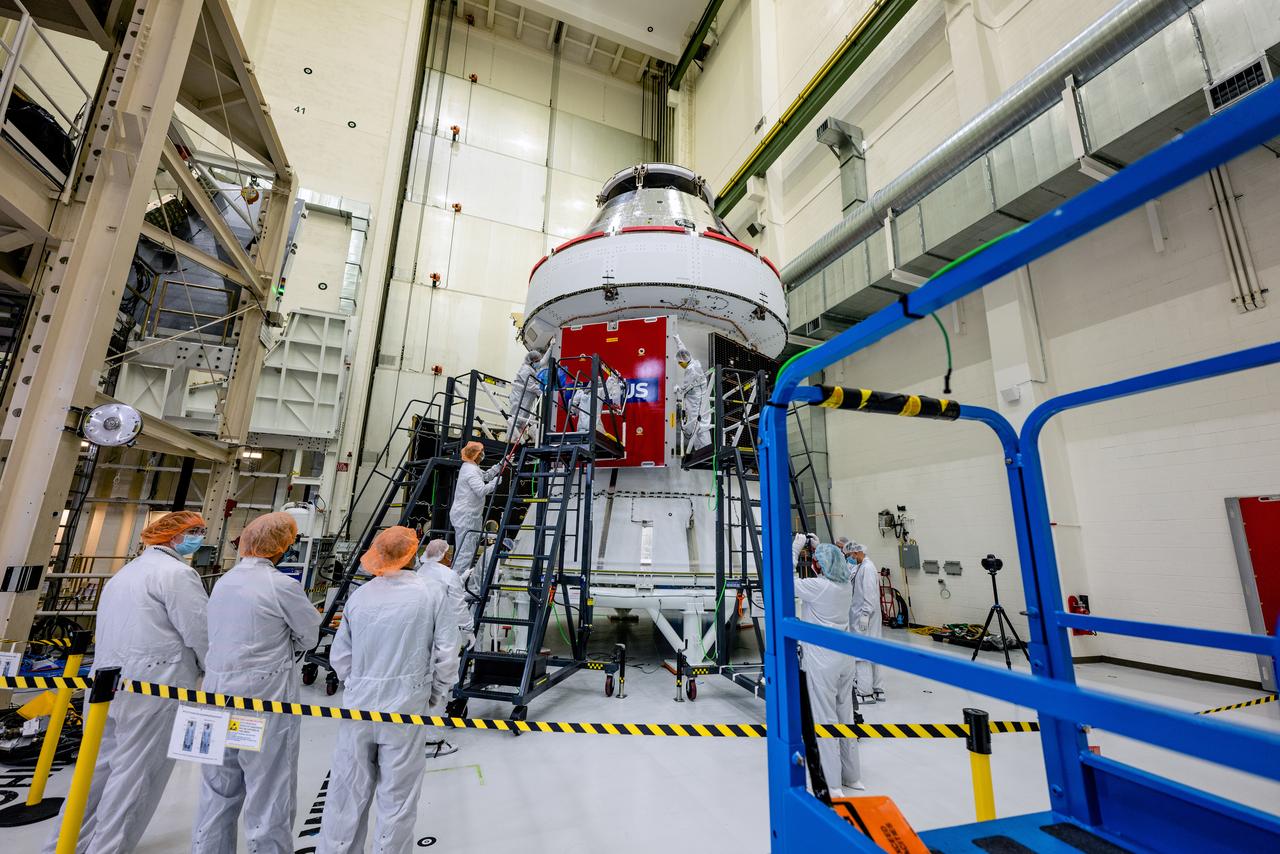

In the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at Kennedy Space Center, three spacecraft adapter jettison (SAJ) fairings are prepared for installation and will be moved into place by technicians with Lockheed Martin, lead contractor for Orion on Oct. 12, 2020. They will be secured around the spacecraft, encapsulating the European Service Module to protect it from the harsh environment as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission. The next time the solar array wings will be visible will be when Orion is in space. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
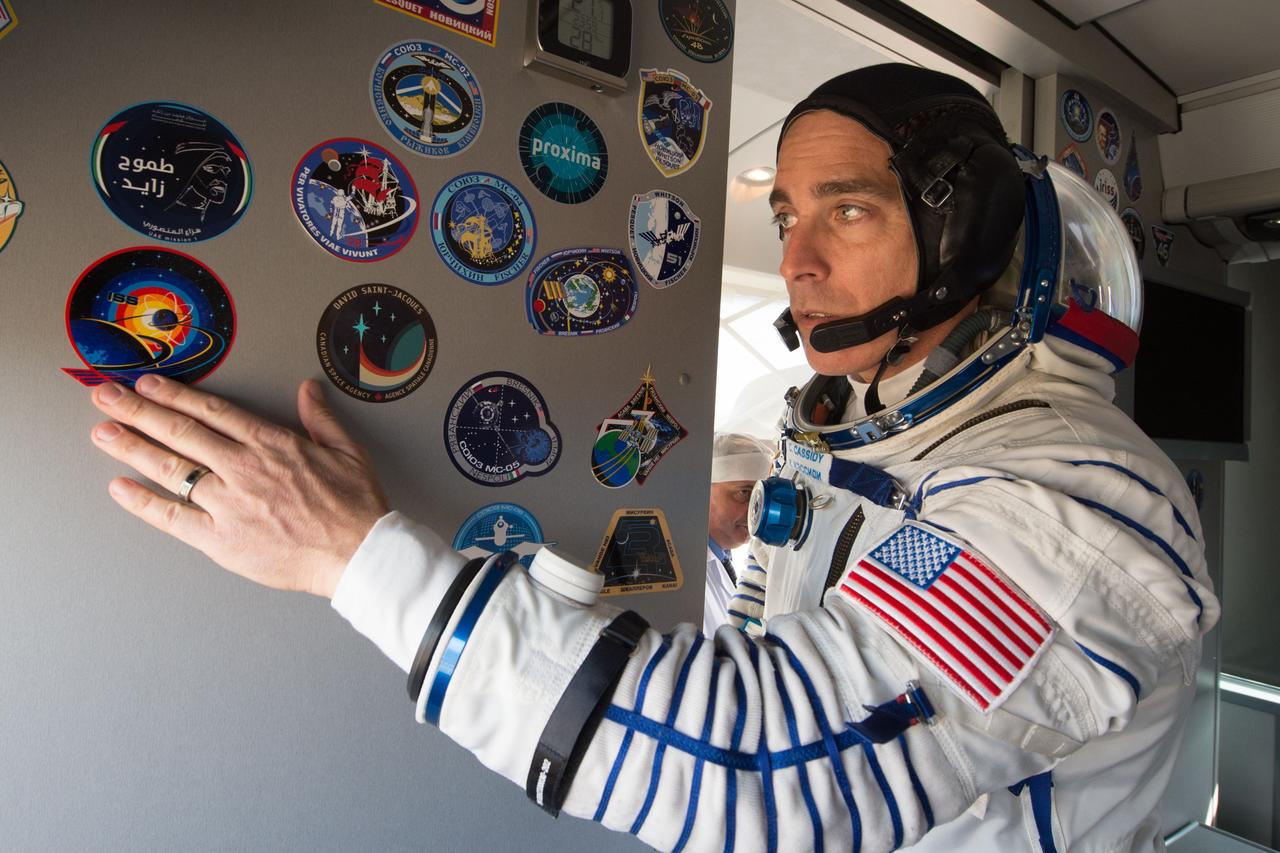

jsc2020e017112 - Expedition 63 Preflight - Expedition 63 crewmember Chris Cassidy of NASA applies a mission sticker to the interior of the crew bus as he, Anatoly Ivanishin, and Ivan Vagner of Roscosmos arrive at the launch pad, Thursday, April 9, 2020 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. A few hours later, they lifted off on a Soyuz rocket for a six-and-a-half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)...

Telemetry testing begins on the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane, as the operations crew at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center records the results. Telemetry testing is a critical phase in X-57’s functional test series. In addition to confirming the ability of the X-57 aircraft to transmit speed, altitude, direction, and location to teams on the ground, telemetry testing also confirms the ability to transmit mission-critical-data, such as voltage, power consumption, and structural integrity. X-57’s goal is to help set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.
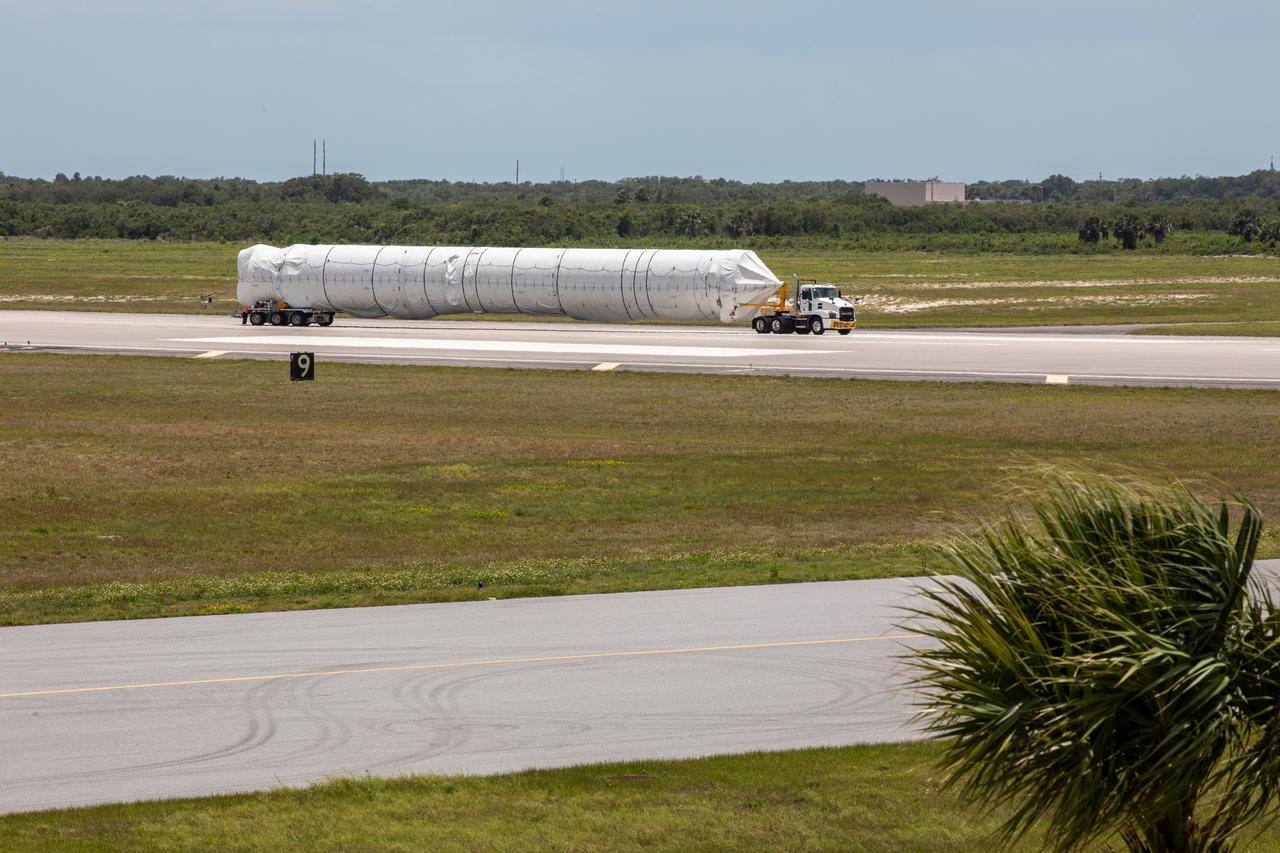

A flatbed truck carrying the United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover departs the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The booster arrived aboard the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip on May 18, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
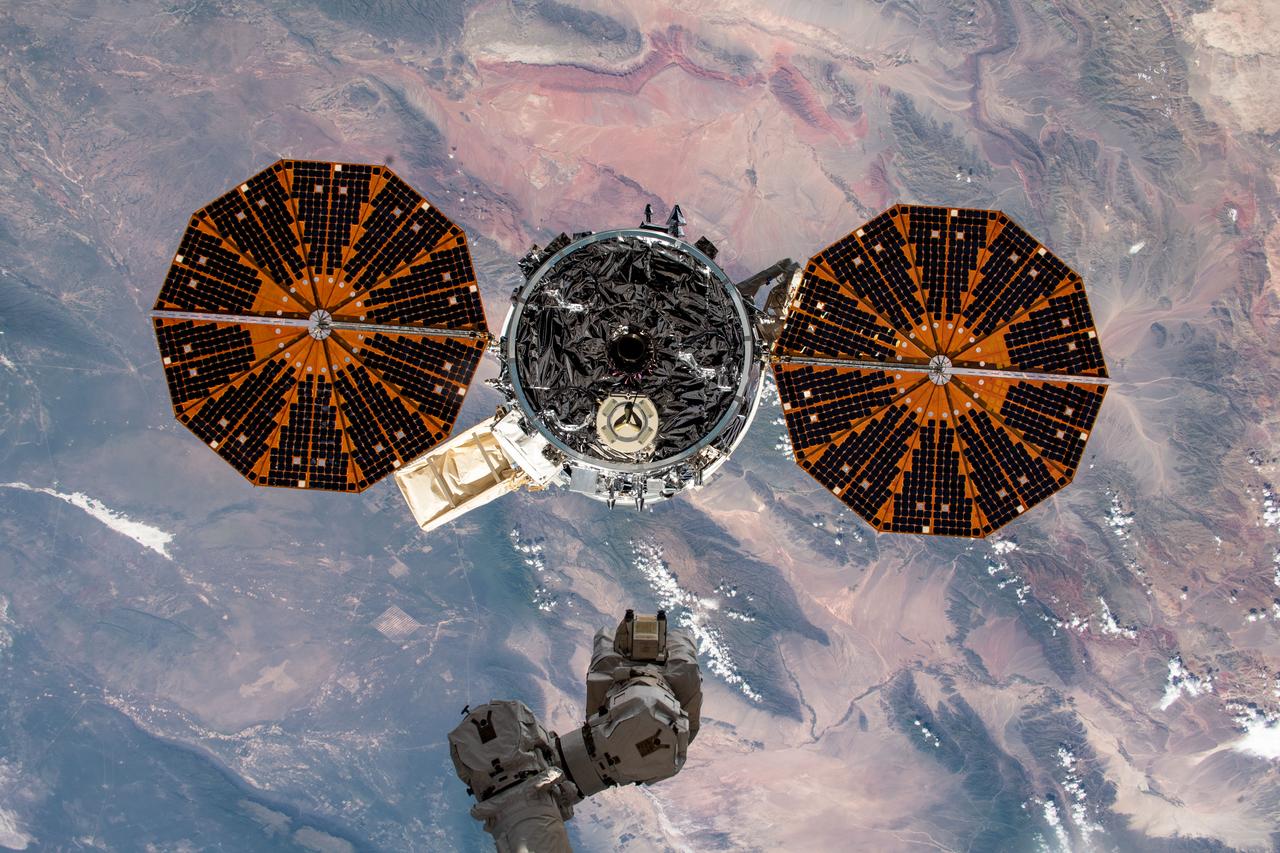

iss061e150257 (Jan. 31, 2020) --- The Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is pictured moments after its release from the Canadarm2 robotic arm as the International Space Station orbited over the South Pacific just off the West Coast of Chile. Cygnus had completed an 88-day stay attached to the Unity module after delivering nearly 8,200 pounds of research and supplies to the space station on Nov. 4, 2019.
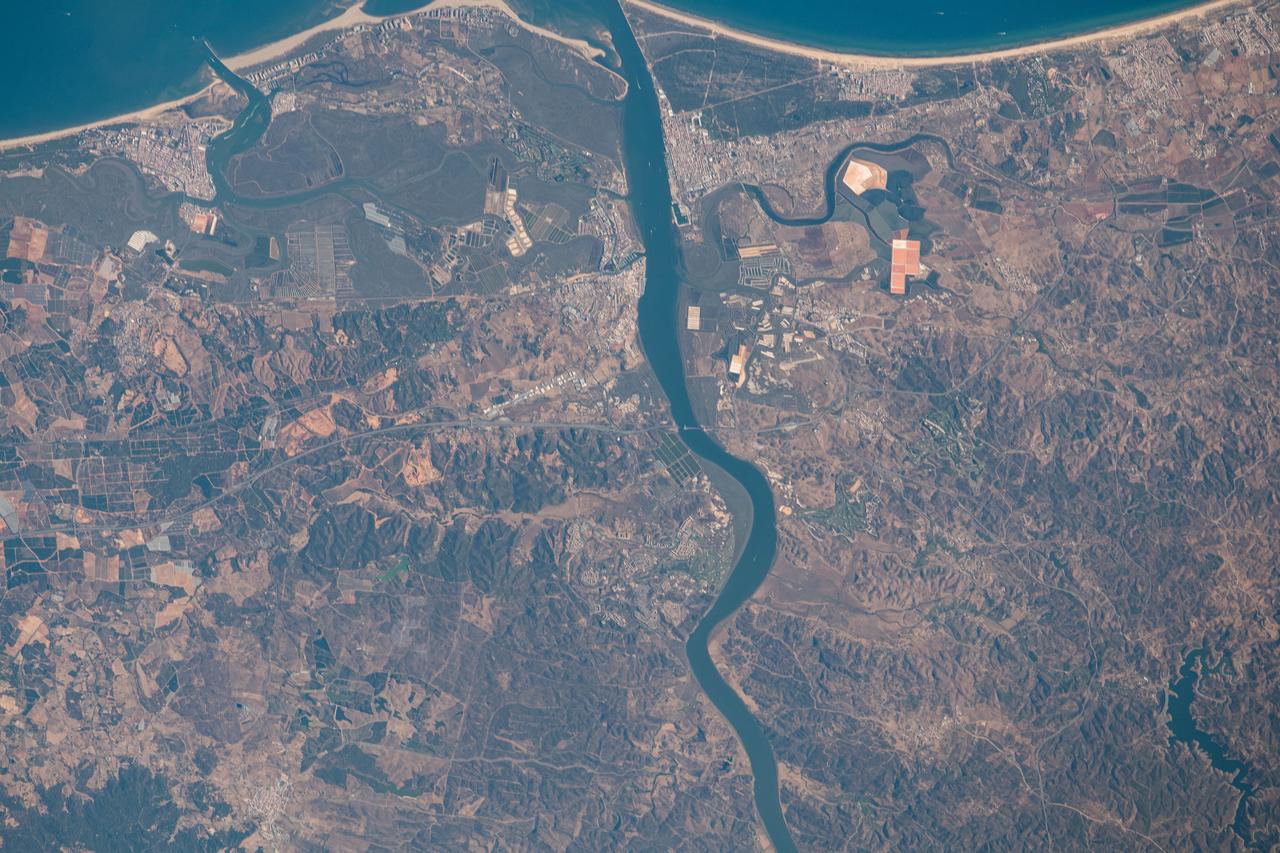

iss063e070330 (Aug. 13, 2020) --- The Guadiana River flows into the Gulf of Cádiz in the Atlantic Ocean and is the border for the southern coastal portions of Portugal (right) and Spain (left)

A flatbed truck, carrying the node structural test article (STA), is on its way to the Launch and Landing Facility from the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 20, 2020. In view is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. The Node STA was used to prove the manufacturing processes and procedures were robust for extended human spaceflight. Those same processes and procedures were then used to build Node 1, which Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana flew to the space station on STS 88. NASA has stored the node STA in the SSPF, and it is moving to a new location to allow for more space in the facility’s high bay to support the agency’s space exploration and commercialization efforts in low-Earth orbit.
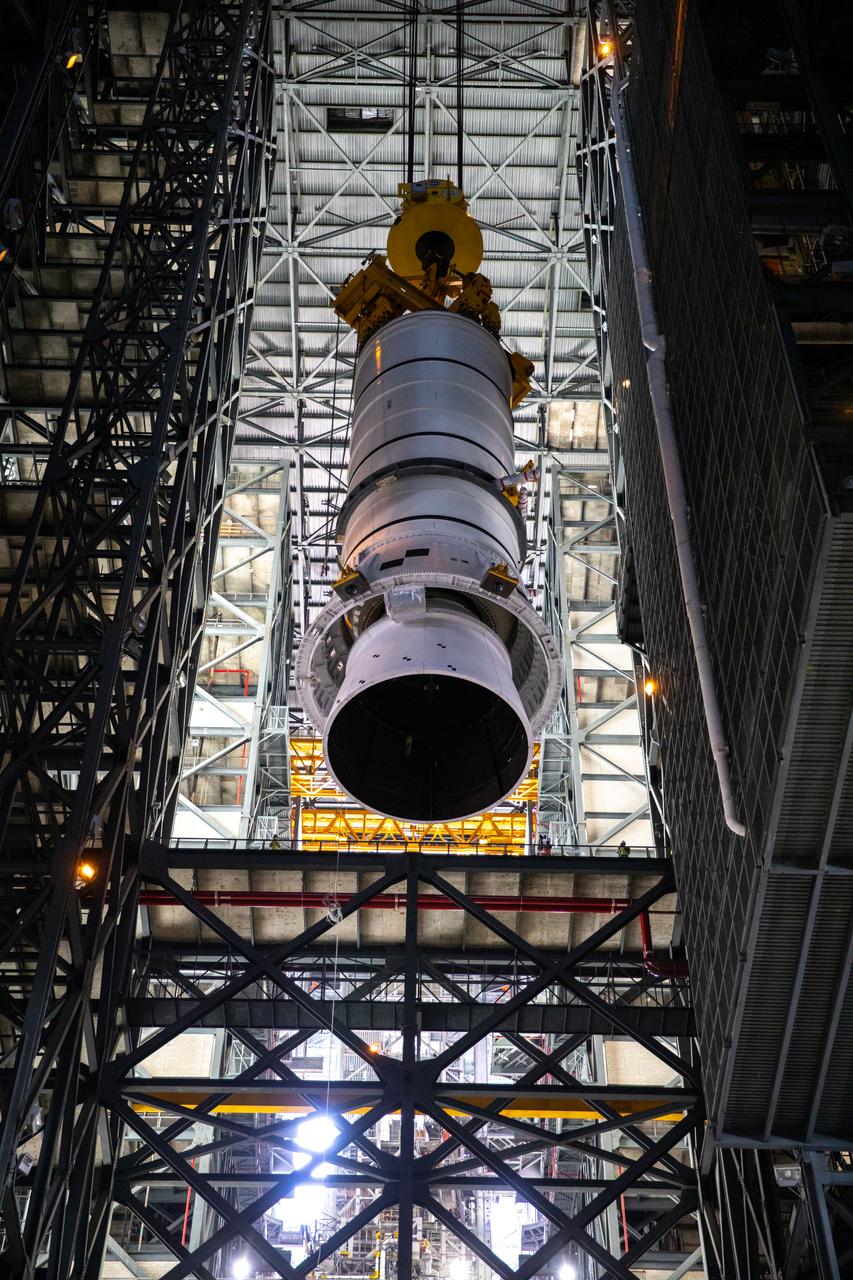

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems rehearse lifting operations using a mock-up of the Space Launch System (SLS) aft booster segment, referred to as a pathfinder, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 11, 2020, in preparation for Artemis I. The exercise involved preparing the aft pathfinder segment in High Bay 4 of the VAB and moving it over to High Bay 3, where it was placed on the mobile launcher. Stacking of the actual booster segments will occur later this year, before the SLS core stage arrives at Kennedy. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
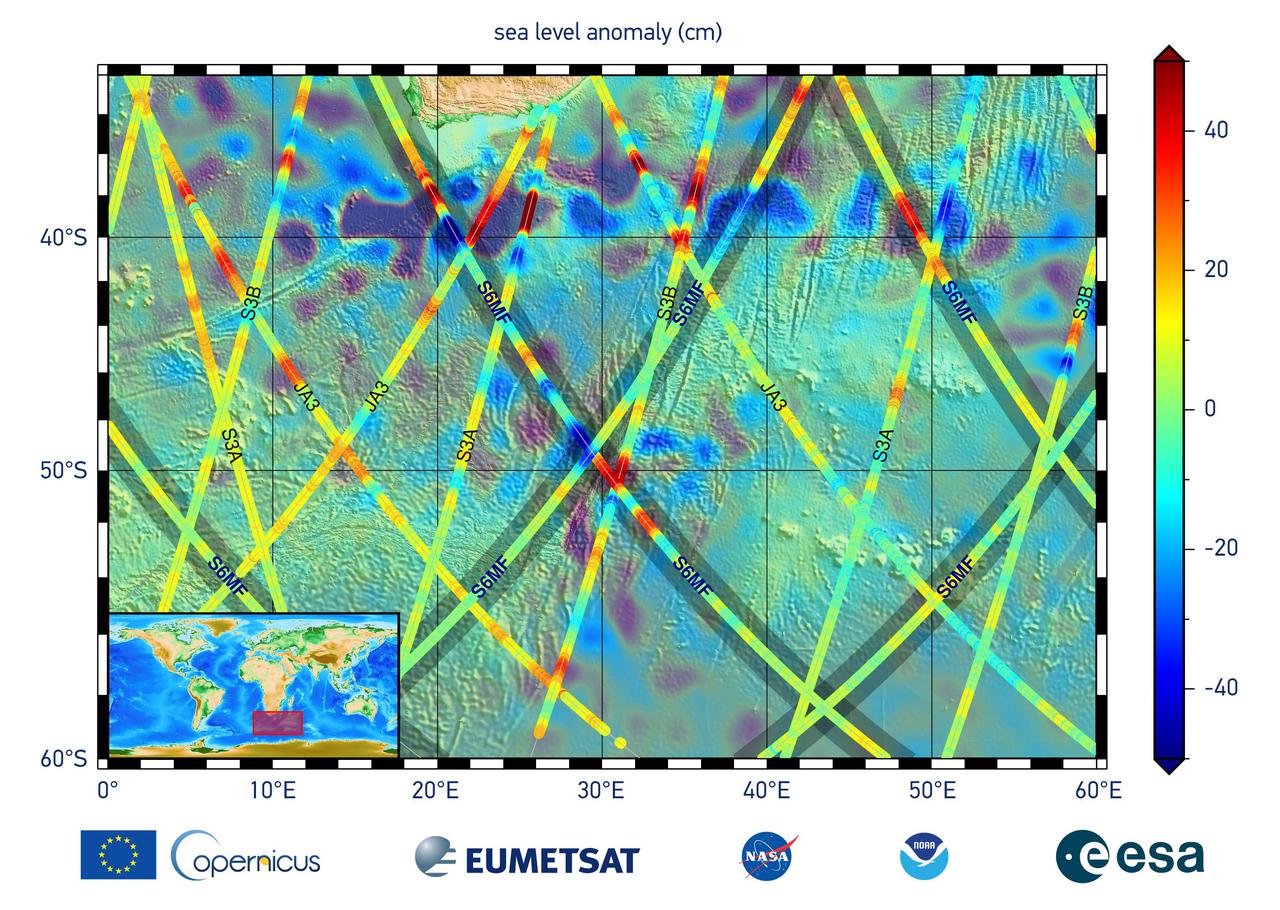
This graphic, released on Dec. 10, 2020, shows the first sea level measurements taken by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich (S6MF), which launched Nov. 21, 2020. It focuses on the ocean off the southern tip of Africa, where red colors indicate higher sea level relative to blue areas, which are lower. Also included are sea surface height measurements from three other satellites for comparison: Jason-3 (JA3), Sentinel-3A (S3A), and Sentinel-3B (S3B). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24135

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
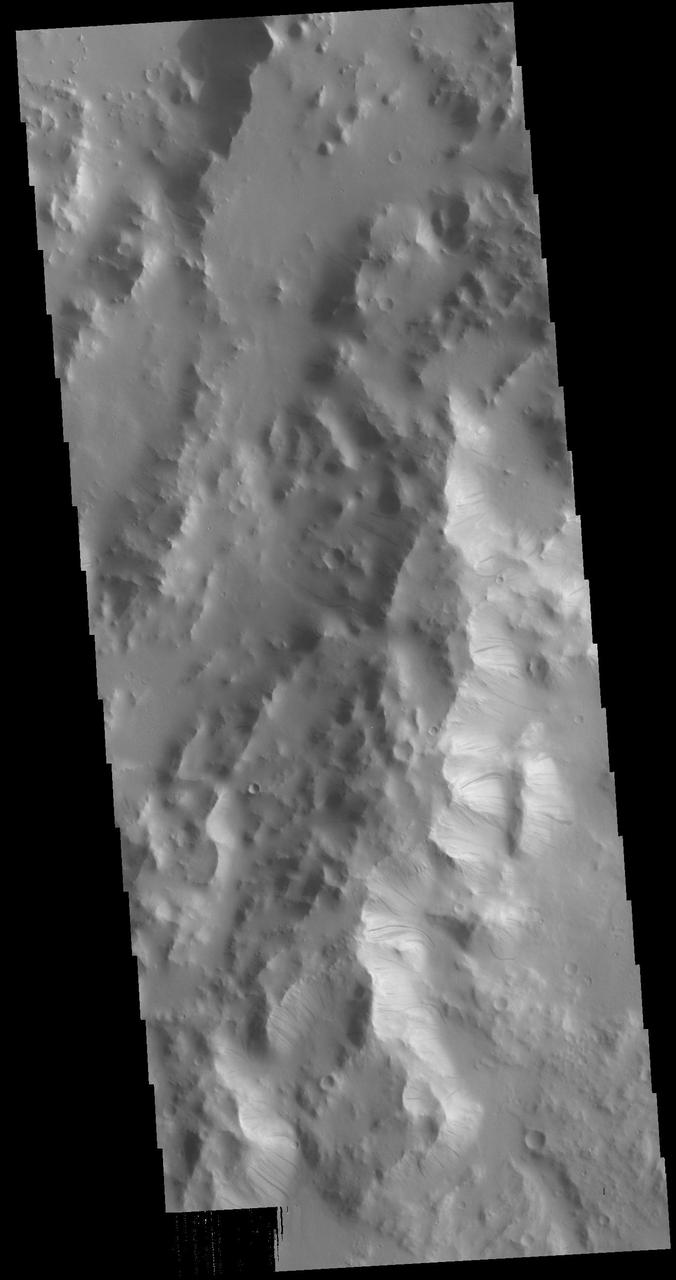

Today's VIS image is located on the eastern margin of Orcus Patera. Dark slope streaks are present on most ridges in the image. Formation of these features is linked to a change in the surface, either removal of the dusty surface revealing darker rock beneath the dust, or a volatile flow along the cliff face. The mechanism that formed Orcus Patera is unknown. While the term "patera" is tied to volcanic activity, the elongate shape might also have been caused by a low angle meteor impact. Orbit Number: 79232 Latitude: 12.9315 Longitude: 179.284 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2019-10-25 06:48 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23640
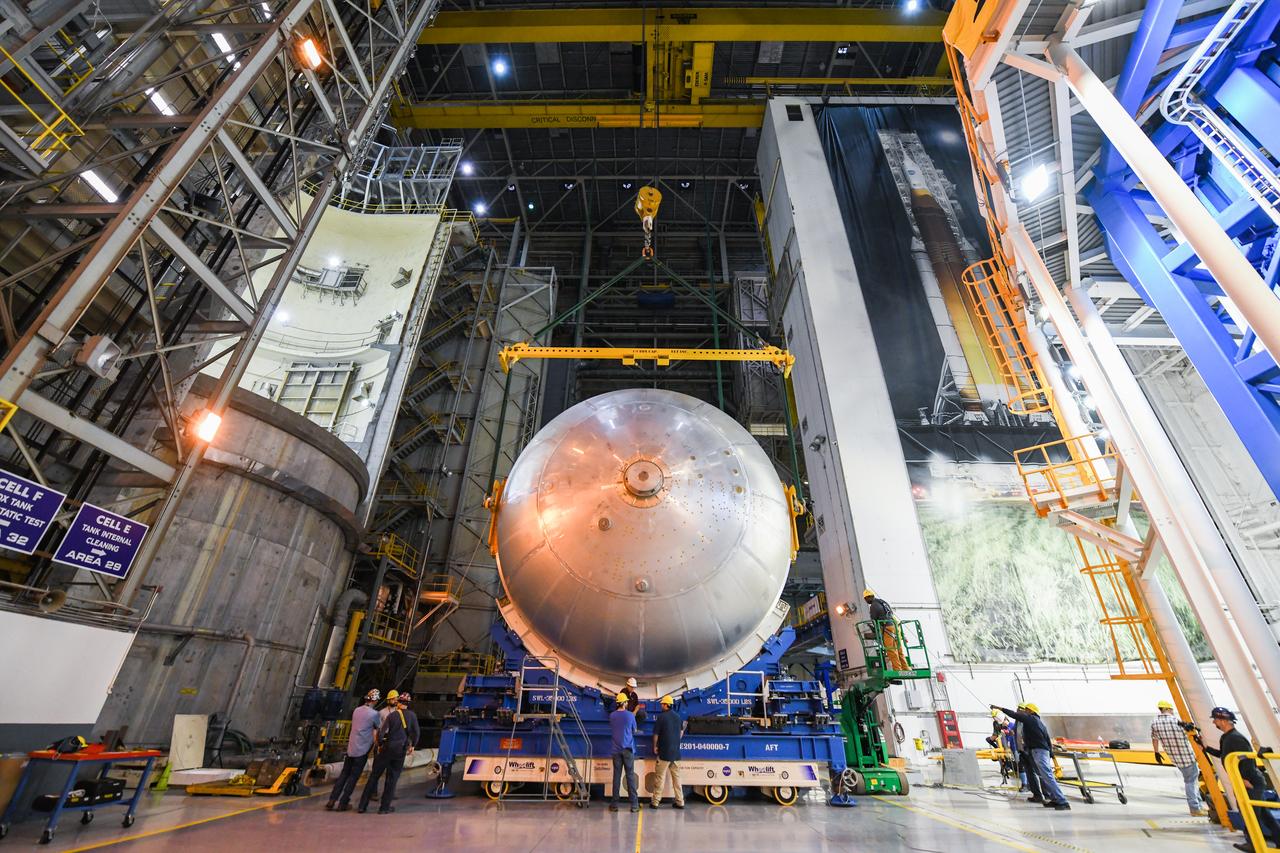

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro participates in a virtual town hall at the Florida spaceport’s Press Site auditorium on June 10, 2020, to share the plan for employees to safely return to on-site work during the time of COVID-19. Also participating were Center Director Bob Cabana and Dr. David Tipton, chief medical officer, not pictured.
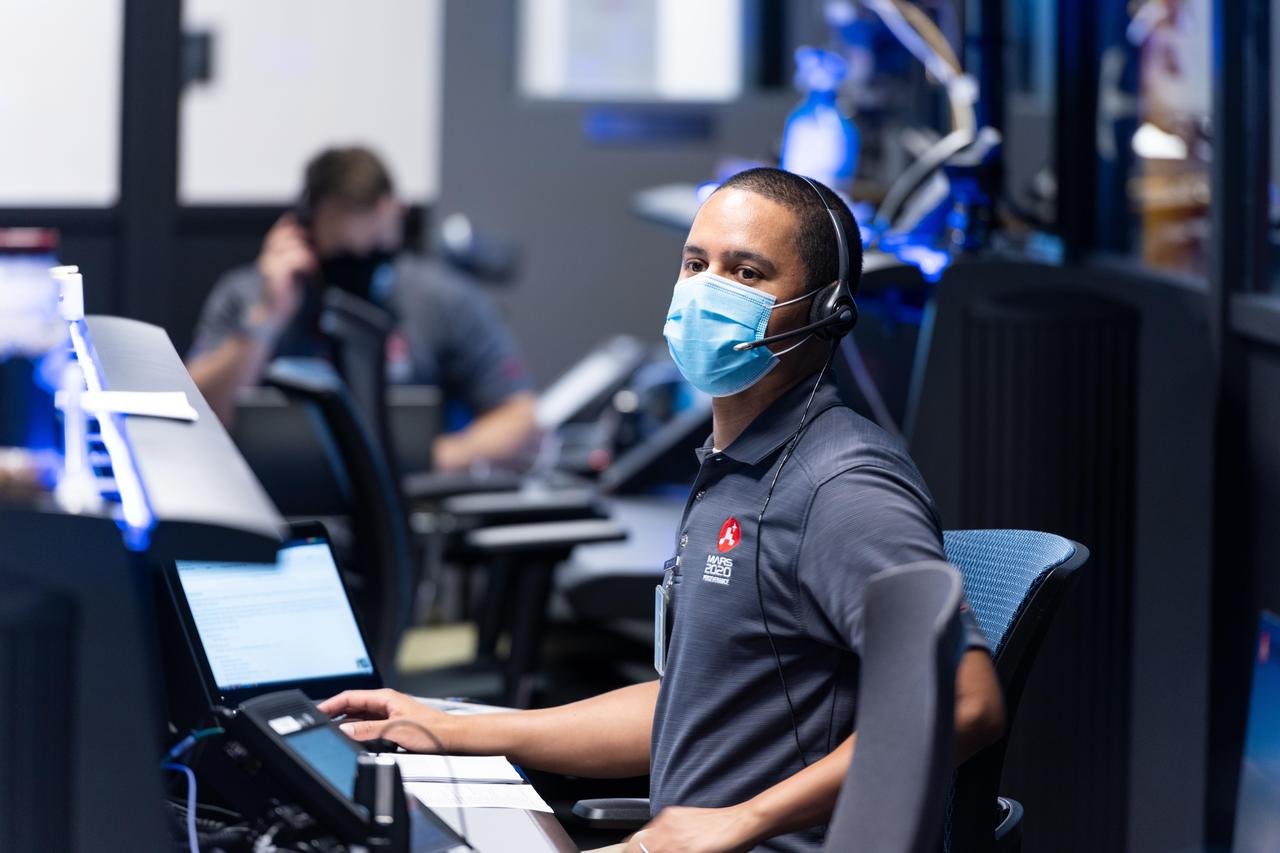

Matt Smith, flight director for the second Mars 2020 mission trajectory correction maneuver (TCM-2), studying the screens at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. TCMs are a series of planned adjustments to put the rover on the correct path to land on Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24193
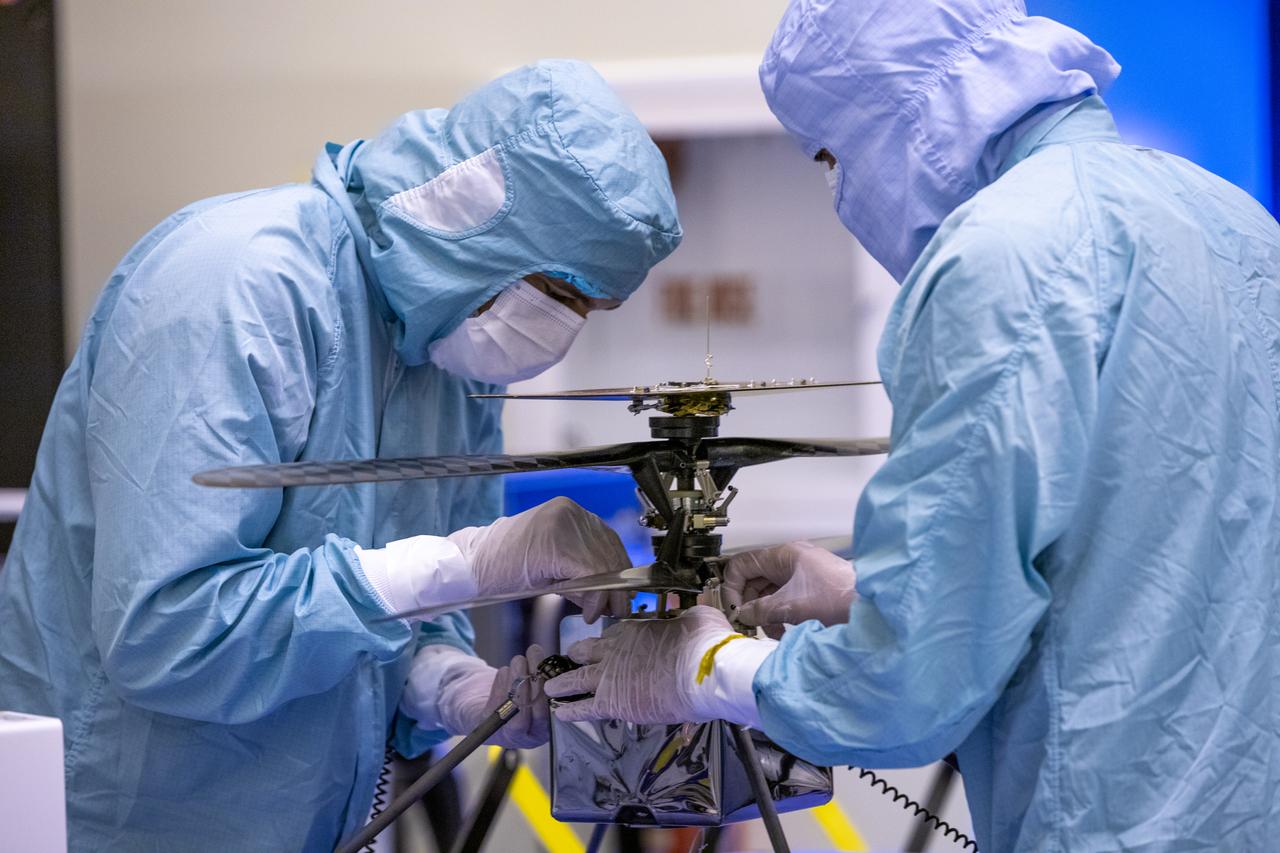

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
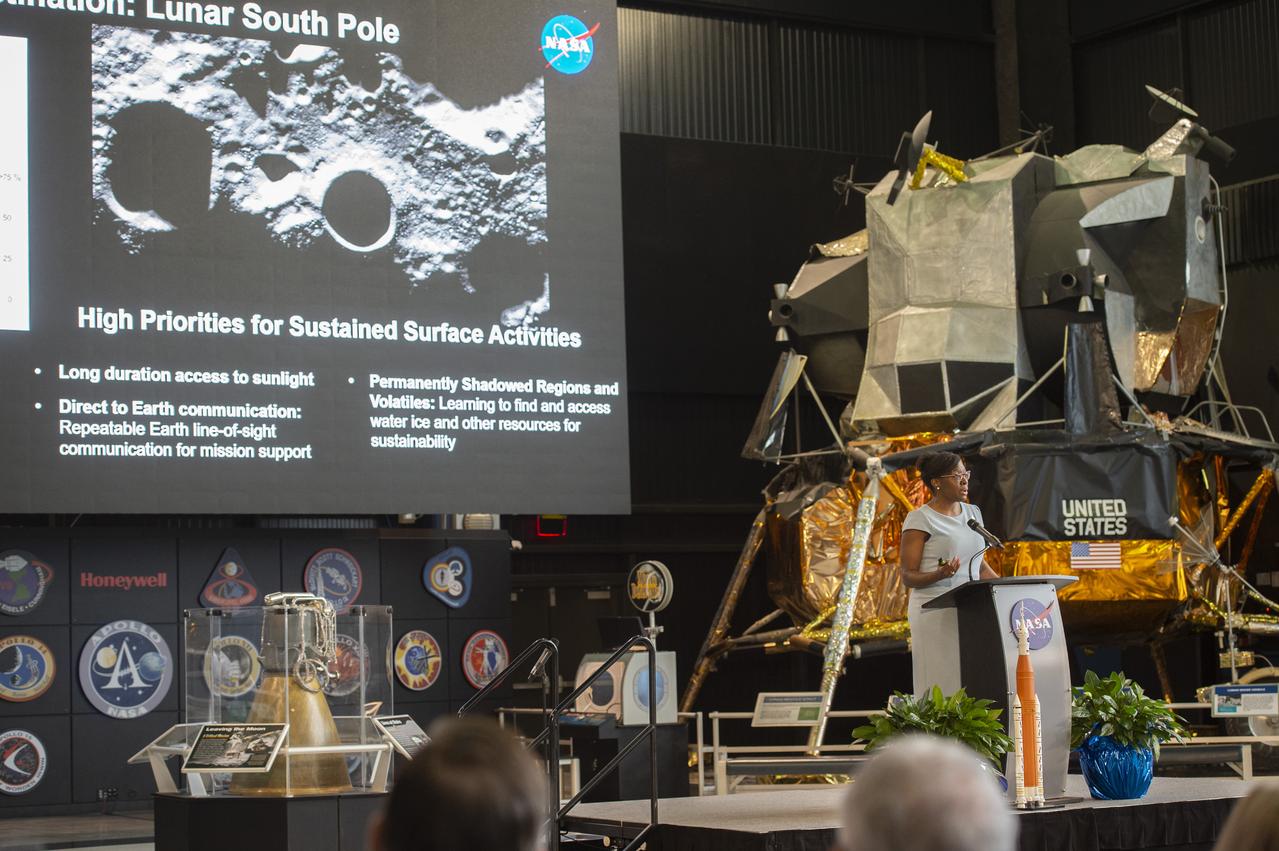

Lakiesha Hawkins delivers Human Landing System update at the 2020 Small Business Alliance meeting at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center's Davidson Center.

The small dunes in this VIS image are located in an unnamed crater in southern Noachis Terra. Orbit Number: 82059 Latitude: -56.2948 Longitude: 353.028 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-06-14 01:00 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24119

On Oct. 23, 2020, an engineer with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) is at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as a brilliant sunrise illuminates the sky. The mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission is at the pad to allow engineers with EGS and Jacobs to complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

iss062e115956 (3/28/2020) --- A view of the Space Tango CubleLab for the the Microgravity Exposure on Medicinal Plant Seeds investigation aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Microgravity Exposure on Medicinal Plant Seeds evaluates microgravity’s effects on Cannibis sativa (Victoria) seeds. The cannabinoid content of plants grown from seeds exposed to microgravity conditions aboard the International Space Station (ISS) are compared to plants grown from seeds maintained on the ground.
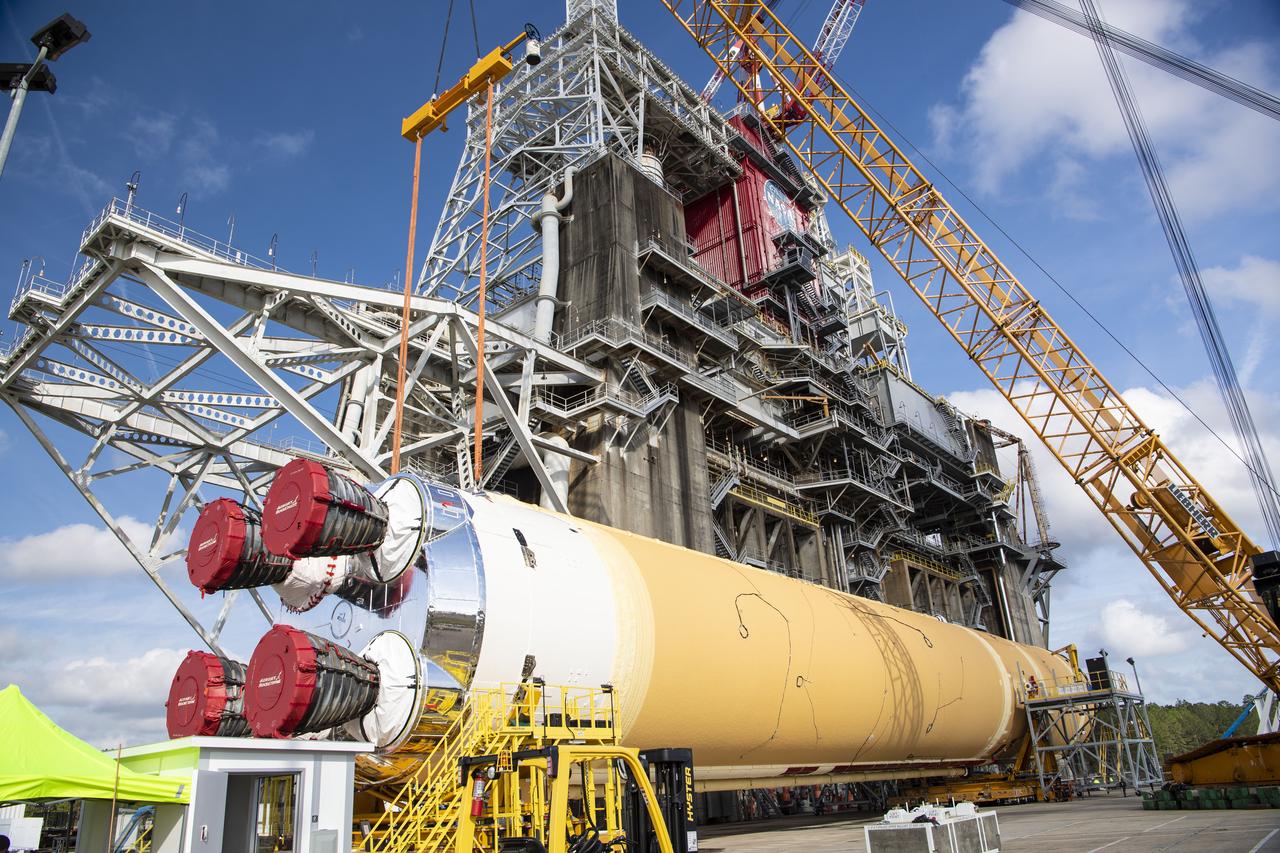

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.
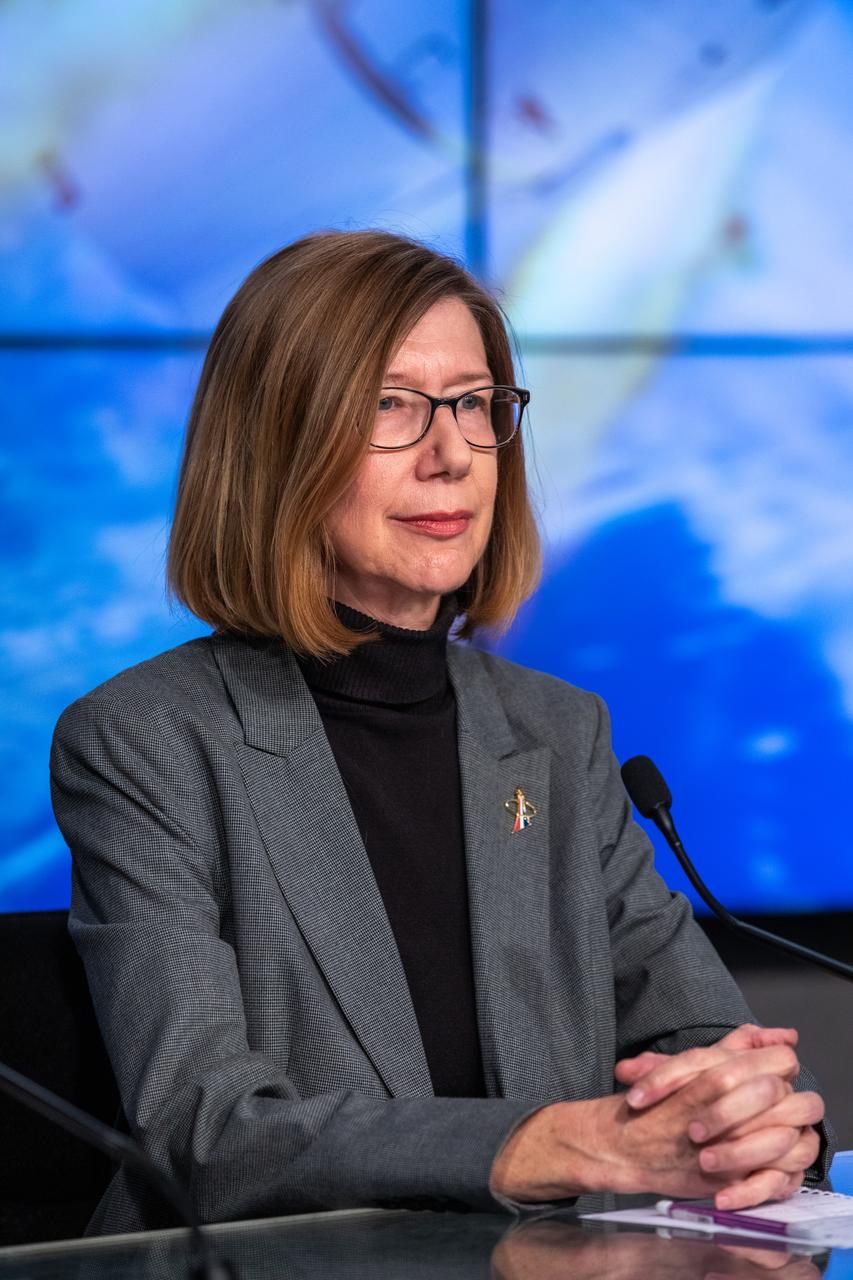

Kathy Lueders, manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, participates in a briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the company’s uncrewed In-Flight Abort Test on Jan. 19, 2020. During the flight test, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifted off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A and began a planned launch-abort sequence demonstrating the spacecraft’s escape capabilities. The Crew Dragon splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean as expected. The In-Flight Abort Test is a critical milestone in preparation for crewed flights to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.

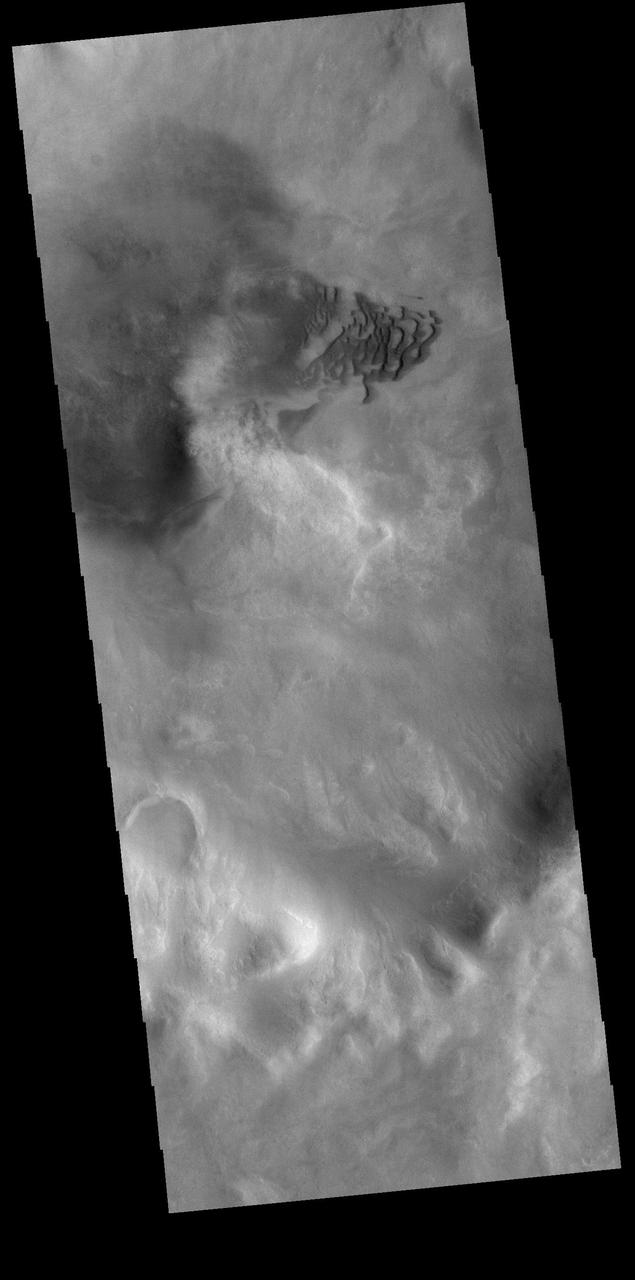
The linear depression in this VIS image is part of Sirenum Fossae. Depressions of this type are called graben, which form by the down drop of material between two parallel faults. The faults are caused by tectonic stresses in the region. The Sirenum Fossae graben are 2735km (1700 miles) long. Orbit Number: 83743 Latitude: -37.2437 Longitude: 191.251 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-10-30 16:21 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24280
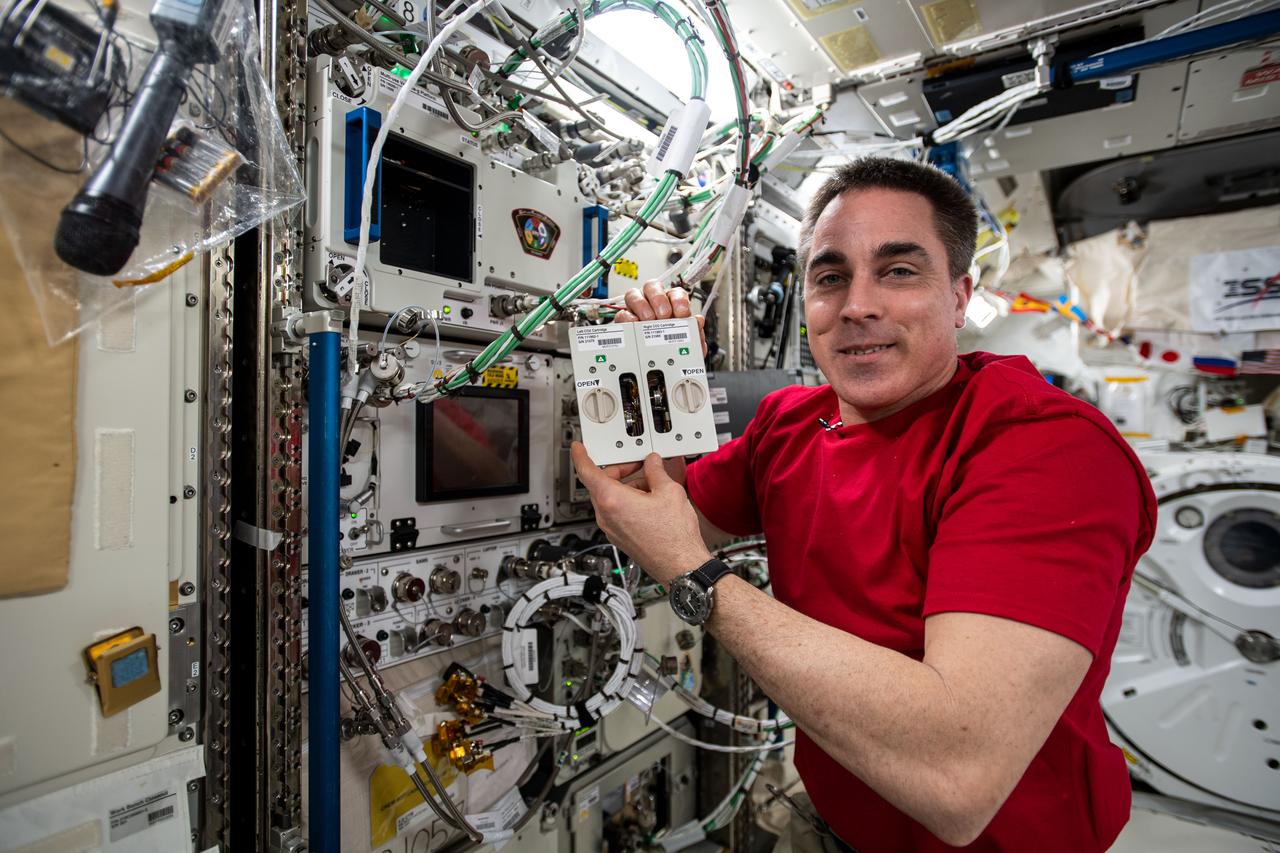

iss063e110548 (Oct. 19, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 63 Commander Chris Cassidy works on research hardware inside the JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Kibo laboratory module.
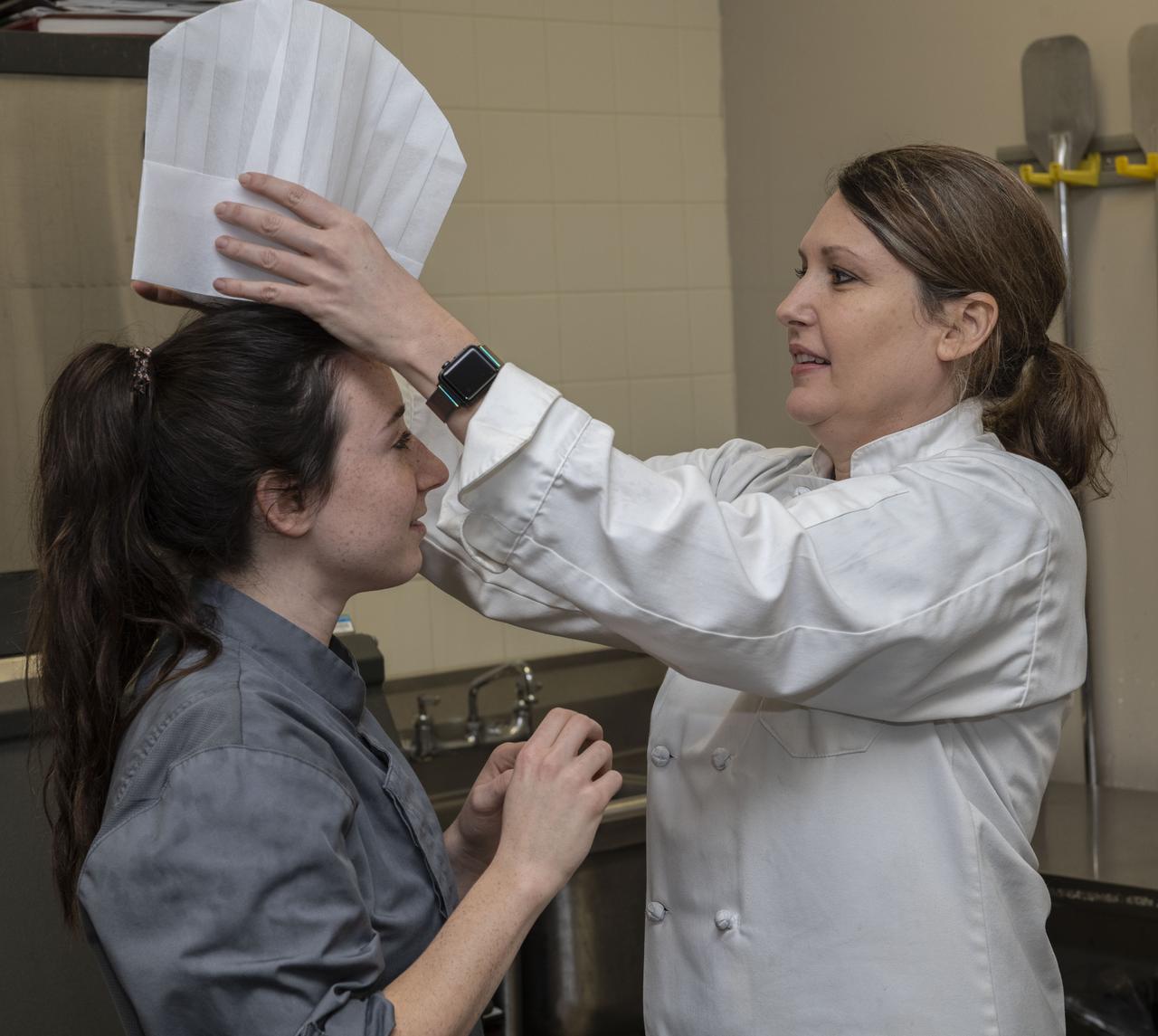
HUNCH (High School Students United with NASA to Create Hardware) students came together at the U.Sl Space and Rocket Center (USSRC) in a competition to create recipes for food to feed astronauts in space. Six teams from North Alabama and George participated. The winner will compete with students from competitions at other NASA centers later at the Johnson Space Flight Center.
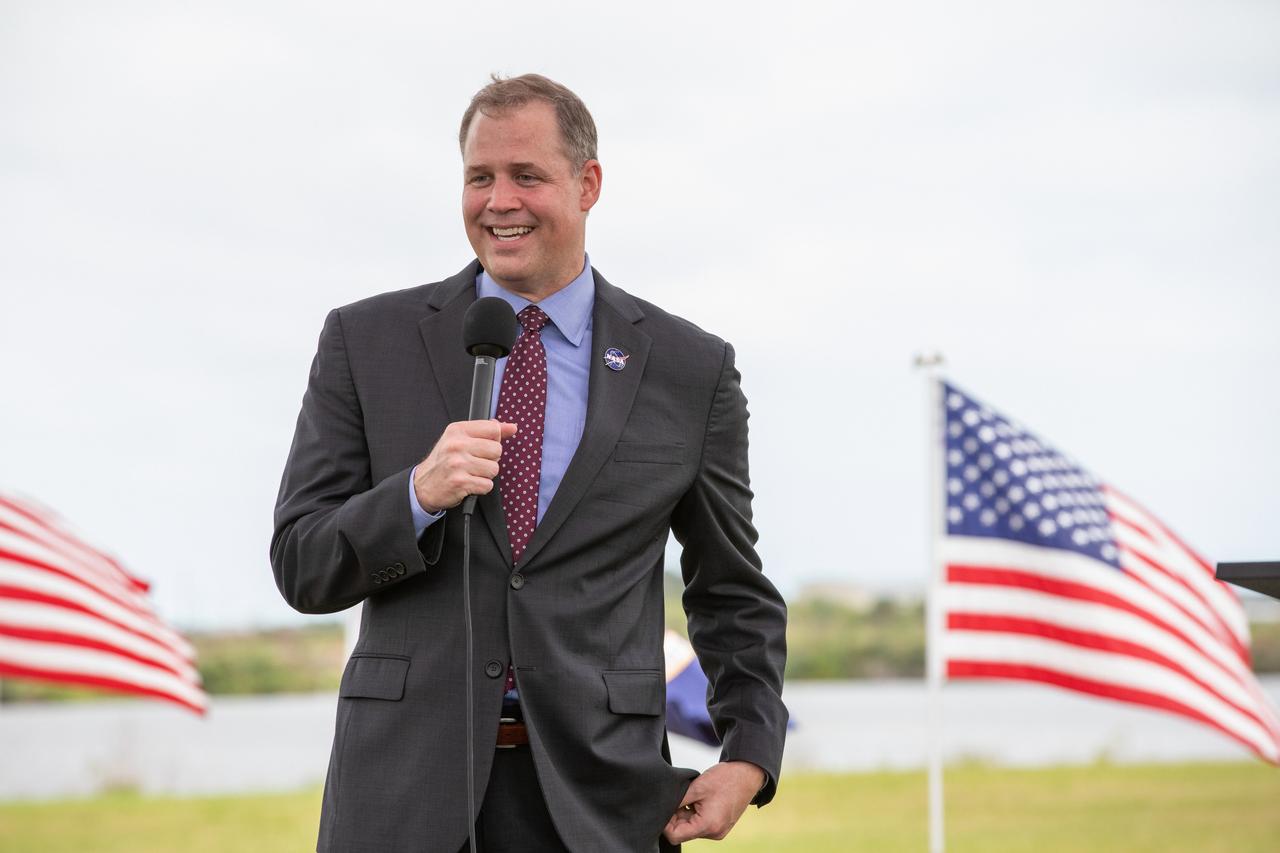

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks to members of the media during a press briefing Nov. 13, 2020, near the Press Site countdown clock at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 launch. Crew-1 is the first regular crew mission of a U.S. commercial spacecraft with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience capsule will launch atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A to the space station for a six-month science mission.
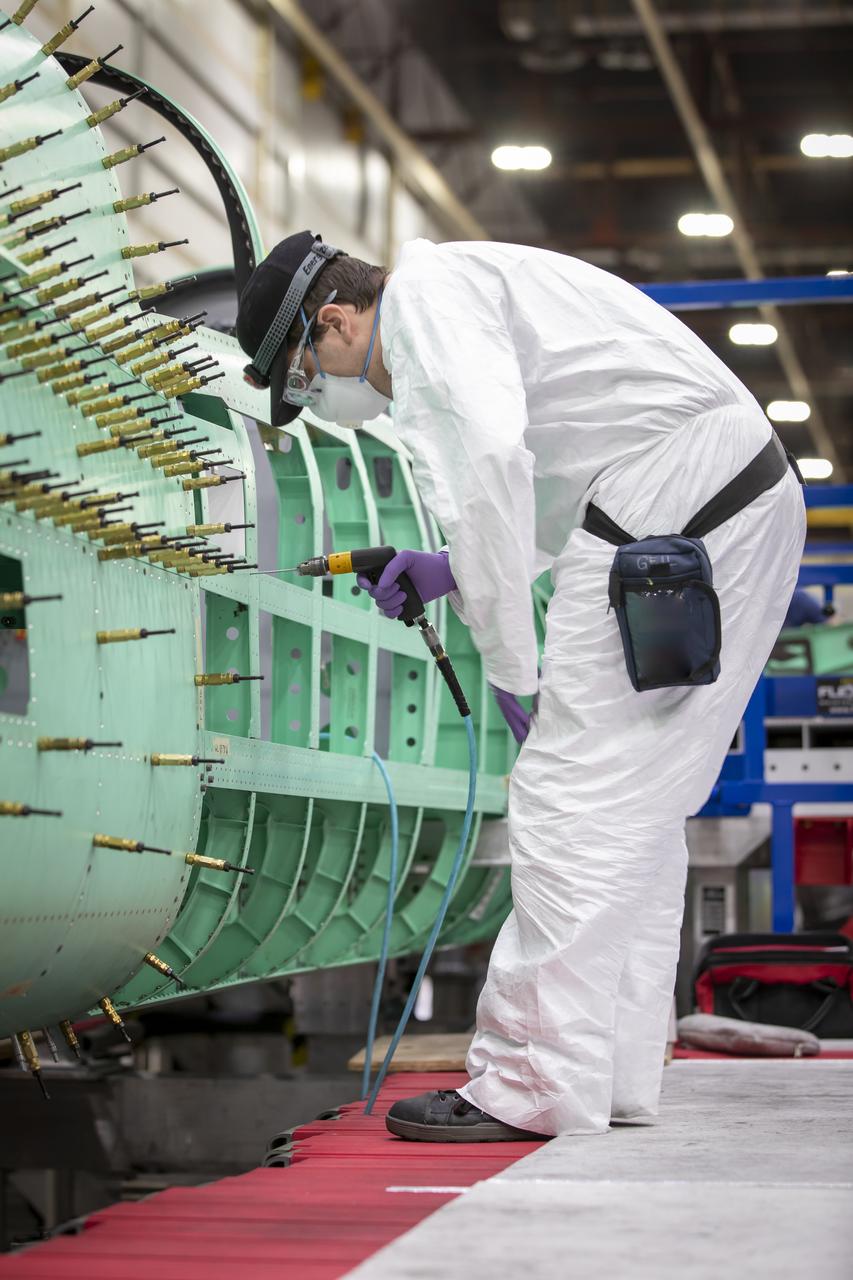

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician prepares to install the left fuselage skins onto the X-59. Once in the air, the aircraft, currently under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
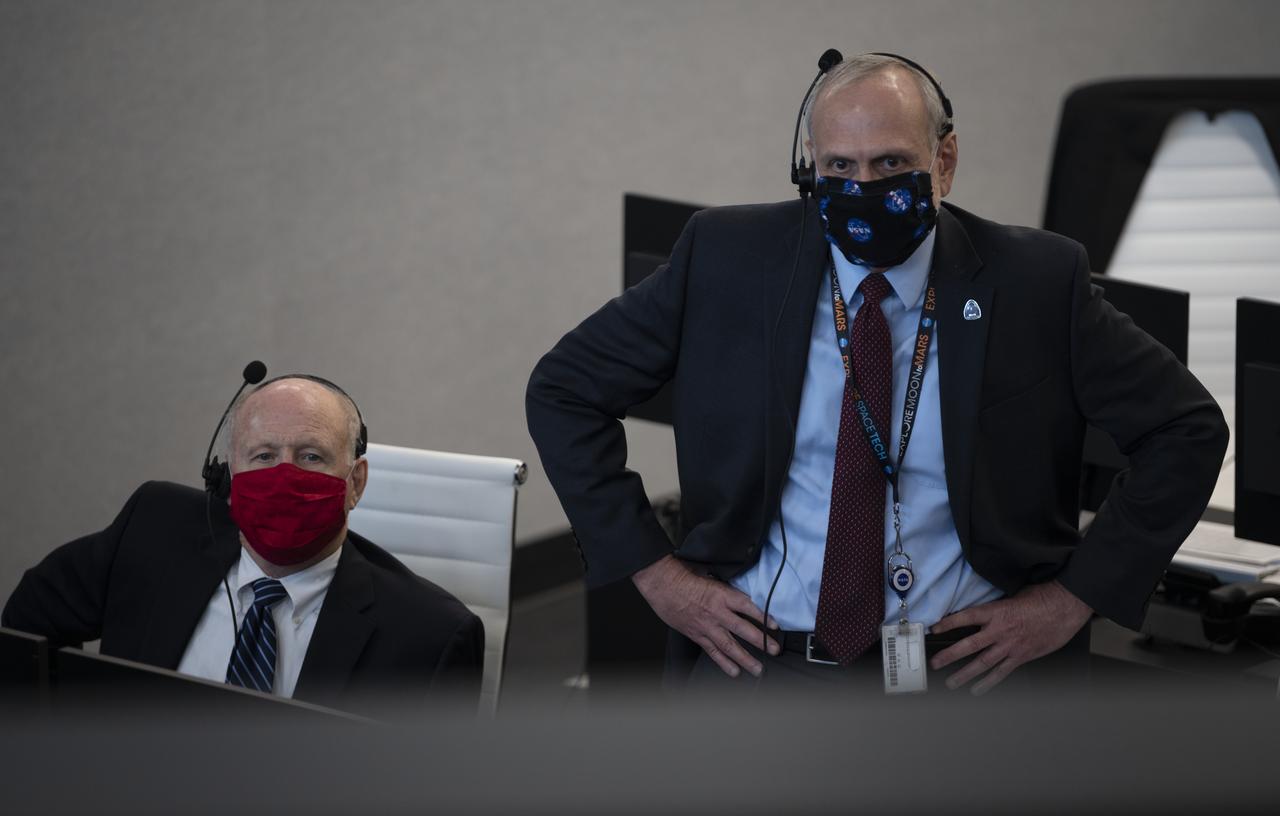

Ken Bowersox, acting Associate Administrator for NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, left, and NASA Associate Administrator Steve Jurczyk monitor the launch of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft on the Demo-2 mission with NASA astronauts Douglas Hurley and Robert Behnken onboard, Saturday, May 30, 2020, in firing room four of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The test flight serves as an end-to-end demonstration of SpaceX’s crew transportation system. Behnken and Hurley launched at 3:22 p.m. EDT on Saturday, May 30, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. A new era of human spaceflight is set to begin as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from American soil to low-Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Painting of the NASA logo, also called the meatball, is underway on the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 8, 2020. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, are repainting the meatball and the American Flag on the iconic building. High Bay 3 inside the VAB has been upgraded with 10 new levels of work platforms that will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing upgrades to the VAB to support the launch of the SLS and Orion for Artemis missions. Under the Artemis program, NASA will send the first woman and next man to the Moon.

The linear depressions in this VIS image are part of Sirenum Fossae. These depressions are called graben, which form by the down drop of material between two parallel faults. The faults are caused by tectonic stresses in the region. The Sirenum Fossae graben are 2735km (1700 miles) long. Orbit Number: 83262 Latitude: -33.4902 Longitude: 203.133 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-09-21 02:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24246

Rachid Amekrane, Airbus Defence and Space Integration test director, assists with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
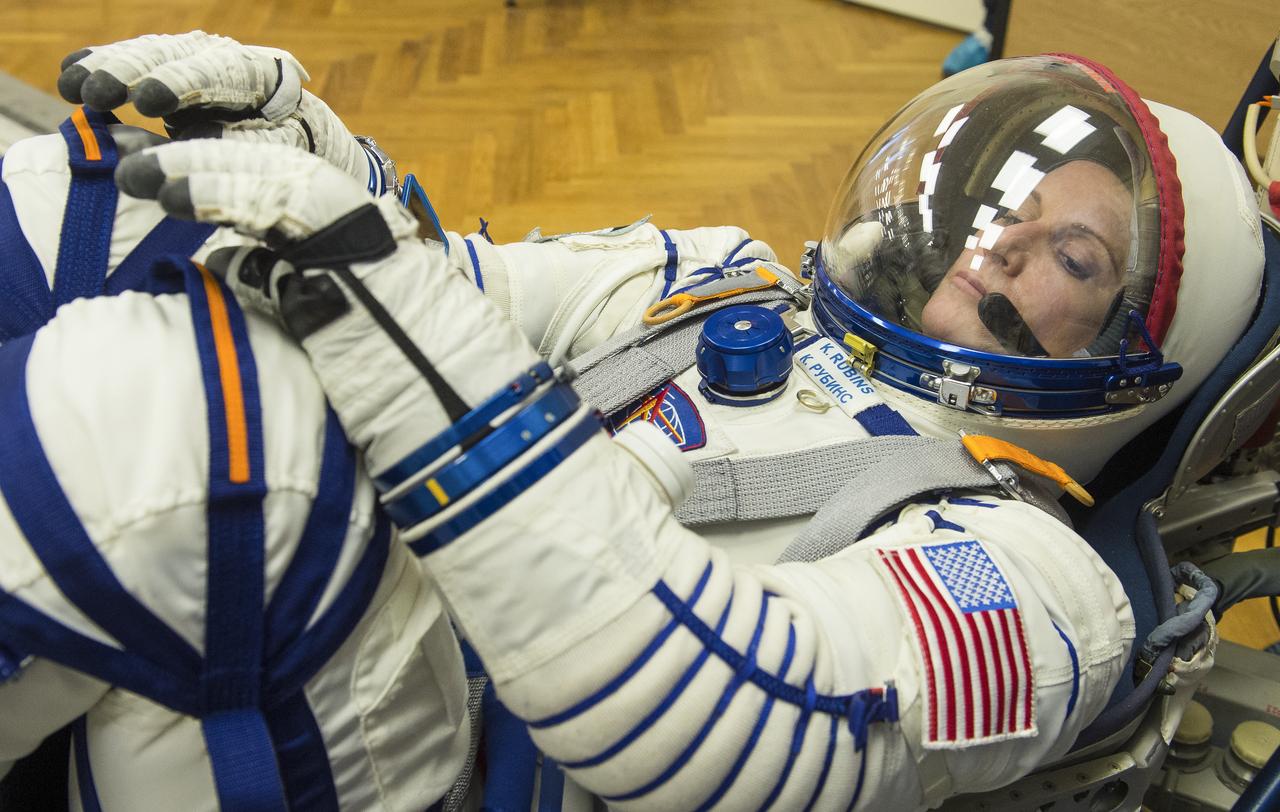

Expedition 64 NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is seen while having her Sokol suit pressure checked during the Soyuz MS-17 spacecraft fit check, Monday, Sept. 28, 2020, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Rubins, and Russian cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov and Sergey Kud-Sverchkov of Roscosmos are preparing for launch to the International Space Station in their Soyuz MS-17 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on October 14, Baikonur time. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
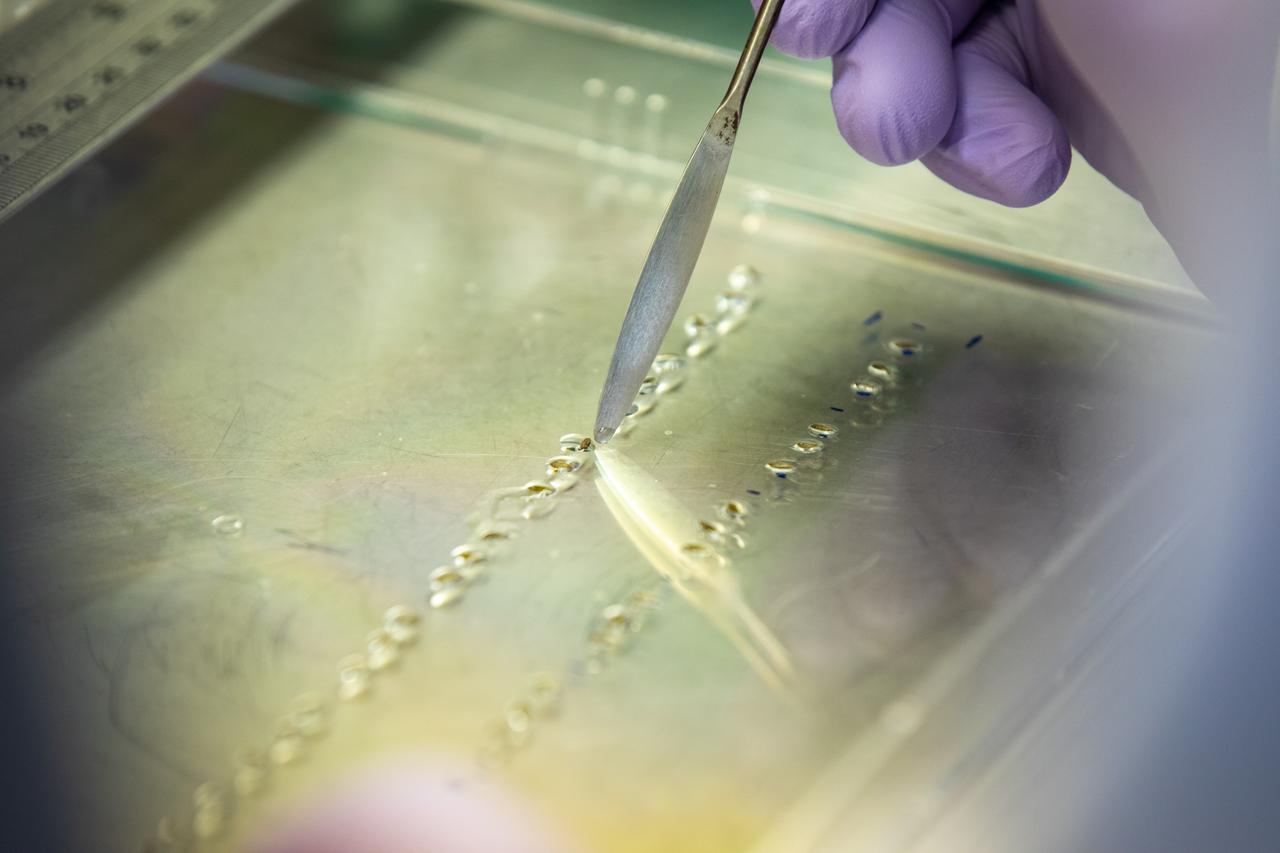
Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a researcher prepares red romaine lettuce seeds in seed film – a new seed handling material– on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
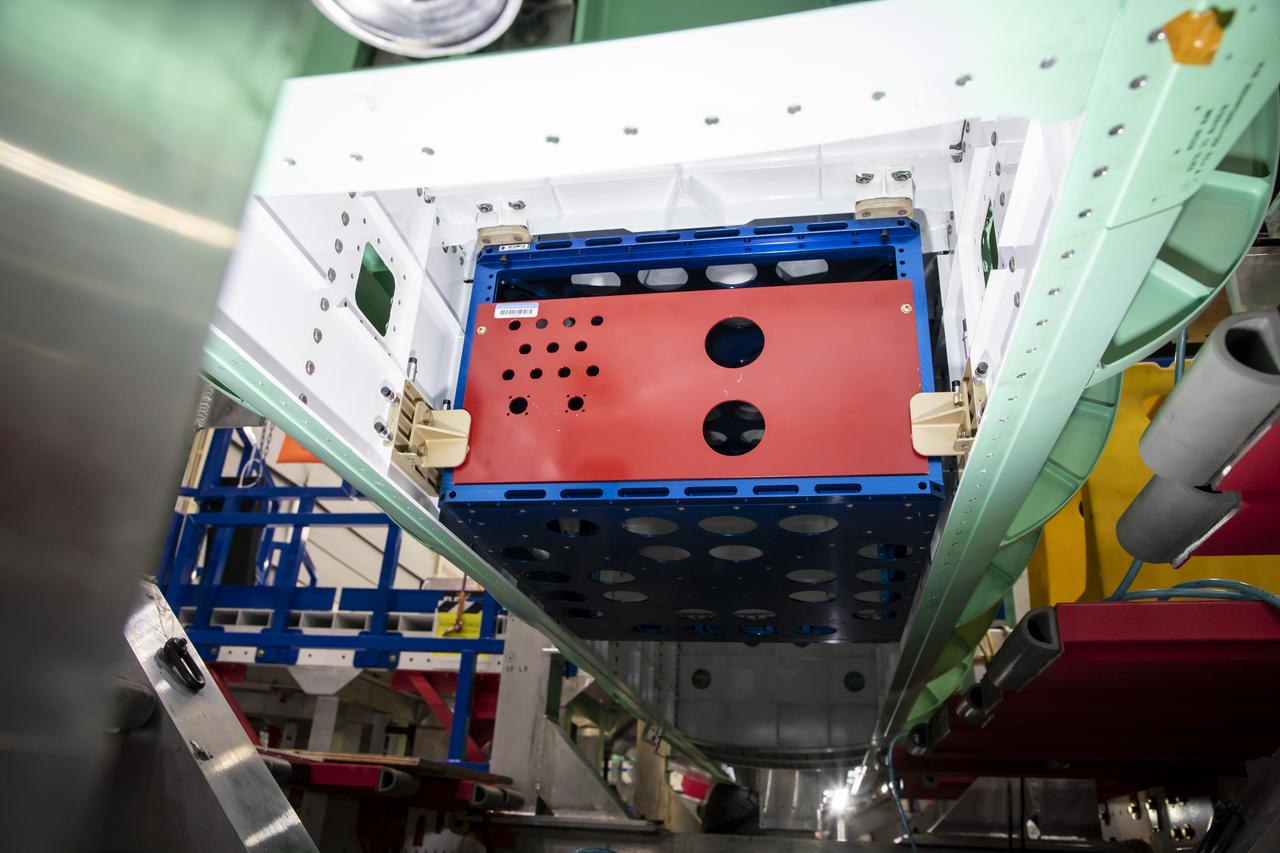
Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: NASA Payload Pallet XVS Mock-Up Date: 7/01/2020 Additional Info:
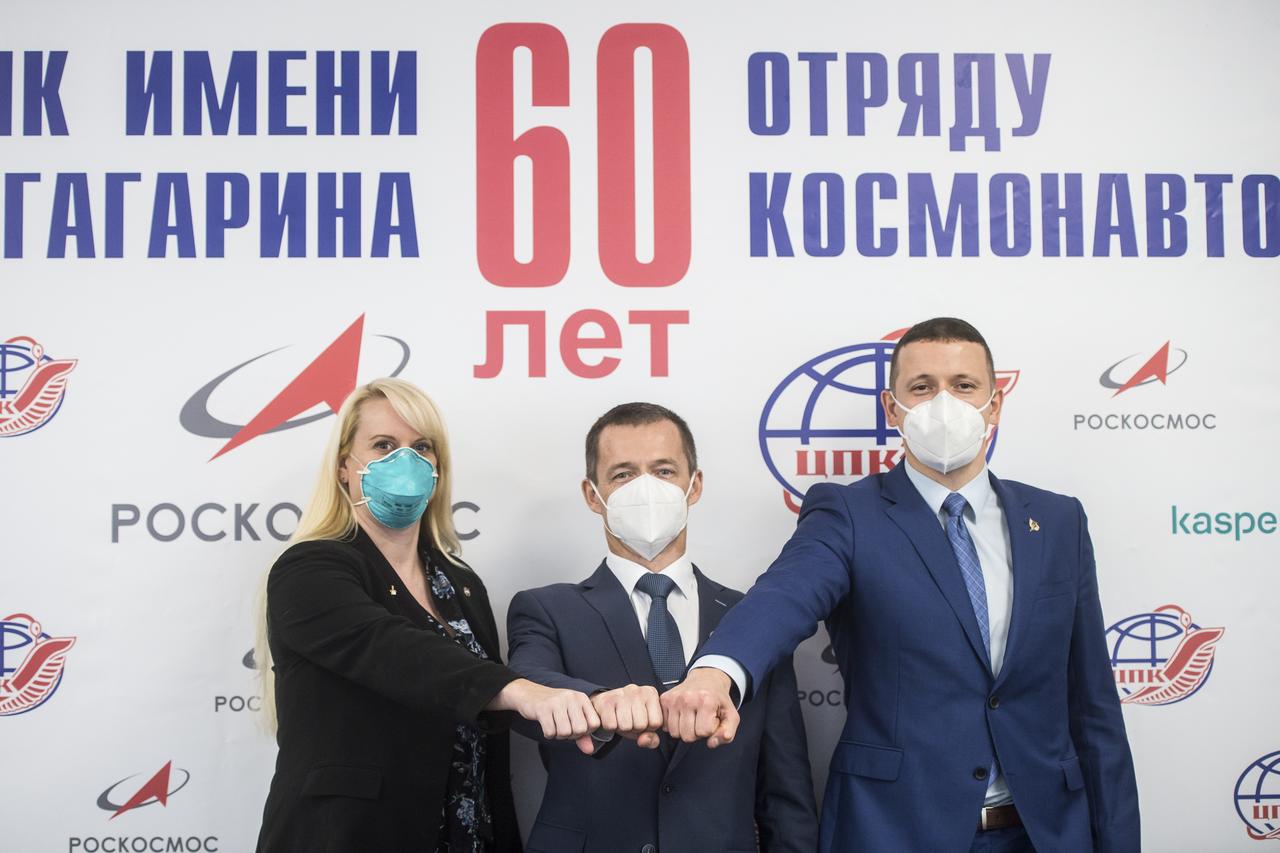

From left to right, Expedition 64 prime crew members, NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, Russian cosmonaut Sergey Ryzhikov of Roscosmos, and Russian cosmonaut Sergey Kud-Sverchkov of Roscosmos, pose for a photo at the conclusion of a press conference prior to their scheduled launch October 14 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, Thursday, Sept. 24, 2020 at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center (GCTC) in Star City, Russia. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
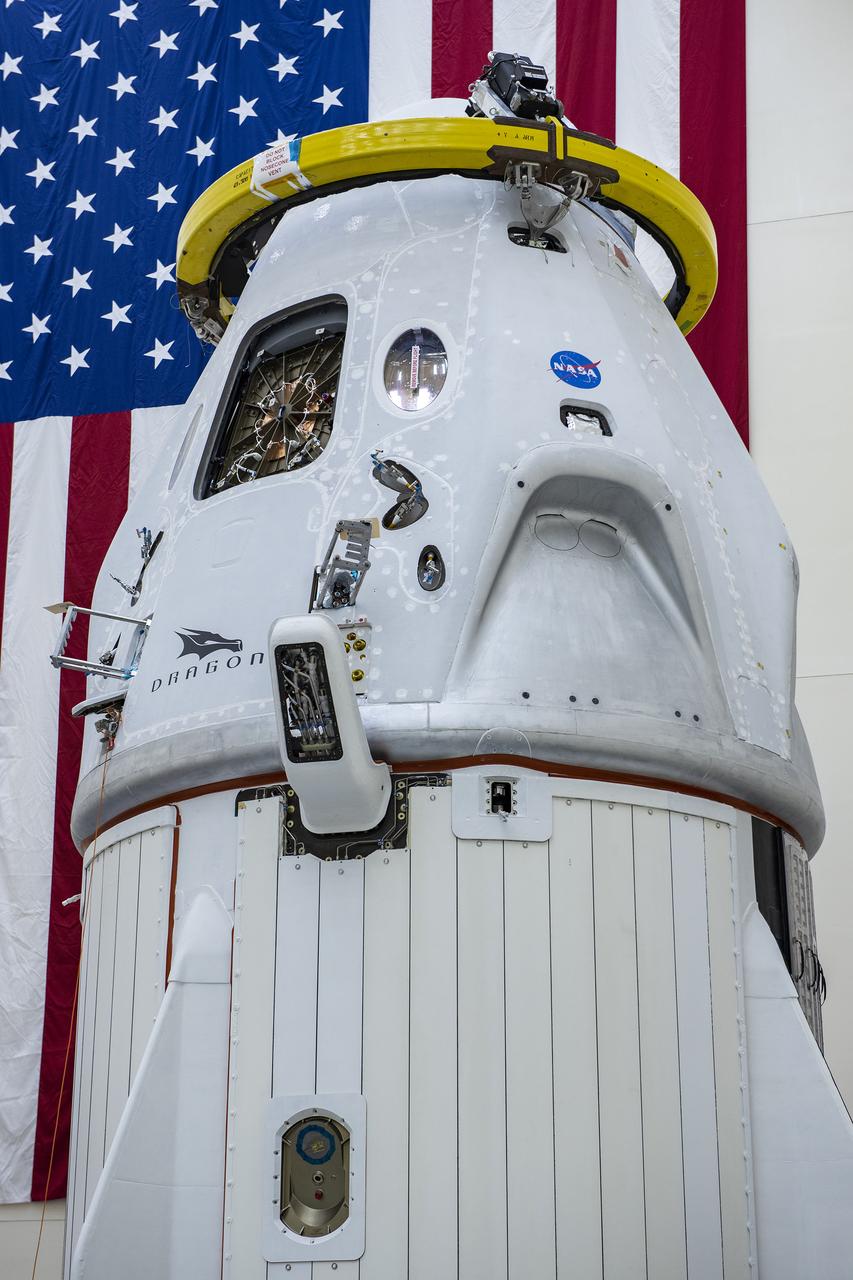

The SpaceX Crew Dragon trunk was secured to the spacecraft on Thursday, April 30, 2020, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, in preparation for the Demo-2 launch with NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew Dragon will carry Behnken and Hurley atop a Falcon 9 rocket, returning crew launches to the space station from U.S. soil for the first time since the Space Shuttle Program ended in 2011.
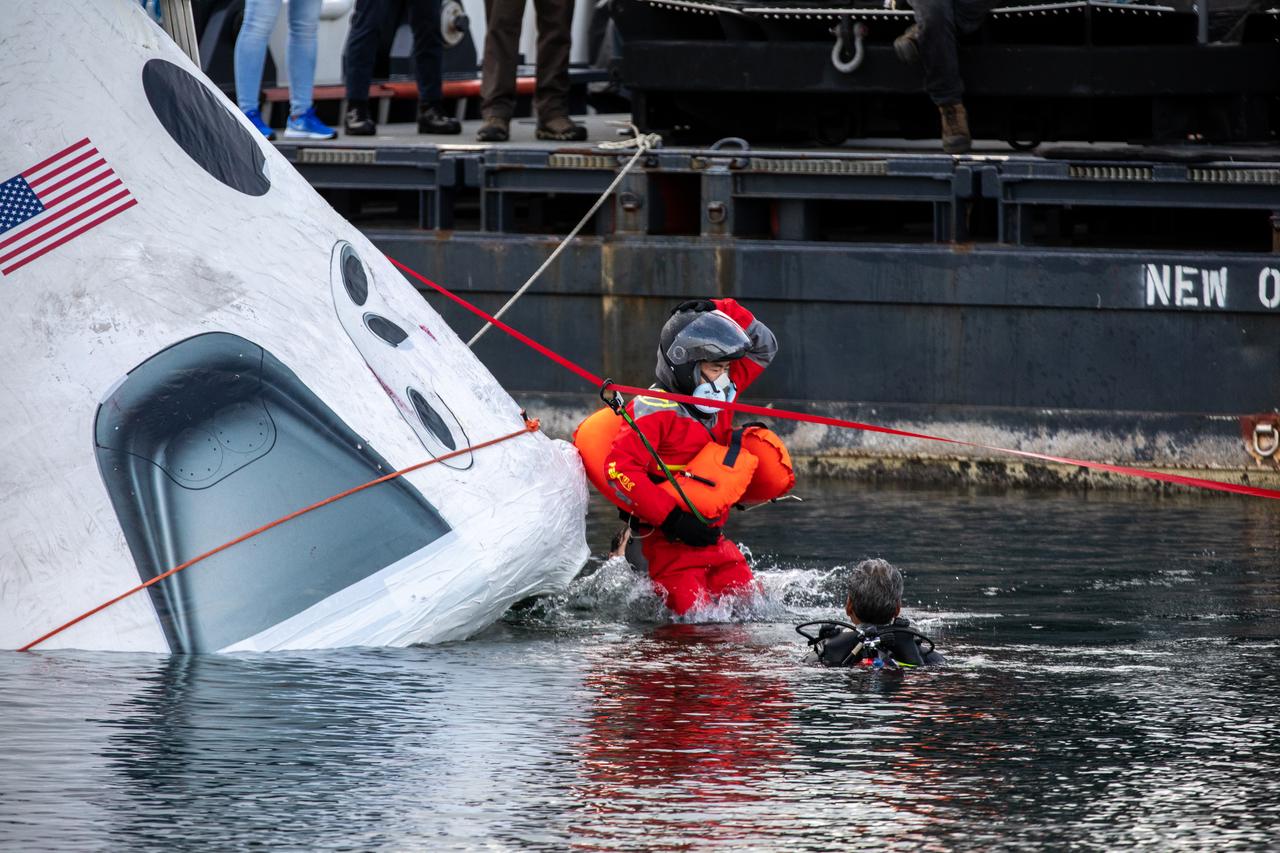

NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Megan McArthur, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Akihiko Hoshide, and European Space Agency astronaut Thomas Pesquet participate in an egress training exercise in Port Canaveral, Florida, on Oct. 1, 2020, in preparation for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-2 mission as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The exercise involved simulating an emergency situation after splashdown of the Crew Dragon spacecraft. Using a mock-up of the Crew Dragon, the crew practiced exiting the capsule and jumping into the water. Crew-2 is targeted to launch from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in spring 2021.
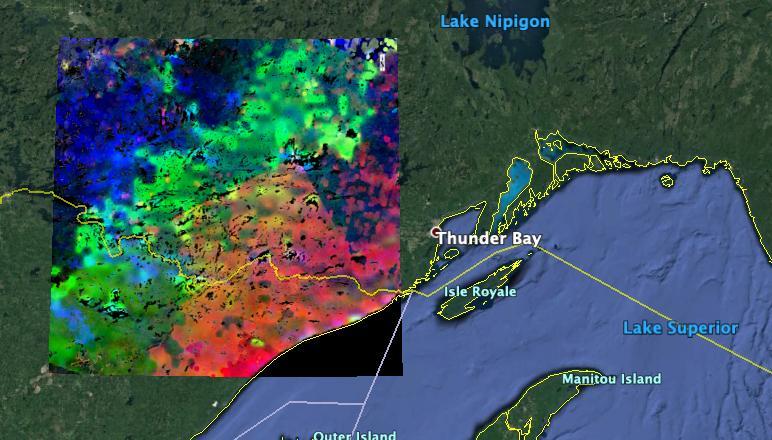
The image shows plants "waking up" west of Lake Superior near the U.S.-Canada border. Plants in the red and pink areas began to wake up around 7 a.m. local time. Those in green areas became active closer to 8 am., while those in blue areas did so closer to 9 a.m. The mission team collected and combined all of ECOSTRESS's morning data for the summer season. In doing so, they observed that the earliest risers were near the lake, with plant activity spreading gradually northwestward as the morning progressed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23430
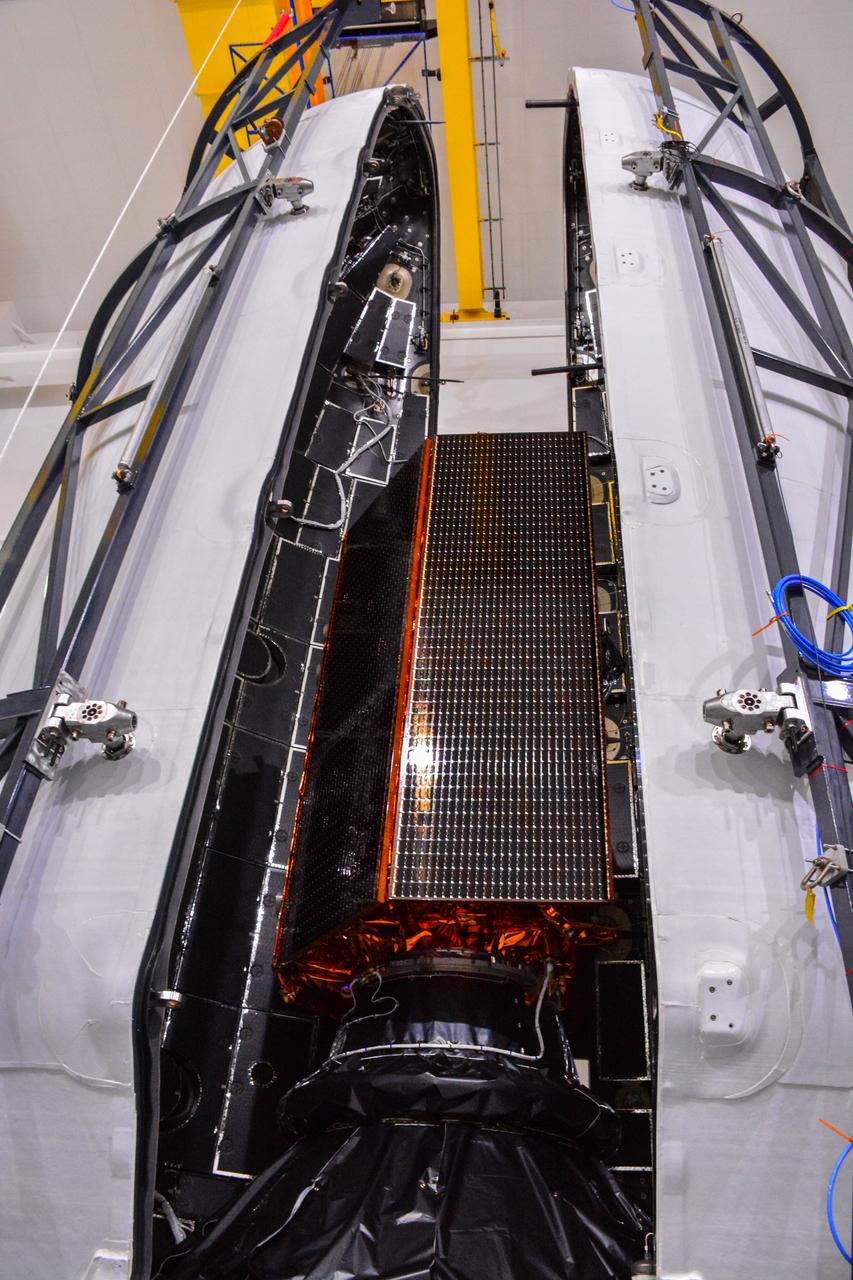
The U.S.-European Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich ocean-monitoring satellite is encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket’s payload fairing on Nov. 3, 2020, inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. Sentinel-6 is scheduled to launch on Nov. 21, 2020, at 12:17 p.m. EST (9:17 a.m. PST), from Space Launch Complex 4E at VAFB. The Launch Services Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
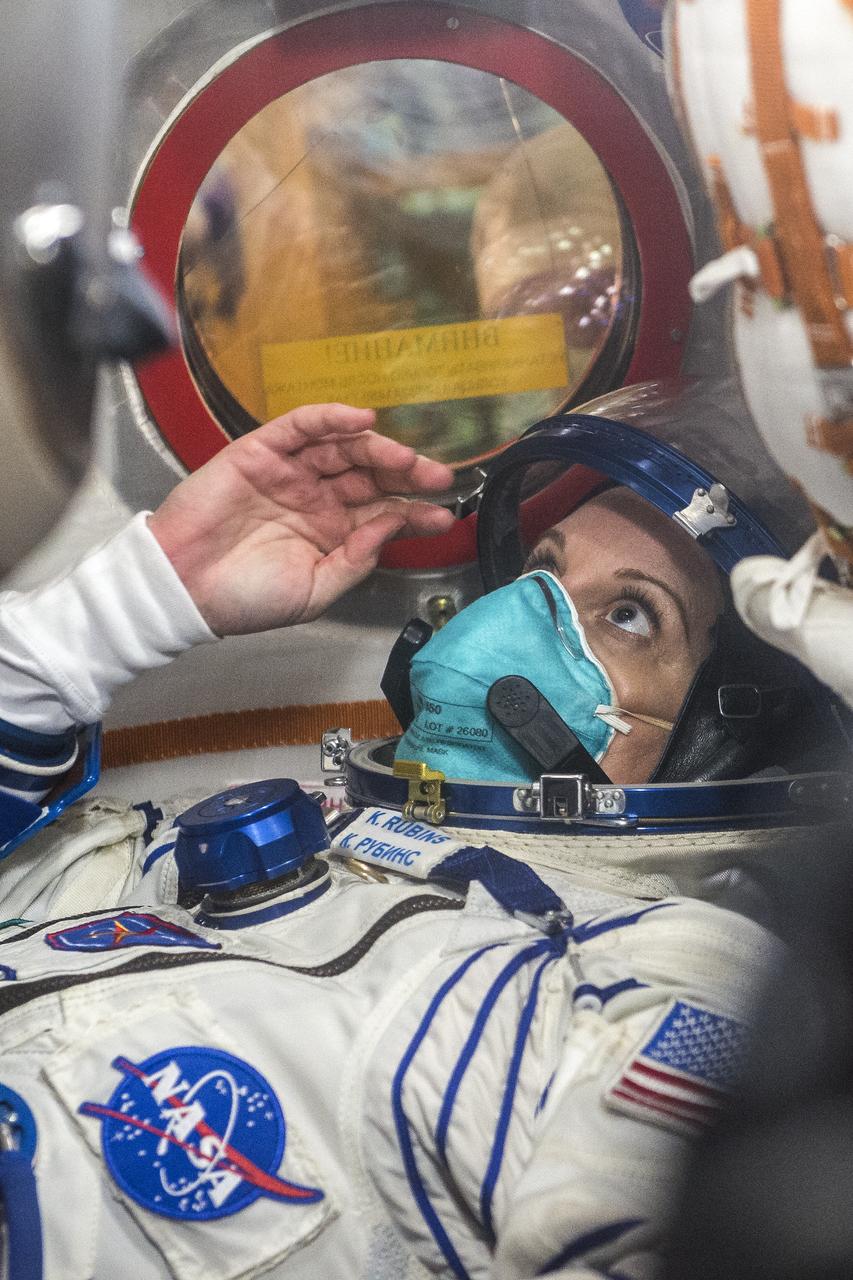

Expedition 64 NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is seen inside the Soyuz MS-17 spacecraft during the fit check to with Russian cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov and Sergey Kud-Sverchkov of Roscosmos, Monday, Sept. 28, 2020, Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The trio are preparing for launch to the International Space Station in their Soyuz MS-17 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on October 14, Baikonur time. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
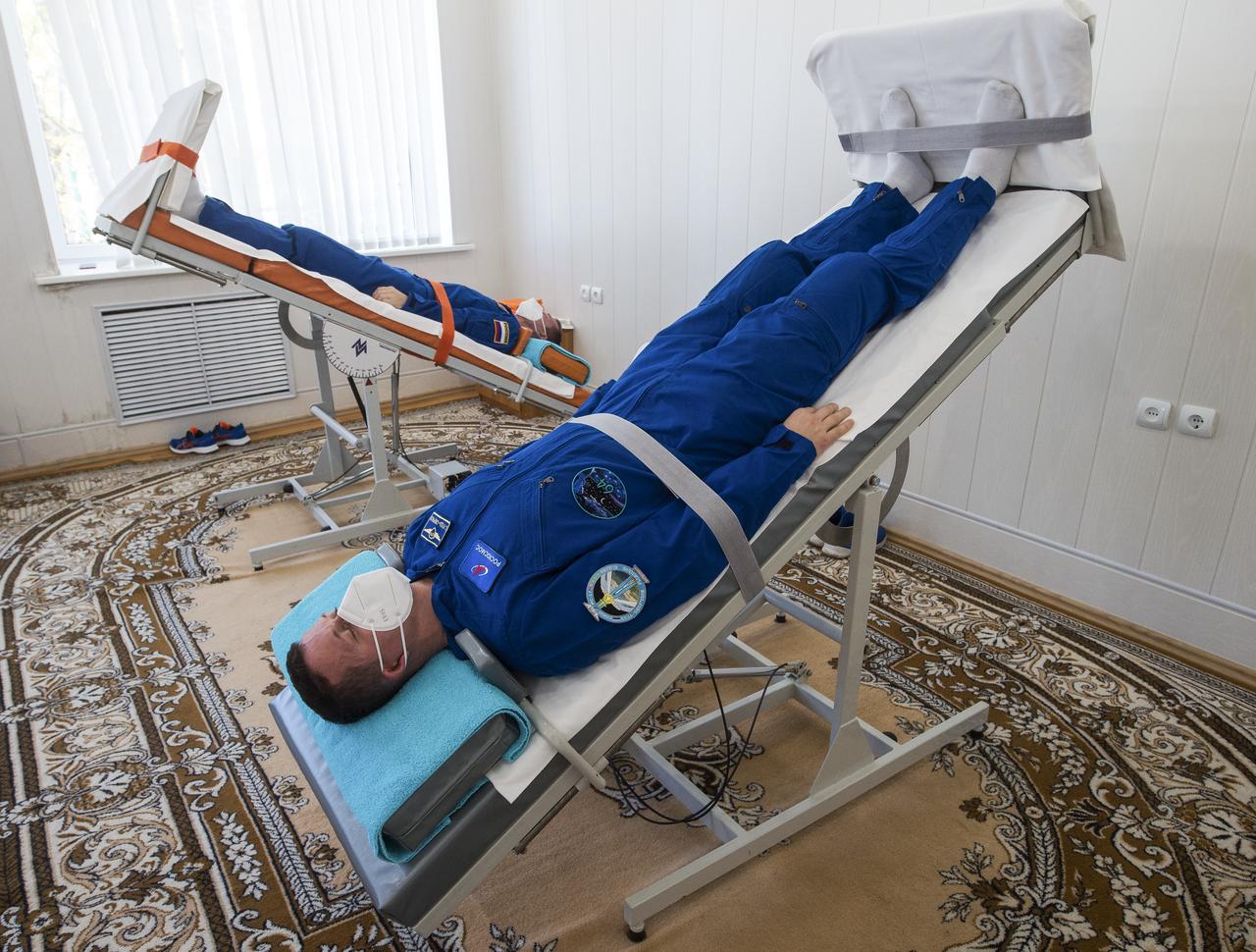
Expedition 64 Russian cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov, back, and Sergey Kud-Sverchkov of Roscosmos, front, take part in tilt table training, Tuesday, Oct. 6, 2020, at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Ryzhikov, Kud-Sverchkov, and Kate Rubins of NASA are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz MS-17 spacecraft on October 14. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Day In The Life of Artemis Employees
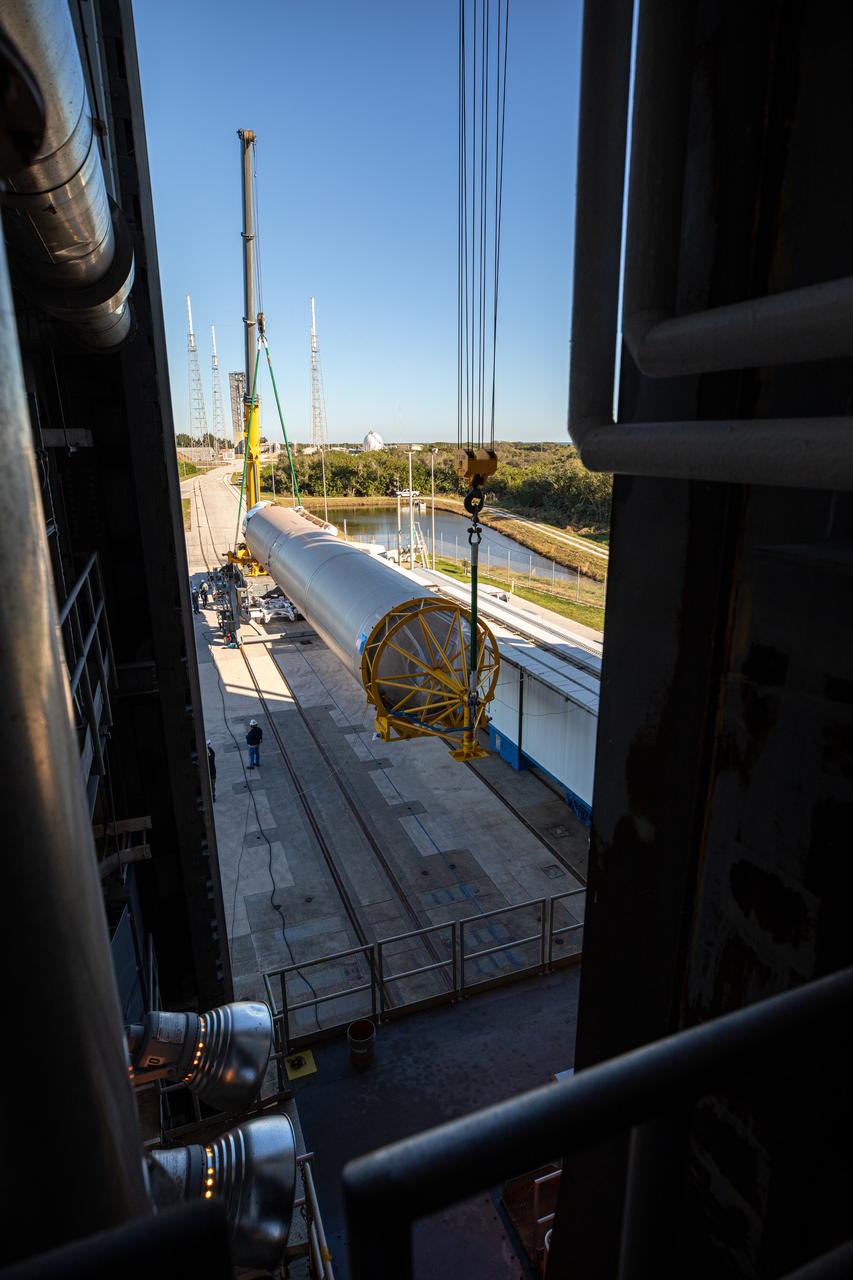

The booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is lifted into the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Jan. 6, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the launch.
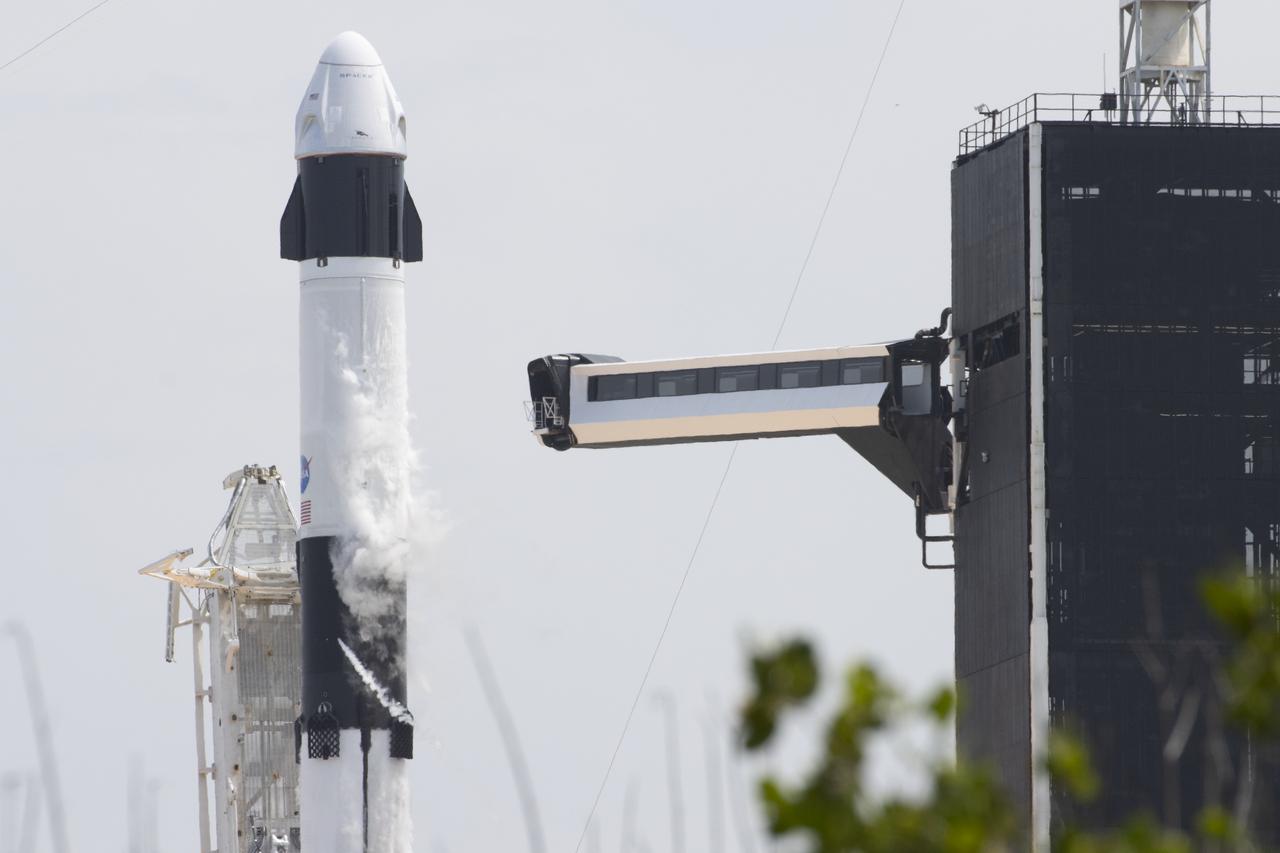

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft is launched from Launch Complex 39A on NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission to the International Space Station with NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley onboard, Saturday, May 30, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The test flight serves as an end-to-end demonstration of SpaceX’s crew transportation system. Behnken and Hurley launched at 3:22 p.m. EDT on Saturday, May 30, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. A new era of human spaceflight is set to begin as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from American soil to low-Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
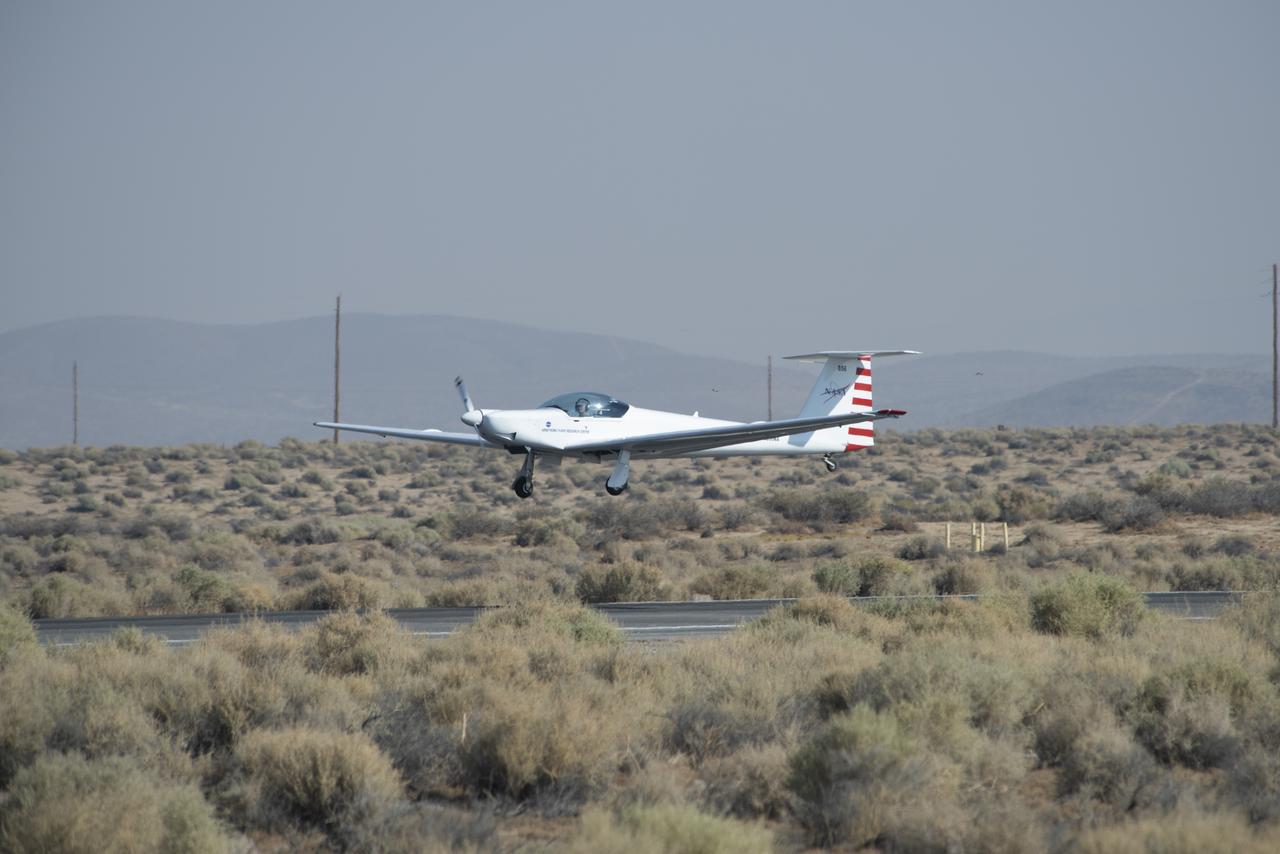

The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project conducted connectivity and infrastructure flight tests with a NASA TG-14 glider aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center Sept. 30-Oct. 1, 2020. The flights were preparation for the NC Integrated Dry Run Test in December and allowed pilots to view the routes they will fly during the helicopter test.
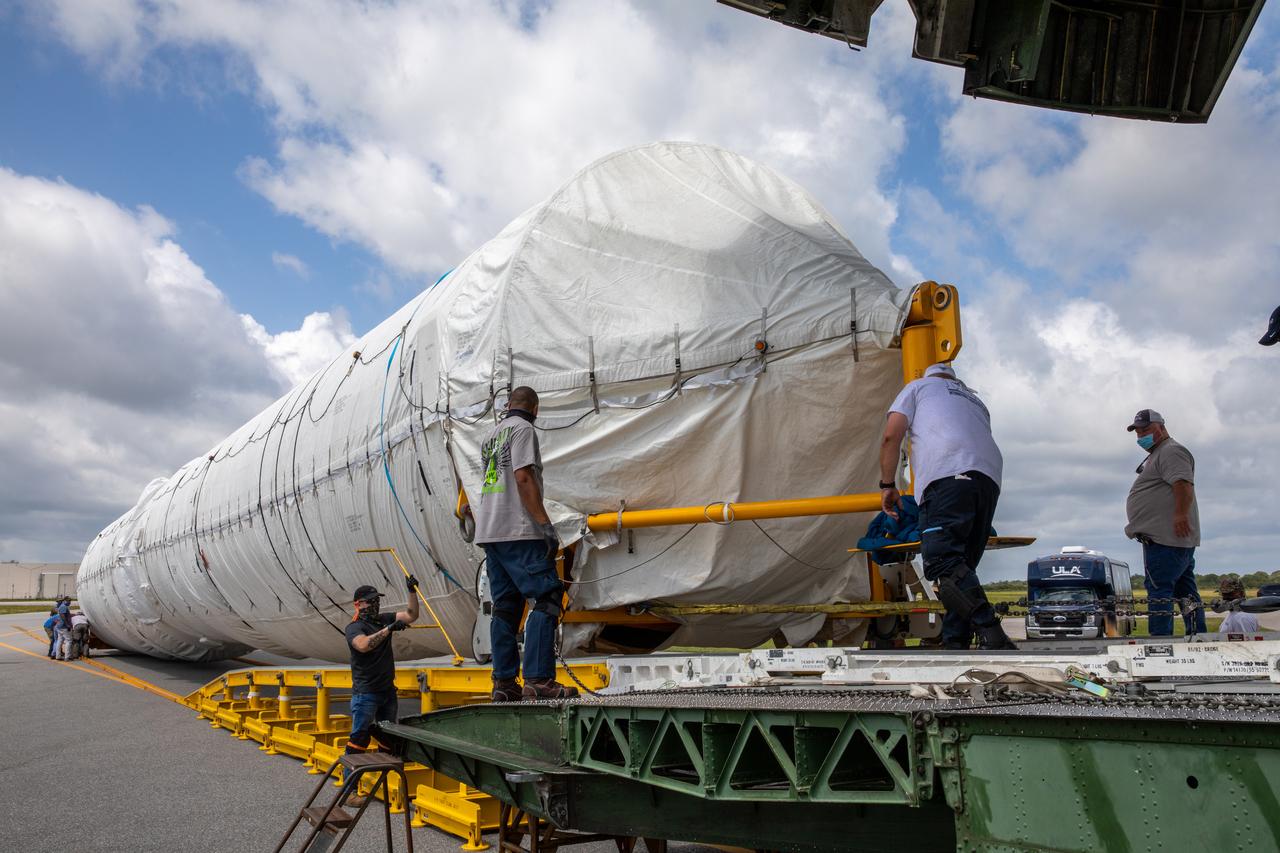

Workers secure the United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover as it is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
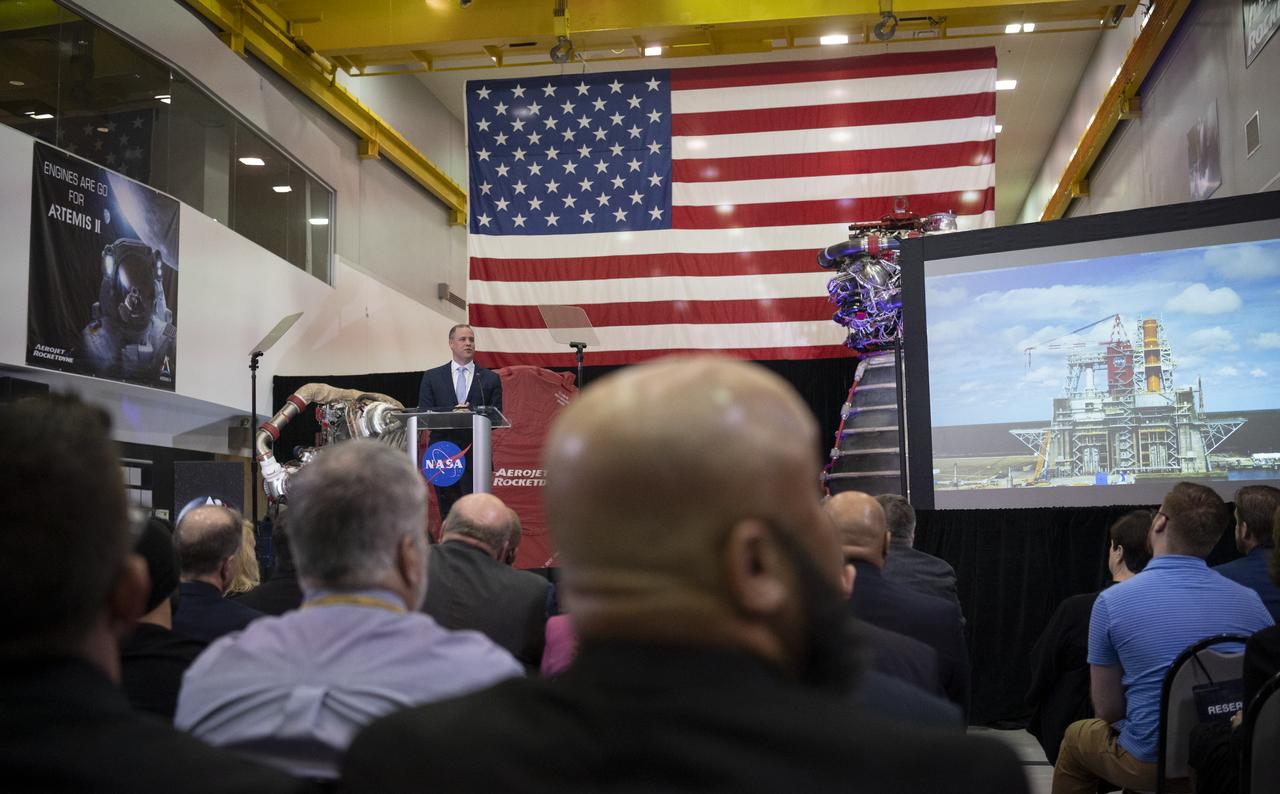

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine discusses the fiscal year 2021 budget proposal during a State of NASA address, Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at Aerojet Rocketdyne’s facility at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

EUMETSAT director-general, Alain Ratier, speaks at a renaming ceremony for the international ocean science satellite previously known as Sentinel-6A/Jason-CS, Tuesday, January 28, 2020, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and its European partners renamed the satellite Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich after NASA’s former director of the Earth Science division, Dr. Michael Freilich. Sentinel-6A Michael Freilich will observe and record global sea level changes and will be joined by an identical satellite slated to launch in 2025 for a total of ten years of targeted observations.” Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

HUNCH (High School Students United with NASA to Create Hardware) students came together at the U.Sl Space and Rocket Center (USSRC) in a competition to create recipes for food to feed astronauts in space. Six teams from North Alabama and George participated. The winner will compete with students from competitions at other NASA centers later at the Johnson Space Flight Center.
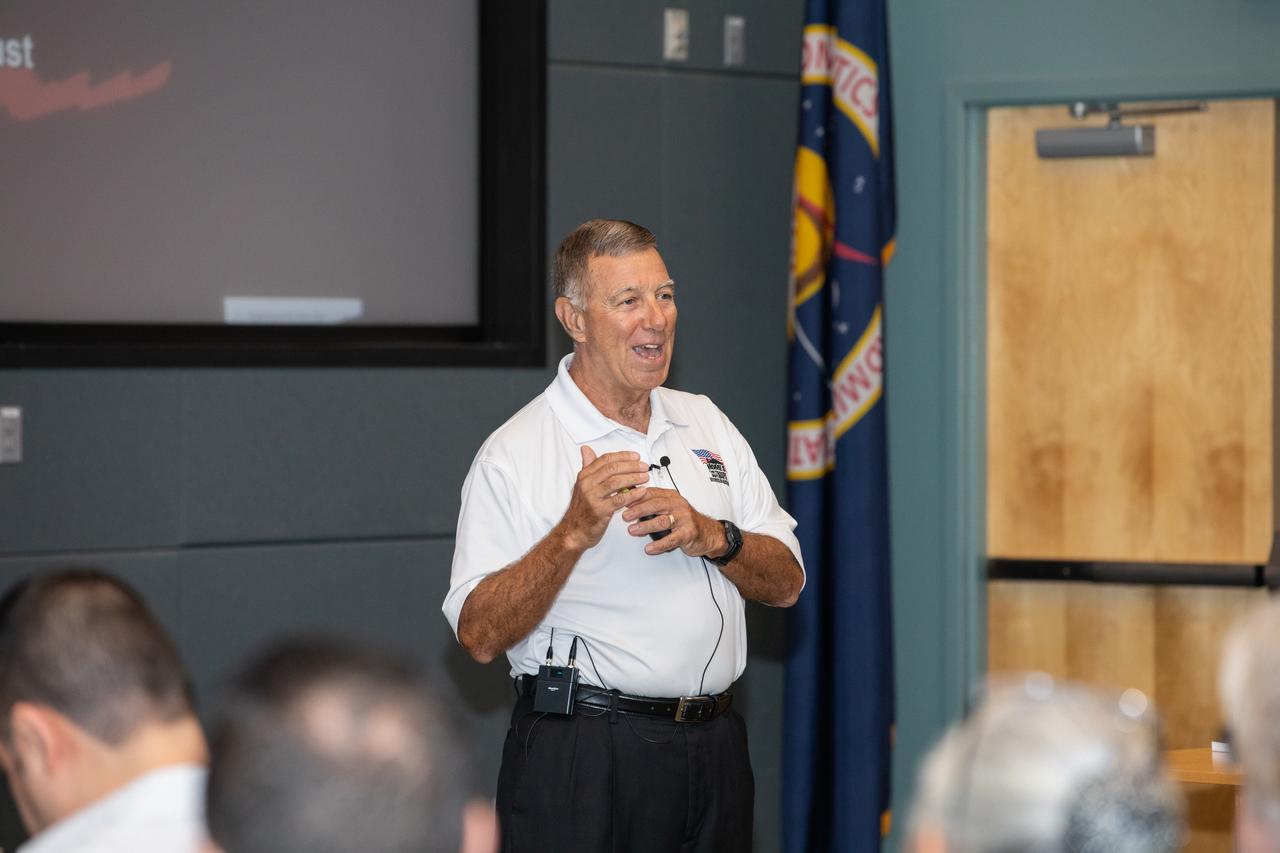

Danny McKnight, a U.S. Army retired colonel, speaks to Kennedy Space Center employees inside the Florida spaceport’s Operations Support Building II on March 3, 2020, during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days. Taking place March 2 through March 6, Safety and Health Days provides Kennedy employees with a variety of presentations to attend – all of which focus on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce. McKnight’s presentation included information on the commitment and leadership required to be successful when operating in difficult conditions.

A close-up view of the single-engine Centaur upper stage for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover as it is being lifted up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 10, 2020. The Centaur will be lifted up and attached to the rocket’s first stage. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 20, 2020. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
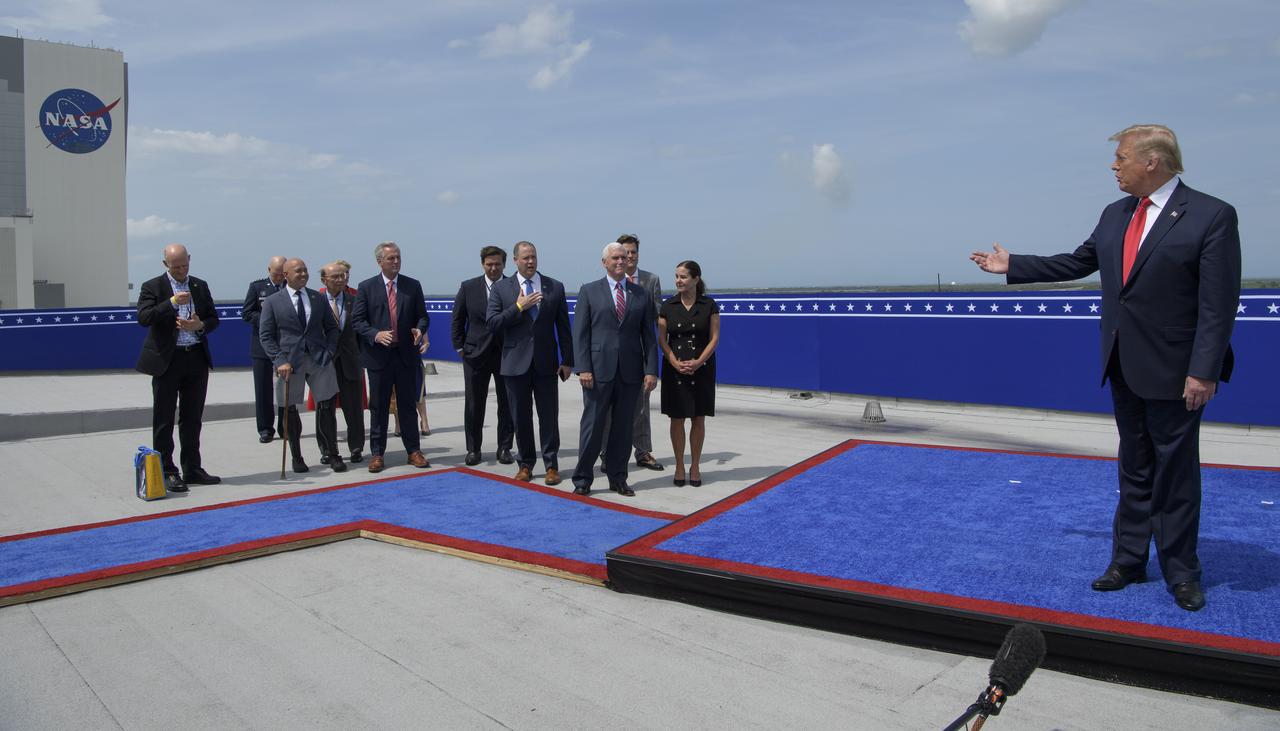

President Donald Trump congratulates NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, hand on chest, at the Operations Support Building II after the launch of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft on NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission with NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley onboard, Saturday, May 30, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The test flight serves as an end-to-end demonstration of SpaceX’s crew transportation system. Behnken and Hurley launched at 3:22 p.m. EDT on Saturday, May 30, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. A new era of human spaceflight is set to begin as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from American soil to low-Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA’s fifth core value – inclusion – is installed in the Central Campus lobby at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 1, 2020. On July 23, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine announced the addition of this fifth core value to the existing values embraced by NASA: safety, integrity, teamwork, and excellence. In his announcement, Bridenstine stated “Incorporating inclusion as a NASA core value is an important step to ensuring this principle remains a long-term focus for our agency and becomes ingrained in the NASA family DNA.”
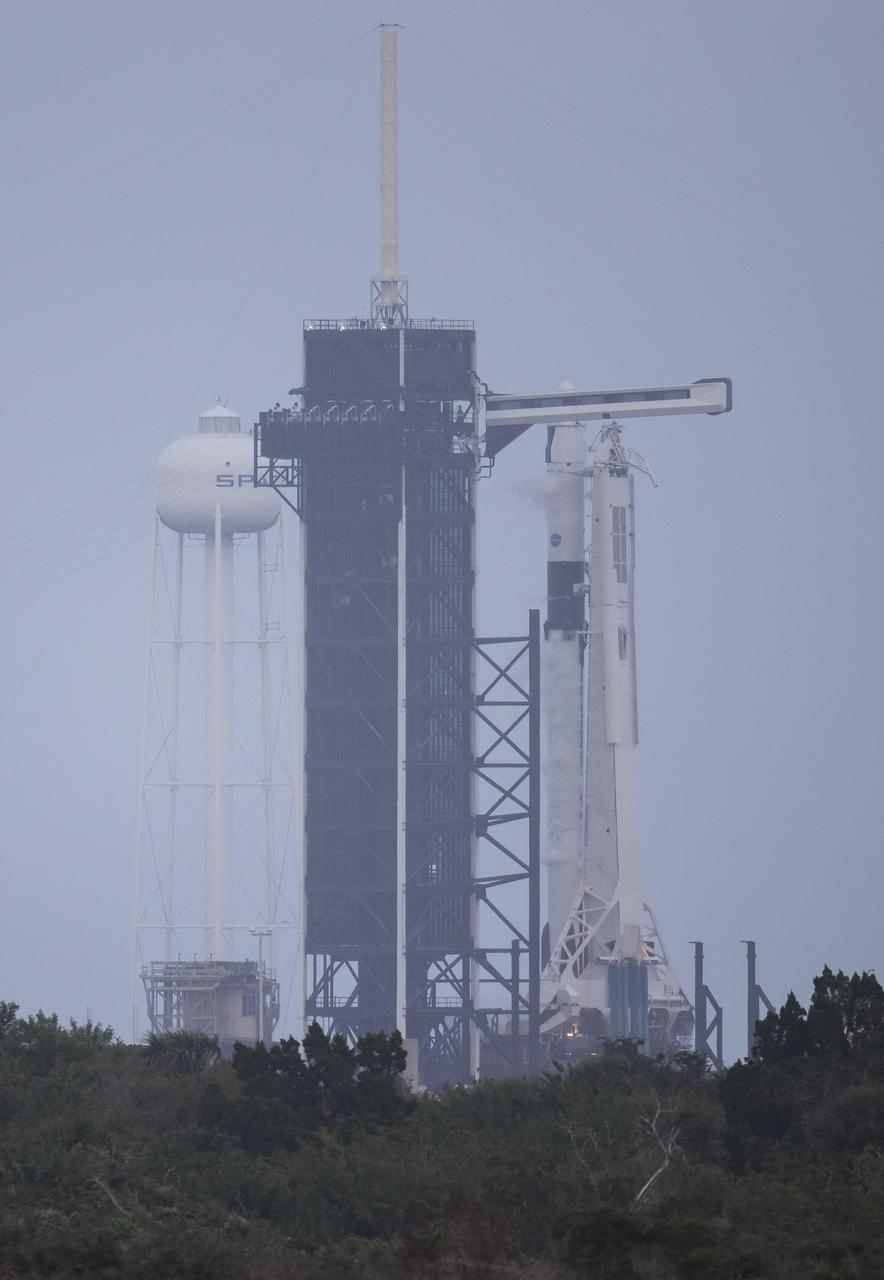

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft onboard is seen on the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A during a brief static fire test ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission, Wednesday, Nov. 11, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first operational mission of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Victor Glover, and Shannon Walker, and astronaut Soichi Noguchi of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 7:49 p.m. EST on Saturday, Nov. 14, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
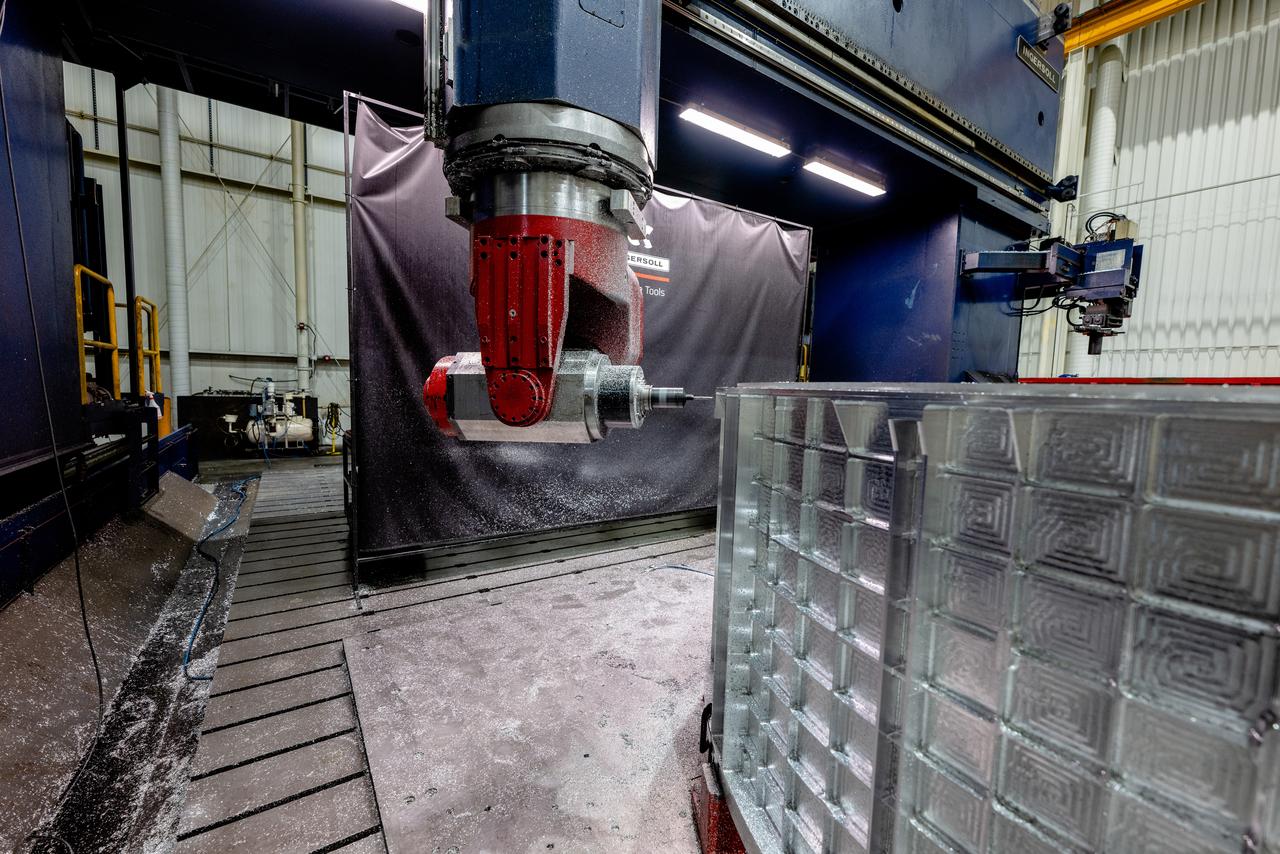

Machining of the tunnel, aft bulkhead, and barrel for the Artemis III Orion pressure vessel takes place at Ingersoll Machine Tool, Inc. in Rockford, Illinois on Sept. 28, 2020.
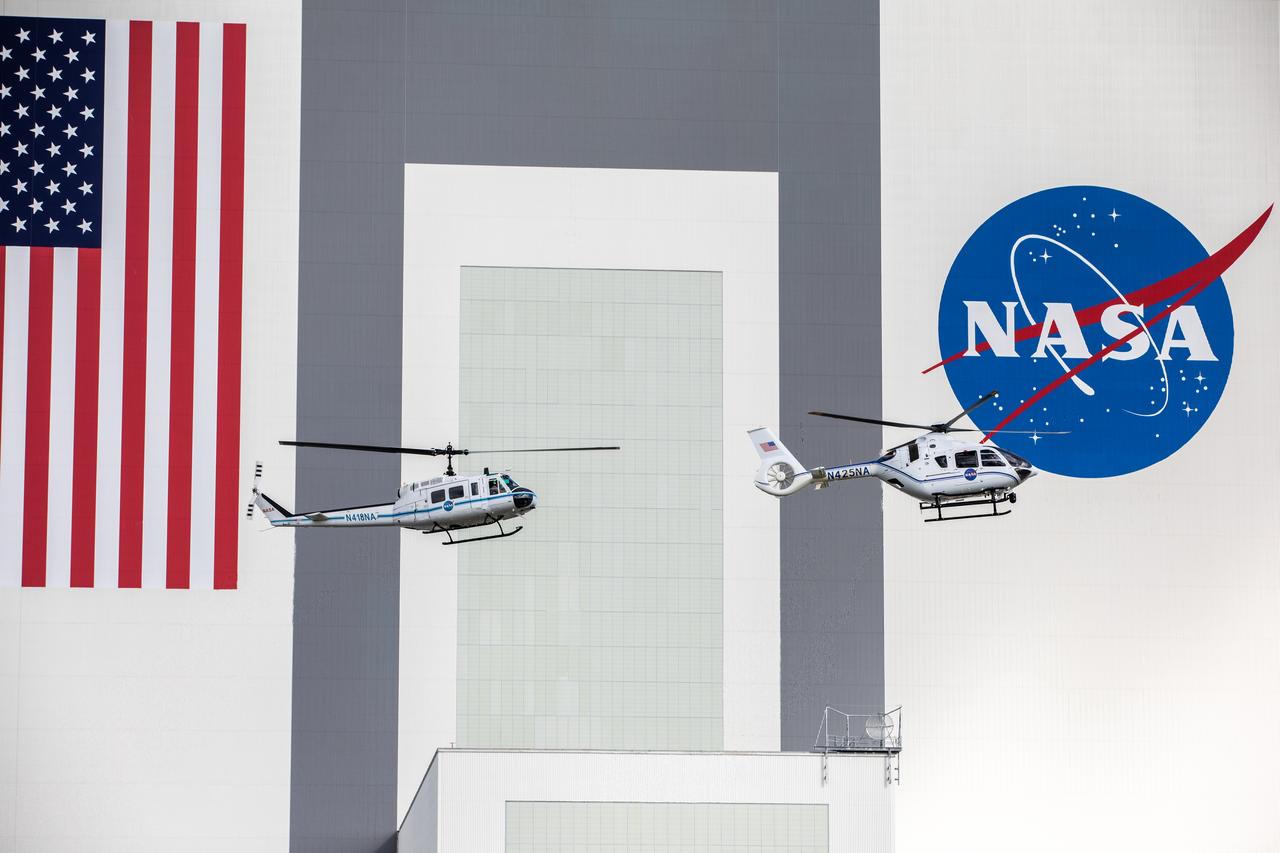

On Oct. 27, 2020, in front of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, the Bell Huey 2 (left) and Airbus H135 helicopters used for security operations at the Florida spaceport perform one flight together before the Hueys are retired from their service. The Airbus H135s are replacing the three Bell Huey 2 aircraft maintained by Kennedy’s Flight Operations team. Kennedy received two of the H135 aircraft on Sept. 30, and the third is expected to arrive in spring 2021. These new helicopters provide a number of technological and safety advantages over the Hueys, such as more lifting power, greater stability in the air, and expanded medical capabilities.
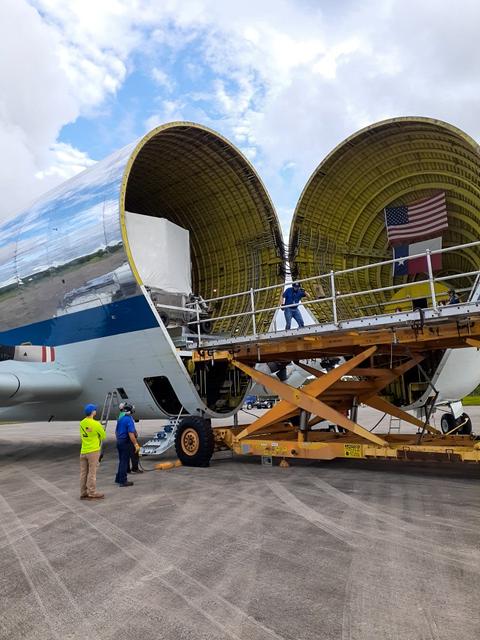

NASA’s Super Guppy arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on Sept. 11, 2020, carrying the Orion Service Module Structural Test Article (SM-STA). Composed of the European Service Module (ESM) and crew module adapter (CMA), these components mark the completion of the test campaign to certify Orion’s Service Module for Artemis I. The Orion SM-STA is being offloaded for transport to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. Photo credit:
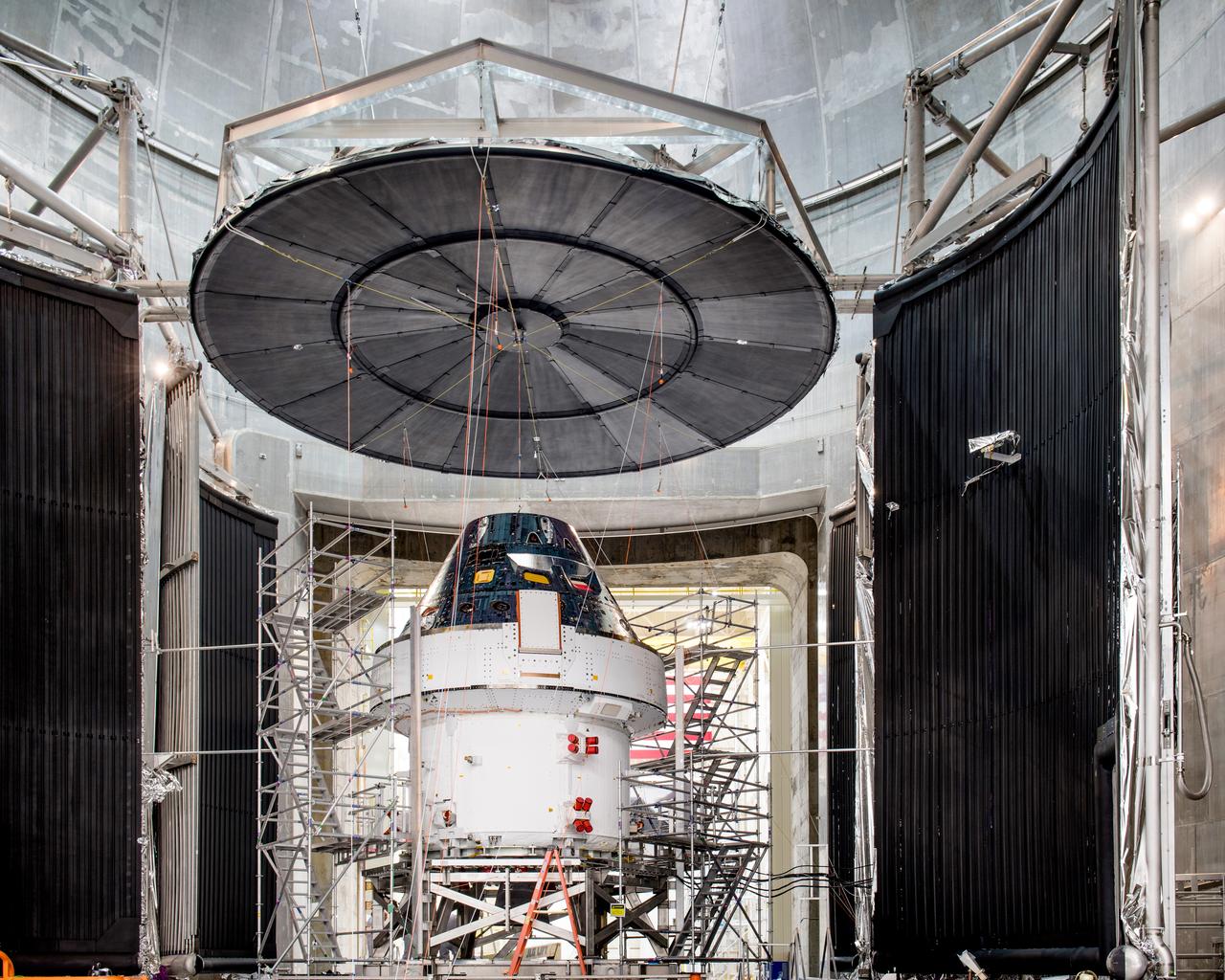

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft is prepared for the final set of environmental tests at NASA Glenn Research Center Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility (formerly Plum Brook Station) in Sandusky, Ohio on Feb. 21, 2020.
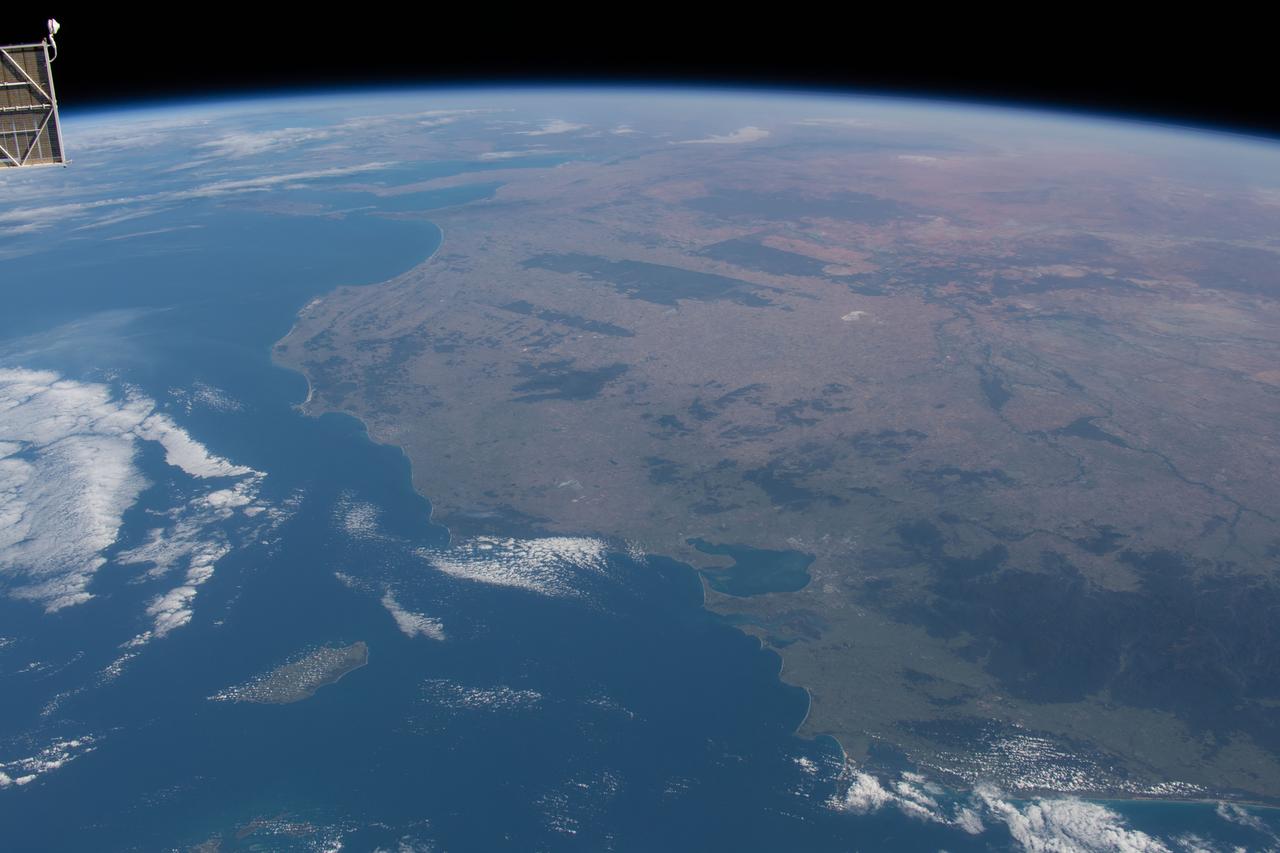

iss062e096440 (March 15, 2020) --- The International Space Station was orbiting 271 miles above Tasmania when this photograph was taken of the southeastern coast of Australia. Landmarks in this picture include the cities of Melbourne on Port Phillip Bay (lower center) and Adelaide on St. Vincent Gulf (at top).
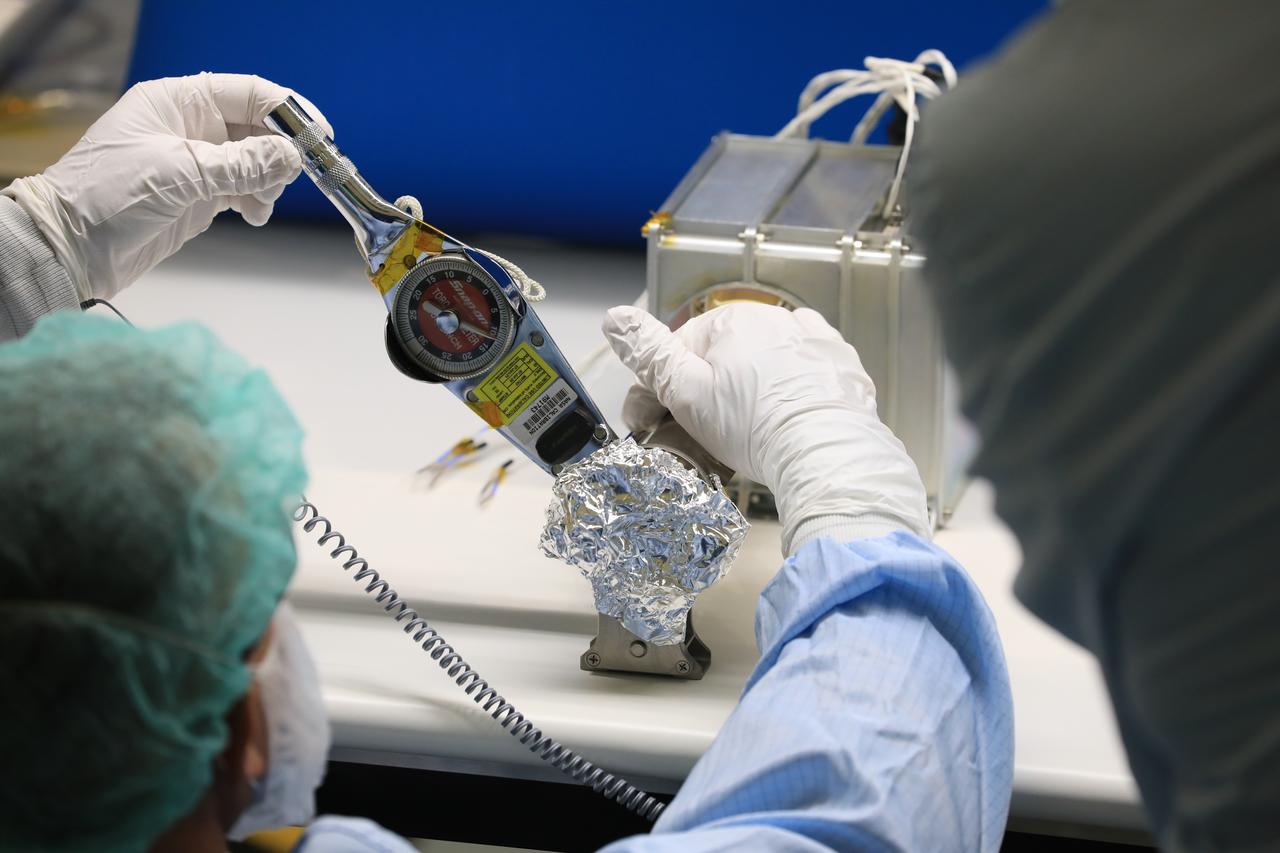

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
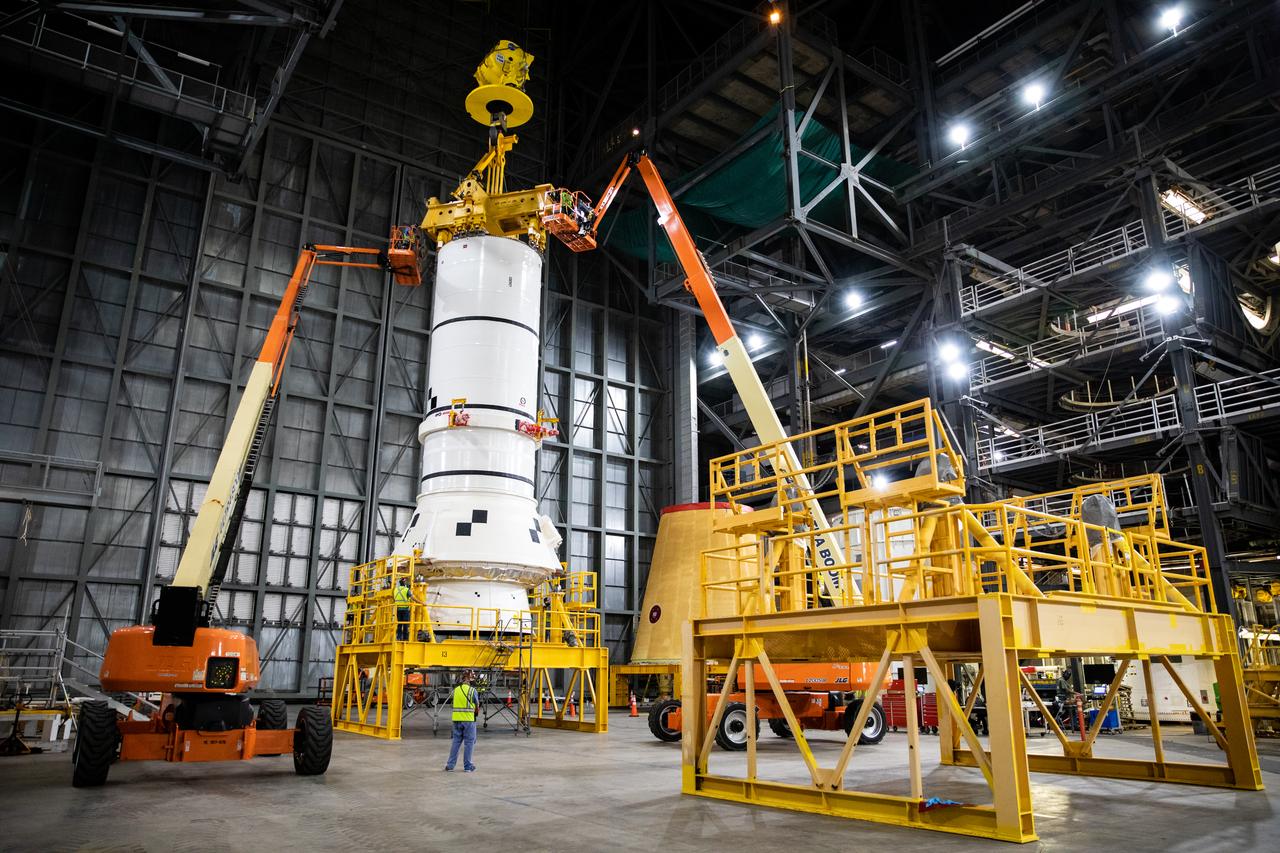

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the second of two Artemis I aft booster segments for the Space Launch System is being prepared for its move into High Bay 3 on Nov. 24, 2020. Workers with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams will stack the twin five-segment boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. The SLS is managed by Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
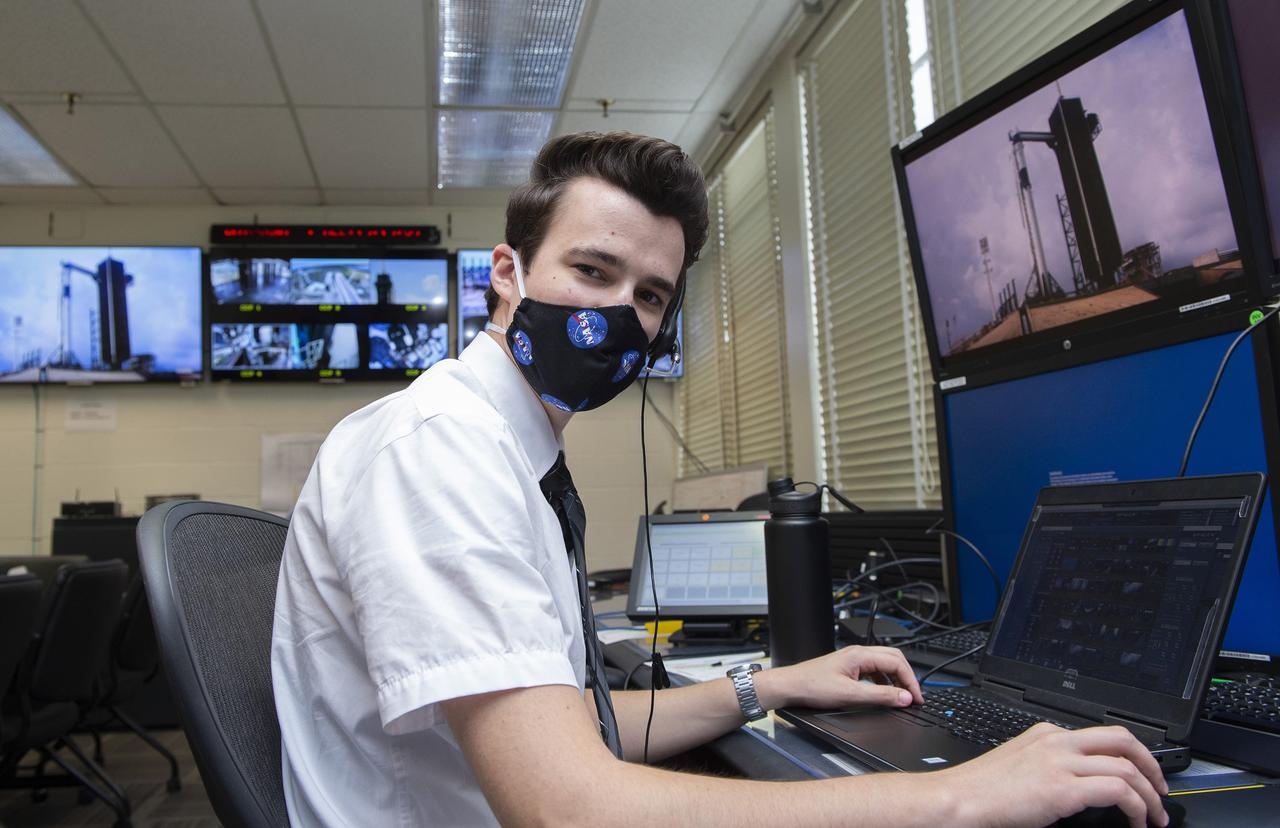

Stewart Whaley and teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Demo-2 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center, HOSC.
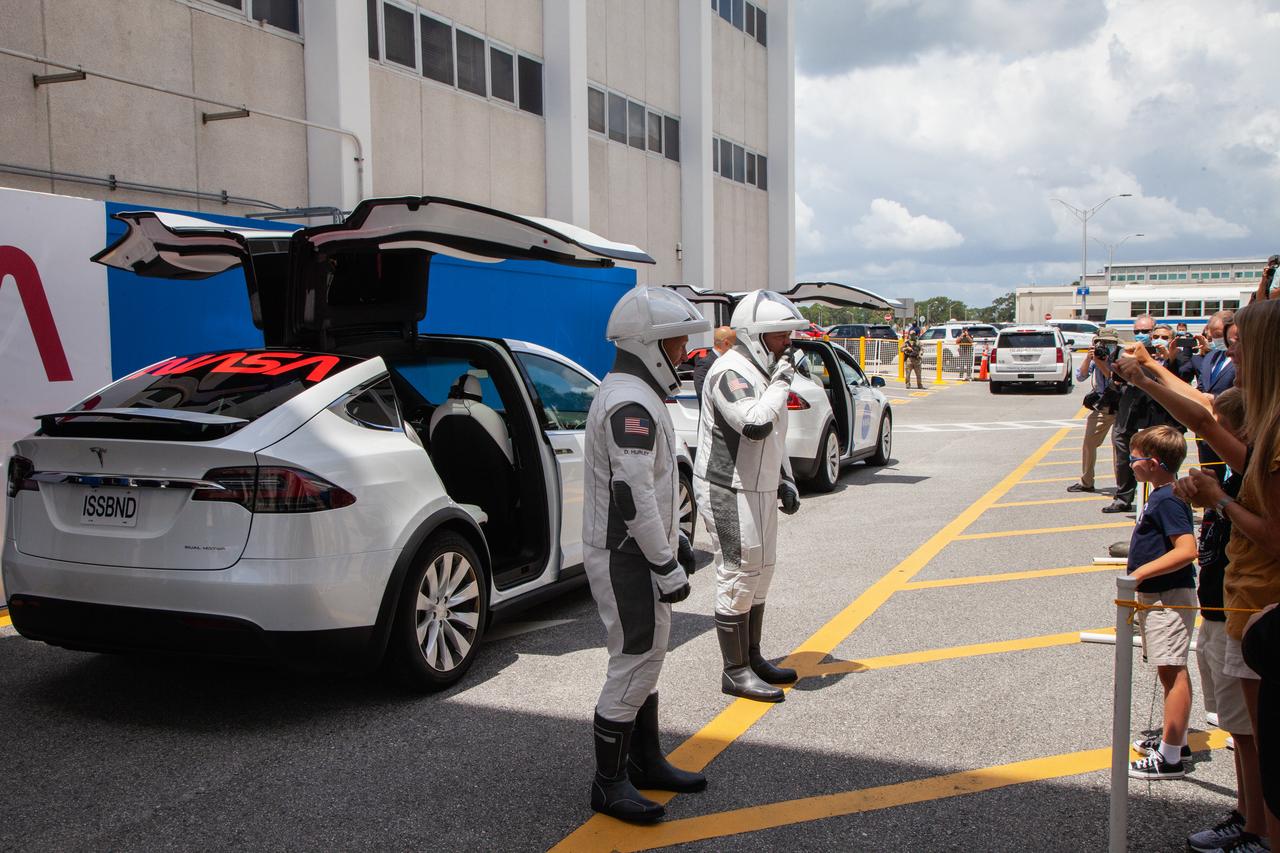

NASA astronauts Douglas Hurley (left) and Robert Behnken speak to their families before entering the Tesla Model X that will transport them from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to historic Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 launch on May 30, 2020. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifted off at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch to the International Space Station from U.S. soil since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
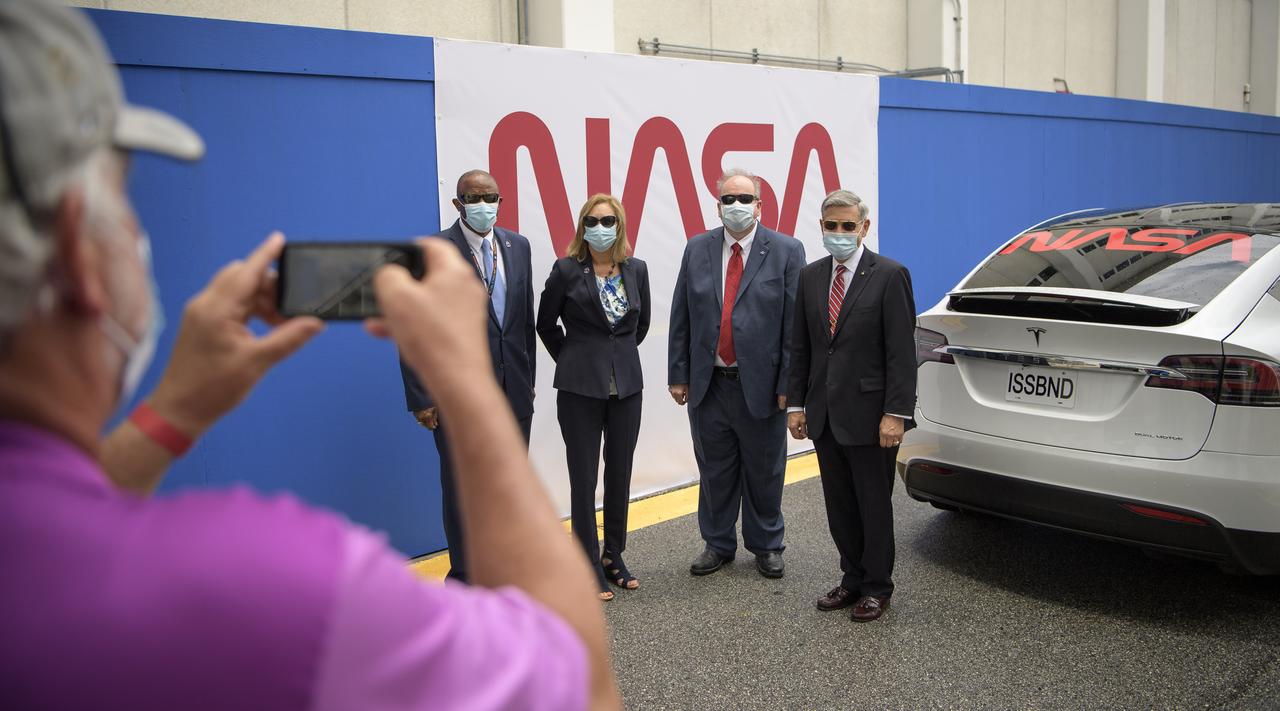

NASA Kennedy Space Center Associate Technical Director Kelvin Manning, left, Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro, Kennedy Space Center Associate Director, Management, Burt Summerfield, and Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, right, pose for a group photograph as they wait to see NASA astronauts Douglas Hurley and Robert Behnken depart the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building for Launch Complex 39A to board the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft for the Demo-2 mission launch, Wednesday, May 27, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The test flight serves as an end-to-end demonstration of SpaceX’s crew transportation system. Today’s launch of Behnken and Hurley was scrubbed due to weather and is now scheduled for 3:22 p.m. EDT on Saturday, May 30, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. A new era of human spaceflight is set to begin as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from American soil to low-Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
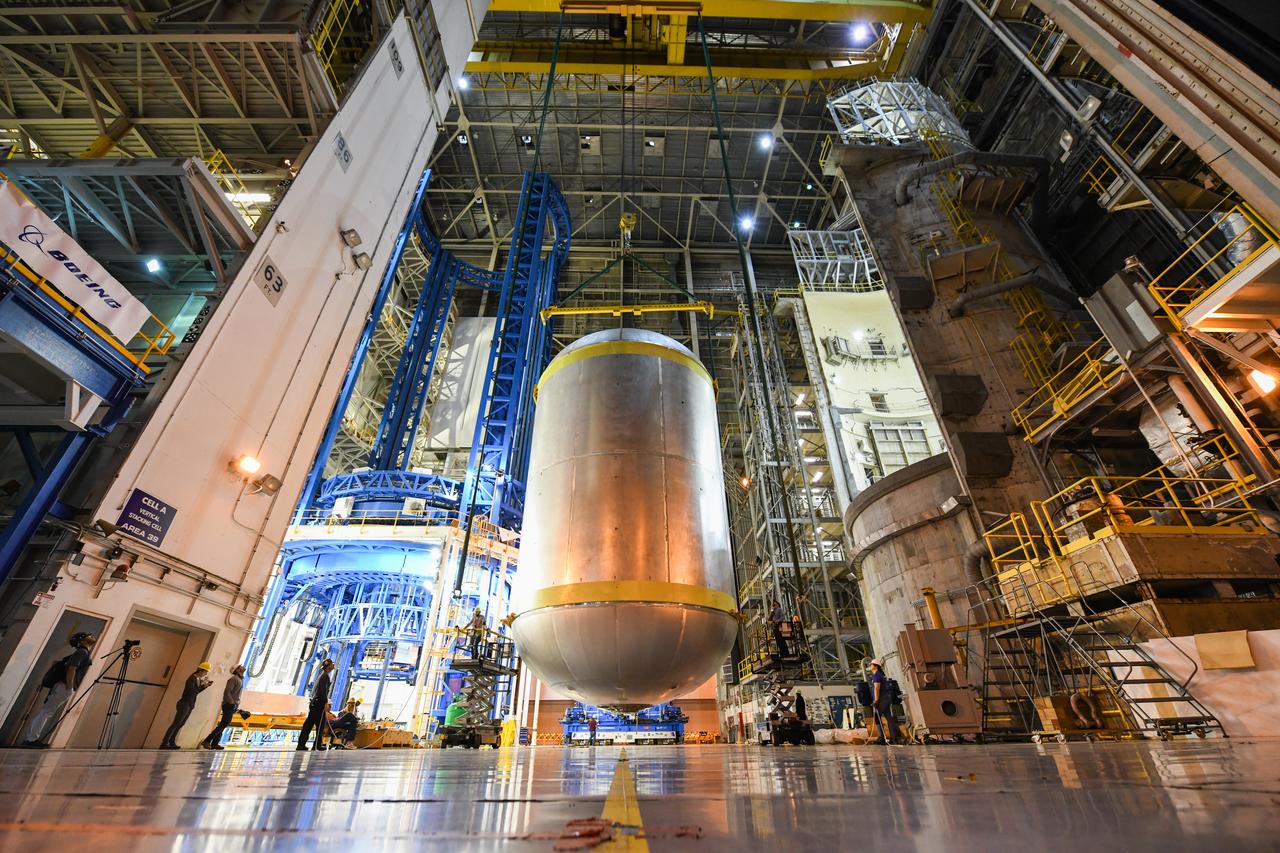

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
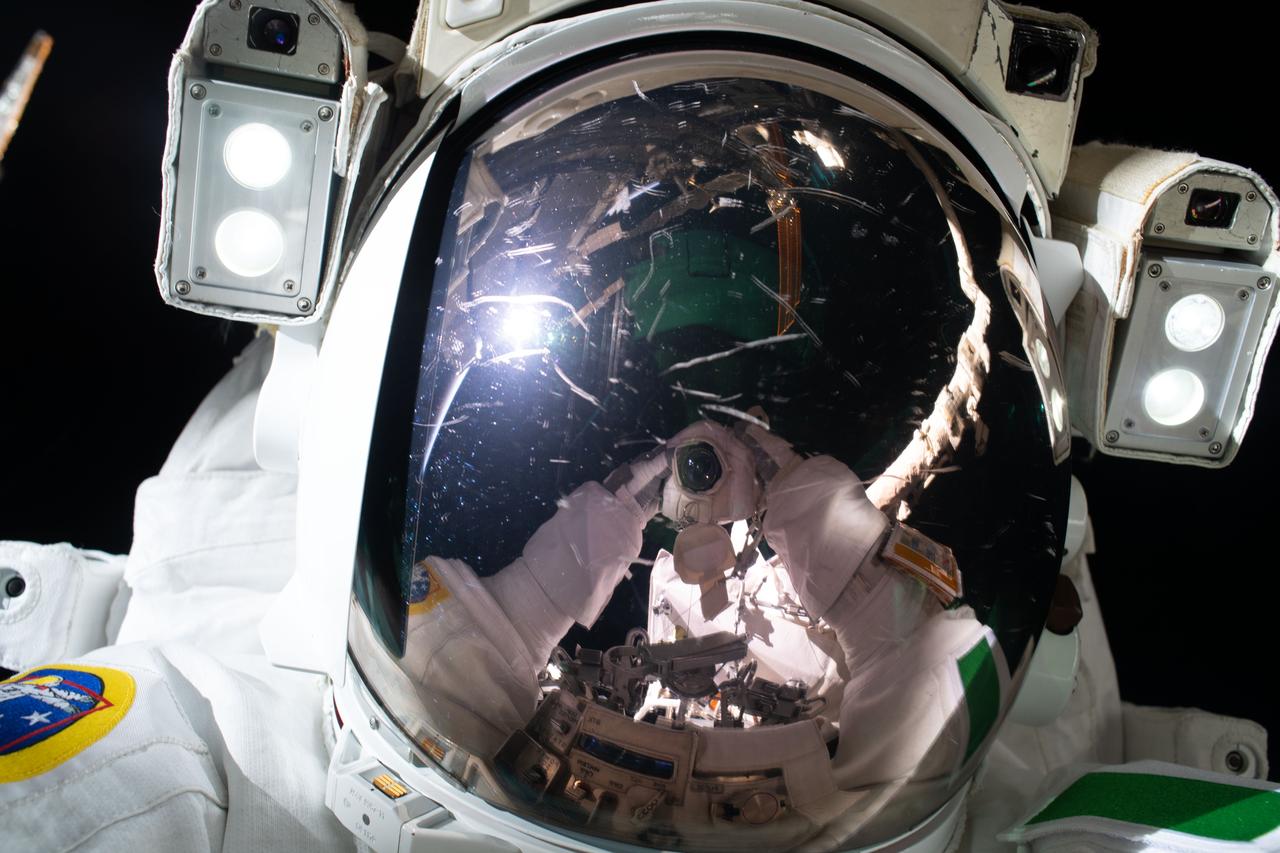

iss061e144502 (Jan. 25, 2020) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Luca Parmitano takes a "space-selfie" with his camera's reflection on his spacesuit's helmet visor. He and NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan were finalizing thermal repairs on the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a dark matter and antimatter detector, during a spacewalk that lasted 6 hours and 16 minutes.
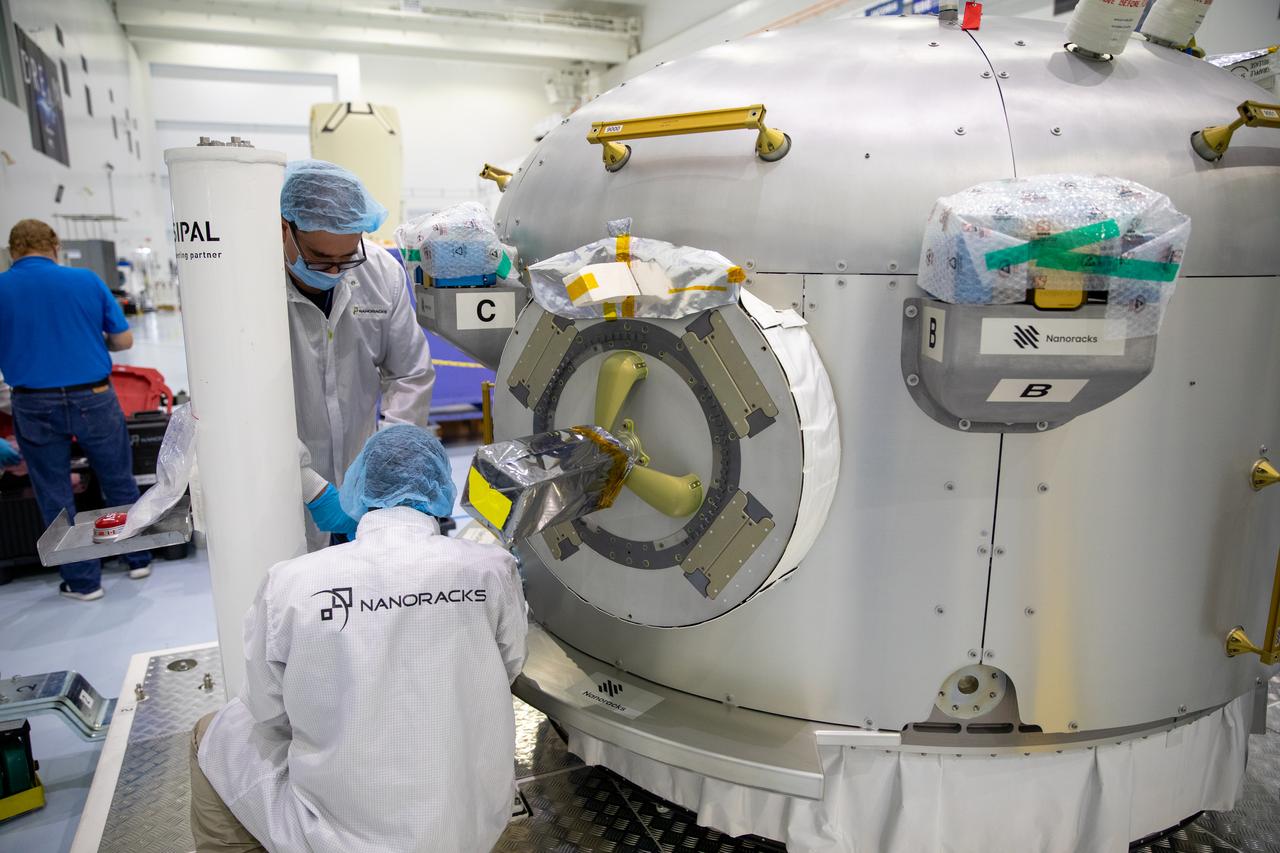

Nanoracks technicians work on the NanoRacks Bishop Airlock inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 29, 2020. The next-generation Nanoracks payload facility is being prepared for its flight to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21) to the International Space Station. The Bishop Airlock is the first commercially funded airlock for the space station. It will provide payload hosting, robotics testing, satellite deployment, serve as an outside toolbox for station crew spacewalks, and more. CRS-21 is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than November from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center.
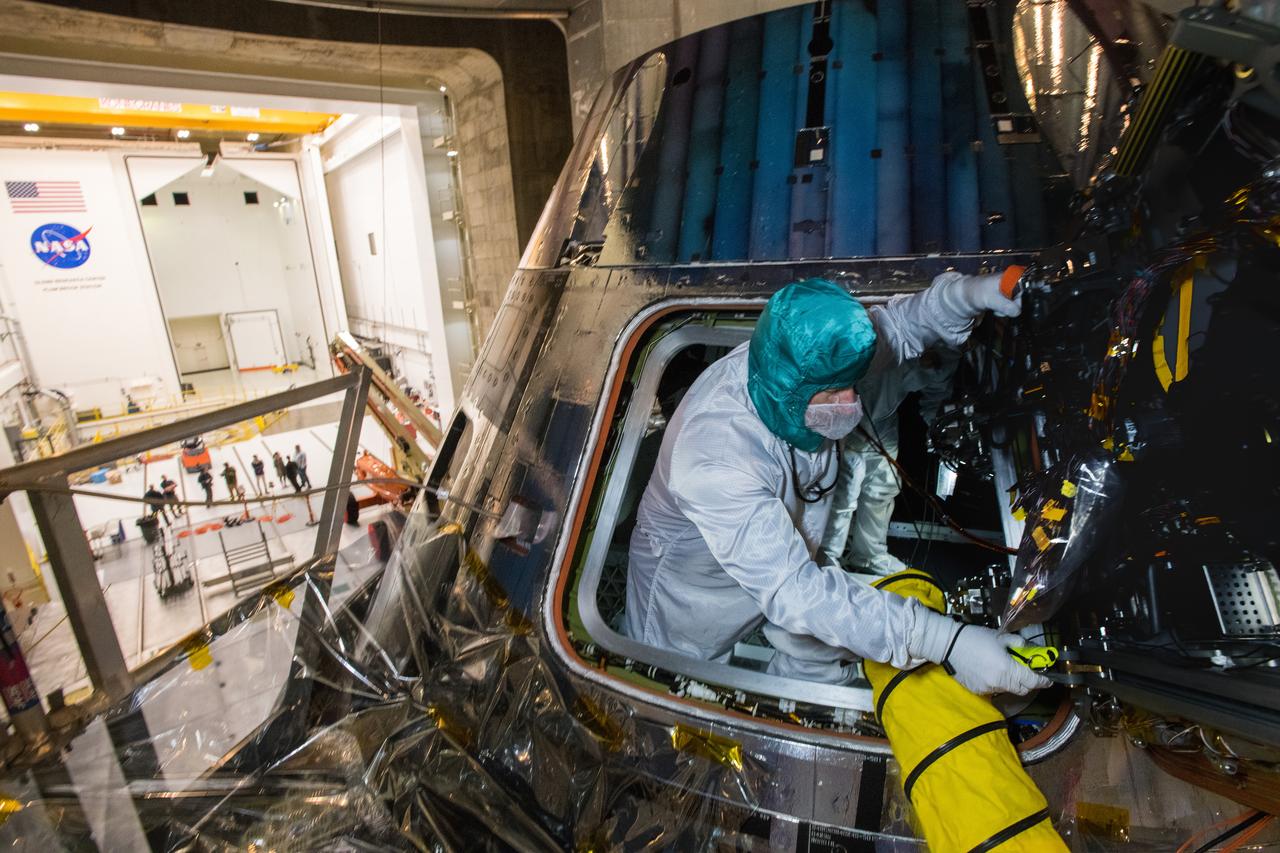

Glenn Research Center's Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility (formerly Plum Brook Station) in Ohio houses the world’s largest space simulation vacuum chamber where the Orion spacecraft, shown here on March 11, 2020, was rigorously tested for Artemis missions to the Moon.

The Soyuz MS-17 rocket is launched with Expedition 64 Russian cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov and Sergey Kud-Sverchkov of Roscosmos and NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, Wednesday, Oct. 14, 2020, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Ryzhikov, Kud-Sverchkov, and Rubins launched at 1:45 a.m. EDT to begin a six-month mission onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Day In The Life of Artemis Employees
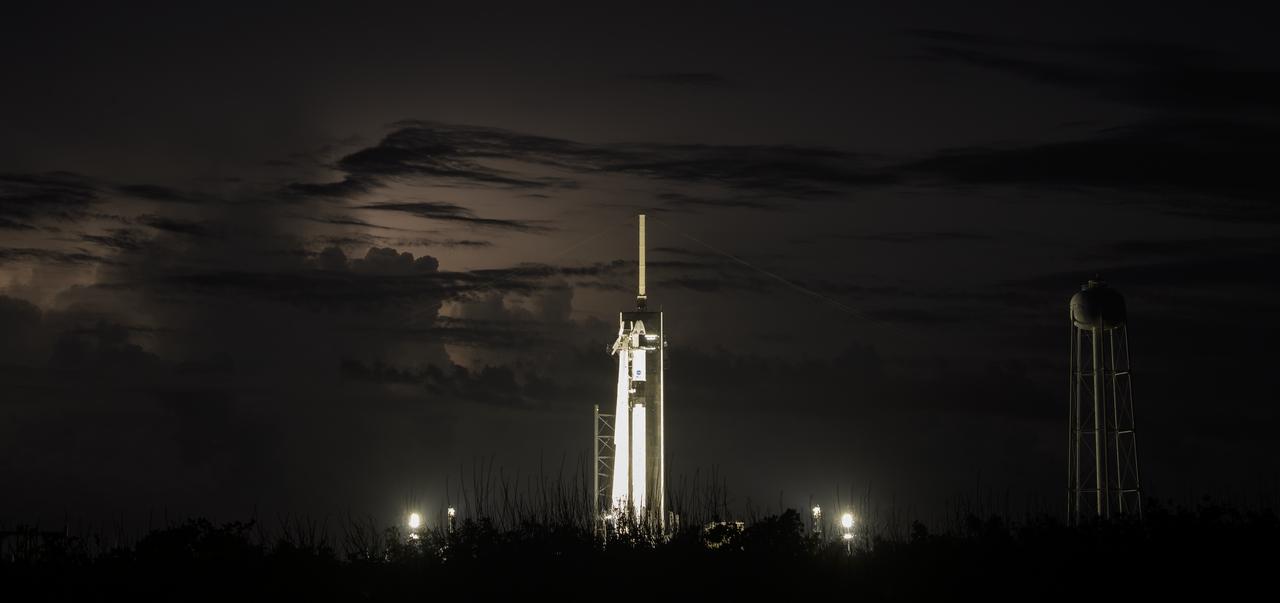

Distant storms illuminate the night sky behind a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft onboard at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Demo-2 mission, Friday, May 29, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The test flight serves as an end-to-end demonstration of SpaceX’s crew transportation system. Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are scheduled to launch at 3:22 p.m. EDT on Saturday, May 30, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. A new era of human spaceflight is set to begin as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from American soil to low-Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
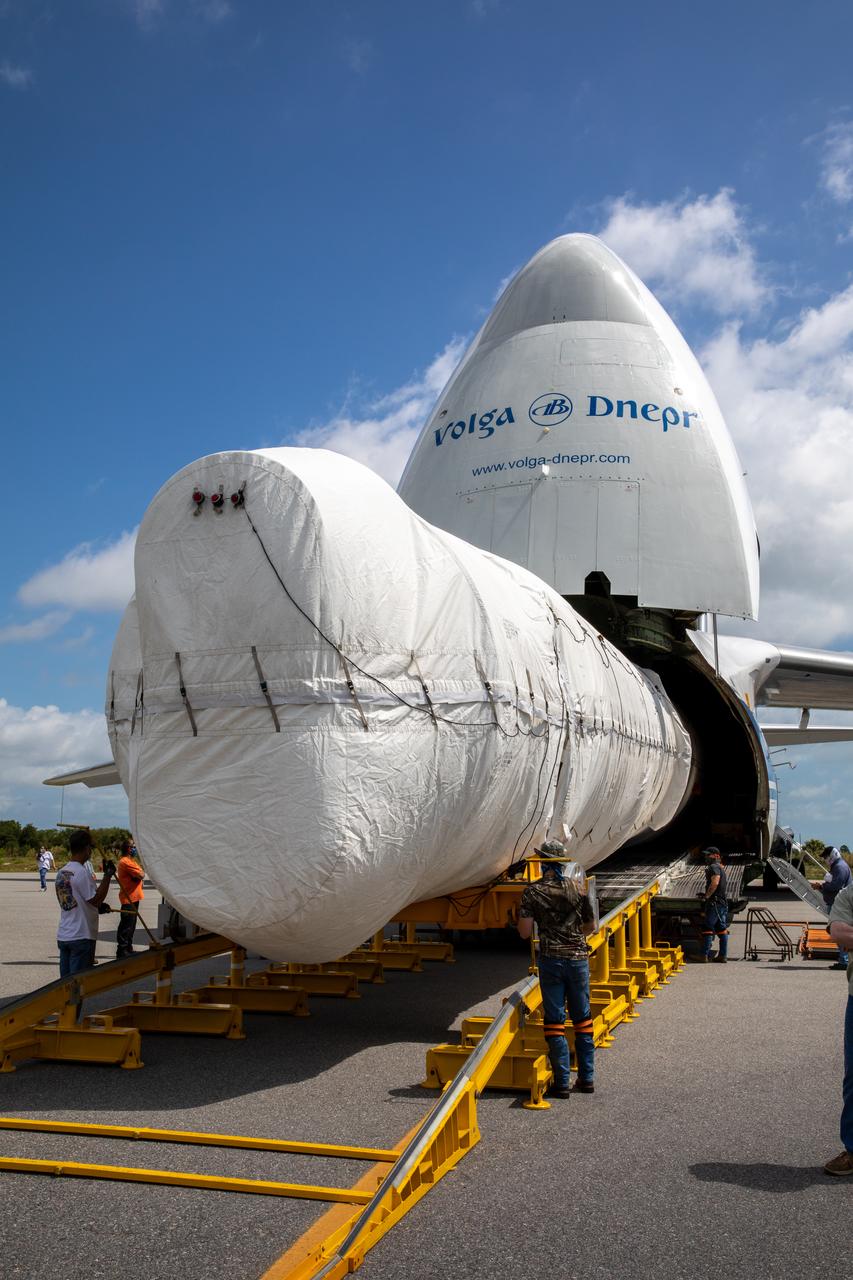

The United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The Worm is Back
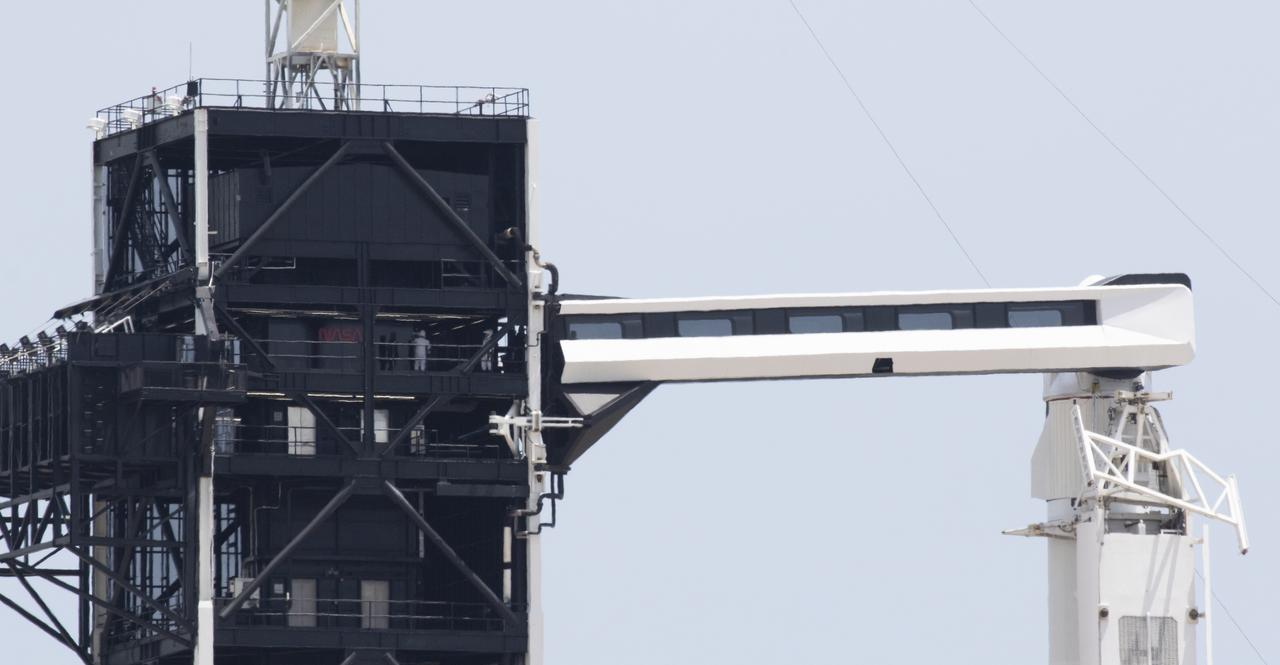

NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are seen on the fixed service structure of Launch Complex 39A before boarding SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft atop the company’s Flacon 9 rocket before launch of NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission to the International Space Station, Saturday, May 30, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The test flight serves as an end-to-end demonstration of SpaceX’s crew transportation system. Behnken and Hurley launched at 3:22 p.m. EDT on Saturday, May 30, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. A new era of human spaceflight is set to begin as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from American soil to low-Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
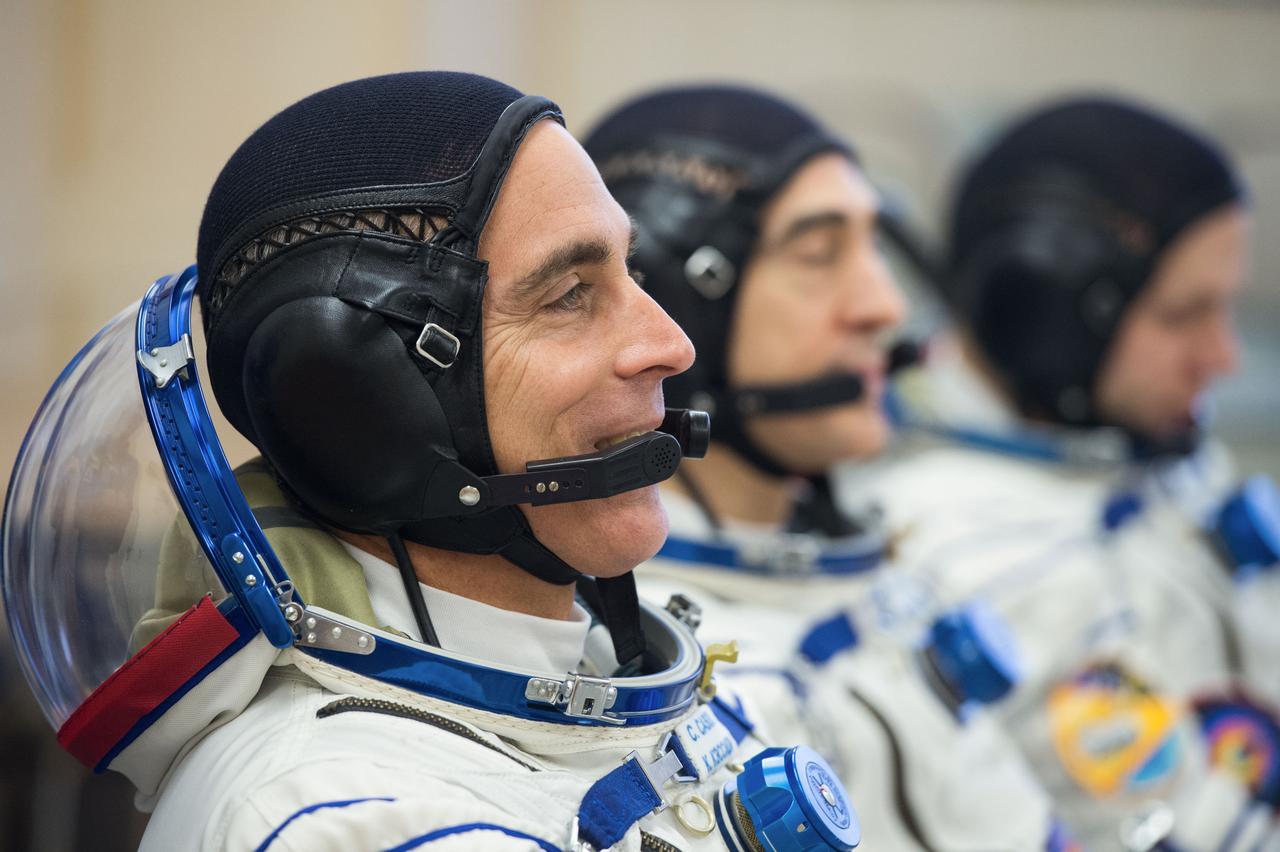

jsc2020e017101 - Expedition 63 Preflight - Expedition 63 crewmembers Chris Cassidy of NASA, left, Anatoly Ivanishin and Ivan Vagner of Roscosmos, right, talk to mission managers prior to departing for the launch pad, Thursday, April 9, 2020 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. A few hours later, they lifted off on a Soyuz rocket for a six-and-a-half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)...
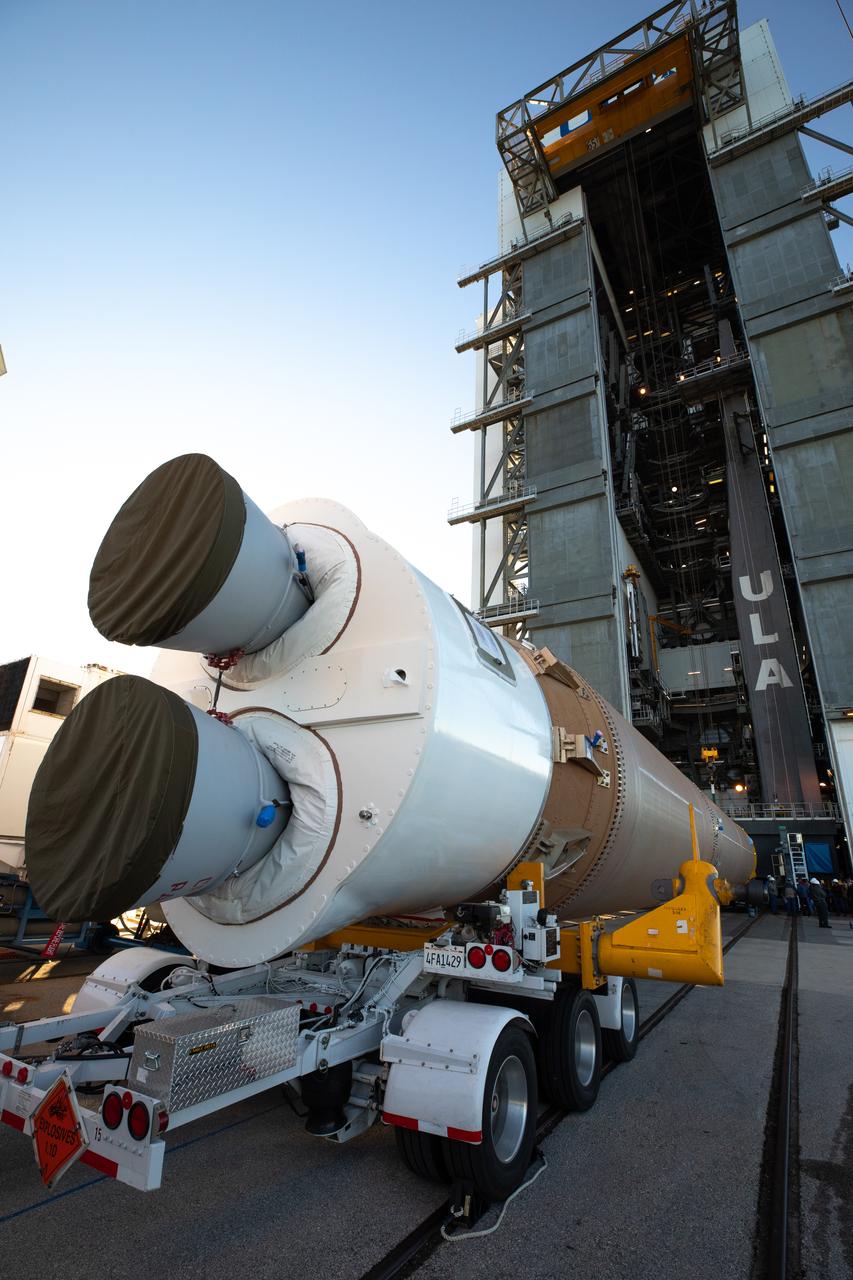

The booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Jan. 6, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the launch.
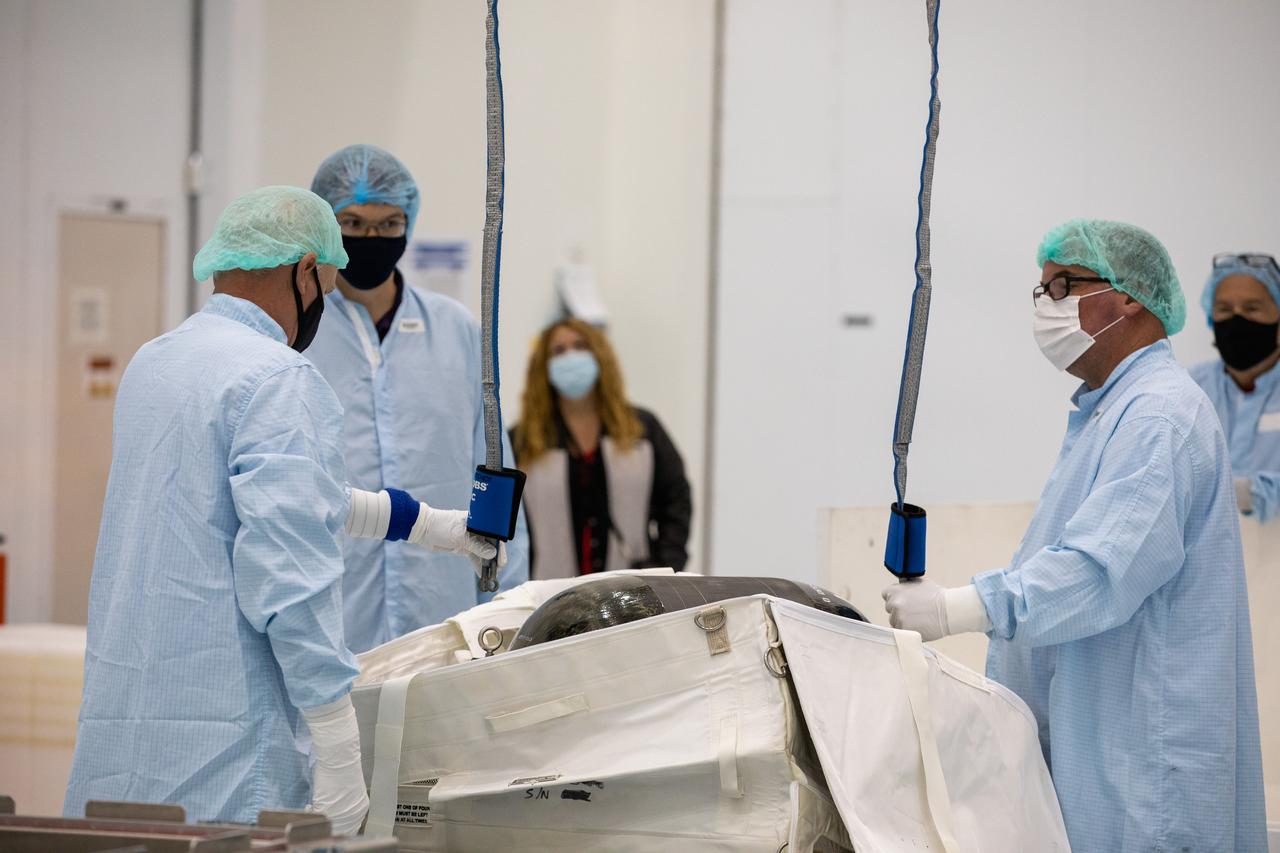

Technicians prepare to unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.

Visit to GRC by the Deputy Administrator, James Morhard

Day In The Life of Artemis Employees
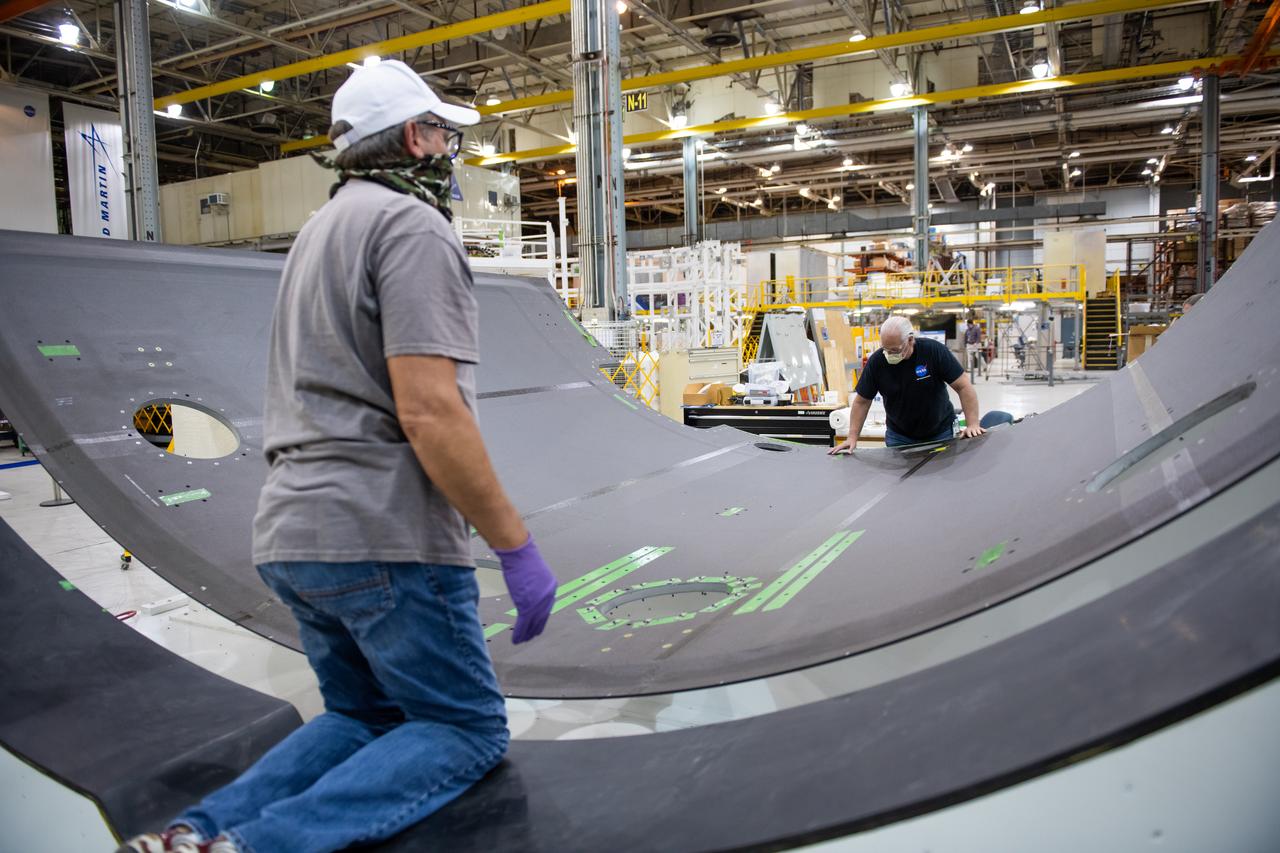

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
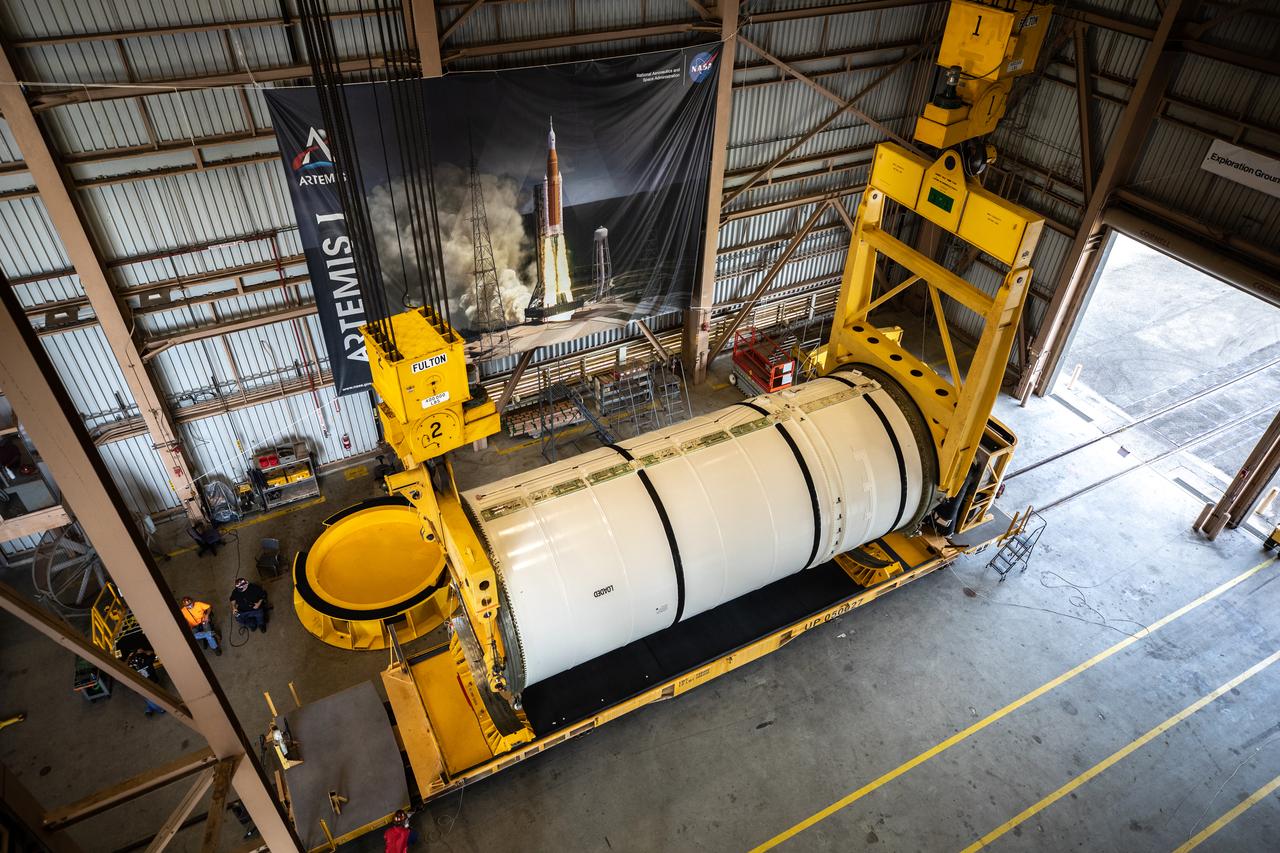

Technicians ready two NASA Space Launch System (SLS) solid rocket boosters for mating to the rocket’s two aft skirts on June 19, 2020, inside Kennedy Space Center’s Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility. Together, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Promontory, Utah, the boosters arrived at Kennedy via train. The cross-country journey was an important milestone for the agency’s Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system prior to crewed missions to the Moon. Once the boosters are mated with the aft skirts, they will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher.
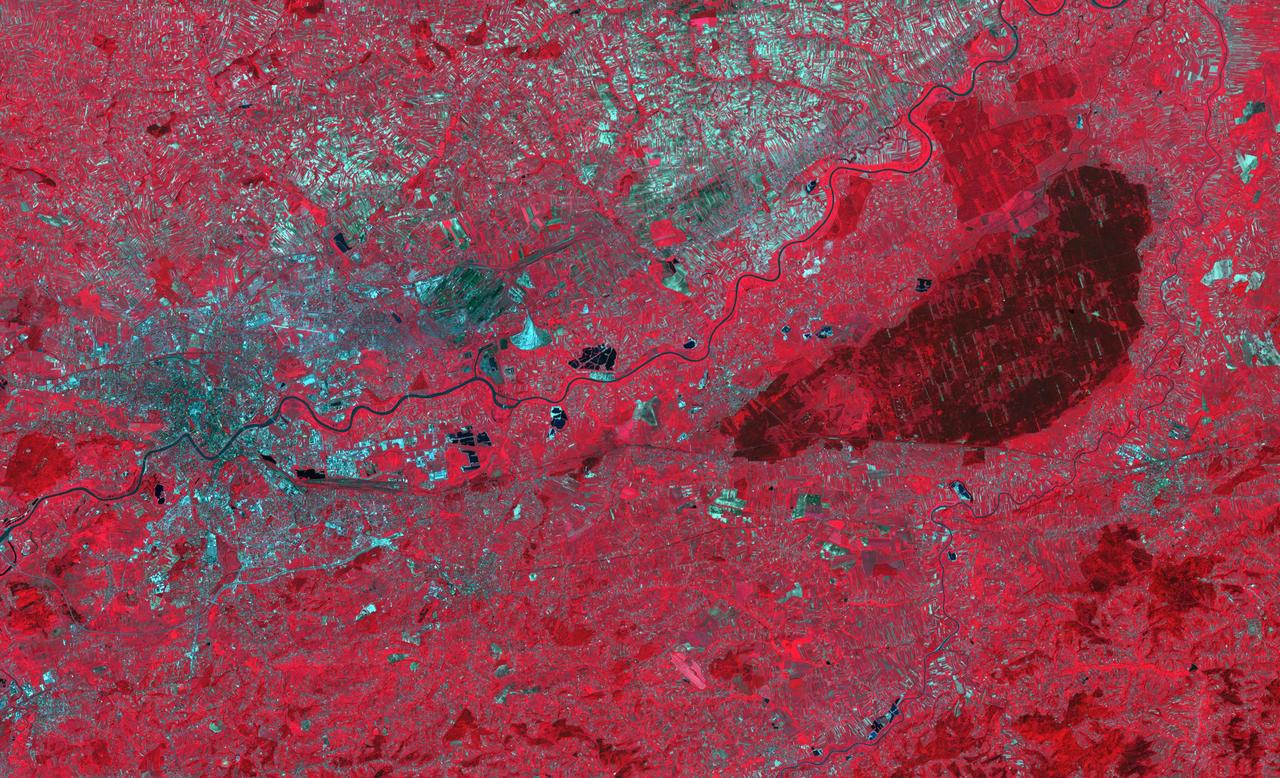

The Niepolmice Forest in Poland consists of six nature reserves, providing sanctuary for such threatened animals as lynx, wild cats and European Bison. Because of its proximity to Krakow, the old capital of Poland (left side of image), the forest (right side of image, dark red area) was a hunting ground for Polish Royalty beginning in the 13th century. The image was acquired May 25, 2003, covers an area of 29.5 by 48.5 km, and is located at 50 degrees north, 20.4 degrees east. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of about 50 to 300 feet (15 to 90 meters), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and data products. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23678
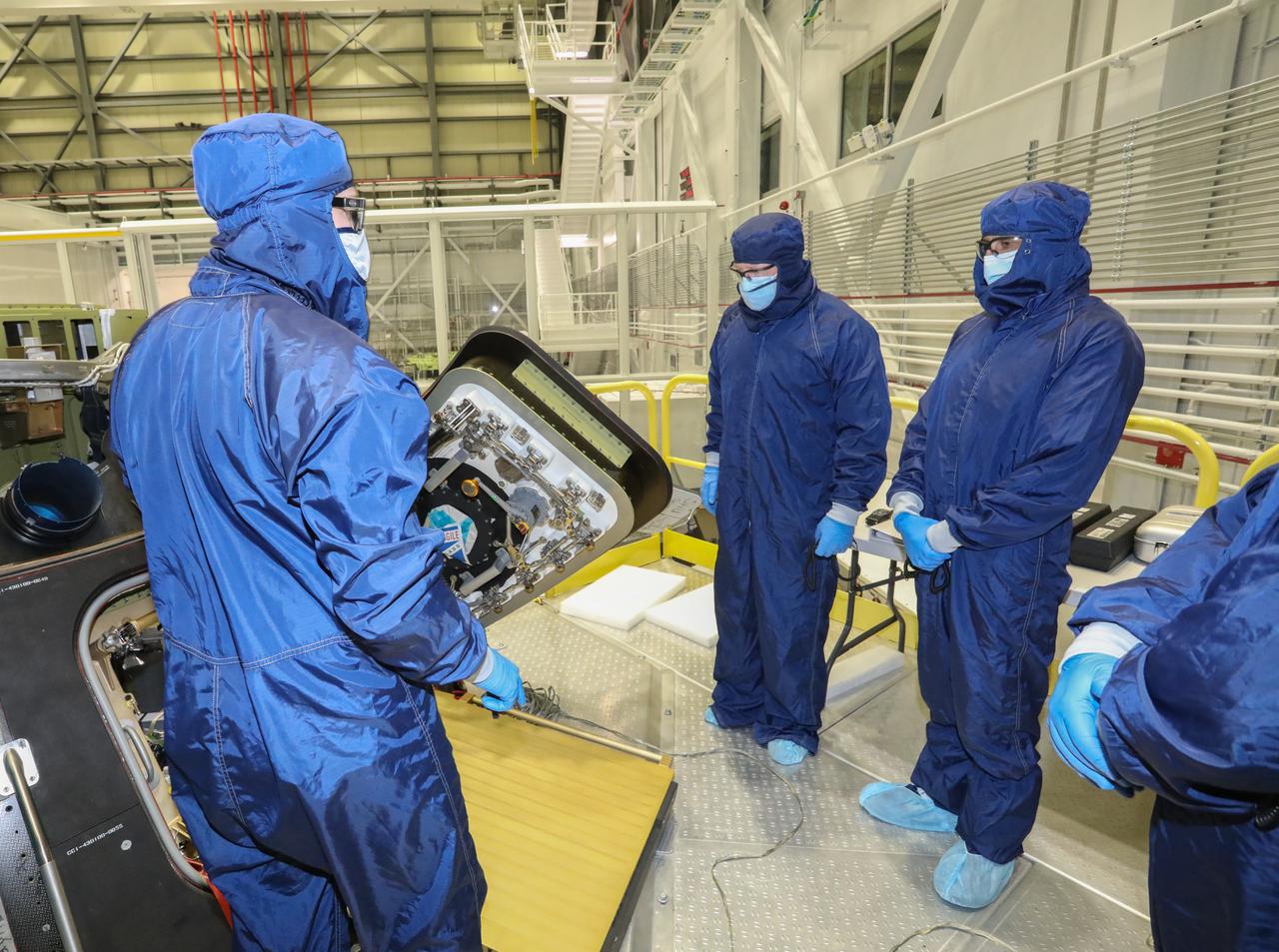

NASA astronauts Barry “Butch” Wilmore and Sunita "Suni" Williams visit the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 17, 2020. The astronauts are at Kennedy to prepare for their flights to the International Space Station on Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Wilmore and Williams will command the Crew Flight Test and the Starliner-1 mission, respectively.
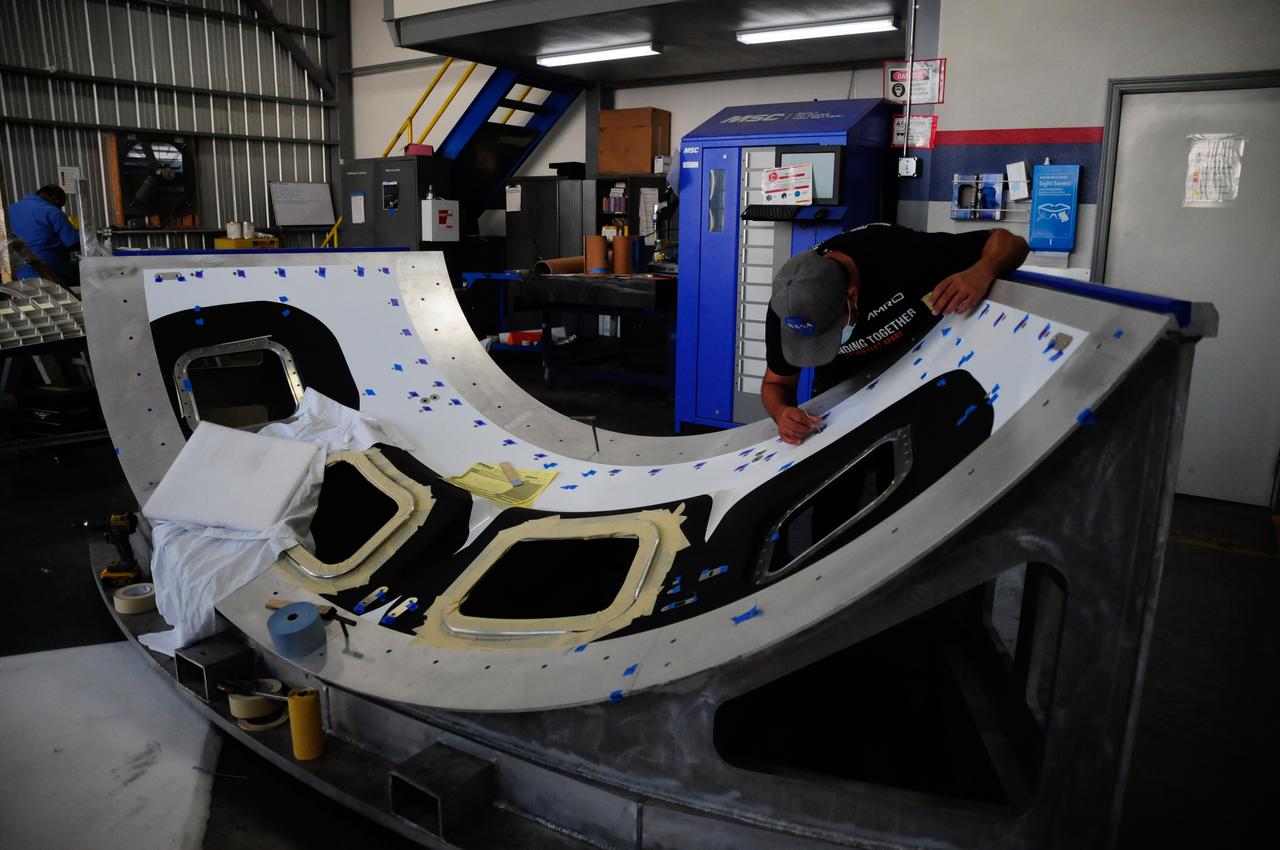

The first element machined for the Artemis III Orion crew module – a cone panel with openings for windows, designed by Orion’s lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, and manufactured by AMRO Fabricating Corp., of South El Monte, California, is shown here on Aug. 14, 2020. The completed panel is on its way to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana, where engineers will weld it with other panels as part of Orion’s pressure vessel.
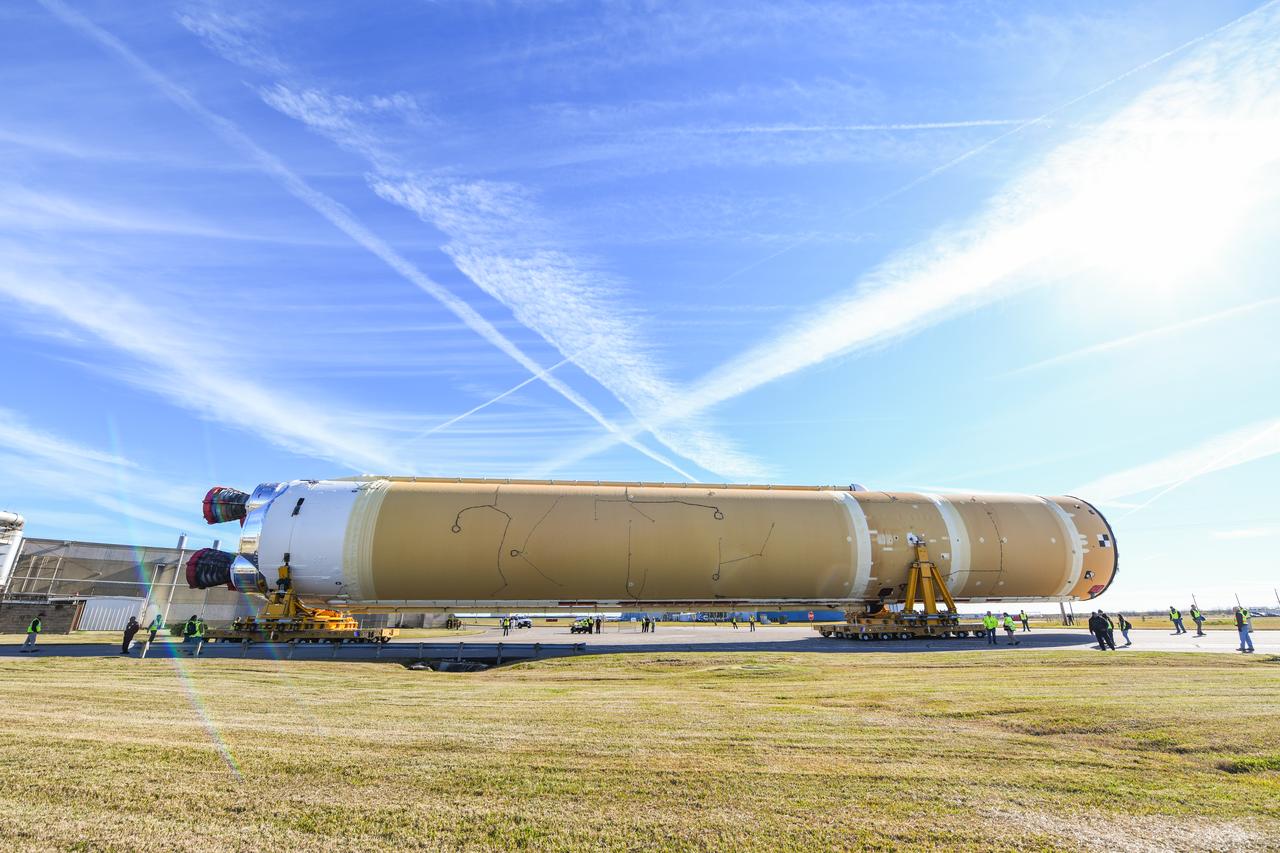

These images show how the team rolled out the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
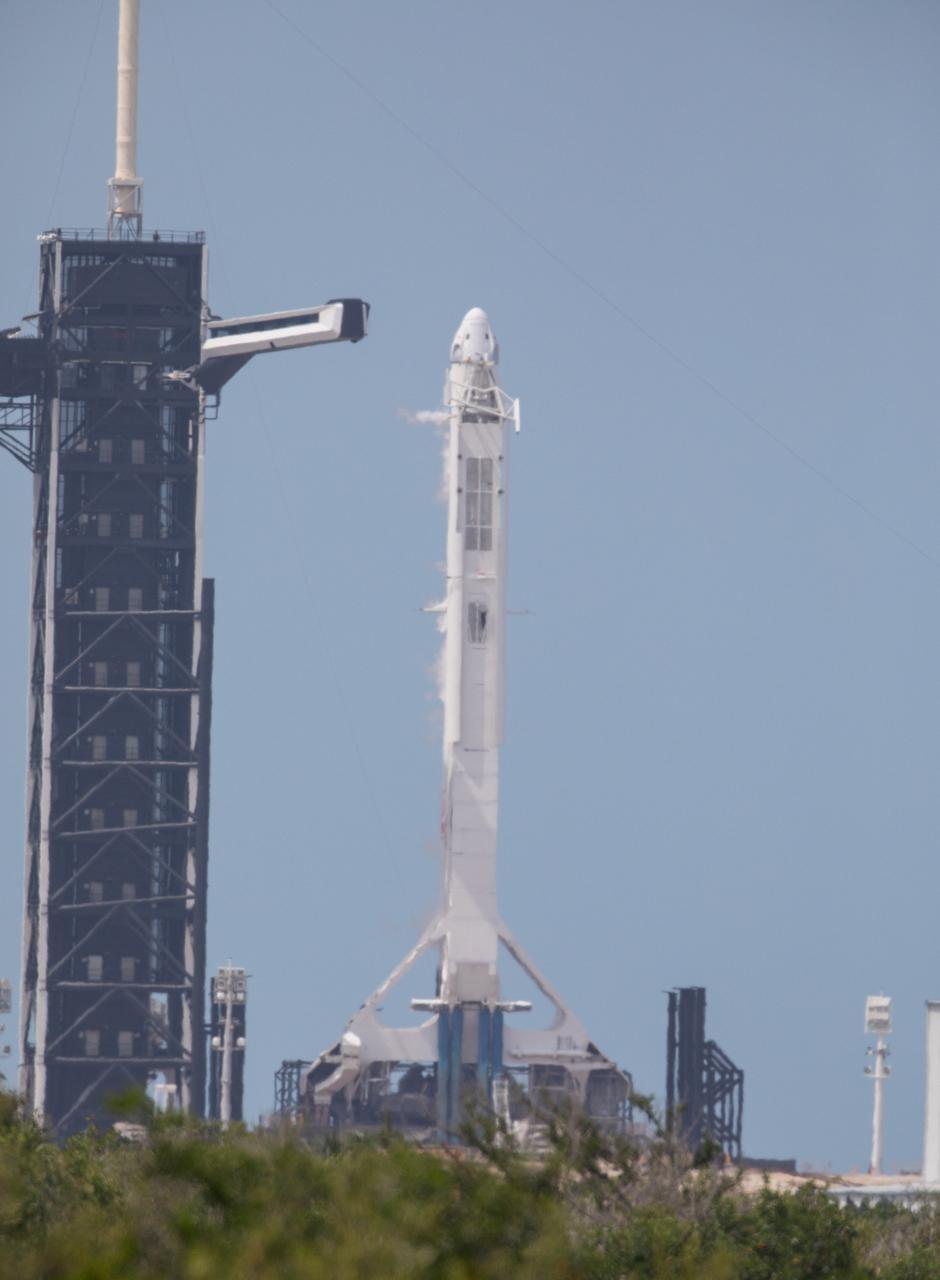

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft stand poised for launch at historic Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.

A prototype of Organic Processor Assembly (OPA) – technology capable of treating mixed organic wastes – arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 19, 2020. At the heart of the OPA is an anaerobic membrane bioreactor – a hybrid technology that couples anaerobic digestion with membrane filtration. Developed through a collaboration between Kennedy’s Dr. Luke Roberson and the University of South Florida’s Dr. Daniel Yeh, the OPA was designed for an early planetary base scenario to help close the resource recovery loop, decreasing the agency’s dependence on resupply missions.
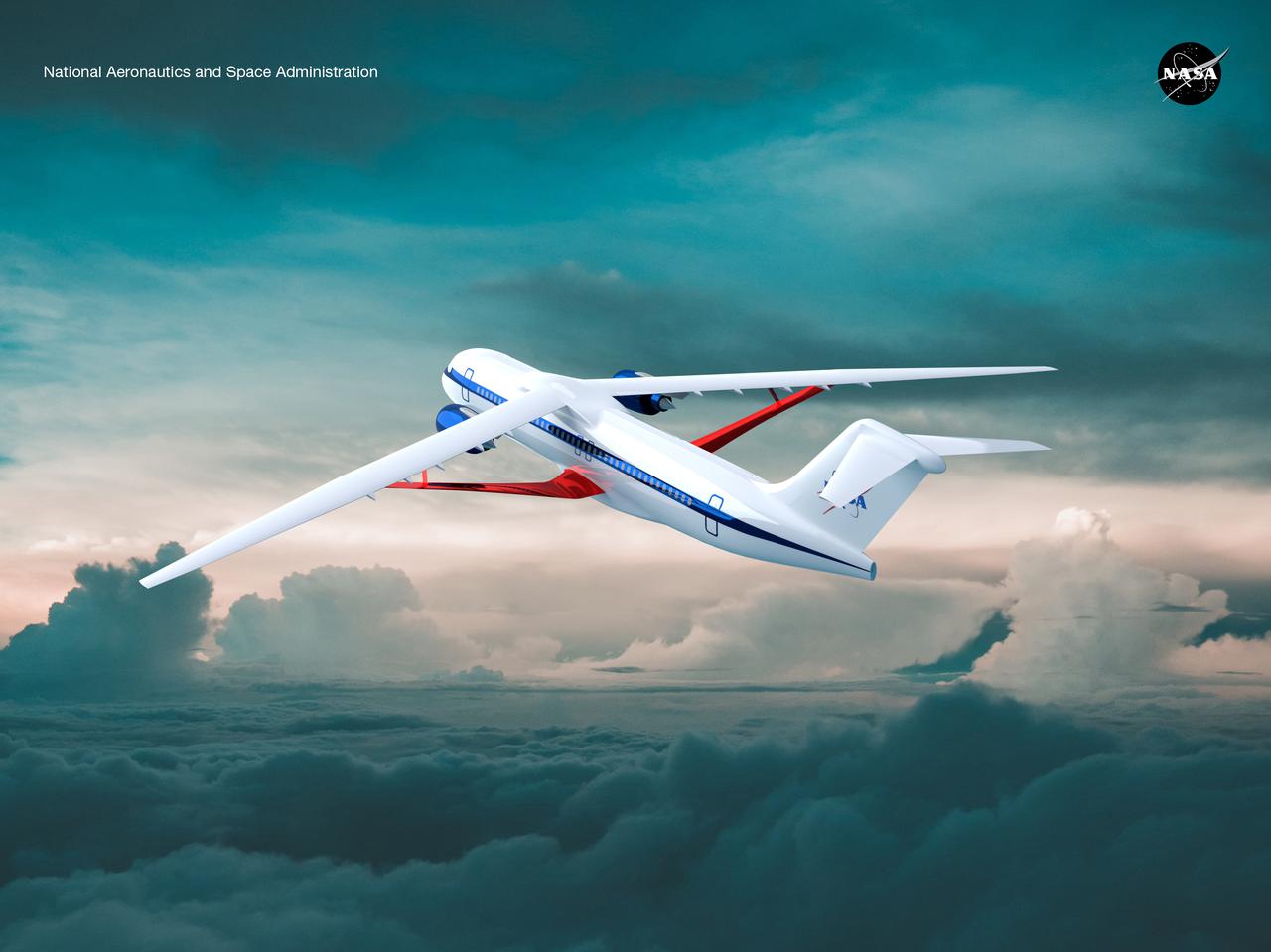

Notice anything different about the wings on this airliner? This conceptual truss-braced wing narrowbody is an aircraft with a 170ft span folding wing. By utilizing trusses, the aircraft can have longer, thinner wings with greater aspect ratios. This, in turn, translates into less drag and 5-10% less fuel burned. The Transonic Truss-Braced Wing aircraft originated from a joint effort by NASA and Boeing to develop subsonic commercial transport concepts – meeting NASA-defined metrics in terms of reduced noise, emissions, and fuel consumption. The design is currently undergoing wind tunnel testing and other studies by NASA researchers.
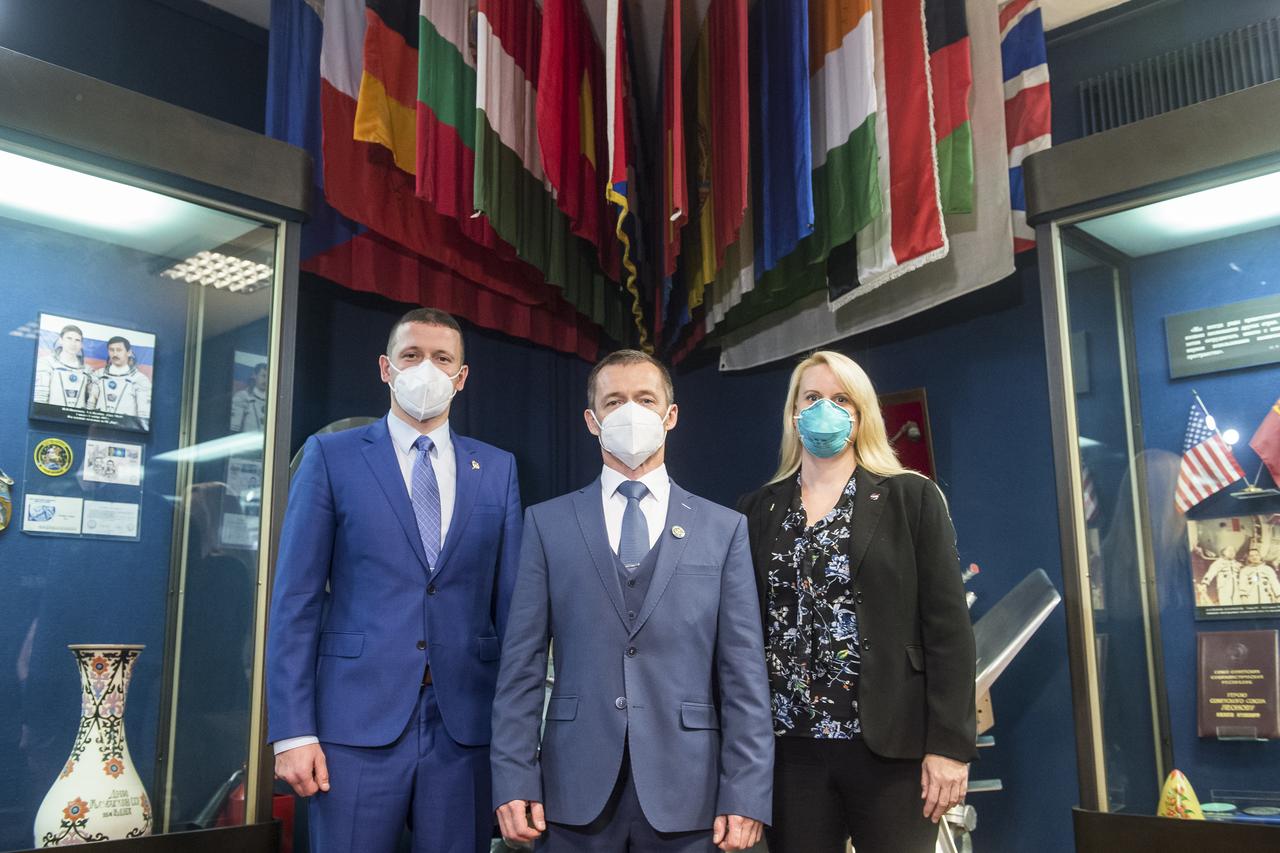

Expedition 64 prime crew members, Russian cosmonaut Sergey Kud-Sverchkov of Roscosmos, left, Russian cosmonaut Sergey Ryzhikov of Roscosmos, center, and NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, pose for a photo after a press conference, Thursday, Sept. 24, 2020 at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center (GCTC) in Star City, Russia. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
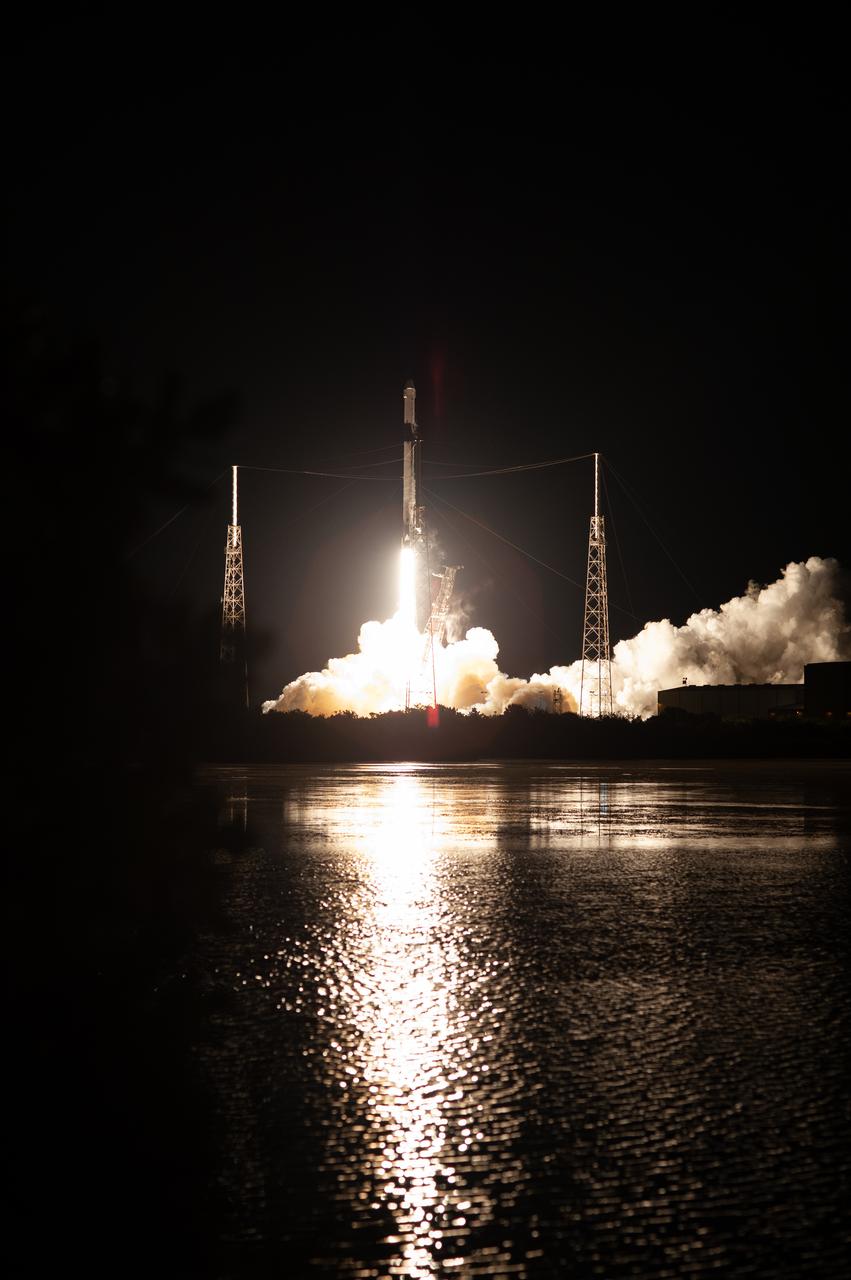

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 11:50 p.m. EST on March 6, 2020, carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 5,600 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory.
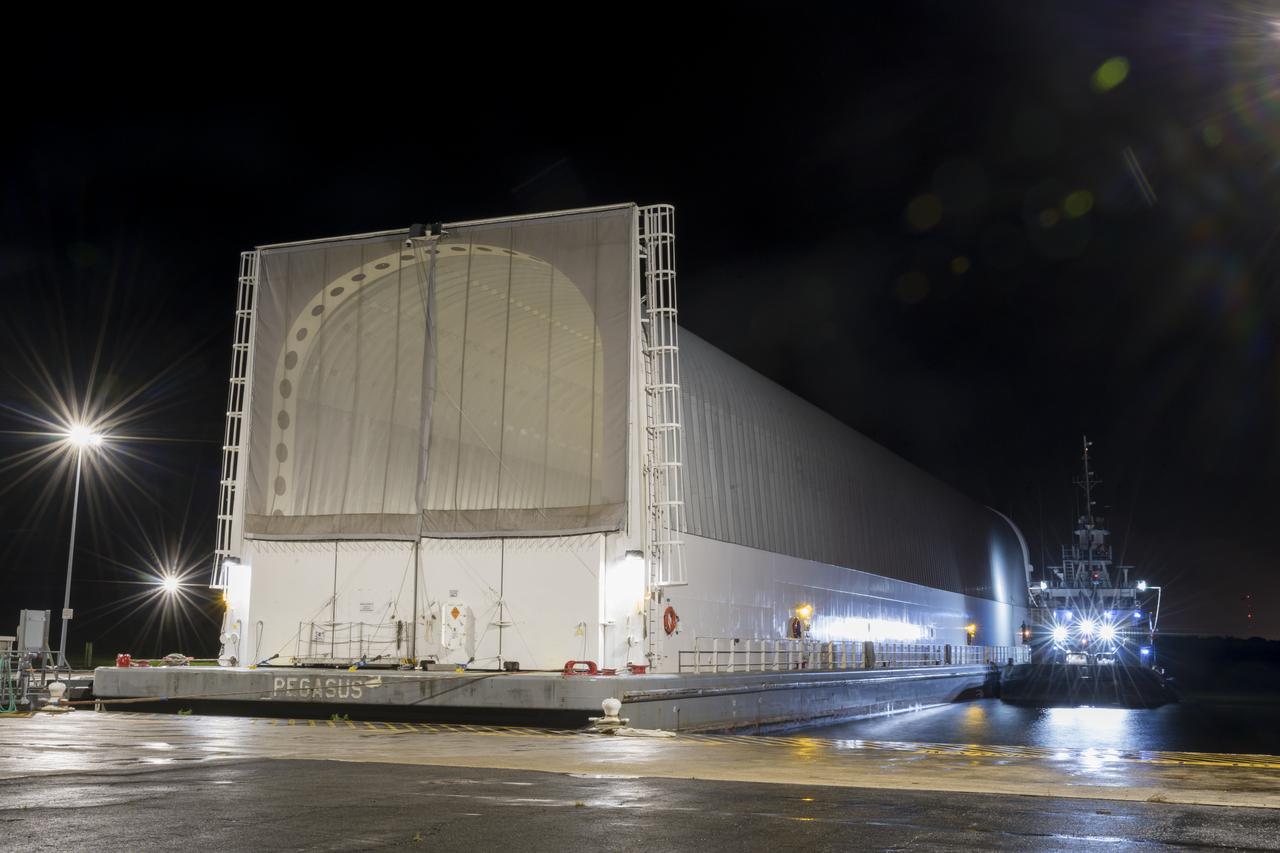

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

ESA (European Space Agency) director of Earth Observation Programmes, Josef Aschbacher, left, presents NASA’s former director of the Earth Science division, Dr. Michael Freilich with an award after announcing that the international ocean science satellite previously known as Sentinel-6A/Jason-CS has been renamed Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich after him, Tuesday, January 28, 2020, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Sentinel-6A Michael Freilich will observe and record global sea level changes and will be joined by an identical satellite slated to launch in 2025 for a total of ten years of targeted observations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

These images show how the team rolled out the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
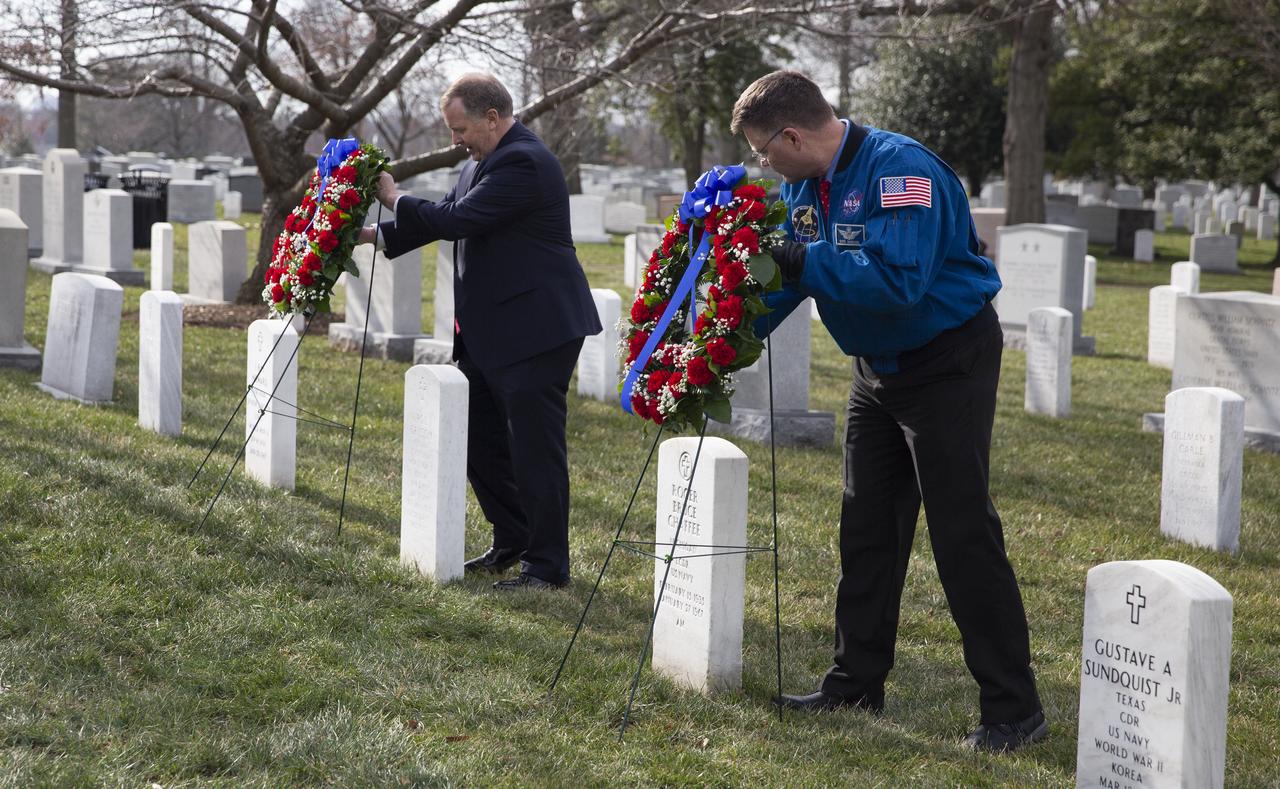

NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, left, and NASA astronaut Doug Wheelock, right, place wreaths at the graves of Apollo 1 astronauts Virgil “Gus” Grissom, and Roger Chaffee as part of NASA’s Day of Remembrance, Thursday, Jan. 30, 2020, at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The wreaths were laid in memory of those men and women who lost their lives in the quest for space exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)