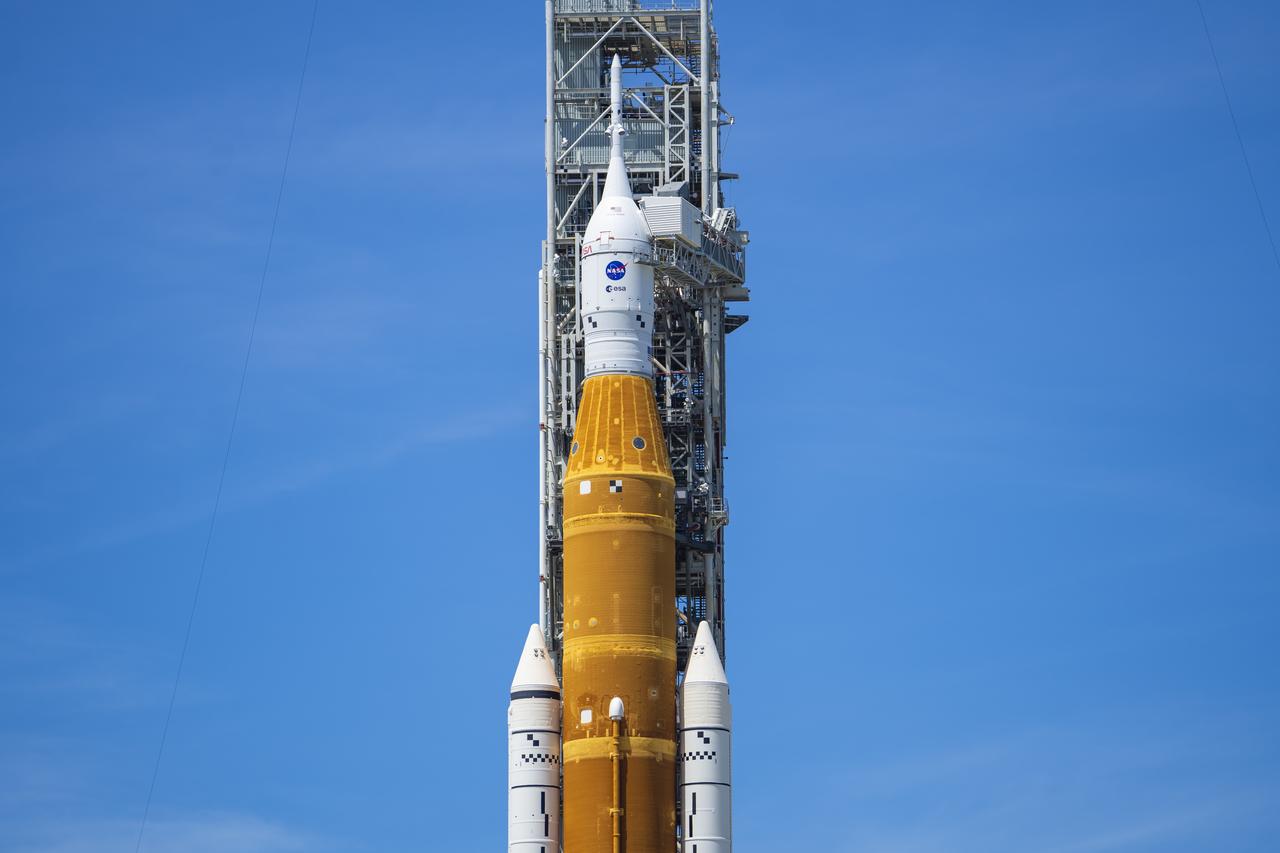

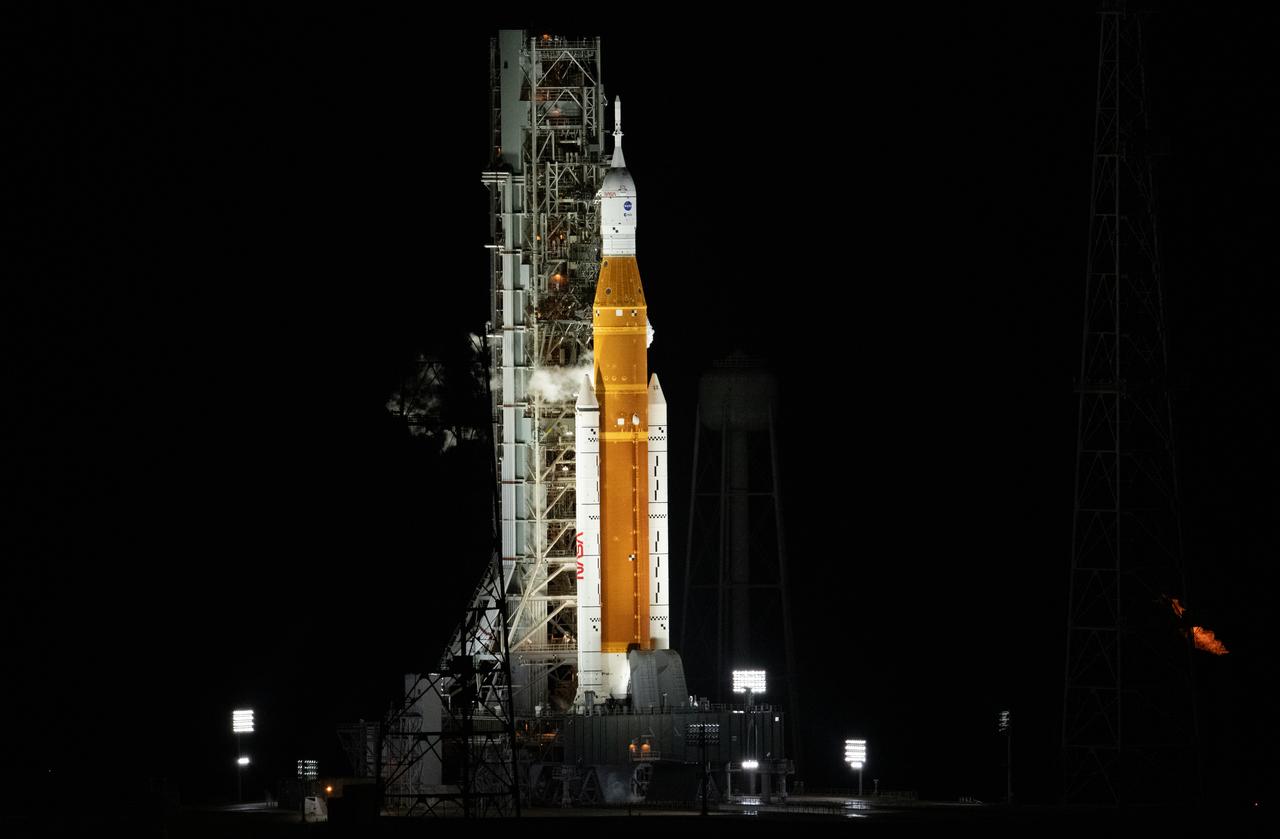
NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

French President Emmanuel Macron and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson participate in an industry roundtable, Wednesday, Nov. 30, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Administrator Nelson and French President Emmanuel Macron met to highlight space cooperation between the United States and France. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

Nuclear Emerging Technologies for Space, NETS 2022 Conference

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives welcoming remarks during an executive session of the NASA Advisory Council (NAC), Monday, Feb. 28, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
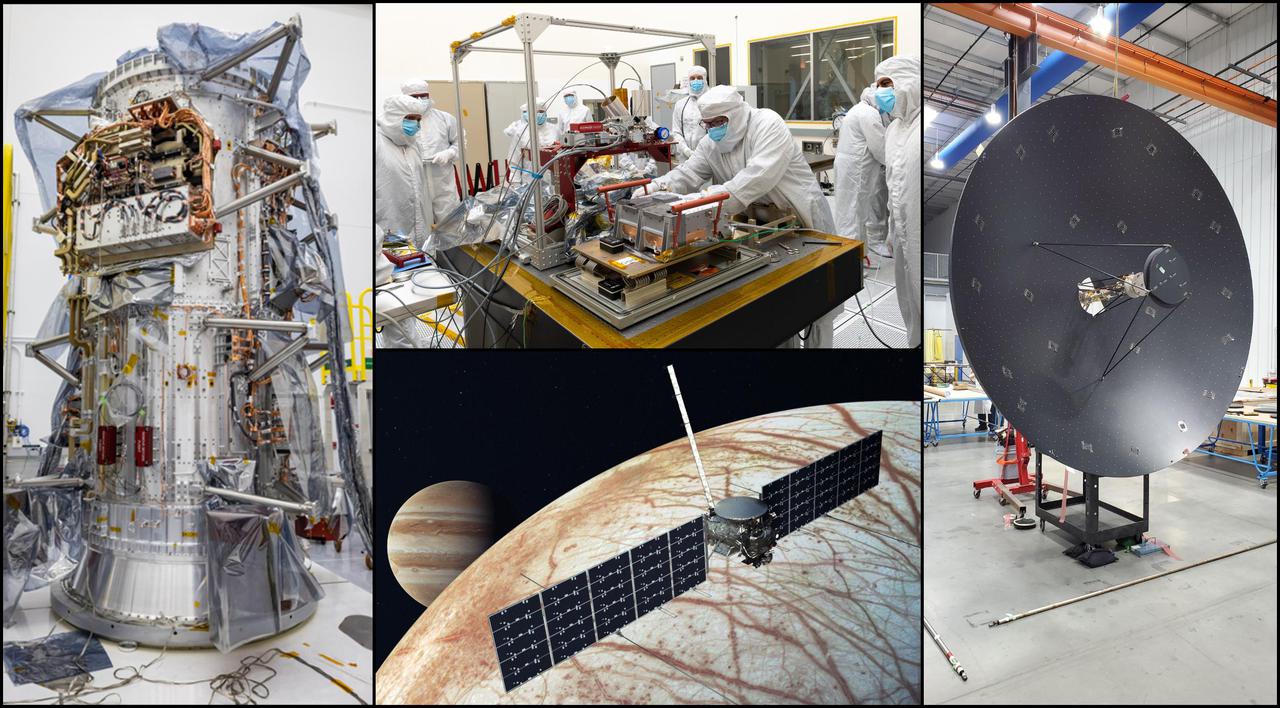

Science instruments and other hardware for NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft will come together in the mission's final phase before launching to Jupiter's icy moon Europa in 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25125
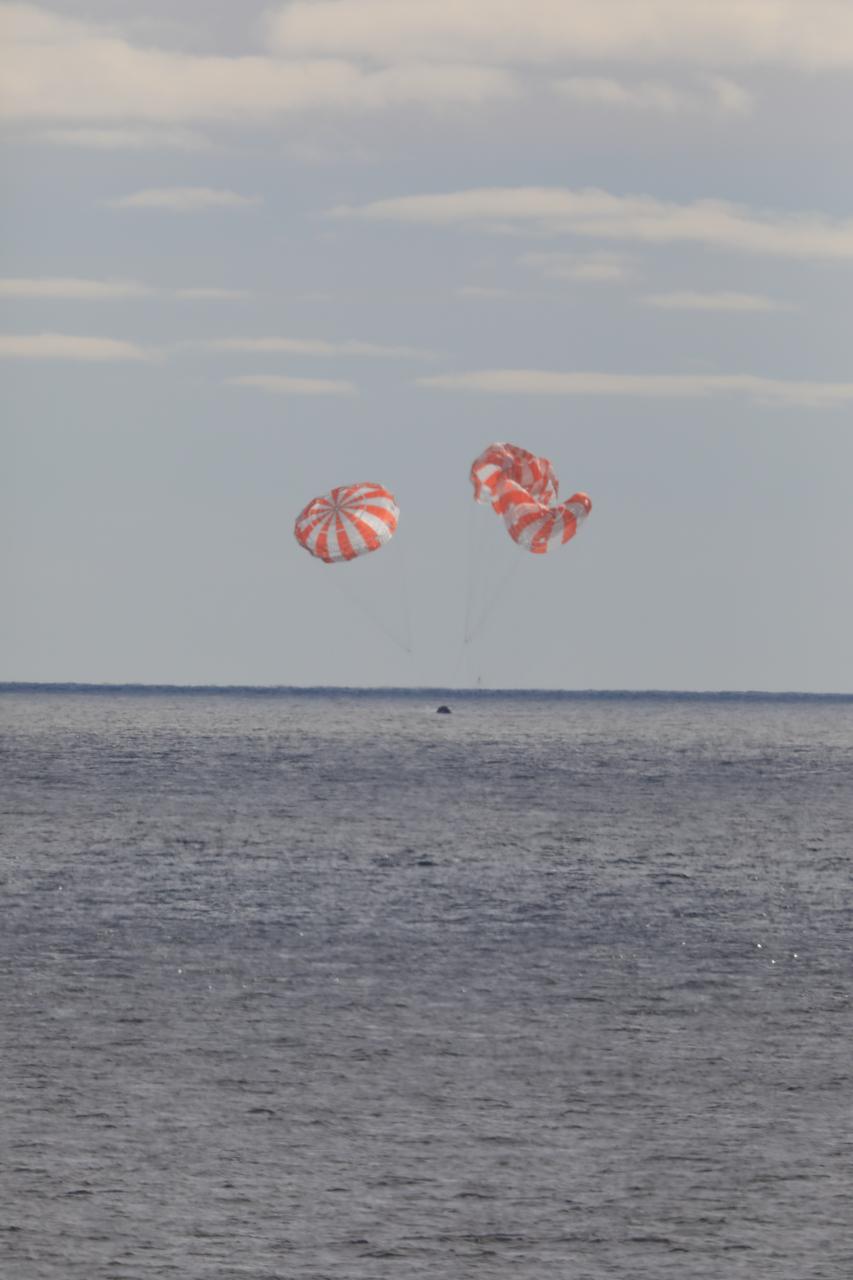

At 12:40 p.m. EST, Dec. 11, 2022, NASA’s Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission splashed down in the Pacific Ocean after a 25.5 day mission to the Moon. Orion will be recovered by NASA’s Landing and Recovery team, U.S. Navy and Department of Defense partners aboard the USS Portland.
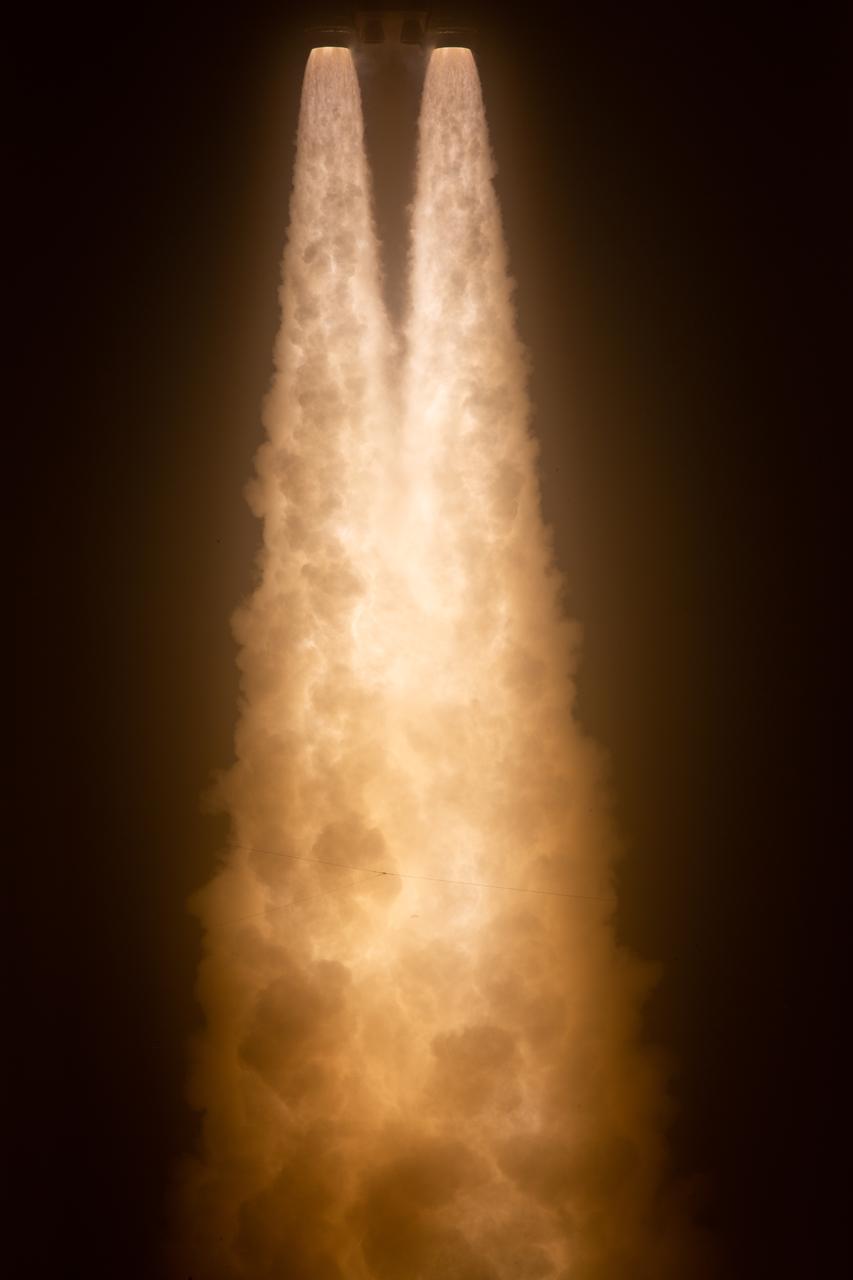

NASA’s Space Launch System rocket carrying the Orion spacecraft launches on the Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16, 2022, from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Artemis I mission is the first integrated flight test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, and ground systems. SLS and Orion launched at 1:47 a.m. EST, from Launch Pad 39B at the Kennedy Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
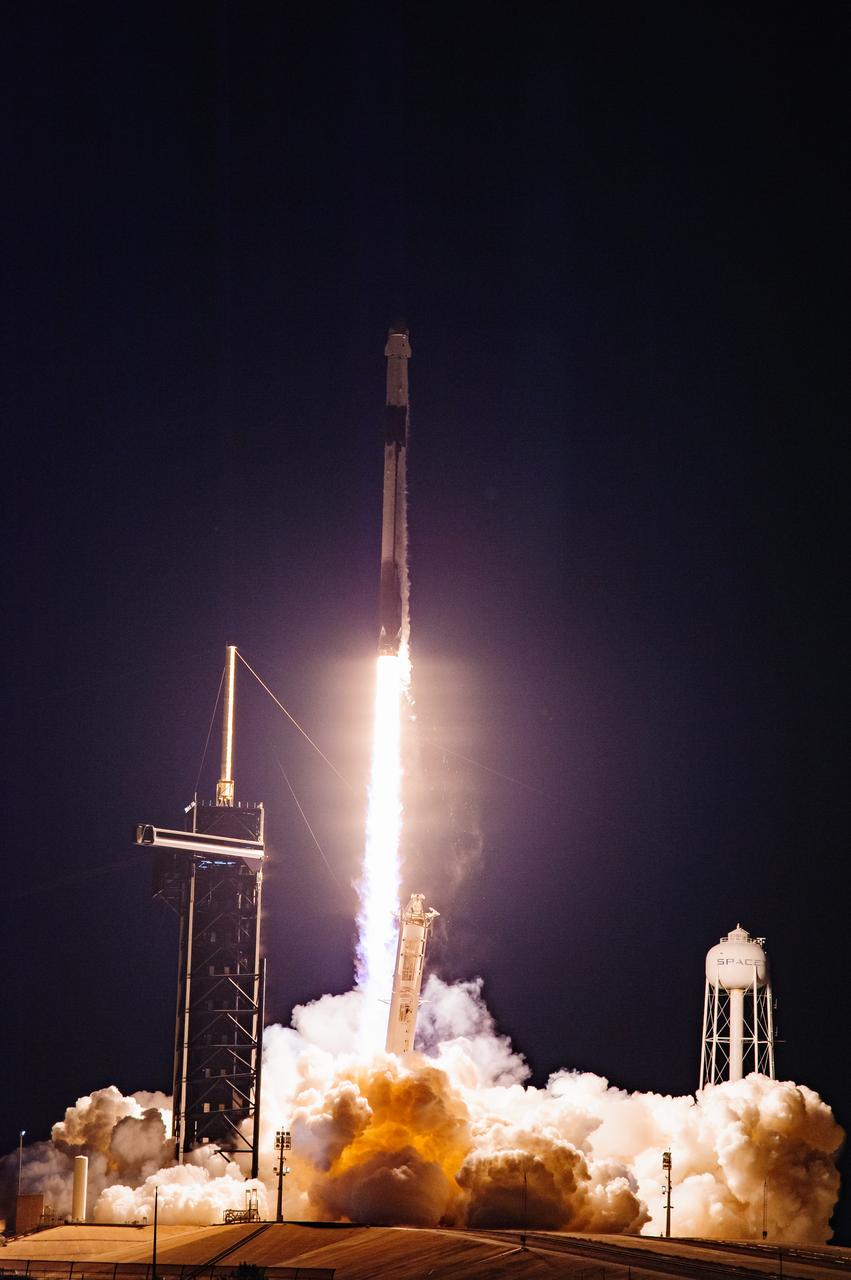

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon capsule soars upward after lifting off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 14, 2022, on the company’s 25th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:44 p.m. EDT. Dragon will deliver more than 5,800 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, to the space station. The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B, Monday, Aug. 29, 2022, as the Artemis I launch teams load more than 700,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants including liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as the launch countdown progresses at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Artemis I flight test is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, SLS rocket, and supporting ground systems. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than 8:33 a.m. ET. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
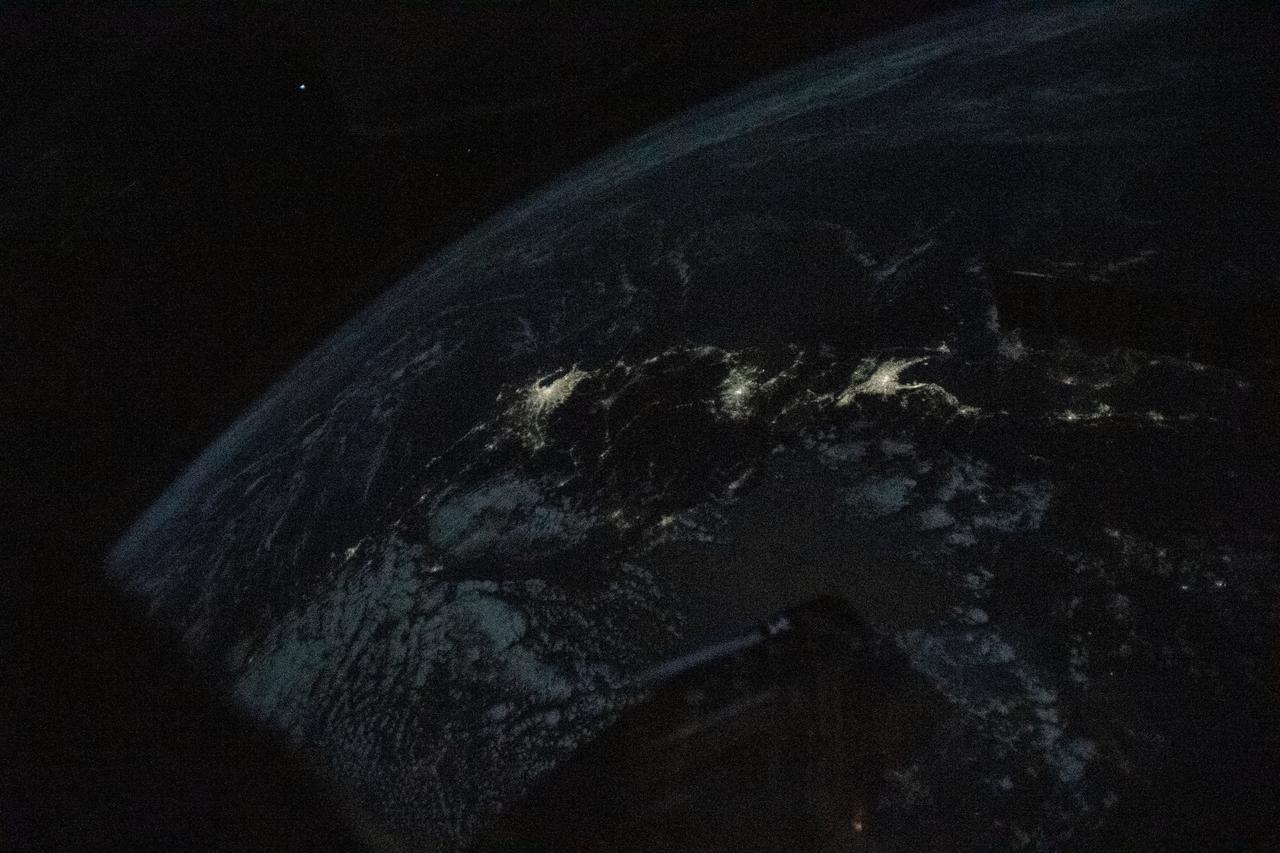

iss068e021122 (Nov. 8, 2022) --- The night lights of the Japanese cities of Tokyo, Nagoya, and Osaka, are pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 258 miles above the Sea of Japan.
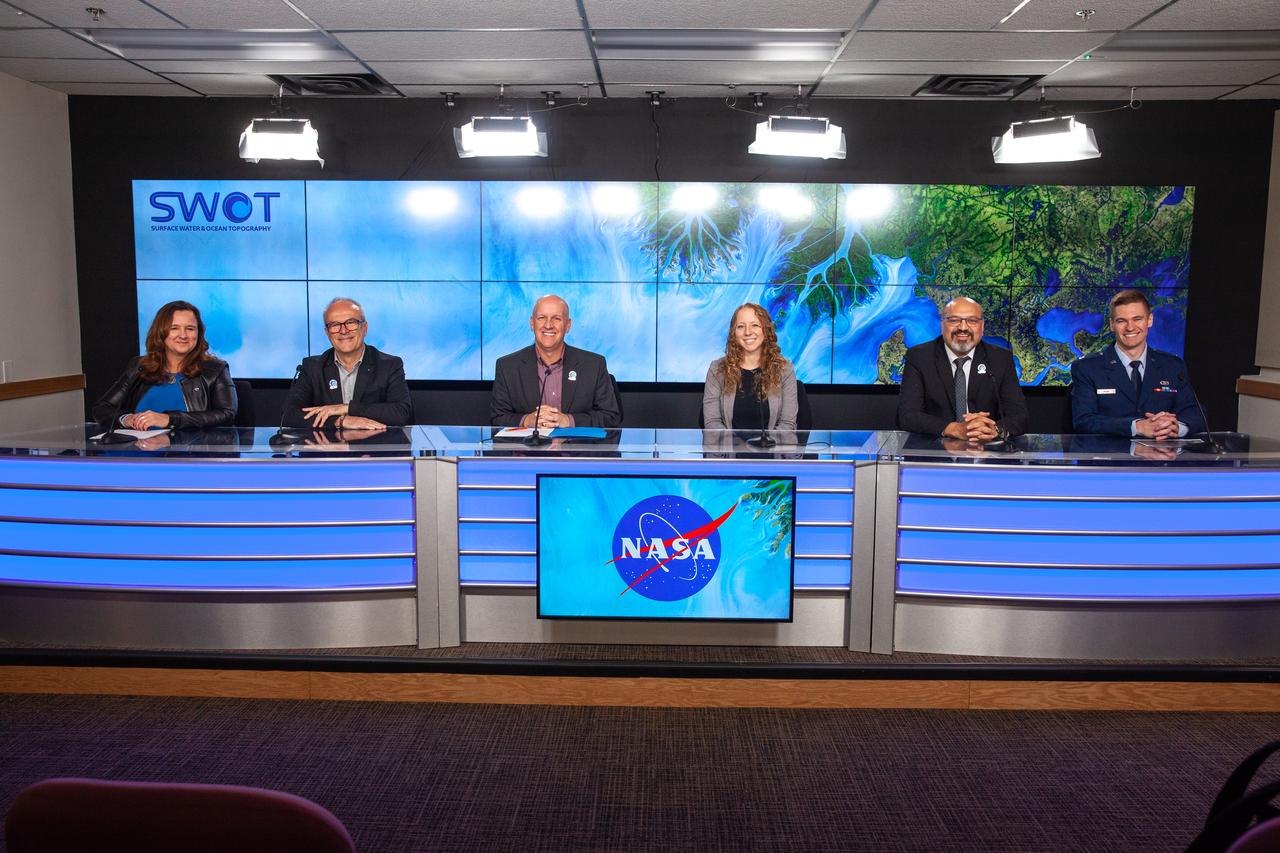

NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) hold a prelaunch news conference for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Participating from left are Karen St. Germain, Earth Science Division director, NASA; Thierry Lafon, SWOT project manager, CNES; Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program; Julianna Scheiman, civil satellite missions director, SpaceX; Parag Vaze, SWOT project manager, Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Capt. Max Rush, launch weather officer, U.S. Air Force. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
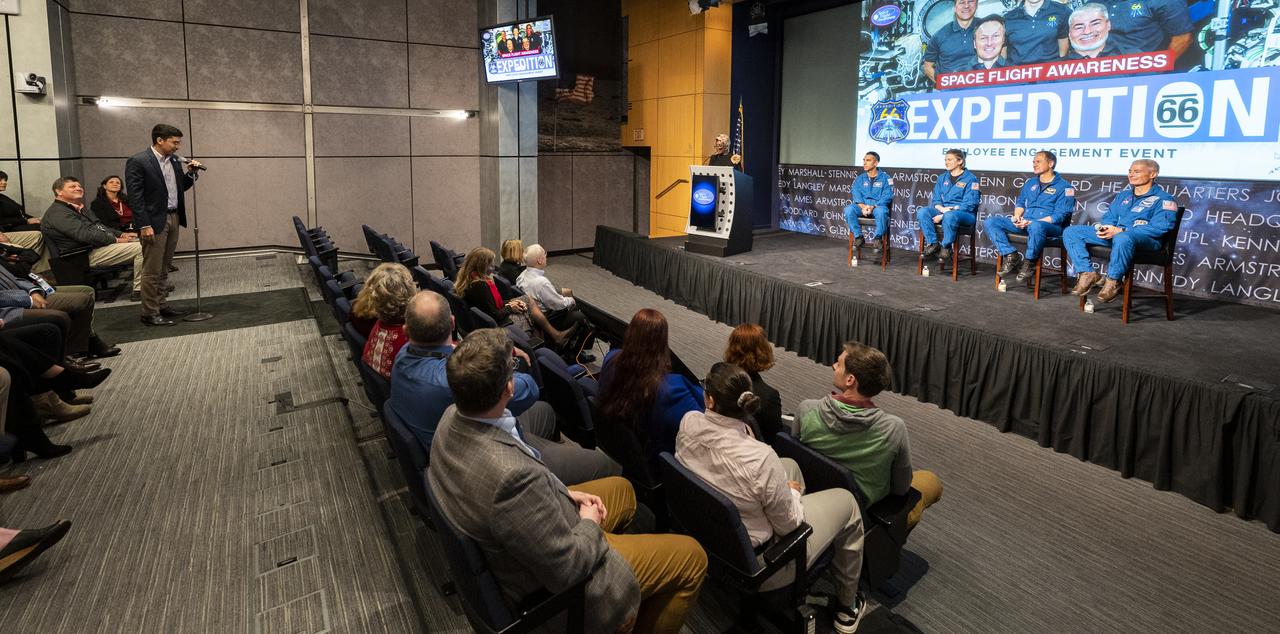

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts, from left to right, Raja Chari, Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, and Mark Vande Hei participate in an employee engagement event, Wednesday, Dec. 7, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
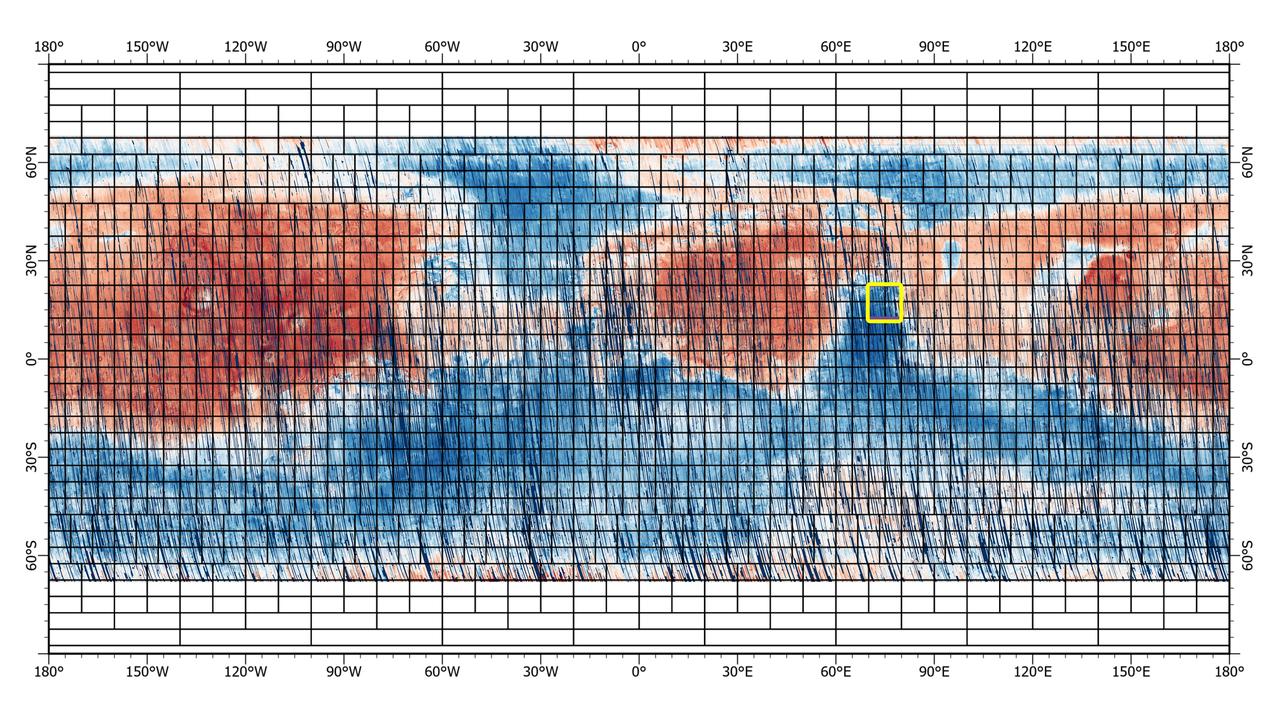
This 72-color near-global map of the Red Planet was captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) using its Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars, or CRISM. The yellow square indicates the Nili Fossae region of Mars, which is highlighted in six views in PIA25364. The map is one of the last major datasets CRISM will ever produce; the instrument will be decommissioned by the end of 2022. Data for the 6.3-gigapixel map was collected over 11 years of CRISM operations. The instrument arrived at Mars with three cryocoolers that allowed it to see in a range of wavelengths, including infrared; in 2017, the last of those cryocoolers stopped working, severely limiting the number of wavelengths CRISM could "see." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25363
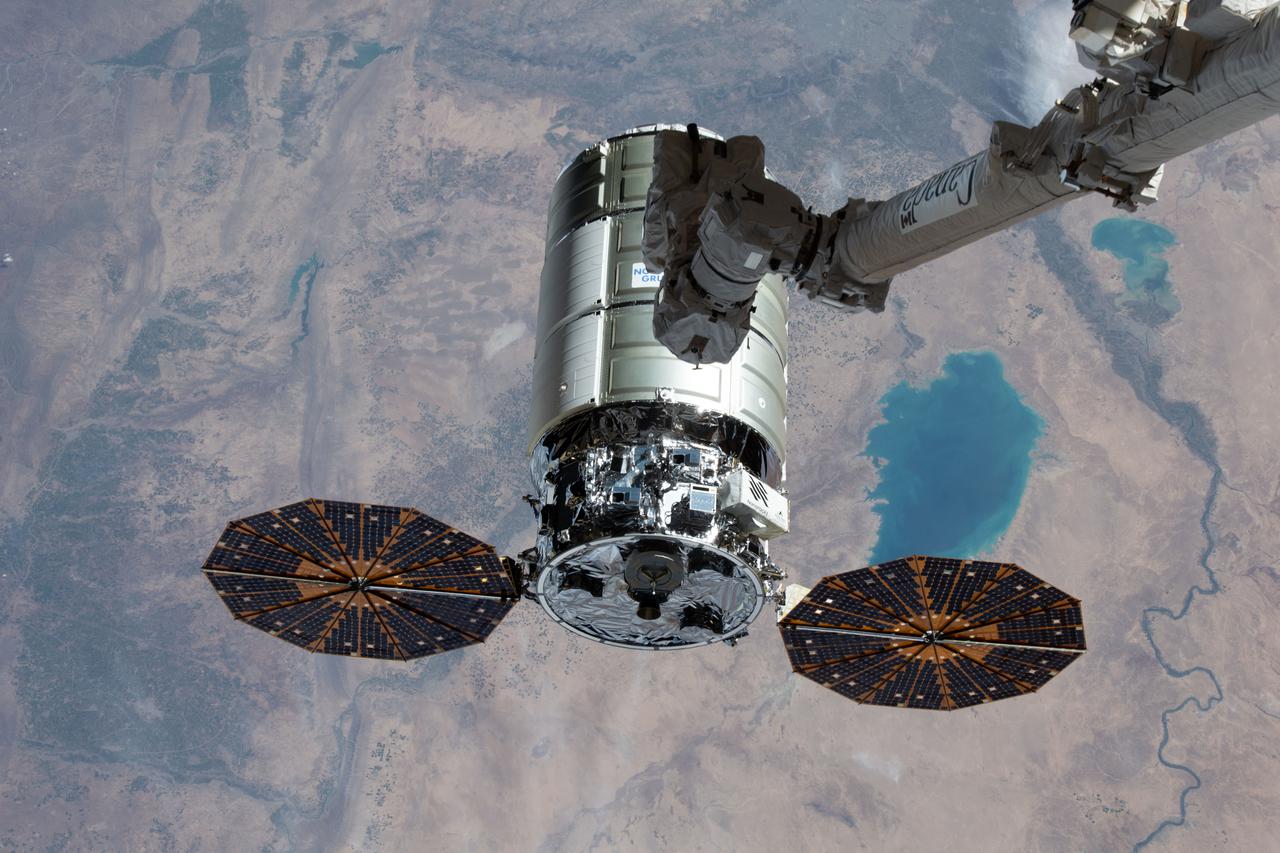
iss066e147543 (Feb. 21, 2022) --- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus space freighter is pictured moments away from being captured with the Canadarm2 robotic arm being commanded by NASA astronaut Raja Chari as the International Space Station orbited 259 miles above northern Iraq. This is Northrop Grumman’s 17th contracted resupply mission under the second Commercial Resupply Services contract with NASA.
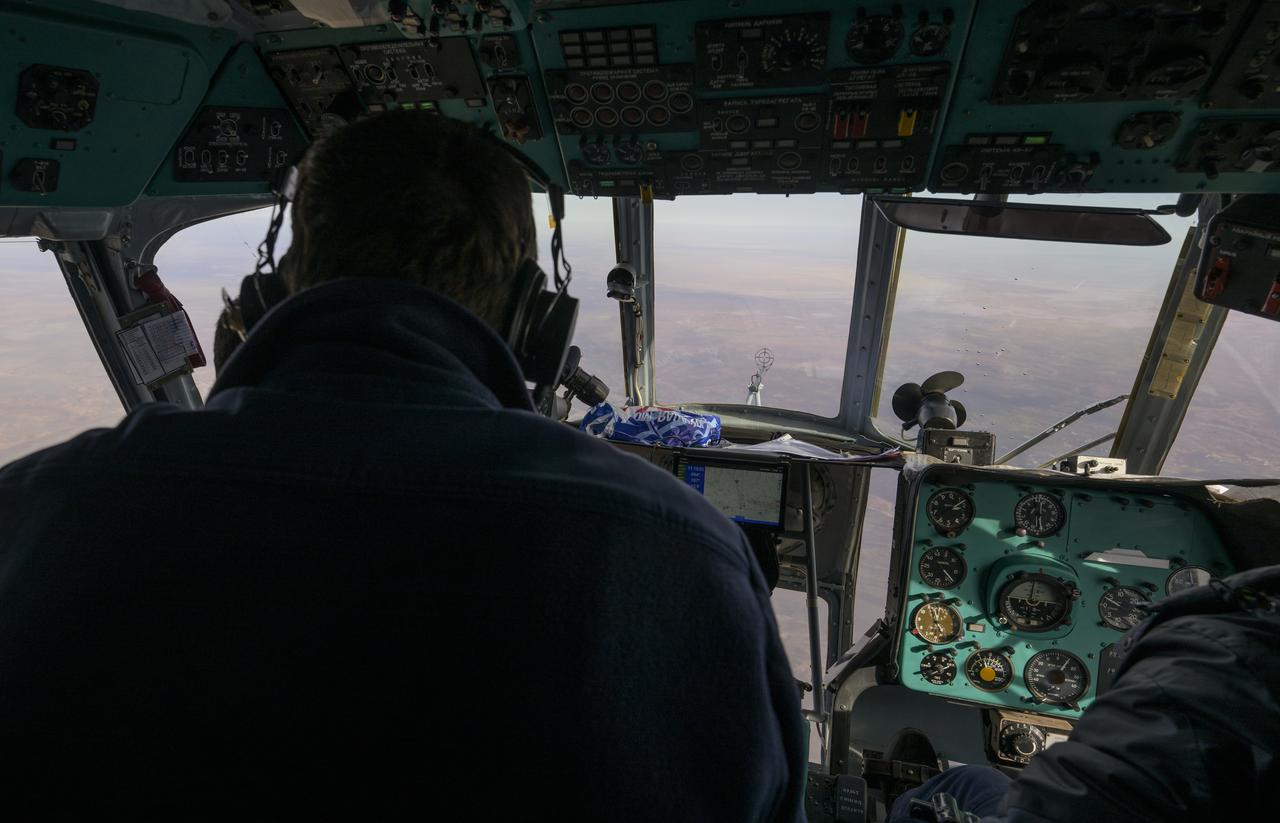

Russian Search and Rescue helicopter teams survey the sky for the Soyuz MS-19 spacecraft as it lands in a remote area near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan with Expedition 66 crew members Mark Vande Hei of NASA, and cosmonauts Pyotr Dubrov, and Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, Wednesday, March 30, 2022. Vande Hei and Dubrov are returning to Earth after logging 355 days in space as members of Expeditions 64-66 aboard the International Space Station. For Vande Hei, his mission is the longest single spaceflight by a U.S. astronaut in history. Shkaplerov is returning after 176 days in space, serving as a Flight Engineer for Expedition 65 and commander of Expedition 66. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
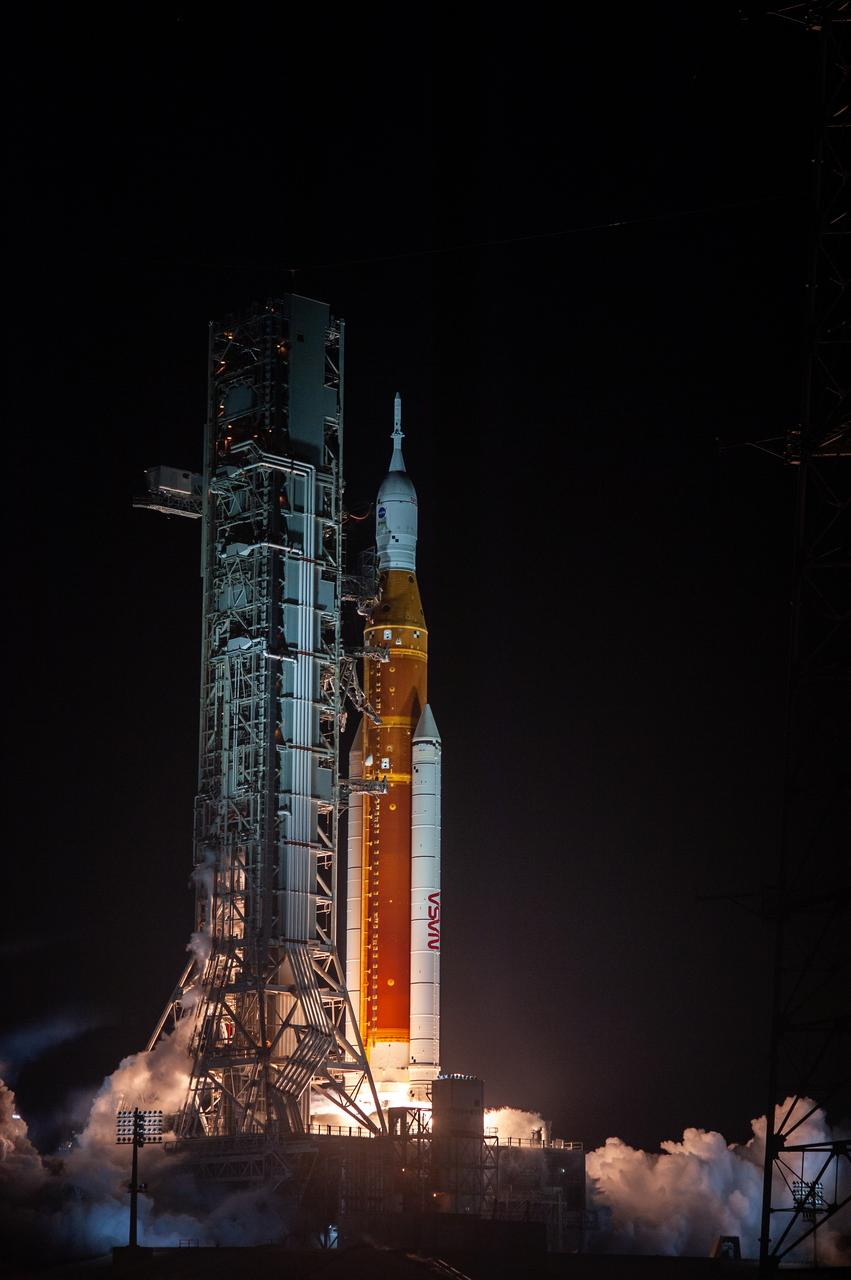

Liftoff! NASA’s Space Launch System carrying the Orion spacecraft lifts off the pad at Launch Complex 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
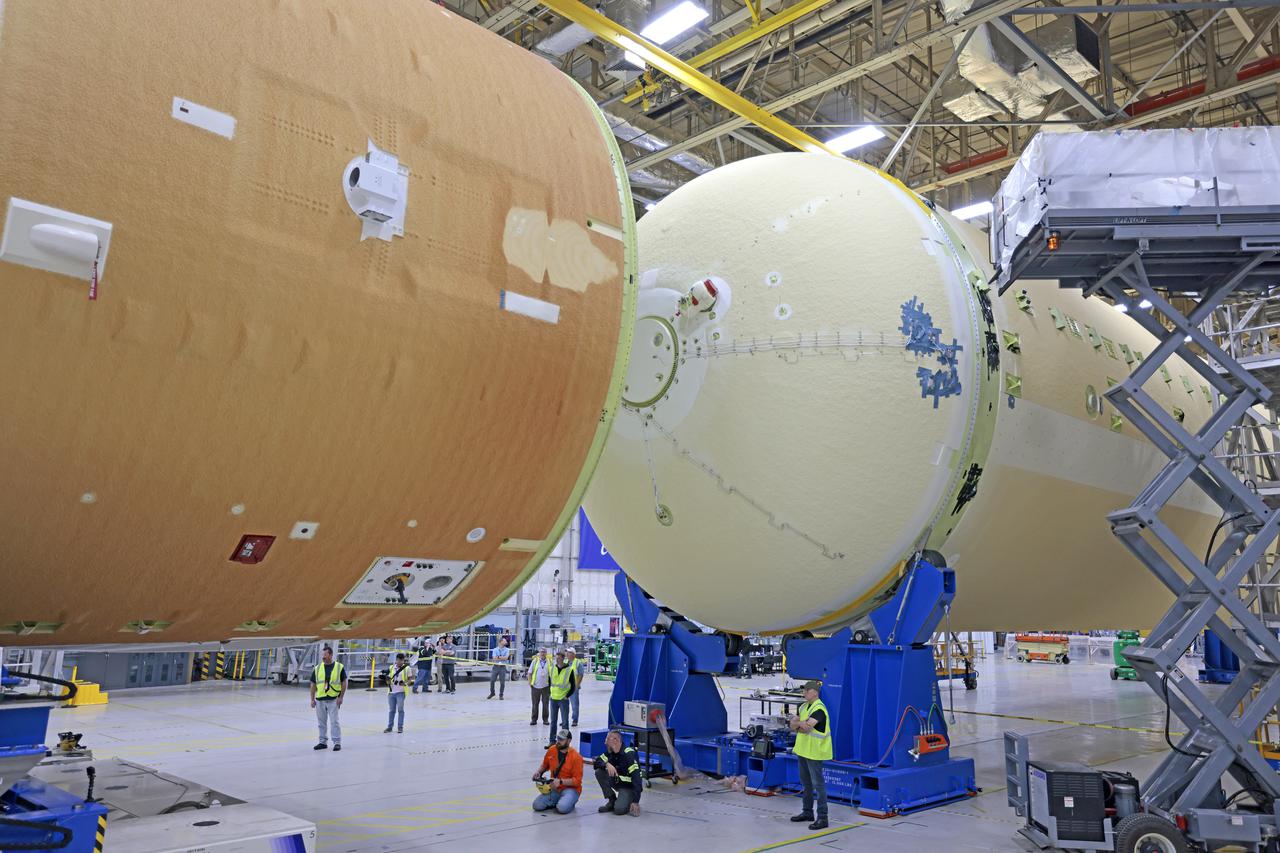

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Nuclear Emerging Technologies for Space, NETS 2022 Conference
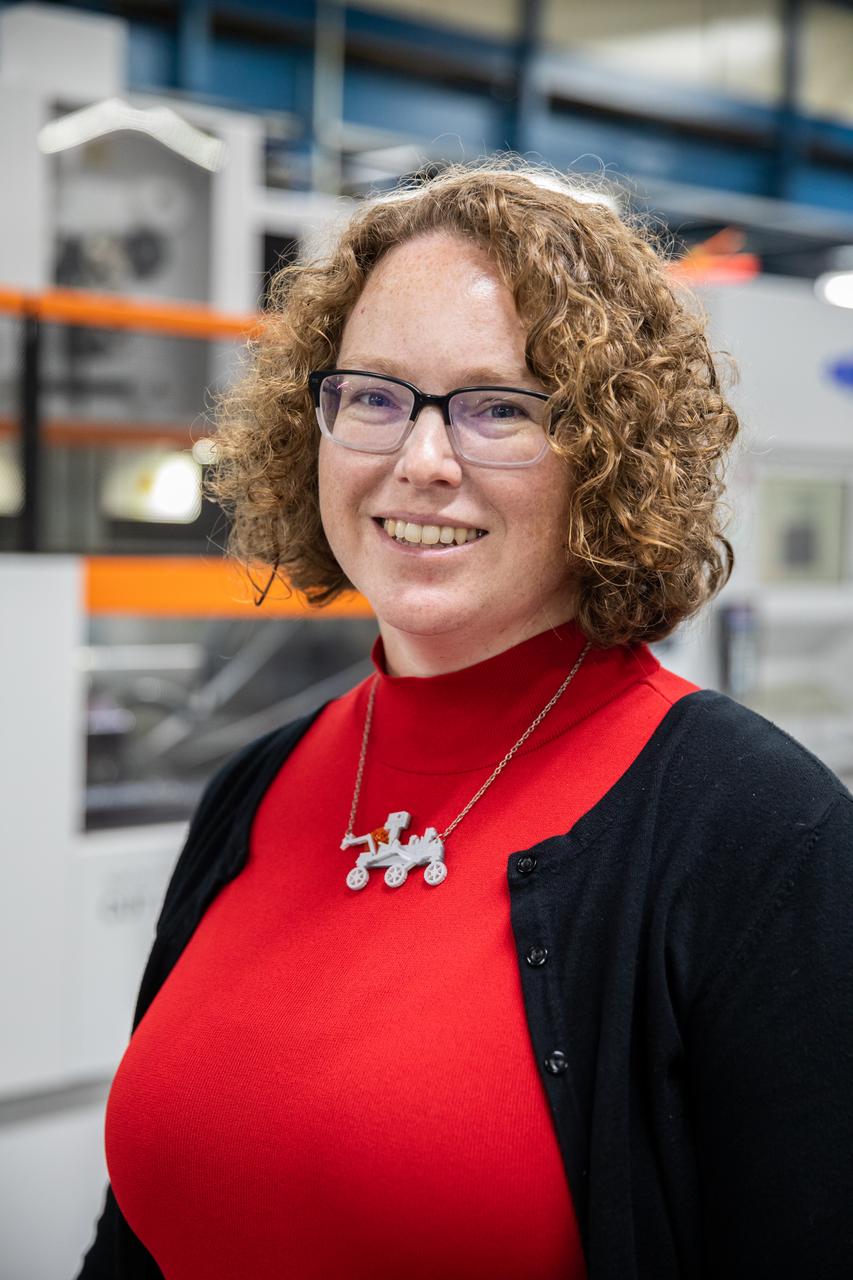

Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, is inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to begin testing on the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.
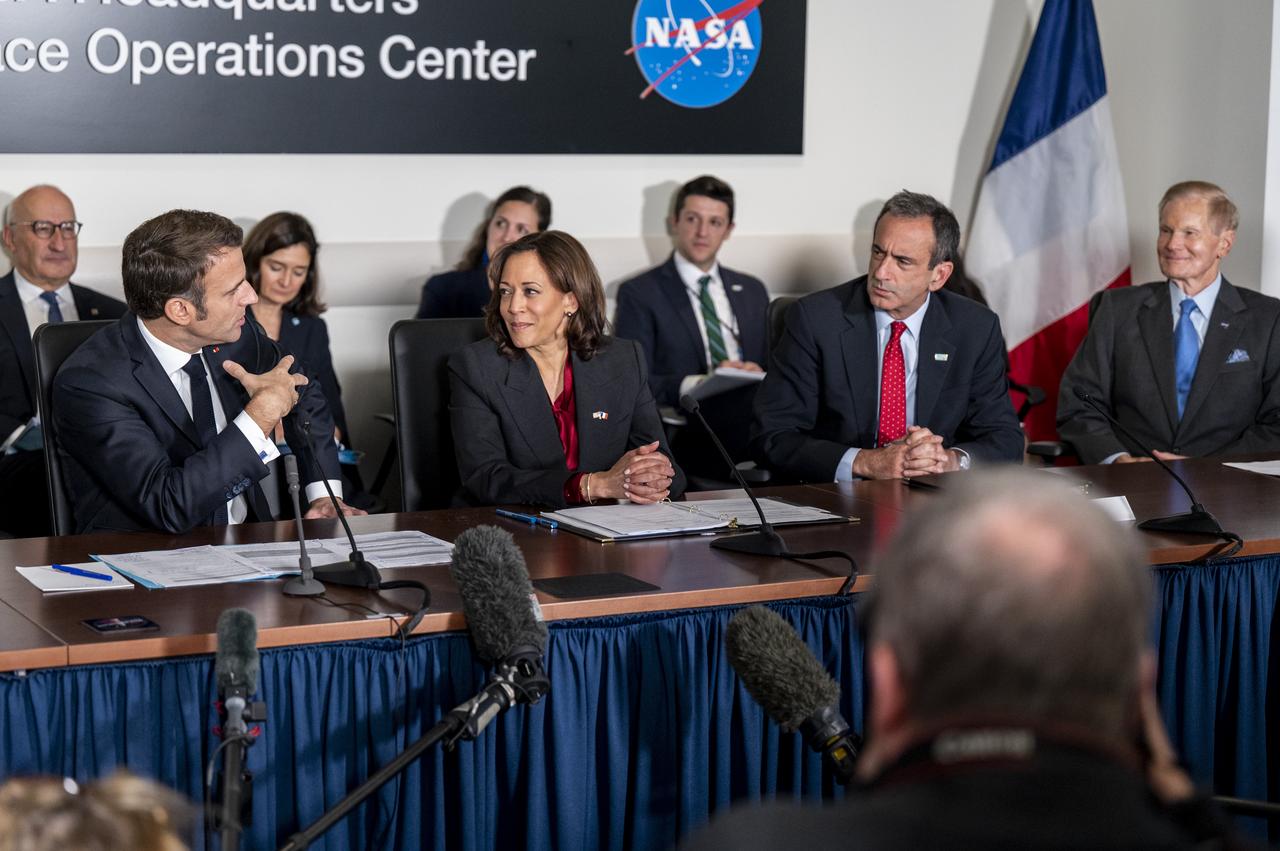

French President Emmanuel Macron delivers remarks prior to meeting with Vice President Kamala Harris and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson for an Earth Science briefing, Wednesday, Nov. 30, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Administrator Nelson and Vice President Harris met with French President Emmanuel Macron to highlight space cooperation between the United States and France. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

Guests at the Banana Creek viewing site watch NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B, Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022, as the Artemis I launch teams load more than 700,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants including liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as the launch countdown progresses at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Artemis I flight test is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, SLS rocket, and supporting ground systems. The launch director waived off today’s Artemis I launch attempt at approximately 11:17 a.m. EDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

Work Request Description: Photographic coverage of ASCAN 2021 Class Wilderness Survival Training at Ft. Rucker, Alabama
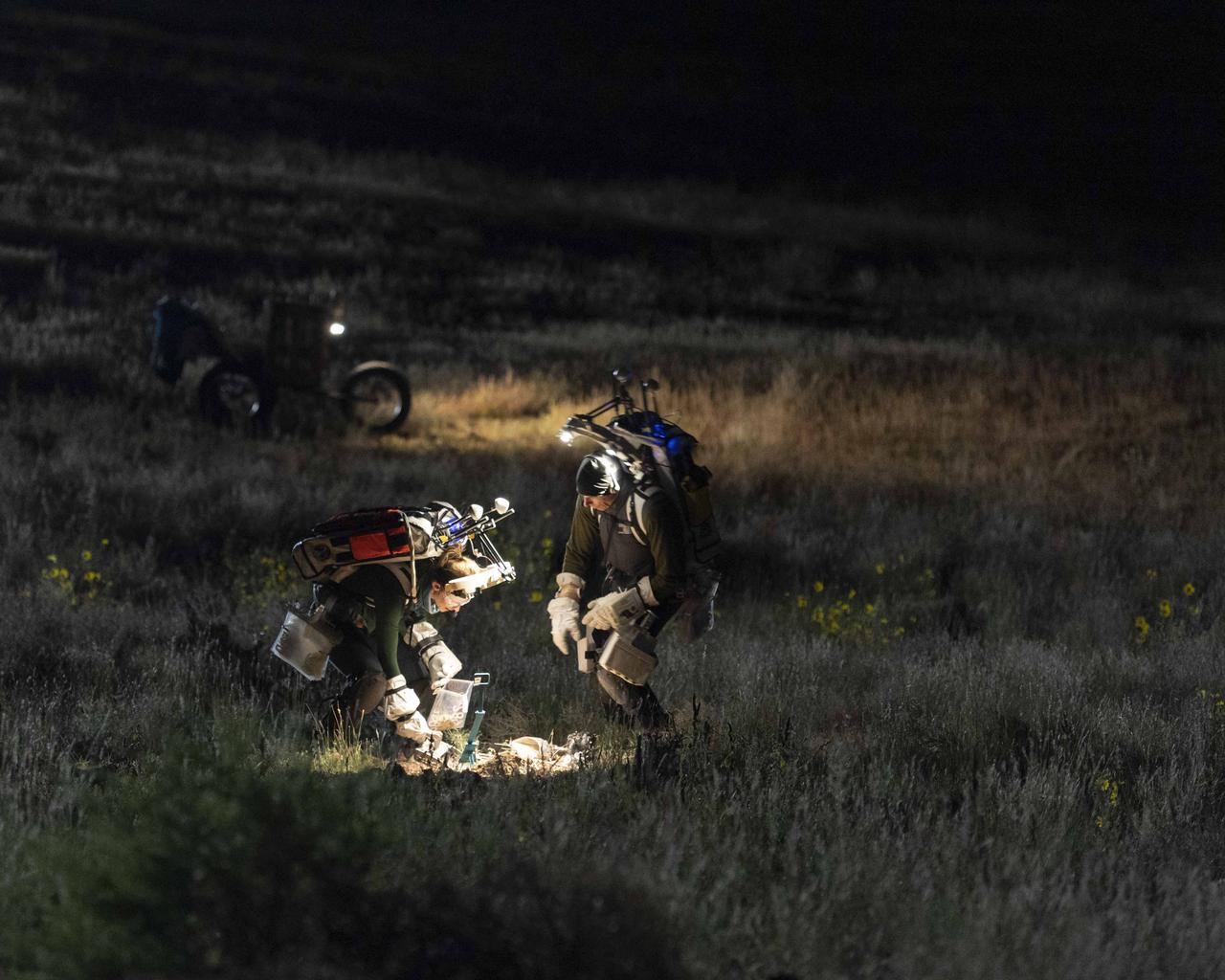

PHOTO DATE: 10-09-22 LOCATION: Flagstaff, Arizona SUBJECT: Photographic coverage of JETTS3 engineering night run 4. Joint EVA Test Team (JETT) Field Testing - JETT 3 fully integrated mission scale test to ensure successful surface operations and technology development for Artemis III. PHOTOGRAPHER: BILL STAFFORD
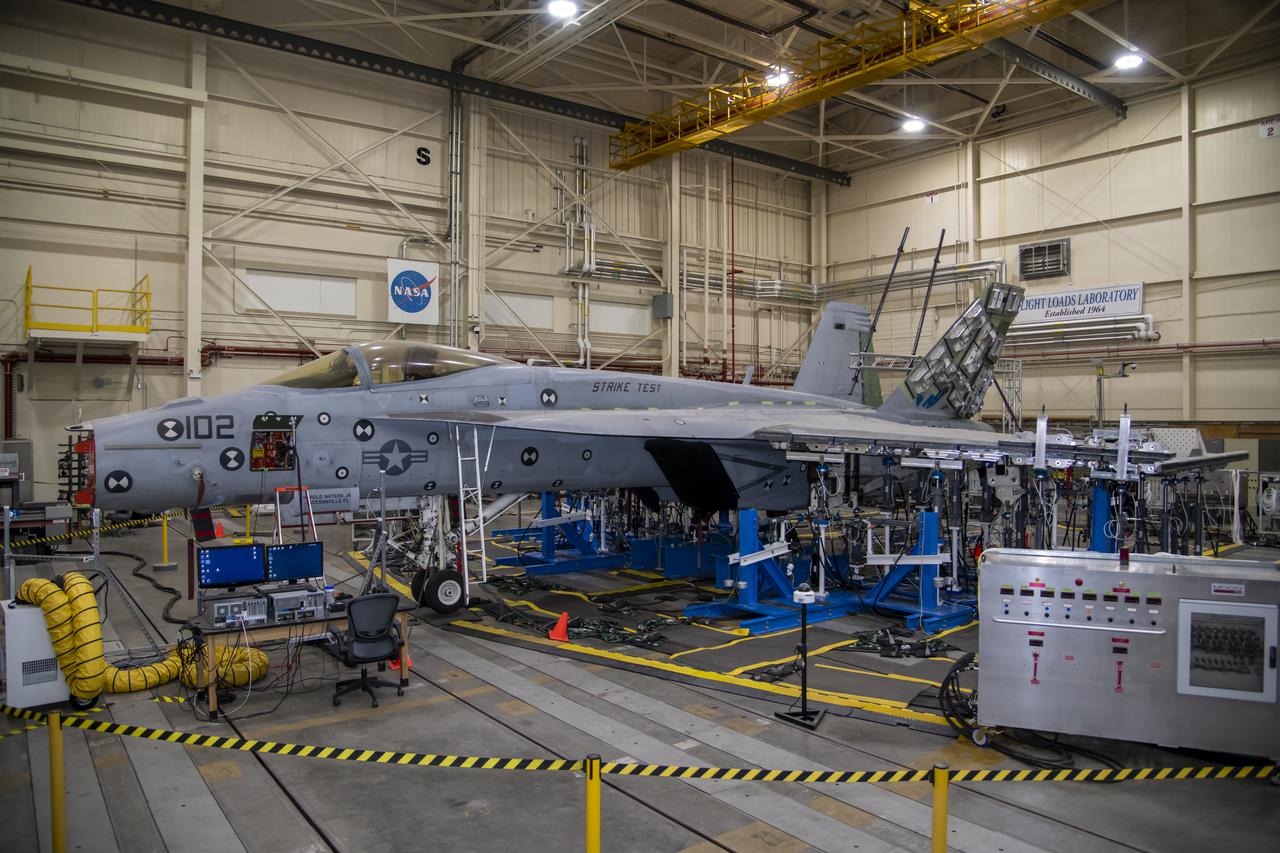

This view shows the left wing loading test configuration and testing area of an F/A-18E from the Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) in Patuxent River, Maryland. The aircraft is in NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center Flight Loads Laboratory in Edwards, California, for the center's biggest load calibrations tests. This testing is needed before the aircraft can serve as a test vehicle for determining if it can safely manage maneuvers and proposed upgrades.
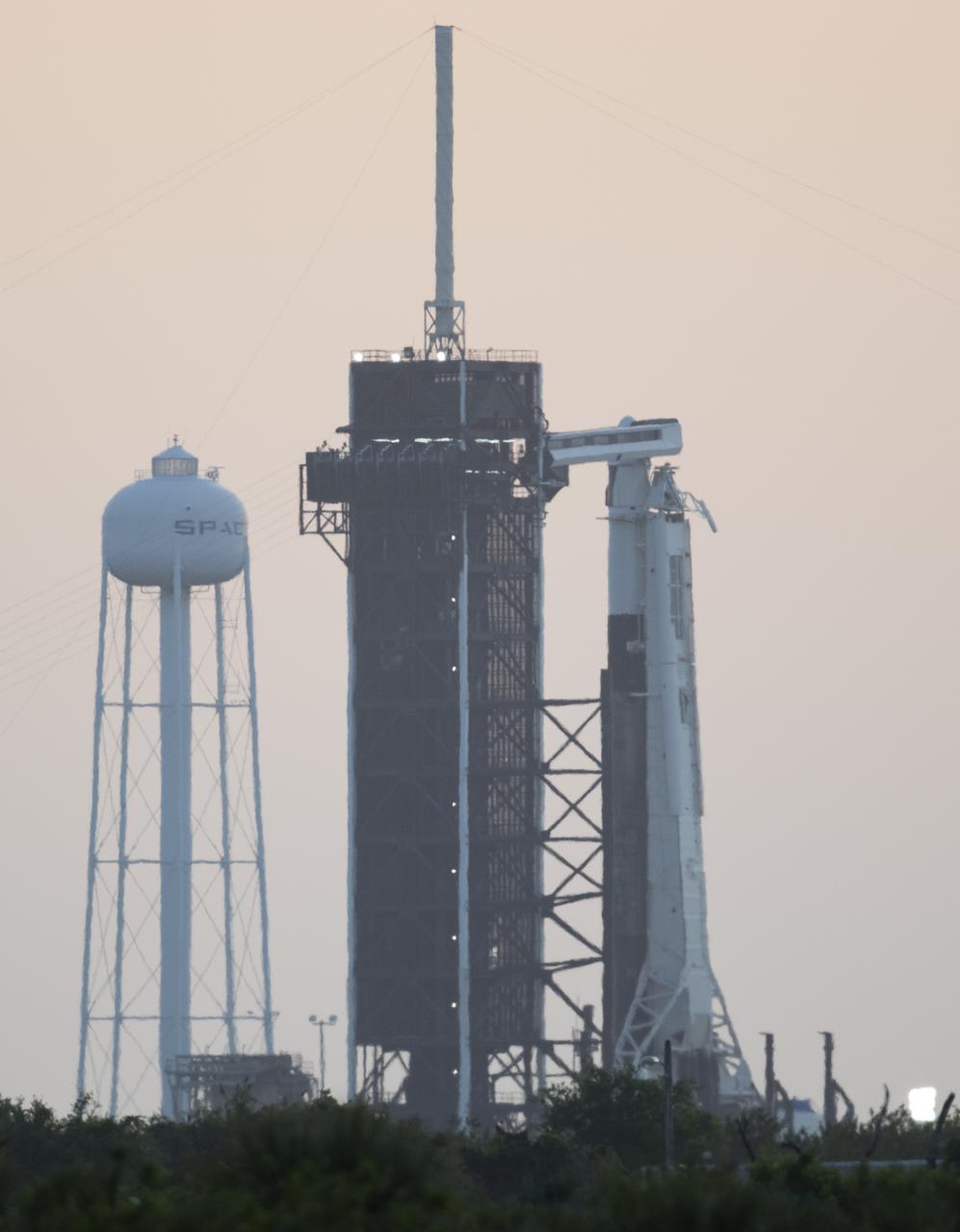

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company's Crew Dragon spacecraft aboard is seen at sunrise on the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for Axiom Mission 1 (Ax-1), Friday, April 8, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ax-1 mission is the first private astronaut mission to the International Space Station. Ax-1 crew members Commander Michael López-Alegría of Spain and the United States, Pilot Larry Connor of the United States, and Mission Specialists Eytan Stibbe of Israel, and Mark Pathy of Canada are scheduled to launch at 11:17 a.m. EDT from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
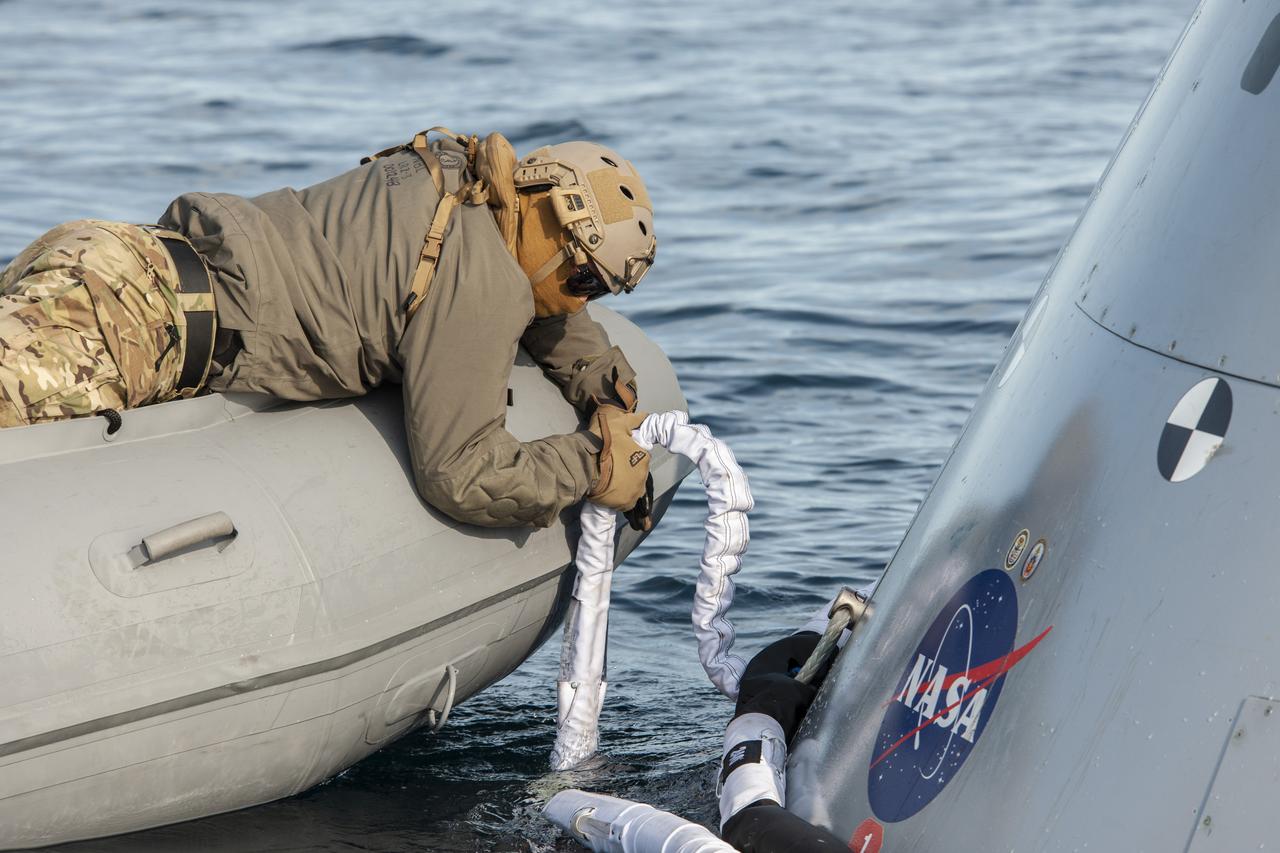

NASA's Landing and Recovery Team practices bringing a mock Orion capsule into the well deck of the USS Portland (LPD 27) ahead of the Artemis I Orion splashdown slated for Dec. 11.
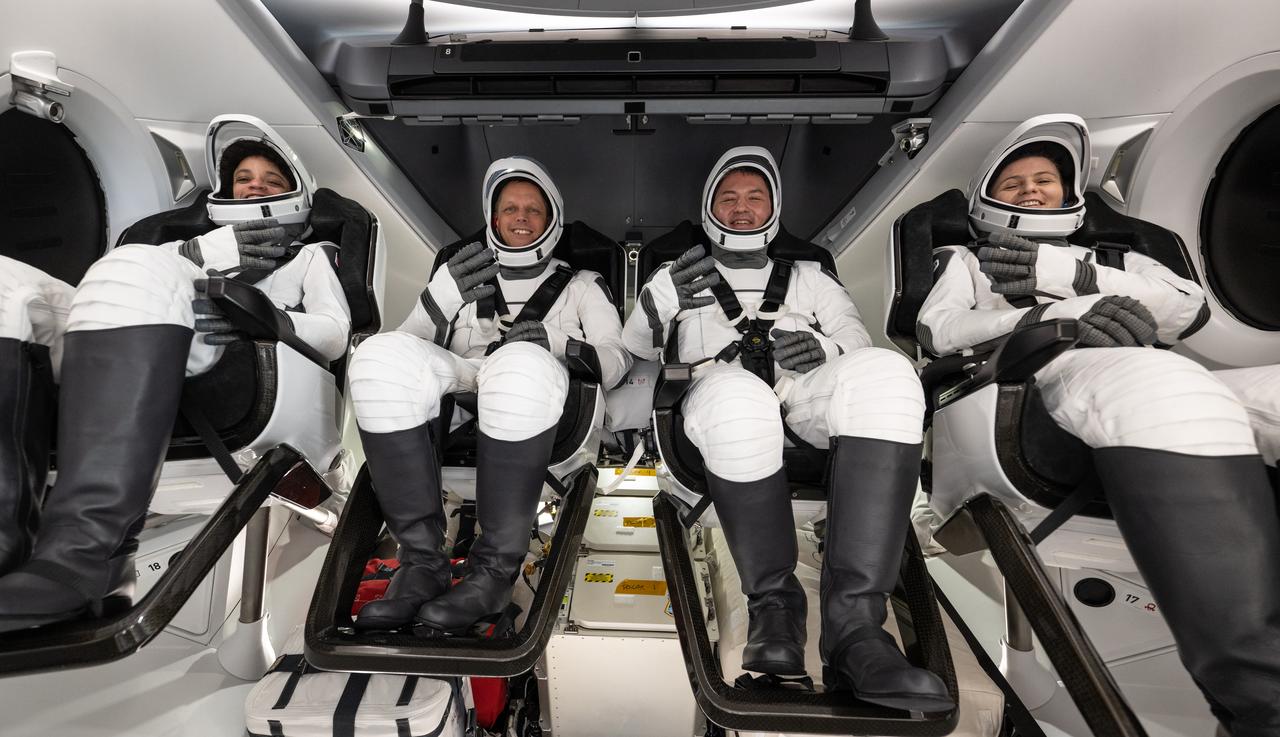

NASA astronauts Jessica Watkins, left, Robert Hines, Kjell Lindgren, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti, right, are seen inside the SpaceX Crew Dragon Freedom spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship Megan shortly after having landed in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Jacksonville, Florida, Friday, Oct. 14, 2022. Lindgren, Hines, Watkins, and Cristoforetti are returning after 170 days in space as part of Expeditions 67 and 68 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
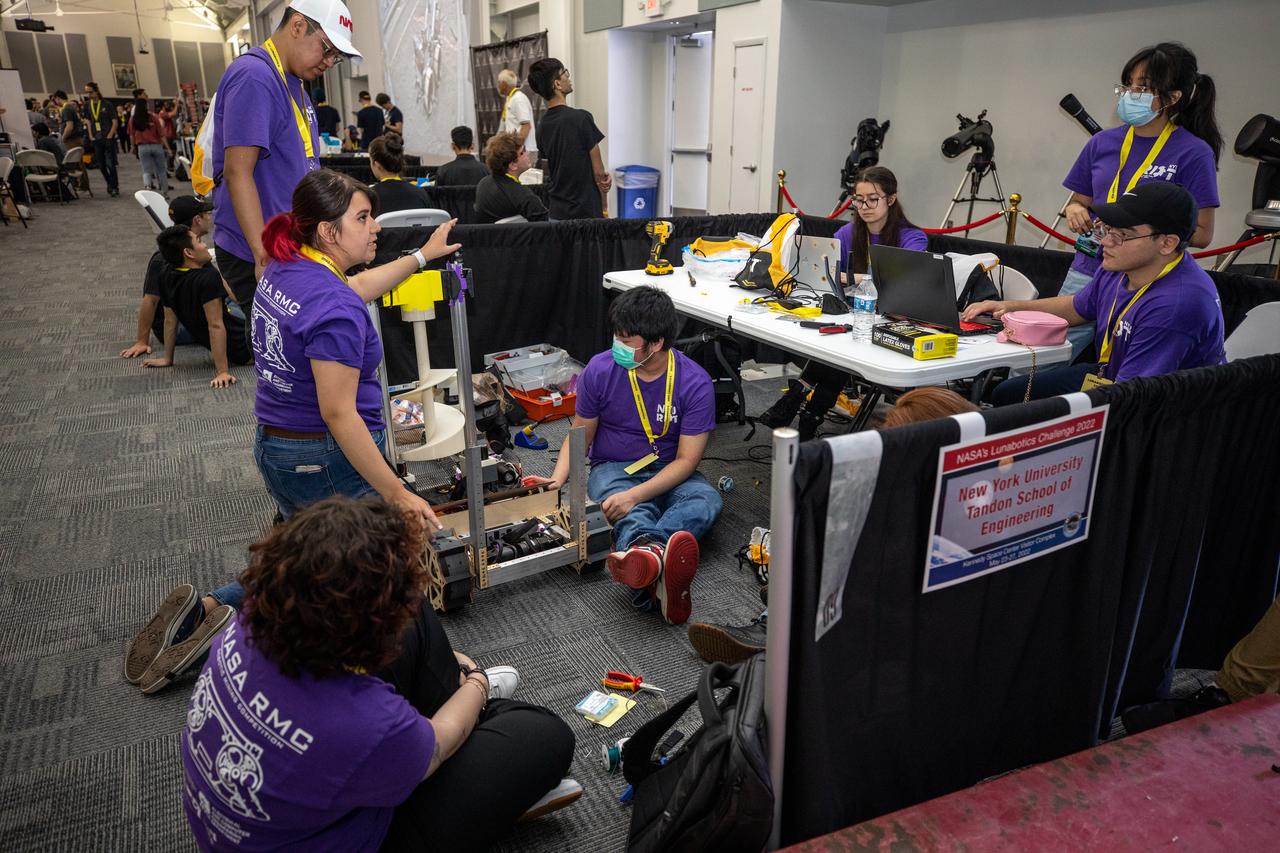

Students from the New York University Tandon School of Engineering prepare their robot for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.

Nuclear Emerging Technologies for Space, NETS 2022 Conference
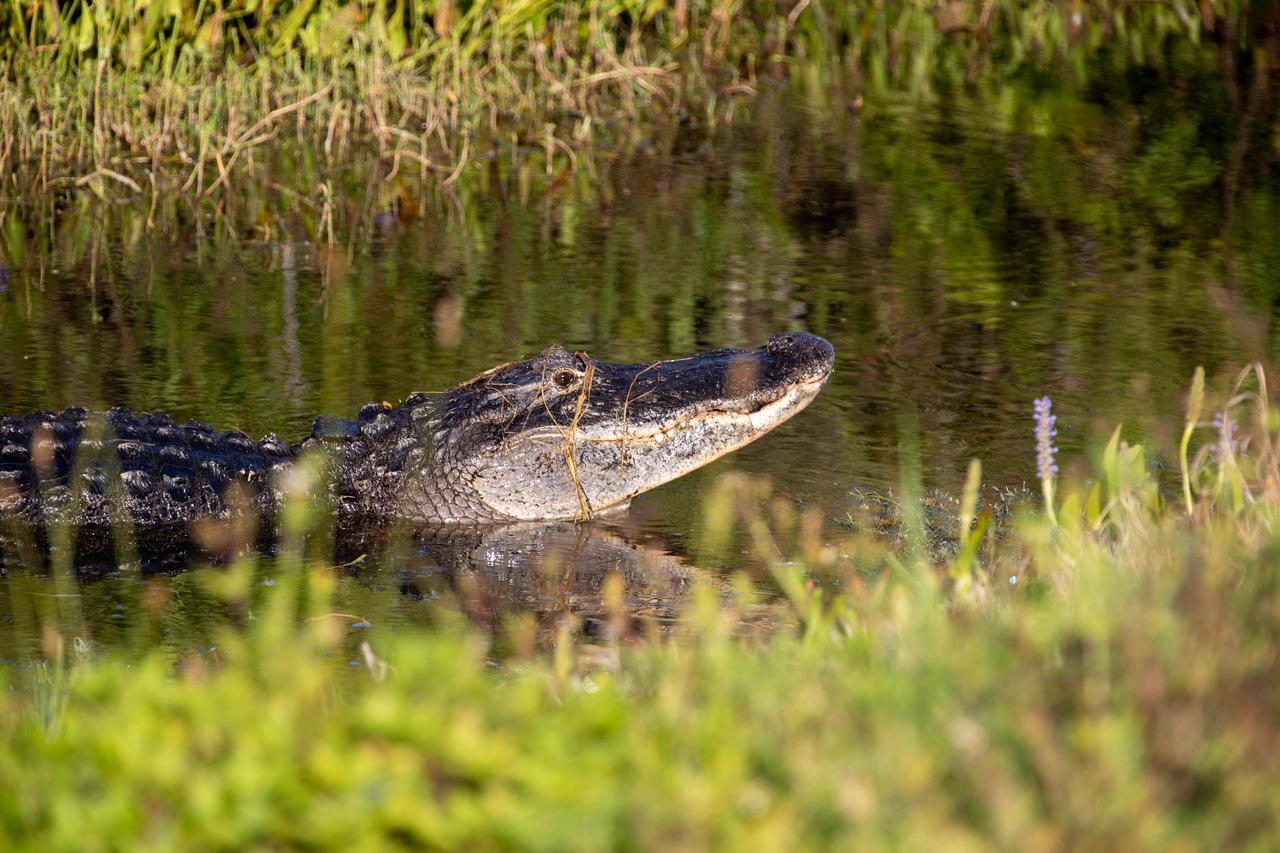

An alligator is in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 16, 2022. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island Wildlife Refuge. More than 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
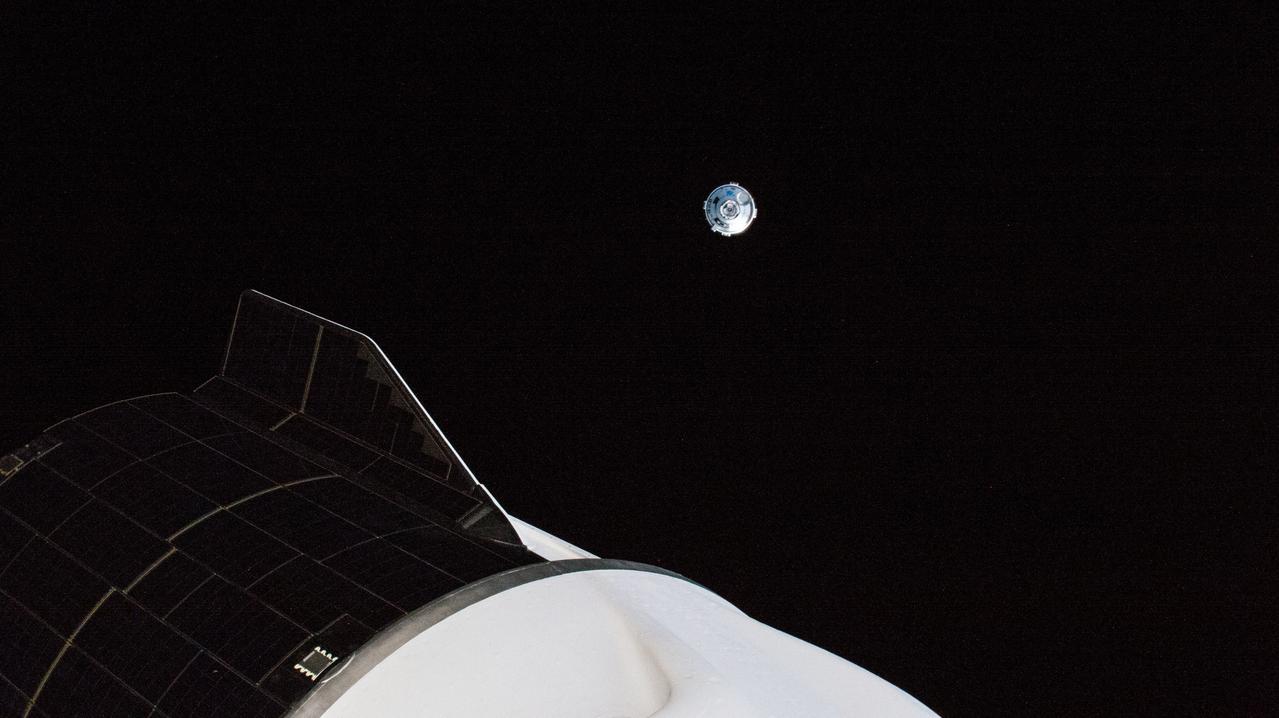

iss067e075991 (May 25, 2022) --- Boeing's CST-100 Starliner crew ship is pictured maneuvering away from the International Space Station after undocking from the Harmony module's forward port. In the foreground, is the aft end of the SpaceX Dragon Freedom crew ship that delivered the Crew-4 astronauts to the orbiting lab.
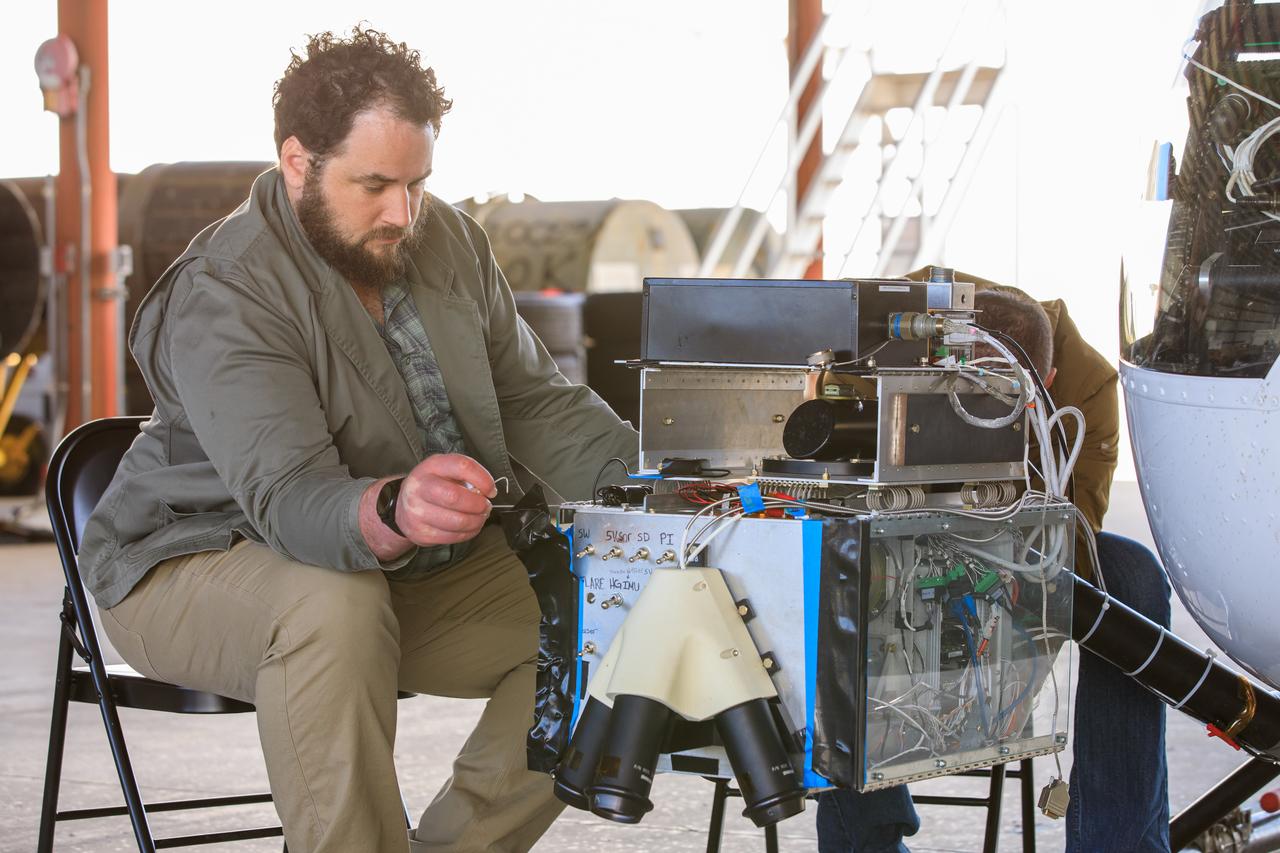

Two Intuitive Machines employees ready navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander in preparation for testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
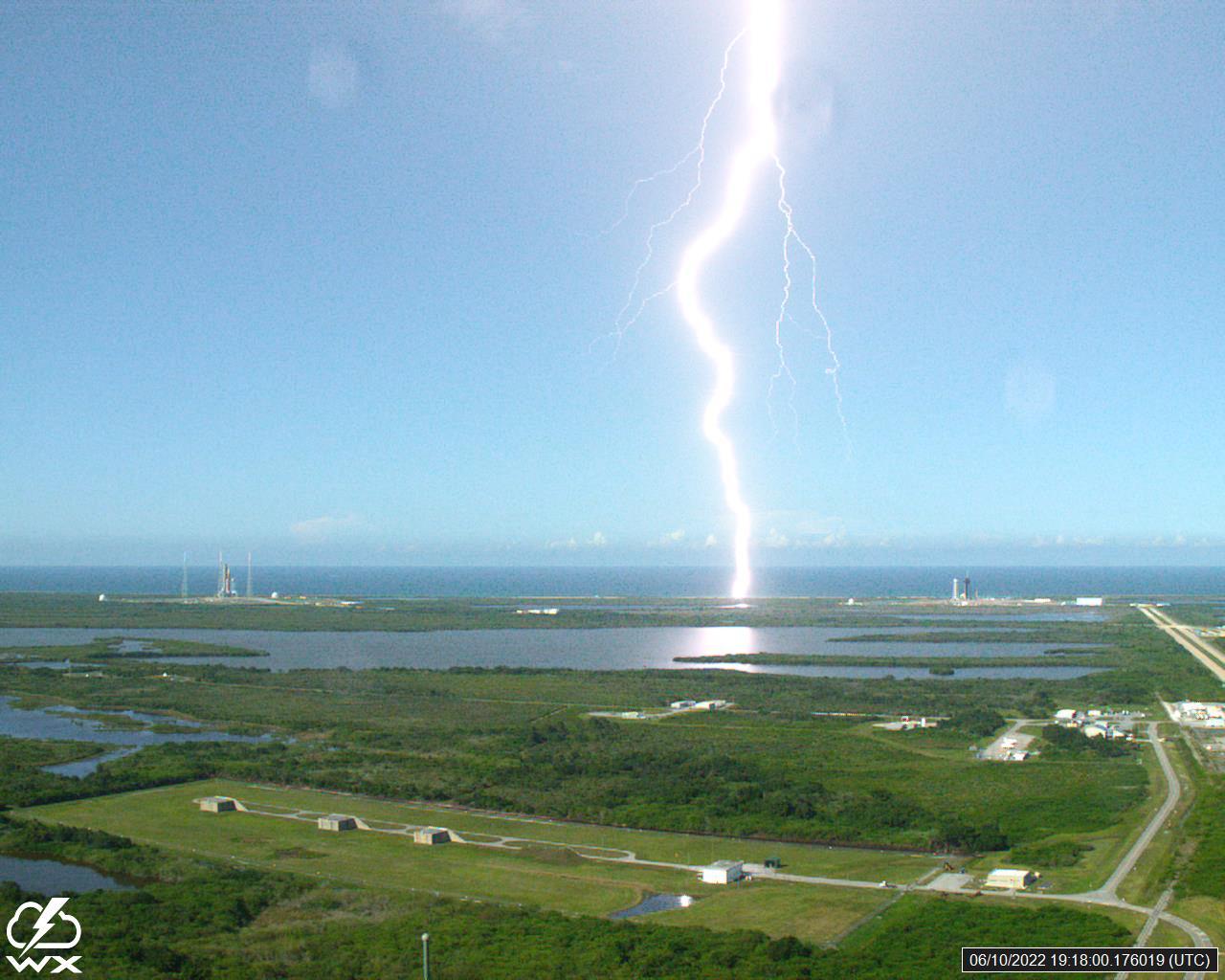

A lightning strike was recorded at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher are on the launch pad in preparation for the Artemis I mission. The lightning strike was recorded by cameras stationed at the pad and mobile launcher using a special filter called a “clear day frame,” which provides an overlay of the raw frame on a reference image. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first woman of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
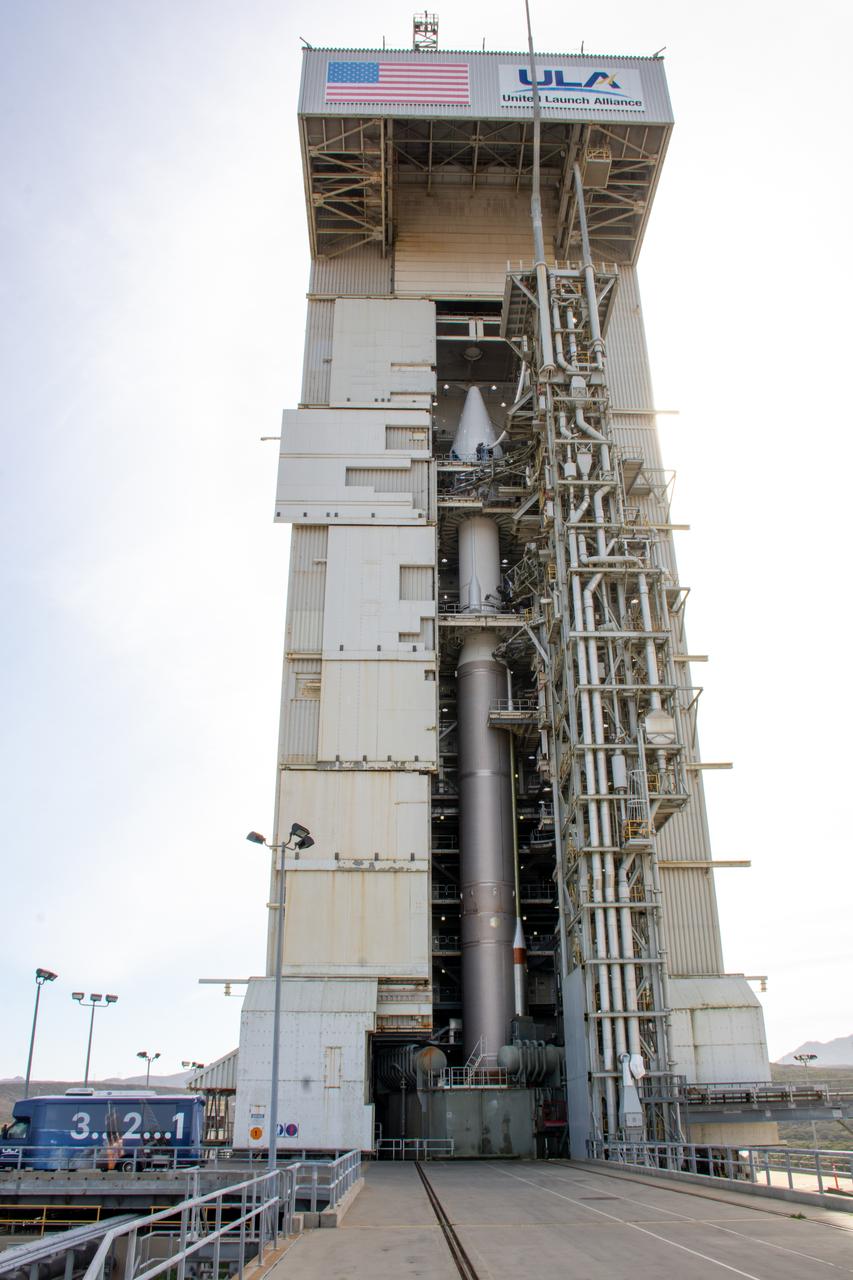
The mobile service tower doors are open at Space Launch Complex-3 (SLC-3) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 28, 2022, revealing the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) and NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) atop. NASA and ULA are targeting launch for no earlier than Wednesday, Nov. 9, pending range availability. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day. The NOAA/NASA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite, and NOAA-20, previously known as JPSS-1, are both already in orbit. Each satellite carries at least four advanced instruments to measure weather and climate conditions on Earth. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
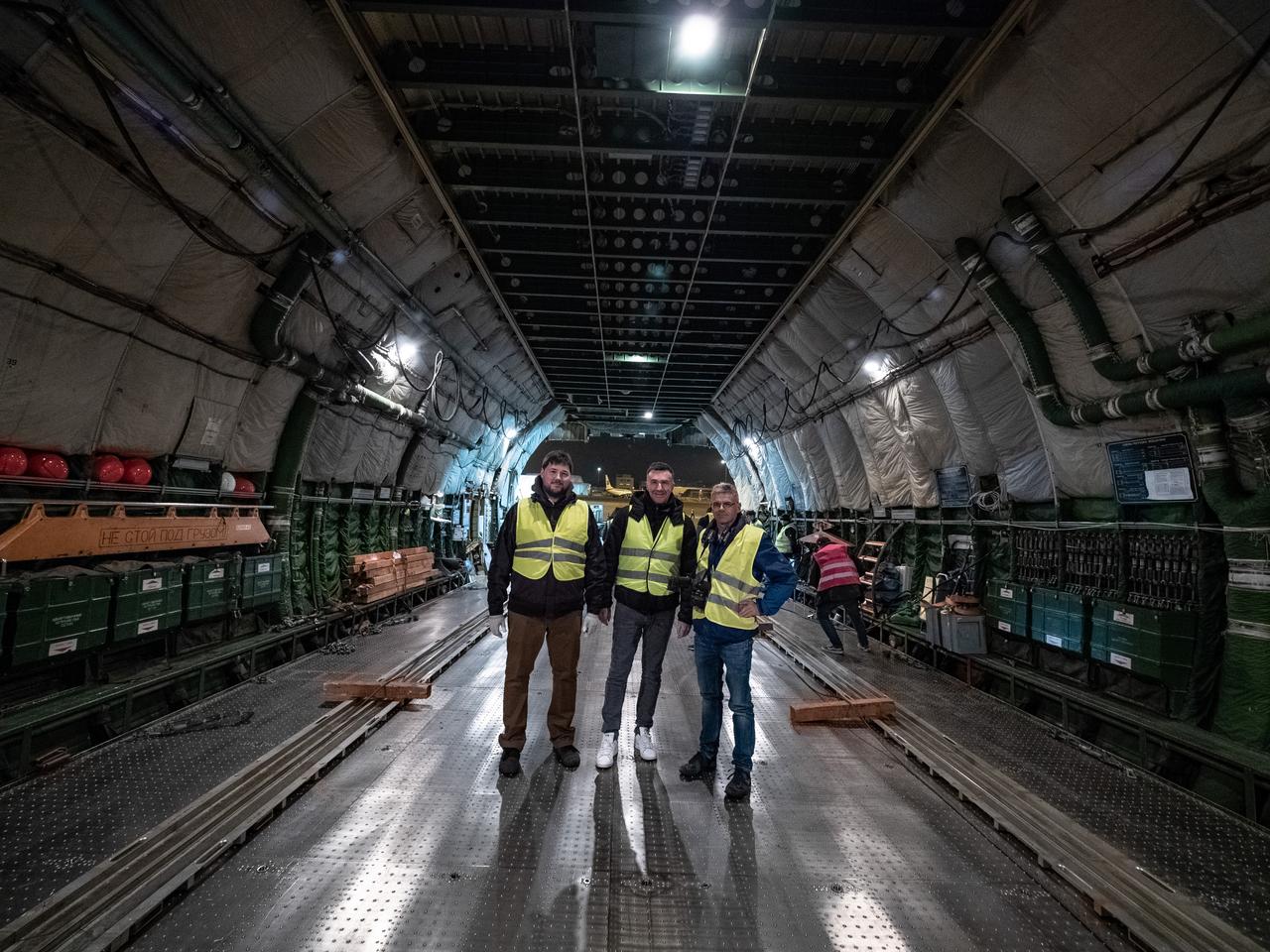

Orion's European Service Module is loaded on the Antonov airplane in Bremen, Germany on Nov. 5, 2018 for transport to Kennedy Space Center...For the first time, NASA will use a European-built system as a critical element to power an American spacecraft, extending the international cooperation of the International Space Station into deep space. The European Service Module is a unique collaboration across space agencies and industry including ESA’s prime contractor, Airbus, and 10 European countries. The completion of service module work in Europe and shipment to Kennedy signifies a major milestone toward NASA’s human deep space exploration missions to the Moon and beyond.
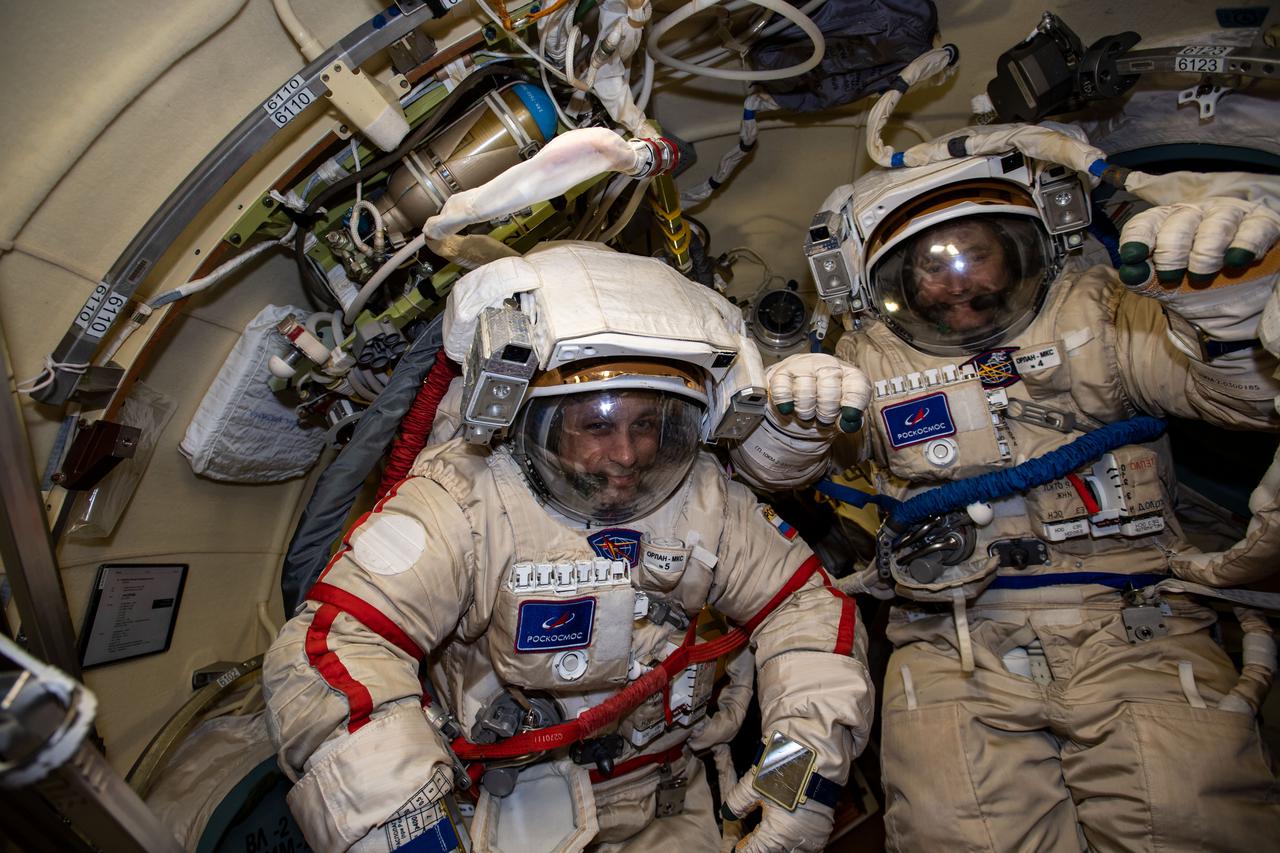

iss066e113704 (Jan. 14, 2022) --- Cosmonauts (from left) Anton Shkaplerov and Pyotr Dubrov are pictured in their Russian Orlan spacesuits for a fit check and leak checks a few days before they begin a spacewalk to outfit the Prichal and Nauka modules at the International Space Station.
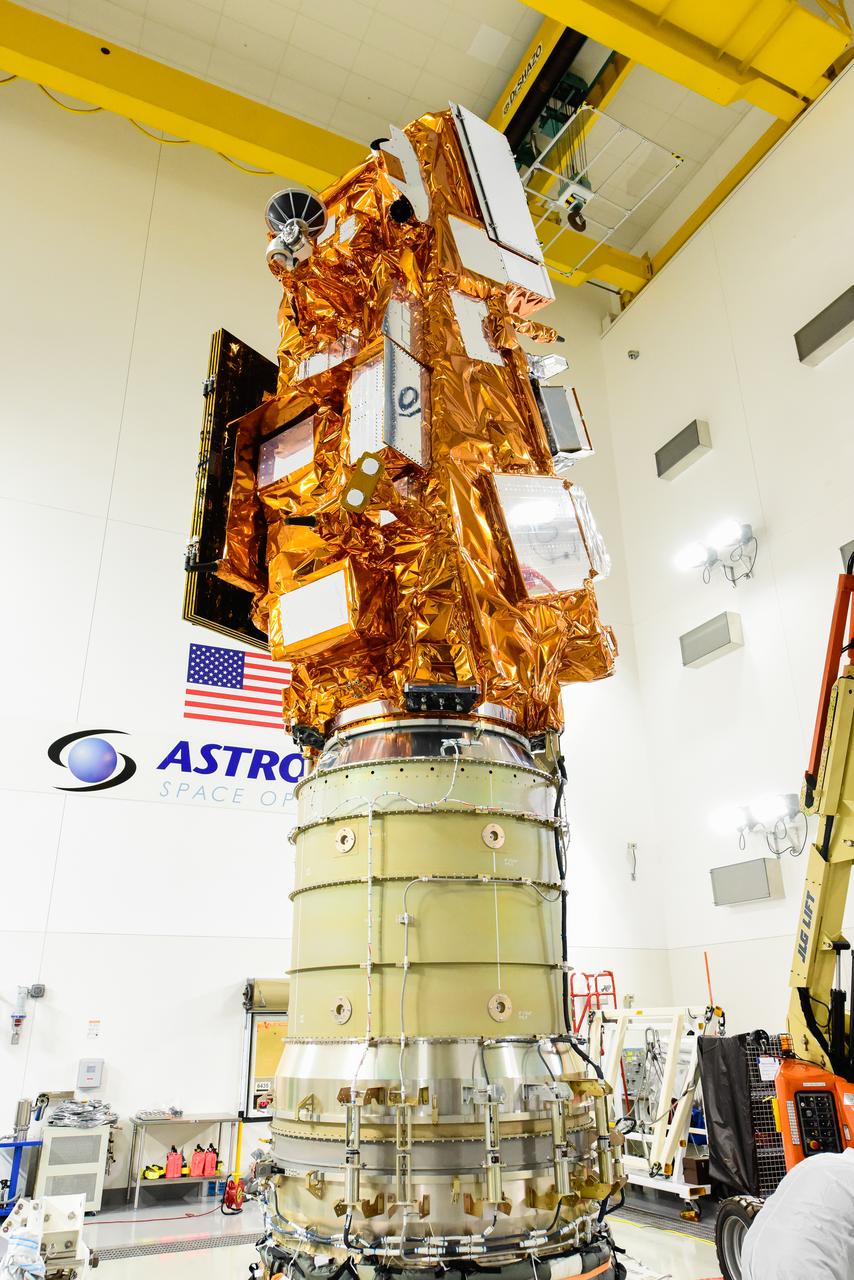

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2), stacked atop NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) secondary payload is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Oct. 12, 2022. JPSS-2 is being prepared for encapsulation inside the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairing. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. The NOAA/NASA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite, and NOAA-20, previously known as JPSS-1, are both already in orbit. Each satellite carries at least four advanced instruments to measure weather and climate conditions on Earth. LOFTID is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
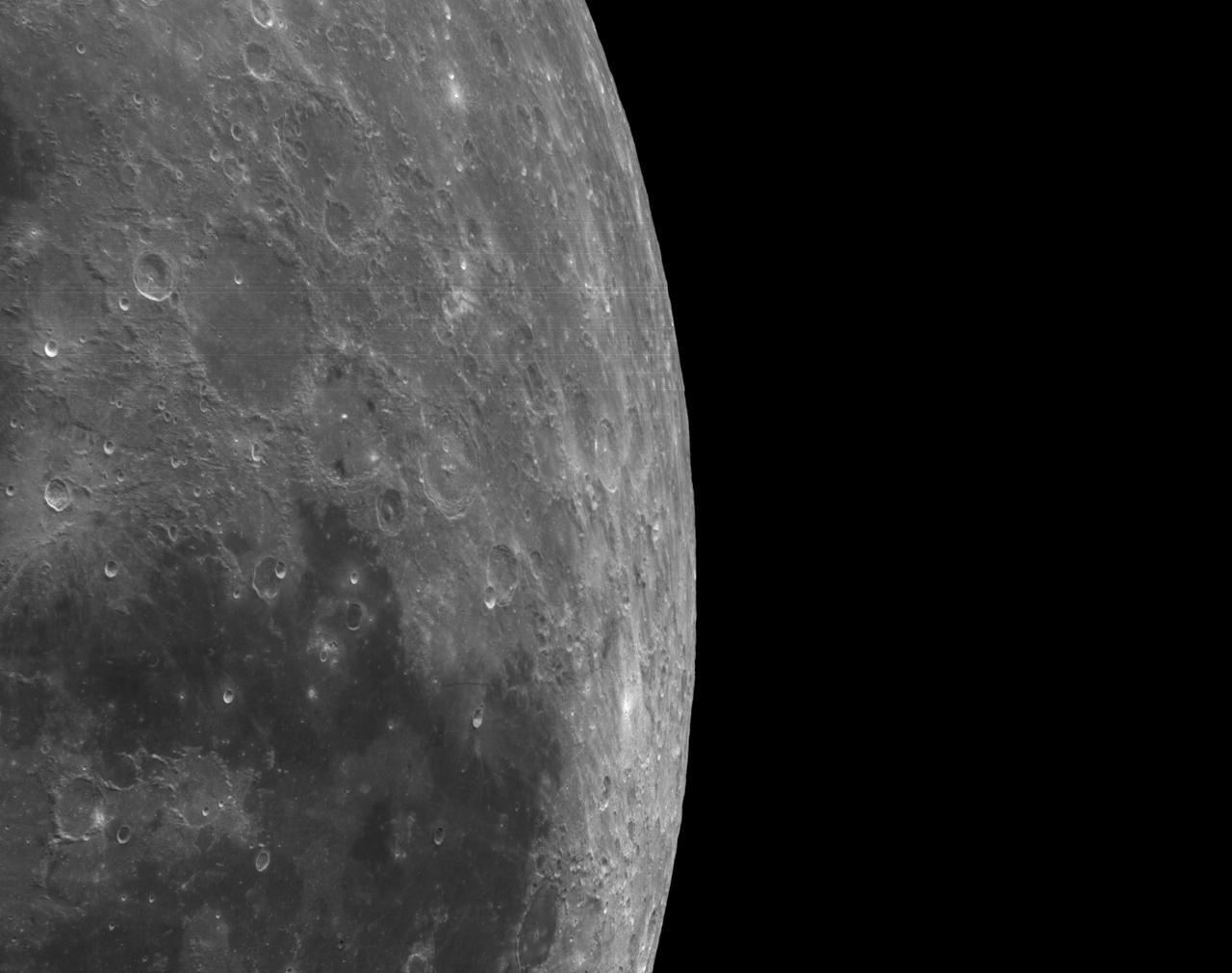

art001e002581 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
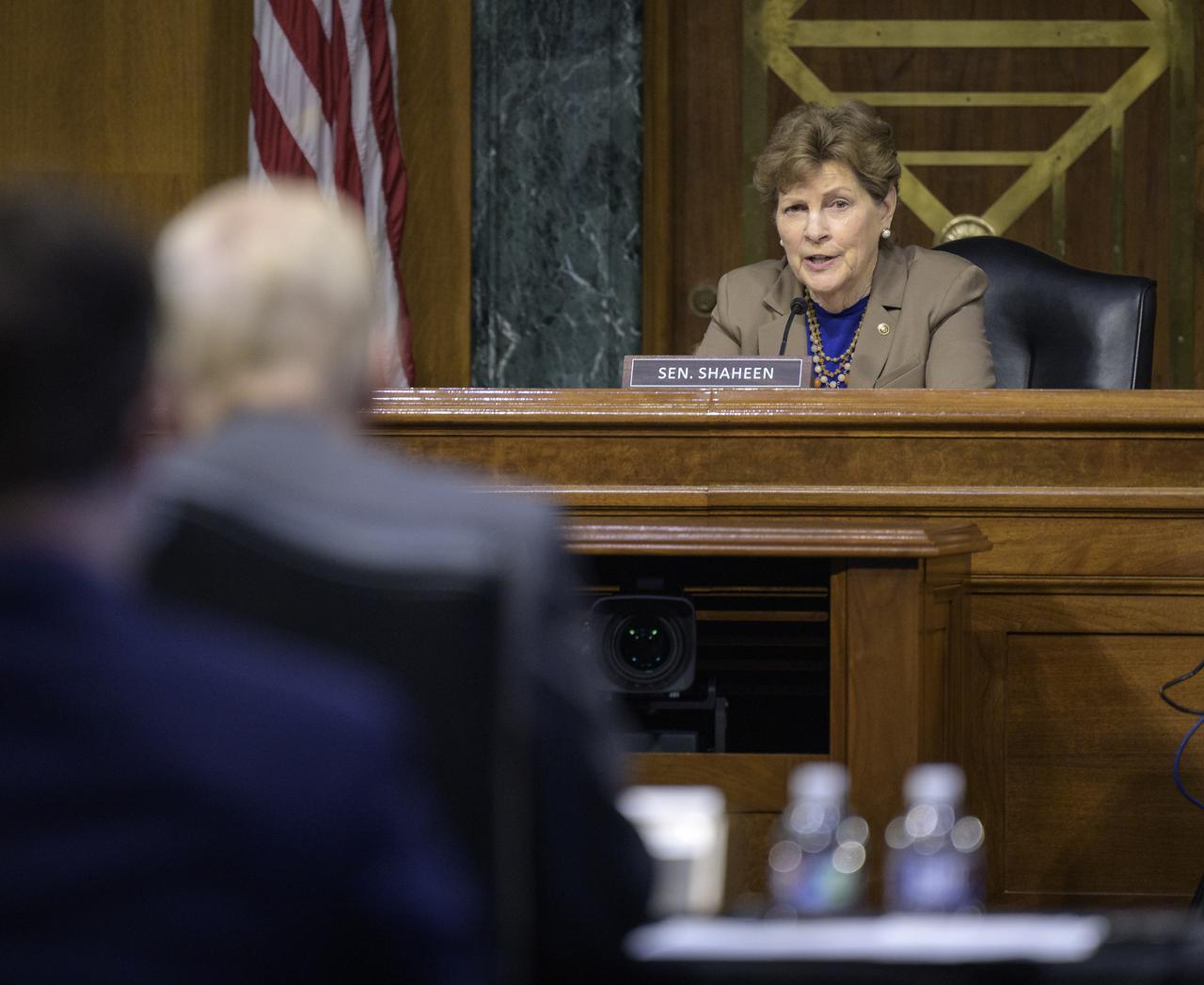

Senator Jeanne Shaheen, D-N.H., Chair Senate Appropriations’ Commerce, Justice, Science, and Related Agencies subcommittee questions NASA Administrator Bill Nelson during a hearing on NASA’s budget, Tuesday, May 3, 2022, at the Dirksen Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
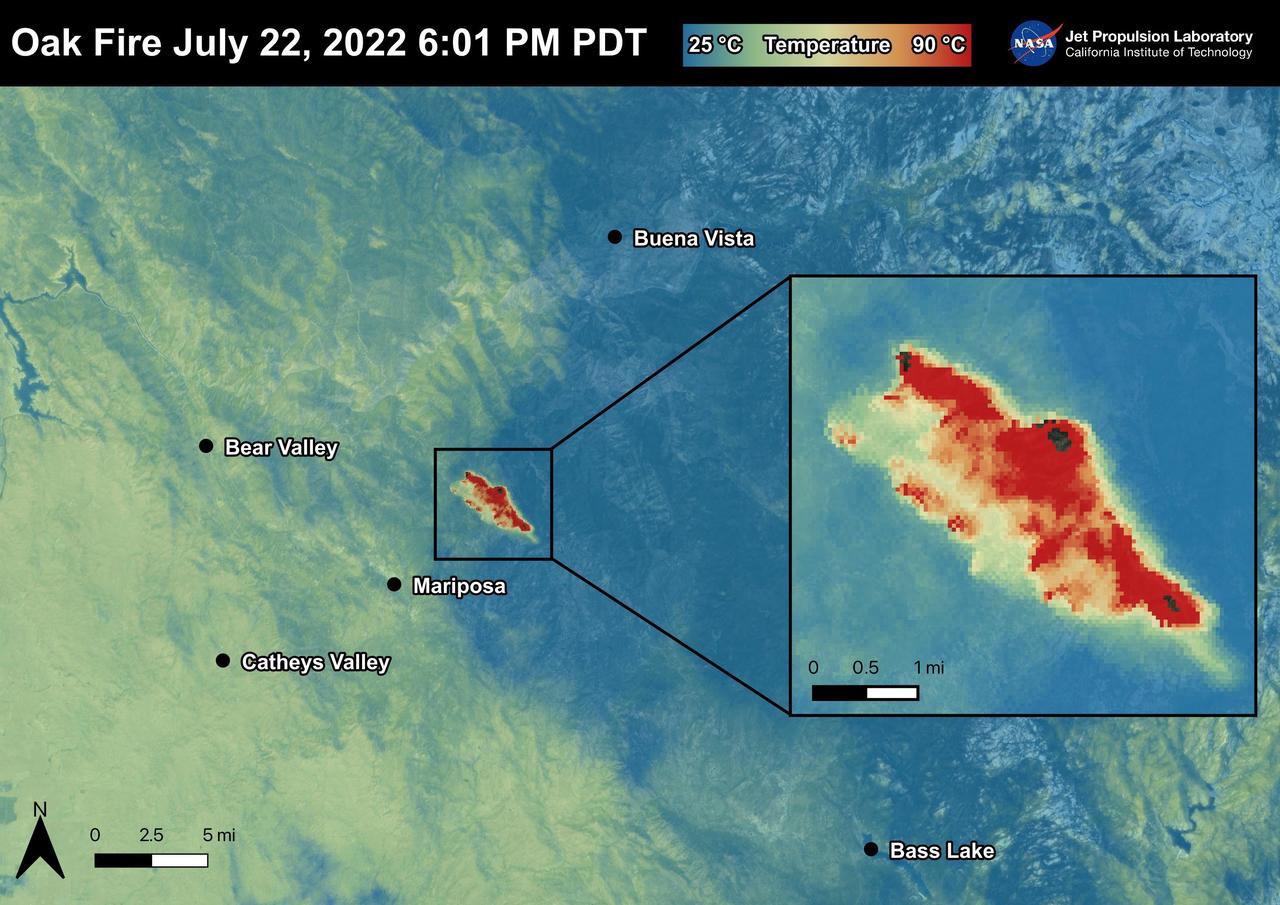
The Oak Fire started on July 22nd, 2022 at 2:10 PM PDT near Carstens Road and Highway 140 in Mariposa County, west of Yosemite. The fire has burned over 19,000 acres. In the first few days of the Oak Fire, over 1,400 structures were threatened, 3 were damaged, and 41 destroyed. Evacuation orders and road closures were issued throughout the region. The Oak Fire was captured in an ECOSTRESS Land Surface Temperature image on July 22nd with temperatures exceeding 90 degrees Celsius. ECOSTRESS is a thermal instrument on the International Space Station that measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the day. It was launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify critical thresholds of water use and water stress in plants and to detect the timing, location, and predictive factors leading to plant water uptake decline and/or cessation. The nature of the high-resolution data provided by ECOSTRESS allows it to record heat related phenomena such as heat waves and wildfires. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25481
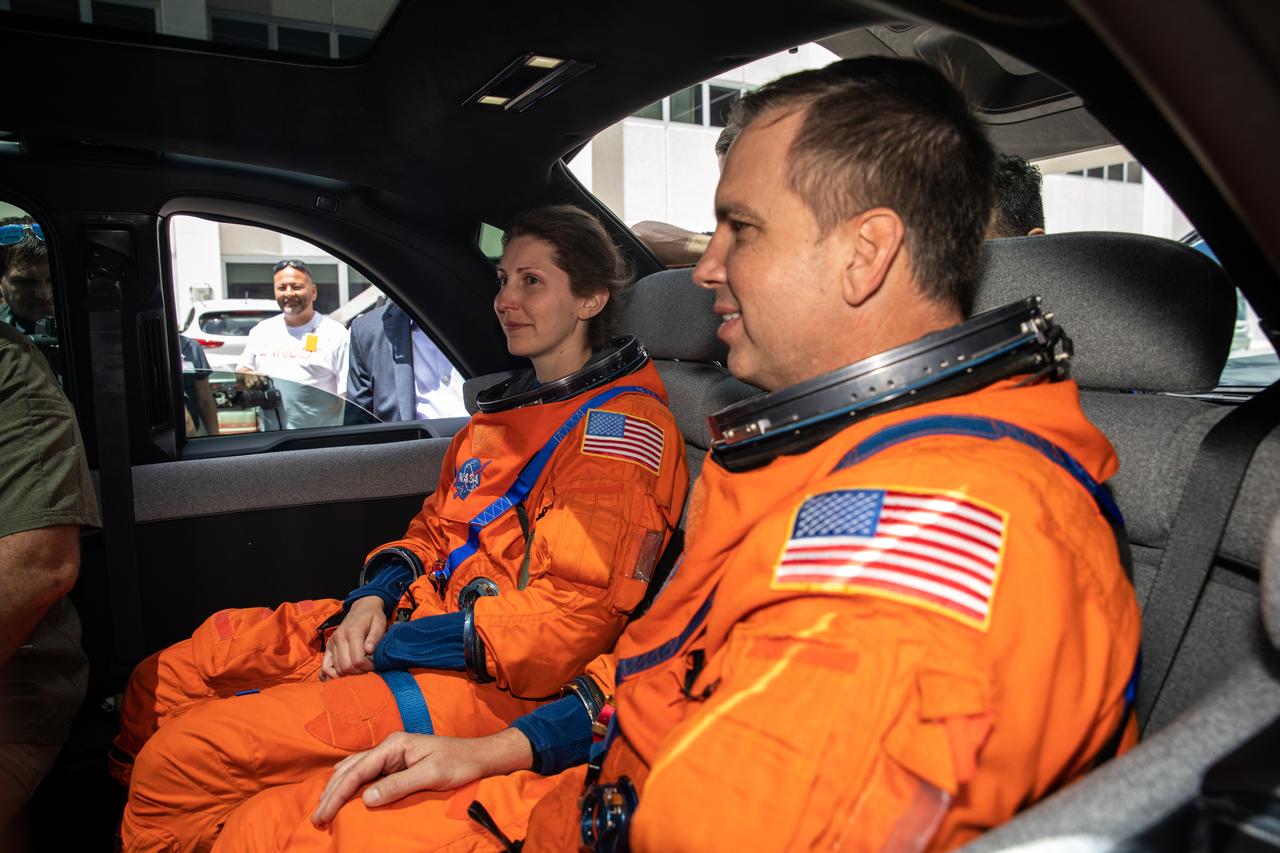

Technicians from Johnson Space Center, dressed in flight suits, secure themselves inside a prototype of a crew transportation vehicle (CTV) for Artemis crewed missions outside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 11, 2022. Canoo Technologies Inc., was awarded a contract to design and provide the next generation of CTVs for the Artemis crewed missions. Representatives with Canoo were at the spaceport demonstrating the environmentally friendly fleet of vehicles. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
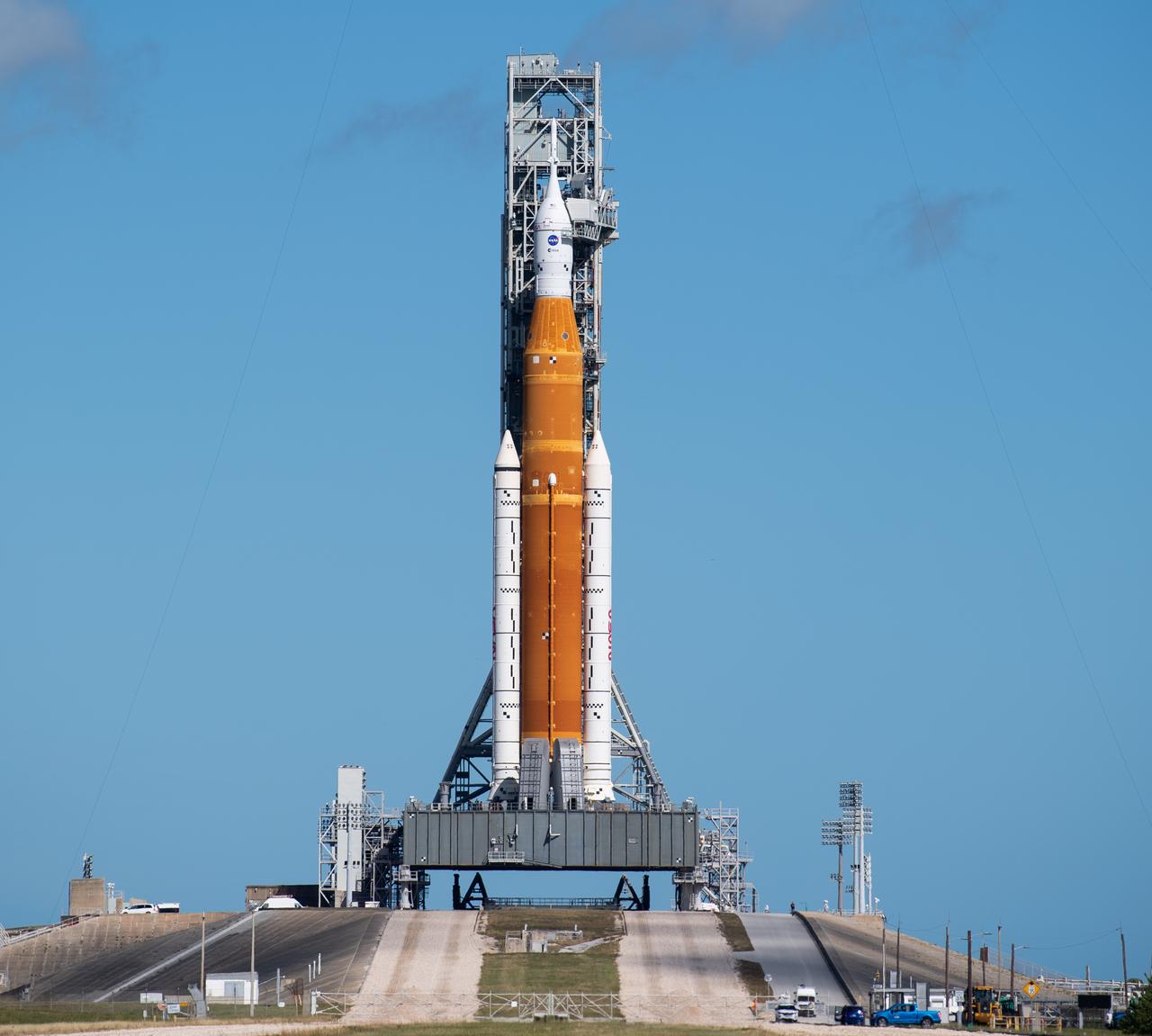

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B, Friday, Nov. 11, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams began walkdowns and inspections at the pad to assess the status of the rocket and spacecraft after the passage of Hurricane Nicole. NASA’s Artemis I flight test is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, SLS rocket, and supporting ground systems. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Nov. 16 at 1:04 a.m. EST. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
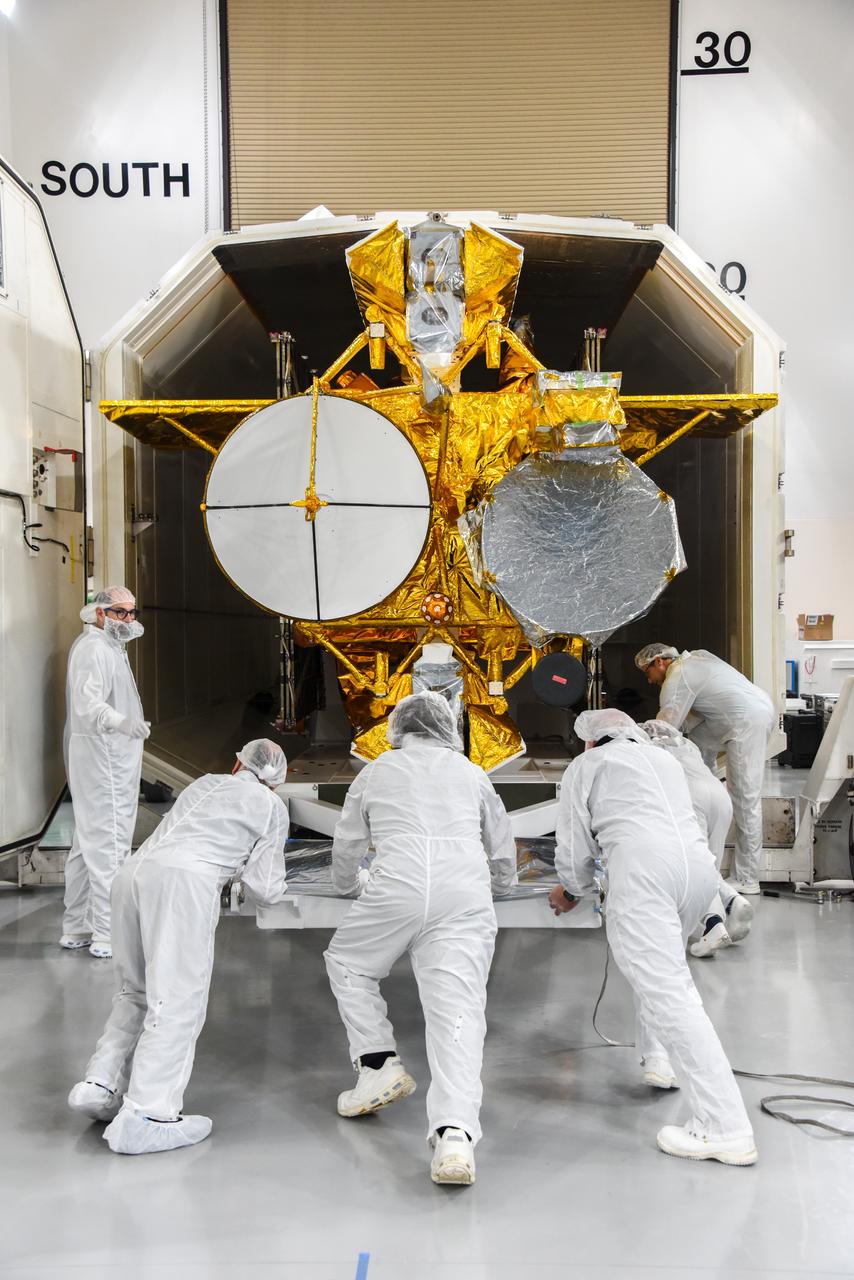

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is moved into a transport container inside the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 18, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
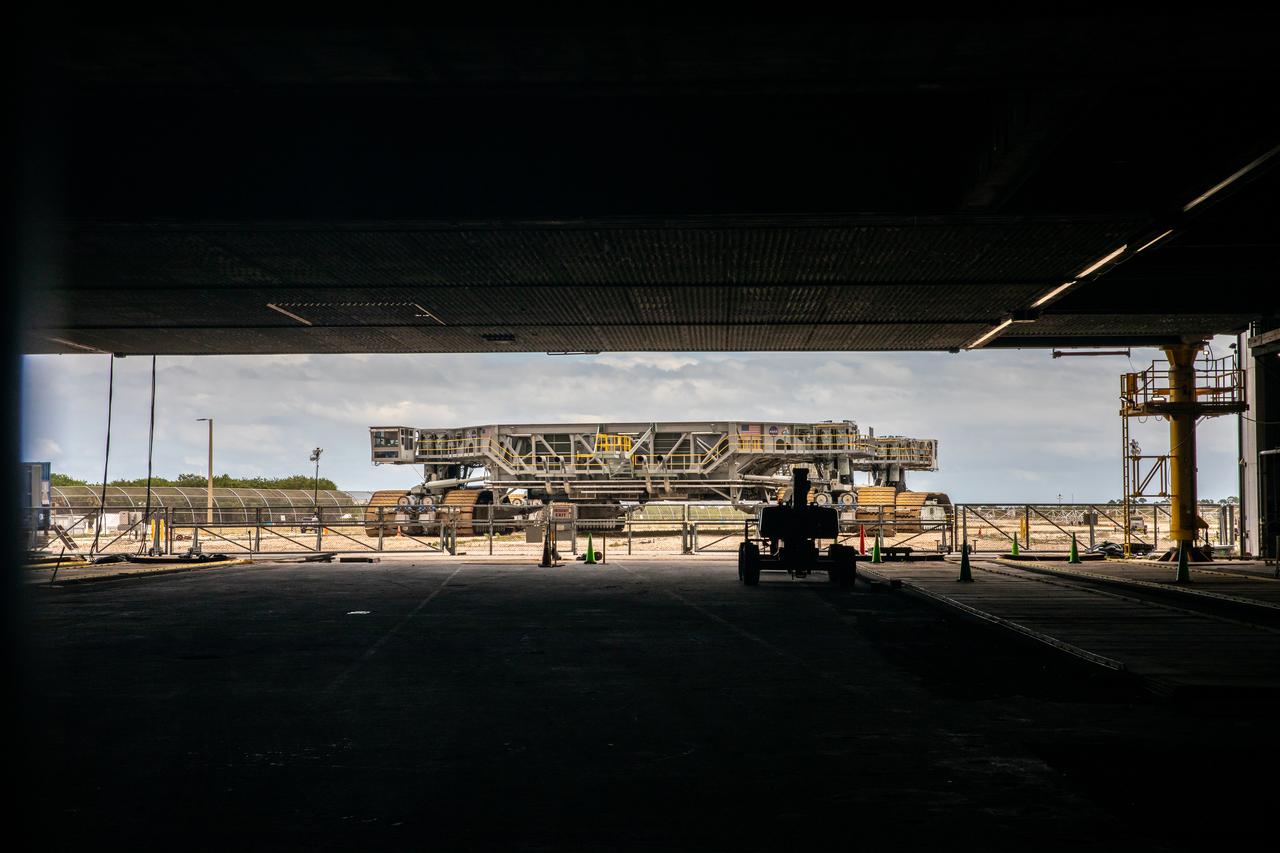

Crawler-transporter 2 is in view just outside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 14, 2022. Soon the crawler will be driven inside to transport the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft stack atop the mobile launcher for a trip along the crawlerway to Launch Complex 39B for a wet dress rehearsal. The Kennedy ground systems team is working to remove equipment and scaffolding away from the rocket and will continue retracting the platforms until the entire rocket is revealed ahead of the wet dress rehearsal test, which is scheduled to occur approximately two weeks after it arrives to 39B. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration to the Moon and Mars.
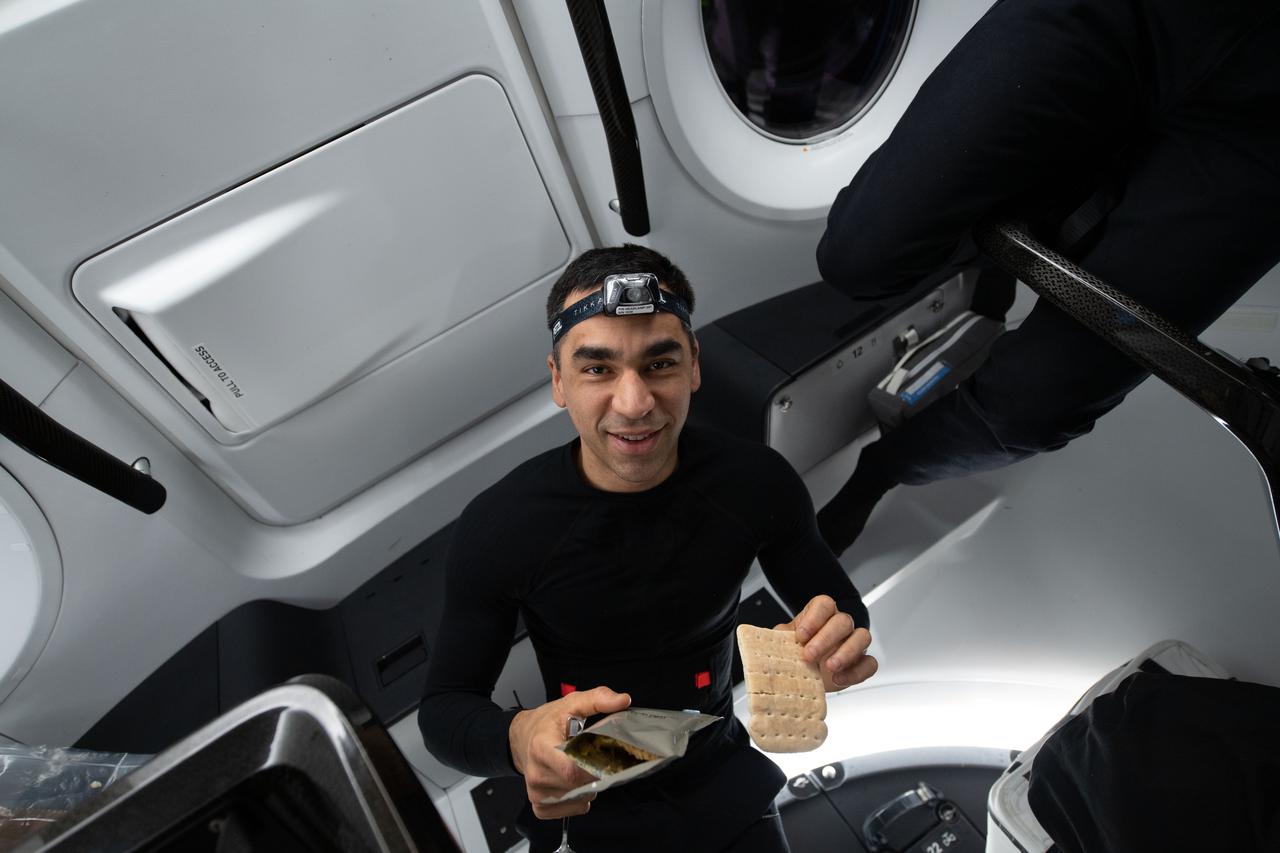

iss067e075881 (May 5, 2022) --- Crew-3 Commander Raja Chari of NASA is pictured journeying back to Earth inside the SpaceX Dragon Endurance spacecraft following its undocking from the International Space Station.
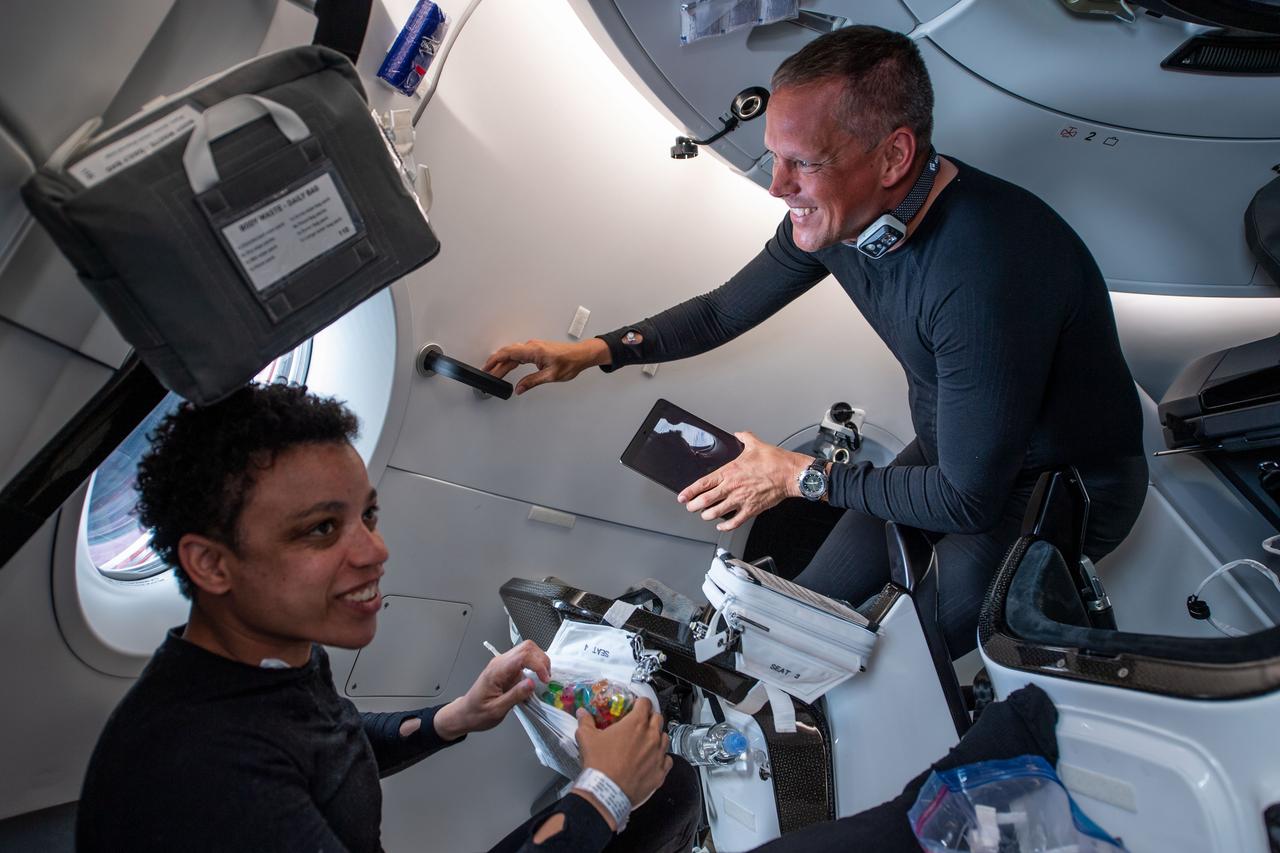

iss067e034503 (April 27, 2022) --- NASA astronauts Bob Hines and Jessica Watkins, Crew-4 Pilot and Mission Specialist respectively, are pictured inside the SpaceX Dragon Freedom spacecraft during their journey to the International Space Station.

iss066e115544 (Jan. 16, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Kayla Barron peers out from a window inside the cupola, the International Space Station's "window to the world." Prominent components in this photograph include the Tranquility module to which the cupola is attached to and the BEAM module.
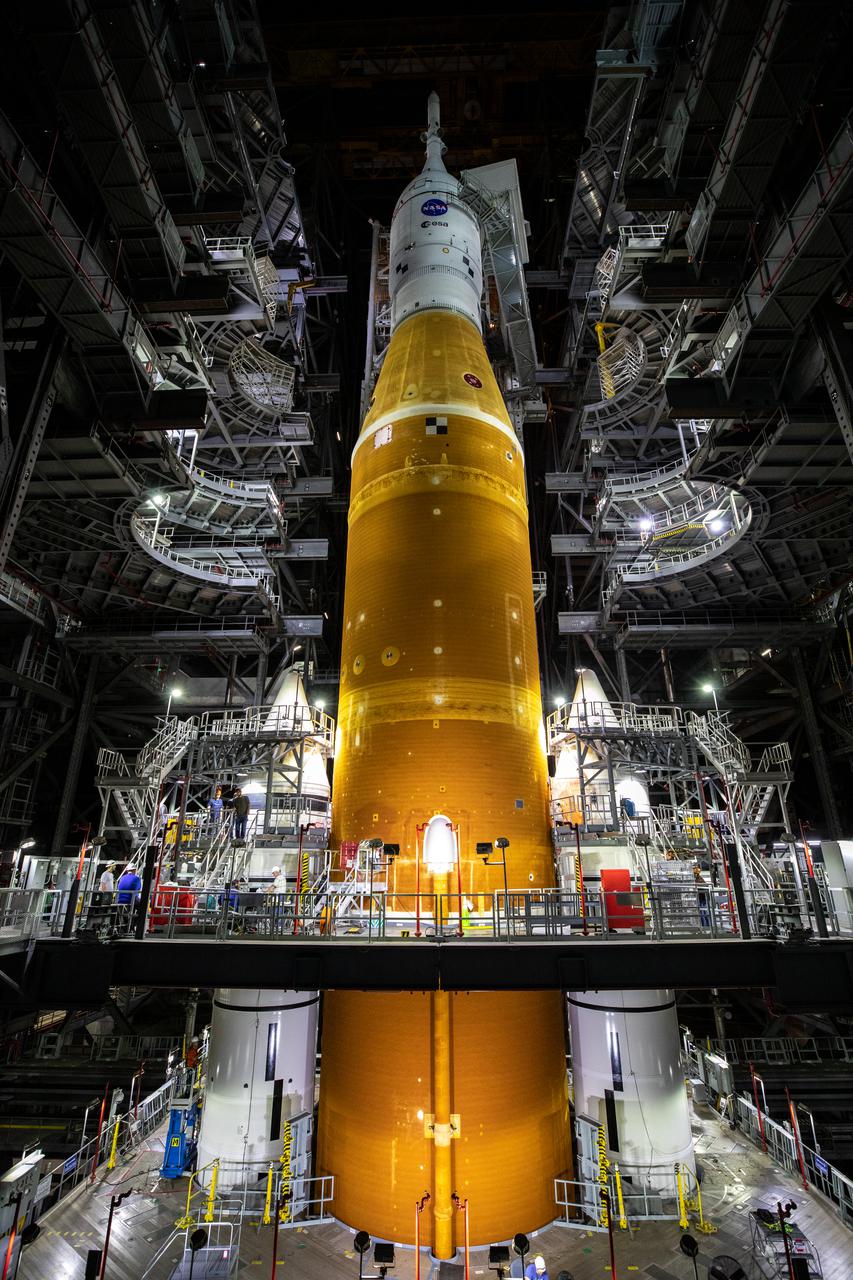

In this view looking up inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 10, 2022, the work platforms are being retracted from around the Artemis I Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation to roll out to launch pad 39B. The Kennedy ground systems team is working to remove equipment and scaffolding away from the rocket and will continue retracting the platforms until the entire rocket is revealed ahead of the wet dress rehearsal test, which is scheduled to occur approximately two weeks after it arrives at the pad.

The Mars Sample Return Campaign Science Group gathered for their first meeting, at the Keck Institute for Space Studies at Caltech, and took a group photo. This June 28 photo includes team members who attended in person; several others attended virtually or were not able to participate. The committee will provide oversight with the goal of maximizing the scientific potential of Mars rock and sediment samples that would be returned to Earth for in-depth analysis, as part of the Campaign. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25443
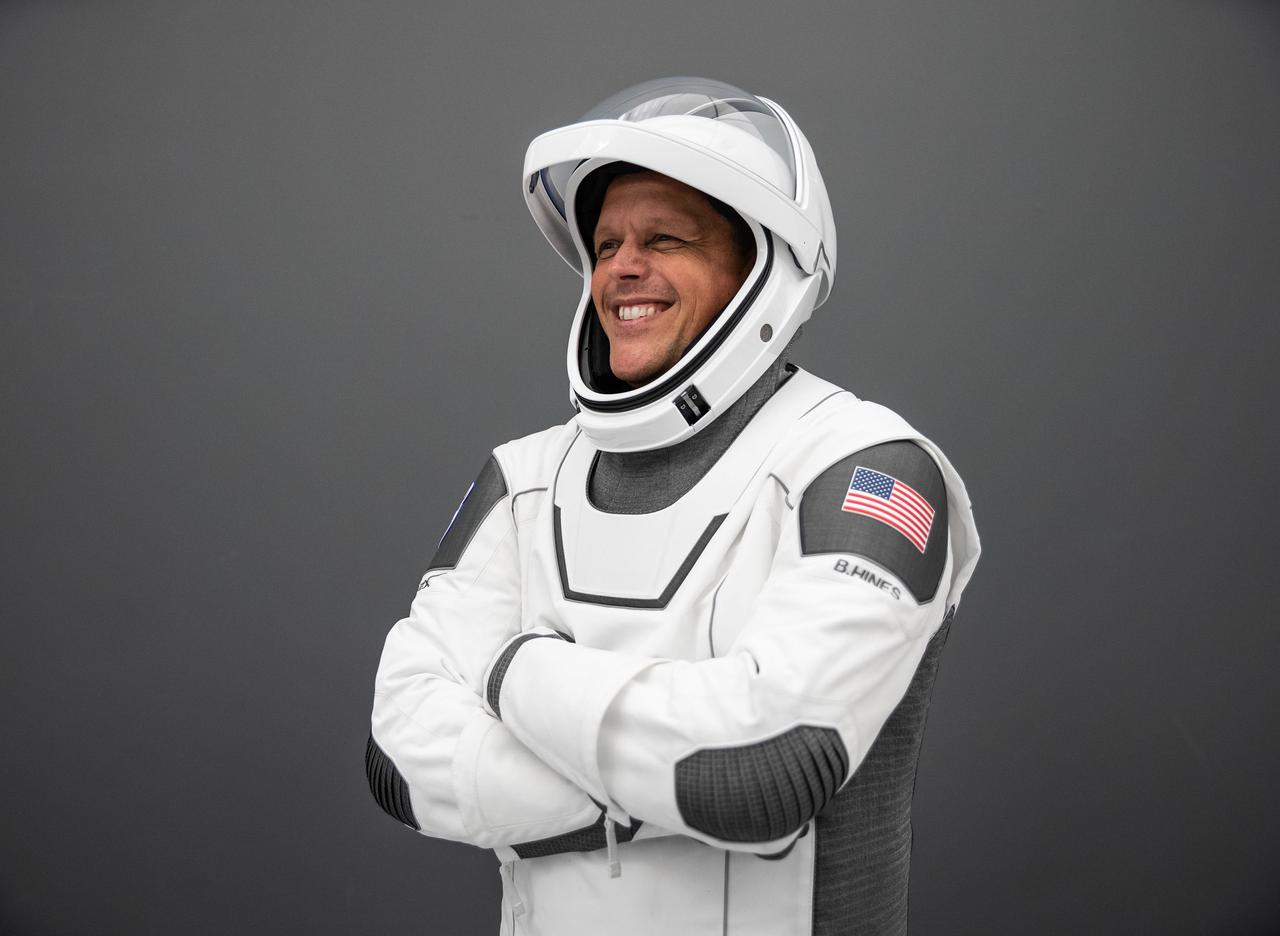

jsc2022e011414 (Feb. 15, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and SpaceX Crew-4 Pilot Robert Hines, representing NASA's Commercial Crew Program, poses for a portrait at SpaceX Headquarters in Hawthorne, California.
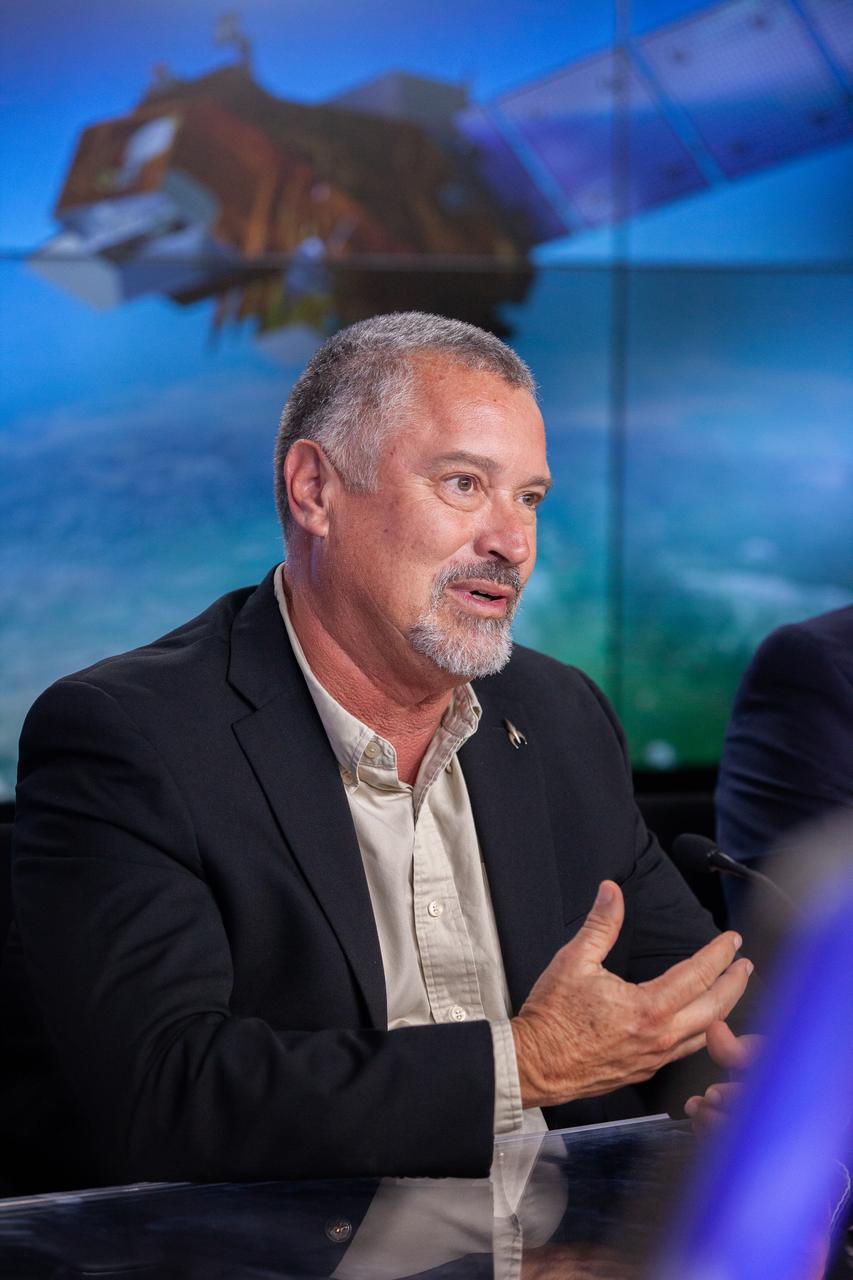

Omar Baez, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program, participates in a prelaunch news conference for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) and NASA Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) technology demonstration at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 28, 2022. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the polar satellite series and is expected to capture data to improve weather forecasts, helping scientists predict and prepare for extreme weather events and climate change. JPSS-2 is scheduled to launch at 2:25 a.m. PDT Tuesday, Nov. 1, on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Launching with JPSS-2 is NASA’s LOFTID technology demonstration. After JPSS-2 safely reaches orbit, LOFTID will follow a re-entry trajectory from low-Earth orbit to demonstrate the inflatable heat shield’s ability to slow down and survive re-entry. LOFTID is a partnership with ULA and is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, one of the company’s engineers who played a key role in developing the technology. LOFTID will demonstrate how the inflatable aeroshell, or heat shield, can slow down and survive re-entry in conditions relevant to many potential applications, whether landing humans on Mars, new missions to Venus and Titan, or returning heavier payloads and samples from low-Earth orbit.
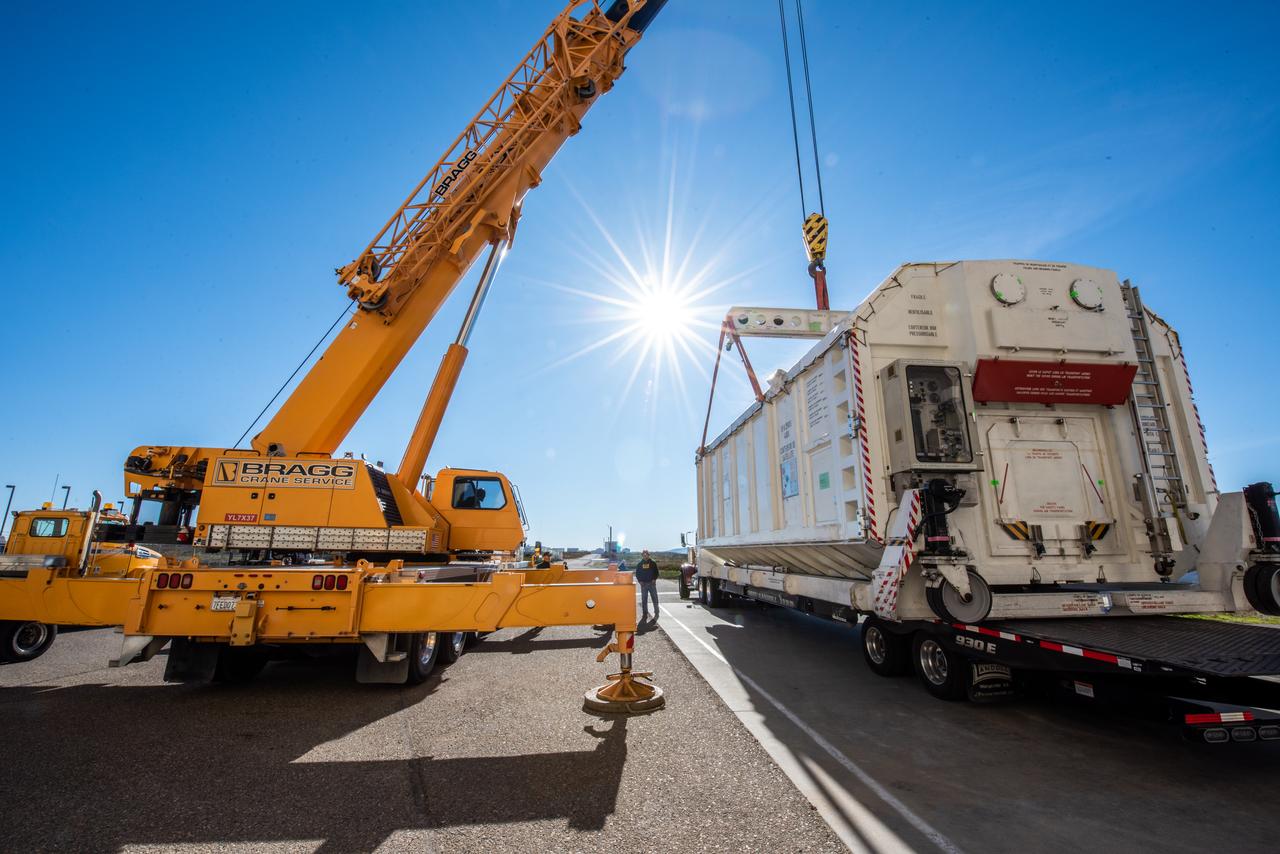

A container, with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft inside, is moved to a trailer at the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 19, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
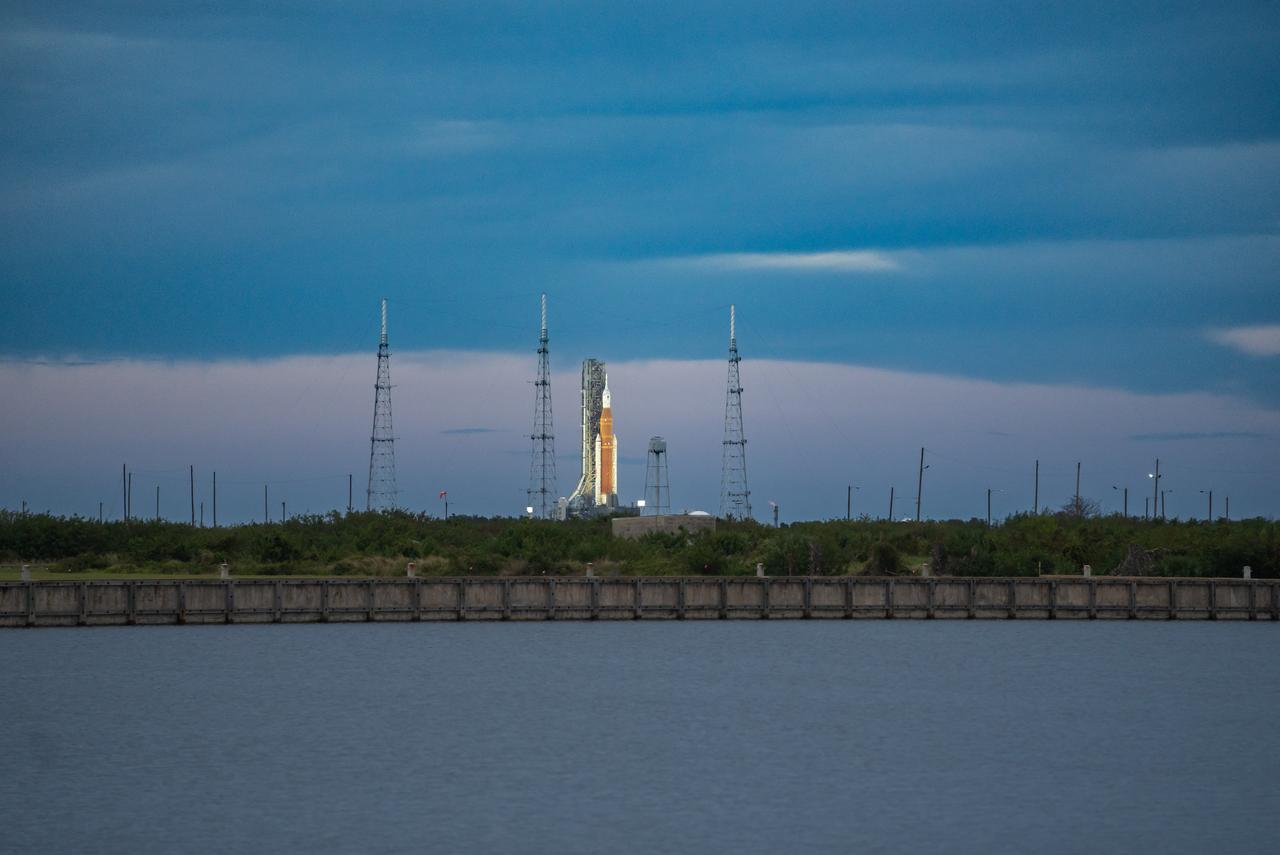

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

Standing atop the mobile launcher, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft can be seen at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 18, 2022. The Artemis I stack was carried from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the pad – a 4.2-mile journey that took nearly 11 hours to complete – by the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 for a wet dress rehearsal ahead of the uncrewed launch. Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
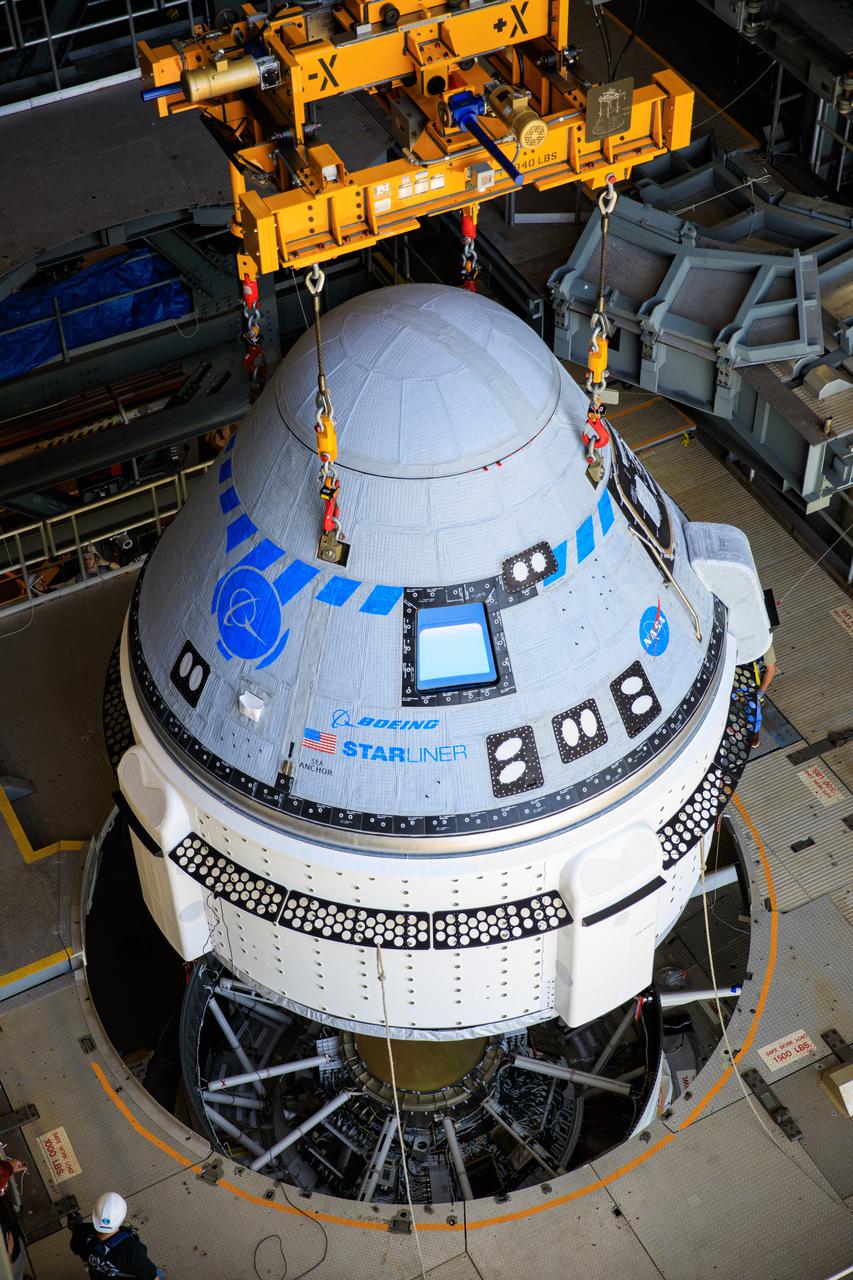

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
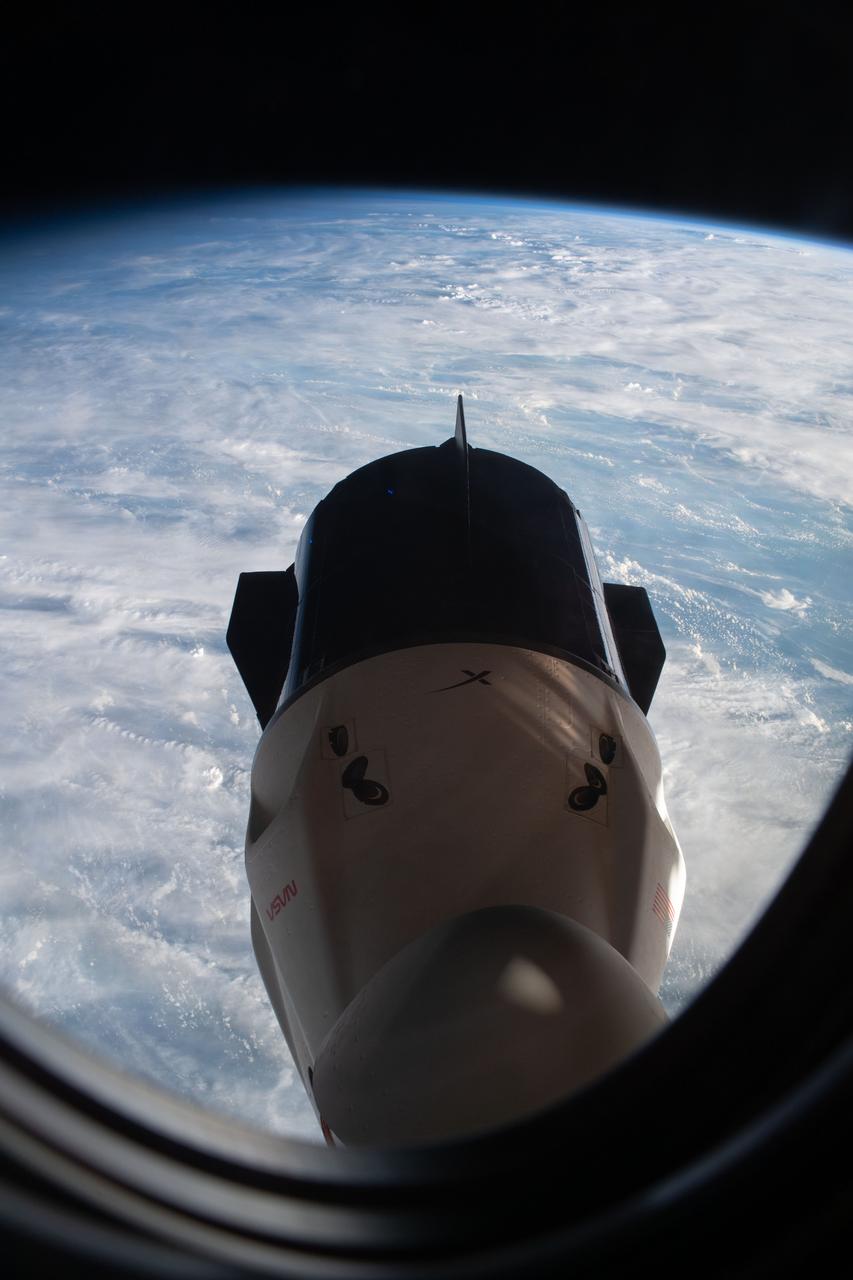

iss068e017228 (Oct. 14, 2022) --- The SpaceX Dragon Endurance crew ship is pictured docked to the forward port of the International Space Station's Harmony module. Endurance was photographed from a window inside the Dragon Freedom crew ship docked to Harmony's space-facing port. Credit: JAXA/Koichi Wakata
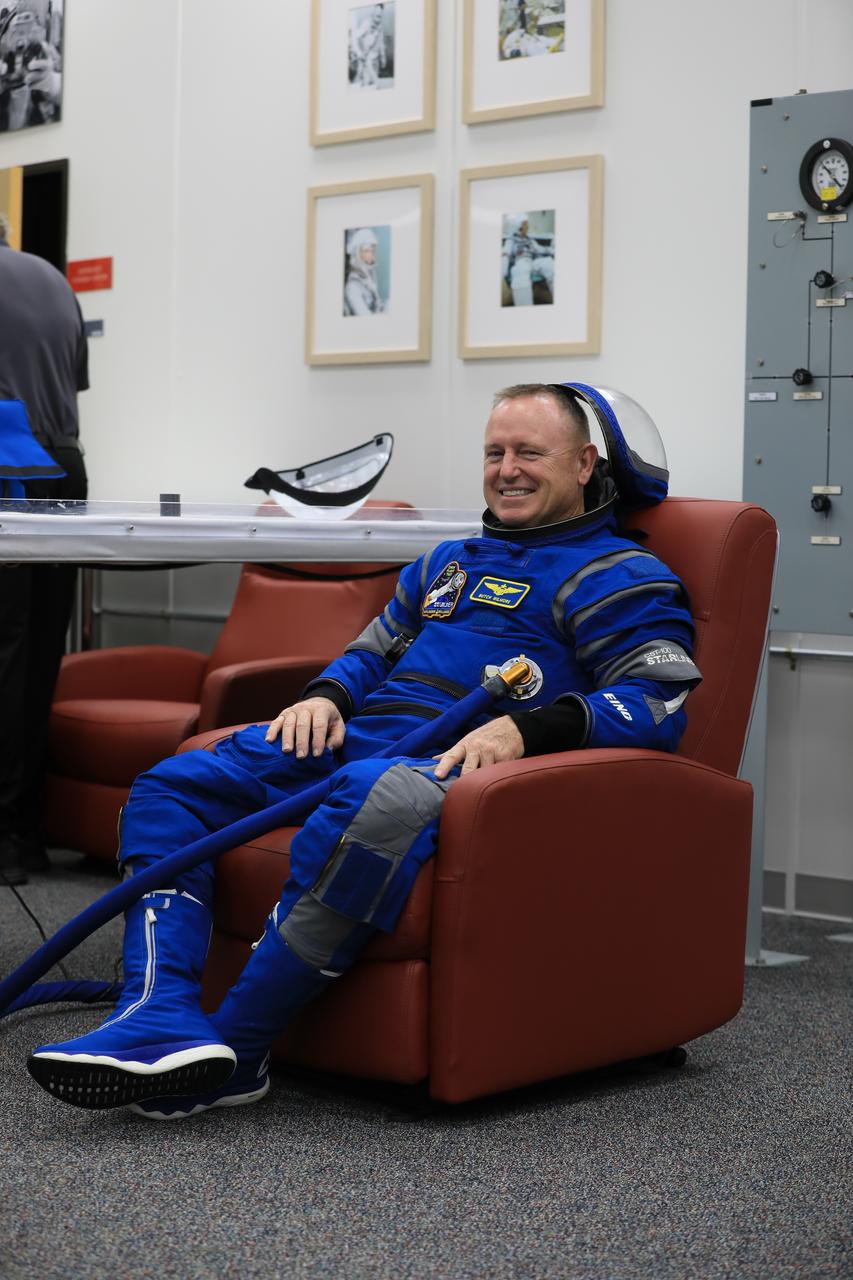

NASA astronaut Barry “Butch” Wilmore, Boeing Crew Flight Test (CFT) commander, checks his spacesuit during a crew validation test inside the Astronaut Crew Quarters at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 18, 2022. Wilmore, along with NASA astronauts Suni Williams, CFT pilot, and Mike Fincke, CFT backup spacecraft test pilot, with assistance from the Boeing team, successfully completed the validation test during which they suited up and tested out the pressurized crew module to ensure seat fit, suit functionality, cabin temperature, audio system, and day of launch operations. Boeing’s CFT is scheduled to launch in April 2023.
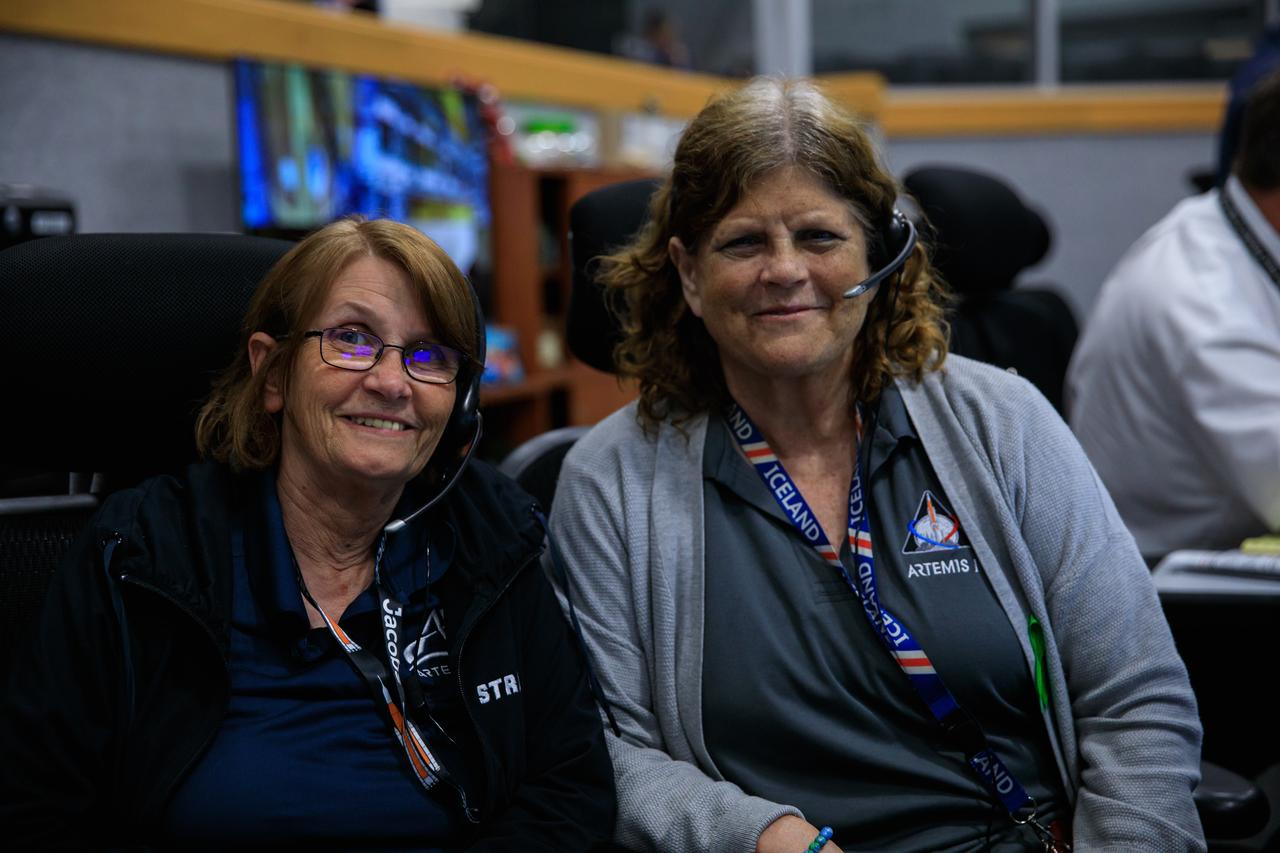

NASA Test Conductors Teresa Annulis, at left, and Roberta Wyrick, monitor launch countdown activities inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022. Liftoff of the agency’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft from Launch Complex 39B was at 1:47 a.m. EST. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
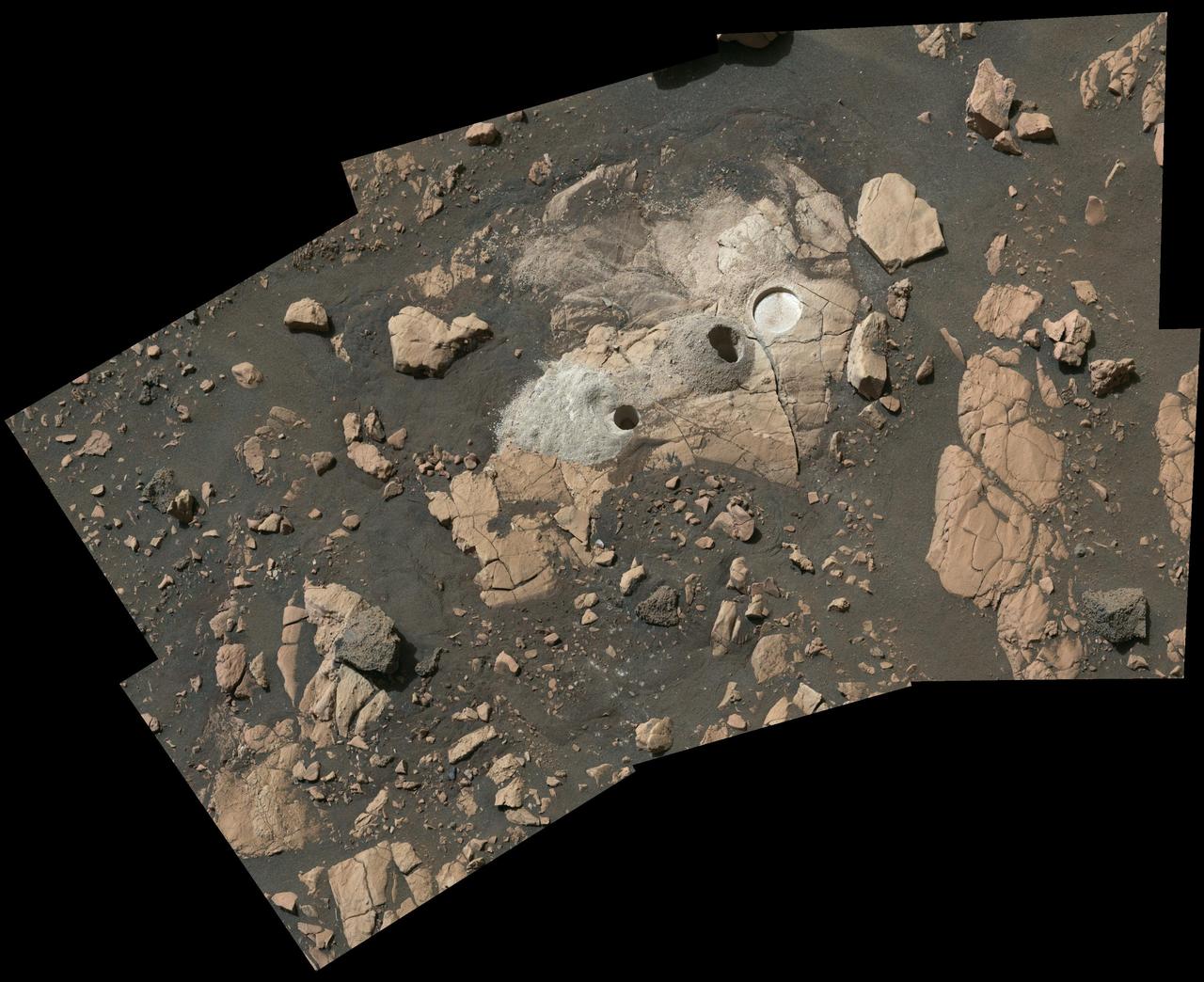

Composed of multiple images from NASA's Perseverance Mars rover, this mosaic shows a rocky outcrop called "Wildcat Ridge," where the rover extracted two rock cores and abraded a circular patch to investigate the rock's composition. The site is in the delta, a fan-shaped area where, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake in Jezero Crater. Scientists consider this area one of the best places on Mars to search for potential signs of ancient microbial life. The images were obtained by the Mastcam-Z instrument on Aug. 4, 2022, the 518th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's mission. For scale, the bright circular abrasion patch on the right is approximately 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter. The color bands of the image have been processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences. The rock cores obtained by Perseverance – each about the size of a piece of classroom chalk – were sealed in ultra-clean sample tubes. They are currently stored in the rover's Sampling and Caching System. The verification of ancient life on Mars carries an enormous burden of proof. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24928
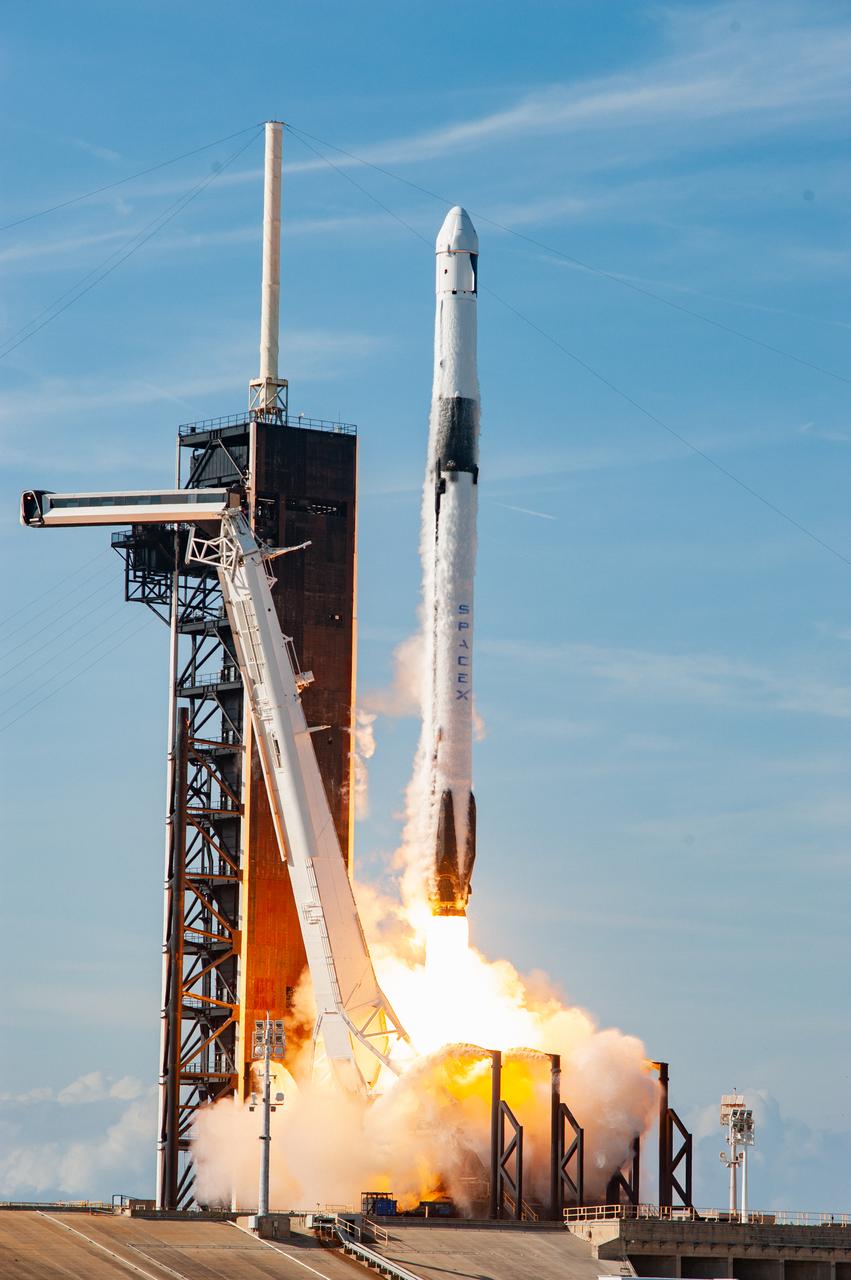

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
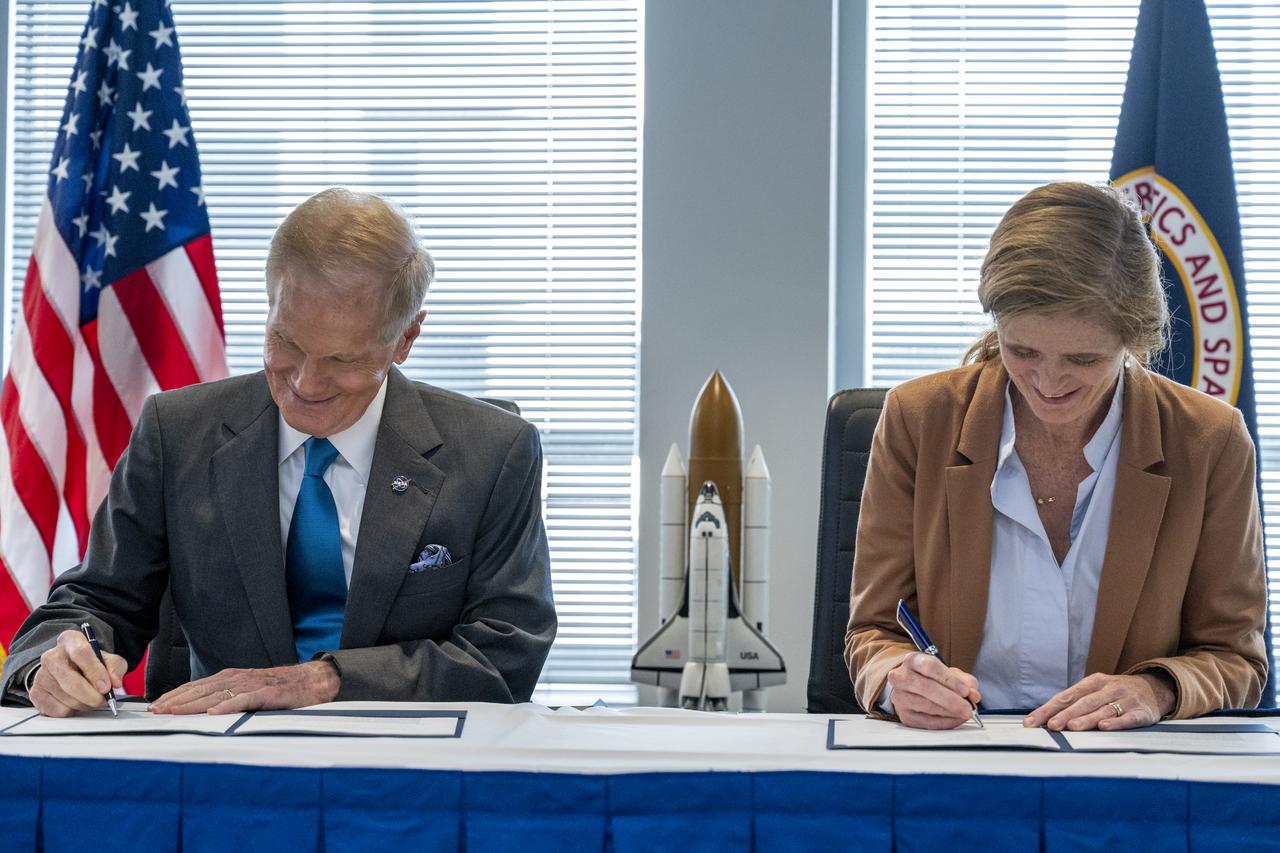

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and USAID Administrator Samantha Power participate in a NASA-USAID Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signing ceremony Friday, Nov. 4, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The MoU will enhance and expand the Agencies’ longstanding partnership that promotes science and technology solutions to address international development challenges in areas such as global health, climate change, food security, disaster mitigation and response, biodiversity conservation, and environmental management for sustainable development. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

David Zahn pilots the ownship aircraft in the VMS’s R-Cab during the AVA-1h simulation in the VMS, N243.
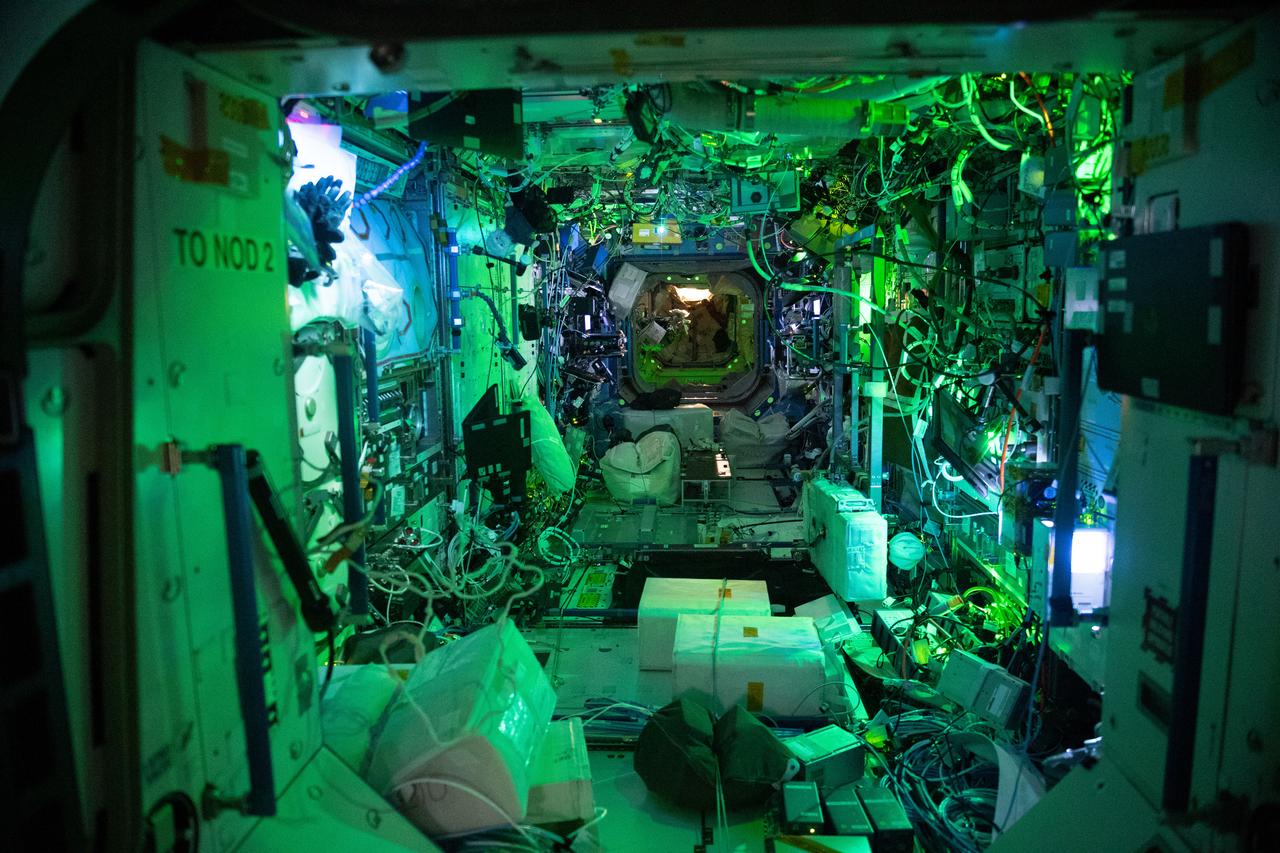

iss068e022293 (Nov. 14, 2022) --- An interior view of the Destiny U.S. Laboratory at night under ambient light with the main lights turned off. The Destiny module supports a variety of life and physical sciences, technology demonstrations, and educational events. In 2022, hardware for the Solid Fuel Ignition and Extinction (SOFIE) facility was installed inside Destiny's Combustion Integrated Rack opening opportunities for new combustion studies.

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022.
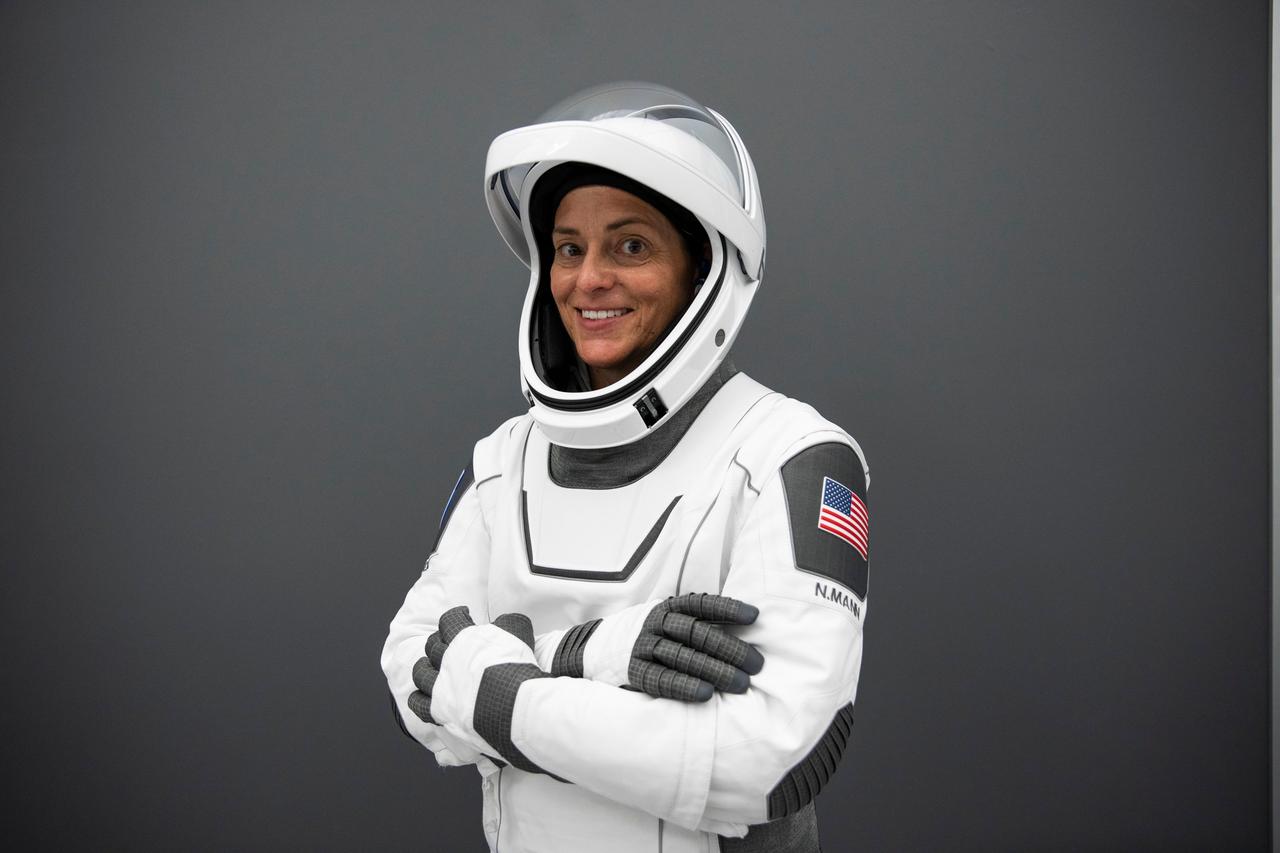

jsc2022e068614 (June 13, 2022) --- SpaceX Crew-5 Commander Nicole Aunapu Mann from NASA poses for a portrait in her Crew Dragon flight suit at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
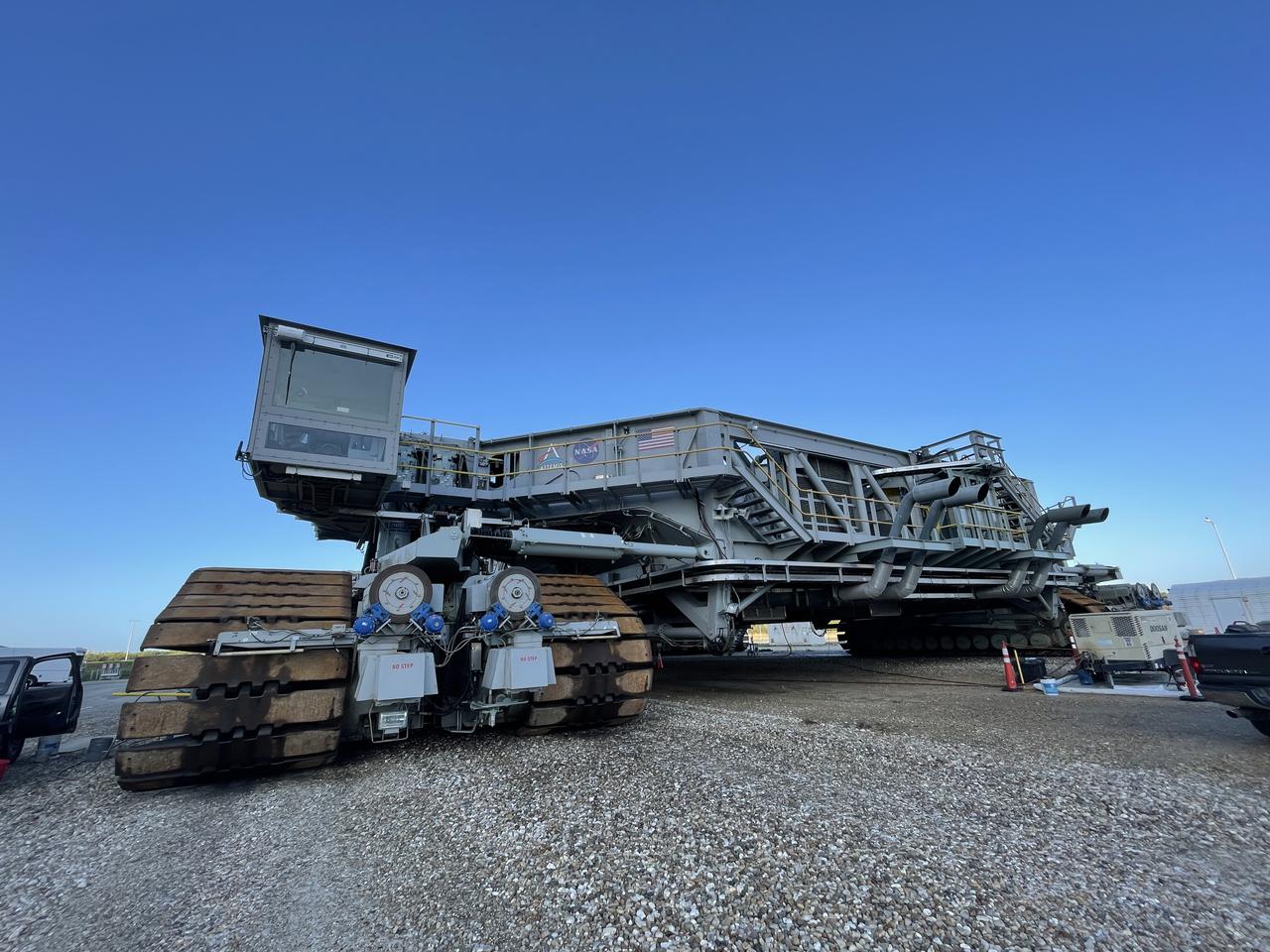

Eight new NASA Artemis logos (four large, four small) were installed on Crawler-Transporter 2 at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the upcoming launch of Artemis I. Named after the twin sister of Apollo, Artemis is the Goddess of the Moon. The Artemis missions will take humanity back to the Moon and beyond, beginning a new legacy of deep space exploration.

(jsc2022e089789) (Nov.25, 2022) During day 10 of the of the 25.5-day Artemis I mission, flight controllers monitor the progress of the Distant Retrograde Orbit Insertion (DRI) burn. The Distant Retrograde Orbit Insertion (DRI) burn, inserted Orion into a Distant Retrograde Orbit (DRO) where at it's furthest distance Orion will be nearly 270,000 miles from Earth.

Technicians assist as the engine section of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage for NASA’s Artemis III mission is moved into the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 15, 2022. The section was shipped from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Dec. 10, 2022 aboard the Pegasus barge, was offloaded, and transferred to the SSPF. Teams will begin processing operations ahead of final integration in the Vehicle Assembly Building. Artemis III will send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission aboard the Orion spacecraft to the surface of the Moon.
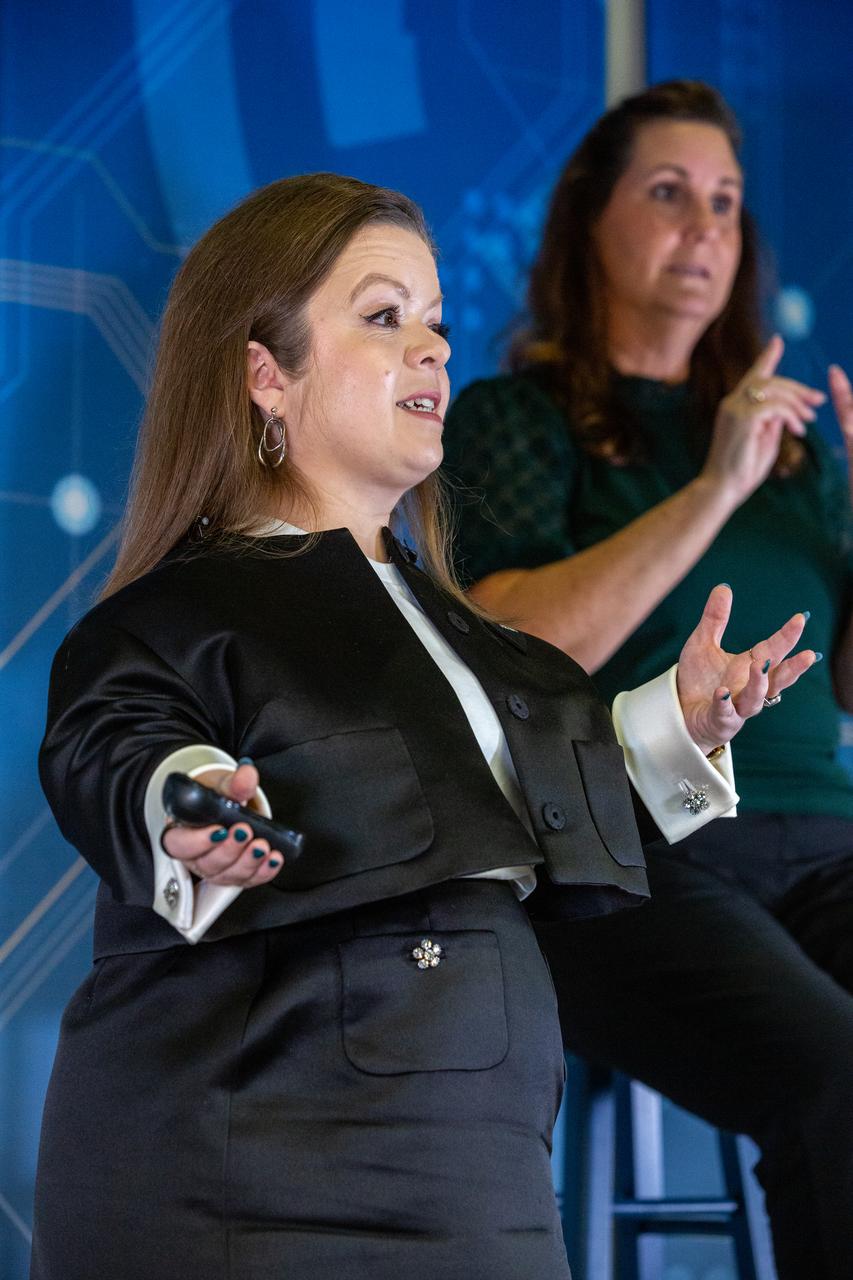

Guest speaker Sinead Burke, from Ireland, gave a presentation on “Breaking the Mould – A Lesson in Equity,” to Kennedy Space Center employees on Nov. 30, 2022, and to employees at other NASA centers via live stream on YouTube. The event was sponsored by the center’s Disability Awareness and Action Working Group (DAAWG) and the Spaceport Integration Directorate. Burke, who is an advocate for the inclusion of all, amplifies the voices who are often not considered.
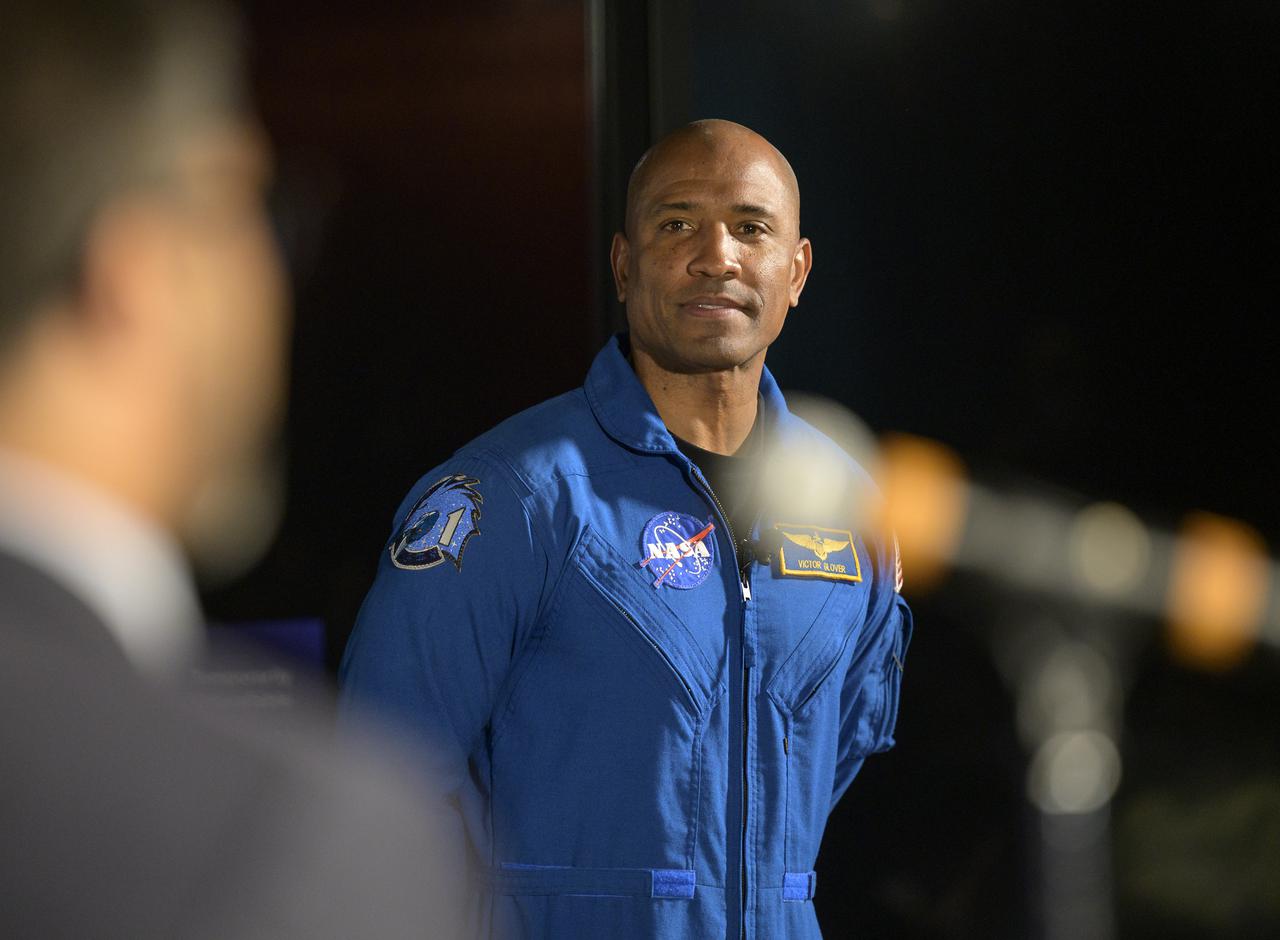

NASA astronaut Victor Glover listens as Chirag Parikh from the National Space Council reads a letter from Vice President Kamala Harris to Glover during an educational event, Thursday, April 28, 2022, at the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington. Glover most recently served as pilot and second-in-command on the Crew-1 SpaceX Crew Dragon, named Resilience, which landed after a long duration mission aboard the International Space Station, May 2, 2021. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
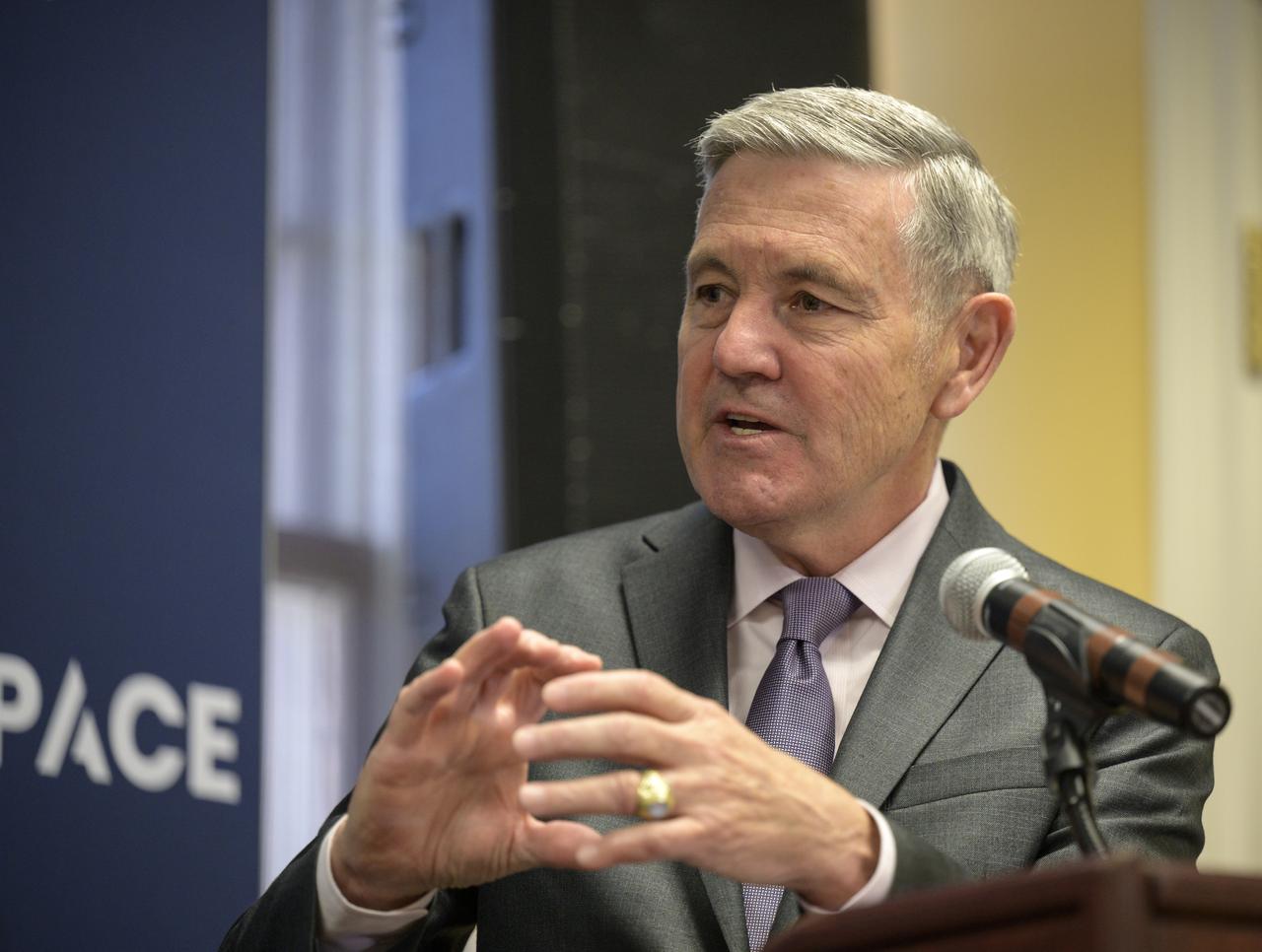

NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana speaks at “Small Satellites, Big Missions: Pathfinding CubeSats Exploring the Moon and Beyond,” a news conference during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

iss067e141214 (June 20, 2022) --- An orbital sunset is pictured from the International Space Station as it was soaring 267 miles above the south Pacific Ocean.
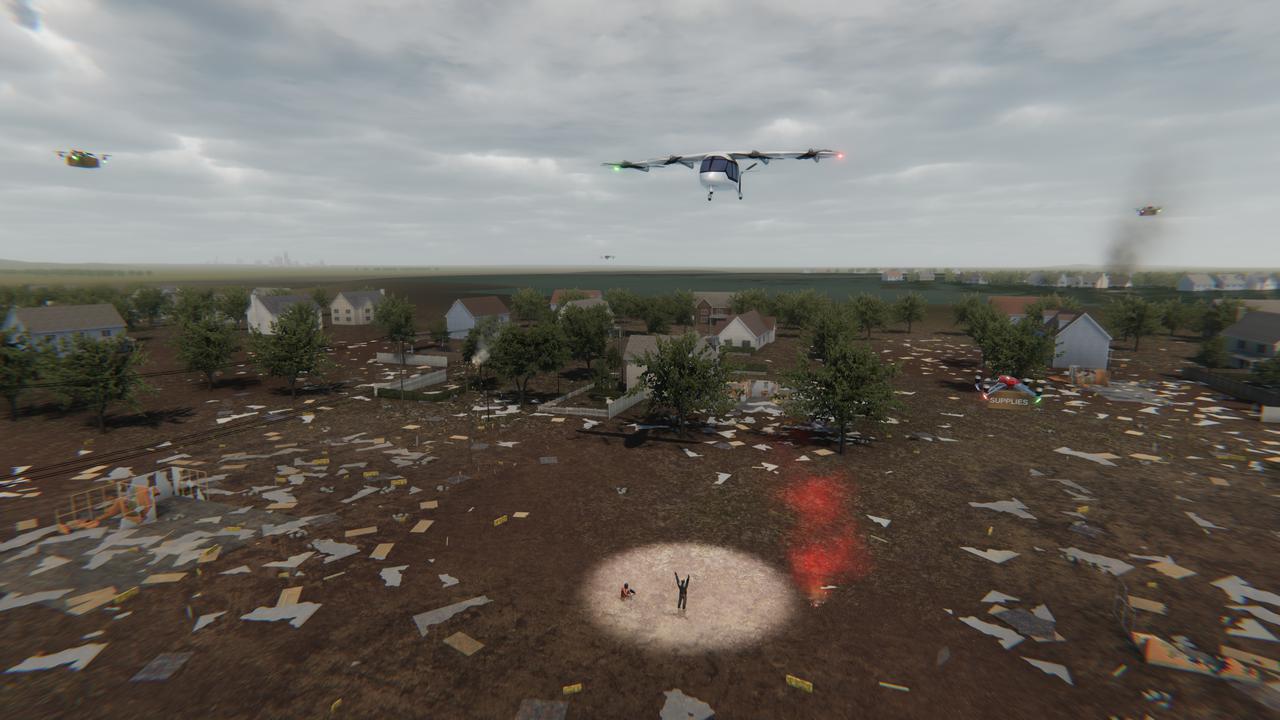

Several projects under NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality in emergency operations. This concept graphic shows how a future AAM vehicle could aid in disaster response.
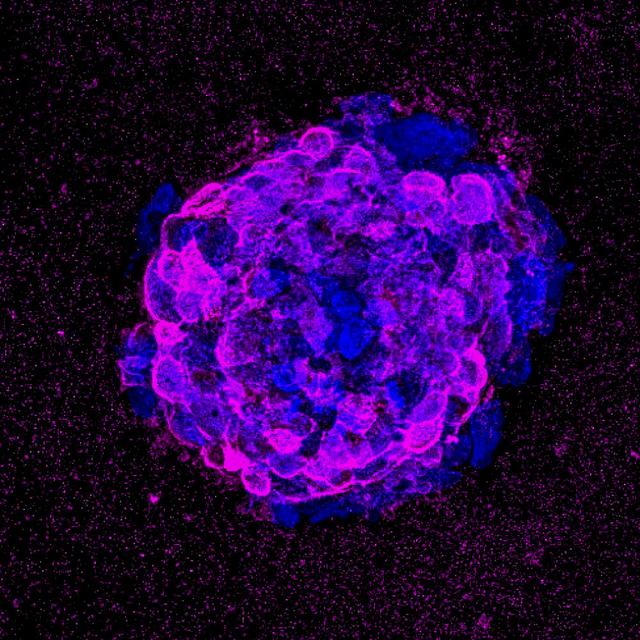
jsc2022e042483 (5/19/2022) --- Image showing impaired wound healing due to immunosenescence. Image courtesy of Prof. Sonja Schrepfer, UCSF.

In early 2022, the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) project – led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California – successfully integrated special gears into pieces of a robotic arm that is planned to perform a robot-controlled lunar surface experiment with imagery in the coming years. These bulk metallic glass (BMG) gears, integrated into COLDArm's joints and actuators, were developed through the Game Changing Development bulk metallic glass gears project to operate at extreme temperatures below minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). The gear alloys have a disordered atomic-scale structure, making them both strong and elastic enough to withstand these exceptionally low temperatures. Typical gearboxes require heating to operate at such cryogenic temperatures. The BMG gear motors have been tested and successfully operated at roughly minus 279 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius) without heating assistance. This gear motor is one of the key technologies to enable the robotic arm to operate in extremely cold environments, such as during lunar night. Each of the four joints containing BMG gears will be tested once the arm is fully assembled, which is scheduled for spring of 2022. Robotic joint testing will include dynamometer testing to measure torque/rotational speed, as well as cryogenic thermal vacuum testing to understand how the equipment would perform in an environment similar to space. Once proven, the BMG gears and COLDArm capabilities will enable future missions to work in extreme environments on the Moon, Mars, and ocean worlds. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24567
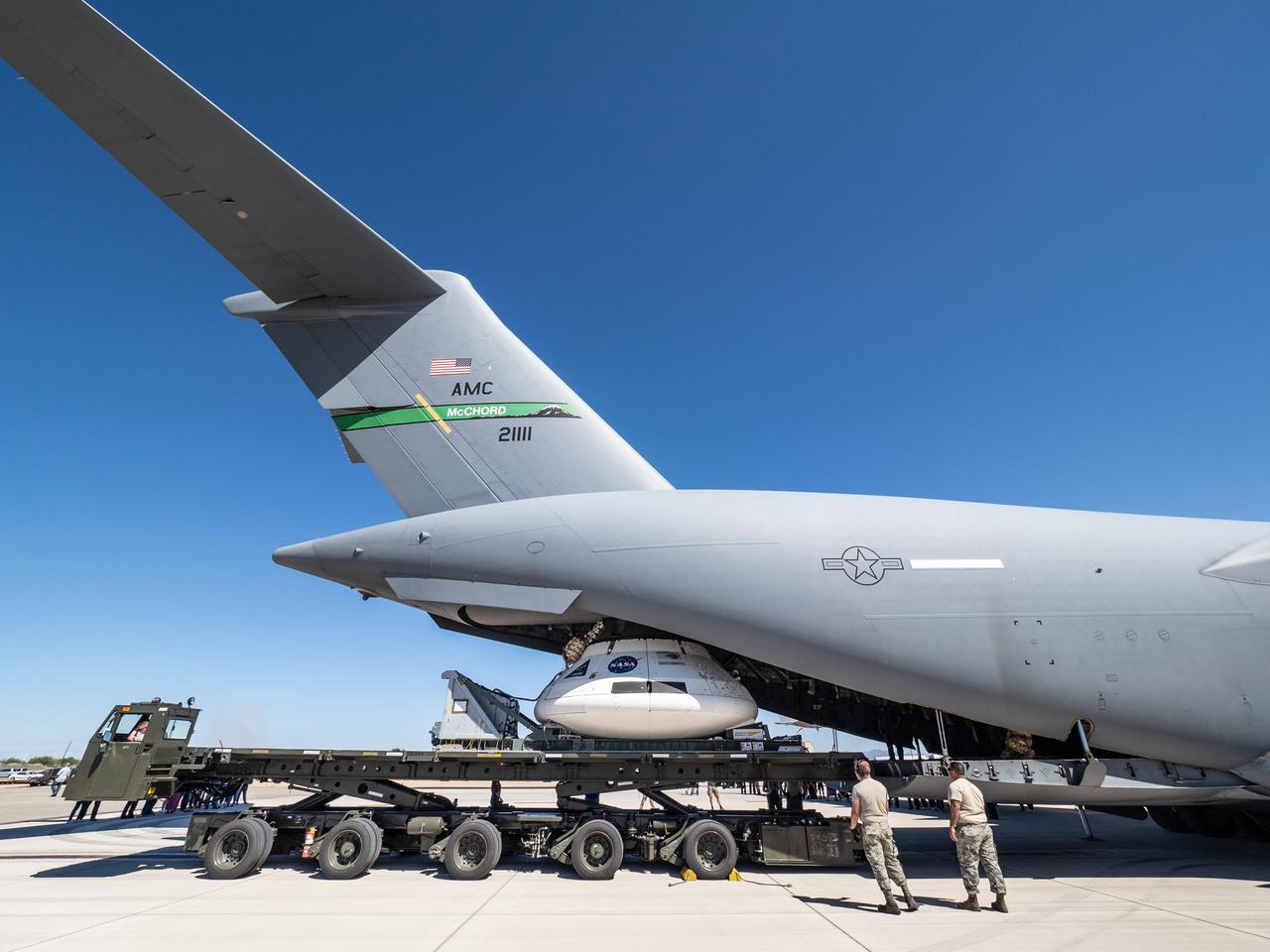

The Orion team prepares the parachute test vehicle for the final drop test which will qualify Orion's parachutes for human flight on Sept. 10, 2018...On September 12, 2018 an Orion test capsule will be dropped from a C-17 aircraft at an altitude of more than six miles to verify the spacecraft’s complex system of 11 parachutes, cannon-like mortars, and pyrotechnic devices work in sequence to slow the capsule’s descent for a safe landing on Earth.
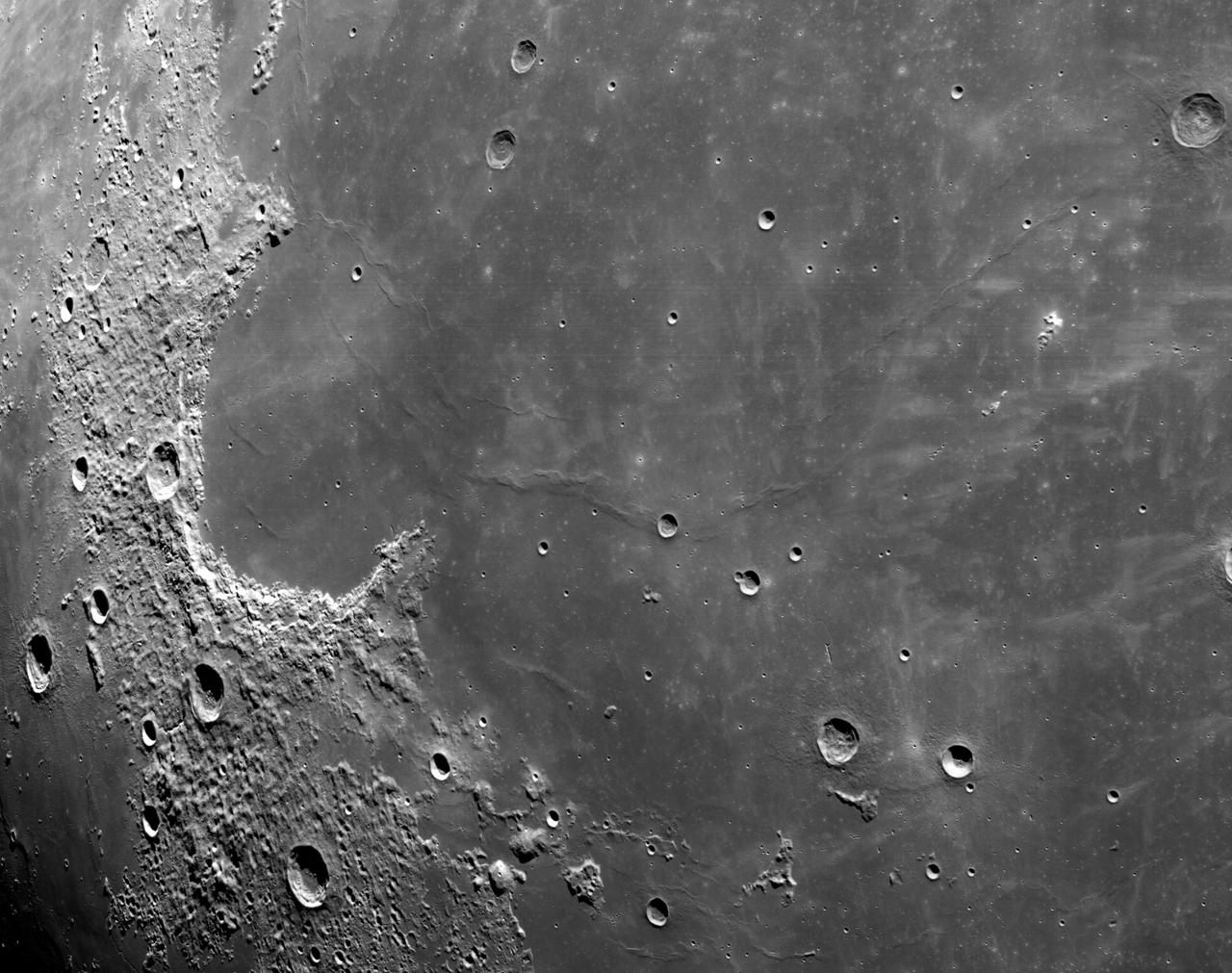

art001e002164 (Dec. 5, 2022): Cameras mounted on the crew module of the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn.

Support teams raise the SpaceX Crew Dragon Freedom spacecraft aboard the recovery ship Megan shortly after it landed with NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Robert Hines, Jessica Watkins, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti aboard in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Jacksonville, Florida, Friday, Oct. 14, 2022. Lindgren, Hines, Watkins, and Cristoforetti are returning after 170 days in space as part of Expeditions 67 and 68 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
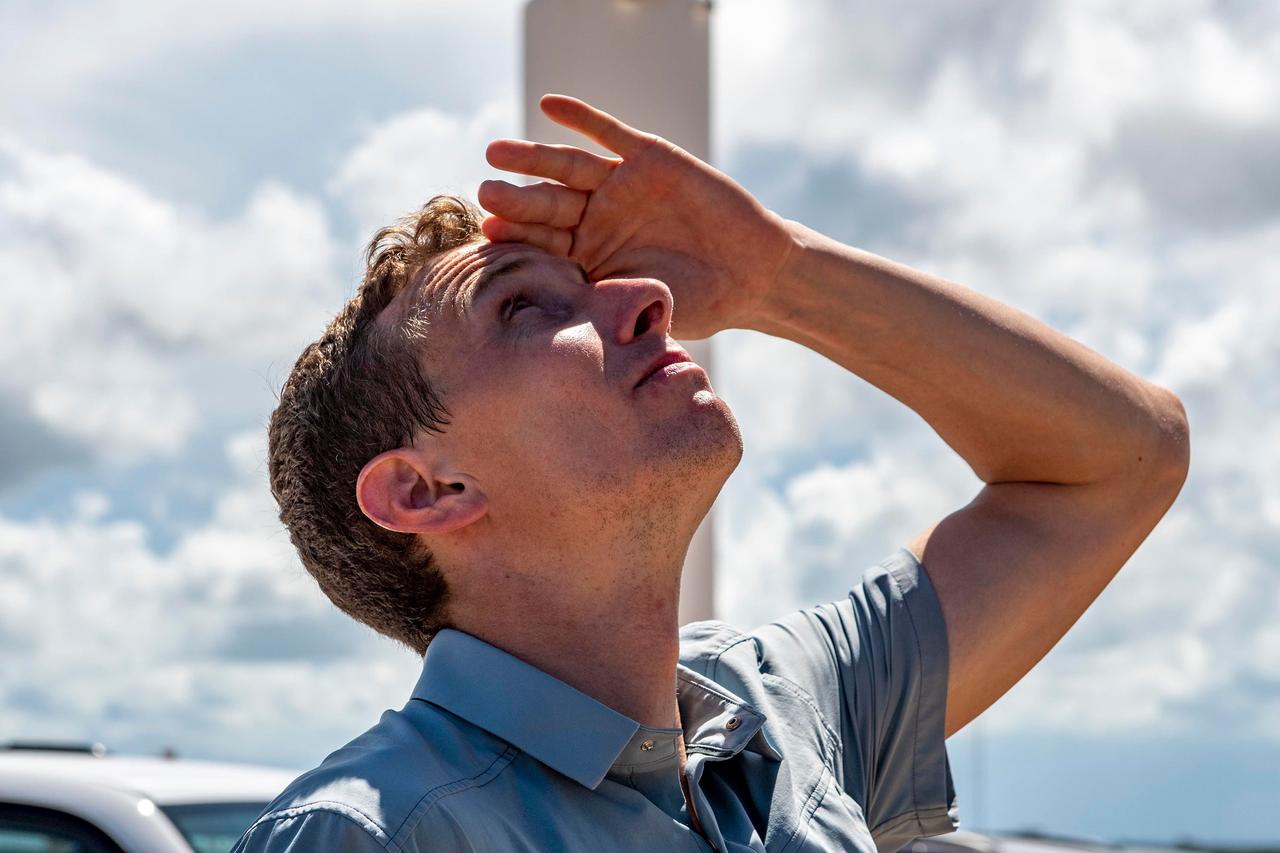

jsc2022e065080 (Aug. 8, 2022) --- Pilot Warren "Woody" Hoburg from NASA of the SpaceX Crew-6 mission is pictured during a training session at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A in Florida. Credit: SpaceX

Seen here is a close-up view of stickers for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3, Crew-4, and Crew-5 missions that were placed on one of the Tesla Model X cars that carry astronauts from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronauts participated in a countdown dress rehearsal on Oct. 2, 2022, in preparation for the upcoming Crew-5 launch. SpaceX’s Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Nicole Aunapu Mann and Josh Cassada, Roscosmos cosmonaut Anna Kikina, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Koichi Wakata to the International Space Station for a science expedition mission as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for noon EDT on Oct. 5, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
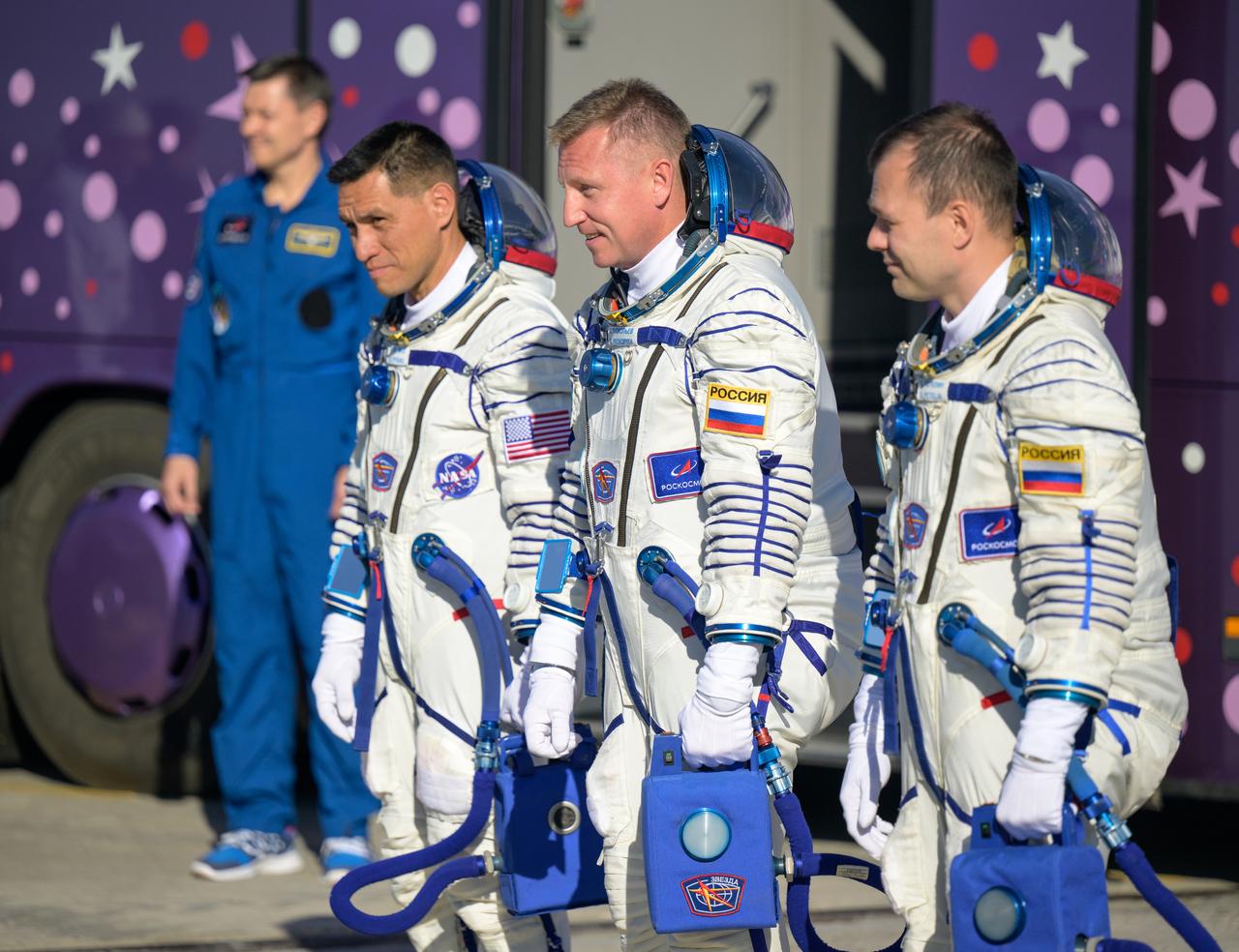

Expedition 68 astronaut Frank Rubio of NASA, left, and cosmonauts Sergey Prokopyev and Dmitri Petelin of Roscosmos, right, arrive at the launch pad to board their Soyuz MS-22 spacecraft for launch, Wednesday, Sept. 21, 2022, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Rubio, Prokopyev and Petelin launched onboard the Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome for a mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Monday, May 23, 2022. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Astronaut Frank Rubio trains with hardware at the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center before his flight to the International Space Station.
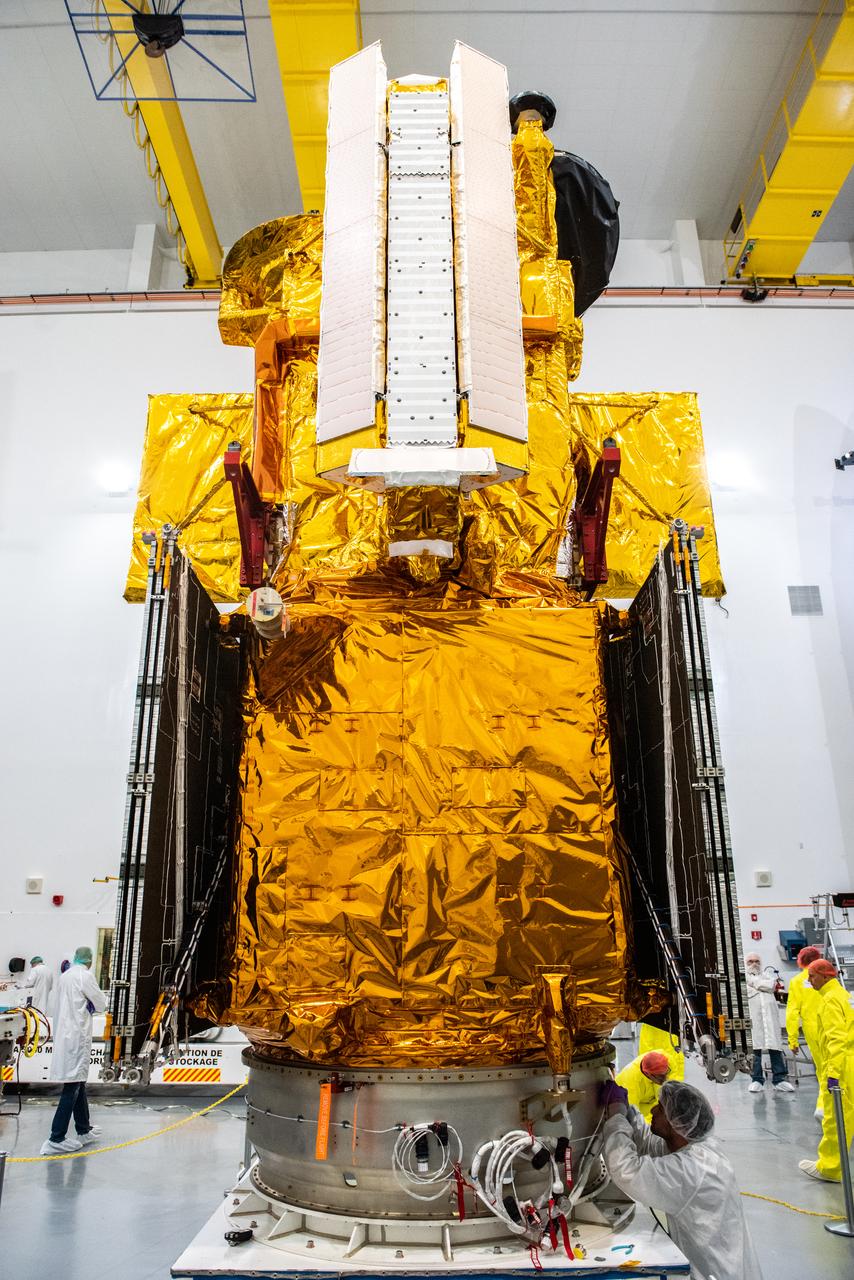

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a crane lifts the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite onto the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
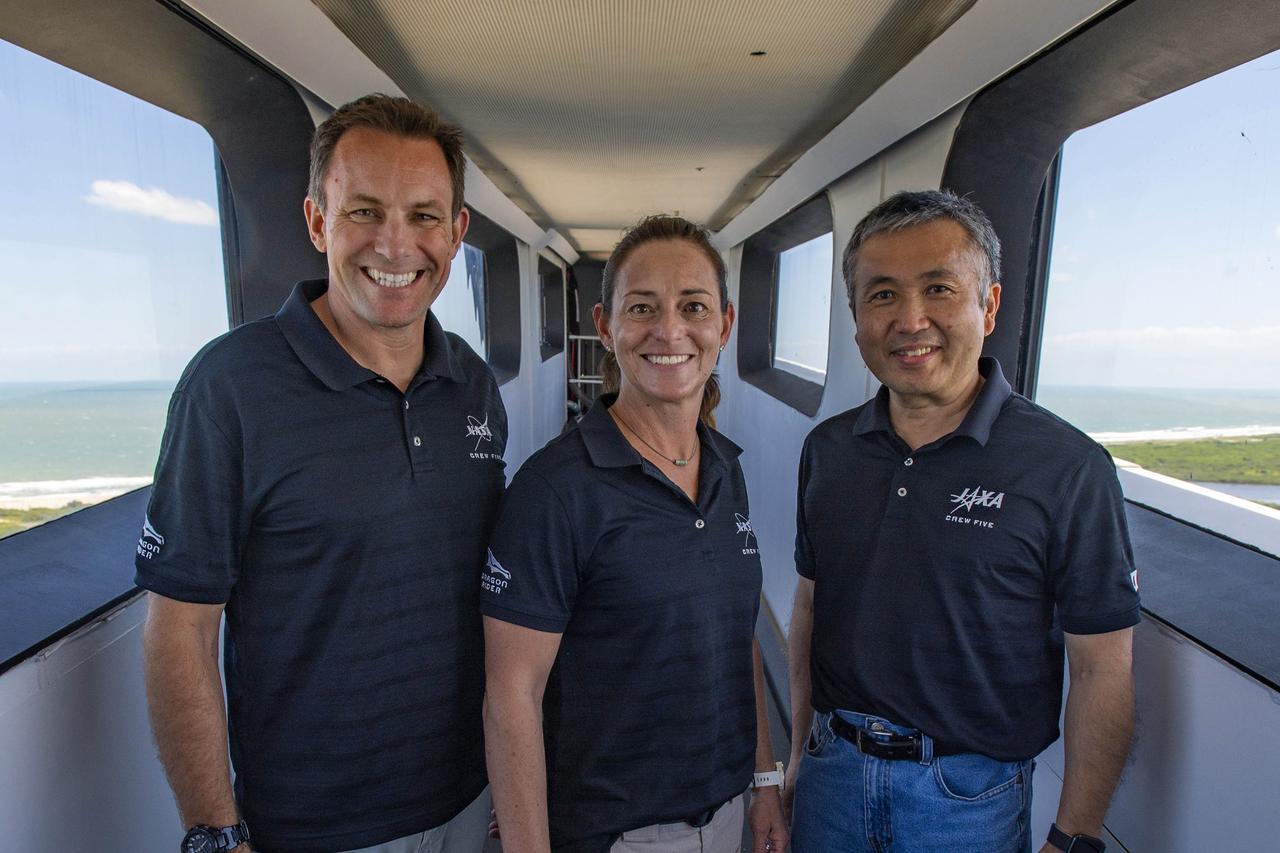

From left, NASA astronauts Josh Cassada and Nicole Mann, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Koichi Wakata, are photographed inside the crew access arm at Launch Complex 39A during a visit to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 10, 2022. Cassada, Mann, and Wakata, along with Roscosmos cosmonaut Anna Kikina, will launch to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 mission for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Liftoff of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft is scheduled for Oct. 3, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
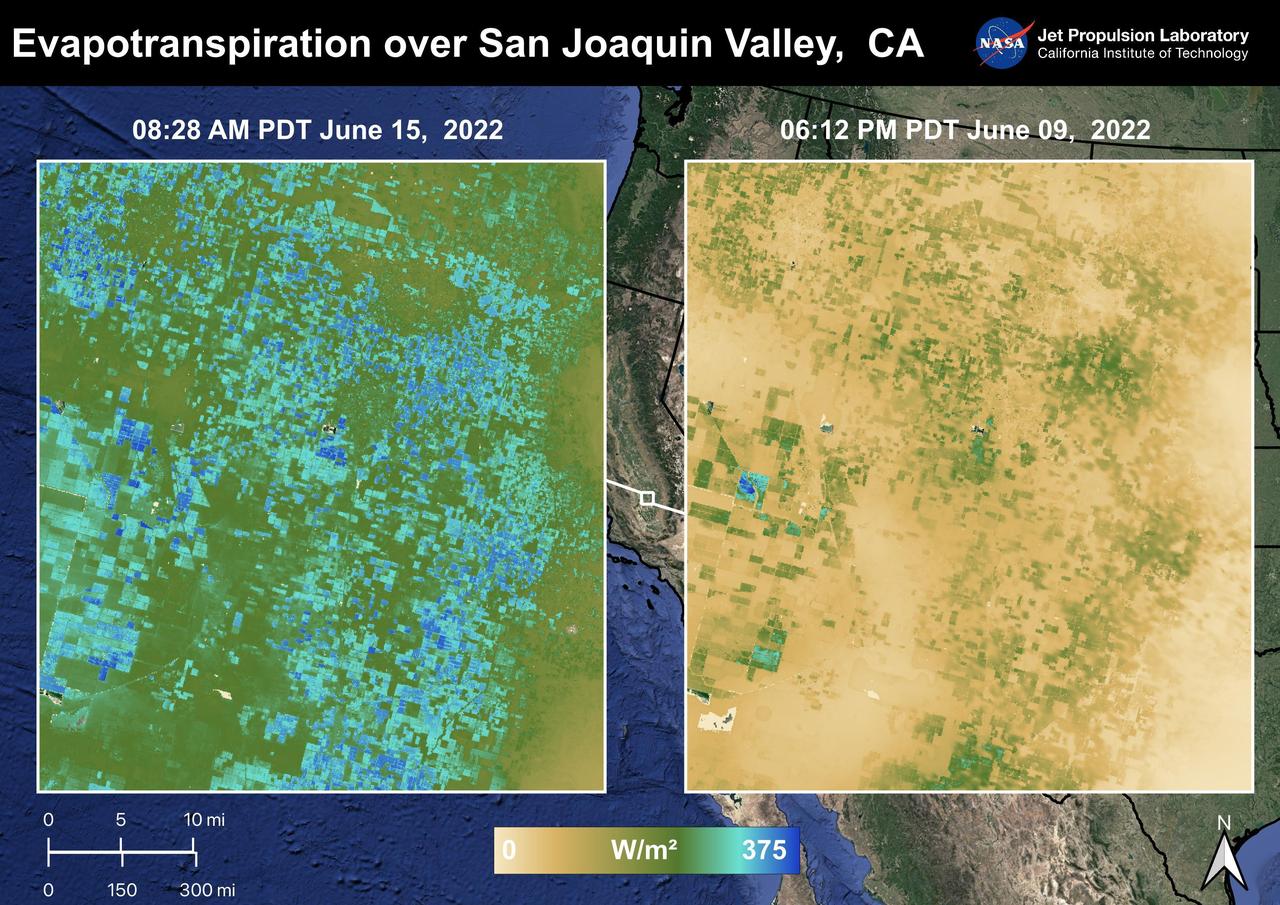
The Central Valley, CA is one of the most productive agricultural regions in the United States and the world. As California is in a continuing drought, it is important to monitor agricultural plant life to ensure maximized productivity. ECOSTRESS has the ability to monitor Evapotranspiration over agricultural fields. This Evapotranspiration image on the right was captured on June 09, 2022 at 06:12 PM PDT. The image on the left was captured by ECOSTRESS on June 15, 2022 at 08:27 AM PDT. Blue indicates high water use while brown indicates dry conditions. ECOSTRESS is a thermal instrument on the International Space Station that measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the day. It was launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify critical thresholds of water use and water stress in plants and to detect the timing, location, and predictive factors leading to plant water uptake decline and/or cessation. The nature of the high-resolution data provided by ECOSTRESS allows it to record heat related phenomena such as heat waves and wildfires. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25486
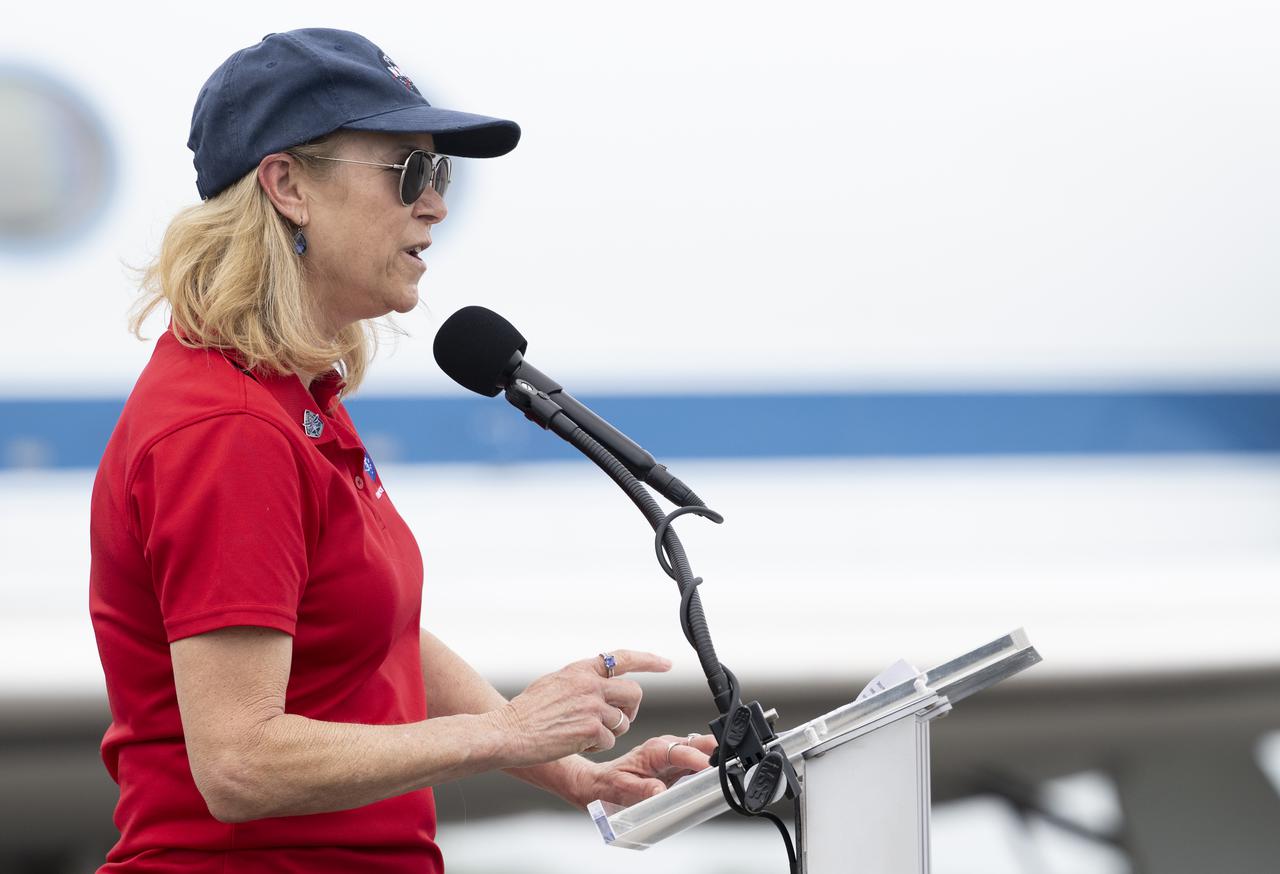

Kennedy Space Center director Janet Petro speaks to members of the media after the arrival of NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Robert Hines, Jessica Watkins, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center ahead of SpaceX’s Crew-4 mission, Monday, April 18, 2022, in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 mission is the fourth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Lindgren, Hines, Watkins, and Cristoforetti are scheduled to launch at April 23 at 5:26 a.m. EDT, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
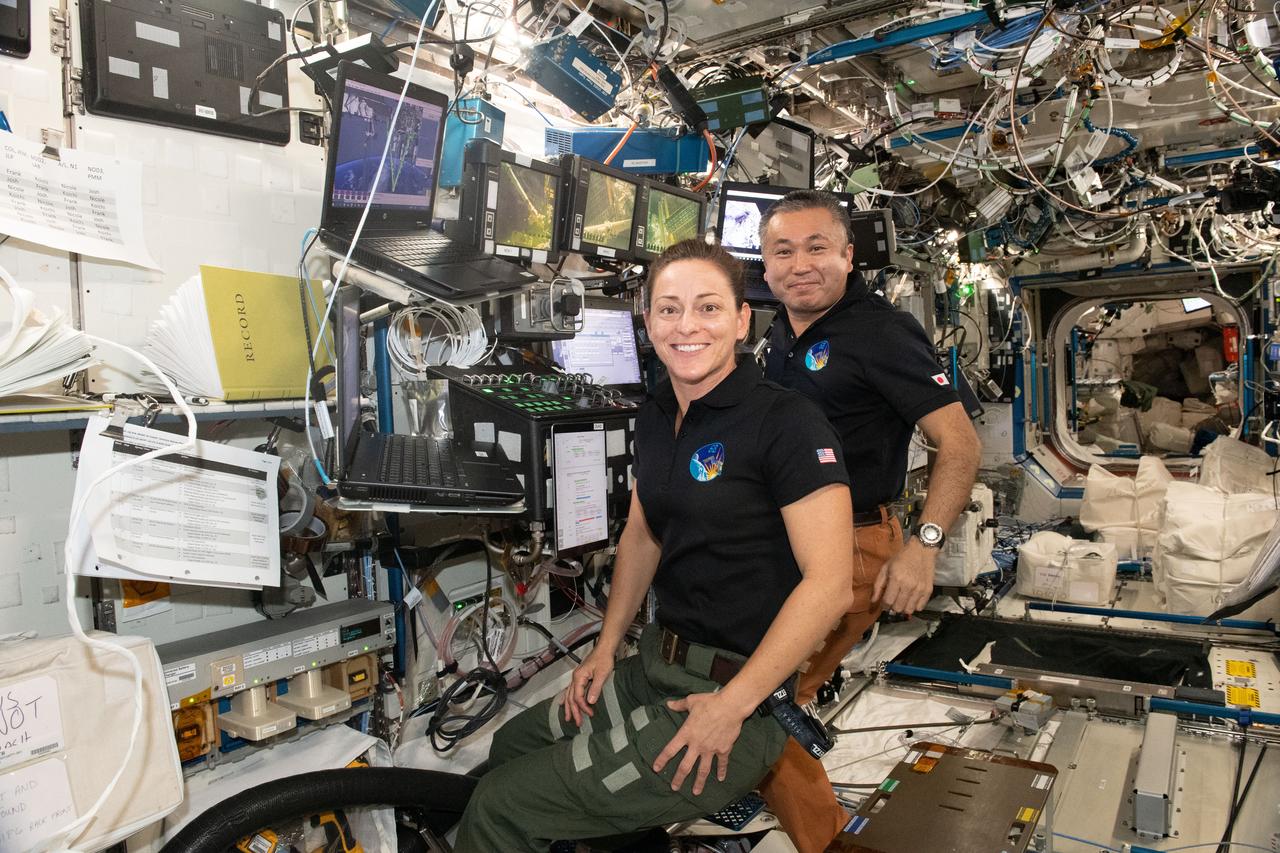

iss068e026335 (Dec. 3, 2022) --- Flight Engineers Nicole Mann of NASA and Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are pictured at the robotics workstation that controls the Canadarm2 robotic arm from inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. The duo assisted NASA spacewalkers Josh Cassada and Frank Rubio (out of frame) who were on the outside of the orbiting lab installing a roll-out solar array on the Starboard-4 truss segment.
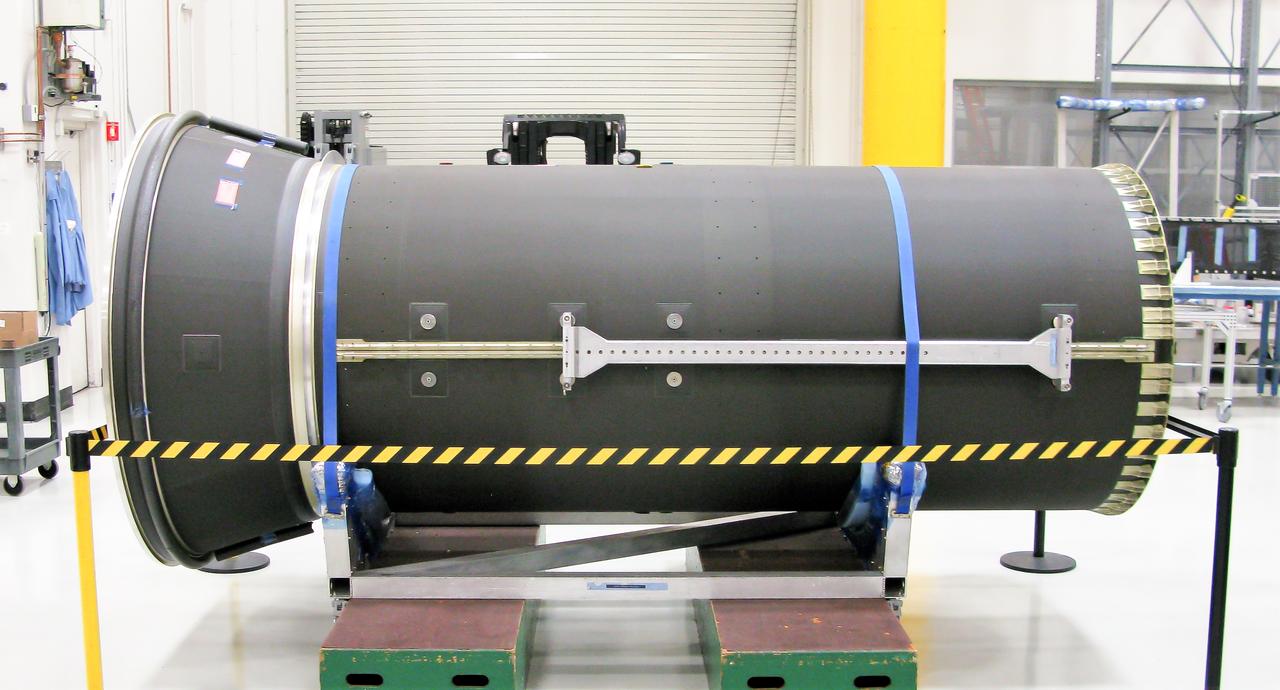

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
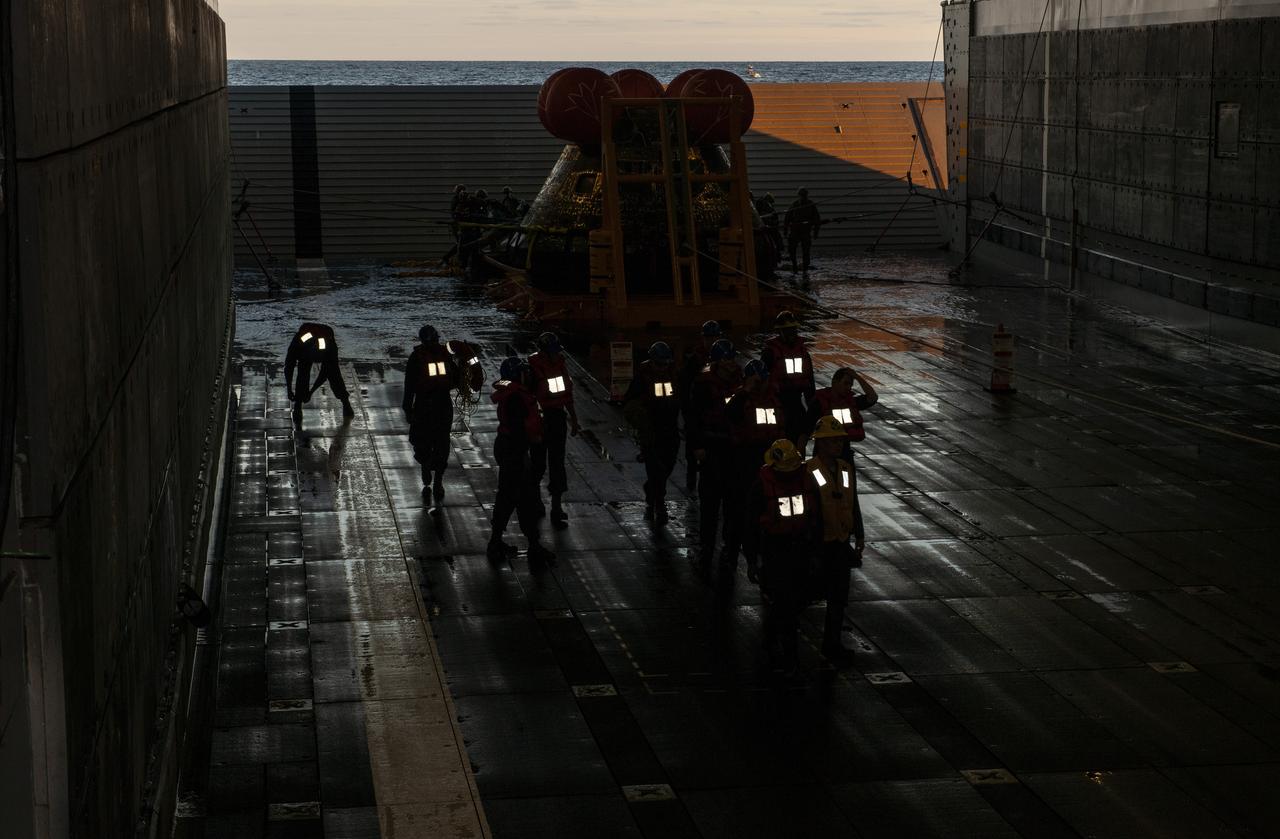

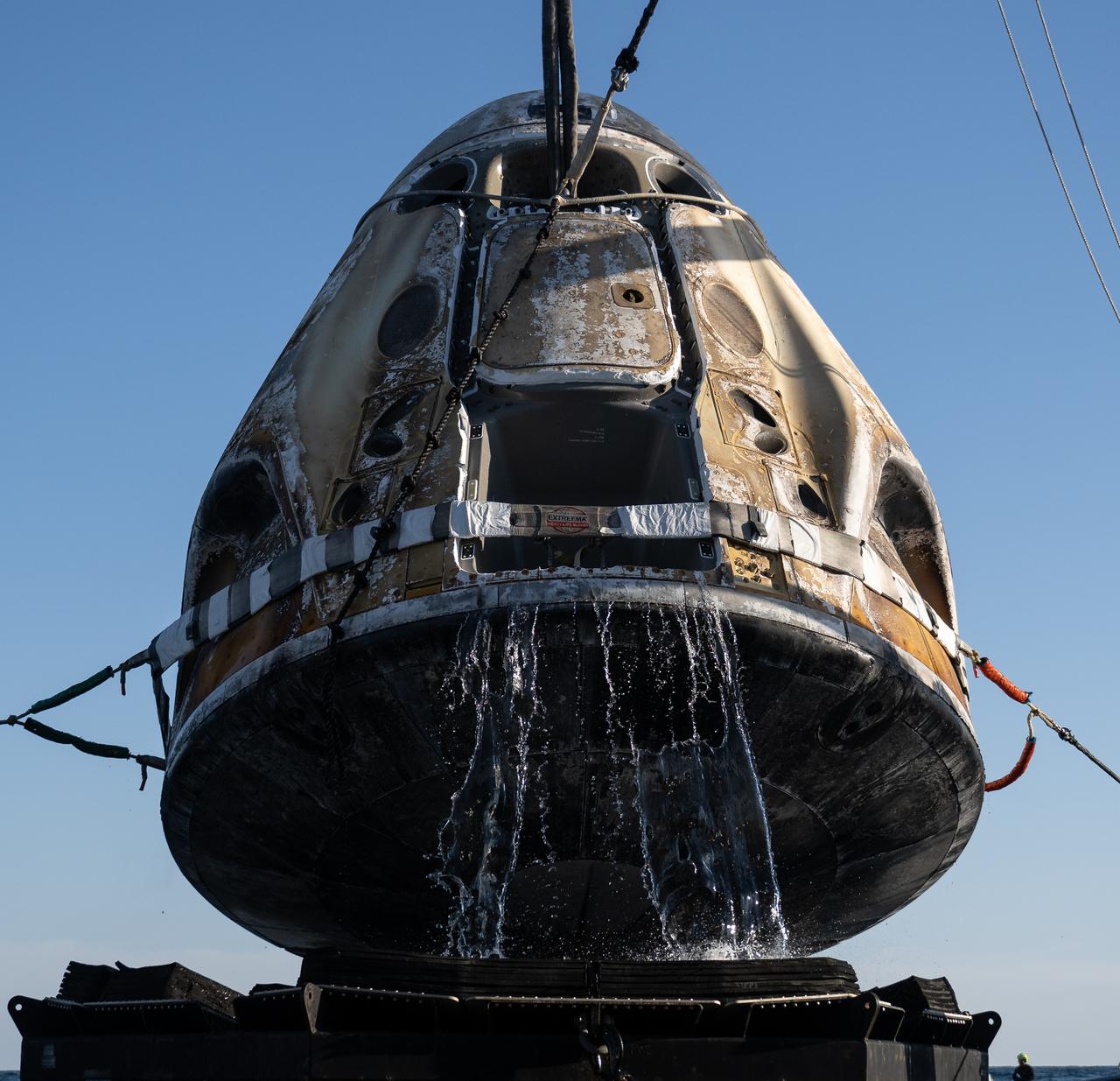
NASA’s Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission was successfully recovered inside the well deck of the USS Portland on Dec. 11, 2022 off the coast of Baja California. After launching atop the Space Launch System rocket on Nov. 16, 2022 from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Orion spent 25.5 days in space before returning to Earth, completing the Artemis I mission.
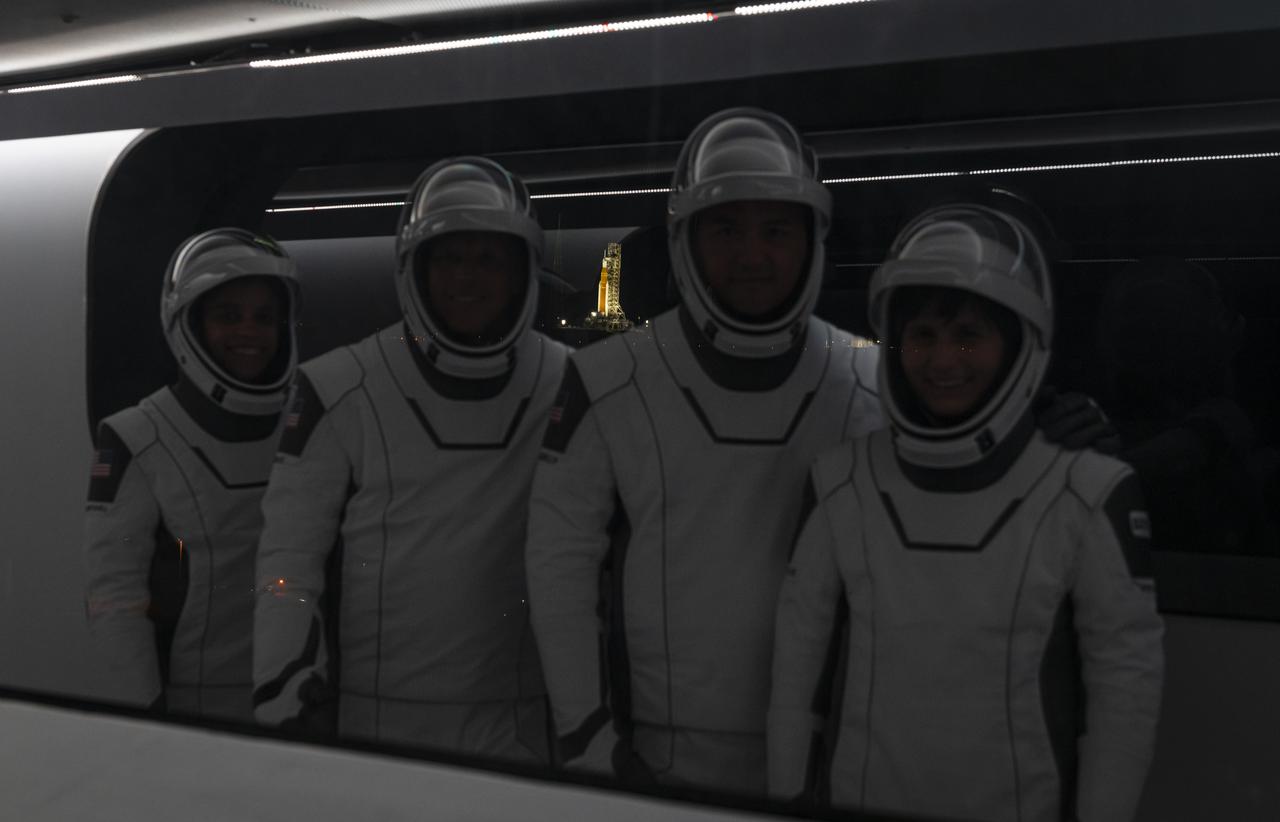

Crew-4 astronauts, from left, Jessica Watkins, Bob Hines, Kjell Lindgren, and Samantha Cristoforetti stand inside the crew access arm at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A during a dry dress rehearsal on April 20, 2022. Reflected and lit up in the background is NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission at Launch Complex 39B. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, with the company’s Crew Dragon, named Freedom by the Crew-4 crew, is targeted for liftoff no earlier than 4:15 a.m. EDT on Tuesday, April 26, 2022, from Pad 39A. The Crew-4 mission will carry the astronauts to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
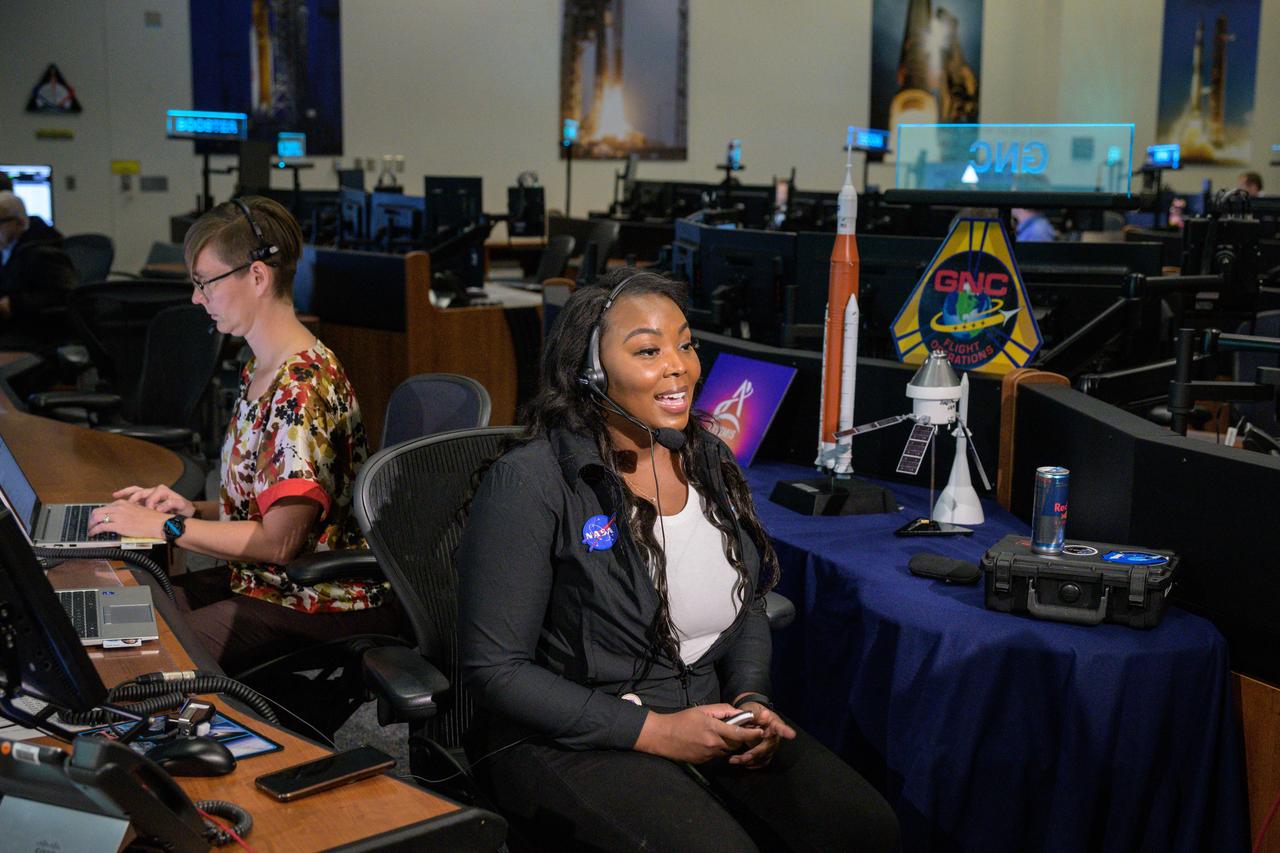

jsc2022e090743 (Dec. 1, 2022): Public Affairs Officer Shaneequa Vereen speaks on camera in Houston’s Mission Control Center as the Orion spacecraft departs its distant retrograde orbit on flight day 16 of the Artemis I mission – one of the steps needed to bring the spacecraft home from the Moon. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
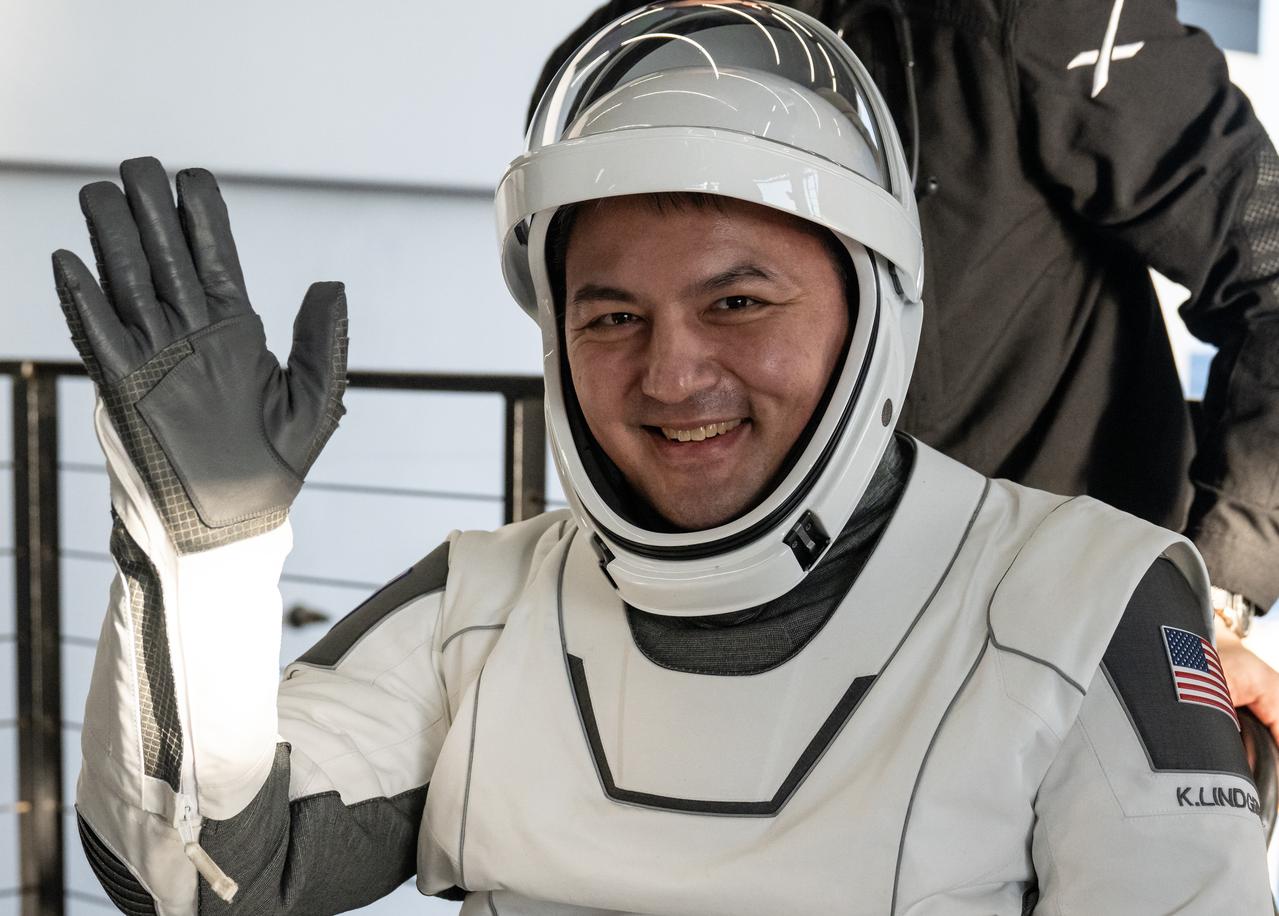

NASA astronaut Kjell Lindgren is helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Freedom spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship Megan after he, NASA astronaut Robert Hines, NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti, landed in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Jacksonville, Florida, Friday, Oct. 14, 2022. Lindgren, Hines, Watkins, and Cristoforetti are returning after 170 days in space as part of Expeditions 67 and 68 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
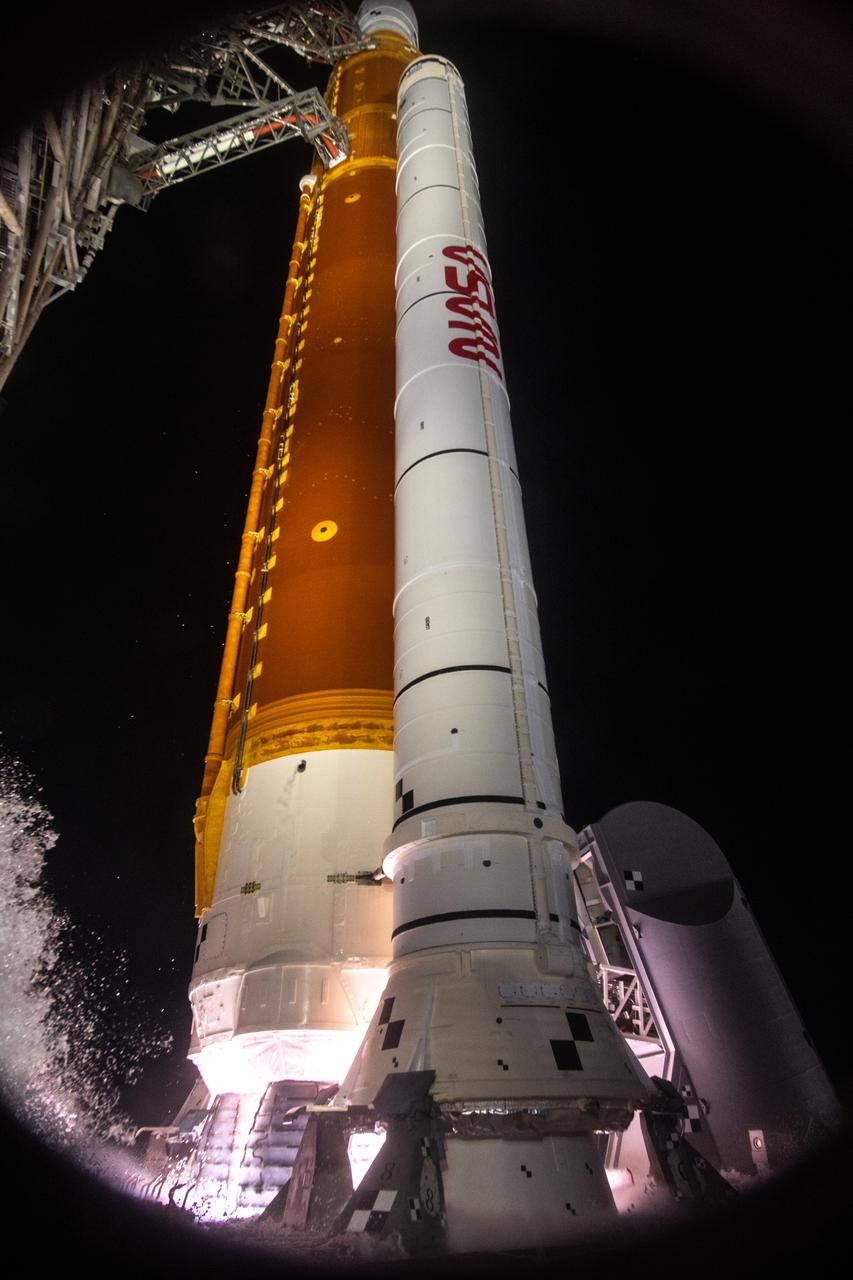

Liftoff! NASA’s Space Launch System carrying the Orion spacecraft lifts off the pad at Launch Complex 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2022. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
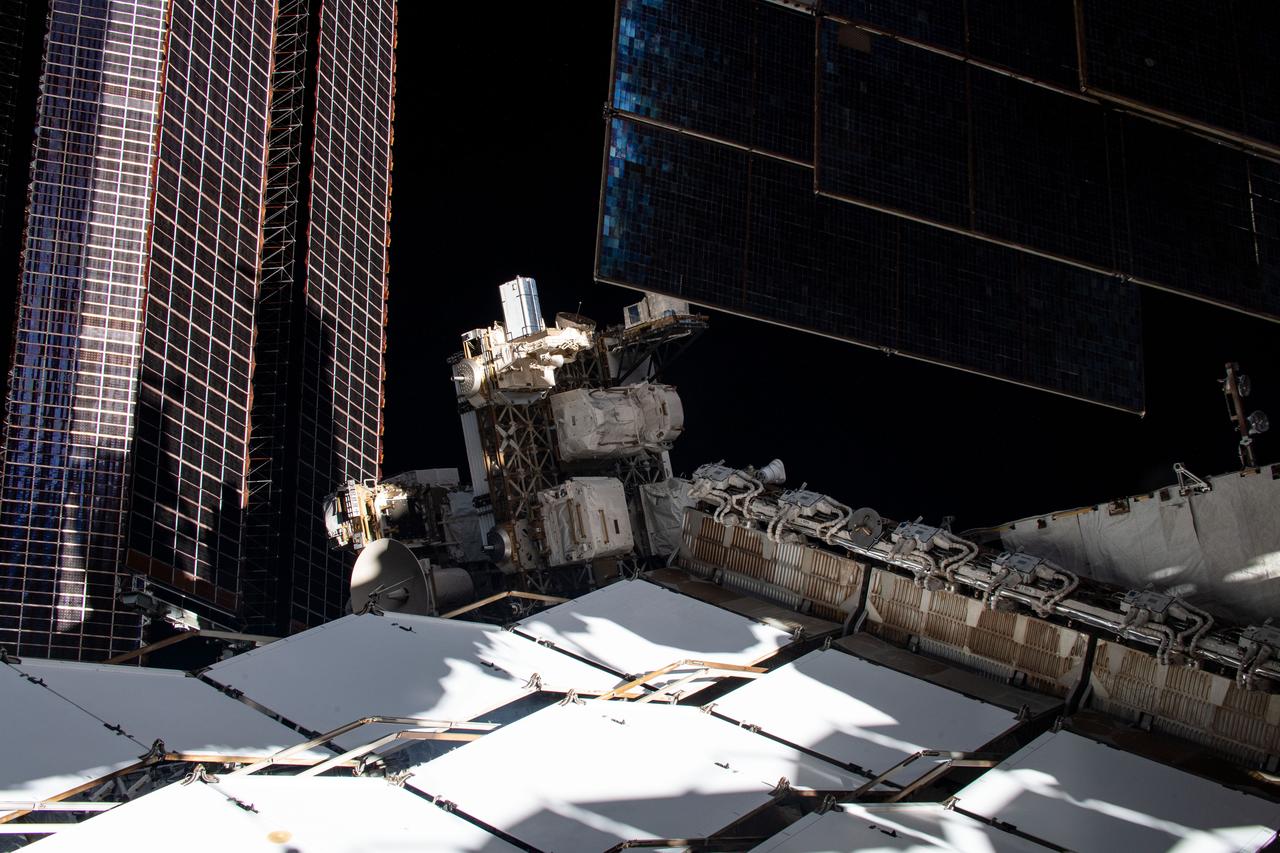

iss067e055839 (5/16/2022) --- Multiple User System for Earth Sensing (MUSES) is the first multi-user facility on an ISS ExPRESS Logistics Carrier (ELC). The facility primarily serves as a platform for earth-viewing sensors and other technologies requiring long-term access to the space environment.
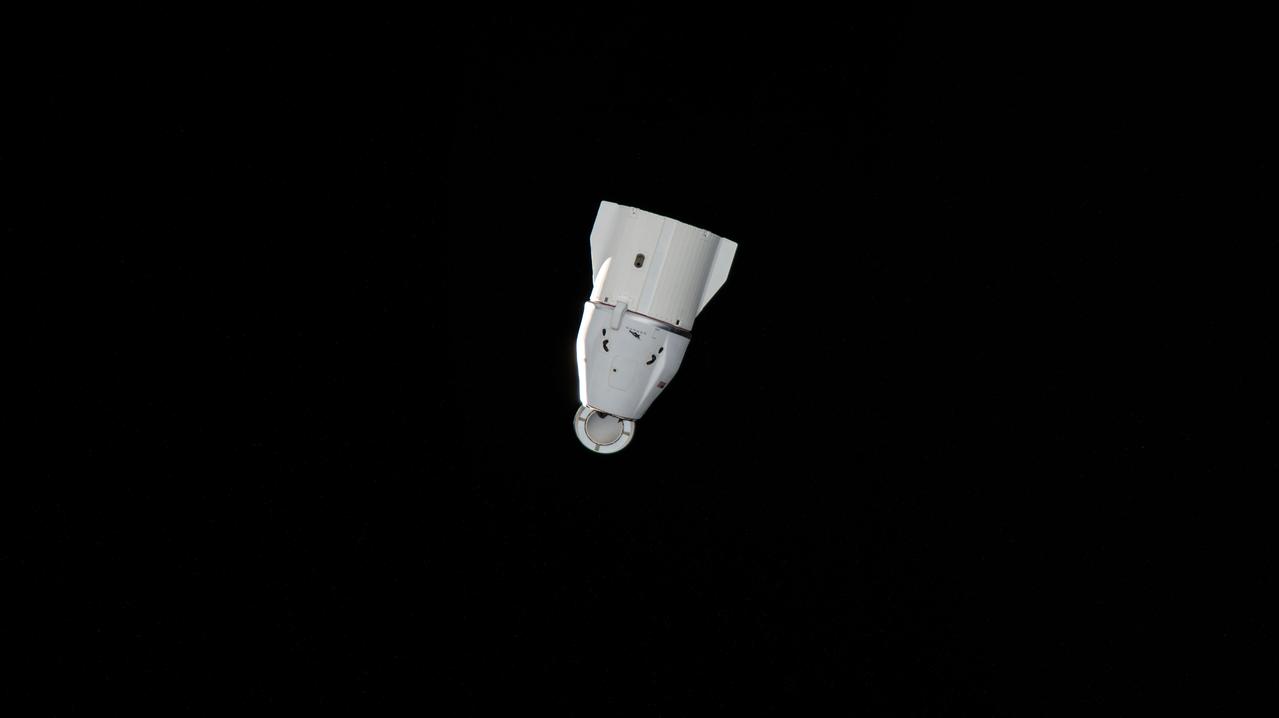

iss067e274277 (Aug. 19, 2022) --- The SpaceX Dragon resupply ship, packed with over 4,000 pounds of return cargo and science experiments for analysis, is pictured departing the vicinity of the International Space Station several minutes after undocking from the Harmony module's forward port.
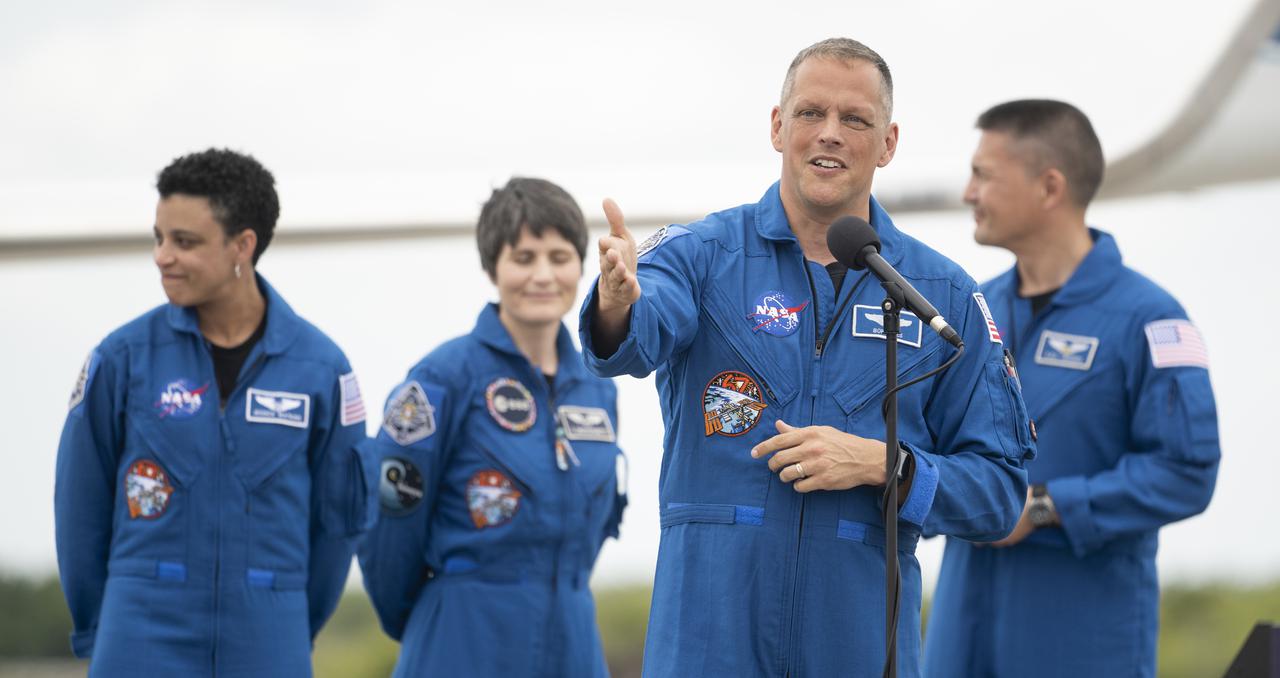

NASA astronaut Robert Hines speaks to members of the media after arriving at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center with fellow crewmates NASA astronauts Jessica Watkins, Kjell Lindgren, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti ahead of SpaceX’s Crew-4 mission, Monday, April 18, 2022, in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 mission is the fourth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Lindgren, Hines, Watkins, and Cristoforetti are scheduled to launch at April 23 at 5:26 a.m. EDT, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
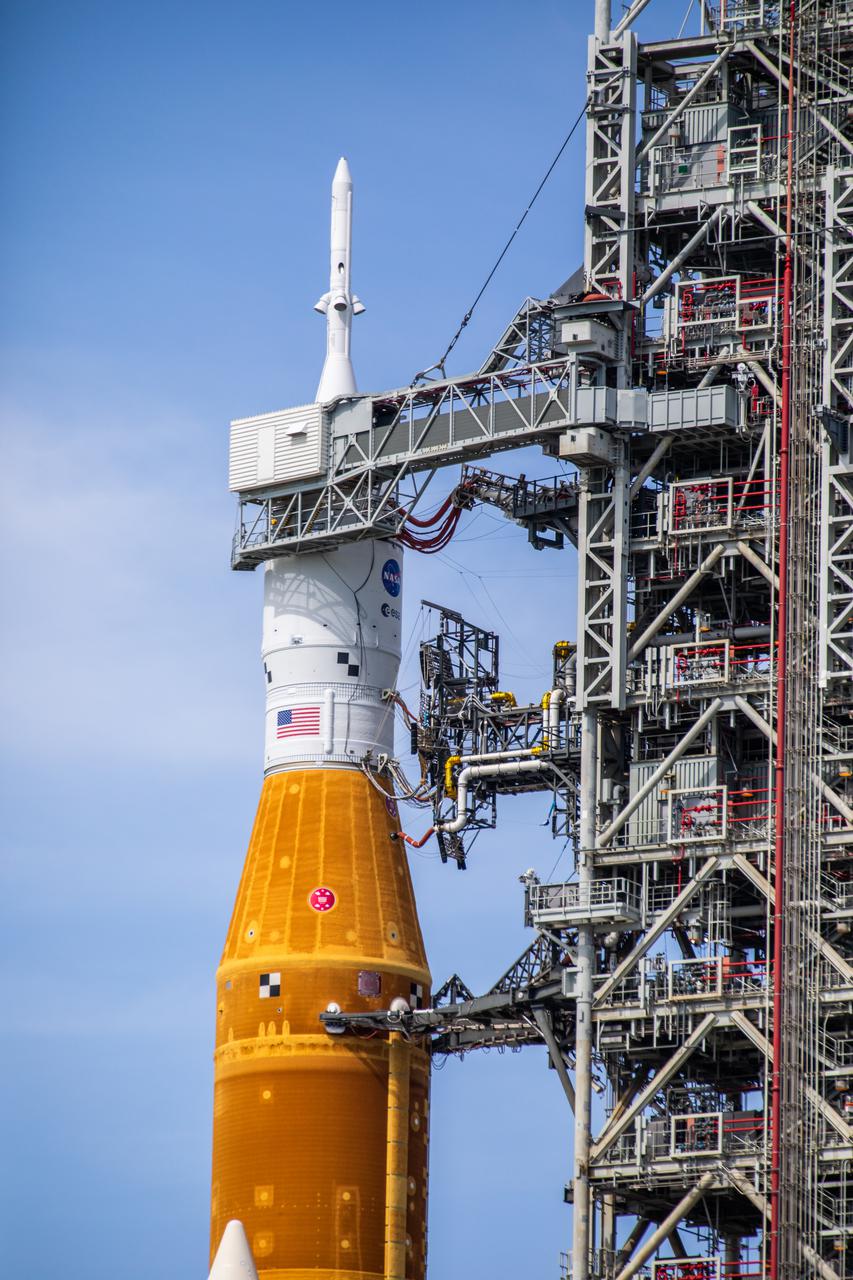

A close-up view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. A portion of the mobile launcher and umbilical connections are in view, as well as the crew access arm. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.

Director of Marshall Space Flight Center, Jody Singer, right, speaks on a panel with NASA's three other female center directors: Dr. Marla Peréz-Davis of Glenn Research Center, second from left, Vanessa Wyche of Johnson Space Center, center, and Janet Petro of Kennedy Space Center, second from right, moderated by NASA General Counsel, Sumara Thompson-King, left, during the "DirectHERS" - Launching Through the Glass Ceiling event, Tuesday, June 7, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)