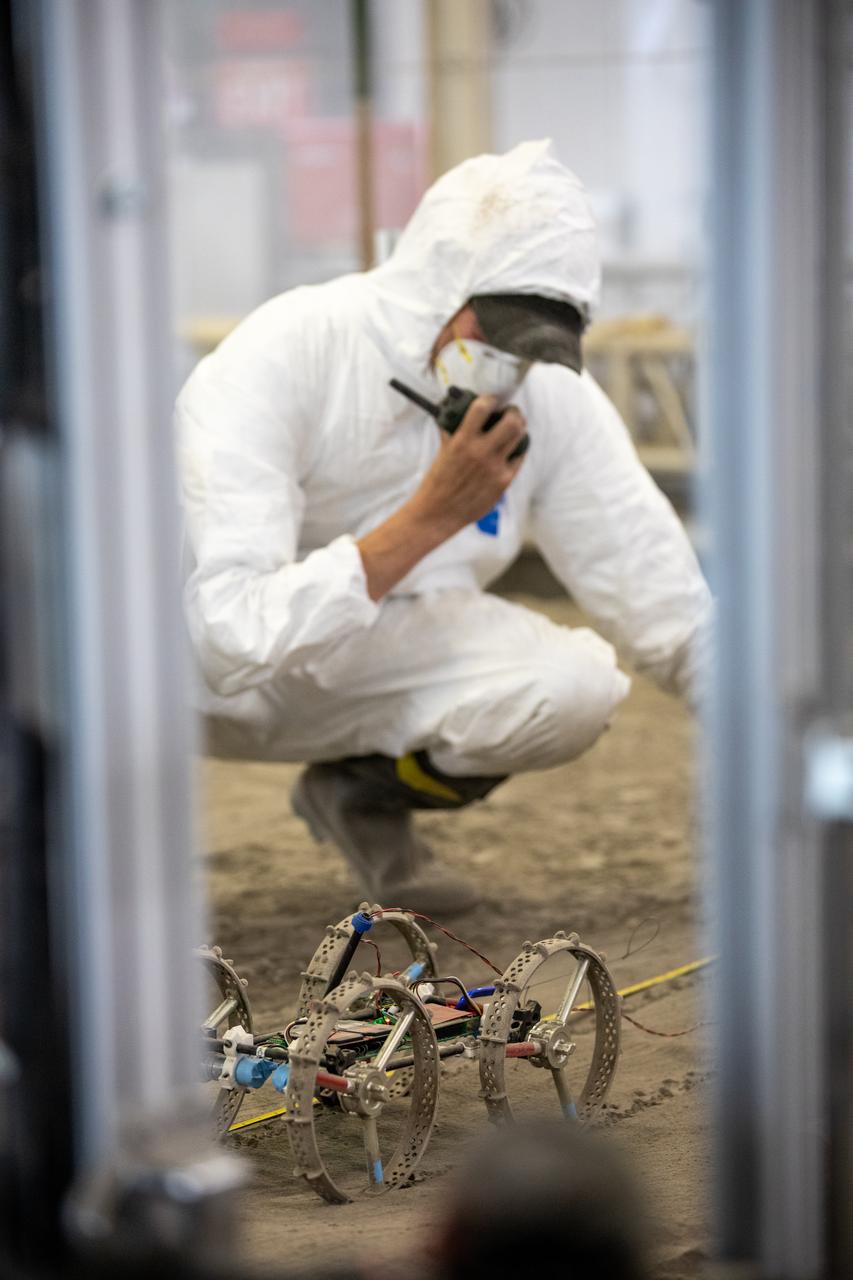

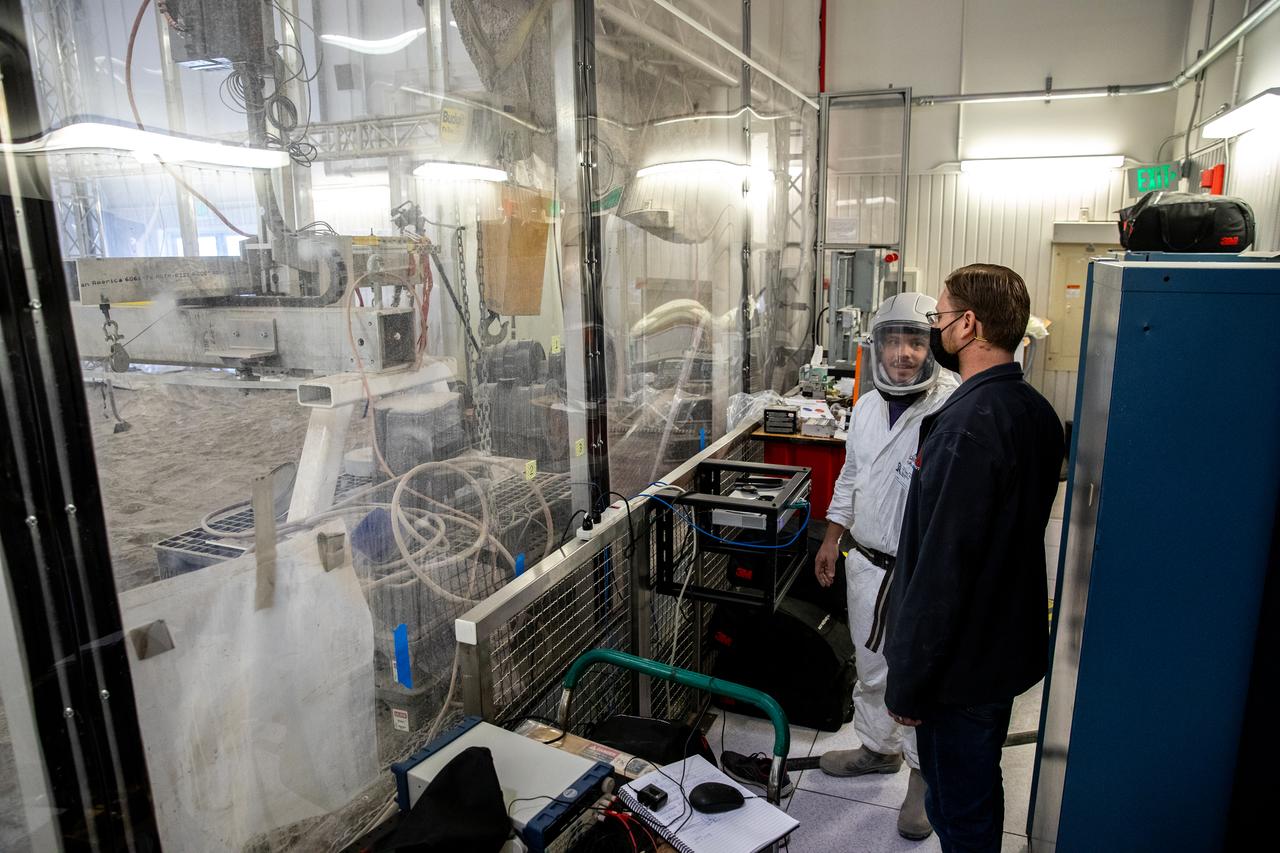
Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker reports the results of a drawbar pull run to Astrobotic staff outside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
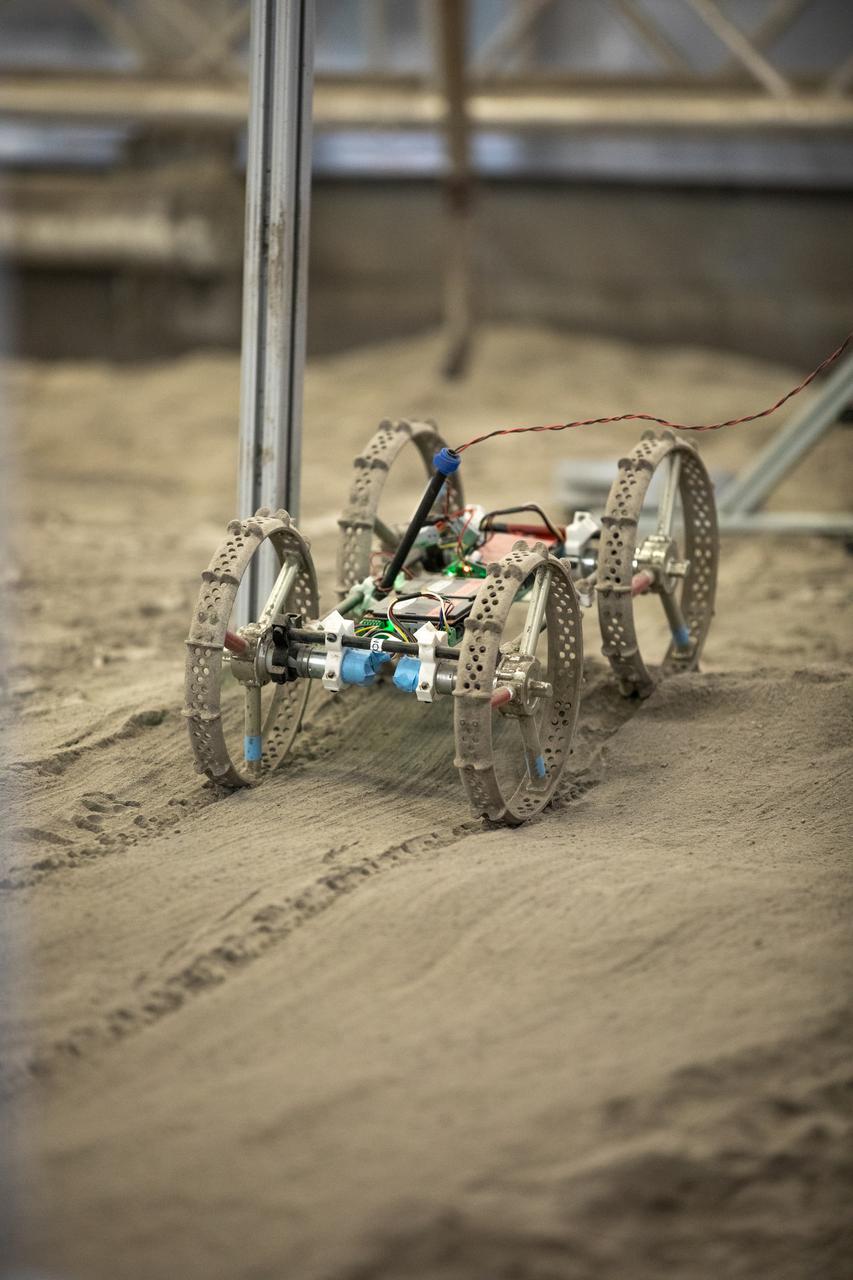

Astrobotic’s mass-offloaded CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – undergoes mobility testing inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
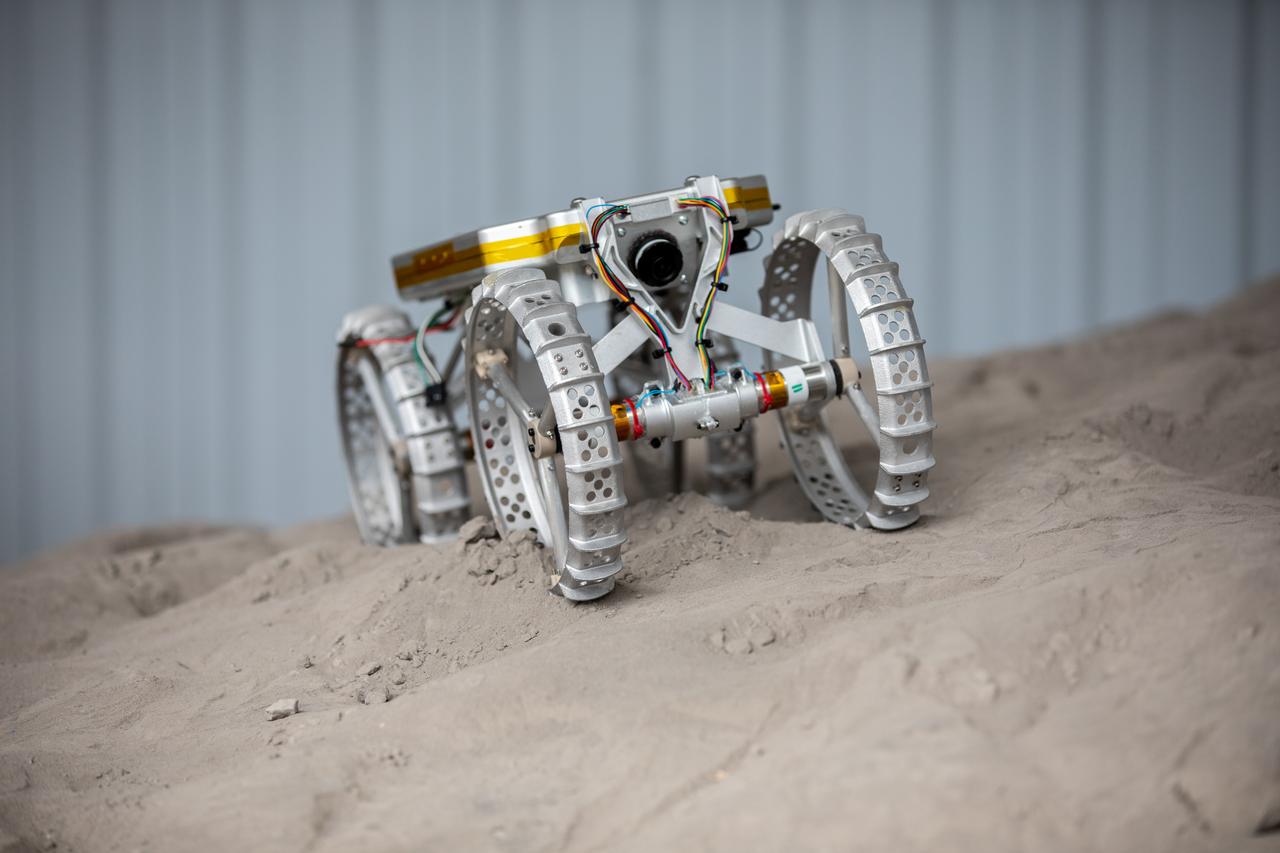
Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – undergoes mobility testing inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
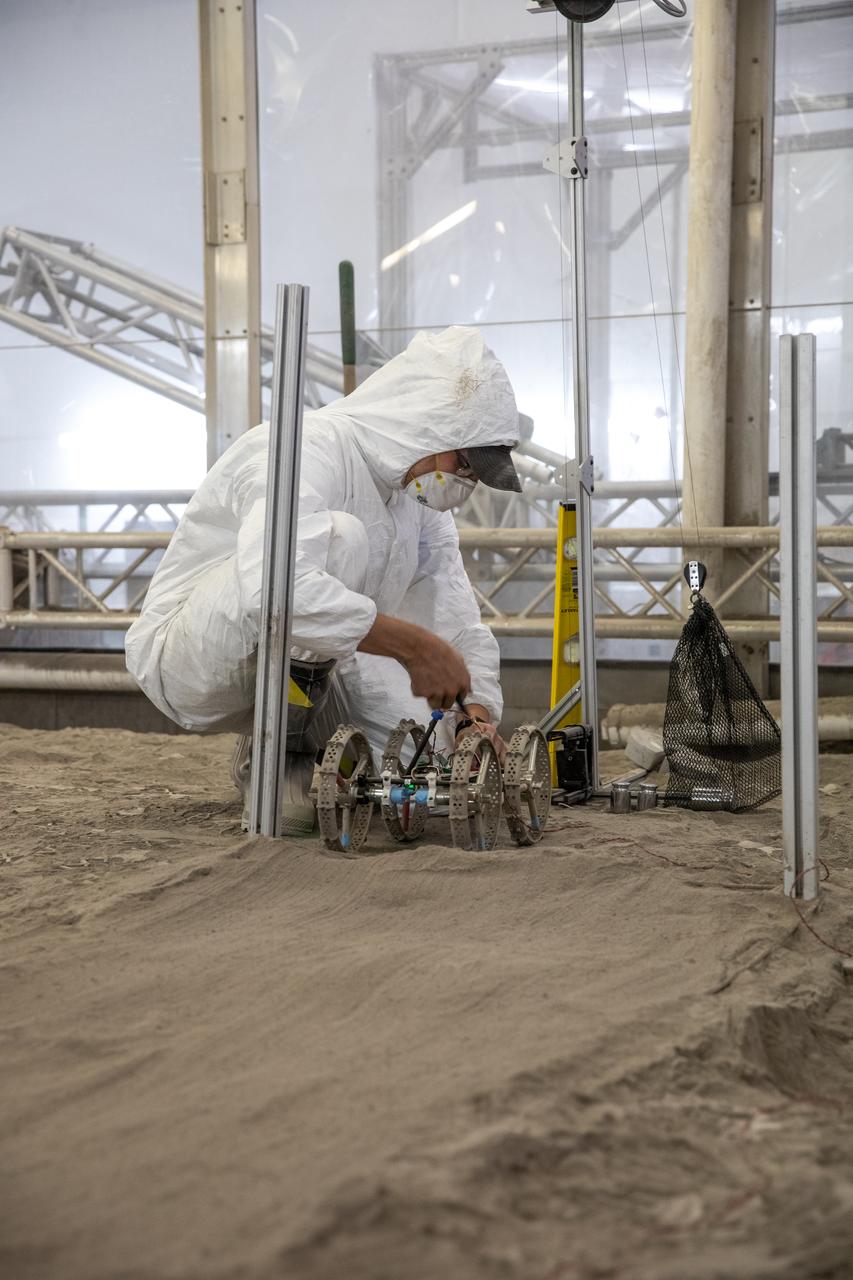

Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker stages Astrobotic’s mass-offloaded CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – for a drawbar pull test inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
A mass-offloaded version of Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – is used to simulate mobility in low lunar gravity inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
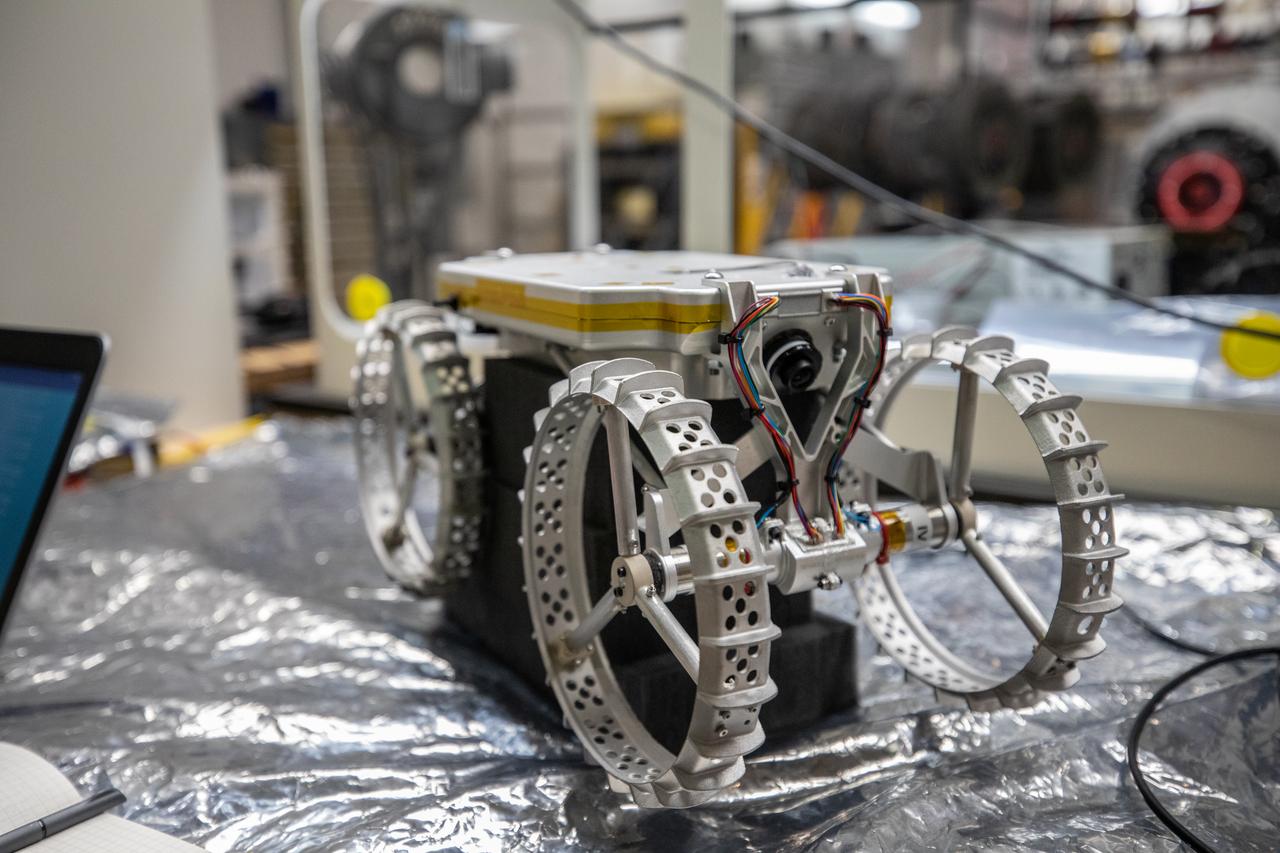
Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – is photographed in its benchtop testing configuration at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is planning to use the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
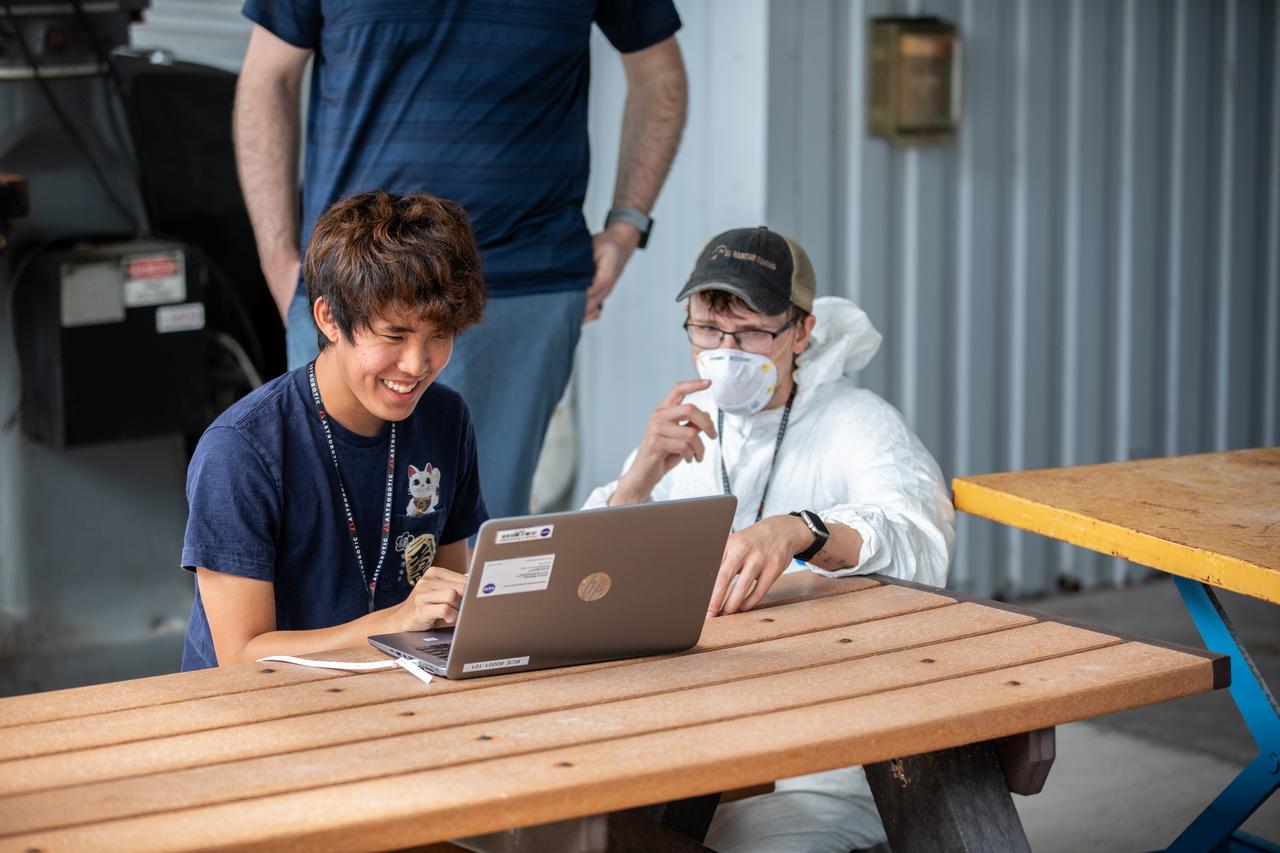

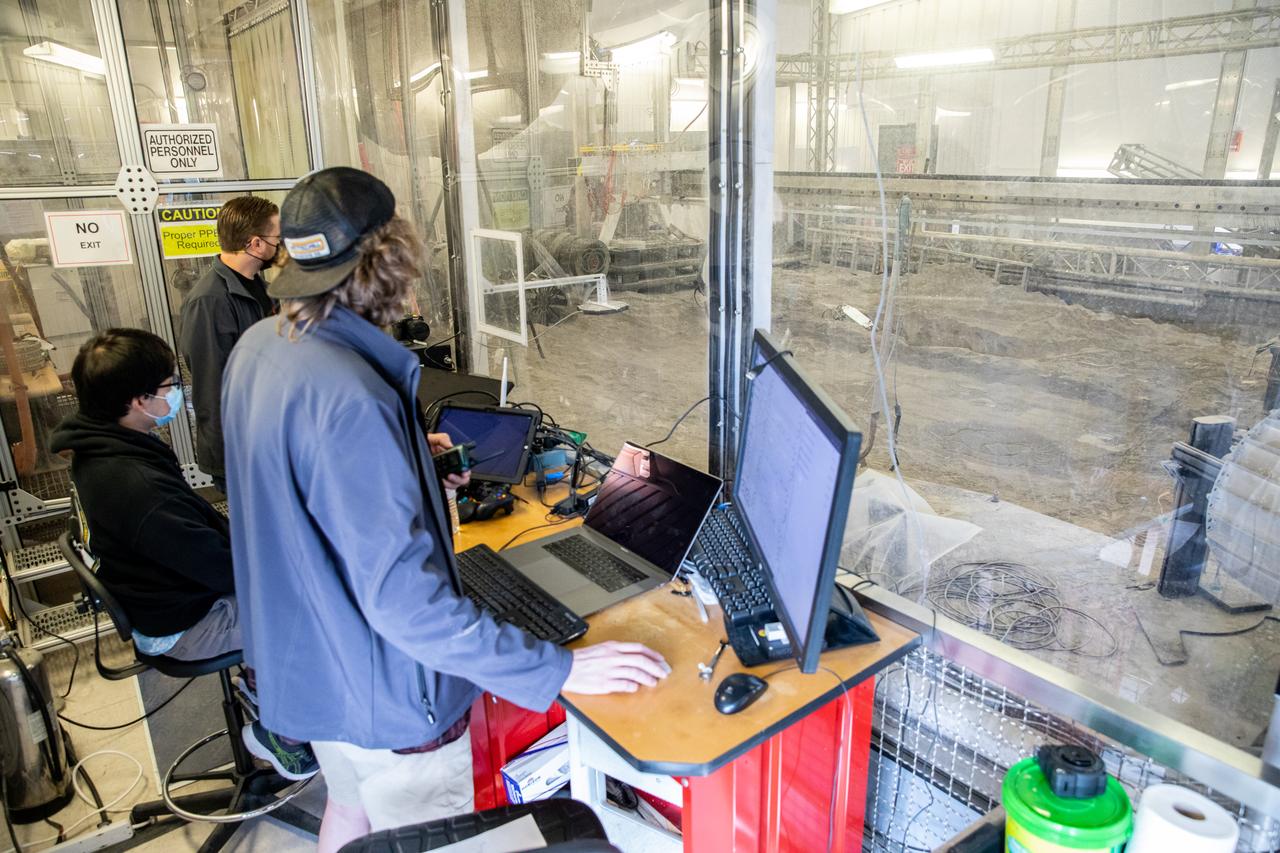
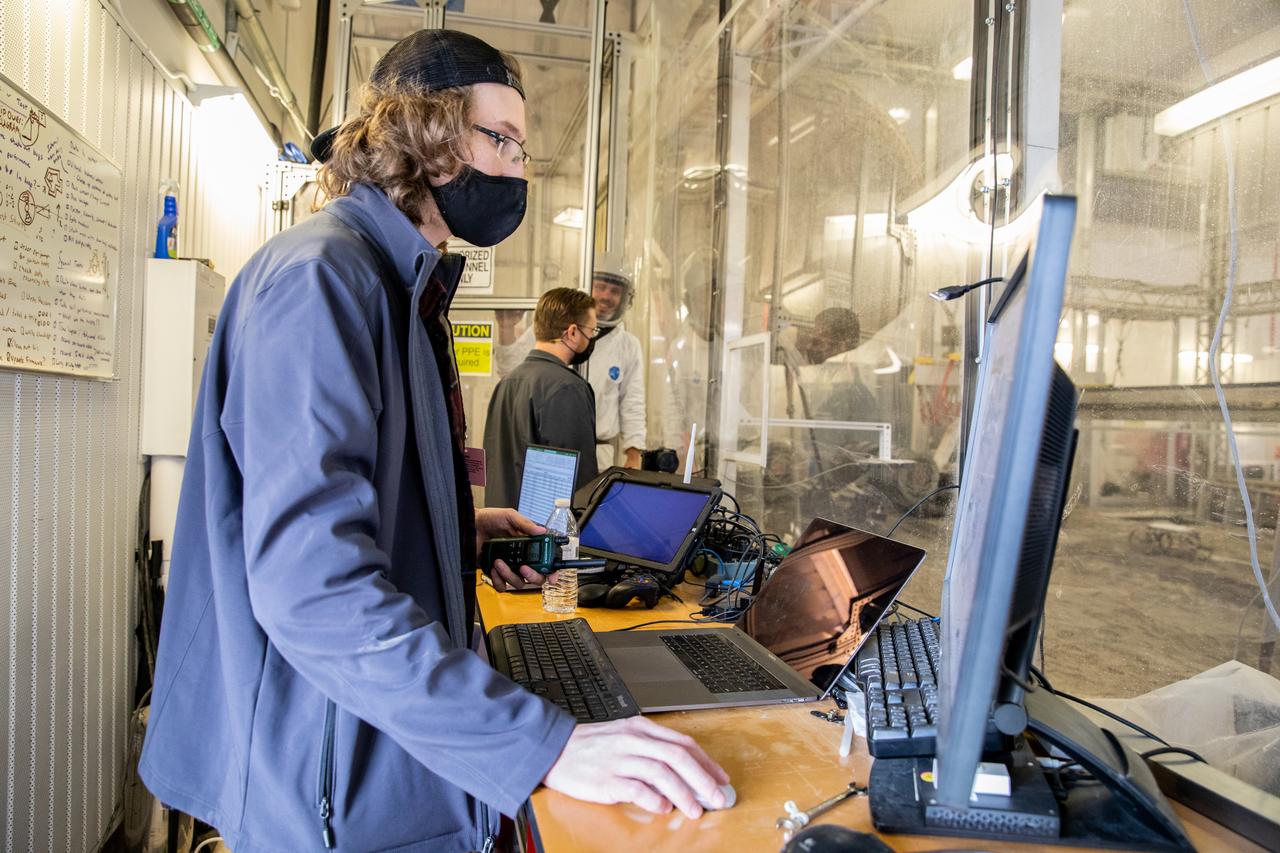
Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker (right) and Software Engineering intern Ashten Akemoto create a mobility routine for Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – using the company’s ground software at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
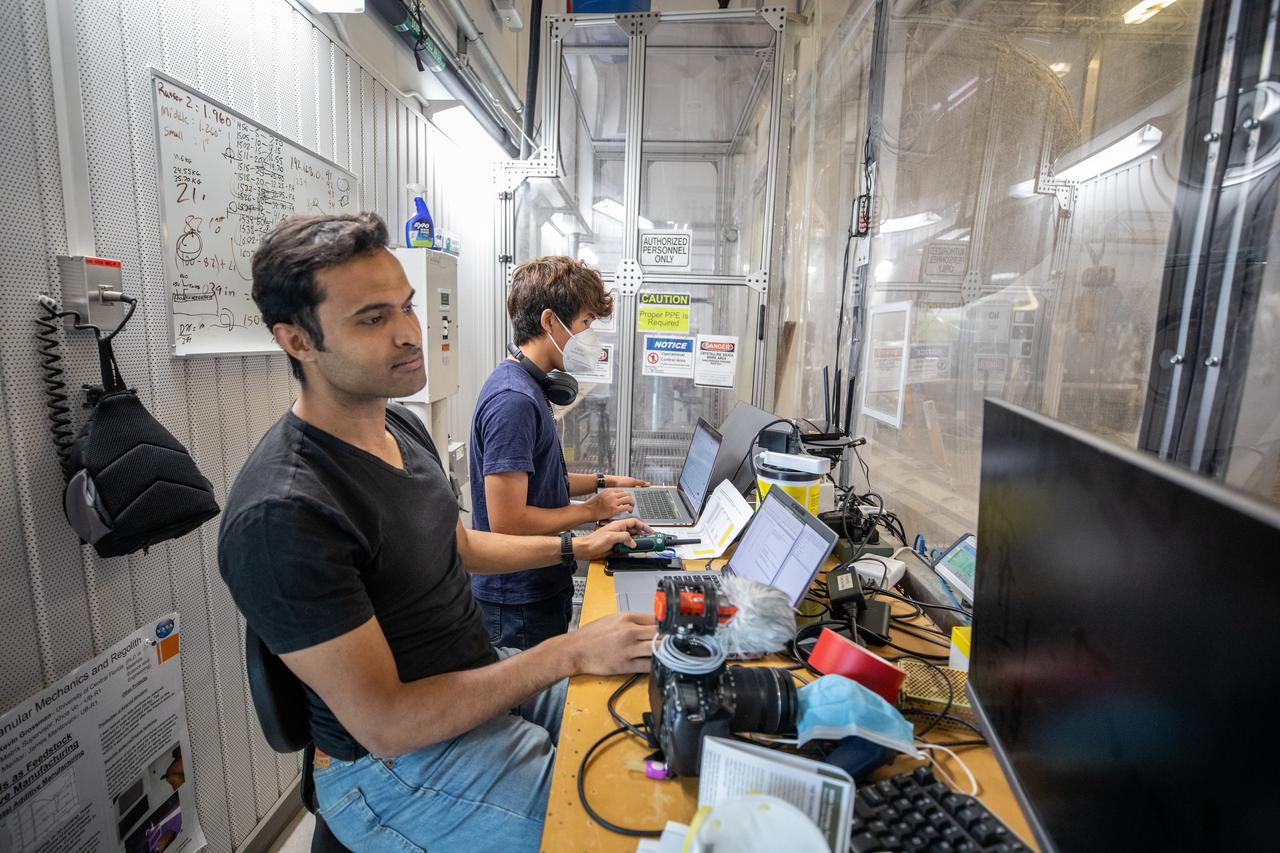

Senior Embedded Software Engineer Aamer Almujahed (left) and Software Engineering intern Ashten Akemoto run the ground software for Astrobotic’s CubeRover drawbar pull test inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.

Robotics Software Engineer II Chris Rampolla (right) and Software Engineering intern Ashten Akemoto issue commands to Astrobotic’s CubeRover using the company’s ground software during mobility testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
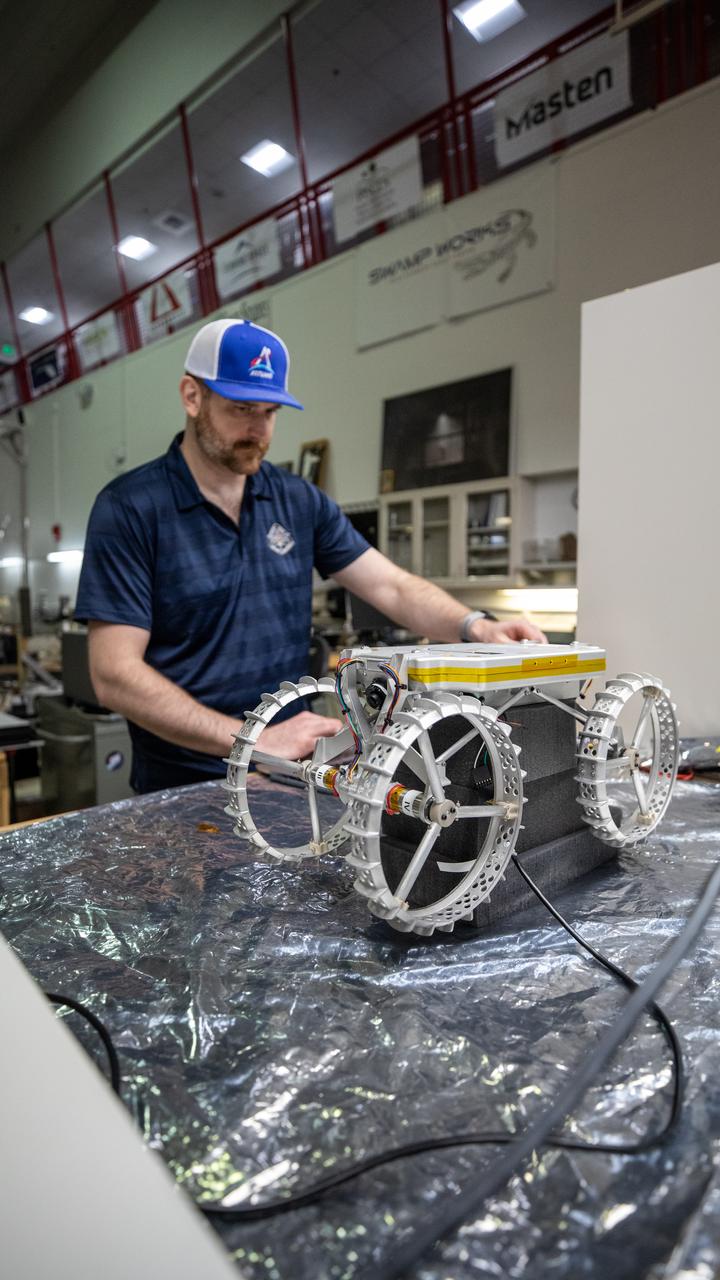

Robotics Software Engineer II Chris Rampolla runs benchtop verifications on Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – before delivery to Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is planning to use Swamp Work’s Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
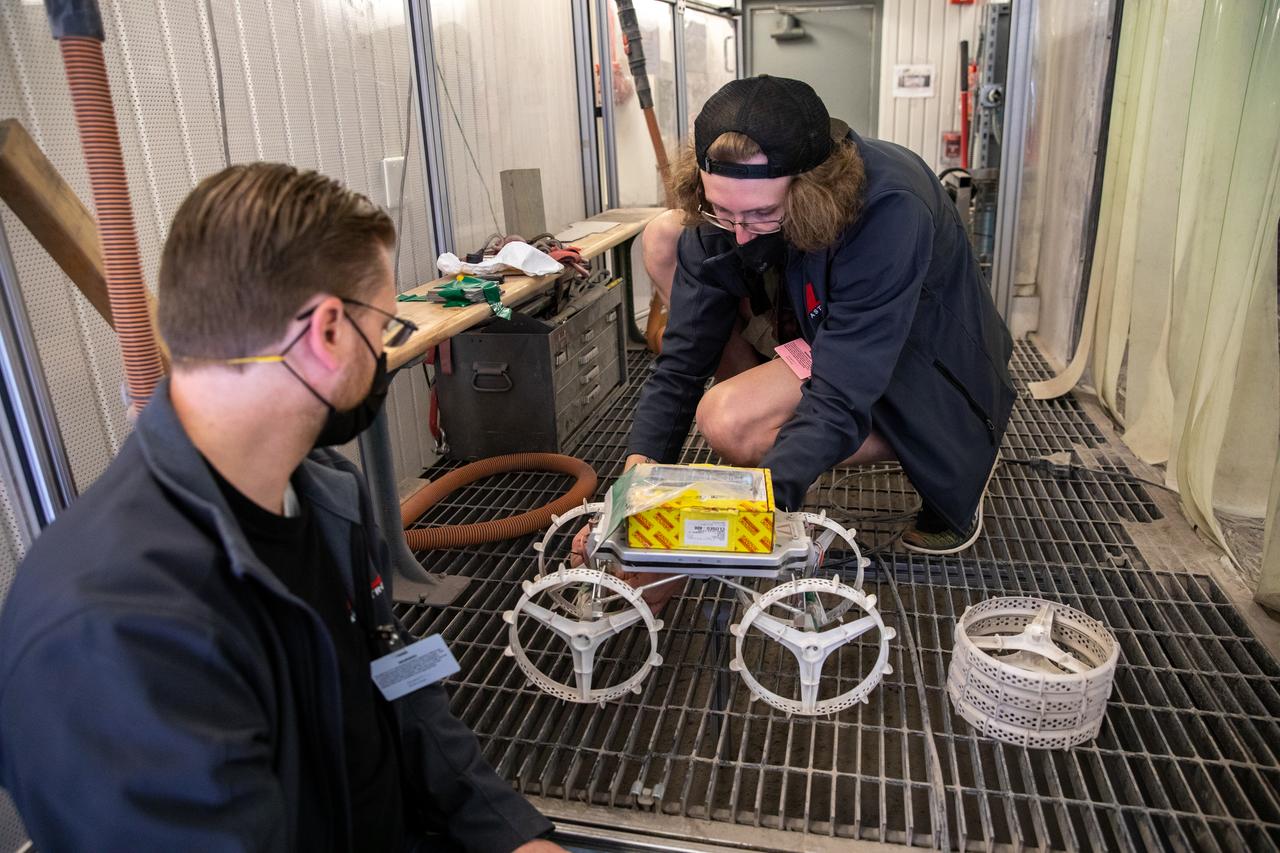

Astrobotic employees Troy Arbuckle, at left, Planetary Mobility lead mechanical engineer, and Taylor Whitaker, flight software engineer, prepare the Astrobotic CubeRover for its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

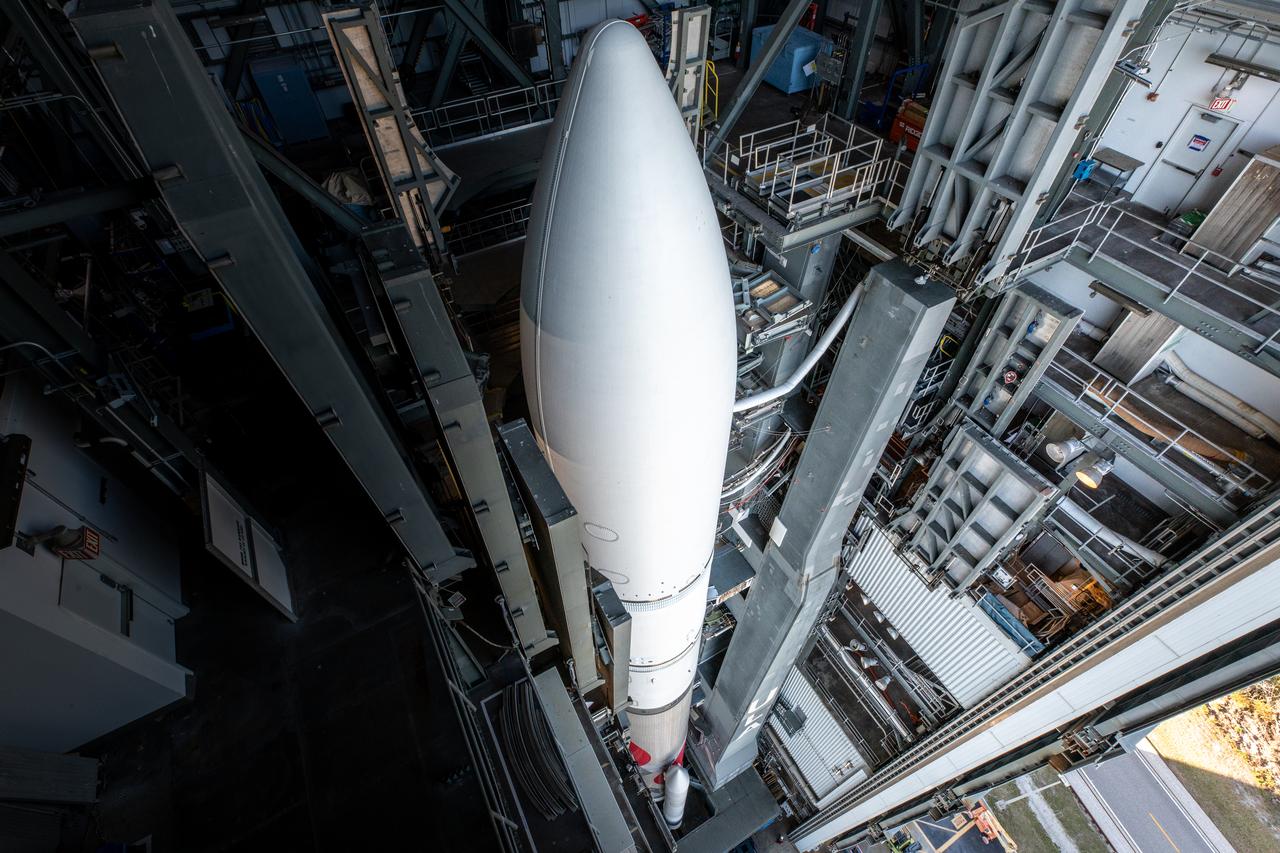
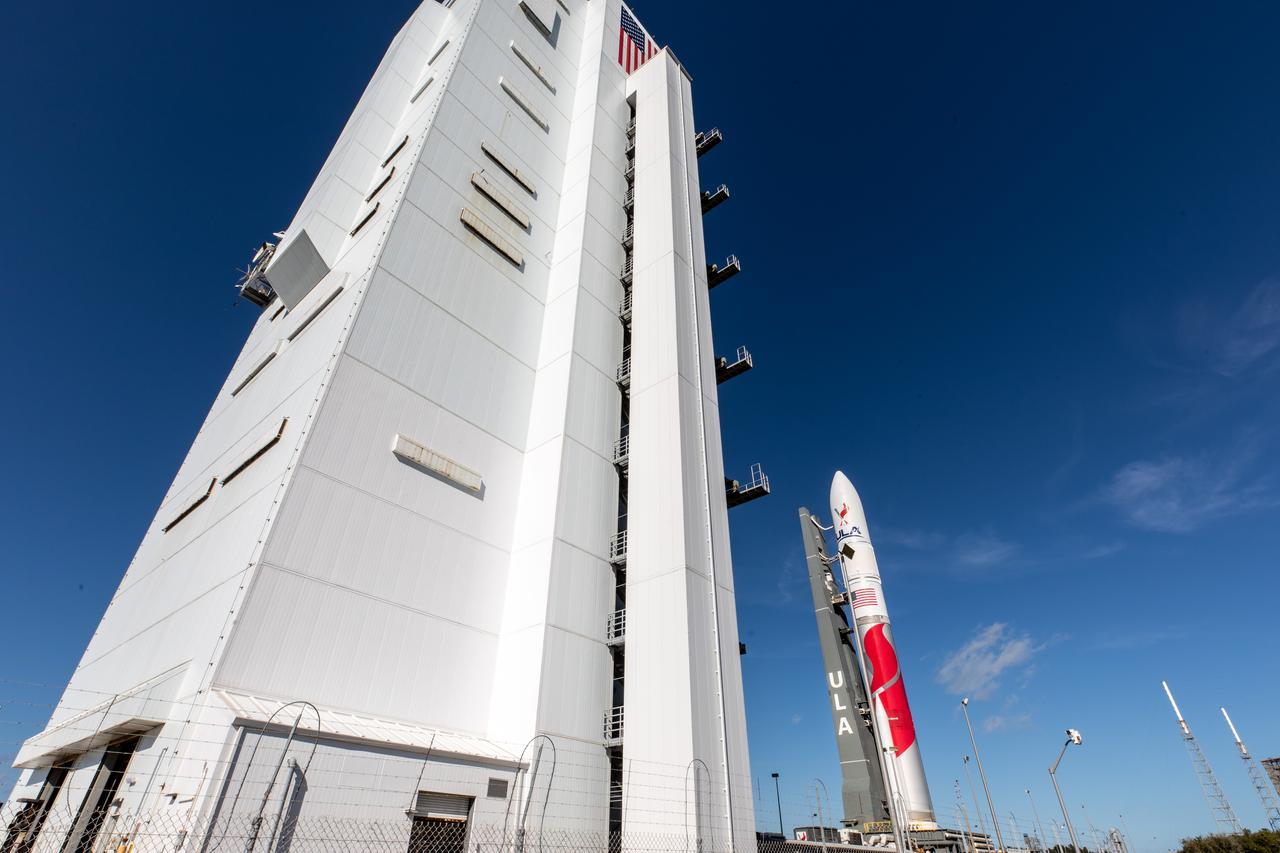
Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Astrobotic employees Troy Arbuckle, at far left, Planetary Mobility lead mechanical engineer; Takuto Oikawa, mechanical engineer; and Taylor Whitaker, flight software engineer, monitor the progress of the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

Astrobotic employee Troy Arbuckle, at right, Planetary Mobility lead mechanical engineer, and NASA employee A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, observe the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is preparing to be encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
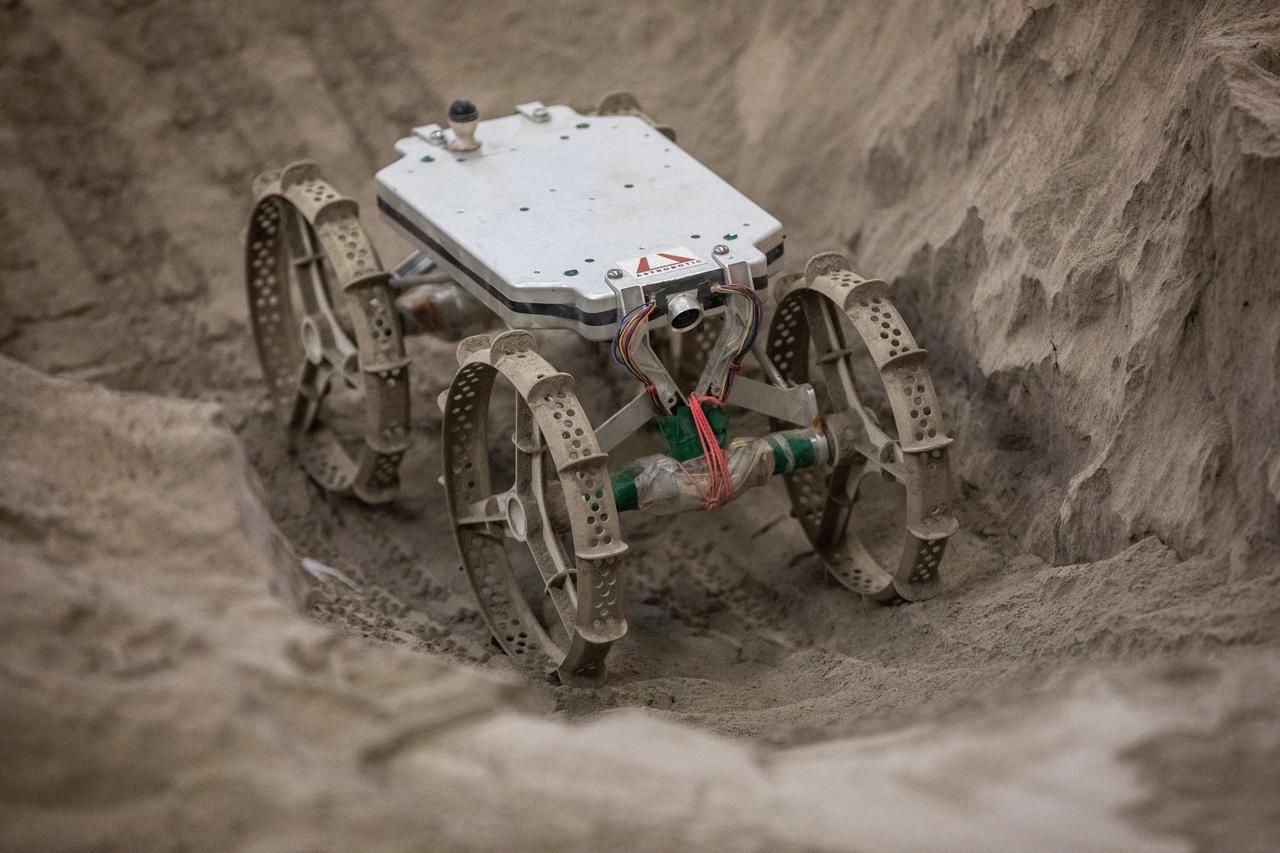

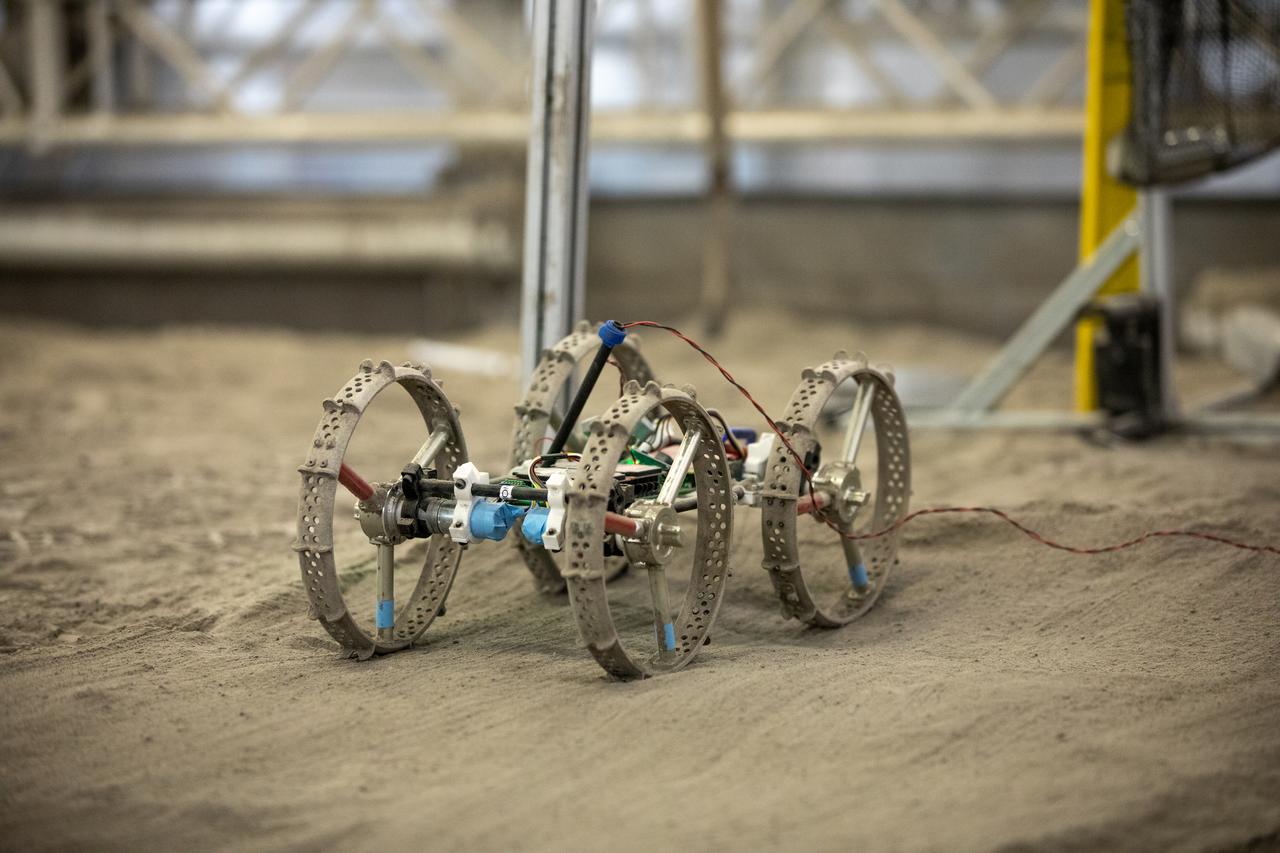
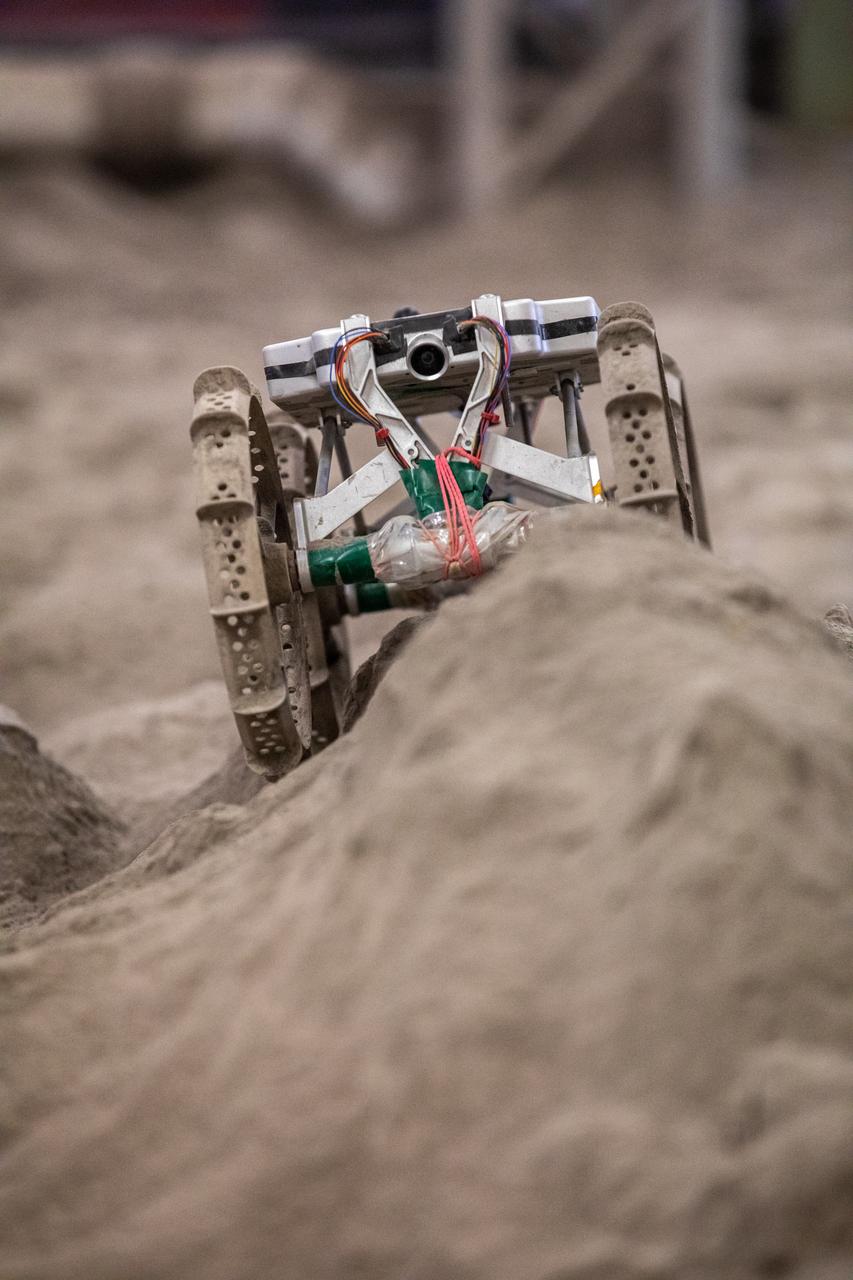
The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
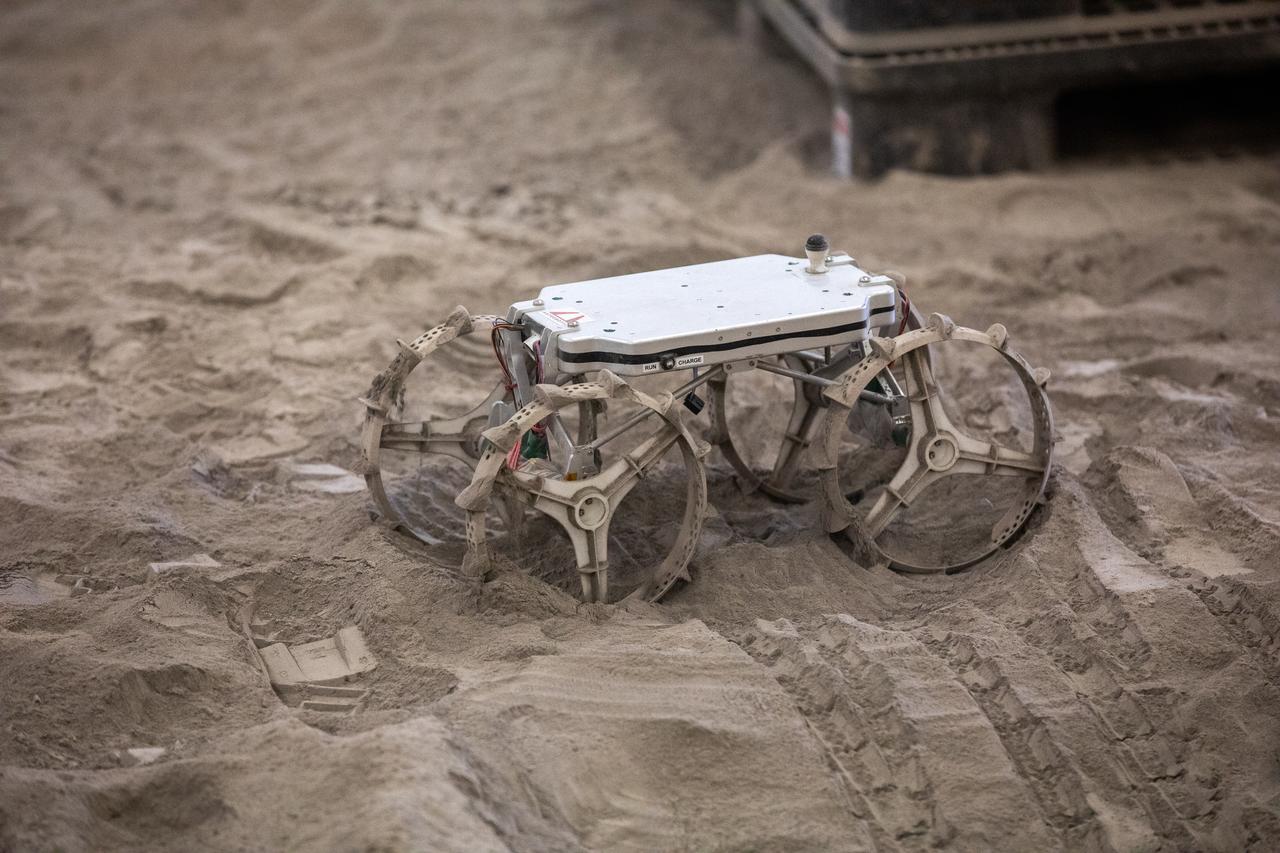

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

Taylor Whitaker, flight software engineer, monitors the progress of the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
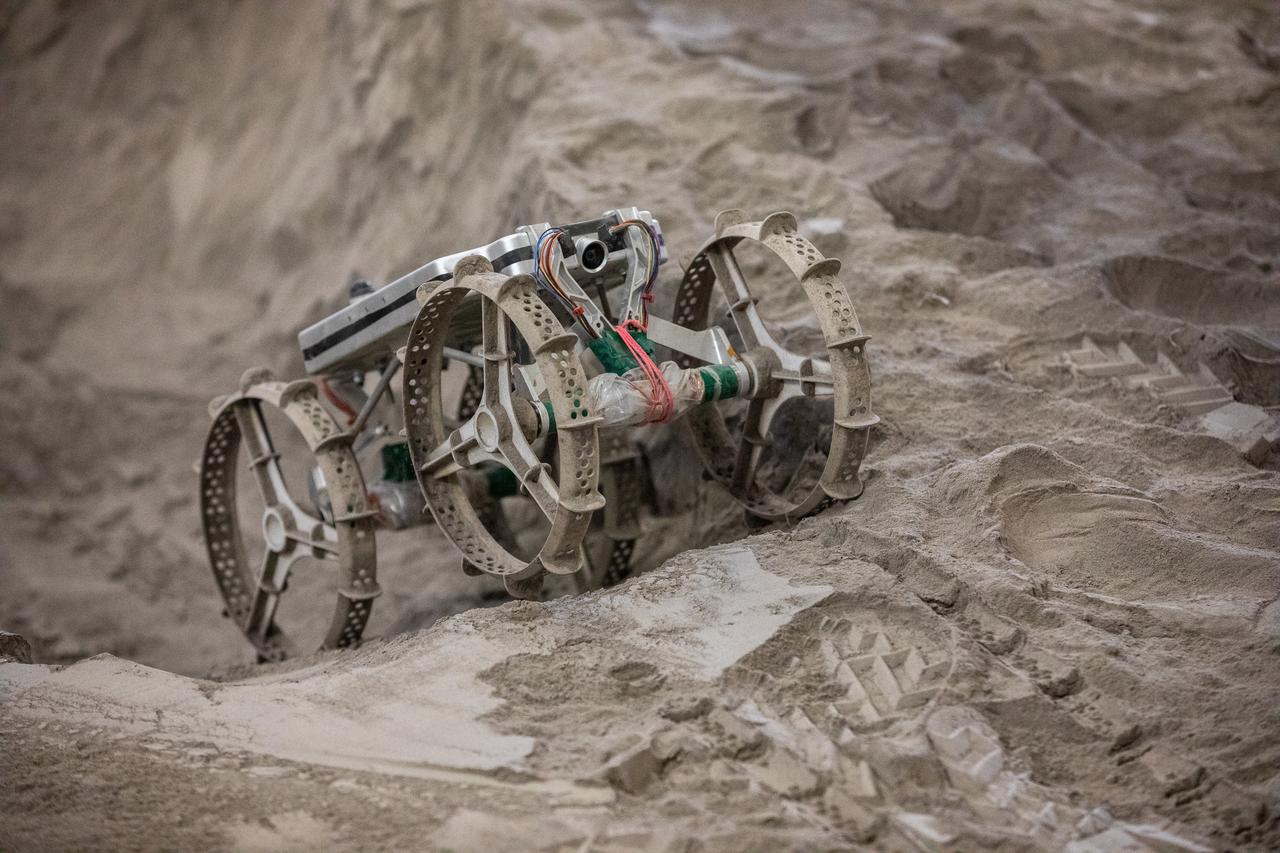

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses obstacles in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
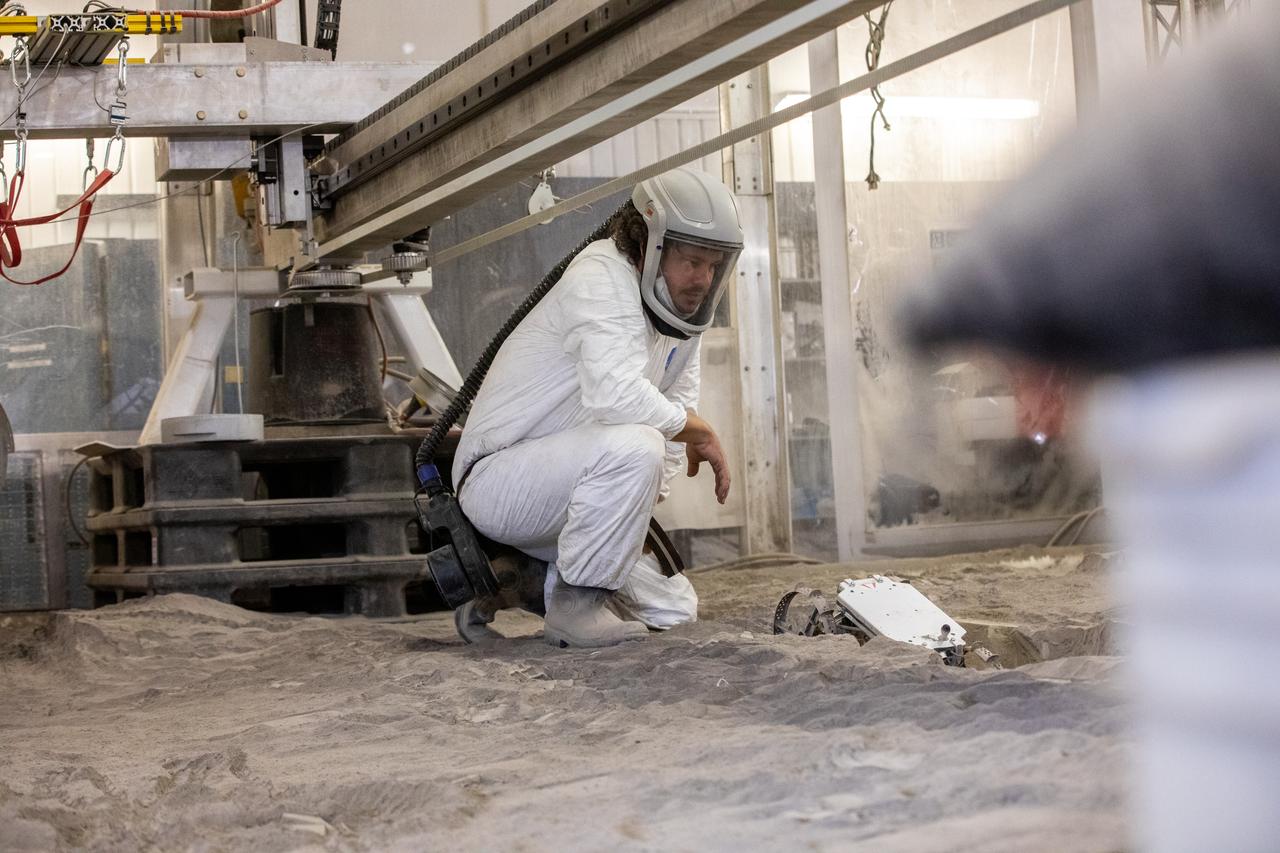

A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, checks the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the regolith bin at Kennedy on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
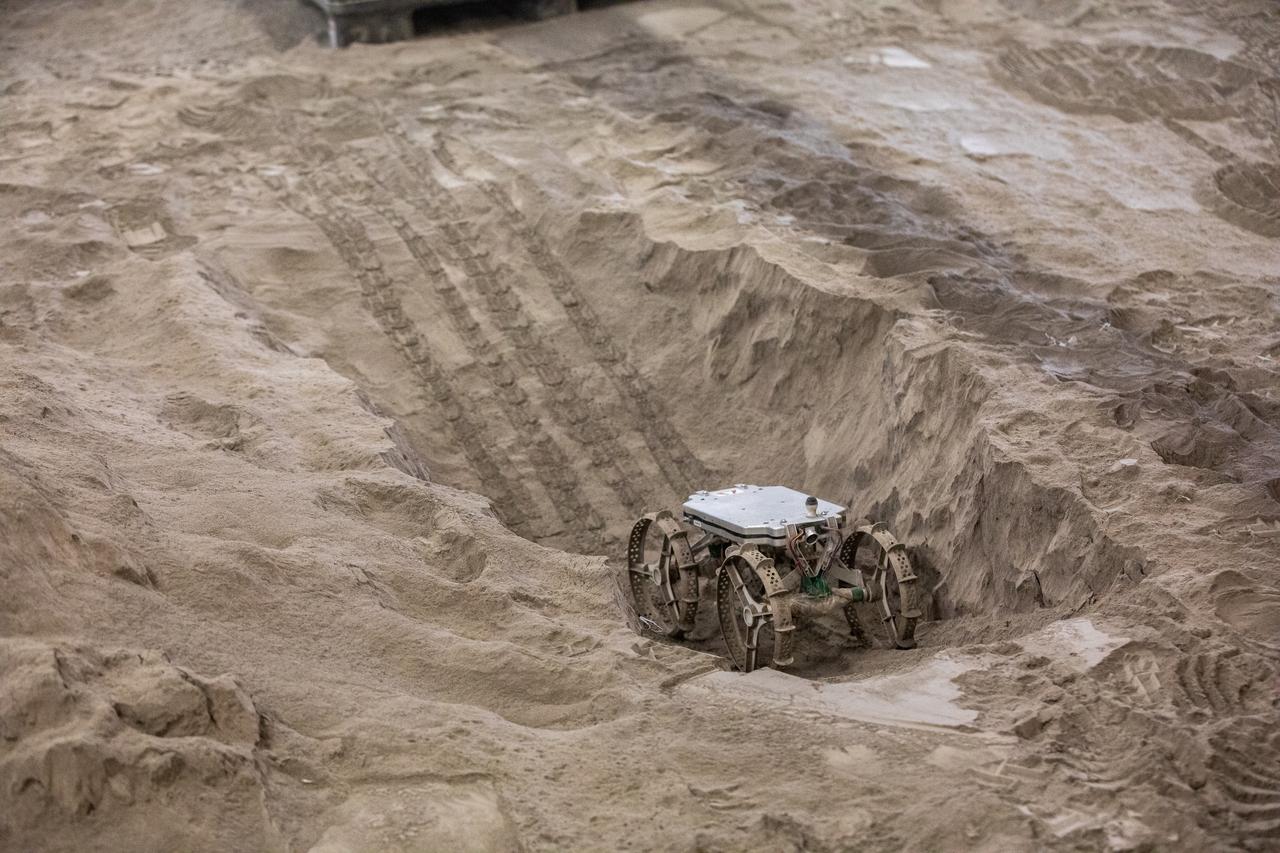

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses a trench in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
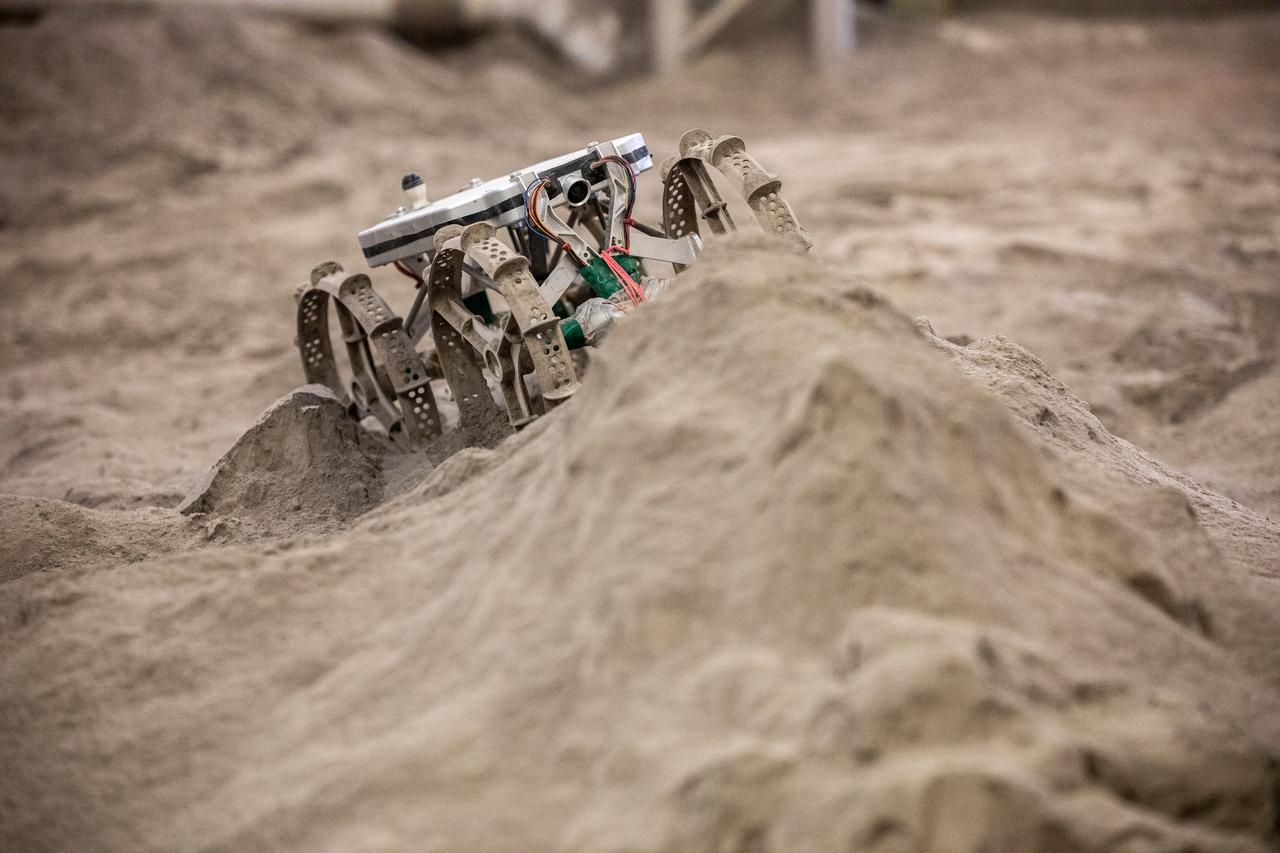

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses obstacles in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
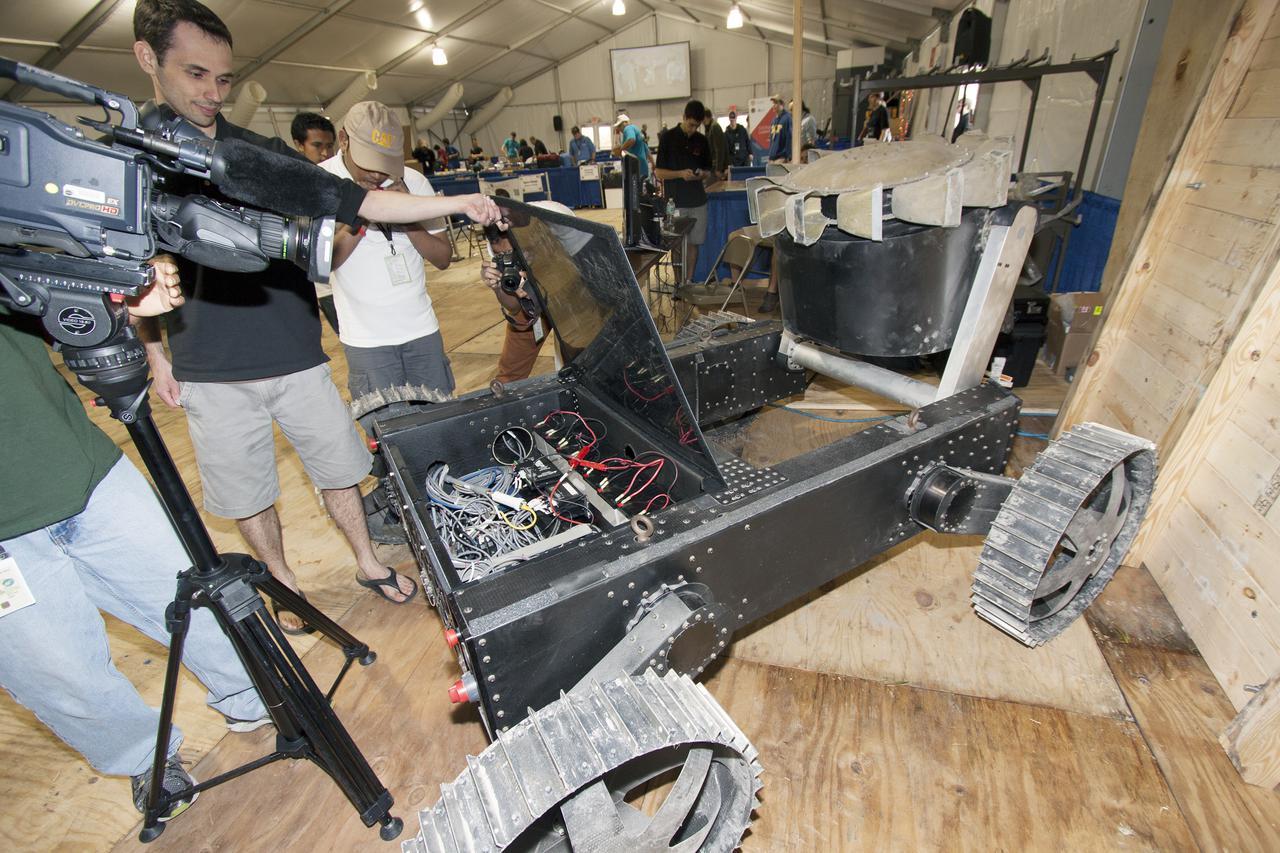

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A team from Astrobotic Technology, Inc., demonstrates the Polaris rover at a robotics mining competition at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Astrobotic developed the Polaris to prospect water at the lunar poles. Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
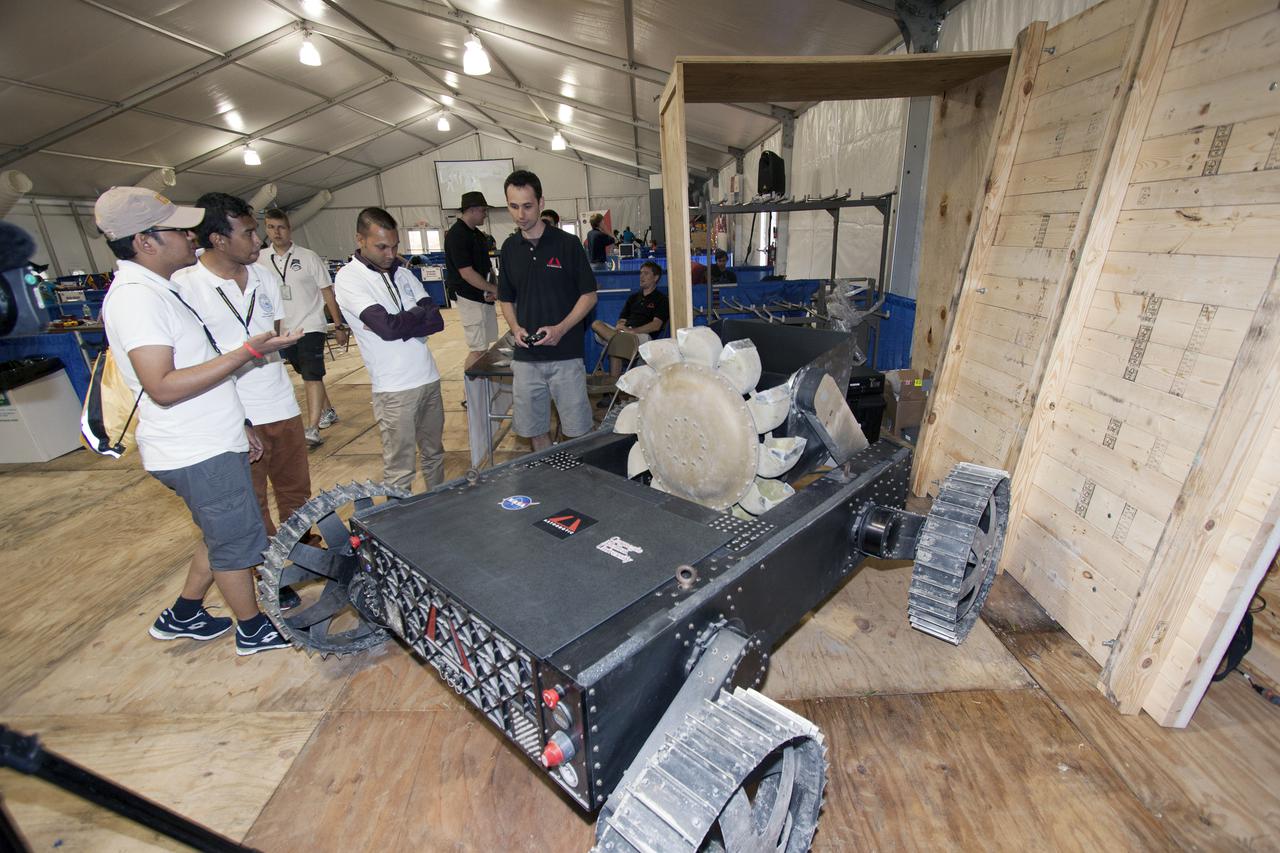

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A team from Astrobotic Technology, Inc., demonstrates the Polaris rover at a robotics mining competition at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Astrobotic developed the Polaris to prospect water at the lunar poles. Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
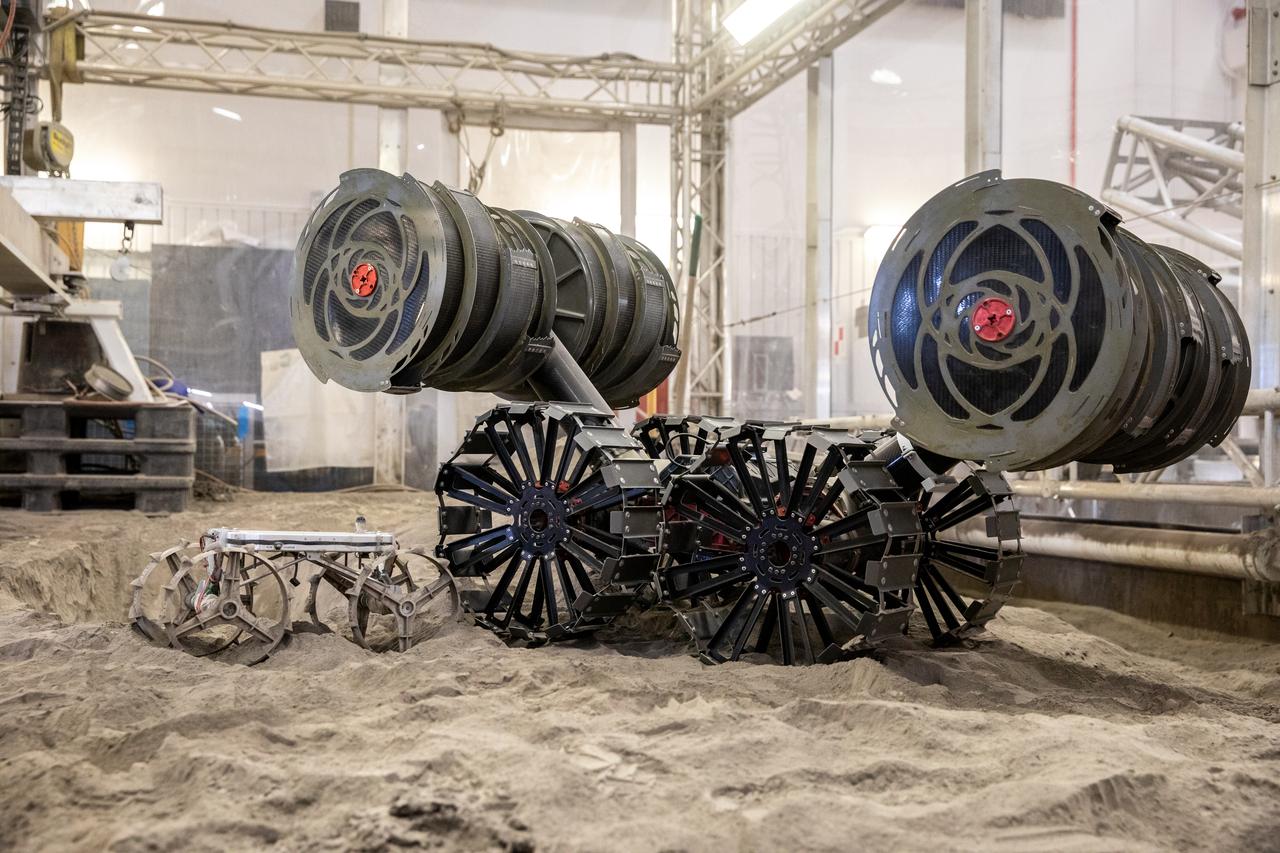

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design. Also in the bin is NASA’s Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), a robotic platform designed to dig on the Moon. The regolith bin simulates the Moon’s surface.
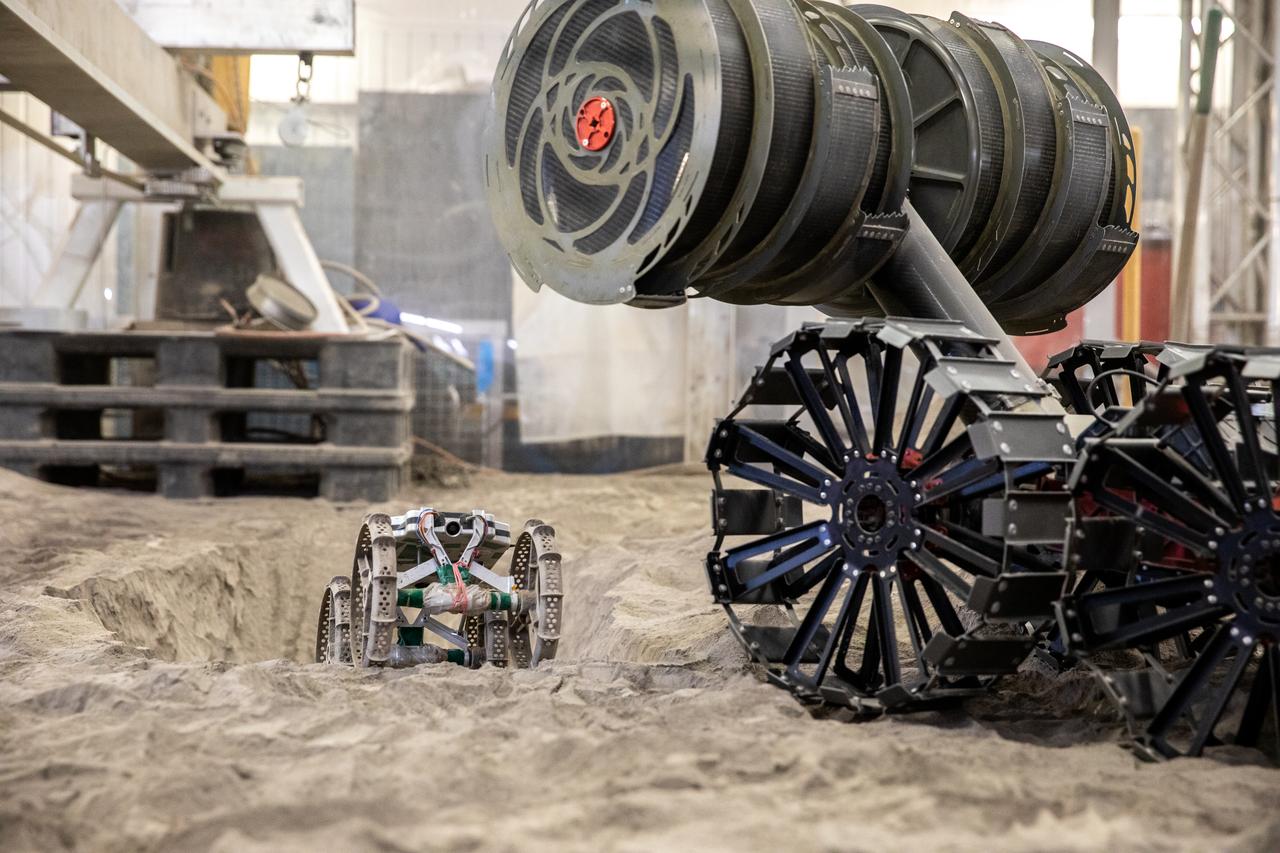

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design. Also in the bin is NASA’s Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), a robotic platform designed to dig on the Moon. The regolith bin simulates the Moon’s surface.
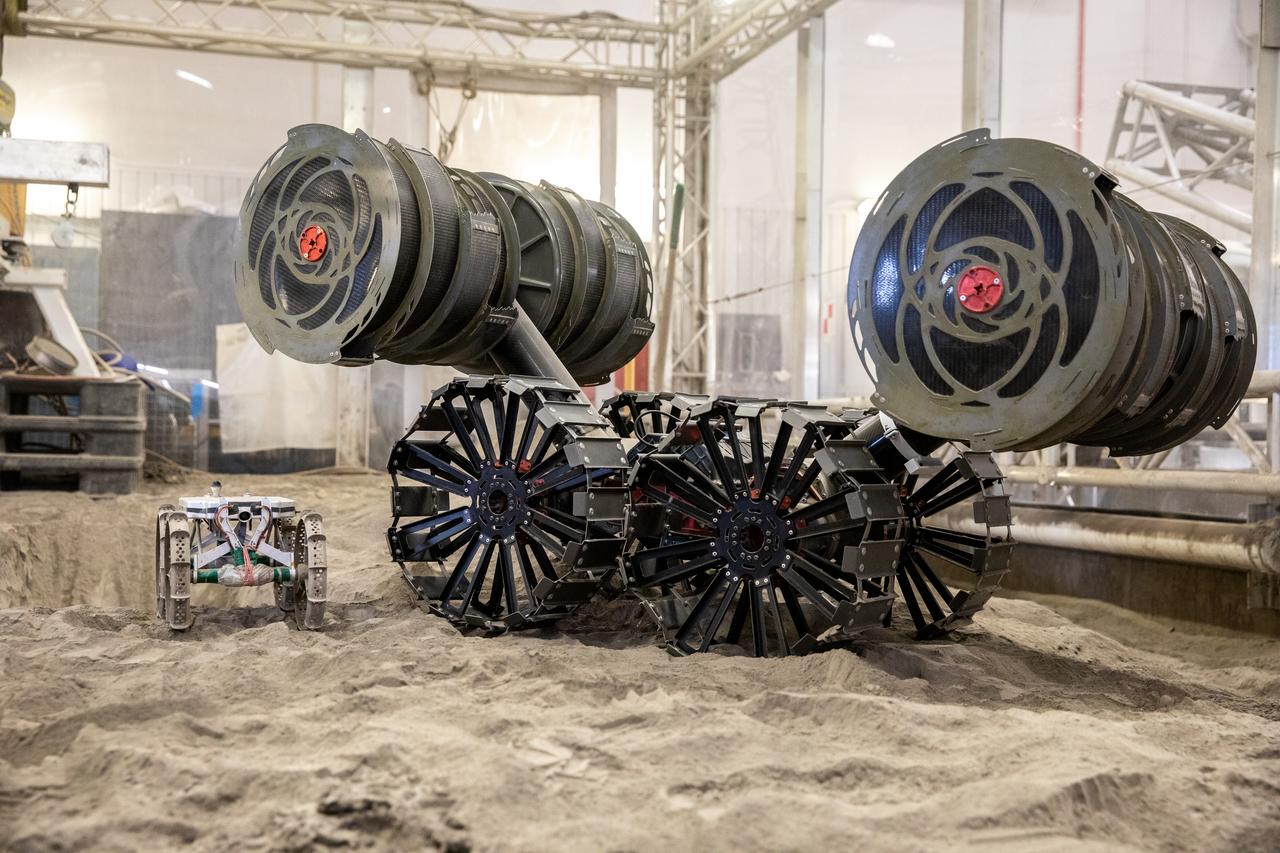

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design. Also in the bin is NASA’s Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), a robotic platform designed to dig on the Moon. The regolith bin simulates the Moon’s surface.
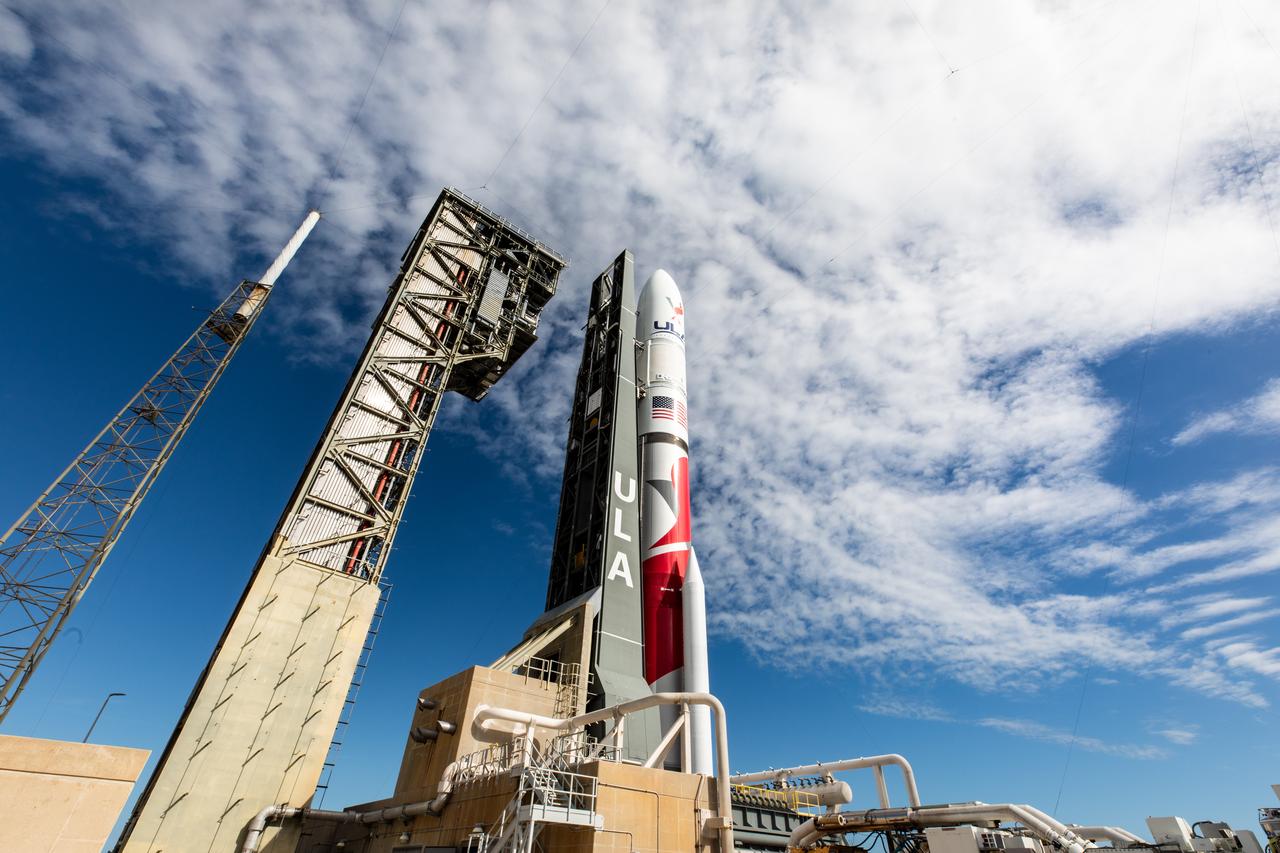

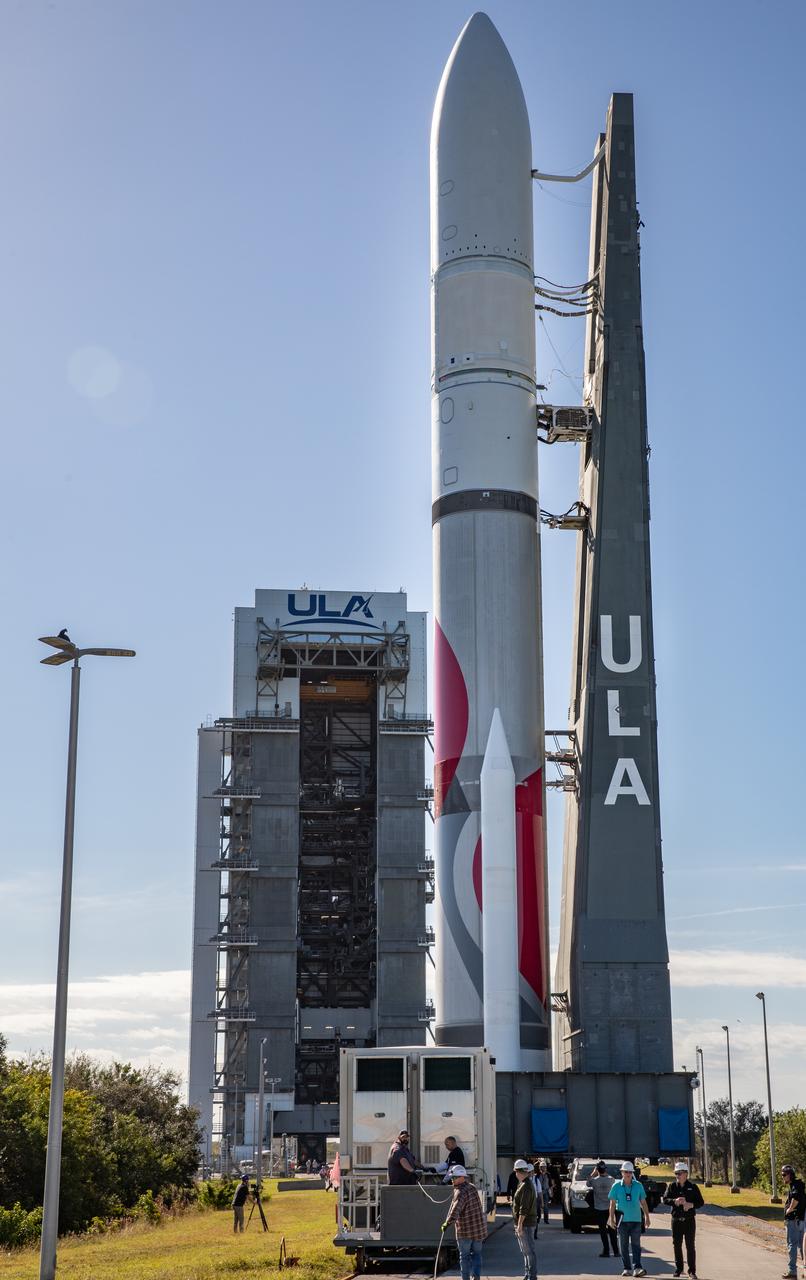
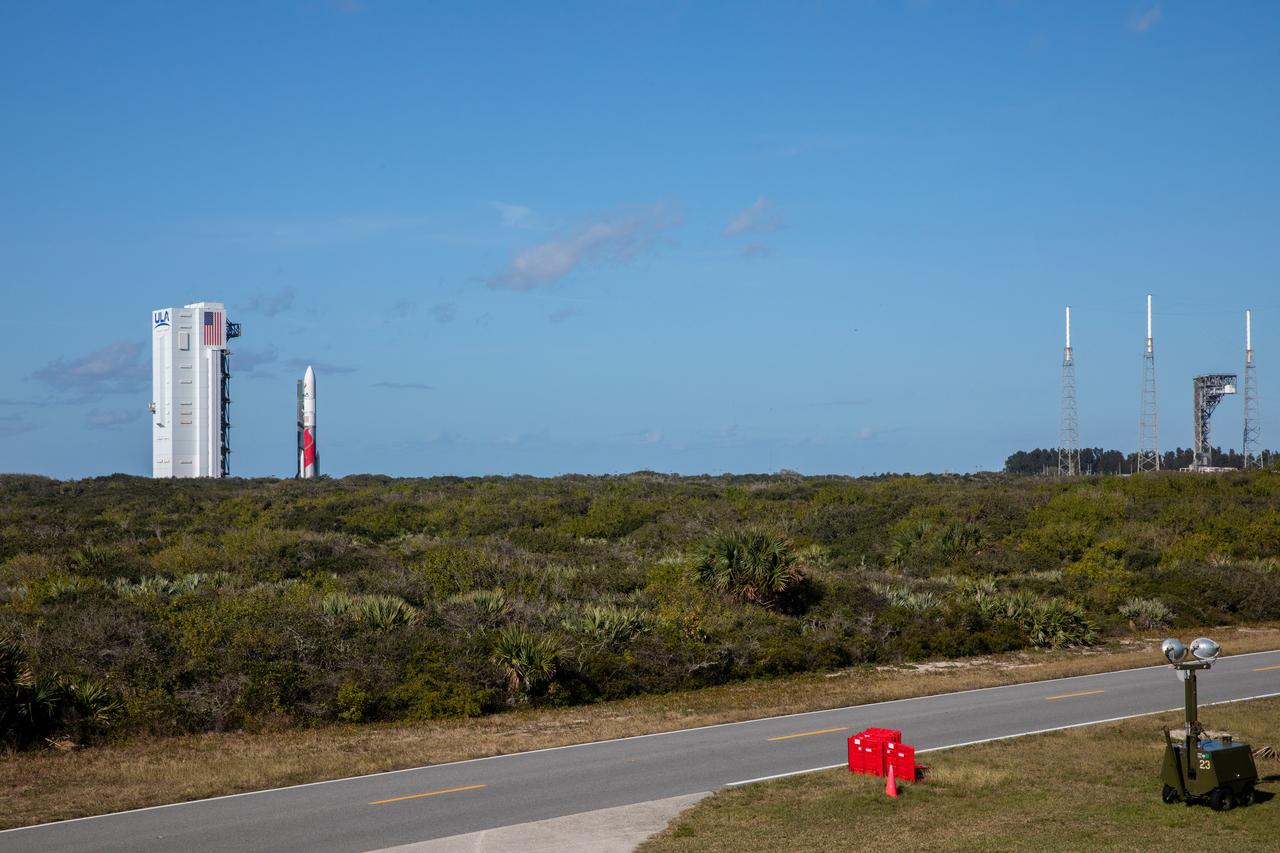
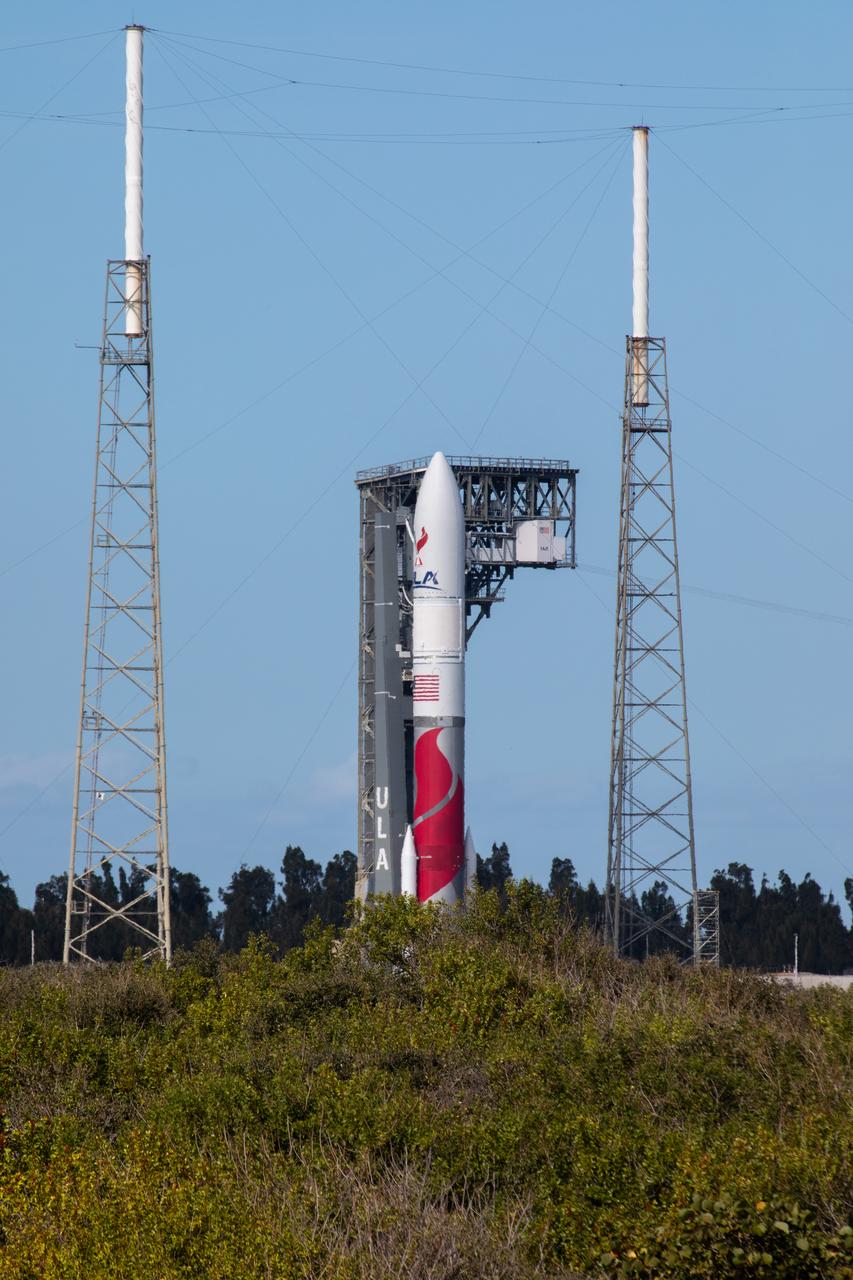
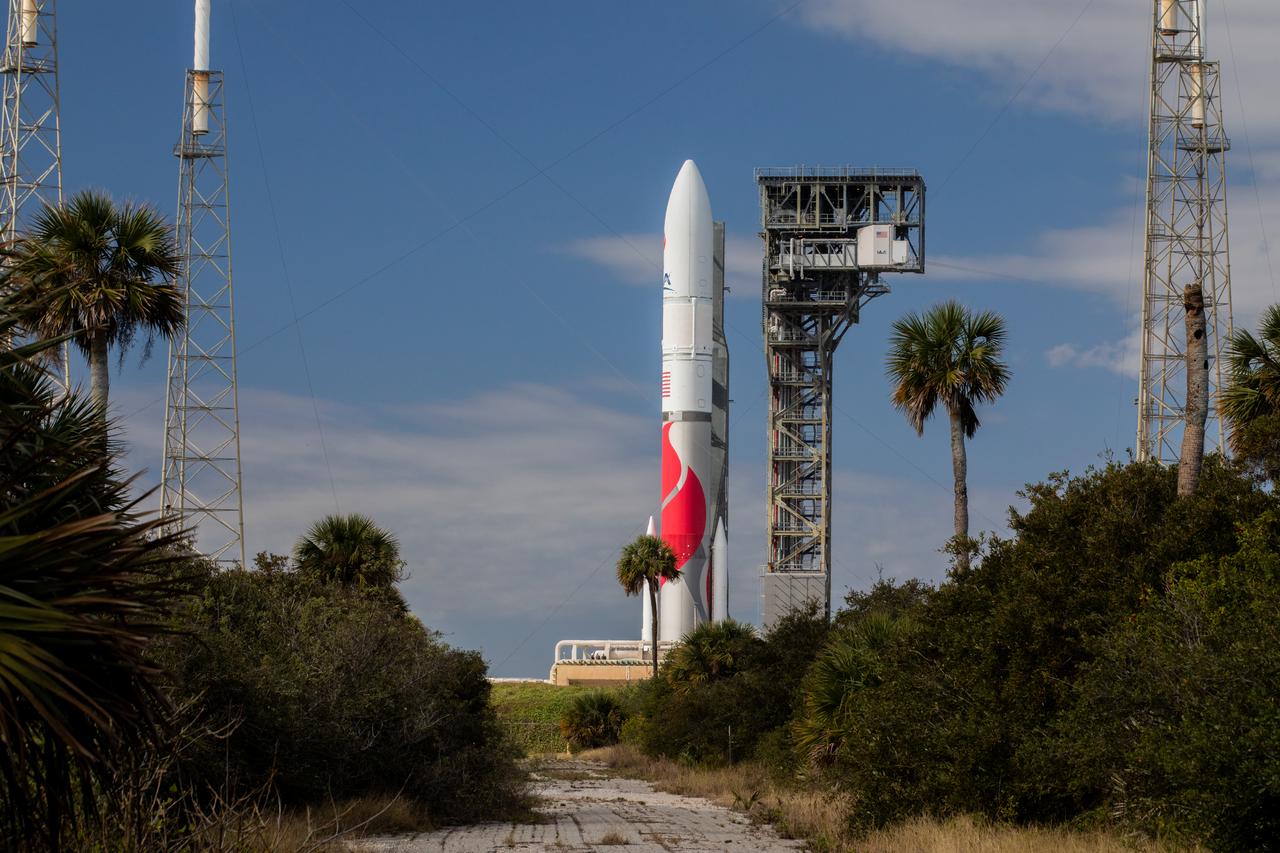
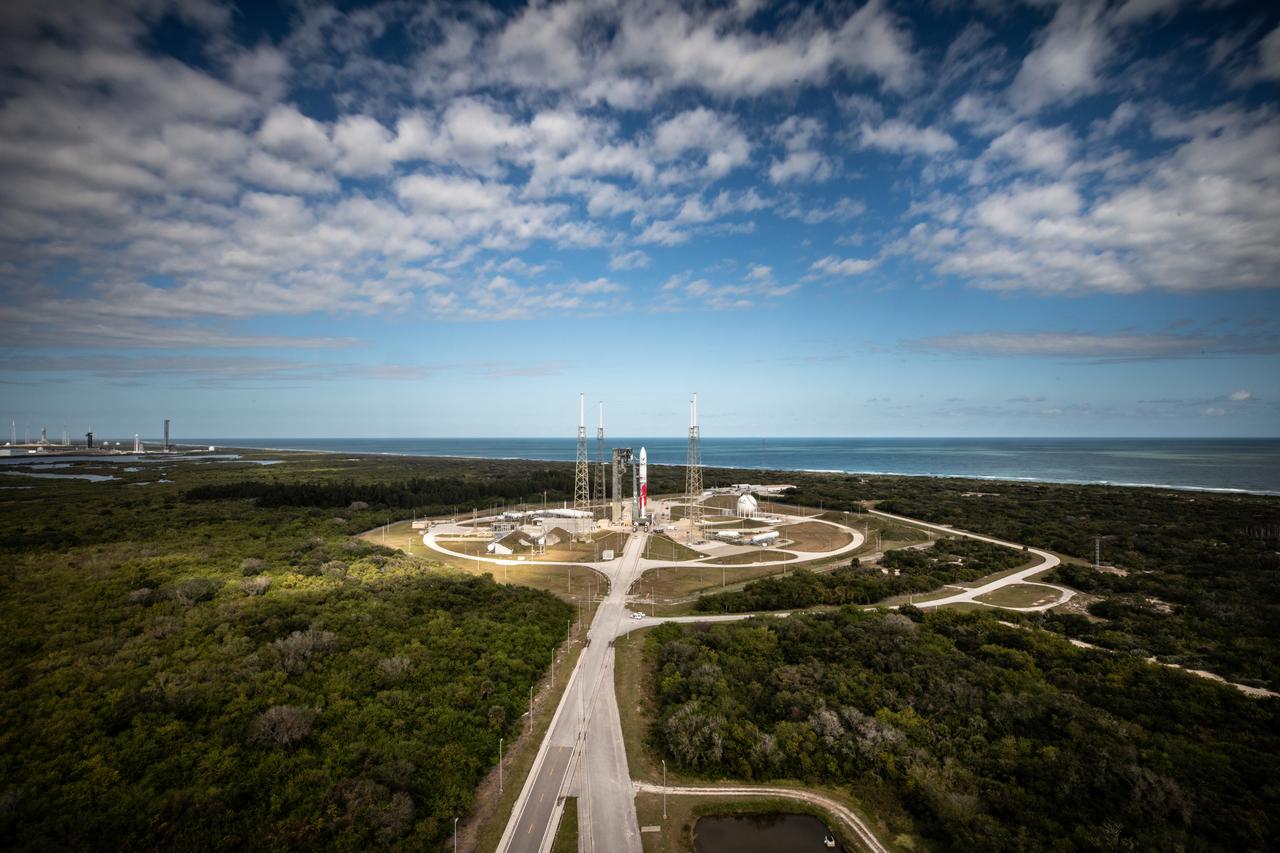
On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
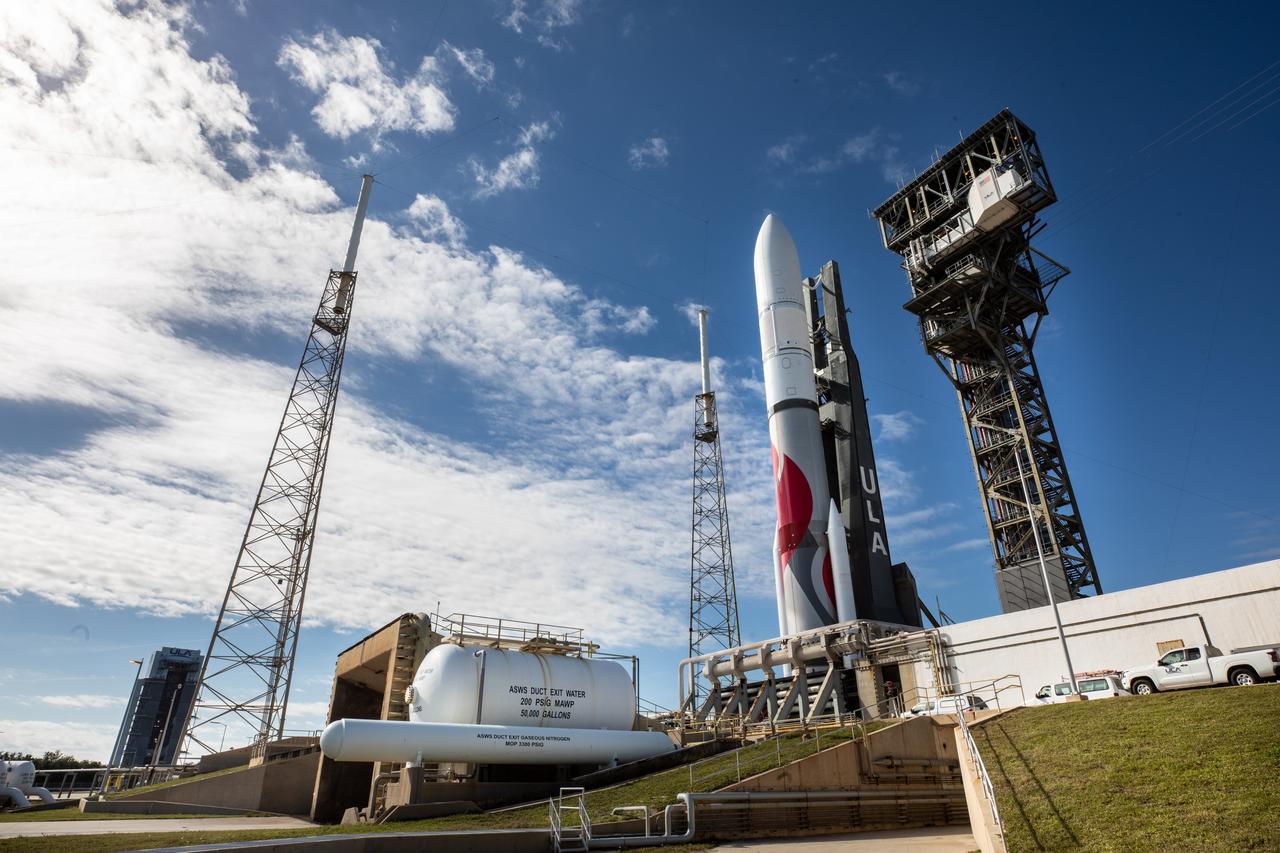

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
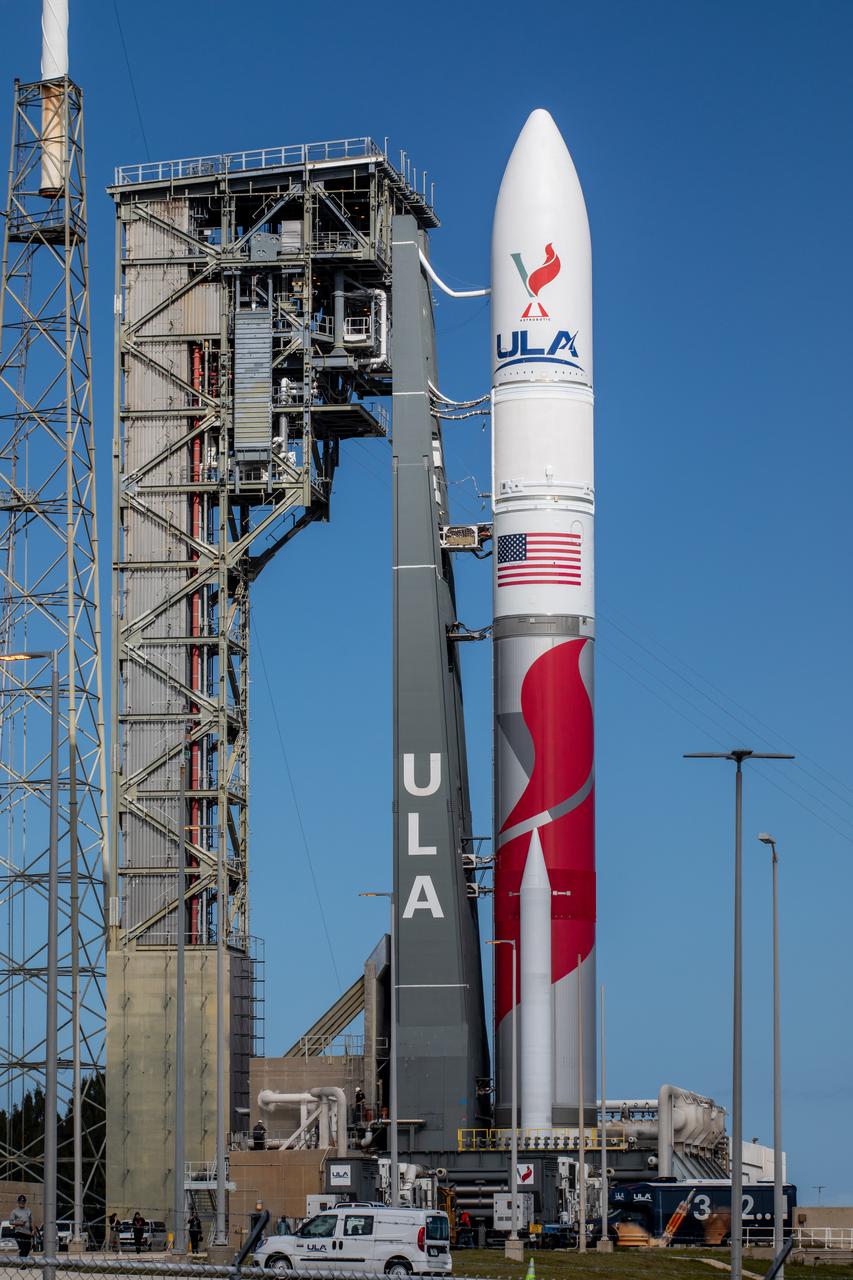

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
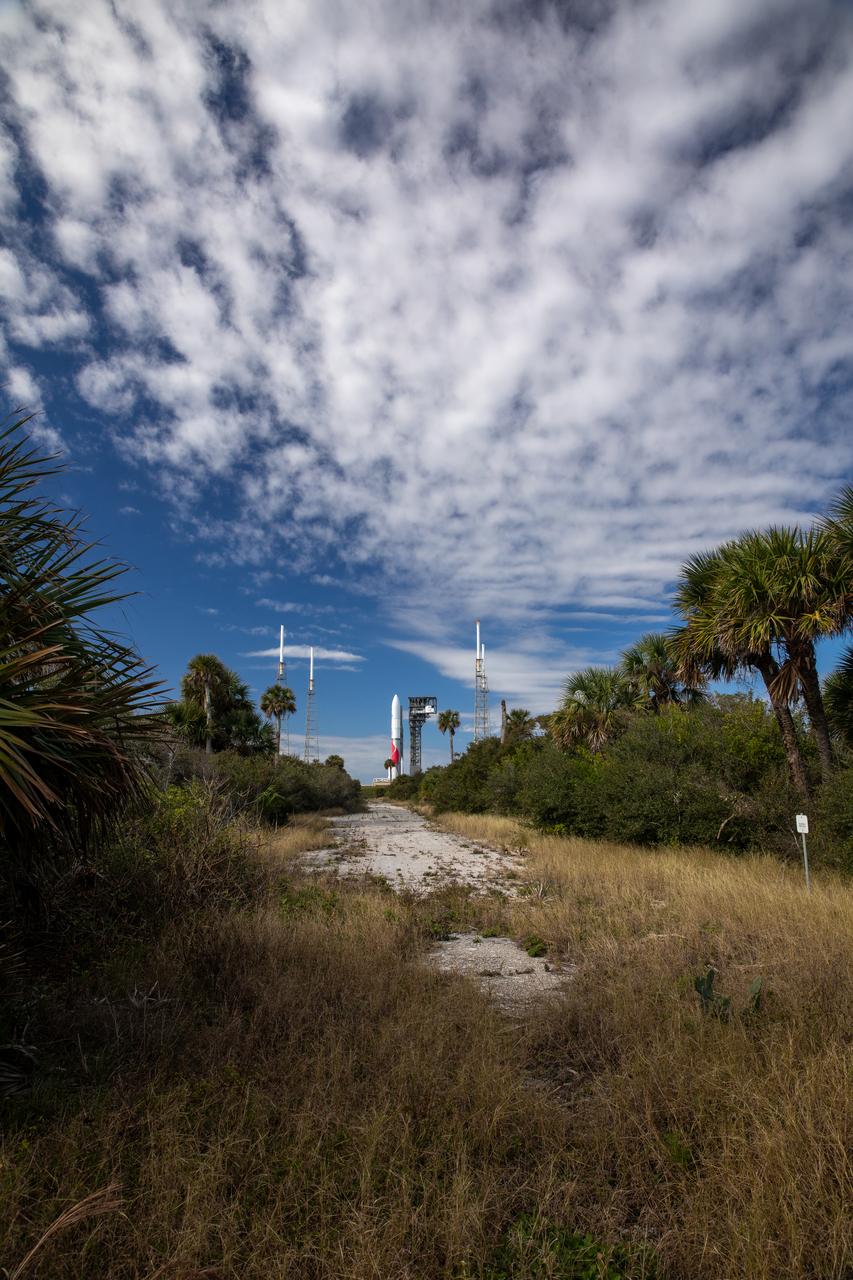

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
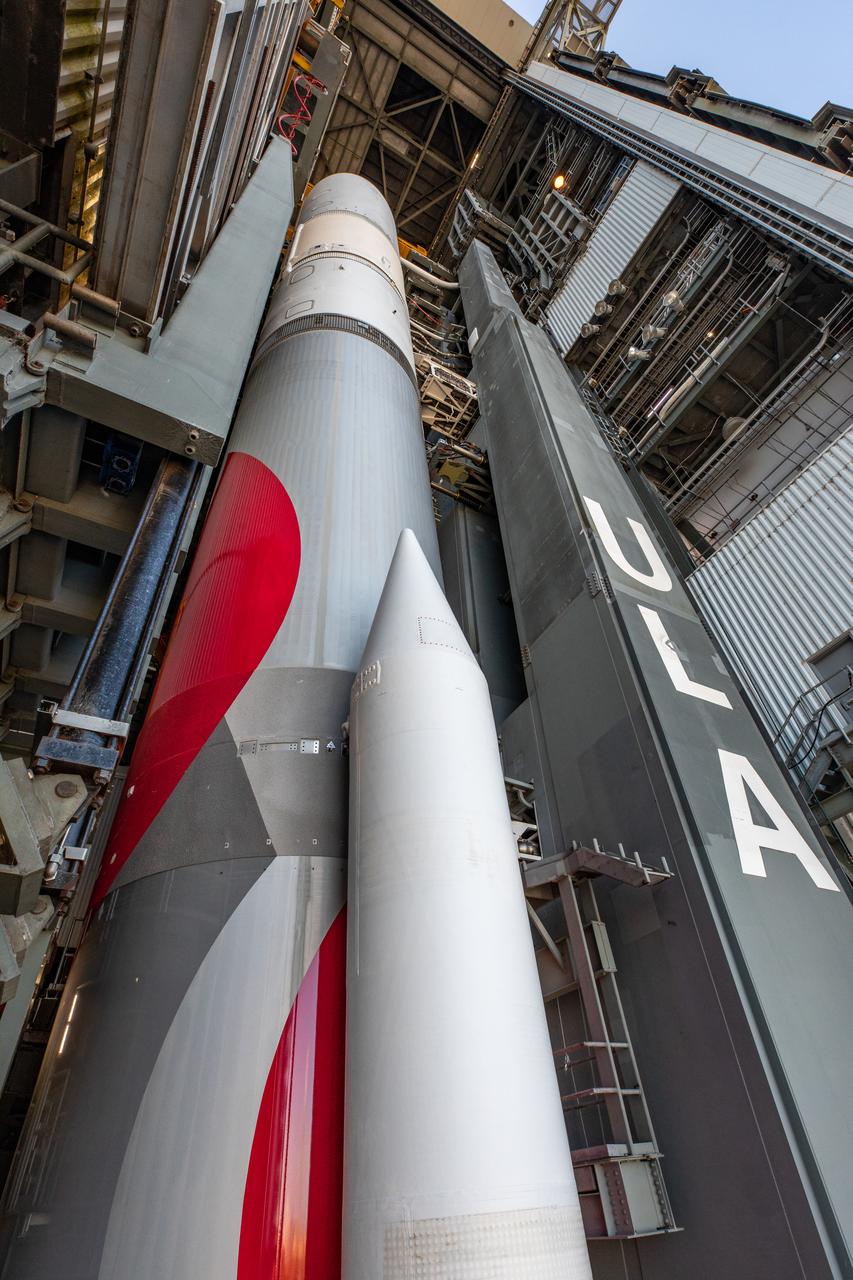

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
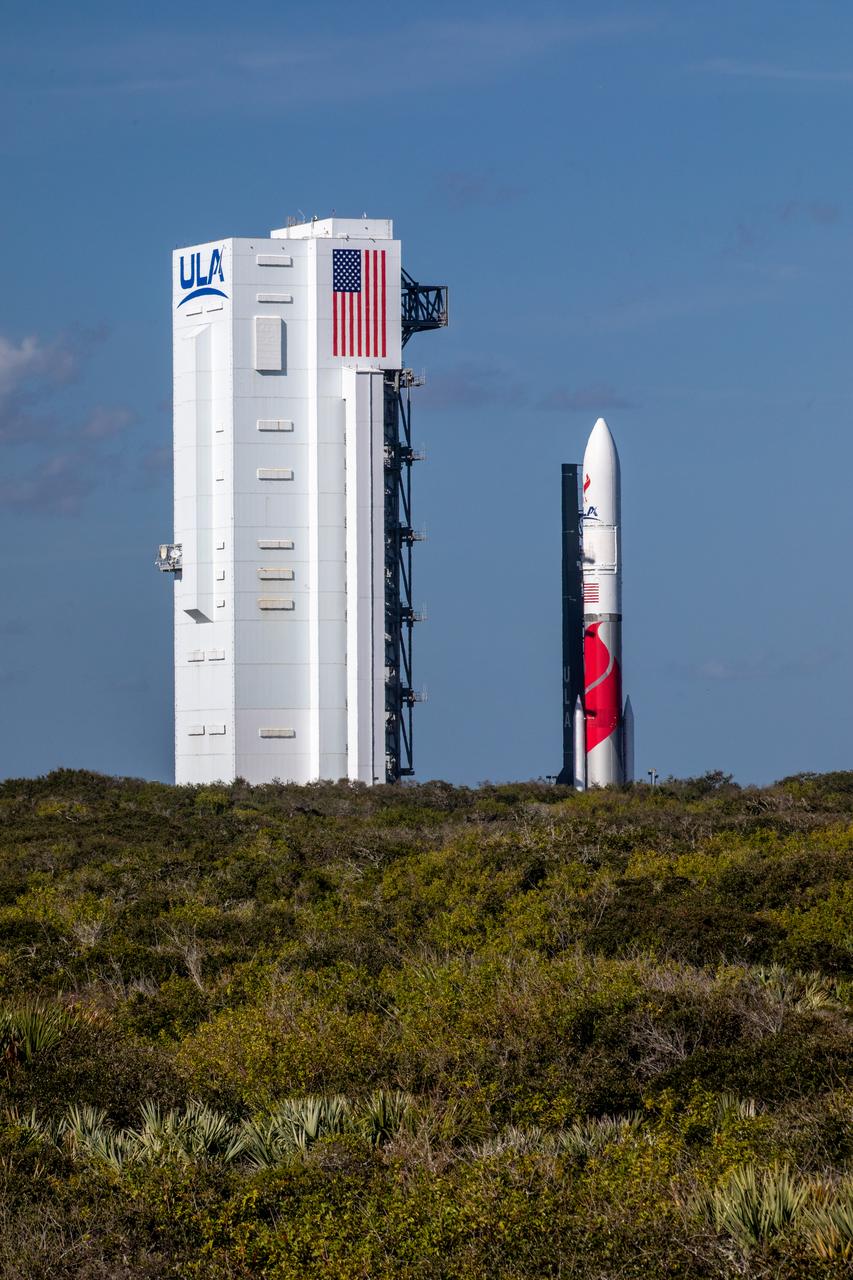

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
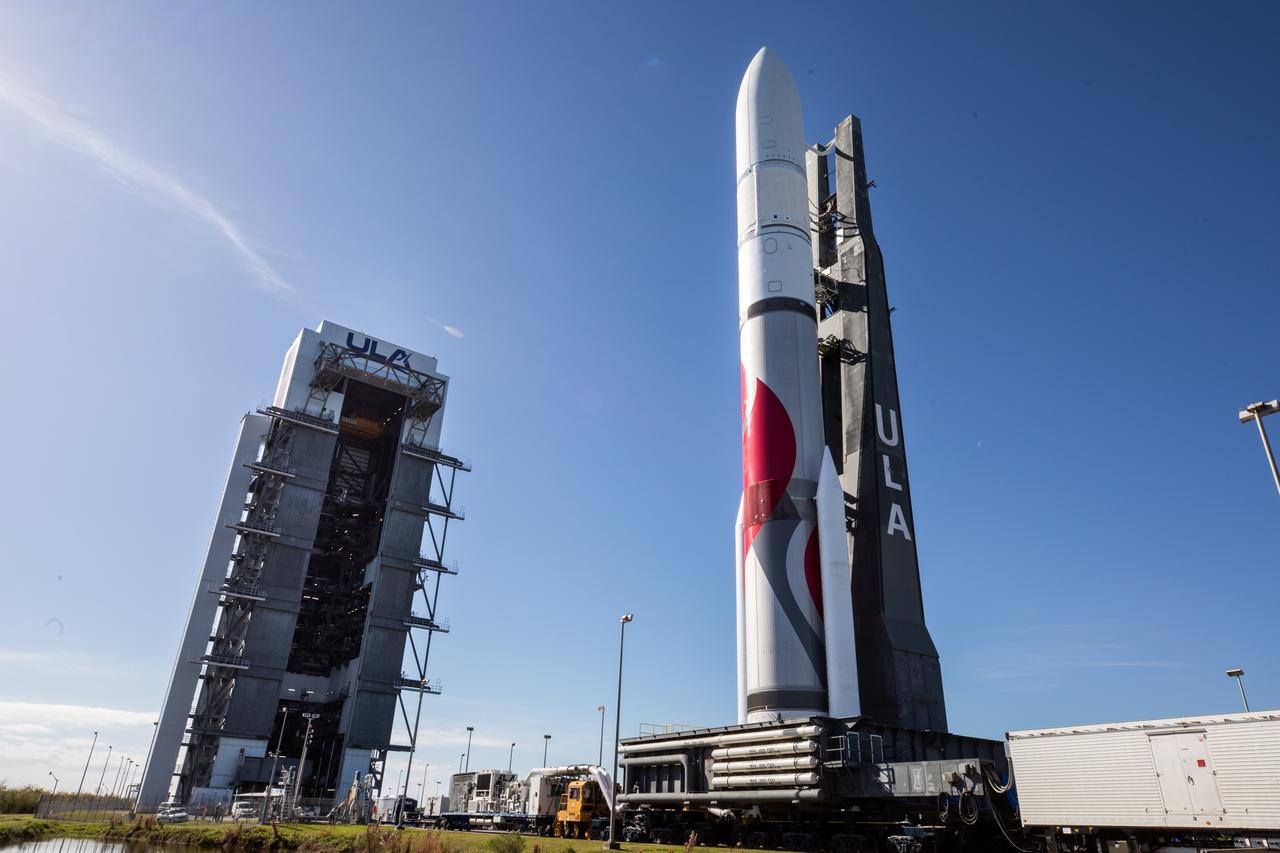

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
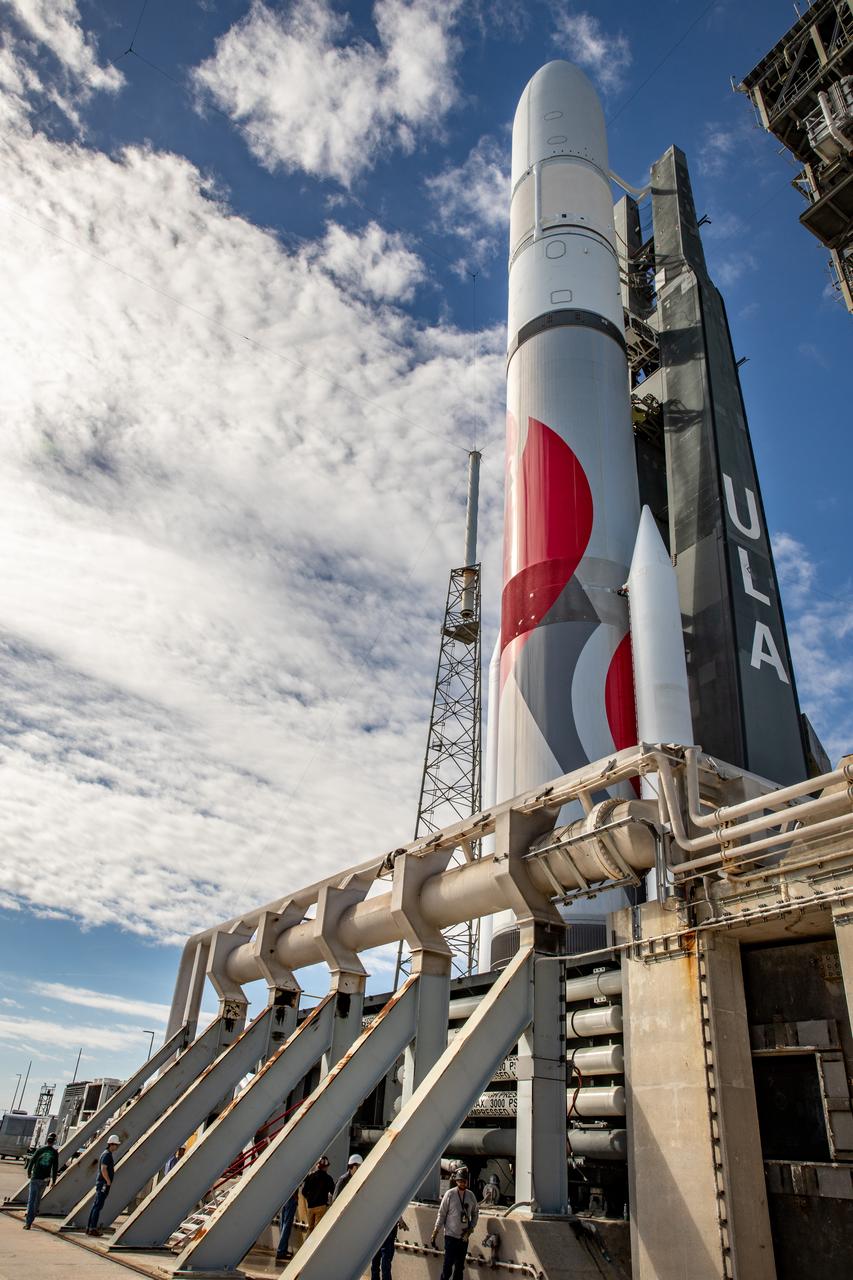

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
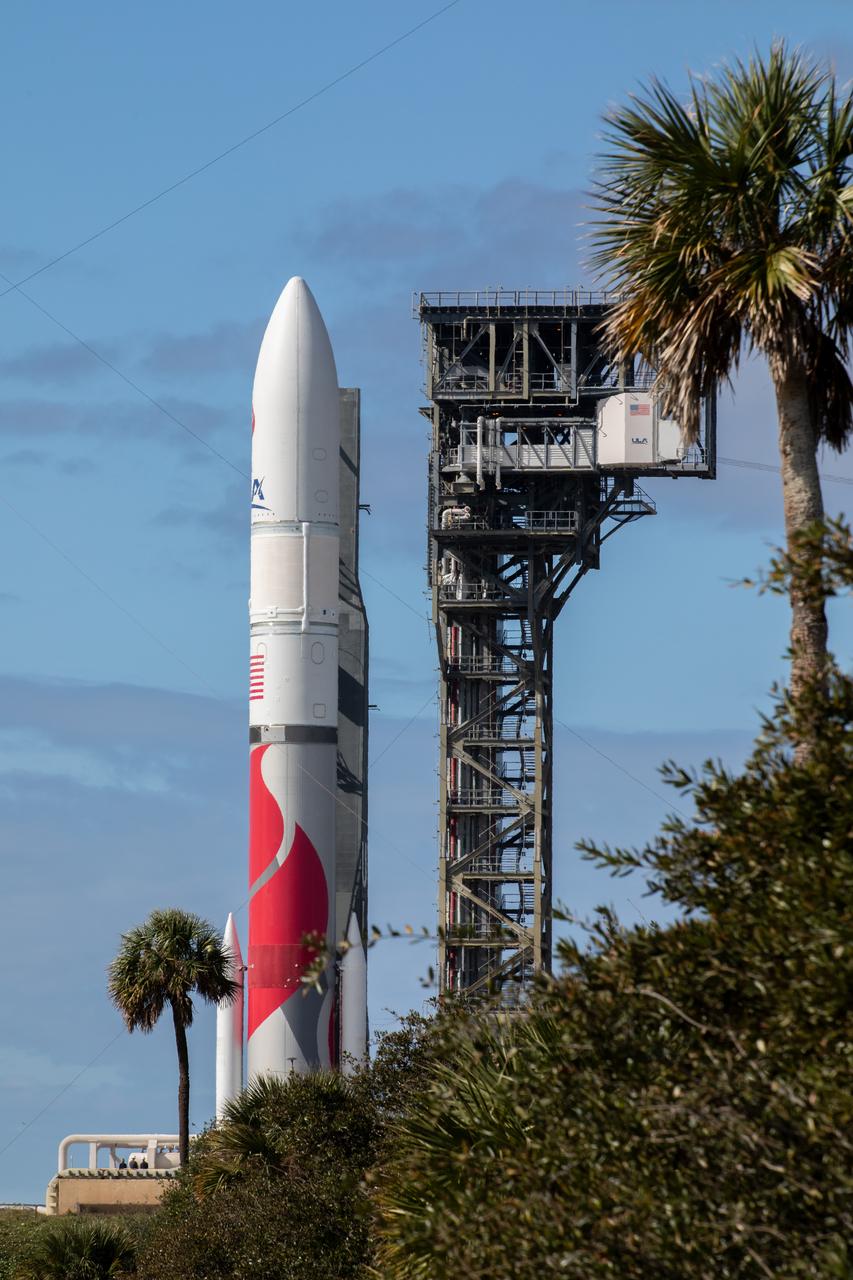

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
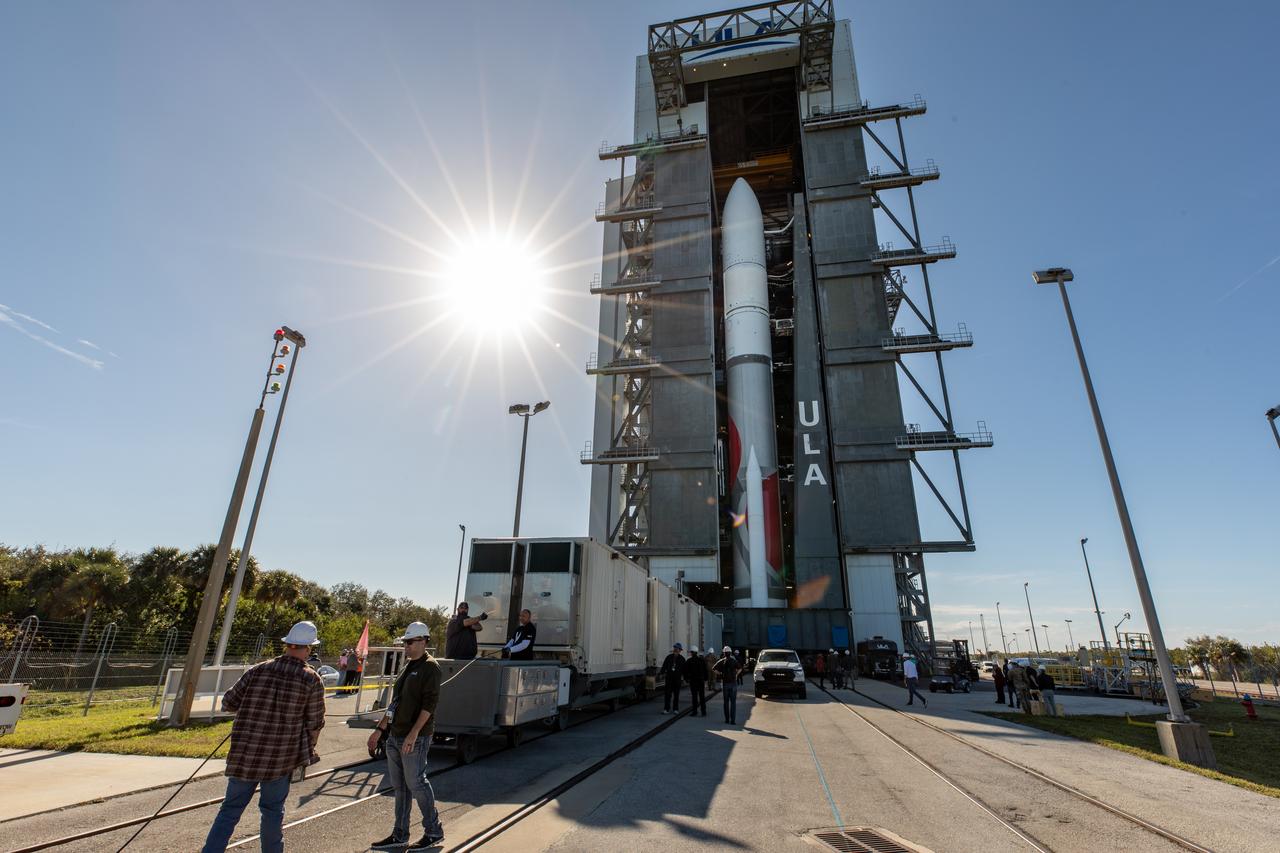

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
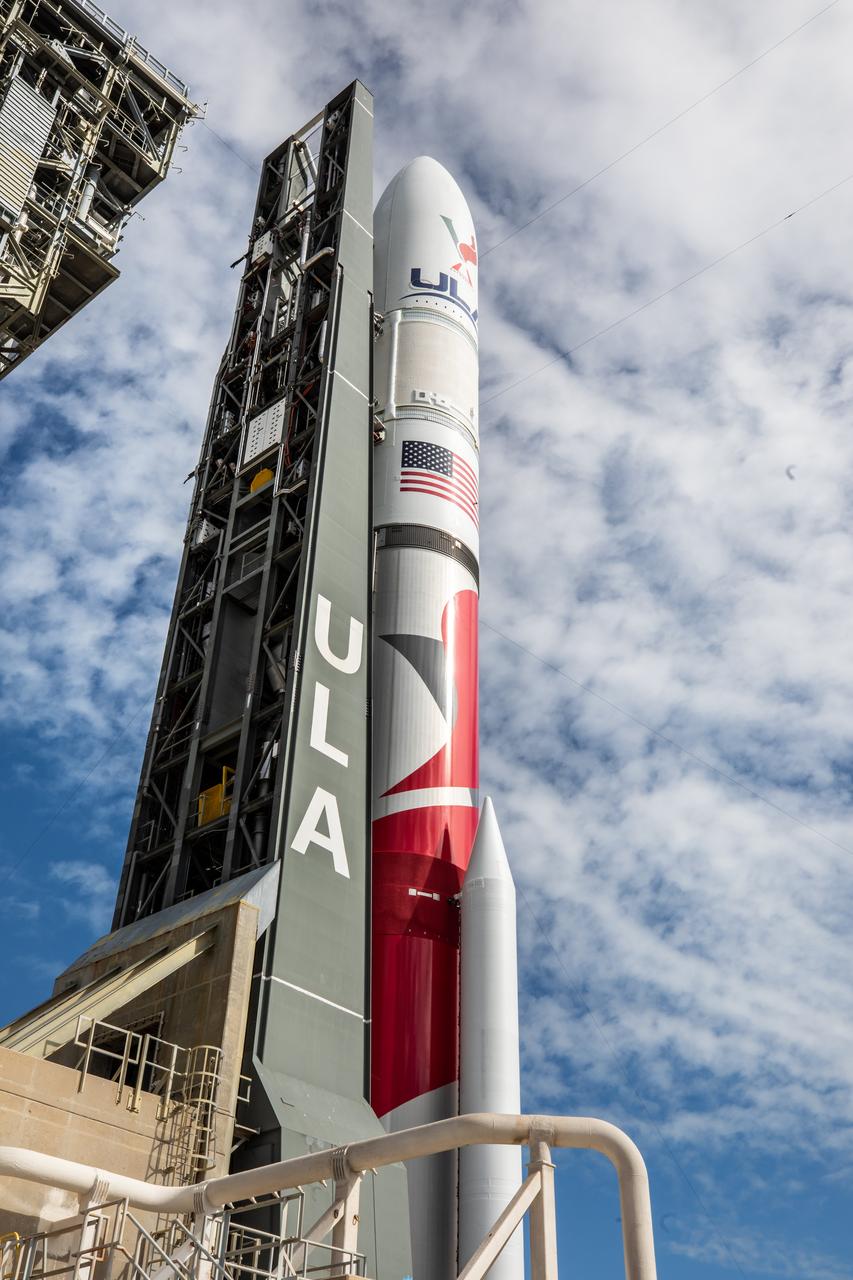
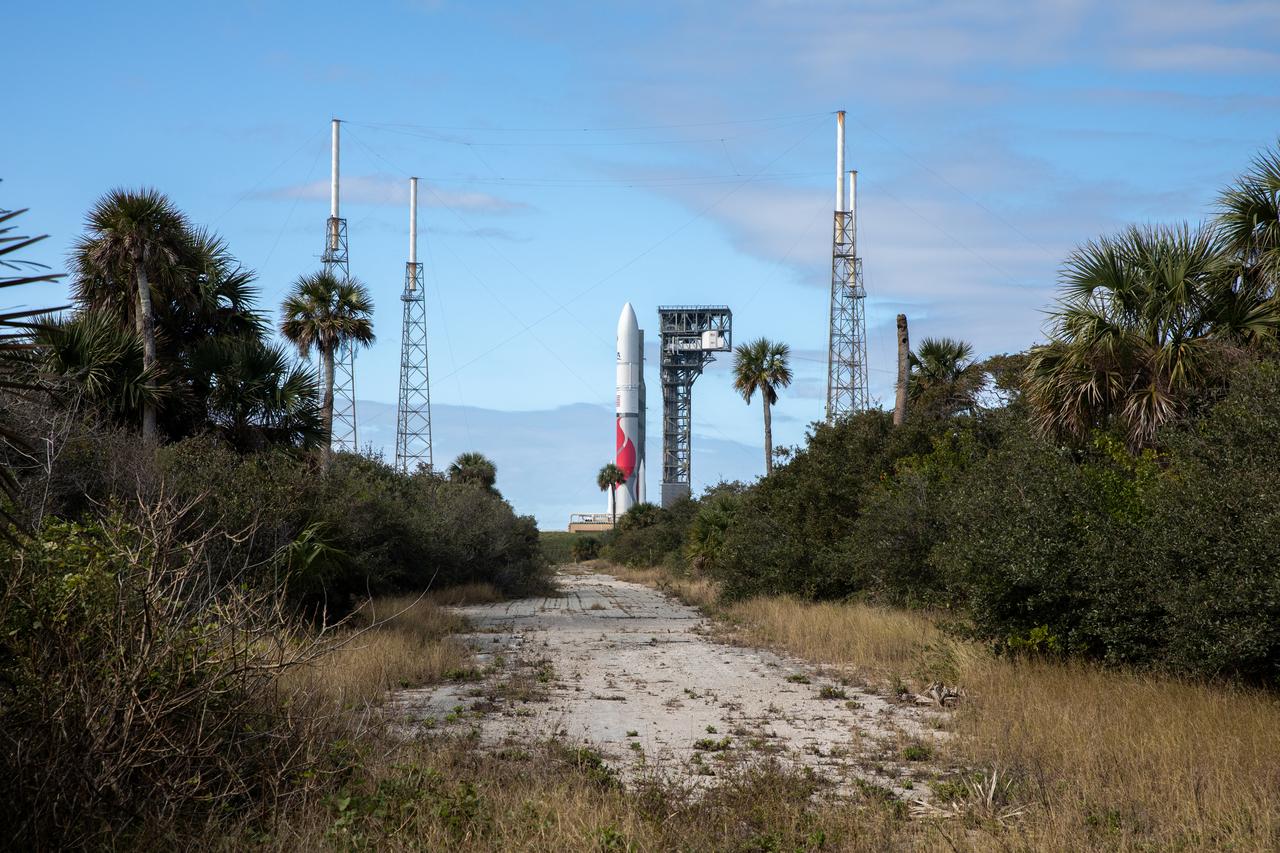
On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

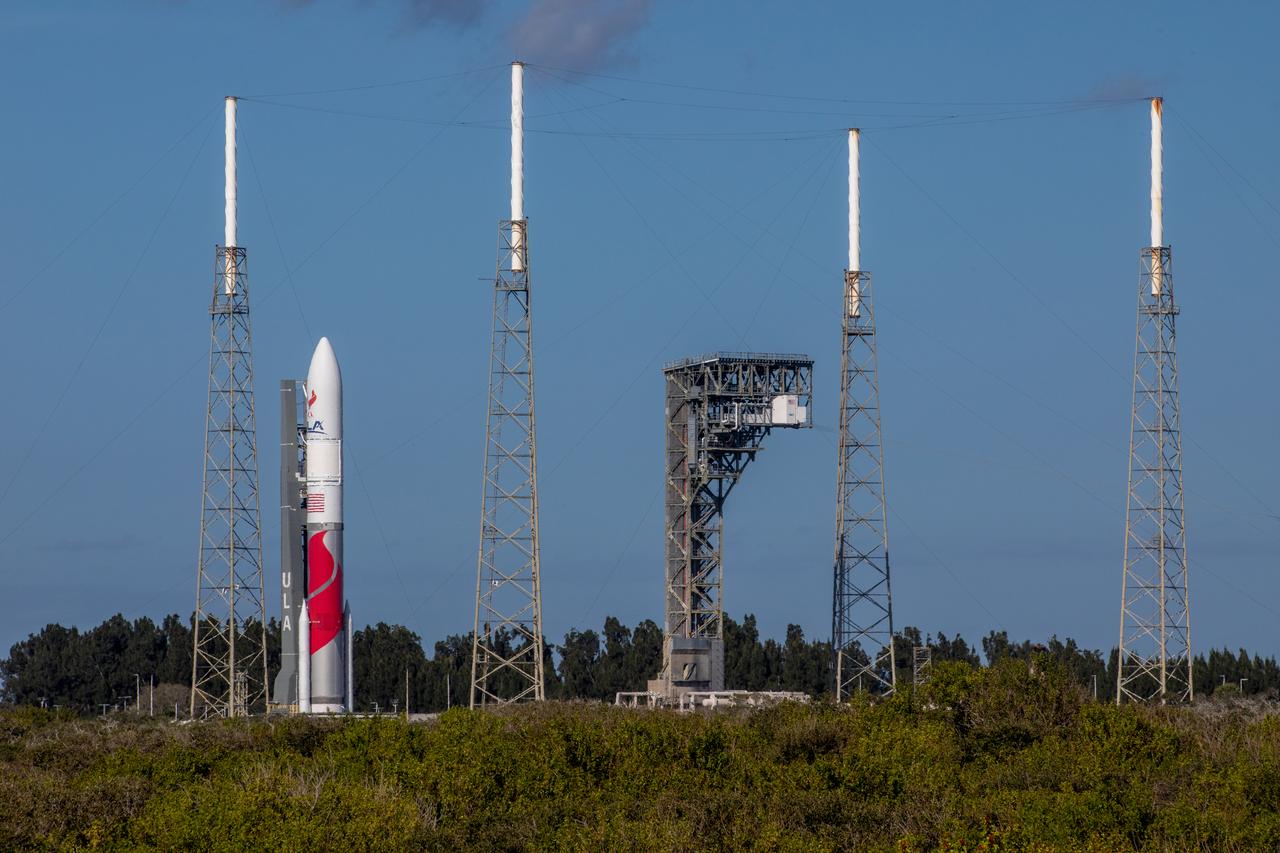
On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
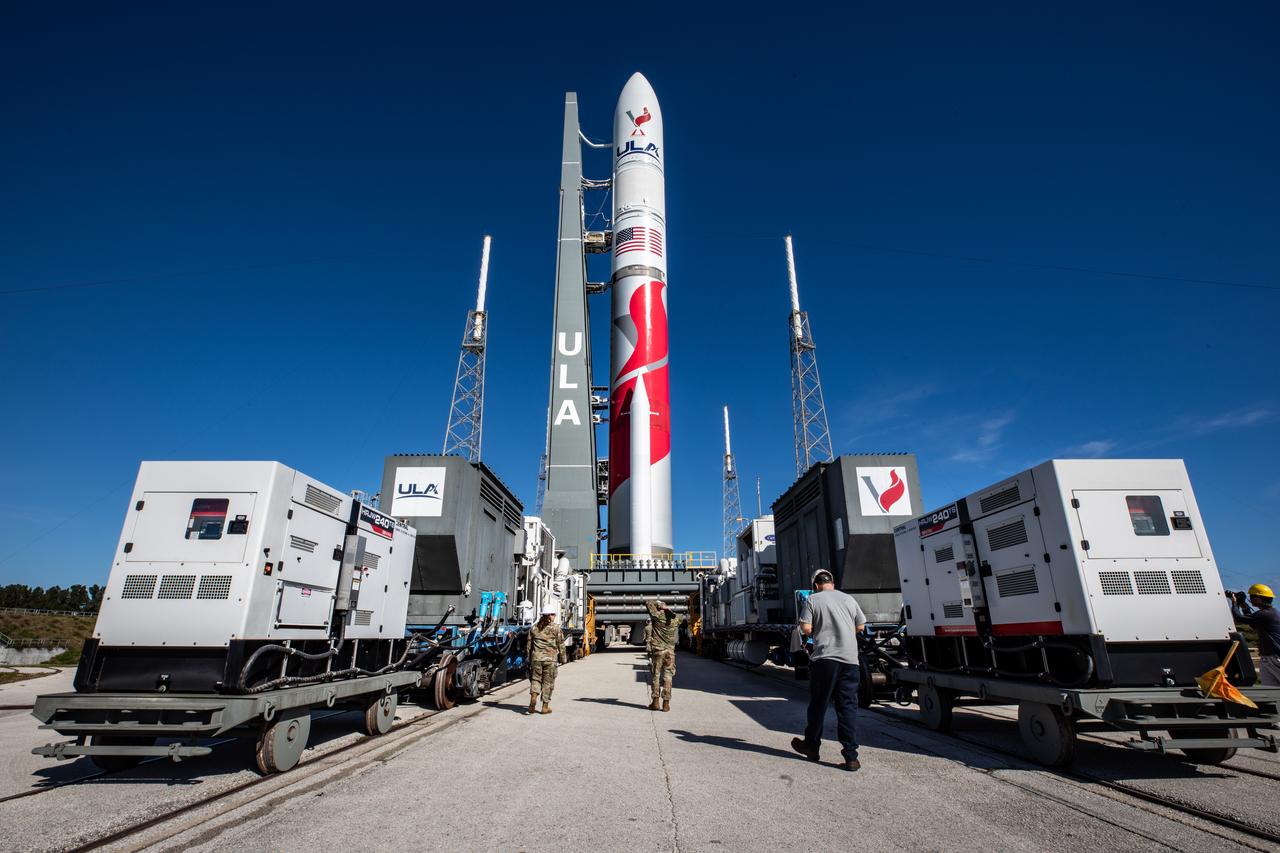

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
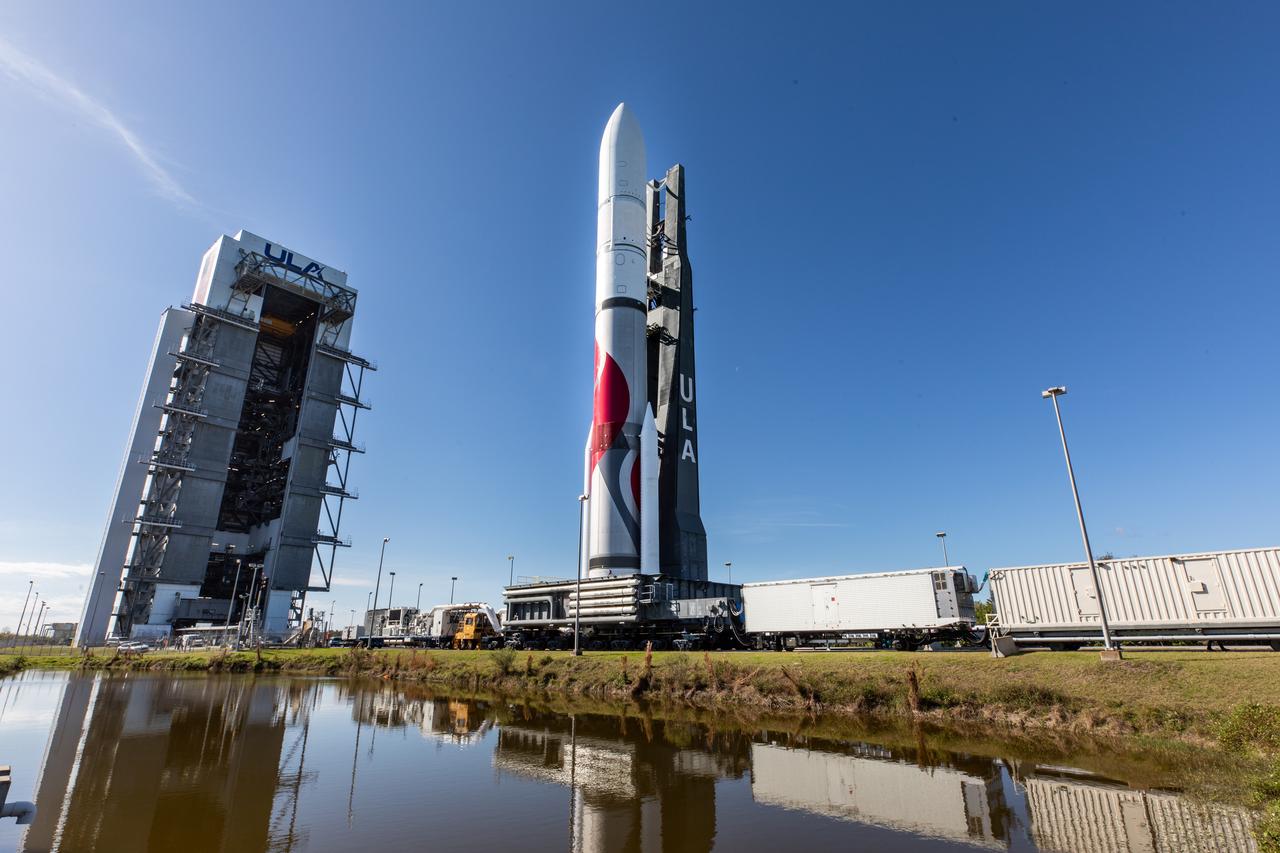

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
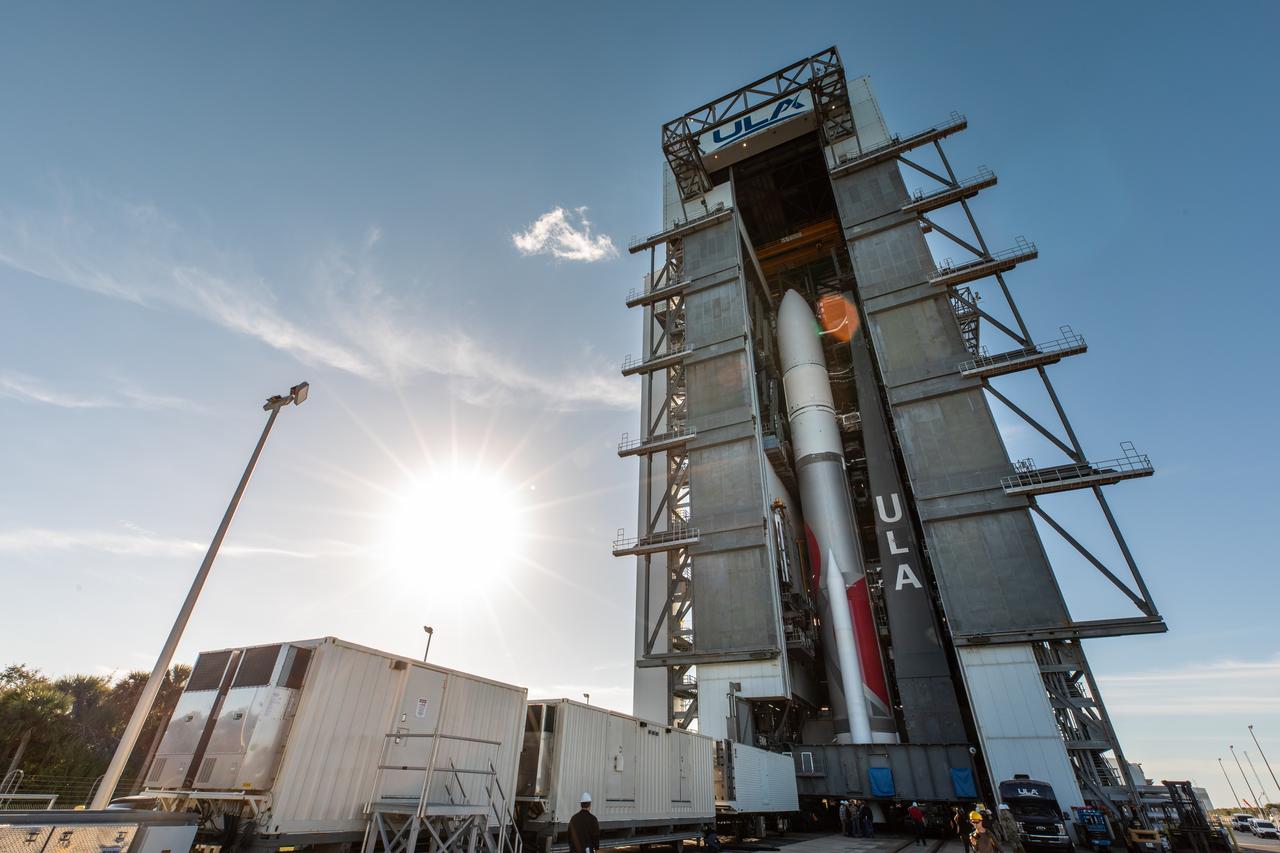

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
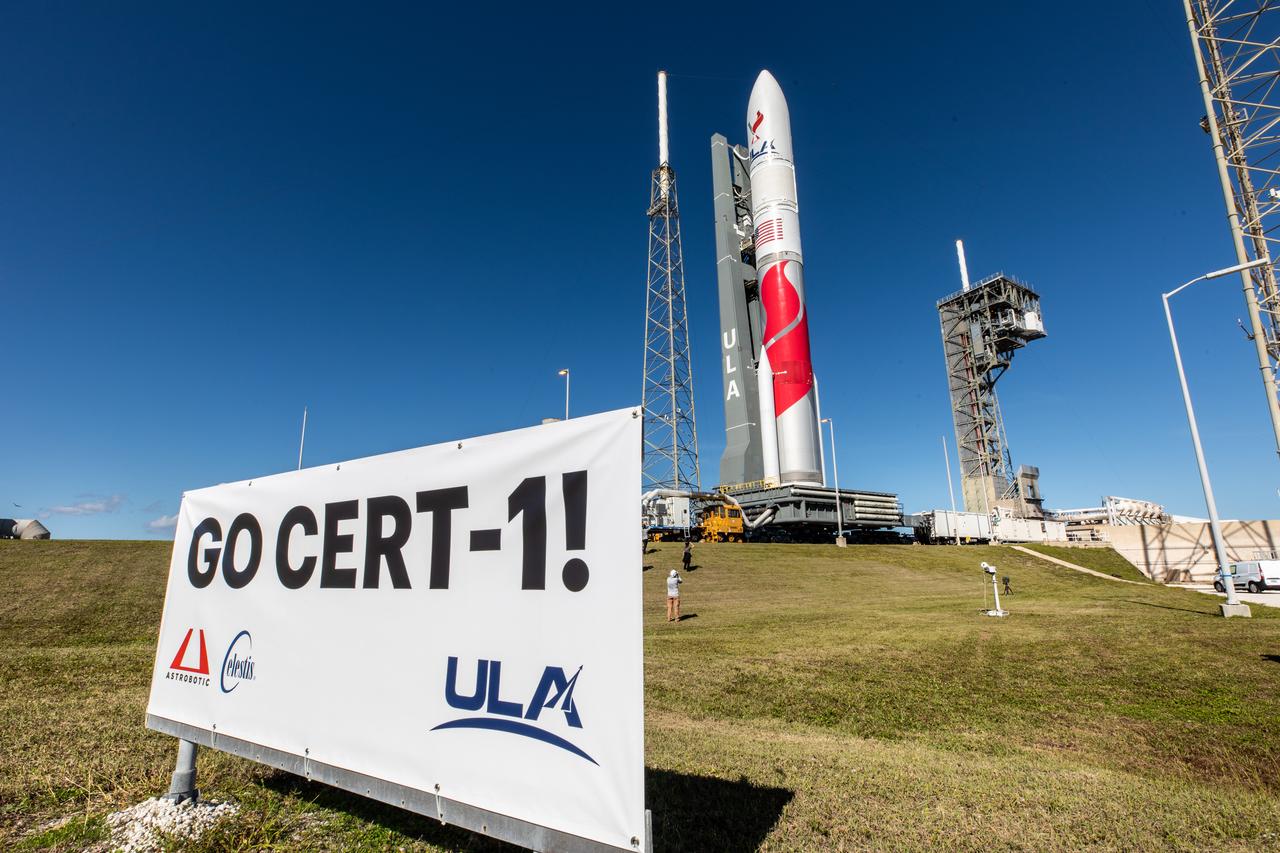

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
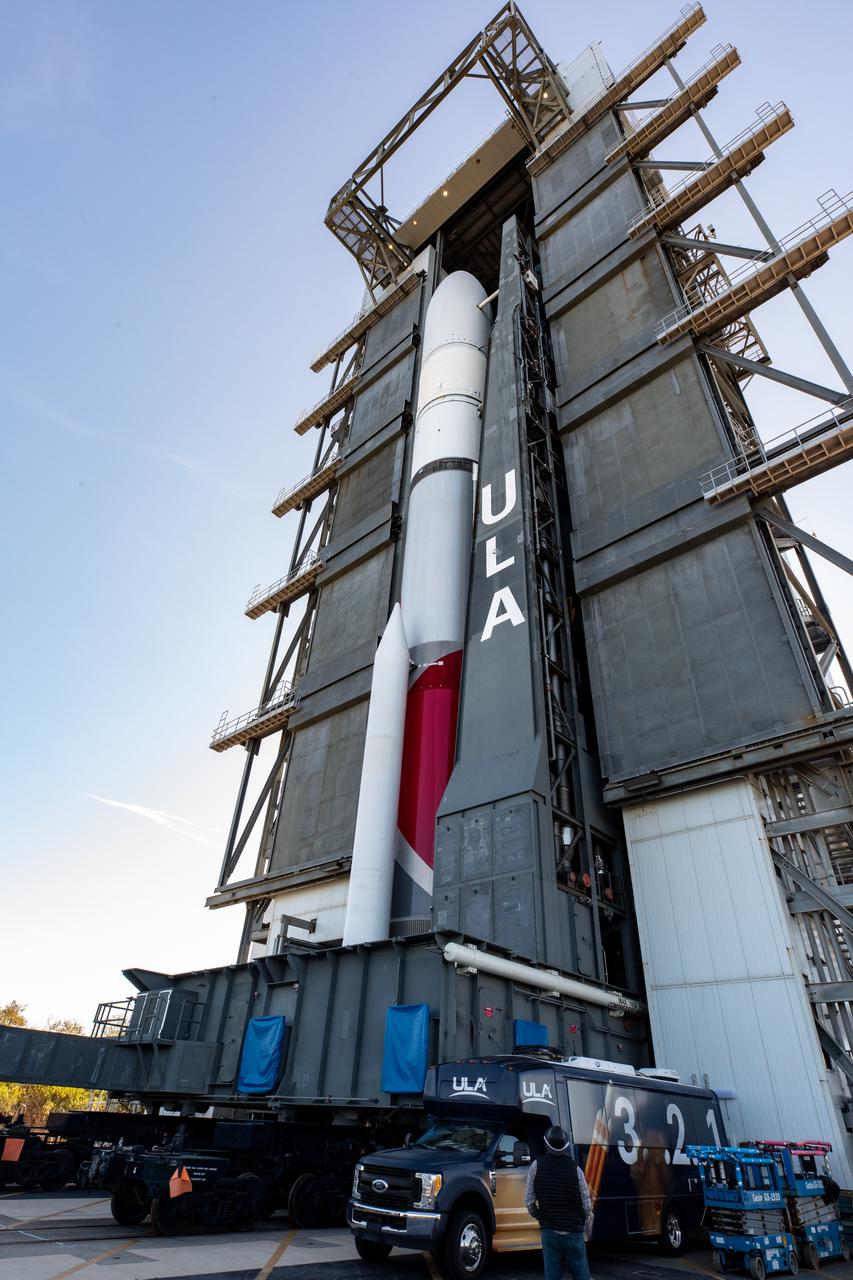

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
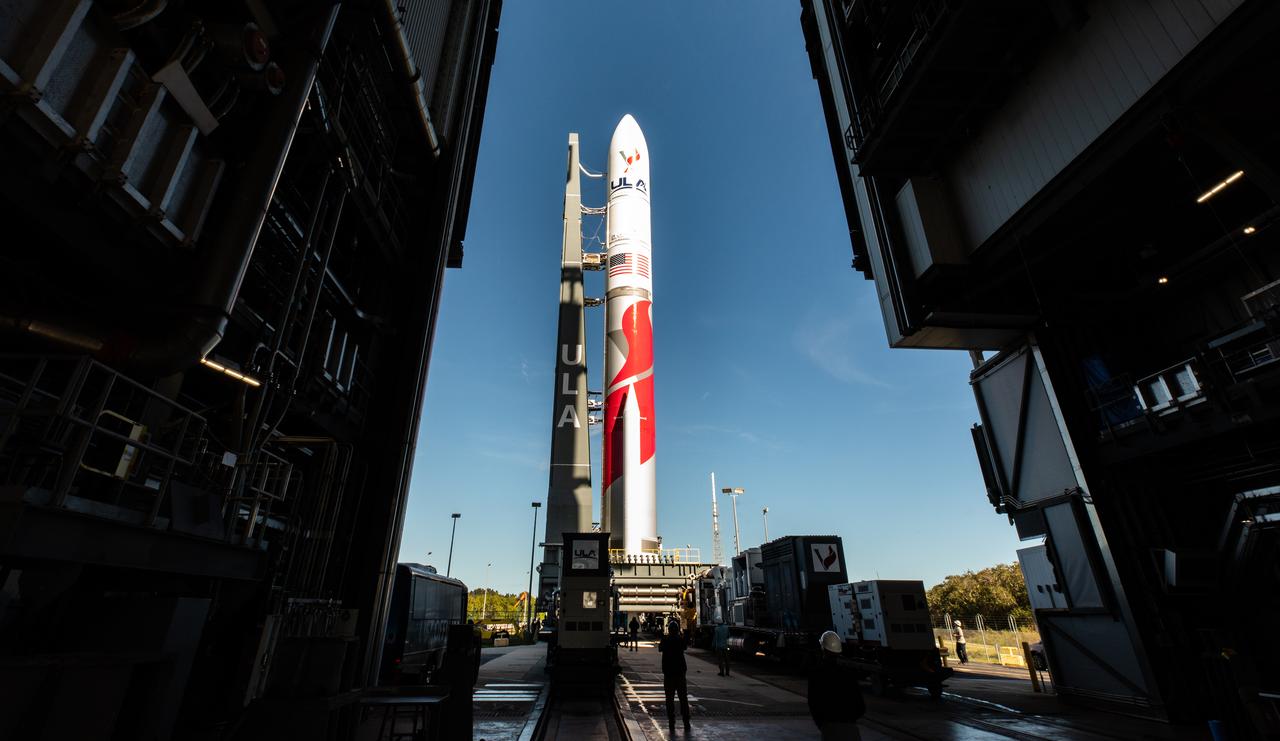

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
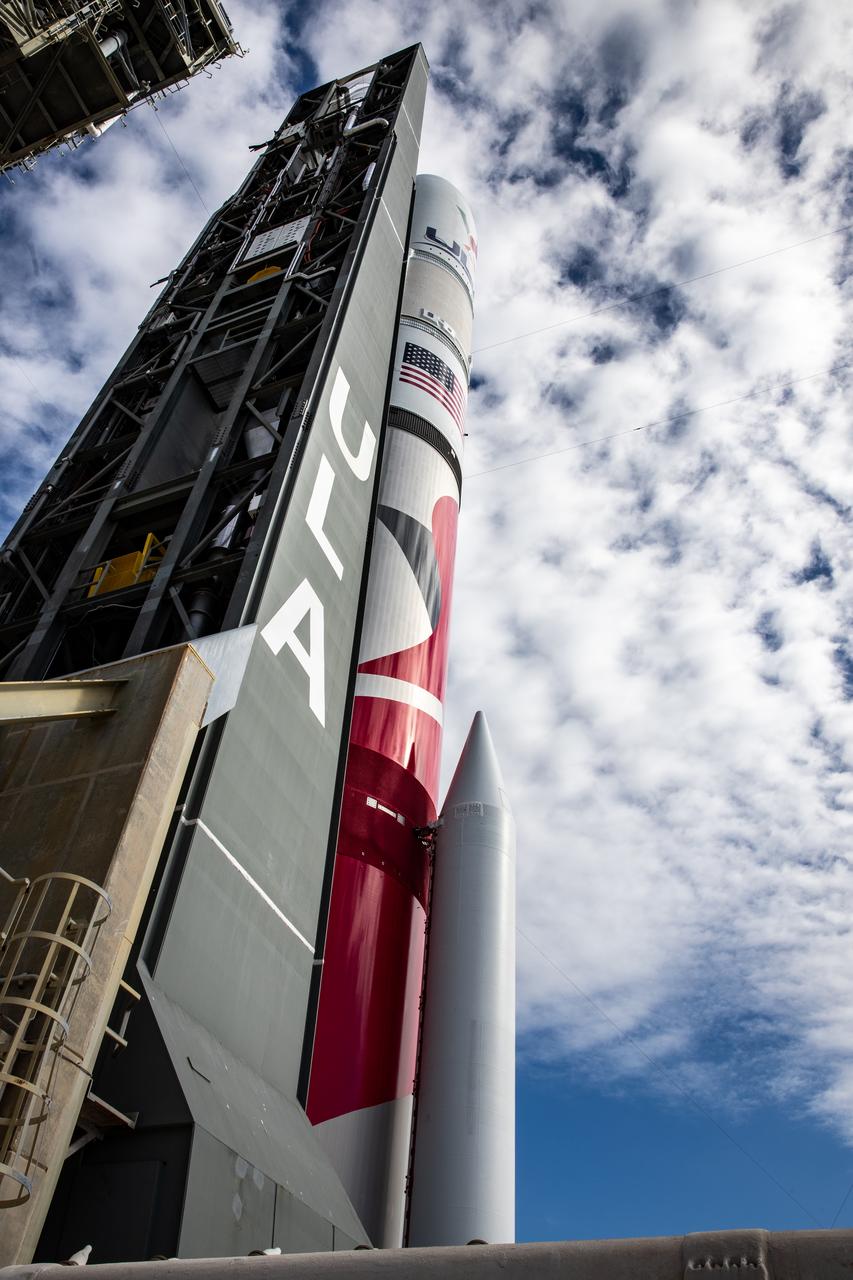

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
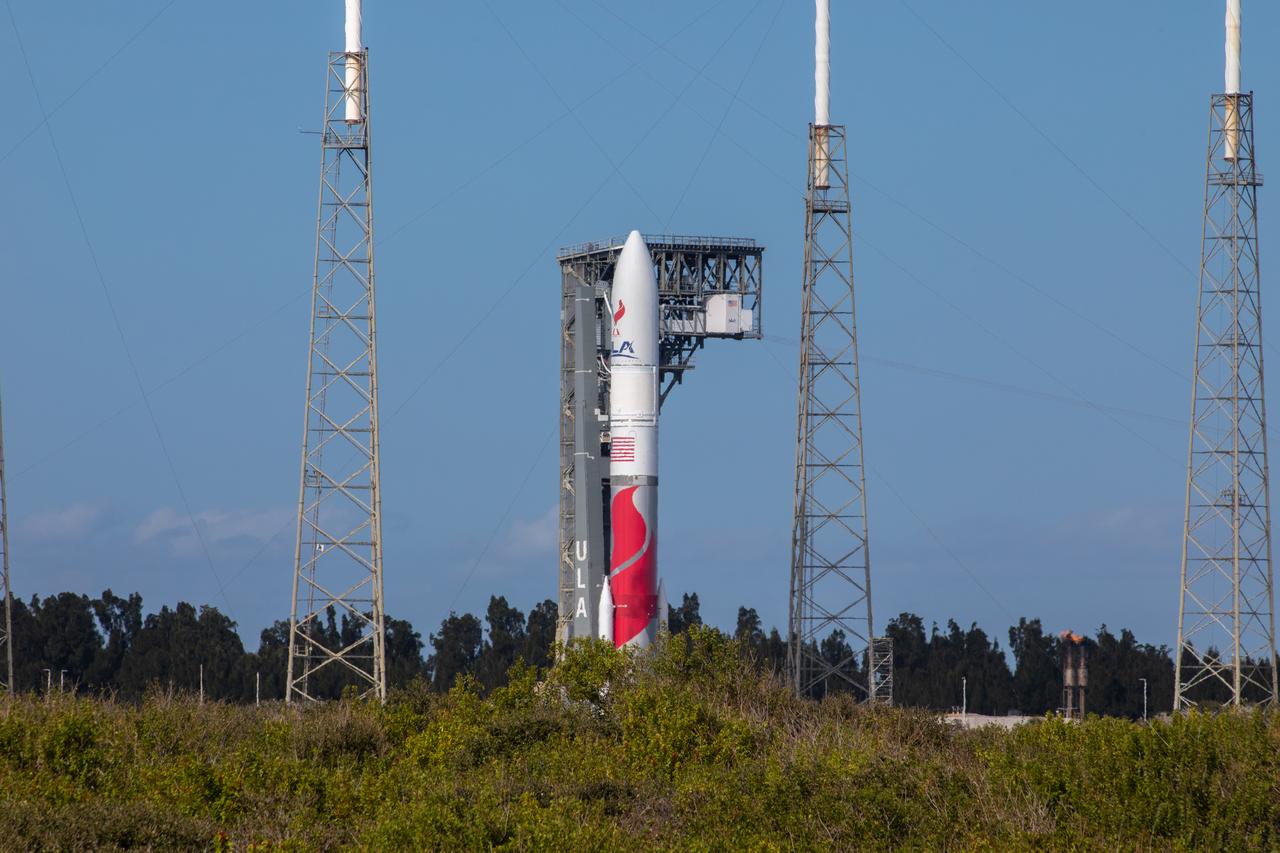

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
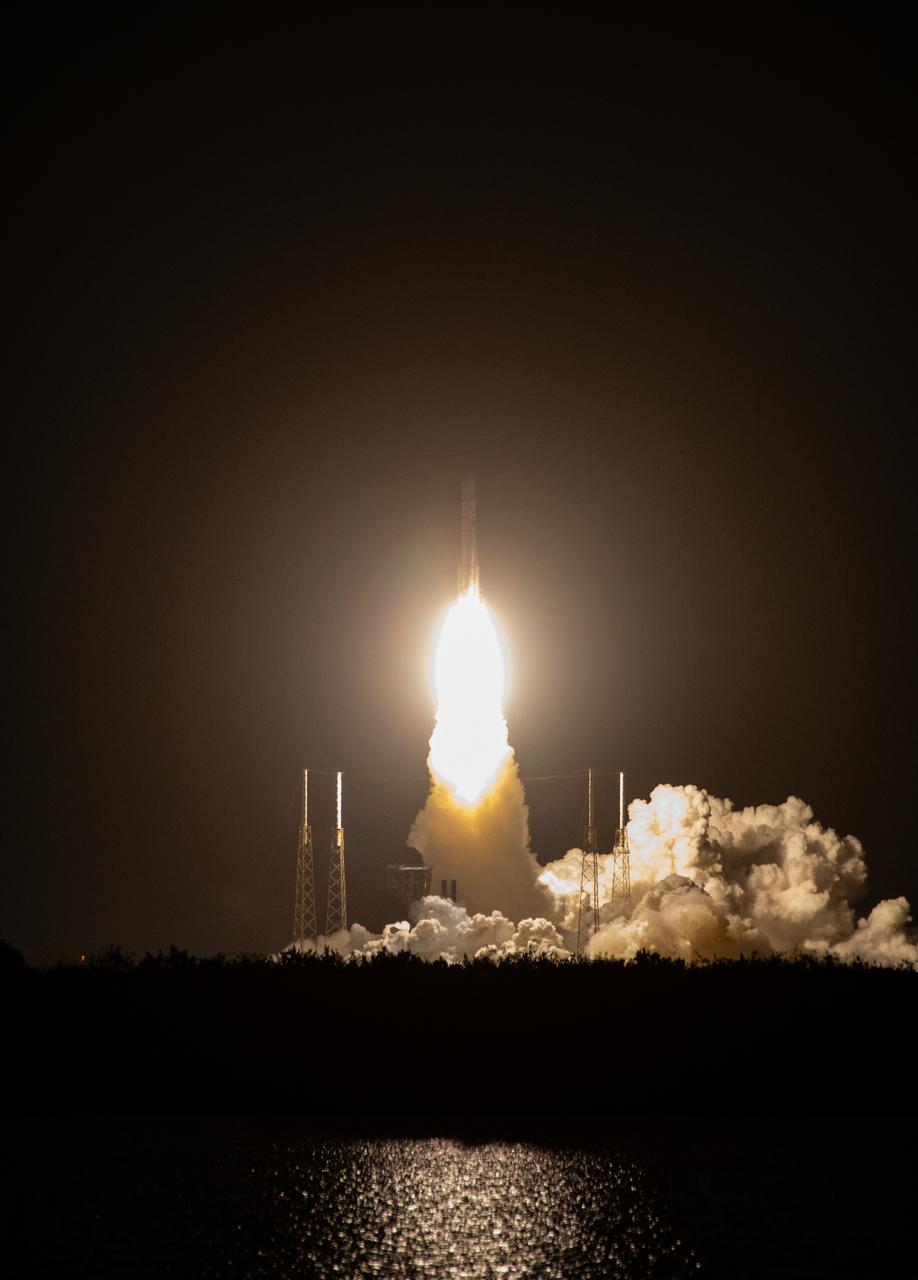

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
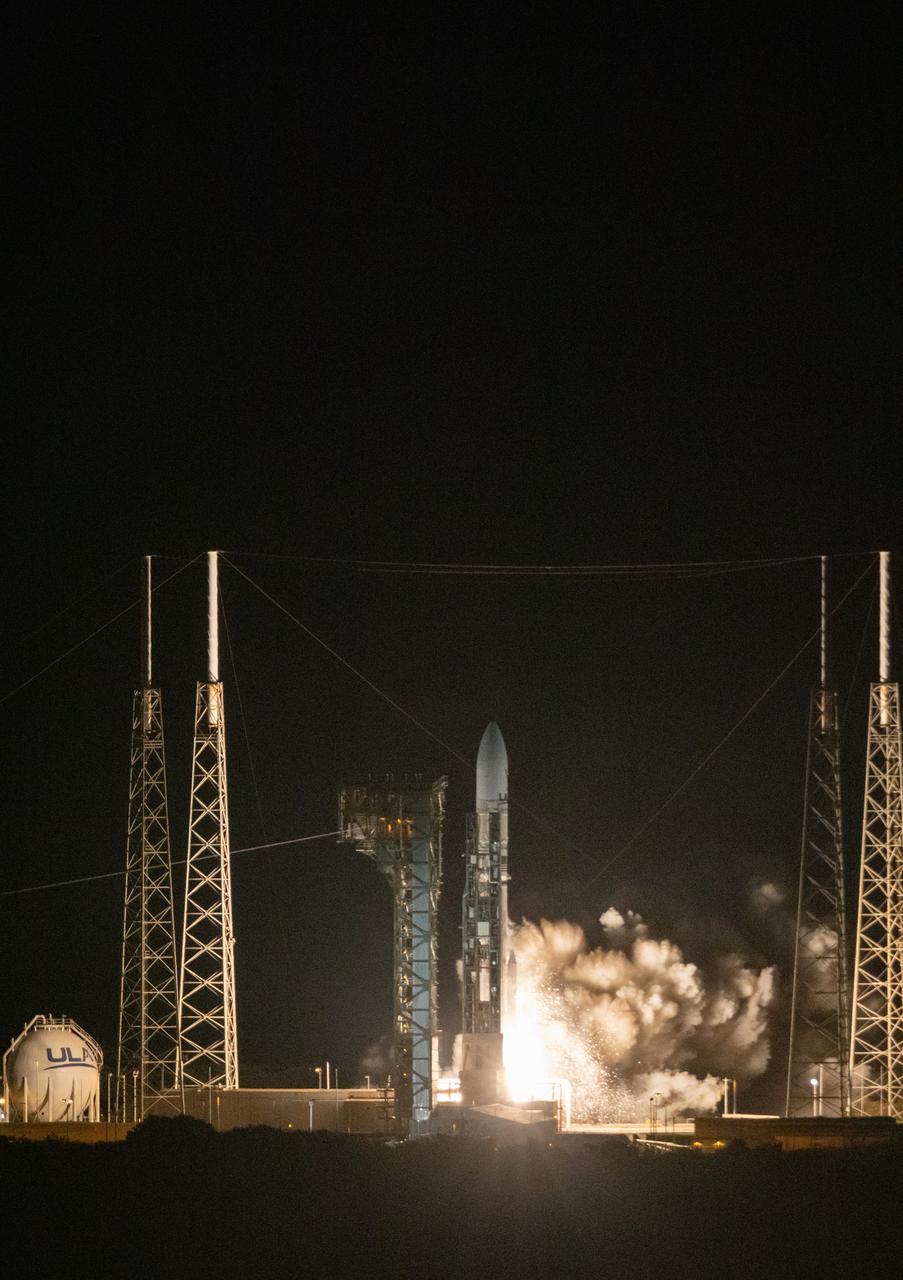

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
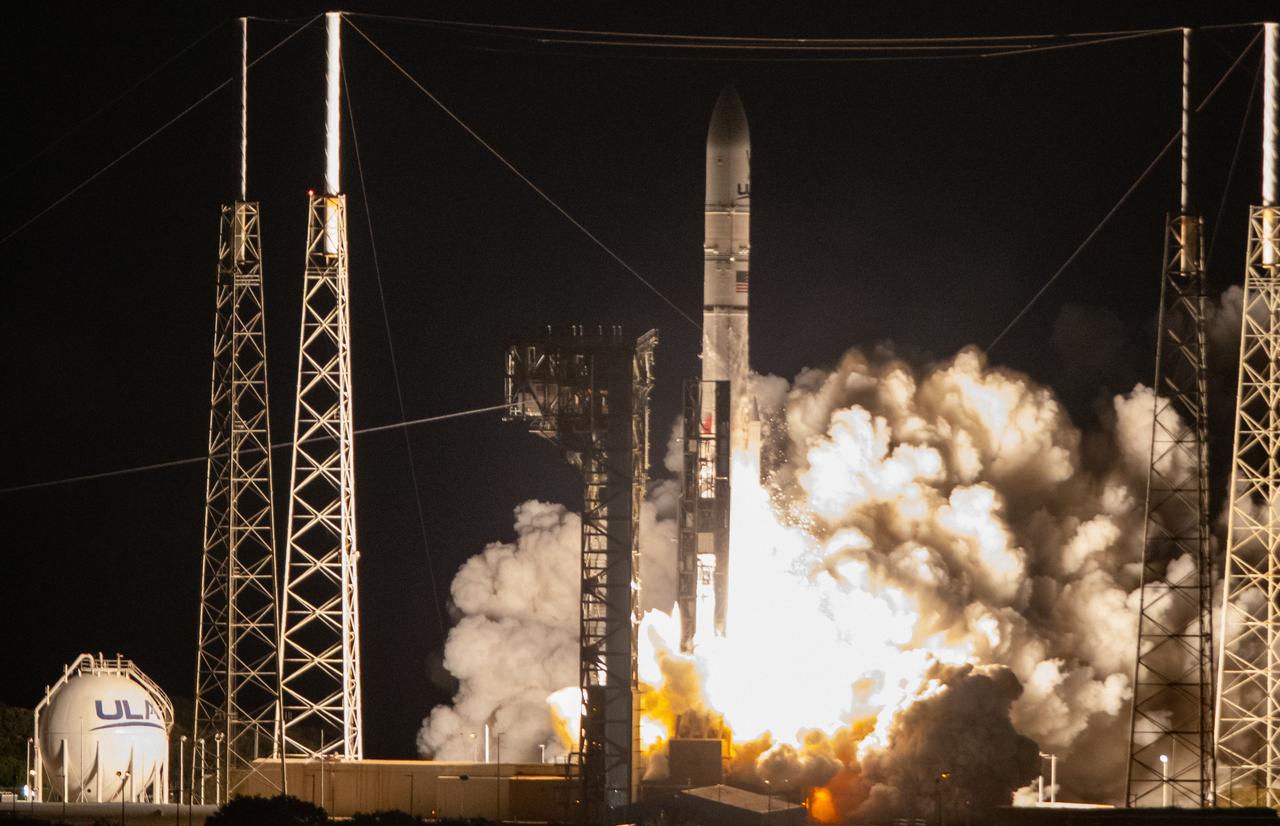

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
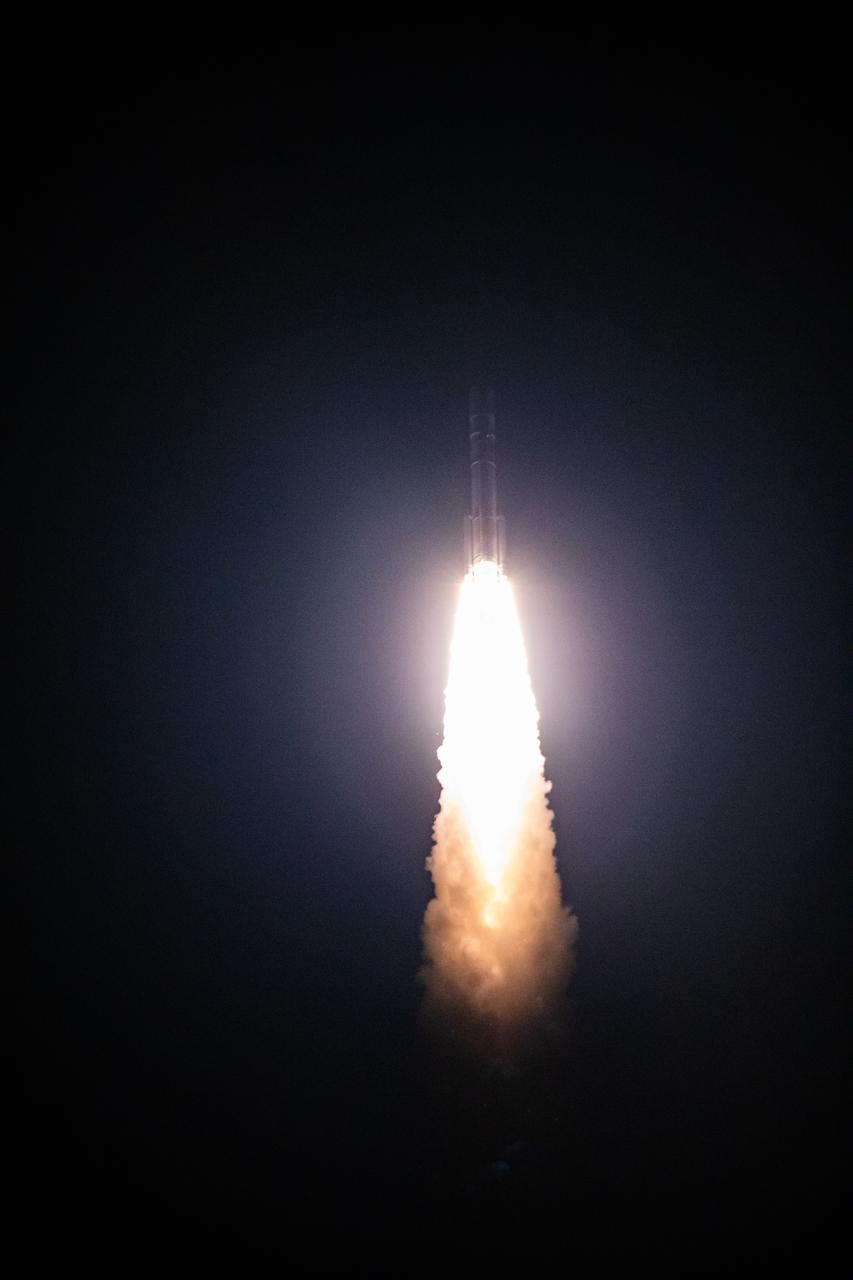

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.

Sharad Bhaskaran, mission director for Pittsburgh-based Astrobotic, delivers the monthly Tech Talk on Sept. 12 in Building 4221 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. Bhaskaran presented Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander which will deliver payloads to the surface of the Moon for government and commercial customers, including NASA.
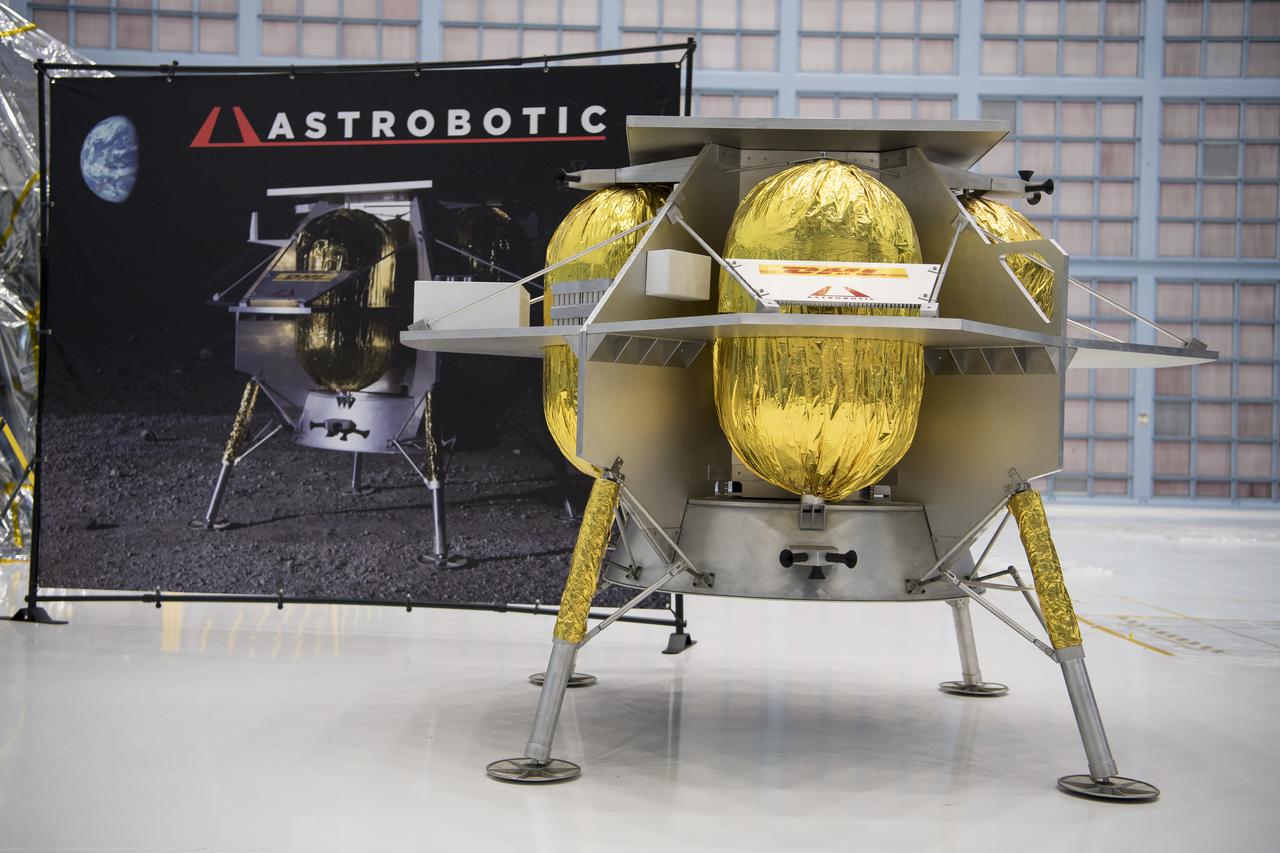

The Astrobotic lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from right, speaks to Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, second from left, and Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran, left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
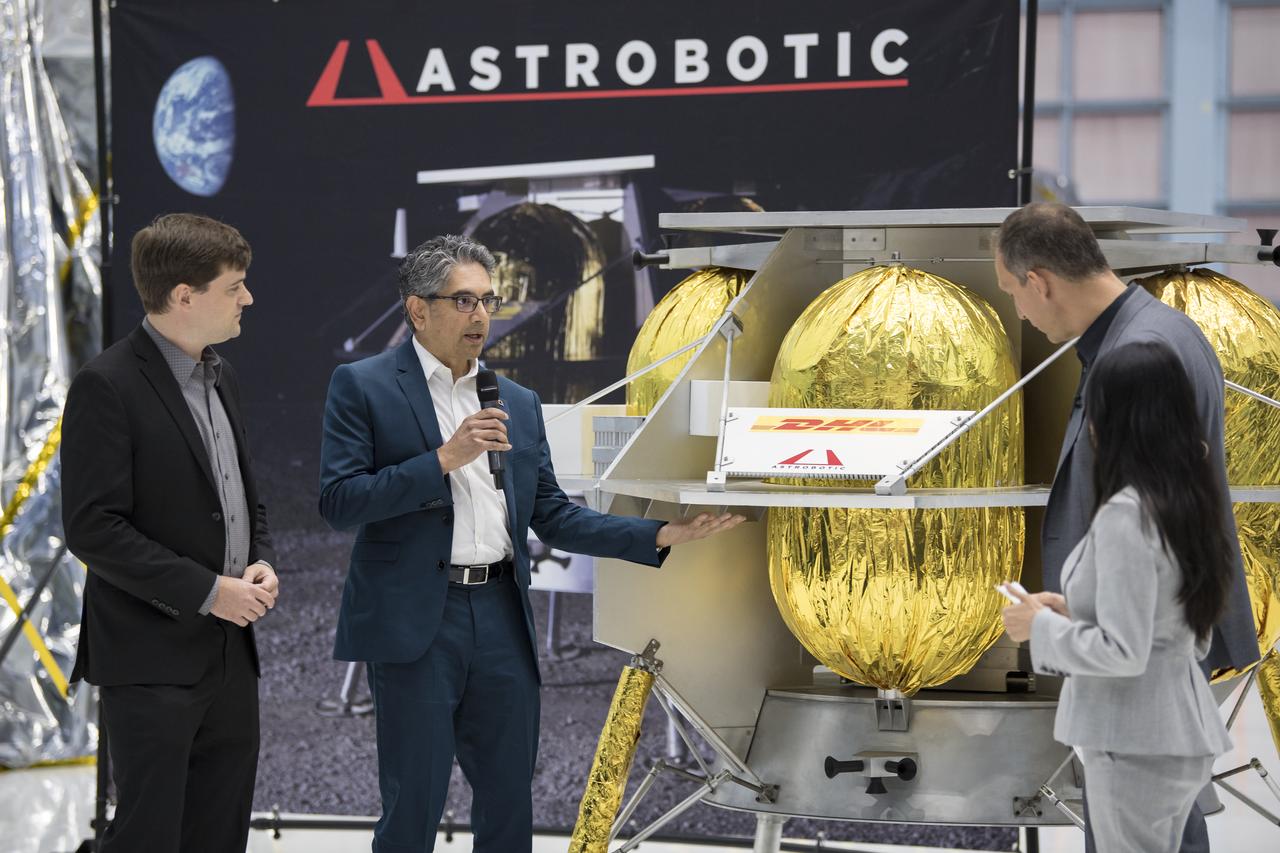

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from right, speaks to Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, left, and Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran, second from left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
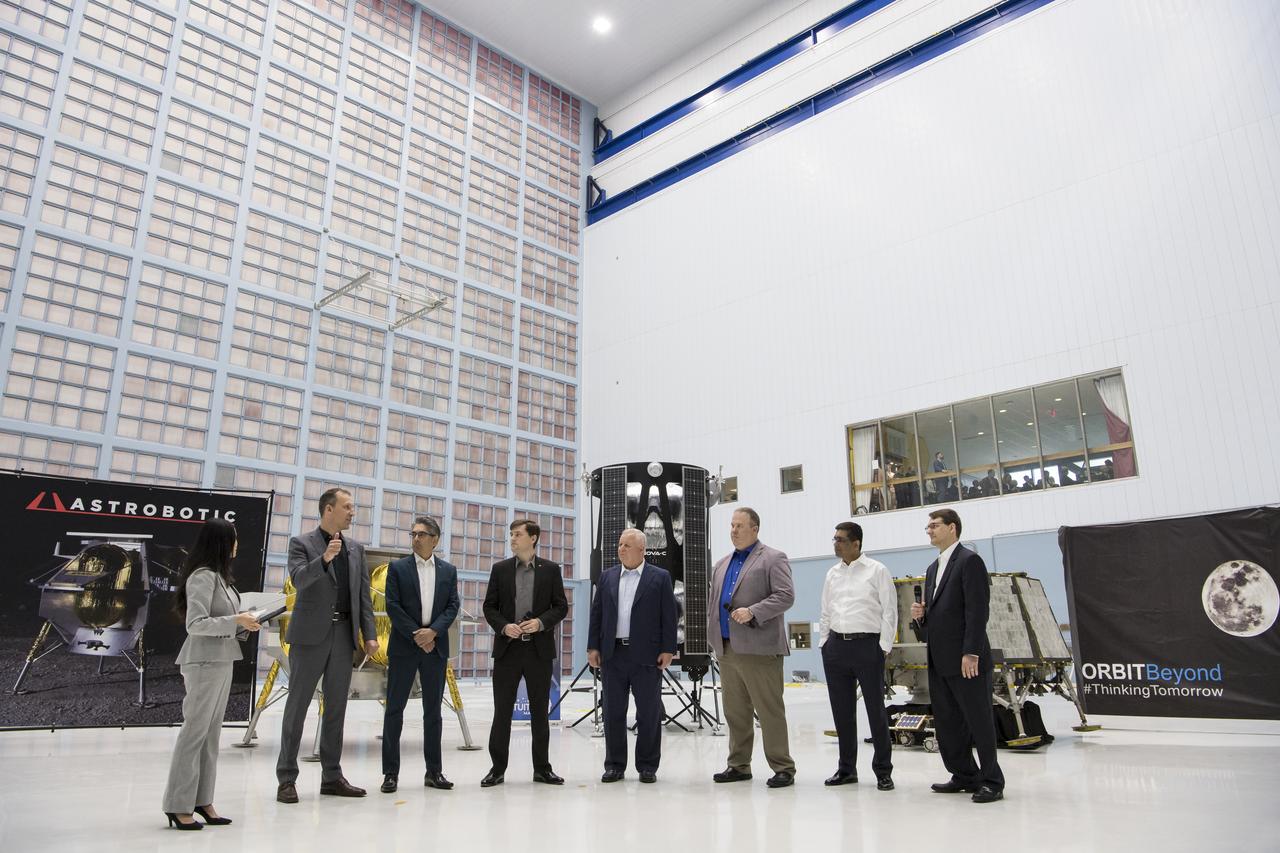

From left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse talk about their lunar landers, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
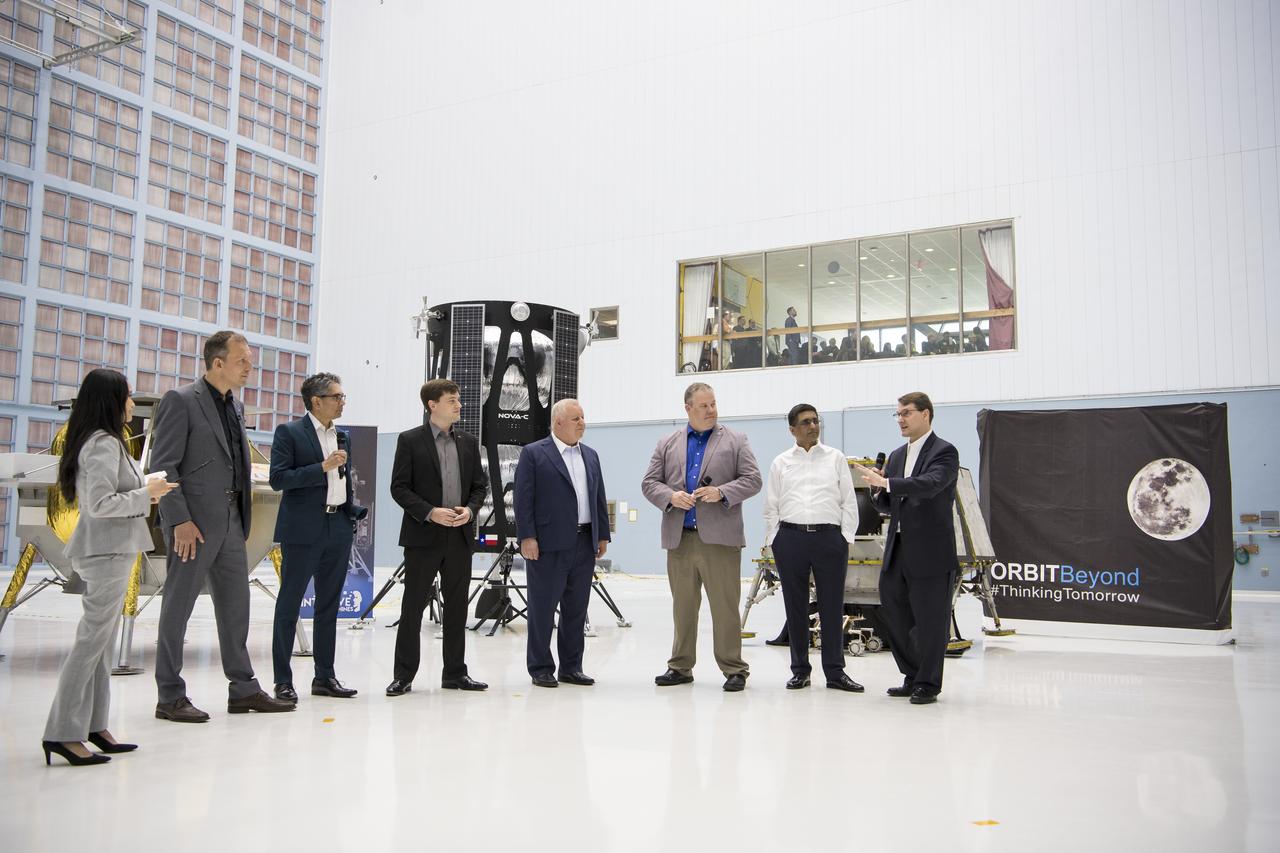

Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse speaks about their lunar lander with, from left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
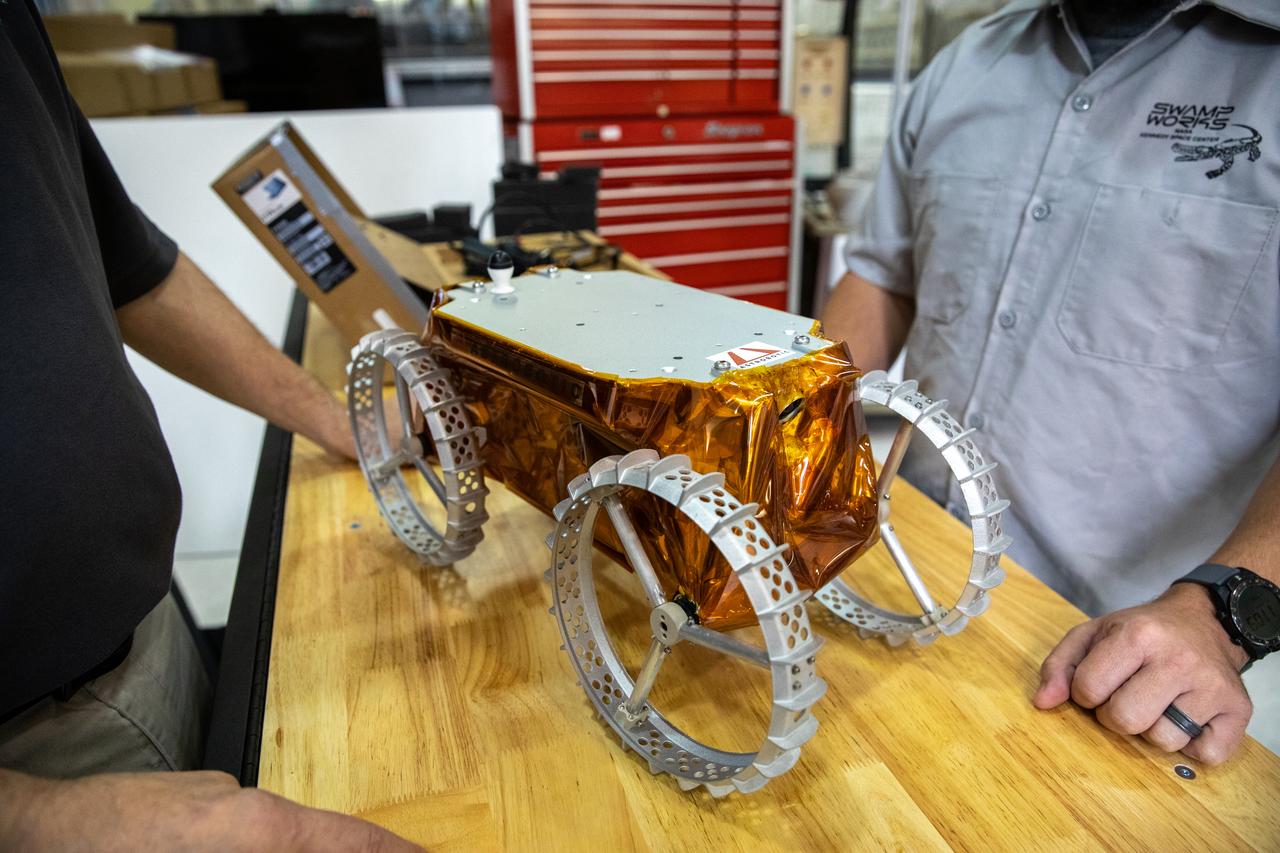

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
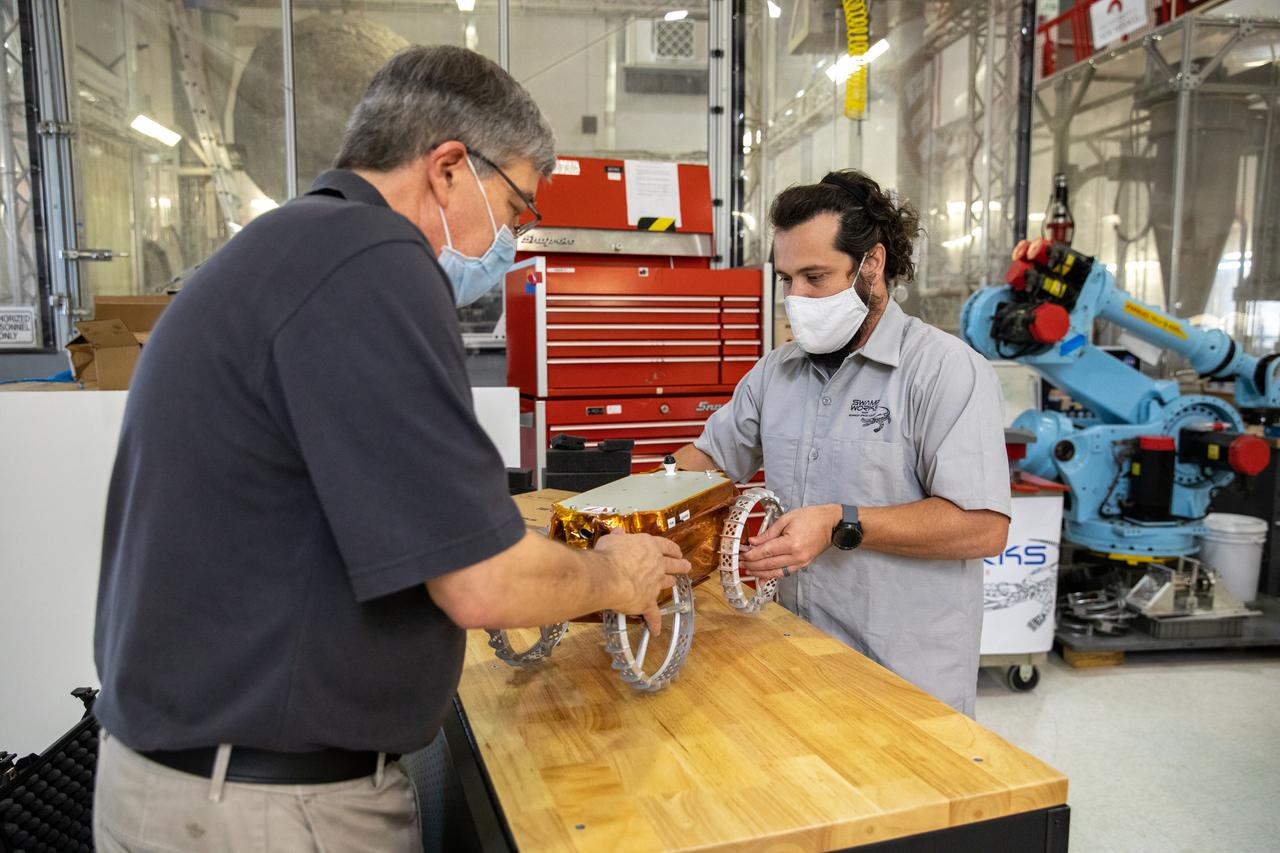

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
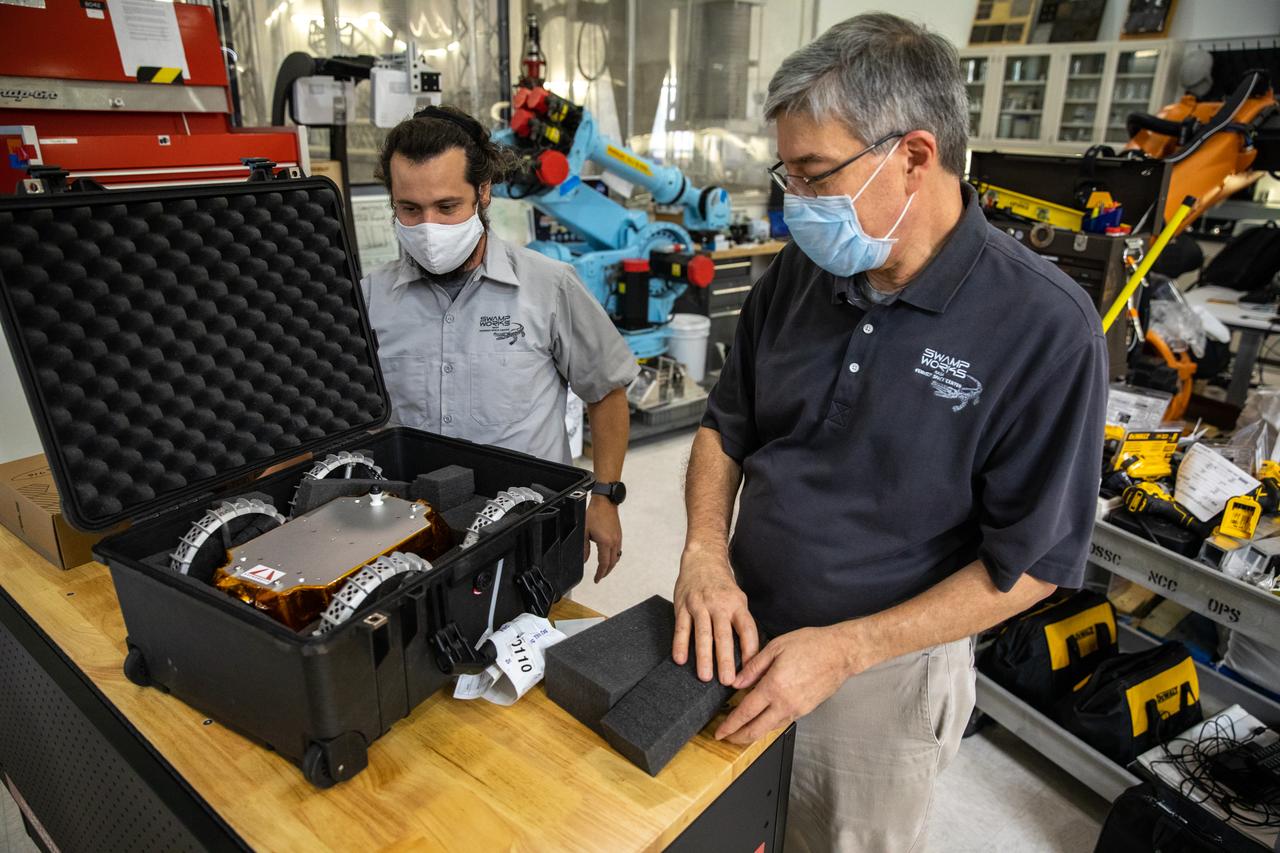

A.J. Nick, left, and Jim Mantovani, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
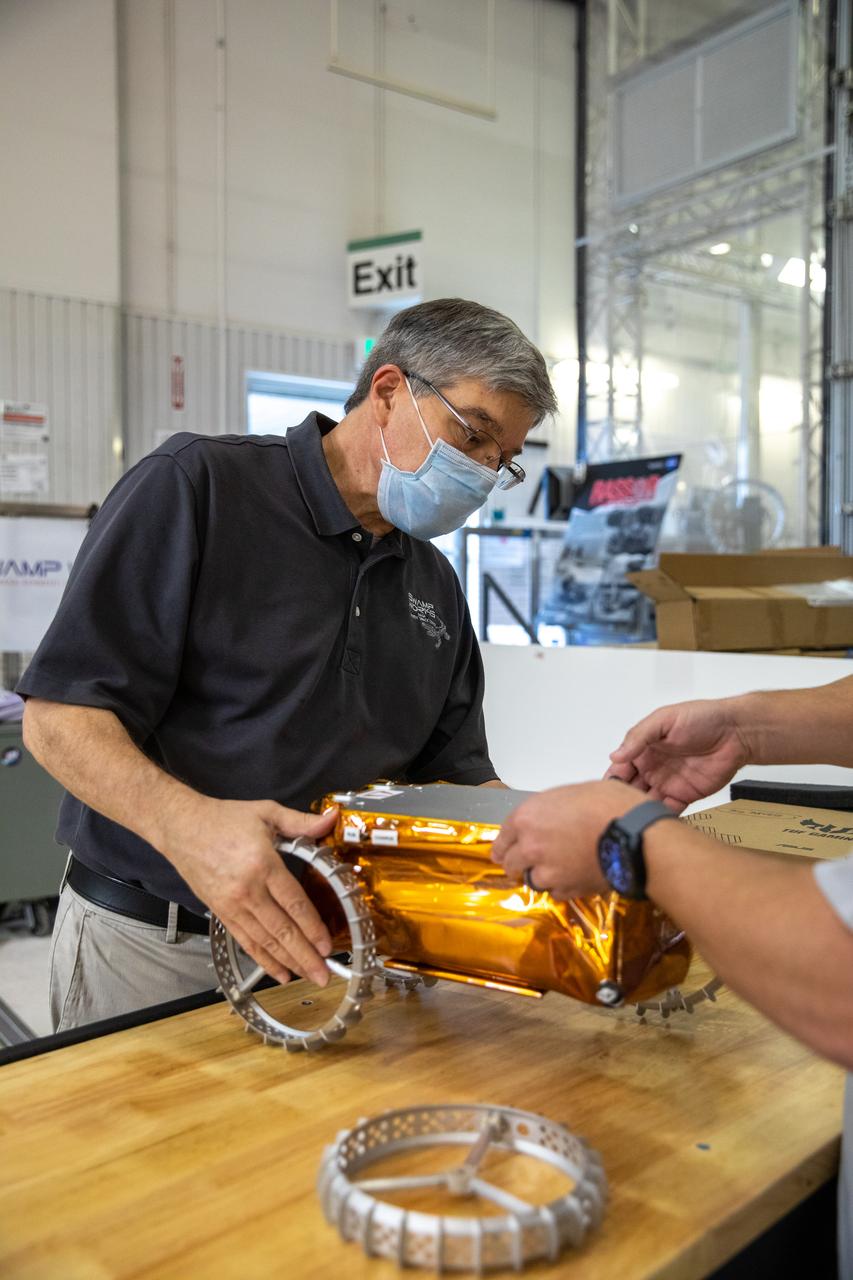

Jim Mantovani, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Kennedy’s A.J. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
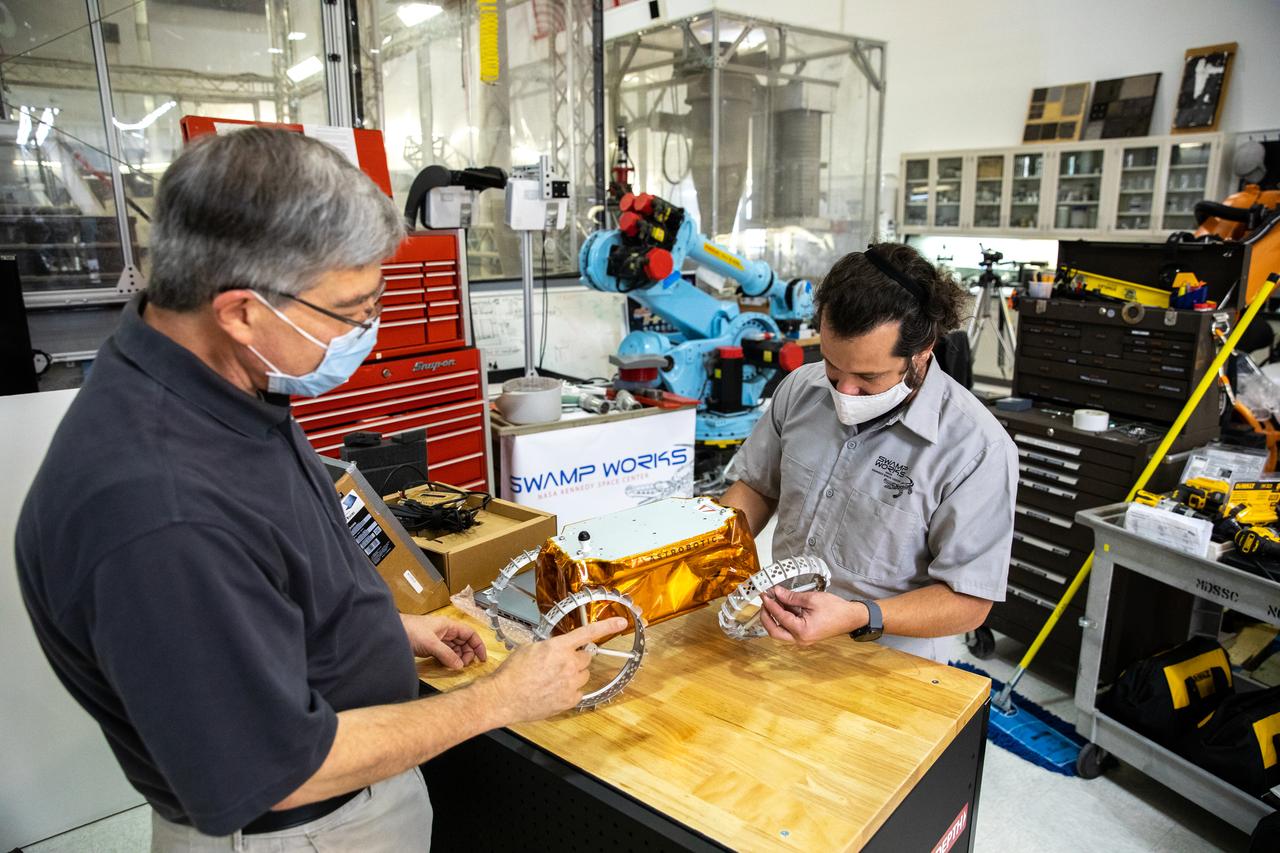

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
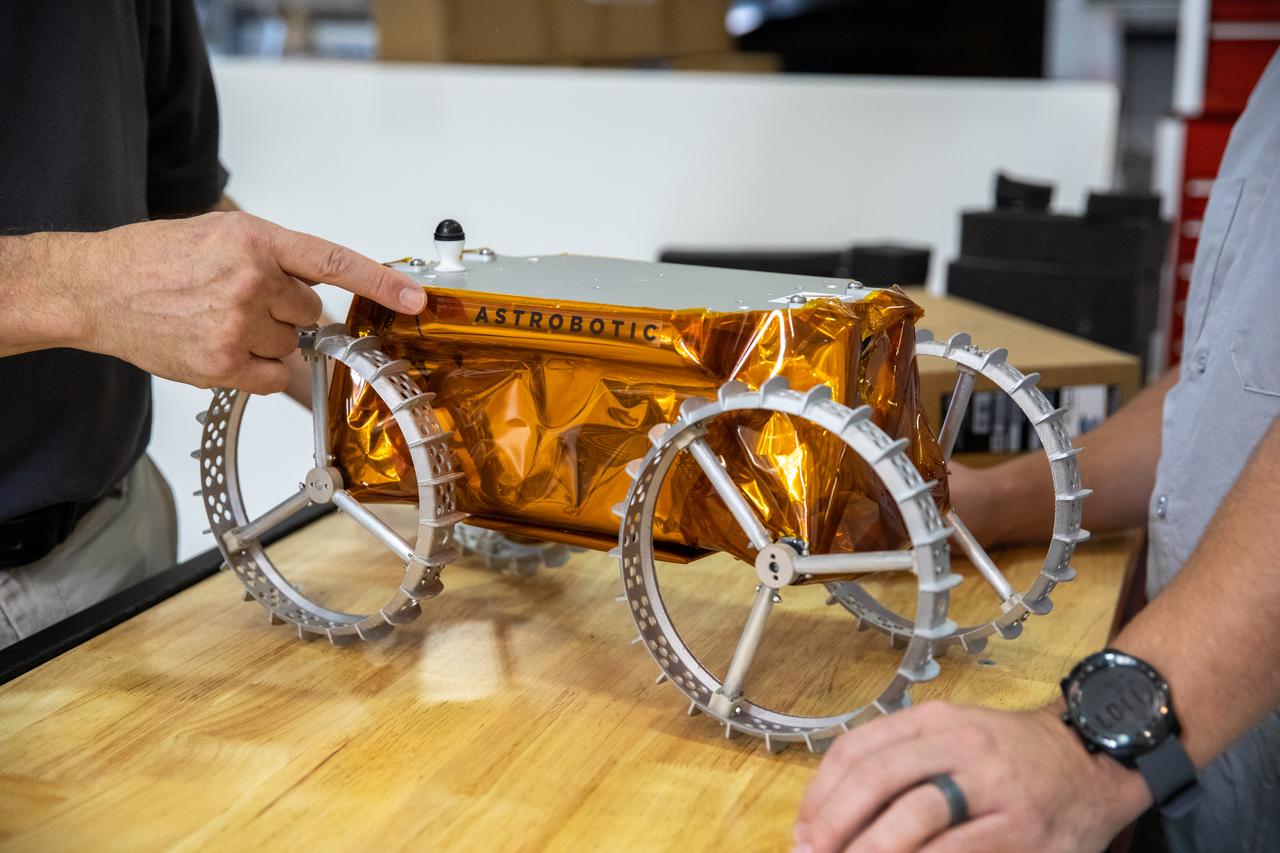

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
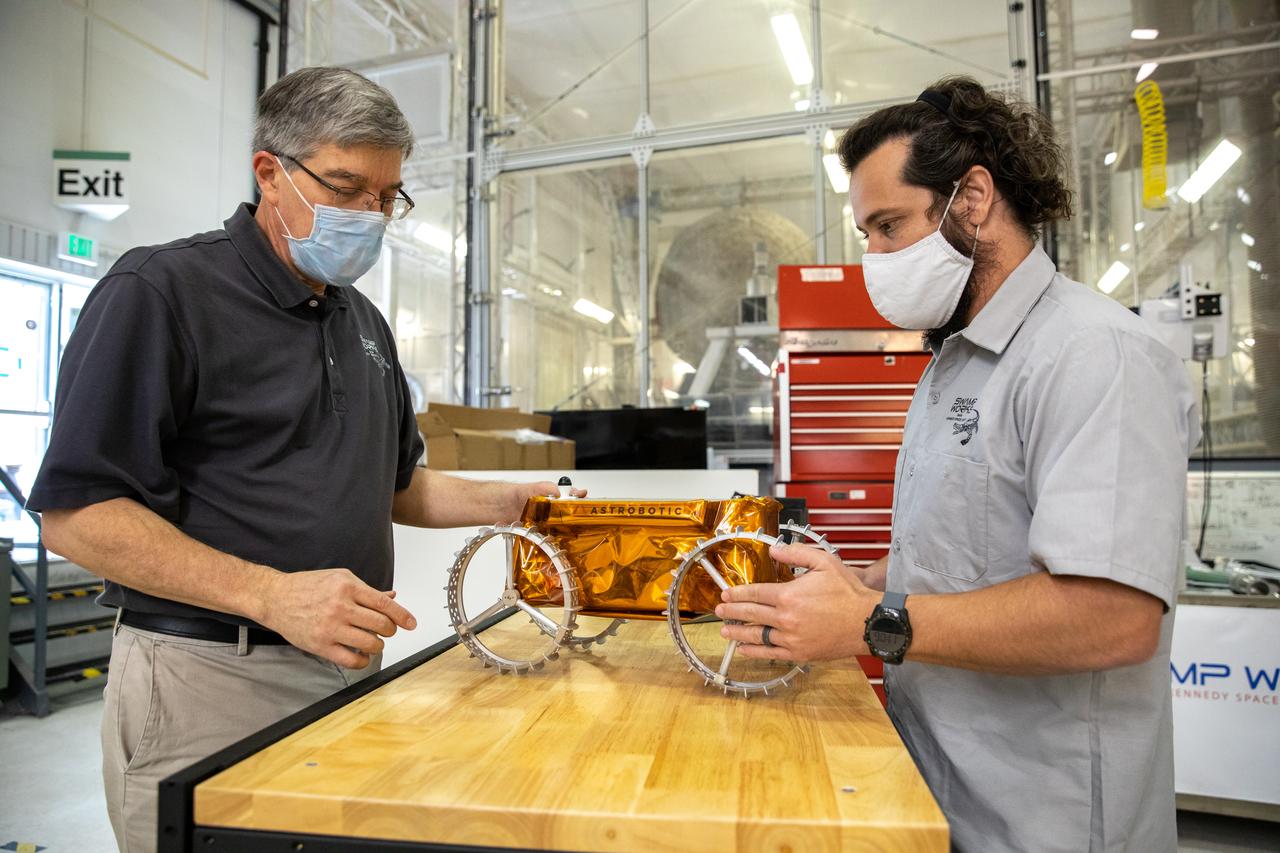

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.

A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
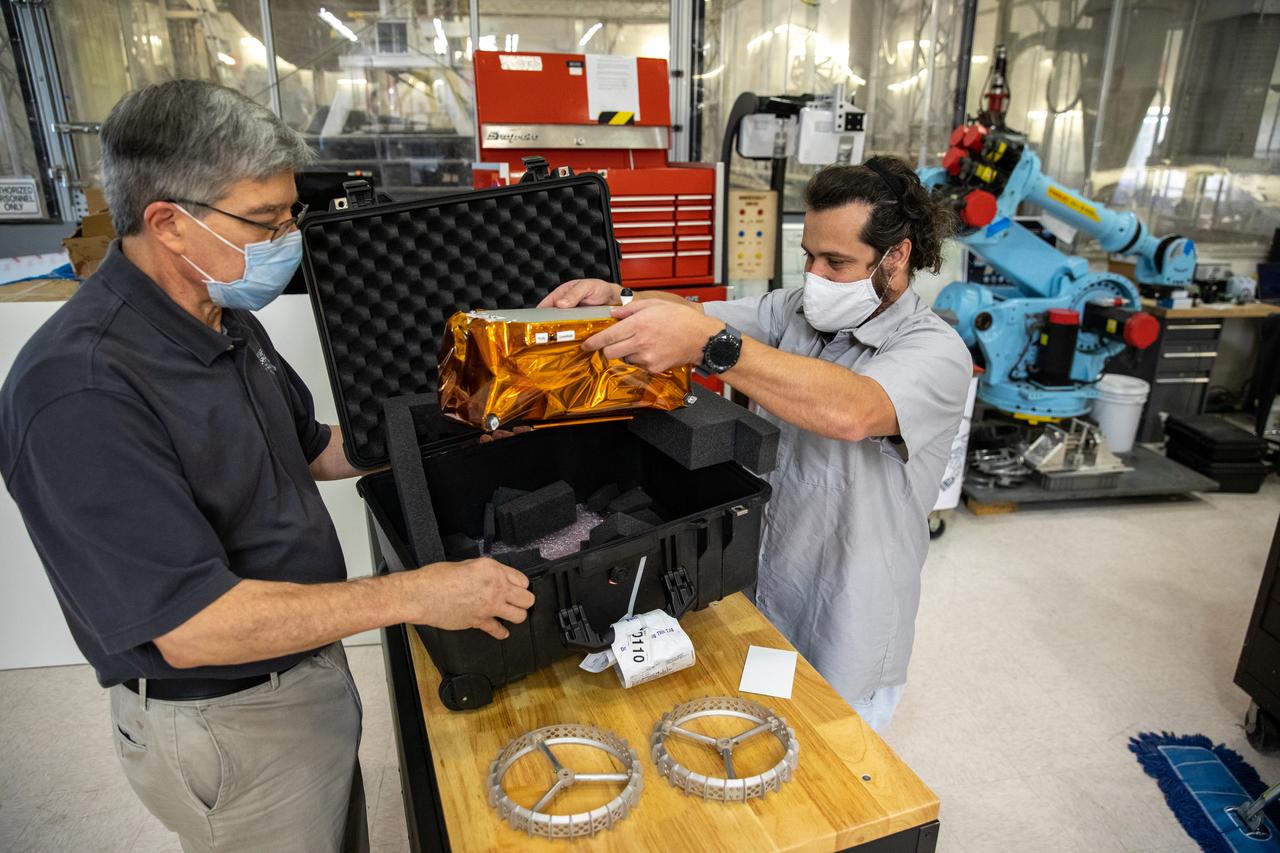

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
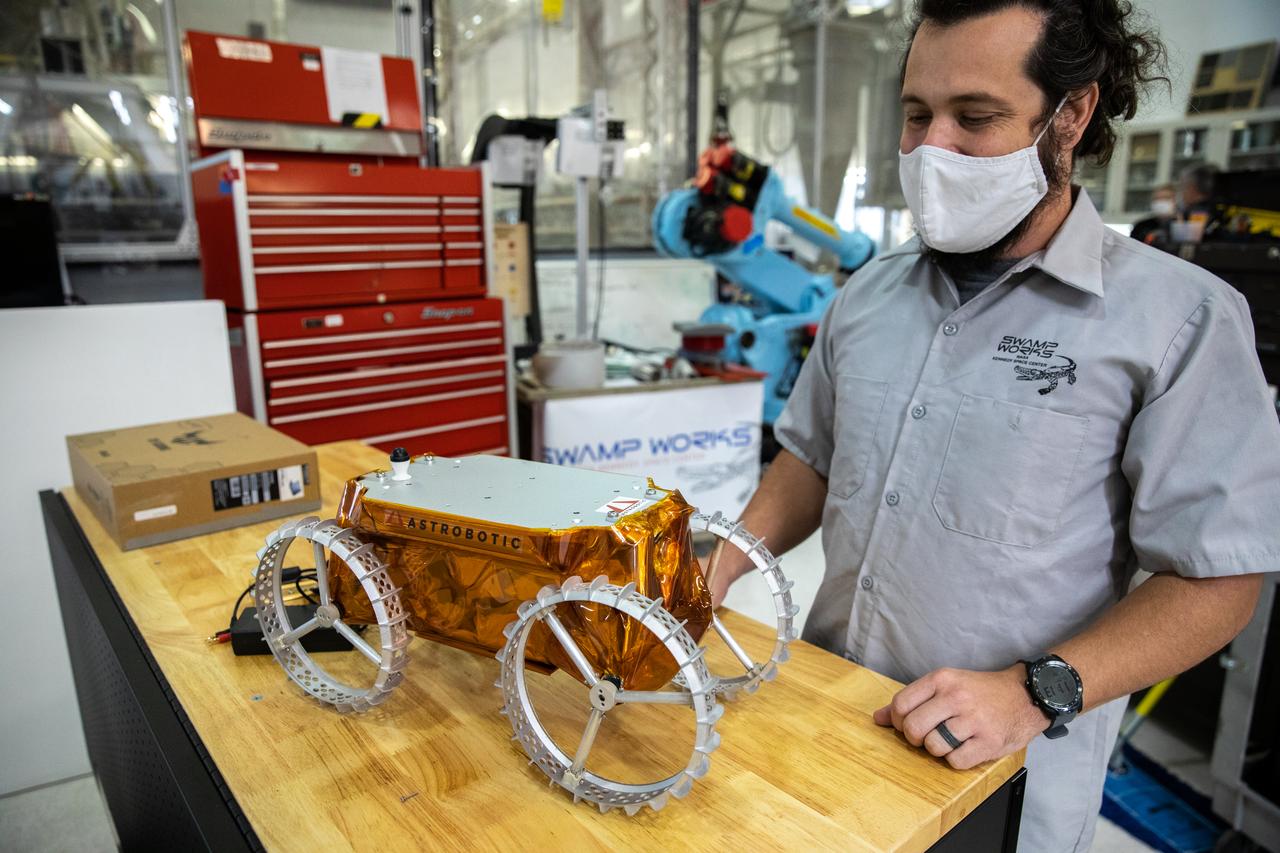

A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
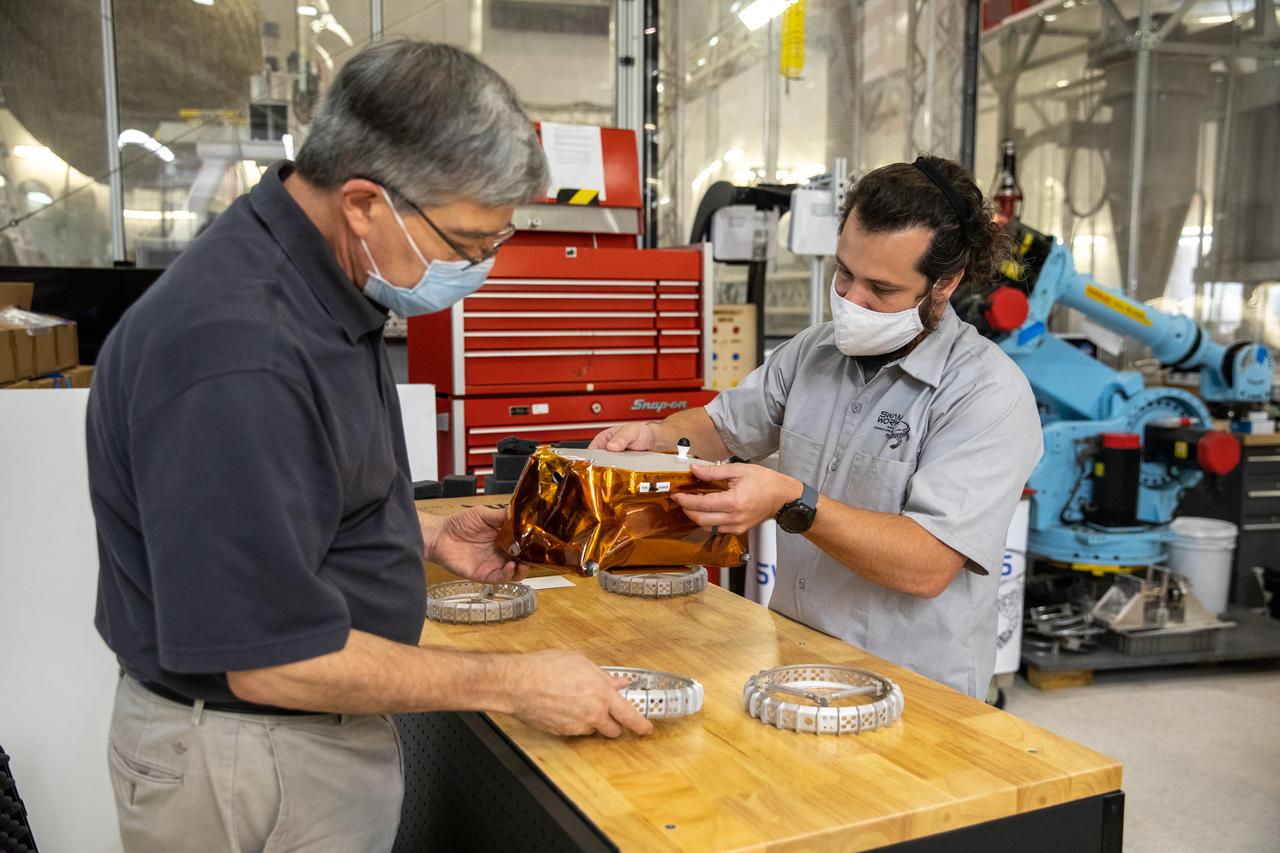

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
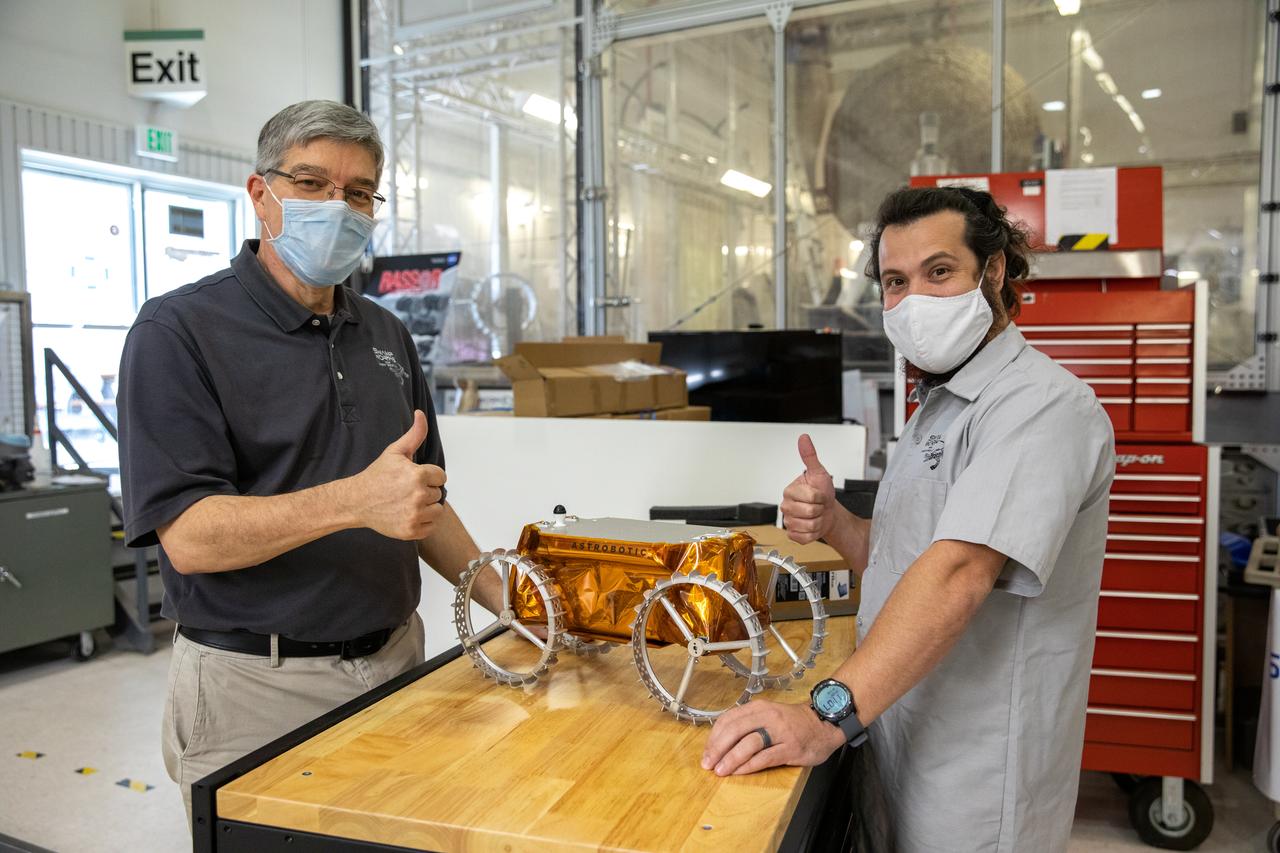

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
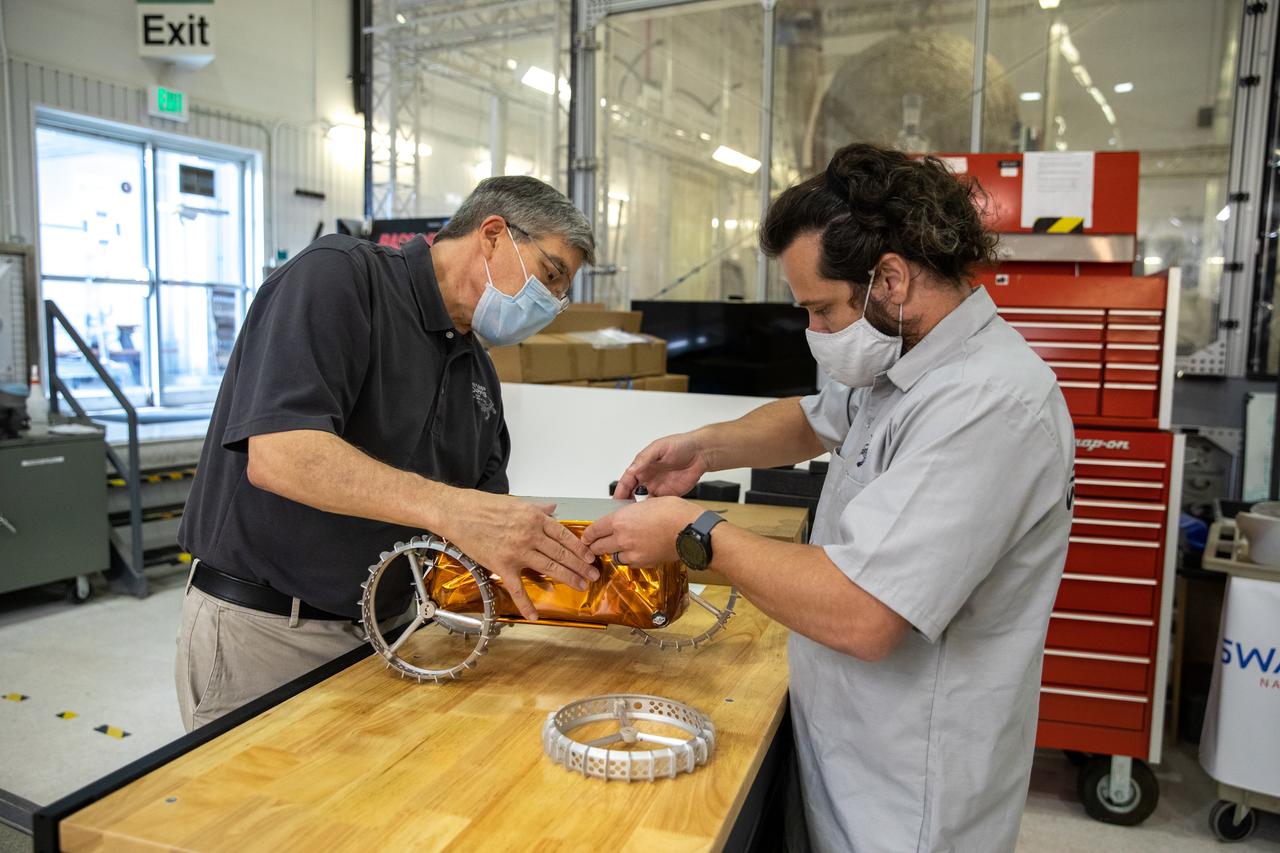

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
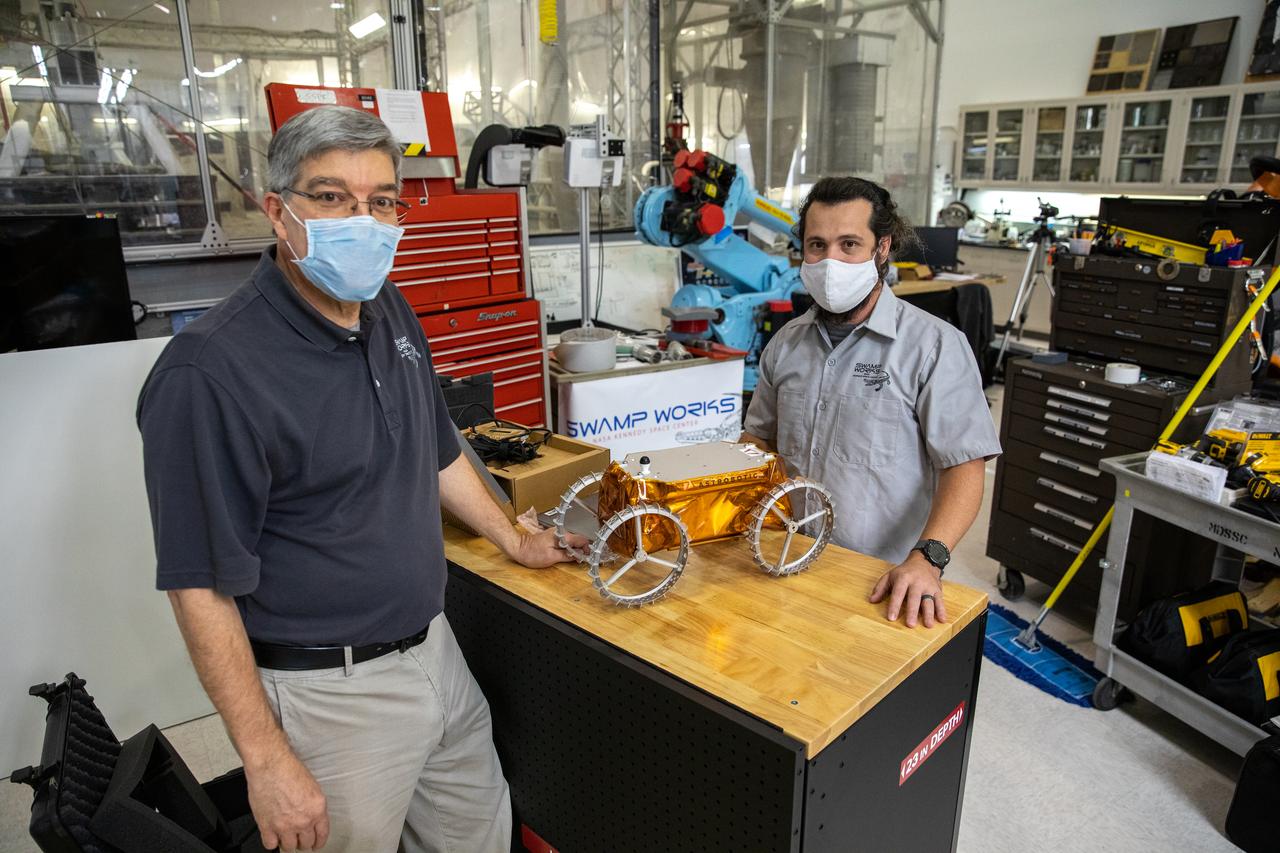

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
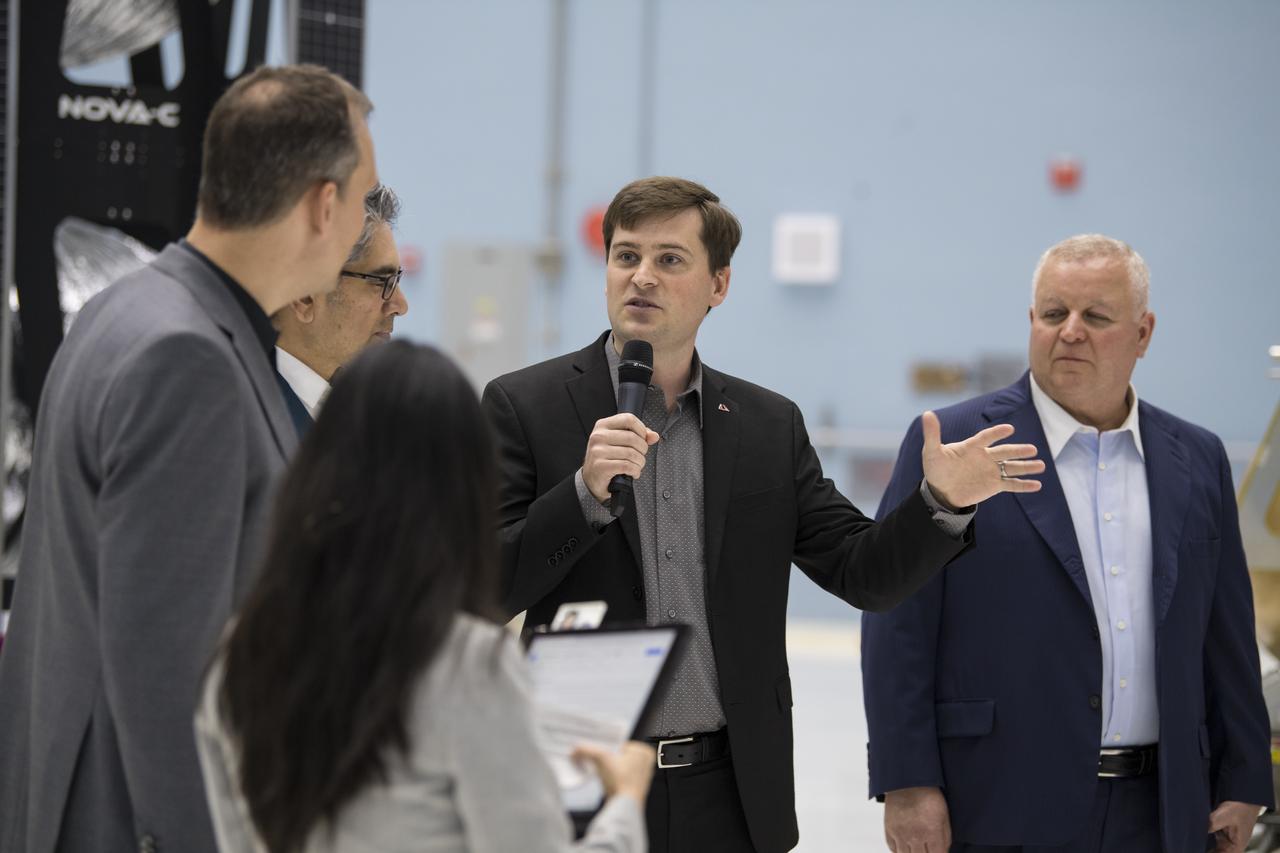

Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, second from right, speaks about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
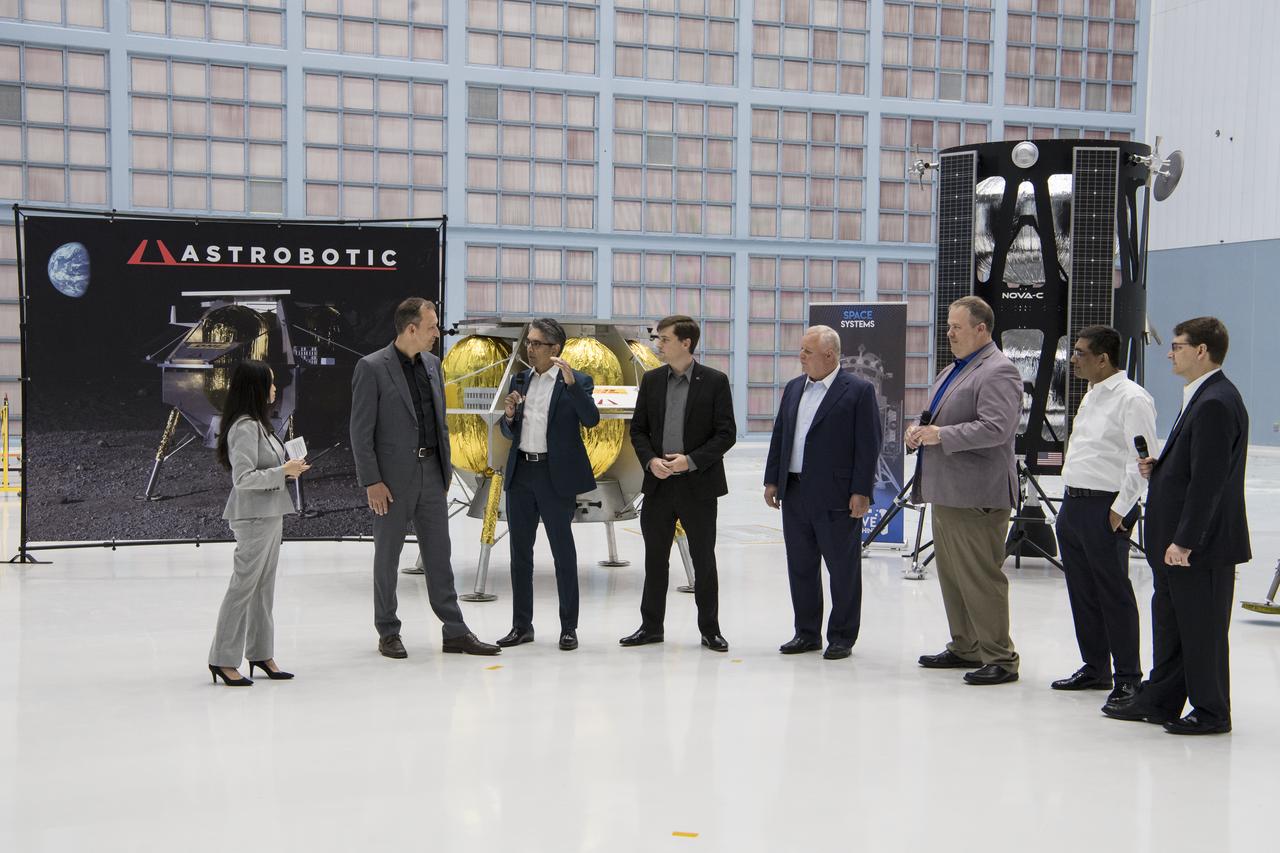

Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran , third from left, speaks about their lunar lander with, from left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, fourth from left, speaks about their lunar lander with, from left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
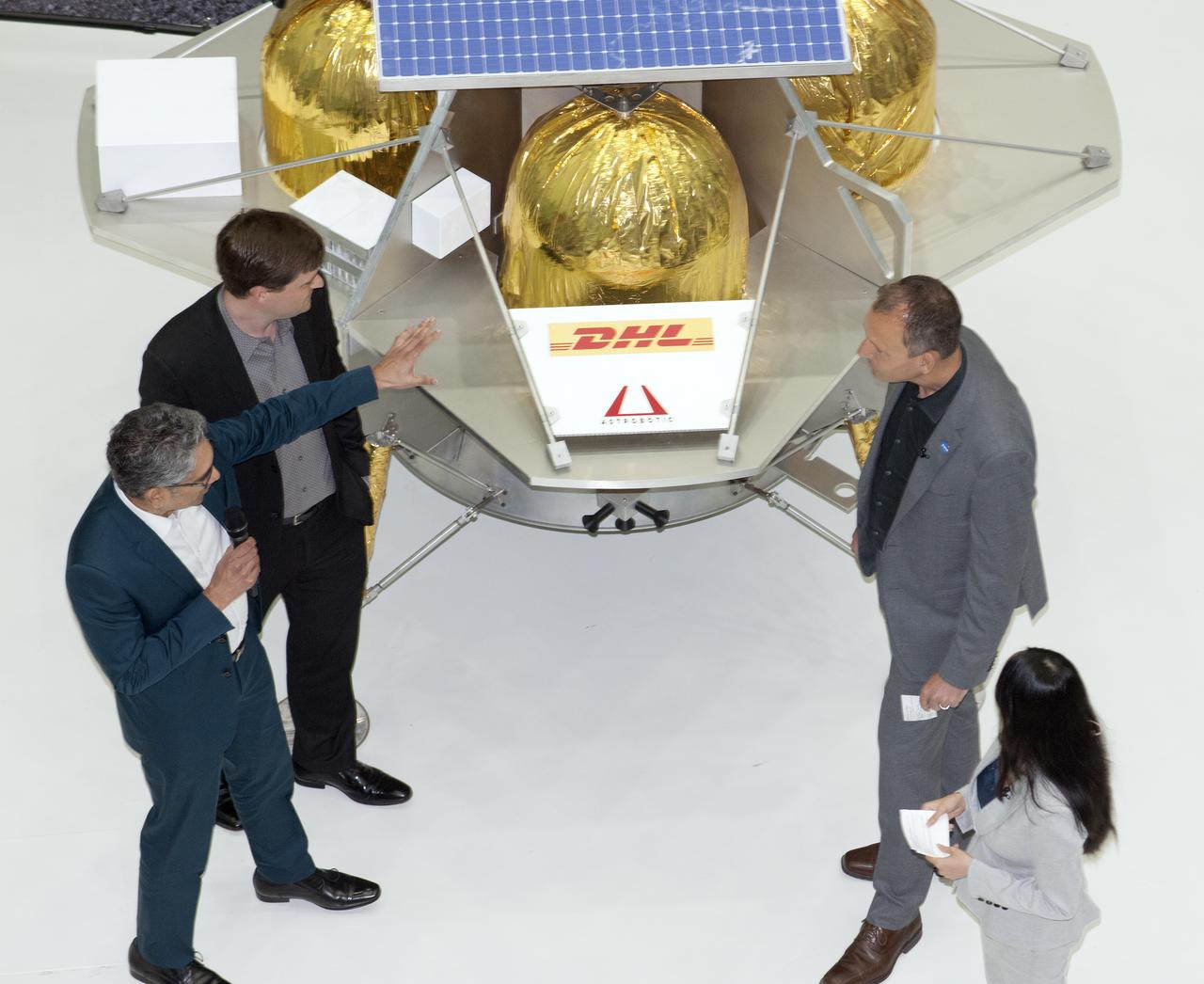

Commercial Lunar Payload Services Announcement was made at Goddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen, AA Science Mission Directorate, congratulated three companies for providing lunar landers for Artermis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond

Commercial Lunar Payload Services Announcemnt was made at Goddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen- AA Science Mission Directorate, congratulated three companies for providing lunar landers for Artemis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines and OrbitBeyond.

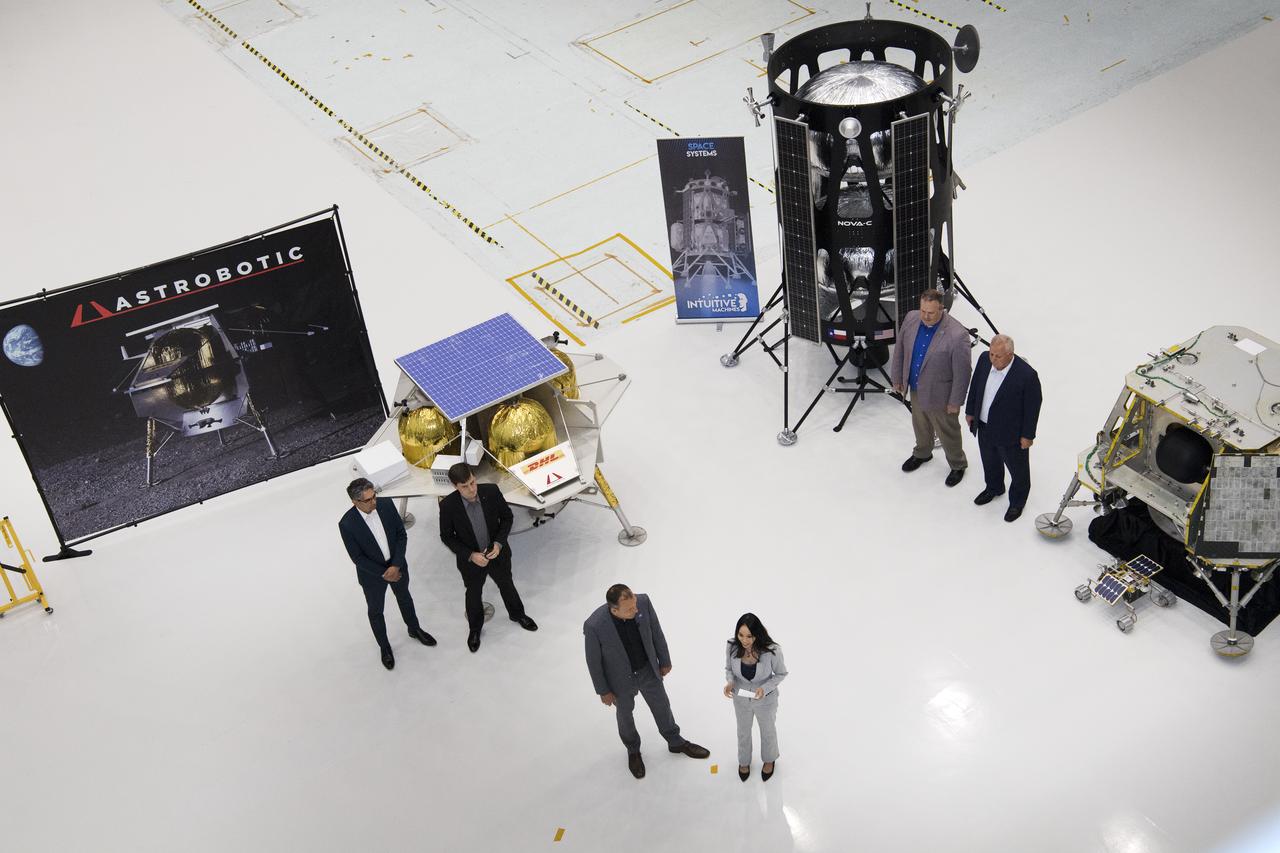
Lunar Commericial Payload Services Announcement was made at Godddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen, AA Science Mission Directorate congratulated three companies for providing first lunar landers for Artemis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines and OrbitBeyond
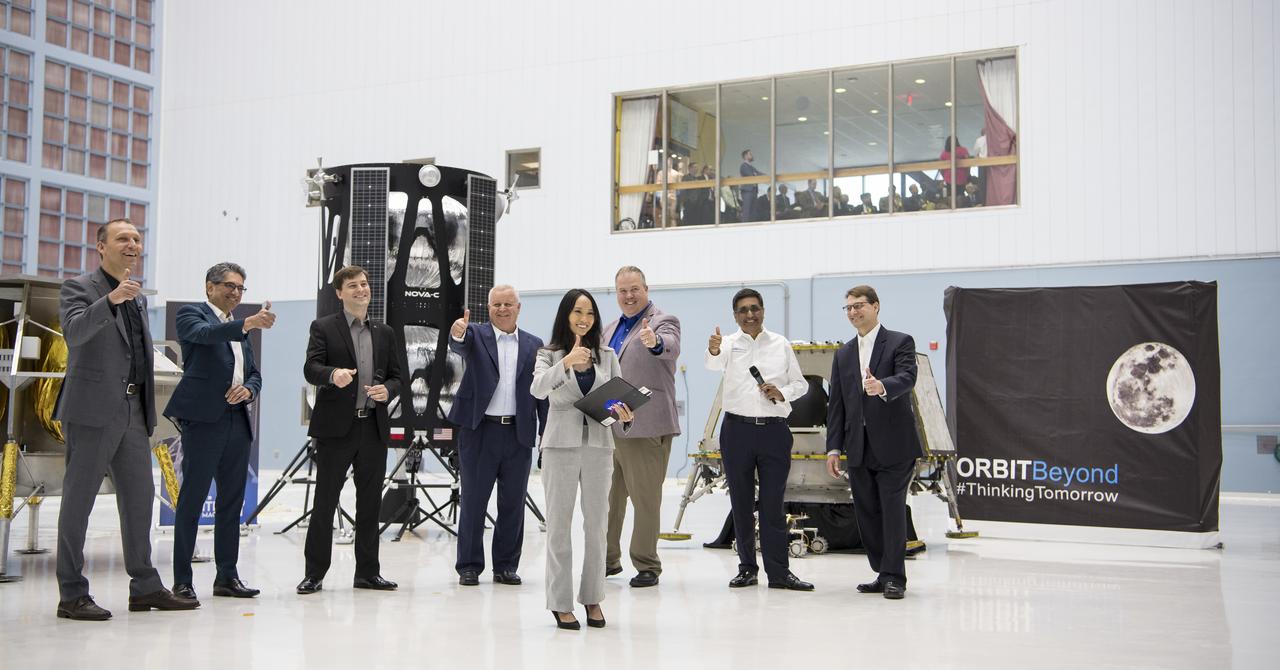

From left to right, NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse; and NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou, front center, put their thumbs up at the conclusion of an event announcing the companies that will provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
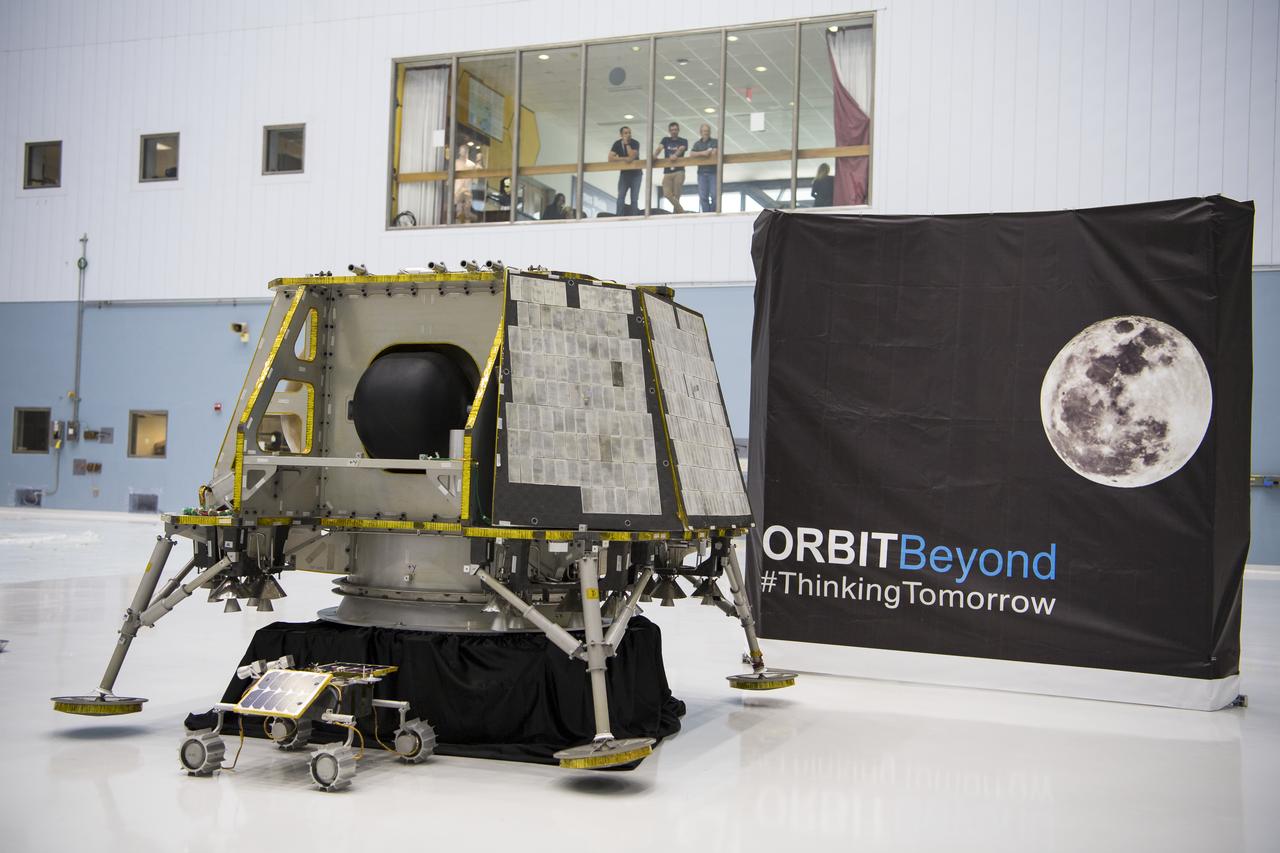

The OrbitBeyond lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
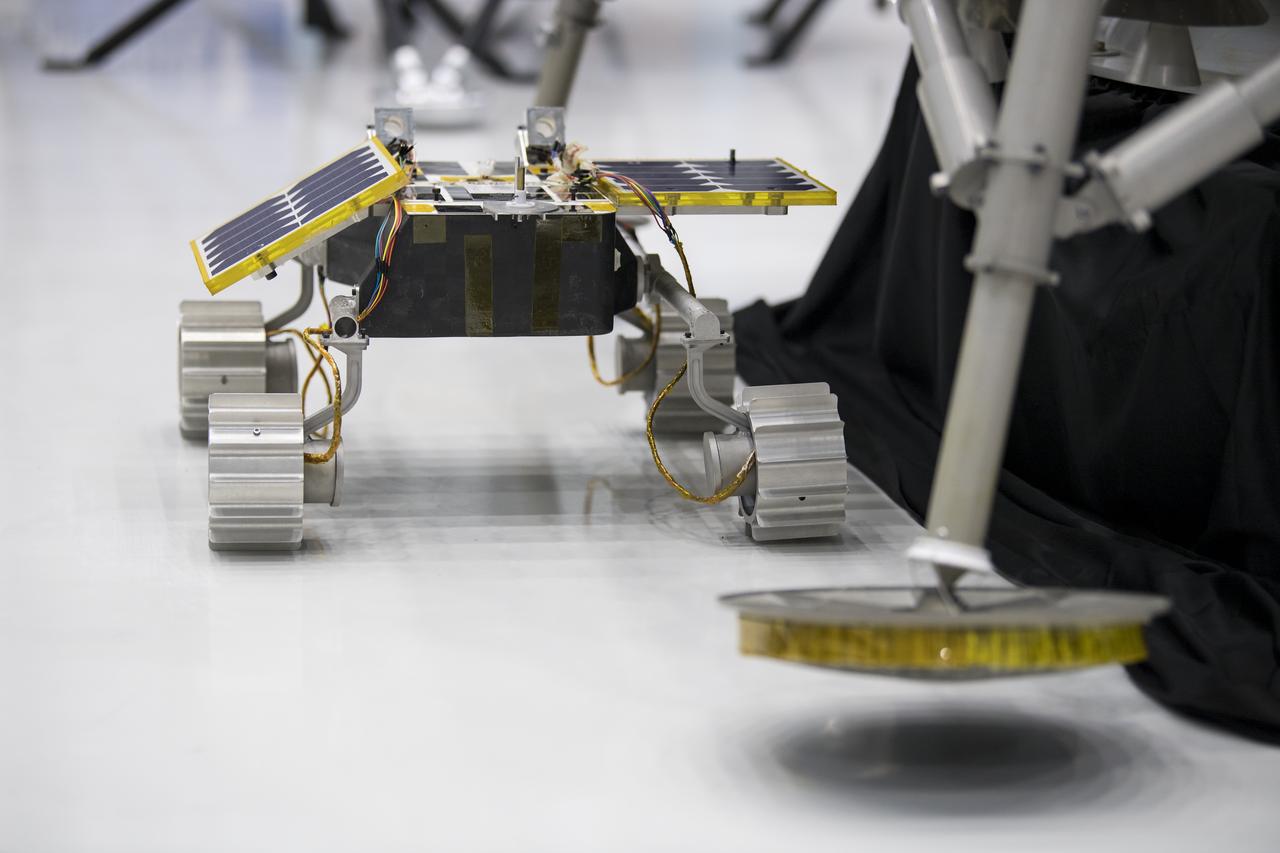

The OrbitBeyond lunar rover is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
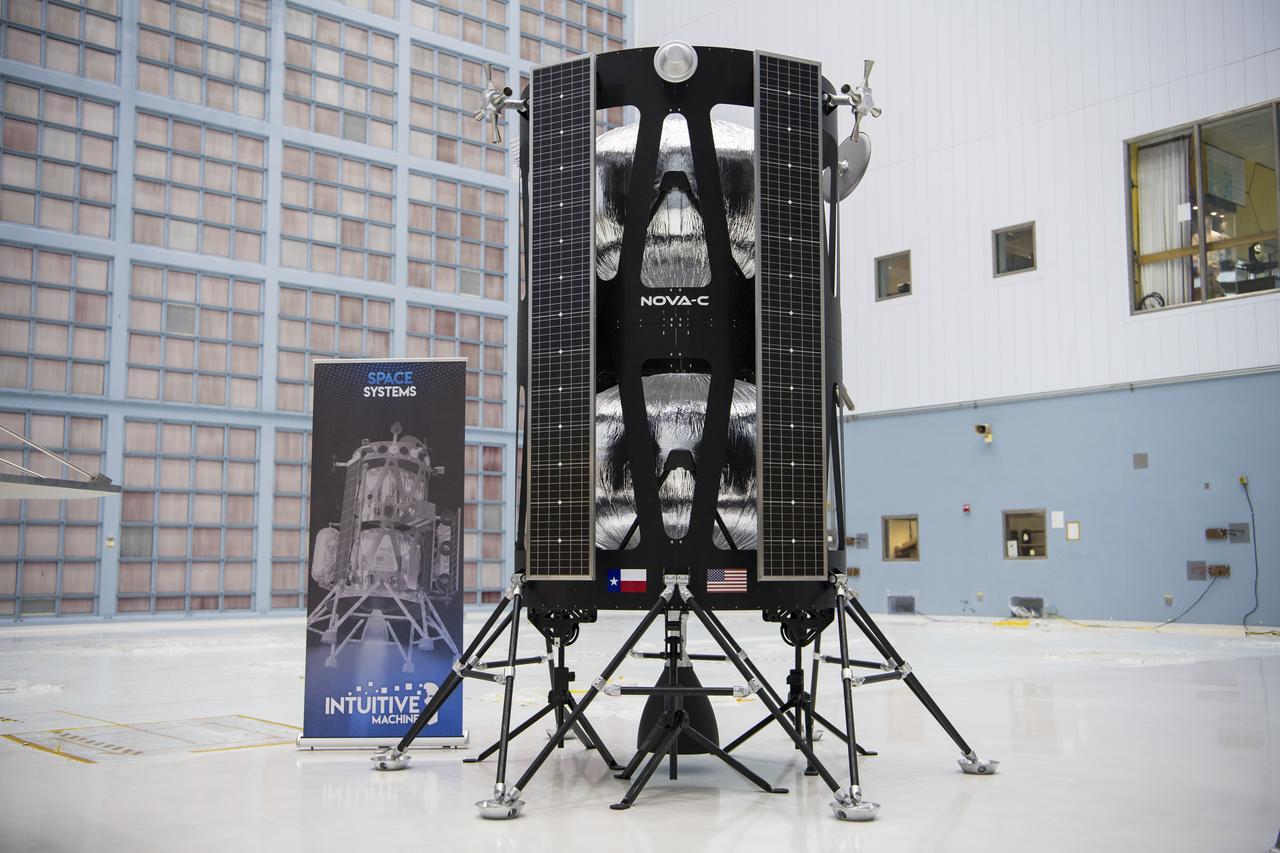

The Intuitive Machines lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
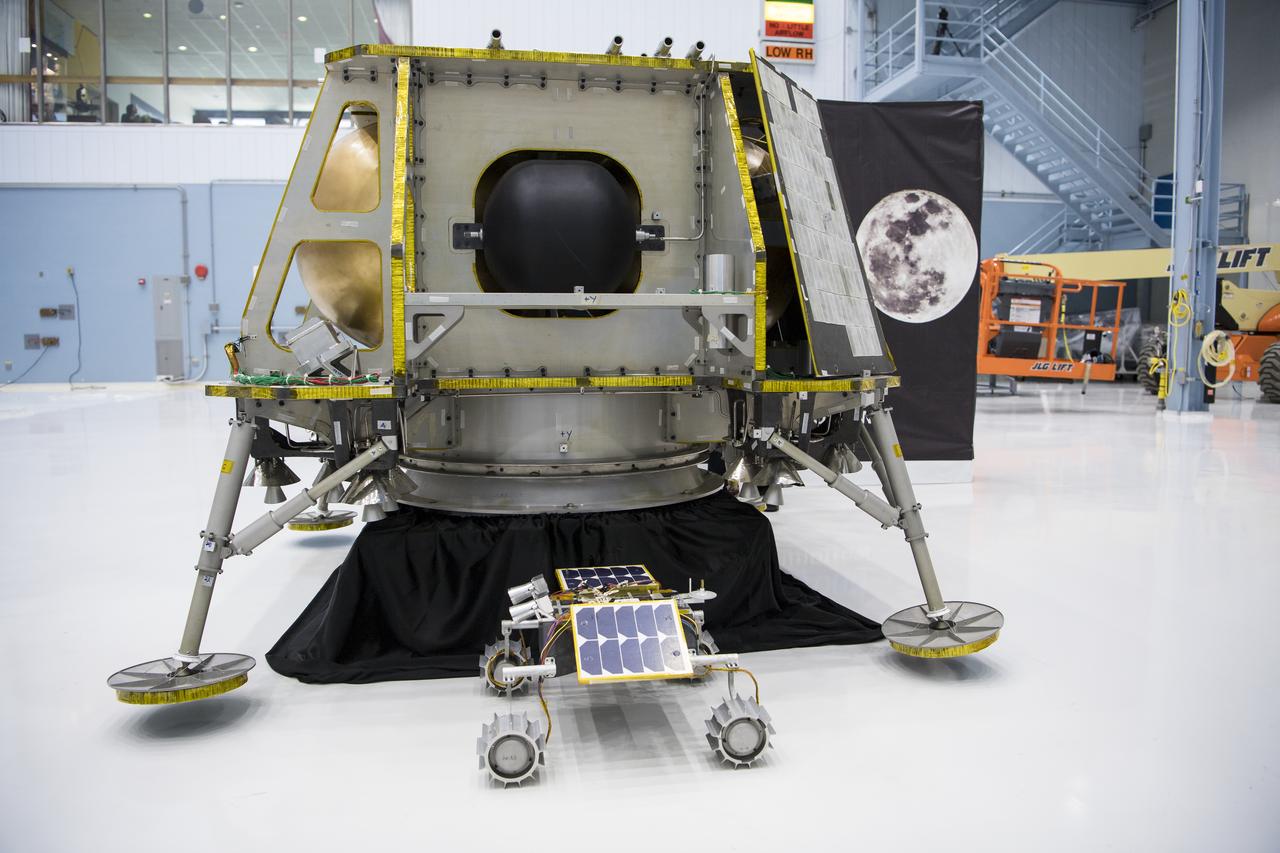

The OrbitBeyond lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)