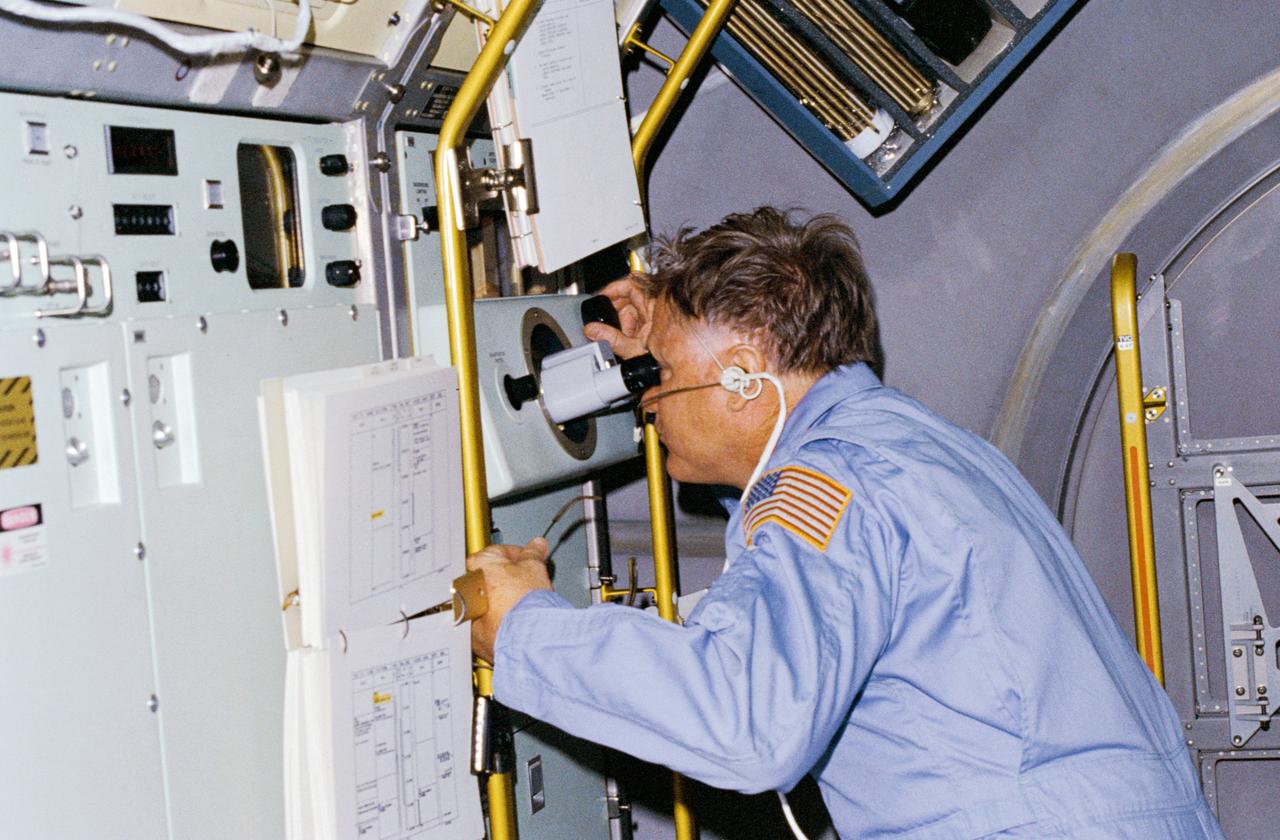

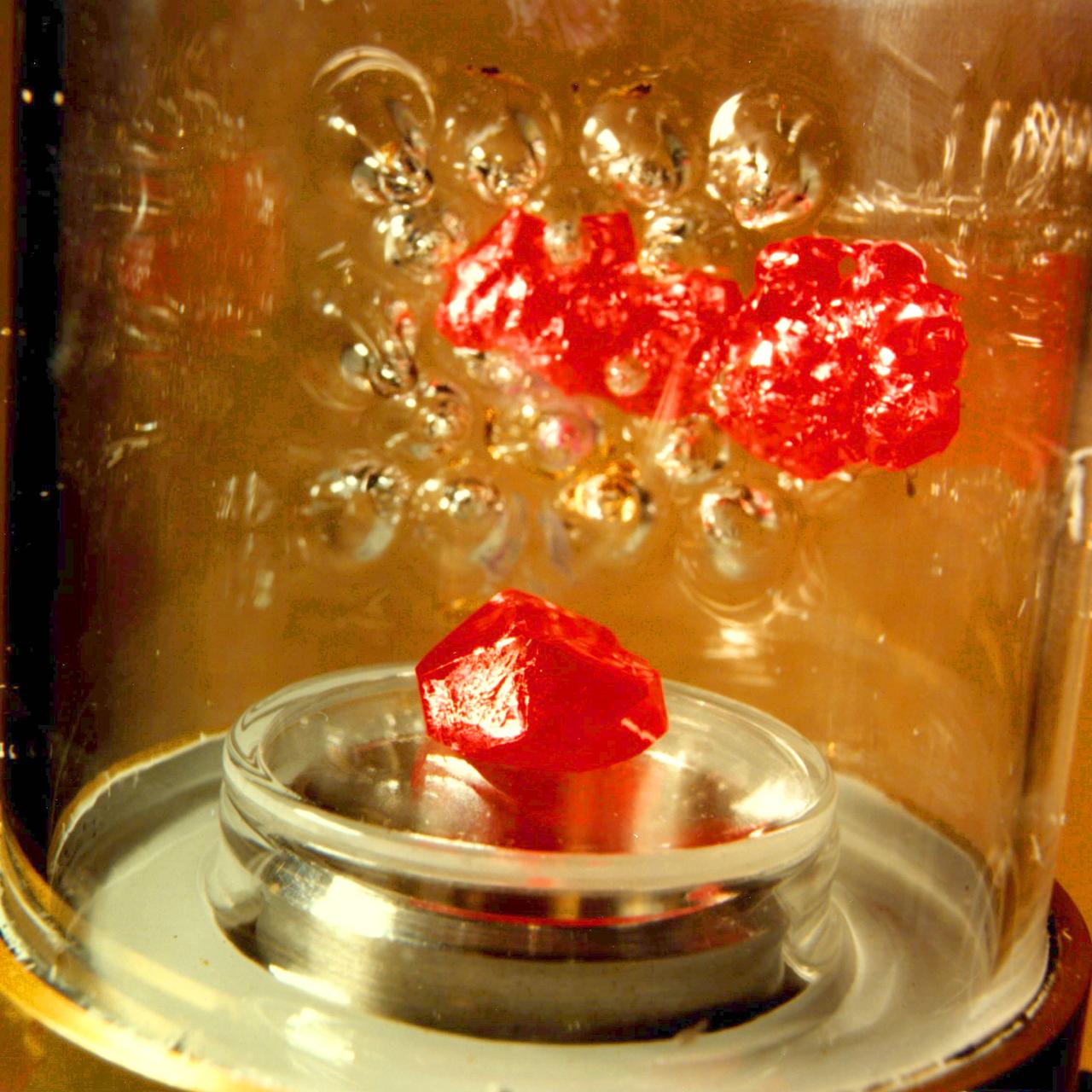
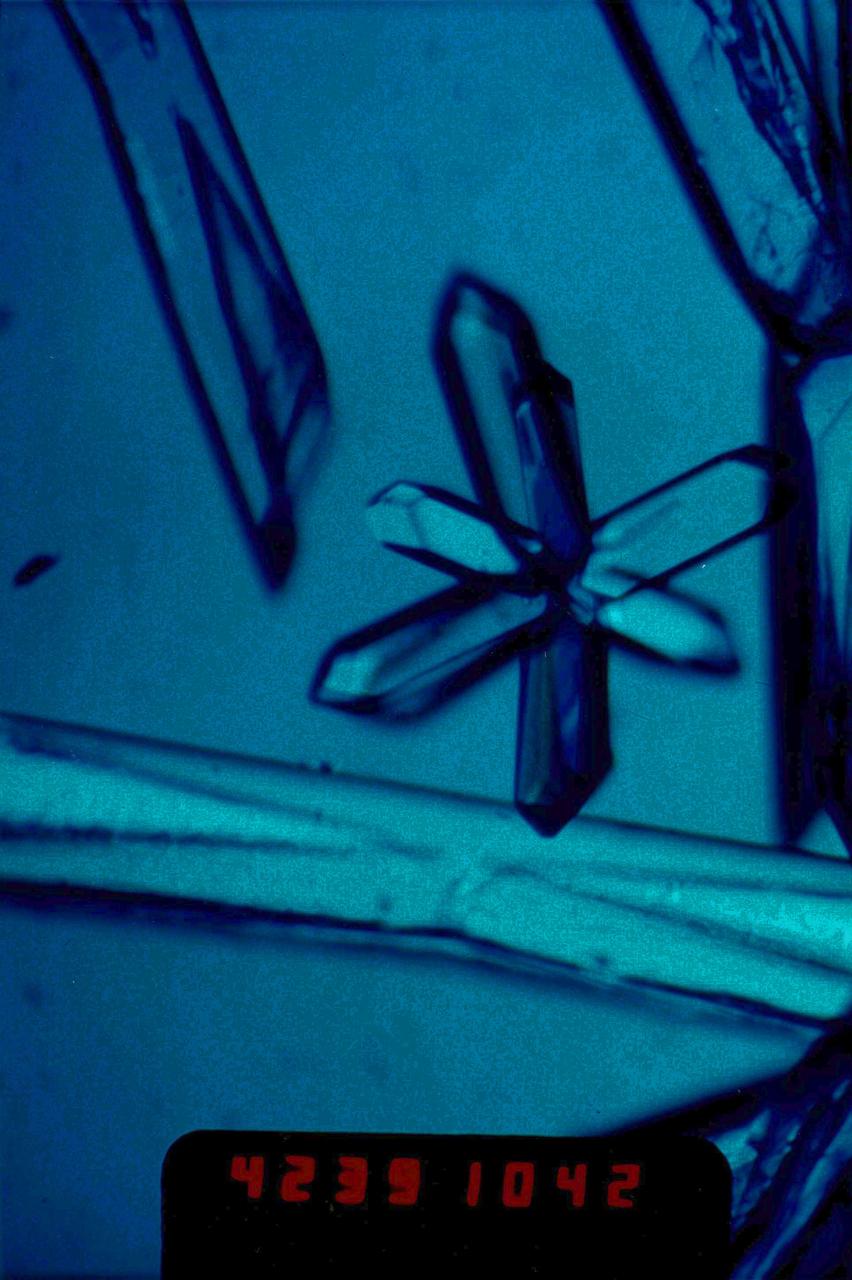
51B-01-007 (30 April 1985) --- Astronaut Don L. Lind, 51-B Spacelab 3 mission specialist, observes the growth of mercuric iodide crystal in the vapor crystal growth system (VCGS) on the Spacelab 3 science module aboard the orbiter Challenger.

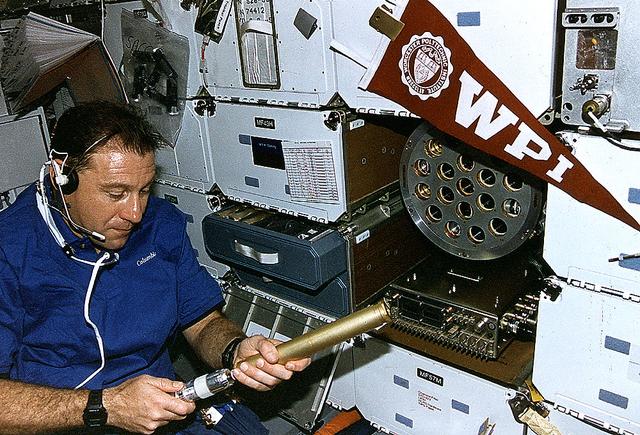
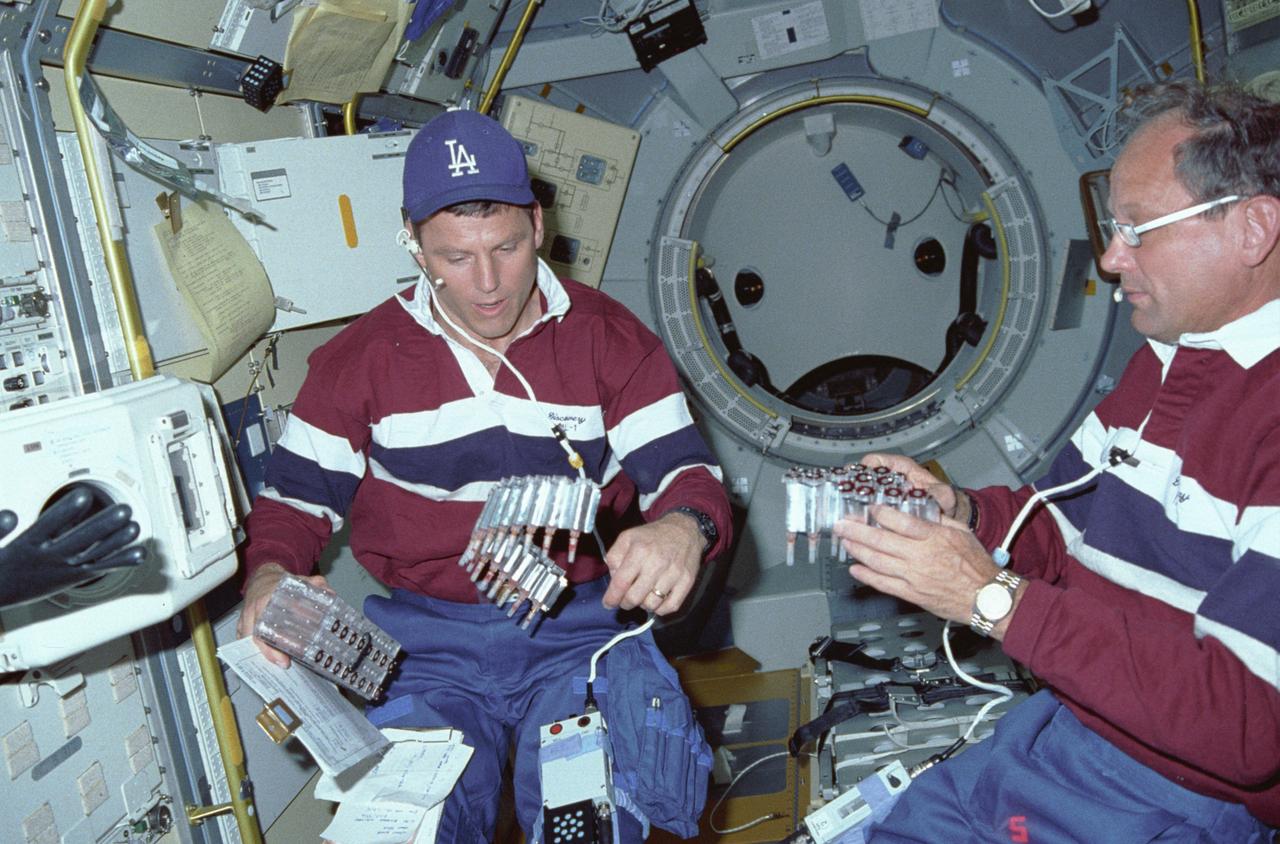
61C-05-036 (12-18 Jan. 1986) --- U.S. Representative Bill Nelson (Democrat - Florida), STS-61C payload specialist, prepares to photograph individual samples in the Handheld Protein Crystal Growth Experiment (HPCG) on Columbia's middeck. The operations involve the use of four pieces of equipment to attempt the growth of 60 different types of crystals -- 12 by means of dialysis and 48 via the vapor diffusion method. The photo was used by members of the STS-61C crew at their Jan. 23, 1986, Post-Flight Press Conference.
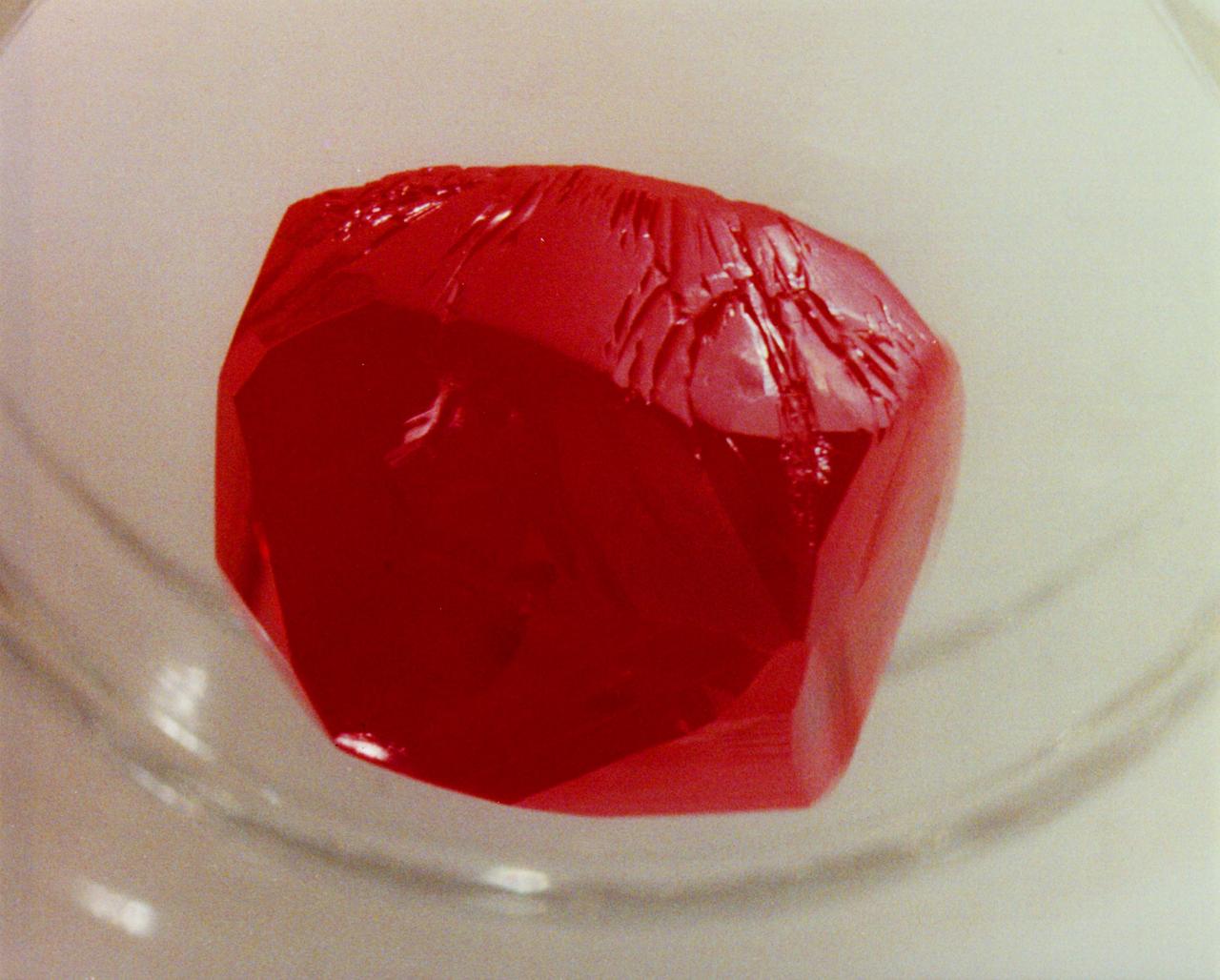

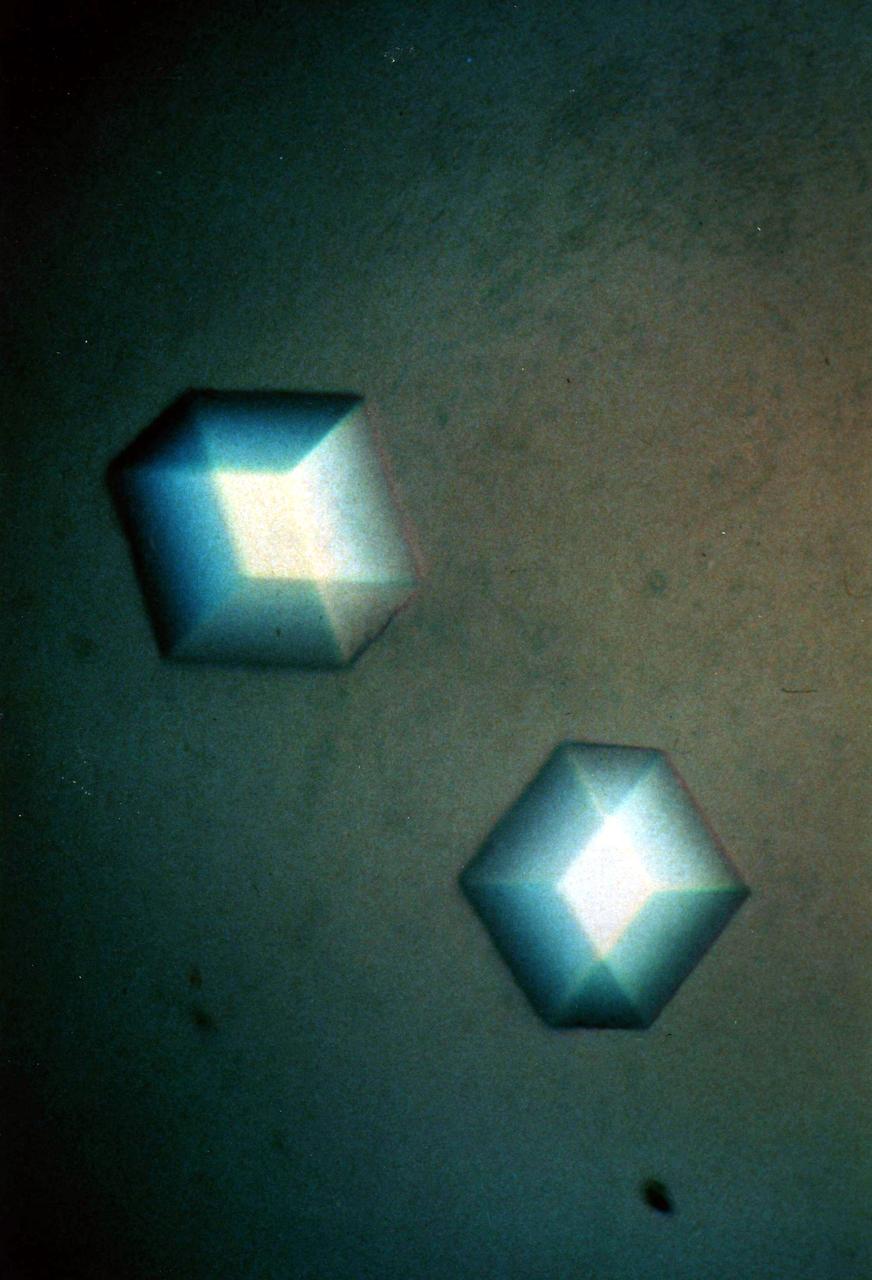
Vapor Crystal Growth System developed in IML-1, Mercuric Iodide Crystal grown in microgravity FES/VCGS (Fluids Experiment System/Vapor Crystal Growth Facility). During the mission, mercury iodide source material was heated, vaporized, and transported to a seed crystal where the vapor condensed. Mercury iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive X-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their excellent optical properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature, which makes them useful for portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications, and astronomical observing.

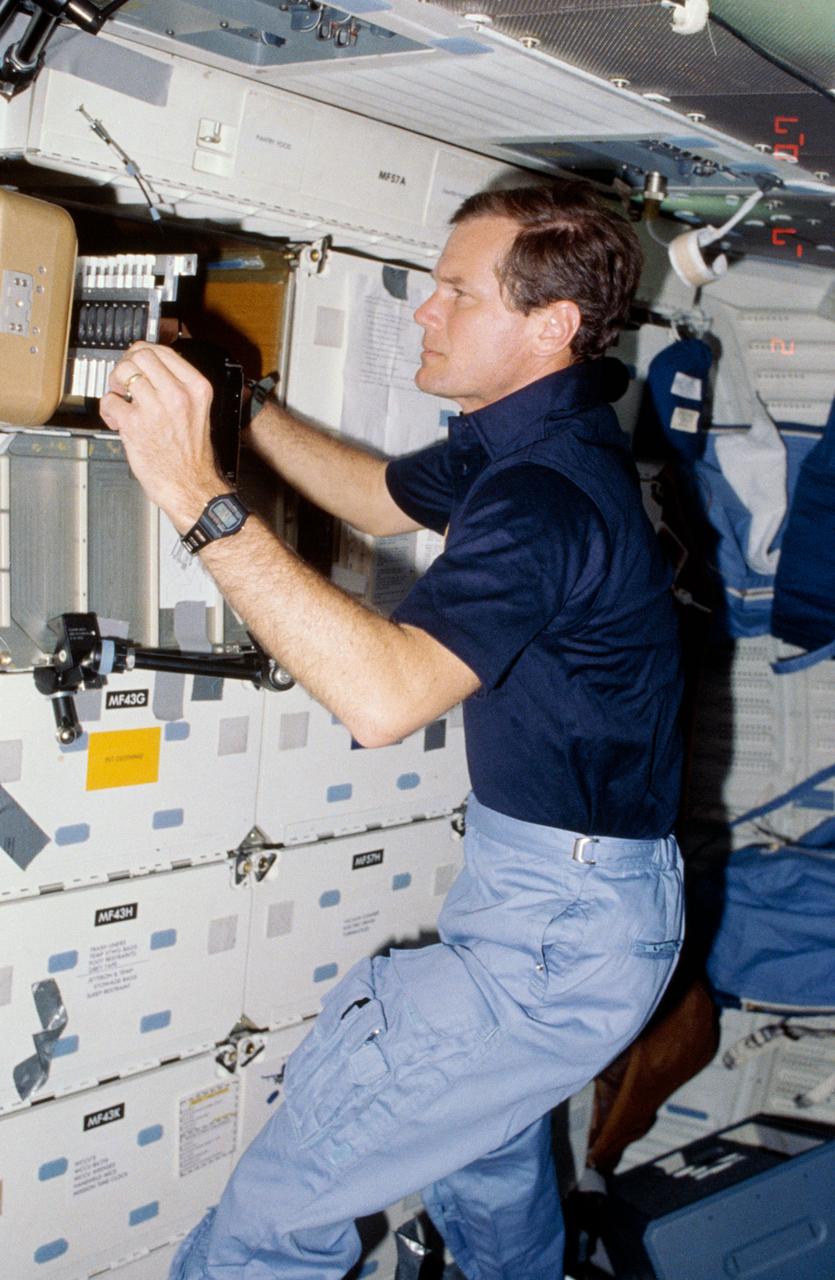
STS060-21-031 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- Using a lap top computer, astronaut N. Jan Davis monitors systems for the Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG) experiment onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. Davis joined four other NASA astronauts and a Russian cosmonaut for eight days in space aboard Discovery.
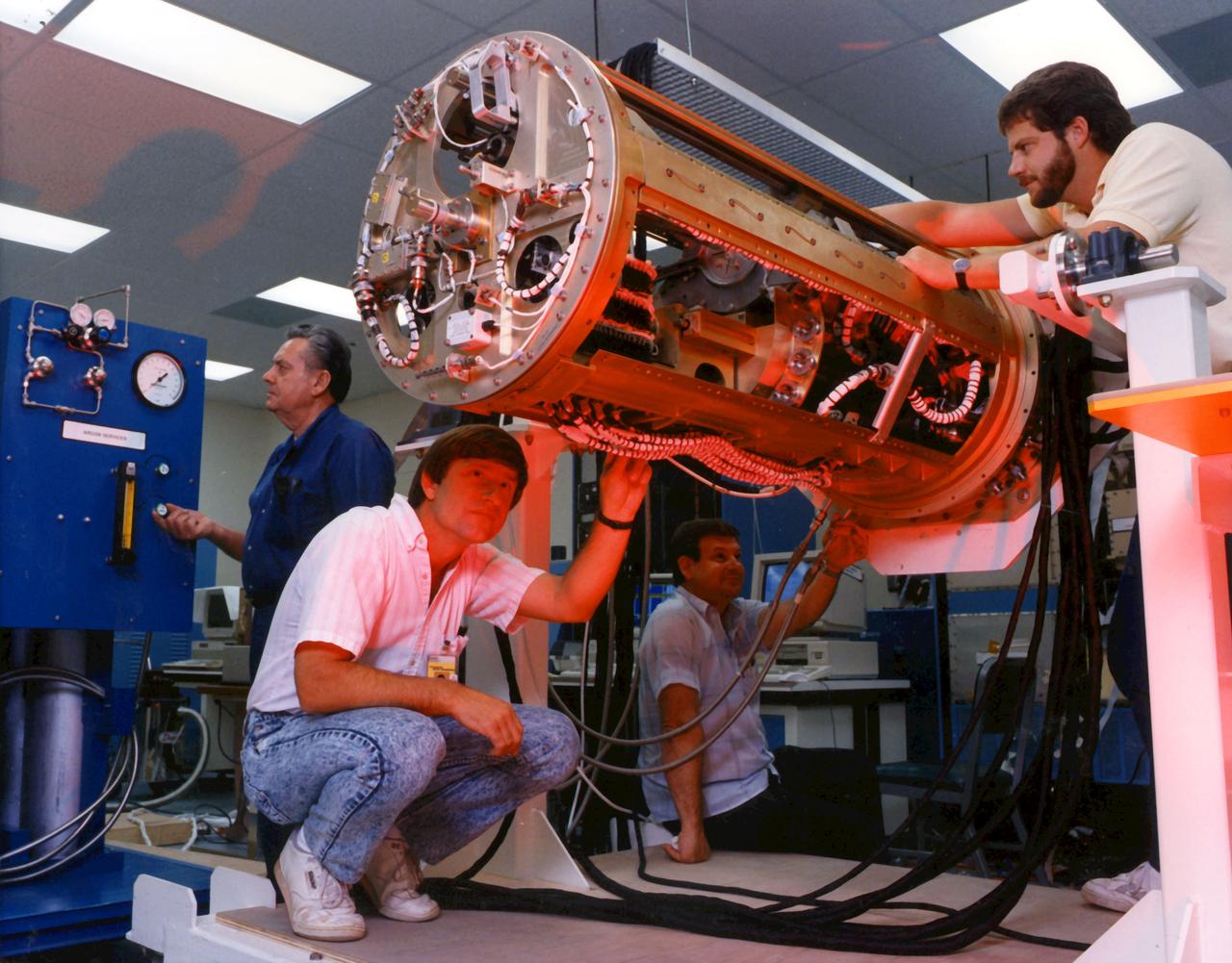
Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) Being Tested at Manufacturing Facilty

iss047e055611 (4/11/2016) --- A view of the JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Demo Sample, in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International space Station (ISS). The objective of JAXA High Quality Protein Crystal Growth Demonstration Experiment (JAXA PCG-Demo) is to grow high quality protein crystals in microgravity.
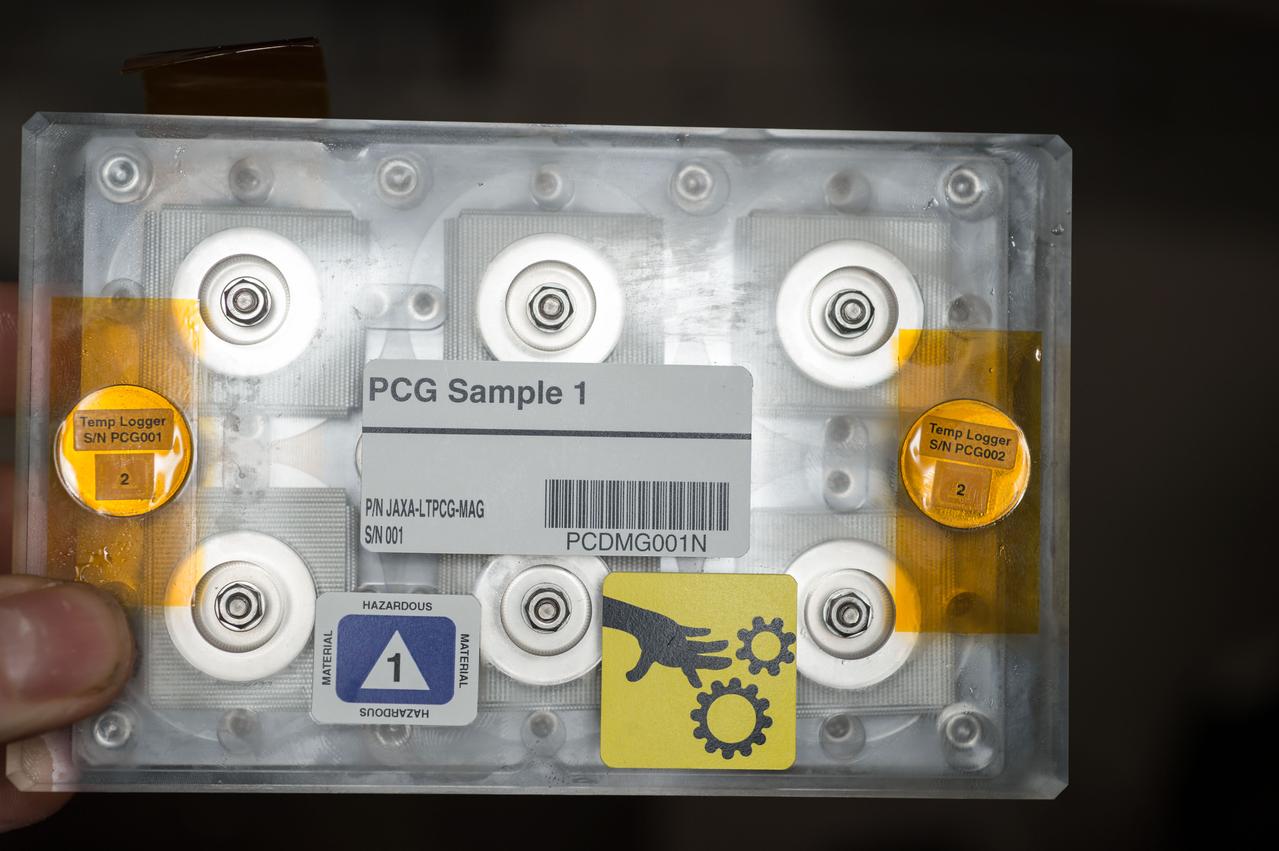

iss047e055613 (4/11/2016) --- A view of the JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Demo Sample, in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International space Station (ISS). The objective of JAXA High Quality Protein Crystal Growth Demonstration Experiment (JAXA PCG-Demo) is to grow high quality protein crystals in microgravity.

Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS), Flown on IML-1, Spacelab 3, Principal Investigator: Lodewijk van den Berg

Scientist photographs STS- 26 Post-flight (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus Tray with (PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Samples.
Orbital Documentation of Porcine Elastase grown in (PCG) Protein Crystal Growth (RIM) Refrigerator Incubator Module
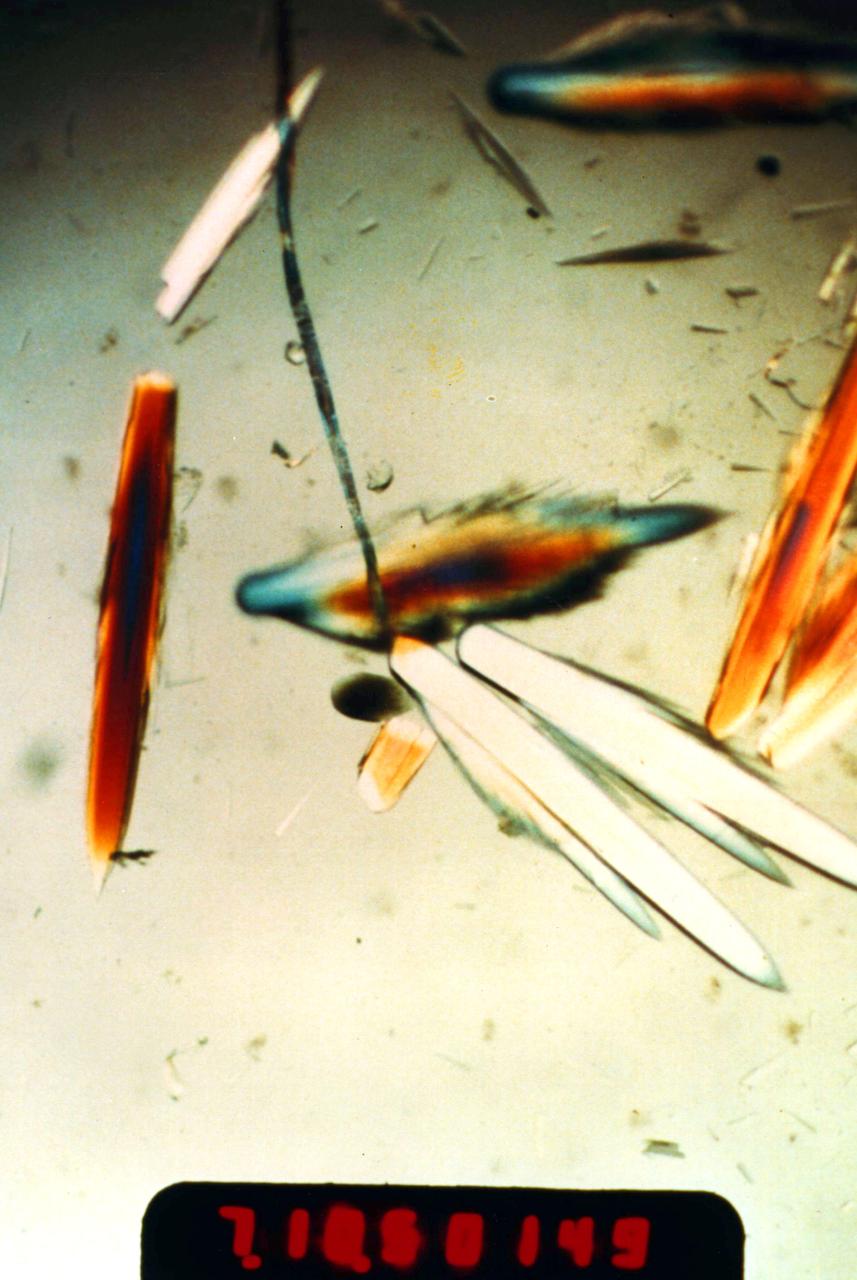
Horse Serum Albumin crystals grown during the USML-1 (STS-50) mission's Protein Crystal Growth Glovebox Experiment. These crystals were grown using a vapor diffusion technique at 22 degrees C. The crystals were allowed to grow for nine days while in orbit. Crystals of 1.0 mm in length were produced. The most abundant blood serum protein, regulates blood pressure and transports ions, metabolites, and therapeutic drugs. Principal Investigator was Edward Meehan.
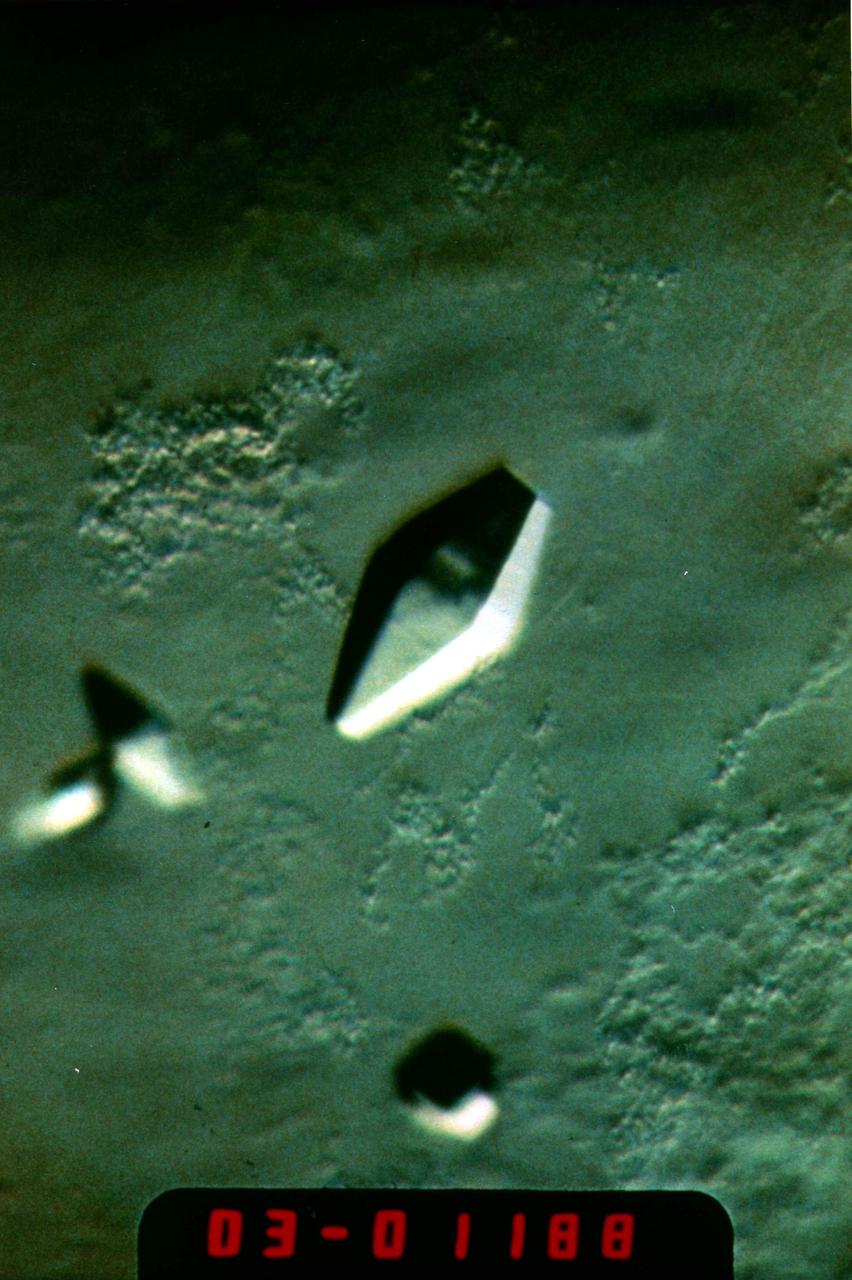
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth C-reactive Protein. Plays a major role in human immune system response. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
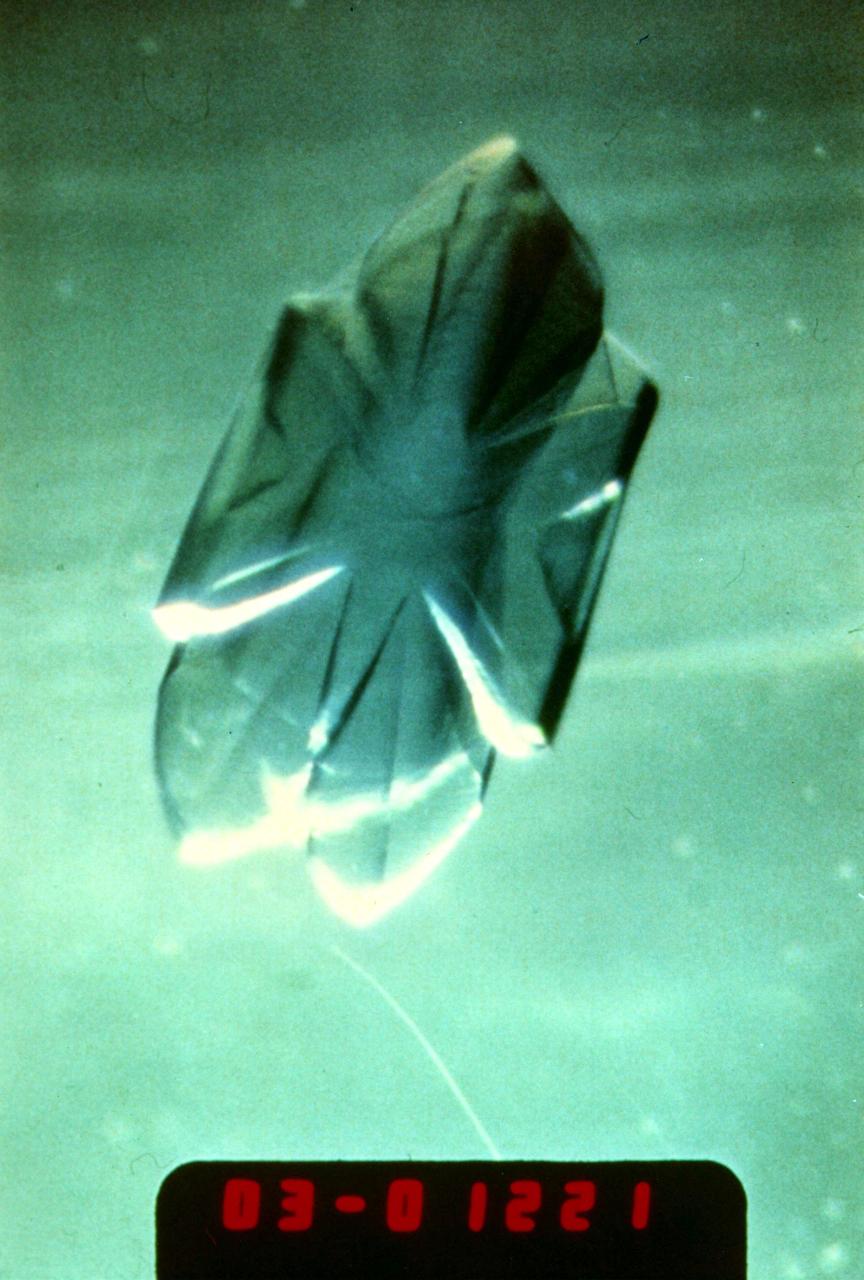

(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Isocitrate Lyase. Target enzyme for fungicides. A better understanding of this enzyme should lead to the discovery of more potent fungicides to treat serious crop diseases such as rice blast. It regulates the flow of metabolic intermediates required for cell growth. Principal Investigator for STS-26 was Charles Bugg.

(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Isocitrate Lysase. Target enzyme for fungicides. A better understanding of this enzyme should lead to the discovery of more potent fungicides to treat serious crop diseases such as rice blast. It regulates the flow of metabolic intermediates required for cell growth. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Porcine Elastase. This enzyme is associated with the degradation of lung tissue in people suffering from emphysema. It is useful in studying causes of this disease. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Renin. Enzyme produced by the kidneys, plays a major role in the chemical reaction that controls blood pressure. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
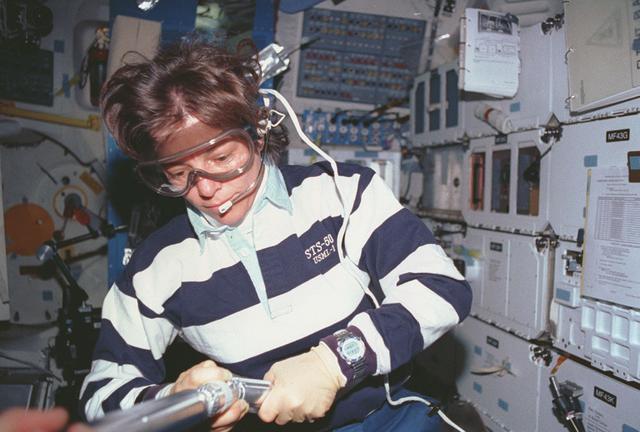

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) astronaut Bornie Dunbar wears protective goggles to assemble a zeolite sample cartridge for the Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) in the United States Microgravity Laboratory-1 (USML-1) science module.
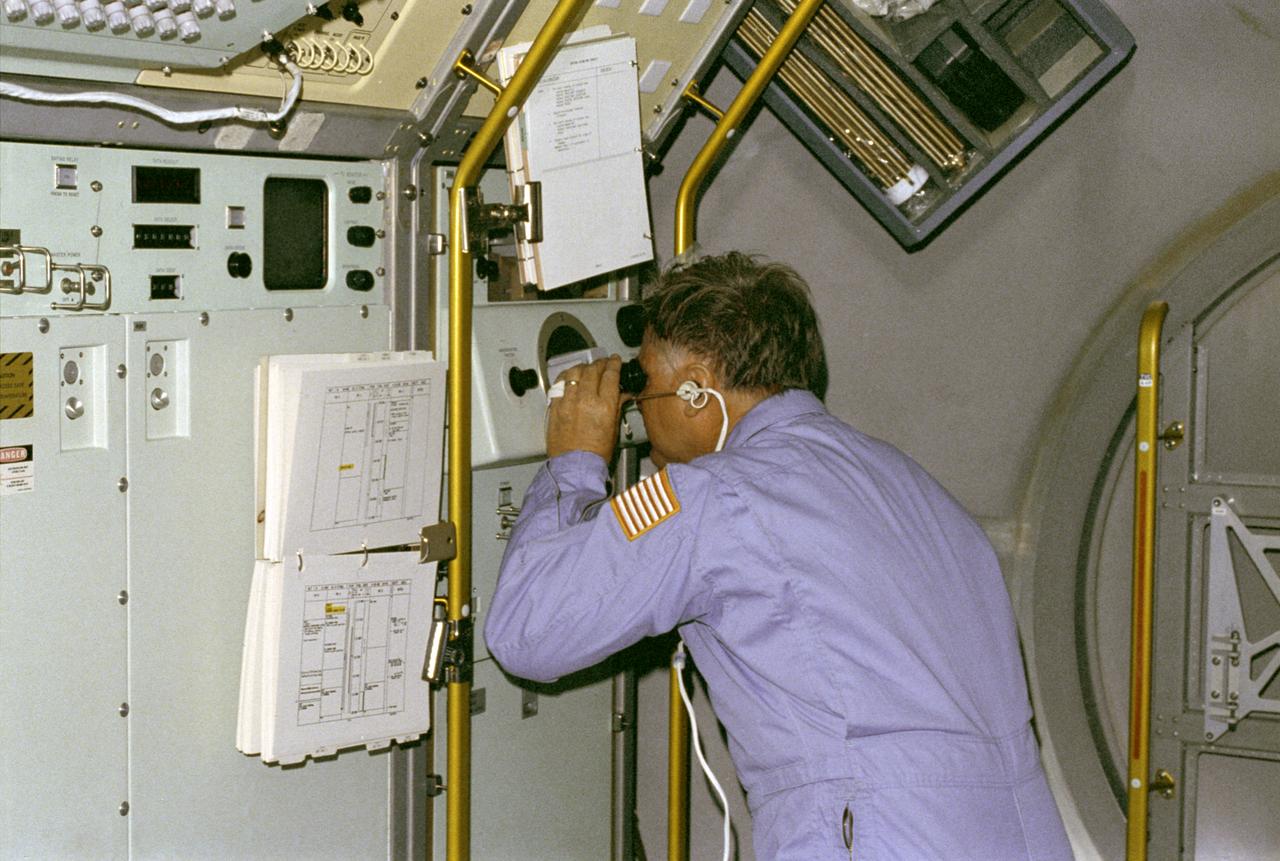

The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew performed research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new minilabs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. In this photograph, astronaut Don Lind observes the mercuric iodide growth experiment through a microscope at the vapor crystal growth furnace. The goals of this investigation were to grow near-perfect single crystals of mercuric iodide and to gain improved understanding of crystal growth by a vapor process. Mercuric iodide crystals have practical use as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors, and in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and in astronomical instruments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, Spacelab-3 (STS-51B) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on April 29, 1985.
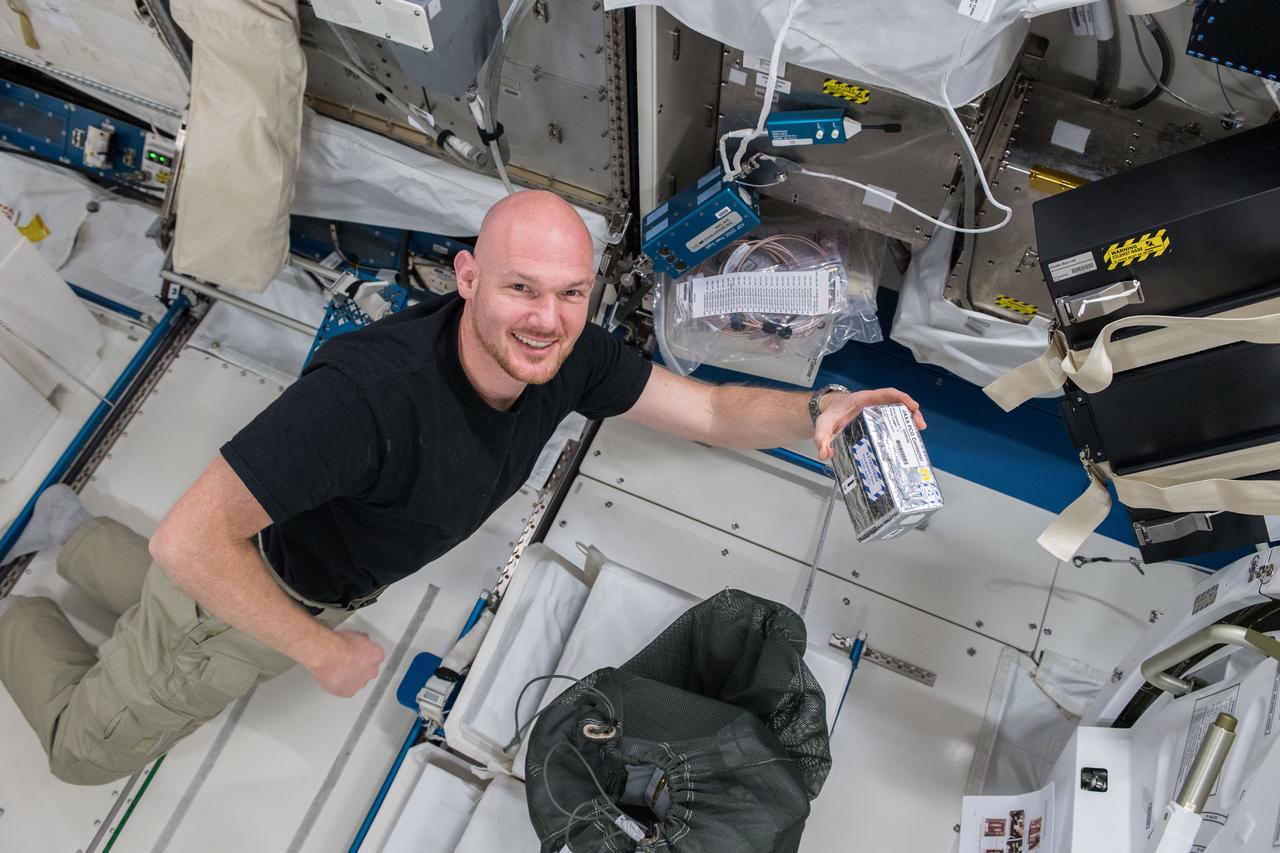

iss056e075928 (7/3/2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency), during the JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) sample retrieval from the Freezer-Refrigerator Of Stirling Cycle 2 (FROST2) and initiation of the crystallization of the samples before inserting them back into the FROST2, where crystallization will continue.
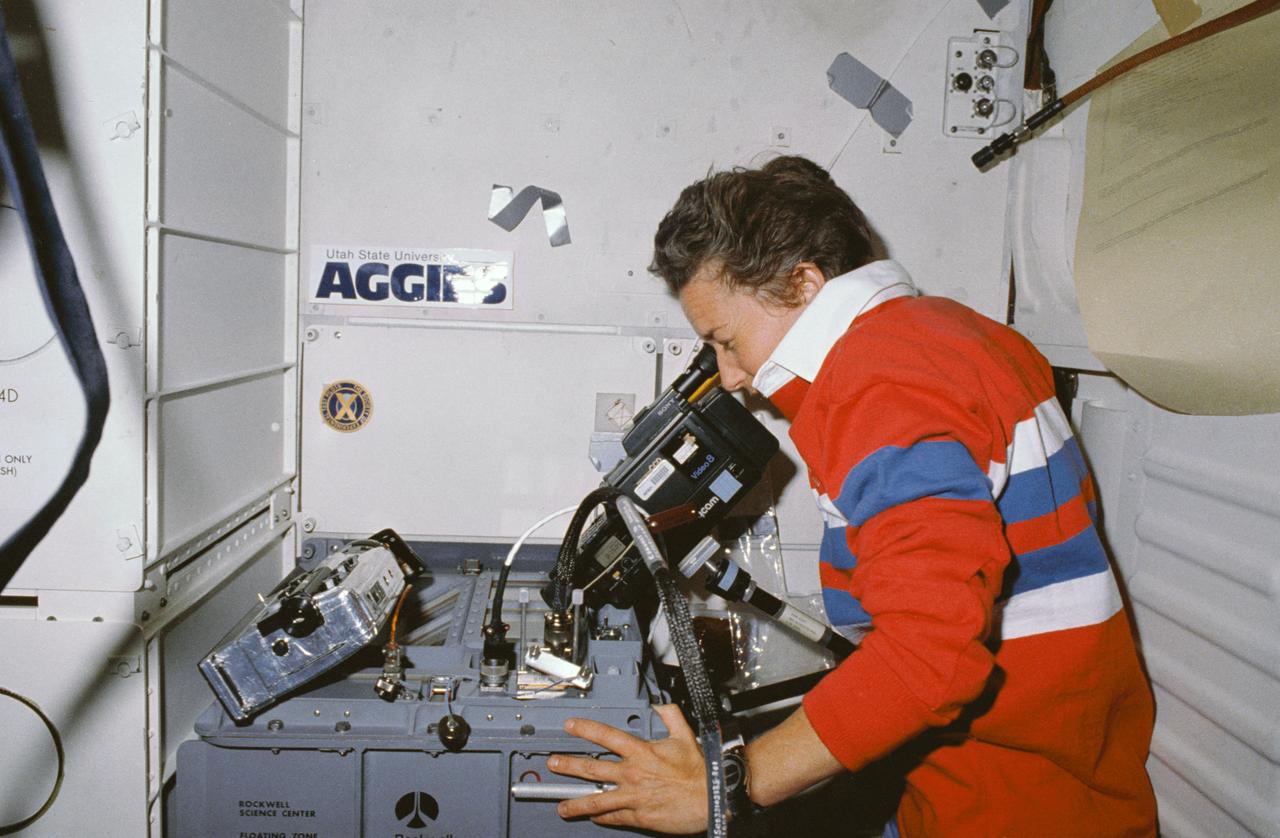

STS030-10-002 (8 May 1989) --- STS-30 Mission Specialist Mary L. Cleave operates 8mm video camcorder at Fluids Experiment Apparatus 2 (FEA-2) (SK73-000102) unit located in aft middeck locker onboard Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Two 8mm video camcorders are positioned above FEA-2 unit to record experiment titled "Floating Zone Crystal Growth and Purification". Rockwell International (RI) through its Space Transportation Systems Division, Downey, California, is engaged in a joint endeavor agreement (JEA) with NASA's Office of Commercial Programs in the field for floating zone crystal growth research. Utah State University Aggies decal appears on aft bulkhead above FEA-2 unit.
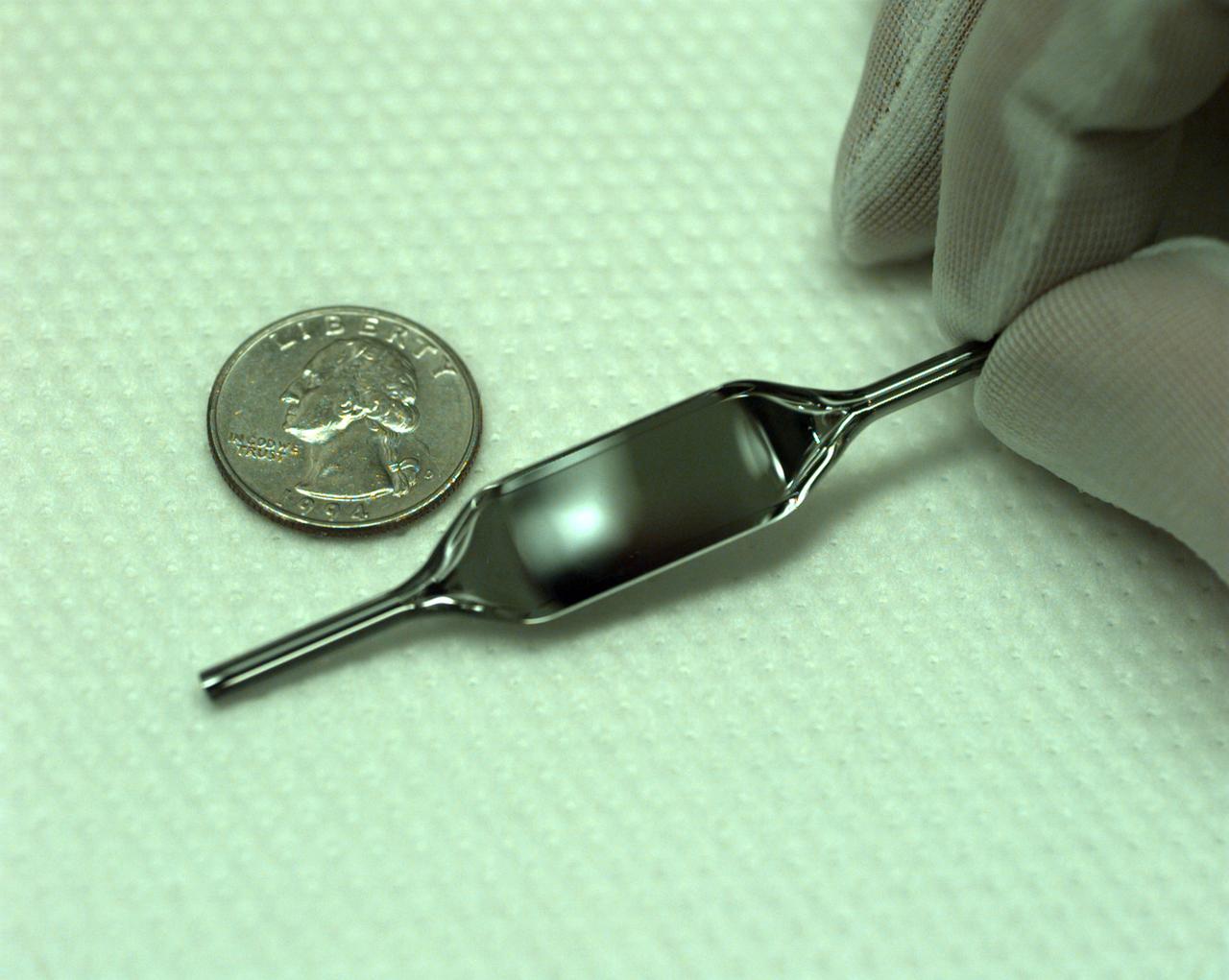
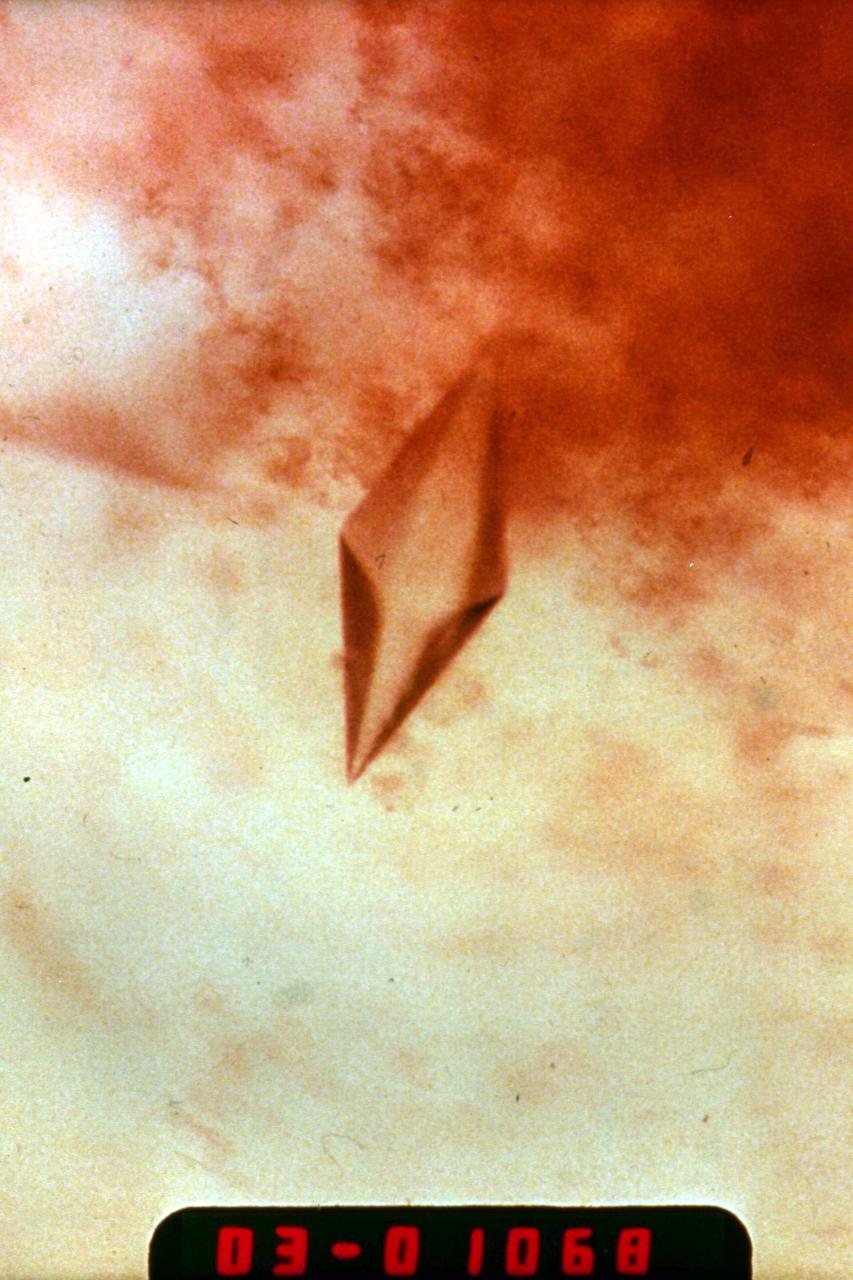
The Interferometer Protein Crystal Growth (IPCG) experiment was designed to measure details of how protein molecules move through a fluid. It was flown on the STS-86 mission for use aboard Russian Space Station Mir in 1998. It studied aspects of how crystals grow - and what conditions lead to the best crystals, details that remain a mystery. IPCG produces interference patterns by spilitting then recombining laser light. This let scientists see how fluid densities - and molecular diffusion - change around a crystal as it grows in microgravity. The heart of the IPCG apparatus is the interferometer cell comprising the optical bench, microscope, other optics, and video camera. IPCG experiment cells are made of optical glass and silvered on one side to serve as a mirror in the interferometer system that visuzlizes crystals and conditions around them as they grow inside the cell. This view shows a large growth cell. The principal investigator was Dr. Alexander McPherson of University of California, Irvine. Co-investigators are William Witherow and Dr. Marc Pusey of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
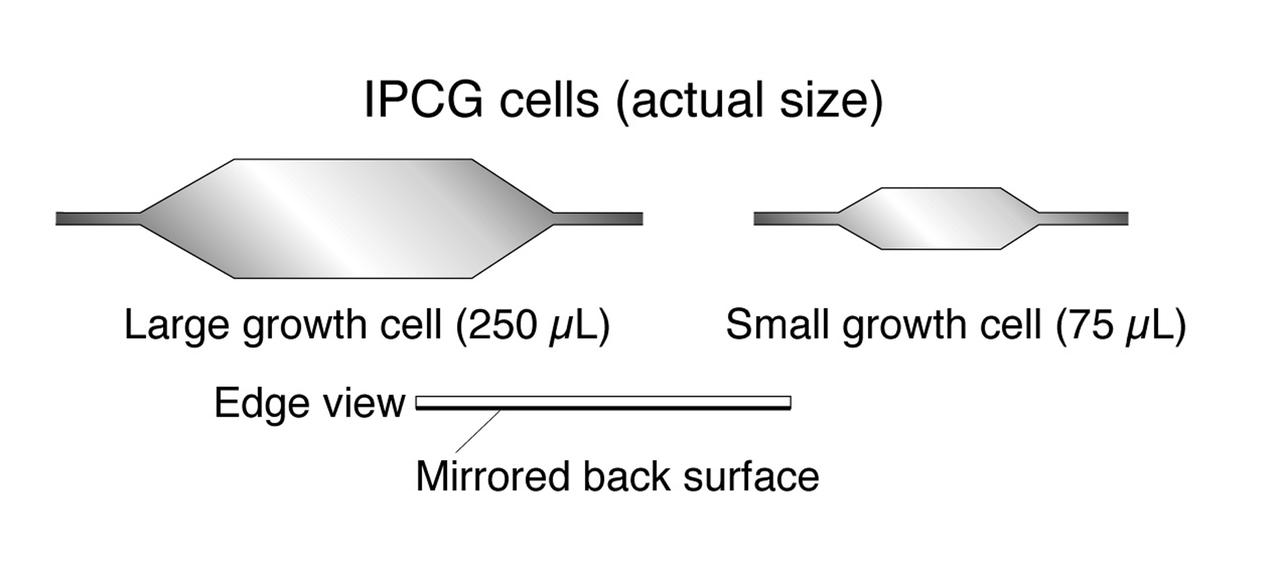
The Interferometer Protein Crystal Growth (IPCG) experiment was designed to measure details of how protein molecules move through a fluid. It was flown on the STS-86 mission for use aboard Russian Space Station Mir in 1998. It studied aspects of how crystals grow - and what conditions lead to the best crystals, details that remain a mystery. IPCG produces interference patterns by spilitting then recombining laser light. This let scientists see how fluid densities - and molecular diffusion - change around a crystal as it grows in microgravity. The heart of the IPCG apparatus is the interferometer cell comprising the optical bench, microscope, other optics, and video camera. IPCG experiment cells are made of optical glass and silvered on one side to serve as a mirror in the interferometer system that visuzlizes crystals and conditions around them as they grow inside the cell. This diagram shows the growth cells. The principal investigator was Dr. Alexander McPherson of University of California, Irvine. Co-investigators are William Witherow and Dr. Marc Pusey of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
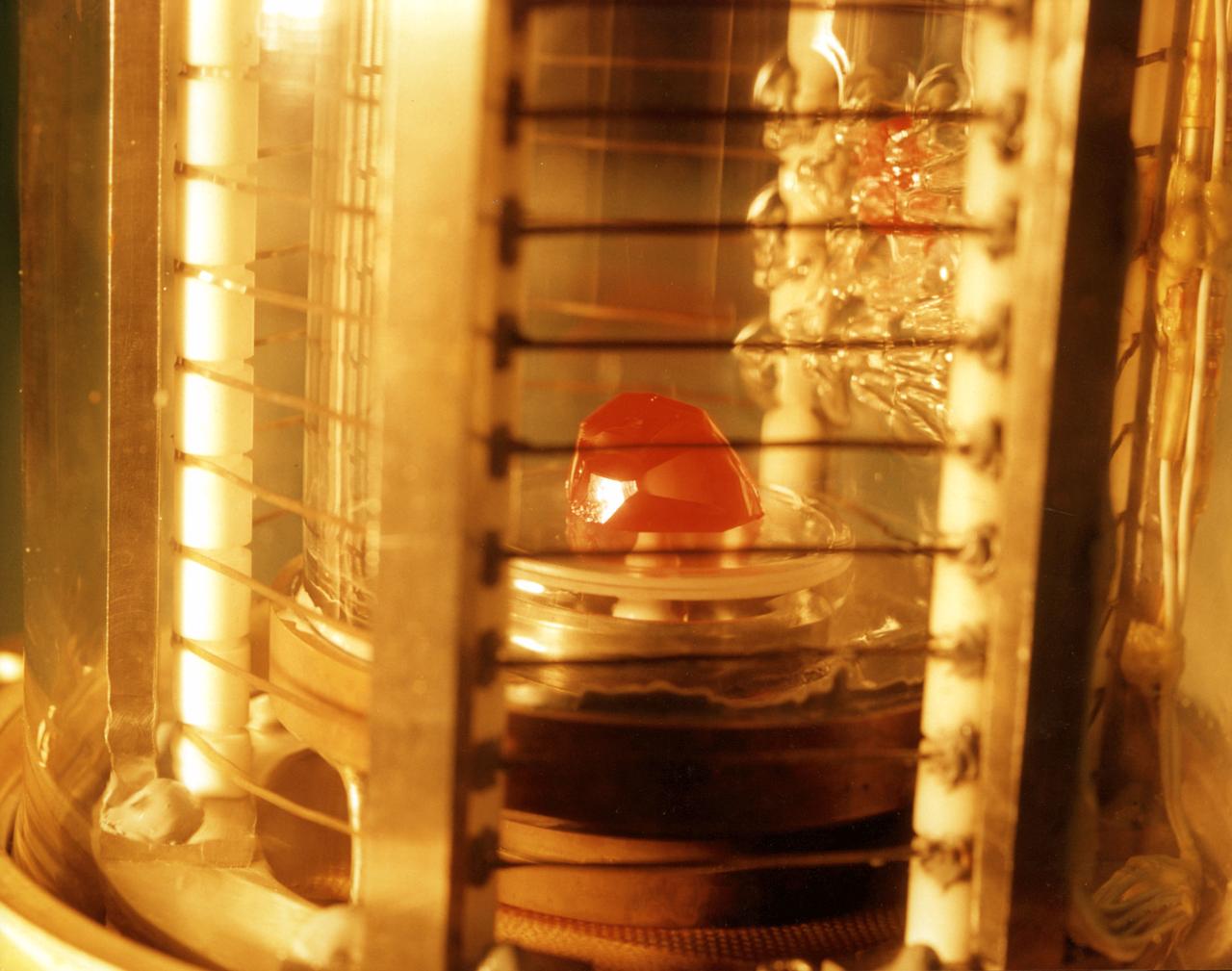

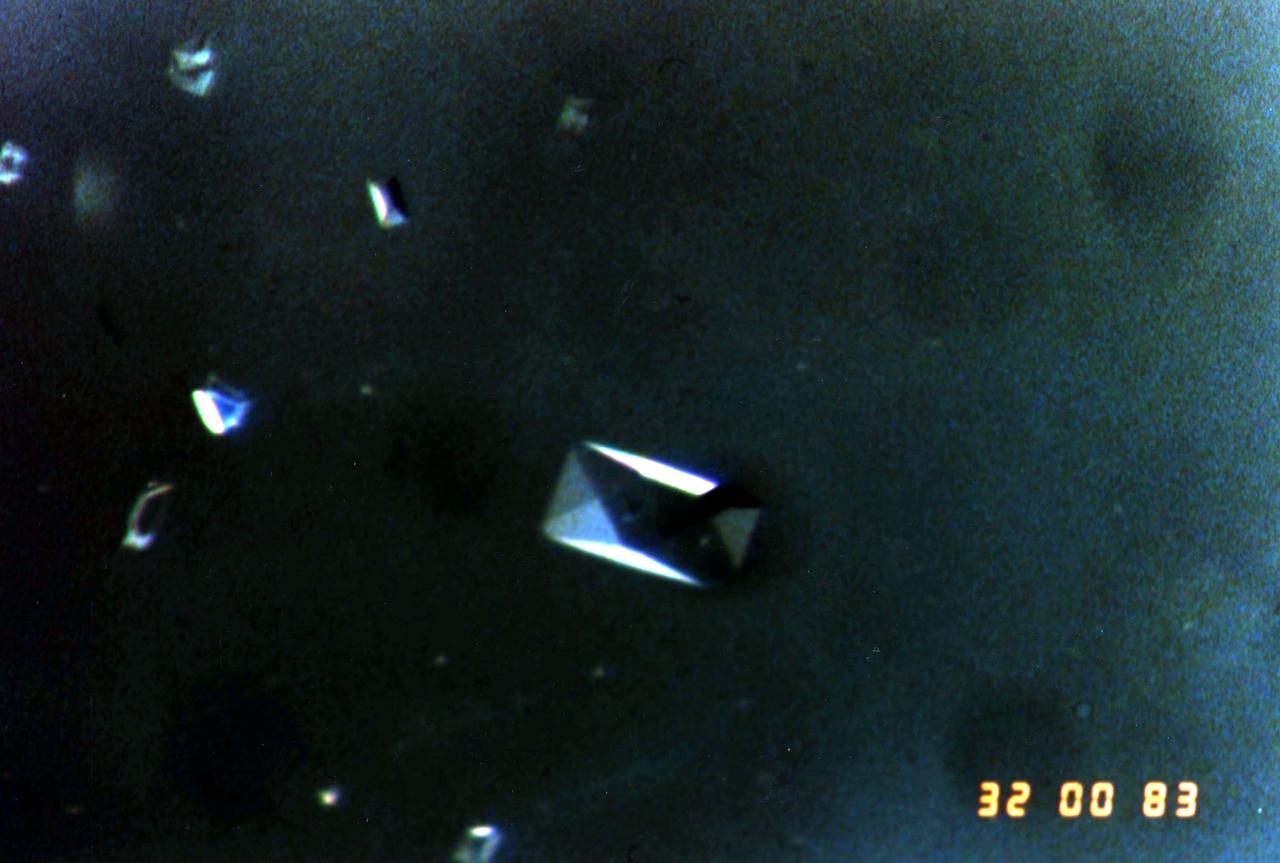
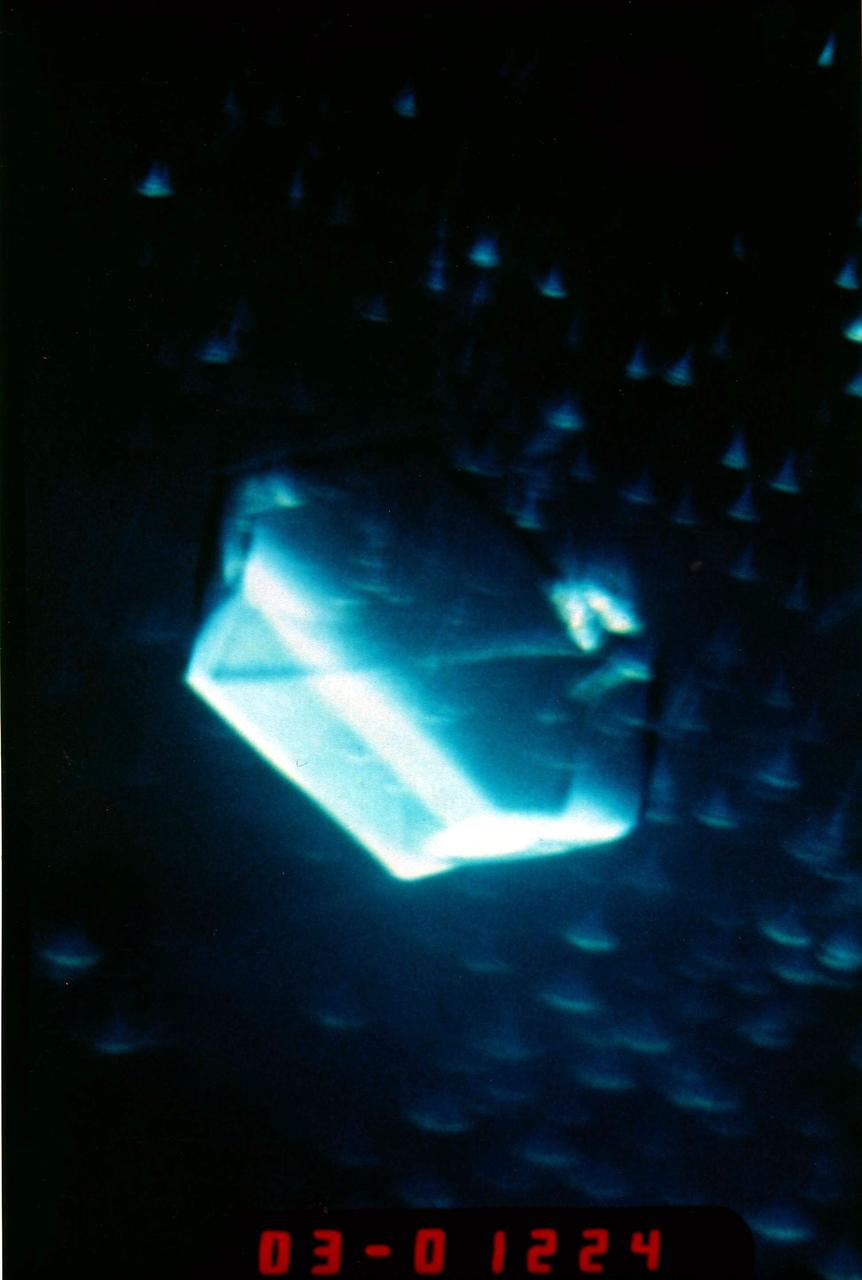
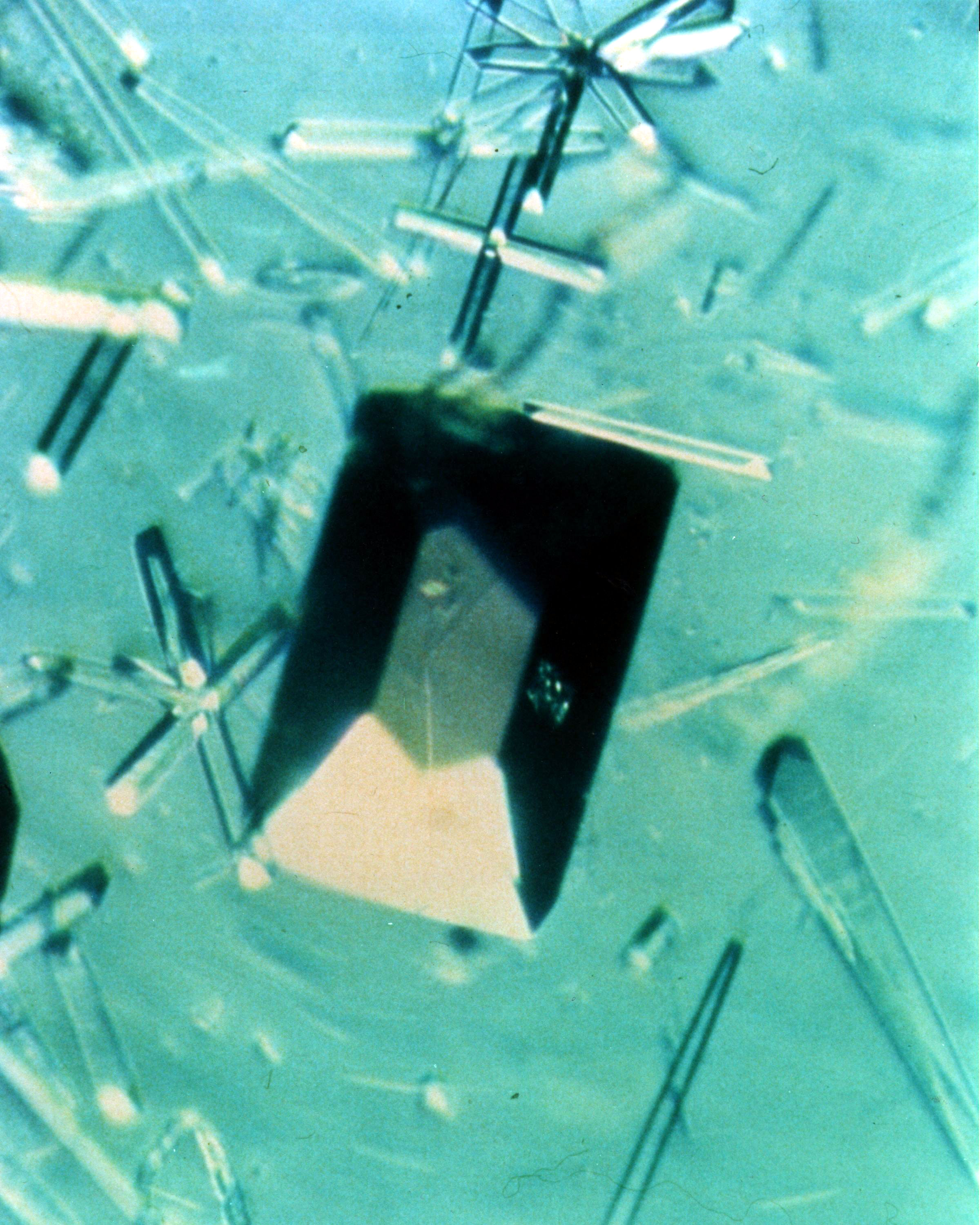
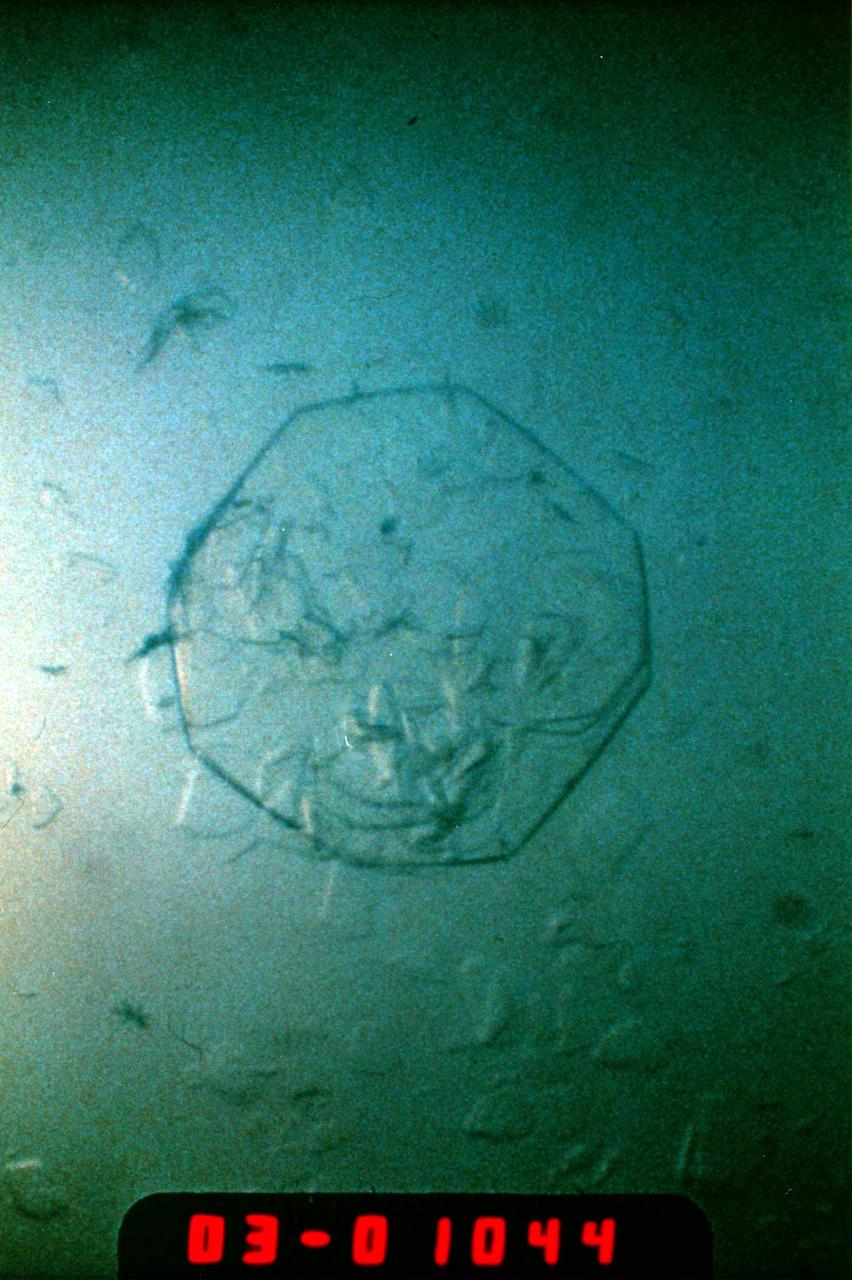
The image shows a test cell of Crystal Growth experiment inside the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) furnace aboard the STS-42, International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), mission. The goal of IML-1, a pressurized marned Spacelab module, was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. More than 200 scientists from 16 countires participated in the investigations.
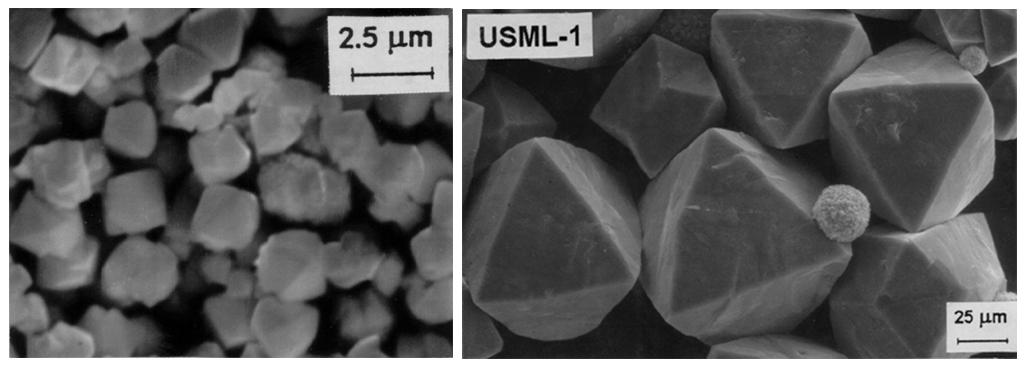
Zeolites are crystalline aluminosilicates that have complex framework structures. However, there are several features of zeolite crystals that make unequivocal structure determinations difficult. The acquisition of reliable structural information on zeolites is greatly facilitated by the availability of high-quality specimens. For structure determinations by conventional diffraction techniques, large single-crystal specimens are essential. Alternatively, structural determinations by powder profile refinement methods relax the constraints on crystal size, but still require materials with a high degree of crystalline perfection. Studies conducted at CAMMP (Center for Advanced Microgravity Materials Processing) have demonstrated that microgravity processing can produce larger crystal sizes and fewer structural defects relative to terrestrial crystal growth. Principal Investigator: Dr. Albert Sacco

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-73) Payload Specialist Albert Sacco loads autoclaves using a power screwdriver into the Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the middeck for the United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) Spacelab mission.
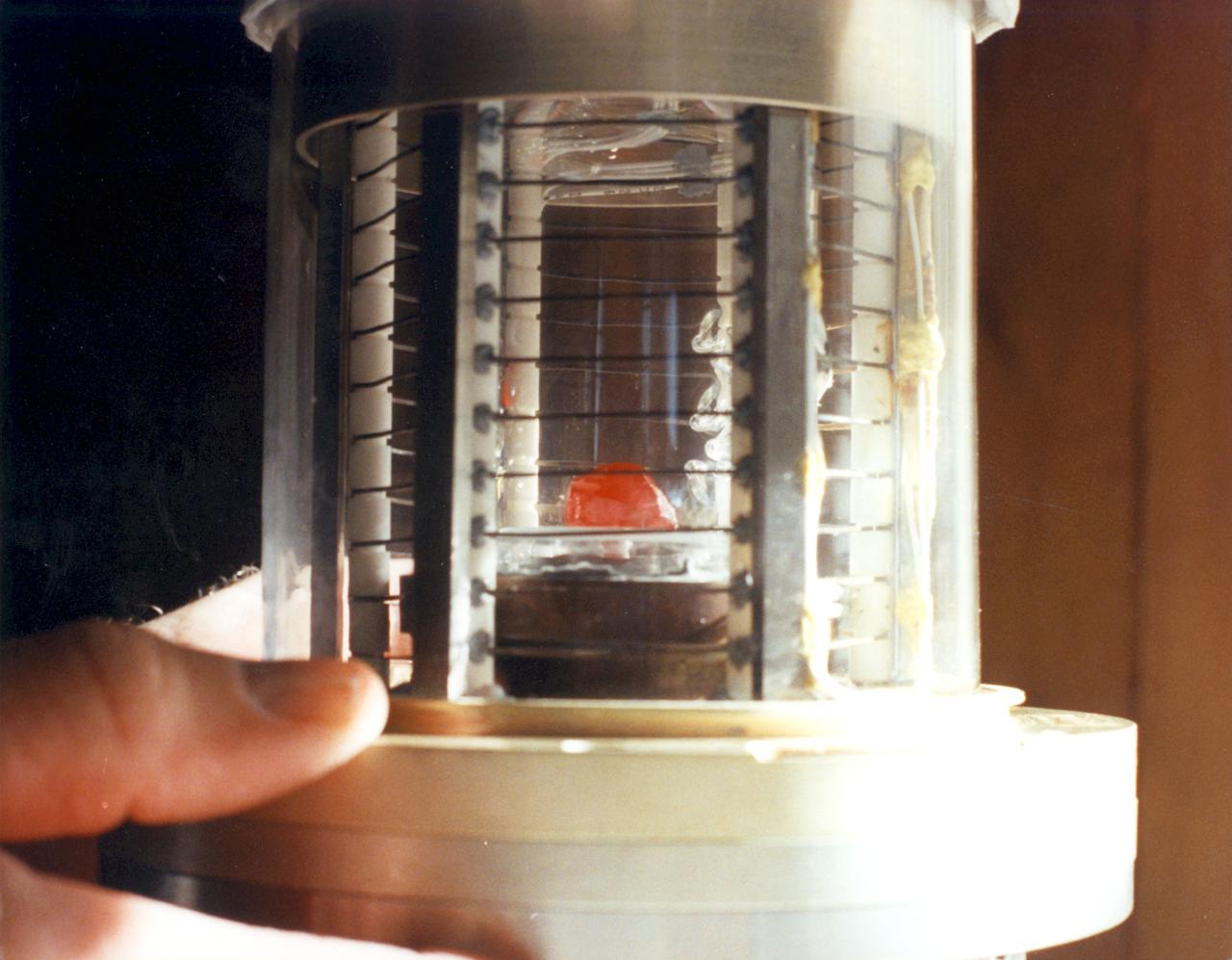
Ampoule view of the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) Furnace. Used on IML-1 International Microgravity Laboratory Spacelab 3. Prinicipal Investigator and Payload Specialist was Lodewijk van den Berg.
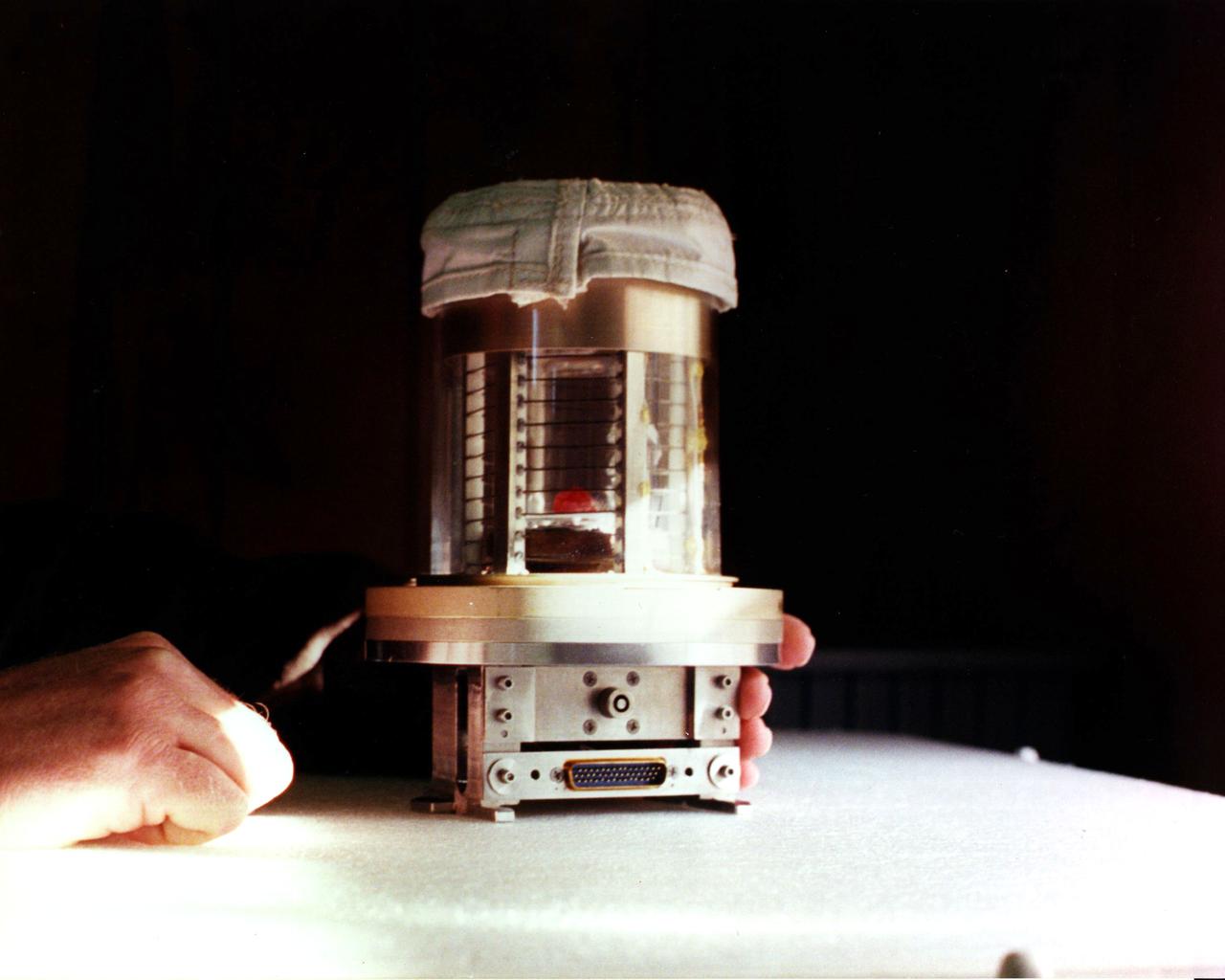
Overall view of the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) Furnace. Used on IML-1 International Microgravity Laboratory Spacelab 3. Principal Investigator and Payload Specialist was Lodewijk van den Berg.
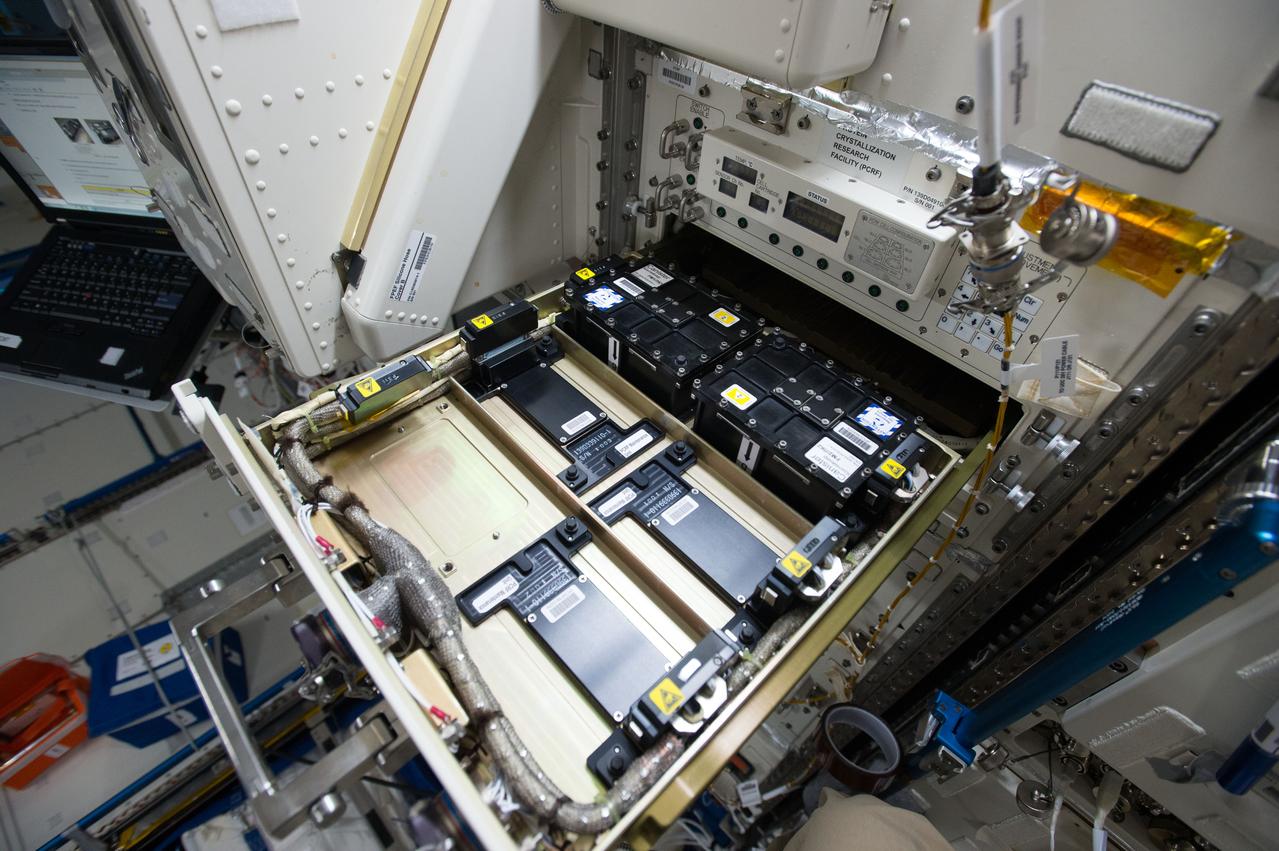

iss049e045287 (10/21/2016) --- Photographic documentation taken during JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Installation into the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF) of the Ryutai Rack.

jsc2025e036383 (4/4/2025) --- The blue box is The Redwire Industrial Crystallization Cassette (ICC), a facility capable of large quantities of crystal growth. The white cylindrical growth chamber below the ICC is capable of holding 200mL in volume, compared to <1mL held by the PIL-BOX cassettes. The ADSEP Industrial Crystallization Cassette Technology Demonstration (ADSEP-ICC) investigation validates the ICC’s capability to grow large quantities of crystals in its high-volume crystal growth chambers aboard the International Space Station. Image courtesy of Redwire.
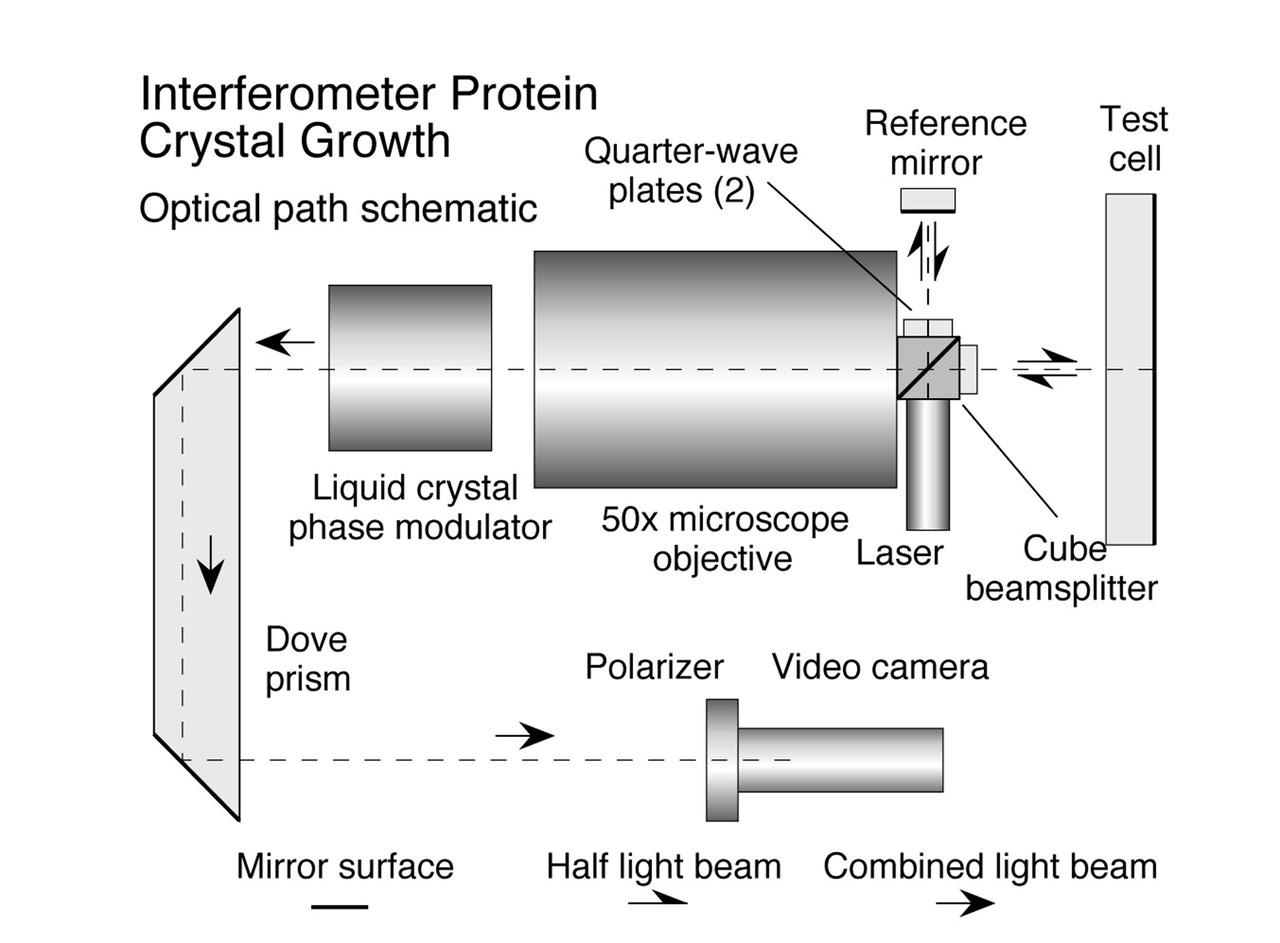
The Interferometer Protein Crystal Growth (IPCG) experiment was designed to measure details of how protein molecules move through a fluid. It was flown on the STS-86 mission for use aboard Russian Space Station Mir in 1998. It studied aspects of how crystals grow - and what conditions lead to the best crystals, details that remain a mystery. IPCG produces interference patterns by spilitting then recombining laser light. This let scientists see how fluid densities - and molecular diffusion - change around a crystal as it grows in microgravity. The heart of the IPCG apparatus is the interferometer cell comprising the optical bench, microscope, other optics, and video camera. IPCG experiment cells are made of optical glass and silvered on one side to serve as a mirror in the interferometer system that visuzlizes crystals and conditions around them as they grow inside the cell. This diagram shows the optical layout. The principal investigator was Dr. Alexander McPherson of University of California, Irvine. Co-investigators are William Witherow and Dr. Marc Pusey of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
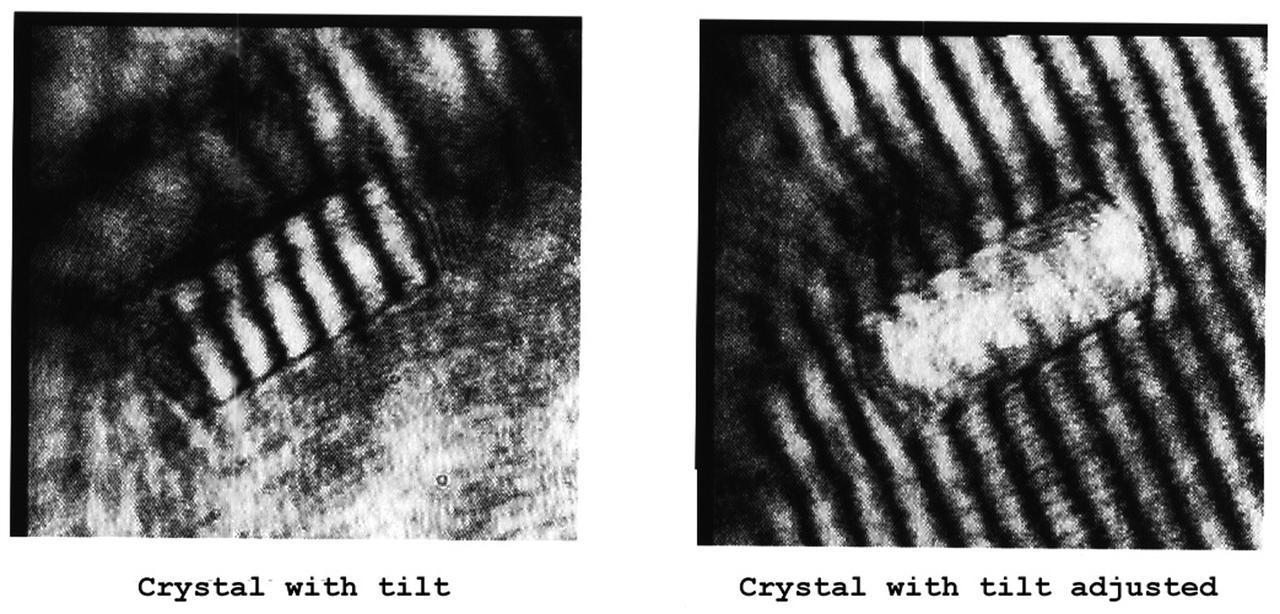
The Interferometer Protein Crystal Growth (IPCG) experiment was designed to measure details of how protein molecules move through a fluid. It was flown on the STS-86 mission for use aboard Russian Space Station Mir in 1998. It studied aspects of how crystals grow - and what conditions lead to the best crystals, details that remain a mystery. IPCG produces interference patterns by spilitting then recombining laser light. This let scientists see how fluid densities - and molecular diffusion - change around a crystal as it grows in microgravity. The heart of the IPCG apparatus is the interferometer cell comprising the optical bench, microscope, other optics, and video camera. IPCG experiment cells are made of optical glass and silvered on one side to serve as a mirror in the interferometer system that visuzlizes crystals and conditions around them as they grow inside the cell. This view shows interferograms produced in ground tests. The principal investigator was Dr. Alexander McPherson of University of California, Irvine. Co-investigators are William Witherow and Dr. Marc Pusey of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
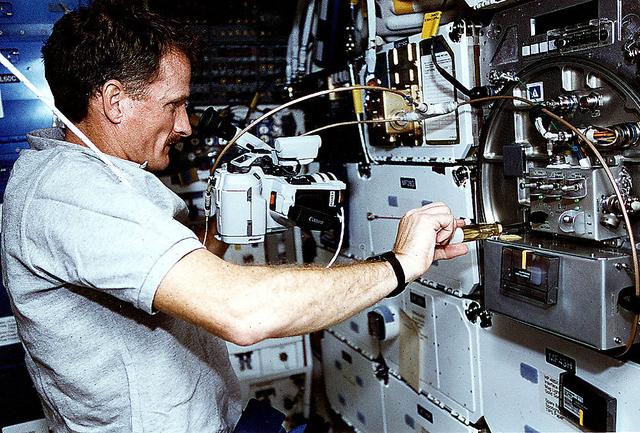

On the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis' middeck, Astronaut Joseph R. Tarner, mission specialist, works at an area amidst several lockers which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment during the STS-66 mission. This particular section is called the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES). Together with the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (SLTES), the COS/TES represents the continuing research into the structure of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses.
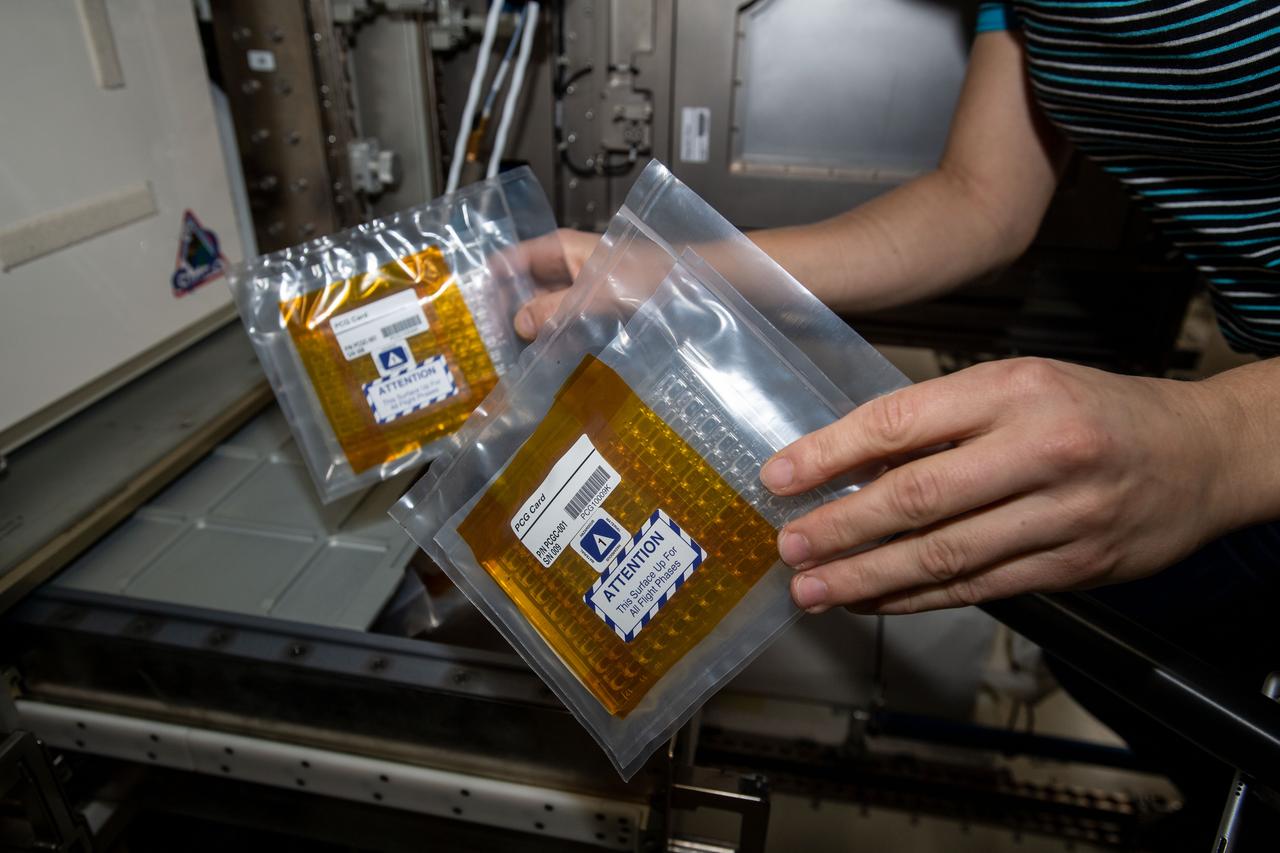

iss062e087808 (3/11/2020) --- A view of Protein Crystal Growth-10 experiment hardware inside JAXA's (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Kibo laboratory module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Microgravity Crystallization of Glycogen Synthase-Glycogenin Protein Complex (CASIS PCG 10) crystallizes human glycogen synthase proteins on the space station. Determining the structure of the human glycogen synthase and full-length glycogenin protein complex could facilitate the development of treatments on Earth for metabolic disorders such as Type 2 diabetes, obesity, rare genetic disorders, and some forms of cancer.
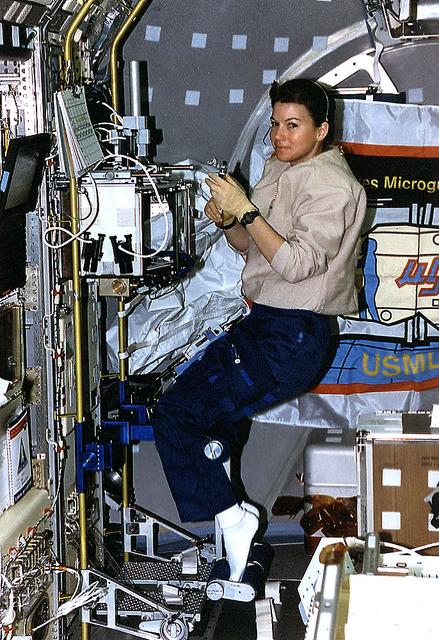

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-73) Mission Specialists Catherine Cady Coleman works at the glovebox facility in support of the Protein Crystal Growth Glovebox (PCG-GBX) experiment in the United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) Spacelab science module.
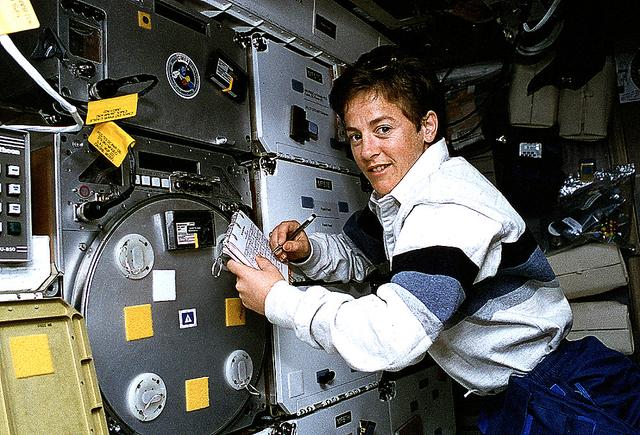

Astronaut Wendy B. Lawrence, flight engineer and mission specialist for STS-67, scribbles notes on the margin of a checklist while monitoring an experiment on the Space Shuttle Endeavour's mid-deck. The experiment is the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG), which takes up locker space near the Commercial Materials Dispersion Apparatus Instruments Technology Associates Experiment (CMIX).
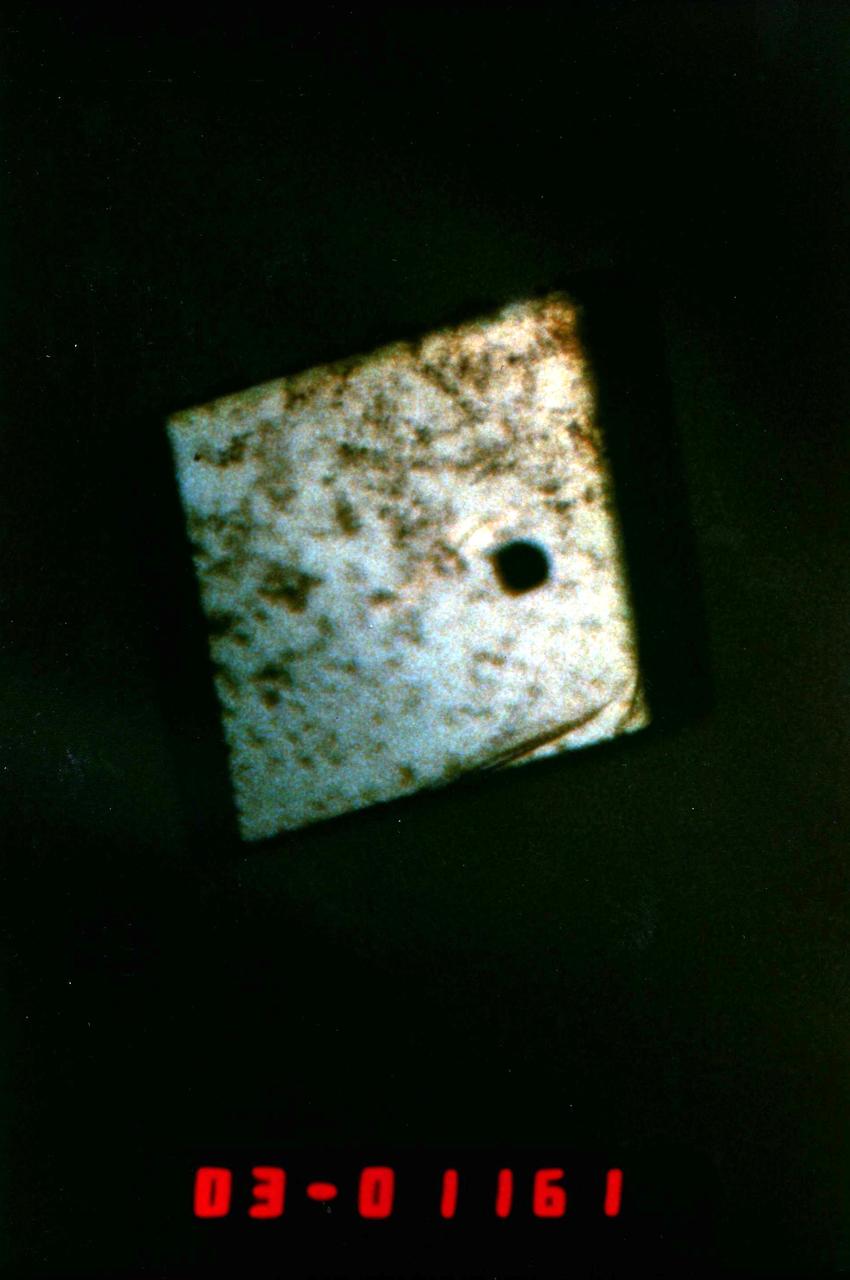

(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Gamma-Interferon. Stimulates the body's immune system and is used clinically in the treatment of cancer. Potential as an anti-tumor agent against solid tumors as well as leukemia's and lymphomas. It has additional utility as an anti-ineffective agent, including antiviral, anti-bacterial, and anti-parasitic activities. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Canavalin. The major storage protein of leguminous plants and a major source of dietary protein for humans and domestic animals. It is studied in efforts to enhance nutritional value of proteins through protein engineerings. It is isolated from Jack Bean because of it's potential as a nutritional substance. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Alex McPherson.
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Human Serum Albumin. Contributes to many transport and regulatory processes and has multifunctional binding properties which range from various metals, to fatty acids, hormones, and a wide spectrum of therapeutic drugs. The most abundant protein of the circulatory system. It binds and transports an incredible variety of biological and pharmaceutical ligands throughout the blood stream. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Larry DeLucas.
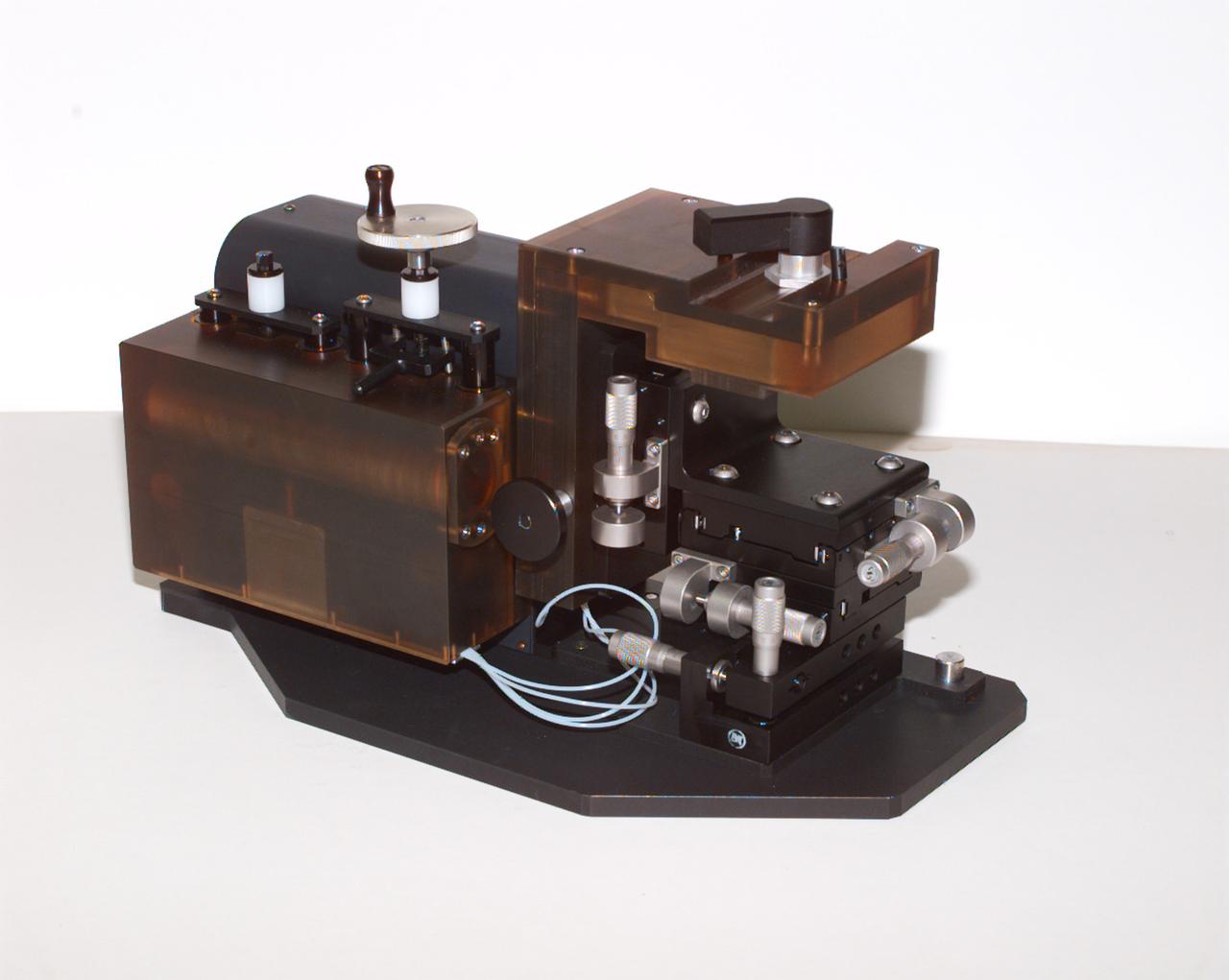

The Interferometer Protein Crstal Growth (IPCG) experiment was designed to measure details of how protein molecules move through a fluid. It was flown on the STS-86 mission for use aboard Russin Space Station Mir in 1998. It studied aspects of how crystals grow - and what conditions lead to the best crystals, details that remain a mystery. IPCG produces interference patterns by splitting then recombining laser light. This let scientists see how fluid densities - and molecular diffusion - change around a crystal as it grows in microgravity. The heart of the IPCG apparatus is the interferometer cell comprising the optical bench, microscope, other optics, and video camera. IPCG experiment cells are made of optical glass and silvered on one side to serve as a mirror in the interferometer system that visualizes crystals and conditions around them as they grow inside the cell. This view shows the complete apparatus. The principal investigator was Dr. Alexander McPherson of the University of California, Irvin. Co-investigators are William Witherow and Dr. Marc Pusey of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center
This is an image of a colloidal crystal from the CDOT-2 investigation flown on STS-95. There are so many colloidal particles in this sample that it behaves like a glass. In the laboratory on Earth, the sample remained in an amorphous state, showing no sign of crystal growth. In microgravity the sample crystallized in 3 days, as did the other glassy colloidal samples examined in the CDOT-2 experiment. During the investigation, crystallization occurred in samples that had a volume fraction (number of particles per total volume) larger than the formerly reported glass transition of 0.58. This has great implications for theories of the structural glass transition. These crystals were strong enough to survive space shuttle re-entry and landing.

51B-06-010 (29 April-6 May 1985) --- Lodewijk van den Berg, 51-B payload specialist, observes the growth of mercuric iodide crystal in the vapor crystal growth system (VCGS) on the Spacelab 3 science module aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger.
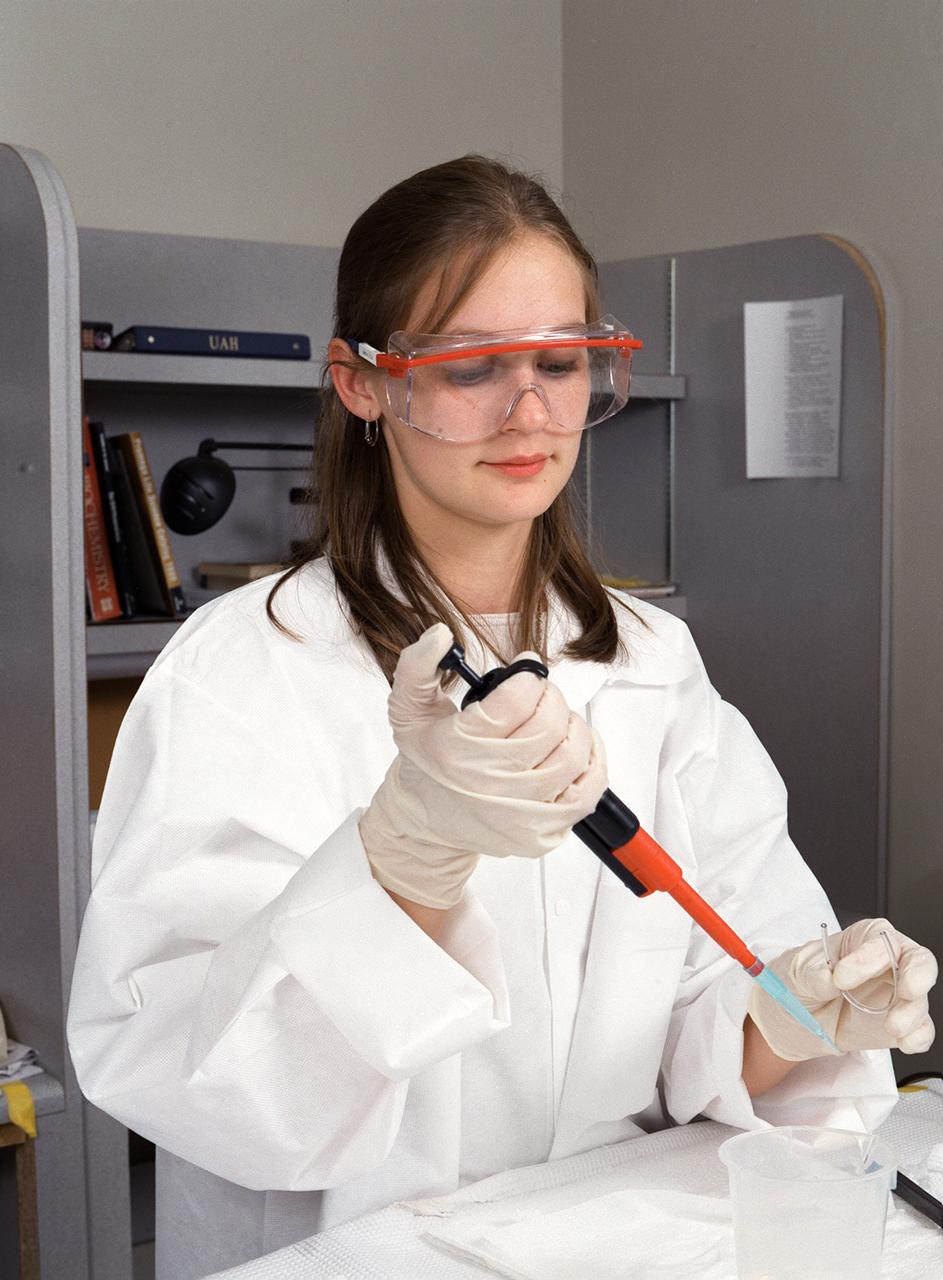

A Memphis student working at the University of Alabama in Huntsville prepares samples for the first protein crystal growth experiments plarned to be performed aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The proteins are placed in plastic tubing that is heat-sealed at the ends, then flash-frozen and preserved in a liquid nitrogen Dewar. Aboard the ISS, the nitrogen will be allowed to evaporated so the samples thaw and then slowly crystallize. They will be analyzed after return to Earth. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)

A Memphis student working at the University of Alabama in Huntsville prepares samples for the first protein crystal growth experiments plarned to be performed aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The proteins are placed in plastic tubing that is heat-sealed at the ends, then flash-frozen and preserved in a liquid nitrogen Dewar. Aboard the ISS, the nitrogen will be allowed to evaporated so the samples thaw and then slowly crystallize. They will be analyzed after return to Earth. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
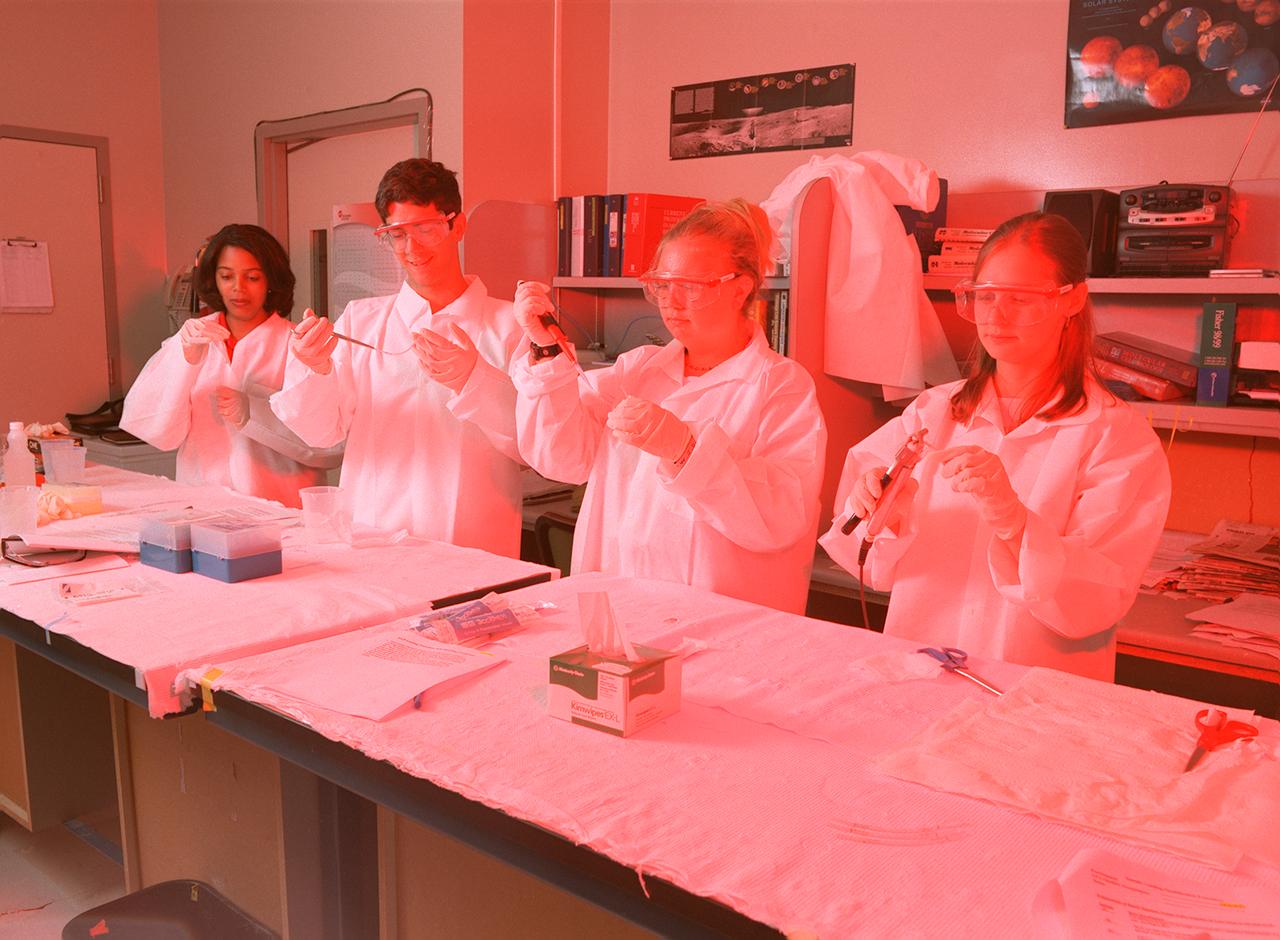

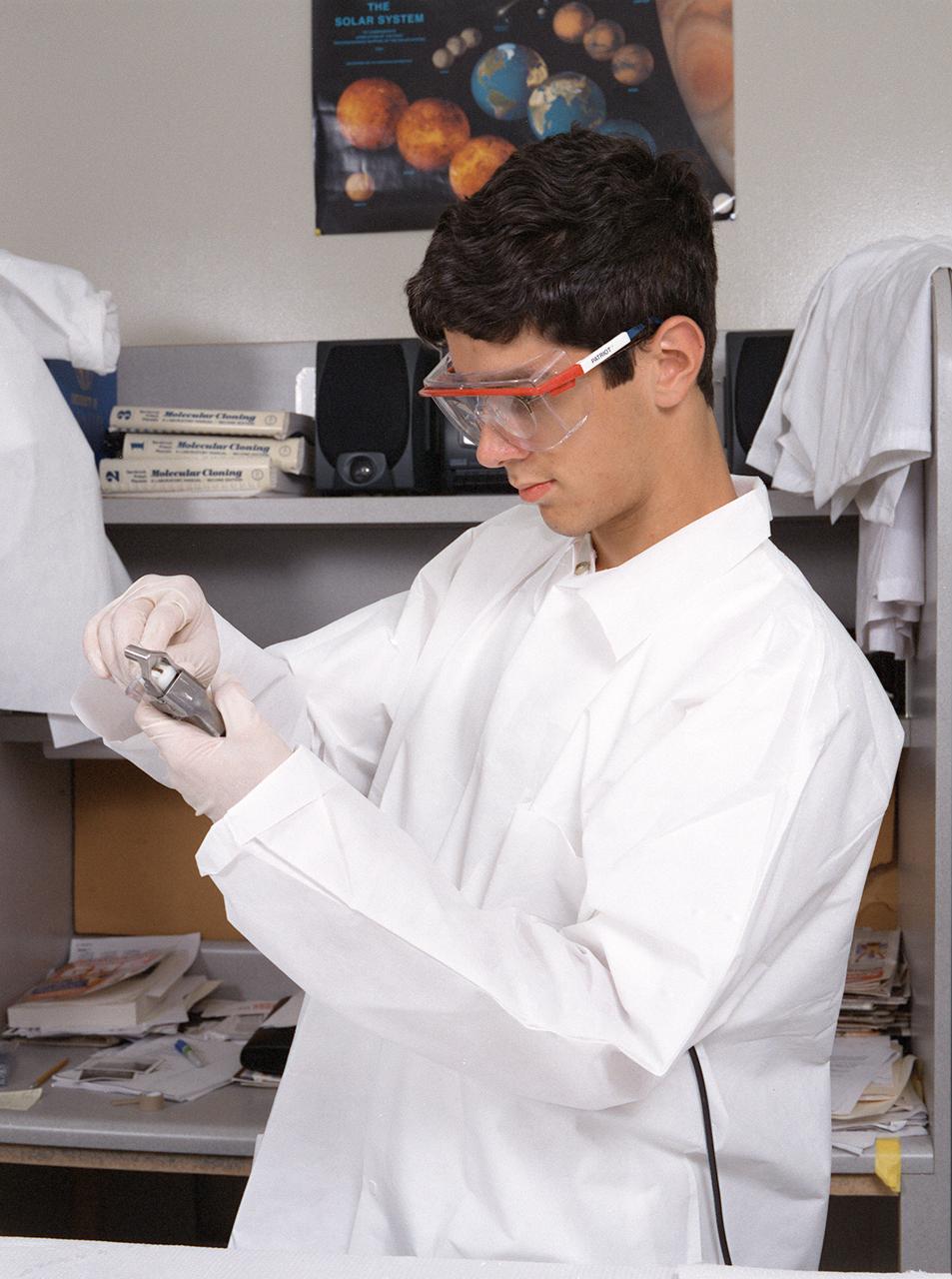
Memphis students working at the University of Alabama in Huntsville prepare samples for the first protein crystal growth experiments plarned to be performed aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The proteins are placed in plastic tubing that is heat-sealed at the ends, then flash-frozen and preserved in a liquid nitrogen Dewar. Aboard the ISS, the nitrogen will be allowed to evaporated so the samples thaw and then slowly crystallize. They will be analyzed after return to Earth. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
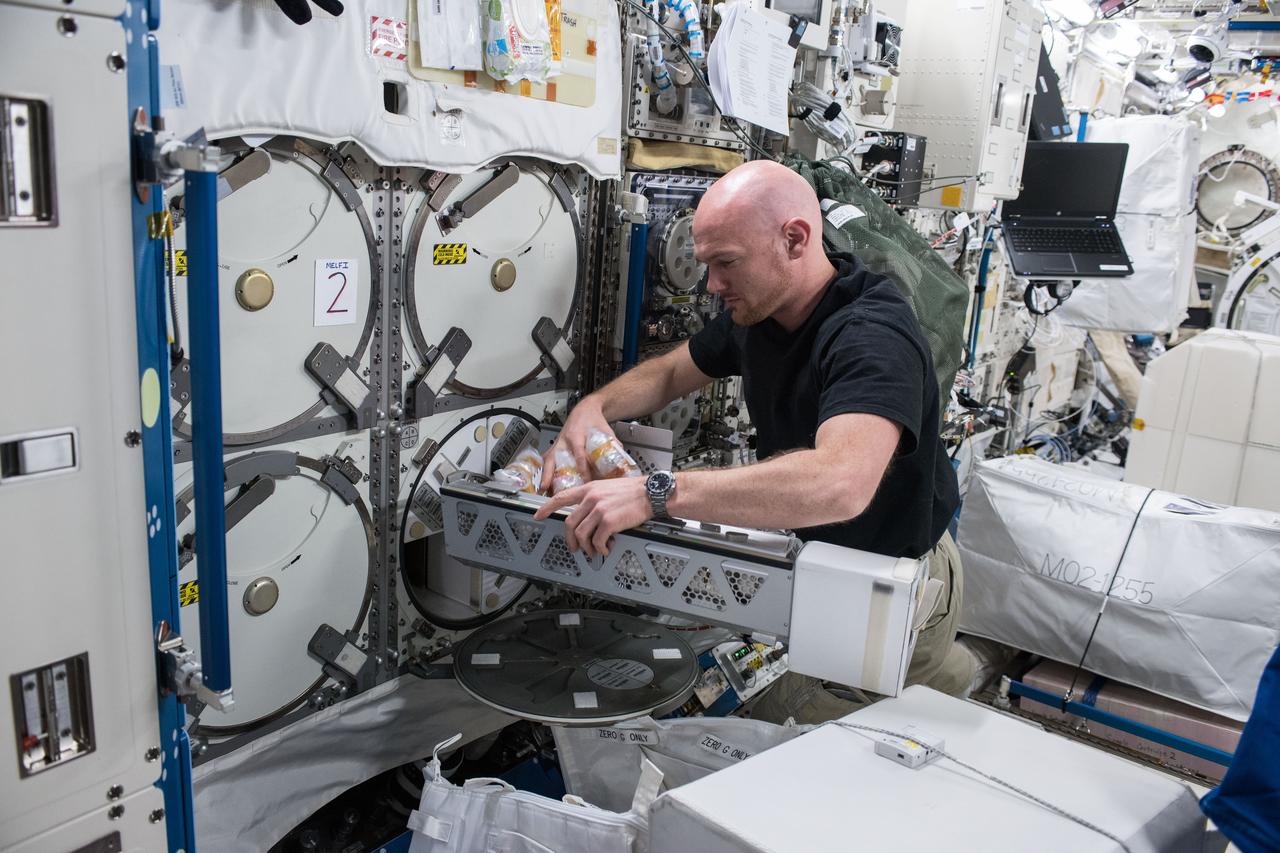

iss056e075950 (July 3, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) works inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module retrieving Protein Crystal Growth samples from a science freezer, also known as the Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI).
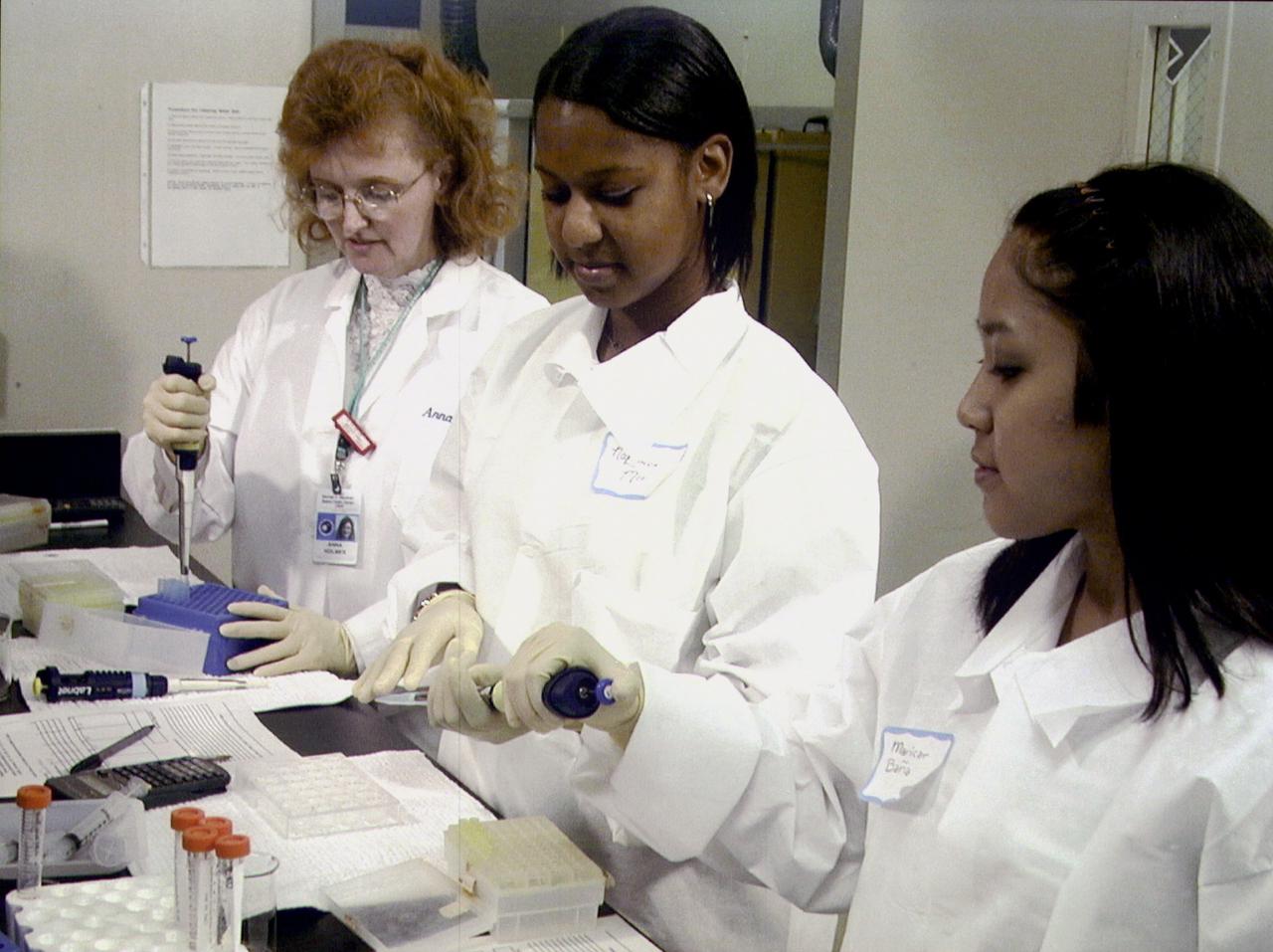

Chemist Arna Holmes, left, from the University of Alabama in Huntsville, teaches NaLonda Moorer, center, and Maricar Bana, right, both from Terry Parker High School in Jacksonville, Fl, procedures for preparing protein crystal growth samples for flight aboard the International Space Station (ISS). NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL, is a sponsor for this educational activity. The proteins are placed in plastic tubing that is heat-sealed at the ends, then flash-frozen and preserved in a liquid nitrogen Dewar. Aborad the ISS, the nitrogen will be allowed to evaporated so the samples thaw and then slowly crystallize. They will be analyzed after return to Earth. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
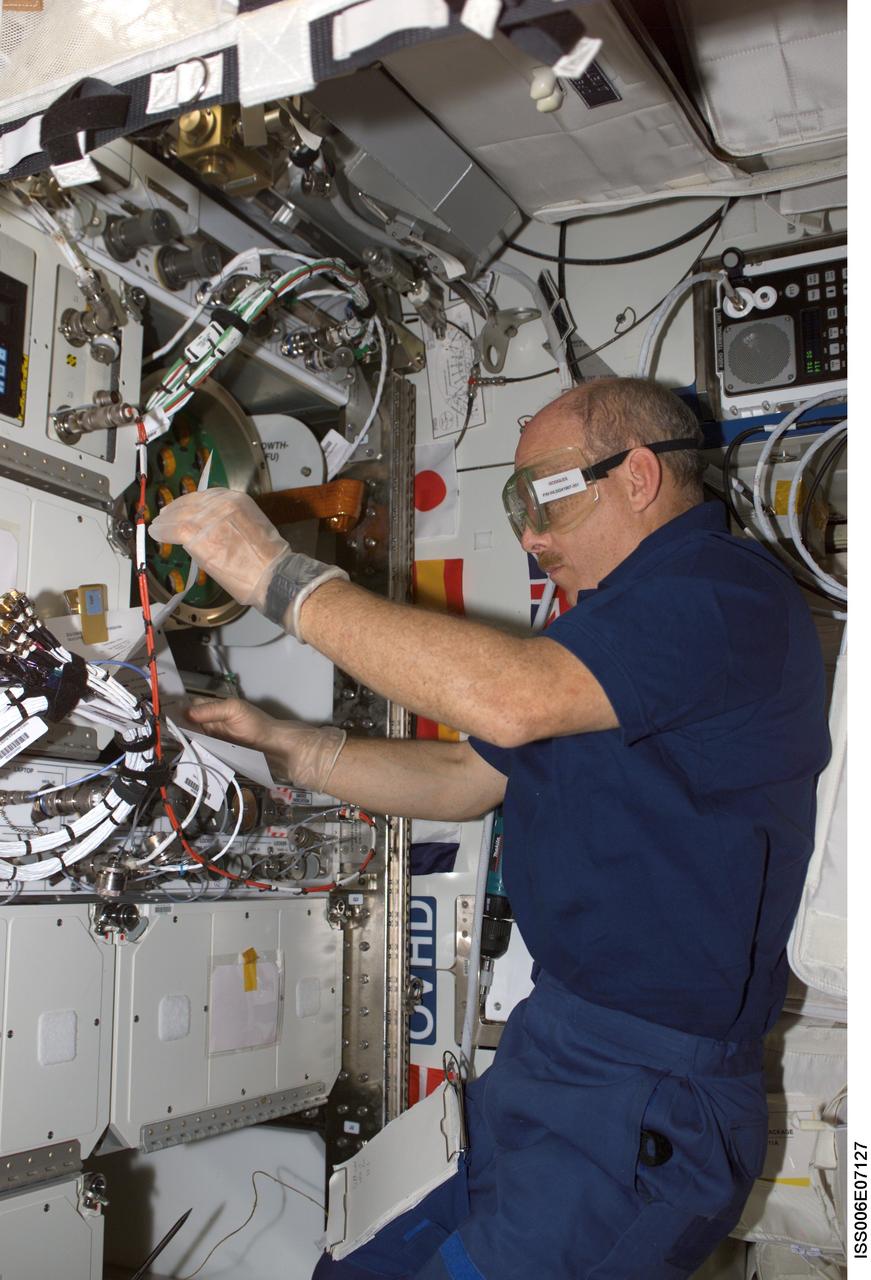

ISS006-E-07127 (5 December 2002) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, Expedition Six mission commander, works with the Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
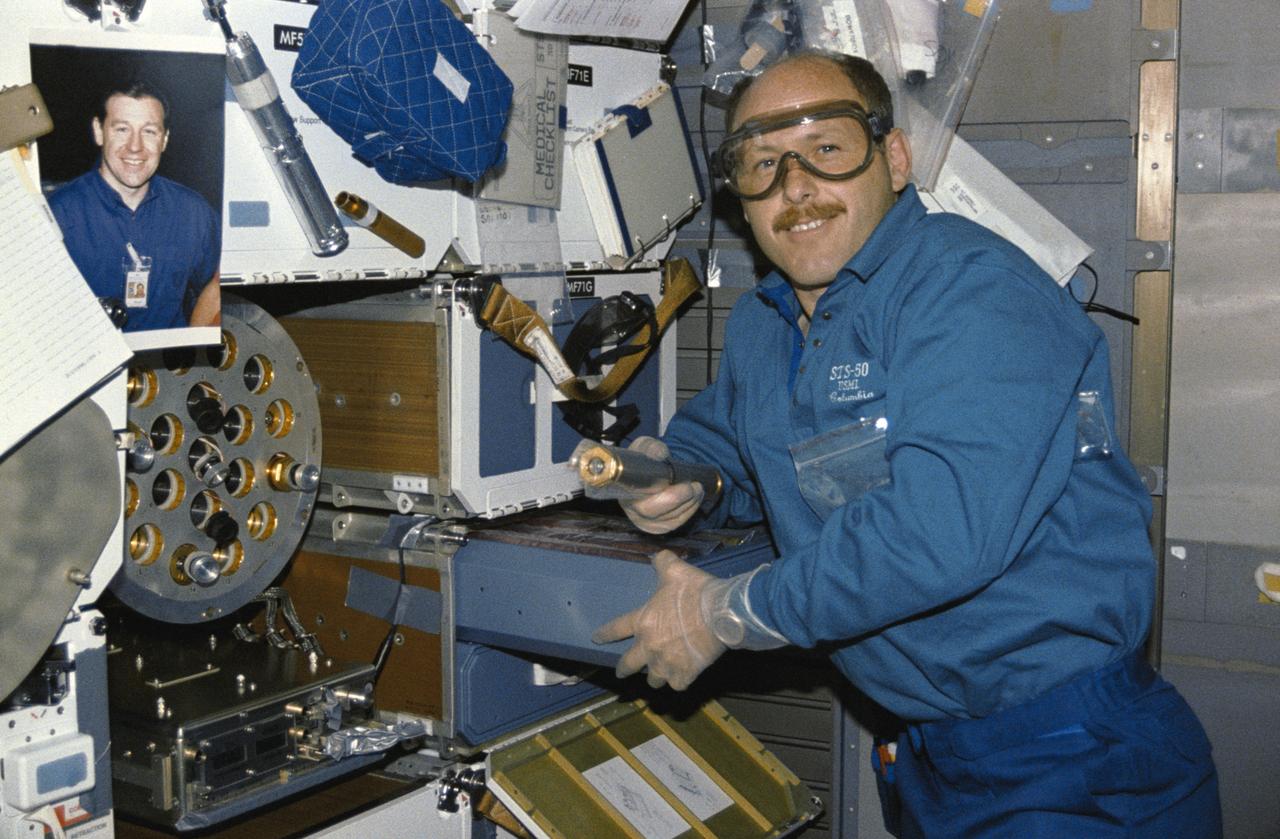

STS50-262-004 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, STS-50 pilot, holds an autoclave used in the growing of zeolite crystals on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. He is standing near the Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) furnace, which is housed in the space of two stowage lockers. On the 14-day U.S. Microgravity Laboratory mission, zeolite crystals were grown in 38 individual autoclaves, which were joined in pairs to be inserted into the 19 furnace orifices. While the autoclaves appear the same externally, there are several types of internal arrangements that were tested to determine which one provides the best mixing of the component solutions. The portrait of alternate payload specialist Albert Sacco, Jr. is mounted nearby. Sacco, serving as a ground controller at Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, worked in conjunction with the red shift crew in the science module.
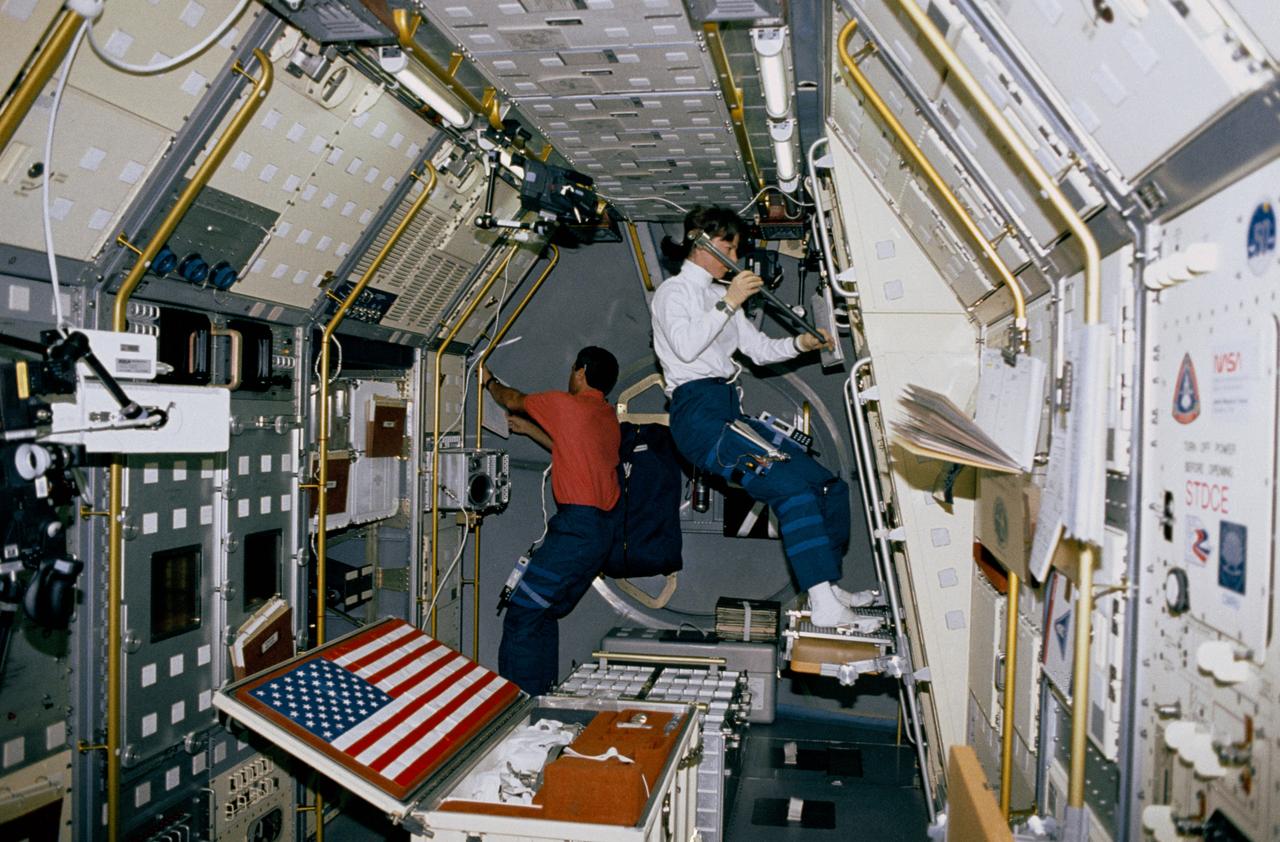

STS050-02-001 (9 July 1992) --- View showing Payload Specialists Bonnie Dunbar and Larry DeLucas in the aft section of the U. S. Microgravity Laboratory-1. Dunbar is preparing to load a sample in the Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) Integrated Furnace Experiment Assembly (IFEA) in rack 9 of the Microgravity Laboratory. DeLucas is checking out the multipurpose Glovebox Facility.
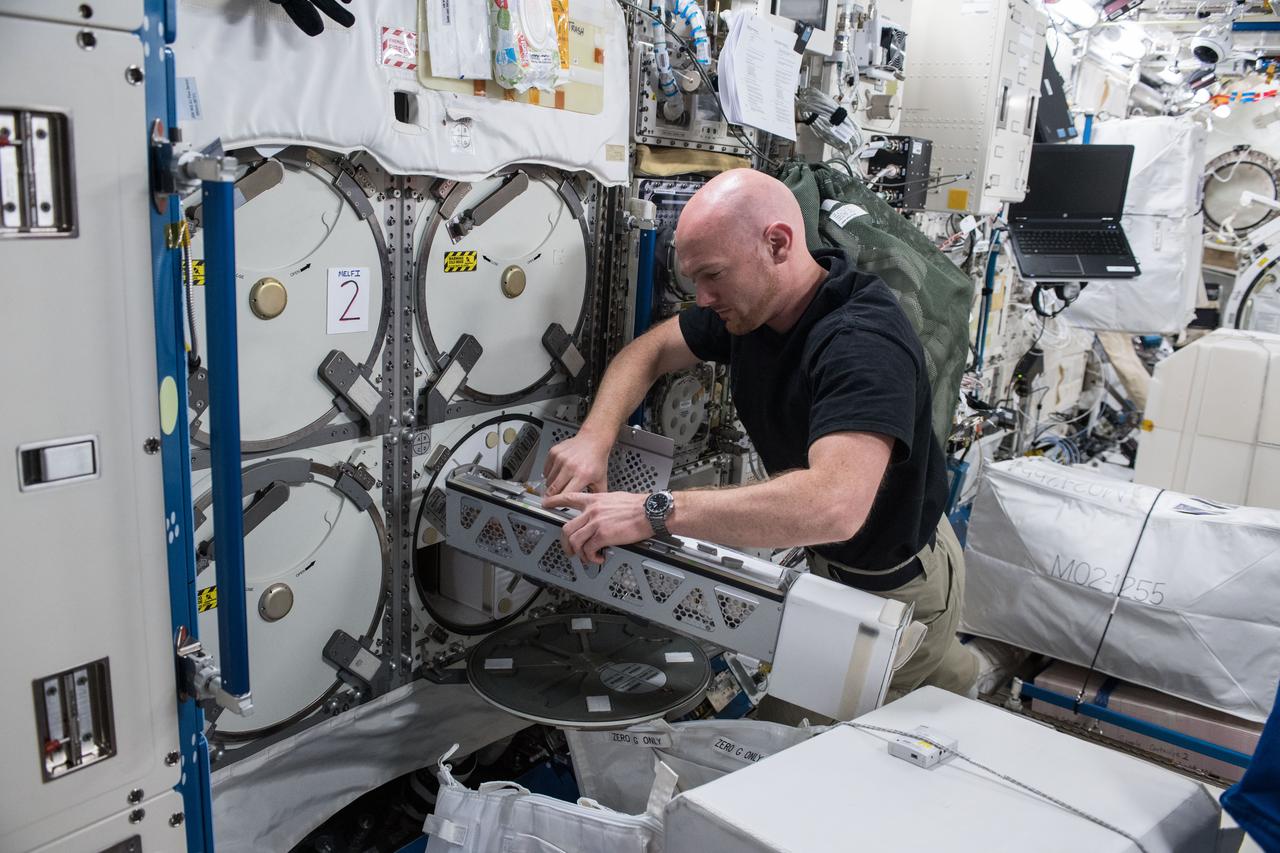

iss056e075951 (July 3, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) works inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module retrieving Protein Crystal Growth samples from a science freezer, also known as the Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI).
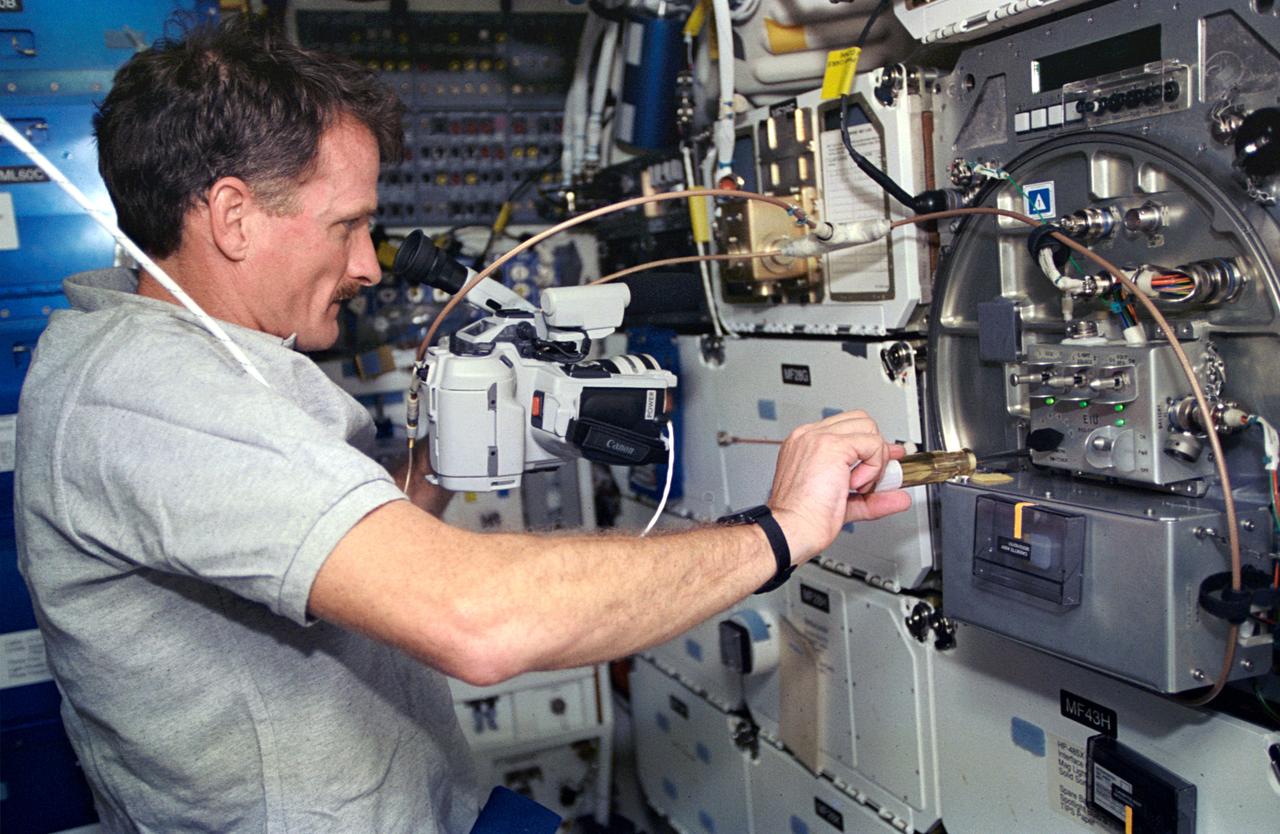

On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, works at area amidst several lockers onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES). Together with the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (SLTES) which is out of frame, the Cos/TES represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses.
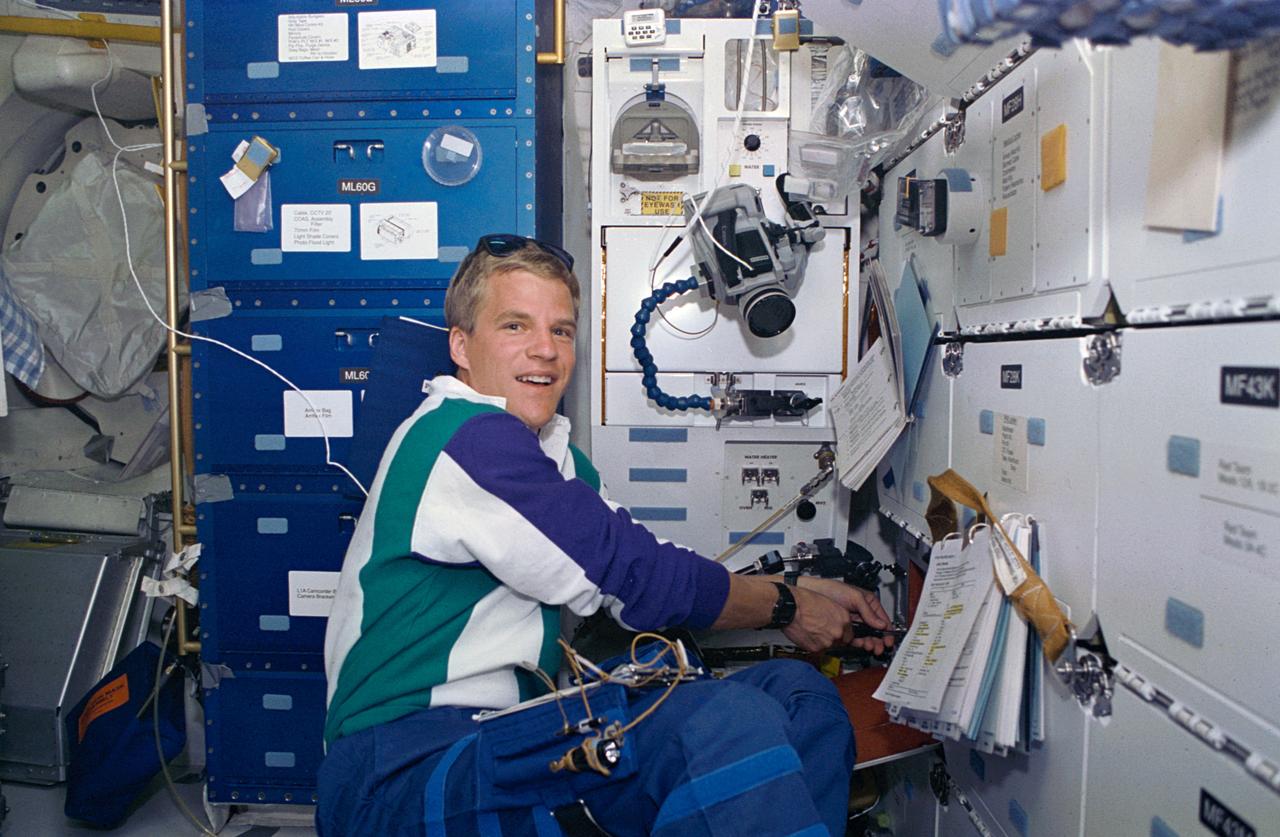

STS066-13-029 (3-14 Nov 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Scott E. Parazynski, mission specialist, works at one of two areas onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (STES). Together with the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES) the VDA represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses. In addition to using the microgravity of space to grow high-quality protein crystals for structural analyses, the experiments are expected to help develop technologies and methods to improve the protein crystallization process on Earth as well as in space.
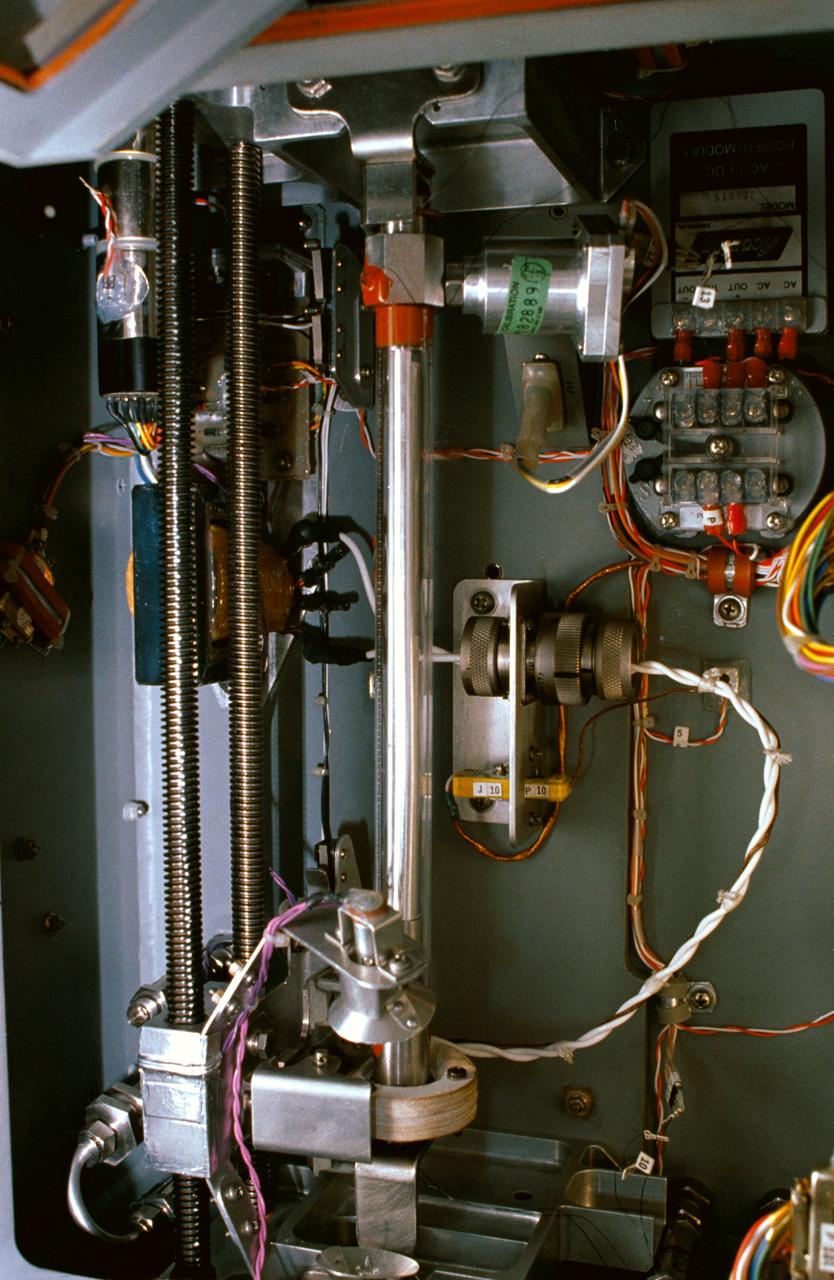
STS030-01-015 (4-8 May 1989) --- A 35mm close-up view of the Fluids Experiment Apparatus (FEA) aboard Atlantis for NASA’s STS-30 mission. Rockwell International is engaged in a joint endeavor agreement with NASA’s Office of Commercial Programs in the field of floating zone crystal growth and purification research. The March 1987 agreement provides for microgravity experiments to be performed in the company’s Microgravity Laboratory, the FEA. Crewmembers, especially Mary L. Cleave, devoted a great deal of onboard time to the monitoring of various materials science experiments using the apparatus.
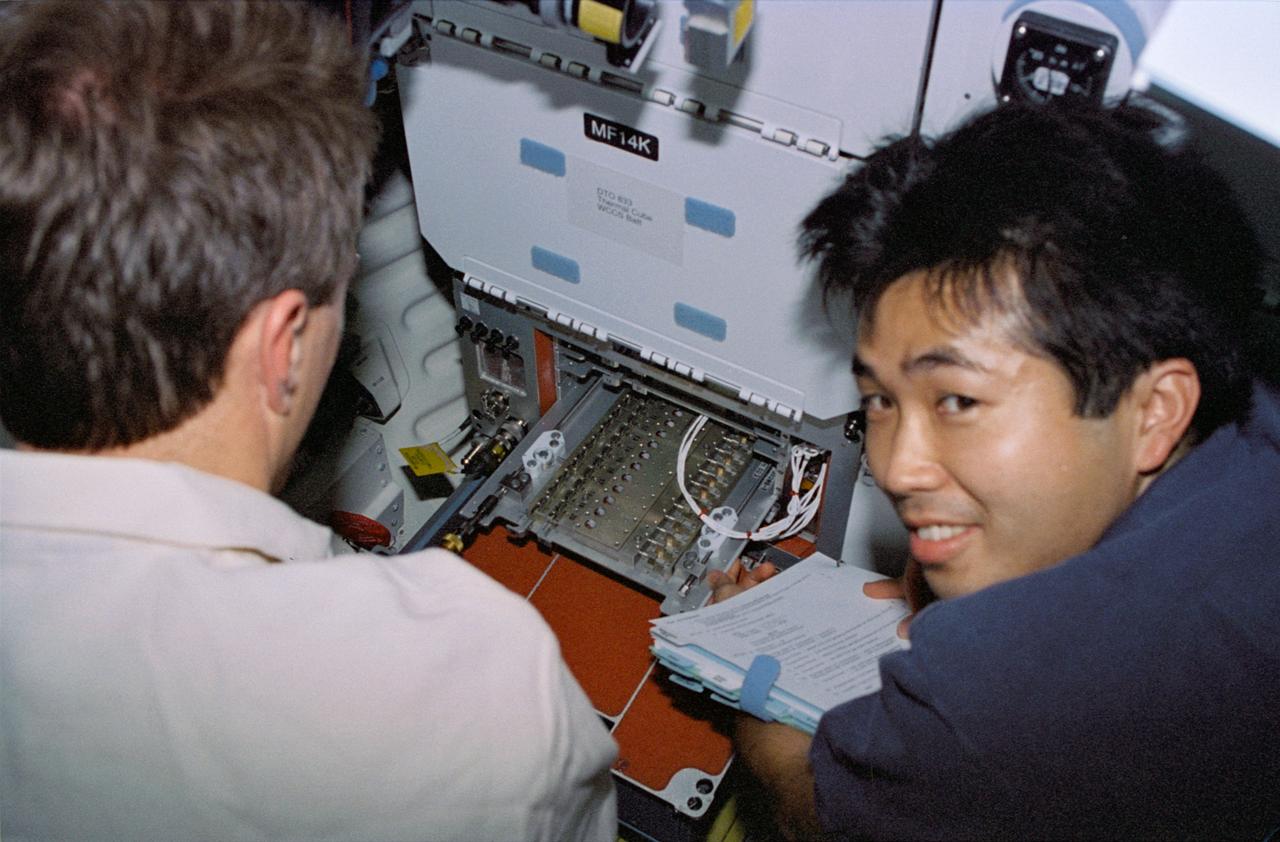
STS072-310-007 (11-20 Jan. 1996) --- Astronauts Brent W. Jett Jr. (left) and Koichi Wakata work with the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment at the Single Locker Thermal Enclosure System (STES) on the Space Shuttle Endeavour’s mid-deck. Jett, making his first flight in space, served as the crew’s pilot, while Wakata served as a mission specialist. Wakata, also a first time Shuttle crew member, represents Japan’s National Space Development Agency (NASDA).
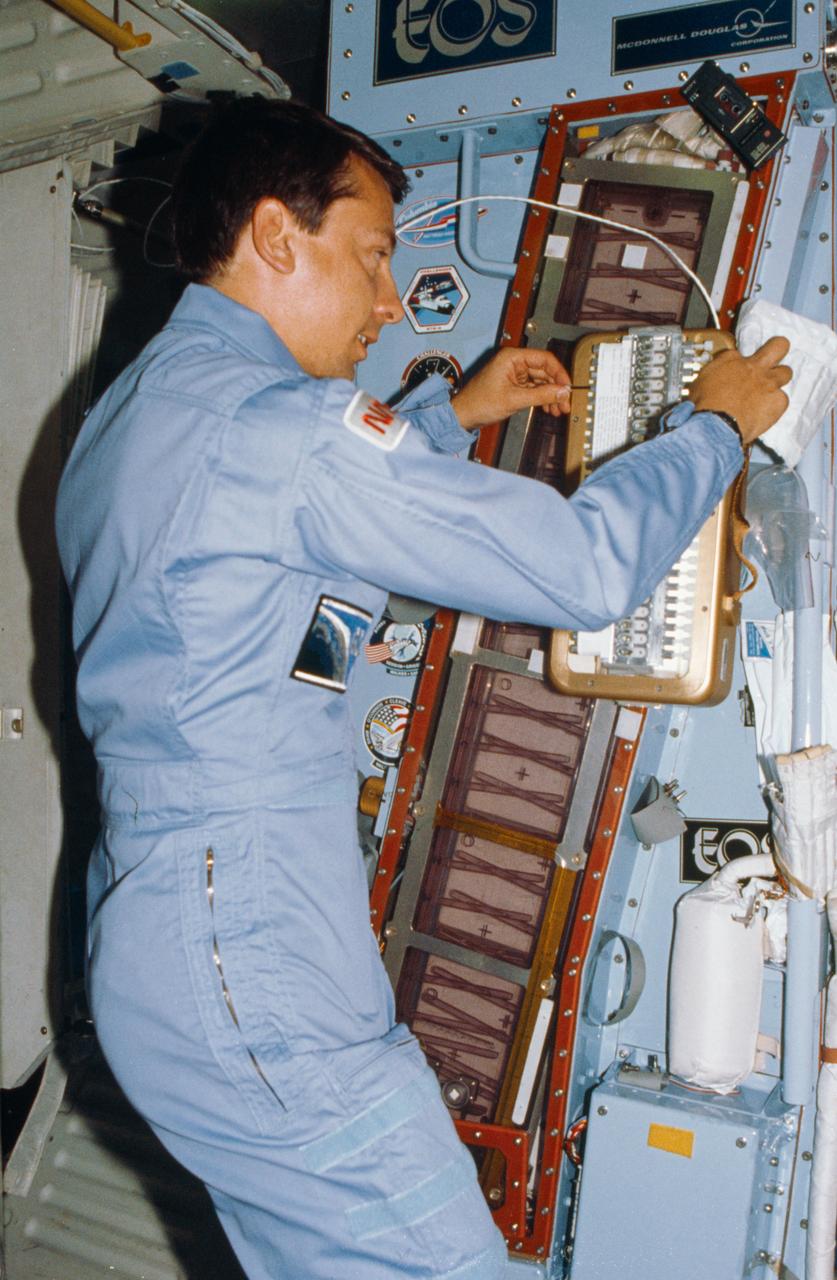

61B-02-014 (26 Nov-3 Dec 1985) --- Payload Specialist Charles D. Walker works with the handheld protein growth experiment -- one of a series of tests being flown to study the possibility of crystallizing biological materials. Walker rests the experiment against the larger continuous flow electrophoresis systems experiment.
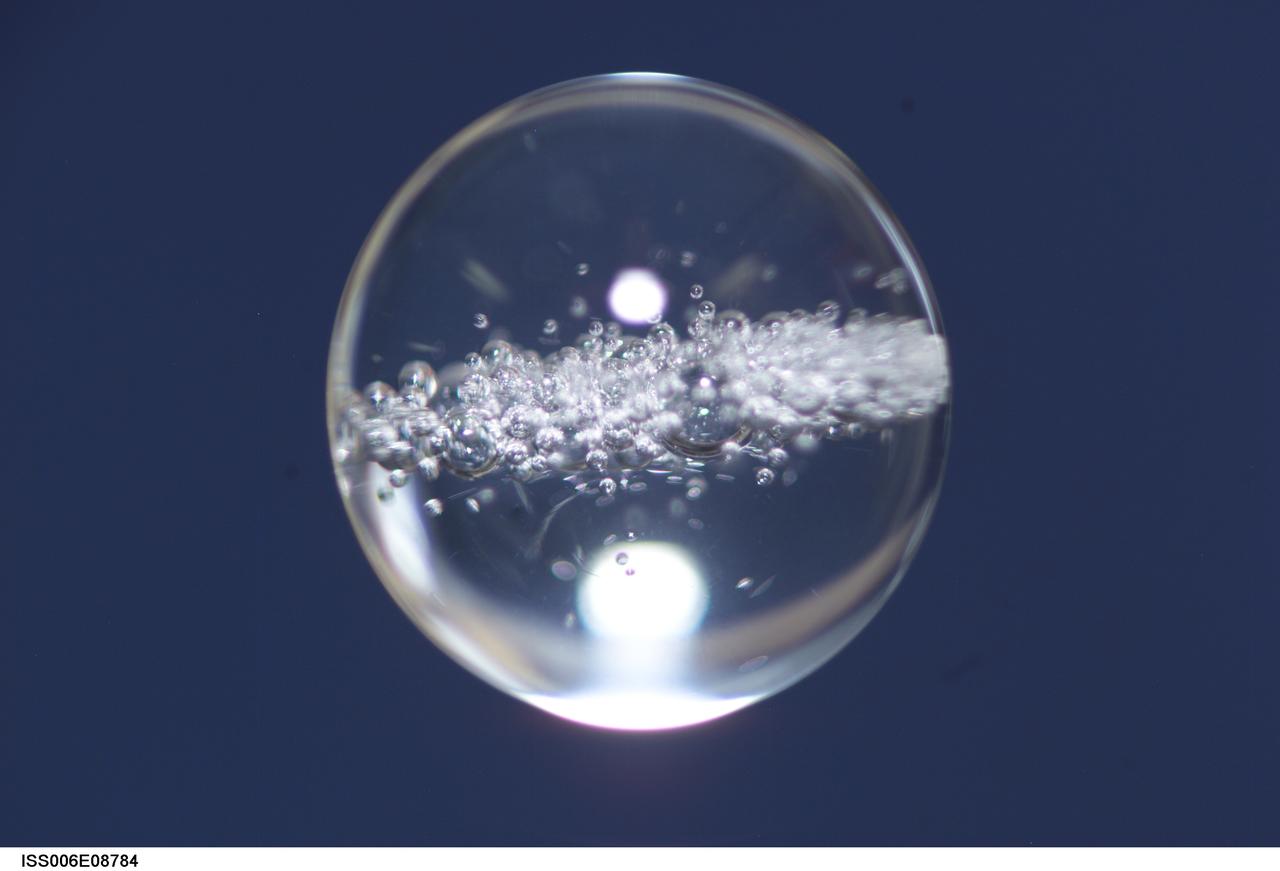

ISS006-E-08784 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
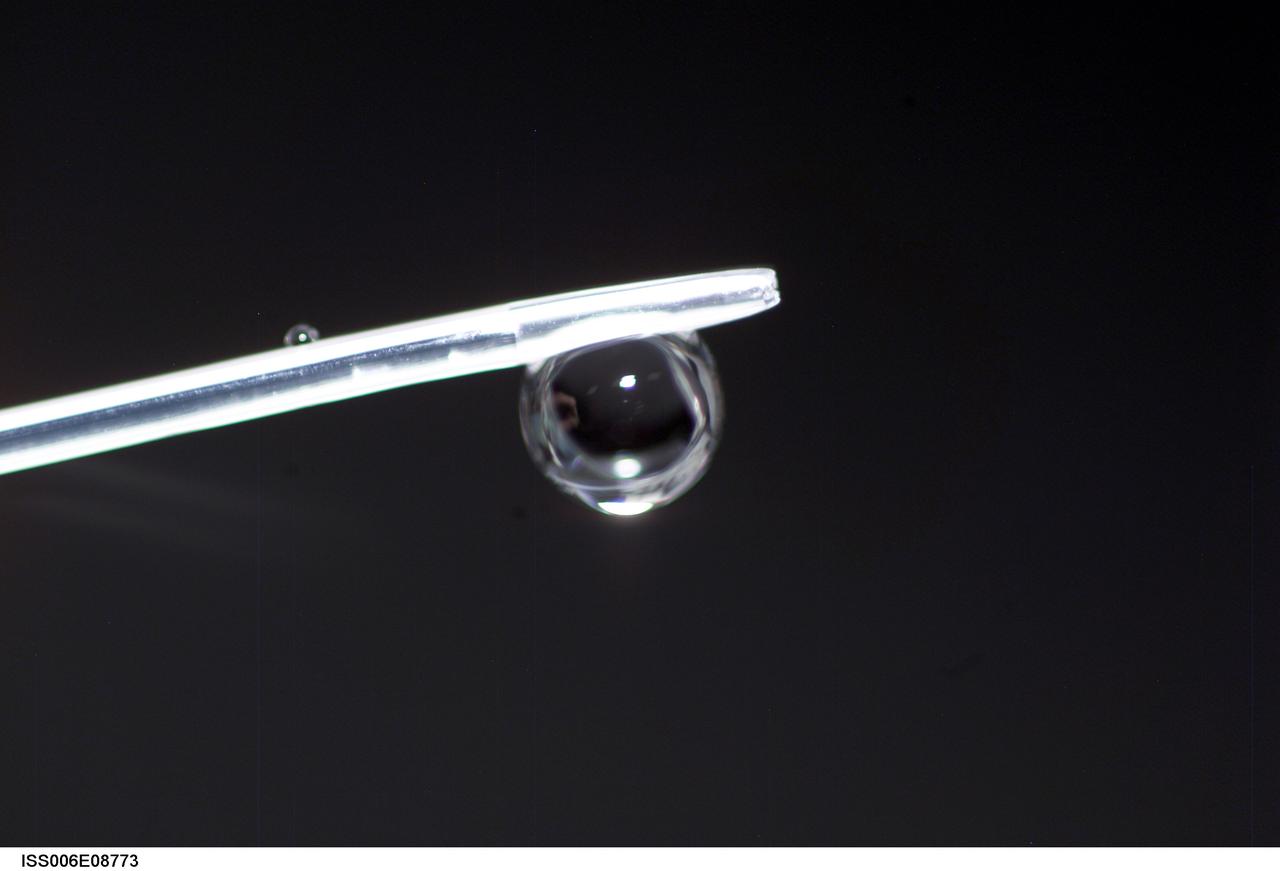

ISS006-E-08773 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
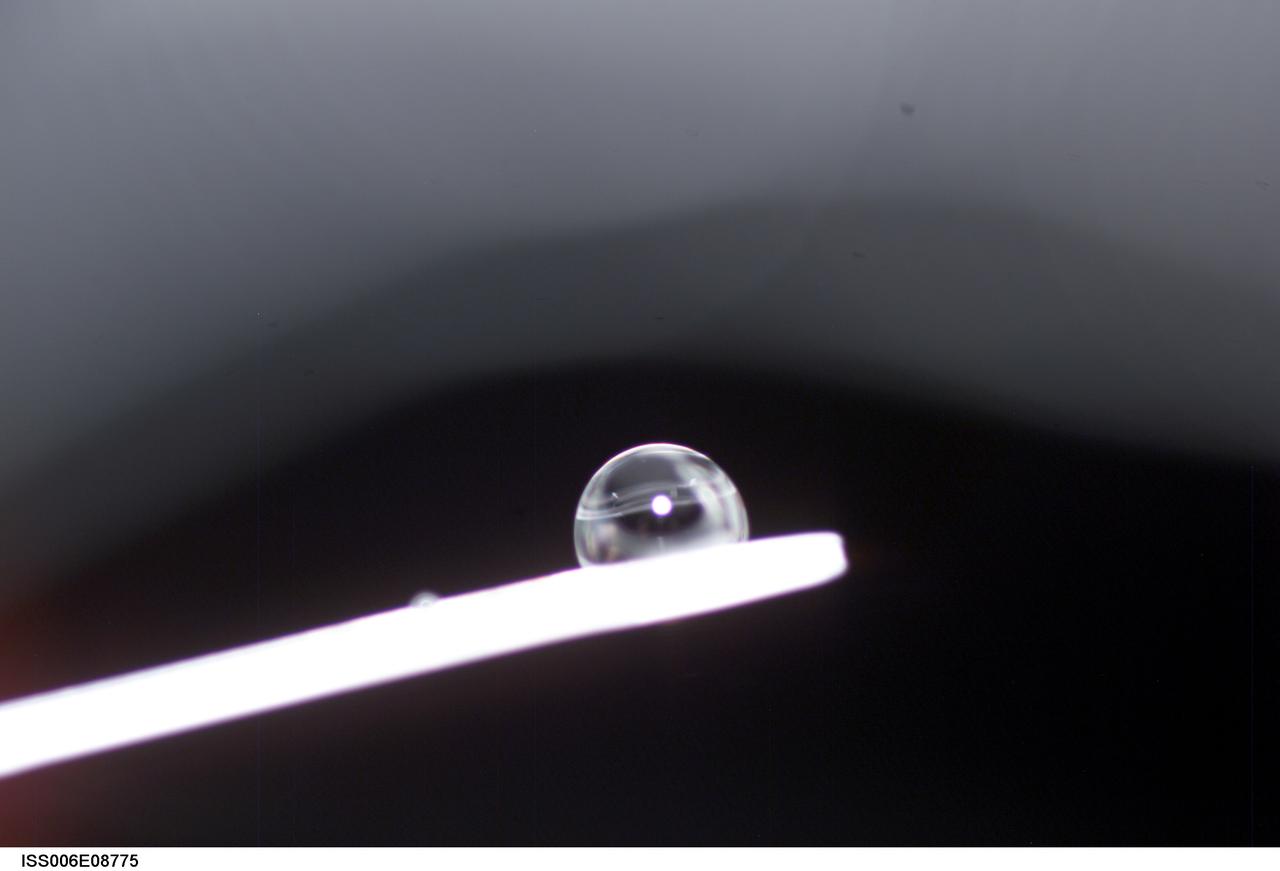

ISS006-E-08775 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
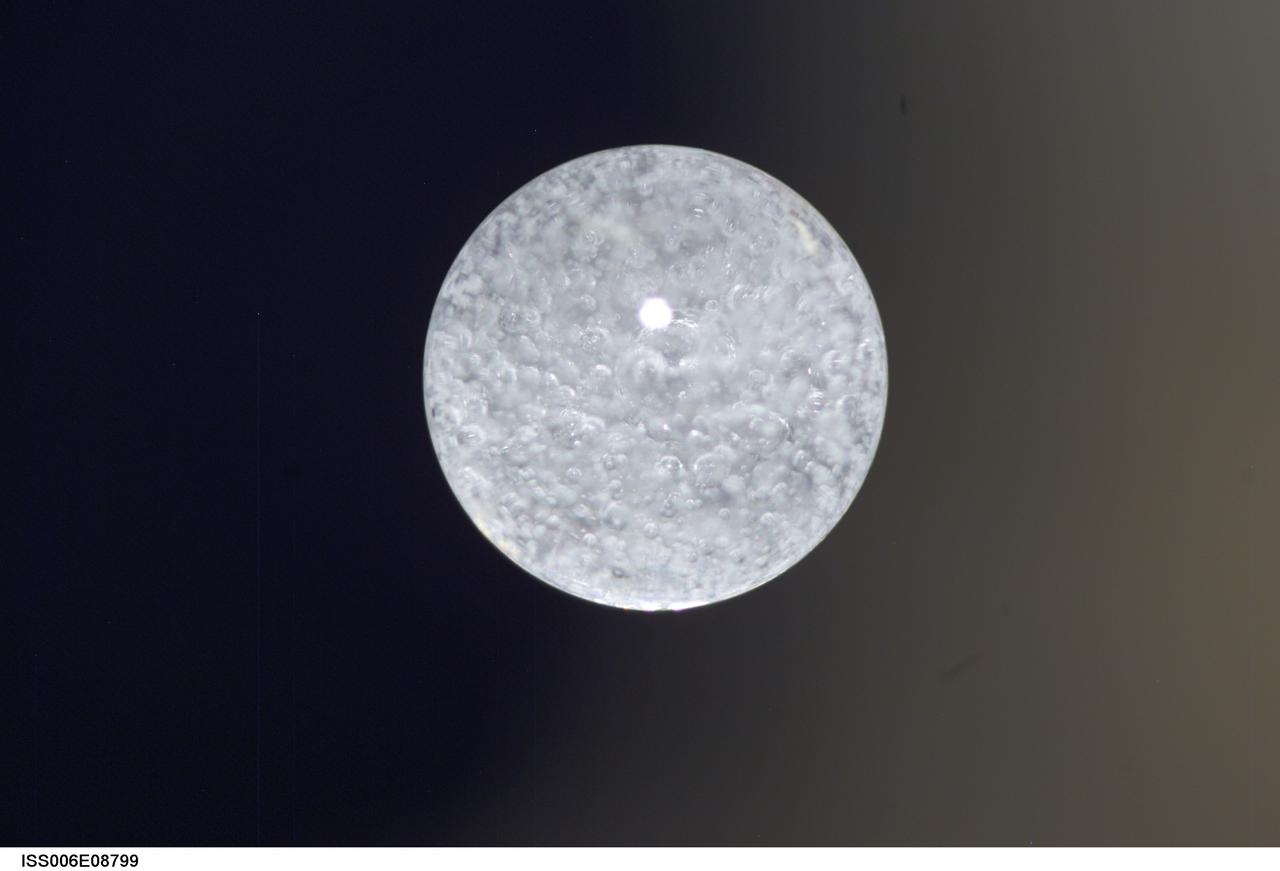

ISS006-E-08799 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
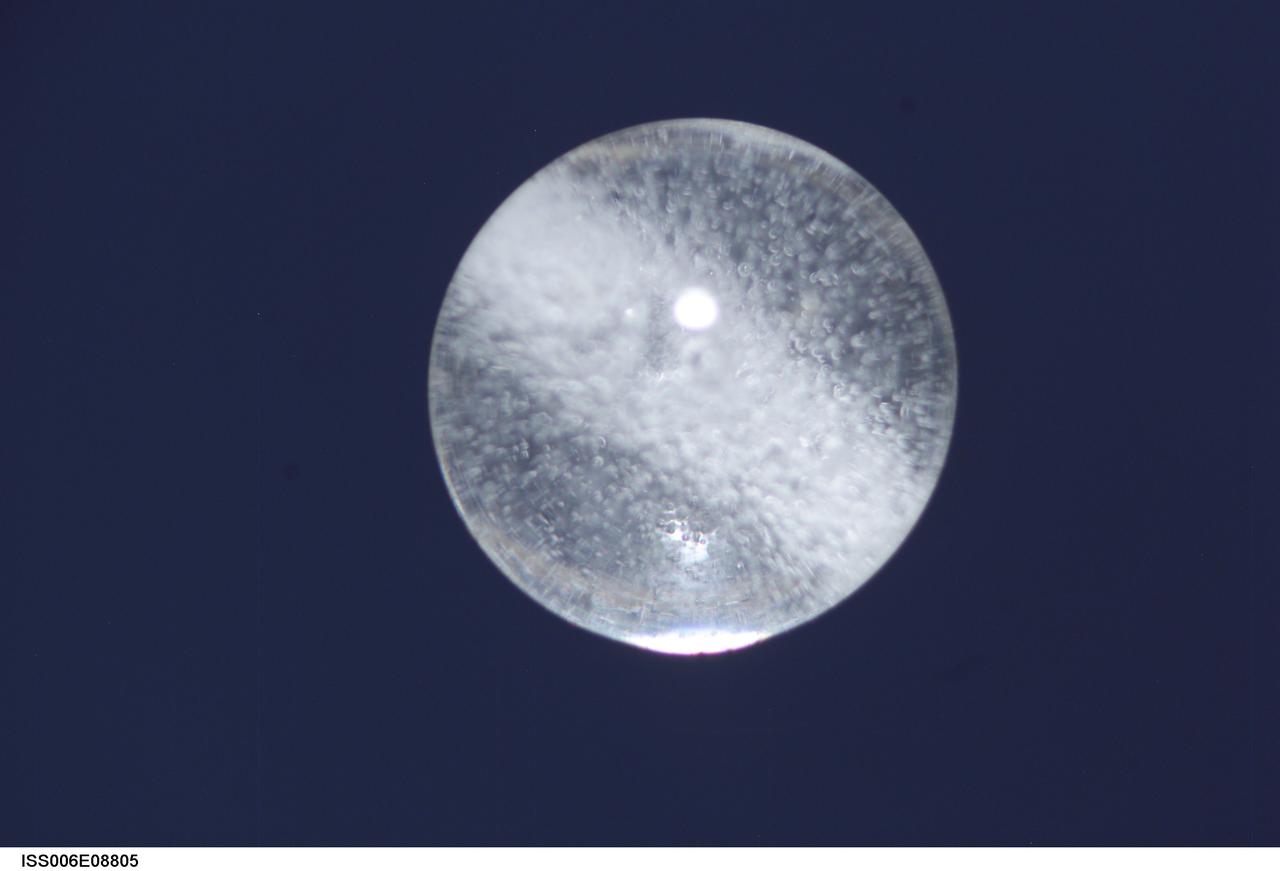
ISS006-E-08805 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
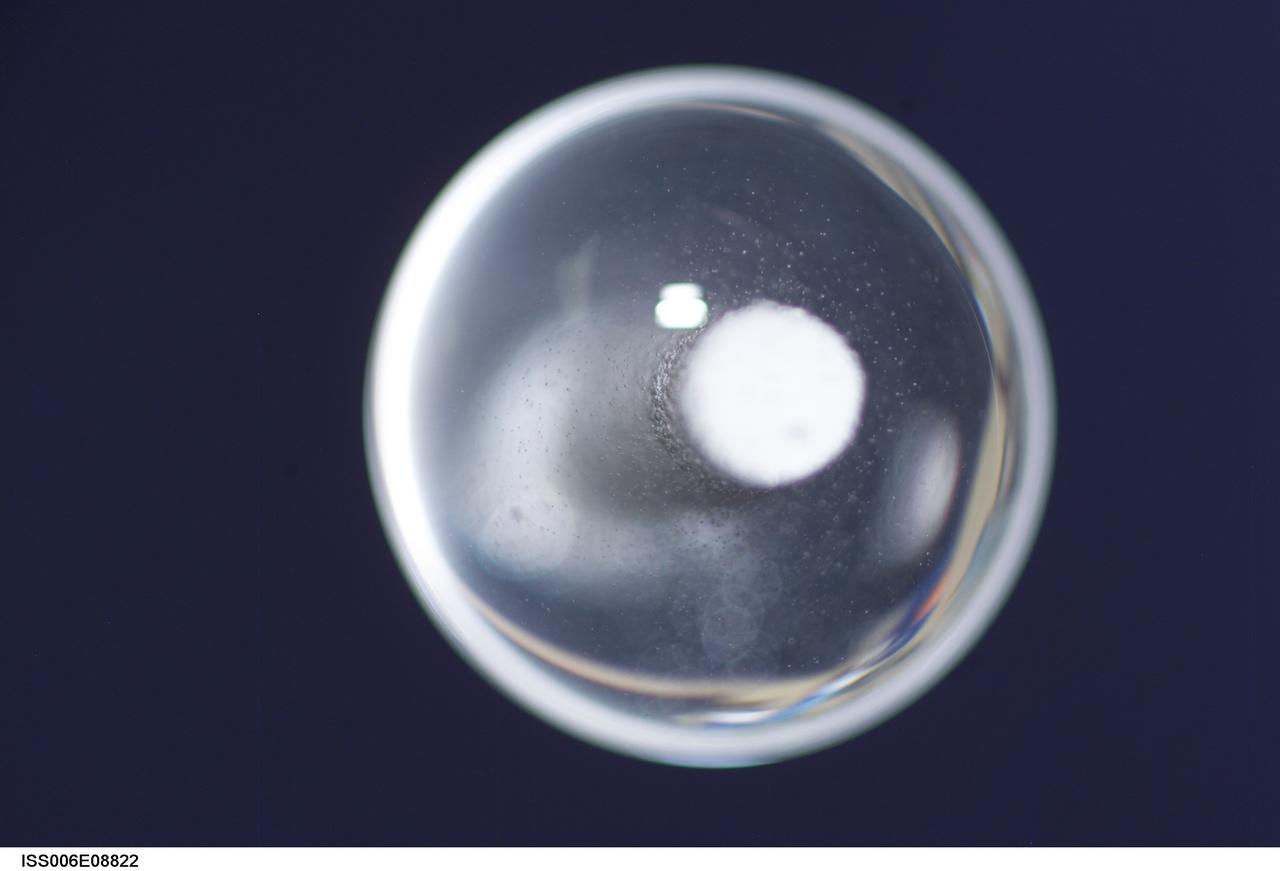
ISS006-E-08822 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
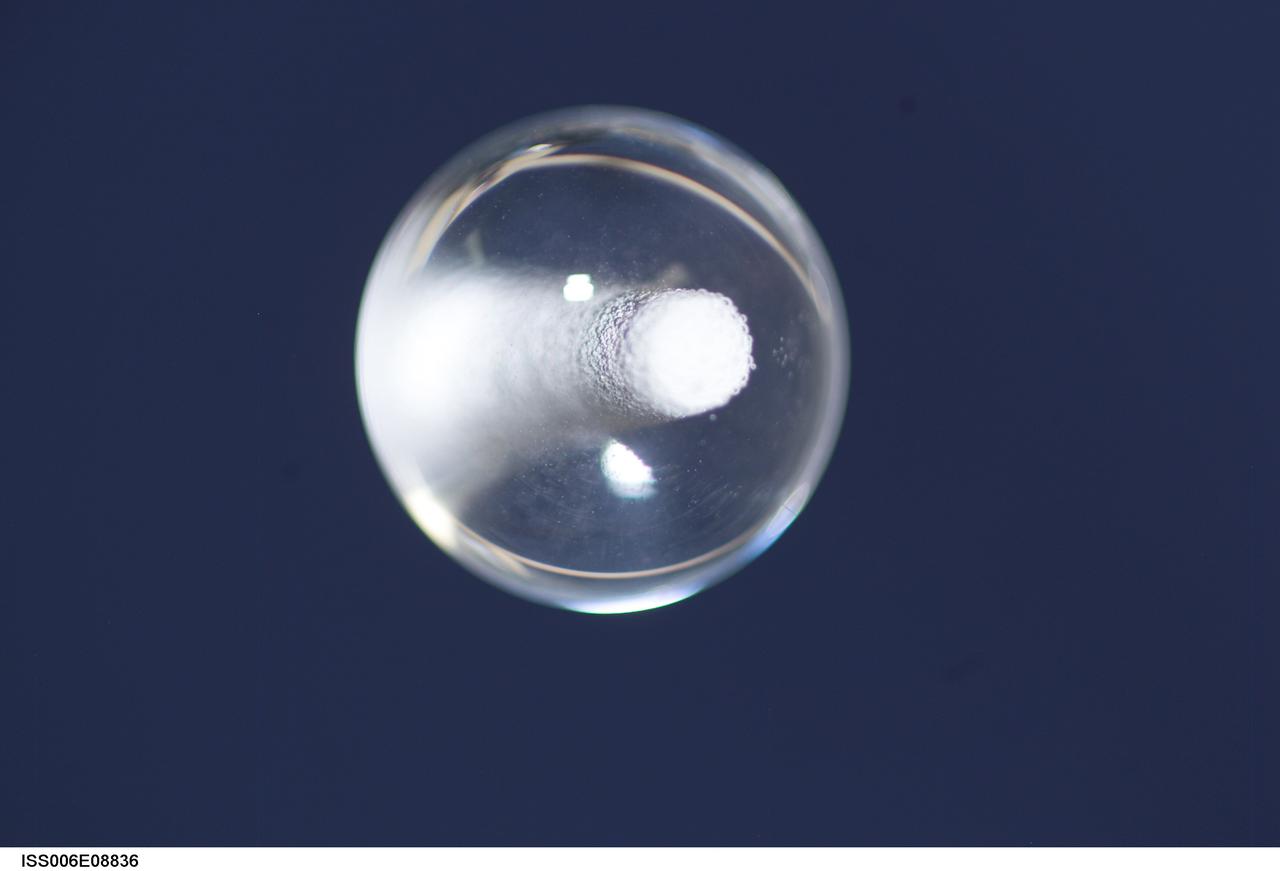
ISS006-E-08836 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
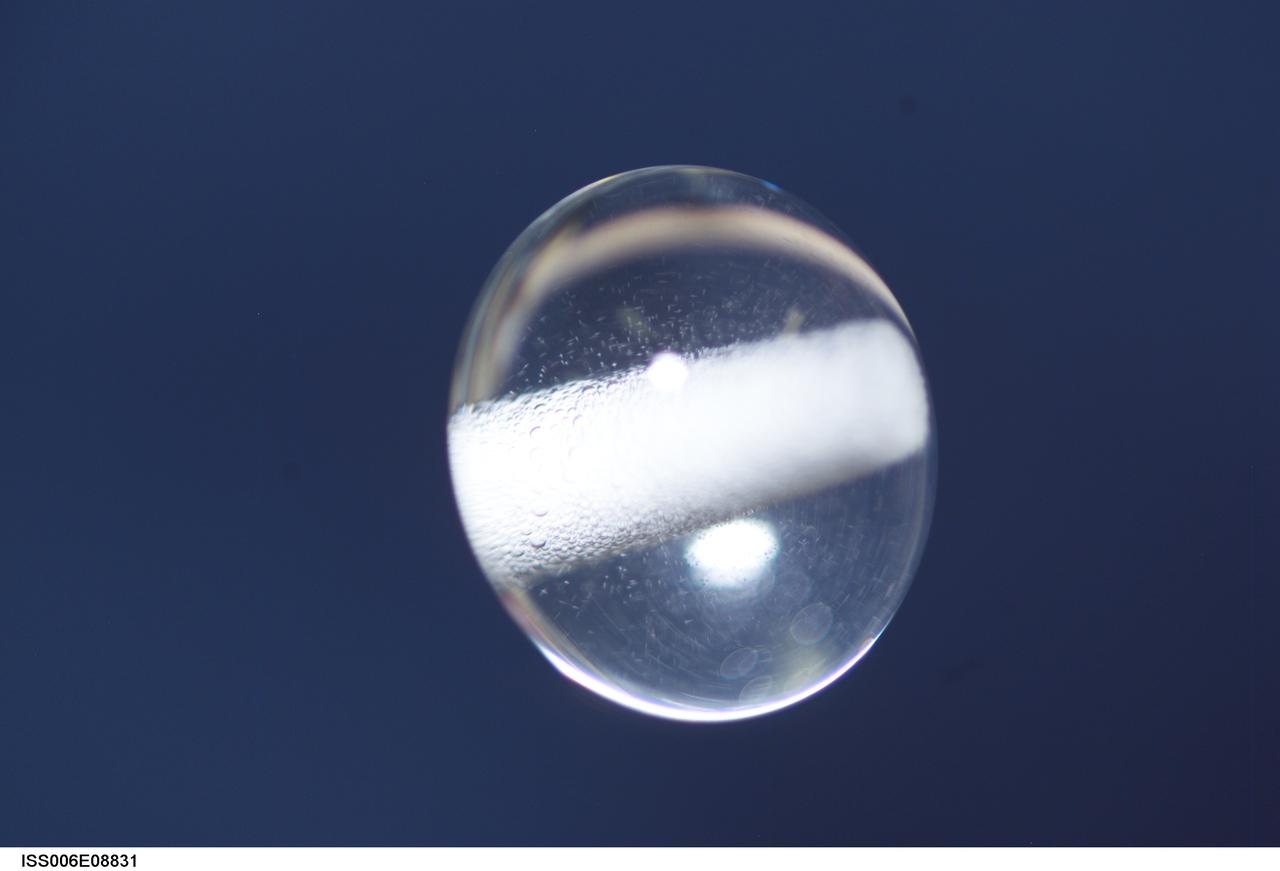

ISS006-E-08831 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
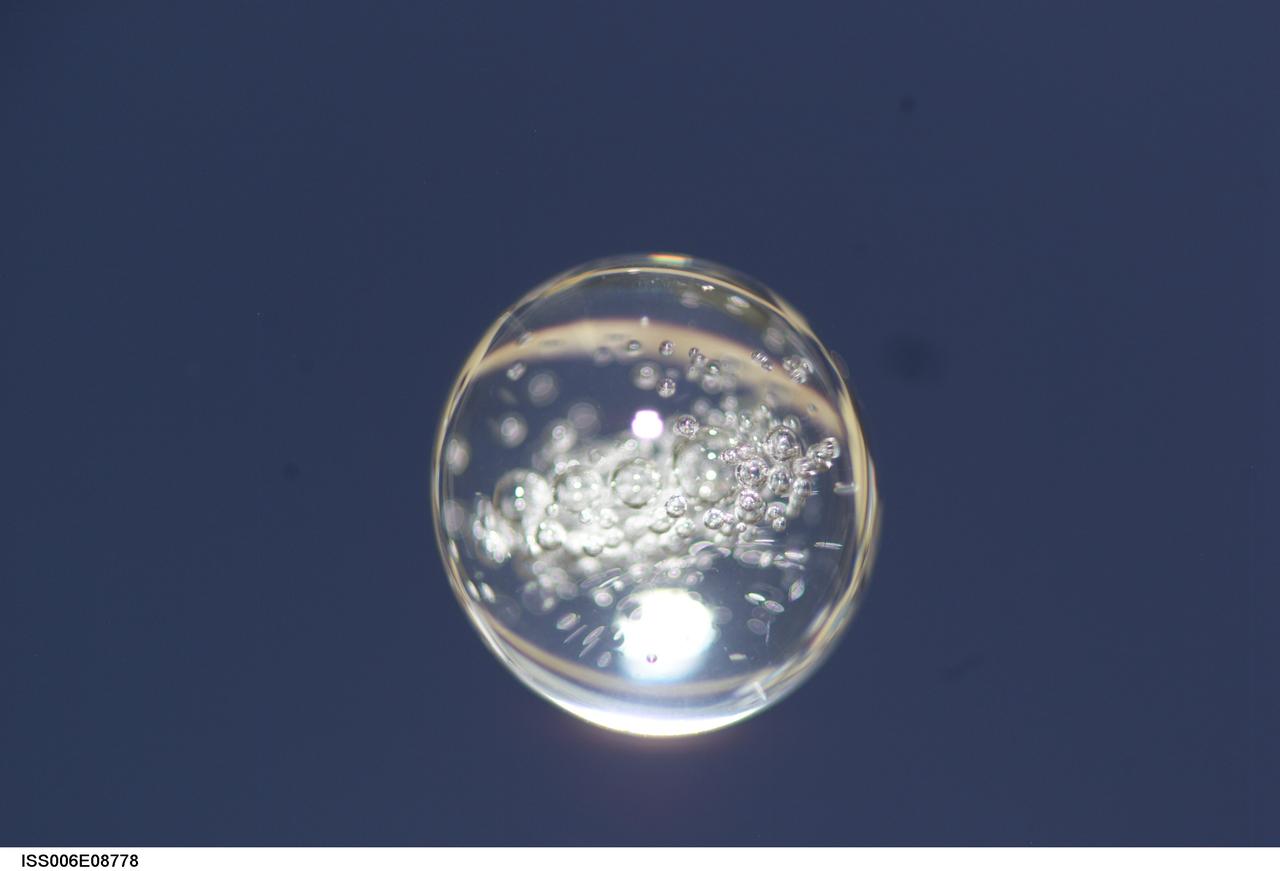
ISS006-E-08778 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
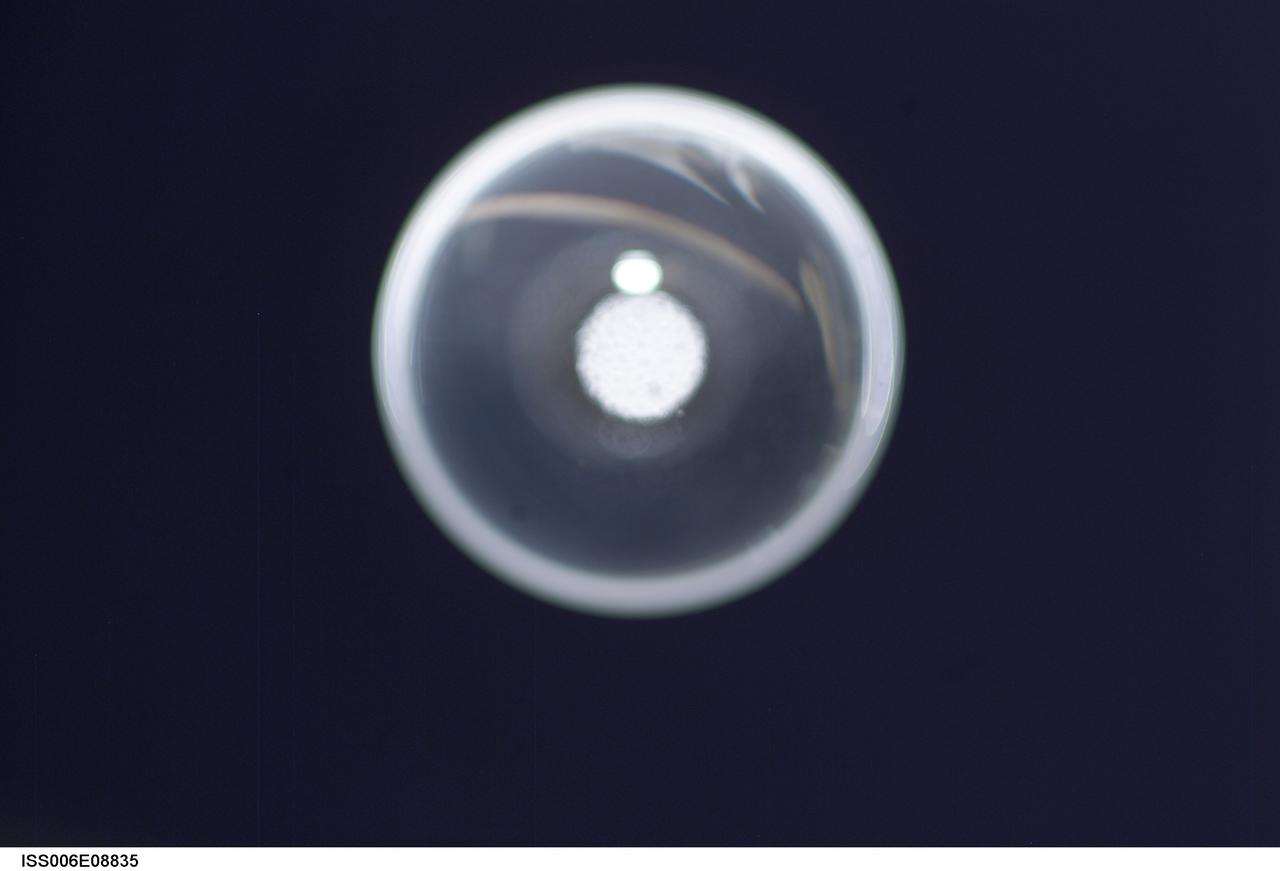

ISS006-E-08835 (14 December 2002) --- View of a bubble formed as a result of a Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) experiment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Expedition Six Commander Kenneth D. Bowersox used a Space Station drill to mix 12 Zeolite samples in clear tubes. Scientists on the ground watching on TV noticed bubbles in the samples. Bowersox used a modified mixing procedure to process autoclaves to isolate bubbles. He re-inserted the samples in the ZCG furnace in Express Rack 2 in the U.S. laboratory/Destiny. This experiment has shown that the bubbles could cause larger number of smaller deformed crystals to grow. Bowersox rotated the samples so that the heavier fluid was thrown to the outside while the lighter bubbles stayed on the inside.
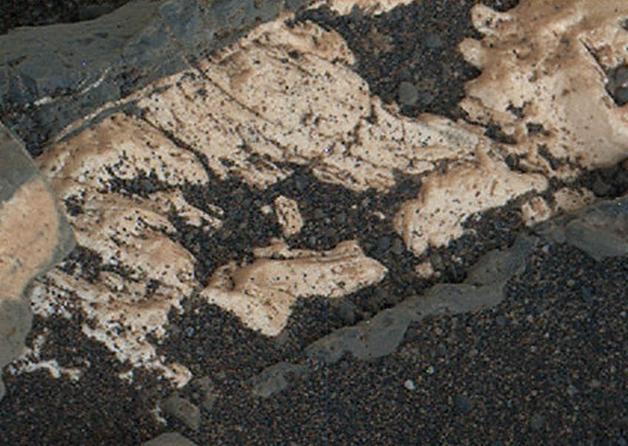

This view from the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on the arm of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows texture within a light-toned vein at a site called "Garden City" on lower Mount Sharp. The area shown is roughly 0.9 inch (2.2 centimeters) wide. It was taken during the 946th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars (April 4, 2015). Differences in textures of light-toned veins in the Garden City complex of crisscrossing mineral veins are clues that these veins may result from distinct fluid events. This vein's texture shows indications of crystal growth, suggesting that crystallization may have exerted a force for opening the fracture filled by the vein. Different examples are at PIA19926 and PIA19927. Mineral veins often form where fluids move through fractured rocks, depositing minerals in the fractures and affecting chemistry of the surrounding rock. At Garden City, the veins have been more resistant to erosion than the surrounding host rock. The fluid movement through fractures at Garden City occurred later than wet environmental conditions in which the host rock formed, before it hardened and cracked. Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego, built and operates MAHLI. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19925

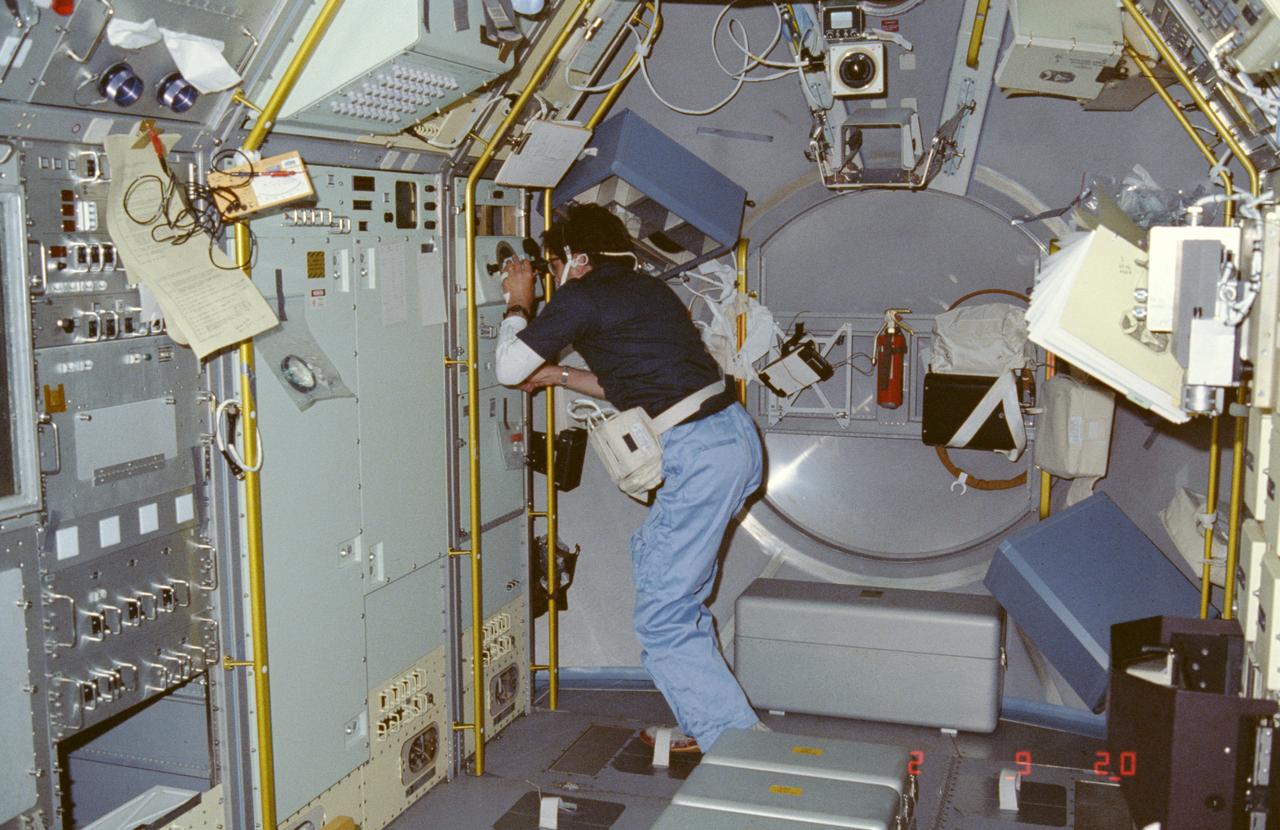
International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. In this photograph, Astronauts Stephen S. Oswald and Norman E. Thagard handle ampoules used in the Mercuric Iodide Crystal Growth (MICG) experiment. Mercury Iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their exceptional electronic properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature rather than at the extremely low temperatures usually required by other materials. Because a bulky cooling system is urnecessary, these crystals could be useful in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and astronomical observation. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).
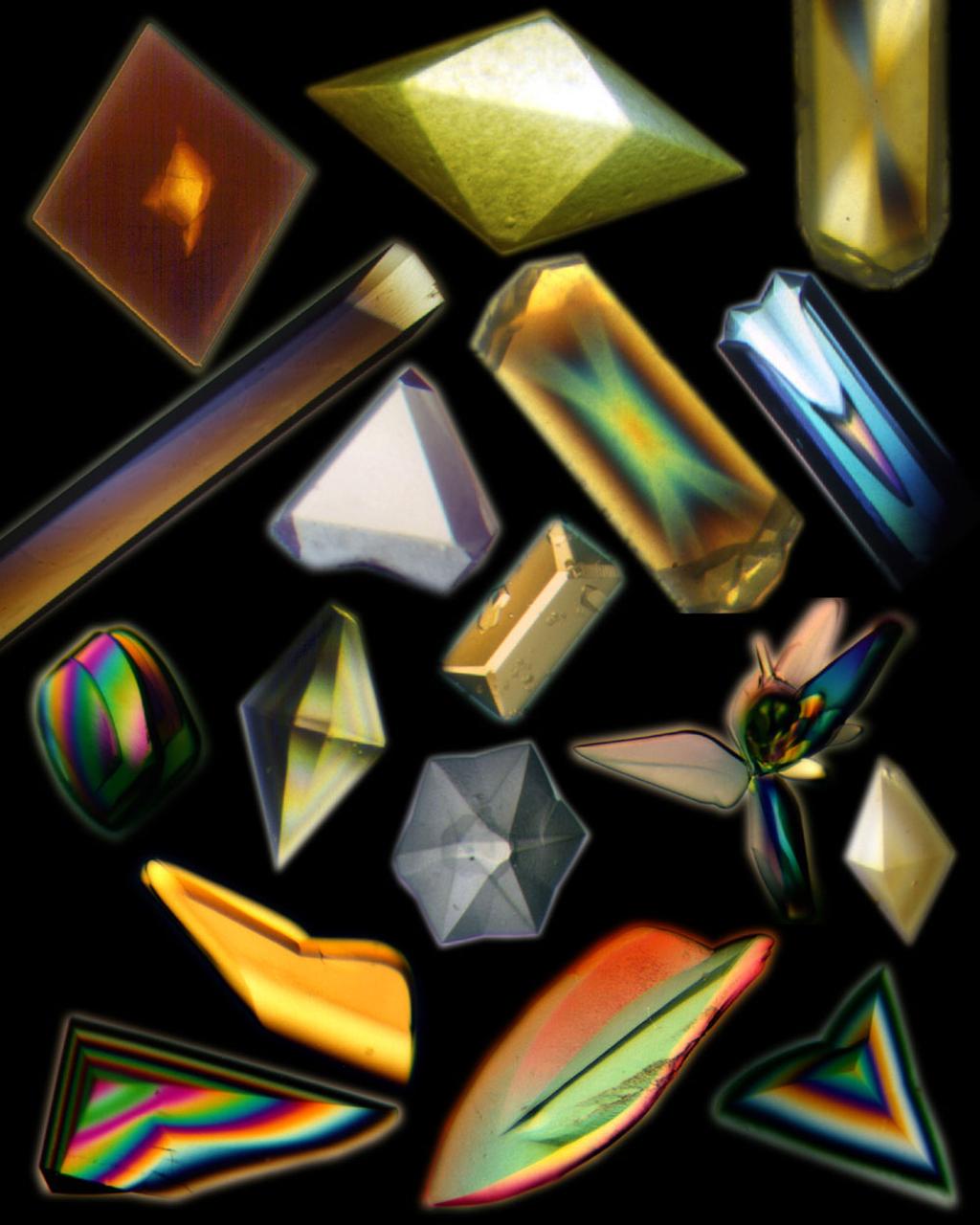

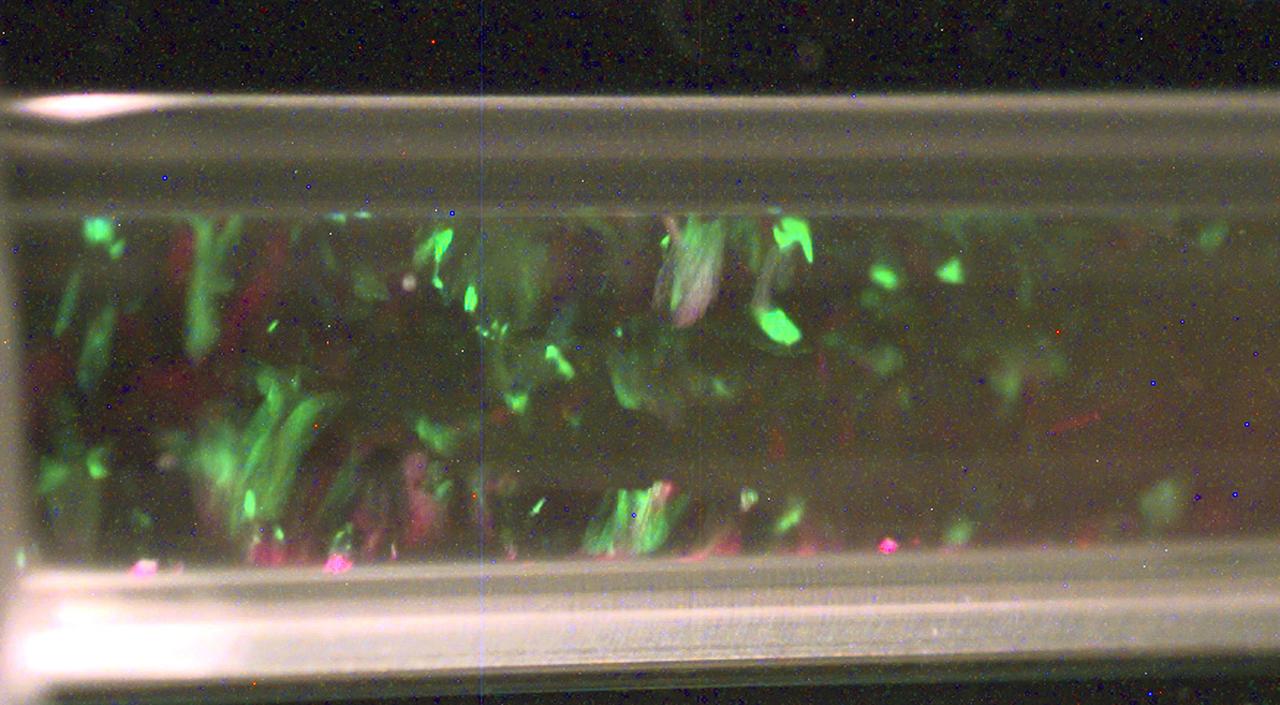
A collage of protein and virus crystals, many of which were grown on the U.S. Space Shuttle or Russian Space Station, Mir. The crystals include the proteins canavalin; mouse monoclonal antibody; a sweet protein, thaumatin; and a fungal protease. Viruses are represented here by crystals of turnip yellow mosaic virus and satellite tobacco mosaic virus. The crystals are photographed under polarized light (thus causing the colors) and range in size from a few hundred microns in edge length up to more than a millimeter. All the crystals are grown from aqueous solutions and are useful for X-ray diffraction analysis. Credit: Dr. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine.
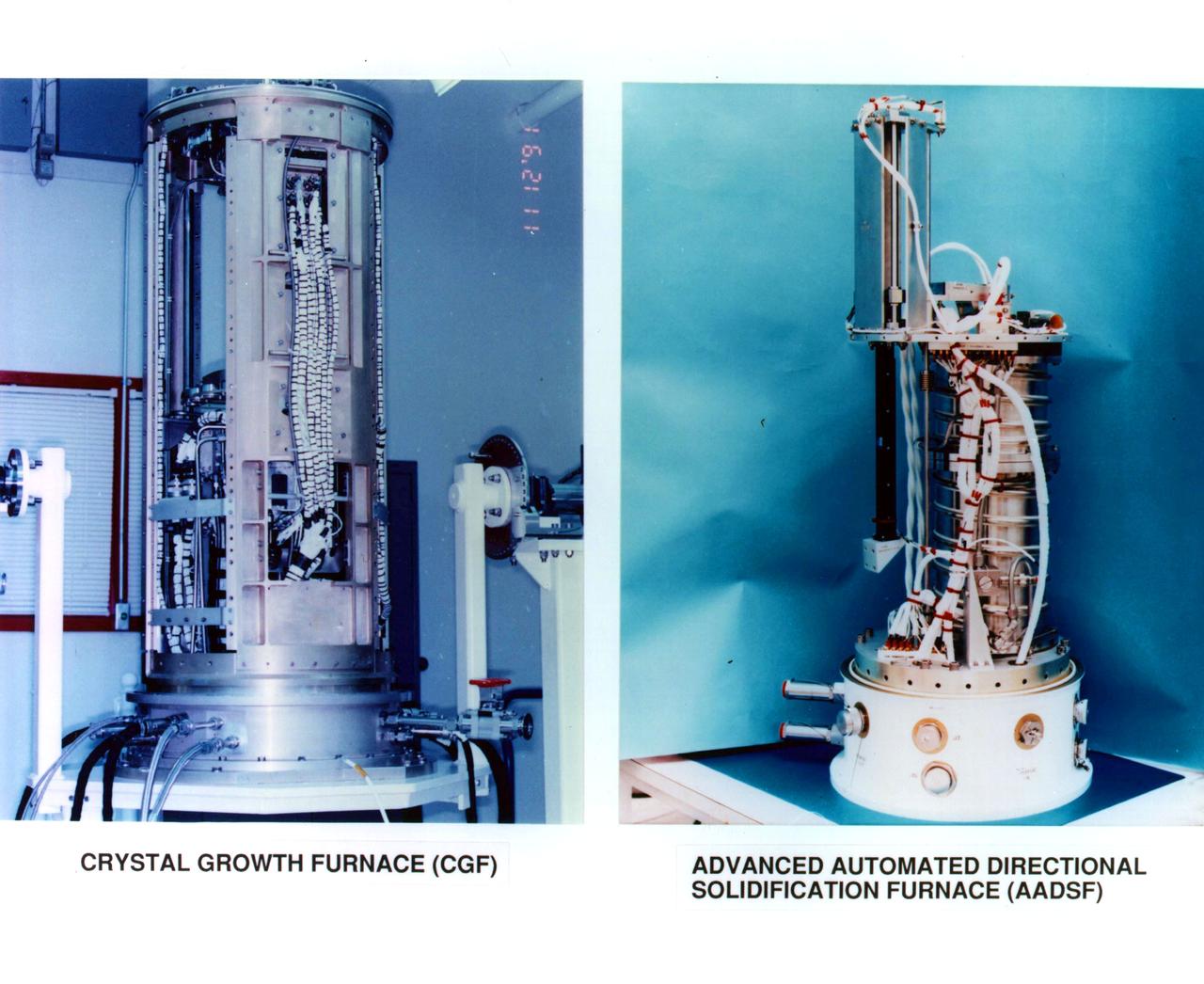
Evolution of Furnaces for Crystal Growth. Left view: Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) Right view: Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF)
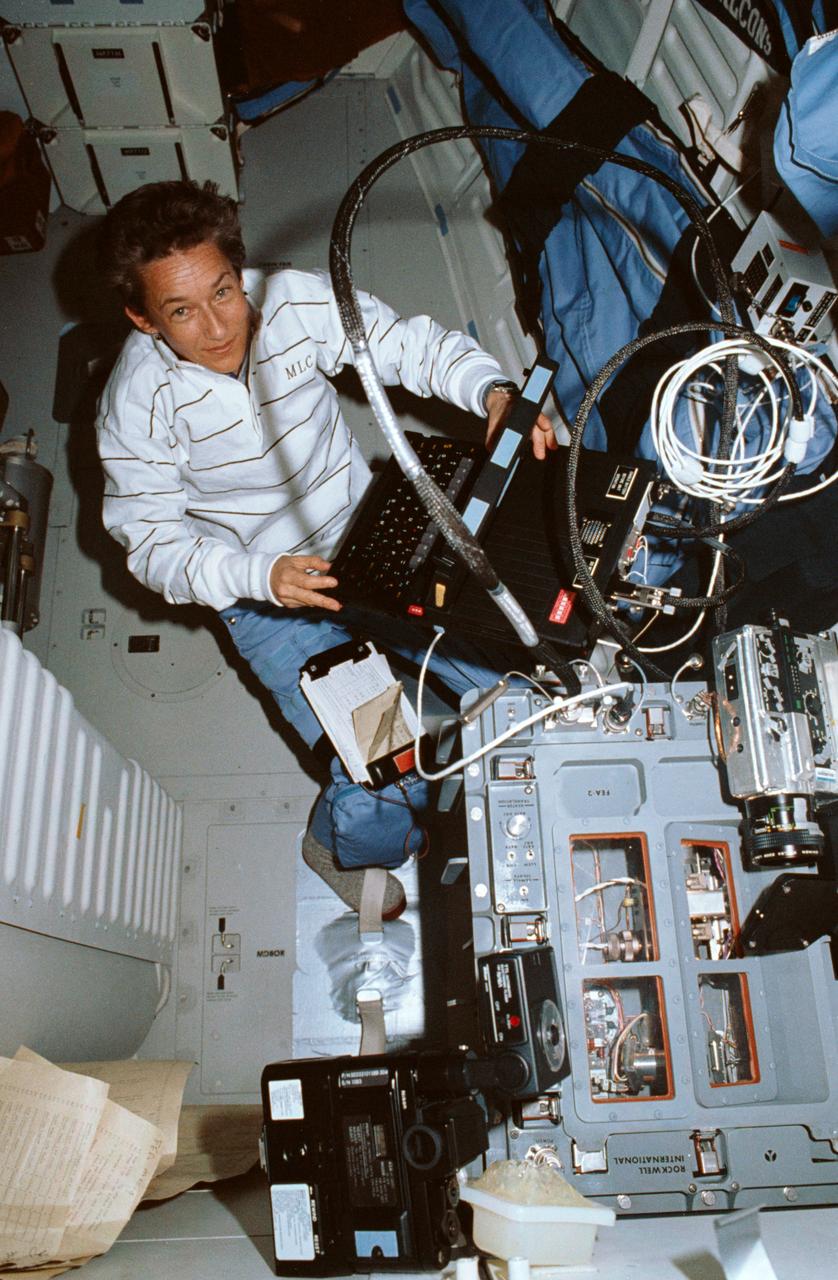

STS030-02-018 (4-8 May 1989) --- A 35mm overall scene of the operations devoted to the fluids experiment apparatus (FEA) aboard Atlantis for NASA’s STS-30 mission. Astronaut Mary L. Cleave, mission specialist, is seen with the computer which is instrumental in the carrying out of a variety of materials science experiments. Rockwell International is engaged in a joint endeavor agreement with NASA’s Office of Commercial Programs in the field of floating zone crystal growth and purification research. The March 1987 agreement provides for microgravity experiments to be performed in the company’s Microgravity Laboratory, the FEA. An 8 mm camcorder which documented details inside the apparatus is visible at bottom of the frame.
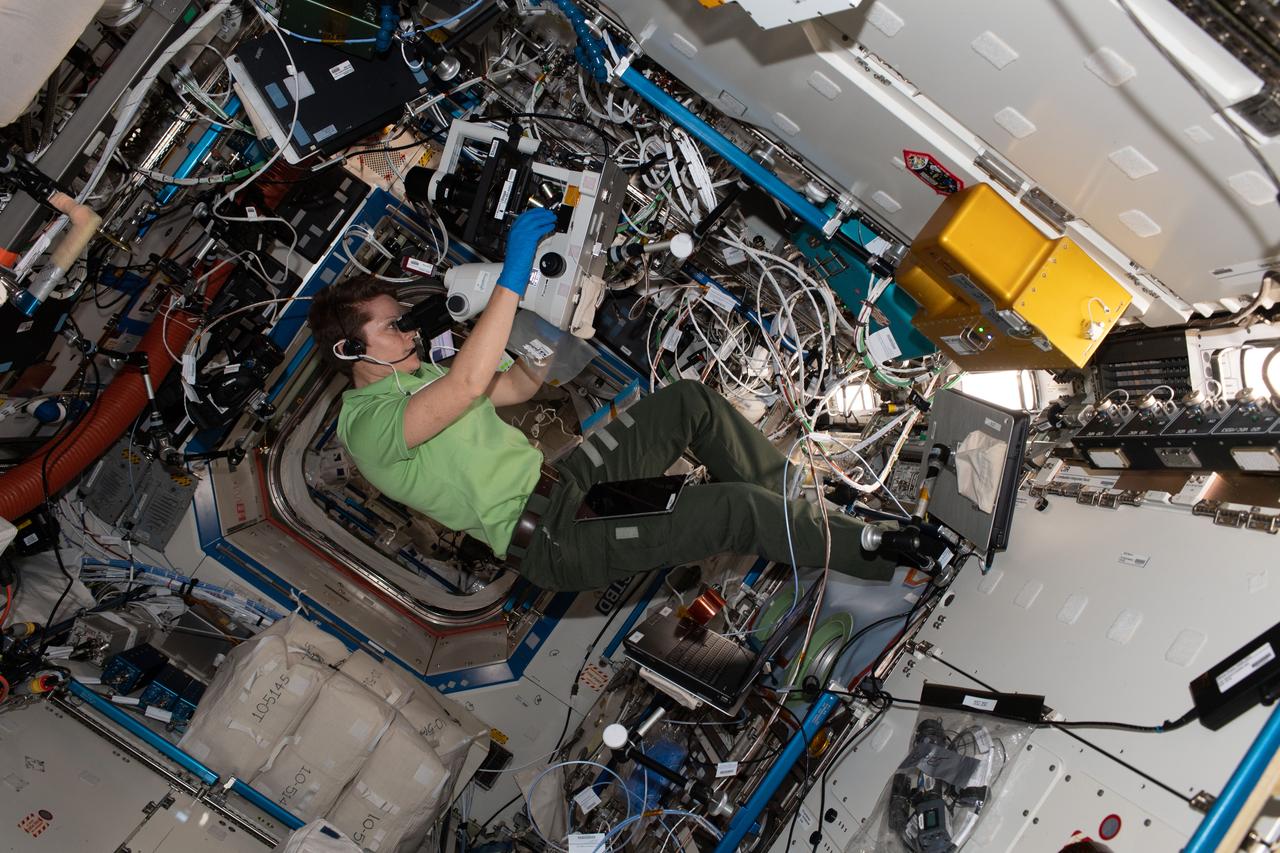

iss058e001945 (Jan. 3, 2019) --- Expedition 58 Flight Engineer and astronaut Anne McClain of NASA peers into a microscope and takes photographs for the Protein Crystal Growth-16 experiment that is exploring therapies for Parkinson's disease.
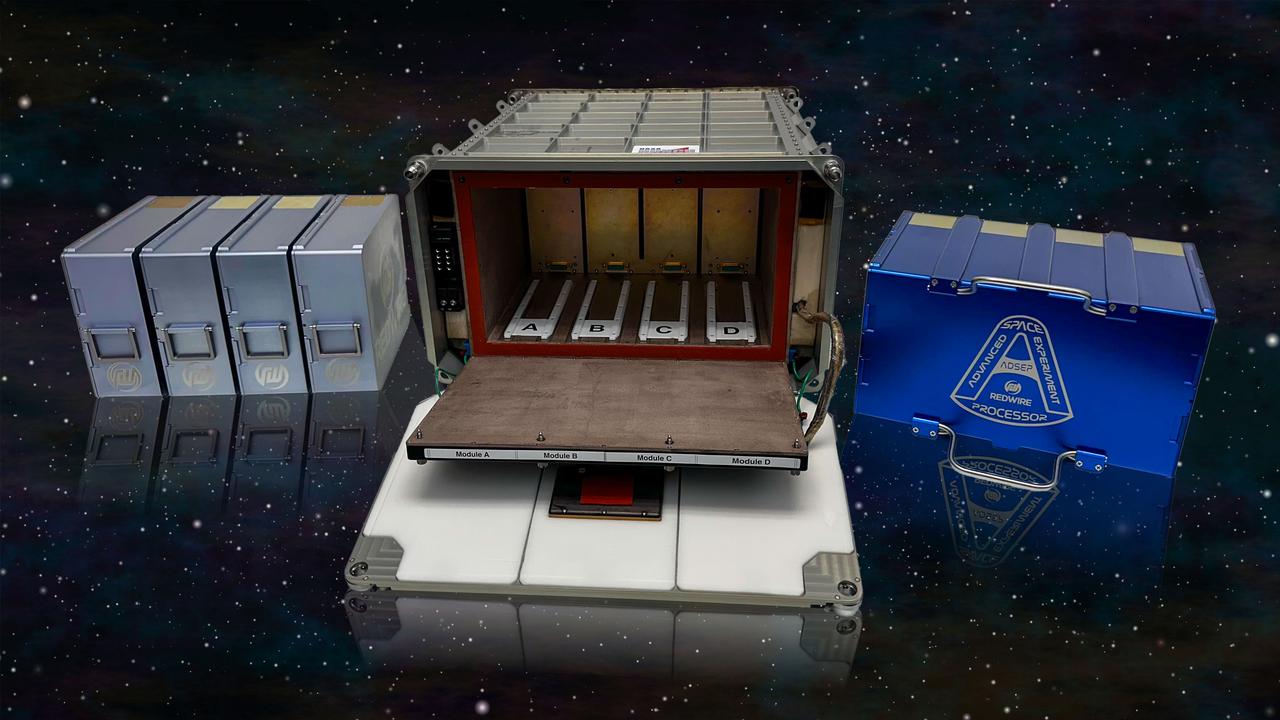

jsc2025e036385 (4/4/2025) --- A lineup of Redwire hardware. Left: Redwire’s in-space pharmaceutical manufacturing system (PIL-BOX) system are chambers that allow crystal growth in small batches. Middle: The Redwire Advanced Space Experiment Processor (ADSEP) in an open configuration onto which either the PIL-BOX or ICC can be installed. Right: The Redwire Industrial Crystallization Cassette (ICC), a facility capable of larger quantities of crystal growth than the PIL-BOX. The ADSEP Industrial Crystallization Cassette Technology Demonstration (ADSEP-ICC) investigation validates the ICC’s capability to grow large quantities of crystals in its high-volume crystal growth chambers aboard the International Space Station. Image courtesy of Redwire.
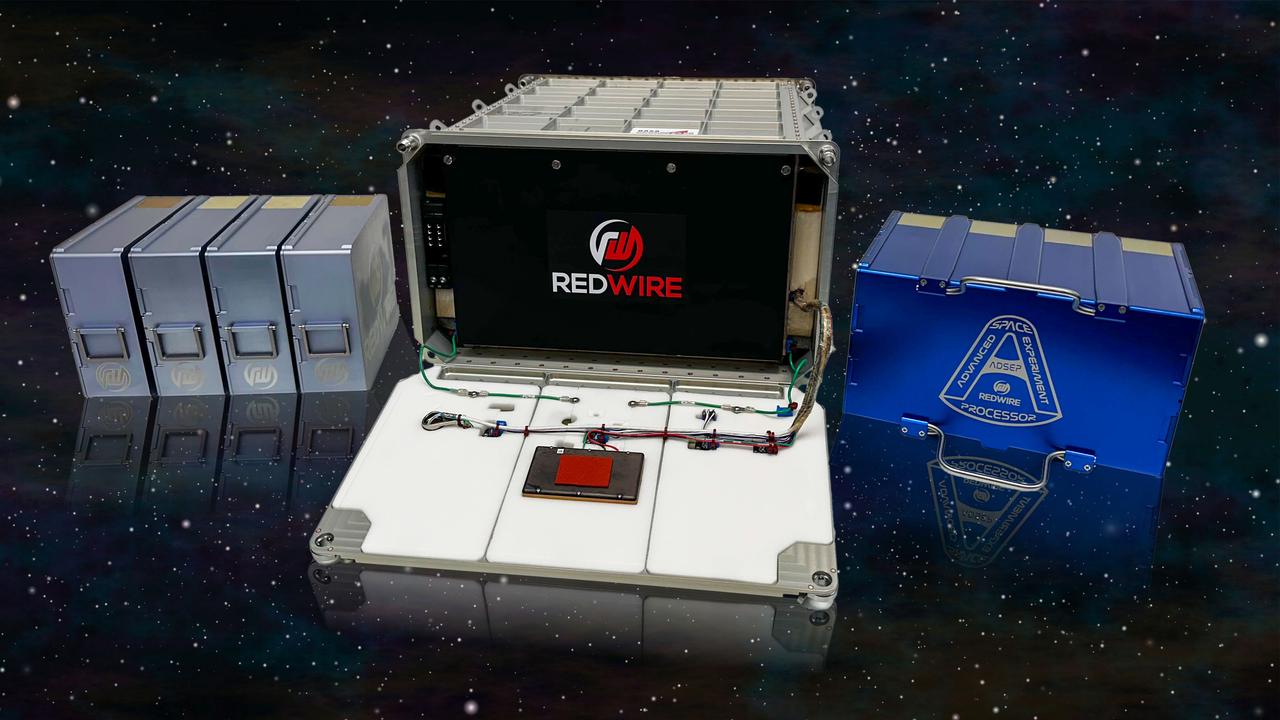

jsc2025e036384 (4/4/2025) --- A lineup of Redwire hardware. Left: Redwire’s in-space pharmaceutical manufacturing system (PIL-BOX) system are chambers that allow crystal growth in small batches. Middle: The Redwire Advanced Space Experiment Processor (ADSEP) in a close configuration onto which either the PIL-BOX or ICC can be installed. Right: The Redwire Industrial Crystallization Cassette (ICC), a facility capable of larger quantities of crystal growth than the PIL-BOX. The ADSEP Industrial Crystallization Cassette Technology Demonstration (ADSEP-ICC) investigation validates the ICC’s capability to grow large quantities of crystals in its high-volume crystal growth chambers aboard the International Space Station. Image courtesy of Redwire.

Facilitates the incorporation of glucose into cells. In diabetics, there is either a decrease in or complete lack of insulin, therby leading to several harmful complications. Principal Investigator was Charles Bugg.
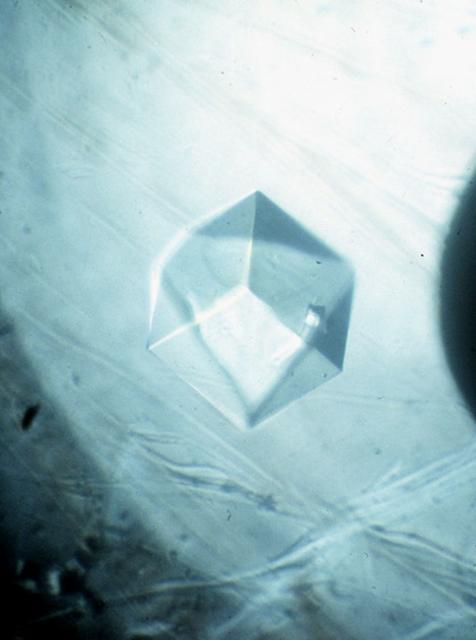
Malic Enzyme is a target protein for drug design because it is a key protein in the life cycle of intestinal parasites. After 2 years of effort on Earth, investigators were unable to produce any crystals that were of high enough quality and for this reason the structure of this important protein could not be determined. Crystals obtained from one STS-50 were of superior quality allowing the structure to be determined. This is just one example why access to space is so vital for these studies. Principal Investigator is Larry DeLucas.

Payload Commander, Bornie Dunbar activating ZCG autoclave onboard STS-50, USML-1
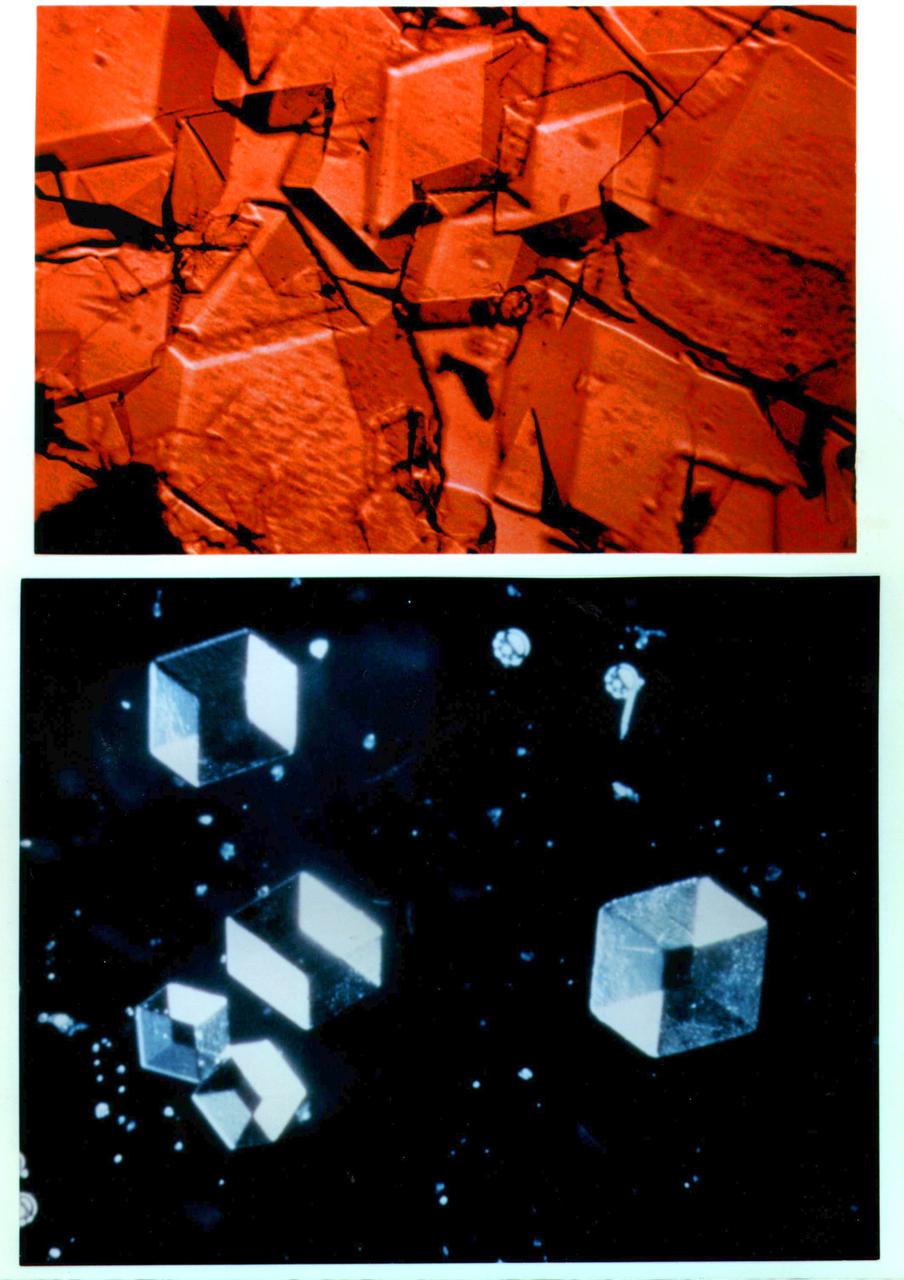
The major storage protein of leguminous plants and a major source of dietary protein for humans and domestic animals. It is studied in efforts to enhance nutritional value of proteins through protein engineerings. It is isolated from Jack Bean because of it's potential as a nutritional substance. Principal Investigator was Alexander McPherson.
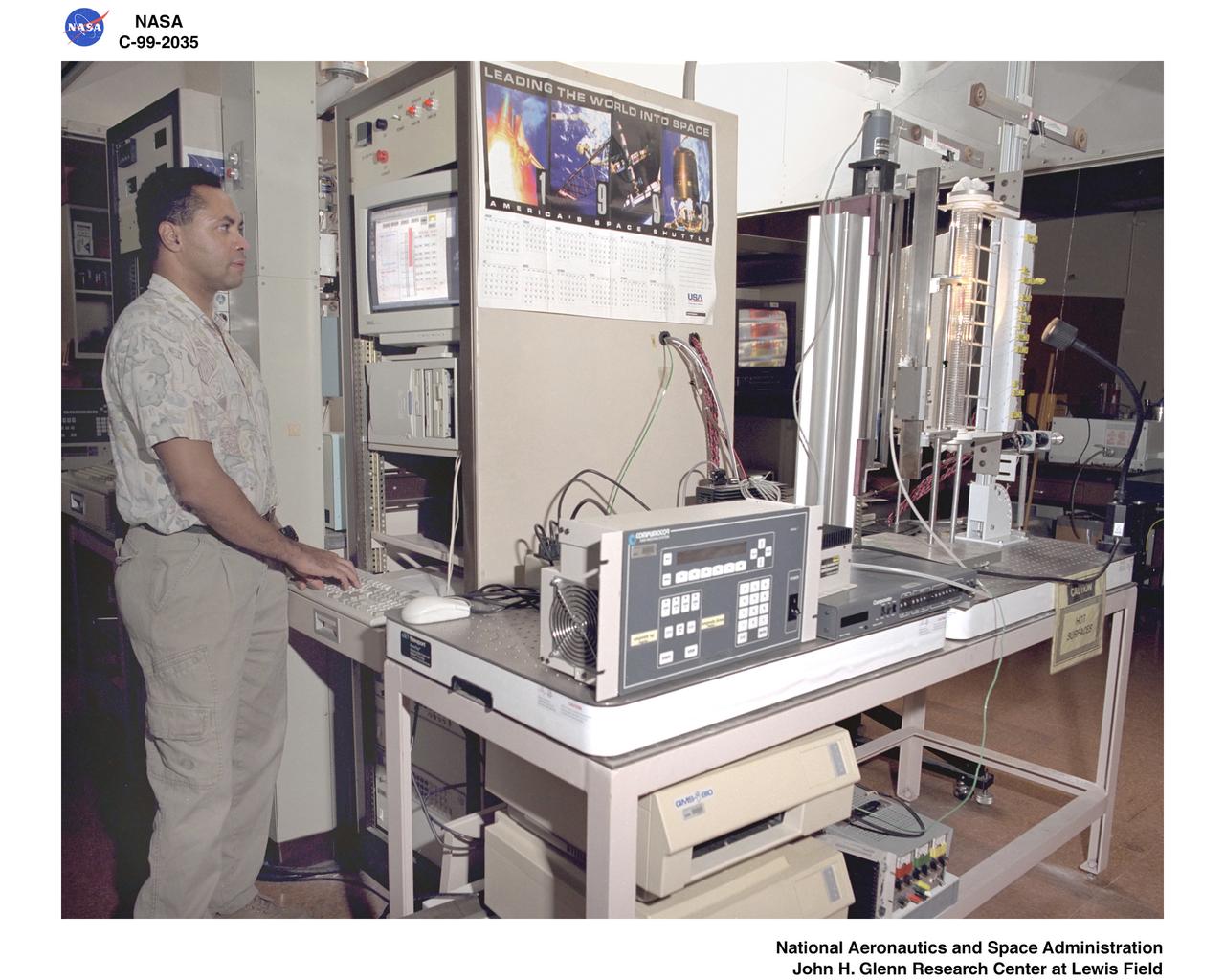

CRYSTAL GROWTH EXPERIMENTS MULTI ZONE TRANSPARENT FURNACE
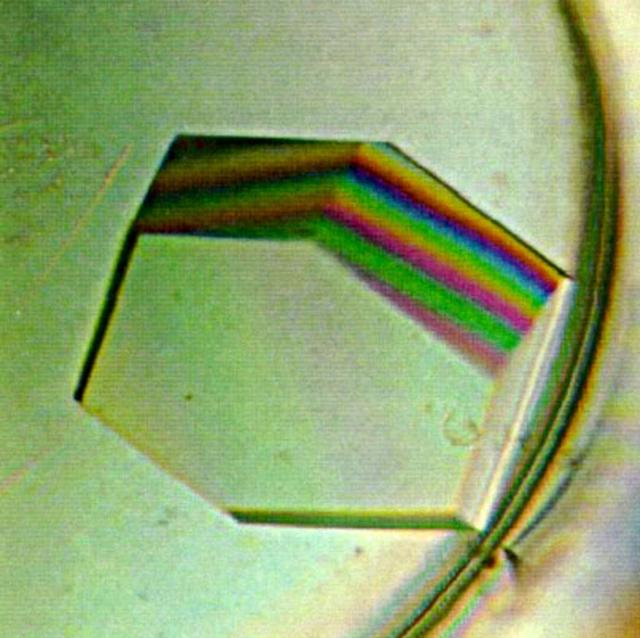
Lysozyme crystal grown on STS-81. A protein model for documentation of the effects of microgravity on crystal growth. Principal Investigator Dan Carter of New Century Pharmaceuticals.
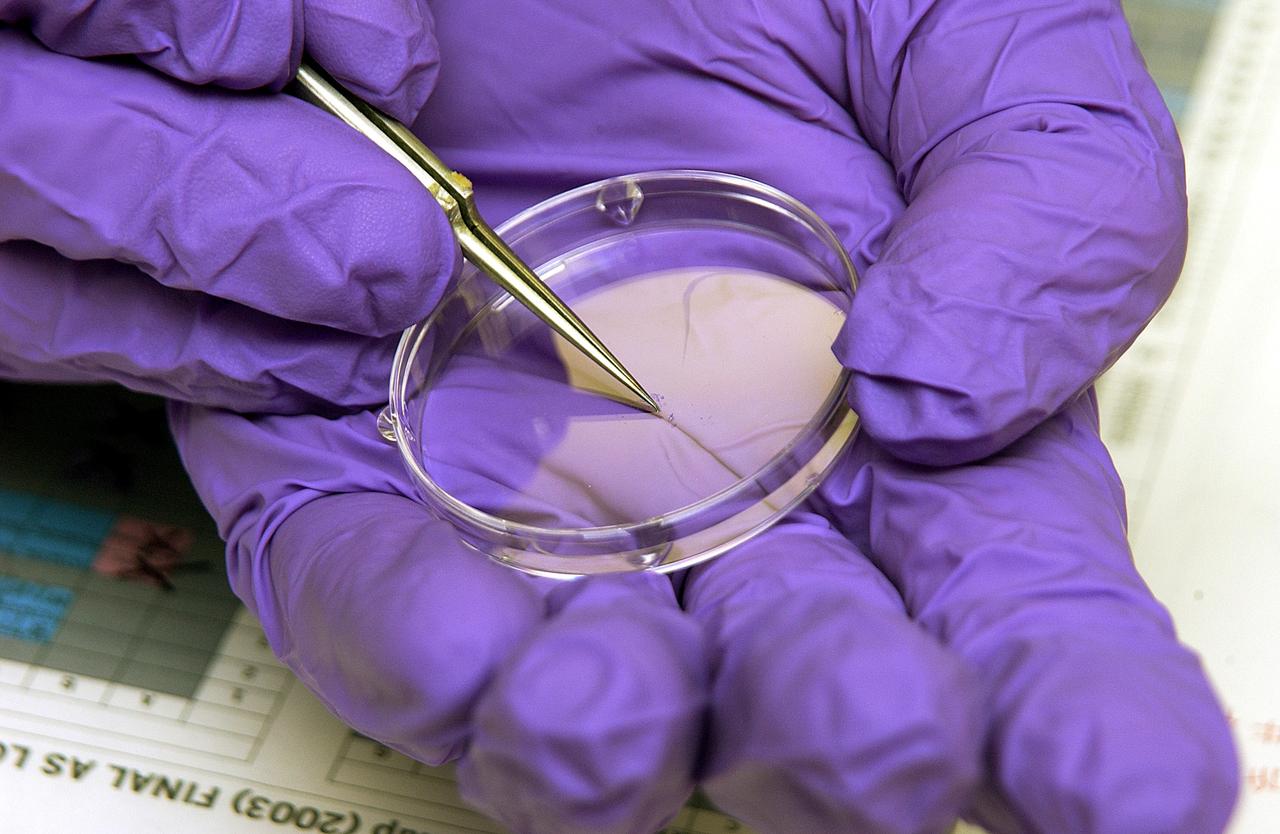
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The crystals visible in this laboratory dish were part of an experiment carried on mission STS-107. Several experiments were found during the search for Columbia debris. Included in the Commercial ITA Biomedical Experiments payload on mission STS-107 are urokinase cancer research, microencapsulation of drugs, the Growth of Bacterial Biofilm on Surfaces during Spaceflight (GOBBSS), and tin crystal formation.
![iss035e006283 (3/18/2013) --- Photo documentation of the Hicari (Growth of Homogeneous Silicon-Germanium [SiGe] Crystals in Microgravity by the Traveling Liquidous Zone [TLZ] Method) Experiment Sample Cartridge (SC) following its removal from the Kobairo Rack during Expedition 35. The materials science investigation Growth of Homogeneous SiGe Crystals in Microgravity by the TLZ Method (Hicari) aims to verify the crystal-growth by Travelling Liquidous Zone method, and to produce high-quality crystals of Silicon-Germanium (SiGe) semiconductor using the Japanese Experiment Module-Gradient Heating Furnace (JEM-GHF).](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss035e006283/iss035e006283~medium.jpg)
iss035e006283 (3/18/2013) --- Photo documentation of the Hicari (Growth of Homogeneous Silicon-Germanium [SiGe] Crystals in Microgravity by the Traveling Liquidous Zone [TLZ] Method) Experiment Sample Cartridge (SC) following its removal from the Kobairo Rack during Expedition 35. The materials science investigation Growth of Homogeneous SiGe Crystals in Microgravity by the TLZ Method (Hicari) aims to verify the crystal-growth by Travelling Liquidous Zone method, and to produce high-quality crystals of Silicon-Germanium (SiGe) semiconductor using the Japanese Experiment Module-Gradient Heating Furnace (JEM-GHF).
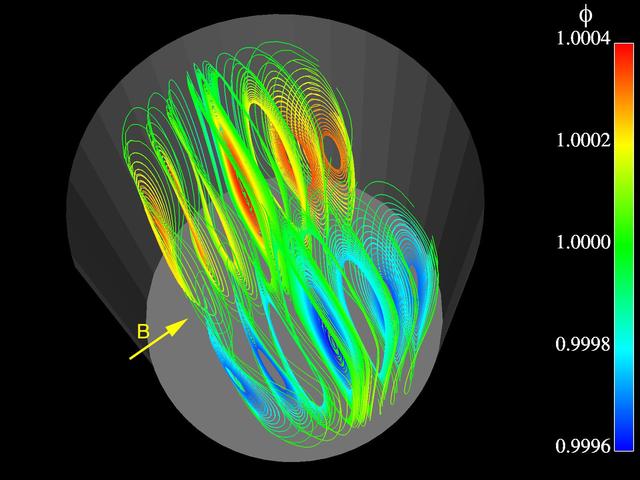
Advanced finite element models are used to study three-dimensional, time-dependent flow and segregation in crystal growth systems. In this image of a prototypical model for melt and crystal growth, pathlines at one instant in time are shown for the flow of heated liquid silicon in a cylindrical container. The container is subjected to g-jitter disturbances along the vertical axis. A transverse magnetic field is applied to control them. Such computations are extremely powerful for understanding melt growth in microgravity where g-jitter drives buoyant flows. The simulation is part of the Theoretical Analysis of 3D, Transient Convection and Segregation in Microgravity Bridgman Crystal Growth investigation by Dr. Jeffrey J. Derby of the University of Mirnesota, Minneapolis.
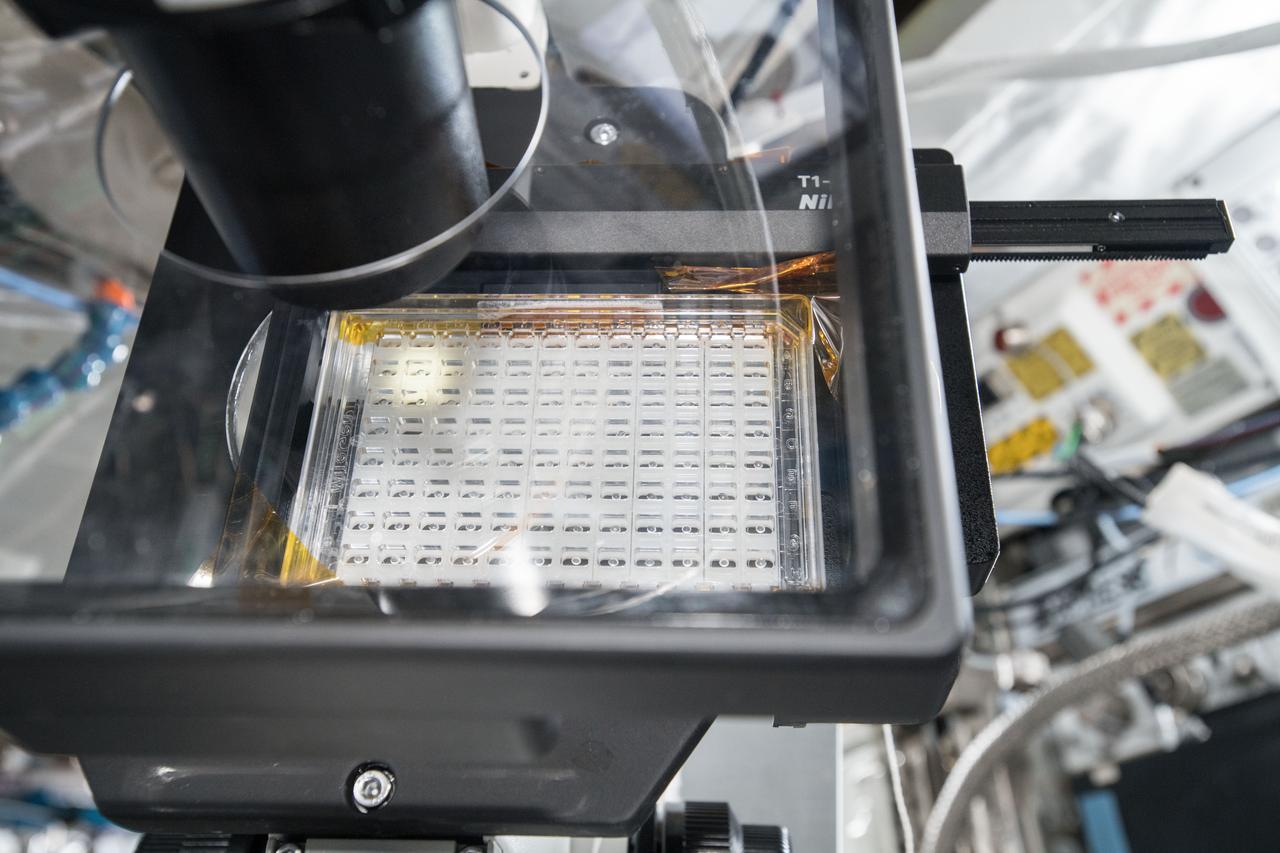
iss057e106419 (Nov. 30, 2018) --- Samples from the Protein Crystal Growth Card are examined using a microscope for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
iss057e106417 (Nov. 30, 2018) --- Samples from the Protein Crystal Growth Card are examined using a microscope for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
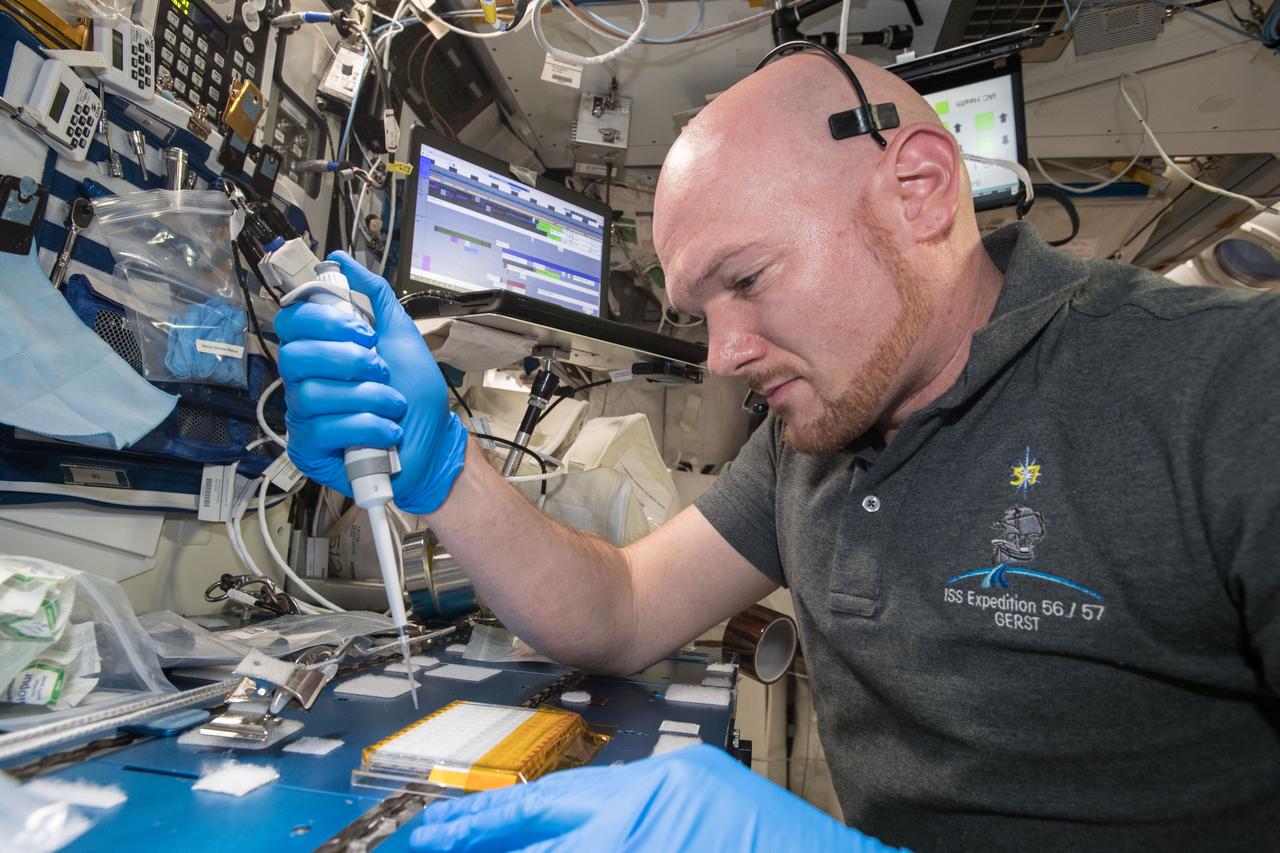

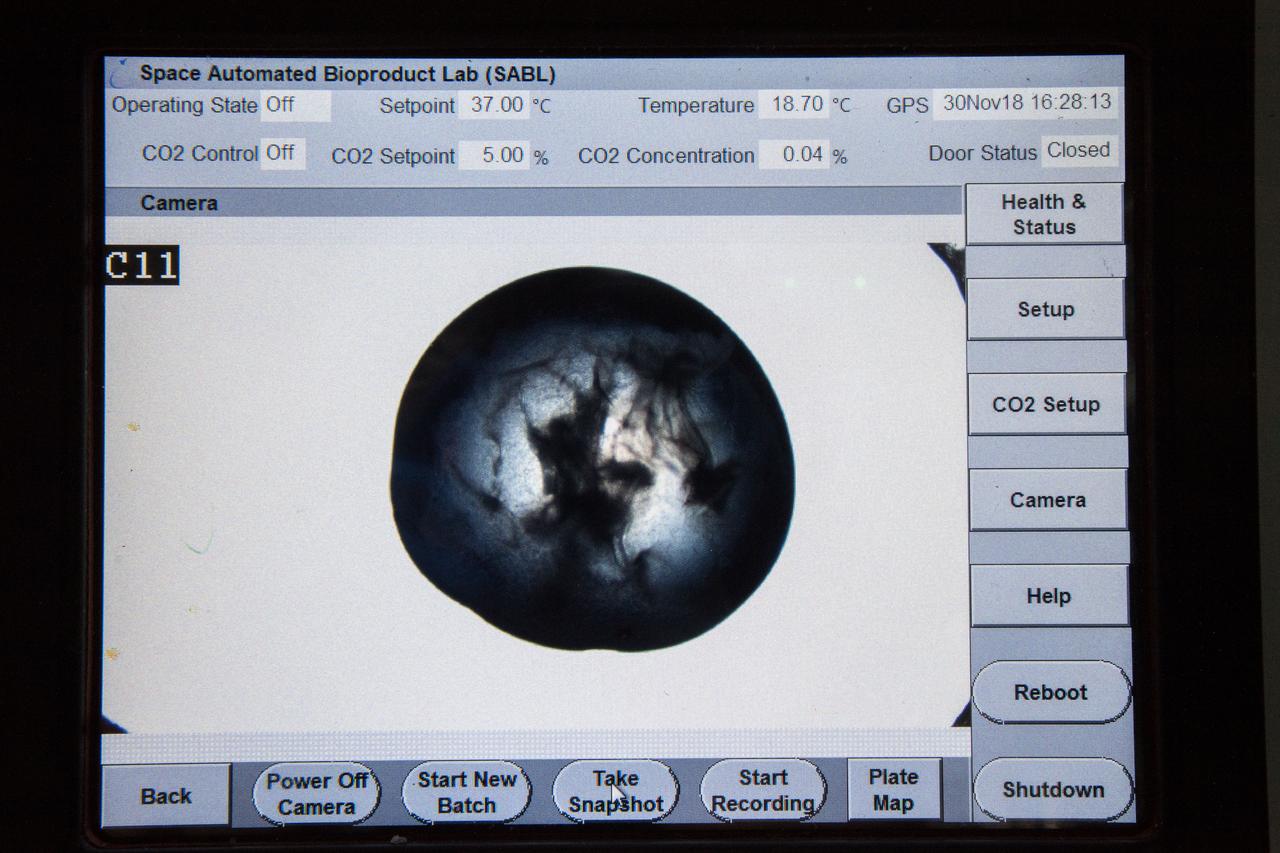
iss057e106231 (Nov. 26, 2018) --- European Space Agency (ESA) asrtonaut Alexander Gerst uses a uses a pipette to transfer a protein solution into the Protein Crystal Growth Card for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Valerie Cassanto is one of the scientists recovering experiments found during the search for Columbia debris. Included in the Commercial ITA Biomedical Experiments payload on mission STS-107 are urokinase cancer research, microencapsulation of drugs, the Growth of Bacterial Biofilm on Surfaces during Spaceflight (GOBBSS), and tin crystal formation.
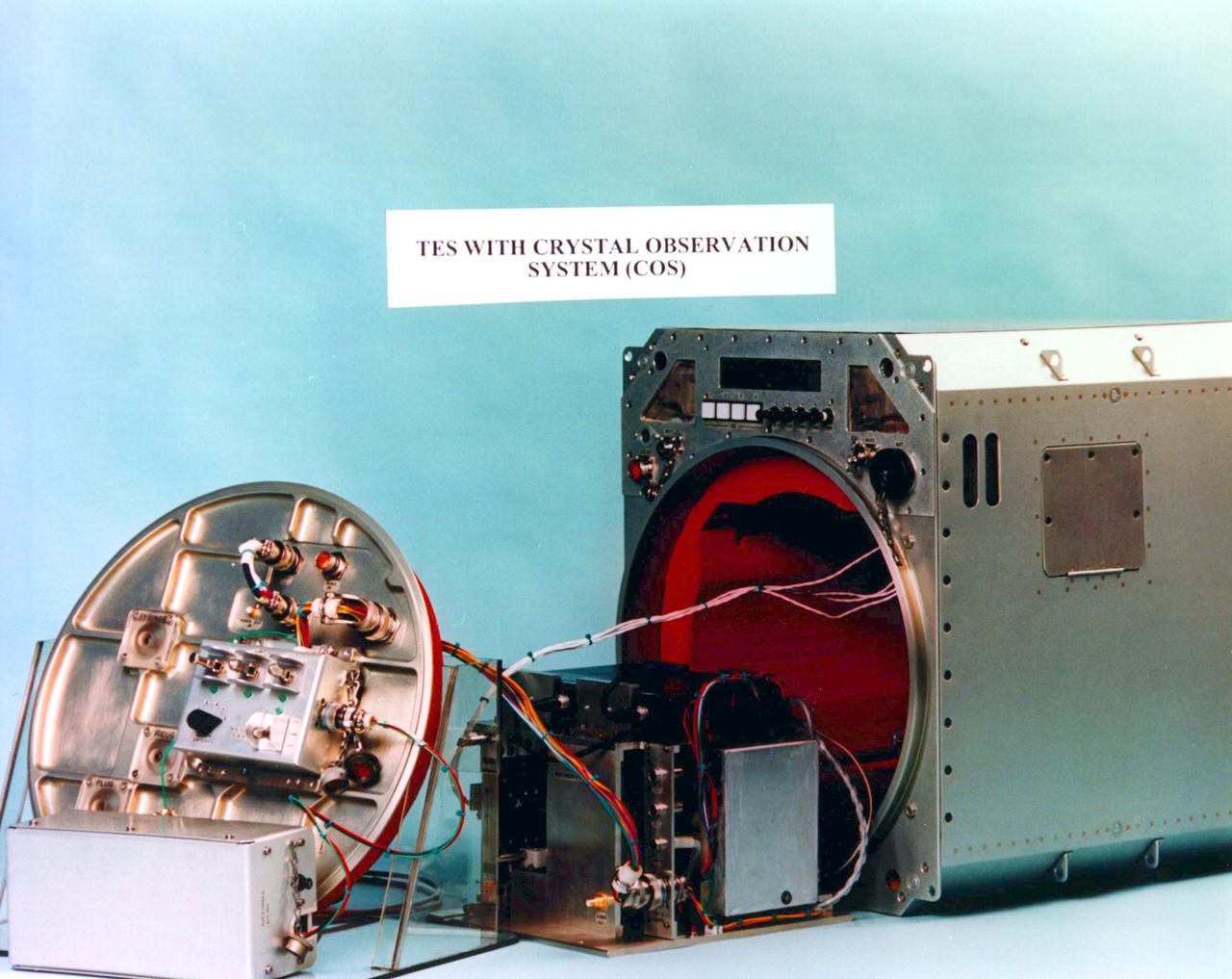
The COS consists of a specially designed (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus tray with 6 chambers, a video camera for each chamber, a lighting system, and associated hardware. By observing the crystal growth in each chamber, researchers can identify which conditions and concentrations of proteins and precipitants are best for promoting the crystal growth to a particular protein.
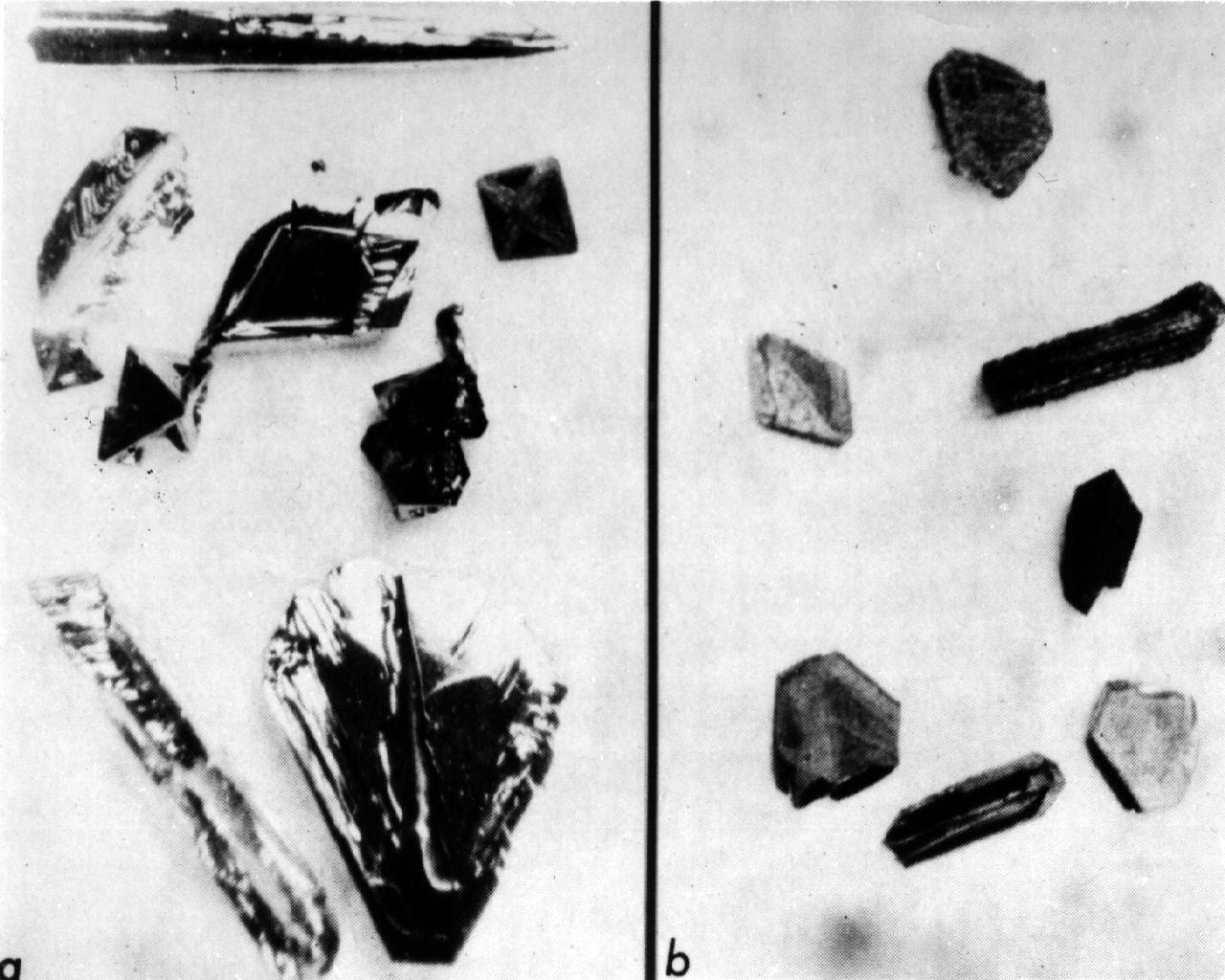
Comparison of Germanium Telluride (GeTe) Crystals grown on Earth (left) and in space (right) during the Skylab SL-3 mission. These crystals were grown using a vapor transport crystal growth method in the Multipurpose Electric Furnace System (MEFS). Crystals grown on earth are needles and platelettes with distorted surfaces and hollow growth habits. The length of the ground-based needle is approximately 2 mm and the average lenth of the platelets is 1 mm. The dull appearance of the Skylab crystals resulted from condensation of the transport agent during the long cooling period dictated by the Skylab furnace. In a dedicated process, this would be prevented by removing the ampoule from the furnace and quenching the vapor source.
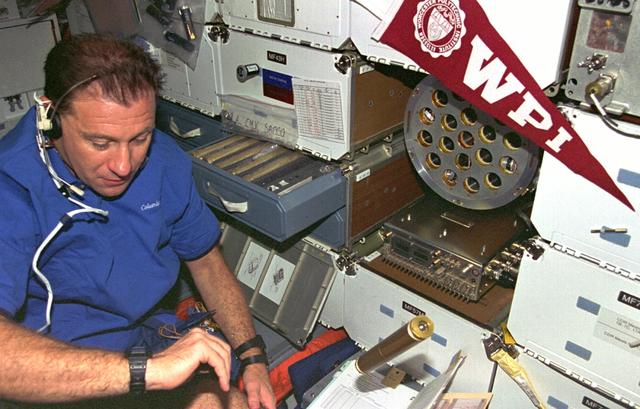

STS073-353-010 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. checks out the Zeolite Crystal Growth (ZCG) on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. ZCG evaluated Zeolite crystallization and growth in the microgravity environment aboard Columbia in order to achieve high yields of large, nearly perfect crystals in space. Zeolites are complex arrangements of silica and alumina that occur naturally as well as synthetically.
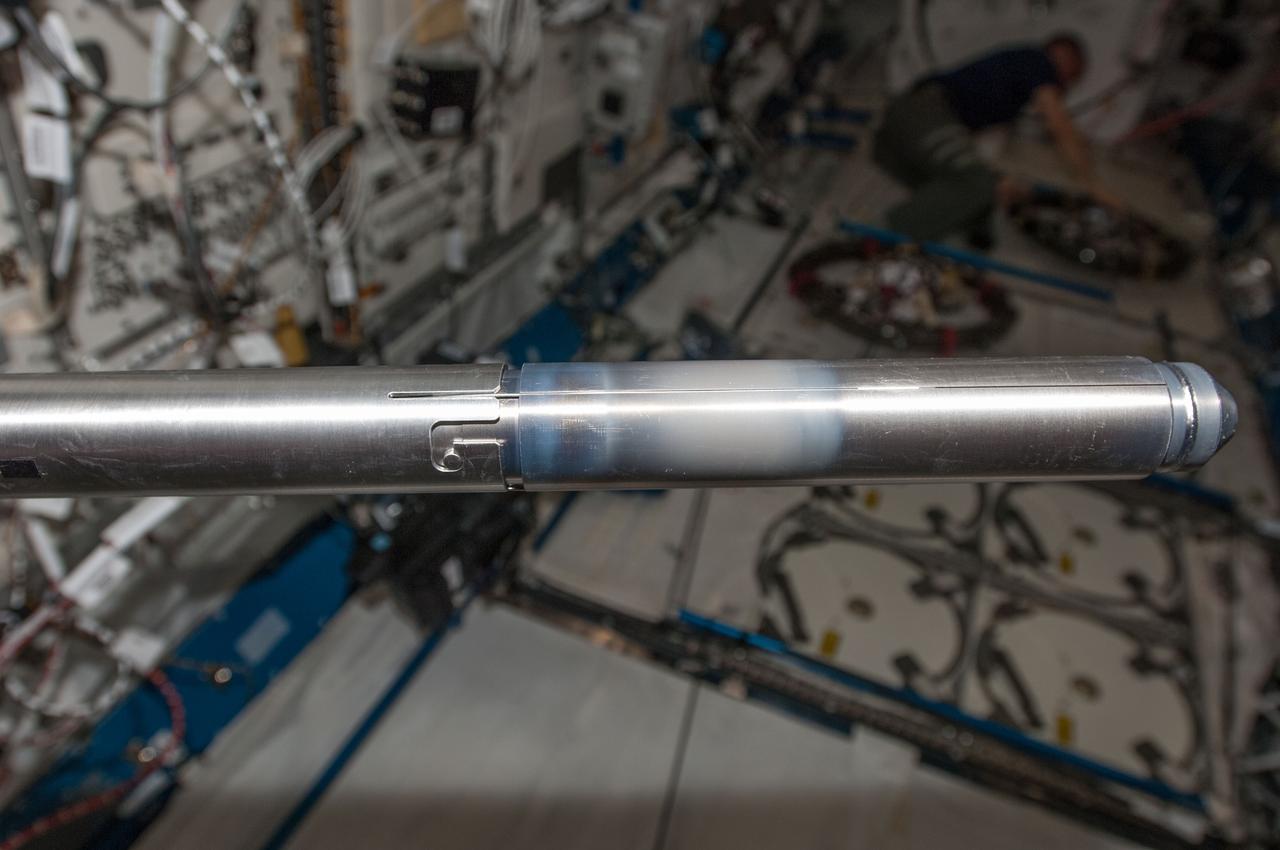
iss040e054526 (7/10/2014) --- A photo of Hicari sample cartridge 2 from the Gradient Heating Furnace (GHF) removed in preparation for return on SpaceX-4. The materials science investigation Growth of Homogeneous SiGe Crystals in Microgravity by the TLZ Method (Hicari) aims to verify the crystal-growth by Travelling Liquidous Zone method, and to produce high-quality crystals of Silicon-Germanium (SiGe) semiconductor using the Japanese Experiment Module-Gradient Heating Furnace (JEM-GHF).
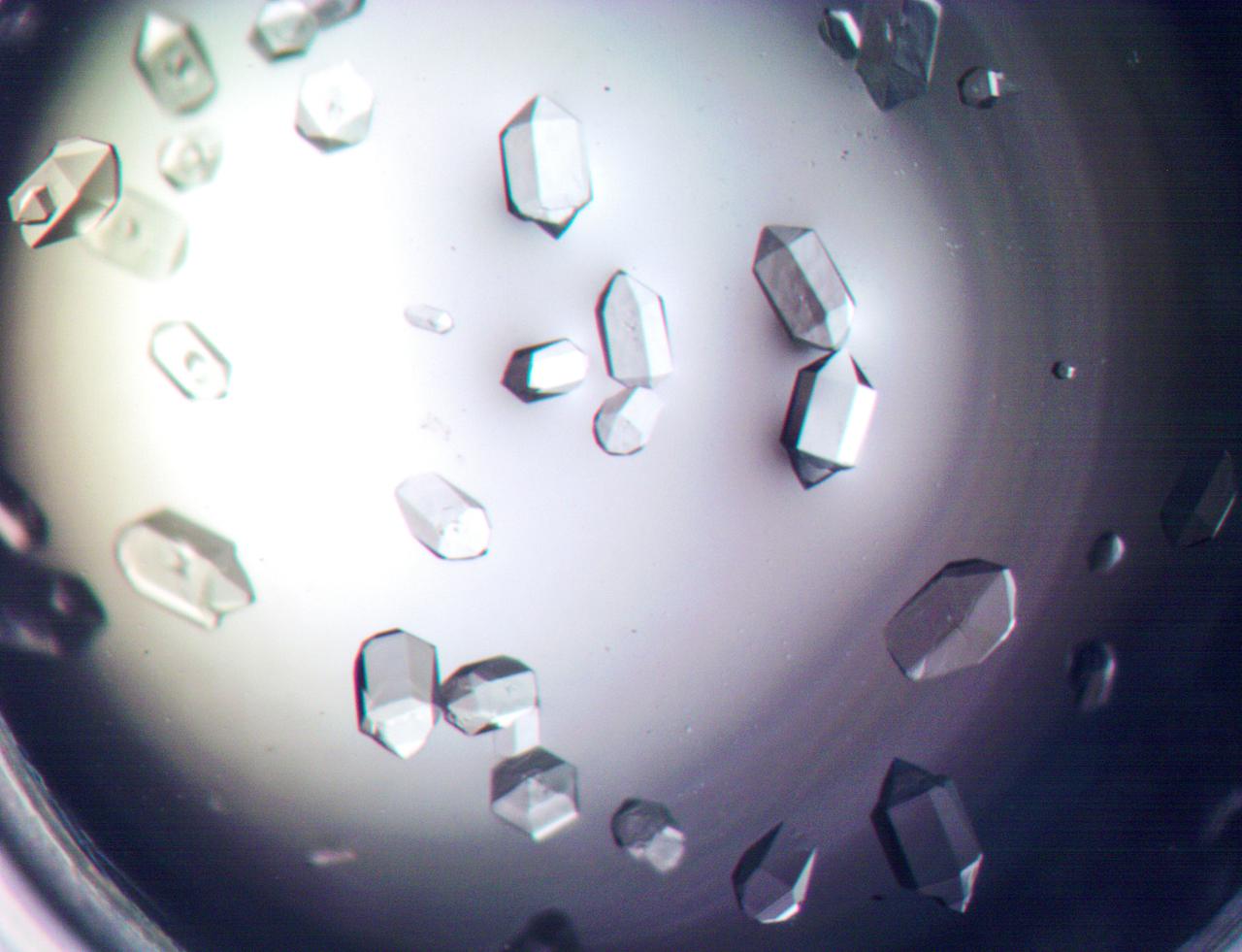
jsc2021e007777 - Aeropyrum pernix Flap Endonuclease-1 (FEN-1) protein crystals are shown grown under Earth gravity conditions. FEN-1 serves as the experimental protein for the Phase II Real-time Protein Crystal Growth on Board the International Space Station (Real-Time Protein Crystal Growth-2) investigation. Image courtesy of University of Toledo.
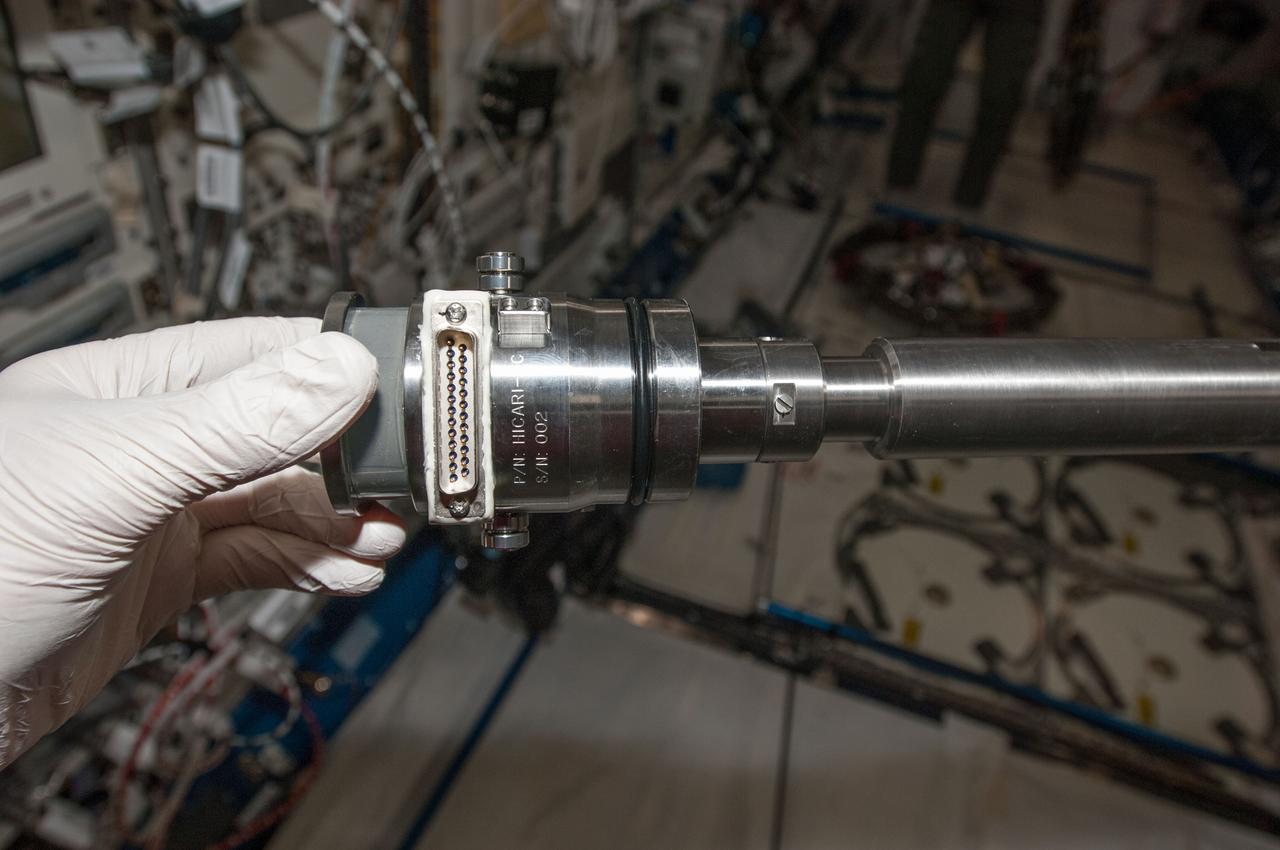

iss040e054521 (7/10/2014) --- A photo of Hicari sample cartridge 2 from the Gradient Heating Furnace (GHF) removed in preparation for return on SpaceX-4. The materials science investigation Growth of Homogeneous SiGe Crystals in Microgravity by the TLZ Method (Hicari) aims to verify the crystal-growth by Travelling Liquidous Zone method, and to produce high-quality crystals of Silicon-Germanium (SiGe) semiconductor using the Japanese Experiment Module-Gradient Heating Furnace (JEM-GHF).
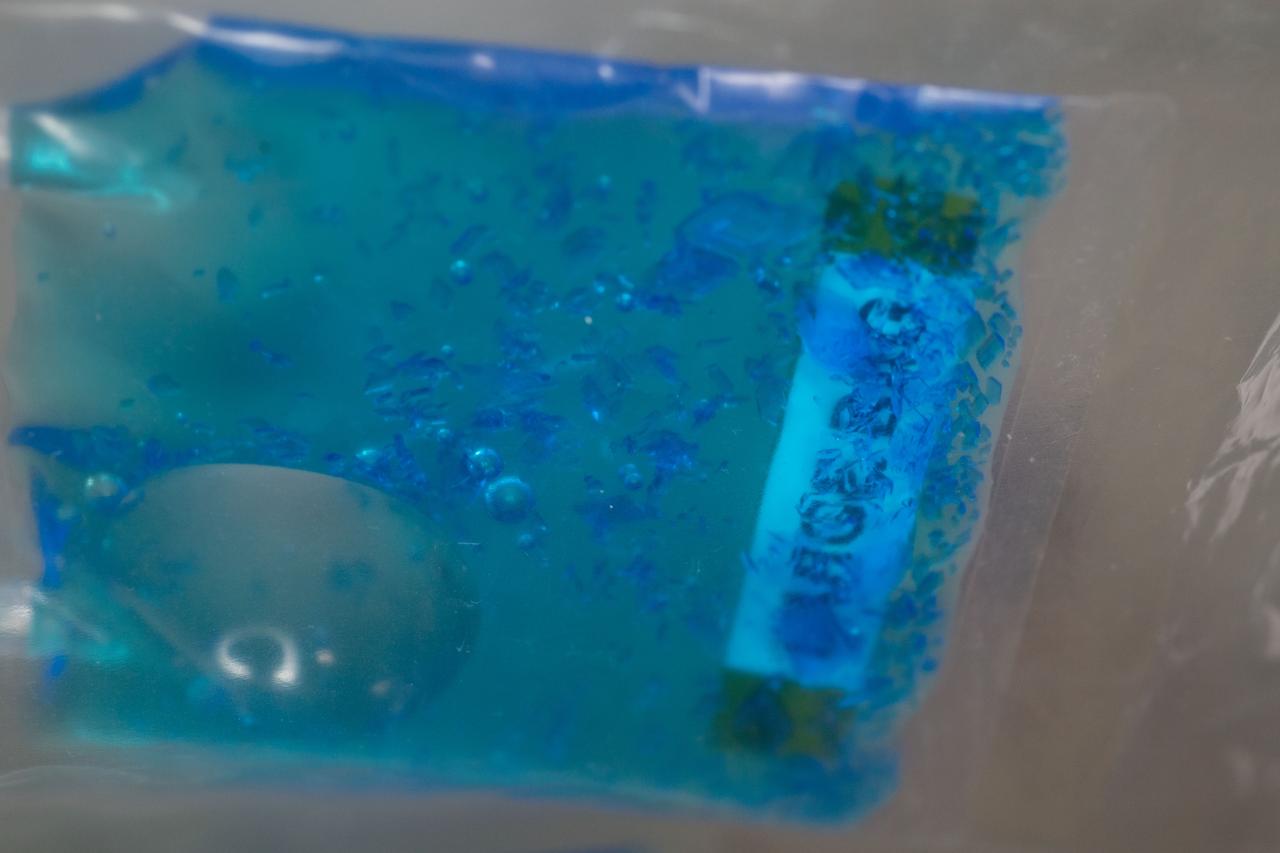

iss055e043707 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- A close look at crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation to examine the effects of microgravity on crystal growth.
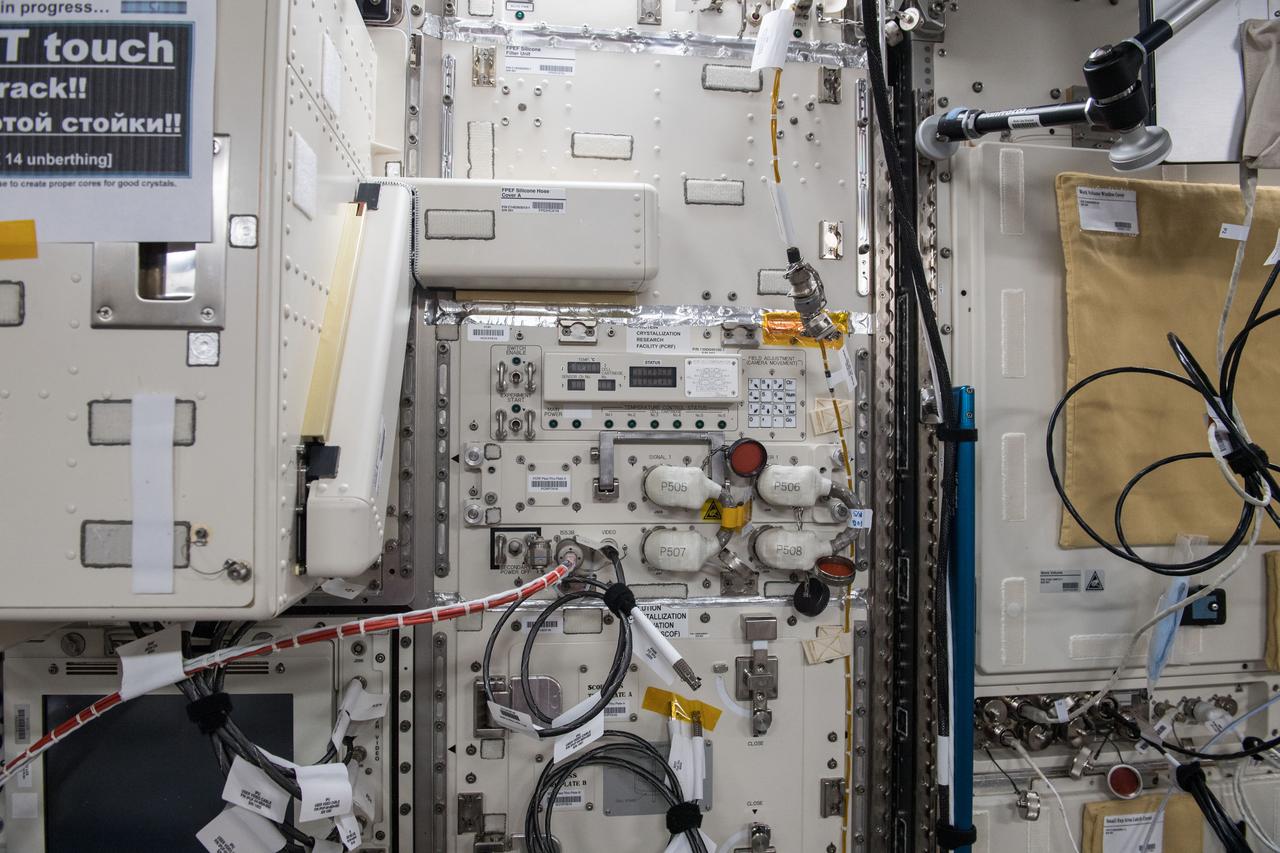

iss055e004890 (3/24/2018) --- Photographic documentation taken during JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Installation into the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF) of the Ryutai Rack.
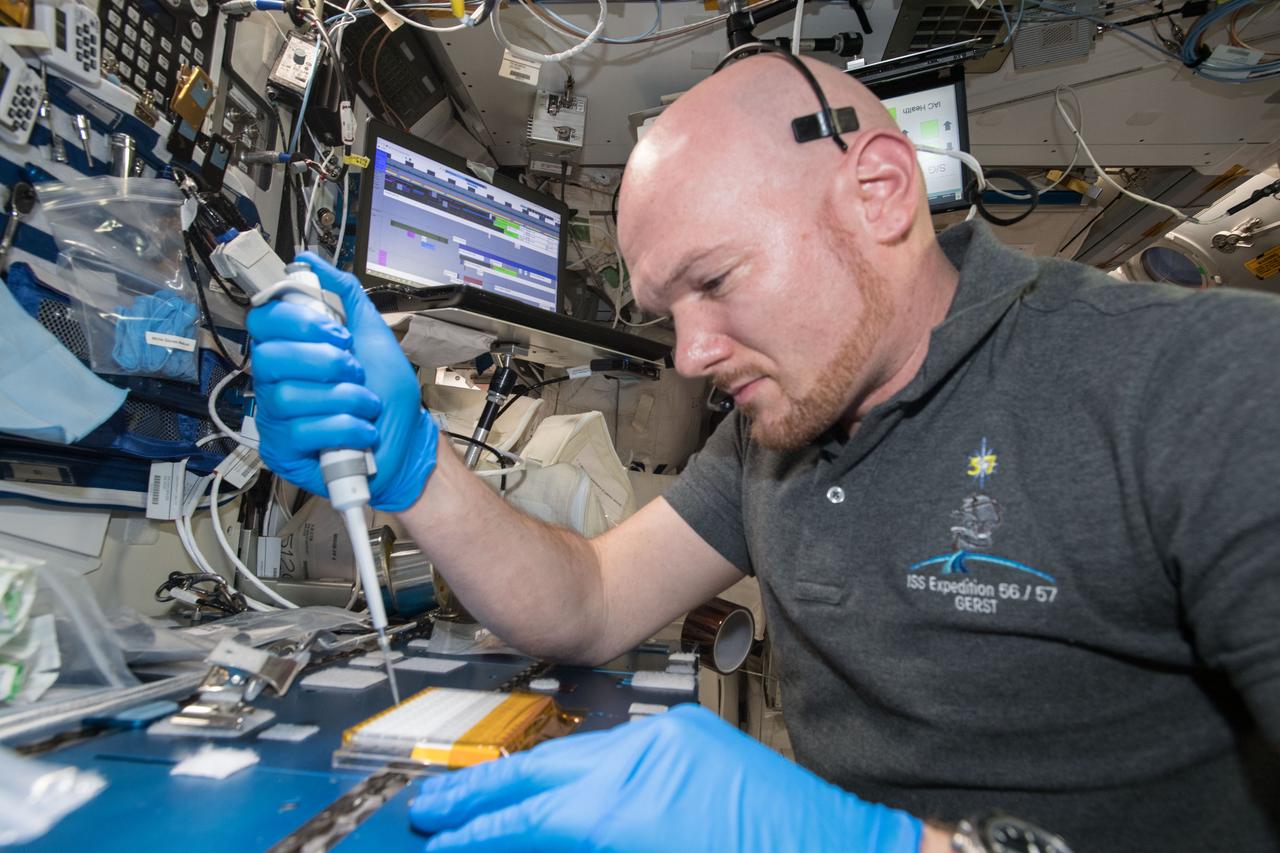

iss057e106232 (Nov. 26, 2018) --- Commander Alexander Gerst uses a uses a pipette to transfer a protein solution into the Protein Crystal Growth Card for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth.
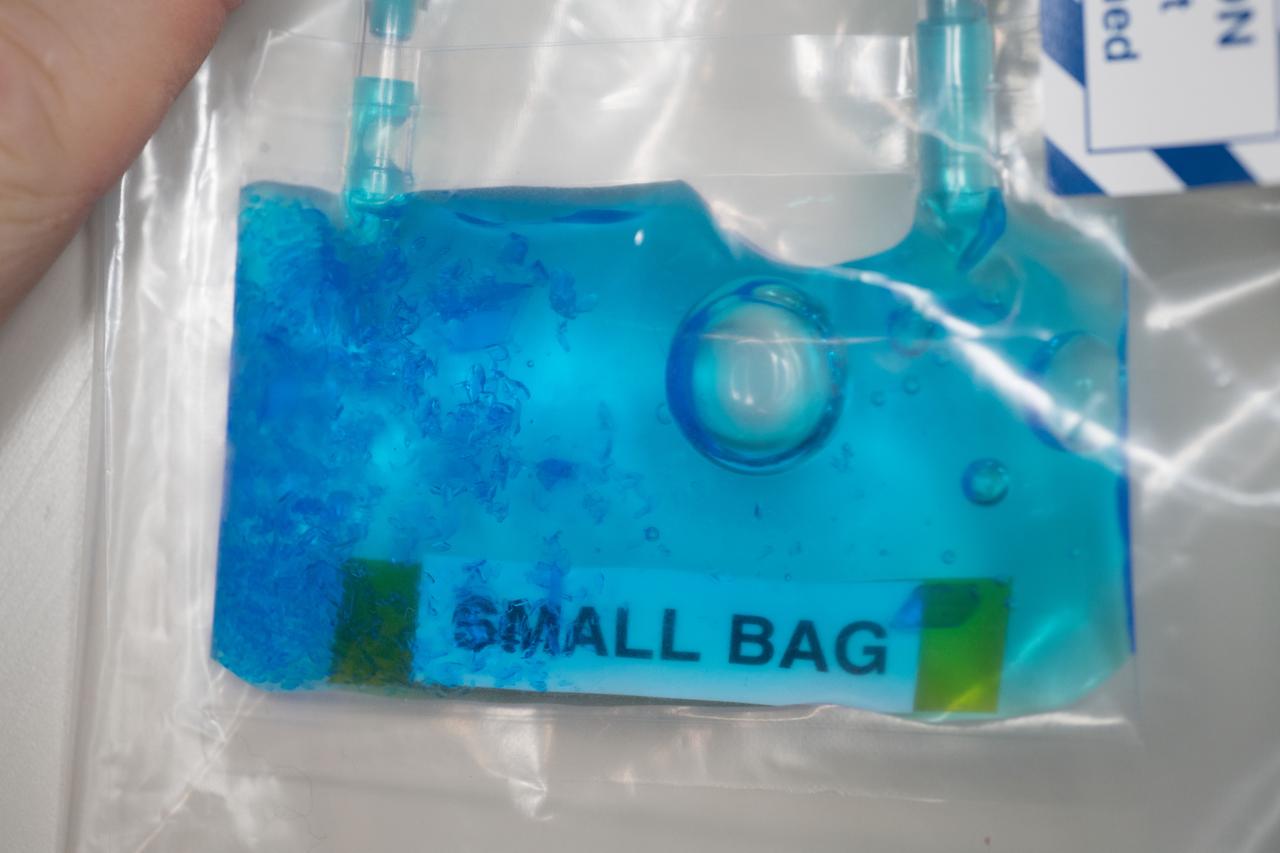
iss055e043718 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- A close look at crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation to examine the effects of microgravity on crystal growth.
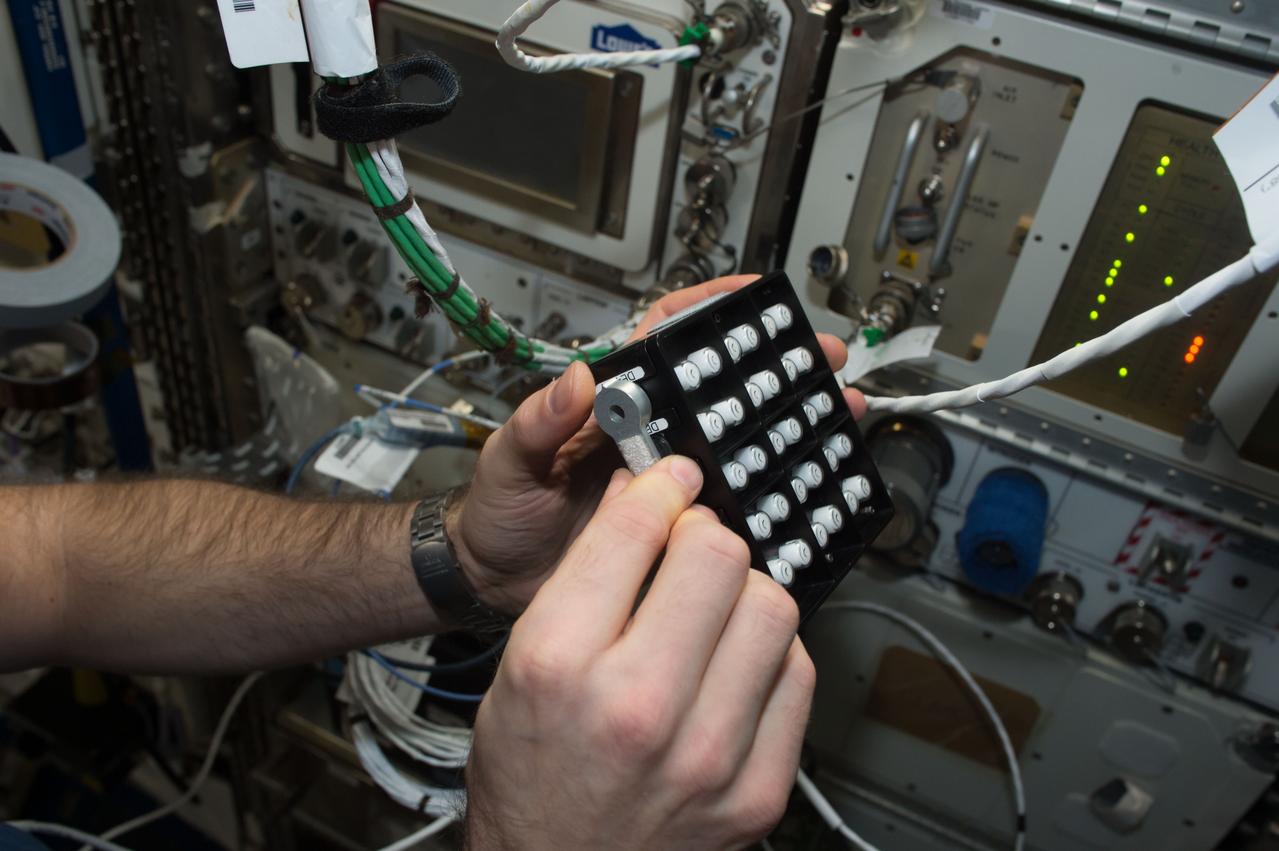

iss050e058807 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
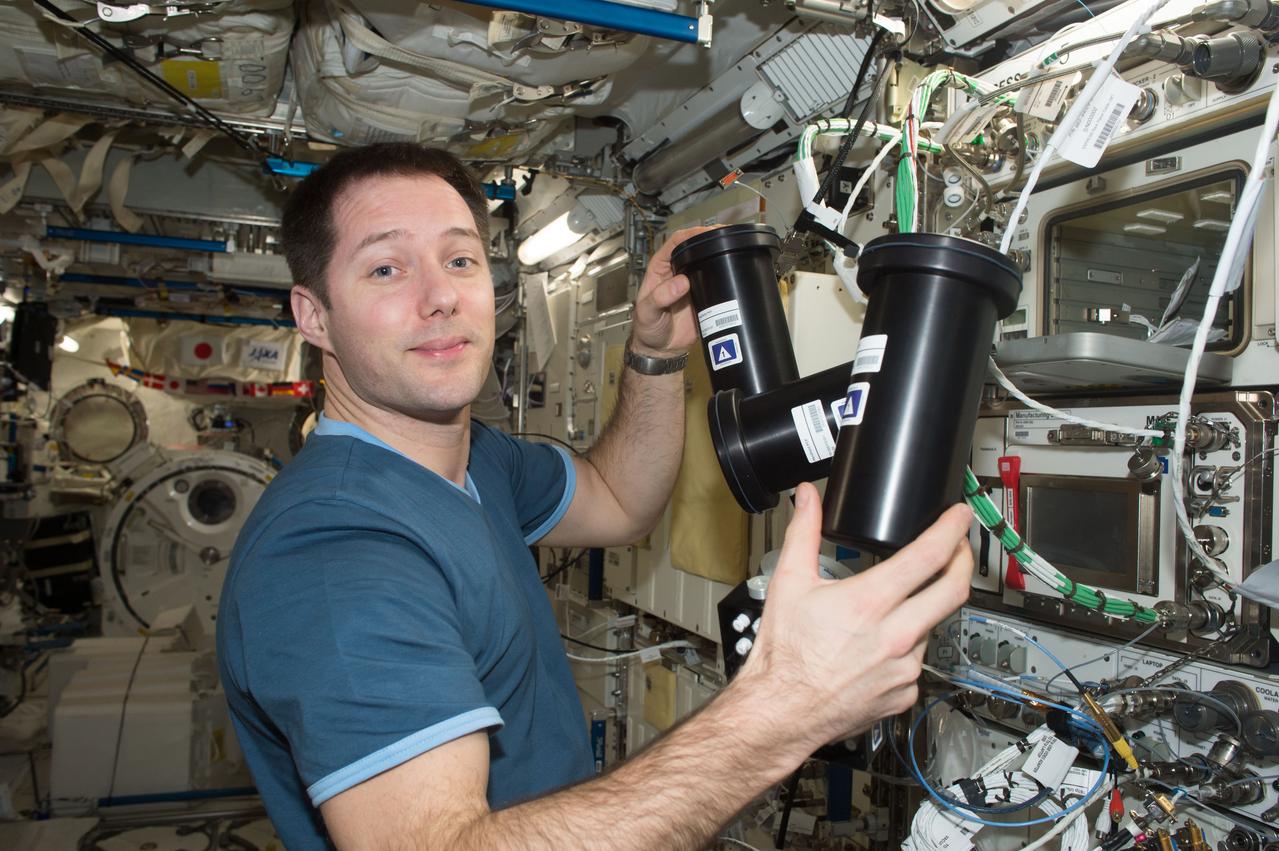

iss050e058812 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
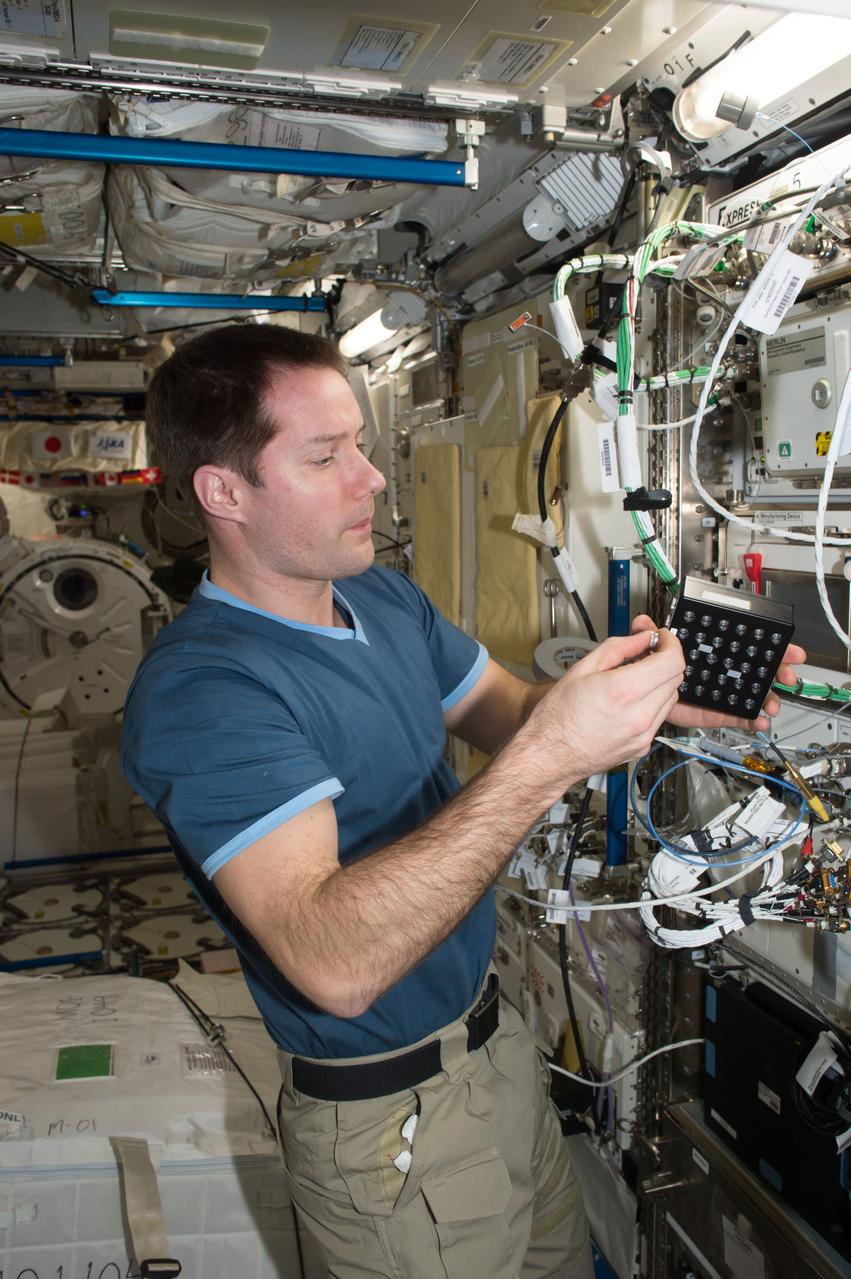

iss050e058802 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
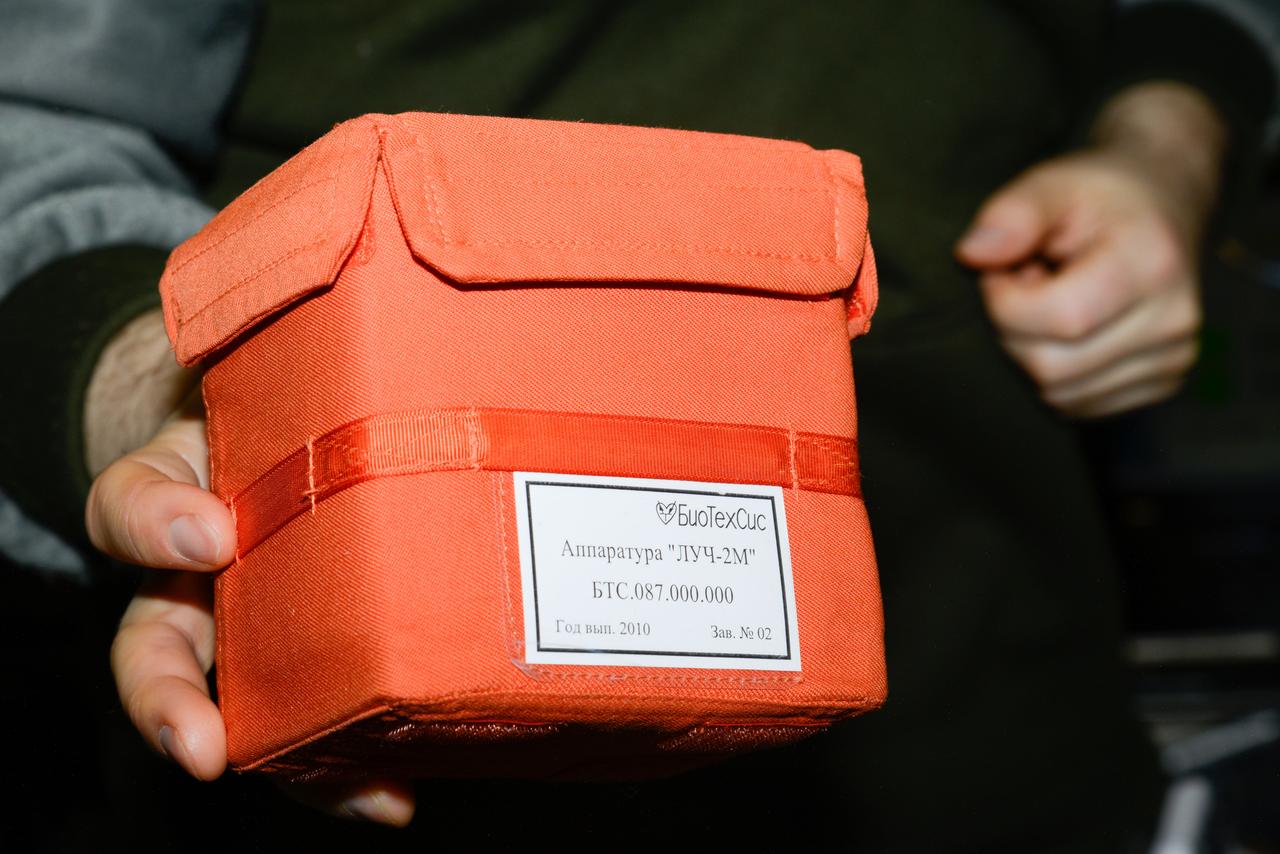

iss047e154711 (6/17/2016) --- Photographic documentation of Luch-2M Multipurpose Crystallization Cassette (УБК) within orange case. Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.