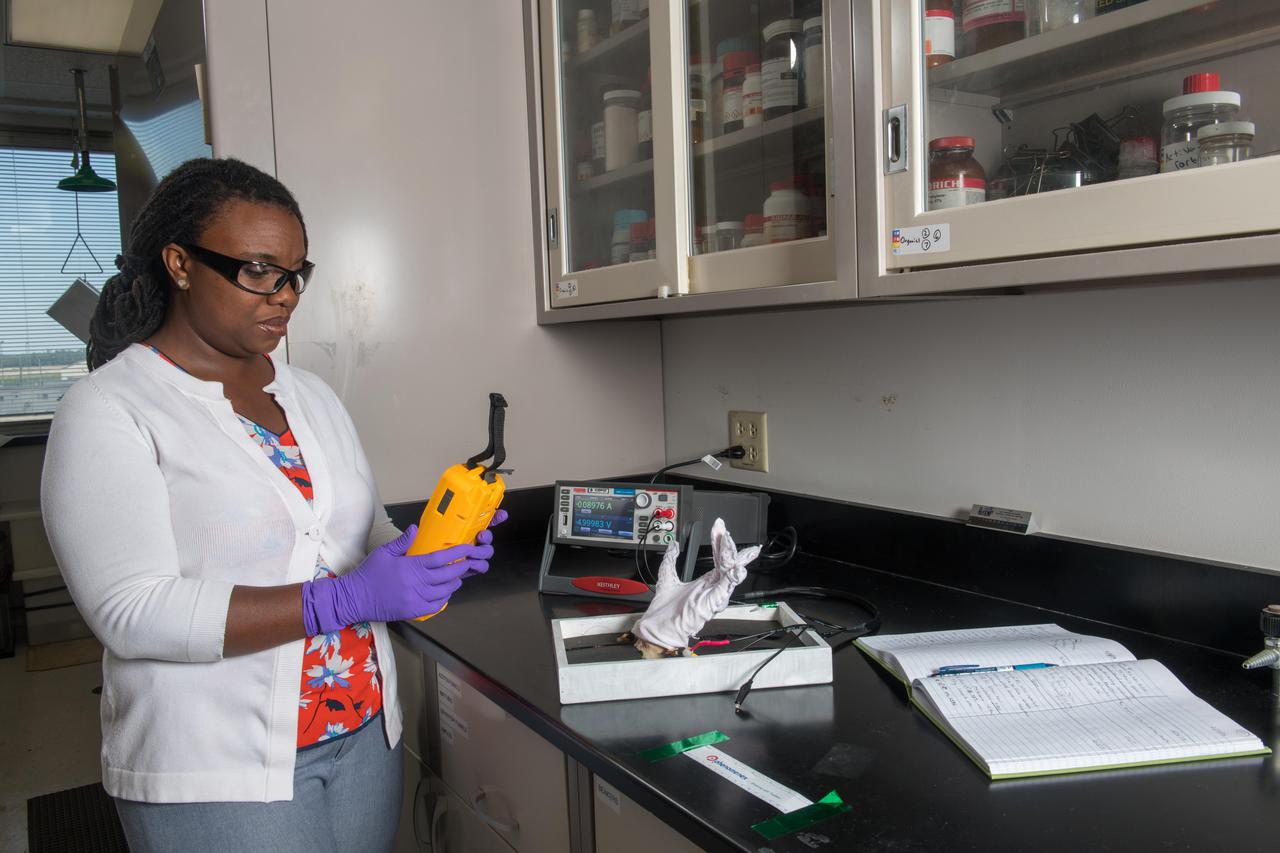

Development of Lightweight, Electrically Conductive, Multi-functional Textiles and Composites
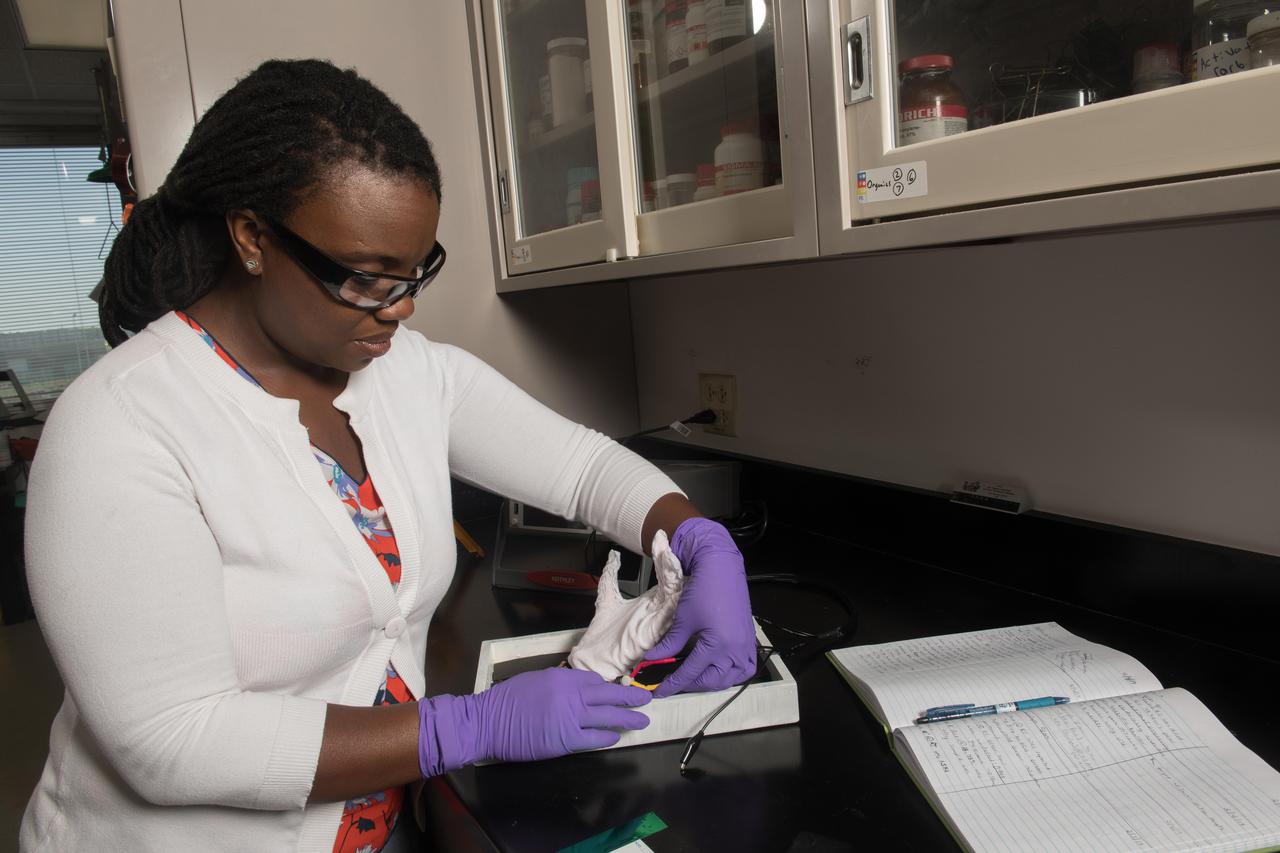

Development of Lightweight, Electrically Conductive, Multi-functional Textiles and Composites
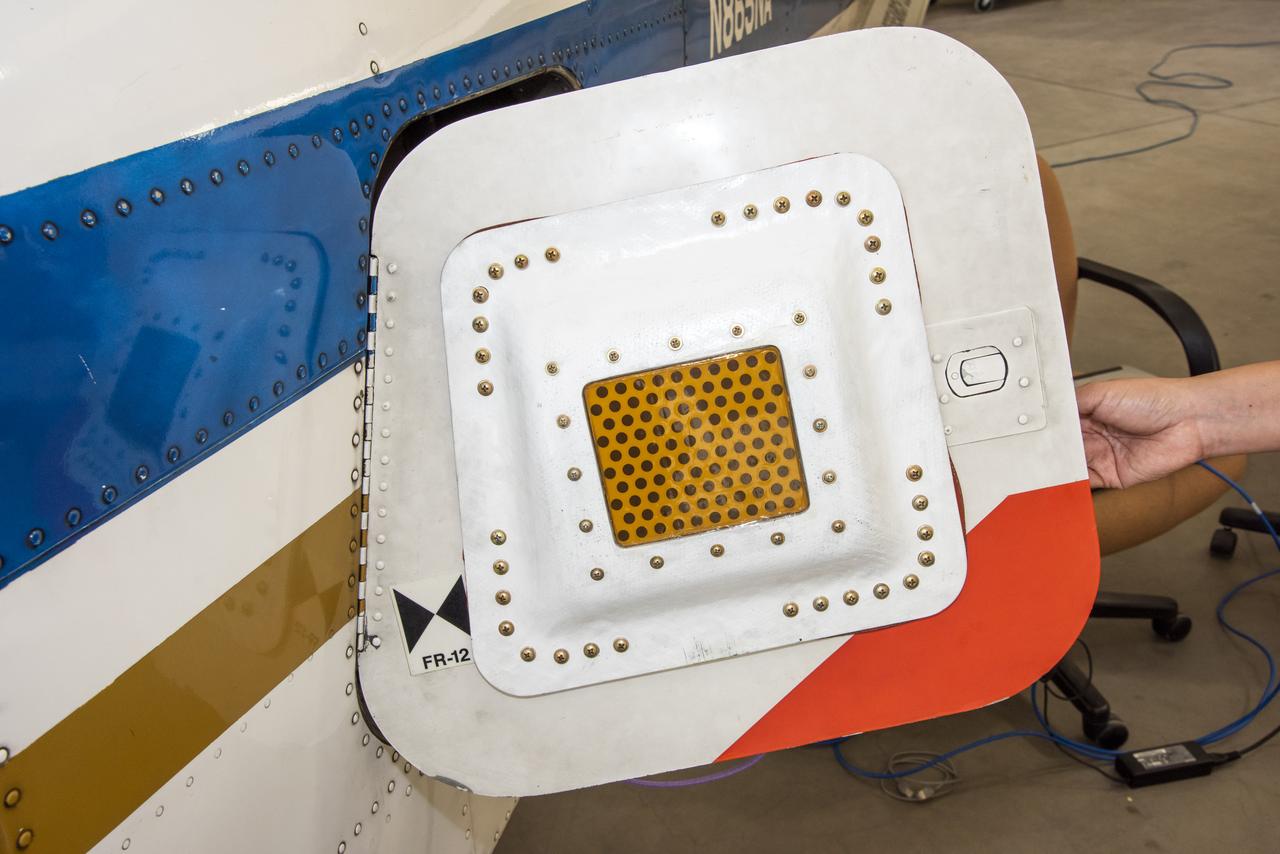

A photo of the conformal antenna installed on the door of T-34C aircraft. The conformal antenna was developed and designed by members of the Conformal Lightweight Antenna Structures for Aeronautical Communications Technologies activity within the Convergent Aeronautics Solutions project. The antenna is made of aerogels which have resulted in a thin, flexible antenna substrate with improved gain, bandwidth and efficiency.
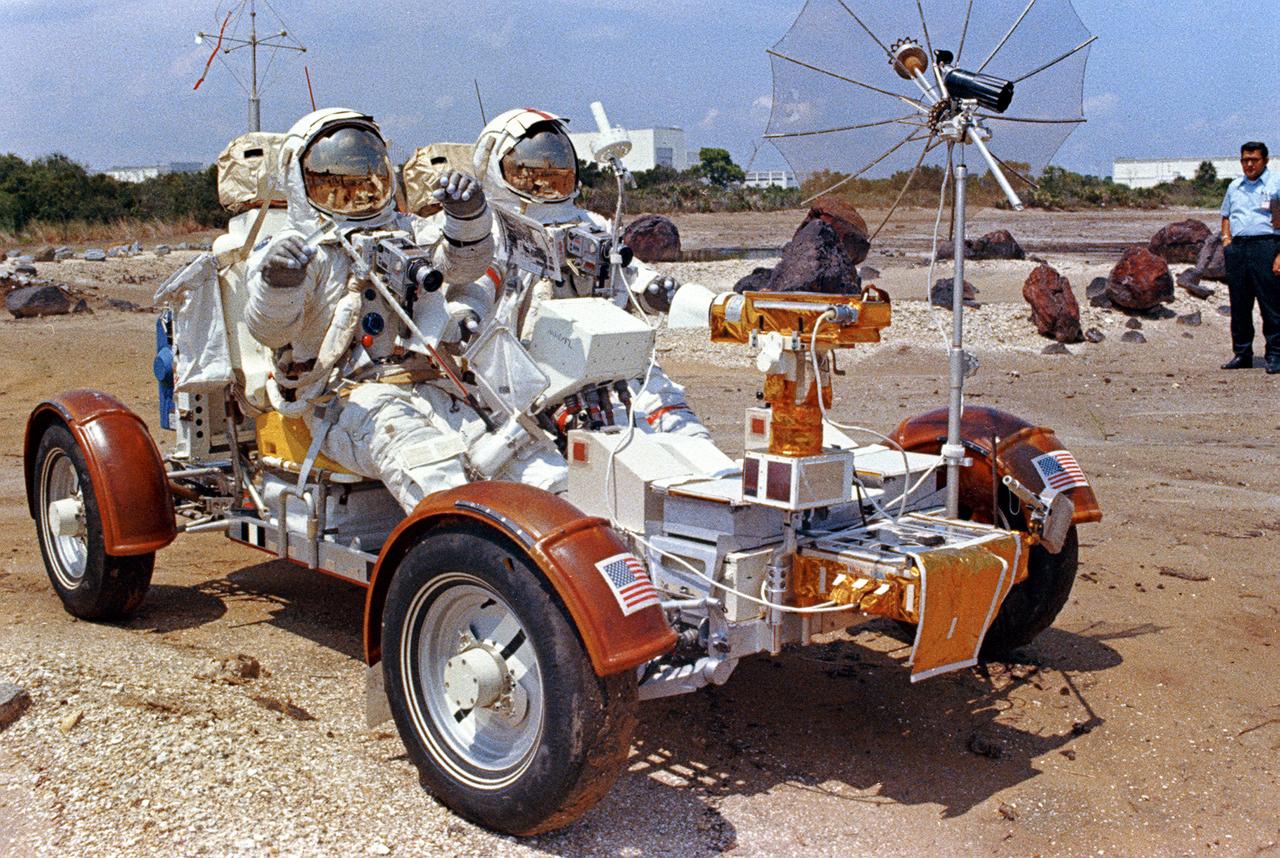
This photograph was taken during the testing of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Johnson Space Center. Developed by the MSFC, the LRV was the lightweight electric car designed to increase the range of mobility and productivity of astronauts on the lunar surface. It was used on the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
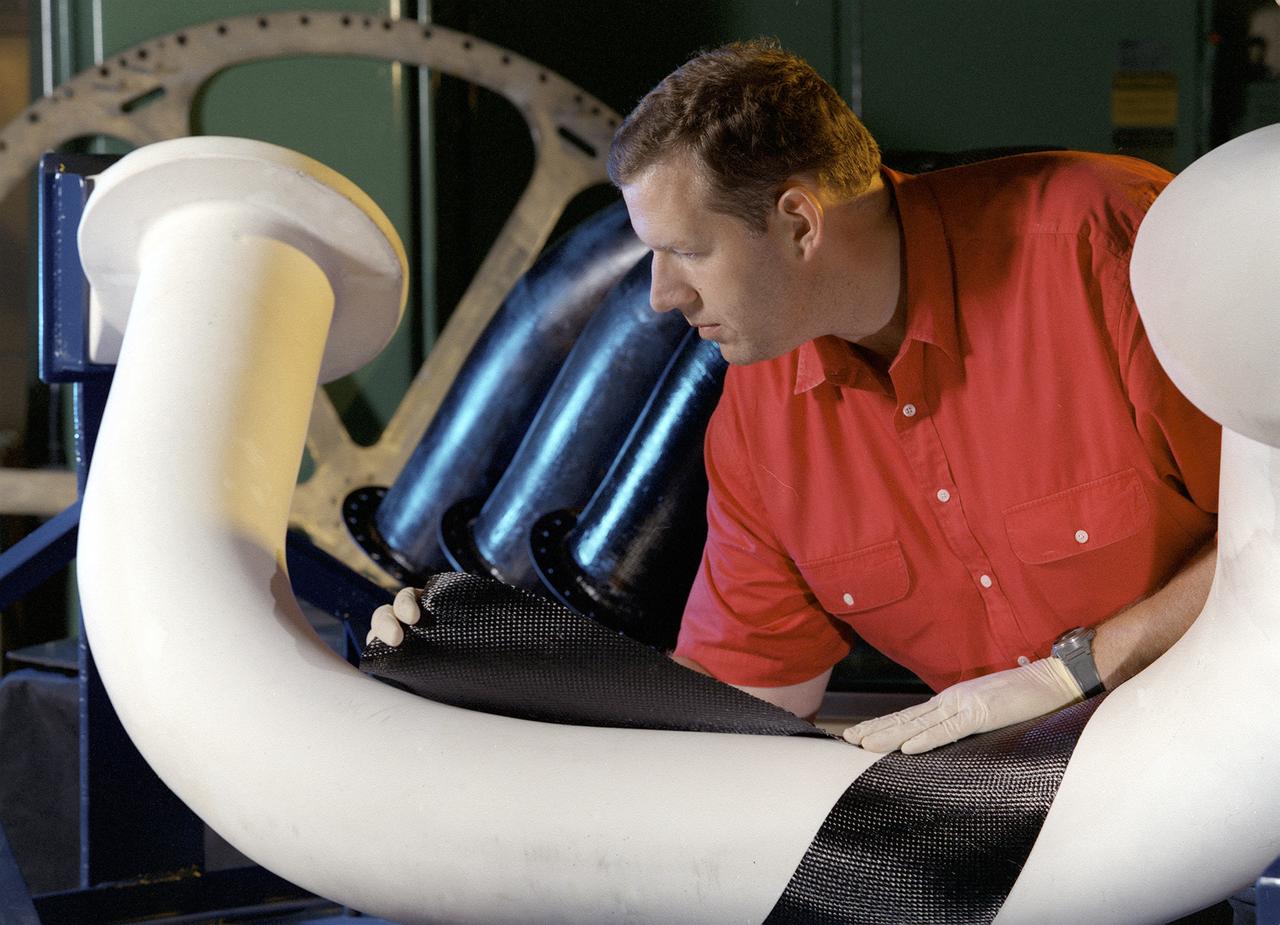

Engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are working with industry partners to develop a new generation of more cost-efficient space vehicles. Lightweight fuel tanks and components under development will be the critical elements in tomorrow's reusable launch vehicles and will tremendously curb the costs of getting to space. In this photo, Tom DeLay, a materials processes engineer for MSFC, uses a new graphite epoxy technology to create lightweight cryogenic fuel lines for futuristic reusable launch vehicles. He is wrapping a water-soluble mandrel, or mold, with a graphite fabric coated with an epoxy resin. Once wrapped, the pipe will be vacuum-bagged and autoclave-cured. The disposable mold will be removed to reveal a thin-walled fuel line. In addition to being much lighter and stronger than metal, this material won't expand or contract as much in the extreme temperatures encountered by launch vehicles.
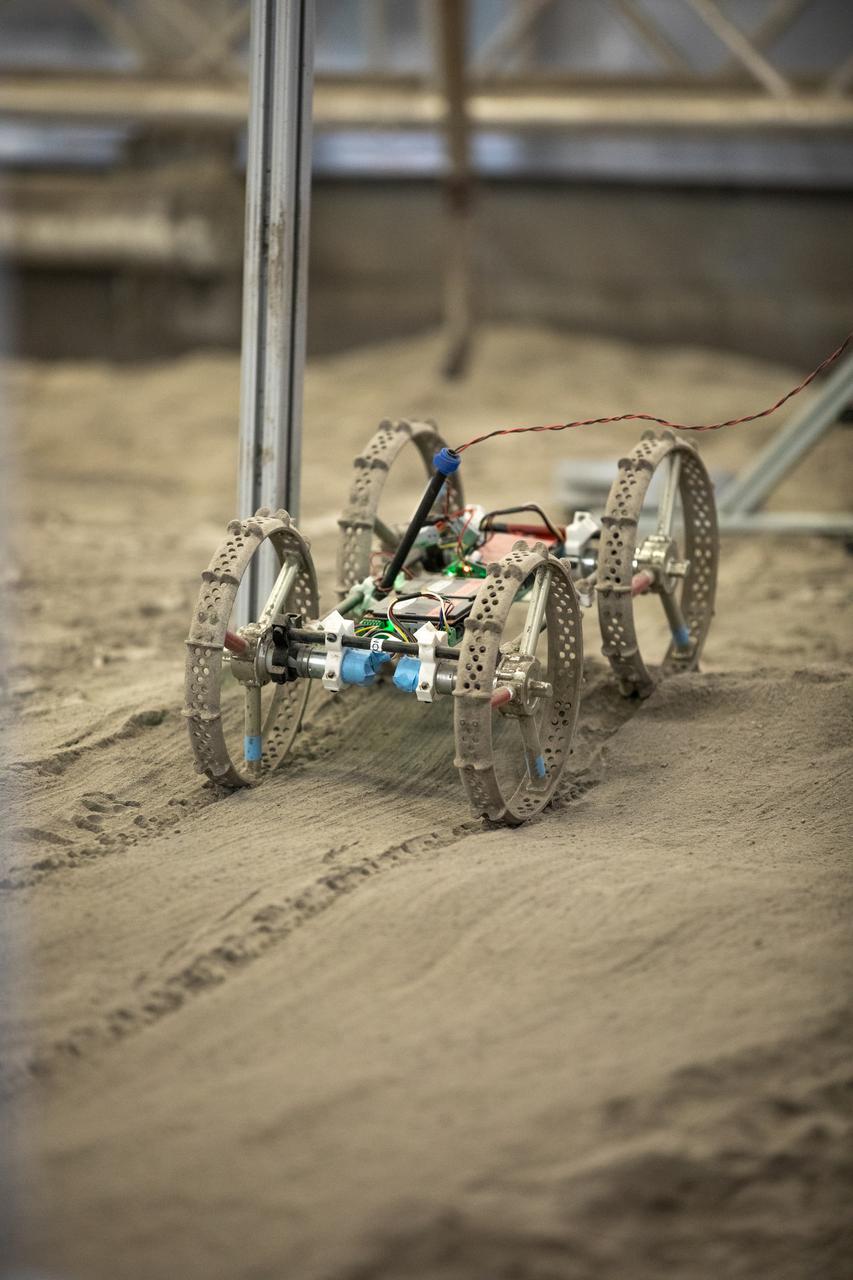

Astrobotic’s mass-offloaded CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – undergoes mobility testing inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
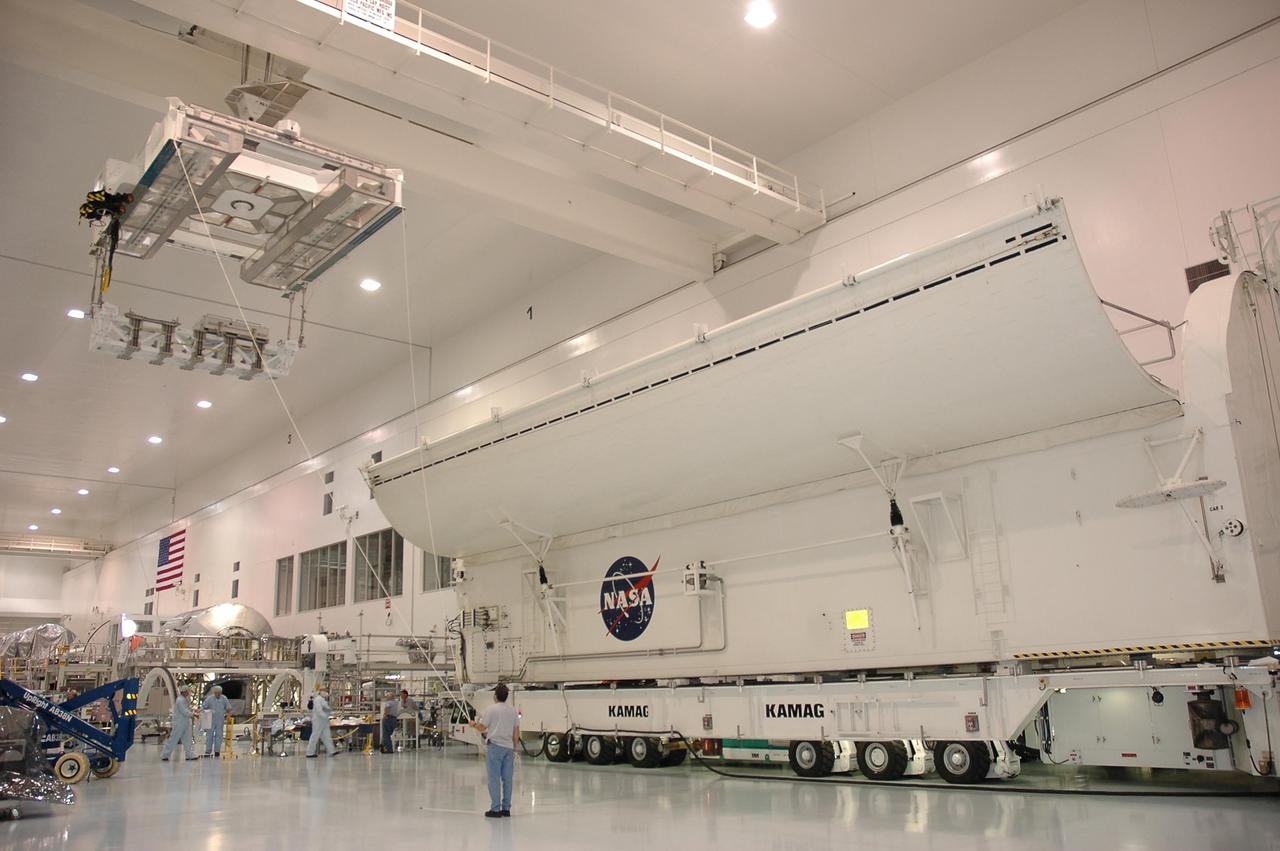

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, a crane moves the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC) toward a payload canister, doors open to receive it. Slated to fly on space shuttle mission STS-121, the LMC is ready to be delivered to Launch Pad 39B for installation into orbiter Discovery. It is a cross-bay carrier for hardware required to perform development test objective 848. Test objective 848 is a demonstration of the tools and techniques developed to repair damaged orbiter thermal protection system tiles during a spacewalk, or extravehicular activity. The target launch window for STS-121 is July 1 to July 19, 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Husten

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, a crane moves the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC) over an abundance of hardware and equipment. Slated to fly on space shuttle mission STS-121, the LMC is ready to be delivered to Launch Pad 39B for installation into orbiter Discovery. It is a cross-bay carrier for hardware required to perform development test objective 848. Test objective 848 is a demonstration of the tools and techniques developed to repair damaged orbiter thermal protection system tiles during a spacewalk, or extravehicular activity. The target launch window for STS-121 is July 1 to July 19, 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Husten

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers monitor the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC) as it is lifted by a crane. Slated to fly on space shuttle mission STS-121, the LMC is ready to be delivered to Launch Pad 39B for installation into orbiter Discovery. It is a cross-bay carrier for hardware required to perform development test objective 848. Test objective 848 is a demonstration of the tools and techniques developed to repair damaged orbiter thermal protection system tiles during a spacewalk, or extravehicular activity. The target launch window for STS-121 is July 1 to July 19, 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Husten
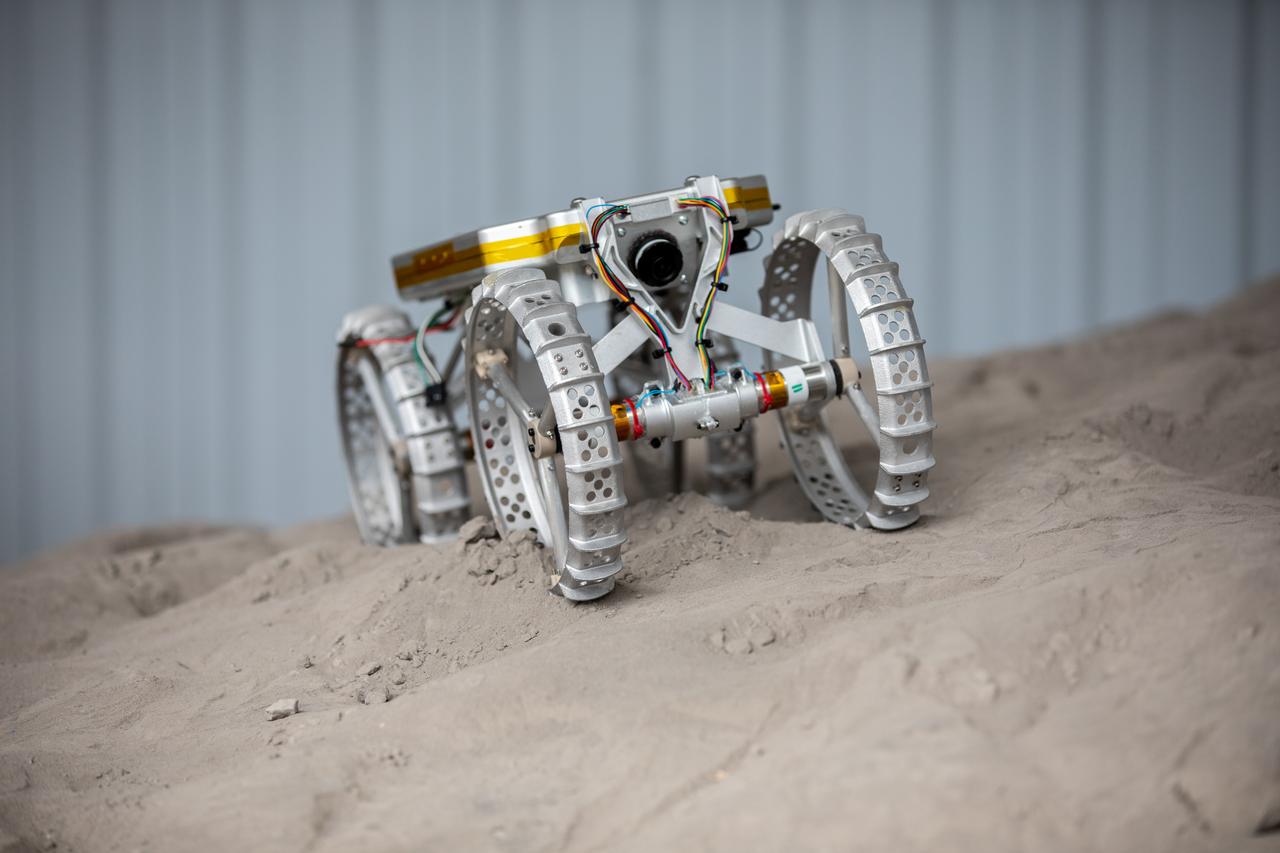
Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – undergoes mobility testing inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
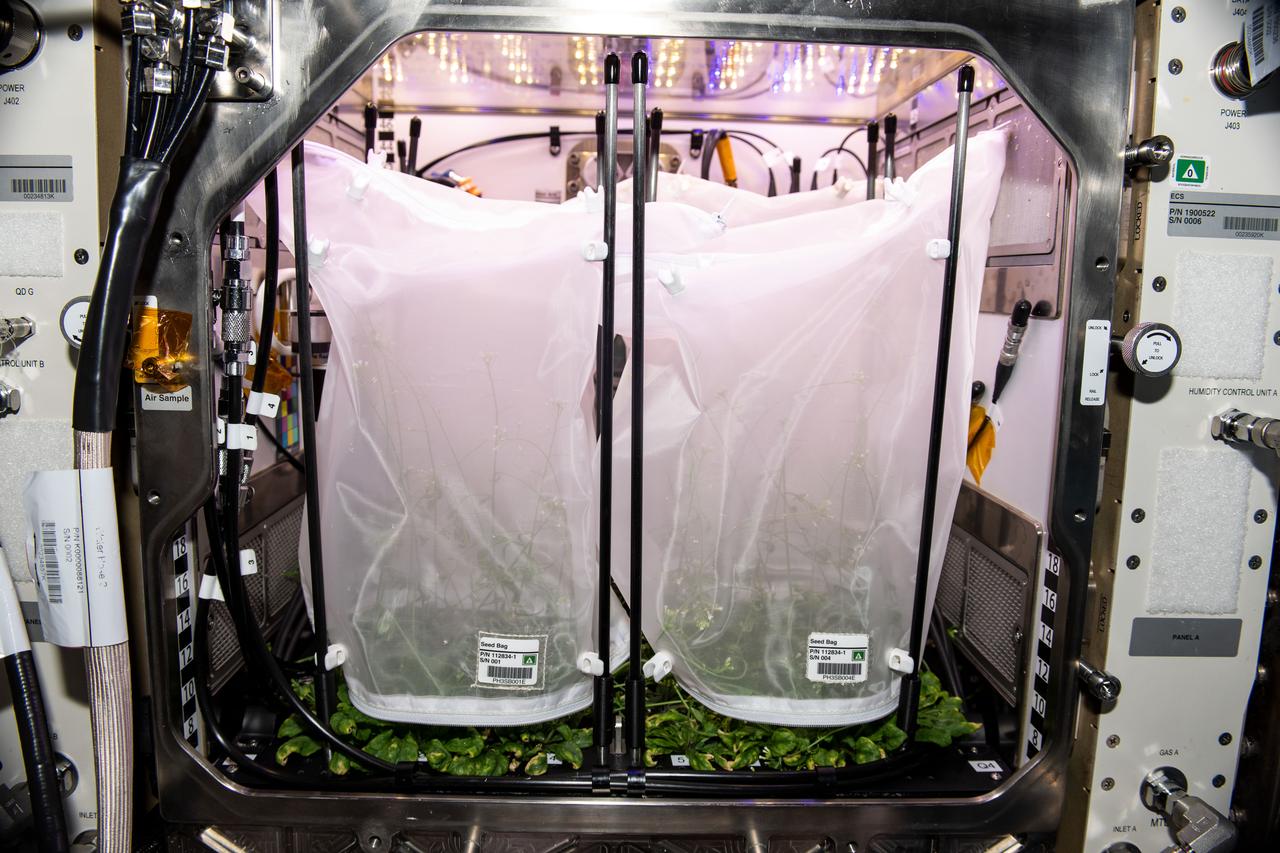

iss068e047055 (2/7/2023) --- Lightweight mesh bags are installed over plant stalks for the Plant Habitat-03 (PH-03) investigation aboard the International Space Station, helping contain them as seeds mature. Astronauts harvest the seed stalks when they mature and begin to dry, preserving them for a return to Earth and further analysis. PH-03 aims to discover whether genetic changes persist through multiple plant generations, a first step in developing plants better suited for future space exploration.
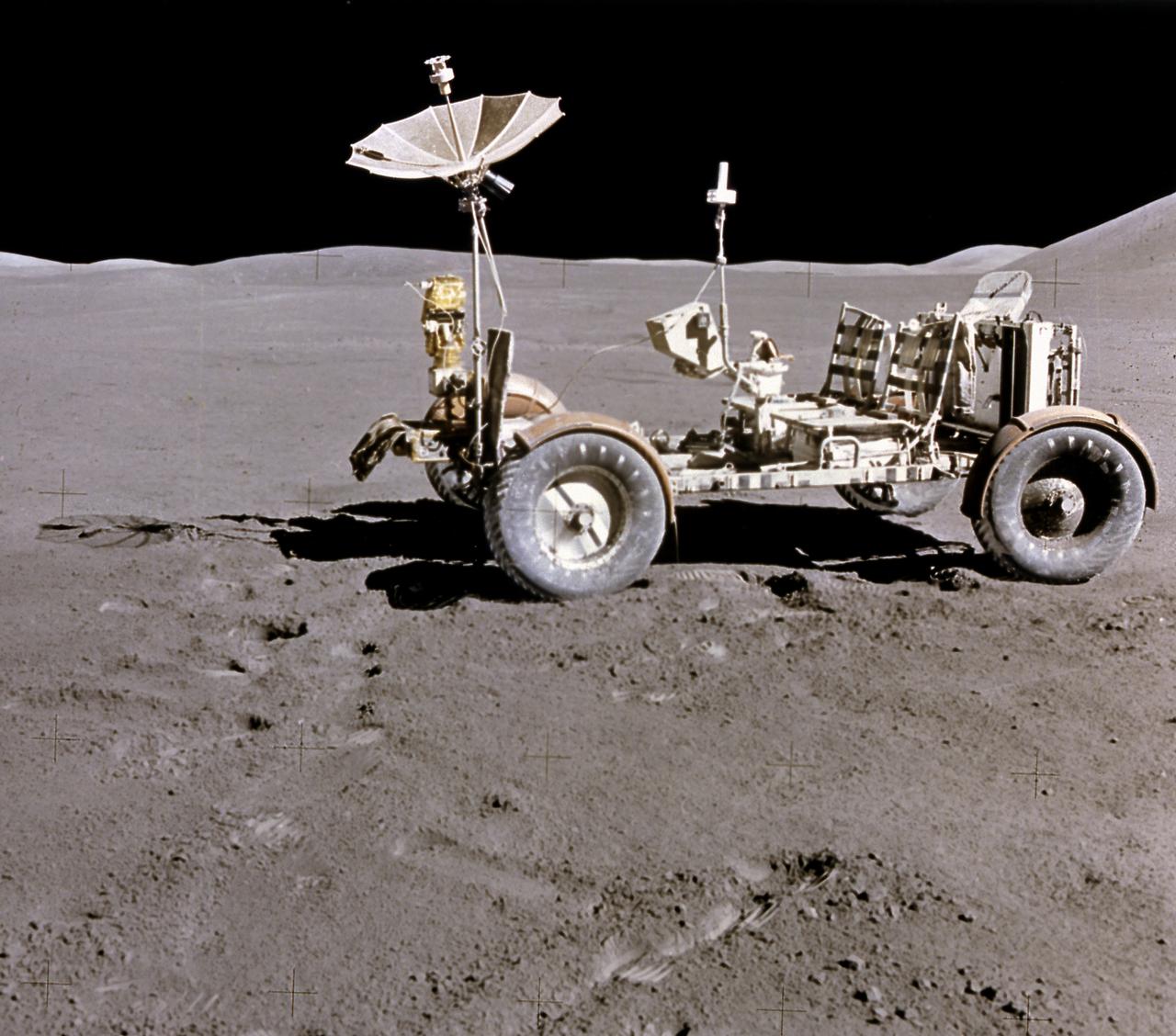
This photograph of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was taken during the Apollo 15 mission. Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
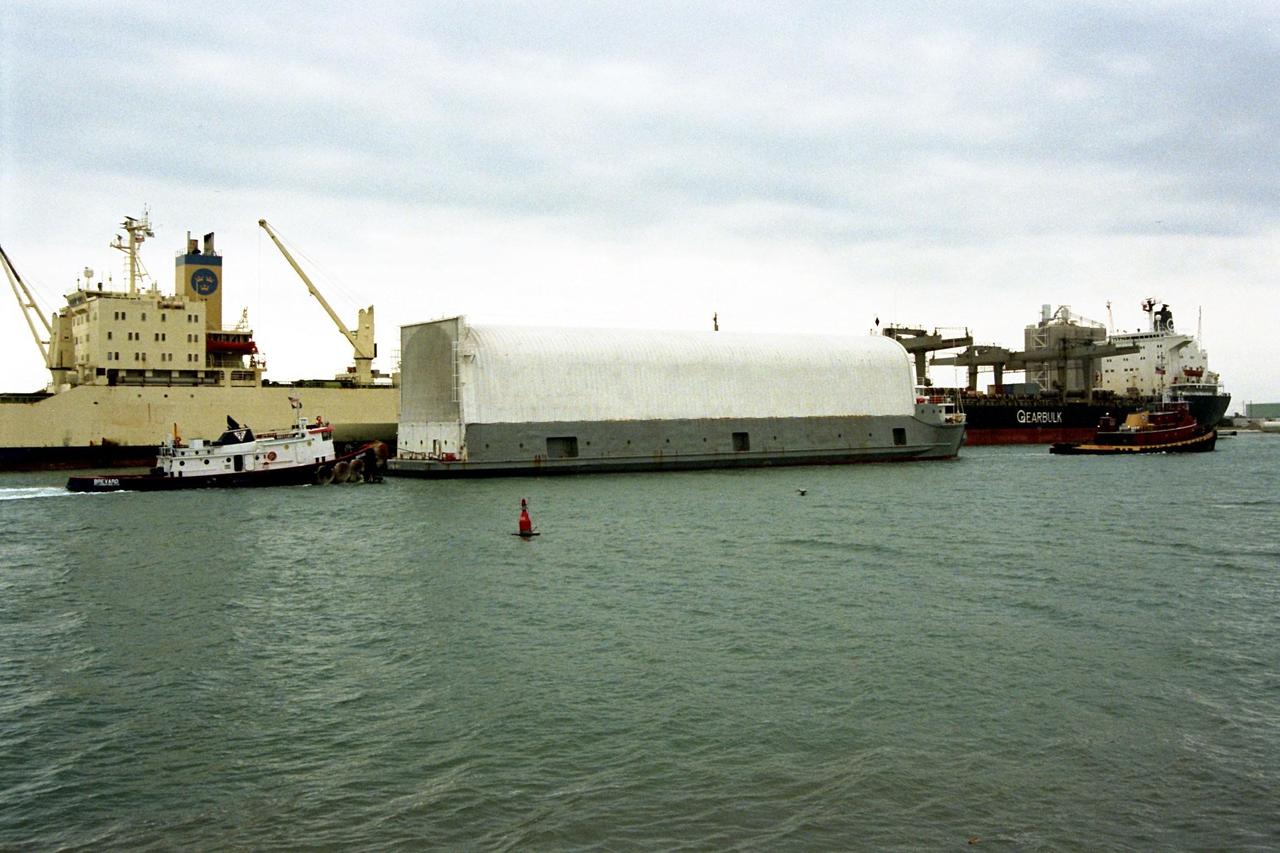

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is moved on a barge by two tug boats toward a pier at Port Canaveral, Fla. The tank is scheduled to undergo processing at Kennedy Space Center for flight on STS-91, targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. The tank was sent from the NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans
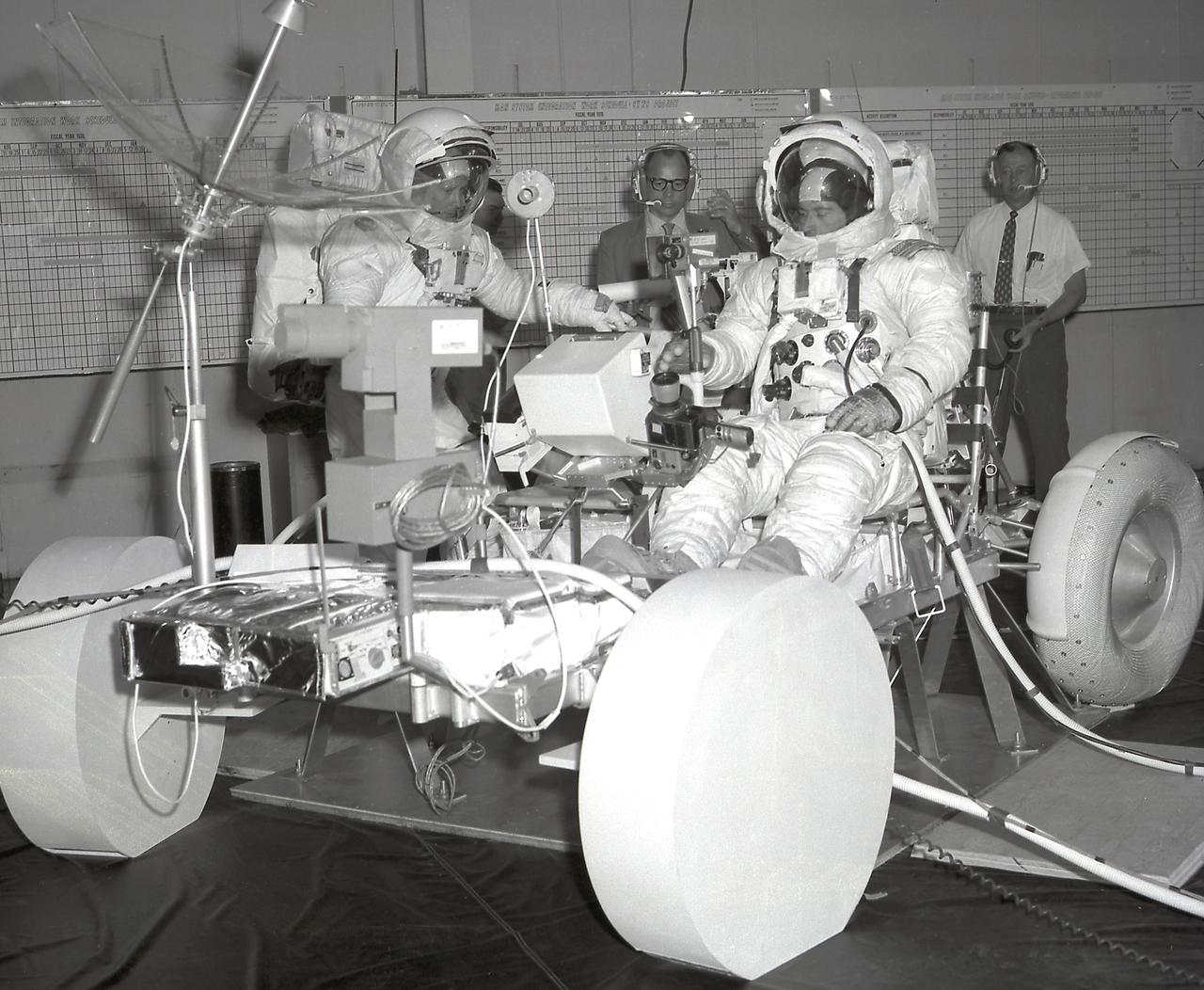
This image depicts the Apollo 16 mission astronauts John Young (right) and Charles Duke (left) in pressure suits during a final crew training on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), building 4619. Developed by the MSFC, the LRV was the lightweight electric car designed to increase the range of mobility and productivity of astronauts on the lunar surface. It was used on the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
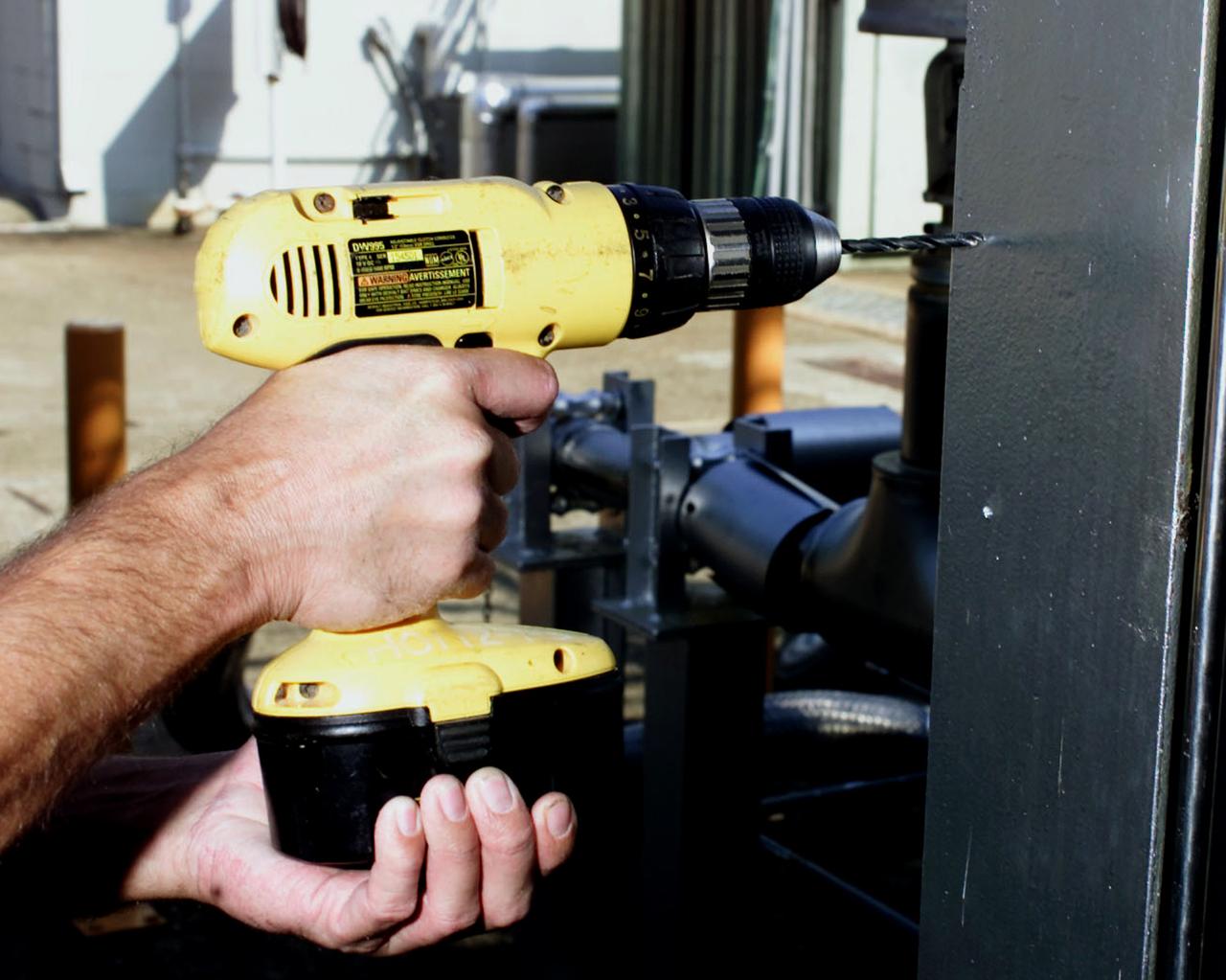

Apollo-era technology spurred the development of cordless products that we take for granted everyday. In the 1960s, NASA asked Black Decker to develop a special drill that would be powerful enough to cut through hard layers of the lunar surface and be lightweight, compact, and operate under its own power source, allowing Apollo astronauts to collect lunar samples further away from the Lunar Experiment Module. In response, Black Decker developed a computer program that analyzed and optimized drill motor operations. From their analysis, engineers were able to design a motor that was powerful yet required minimal battery power to operate. Since those first days of cordless products, Black Decker has continued to refine this technology and they now sell their rechargeable products worldwide (i.e. the Dustbuster, cordless tools for home and industrial use, and medical tools.)
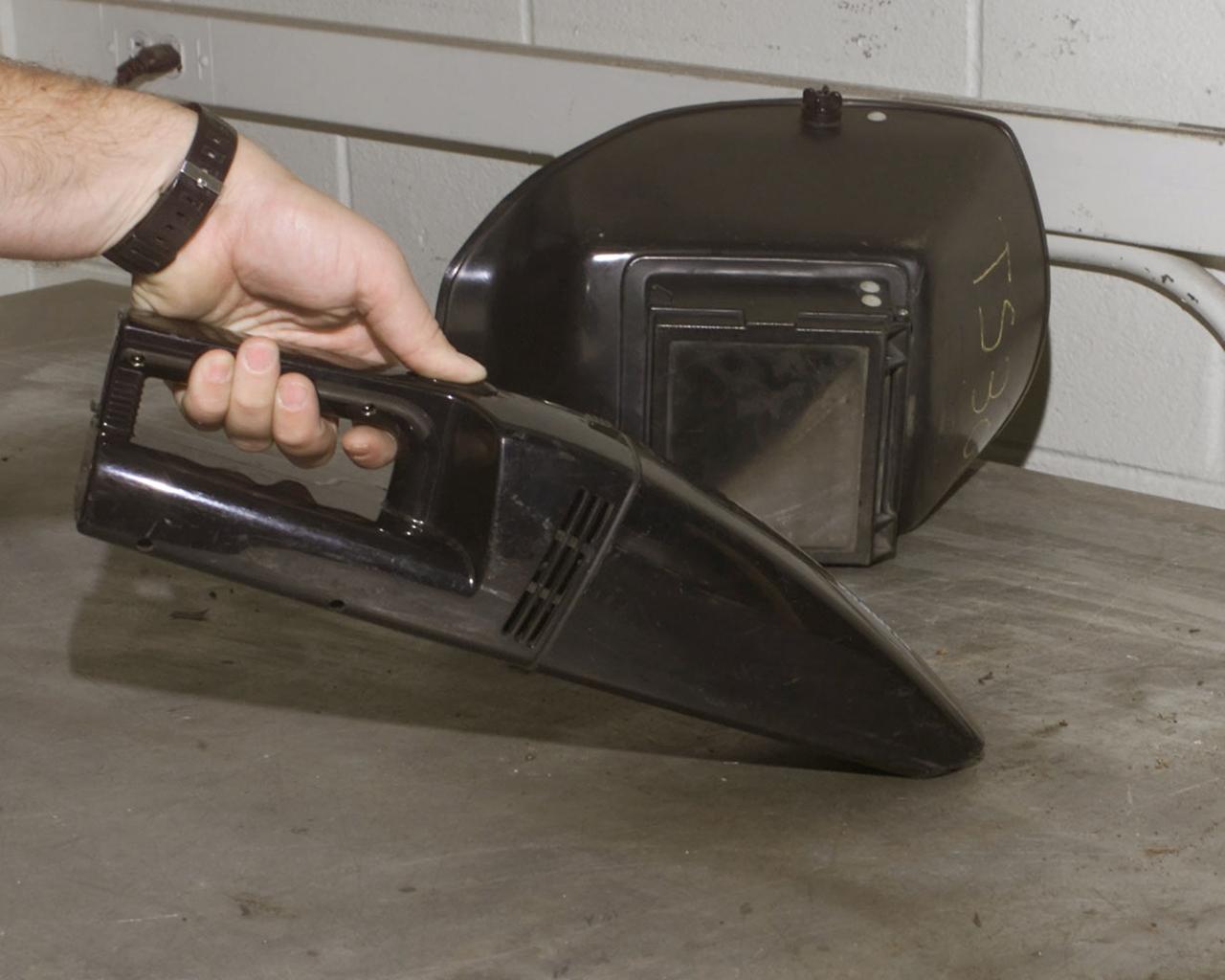

Apollo-era technology spurred the development of cordless products that we take for granted everyday. In the 1960s, NASA asked Black Decker to develop a special drill that would be powerful enough to cut through hard layers of the lunar surface and be lightweight, compact, and operate under its own power source, allowing Apollo astronauts to collect lunar samples further away from the Lunar Experiment Module. In response, Black Decker developed a computer program that analyzed and optimized drill motor operations. From their analysis, engineers were able to design a motor that was powerful yet required minimal battery power to operate. Since those first days of cordless products, Black Decker has continued to refine this technology and they now sell their rechargeable products worldwide (i.e. the Dustbuster, cordless tools for home and industrial use, and medical tools.)
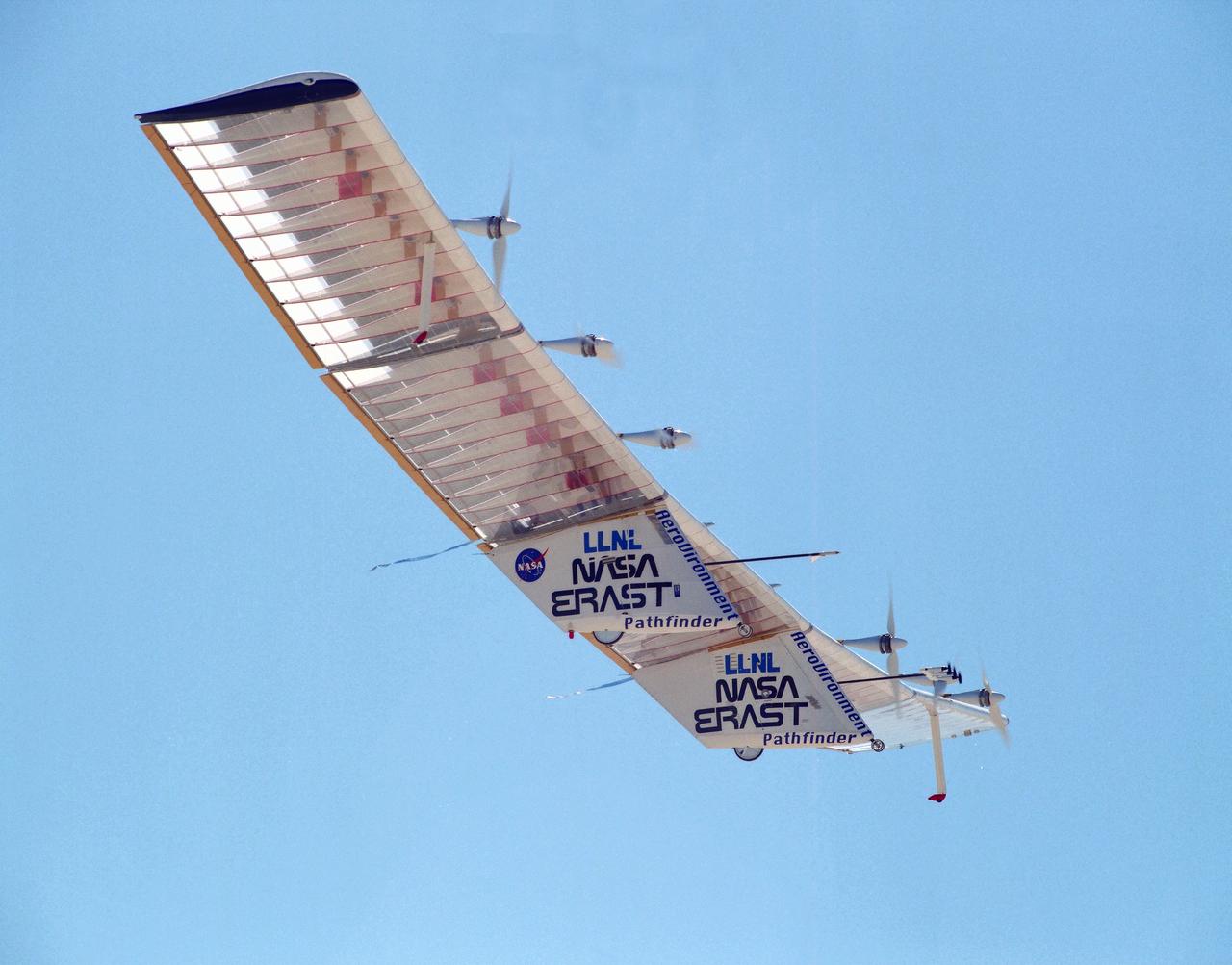

The Pathfinder research aircraft's wing structure was clearly defined as it soared under a clear blue sky during a test flight July 27, 1995, from Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The center section and outer wing panels of the aircraft had ribs constructed of thin plastic foam, while the ribs in the inner wing panels are fabricated from lightweight composite material. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., the Pathfinder was one of several unmanned aircraft being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
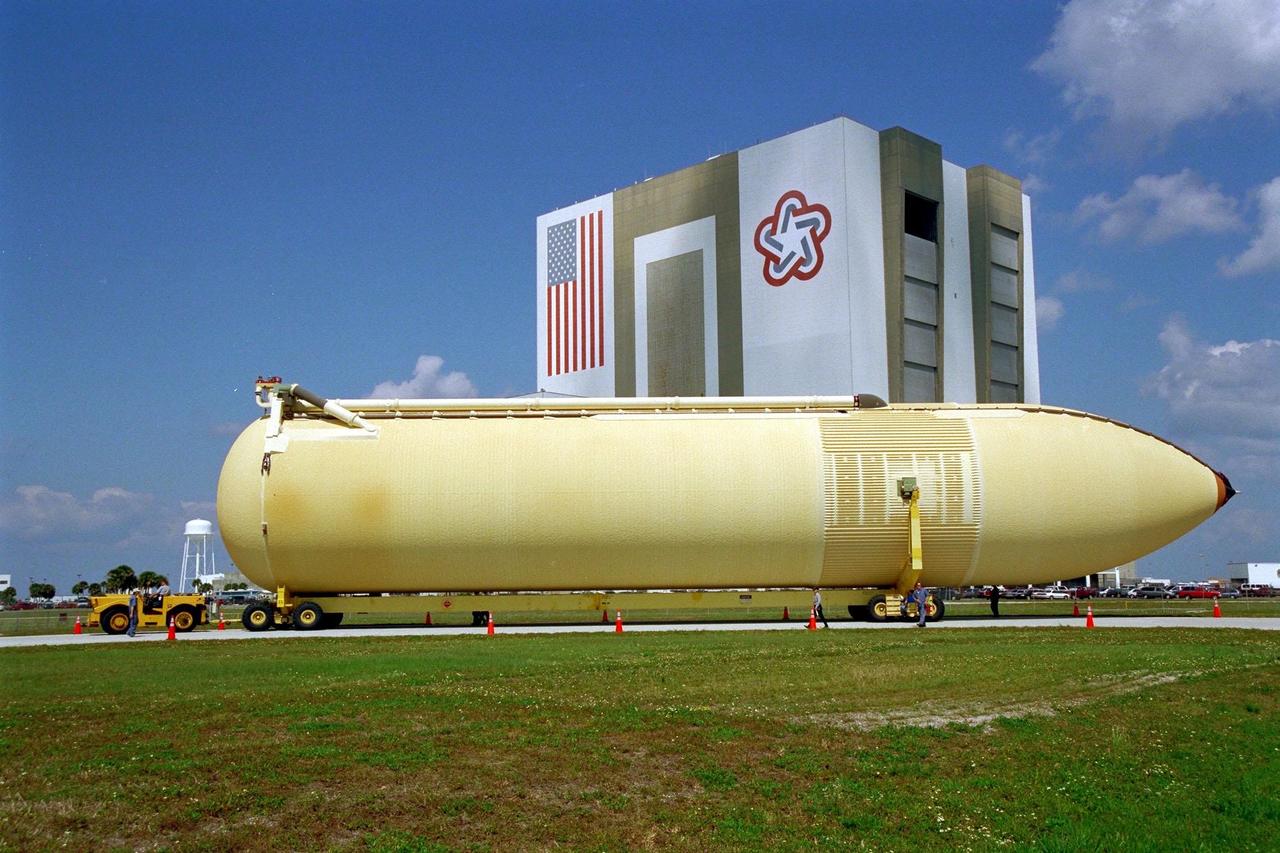

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's second lightweight external tank arrives at Kennedy Space Center and is moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building after removal from the barge by which it was delivered to the Launch Complex 39 Turn Basin. This external tank is slated for use on the STS-88 launch, the first International Space Station assembly flight. The improved tank is about 7,000 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. The tank was sent from the NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is moved on a barge toward the turn basin at Kennedy Space Center from Port Canaveral, Fla. The tank is scheduled to undergo processing at KSC's Vehicle Assembly Building for flight on STS-91, targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. The tank was sent from the NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans
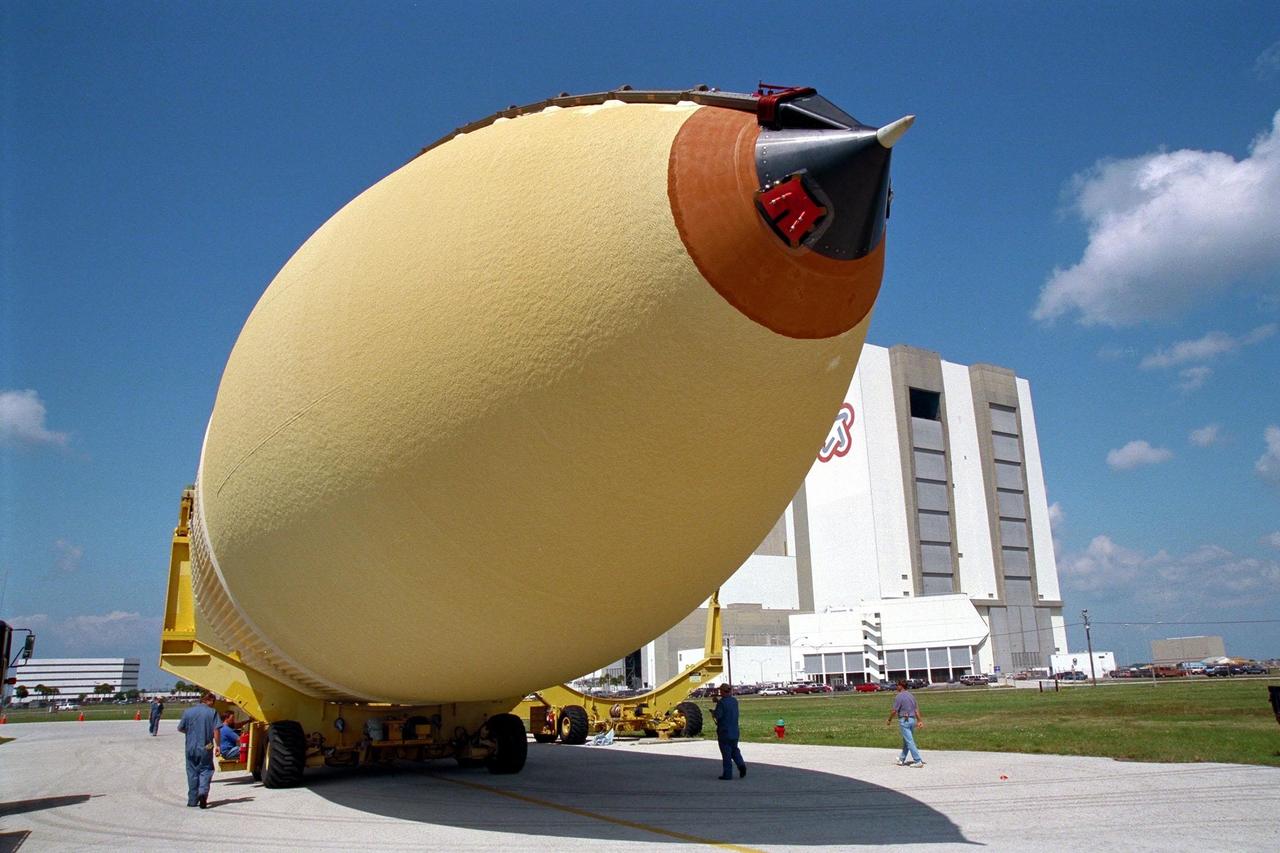

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's second lightweight external tank arrives at Kennedy Space Center and is moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building after removal from the barge by which it was delivered to the Launch Complex 39 Turn Basin. This external tank is slated for use on the STS-88 launch, the first International Space Station assembly flight. The improved tank is about 7,000 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. The tank was sent from the NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans.
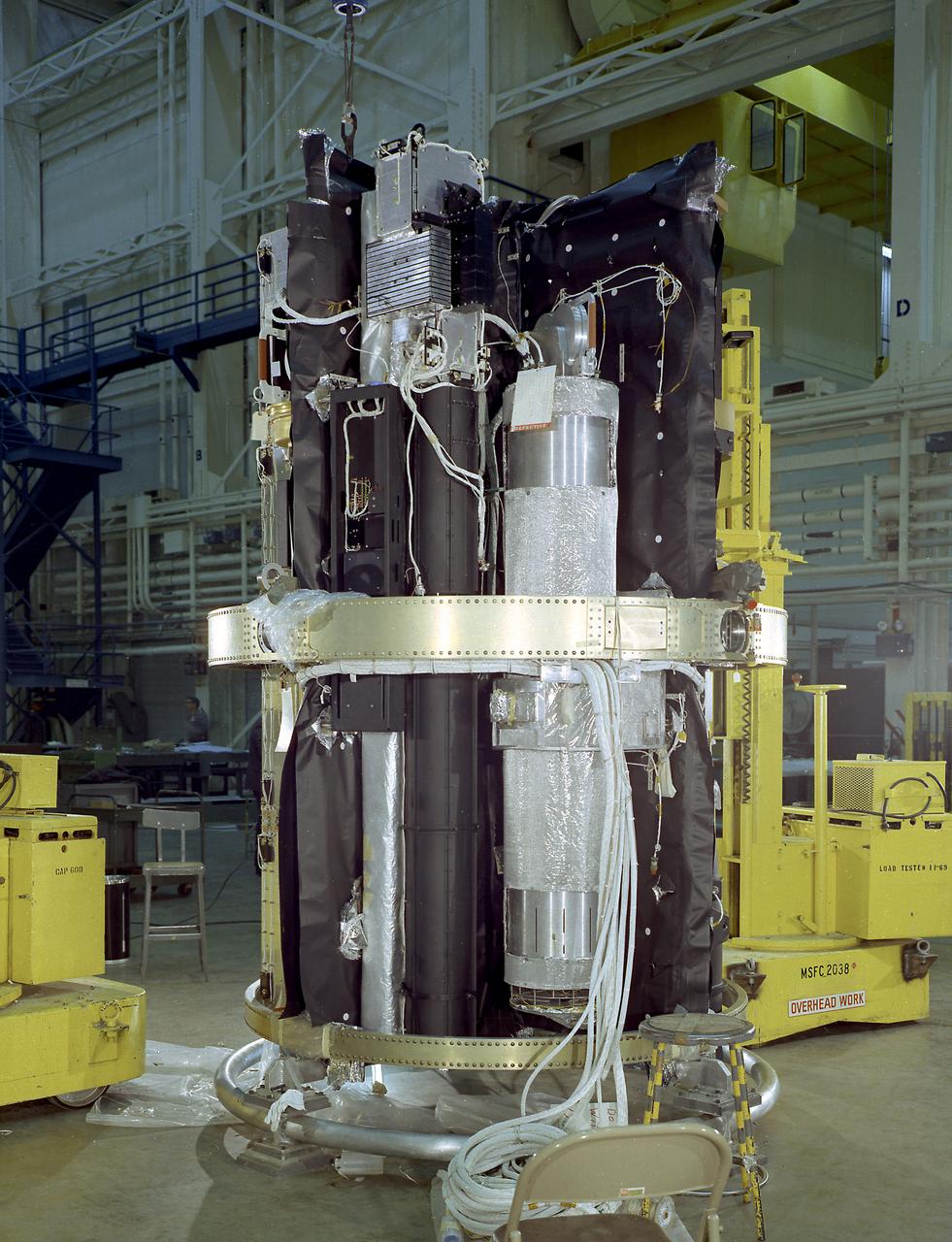
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This image shows the ATM spar assembly. All solar telescopes, the fine Sun sensors, and some auxiliary systems are mounted on the spar, a cruciform lightweight perforated metal mounting panel that divides the 10-foot long canister lengthwise into four equal compartments. The spar assembly was nested inside a cylindrical canister that fit into the rack, a complex frame, and was protected by the solar shield.
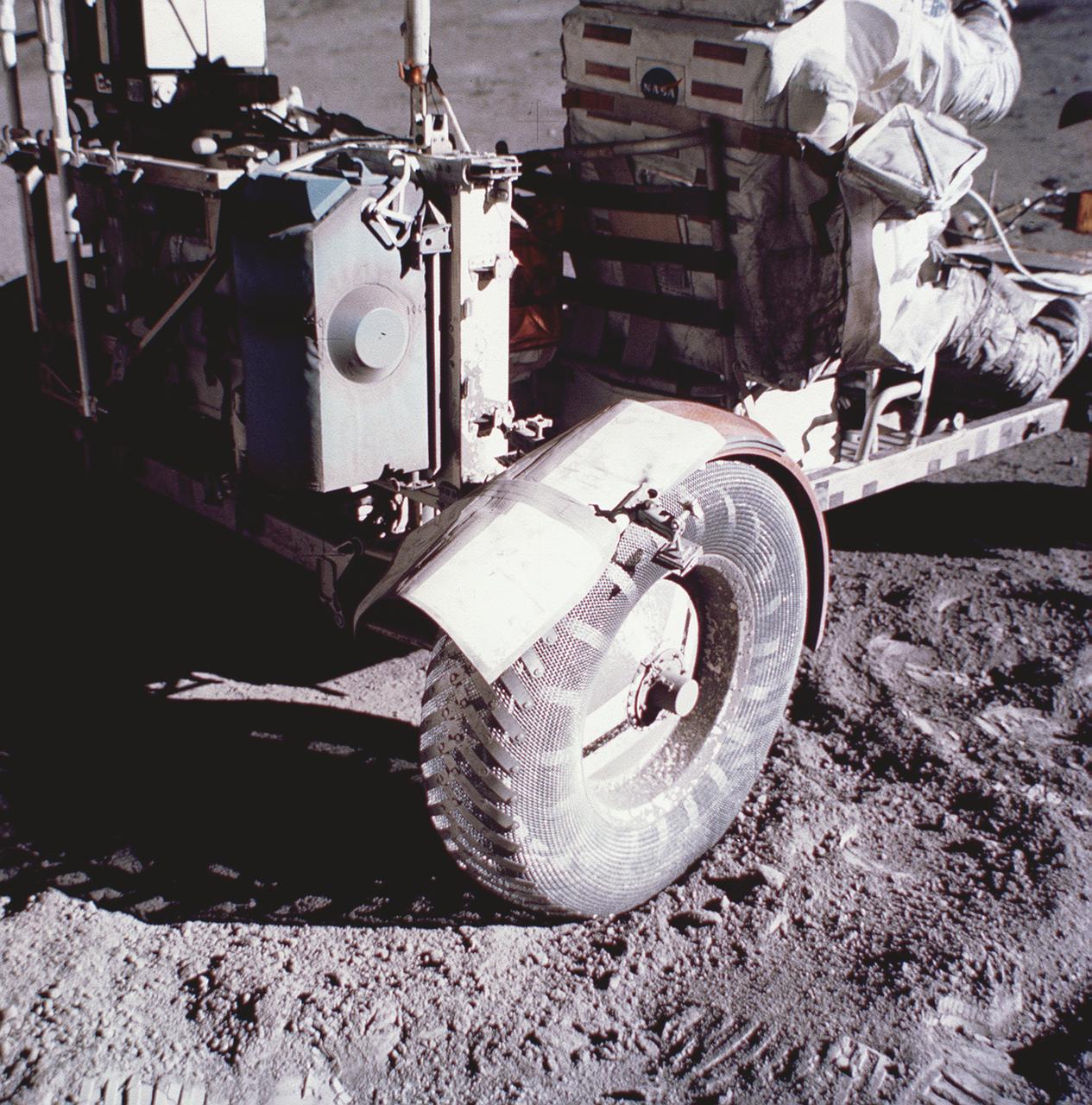

This photograph taken during the Apollo 17 mission (the last mission of the Apollo Program), depicts stiff plasticized maps being taped together and fastened by clamps to patch a broken fender of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard the Skylab. The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This image shows the ATM spar assembly. All solar telescopes, the fine Sun sensors, and some auxiliary systems are mounted on the spar, a cruciform lightweight perforated metal mounting panel that divides the 10-foot long canister lengthwise into four equal compartments. The spar assembly was nested inside a cylindrical canister that fit into the rack, a complex frame, and was protected by the solar shield.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's second lightweight external tank arrives at Kennedy Space Center and is moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building after removal from the barge by which it was delivered to the Launch Complex 39 Turn Basin. This external tank is slated for use on the STS-88 launch, the first International Space Station assembly flight. The improved tank is about 7,000 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. The tank was sent from the NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans
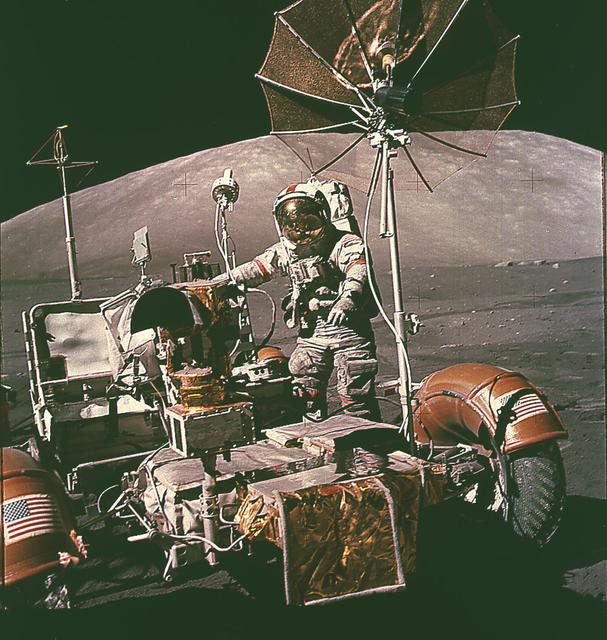

This is an Apollo 17 onboard photo of an astronaut beside the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface. Designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company, the LRV was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and increased the range of astronauts' mobility and productivity on the lunar surface. This lightweight electric car had battery power sufficient for about 55 miles. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear, cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees.
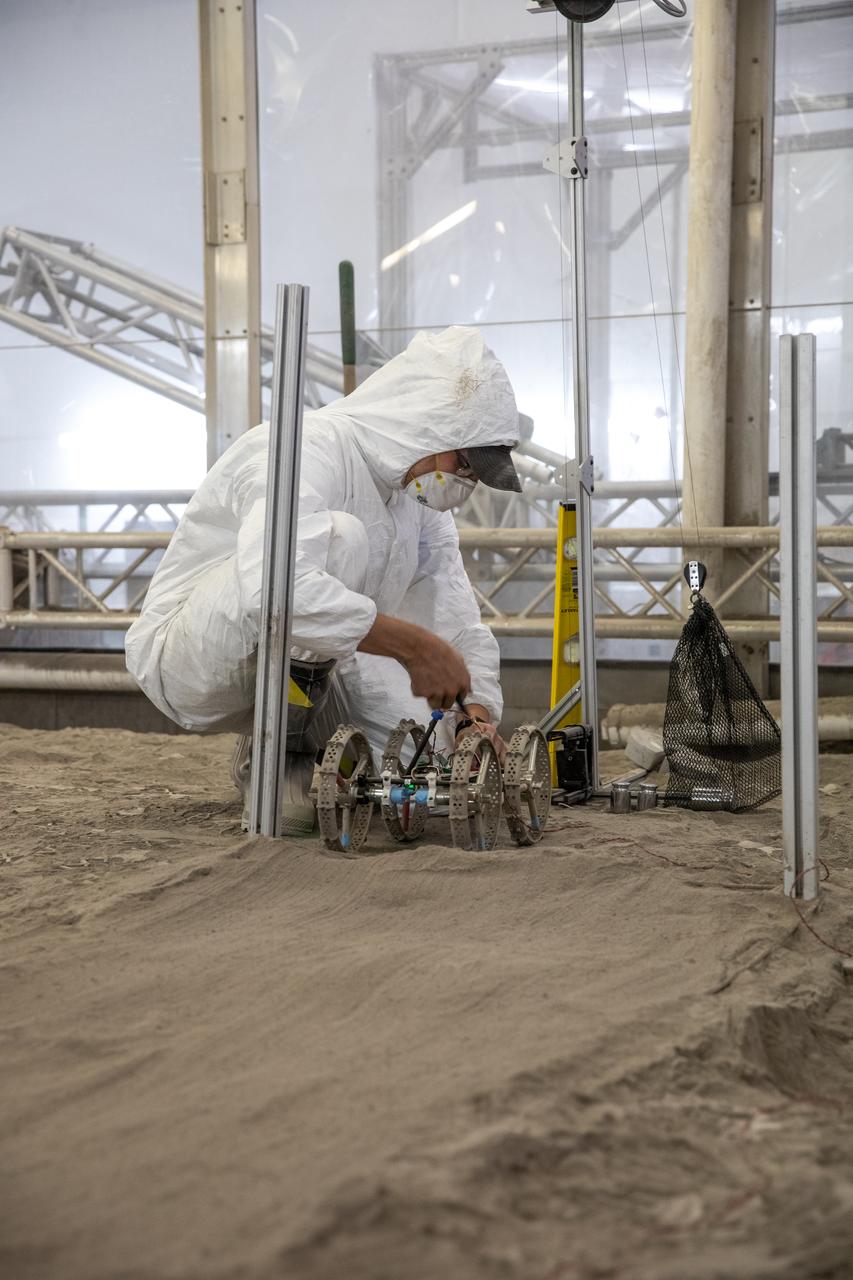

Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker stages Astrobotic’s mass-offloaded CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – for a drawbar pull test inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
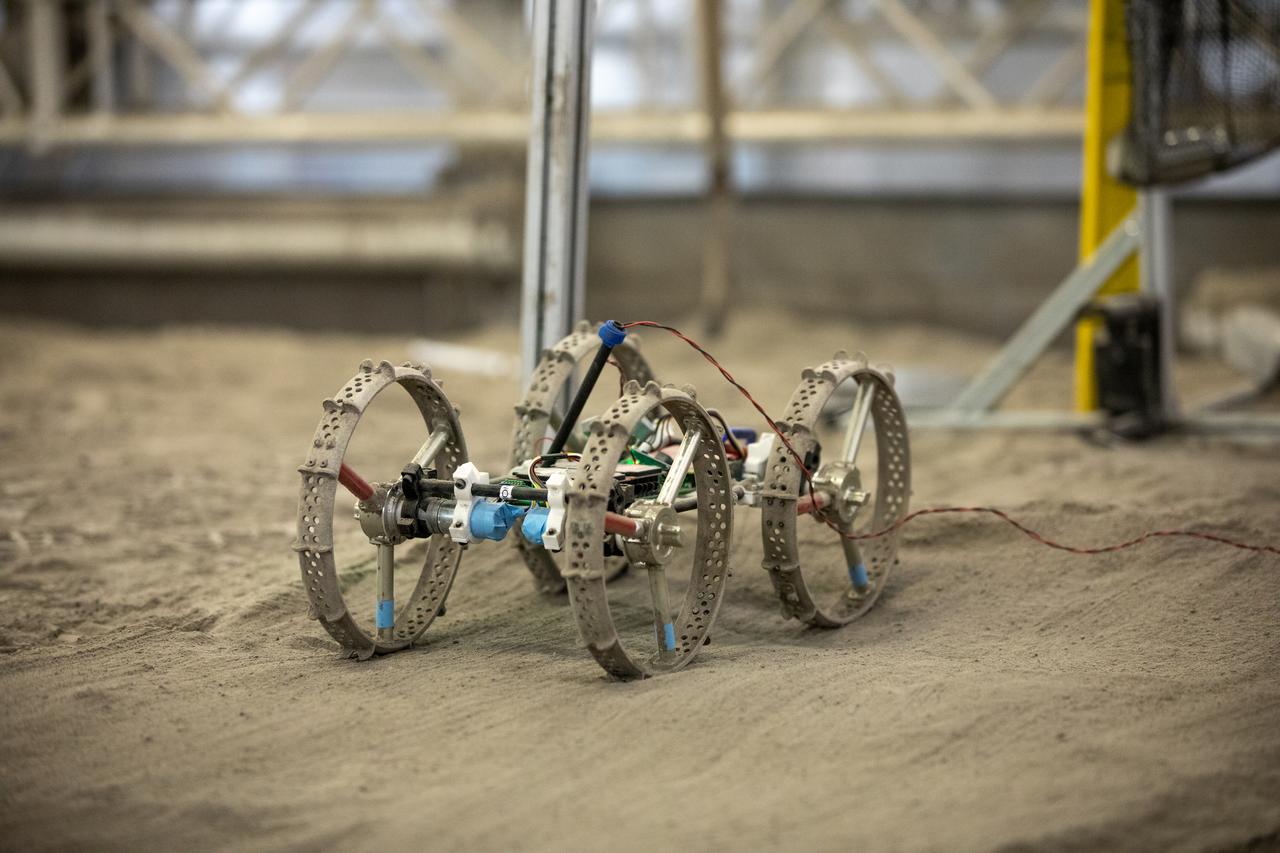
A mass-offloaded version of Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – is used to simulate mobility in low lunar gravity inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
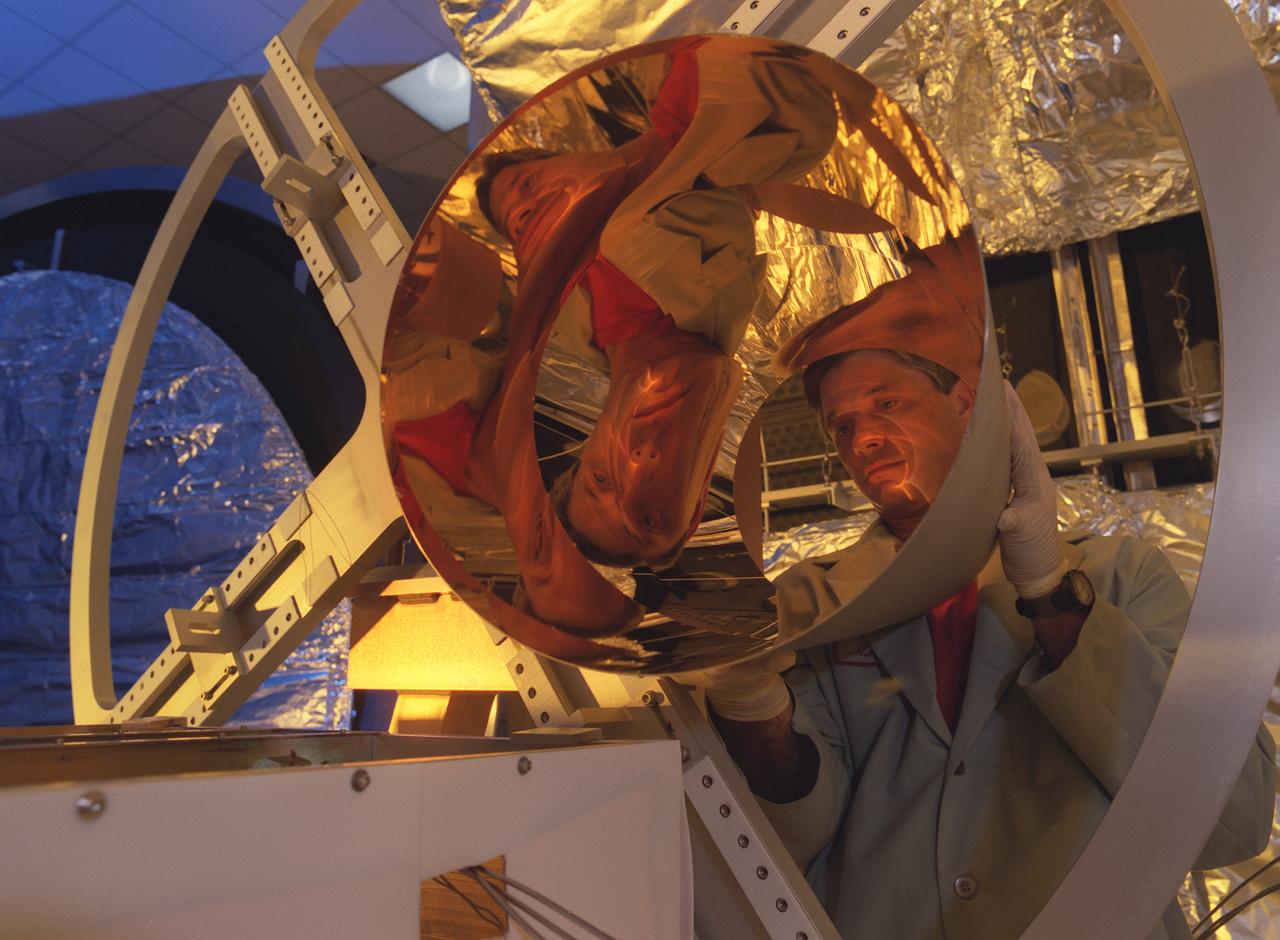

NASA's Space Optics Manufacturing Center has been working to expand our view of the universe via sophisticated new telescopes. The Optics Center's goal is to develop low-cost, advanced space optics technologies for the NASA program in the 21st century - including the long-term goal of imaging Earth-like planets in distant solar systems. To reduce the cost of mirror fabrication, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) has developed replication techniques, the machinery and materials to replicate electro-formed nickel mirrors. The process allows fabricating precisely shaped mandrels to be used and reused as masters for replicating high-quality mirrors. This image shows a lightweight replicated x-ray mirror with gold coatings applied.
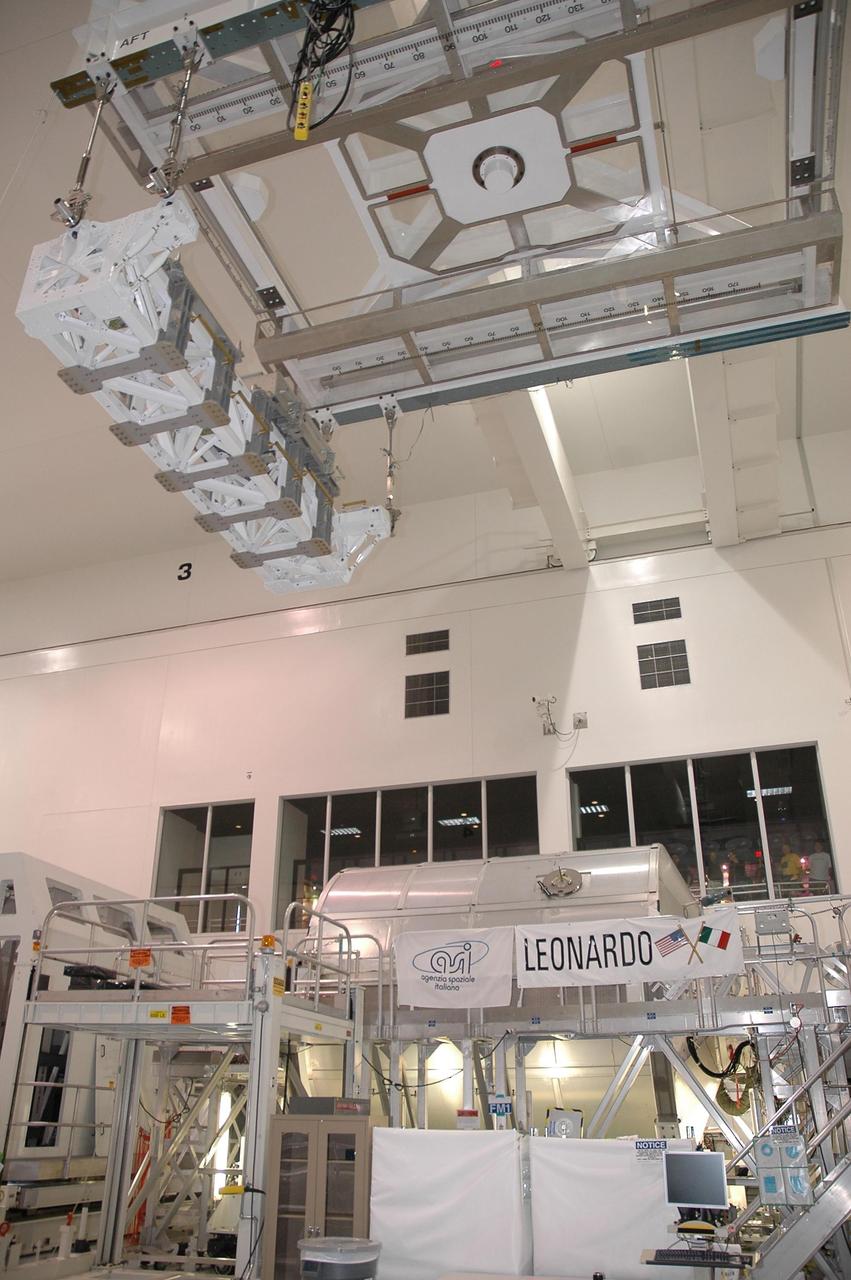

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, a crane moves the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC) over an abundance of hardware and equipment including the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. Slated to fly on space shuttle mission STS-121, the LMC is ready to be delivered to Launch Pad 39B for installation into orbiter Discovery. It is a cross-bay carrier for hardware required to perform development test objective 848. Test objective 848 is a demonstration of the tools and techniques developed to repair damaged orbiter thermal protection system tiles during a spacewalk, or extravehicular activity. The target launch window for STS-121 is July 1 to July 19, 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Husten

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers monitor the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC) as it is lifted by a crane toward a payload canister, doors open to receive it. Slated to fly on space shuttle mission STS-121, the LMC is ready to be delivered to Launch Pad 39B for installation into orbiter Discovery. It is a cross-bay carrier for hardware required to perform development test objective 848. Test objective 848 is a demonstration of the tools and techniques developed to repair damaged orbiter thermal protection system tiles during a spacewalk, or extravehicular activity. The target launch window for STS-121 is July 1 to July 19, 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Husten
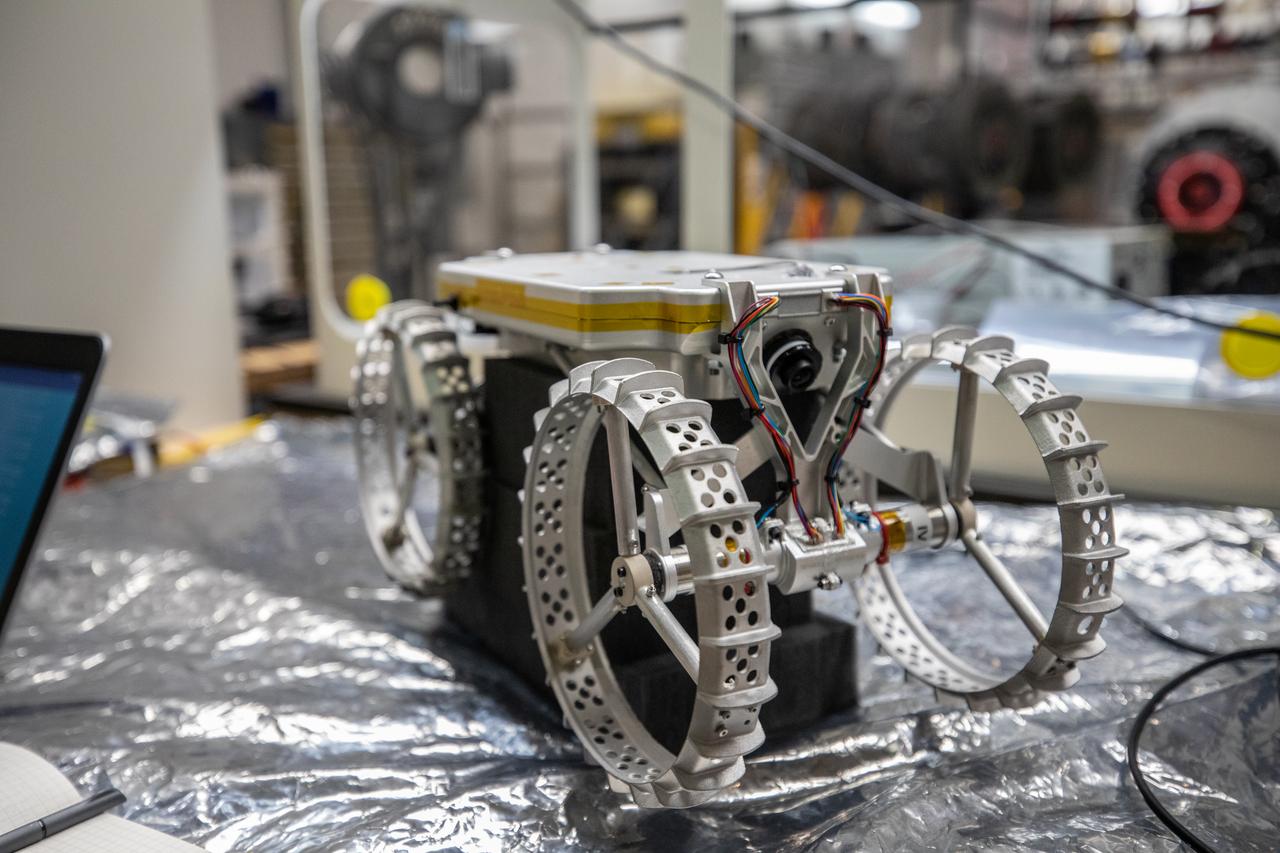
Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – is photographed in its benchtop testing configuration at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is planning to use the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
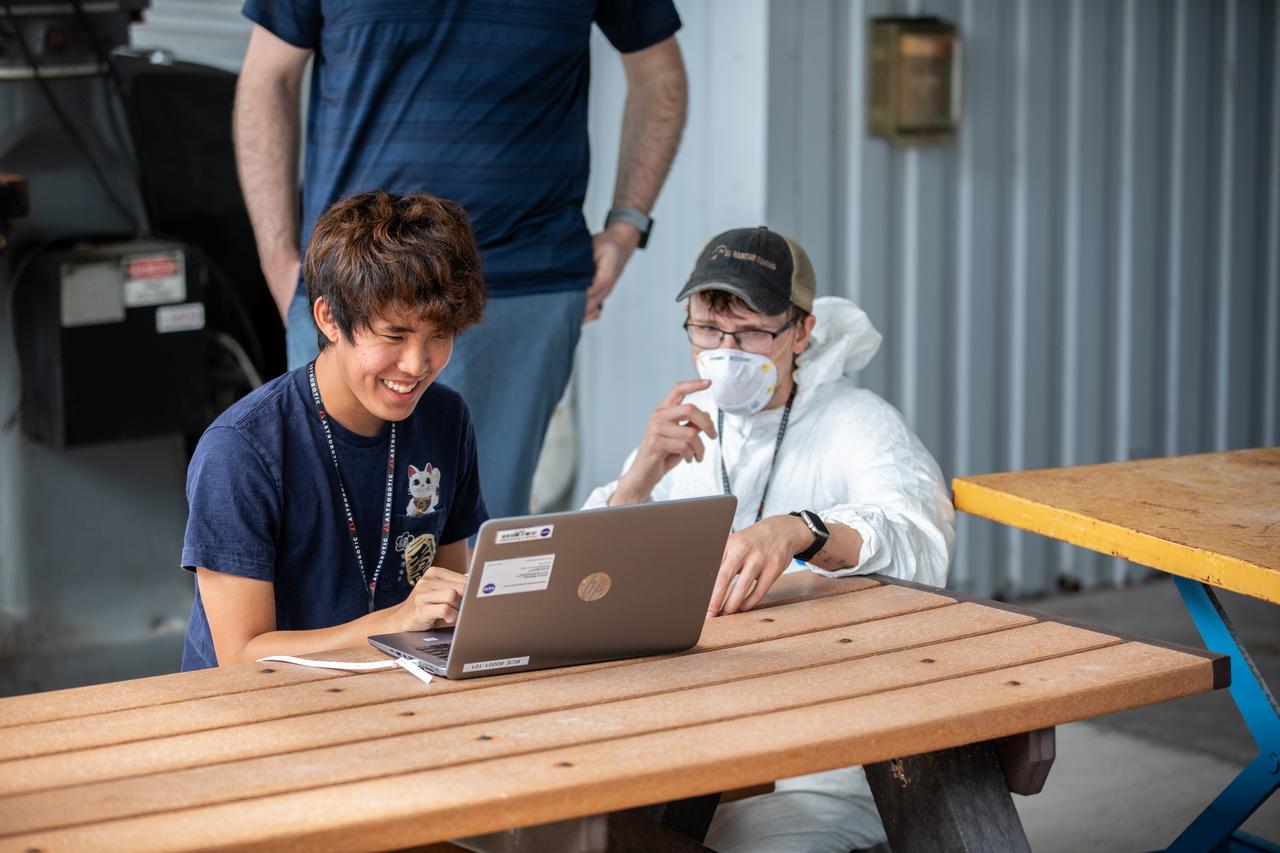

Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker (right) and Software Engineering intern Ashten Akemoto create a mobility routine for Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – using the company’s ground software at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
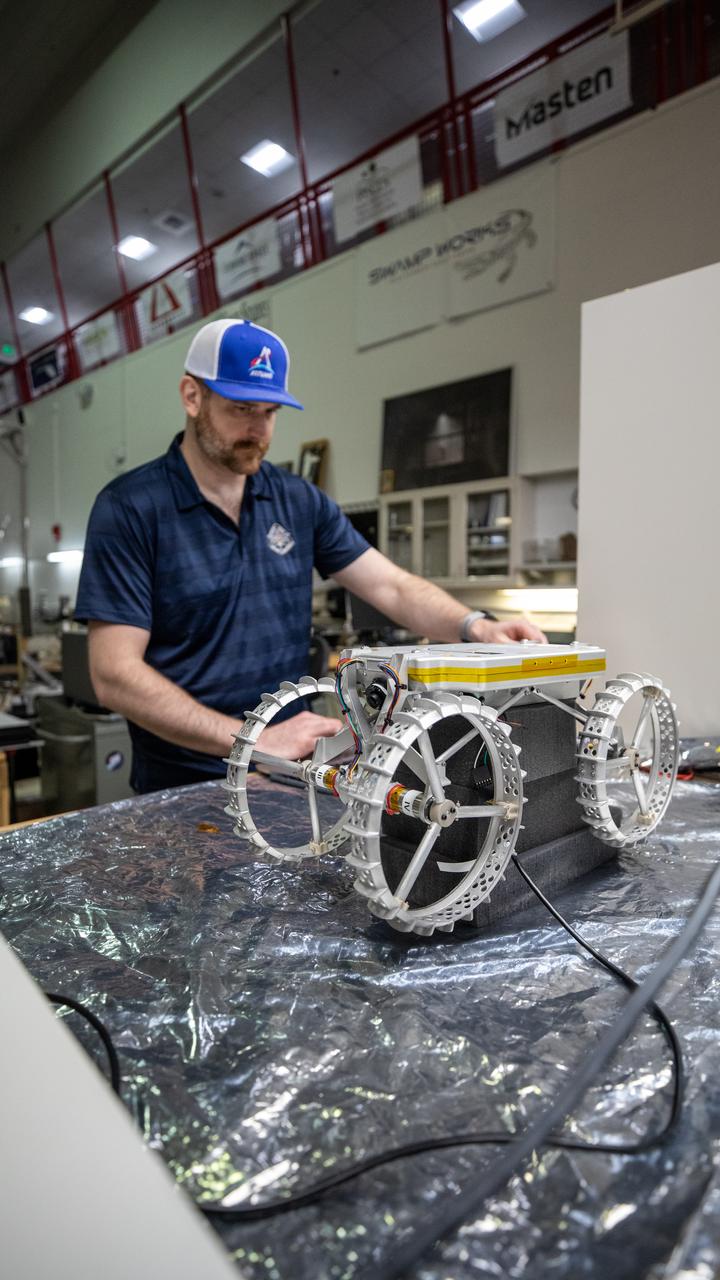

Robotics Software Engineer II Chris Rampolla runs benchtop verifications on Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – before delivery to Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is planning to use Swamp Work’s Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
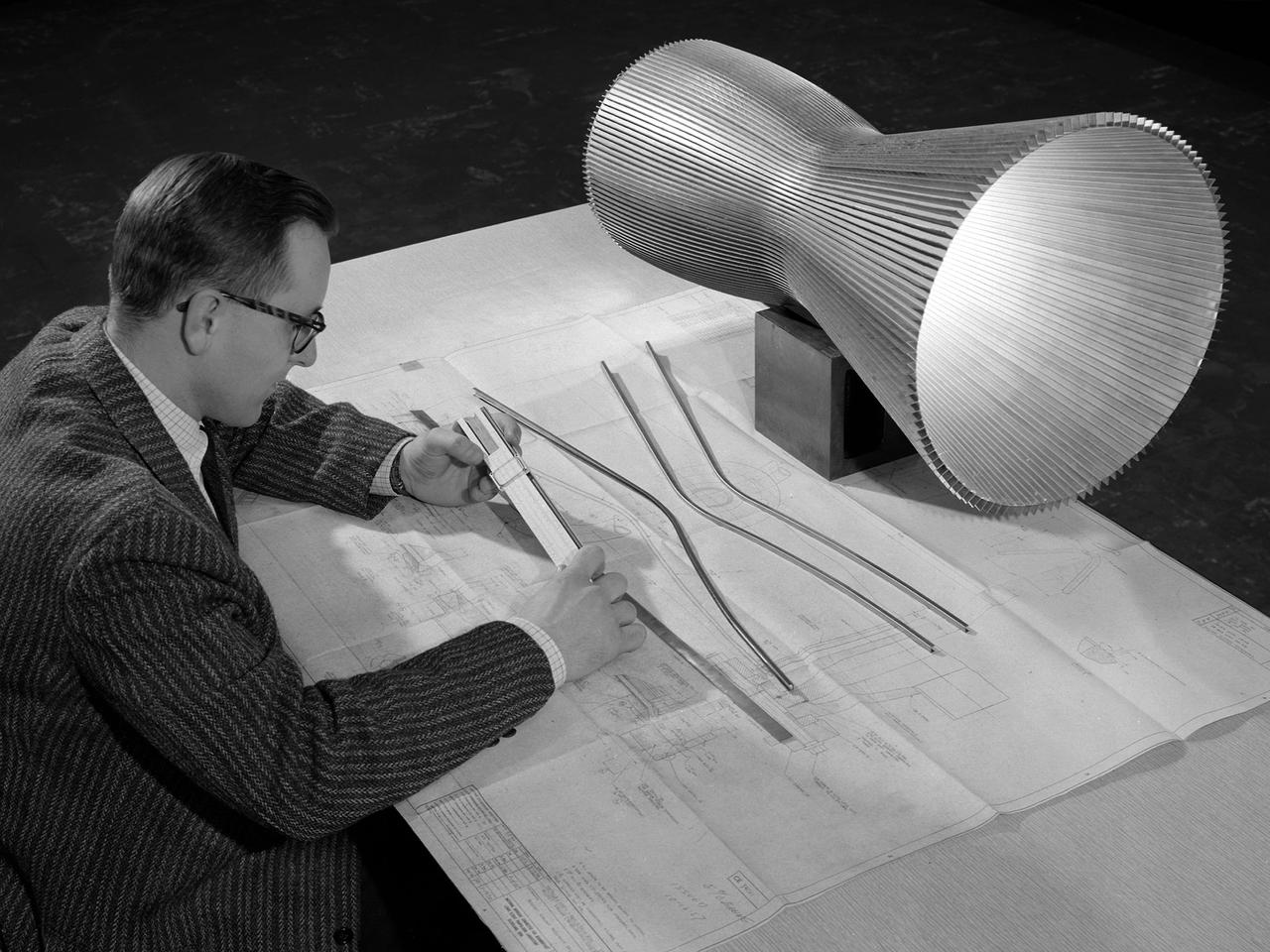
An engineer at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center examines a drawing showing the assembly and details of a 20,000-pound thrust regeneratively cooled rocket engine. The engine was being designed for testing in Lewis’ new Rocket Engine Test Facility, which began operating in the fall of 1957. The facility was the largest high-energy test facility in the country that was capable of handling liquid hydrogen and other liquid chemical fuels. The facility’s use of subscale engines up to 20,000 pounds of thrust permitted a cost-effective method of testing engines under various conditions. The Rocket Engine Test Facility was critical to the development of the technology that led to the use of hydrogen as a rocket fuel and the development of lightweight, regeneratively-cooled, hydrogen-fueled rocket engines. Regeneratively-cooled engines use the cryogenic liquid hydrogen as both the propellant and the coolant to prevent the engine from burning up. The fuel was fed through rows of narrow tubes that surrounded the combustion chamber and nozzle before being ignited inside the combustion chamber. The tubes are visible in the liner sitting on the desk. At the time, Pratt and Whitney was designing a 20,000-pound thrust liquid-hydrogen rocket engine, the RL-10. Two RL-10s would be used to power the Centaur second-stage rocket in the 1960s. The successful development of the Centaur rocket and the upper stages of the Saturn V were largely credited to the work carried out Lewis.

The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
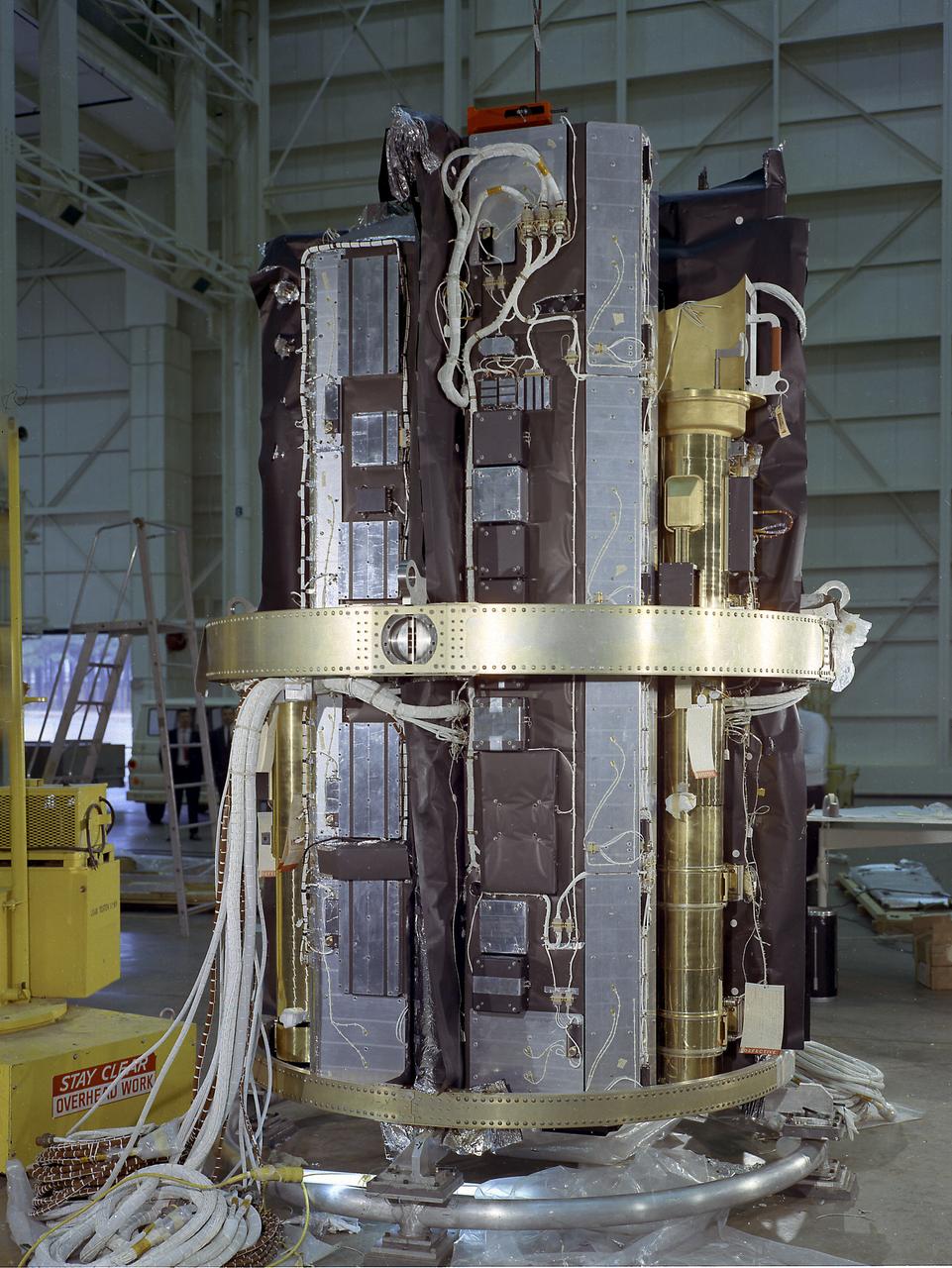
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This image depicts the sun end and spar of the ATM flight unit showing individual telescopes. All solar telescopes, the fine Sun sensors, and some auxiliary systems are mounted on the spar, a cruciform lightweight perforated metal mounting panel that divides the canister lengthwise into four equal compartments. The spar assembly was nested inside a cylindrical canister that fit into a complex frame named the rack, and was protected by the solar shield.
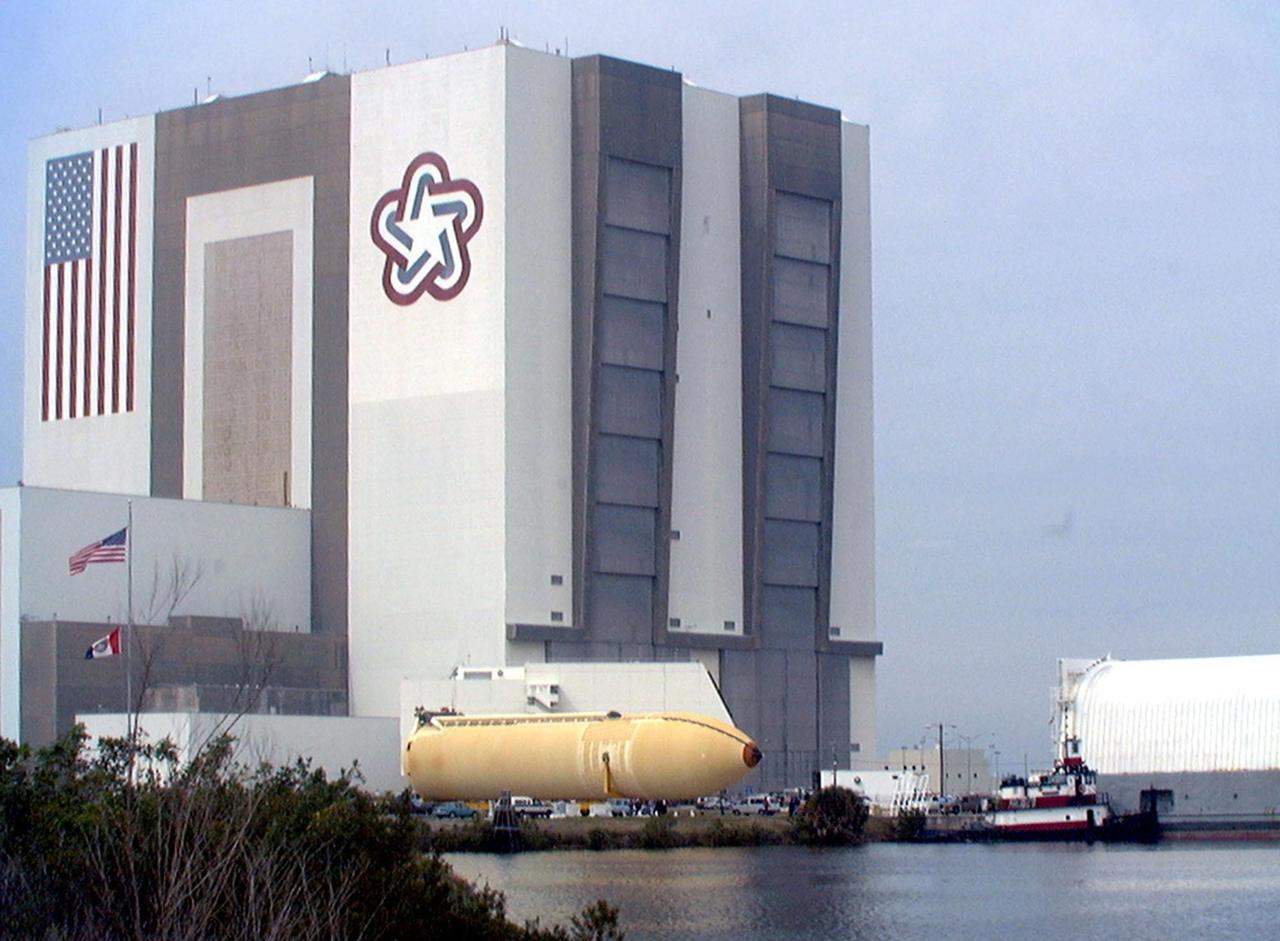

The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
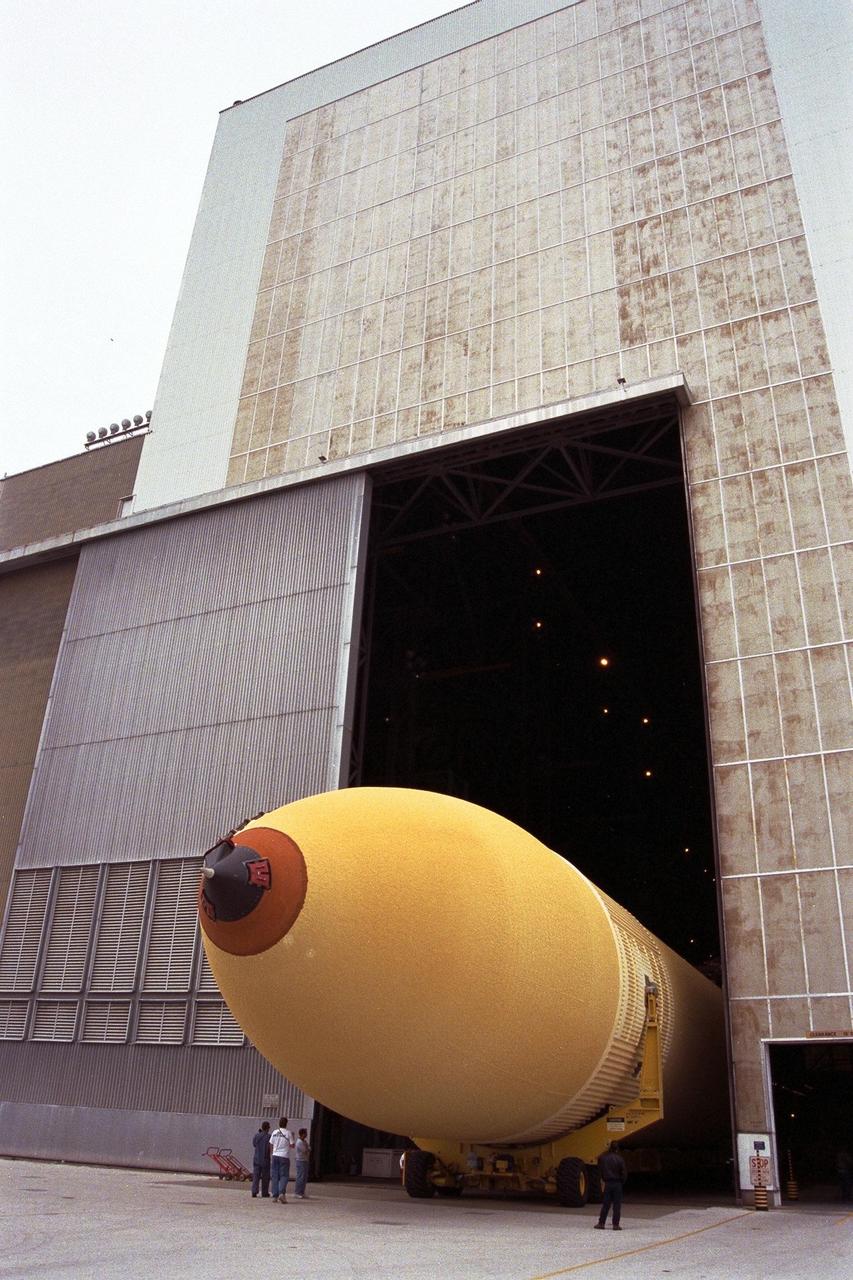

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way into Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
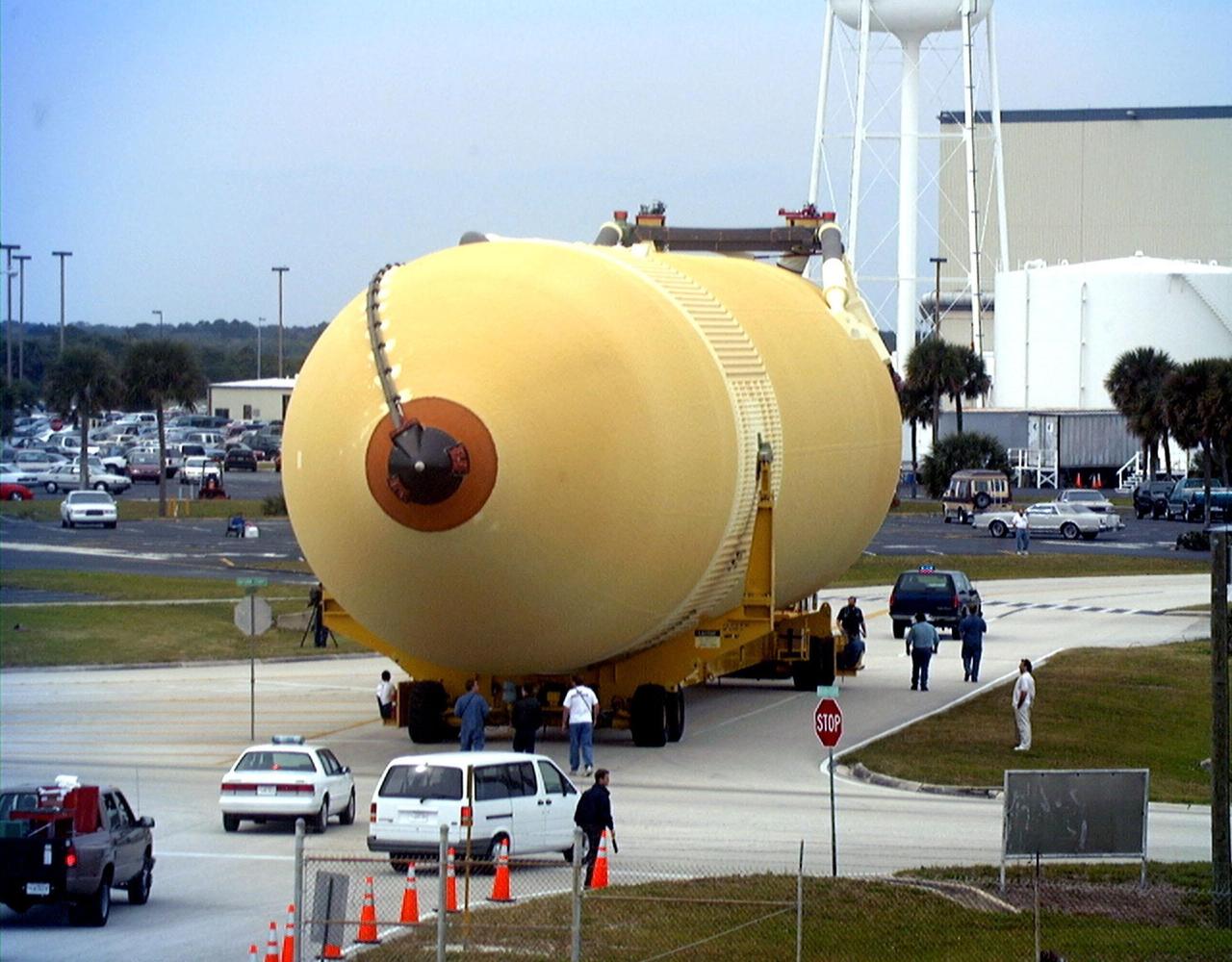

The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well

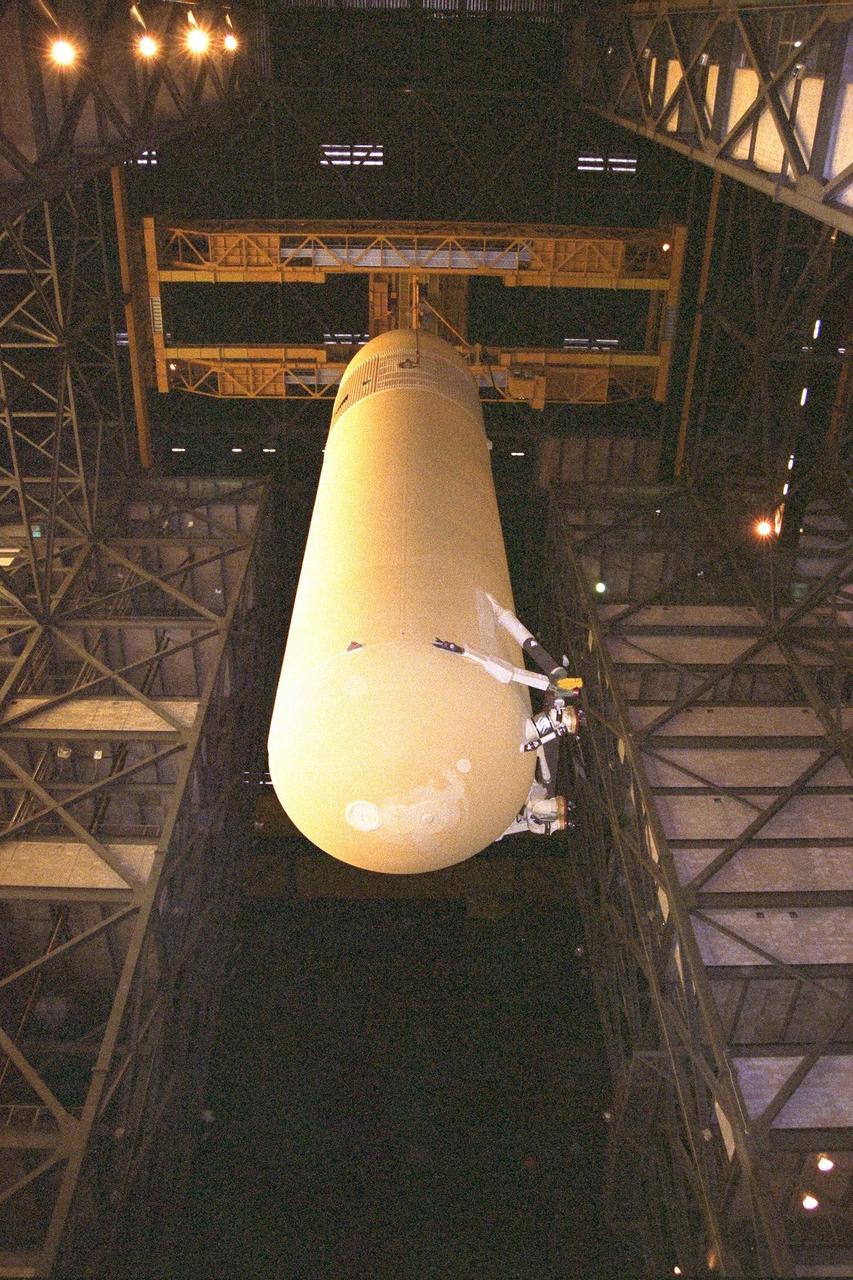
The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
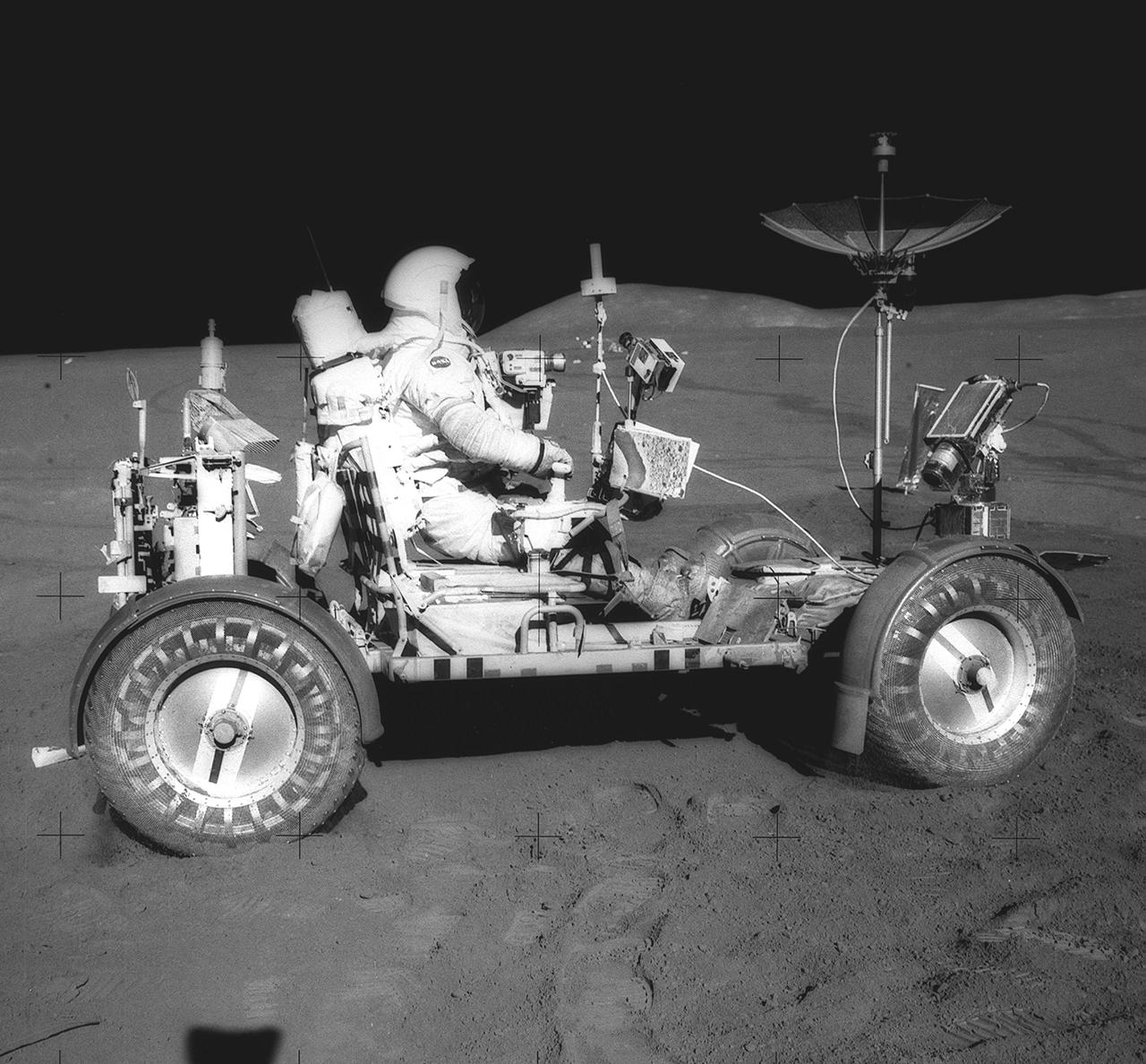

This photograph was taken during the Apollo 15 mission on the lunar surface. Astronaut David R. Scott waits in the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) for astronaut James Irwin for the return trip to the Lunar Module, Falcon, with rocks and soil collected near the Hadley-Apernine landing site. The Apollo 15 was the first mission to use the LRV. Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
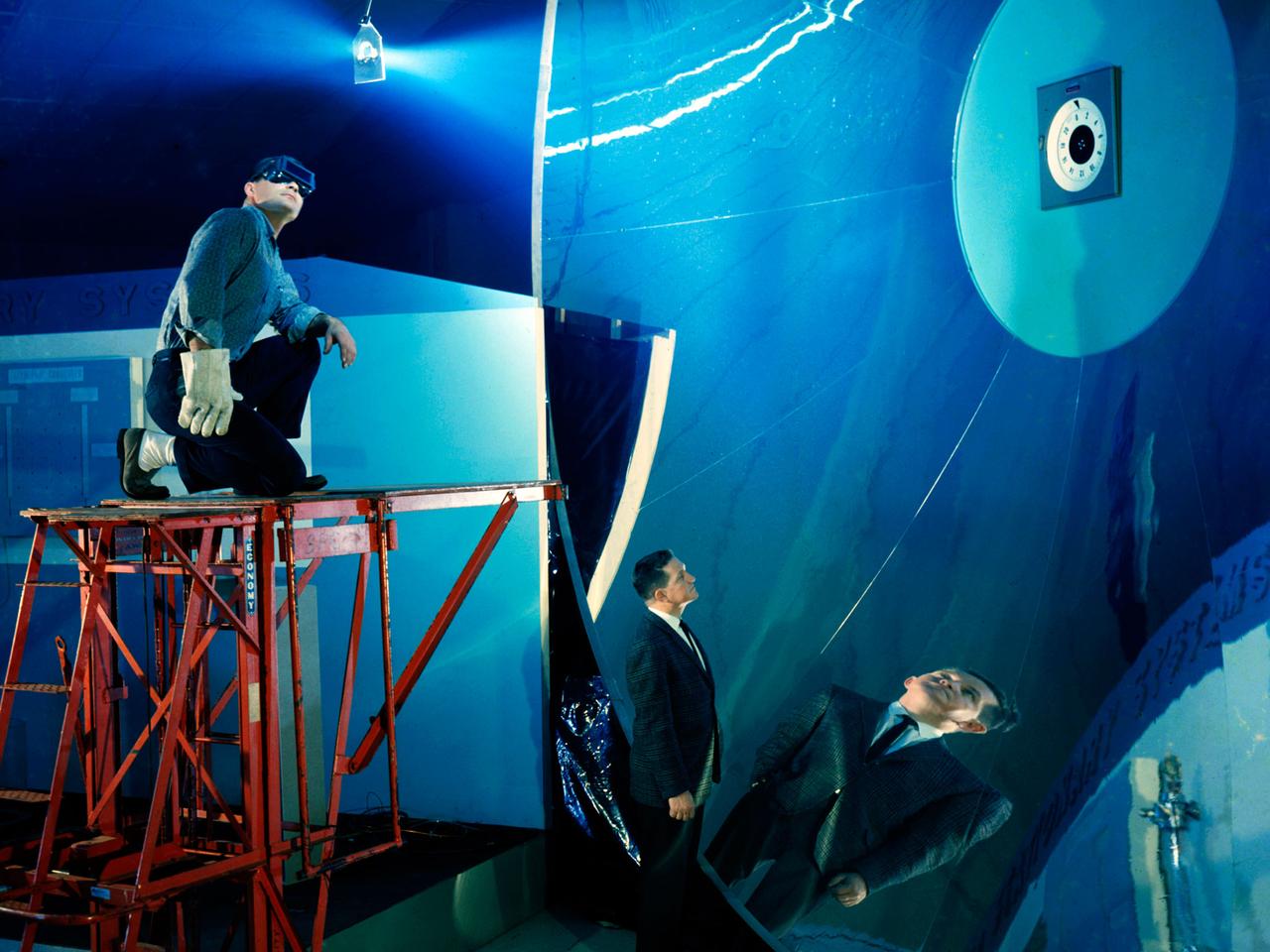

NASA’s Lewis Research Center conducted extensive research programs in the 1960s and 1970s to develop systems that provide electrical power in space. One system, the Brayton cycle engine, converted solar thermal energy into electrical power. This system operated on a closed-loop Brayton thermodynamic cycle. The Brayton system relied on this large mirror to collect radiation from the sun. The mirror concentrated the Sun's rays on a heat storage receiver which warmed the Brayton system’s working fluid, a helium-xenon gas mixture. The heated fluid powered the system’s generator which produced power. In the mid-1960s Lewis researchers constructed this 30-foot diameter prototype of a parabolic solar mirror for the Brayton cycle system. The mirror had to be rigid, impervious to micrometeorite strikes, and lightweight. This mirror was comprised of twelve 1-inch thick magnesium plate sections that were coated with aluminum. The mirror could be compactly broken into its sections for launch.

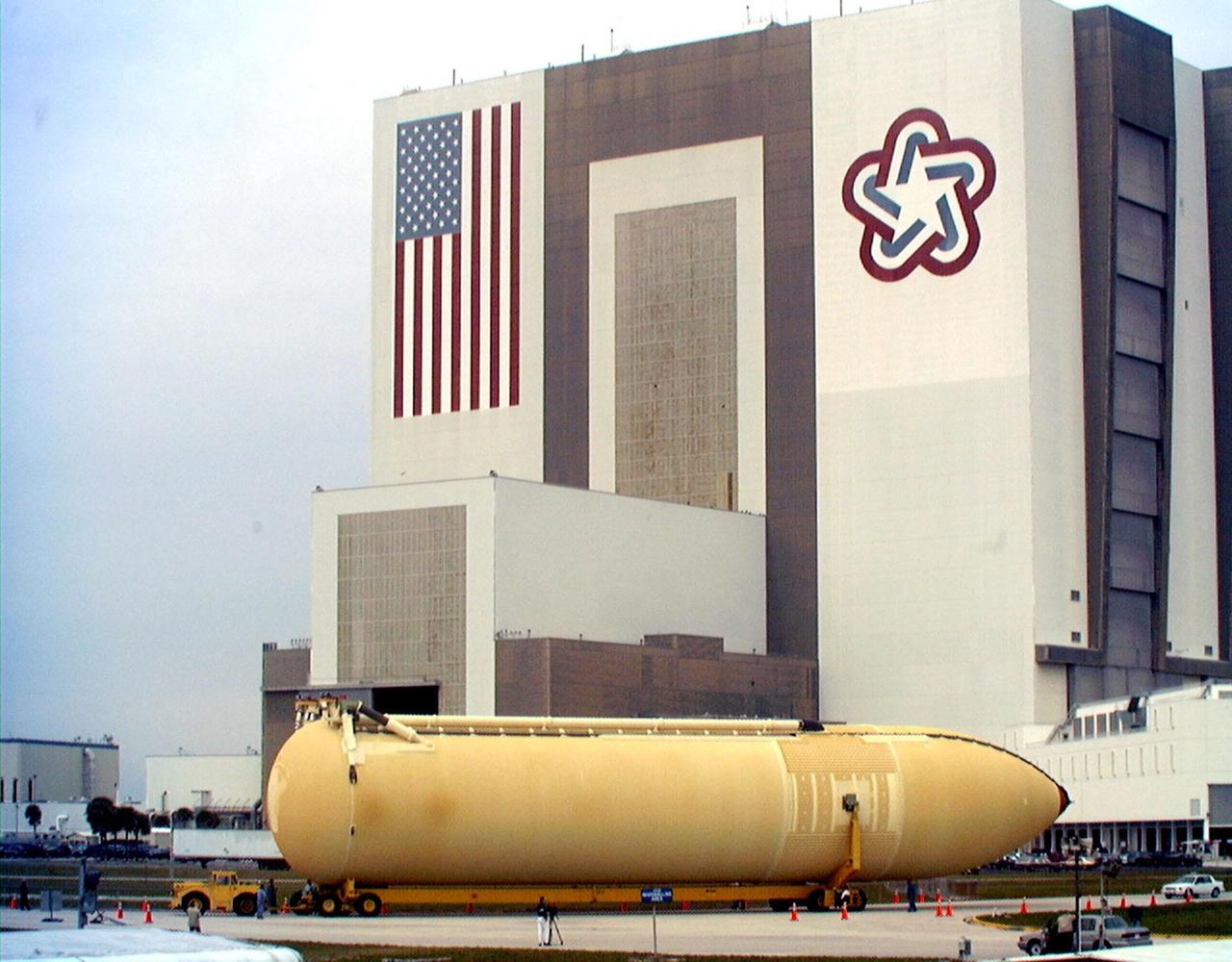
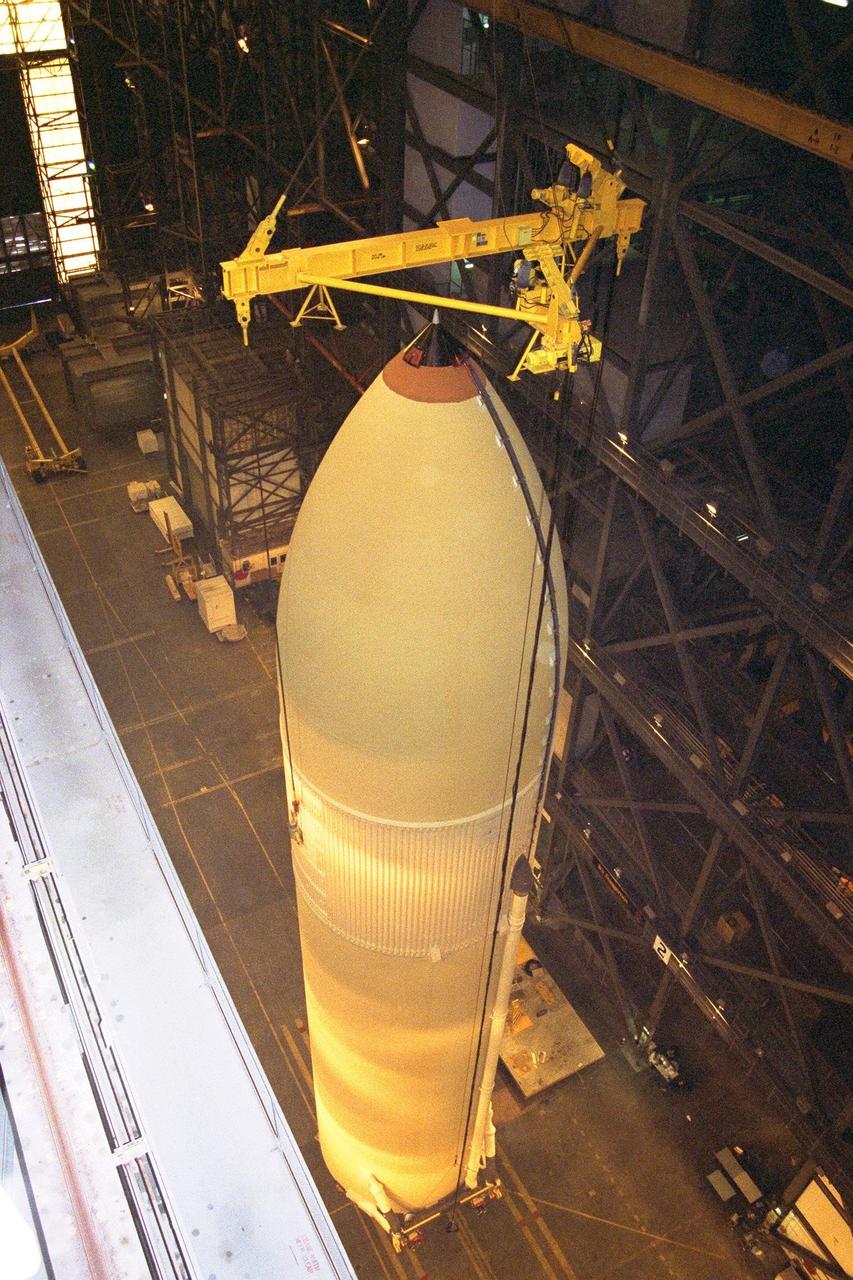
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is lifted in KSC's Vehicle Assembly Building for STS-91 pre-flight processing. STS-91 is targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
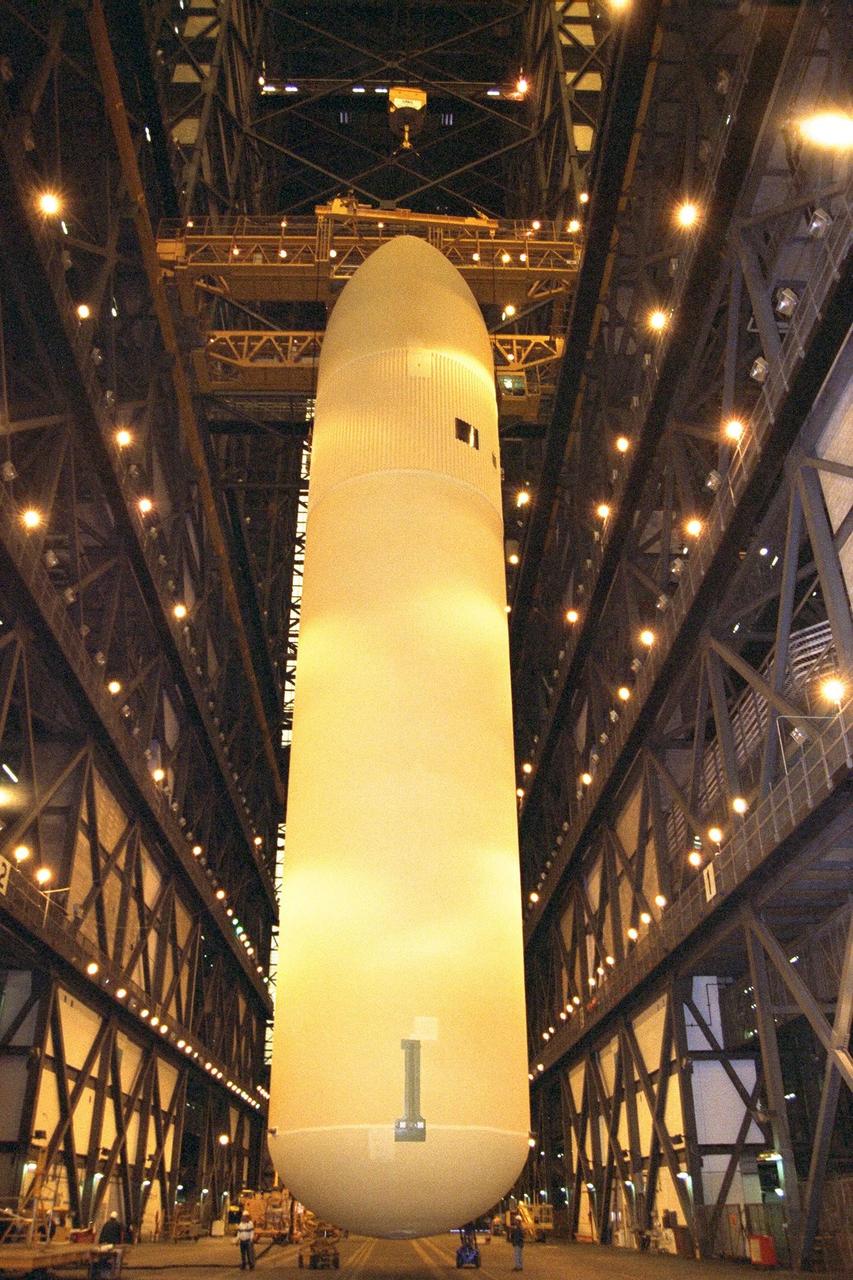

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is lifted in KSC's Vehicle Assembly Building for STS-91 pre-flight processing. STS-91 is targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. It was moved by barge to KSC on Feb. 6. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is lifted in KSC's Vehicle Assembly Building for STS-91 pre-flight processing. STS-91 is targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
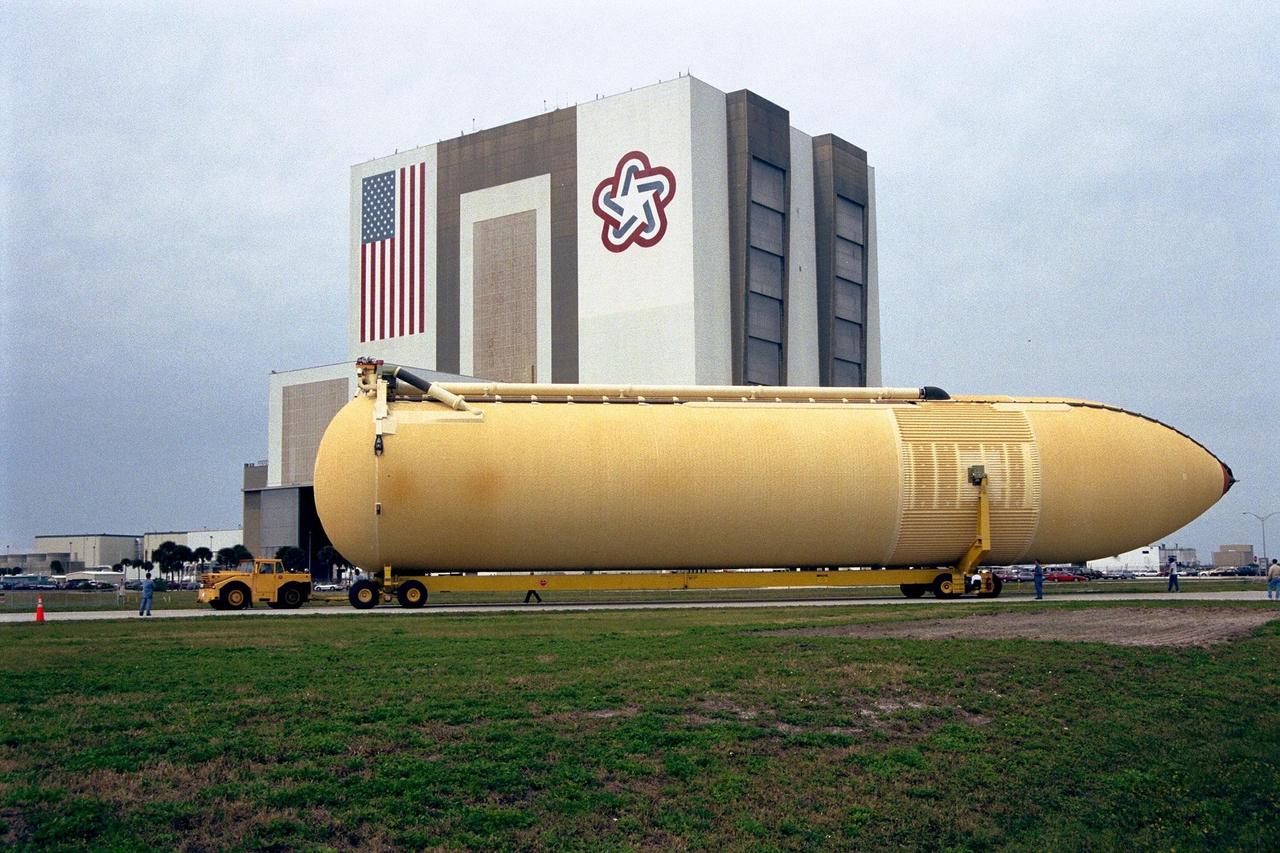

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
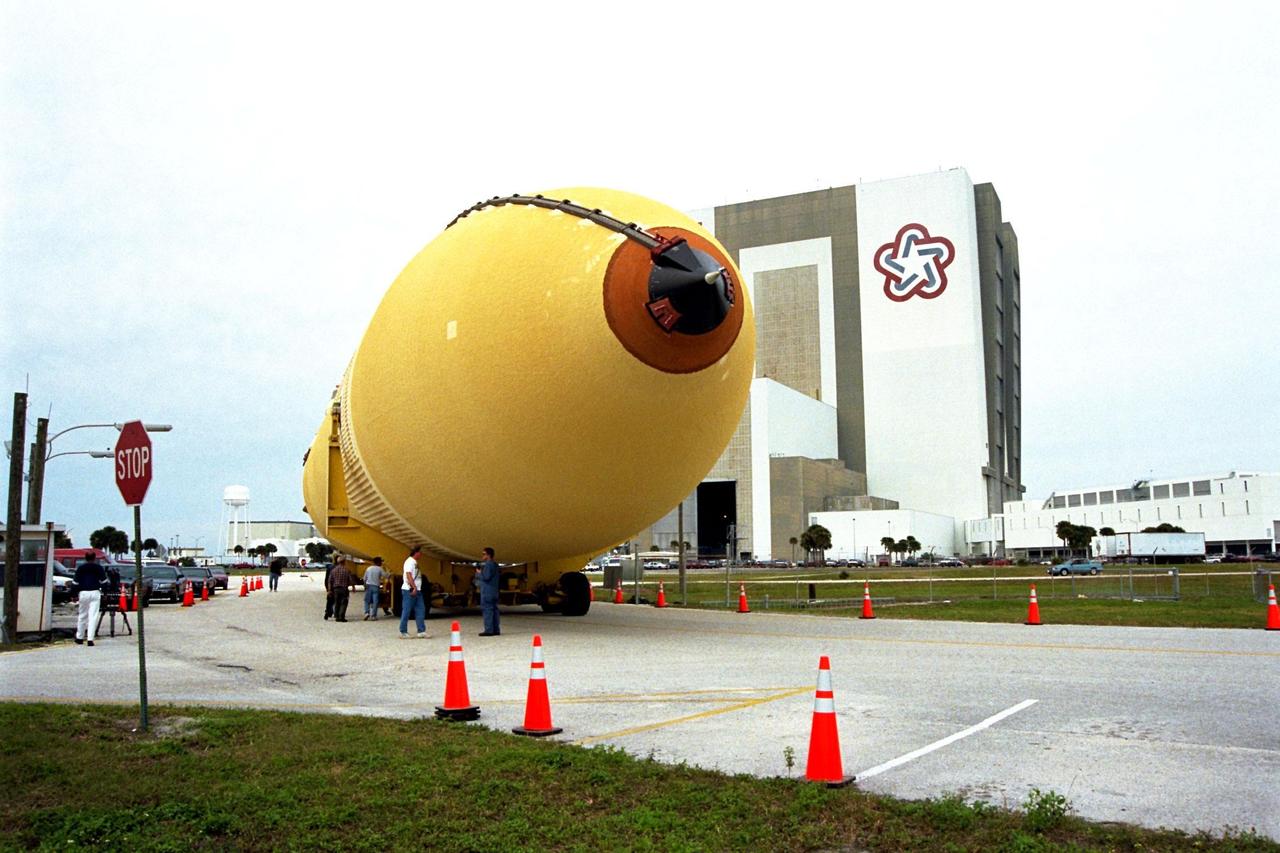

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
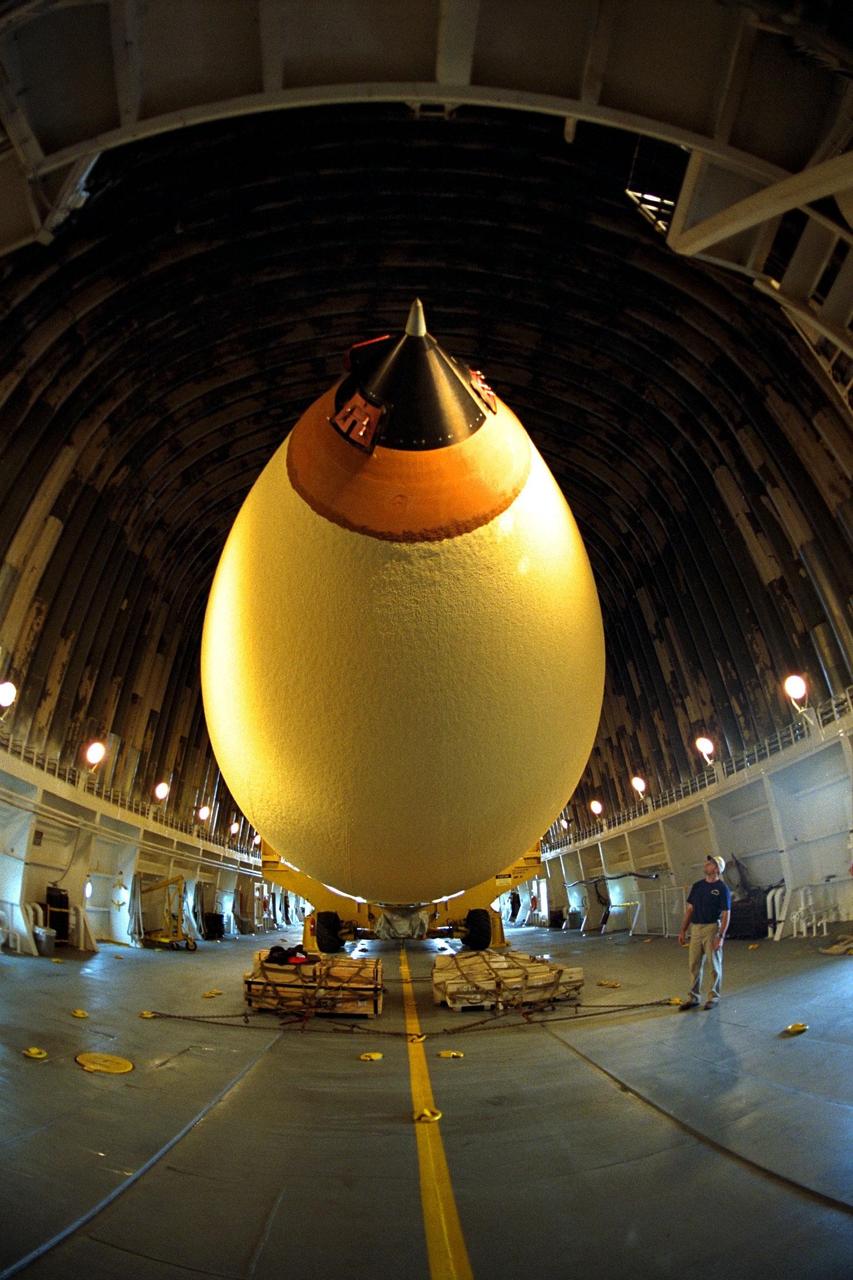

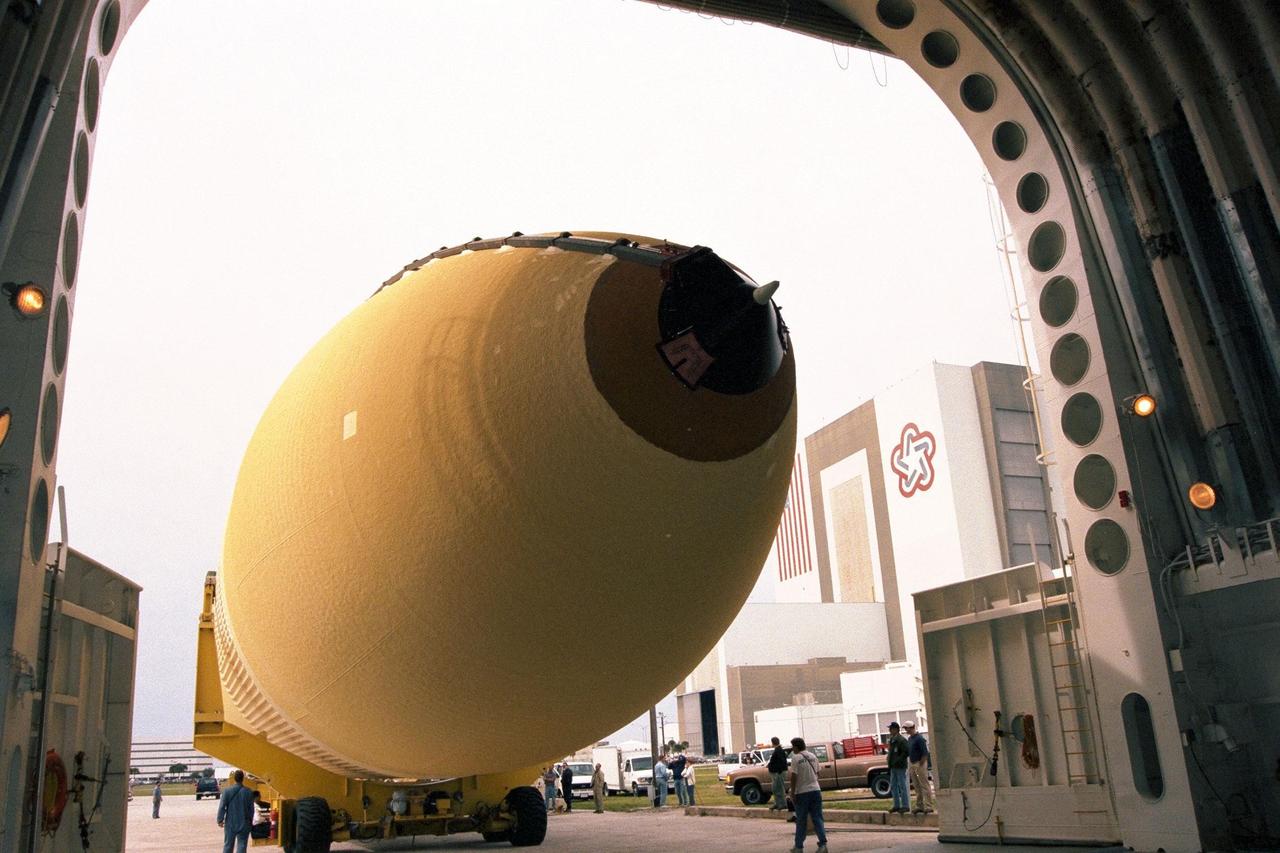
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Bren Wade, chief mate of the "Liberty Star," looks up at the Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank as it is moved on a barge to Port Canaveral, Fla. The tank is scheduled to undergo processing at Kennedy Space Center for flight on STS-91, targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. From the outside, the new orange-colored tank appears identical to tanks currently used on Shuttle flights. Major changes, however, include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well. This photograph was taken with a wide-angle lens
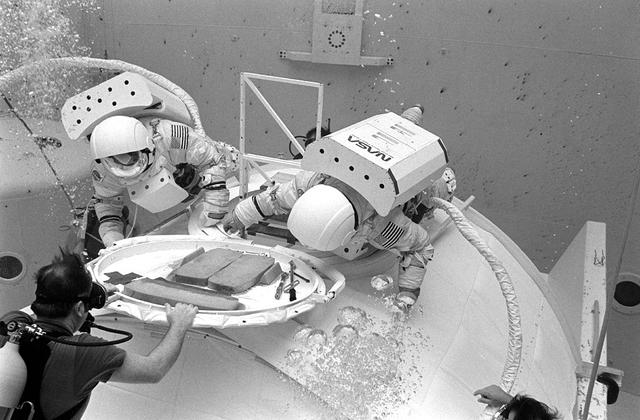
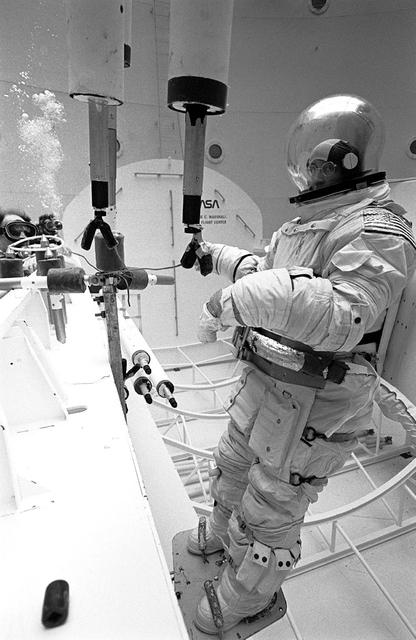
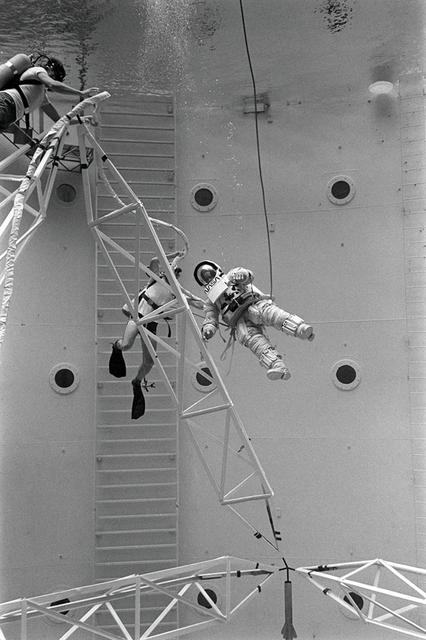
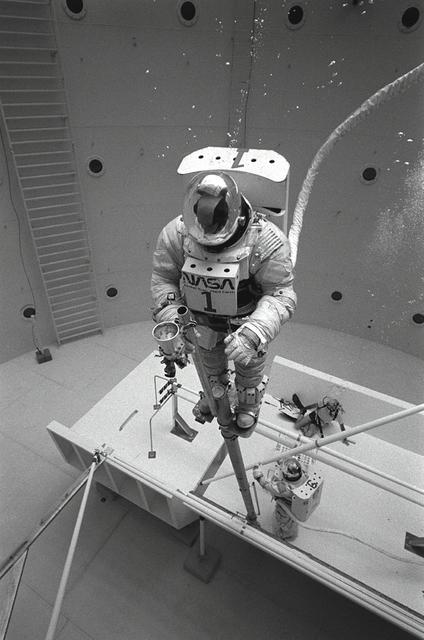
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. Pictured is Astronaut Paul Weitz training on a mock-up of Spacelab's airlock-hatch cover. Training was also done on the use of foot restraints which had recently been developed to help astronauts maintain their positions during space walks rather than having their feet float out from underneath them while they tried to perform maintenance and repair operations. Every aspect of every space mission was researched and demonstrated in the NBS. Using the airlock hatch cover and foot restraints were just a small example of the preparation that went into each mission.

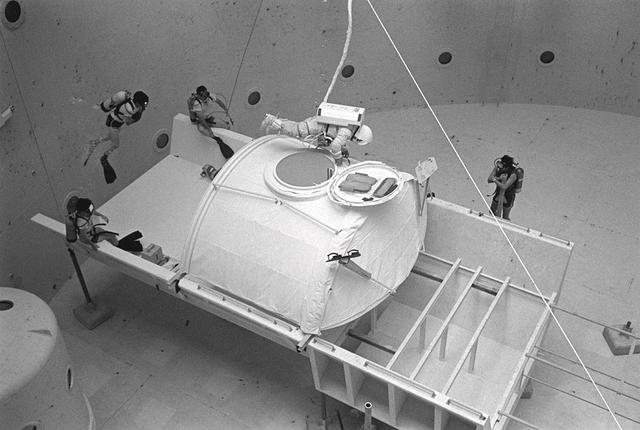
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.
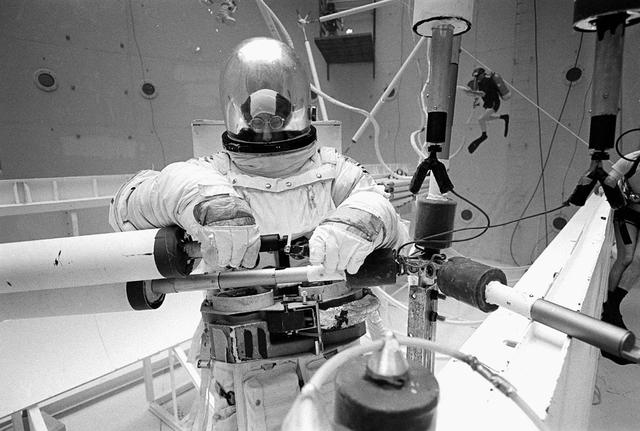
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.
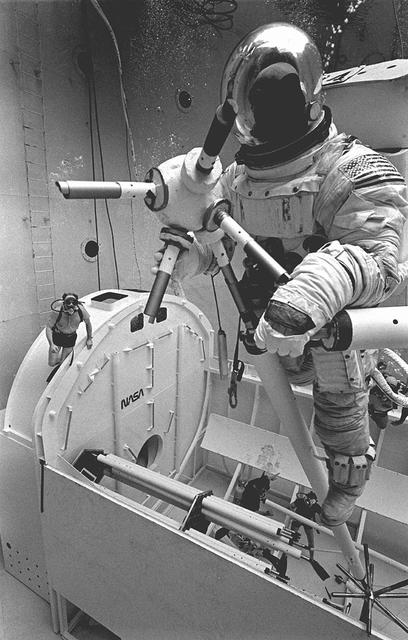

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.
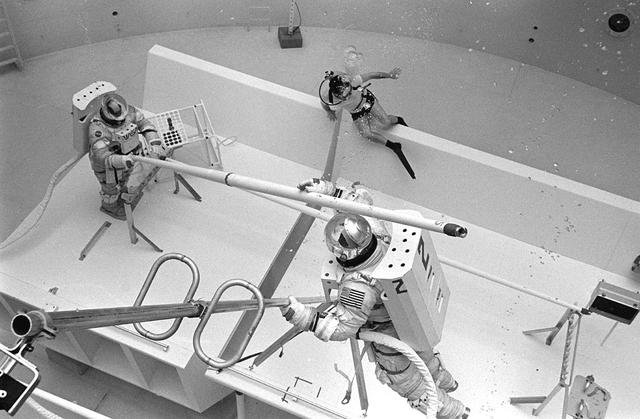
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. As part of this experimentation, the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. Pictured is an entire unit that has been constructed and is sitting in the bottom of a mock-up shuttle cargo bay pallet.
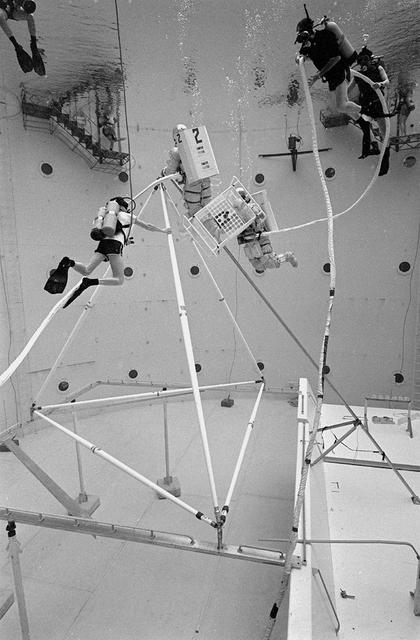

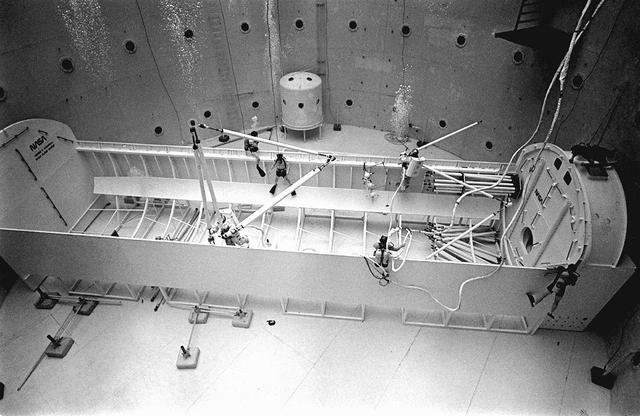
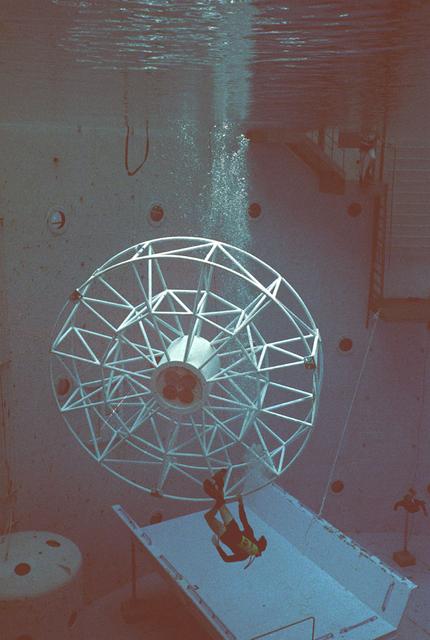
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.
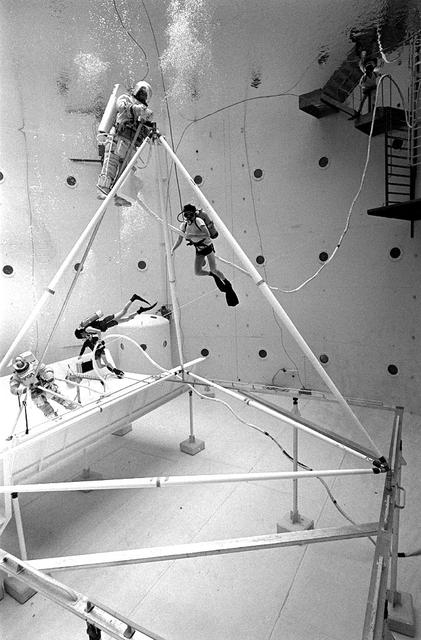
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, theprospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. Pictured is Astronaut Paul Weitz training on a mock-up of Spacelab's airlock-hatch cover. Training was also done on the use of foot restraints which had recently been developed to help astronauts maintain their positions during space walks rather than having their feet float out from underneath them while they tried to perform maintenance and repair operations. Every aspect of every space mission was researched and demonstrated in the NBS. Using the airlock hatch cover and foot restraints were just a small example of the preparation that went into each mission.
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.
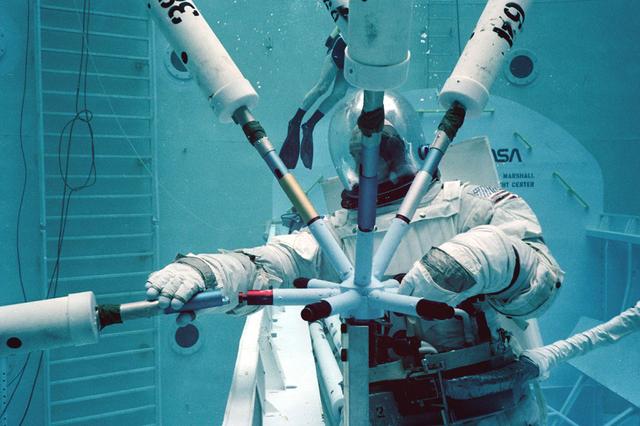

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle.

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia and the MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.
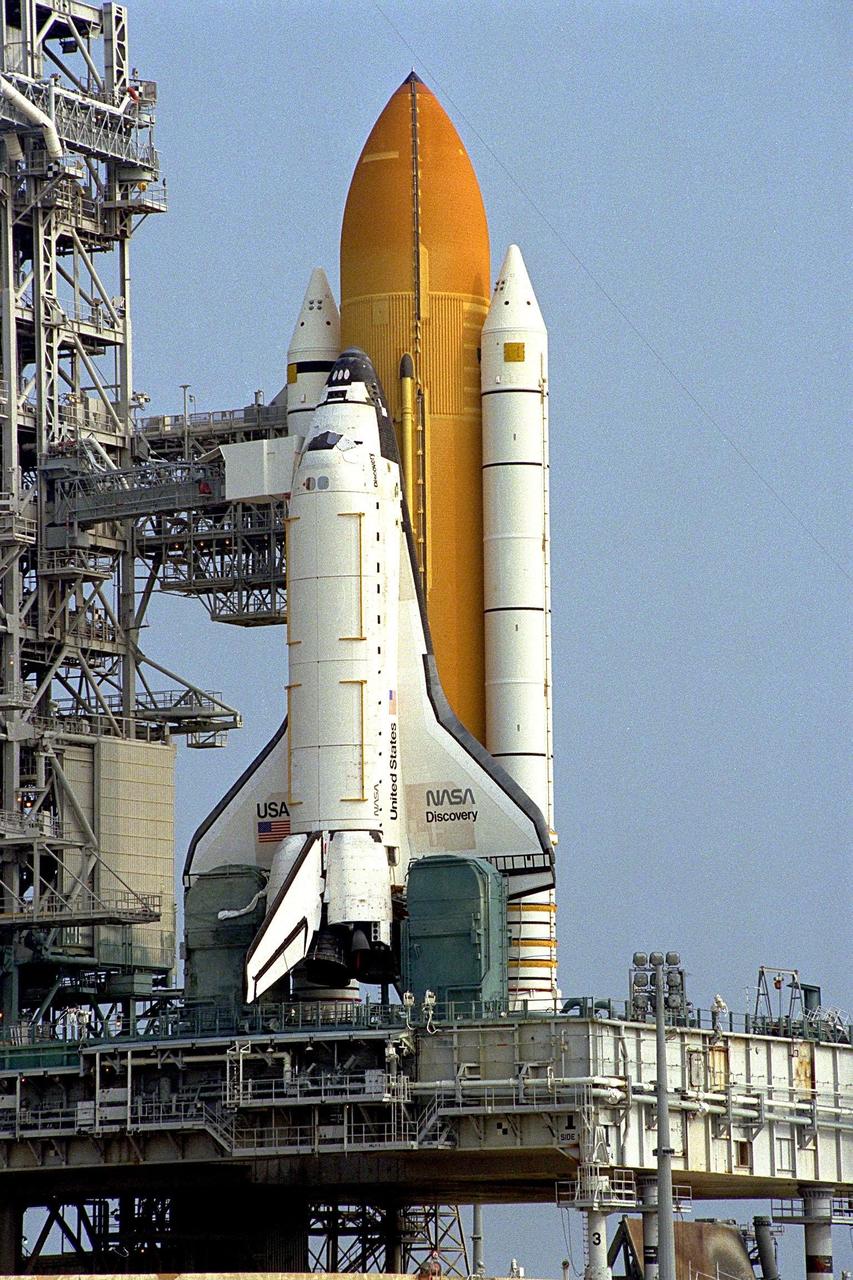

Preliminary reports indicate the Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank (SLWT) is in excellent condition following the completion of a tanking test yesterday during a simulated launch countdown at Launch Pad 39A. The pad's Rotating Service Structure will be closed around Discovery later today as preparations for the STS-91 launch on June 2 continue. The primary objectives of the test were to evaluate the strut loads between the tank and the solid rocket boosters and to verify the integrity of the new components of the tank. The SLWT is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability, as well. The STS-91 mission will also feature the ninth Shuttle docking with the Russian Space Station Mir, the first Mir docking for Discovery, and the conclusion of Phase I of the joint U.S.-Russian International Space Station Program
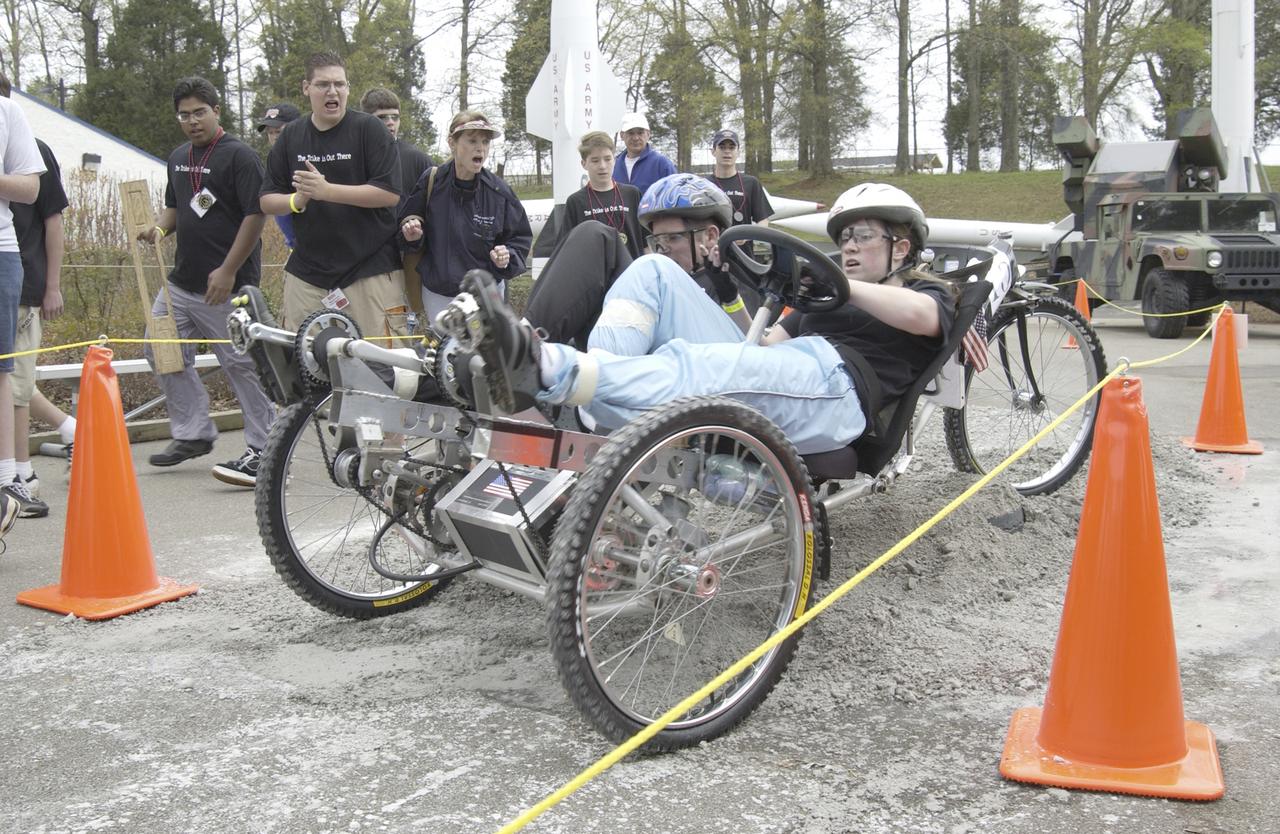

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. In this photograph, the New Orleans area schools team #2 from New Orleans, Louisiana maneuvers through an obstacle course. The team captured second place in the high school division competition. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by the development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems, similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
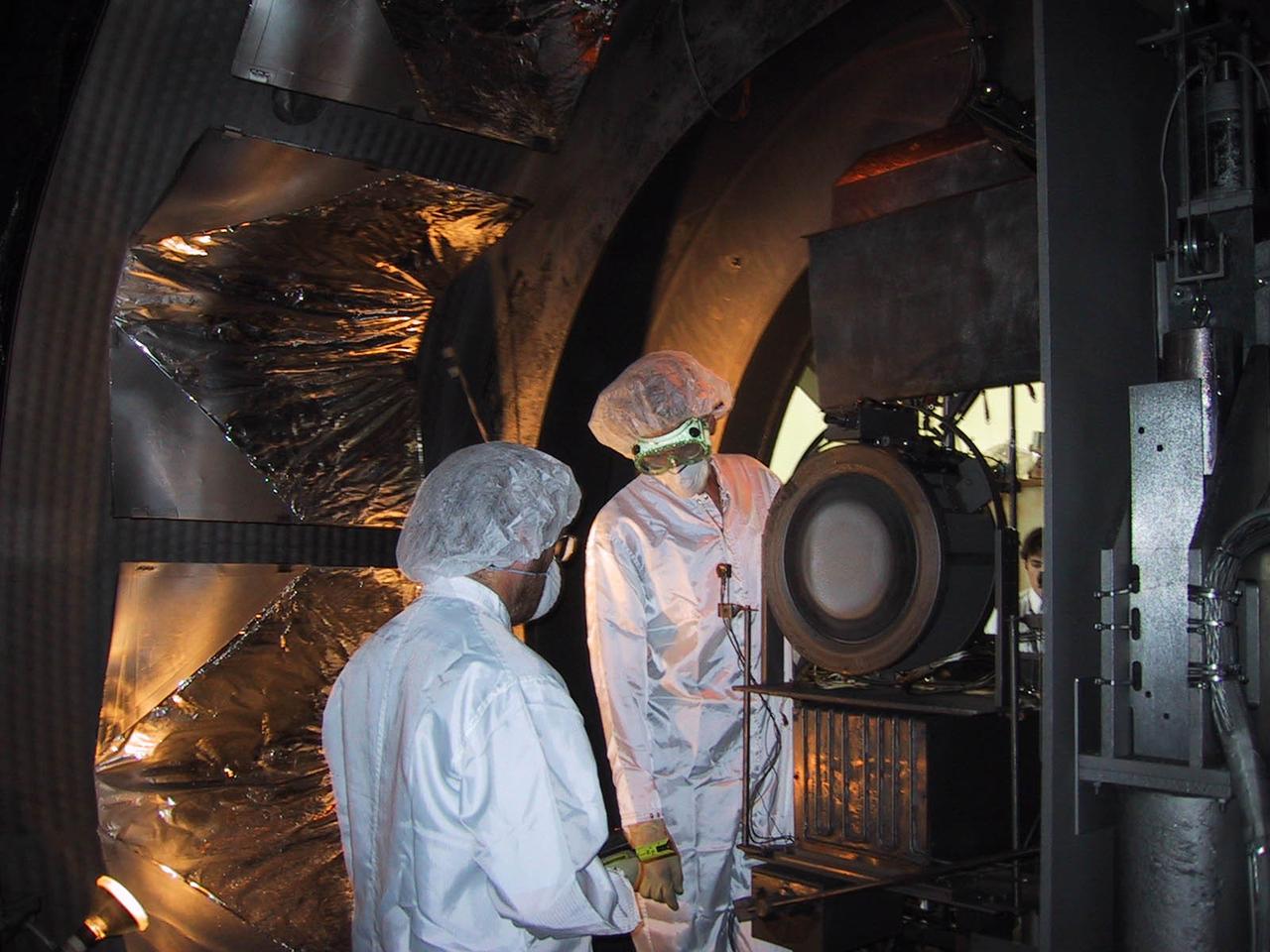

An ion thruster is removed from a vacuum chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The thruster, a spare engine from NASA's Deep Space 1 mission, with a designed life of 8,000 hours, ran for a record 30,352 hours (nearly 5 years) giving researchers the ability to observe its performance and wear at different power levels throughout the test. This information will be vital to future missions that use ion propulsion. Ion propulsion systems can be very lightweight, rurning on just a few grams of xenon gas a day. Xenon is the same gas that is found in photo flash bulbs. This fuel efficiency can lower launch vehicle costs. The successful Deep Space 1 mission featured the first use of an ion engine as the primary means of propulsion on a NASA spacecraft. NASA's next-generation ion propulsion efforts are implemented by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The program seeks to develop advanced propulsion technologies that will significantly reduce cost, mass, or travel times.
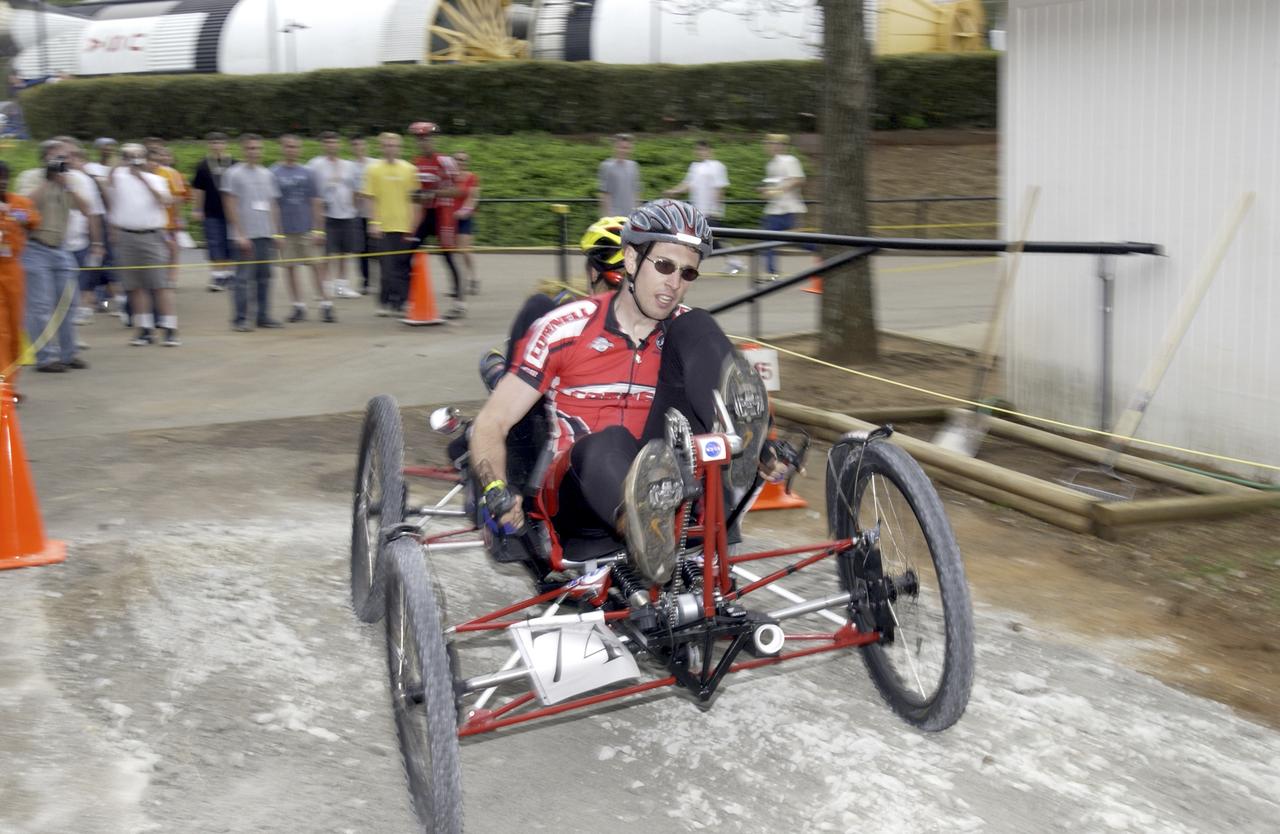

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. A team from Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, took the first place honor in the college division. In this photograph, the Cornell #1 team, the collegiate first place winner, maneuvers their vehicle through the course. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a humanpowered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
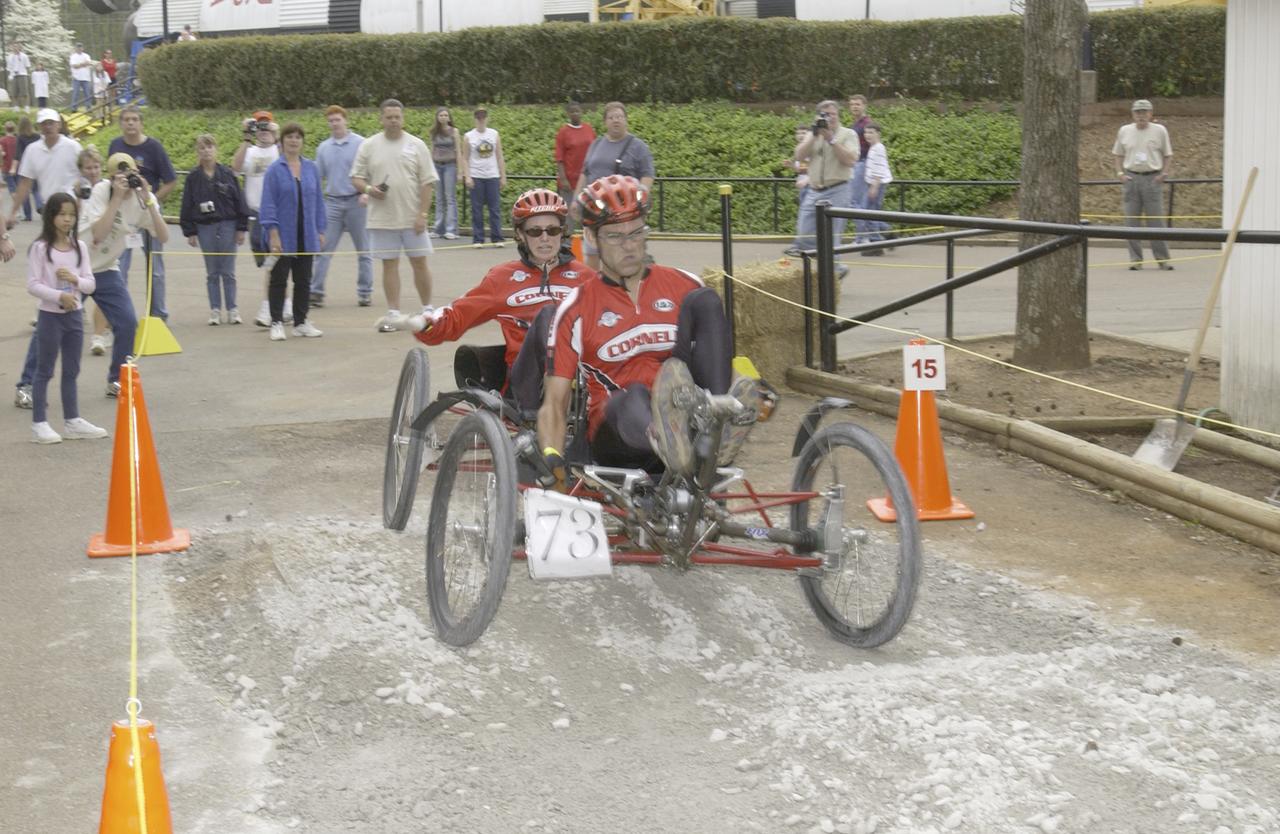

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. A team from Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, took the first place honor in the college division. This photograph shows the Cornell #2 team driving their vehicle through the course. The team finished the race in second place in the college division. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle, that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems, similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
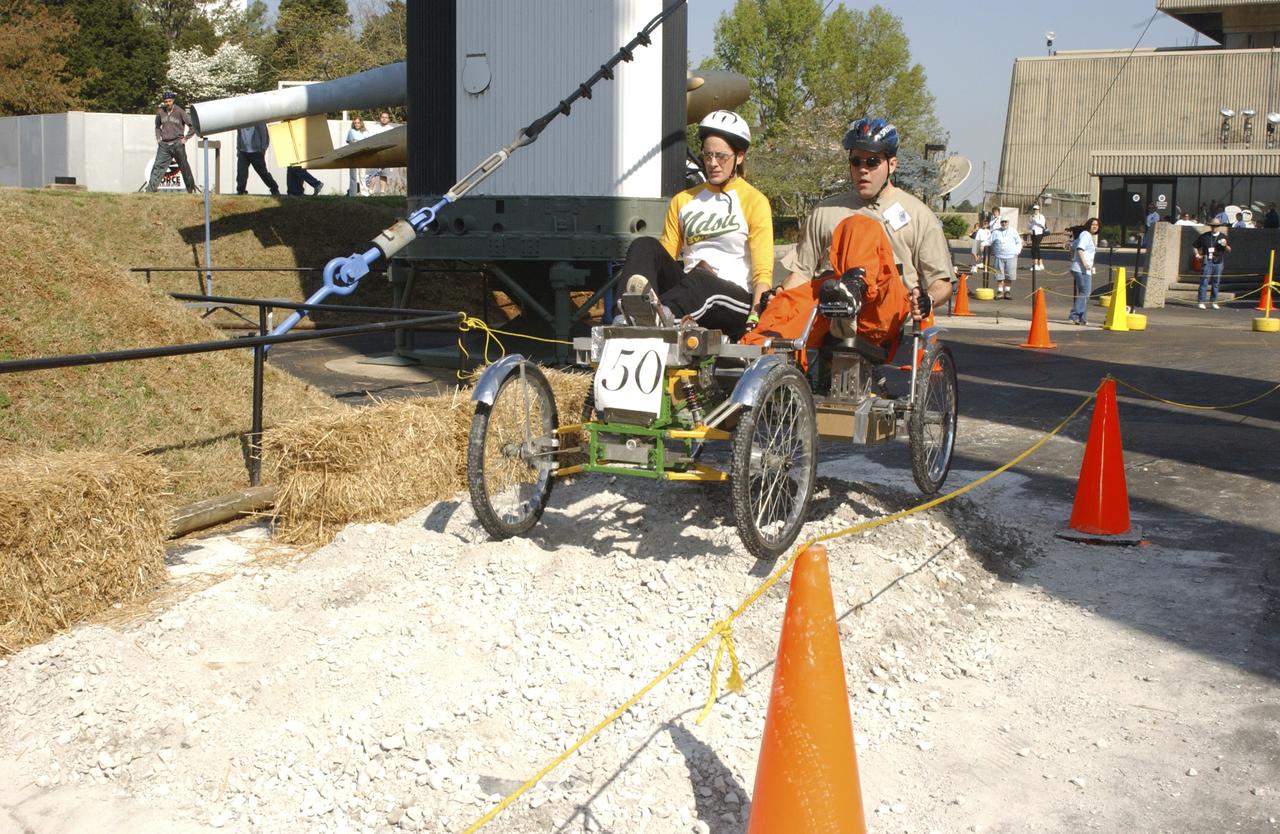

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 10th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Sixty-eight teams, representing high schools and colleges from all over the United States, and Puerto Rico, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team. In this photograph, Team No. 1 from North Dakota State University in Fargo conquers one of several obstacles on their way to victory. The team captured first place honors in the college level competition.
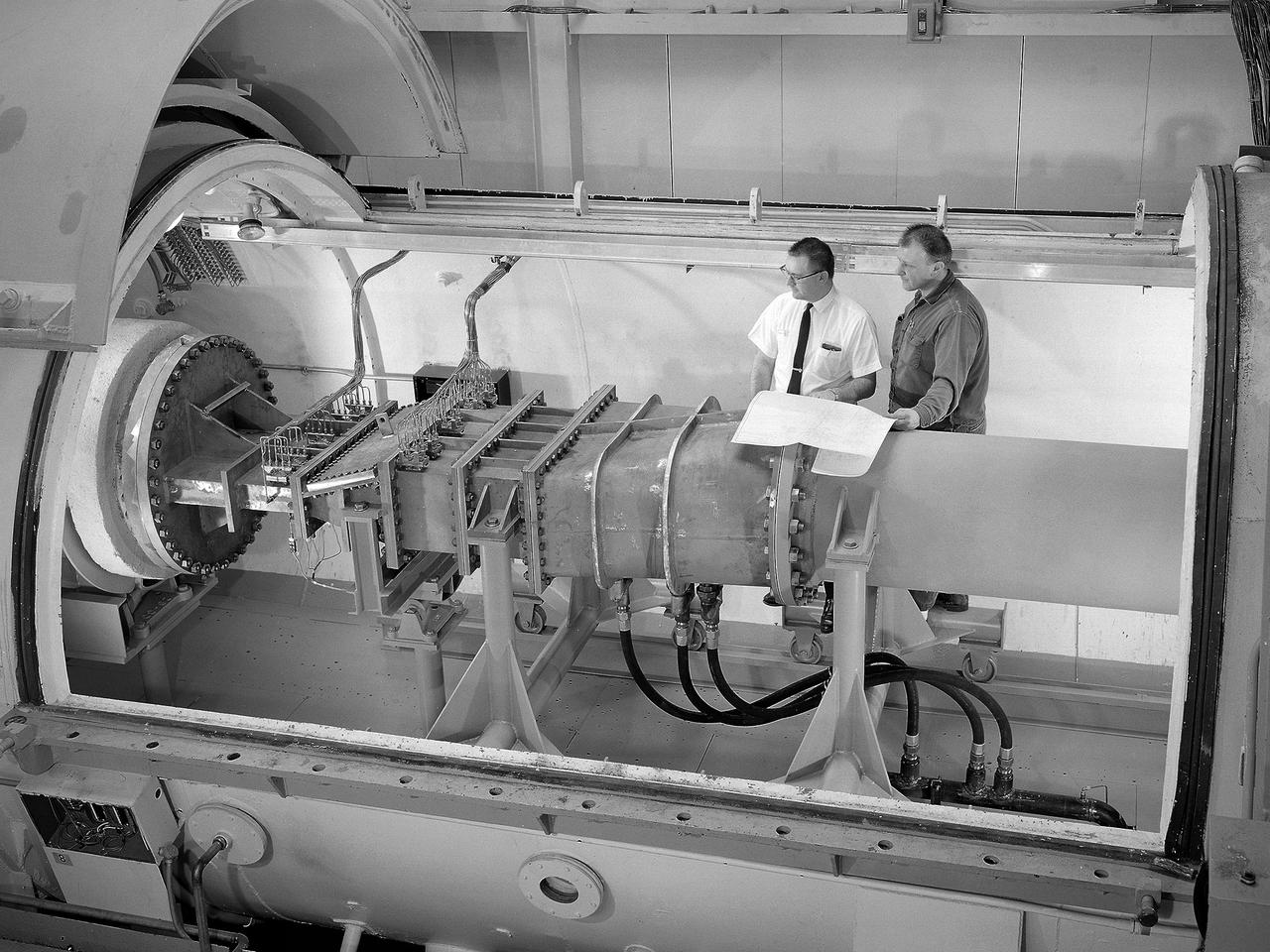

Engineer Frank Kutina and a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) mechanic examine the setup of an advanced combustor rig inside one of the test cells at the Lewis Research Center’s Four Burner Area in the Engine Research Building. Kutina, of the Research Operations Branch, served as go-between for the researchers and the mechanics. He helped develop the test configurations and get the hardware installed. At the time of this photograph, Lewis Center Director Abe Silverstein had just established the Airbreathing Engine Division to address the new propulsion of the 1960s. After nearly a decade of focusing almost exclusively on space, NASA Lewis began tackling issues relating to the new turbofan engine, noise reduction, energy efficiency, supersonic transport, and the never-ending quest for higher performance levels with smaller and more lightweight engines. The Airbreathing Engine Division’s Combustion Branch was dedicated to the study and mitigation of the high temperatures and pressures found in advanced combustor designs. These high temperatures and pressures could destroy engine components. The Lewis investigation included film cooling, diffuser flow, and jet mixing. Components were tested in smaller test cells, but a full-scale augmenting burner rig, seen here, was tested extensively in the Four Burner Area test cell.
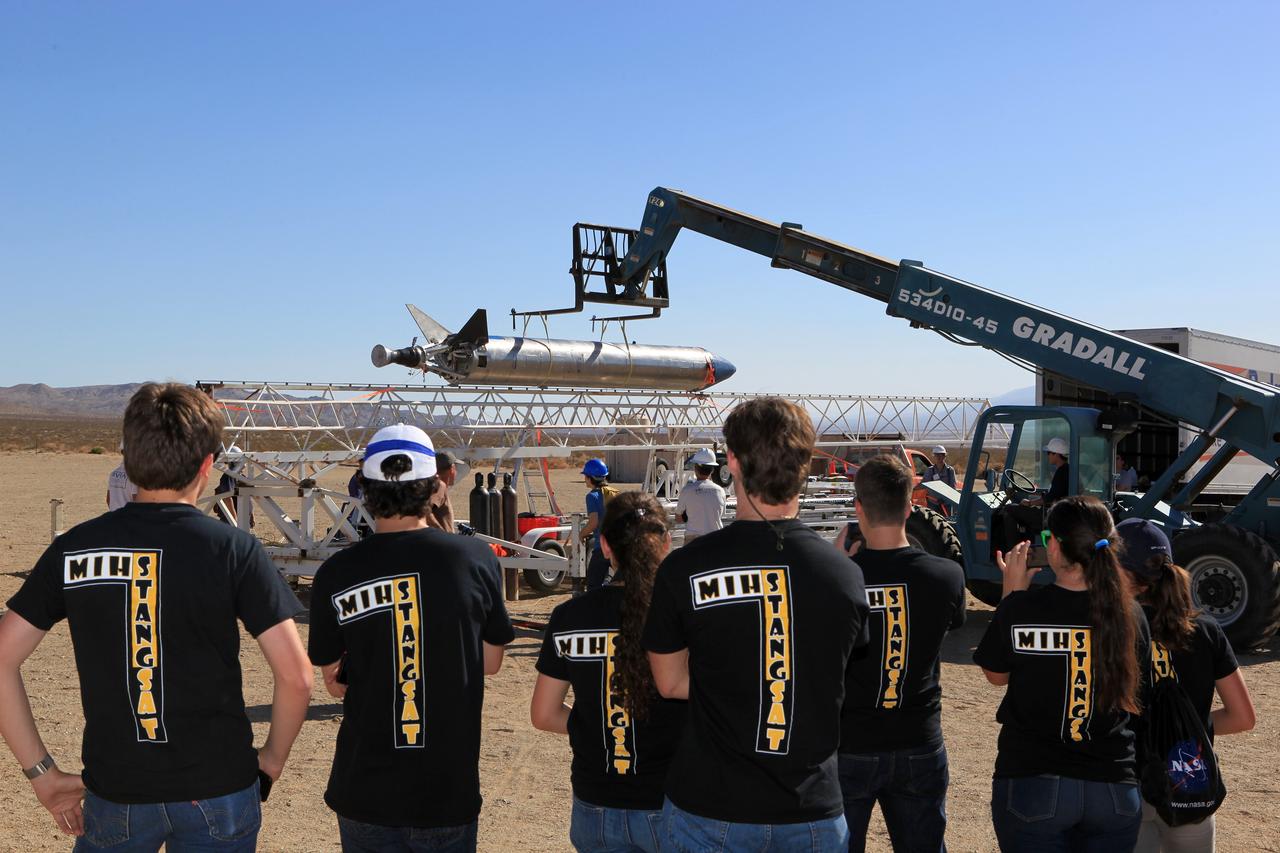

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students from Merritt Island High School in Florida watch as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections, one developed by students from the school that is located near the Kennedy Space Center. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
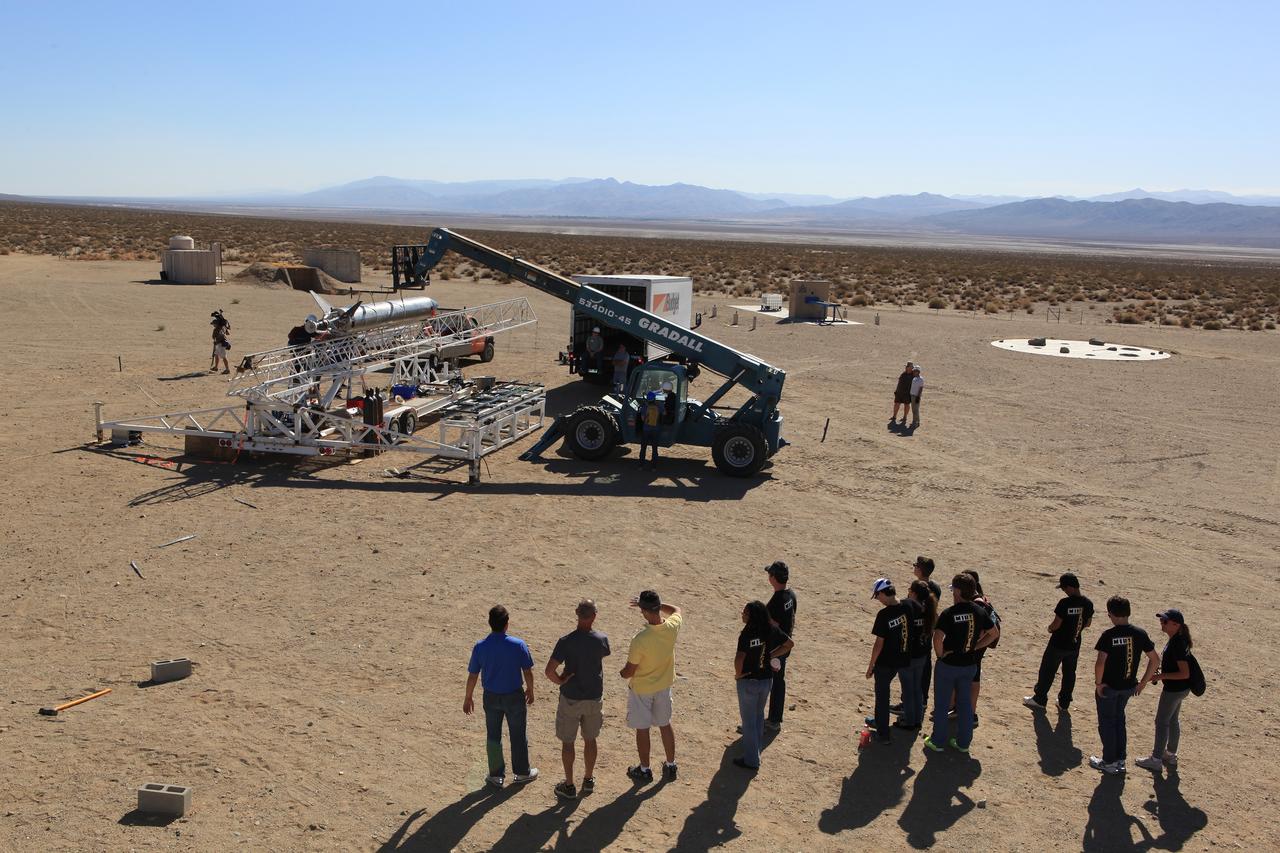

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students from Merritt Island High School in Florida watch as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section, one developed by students from the school that is located near the Kennedy Space Center. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
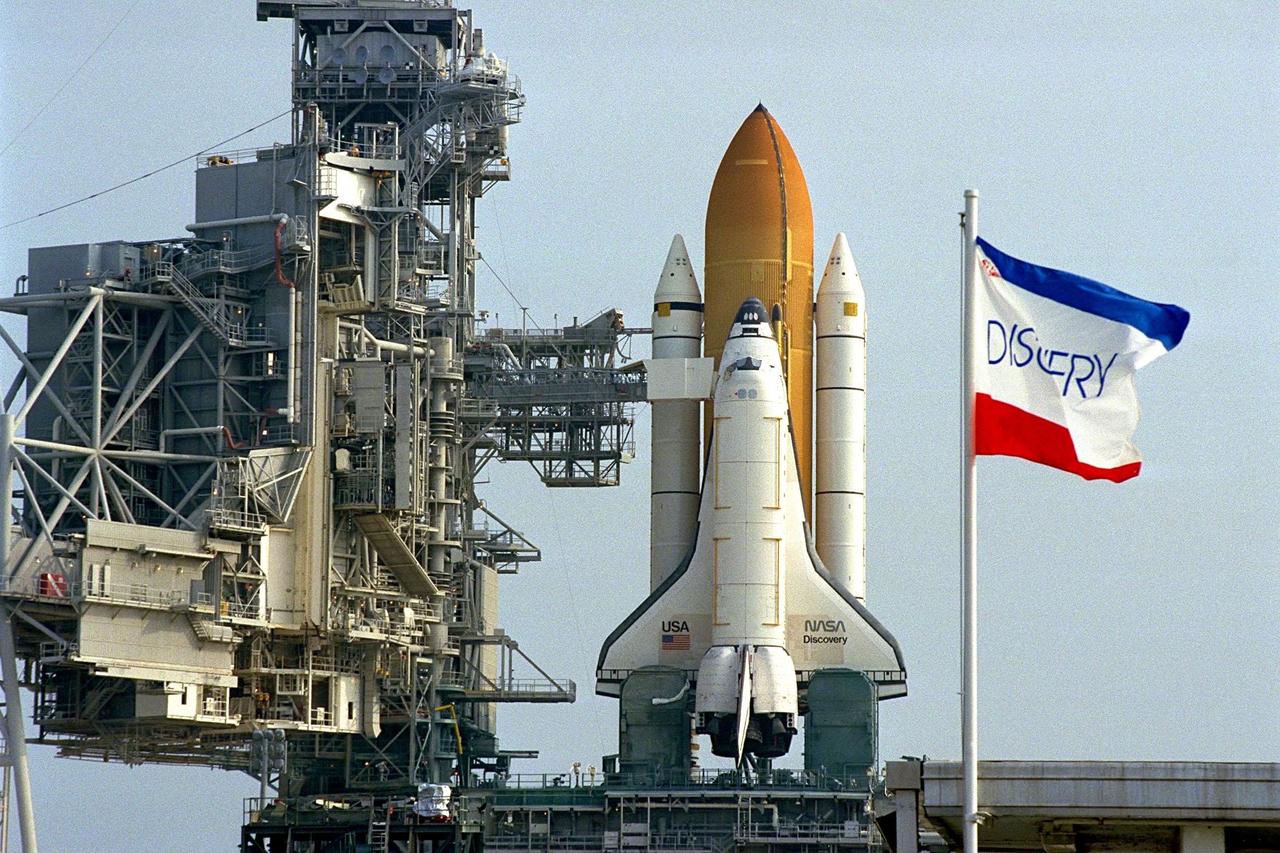
Preliminary reports indicate the Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank (SLWT) is in excellent condition following the completion of a tanking test yesterday during a simulated launch countdown at Launch Pad 39A. The pad's Rotating Service Structure will be closed around Discovery later today as preparations for the STS-91 launch on June 2 continue. The primary objectives of the test were to evaluate the strut loads between the tank and the solid rocket boosters and to verify the integrity of the new components of the tank. The SLWT is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability, as well. The STS-91 mission will also feature the ninth Shuttle docking with the Russian Space Station Mir, the first Mir docking for Discovery, and the conclusion of Phase I of the joint U.S.-Russian International Space Station Program
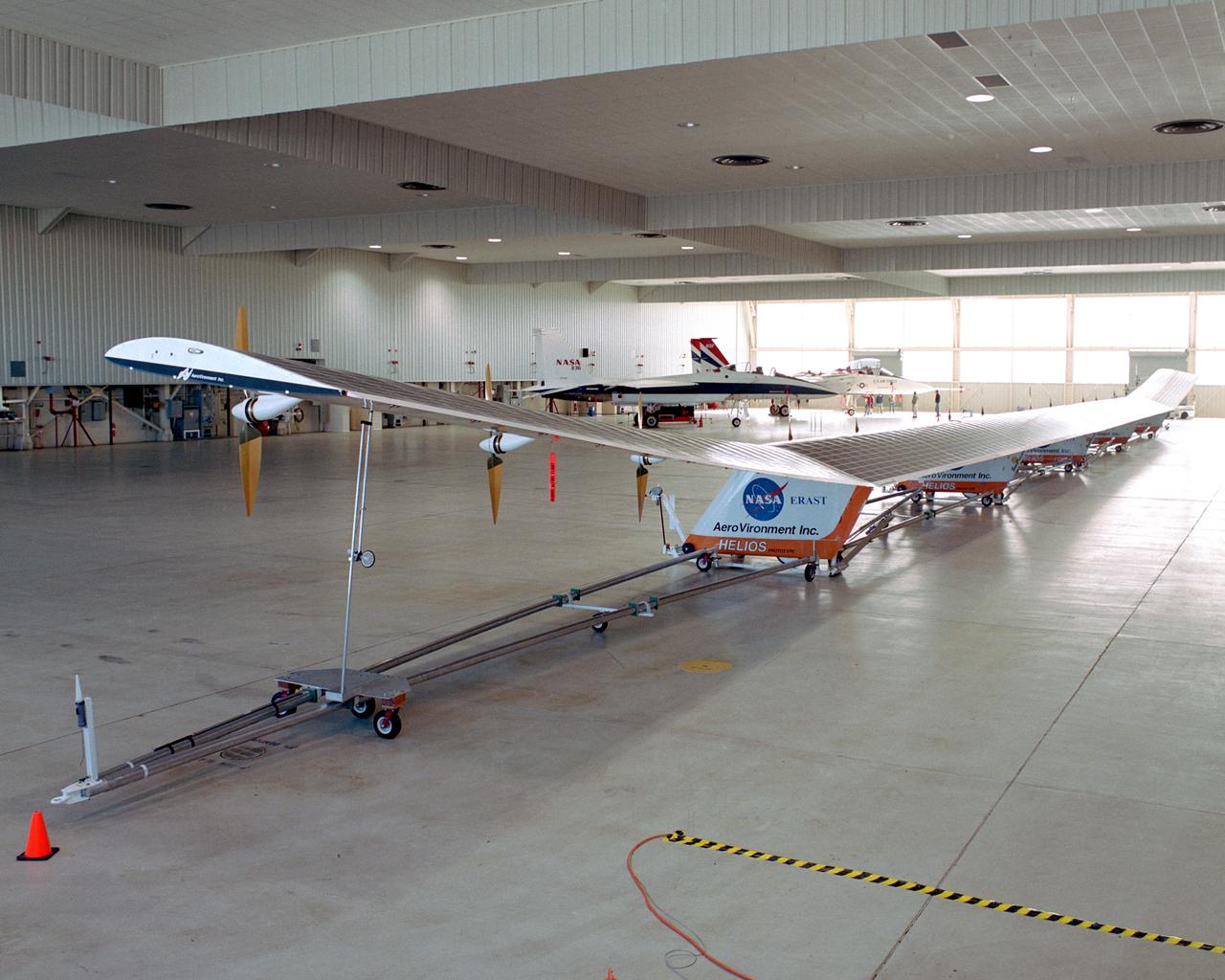

The solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing frames two modified F-15 research aircraft in a hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The elongated 247-foot span lightweight aircraft, resting on its ground maneuvering dolly, stretched almost the full length of the 300-foot long hangar while on display during a visit of NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and other NASA officials on Jan. 31, 2002. The unique solar-electric flying wing reached an altitude of 96,863 feet during an almost 17-hour flight near Hawaii on Aug. 13, 2001, a world record for sustained horizontal flight by a non-rocket powered aircraft. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the Helios Prototype is the forerunner of a planned fleet of slow-flying, long duration, high-altitude uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) which can serve as "atmospheric satellites," performing Earth science missions or functioning as telecommunications relay platforms in the stratosphere.
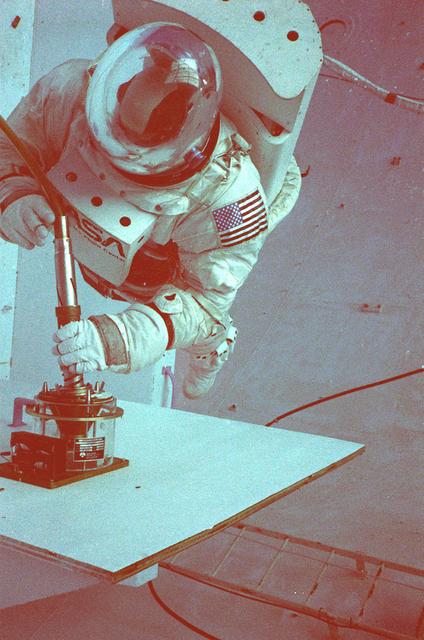

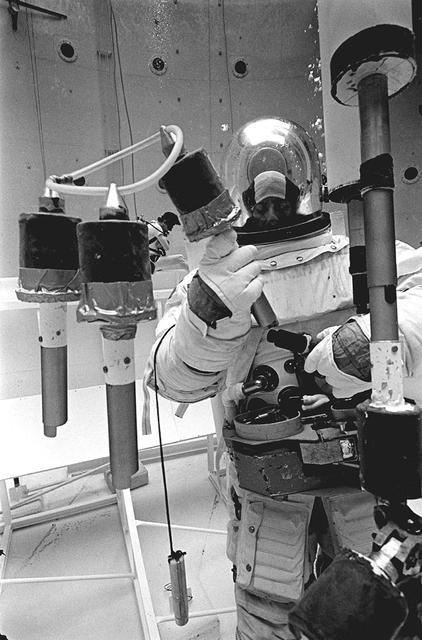
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Another facet of the space station would be electrical cornectors which would be used for powering tools the astronauts would need for construction, maintenance and repairs. Shown is an astronaut training during an underwater electrical connector test in the NBS.
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Included in the plans for the space station was a space telescope. This telescope would be attached to the space station and directed towards outerspace. Astronomers hoped that the space telescope would provide a look at space that is impossible to see from Earth because of Earth's atmosphere and other man made influences. Pictured is a large structure that is being used as the antenna base for the space telescope.

Pictured is the chosen artist's rendering of NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, was named the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. To further our understanding of the way our present universe formed following the the big bang, NASA is developing the JWST to observe the first stars and galaxies in the universe. This grand effort will help to answer the following fundamental questions: How galaxies form and evolve, how stars and planetary systems form and interact, how the universe builds up its present elemental/chemical composition, and what dark matter is. To see into the depths of space, the JWST is currently plarning to carry instruments that are sensitive to the infrared wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. The new telescope will carry a near-infrared camera, a multi-object spectrometer, and a mid-infrared camera/spectrometer. The JWST is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by creating an ultra-lightweight mirror for the telescope at MSFC's Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center. GSFC, Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the JWST, and TRW will design and fabricate the observatory's primary mirror and spacecraft. The program has a number of industry, academic, and government partners, as well as the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. (Image: Courtesy of TRW)
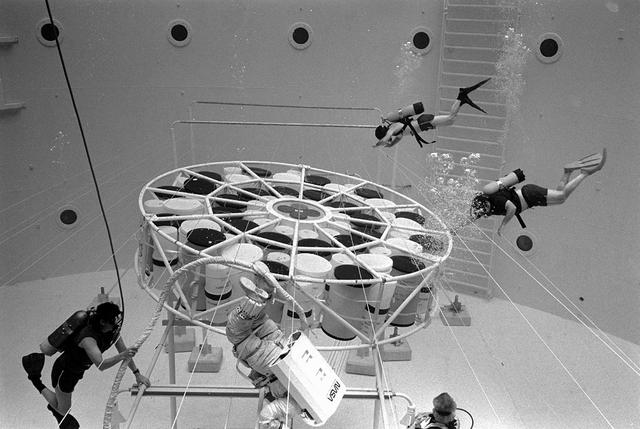

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built.Pictured is an experiment where the astronaut is required to move a large object which weighed 19,000 pounds. It was moved with realitive ease once the astronaut became familiar with his environment and his near weightless condition. Experiments of this nature provided scientists with the information needed regarding weight and mass allowances astronauts could manage in preparation for building a permanent space station in the future.
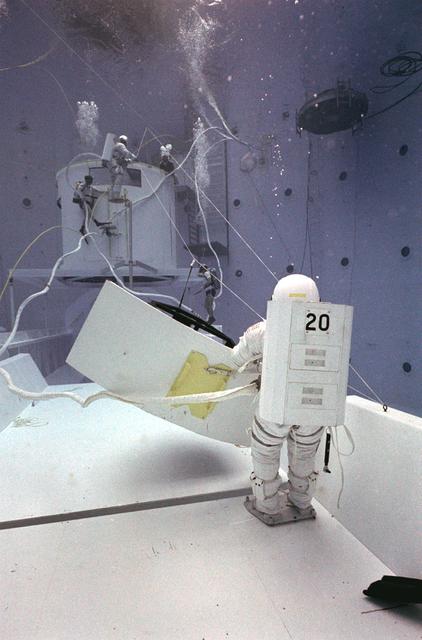

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Included in the plans for the space station was a space telescope. This telescope would be attached to the space station and directed towards outerspace. Astronomers hoped that the space telescope would provide a look at space that is impossible to see from Earth because of Earth's atmosphere and other man made influences. In an effort to make replacement and repairs easier on astronauts the space telescope was designed to be modular. Practice makes perfect as demonstrated in this photo: an astronaut practices moving modular pieces of the space telescope in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at MSFC. The space telescope was later deployed in April 1990 as the Hubble Space Telescope.
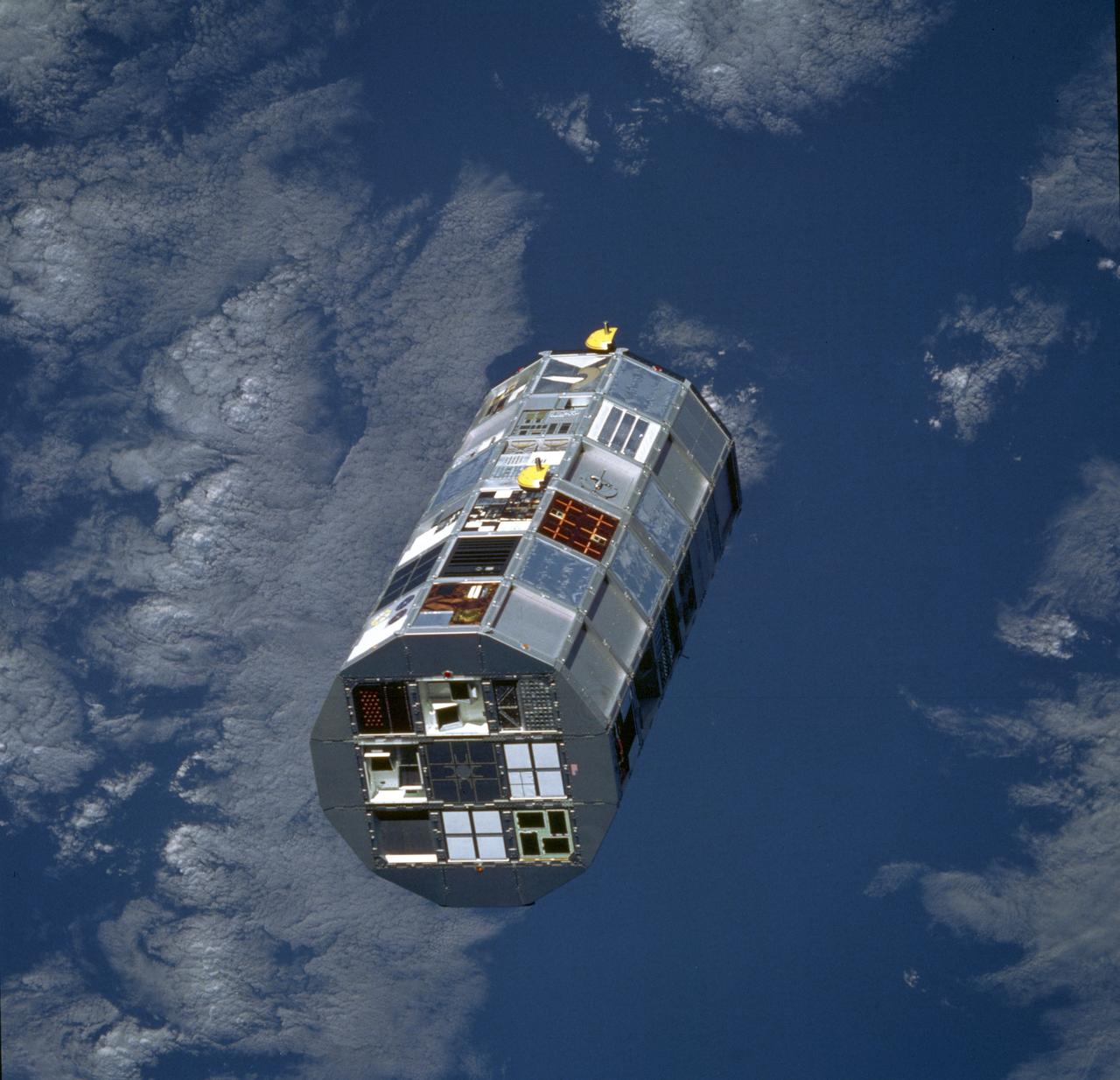

The Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) was designed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) to test the performance of spacecraft materials, components, and systems that have been exposed to the environment of micrometeoroids and space debris for an extended period of time. The LDEF proved invaluable to the development of future spacecraft and the International Space Station (ISS). The LDEF carried 57 science and technology experiments, the work of more than 200 investigators. MSFC`s experiments included: Trapped Proton Energy Determination to determine protons trapped in the Earth's magnetic field and the impact of radiation particles; Linear Energy Transfer Spectrum Measurement Experiment which measures the linear energy transfer spectrum behind different shielding configurations; Atomic oxygen-Simulated Out-gassing, an experiment that exposes thermal control surfaces to atomic oxygen to measure the damaging out-gassed products; Thermal Control Surfaces Experiment to determine the effects of the near-Earth orbital environment and the shuttle induced environment on spacecraft thermal control surfaces; Transverse Flat-Plate Heat Pipe Experiment, to evaluate the zero-gravity performance of a number of transverse flat plate heat pipe modules and their ability to transport large quantities of heat; Solar Array Materials Passive LDEF Experiment to examine the effects of space on mechanical, electrical, and optical properties of lightweight solar array materials; and the Effects of Solar Radiation on Glasses. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger's STS-41C mission April 6, 1984, the LDEF remained in orbit for five years until January 1990 when it was retrieved by the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia STS-32 mission and brought back to Earth for close examination and analysis.
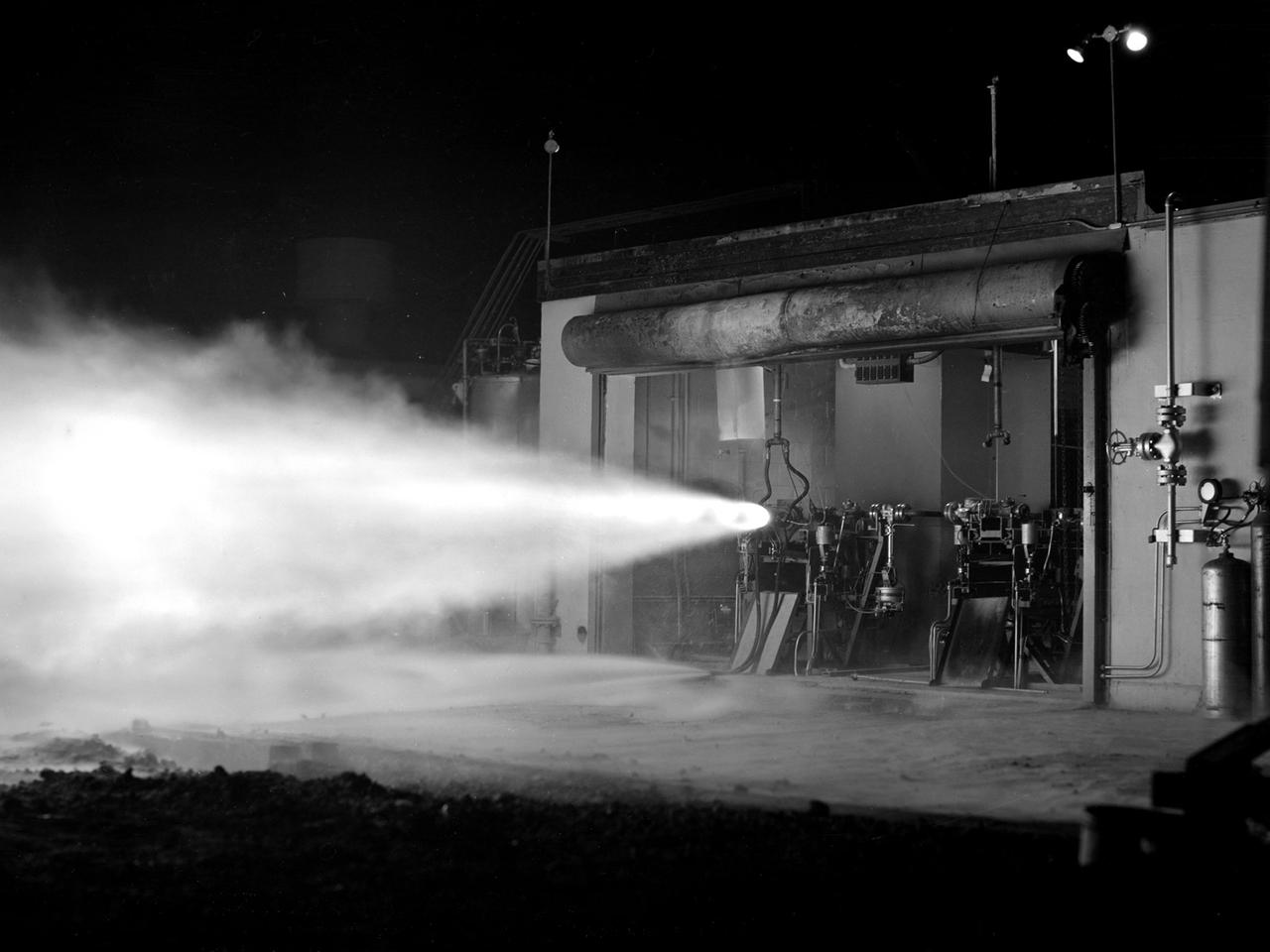

A rocket using high-energy propellant is fired from the Rocket Laboratory at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The Rocket Lab was a collection of ten one-story cinderblock test cells located behind earthen barriers at the western edge of the campus. The rocket engines tested there were comparatively small, but the Lewis researchers were able to study different configurations, combustion performance, and injectors and nozzle design. The rockets were generally mounted horizontally and fired, as seen in this photograph of Test Cell No. 22. A group of fuels researchers at Lewis refocused their efforts after World War II in order to explore high energy propellants, combustion, and cooling. Research in these three areas began in 1945 and continued through the 1960s. The group of rocket researches was not elevated to a division branch until 1952. The early NACA Lewis work led to the development of liquid hydrogen as a viable propellant in the late 1950s. Following the 1949 reorganization of the research divisions, the rocket group began working with high-energy propellants such as diborane, pentaborane, and hydrogen. The lightweight fuels offered high levels of energy but were difficult to handle and required large tanks. In late 1954, Lewis researchers studied the combustion characteristics of gaseous hydrogen in a turbojet combustor. Despite poor mixing of the fuel and air, it was found that the hydrogen yielded more than a 90-percent efficiency. Liquid hydrogen became the focus of Lewis researchers for the next 15 years.

A team of NASA researchers from Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and Dryden Flight Research center have proven that beamed light can be used to power an aircraft, a first-in-the-world accomplishment to the best of their knowledge. Using an experimental custom built radio-controlled model aircraft, the team has demonstrated a system that beams enough light energy from the ground to power the propeller of an aircraft and sustain it in flight. Special photovoltaic arrays on the plane, similar to solar cells, receive the light energy and convert it to electric current to drive the propeller motor. In a series of indoor flights this week at MSFC, a lightweight custom built laser beam was aimed at the airplane `s solar panels. The laser tracks the plane, maintaining power on its cells until the end of the flight when the laser is turned off and the airplane glides to a landing. The laser source demonstration represents the capability to beam more power to a plane so that it can reach higher altitudes and have a greater flight range without having to carry fuel or batteries, enabling an indefinite flight time. The demonstration was a collaborative effort between the Dryden Center at Edward's, California, where the aircraft was designed and built, and MSFC, where integration and testing of the laser and photovoltaic cells was done. Laser power beaming is a promising technology for consideration in new aircraft design and operation, and supports NASA's goals in the development of revolutionary aerospace technologies. Photographed with their invention are (from left to right): David Bushman and Tony Frackowiak, both of Dryden; and MSFC's Robert Burdine.

Engineer Emmanuel Decrossas of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California makes an adjustment to an antenna's connector, part of a NASA telecommunications payload called User Terminal, at Firefly Aerospace's facility in Cedar Park, Texas, in August 2025. Figure A (https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/figures/PIA26596_figA.jpg) shows members of the team from JPL and NASA (dark blue) and Firefly (white) with the User Terminal antenna, radio, and other components on the bench behind them. Managed by JPL, the User Terminal will test a new, low-cost lunar communications system that future missions to the Moon's far side could use to transfer data to and from Earth via lunar relay satellite. The User Terminal payload will be installed atop Firefly's Blue Ghost Mission 2 lunar lander, which is slated to launch to the Moon's far side in 2026 under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. NASA's Apollo missions brought large and powerful telecommunications systems to the lunar near-side surface to communicate directly with Earth. But spacecraft on the far side will not have that option because only the near side of the Moon is visible to Earth. Sending messages between the Moon and Earth via a relay orbiter enables communication with the lunar far side and improves it at the Moon's poles. The User Terminal will for the first time test such a setup for NASA by using a compact, lightweight software defined radio, antenna, and related hardware to communicate with a satellite that Blue Ghost Mission 2 is delivering to lunar orbit: ESA's (the European Space Agency's) Lunar Pathfinder. The User Terminal radio and antenna installed on the Blue Ghost lander will be used to commission Lunar Pathfinder, sending test data back and forth. After the lander ceases operations as planned at the end of a single lunar day (about 14 Earth days), a separate User Terminal radio and antenna installed on LuSEE-Night – another payload on the lander – will send LuSEE-Night's data to Lunar Pathfinder, which will relay the information to a commercial network of ground stations on Earth. LuSEE-Night is a radio telescope that expected to operate for at least 1½ years; it is a joint effort by NASA, the U.S. Department of Energy, and University of California, Berkeley's Space Sciences Laboratory. Additionally, User Terminal will be able to communicate with another satellite that's being delivered to lunar orbit by Blue Ghost Mission 2: Firefly's own Elytra Dark orbital vehicle. The hardware on the lander is only part of the User Terminal project, which was also designed to implement a new S-band two-way protocol, or standard, for short-range space communications between entities on the lunar surface (such as rovers and landers) and lunar orbiters, enabling reliable data transfer between them. The standard is a new version of a space communications protocol called Proximity-1 that was initially developed more than two decades ago for use at Mars by an international standard body called the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS), of which NASA is a member agency. The User Terminal team made recommendations to CCSDS on the development of the new lunar S-band standard, which was specified in 2024. The new standard will enable lunar orbiters and surface spacecraft from various entities – NASA and other civil space agencies as well as industry and academia – to communicate with each other, a concept known as interoperability. At Mars, NASA rovers communicate with various Red Planet orbiters using the Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) radio band version of the Proximity-1 standard. On the Moon's far side, use of UHF is reserved for radio astronomy science; so a new lunar standard was needed using a different frequency range, S-band, as were more efficient modulation and coding schemes to better fit the available frequency spectrum specified by the new standard. User Terminal is funded by NASA's Exploration Science Strategy and Integration Office, part of the agency's Science Mission Directorate, which manages the CLPS initiative. JPL manages the project and supported development of the new S-band radio standard and the payload in coordination with Vulcan Wireless in Carlsbad, California, which built the radio. Caltech in Pasadena manages JPL for NASA. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26596