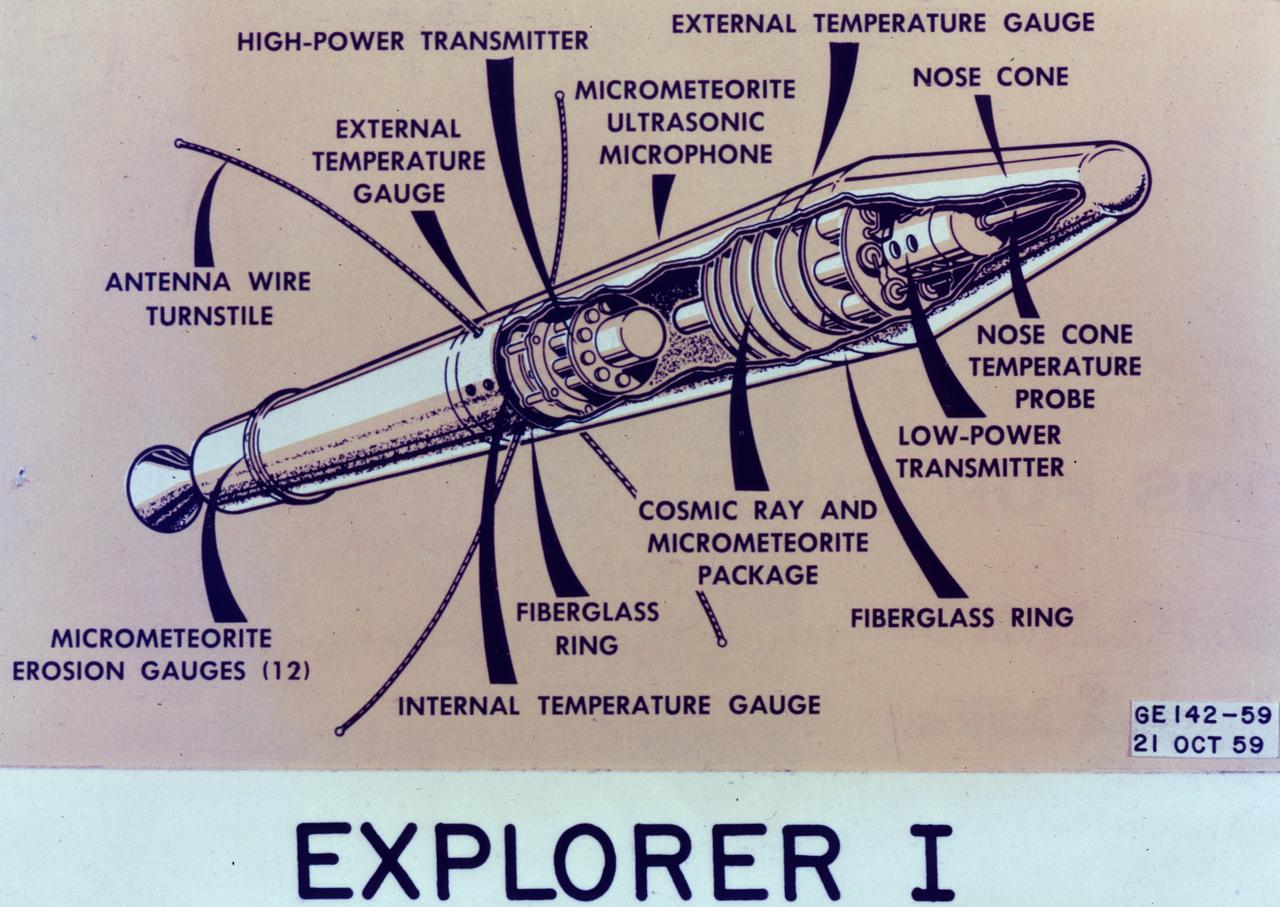
This image is a cutaway illustration of the Explorer I satellite with callouts. The Explorer I satellite was America's first scientific satellite launched aboard the Jupiter C launch vehicle on January 31, 1958. The Explorer I carried the radiation detection experiment designed by Dr. James Van Allen and discovered the Van Allen Radiation Belt.

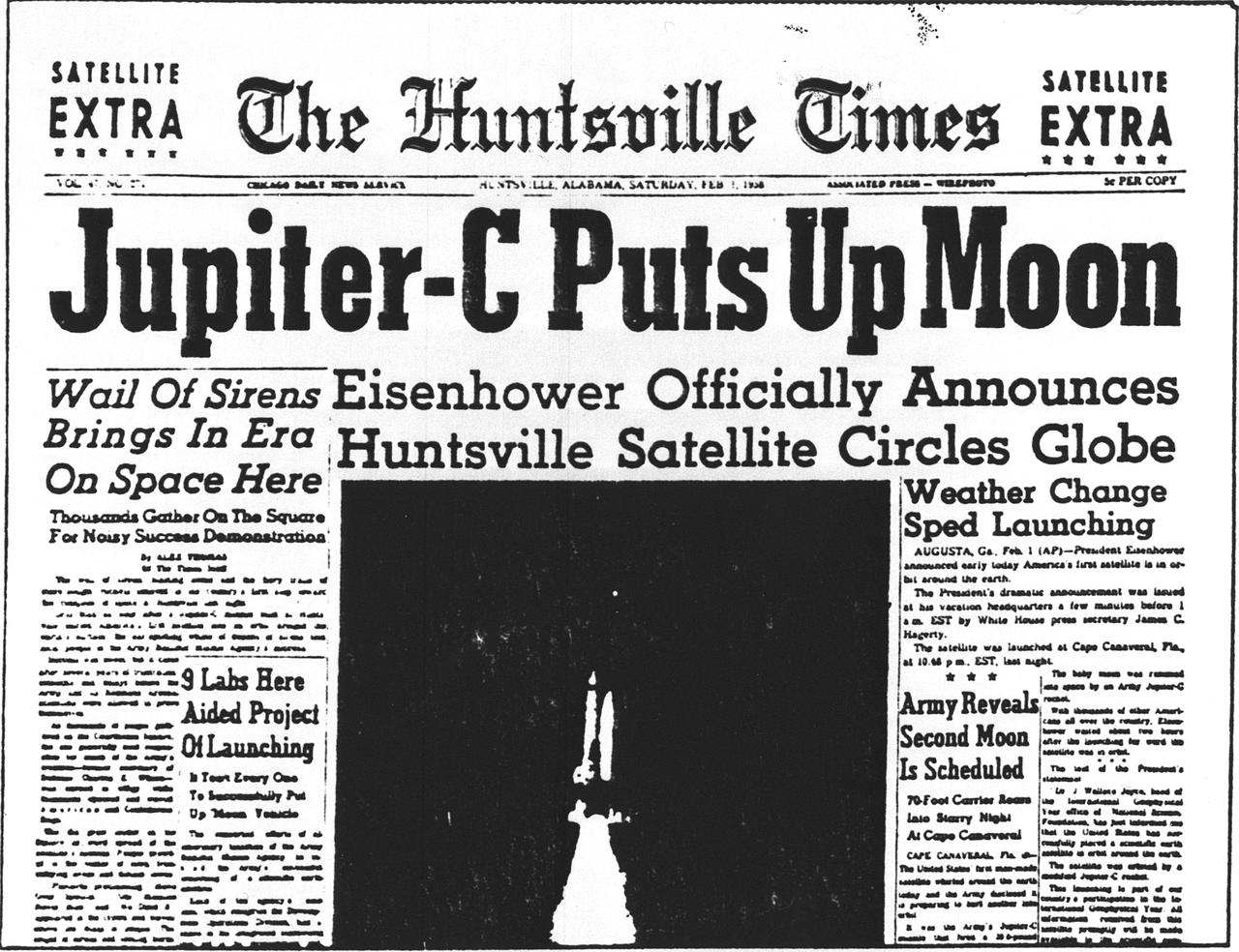
Dr. von Braun is presented with the front page of the Huntsville Times arnouncing the launch of Explorer I, the first U.S. Earth satellite, which was boosted by the Jupiter-C launch vehicle developed by Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The occasion was the fifth Anniversary of the Explorer I launch in January 1958.
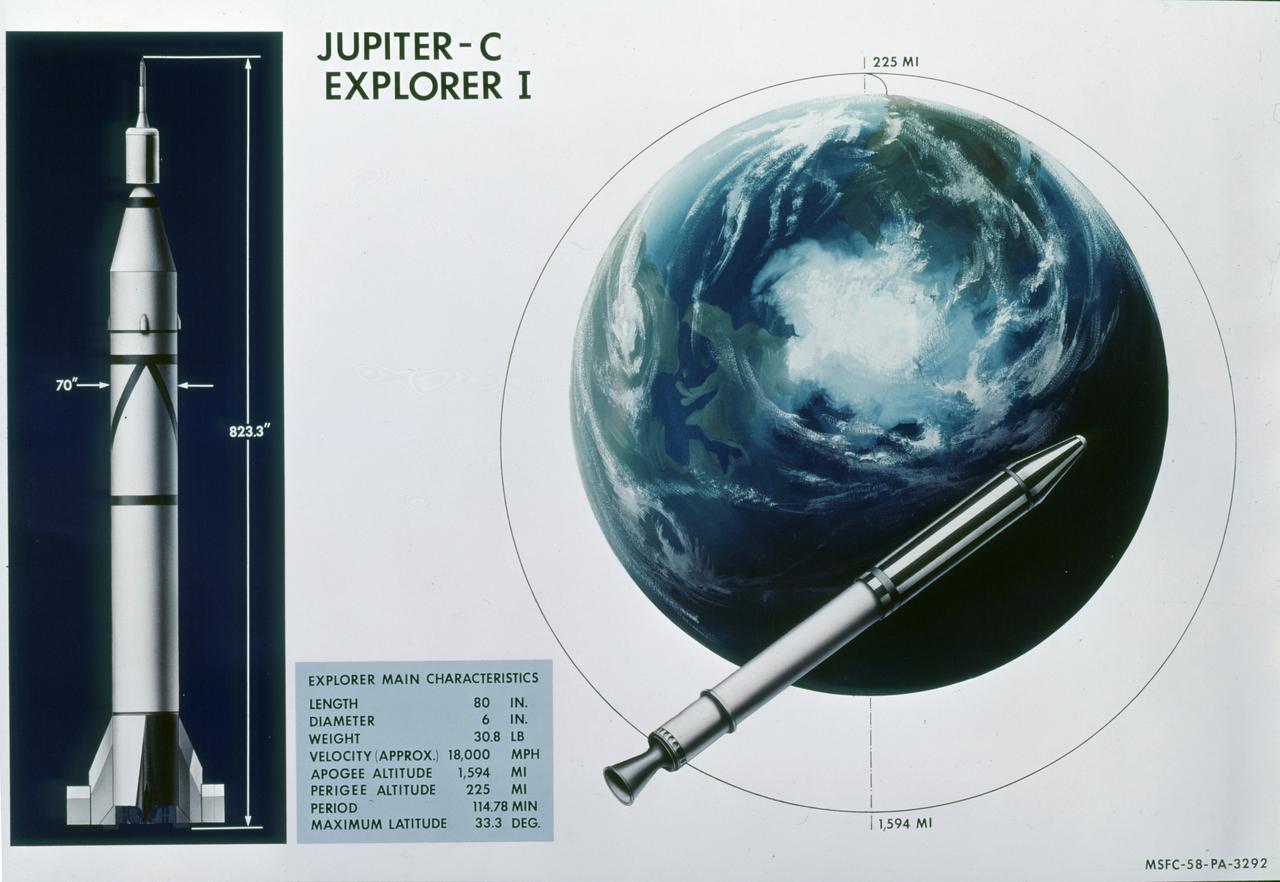
This illustration shows the main characteristics of the Jupiter C launch vehicle and its payload, the Explorer I satellite. The Jupiter C, America's first successful space vehicle, launched the free world's first scientific satellite, Explorer 1, on January 31, 1958. The four-stage Jupiter C measured almost 69 feet in length. The first stage was a modified liquid fueled Redstone missile. This main stage was about 57 feet in length and 70 inches in diameter. Fifteen scaled down SERGENT solid propellant motors were used in the upper stages. A "tub" configuration mounted on top of the modified Redstone held the second and third stages. The second stage consisted of 11 rockets placed in a ring formation within the tub. Inserted into the ring of second stage rockets was a cluster of 3 rockets making up the third stage. A fourth stage single rocket and the satellite were mounted atop the third stage. This "tub", all upper stages, and the satellite were set spirning prior to launching. The complete upper assembly measured 12.5 feet in length. The Explorer I carried the radiation detection experiment designed by Dr. James Van Allen and discovered the Van Allen Radiation Belt.
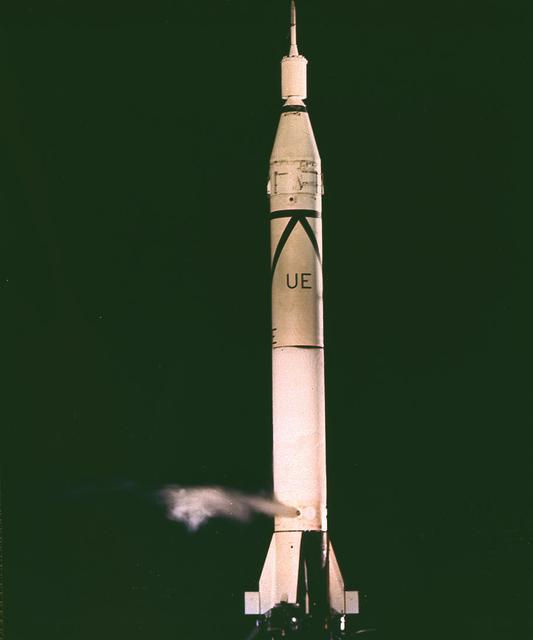

Juno I, a slightly modified Jupiter-C launch vehicle, shortly before the January 31, 1958 launch of America's first satellite, Explorer I. The Jupiter-C, developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the rocket team at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama, consisted of a modified version of the Redstone rocket's first stage and two upper stages of clustered Baby Sergeant rockets developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
In January 1958, a modified Redstone rocket lifted the first American satellite into orbit just 3 months after the the von Braun team received the go-ahead. This modified Redstone rocket was known as a Jupiter-C. Its satellite payload was called Explorer I.
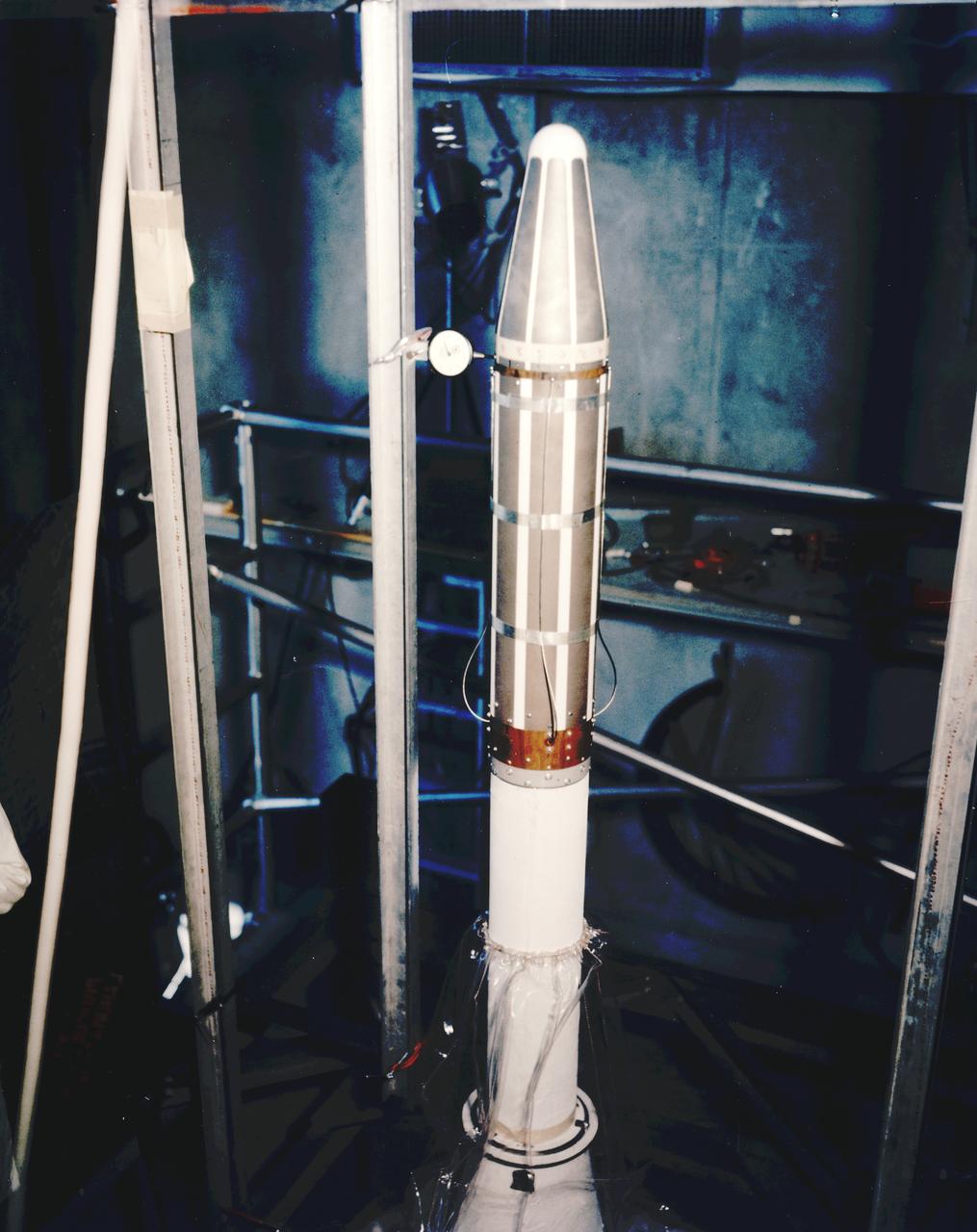

America’s first scientific satellite, the Explorer I, carried the radiation detection experiment designed by Dr. James Van Allen and discovered the Van Allen Radiation Belt. It was launched aboard a modified redstone rocket known as the Jupiter C, developed by Dr. von Braun’s rocket team at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama. The satellite launched on January 31, 1958, just 3 months after the the von Braun team received the go-ahead.
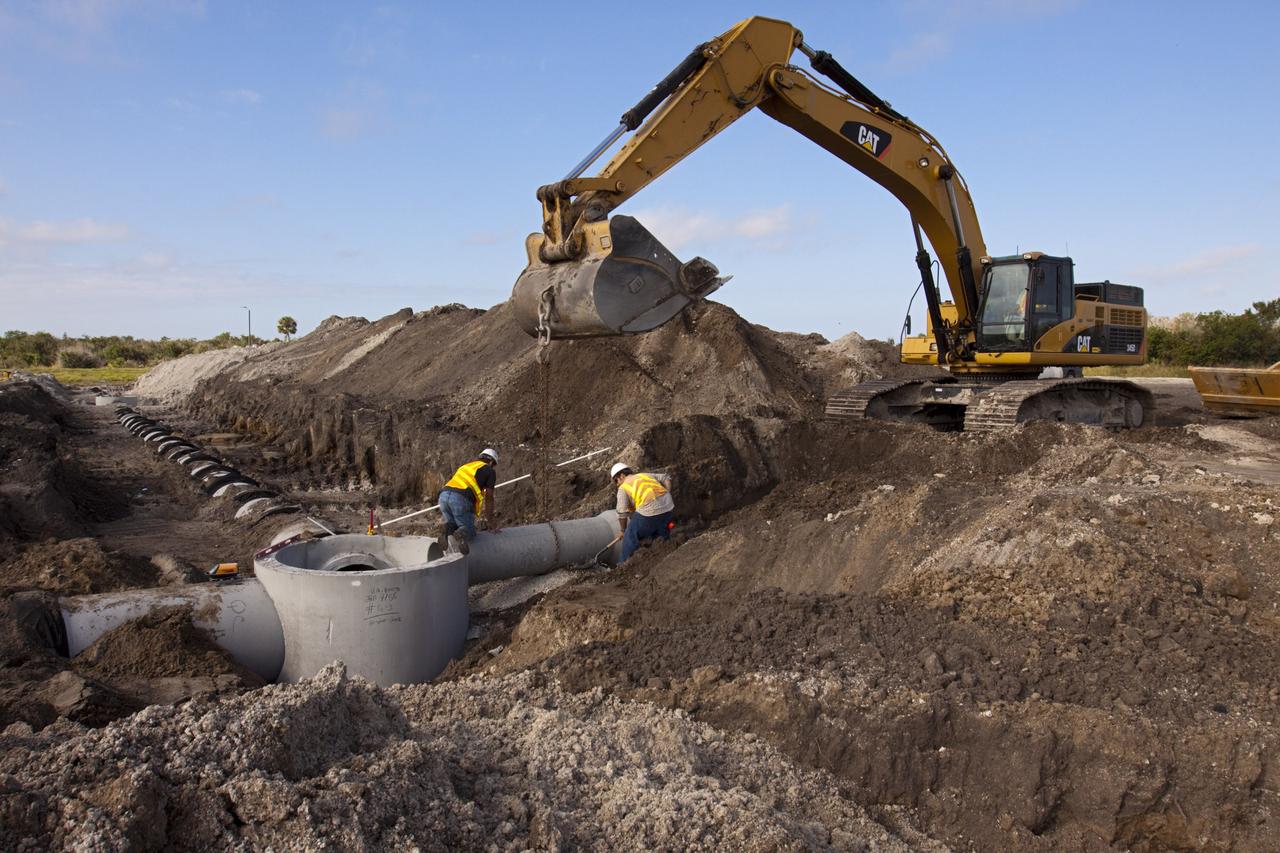

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
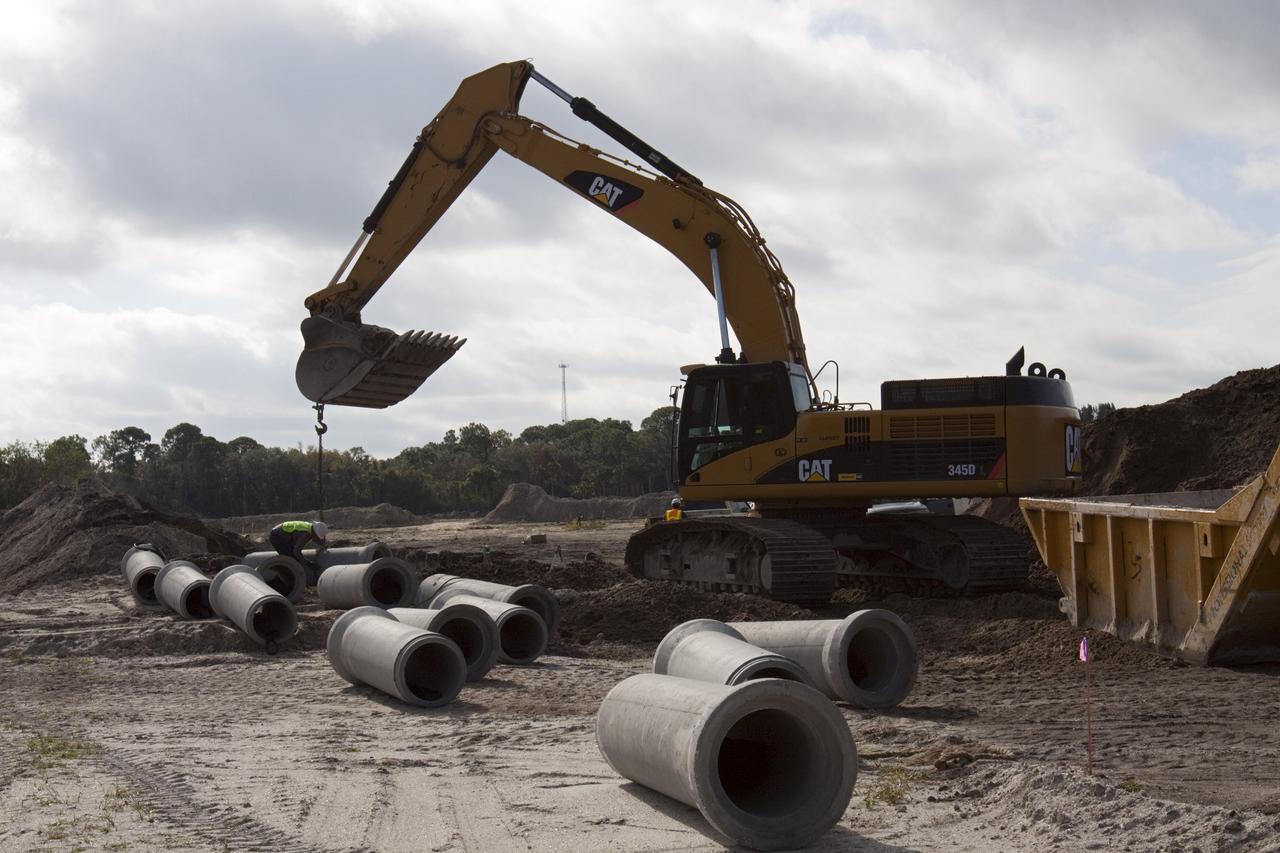

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
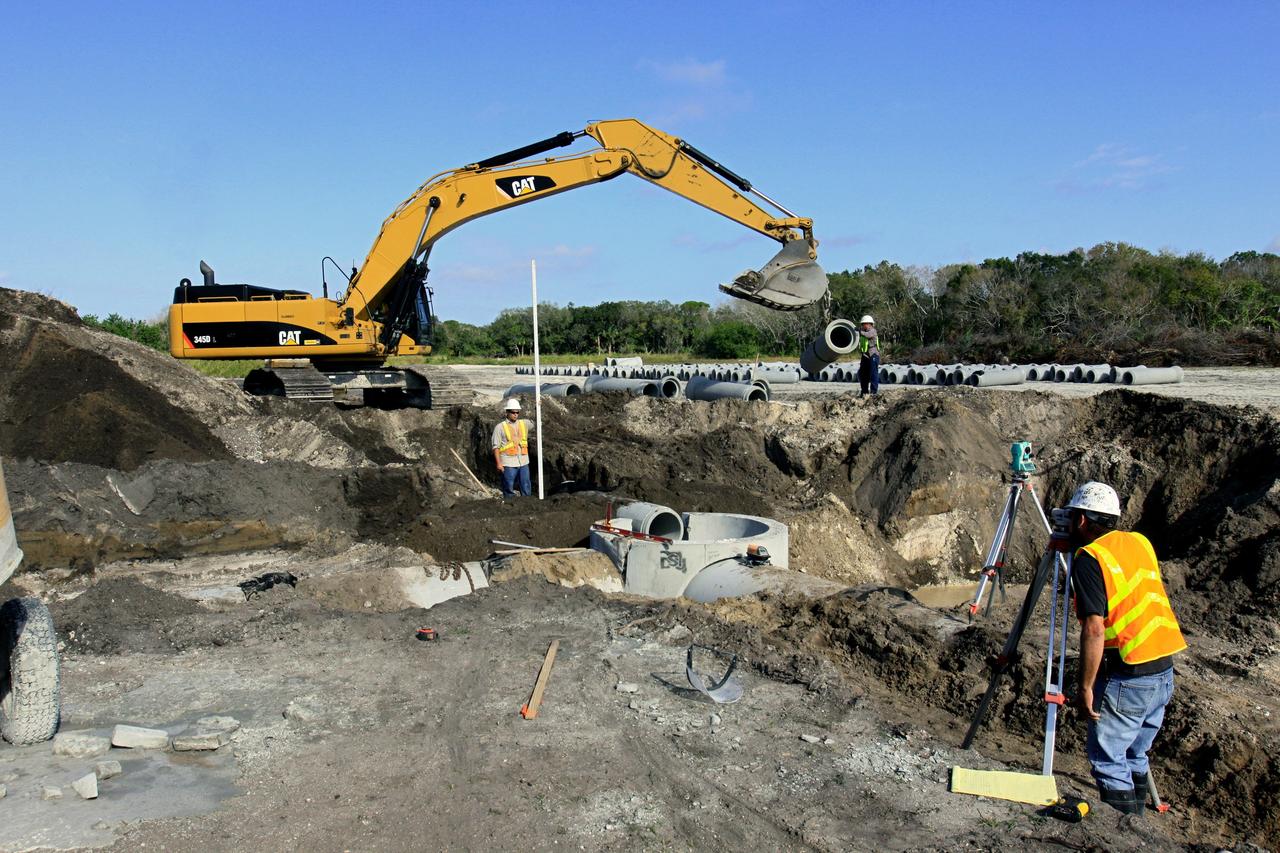

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
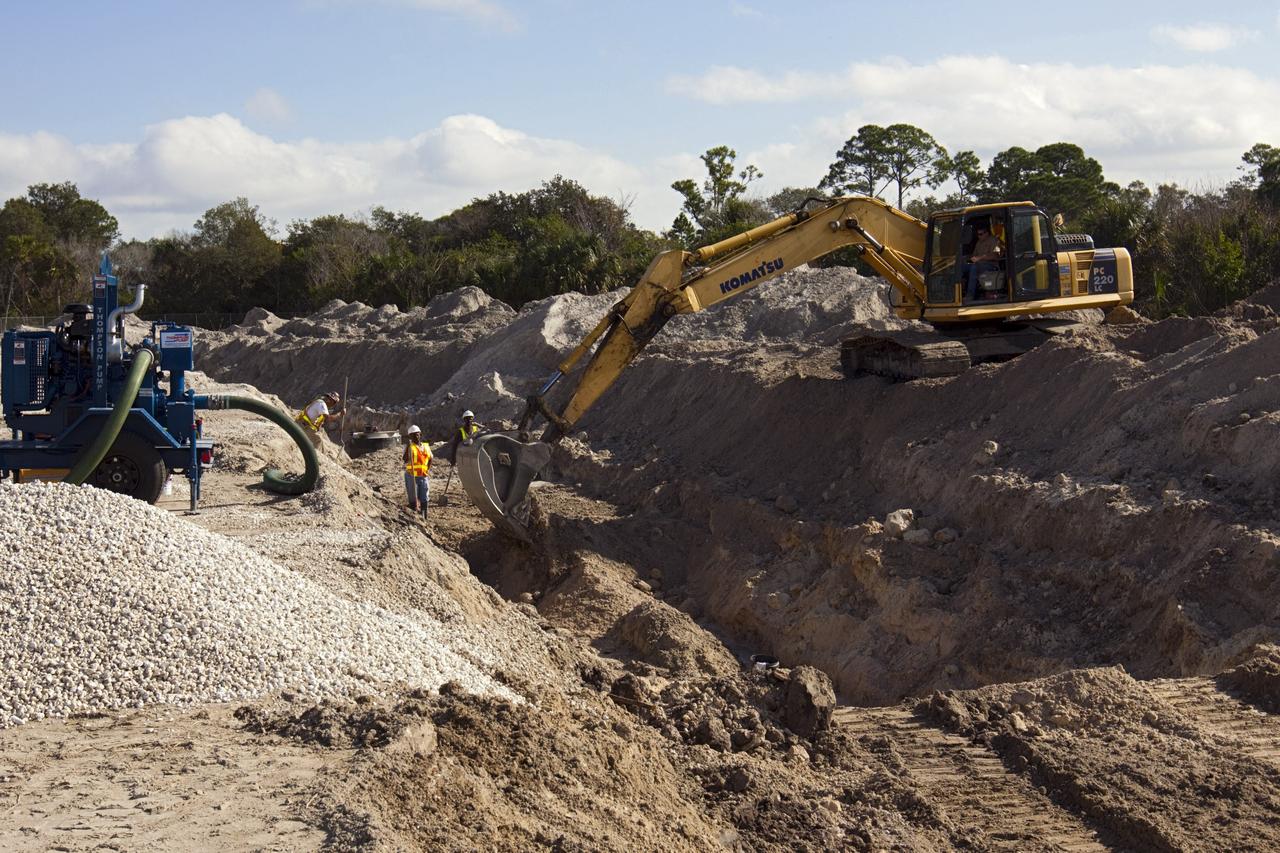

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
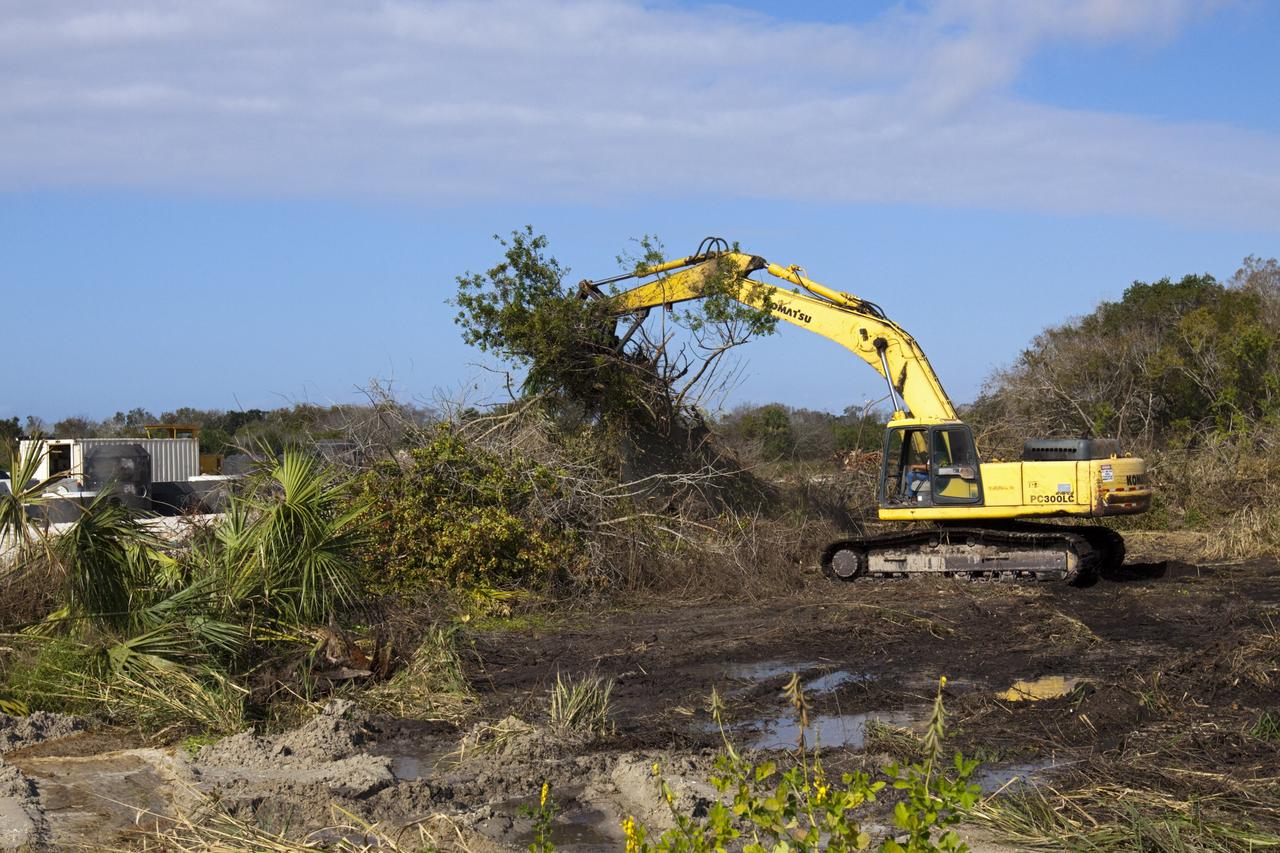

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Land is cleared as construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
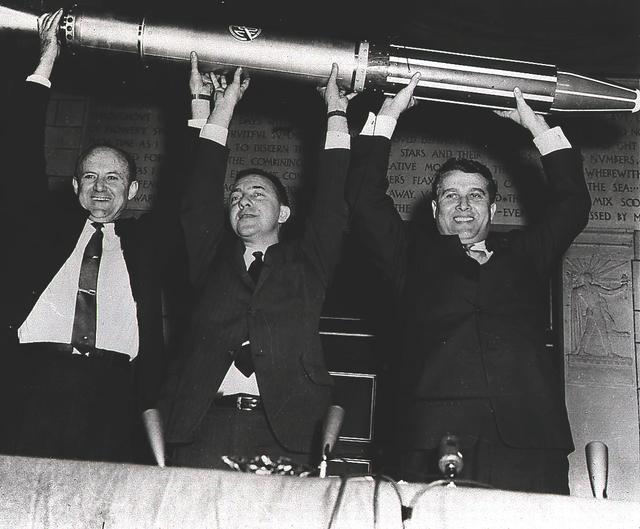

Jet Propulsion Laboratory Director Dr. William Pickering, Dr. James van Allen of the State University of Iowa, and Army Ballistic missionile Agency Technical Director Dr. Wernher von Braun triumphantly display a model of the Explorer I, America's first satellite, shortly after the satellite's launch on January 31, 1958. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory packed and tested the payload, a radiation detection experiment designed by Dr. van Allen. Dr. von Braun's rocket team at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama, developed the Juno I launch vehicle, a modified Jupiter-C.
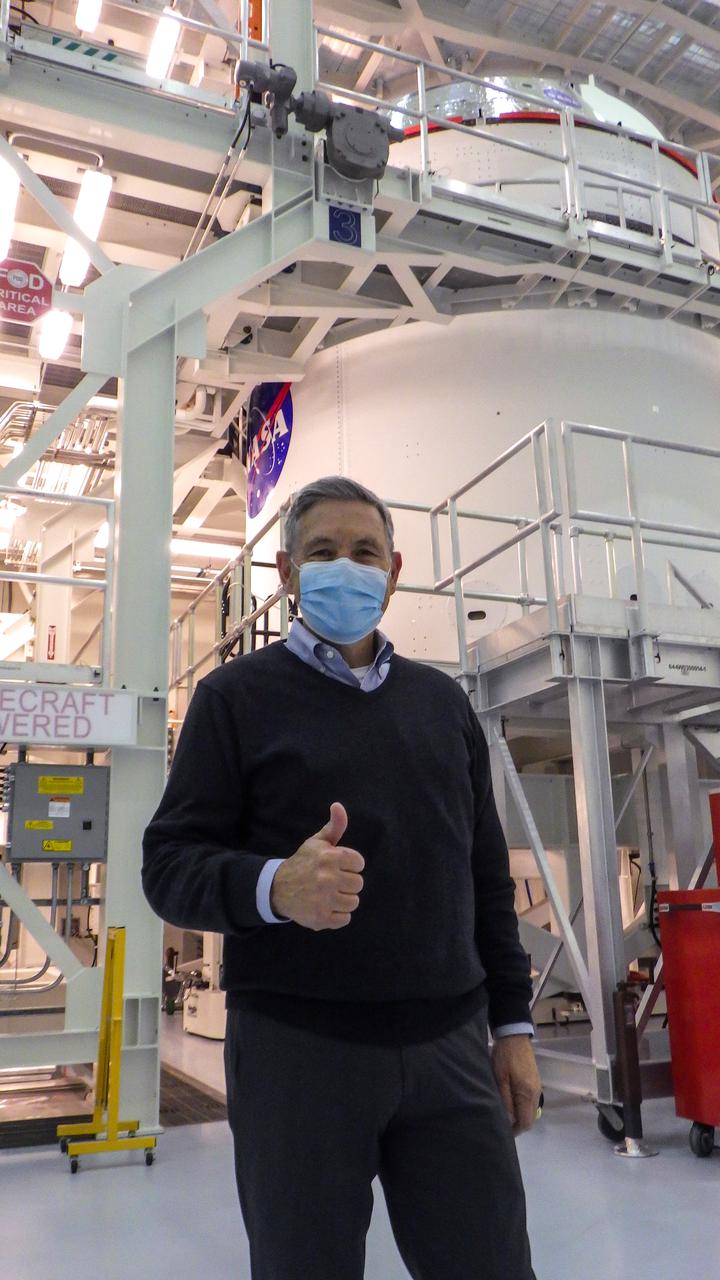

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana gives a thumbs up inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at the center on Jan. 20, 2021. Behind him is the Artemis I Orion spacecraft with NASA’s famous “meatball” insignia is affixed to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft adapter jettison fairings, which protect the European built service module. Shown inside its servicing stand, ground processing begins on Orion, with the Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams performing checkouts and fueling the spacecraft with commodities as part of preparations ahead of the Artemis I mission.
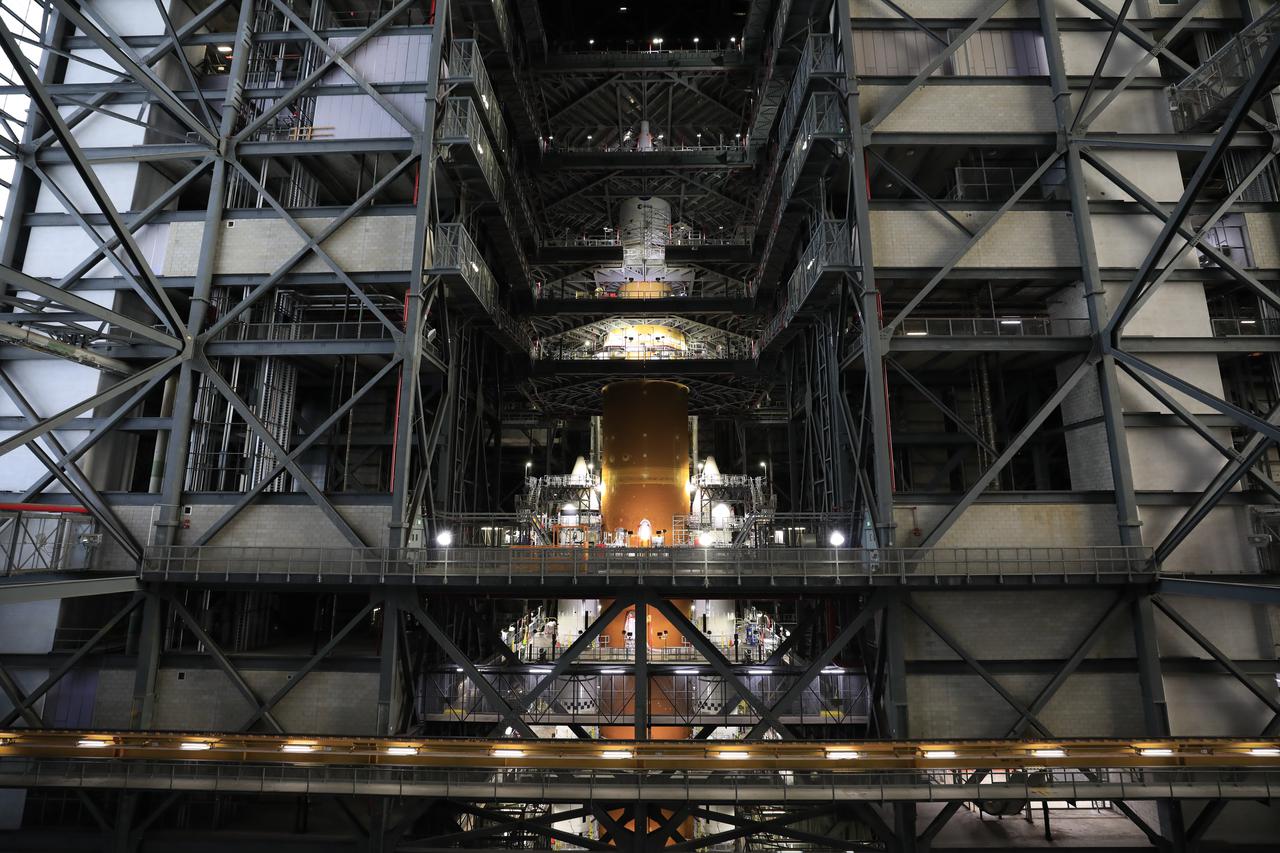

NASA’s massive Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission is shown fully stacked – with NASA’s Orion spacecraft atop – inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Dec. 13, 2021. Artemis I is the inaugural launch of SLS and Orion as an integrated system. With Artemis missions, NASA will explore more of the lunar surface than ever before, using what we learn on and around the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
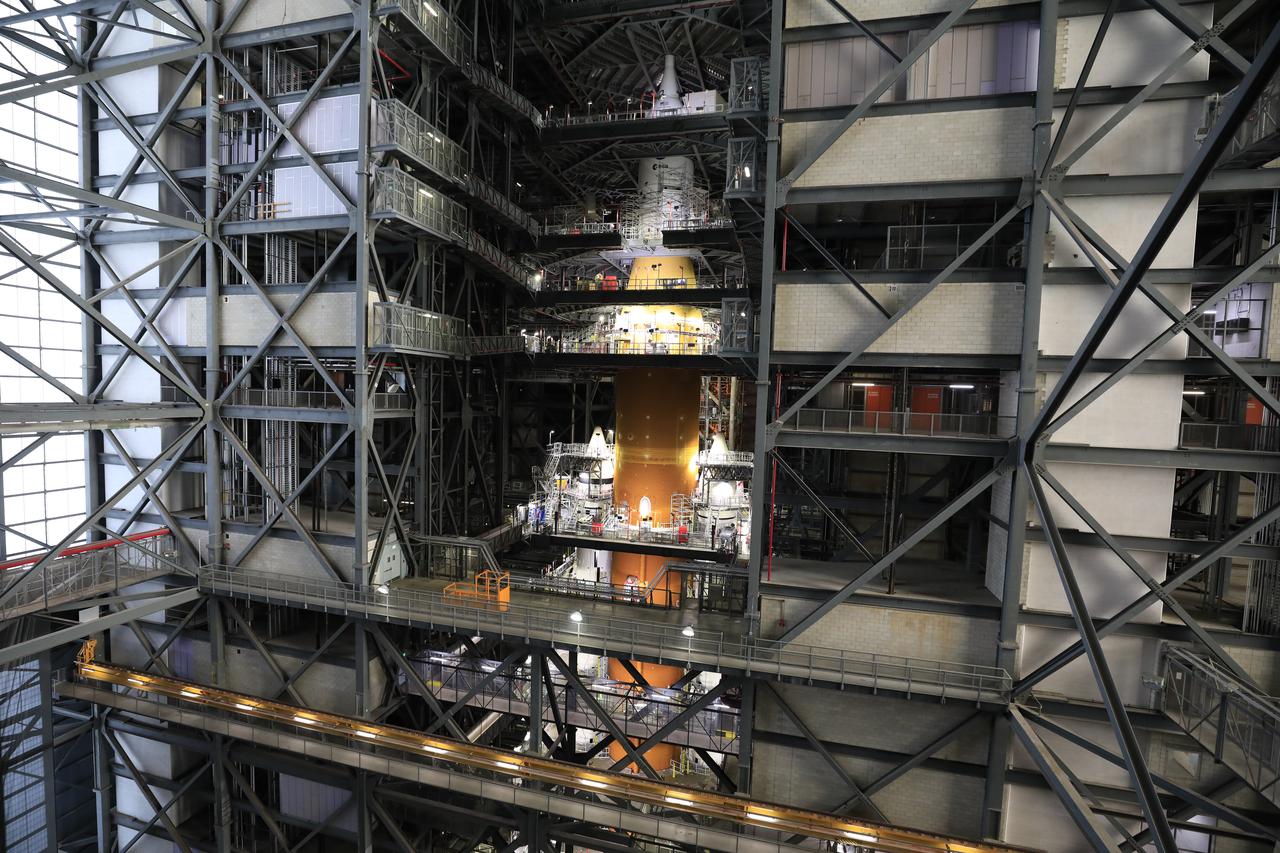
NASA’s massive Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission is shown fully stacked – with NASA’s Orion spacecraft atop – inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Dec. 13, 2021. Artemis I is the inaugural launch of SLS and Orion as an integrated system. With Artemis missions, NASA will explore more of the lunar surface than ever before, using what we learn on and around the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
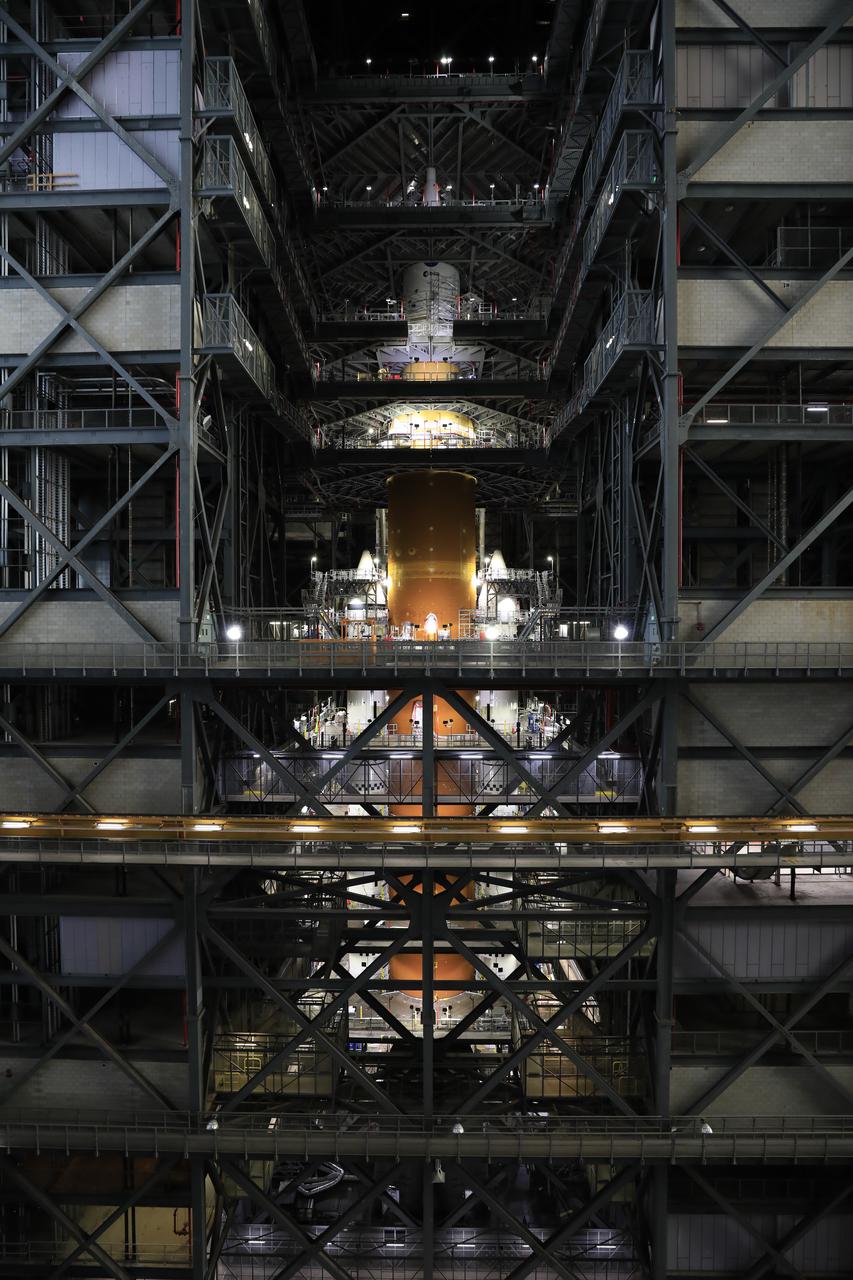

NASA’s massive Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission is shown fully stacked – with NASA’s Orion spacecraft atop – inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Dec. 13, 2021. Artemis I is the inaugural launch of SLS and Orion as an integrated system. With Artemis missions, NASA will explore more of the lunar surface than ever before, using what we learn on and around the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
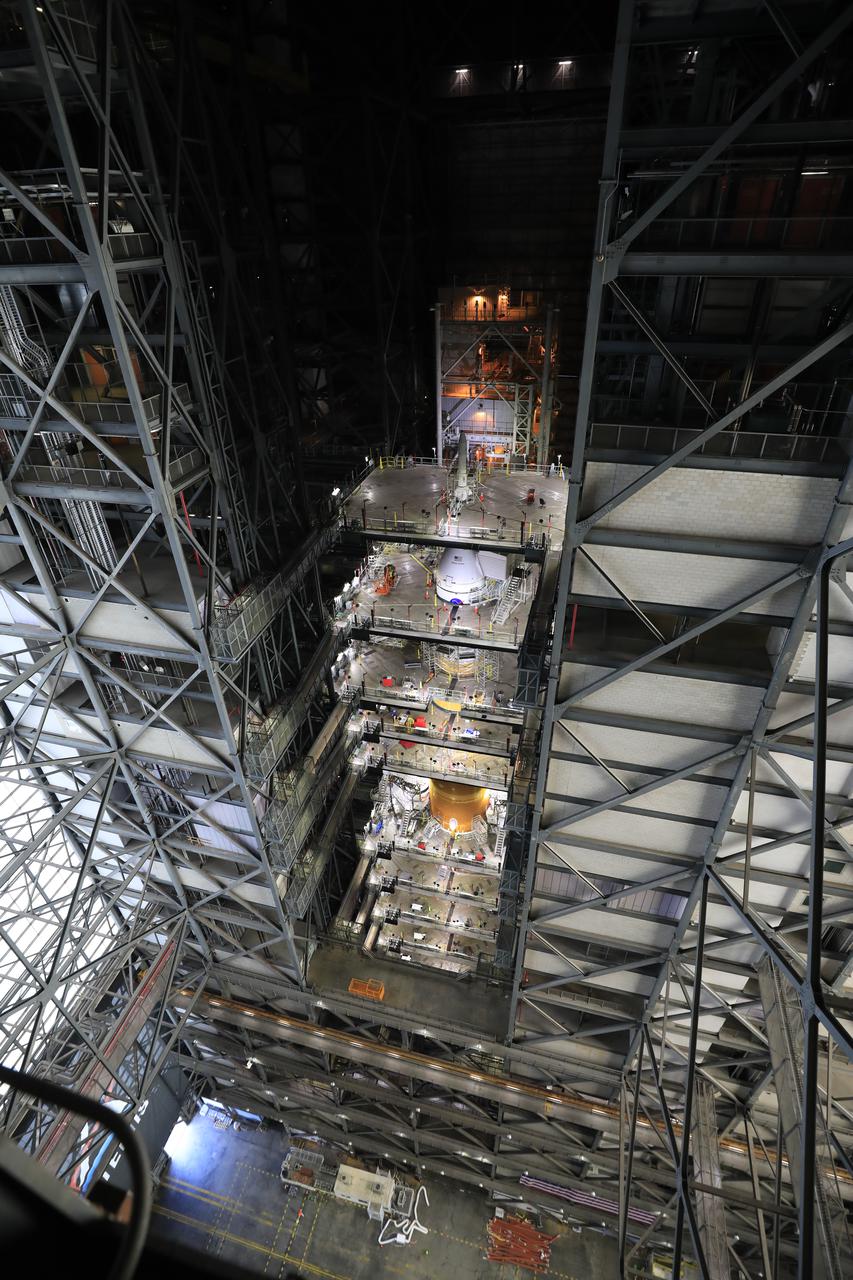

NASA’s massive Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission is shown fully stacked – with NASA’s Orion spacecraft atop – inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Dec. 13, 2021. Artemis I is the inaugural launch of SLS and Orion as an integrated system. With Artemis missions, NASA will explore more of the lunar surface than ever before, using what we learn on and around the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
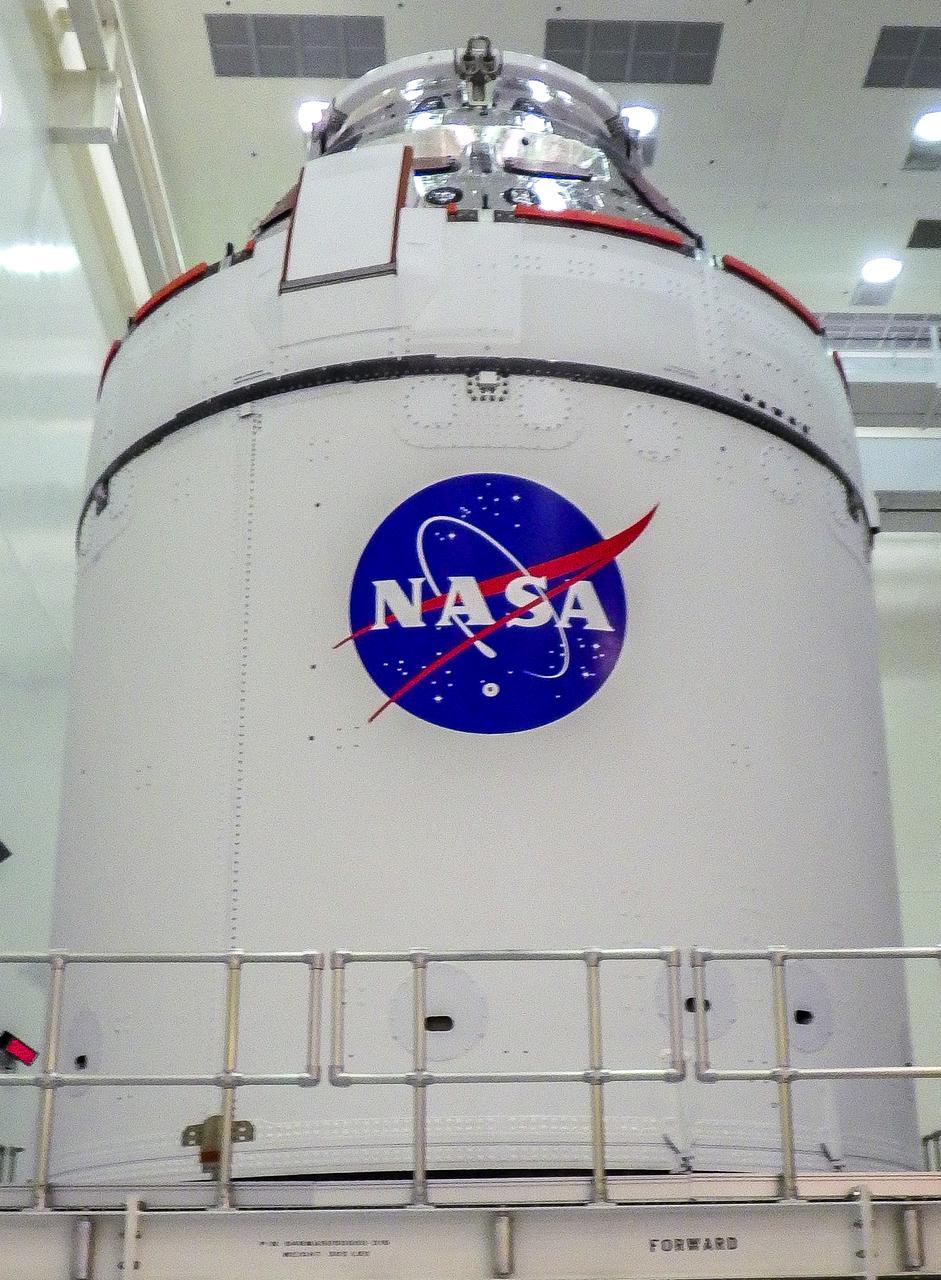

A close-up view of the Artemis I Orion spacecraft with NASA’s famous “meatball” insignia is affixed to the spacecraft adapter jettison fairings, which protect the European built service module, inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center on Jan. 20, 2021. Ground processing will begin on Orion, with the Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams performing checkouts and fueling the spacecraft with commodities as part of preparations ahead of the Artemis I mission.

NASA’s famous “meatball” insignia is affixed to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft adapter jettison fairings, which protect the European built service module, Jan. 20, 2021, inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Shown inside its servicing stand, ground processing begins on Orion, with the Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams performing checkouts and fueling the spacecraft with commodities as part of preparations ahead of the Artemis I mission.
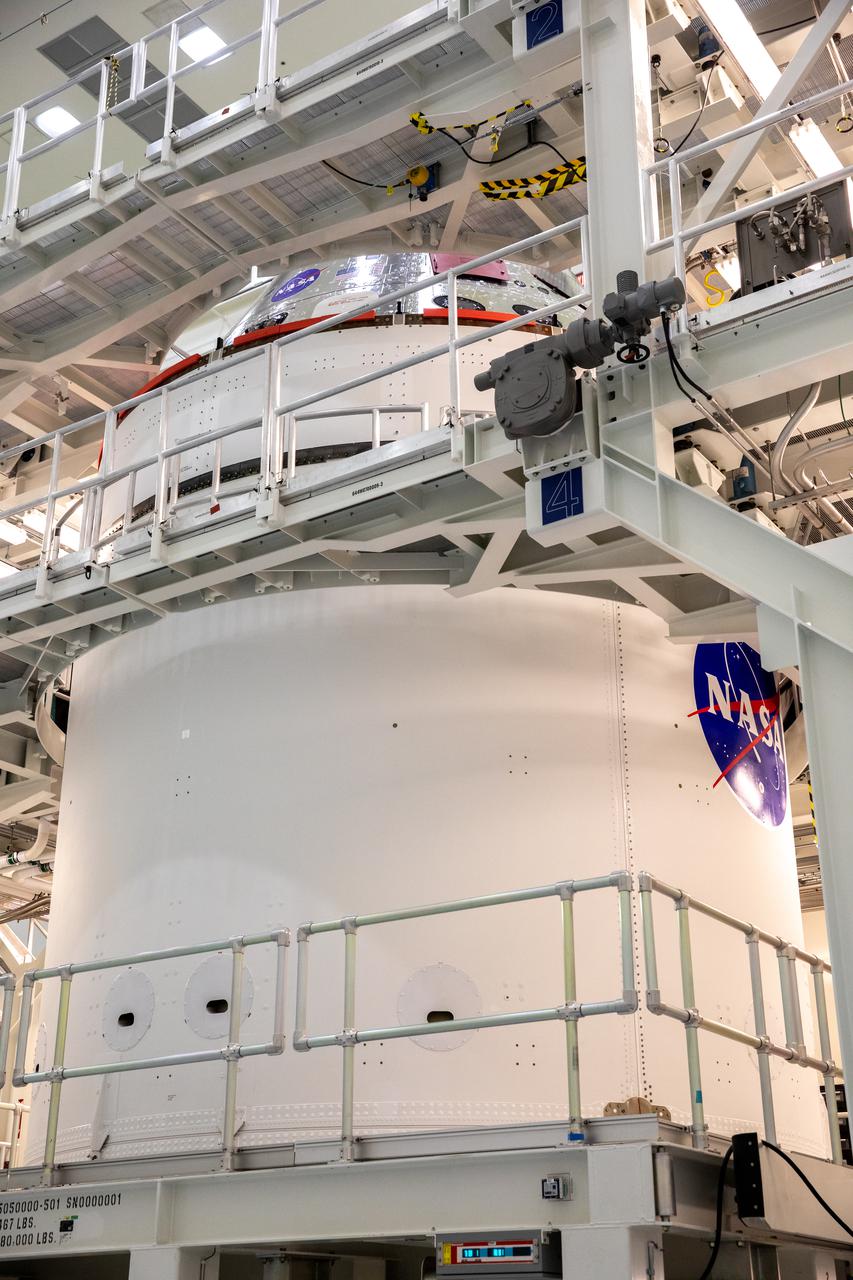

NASA’s famous “meatball” insignia is affixed to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft adapter jettison fairings, which protect the European built service module, Jan. 20, 2021, inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Shown inside its servicing stand, ground processing begins on Orion, with the Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams performing checkouts and fueling the spacecraft with commodities as part of preparations ahead of the Artemis I mission.
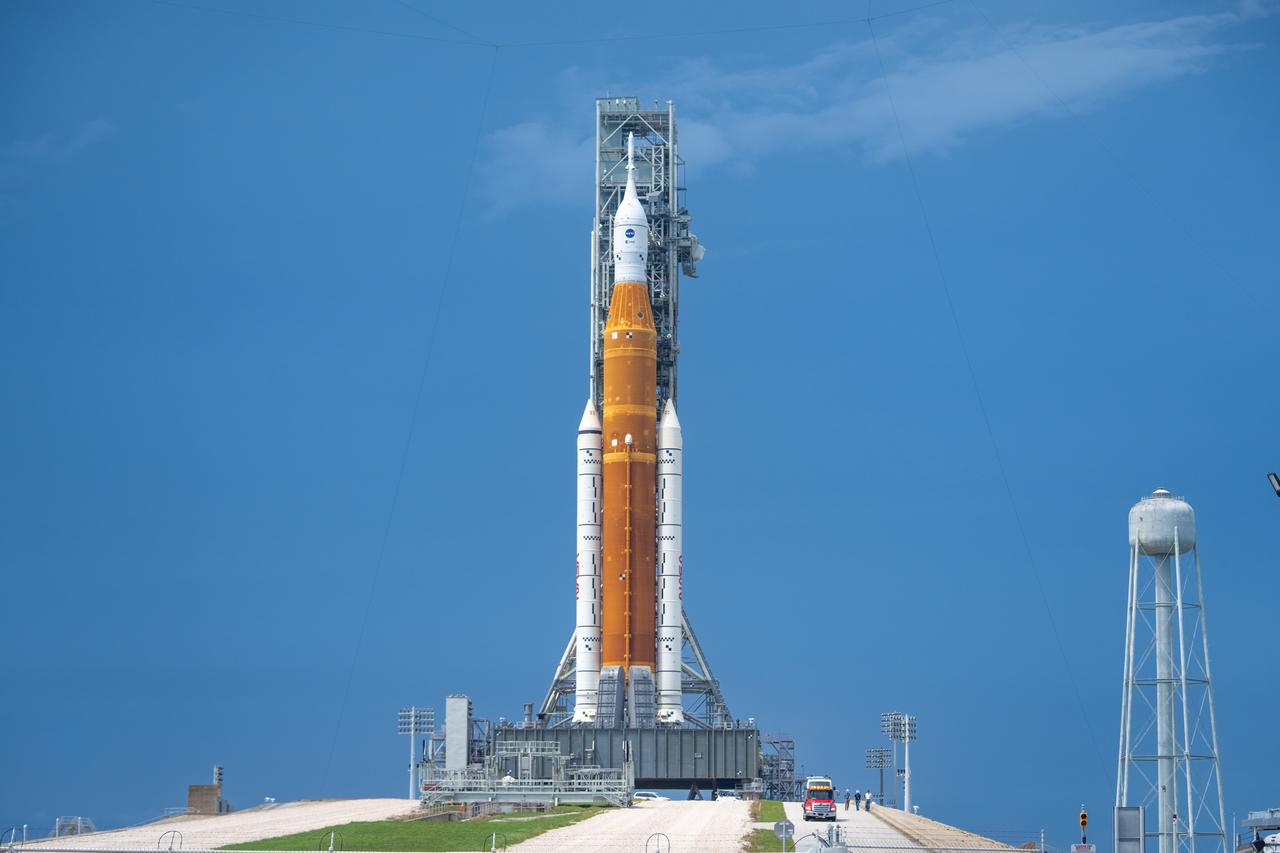

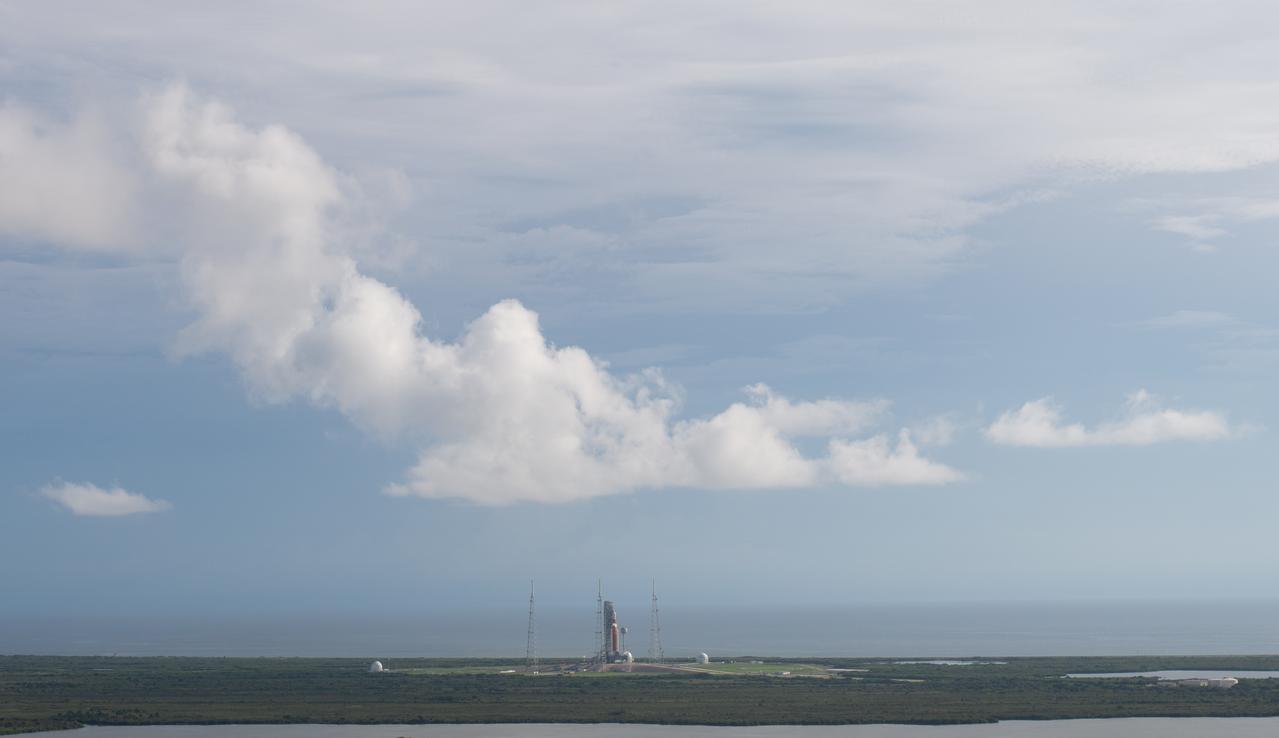
NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

Jim Free, associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in a press conference on Aug. 29, 2022, at the agency’s NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after waving-off of the launch of the Artemis I mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Mike Bolger, Exploration Ground Systems Program manager, Kennedy, participates in a postlaunch news conference on Nov. 16, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I at 1:47 a.m. EST from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

From left, Jeremy Parsons, Exploration Ground Systems, deputy program manager, NASA Kennedy; and Melody Lovin, weather officer, Space Launch Delta 45, participate in a prelaunch media briefing on the status of the Artemis I countdown on Sept. 2, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Jim Free, Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following completion of NASA’s Flight Readiness Review for Artemis I on Aug. 22, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
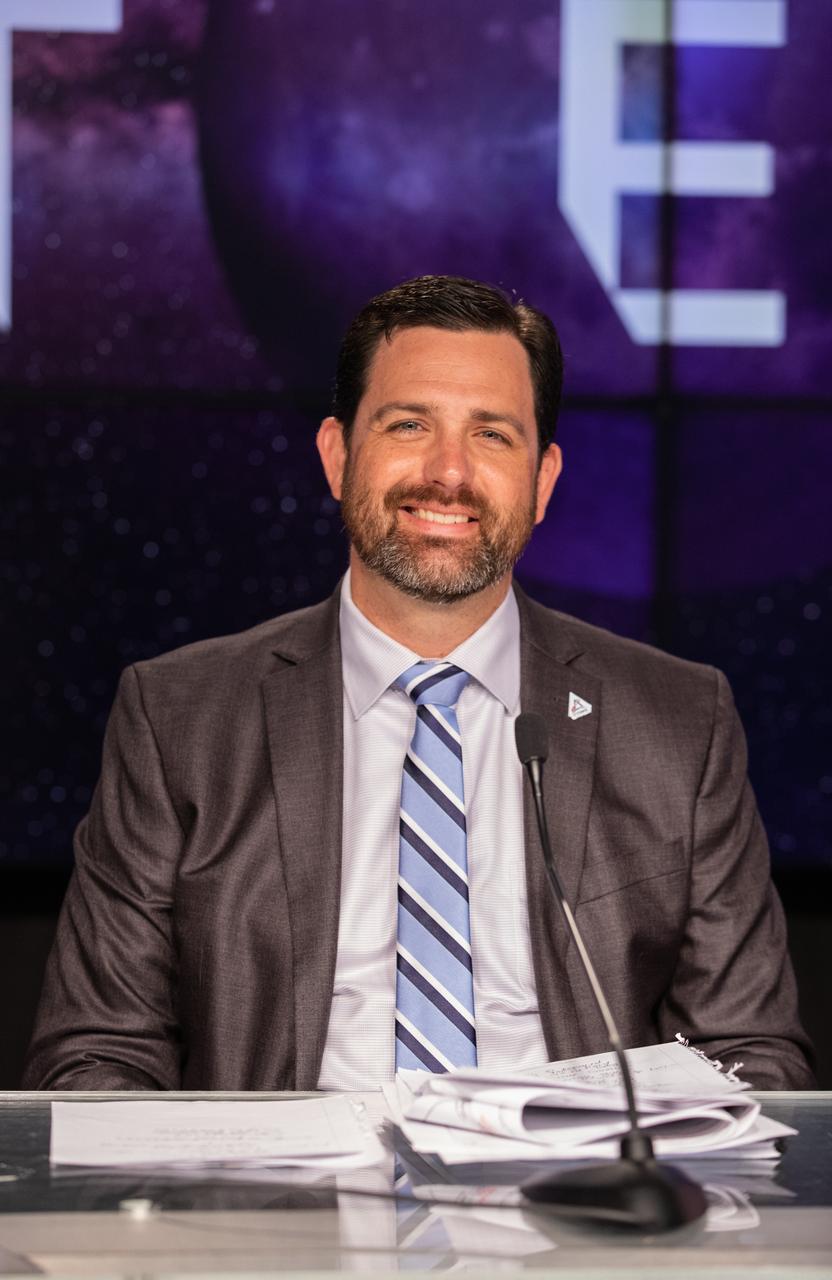

Jeremy Parsons, Exploration Ground Systems, deputy program manager, NASA Kennedy Space Center, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the status of the Artemis I countdown on Sept. 2, 2022, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
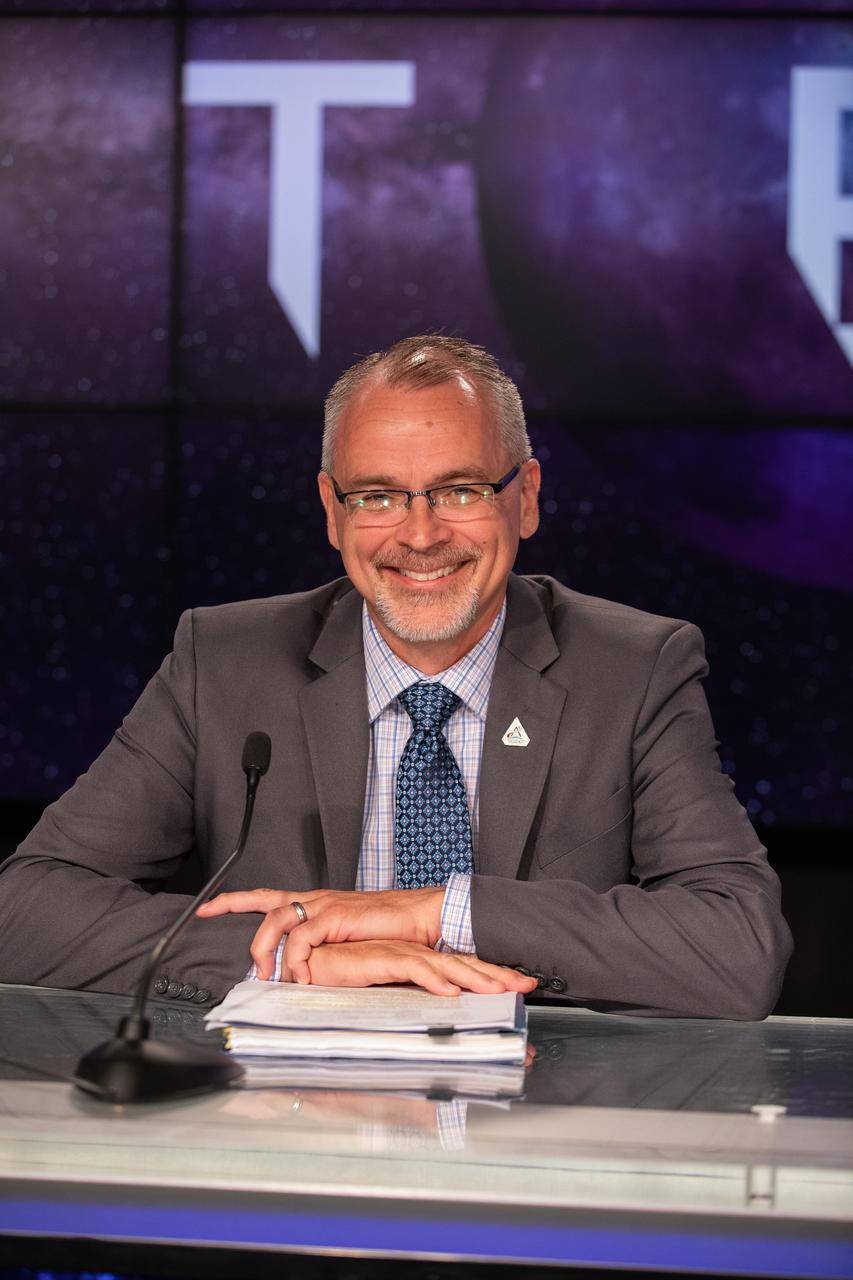

Jim Free, NASA associate administrator, Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

NASA holds a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Participants, from left are Kathryn Hambleton, NASA Communications; Jim Free, association administrator, Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters; and Randy Lycans, vice president/general manager of NASA Enterprise Solutions, Jacobs. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
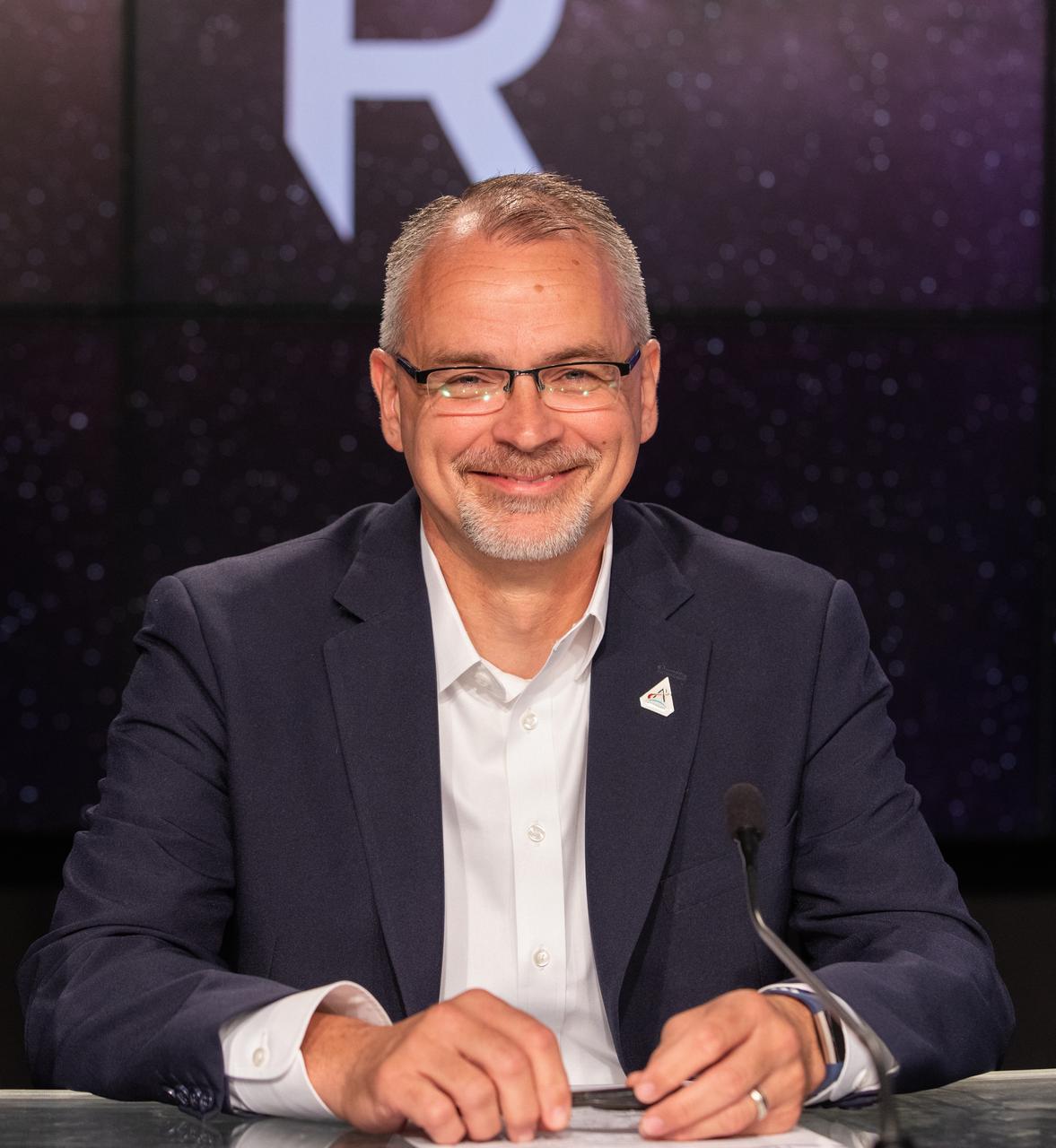

Jim Free, association administrator, Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
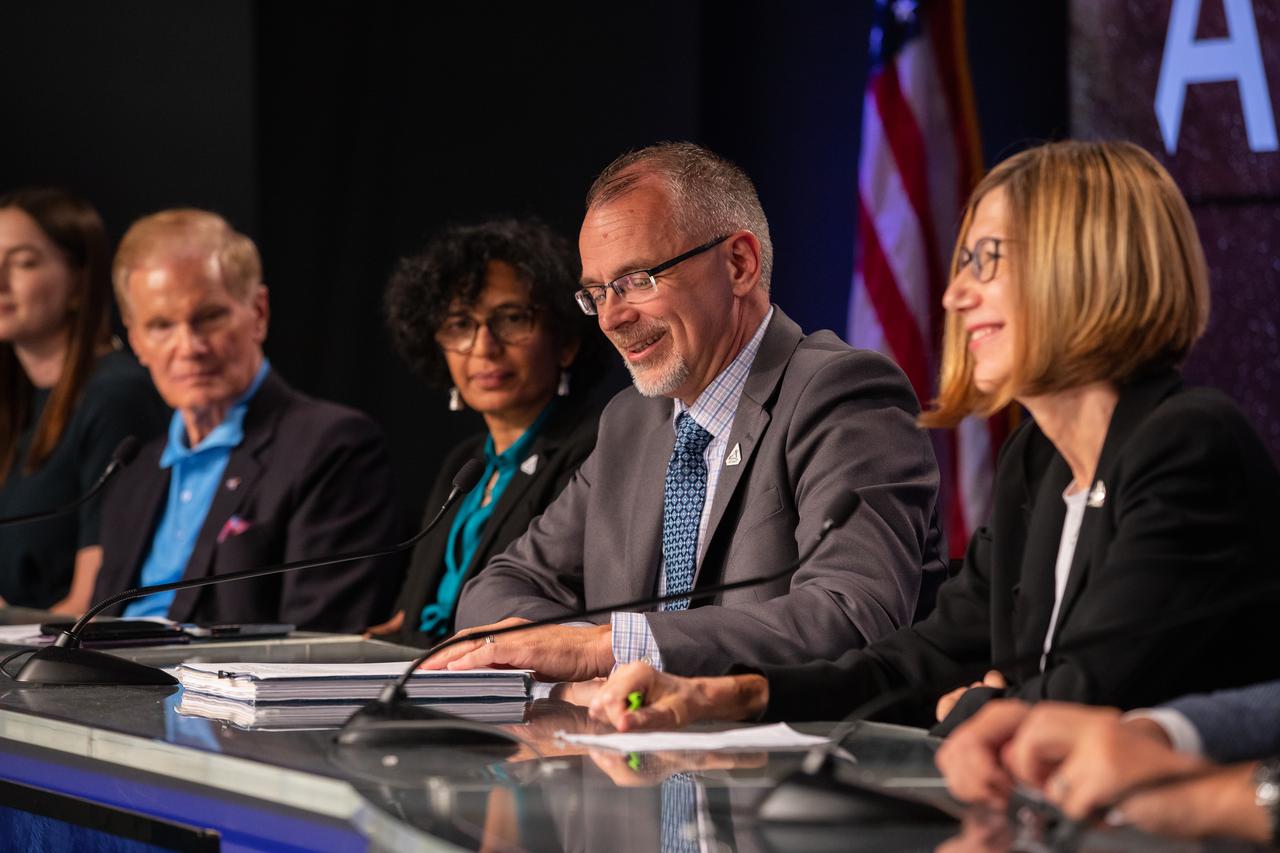

Jim Free, NASA associate administrator, Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, second from right, speaks during a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
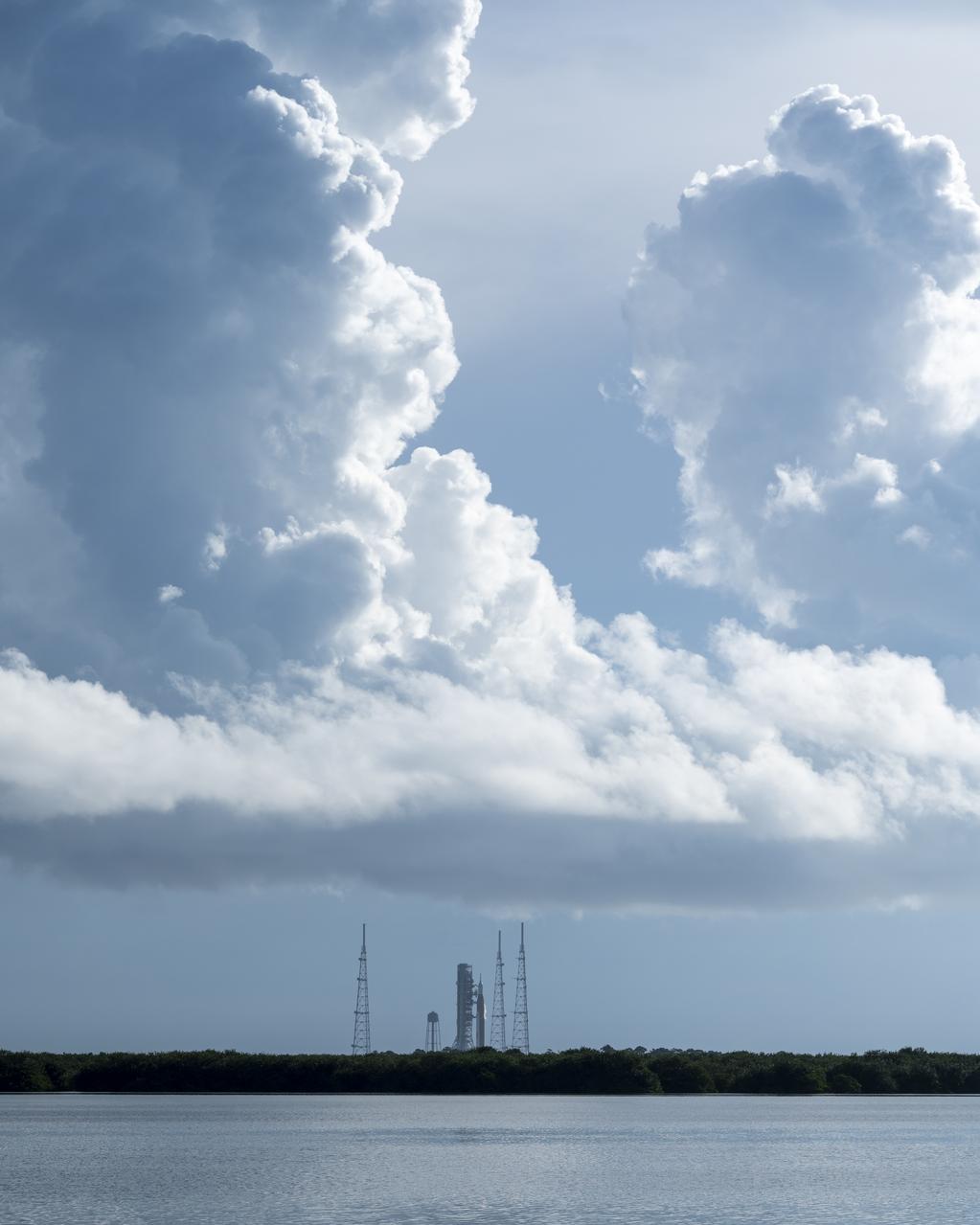

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B, Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022, as the Artemis I launch teams load more than 700,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants including liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as the launch countdown progresses at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Artemis I flight test is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, SLS rocket, and supporting ground systems. The launch director waived off today’s Artemis I launch attempt at approximately 11:17 a.m. EDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B, Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022, as the Artemis I launch teams load more than 700,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants including liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as the launch countdown progresses at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Artemis I flight test is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, SLS rocket, and supporting ground systems. The launch director waived off today’s Artemis I launch attempt at approximately 11:17 a.m. EDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A prelaunch media briefing is held following completion of NASA’s Flight Readiness Review for Artemis I on Aug. 22, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, Megan Cruz, NASA Communications; Bob Cabana, NASA Associate Administrator; Janet Petro, Director, Kennedy Space Center; Jim Free, Associate Administrator, Exploration Systems Development; Mike Sarafin, Mission Manager, Artemis I; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Launch Director, Artemis I; Howard Hu, Manager, Orion Program; Chris Cianciola, Deputy Manager, SLS Program. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

A prelaunch media briefing is held following completion of NASA’s Flight Readiness Review for Artemis I on Aug. 22, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, Megan Cruz, NASA Communications; Bob Cabana, NASA Associate Administrator; Janet Petro, Director, Kennedy Space Center; Jim Free, Associate Administrator, Exploration Systems Development; Mike Sarafin, Mission Manager, Artemis I; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Launch Director, Artemis I; Howard Hu, Manager, Orion Program; Chris Cianciola, Deputy Manager, SLS Program. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

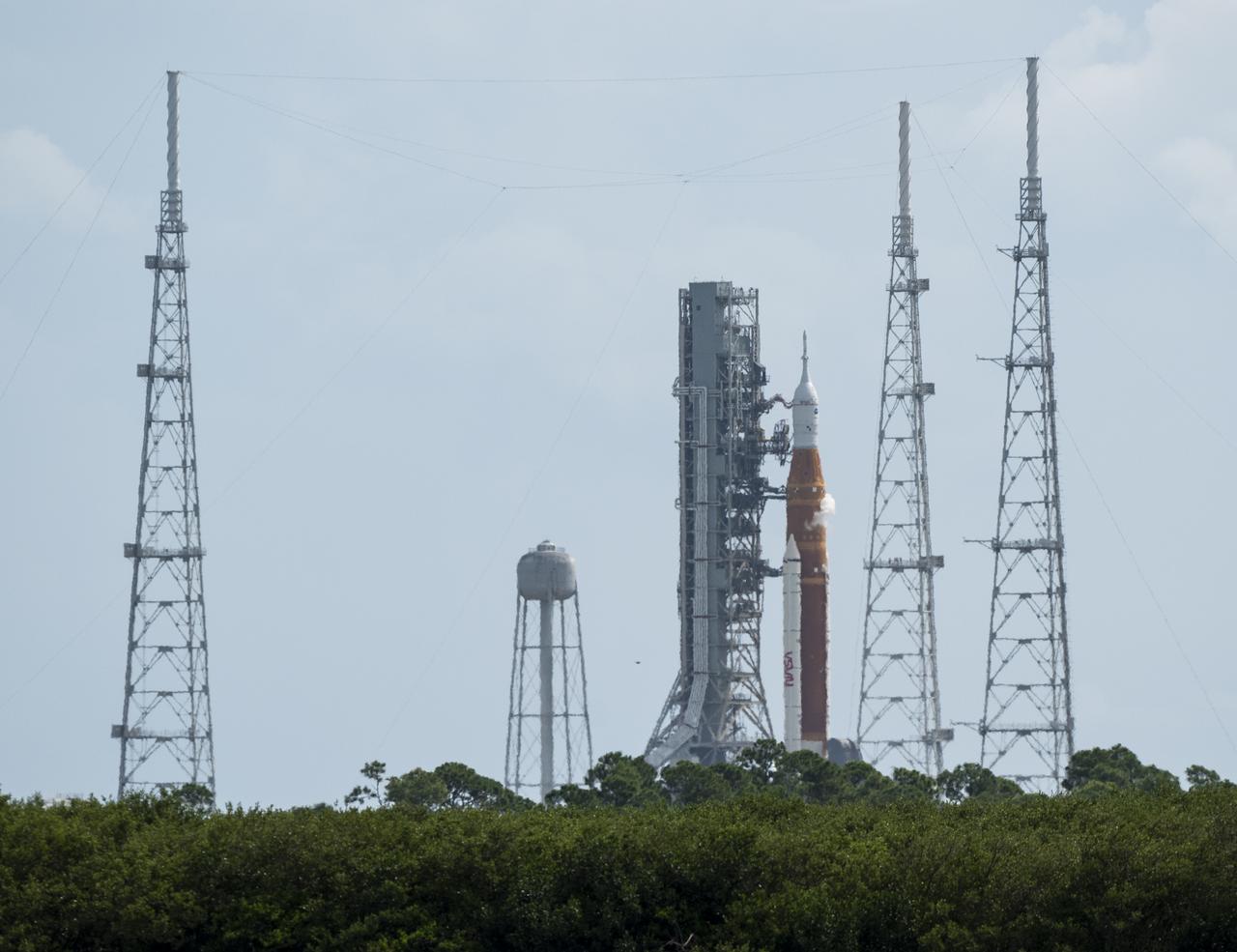
NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B, Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Artemis I flight test is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, SLS rocket, and supporting ground systems. The launch director waived off today’s Artemis I launch attempt at approximately 11:17 a.m. EDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
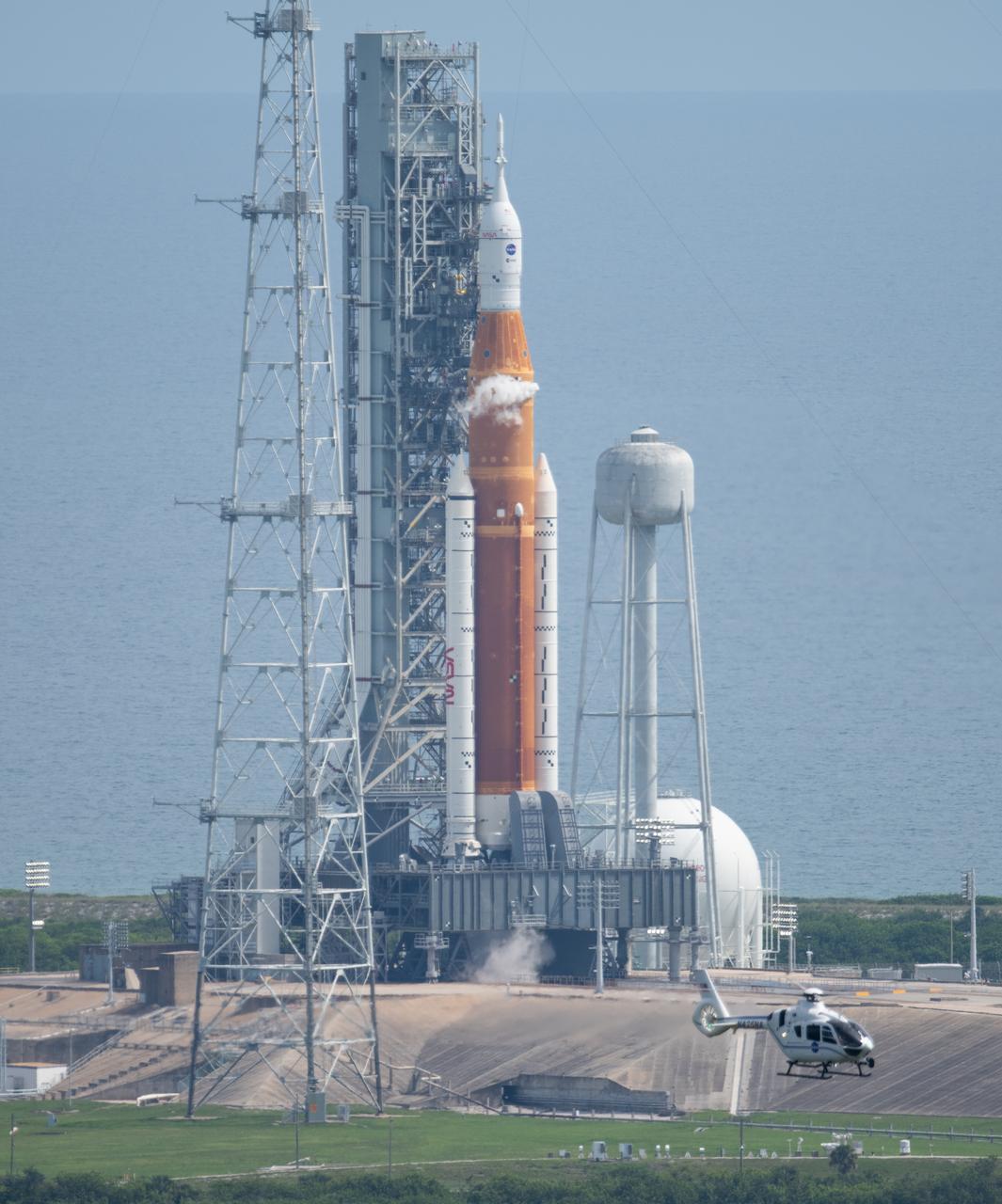

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B, Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Artemis I flight test is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Orion spacecraft, SLS rocket, and supporting ground systems. The launch director waived off today’s Artemis I launch attempt at approximately 11:17 a.m. EDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
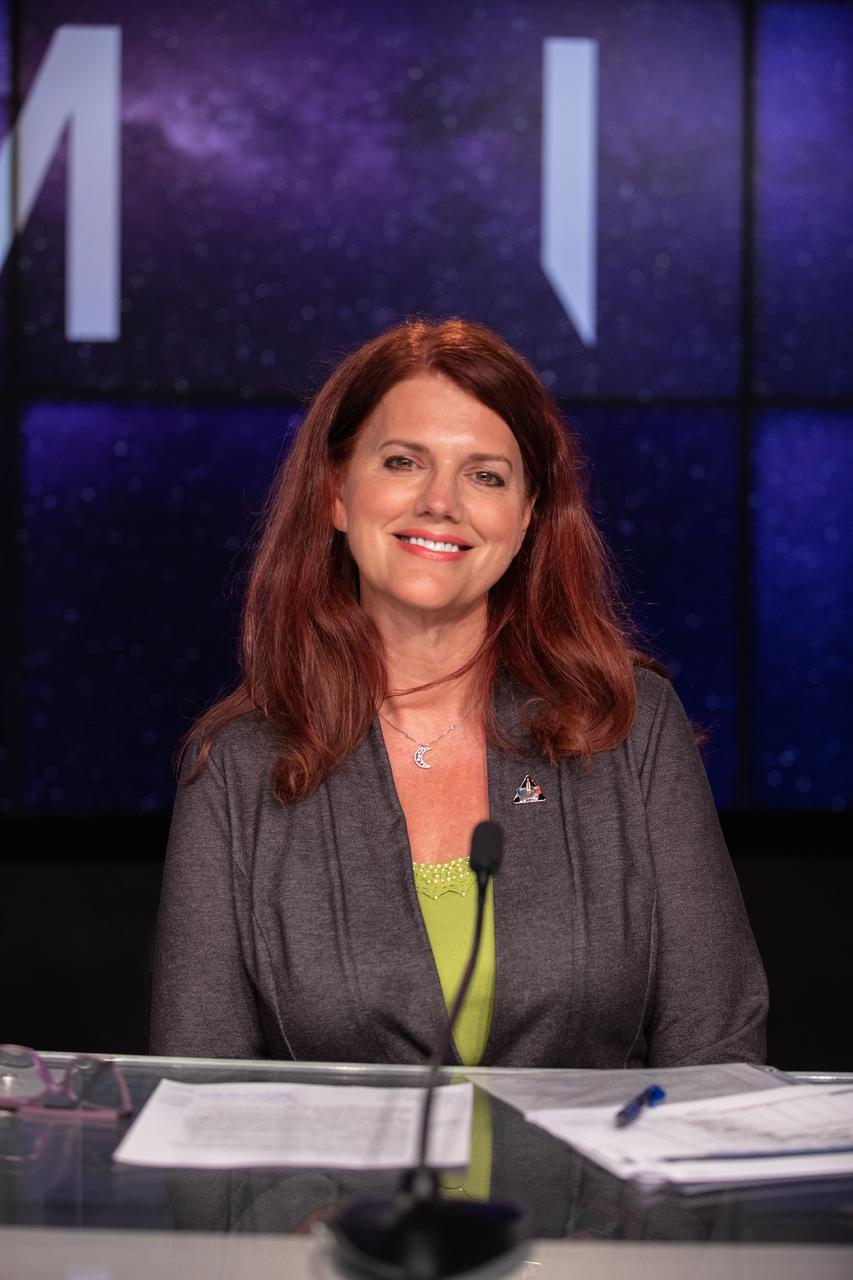

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Launch Director, Artemis I, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following completion of NASA’s Flight Readiness Review for Artemis I on Aug. 22, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
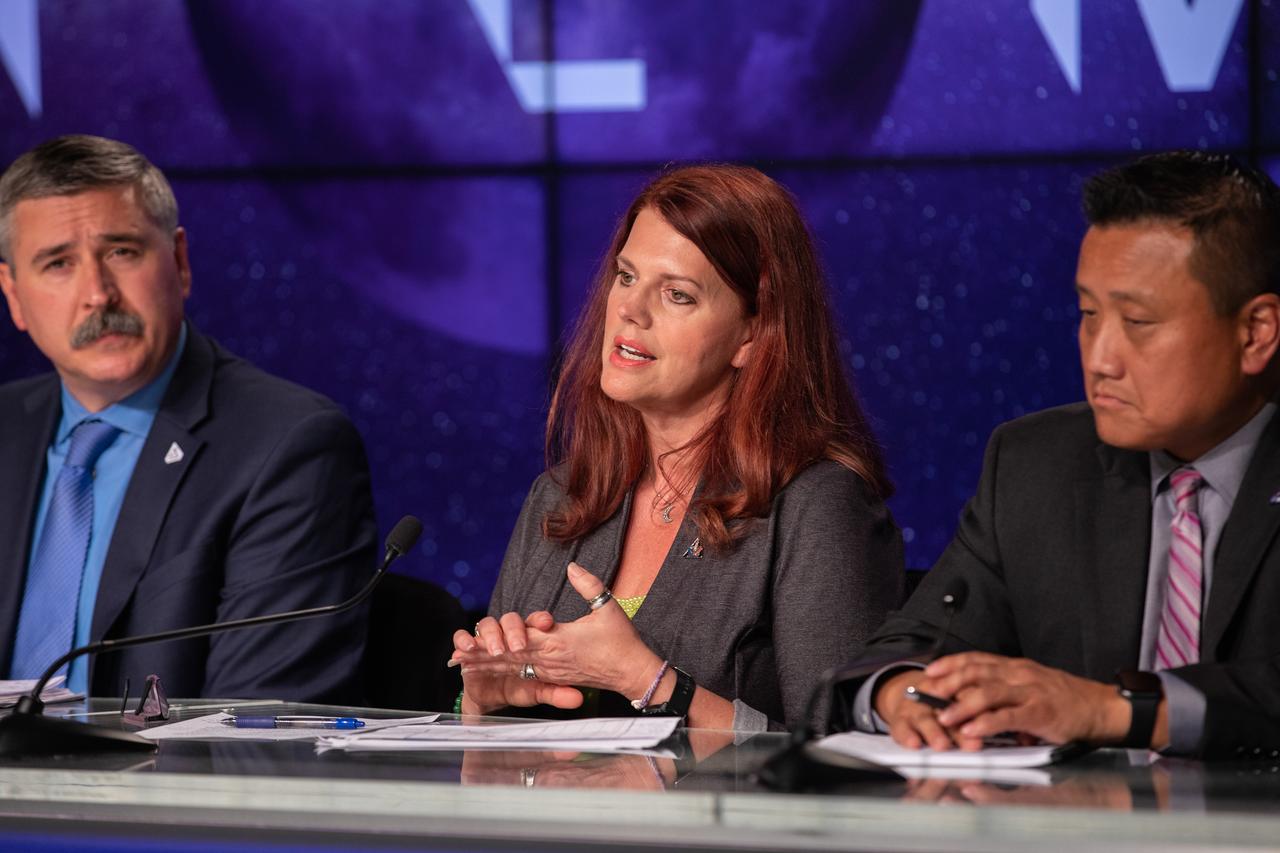

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Launch Director, Artemis I, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following completion of NASA’s Flight Readiness Review for Artemis I on Aug. 22, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Inside Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Artemis I launch team members and Artemis I Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, at right, celebrate the successful launch of the agency’s Artemis I Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft from Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022. Liftoff was at 1:47 a.m. EST. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
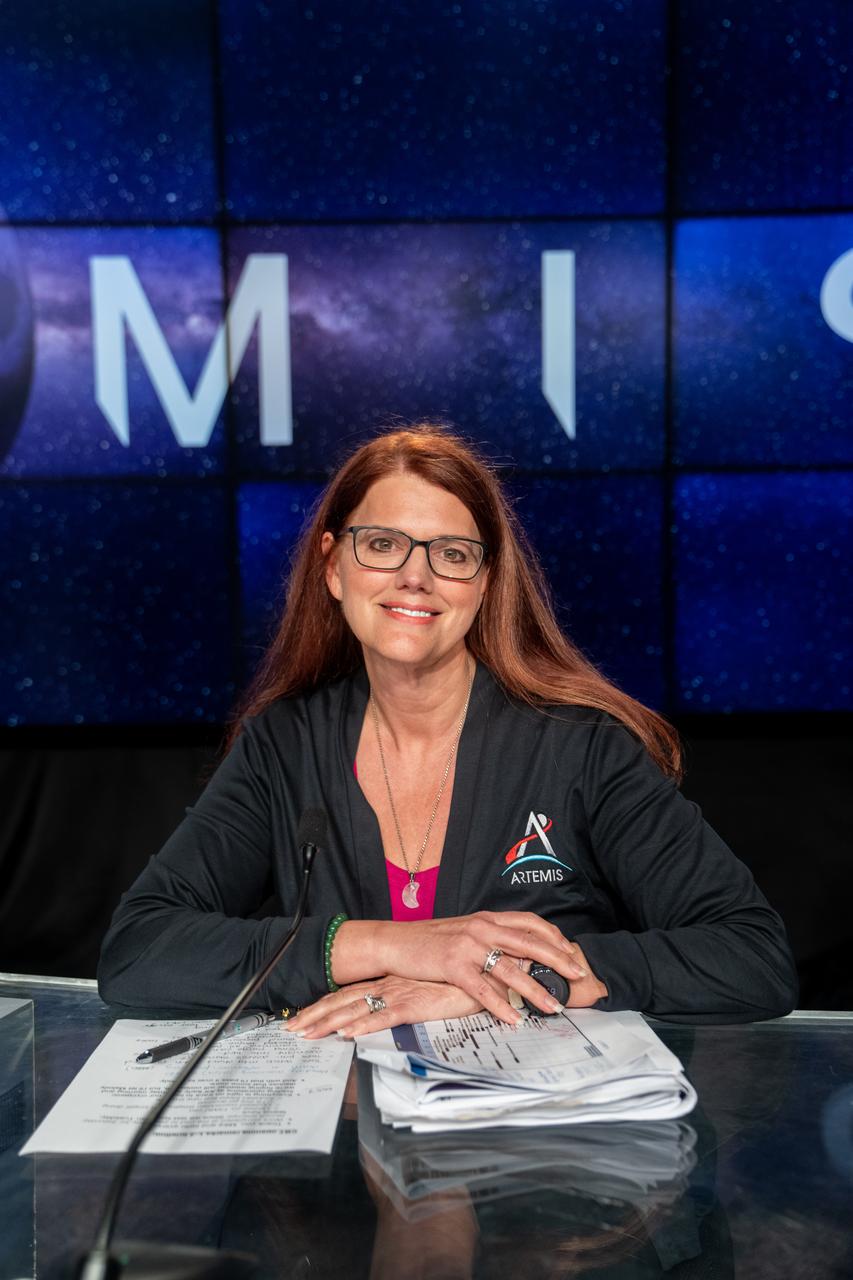

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis I launch director, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
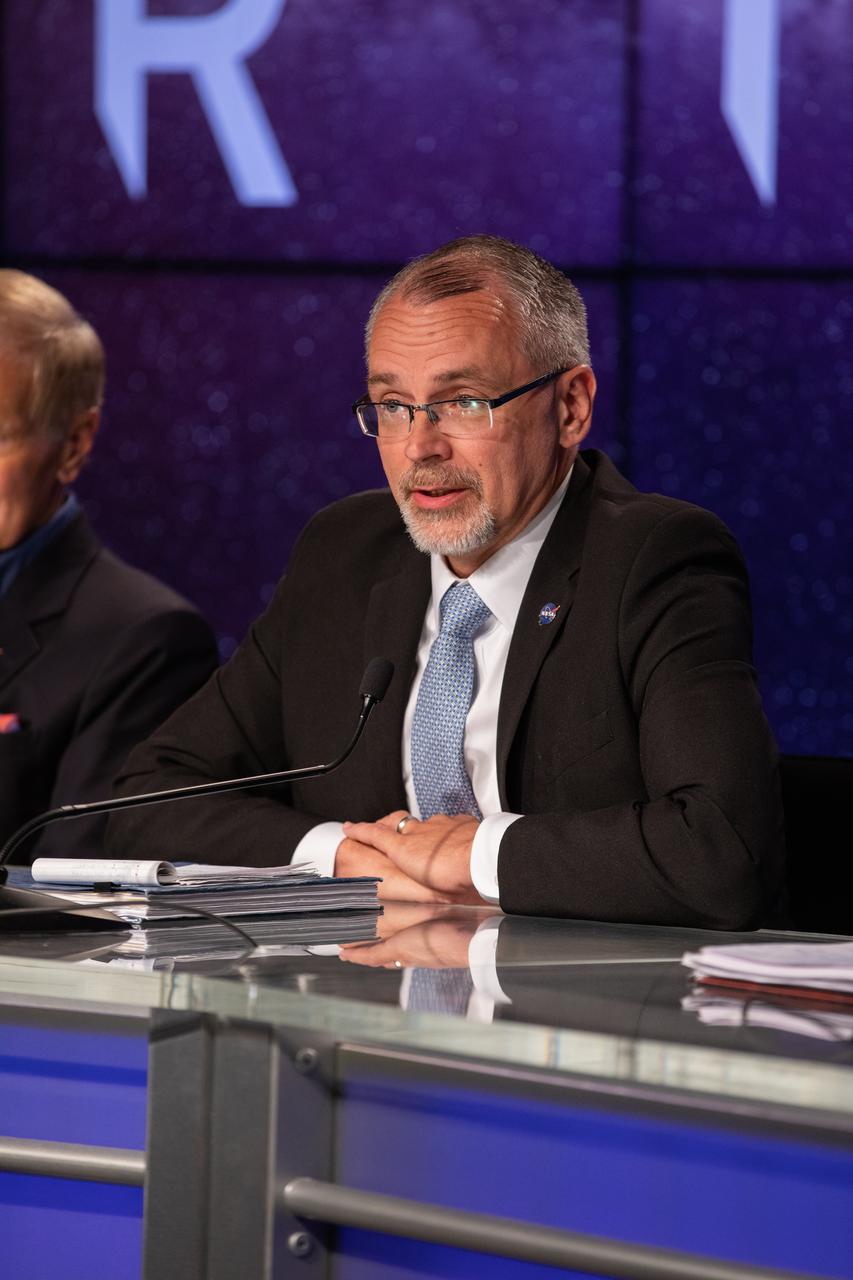

Jim Free, associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, participates in a news conference Sept. 3, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I was waived off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Teams encountered a liquid hydrogen leak while loading propellant into the core stage of the Space Launch System rocket. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
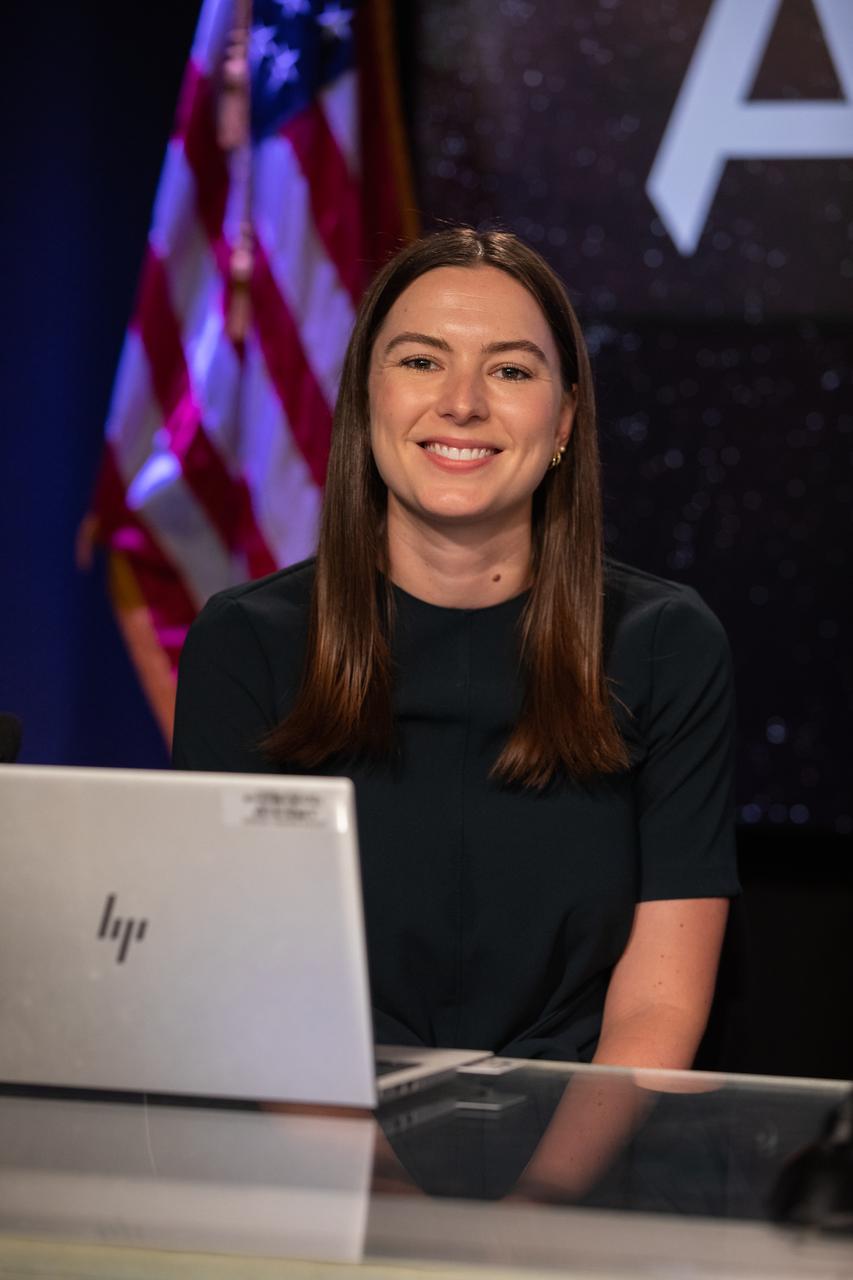

NASA Press Secretary Jackie McGuinness moderates a prelaunch media briefing on the NASA’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

A news conference is held Sept. 3, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I was waived off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Teams encountered a liquid hydrogen leak while loading propellant into the core stage of the Space Launch System rocket. Participants are, from left, Jackie McGuinness, NASA press secretary; Bill Nelson, NASA administrator; Jim Free, associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate; and Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
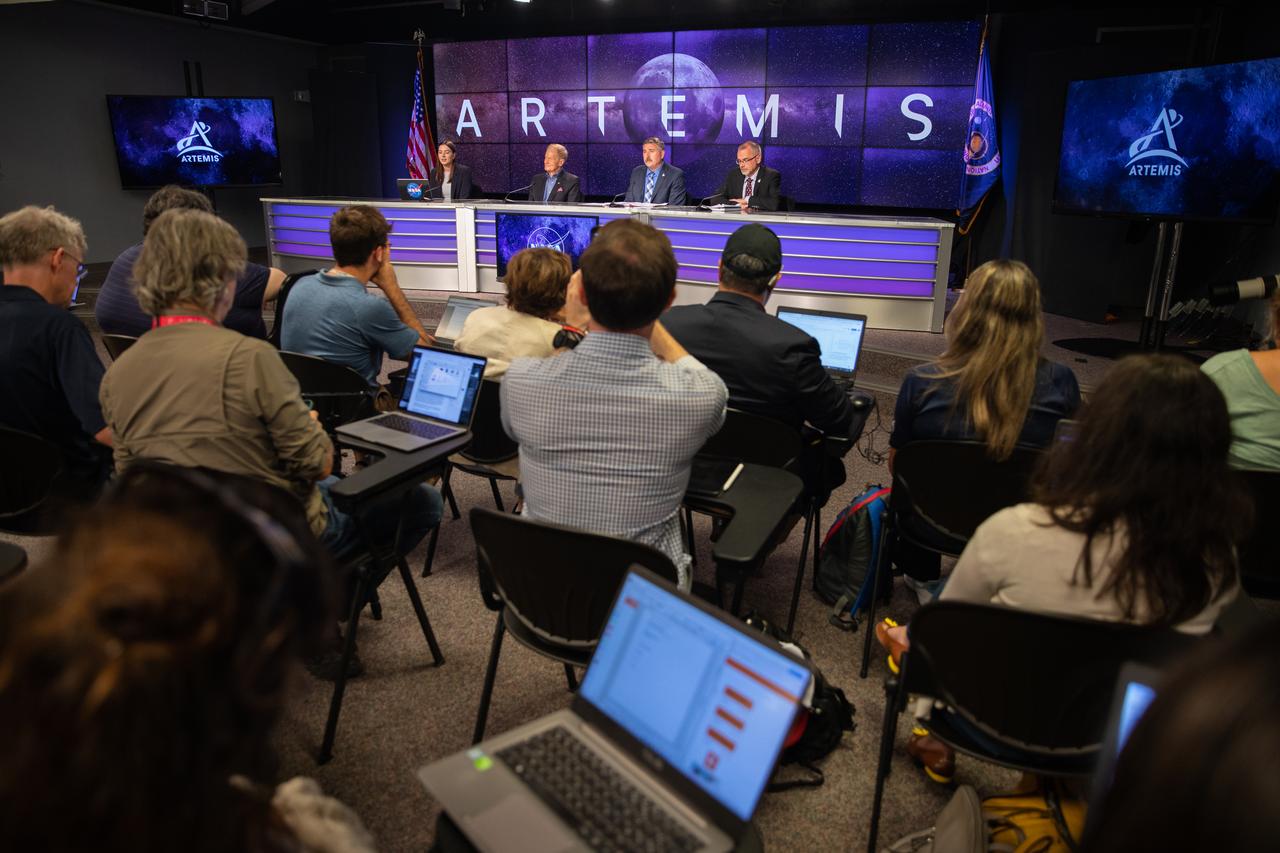

A press conference is held on Aug. 29, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after waving-off of the launch of the agency’s Artemis I mission. Participants from left, are NASA Press Secretary Jackie McGuiness; Bill Nelson, NASA administrator; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters; and Jim Free, associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
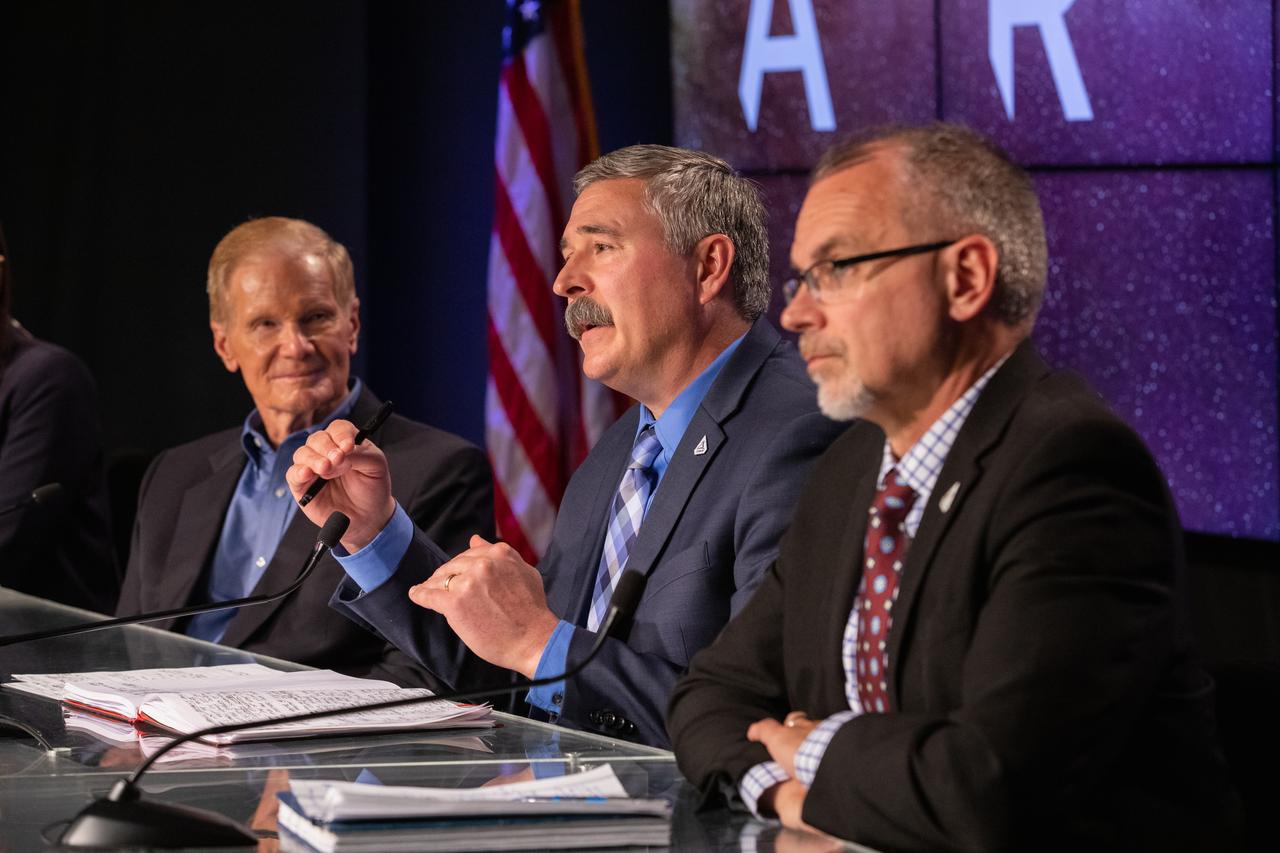

A press conference is held on Aug. 29, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after waving-off of the launch of the agency’s Artemis I mission. Participants from left, are NASA Administrator Bill Nelson; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters; and Jim Free, associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Members of the media attend a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
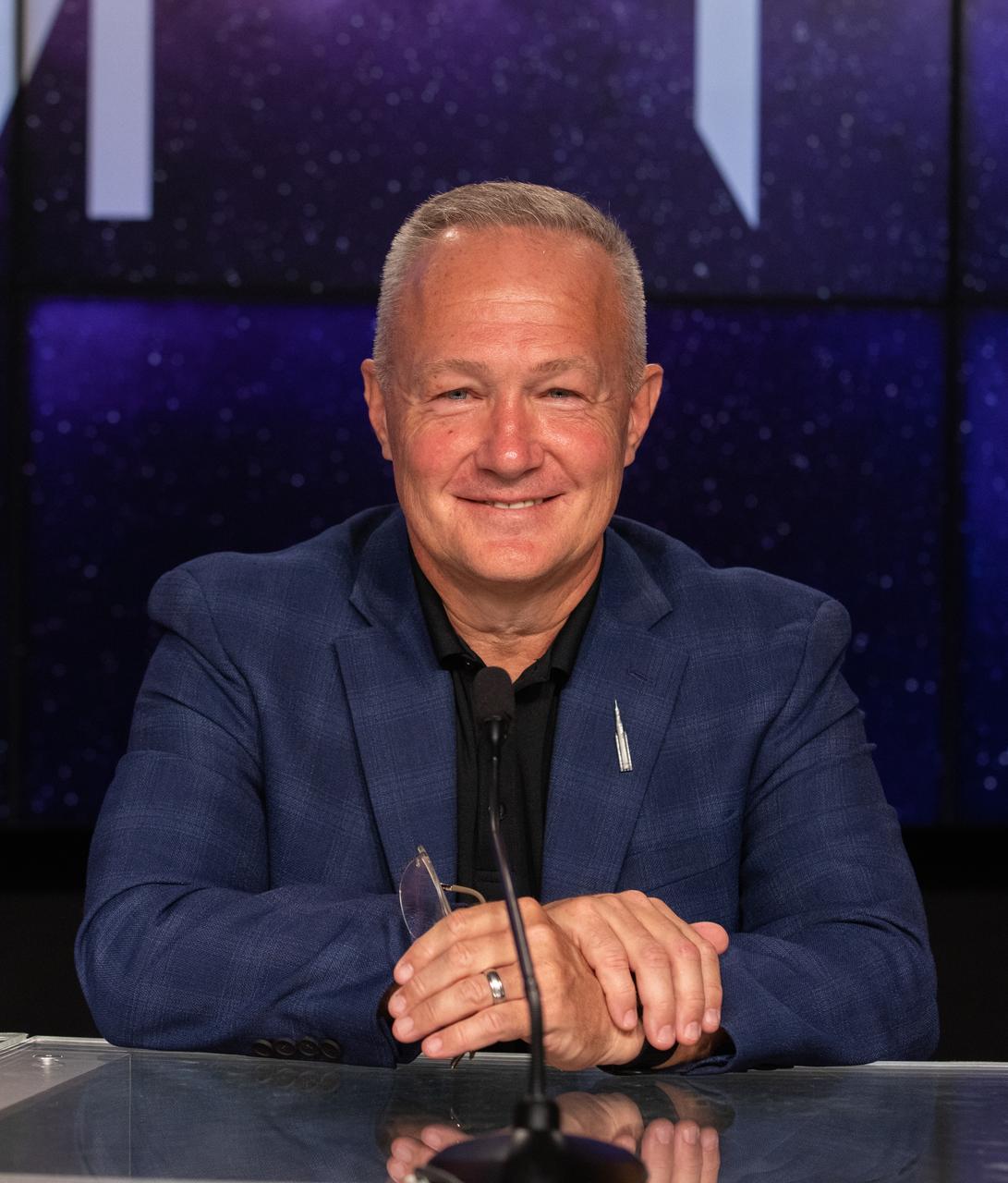

Doug Hurley, senior director of business development, Northrop Grumman, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
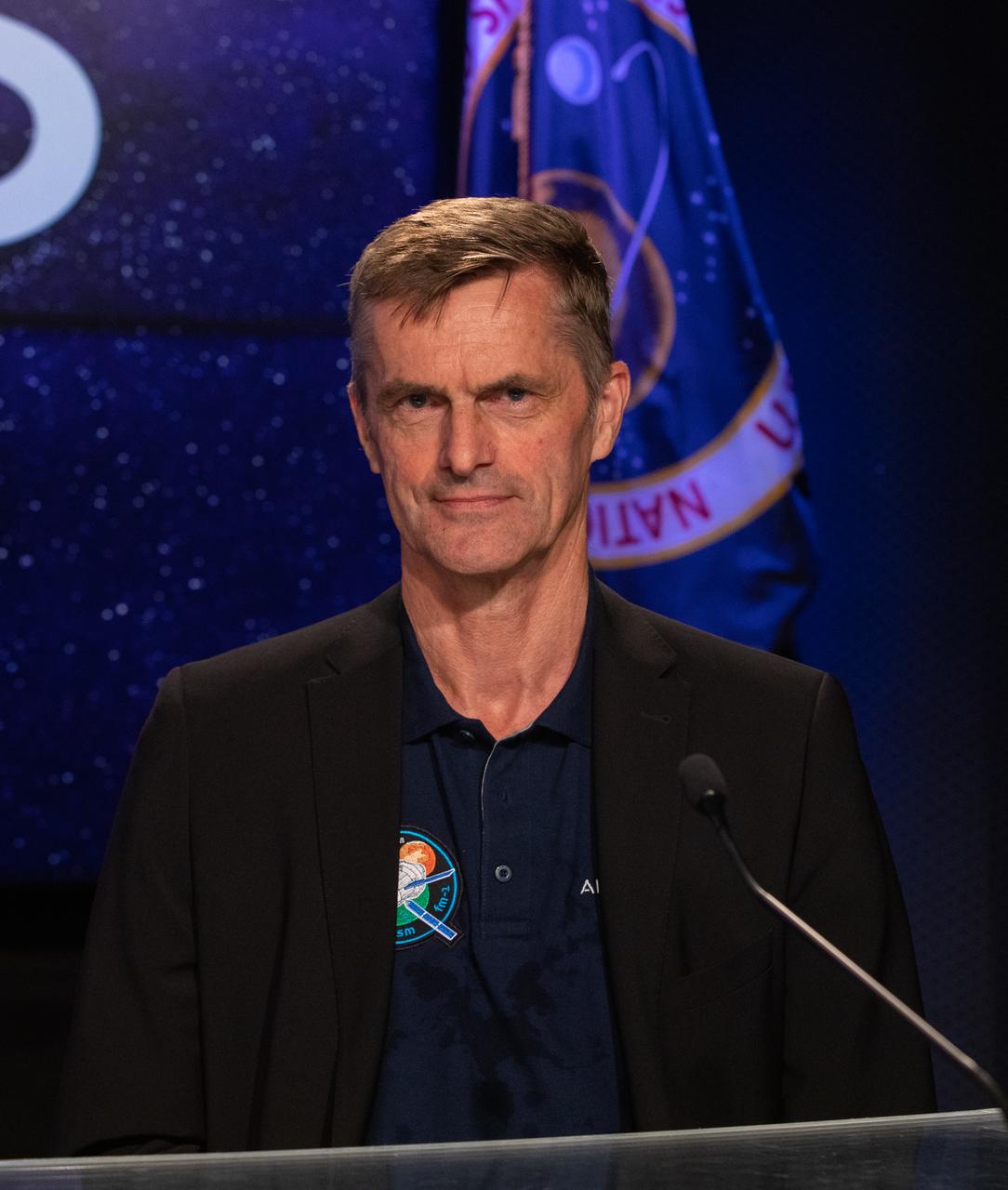

Ralf Zimmerman, head of Moon programs and Orion European Service Module, Airbus, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
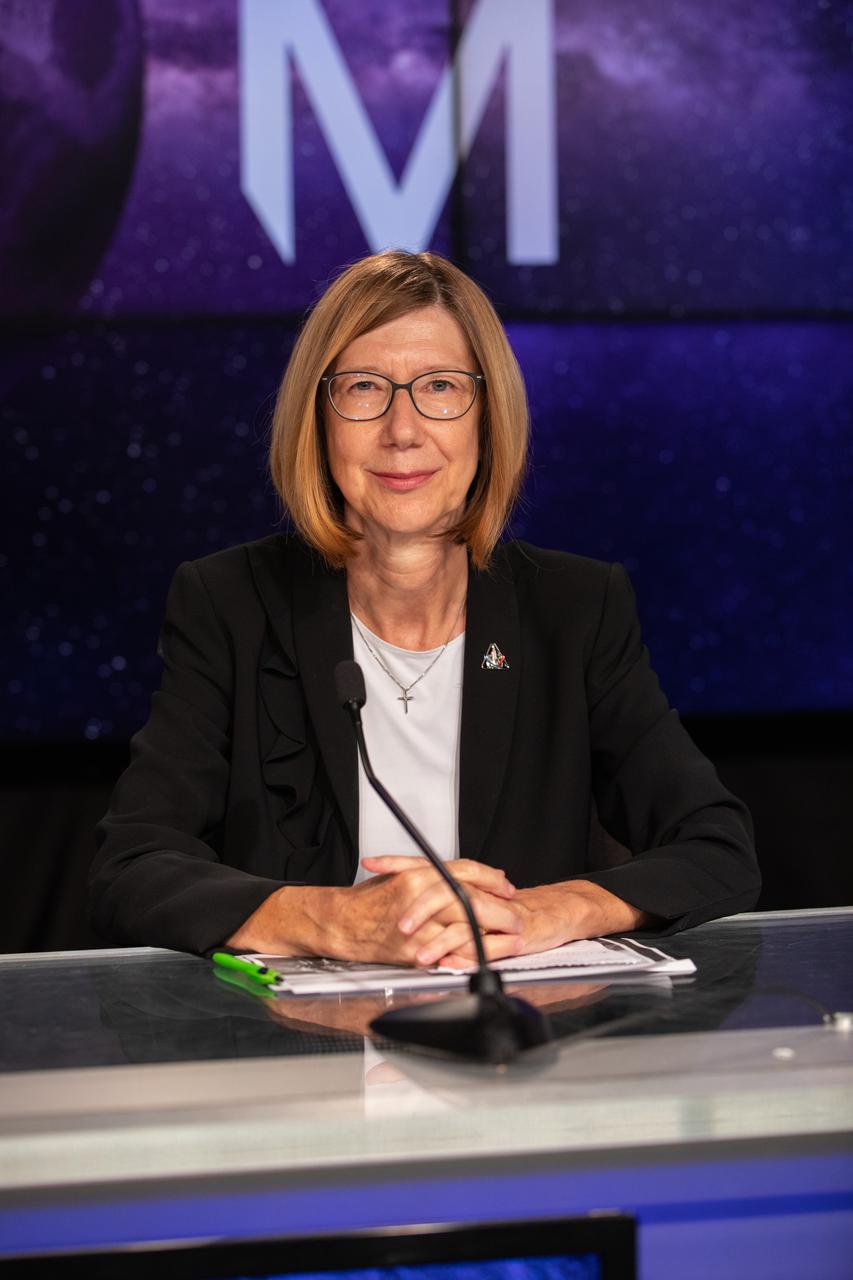

Kathy Lueders, NASA associate administrator, Space Operations Mission Directorate, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Bhavya Lal, NASA associate administrator for technology, policy and strategy, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
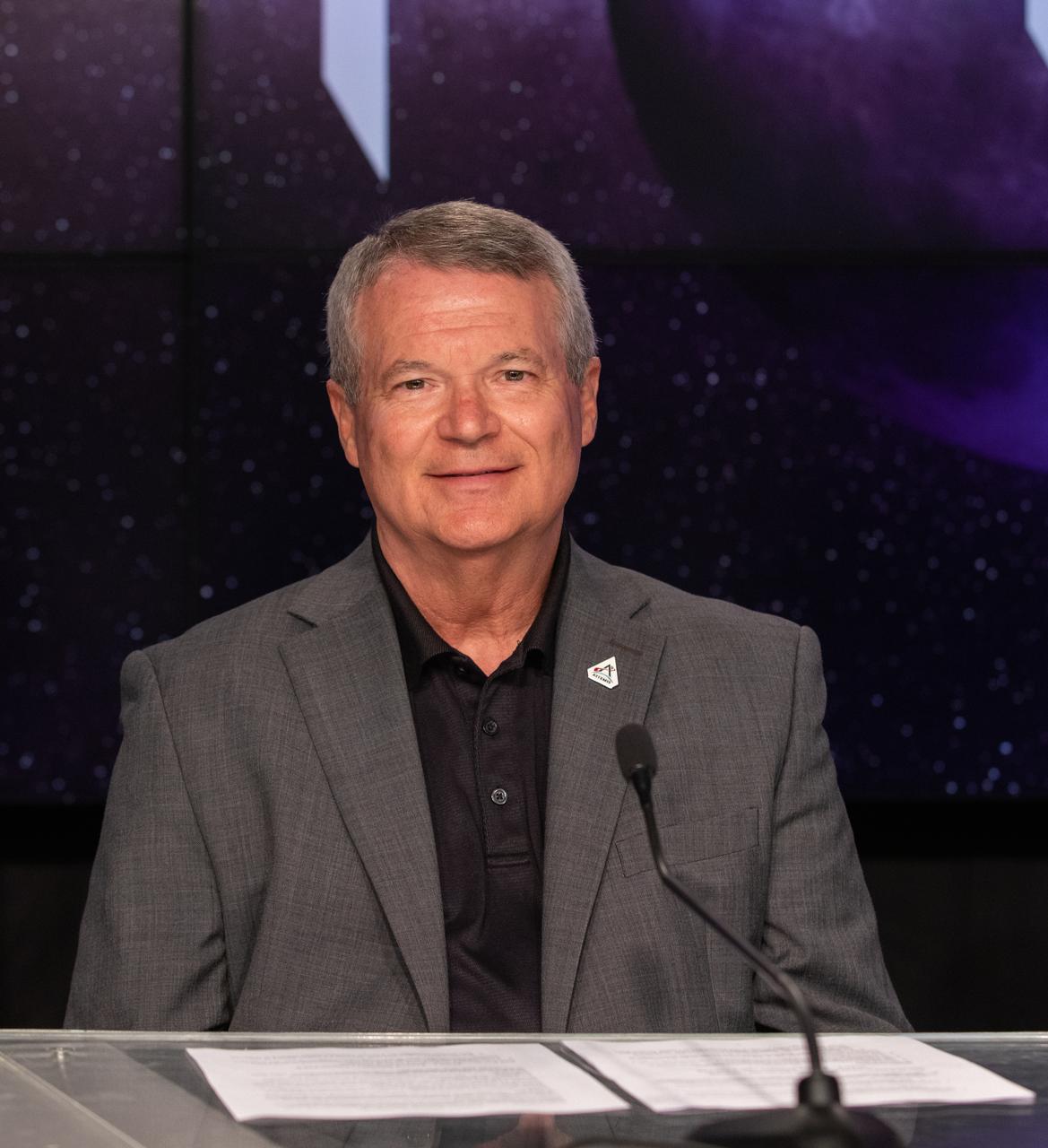

Randy Lycans, vice president/general manager of NASA Enterprise Solutions, Jacobs, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

A news conference is held Sept. 3, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I was waived off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Teams encountered a liquid hydrogen leak while loading propellant into the core stage of the Space Launch System rocket. Participants are, from left, Jackie McGuinness, NASA press secretary; Bill Nelson, NASA administrator; Jim Free, associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate; and Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
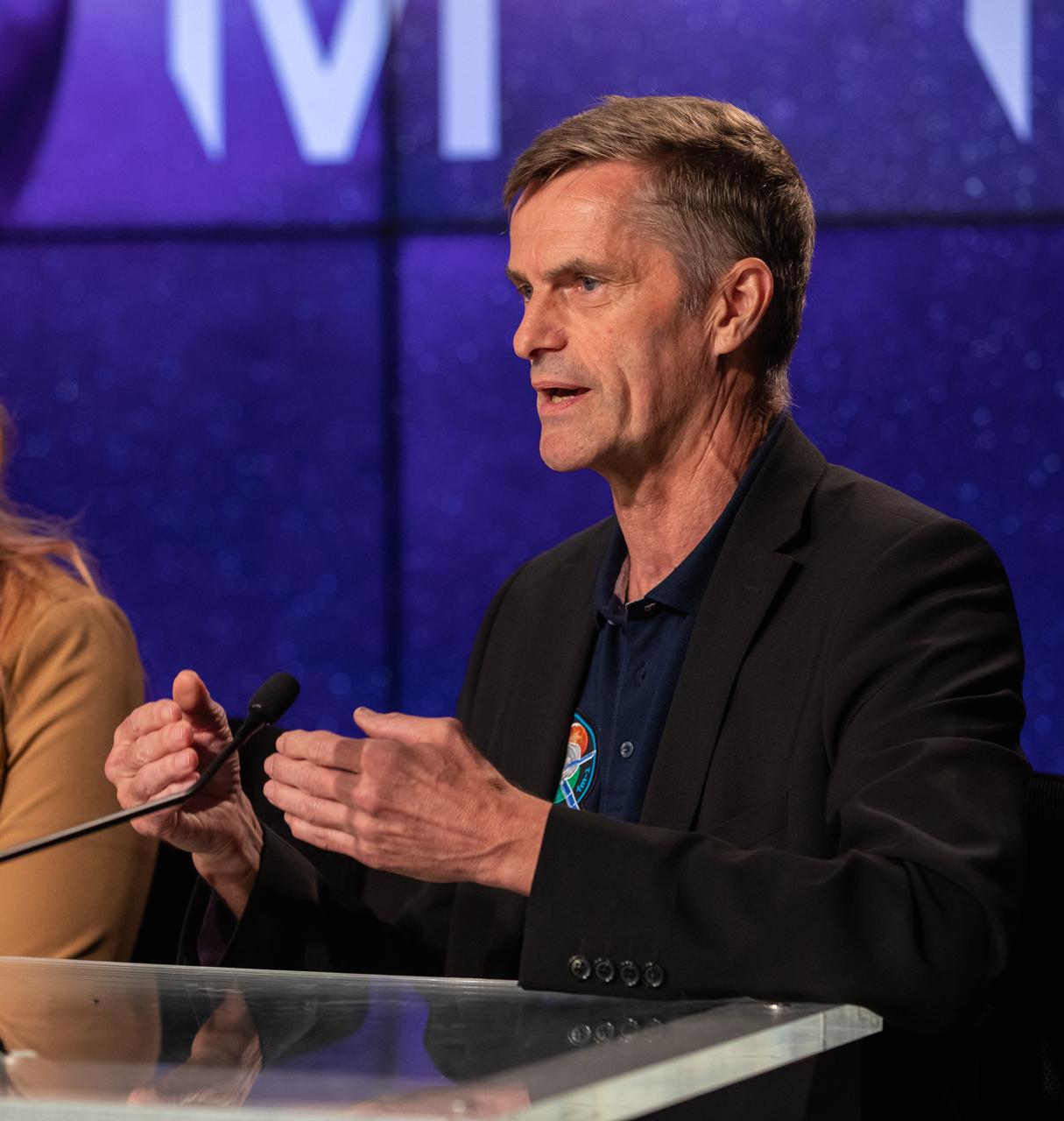

Ralf Zimmerman, head of Moon programs and Orion European Service Module, Airbus, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
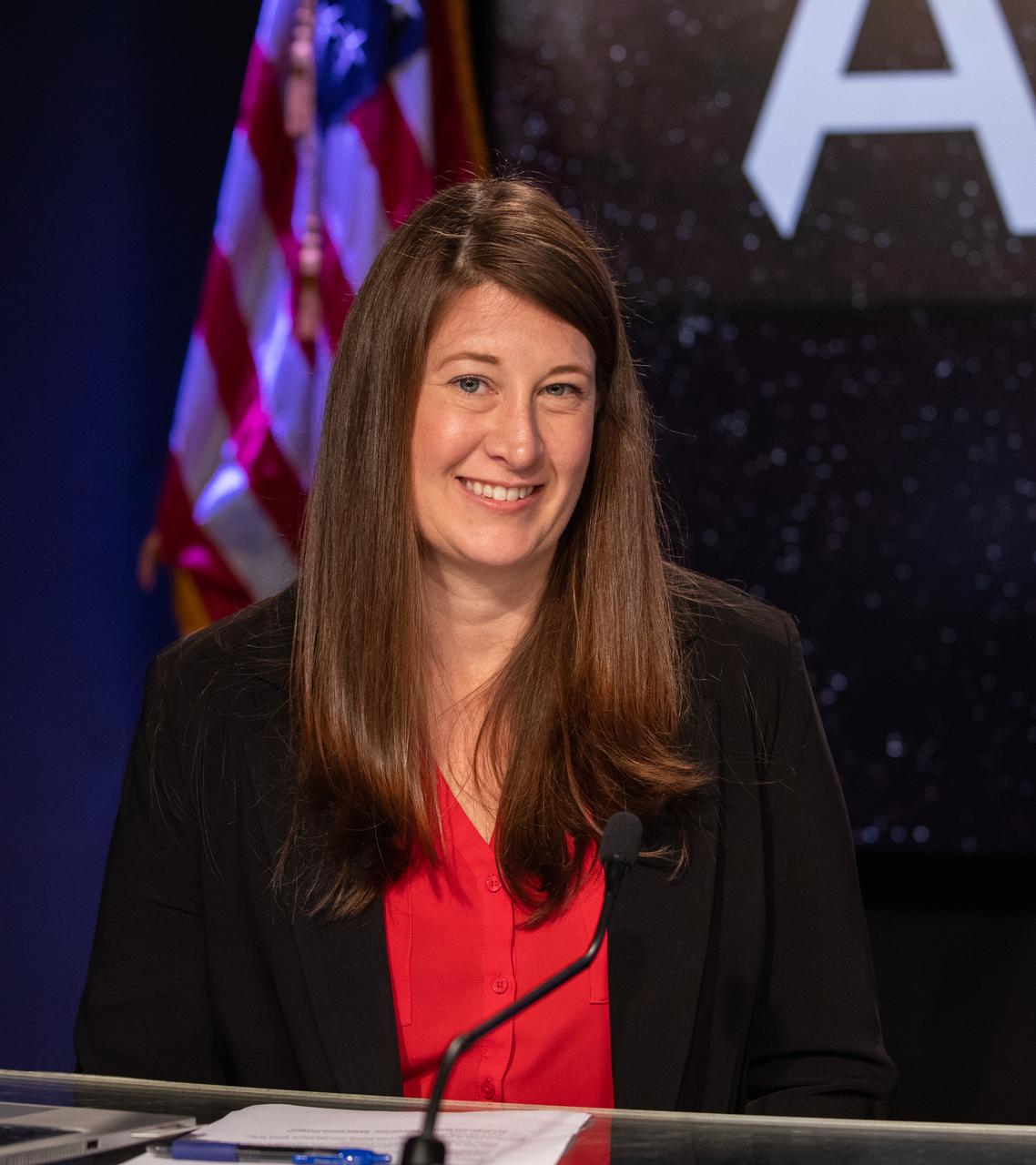

Kathryn Hambleton, NASA Communications, moderates a prelaunch briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
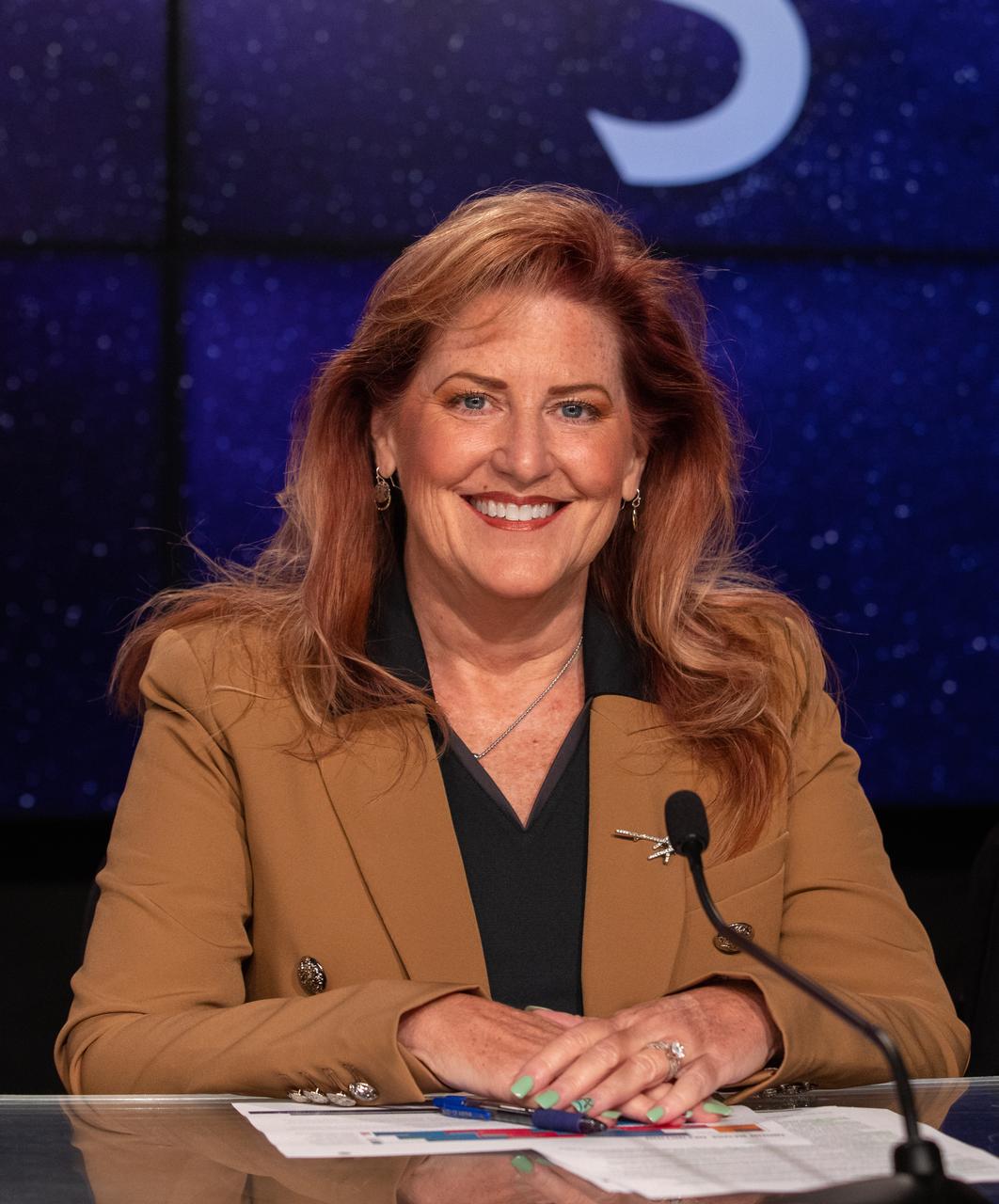

Kelly DeFazio, director of Orion production, Lockheed Martin, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins speaks from the International Space Station during a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Prasun Desai, NASA deputy associate administrator, Space Technology Mission Directorate, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
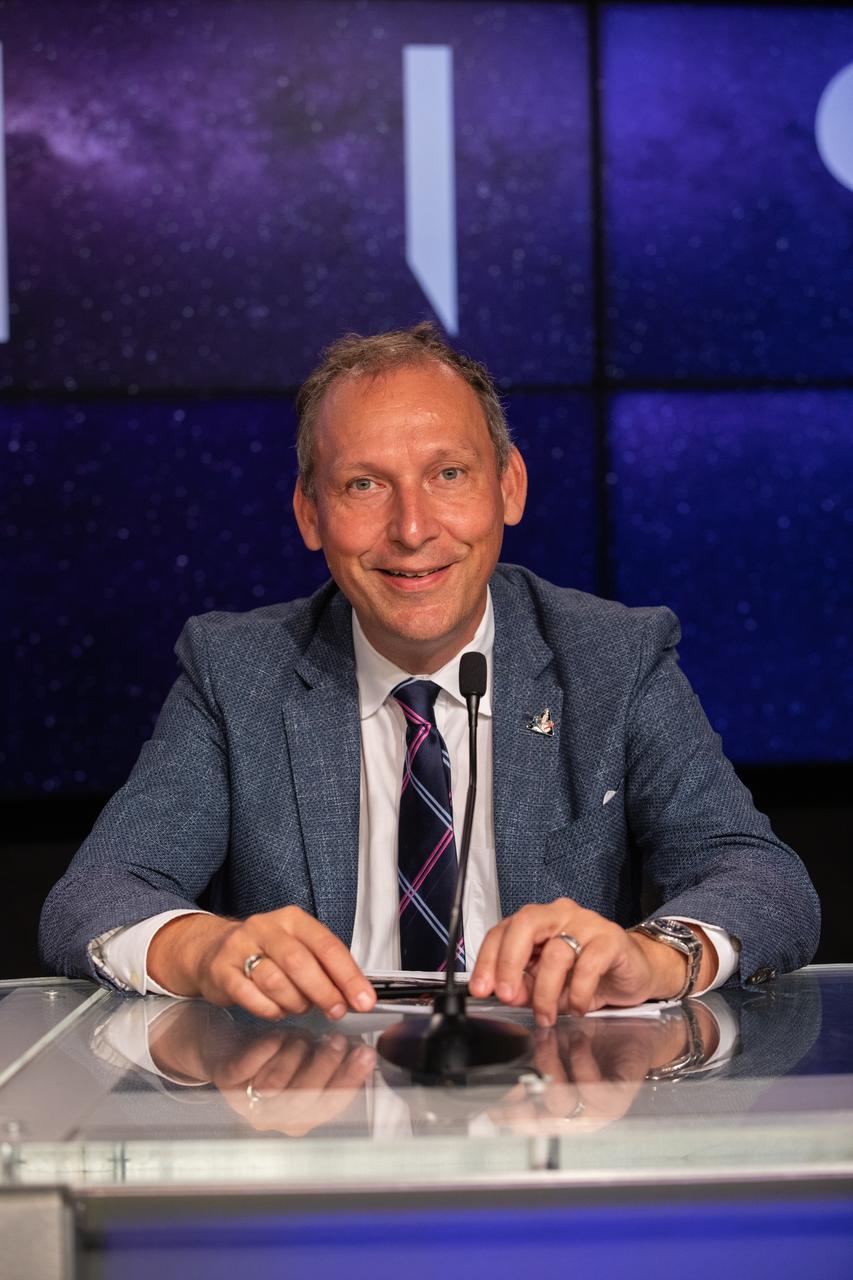

Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
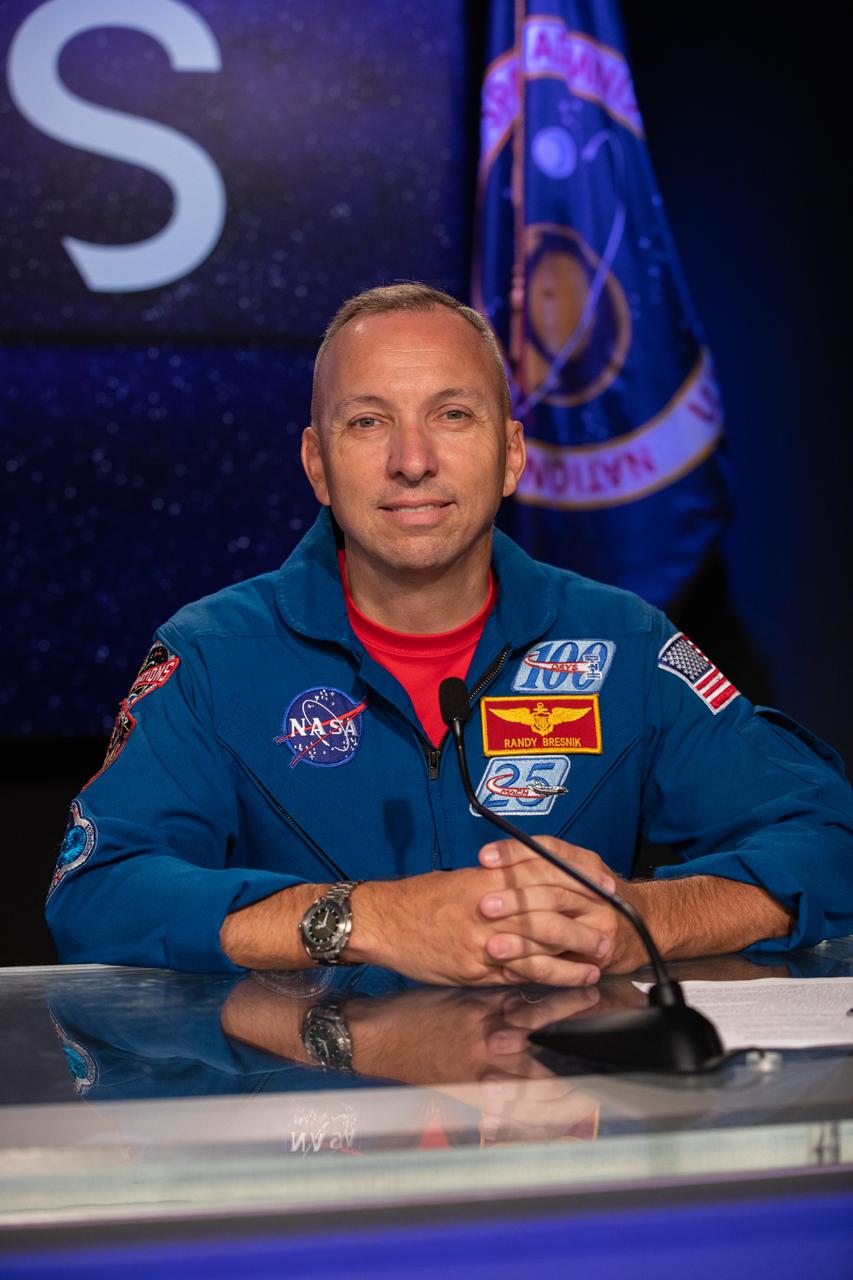

NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
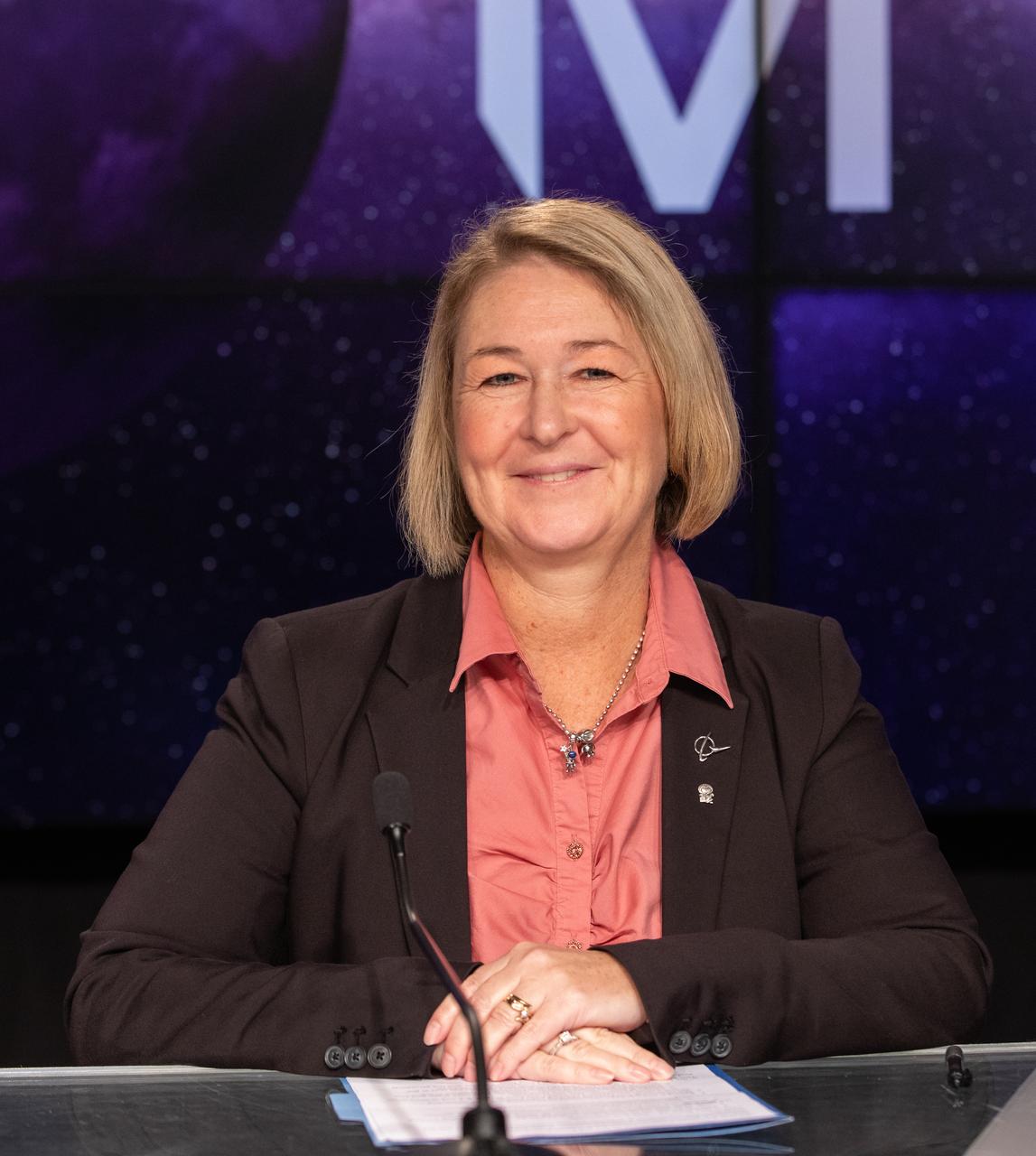

Jennifer Boland-Masterson, director of operations, Michoud Assembly Facility, Boeing, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik speaks during a prelaunch media briefing on the agency’s Moon to Mars exploration plans on Aug. 27, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the clock counts down to the launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

A news conference is held Sept. 3, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I was waived off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Teams encountered a liquid hydrogen leak while loading propellant into the core stage of the Space Launch System rocket. Participants are, from left, Bill Nelson, NASA administrator; Jim Free, associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate; and Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
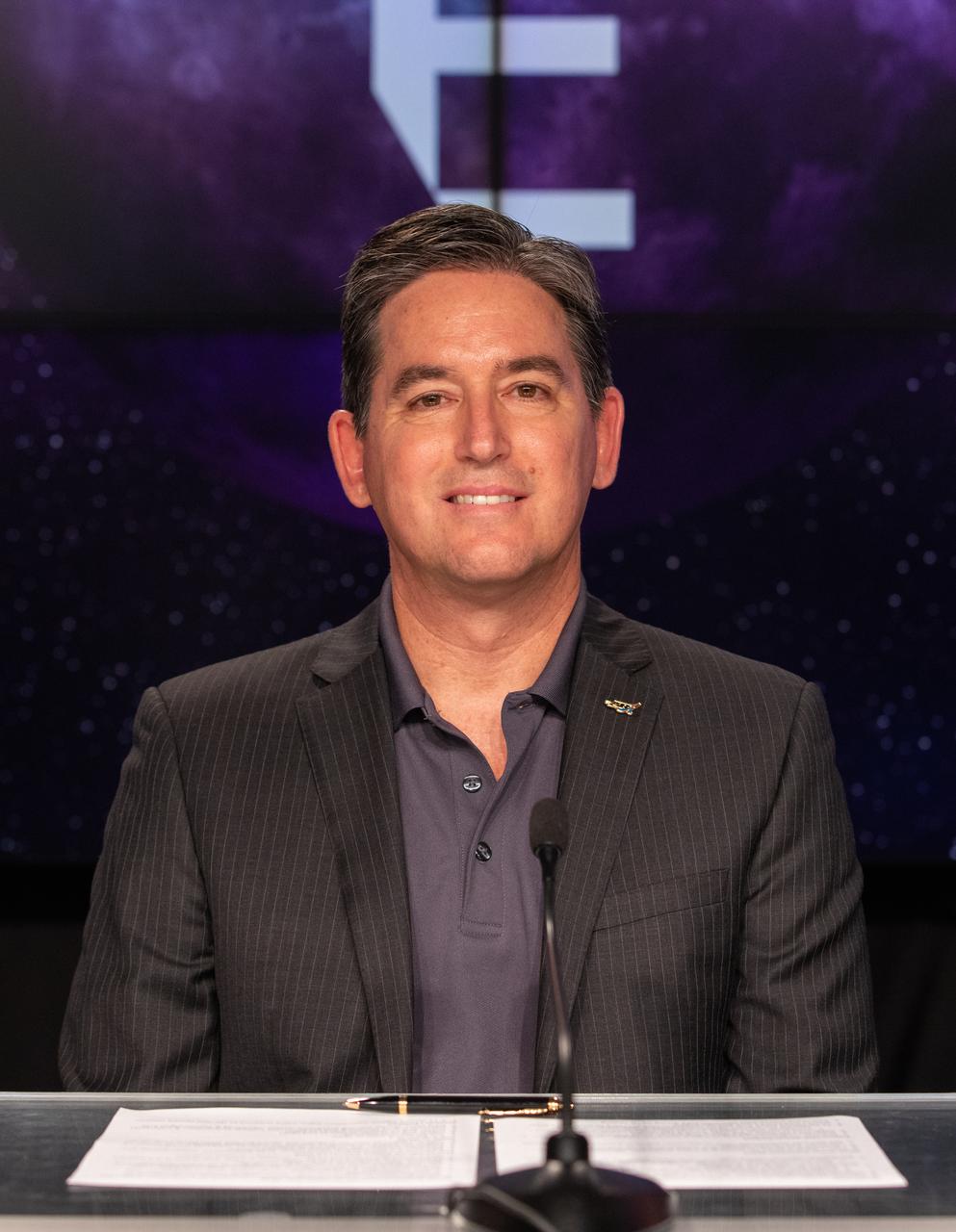

Jeff Zotti, RS-25 program director, Aerojet Rocketdyne, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the role of industry in advancing human exploration on Aug. 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the agency prepares for launch of Artemis I scheduled for Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

A press conference is held on Aug. 29, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after waving-off of the launch of the agency’s Artemis I mission. Participants from left, are NASA Press Secretary Jackie McGuiness; Bill Nelson, NASA administrator; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters; and Jim Free, associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
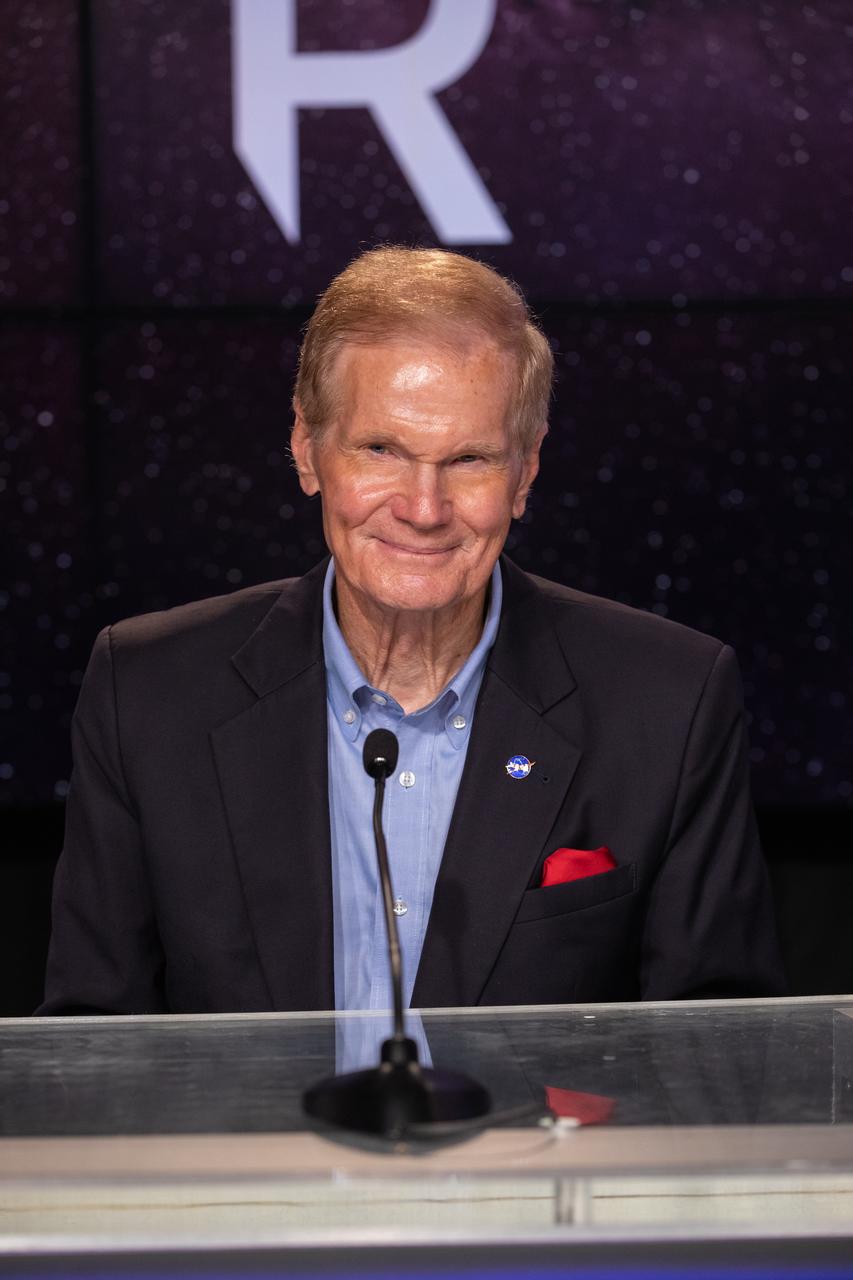

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson participates in a postlaunch news conference on Nov. 16, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I at 1:47 a.m. EST from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
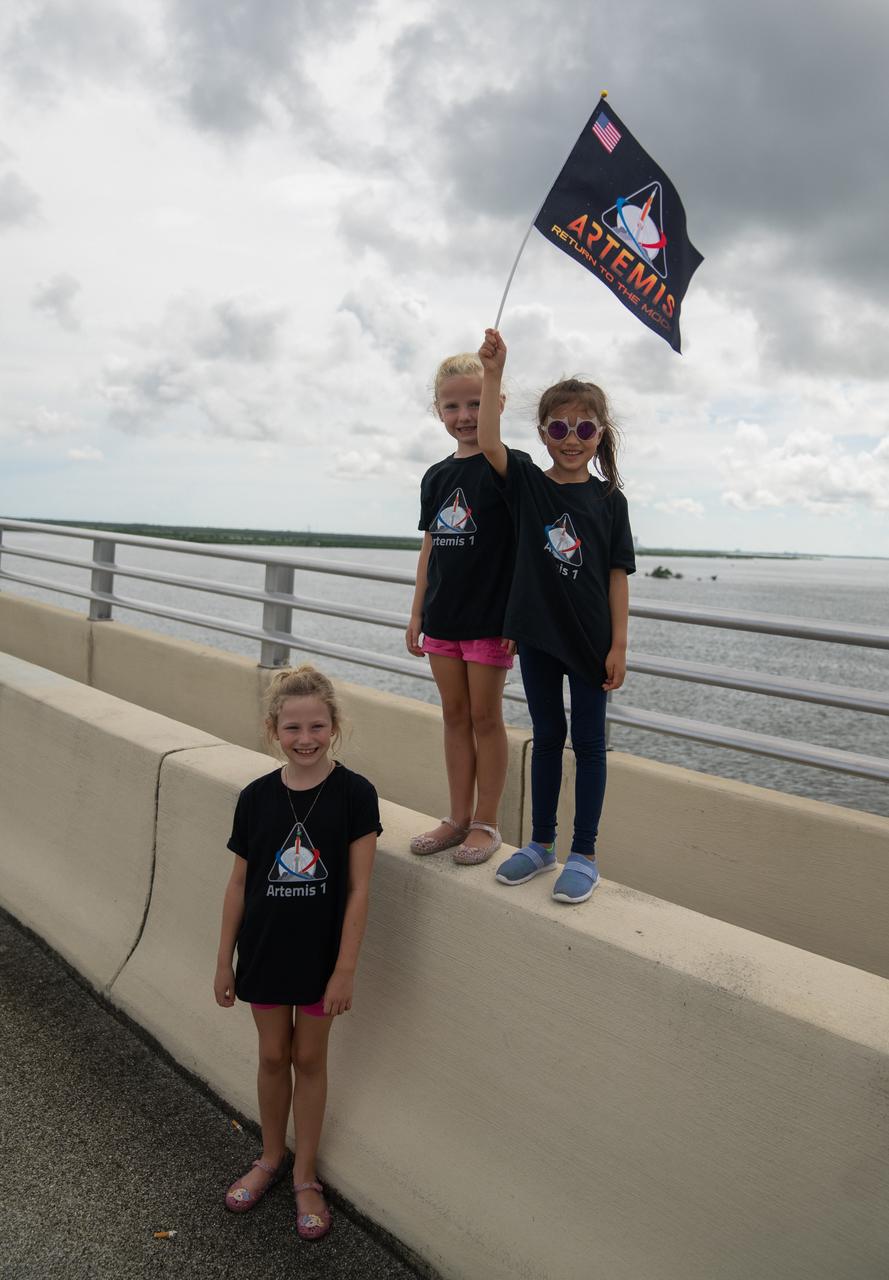

A group of young children with an Artemis flag are photographed on the Max Brewer Bridge in Titusville, Florida, as they wait to watch the launch of NASA’s Artemis I mission on Sept. 3, 2022. The launch was waived off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
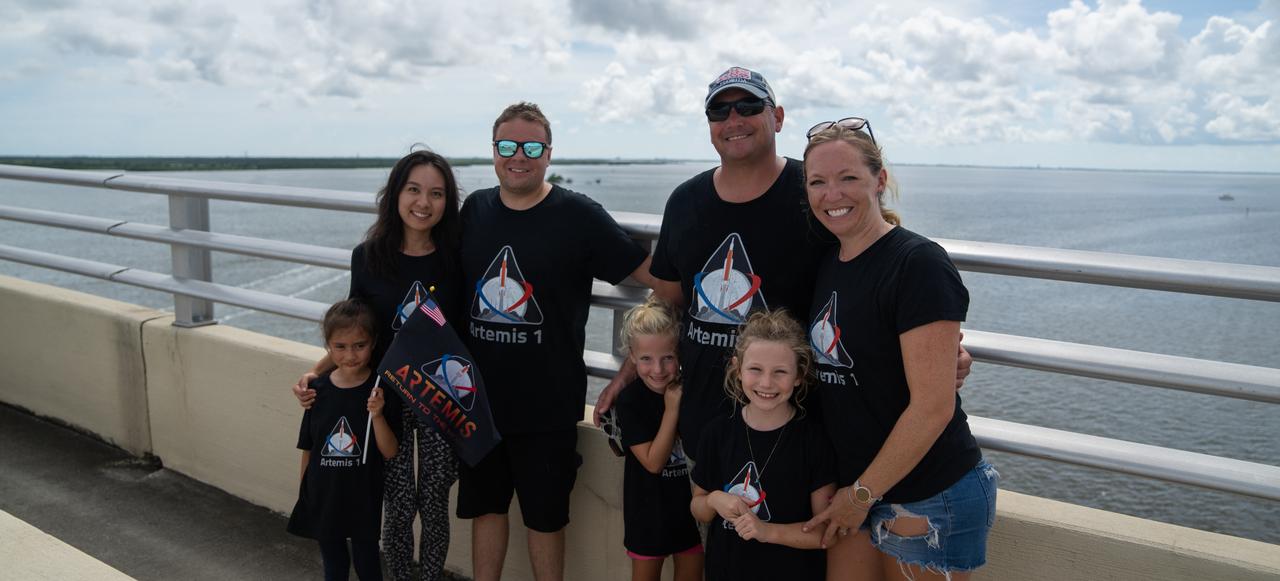

A family wearing matching Artemis shirts are on the Max Brewer Bridge in Titusville, Florida, to witness the launch of NASA’s Artemis I mission on Sept. 3, 2022. The launch was waived off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
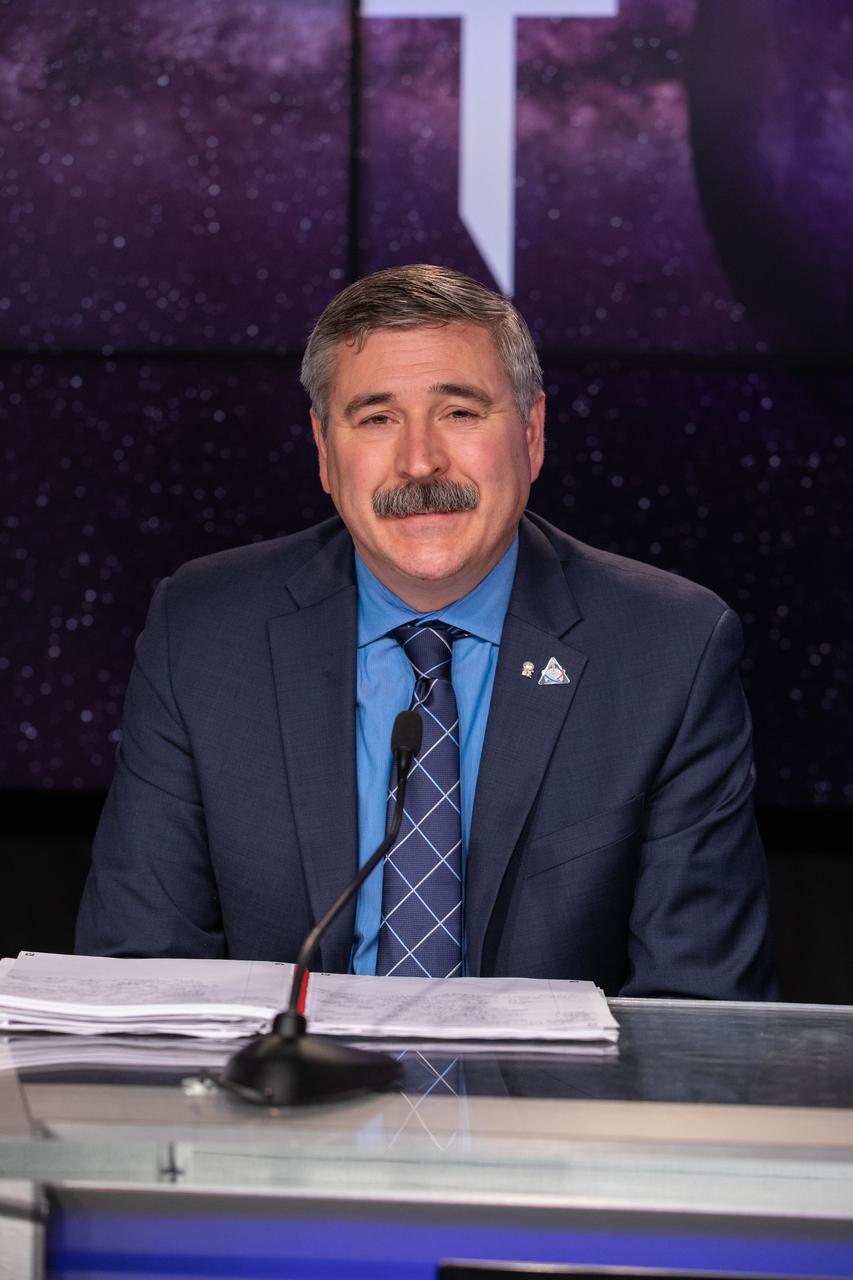

Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters, participates in a postlaunch news conference on Nov. 16, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I at 1:47 a.m. EST from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
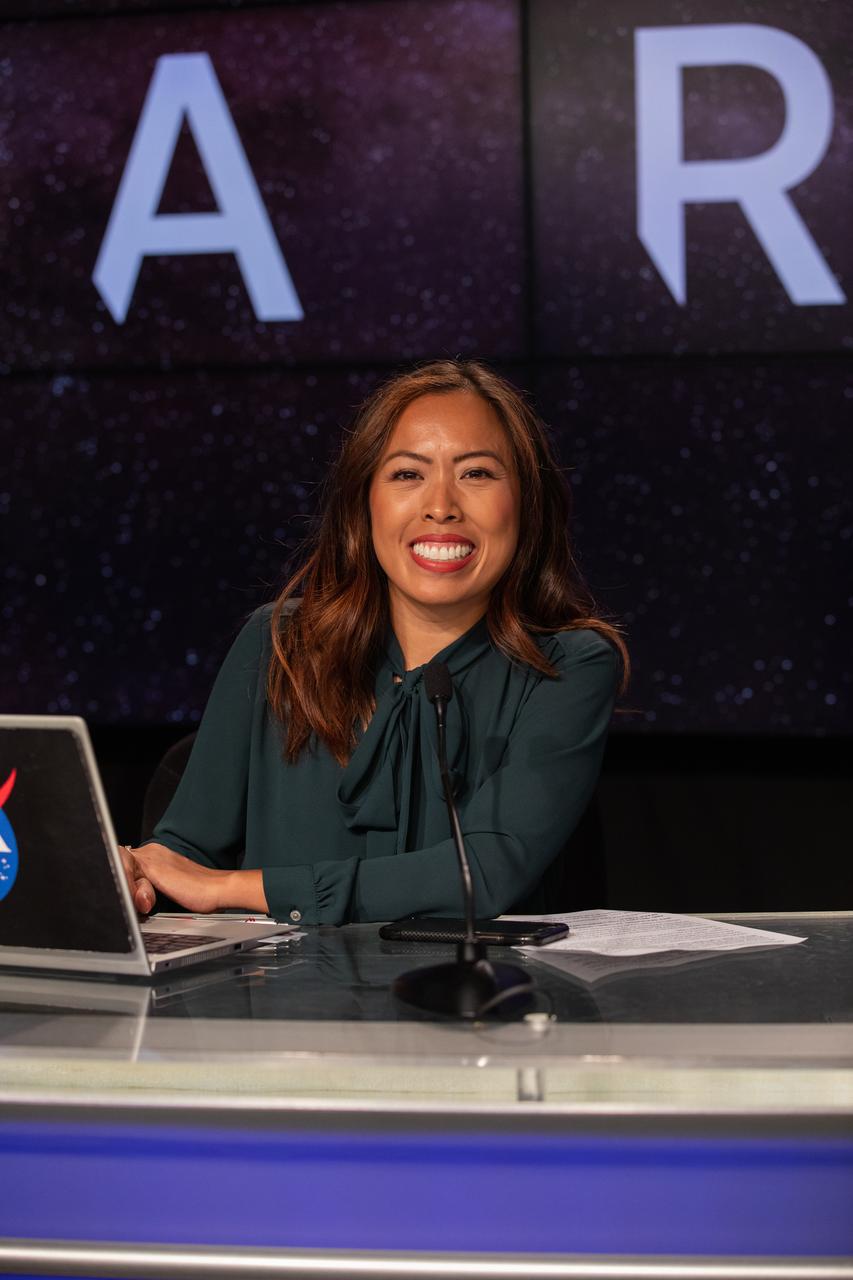

Megan Cruz, NASA Communications, participates in a prelaunch media briefing on the status of the Artemis countdown is held on Aug. 28, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch Aug. 29, at 8:33 a.m. EDT from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
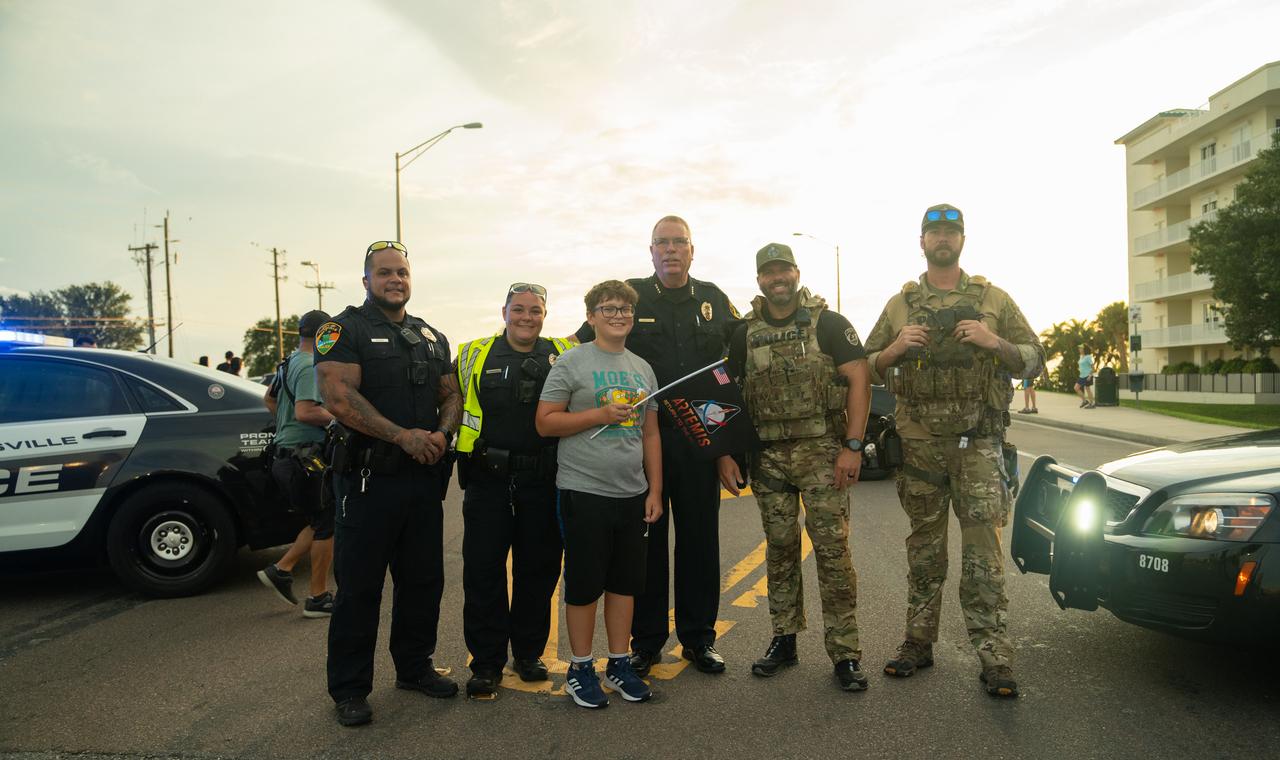

A young child waving an Artemis flag poses with members of the Titusville Police Dept. on the Max Brewer Bridge on Aug. 29, 2022, during Artemis I countdown festivities. The launch was waved off for the day at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
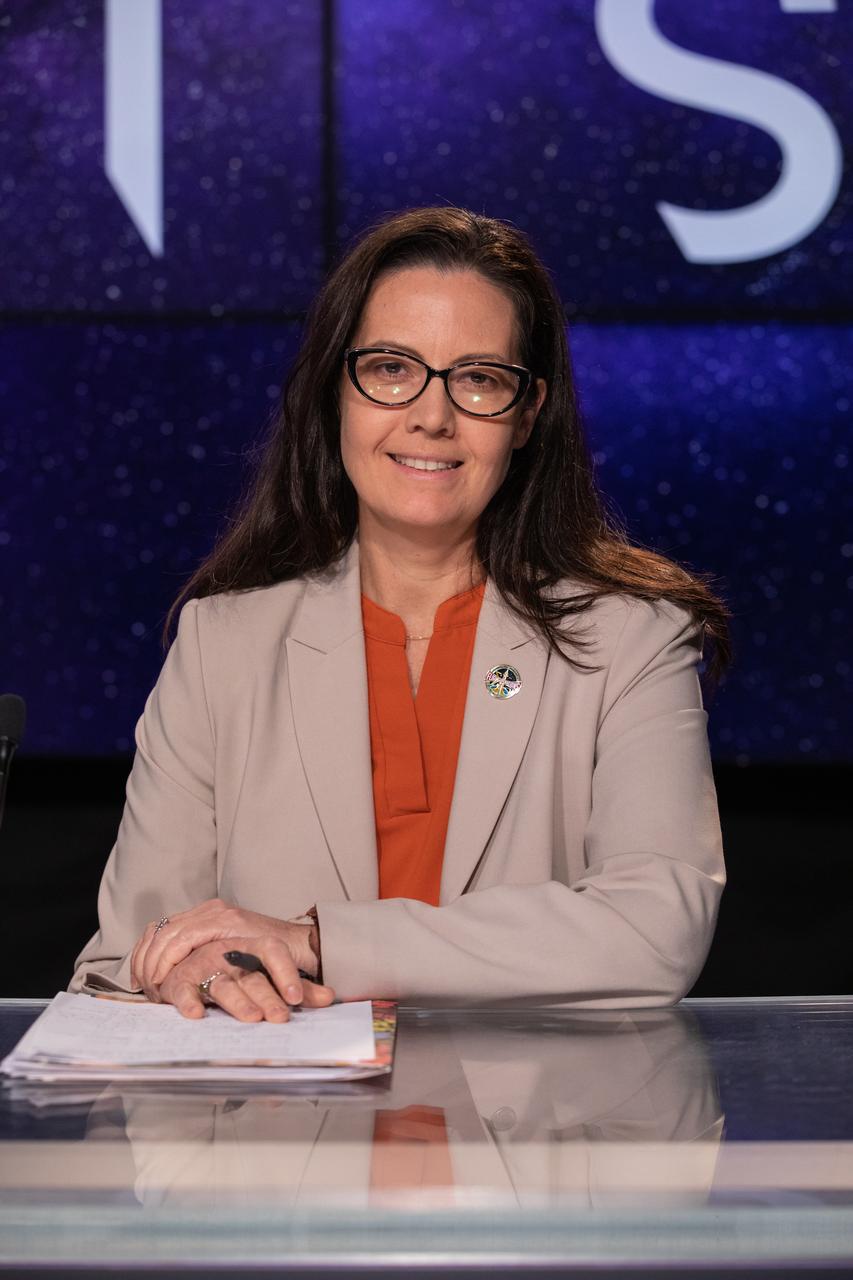

Emily Nelson, chief flight director, Johnson Space Center, participates in a postlaunch news conference on Nov. 16, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I at 1:47 a.m. EST from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
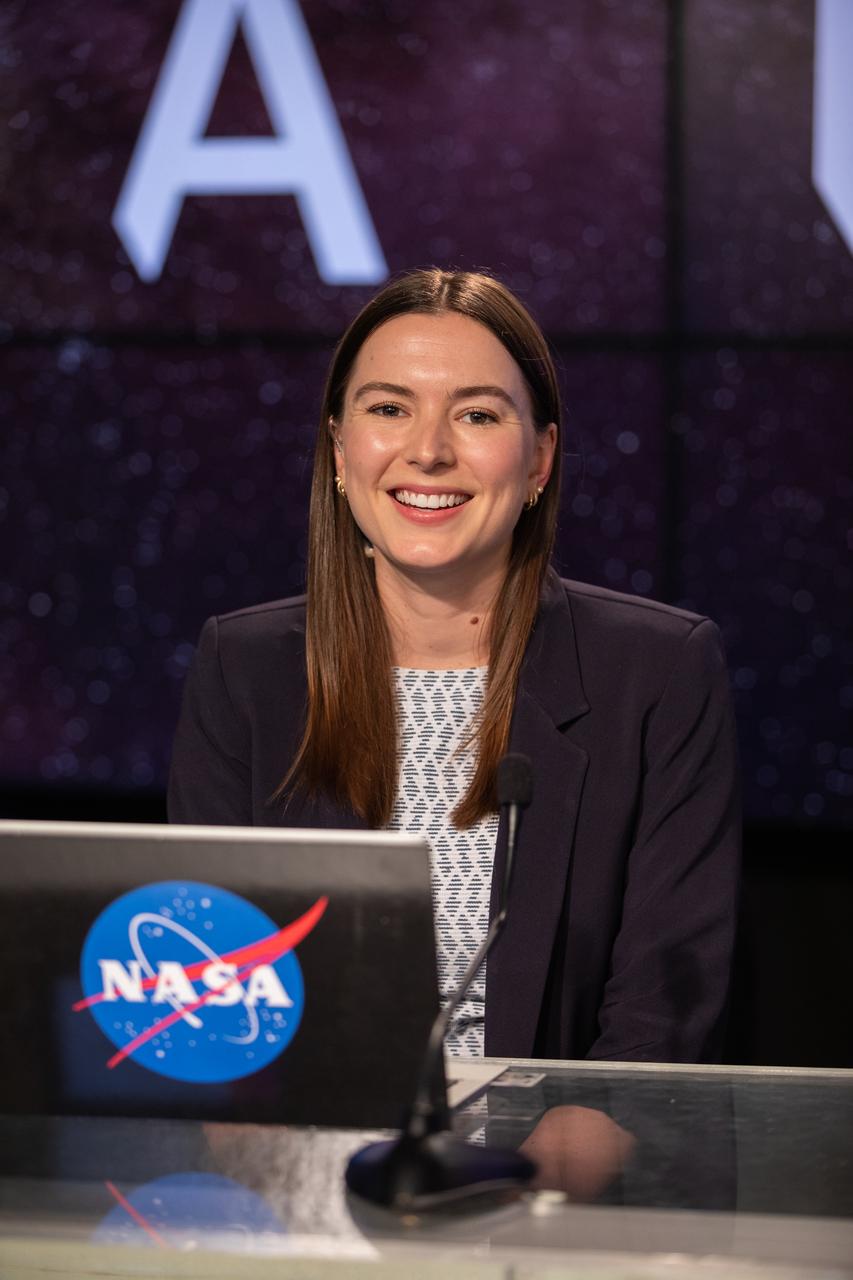

NASA Press Secretary Jackie McGuiness moderates a press conference on Aug. 29, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after waving-off of the launch of the agency’s Artemis I mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
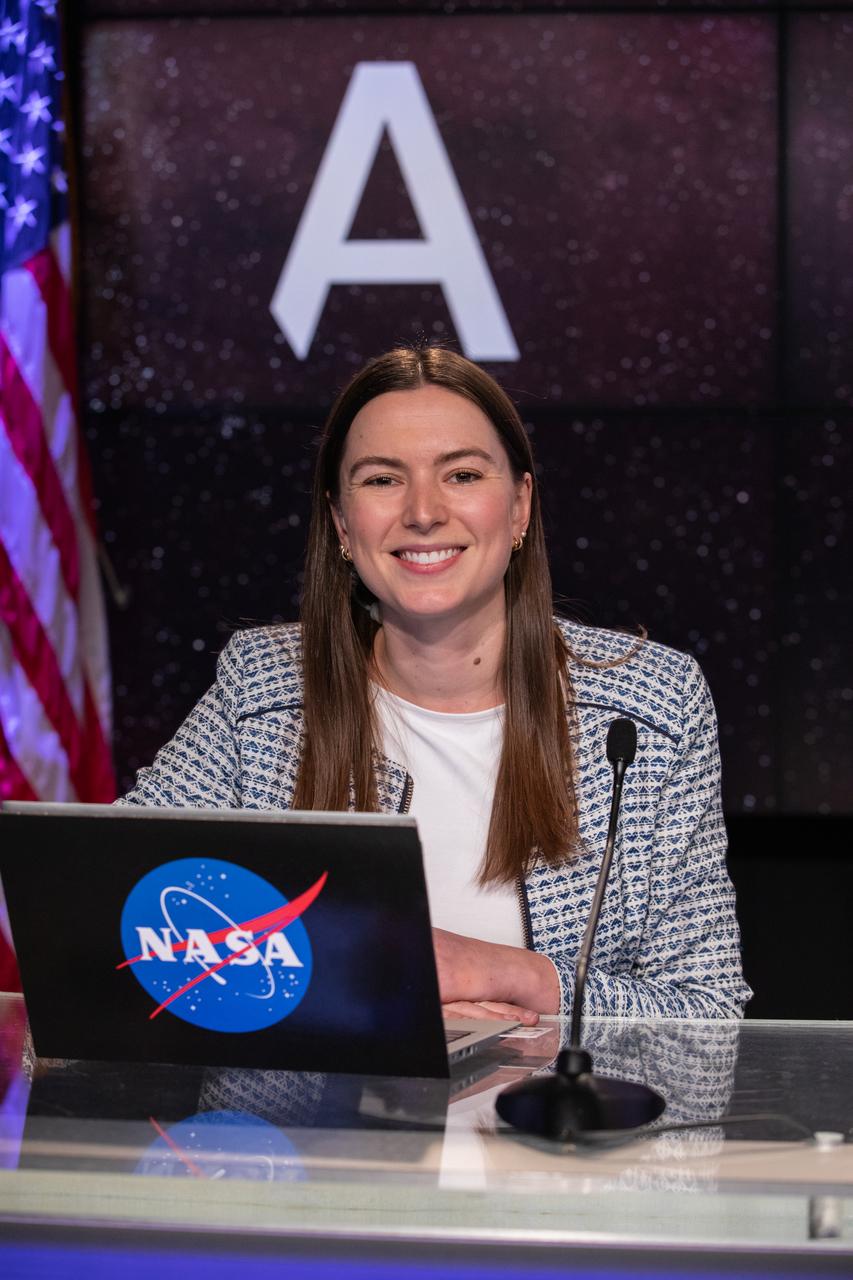

Jackie McGuiness, NASA Communications, moderates a postlaunch news conference on Nov. 16, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I at 1:47 a.m. EST from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Howard Hu, Orion Program manager, NASA’s Johnson Space Center, participates in a postlaunch news conference on Nov. 16, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after launch of Artemis I at 1:47 a.m. EST from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
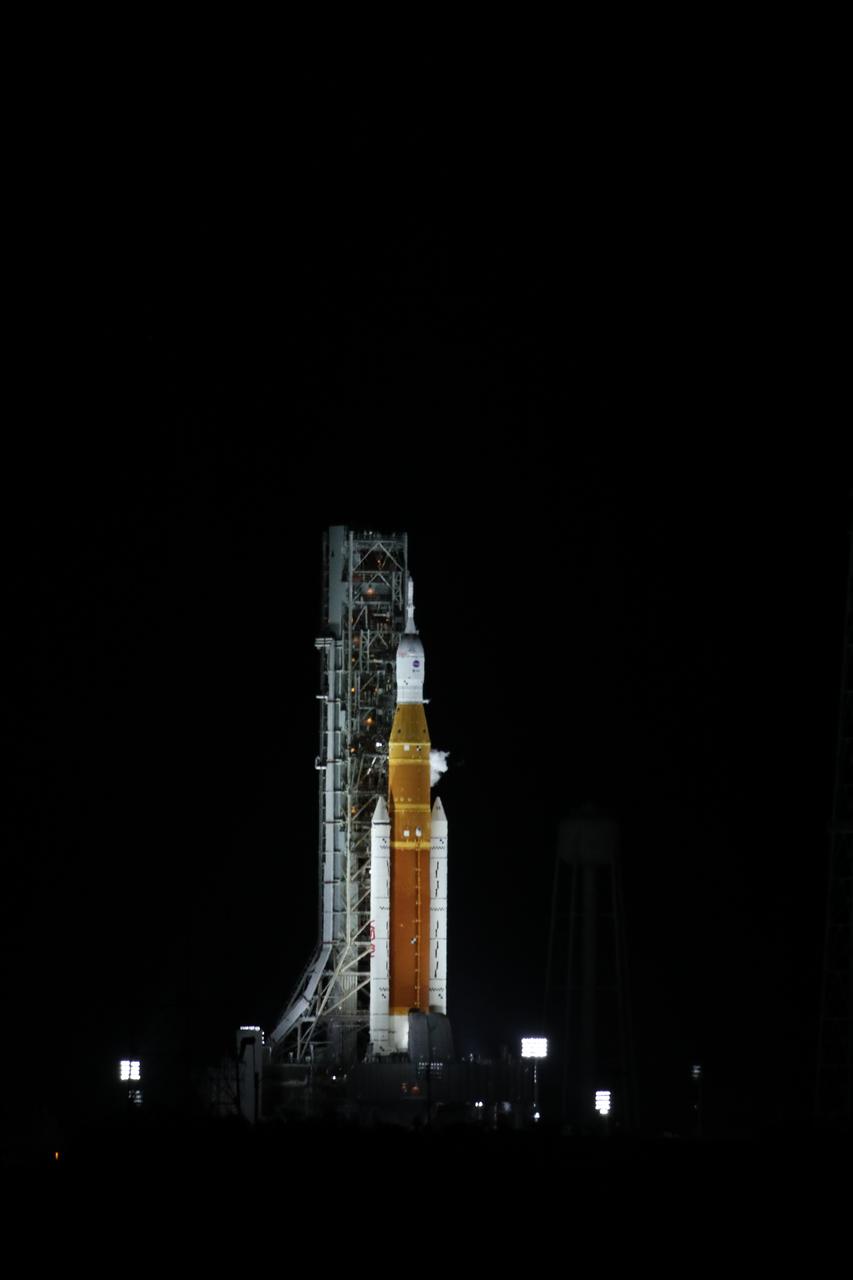

NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher await ignition and liftoff on Artemis I from the pad at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022. Liftoff was at 1:47 a.m. EST. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Former NASA astronaut Gen. Tom Stafford attends an Artemis I guest briefing during launch countdown activities on Aug. 29, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch was waved off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson participates in a press conference on Aug. 29, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after waving-off of the launch of the agency’s Artemis I mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

A half Moon illuminates the sky after the launch of NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft on Artemis I from Launch Complex 39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022. Liftoff was at 1:47 a.m. EST. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
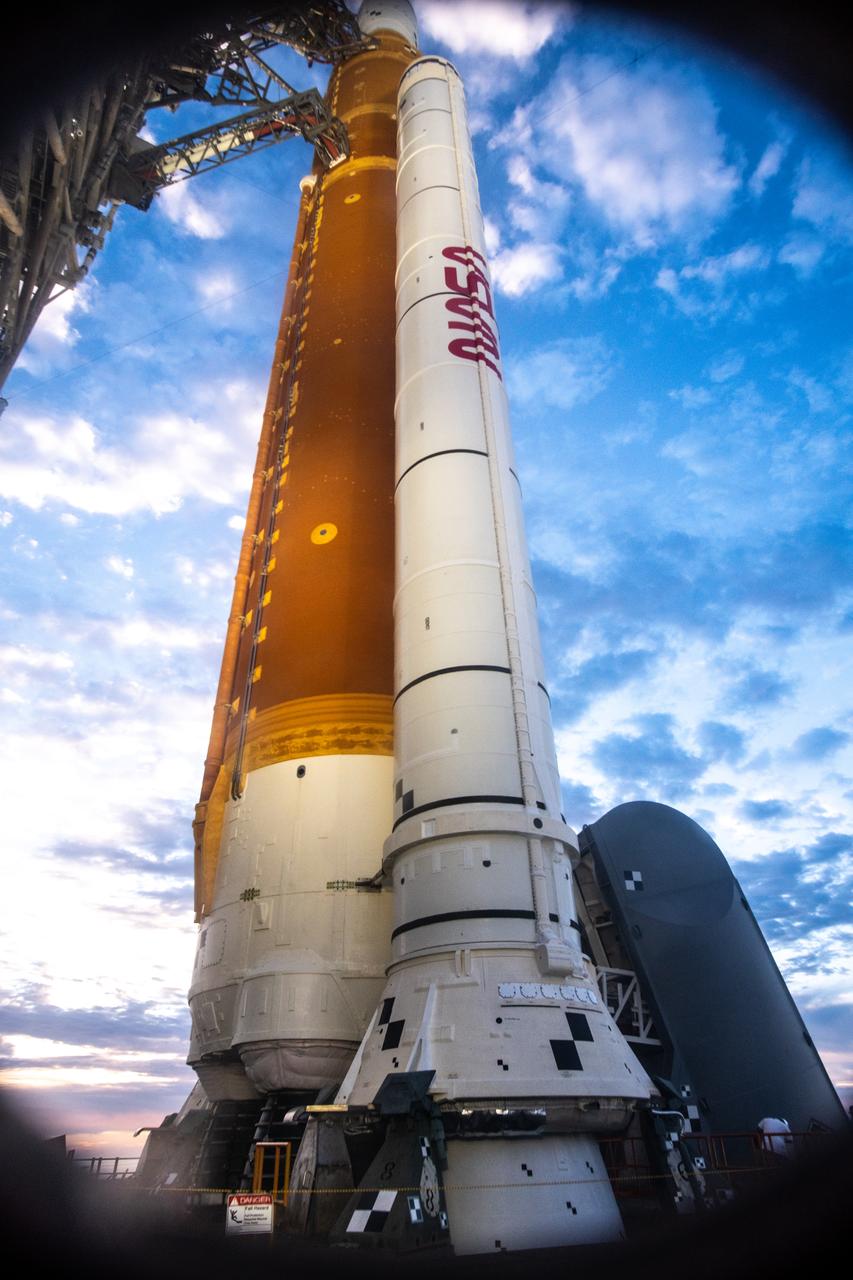

NASA’s Artemis I Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher are in view on the pad at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 15, 2022. Liftoff was at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
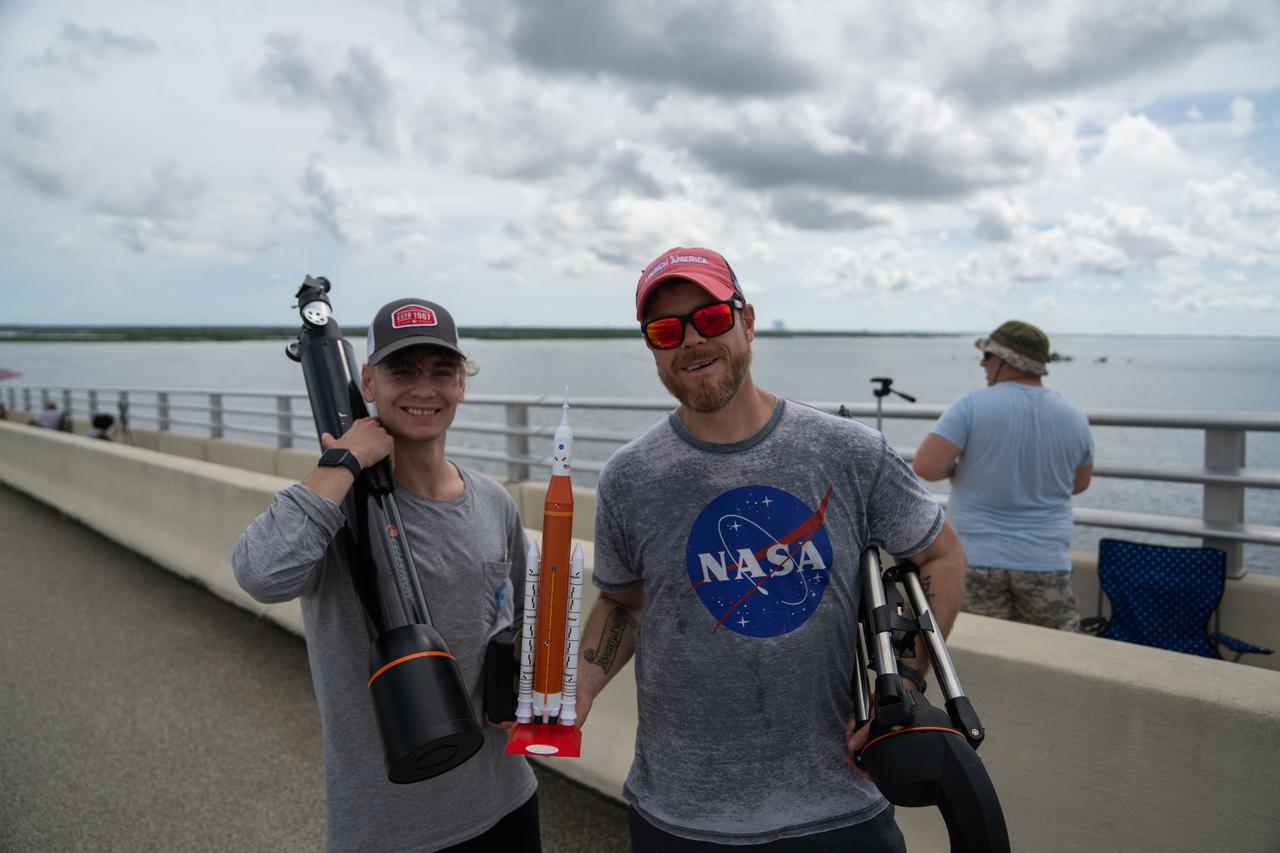

Two individuals wearing NASA shirts and holding a model Space Launch System rocket are on the Max Brewer Bridge in Titusville, Florida, to witness the launch of NASA’s Artemis I mission on Sept. 3, 2022. The launch was waived off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters, participates in a press conference on Aug. 29, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after waving-off of the launch of the agency’s Artemis I mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown
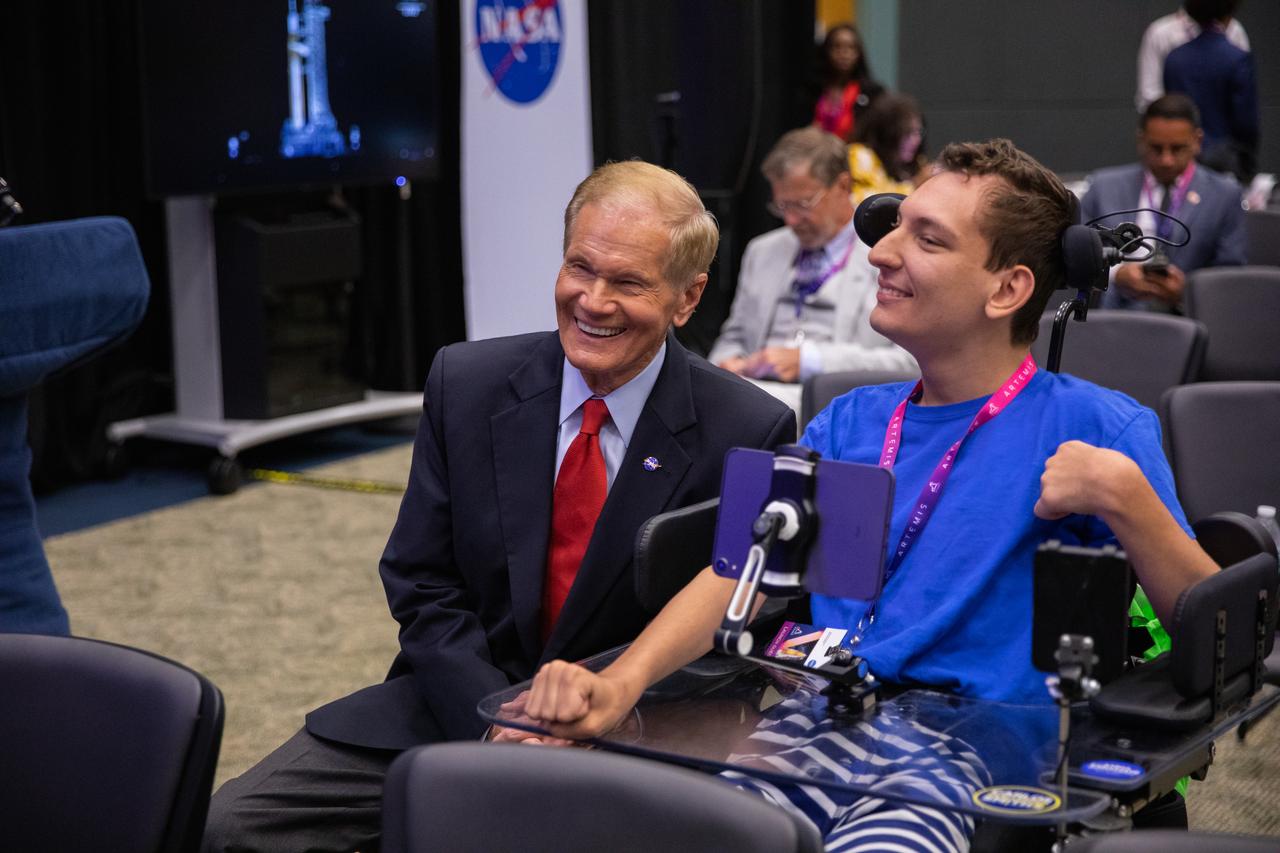

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, at left, visits with a launch guest during launch countdown activities for NASA’s Artemis I mission on Aug. 29, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch was waved off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
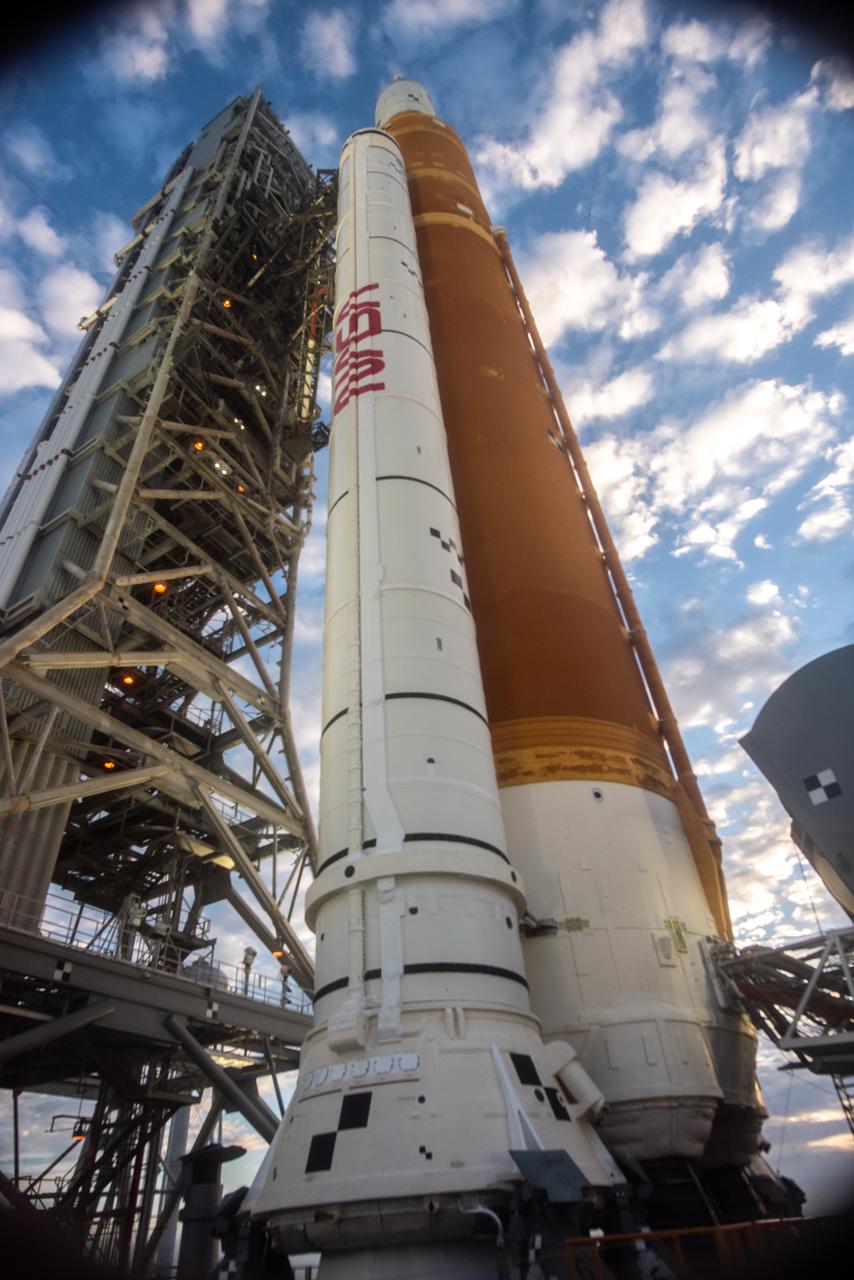

NASA’s Artemis I Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher are in view on the pad at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 15, 2022. Liftoff was at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
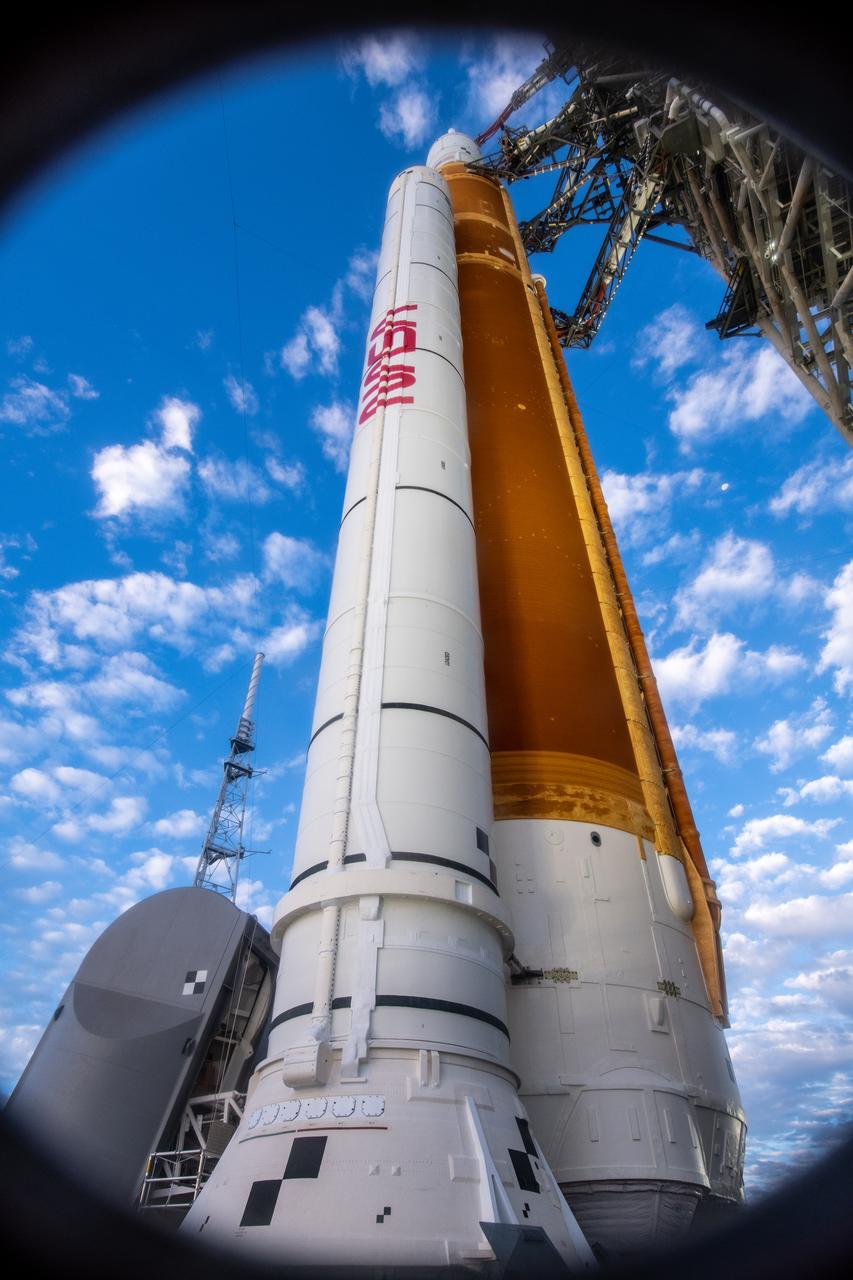

NASA’s Artemis I Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher are in view on the pad at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 15, 2022. Liftoff was at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
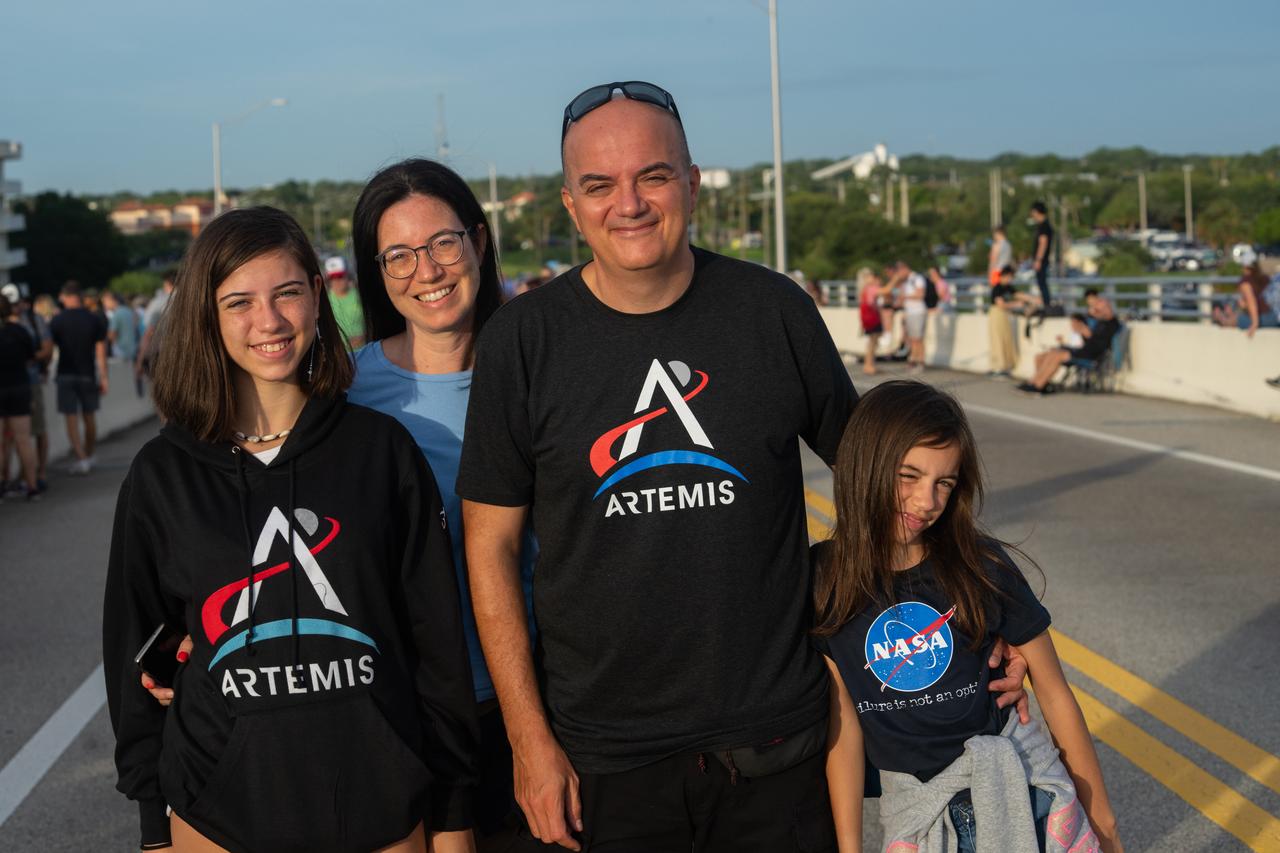

A family wearing NASA and Artemis shirts are on the Max Brewer Bridge in Titusville, Florida, to witness the launch of NASA’s Artemis I mission on Aug. 29, 2022. The launch was waved off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
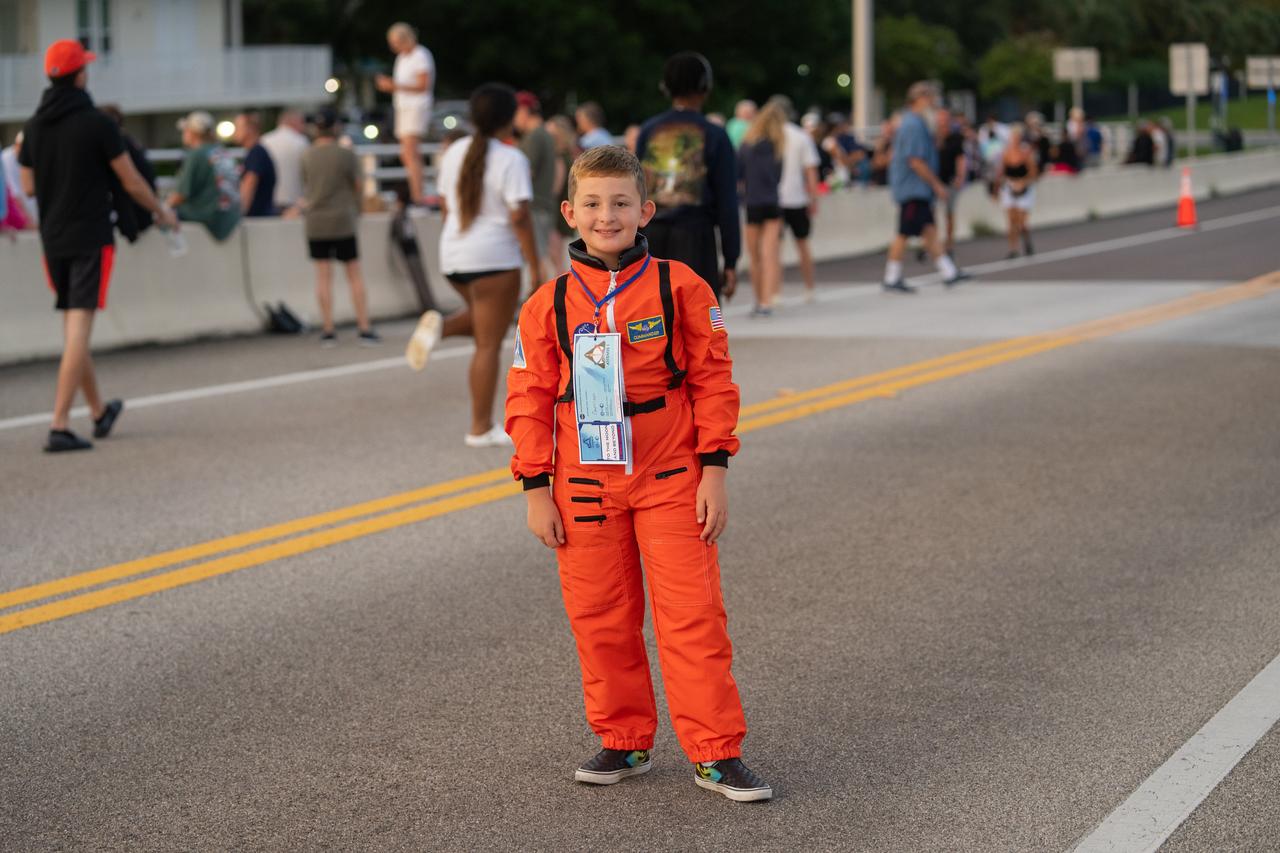

A young child dressed in an astronaut spacesuit is one of the spectators gathering on the Max Brewer Bridge in Titusville, Florida, to witness NASA’s Artemis I launch on Aug. 29, 2022. The launch was waved off for the day at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
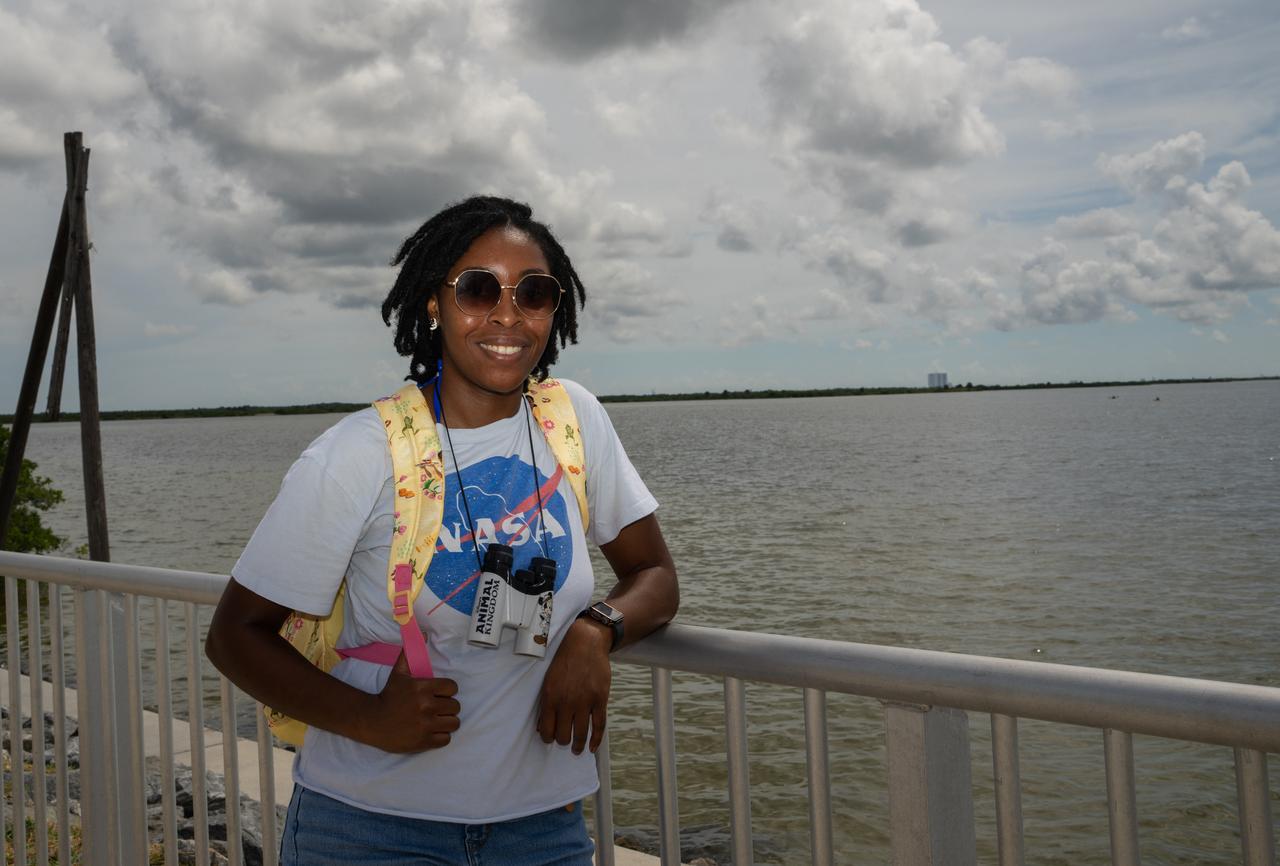

A woman wearing a NASA shirt is on the Max Brewer Bridge in Titusville, Florida, waiting to witness the launch of NASA’s Artemis I mission on Sept. 3, 2022. The launch was waived off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
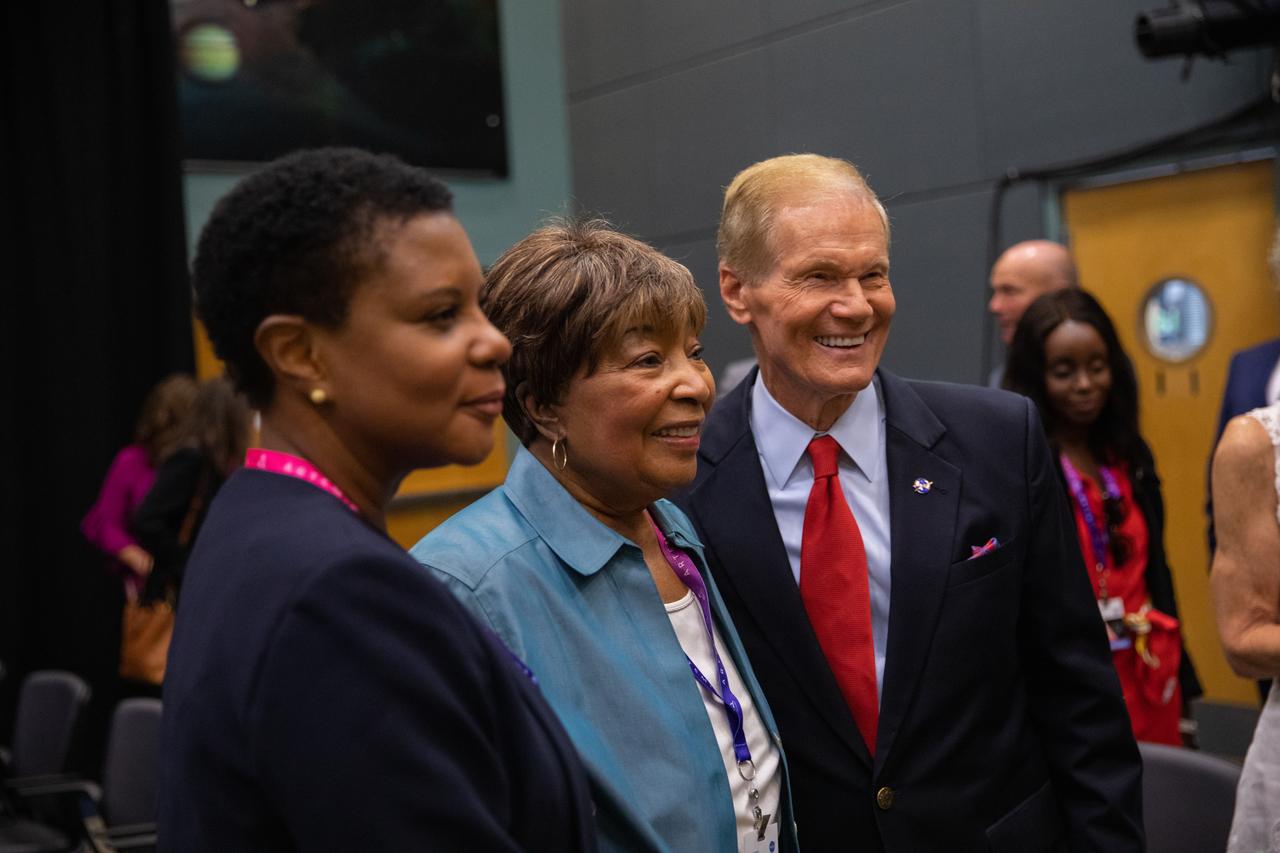

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, far right, visits with Congresswoman (TX) Eddie Bernice Johnson, center, during launch countdown activities for NASA’s Artemis I mission on Aug. 29, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch was waved off for the day. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
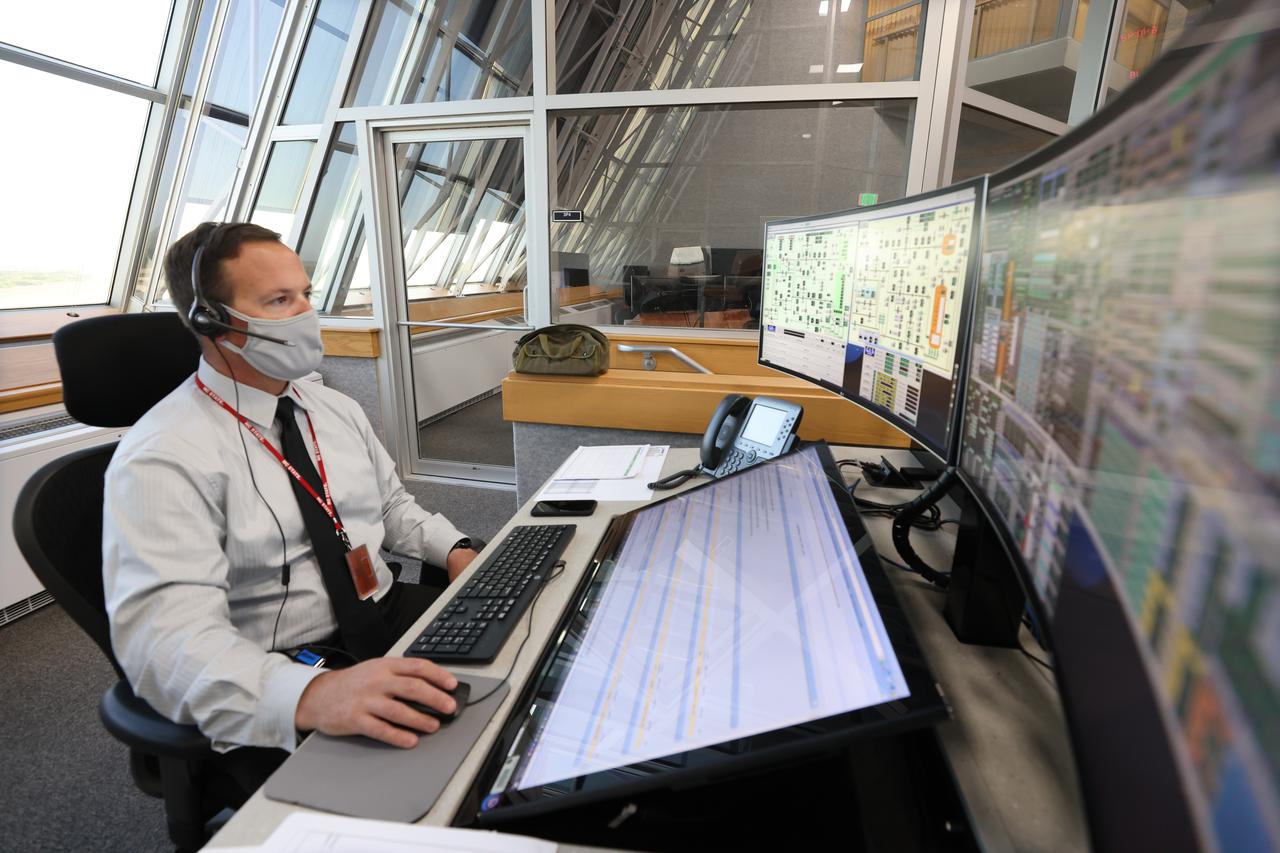

Wes Mosedale, Technical Assistant to the Launch Director, with Exploration Ground Systems, is seated at console inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. He is participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
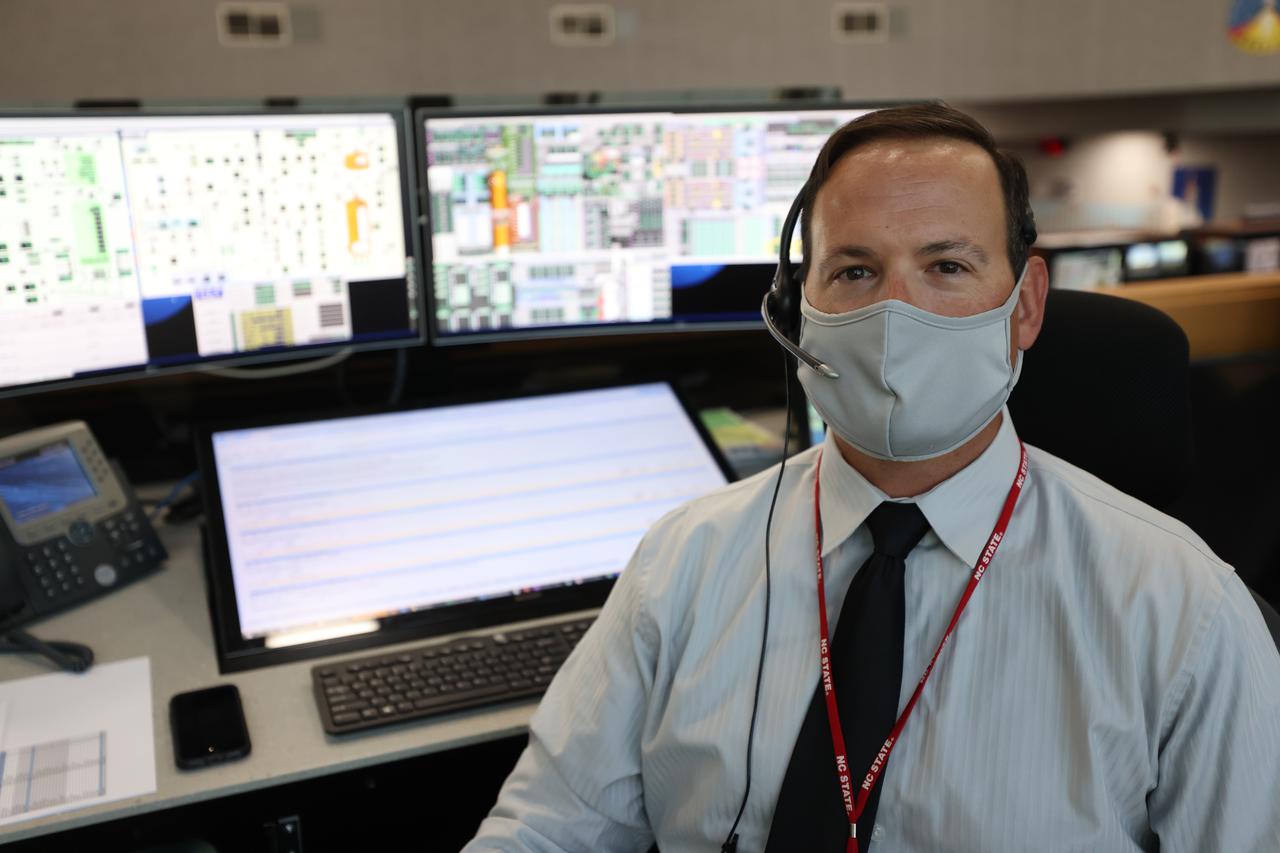

Wes Mosedale, Technical Assistant to the Launch Director, with Exploration Ground Systems, is seated at console inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. He is participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
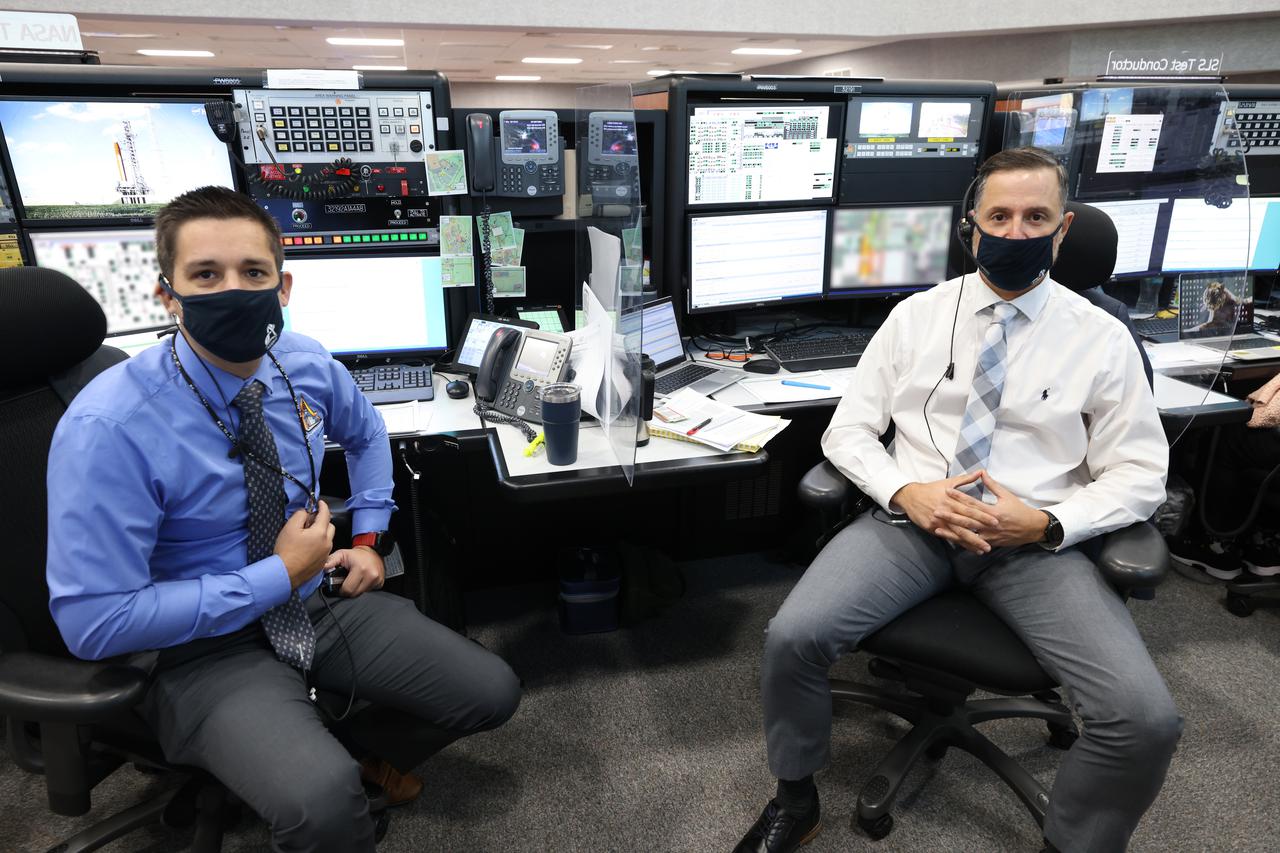

NASA Test Directors Daniel Florez, left, and Carlos Monje, right, with Exploration Ground Systems, are seated at their consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.

NASA Test Directors Daniel Florez, right, and Carlos Monje, left, with Exploration Ground Systems, are seated at their consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
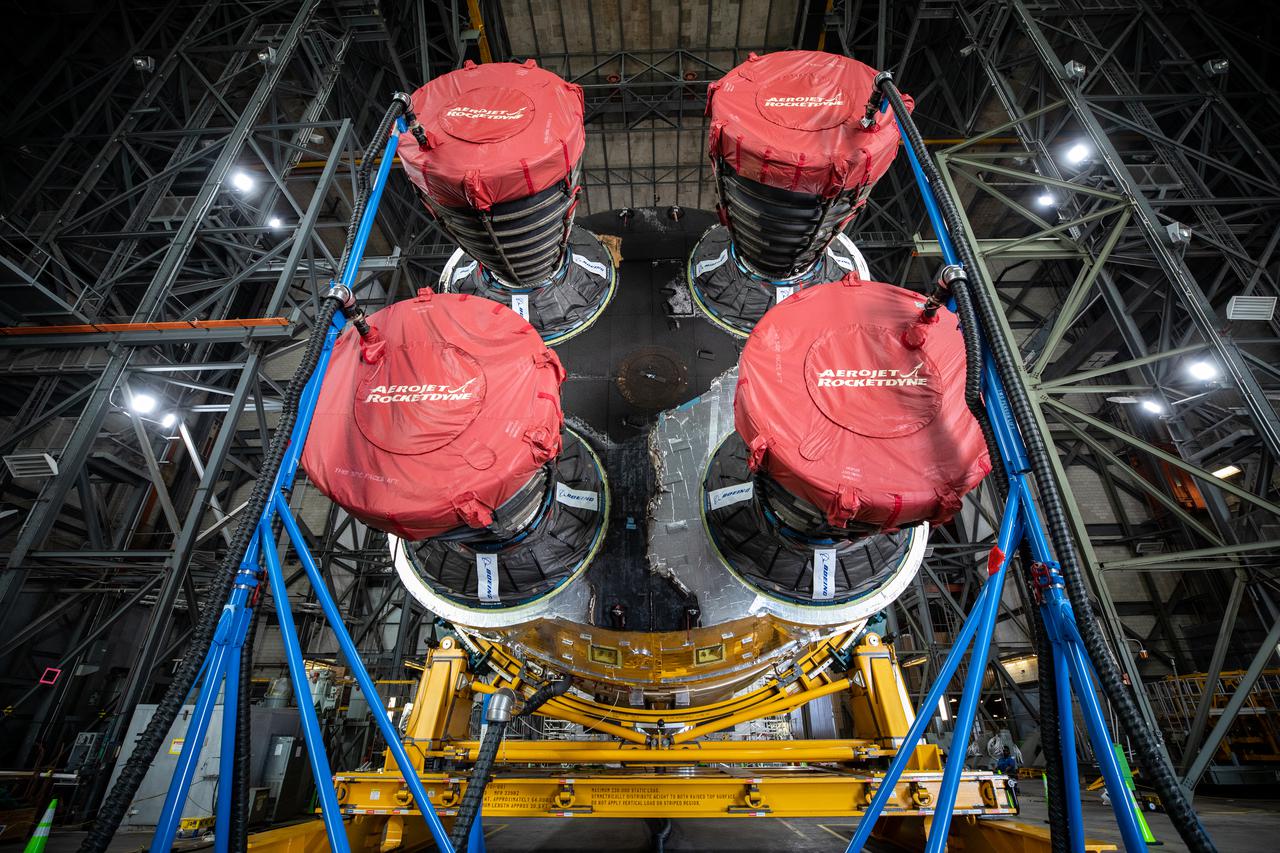

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage for NASA’s Artemis I mission is in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 5, 2021. In view are the core stage’s four RS-25 engines in protective covers. Teams from the center’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will perform checkouts ahead of integrating the massive rocket stage with the twin solid rocket boosters, Orion spacecraft, and additional flight hardware ahead of the Artemis I launch. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of SLS and Orion and will pave the way for landing the first woman and first person of color on the lunar surface. It will be a proving ground for deep space exploration, leading the agency’s efforts under the Artemis program for a sustainable presence on the Moon and preparing for human missions to Mars.
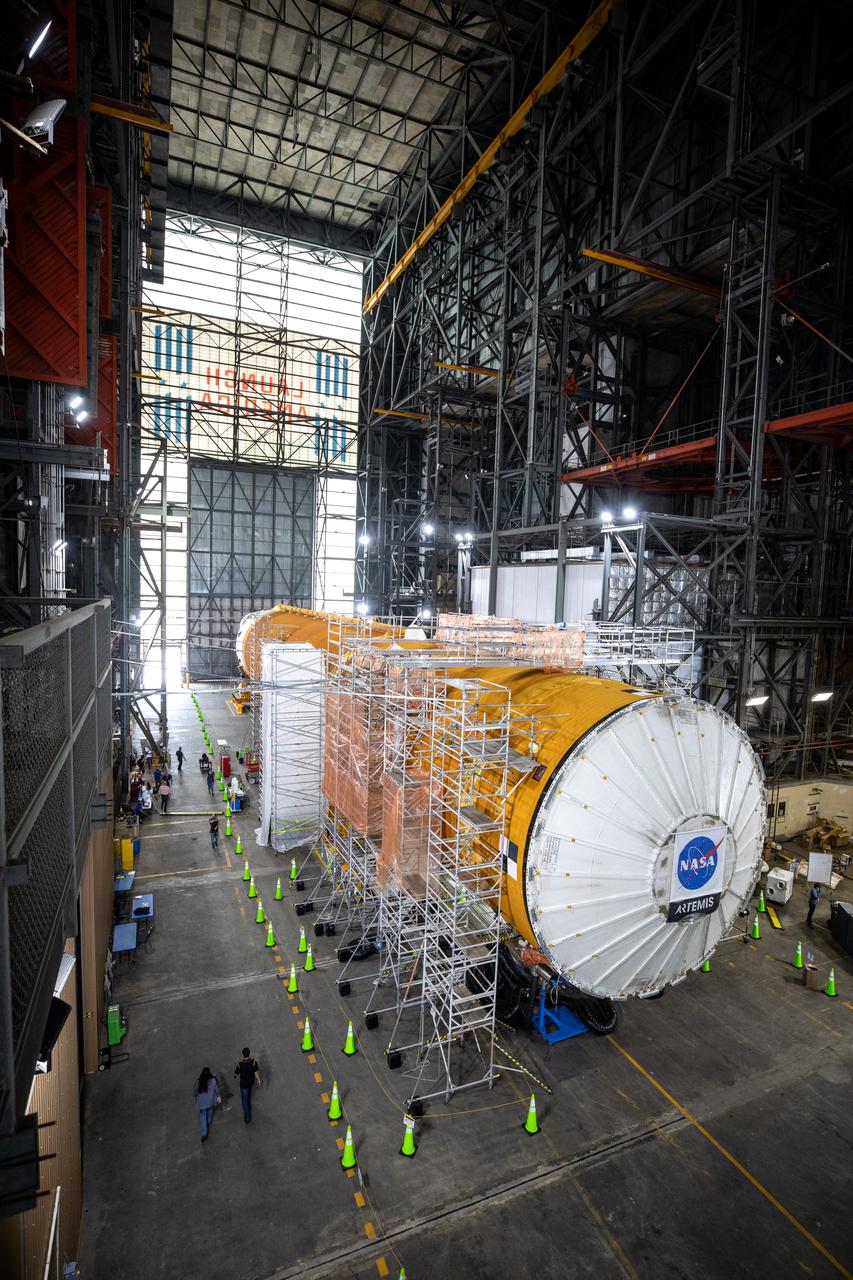

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage for NASA’s Artemis I mission is in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 5, 2021. Teams from the center’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will perform checkouts ahead of integrating the massive rocket stage with the twin solid rocket boosters, Orion spacecraft, and additional flight hardware ahead of the Artemis I launch. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of SLS and Orion and will pave the way for landing the first woman and first person of color on the lunar surface. It will be a proving ground for deep space exploration, leading the agency’s efforts under the Artemis program for a sustainable presence on the Moon and preparing for human missions to Mars.
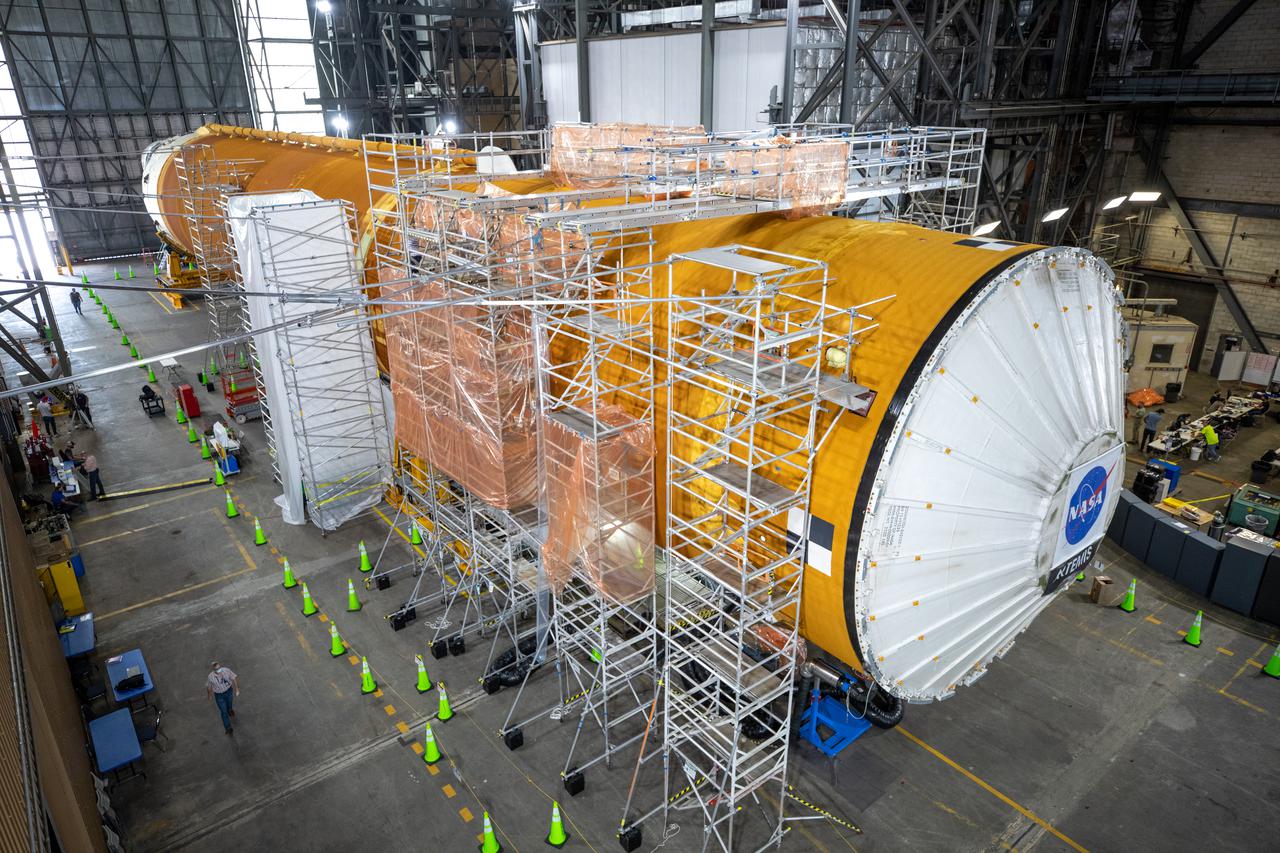

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage for NASA’s Artemis I mission is in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 5, 2021. Teams from the center’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will perform checkouts ahead of integrating the massive rocket stage with the twin solid rocket boosters, Orion spacecraft, and additional flight hardware ahead of the Artemis I launch. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of SLS and Orion and will pave the way for landing the first woman and first person of color on the lunar surface. It will be a proving ground for deep space exploration, leading the agency’s efforts under the Artemis program for a sustainable presence on the Moon and preparing for human missions to Mars.

Howard Hu, Orion Program Manager, NASA’s Johnson Space Center, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following completion of NASA’s Flight Readiness Review for Artemis I on Aug. 22, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Bob Cabana, NASA Associate Administrator, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following completion of NASA’s Flight Readiness Review for Artemis I on Aug. 22, 2022, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.