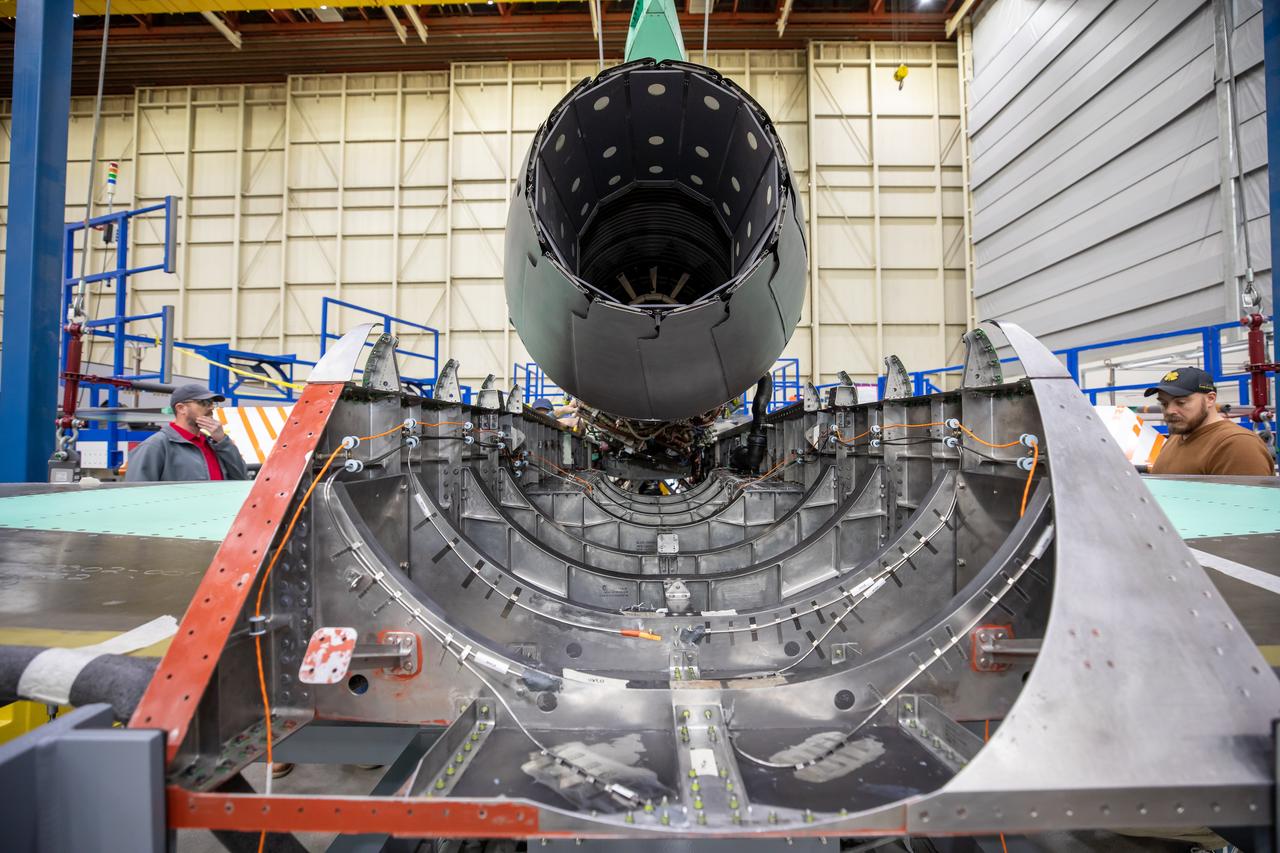

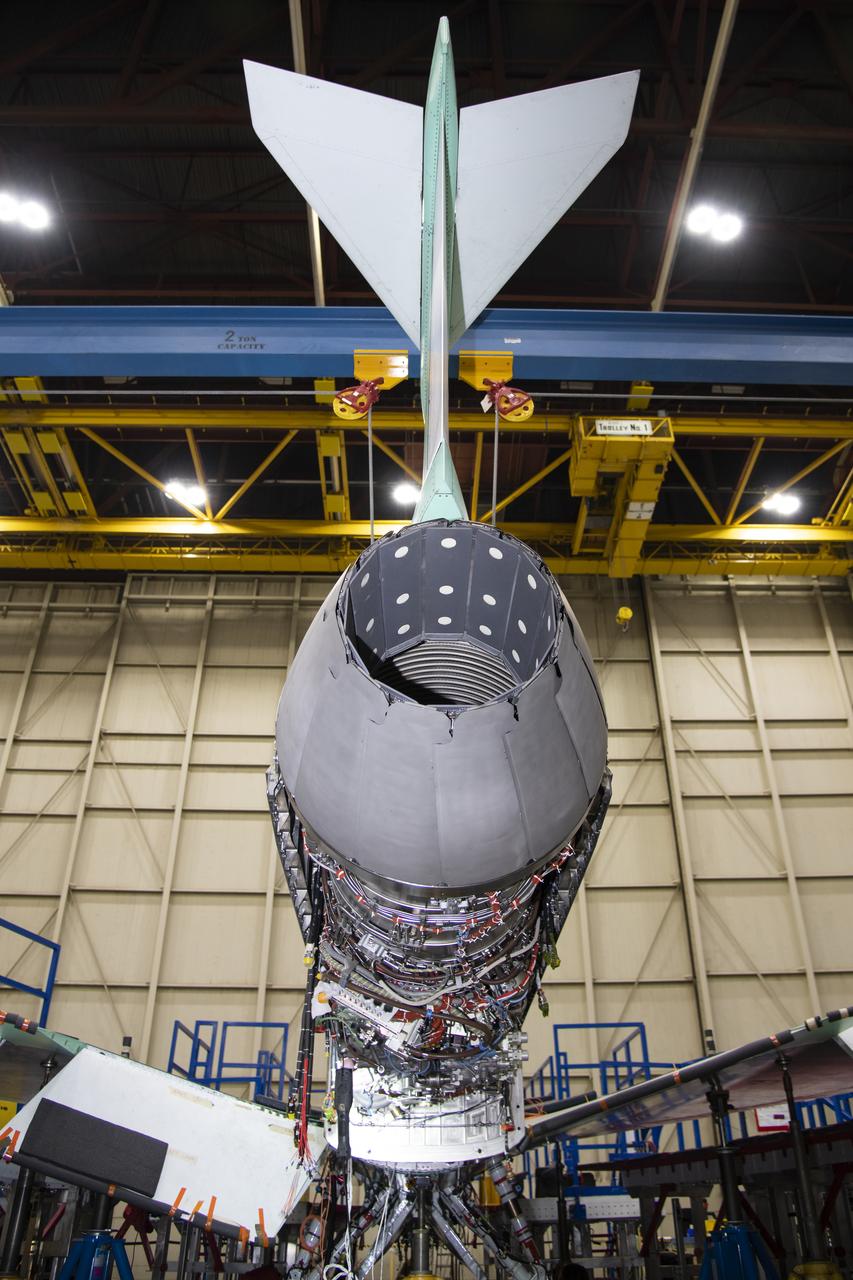
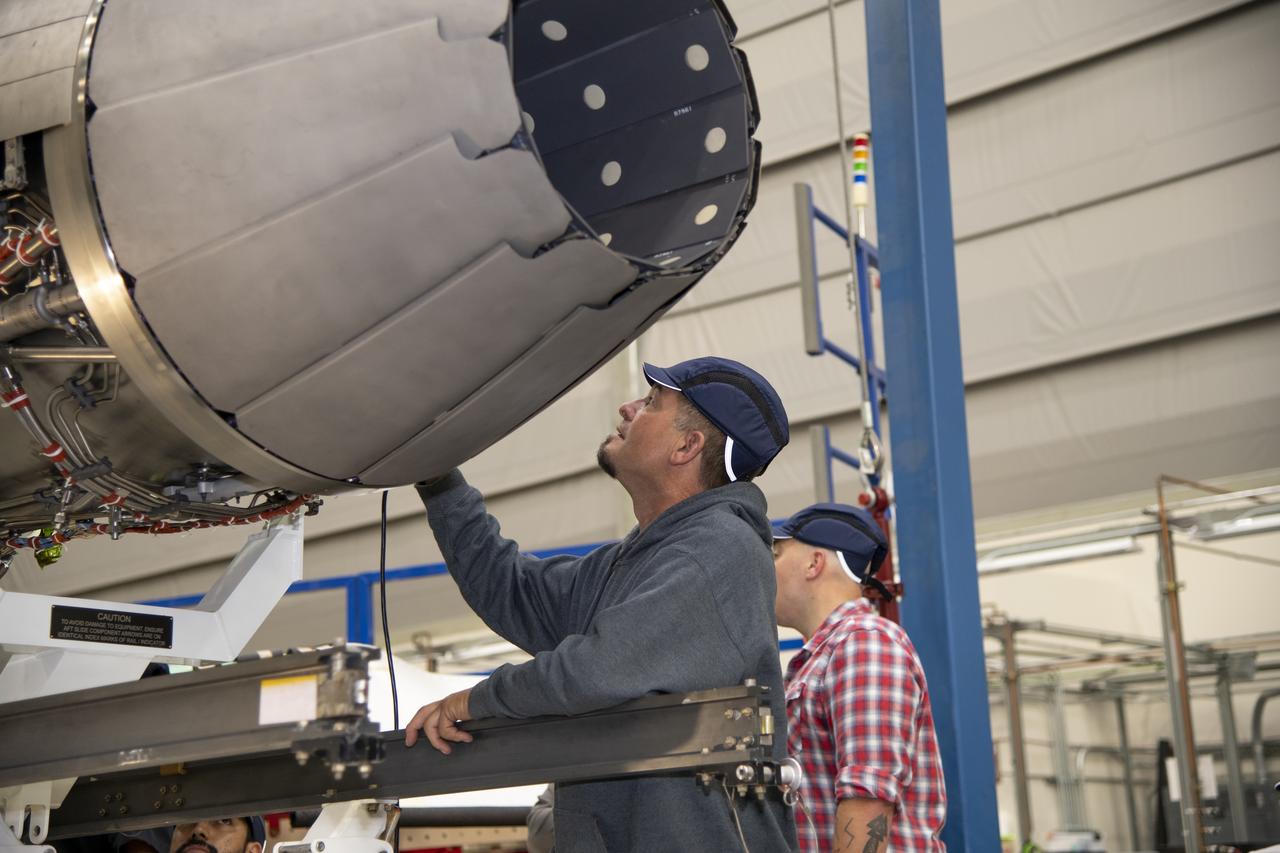
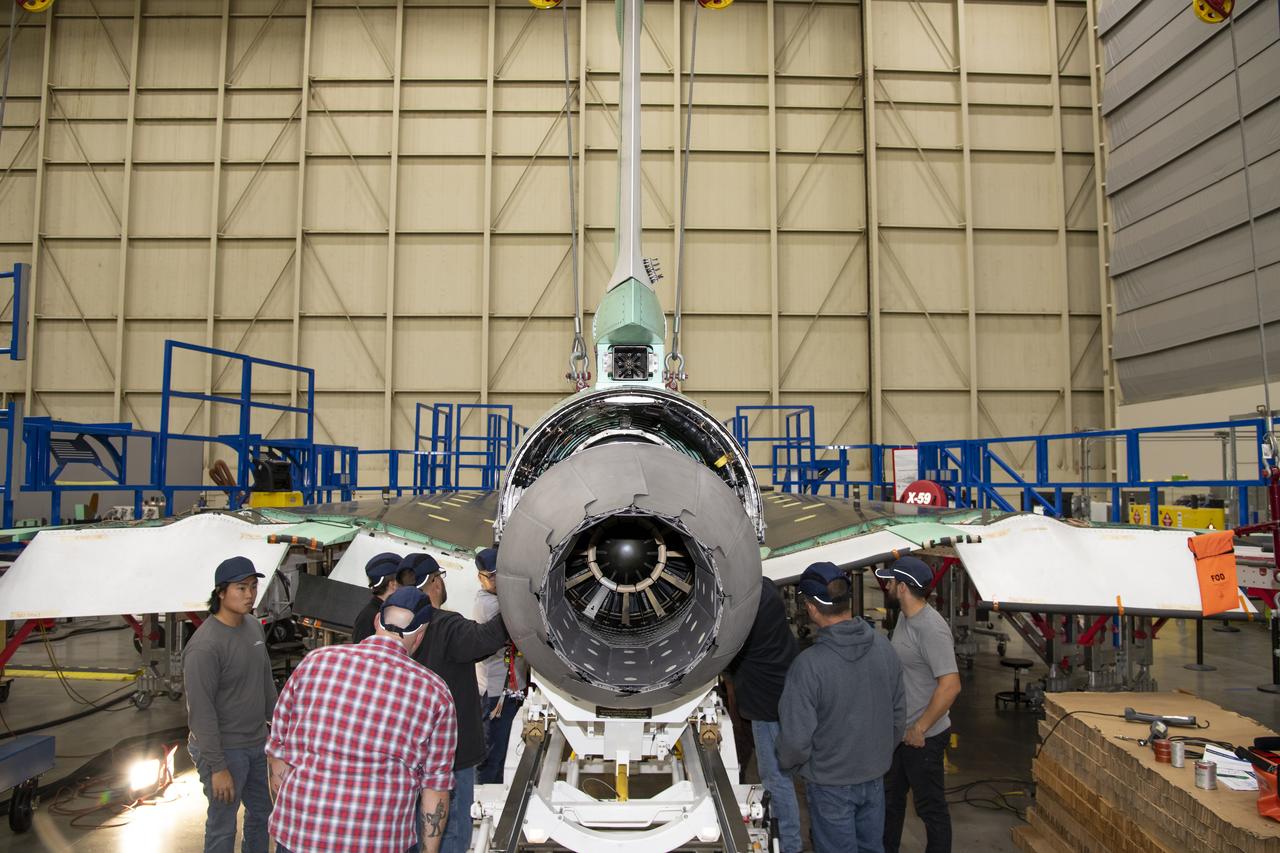
Here is a close-up of the GE F414 engine, from the aft deck or rear, before the tail section of the X-59 is lifted into place and attached to the aircraft. The aft deck helps control the shockwaves at the end of the aircraft and reduce the noise of a sonic boom to more of a sonic thump.

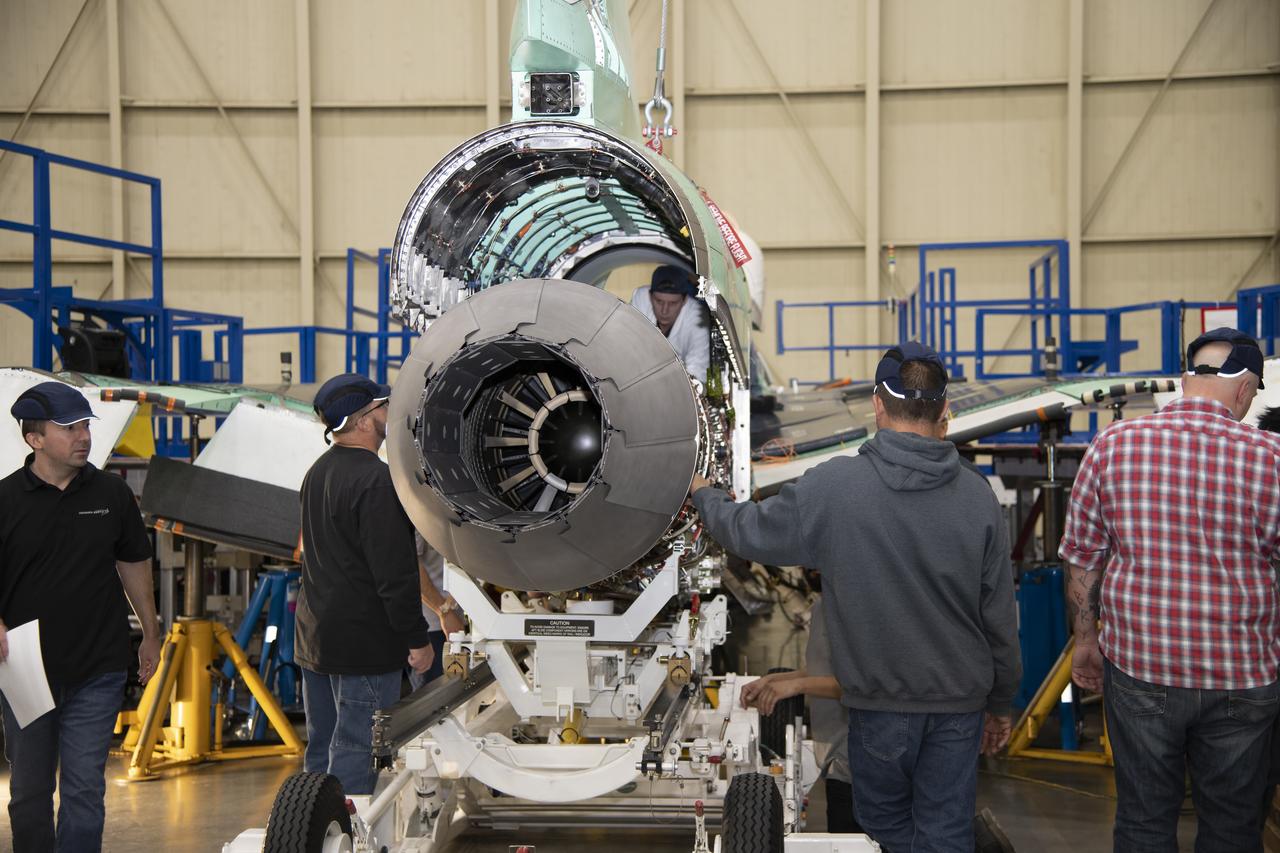
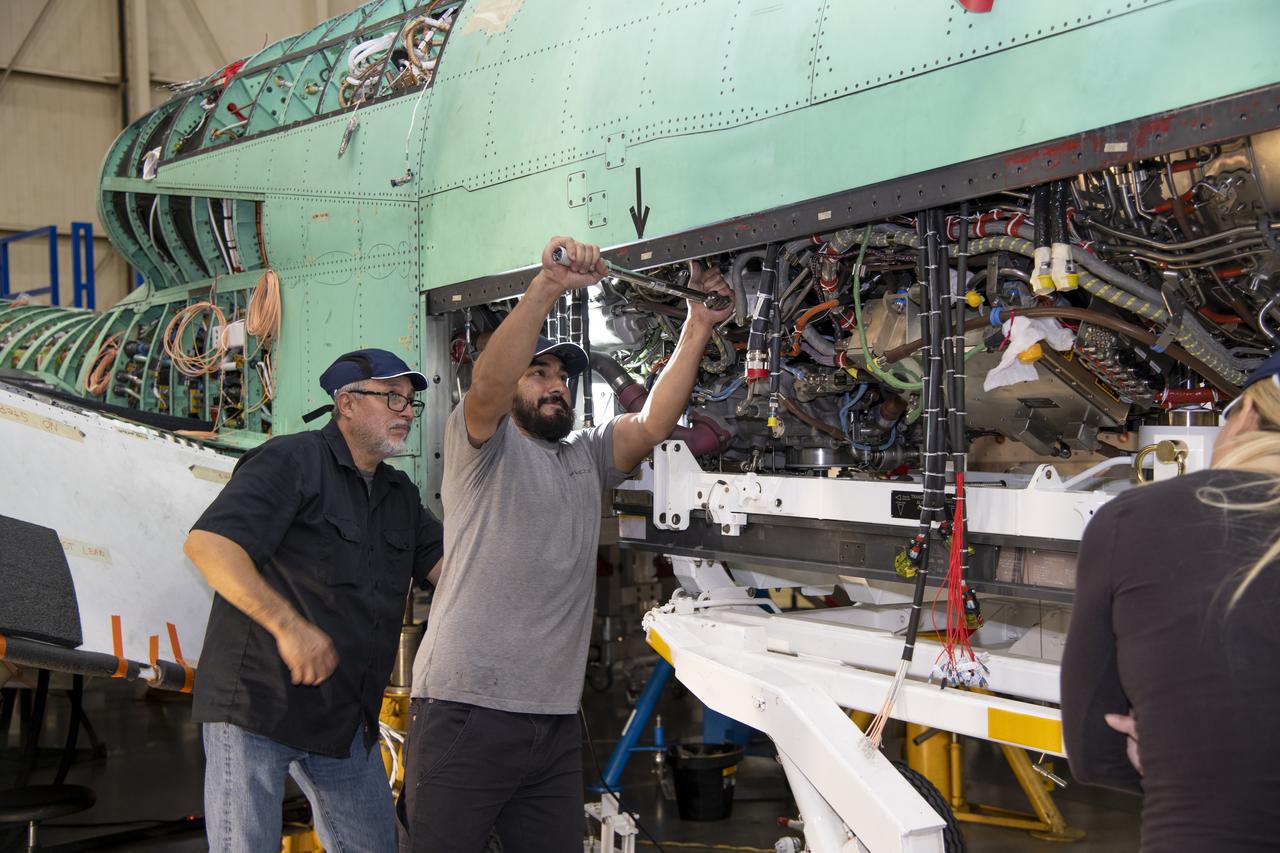
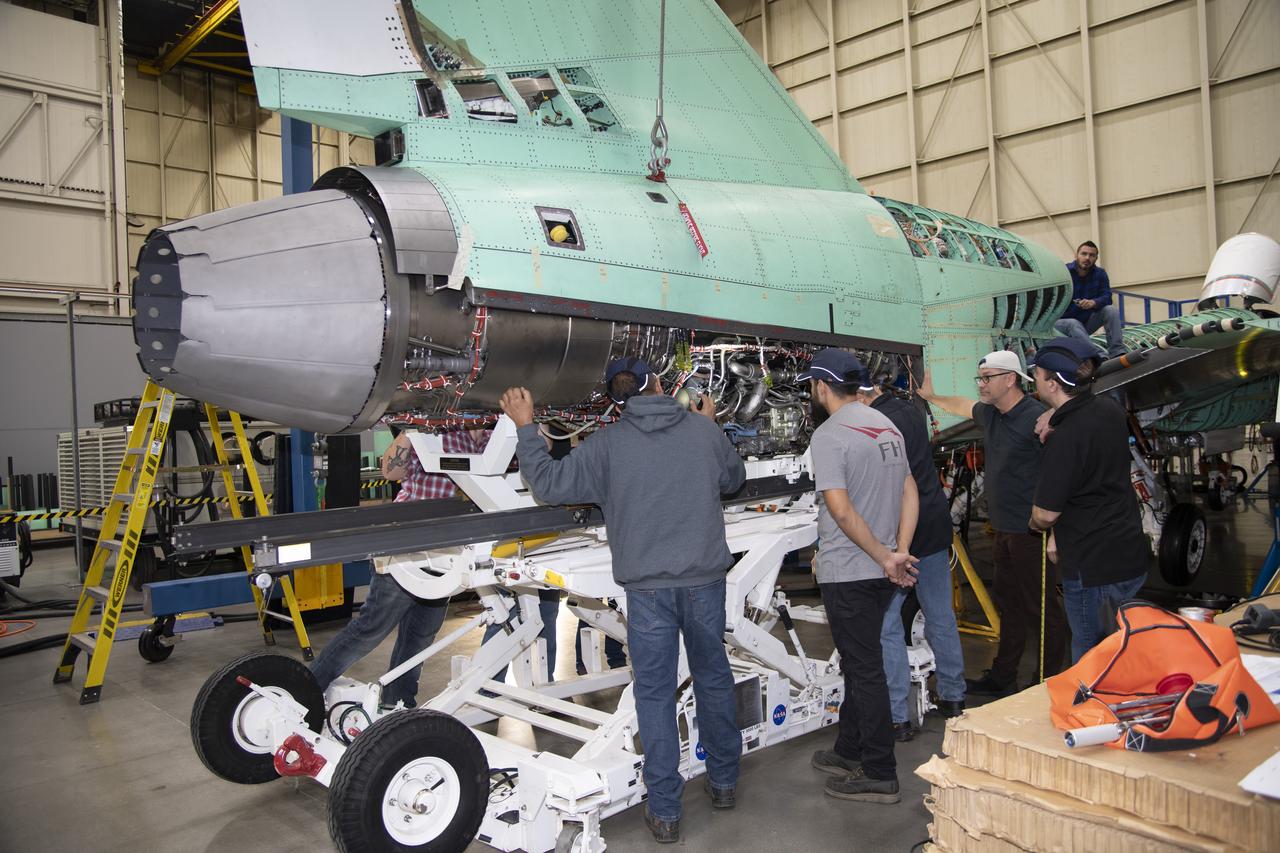
Here is an image of the X-59’s 13-foot General Electric F414 engine as the team prepares for a fit check. Making sure components, like the aircraft’s hydraulic lines, which help control functions like brakes or landing gear, and wiring of the engine, fit properly is essential to the aircraft’s safety. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

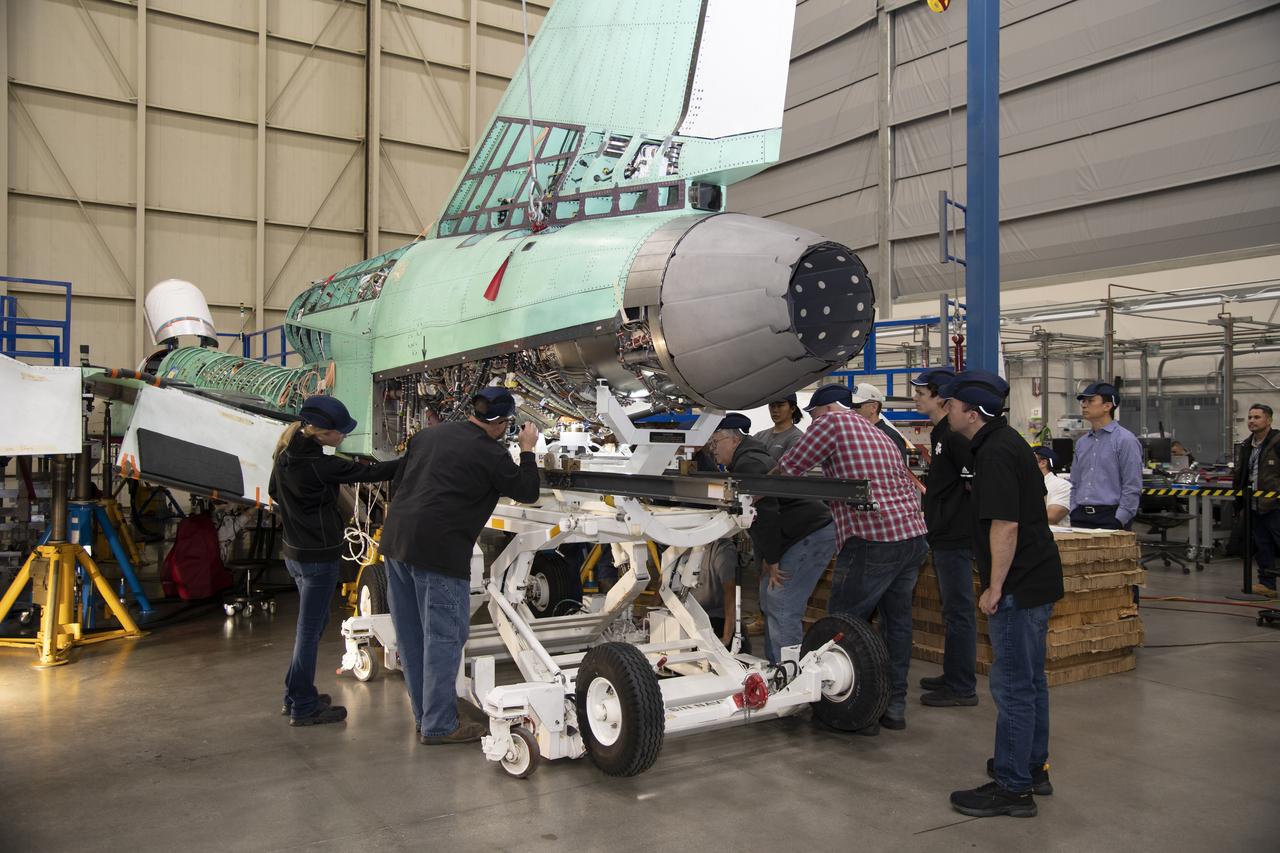
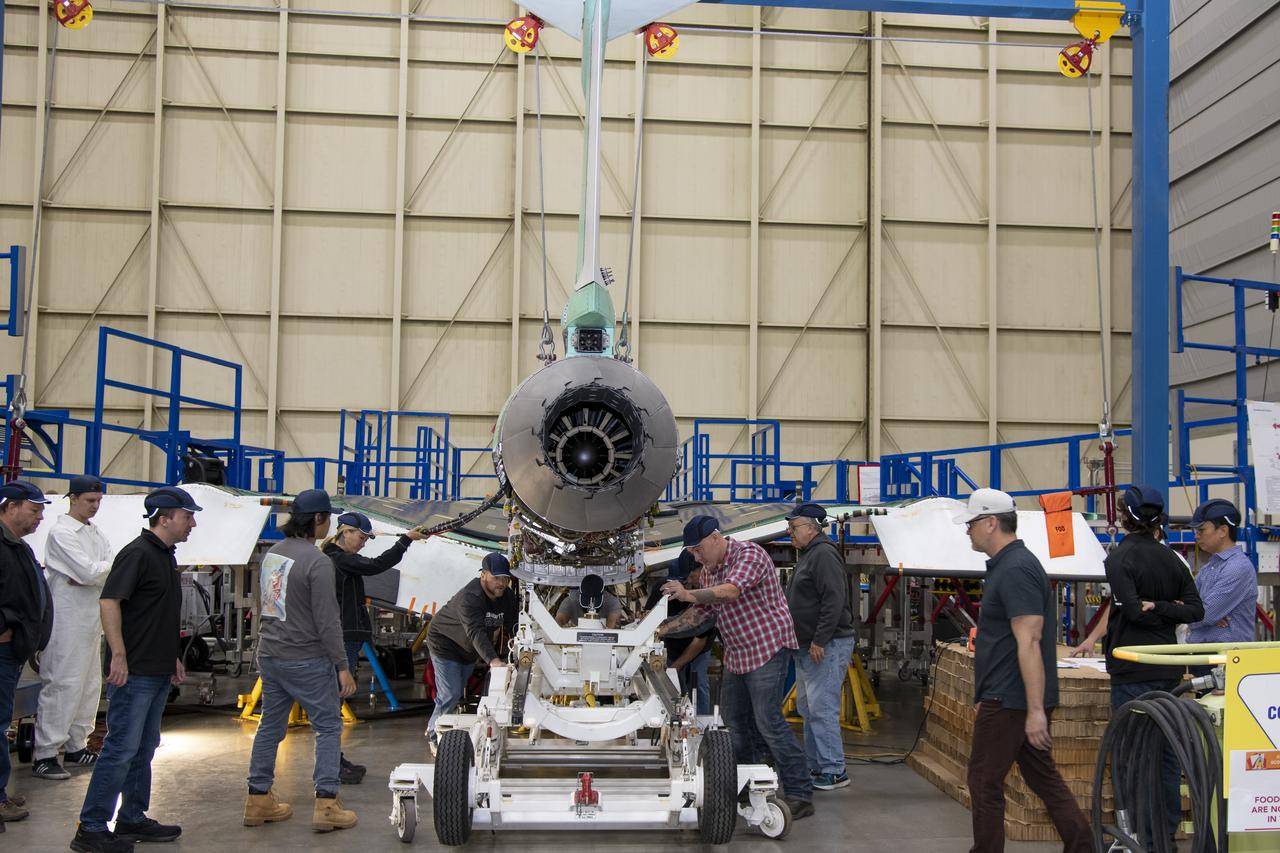
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
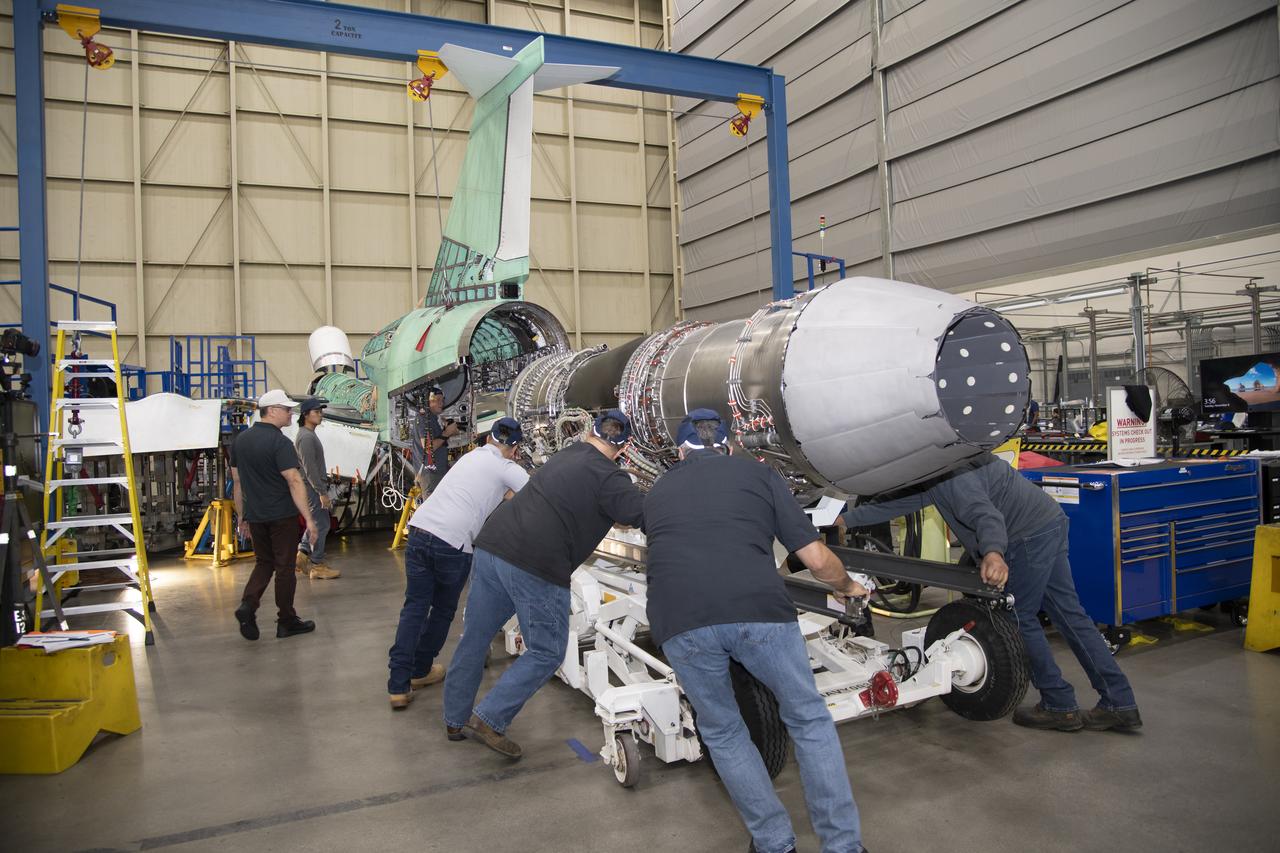

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
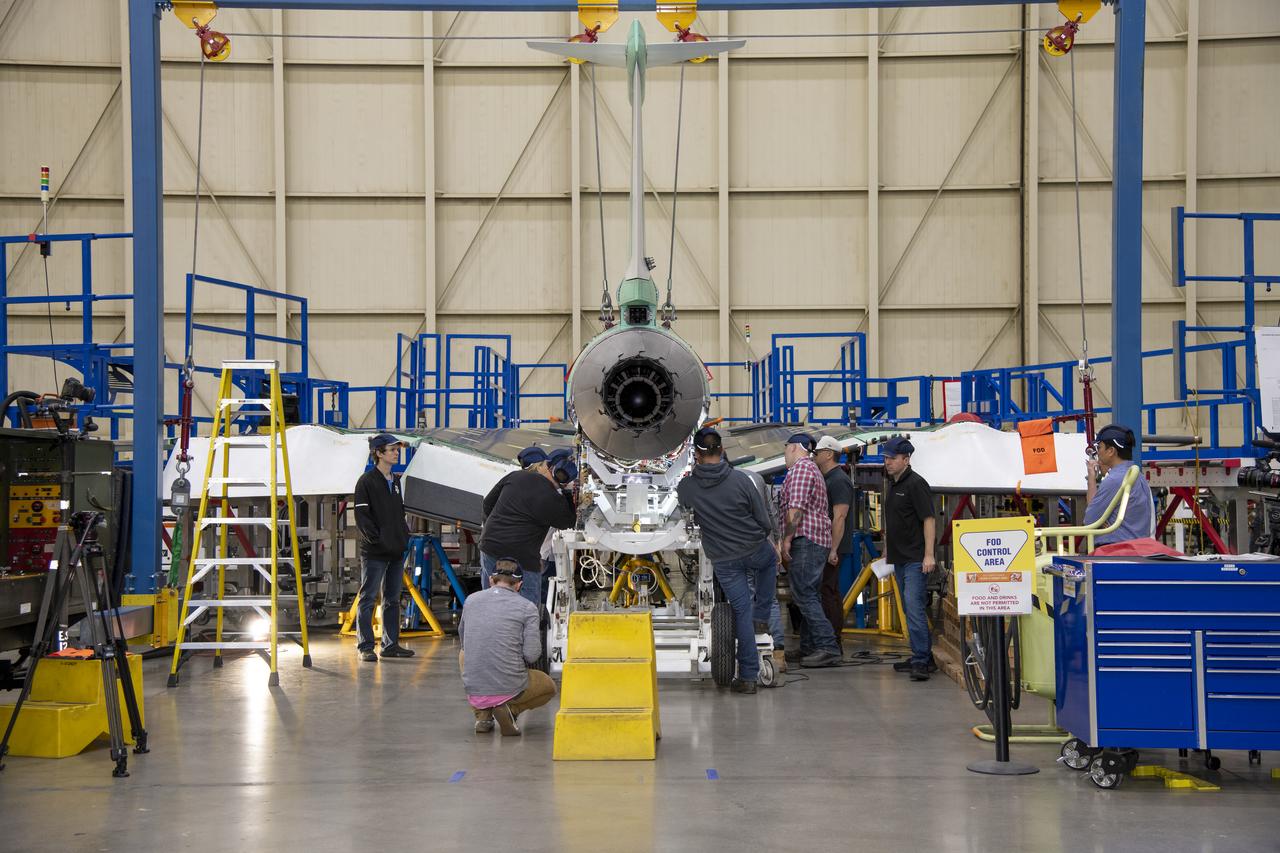

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
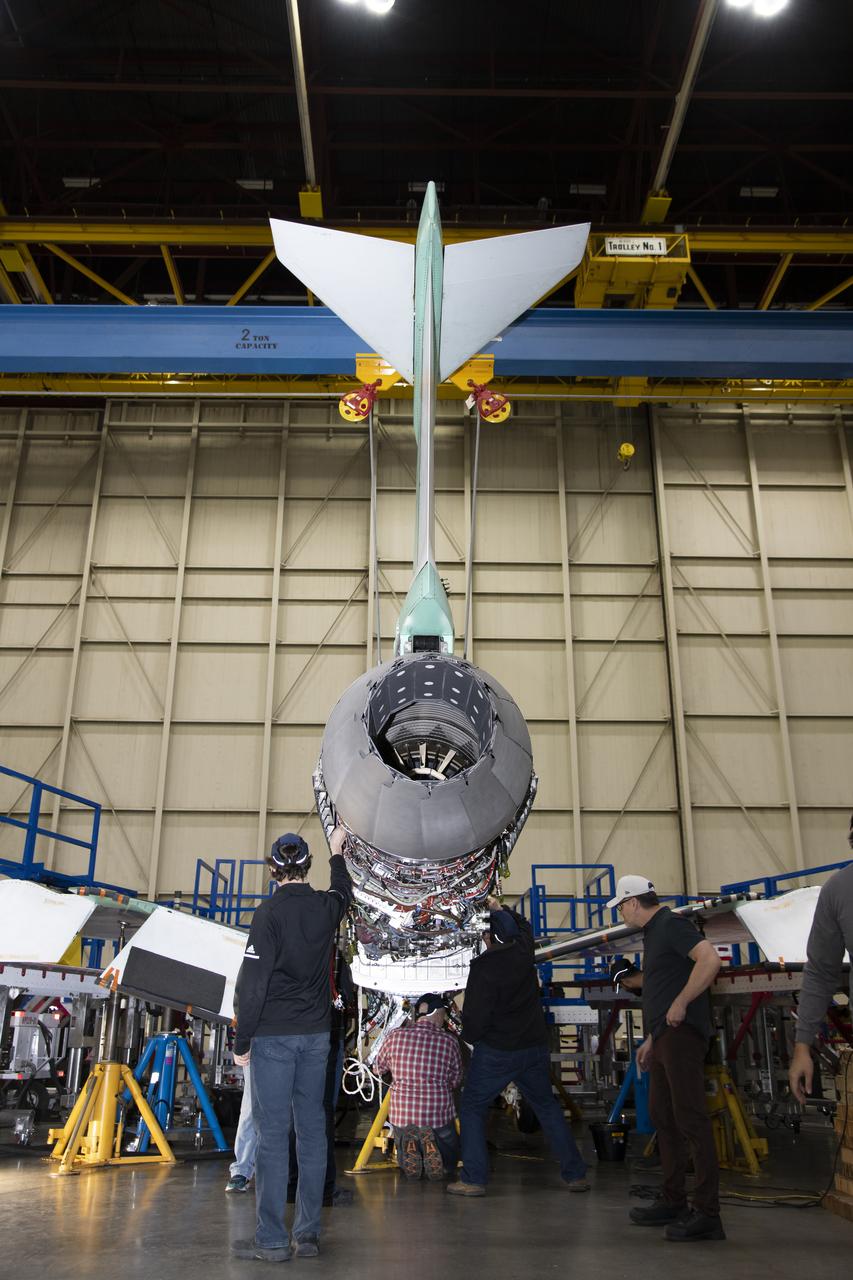

The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
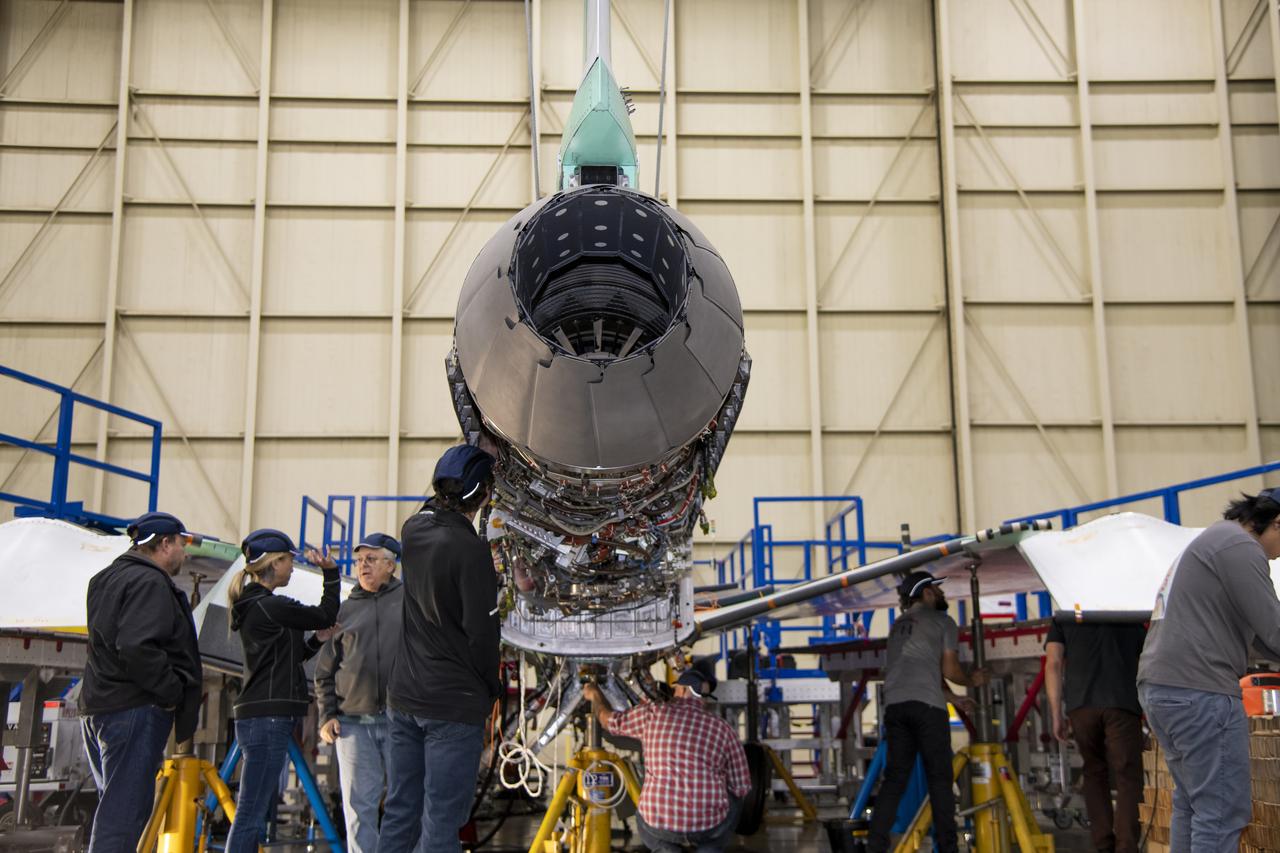

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
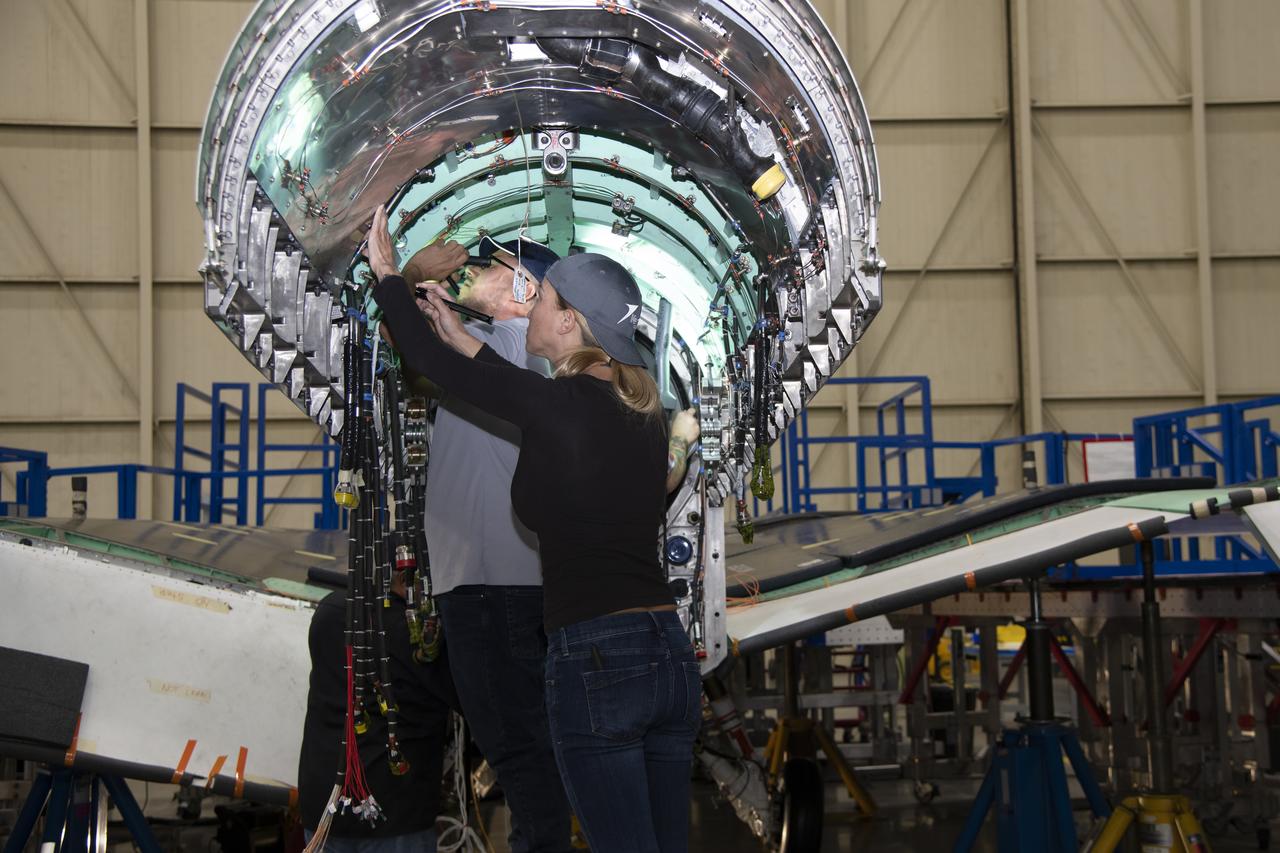

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
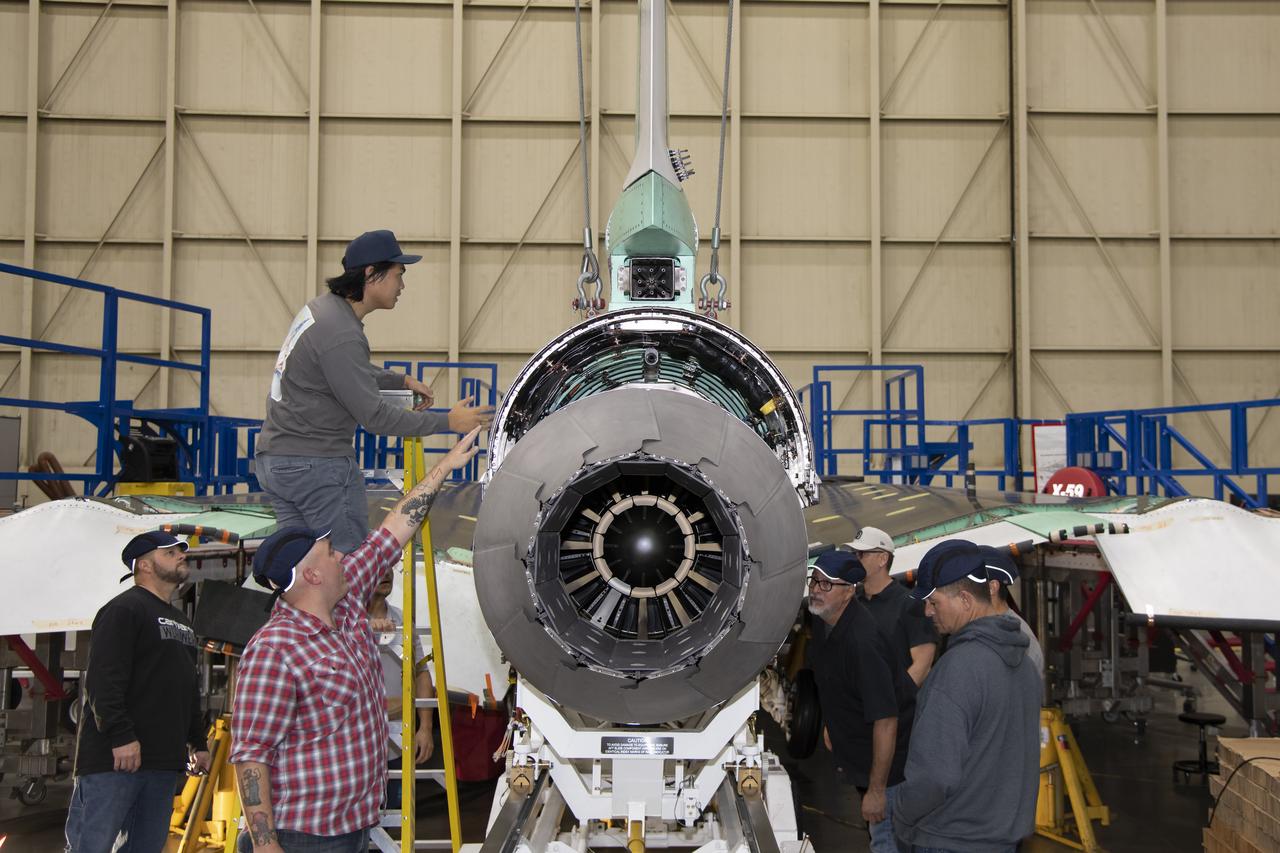

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
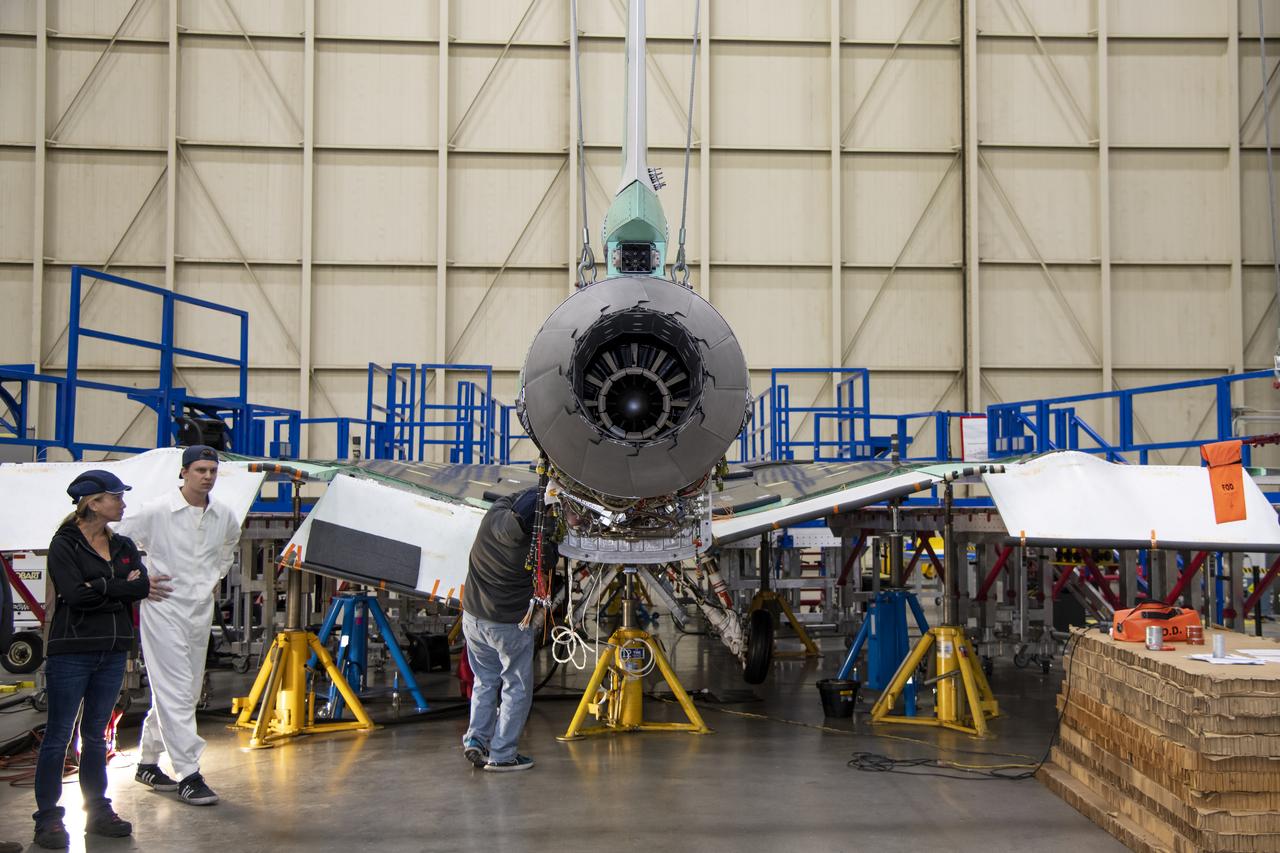

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
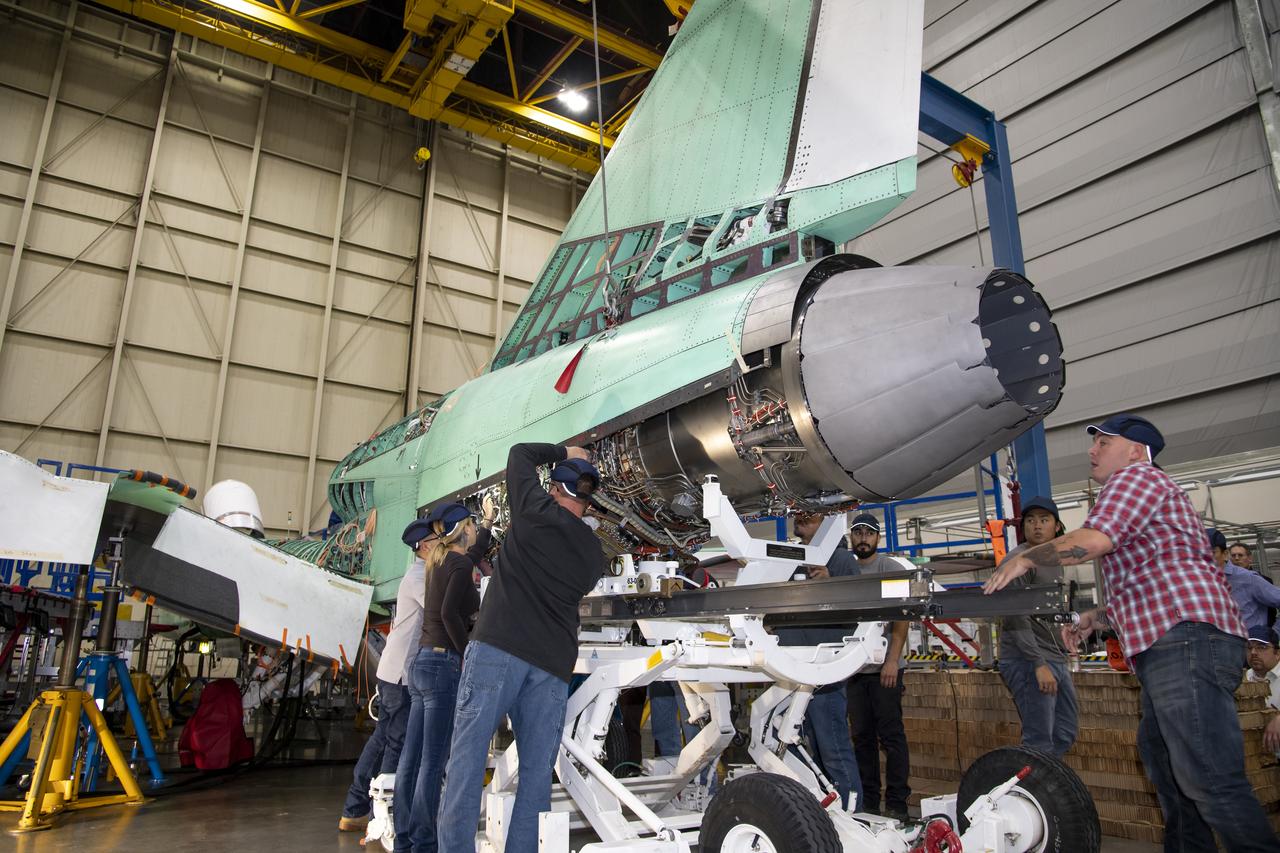

The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
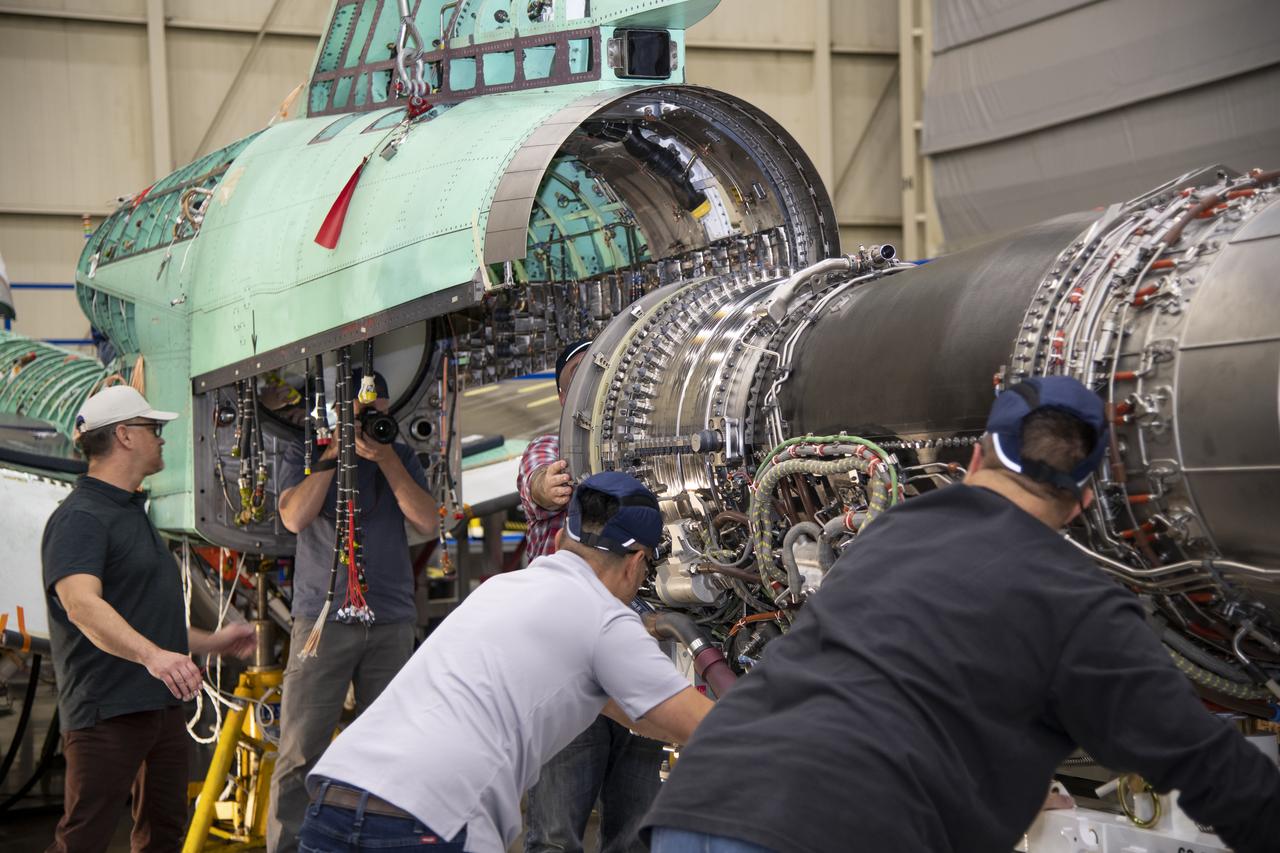

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
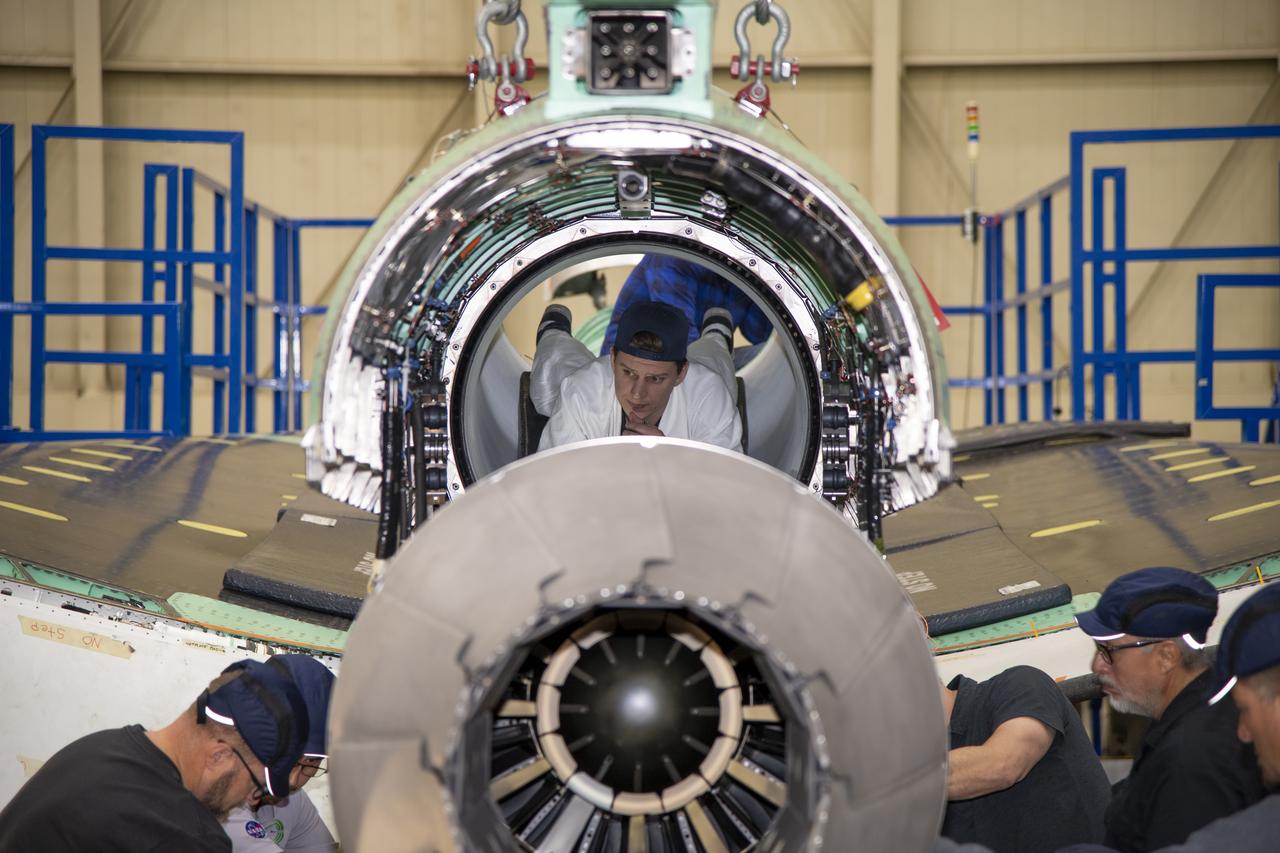

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
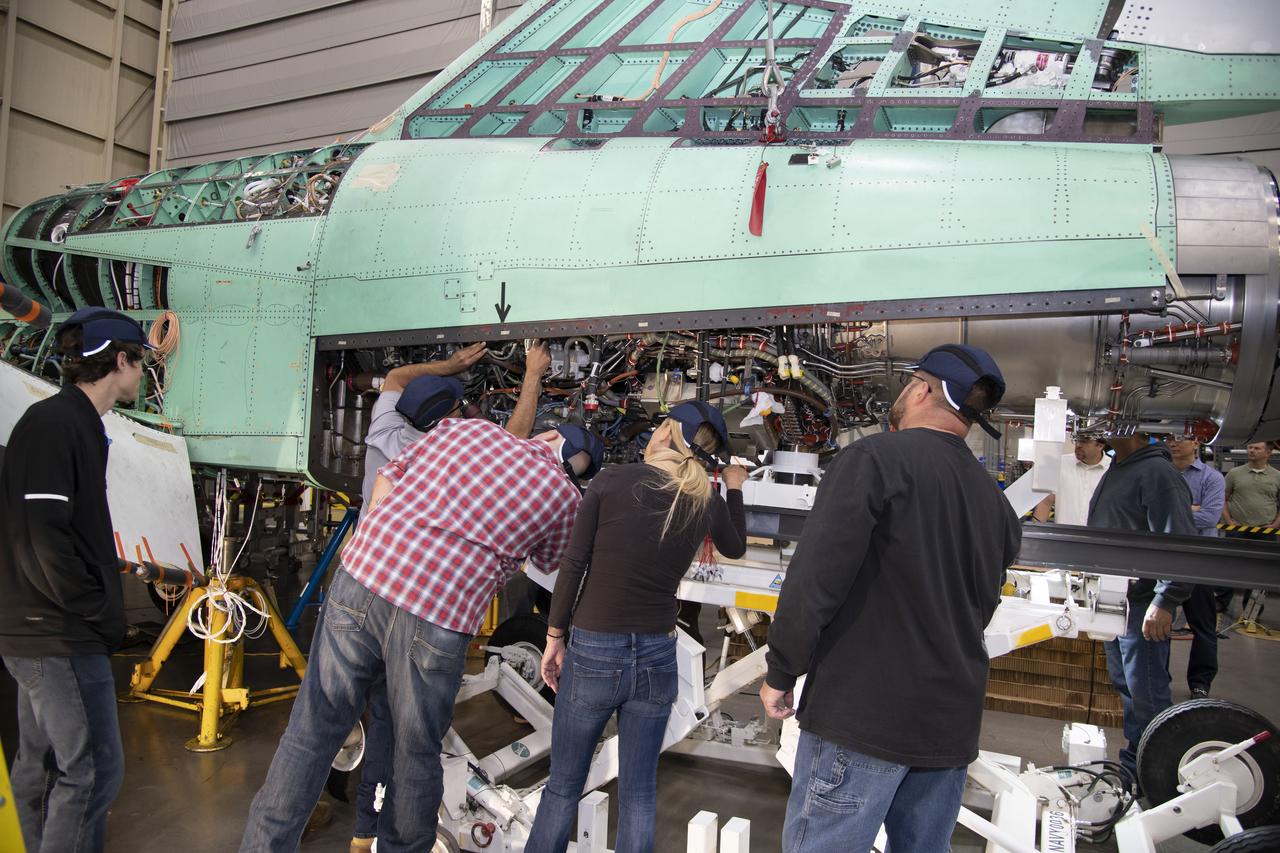

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
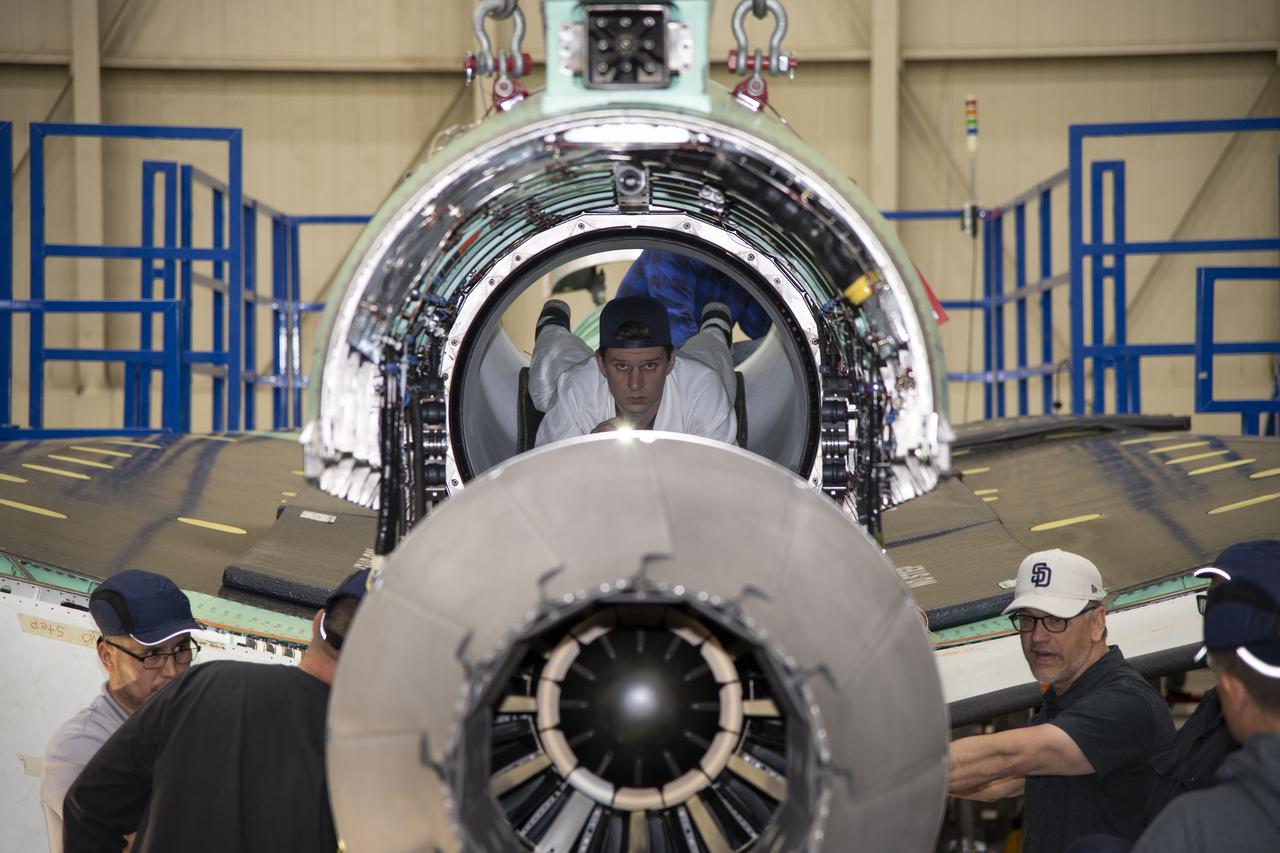

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

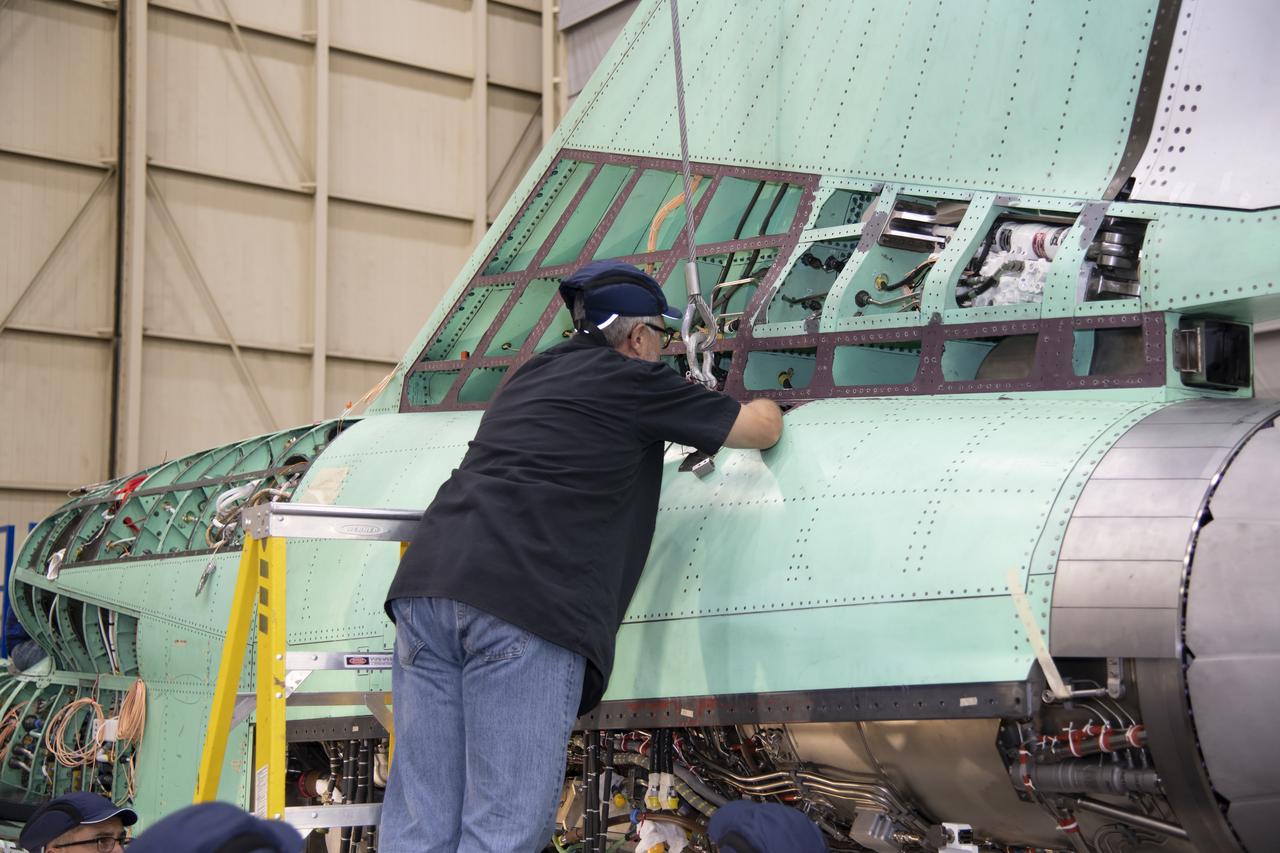
Here is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft (left) prior to the installation of the General Electric F414 engine (center, located under the blue cover). After the engine is installed, the lower empennage (right), the last remaining major aircraft component, will be installed in preparation for integrated system checkouts. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
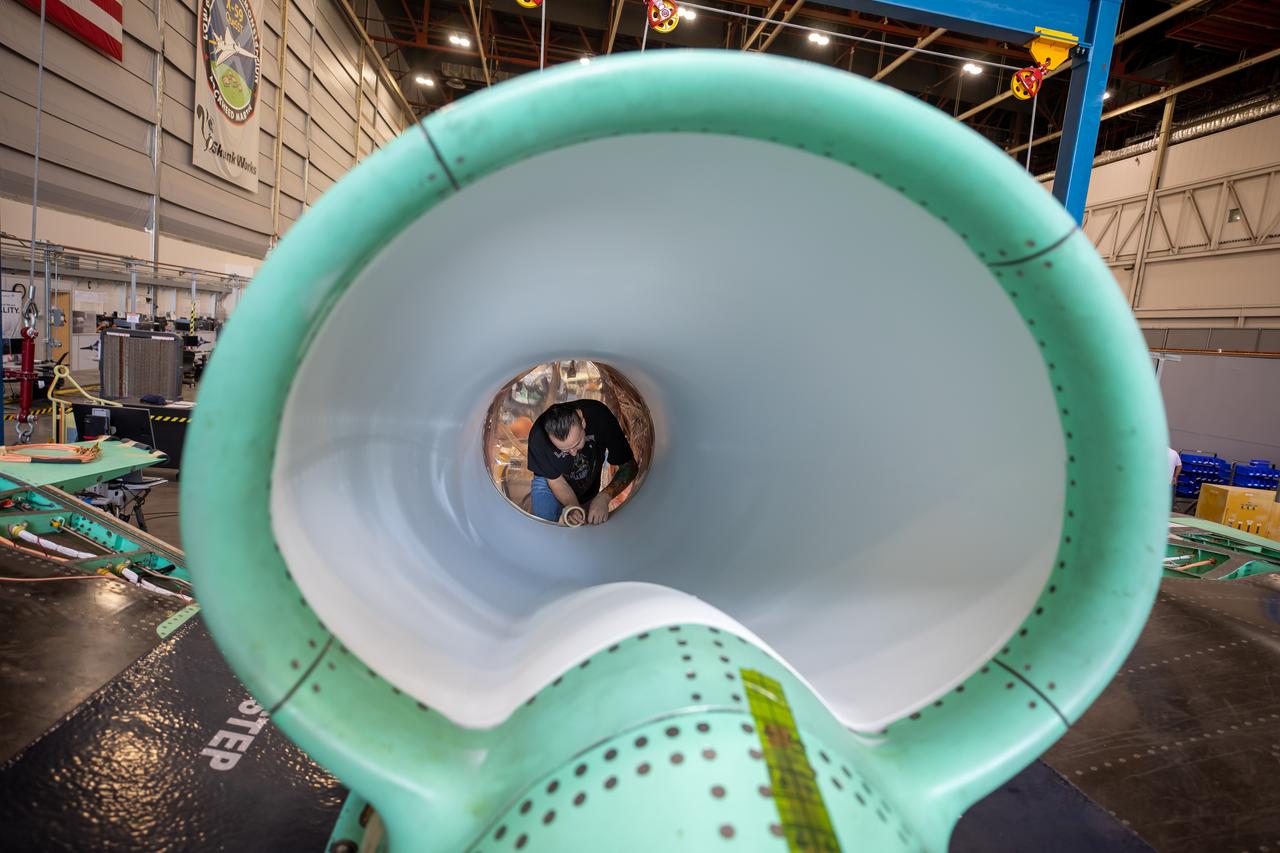

This is an up-close view of the X-59’s engine inlet – fresh after being painted. The 13-foot F414-GE-100 engine will be placed inside the inlet bringing the X-59 aircraft one step closer to completion. Once fully assembled, the X-59 aircraft will begin flight operations, working toward demonstration of the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump, helping to enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
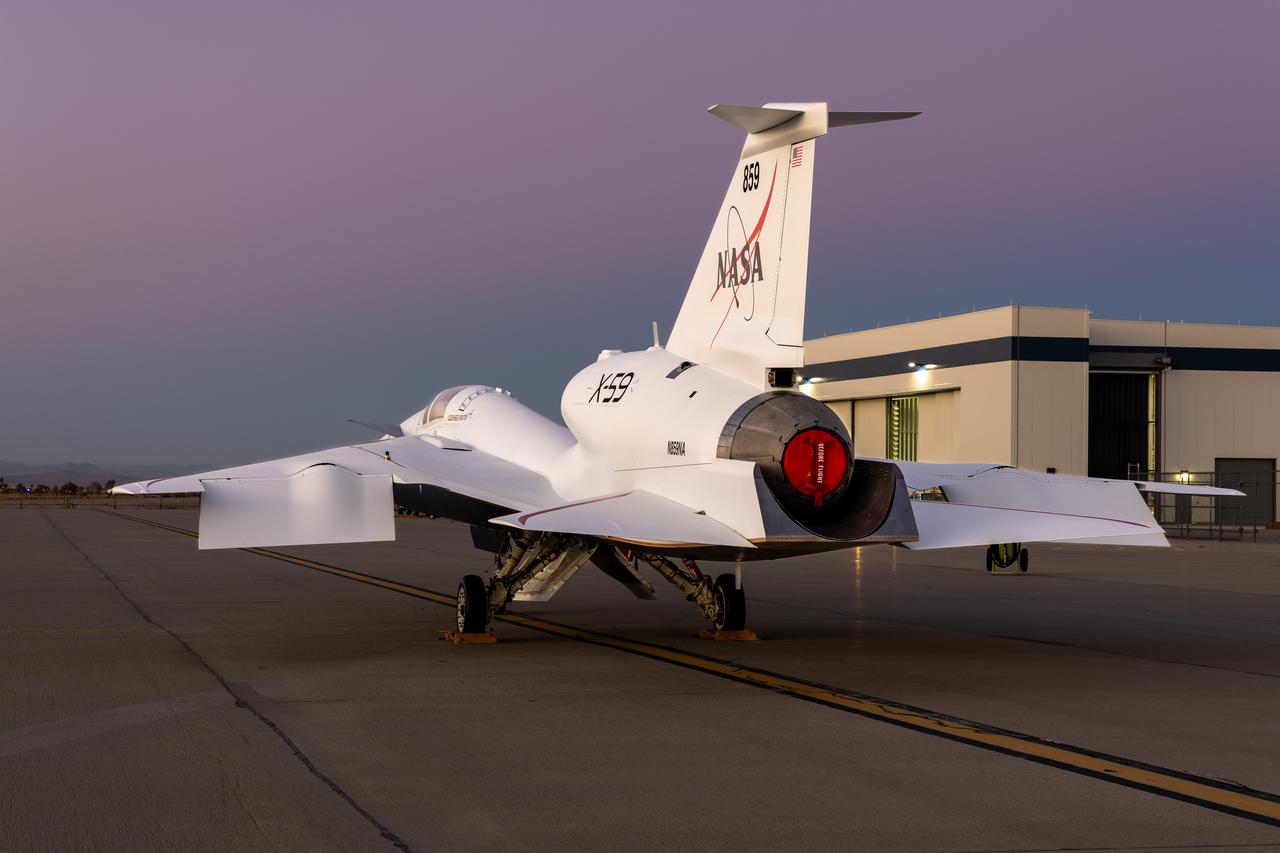

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.
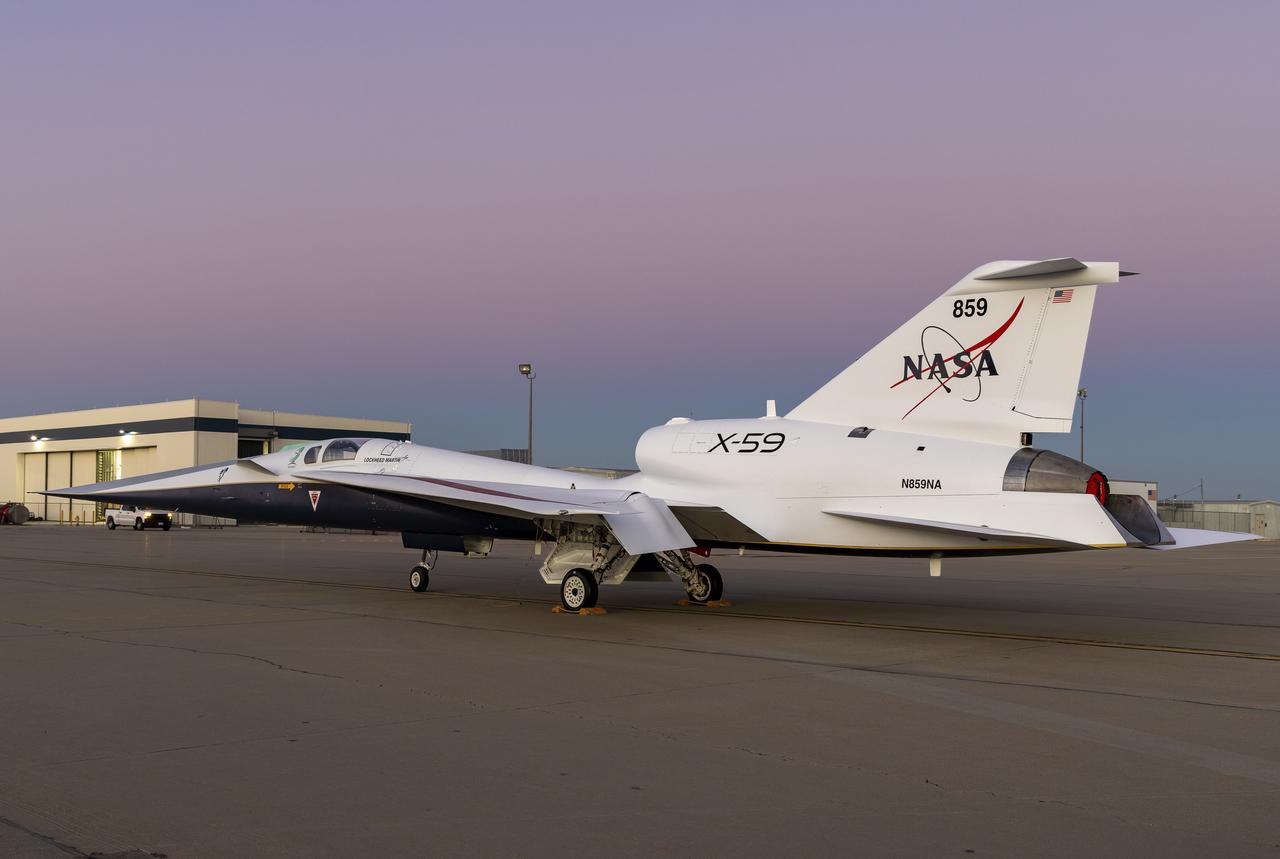

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.
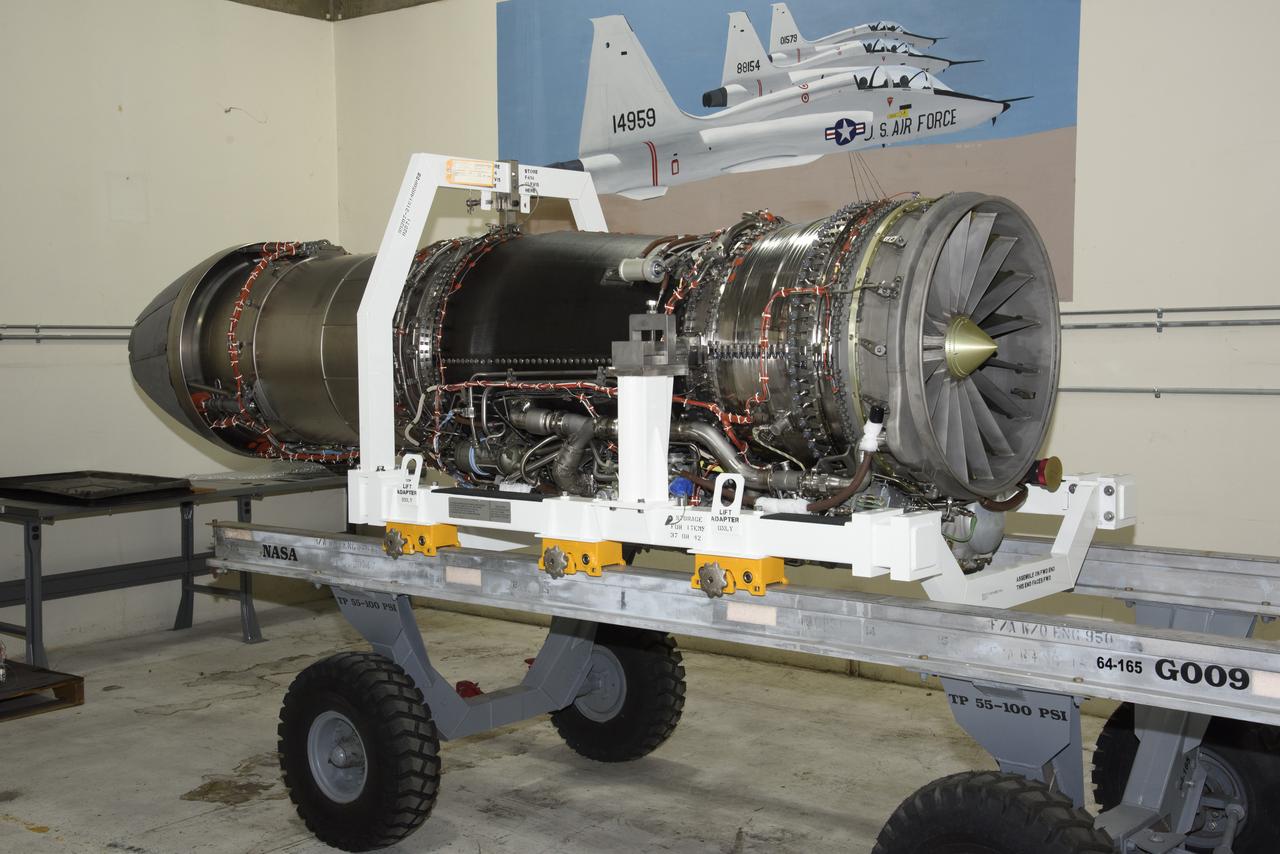

The F414-GE-100 engine, which will power NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane (QueSST) in flight, is unboxed at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The engine, one of two delivered by GE, is approximately 13 feet long, and will power X-59 on missions to gather information about how the public perceives the sounds of quieter supersonic flight.
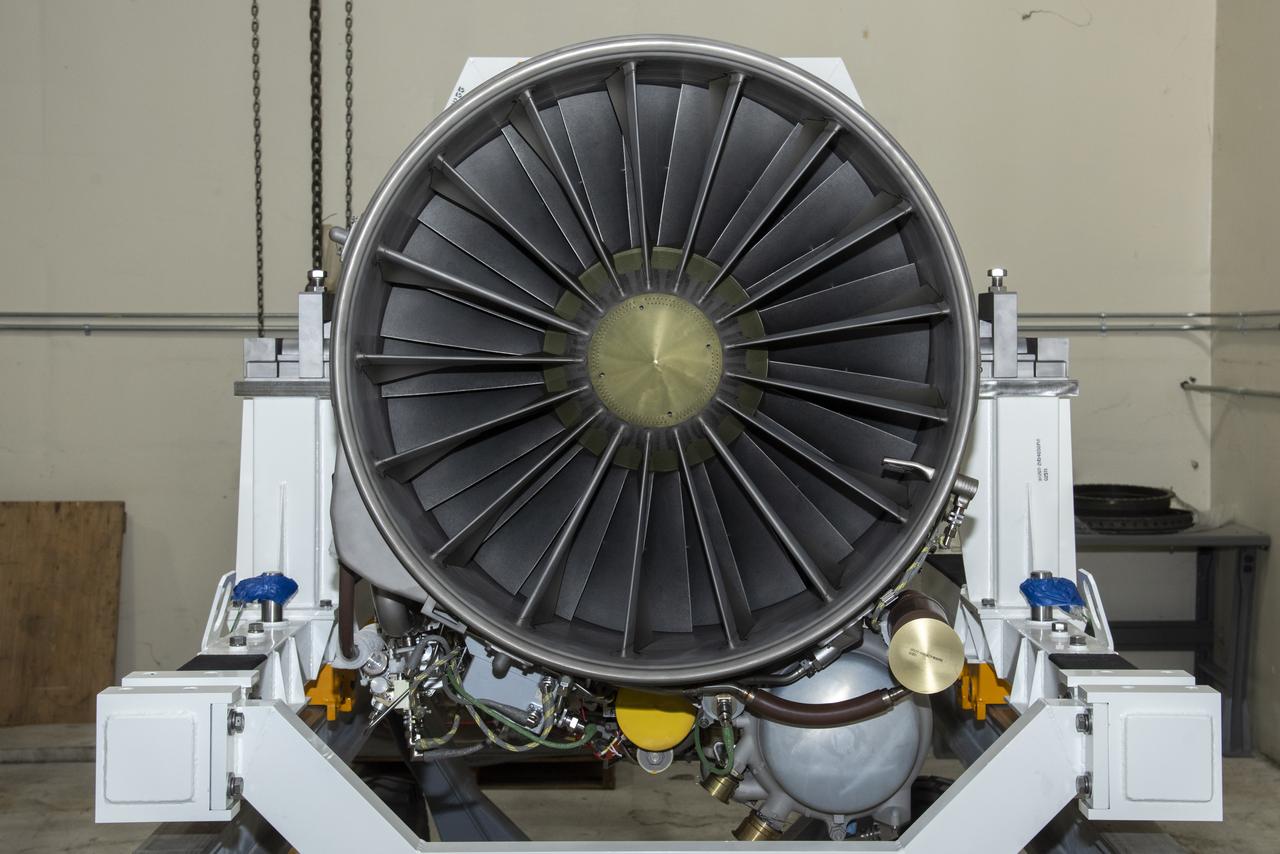

The F414-GE-100 engine, which will power NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane (QueSST) in flight, is unboxed at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The engine, one of two delivered by GE, is approximately 13 feet long, and will power X-59 on missions to gather information about how the public perceives the sounds of quieter supersonic flight.
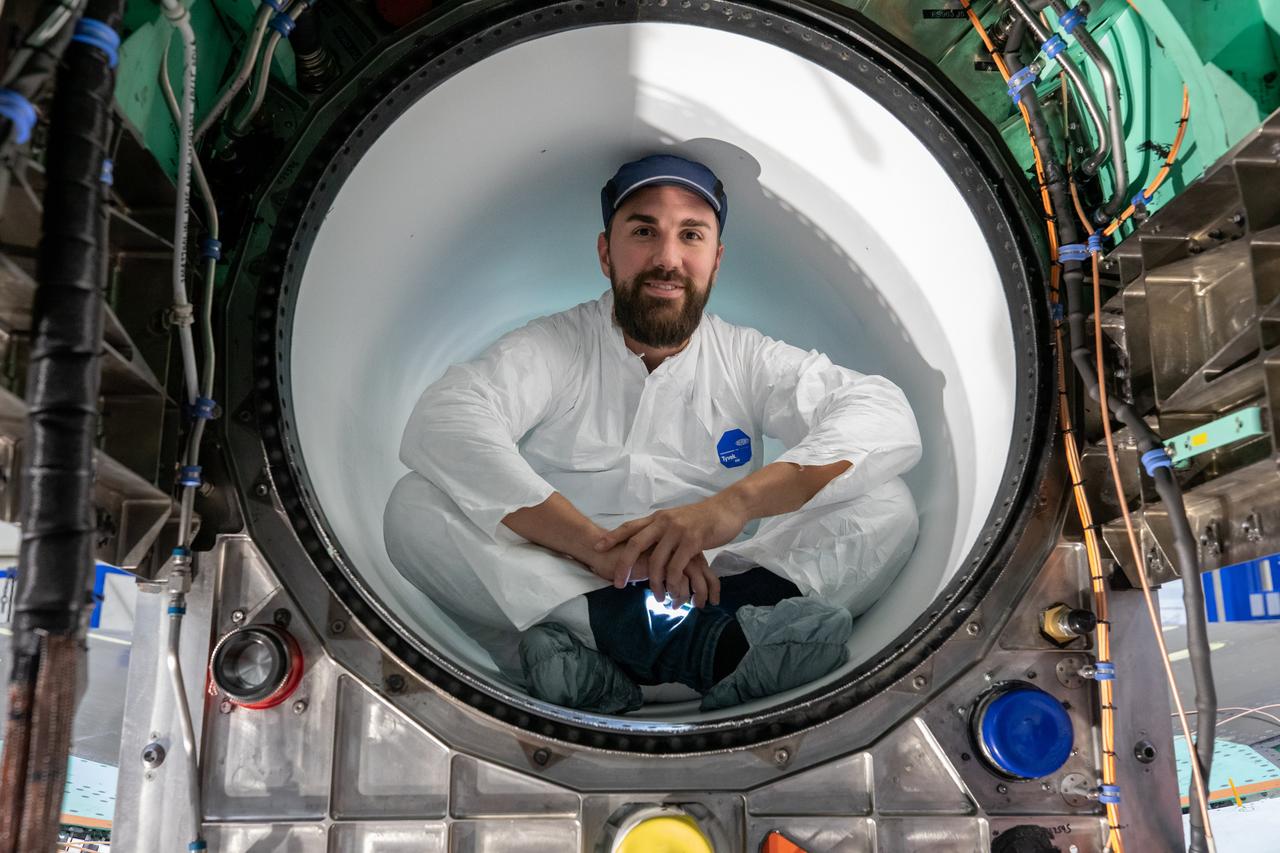

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician takes a break for a photo. Note that the technician is wearing protective clean gear while sitting inside the X-59 engine inlet. Wearing this gear reduces the chance of any foreign objects from damaging the engine inlet.
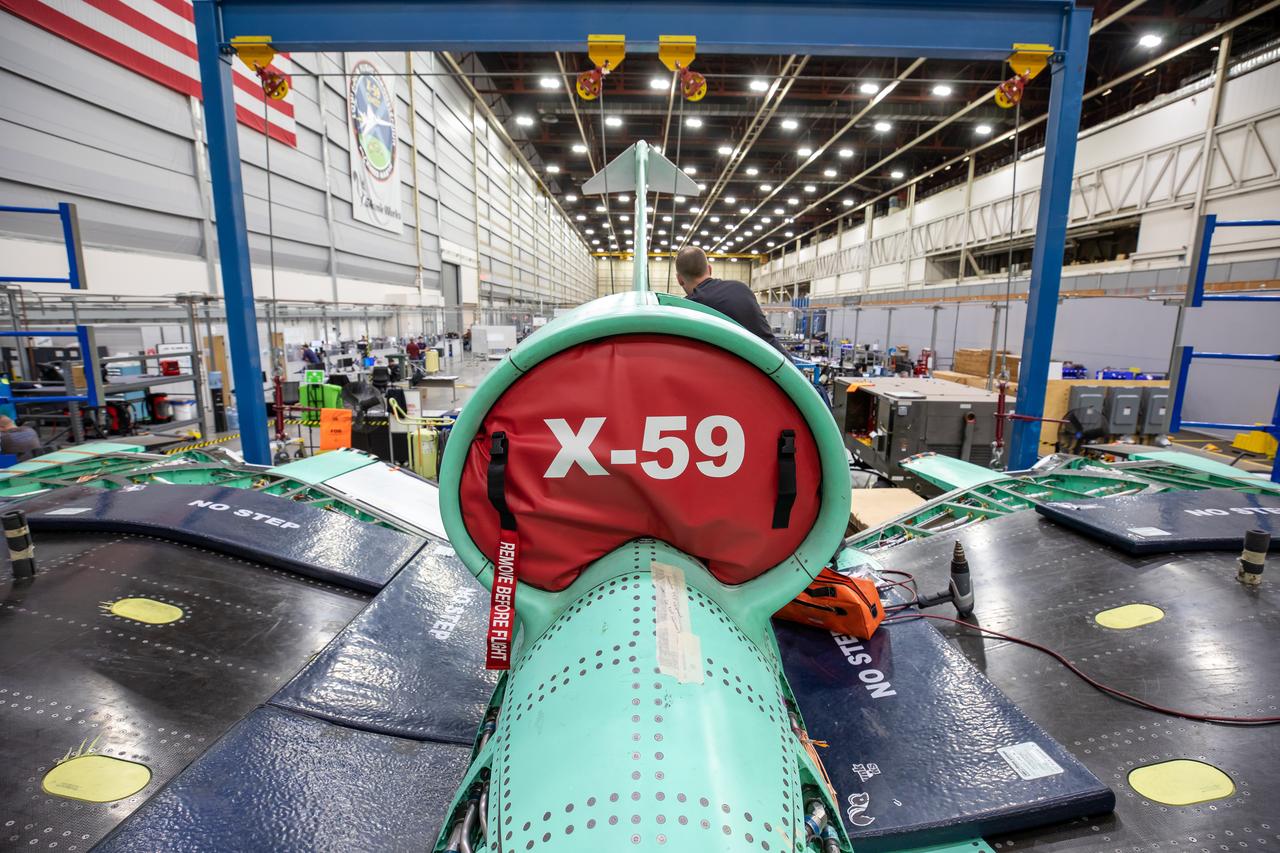

This is an image of the X-59 inlet with a safety covering. The inlet’s purpose is to adjust air speeds before they pass through the aircraft’s engine. The purpose of the covering is to protect the inlet and engine from foreign objects.
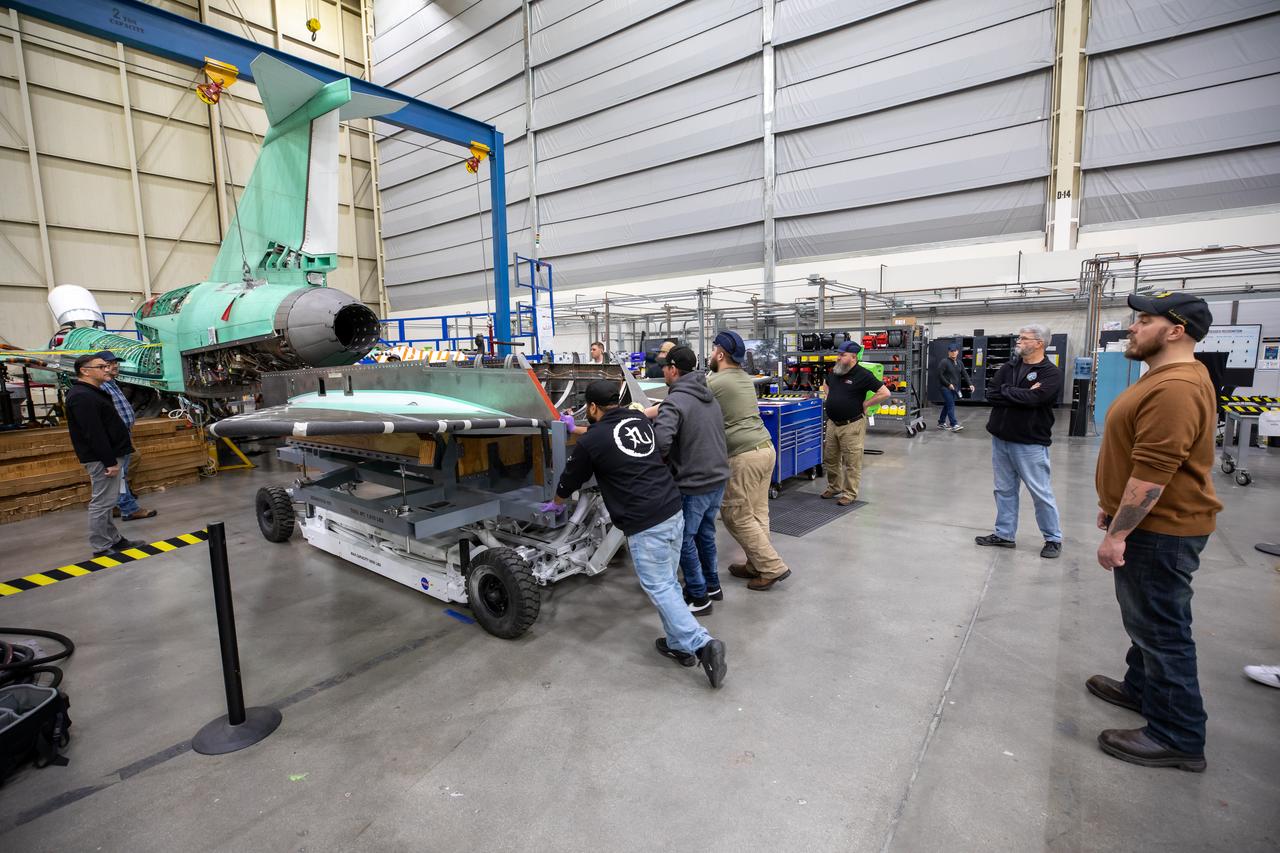

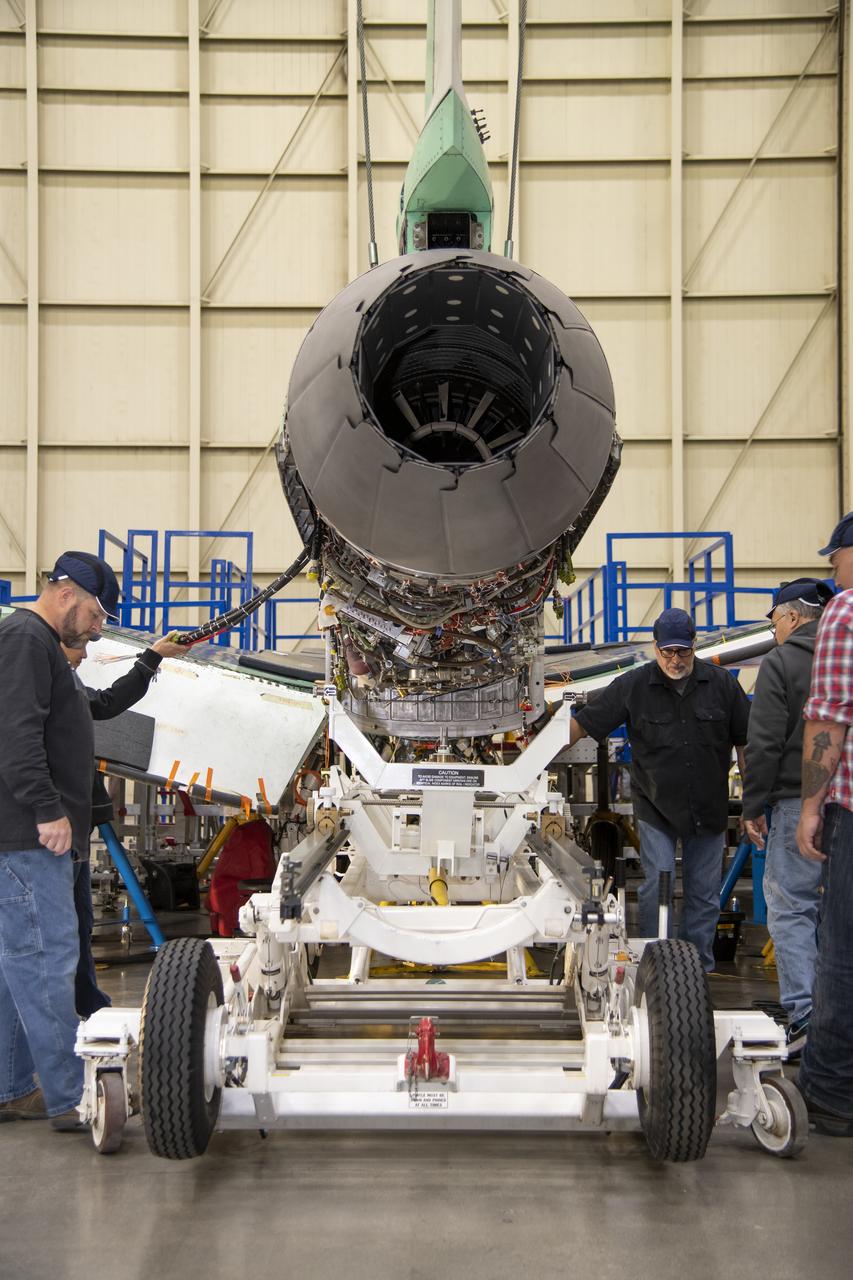
The X-59 team at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, load the lower empennage - the tail section - into place. The surfaces used to control the tilt of the airplane are called stabilators and are connected to the lower empennage. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which could help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
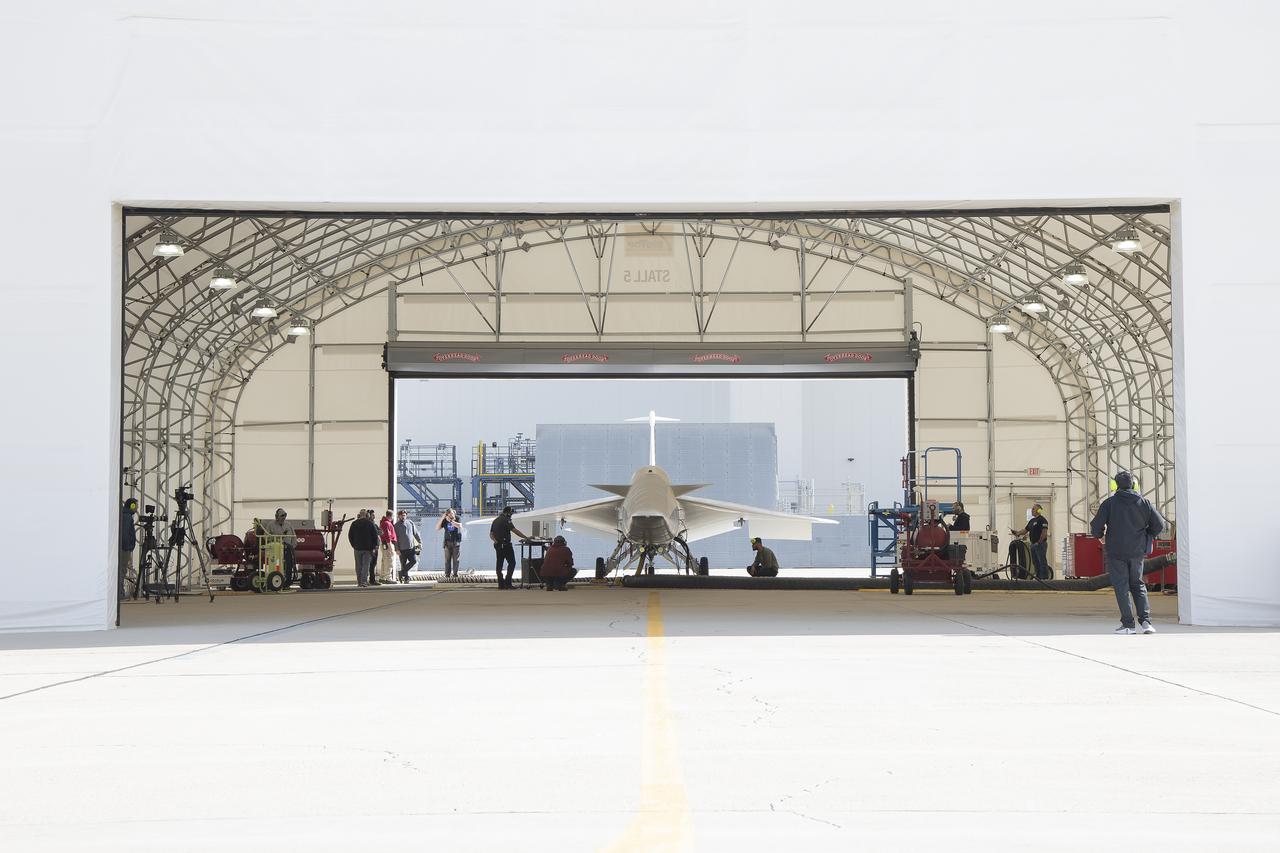

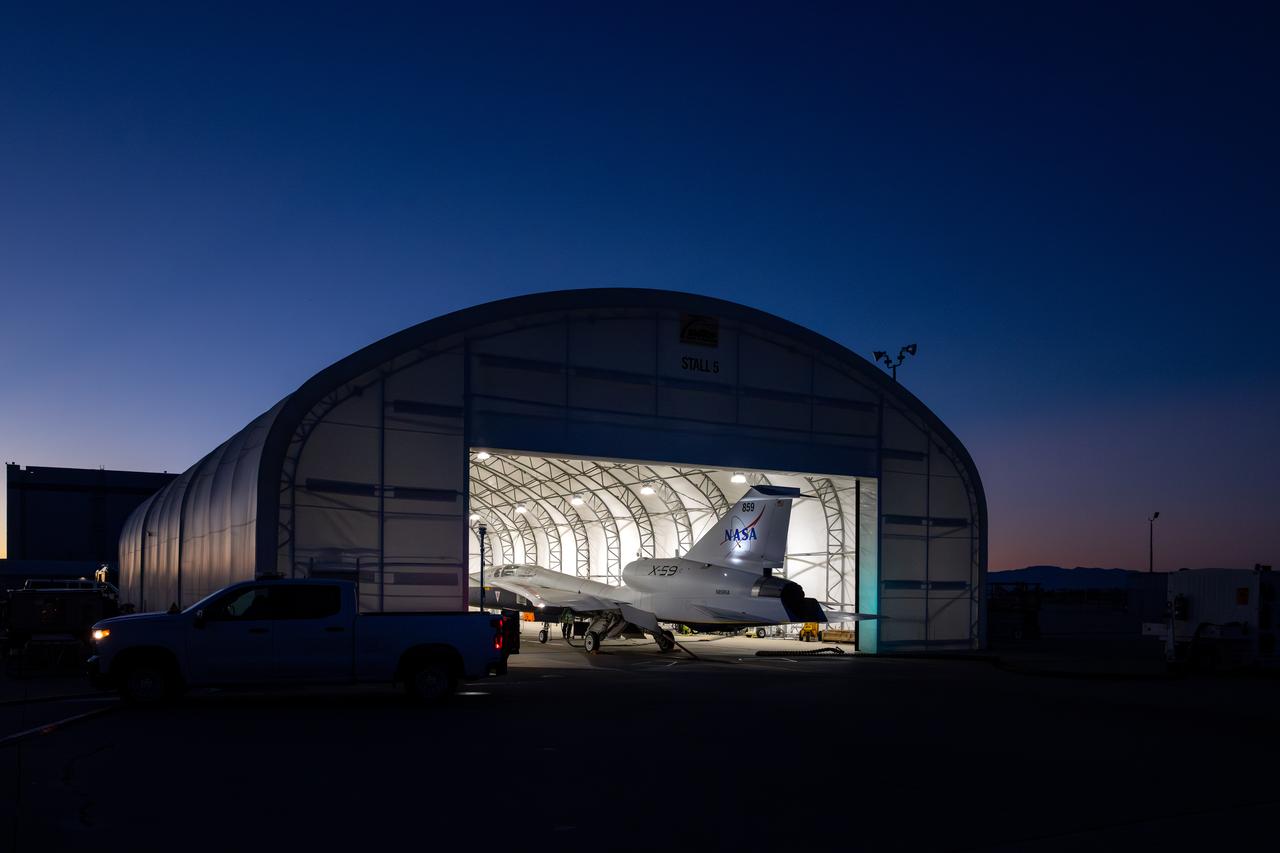
NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in its run stall at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, prior to its first engine run. Engine runs are part of a series of integrated ground tests needed to ensure safe flight and successful achievement of mission goals. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land by making sonic booms quieter.
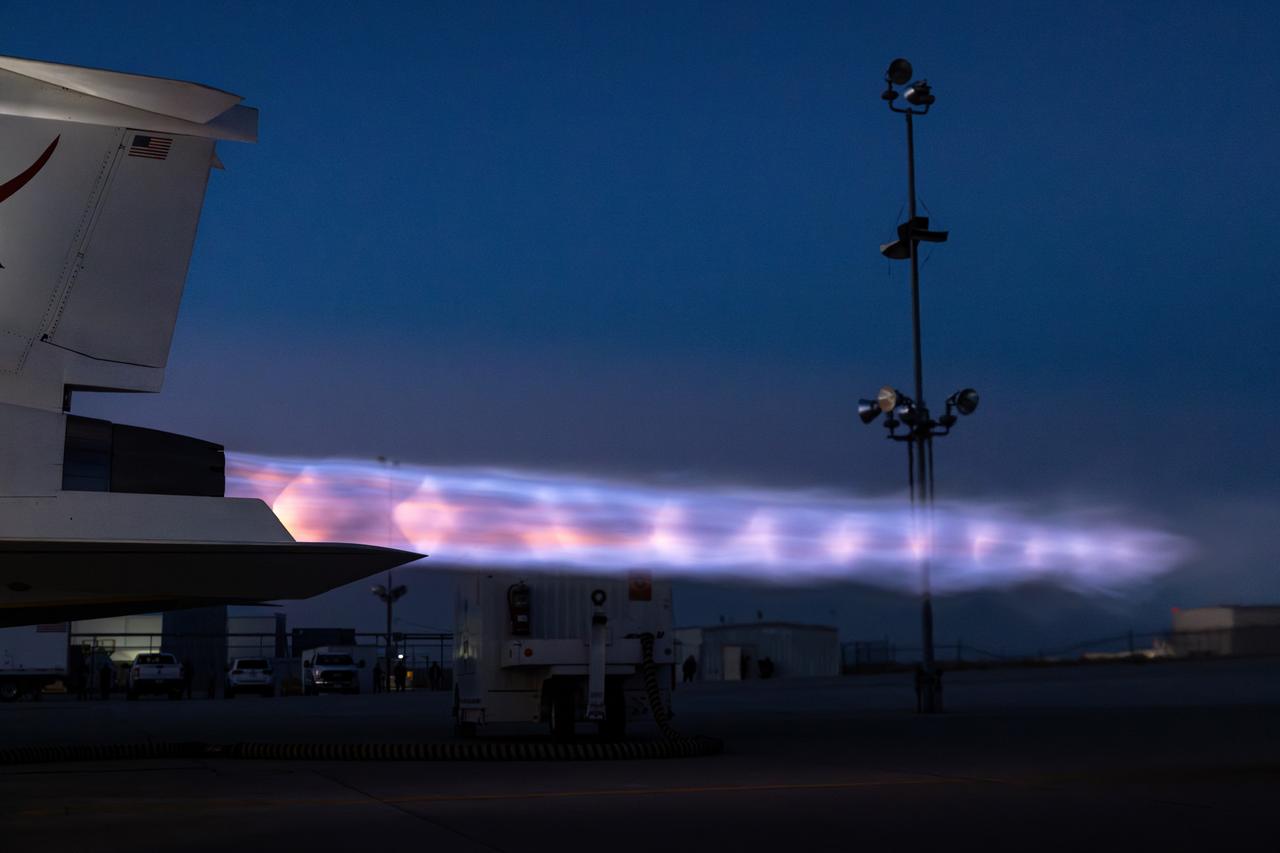

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.

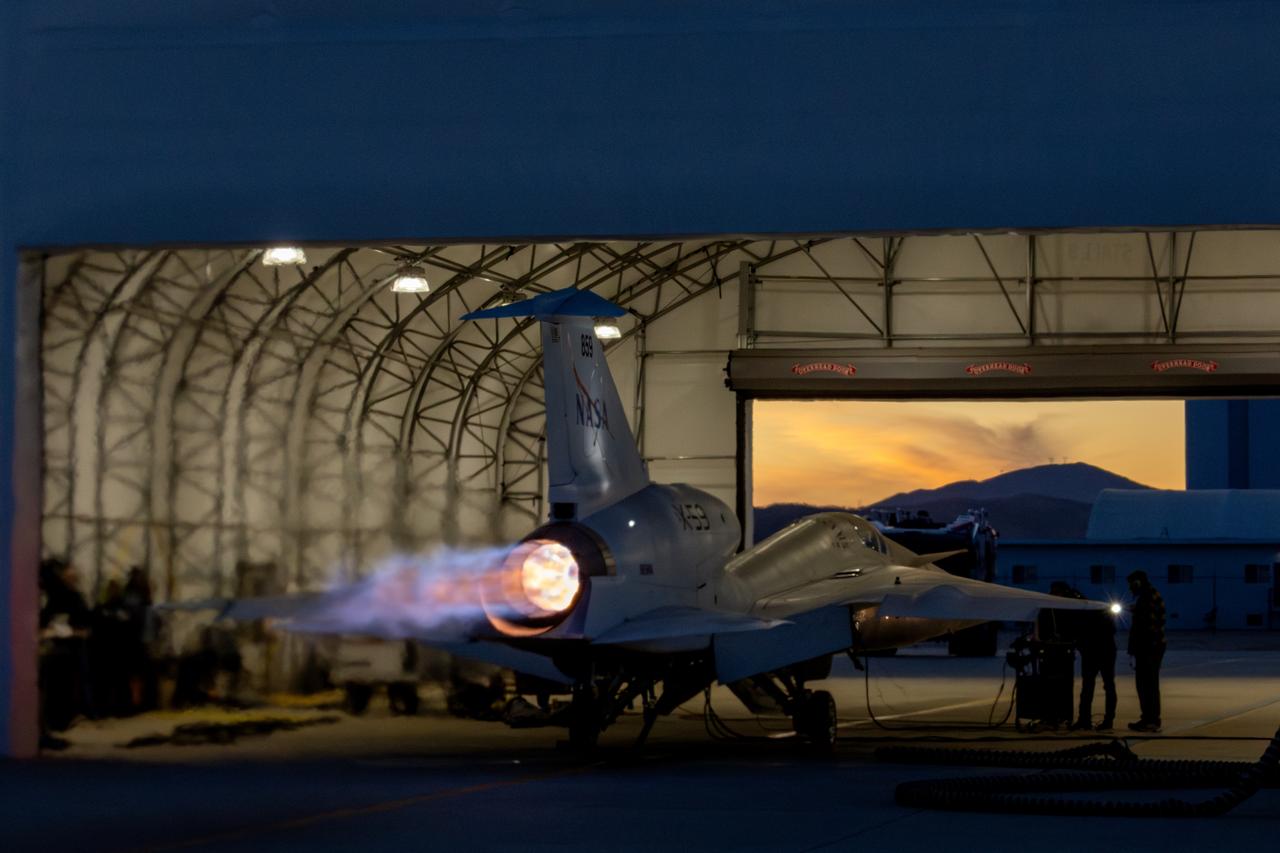
NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall following maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the mission, designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
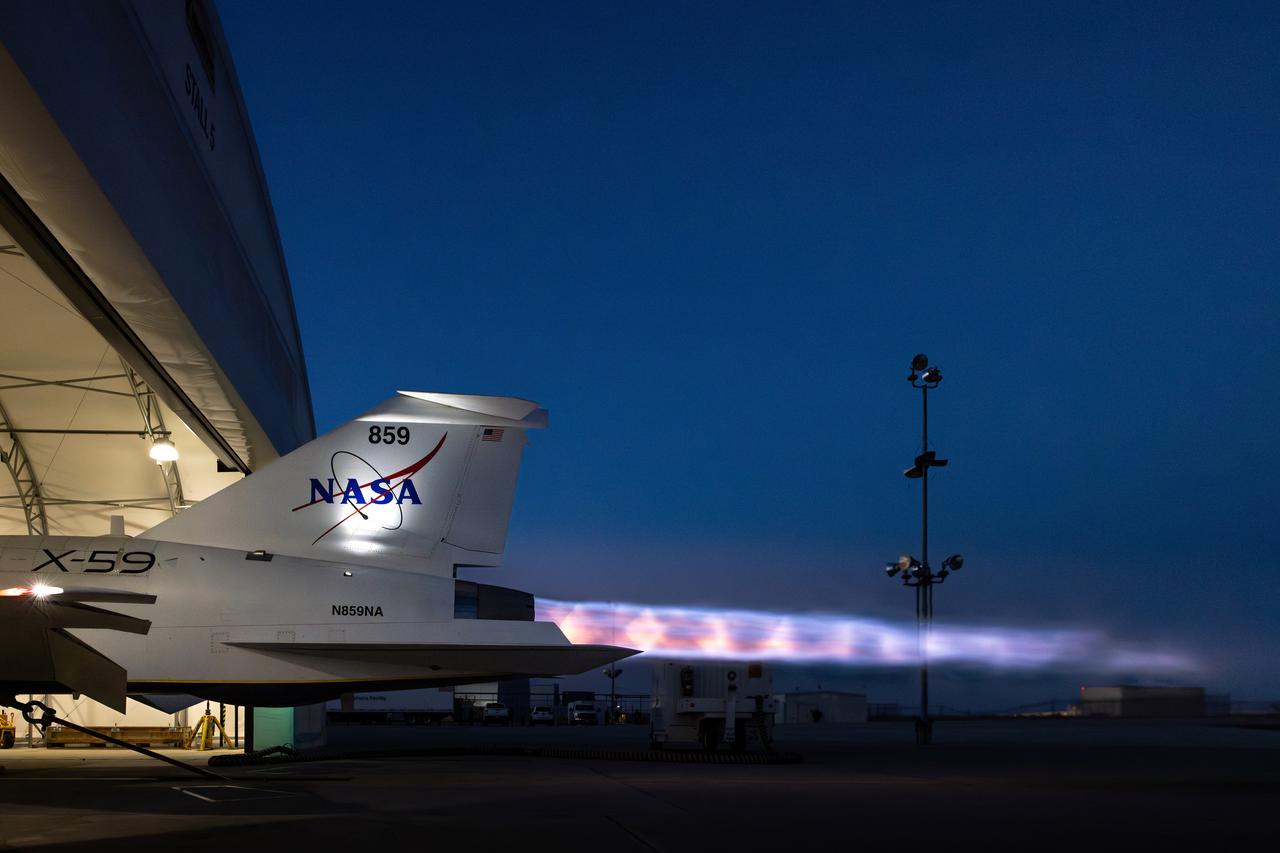

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
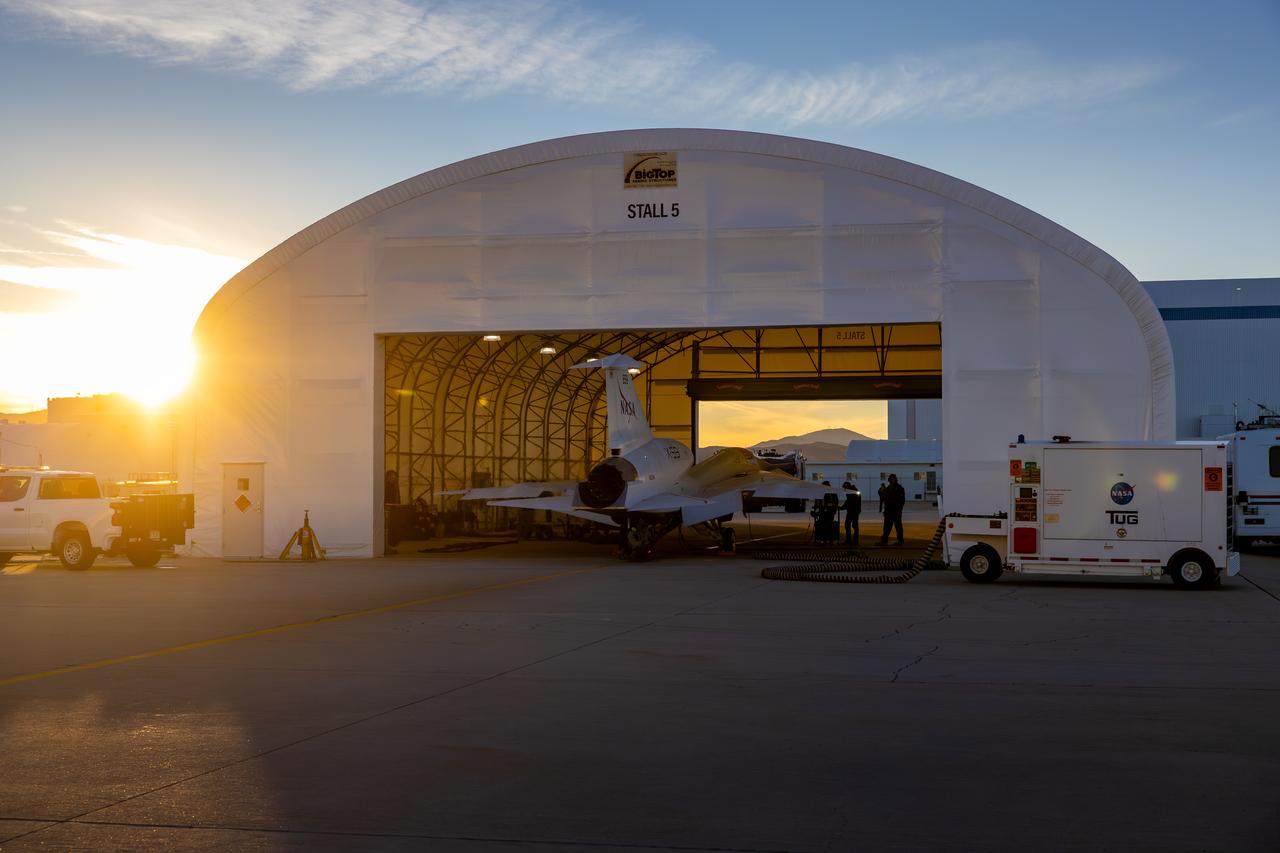

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall in preparation for maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Teams conduct final checks on the aircraft before its high-thrust engine runs. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.
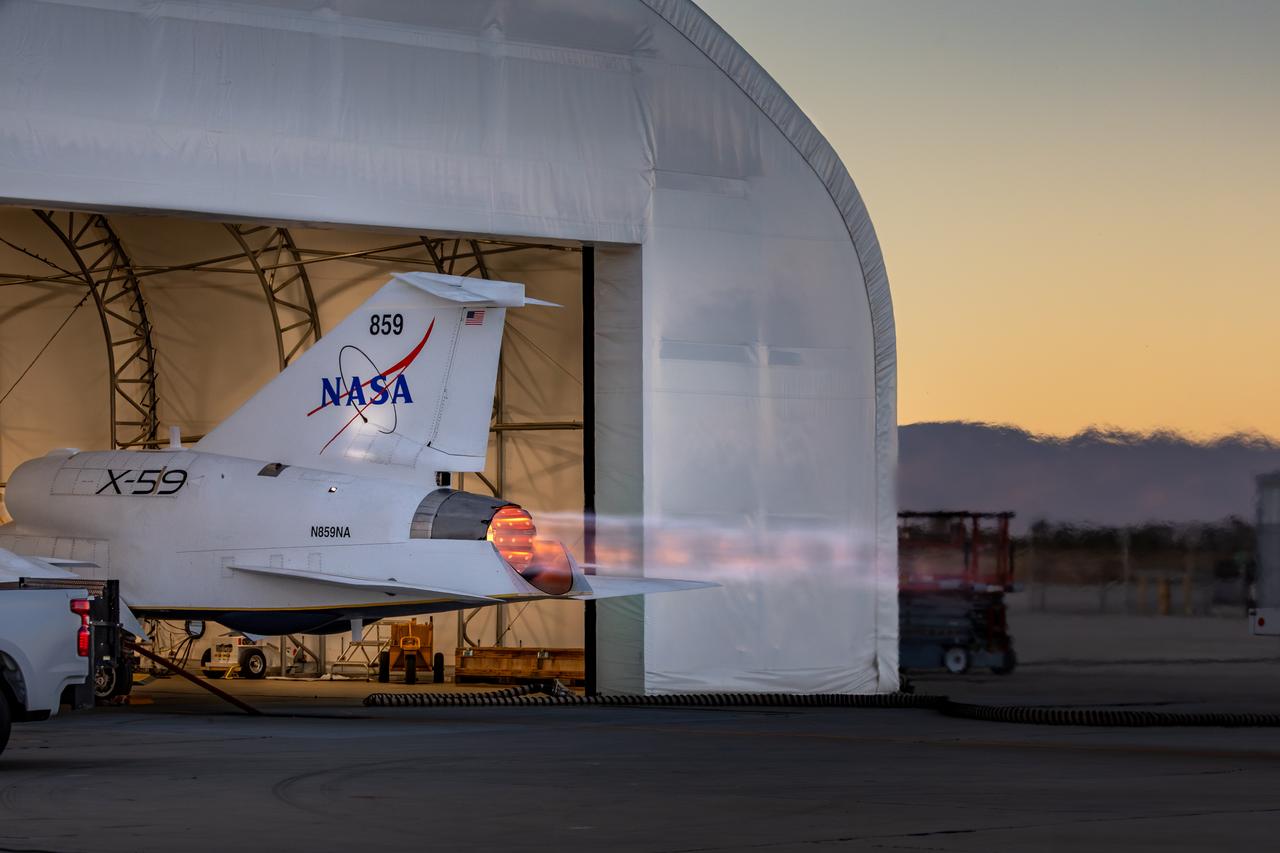

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
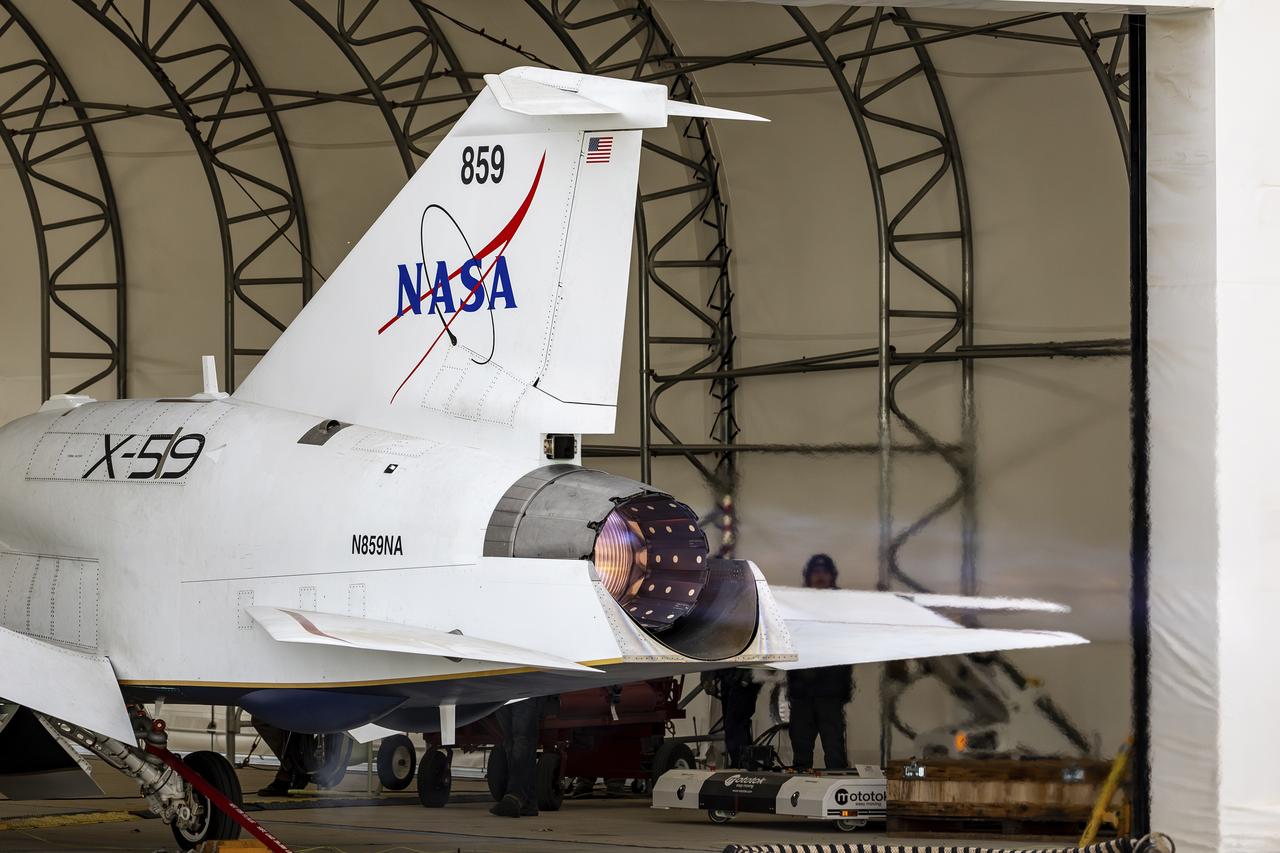

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft completed its first maximum afterburner test at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. This full-power test, during which the engine generates additional thrust, validates the additional power needed for meeting the testing conditions of the aircraft. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to overcome a major barrier to supersonic flight over land by reducing the noise of sonic booms.
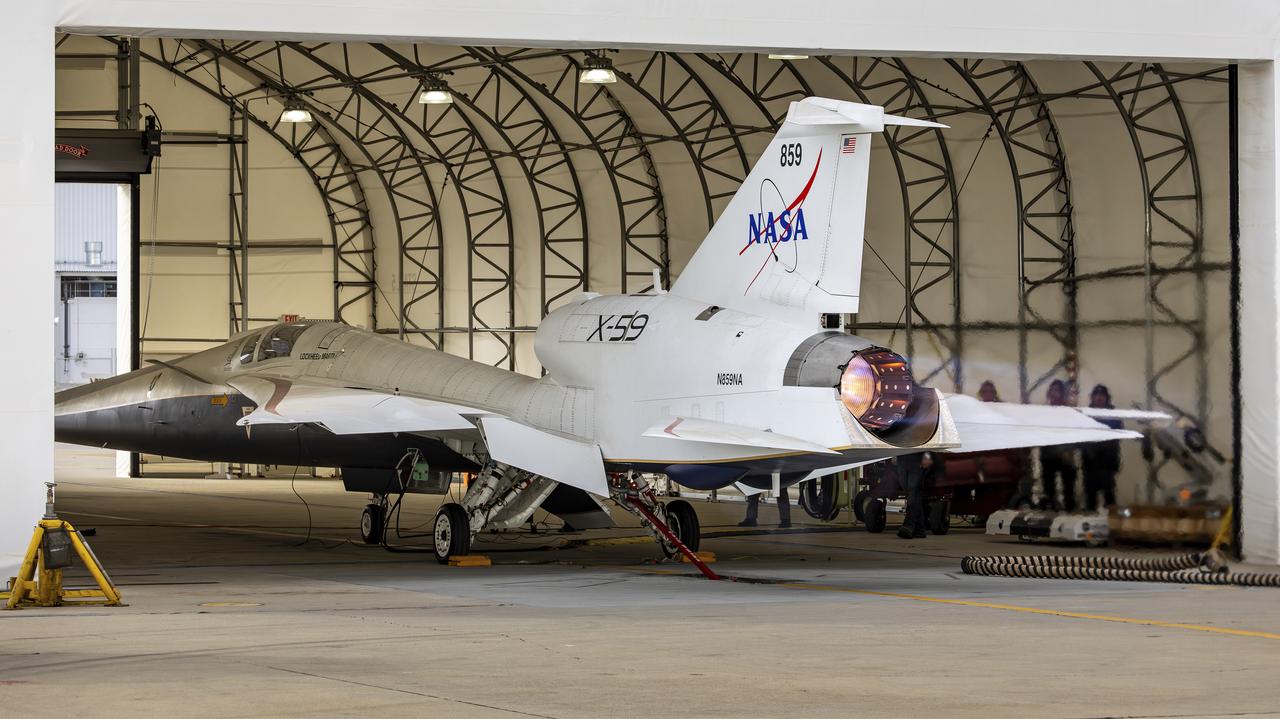

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft completed its first maximum afterburner test at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. This full-power test, during which the engine generates additional thrust, validates the additional power needed for meeting the testing conditions of the aircraft. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to overcome a major barrier to supersonic flight over land by reducing the noise of sonic booms.
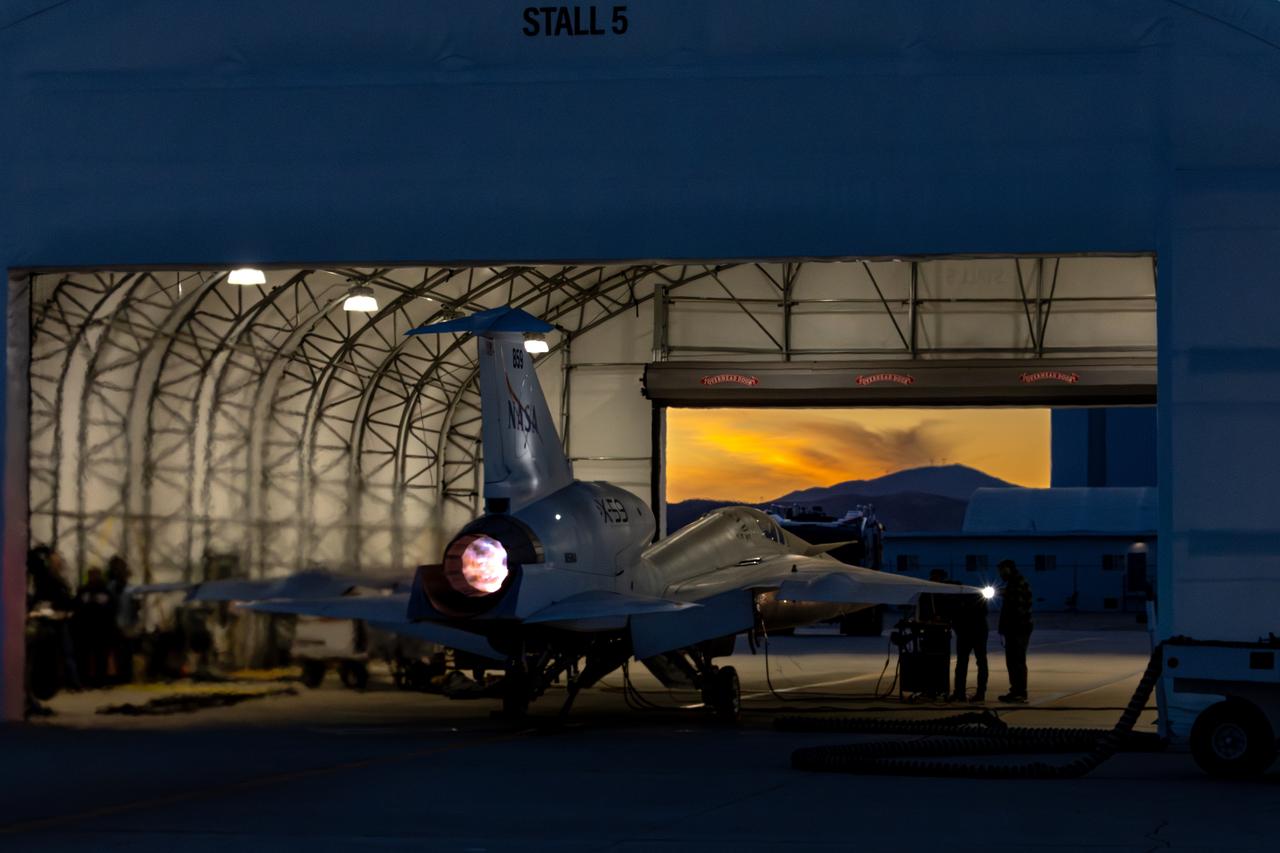

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
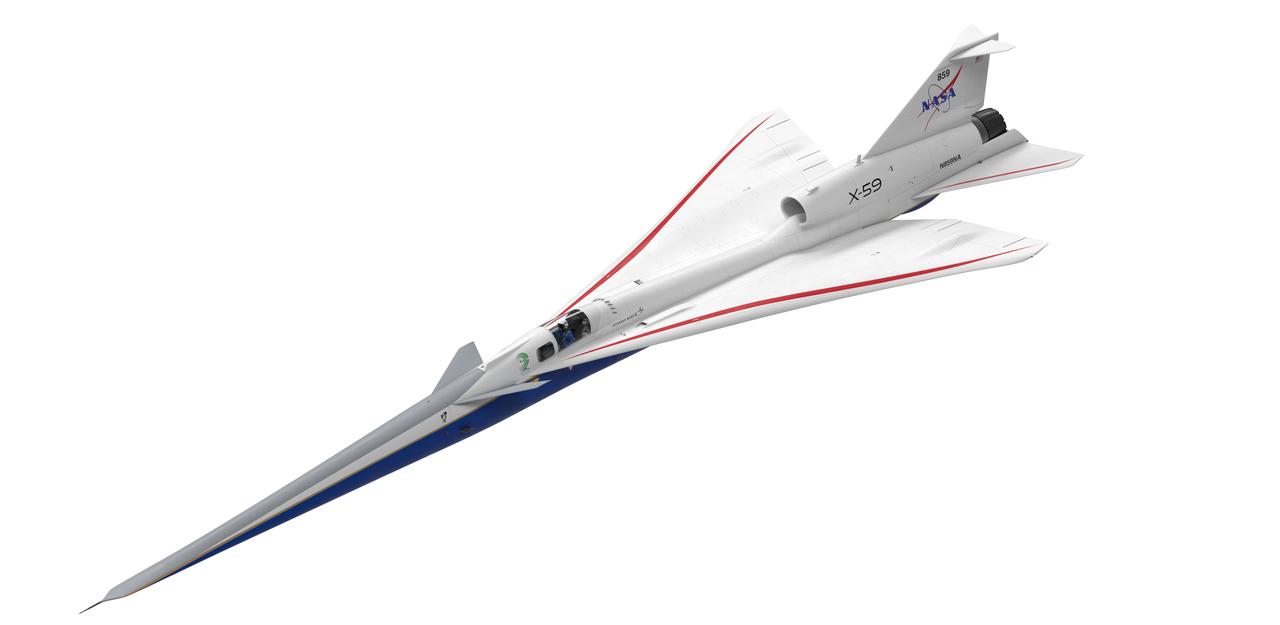

Artist concept of the X-59 three forths view top
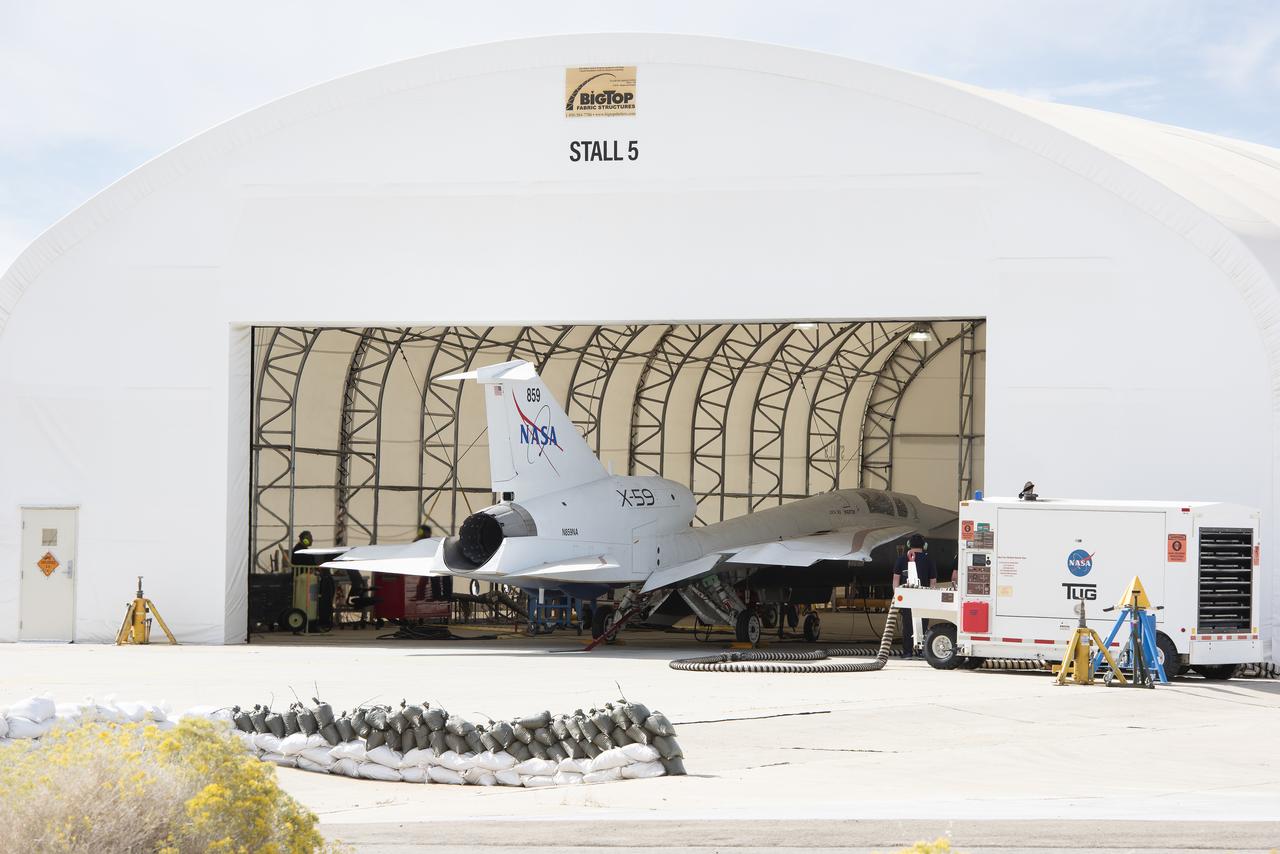

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in its run stall at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, firing up its engine for the first time. These engine-run tests start at low power and allow the X-59 team to verify the aircraft’s systems are working together while powered by its own engine. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land by making sonic booms quieter.
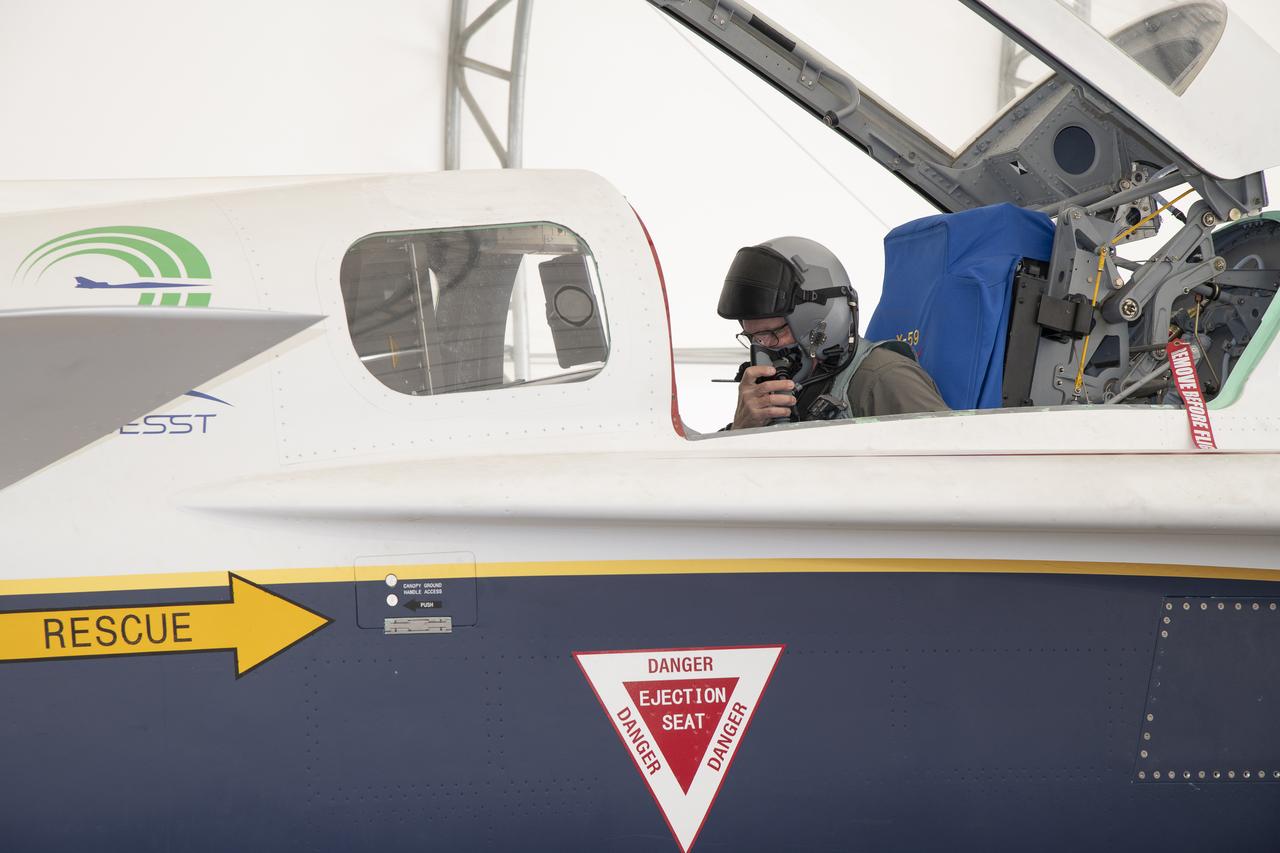

Lockheed Martin test pilot Dan “Dog” Canin sits in the cockpit of NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft in a run stall at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California prior to its first engine run. These engine-run tests featured the X-59 powered by its own engine, whereas in previous tests, the aircraft depended on external sources for power. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land by making sonic booms quieter.
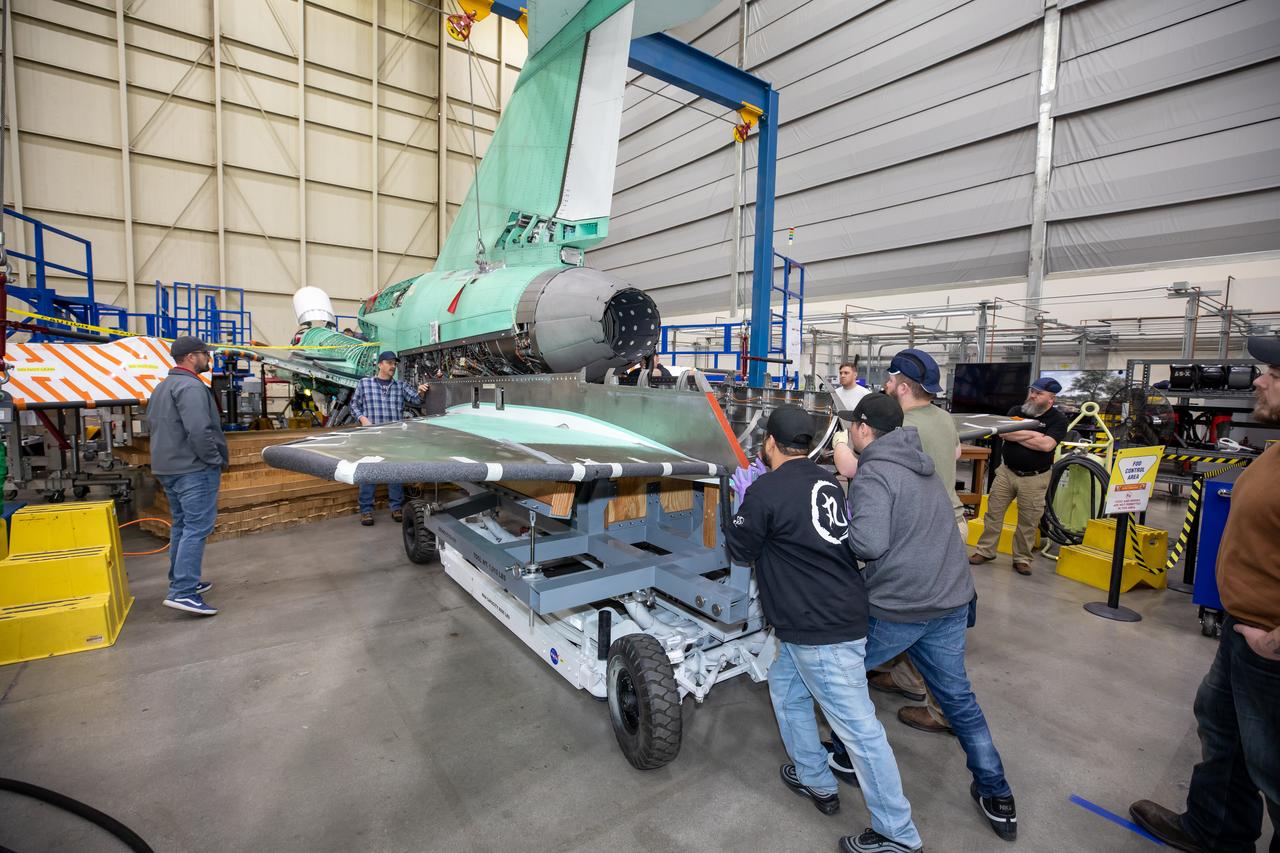

The X-59 team at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, load the lower empennage - the tail section - into place. The surfaces used to control the tilt of the airplane are called stabilators and are connected to the lower empennage. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which could help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
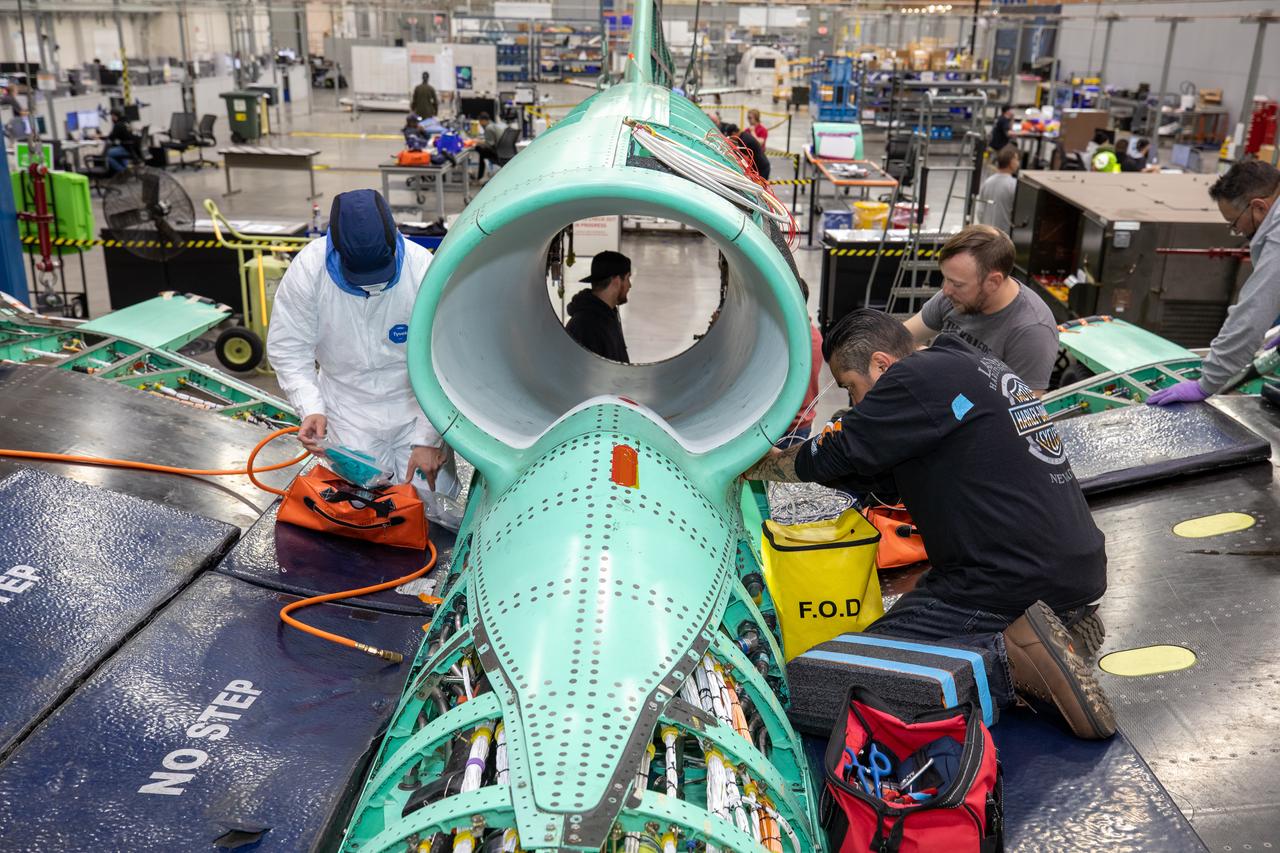

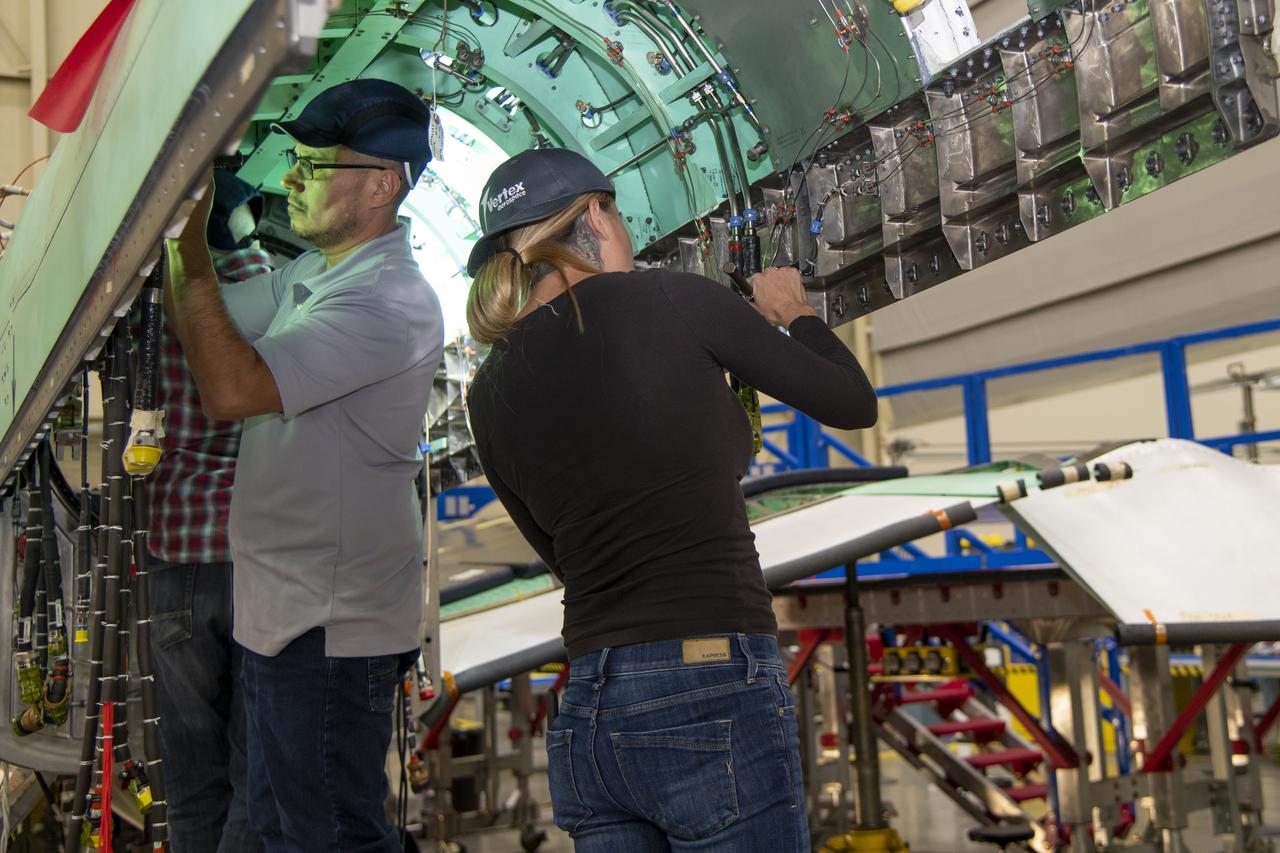
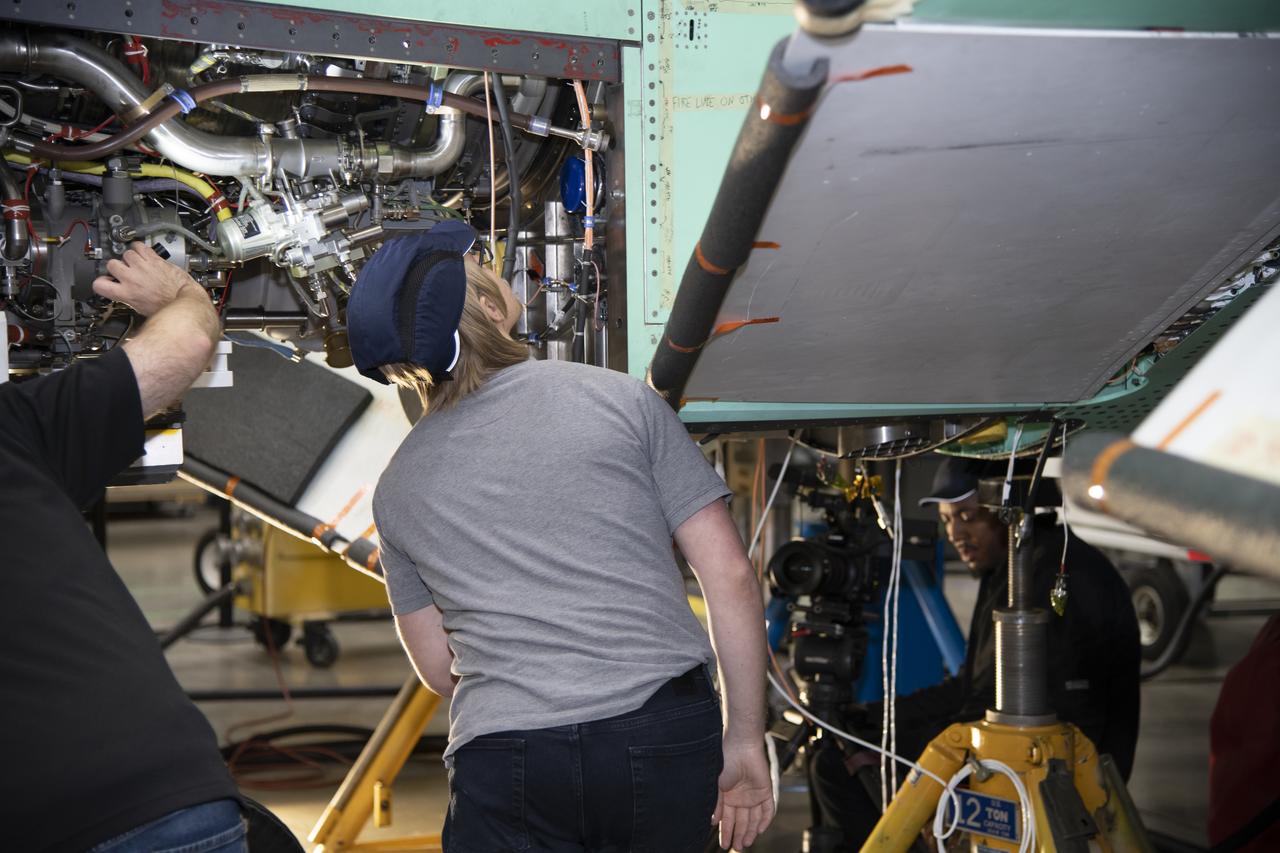
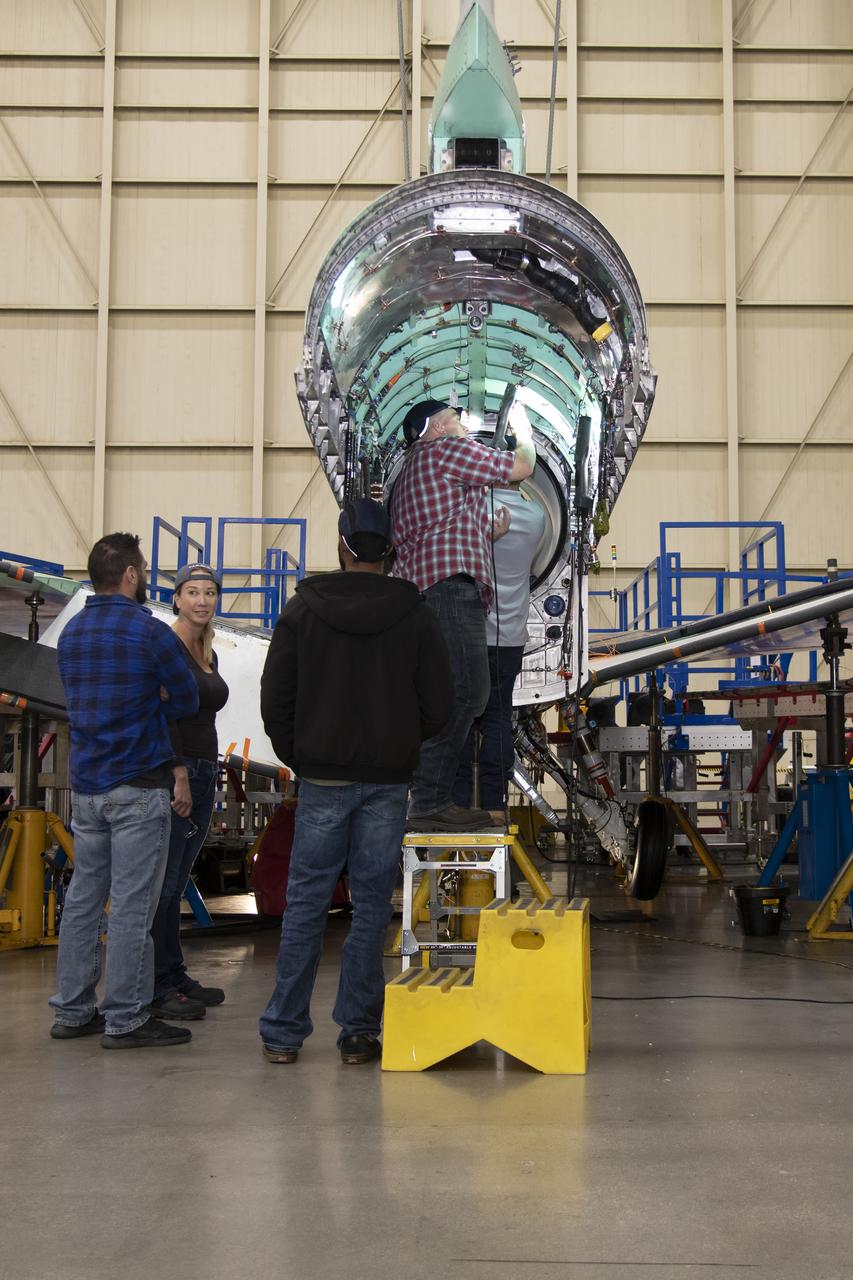
The X-59 team working on the aircraft’s wiring around the engine inlet prior to the engine being installed. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
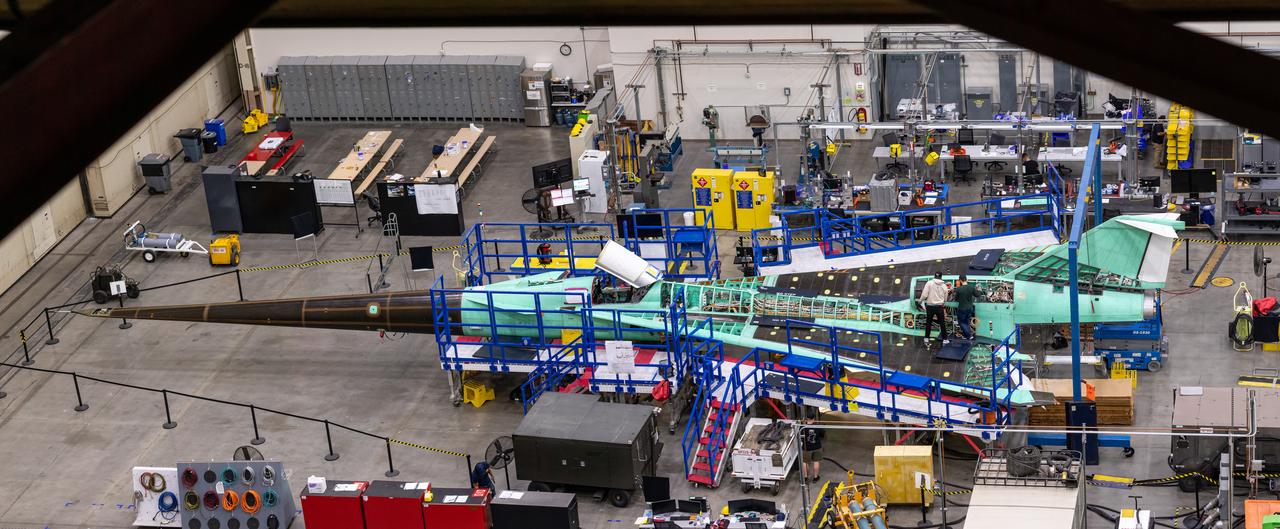

This is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The nose was installed, and the plane awaits engine installation. Technicians continue to wire the aircraft as the team preforms several system checkouts to ensure the safety of the aircraft. The X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
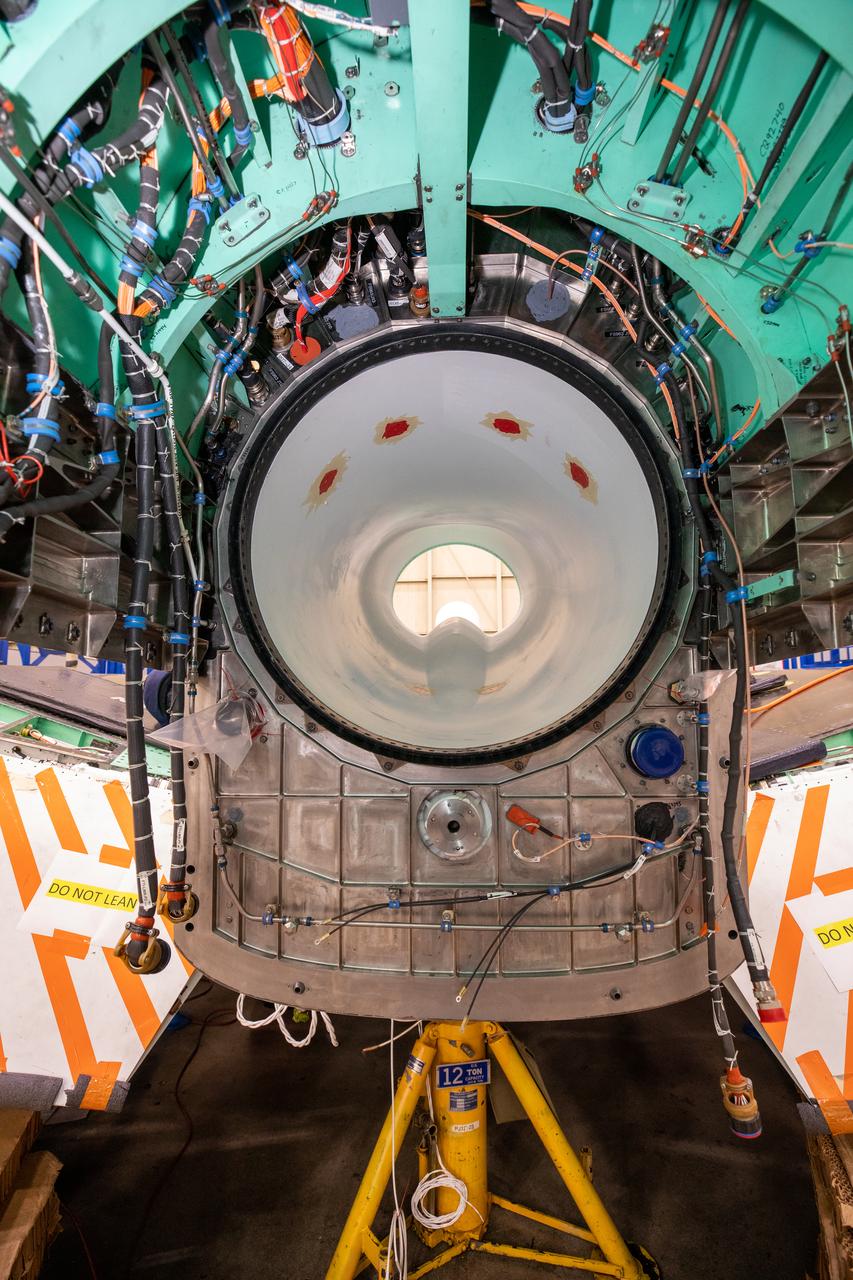

This image shows the X-59’s engine inlet from the aft view, which is the rear of the airplane, looking forward. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land again.