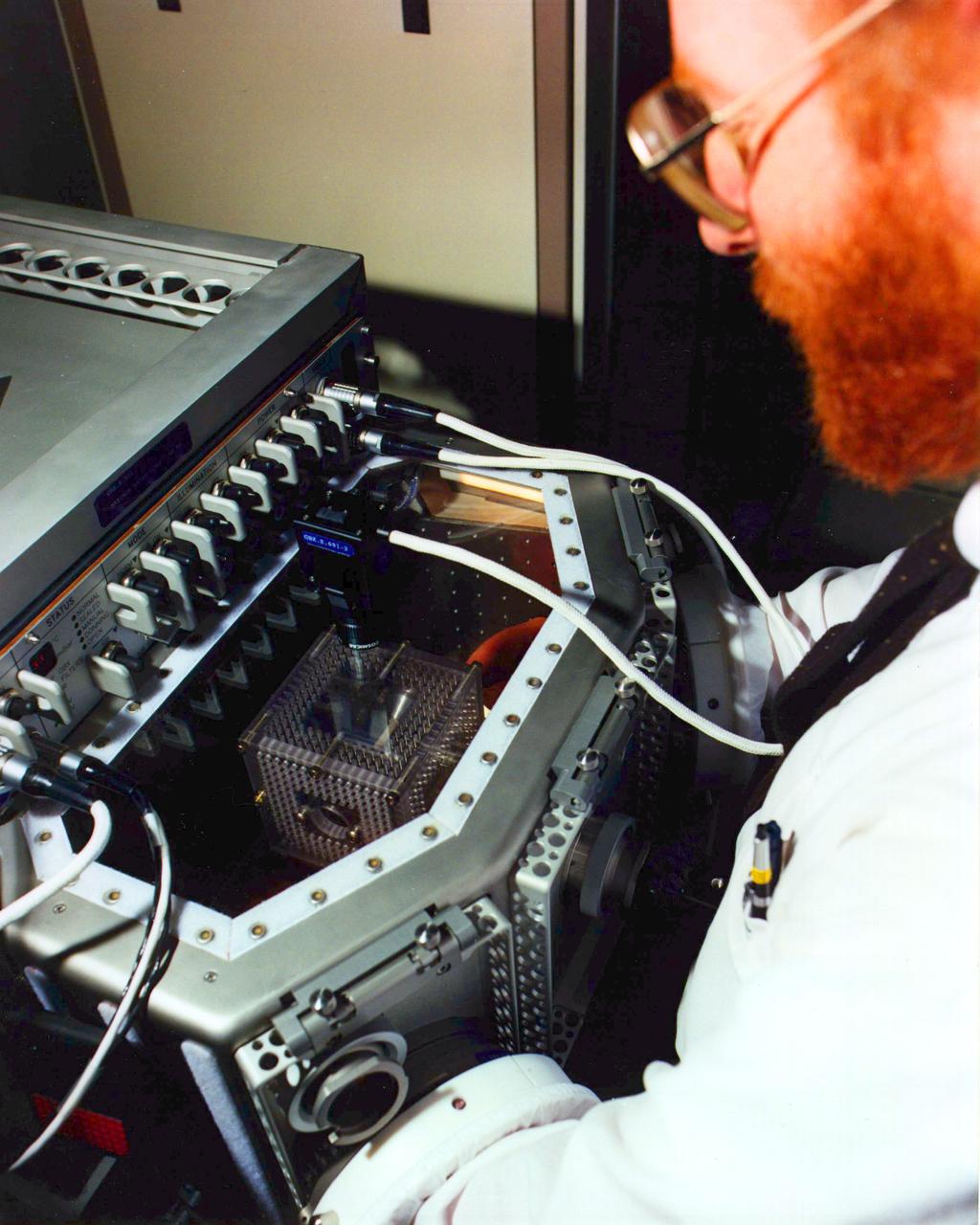

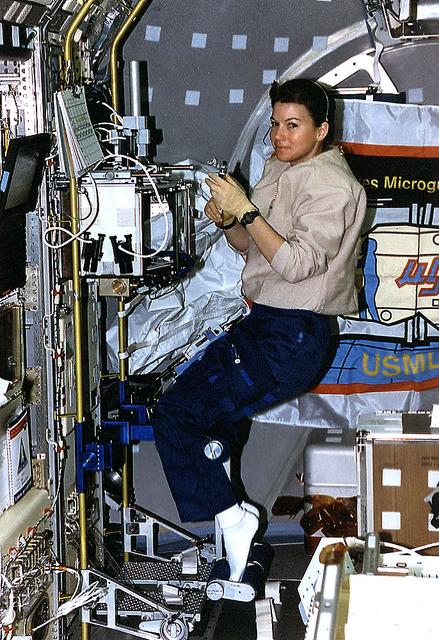
USML-1, Howard Ross working with the Glovebox Module
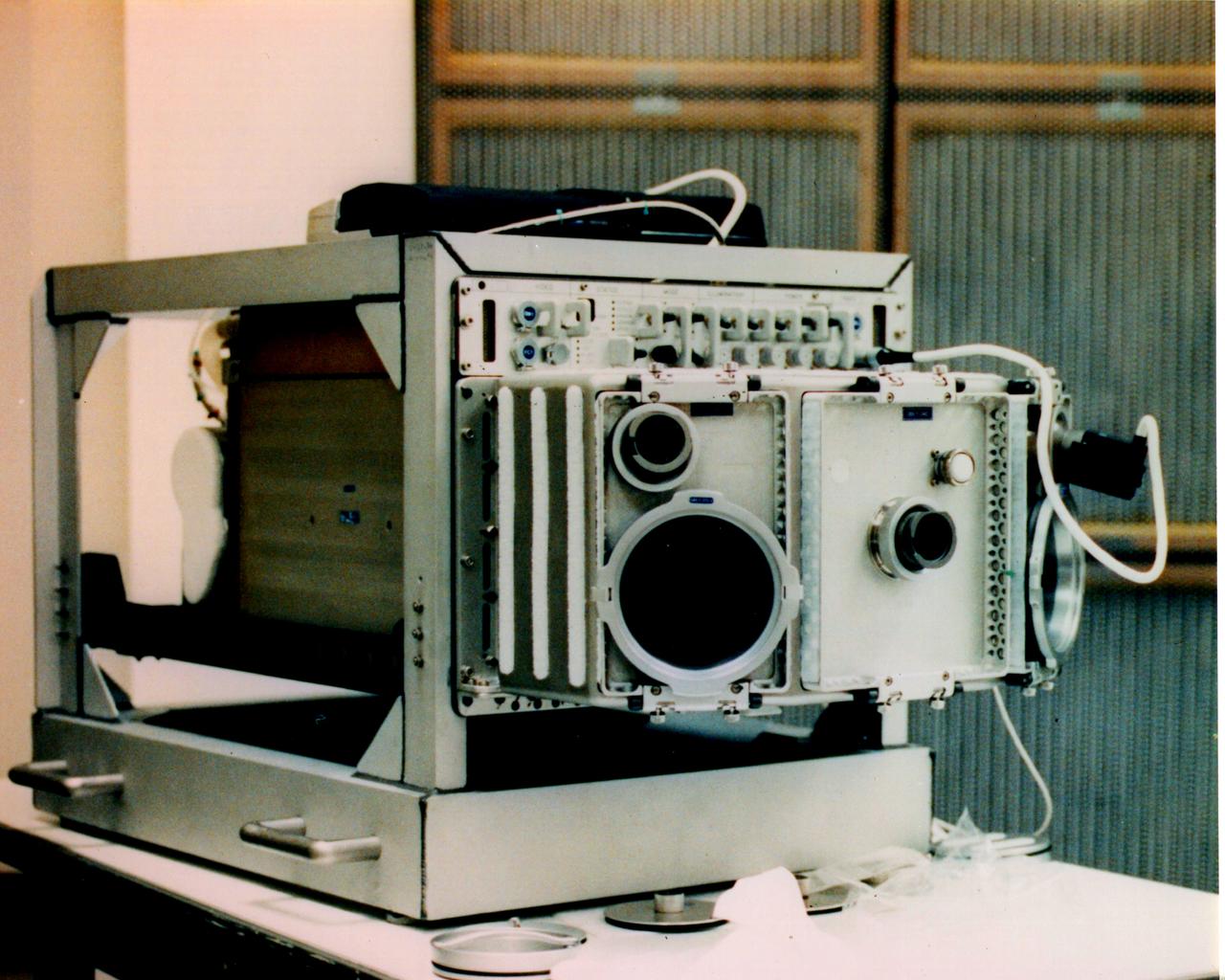
The USML-1 Glovebox (GBX) is a multi-user facility supporting 16 experiments in fluid dynamics, combustion sciences, crystal growth, and technology demonstration. The GBX has an enclosed working space which minimizes the contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. The GBX supports four charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras (two of which may be operated simultaneously) with three black-and-white and three color camera CCD heads available. The GBX also has a backlight panel, a 35 mm camera, and a stereomicroscope that offers high-magnification viewing of experiment samples. Video data can also be downlinked in real-time. The GBX also provides electrical power for experiment hardware, a time-temperature display, and cleaning supplies.
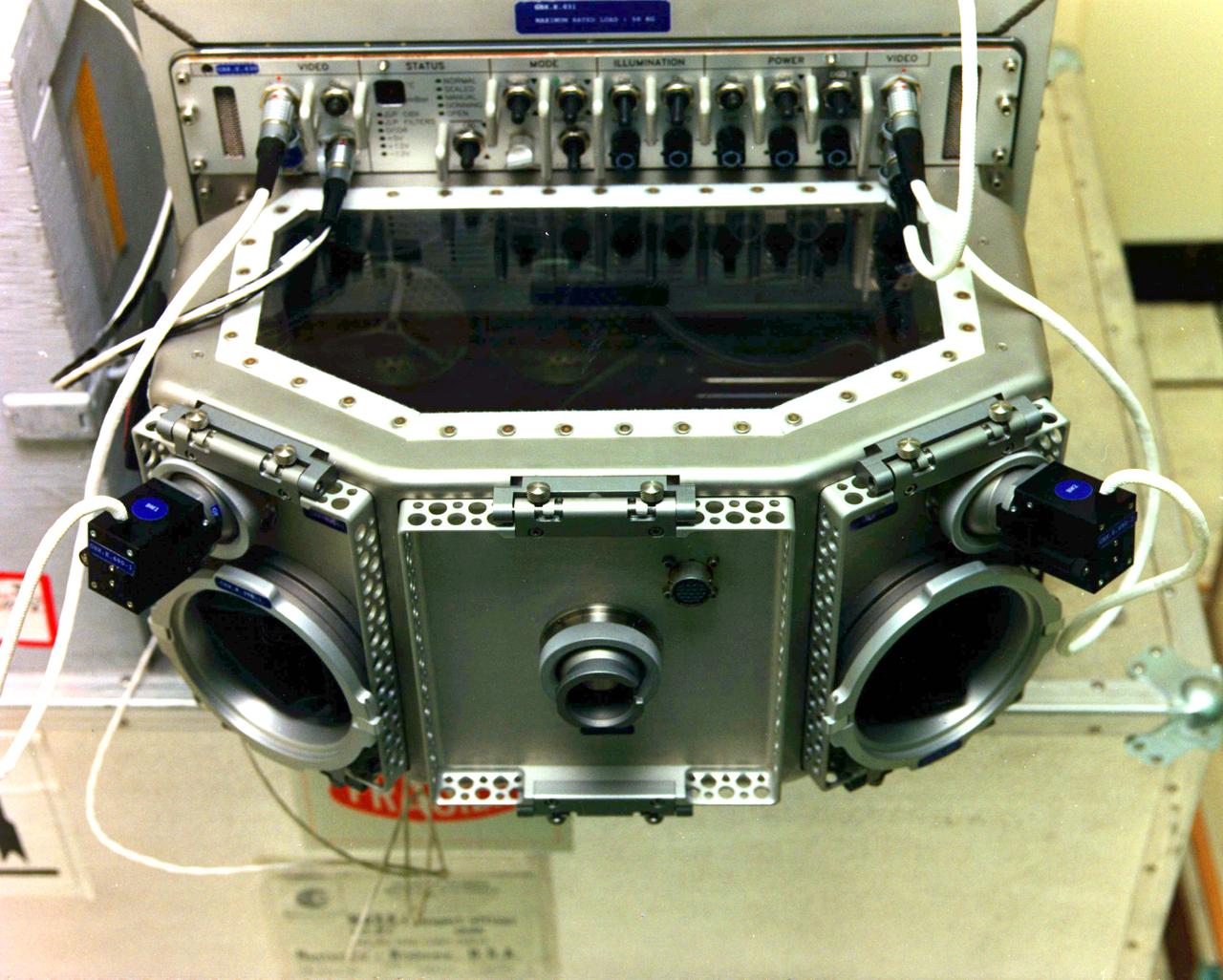

The USML-1 Glovebox (GBX) is a multi-user facility supporting 16 experiments in fluid dynamics, combustion sciences, crystal growth, and technology demonstration. The GBX has an enclosed working space which minimizes the contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. The GBX supports four charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras (two of which may be operated simultaneously) with three black-and-white and three color camera CCD heads available. The GBX also has a backlight panel, a 35 mm camera, and a stereomicroscope that offers high-magnification viewing of experiment samples. Video data can also be downlinked in real-time. The GBX also provides electrical power for experiment hardware, a time-temperature display, and cleaning supplies.

STS095-E-5163 (1 Nov. 1998) --- Astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, mission specialist, works with an experiment in the glove box located in the Spacehab facility onboard Discovery. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 01:53:47 GMT, Nov. 1.
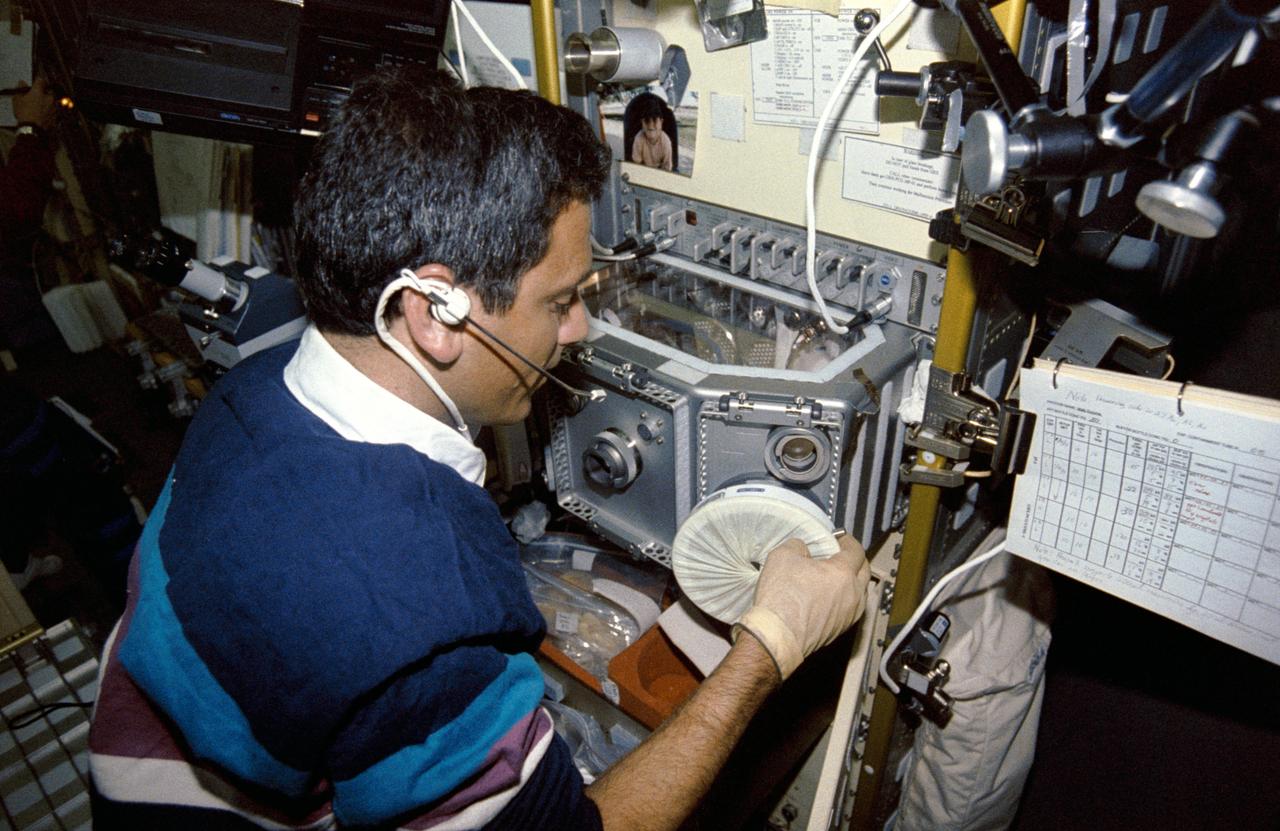

STS050-259-016 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Payload specialist Lawrence J. DeLucas works at the Multipurpose Glovebox (MPGB) in the science module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Provided by the European Space Agency, the glovebox enables crewmembers to handle, transfer and otherwise manipulate materials in ways that are impractical in the open science module. At least 16 experiments were accommodated in the glovebox during this 14-day record-setting mission.
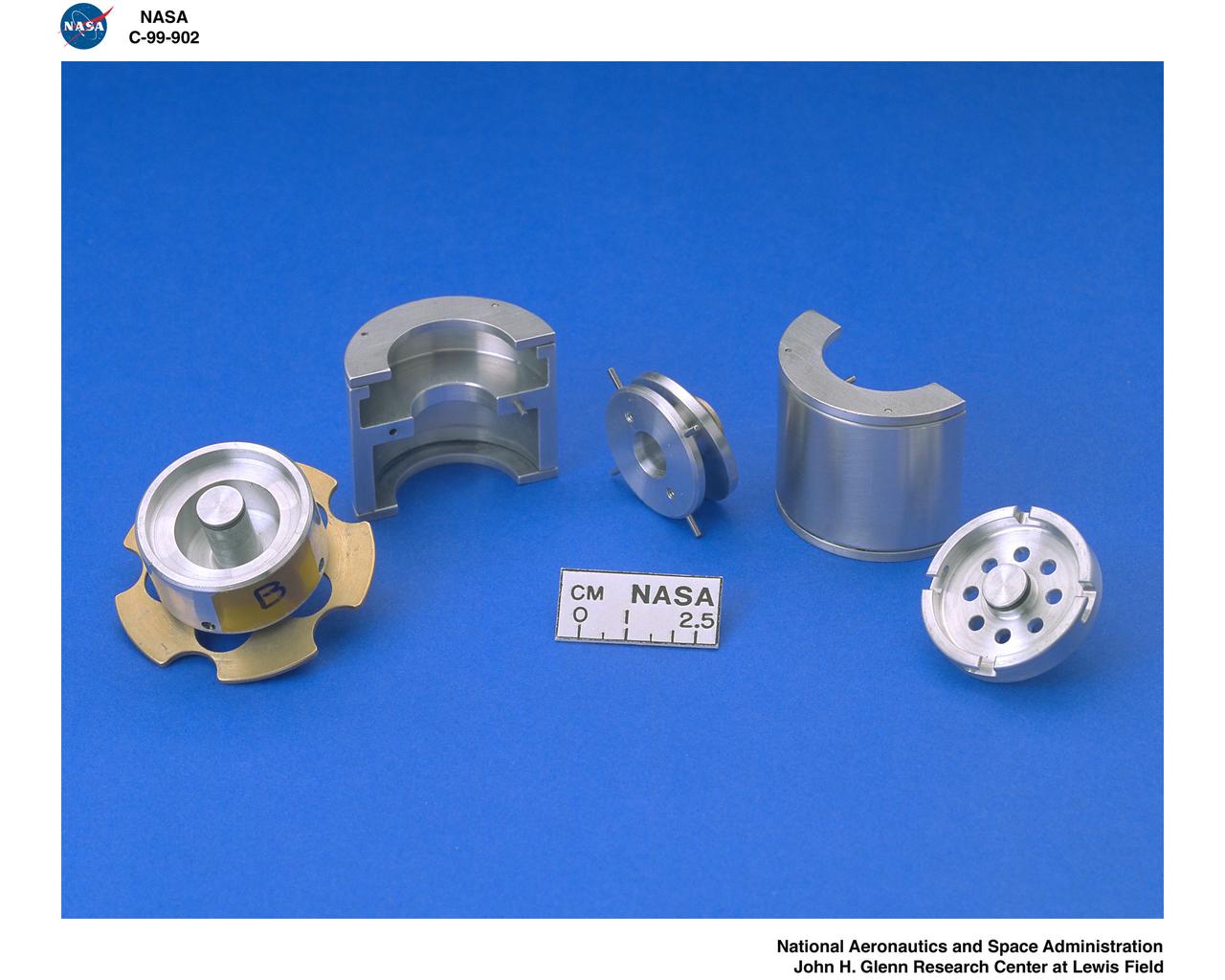

SHEAR EXTENSIONAL RHEOLOGY EXPERIMENT FLUID MODULE AND KC135 AIRCRAFT TEST FIXTURE FOR THE EXTENSIONAL RHEOLOGY GLOVEBOX INVESTIGATION
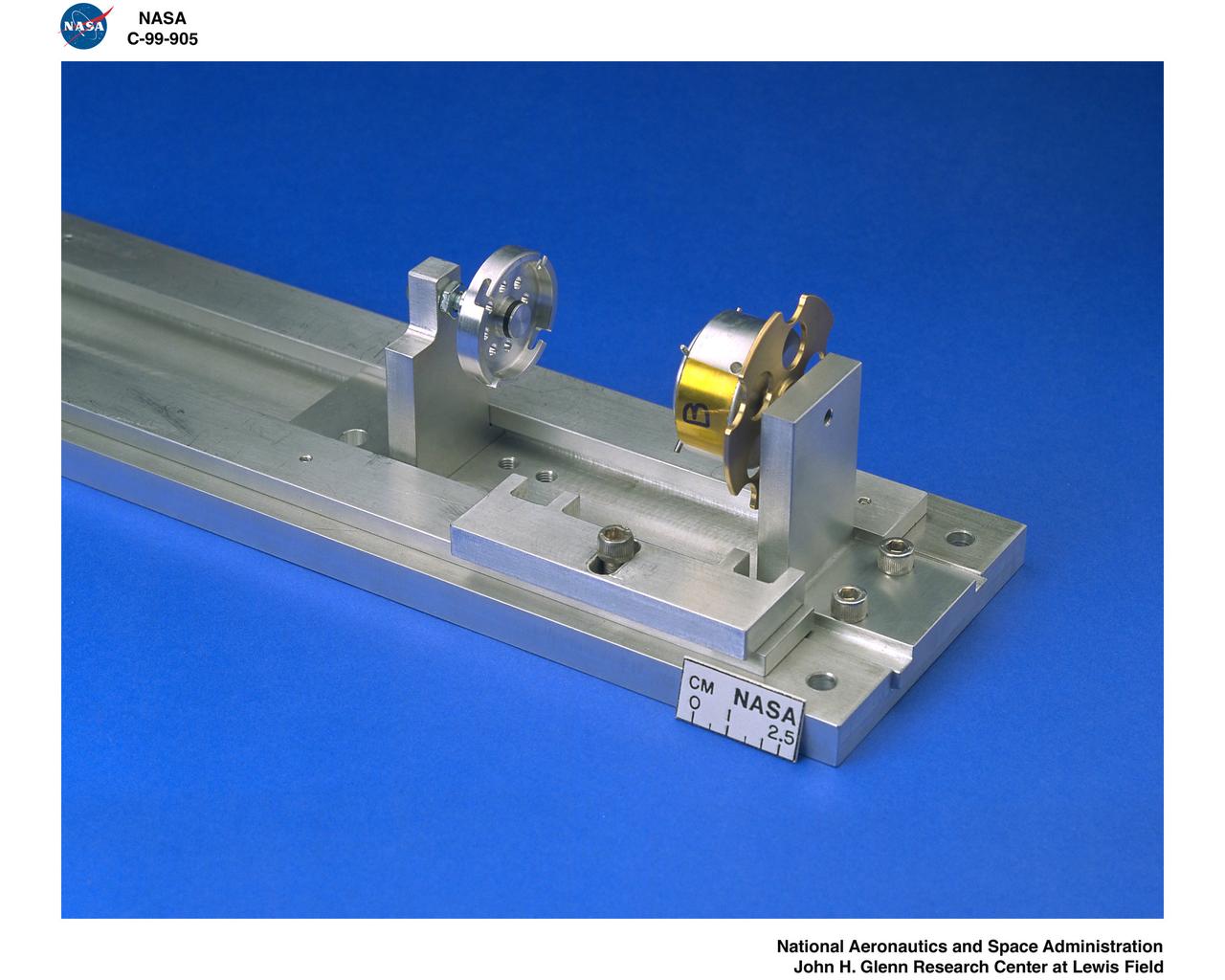
SHEAR EXTENSIONAL RHEOLOGY EXPERIMENT FLUID MODULE AND KC135 AIRCRAFT TEST FIXTURE FOR THE EXTENSIONAL RHEOLOGY GLOVEBOX INVESTIGATION
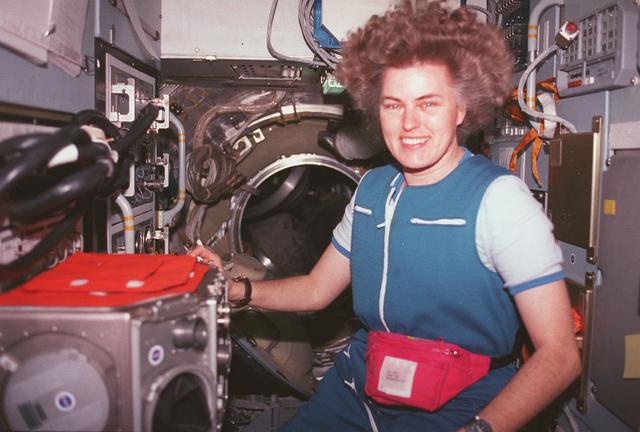

Sharnon Lucid aboard STS-79, with the Glovebox in MIR Priroda module. Priroda is the Russian word for nature.
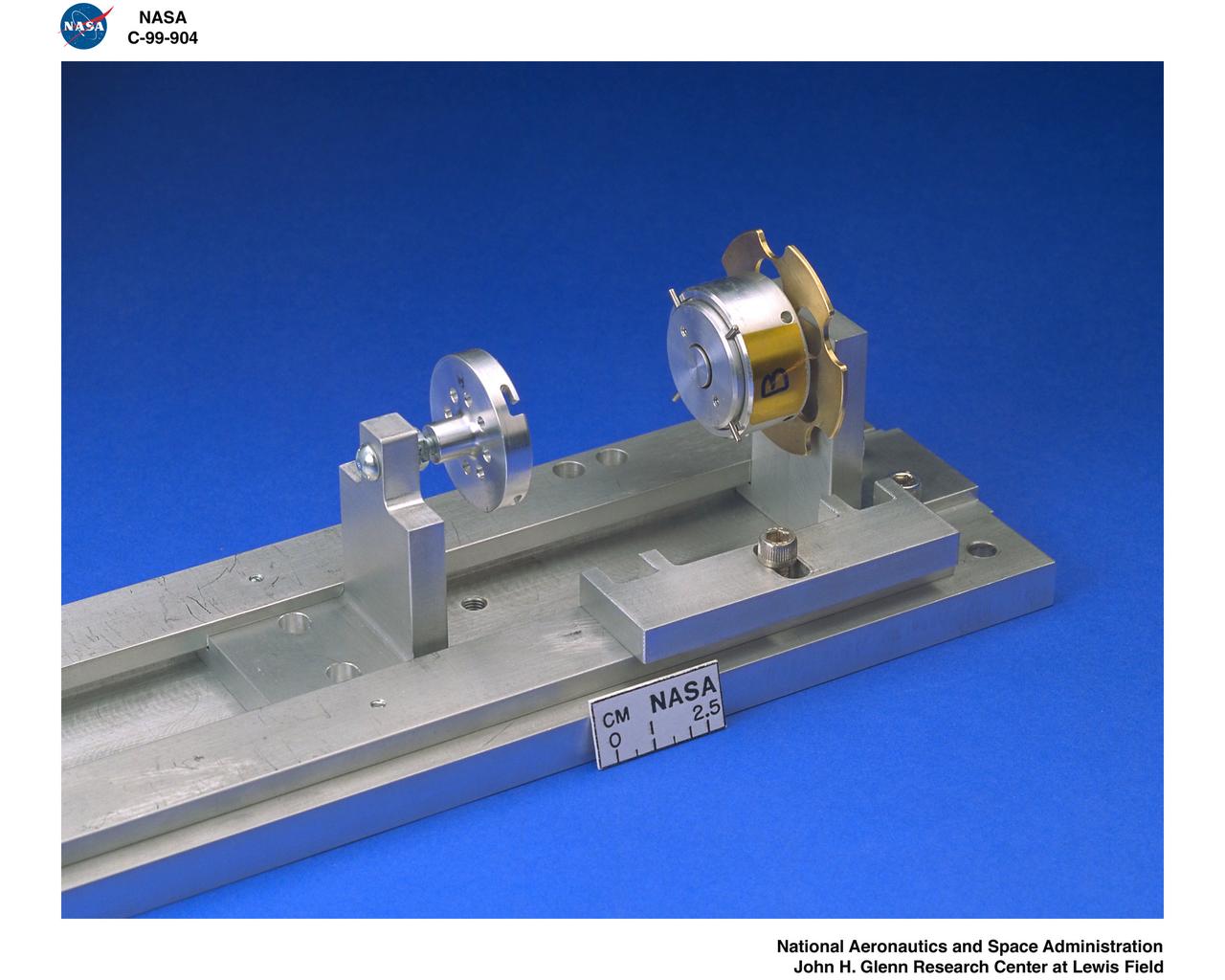
SHEAR EXTENSIONAL RHEOLOGY EXPERIMENT FLUID MODULE AND KC135 AIRCRAFT TEST FIXTURE FOR THE EXTENSIONAL RHEOLOGY GLOVEBOX INVESTIGATION
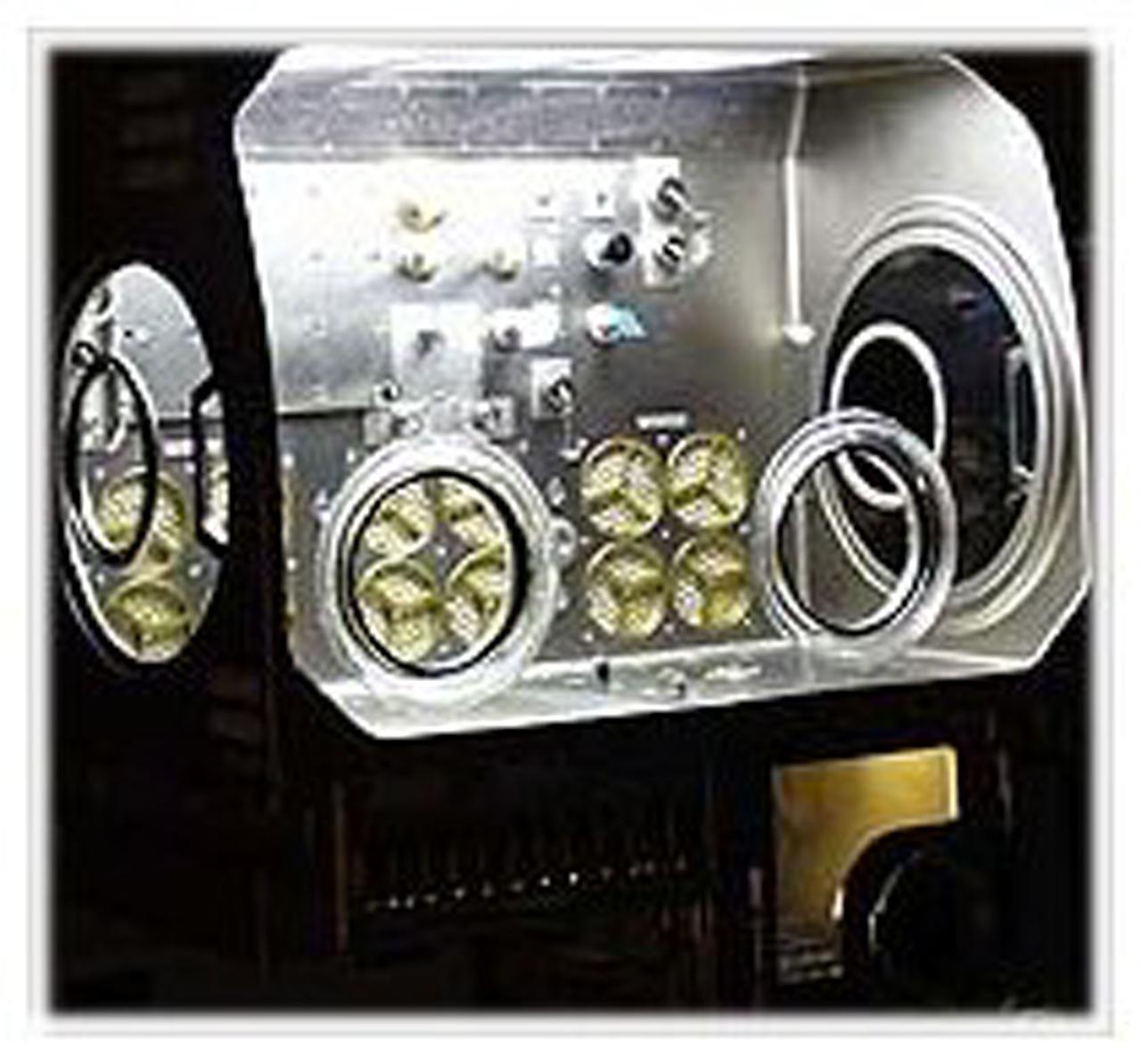

A versatile experiment facility for the International Space Station moved closer to flight recently with delivery of the ground-test model to NASA's Marshall Flight Center. The Microgravity Science Glovebox Ground Unit was delivered to the Microgravity Development Laboratory will be used to test hardware and procedures for the flight model of the glovebox aboard the ISS's Laboratory Module, Destiny.

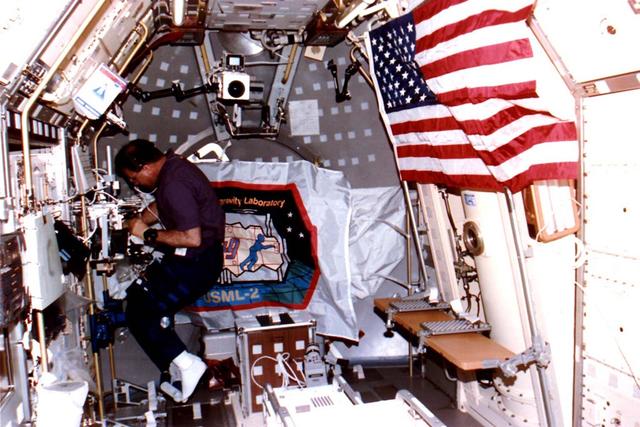
Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-73) Mission Specialists Catherine Cady Coleman works at the glovebox facility in support of the Protein Crystal Growth Glovebox (PCG-GBX) experiment in the United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) Spacelab science module.
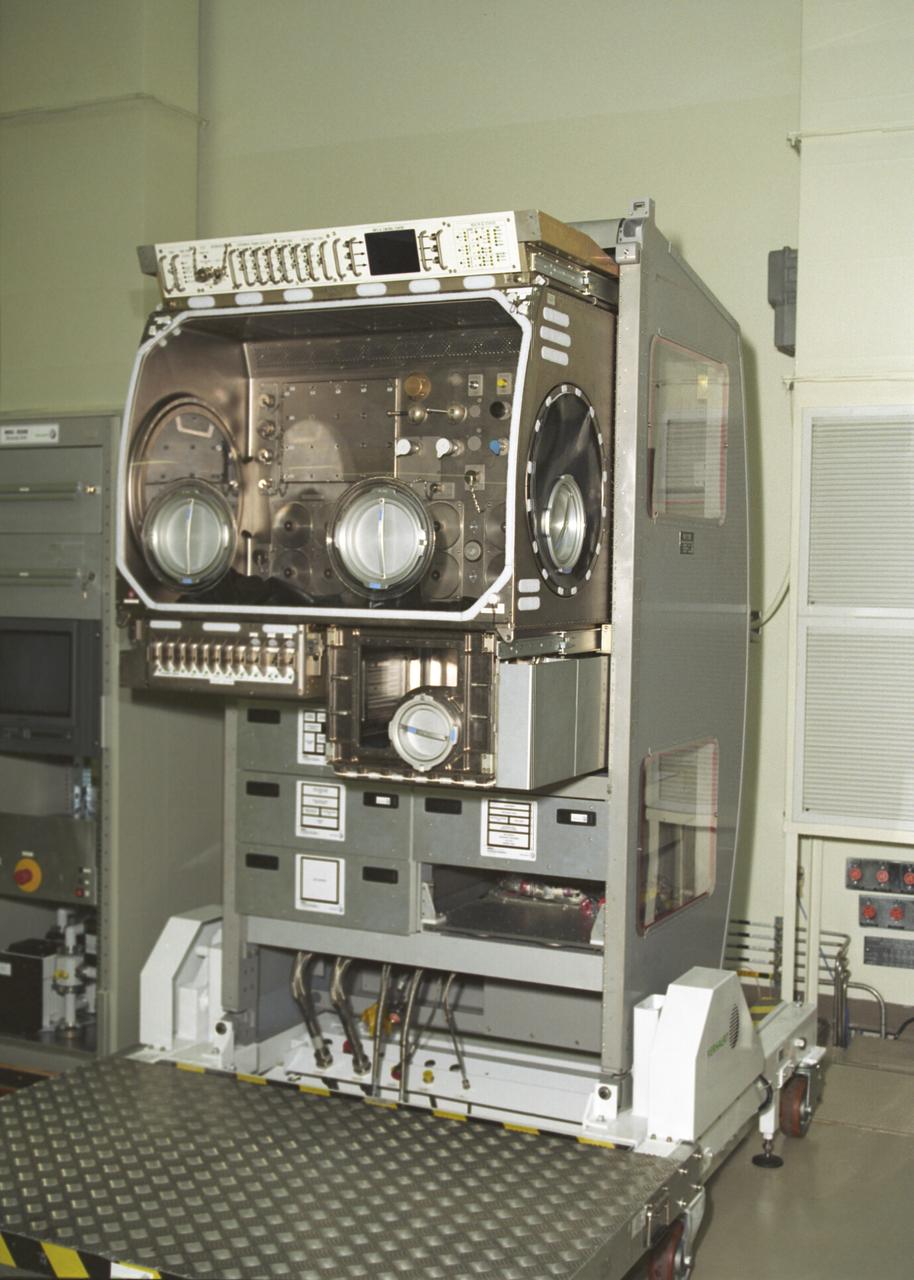

The Microgravity Science Glovebox Ground Unit, delivered to the Marshall Space Flight Center on August 30, 2002, will be used at Marshall's Microgravity Development Laboratory to test experiment hardware before it is installed in the flight glovebox aboard the International Space Station (ISS) U.S. Laboratory Module, Destiny. The glovebox is a sealed container with built in gloves on its sides and fronts that enables astronauts to work safely with experiments that involve fluids, flames, particles, and fumes that need to be safely contained.
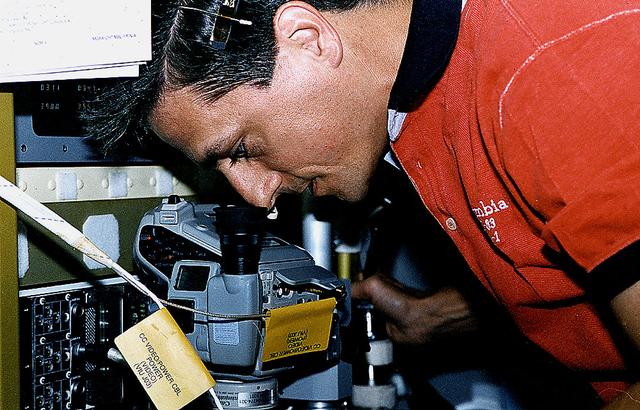

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-94) Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas observes an experiment in the glovebox aboard the Spacelab Science Module. Thomas is looking through an eye-piece of a camcorder and recording his observations on tape for post-flight analysis. Other cameras inside the glovebox are also recording other angles of the experiment or downlinking video to the experiment teams on the ground. The glovebox is thought of as a safety cabinet with closed front and negative pressure differential to prevent spillage and contamination and allow for manipulation of the experiment sample when its containment has to be opened for observation, microscopy and photography. Although not visible in this view, the glovebox is equipped with windows on the top and each side for these observations.
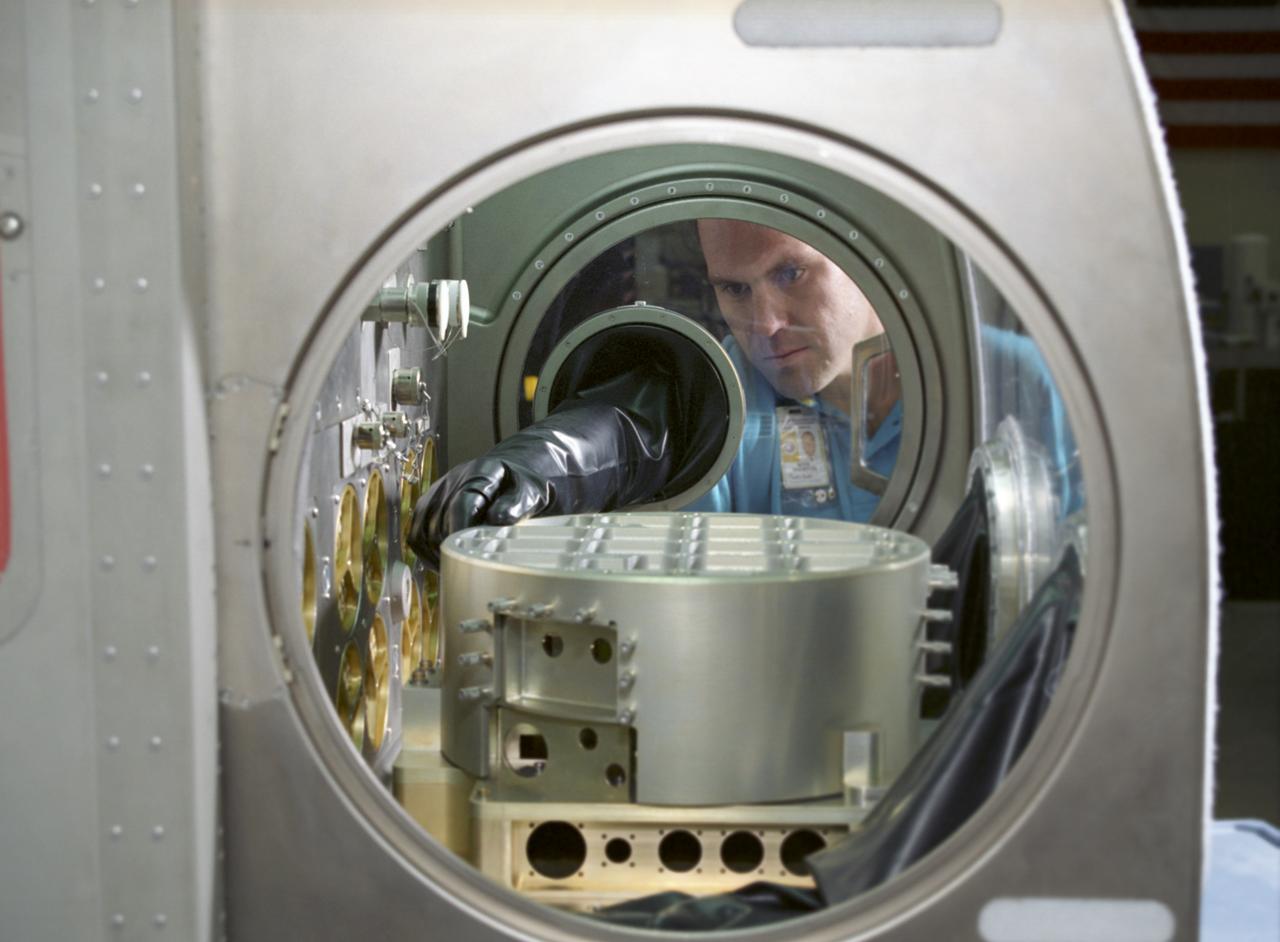

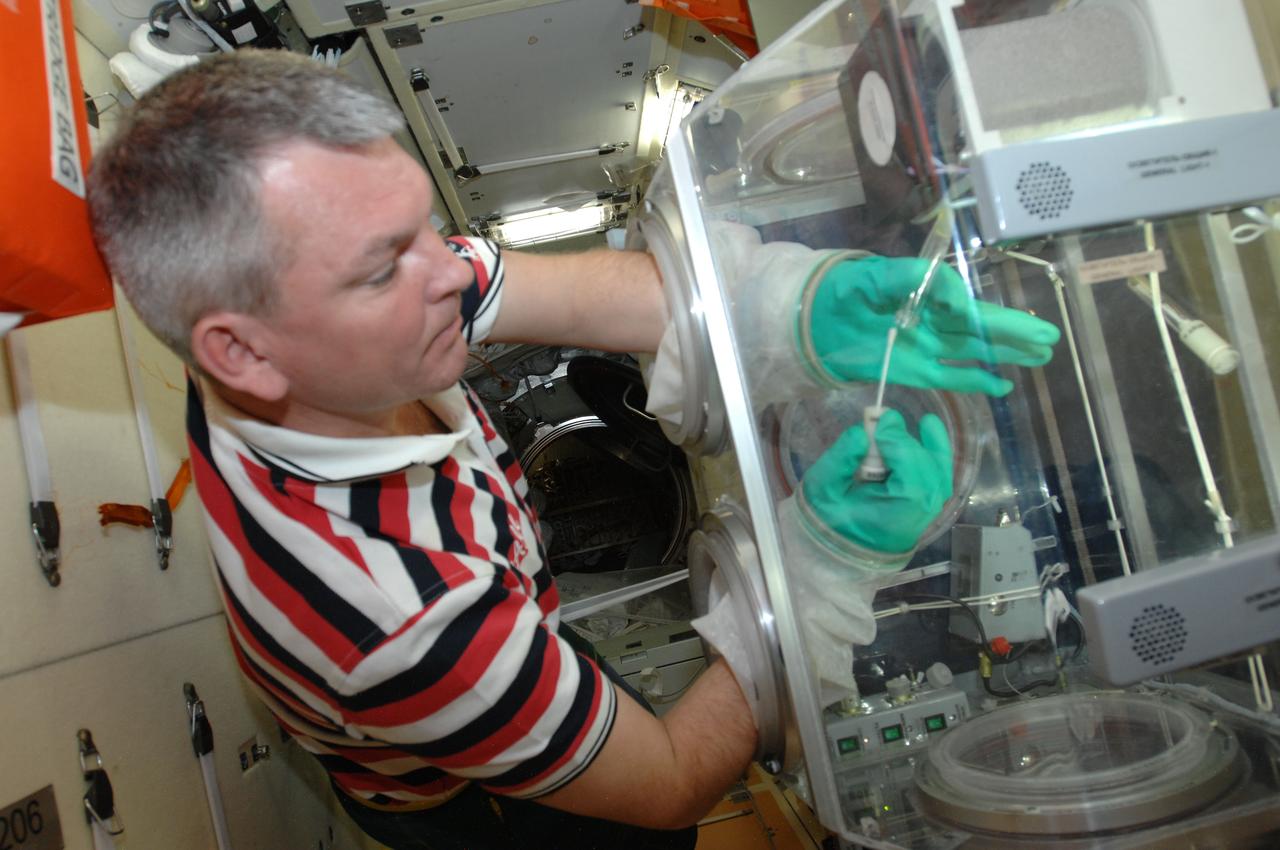
This excellent shot of Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Mark Whorton, testing experiment hardware in the Microgravity Science Glovebox Ground Unit delivered to MSFC on August 30, 2002, reveals a close look at the components inside of the Glovebox. The unit is being used at Marshall's Microgravity Development Laboratory to test experiment hardware before it is installed in the flight Glovebox aboard the International Space Station (ISS) U.S. Laboratory Module, Destiny. The glovebox is a sealed container with built in gloves on its sides and fronts that enables astronauts to work safely with experiments that involve fluids, flames, particles, and fumes that need to be safely contained.

Astronaut Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialist for STS-73, works in the glovebox on the portside of the science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in earth-orbit.

Albert Sacco Jr., payload specialist for STS-73, works in the glovebox on the portside of the science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in earth orbit.

iss065e021207 (May 6, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Flight Engineers (from left) Shane Kimbrough of NASA and Oleg Novitskiy of Roscosmos unpack hardware for installation inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox.

ISS041-E-042459 (30 Sept. 2014) --- Russian cosmonaut Alexander Samokutyaev, Expedition 41 flight engineer, works with test samples in a glovebox in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.

iss067e008088 (April 10, 2022) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition Flight Engineer Matthias Maurer is pictured in front of the Microgravity Science Glovebox located inside the International Space Station's U.S. Destiny laboratory module.
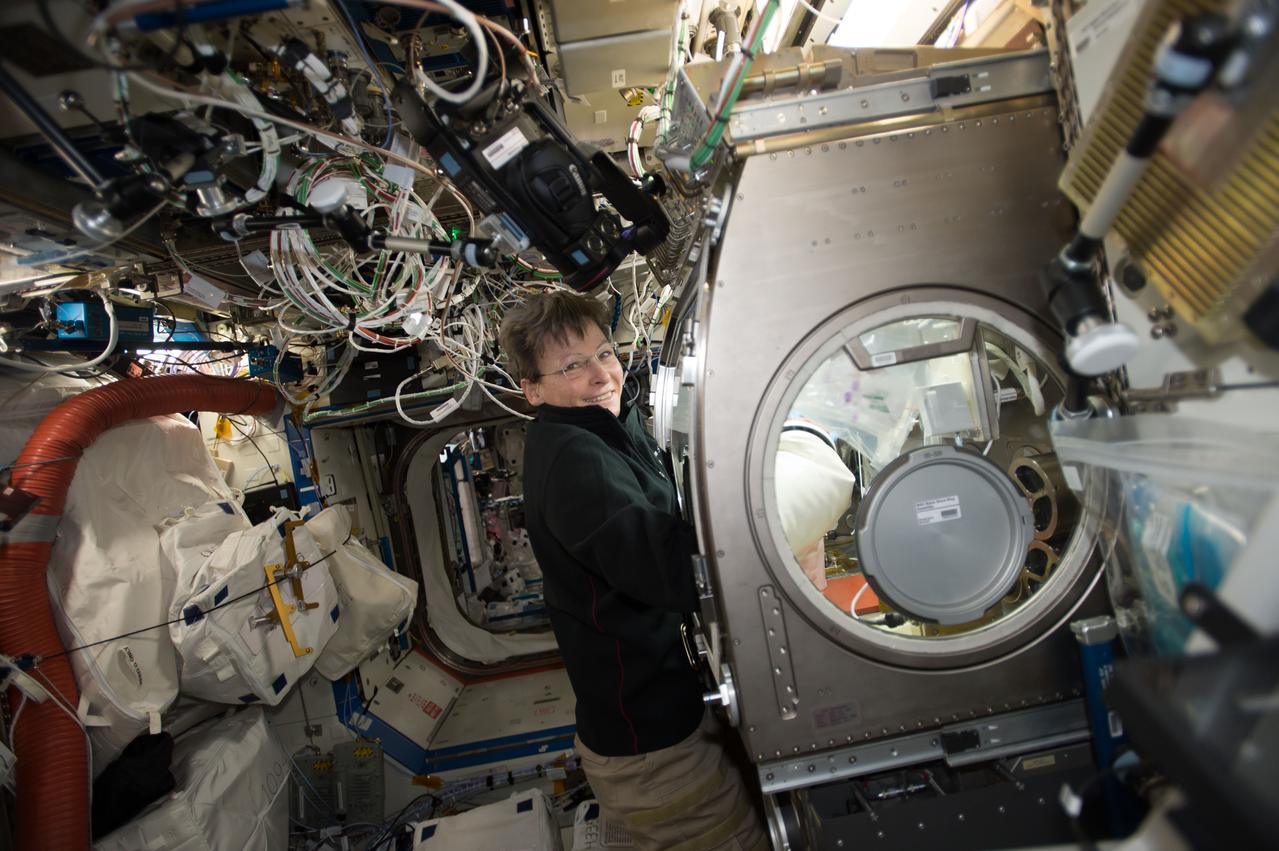

iss050e053302 (Feb. 28, 2017) --- Peggy Whitson, Expedition 50 Flight Engineer, works on an experiment inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module.

S94-E-5001 (5 July 1997) --- Astronaut Donald Thomas, mission specialist, uses a microscope at the glovebox onboard the Space Shuttle Columbia's Spacelab Module during flight day five activities.
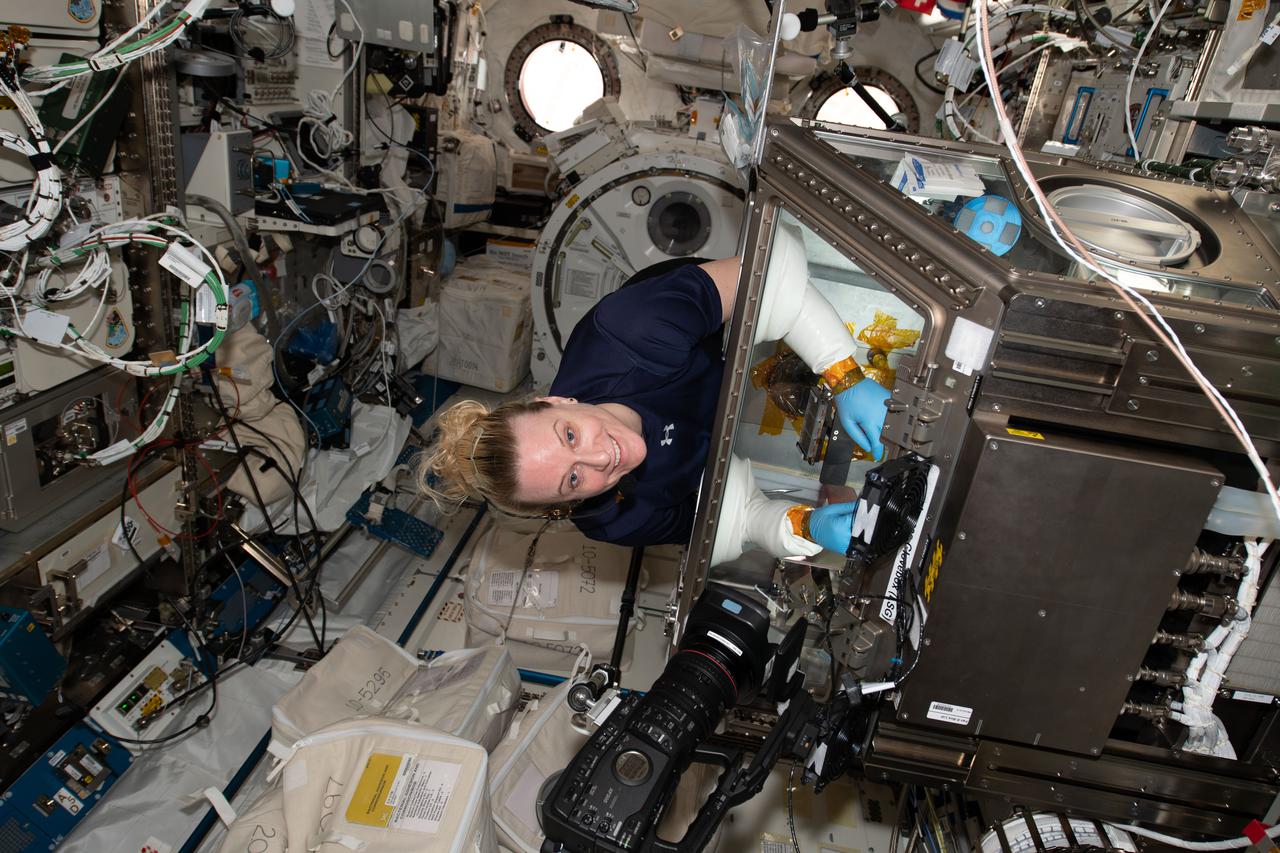

iss064e020688 (Jan. 7, 2021) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins works in the Kibo laboratory module's Life Sciences Glovebox servicing samples of microbes for an experiment that seeks to understand the microbial risk to a spacecraft’s environment.
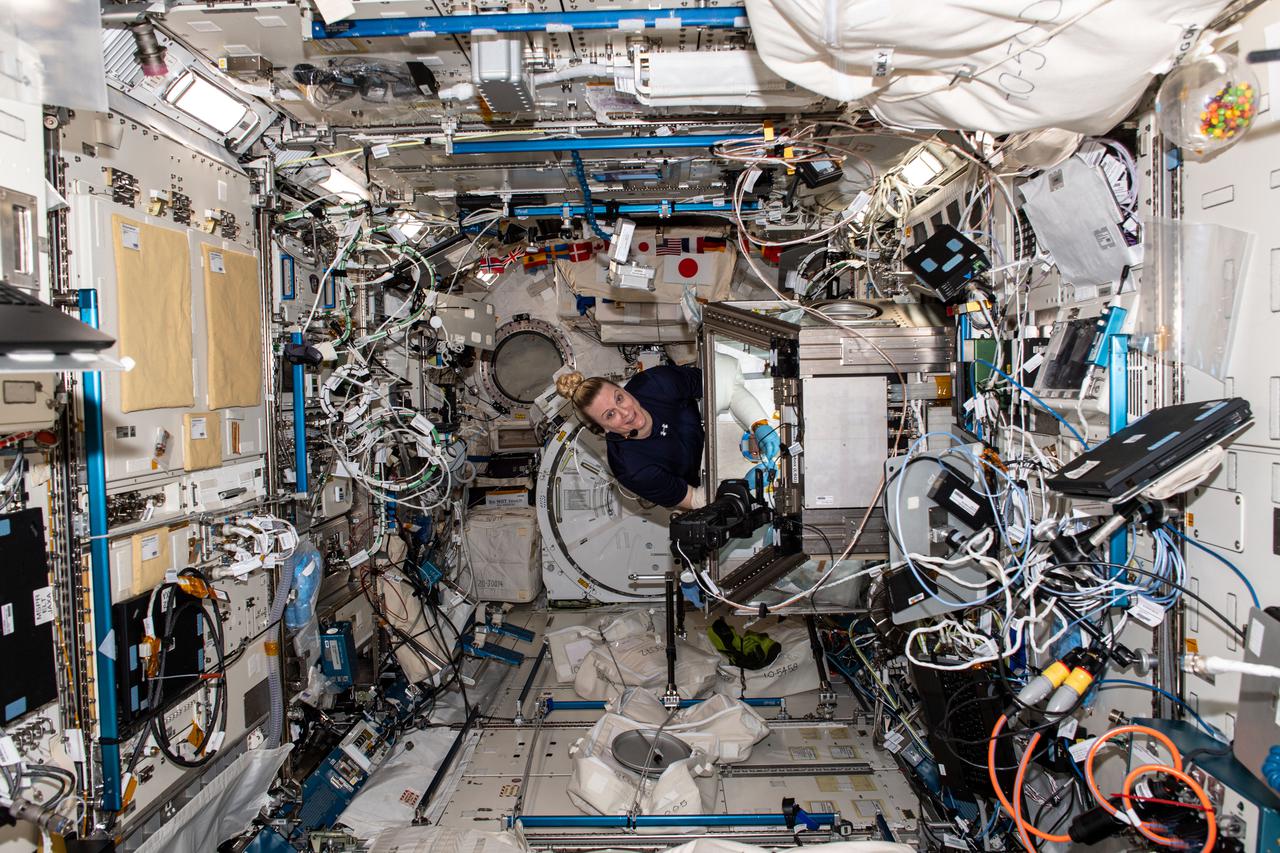

iss064e020031 (Jan. 5, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Kate Rubins works inside the JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Kibo laboratory module conducting research operations in the Life Sciences Glovebox.
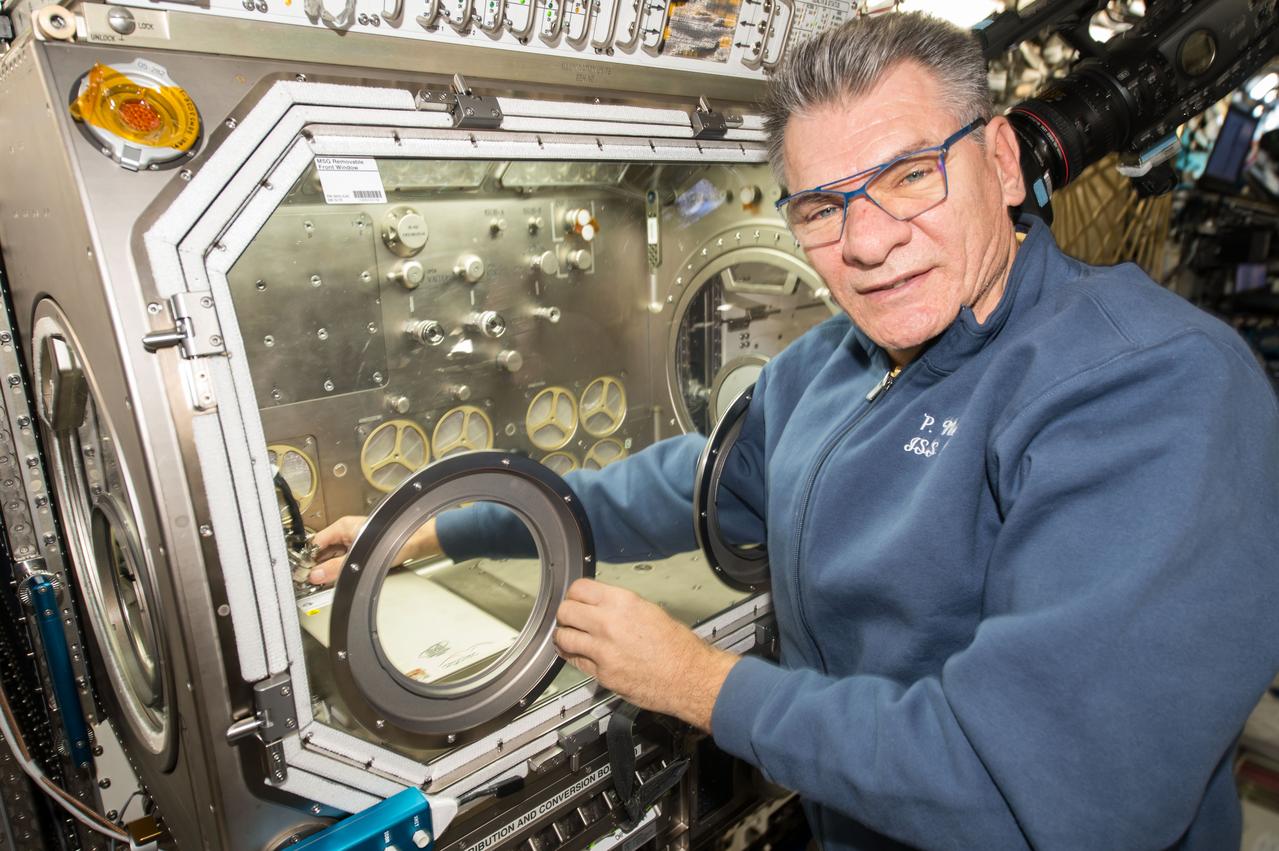

iss053e020149 (Sept. 14, 2017) --- Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli sets up thermal exchange hardware inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox located in the U.S. Destiny laboratory module.
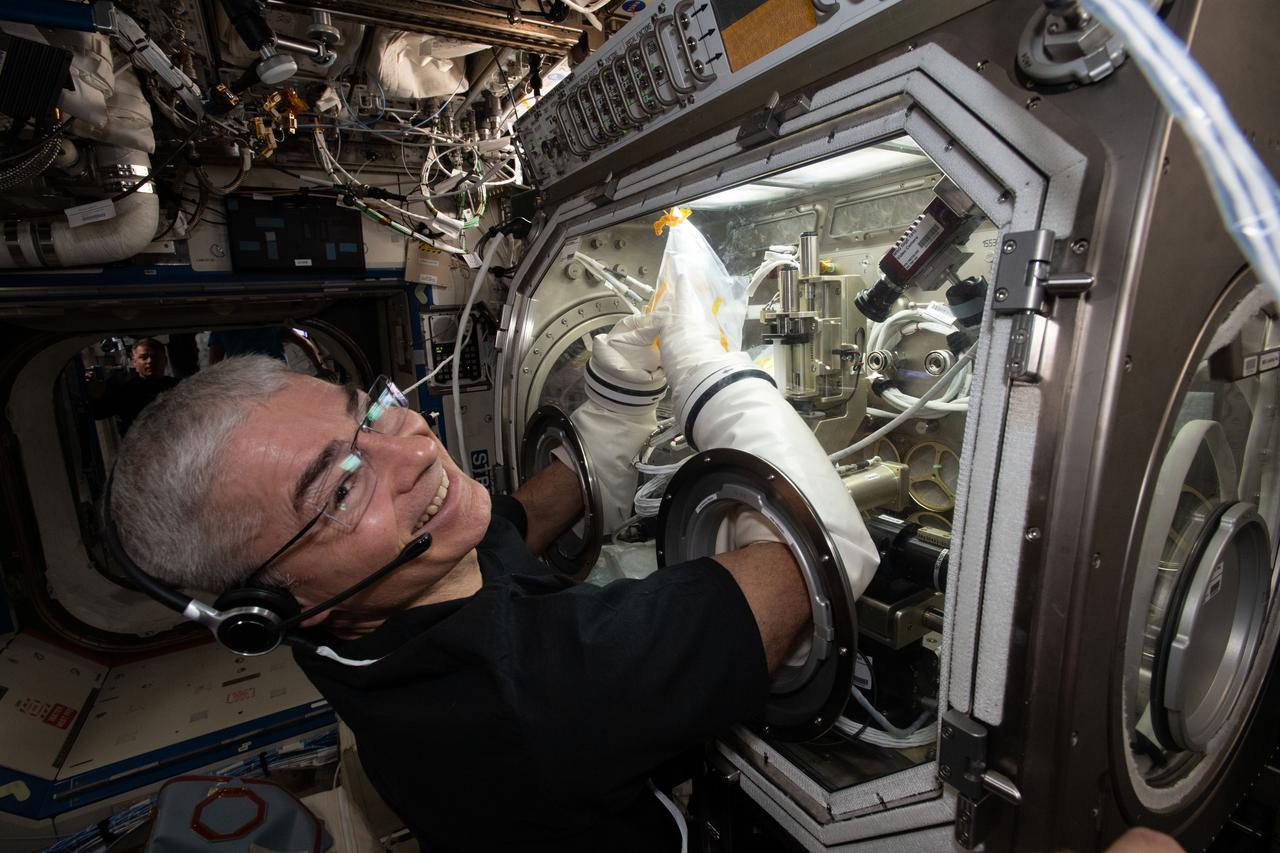

iss065e276849 (Aug. 16, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei works inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Ring Sheared Drop fluid physics study.

ISS041-E-042451 (30 Sept. 2014) --- Russian cosmonaut Alexander Samokutyaev, Expedition 41 flight engineer, works with test samples in a glovebox in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
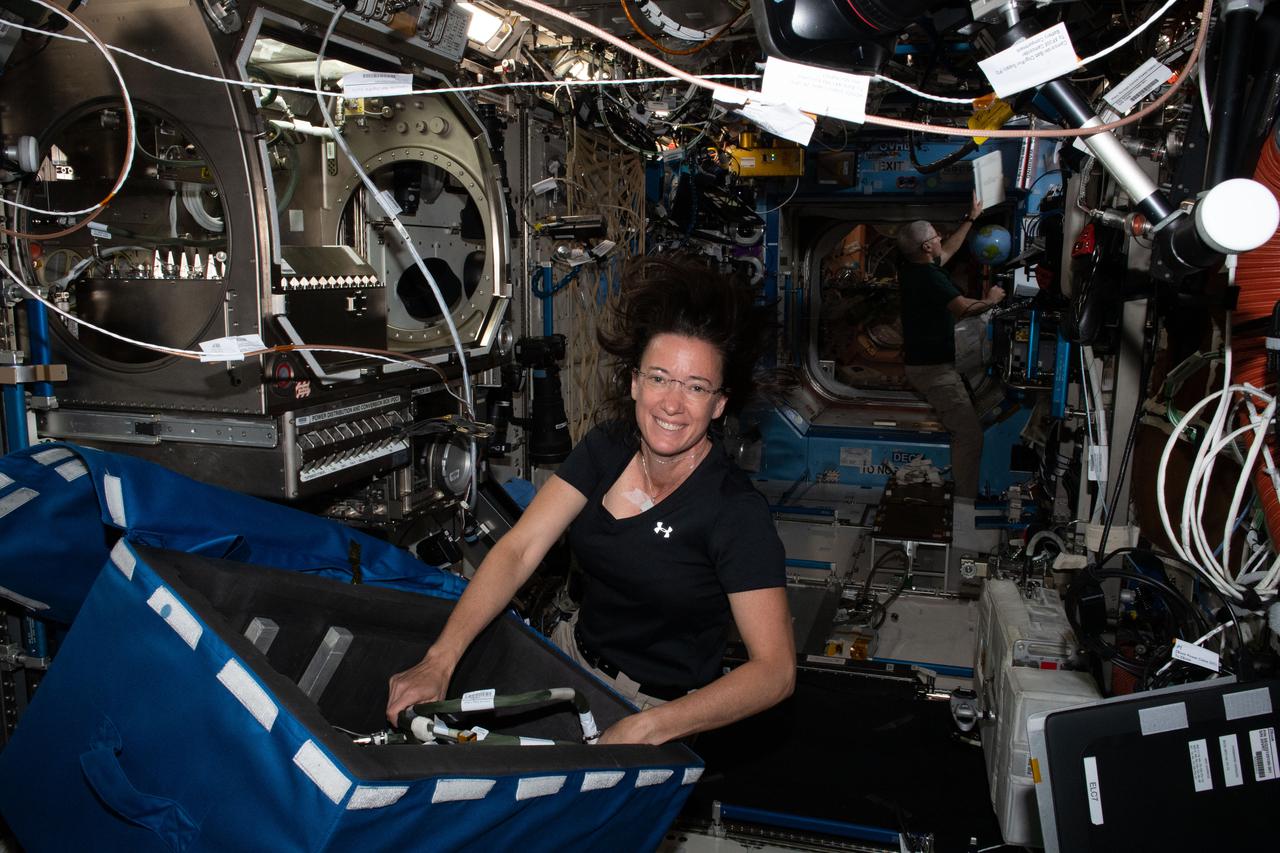

iss065e012827 (May 3, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur stows science hardware and reconfigures the Microgravity Science Glovebox inside the International Space Station's U.S. Destiny laboratory module.
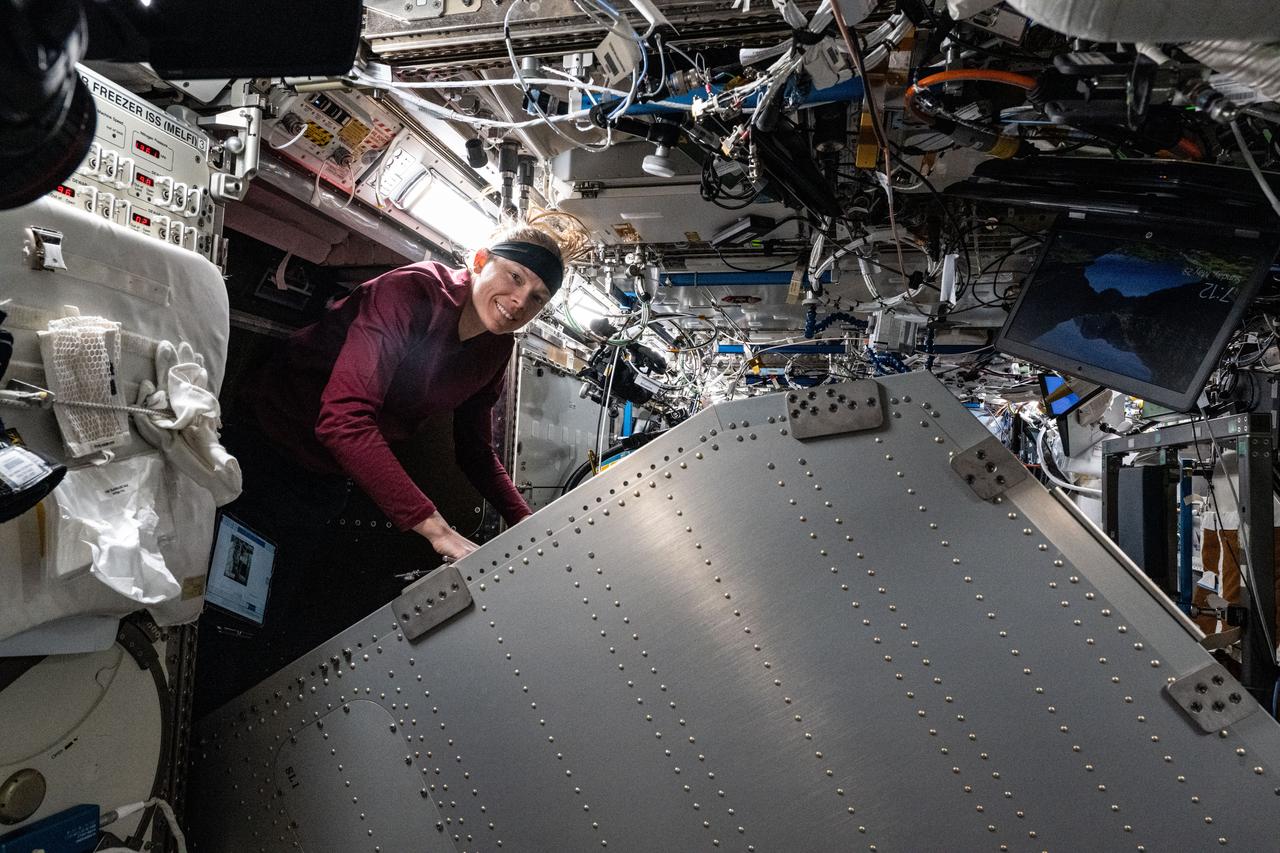

iss073e0379975 (July 17, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers works inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module and cleans components behind the Microgravity Science Glovebox.
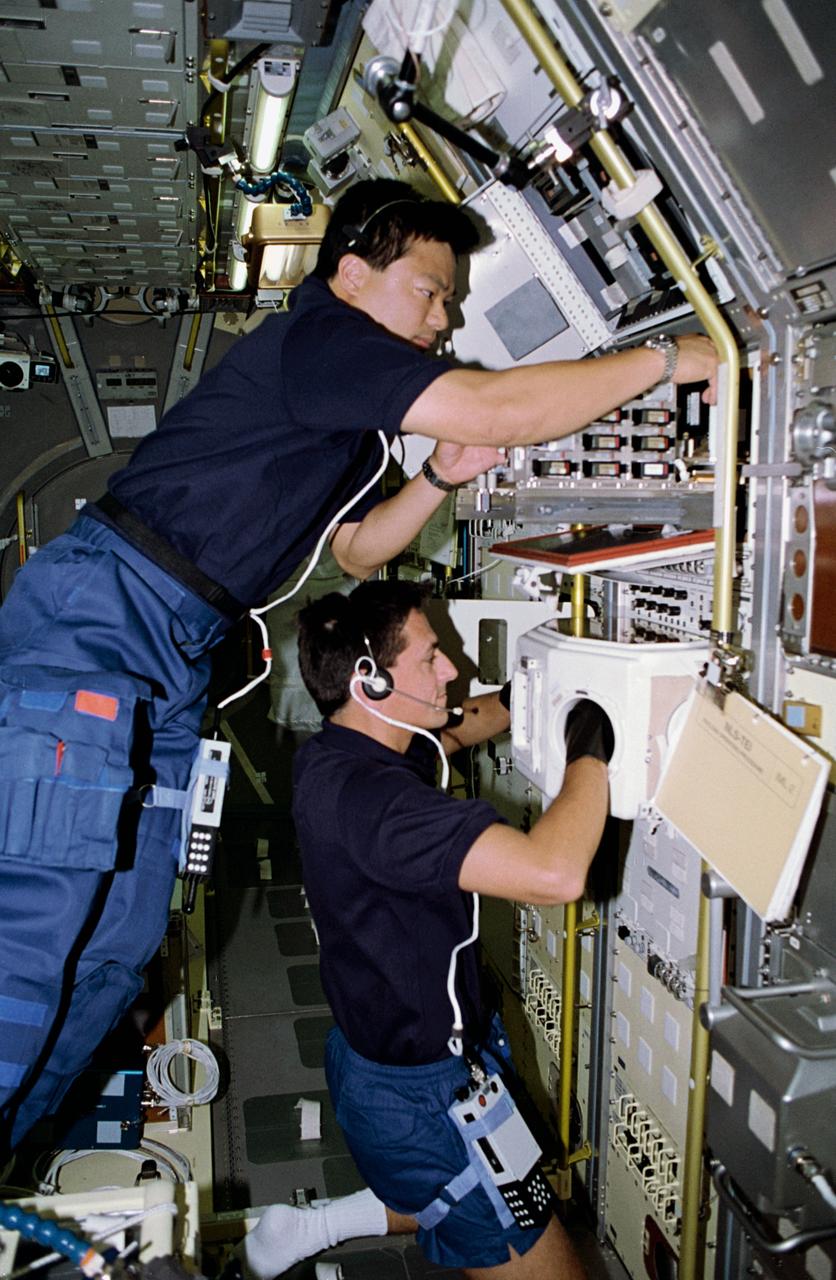

STS-65 Mission Specialist (MS) Leroy Chiao (top) and MS Donald A. Thomas are seen at work in the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) spacelab science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102. The two crewmembers are conducting experiments at the IML-2 Rack 5 Biorack (BR). Chiao places a sample in the BR incubator as Thomas handles another sample inside the BR glovebox. The glovebox is used to prepare samples for BR and slow rotating centrifuge microscope (NIZEMI) experiments.
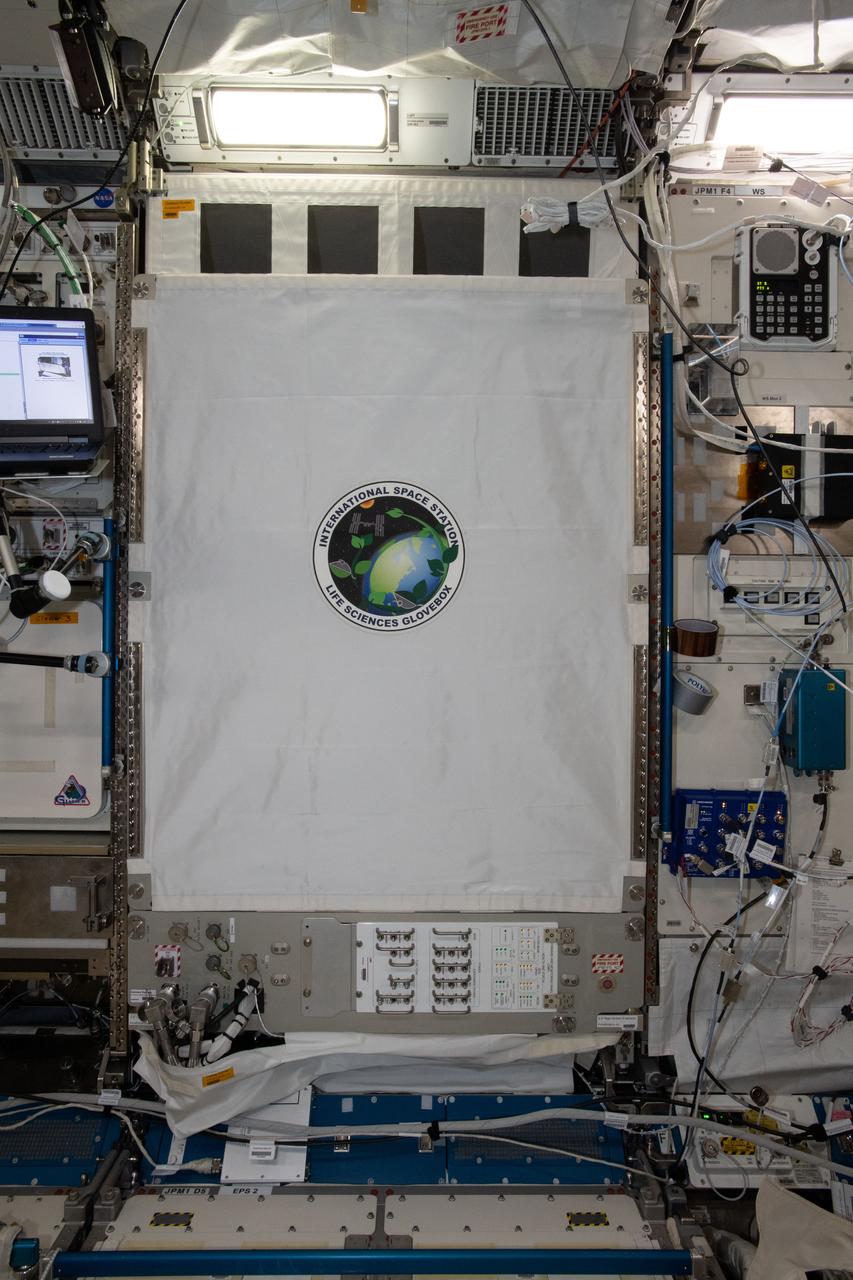

iss057e057787 (10/31/2018) --- A view of the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) with Closeout Screen and Front Cover installed during rack configuration operations (OPS) in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM). The Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) is a sealed work area that accommodates life science and technology investigations in a “workbench” type environment. Due to its larger size design, two crew members can work in the LSG simultaneously.
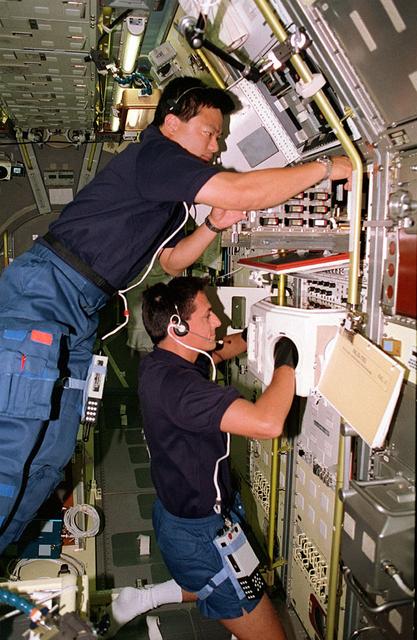

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) Mission Specialist Leroy Chiao (top) and Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas are seen at work in the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) spacelab science module. The two crewmembers are conducting experiments at the IML-2 Rack 5 Biorack (BR). Chiao places a sample in the BR incubator as Thomas handles another sample inside the BR glovebox. The glovebox is used to prepare samples for BR and slow rotating centrifuge microscope (NIZEMI) experiments.
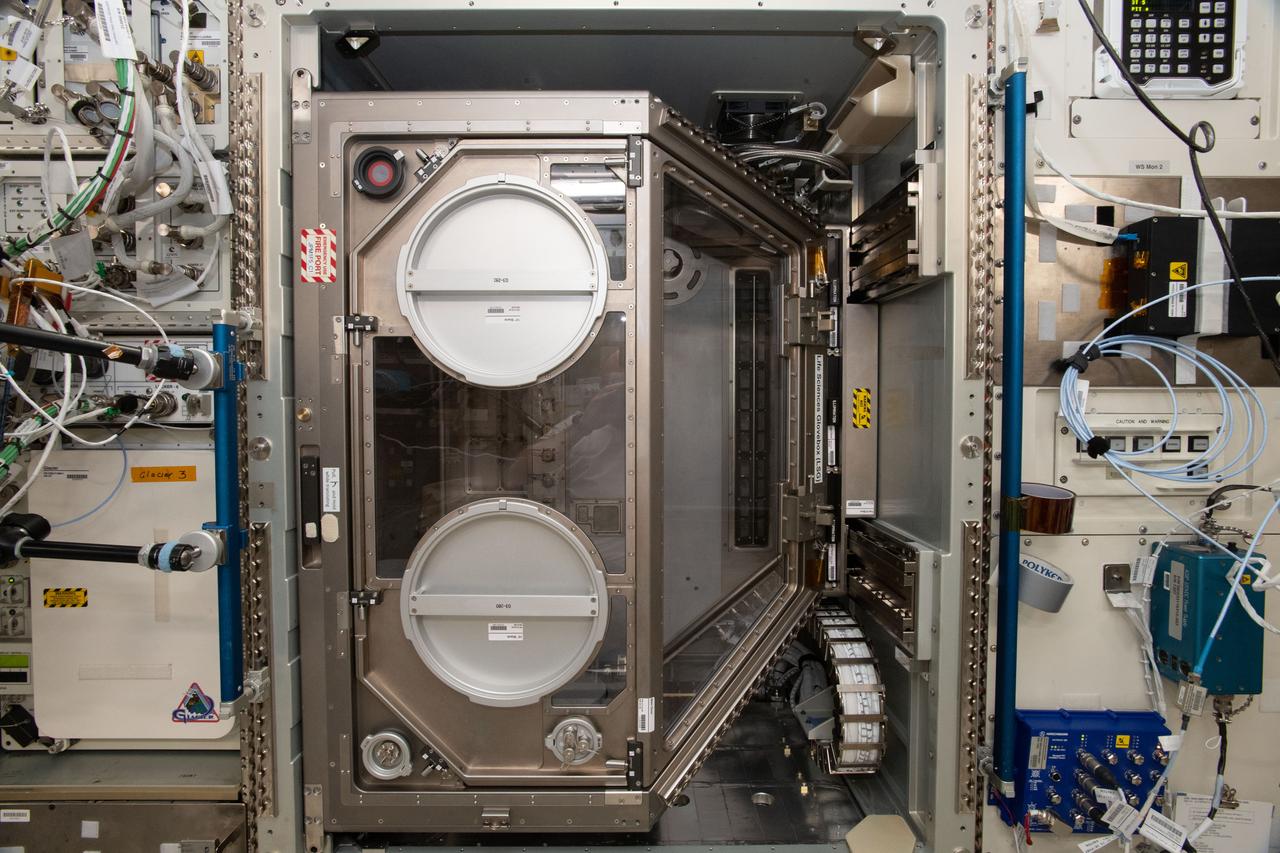

iss057e057774 (10/31/2018) --- A view of the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) during rack configuration operations (OPS) in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM). The Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) is a sealed work area that accommodates life science and technology investigations in a “workbench” type environment. Due to its larger size design, two crew members can work in the LSG simultaneously.
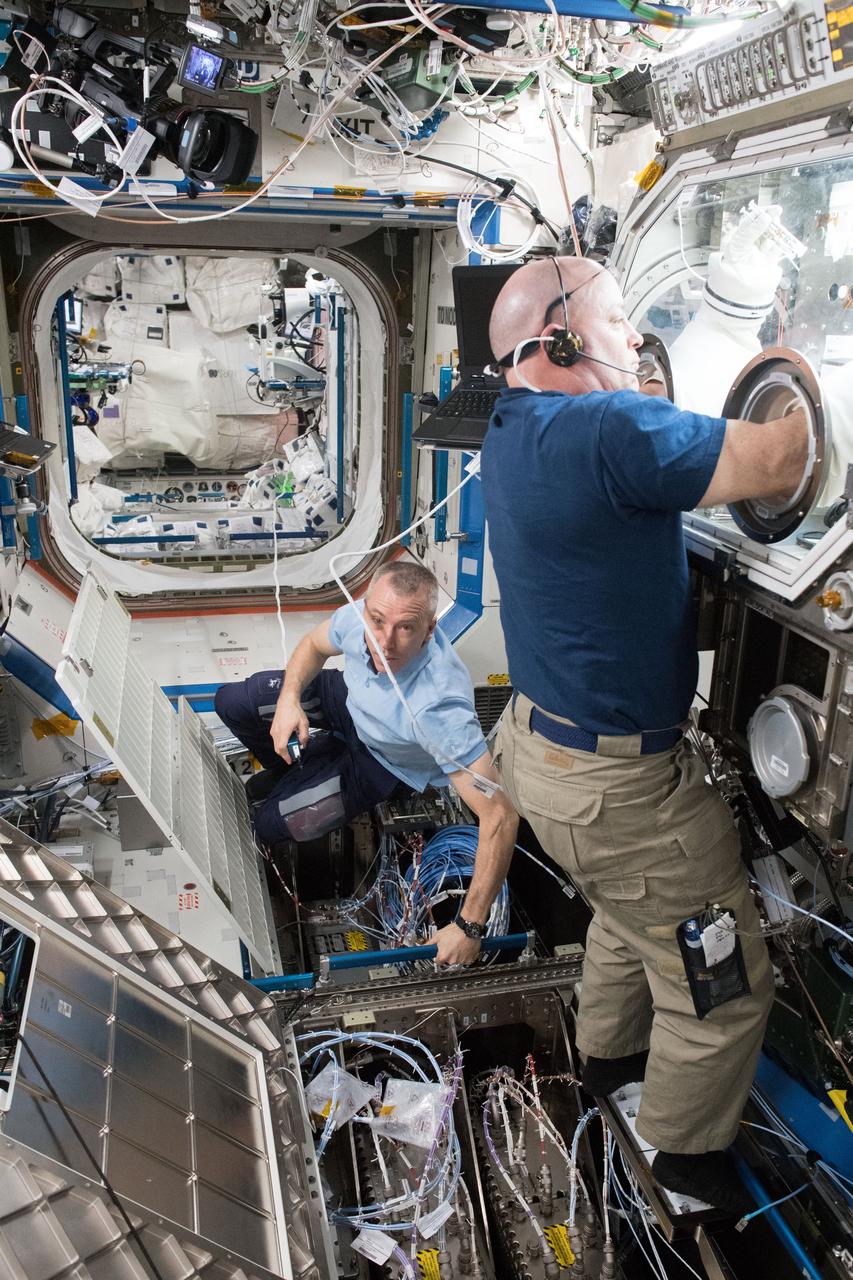

iss055e024310 (April 17, 2018) --- NASA astronauts Drew Feustel and Scott Tingle are at work inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module. Feustel works on routing and installing ethernet cables throughout the International Space Station. Tingle conducts research for the Metabolic Tracking experiment inside the lab module's Microgravity Science Glovebox.
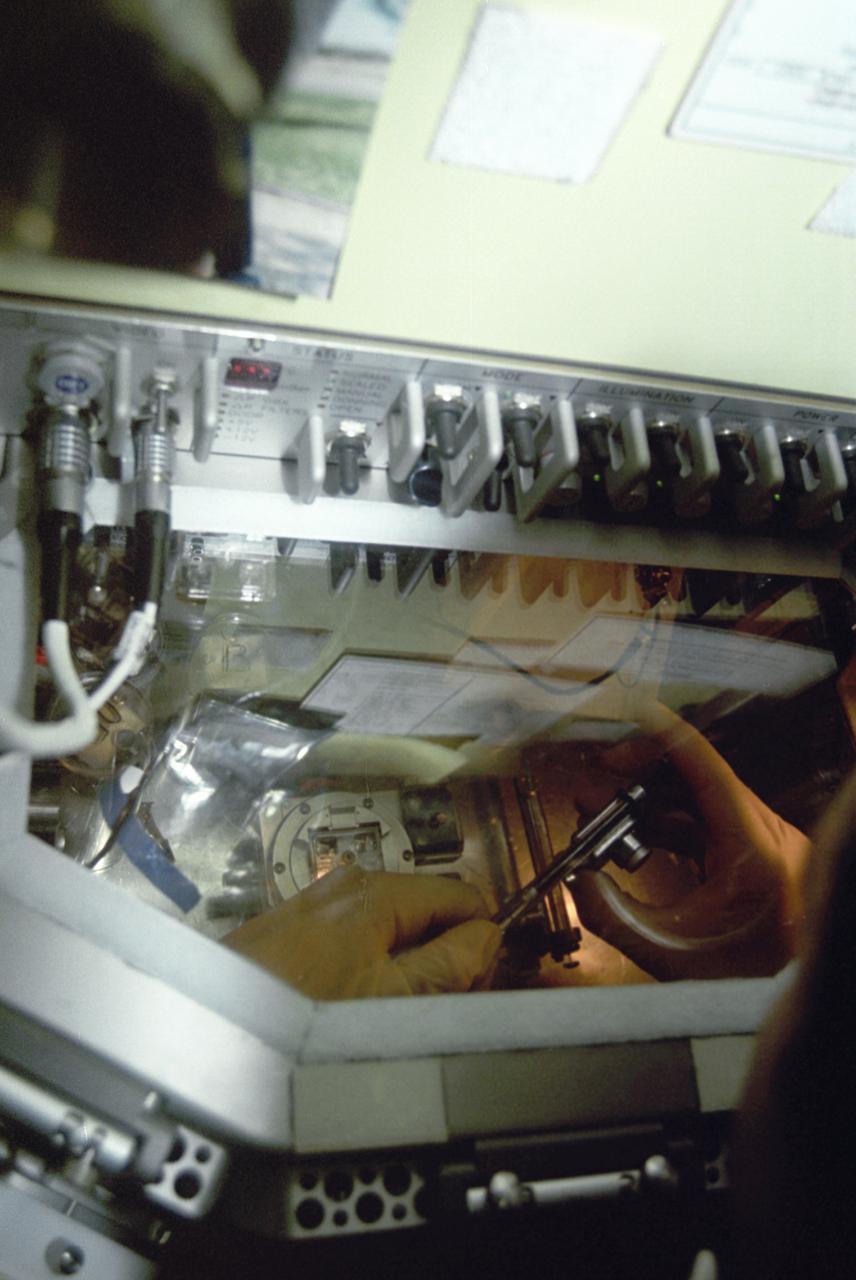

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) provided scientific research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology, and combustion science in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. This photograph is a close-up view of the Glovebox in operation during the mission. The Spacelab Glovebox, provided by the European Space Agency, offers experimenters new capabilities to test and develop science procedures and technologies in microgravity. It enables crewmembers to handle, transfer, and otherwise manipulate materials in ways that are impractical in the open Spacelab. The facility is equipped with three doors: a central port through which experiments are placed in the Glovebox and two glovedoors on both sides with an attachment for gloves or adjustable cuffs and adapters for cameras. The Glovebox has an enclosed compartment that offers a clean working space and minimizes the contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. Although fluid containment and ease of cleanup are major benefits provided by the facility, it can also contain powders and bioparticles; toxic, irritating, or potentially infectious materials; and other debris produced during experiment operations. The facility is equipped with photographic/video capabilities and permits mounting a microscope. For the USML-1 mission, the Glovebox experiments fell into four basic categories: fluid dynamics, combustion science, crystal growth, and technology demonstration. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission in June 1992.
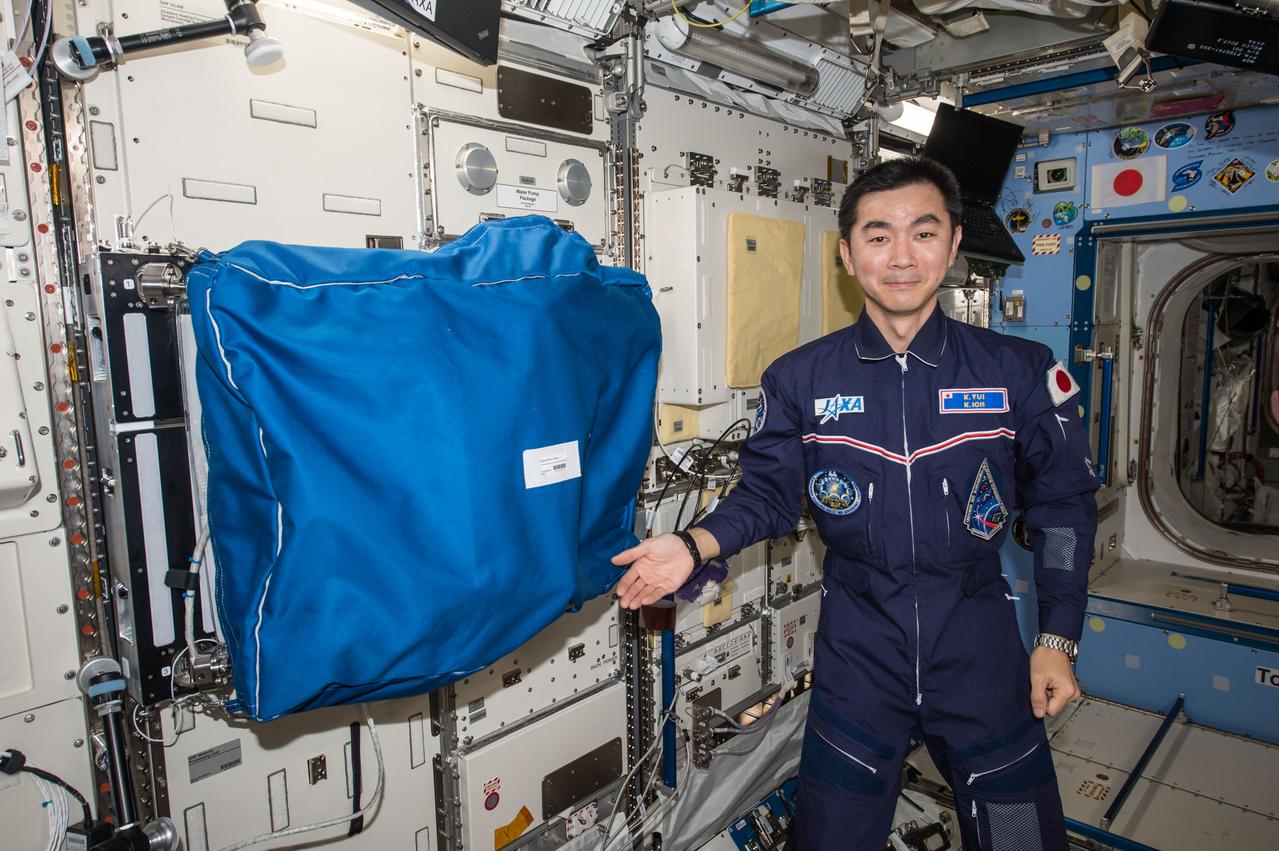

iss045e152163 (12/1/2015) --- A view of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Kimiya Yui photographed next to the Kobairo rack, JPM1F3 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The rack contains the Gradient Heating Furnace (GHF) and has a Glovebox attached to the rack front.
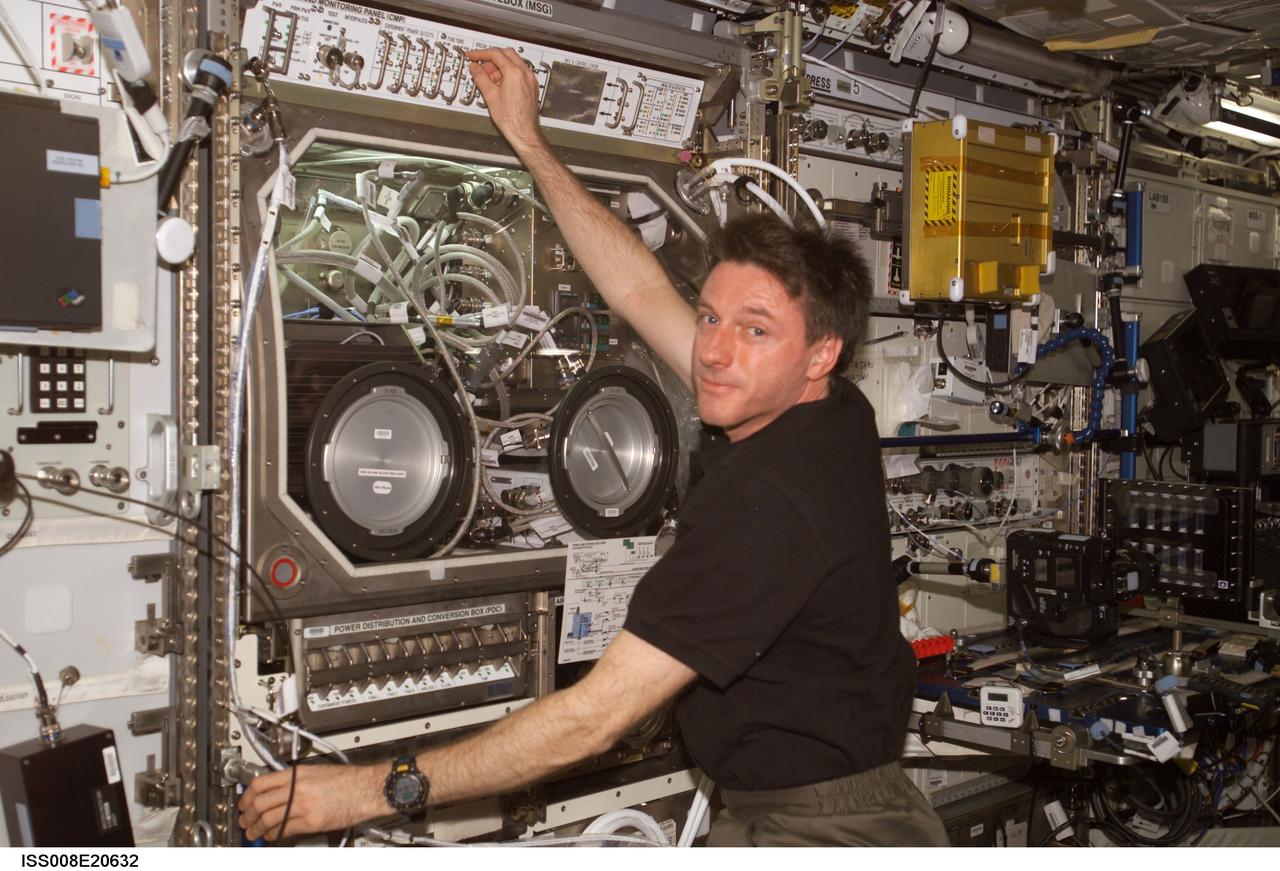

ISS008-E-20632 (5 April 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, conducts an inspection of the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) / Exchangeable Standard Electronic Module (ESEM) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS).
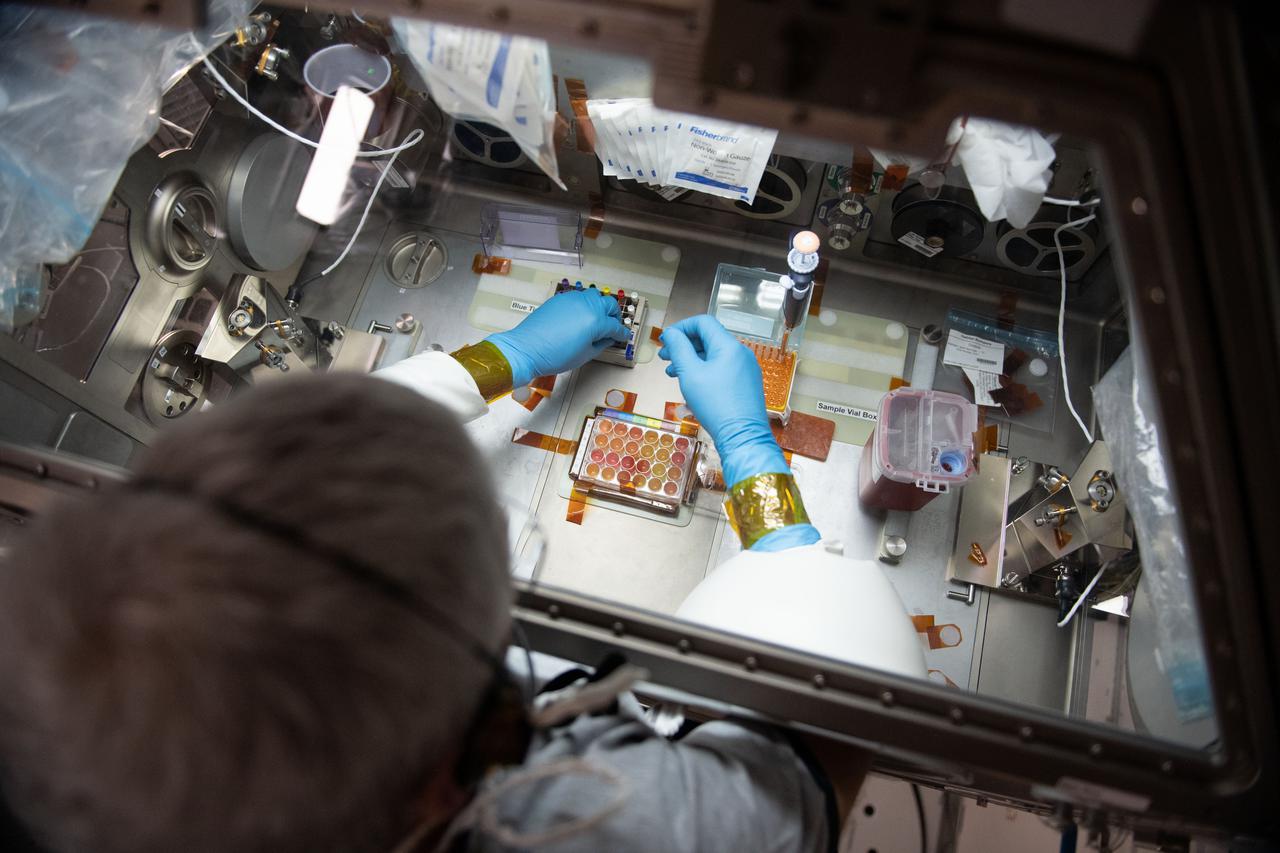

iss065e056805 (5/22/2021) --- NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei works inside the Life Science Glovebox (LSG) for the Celestial Immunity study that may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space. The LSG is located in the Kibo laboratory module from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
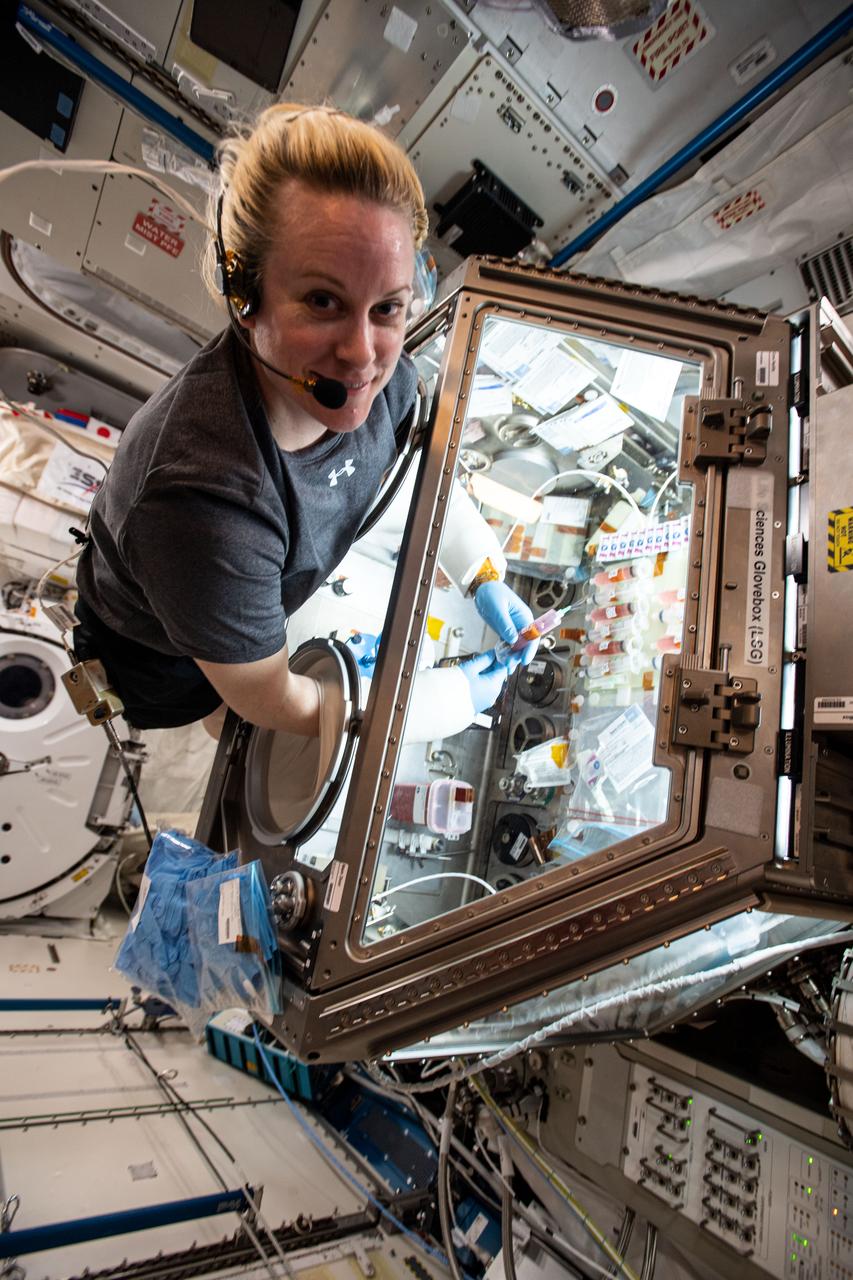

iss064e015250 (Dec. 24, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Kate Rubins works inside the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) servicing engineered heart tissue samples for the Cardinal Heart study that seeks to understand space-caused cell and tissue abnormalities. The LSG is located inside Japan's Kibo laboratory module.
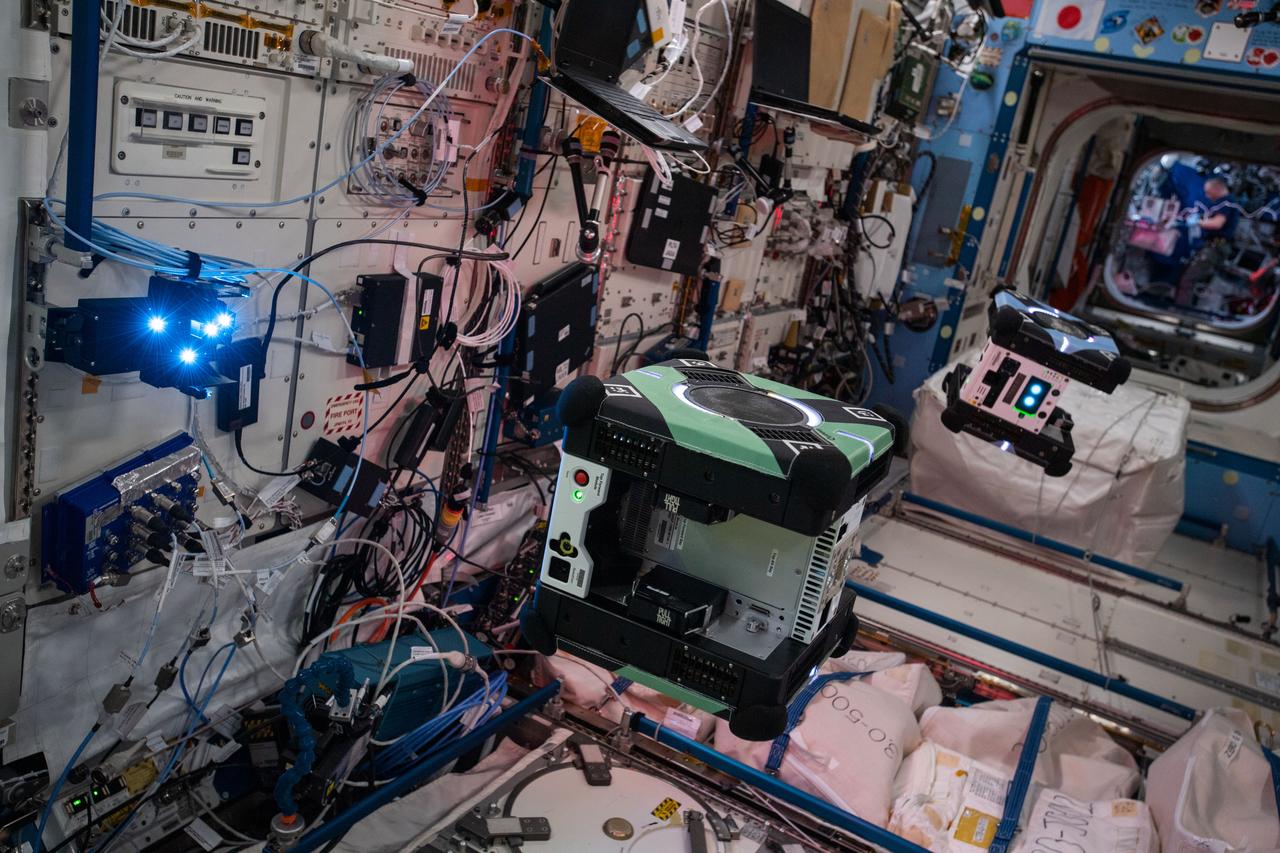

Documentation of two free-flying Astrobee robots (Queen and Bumble), equipped with LED Targets for the Smartphone Video Guidance Sensor (SVGS) experiment, during SVGS science 3 session. An SVGS LED Target is attached to the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) rack, JPM1F5 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
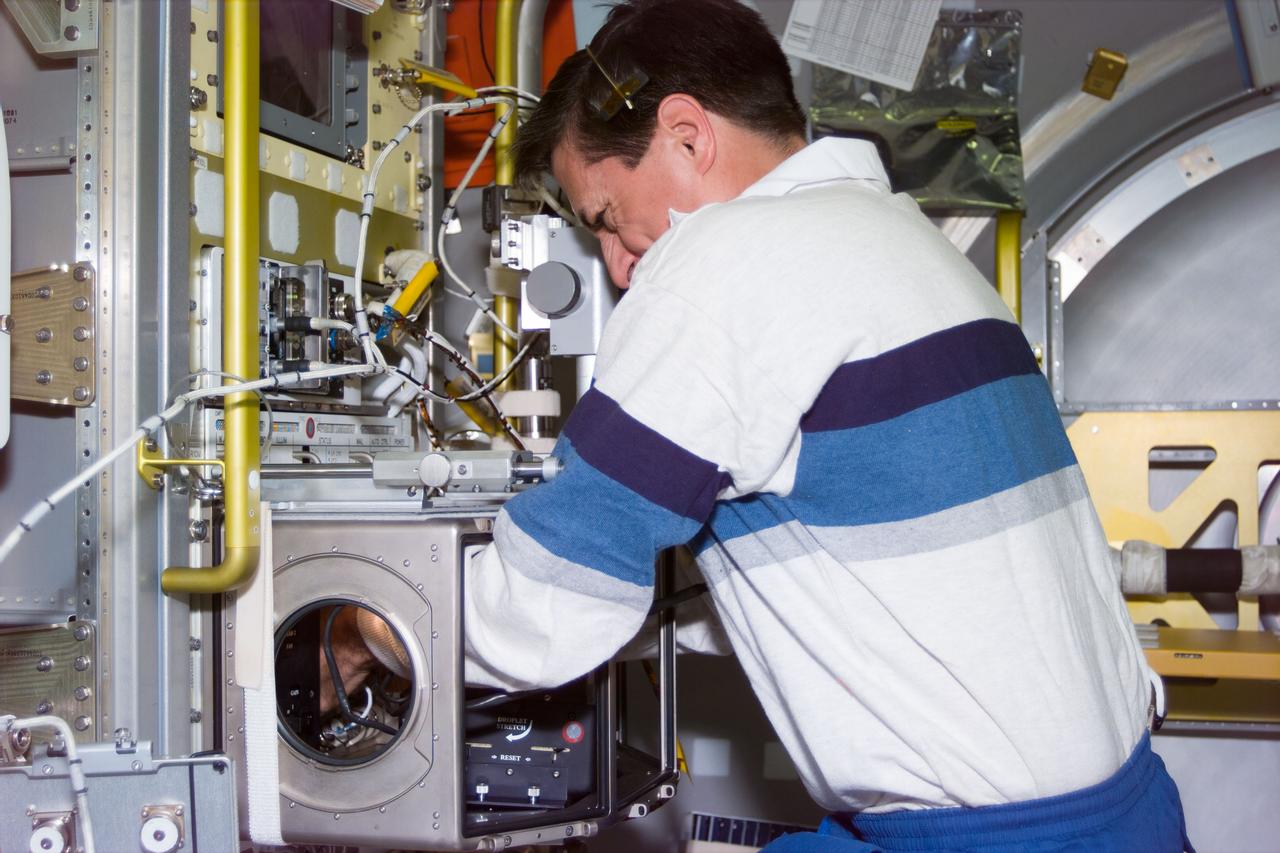

S94-E-5046 (July 1997) --- Astronaut Donald Thomas, mission specialist, sets up an experiment in the glovebox onboard the Spacelab science module. Thomas joins four other NASA astronauts and two payload specialists who are supporting the Microgravity Science Laboratory (MSL-1) mission aboard the Space Shuttle Columiba.
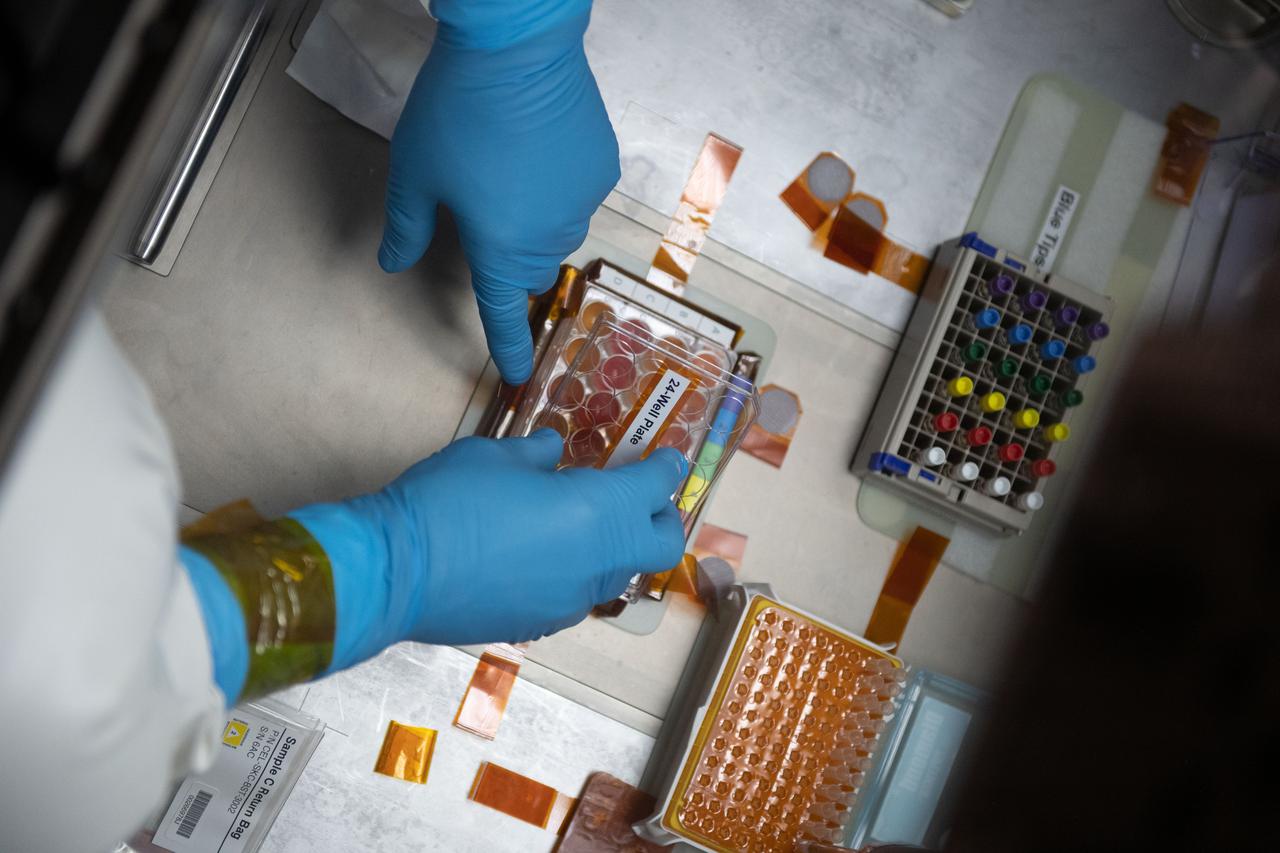

iss065e056810 (5/22/2021) --- NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei works inside the Life Science Glovebox (LSG) for the Celestial Immunity study that may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space. The LSG is located in the Kibo laboratory module from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
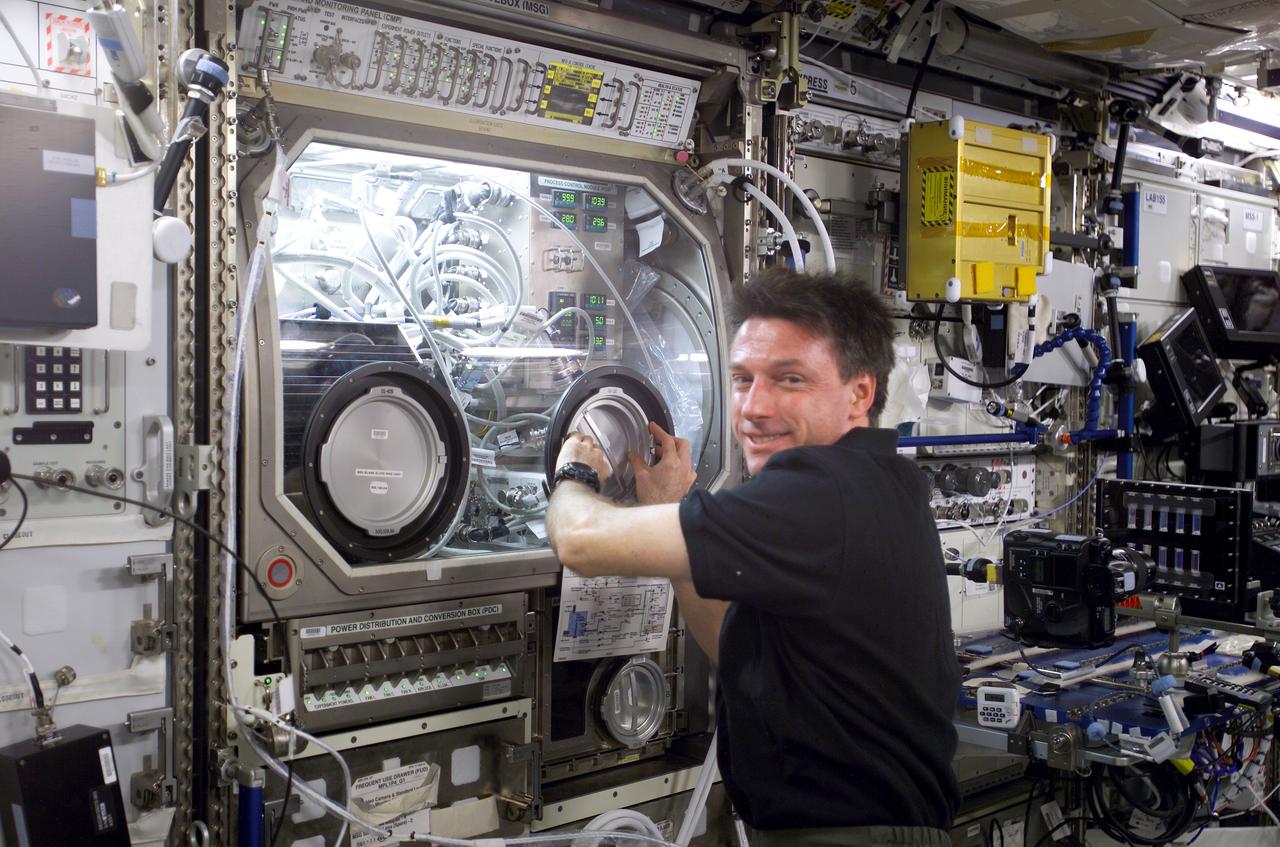

ISS008-E-20622 (5 April 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, conducts an inspection of the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) / Exchangeable Standard Electronic Module (ESEM) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS).
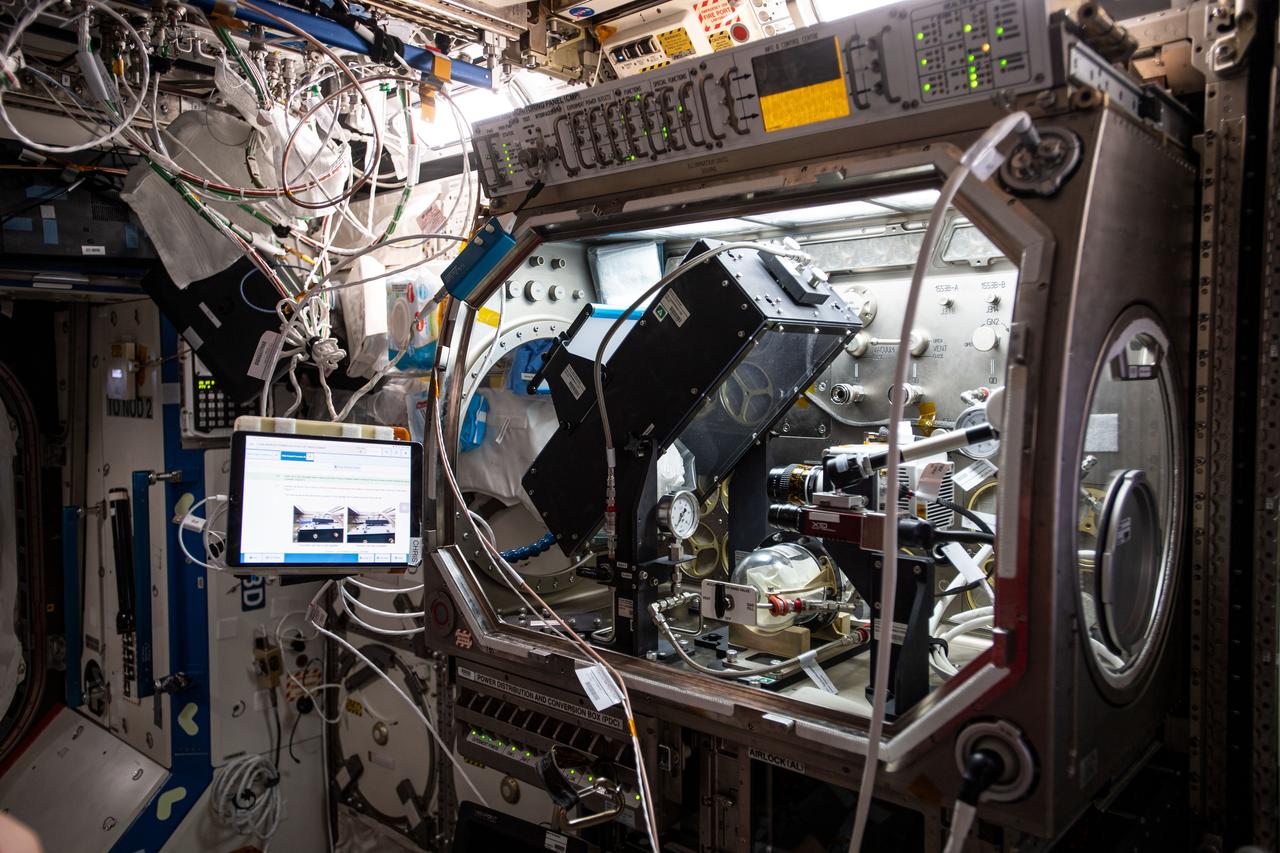

iss063e062018 (7/29/2020) --- Photo documentation of the Droplet Formation Study inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Droplet Formation Study observes how microgravity shapes water droplets, possibly improving water conservation and water pressure techniques on Earth.
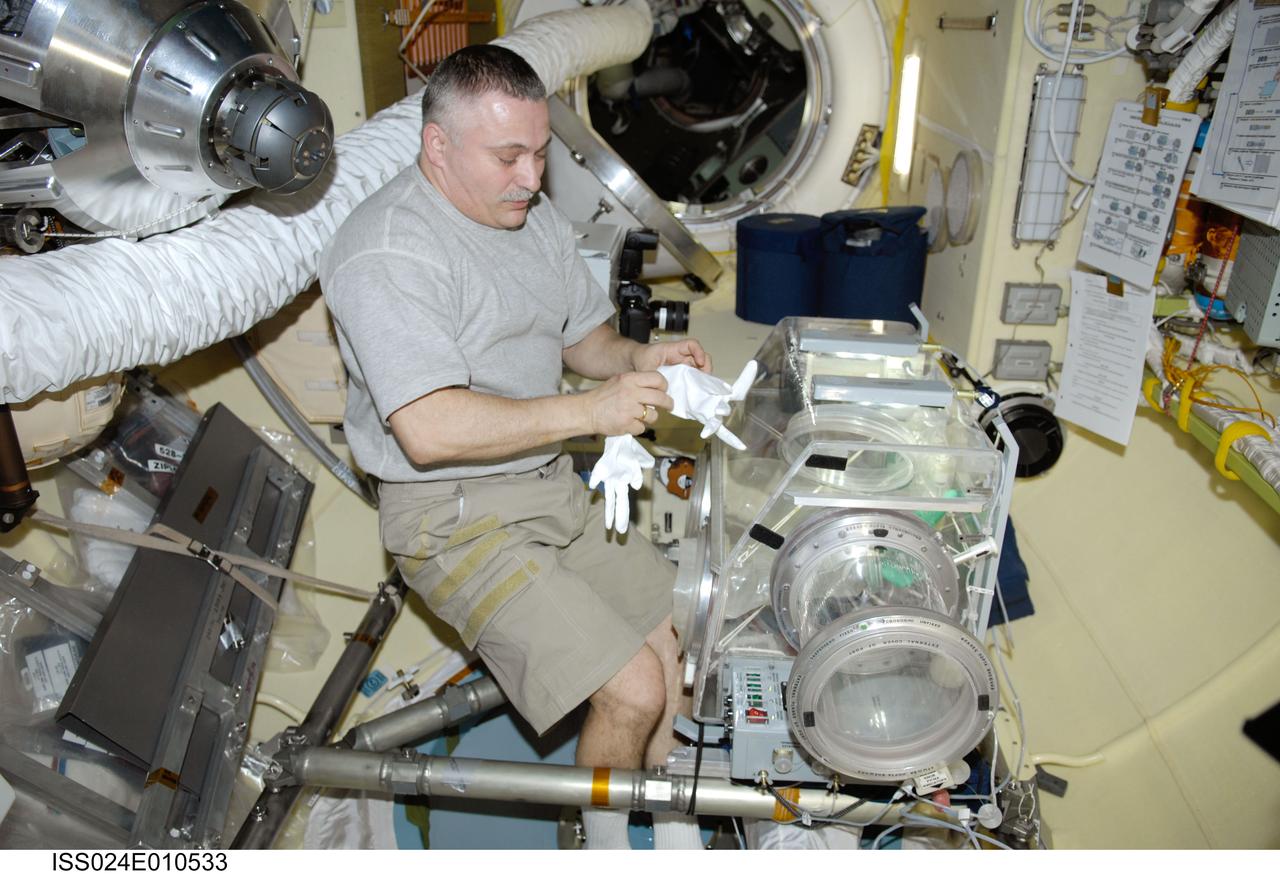

ISS024-E-010533 (3 Aug. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Fyodor Yurchikhin, Expedition 24 flight engineer, prepares the Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) for the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
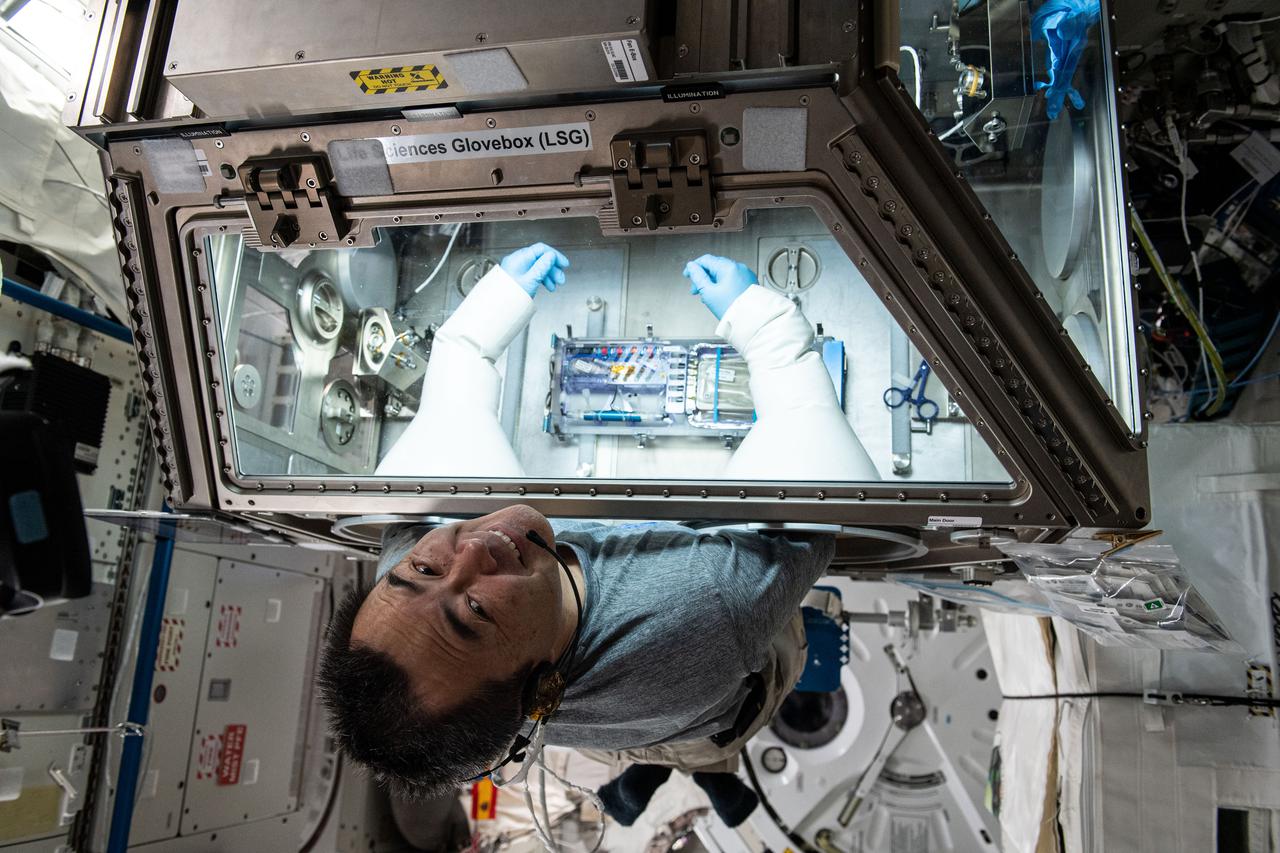

Expedition 65 Commander Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) studies microbes called tardigrades, also known as "water bears", inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Sciences Glovebox for the Cell Science-04 biology experiment. The study seeks to identify genes that adapt best to the harsh environment of microgravity.
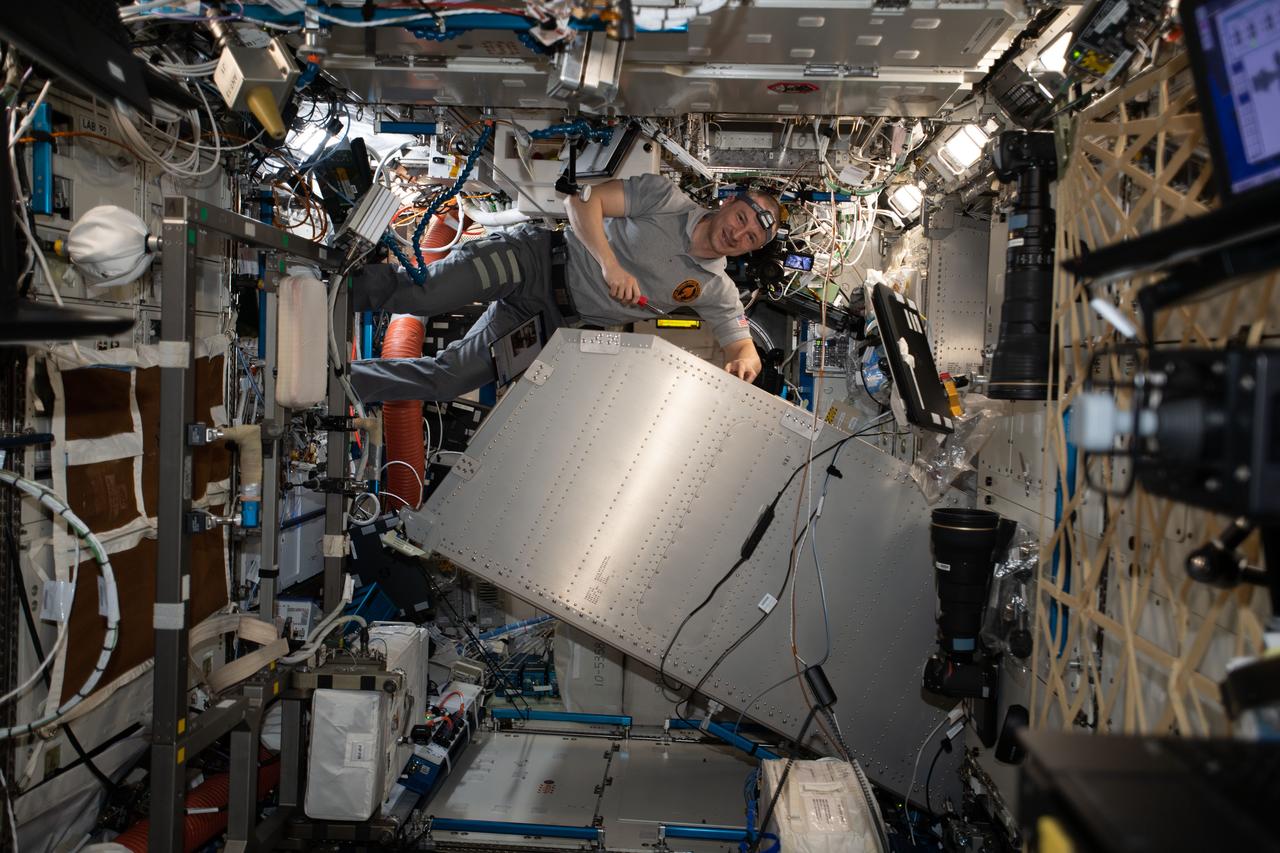

iss062e014085 (Feb. 22, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 62 Flight Engineer Andrew Morgan services the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module. Morgan was cleaning and lubricating the MSG components and photographing the maintenance work for inspection.
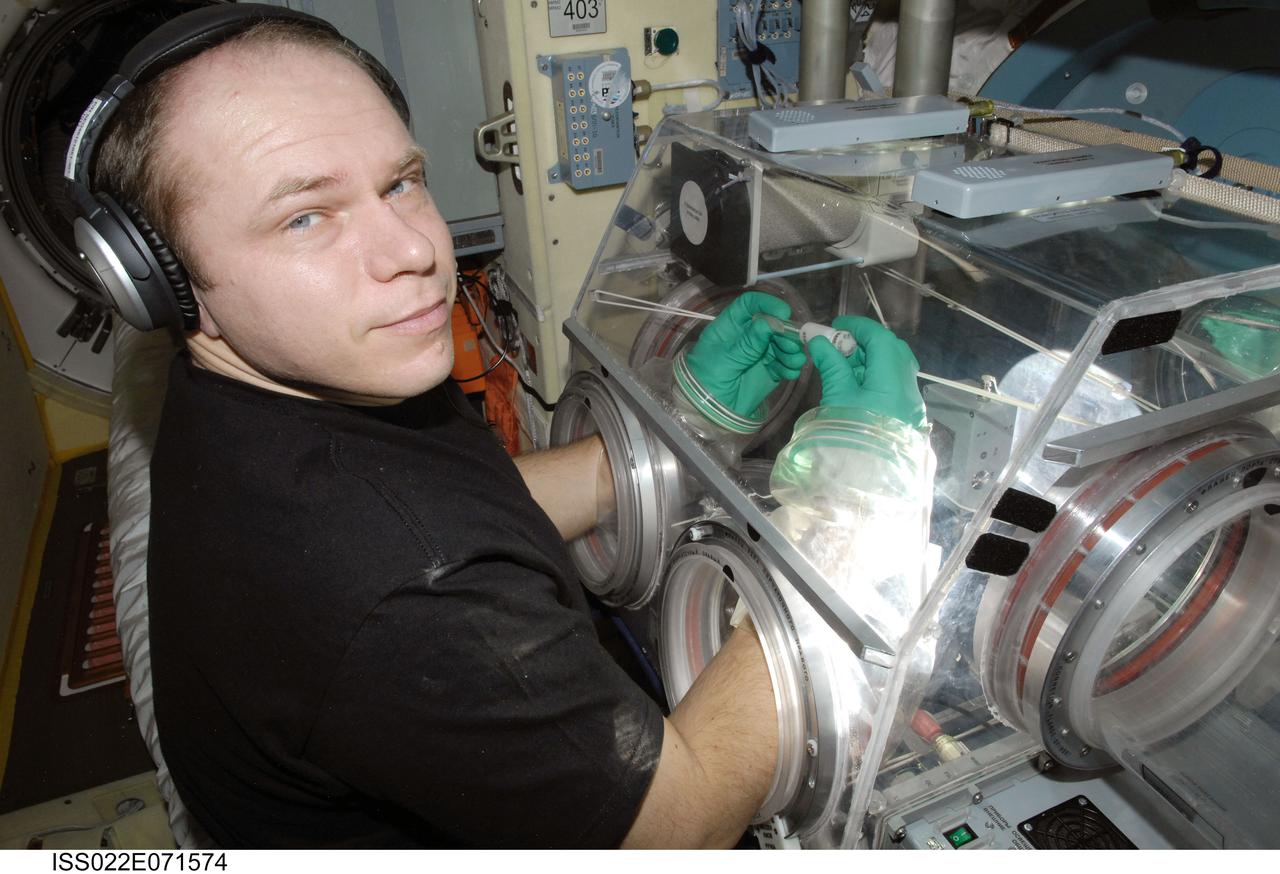

ISS022-E-071574 (24 Feb. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with samples from the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
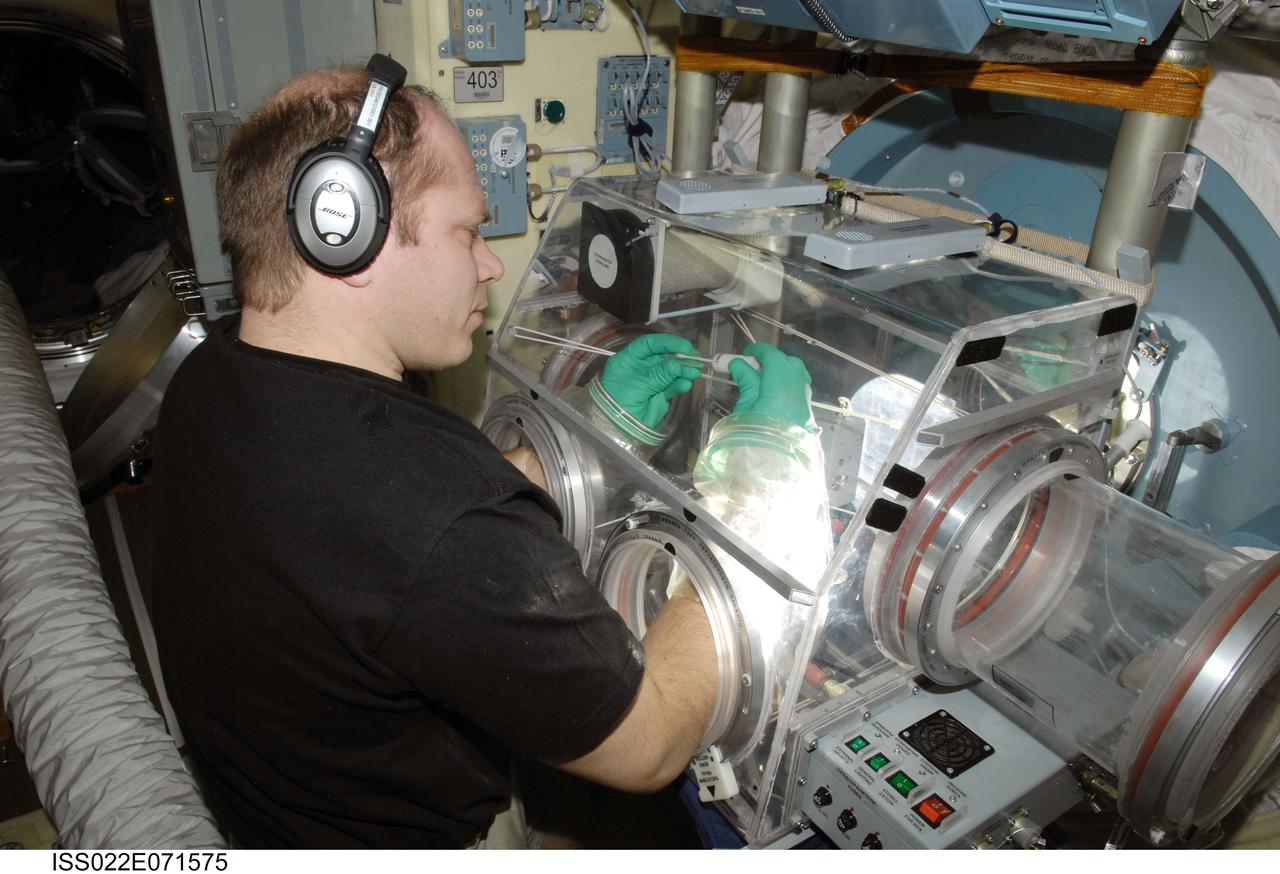

ISS022-E-071575 (24 Feb. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with samples from the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.

ISS022-E-068645 (18 Feb. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with samples from the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the new Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
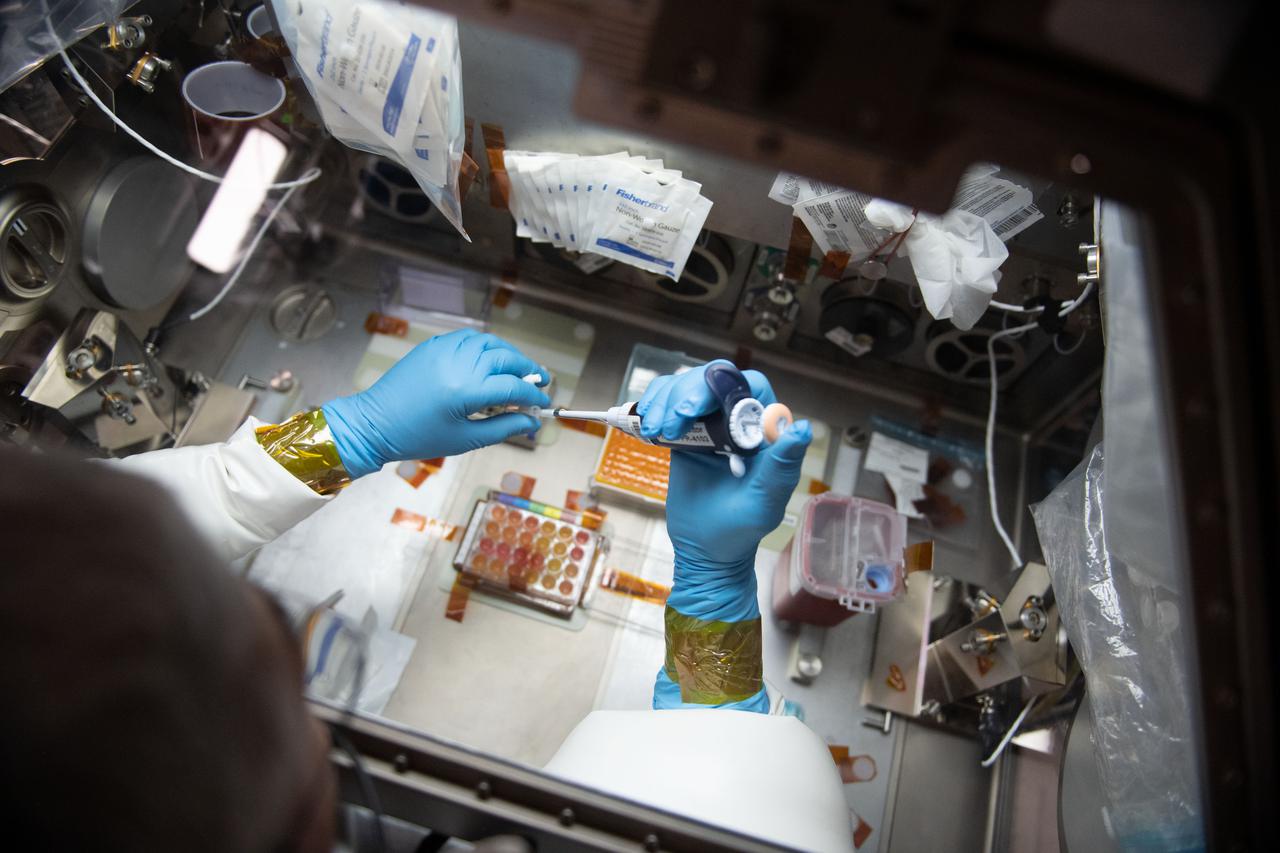
iss065e056791 (5/22/2021) --- NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei works inside the Life Science Glovebox (LSG) for the Celestial Immunity study that may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space. The LSG is located in the Kibo laboratory module from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
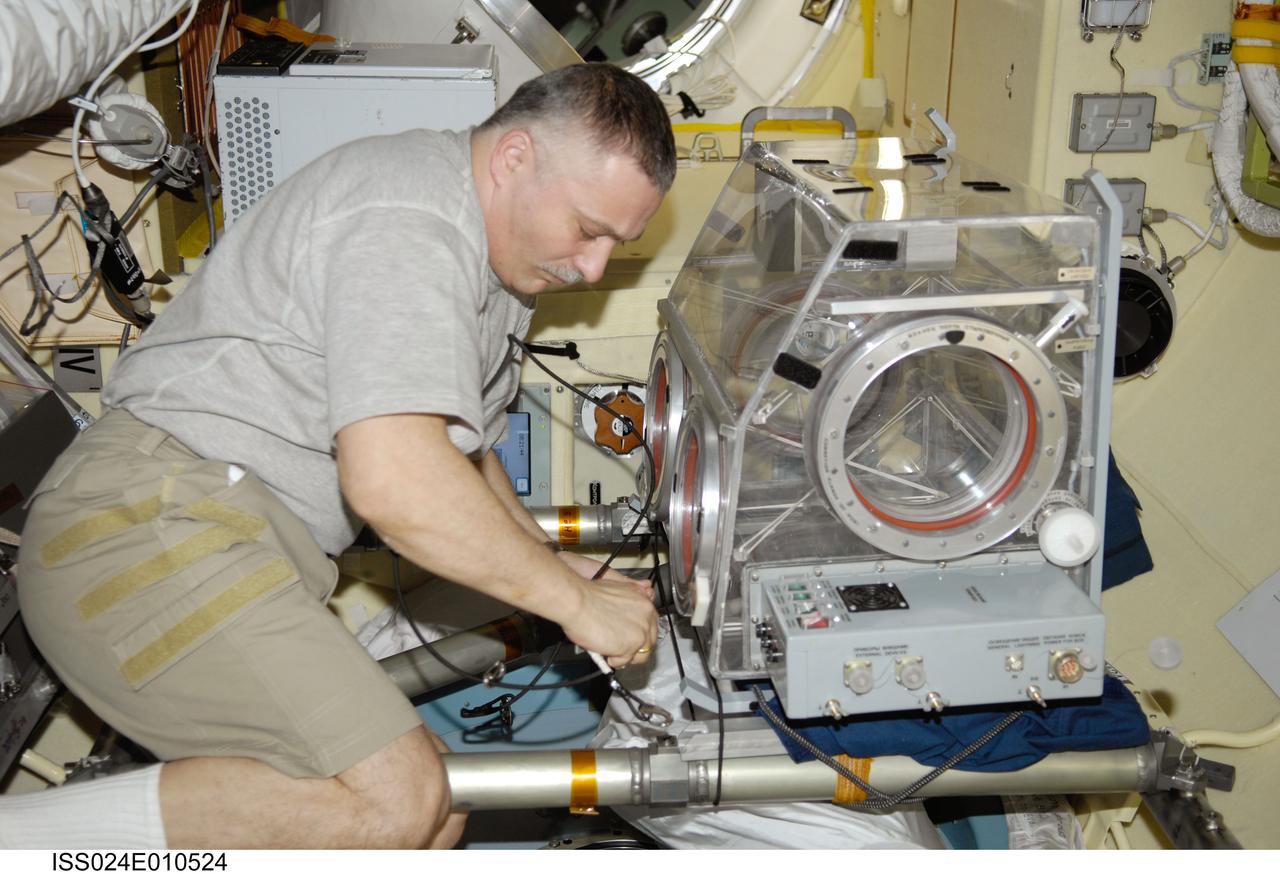

ISS024-E-010524 (3 Aug. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Fyodor Yurchikhin, Expedition 24 flight engineer, prepares the Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) for the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
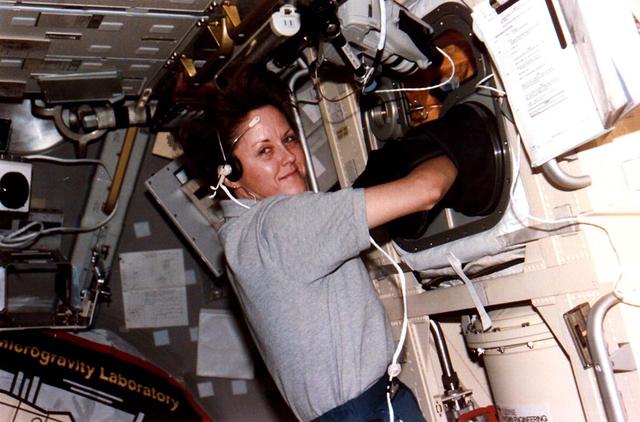

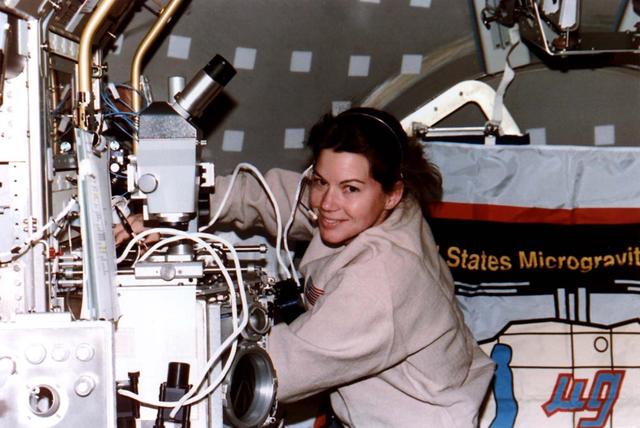
Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander, works in the glovebox of the science module supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission. Five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists are in the last few days of a scheduled 16 day mission.
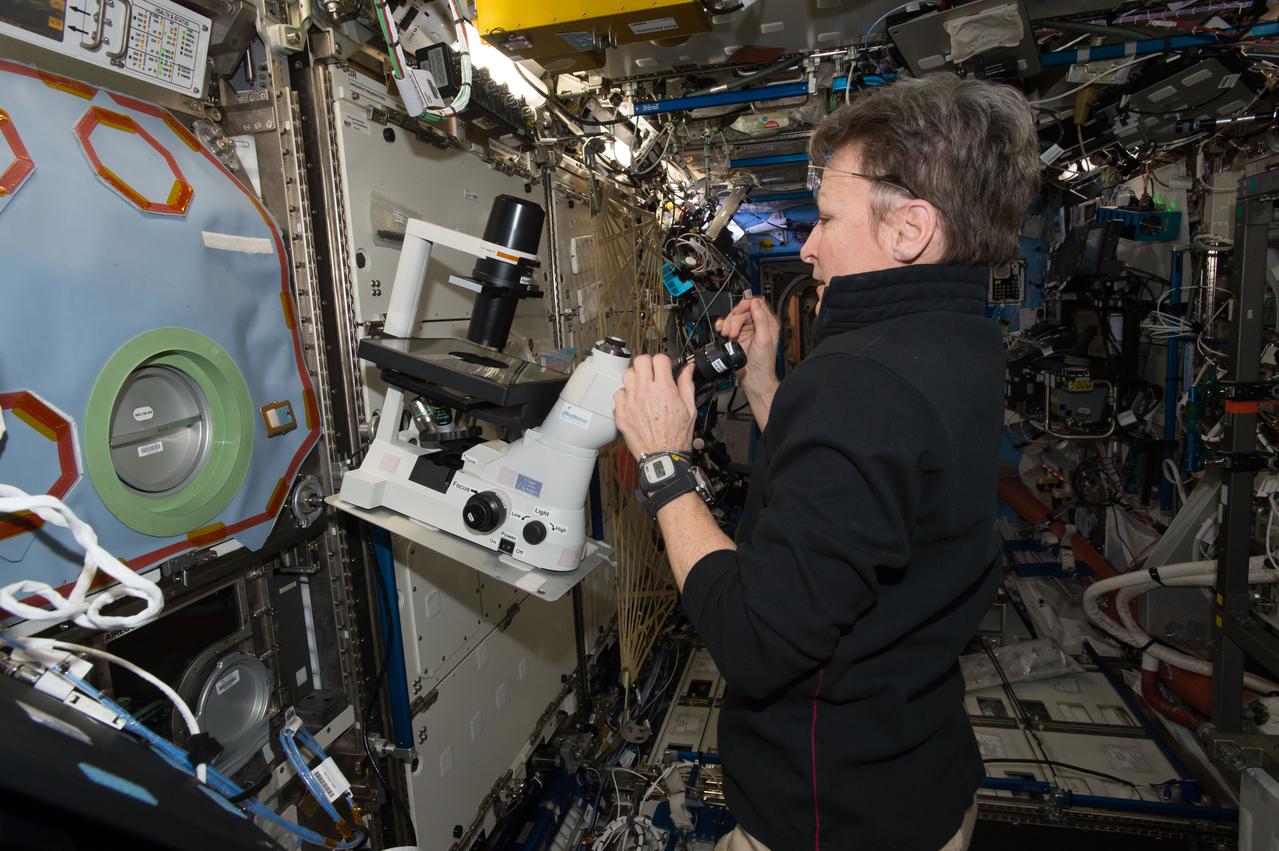

iss050e052142 (Feb. 21, 2017) --- Expedition 50 Flight Engineer Peggy Whitson sets up a microscope in support of the Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells payload outside the Microgravity Science Glovebox housed inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module.

iss070e00391 (Sept. 28, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Loral O'Hara removes space physics research hardware from inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station.
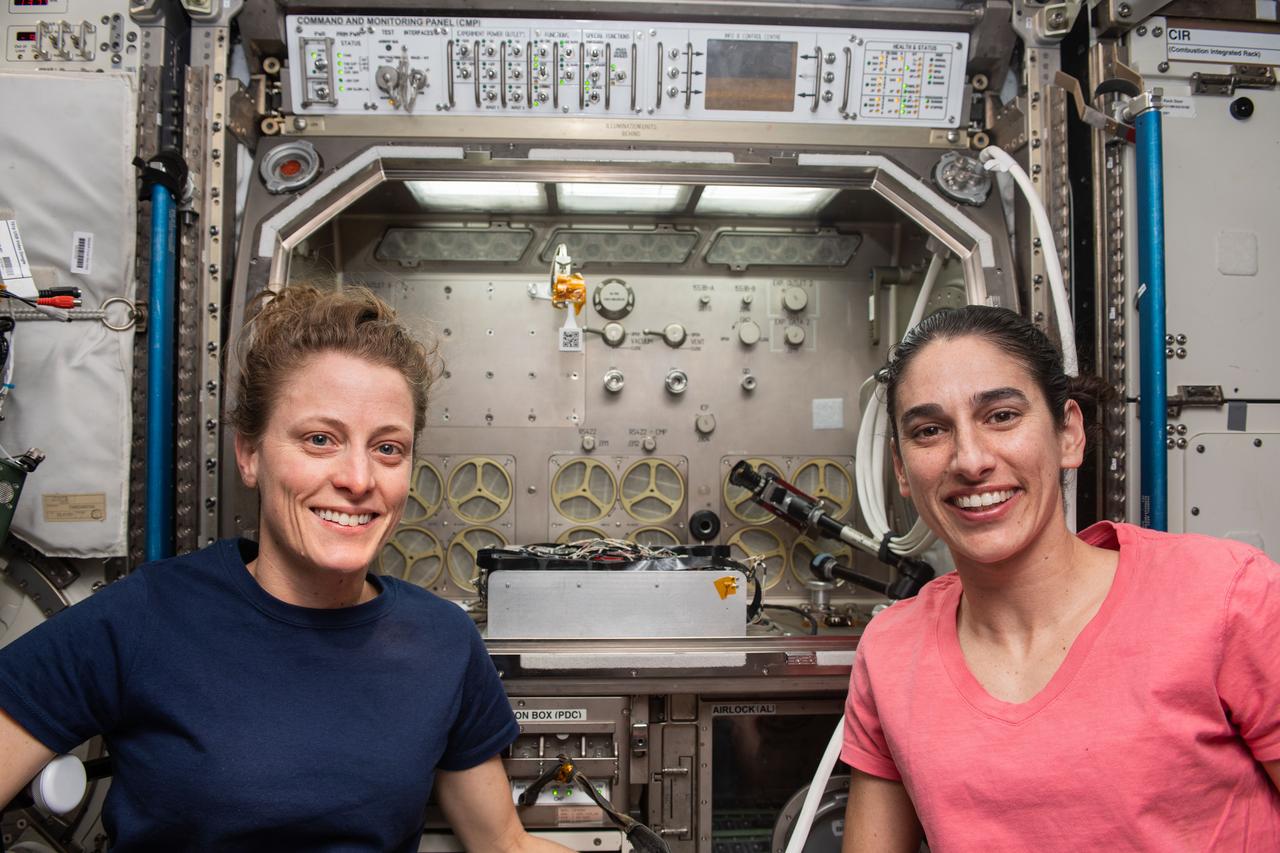
iss070e085869 (Feb. 2, 2024) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineers (from left) Loral O'Hara and Jasmin Moghbeli are pictured in front of the Microgravity Science Glovebox, a research facilty that can host a variety of biology and physics experiments, located in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module.
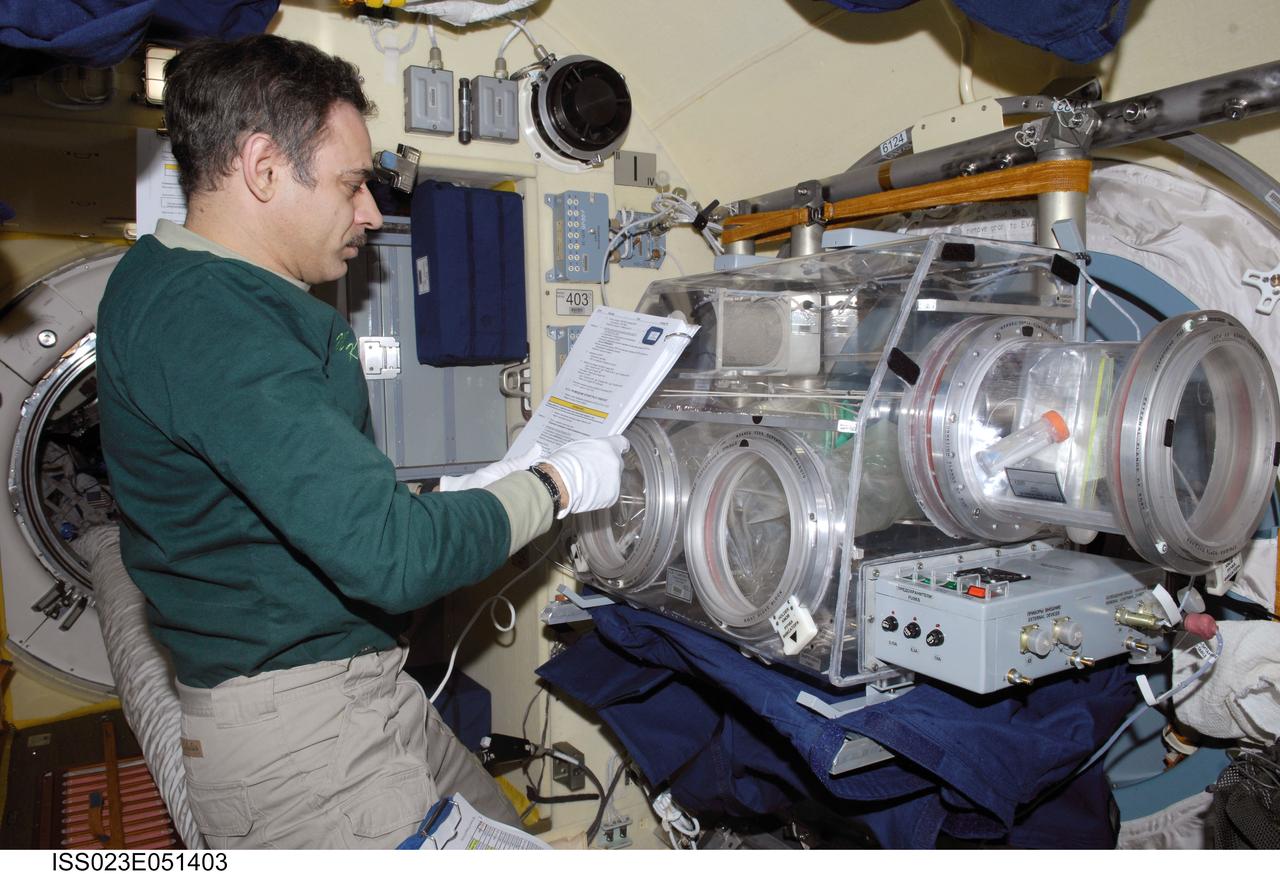

ISS023-E-051403 (26 May 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko, Expedition 23 flight engineer, performs the BTKh-16 KASKAD (Cascade) experiment in the Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
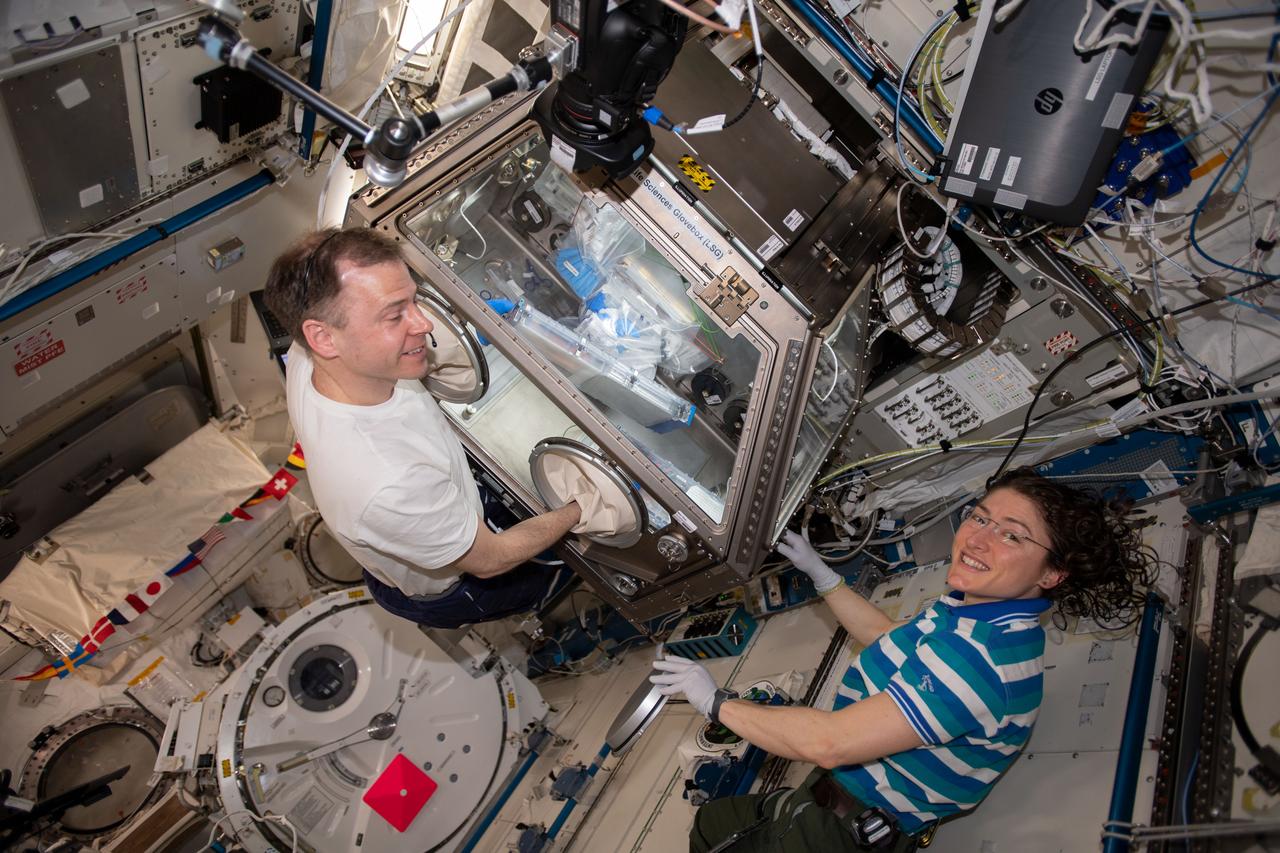

iss060e021469 (Aug. 3, 2019) --- NASA astronauts Nick Hague and Christina Koch work inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module supporting research activities with the Life Sciences Glovebox. The Expedition 60 crewmates were conducting science operations for the Cell Science-02 bone healing and tissue regeneration experiment.
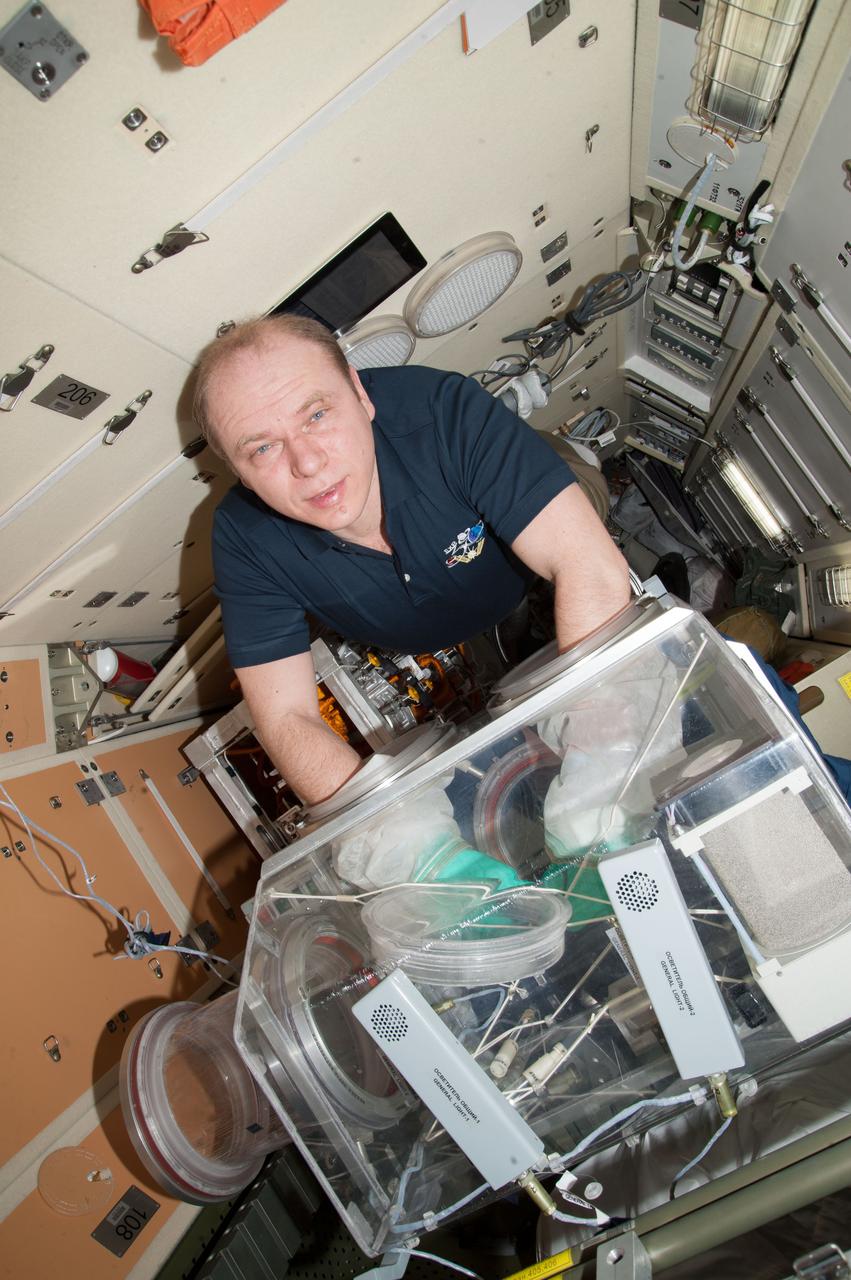

ISS038-E-066110 (7 Feb. 2014) --- In the Rassvet Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM1) of the Earth-orbiting International Space Station, Expedition 38 Commander Oleg Kotov of Russia's Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) works with the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC in the Russian Glavboks (Glovebox).
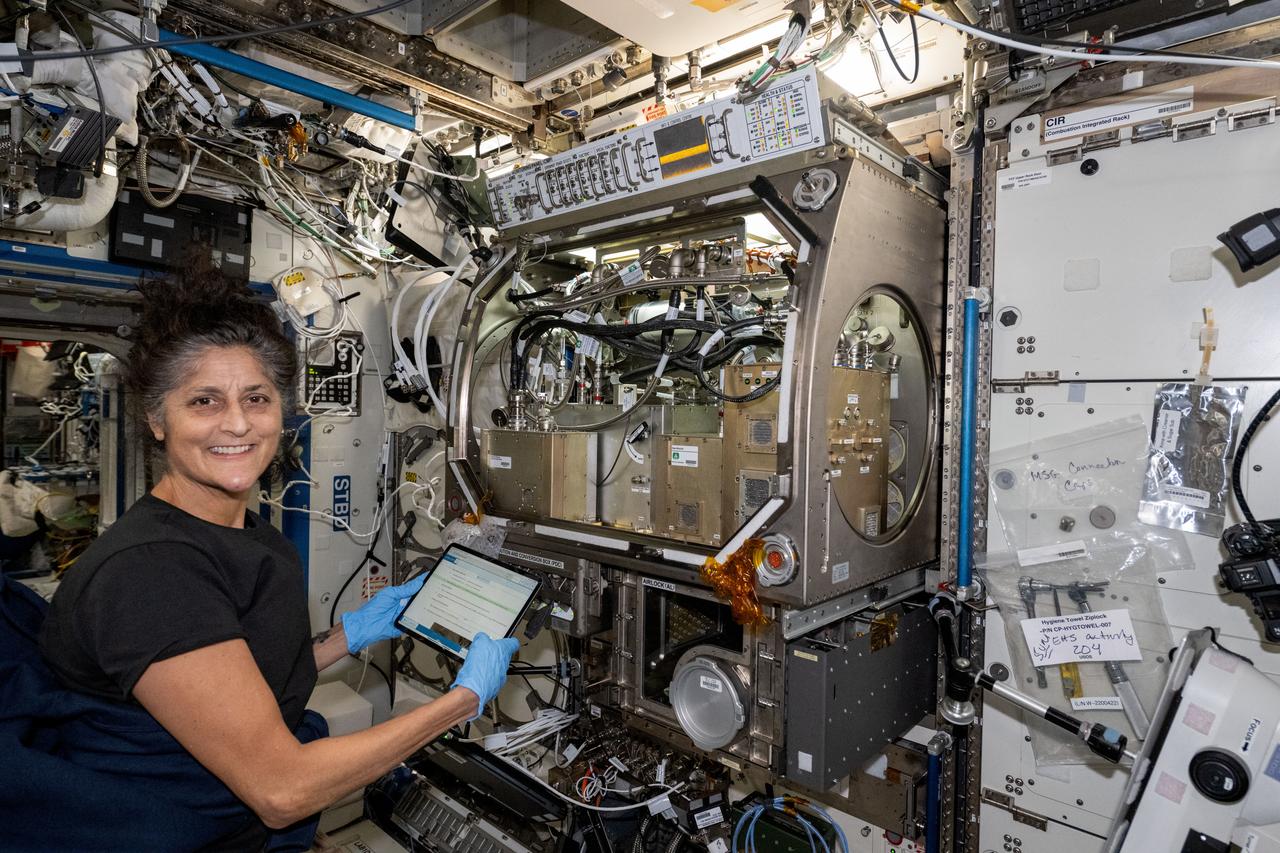

iss071e485839 (Aug. 15, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Boeing Crew Flight Test Pilot Suni Williams installs the Packed Bed Reactor Experiment, experimental life support hardware, inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox located aboard the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module.
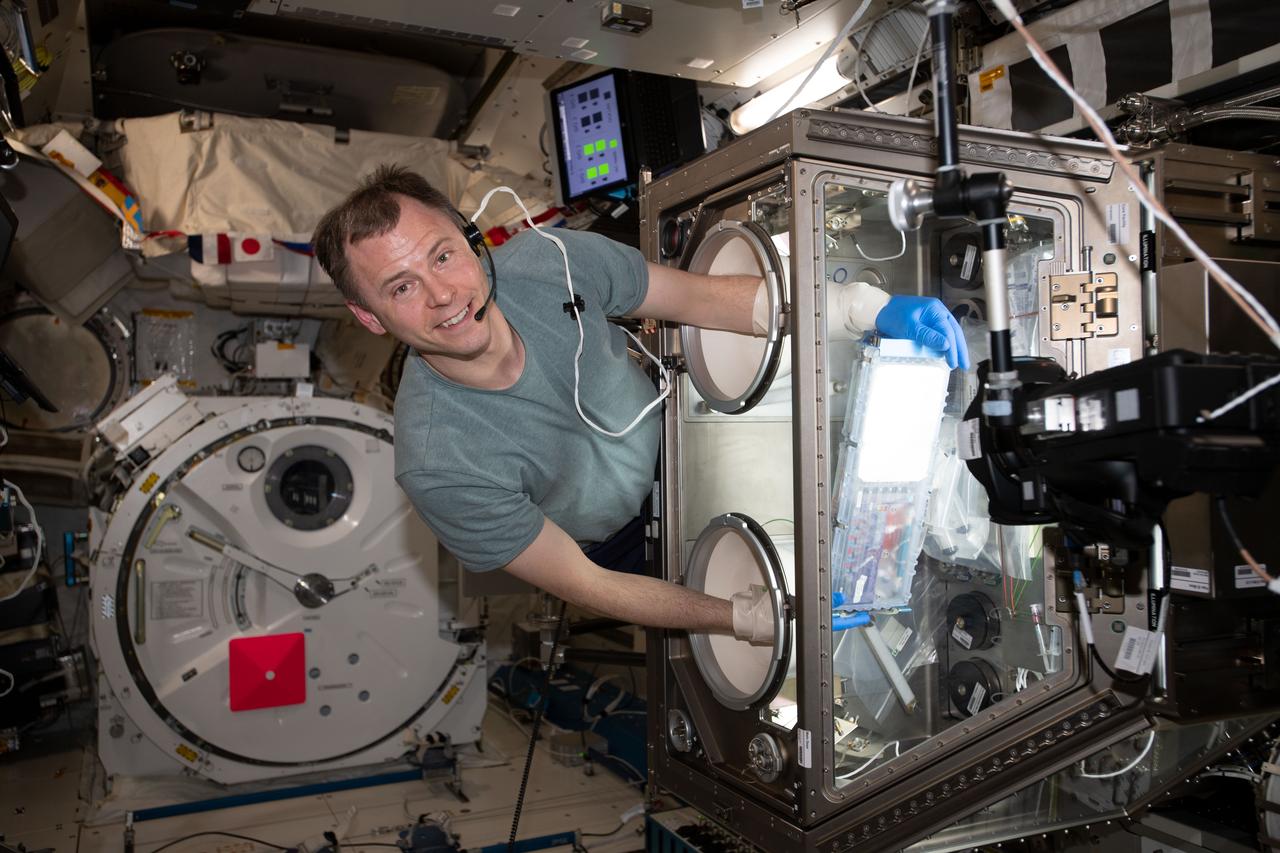

iss060e019982 (July 30, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague works inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module supporting research activities with the Life Sciences Glovebox. Hague is conducting science operations for the Cell Science-02 bone healing and tissue regeneration experiment.
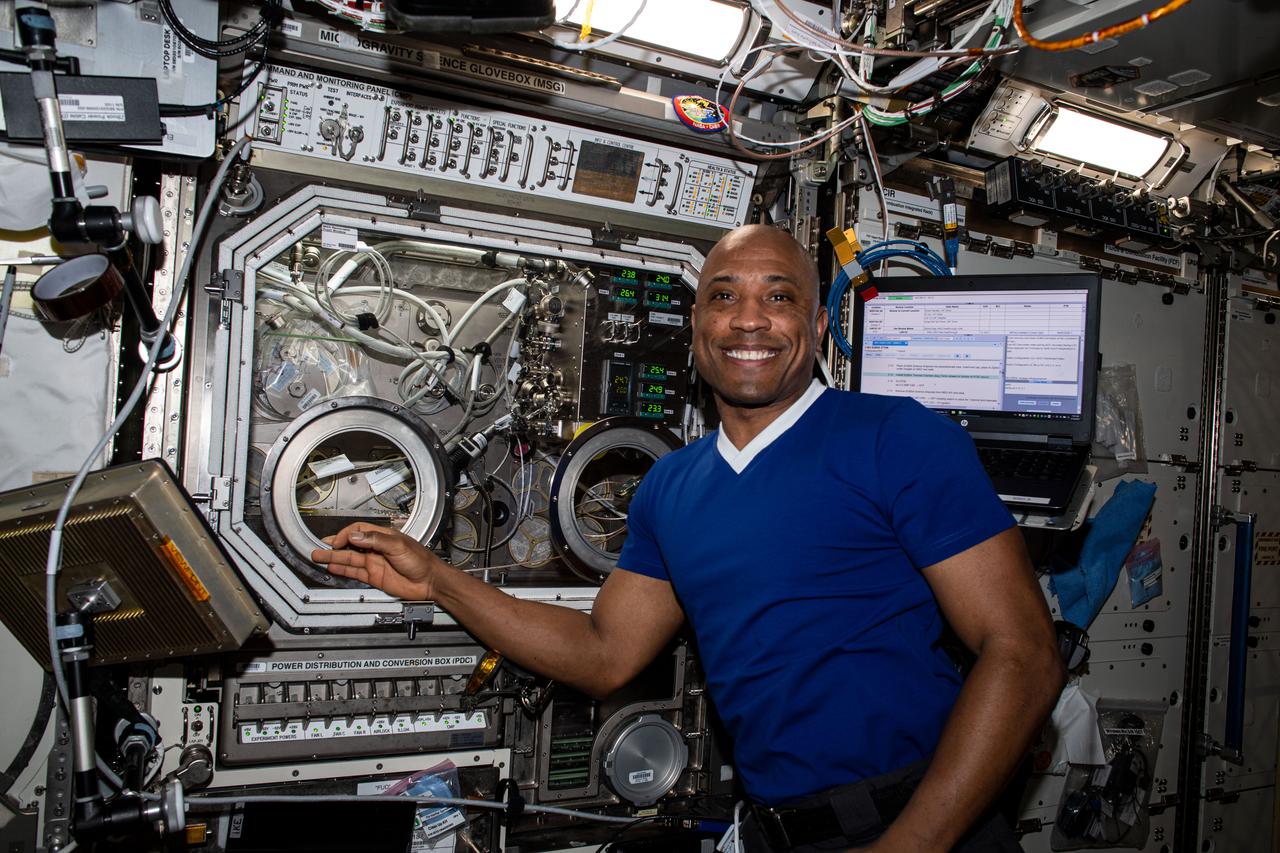

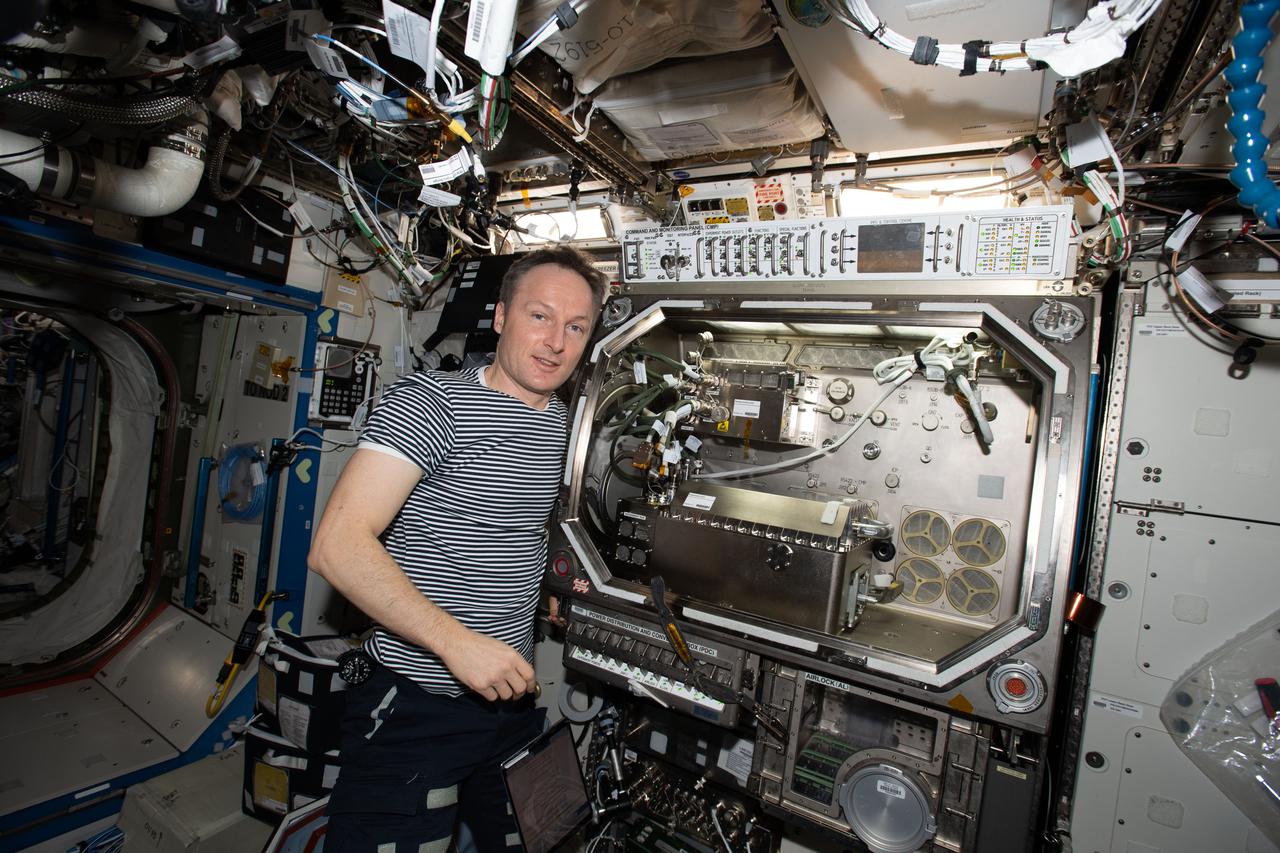
iss064e033239 (Feb. 16, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Victor Glover poses for a portrait in front of the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) located inside the International Space Station's U.S. Destiny laboratory module. The MSG supports a wide variety of space studies exploring everything from physics to biology.
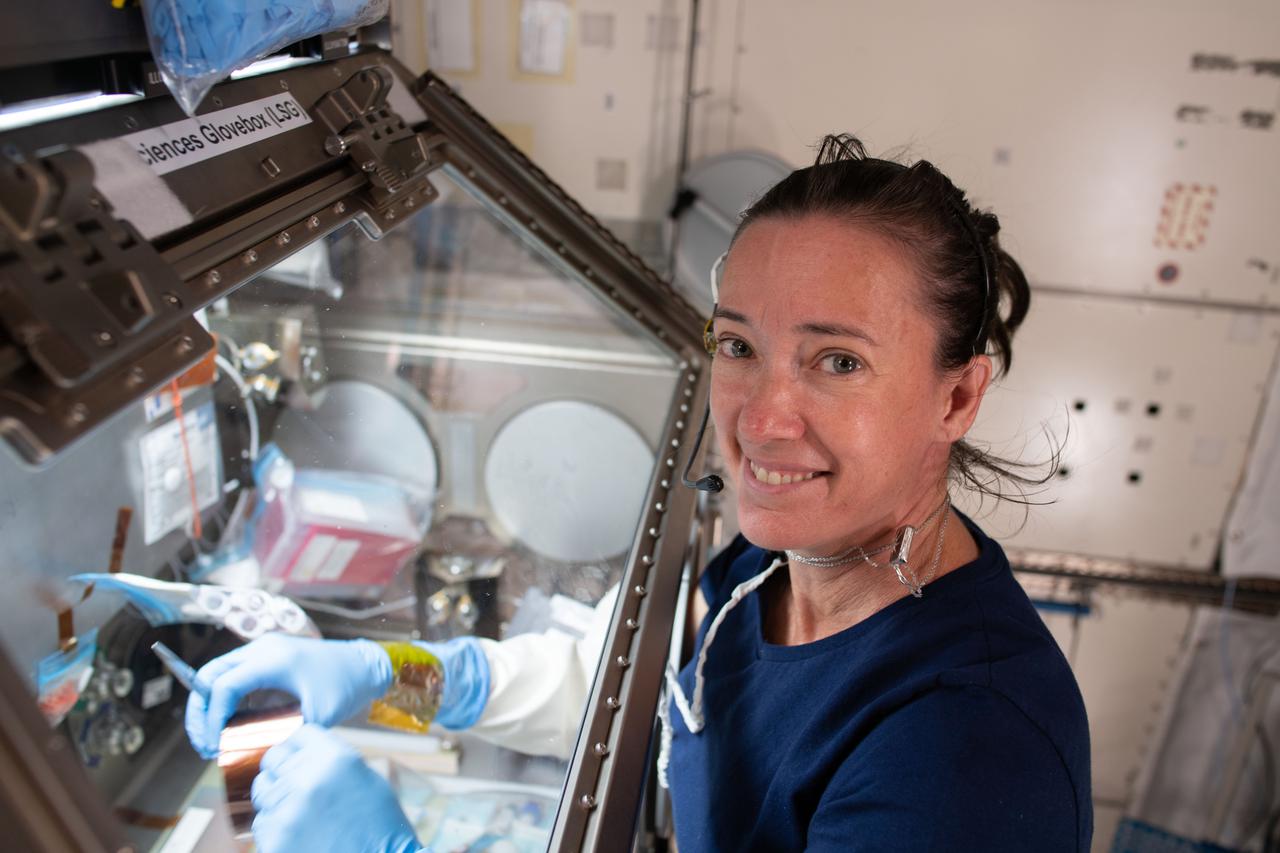

iss065e026426 (May 6, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur services donor cells inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox for the Celestial Immunity study. The human research investigation may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space.
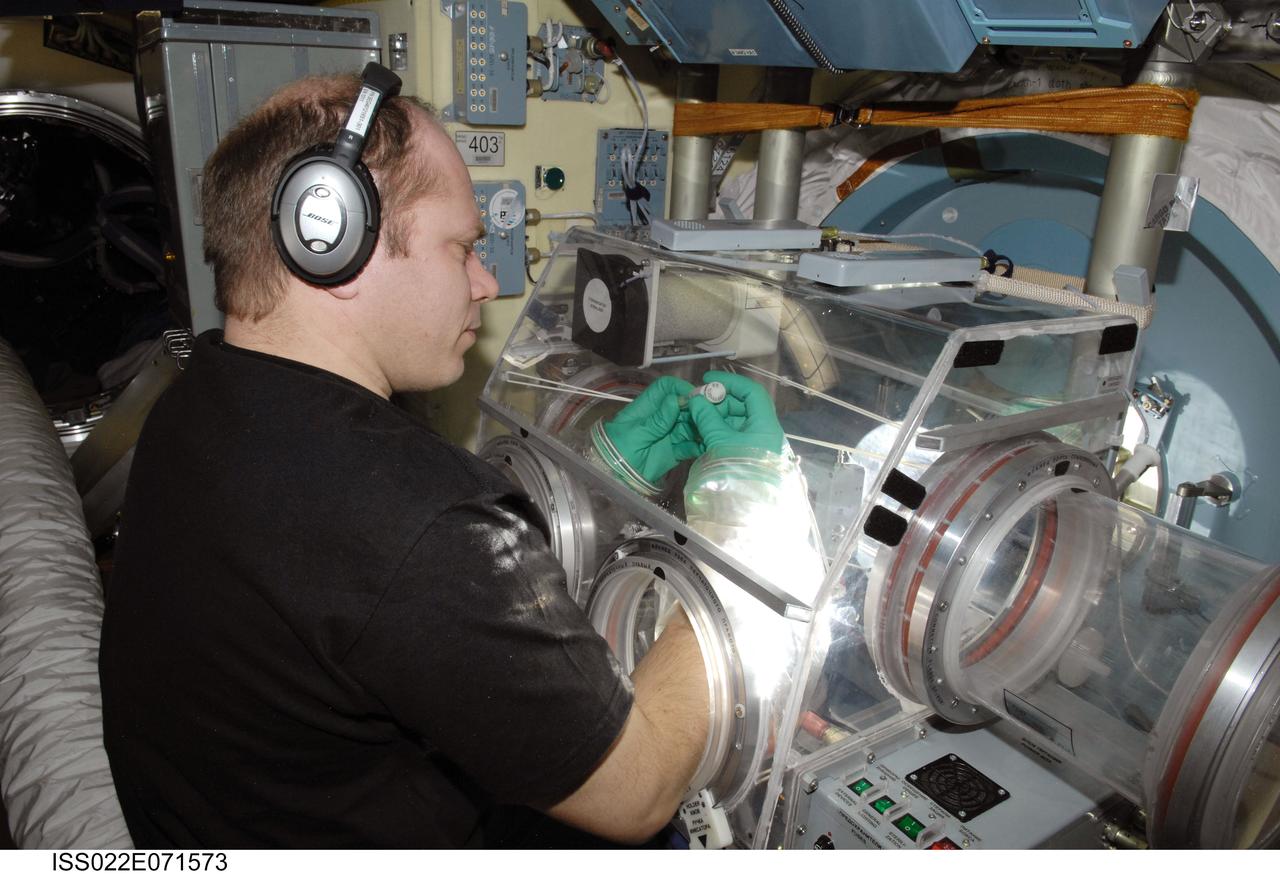

ISS022-E-071573 (24 Feb. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with samples from the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
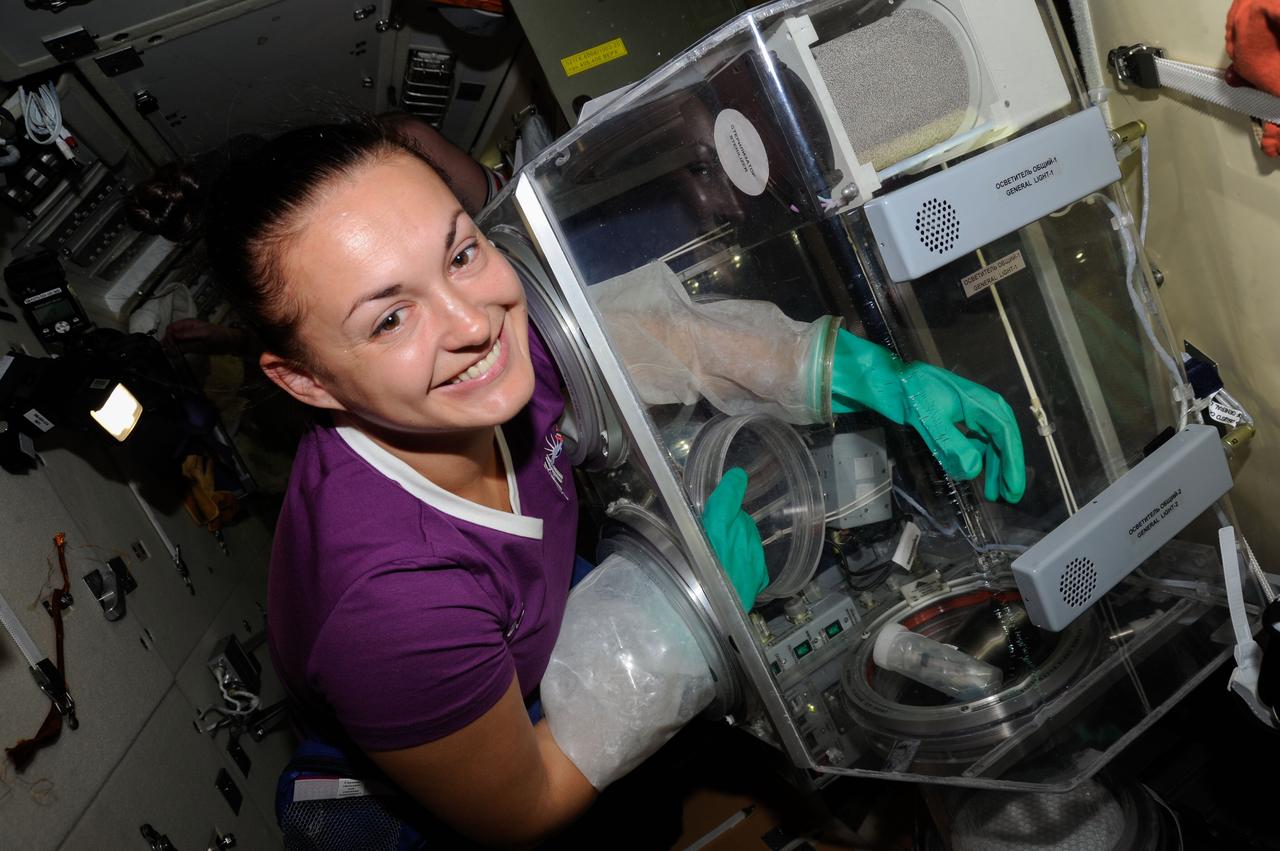

ISS041-E-037551 (29 Sept. 2014) --- Russian cosmonaut Elena Serova, Expedition 41 flight engineer, works with test samples from the Kaskad cell cultivation experiment in a glovebox in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
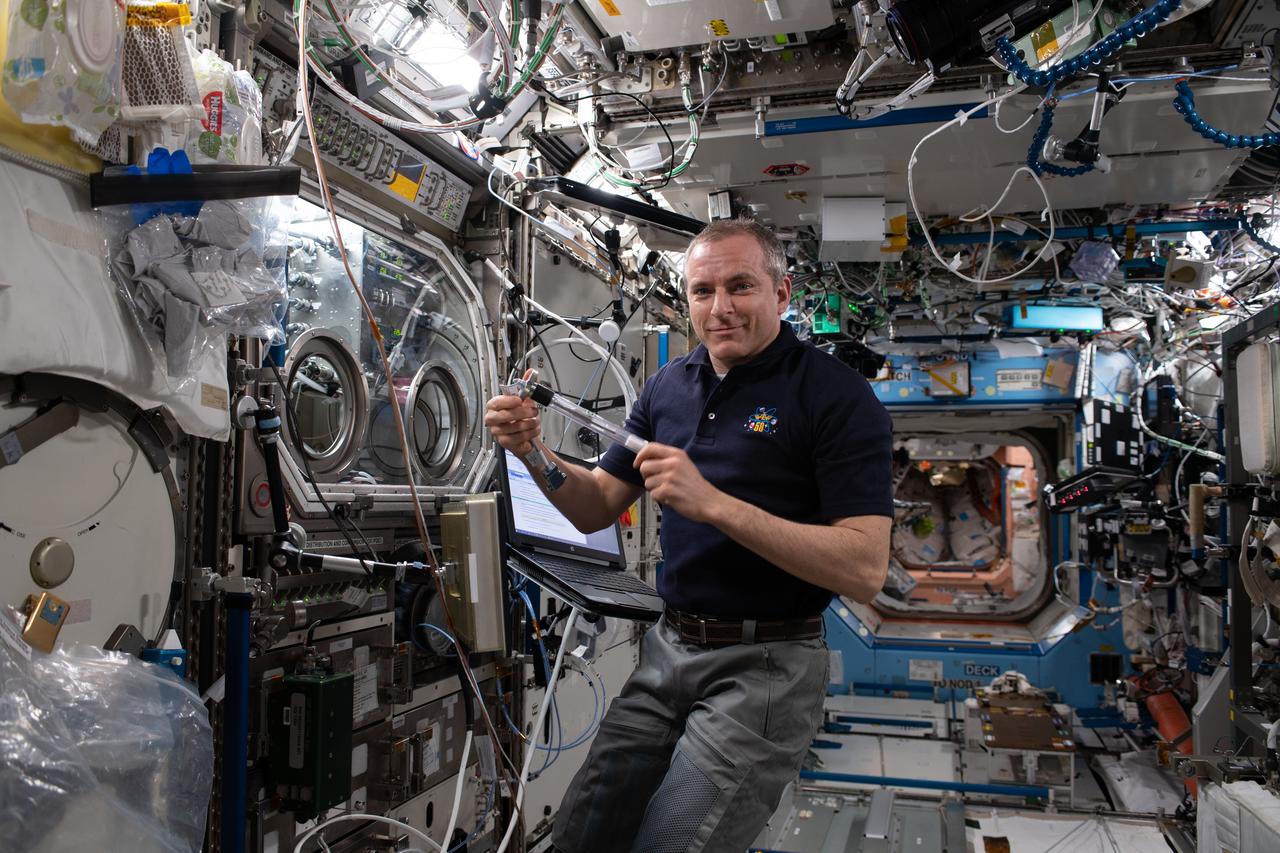

iss059e027344 (April 19, 2019) --- Astronaut David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency studies how crystals melt and solidify using the Microgravity Science Glovebox inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module. The Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules study explores how to produce high-quality semi-conductor crystals in microgravity.
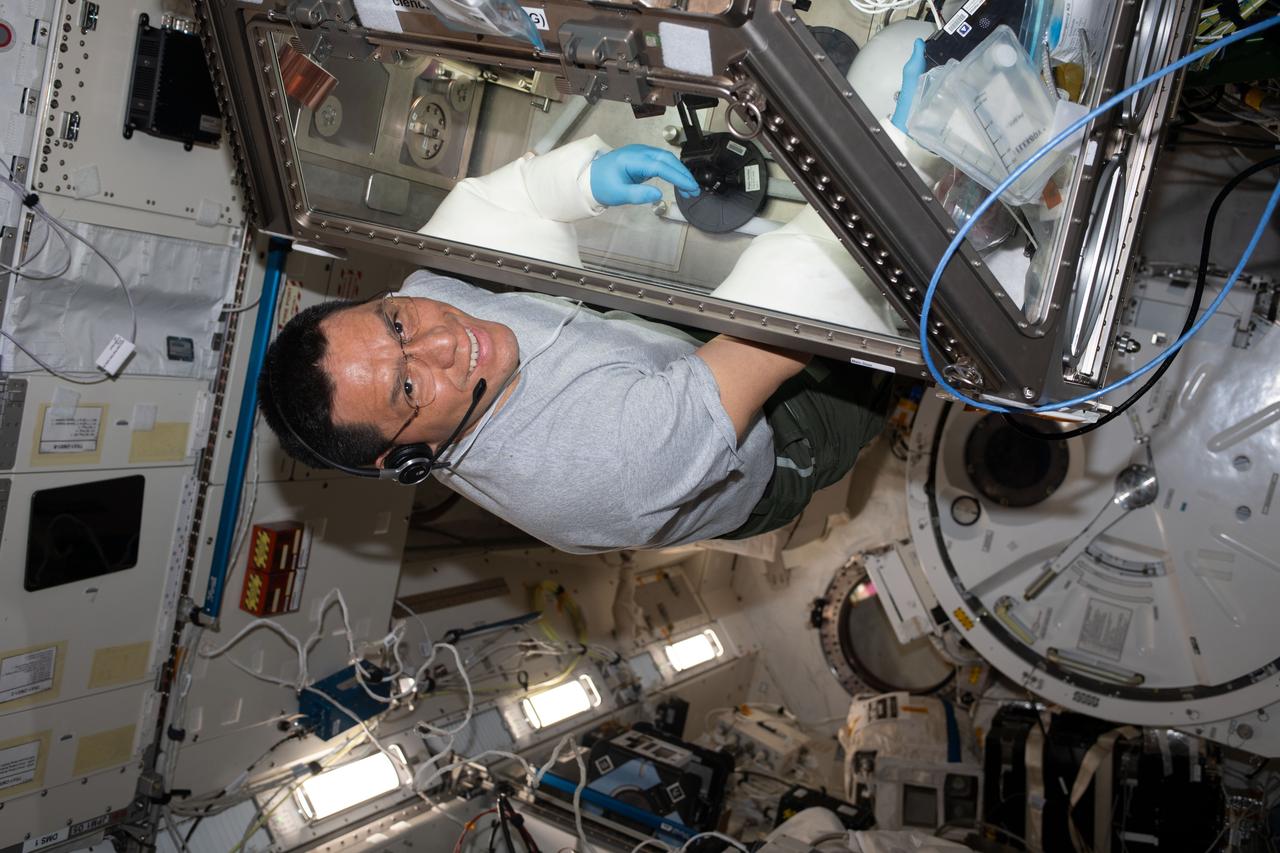

iss069e055093 (Aug. 8, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Frank Rubio works in the Kibo laboratory module's Life Sciences Glovebox servicing stem cell samples for the StemCellEX-H Pathfinder study. The biotechnology investigation seeks to improve therapies for blood diseases and cancers such as leukemia.
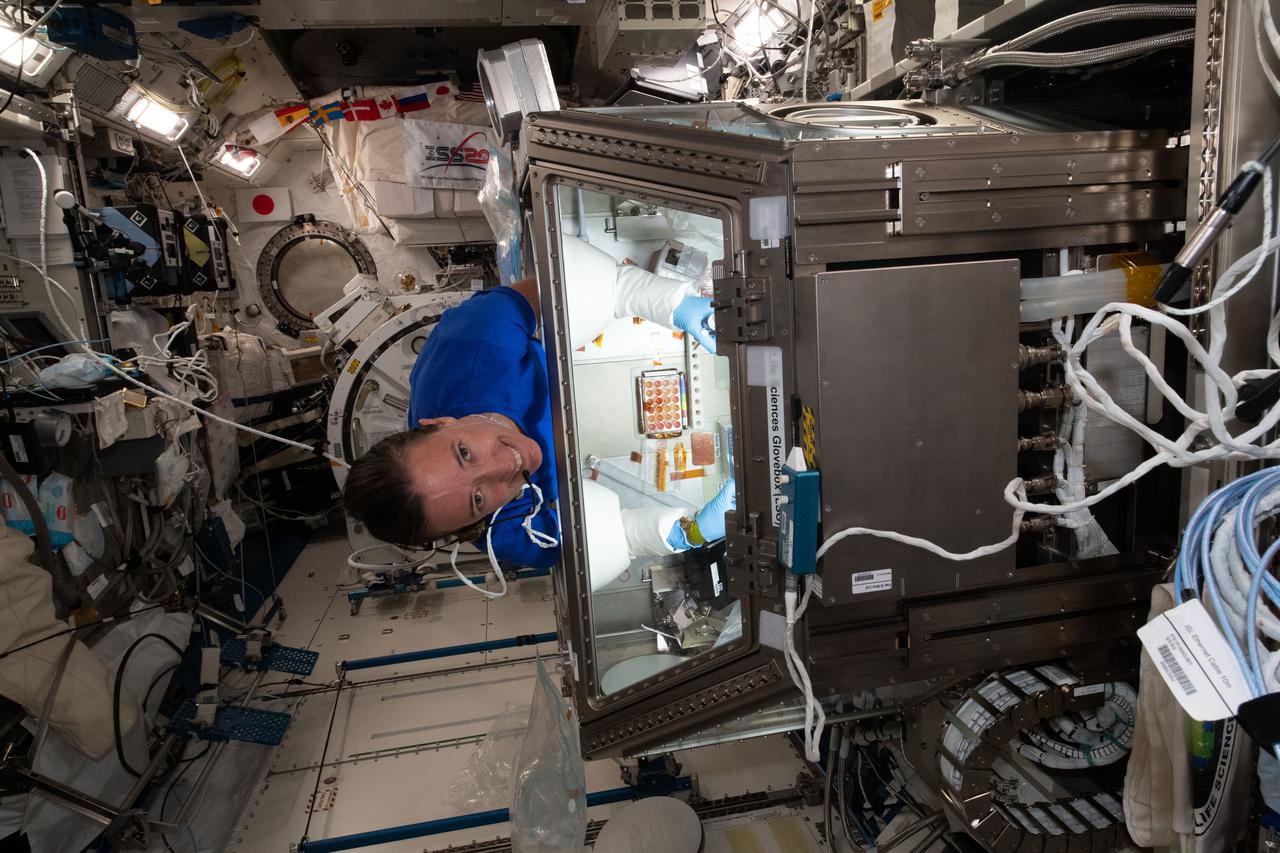

iss065e026996 (5/8/2021) --- NASA astronaut Megan McArthur services donor cells inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox for the Celestial Immunity study. The human research investigation may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space.
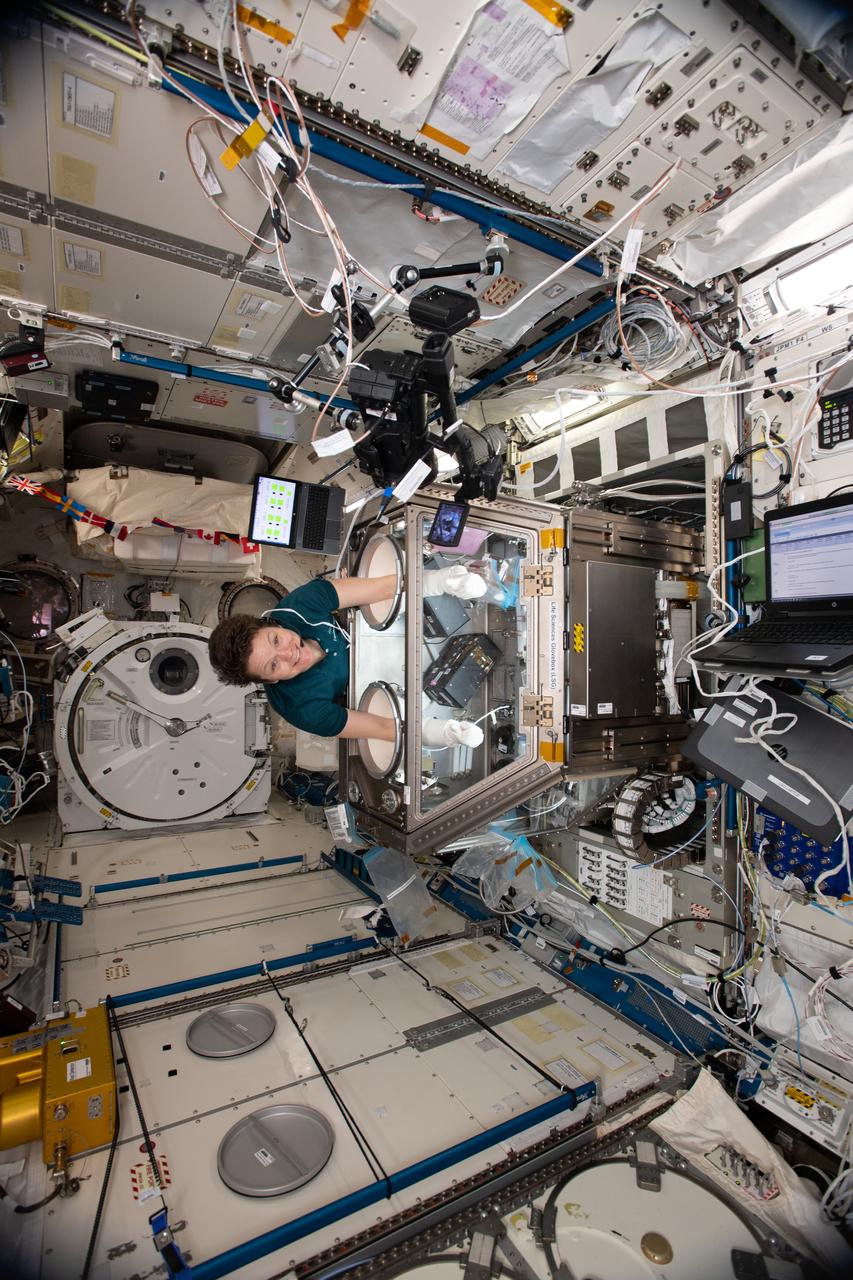

iss059e060922 (May 10, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Anne McClain works on Kidney Cells hardware inside the Life Sciences Glovebox located in Japan's Kibo laboratory module. Kidney Cells is an investigation that is seeking innovative treatments for kidney stones, osteoporosis and toxic chemical exposures to protect the health of astronauts in space and humans on Earth.
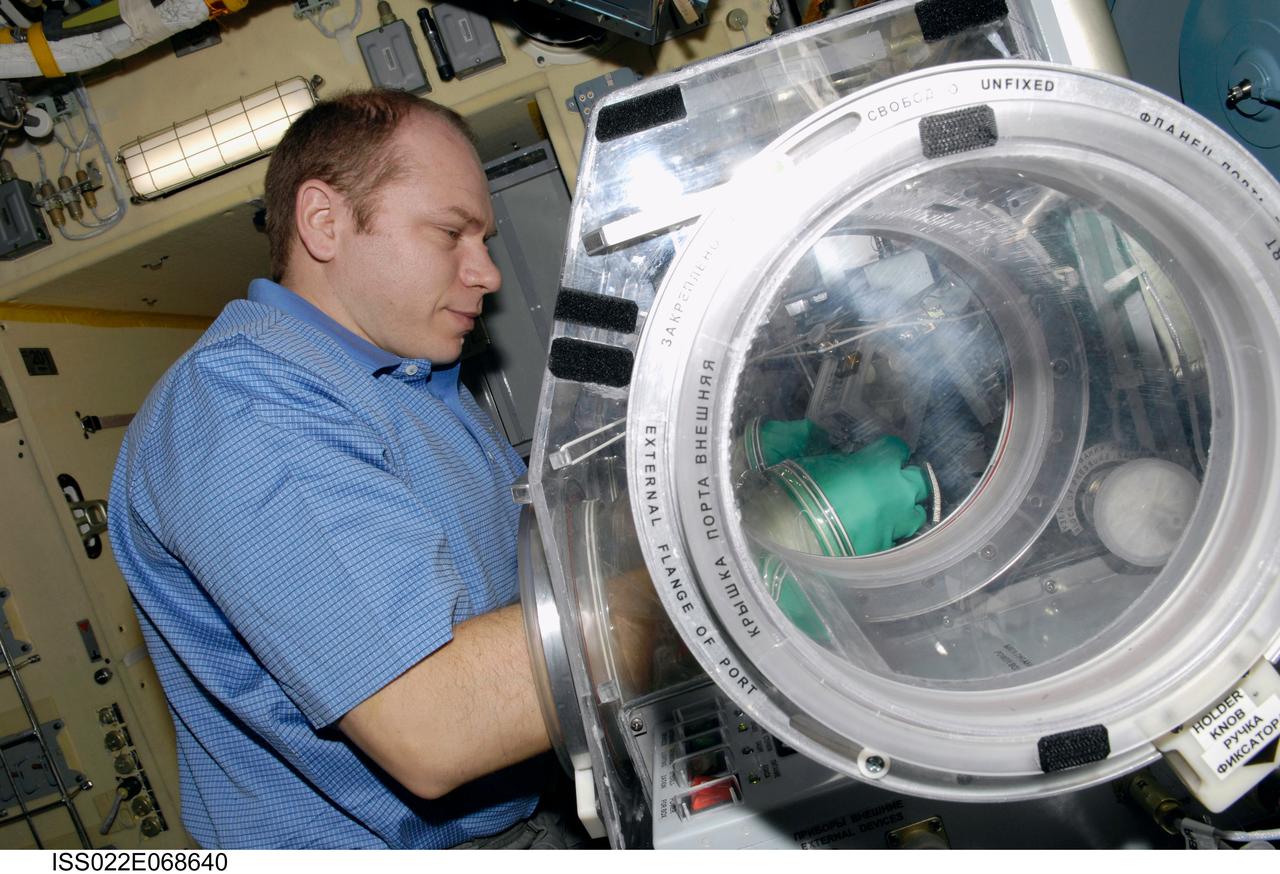

ISS022-E-068640 (18 Feb. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with samples from the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the new Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
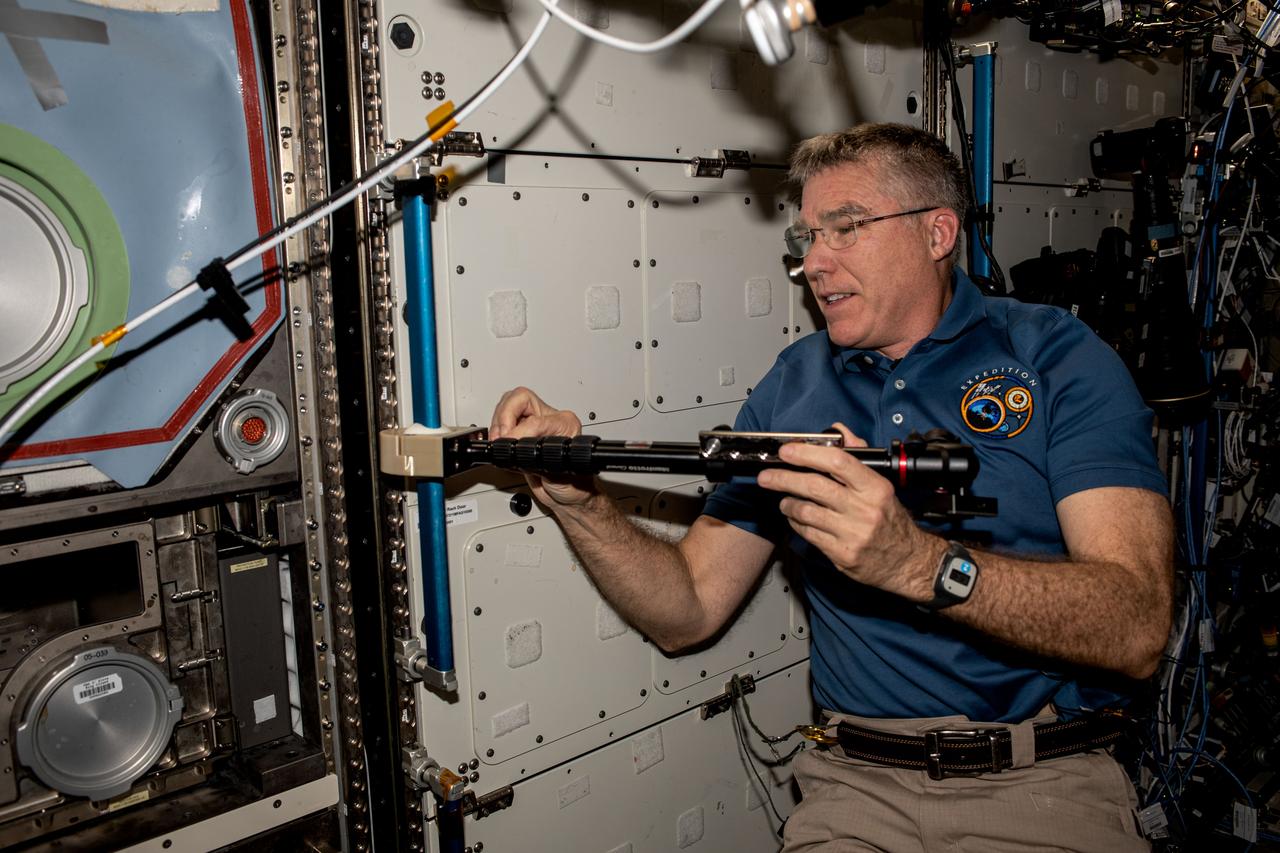

iss069e009790 (May 9, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen installs student-made hardware next to the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox to test a platform that improves the stability of cameras used to track targets on the ground or take images and video inside the International Space Station.
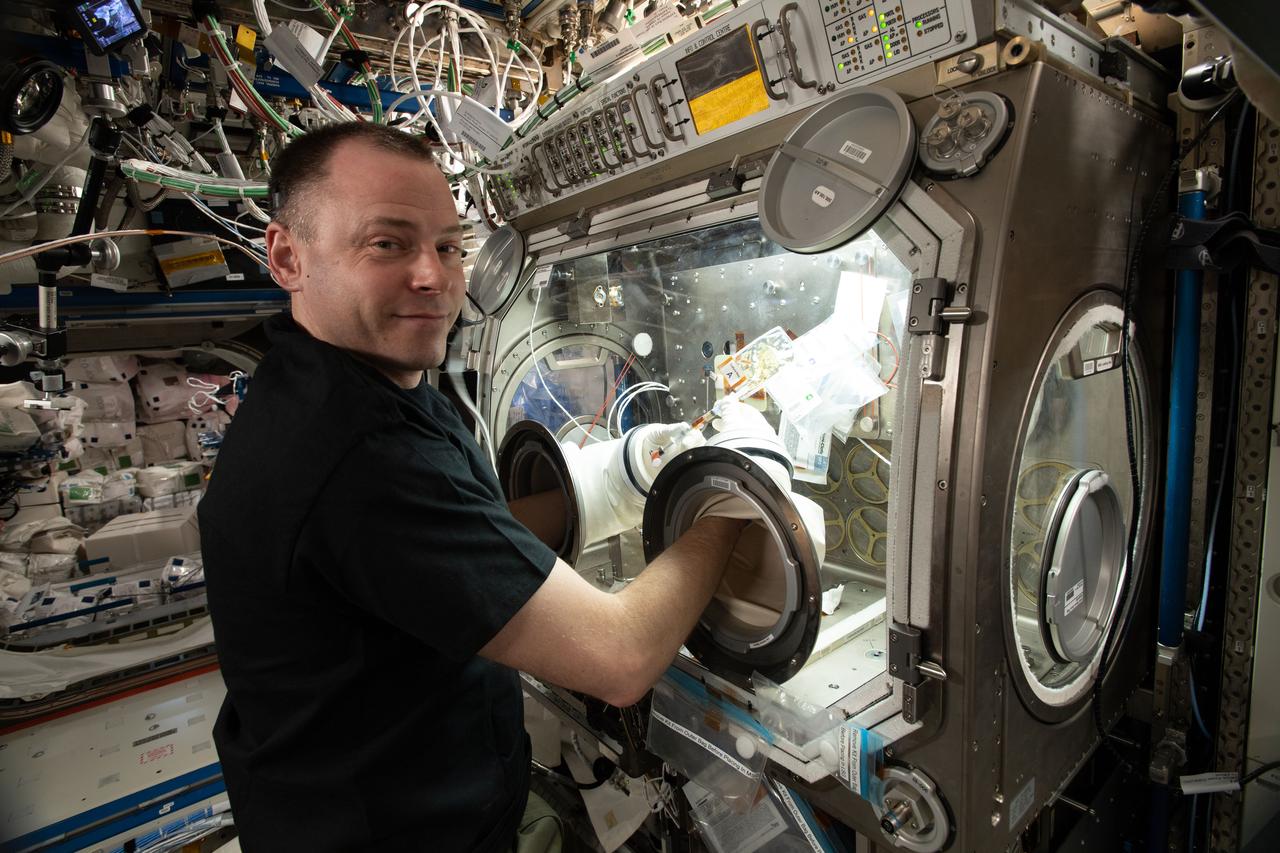

iss059e061135 (May 13, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague conducts research operations in the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Sciences Glovebox. Hague is exploring why pathogens become more virulent in the weightless environment of outer space posing a flight risk to astronauts.
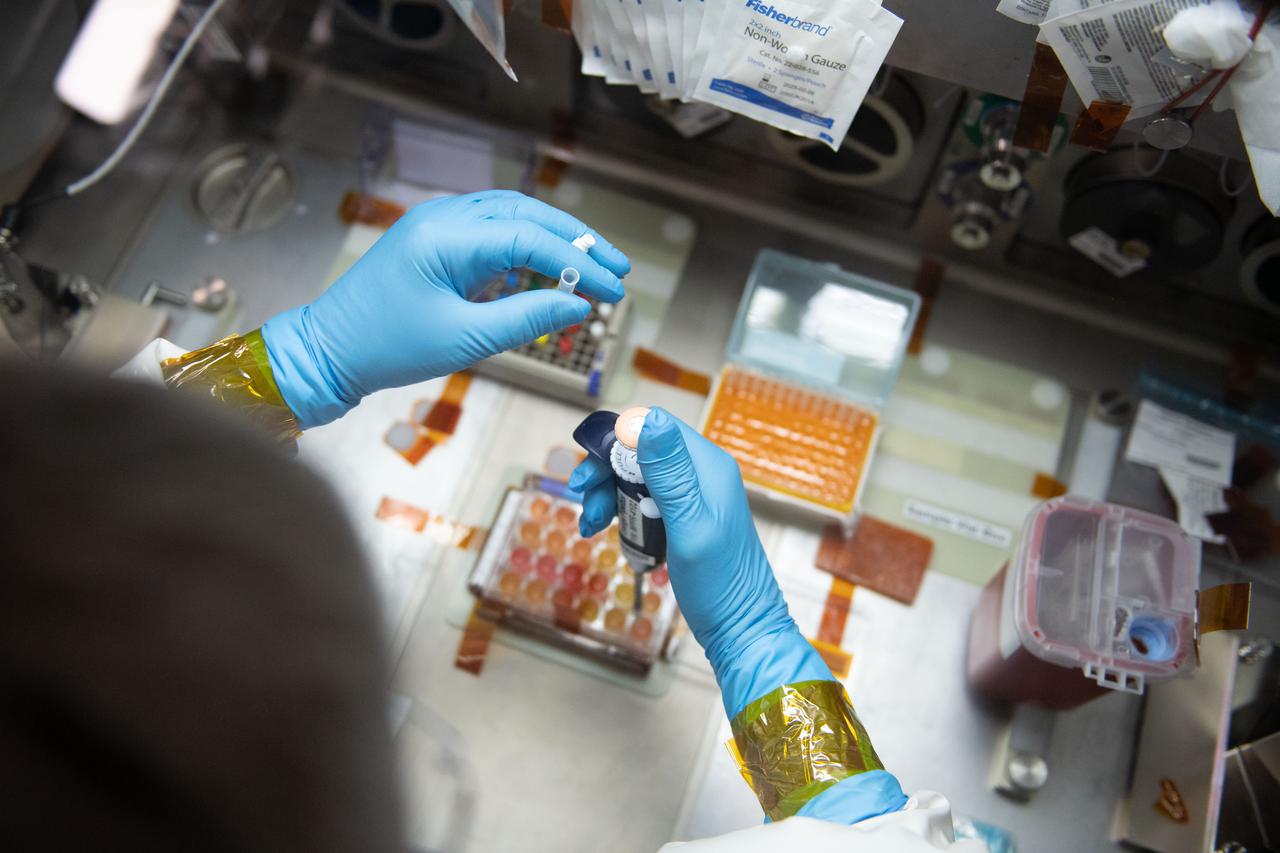
iss065e056790 (5/22/2021) --- NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei works inside the Life Science Glovebox (LSG) for the Celestial Immunity study that may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space. The LSG is located in the Kibo laboratory module from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
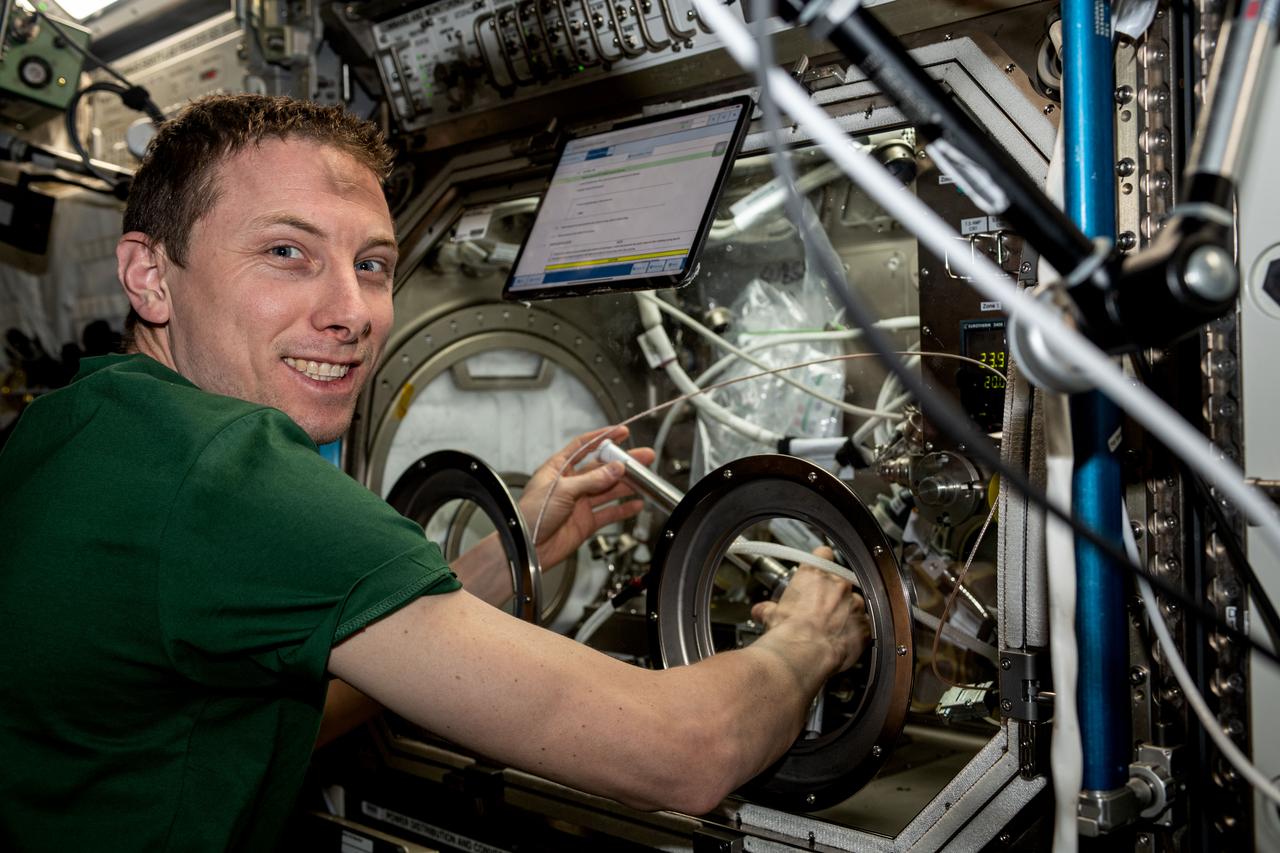

iss069e060322 (August 15, 2023) -- NASA astronaut Woody Hoburg swaps samples for a space manufacturing study inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the International Space Station's U.S. Destiny Laboratory Module. MSG allows crews to investigate physical science and biological research in a safe, contained environment in microgravity.
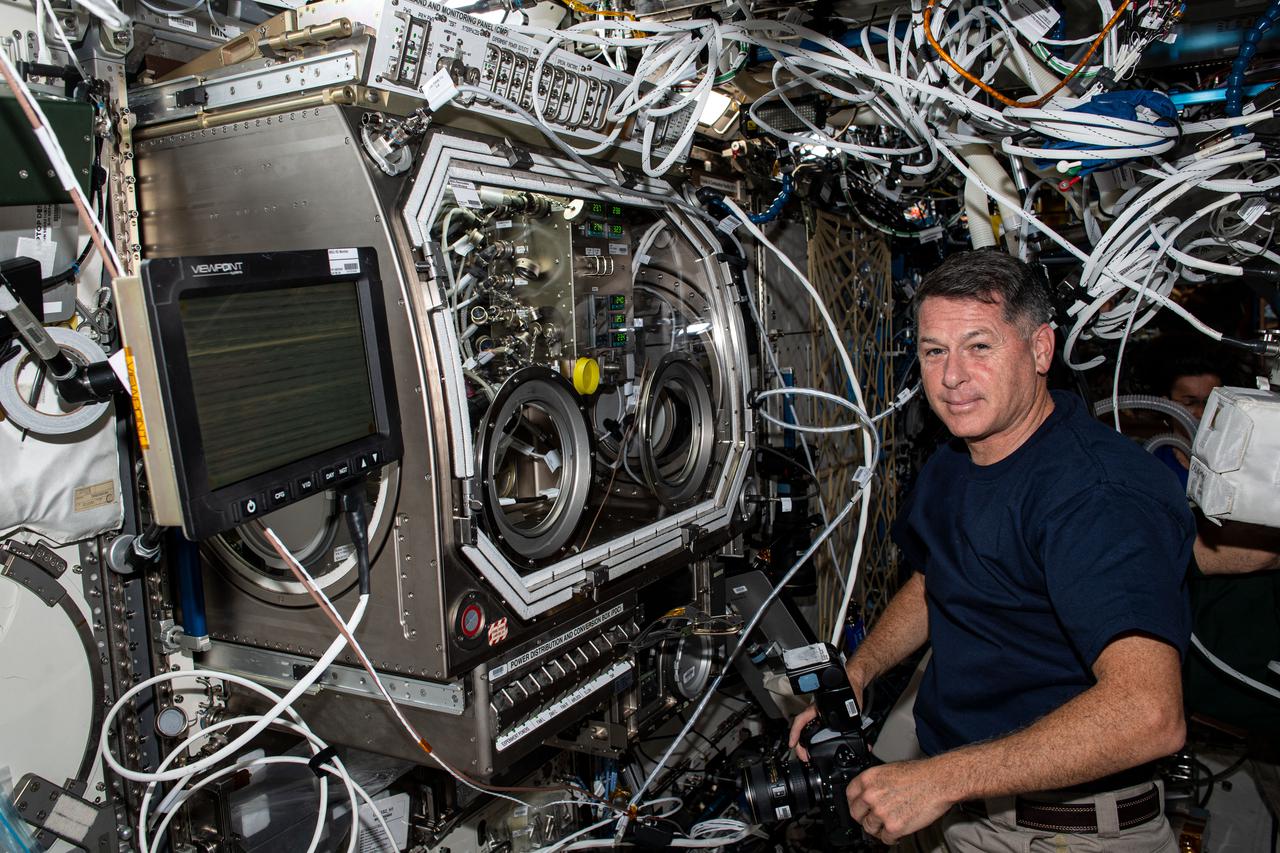

iss065e020575 (May 6, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough sets up the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox for a physics investigation. The study known as Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA, explores improving technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.
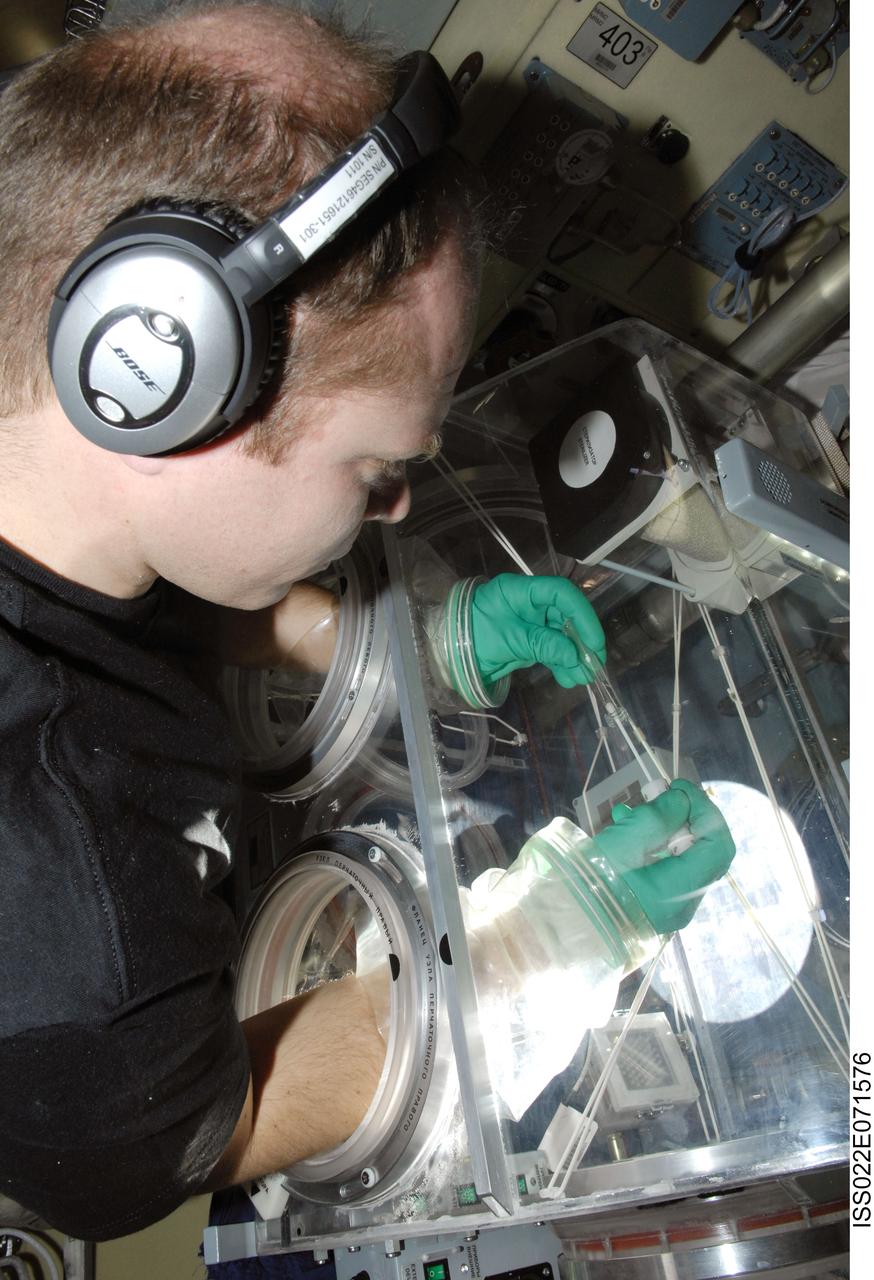

ISS022-E-071576 (24 Feb. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with samples from the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
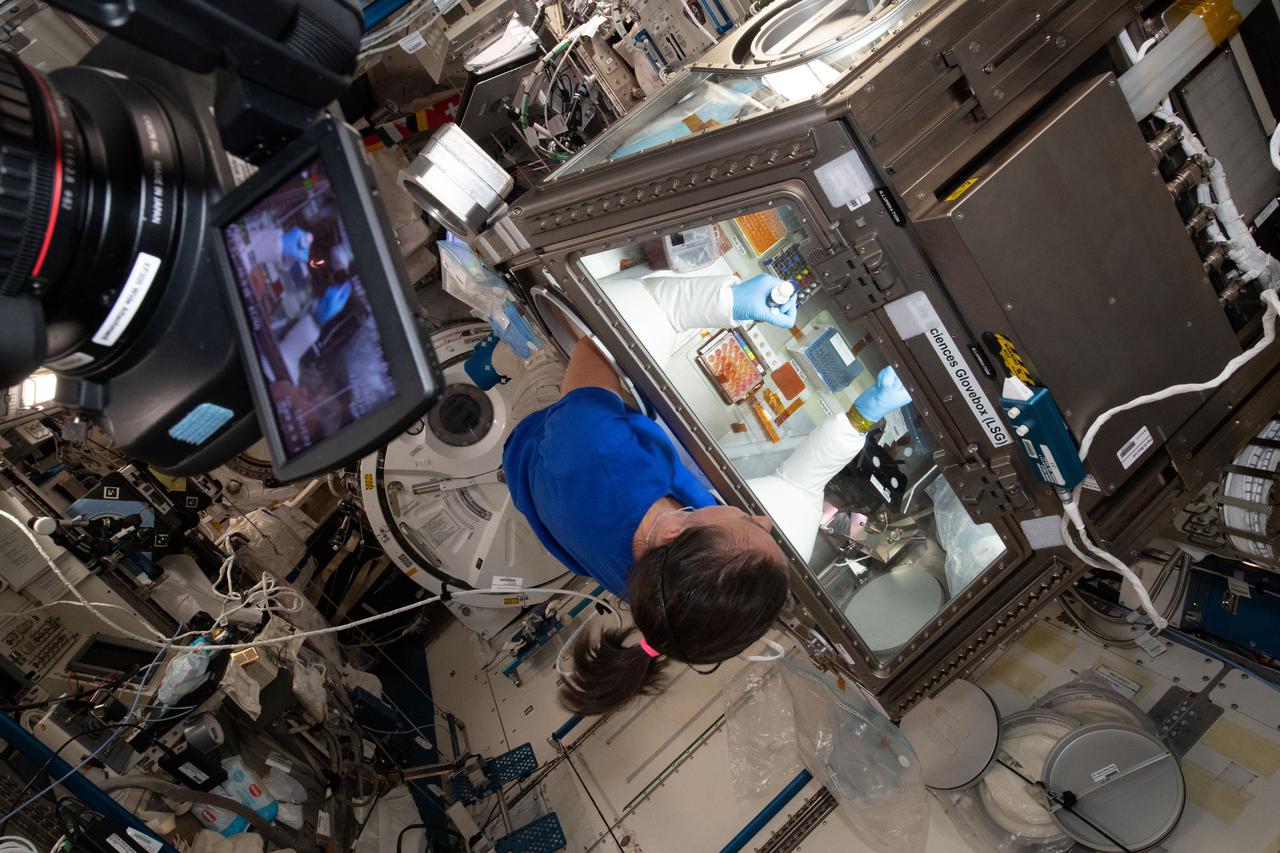

iss065e026994 (5/8/2021) --- NASA astronaut Megan McArthur services donor cells inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox for the Celestial Immunity study. The human research investigation may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space.
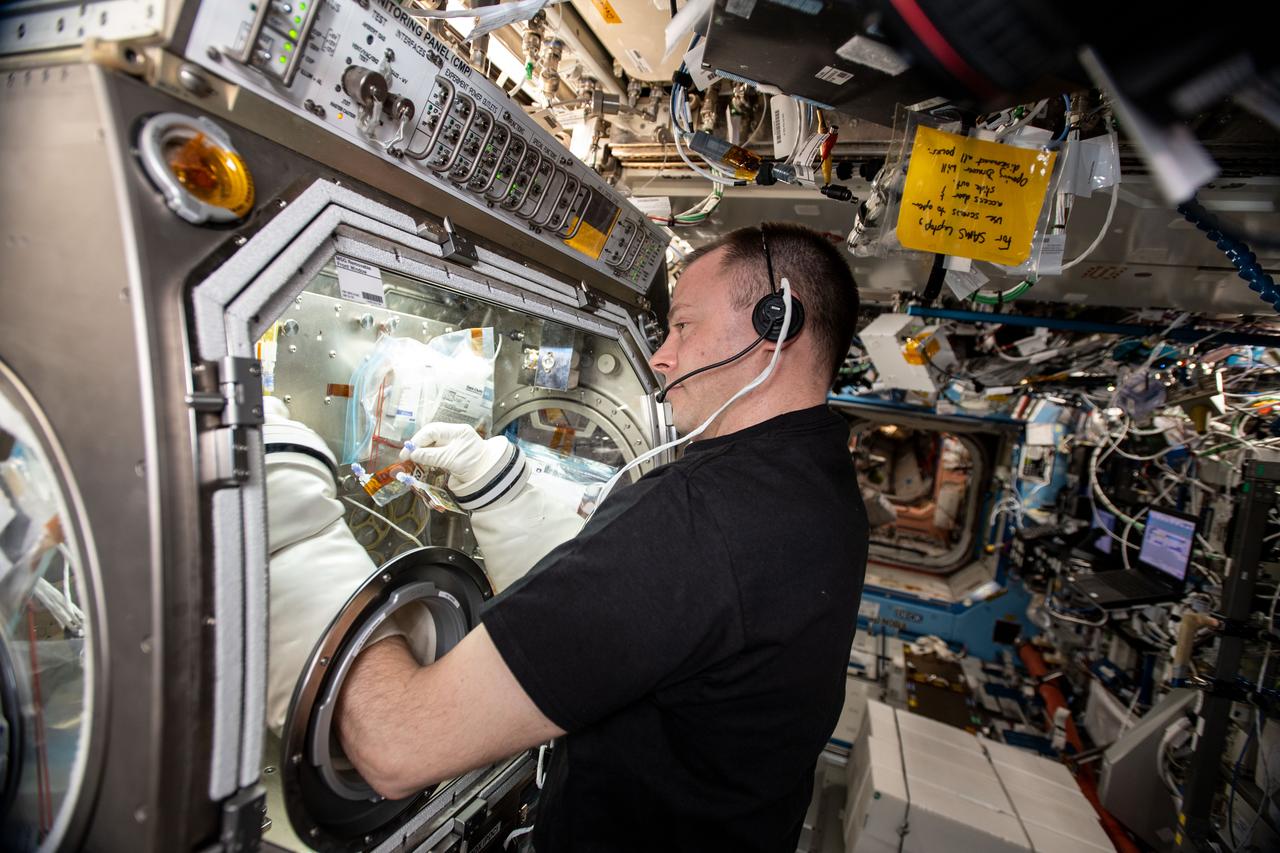

iss059e061522 (May 14, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague conducts research operations in the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Sciences Glovebox. Hague is exploring why pathogens become more virulent in the weightless environment of outer space posing a flight risk to astronauts.
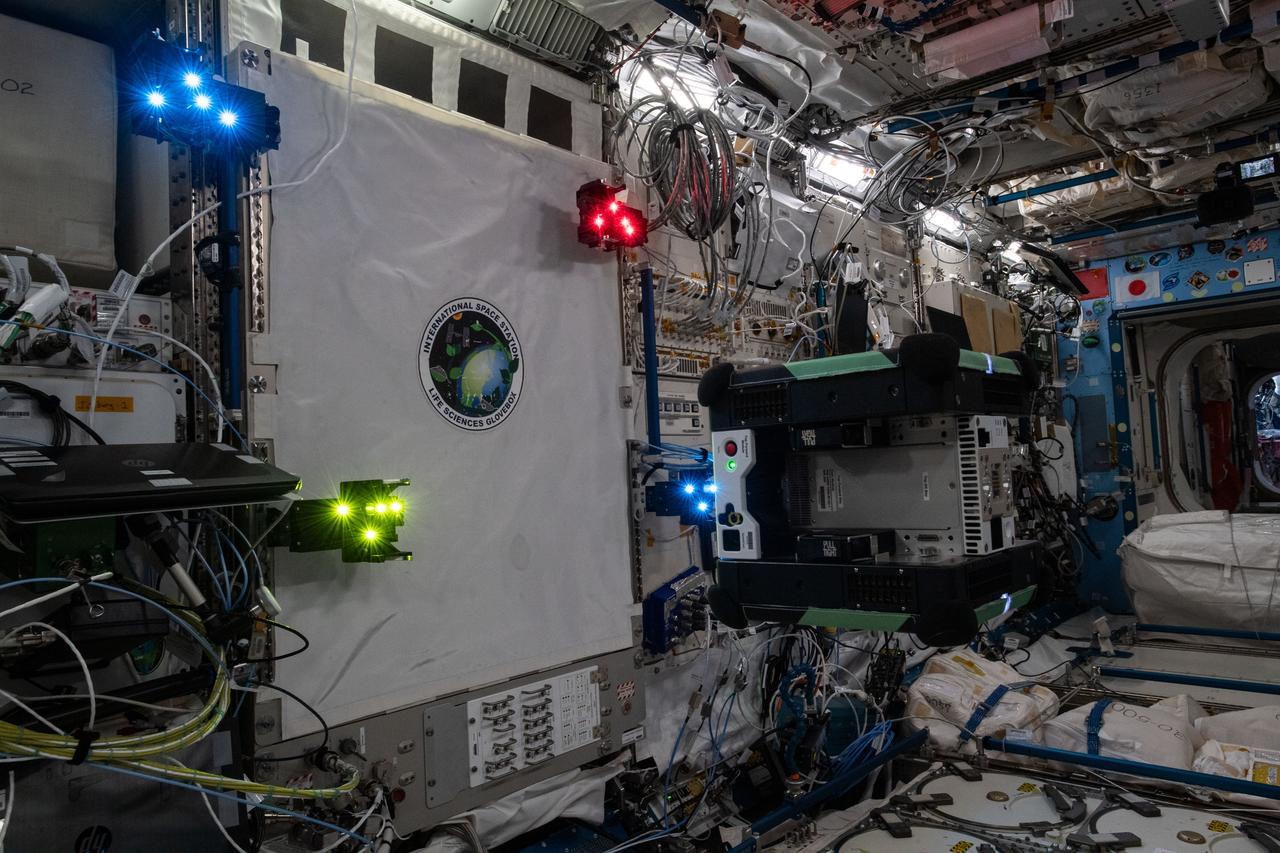

Documentation of a free-flying Astrobee robot (Queen), equipped with an LED Target for the Smartphone Video Guidance Sensor (SVGS) experiment, during SVGS science 3 session. Four SVGS LED Targets are attached to the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) rack, JPM1F5 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
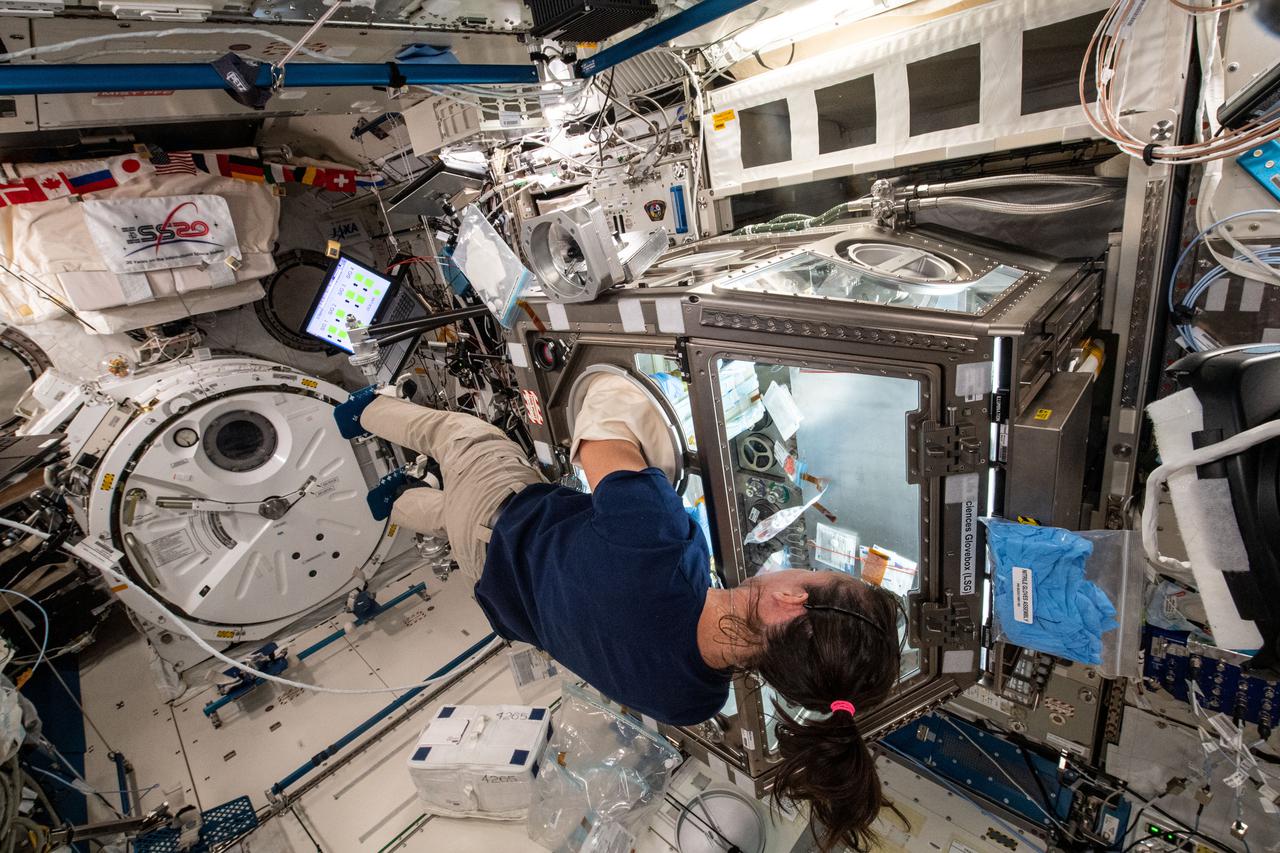

iss065e023172 (May 6, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur services donor cells inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox for the Celestial Immunity study. The human research investigation may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space.
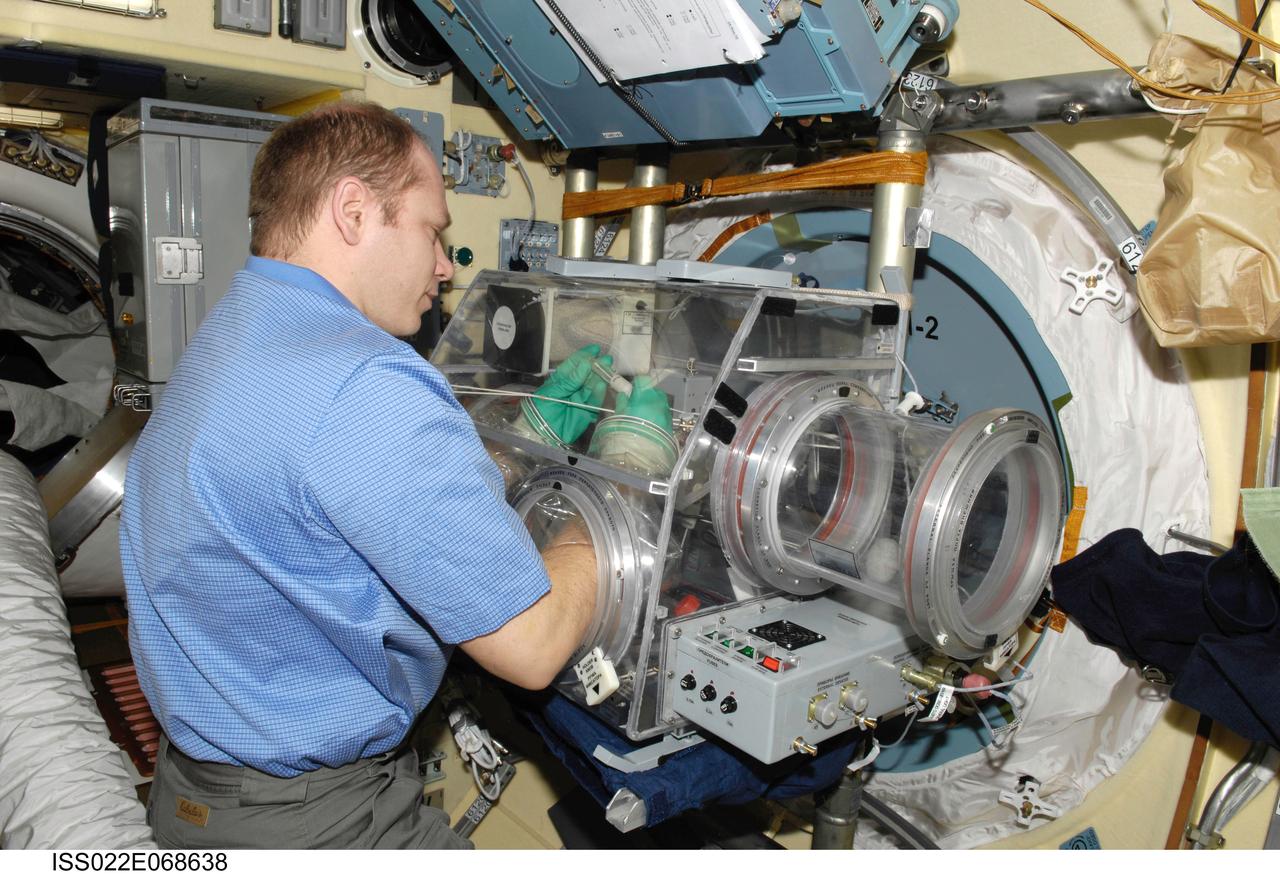

ISS022-E-068638 (18 Feb. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with samples from the bioscience experiment ASEPTIC (BTKh-39) in the new Russian Glavboks-S (Glovebox) located in the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) of the International Space Station.
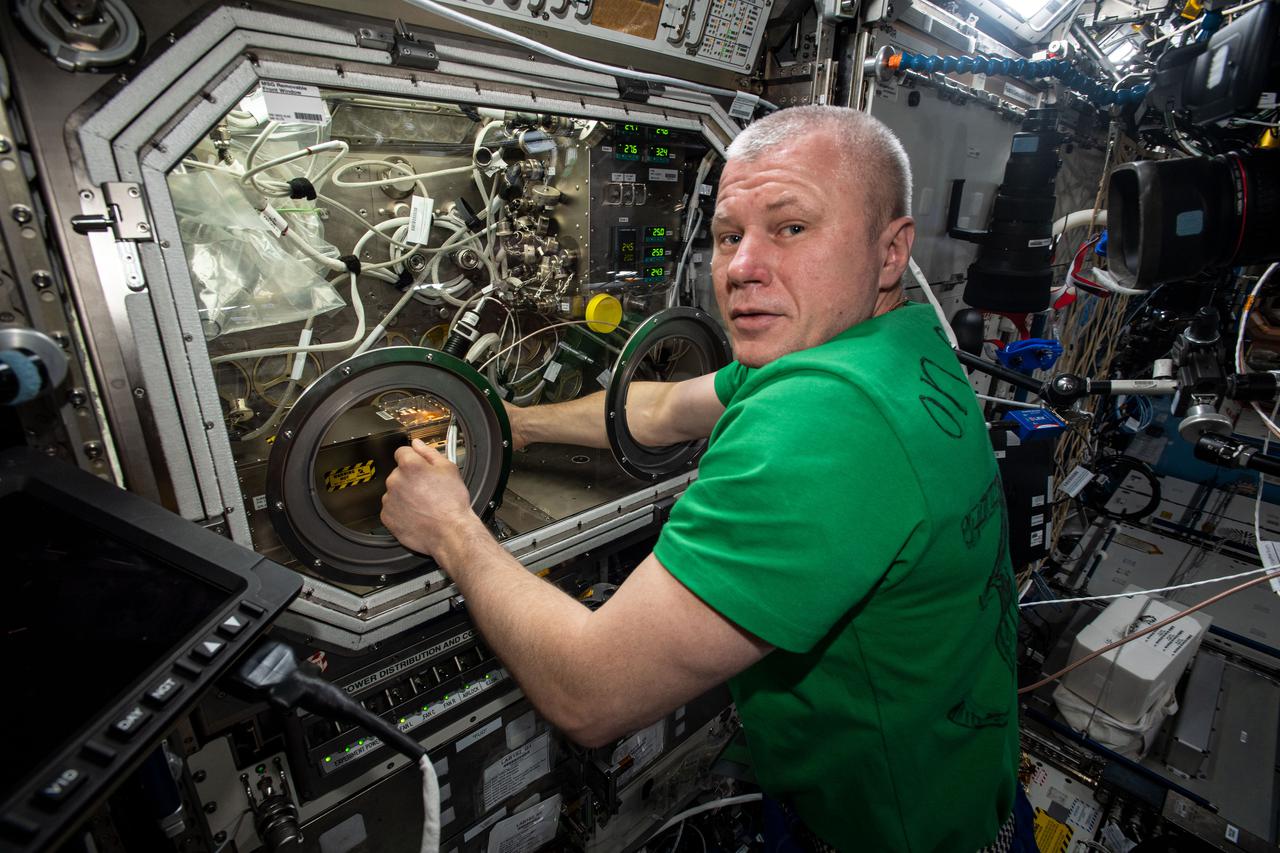

iss065e021208 (May 6, 2021) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Oleg Novitskiy swaps hardware inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox for a physics investigation. The study known as Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA, explores improving technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.
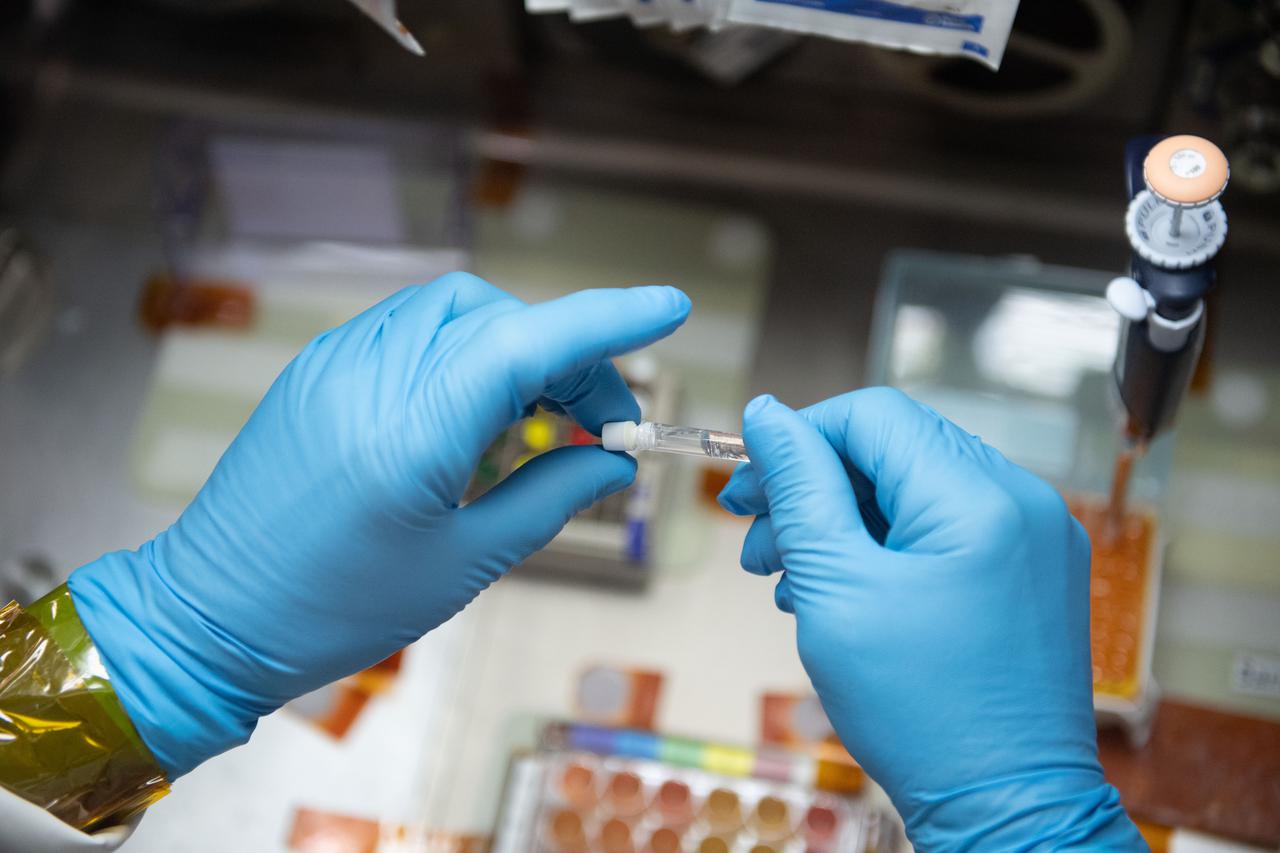
iss065e056800 (5/22/2021) --- NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei works inside the Life Science Glovebox (LSG) for the Celestial Immunity study that may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space. The LSG is located in the Kibo laboratory module from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.

iss073e0178587 (June 16, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers conducts research operations inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Ayers swapped syringes containing protein samples and installed test cells inside the glovebox for the Ring-Sheared Drop Interfacial Bioprocessing of Pharmaceuticals investigation that explores using surface tension to contain liquids and study proteins without contacting solid walls. Results may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing and 3D printing techniques on and off the Earth.
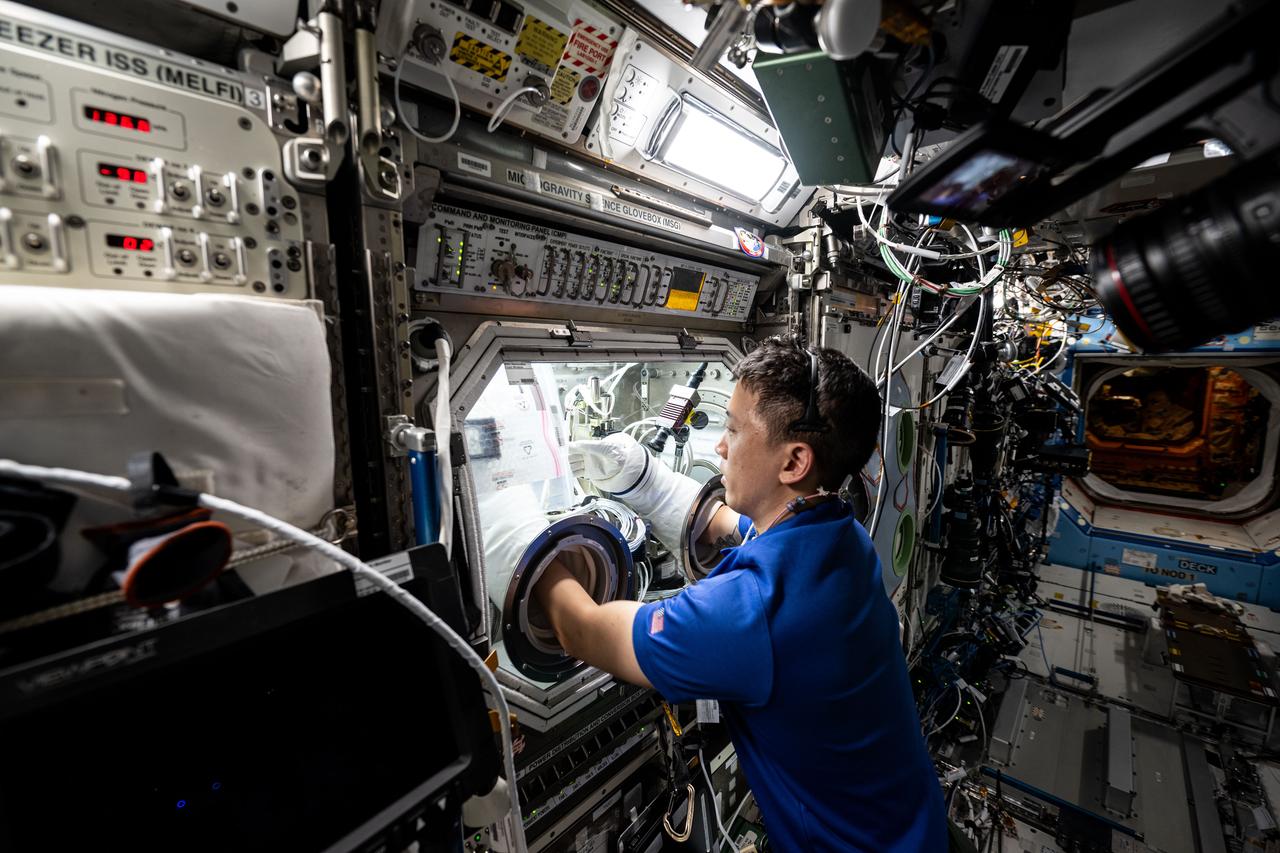

iss073e0177791 (June 12, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim conducts research operations inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Kim swapped syringes containing protein samples and installed test cells inside the glovebox for the Ring-Sheared Drop Interfacial Bioprocessing of Pharmaceuticals investigation that explores using surface tension to contain liquids and study proteins without contacting solid walls. Results may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing and 3D printing techniques on and off the Earth.
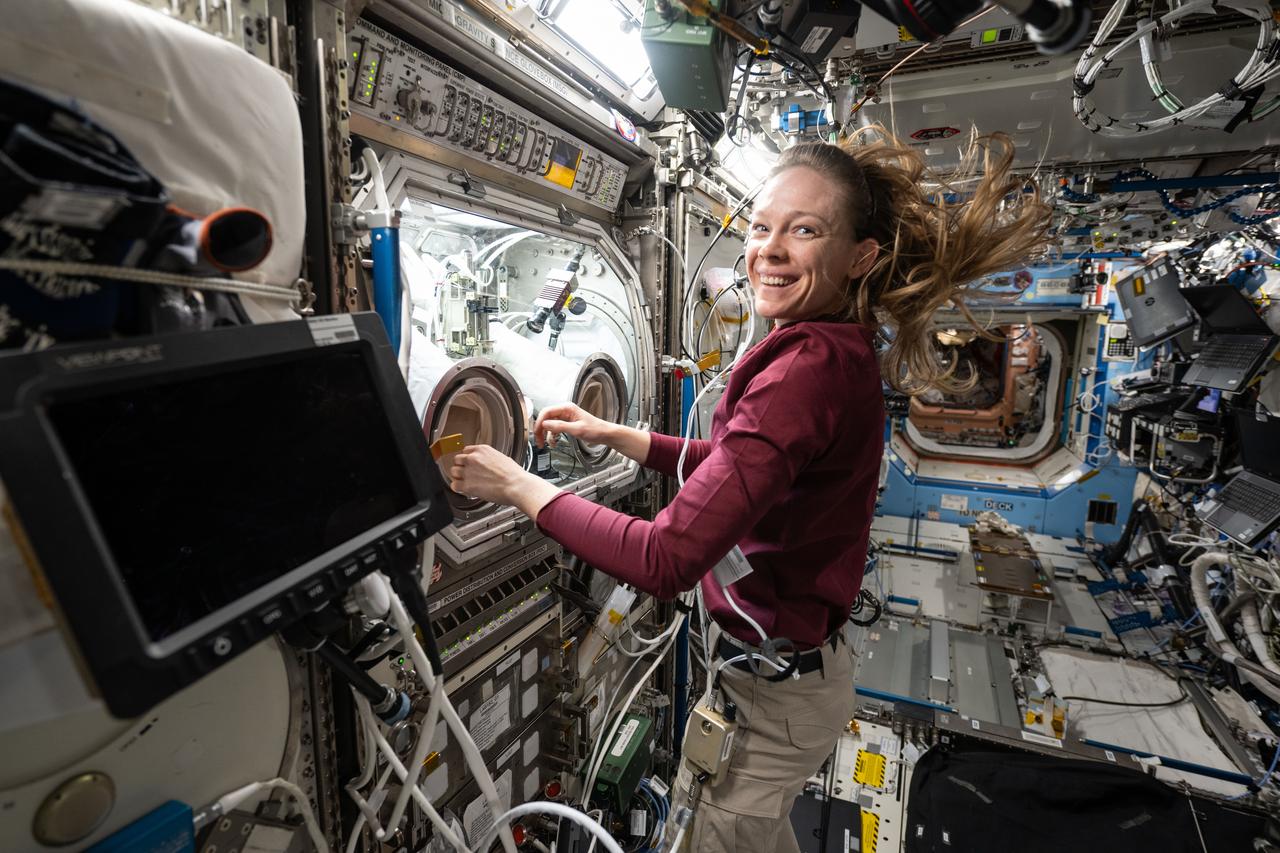

iss073e0248499 (June 25, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers conducts research operations inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Ayers swapped syringes containing protein samples and installed test cells inside the glovebox for the Ring-Sheared Drop Interfacial Bioprocessing of Pharmaceuticals investigation that explores using surface tension to contain liquids and study proteins without contacting solid walls. Results may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing and 3D printing techniques on and off the Earth.

STS073-E-5003 (23 Oct. 1995) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, STS-73 payload commander, works at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) on the portside of the science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in Earth orbit. Payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. conducts an experiment at the Glovebox. This frame was exposed with the color Electronic Still Camera (ESC) assigned to the 16-day United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
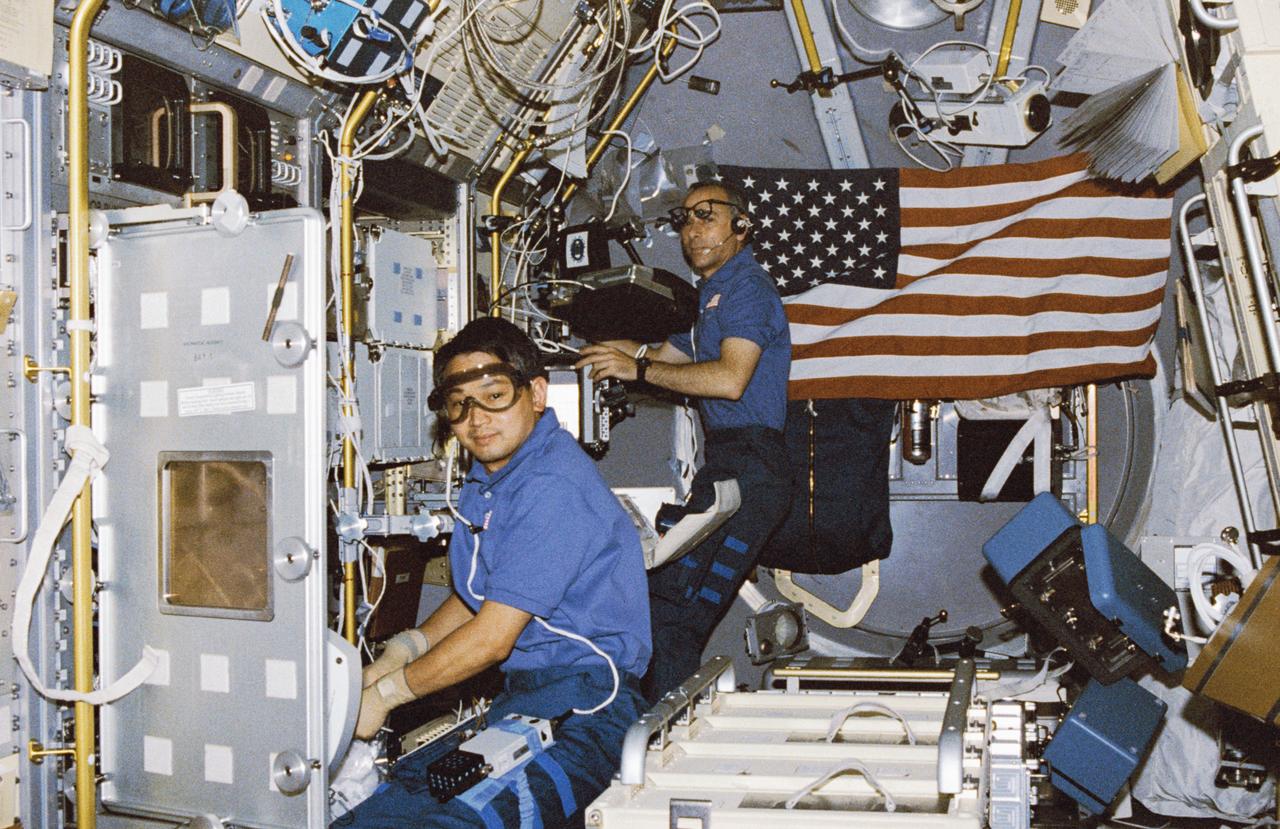
STS050-255-027 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Payload specialist Eugene H. Trinh, left, and astronaut Carl J. Meade, mission specialist, go to work in the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) science module as the blue shift crew takes over from the red. Trinh is working with an experiment at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) and Meade prepares to monitor an experiment in the Glovebox. The two joined four other astronauts and a second scientist from the private sector for 14-days of scientific data-gathering.
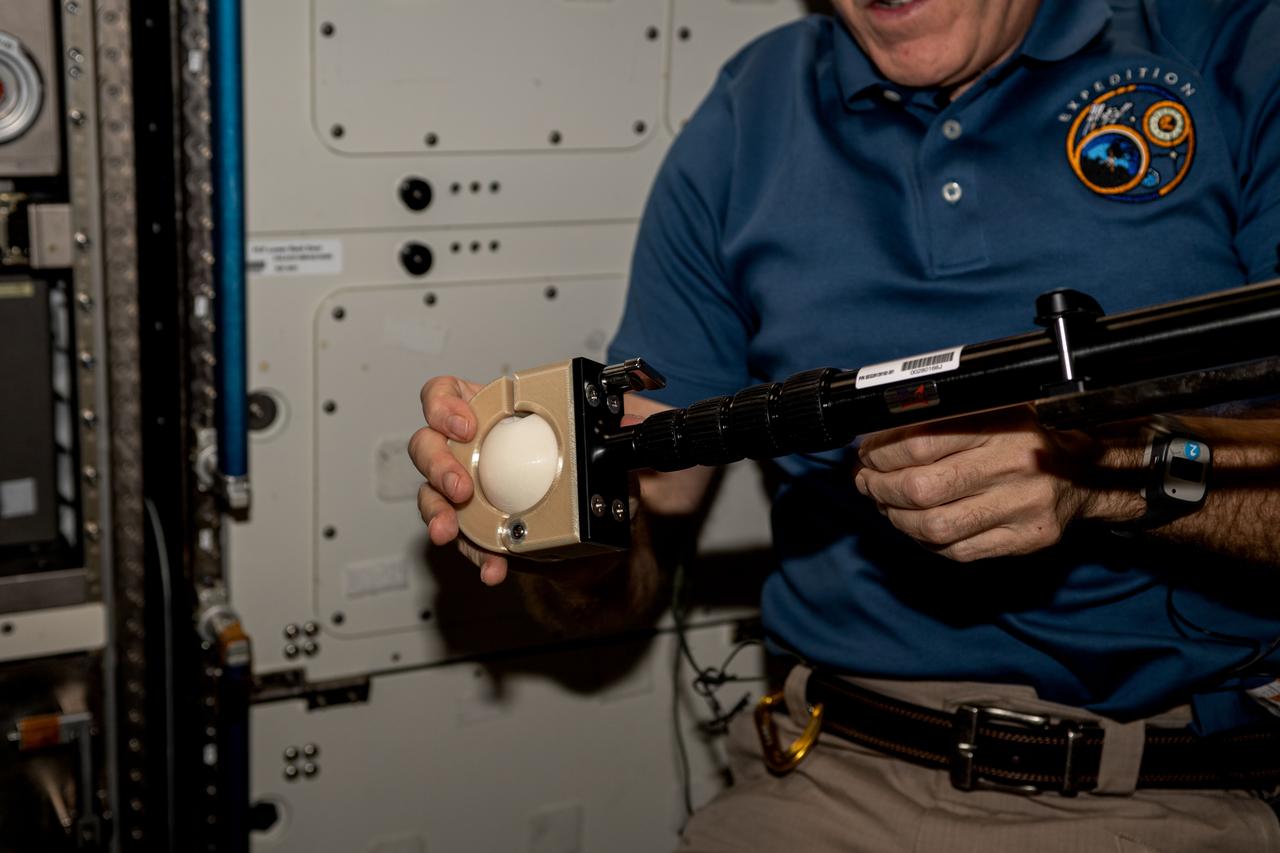

iss069e009795 (May 9, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen installs student-made hardware next to the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox. The High school students United with NASA to Create Hardware (HUNCH) Ball Clamp Monopod (HUNCH Ball Clamp Monopod) investigation tests a platform for holding cameras used to track targets on the ground or take images and video within space station modules
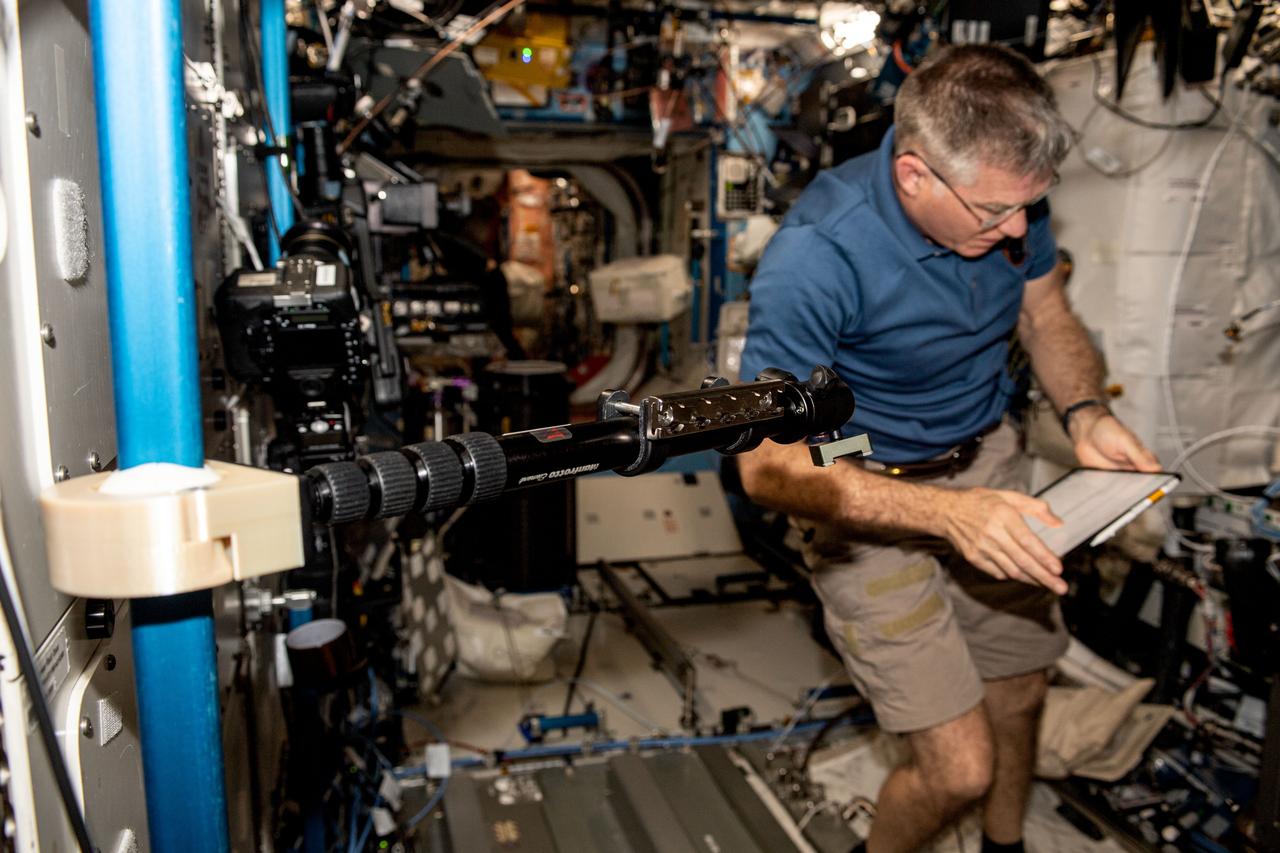

iss069e009786 (May 9, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen installs student-made hardware next to the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox. The High school students United with NASA to Create Hardware (HUNCH) Ball Clamp Monopod (HUNCH Ball Clamp Monopod) investigation tests a platform for holding cameras used to track targets on the ground or take images and video within space station modules

iss069e009796 (May 9, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen installs student-made hardware next to the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox. The High school students United with NASA to Create Hardware (HUNCH) Ball Clamp Monopod (HUNCH Ball Clamp Monopod) investigation tests a platform for holding cameras used to track targets on the ground or take images and video within space station modules
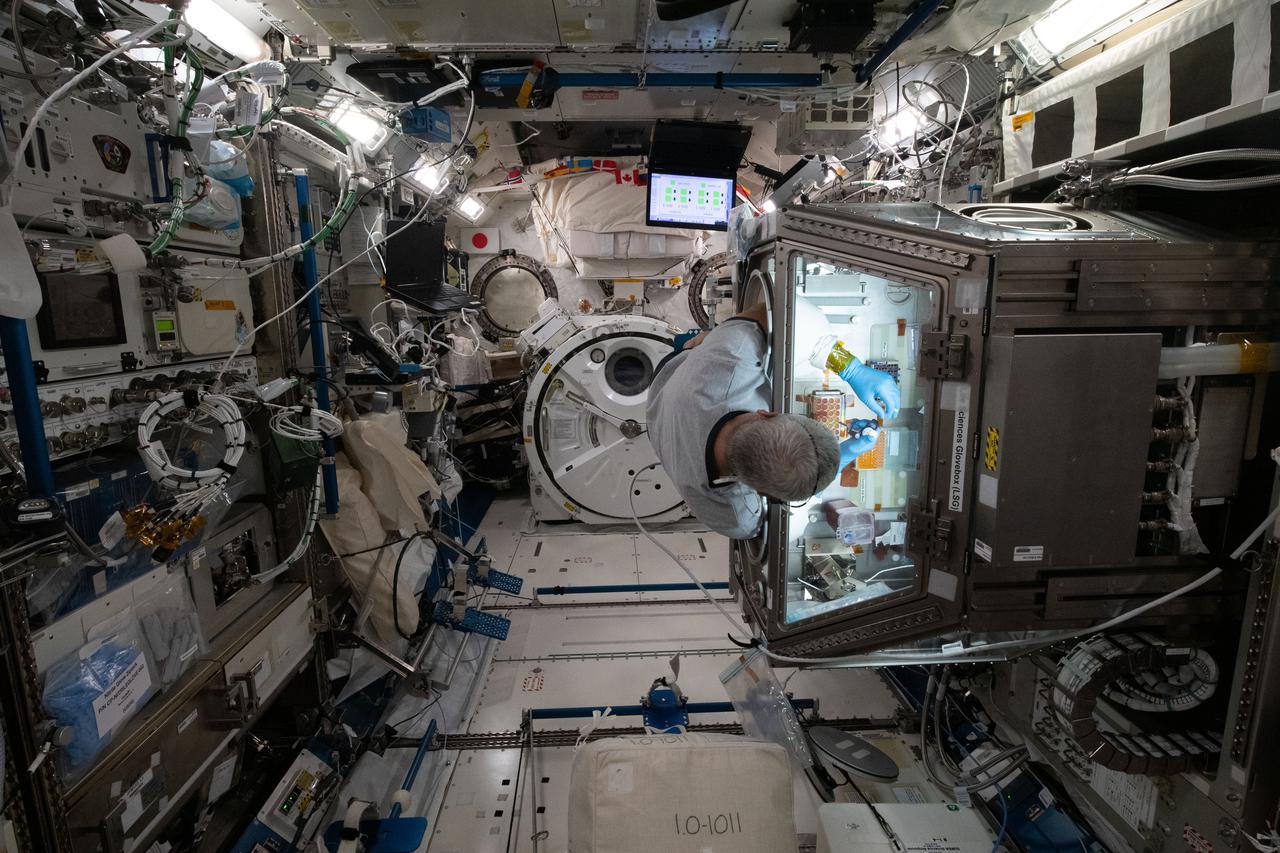

Photo (part of time lapse) taken during Celestial Immunity Plate Second Sampling in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). View is of the empty module with Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) in the forefront. Astronaut Mark Vande Hei is also visible to conduct the operations. Dissecting the Influence of Gravity on Human Immune Function in Adults and the Elderly (Celestial Immunity) builds on earlier studies to evaluate how gravity affects functional immune response, from innate mechanisms of defense to adaptive responses.
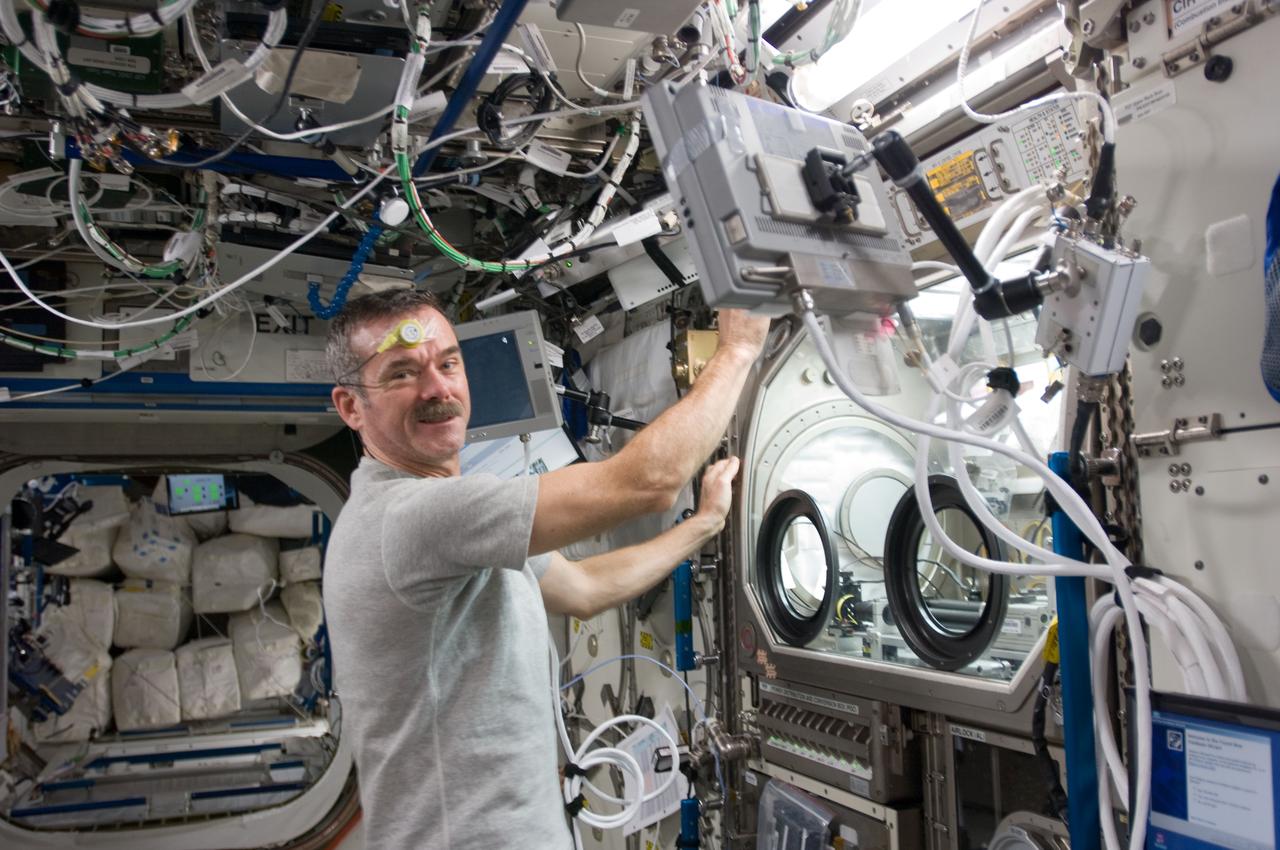

View of Canadian Space Agency (CSA) Chris Hadfield,Expedition 34 Flight Engineer (FE), during the Investigating the Structure of Paramagnetic Aggregates from Colloidal Emulsions 3 (InSPACE-3) experiment. InSPACE-3 collects and records data on fluids containing ellipsoid-shaped particles that change the physical properties of the fluids in response to magnetic fields. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.
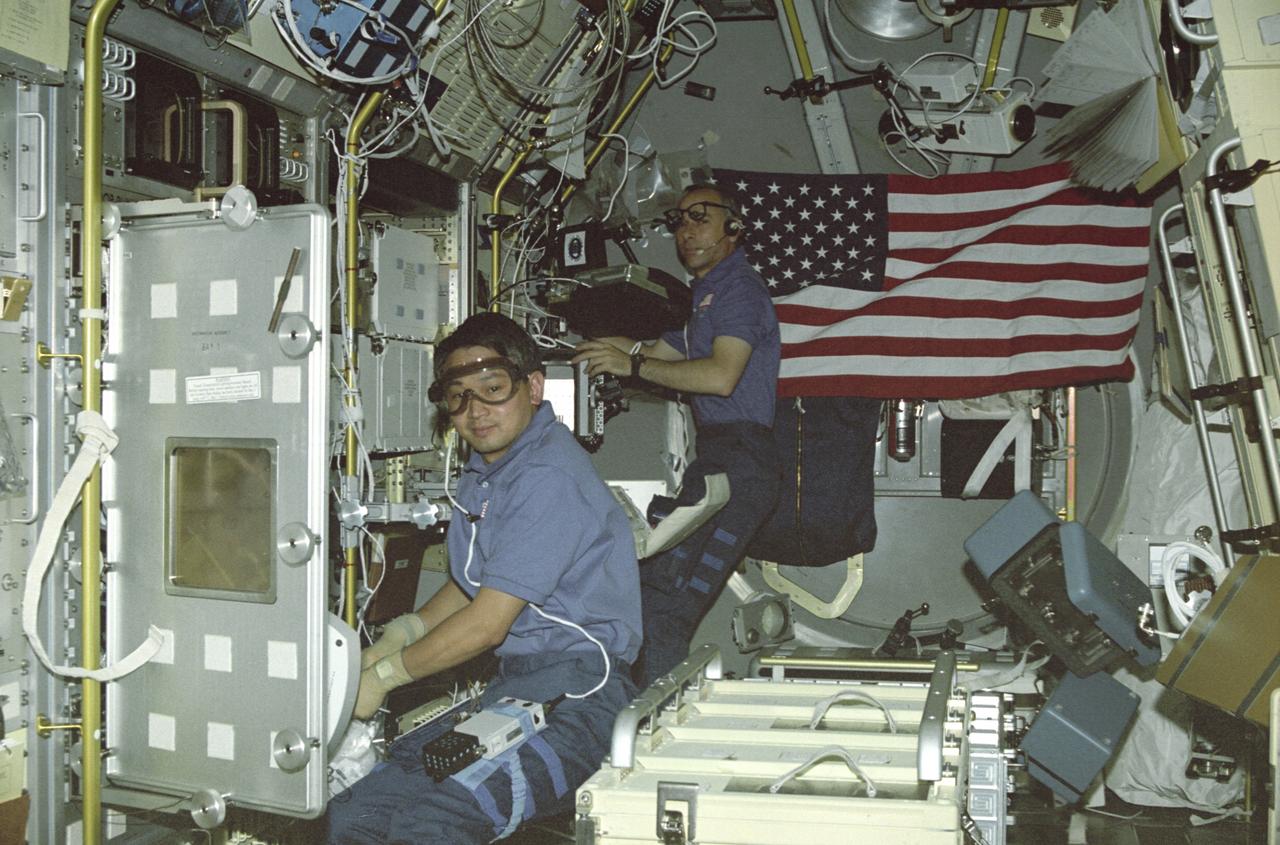

In this photograph, astronaut Eugene Trinh, a payload specialist for this mission, is working at the Drop Physics Module (DPM), and mission specialist Carl Meade is working on the experiment at the Glovebox inside the first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) Science Module. The USML-1 was one of NASA's missions dedicated to scientific investigations in a microgravity environment inside the Spacelab module. Investigations aboard the USML-1 included: materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. The DPM is dedicated to the detailed study of the dynamics of fluid drops in microgravity. The Glovebox offers experimenters new capabilities and technologies in microgravity with a clean working space and minimizes contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. Payload specialists are professional scientists or engineers whose only assignment on a space flight is to carry out scientific and technological experiments. Their specific training for a space flight is usually limited to a short period of learning how to live and work in weightlessness. Mission Specialists are both professional scientists and career astronauts. Thus they are a link or bridge between the other crew members, and combine the functions of resident maintenance engineers, in-space counterparts of flight engineers in aircraft, and fully qualified scientists. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992, and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
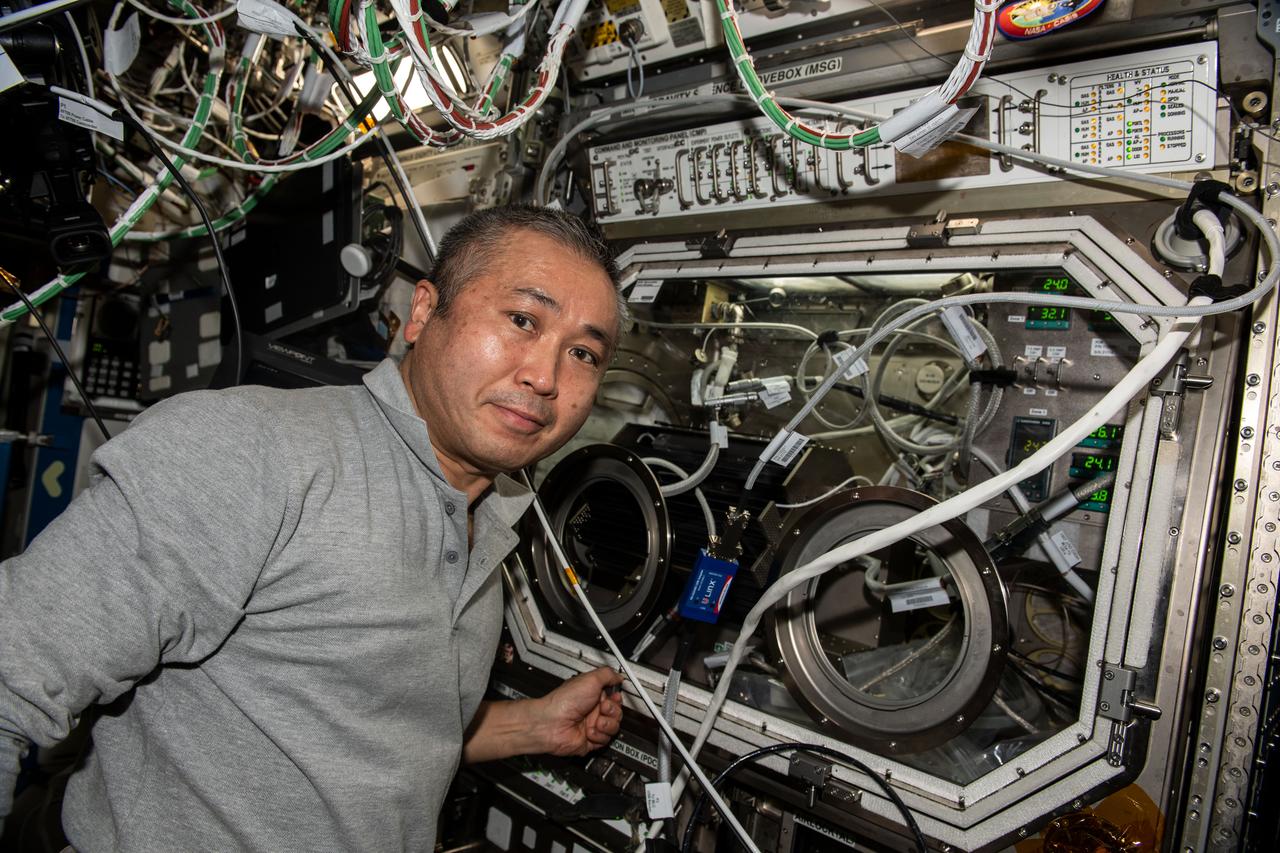
iss068e029939 (Dec. 15, 2022) --- Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) performs research operations inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG). Wakata was swapping samples inside the MSG for a space physics experiment demonstrating a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity.
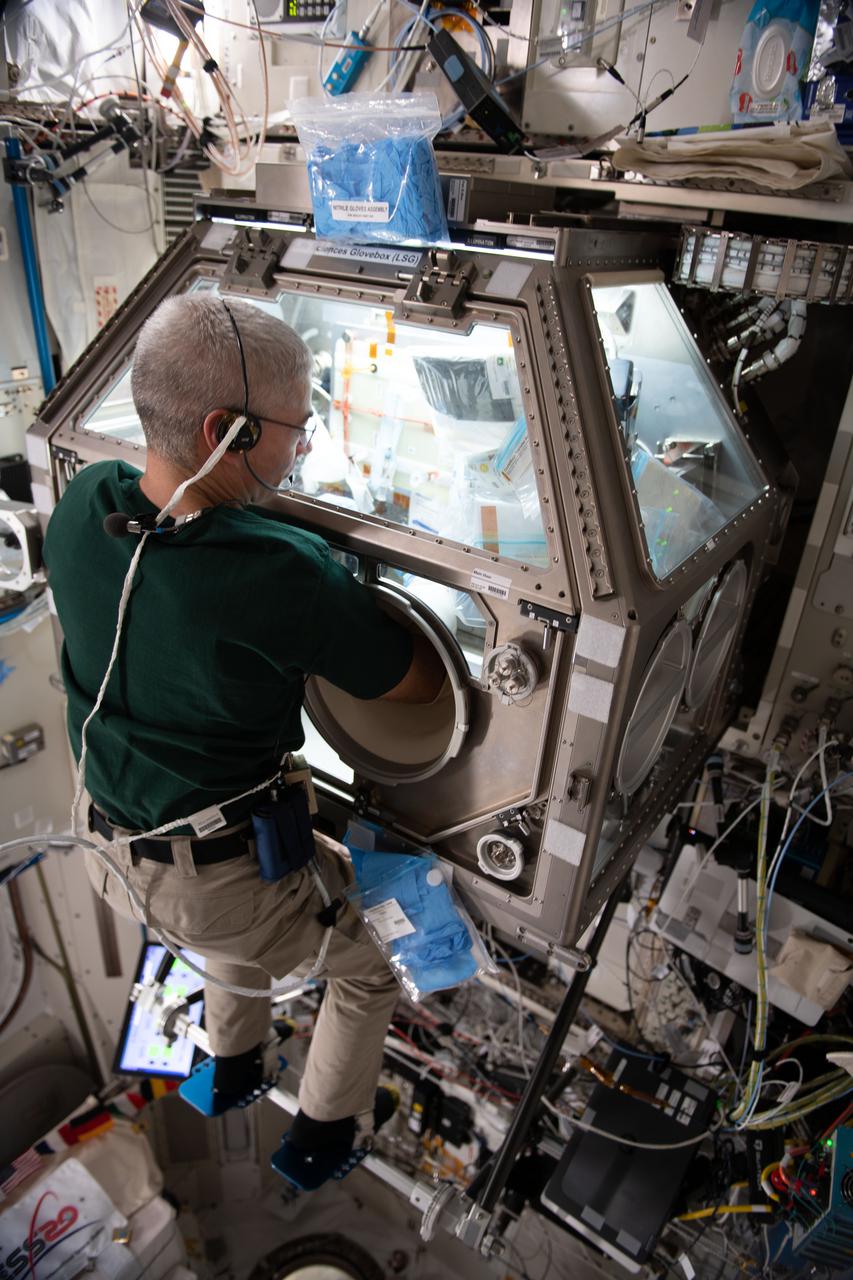

iss065e018996 (May 4, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei works inside the Life Science Glovebox (LSG) for the Celestial Immunity study that may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs possibly advancing the commercialization of space. The LSG is located in the Kibo laboratory module from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
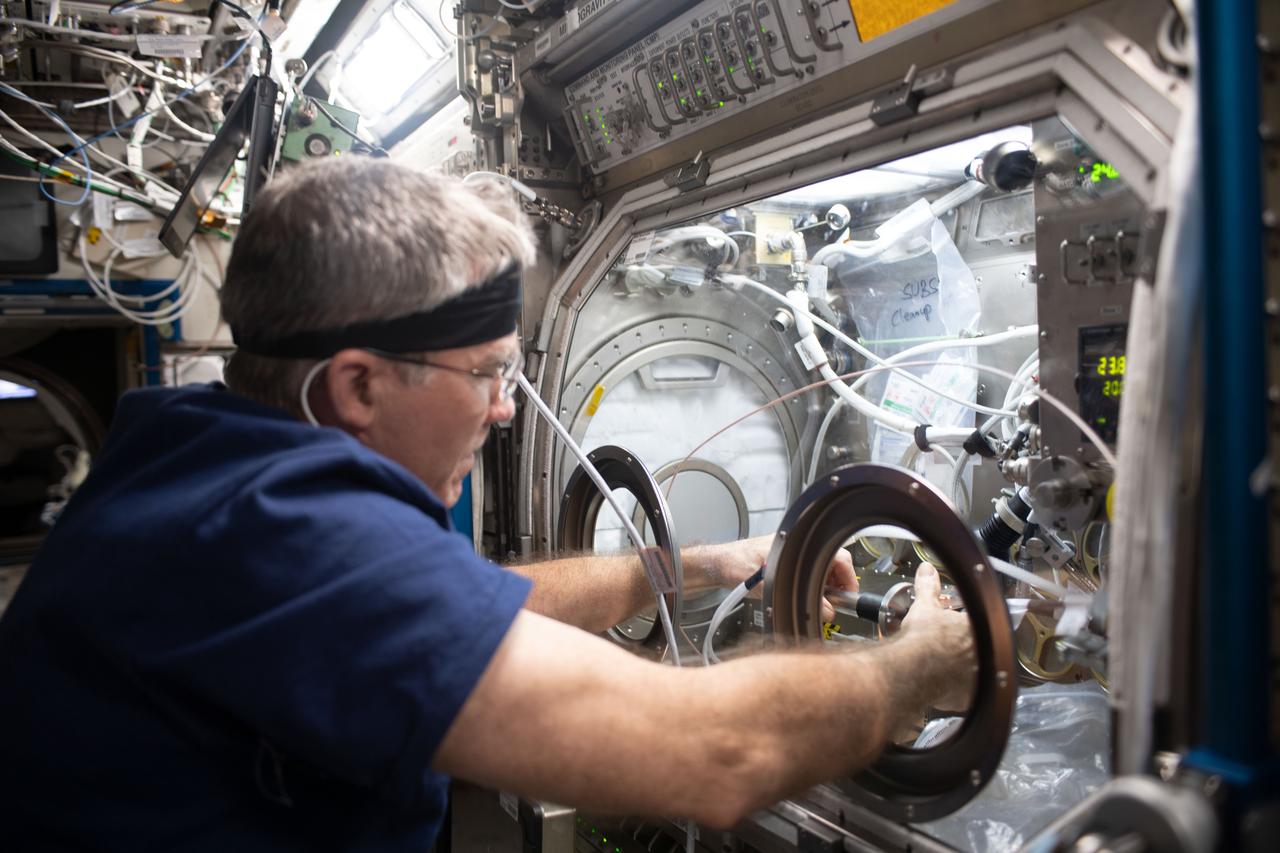

iss069e056172 (Aug. 11, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen works on physics research inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox. The SUBSA-μgGA investigation seeks to create a superior graphene aerogel, a synthetic material with high porosity and low density, in microgravity benefitting both Earth and space industries such as power storage, environmental protection, and chemical sensing.
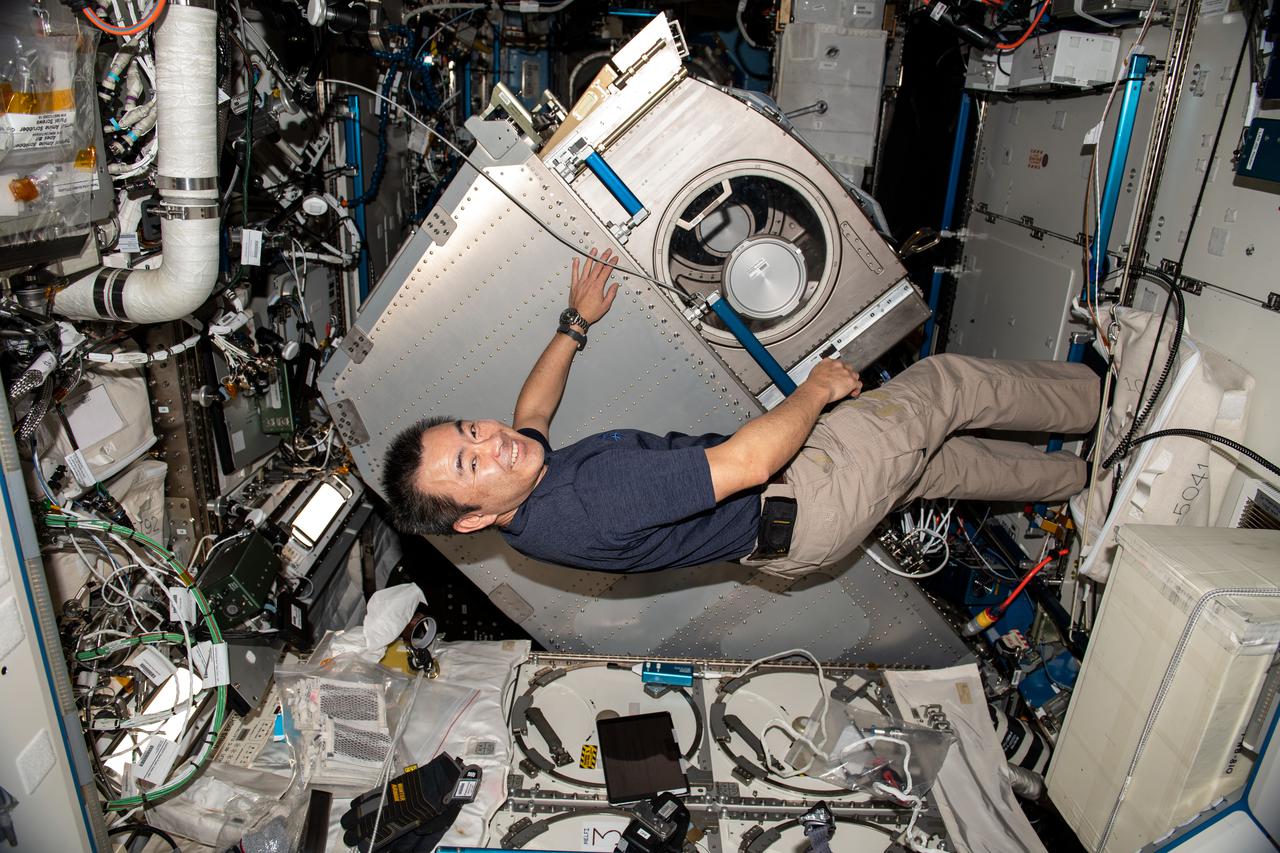

iss065e241905 (Aug. 11, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Commander Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) rotates the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) from its rack position inside the International Space Station's U.S. Destiny laboratory module. Hoshide cleaned electronic components inside the MSG following completion of the InSpace-4 physics experiment that studied the assembly of tiny structures from colloids using magnetic fields.
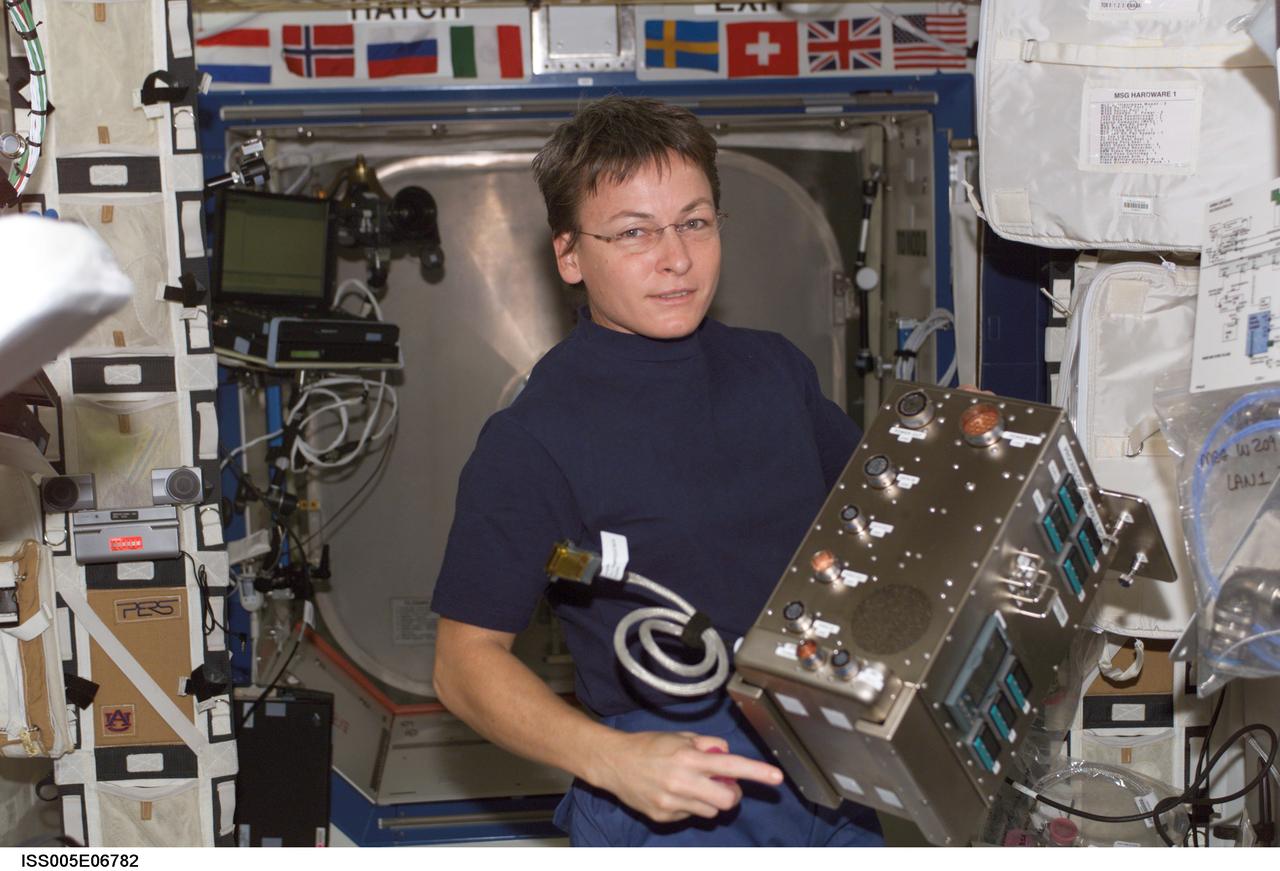

iss005e06782 (7/5/2002) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson installs a Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules (SUBSA) Process Control Module in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG). The SUBSA objective is to advance our understanding of the processes involved in semiconductor crystal growth. It offers a gradient freeze furnace for materials science investigations that can reach 850°C. Samples are contained in transparent quartz or ceramic ampoules with high definition video imaging available in real-time along with remote commanding of thermal control parameters.
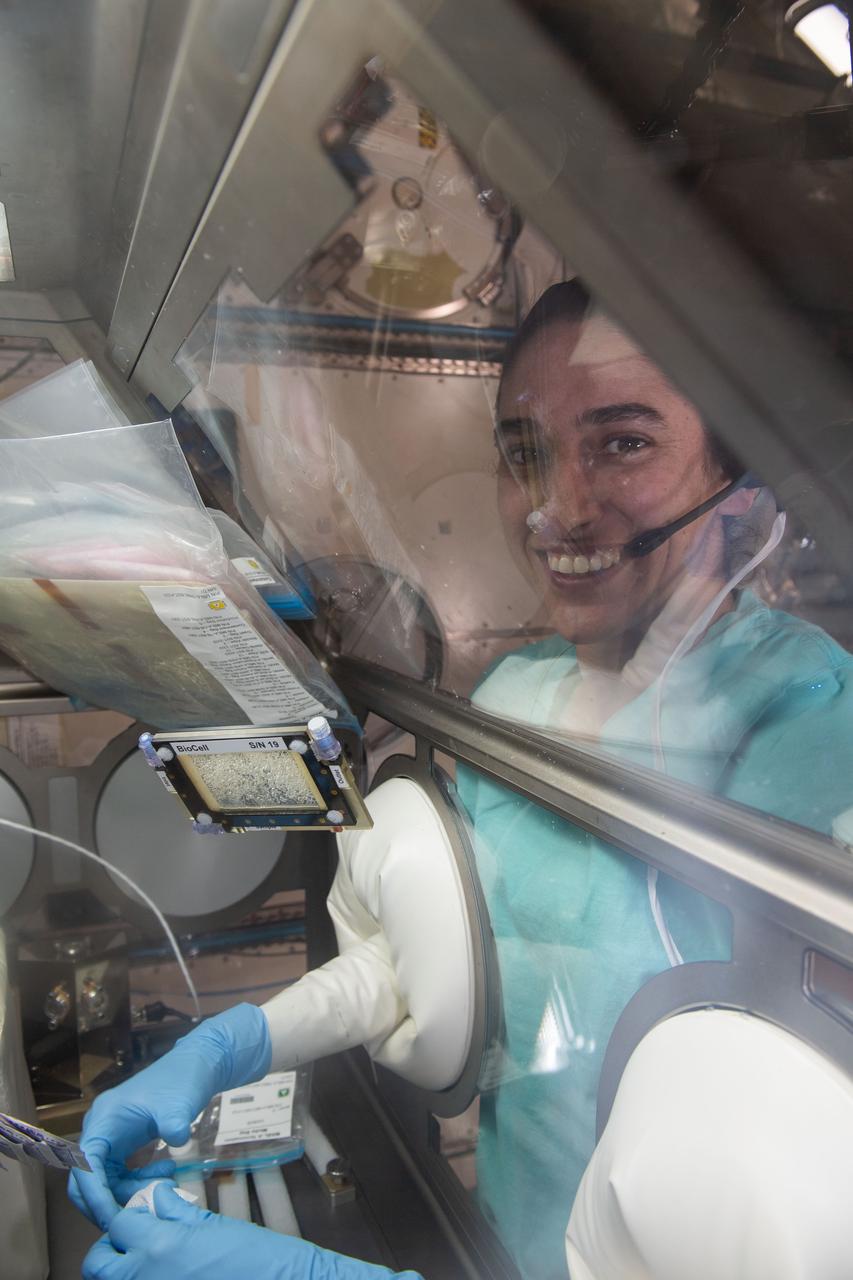

iss070e094541 (Feb. 16, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Jasmin Moghbeli works on a bone cell study inside the Life Science Glovebox located inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. Moghbeli was working on the Microgravity Associated Bone Loss-A investigation that may provide a better understanding of space-caused bone loss and aging-related bone conditions on Earth.
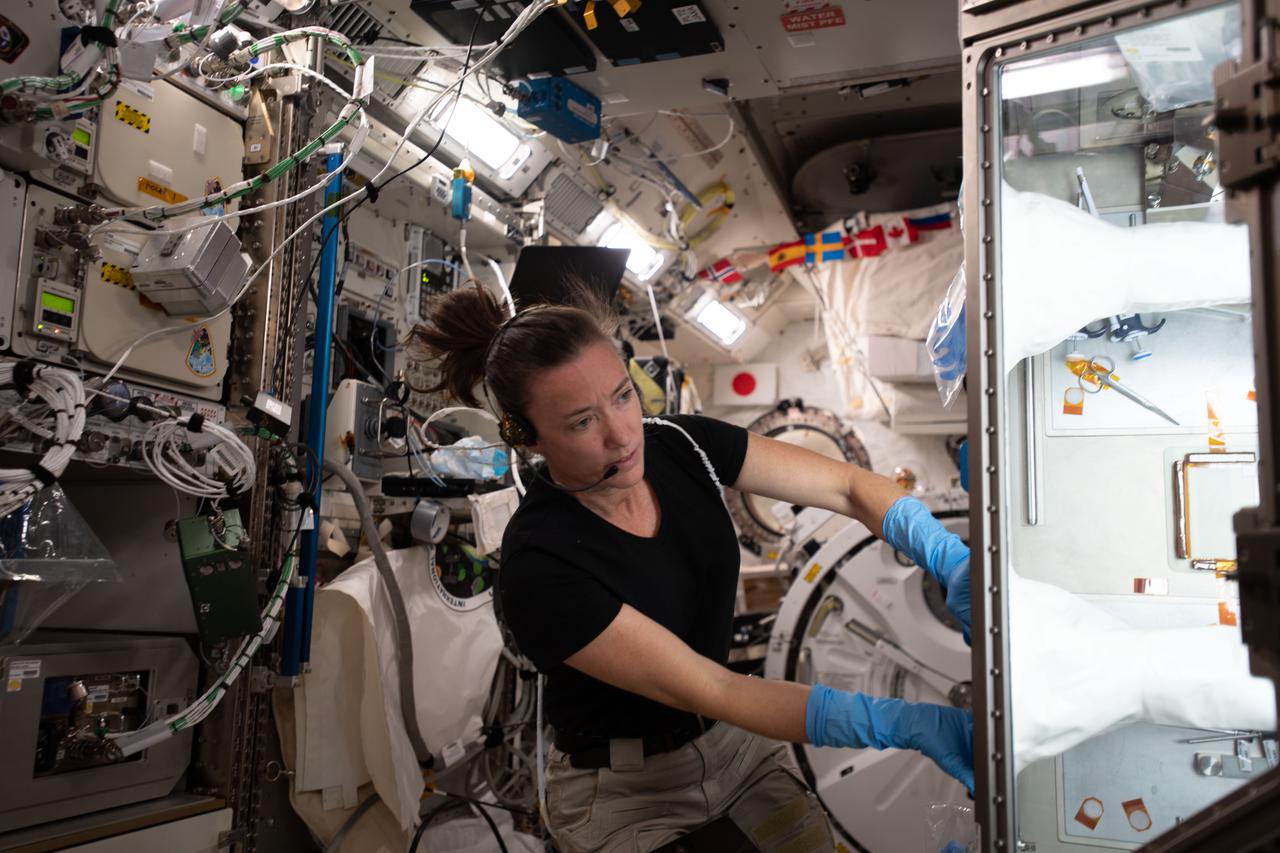

iss065e033958 (May 12, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur services donor cell samples inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox. The samples are being compared to cells on Earth so scientists can document the significant differences in microgravity. The Celestial Immunity study’s results may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs and advance the commercialization of space.