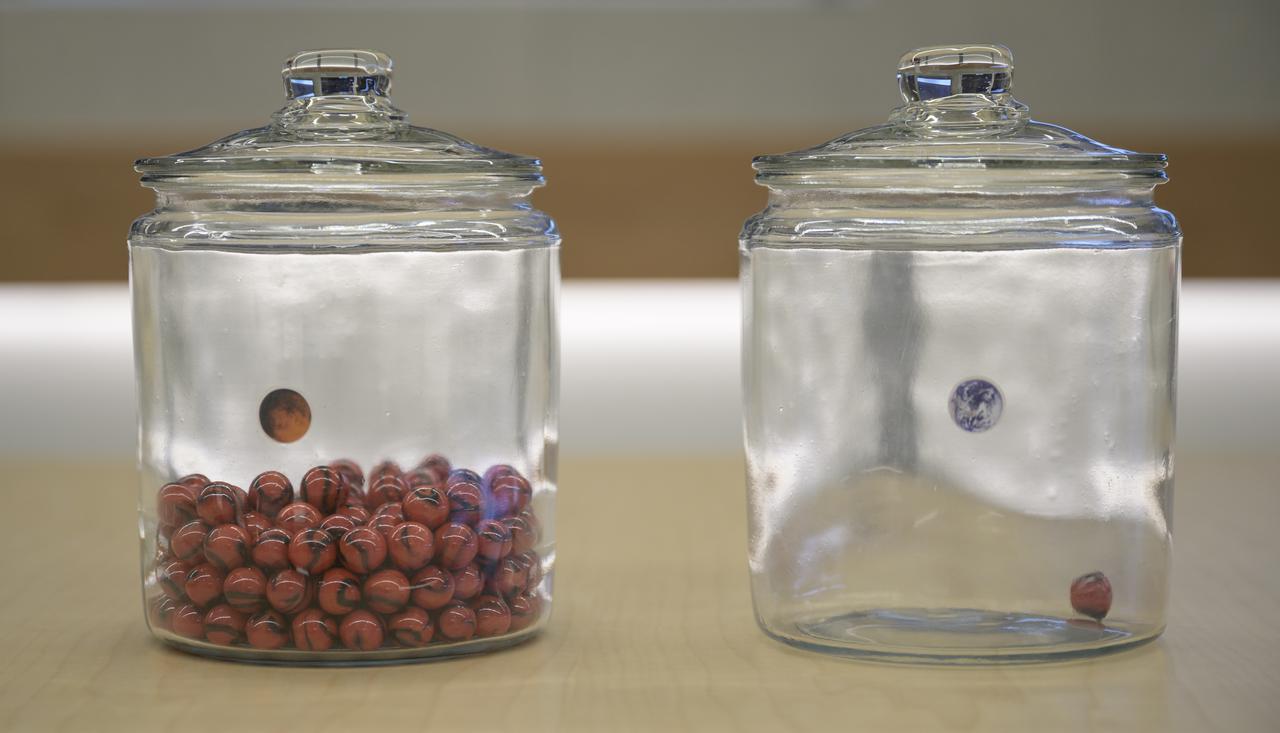

A jar with an Earth sticker and one marble inside and a jar with a Mars sticker full of marbles are seen on a conference room table of the Mission Support Area (MSA)on Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover team has been moving one marble a day since launch from jar to jar. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
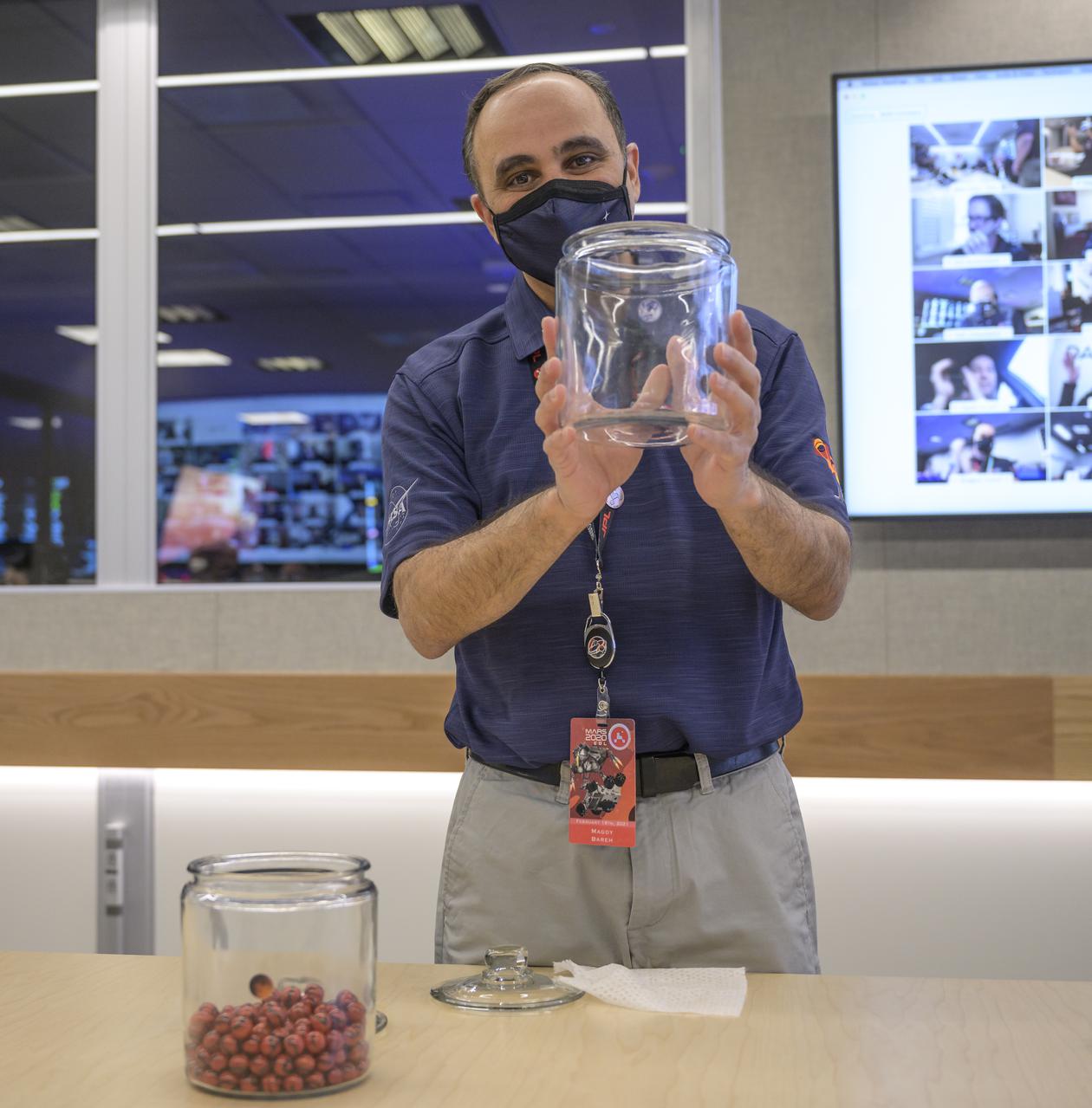

Perseverance flight director Magdy Bareh holds an empty jar after moving the final marble from the Perseverance Mars rover Earth launch jar to the Mars landing jar in a conference room of the Mission Support Area (MSA) Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover team has been moving one marble a day since launch from jar to jar. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
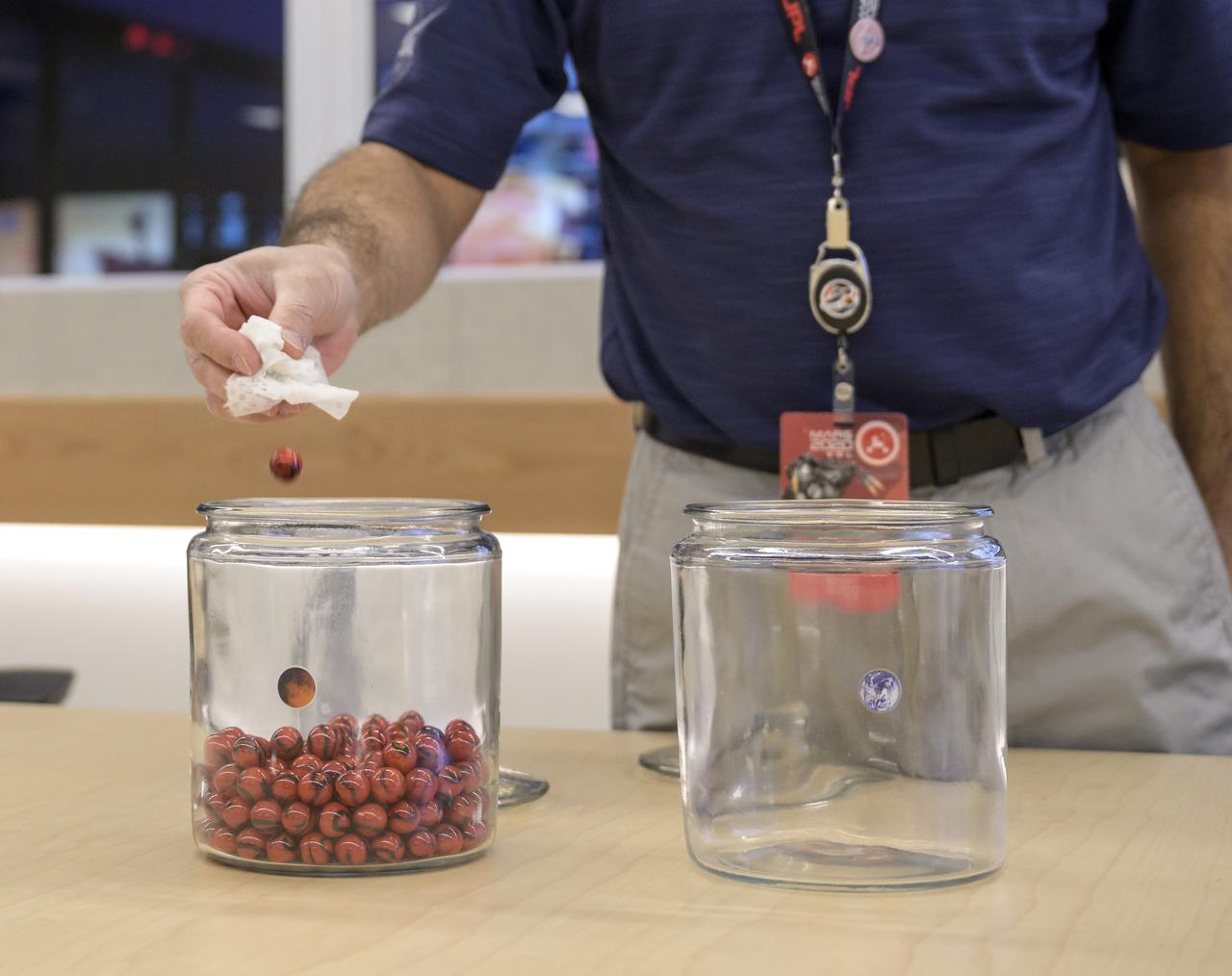

Perseverance flight director Magdy Bareh moves the final marble from the Perseverance Mars rover Earth launch jar to the Mars landing in a conference room of the Mission Support Area (MSA) Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover team has been moving one marble a day since launch from jar to jar. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA JSC Electronic Imagery
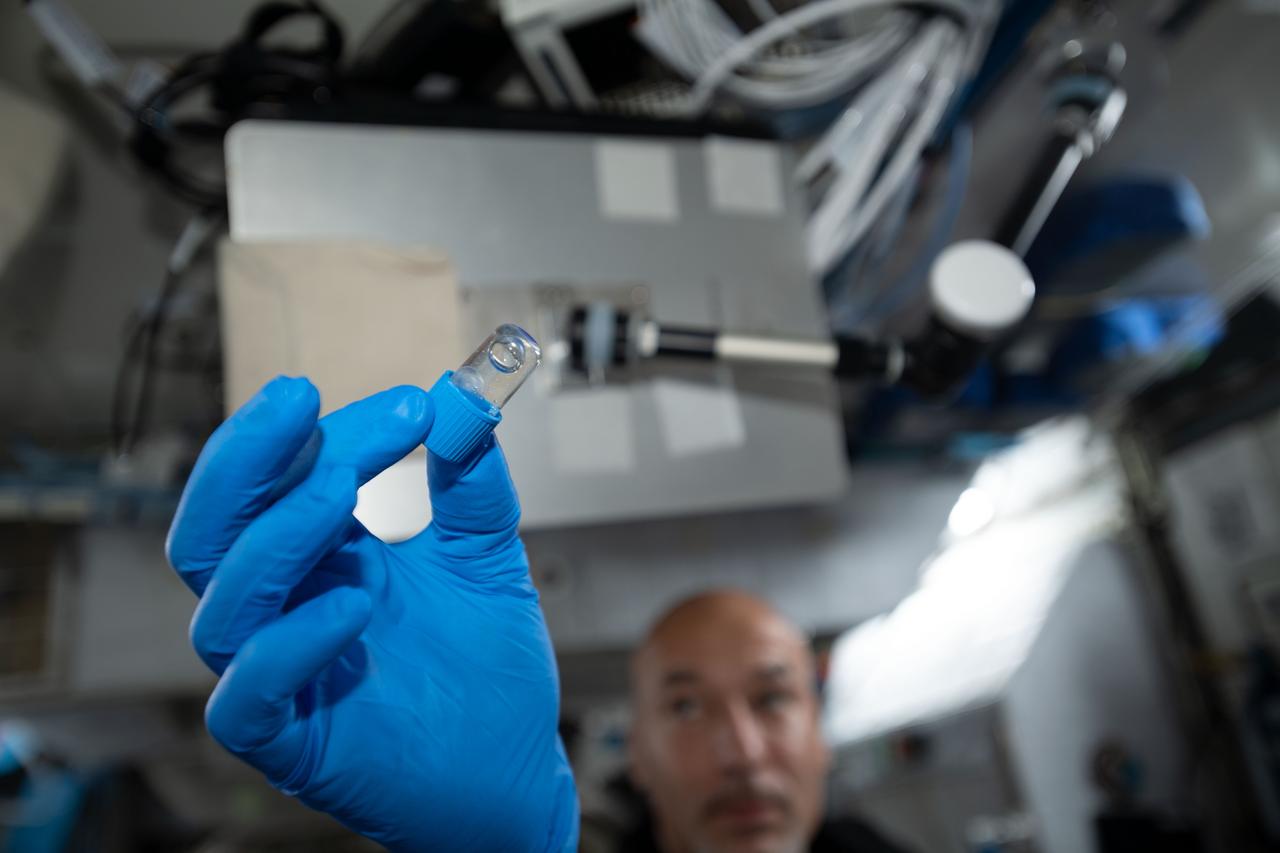

iss060e023994 (8/7/2019) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Luca Parmitano is shown holding a Amyloid Aggregation Blue Jar. The cap colors are used to distinguish the incubation times. The aim of the Amyloid Aggregation investigation is to assess if amyloid fibrils aggregation is affected by microgravity in order to identify a possible professional risk in astronauts spending long periods on board the ISS. The knowledge gained could contribute to the designing of innovative therapeutic strategies for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and for other diseases characterized by protein accumulation.
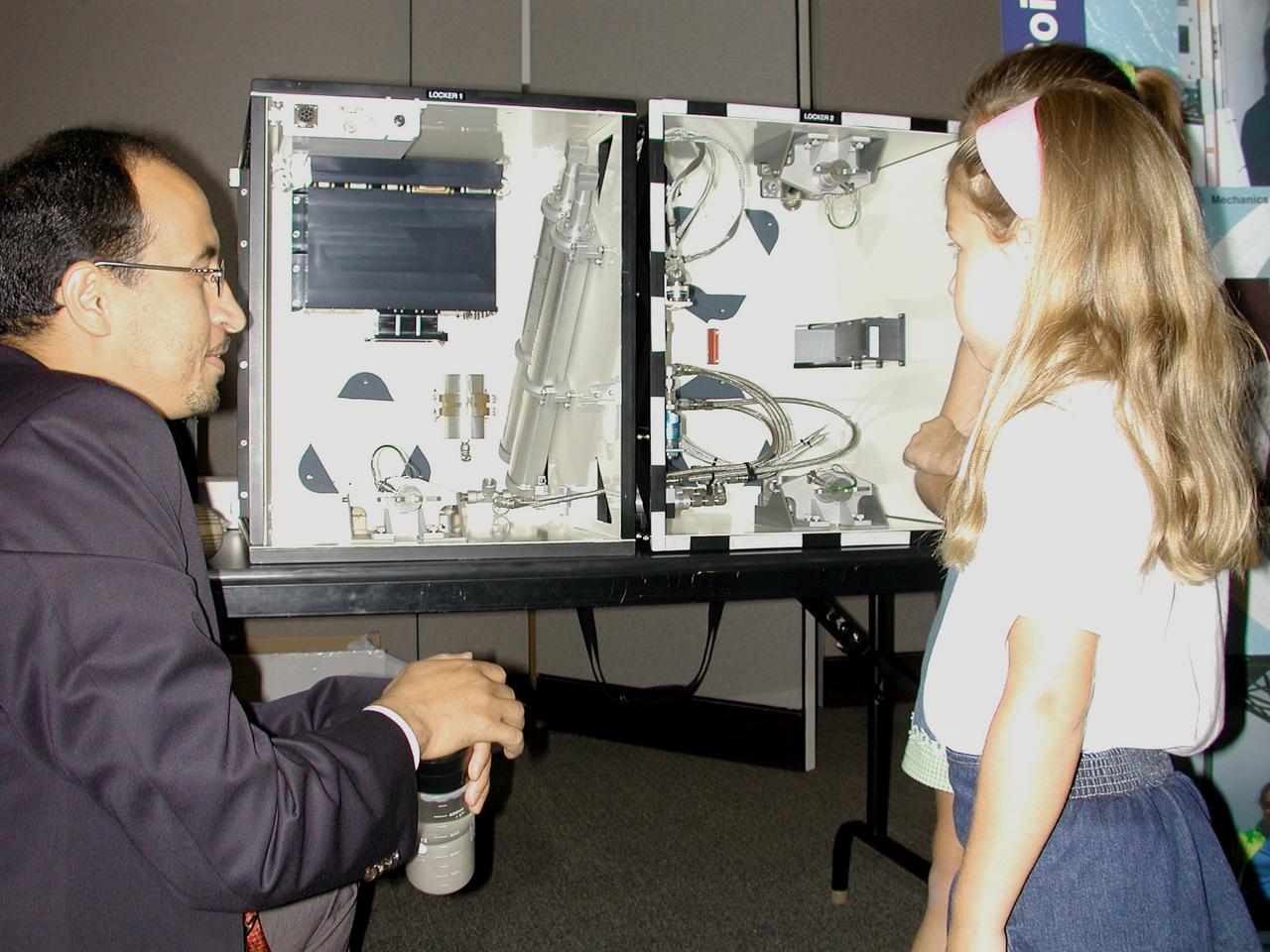

Khalid Alshibli of Louisiana State University, project scientist for the Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM-III) experiment, uses a jar of sand and a training model of the MGM apparatus to explain the experiment to two young Virginia students. The activity was part of the Space Research and You education event held by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research on June 25, 2002, in Arlington, VA, to highlight the research that will be conducted on STS-107.
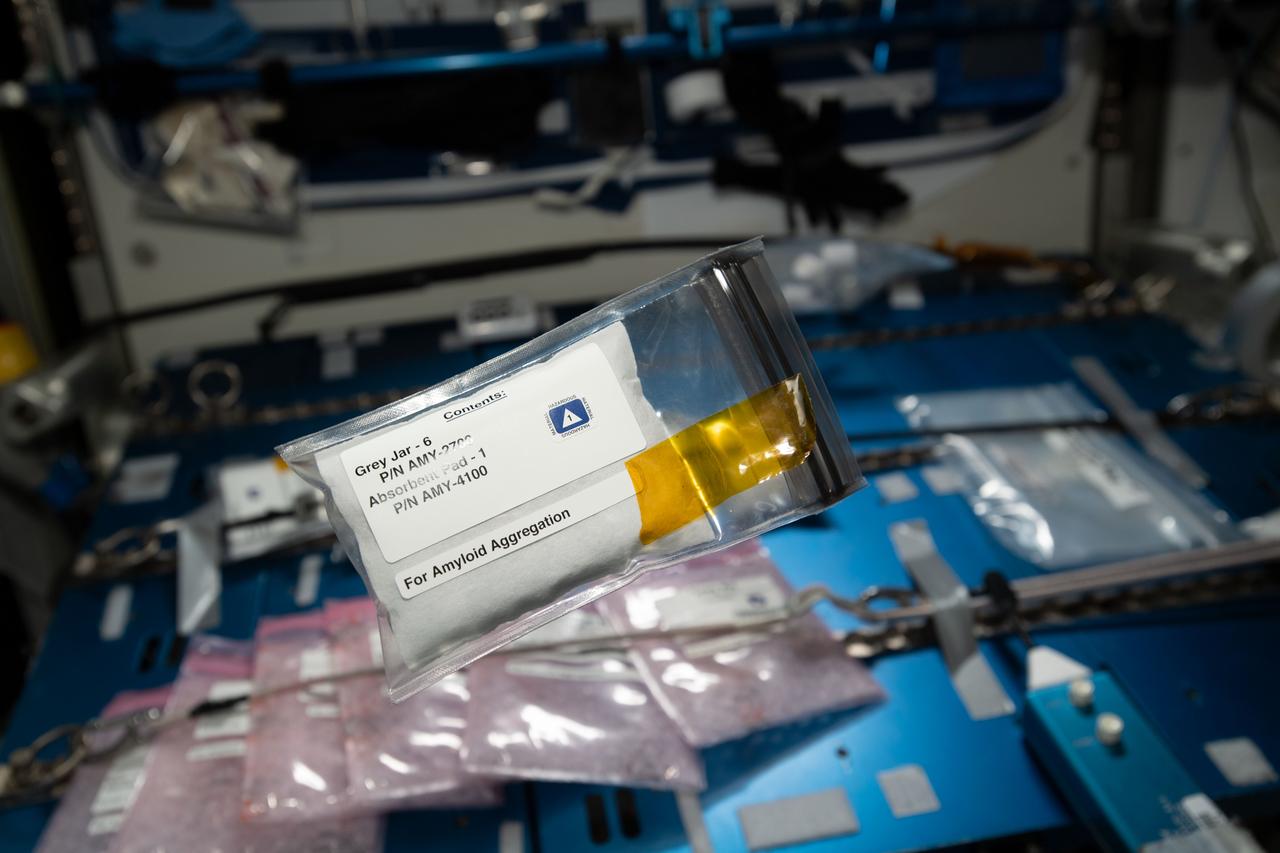

iss060e023981 (8/7/2019) --- Photo documentation of an Amyloid Aggregation Grey Jar sample pack, aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The cap colors are used to distinguish the incubation times. The aim of the Amyloid Aggregation investigation is to assess if amyloid fibrils aggregation is affected by microgravity in order to identify a possible professional risk in astronauts spending long periods on board the ISS. The knowledge gained could contribute to the designing of innovative therapeutic strategies for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and for other diseases characterized by protein accumulation.
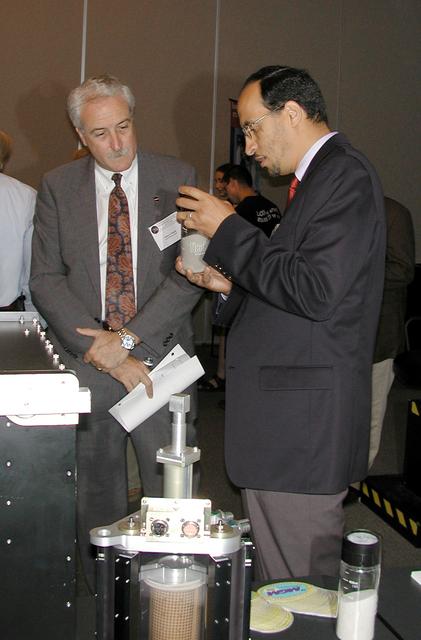

Khalid Alshibli of Louisiana State University, project scientist for the Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM-III) experiment, uses a jar of sand as he explains MGM to NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe. A training model of an MGM test cell is in the foreground. The activity was part of the Space Research and You education event held by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research on June 25, 2002, in Arlington, VA, to highlight the research that will be conducted on STS-107.
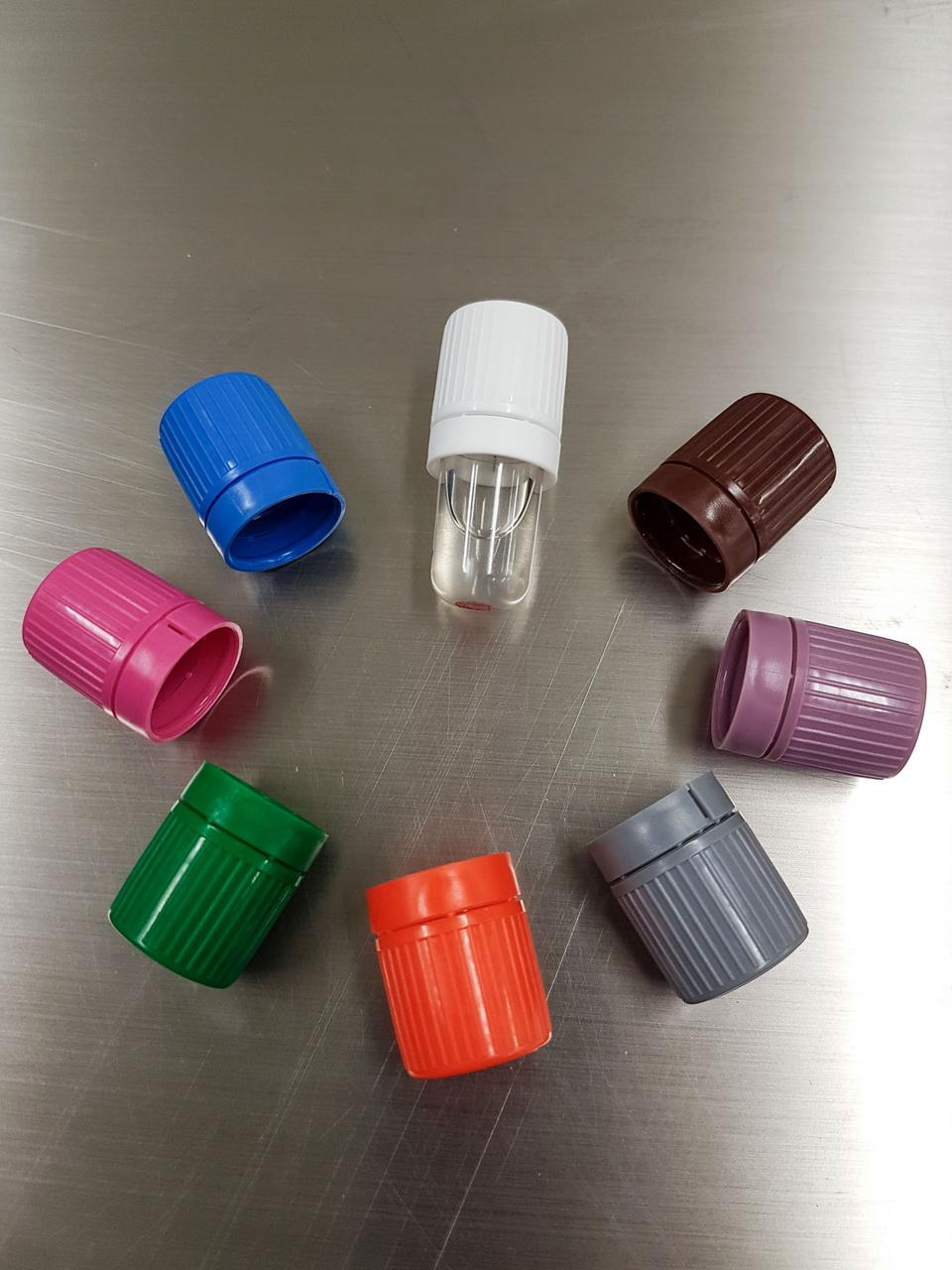

jsc2019e039817 (7/16/2019) --- A preflight view of an Amyloid Aggregation White Jar and different colored caps, used to distinguish within several incubation times by means of color code. The aim of the Amyloid Aggregation investigation is to assess if amyloid fibrils aggregation is affected by microgravity in order to identify a possible professional risk in astronauts spending long periods on board the International Space Station (ISS). (Image Courtesy of: ASI)
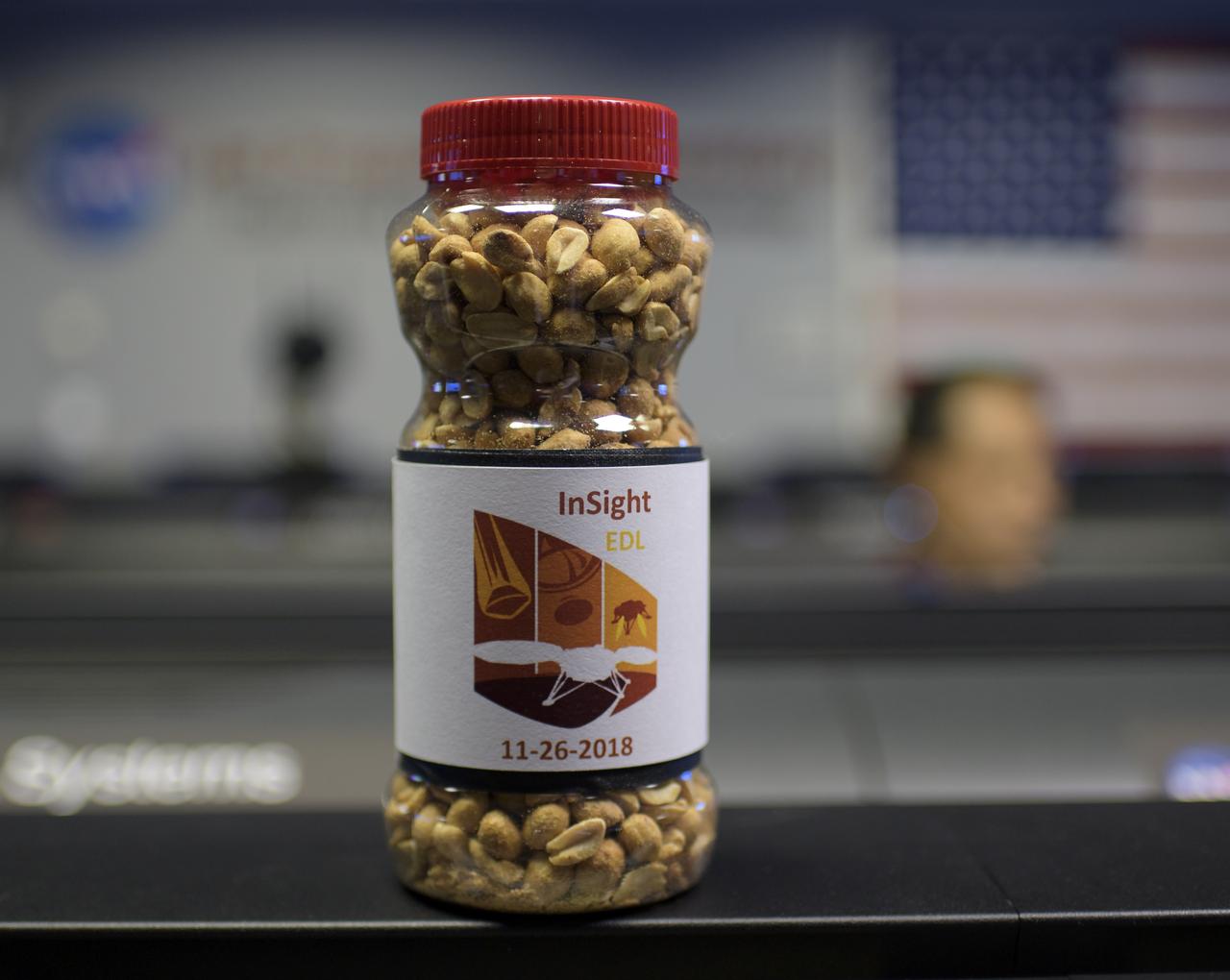

A jar of nuts is seen inside the Mission Control Area (MSA) where teams are starting to gather for the Mars InSight landing, Monday, Nov. 26, 2018 inside the Mission Support Area at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Good-luck peanuts made their first appearance at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Space Flight Operations Facility in 1964 during the Ranger 7 mission. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to study the "inner space" of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
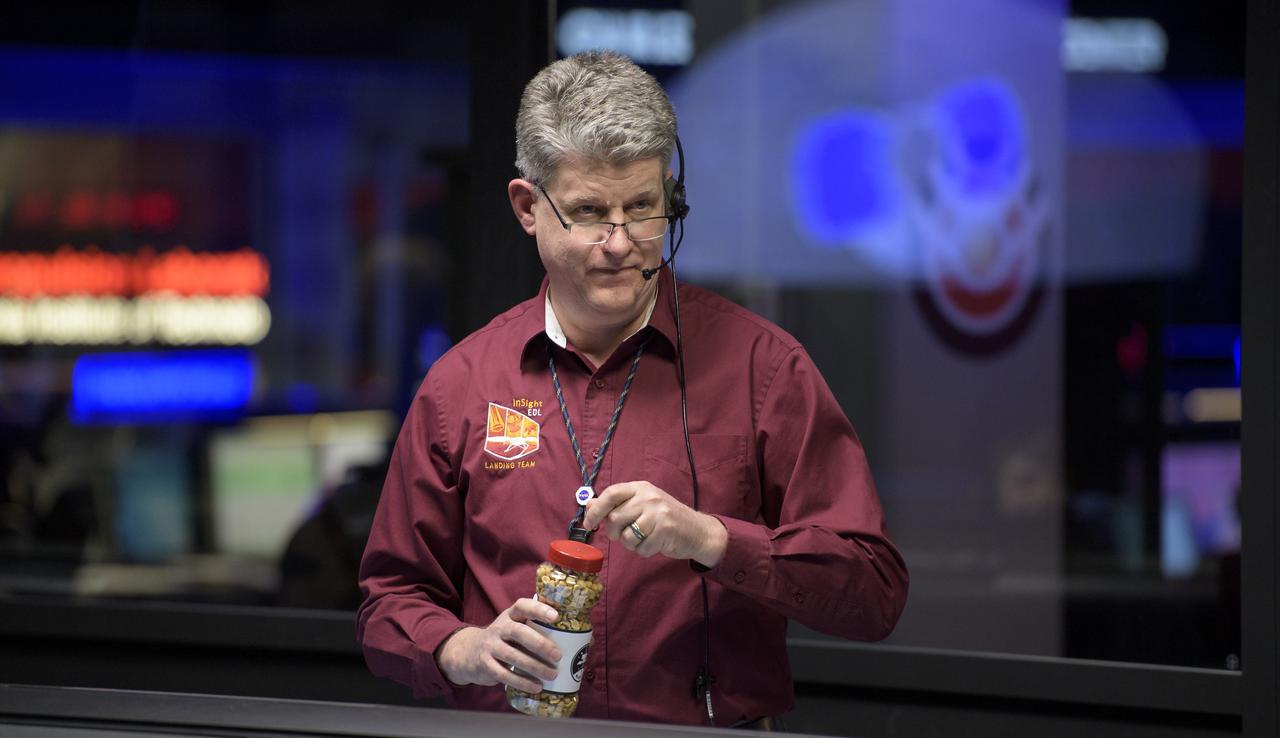

Rob Grover, EDL Phase Lead, NASA JPL, holds a jar of good-luck peanuts as he and other Mars InSight team members monitor the status of the lander prior to it touching down on Mars, Monday, Nov. 26, 2018 inside the Mission Support Area at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to study the "inner space" of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
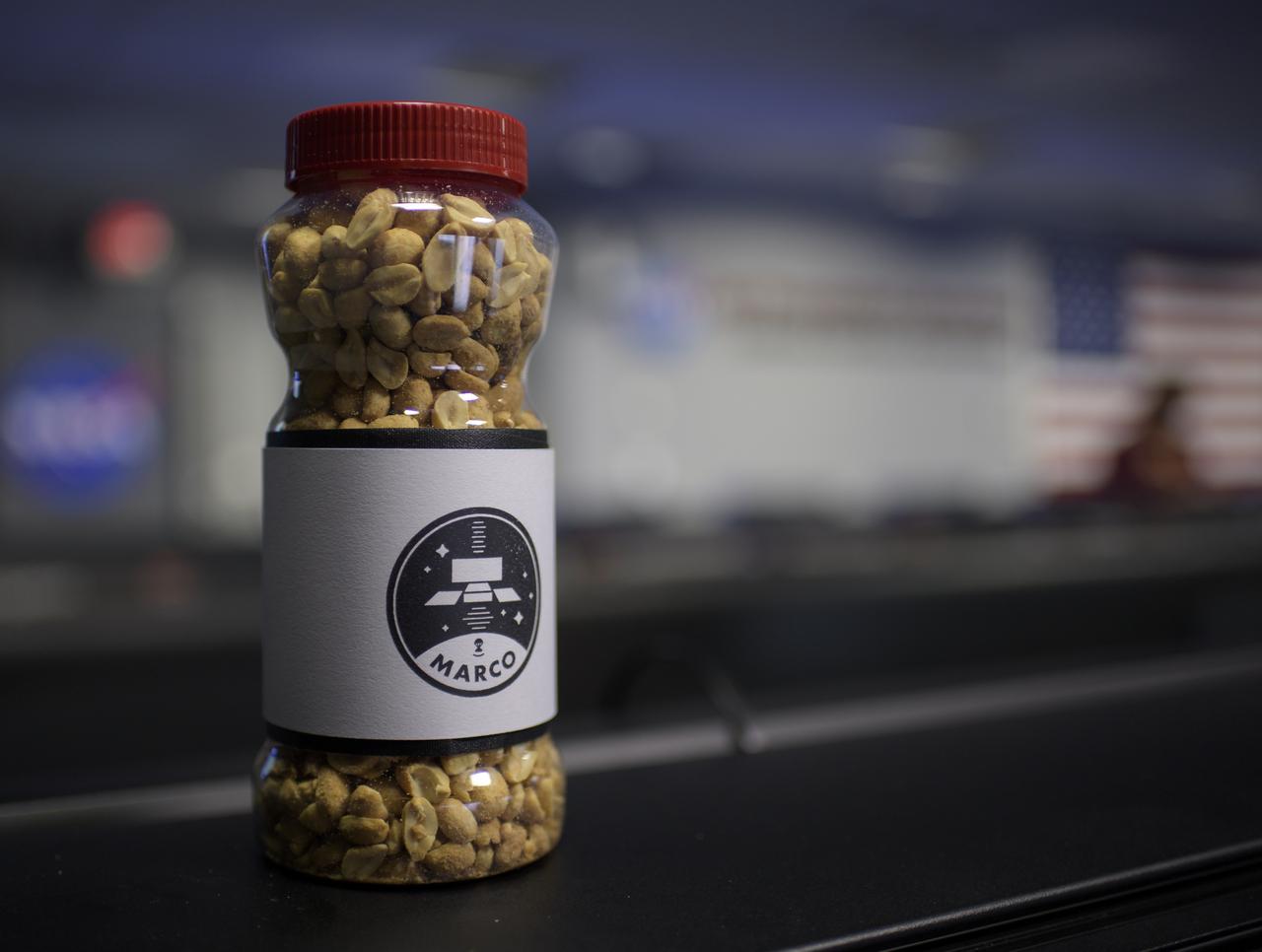

A jar of nuts with the Mars Cube One (MarCO) logo is seen inside the Mission Control Area (MSA) where teams are starting to gather for the Mars InSight landing, Monday, Nov. 26, 2018 inside the Mission Support Area at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Good-luck peanuts made their first appearance at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Space Flight Operations Facility in 1964 during the Ranger 7 mission. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to study the "inner space" of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
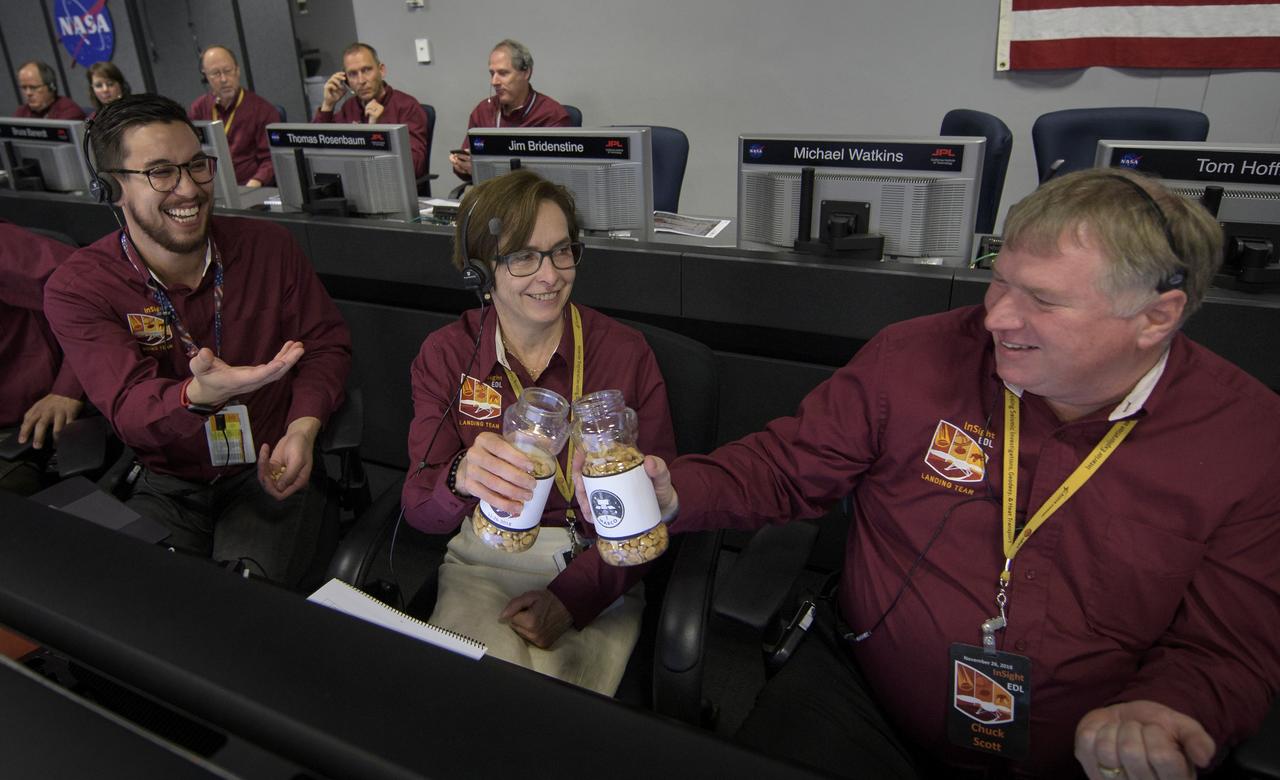

Sue Smrekar, InSight deputy principal investigator, NASA JPL, center, and Charles Scott, InSight Deputy Project Manager, NASA JPL, say cheers with two jars of good-luck peanuts as Thomas Thammasuckdi, Software Systems Engineer, NASA JPL, left, looks on, Monday, Nov. 26, 2018 inside the Mission Support Area at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to study the "inner space" of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
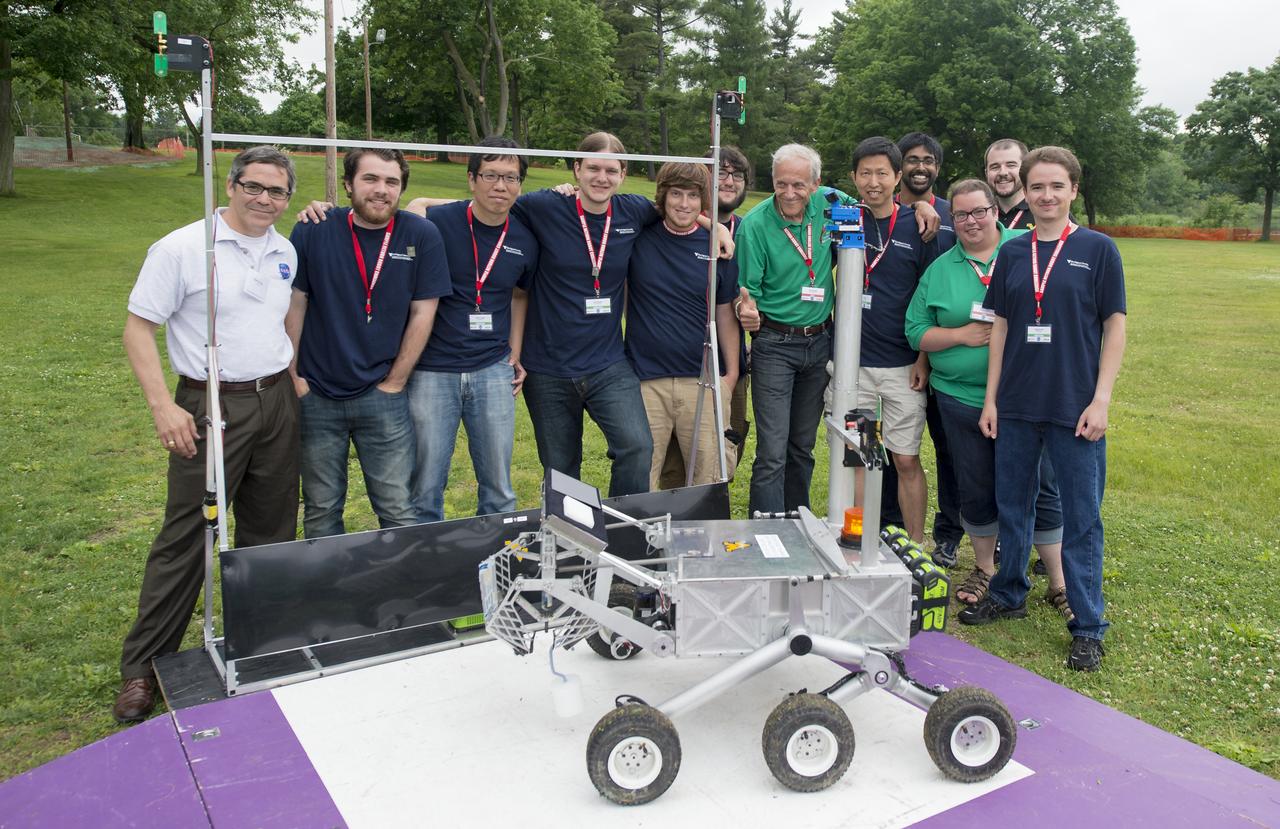

Members of team Mountaineers pose with officials from the 2014 NASA Centennial Challenges Sample Return Robot Challenge on Saturday, June 14, 2014 at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Worcester, Mass. Team Mountaineer was the only team to complete the level one challenge this year. Team Mountaineer members, from left (in blue shirts) are: Ryan Watson, Marvin Cheng, Scott Harper, Jarred Strader, Lucas Behrens, Yu Gu, Tanmay Mandal, Alexander Hypes, and Nick Ohi Challenge judges and competition staff (in white and green polo shirts) from left are: Sam Ortega, NASA Centennial Challenge program manager; Ken Stafford, challenge technical advisor, WPI; Colleen Shaver, challenge event manager, WPI. During the competition, teams were required to demonstrate autonomous robots that can locate and collect samples from a wide and varied terrain, operating without human control. The objective of this NASA-WPI Centennial Challenge was to encourage innovations in autonomous navigation and robotics technologies. Innovations stemming from the challenge may improve NASA's capability to explore a variety of destinations in space, as well as enhance the nation's robotic technology for use in industries and applications on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The NASA Centennial Challenges prize, level one, is presented to team Mountaineers for successfully completing level one of the NASA 2014 Sample Return Robot Challenge, from left, Ryan Watson, Team Mountaineers; Lucas Behrens, Team Mountaineers; Jarred Strader, Team Mountaineers; Yu Gu, Team Mountaineers; Scott Harper, Team Mountaineers; Dorothy Rasco, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for the Space Technology Mission Directorate; Laurie Leshin, Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) President; David Miller, NASA Chief Technologist; Alexander Hypes, Team Mountaineers; Nick Ohi,Team Mountaineers; Marvin Cheng, Team Mountaineers; Sam Ortega, NASA Program Manager for Centennial Challenges; and Tanmay Mandal, Team Mountaineers;, Saturday, June 14, 2014, at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Worcester, Mass. Team Mountaineers was the only team to complete the level one challenge. During the competition, teams were required to demonstrate autonomous robots that can locate and collect samples from a wide and varied terrain, operating without human control. The objective of this NASA-WPI Centennial Challenge was to encourage innovations in autonomous navigation and robotics technologies. Innovations stemming from the challenge may improve NASA's capability to explore a variety of destinations in space, as well as enhance the nation's robotic technology for use in industries and applications on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
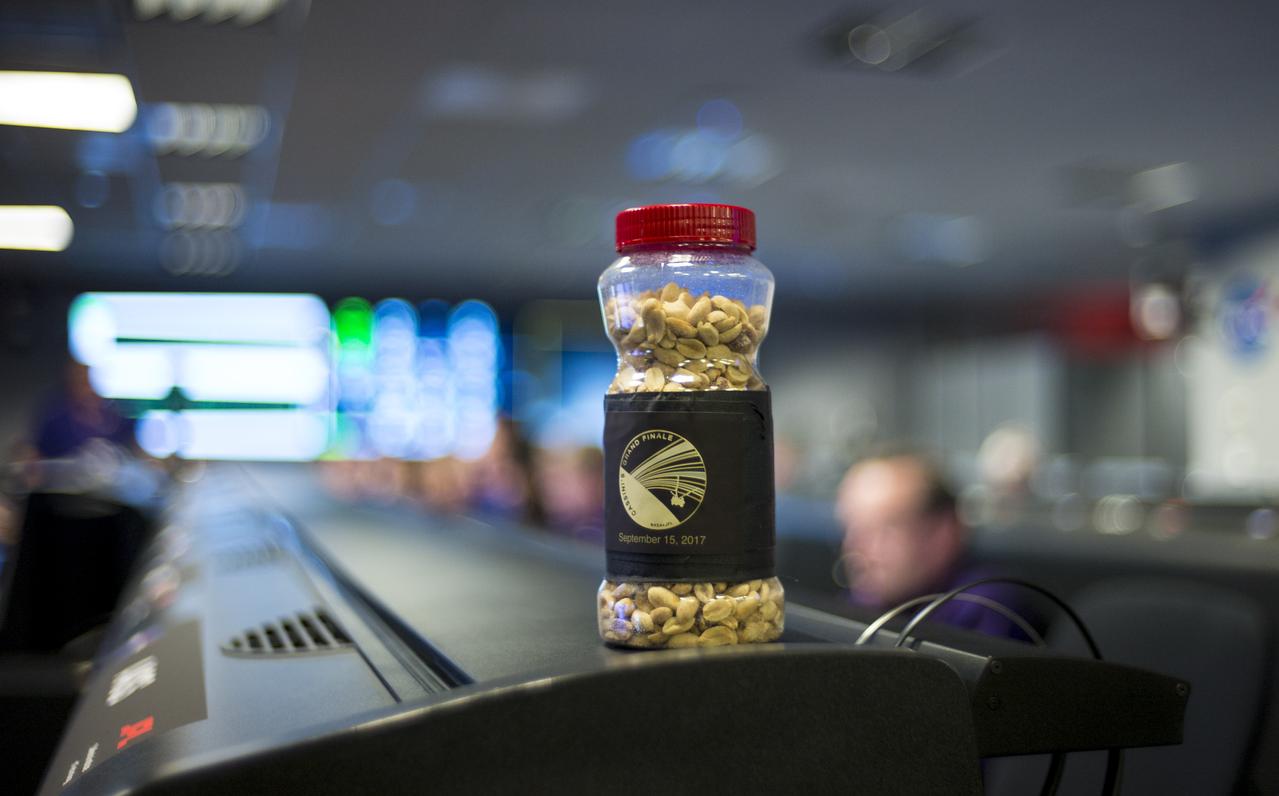

A jar of peanuts is seen sitting on a console in mission control of the Space Flight Operations Center as the Cassini mission team await the final downlink of the spacecraft's data recorder, Thursday, Sept. 14, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
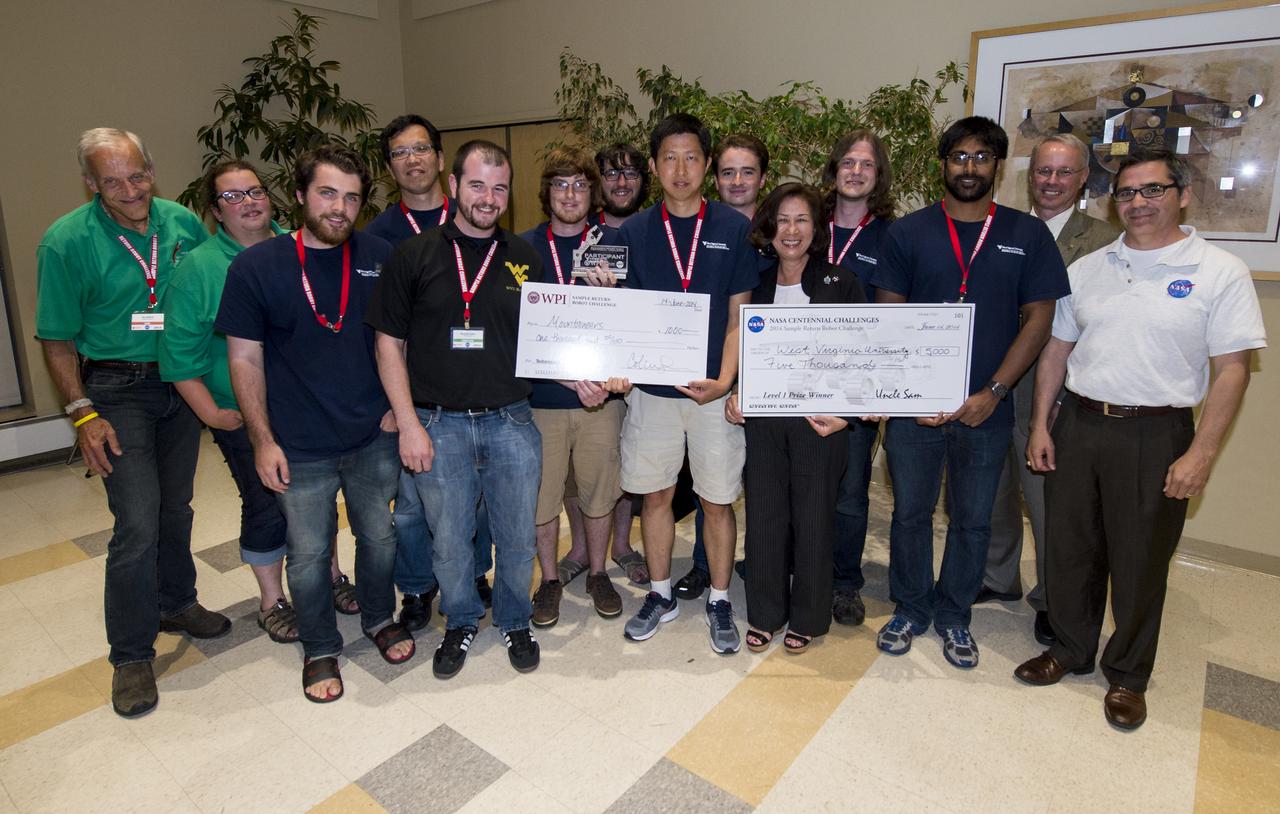

The NASA Centennial Challenges prize, level one, is presented to team Mountaineers for successfully completing level one of the NASA 2014 Sample Return Robot Challenge, from left, Ken Stafford, WPI Challenge technical advisor; Colleen Shaver, WPI Challenge Manager; Ryan Watson, Team Mountaineers; Marvin Cheng, Team Mountaineers; Alexander Hypes, Team Mountaineers; Jarred Strader, Team Mountaineers; Lucas Behrens, Team Mountaineers; Yu Gu, Team Mountaineers; Nick Ohi, Team Mountaineers; Dorothy Rasco, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for the Space Technology Mission Directorate; Scott Harper, Team Mountaineers; Tanmay Mandal, Team Mountaineers; David Miller, NASA Chief Technologist; Sam Ortega, NASA Program Manager for Centennial Challenges, Saturday, June 14, 2014, at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Worcester, Mass. Team Mountaineers was the only team to complete the level one challenge. During the competition, teams were required to demonstrate autonomous robots that can locate and collect samples from a wide and varied terrain, operating without human control. The objective of this NASA-WPI Centennial Challenge was to encourage innovations in autonomous navigation and robotics technologies. Innovations stemming from the challenge may improve NASA's capability to explore a variety of destinations in space, as well as enhance the nation's robotic technology for use in industries and applications on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
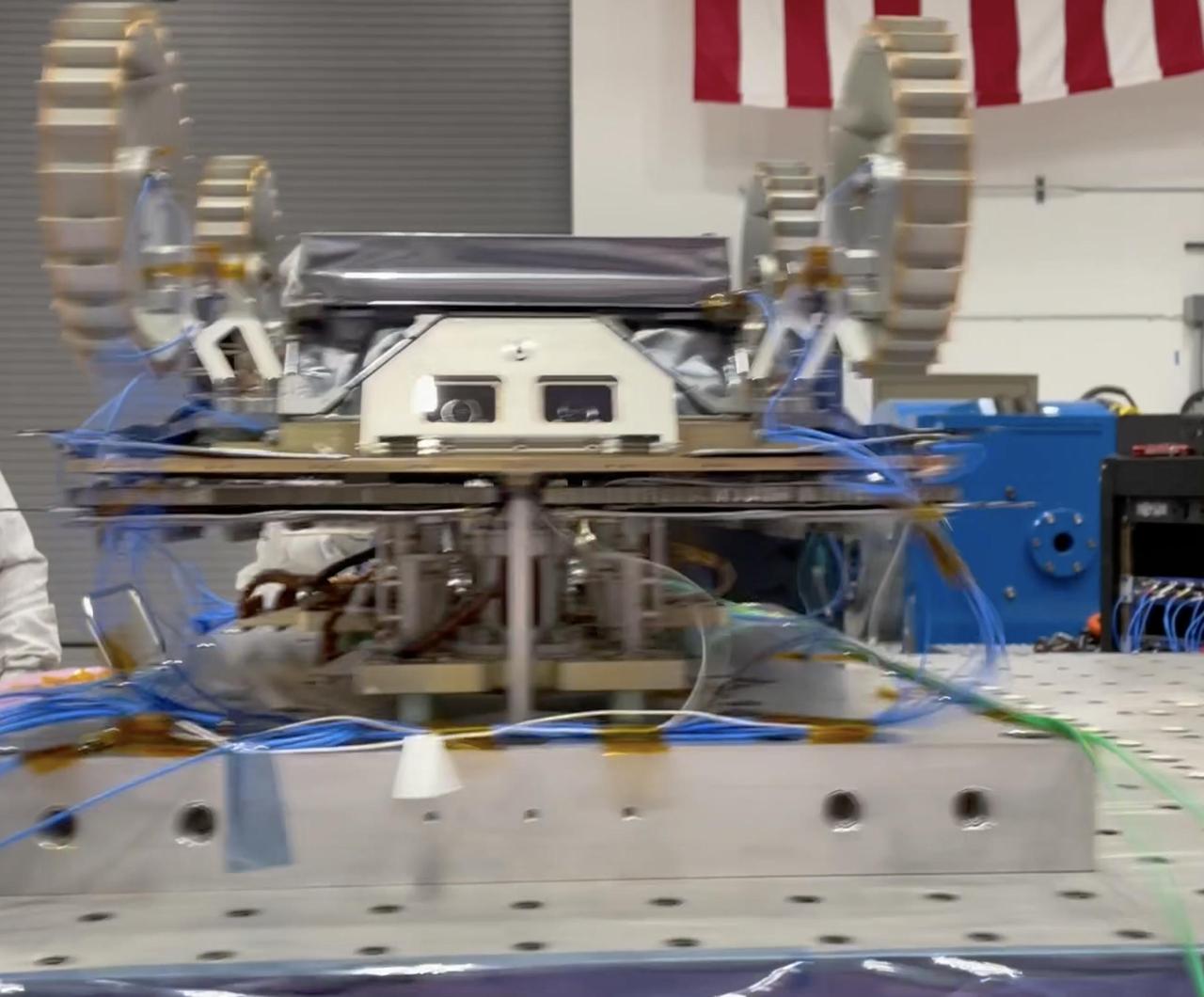
A small Moon-bound rover is clamped to a special "shaker table" that vibrates intensely to make sure the hardware will survive the jarring rocket ride out of Earth's atmosphere. This is one of three rovers – each about the size of a carry-on suitcase – that are part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration. This vibration testing took place in November 2023 at a National Technical Systems test facility in Santa Clarita, California. In the video, the rover is shaken in two directions – first along the "z" axis and then the "x" axis. Another test, not shown, subjected the rover to a "y" axis vibration test. CADRE is designed to show that a group of robotic spacecraft can work together as a team to accomplish tasks and record data autonomously &ndash without explicit commands from mission controllers on Earth. The three small rovers will ride aboard a lunar lander that will carry the project's base station and camera assembly. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26167