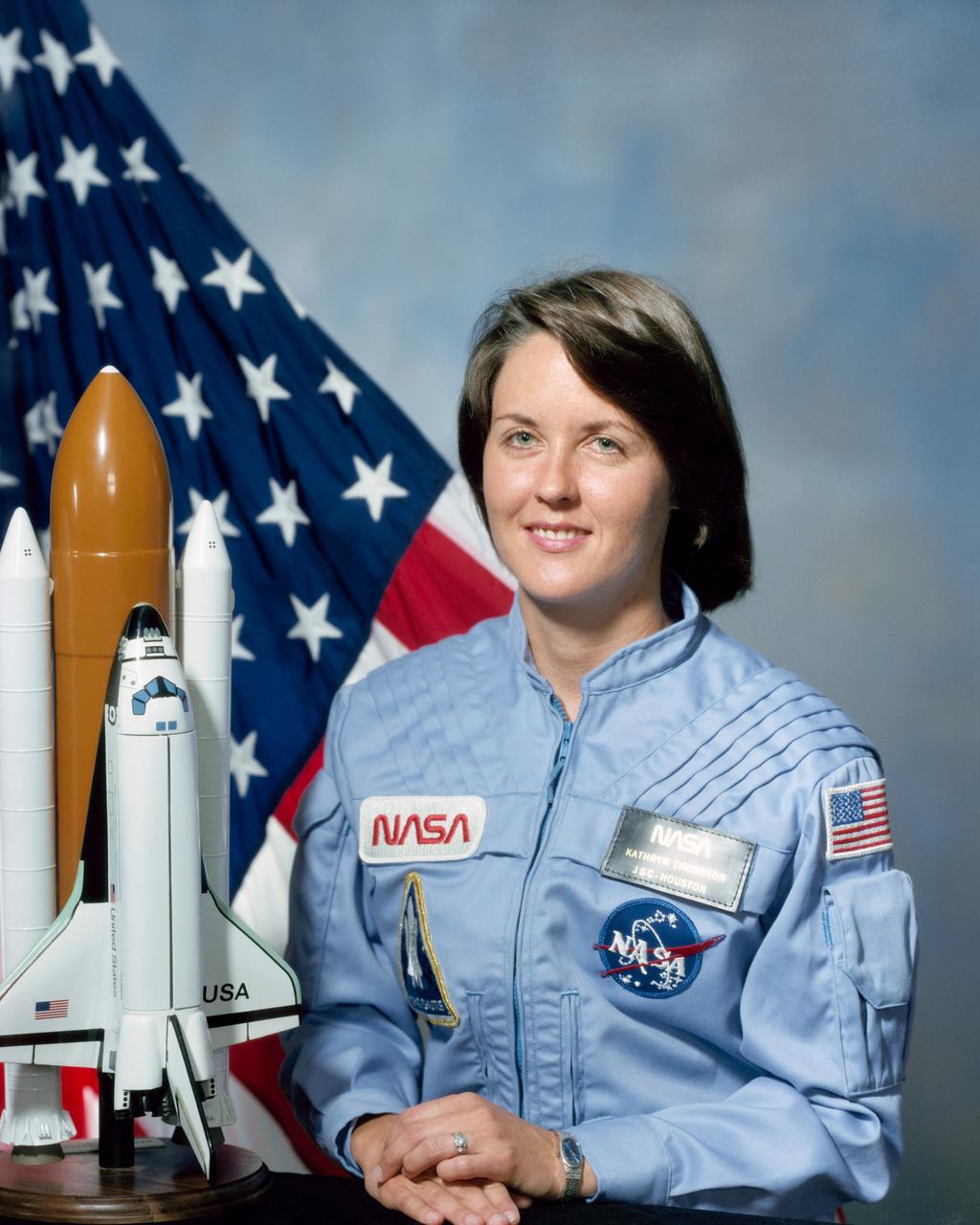

S84-40237 (July 1984) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, Astronaut Candidate Group 11.
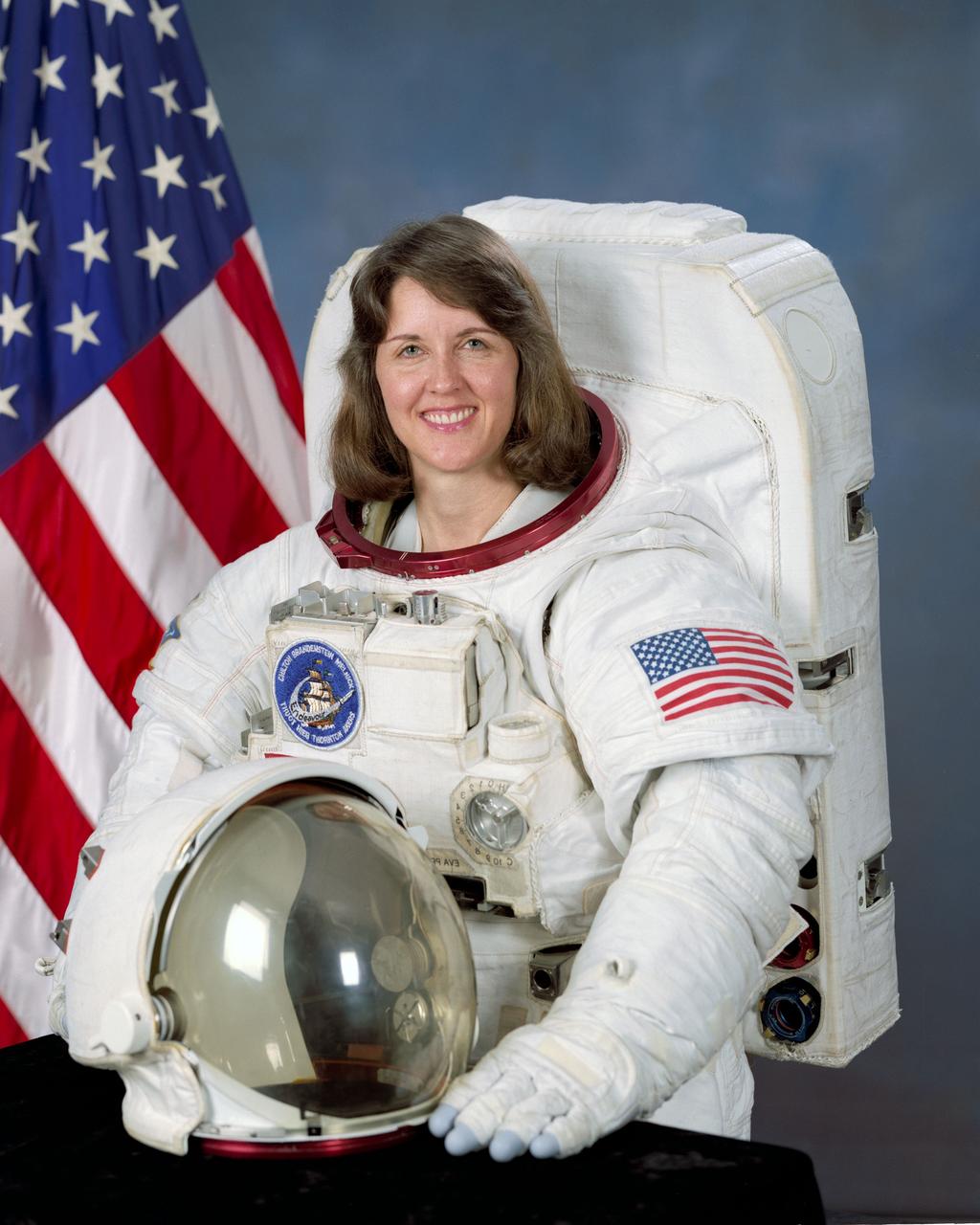

S92-42897 (7 August 1992) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialist
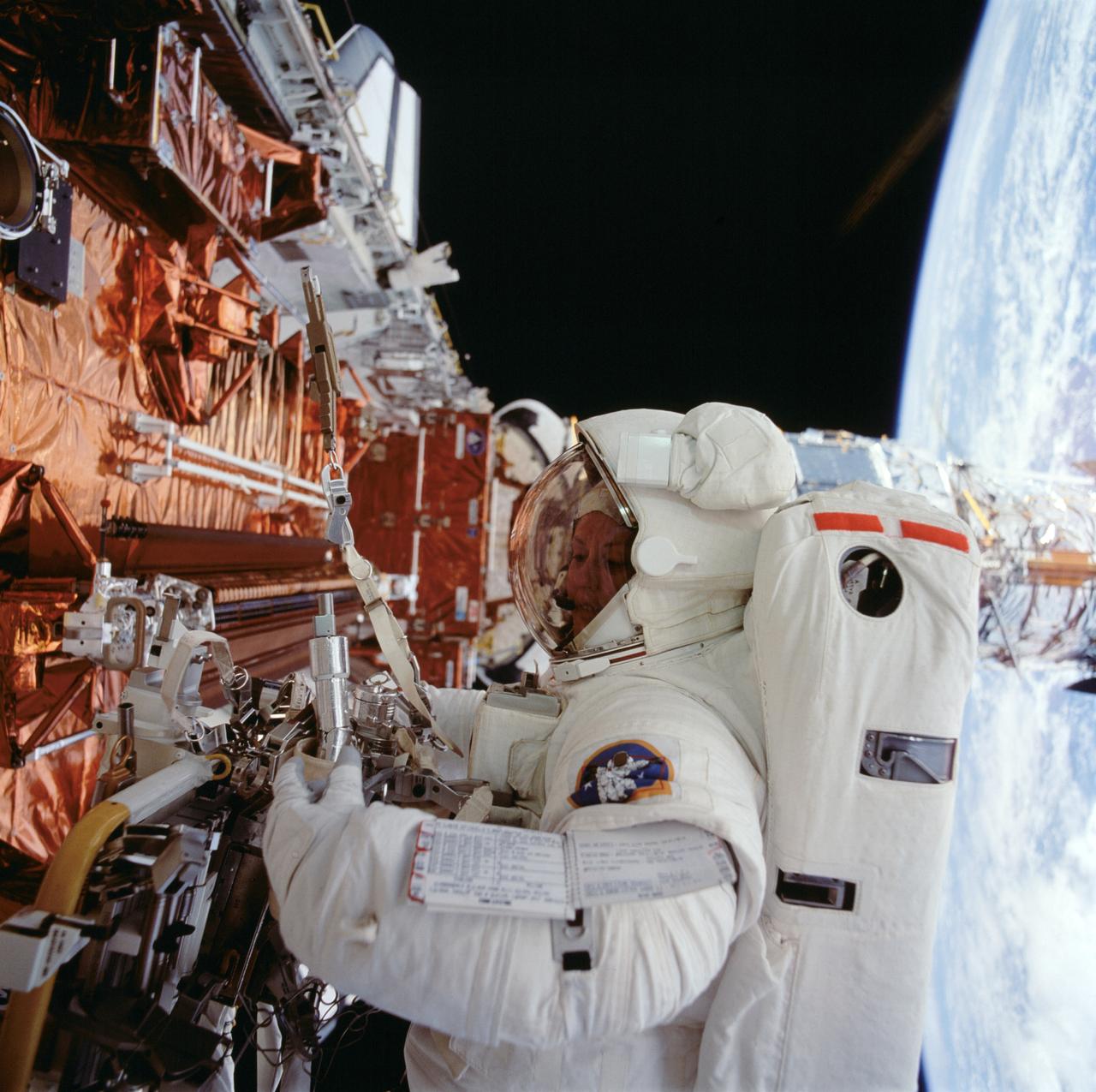

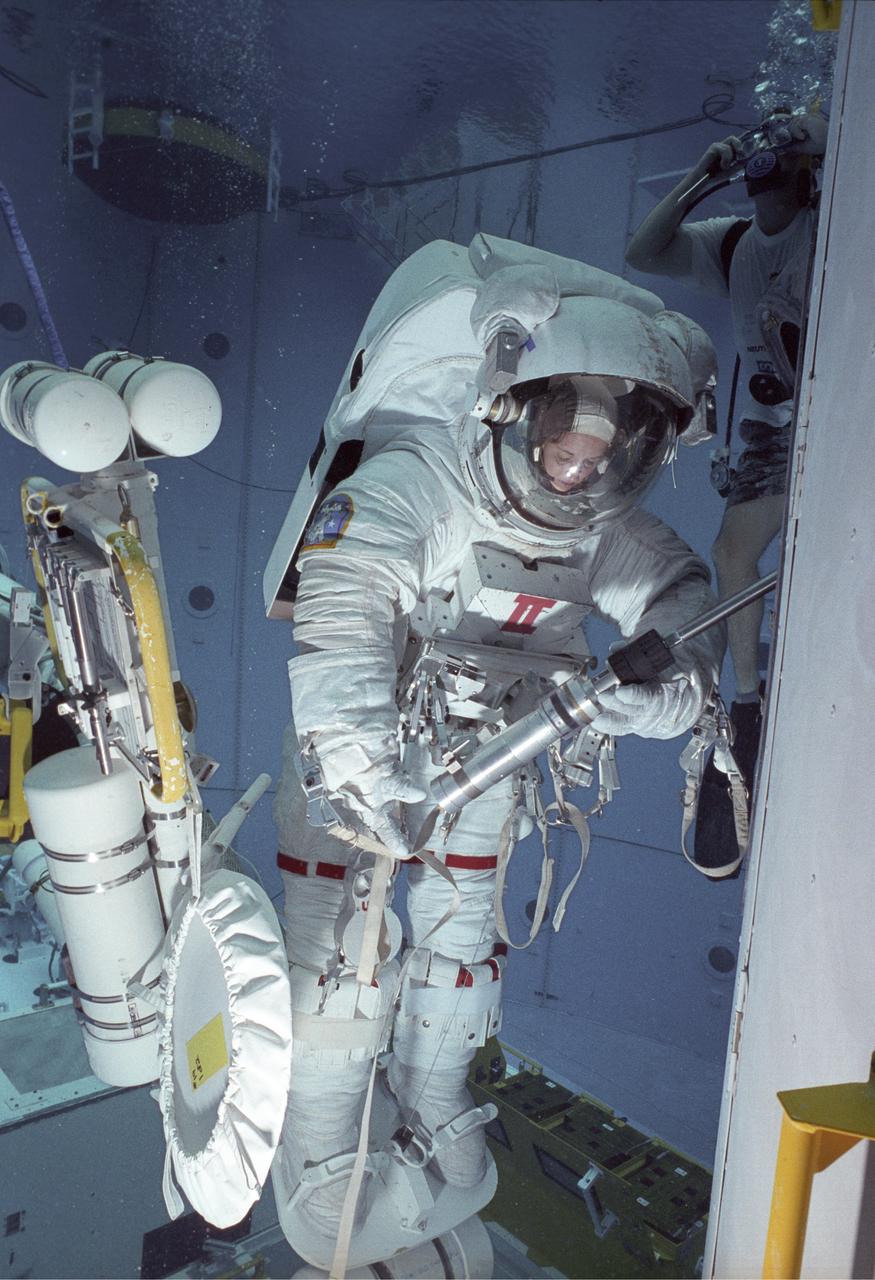
STS061-098-000K (8 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton works with equipment associated with servicing chores on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during the fourth extravehicular activity (EVA) on the eleven-day mission.
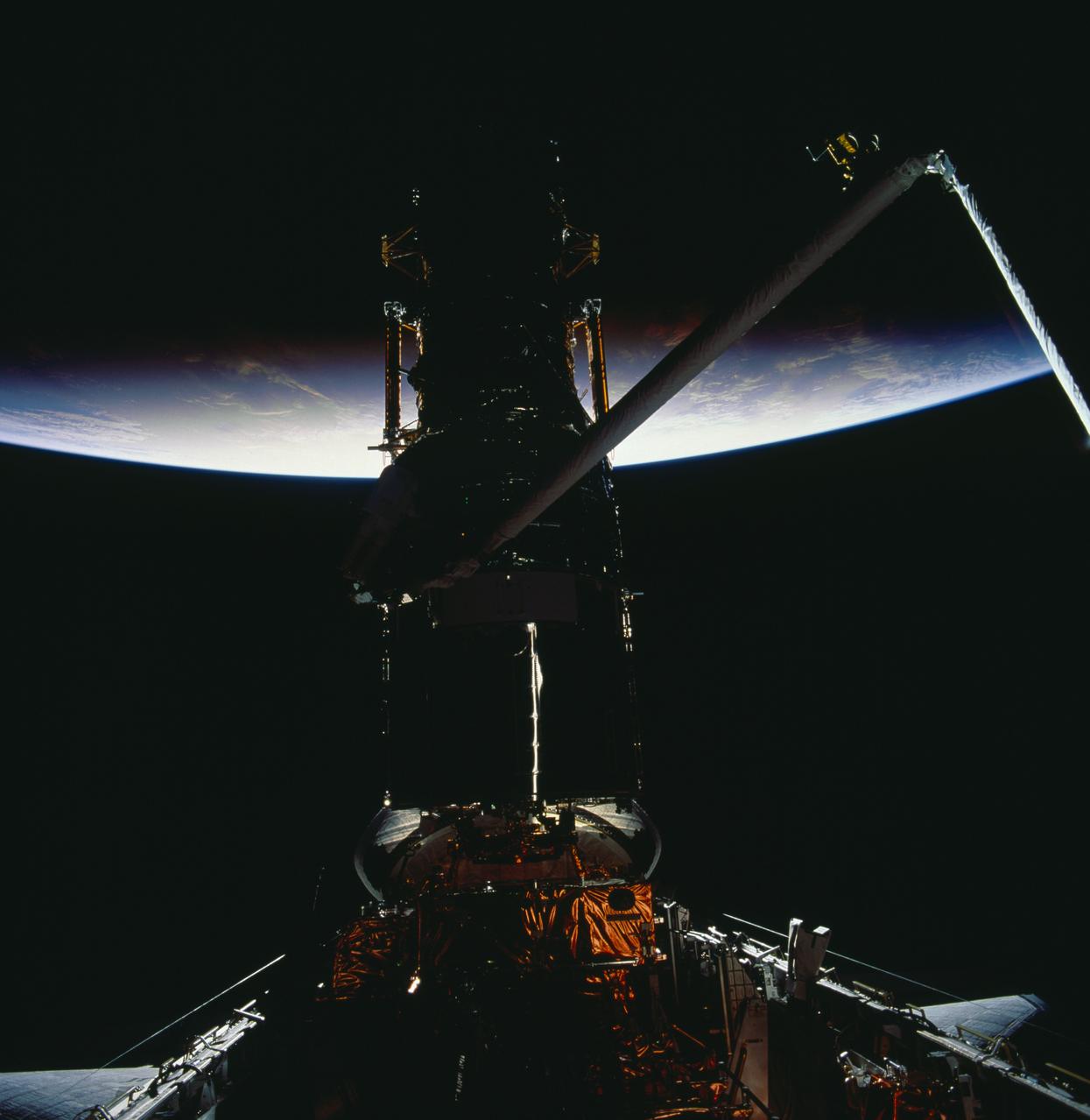

STS061-98-0AR (8 Dec 1993) --- Earth is partially illuminated but the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Space Shuttle Endeavour are still mostly in darkness, in this 70mm frame photographed during the fourth of five space walks. Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, barely visible above left center in the frame, works to install the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR).
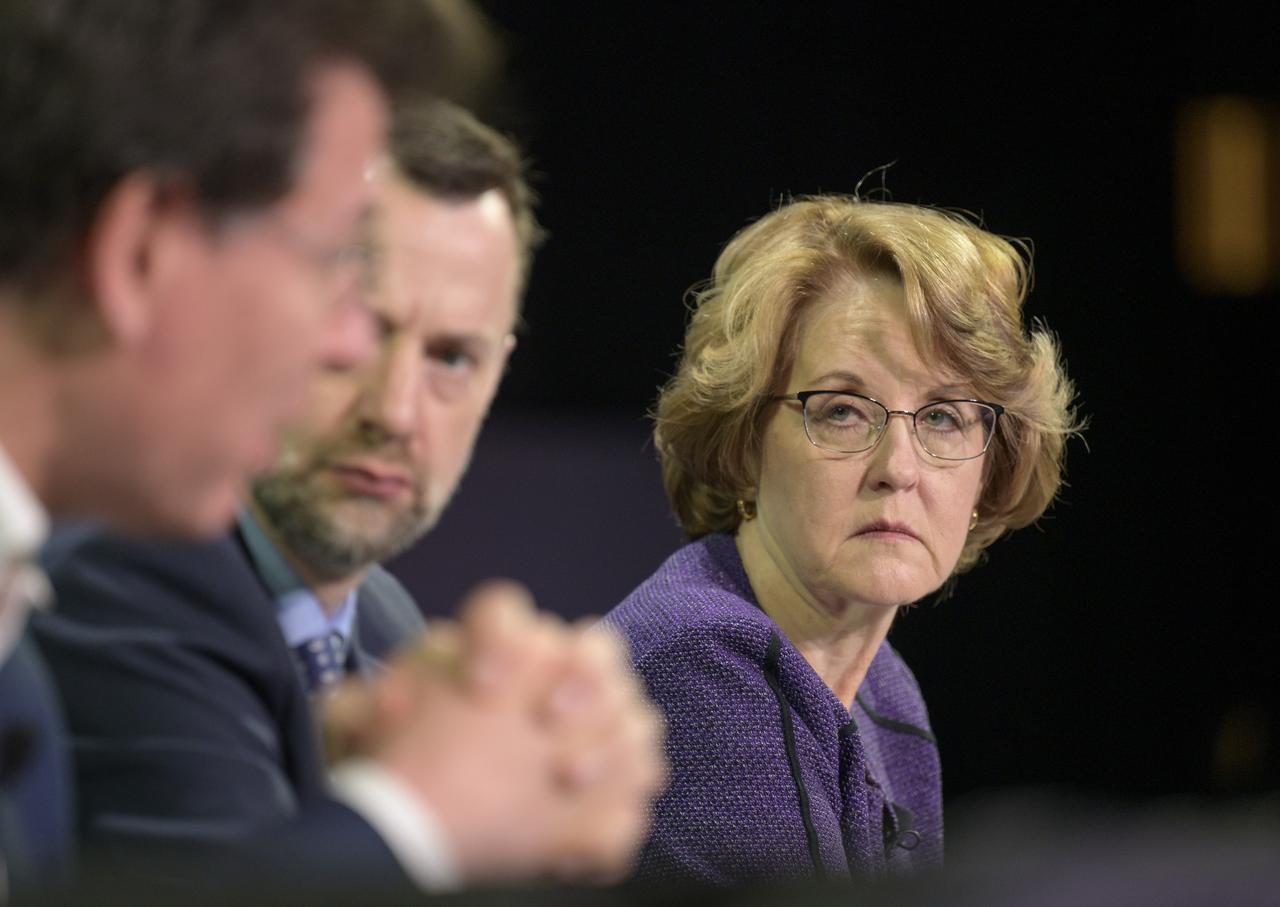

Dr. Kathryn C. Thornton, Chairwoman, Space Foundation, moderates a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
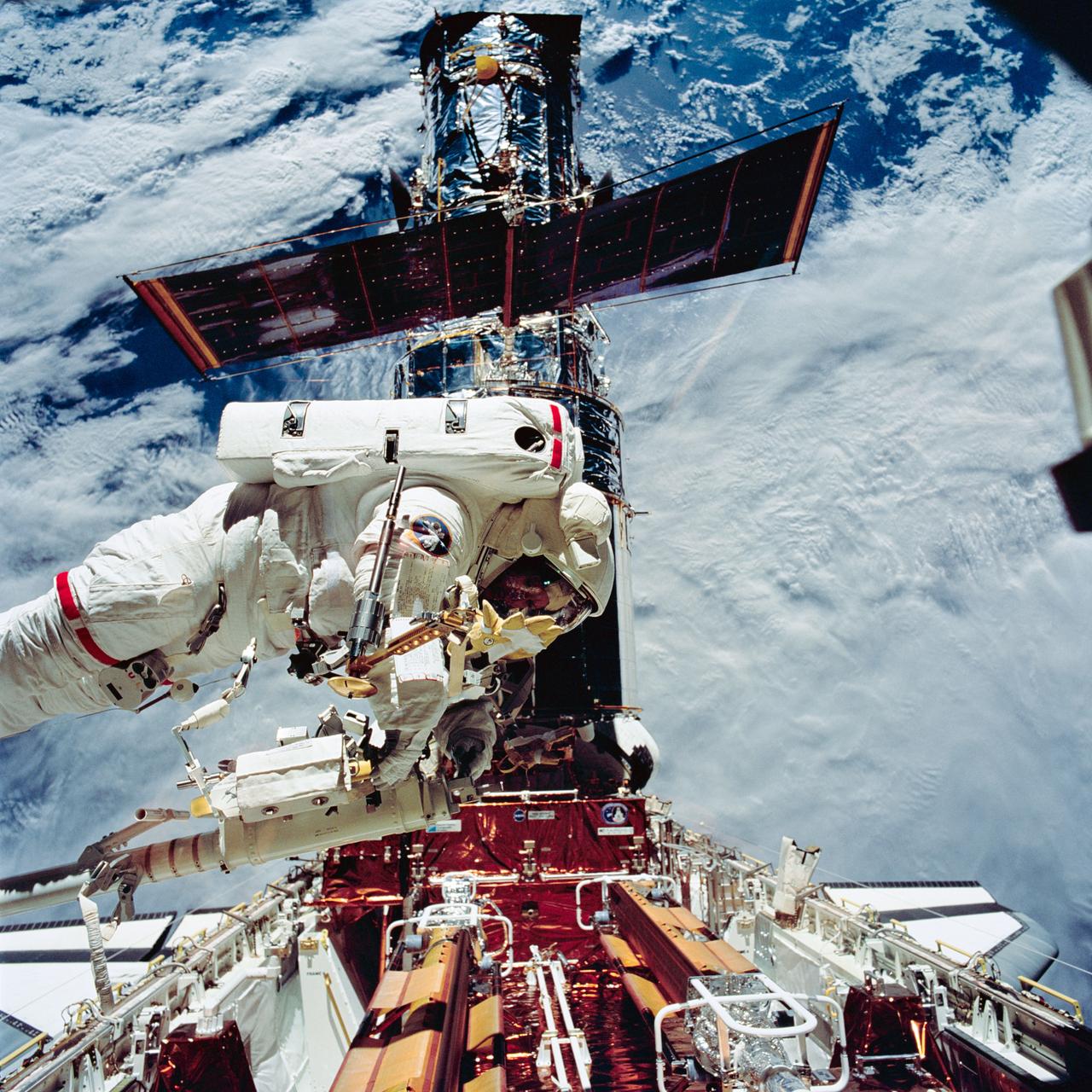

STS061-95-028 (6 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, hovers over equipment associated with servicing chores on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during the second extravehicular activity (EVA) on the eleven-day mission. Astronauts Thornton and Thomas D. Akers changed out the solar array panels during this EVA.
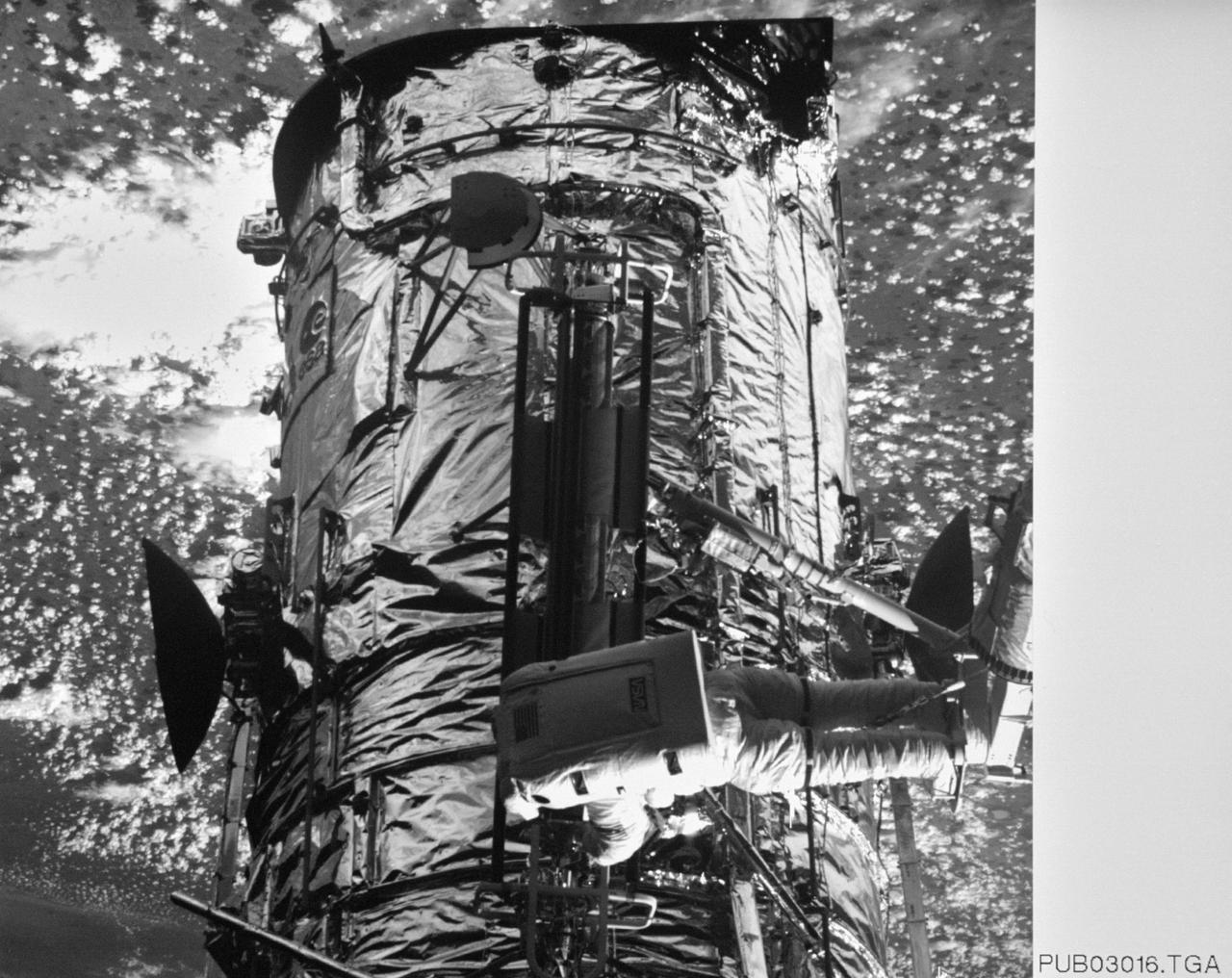

S61-E-011 (5 Dec 1993) --- This view of astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton working on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was photographed with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC), and down linked to ground controllers soon afterward. Thornton, anchored to the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is installing the +V2 Solar Array Panel as a replacement for the original one removed earlier. Electronic still photography is a relatively new technology which provides the means for a handheld camera to electronically capture and digitize an image with resolution approaching film quality. The electronic still camera has flown as an experiment on several other shuttle missions.
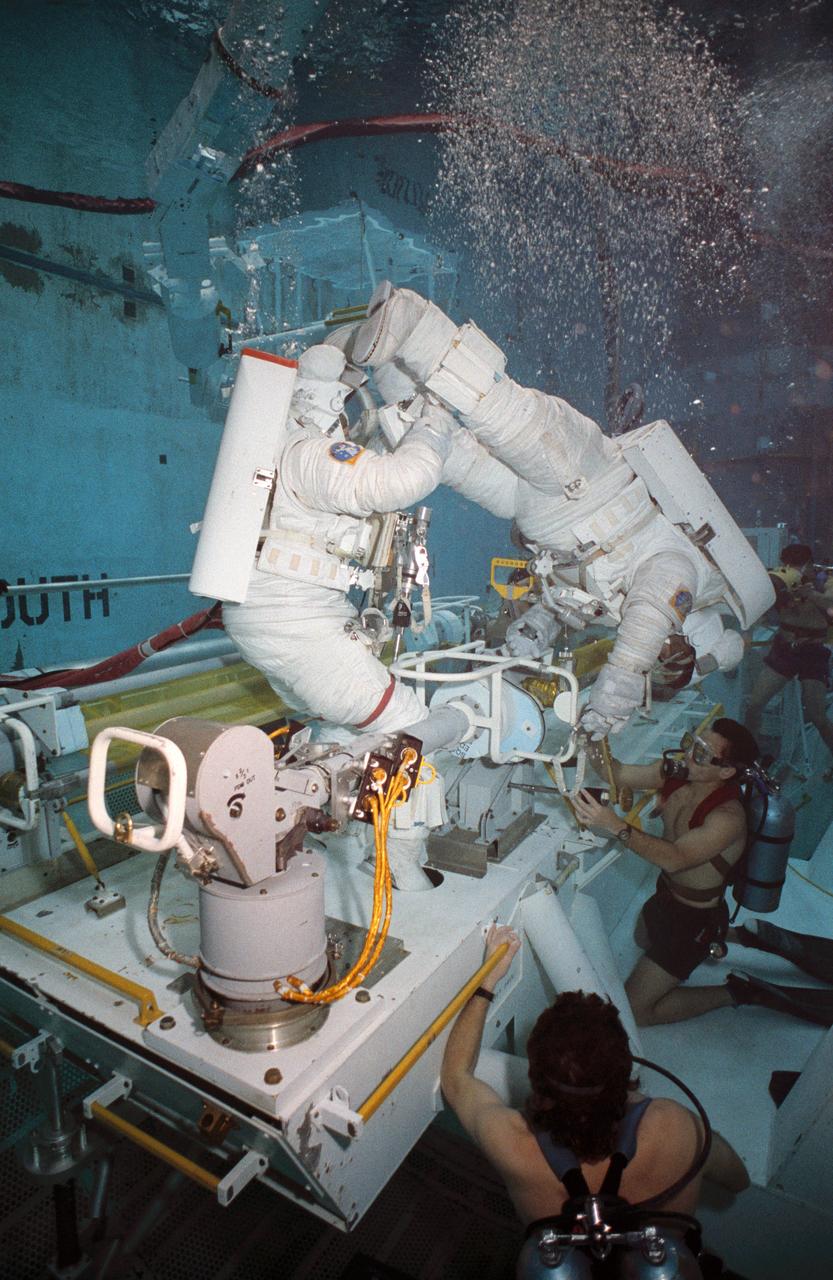
S93-30238 (5 Mar 1993) --- Wearing training versions of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMU), astronauts Thomas D. Akers (red stripe) and Kathryn C. Thornton use the spacious pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. They are working with a full scale mockup of a solar array fixture.
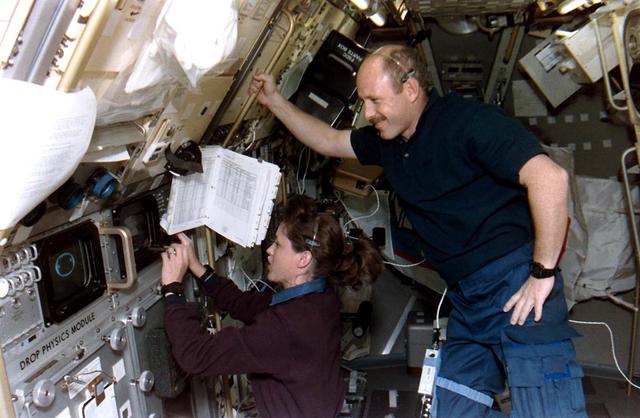

Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander, works at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) on the portside of the science module supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2). Astronaut Kerneth D. Bowersox, mission commander, looks on.
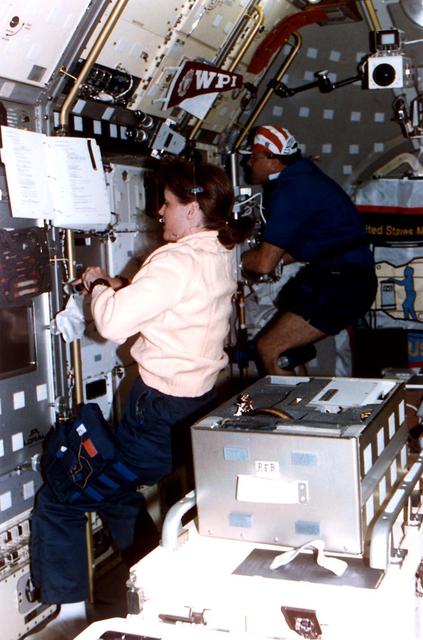

Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander for STS-73, works at the drop physics module (DPM) on the portside of the science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in Earth orbit.
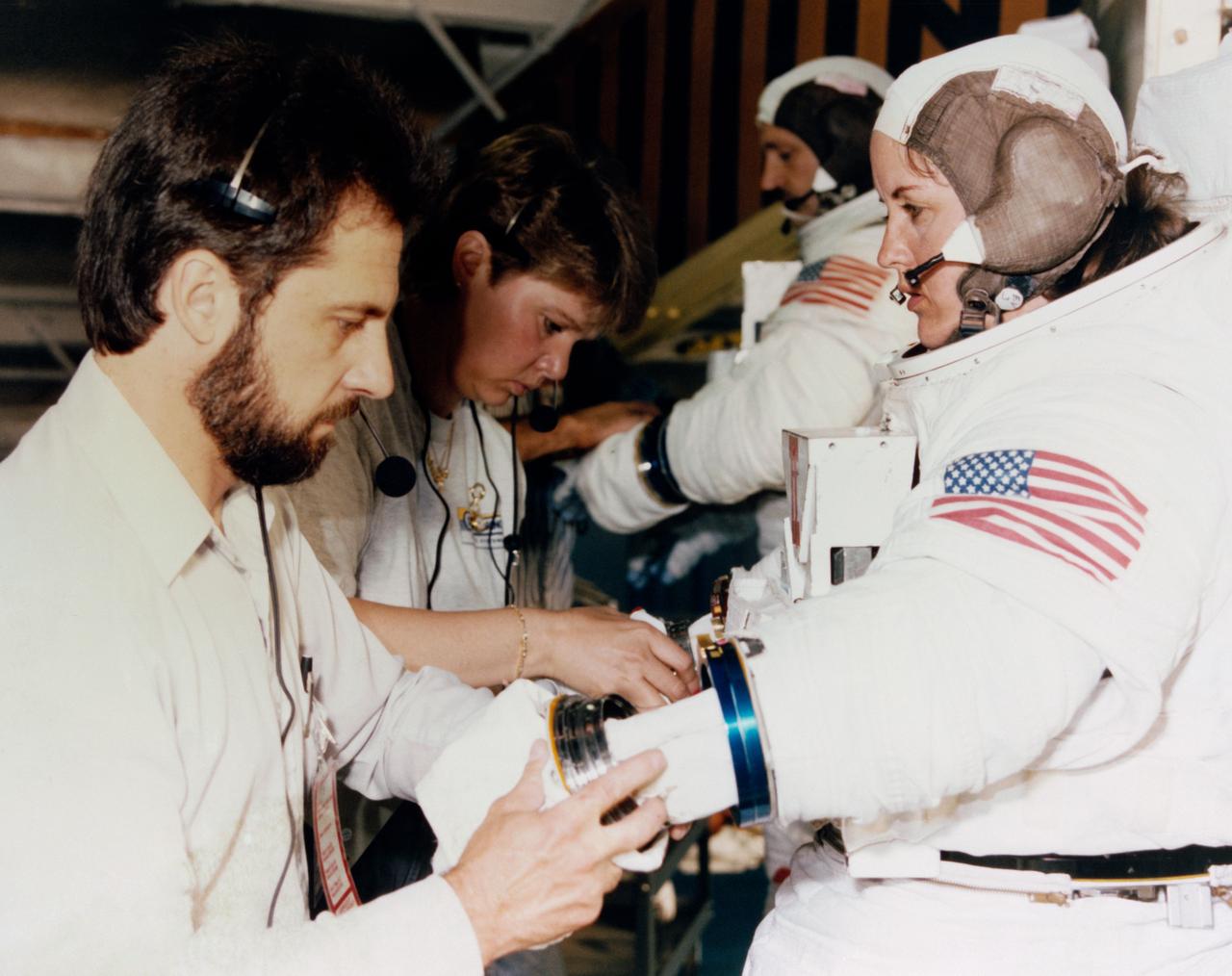

Astronaut Thomas D. Akers gets assistance in donning a training version of the Shuttle extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) space suit prior to a training session in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) (39735); Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton (foreground) and Thomas Akers, STS-61 mission specialists scheduled for extravehicular activity (EVA) duty, prepare for an underwater rehearsal session. Thornton recieves assistance from a technician in donning her EMU gloves (39736).
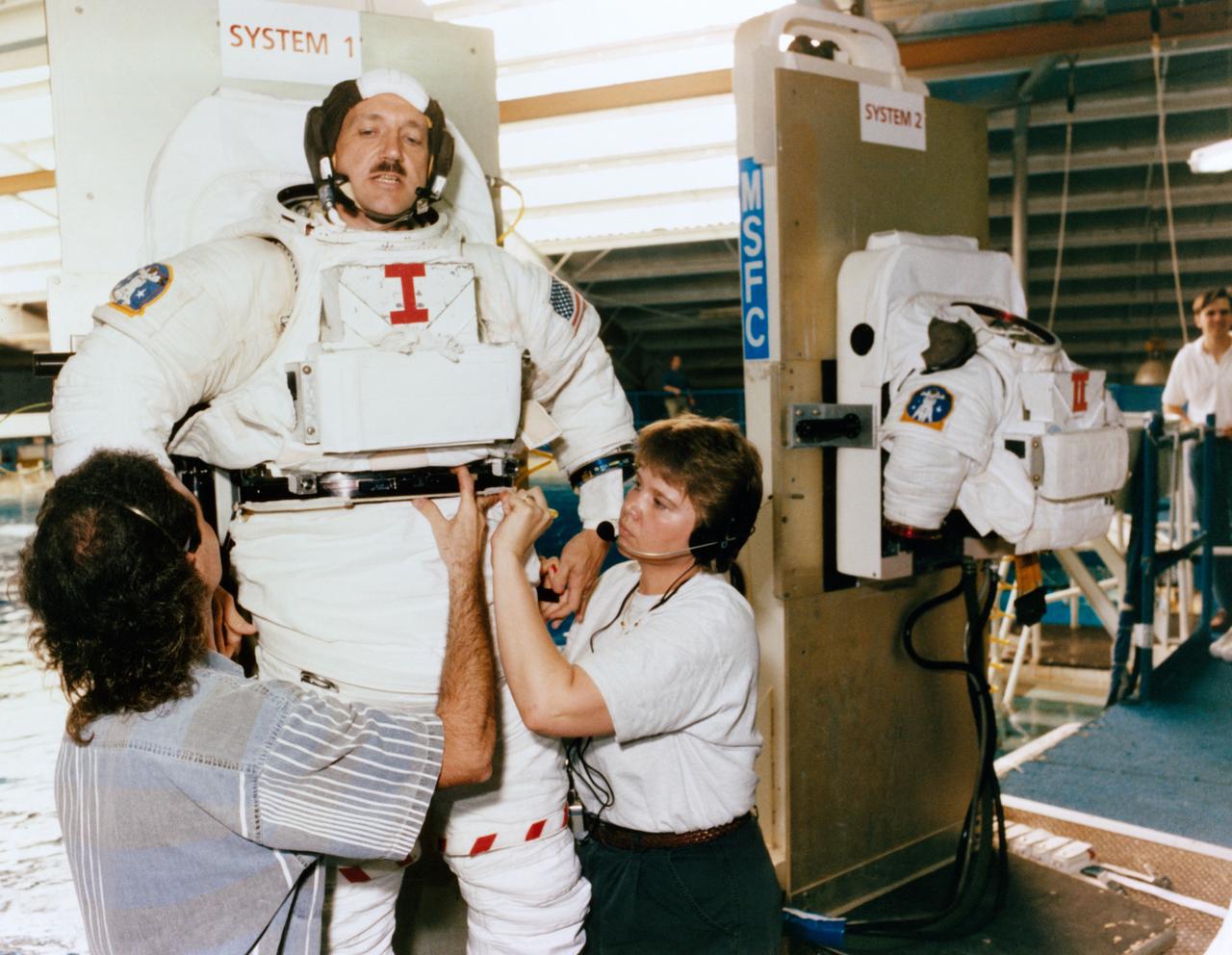
Astronaut Thomas D. Akers gets assistance in donning a training version of the Shuttle extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) space suit prior to a training session in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) (39735); Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton (foreground) and Thomas Akers, STS-61 mission specialists scheduled for extravehicular activity (EVA) duty, prepare for an underwater rehearsal session. Thornton recieves assistance from a technician in donning her EMU gloves (39736).
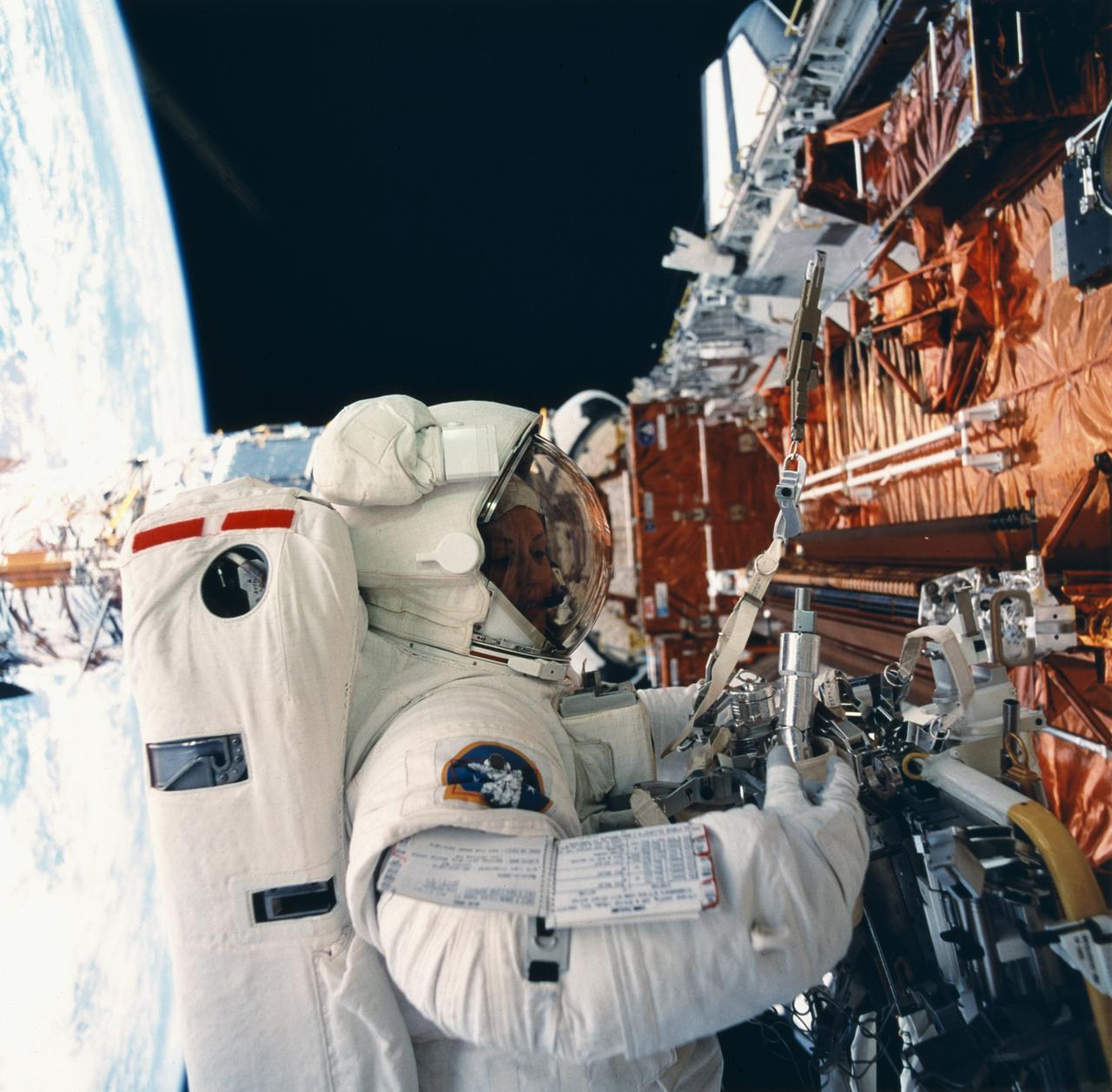

This STS-61 onboard photo depicts Astronaut and mission specialist Kathryn Thornton performing the 2nd extra-vehicular activity (EVA) of the STS-61 mission. Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers (out of frame), performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes. Launched December 1, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, the STS-61 mission was solely dedicated to servicing the HST.
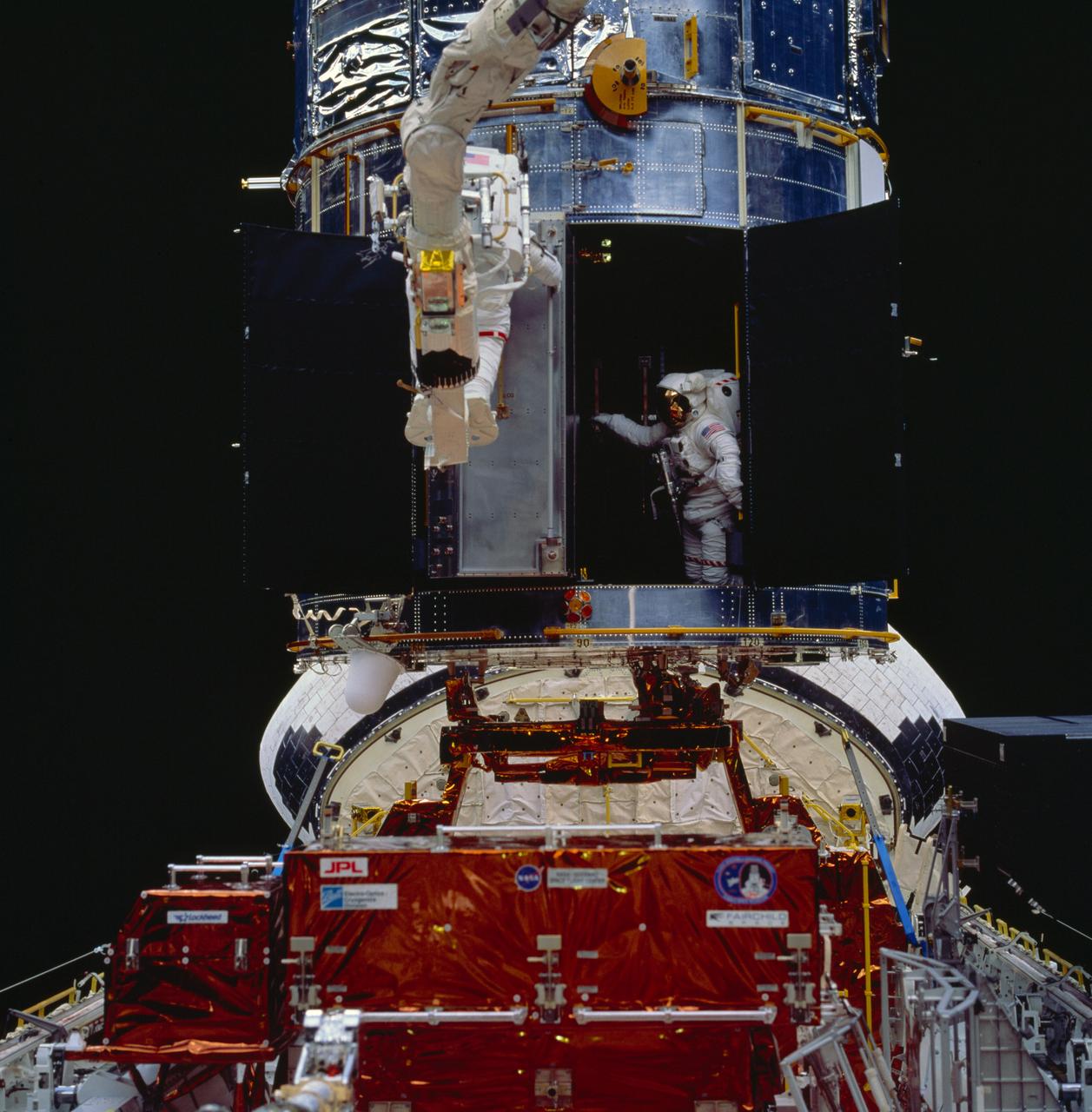

STS061-94-050 (8 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers maneuvers inside the bay which will house the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) while assisting astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton with the installation of the 640-pound instrument. Thornton, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is partially visible as she prepares to install the COSTAR, during their extravehicular activity (EVA).
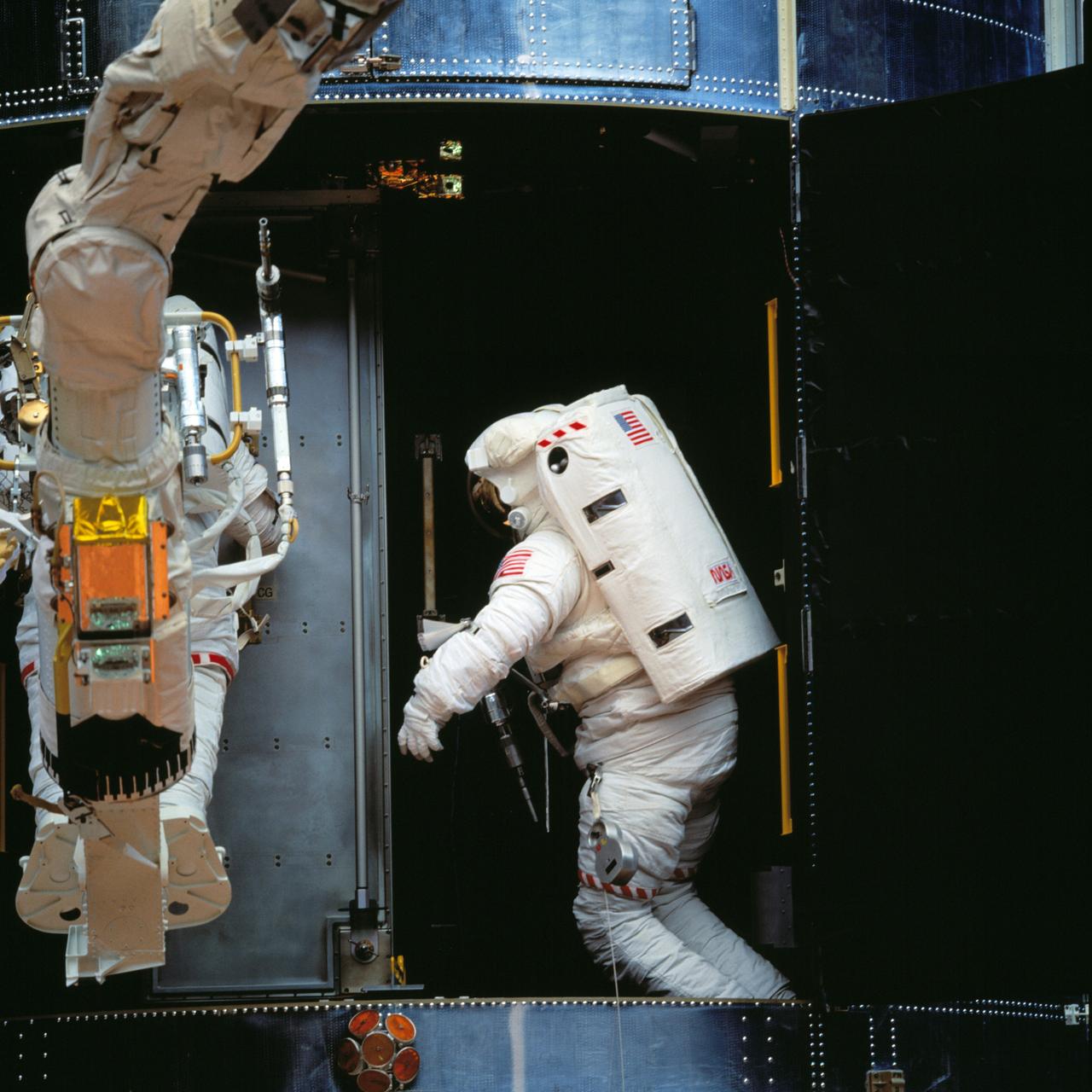
STS061-94-059 (8 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers maneuvers inside the bay which will house the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) while assisting astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton with the installation of the 640-pound instrument. Thornton, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is partially visible as she prepares to install the COSTAR.
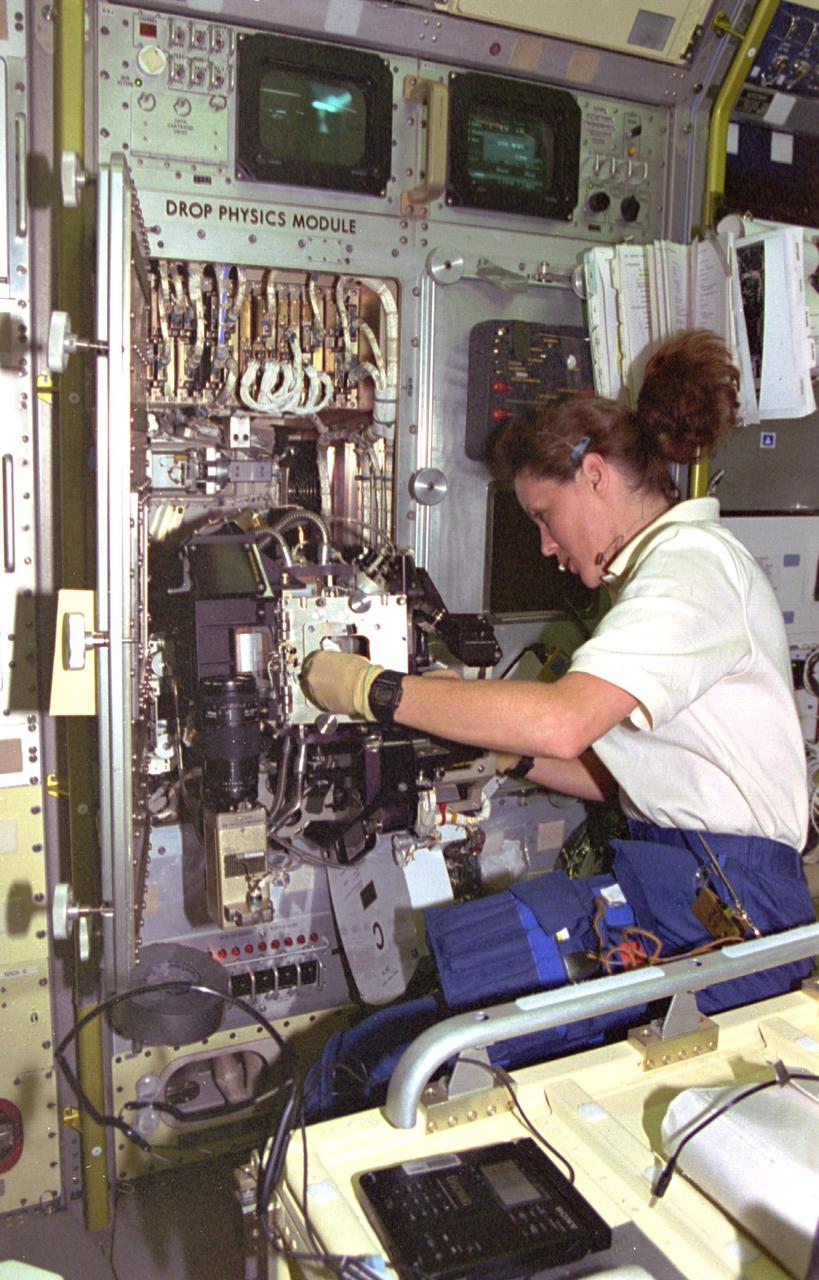

STS073-143-026 (20 October-5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, STS-73 payload commander for the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2), explores the inner workings of the Drop Physics Module (DPM). Thornton was joined by four other NASA astronauts and two guest researchers for almost 16 days of research aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in Earth-orbit.
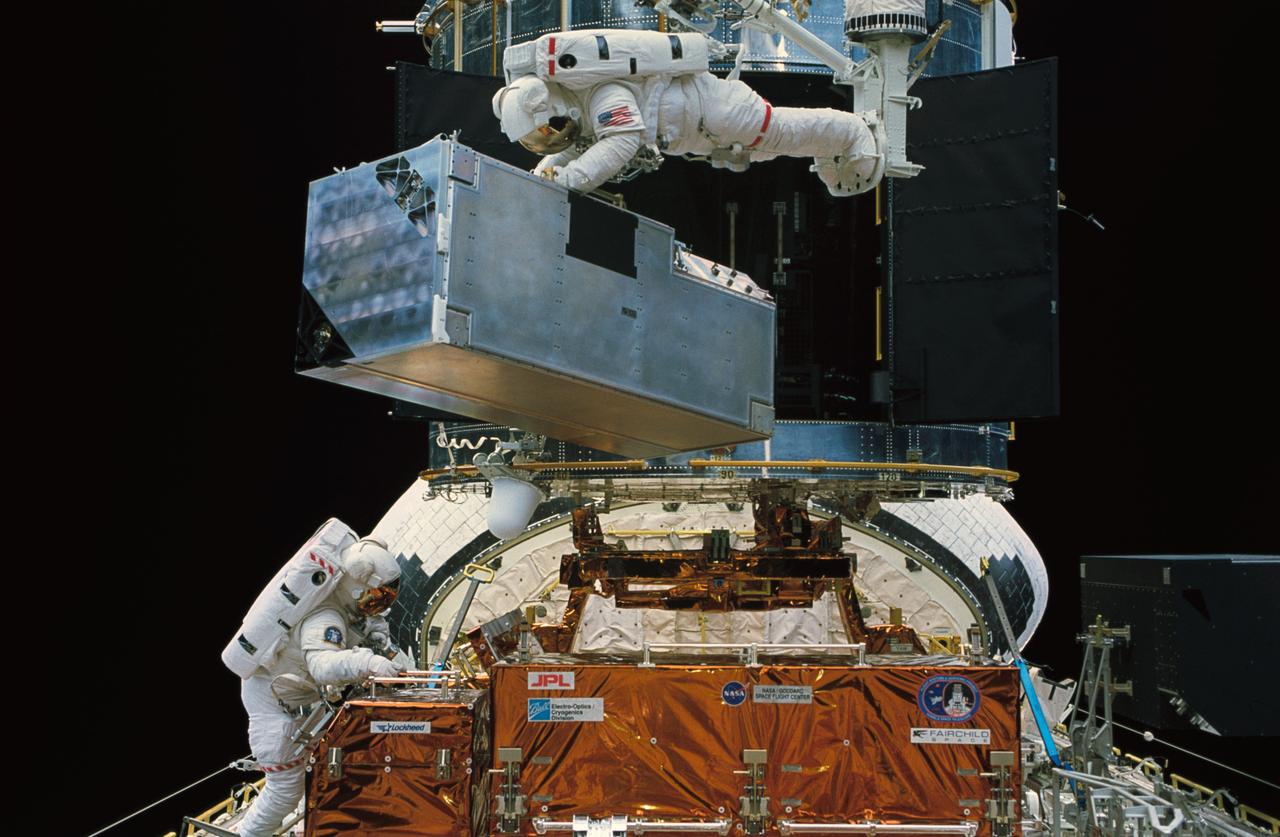
STS061-47-014 (8 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton lifts the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) prior to its installation on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Thornton is anchored to a foot restraint on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. Astronaut Thomas D. Akers, who assisted in the COSTAR installation, is at lower left.
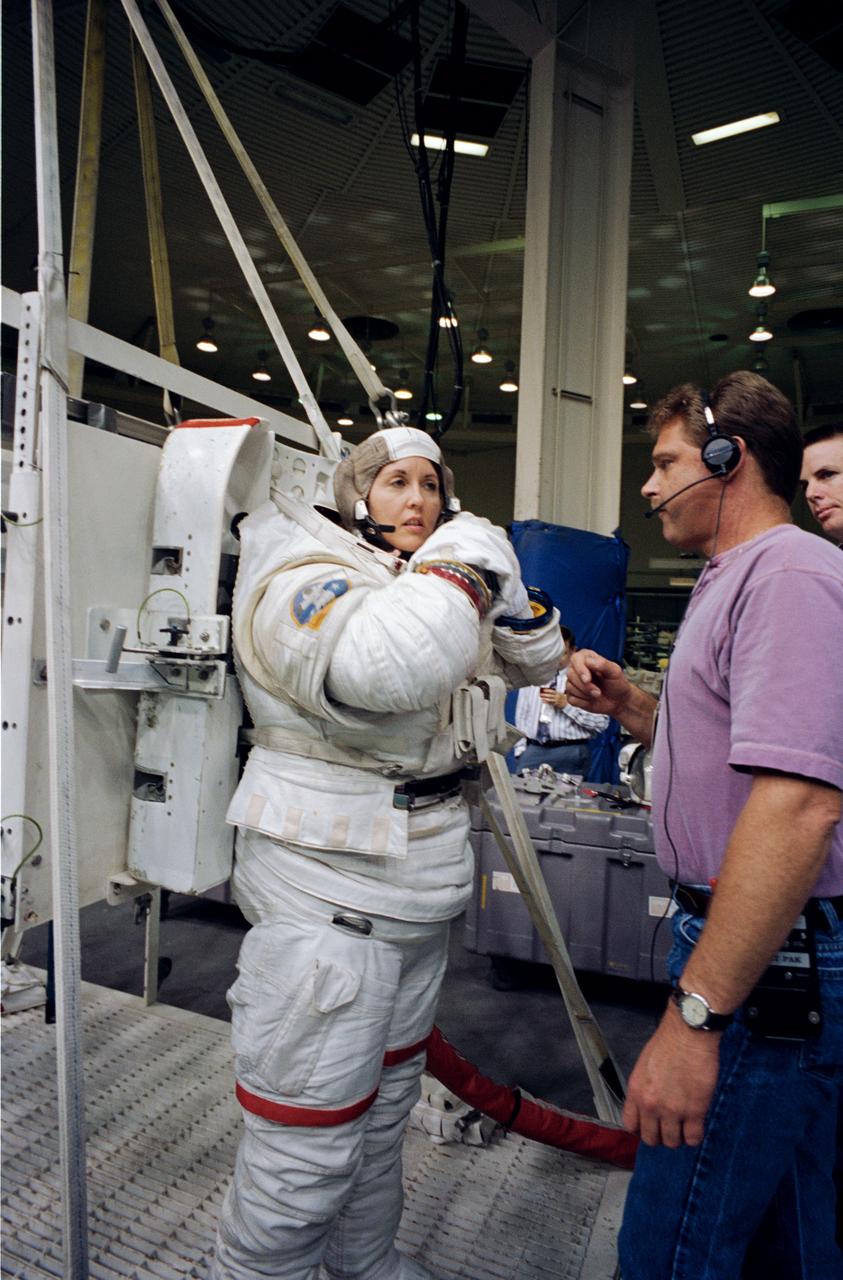

S95-08375 (August 1995) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander for the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission, prepares to go underwater in the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) pool. Thornton was about to rehearse contingency space walk tasks; there is no Extravehicular Activity (EVA) planned for the STS-73 mission.
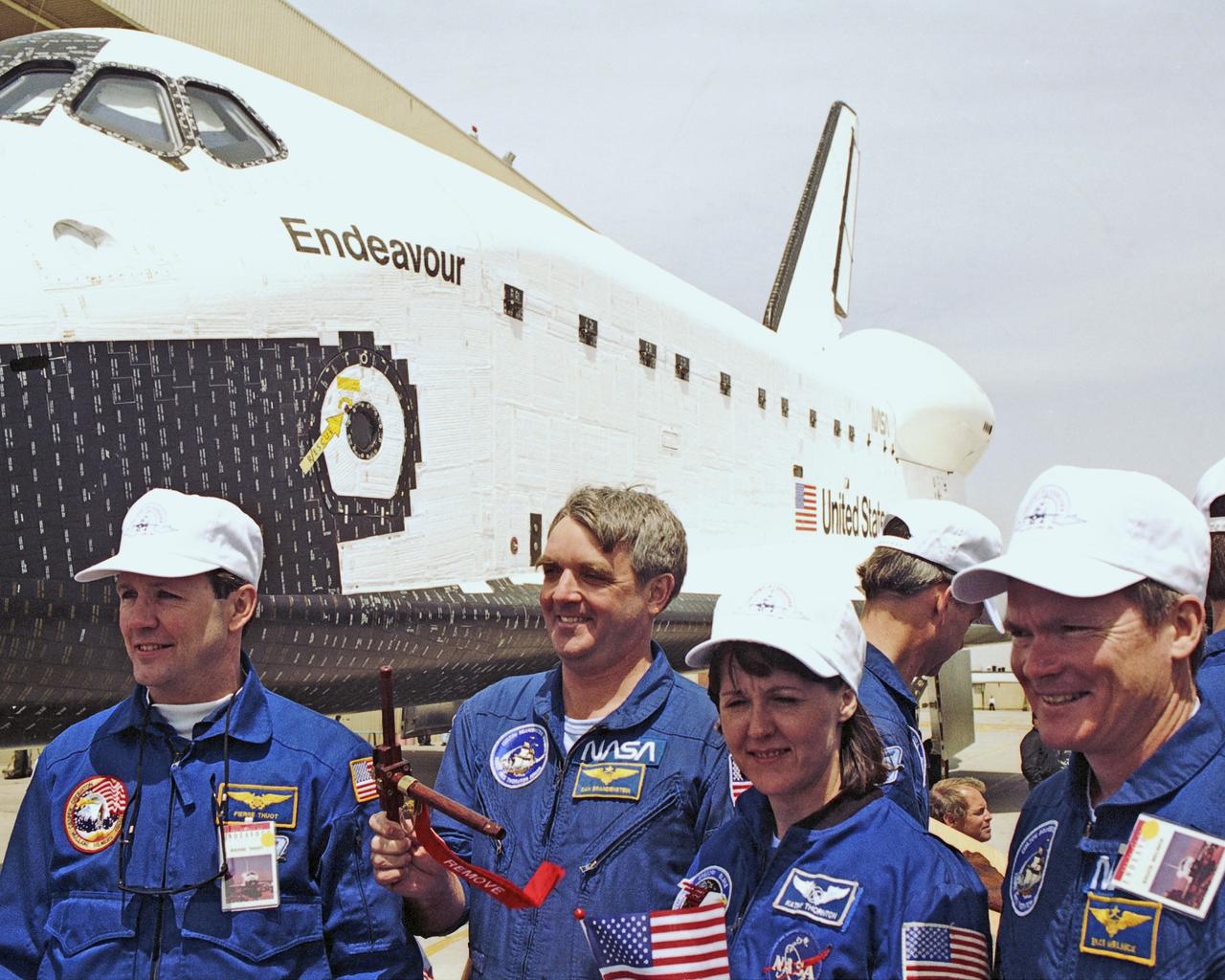

Chief astronaut Daniel Brandenstein second from left, and astronauts Pierre Thuot left, Kathryn Thornton, and Bruce Melnick are on hand for a proud moment in the history of manned spaceflight: the debut of the newest space shuttle orbiter, Endeavour, at Palmdale, Calif. Photo credit: NASA
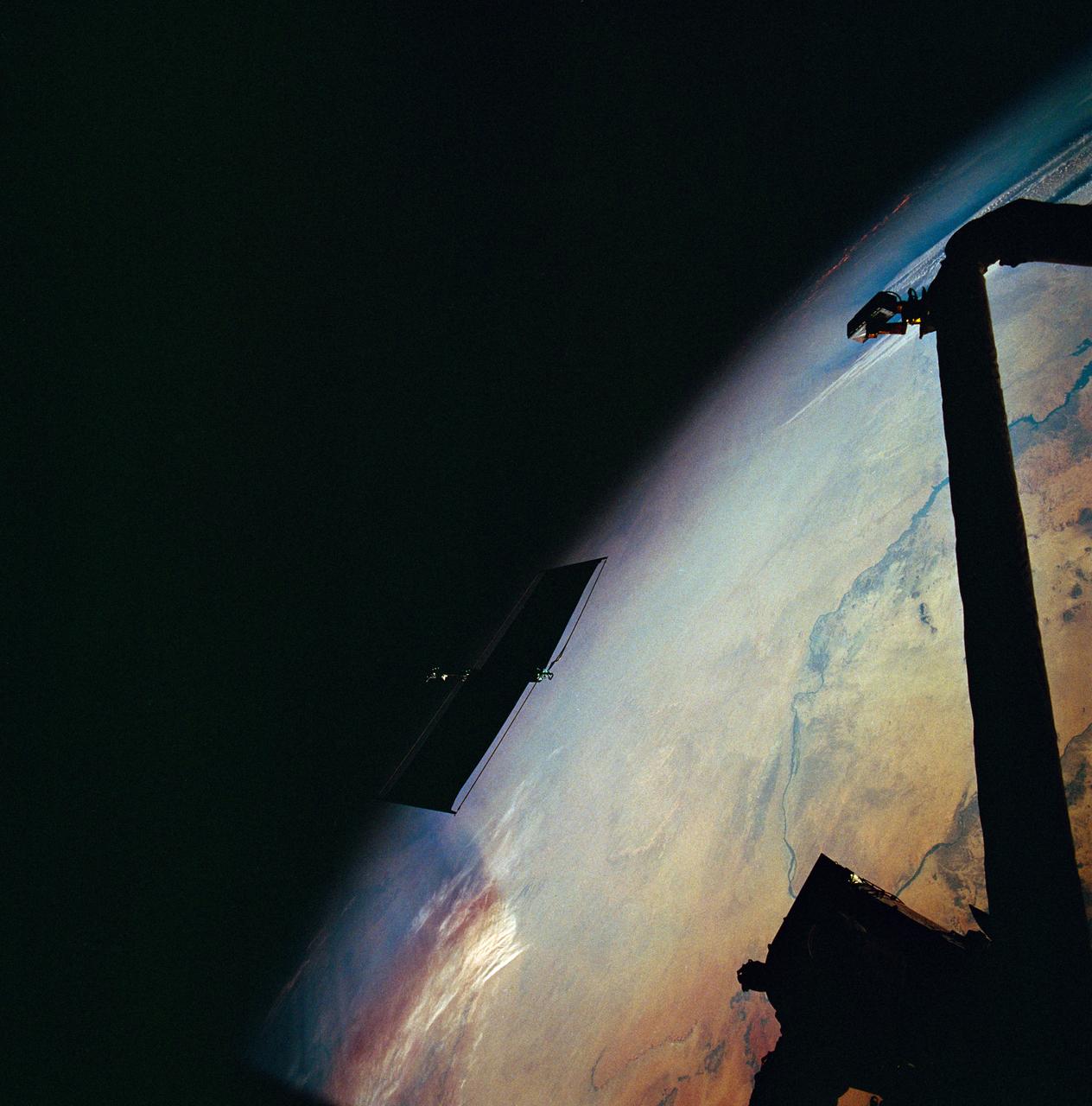

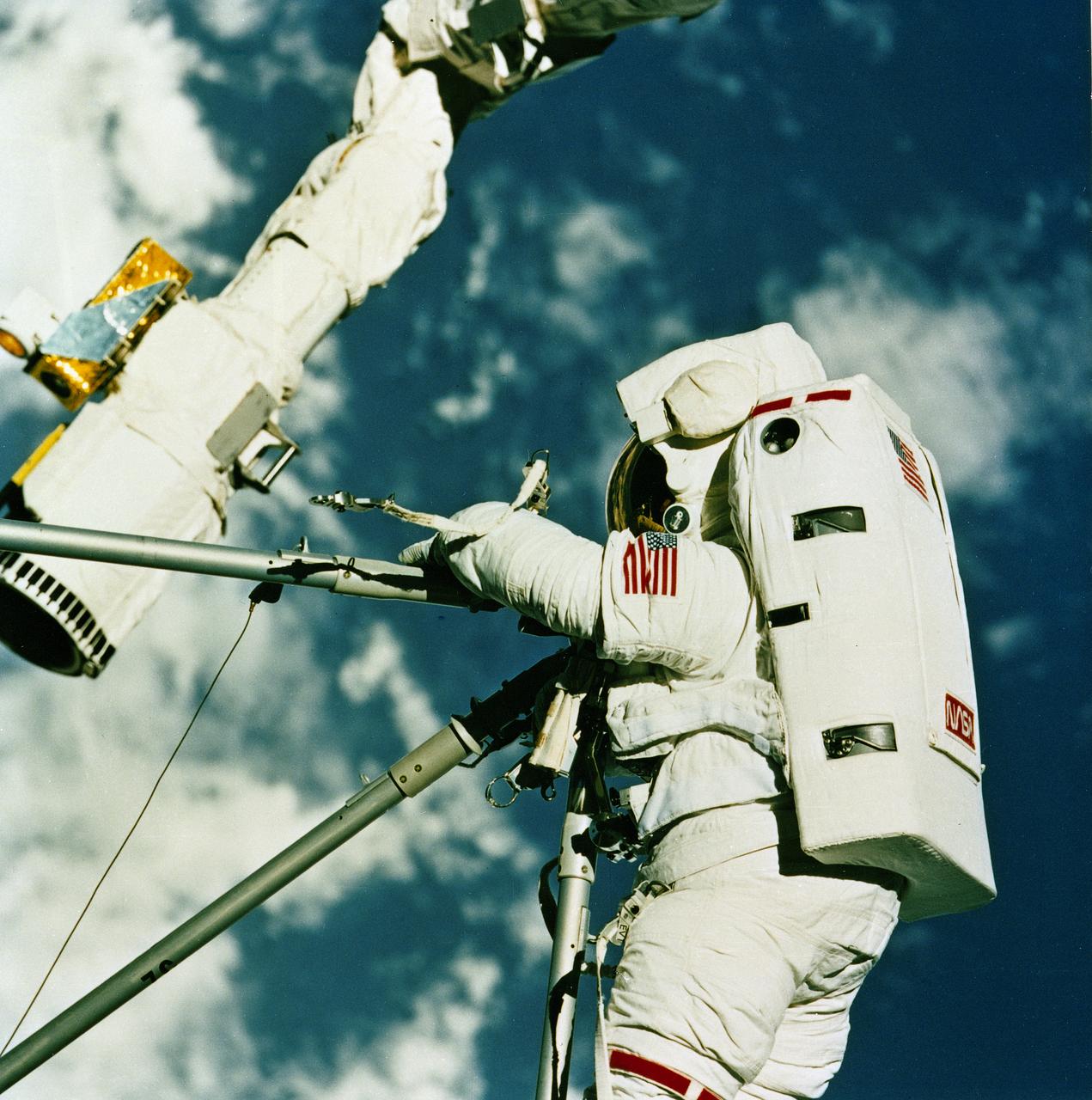
STS061-95-031 (6 Dec 1993) --- The damaged solar array panel removed from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is backdropped over northern Sudan. Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, just out of frame at top right, watched the panel after releasing it moments earlier.
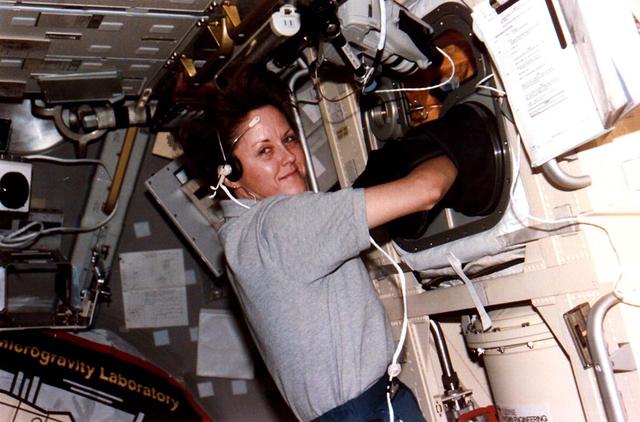

Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander, works in the glovebox of the science module supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission. Five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists are in the last few days of a scheduled 16 day mission.
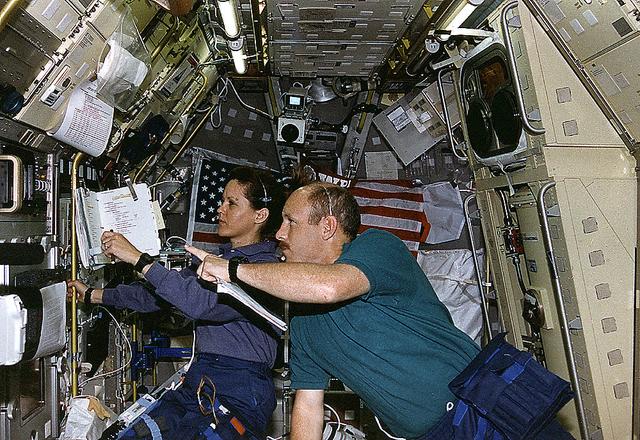

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-73) Payload Commander Kathryn Thornton and Commander Ken Bowersox discuss the Drop Physics Module (DPM) experiment in the United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) spacelab science module.
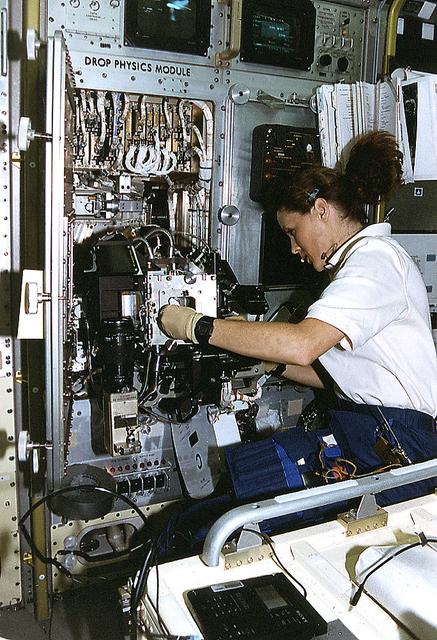

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-73) Payload Commander Kathryn Thornton works with the Drop Physics Module (DPM) in the United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) Spacelab Science Module cleaning the experiment chamber of the DPM.
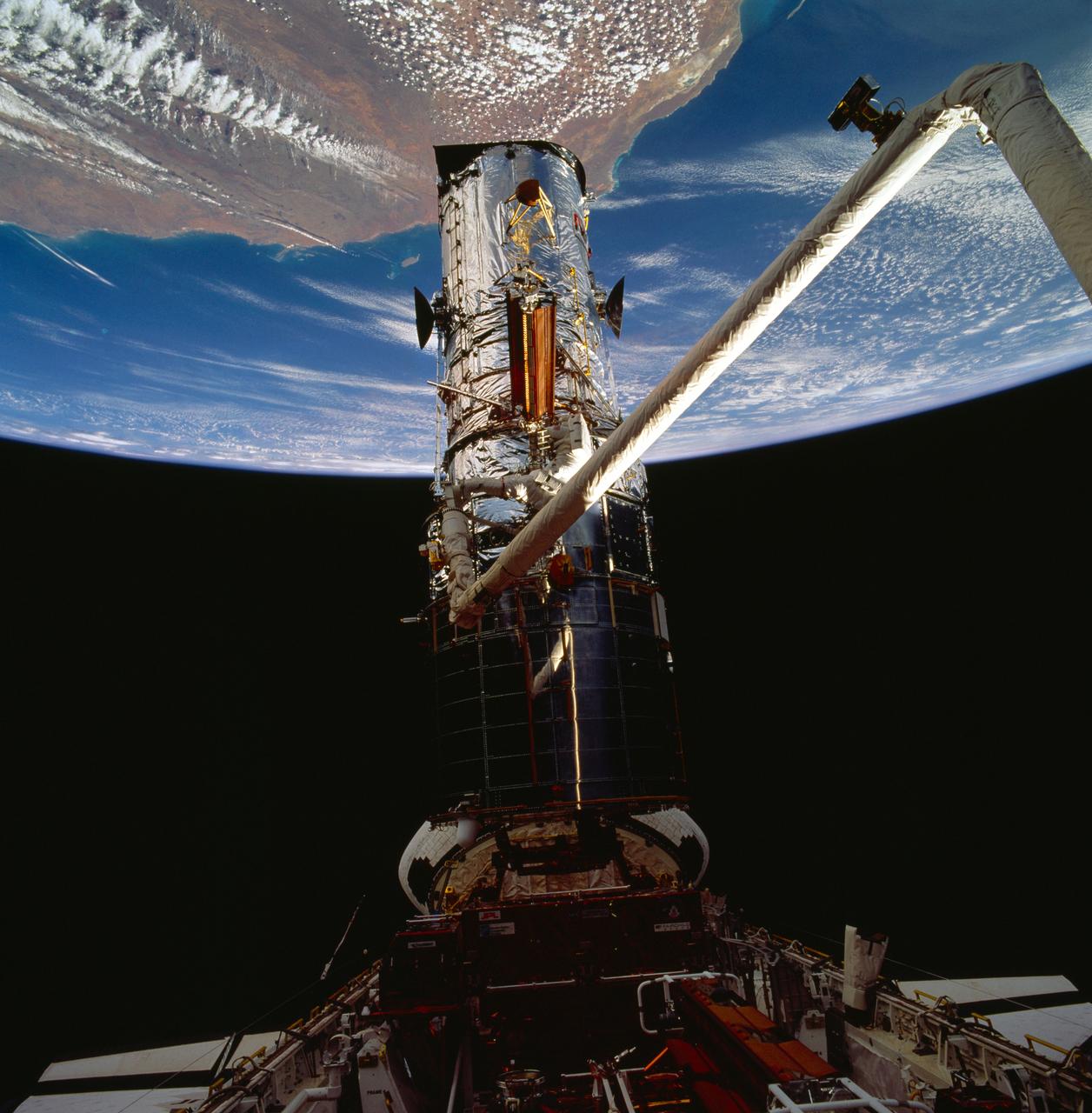

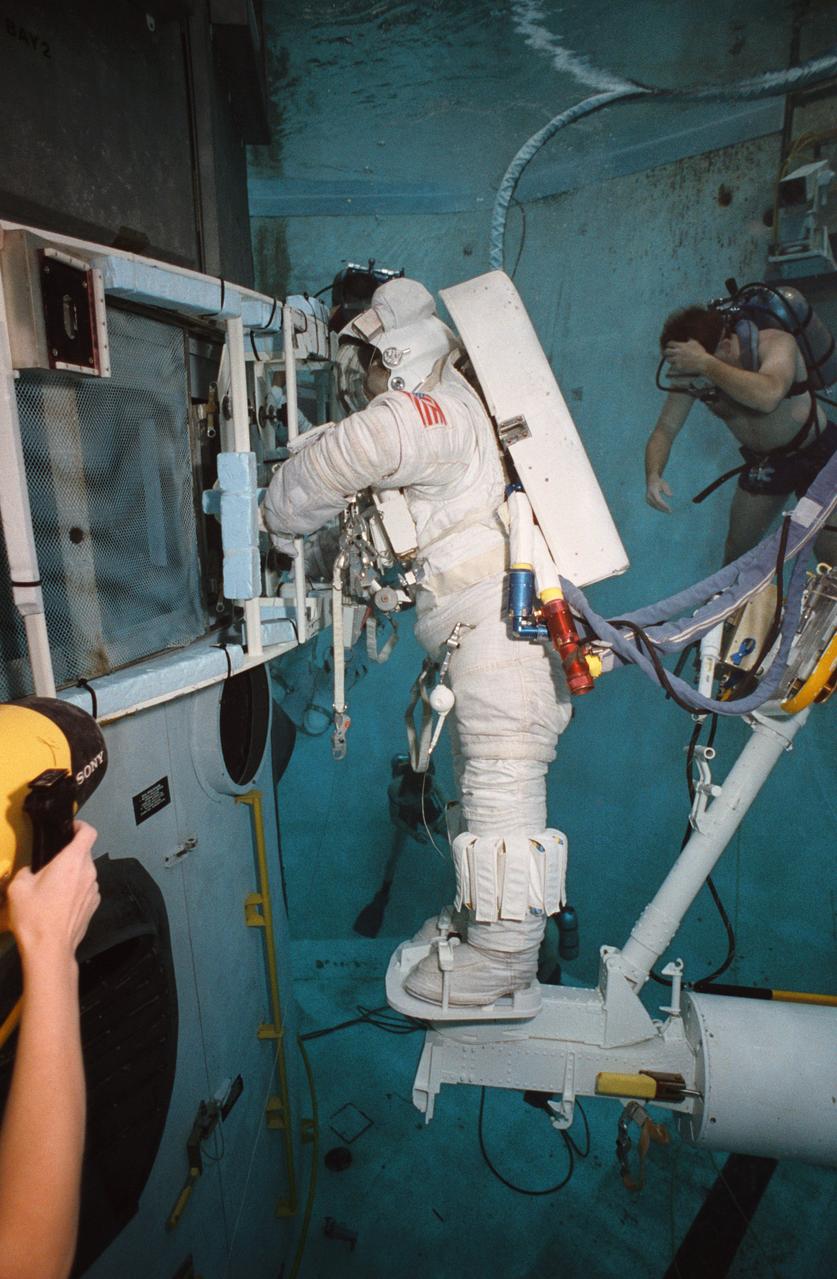
STS061-95-075 (6 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers work to remove one of the solar arrays on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on the second of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA). The two space walkers later replaced both solar array panels. Part of Australia is in the background.
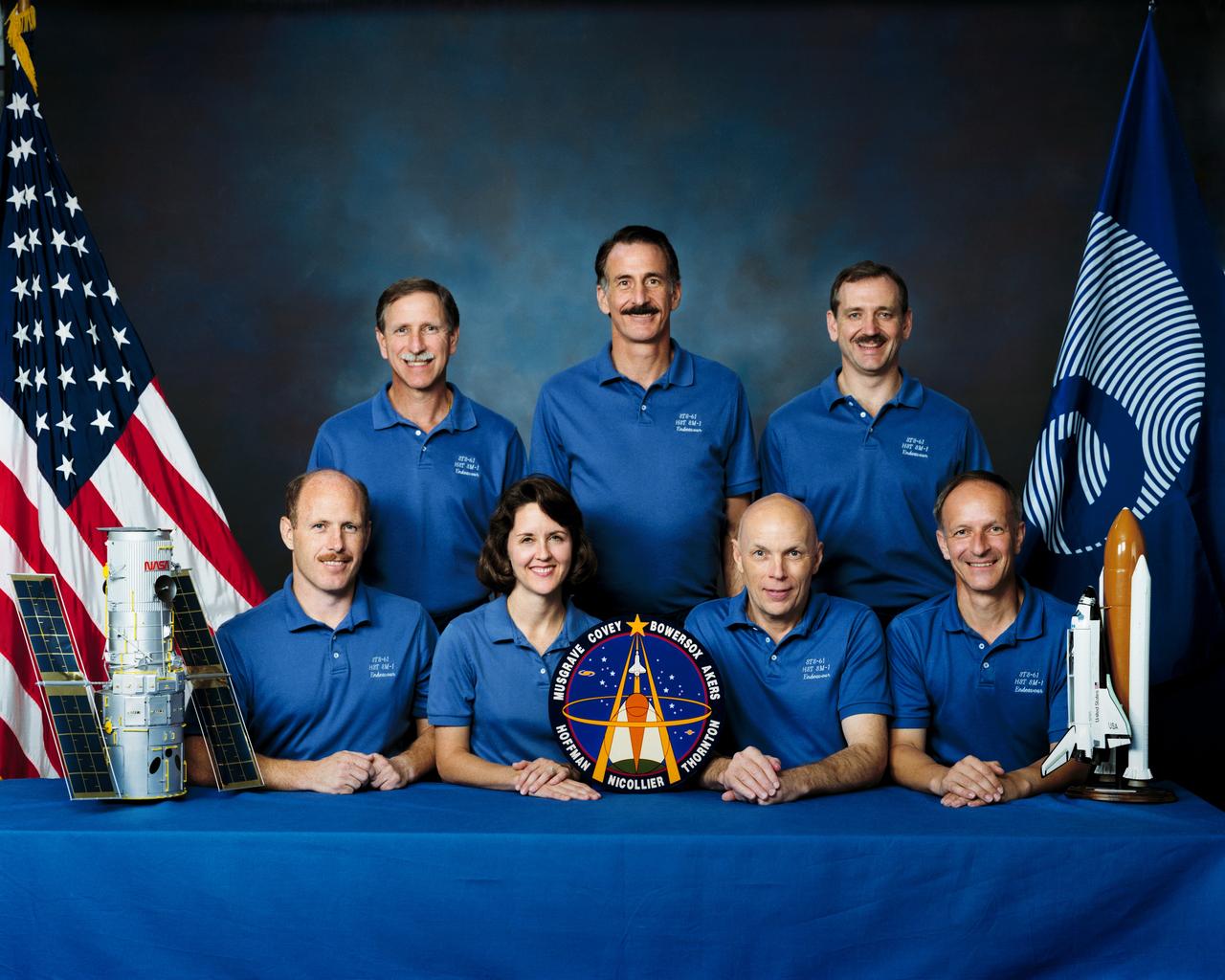

STS061-S-002 (1 Oct. 1993) --- These seven NASA astronauts are currently in training for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission, scheduled for later this year. Astronaut Richard O. Covey, mission commander, is standing at left, with astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot, seated at left. The five mission specialists for the mission are (left to right, seated) astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton and F. Story Musgrave, and the European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Claude Nicollier; and (left to right, standing), astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman and Thomas D. Akers. Musgrave, Akers, Thornton and Hoffman are all assigned to participate in five total sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) for the servicing tasks.
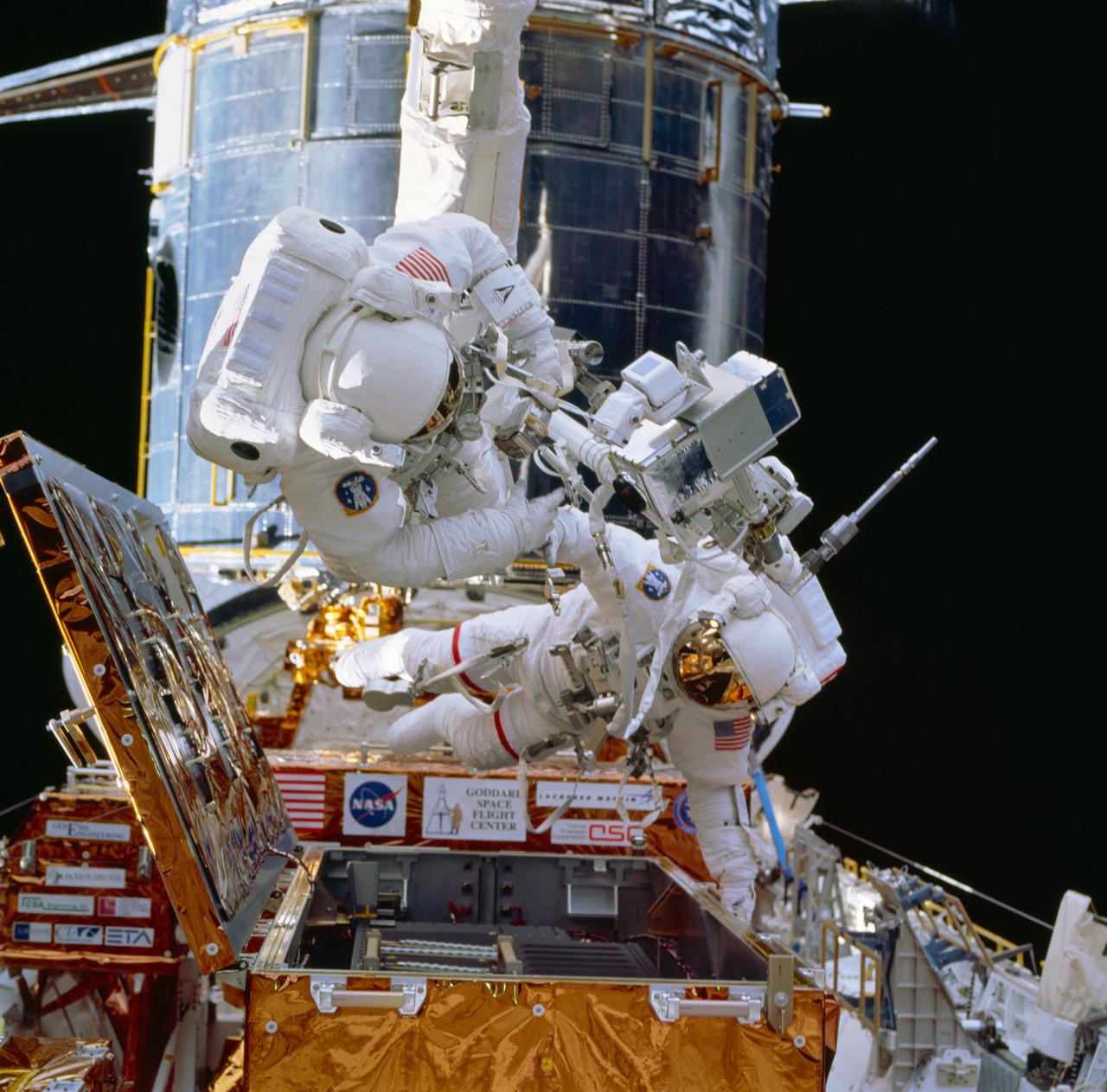

STS049-81-093 (14 May 1992) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton joins three struts together, as fourth period of extravehicular activity (EVA) proceeds in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. The purpose of the final EVA on this nine-day mission was the evaluation of Assembly of Station by EVA Methods (ASEM). Clouds over the ocean share the background with part of Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The scene was recorded on 70mm film from the Space Shuttle's flight deck. Astronaut Thomas D. Akers (out of frame) joined Thornton on the 7 1/2 hour EVA.
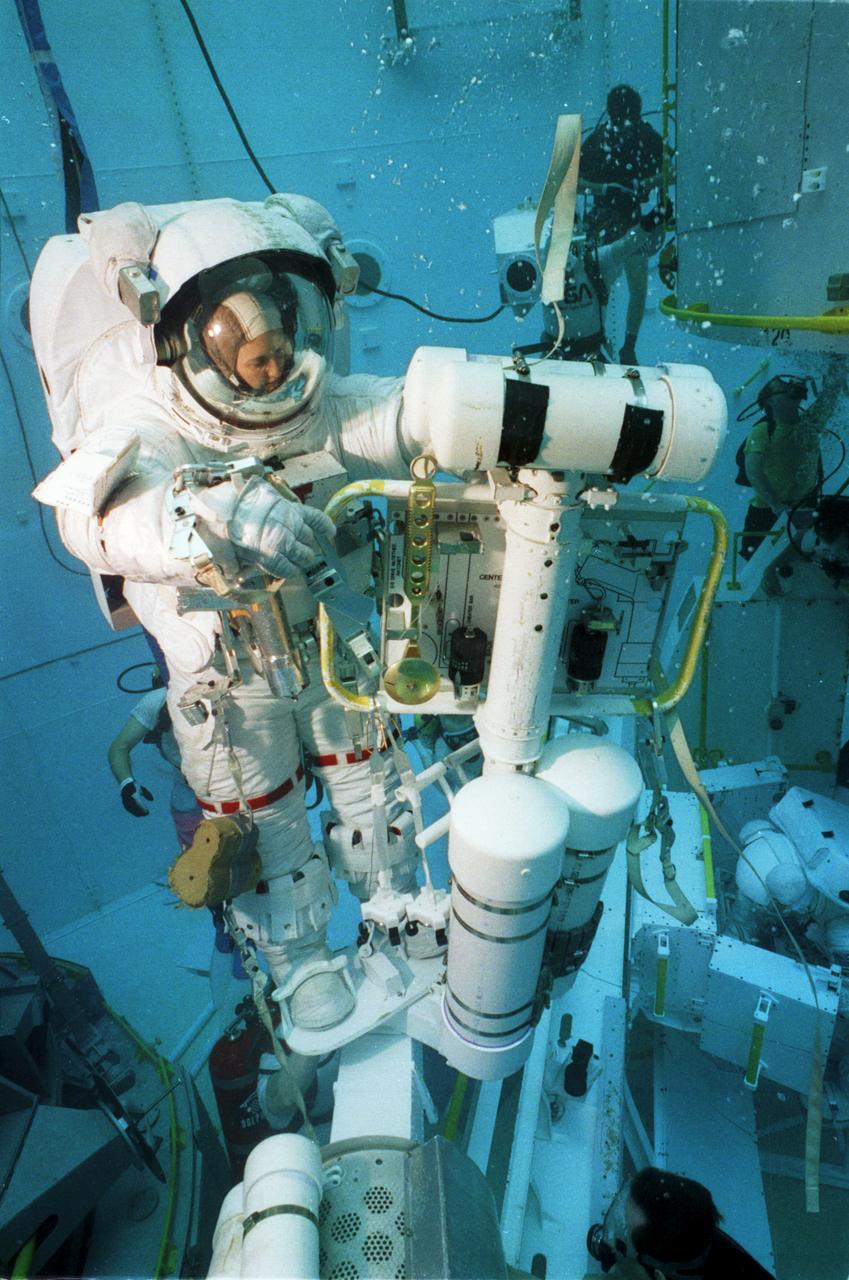
This close-up of astronaut and mission specialist, Kathryn Thornton, was captured under water in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neural Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) where she is participating in a training session for the STS-61 mission. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA). Launched on December 2, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, STS-61 was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) serving mission. During the 2nd EVA of the mission, Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers, performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes.
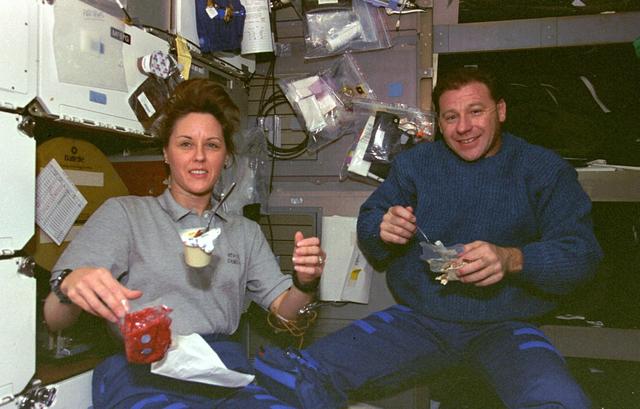

STS073-356-024 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. joins astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander, for mealtime on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Thornton is about to open a packet of strawberries, while a can of vanilla pudding floats before her. Sacco is about to grab a spoonful of rice pilaf while holding a peanut butter and jelly sandwich on a tortilla. The two were joined by five other crewmembers in support of 16-days' in-space research in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.

This close-up of astronaut and mission specialist Kathryn Thornton was captured under water in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neural Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) where she is participating in a training session for the STS-61 mission. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA). Launched on December 2, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, STS-61 was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) serving mission. During the 2nd EVA of the mission, Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers, performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes.
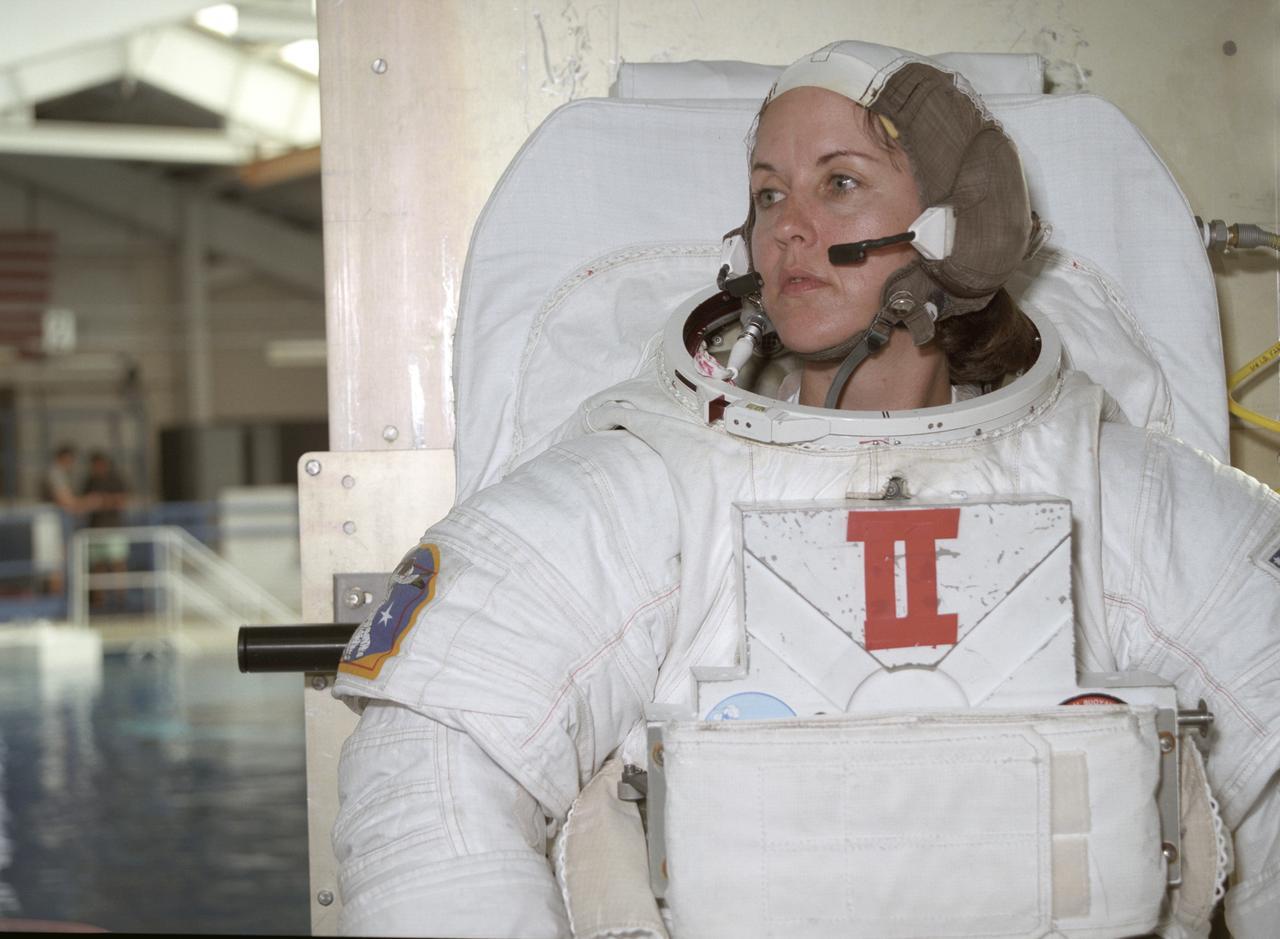

This close-up of astronaut and mission specialist Kathryn Thornton readies herself for submersion into the water in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) where she is participating in a training session for the STS-61 mission. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA). Launched on December 2, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, STS-61 was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) serving mission. During the 2nd EVA of the mission, Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers, performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes.

S93-33101 (5 Apr 1993) --- Wearing a training version of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton uses the giant pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. Standing on a mobile foot restraint connected to the Shuttle's robot arm, Thornton grasps a large structure which attaches to the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC). The current WF/PC on the HST will be replaced with WF/PC-2. Out of frame is astronaut Thomas D. Akers, who will join Thornton in STS-61 EVA. A SCUBA-equipped diver can be seen in the background. A number of divers are on hand for all training sessions in the WET-F. A total of five extravehicular activity (EVA) sessions will be conducted during the scheduled December mission of the Endeavour.

Heads of Agency participate in a panel discussion, from left, Dr. Josef Aschbacher, Director General, European Space Agency (ESA); Dr. Philippe Baptiste, President, French Space Agency (CNES); Dr. Paul Bate, Chief Executive Officer UK Space Agency (UKSA); moderator Dr. Kathryn C. Thornton, Chairwoman, Space Foundation; Lisa Campbell, President, Canadian Space Agency (CSA); NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy; Dr. Walther Pelzer, Executive Board Member and Head of the German Space Agency at the German Aerospace Center (DLR); and Dr. Hiroshi Yamakawa, President, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), right, during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
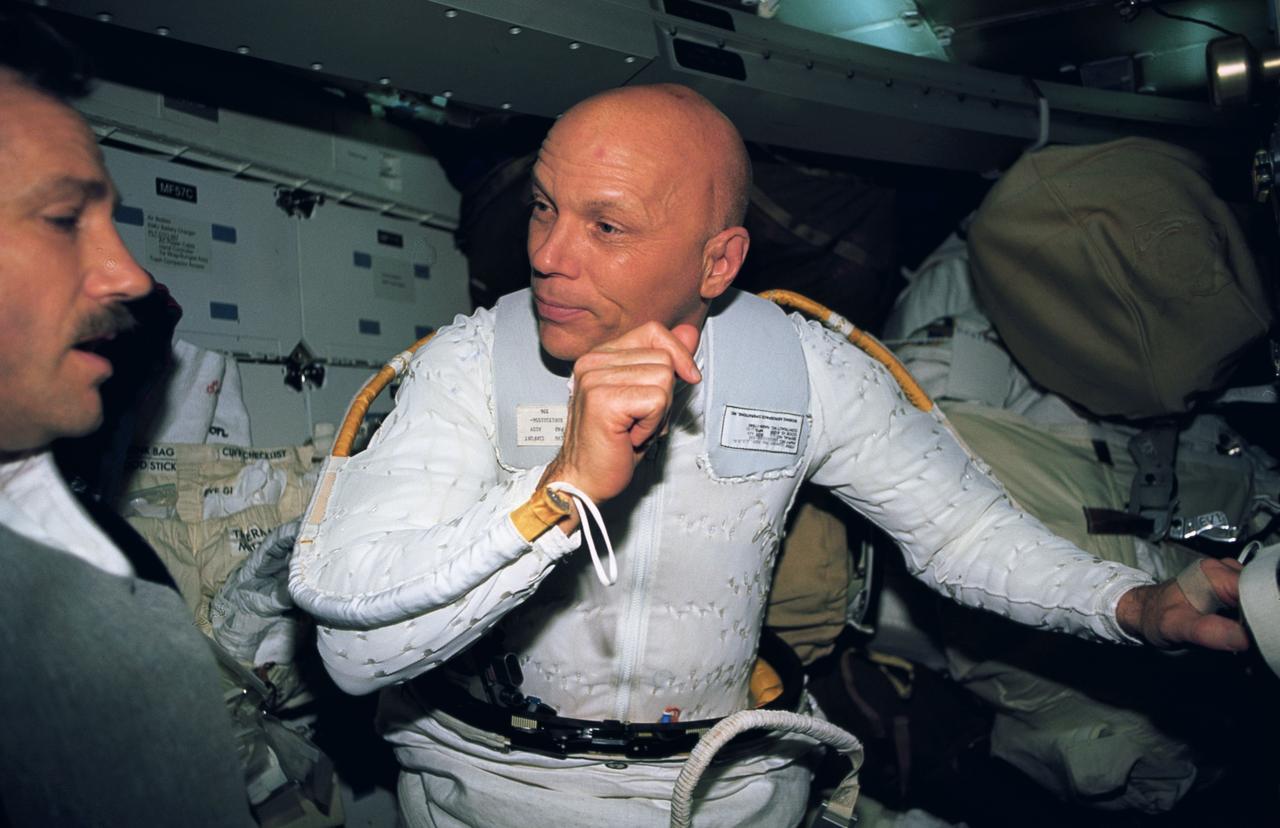

STS061-38-014 (9 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave gets assistance from astronaut Thomas D. Akers while suiting up for the final space walk on the eleven-day, Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. Musgrave joined astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman (out of frame) on three space walks, while Akers teamed with astronaut Kathryn D. Thornton for two.
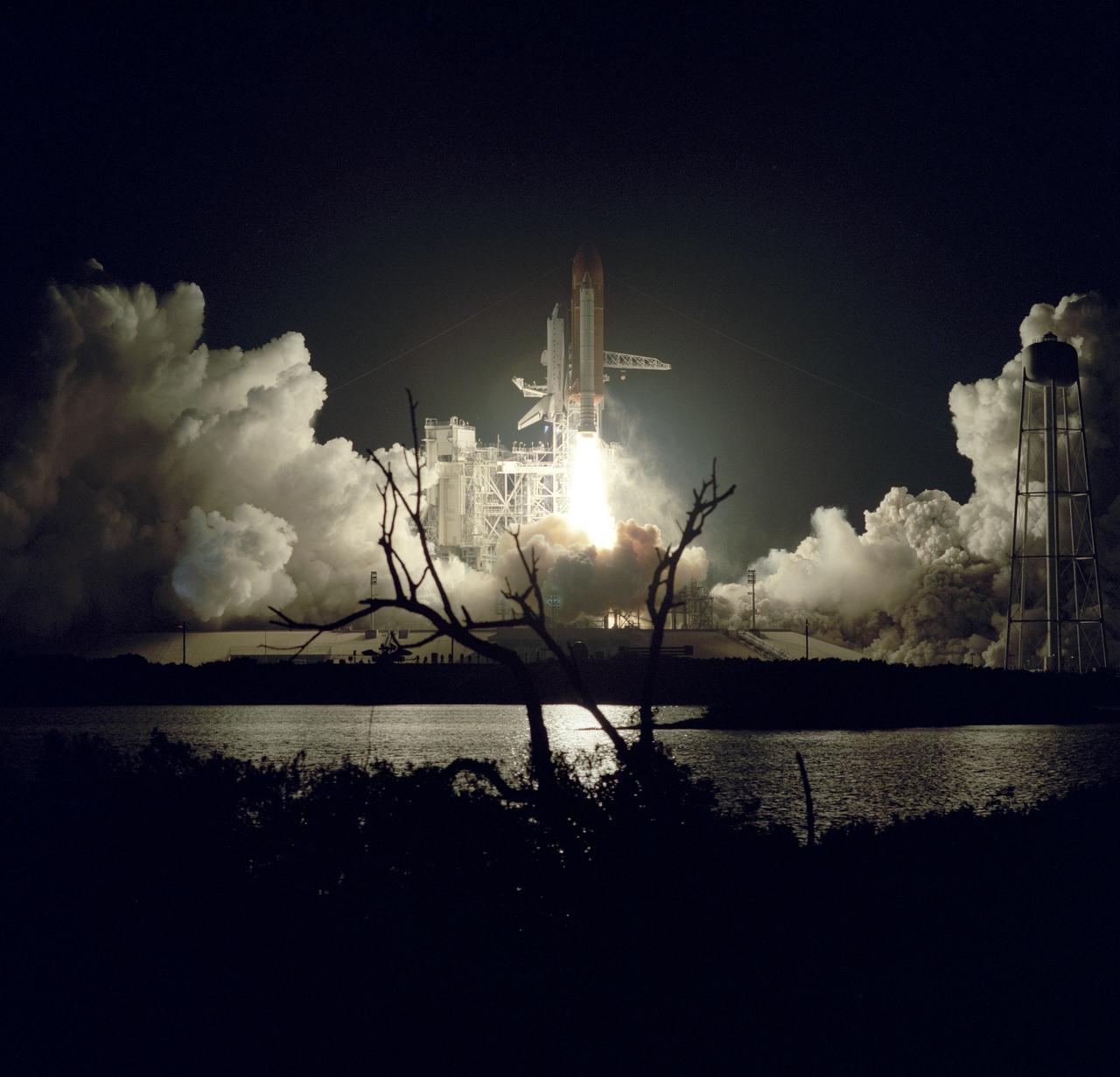

On November 22, 1989, at 7:23:30pm (EST), five astronauts were launched into space aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the 5th Department of Defense (DOD) mission, STS-33. Crew members included Frederick D. Gregory, commander; John E. Blaha, pilot; and mission specialists Kathryn C. Thornton, Manley L. (Sonny) Carter, and F. Story Musgrave.
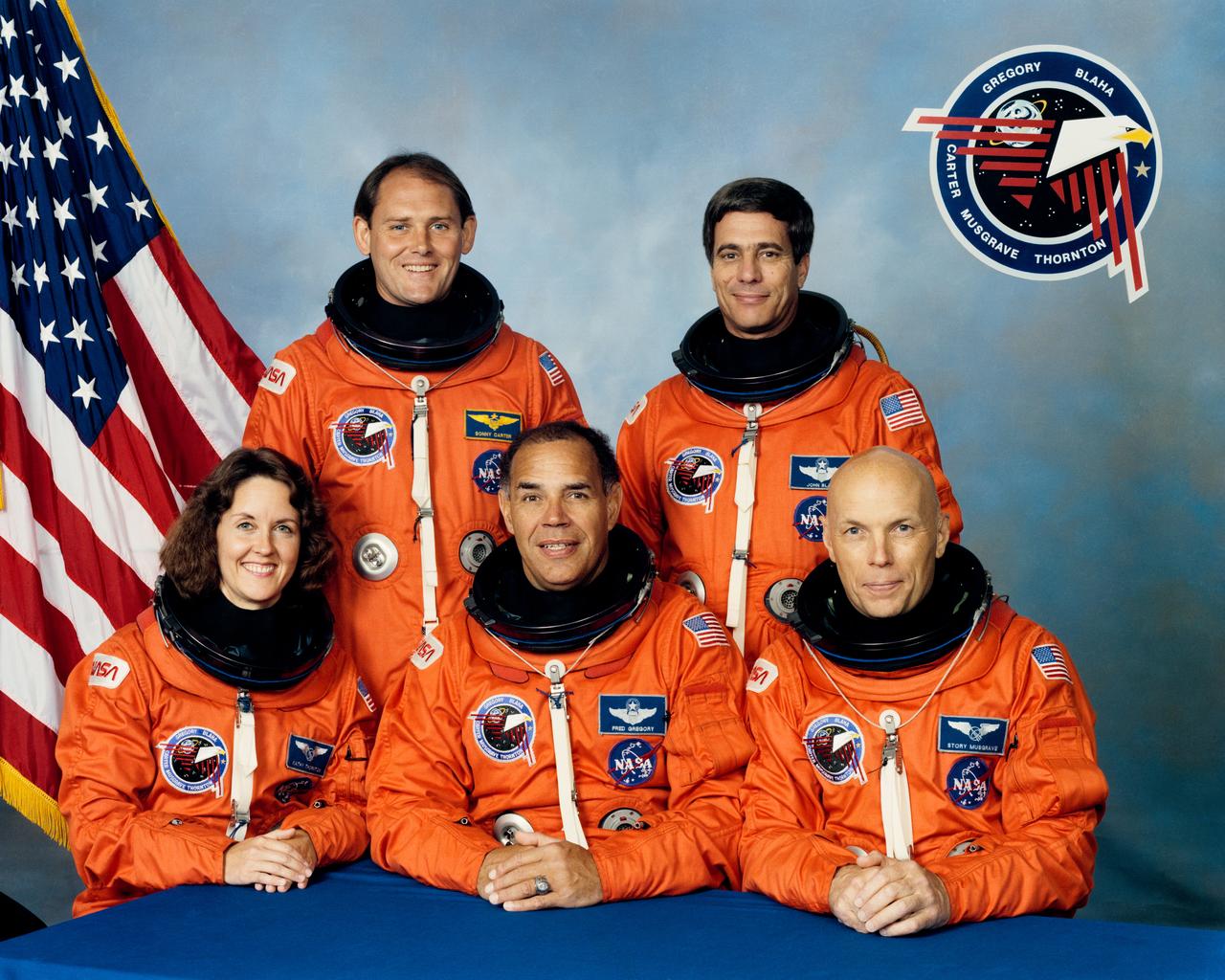

S89-45737 (19 September 1989) --- Official STS-33 crew portrait. These five astronauts will be aboard the space shuttle Discovery for a scheduled November 1989 mission for the Department of Defense (DOD). Frederick D. Gregory (center, front) is mission commander. He is flanked by Kathryn C. Thornton and F. Story Musgrave, mission specialists. At rear are Manley L. Carter, Jr., mission specialist, and John E. Blaha, pilot.
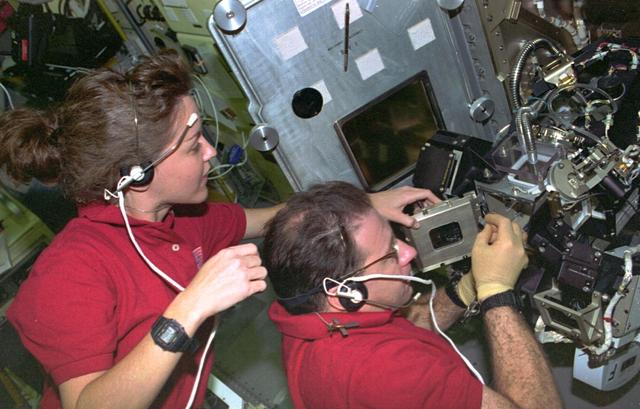

STS073-108-005 (20 October-5 November 1995) --- Two members of the crew perform an in-flight maintenance on the Drop Physics Module (DPM) in the science module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Payload commander Kathryn C. Thornton and payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. were part of a seven-member crew that spent 16 full days in space in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
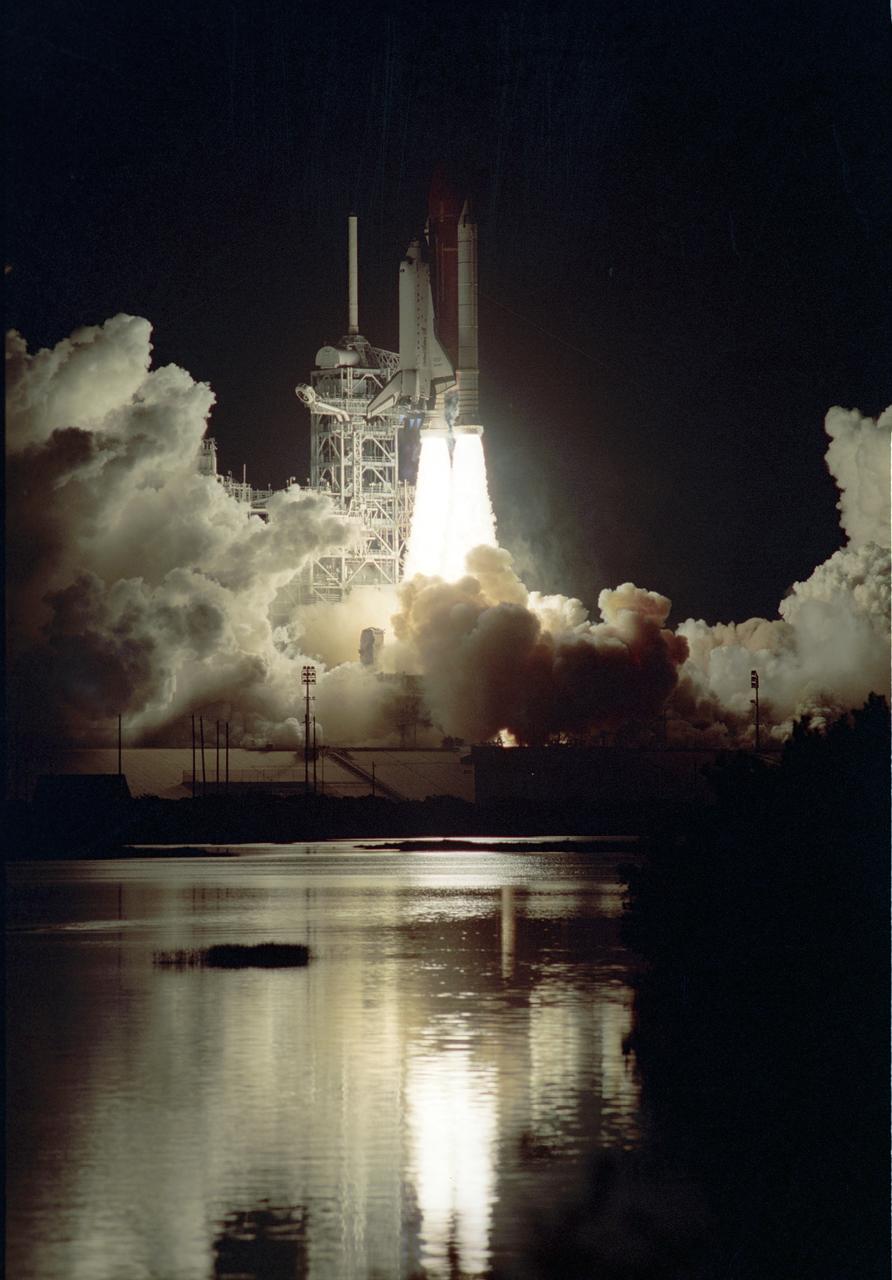

On November 22, 1989, at 7:23:30pm (EST), five astronauts were launched into space aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the 5th Department of Defense (DOD) mission, STS-33. Crew members included Frederick D. Gregory, commander; John E. Blaha, pilot; and mission specialists Kathryn C. Thornton, Manley L. (Sonny) Carter, and F. Story Musgrave.
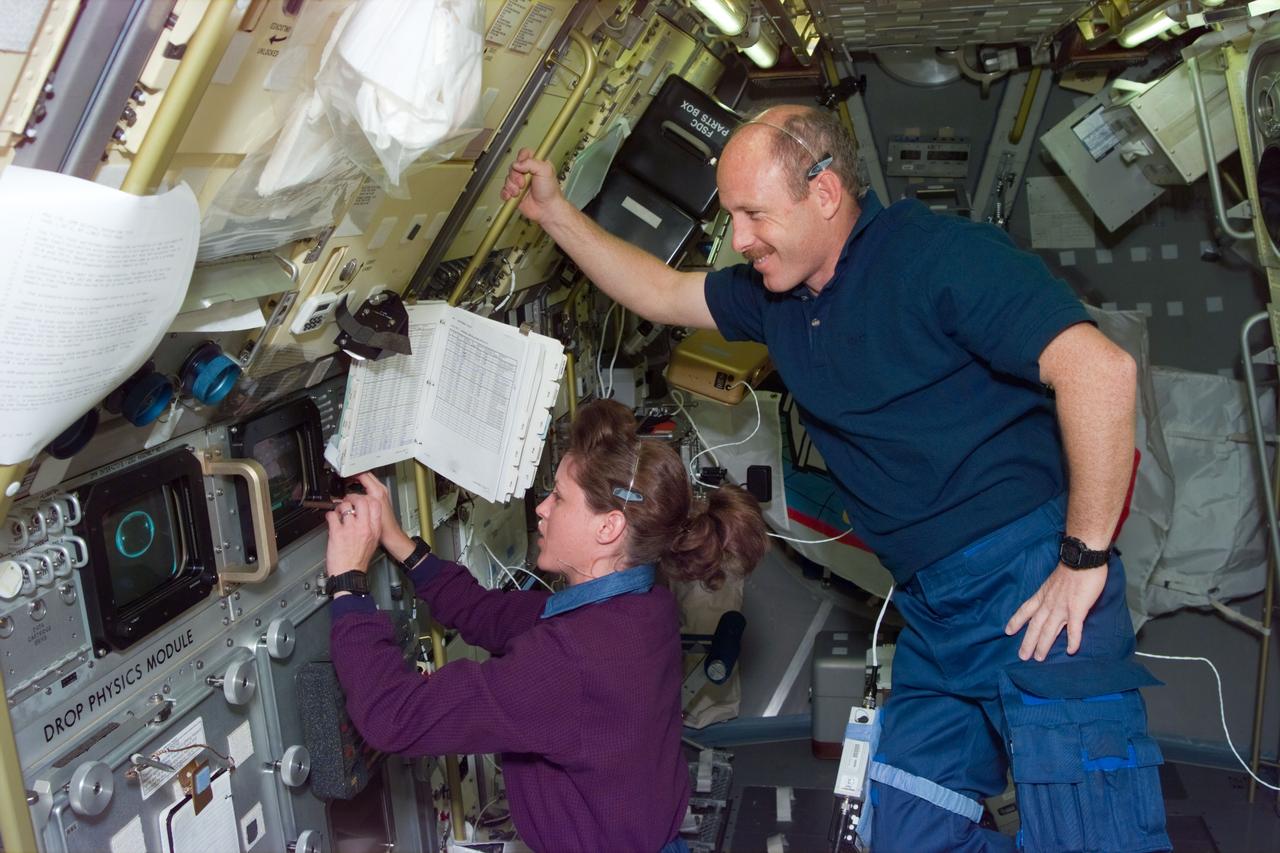

STS073-E-5311 (3 Nov. 1995) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, STS-73 payload commander, works at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) on the portside of the science module supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2). Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, mission commander, looks on. Five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists are in the last few days of a scheduled 16-day mission. This frame was exposed with the Electronic Still Camera (ESC).

STS073-E-5003 (23 Oct. 1995) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, STS-73 payload commander, works at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) on the portside of the science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in Earth orbit. Payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. conducts an experiment at the Glovebox. This frame was exposed with the color Electronic Still Camera (ESC) assigned to the 16-day United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
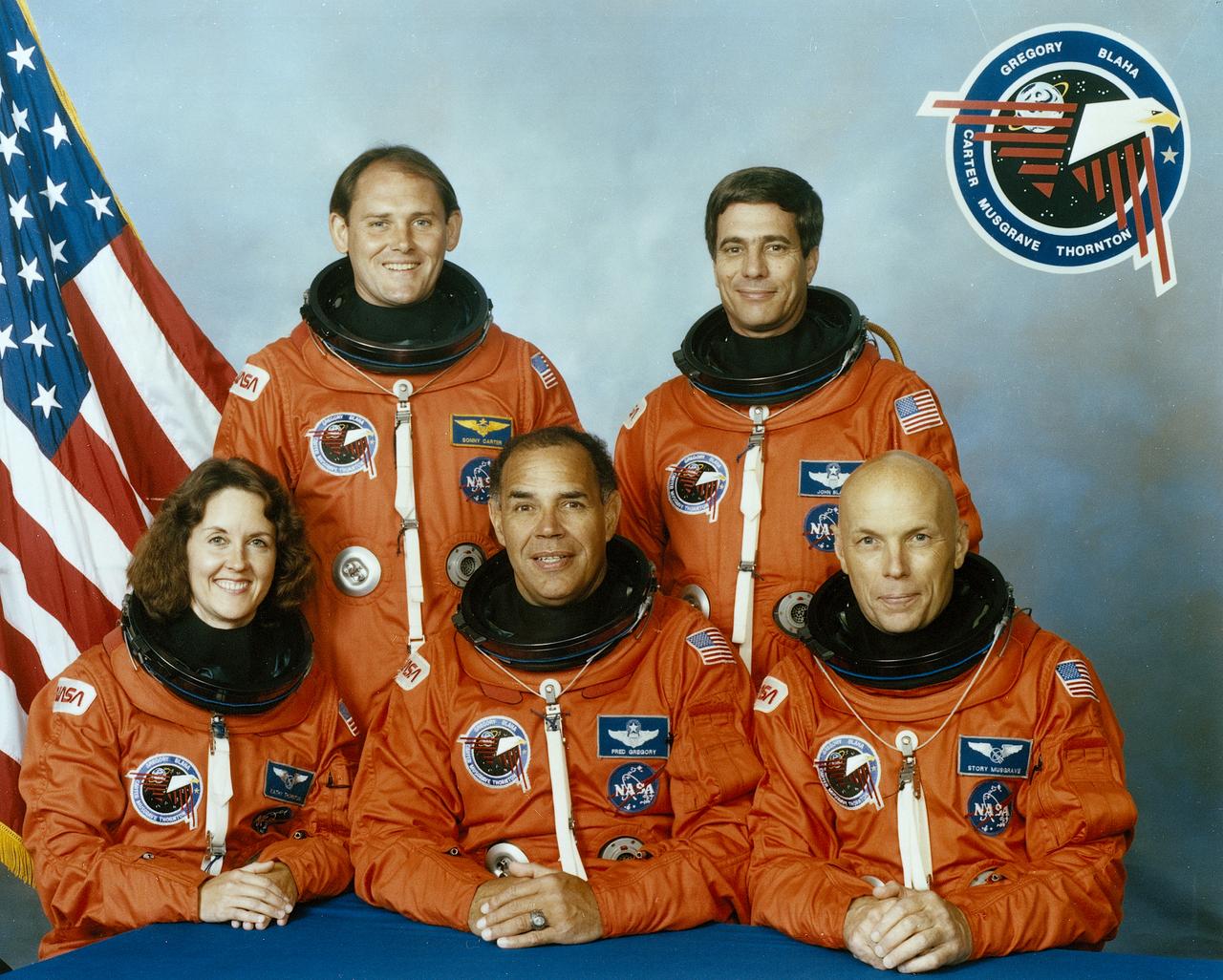

On November 22, 1989, at 7:23:30pm (EST), 5 astronauts were launched into space aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the 5th Department of Defense mission, STS-33. Photographed from left to right are Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialist 3; Manley L. (Sonny) Carter, mission specialist 2; Frederick D. Gregory, commander; John E. Blaha, pilot; and F. Story Musgrave, mission specialist 1.
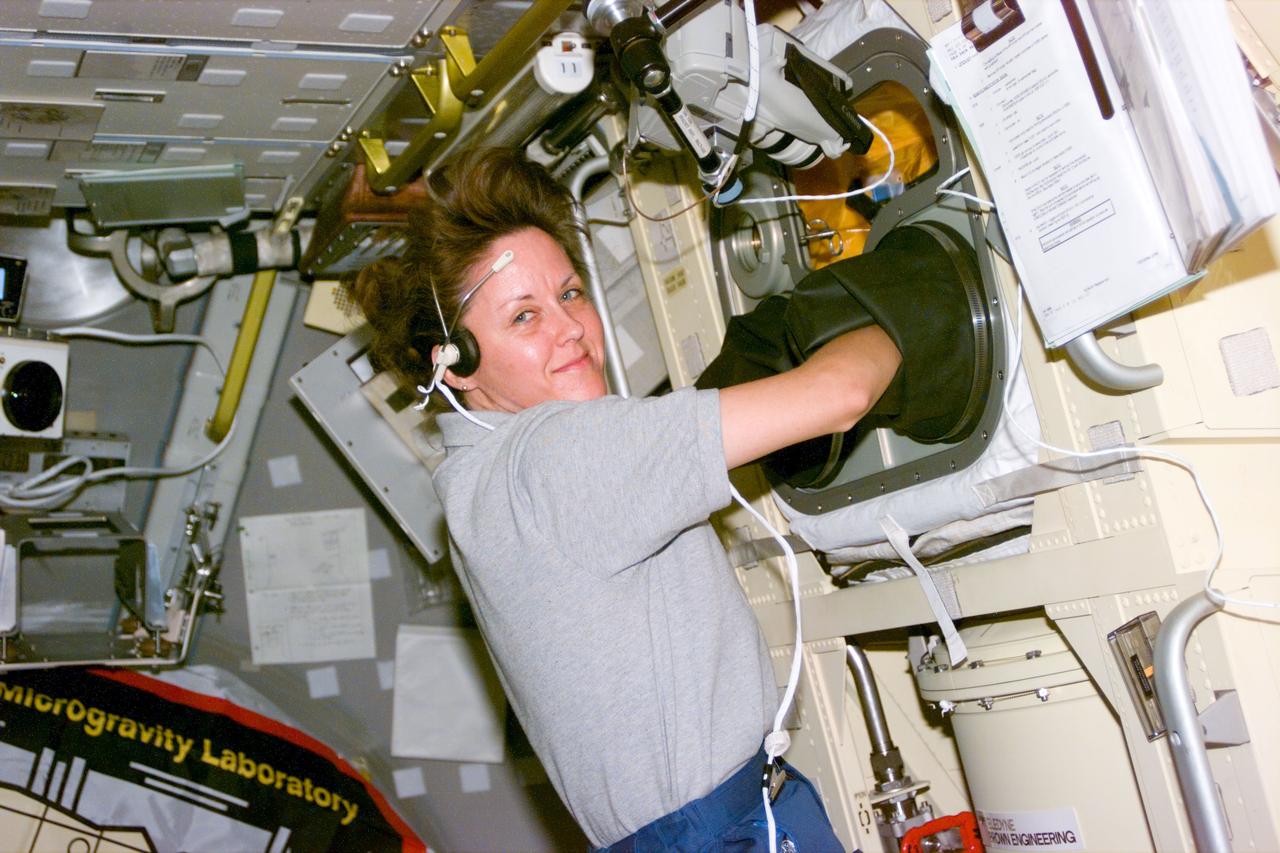

STS073-E-5246 (3 Nov. 1995) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, STS-73 payload commander, works in the Glovebox of the science module supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission. Five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists are in the last few days of a scheduled 16-day mission. This frame was exposed with the Electronic Still Camera (ESC).

STS049-S-269 (16 May 1992) --- The seven crewmembers of STS-49 pose near Endeavour for a post-flight shot soon after getting their feet on terra firma following nine days in Earth orbit. Left to right are astronauts Richard J. Hieb, Kevin P. Chilton, Daniel C. Brandenstein, Thomas D. Akers, Pierre J. Thuot, Kathryn C. Thornton and Bruce E. Melnick. Brandenstein was mission commander; Chilton, pilot; and the others, mission specialists.
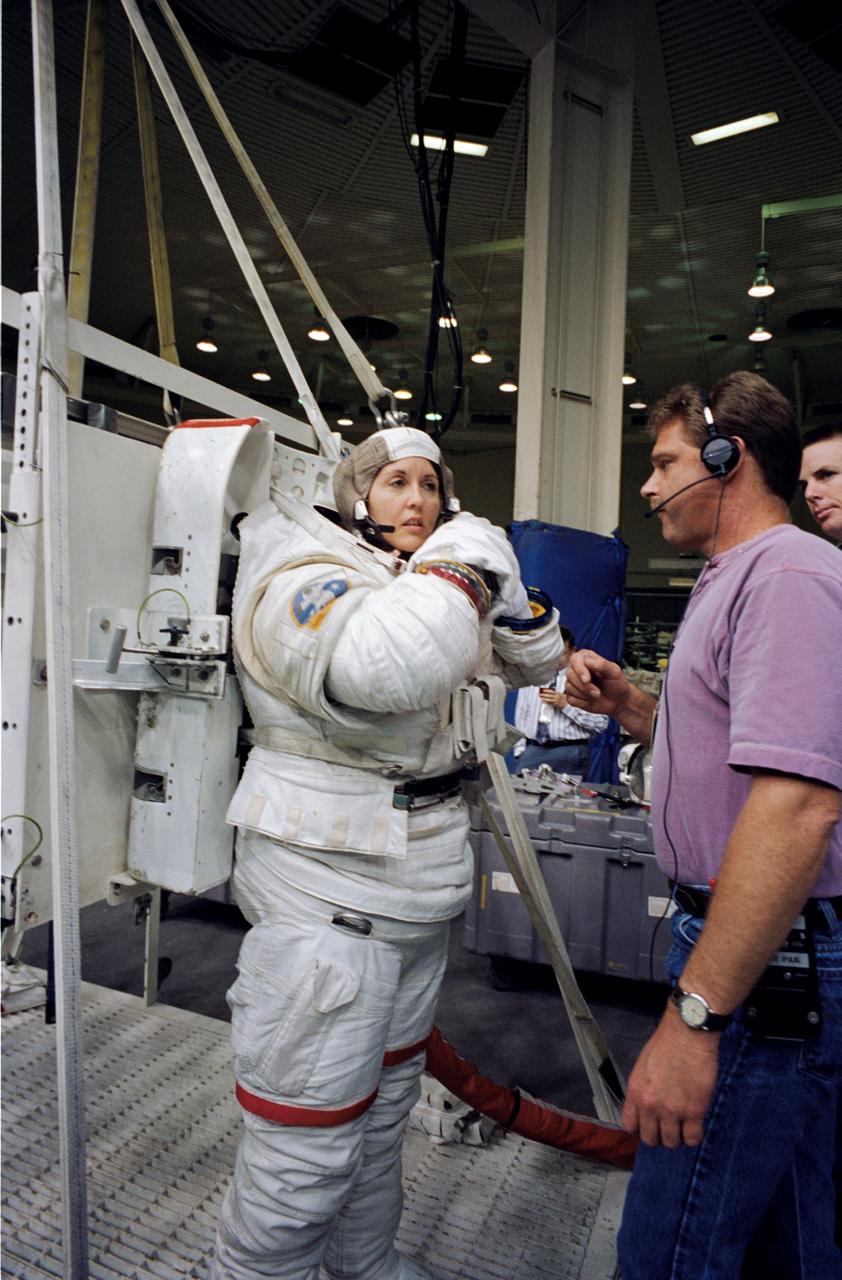

Astronaut Kathryn Thornton, payload commander for the STS-73 mission, attired in a high fidelity training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit, prepares to go underwater in the Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). The STS-73 mission was the second flight of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2), managed by scientists and engineers from the Marshall Space Flight Center.
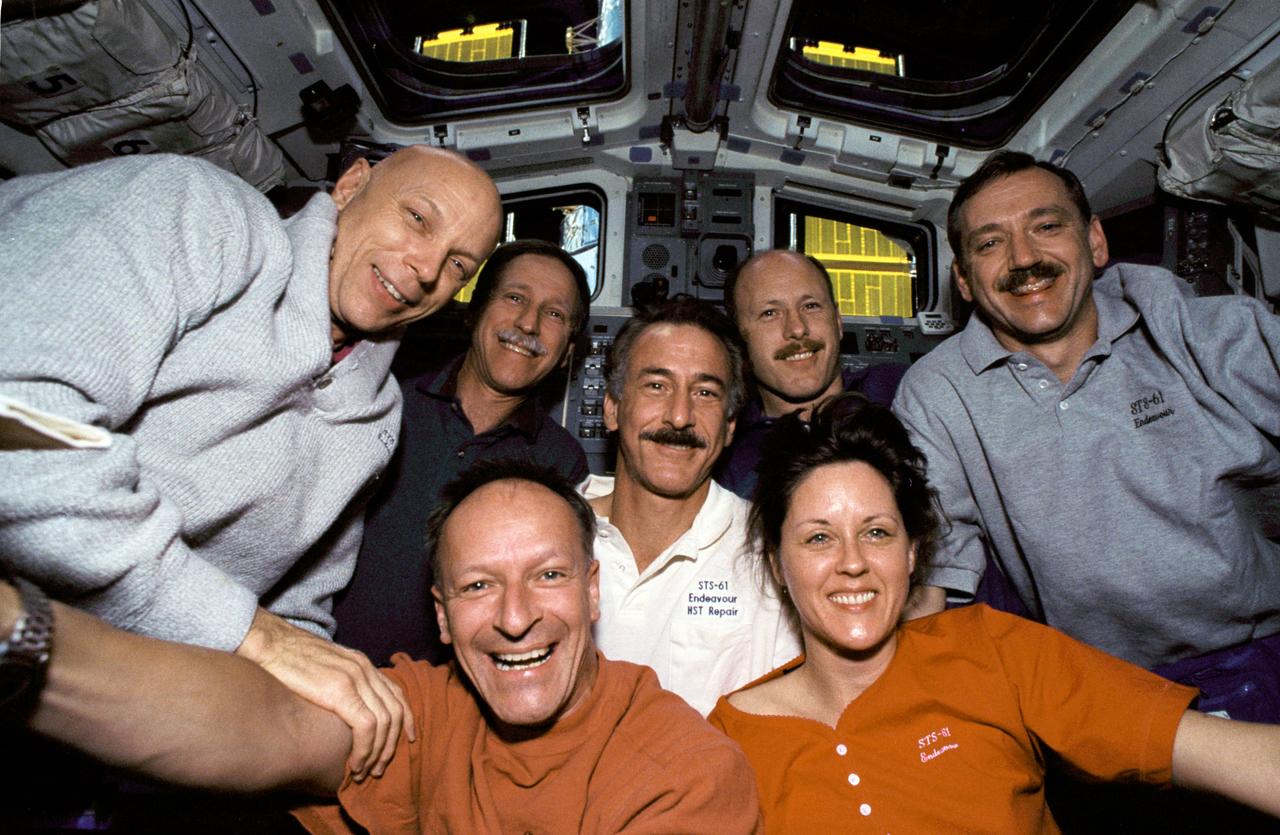

STS061-05-031 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- With the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) berthed in Endeavour's cargo bay, crew members for the STS-61 mission pause for a crew portrait on the flight deck. Left to right are F. Story Musgrave, Richard O. Covey, Claude Nicollier, Jeffrey A. Hoffman, Kenneth D. Bowersox, Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers.
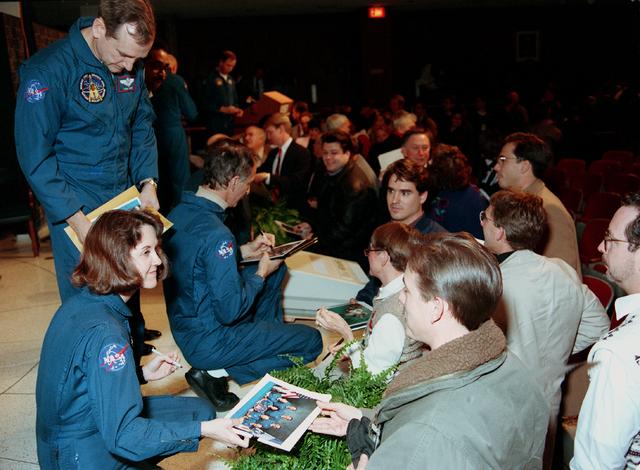

STS-61 astronauts Kathryn Thornton, Jeffrey Hoffman and Thomas Akers (standing) sign autographs in Marshall Space Flight Center's Morris Auditorium, January 19, 1994. Space Shuttle crews traditionally visited NASA field centers following each mission to present mission highlights and recognize employees who made contributions to the Shuttle program. Many of the techniques used during the STS-61 Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission were rehearsed at the Center's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator.
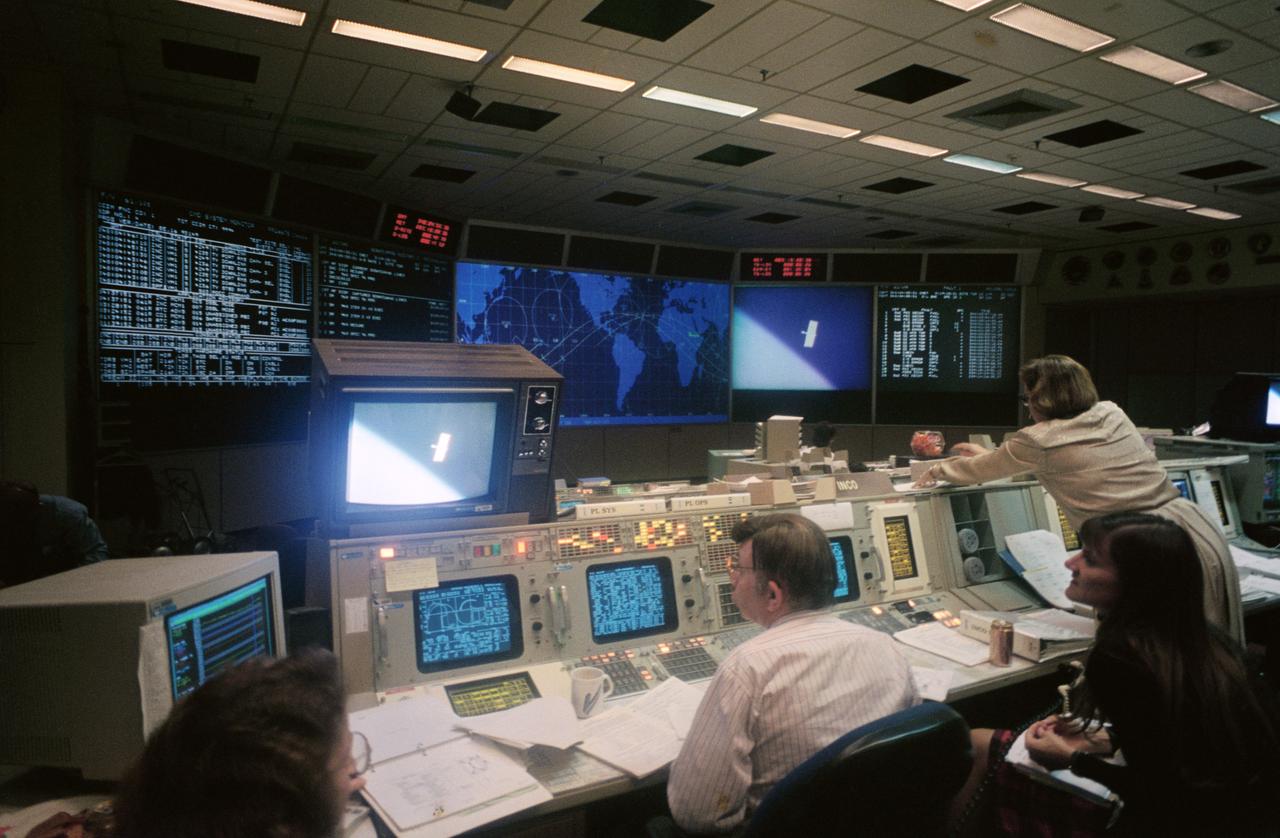

Harry Black, at the Integrated Communications Officer's console in the Mission Control Center (MCC), monitors the second extravehicular activity (EVA-2) of the STS-61 Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. Others pictured, left to right, are Judy Alexander, Kathy Morrison and Linda Thomas. Note monitor scene of one of HST's original solar array panels floating in space moments after being tossed away by Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton.
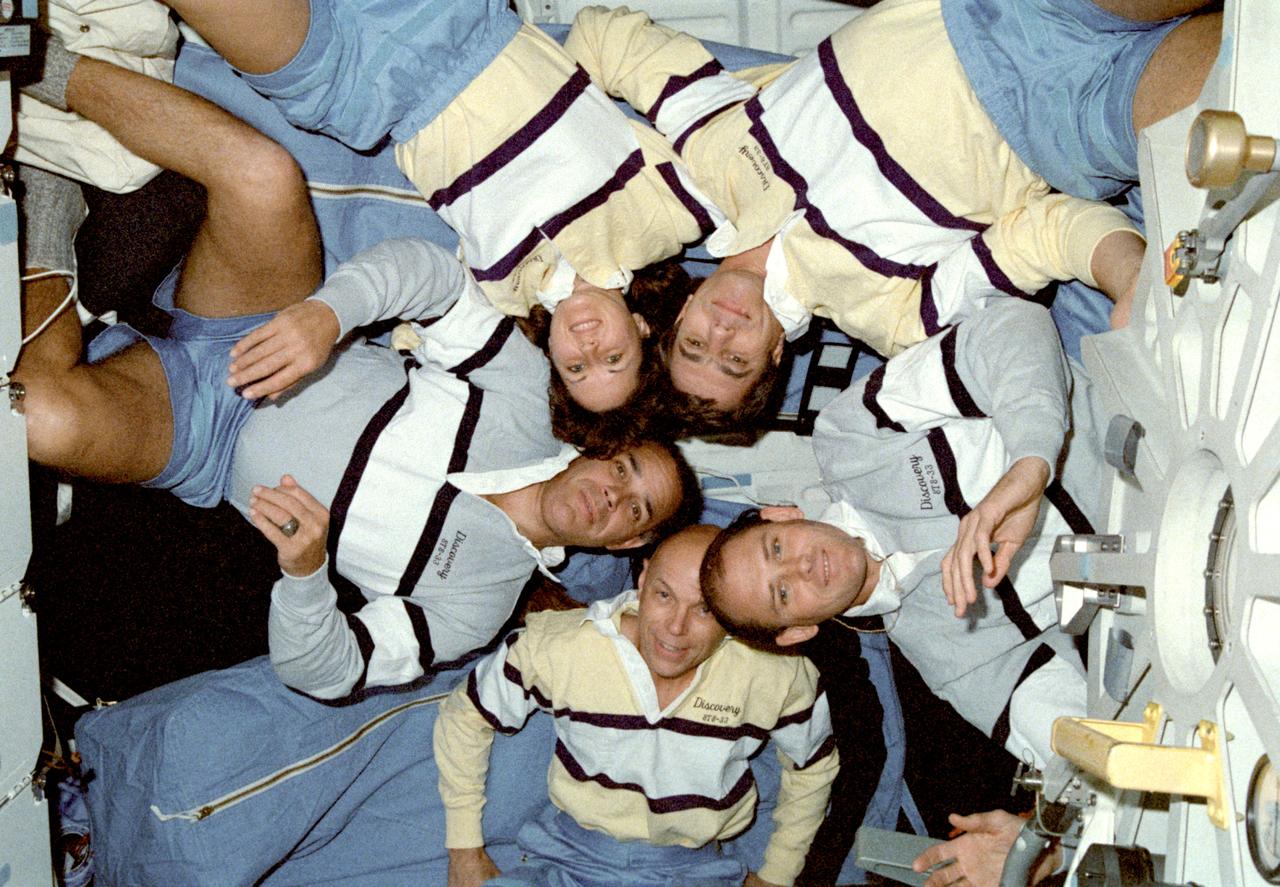

STS033-22-035 (22-27 Nov. 1989) --- STS-33 crewmembers, wearing mission polo shirts, pose on the middeck of the Space Shuttle Discovery for an in-flight crew portrait. Clockwise (starting at left) are astronauts Frederick D. Gregory, commander; Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialist; John E. Blaha, pilot; Manley L. (Sonny) Carter Jr., and F. Story Musgrave, mission specialists.
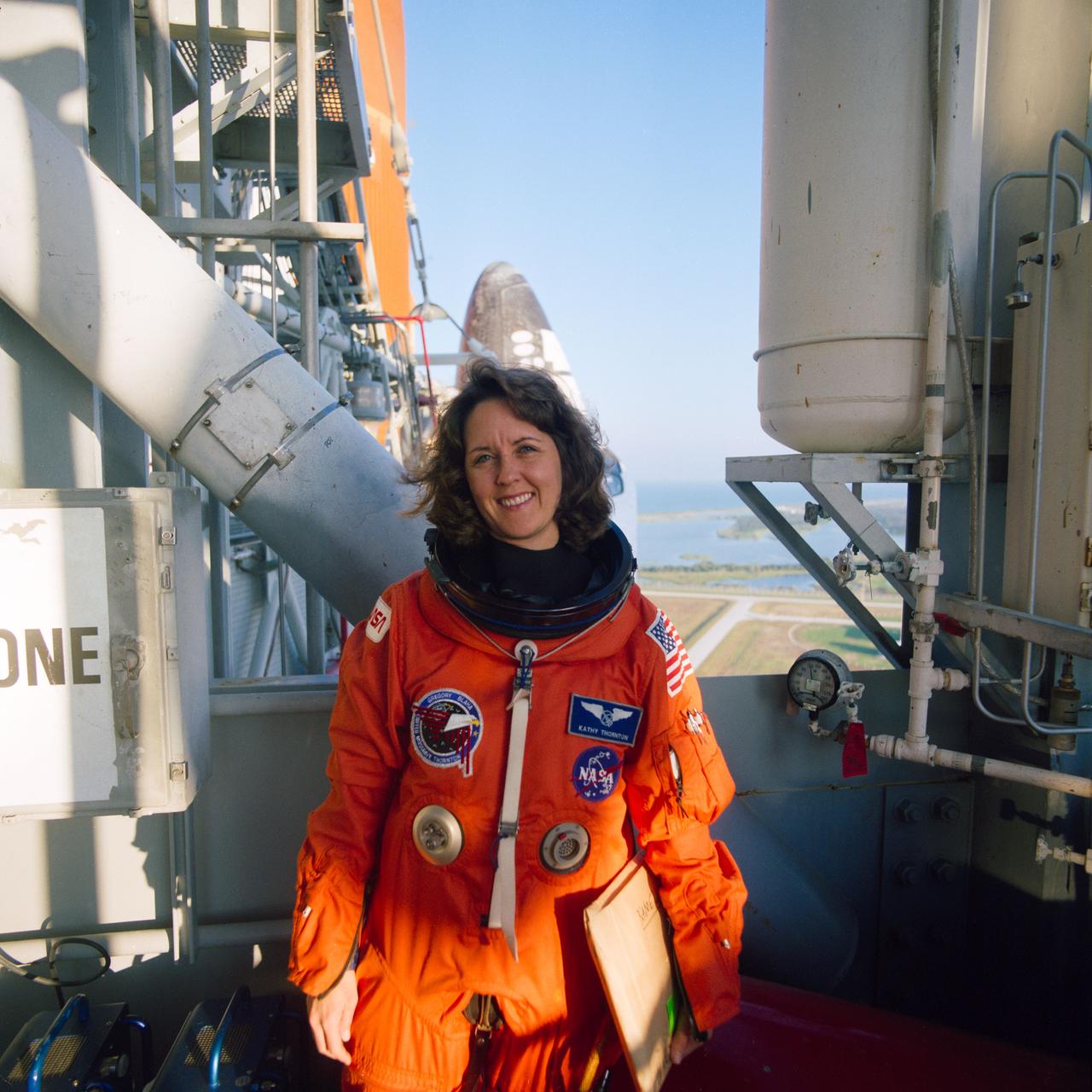

STS-33 Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn C. Thornton, wearing launch and entry suit (LES) and holding file folder, poses in front of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, at the 195 ft level elevator entrance at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B. Visible in the background is the catwalk to OV-103's side hatch and the Atlantic Ocean.
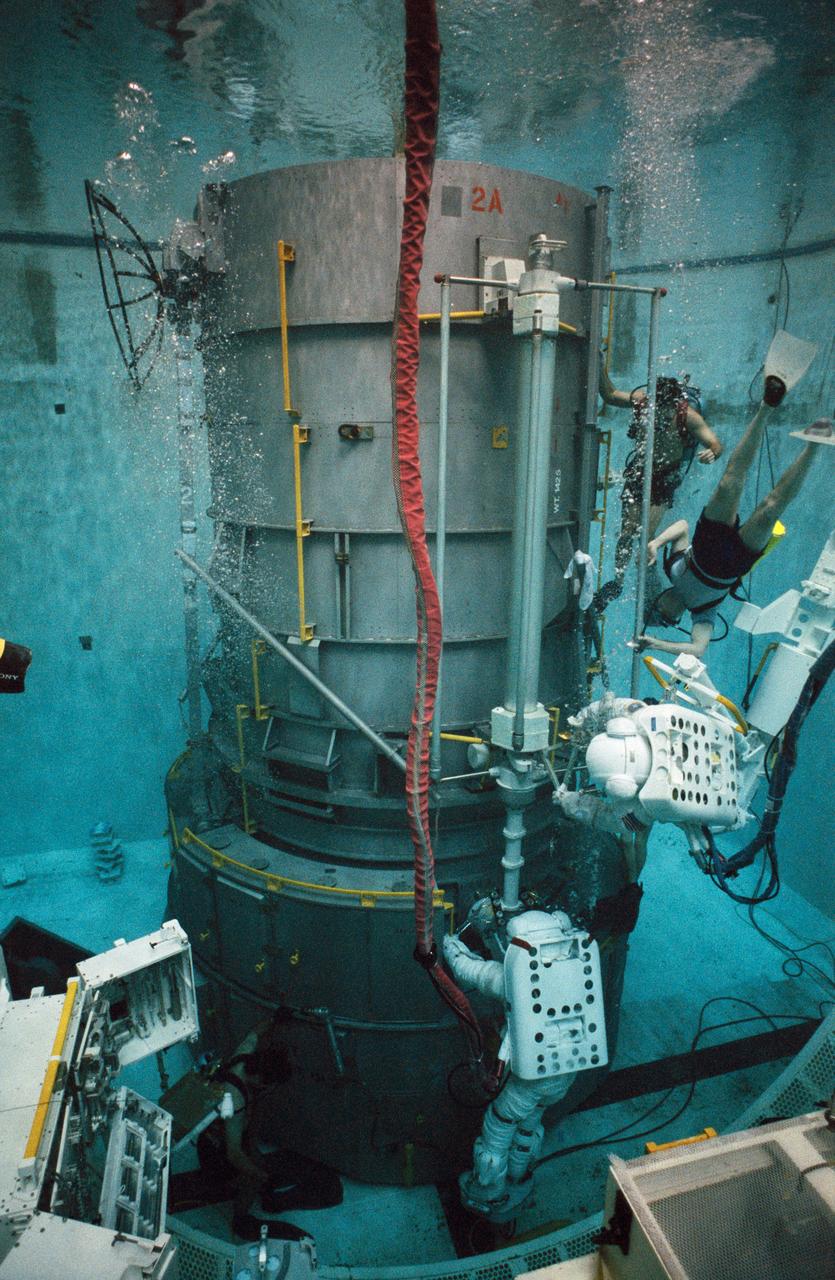
S93-30237 (5 Mar 1993) --- Wearing training versions of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMU), astronauts Thomas D. Akers (red stripe) and Kathryn C. Thornton use the spacious pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. They are working with part of a full-scale mockup of HST.
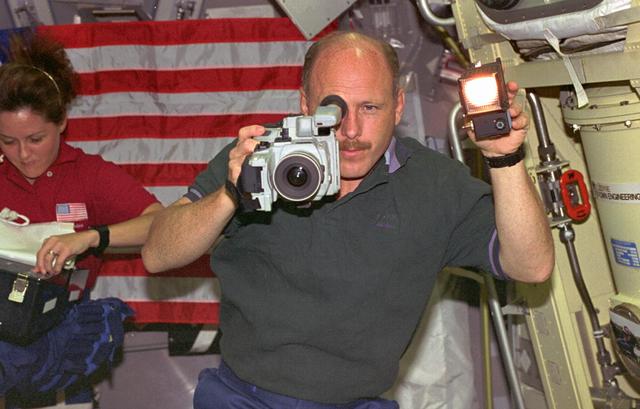

STS073-230-014 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, STS-73 mission commander, uses a camcorder to record United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) activities onboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. Nearby, astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander, prepares to open a supply chest to support one of many science experiments conducted by the seven-member crew during the 16-day USML-2 flight.

STS049-S-002 (16 Jan. 1992) --- These seven NASA astronauts are currently training for the first flight of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, seen in the background. Daniel C. Brandenstein, center, is mission commander; and Kevin P. Chilton, third from right, is pilot. Mission specialists are, left to right, Kathryn C. Thornton, Bruce E. Melnick, Pierre J. Thout, Thomas D. Akers and Richard J. Hieb.
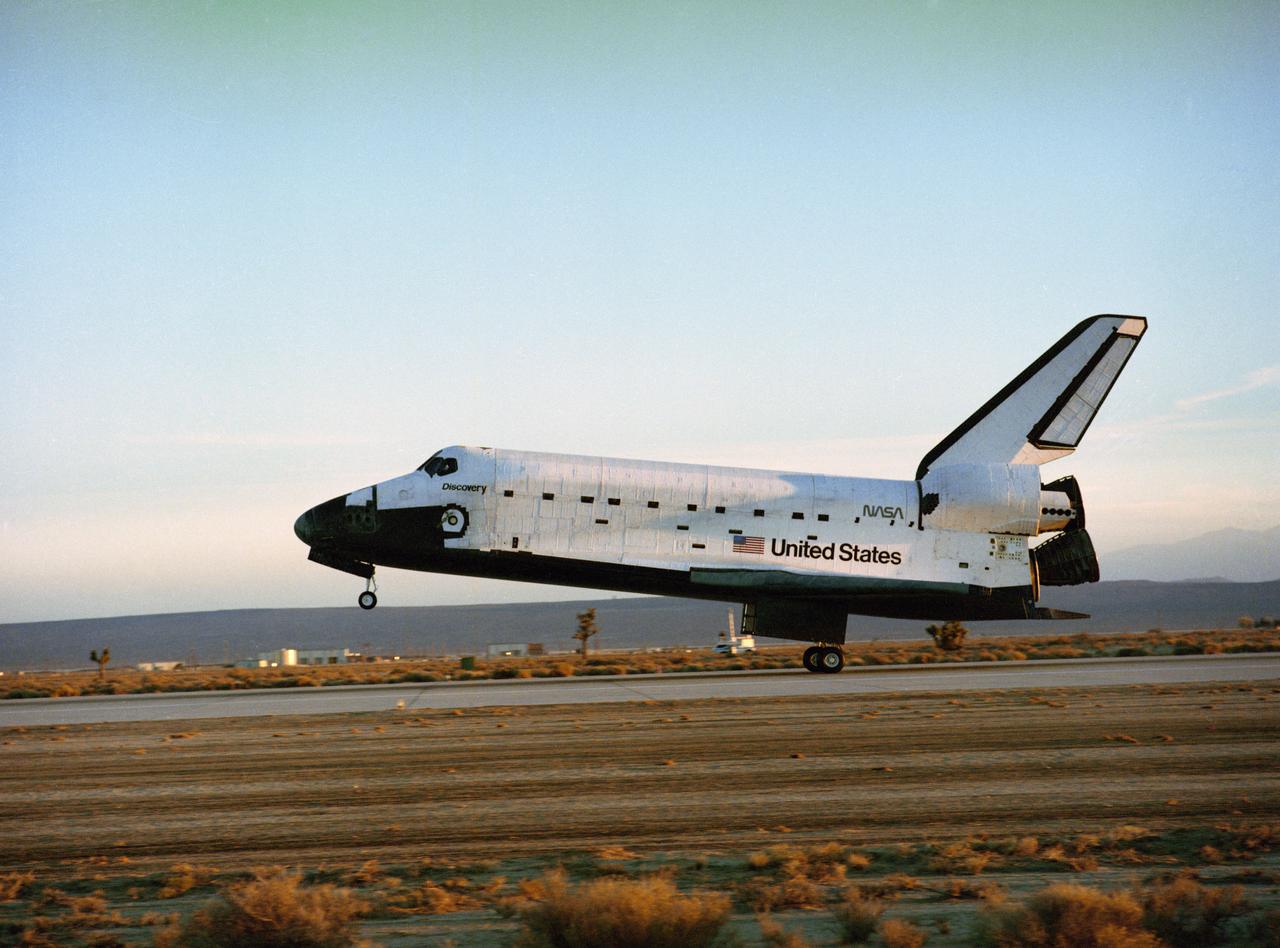

STS033-S-010 (27 Nov 1989) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery, with a crew of five astronauts aboard, touches down on a runway at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California. The landing occurred at 16:31:02 p.m. (PST), Nov. 27, 1989. Onboard Discovery for the DOD-devoted mission were astronauts Frederick D. Gregory, John E. Blaha, Kathryn C. Thornton, F. Story Musgrave and Manley L. Carter.
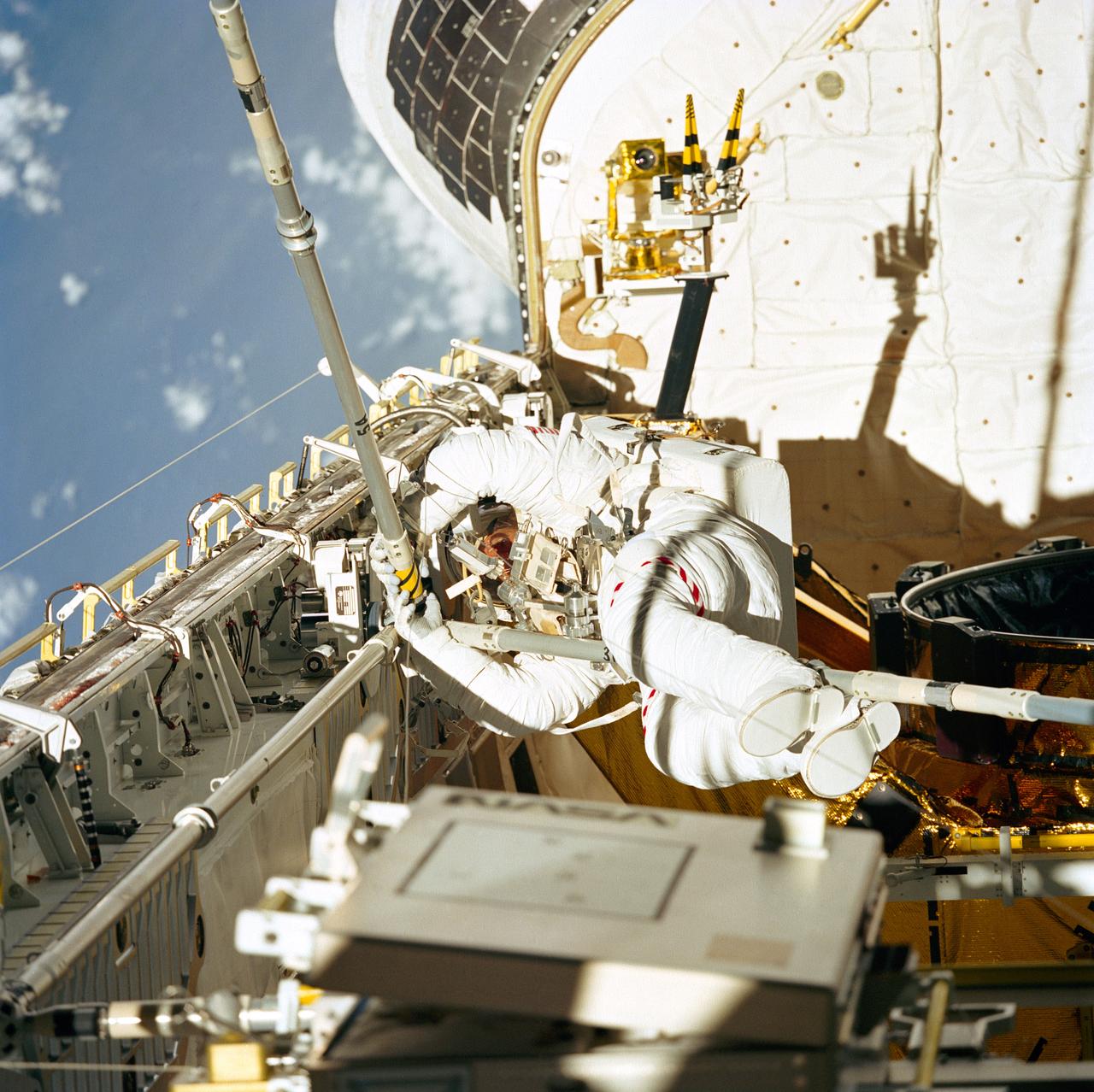

STS049-77-023 (14 May 1992) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers joins three struts together, as fourth period of extravehicular activity (EVA) proceeds in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. The purpose of the final EVA on this nine-day mission was the evaluation of Assembly of Station by EVA Methods (ASEM). The scene was recorded on 70mm film by a fellow crew member in the Space Shuttle's cabin. Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton (out of frame) joined Akers on the 7 1/2 hour EVA.
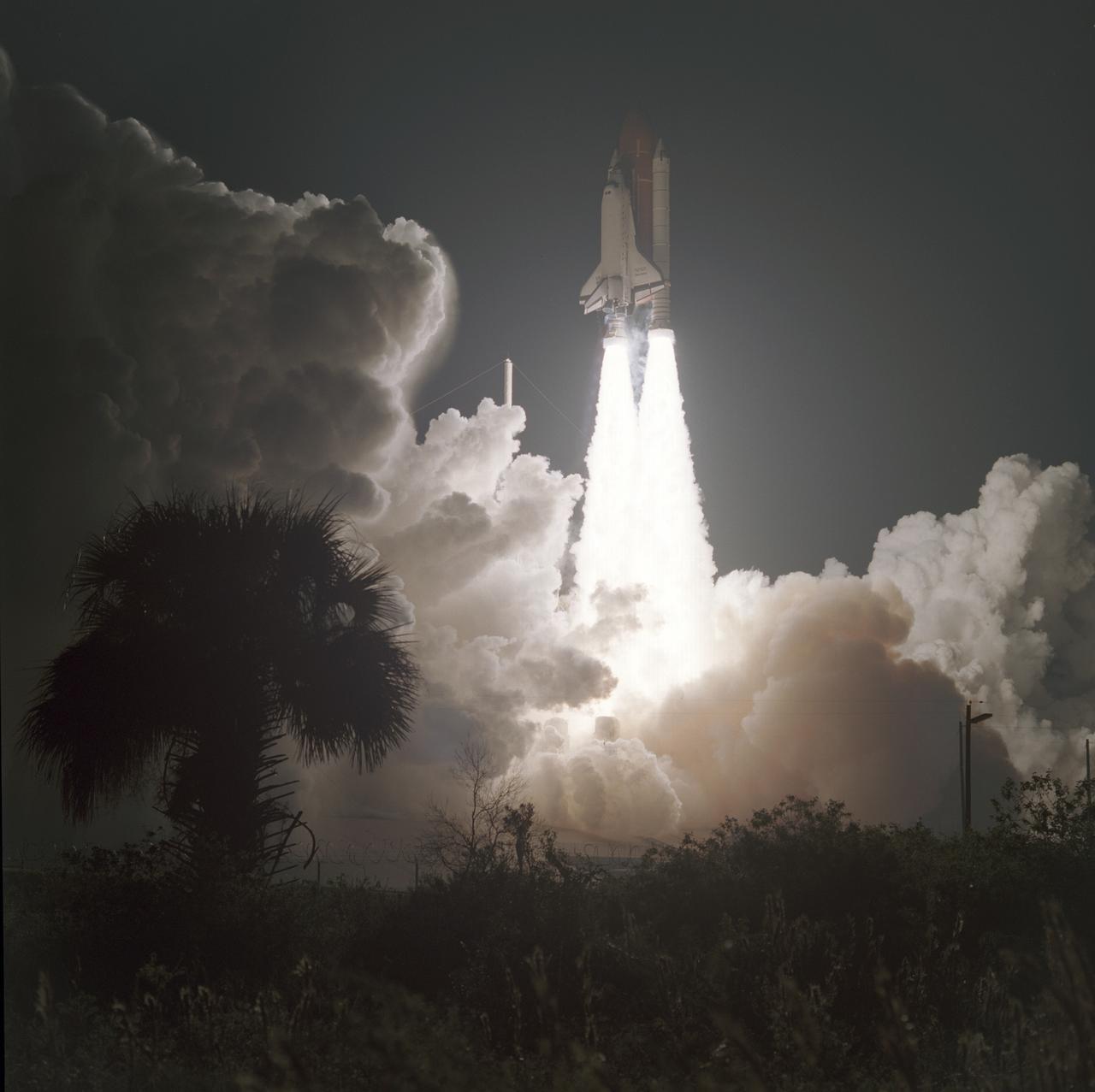

On November 22, 1989, at 7:23:30pm (EST), five astronauts were launched into space aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the 5th Department of Defense (DOD) mission, STS-33. Crew members included Frederick D. Gregory, commander; John E. Blaha, pilot; and mission specialists Kathryn C. Thornton, Manley L. (Sonny) Carter, and F. Story Musgrave.
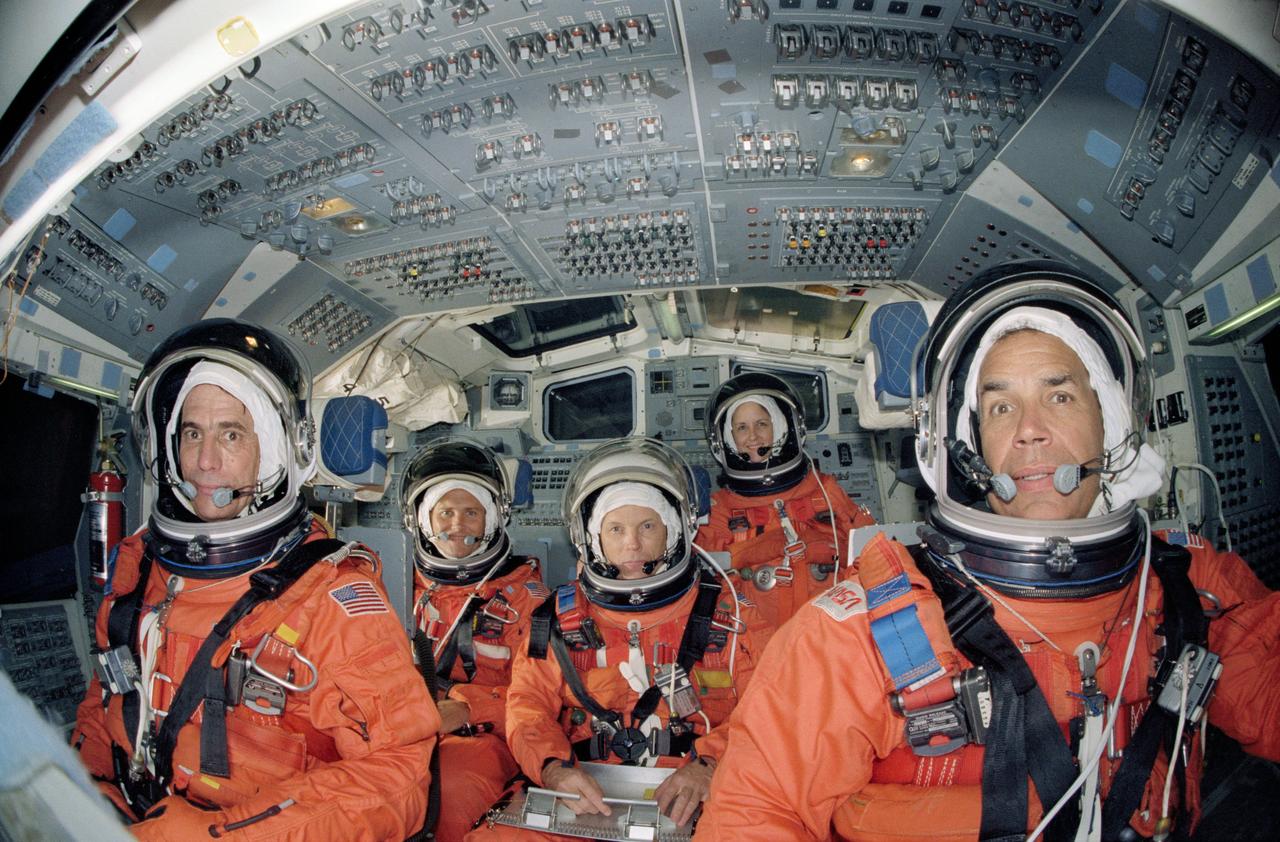

STS-33 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, crewmembers, wearing orange launch and entry suits (LESs) and launch and entry helmets (LEHs), are seated in their launch and entry positions on crew compartment trainer (CCT) flight deck during a training exercise in JSC Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9A. Commander Frederick D. Gregory (far right) is stationed at forward flight deck commanders controls, Pilot John E. Blaha (far left) at the pilots controls and on aft flight deck are mission specialists Manley L. Carter, Jr (left), MS F. Story Musgrave (center, holding clipboard), and MS Kathryn C. Thornton (standing). Overhead forward control panels are visible above the astronauts and aft flight deck onorbit station control panels and windows are visible in the background. Thornton is on the flight deck for this photo but during launch and entry will be seated on the middeck.

S61-E-012 (5 Dec 1993) --- This view of astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton (top) and Thomas D. Akers working on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was photographed with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC), and down linked to ground controllers soon afterward. Thornton, anchored to the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is teaming with Akers to install the +V2 Solar Array Panel as a replacement for the original one removed earlier. Akers uses tethers and a foot restraint to remain in position for the task. Electronic still photography is a relatively new technology which provides the means for a handheld camera to electronically capture and digitize an image with resolution approaching film quality. The electronic still camera has flown as an experiment on several other shuttle missions.

S61-E-014 (5 Dec 1993) --- This view of astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton (bottom) and Thomas D. Akers working on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was photographed with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC), and down linked to ground controllers soon afterward. Thornton, anchored to the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is teaming with Akers to install the +V2 Solar Array Panel as a replacement for the original one removed earlier. Akers uses tethers and a foot restraint to remain in position for the task. Electronic still photography is a relatively new technology which provides the means for a handheld camera to electronically capture and digitize an image with resolution approaching film quality. The electronic still camera has flown as an experiment on several other shuttle missions.
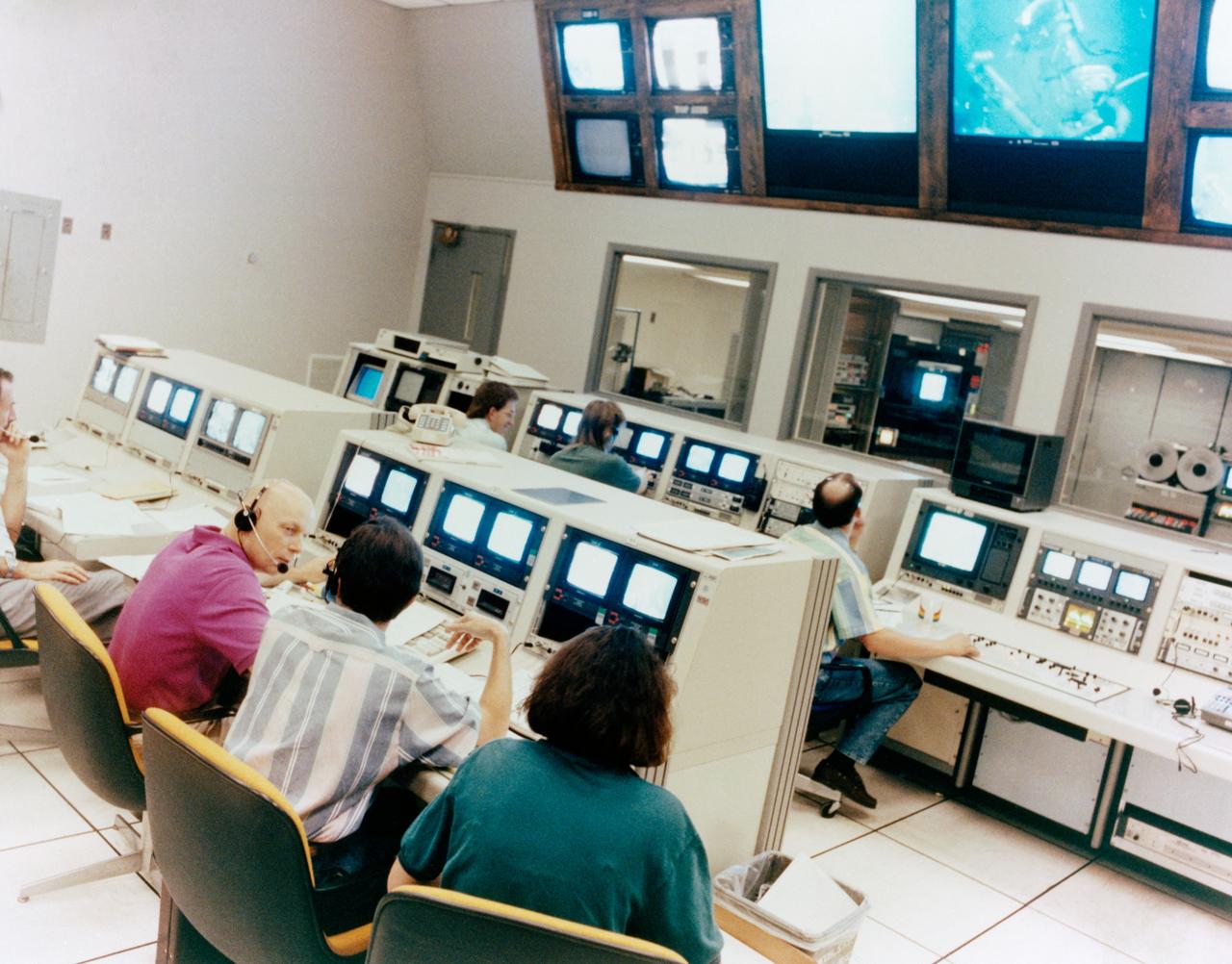

Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (far left) and F. Story Musgrave (second left) monitor a training session from consoles in the control room for the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Seen underwater in the NBS on the big screen and the monitors at the consoles is astronaut Thomas D. Akers. The three mission specialists, along with astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, are scheduled to be involved in a total of five sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) to service the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in orbit during the STS-61 mission, scheduled for December 1993.
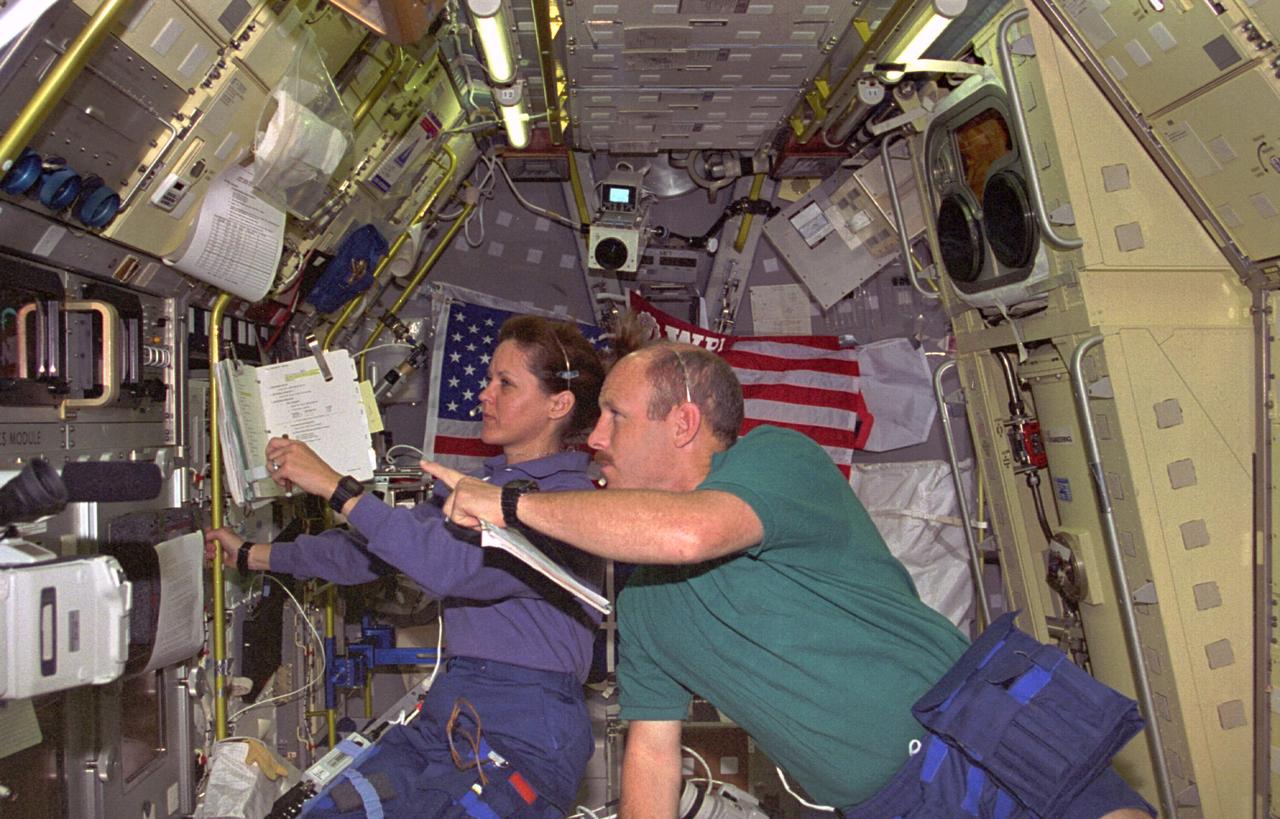

STS073-229-014 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton, STS-73 payload commander, and Kenneth D. Bowersox, mission commander, observe a liquid drop's activity at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) in the science module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. The drop is partially visible at the center of the left edge of the frame. The two were joined by three other NASA astronauts and two guest researchers for almost 16-days of in-orbit research in support of the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
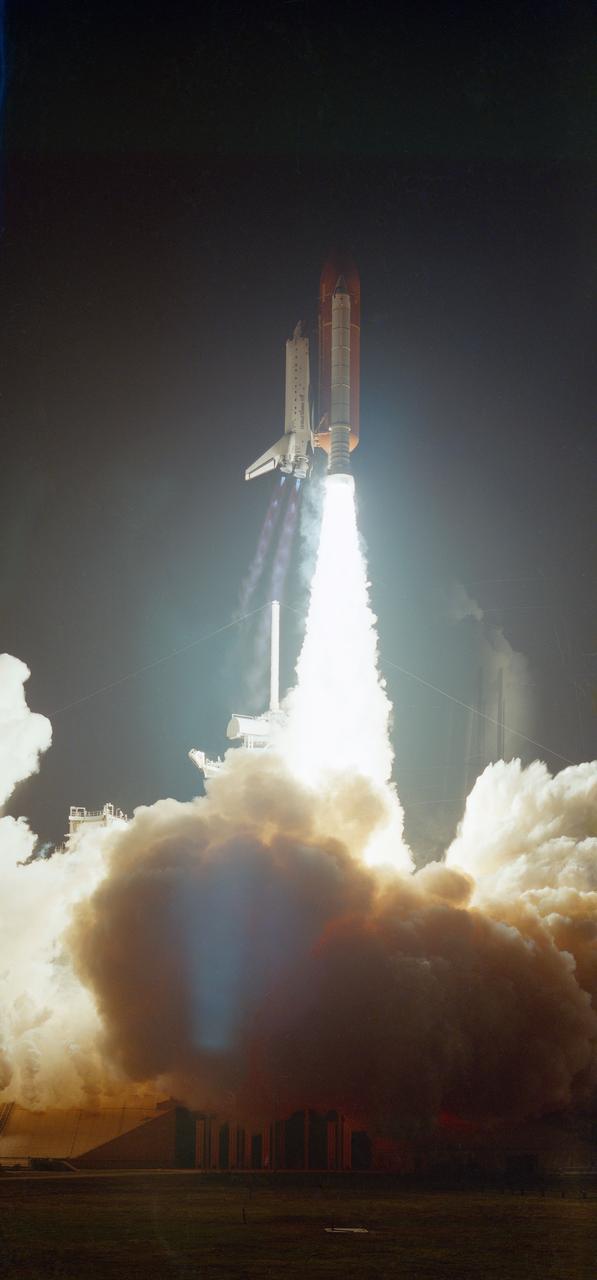

STS033-S-002 (22 Nov 1989) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery heads for Earth orbit on the first post-Challenger nocturnal launch. Liftoff occurred at 7:23:29:989 p.m. (EST), November 22, 1989. This picture shows a side view of Discovery, one of its two solid rocket boosters (SRB) and the external tank. It represents a good example of the "diamond shock" effect, in the plume from the main engine, associated with Shuttle launches. Onboard for the DOD-devoted mission were Astronauts Frederick D. Gregory, John E. Blaha, F. Story Musgrave, Kathryn C. Thornton and Manley L. Carter.
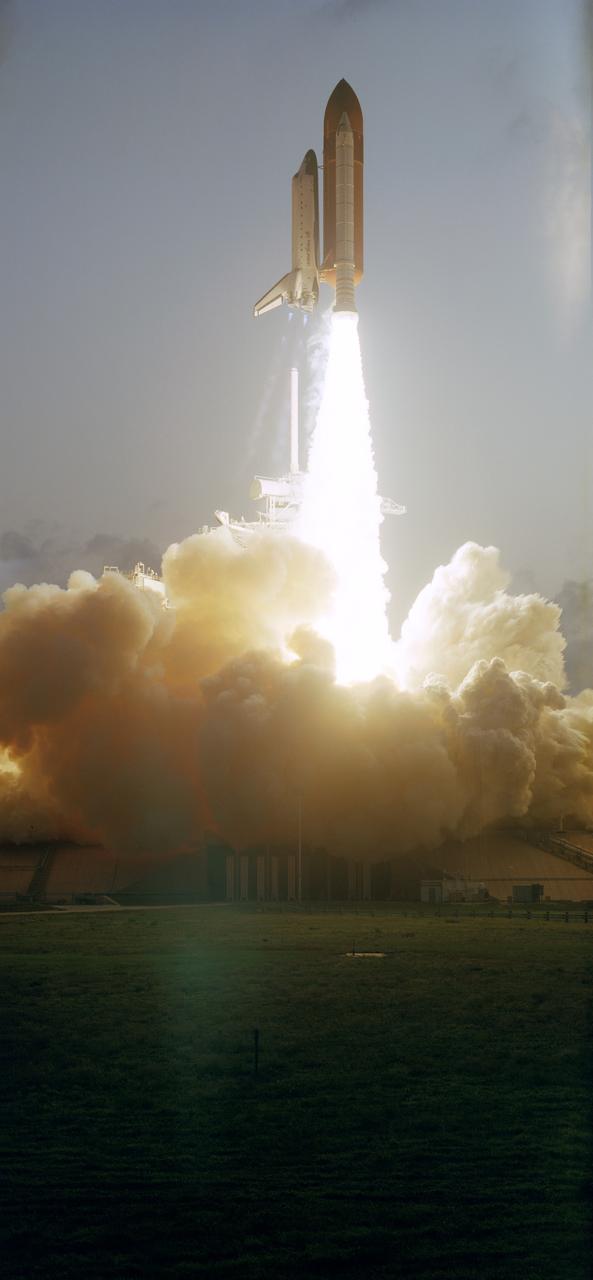

STS049-S-251 (7 May 1992) --- The Space Shuttle Endeavour soars toward Earth orbit where a crew of seven NASA astronauts will spend at least a week. Endeavour, the newest orbiter in NASA's Space Shuttle fleet, lifted off from Pad 39B at 7:40 p.m. (EDT), May 7, 1992. A diamond shock effect can be seen beneath the three main engines. Onboard are astronauts Daniel C. Brandenstein, mission commander; Kevin P. Chilton, pilot; and Richard J. Hieb, Bruce E. Melnick, Pierre J. Thuot, Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers, all mission specialists.

S90-27591 (23 Jan 1990) --- STS-33 crewmembers, wearing launch and entry suit (LES), take a break from training activities to pose for group portrait in front of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, at the 195 ft level elevator entrance at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B. Left to right are Pilot John E. Blaha, Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn C. Thornton, MS Manley L. Carter, Jr, Commander Frederick D. Gregory, and MS F. Story Musgrave. Visible in the background is the catwalk to OV-103's side hatch.

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. In this STS-49 onboard photo, Astronaut Kathryn Thornton joins three struts together during her Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA).
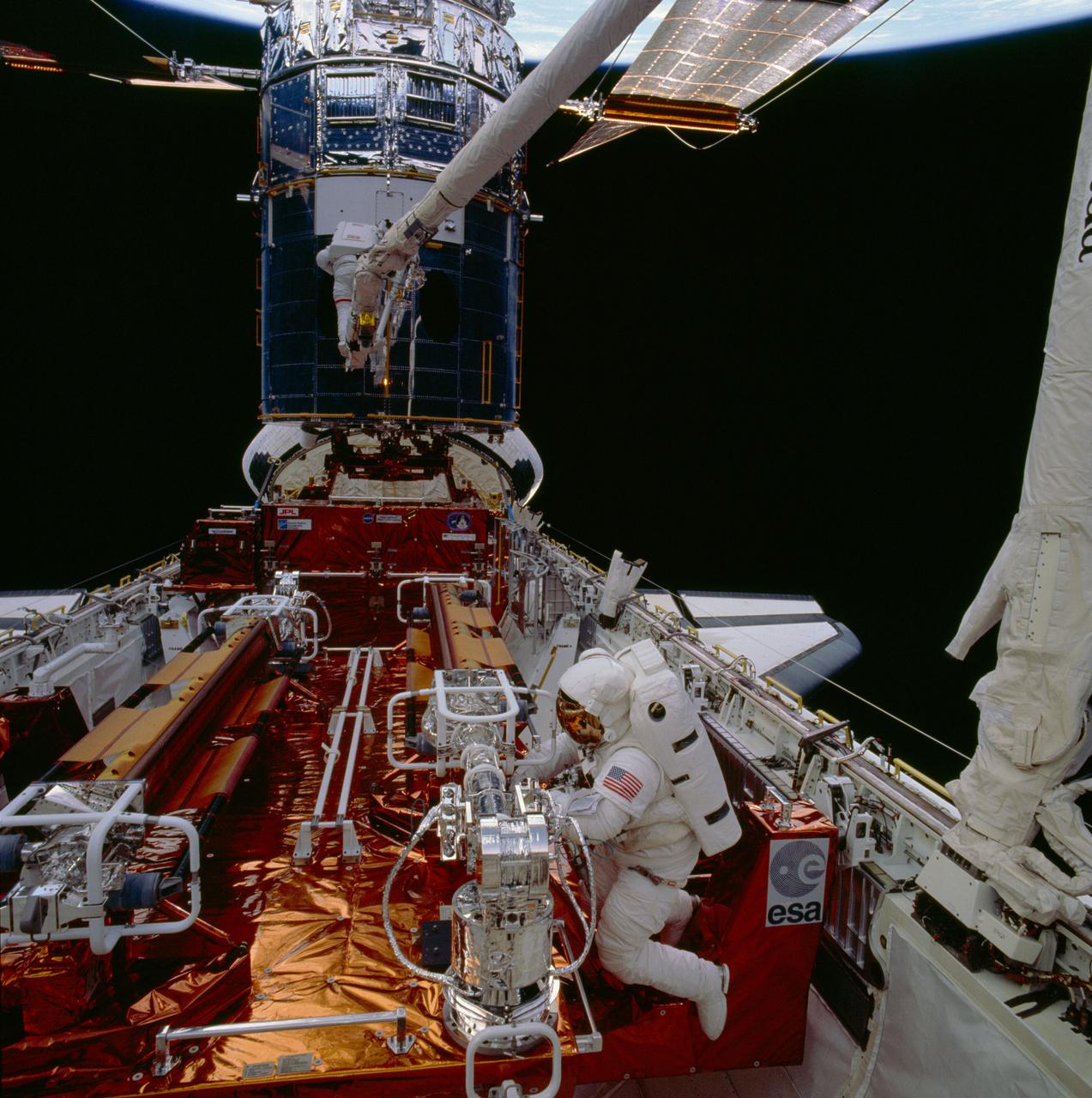
STS061-86-048 (5 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts F. Story Musgrave (foreground) and Jeffrey A. Hoffman are pictured near the end of the first of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA). Musgrave works at the Solar Array Carrier (SAC) in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. Hoffman, anchored to a foot restraint mounted on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, waits to be maneuvered to the forward payload bay. The original solar array panels are partially visible at top, while their replacements remain stowed in foreground. The crew's second pair of space walkers -- astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers -- later changed the solar arrays on the mission's second EVA.

STS061-S-071 (13 Dec 1993) --- A rear view of the Space Shuttle Endeavour as it touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 05:25:57:27 GMT (12:26 a.m. EST) December 13, 1993. Onboard the spacecraft were Richard O. Covey, mission commander; Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot; mission specialists Thomas D. Akers; Jeffrey A. Hoffman; F. Story Musgrave; Kathryn C. Thornton and Swiss scientist Claude Nicollier. This is the second night landing at KSC in the history of the Shuttle Program.
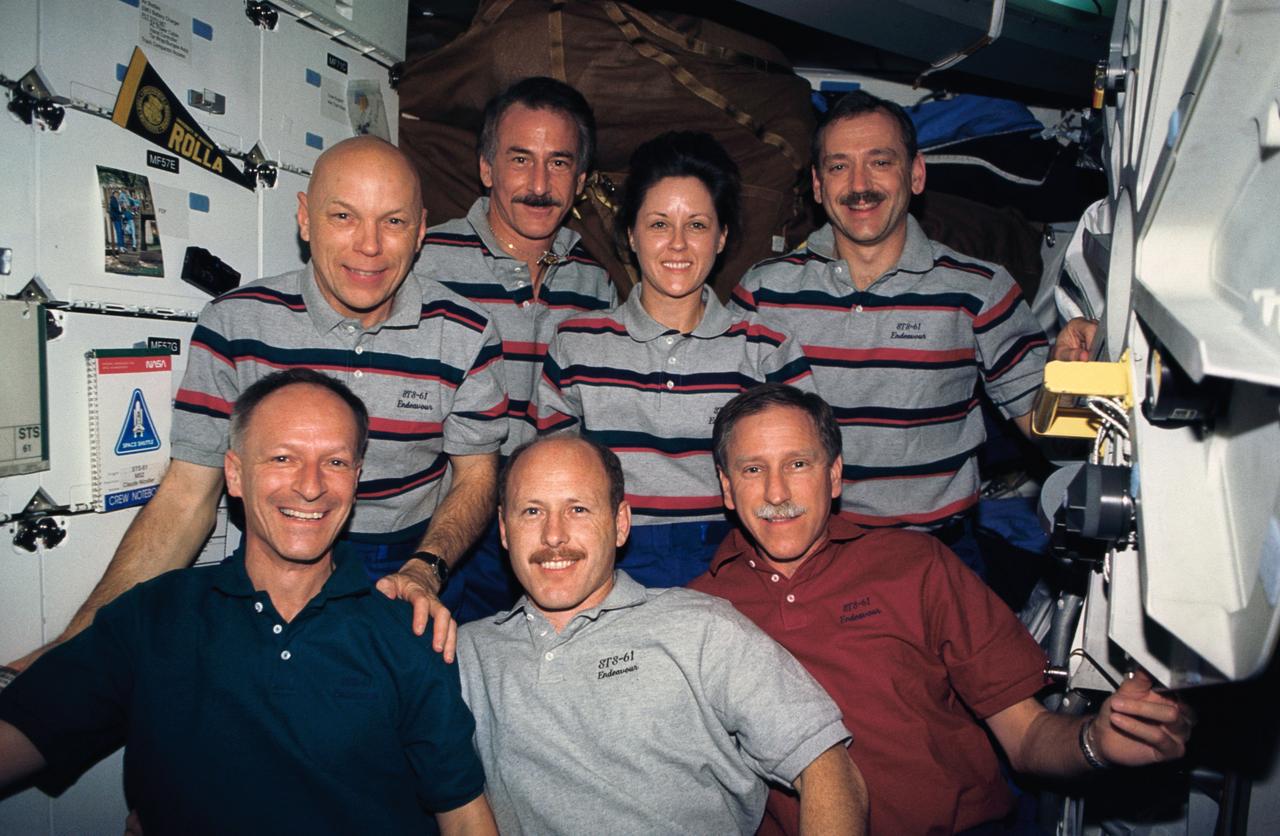

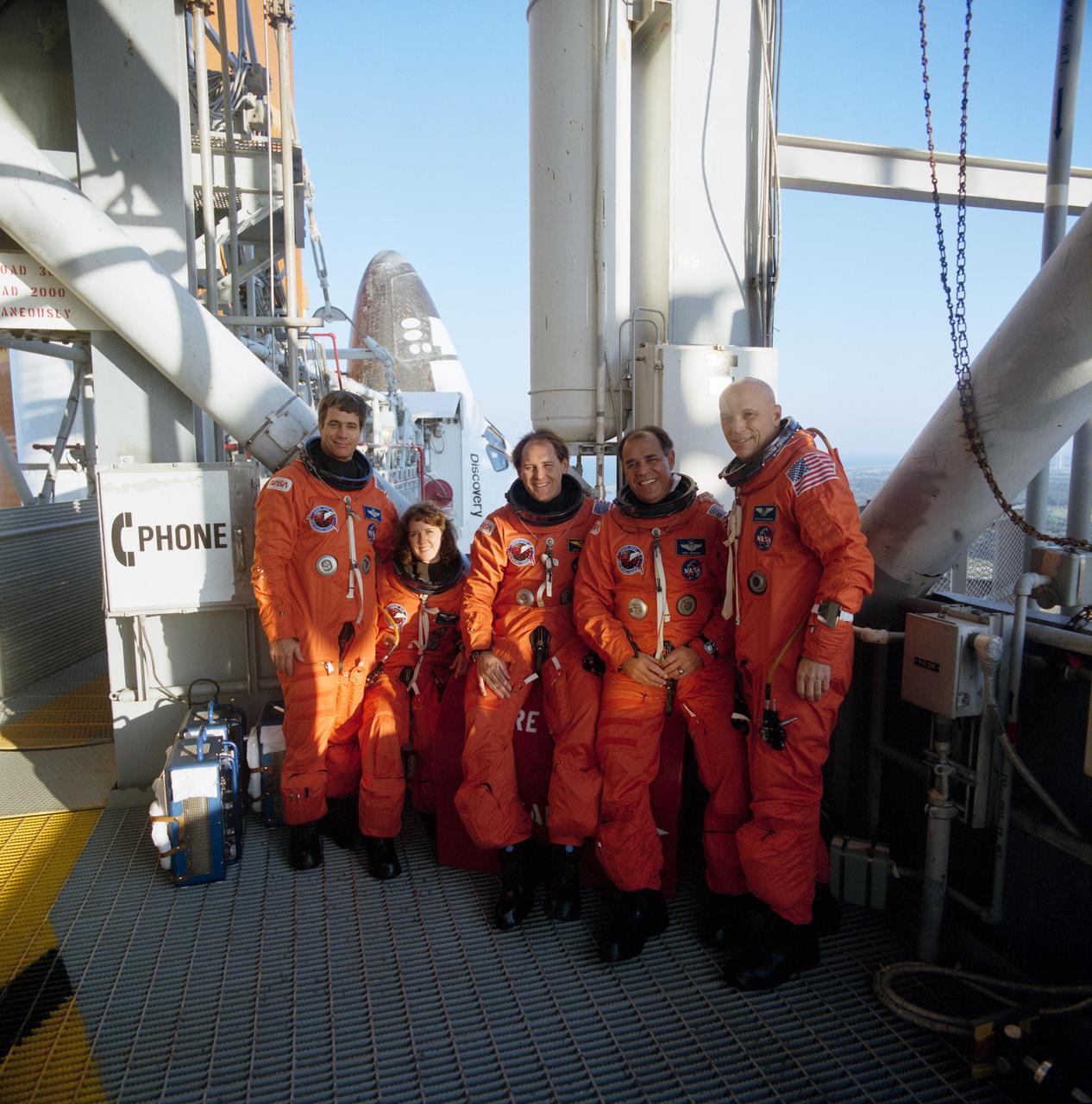
STS061-11-004 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- Traditional inflight portrait for the crew of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. On the front row are the three crew members who assisted from inside the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cabin throughout the five space walks. They are, left to right, Swiss scientist Claude Nicollier, mission specialist, along with astronauts Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot; and Richard O. Covey, mission commander. Back row -- all space walkers on this flight -- are astronauts F. Story Musgrave, payload commander; Jeffrey A. Hoffman, Kathryn D. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers, all mission specialists.
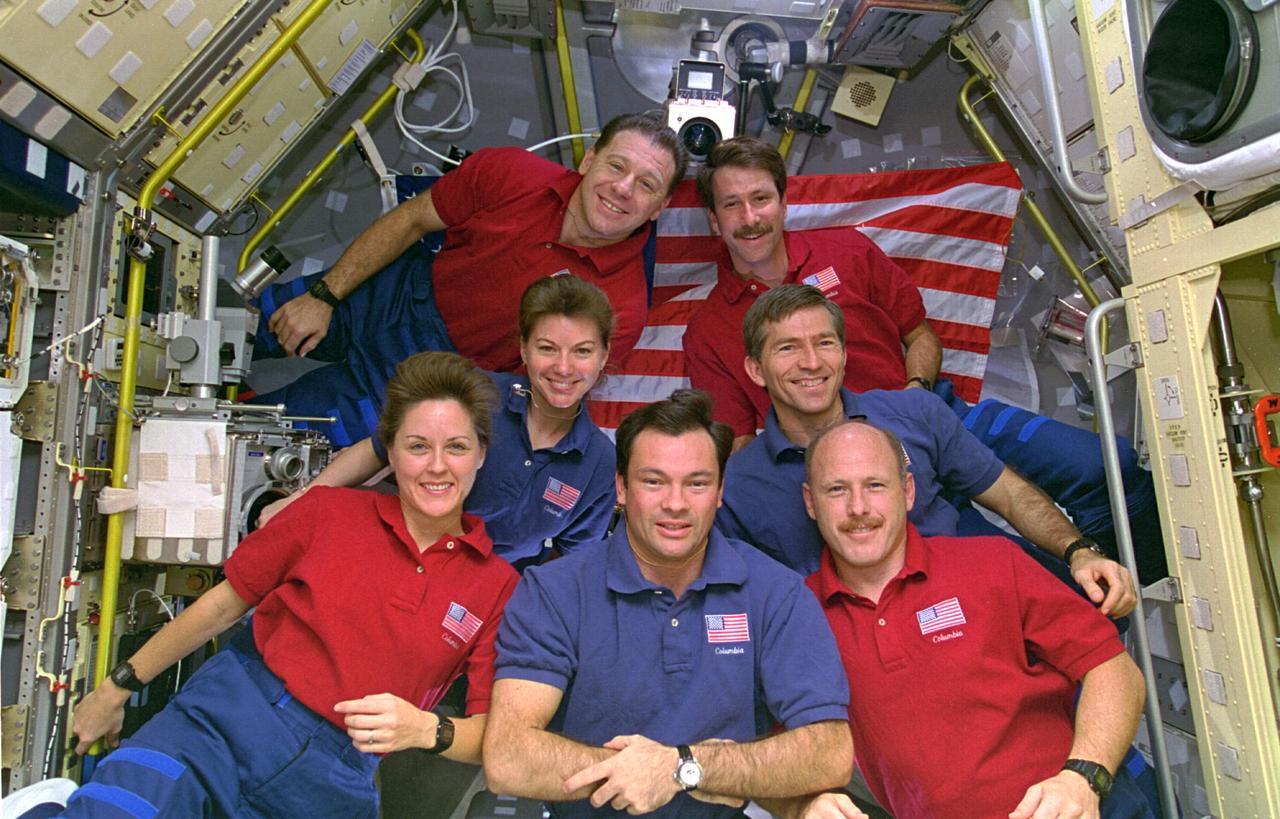

STS073-303-015 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- The crew members picked the site of their busy workdays as the setting for the traditional in-flight crew portrait, as personnel from both work shifts assembled in the science module supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission. Astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, mission specialist, has his arms folded at front center. The others pictured, counter-clockwise from that point, are Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander; Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialist; Albert Sacco, payload specialist; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; Fred W. Leslie, payload specialist; and Kenneth D. Bowersox, mission commander.
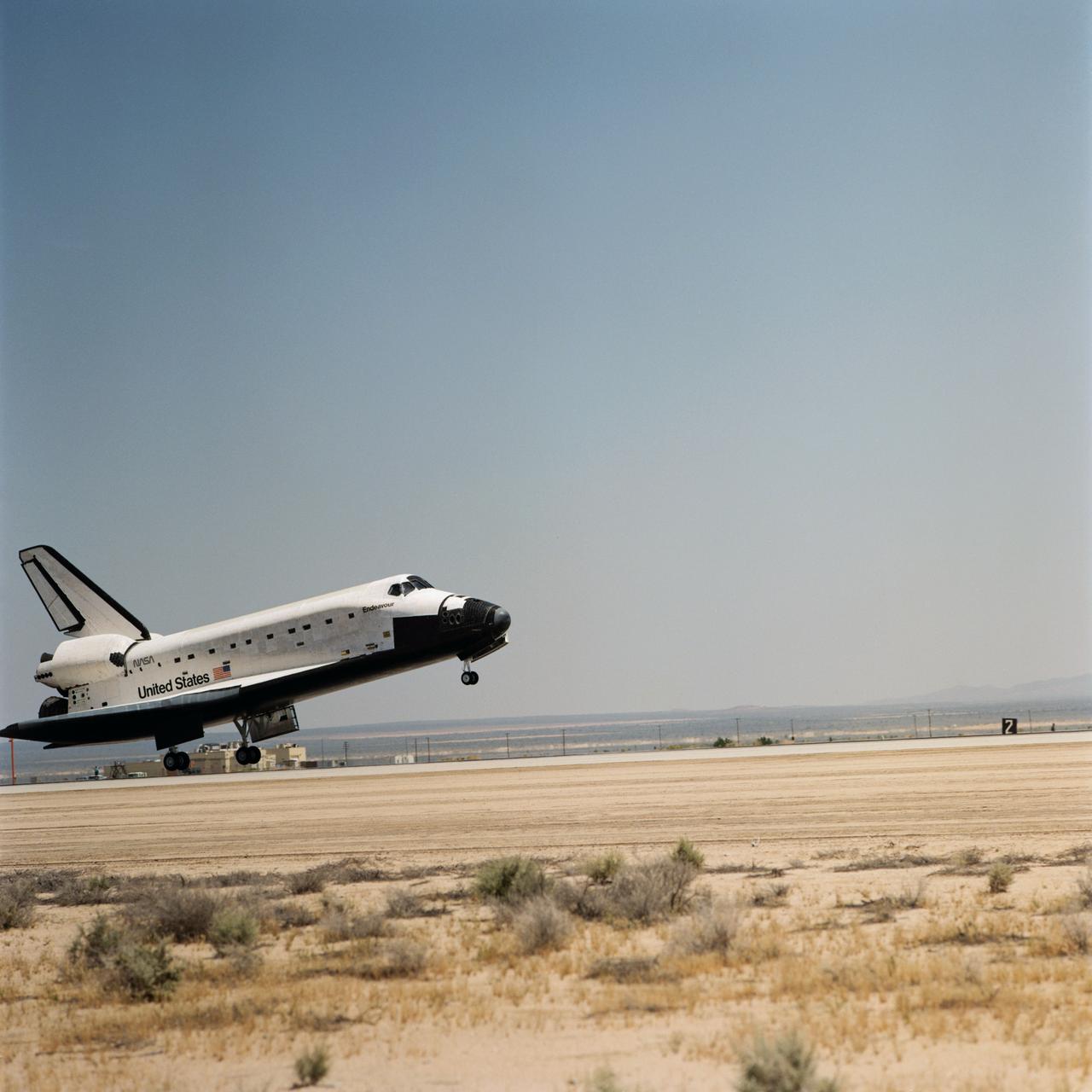

STS049-S-325 (16 May 1992) --- The main landing gear of Endeavour is just about to touch down at Edwards Air Force Base to draw to an end NASA's nine-day STS-49 mission. Crewmembers onboard were astronauts Daniel C. Brandenstein, mission commander; Kevin P. Chilton, pilot; and Thomas D. Akers, Richard J. Hieb, Bruce E. Melnick, Kathryn C. Thornton and Pierre J. Thout, all mission specialists. Landing occurred at 1:36:38 p.m. (PDT), May 16, 1992.
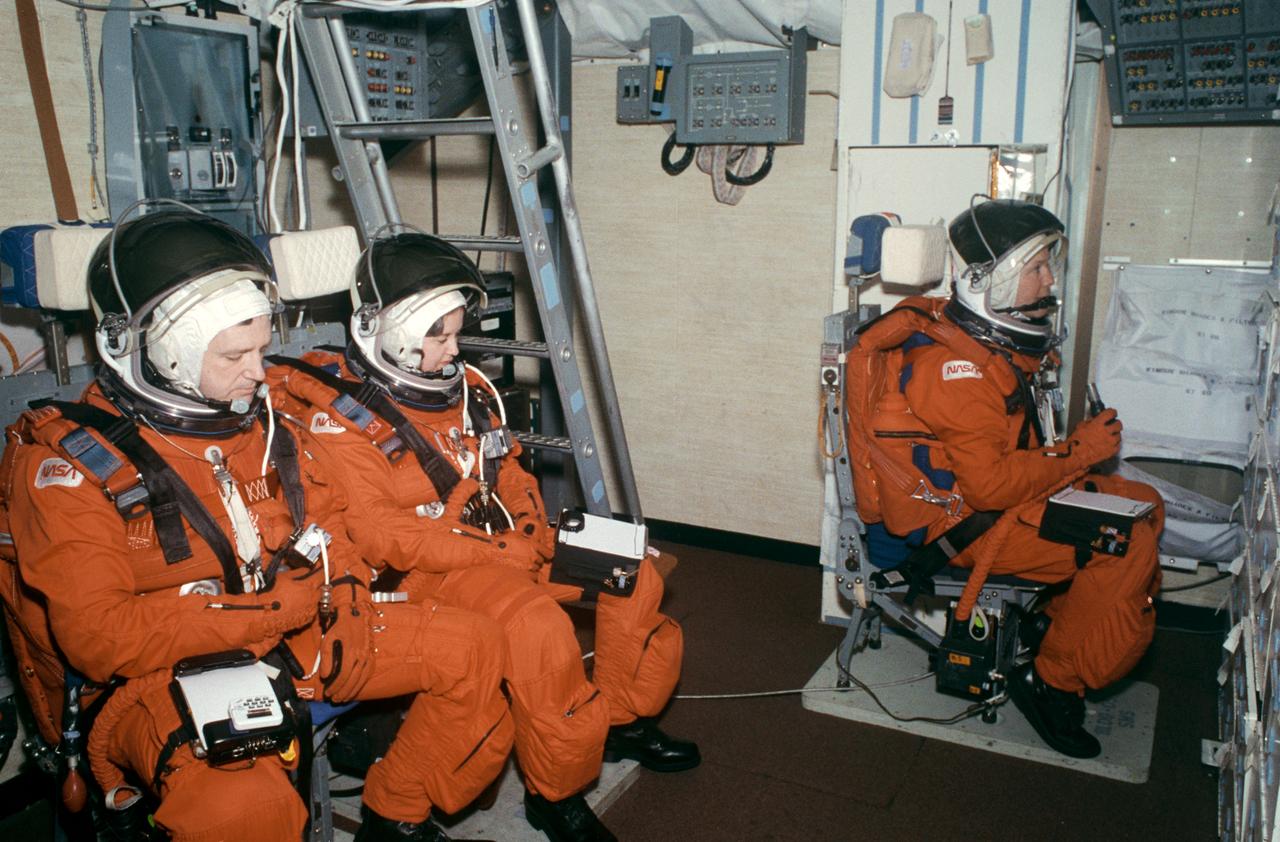

S92-29406 (Feb 1992) --- Three mission specialists assigned to the STS-49 flight occupy temporary stations on the "middeck" of a Johnson Space Center (JSC) Shuttle trainer during a rehearsal of Endeavour's launch and entry phases. Left to right are astronauts Thomas D. Akers, Kathryn C. Thornton and Pierre J. Thuot. The three, along with four other NASA astronauts, will be aboard Endeavour in May for a week-long mission during which a satellite will be retrieved and boosted toward a higher orbit and extravehicular activity evaluations for Space Station Freedom assembly techniques will be conducted.
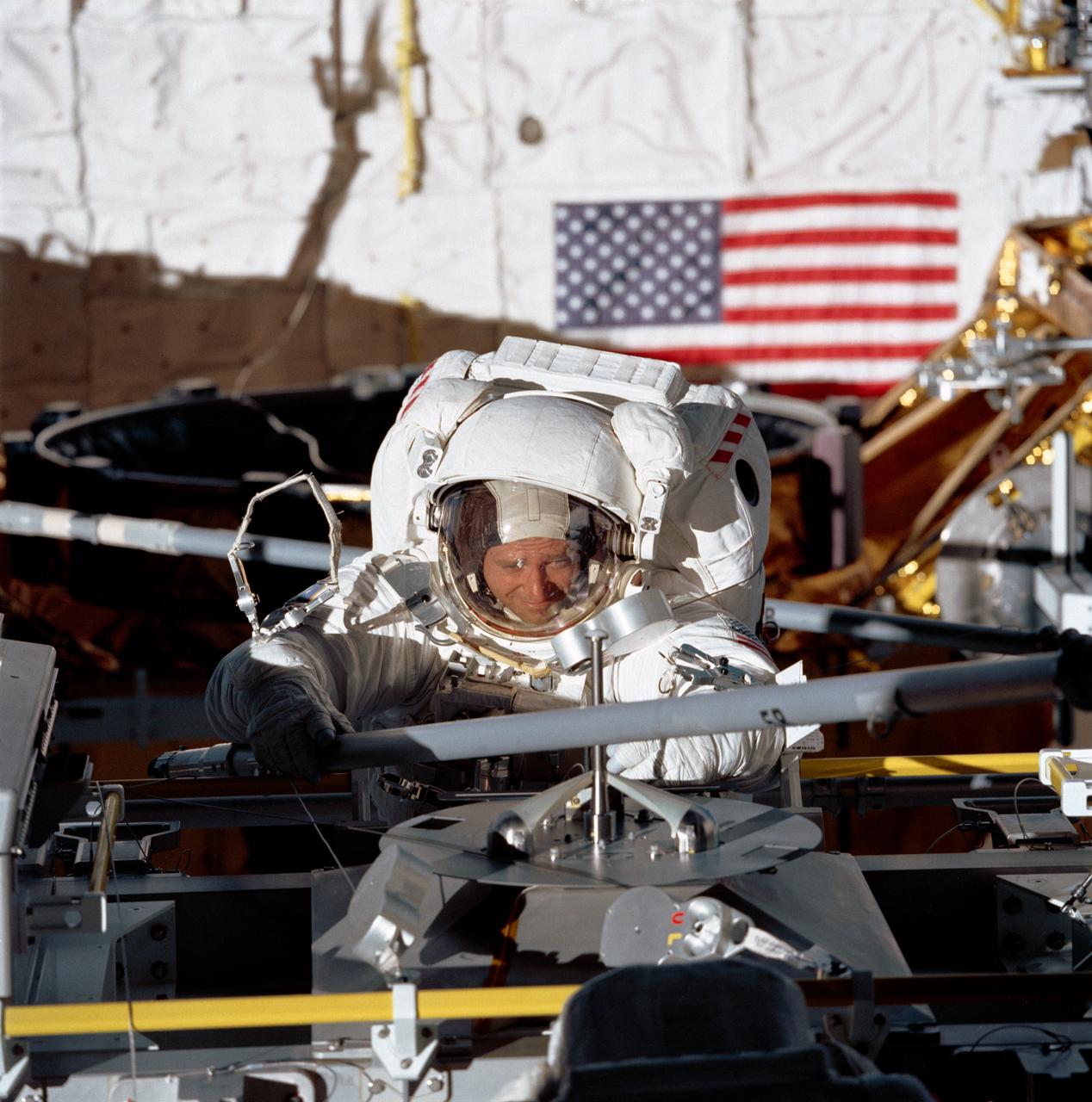

STS049-77-028 (14 May 1992) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers, STS-49 mission specialist, grabs a strut device as fourth period of extravehicular activity (EVA) gets underway in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. Akers is positioned near the Multi-purpose Support Structure (MPESS). The purpose of the final EVA on this nine-day mission was the evaluation of Assembly of Station by EVA Methods (ASEM). The scene was recorded on 70mm film by a fellow crew member in the space shuttle's cabin. Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton (out of frame) joined Akers on the 7 1/2 hour EVA.
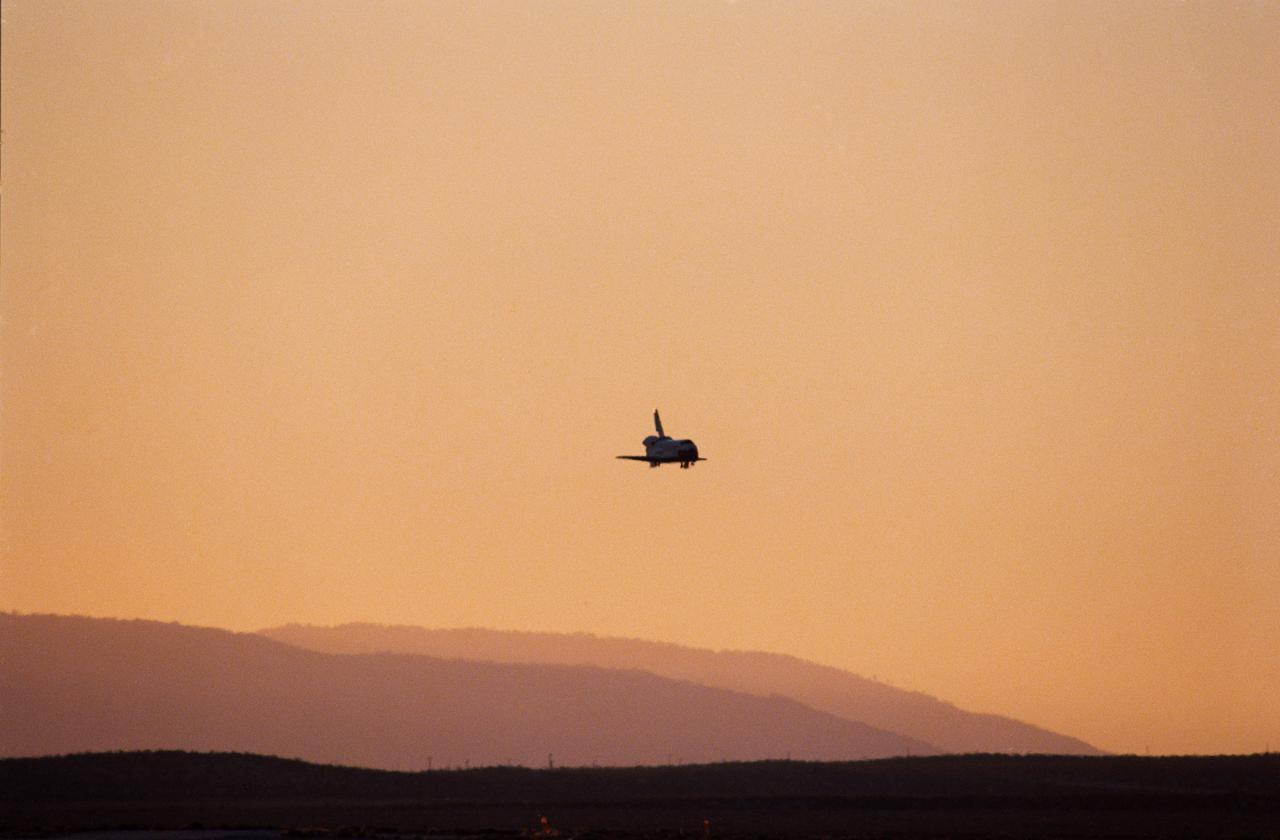

STS033-S-014 (27 Nov 1989) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery is silhouetted against late afternoon California skies as it approaches the runway for landing at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California. A five-member crew aboard was about to complete the DOD-devoted STS-33 mission. The landing occurred at 16:31:02 p.m. (PST), Nov. 27, 1989. Onboard Discovery for the mission were Astronauts Frederick D. Gregory, John E. Blaha, Kathryn C. Thornton, F. Story Musgrave and Manley L. Carter.
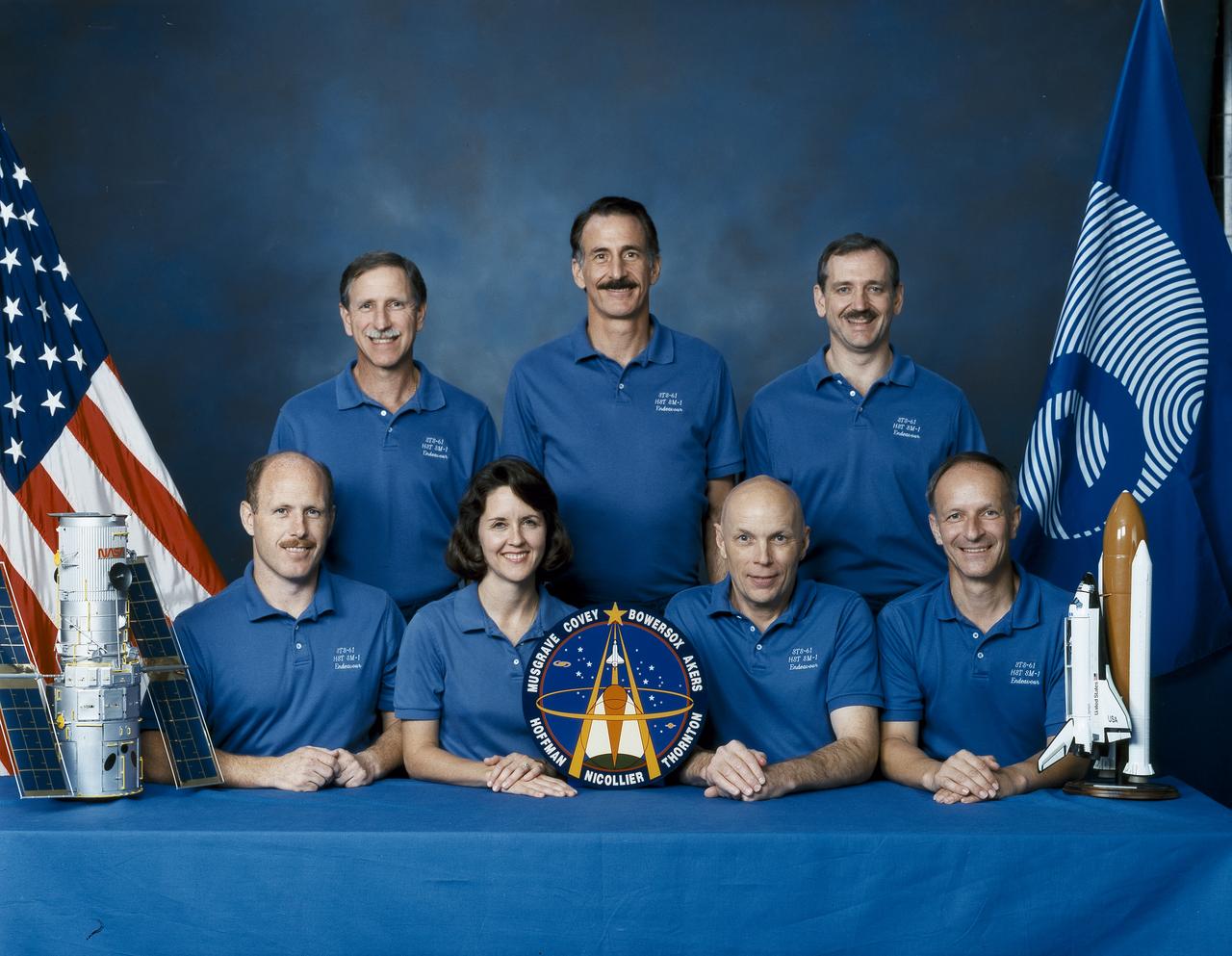

Astronauts included in the STS-61 crew portrait include (standing in rear left to right) Richard O. Covey, commander; and mission specialists Jeffrey A. Hoffman, and Thomas D. Akers. Seated left to right are Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot; Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialist; F. Story Musgrave, payload commander; and Claude Nicollier, mission specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavor on December 2, 1993 at 4:27:00 am (EST), the STS-61 mission was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission, and the last mission of 1993.
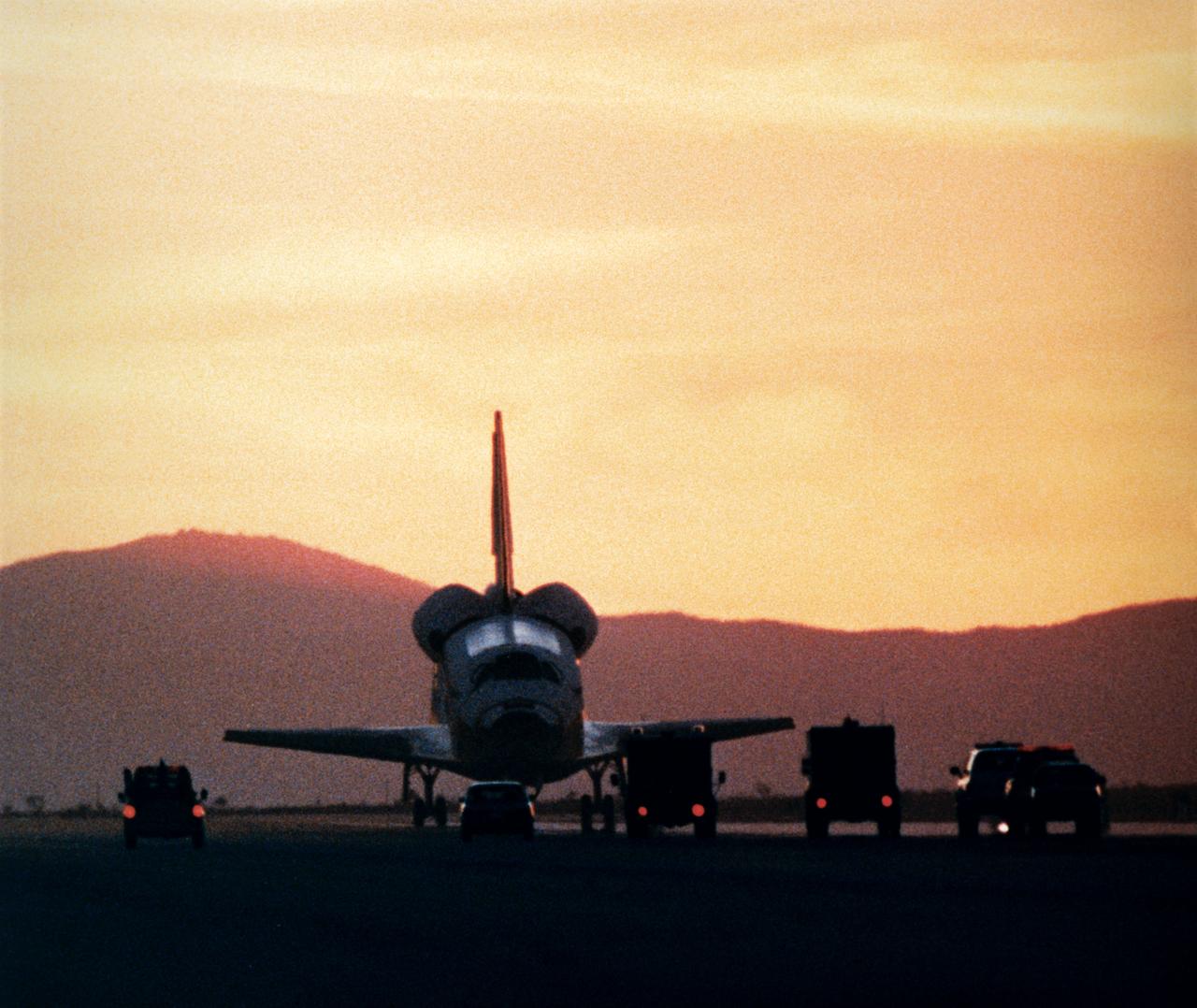

STS033-S-017 (27 Nov 1989) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery is approached by safing vehicles and team members following its late-afternoon landing at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California. A five member crew aboard had just completed the DOD-devoted STS-33 mission. The landing occurred at 16:31:02 p.m. (PST), Nov. 27, 1989. Onboard Discovery for the mission and still aboard the craft when this photo was made were Astronauts Frederick D. Gregory, John E. Blaha, Kathryn C. Thornton, F. Story Musgrave and Manley L. Carter.
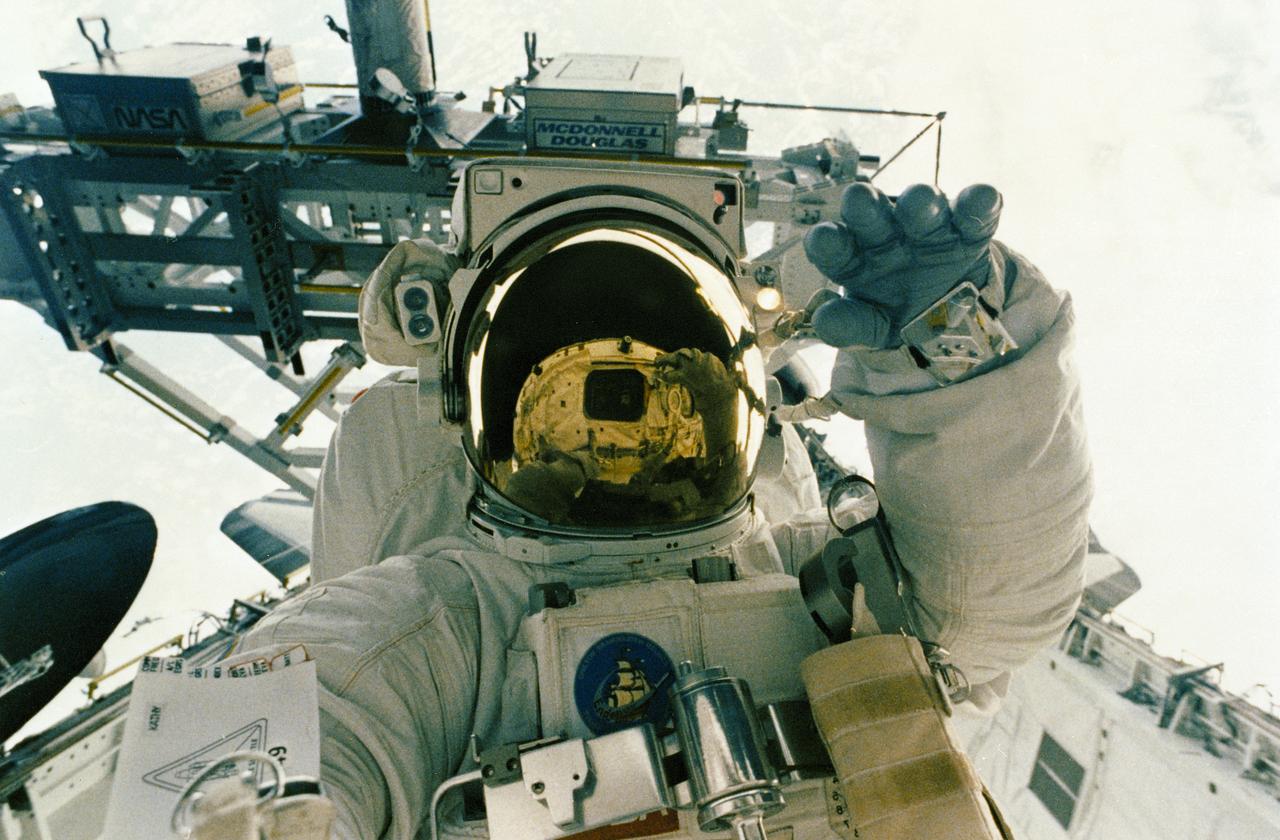

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. In this onboard photo, astronaut Kathryn Thornton is working on the Assembly of Station by EVA Methods (ASEM) in the cargo bay.

STS073-S-002 (July 1995) --- These five astronauts and two United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML) payload specialists pause from a rigid training schedule for the STS-73 crew portrait. On the front row, left to right, are Albert Sacco Jr., payload specialist; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, mission specialist. On the back row are, left to right, Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialist; Kenneth D. Bowersox, commander; Fred W. Leslie, payload specialist; and Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander.
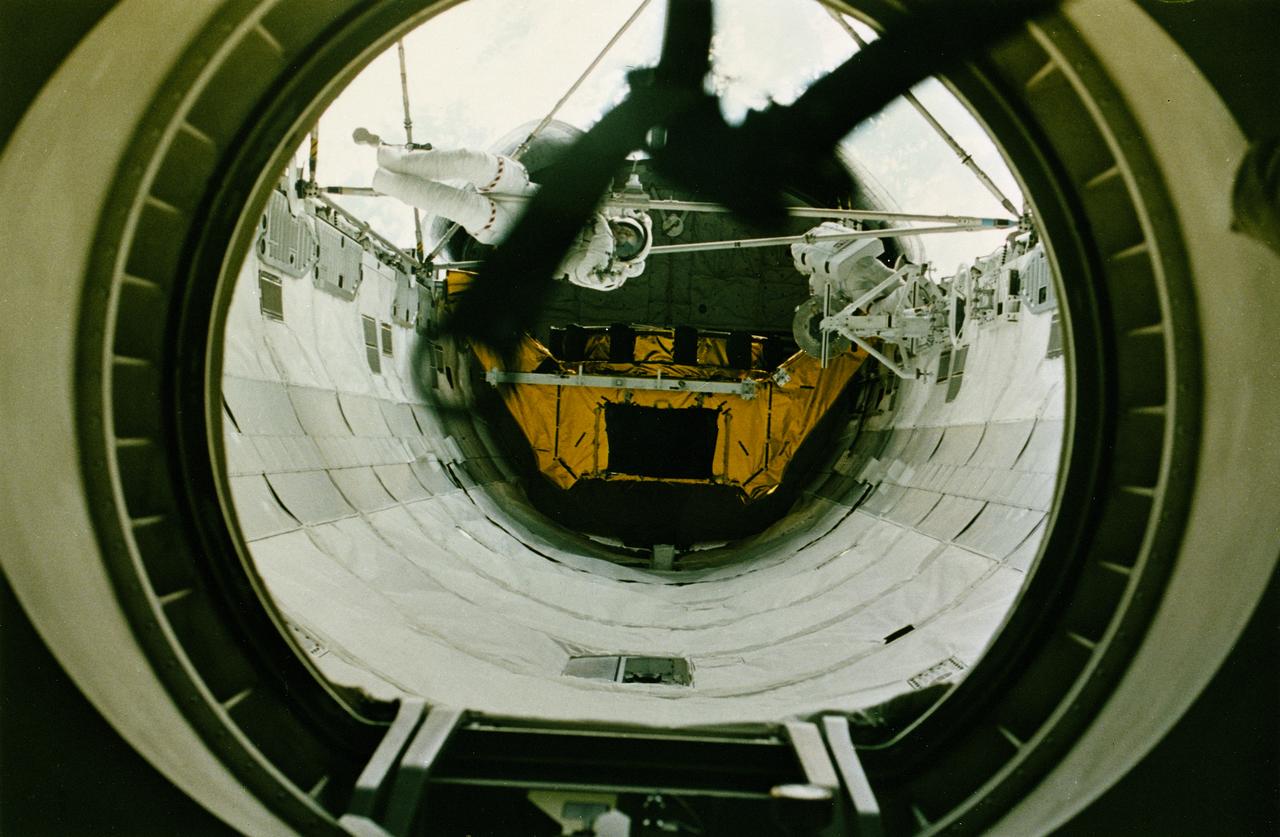

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. A view through Endeavour’s busy airlock reveals astronauts Thomas Akers and Kathryn Thornton.
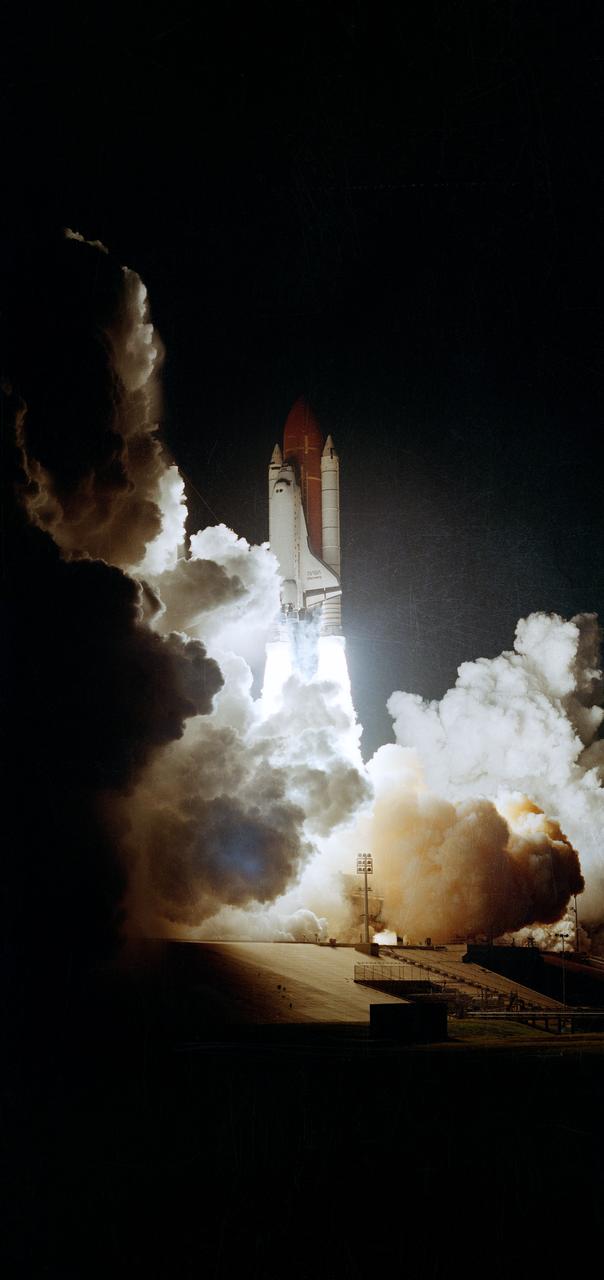

STS033-S-003 (22 Nov 1989) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery heads for Earth-orbit on the first post-Challenger nocturnal launch. Liftoff occurred at 7:23:29:989 p.m. (EST), November 22, 1989. This picture shows almost a full front view of the Space Shuttle Discovery, its two Solid Rocket Boosters (SRB) and the External Tank (ET). Onboard for the Department of the Defense (DOD) devoted mission were astronauts Frederick D. Gregory, John E. Blaha, F. Story Musgrave, Kathryn C. Thornton and Manley L. Carter.
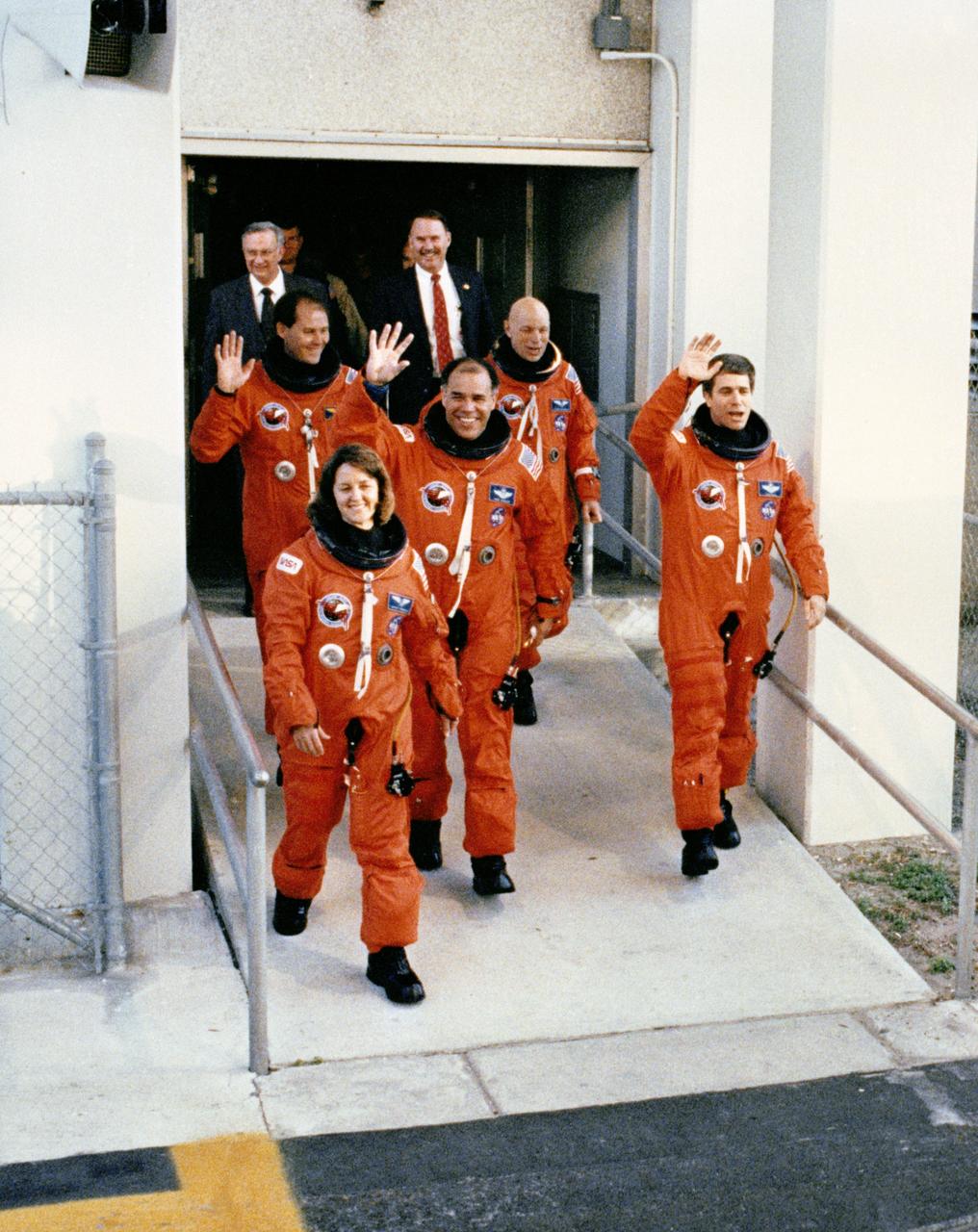

STS033-S-009 (22 Nov 1989) --- Leaving the operations and checkout building for catching a van ride to the launch pad are the five astronaut crewmembers assigned to STS-33, a DOD-devoted mission. Displaying smiles and waves for the crowd on hand are (left to right) Astronauts Manley L. Carter, Kathryn C. Thornton; Frederick D. Gregory, commander; F. Story Musgrave and John E. Blaha. Behind them are (left to right), Olan J. Bertrand, Michael L. Coats (partially obscured) and Donald R. Puddy of the Johnson Space Center (JSC).
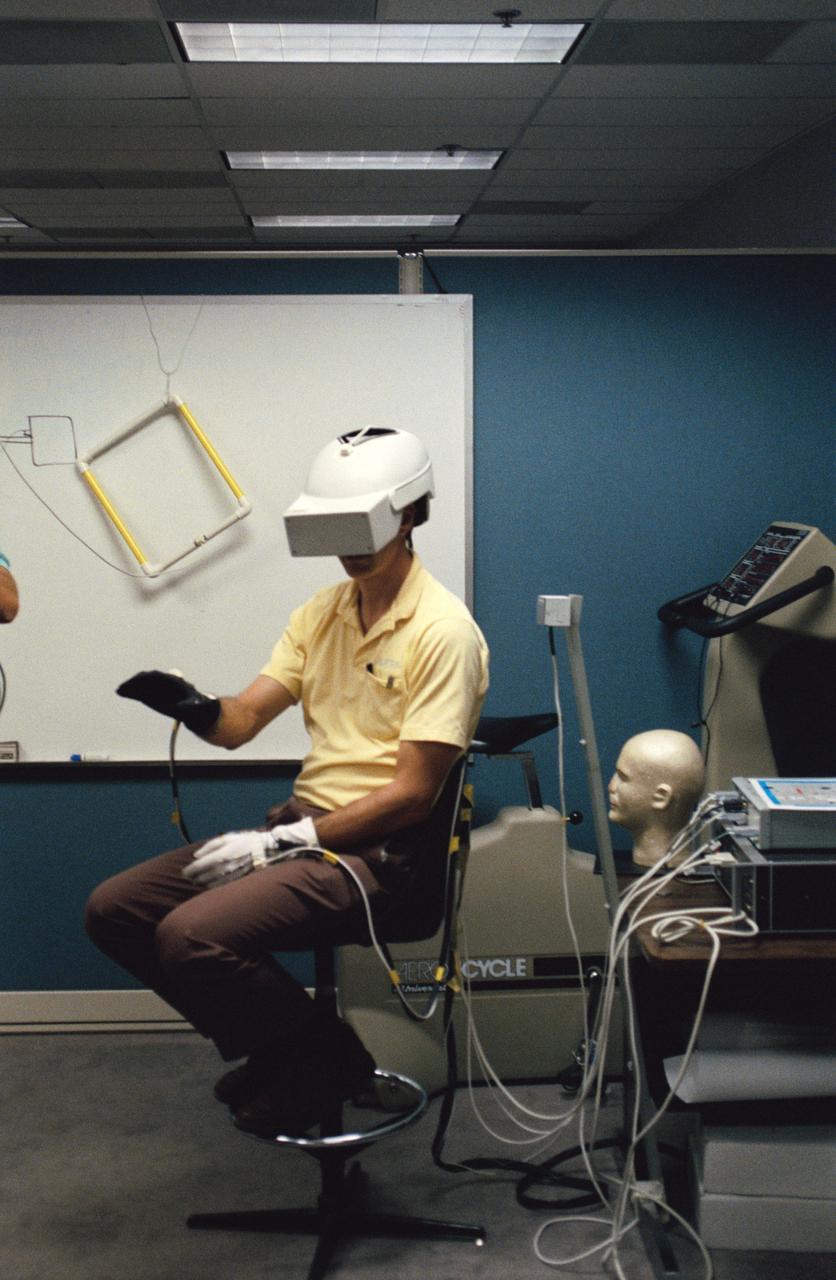
Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
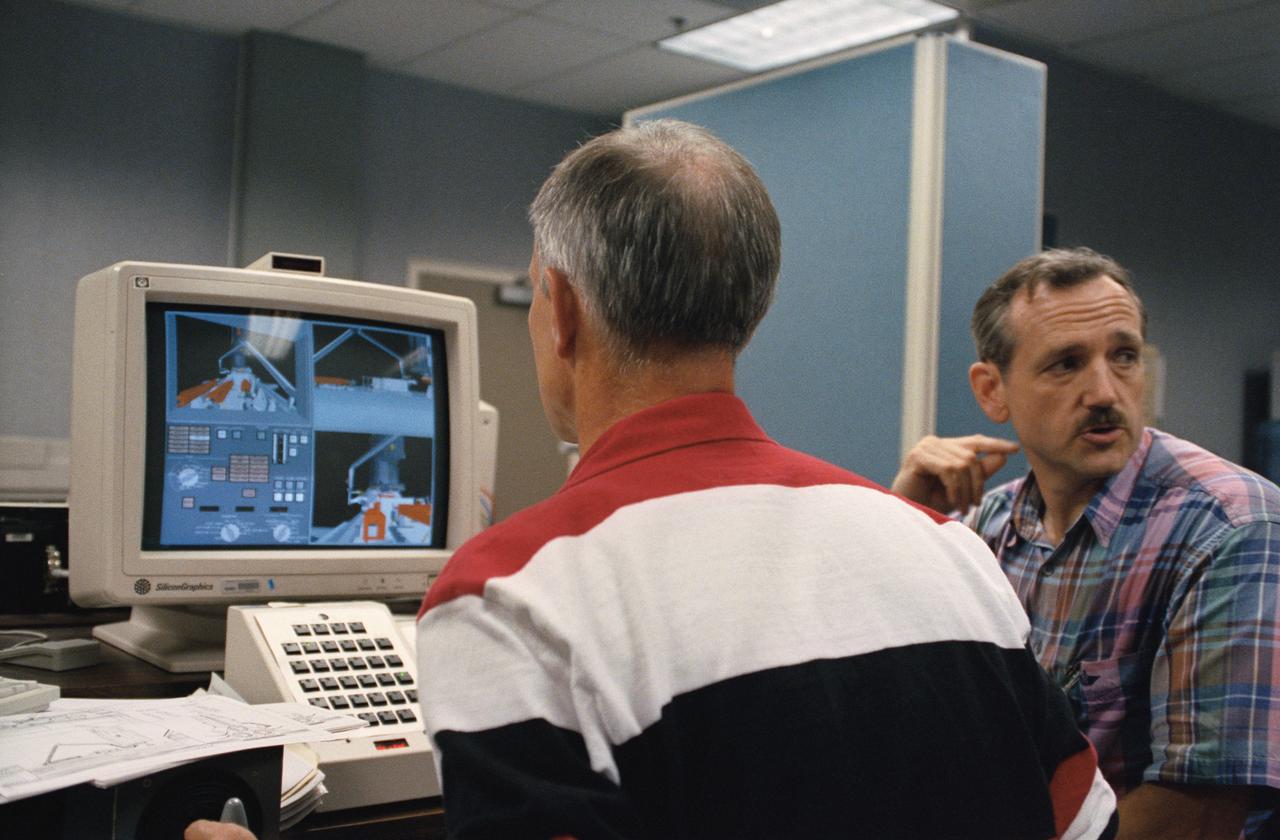

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
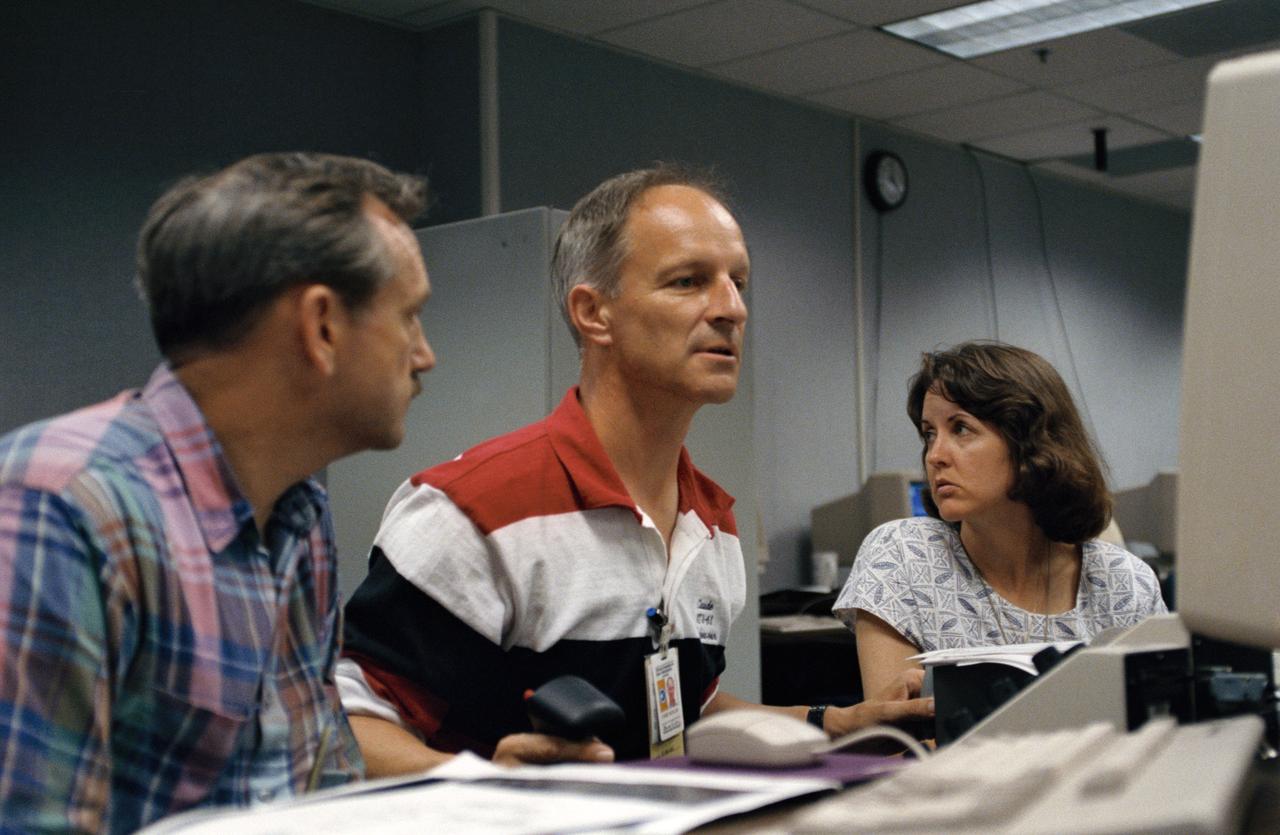

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
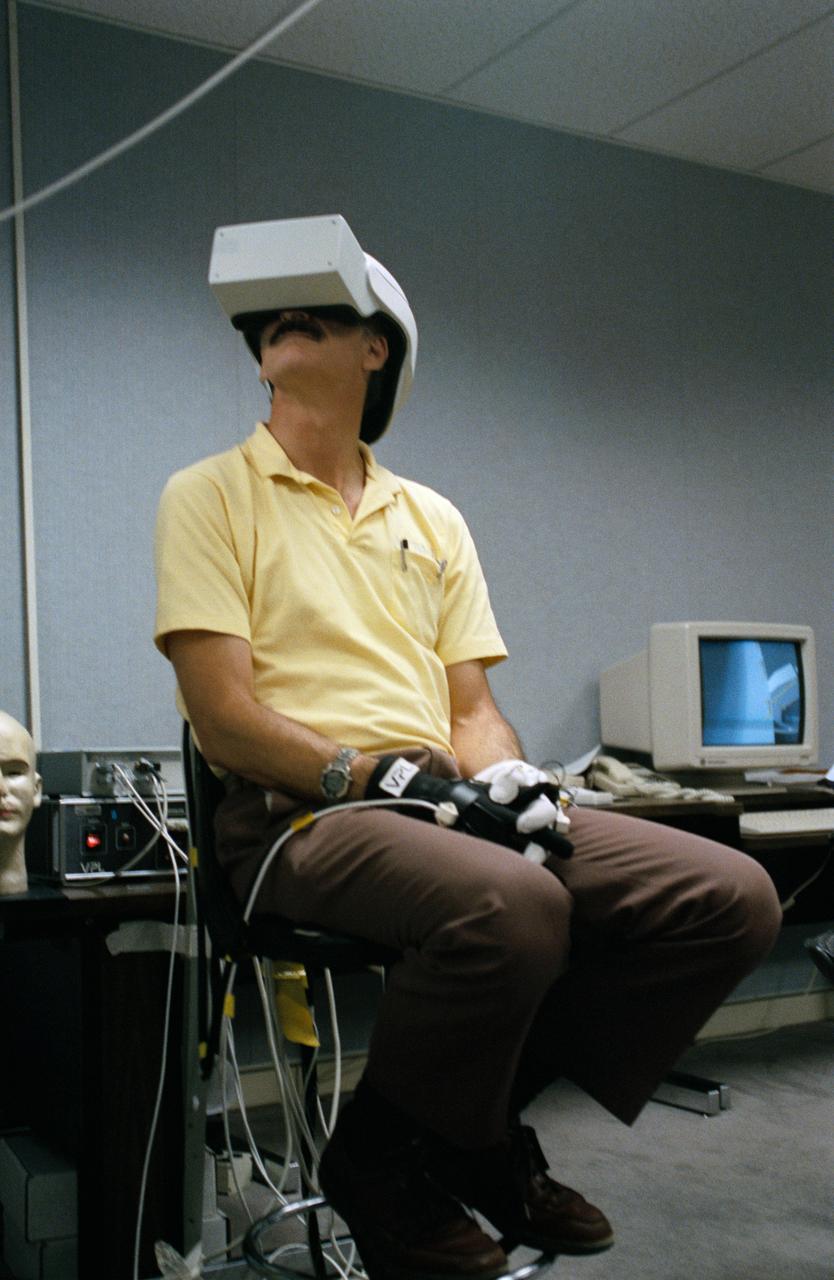

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
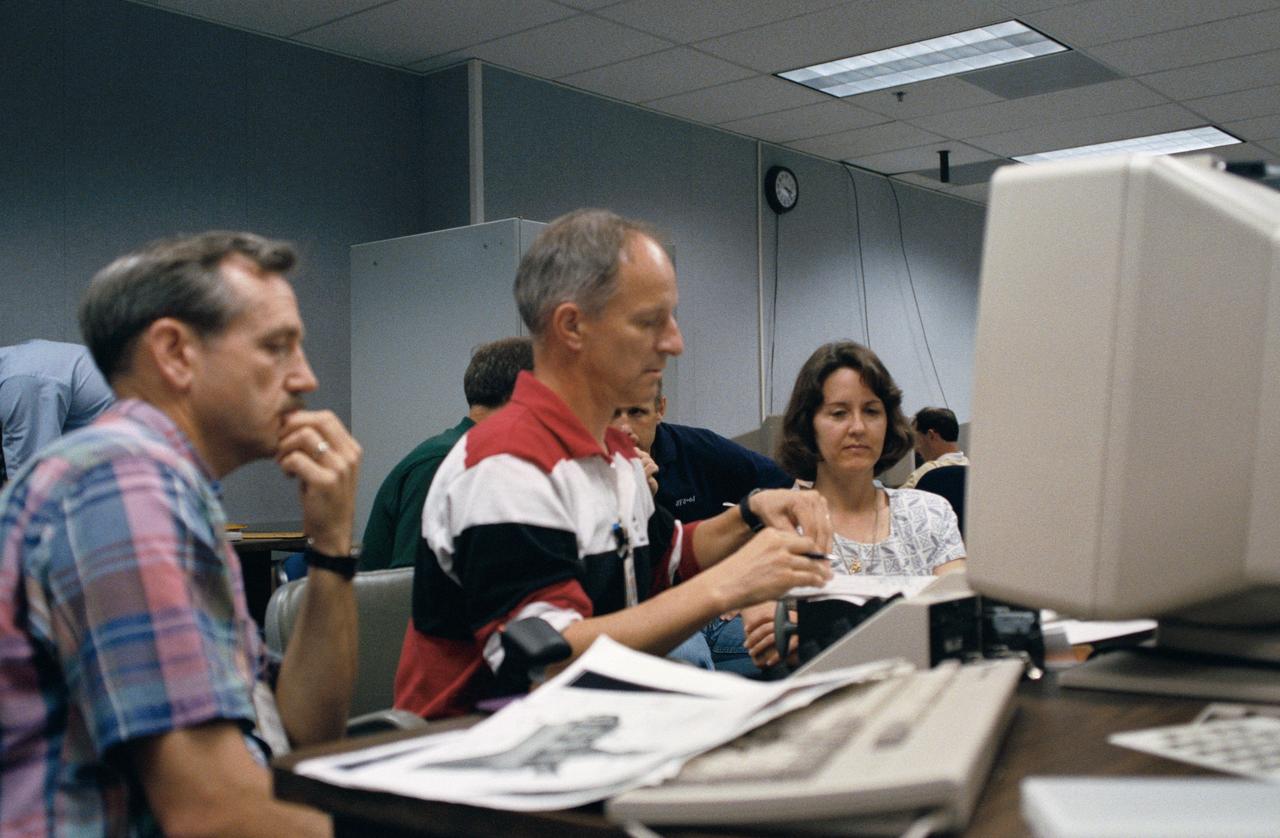

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
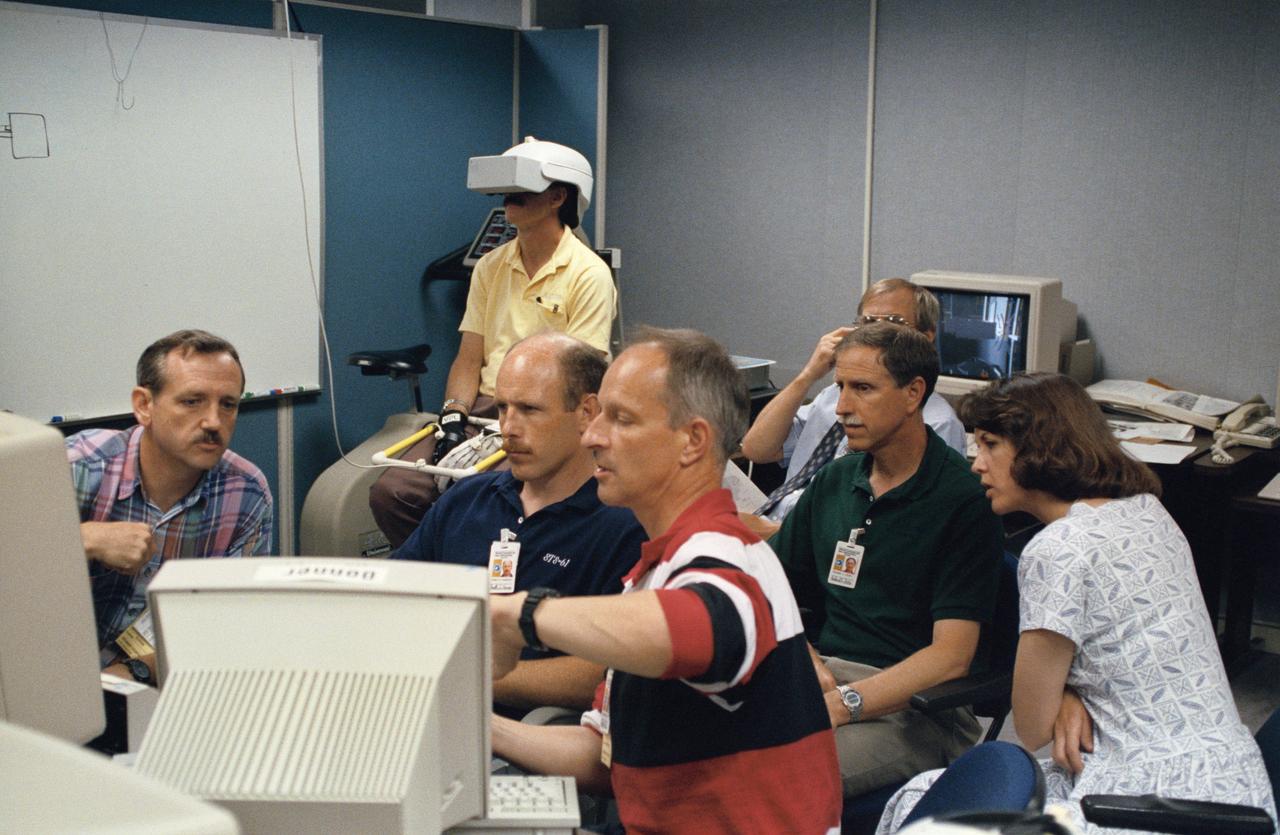

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
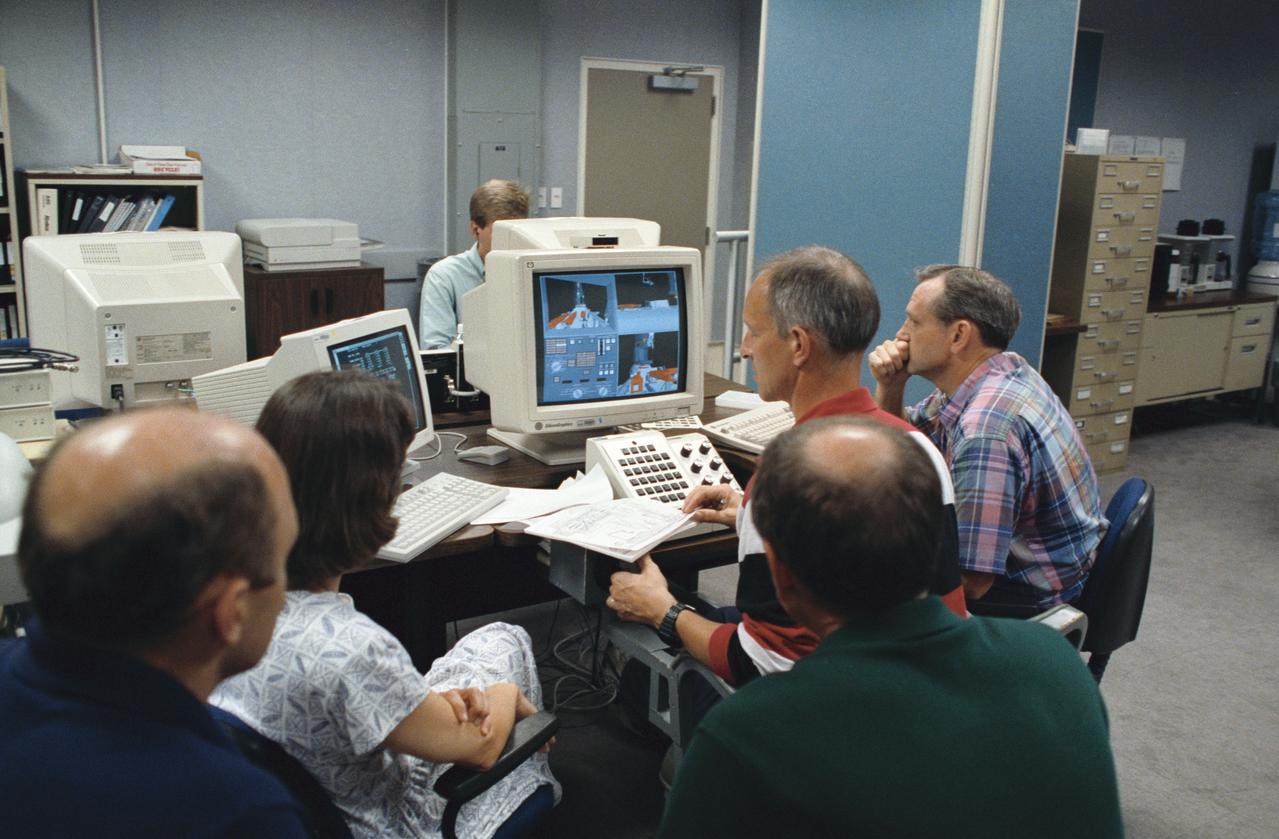

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
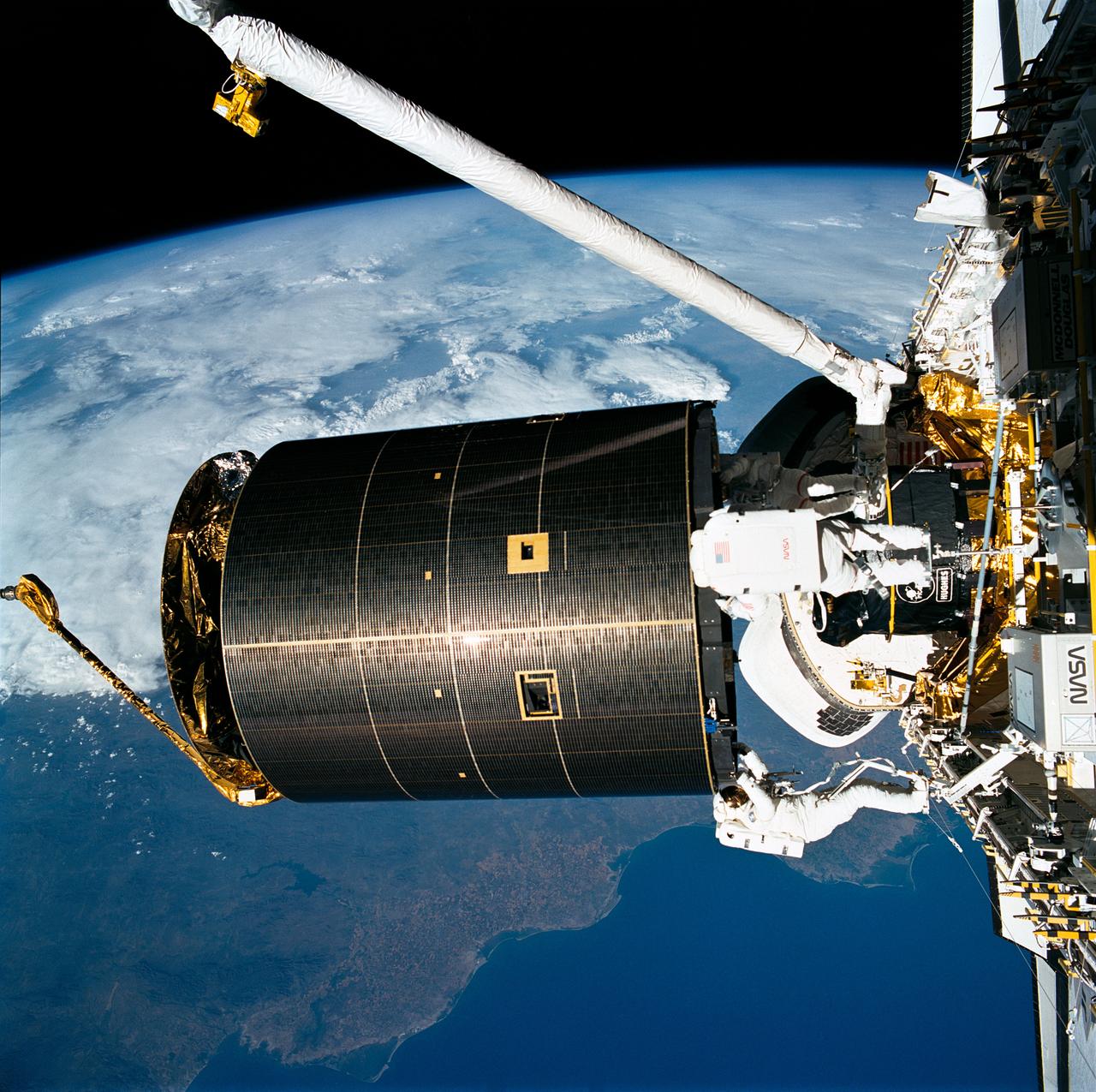

STS049-91-020 (13 May 1992) --- The successful capture of Intelsat VI satellite is recorded over Mexico on this 70mm frame, from inside the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cabin. Left to right, astronauts Richard J. Hieb, Thomas D. Akers and Pierre J. Thuot have handholds on the satellite. Ground coverage in the frame includes an area from Hermosillo, Sonara to Los Mochis in the state of Sinaloa. The nine-day mission accomplished the capture of the Intelsat, subsequent mating of the satellite to a booster and its eventual deployment, as well as a Space Station Freedom preview Extravehicular Activity (EVA). Endeavour's crew members were astronauts Daniel C. Brandenstein, mission commander; Kevin P. Chilton, pilot; and Thomas D. Akers, Richard J. Hieb, Bruce E. Melnick, Kathryn C. Thornton and Pierre J. Thuot, all mission specialists.
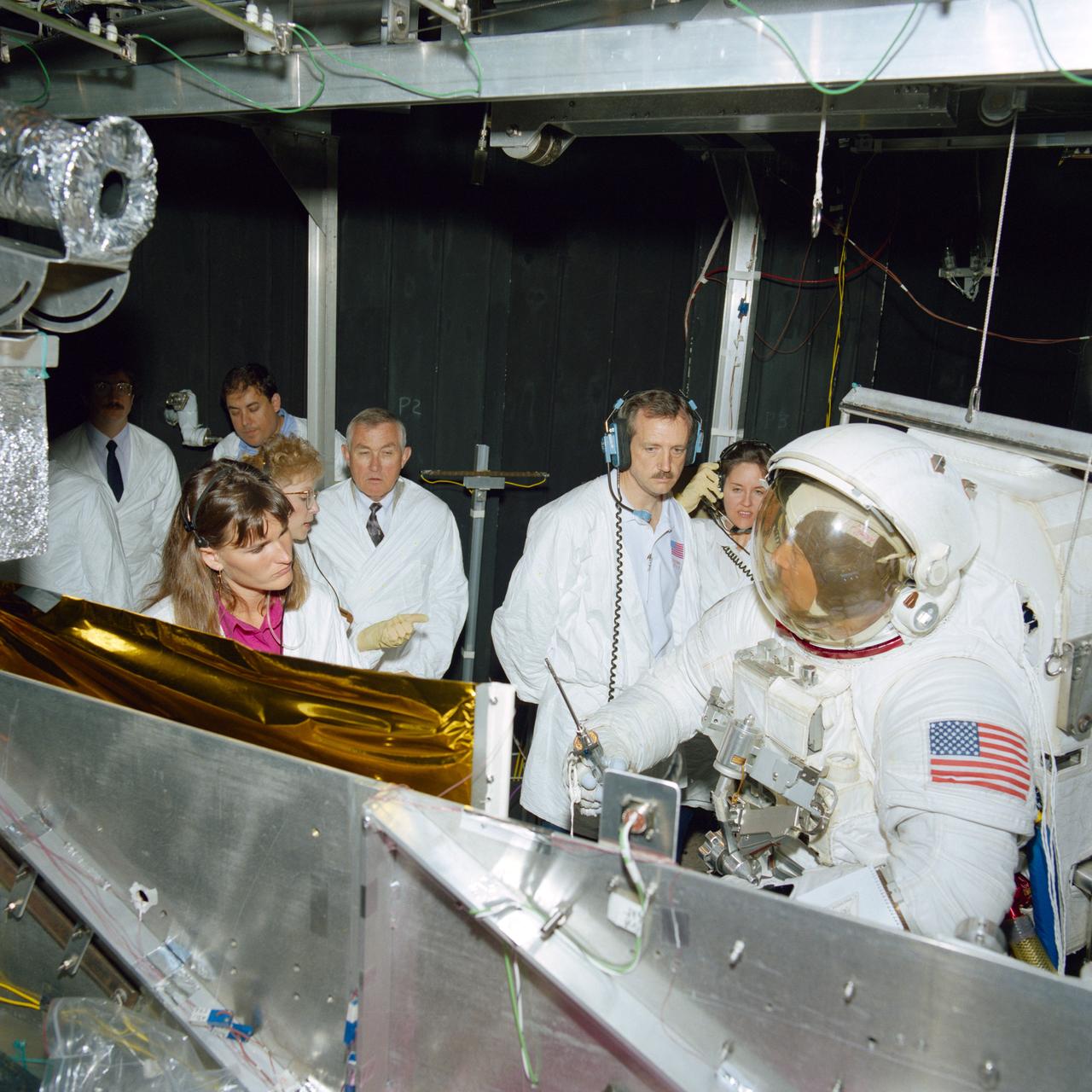

S93-34001 (26 May 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, wearing a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), participates in a dry run for tests in a thermal vacuum chamber. The payload commander will be among four suited crew members participating in task rehearsals and testing the tools that will be used on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. The test, conducted in Chamber B of the Space Environment and Simulation Laboratory (SESL) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC), verified that the tools being designed for the mission will work in the cold vacuum of space. Others pictured, from the left, are Andrea Tullar and Donna Fender, test directors; Leonard S. Nicholson, acting director of engineering; and astronauts Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists, along with Musgrave.
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seventeen new astronaut candidates visited the Vehicle Assembly Building as part of an orientation tour of KSC facilities. Here they are grouped around one of the external fuel tanks in the transfer aisle of the VAB. This latest group of candidates is the tenth chosen since the original seven Mercury astronauts. [From left, Michael J. McCulley, Curtis L. Brown Jr., Frank L. Culbertson Jr., Kathryn C. Thornton, Mark N. Brown, Mark C. Lee, Kenneth D. Cameron, John H. Casper, L. Blaine Hammond Jr., Charles Lacy Veach (deceased), James C. Adamson, William M. Shepherd, Sidney M. Gutierrez, Marsha S. Ivins, David G. Low, Michael J. Smith (deceased), Ellen S. Baker, Sonny Carter (deceased).]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/108-KSC-84P-339/108-KSC-84P-339~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seventeen new astronaut candidates visited the Vehicle Assembly Building as part of an orientation tour of KSC facilities. Here they are grouped around one of the external fuel tanks in the transfer aisle of the VAB. This latest group of candidates is the tenth chosen since the original seven Mercury astronauts. [From left, Michael J. McCulley, Curtis L. Brown Jr., Frank L. Culbertson Jr., Kathryn C. Thornton, Mark N. Brown, Mark C. Lee, Kenneth D. Cameron, John H. Casper, L. Blaine Hammond Jr., Charles Lacy Veach (deceased), James C. Adamson, William M. Shepherd, Sidney M. Gutierrez, Marsha S. Ivins, David G. Low, Michael J. Smith (deceased), Ellen S. Baker, Sonny Carter (deceased).]
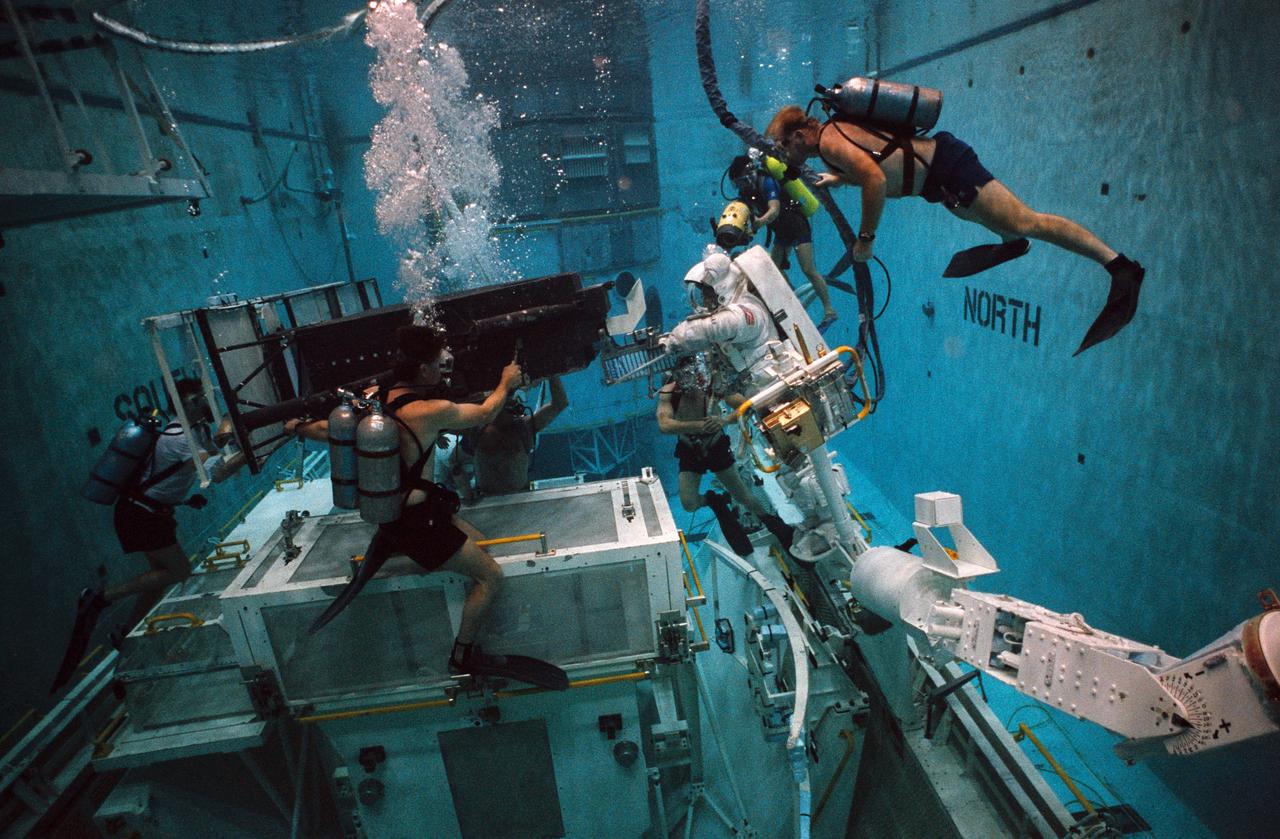

S93-33102 (5 Apr 1993) --- Wearing a training version of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Thomas D. Akers uses the giant pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. Standing on a mobile foot restraint connected to the Shuttle's robot arm, Akers works with a full-scale training version of the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC). The current WF/PC on the HST will be replaced with WF/PC-2. The giant box is a stowage area for both WF/PC facilities. Out of frame is astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, who will join Akers in STS-61 EVA. Several SCUBA-equipped divers assist in the rehearsal. A total of five extravehicular activity (EVA) sessions will be conducted during the scheduled December mission of the Endeavour.

These five astronauts and two United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML) payload specialists pause from a rigid training schedule for the STS-73 crew portrait. On the front row, left to right, are Albert Sacco Jr., payload specialist; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, mission specialist. On the back row are, left to right, Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialist; Kenneth D. Bowersox, commander; Fred W. Leslie, payload specialist; and Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander. The STS-073 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on October 20, 1995 at 9:53:00.069 am (EDT). The mission served as the second flight of the Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2).
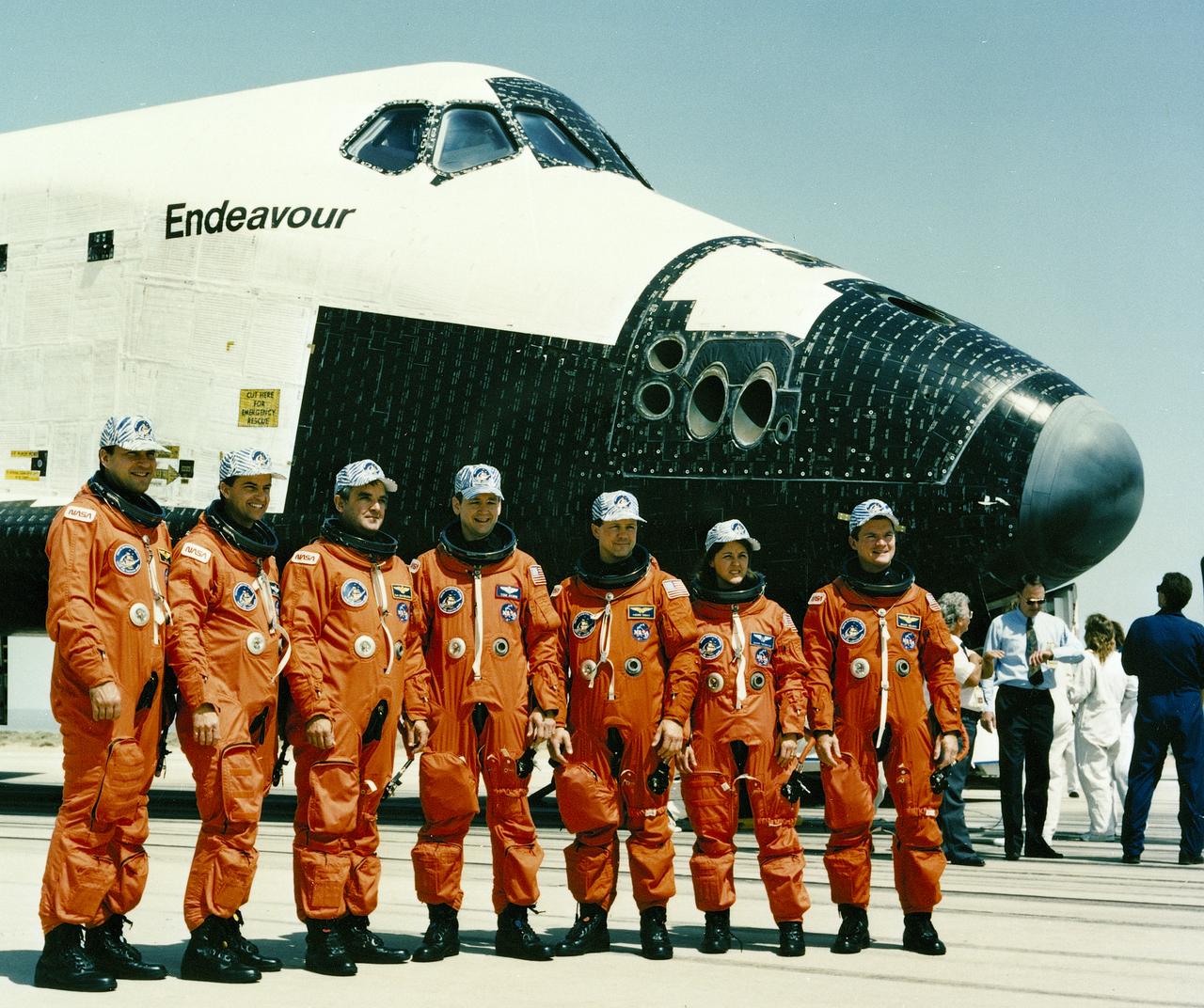

The STS-49 crew members pose near Endeavour after landing. Pictured left to right are: Richard J. Hieb, mission specialist; Kevin P. Chiltin, pilot; Daniel C. Brandenstein, commander; and mission specialists Thomas D. Akers, Pierre J. Thuot, Kathryn C. Thornton, and Bruce E. Melnick. Launched on May 7, 1992 at 7:40:00 pm (EDT), the crew of seven was the first to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavor. The mission was the first US orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members simultaneously working outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
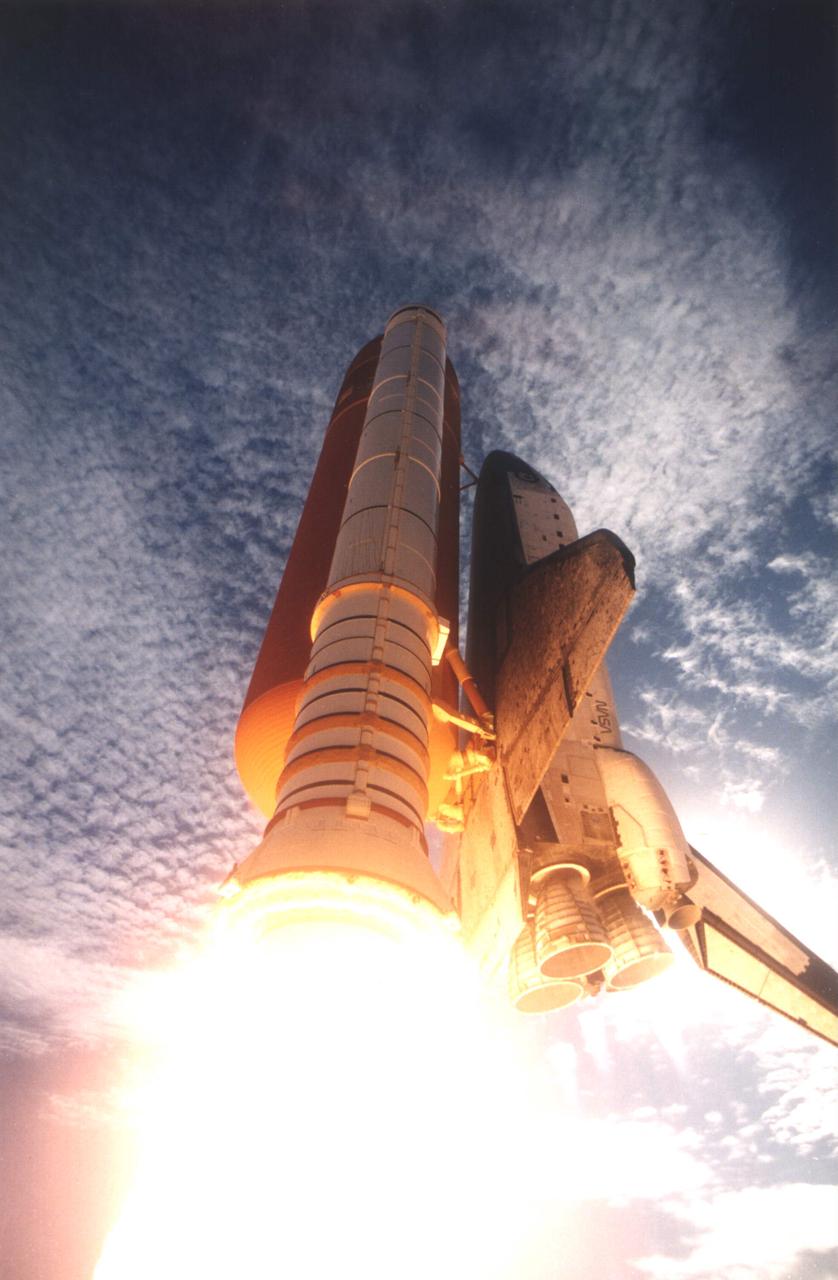

STS073-S-027 (20 October 1995) --- A 35mm camera captured this low-angle view of the Space Shuttle Columbia as it lifted off from Launch Pad 39B, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), to begin a scheduled 16-day mission in Earth-orbit in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2). Five NASA astronauts and two scientists from the private sector were onboard. Liftoff occurred at 9:53:00 a.m. (EDT) on October 20, 1995. The mission represents the 72nd Space Shuttle flight for NASA. The crew will be working around the clock on a diverse assortment of USML-2 experiments located in a science module in Columbia's cargo bay. Fields of study include fluid physics, materials science, biotechnology, combustion science and commercial space processing technologies. The crew is made up of astronauts Kenneth D. Bowersox, commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander; Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialists; along with Fred W. Leslie and Albert Sacco Jr., payload specialists.

STS073-S-029 (20 October 1995) --- A stationary 70mm camera captured this wide view of the Space Shuttle Columbia as it lifted off from Launch Pad 39B, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), to begin a scheduled 16-day mission in Earth-orbit in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2). Five NASA astronauts and two scientists from the private sector were onboard. Liftoff occurred at 9:53:00 a.m. (EDT) on October 20, 1995. The mission represents the 72nd Space Shuttle flight for NASA. The crew will be working around the clock on a diverse assortment of USML-2 experiments located in a science module in Columbia's cargo bay. Fields of study include fluid physics, materials science, biotechnology, combustion science and commercial space processing technologies. The crew is made up of astronauts Kenneth D. Bowersox, commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander; Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialists; along with Fred W. Leslie and Albert Sacco Jr., payload specialists.
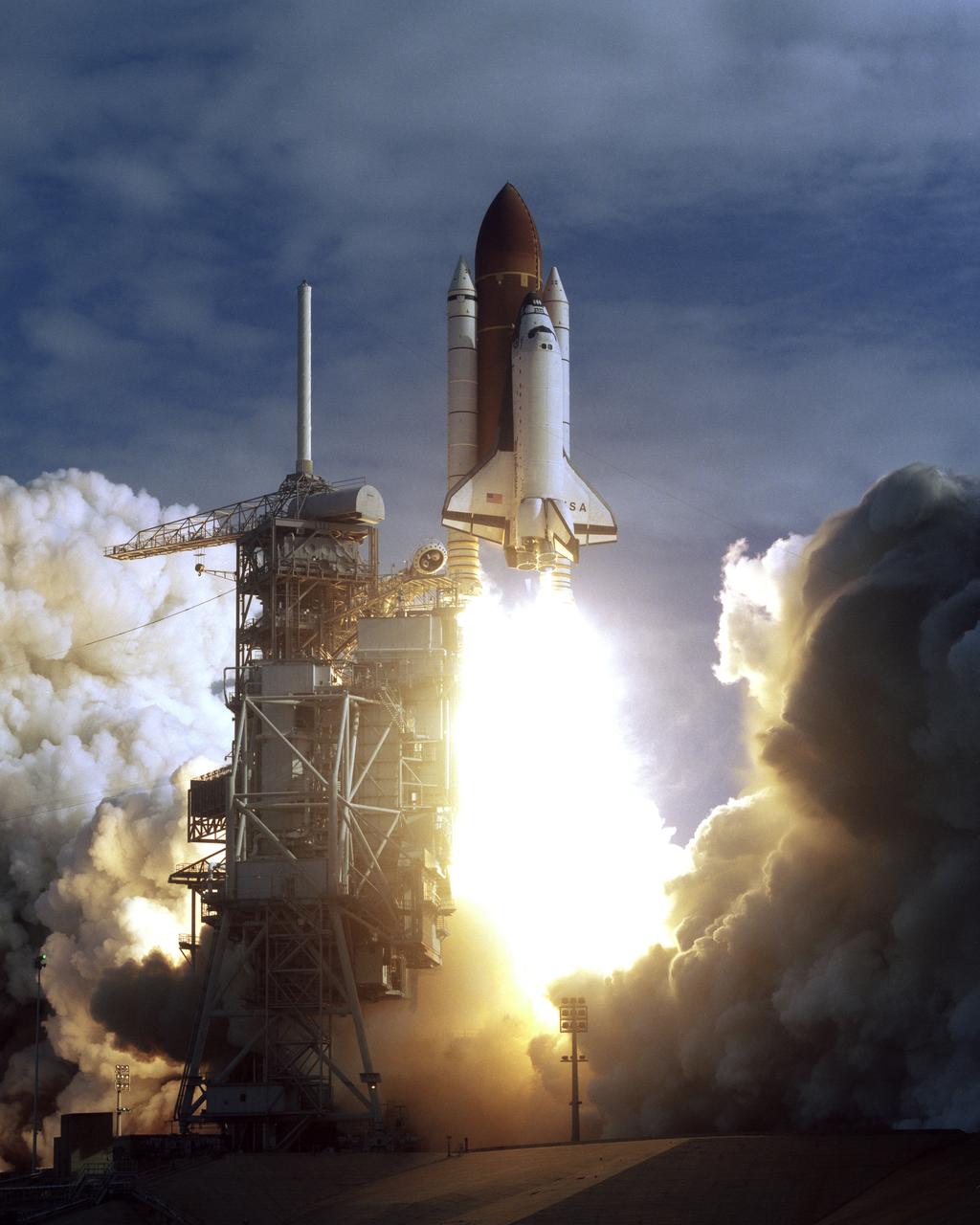

STS073-S-030 (20 Oct. 1995) --- The space shuttle Columbia lifts off from Launch Pad 39B, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), to begin a scheduled 16-day mission in Earth orbit in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2). Five NASA astronauts and two scientists from the private sector were onboard. Liftoff occurred at 9:53:00 a.m. (EDT) on Oct. 20, 1995. The mission represents the 72nd space shuttle flight for NASA. The crew will be working around the clock on a diverse assortment of USML-2 experiments located in a science module in Columbia's cargo bay. Fields of study include fluid physics, materials science, biotechnology, combustion science and commercial space processing technologies. The crew is made up of astronauts Kenneth D. Bowersox, commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander; Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Catherine G. Coleman, both mission specialists; along with Fred W. Leslie and Albert Sacco Jr., payload specialists. Photo credit: NASA