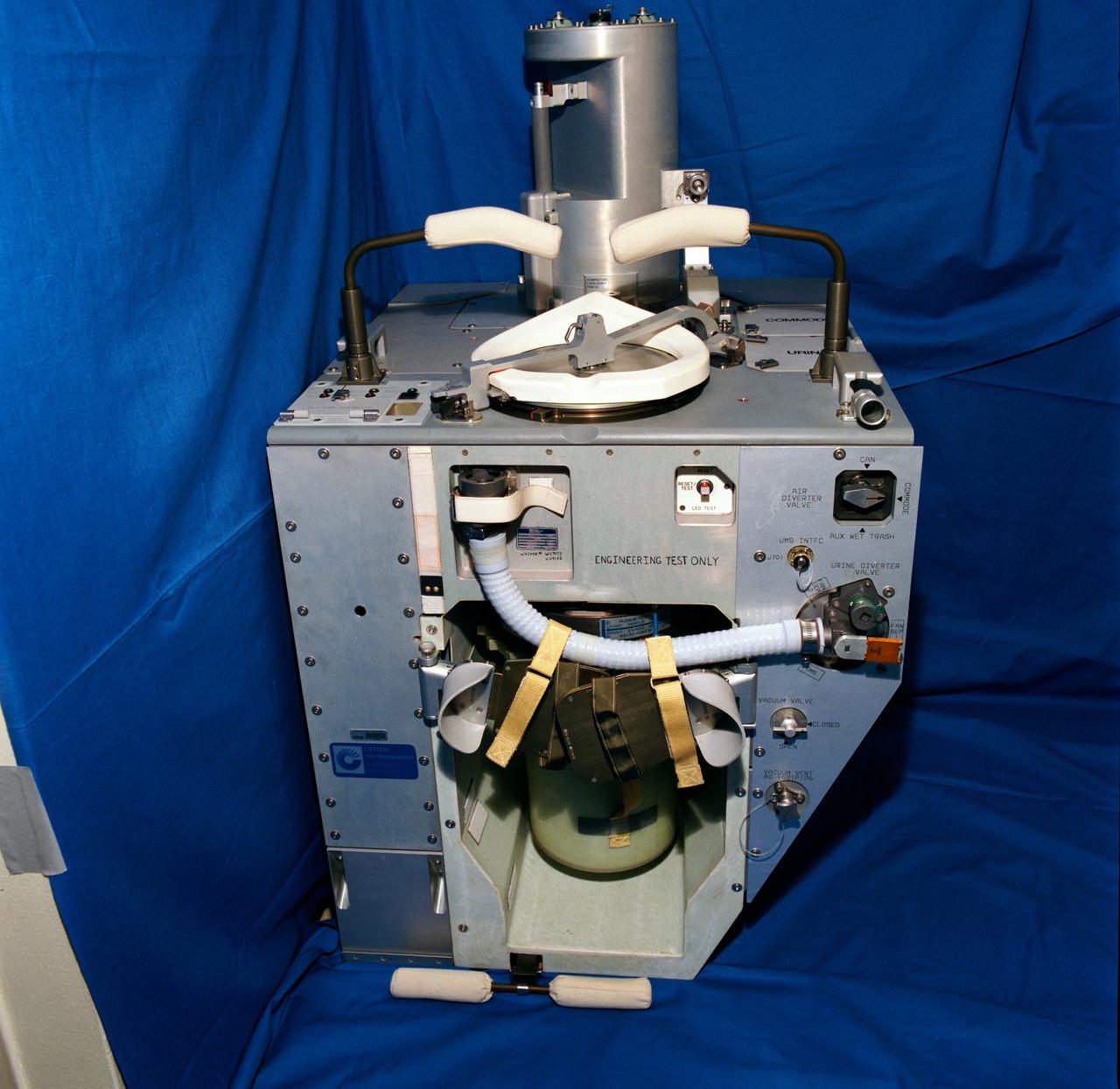

S92-46717 (November 1992) --- A front view of the improved waste collection system (IWCS) scheduled to fly aboard NASA's Space Shuttle Endeavour for the STS-54 mission. Among the advantages the new IWCS is hoped to have over the current WCS are greater dependability, better hygiene, virtually unlimited capacity and more efficient preparation between Shuttle missions. Unlike the previous WCS, the improved version will not have to be removed from the spacecraft to be readied for the next flight.
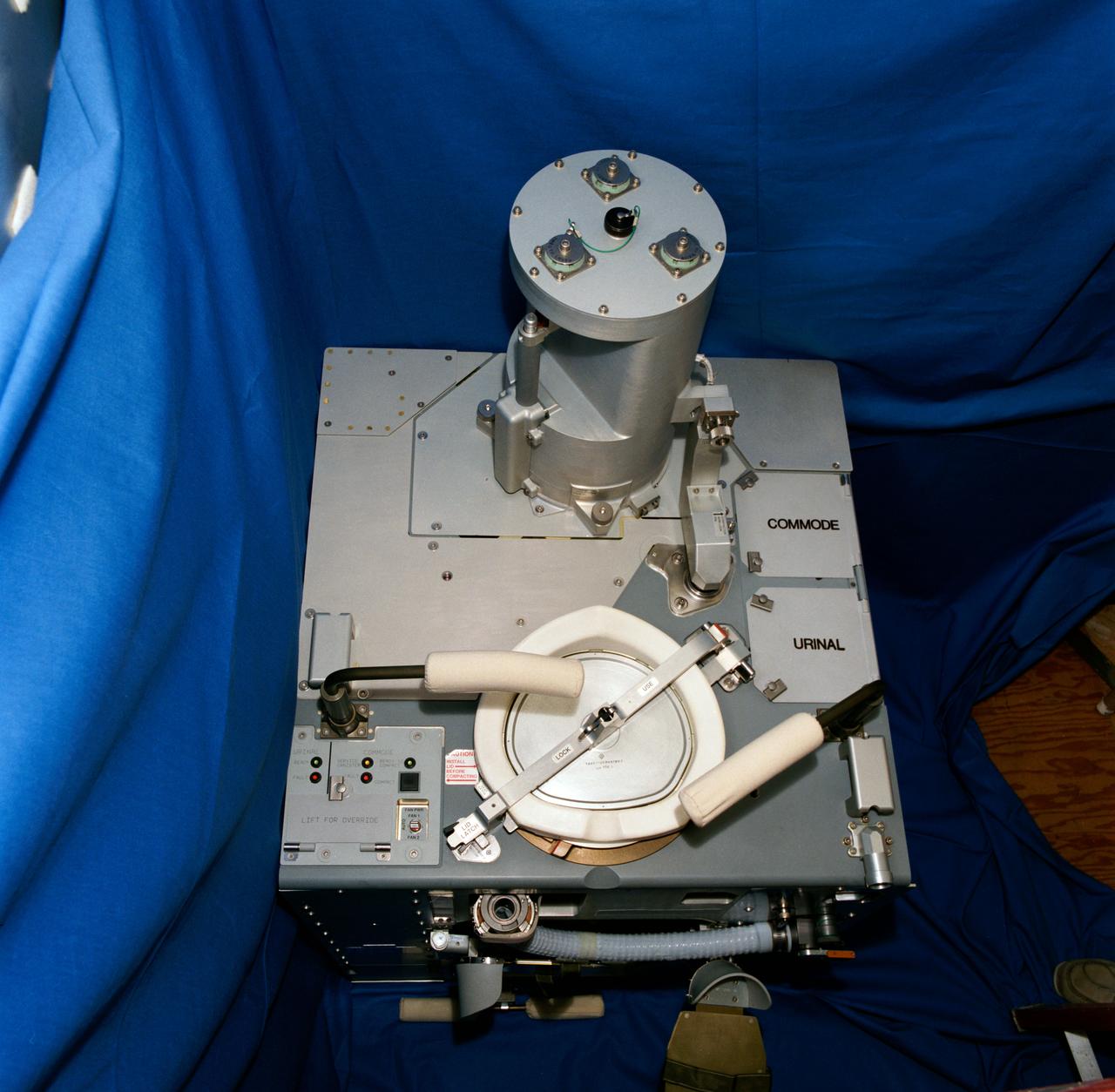

S92-46726 (November 1992) --- A high angle view of the Improved Waste Collection System (IWCS) scheduled to fly aboard NASA's Space Shuttle Endeavour for the STS-54 mission. Among the advantages the new IWCS is hoped to have over the current WCS are greater dependability, better hygiene, virtually unlimited capacity and more efficient preparation between Shuttle missions. Unlike the previous WCS, the improved version will not have to be removed from the spacecraft to be readied for the next flight.
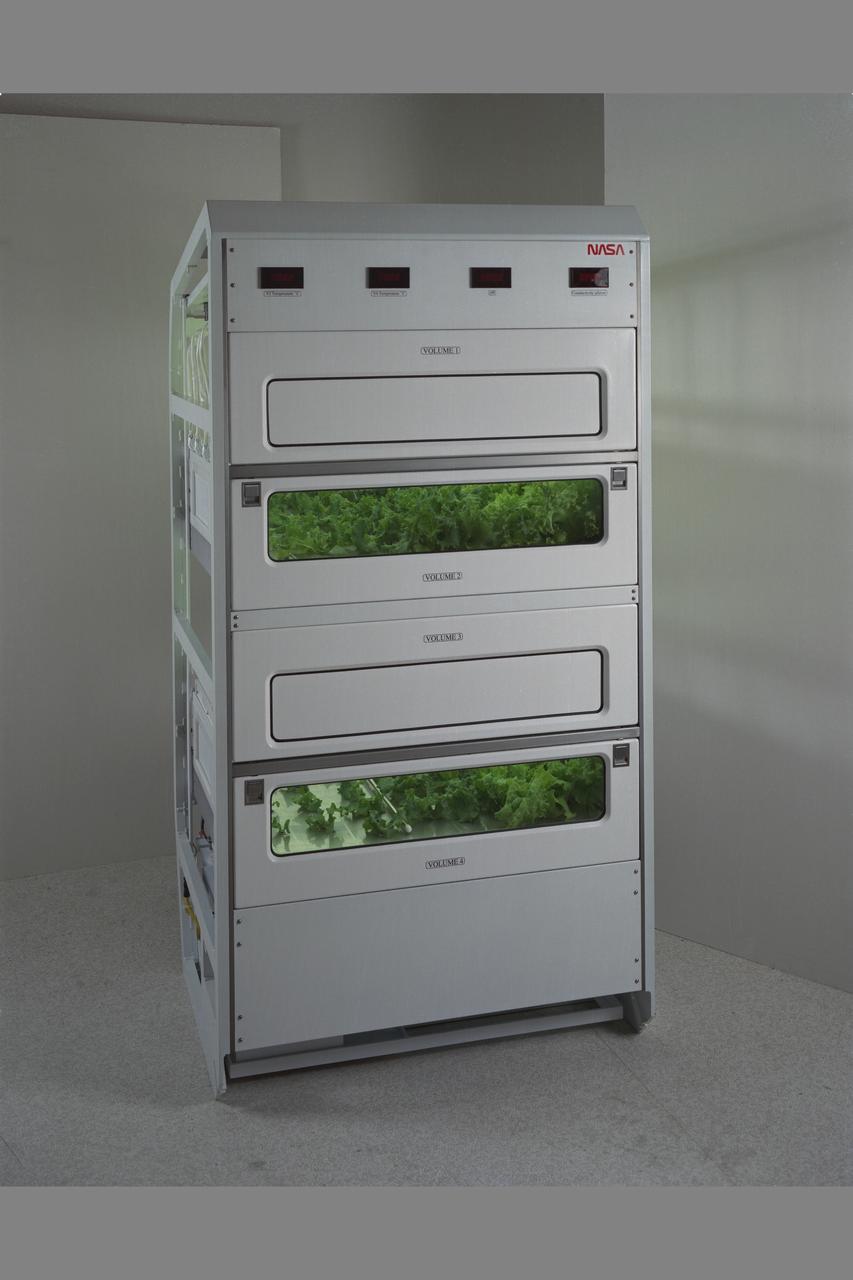

Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
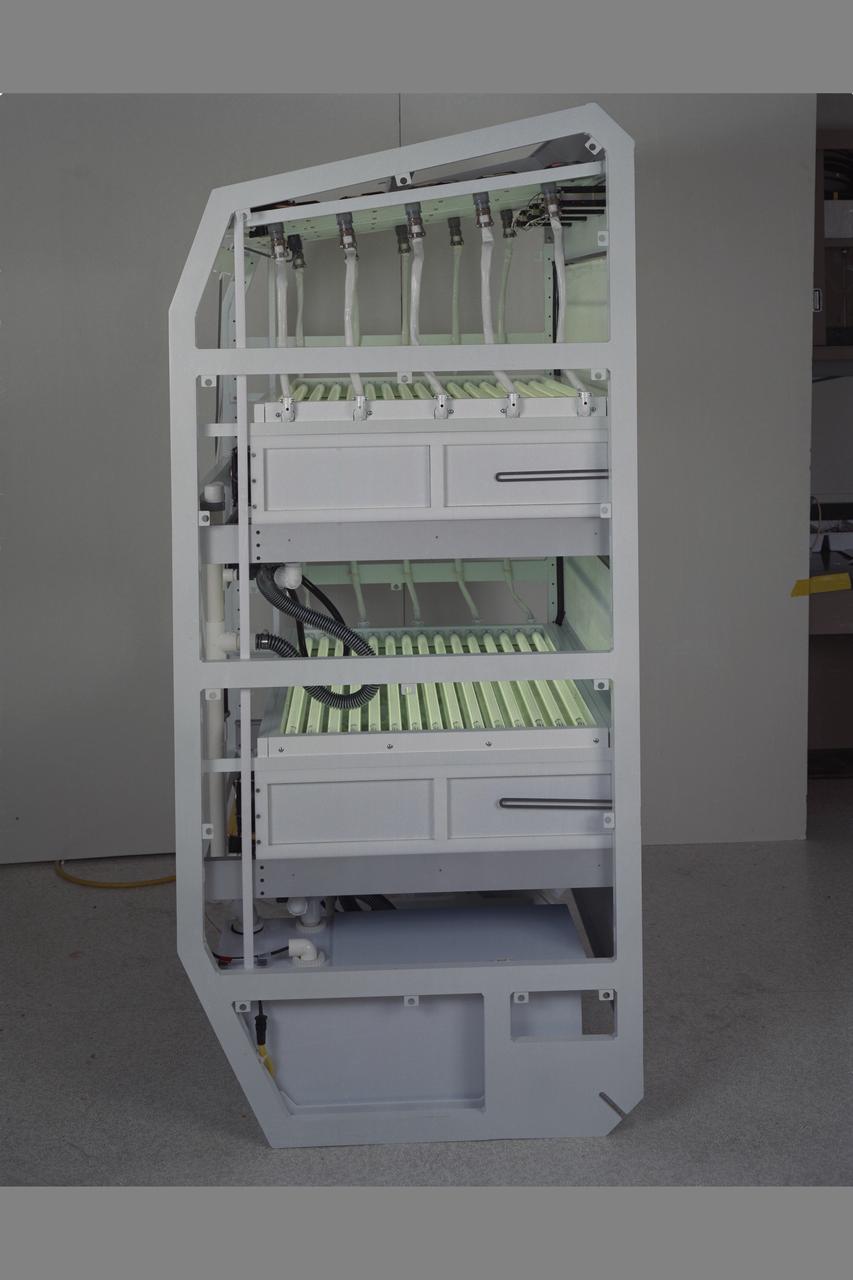

Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
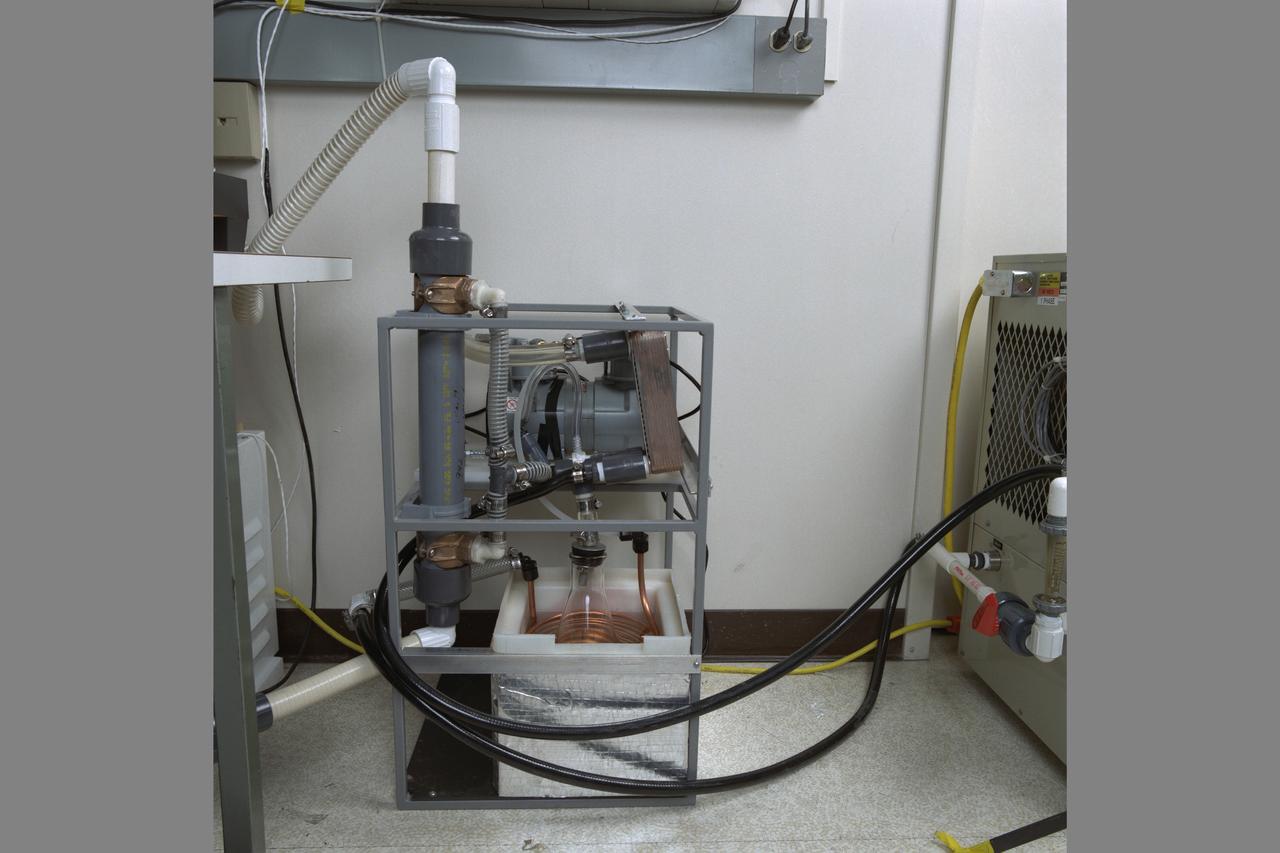
Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
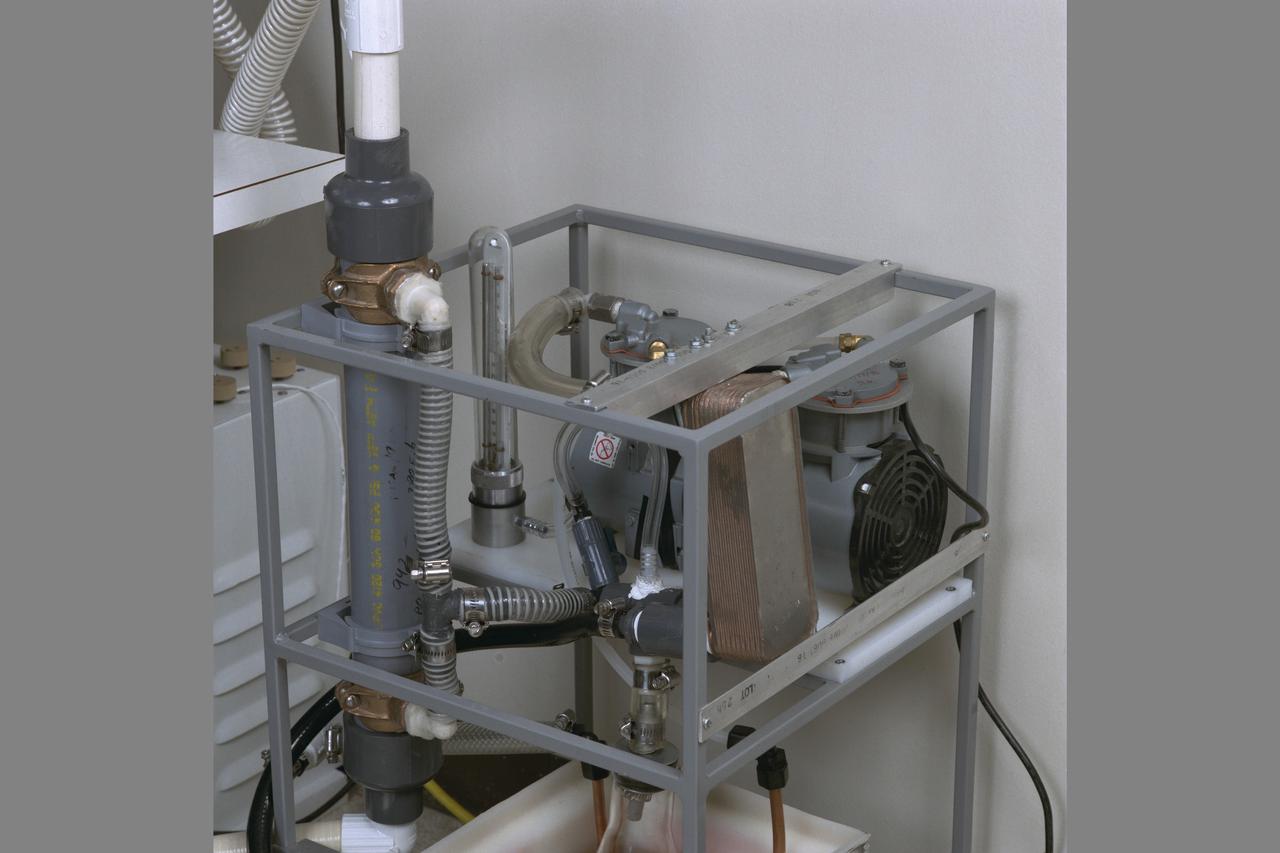
Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
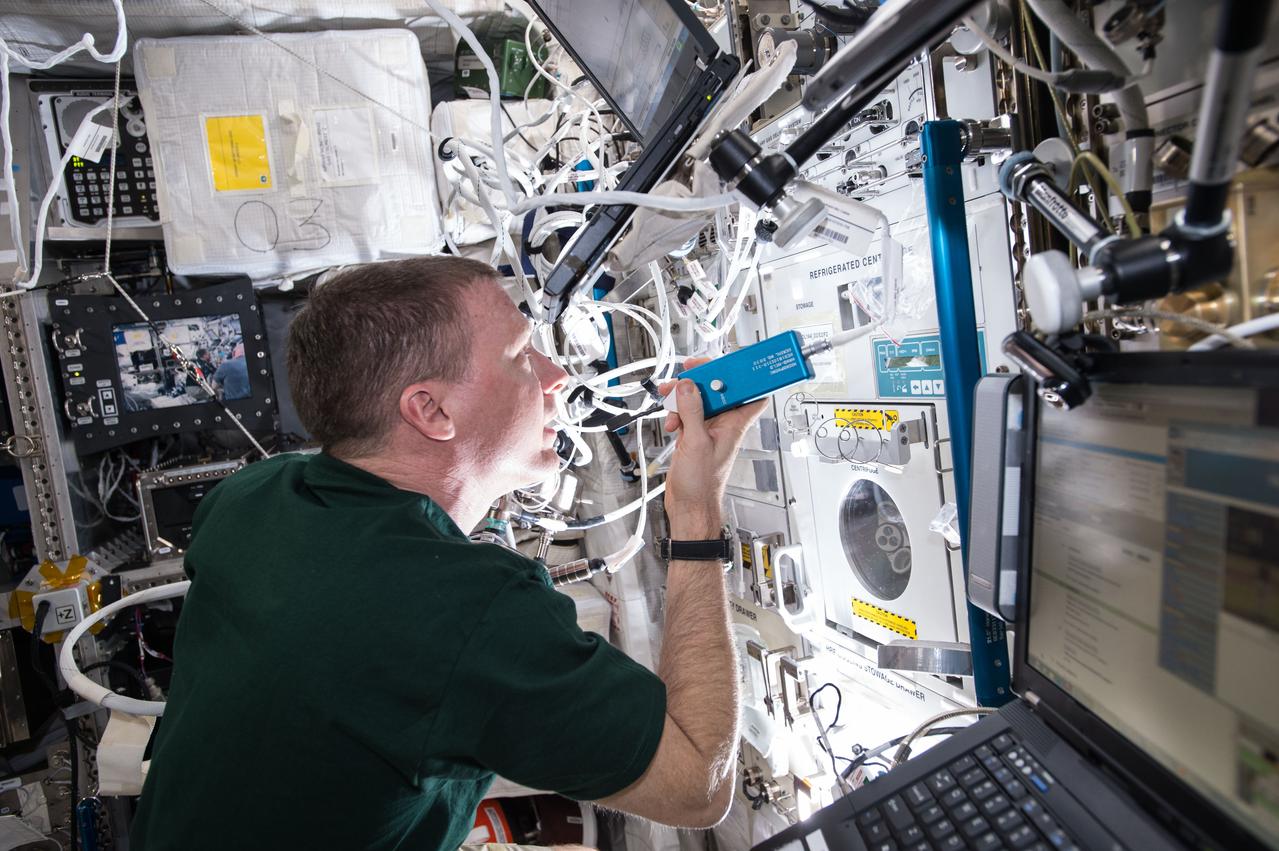

ISS043E091755 (04/07/2015) --- Expedition 43 Commander Terry Virts is seen here working inside of the Columbus laboratory on the Blood Pressure Regulation (BP Reg) experiment. Astronauts returning from long-duration space flights risk experiencing dizziness or fainting when they stand immediately after returning to Earth. This has an important health risk as it reduces the potential for astronauts to safely escape from an emergency situation. BP Reg will help researchers develop appropriate countermeasures so that astronauts returning from long-duration space flights will have very low risk of experiencing dizziness or fainting when they return to Earth.
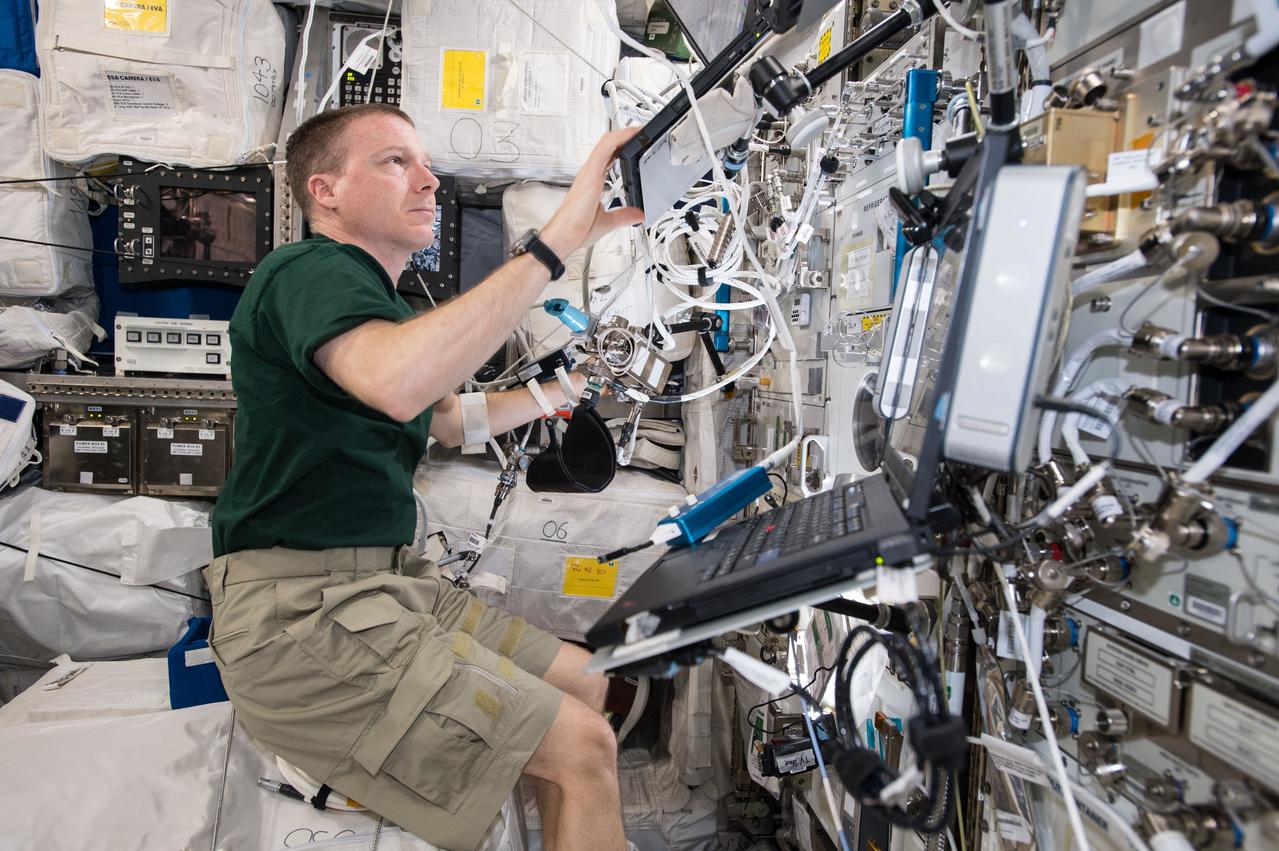

ISS043E091740 (04/07/2015) --- Expedition 43 Commander Terry Virts is seen here working inside of the Columbus laboratory on the Blood Pressure Regulation (BP Reg) experiment. Astronauts returning from long-duration space flights risk experiencing dizziness or fainting when they stand immediately after returning to Earth. This has an important health risk as it reduces the potential for astronauts to safely escape from an emergency situation. BP Reg will help researchers develop appropriate countermeasures so that astronauts returning from long-duration space flights will have very low risk of experiencing dizziness or fainting when they return to Earth.
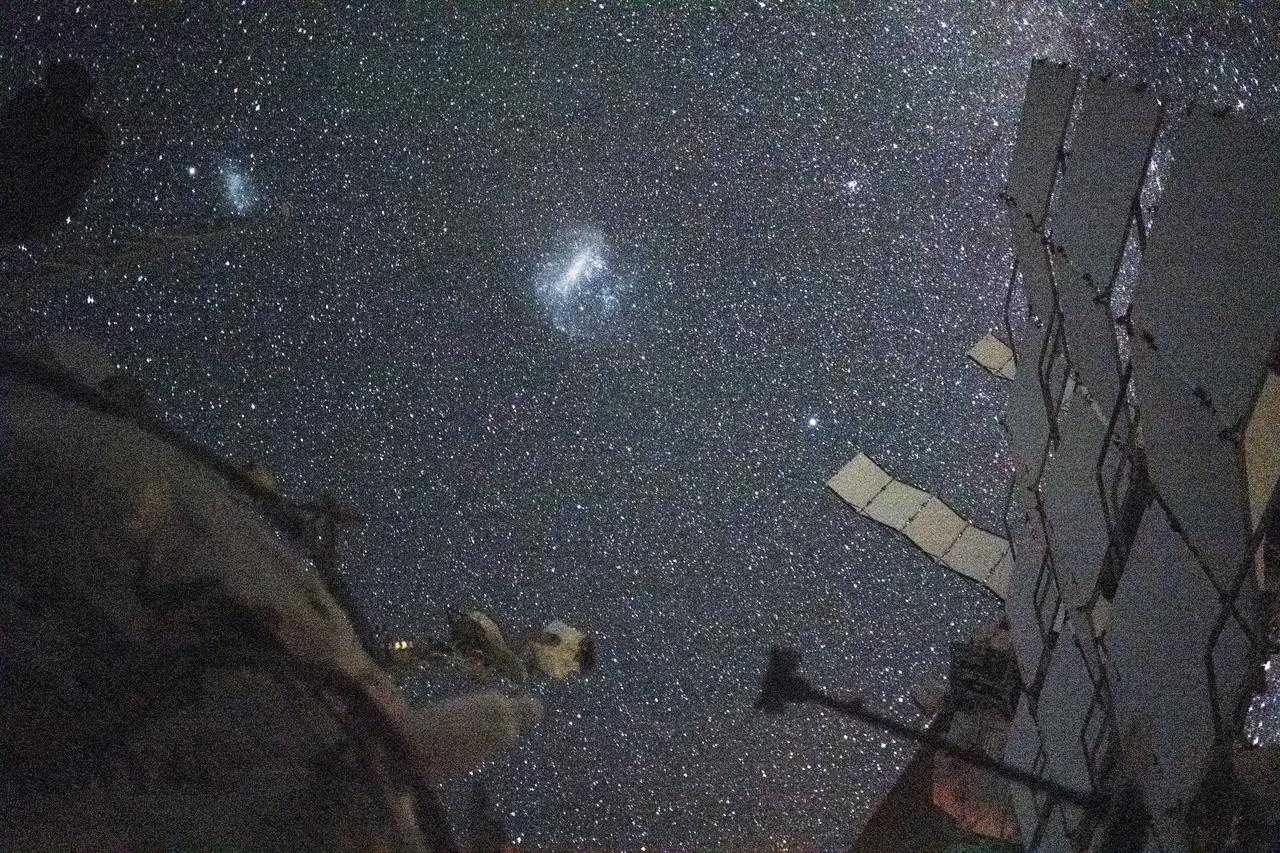

iss071e418742 (Aug. 6, 2024) --- The Large Magellanic Cloud (center) and the Small Magellanic Cloud (upper left), dwarf galaxies in close proximity with the Milky Way galaxy, are pictured from the International Space Station. NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Matthew Dominick took this long-duration photograph with a station camera increasing its sensitivity to account for low light conditions.
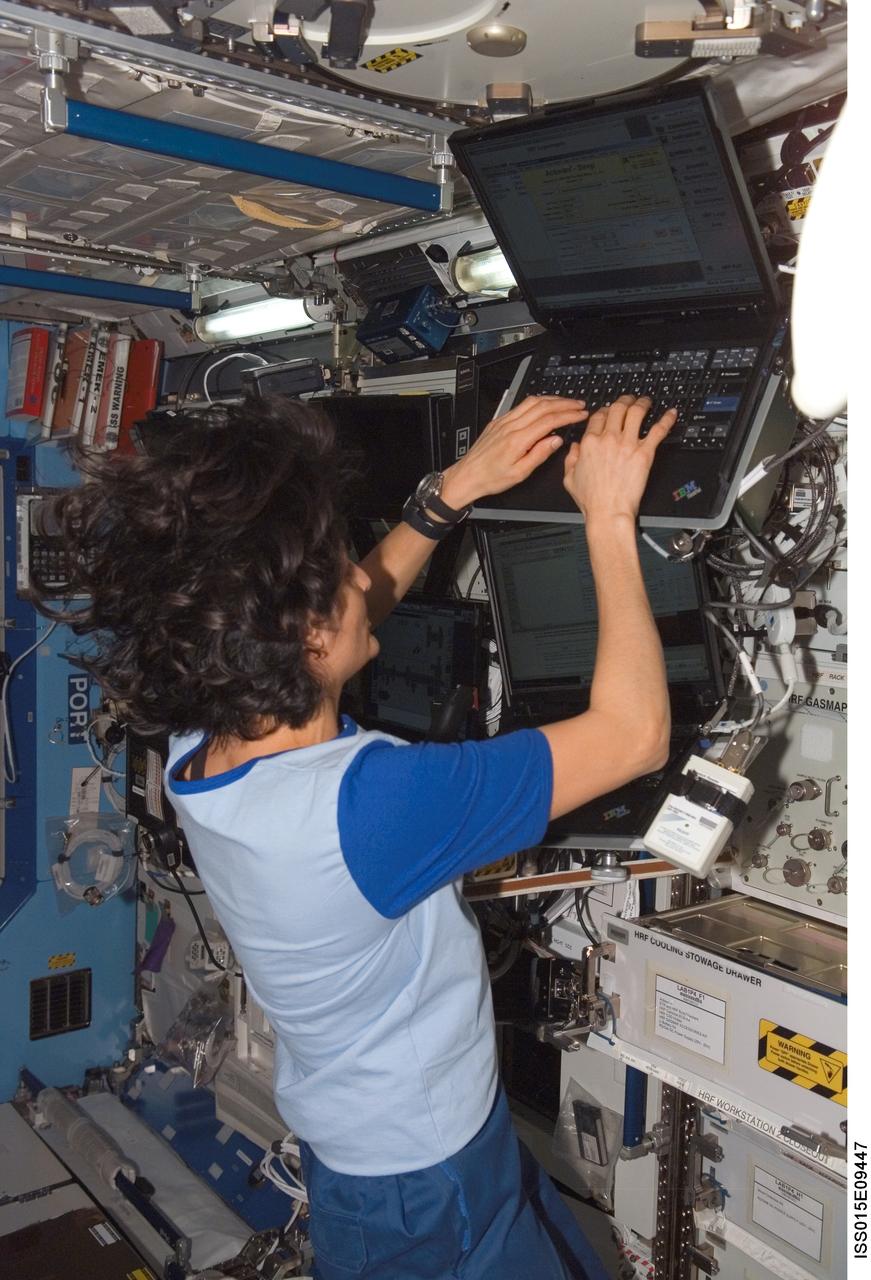

ISS015-E-09447 (24 May 2007) --- Astronaut Sunita L. Williams, Expedition 15 flight engineer, enters data in a computer for the Sleep-Wake Actigraphy and Light Exposure During Spaceflight-Long (Sleep-Long) experiment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. Sleep-Long will examine the effects of spaceflight and ambient light exposure on the sleep-wake cycles of the crewmembers during long-duration stays on the station.
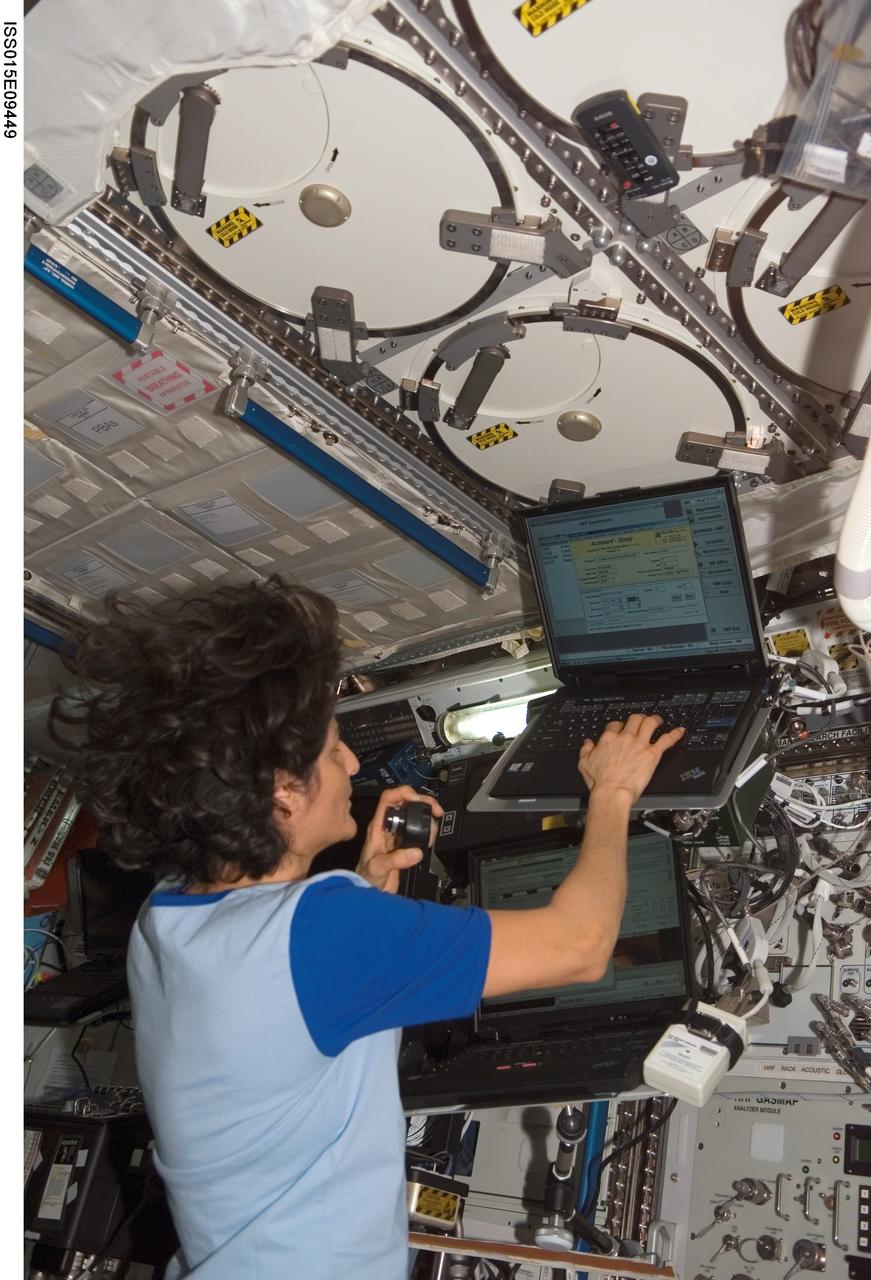

ISS015-E-09449 (24 May 2007) --- Astronaut Sunita L. Williams, Expedition 15 flight engineer, enters data in a computer for the Sleep-Wake Actigraphy and Light Exposure During Spaceflight-Long (Sleep-Long) experiment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. Sleep-Long will examine the effects of spaceflight and ambient light exposure on the sleep-wake cycles of the crewmembers during long-duration stays on the station.
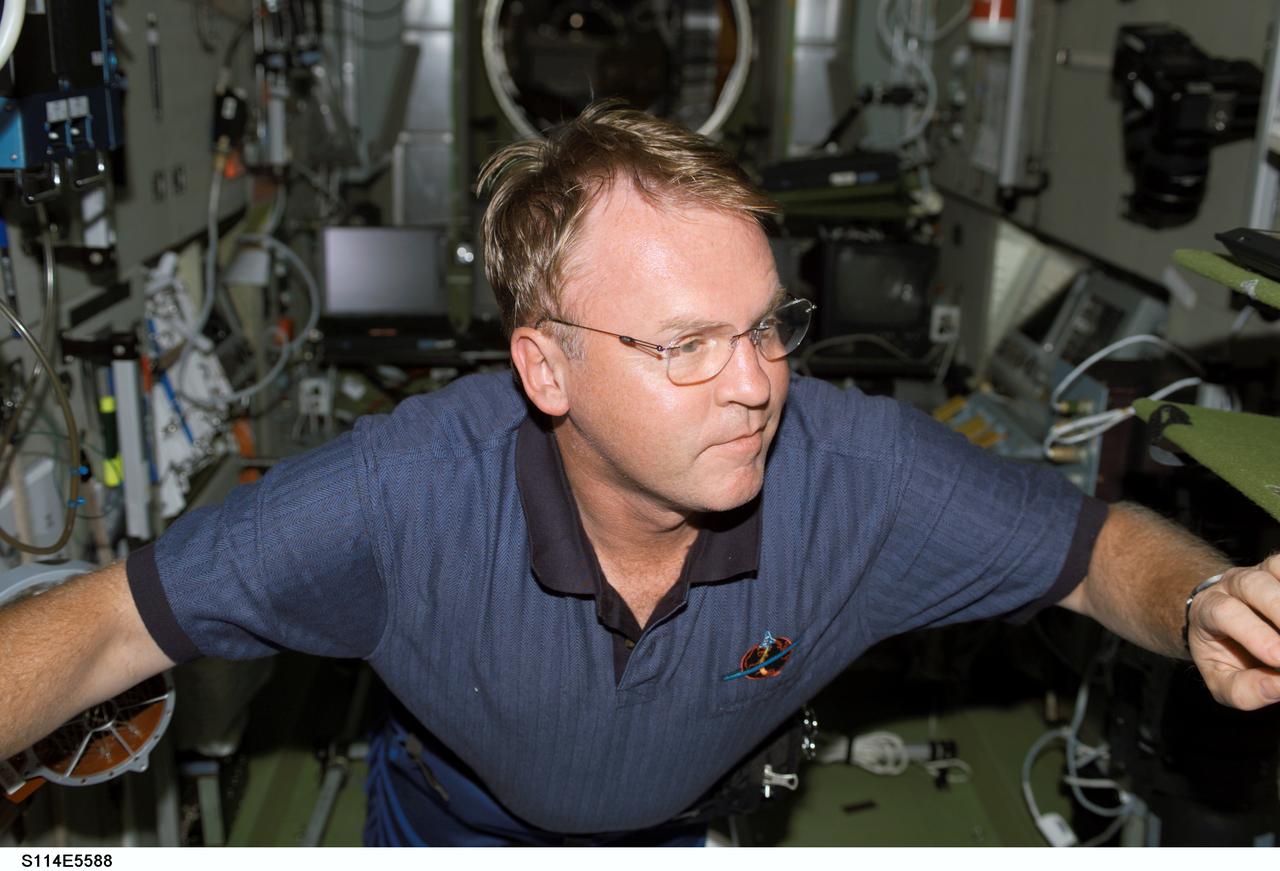

S114-E-5588 (28 July 2005) --- Astronaut Andrew S.W. Thomas may be reminiscing about his long duration stay aboard Russia's late Mir space station as he floats about the International Space Station during STS-114 flight day three activities.

iss071e265137 (July 3, 2024) --- Boeing's Starliner spacecraft that launched NASA's Crew Flight Test astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams to the International Space Station is pictured docked to the Harmony module's forward port. This long-duration photograph was taken at night from the orbital complex as it soared 258 miles above western China.
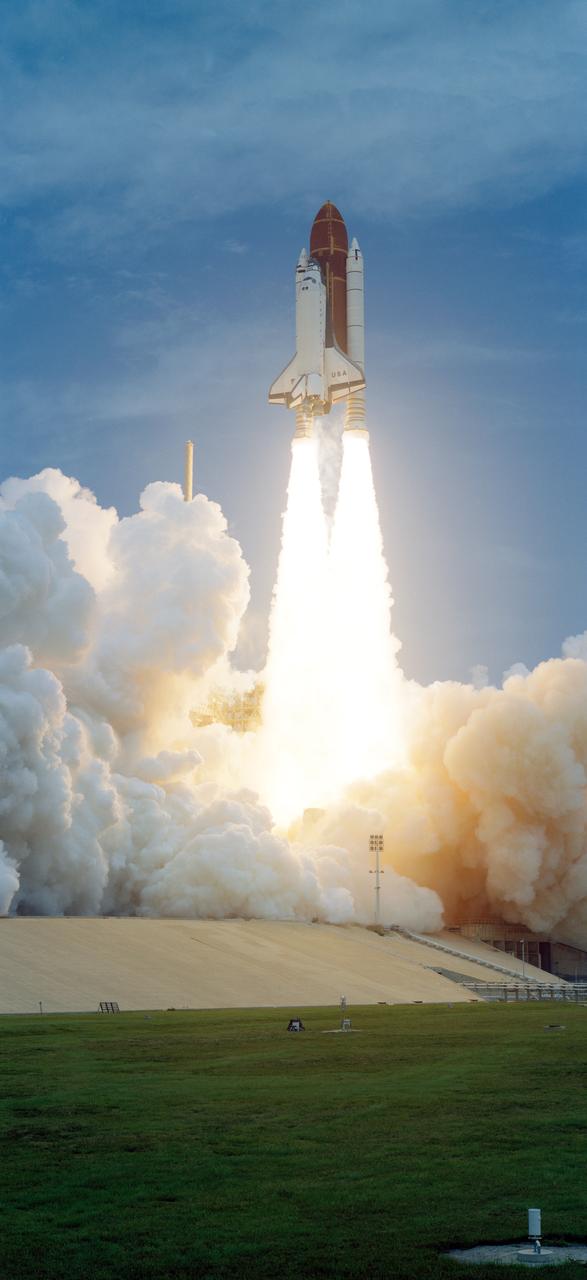

STS050-S-038 (25 June 1992) --- The Space Shuttle Columbia, NASA's first Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO), lifts off on its way toward a scheduled record 13-day mission in Earth-orbit. Liftoff occurred at 12:12:23:0534 p.m. (EDT) on June 25, 1992. Five NASA astronauts and two scientists/payload specialists are aboard. The seven will divide into two shifts to support United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML) research.
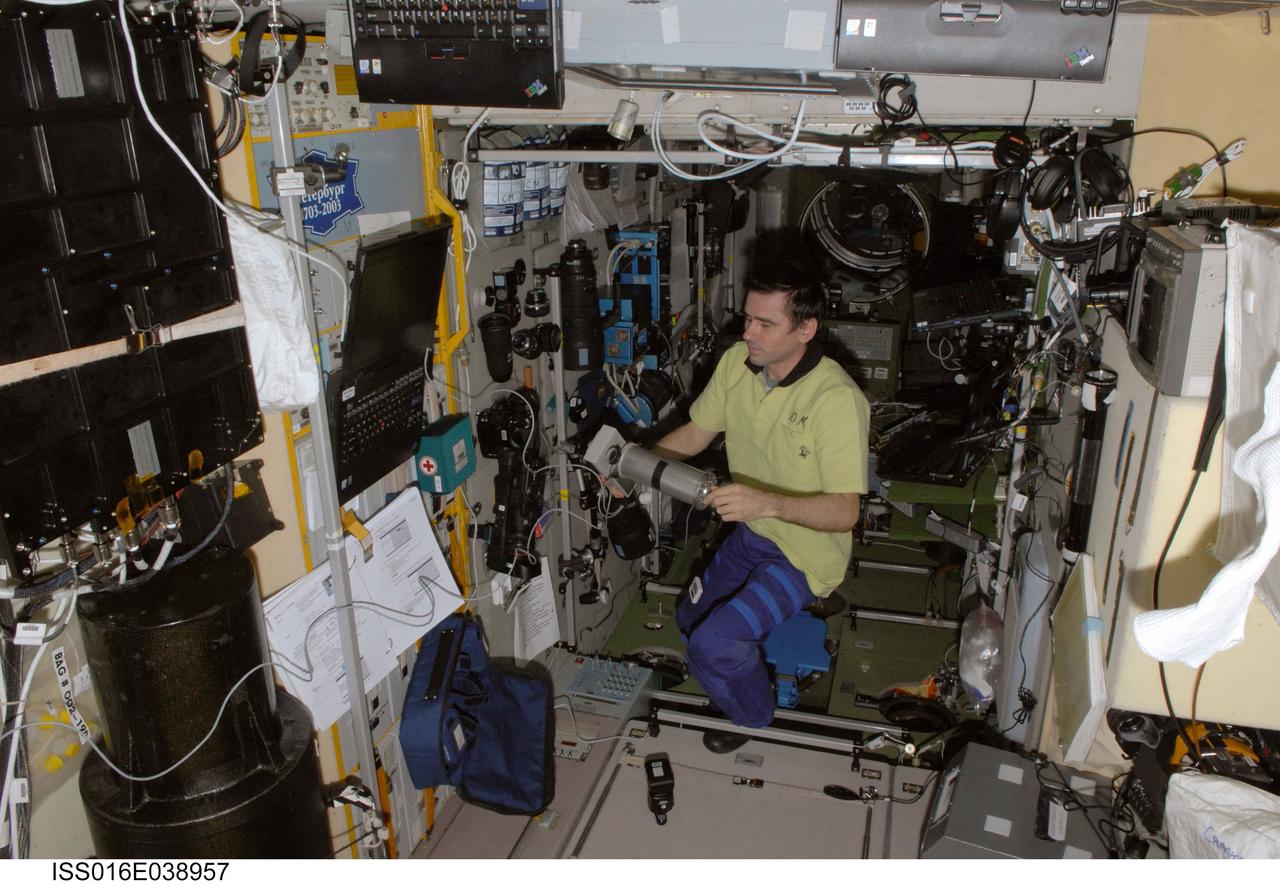

iss016e038957 (3/12/2008) --- Cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko holds the combined signal generation unit with the connected calibrator for the Dykhanie (Respiration) experiment. The Study of the Regulation and Biomechanics of Respiration in Spaceflight (Dykhanie) investigates upper respiratory functions in long-term orbital flight on the International Space Station (ISS) in order to improve the medical monitoring and countermeasures system for future long-duration crew members.
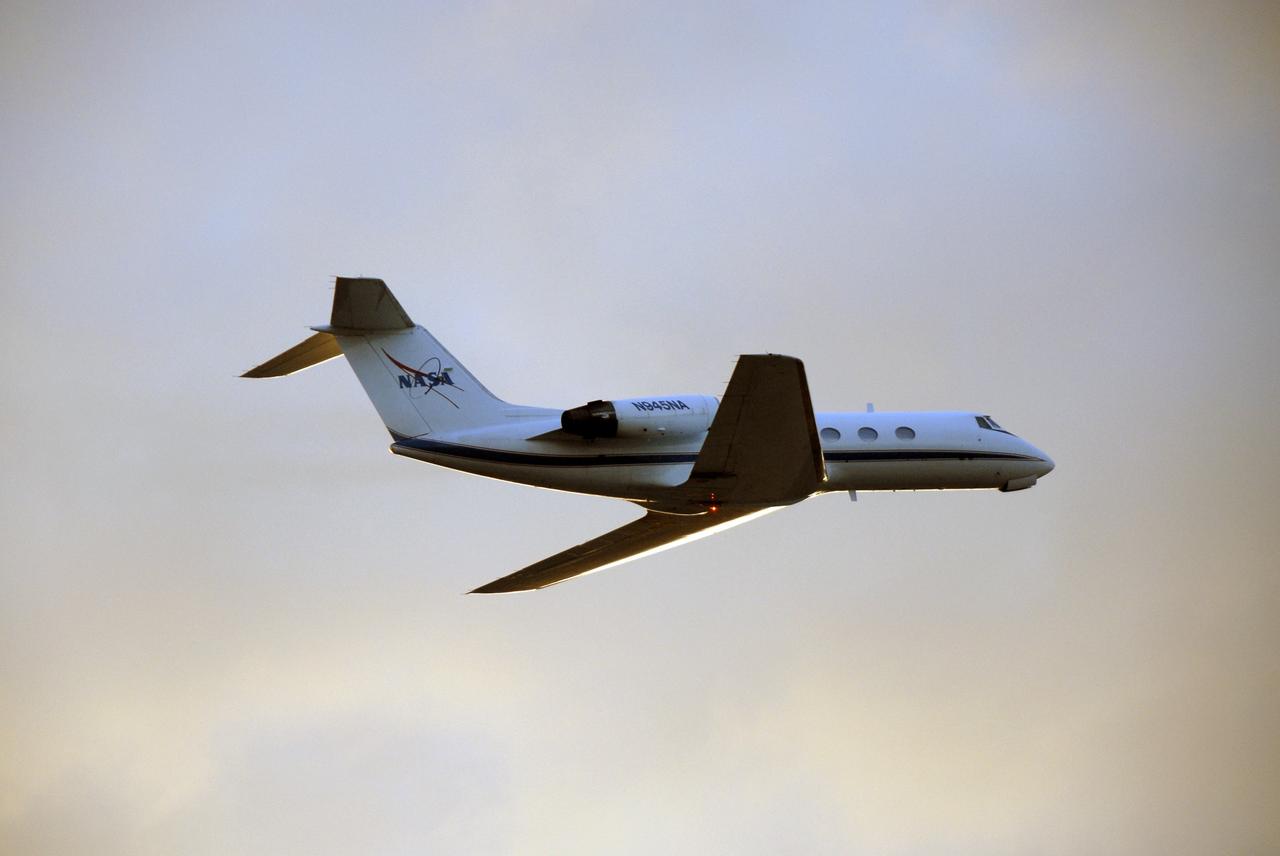

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the skies over the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Shuttle Training Aircraft begins its long turn to achieve the right position for landing. The mission crew members arrived at Kennedy to prepare for launch. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The 15-day mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
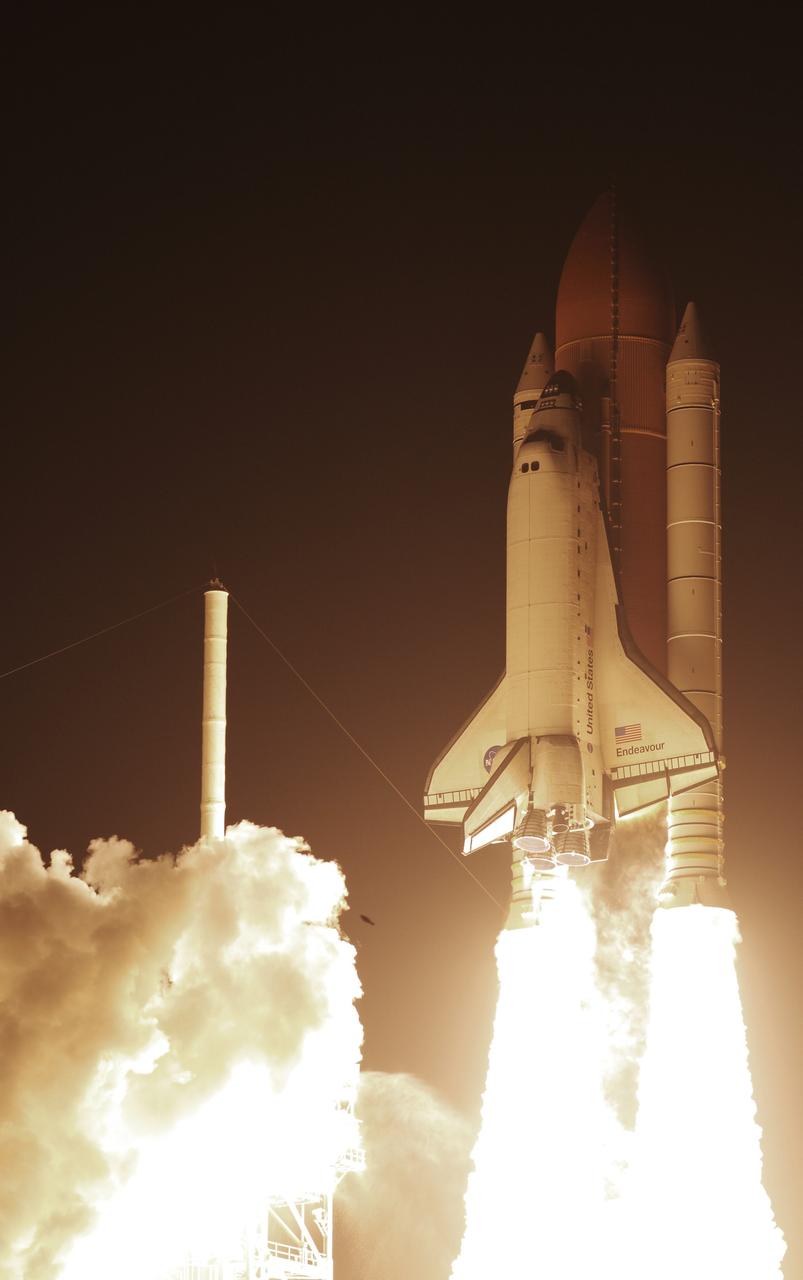

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Atop twin towers of flame, space shuttle Endeavour races past the lightning mast on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, heading into space on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
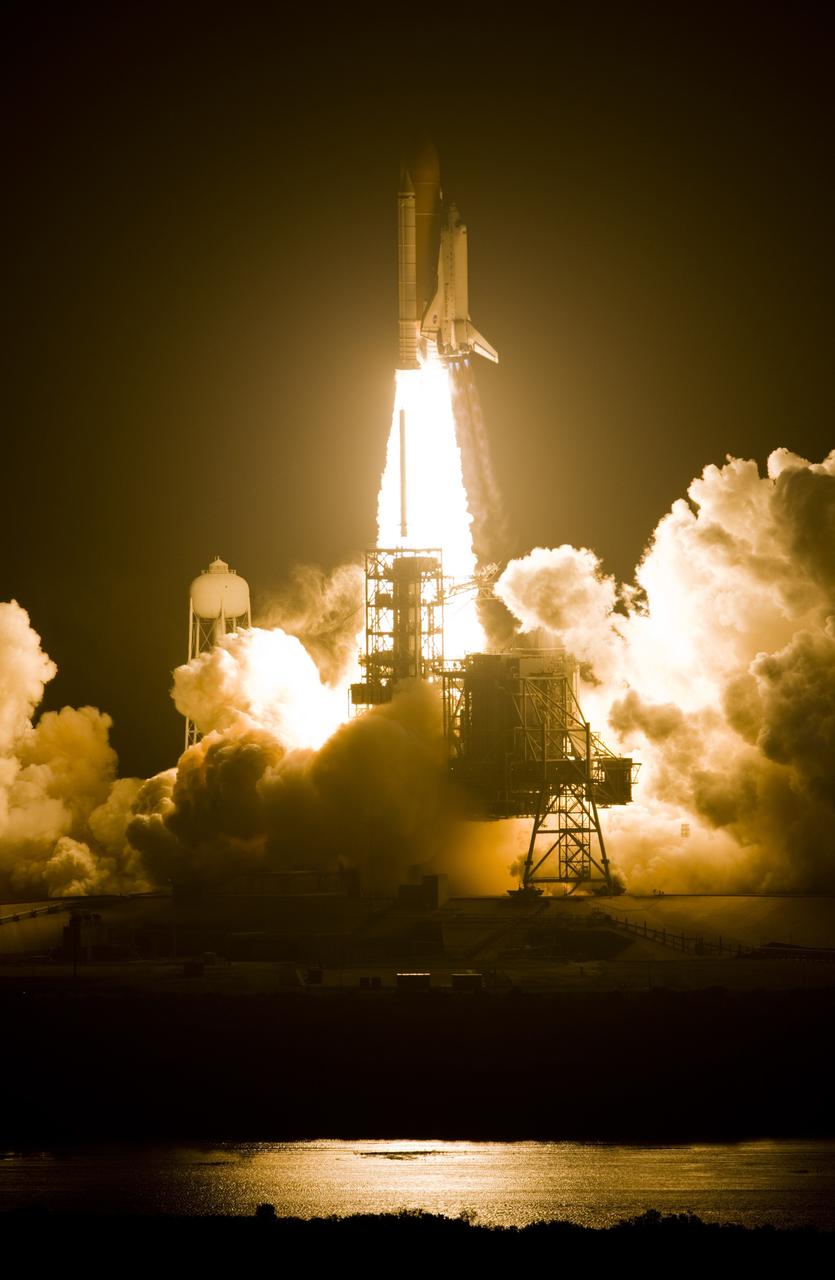

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – From Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour roars into space atop twin columns of fire, lighting the night sky, Liftoff of Endeavour on the STS-126 mission was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
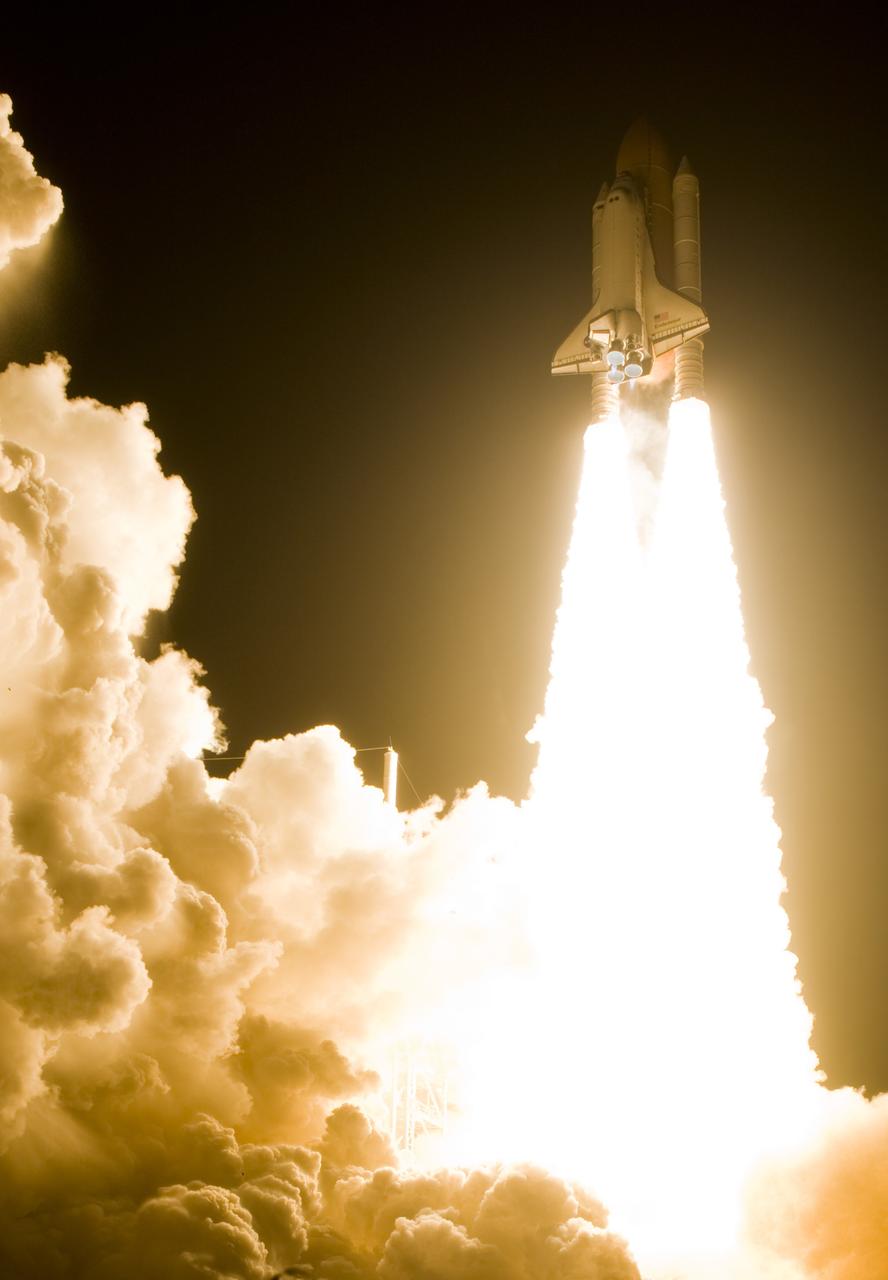

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Atop twin towers of flame, space shuttle Endeavour erupts from the smoke and steam as it hurtles into space from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff on the STS-126 mission was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
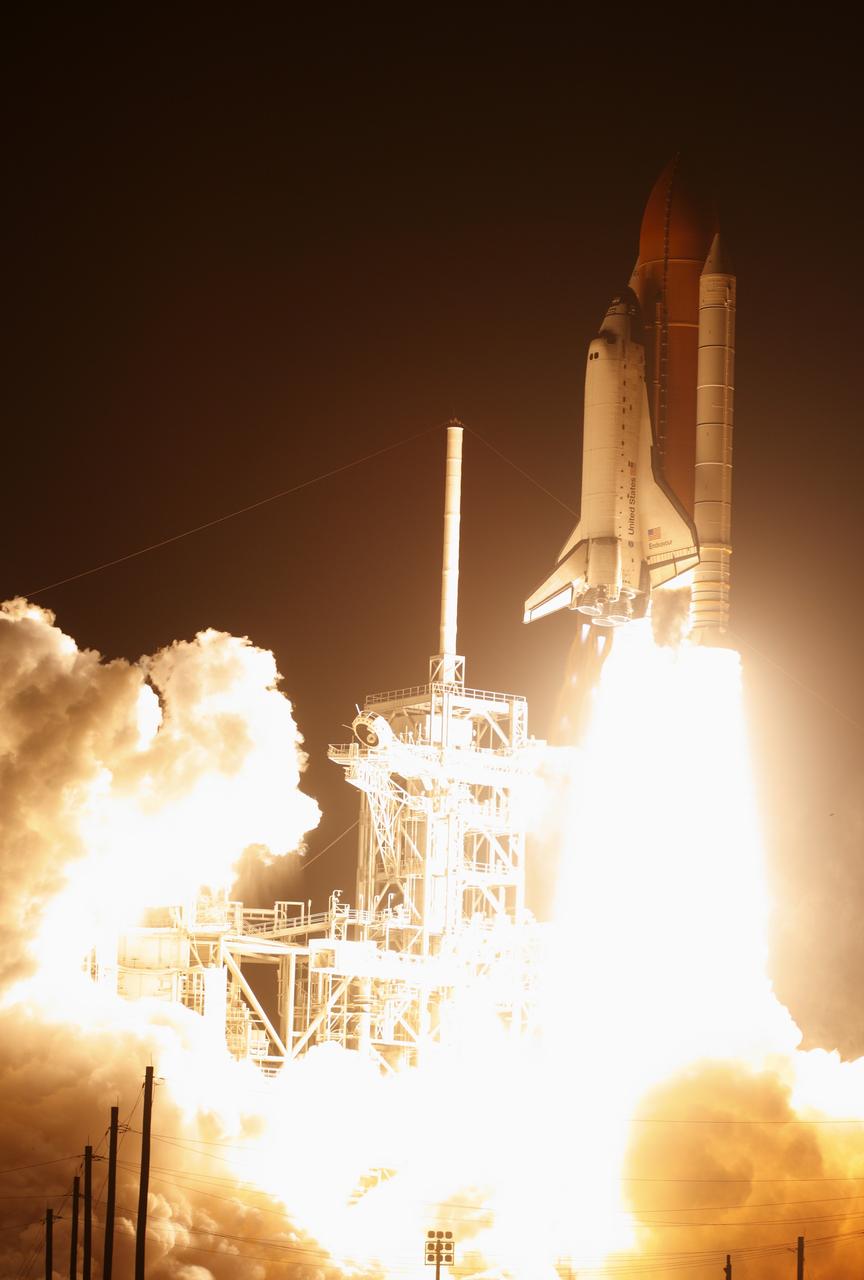

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Atop twin towers of flame, space shuttle Endeavour races past the lightning mast on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, heading into space on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
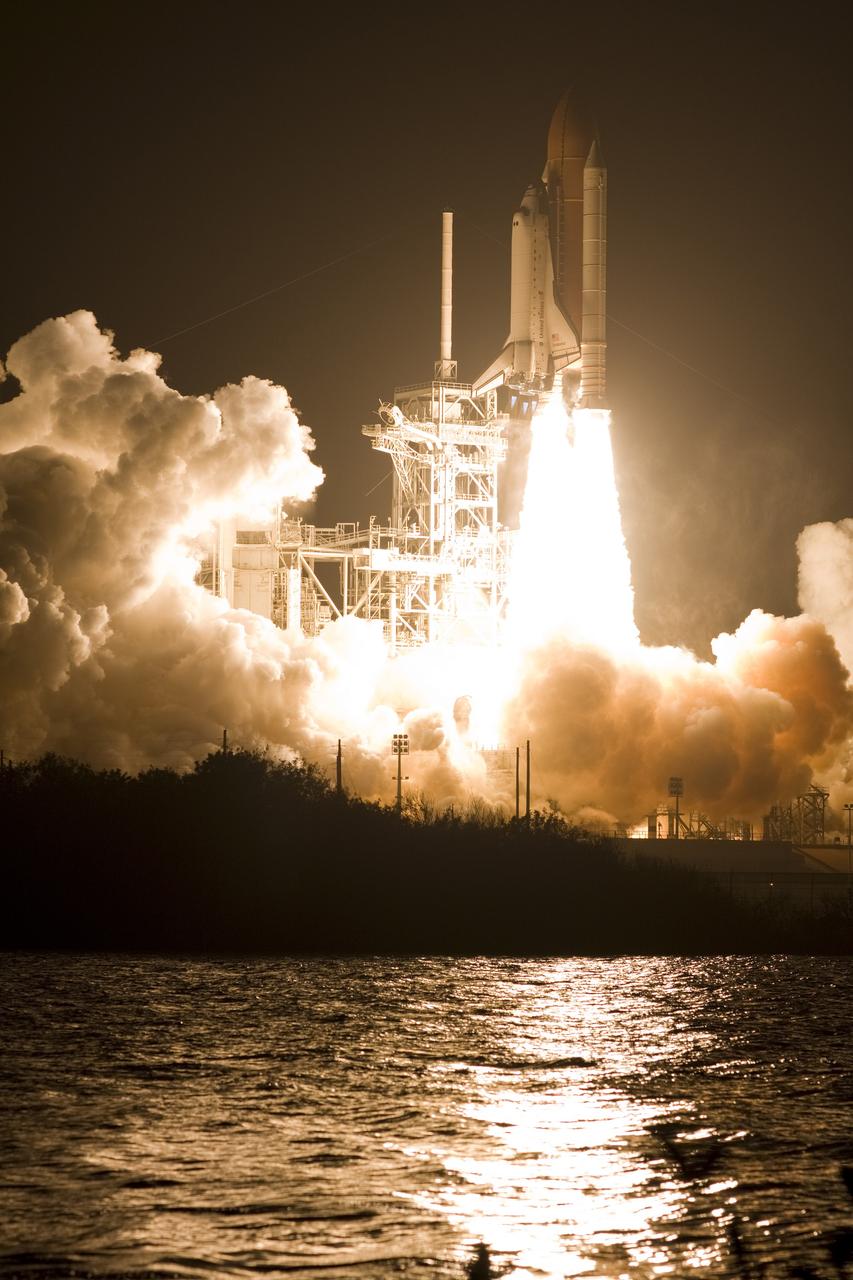

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Atop twin towers of flame, space shuttle Endeavour races past the lightning mast on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, heading into space on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
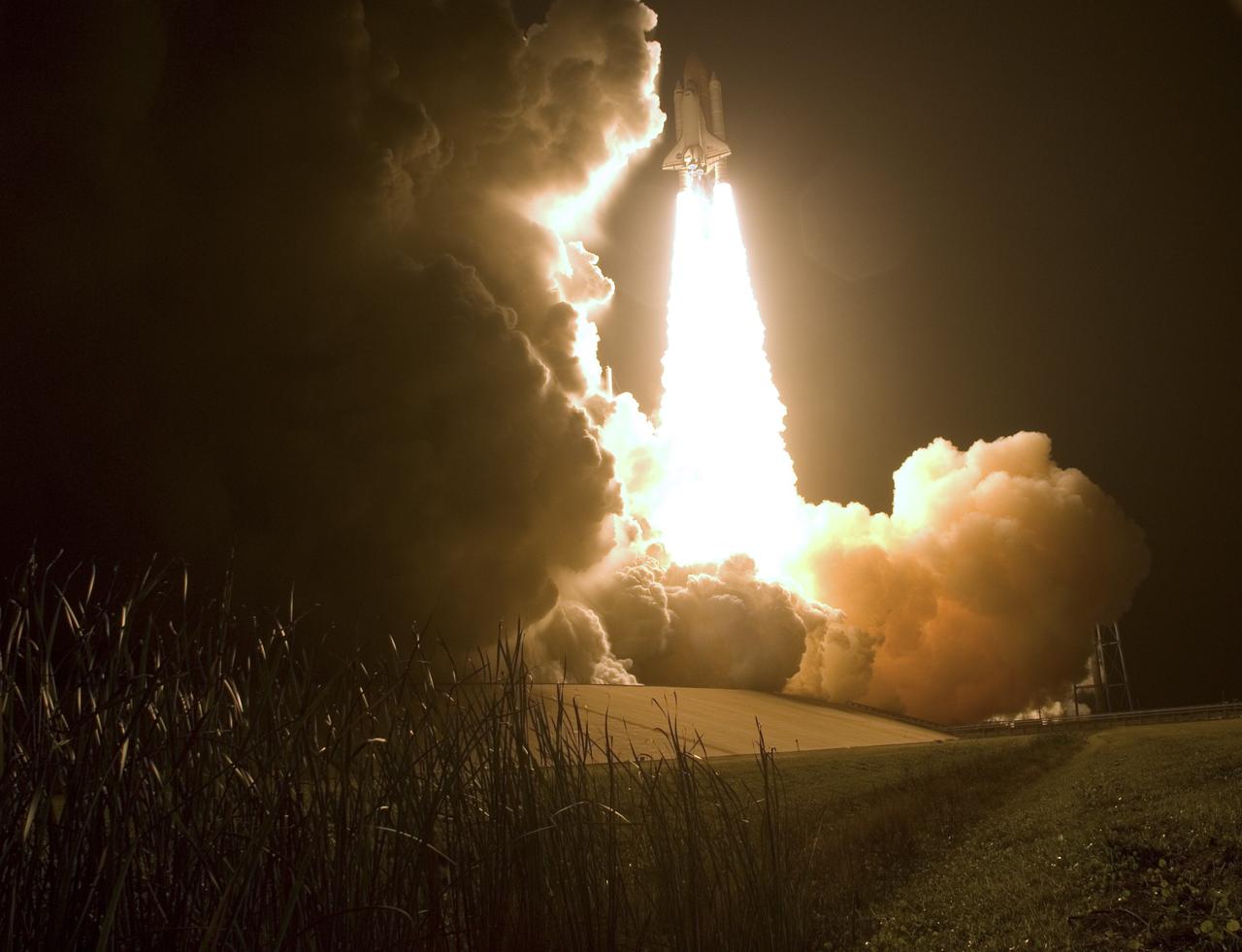

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Twin columns light the night sky as space shuttle Endeavour hurtles into space on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
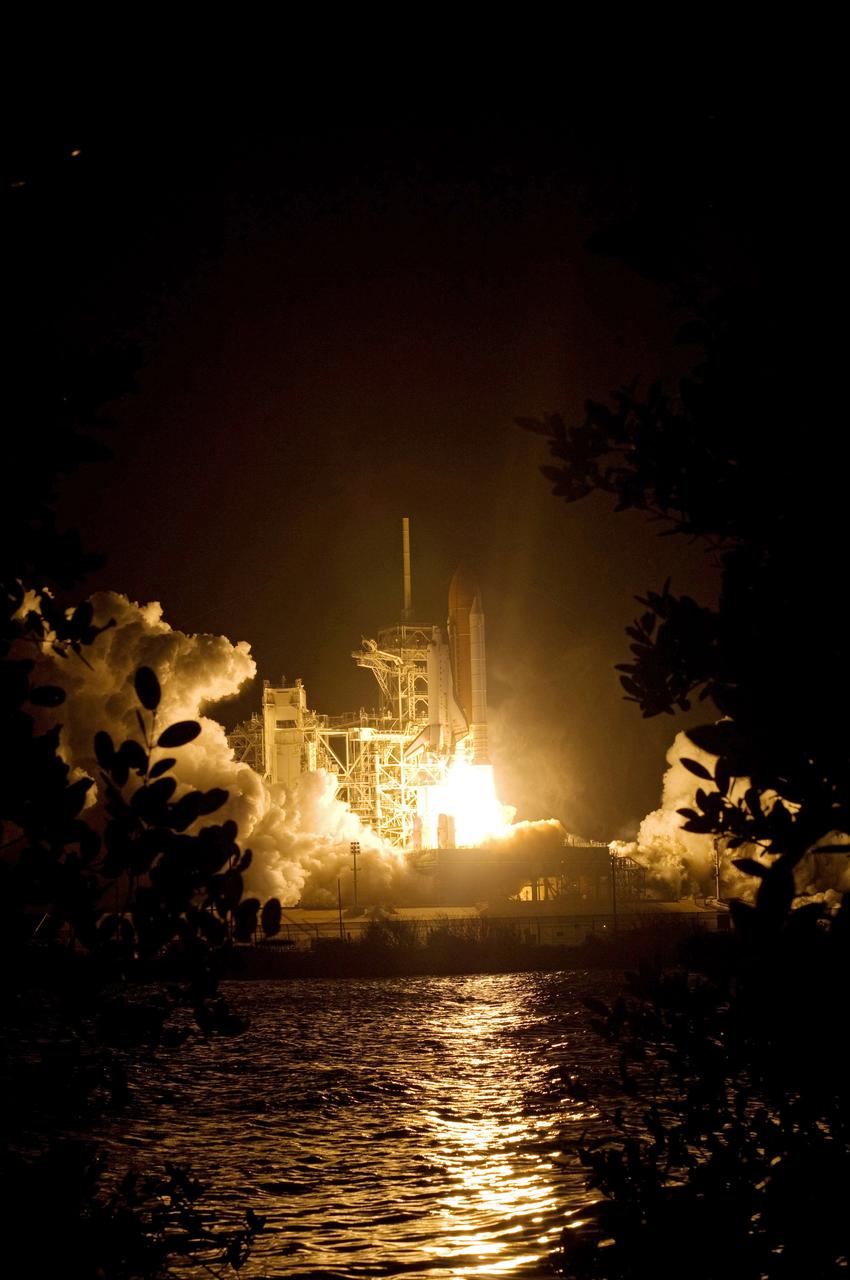

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Blazing light surrounds Launch Pad 39A and glows in the nearby water at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida as space shuttle Endeavour leaps into the sky on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
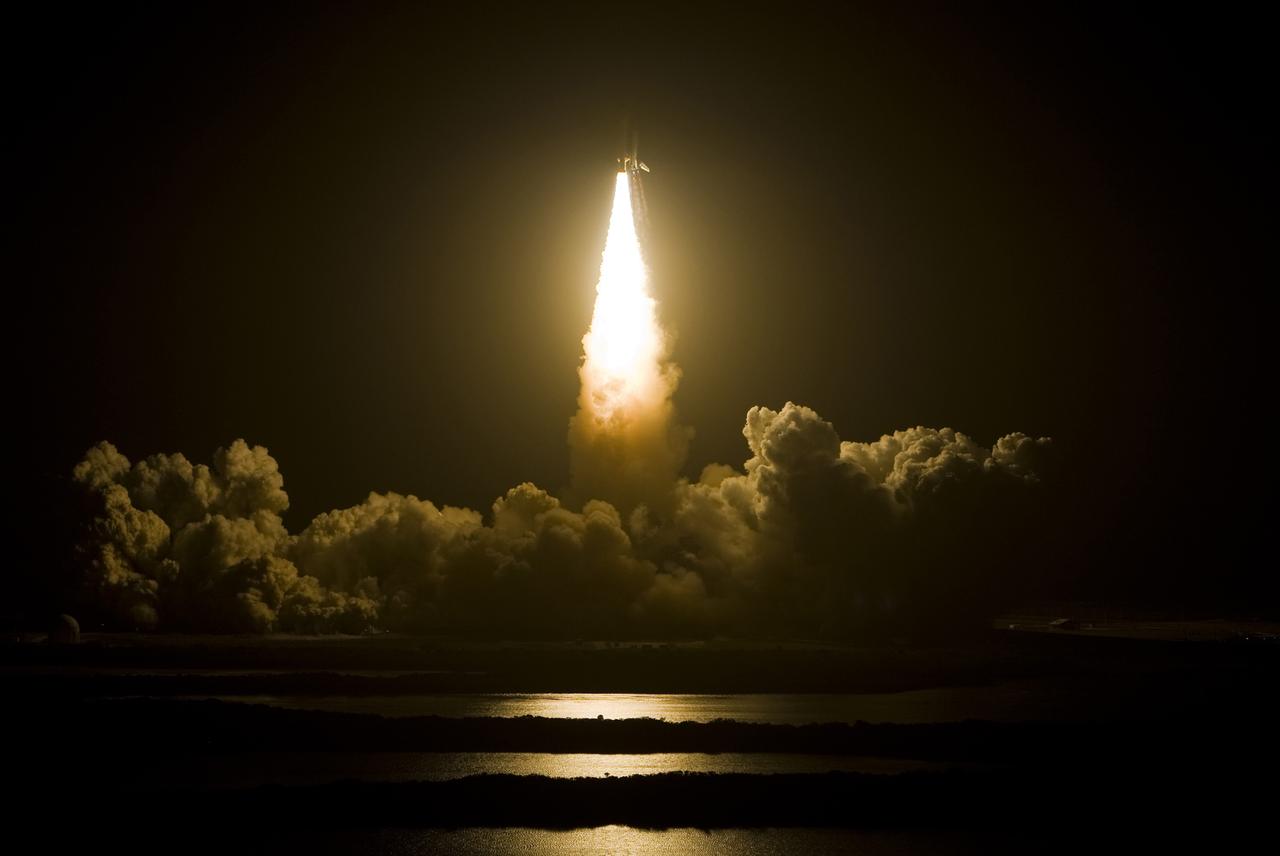

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour punches a hole in the dark of night as it hurtles into the sky atop a column of fire on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
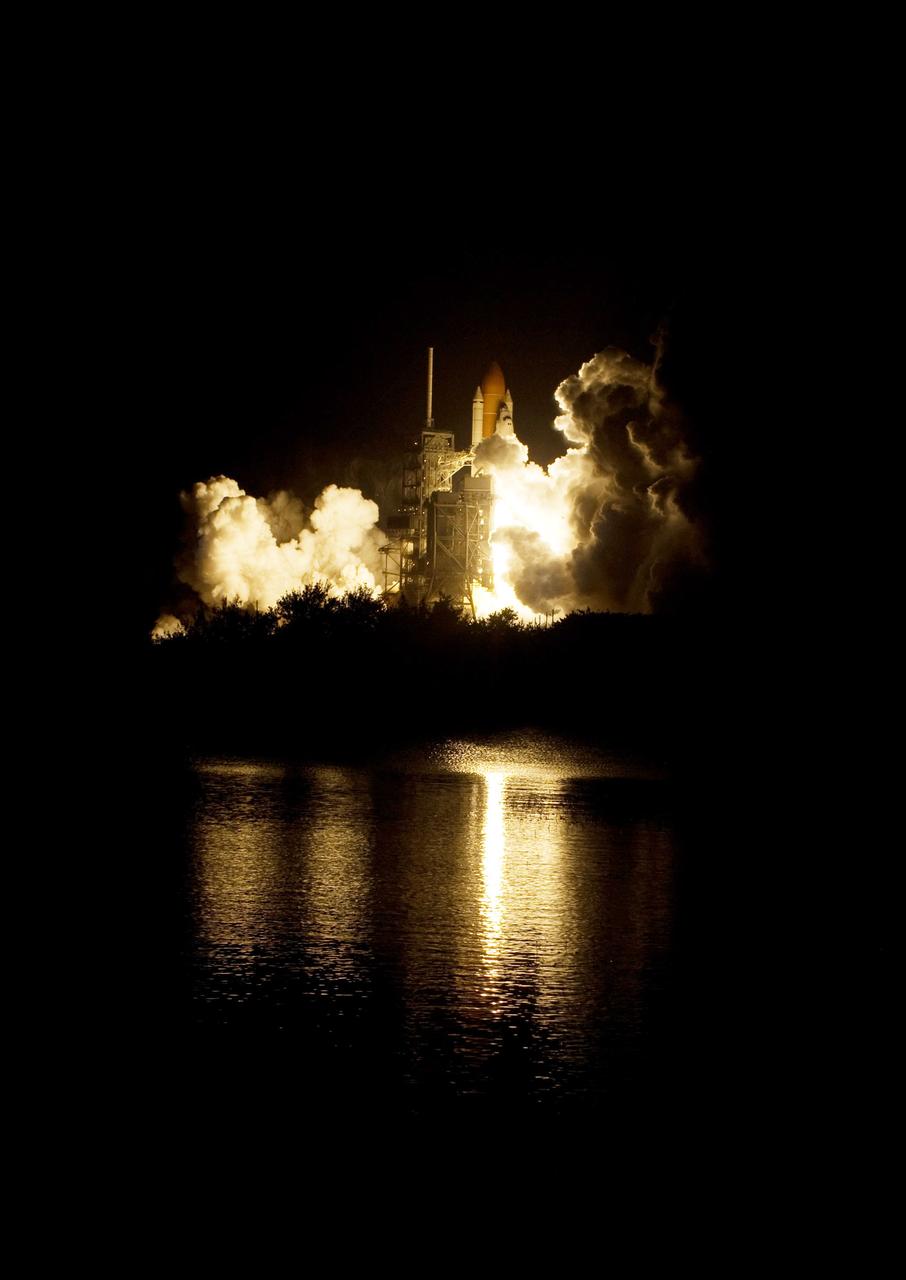

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The fiery glow from the liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission fills the Launch Pad 39A and water nearby at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray-Tom Farrar
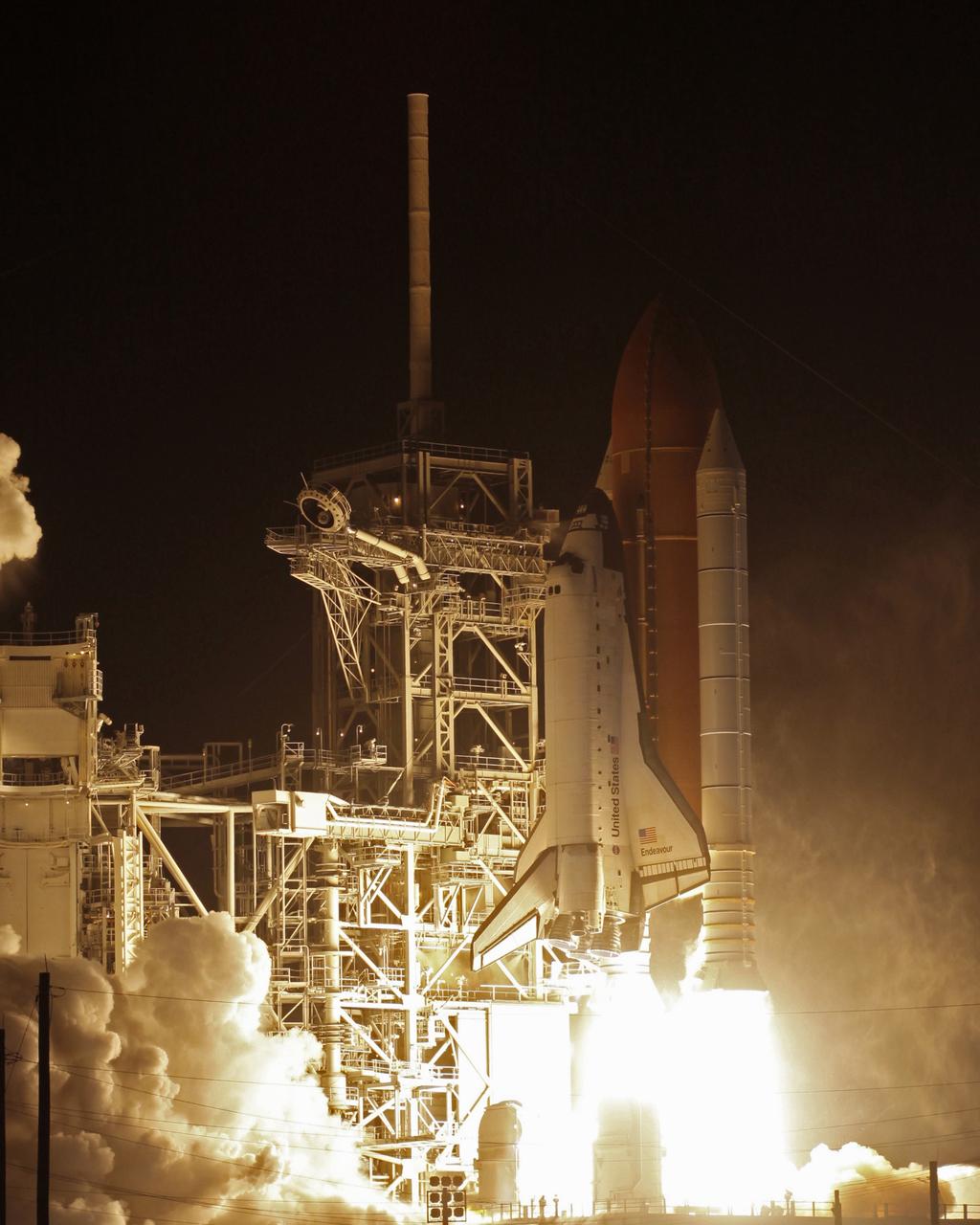

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Light-filled clouds of smoke and steam roll across Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center as space shuttle Endeavour roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
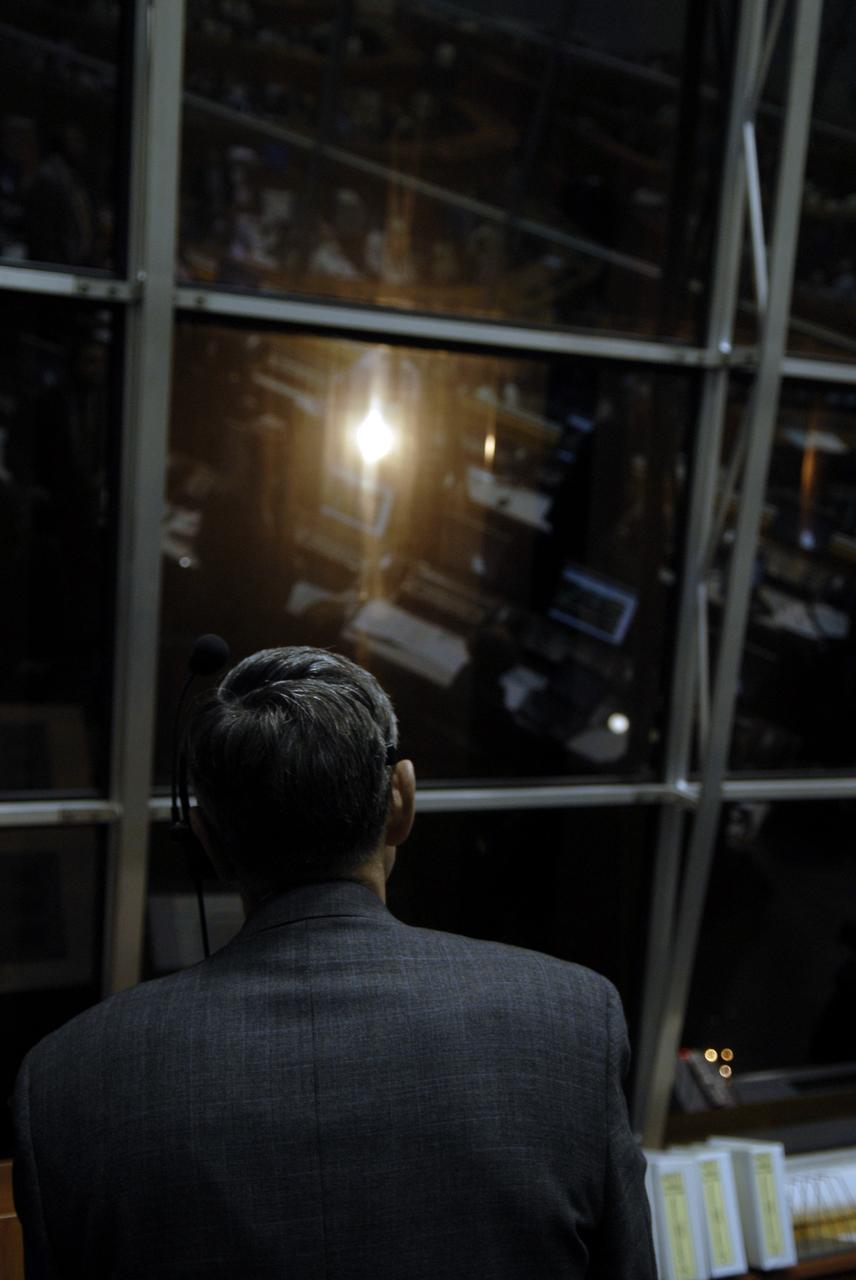

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Center Director Bob Cabana watches the successful launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission in the Firing Room of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
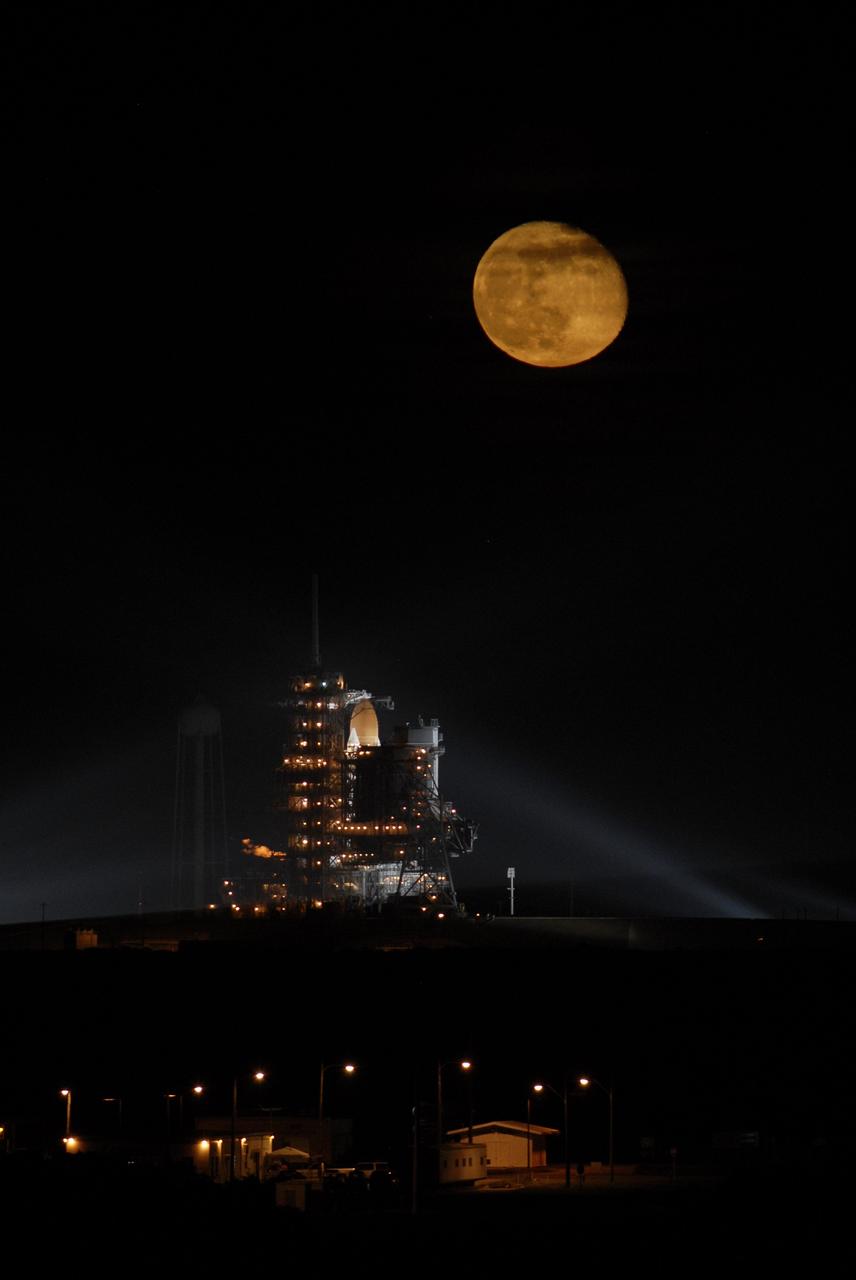

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Above Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the full moon hovers over space shuttle Endeavour waiting for liftoff on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
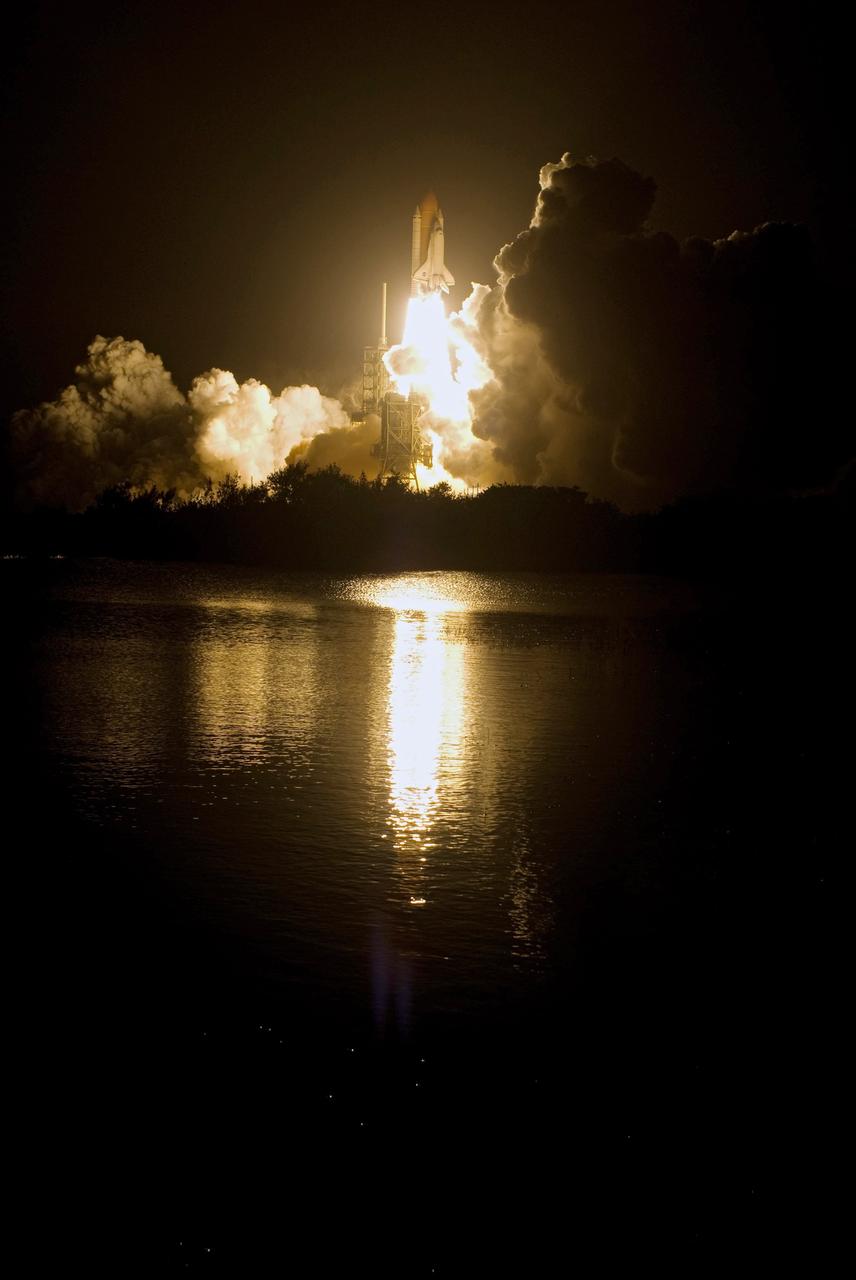

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The light-filled clouds of smoke and steam spotlight space shuttle Endeavour as it lifts off on the STS-126 mission from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray-Tom Farrar
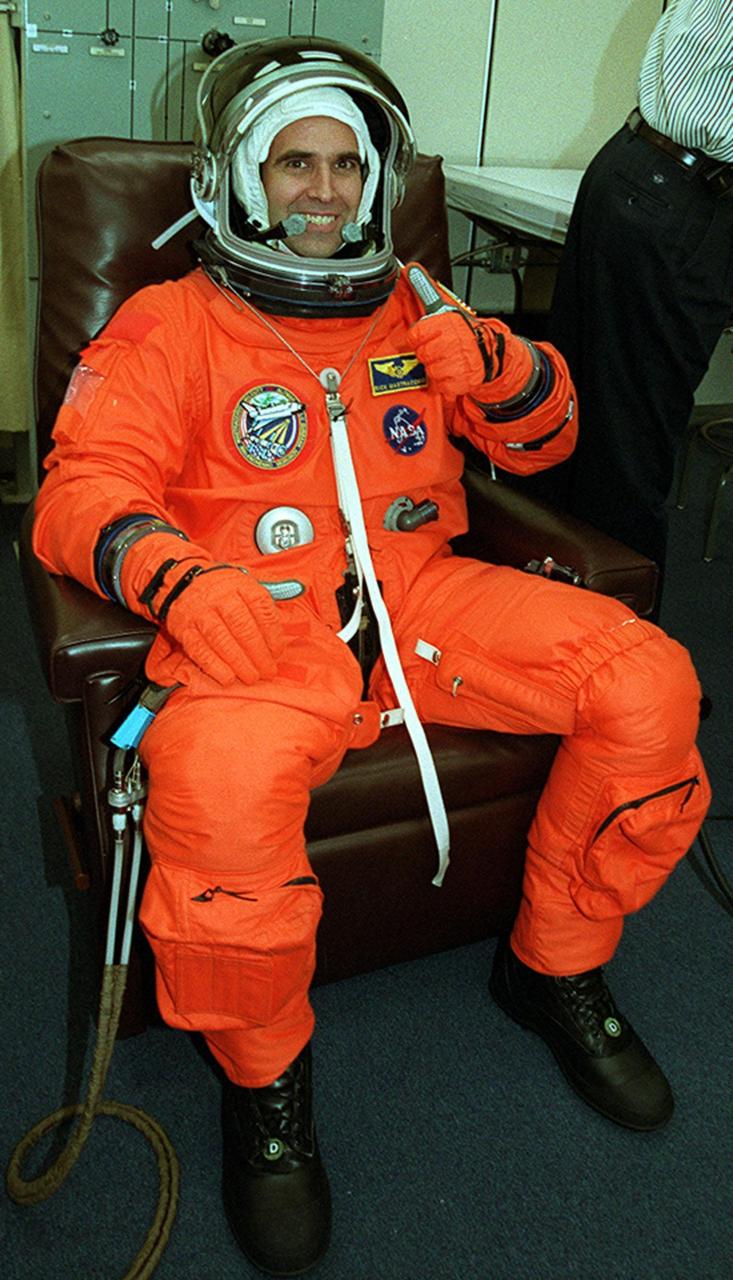

Already suited up, Mission Specialist Richard A. Mastracchio gives thumbs up for launch today. This is Mastracchio’s first space flight. Space Shuttle Atlantis is set to lift off 8:45 a.m. EDT on the fourth flight to the International Space Station. During the 11-day mission, the seven-member crew will perform support tasks on orbit, transfer supplies and prepare the living quarters in the newly arrived Zvezda Service Module. The first long-duration crew, dubbed “Expedition One,” is due to arrive at the Station in late fall
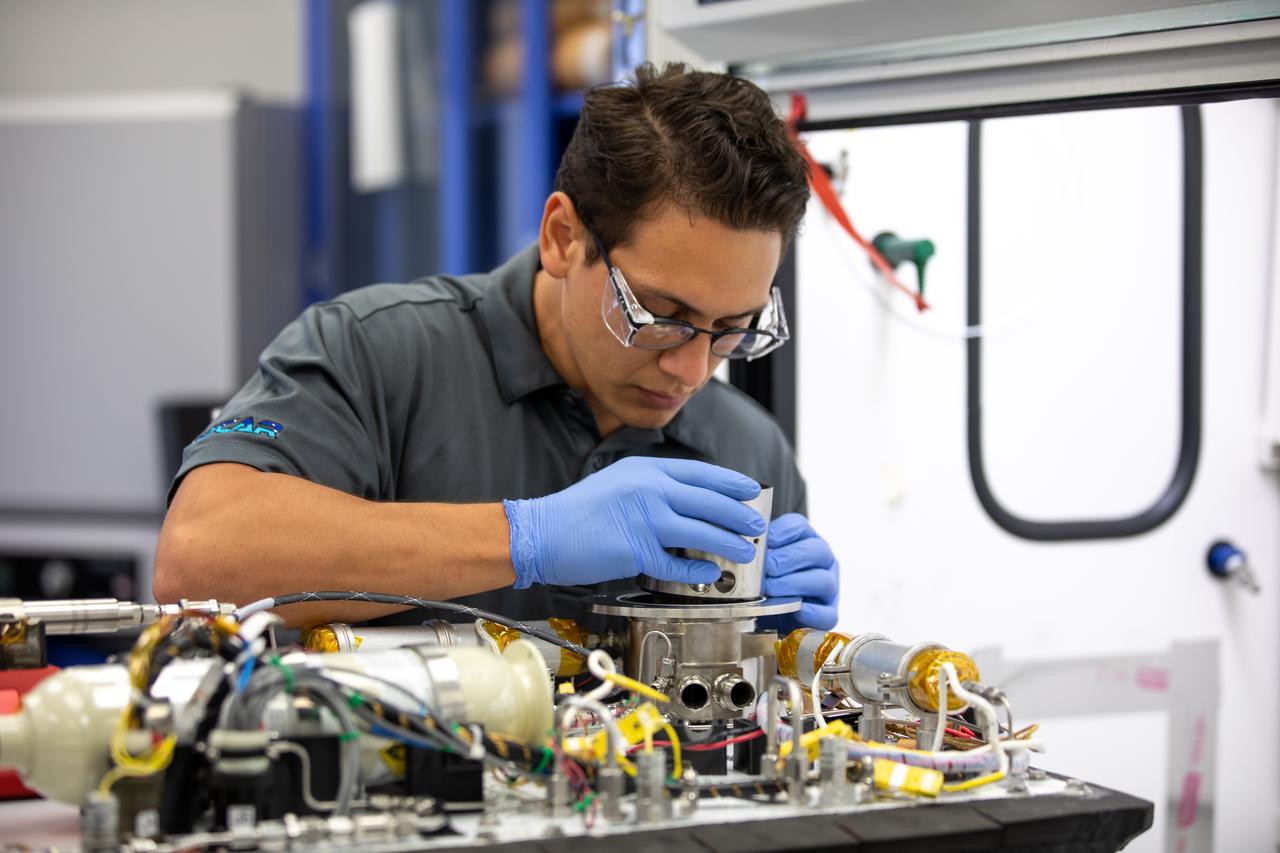

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
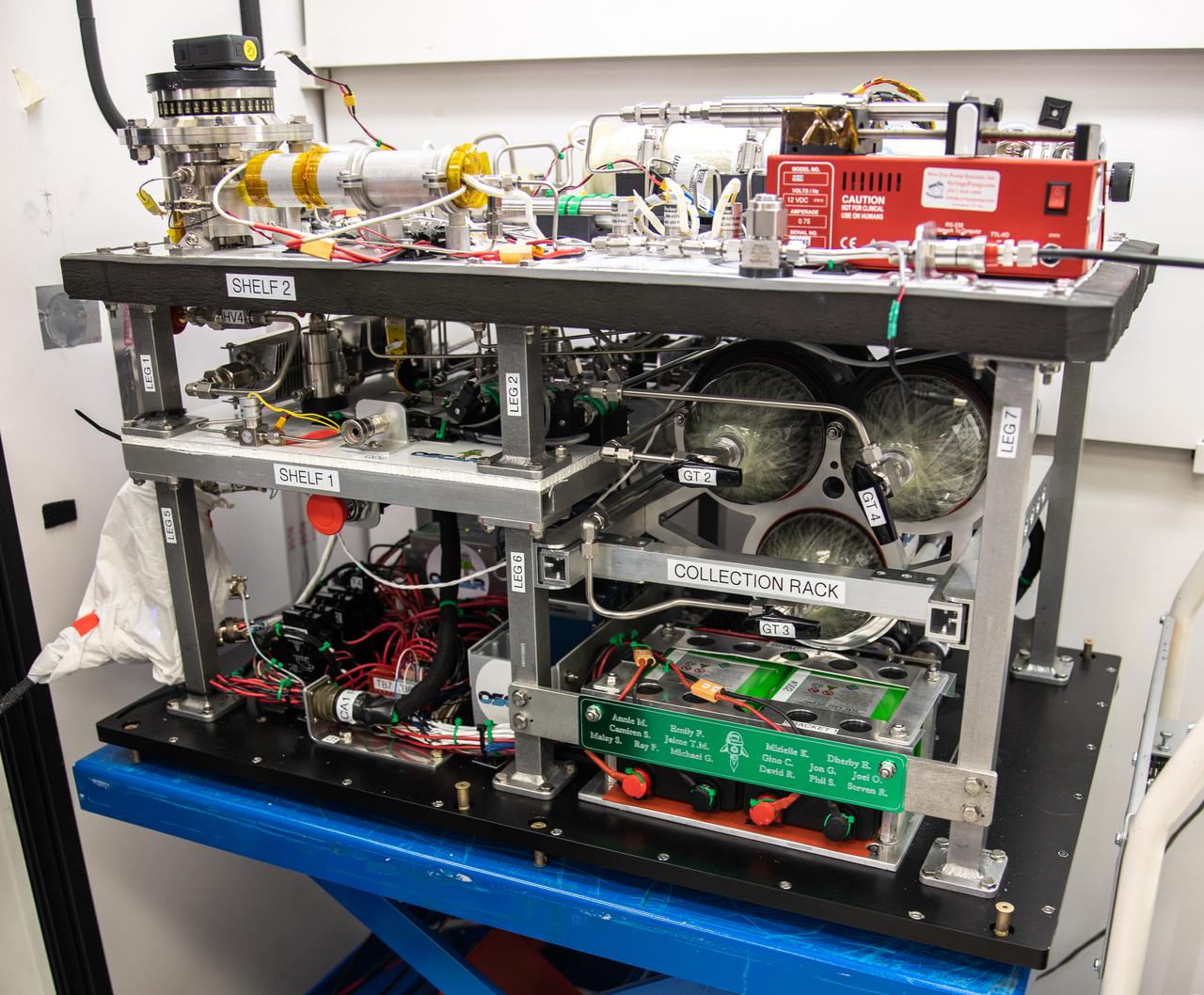
Members of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team perform ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
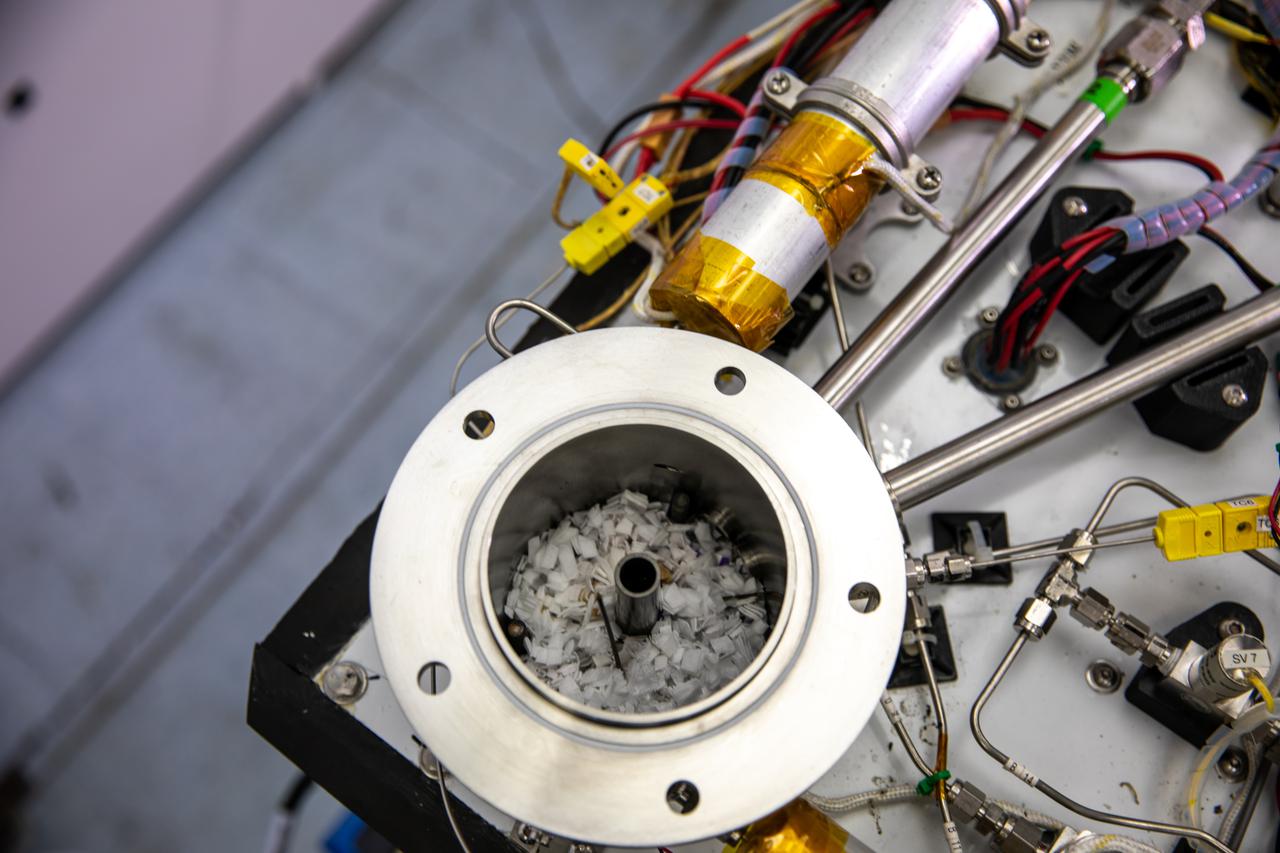
A member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
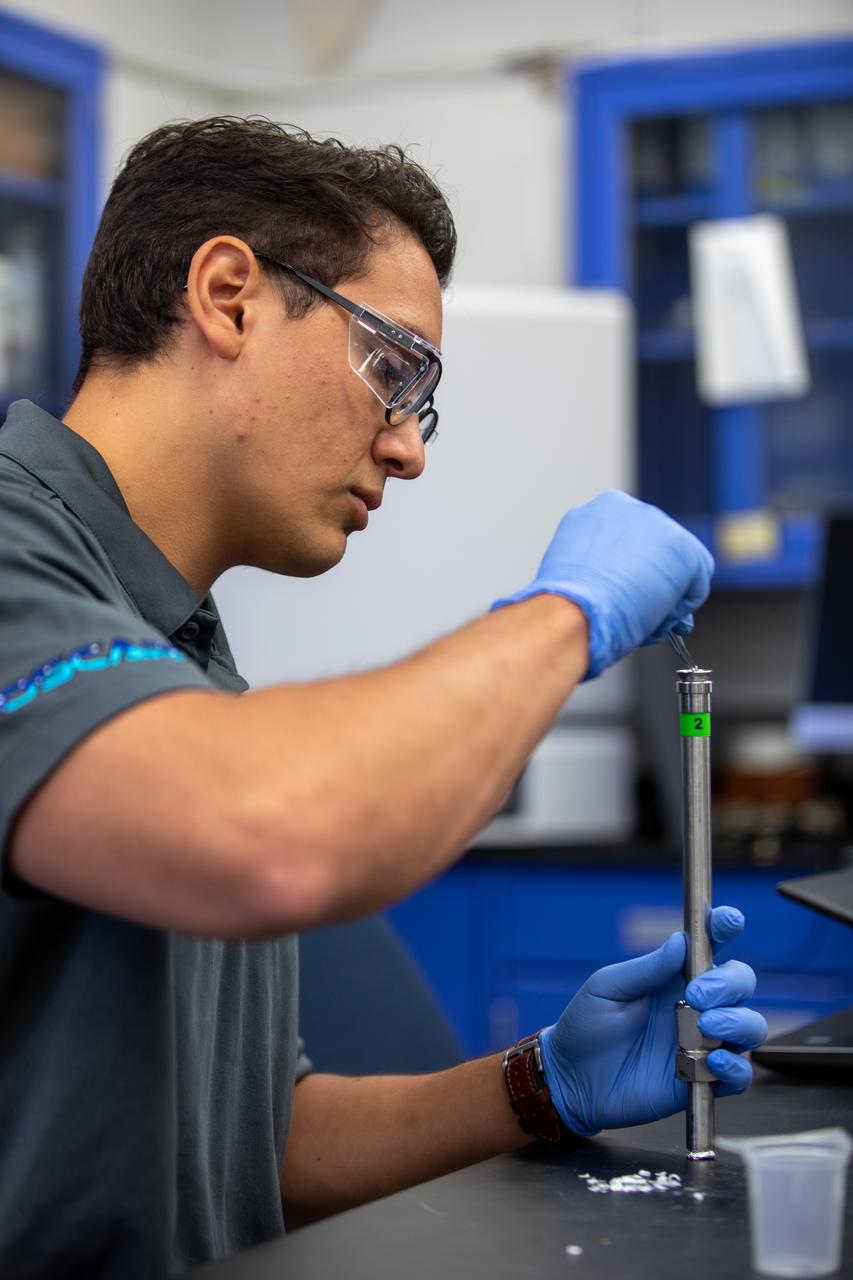

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
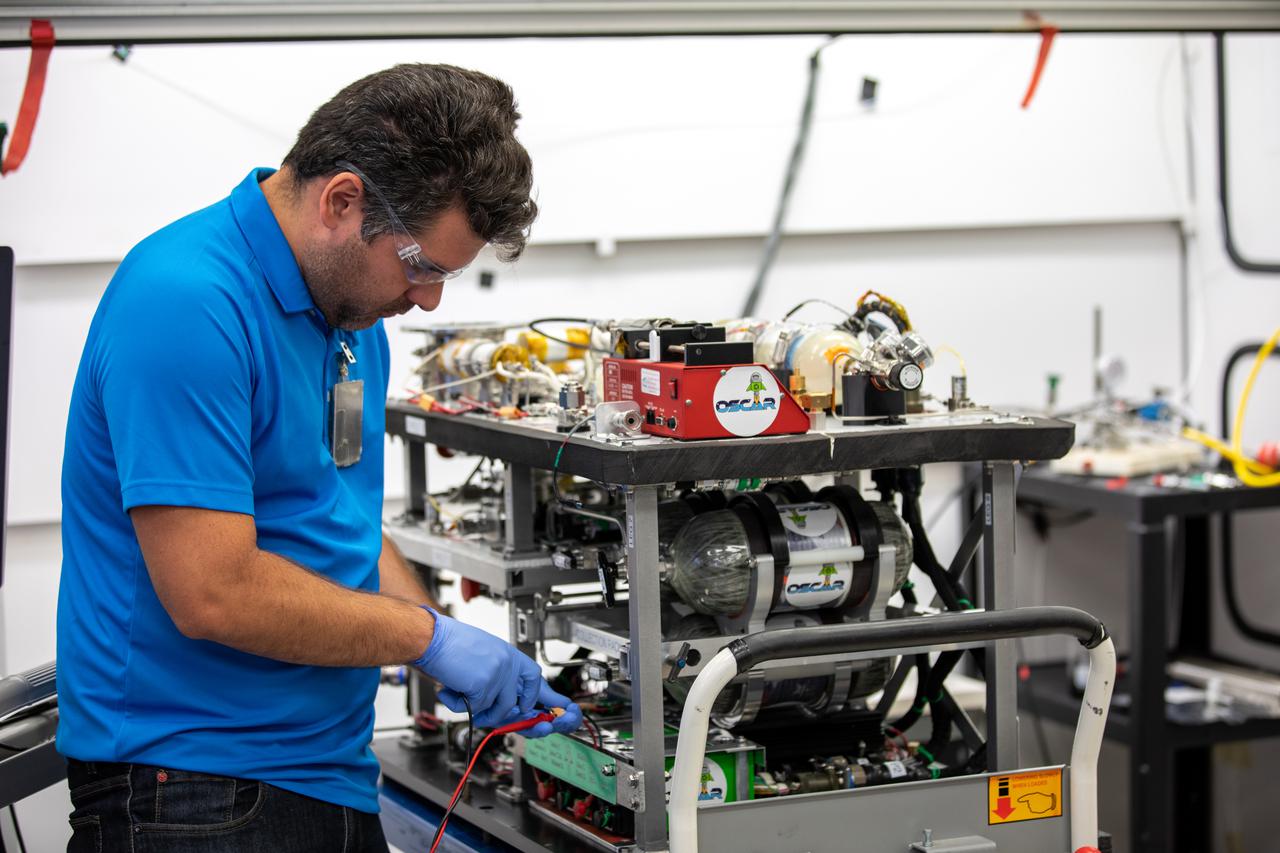

Jaime Toro, an aerospace/mechanical engineer and member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team, performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
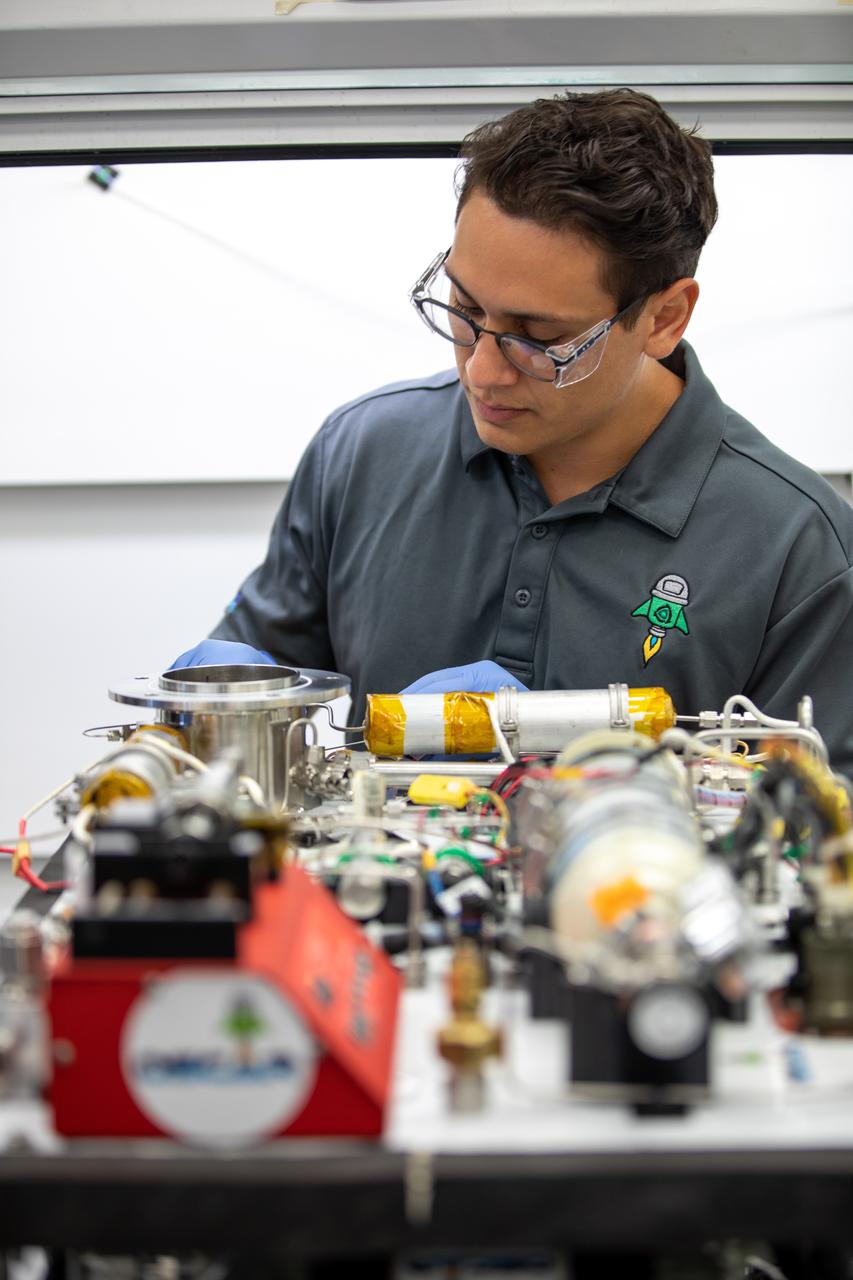

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
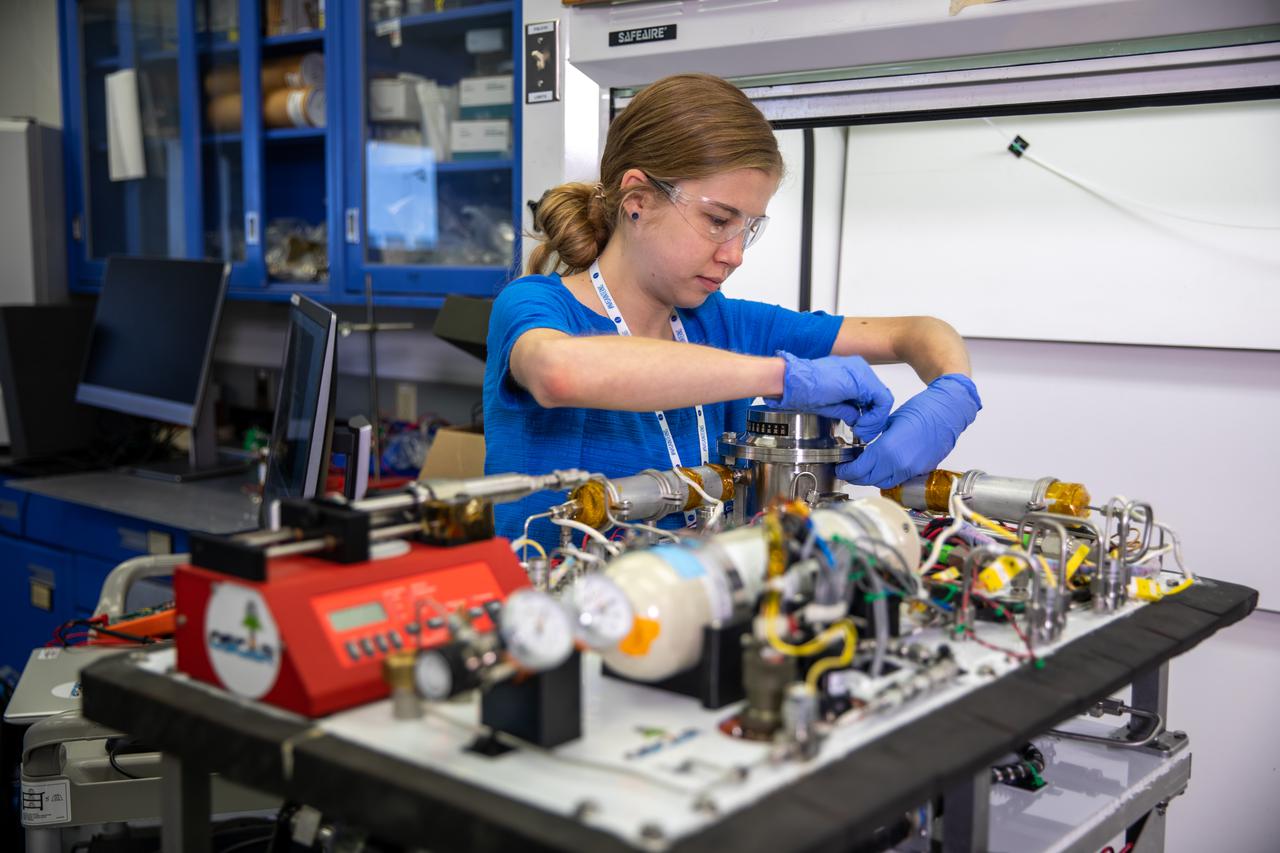
A member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
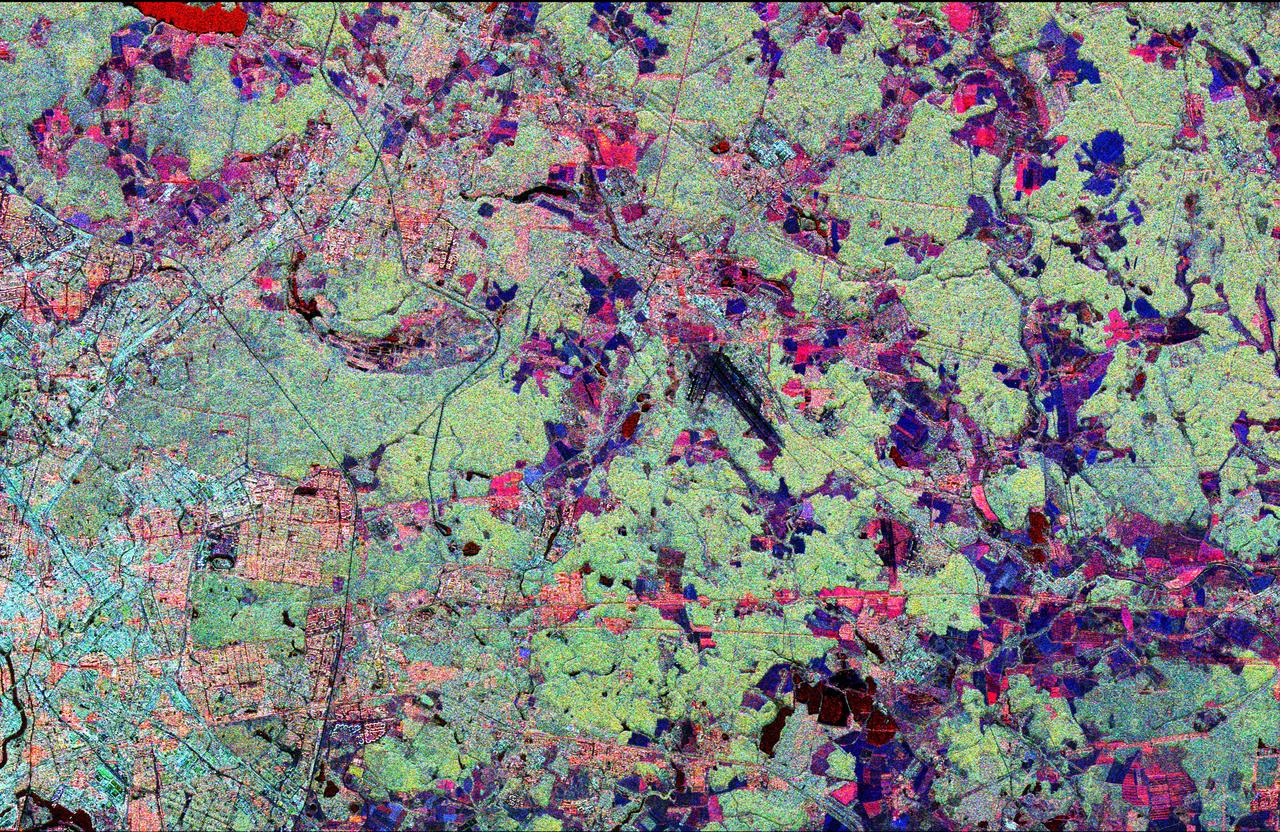
This radar image shows the Star City cosmonaut training center, east of Moscow, Russia. Four American astronauts are training here for future long-duration flights aboard the Russian Mir space station. These joint flights are giving NASA and the Russian Space Agency experience necessary for the construction of the international Alpha space station, beginning in late 1997. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR), on its 62nd orbit on October 3, 1994. This Star City image is centered at 55.55 degrees north latitude and 38.0 degrees east longitude. The area shown is approximately 32 kilometers by 49 kilometers (20 miles by 30 miles). North is to the top in this image. The radar illumination is from the top of the image. The image was produced using three channels of SIR-C radar data: red indicates L-band (23 cm wavelength, horizontally transmitted and received); green indicates L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received); blue indicates C-band (6 cm wavelength, horizontally transmitted and vertically received). In general, dark pink areas are agricultural; pink and light blue areas are urban communities; black areas represent lakes and rivers; dark blue areas are cleared forest; and light green areas are forested. The prominent black runways just right of center are Shchelkovo Airfield, about 4 km long. The textured pale blue-green area east and southeast of Shchelkovo Airfield is forest. Just east of the runways is a thin railroad line running southeast; the Star City compound lies just east of the small bend in the rail line. Star City contains the living quarters and training facilities for Russian cosmonauts and their families. Moscow's inner loop road is visible at the lower left edge of the image. The Kremlin is just off the left edge, on the banks of the meandering Moskva River. The Klyazma River snakes to the southeast from the reservoir in the upper left (shown in bright red), passing just east of Star City and flowing off the lower right edge of the image. The dark blue band of the Vorya River runs north-south in the upper right quadrant, east of Star City. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01775
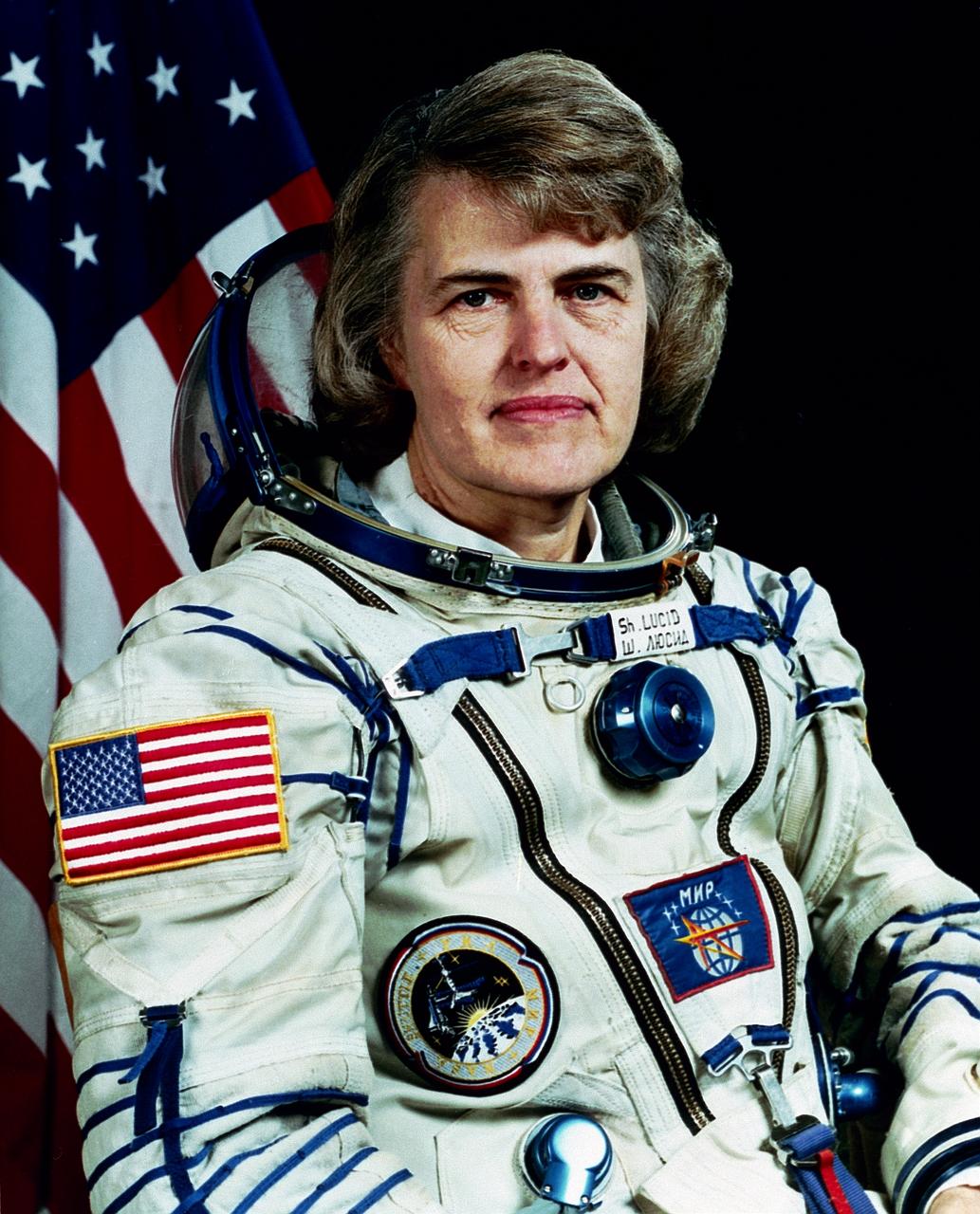

S95-21469 (December 1995) --- Astronaut Shannon W. Lucid, mission specialist, Mir 21/22 flight engineer, cosmonaut guest researcher. EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Lucid will launch aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis, STS-76 mission, to board the Russian Mir Space Station. After a long duration of cosmonaut guest research duties, she will return to Earth aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis STS-79 mission.

ISS014-E-08795 (29 Nov. 2006) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Reiter, Expedition 14 flight engineer, works with the Cognitive Cardiovascular (Cardiocog-2) experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station. Cardiocog-2 will determine the impact of weightlessness on the cardiovascular system and respiratory system and the cognitive reactions of crewmembers. The results of this study will be used to develop additional countermeasures that will continue to keep crewmembers healthy during long-duration space exploration.

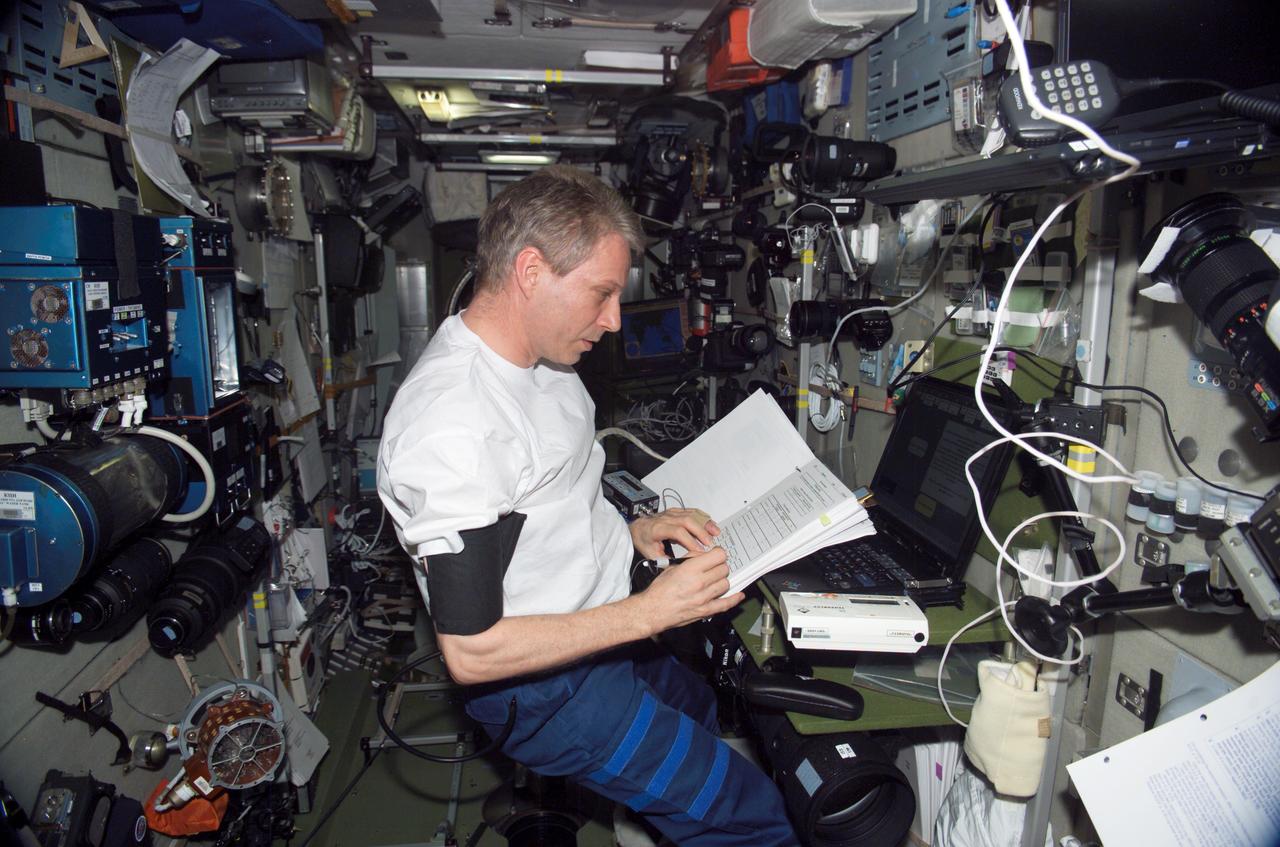
ISS015-E-08659 (May 2007) --- Cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov, Expedition 15 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, checks procedures checklists while collecting medical data for the Cognitive Cardiovascular (Cardiocog-2) experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station. Cardiocog-2 will determine the impact of weightlessness on the cardiovascular system and respiratory system and the cognitive reactions of crewmembers. The results of this study will be used to develop additional countermeasures that will continue to keep crewmembers healthy during long-duration space exploration.
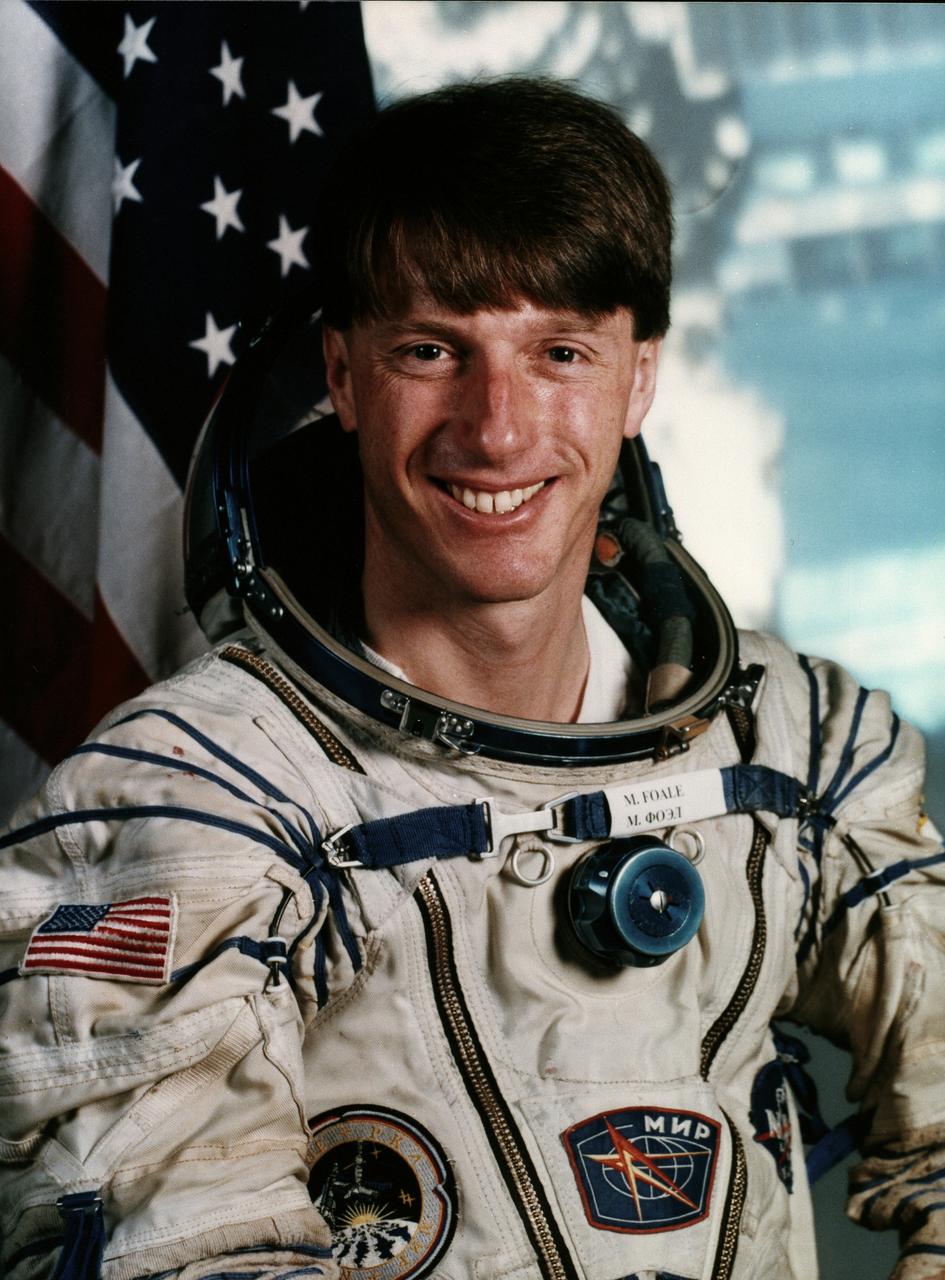

S97-06565 (1997) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, mission specialist/cosmonaut guest researcher Mir 23/24 flight engineer. EDITOR?S NOTE: Astronaut Foale will launch aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis, STS-84 mission, to board the Russia?s Mir Space Station. After a long duration of cosmonaut guest researcher duties, he will return to Earth aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis STS-86 mission.
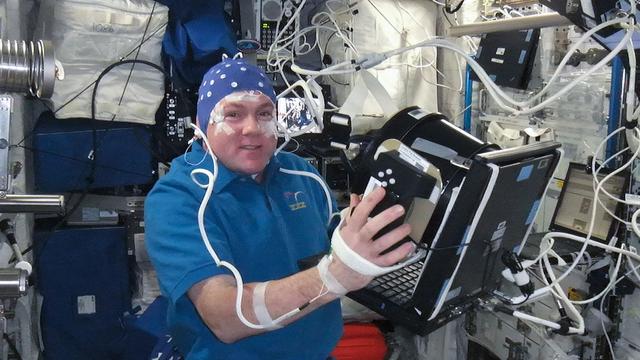
ISS030-E-116907 (13 Feb. 2012) --- Wearing an Electroencephalogram (EEG) electrode cap, European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 30 flight engineer, performs a NeuroSpat science session in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station. NeuroSpat investigates the ways in which crew members’ three-dimensional visual & space perception is affected by long-duration stays in weightlessness.

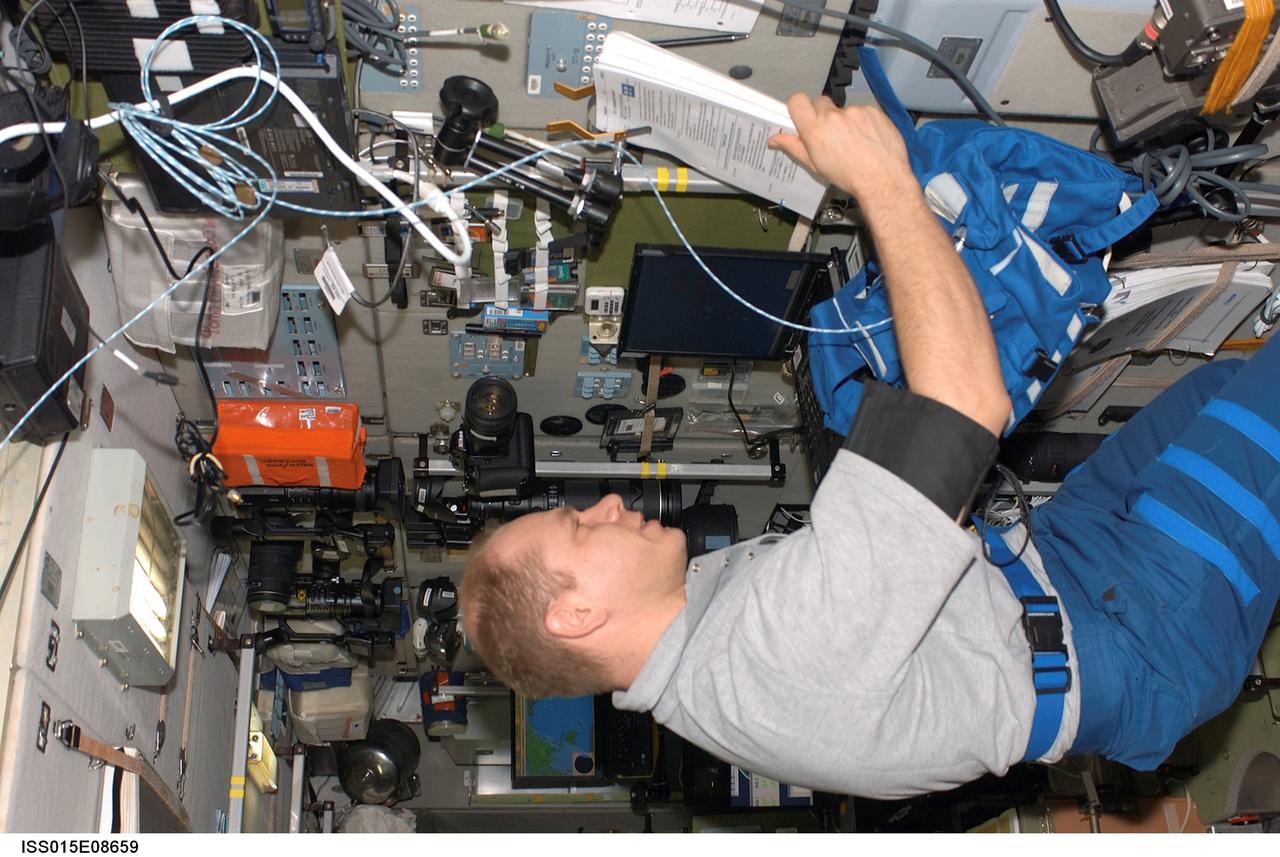
ISS015-E-08660 (May 2007) --- Cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov, Expedition 15 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, collects medical data for the Cognitive Cardiovascular (Cardiocog-2) experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station. Cardiocog-2 will determine the impact of weightlessness on the cardiovascular system and respiratory system and the cognitive reactions of crewmembers. The results of this study will be used to develop additional countermeasures that will continue to keep crewmembers healthy during long-duration space exploration.
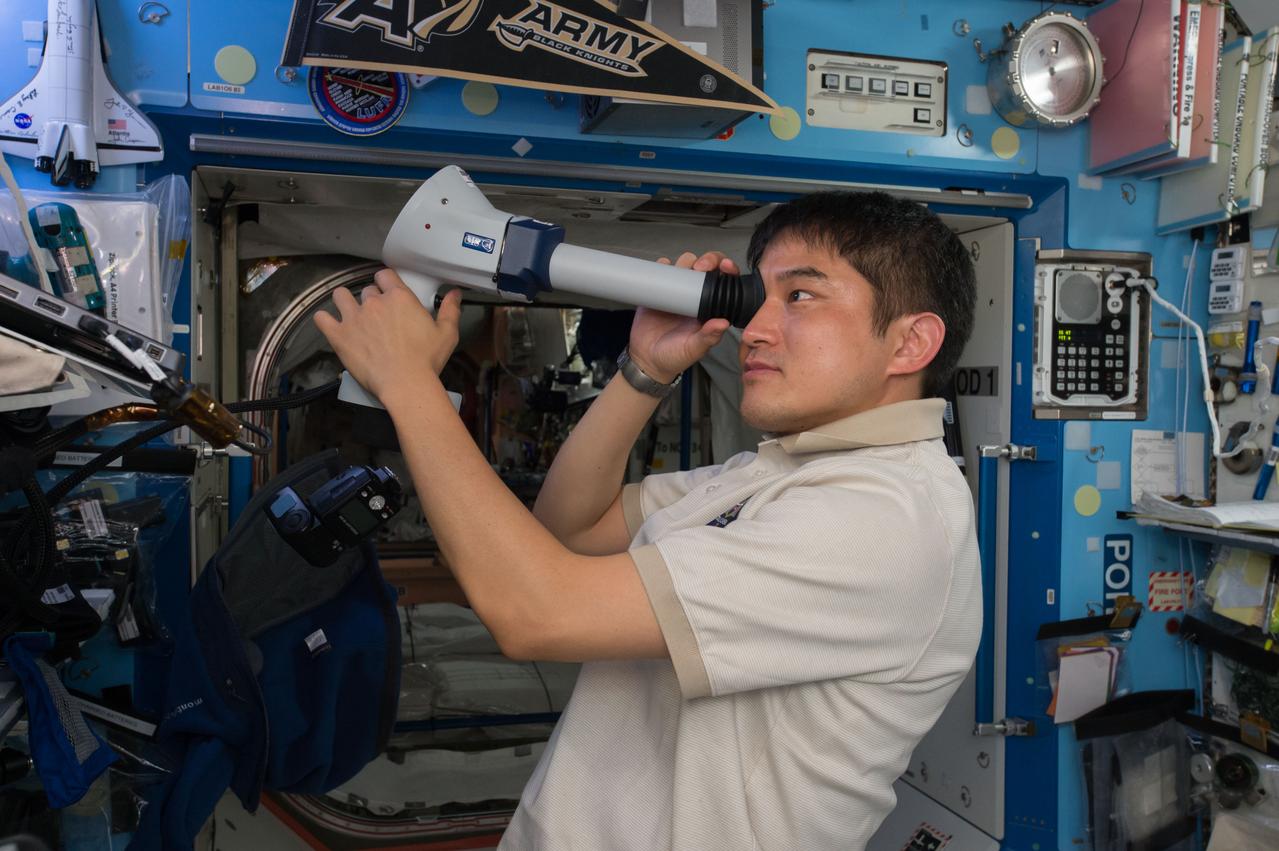

iss048e045079 (07/27/2016) --- Japanese astronaut Takuya Onishi performs eye scans inside of the U.S. Destiny laboratory aboard the International Space Station. Crew members' bodies change in a variety of ways during space flight, and some experience impaired vision. To help develop countermeasures, crew members record their visual health during and after long-duration space station missions.

ISS030-E-116908 (13 Feb. 2012) --- Wearing an Electroencephalogram (EEG) electrode cap, European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 30 flight engineer, performs a NeuroSpat science session in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station. NeuroSpat investigates the ways in which crew members’ three-dimensional visual & space perception is affected by long-duration stays in weightlessness.
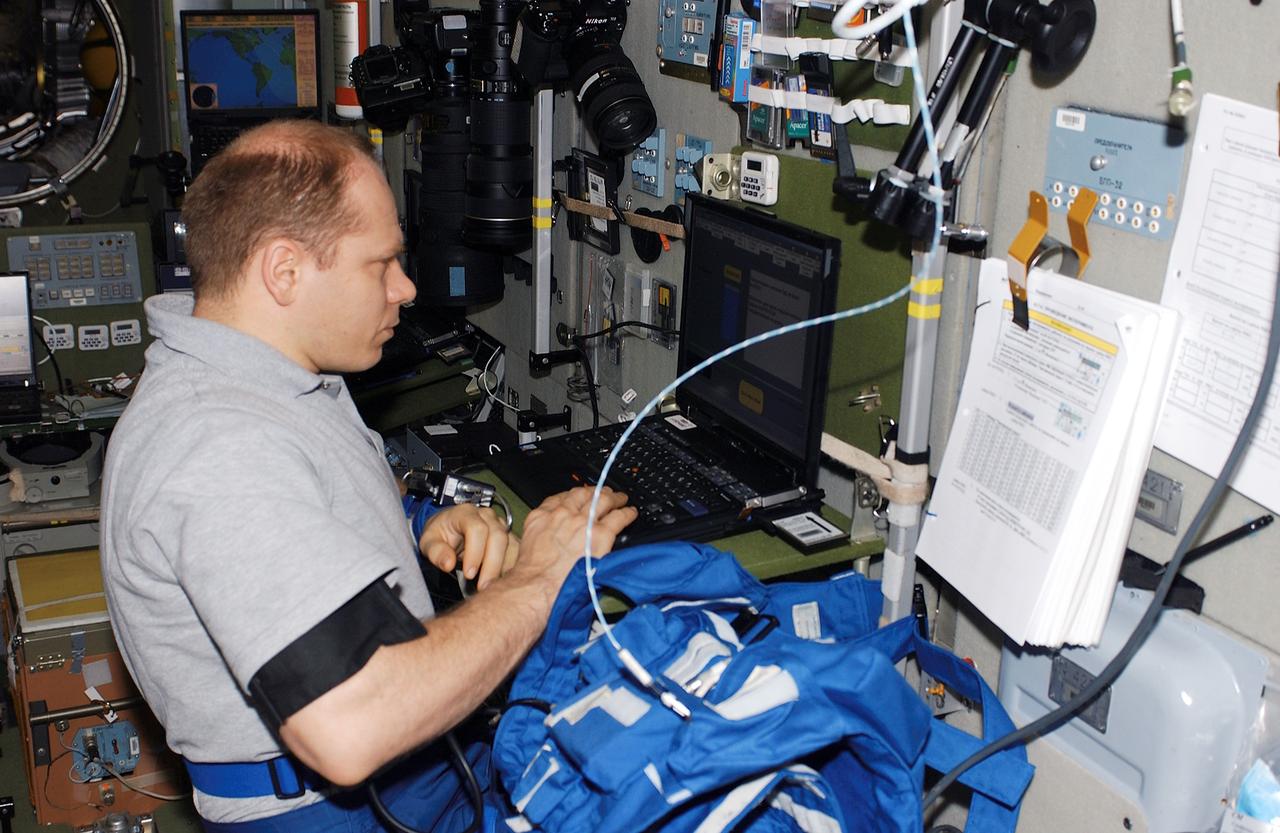

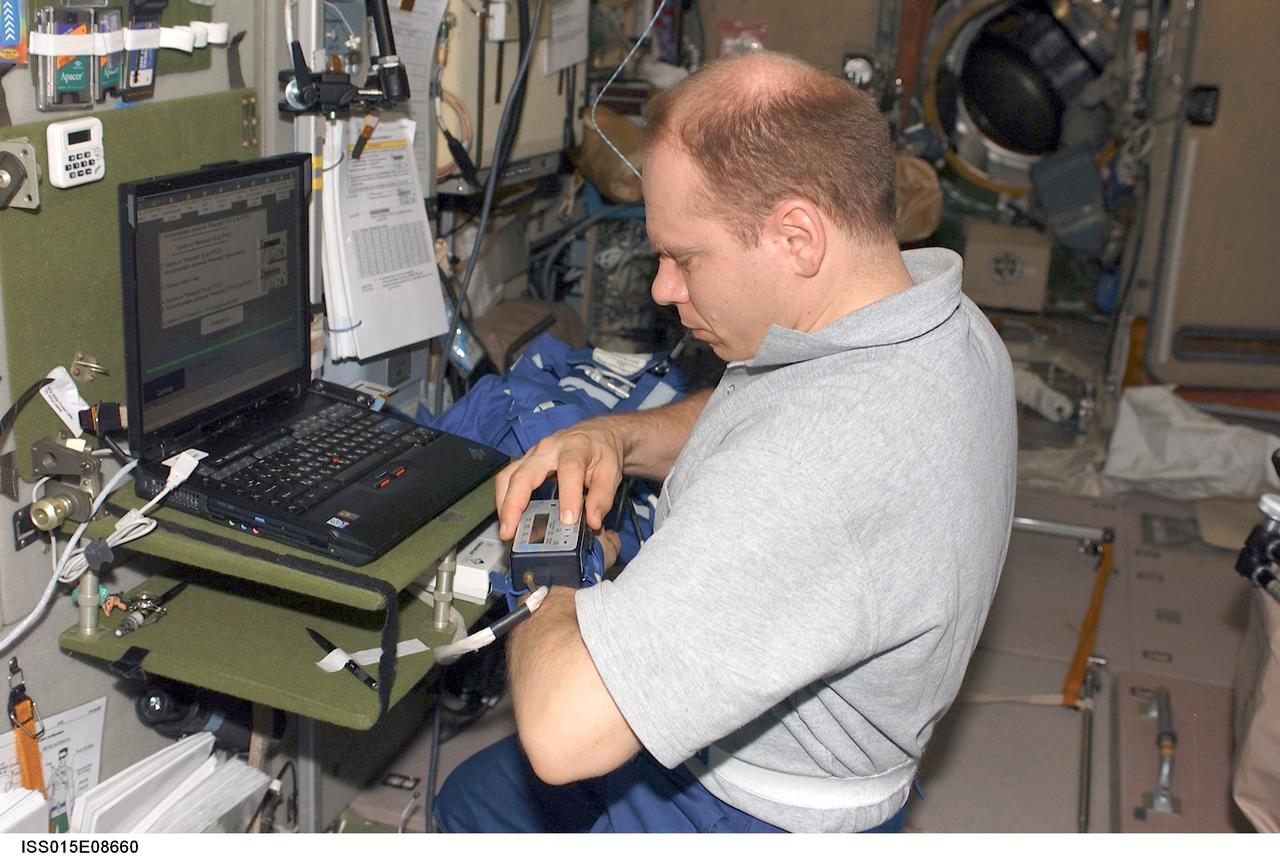
ISS015-E-08661 (May 2007) --- Cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov, Expedition 15 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, collects medical data for the Cognitive Cardiovascular (Cardiocog-2) experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station. Cardiocog-2 will determine the impact of weightlessness on the cardiovascular system and respiratory system and the cognitive reactions of crewmembers. The results of this study will be used to develop additional countermeasures that will continue to keep crewmembers healthy during long-duration space exploration.

Dr. Scott Shipley of Ascentech Enterprises makes an adjustment to the Spectrum unit. He is the project engineer for the effort working under the Engineering Services Contract at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The device is being built for use aboard the International Space Station and is designed to expose different organisms to different color of fluorescent light while a camera records what's happening with time-laps imagery. Results from the Spectrum project will shed light on which living things are best suited for long-duration flights into deep space.
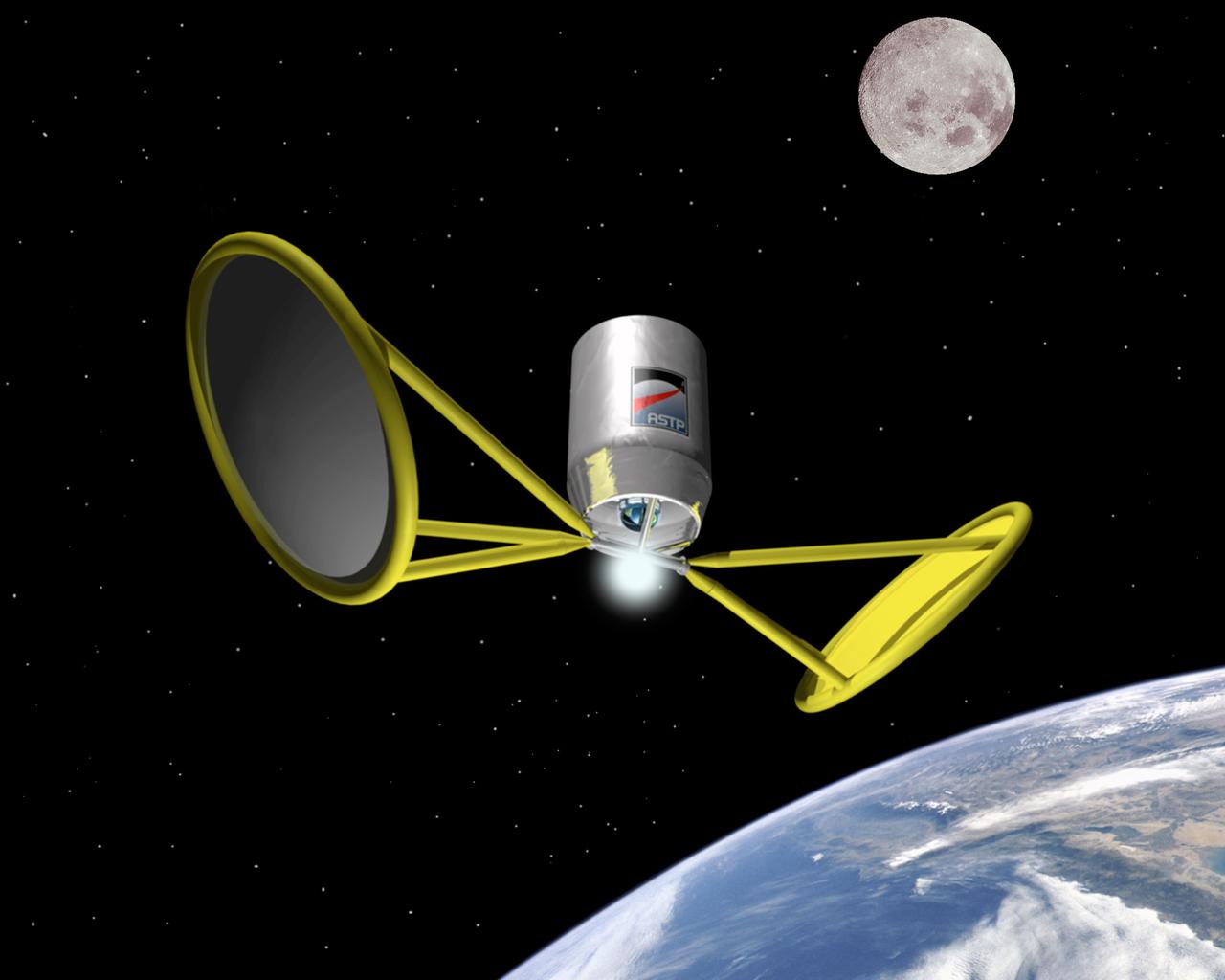
Harnessing the Sun's energy through Solar Thermal Propulsion will propel vehicles through space by significantly reducing weight, complexity, and cost while boosting performance over current conventional upper stages. Another solar powered system, solar electric propulsion, demonstrates ion propulsion is suitable for long duration missions. Pictured is an artist's concept of space flight using solar thermal propulsion.
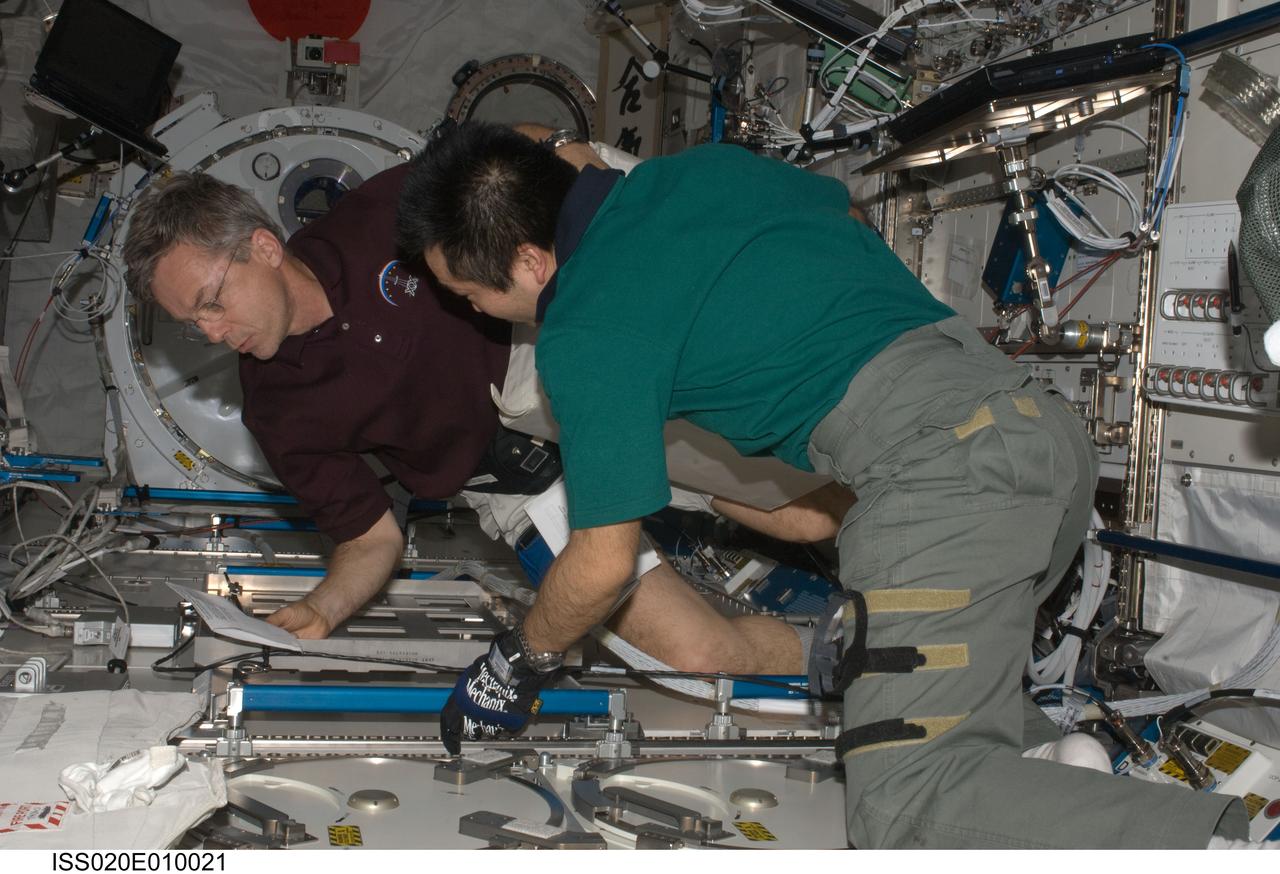

ISS020-E-010021 (15 June 2009) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Robert Thirsk (left) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, both Expedition 20 flight engineers, prepare to put samples in the Minus Eighty Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Samples were taken as part of the Nutritional Status Assessment (Nutrition) with Repository experiment, a study done by NASA to date of human physiologic changes during long-duration spaceflight.

Lori Glaze, acting director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, right, visited NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center March 7 to see firsthand the work done by center scientists. Glaze, along with Marshall planetary scientists Renee Weber, left, and Debra Needham, center, and intern James Mavo, second from right, toured multiple facilities at Marshall – including the Deep Space Habitat facility – to discuss how Marshall is working to support astronauts on long-duration missions.
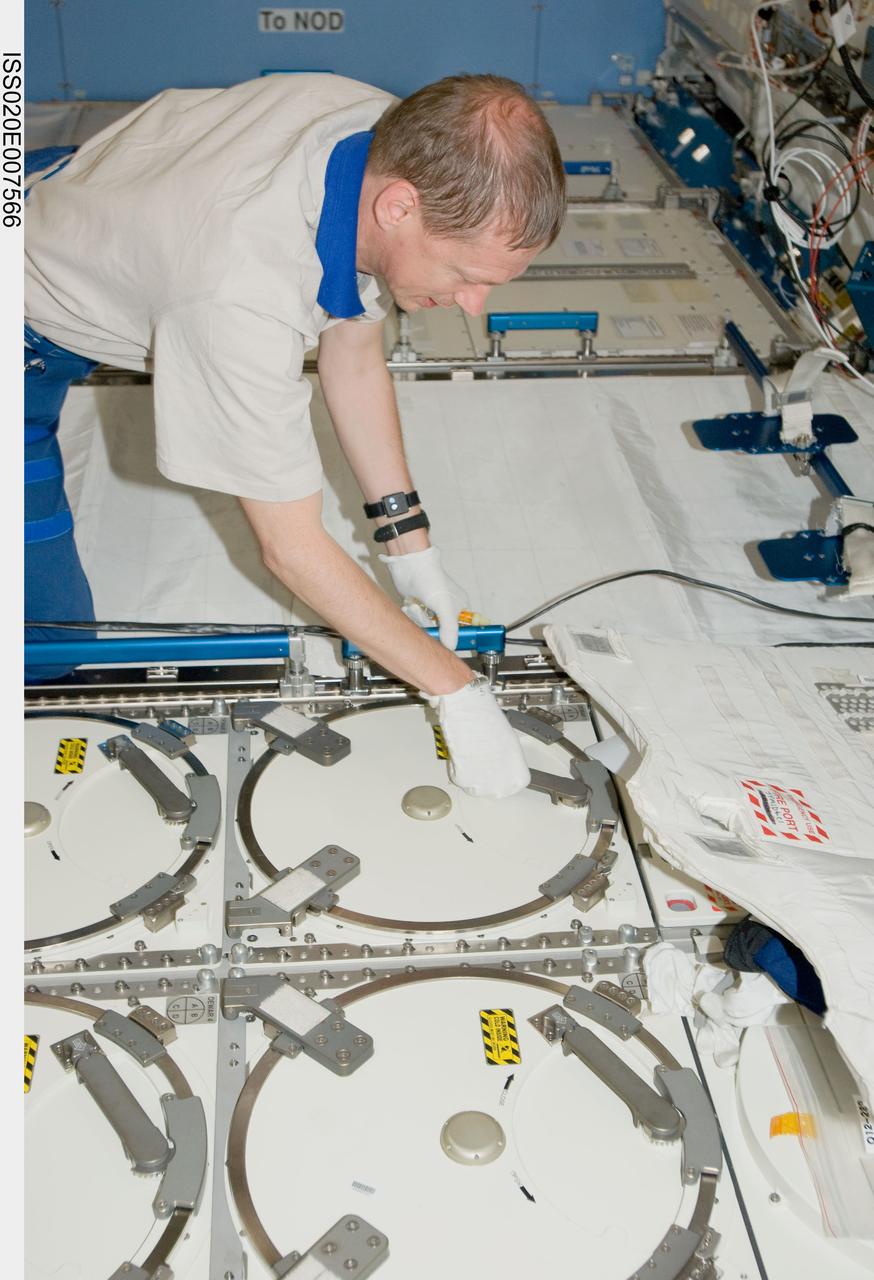

ISS020-E-007566 (6 June 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer, prepares to put samples in the Minus Eighty Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Samples were taken as part of the Nutritional Status Assessment (Nutrition) with Repository experiment, a study done by NASA to date of human physiologic changes during long-duration spaceflight.
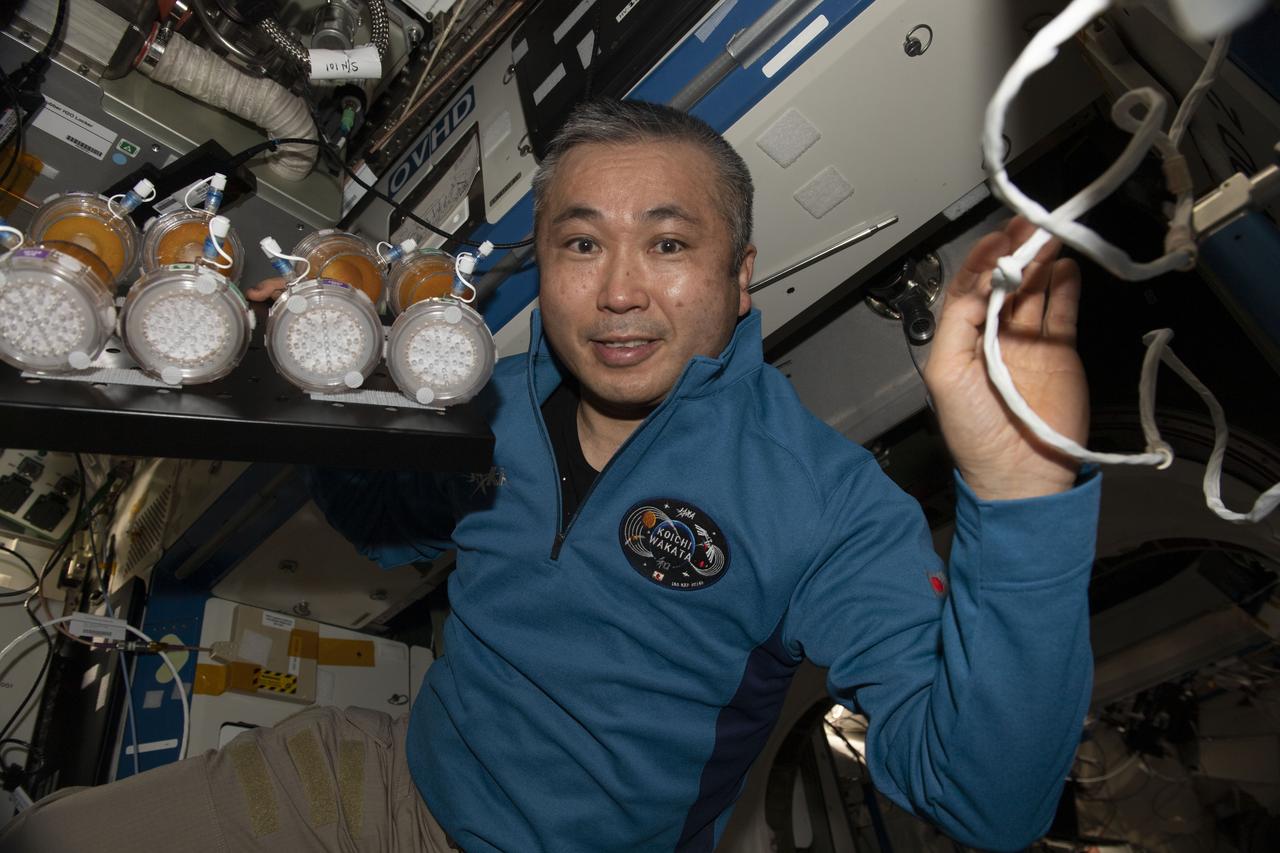

iss068e043110 (Jan. 28, 2023) --- Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) displays incubated nutrient packets removed from the Space Automated Bioproducts Laboratory (SABL). The packets contain generically activated microbes, like yeast, that are hydrated with sterilized water, incubated inside the SABL, then frozen and returned to Earth for analysis. The BioNutrients experiment is demonstrating a technology that enables on-demand production of human nutrients during long-duration space missions.
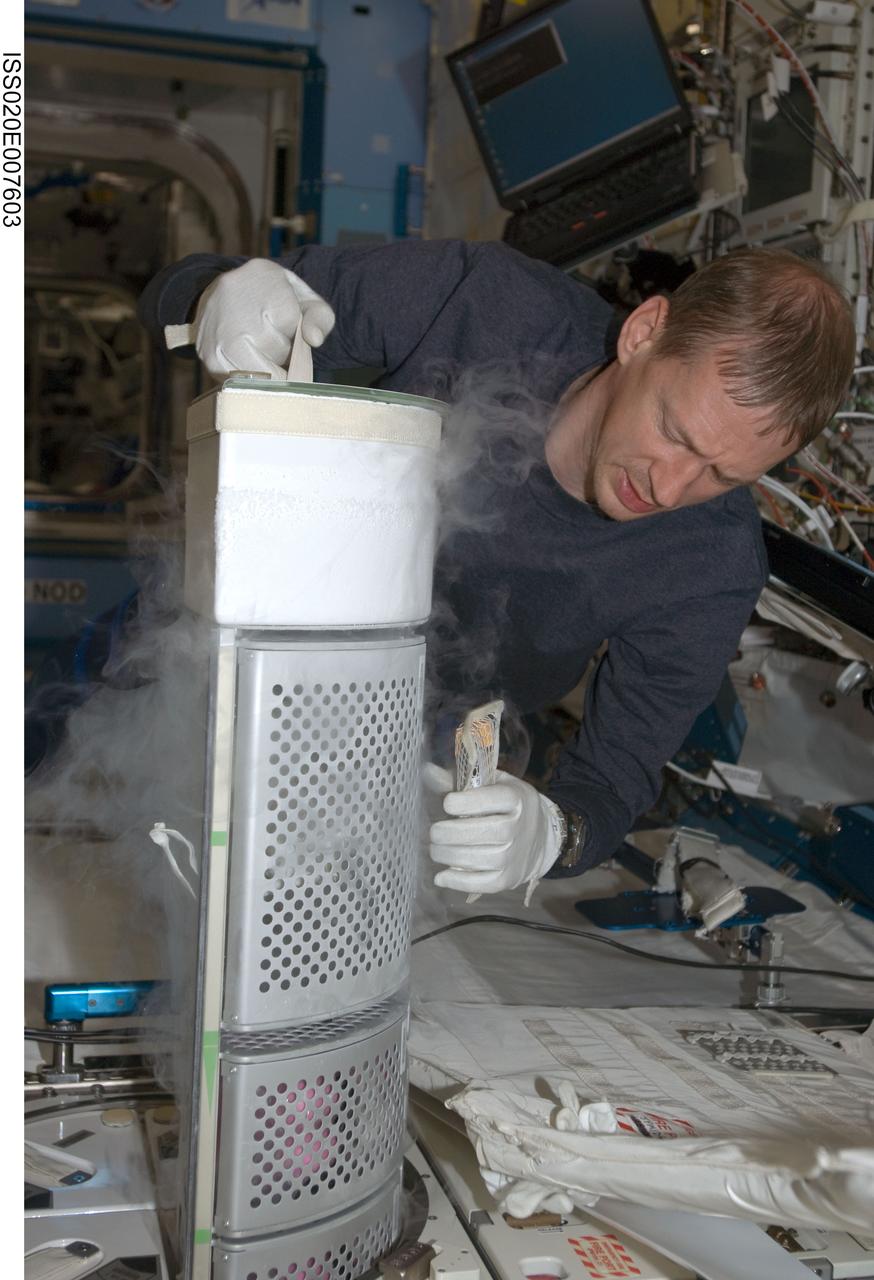

ISS020-E-007603 (7 June 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer, removes a dewar tray from the Minus Eighty Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) in order to insert biological samples into the trays in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Samples were taken as part of the Nutritional Status Assessment (Nutrition) with Repository experiment, a study done by NASA to date of human physiologic changes during long-duration spaceflight.
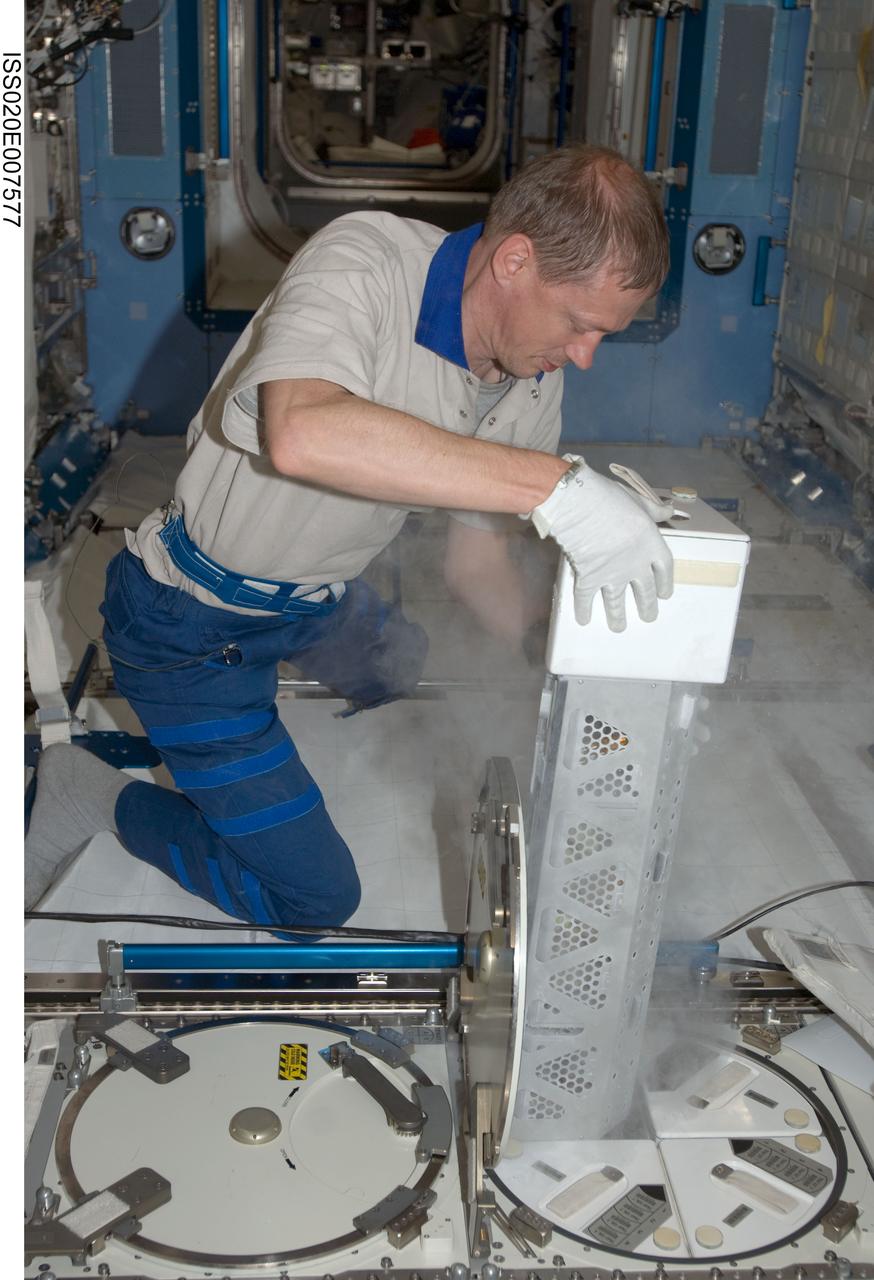

ISS020-E-007577 (6 June 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer, returns a dewar tray to the Minus Eighty Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) after inserting biological samples into the trays in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Samples were taken as part of the Nutritional Status Assessment (Nutrition) with Repository experiment, a study done by NASA to date of human physiologic changes during long-duration spaceflight.
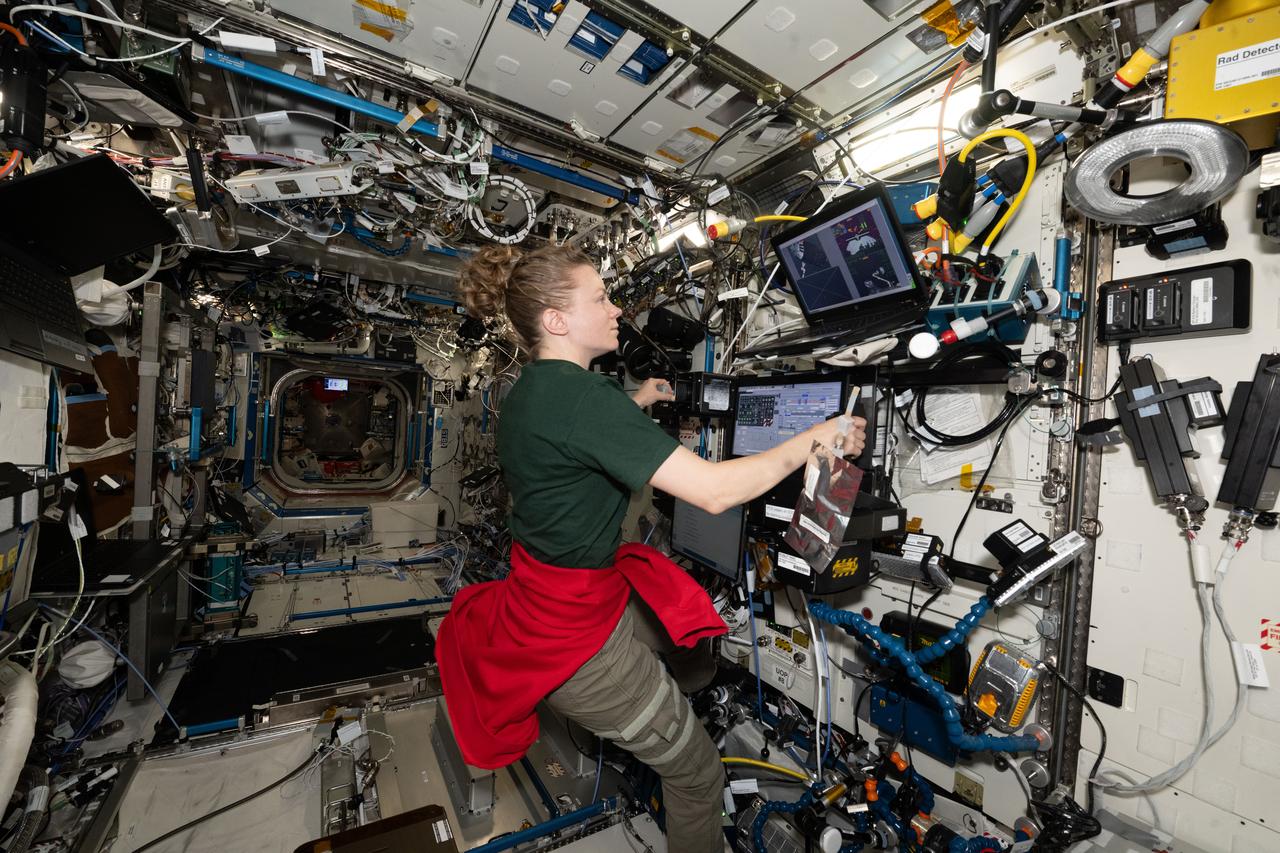

iss073e0505925 (Aug. 15, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Zena Cardman operates the robotics workstation in the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module during a computerized test tracking space-related effects on her brain function. Part of the CIPHER suite of 14 human research investigations, the cognition study could lead to advanced tools like brain scans and task simulations for future long-duration missions.
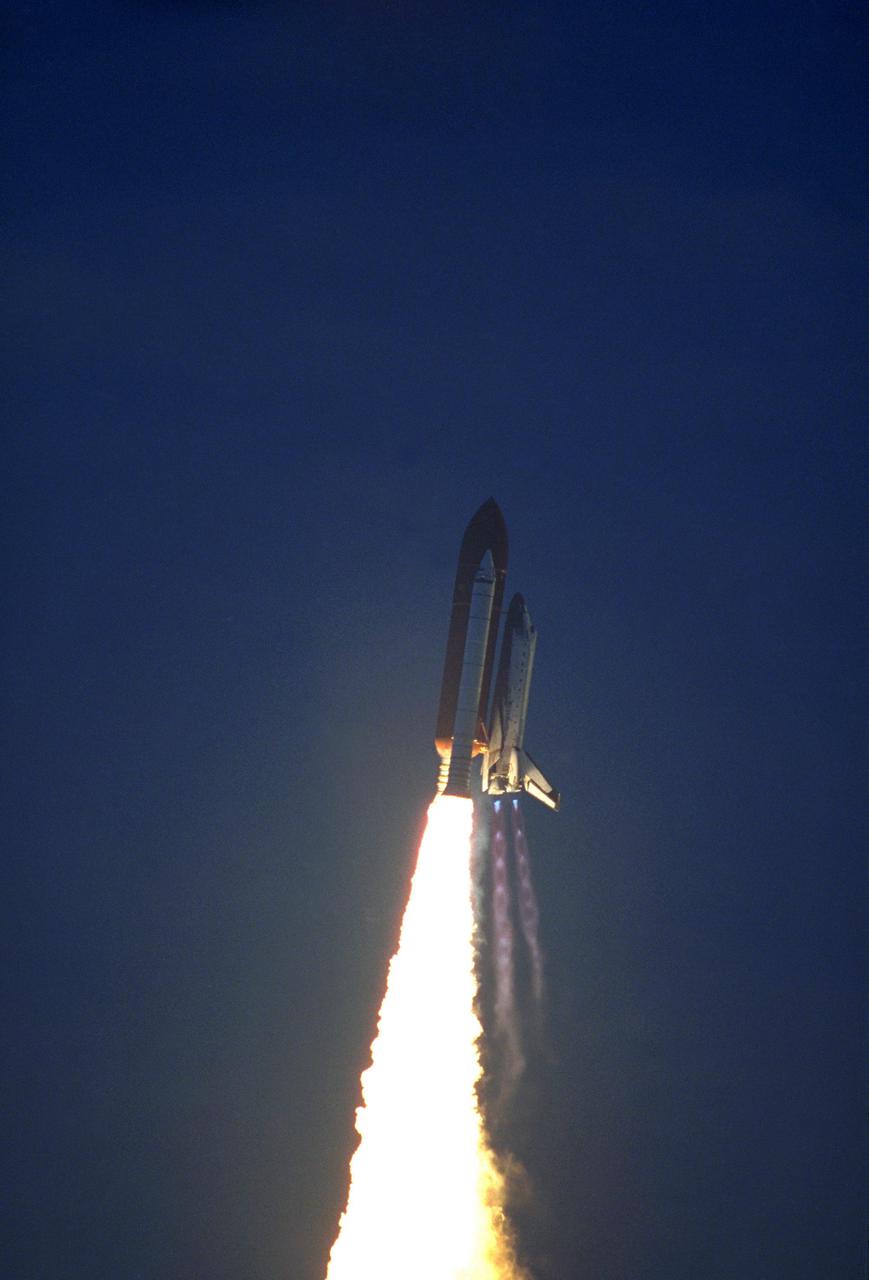

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-32R lifts off from Pad 39-A at 7:35 a.m. EST. Columbia is scheduled to deploy the Syncom IV-5 defense communications satellite and retrieve NASA's Long duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) during a 10-day mission, the longest Shuttle flight to date. The mission also includes a variety of experiments, including Protein Crystal Growth. This photo was taken from the Shuttle Training Aircraft.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-32R lifts off from Pad 39-A at 7:35 a.m. EST. Columbia is scheduled to deploy the Syncom IV-5 defense communications satellite and retrieve NASA's Long duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) during a 10-day mission, the longest Shuttle flight to date. The mission also includes a variety of experiments, including Protein Crystal Growth. This photo was taken from the Shuttle Training Aircraft.
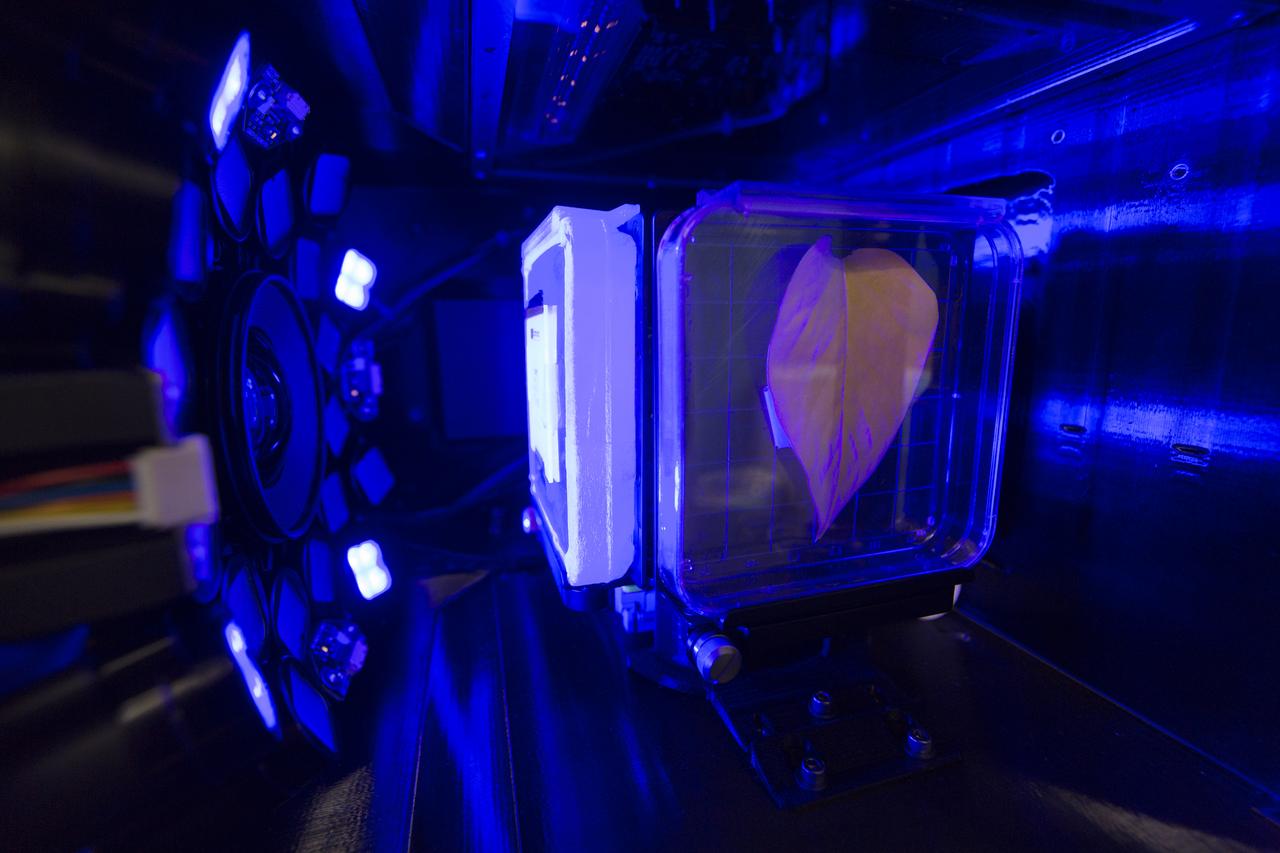

Inside the Spectrum prototype unit, organisms in a Petri plate are exposed to blue excitation lighting. The device works by exposing organisms to different colors of fluorescent light while a camera records what's happening with time-lapse photography. Results from the Spectrum project will shed light on which living things are best suited for long-duration flights into deep space.
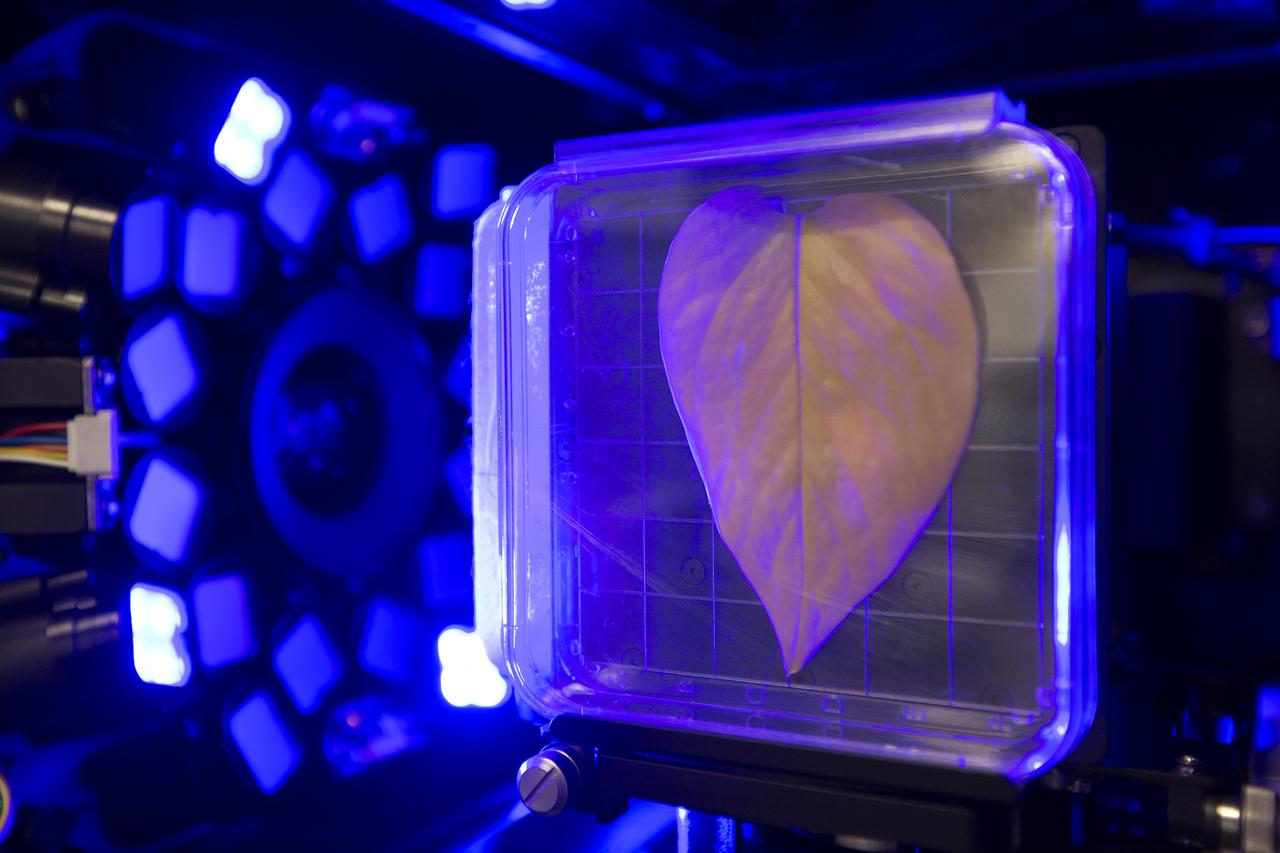
Inside the Spectrum prototype unit, organisms in a Petri plate are exposed to blue excitation lighting. The device works by exposing organisms to different colors of fluorescent light while a camera records what's happening with time-lapse photography. Results from the Spectrum project will shed light on which living things are best suited for long-duration flights into deep space.
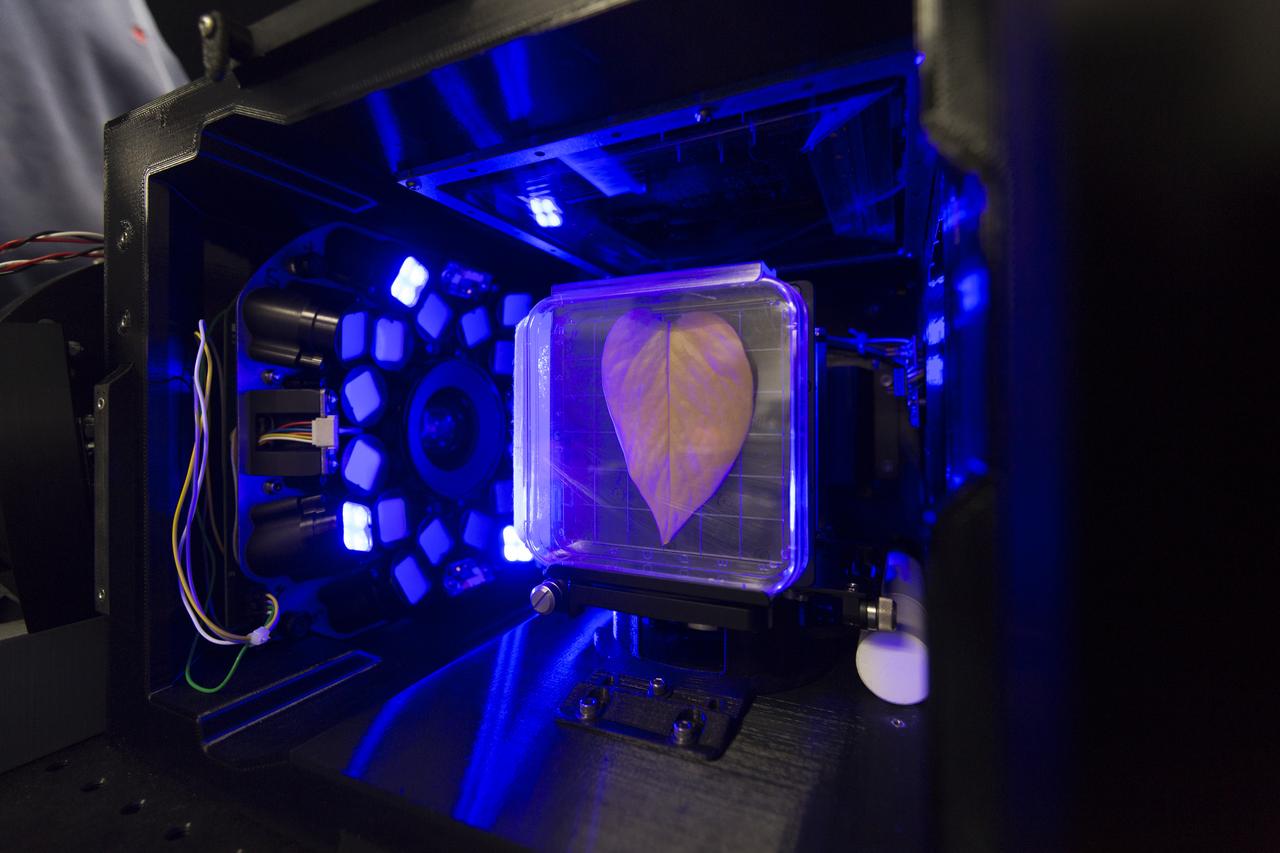
Inside the Spectrum prototype unit, organisms in a Petri plate are exposed to blue excitation lighting. The device works by exposing organisms to different colors of fluorescent light while a camera records what's happening with time-lapse photography. Results from the Spectrum project will shed light on which living things are best suited for long-duration flights into deep space.
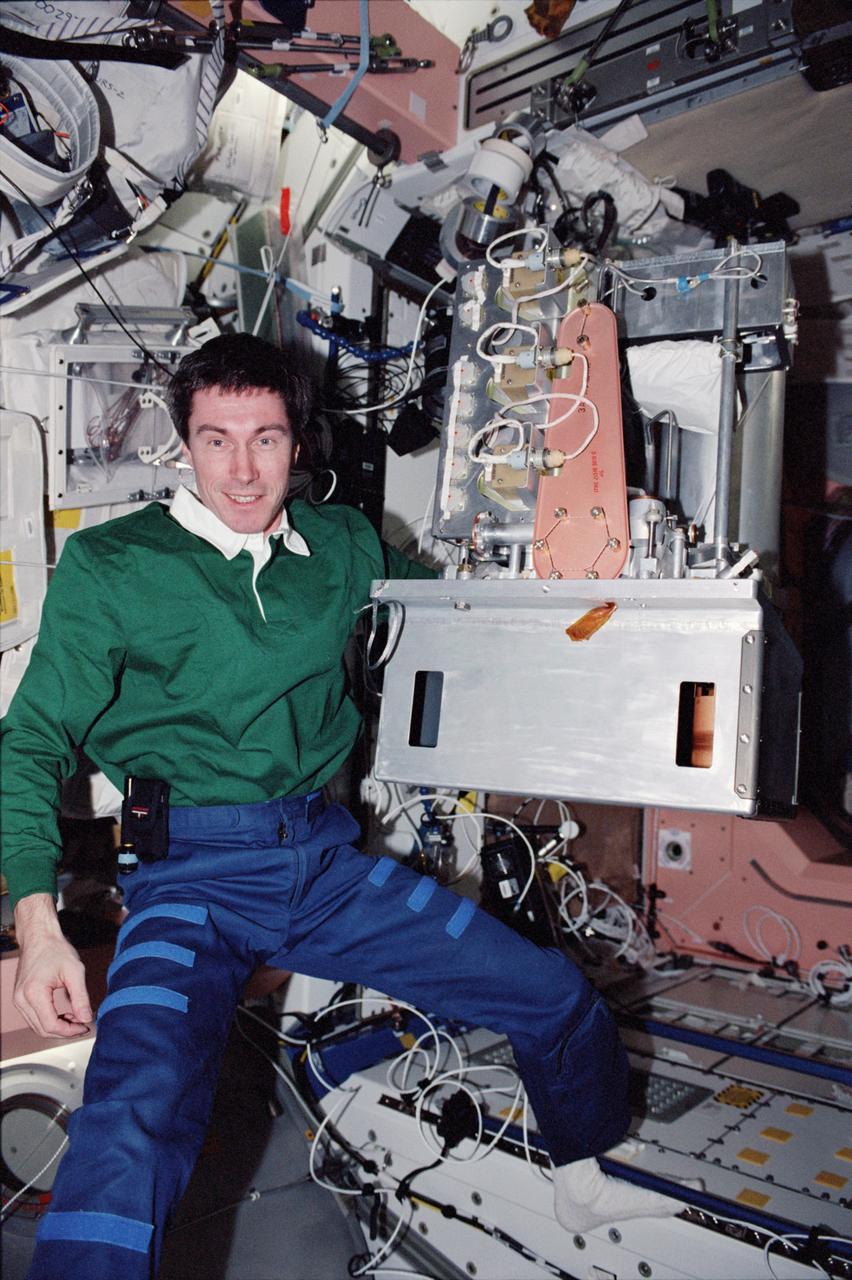

STS098-346-0032 (7-20 February 2001) --- Cosmonaut Sergei K. Krikalev, Expedition One flight engineer representing the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, carries the Vozdukh in the Unity node. Vozdukh is designed to maintain the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the cabin air within the medically permissible range for long-duration exposure. It provides the primary means of removing CO2 from the outpost's atmosphere, and its operation is based on the use of regenerated adsorbers of CO2.
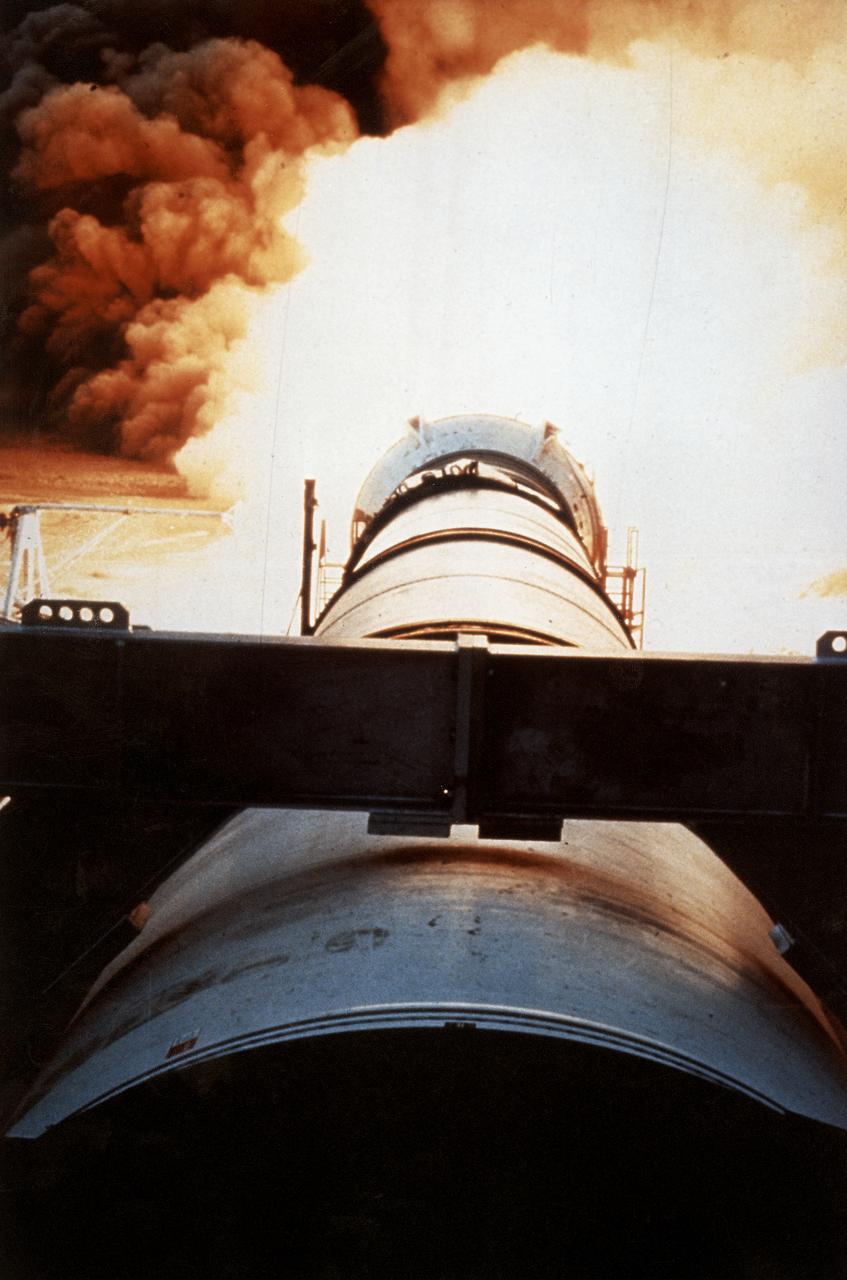

One of the key tests in the effort to return the Space Shuttle to flight following the Challenger accident was testing the development Motor-8 (DM-8). The 126-foot long, 1.2-million-pound motor, designated DM-8, underwent a full-duration horizontal test firing for two minutes at the Thiokol test facility in Utah. It was fitted with more than 500 instruments to measure such things as acceleration, pressure, deflection thrust, strain, temperature, and electrical properties.

Inside the Spectrum prototype unit, organisms in a Petri plate are exposed to different colors of lighting. The device works by exposing organisms to different colors of fluorescent light while a camera records what's happening with time-lapse photography. Results from the Spectrum project will shed light on which living things are best suited for long-duration flights into deep space.
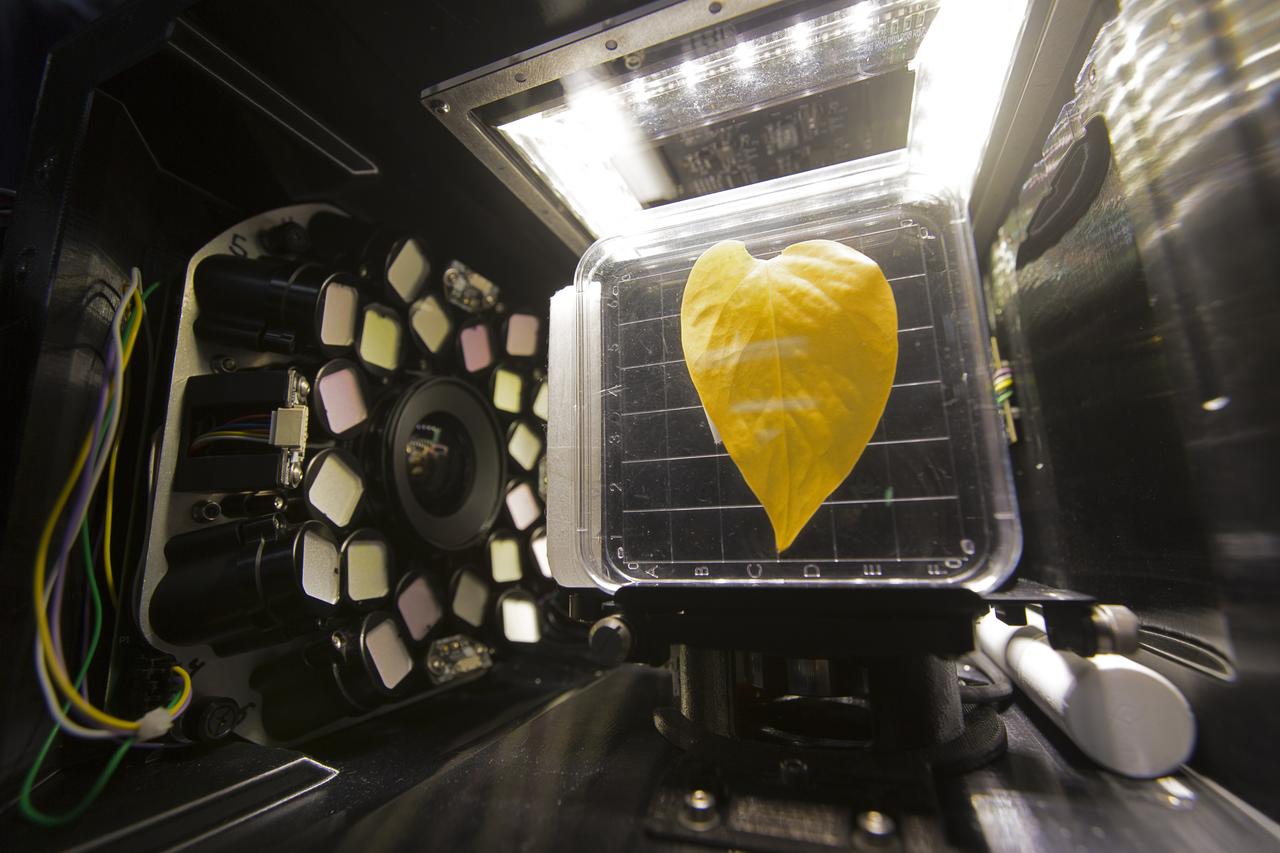

Inside the Spectrum prototype unit, organisms in a Petri plate are exposed to different colors of lighting. The device works by exposing organisms to different colors of fluorescent light while a camera records what's happening with time-lapse photography. Results from the Spectrum project will shed light on which living things are best suited for long-duration flights into deep space.
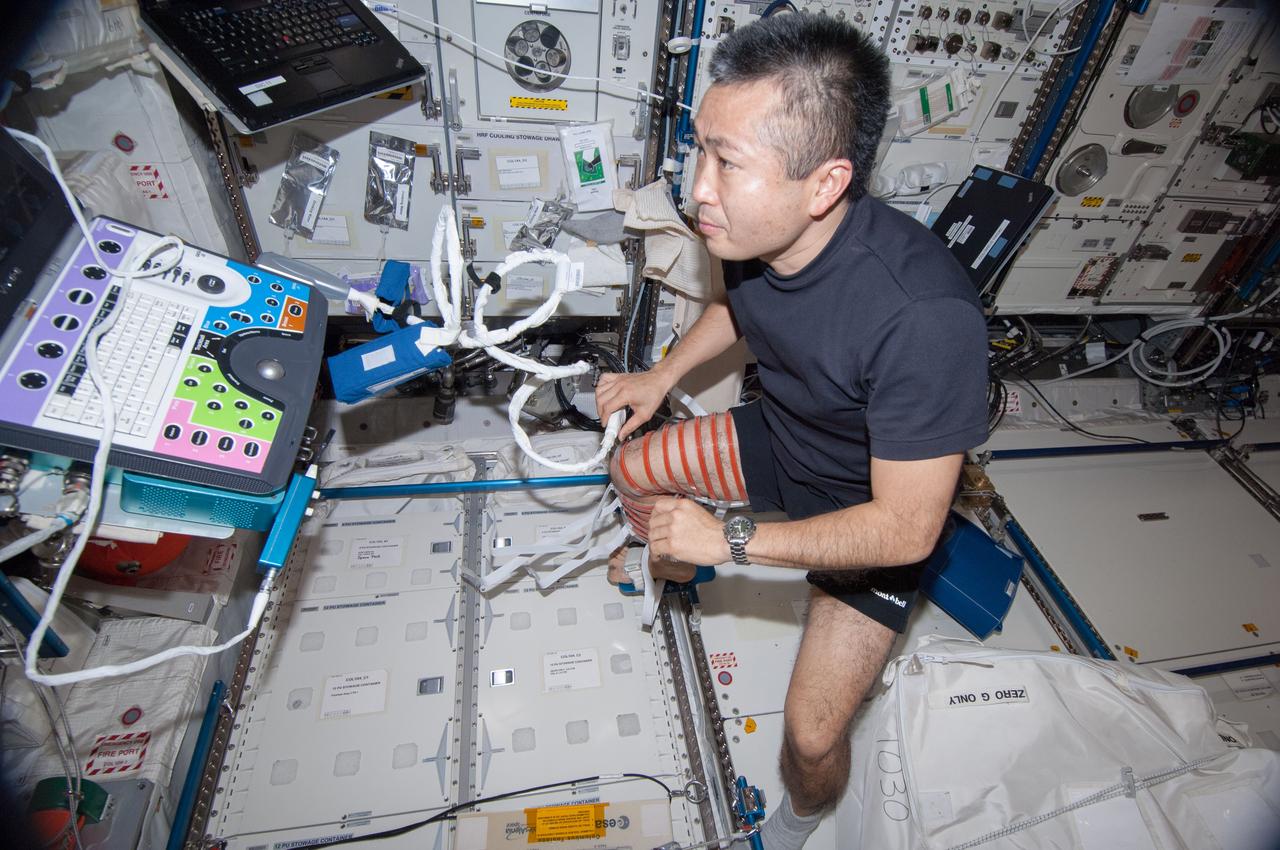

ISS038-E-007119 (21 Nov. 2013) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 38 flight engineer, wears ultrasound gear around his legs while performing the Integrated Resistance and Aerobic Training Study (Sprint) experiment in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station. Sprint evaluates the use of high intensity, low volume exercise training to minimize loss of muscle, bone, and cardiovascular function in station crew members during long-duration missions.
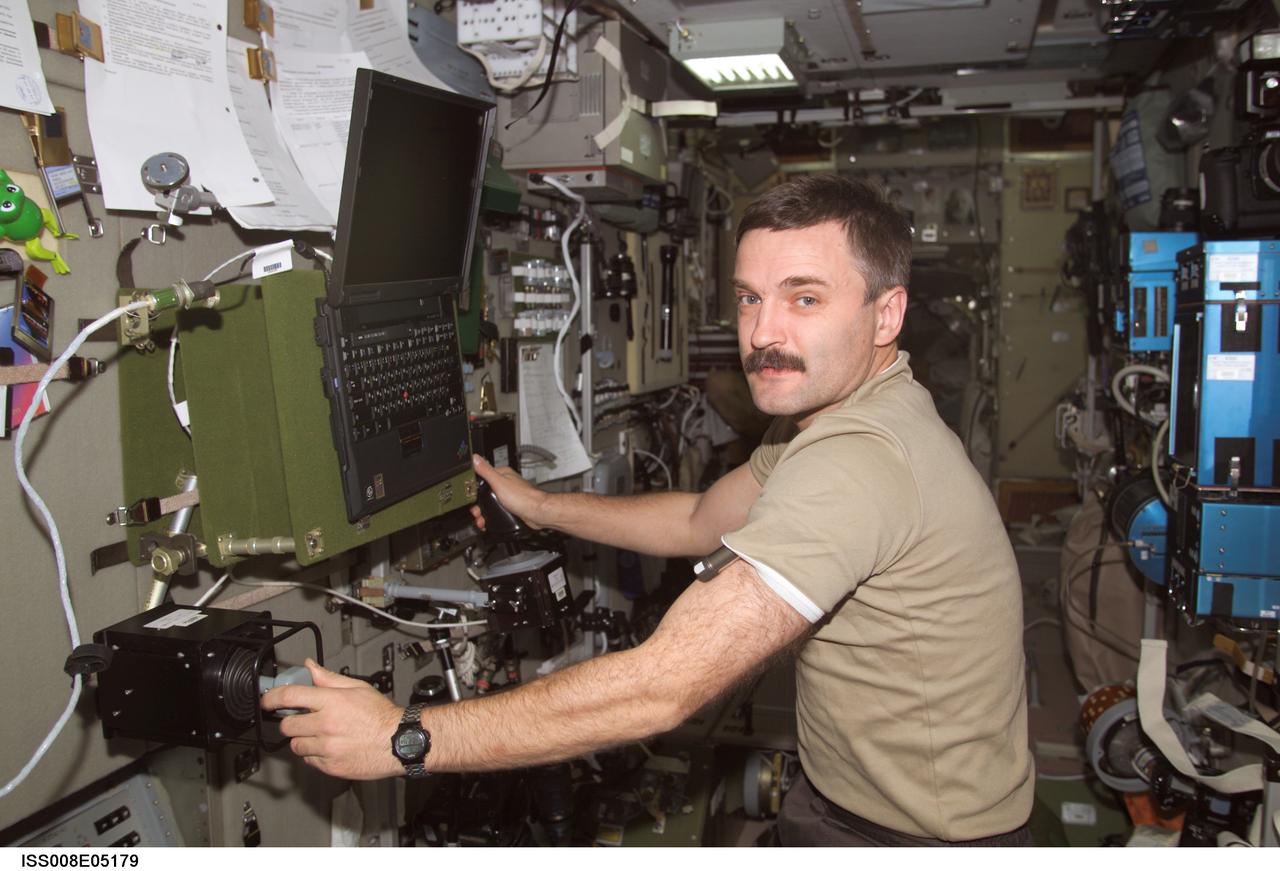

ISS008-E-05179 (31 October 2003) --- Cosmonaut Alexander Y. Kaleri, Expedition 8 flight engineer, works with the Russian biomedical “Pilot” experiment (MBI-15) in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The experiment, which looks at psychological and physiological changes in crew performance during long-duration spaceflight, requires a worktable, ankle restraint system and two control handles for testing piloting skill. Kaleri represents Rosaviakosmos.

iss071e265124 (July 3, 2024) --- Boeing's Starliner spacecraft that launched NASA's Crew Flight Test astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams to the International Space Station is pictured docked to the Harmony module's forward port. This long-duration photograph was taken at night from the orbital complex as it soared 256 miles above the Arabian Sea off the coast of Mumbai, India.
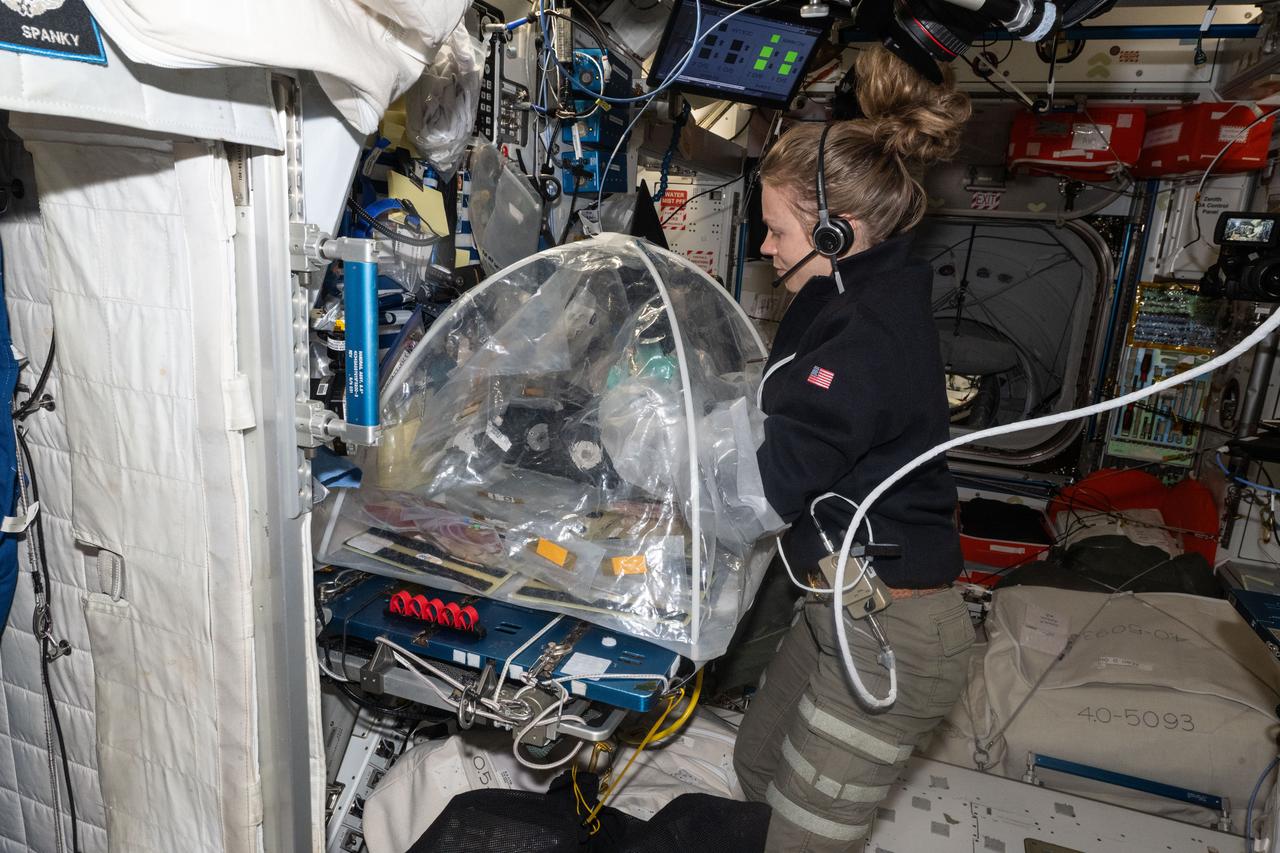

iss073e0606876 (Sept. 5, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Zena Cardman treats bioprinted liver tissues in a portable glovebag inside the International Space Station's Harmony module. The samples will be placed inside an artificial gravity-generating research device to help researchers understand how microgravity affects the formation of blood vessels in engineered tissues. Result may lead to advanced treatments protecting astronauts on long-duration spaceflights and improve bioprinting techniques for patient therapies on Earth.
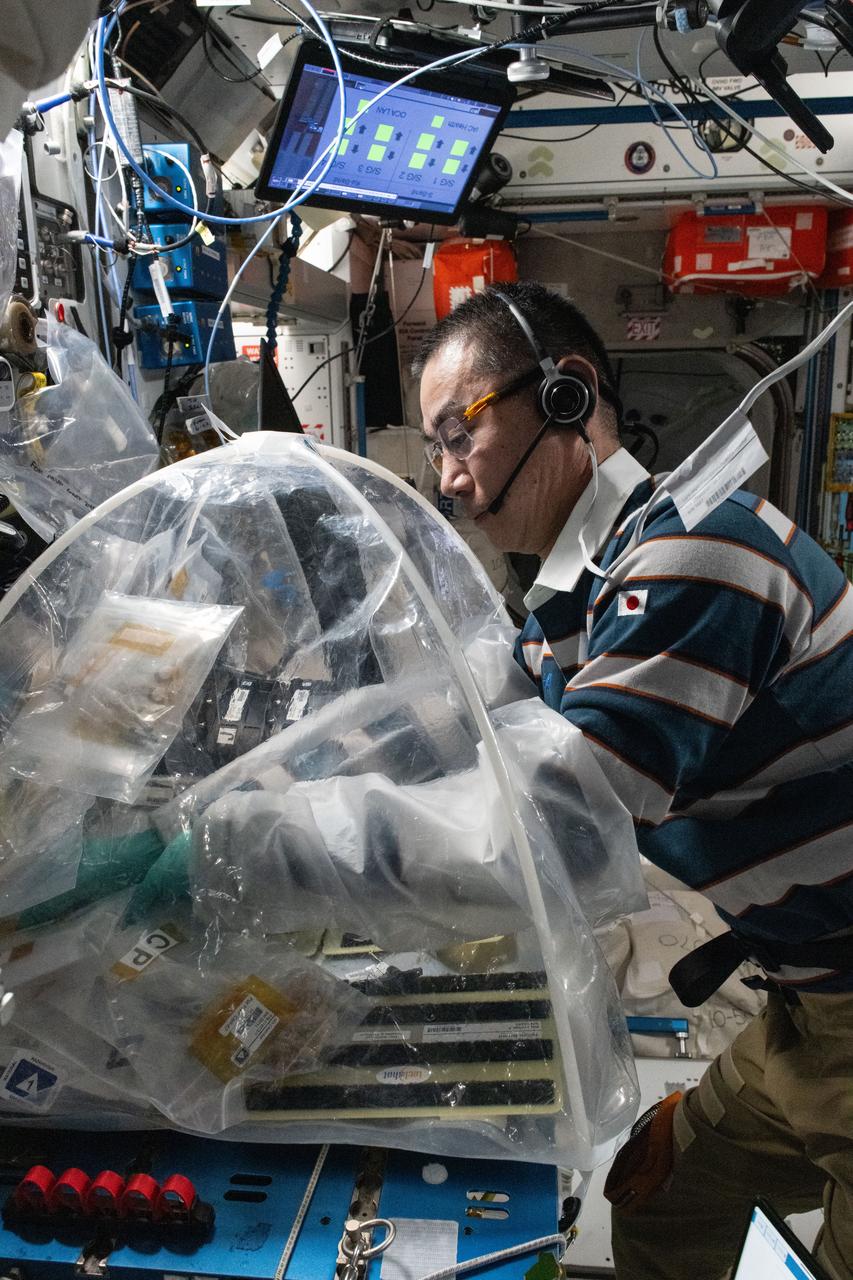

iss073e0606883 (Sept. 5, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Kimiya Yui treats bioprinted liver tissues in a portable glovebag inside the International Space Station's Harmony module. The samples will be placed inside an artificial gravity-generating research device to help researchers understand how microgravity affects the formation of blood vessels in engineered tissues. Result may lead to advanced treatments protecting astronauts on long-duration spaceflights and improve bioprinting techniques for patient therapies on Earth.
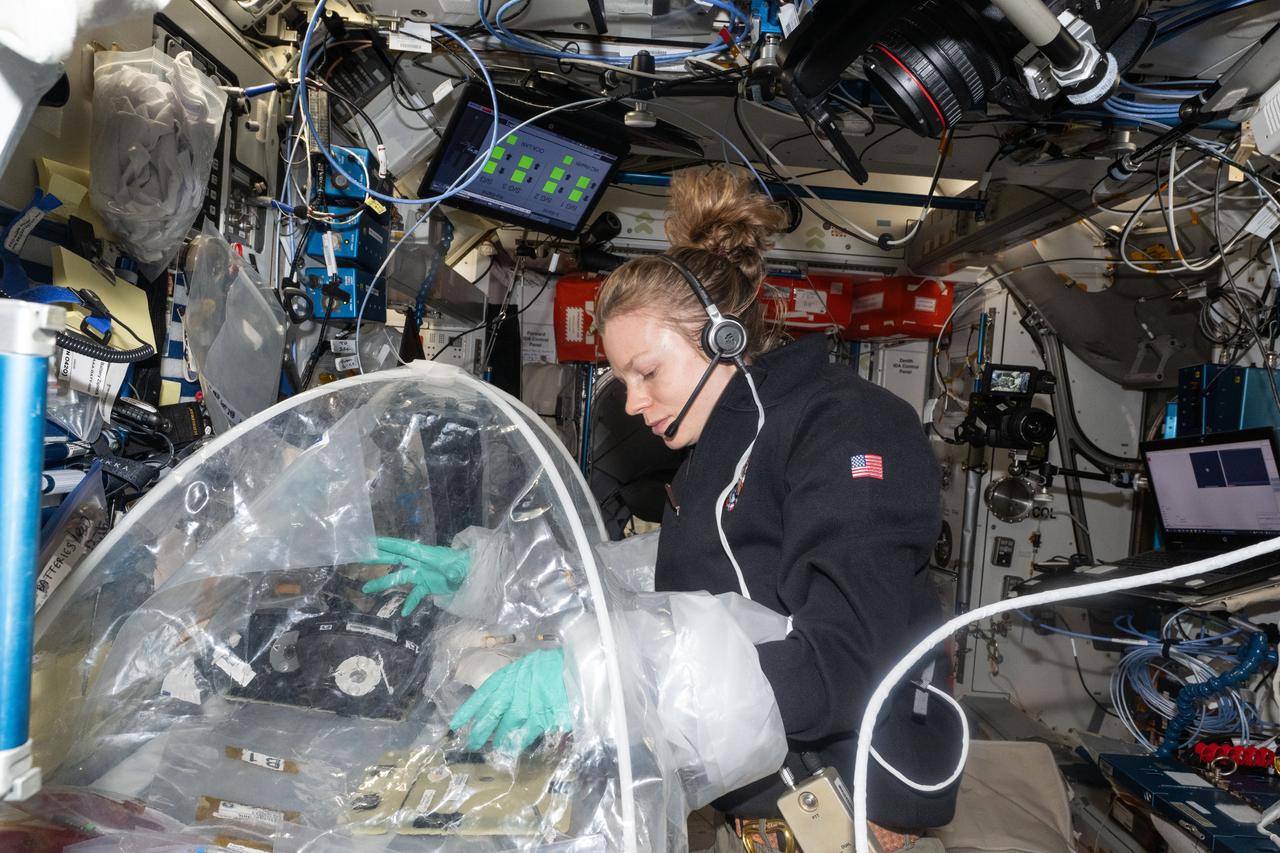

iss073e0606879 (Sept. 5, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Zena Cardman treats bioprinted liver tissues in a portable glovebag inside the International Space Station's Harmony module. The samples will be placed inside an artificial gravity-generating research device to help researchers understand how microgravity affects the formation of blood vessels in engineered tissues. Result may lead to advanced treatments protecting astronauts on long-duration spaceflights and improve bioprinting techniques for patient therapies on Earth.
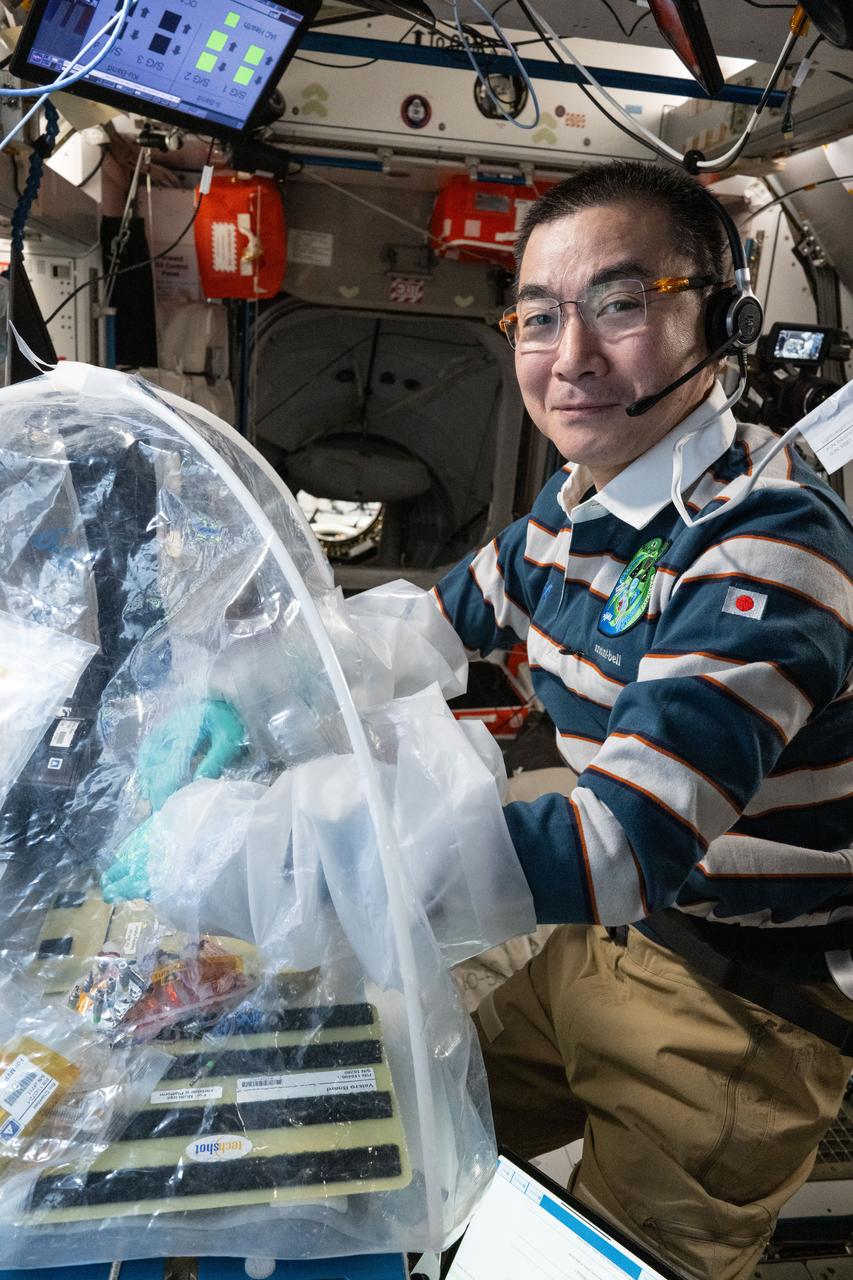

iss073e0606897 (Sept. 5, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Kimiya Yui treats bioprinted liver tissues in a portable glovebag inside the International Space Station's Harmony module. The samples will be placed inside an artificial gravity-generating research device to help researchers understand how microgravity affects the formation of blood vessels in engineered tissues. Result may lead to advanced treatments protecting astronauts on long-duration spaceflights and improve bioprinting techniques for patient therapies on Earth.
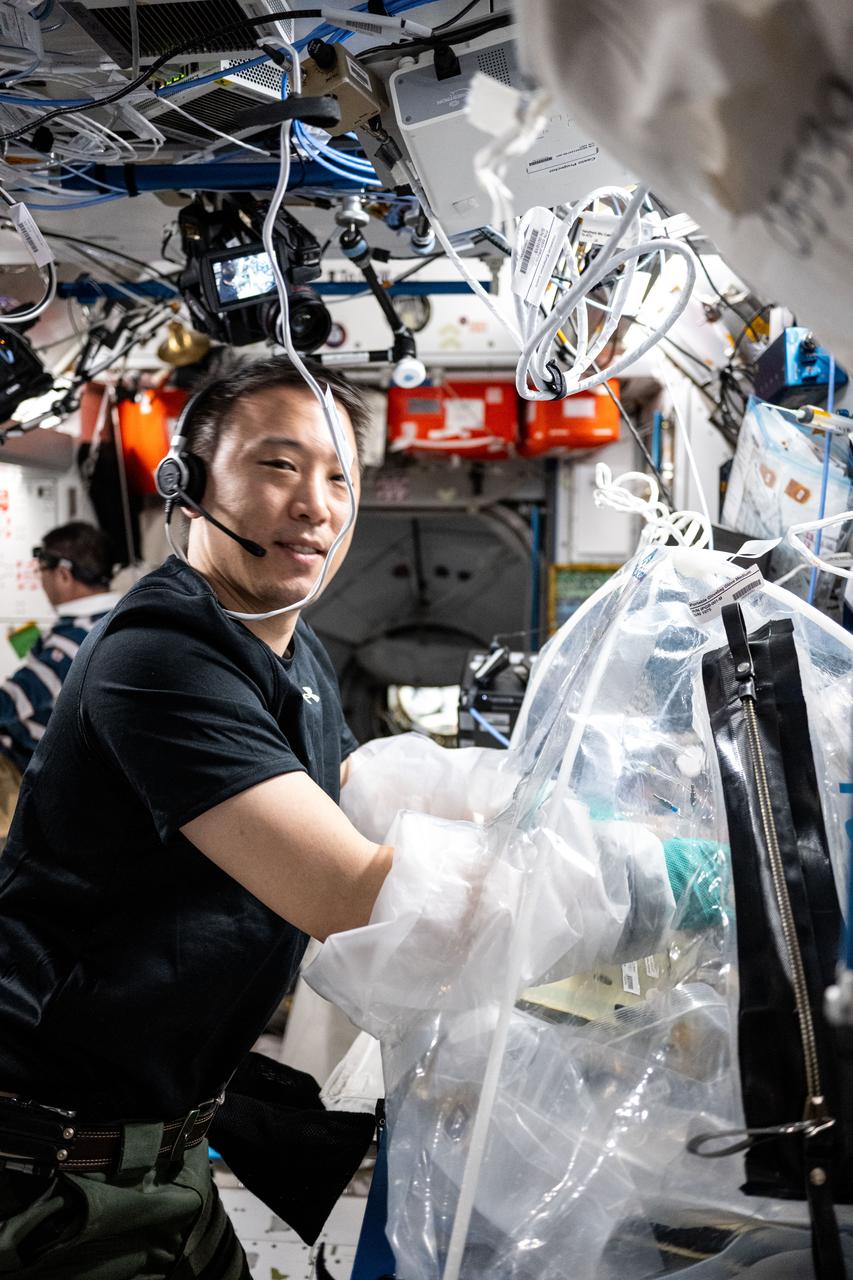

iss073e0702488 (Sept. 17, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim treats bioprinted liver tissues in a portable glovebag inside the International Space Station's Harmony module. The samples were later placed inside an artificial gravity-generating research device to help researchers understand how microgravity affects the formation of blood vessels in engineered tissues. Result may lead to advanced treatments protecting astronauts on long-duration spaceflights and improve bioprinting techniques for patient therapies on Earth.
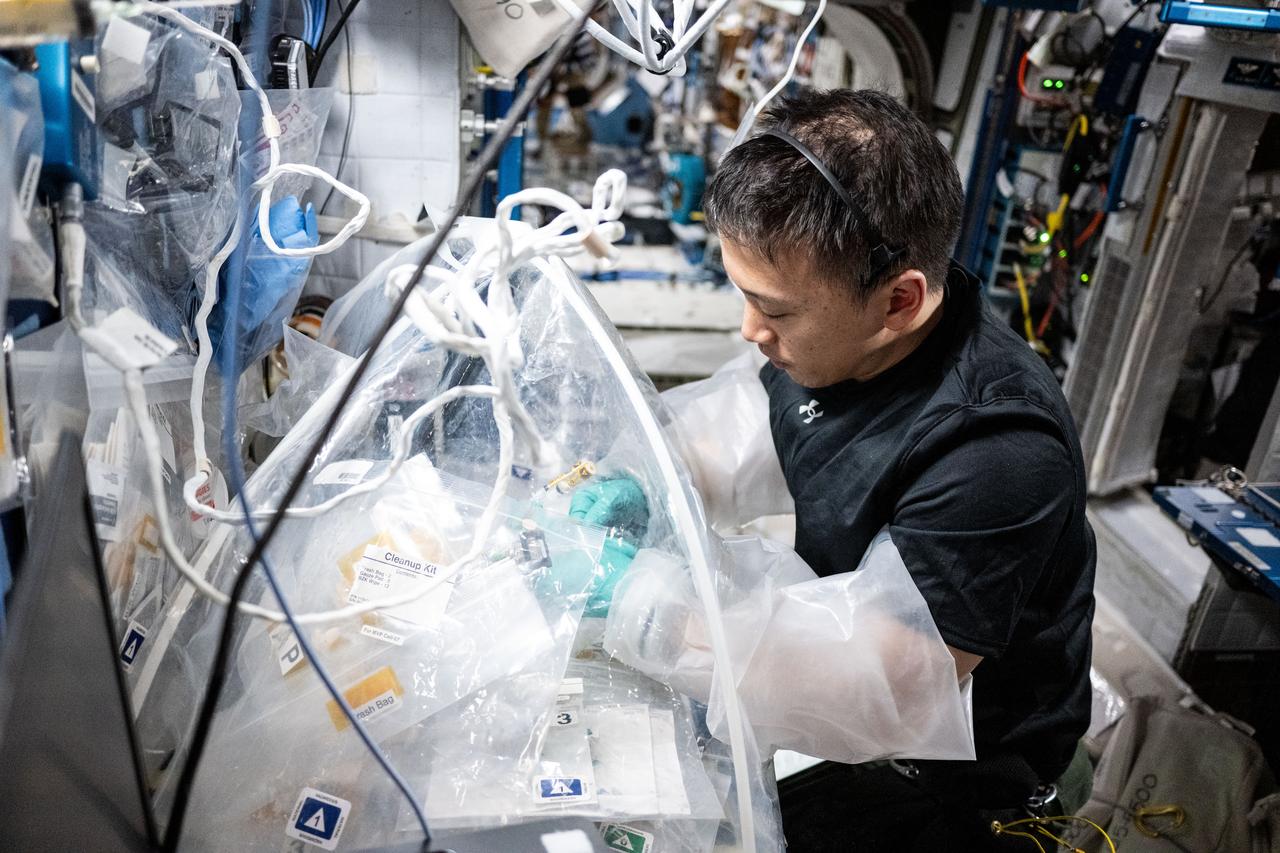

iss073e0702493 (Sept. 17, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim treats bioprinted liver tissues in a portable glovebag inside the International Space Station's Harmony module. The samples were later placed inside an artificial gravity-generating research device to help researchers understand how microgravity affects the formation of blood vessels in engineered tissues. Result may lead to advanced treatments protecting astronauts on long-duration spaceflights and improve bioprinting techniques for patient therapies on Earth.
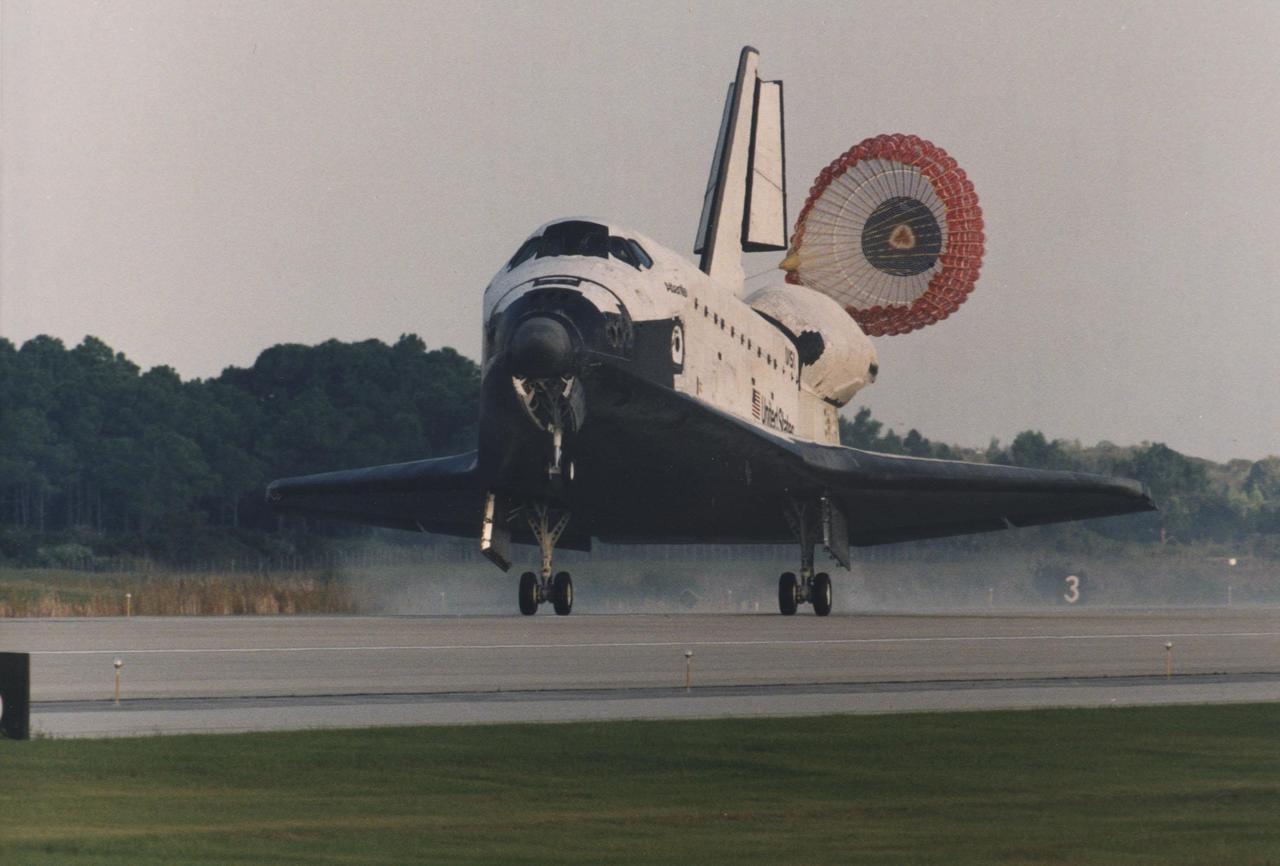

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The drag chute is deployed as the orbiter Atlantis swoops down on Runway 15 of KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility at 8:13:15 a.m. EDT, September 26, bringing to a successful conclusion U.S. astronaut Shannon Lucid's record- setting, 188-day stay in space. Lucid's approximately six-month stay aboard the Russian Space Station Mir establishes a new U.S. record for long-duration spaceflight and also is the longest for a woman, surpassing Russian cosmonaut Elena Kondakovaþs 169-day stay on Mir. Lucid returns to Earth with the flight crew of Mission STS-79: Commander William F. Readdy; Pilot Terrence W. Wilcutt; and Mission Specialists Thomas D. Akers, Jay Apt and Carl E. Walz. Succeeding her aboard Mir for an approximately four-month stay is fellow veteran astronaut John E. Blaha, who traveled to the station with the STS-79 flight crew. The STS-79 mission is part of the NASA/Mir program which is now into the Phase 1B portion, consisting of nine Shuttle-Mir dockings and seven long-duration flights of U.S. astronauts aboard the Russian space station between early 1996 and late 1998
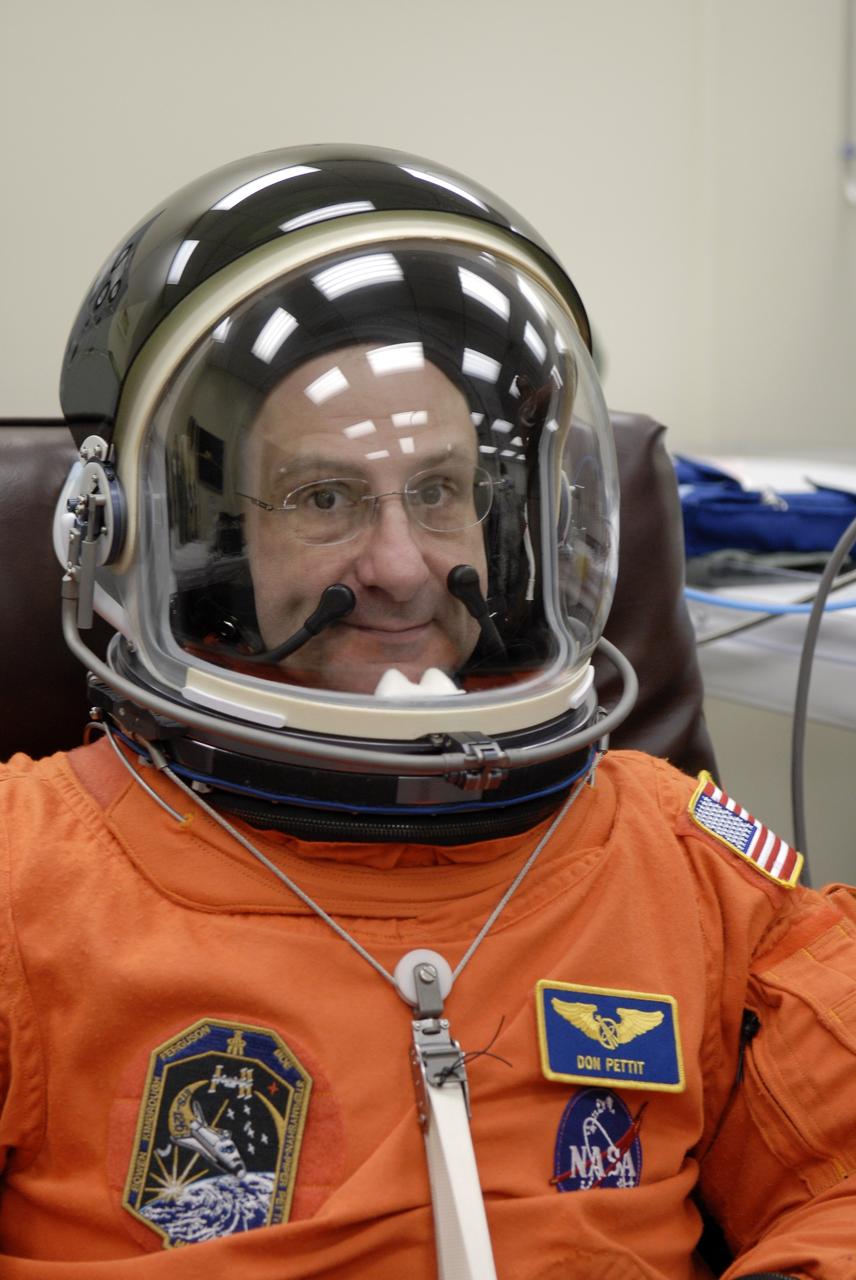

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission put on their launch and entry suits before heading to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Mission Specialist Don Pettit dons his helmet. Pettit is making his second shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
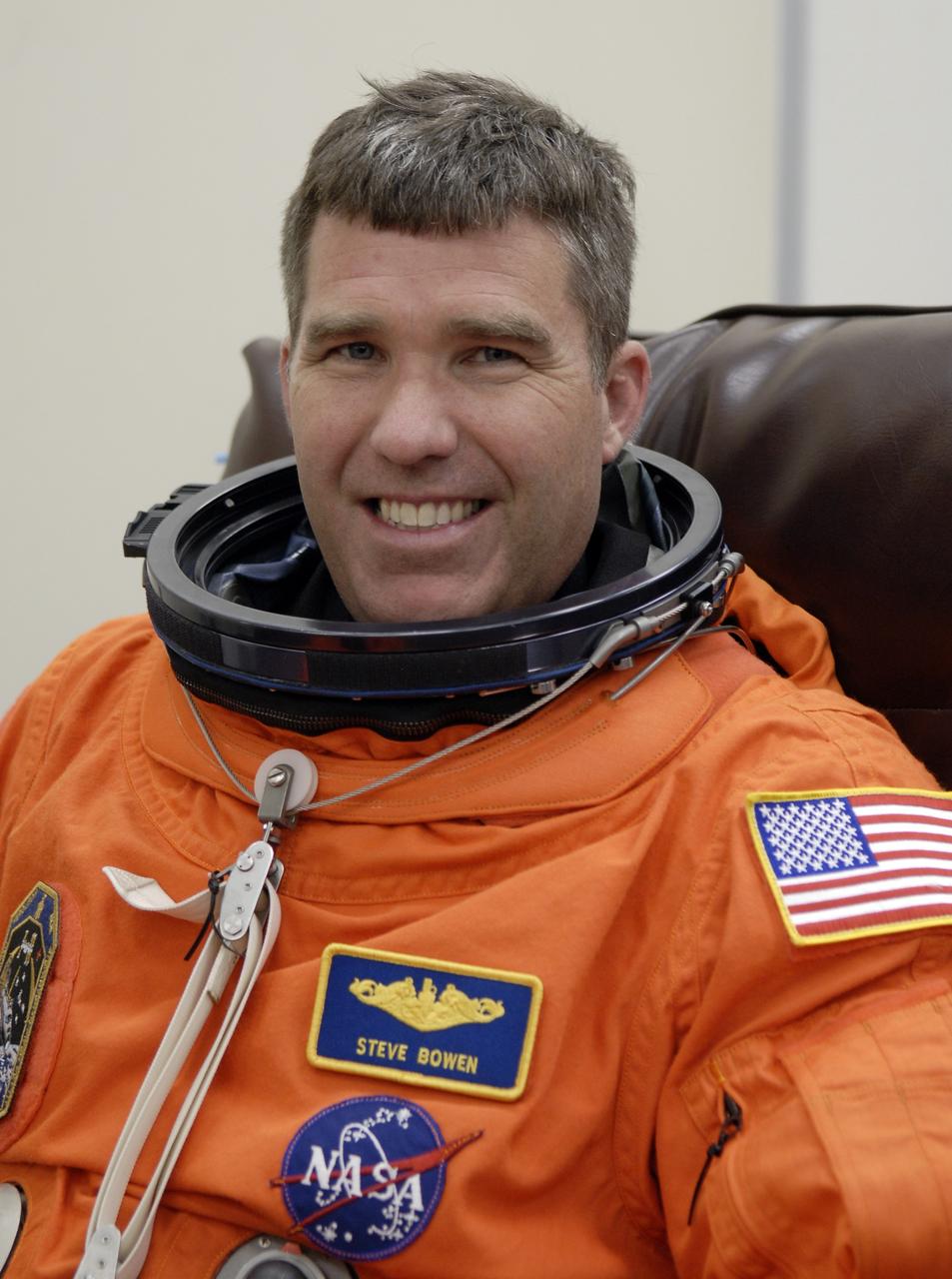

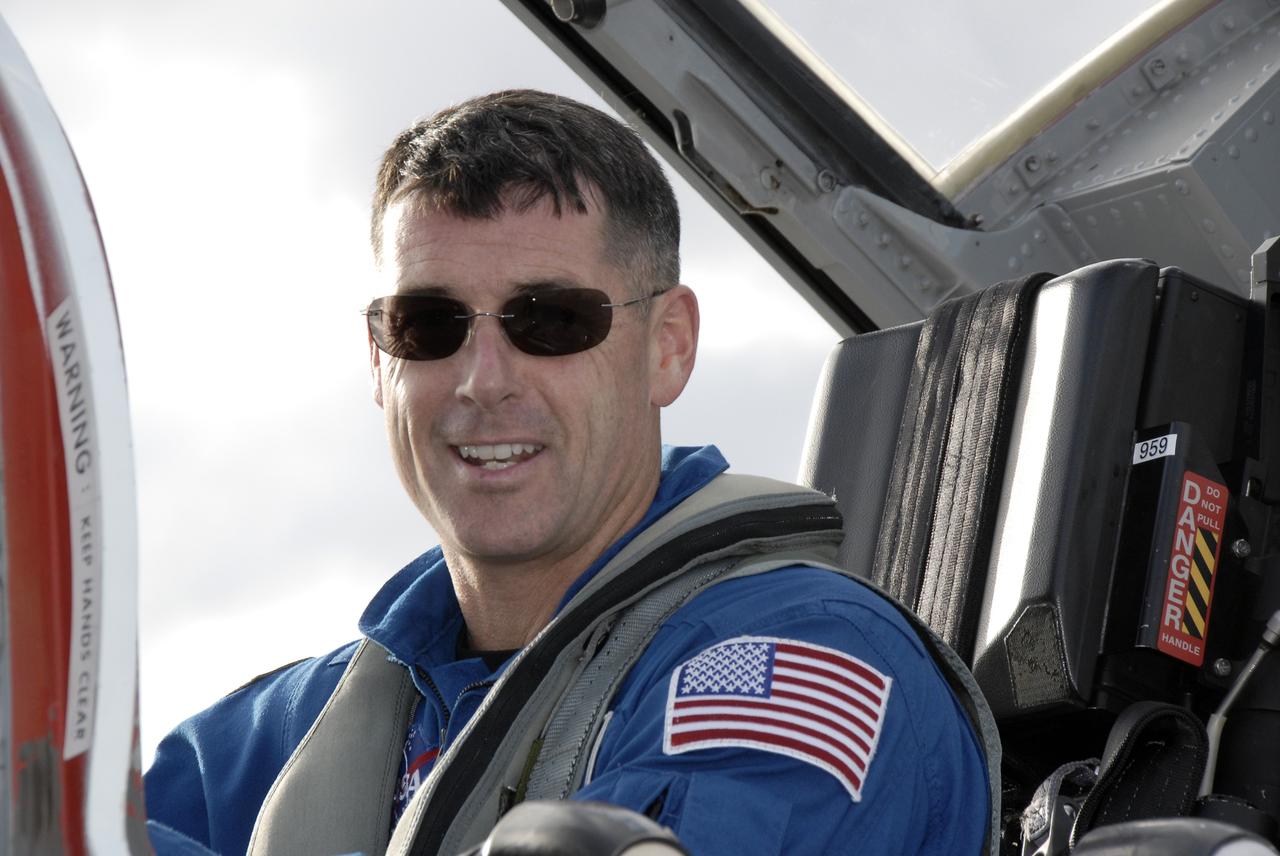
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission put on their launch and entry suits before heading to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Mission Specialist Steve Bowen is making his first shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
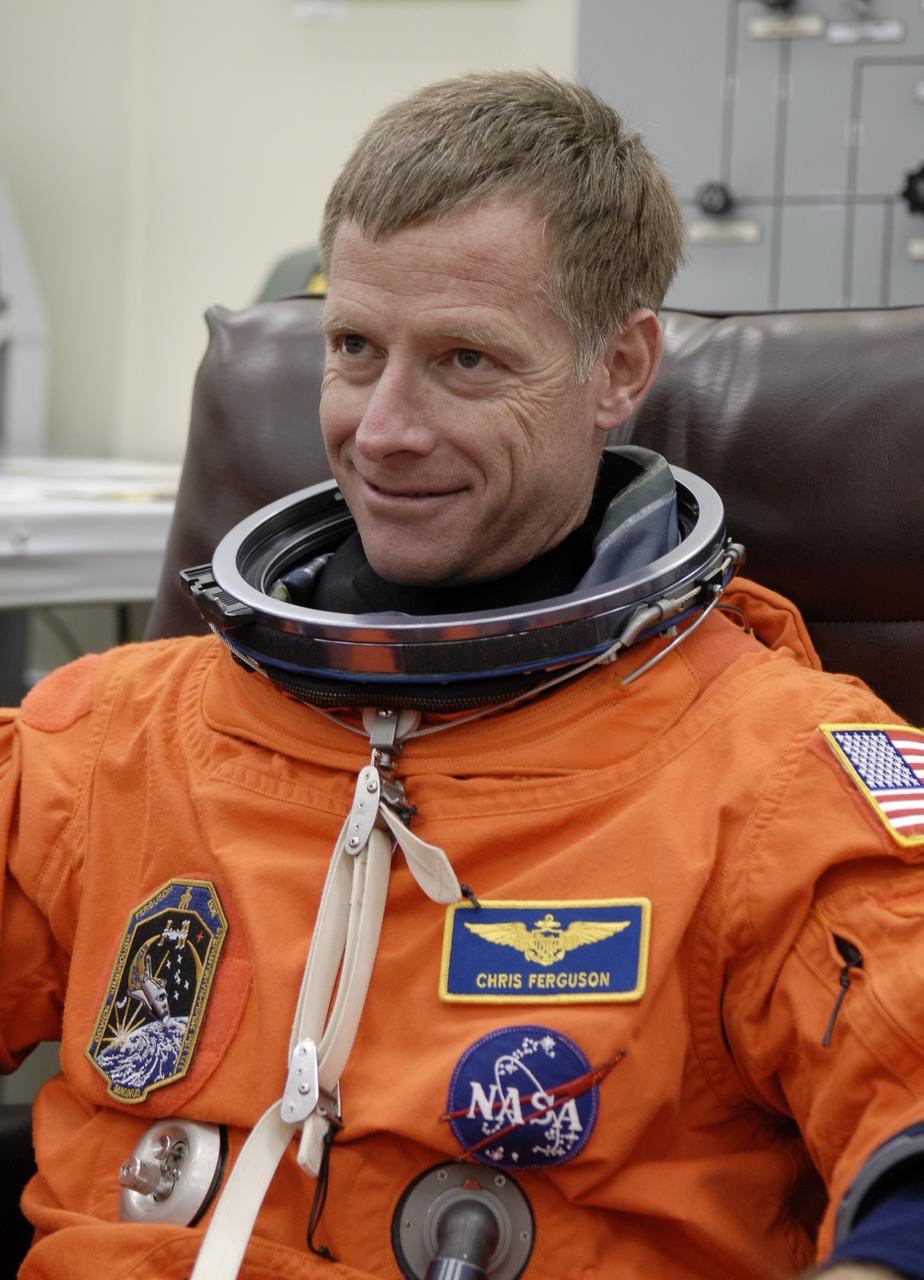

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission put on their launch and entry suits before heading to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson is making his second shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
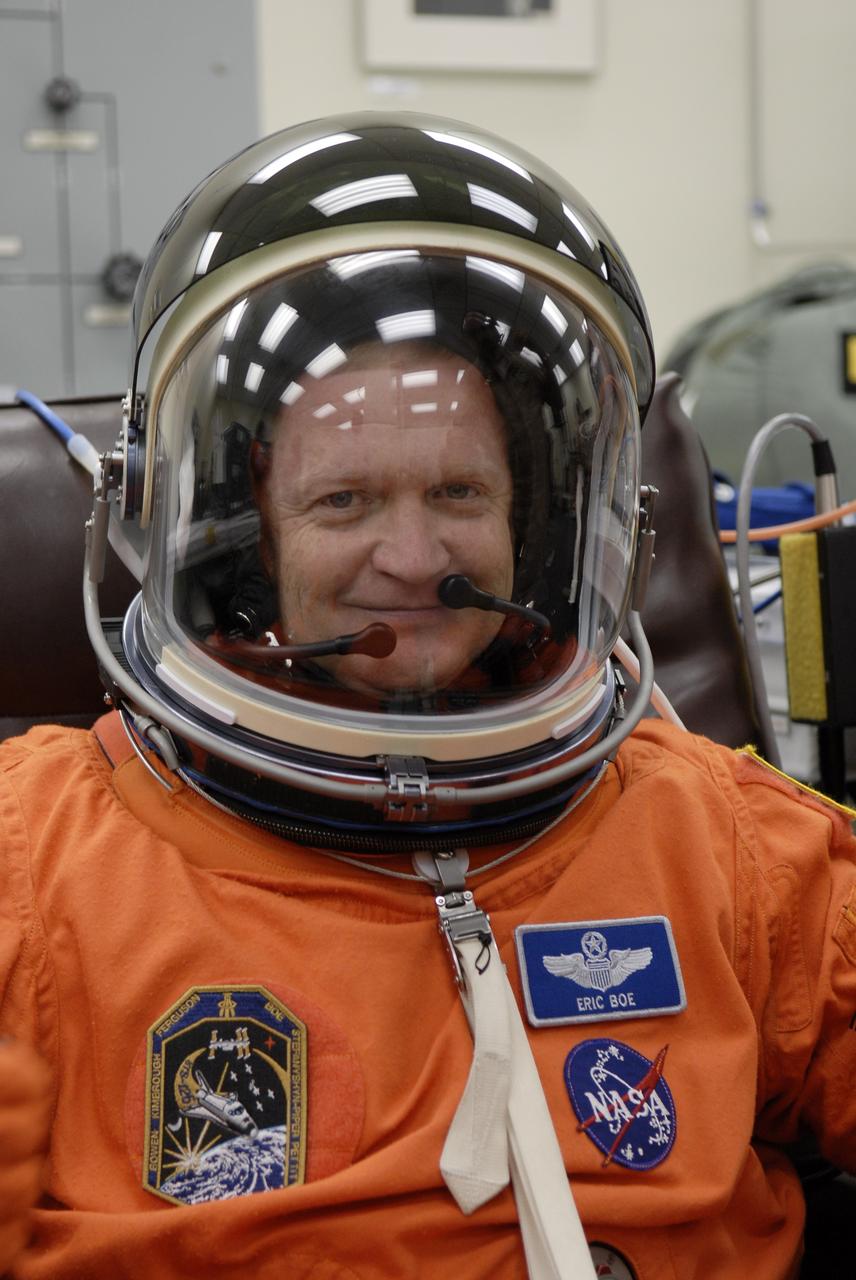

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission put on their launch and entry suits before heading to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pilot Eric Boe, who is making his first shuttle flight, dons his helmet. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
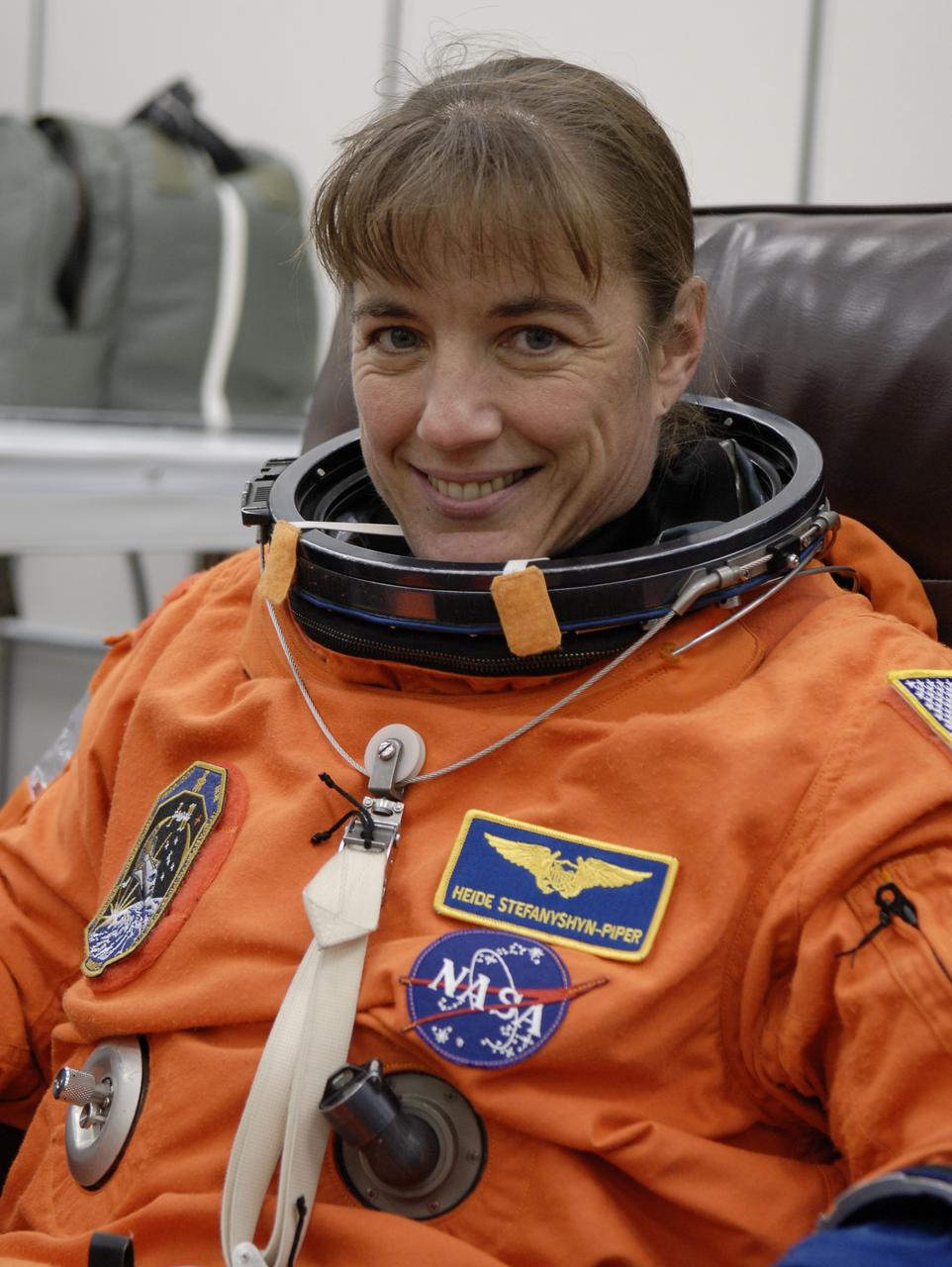

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission put on their launch and entry suits before heading to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Mission Specialist Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper is making her second shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission put on their launch and entry suits before heading to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Mission Specialist Shane Kimbrough waves as he gets his boots on. Kimbrough is making his first shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The first crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission arrive at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for launch. Pilot Eric Boe is greeted by Center Director Bob Cabana. Boe will be making his first shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and important repair work and will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
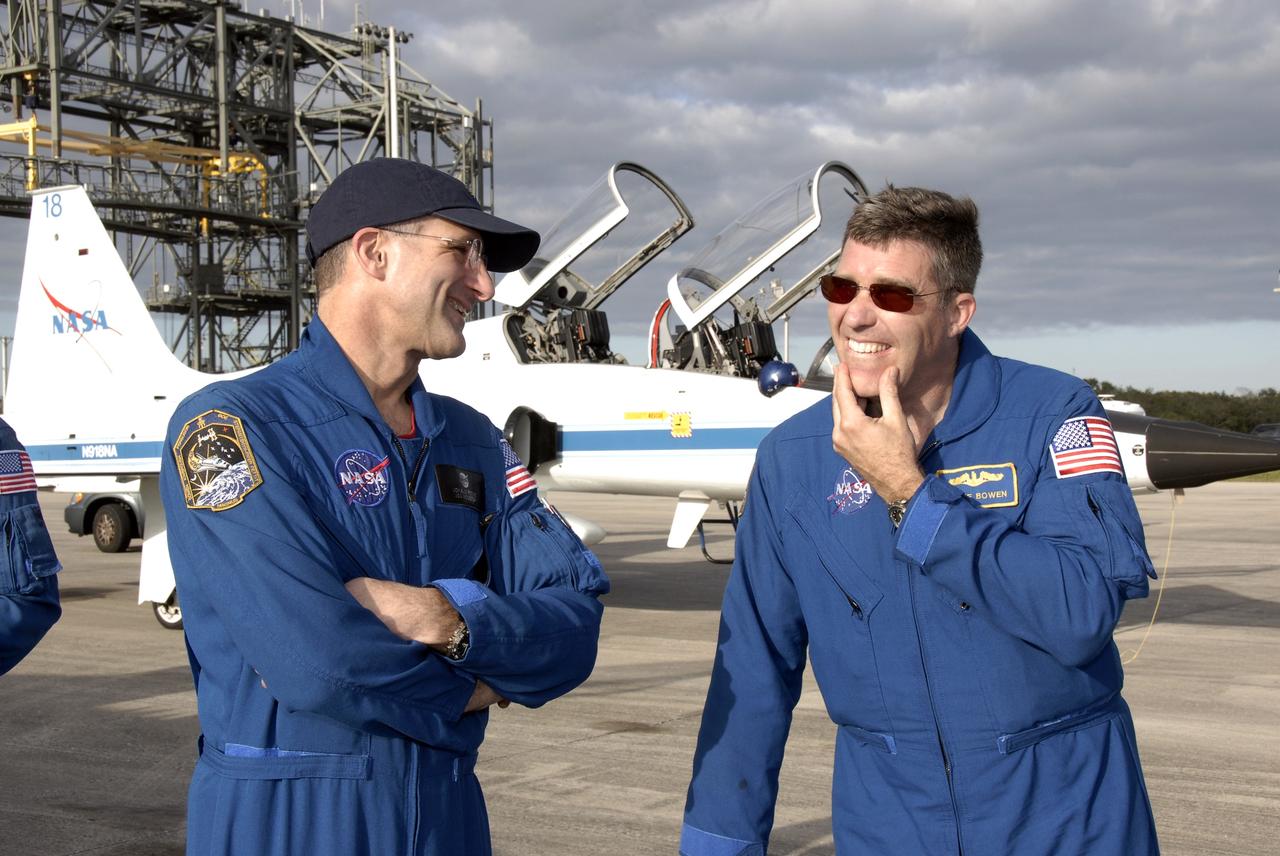

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The crew members for the STS-126 mission arrive at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for launch. At left is Mission Specialist Donald Pettit; at right is Mission Specialist Steve Bowen. Pettit will be making his second shuttle flight while Bowen will be making his first. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and important repair work and will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The crew members for the STS-126 mission arrive at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for launch. Seated in the T-38 training jet is Mission Specialist Shane Kimbrough, who will be making his first shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and important repair work and will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
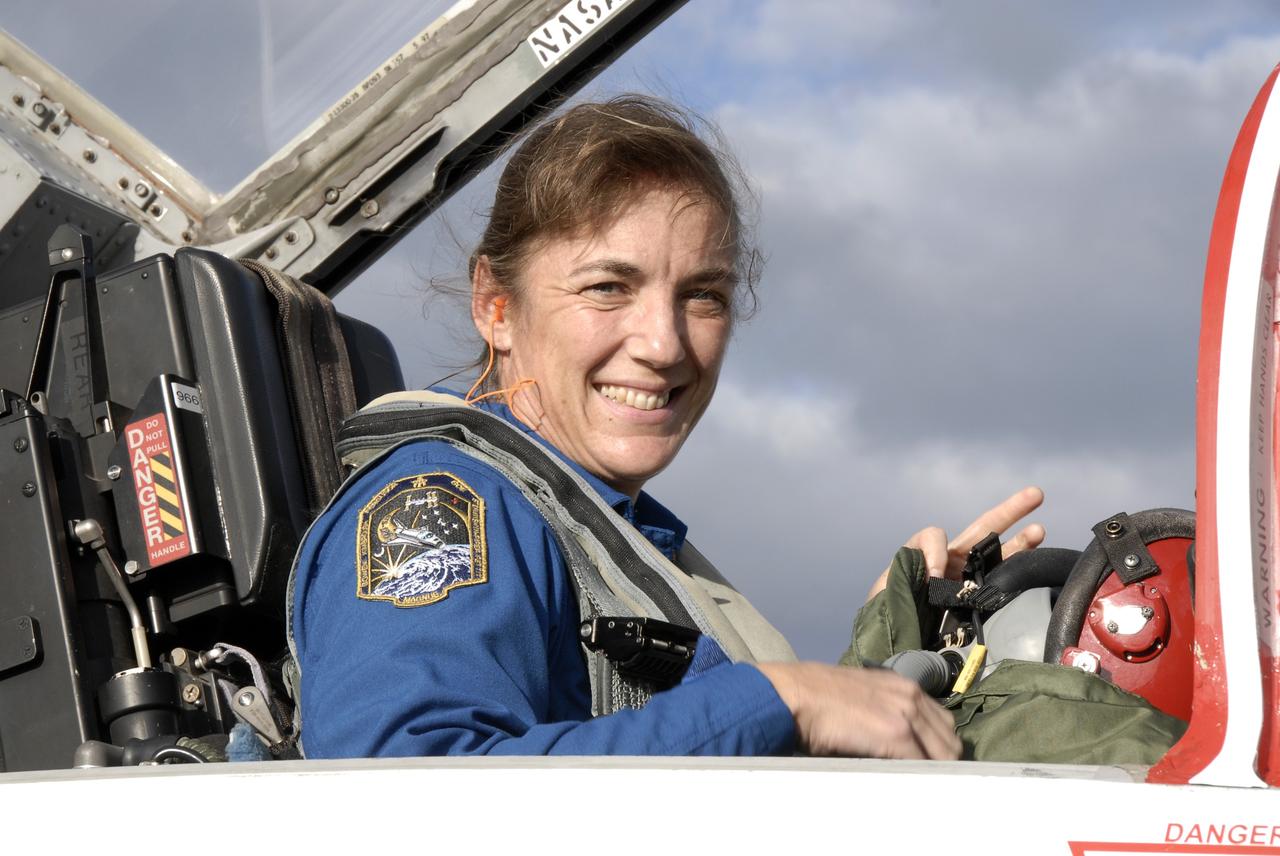

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The crew members for the STS-126 mission arrive at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for launch. Seated in the T-38 training jet is Mission Specialist Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper, who will be making her second shuttle flight. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and important repair work and will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
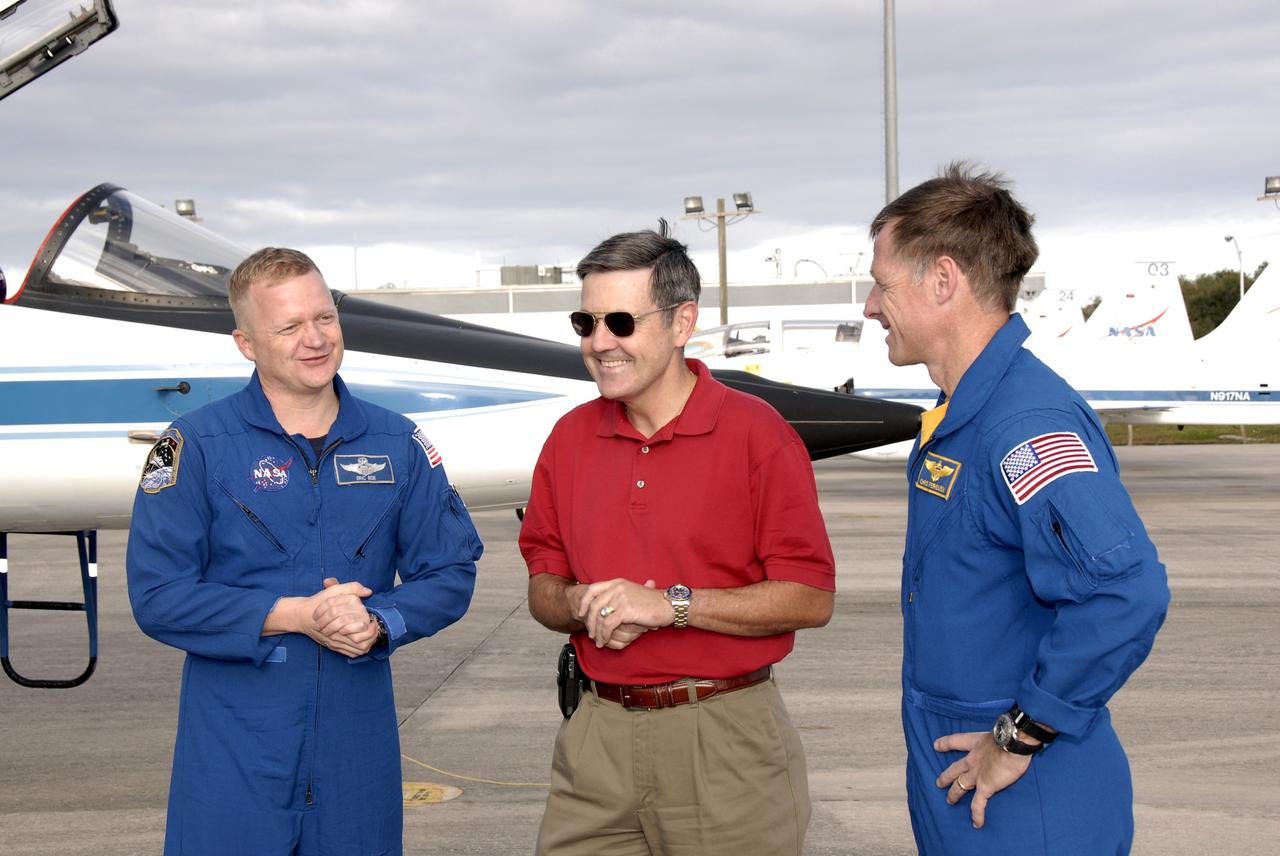

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The crew members for the STS-126 mission arrive at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for launch. Pilot Eric Boe (left) and Commander Chris Ferguson (right) are greeted by Center Director Bob Cabana. Boe will be making his first shuttle flight while Ferguson will make his second. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and important repair work and will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
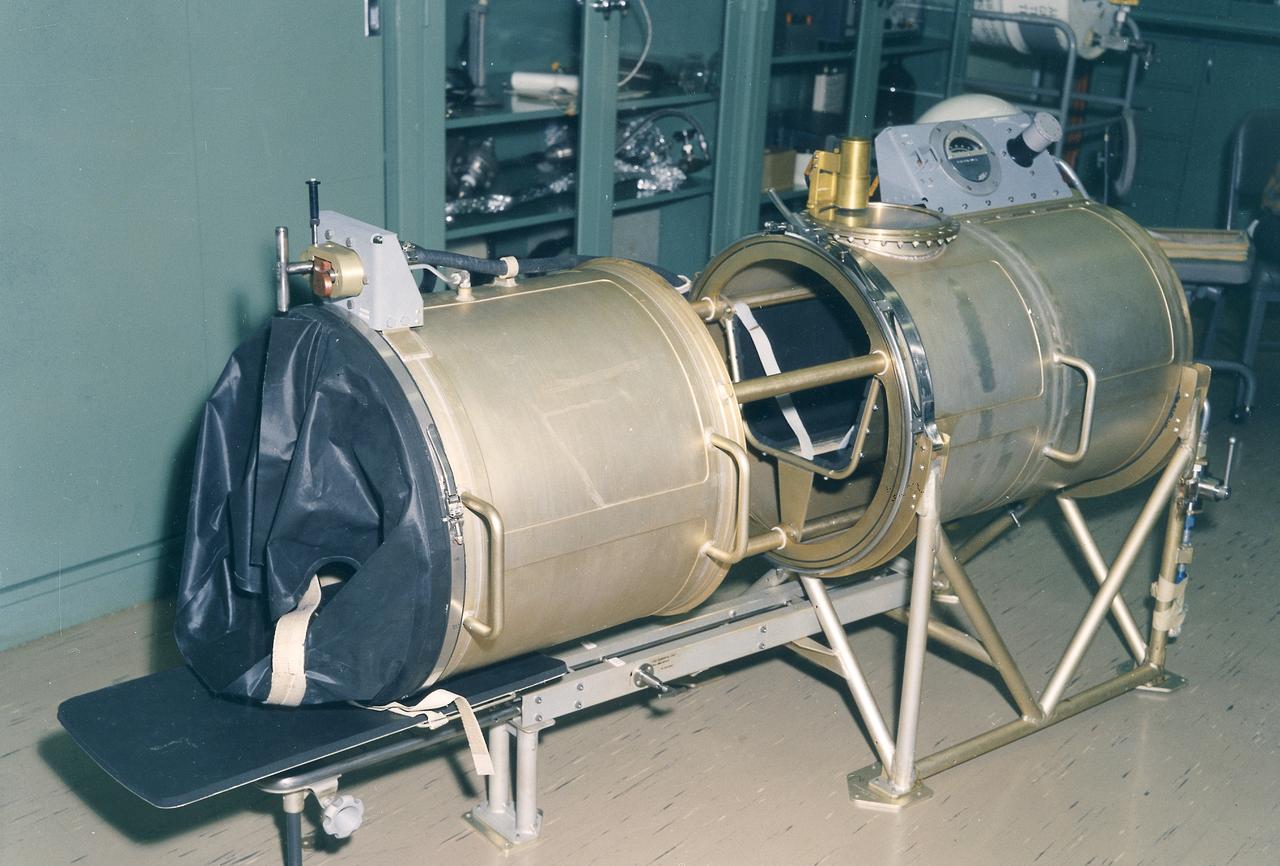
This 1970 photograph shows Skylab's In-Flight Lower Body Negative Pressure experiment facility, a medical evaluation designed to monitor changes in astronauts' cardiovascular systems during long-duration space missions. This experiment collected in-flight data for predicting the impairment of physical capacity and the degree of orthostatic intolerance to be expected upon return to Earth. Data to be collected were blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, vectorcardiogram, lower body negative pressure, leg volume changes, and body mass. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
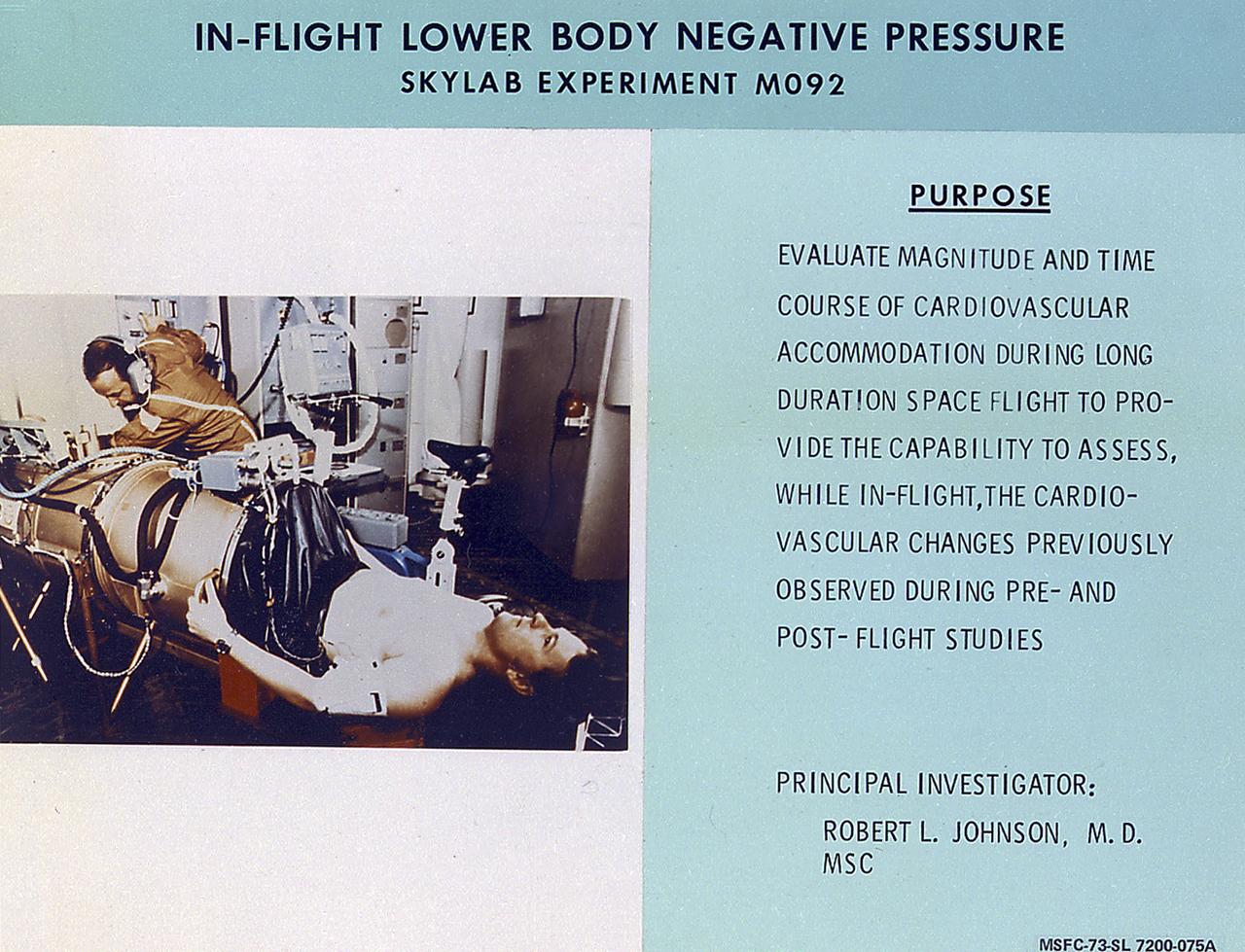
This chart details Skylab's In-Flight Lower Body Negative Pressure experiment facility, a medical evaluation designed to monitor changes in astronauts' cardiovascular systems during long-duration space missions. This experiment collected in-flight data for predicting the impairment of physical capacity and the degree of orthostatic intolerance to be expected upon return to Earth. Data to be collected were blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, vectorcardiogram, lower body negative pressure, leg volume changes, and body mass. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
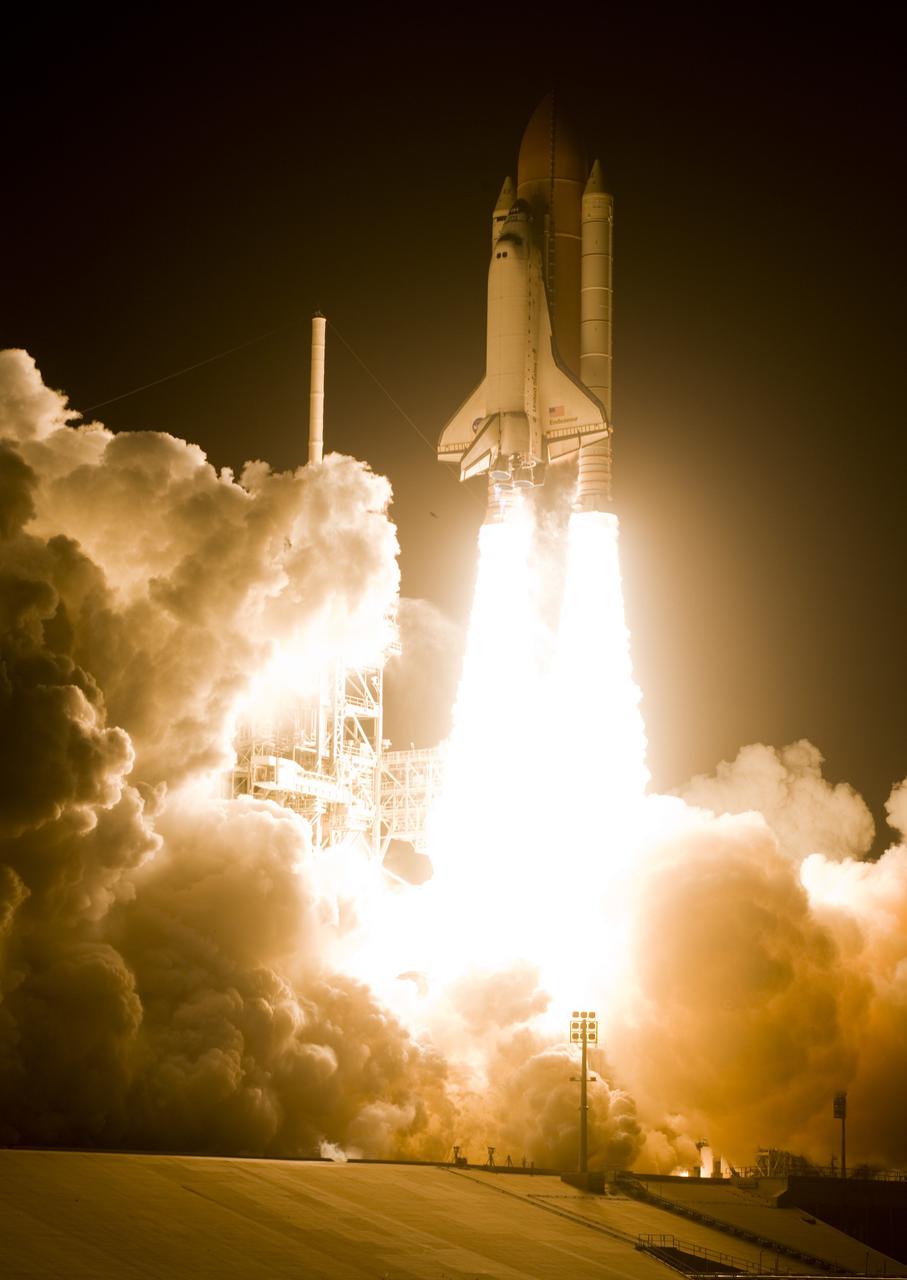

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Atop twin towers of flame, space shuttle Endeavour erupts from the smoke and steam as it hurtles past the lightning mast on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, heading into space on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
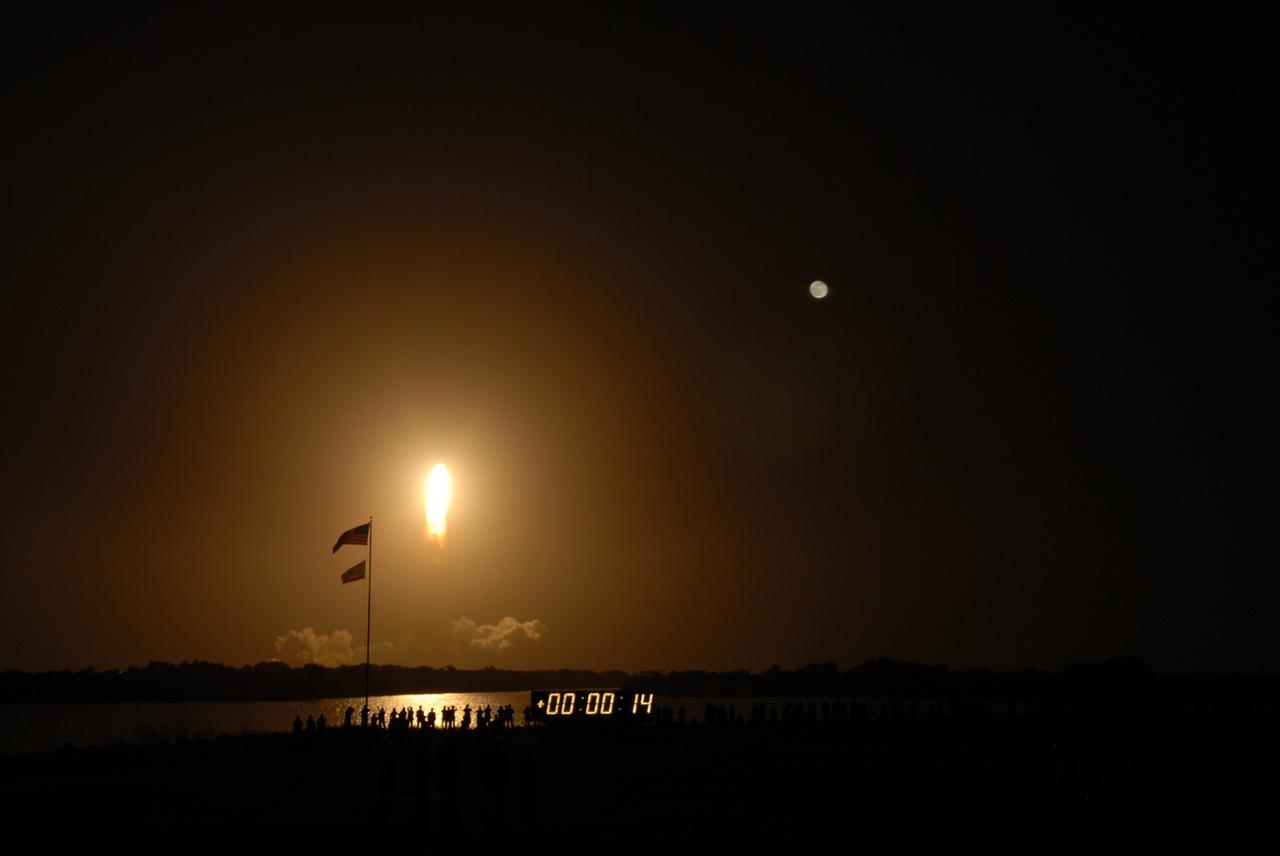

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Blazing light surrounds space shuttle Endeavour, eclipsing the light from the nearby full moon, as it roars into space from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center during the launch of the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
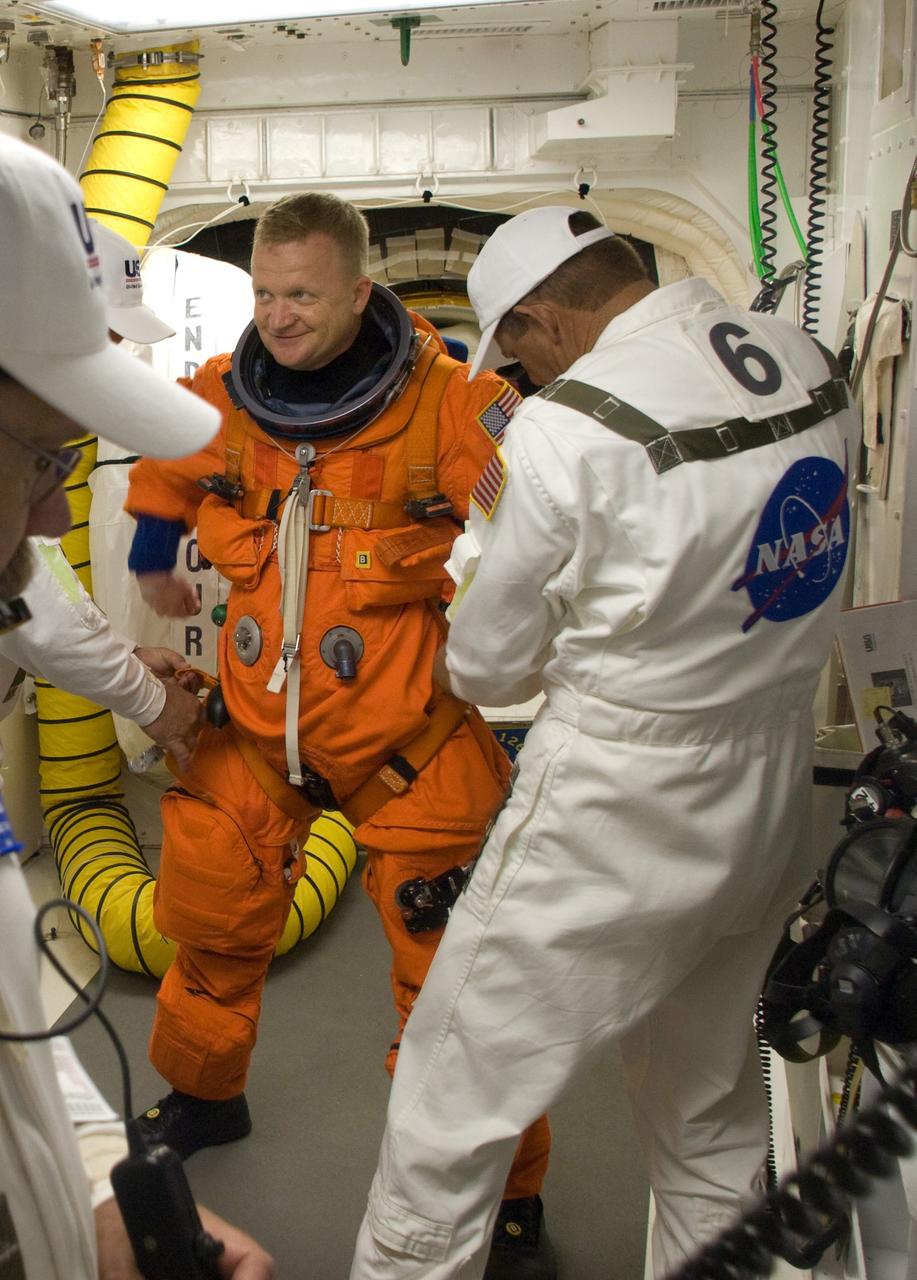

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the White Room on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-126 Pilot Eric Boe is helped by suit technicians to put on a harness over his launch and entry suit. In the background is the hatch for entry into space shuttle Endeavour. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
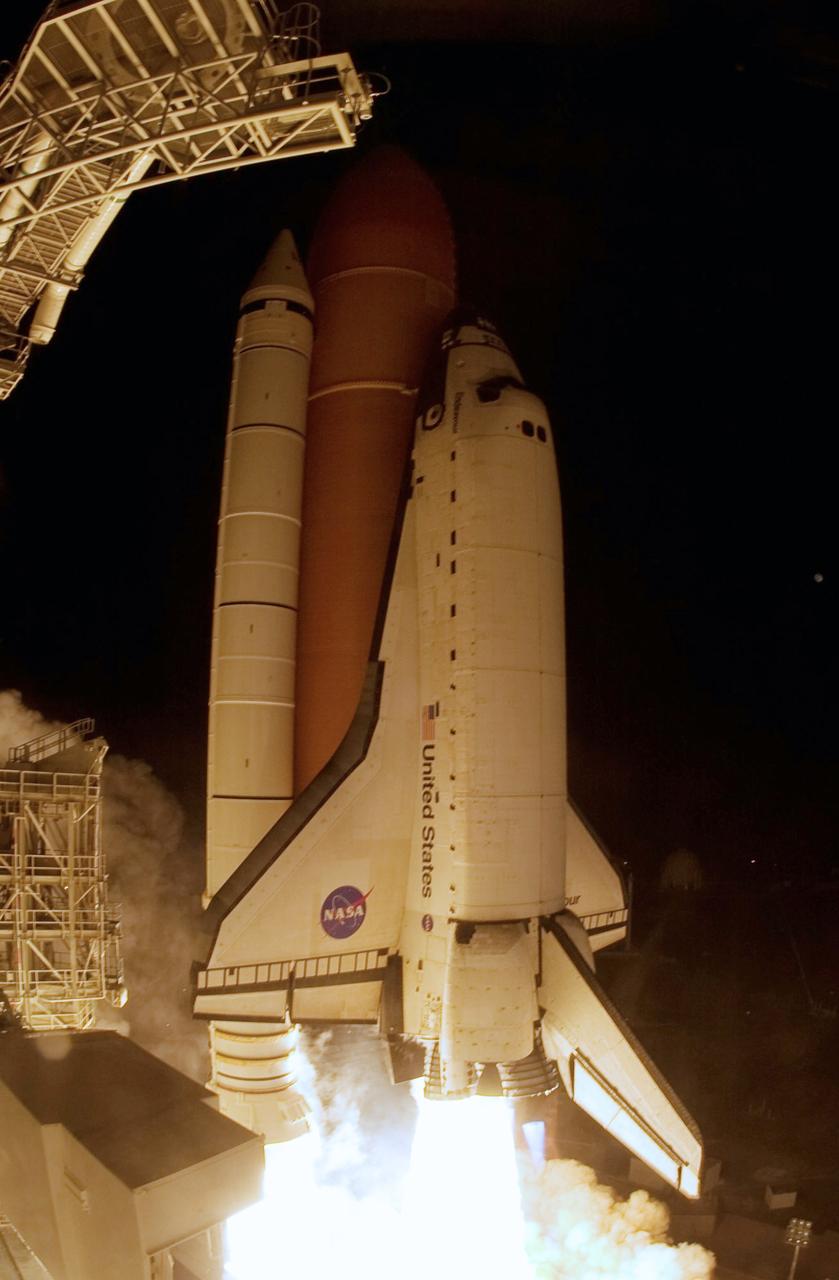

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system can be seen beneath the nozzles of the main engines. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
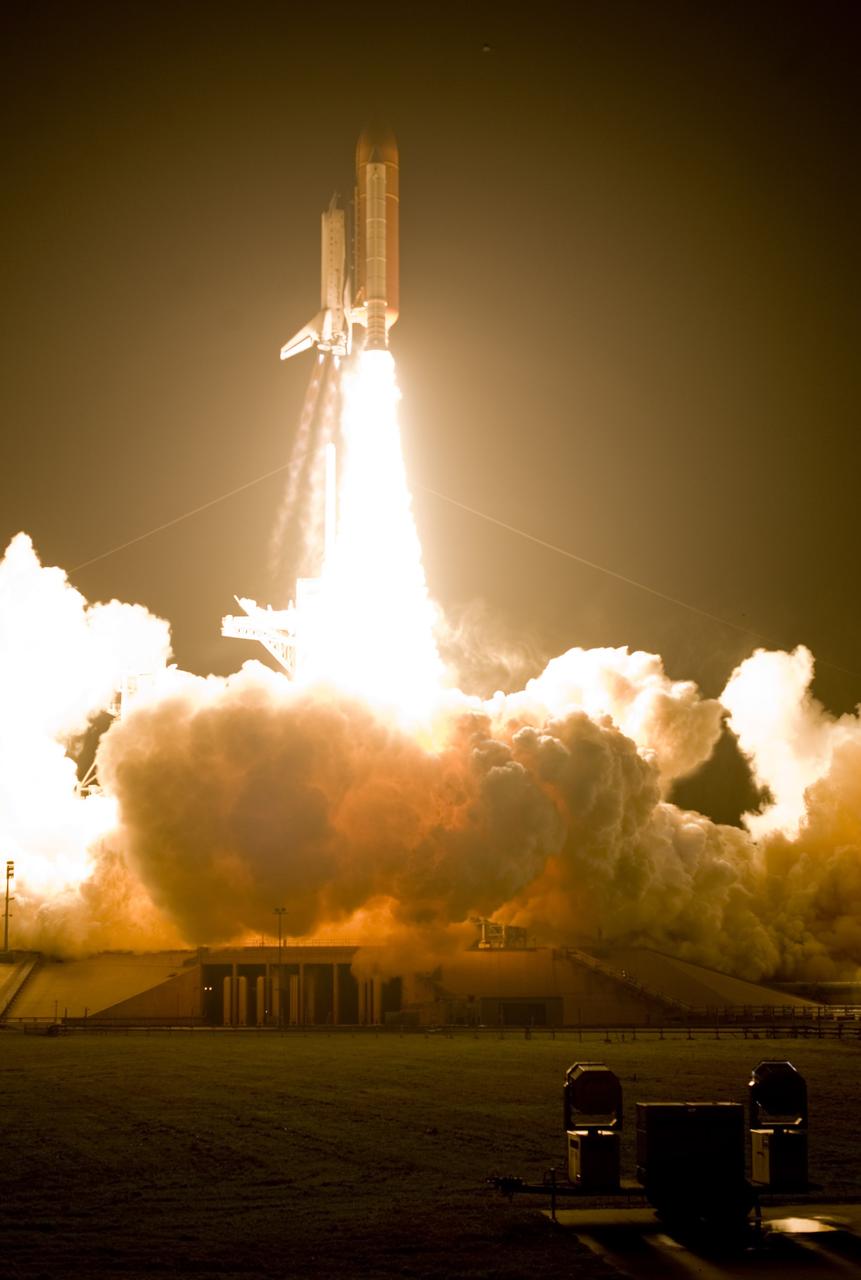

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour erupts from the smoke and steam as it roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system, can be seen beneath the nozzles of the main engines. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
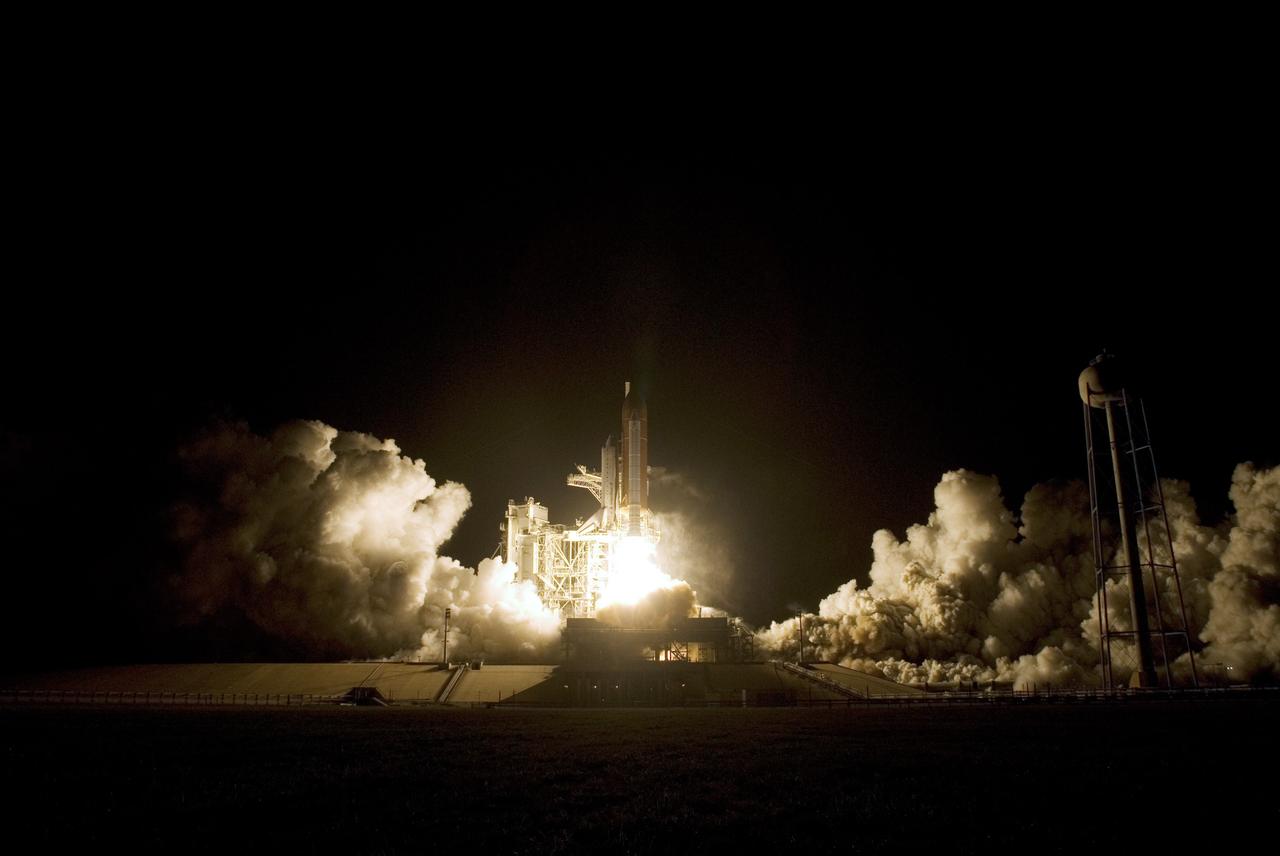

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Clouds of smoke and steam roll across Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida as towers of flame propel space shuttle Endeavour into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray-Tom Farrar
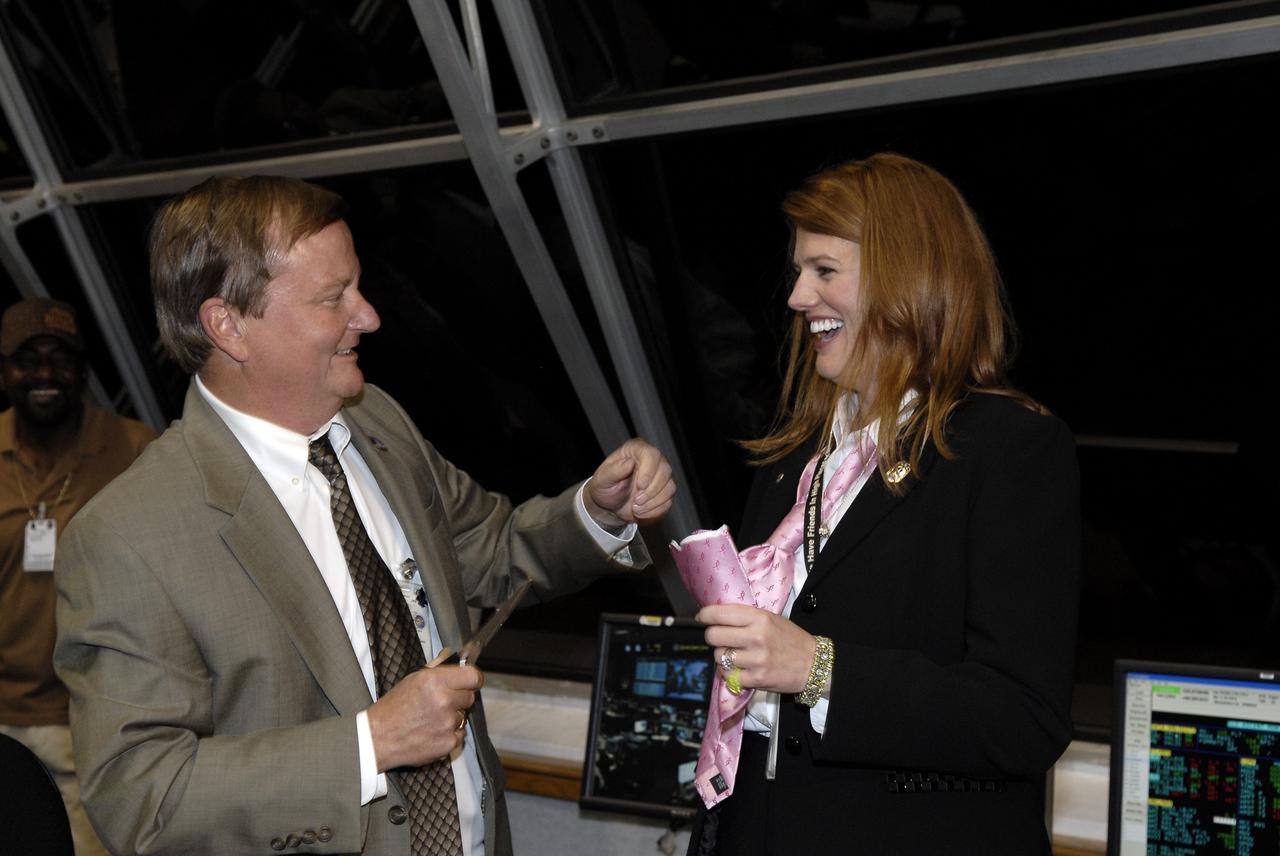

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Firing Room of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach (left) congratulates STS-126 NASA Test Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with the traditional tie-cutting ceremony for a first-time NTD. Congratulations were offered for the successful launch of space shuttle Endeavour. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
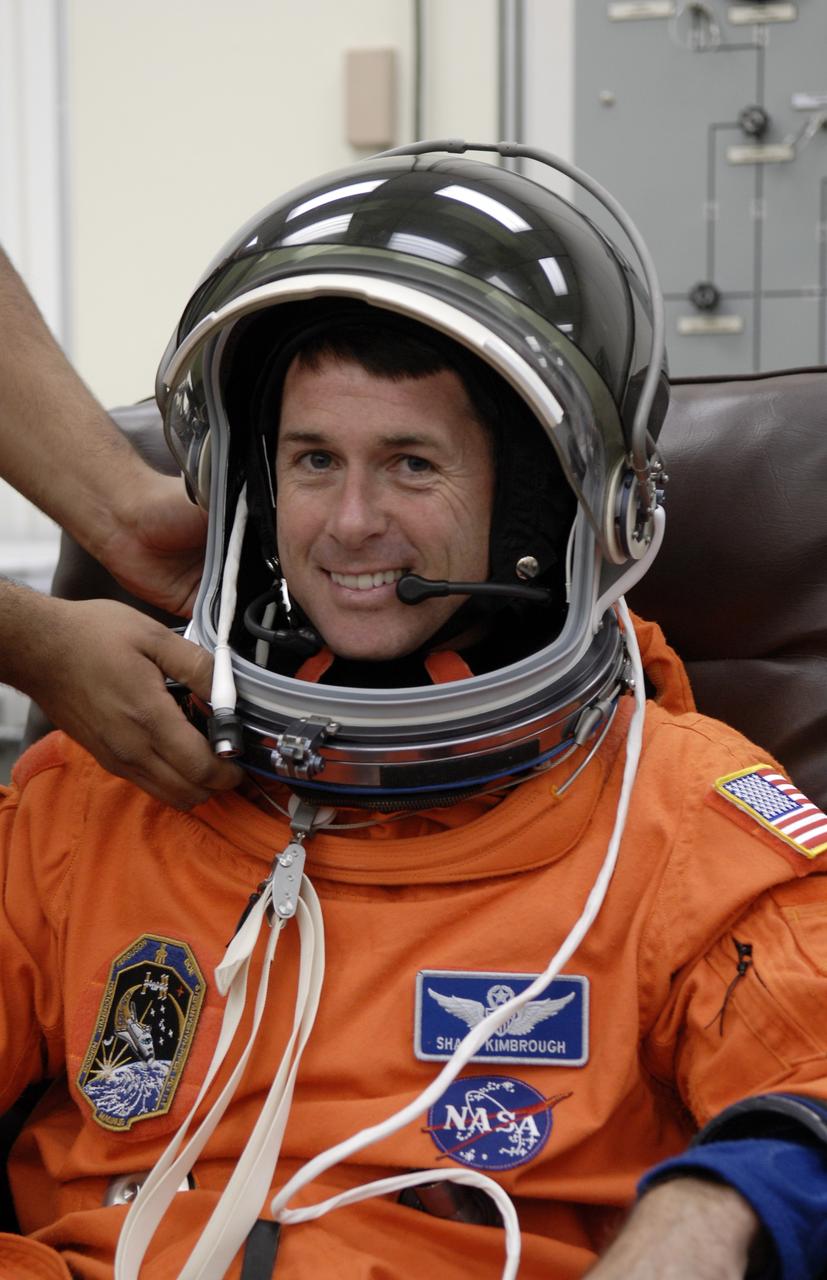

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crew members for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission put on their launch and entry suits before heading to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Mission Specialist Shane Kimbrough dons his helmet. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
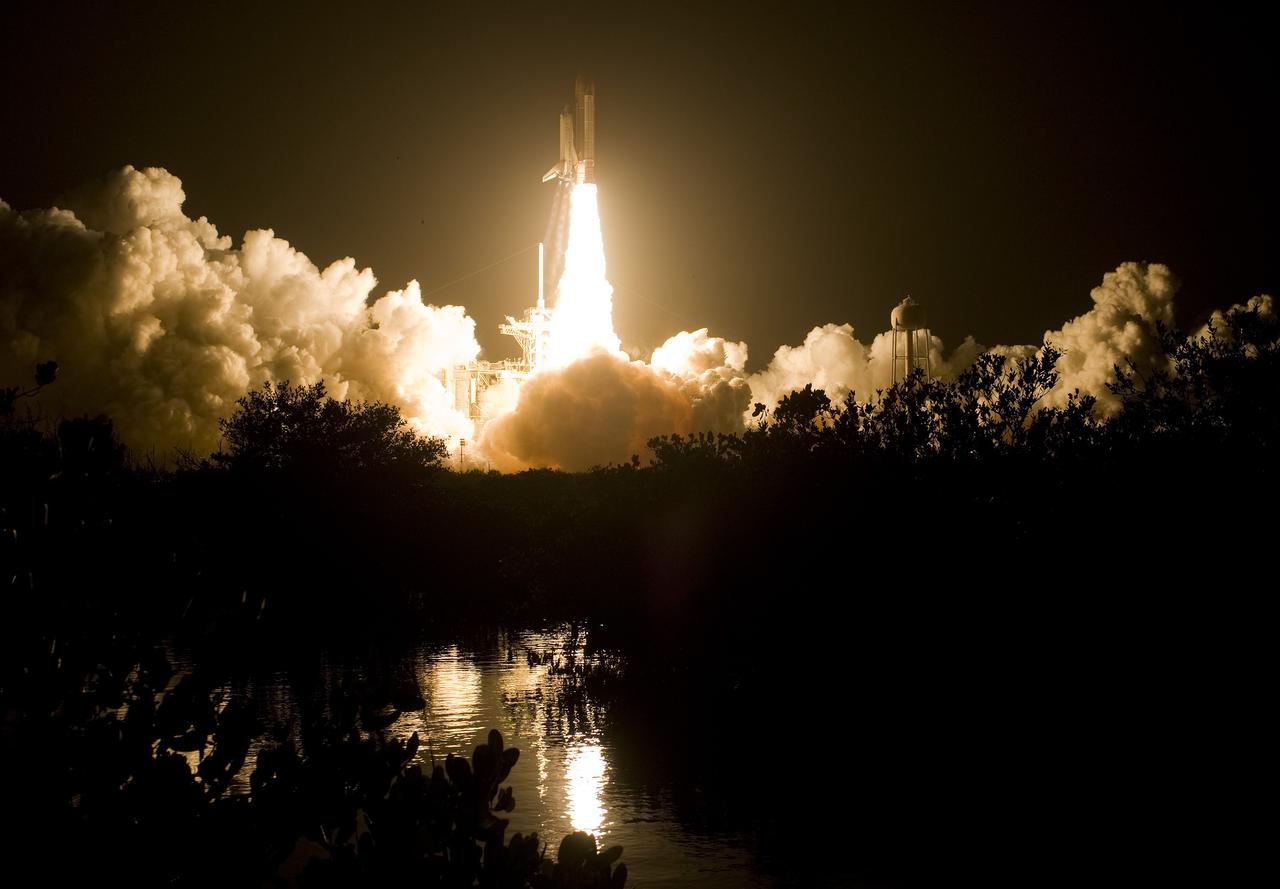

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rising from the billows of smoke below, space shuttle Endeavour roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. The brilliant liftoff is reflected in the water next to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
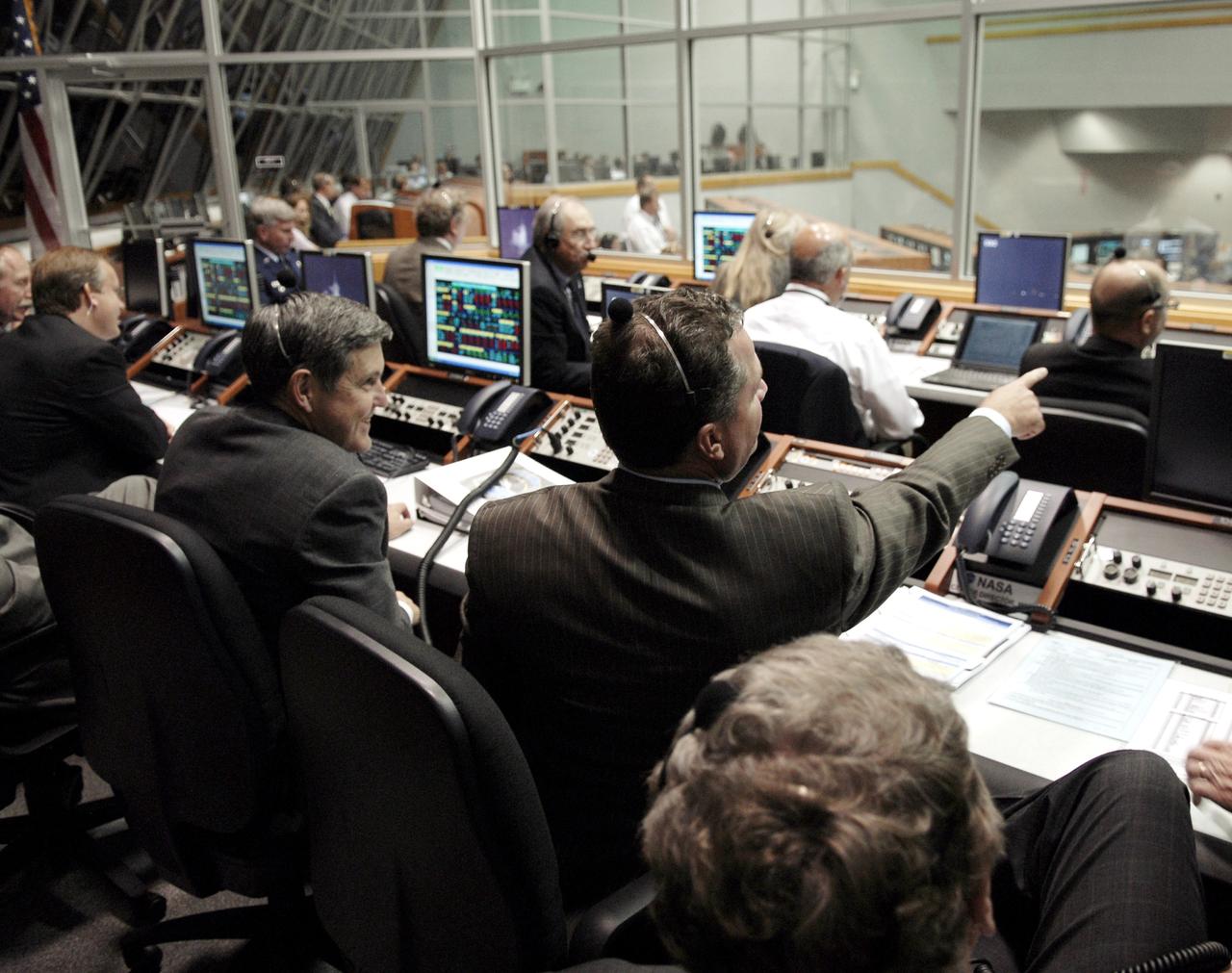

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Center Director Bob Cabana (center left) watches the successful launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission in the Firing Room of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
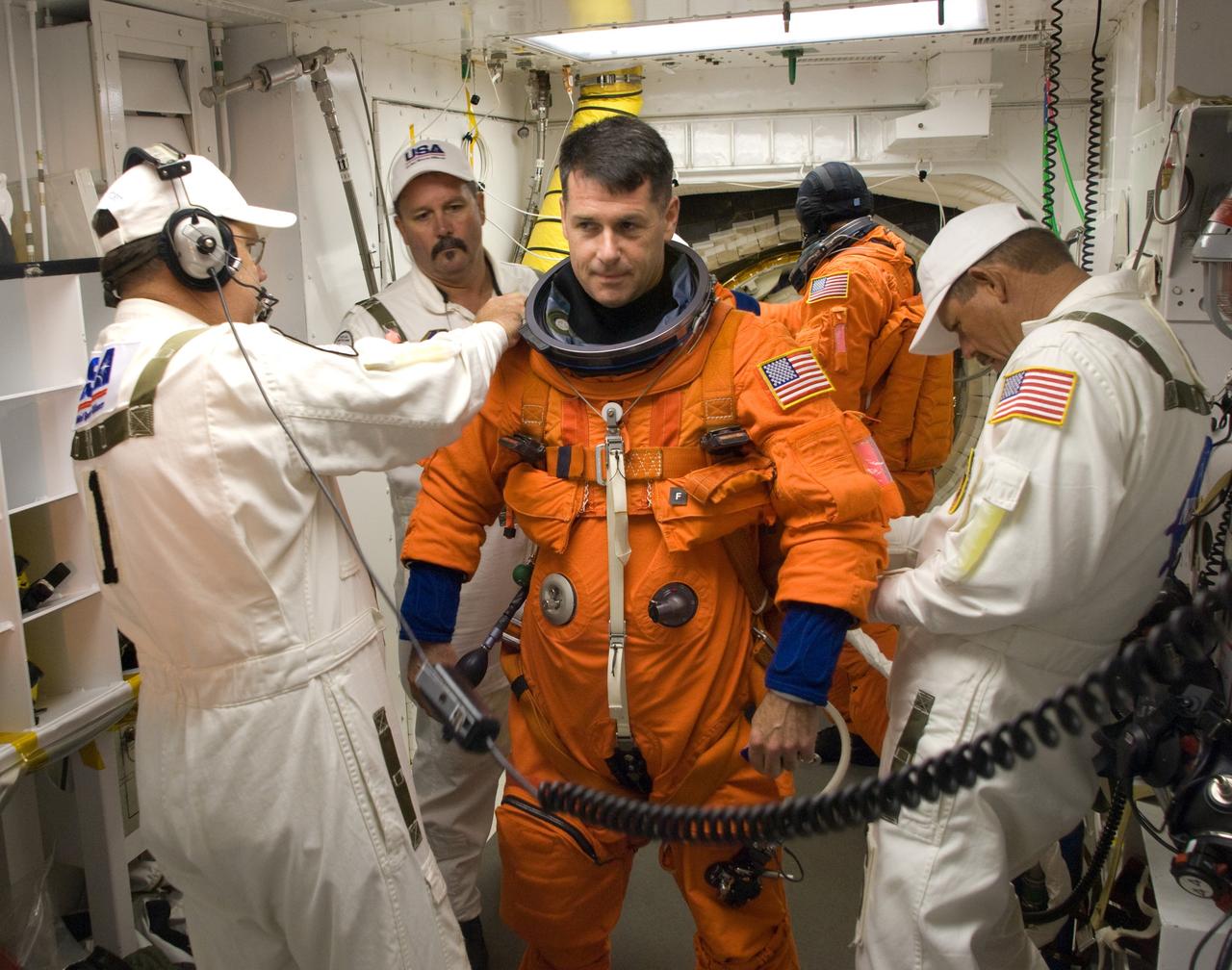

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the White Room on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-126 Mission Specialist Shane Kimbrough is helped by suit technicians to get into his harness. In the background is another crew member waiting to enter space shuttle Endeavour. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
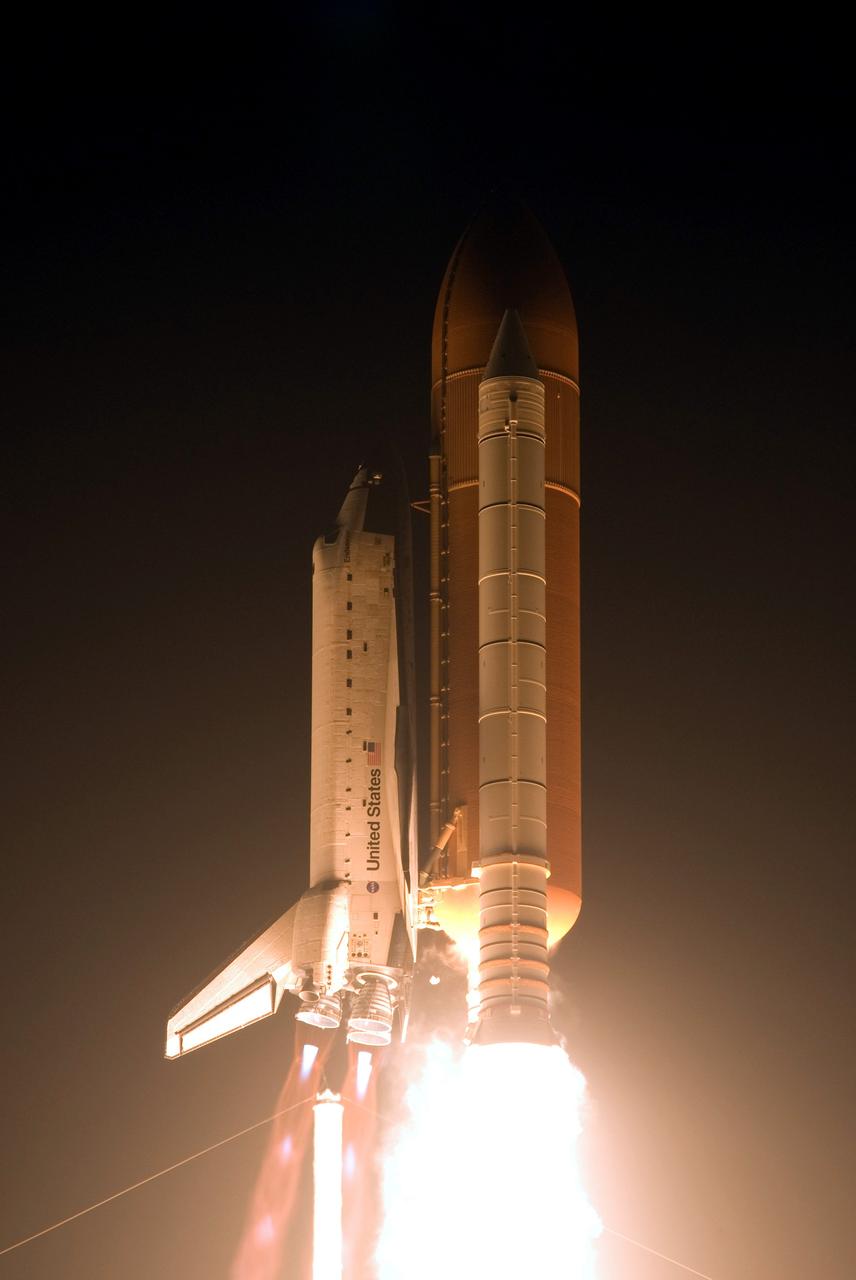

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system can be seen beneath the nozzles of the main engines. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer-George Roberts