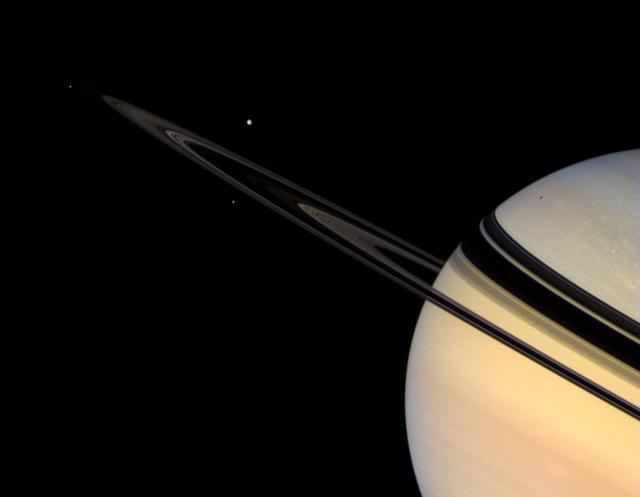

Solar System in Miniature
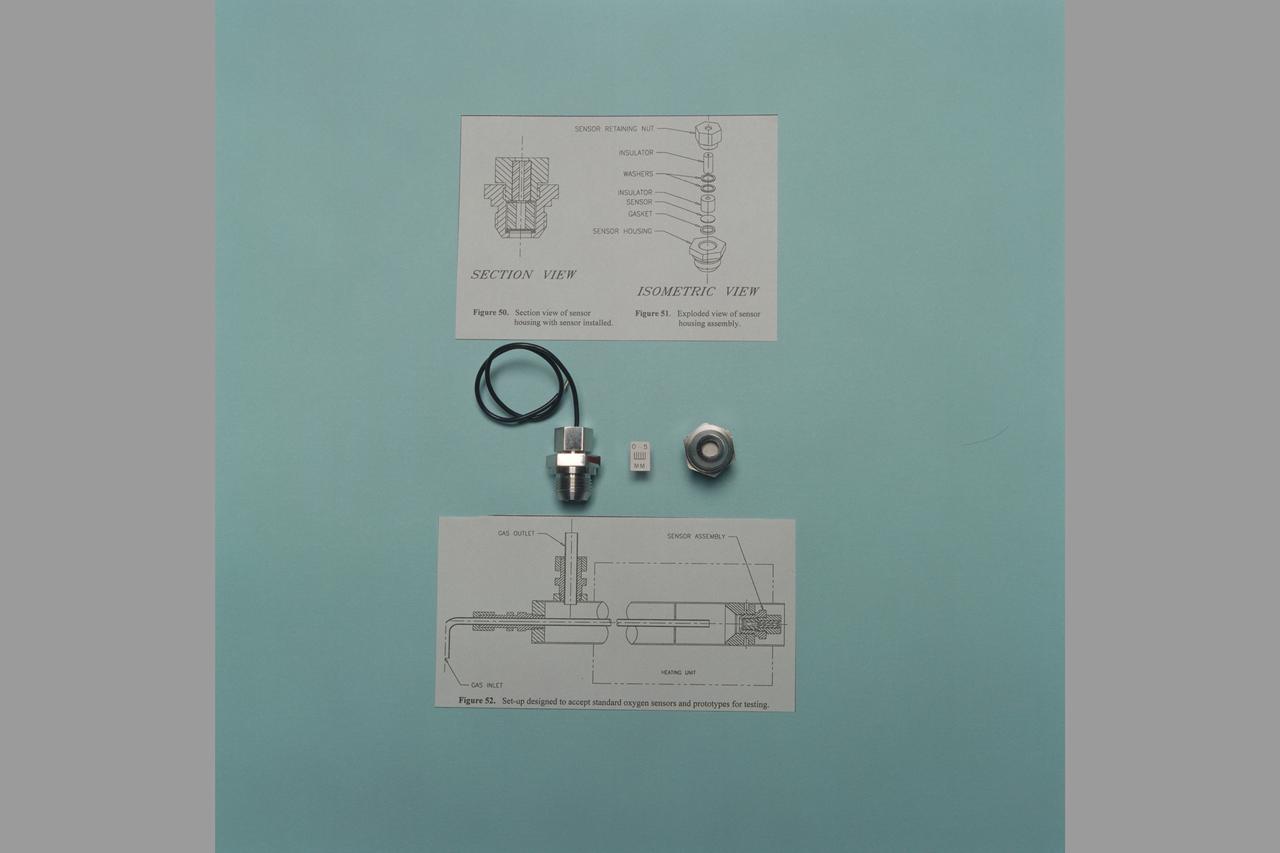
Miniature Oxygen Sensing Device. (sensor & sensors with drawings)
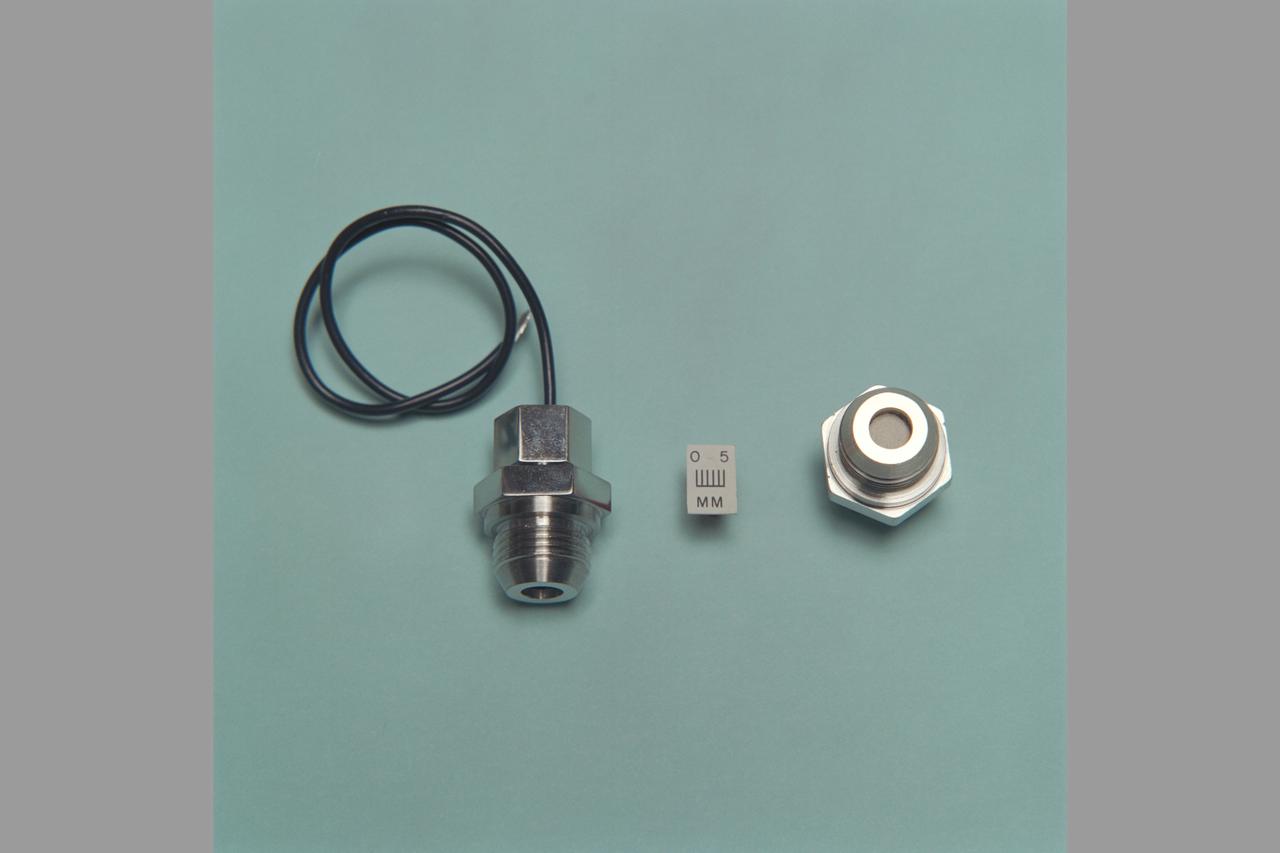

Miniature Oxygen Sensing Device. (sensor & sensors with drawings)

View of miniature bread floating,in the Node 1. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.

Originally devised to observe Saturn stage separation during Apollo flights, Marshall Space Flight Center's Miniature Television Camera, measuring only 4 x 3 x 1 1/2 inches, quickly made its way to the commercial telecommunications market.
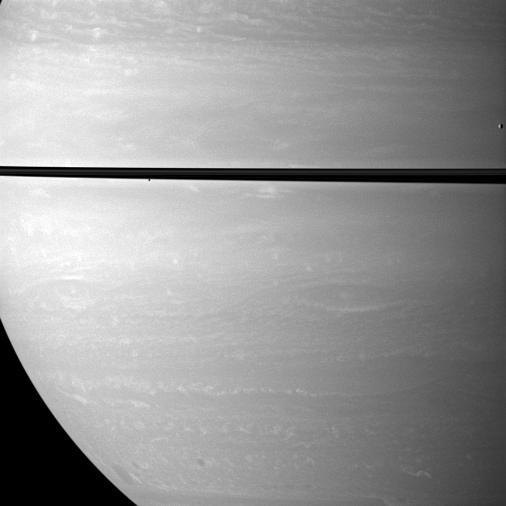

While studying Saturn atmosphere, NASA Cassini spacecraft happens to catch a view of two small, icy satellites. Mimas drifts past on the far right of the image. Janus appears as a black dot just below the rings near the center of the image.
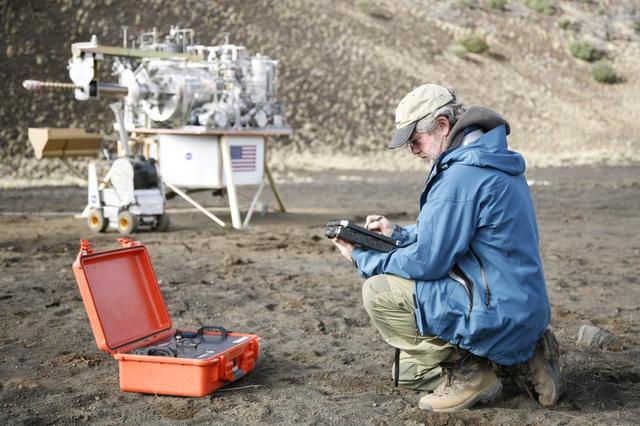

Decades of work preparing a miniaturized laboratory for identifying minerals on Mars have also yielded spinoff versions with diverse applications on Earth and, possibly, the moon.
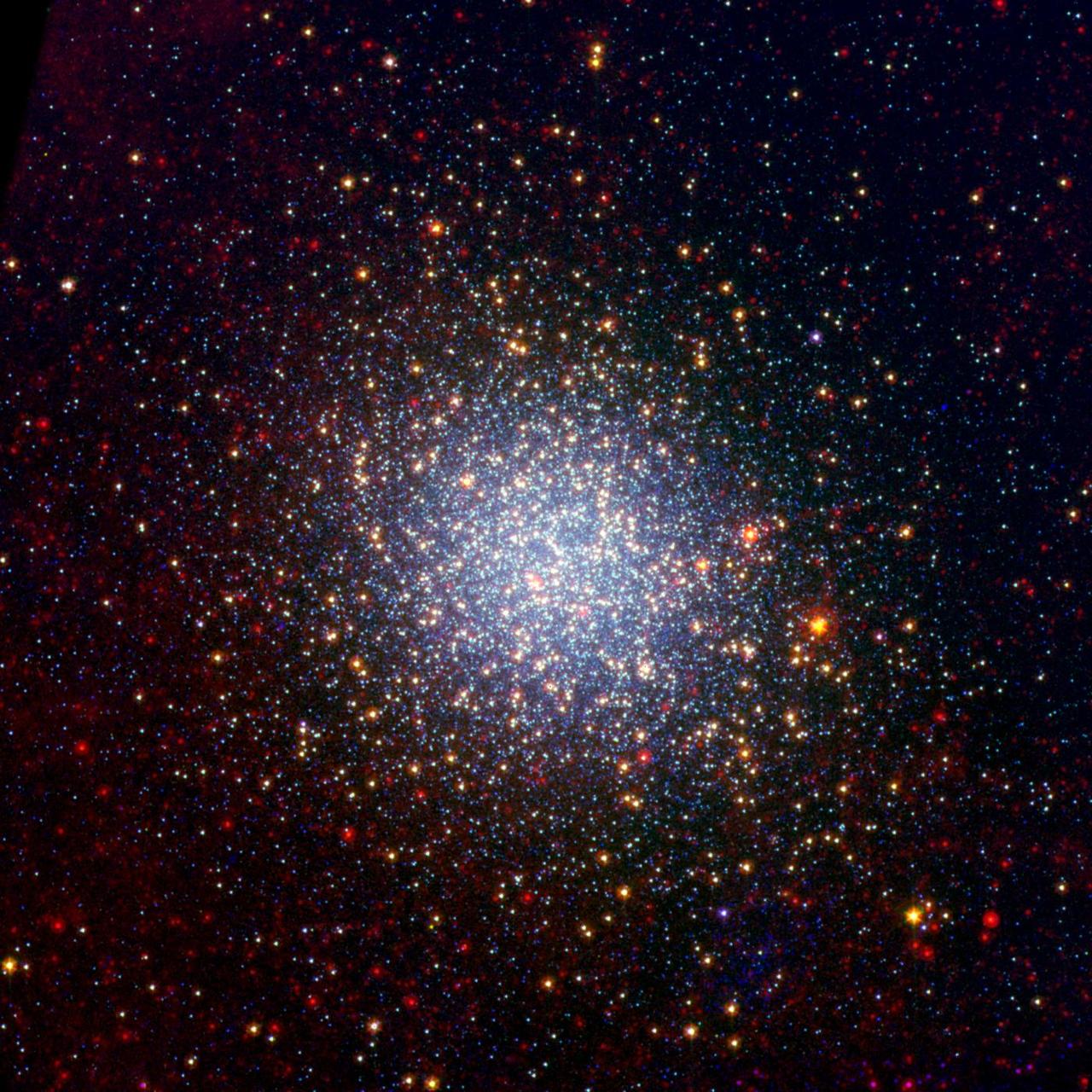

A cluster brimming with millions of stars glistens like an iridescent opal in this image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Called Omega Centauri, the sparkling orb of stars is like a miniature galaxy.
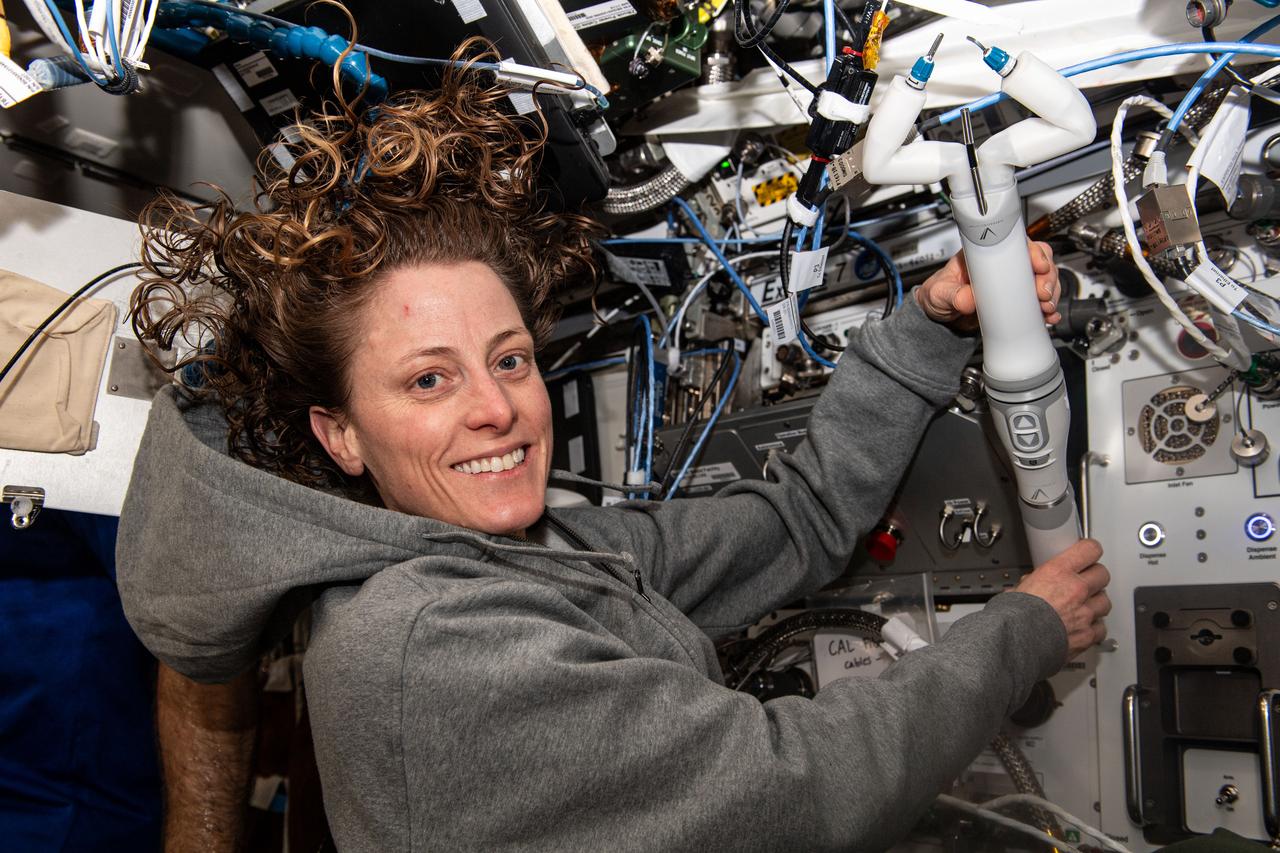

iss070e097708 (Feb. 21, 2024) -- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Loral O’Hara shows off the miniaturized in vivo robotic assistant (MIRA), which is Virtual Incision’s miniaturized robotic assisted surgery system, which was used to conduct a robotic surgery technology demonstration aboard the International Space Station. The hardware tests techniques for performing robotic surgery in microgravity using a miniature surgical robot that can be remotely controlled or teleoperated from Earth.

jsc2019e051830 --- FLUMIAS-DEA miniaturized fluorescence microscope loaded in TangoLab-2. Image courtesy of: Airbus
jsc2019e051831 --- Image of fixed macrophages using three chromophores created by the FLUMIAS-DEA miniaturized fluorescence microscope during Science Verification Test. Image courtesy of: Airbus
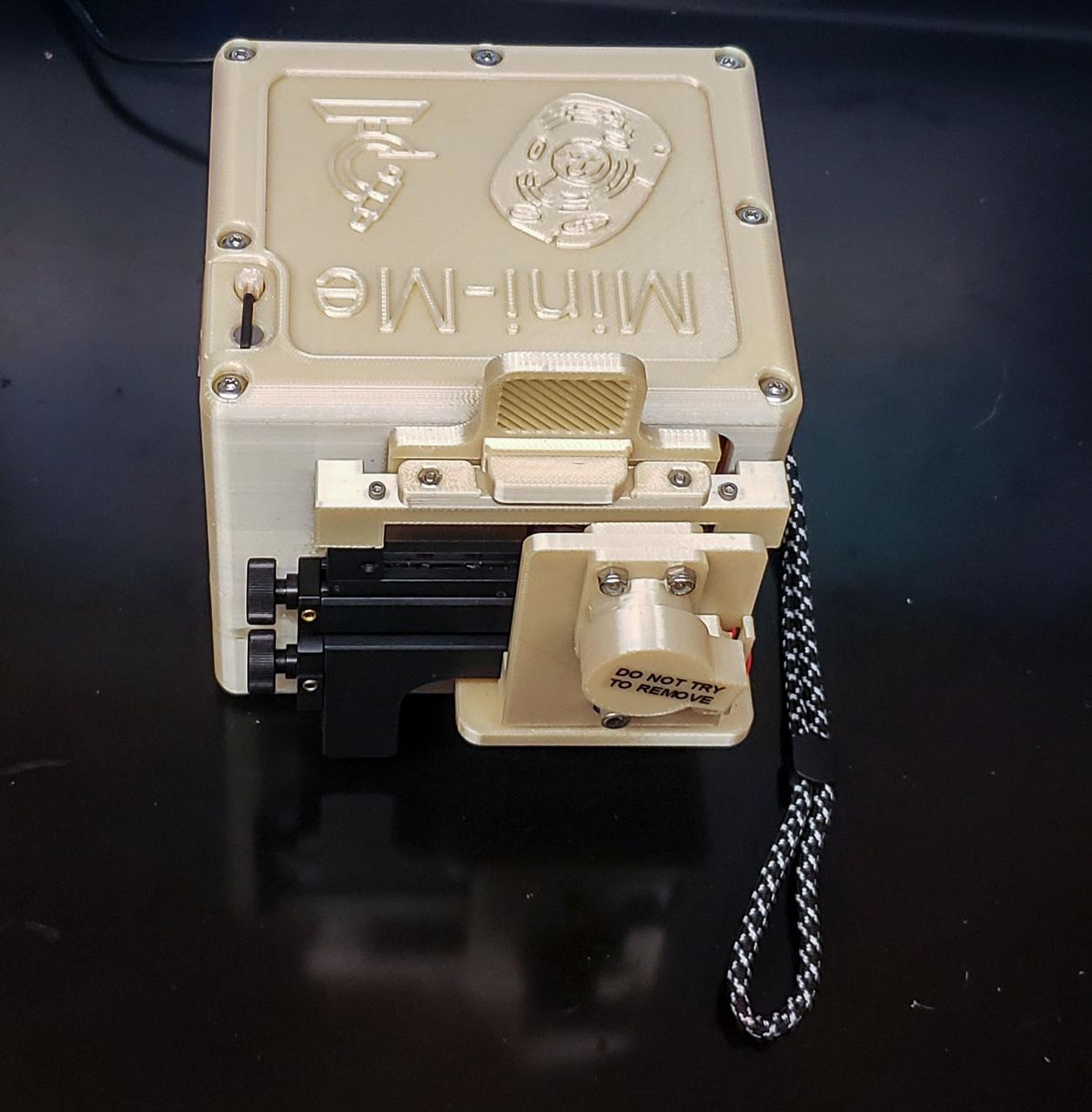

jsc2022e083574 (8/17/2022) --- A preflight image of the miniature microscope developed for the Moon Microscope investigation. Image courtesy of NASA’s Johnson Space Center Immunology/Virology Laboratory.
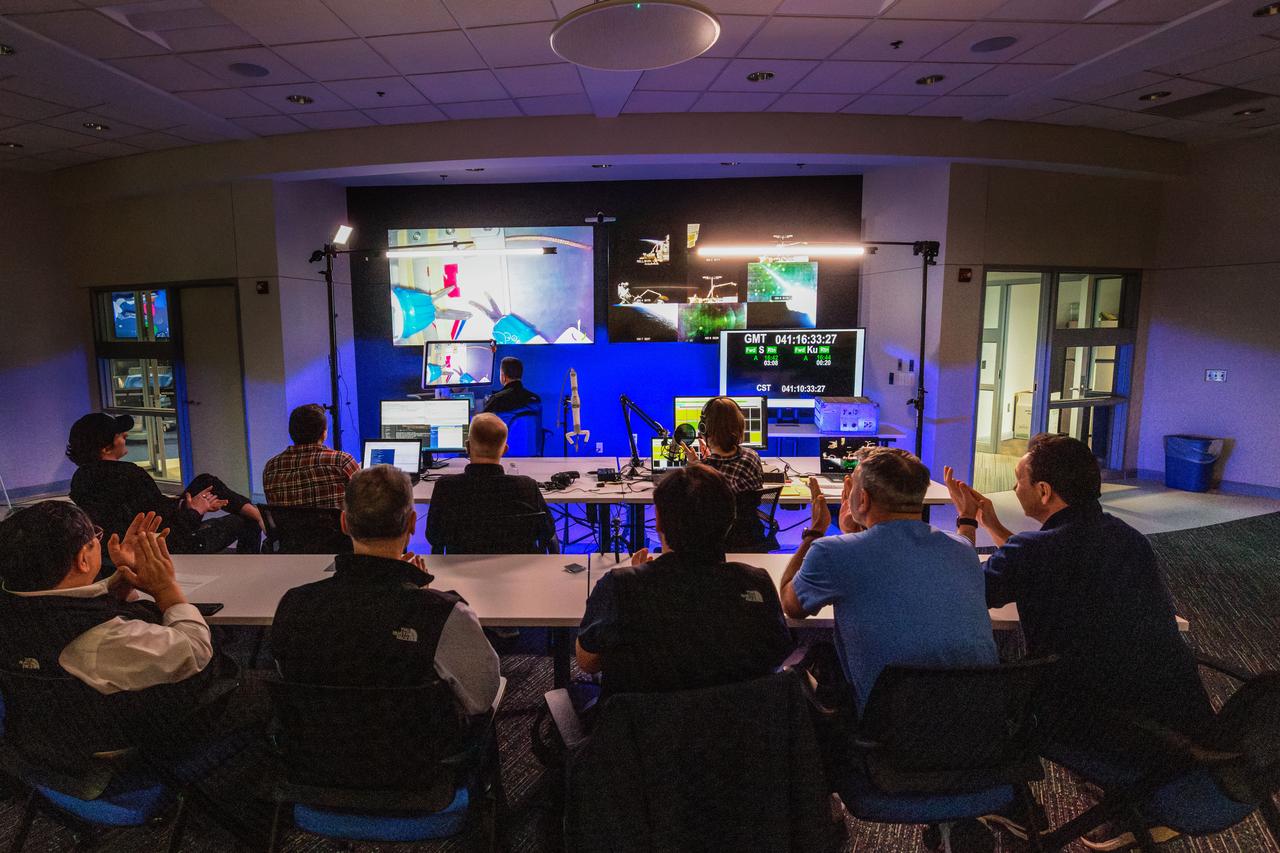

jsc2024e041214 (2/10/2024) --- Dr. Michael Jobst remotely operates a surgical robot aboard the International Space Station using controls at the Virtual Incision offices in Lincoln, Nebraska. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo tests techniques for performing robotic surgery in microgravity using a miniature surgical robot that can be remotely controlled or teleoperated from Earth. Results from this investigation could support the development of robotic systems to perform remote procedures. Miniaturization and the ability to remotely control robots may help to make surgery available anywhere and anytime. Image courtesy of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
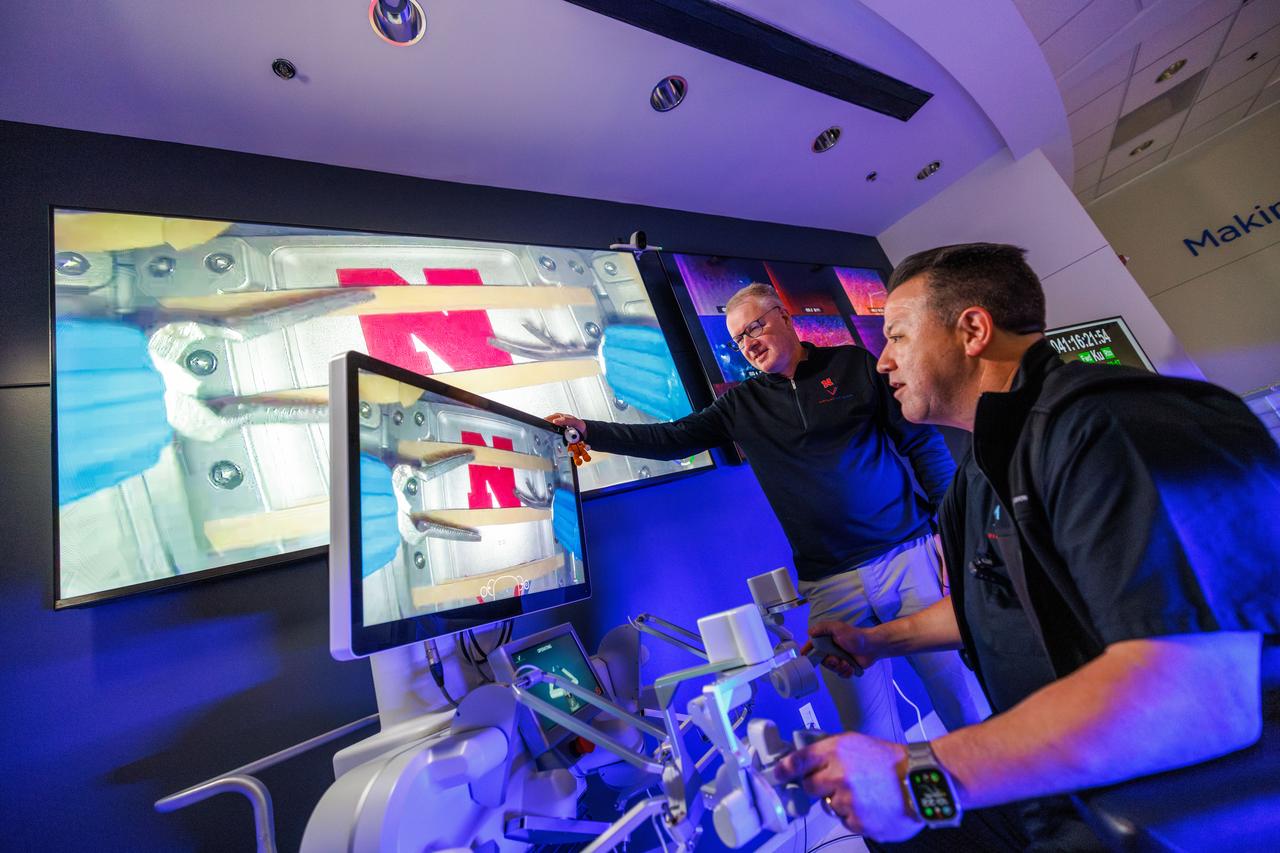

jsc2024e041212 (2/10/2024) --- Professor Shane Farritor (left) watches as Dr. Michael Jobst remotely operates a surgical robot aboard the International Space Station using controls at the Virtual Incision offices in Lincoln, Nebraska. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo tests techniques for performing robotic surgery in microgravity using a miniature surgical robot that can be remotely controlled or teleoperated from Earth. Results from this investigation could support the development of robotic systems to perform these procedures. Miniaturization and the ability to remotely control robots may help to make surgery available anywhere and anytime. Image courtesy of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
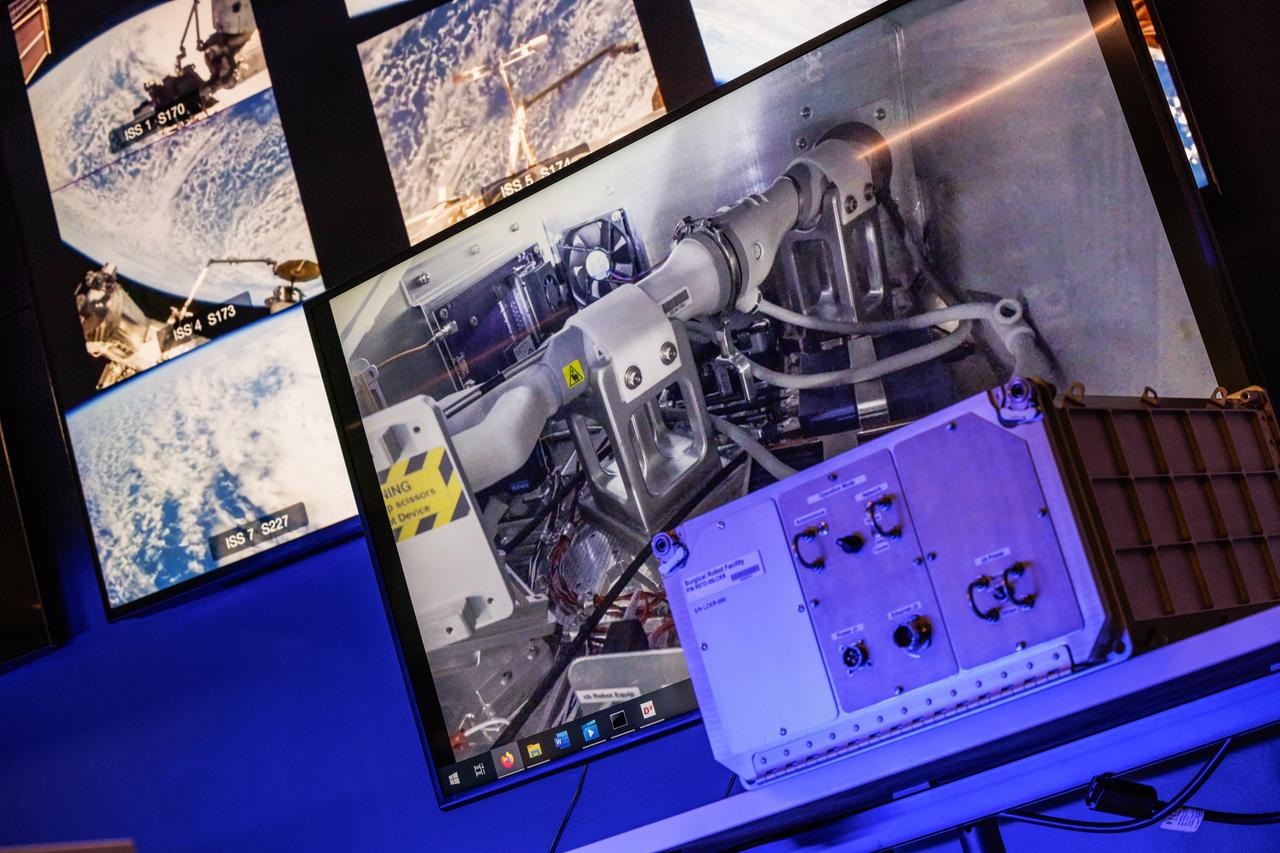

jsc2024e041211 (2/10/2024) --- Robotic Surgery Tech Demo tests techniques for performing robotic surgery in microgravity using a miniature surgical robot that can be remotely controlled or teleoperated from Earth. Several monitors at the Virtual Incision offices in Lincoln, Nebraska show views of the International Space Station during remote operations. Near the center, a larger monitor shows inside the box aboard the space station that houses the surgical robot. Results from this investigation could support the development of robotic systems to perform remote procedures. Miniaturization and the ability to remotely control robots may help to make surgery available anywhere and anytime. Image courtesy of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
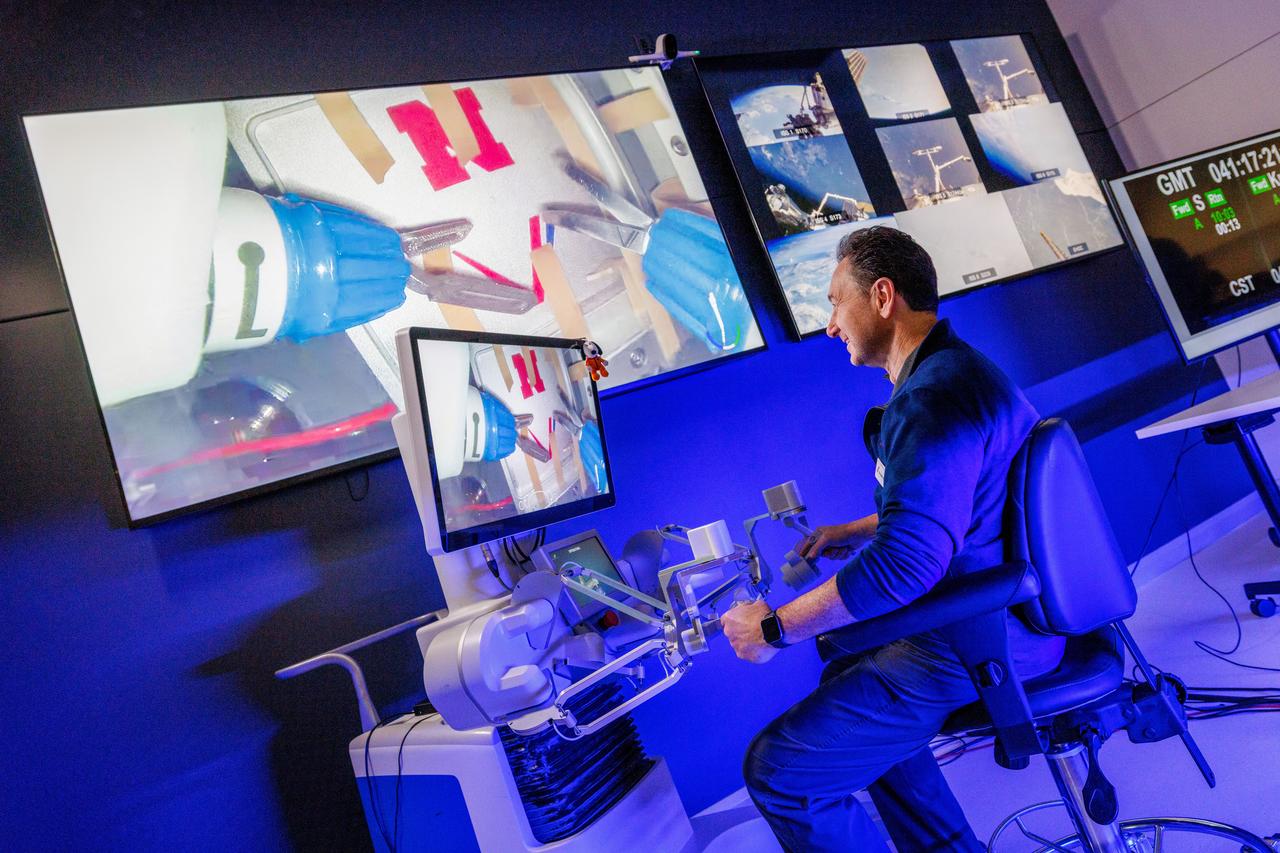

jsc2024e041215 (2/10/2024) --- Dr. Dmitry Oleynikov remotely operates a surgical robot aboard the International Space Station using controls at the Virtual Incision offices in Lincoln, Nebraska. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo tests techniques for performing a simulated surgical procedure in microgravity using a miniature surgical robot that can be remotely controlled or teleoperated from Earth. Results from this investigation could support the development of robotic systems to perform these procedures. Miniaturization and the ability to remotely control robots may help to make surgery available anywhere and anytime. Image courtesy of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
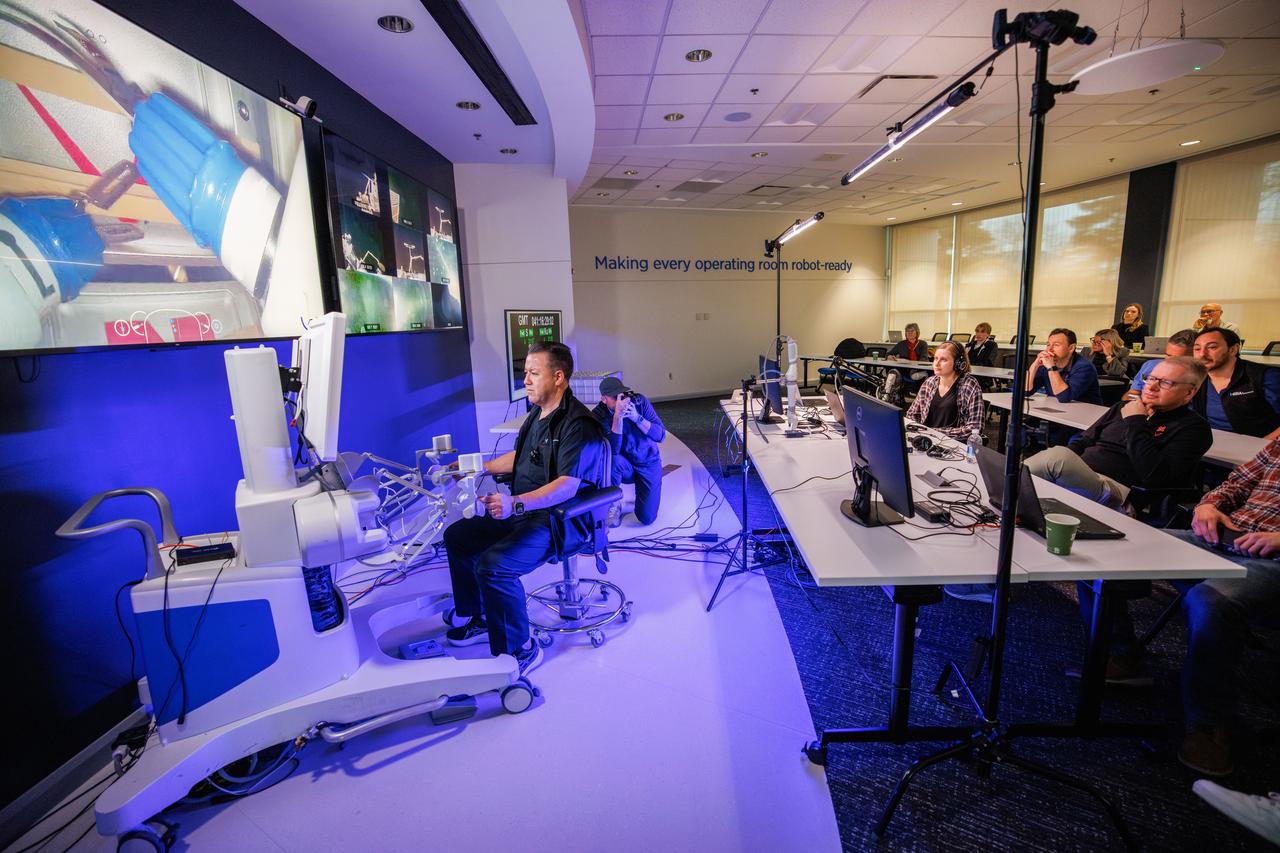

jsc2024e041213 (2/10/2024) --- Dr. Michael Jobst remotely operates a surgical robot aboard the International Space Station using controls at the Virtual Incision offices in Lincoln, Nebraska. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo tests techniques for performing robotic surgery in microgravity using a miniature surgical robot that can be remotely controlled or teleoperated from Earth. Results from this investigation could support the development of robotic systems to perform remote procedures. Miniaturization and the ability to remotely control robots may help to make surgery available anywhere and anytime. Image courtesy of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
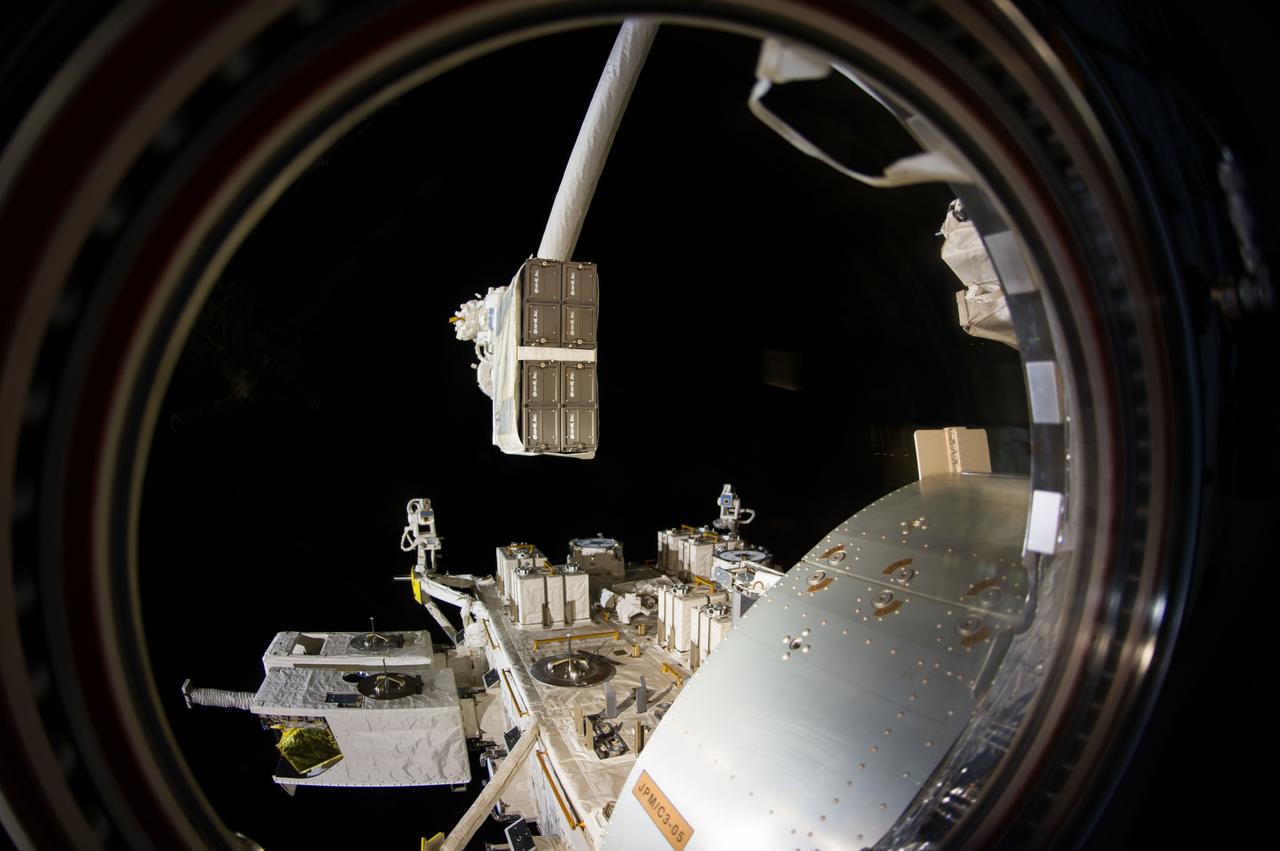

ISS040-E-100890 (19 Aug. 2014) --- Through a window in the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory, an Expedition 40 crew member photographed the CubeSat deployer mechanism in the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm prior to a series of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellite deployments.
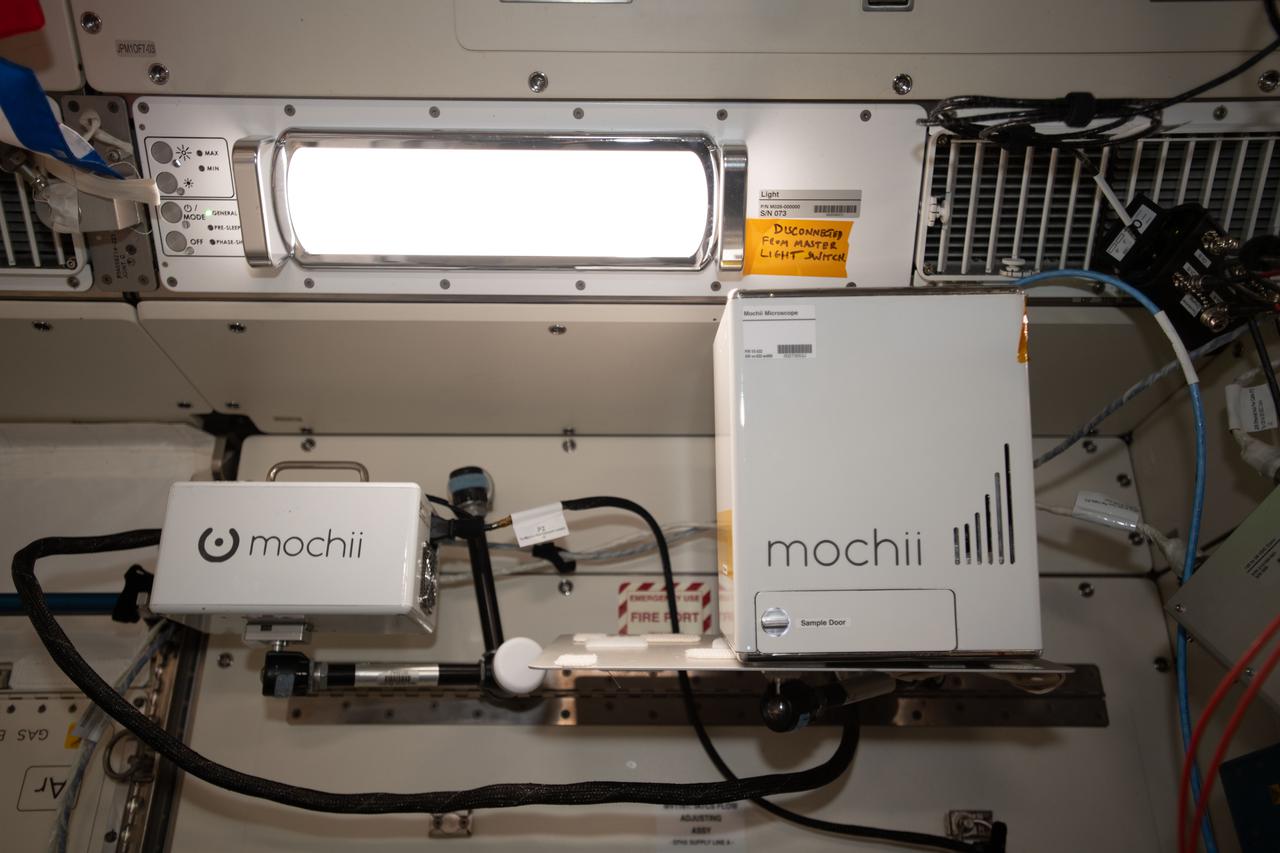

iss066e110545 (1/10/2022) --- A view of the Mochii microscope aboard the International Space Station (ISS. Mochii is a miniature scanning electron microscope (SEM) with spectroscopy to conduct real-time, on-site imaging and compositional measurements of particles on the International Space Station (ISS).
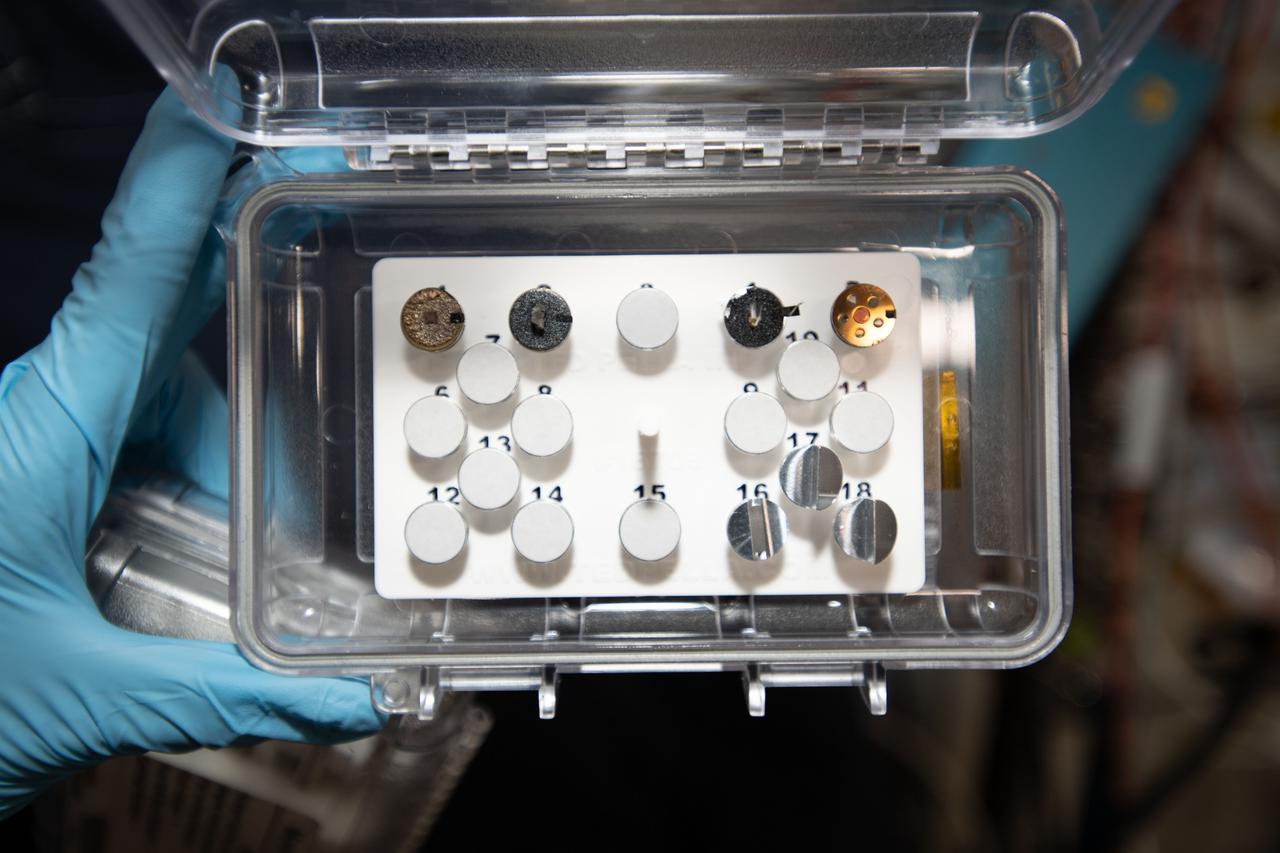

iss066e110547 (1/10/2022) --- A view of the Mochii microscope sample load aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Mochii is a miniature scanning electron microscope (SEM) with spectroscopy to conduct real-time, on-site imaging and compositional measurements of particles on the International Space Station (ISS)
jsc2024e005977 (9/14/2023) --- MIRA, Virtual Incision’s miniaturized robotic assisted surgery system, is pictured in position to reach simulated surgical tissue. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo uses MIRA on the International Space Station to perform a set of pre-programmed movements. Image courtesy of Virtual Incision.

ISS003-E-7261 (October 2001) --- Cosmonaut Vladimir N. Dezhurov, Expedition Three flight engineer, takes a break from his duties, as he plays with a miniature basketball and net in the Unity node on the International Space Station (ISS). Dezhurov represents Rosaviakosmos. This image was taken with a digital still camera.
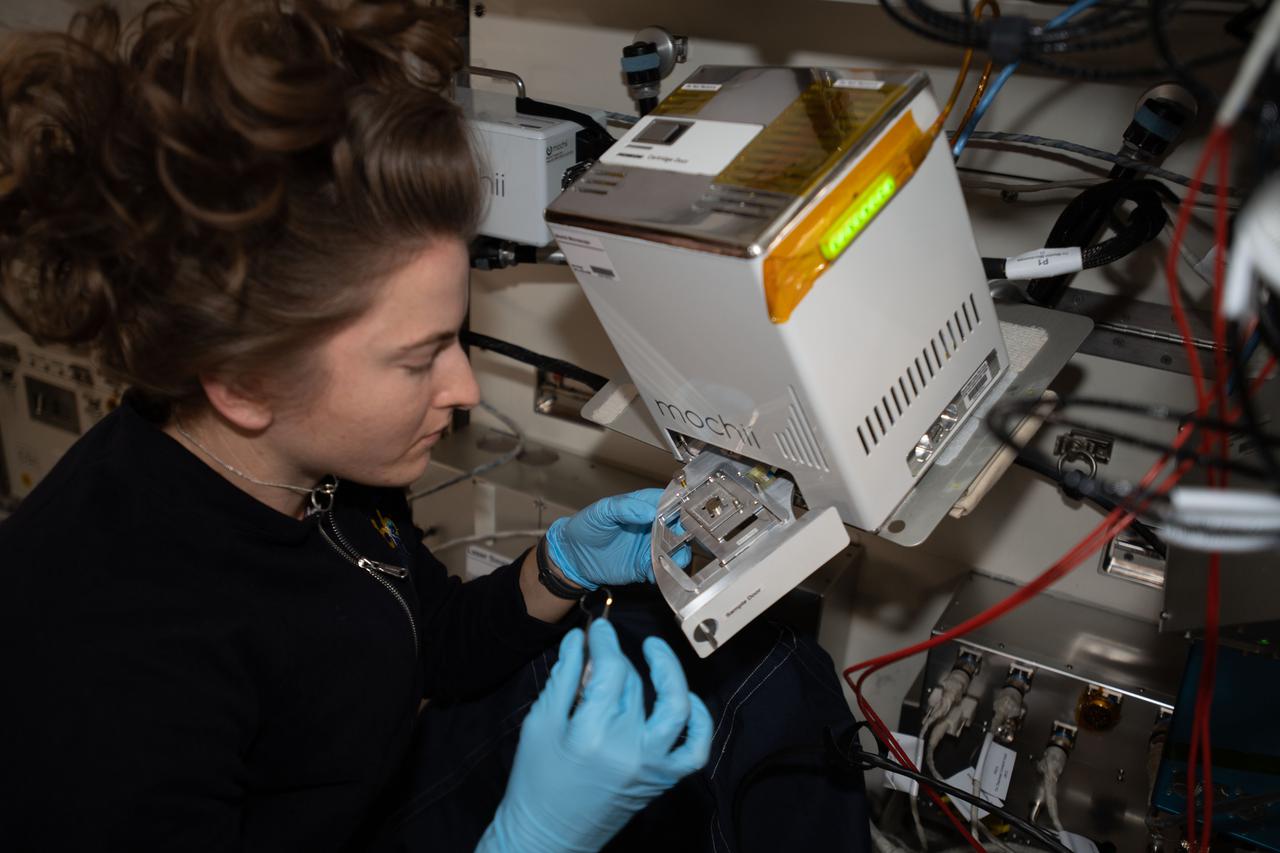

iss066e110566 (1/10/2022) --- NASA astronaut Kayla Barron sets up the Mochii microscope. Mochii is a miniature scanning electron microscope (SEM) with spectroscopy to conduct real-time, on-site imaging and compositional measurements of particles on the International Space Station (ISS).
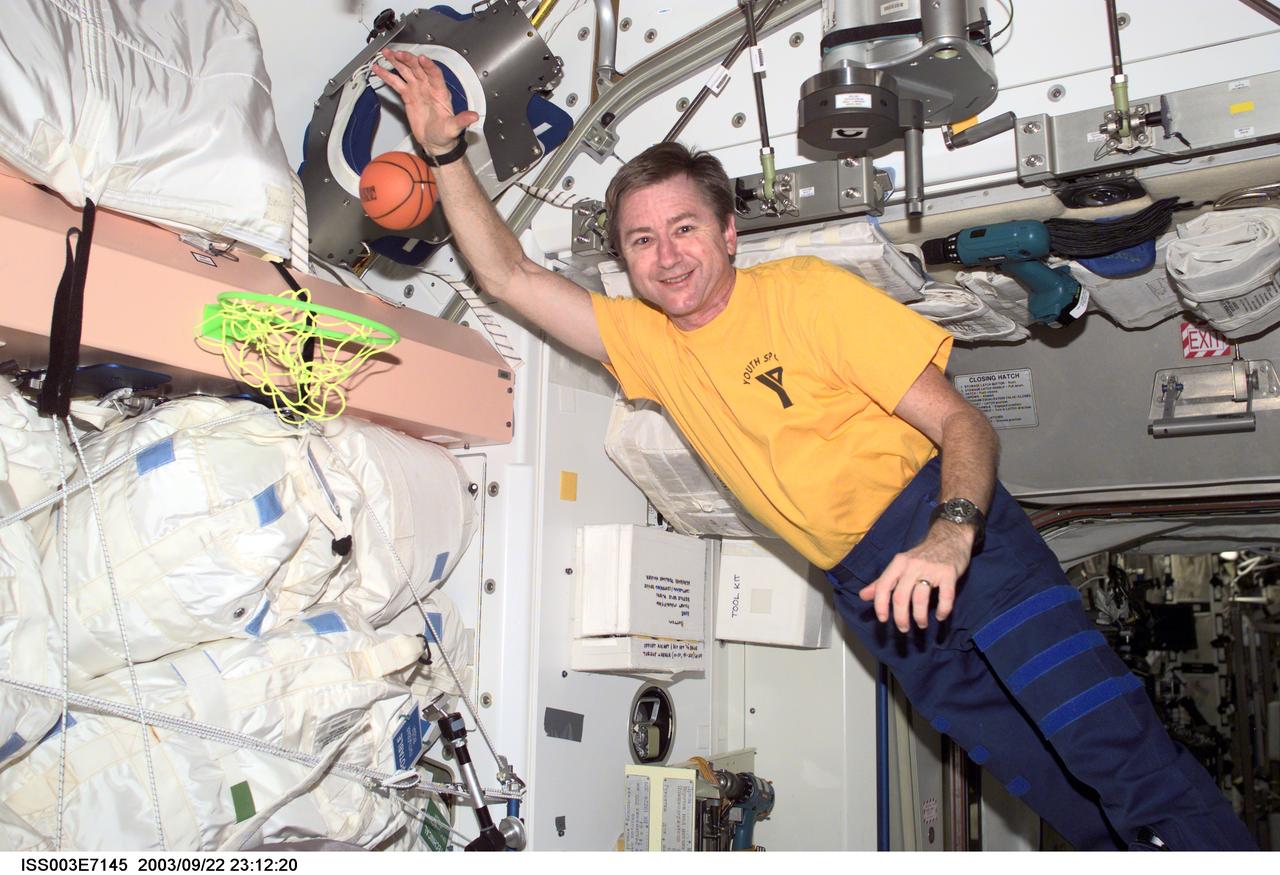

ISS003-E-7145 (OCTOBER 2001) --- Astronaut Frank L. Culbertson, Jr., Expedition Three mission commander, takes a break from his duties, as he plays with a miniature basketball and net in the Unity node on the International Space Station (ISS). This image was taken with a digital still camera.
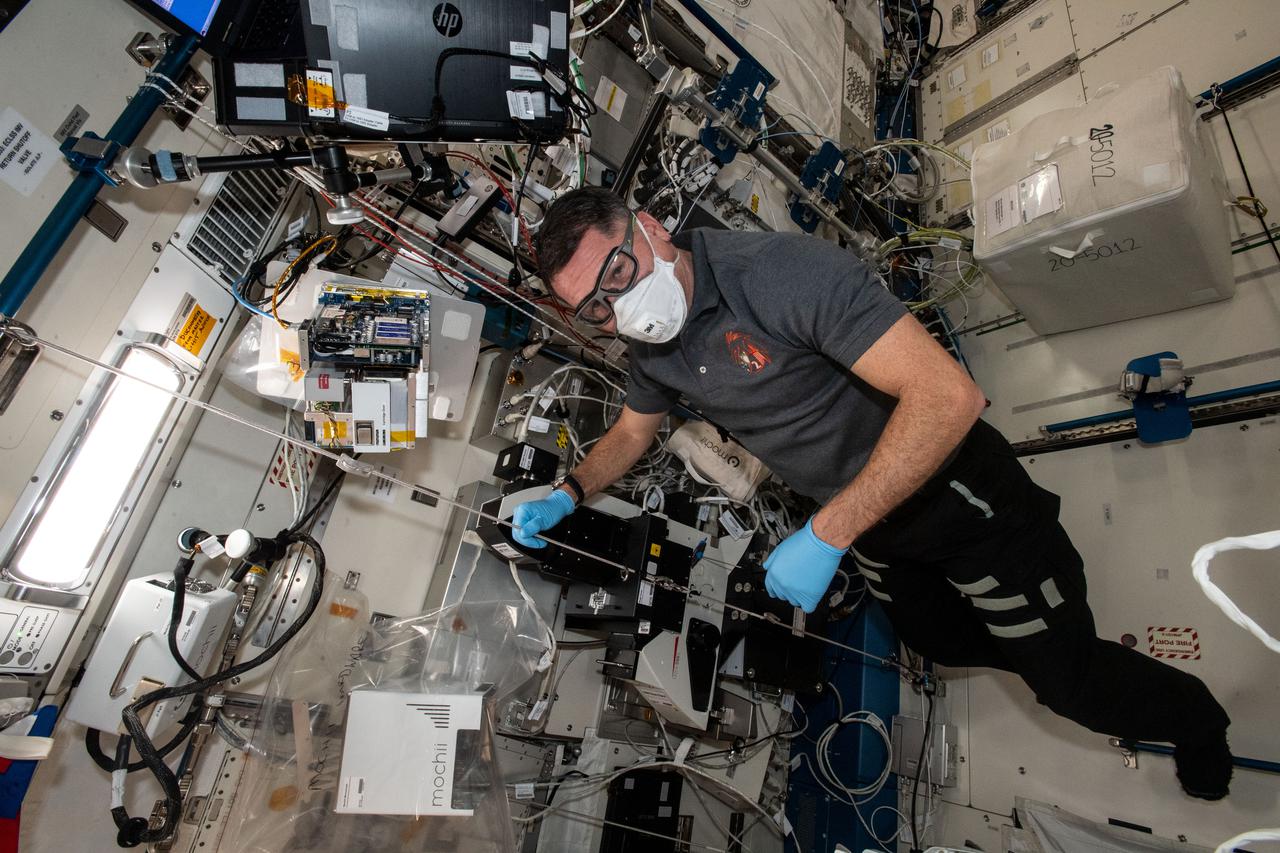

iss065e241981 (Aug. 12, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough conducts maintenance on a miniature electron microscope, called Mochii, to support spectroscopic investigations and analyses of microscopic particles aboard the International Space Station.
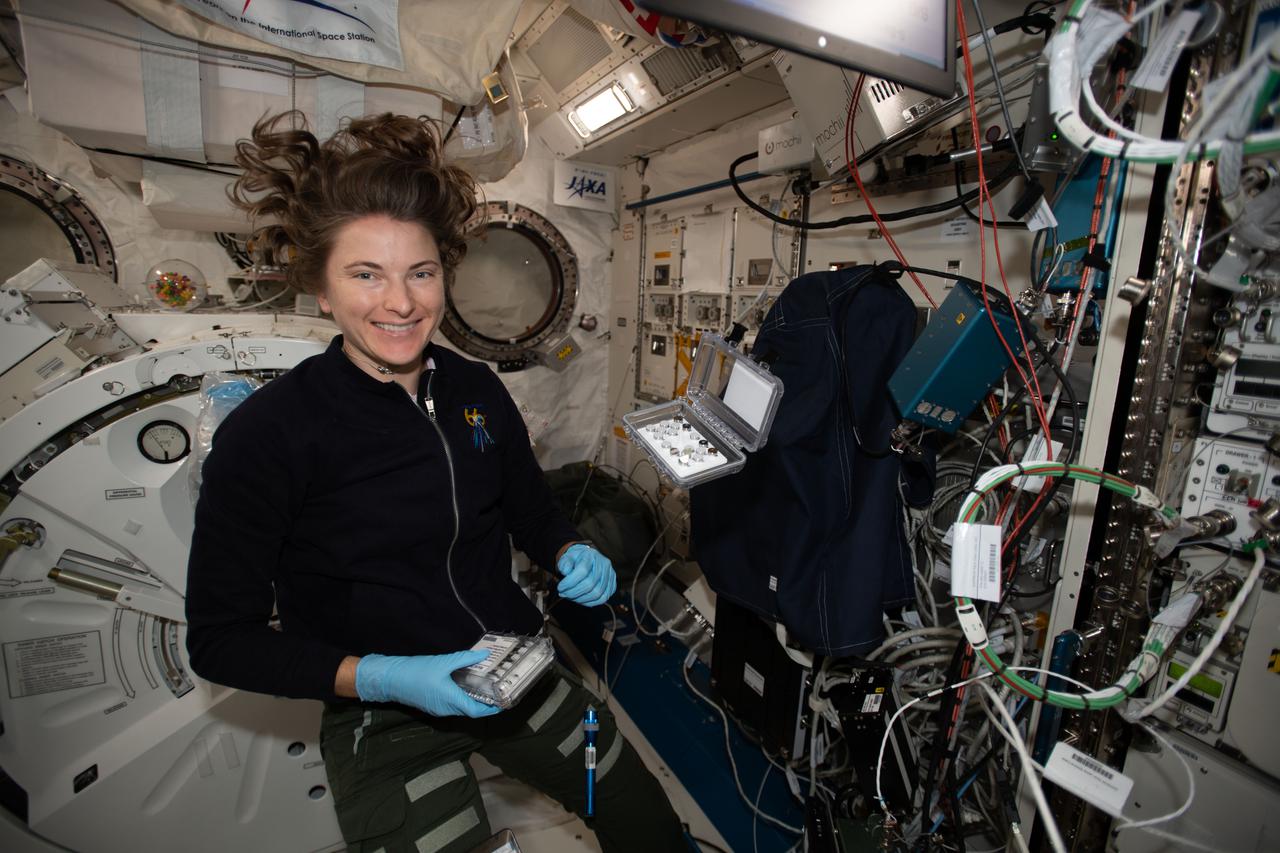

iss066e110556 (1/10/2022) --- NASA astronaut Kayla Barron sets up the Mochii microscope. Mochii is a miniature scanning electron microscope (SEM) with spectroscopy to conduct real-time, on-site imaging and compositional measurements of particles on the International Space Station (ISS).
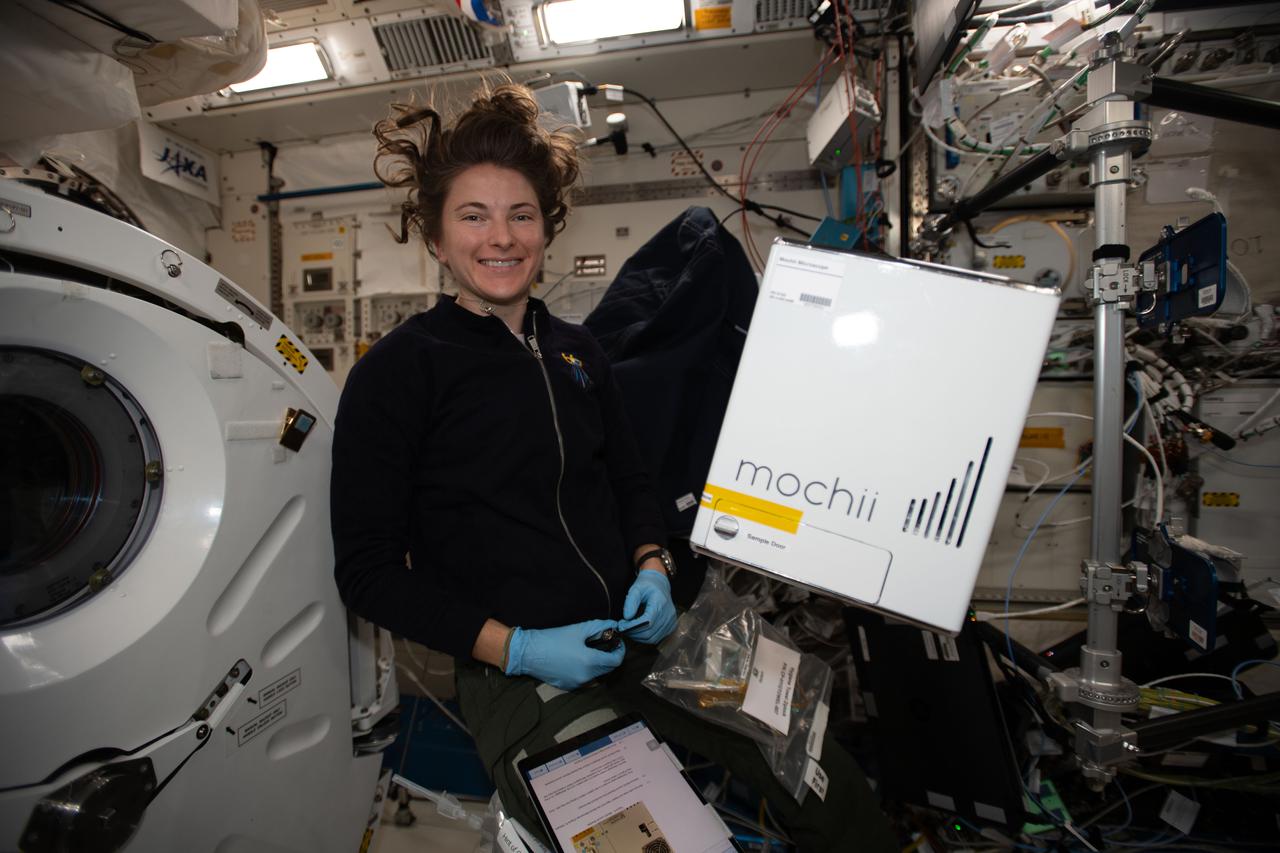

iss066e110531_alt (1/10/2022) --- NASA astronaut Kayla Barron sets up the Mochii microscope. Mochii is a miniature scanning electron microscope (SEM) with spectroscopy to conduct real-time, on-site imaging and compositional measurements of particles on the International Space Station (ISS).

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier, center, talk with a Harding University student about a miniaturized laser sample analysis device that may be used for planetary science research. Terrier attended “NASA Day in Arkansas,” hosted at the university in Searcy, Arkansas on Jan. 27, 2020.
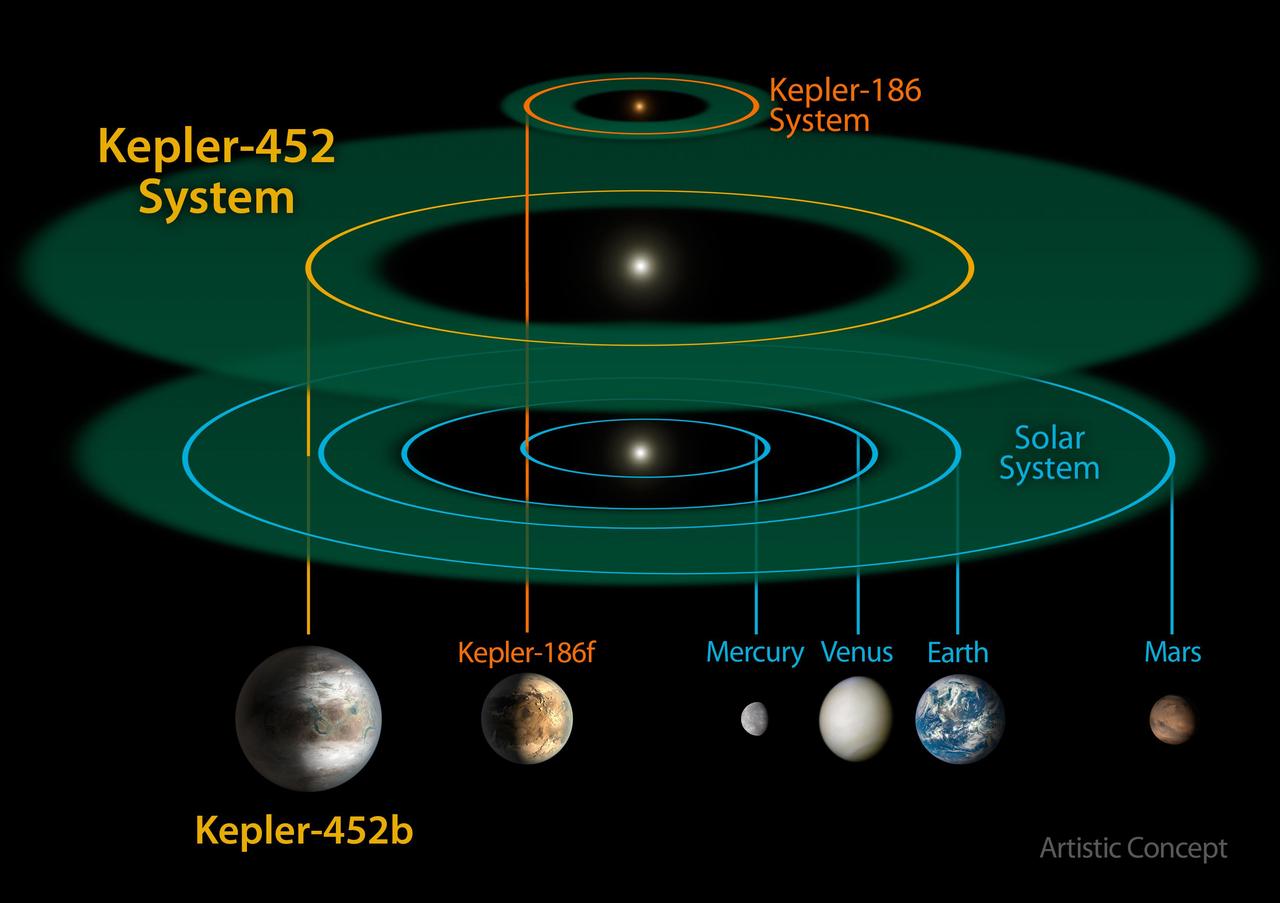
This size and scale of the Kepler-452 system compared alongside the Kepler-186 system and the solar system. Kepler-186 is a miniature solar system that would fit entirely inside the orbit of Mercury. The habitable zone of Kepler-186 is very small compared to that of Kepler-452 or the sun because it is a much smaller, cooler star. The size and extent of the habitable zone of Kepler-452 is nearly the same as that of the sun, but is slightly bigger because Kepler-452 is somewhat older, bigger and brighter. The size of the orbit of Kepler-452b is nearly the same as that of Earth at 1.05 astronomical units (an astronomical unit is the distance between Earth and the sun). Kepler-452b orbits its star once every 385 days. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19826
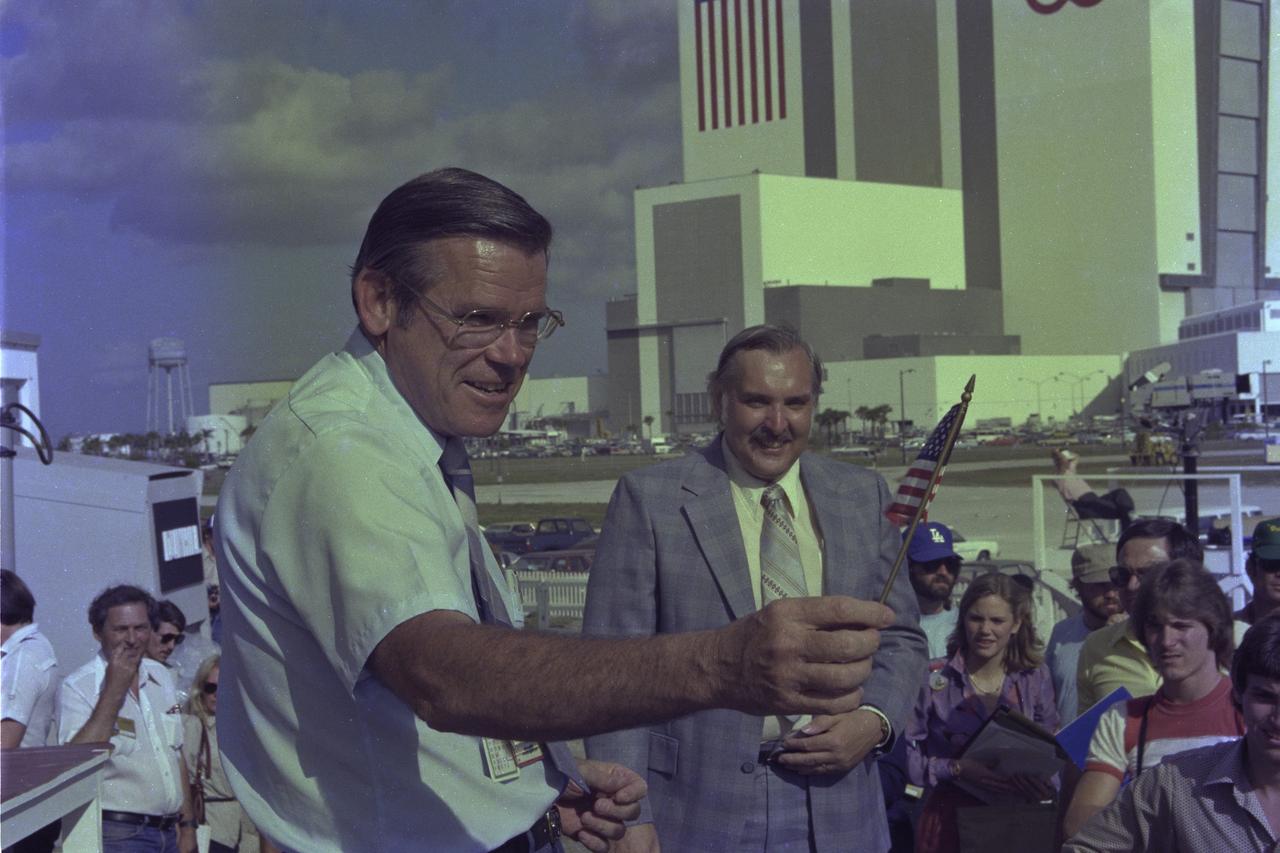

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A smiling George Page, launch director for the historic maiden flight of space shuttle Columbia, waves a miniature American flag at the conclusion of a press conference following the successful launch on April 12. With Page is Hugh Harris, chief of the Public Information Branch, NASA Public Affairs, Kennedy Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
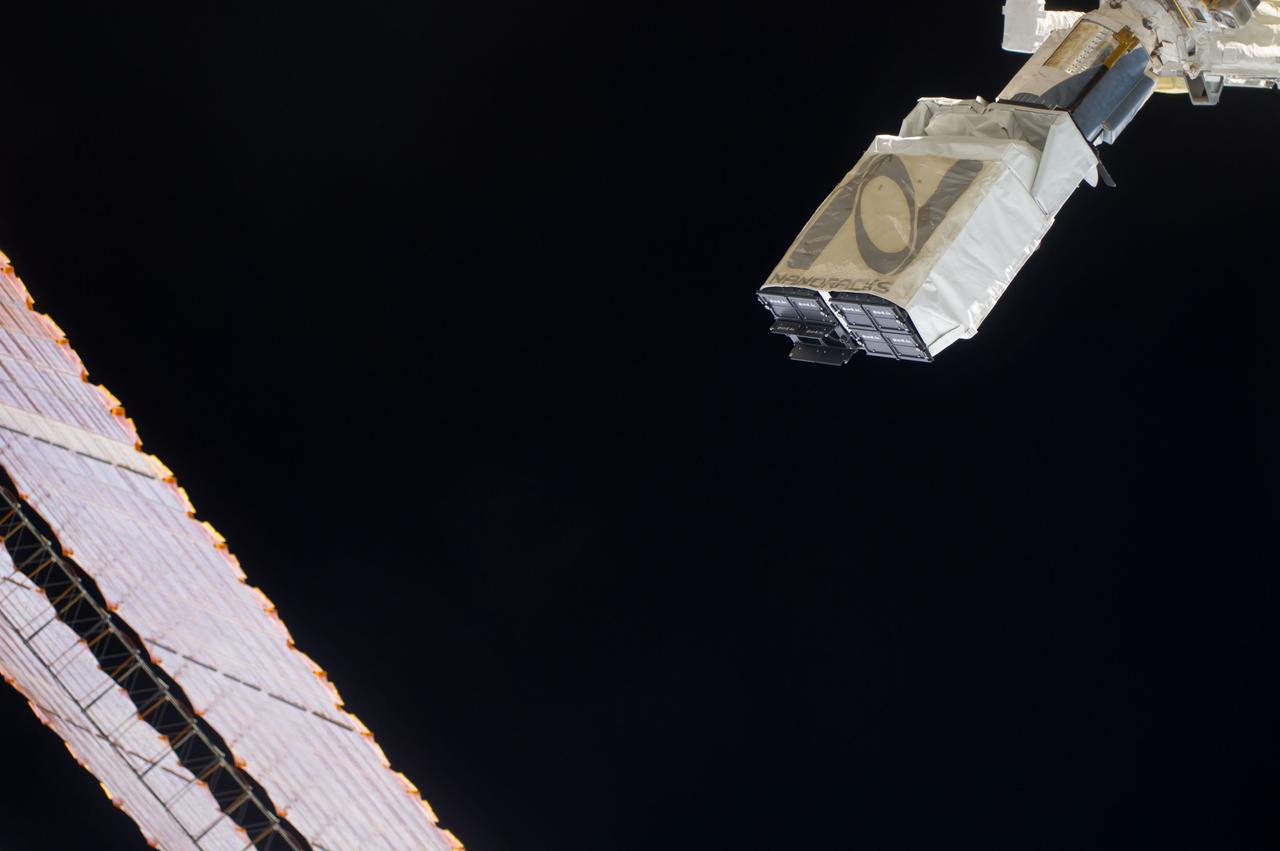

ISS040-E-102410 (20 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer is about to release a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. A section of the station solar array wings is at left.
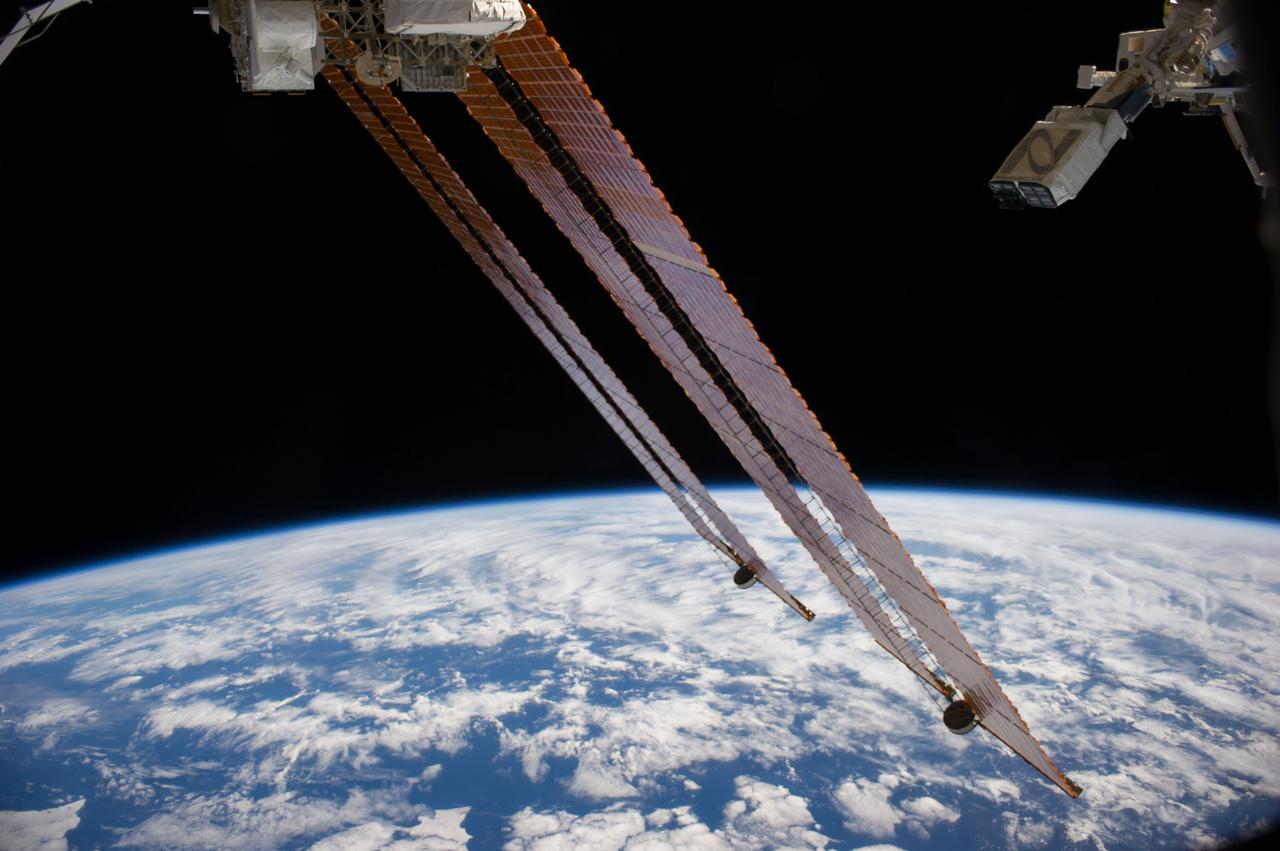

ISS040-E-103327 (20 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer (upper right) is about to release a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. A section of the station solar array wings is at center. A blue and white part of Earth and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
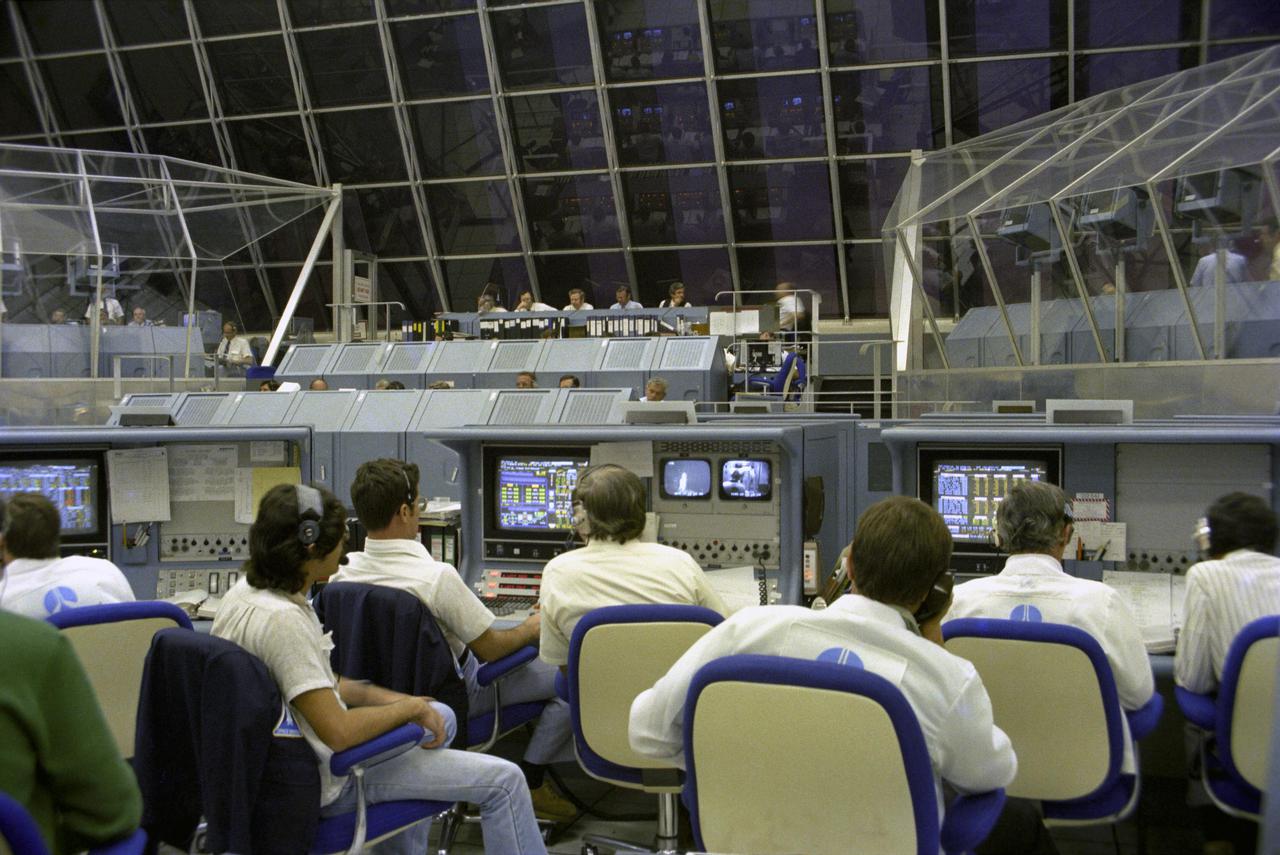

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Heavy, blast-proof steel louvers seal the large windows of the Launch Control Center’s firing room against mishaps that fail to occur when the first flight of the Space Shuttle is launched from Pad 39A 3.5 mile away. Launch staff, intently watching their computer readouts and TV monitors during the critical moments of launch, will cheer and wave miniature American flags when Astronauts John Young and Robert Crippen complete their fiery rocket ascent safely.
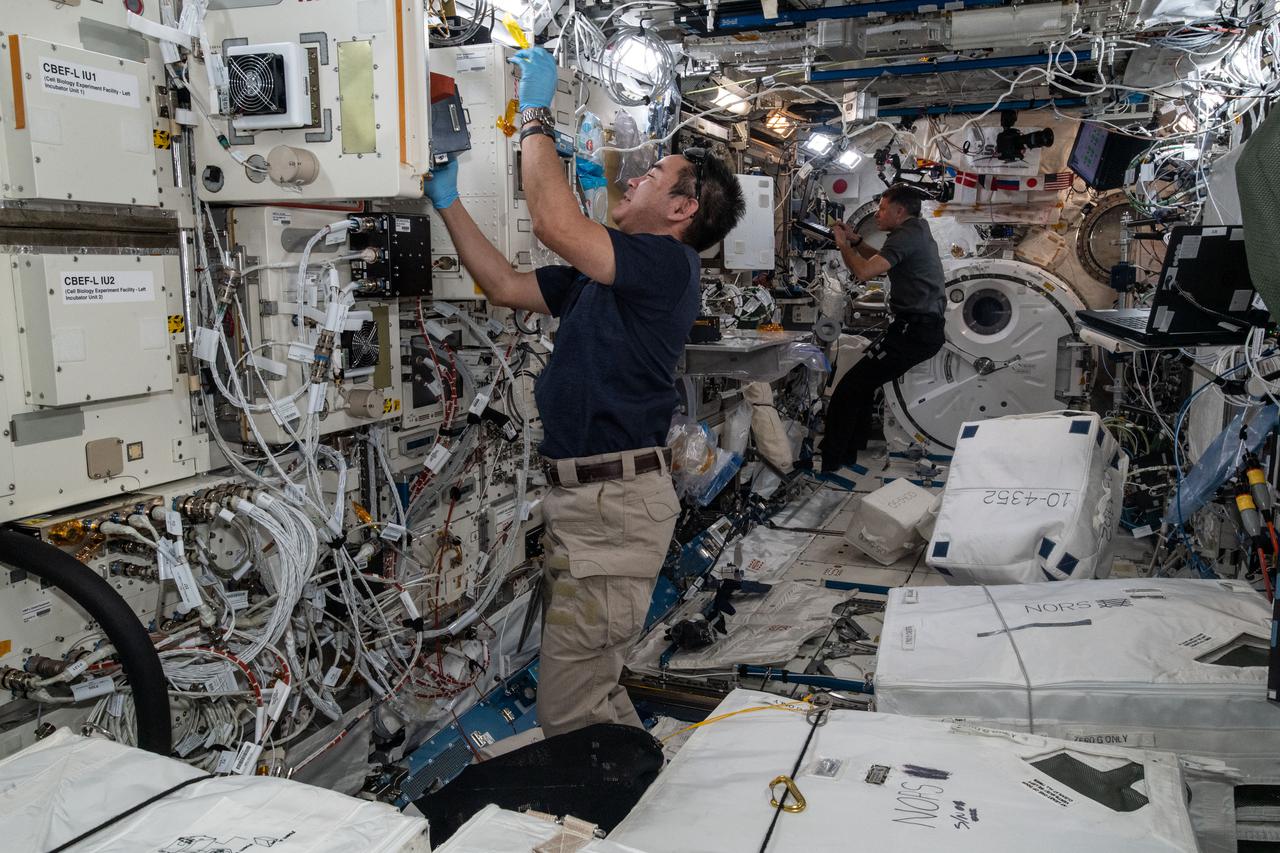

iss065e242201 (Aug. 13, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Commander Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) inserts cell samples into the Kibo laboratory module's Cell Biology Experiment Facility. At the rear of Kibo, NASA Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough trains to use a miniature electron microscope, called Mochii, to support spectroscopic investigations and analyses of microscopic particles aboard the International Space Station.
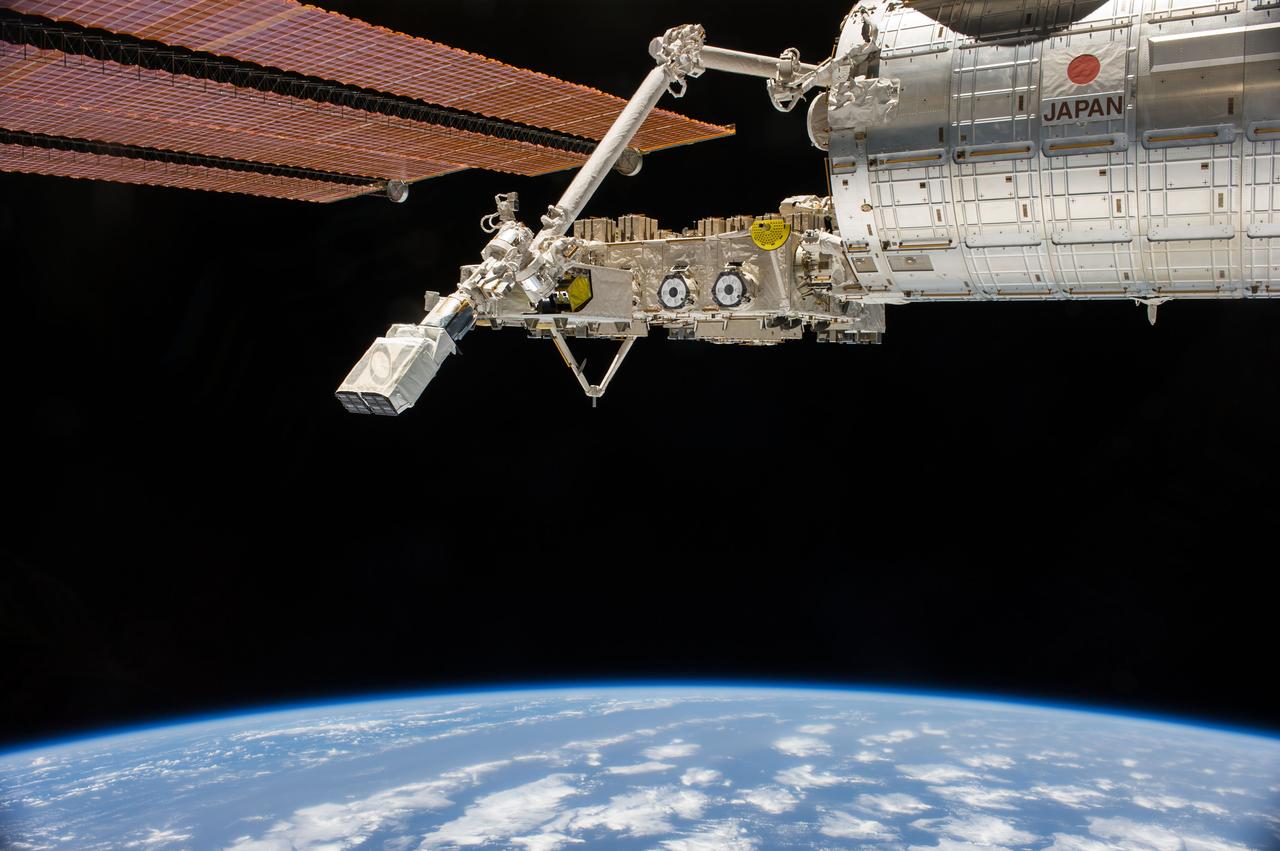

ISS040-E-103506 (19 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer is about to release a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. The station?s Kibo laboratory is at top right. A blue and white part of Earth and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
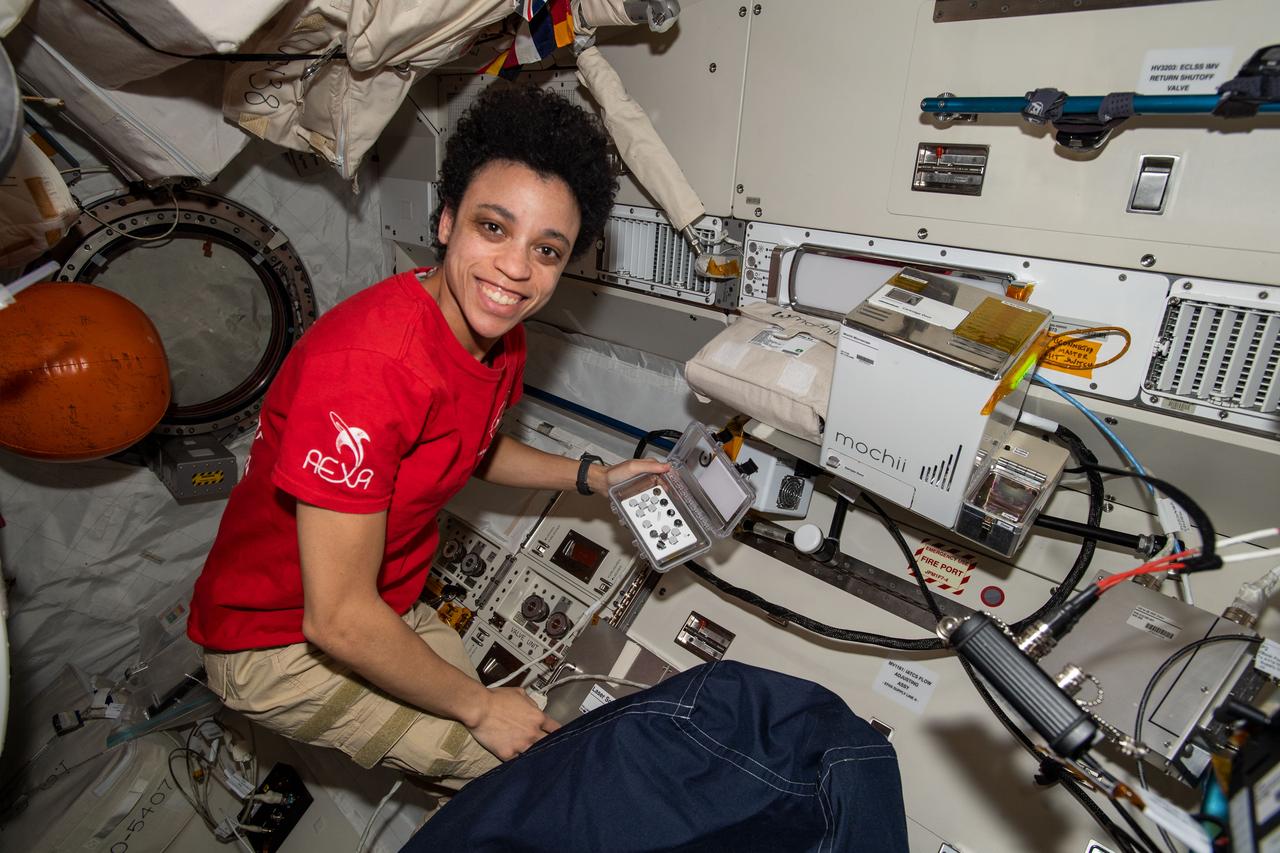

iss068e016422 (Oct. 12, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Jessica Watkins works with Mochii, a miniature scanning electron microscope (SEM) with spectroscopy to conduct real-time, on-site imaging and compositional measurements of particles on the International Space Station (ISS). Such particles can cause vehicle and equipment malfunctions and threaten crew health, but currently, samples must be returned to Earth for analysis, leaving crew and vehicle at risk. Mochii also provides a powerful new analysis platform to support novel microgravity science and engineering.

jsc2021e029976 (6/30/2021) --- A preflight view of the TARGIT cubesat. The Tethering And Ranging Mission of the Georgia Institute of Technology (TARGIT) tests a miniaturized Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) imaging camera. The camera tracks and takes images of a tethered inflatable target to verify its performance and demonstrate precision topographic mapping capability and use of an inflatable as a drag device. These capabilities could help support future planetary missions. Image courtesy of Candler Hobbs
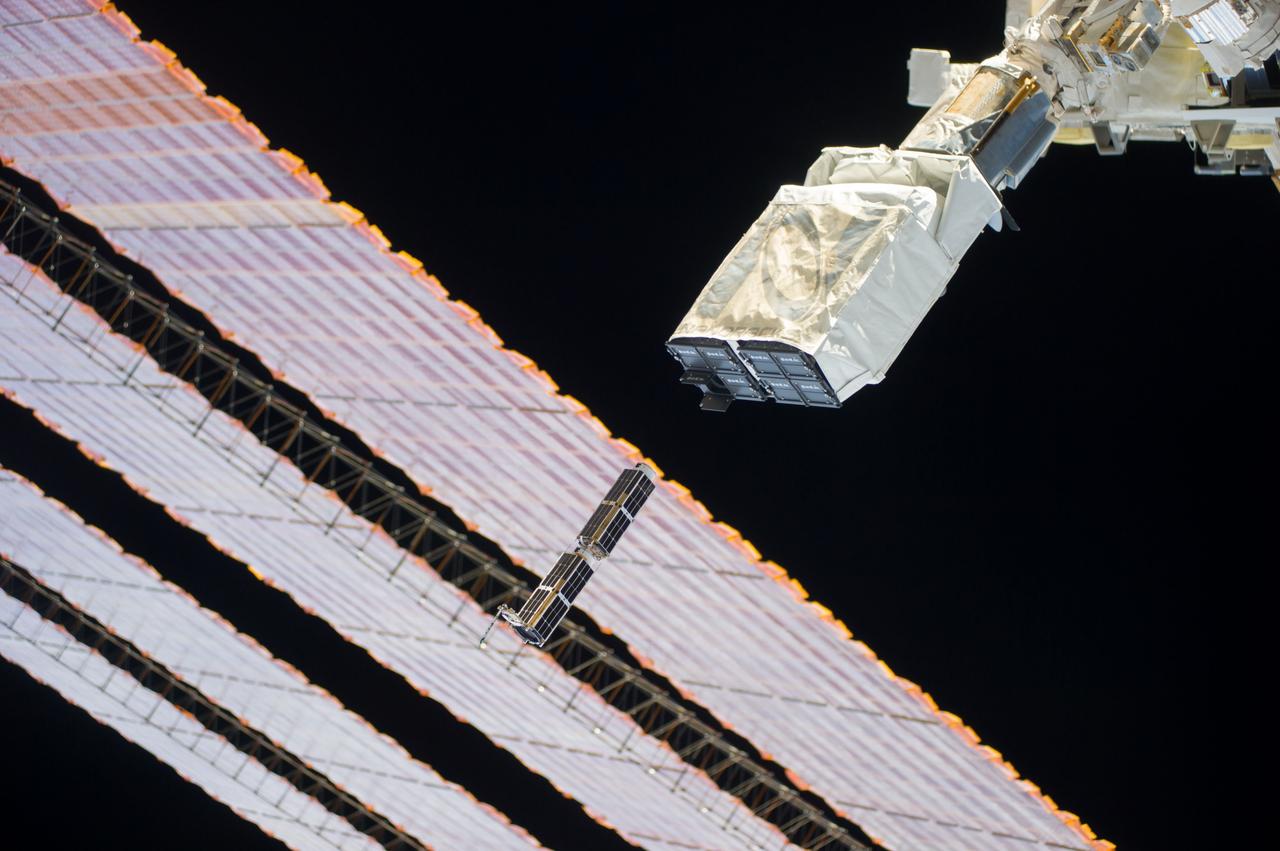

ISS040-E-102490 (19 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer releases a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. A section of the station solar array wings is at left.
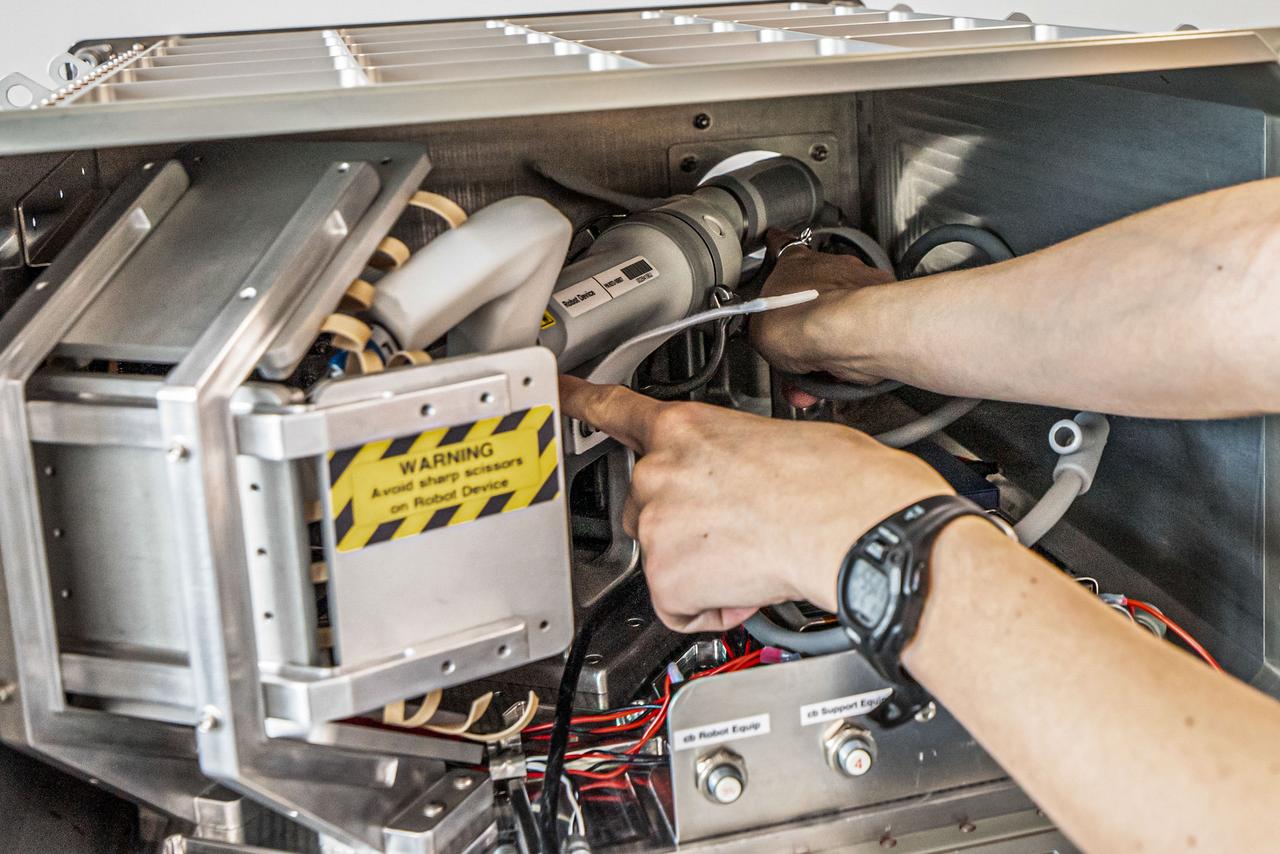
jsc2024e005981 (9/15/2023) --- The robotic surgery device is shown positioned inside the science locker, with the instrument arms and camera oriented toward the simulated surgical tissue on the experiment board. The unique small footprint makes it possible to transport the minibot anywhere, even to space. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo flies a special iteration of MIRA, Virtual Incision’s miniaturized robotic assisted surgery system. Image courtesy of Virtual Incision.

ISS040-E-096126 (18 Aug. 2014) --- In the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory, European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, depressurizes the Kibo airlock in preparation for a series of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellite deployments. The first two pairs of nanosatellites are scheduled for deployment on Aug. 19. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25.
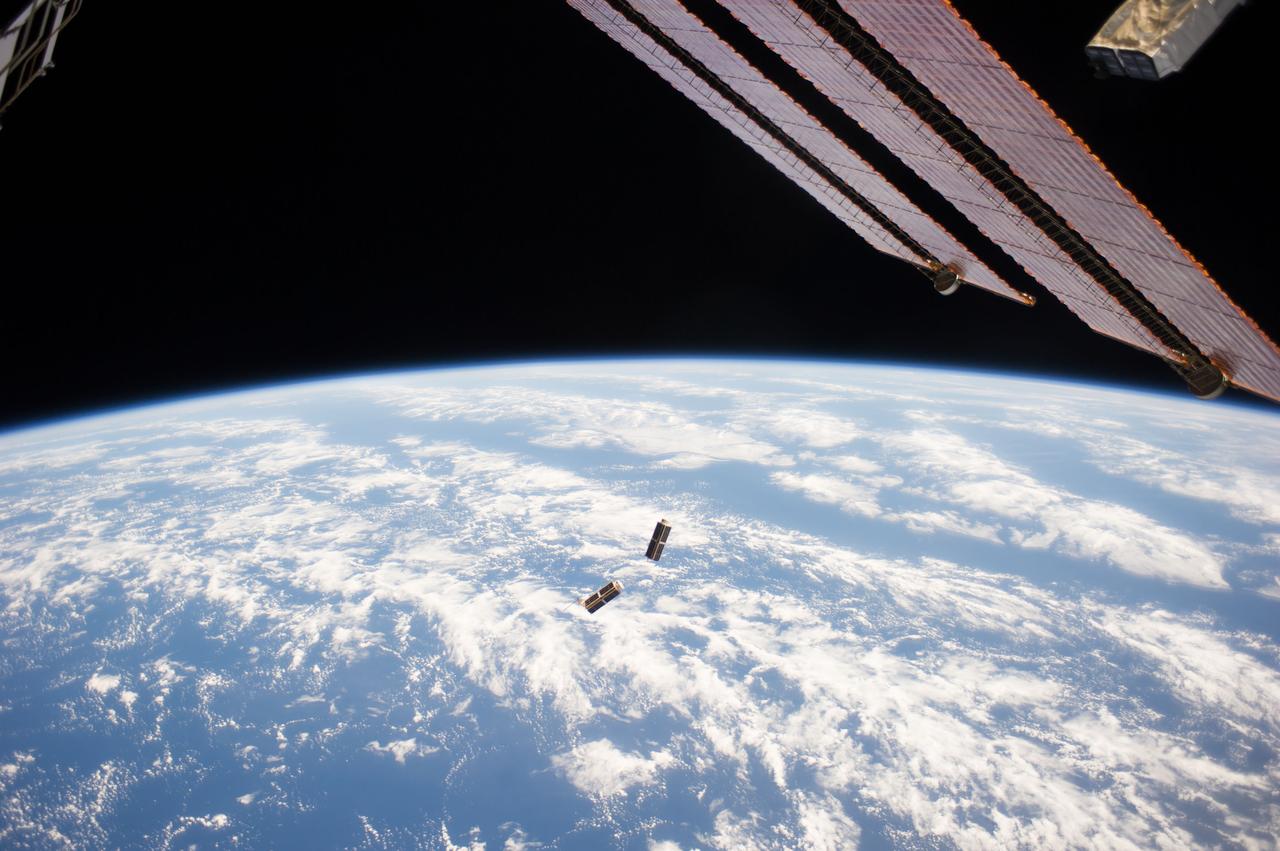

ISS040-E-103545 (19 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer (mostly out of frame, upper right) releases a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites (center). The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. A section of the station solar array wings is at top right. A blue and white part of Earth and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
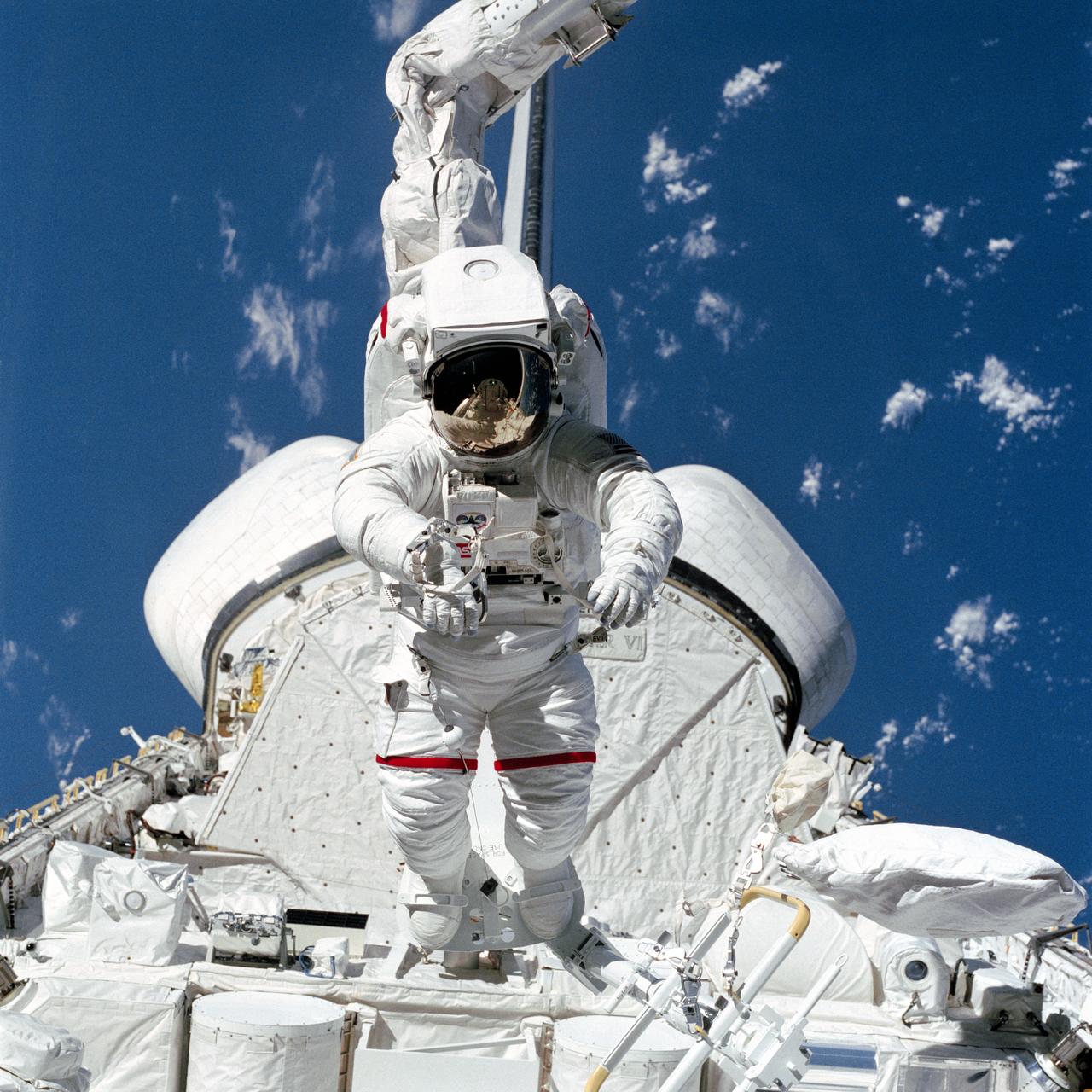

S84-27039 (7 Feb 1984) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, at first glance appears to be walking on cargo in the Space Shuttle Challenger's payload bay. Actually, he is being "flown" around above the stationary cargo. His "flight" is due to the combined configuration of the Mobile Foot Restraint (MFR) and the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). His helmet visor reflects in miniature parts of the payload bay that can't be seen in the larger portion of the photo. A 70mm camera aimed through the aft flight deck windows exposed this frame.
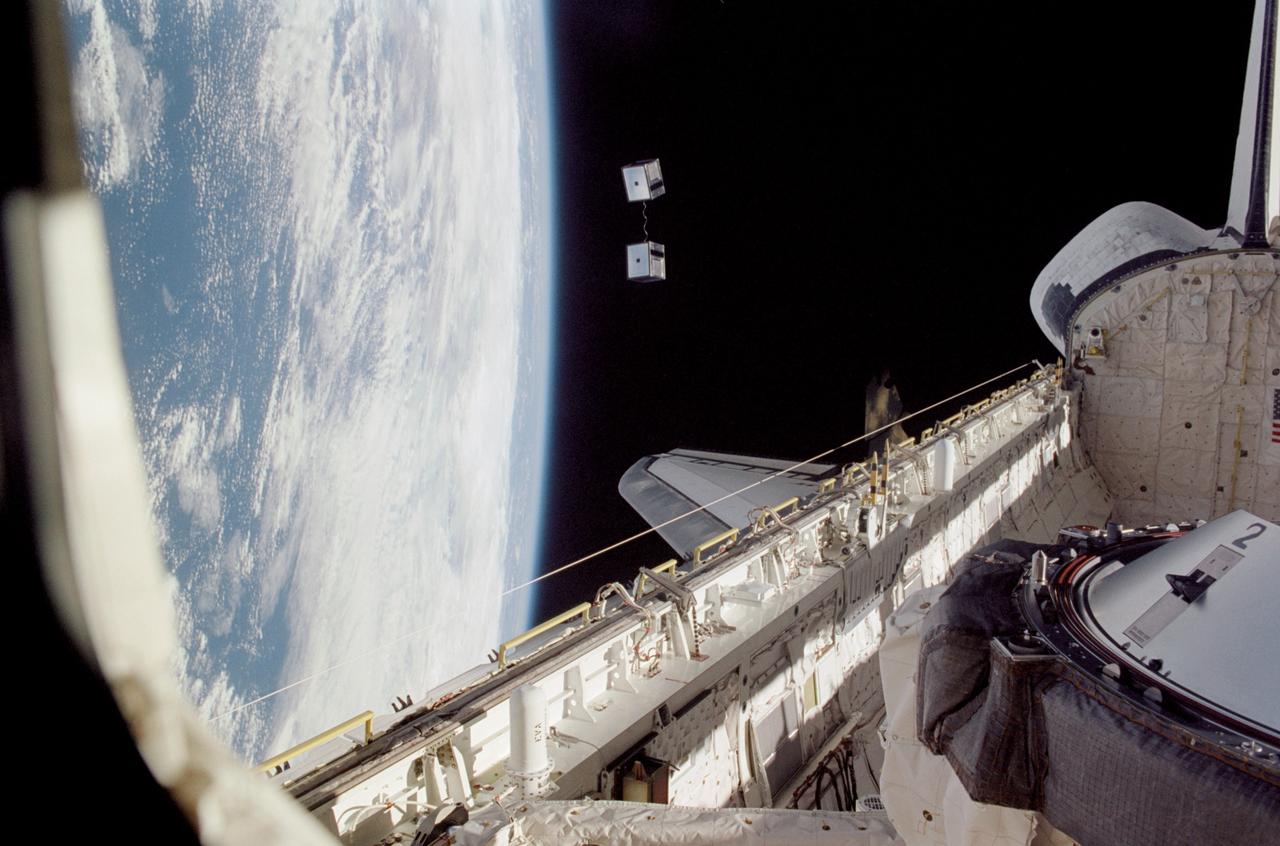

STS113-370-012 (2 December 2002) --- The horizon of a blue and white Earth and the blackness of space form the backdrop for this view, as two miniature satellites are released from the Space Shuttle Endeavour as part of an experiment referred to as MEPSI. Funded by the Defense Advance Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the two small satellites, which are tethered together, were released from Endeavour’s payload bay (visible in foreground) to fly free for three days as a technology demonstration of the launcher and use of micro- and nano-technologies in space systems.

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center showcased it's various projects for the public in Huntsville, Alabama's Big Spring Park. Exhibits were displayed by all of the various directorates of the Center with employee volunteers explaining all aspects of their projects. Adding to the festivities was the attendance of retired NASA astronaut Robert "Hoot" Gibson. Northrup Grumman employees fire a tethered miniature rocket at NASA Day in the Park.
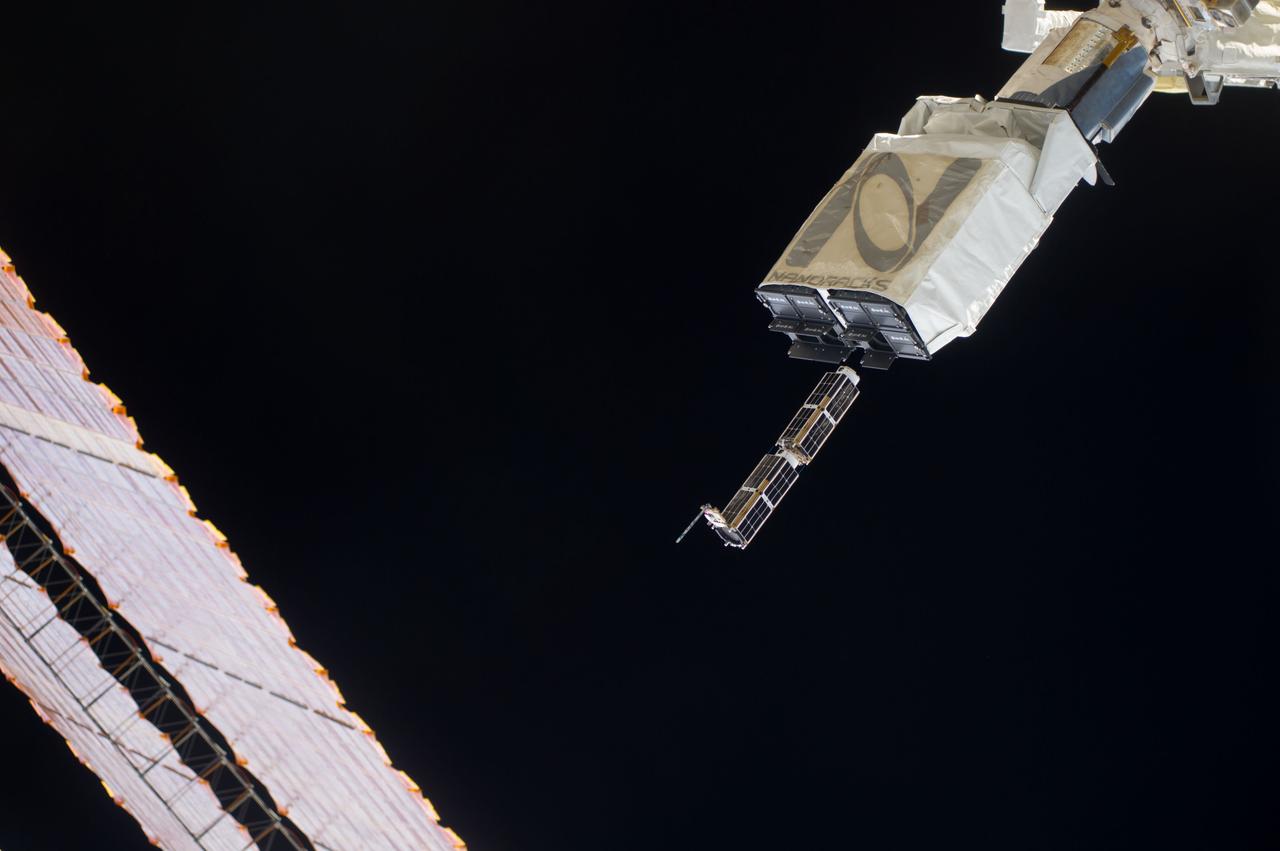

ISS040-E-102420 (20 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer releases a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. A section of the station solar array wings is at left.
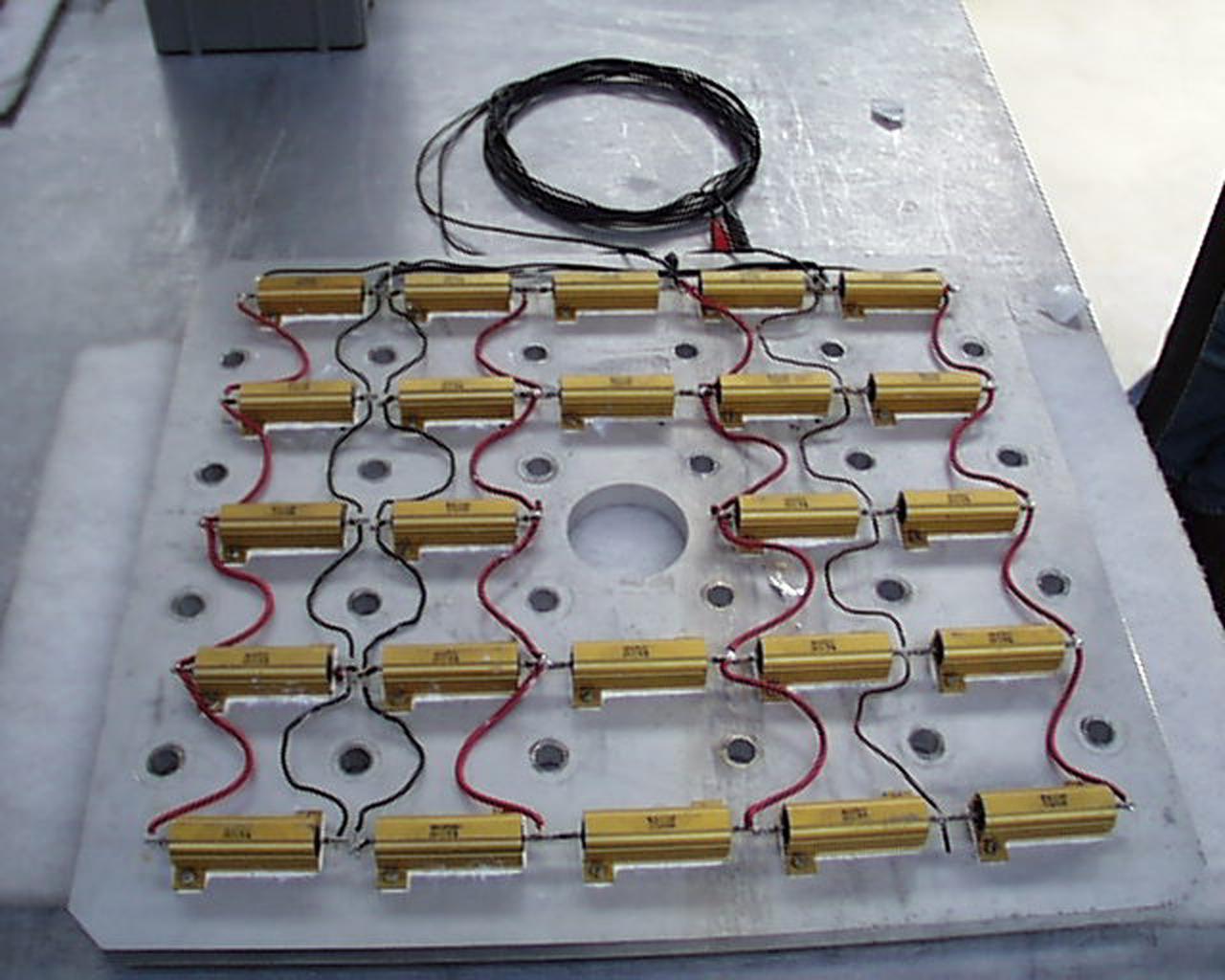
An array of miniature lamps will provide illumination to help scientists as they conduct experiments inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG). The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA are developing the MSG for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC

jsc2024e005979 (9/15/2023) --- The investigation locker for the Robotic Surgery Tech Demo investigation is shown on the ground. The locker was designed so that the astronauts can initiate "autonomous mode" and switch to "telesurgery mode." The miniaturized robotic surgeon is housed inside the microwave-sized locker and will be controlled via remote human control and pre-programmed movements. Image courtesy of Virtual Incision.
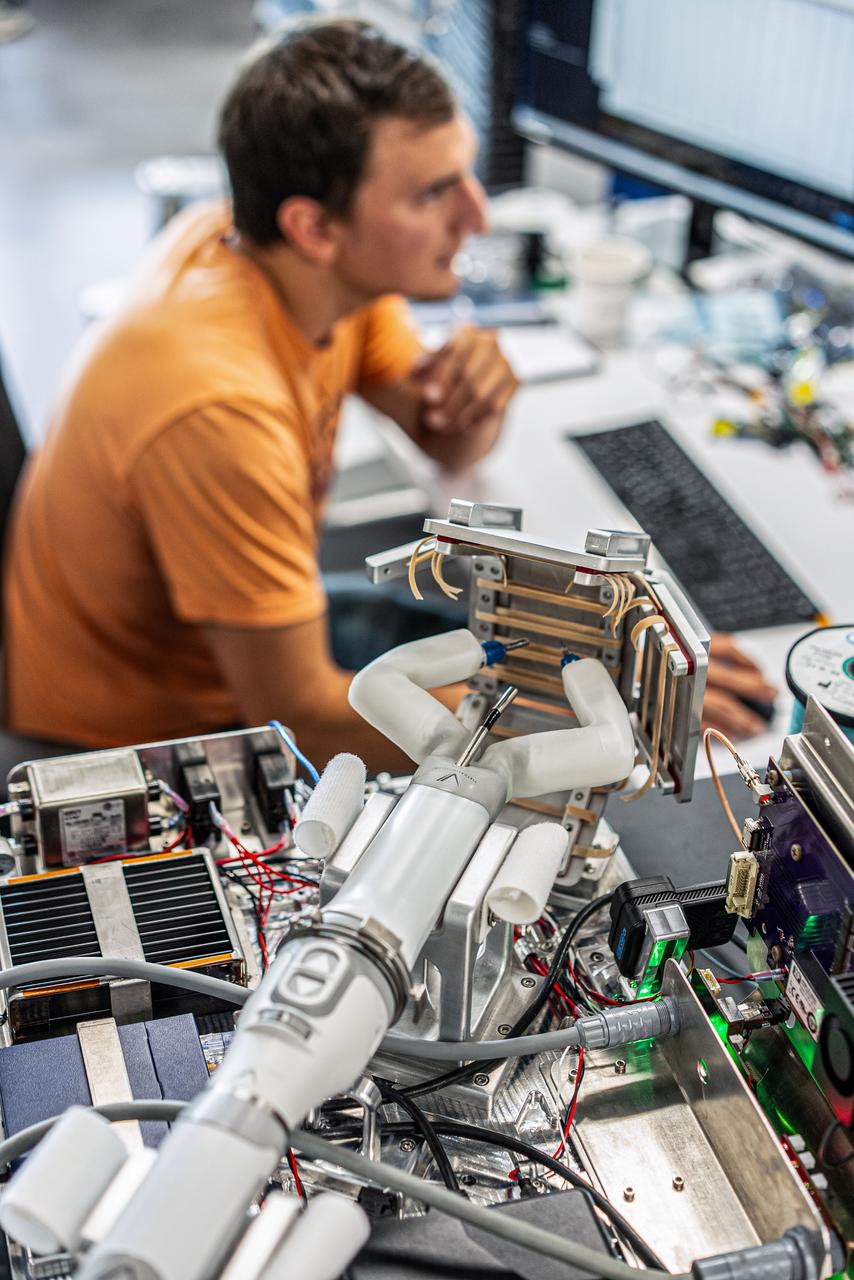
jsc2024e005978 ()9/14/2023) --- MIRA, Virtual Incision’s miniaturized robotic assisted surgery system, is pictured in position to reach simulated surgical tissue. The minibot is able to view the working area with an articulating camera. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo uses MIRA to evaluate human remote control and perform pre-programmed movements. Image courtesy of Virtual Incision.
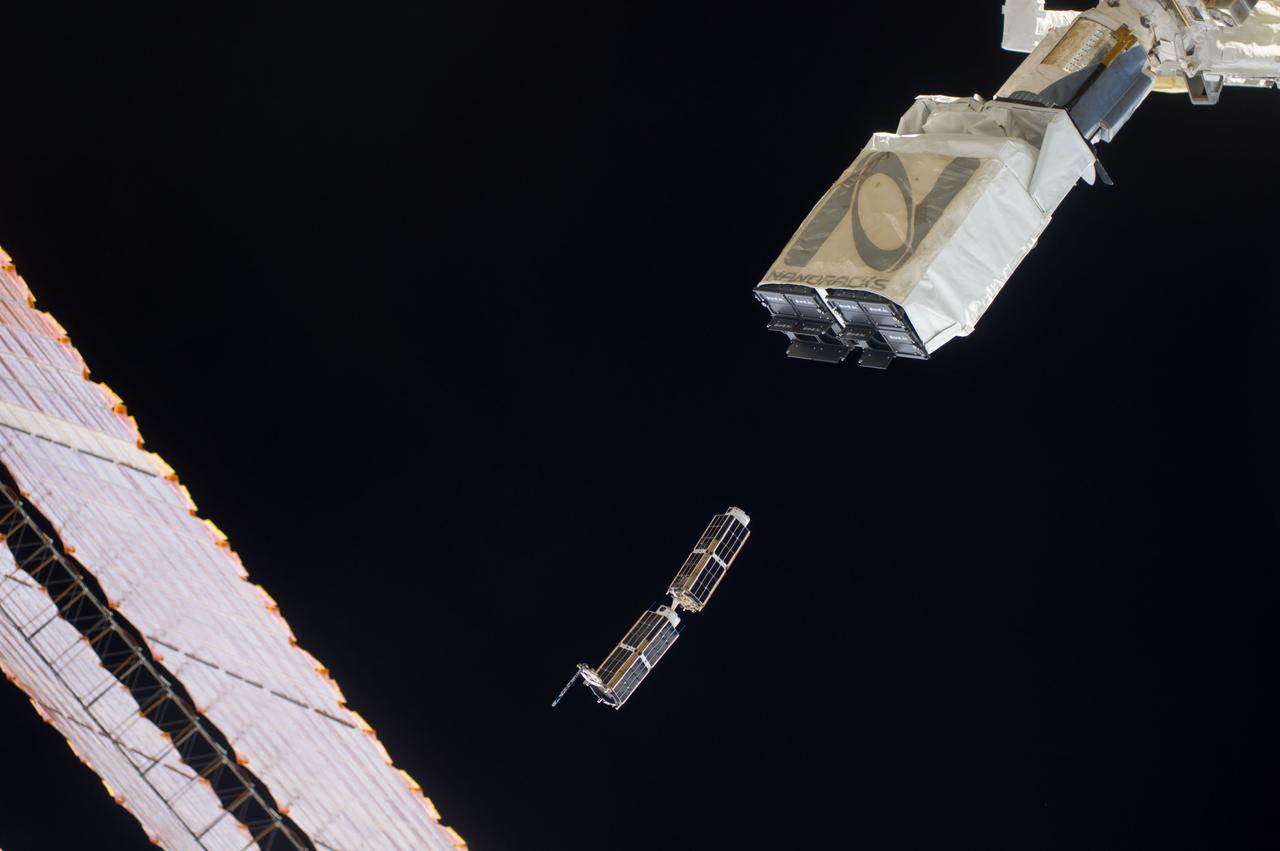

ISS040-E-102425 (20 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer releases a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. A section of the station solar array wings is at left.
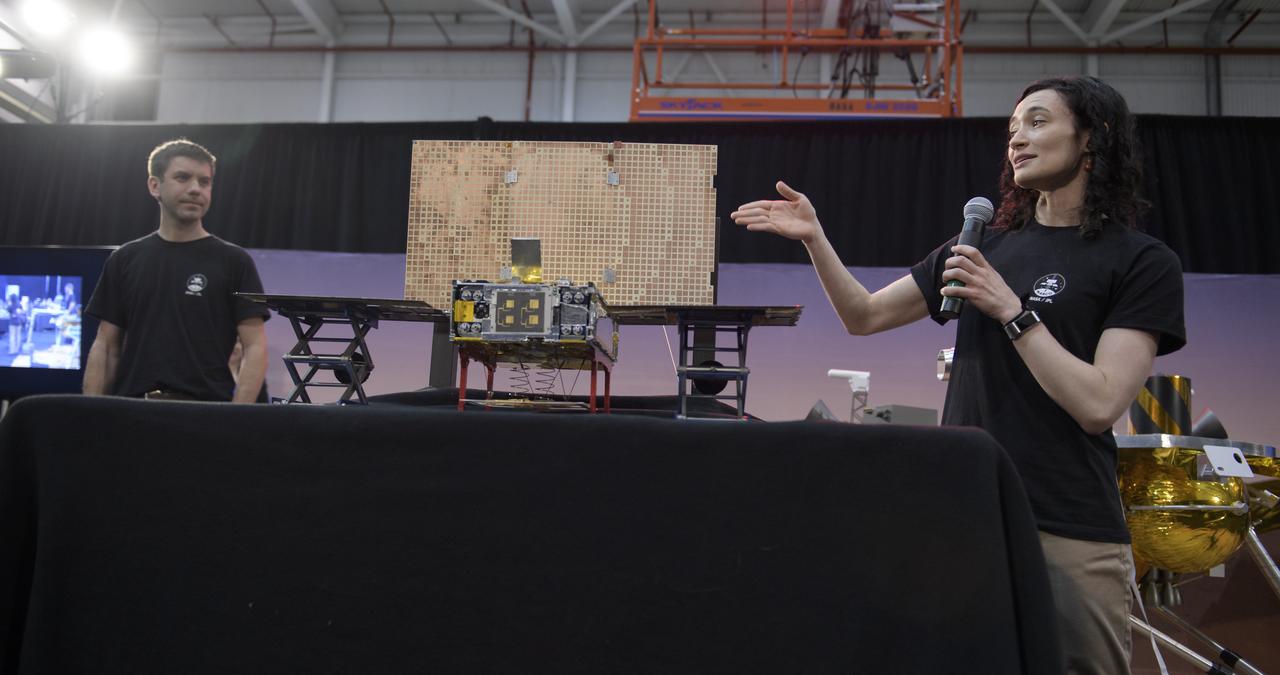
Andy Klesh, MarCO chief engineer, NASA JPL, left, and Annie Marinan, MarCO Systems Engineer, NASA JPL discuss NASA's Mars Cube One (MarCO) technology demonstration mission during a prelaunch media briefing, Thursday, May 3, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. MarCO, which is a separate mission launching on the same rocket at NASA’s InSight mission to Mars, will test new miniaturized deep space communication equipment. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
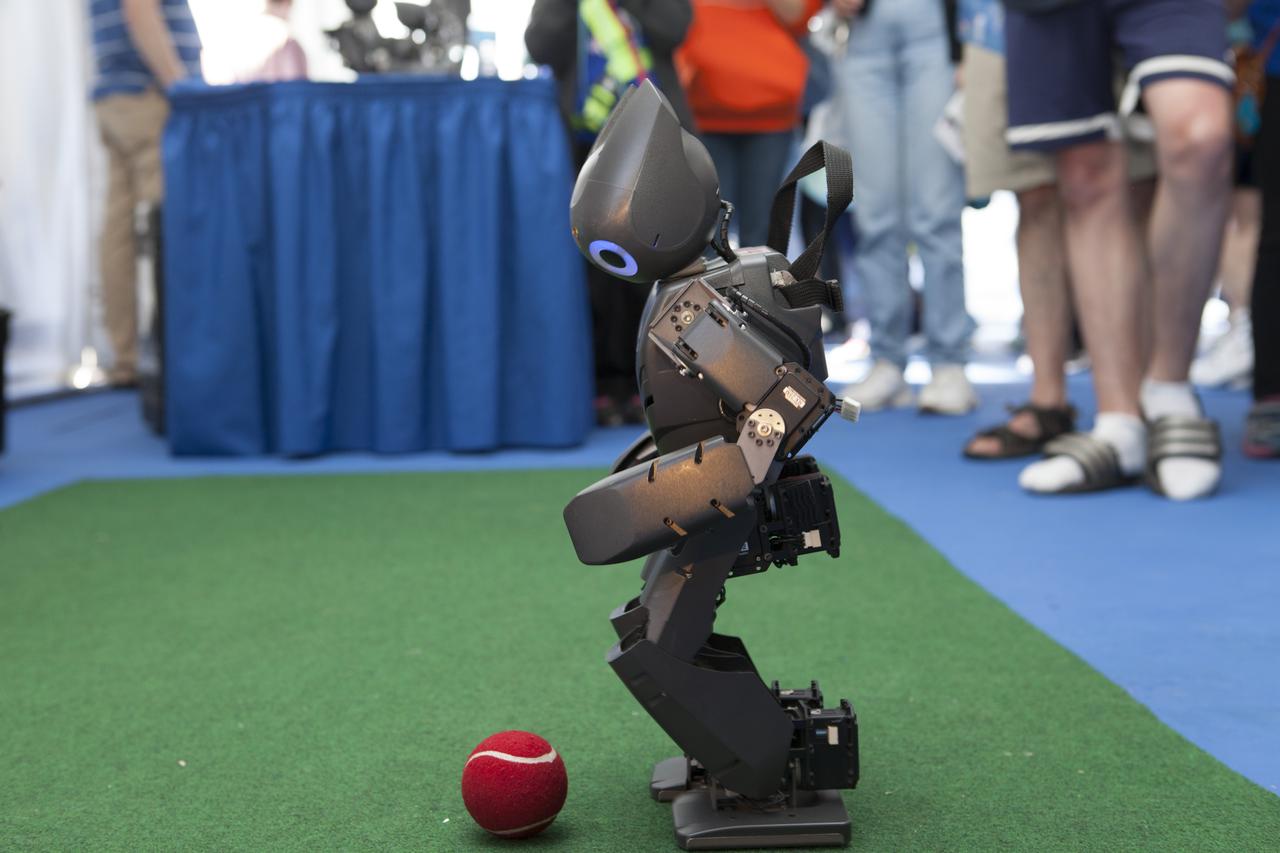

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A miniature humanoid robot known as DARwin-OP, from Virginia Tech Robotics, plays soccer with a red tennis ball for a crowd of students at the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
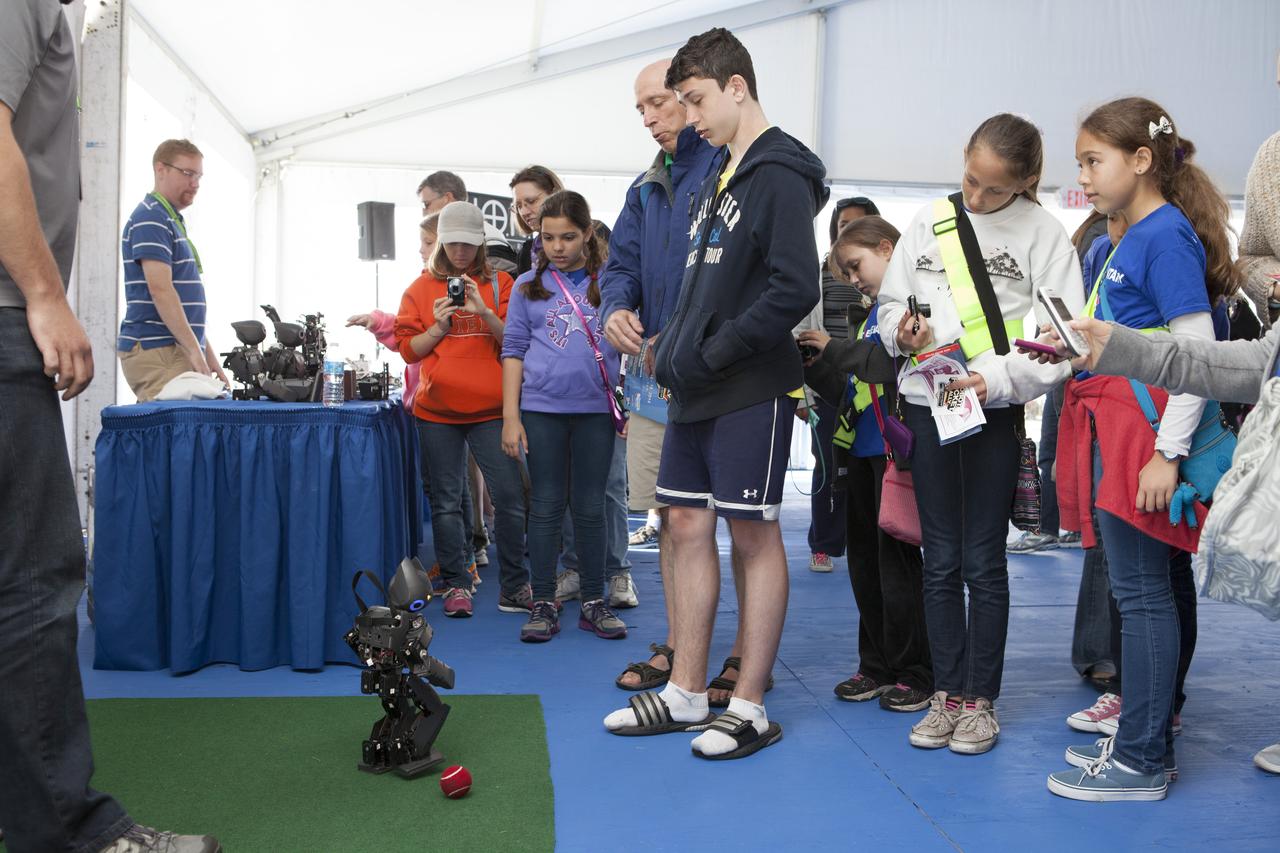

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students gather to watch as a DARwin-OP miniature humanoid robot from Virginia Tech Robotics demonstrates its soccer abilities at the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
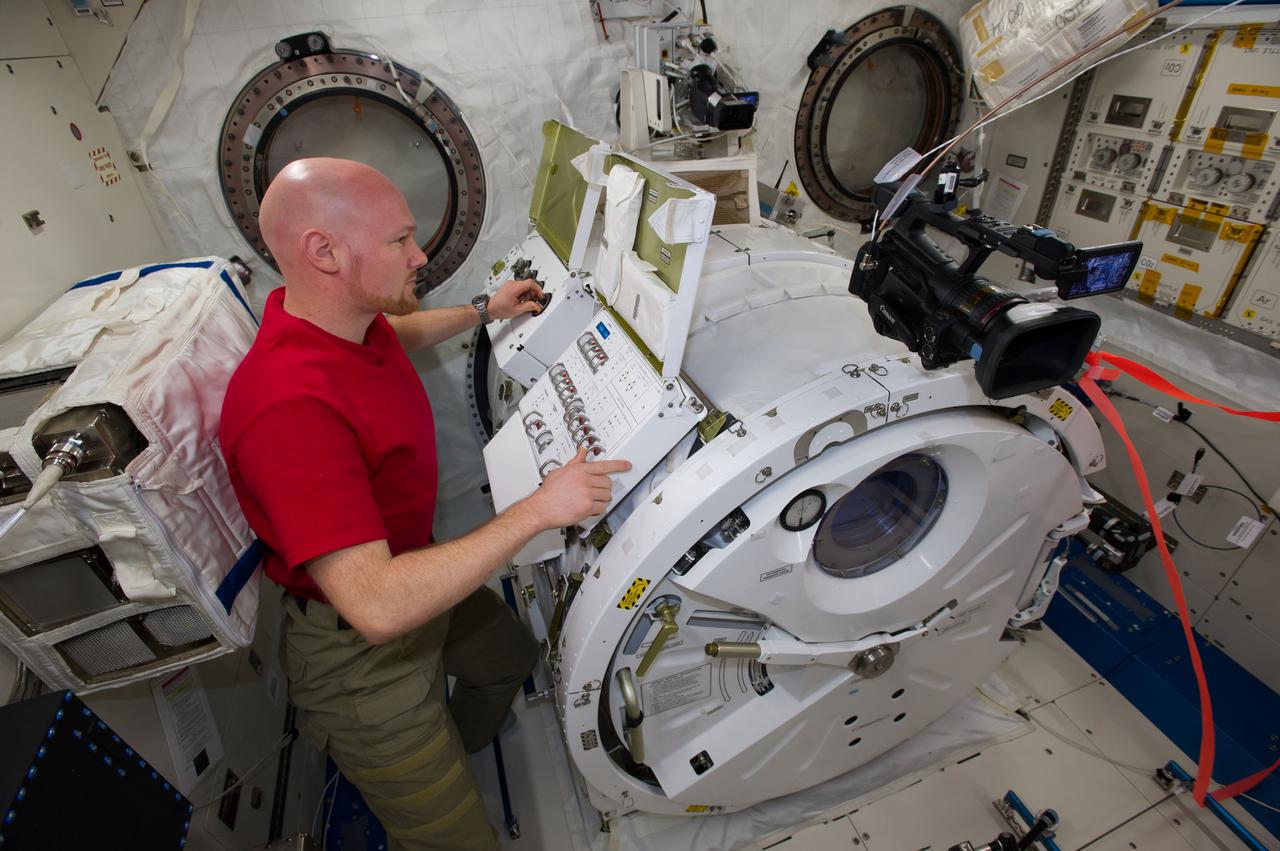

ISS040-E-096122 (18 Aug. 2014) --- In the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory, European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, depressurizes the Kibo airlock in preparation for a series of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellite deployments. The first two pairs of nanosatellites are scheduled for deployment on Aug. 19. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25.
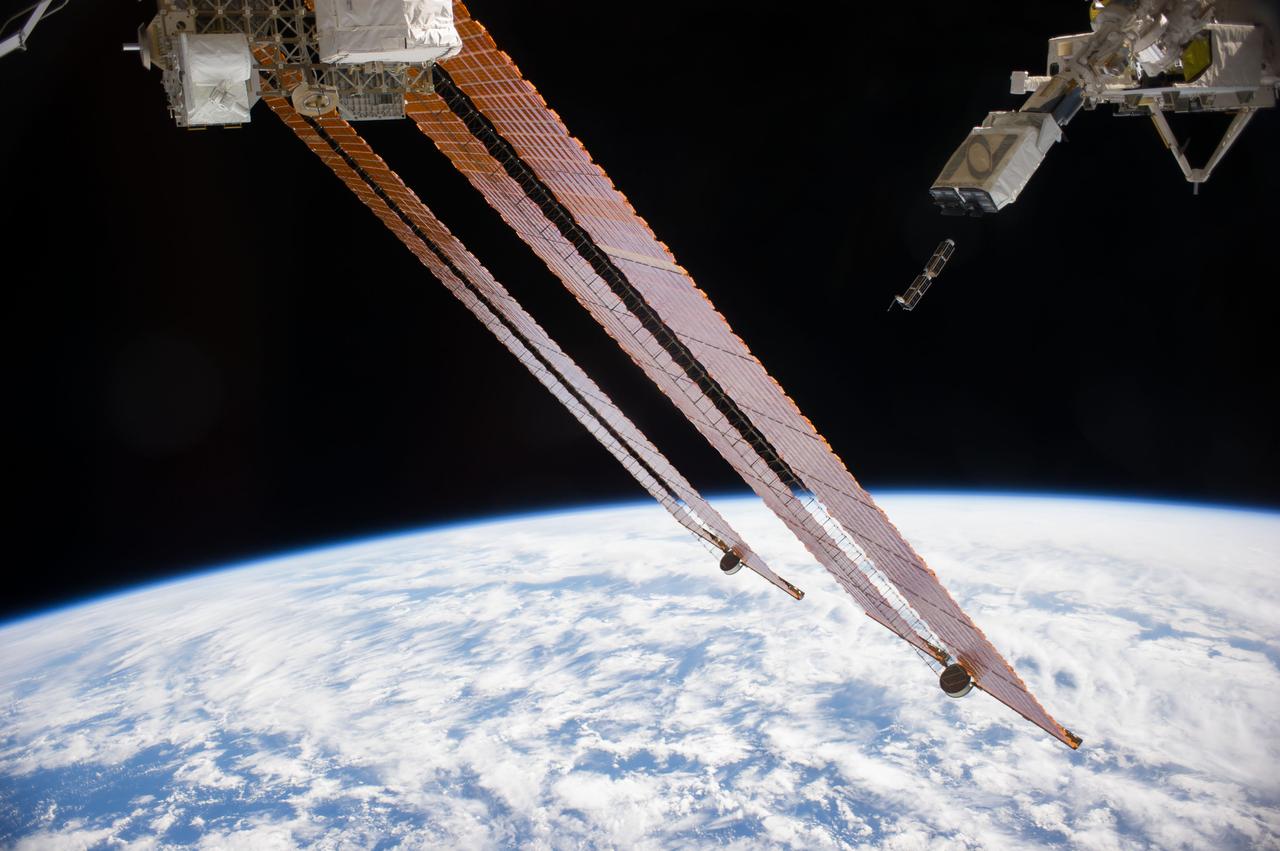

ISS040-E-103340 (20 Aug. 2014) --- In the grasp of the Japanese robotic arm, the CubeSat deployer (upper right) releases a pair of NanoRacks CubeSat miniature satellites. The Planet Labs Dove satellites that were carried to the International Space Station aboard the Orbital Sciences Cygnus commercial cargo craft are being deployed between Aug. 19 and Aug. 25. A section of the station solar array wings is at center. A blue and white part of Earth and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
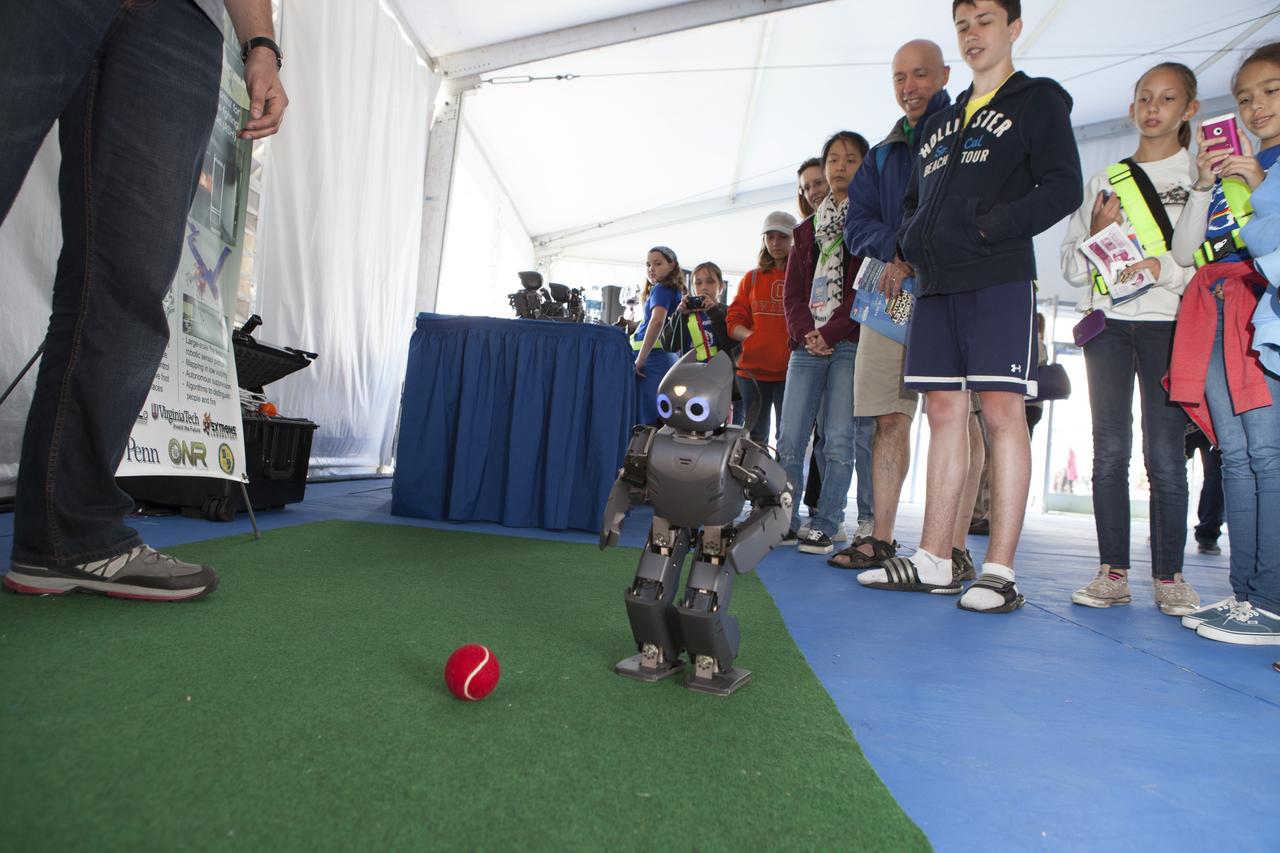

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students gather to watch as a DARwin-OP miniature humanoid robot from Virginia Tech Robotics demonstrates its soccer abilities at the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
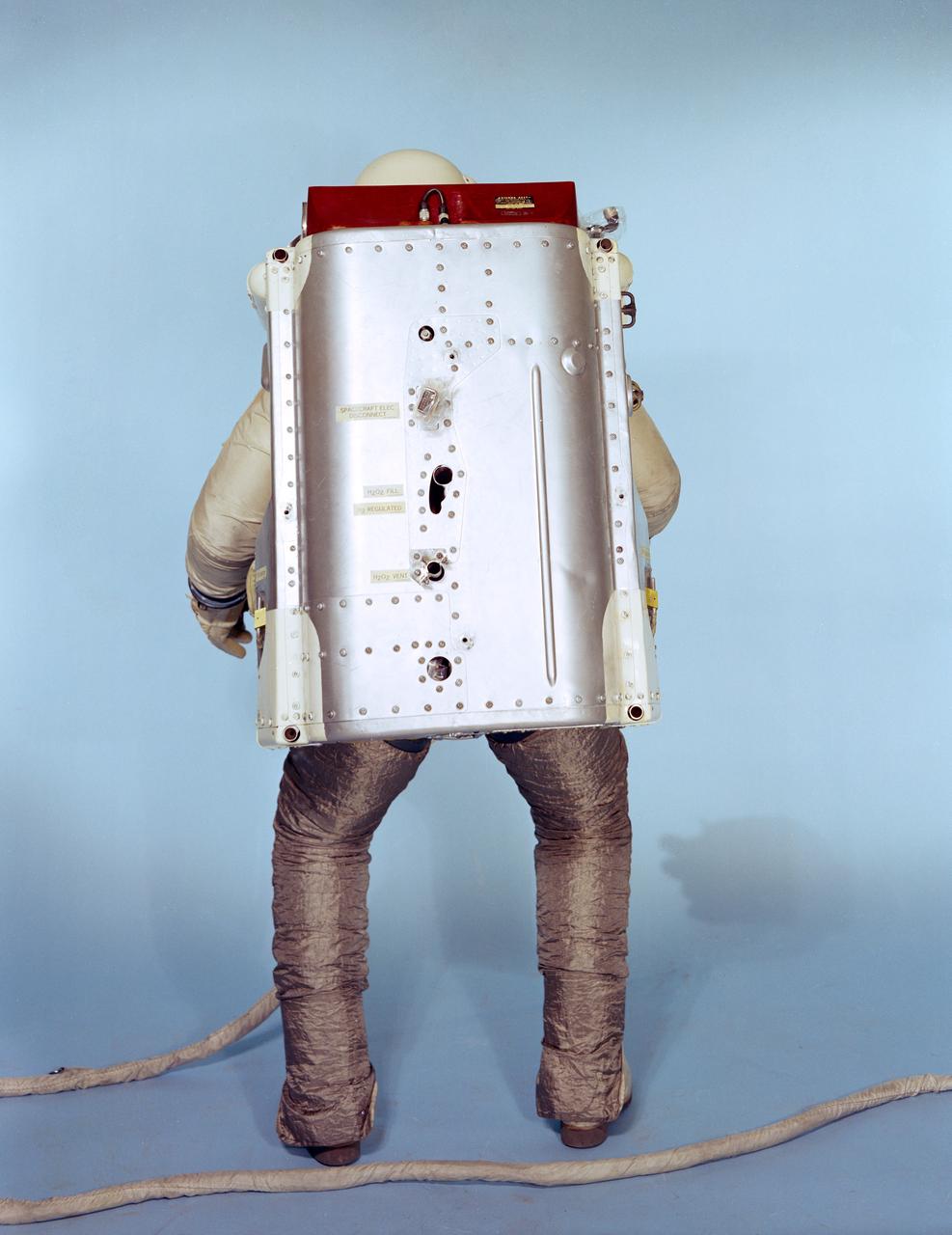

S66-33163 (May 1966) --- Rear view of the Astronaut Maneuvering Unit (AMU), worn by test subject Fred Spross, Crew Systems Division. The Gemini spacesuit, backpack and chest pack comprise the AMU, a system which is essentially a miniature manned spacecraft. The spacesuit legs are covered with Chromel R, which is a cloth woven from stainless steel fibers, used to protect the astronaut and suit from the hot exhaust thrust of the AMU backpack. Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan will wear the AMU during his Gemin-9A extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA
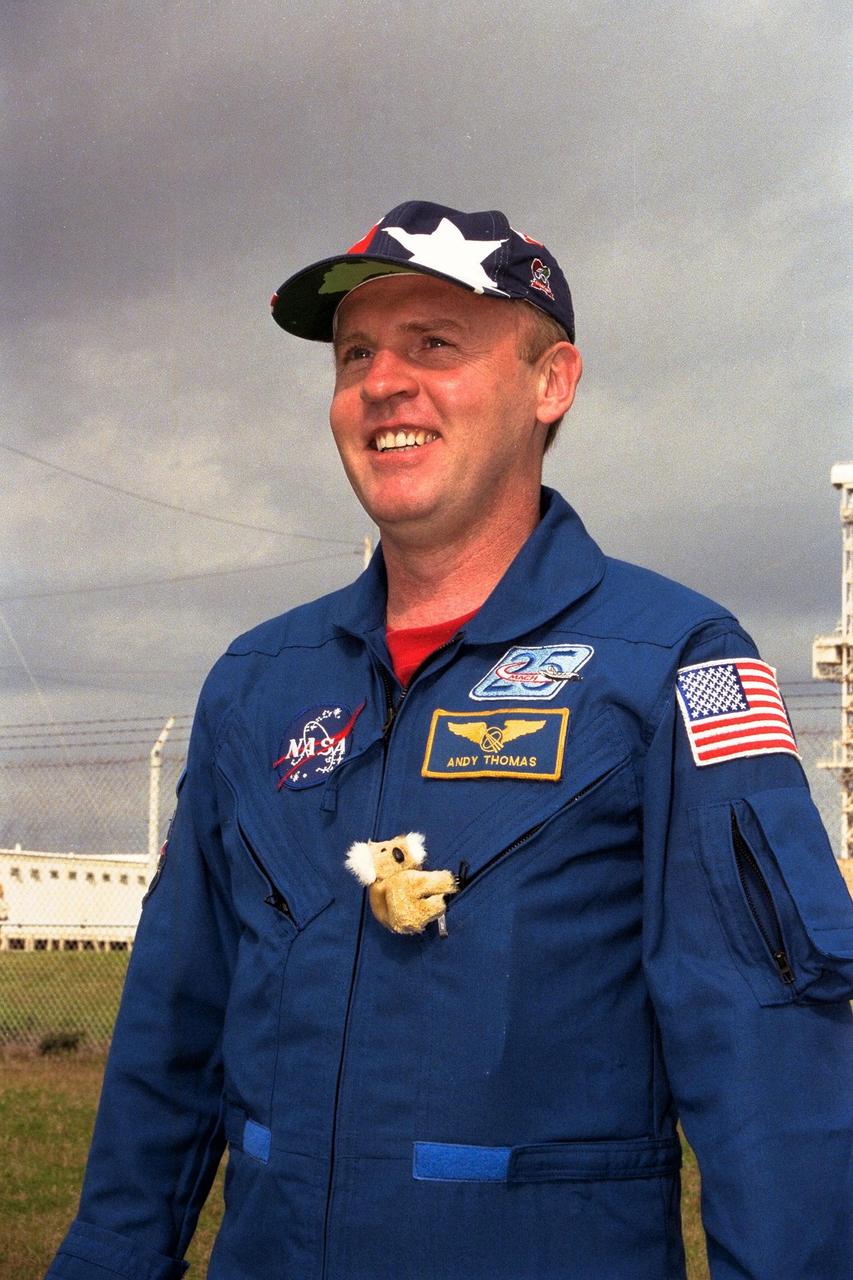

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-89 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas, Ph.D., poses at KSC's Launch Pad 39A wearing a miniature koala bear on the day before the scheduled launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour that will carry him up to the Russian Space Station Mir. Final preparations are under way toward liftoff on Jan. 22 on the eighth mission to dock with Mir. After docking, Dr. Thomas will transfer to the space station, succeeding David Wolf, M.D., who will return to Earth aboard Endeavour. Dr. Thomas, who was born and educated in South Australia, will live and work on Mir until June. STS-89 is scheduled for liftoff at 9:48 p.m. EST
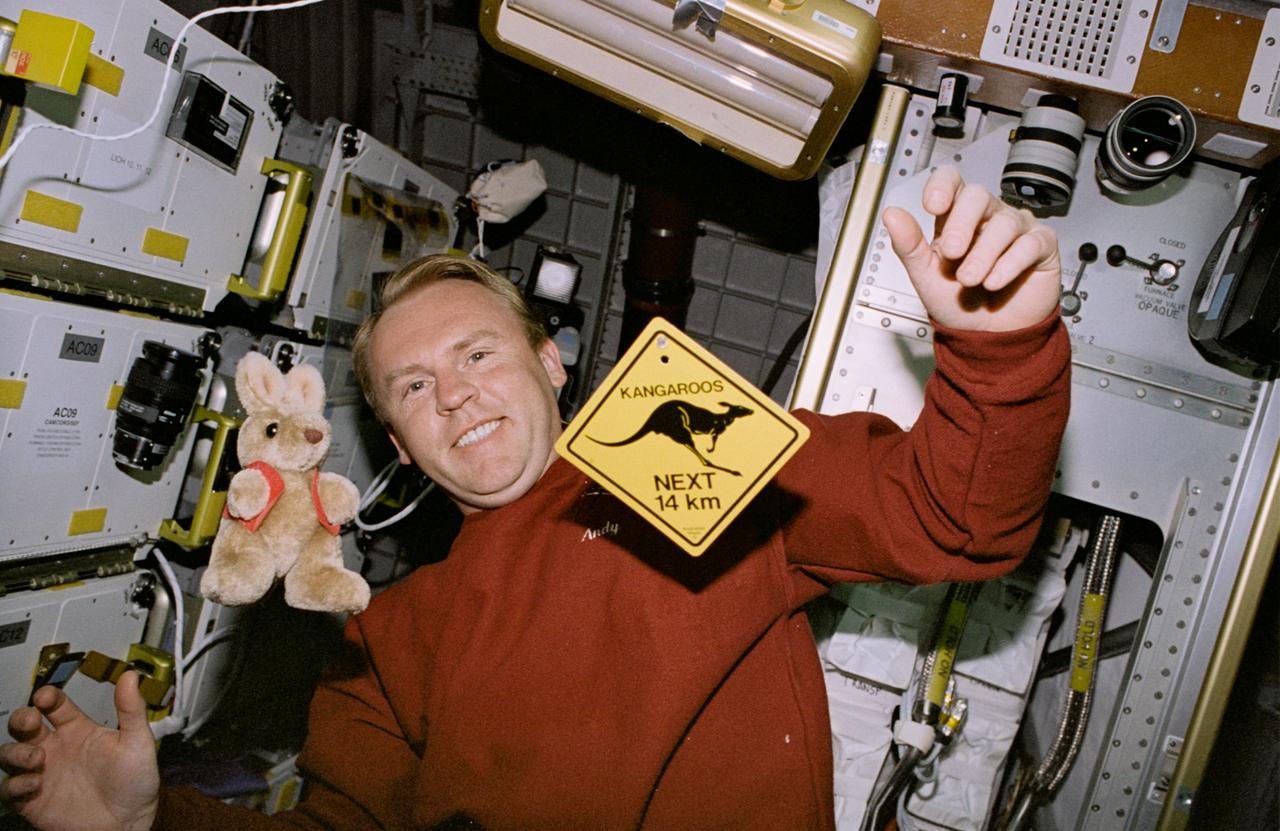

STS077-368-026 (19-29 May 1996) --- On his off-duty time, Australian-native Andrew S. W. Thomas, mission specialist, has a little fun with Australian mementos in the Spacehab Module onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. Floating in the foreground are a stuffed toy kangaroo and a miniaturized typical highway warning sign about the plentiful four-legged Australian resident. Astronaut Thomas and five other crew members went on to spend almost ten-days aboard Endeavour in support of the Spacehab 4 mission and a number of other payloads.
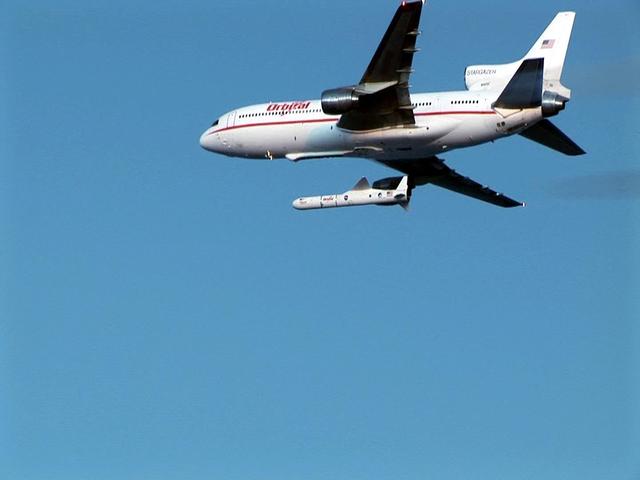

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Orbital Sciences' L-1011 jet aircraft releases the Pegasus rocket carrying the Space Technology 5 spacecraft with its trio of micro-satellites. The Pegasus will launch the trio of satellites in a "string of pearls" sequence on a near-Earth polar elliptical orbit that will take them from approximately 190 miles (300 kilometers) to 2,800 miles (4,500 kilometers) from the planet. The three spacecraft will conduct science validation using measurements of the Earth's magnetic field collected by the miniature boom-mounted magnetometers on each.

S66-33162 (May 1966) --- Test subject Fred Spross, Crew Systems Division, wears configured extravehicular spacesuit assembly and Extravehicular Life Support System chest pack. The spacesuit legs are covered with Chromel R, which is a cloth woven from stainless steel fibers, used to protect the suit and astronaut from the hot exhaust thrust of the Astronaut Maneuvering Unit backpack. The Gemini spacesuit, backpack and chest pack comprise the AMU, a system which is essentially a miniature manned spacecraft. Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan will wear the AMU during his Gemini-9A extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA
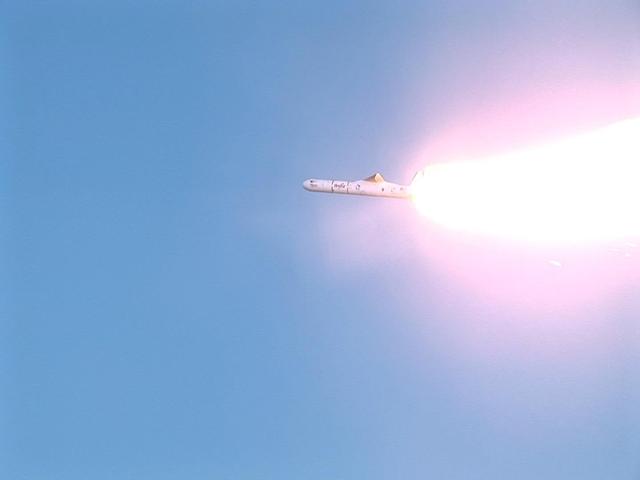

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Orbital Sciences' Pegasus launch vehicle rockets away from the L-1011 jet aircraft after being released. Pegasus carries the Space Technology 5 spacecraft with its trio of micro-satellites that will be launched in a "string of pearls" sequence on a near-Earth polar elliptical orbit that will take them from approximately 190 miles (300 kilometers) to 2,800 miles (4,500 kilometers) from the planet. The three spacecraft will conduct science validation using measurements of the Earth's magnetic field collected by the miniature boom-mounted magnetometers on each.
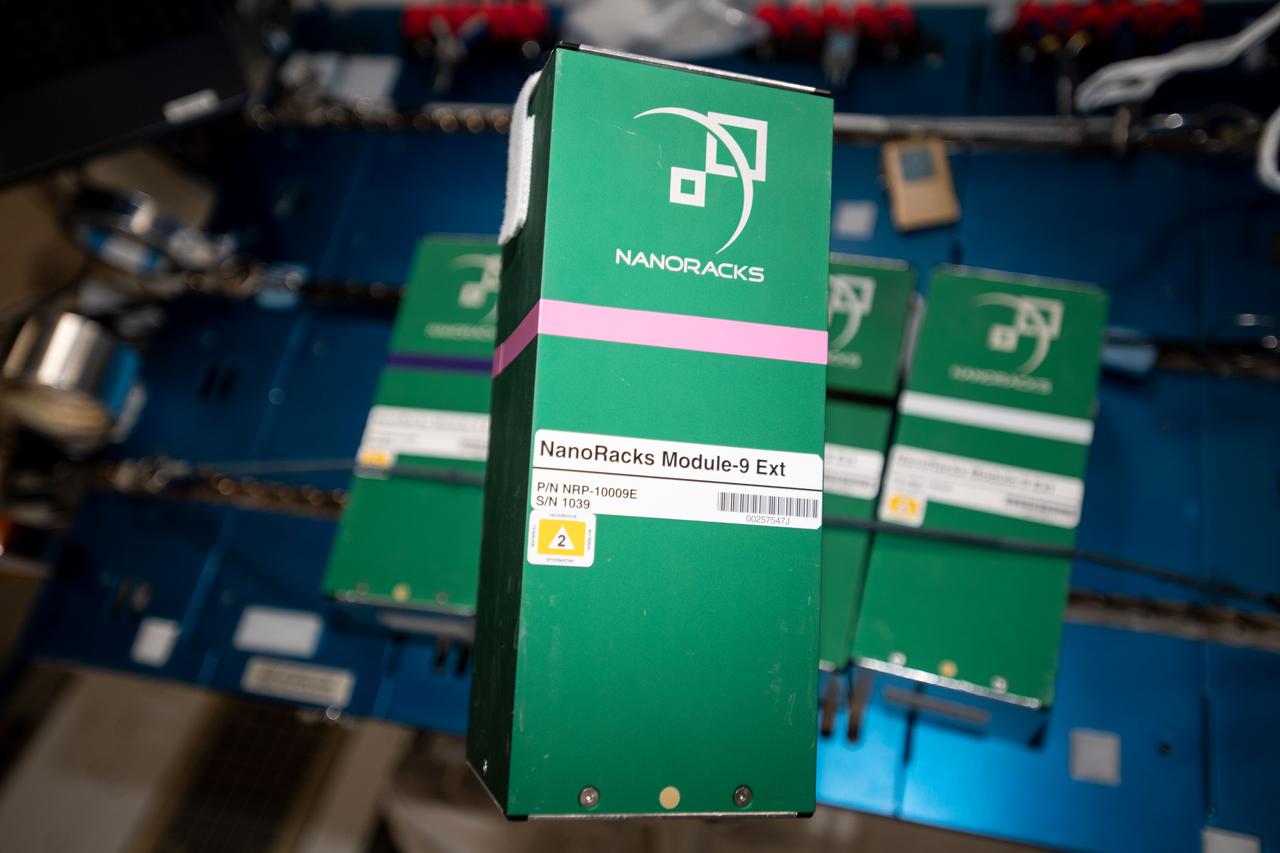

iss060e035407 (8/13/2019) --- A view the NanoRacks-NCESSE-Gemini NanoRacks-National Center for Earth and Space Science-Gemini (SSEP Mission 13) - Part of NanoRacks Module-9 Ext. The experiments range from examinations of water filtration and purification to synthetic soil production, rust formation, antibiotic effectiveness, growth and development of microacquatic organisms, and growth of plant, fungi, and bacteria. Each was chosen from more than 3,000 entries submitted by more than 23,000 U.S., Canadian, and Brazilian students. The experiments use NanoRacks MixStix, miniature laboratories activated by space station crew and eventually returned to the student teams on Earth for analysis.

S66-33167 (May 1966) --- Test subject Fred Spross, Crew Systems Division, wears an Astronaut Maneuvering Unit (AMU). The Gemini spacesuit, AMU backpack, and the Extravehicular Life Support System chest pack comprises the AMU, a system which is essentially a miniature manned spacecraft. The spacesuit legs are covered with Chromel R, which is a cloth woven from stainless steel fibers, used to protect the suit and astronaut from the hot exhaust thrust of the AMU backpack. Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan will wear the AMU during his Gemini-9A extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA
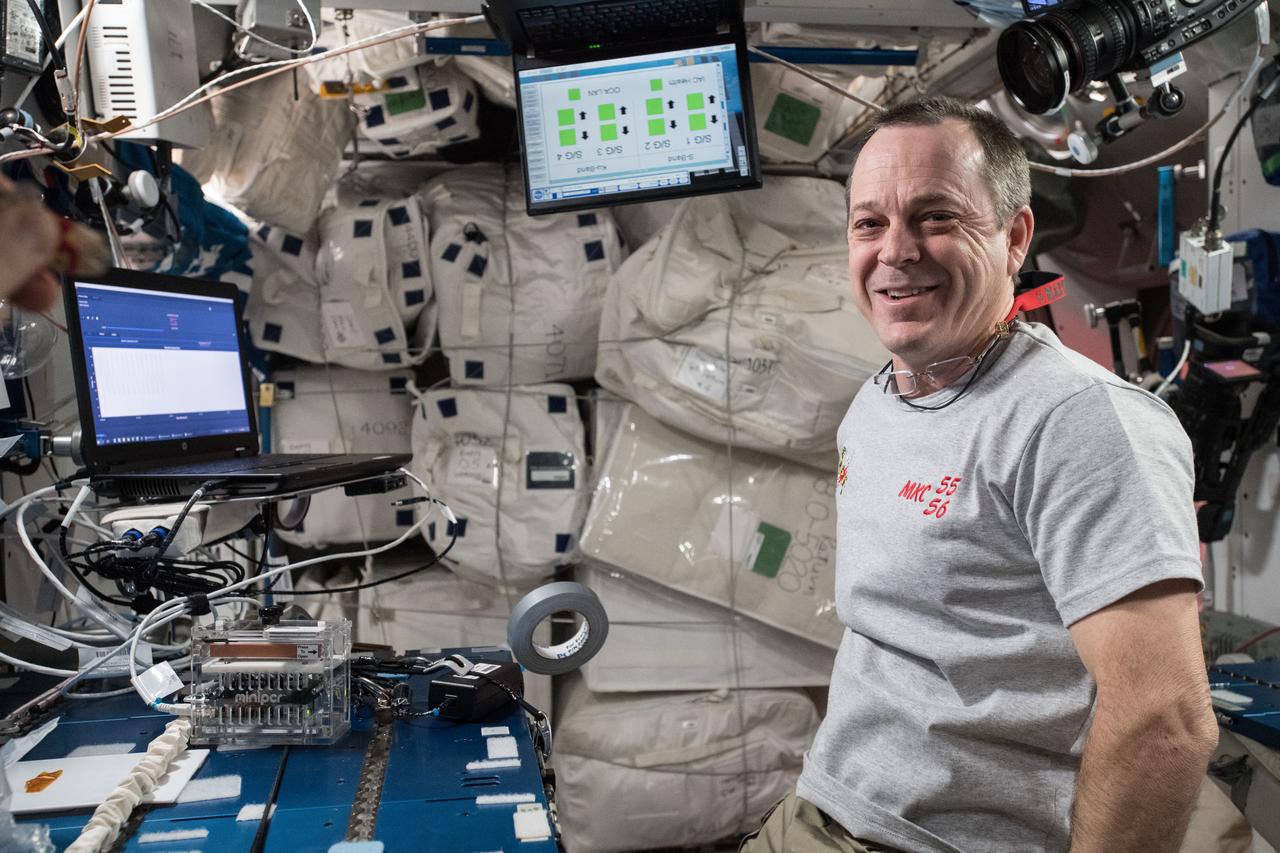

iss055e020319 (April 13, 2018) --- Flight Engineer Ricky Arnold processes of samples inside the Miniature Polymerase Chain Reaction (miniPCR) for the Genes In Space-5 experiment. The research gathered from Genes in Space-5 may be valuable in the development of procedures to maintain astronaut health and prevent an increased risk of cancer on deep space missions. The investigation also provides a deeper understanding of the human immune system, while giving student researchers a direct connection to the space program and offering hands-on educational experiences on Earth and promoting involvement in STEM fields.
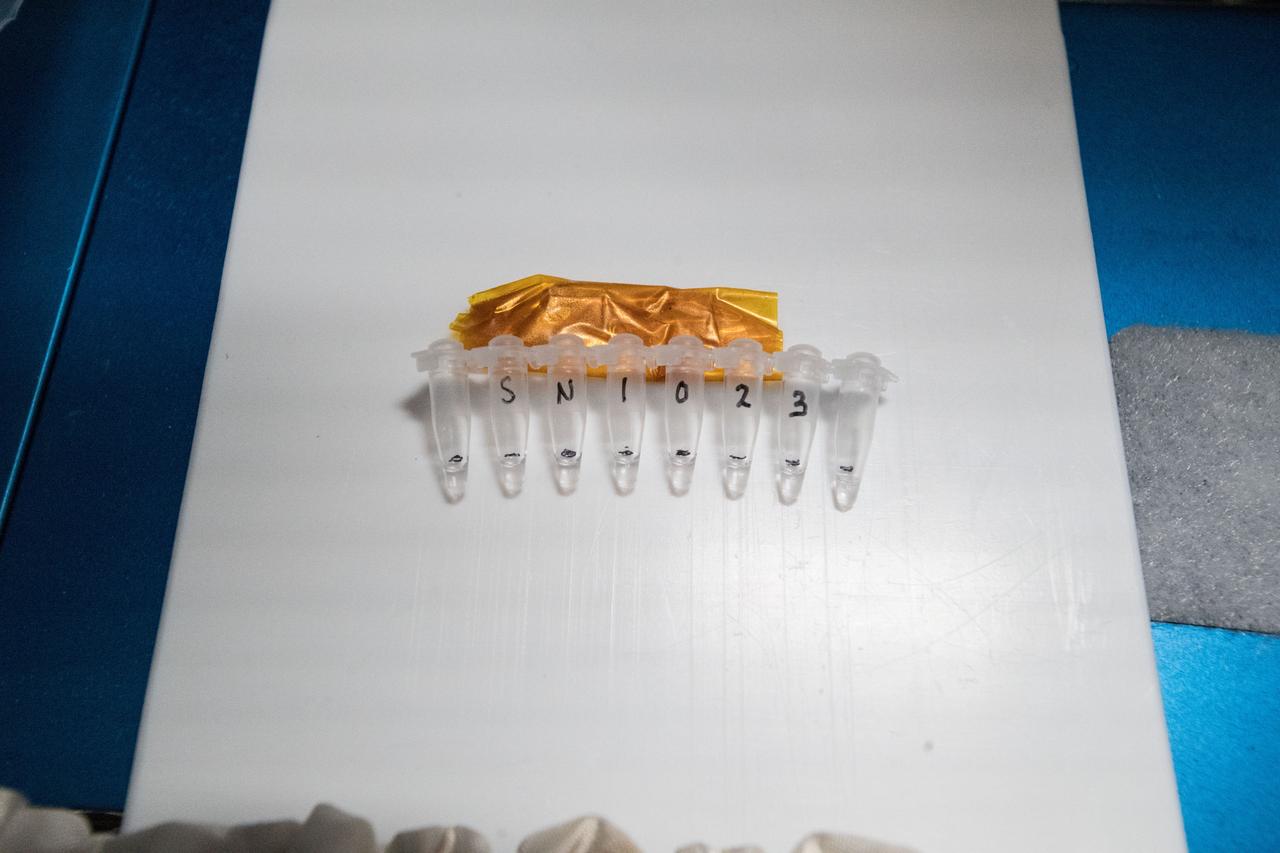

iss055e020316 (4/13/2018) --- Photographic documentation taken during processing of samples in the Miniature Polymerase Chain Reaction (miniPCR) for the Genes In Space-5 experiment onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The genetic research is helping scientists understand the relationship between DNA alterations and weakened immune systems possibly caused by living in space. Genes in Space is an innovation challenge including students and teachers across the United States from grades 7 through 12. Students design a pioneering DNA-related experiment to fly on the ISS, providing real-world training in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) fields and connecting students to the space program.
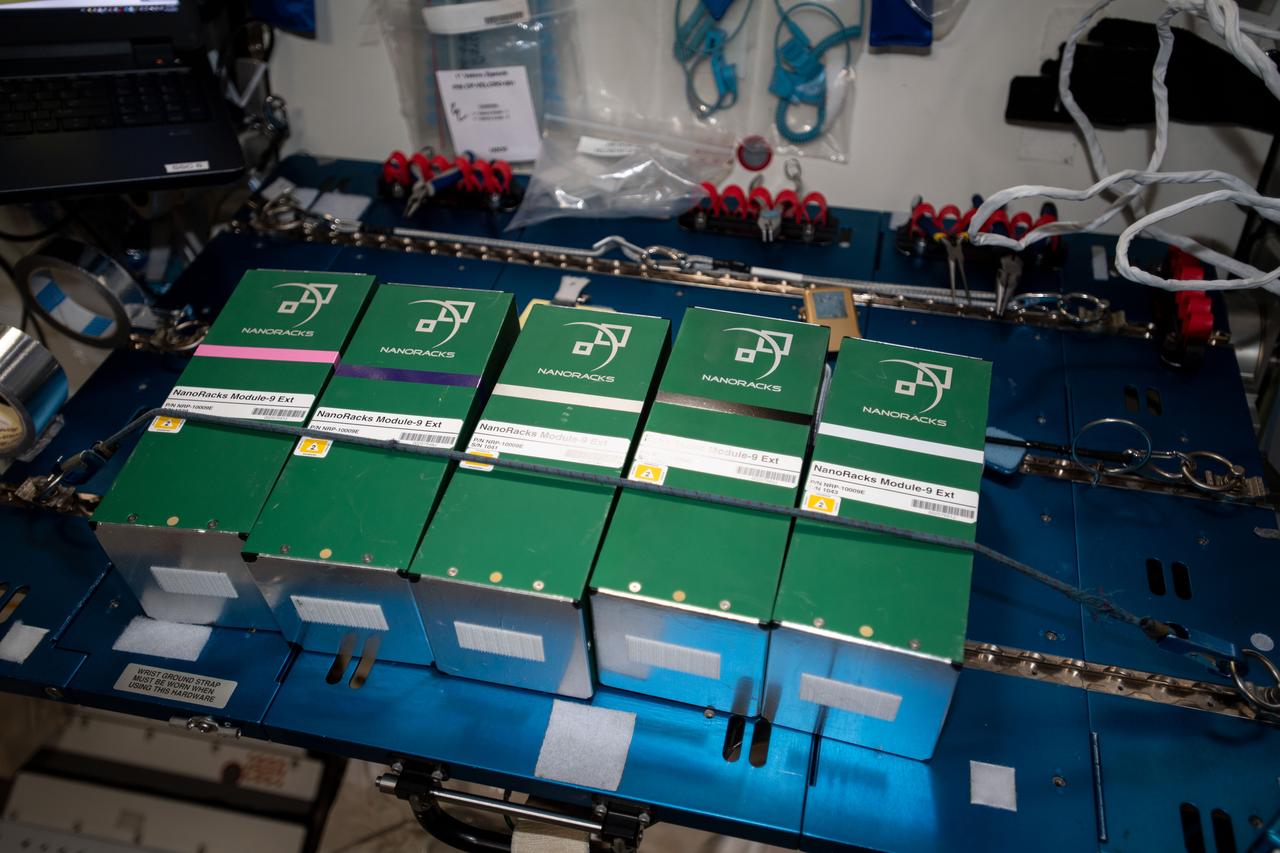

iss060e035405 (8/13/2019) --- A view the NanoRacks-NCESSE-Gemini NanoRacks-National Center for Earth and Space Science-Gemini (SSEP Mission 13) - Part of NanoRacks Module-9 Ext. aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The experiments range from examinations of water filtration and purification to synthetic soil production, rust formation, antibiotic effectiveness, growth and development of microacquatic organisms, and growth of plant, fungi, and bacteria. Each was chosen from more than 3,000 entries submitted by more than 23,000 U.S., Canadian, and Brazilian students. The experiments use NanoRacks MixStix, miniature laboratories activated by space station crew and eventually returned to the student teams on Earth for analysis.
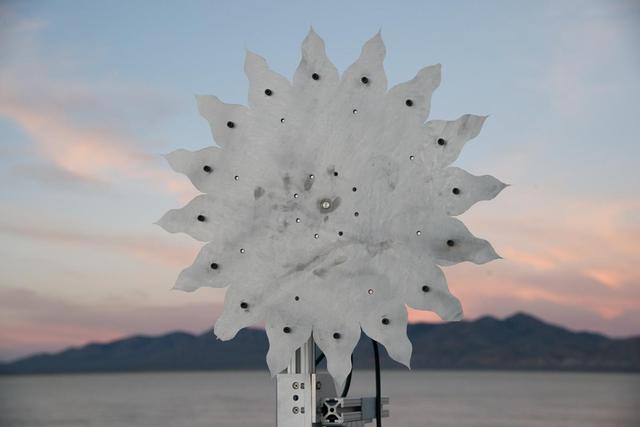

A test of a small-scale starshade model (58 cm), made from metal, in a dry lake bed in central Nevada's Smith Creek, took place from May to June 2014. Nineteen different versions of the miniaturized starshade were tested over five days. The tests revealed that a starshade, or external occulter, is capable of blocking starlight to a degree that reveals the relatively dim reflected light of a planet next to its brighter star. Like holding your hand up to block sunlight, the starshade works to block excessive starlight from the "eyes" of a space telescope like Hubble. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20902
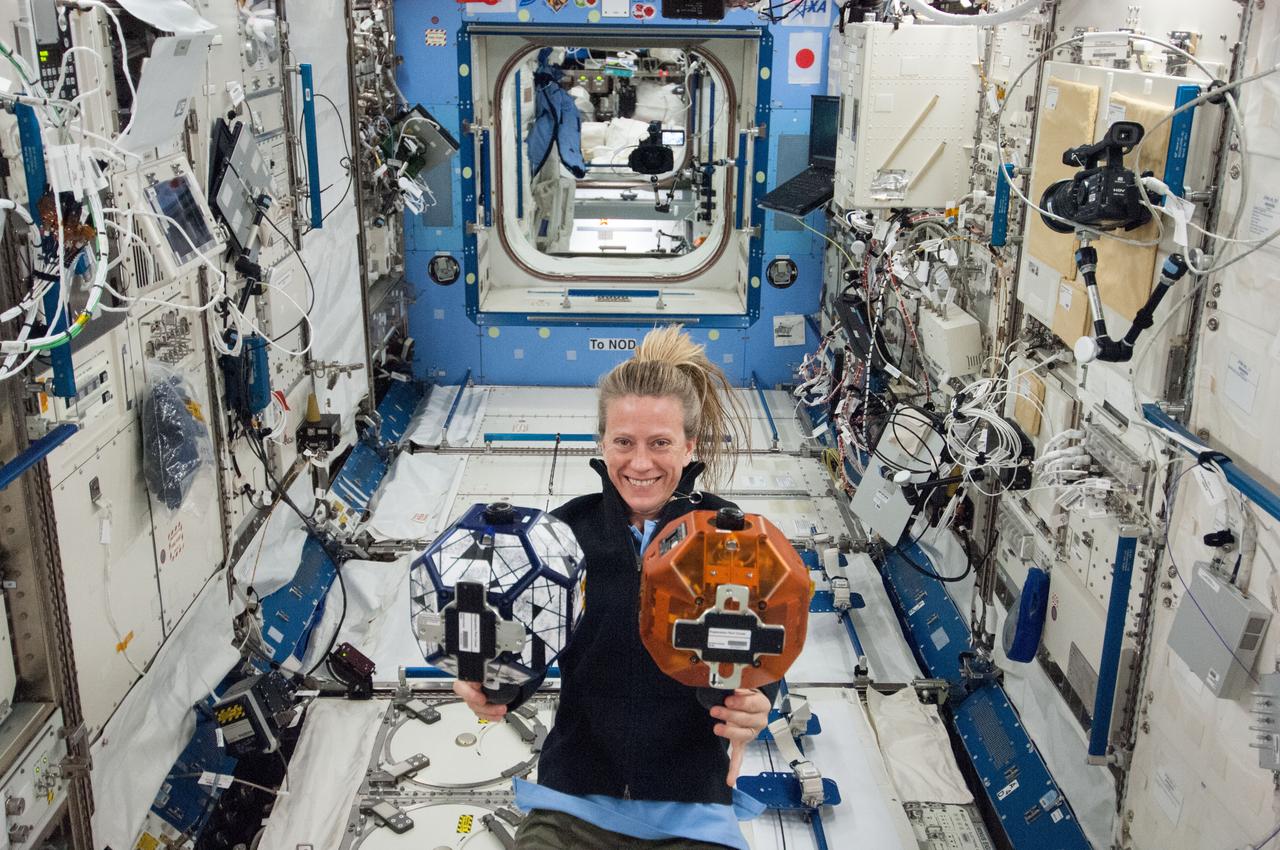

ISS036-E-029545 (7 Aug. 2013) --- In the International Space Station’s Kibo laboratory, NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, conducts a session with a pair of bowling-ball-sized free-flying satellites known as Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES. Nyberg and NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy (not pictured) put the miniature satellites through their paces for a dry run of the SPHERES Zero Robotics tournament scheduled for Aug. 13. Teams of middle school students from Florida, Georgia, Idaho and Massachusetts will gather at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge to see which teams’ algorithms do the best job of commanding the free-flying robots through a series of maneuvers and objectives.
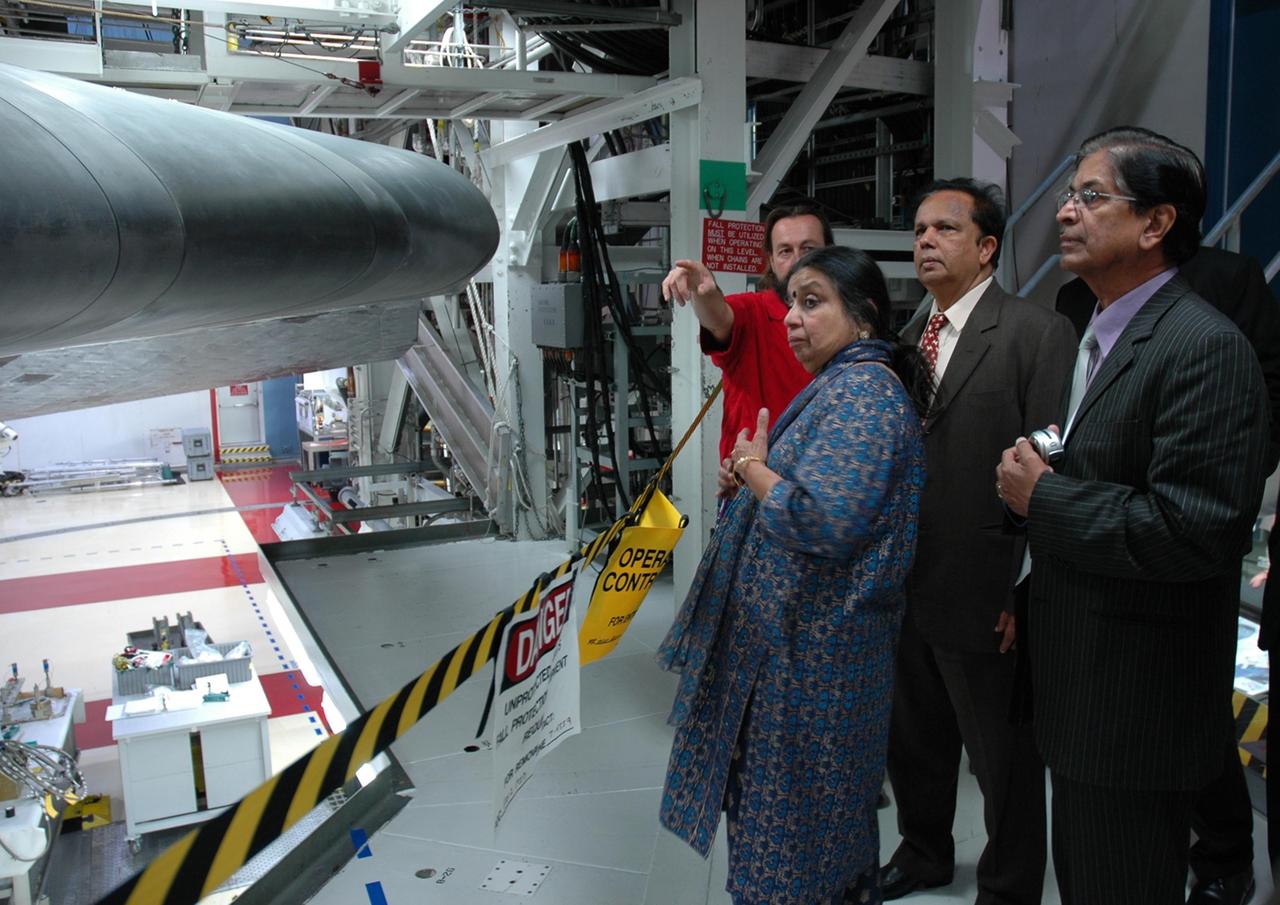

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After signing a framework agreement establishing the terms for future cooperation between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization, Chairman G. Madhavan Nair (center) is given a tour of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The agreement establishes the terms for future cooperation between the two agencies in the exploration and use of outer space for peaceful purposes. According to the framework agreement, the two agencies will identify areas of mutual interest and seek to develop cooperative programs or projects in Earth and space science, exploration, human space flight and other activities. In addition to a long history of cooperation in Earth science, NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization also are cooperating on India's first, mission to the moon, Chandrayaan-1, which will be launched later this year. NASA is providing two of the 11 instruments on the spacecraft: the moon mineralogy mapper instrument and the miniature synthetic aperture radar instrument. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
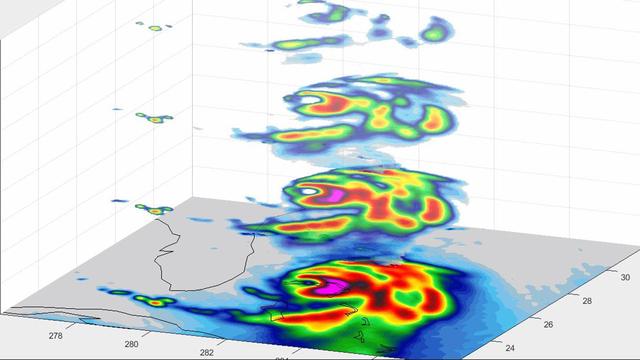
In this animation, TEMPEST-D — a weather-observing satellite the size of a cereal box — captured imagery of Hurricane Dorian off the coast of Florida at 2 a.m. EDT on Sep. 3, 2019 (11 p.m. PDT on Sept. 2, 2019). At a vantage point 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the storm, the CubeSat used its miniaturized radio-wave-based instrument to see through the clouds, revealing different depths of the hurricane with areas with heavy rainfall and moisture being pulled into the storm. The green colors indicate moisture spiraling into the storm's center, and the yellow, red and pink areas correspond to the most intense rainfall. TEMPEST-D — short for Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Demonstration — is an experiment in shrinking weather satellites to a size that makes them inexpensive enough to produce in multiples. The goal is eventual real-time storm coverage with many small satellites that can track storms around the world. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23431
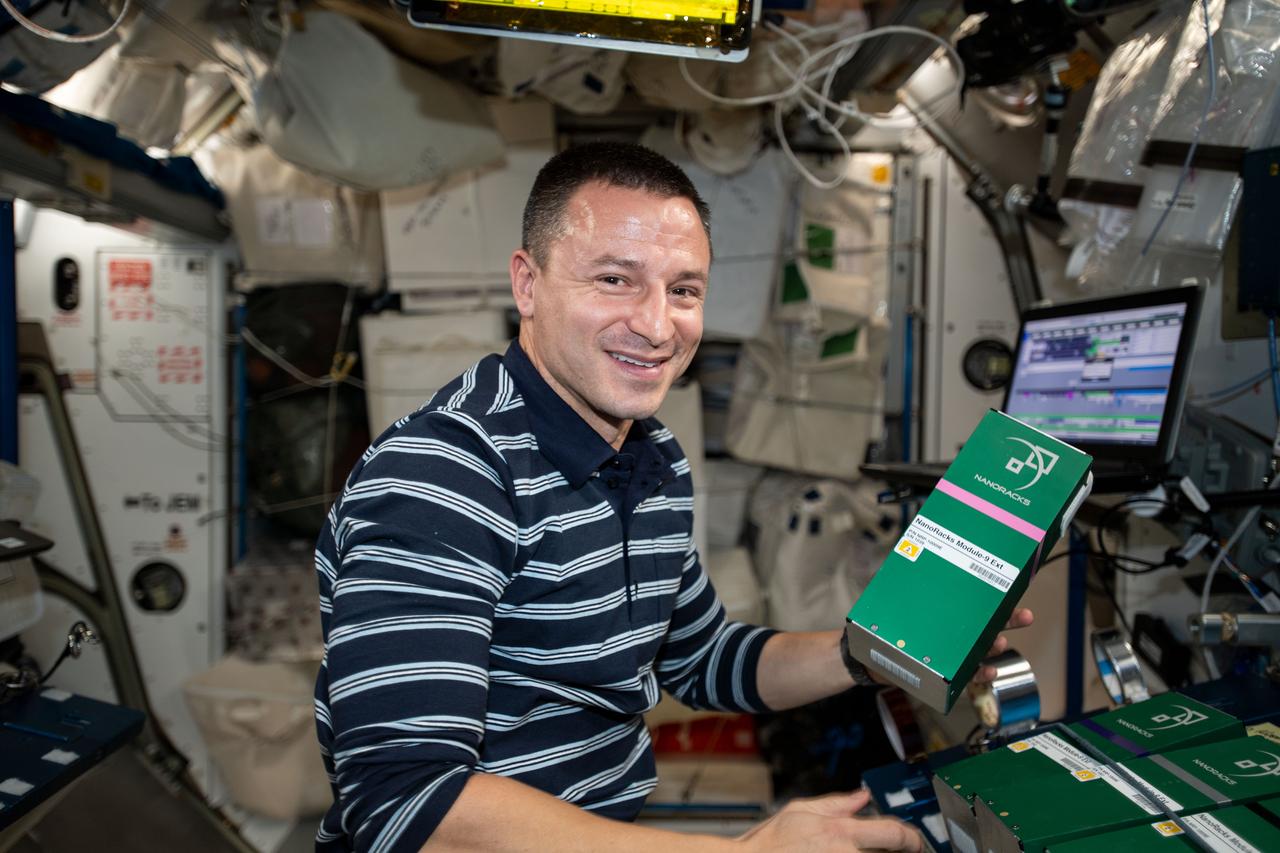

iss060e035409 (8/13/2019) --- A view of NASA astronaut Drew Morgan during the deactivation and/or shaking designated mixture tubes of NanoRacks-NCESSE-Gemini NanoRacks-National Center for Earth and Space Science-Gemini (SSEP Mission 13) - Part of NanoRacks Module-9 Ext. aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The experiments range from examinations of water filtration and purification to synthetic soil production, rust formation, antibiotic effectiveness, growth and development of microacquatic organisms, and growth of plant, fungi, and bacteria. Each was chosen from more than 3,000 entries submitted by more than 23,000 U.S., Canadian, and Brazilian students. The experiments use NanoRacks MixStix, miniature laboratories activated by space station crew and eventually returned to the student teams on Earth for analysis.
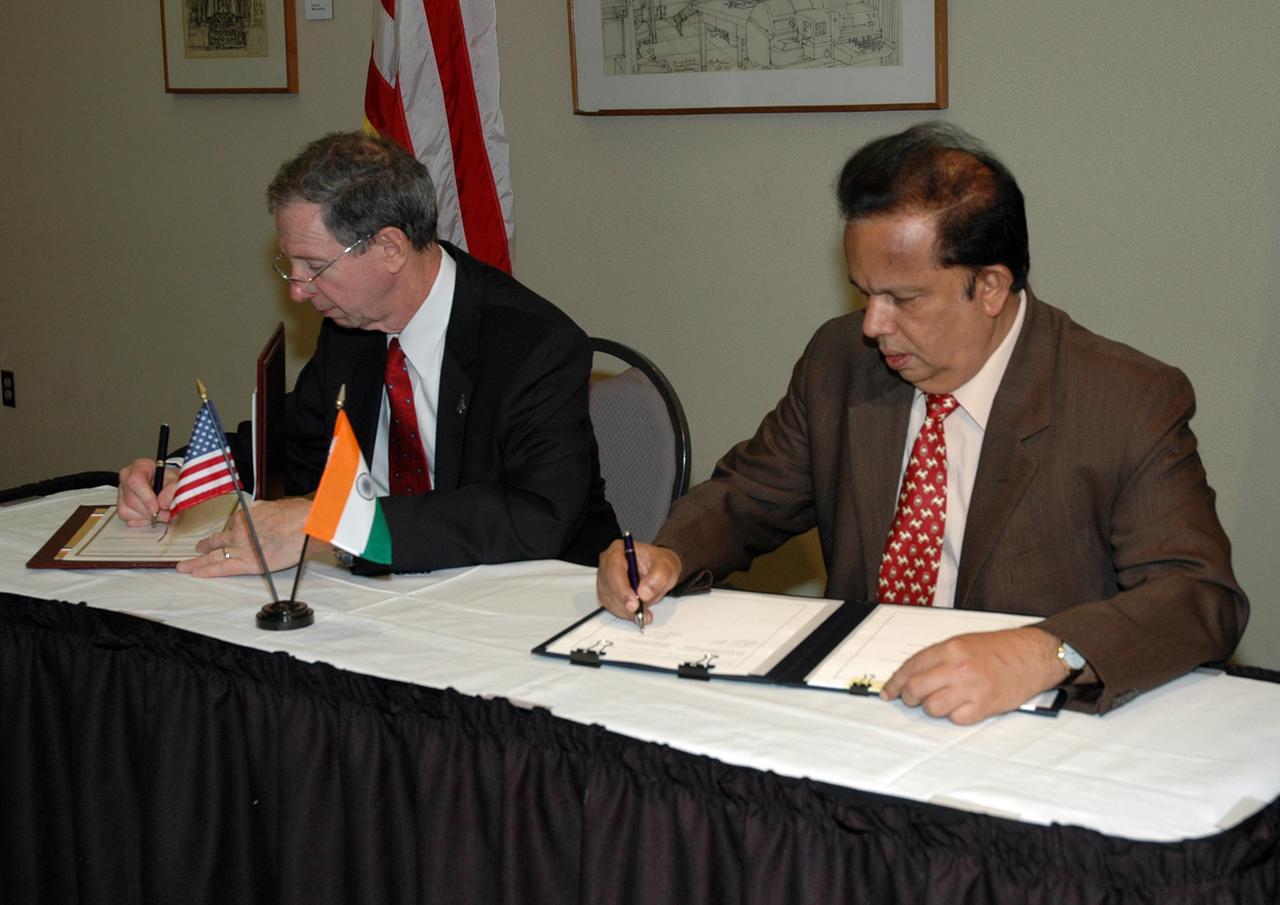

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At a ceremony at the NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, NASA Administrator Michael Griffin (left) and Indian Space Research Organization Chairman G. Madhavan Nair sign a framework agreement establishing the terms for future cooperation between the two agencies in the exploration and use of outer space for peaceful purposes. According to the framework agreement, the two agencies will identify areas of mutual interest and seek to develop cooperative programs or projects in Earth and space science, exploration, human space flight and other activities. In addition to a long history of cooperation in Earth science, NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization also are cooperating on India's first, mission to the moon, Chandrayaan-1, which will be launched later this year. NASA is providing two of the 11 instruments on the spacecraft: the moon mineralogy mapper instrument and the miniature synthetic aperture radar instrument. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
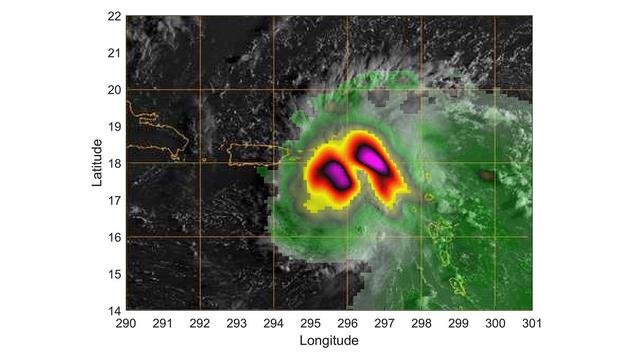
TEMPEST-D — a weather-observing satellite the size of a cereal box — captured imagery of Hurricane Dorian off the coast of Puerto Rico in the early morning hours (local time) of Aug. 28, 2019. At a vantage point 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the storm, the CubeSat used its miniaturized radio-wave-based instrument to see through the clouds, revealing areas with strong rain and moisture being pulled into the storm. The green colors show moisture spiraling into the storm's center, and the yellow to pink colors correspond to the most intense rainfall. TEMPEST-D — short for Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Demonstration — is an experiment in shrinking weather satellites to a size that makes them inexpensive enough to produce in multiples. The goal is eventual real-time storm coverage with many small satellites that can track storms around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23414
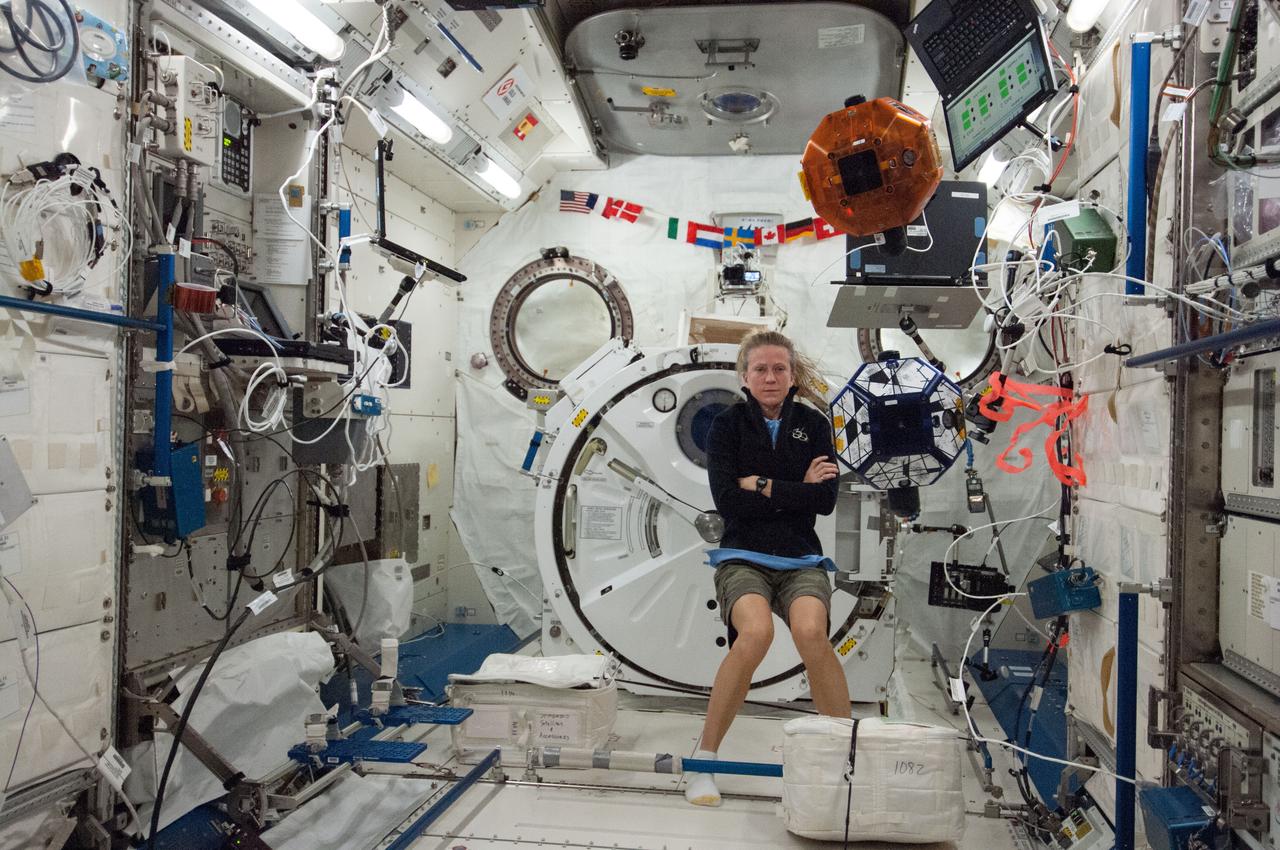

ISS036-E-029522 (7 Aug. 2013) --- In the International Space Station’s Kibo laboratory, NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, conducts a session with a pair of bowling-ball-sized free-flying satellites known as Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES. Nyberg and NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy (not pictured) put the miniature satellites through their paces for a dry run of the SPHERES Zero Robotics tournament scheduled for Aug. 13. Teams of middle school students from Florida, Georgia, Idaho and Massachusetts will gather at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge to see which teams’ algorithms do the best job of commanding the free-flying robots through a series of maneuvers and objectives.
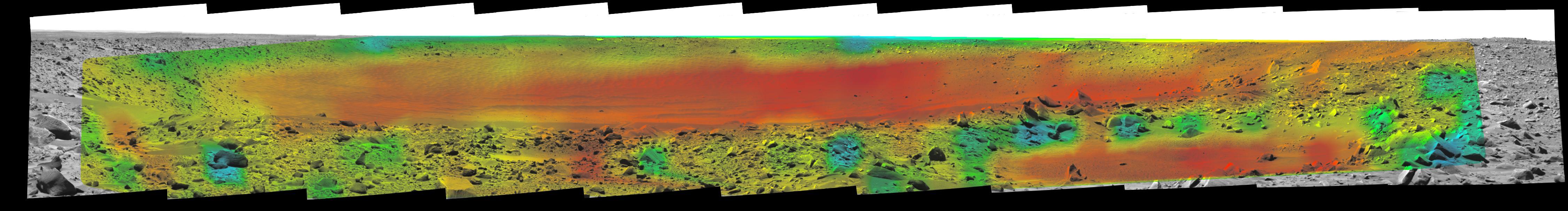
Rates of change in surface temperatures during a martian day indicate differences in particle size in and near "Bonneville Crater." This image is the third in a series of five with color-coded temperature information from different times of day. This one is from 1:35 p.m. local solar time at the site where NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit is exploring Mars. Temperature information from Spirit's miniature thermal emission spectrometer is overlaid onto a view of the site from Spirit's panoramic camera. In this color-coded map, quicker reddening during the day suggests sand or dust. (Red is about 270 Kelvin or 27 degrees Fahrenheit.) An example of this is in the shallow depression in the right foreground. Areas that stay blue longer into the day have larger rocks. (Blue indicates about 230 Kelvin or minus 45 Degrees F.) An example is the rock in the left foreground. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05930

iss060e035415 8/13/2019) --- A view of NASA astronaut Drew Morgan during the deactivation and/or shaking designated mixture tubes of NanoRacks-NCESSE-Gemini NanoRacks-National Center for Earth and Space Science-Gemini (SSEP Mission 13) - Part of NanoRacks Module-9 Ext. aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The experiments range from examinations of water filtration and purification to synthetic soil production, rust formation, antibiotic effectiveness, growth and development of microacquatic organisms, and growth of plant, fungi, and bacteria. Each was chosen from more than 3,000 entries submitted by more than 23,000 U.S., Canadian, and Brazilian students. The experiments use NanoRacks MixStix, miniature laboratories activated by space station crew and eventually returned to the student teams on Earth for analysis.
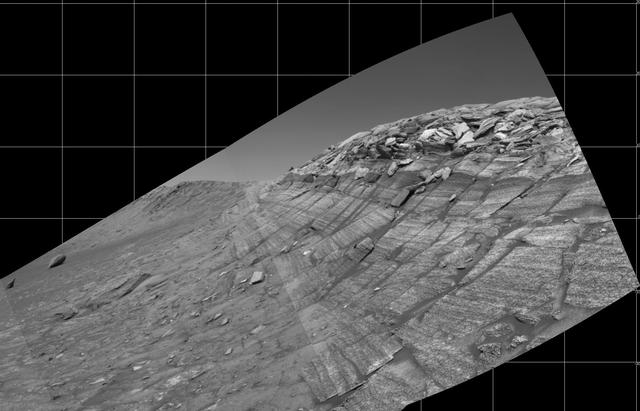

NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity captured this view from the base of "Burns Cliff" during the rover's 280th martian day (Nov. 6, 2004). This cliff in the inner wall of "Endurance Crater" displays multiple layers of bedrock for the rover to examine with its panoramic camera and miniature thermal emission spectrometer. The rover team has decided that the farthest Opportunity can safely advance along the base of the cliff is close to the squarish white rock near the center of this image. After examining the site for a few days from that position, the the rover will turn around and head out of the crater. The view is a mosaic of frames taken by Opportunity's navigation camera. The rover was on ground with a slope of about 30 degrees when the pictures were taken, and the view is presented here in a way that corrects for that tilt of the camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07039
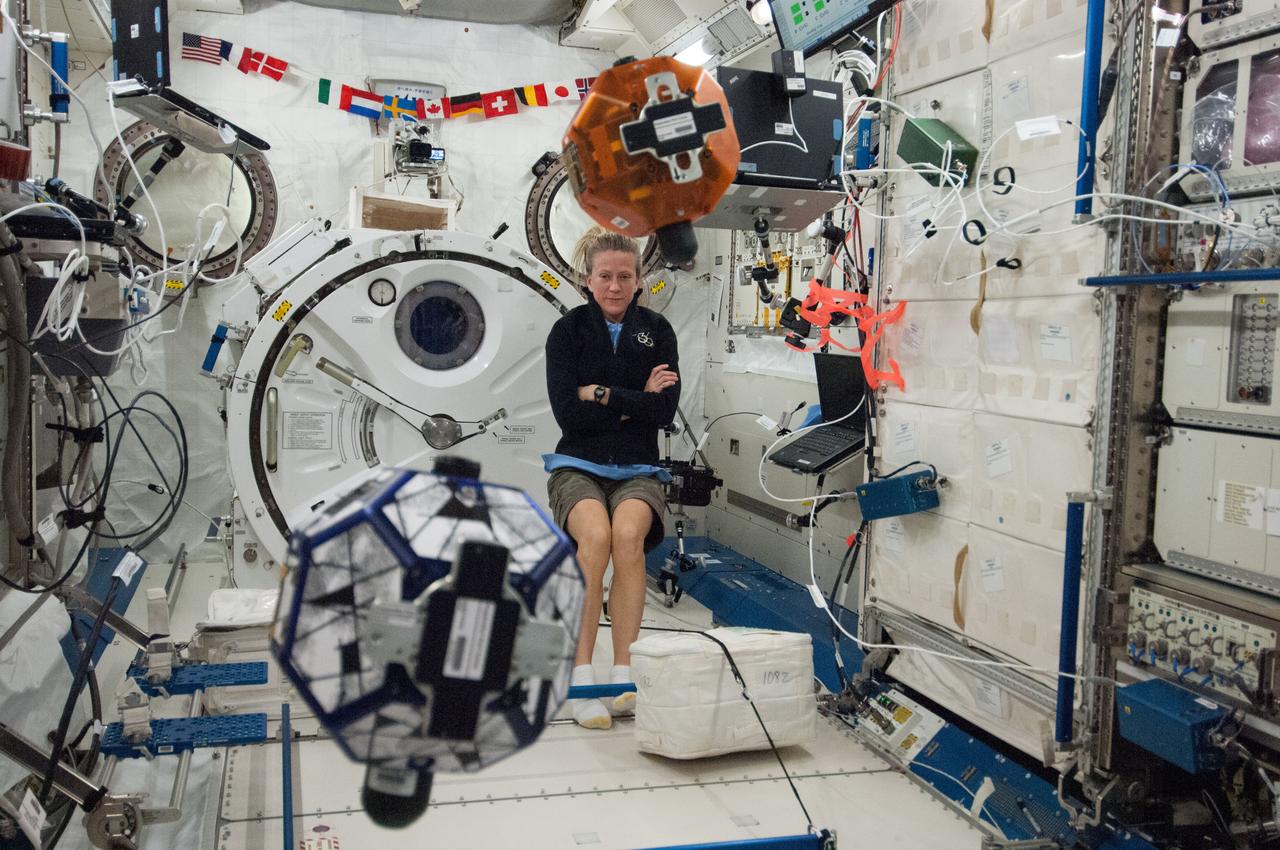

ISS036-E-029539 (7 Aug. 2013) --- In the International Space Station’s Kibo laboratory, NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, conducts a session with a pair of bowling-ball-sized free-flying satellites known as Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES. Nyberg and NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy (not pictured) put the miniature satellites through their paces for a dry run of the SPHERES Zero Robotics tournament scheduled for Aug. 13. Teams of middle school students from Florida, Georgia, Idaho and Massachusetts will gather at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge to see which teams’ algorithms do the best job of commanding the free-flying robots through a series of maneuvers and objectives.
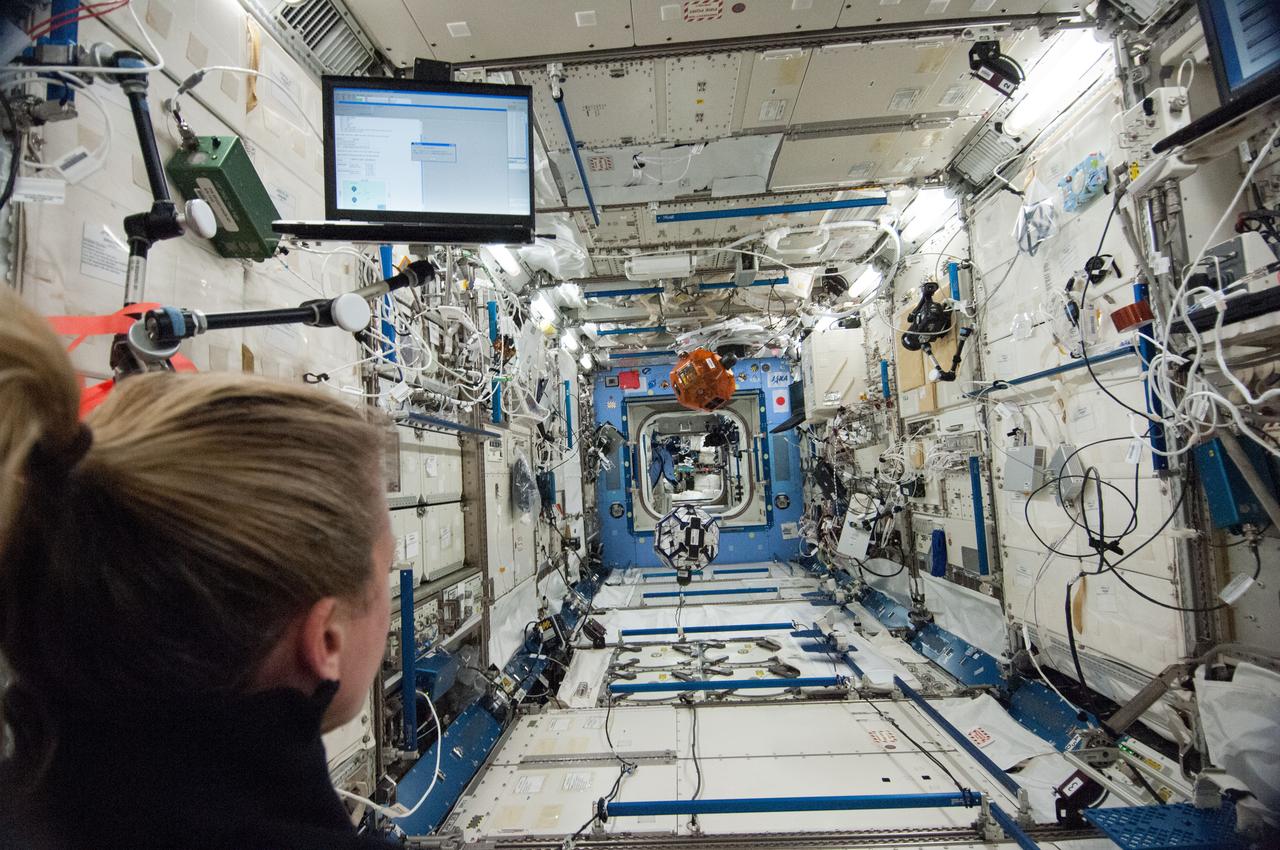

ISS036-E-029521 (7 Aug. 2013) --- In the International Space Station’s Kibo laboratory, NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, conducts a session with a pair of bowling-ball-sized free-flying satellites known as Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES. Nyberg and NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy (not pictured) put the miniature satellites through their paces for a dry run of the SPHERES Zero Robotics tournament scheduled for Aug. 13. Teams of middle school students from Florida, Georgia, Idaho and Massachusetts will gather at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge to see which teams’ algorithms do the best job of commanding the free-flying robots through a series of maneuvers and objectives.
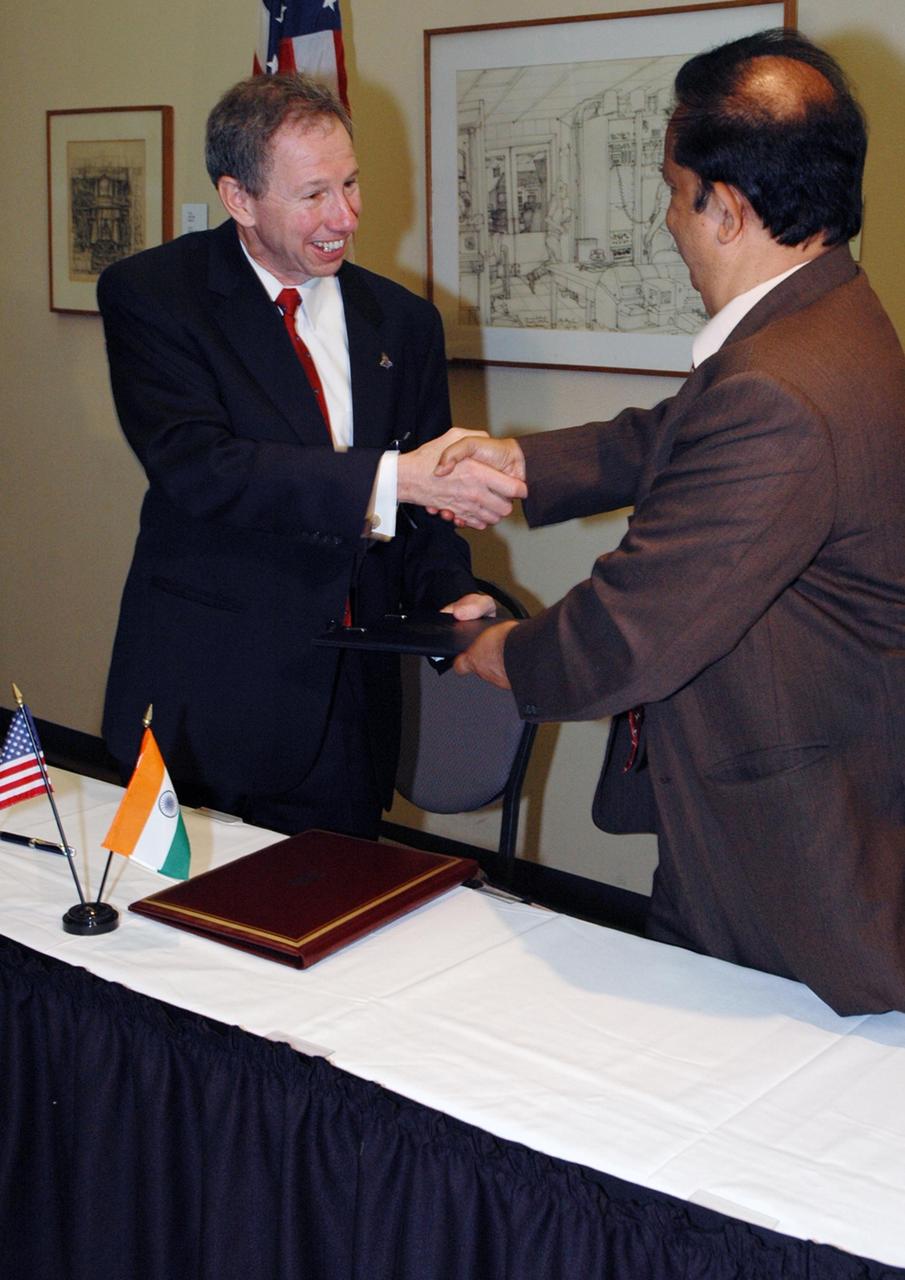

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, NASA Administrator Michael Griffin (left) and Indian Space Research Organization Chairman G. Madhavan Nair show their pleasure after signing a framework agreement establishing the terms for future cooperation between the two agencies in the exploration and use of outer space for peaceful purposes. According to the framework agreement, the two agencies will identify areas of mutual interest and seek to develop cooperative programs or projects in Earth and space science, exploration, human space flight and other activities. In addition to a long history of cooperation in Earth science, NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization also are cooperating on India's first, mission to the moon, Chandrayaan-1, which will be launched later this year. NASA is providing two of the 11 instruments on the spacecraft: the moon mineralogy mapper instrument and the miniature synthetic aperture radar instrument. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
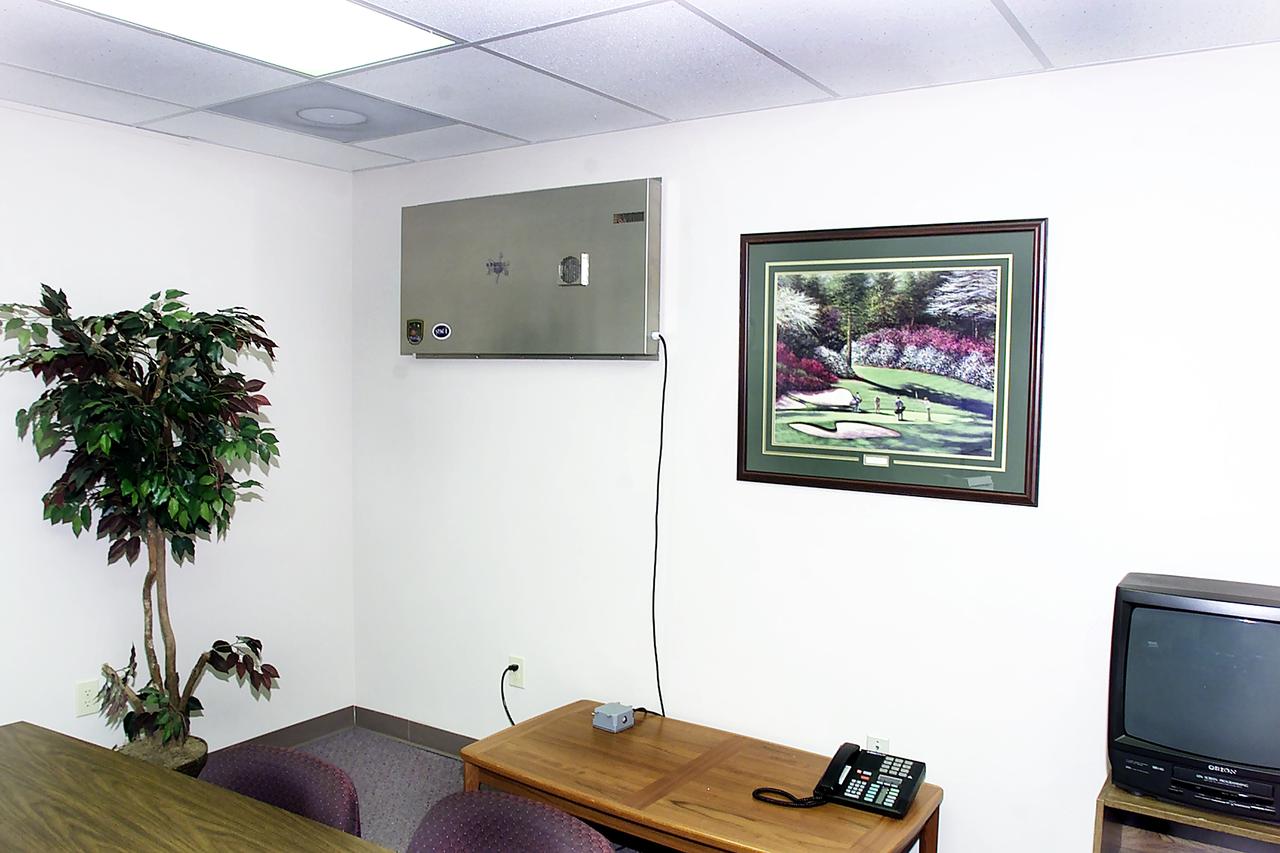

AiroCide Ti02, an anthrax-killing air scrubber manufactured by KES Science and Technology Inc., in Kernesaw, Georgia, looks like a square metal box when it is installed on an office wall. Its fans draw in airborne spores and airflow forces them through a maze of tubes. Inside, hydroxyl radicals (OH-) attack and kill pathogens. Most remaining spores are destroyed by high-energy ultraviolet photons. Building miniature greenhouses for experiments on the International Space Station (ISS) has led to the invention of this device that annihilates anthrax-a bacteria that can be deadly when inhaled. The research enabling the invention started at the University of Wisconsin (Madison) Center for Space Automation and Robotics (WCSAR), one of 17 NASA Commercial Space Centers. A special coating technology used in the anthrax-killing invention is also being used inside WCSAR-built plant growth units on the ISS. This commercial research is managed by the Space Product Development Program at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
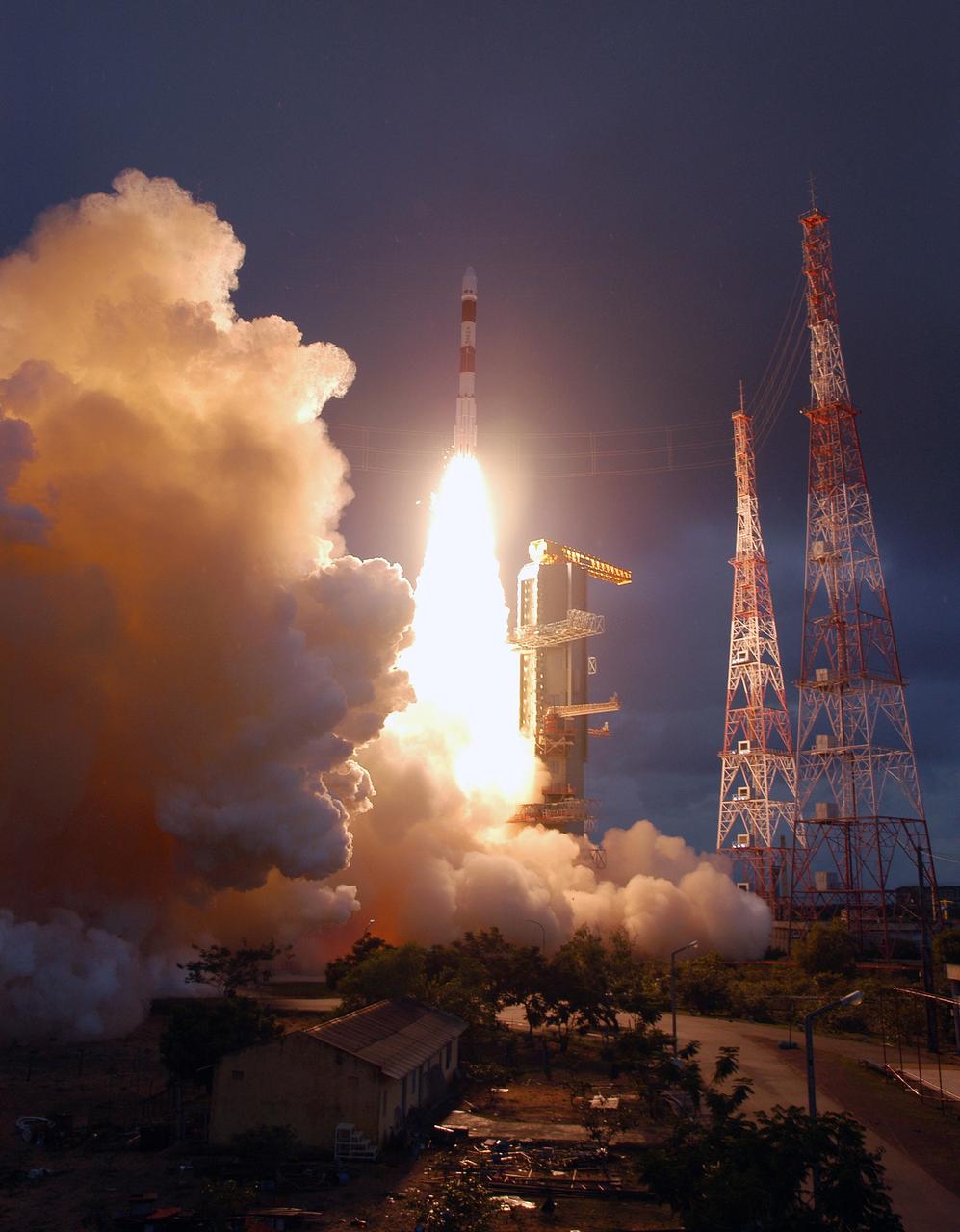

SRIHARIKOTA, India – The Indian Space Research Organization, or ISRO, launches its robotic Chandrayaan-1 rocket with two NASA instruments aboard on India's maiden moon voyage to map the lunar surface. The Moon Mineralogy Mapper will assess mineral resources, and the Miniature Synthetic Aperture Radar, or Mini-SAR, will map the polar regions and look for ice deposits. Data from the two instruments will contribute to NASA's increased understanding of the lunar environment as it implements the nation's space exploration policy, which calls for robotic and human missions to the moon. In addition to the two science instruments, NASA will provide space communications support to Chandrayaan-1. The primary location for the NASA ground tracking station will be at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. Photo credit: NASA
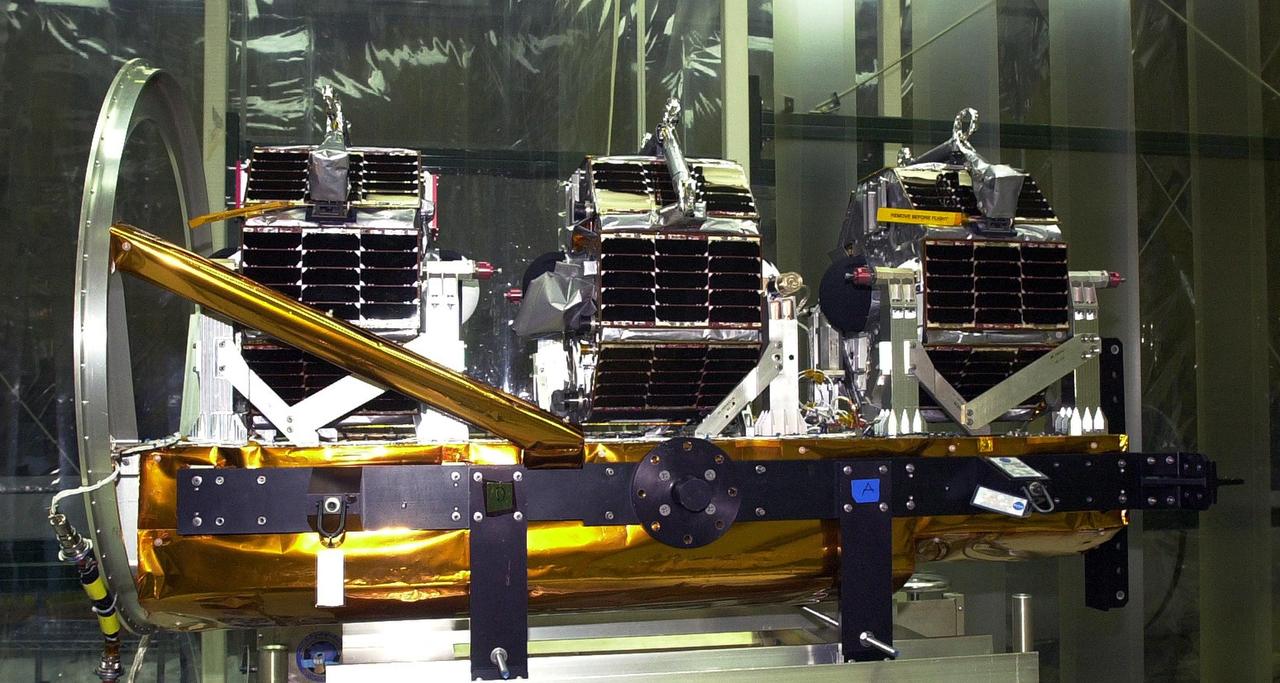

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft is ready for mating to the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Seen in the photo are the three satellites that make up the ST5, containing miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled no earlier than March 6 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
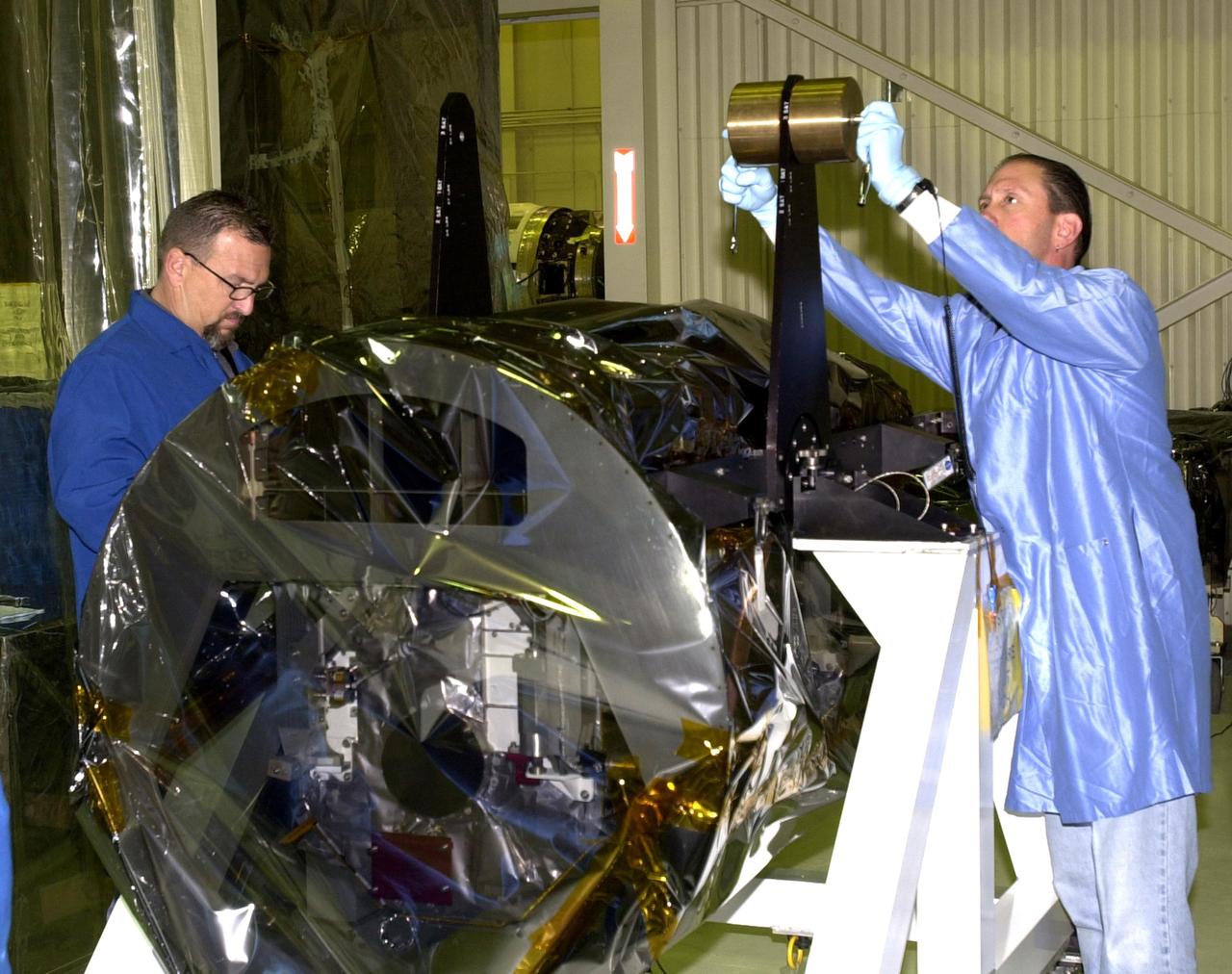

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the wrapped Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft is being prepared for mating to the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
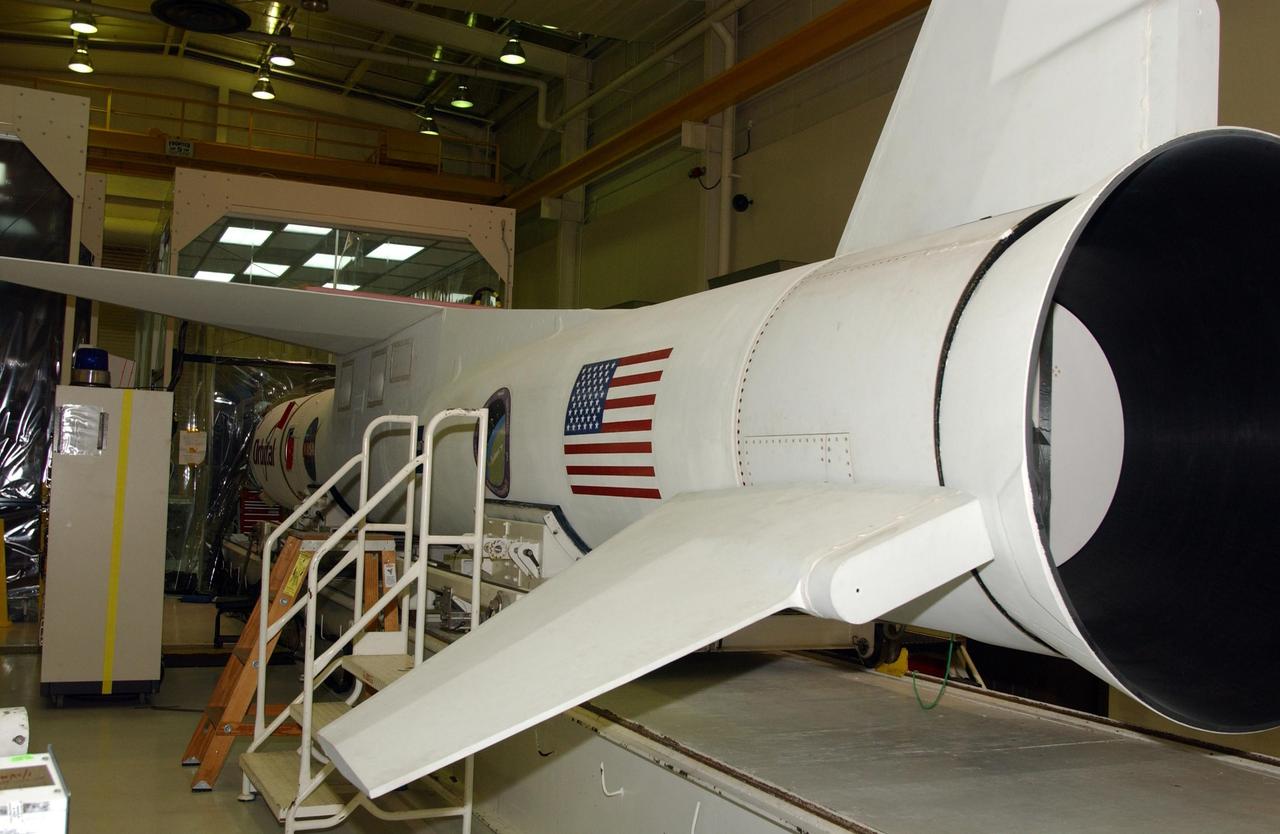

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. -Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California is the Pegasus XL launch vehicle and the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft being prepared for encapsulation before launch. The ST5, mated to Orbital Sciences' Pegasus XL launch vehicle, contains three microsatellites with miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled from the belly of an L-1011 carrier aircraft no earlier than March 14 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
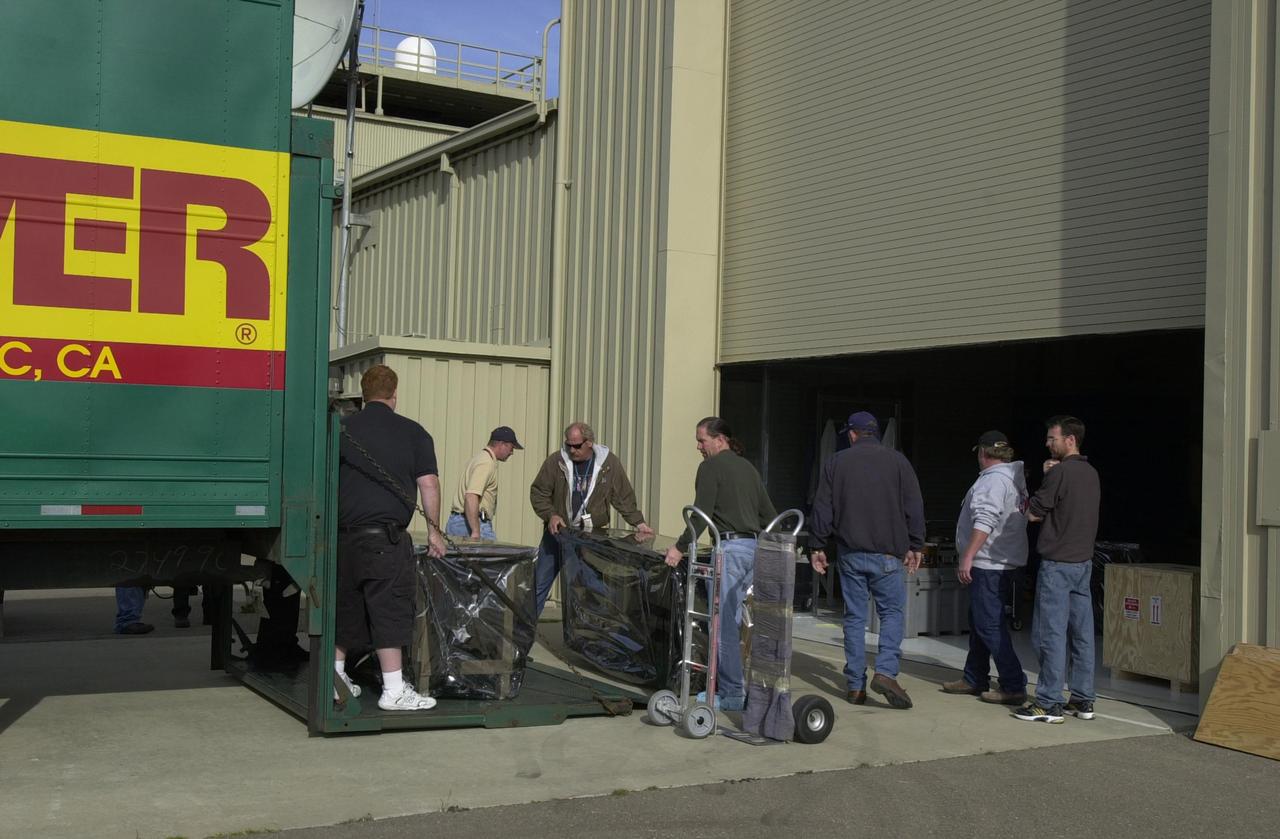

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers are moving the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft out of the Orbital Sciences Building 836 onto a truck for transfer to Building 1555. There it will be mated with the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. ST5 will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
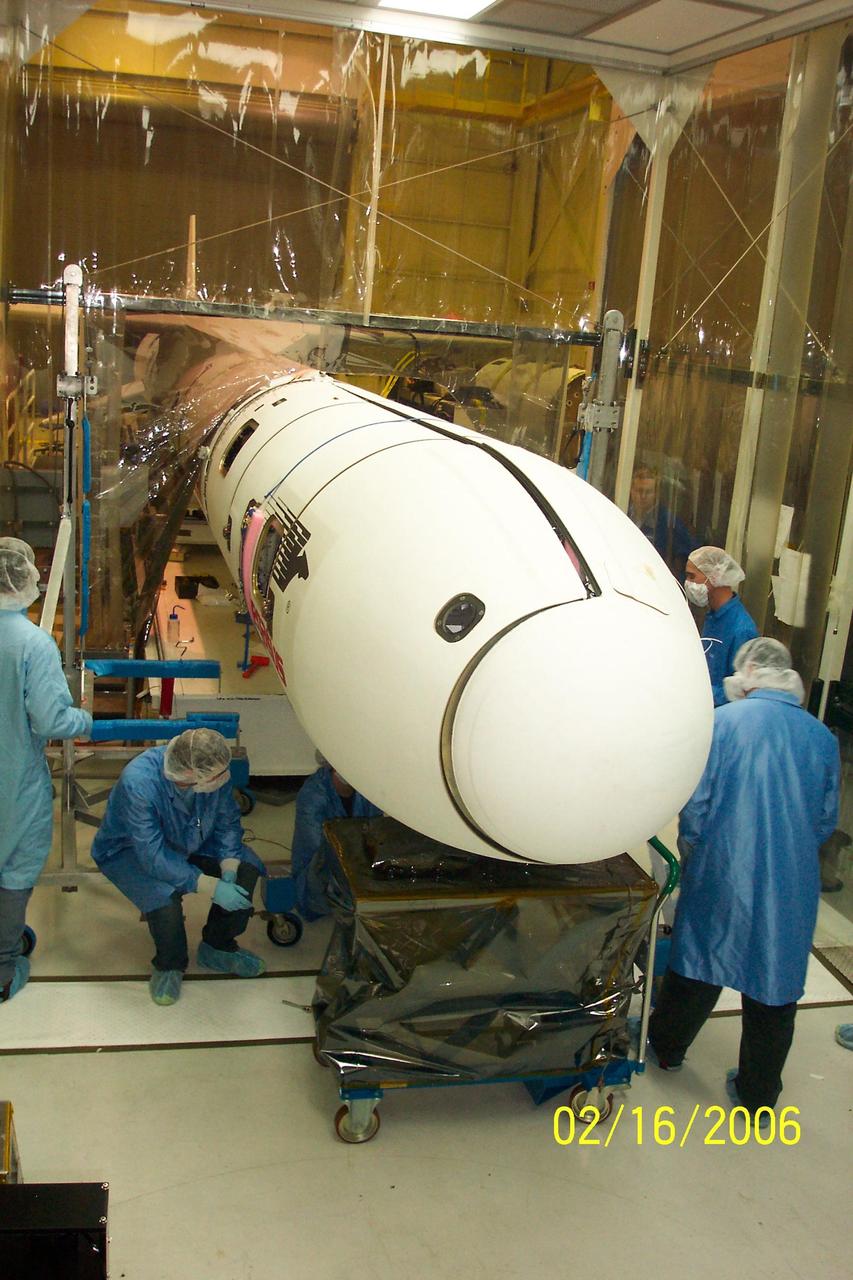

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers continue the installation of the second half of the fairing around the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft. The ST5, which contains three microsatellites with miniaturized redundant components and technologies, is mated to its launch vehicle, Orbital Sciences' Pegasus XL. Each of the ST5 microsatellites will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. Launch of ST5 and the Pegasus XL will be from underneath the belly of an L-1011 carrier aircraft on March 14 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
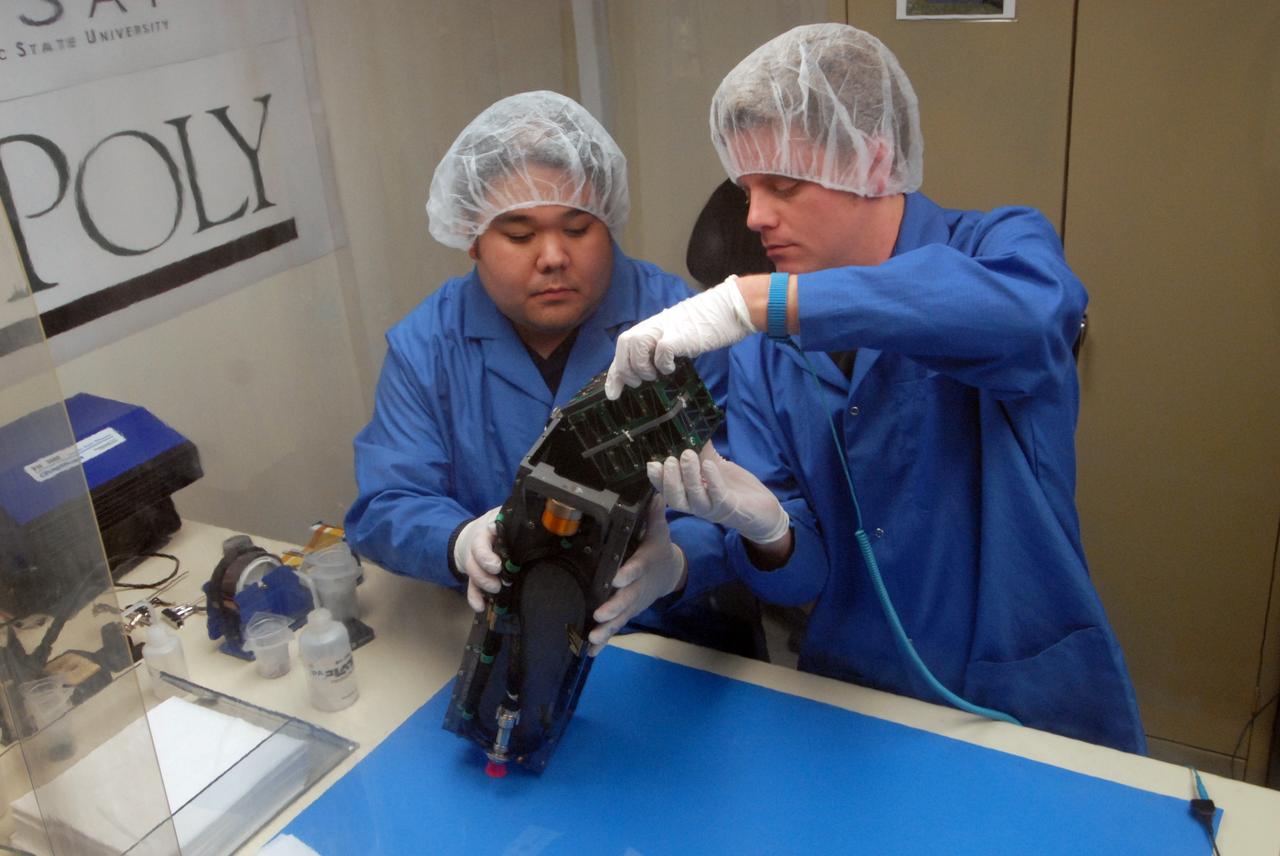

San Luis Obispo, Calif. -- 101116-F-8290C-054 -- Roland Coelho and Ryan Nugent, students at California Polytechnic State University Cal Poly, integrate miniature research satellites called CubeSats into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer PPOD container. The PPOD and CubeSat Project were developed by Cal Poly and Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Lab for use on NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite ELaNa missions. Each CubeSat measures about 4-inches cubed and is about the same volume as a quart. The CubeSats weigh about 2.2 pounds, must conform to standard aerospace materials and must operate without propulsion. The satellites are being prepared to launch with NASA's Glory spacecraft aboard an Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon from its place in low Earth orbit. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: U.S. Air Force/Jerry E. Clemens Jr.
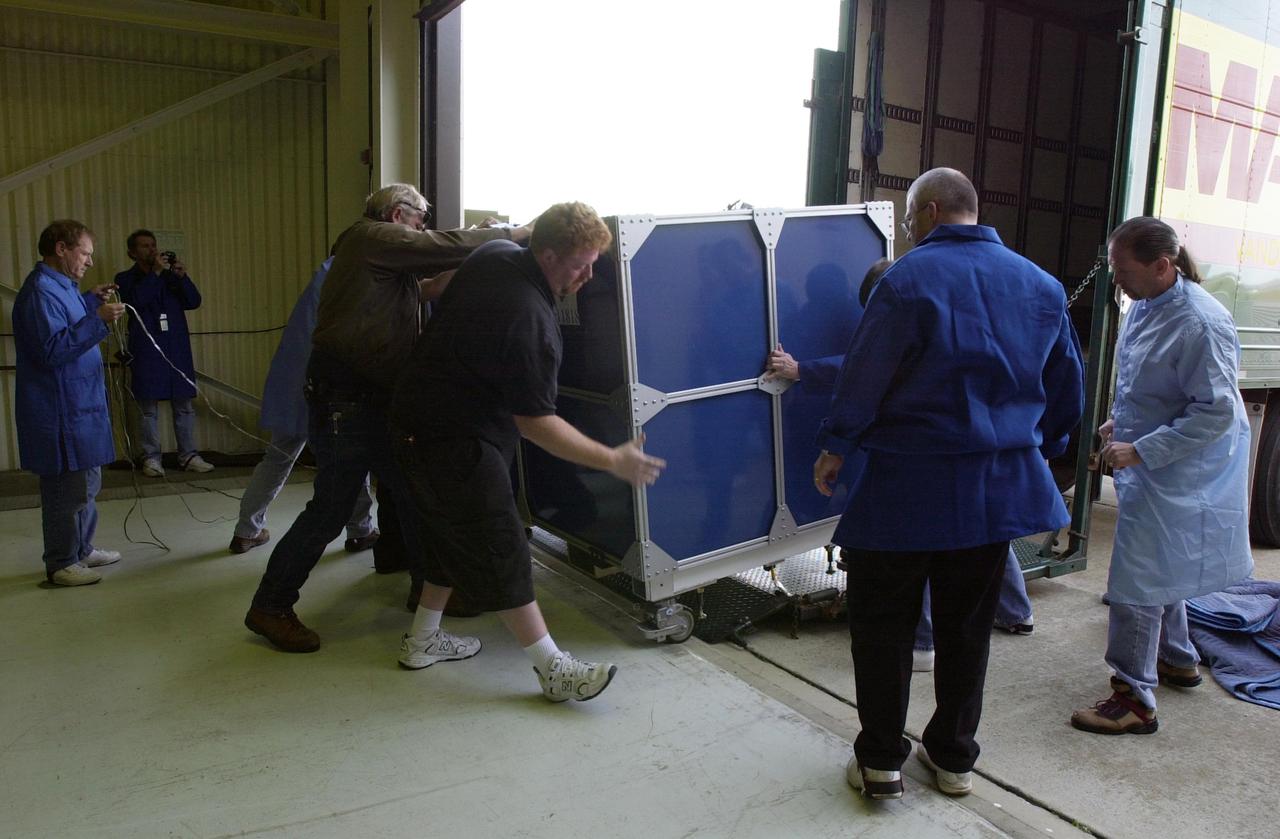

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers are moving the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft into Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555. There it will be mated with the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. ST5 will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
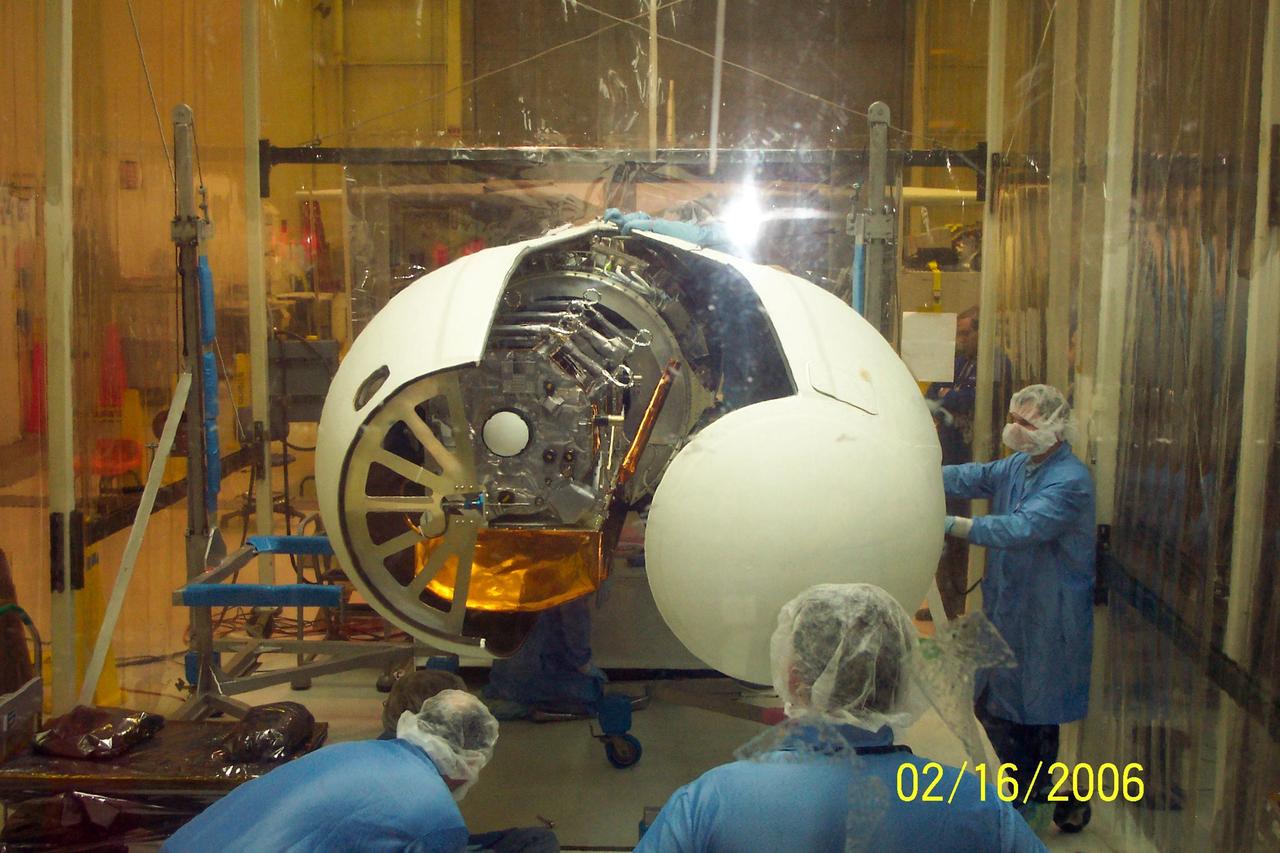

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers move the second half of the fairing into position around the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft. The ST5, which contains three microsatellites with miniaturized redundant components and technologies, is mated to its launch vehicle, Orbital Sciences' Pegasus XL. Each of the ST5 microsatellites will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. Launch of ST5 and the Pegasus XL will be from underneath the belly of an L-1011 carrier aircraft on March 14 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
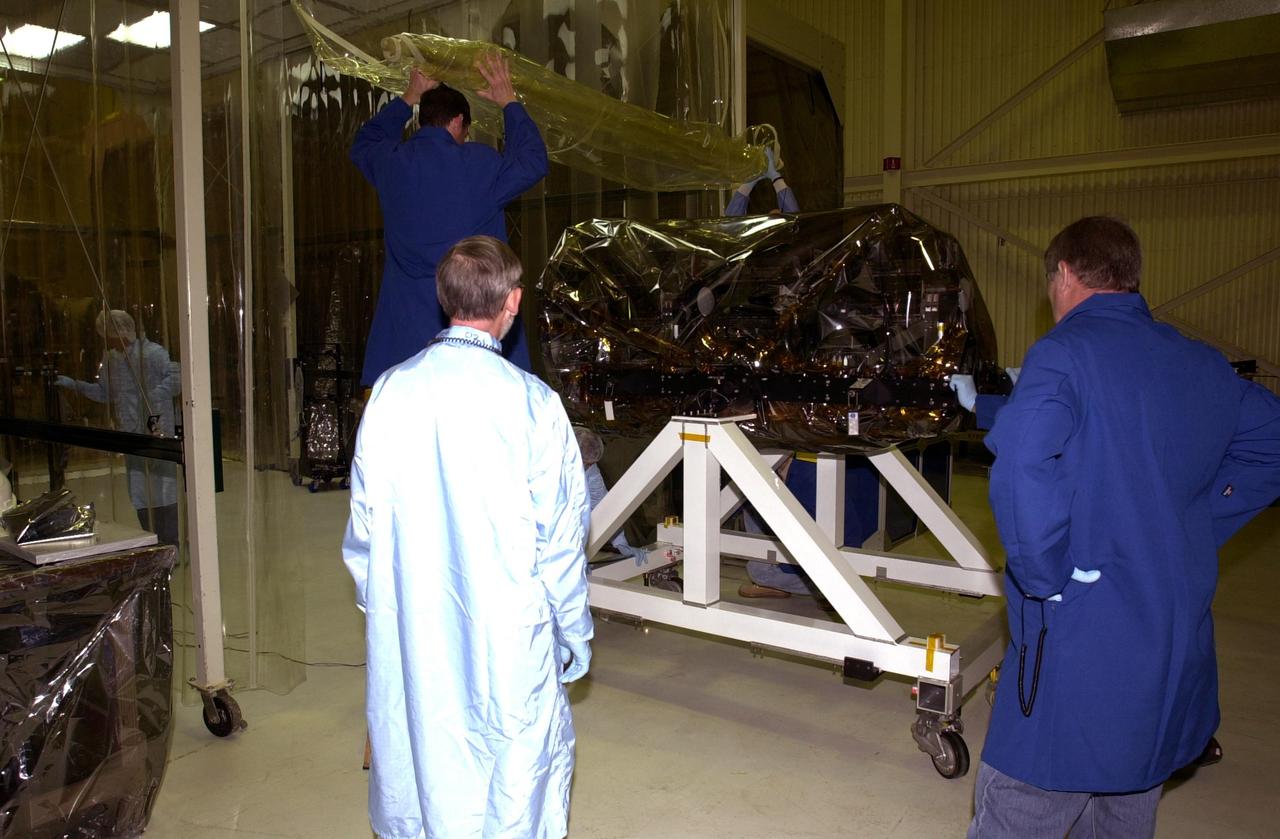

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the wrapped Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft is ready for mating to the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
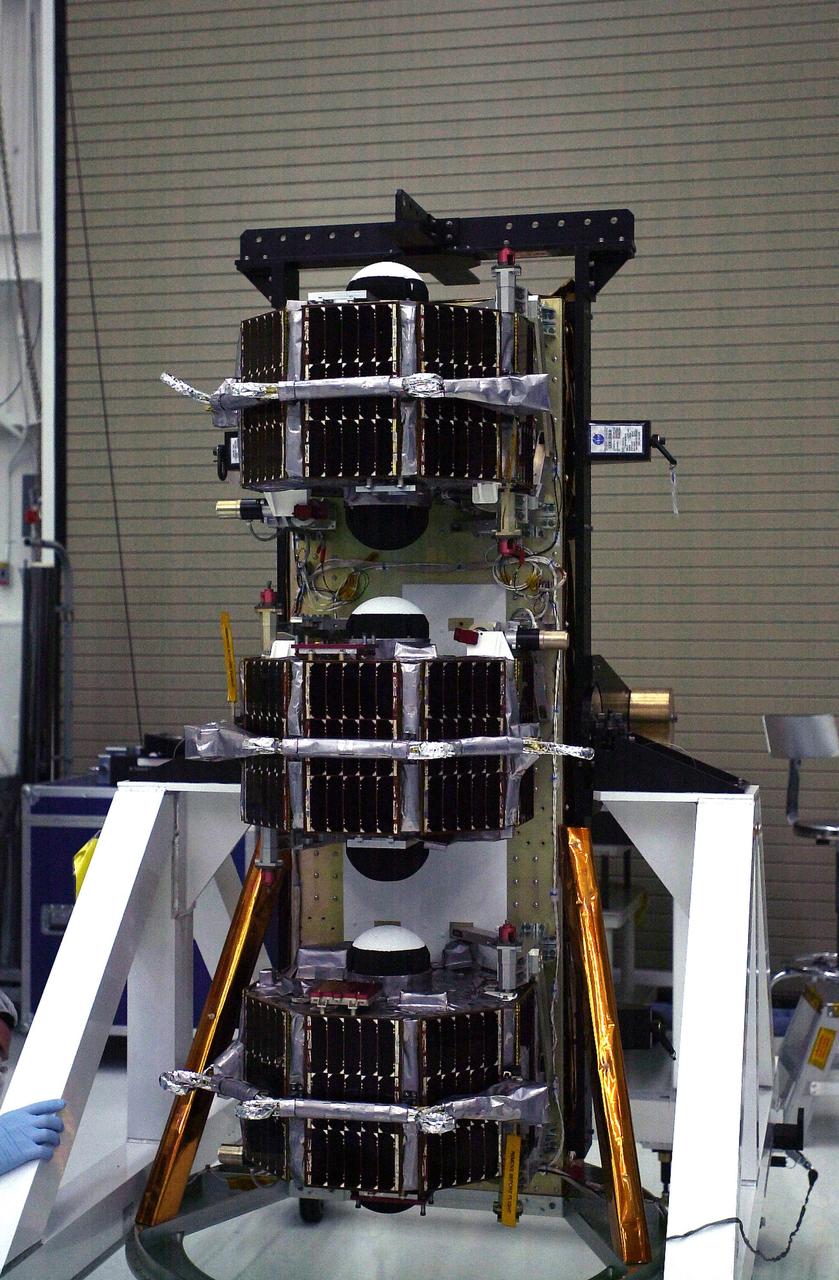
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — In In the Orbital Sciences Building 836 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the payload support structure with the three micro-satellites comprising the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft has been raised to vertical to be weighed. ST5 will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
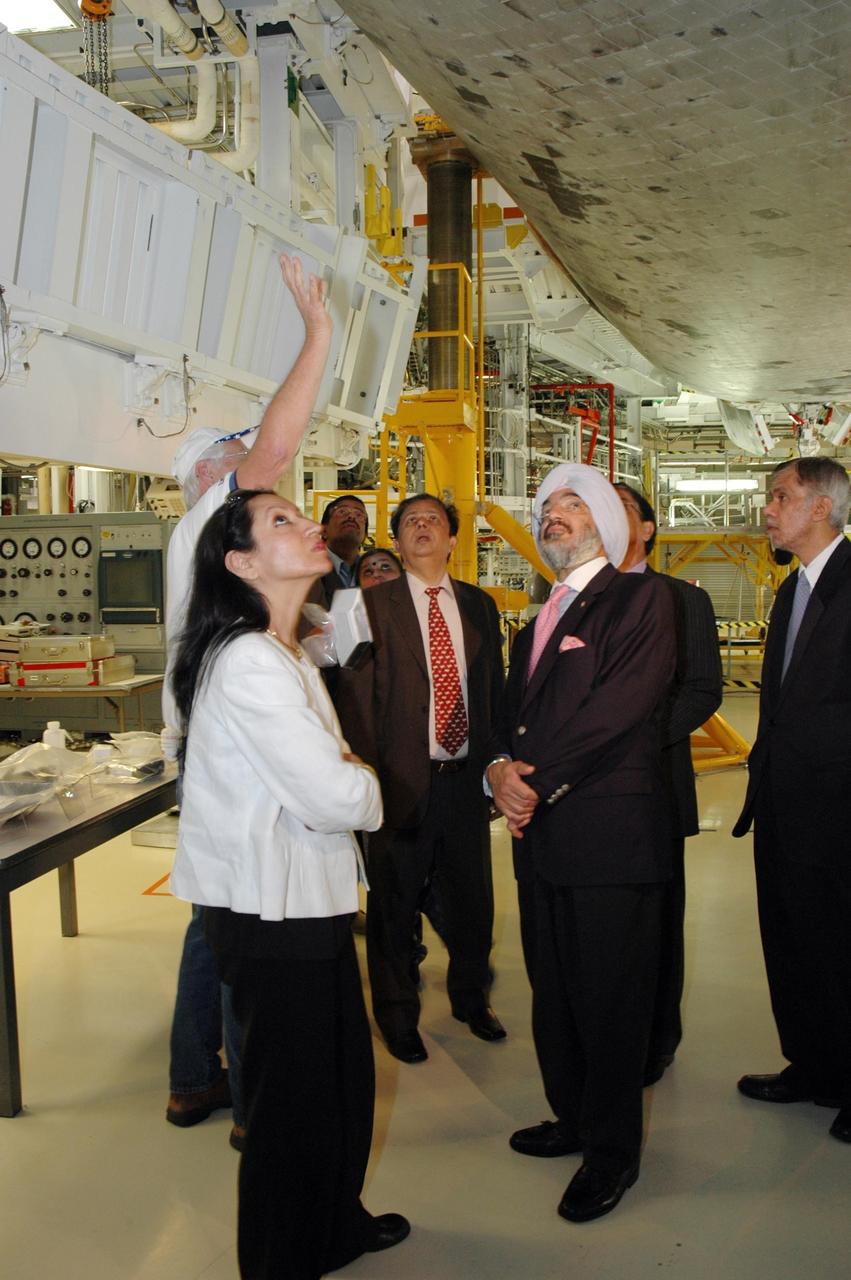

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After signing a framework agreement establishing the terms for future cooperation between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization, Chairman G. Madhavan Nair (center) and other members are given a tour of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The agreement establishes the terms for future cooperation between the two agencies in the exploration and use of outer space for peaceful purposes. According to the framework agreement, the two agencies will identify areas of mutual interest and seek to develop cooperative programs or projects in Earth and space science, exploration, human space flight and other activities. In addition to a long history of cooperation in Earth science, NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization also are cooperating on India's first, mission to the moon, Chandrayaan-1, which will be launched later this year. NASA is providing two of the 11 instruments on the spacecraft: the moon mineralogy mapper instrument and the miniature synthetic aperture radar instrument. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
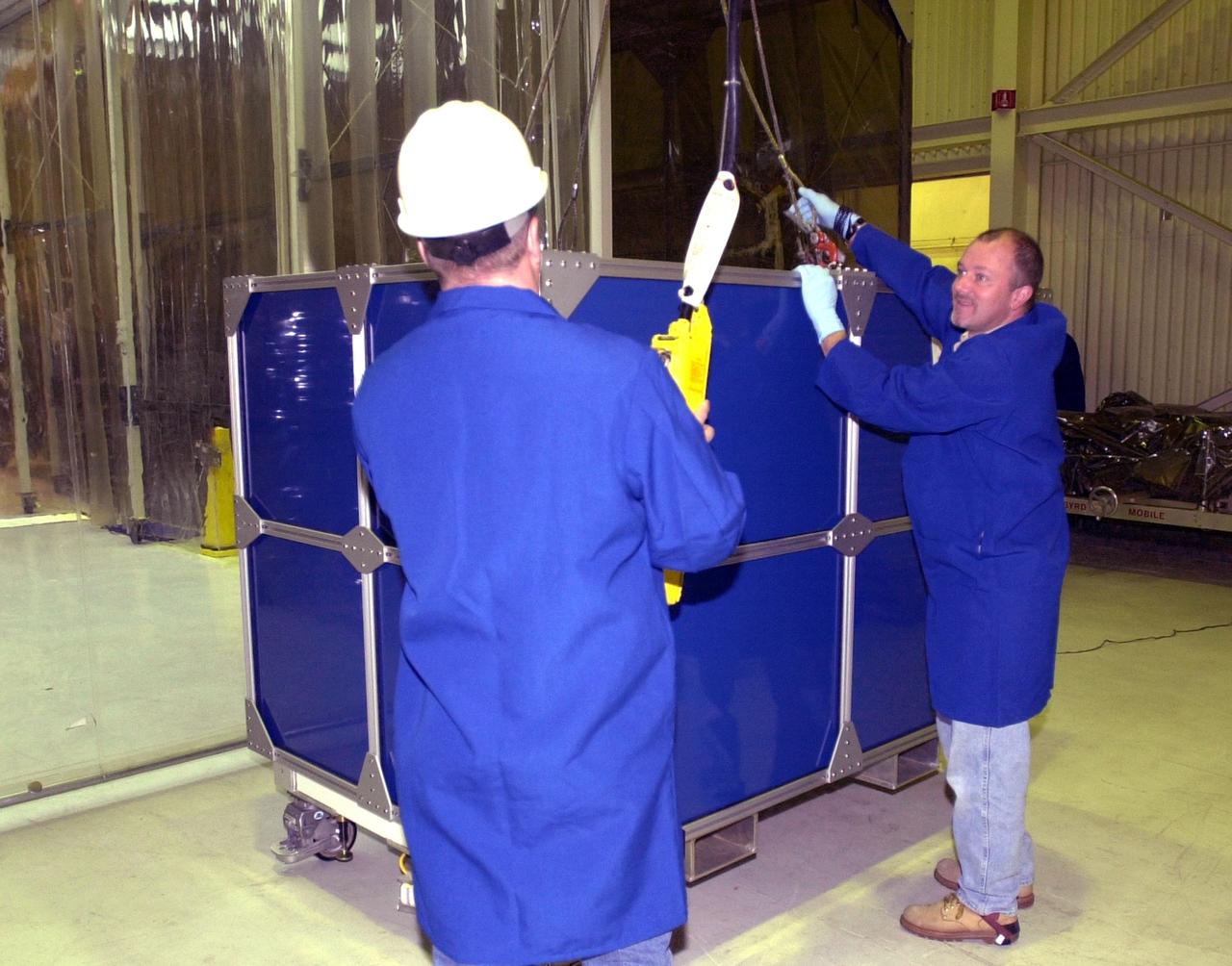

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers attach the wires to lift the shipping container surrounding the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft. ST5 will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
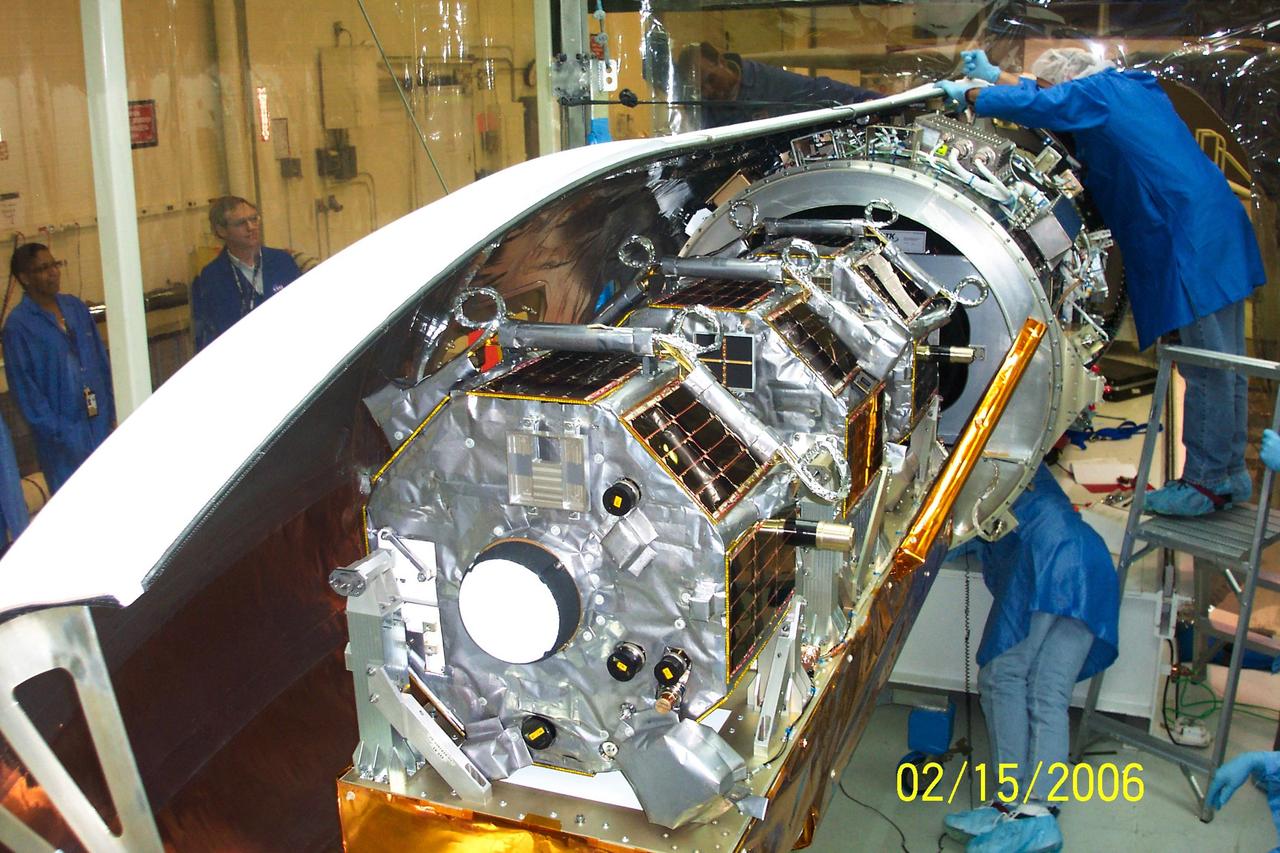

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers adjust the first half of the fairing around the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft. The ST5, which contains three microsatellites with miniaturized redundant components and technologies, is mated to its launch vehicle, Orbital Sciences' Pegasus XL. Each of the ST5 microsatellites will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. Launch of ST5 and the Pegasus XL will be from underneath the belly of an L-1011 carrier aircraft on March 14 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
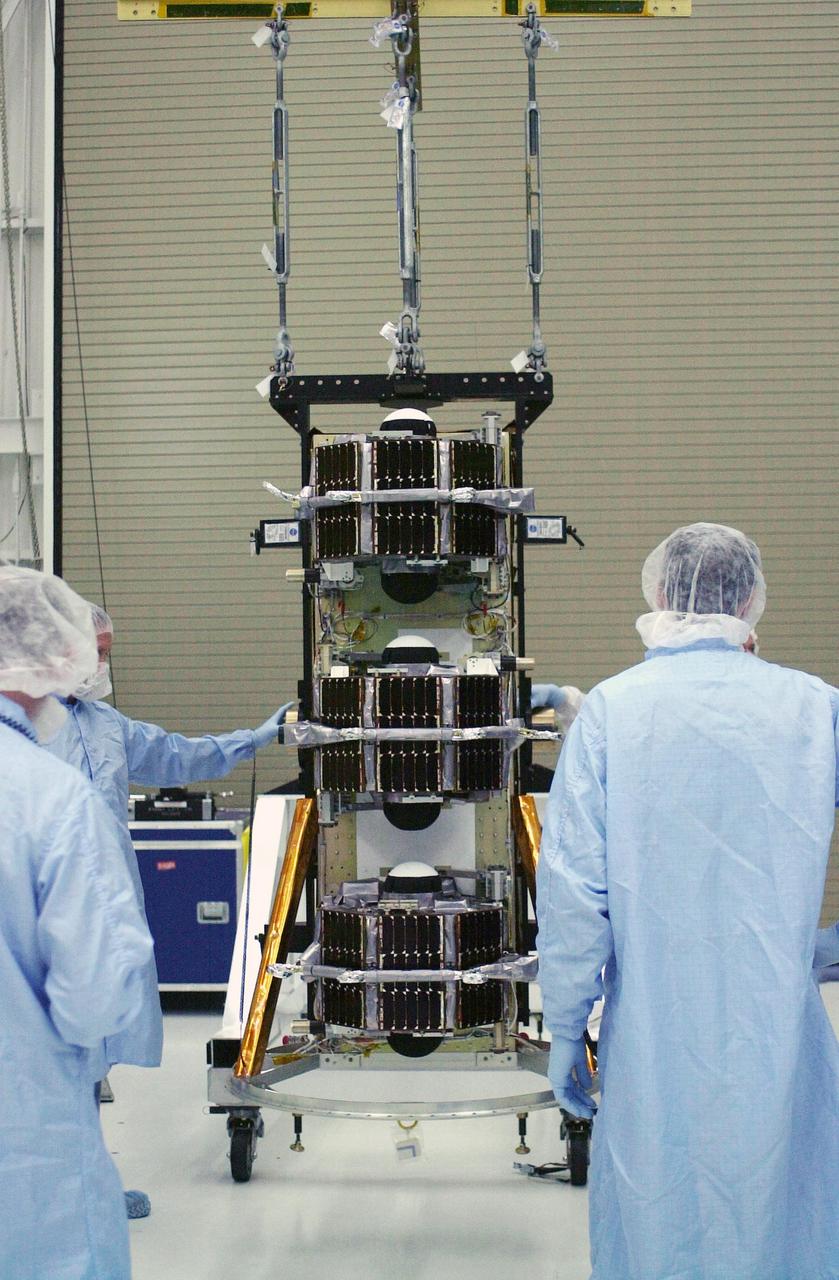

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — In the Orbital Sciences Building 836 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a scale attached to a crane is ready to lift the payload support structure with the three micro-satellites comprising the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft. ST5 will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
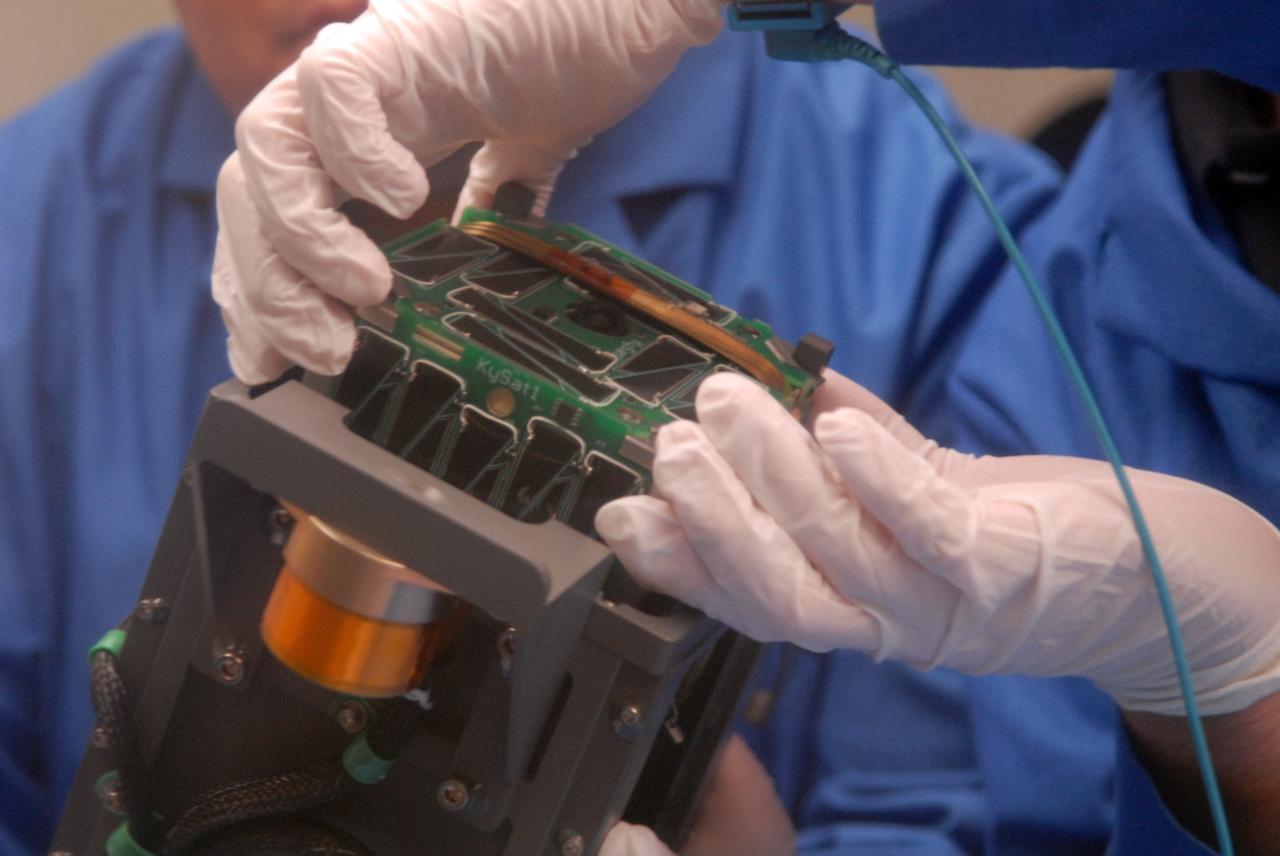
San Luis Obispo, Calif. -- 101116-F-8290C-059 -- Roland Coelho and Ryan Nugent, students at California Polytechnic State University Cal Poly, integrate miniature research satellites called CubeSats into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer PPOD container. The PPOD and CubeSat Project were developed by Cal Poly and Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Lab for use on NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite ELaNa missions. Each CubeSat measures about 4-inches cubed and is about the same volume as a quart. The CubeSats weigh about 2.2 pounds, must conform to standard aerospace materials and must operate without propulsion. The satellites are being prepared to launch with NASA's Glory spacecraft aboard an Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon from its place in low Earth orbit. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: U.S. Air Force/Jerry E. Clemens Jr.
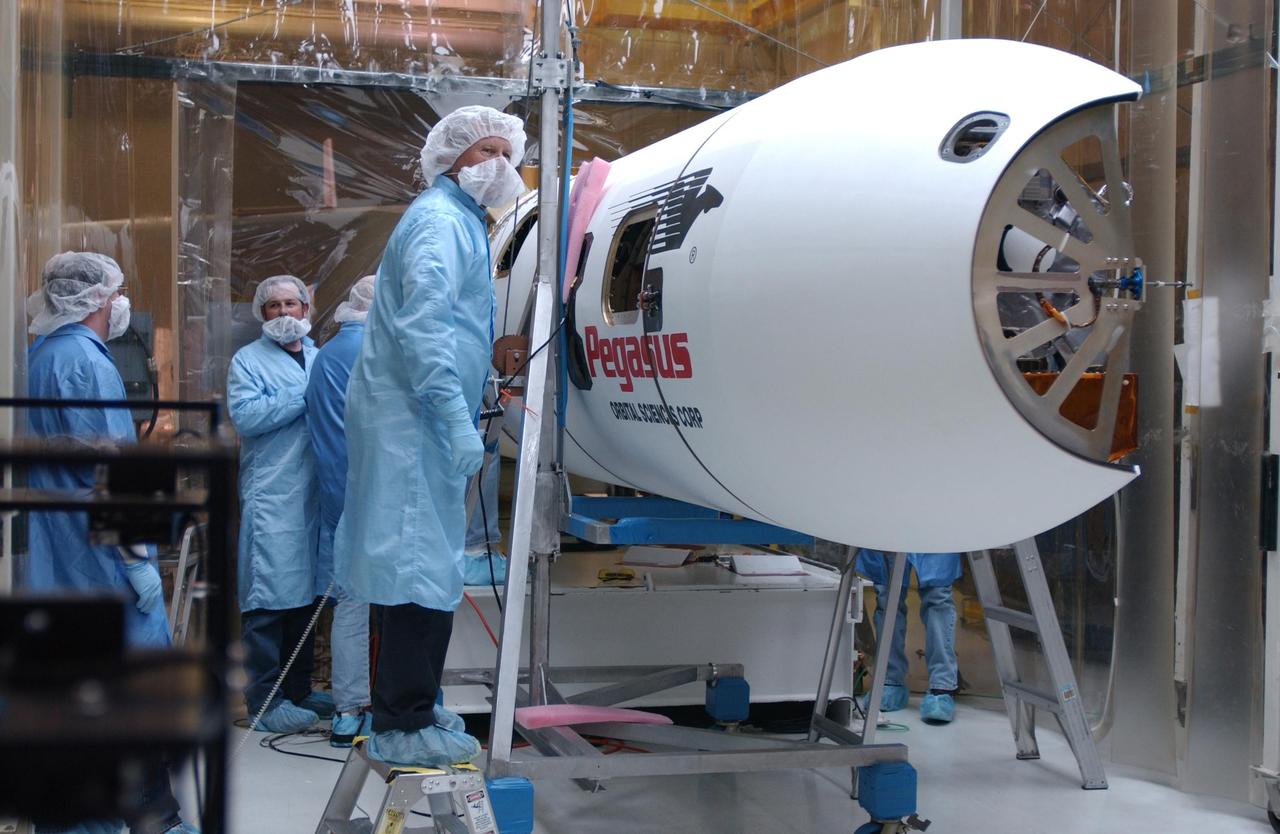

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers check the Orbital Sciences' Pegasus XL launch vehicle before encapsulation of the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft. The ST5 contains three microsatellites with miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled from the belly of an L-1011 carrier aircraft no earlier than March 14 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
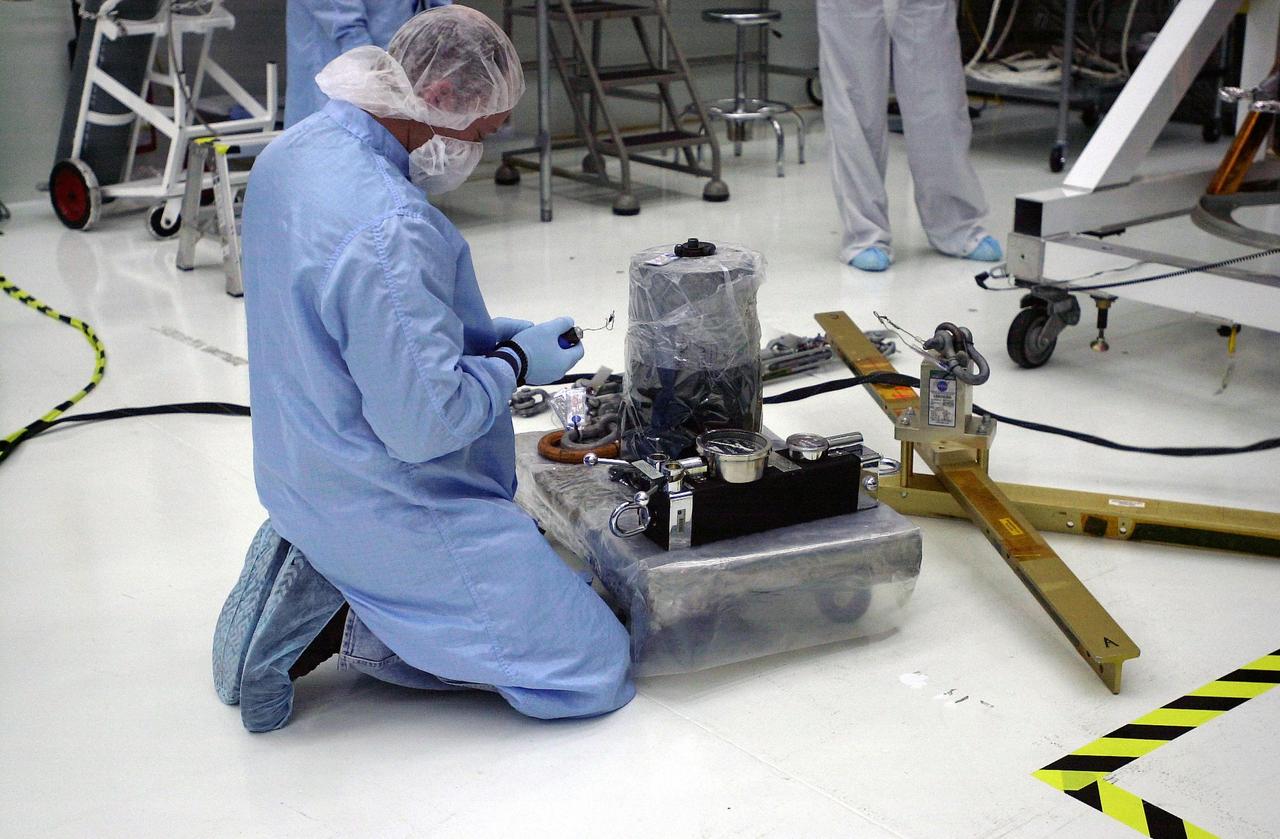

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — In the Orbital Sciences Building 836 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare the scale that will be used to weigh the three micro-satellites comprising the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft. ST5 will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
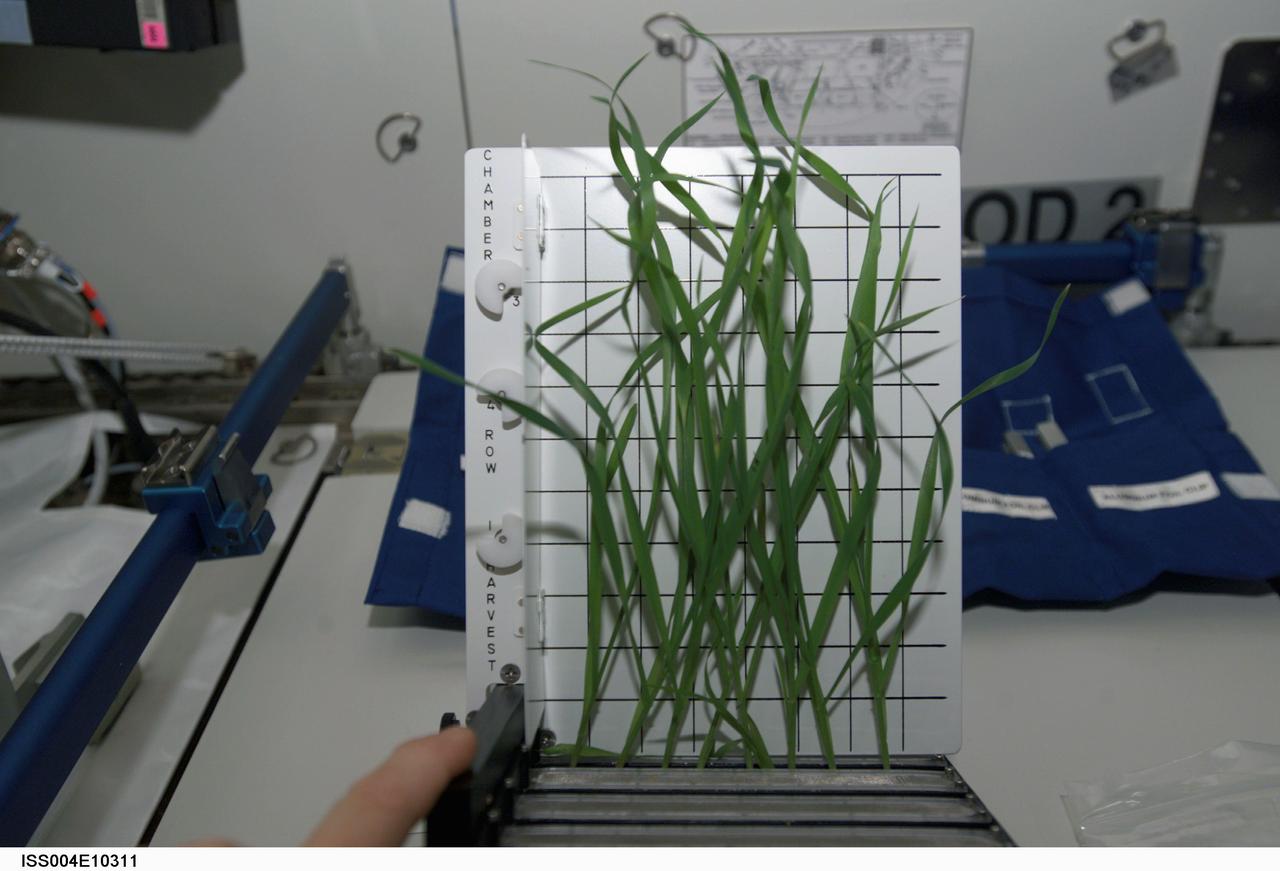

Dwarf wheat were photographed aboard the International Space Station in April 2002. Lessons from on-orbit research on plants will have applications to terrestrial agriculture as well as for long-term space missions. Alternative agricultural systems that can efficiently produce greater quantities of high-quality crops in a small area are important for future space expeditions. Also regenerative life-support systems that include plants will be an important component of long-term space missions. Data from the Biomass Production System (BPS) and the Photosynthesis Experiment and System Testing and Operations (PESTO) will advance controlled-environment agricultural systems and will help farmers produce better, healthier crops in a small area. This same knowledge is critical to closed-loop life support systems for spacecraft. The BPS comprises a miniature environmental control system for four plant growth chambers, all in the volume of two space shuttle lockers. The experience with the BPS on orbit is providing valuable design and operational lessons that will be incorporated into the Plant Growth Units. The objective of PESTO was to flight verify the BPS hardware and to determine how the microgravity environment affects the photosynthesis and metabolic function of Super Dwarf wheat and Brassica rapa (a member of the mustard family).