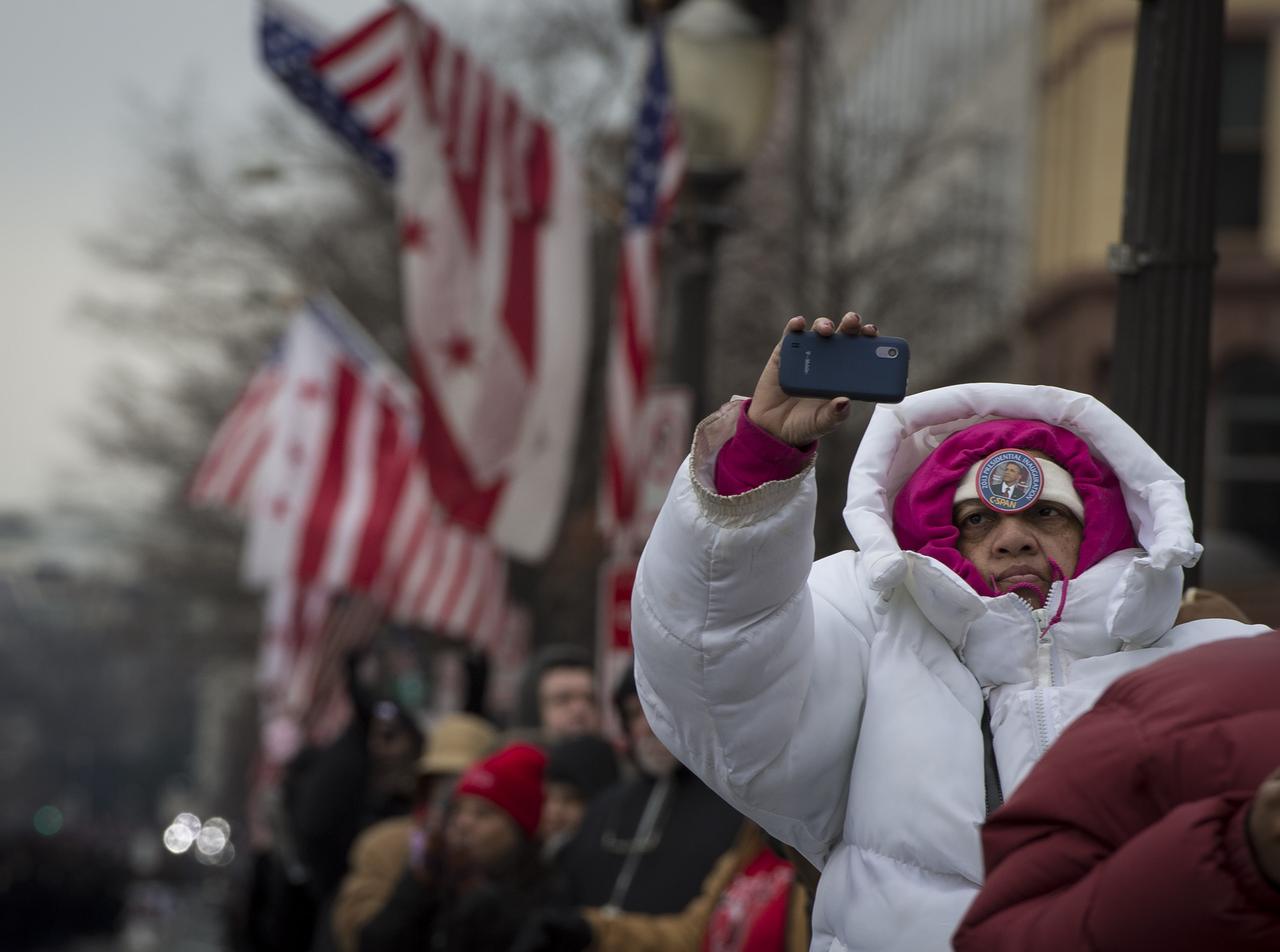

A woman bundled up for the cold temperatures makes a picture with here mobile device as she waits for the Inaugural Parade honoring President Barack Obama, Monday, Jan. 21, 2013, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
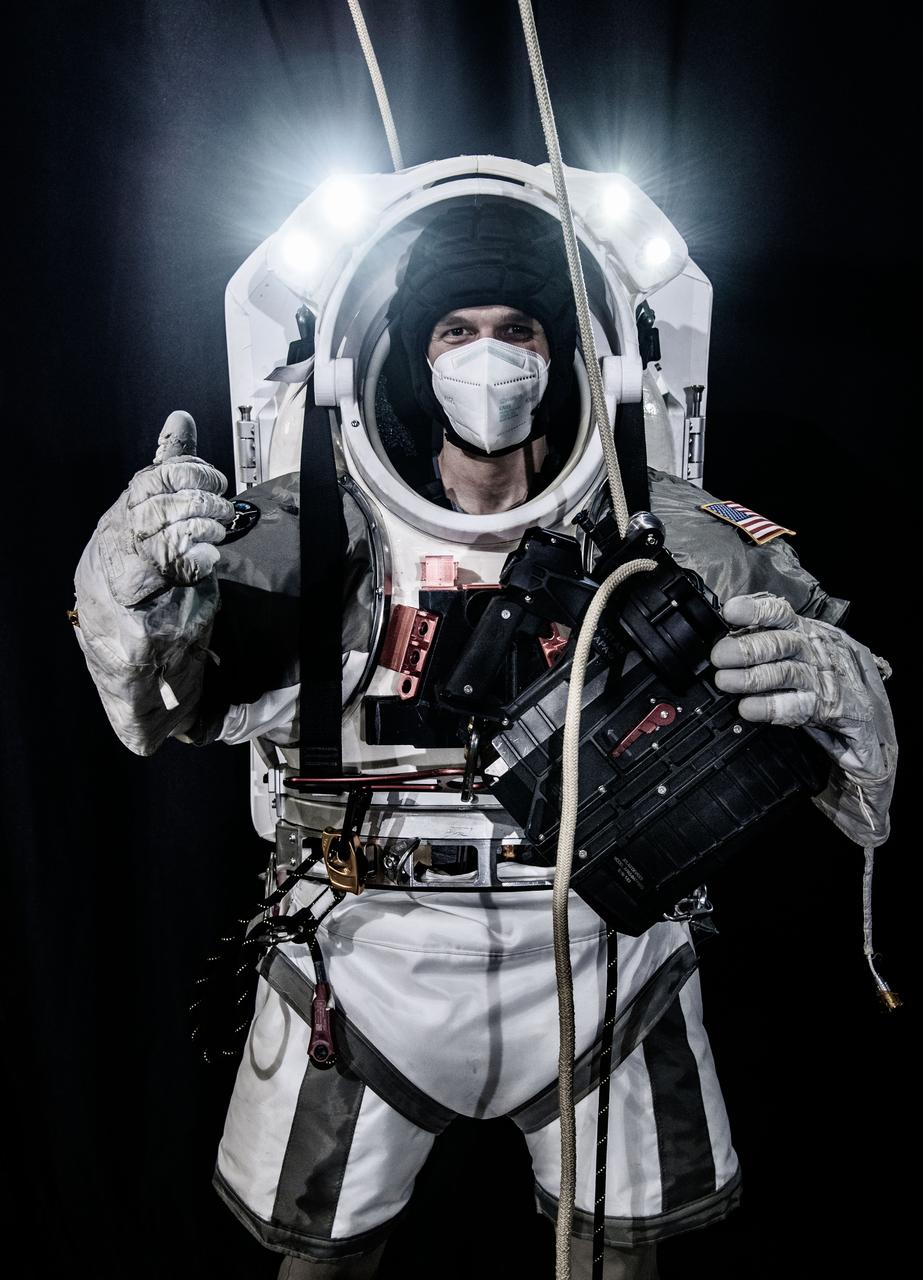

Nate Ball of Atlas Devices prepares to test an APA-5 powered rope ascender with the Exploration Conop (EXCON) Suit, a new xEMU spacesuit simulator. Atlas uses this device in terrestrial applications of powered ascenders including rescue and vertical mobility. This photo was taken when NASA began researching if these capabilities may have analogous applications for lunar surface operations. Photo Date: April 29, 2021. Location: Building 49 High Bay. Photographer: Robert Markowitz

iss068e024574 (Nov. 26, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Frank Rubio works in the Microgravity Science Glovebox setting up hardware for the Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation. The space physics study demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a micro-structured surface.
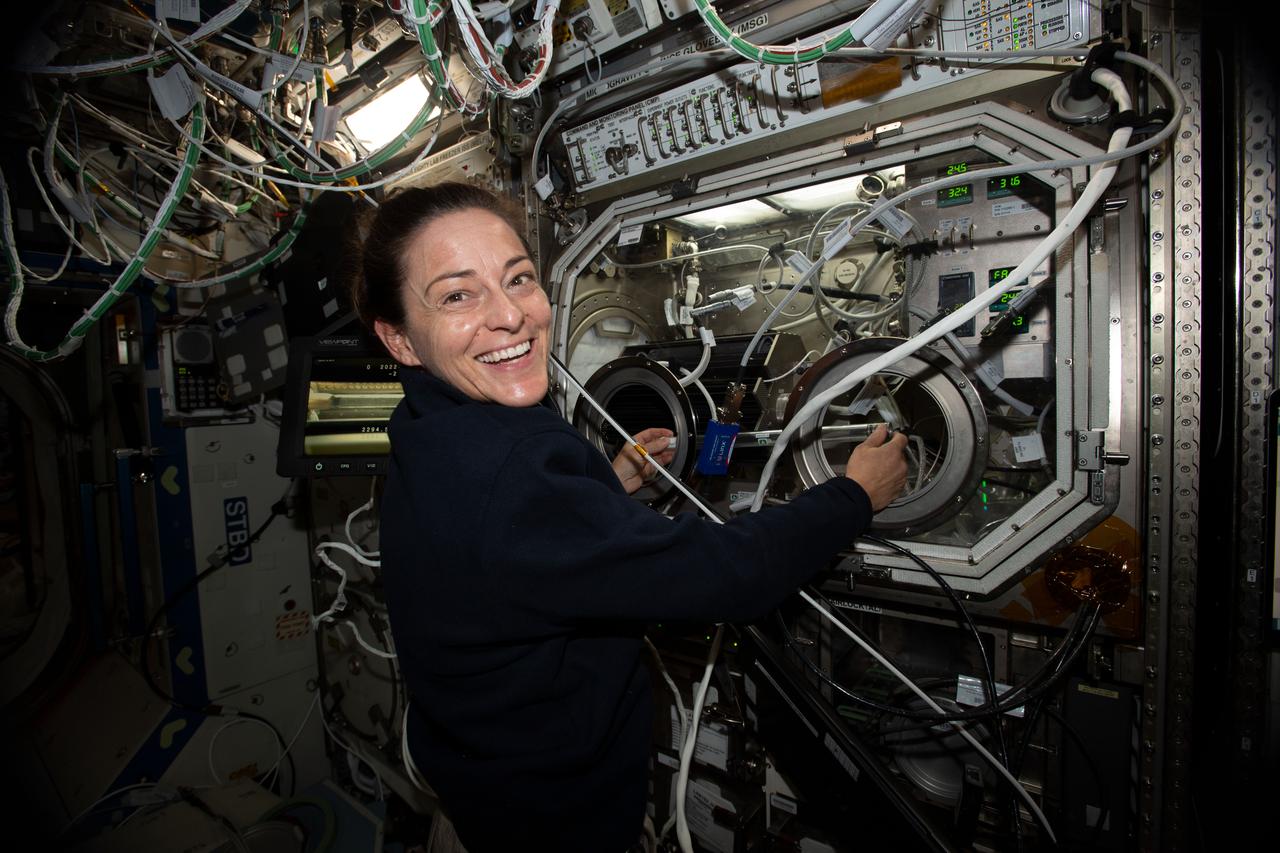

iss068e029599 (Dec. 14, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Nicole Mann exchanges samples inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation. The space physics study demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a micro-structured surface.
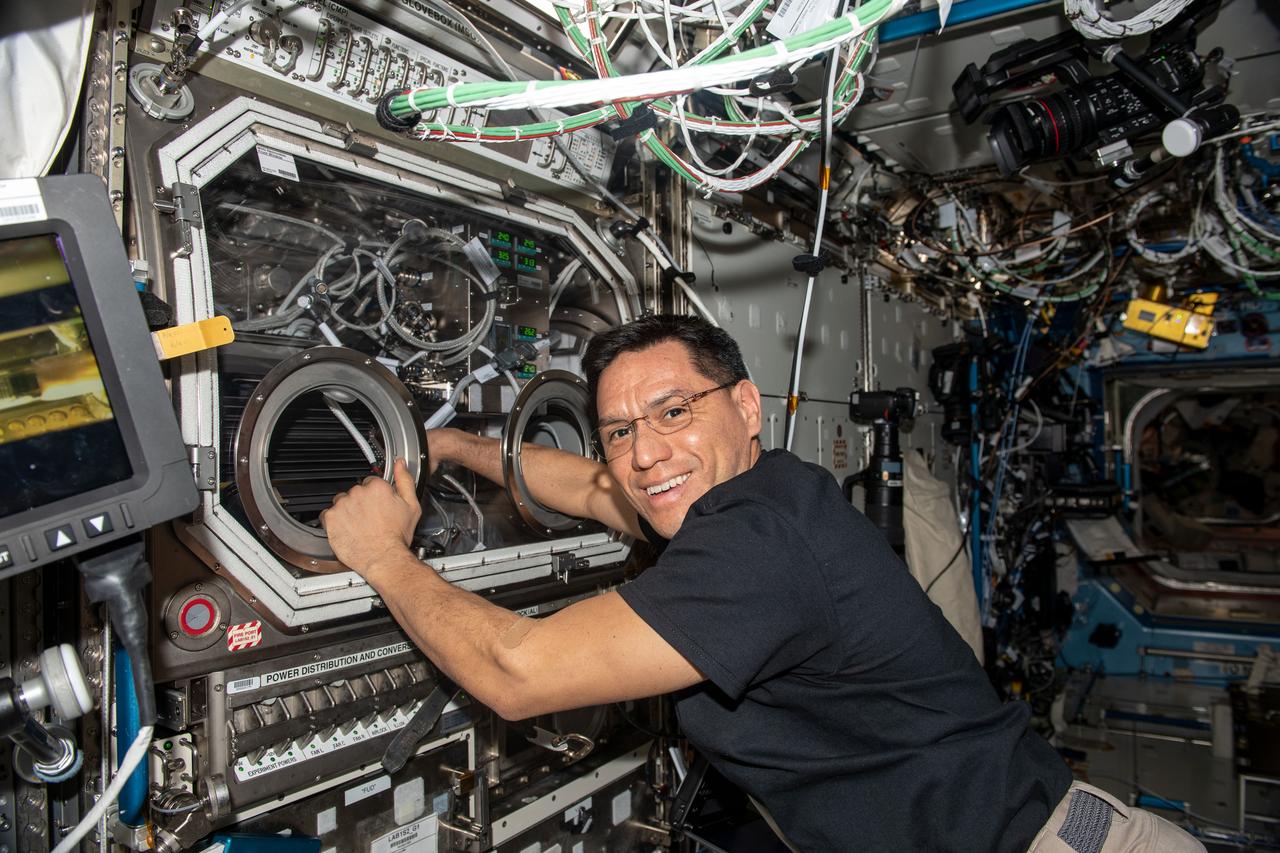

iss068e028262 (Dec. 9, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Frank Rubio exchanges samples inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation. The space physics study demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a micro-structured surface.
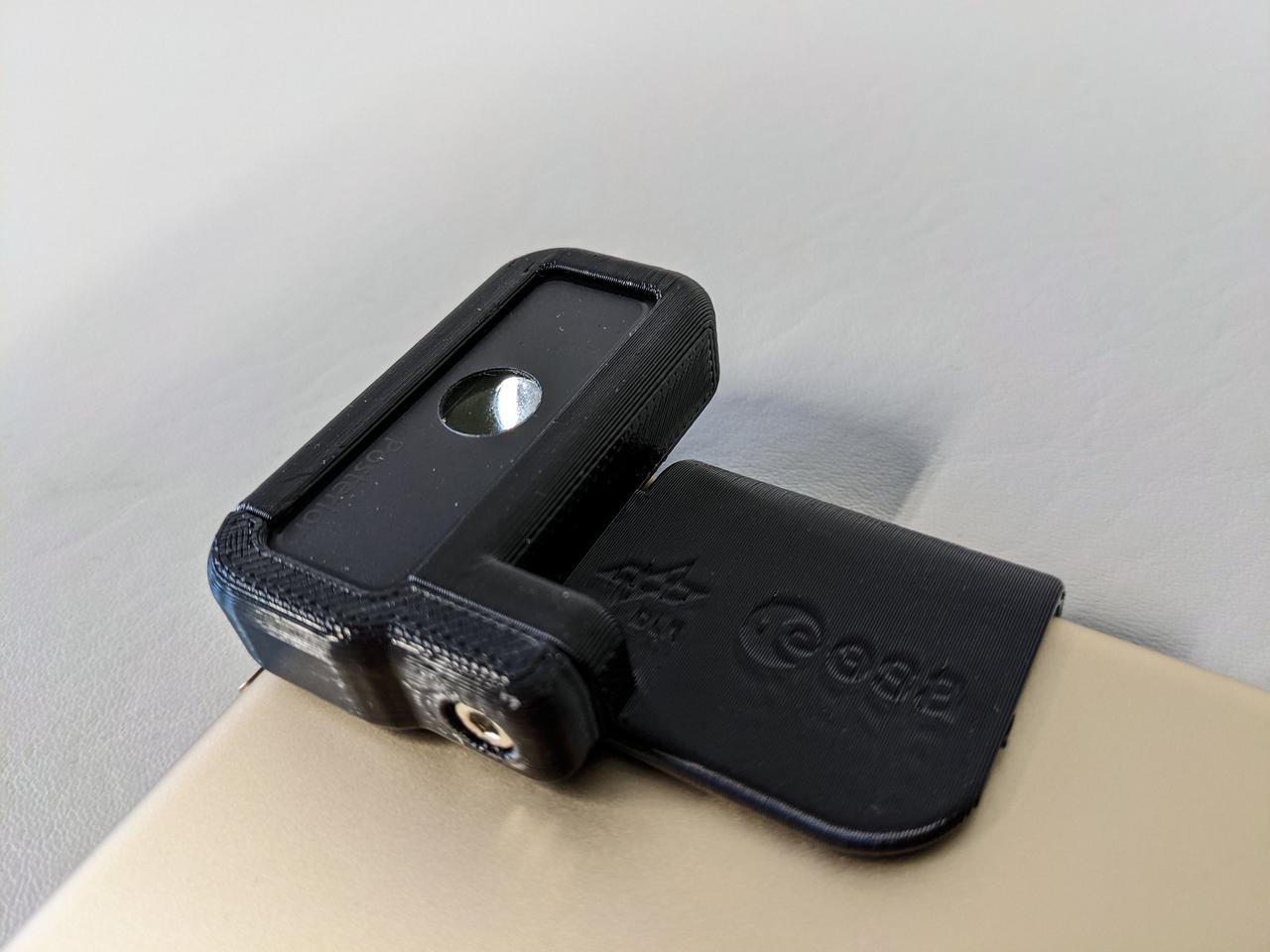

jsc2021e031163 (2/17/2021) --- A preflight view of the experiment hardware for DLR-EAC Retinal Diagnostics Study. The DLR-EAC Retinal Diagnostics Study (Retinal Diagnostics) utilizes a commercially available ophthalmology lens, approved for routine clinical use with mobile devices, to capture images of the human retina in space. Image courtesy of DLR and EAC.

iss068e036994 (Jan. 4, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Josh Cassada conducts research operations inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation. The space physics study demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a micro-structured surface.
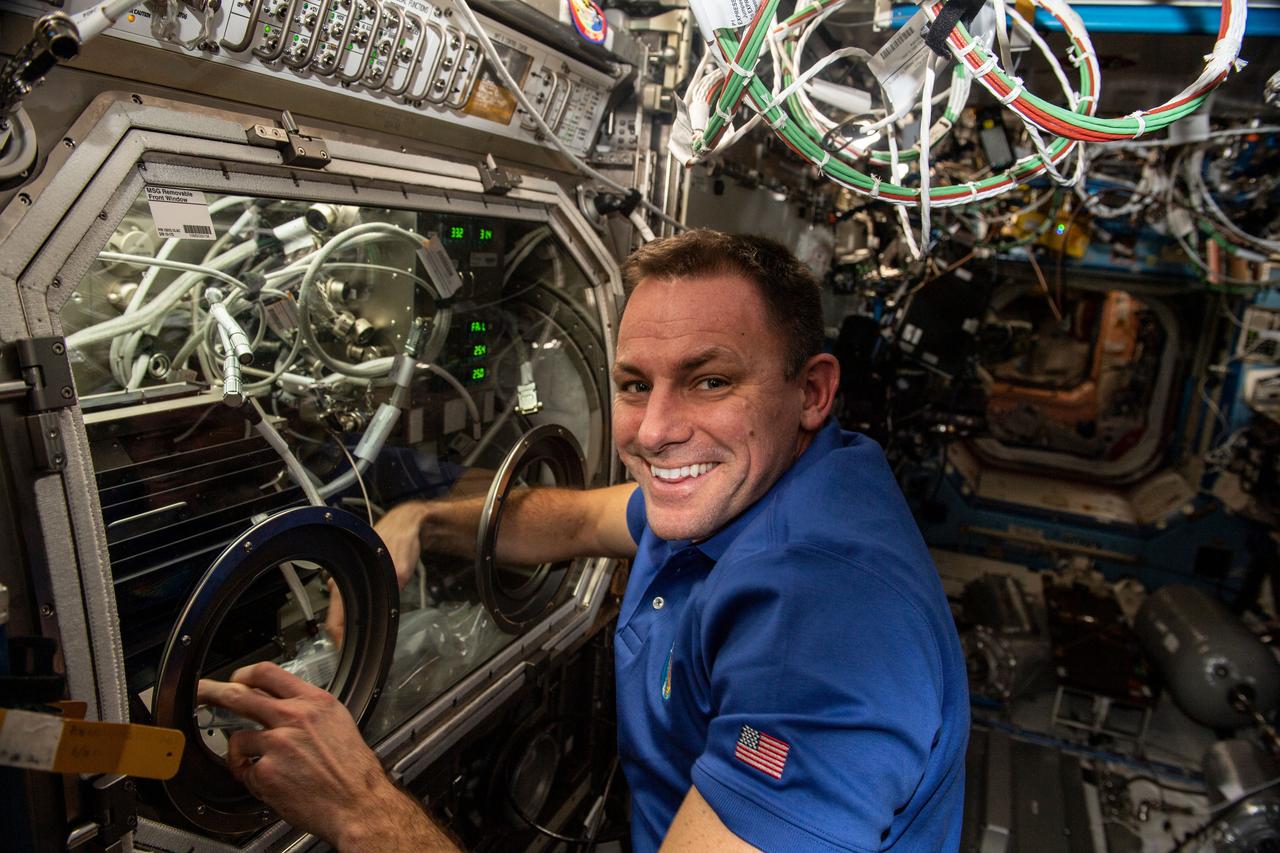

iss068e037083 (Jan. 4, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Josh Cassada swaps samples inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation. The space physics study demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a micro-structured surface.
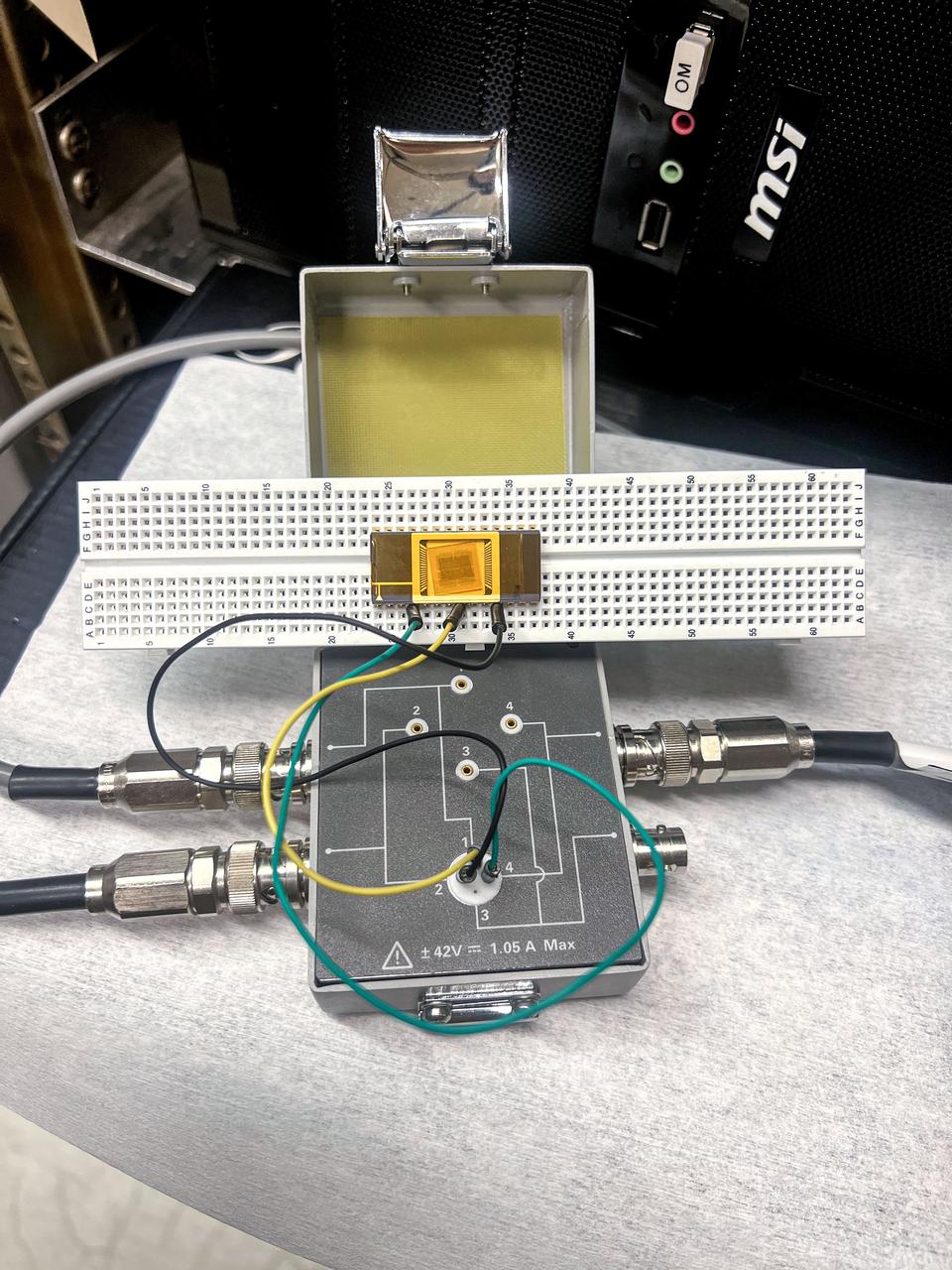
jsc2025e015683 (3/6/2025) --- The chip carrier setup shows the GaN devices are wire bonded to perform electrical measurement as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
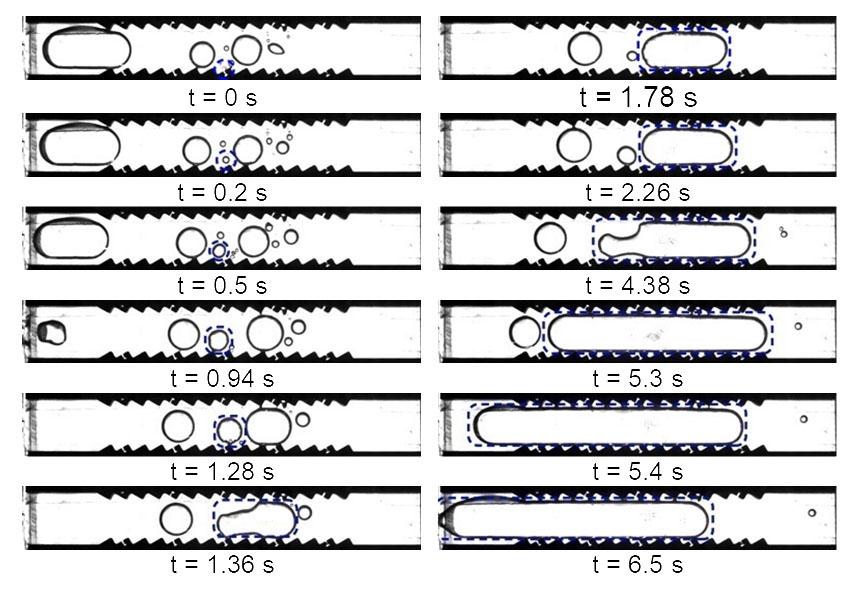
jsc2020e030483 (4/20/2020) --- A preflight image sequence from parabolic flight experiments indicating motion of vapor bubble on heated ratchet surface. Asymmetric Sawtooth and Cavity-Enhanced Nucleation-Driven Transport (PFMI-ASCENT) demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a microstructured surface. When fluids boil over flat heated surfaces in microgravity, vapor bubbles grow larger in size, causing poor heat transfer that can lead to damage of devices. Adding microscopic rachets on the surface may passively enable mobility of vapor bubbles and prevent this damage. (Image courtesy of: Techshot, Inc.)
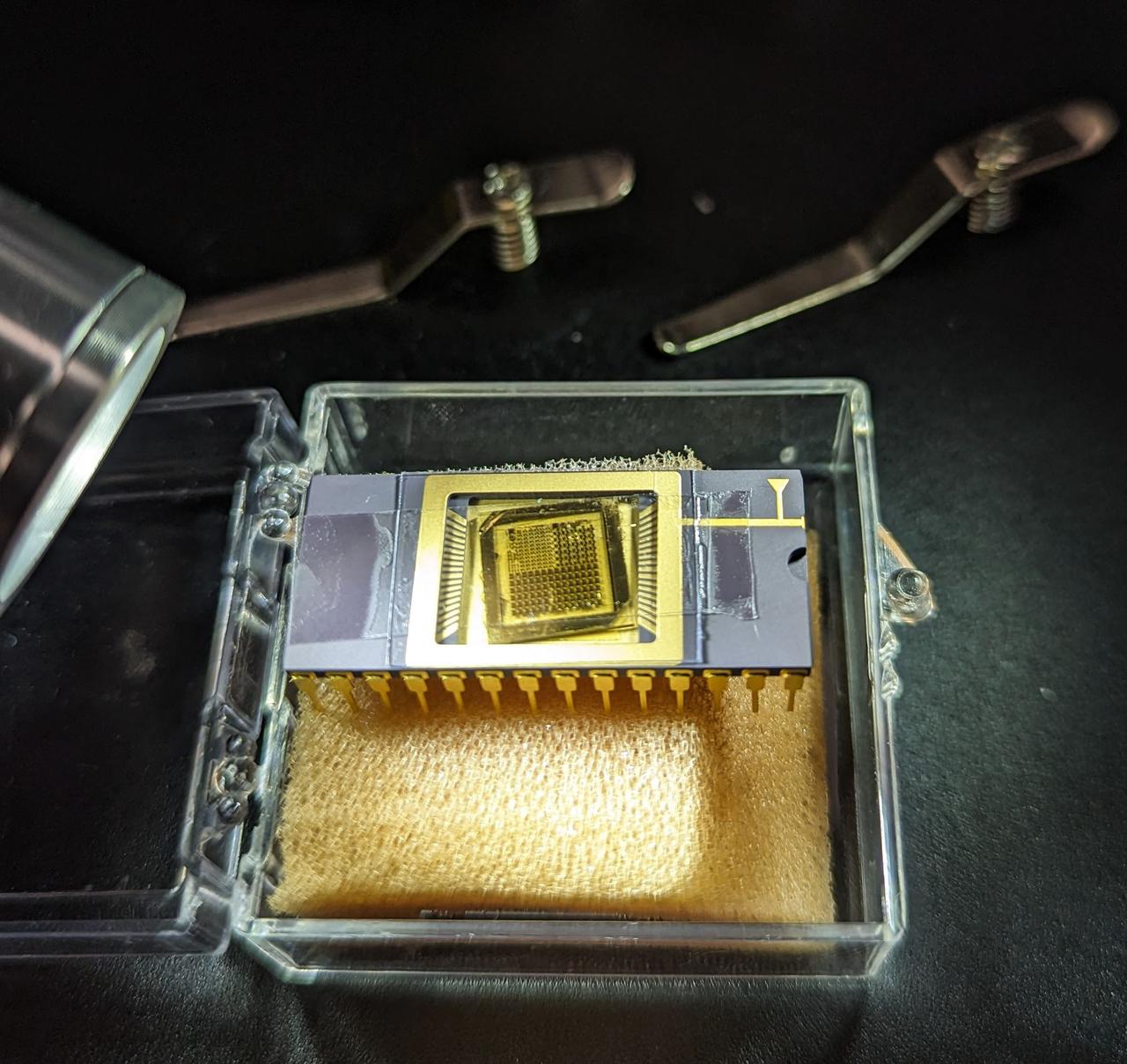
jsc2025e015685c(3/6/2025) --- The GaN devices wire bonded to a chip carrier as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
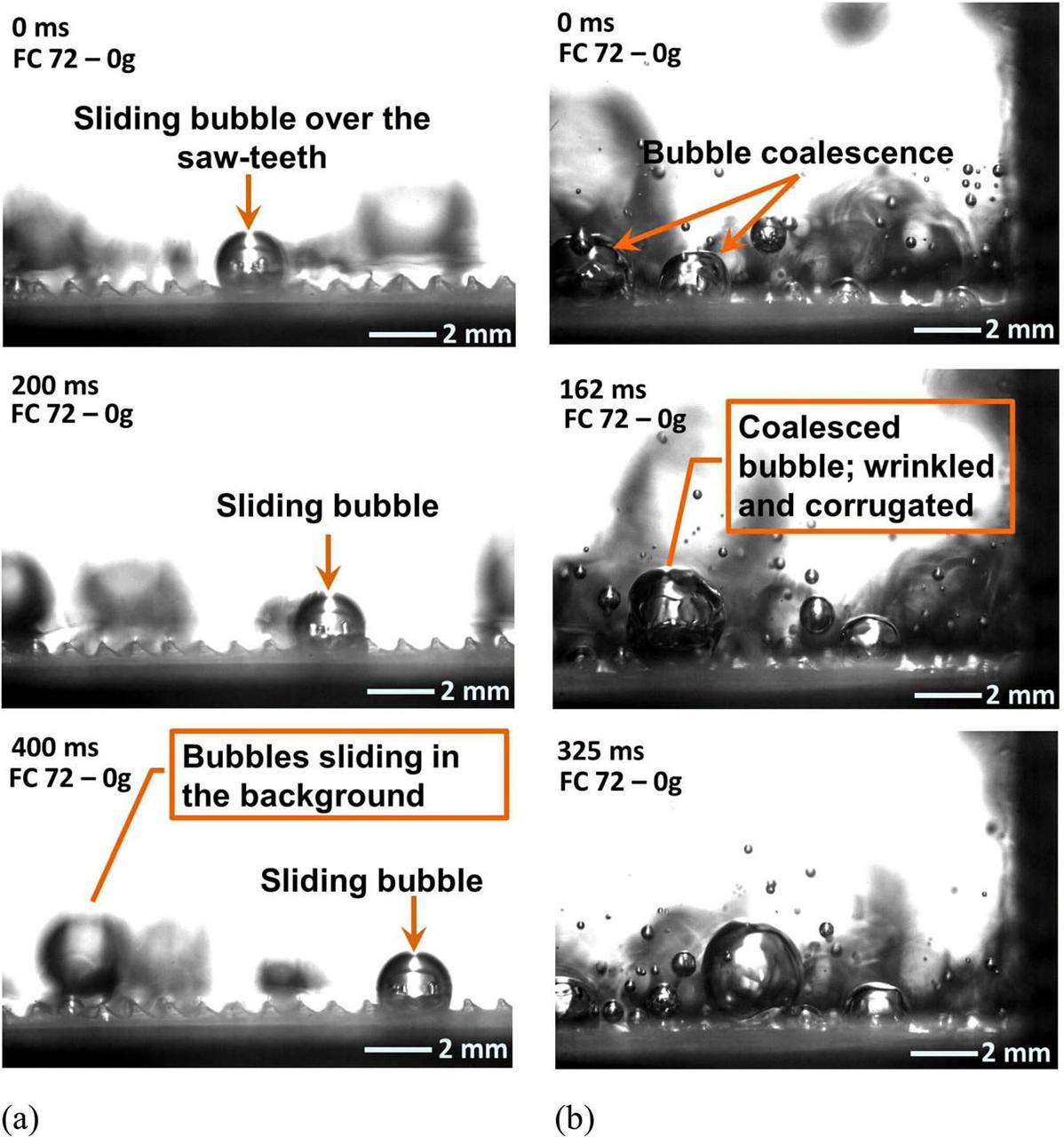
jsc2020e030484 (4/20/2020) --- A preflight image sequence from terrestrial experiments with two vertically oriented ratchet surfaces; subcooling: 9.5 ℃; heat flux: 1.31 W/cm2. Asymmetric Sawtooth and Cavity-Enhanced Nucleation-Driven Transport (PFMI-ASCENT) demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a microstructured surface. When fluids boil over flat heated surfaces in microgravity, vapor bubbles grow larger in size, causing poor heat transfer that can lead to damage of devices. Adding microscopic rachets on the surface may passively enable mobility of vapor bubbles and prevent this damage. (Image courtesy of: Techshot, Inc.)
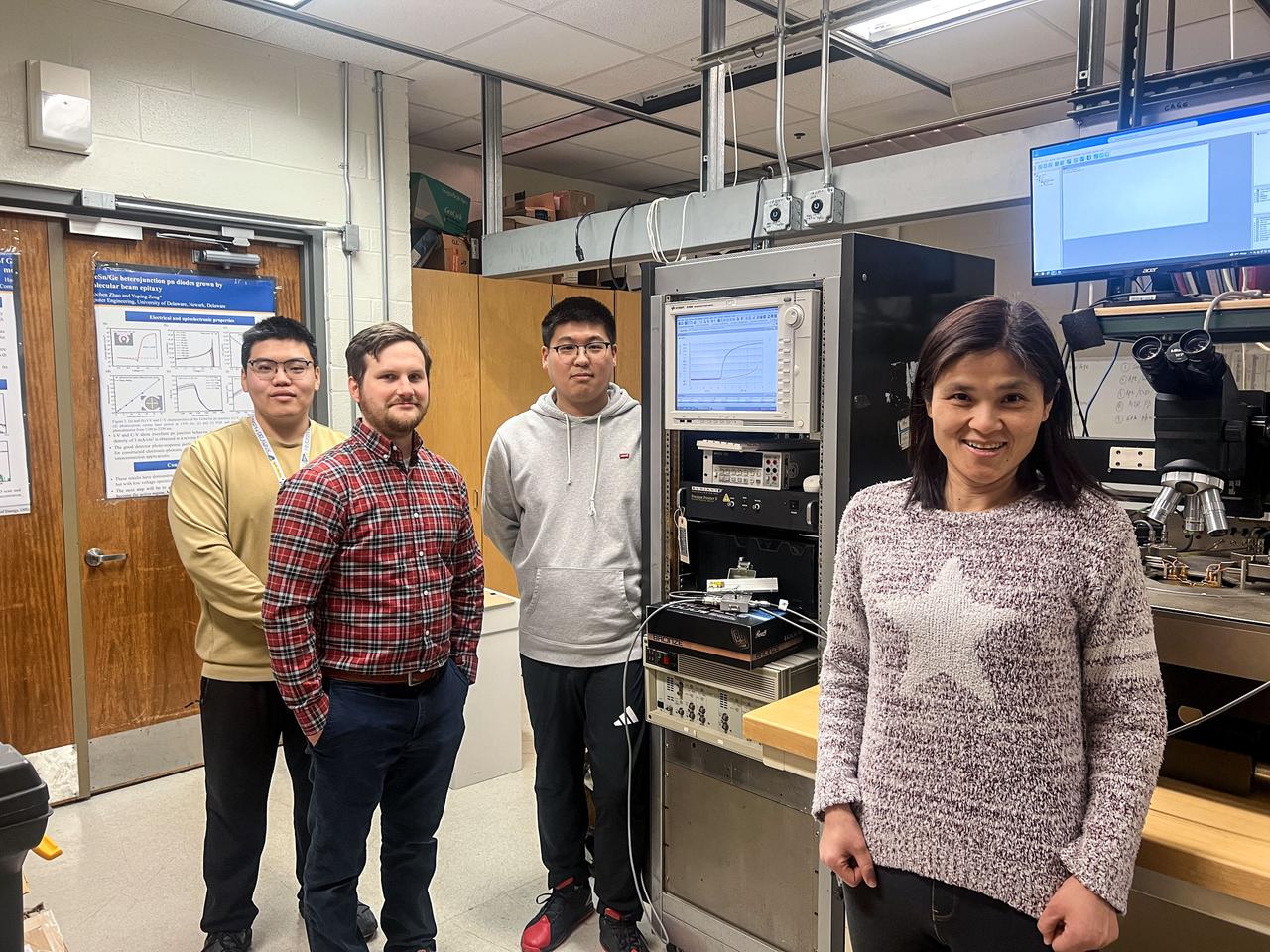
jsc2025e015682 (3/6/2025) --- From left to right: students, Tuofu Zhama, Alex Katorkas, Haochen Zhao, and Principal Investigator Yuping Zeng stand beside the equipment for GaN devices electrical property measurement before the packaging. The High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
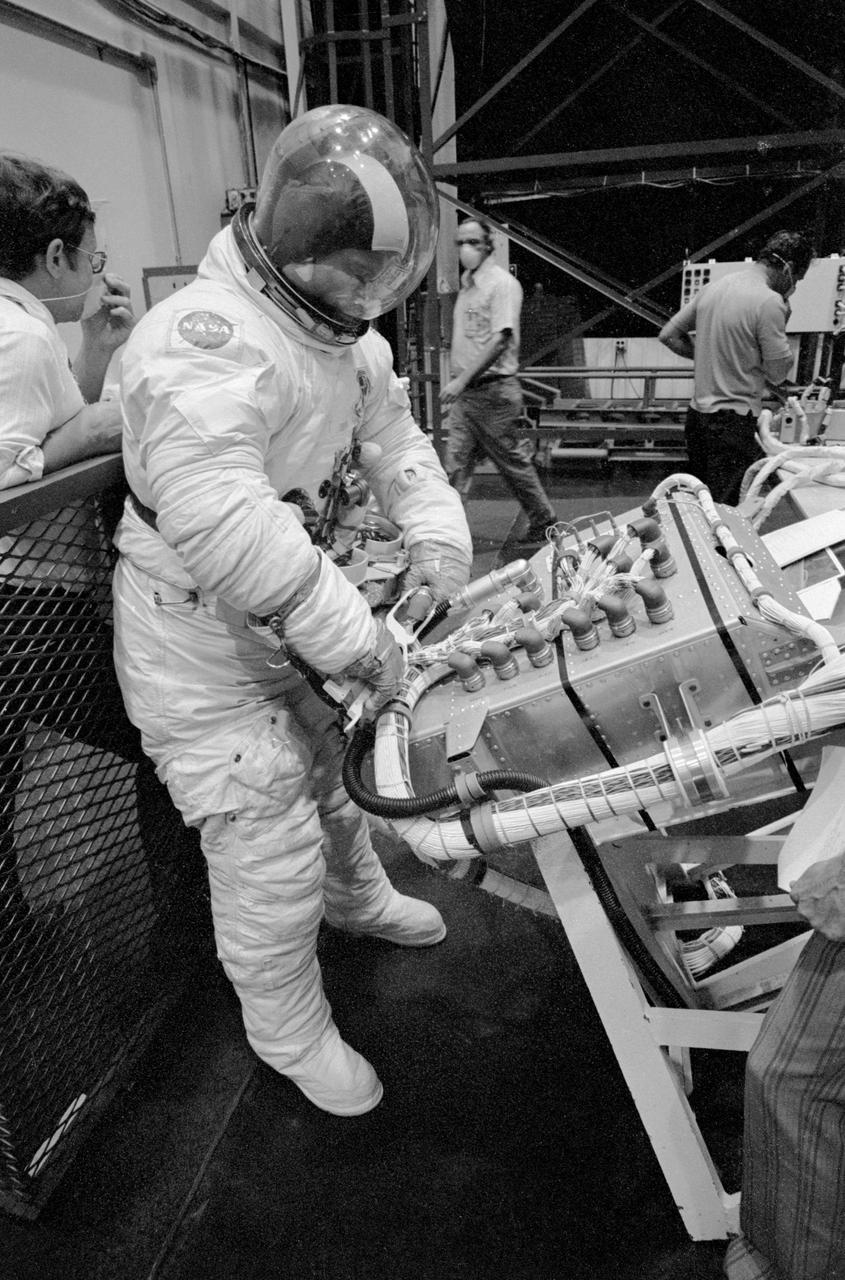

S73-31323 (30 June 1973) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, practices procedures for extravehicular activity (EVA) in his Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit during Skylab 3 prelaunch training at Johnson Space Center. He is working with a mock-up of a trunion plug plate which is on the space station's deployment assembly. Photo credit: NASA
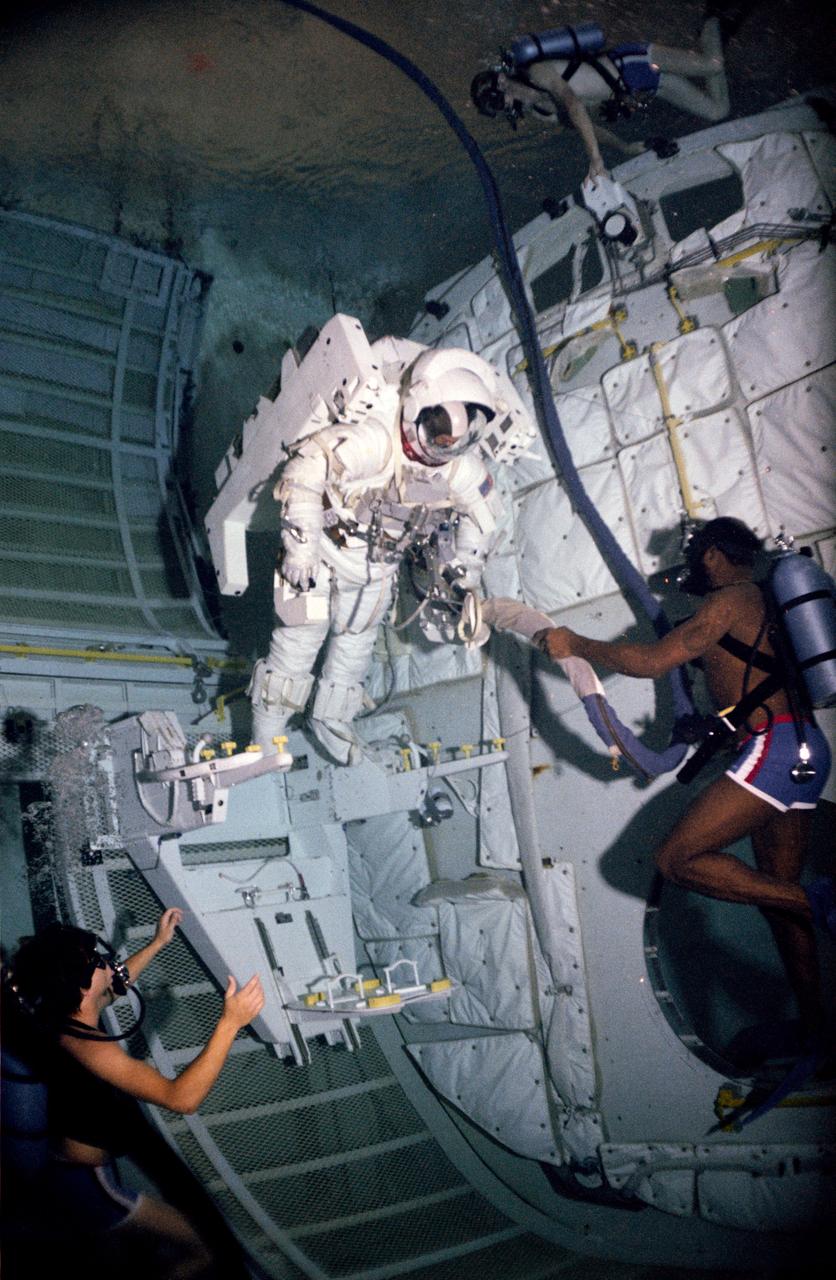

Astronaut Bruce McCandless during an underwater test of the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU) Flight Support Station (FSS) donning and doffing in the Bldg 29 Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF). View is of McCandless wearing the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), stepping into the MMU.
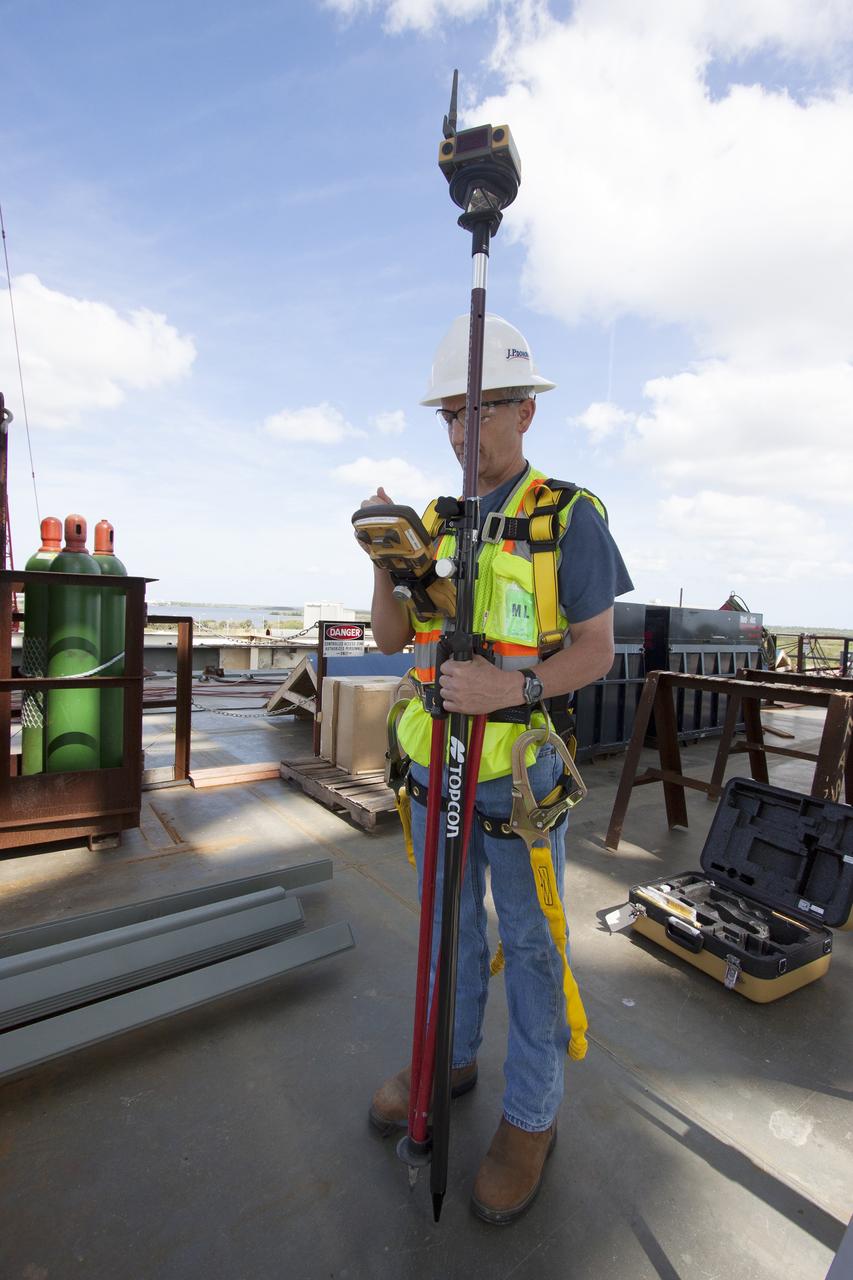

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Mobile Launcher, or ML, at the Mobile Launcher Park Site at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A construction worker uses a measuring device on the surface of the ML. In 2013, the agency awarded a contract to J.P. Donovan Construction Inc. of Rockledge, Fla., to modify the ML, which is one of the key elements of ground support equipment that is being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy. The ML will carry the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for its first mission, Exploration Mission 1, in 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
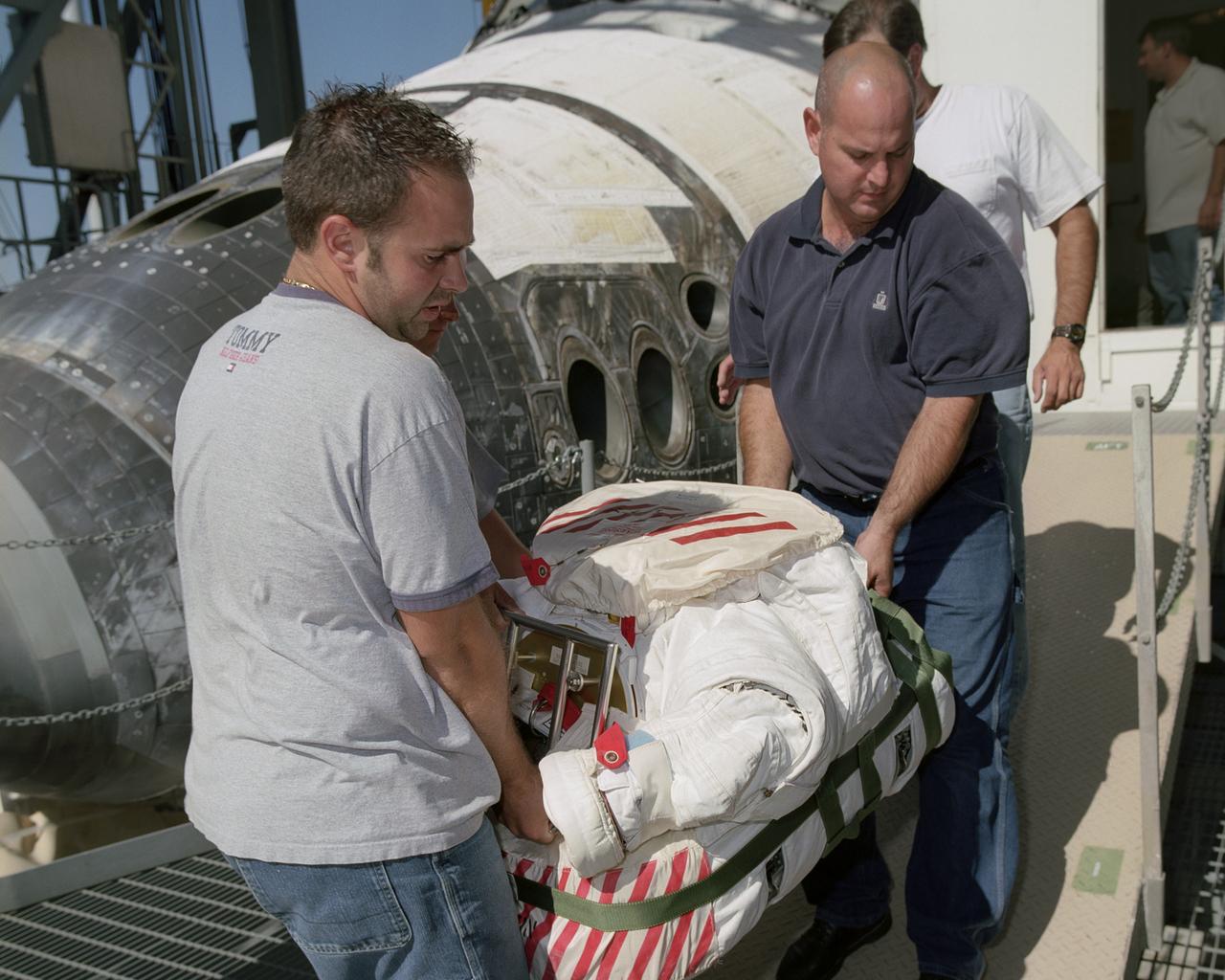

Flight Crew Systems Technicians Ray Smith and Raphael Rodriguez remove one of the Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs, from the Space Shuttle Discovery after it's successful landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Space Shuttles receive post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) following landings at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14
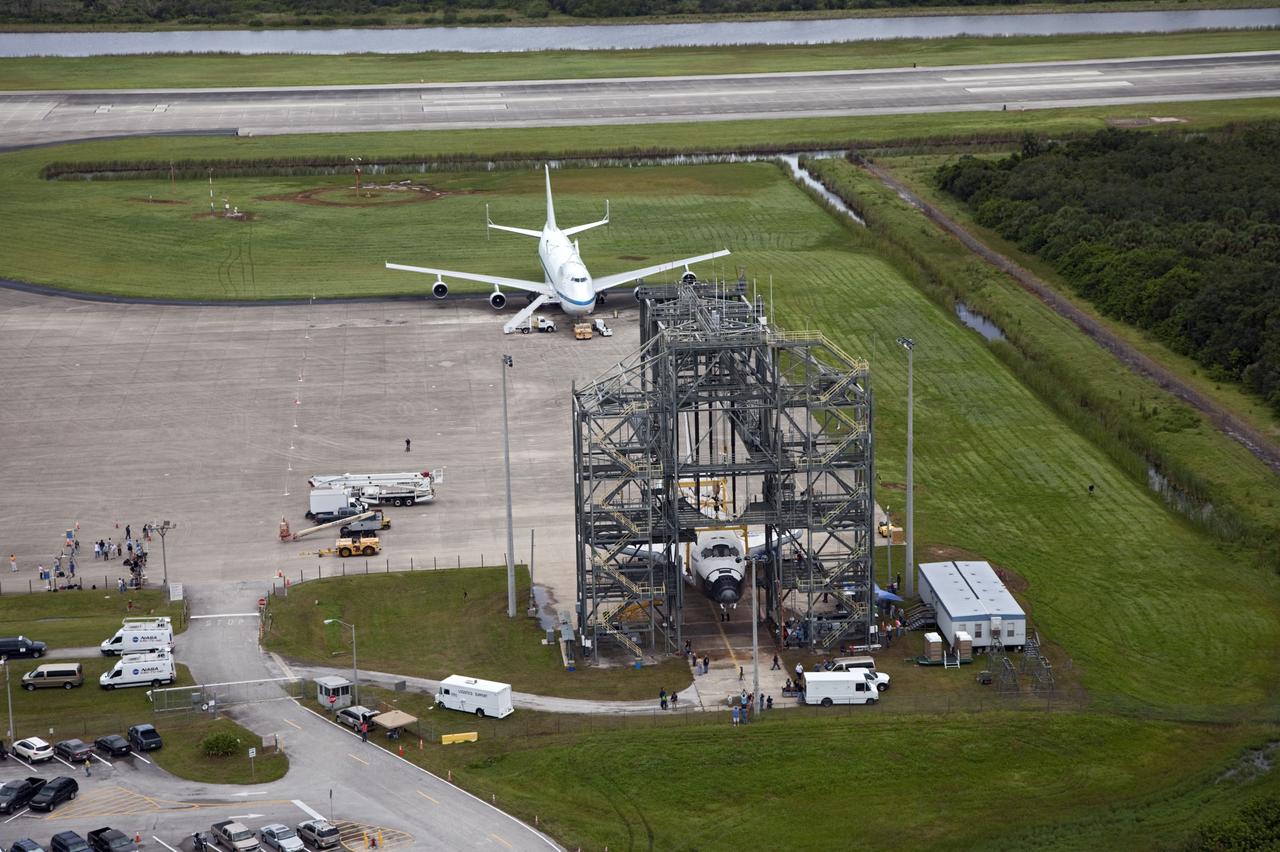

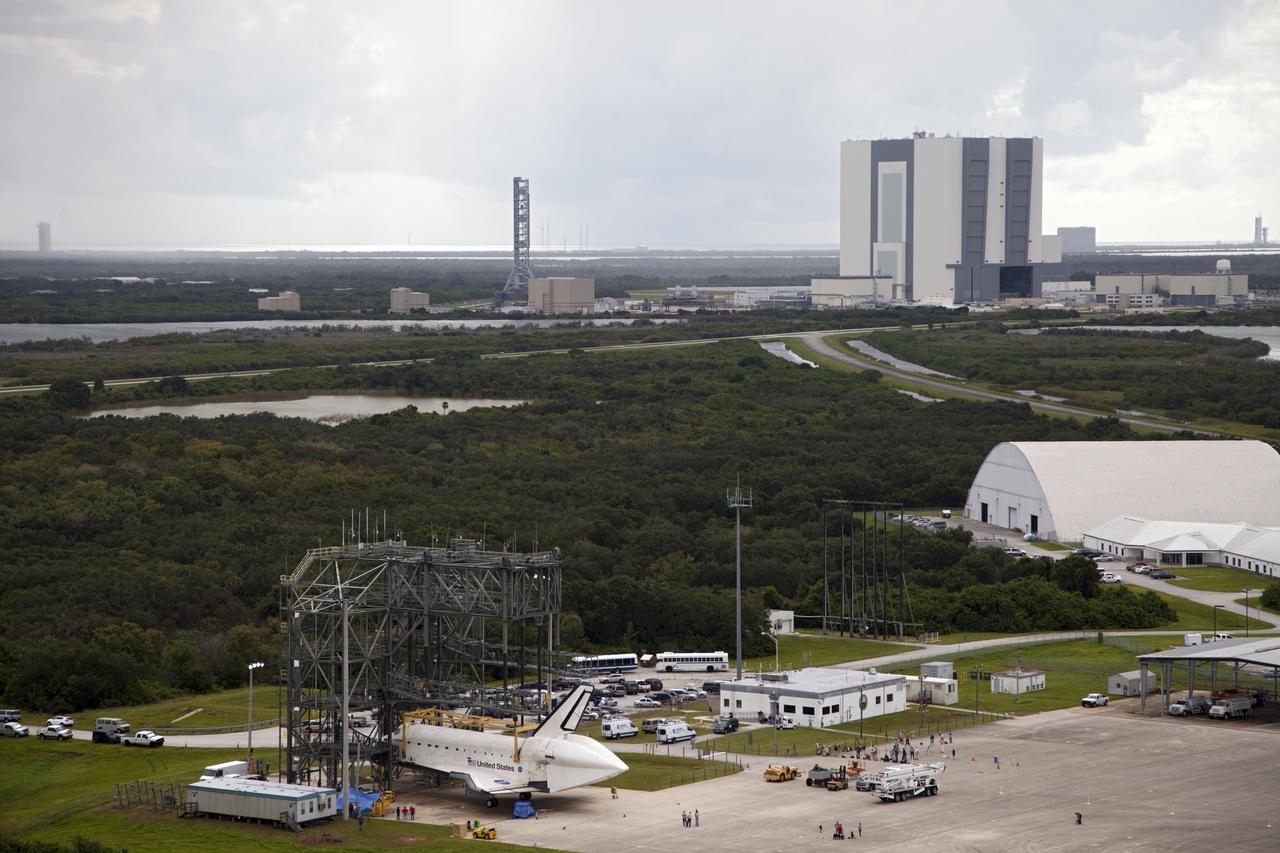
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, is seen on the ramp. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. The center's Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, and the mobile launcher built for the Space Launch System are also visible in the background. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
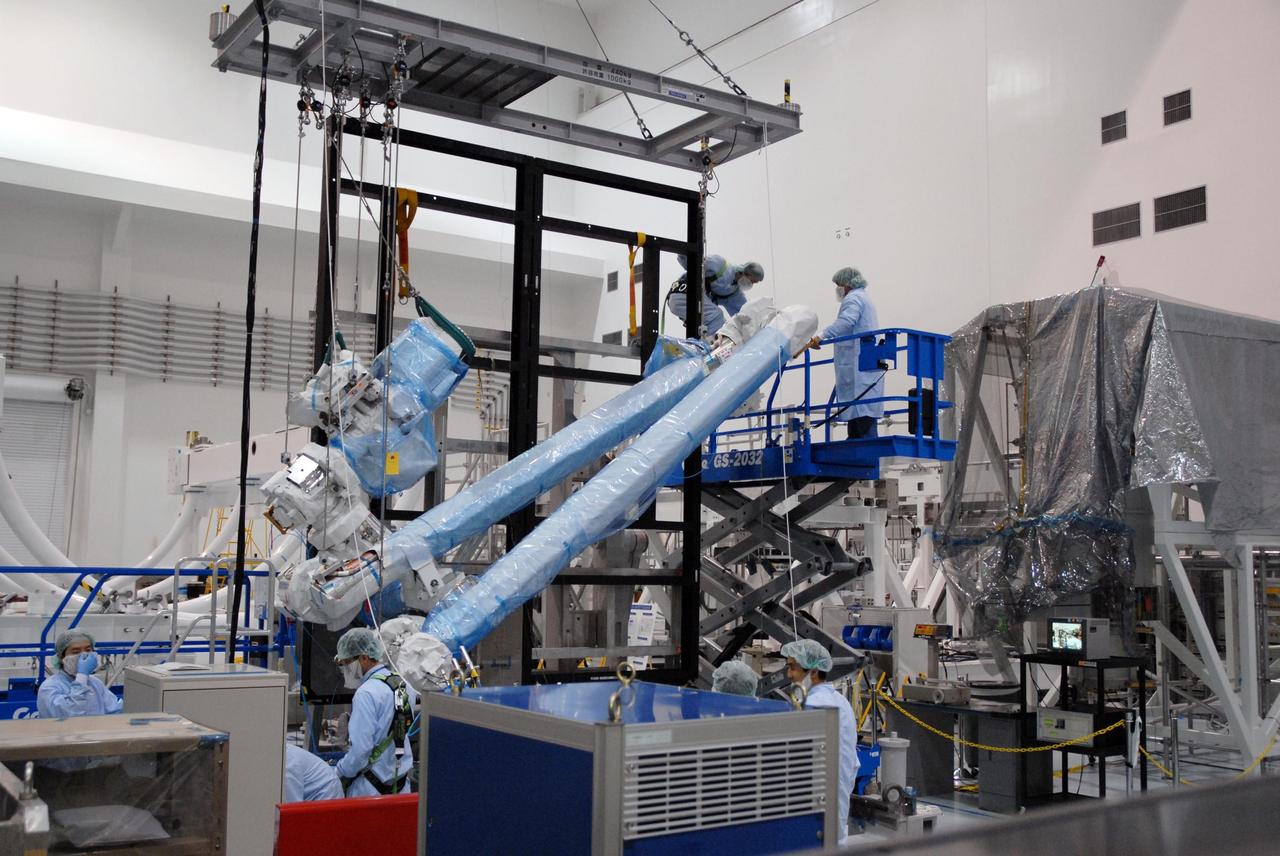

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to a hoisting device to prepare for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
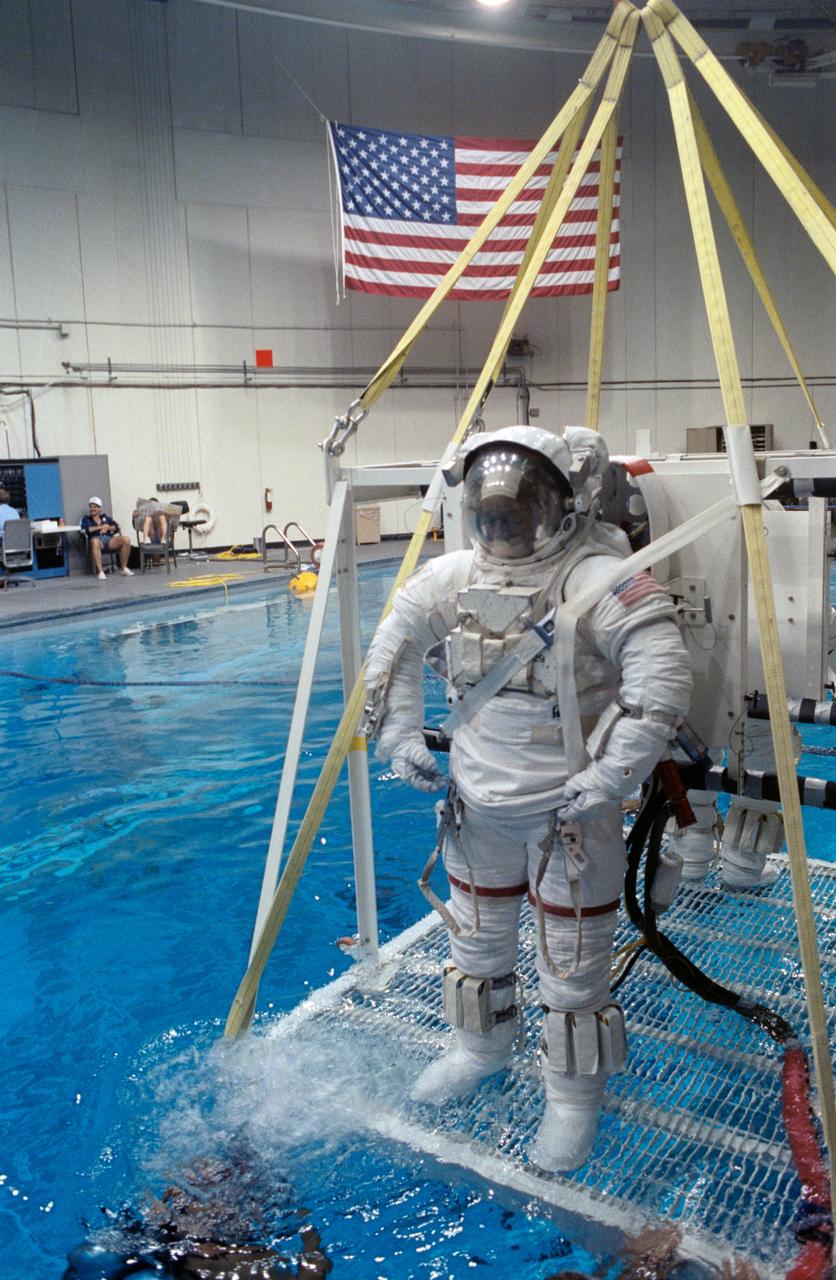

S90-44118 (August 1990) --- Astronaut Guion S. Bluford, mission specialist for STS-39, wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, is lowered by a hoist device prior to participating in an underwater rehearsal of a contingency EVA. The scene is in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F) which houses a 25-ft. deep pool (visible in background).
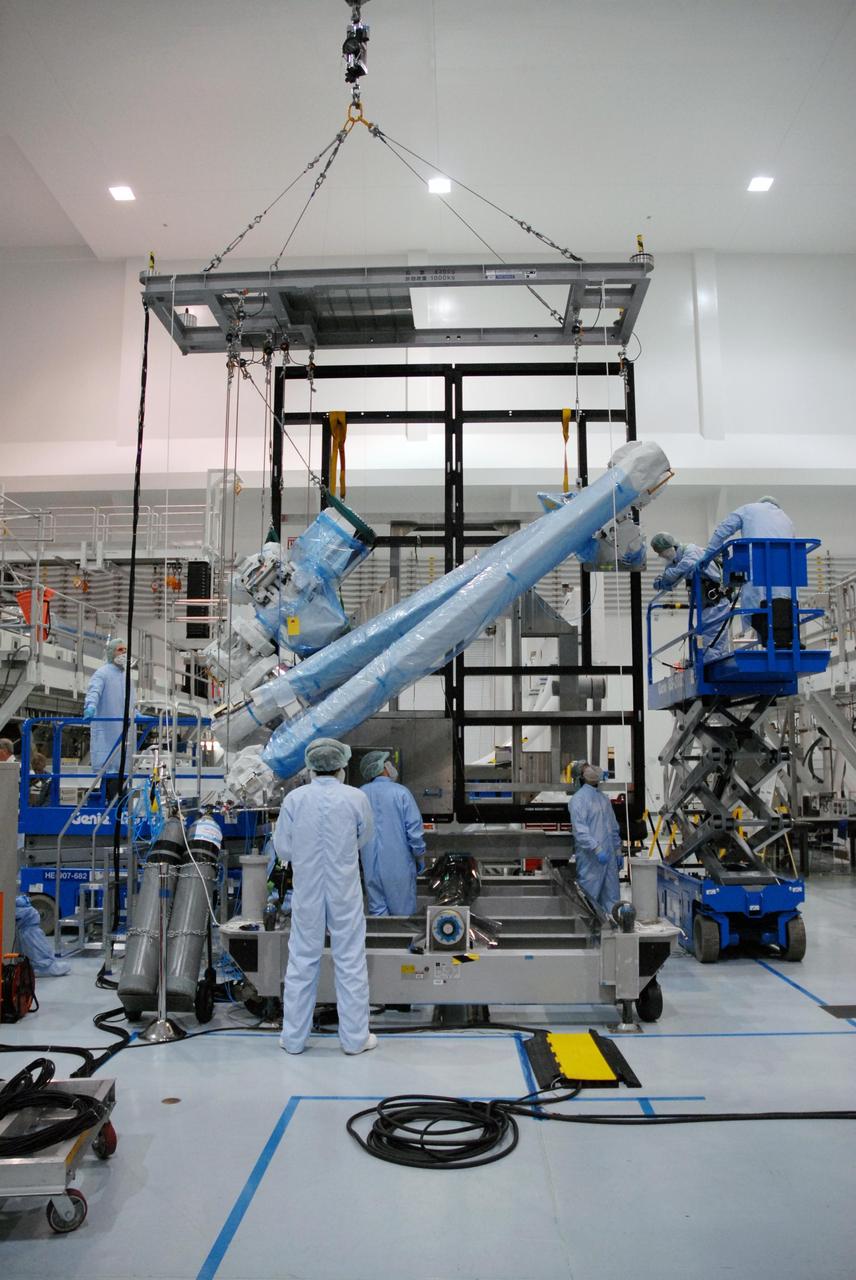

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to a hoisting device to prepare for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
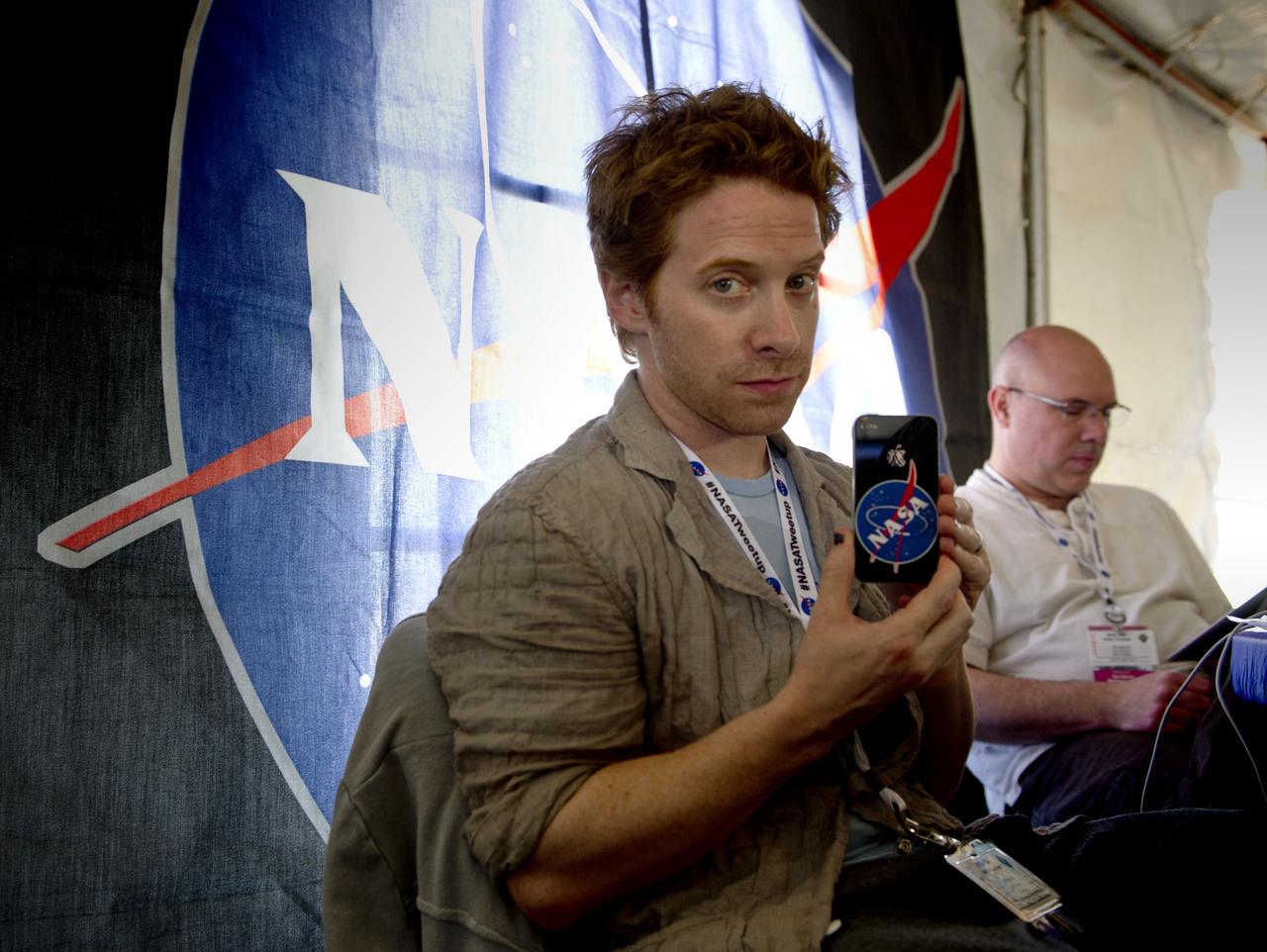

Actor Seth Green, a NASA Twitter follower, holds up his mobile device bearing the NASA emblem during the STS-134 Tweetup, Thursday, April 28, 2011, at Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. About 150 NASA Twitter followers attended the event. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

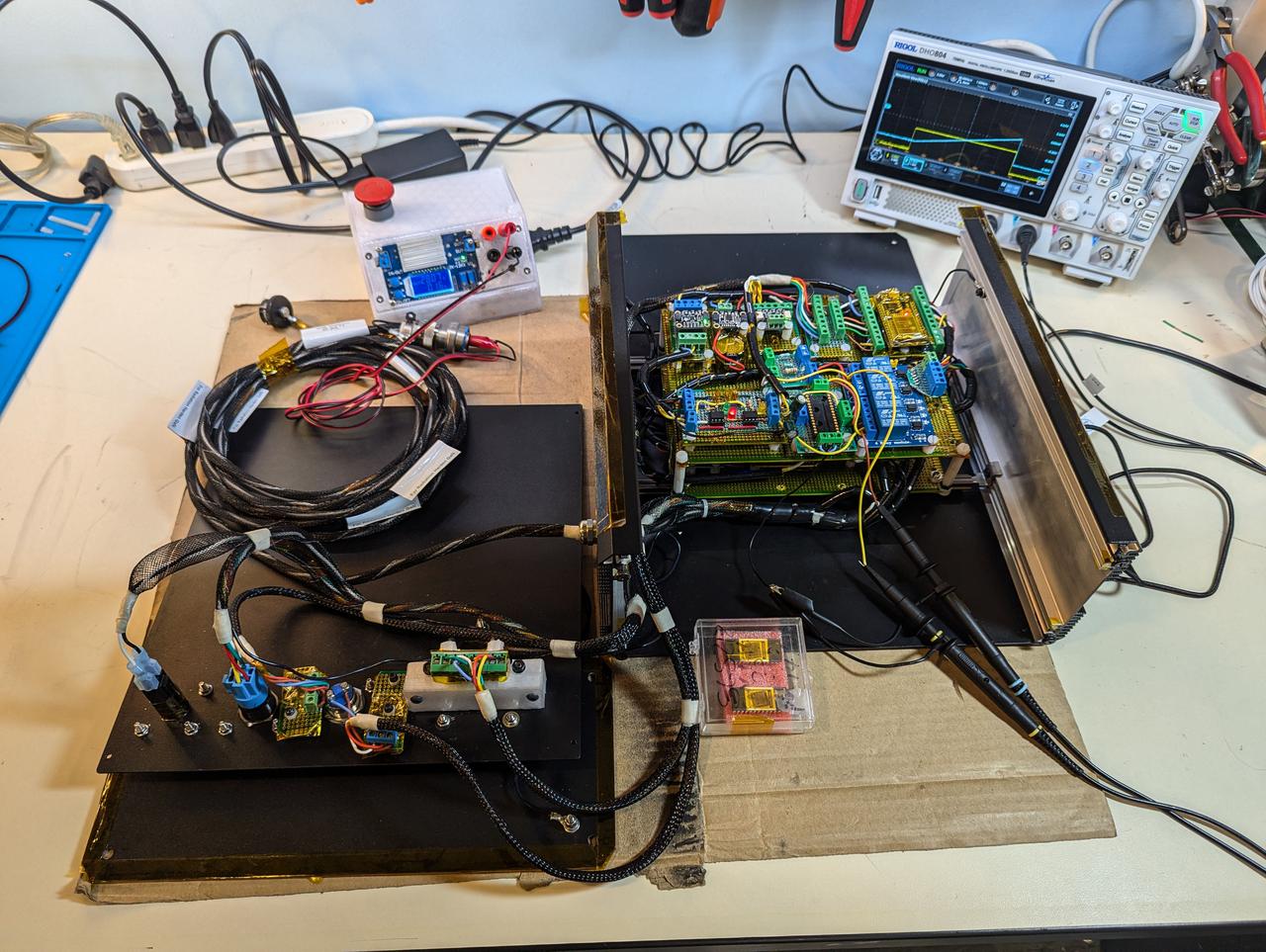
jsc2025e015690 (3/6/2025) --- An overview of the prototype with the various components as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, is seen on the ramp. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. The center's Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, and the mobile launcher built for the Space Launch System are also visible in the background. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center's Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, and the mobile launcher built for the Space Launch System are also visible in the background. The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
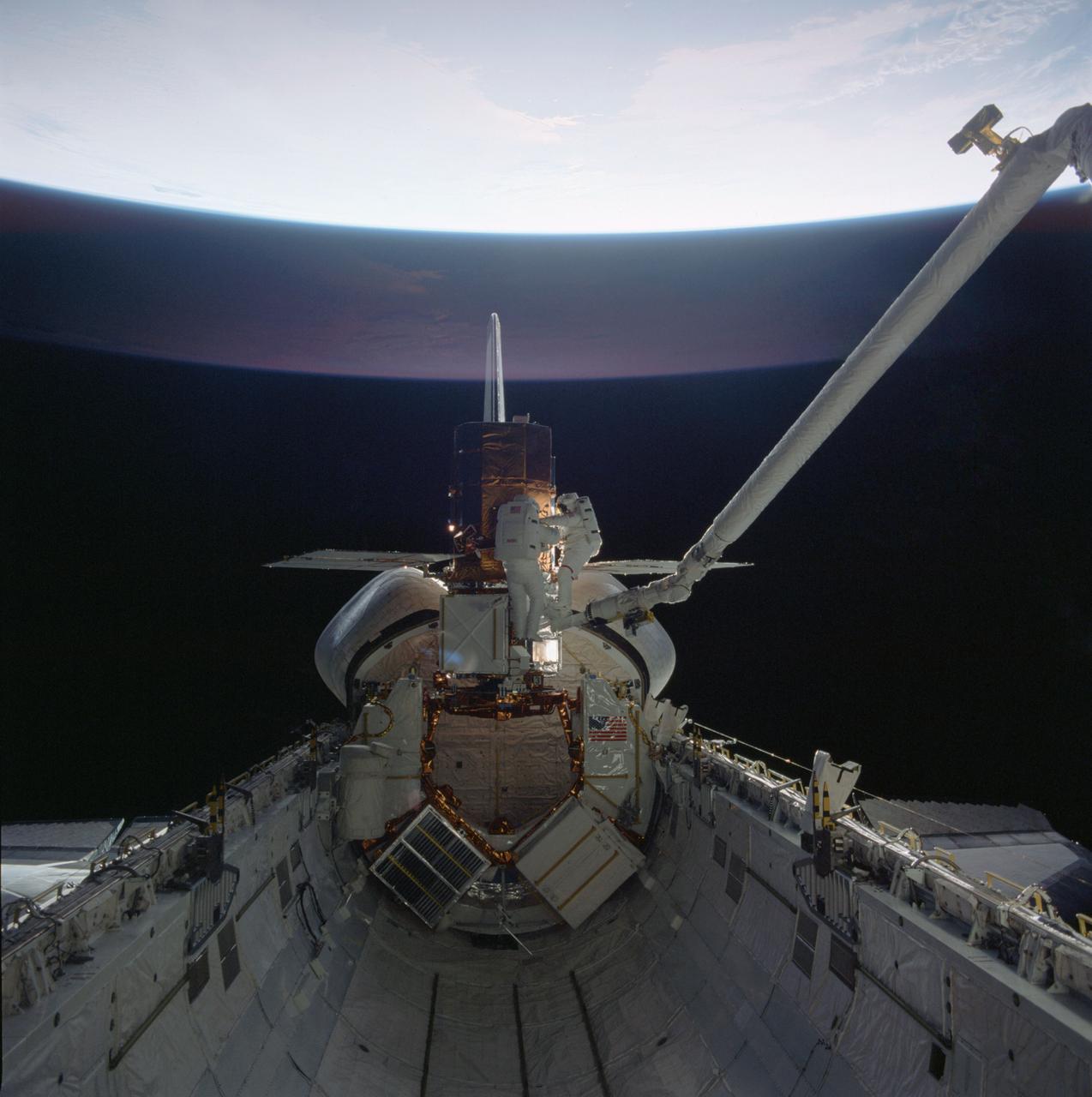

41C-37-1711 (11 April 1984) --- The two mission specialist-EVA participants of Flight 41-C share a repair task at the "captured" Solar Maximum Mission Satellite (SMMS) in the aft end of the Challenger's cargo bay. Astronauts George D. Nelson, right, and James D. van Hoften uses the mobile foot restraint and the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) as a "cherry picker" device for moving about. Later, the RMS lifted the SMMS into space once more.
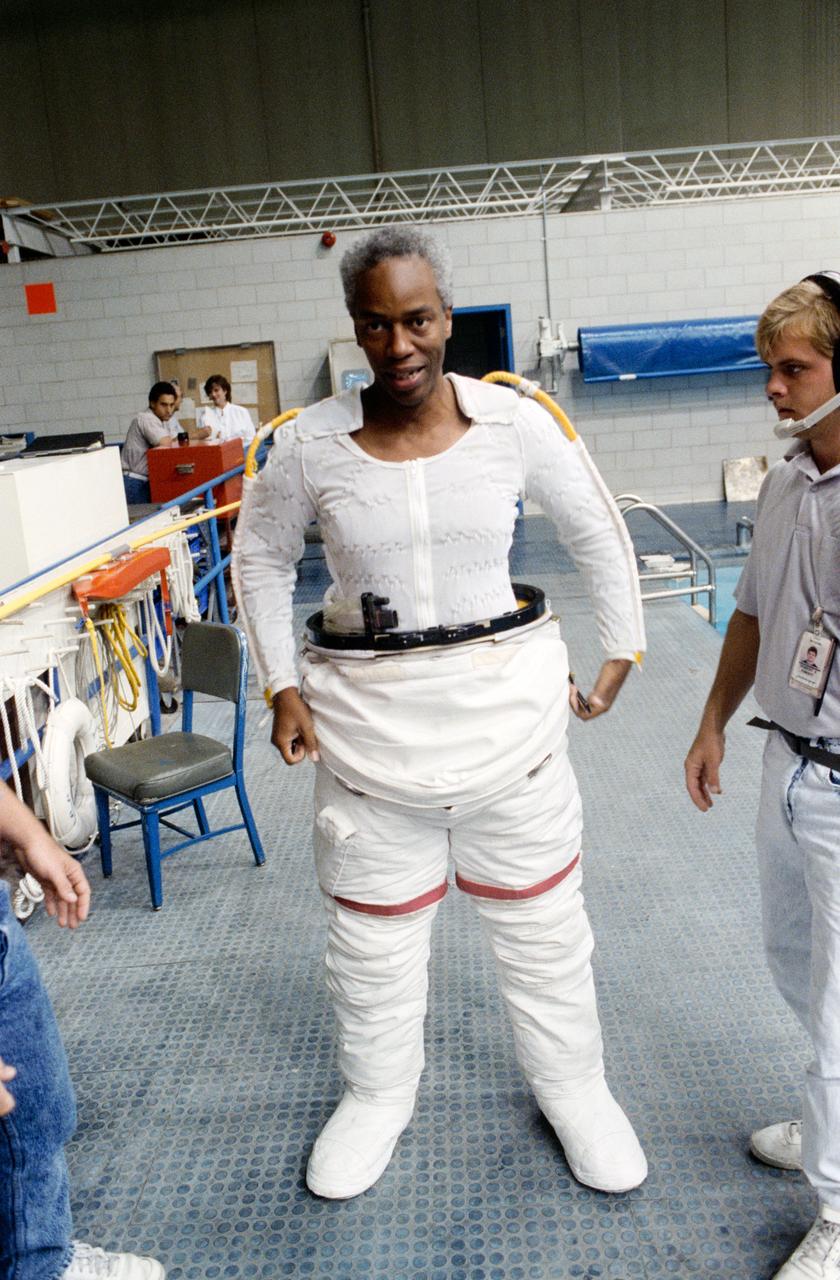

S90-44106 (August 1990) --- Astronaut Guion S. Bluford, mission specialist for STS-39, wearing part of an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, prepares to participate in a training session for the scheduled March 1991 spaceflight. Soon after this picture was taken, Bluford was lowered into water by a hoist device for the underwater rehearsal of a contingency EVA. The scene is in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F) which houses a 25-ft. deep pool (visible in right background).
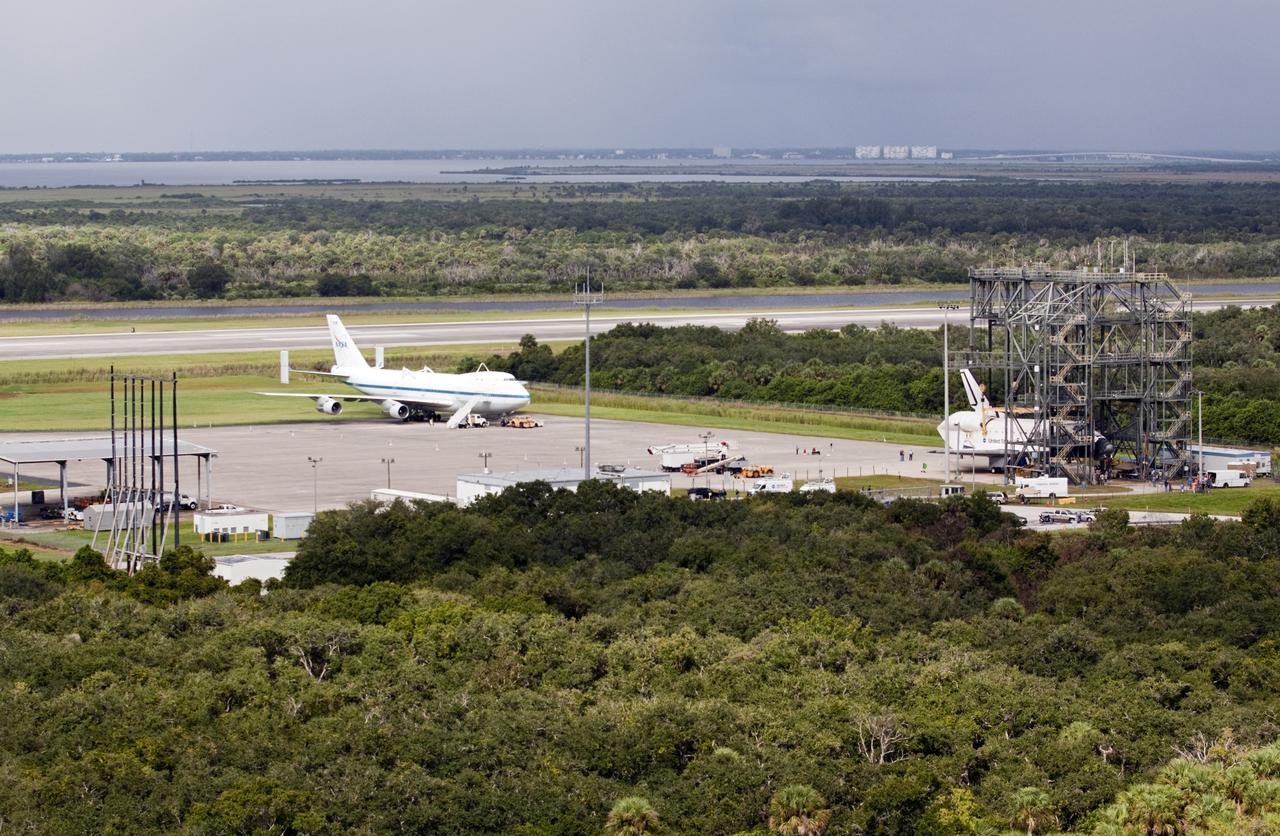

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, is seen on the ramp. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. The center's Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, and the mobile launcher built for the Space Launch System are also visible in the background. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
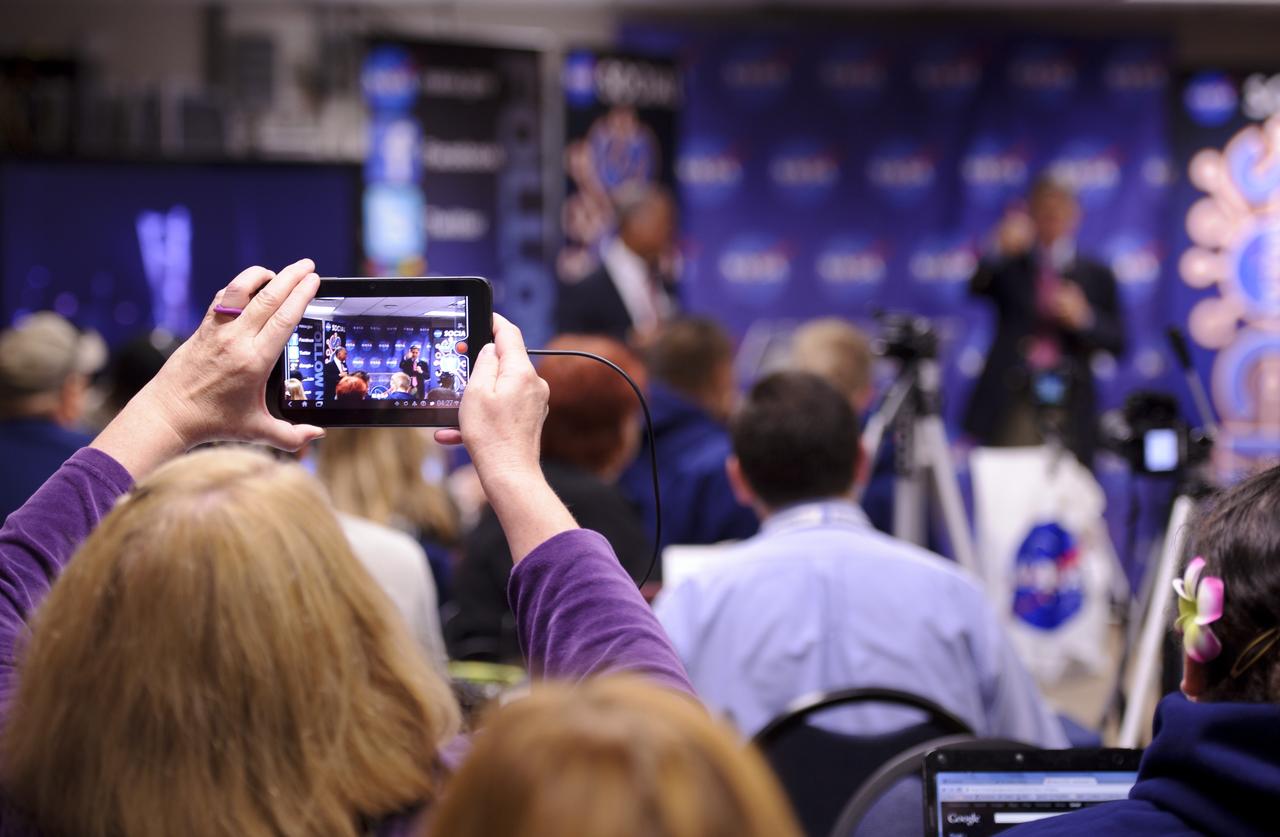

A NASA Social follower holds up a mobile device as NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and Kennedy Space Center director Robert Cabana appear at the NASA Social event, Friday morning, May 19, 2012, at Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. About 50 NASA Social followers attended an event as part of activities surrounding the launch of Space Exploration Technologies, or SpaceX, demonstration mission of the company's Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

An onlooker holds up a mobile device to record space shuttle Atlantis as it rolls to ts new home at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, early Friday, Nov. 2, 2012, in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The spacecraft traveled 125,935,769 miles during 33 spaceflights, including 12 missions to the International Space Station. Its final flight, STS-135, closed out the Space Shuttle Program era with a landing on July 21, 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
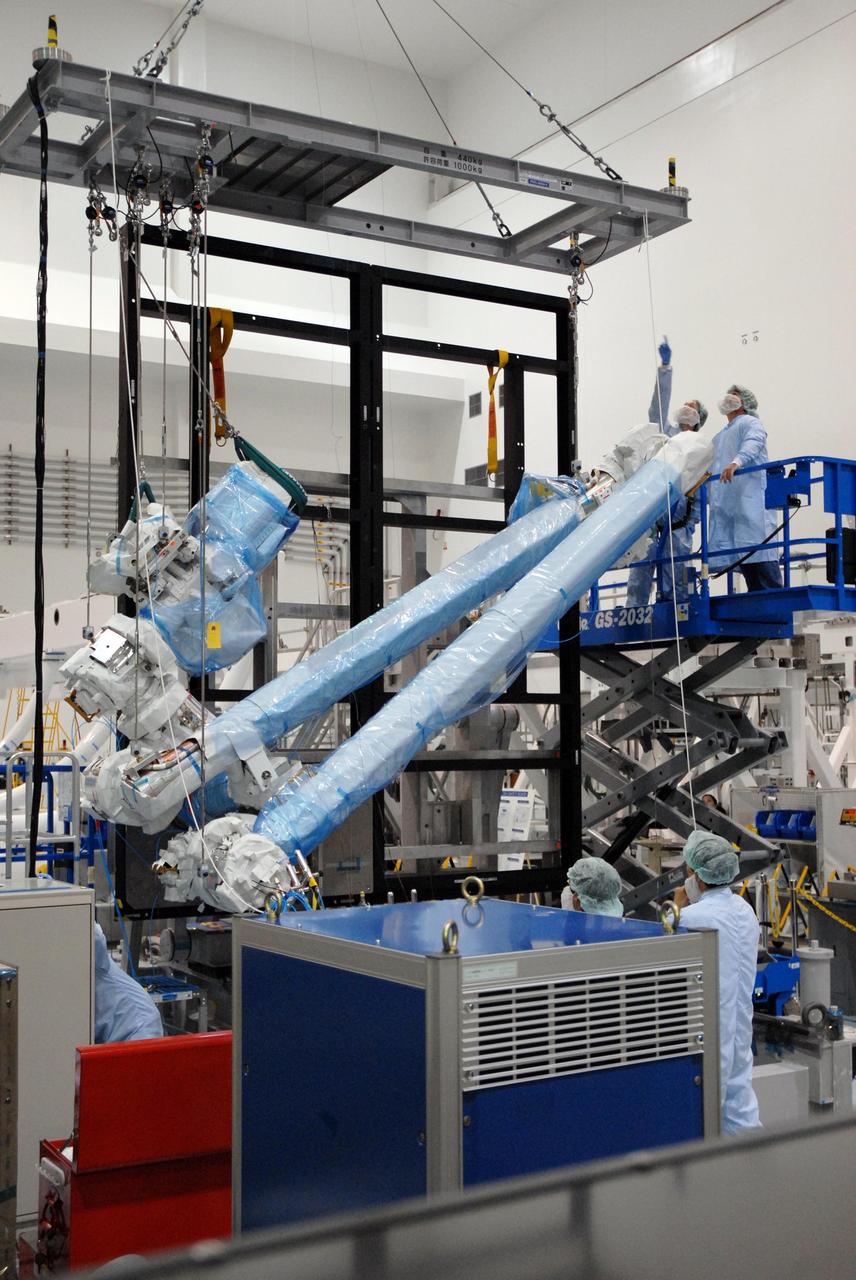
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to a hoisting device to prepare for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, is seen on the ramp. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. The center's Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, and the mobile launcher built for the Space Launch System are also visible in the background. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
jsc2025e015689 (3/6/2025) --- The inside of the prototype is shown during testing for the the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
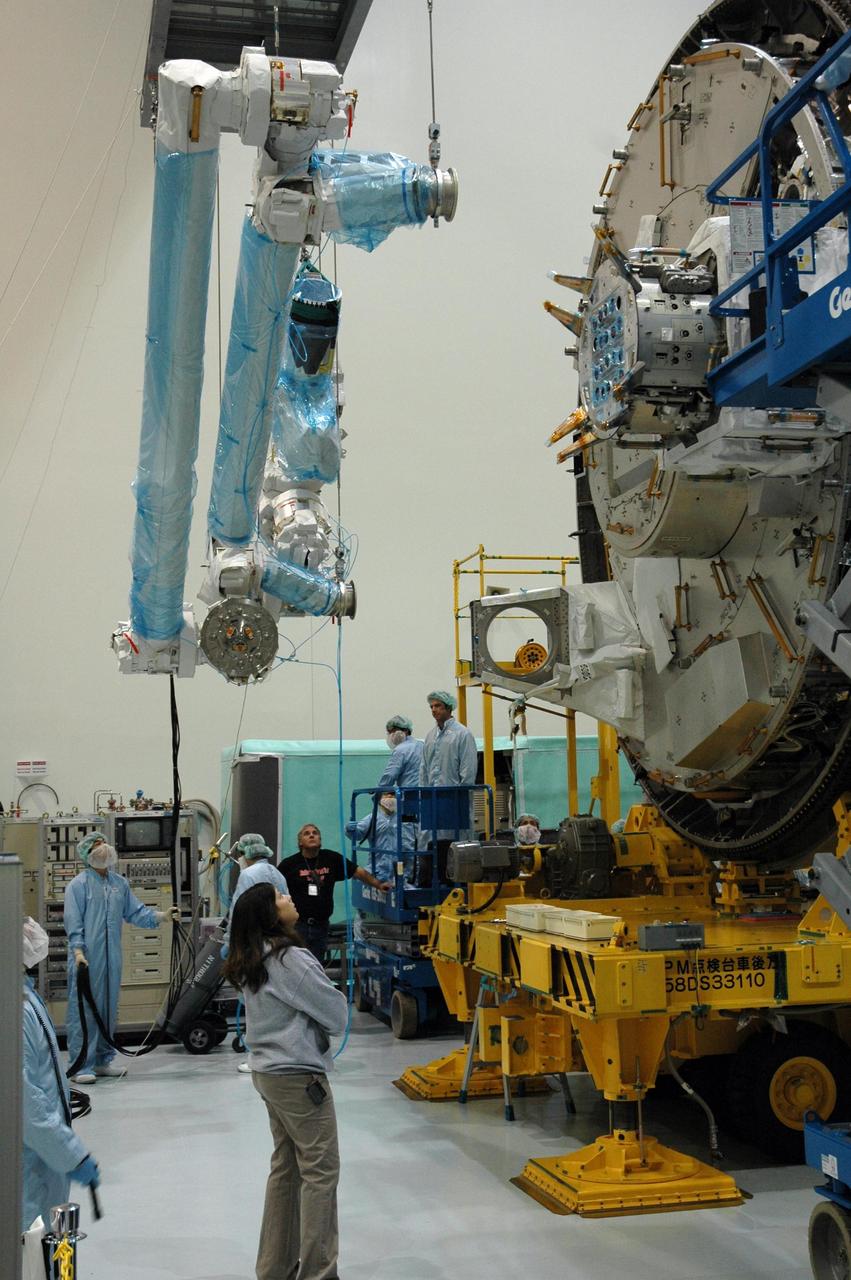

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers use a hoisting device to move the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, toward the Japanese Experiment Module for installation and testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008.The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
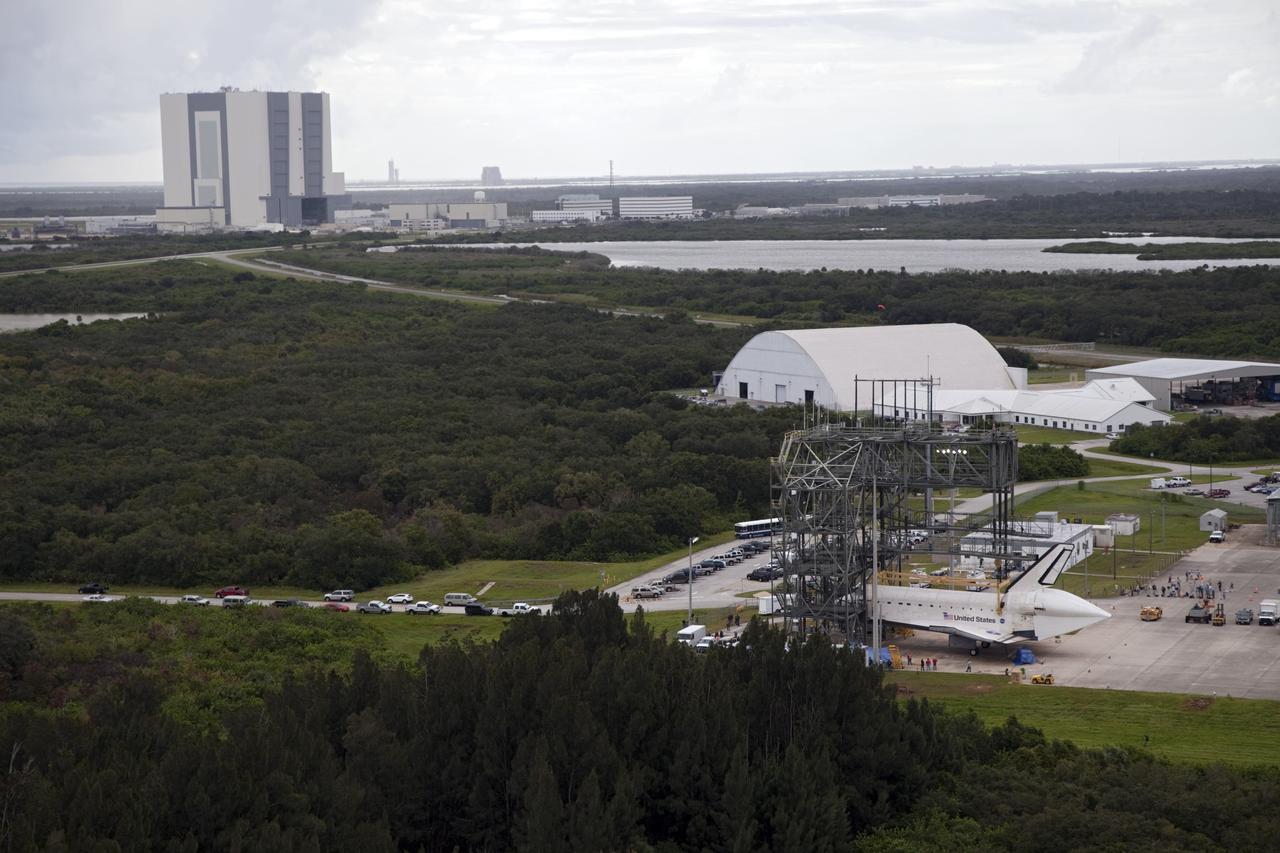

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center's Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, and the mobile launcher built for the Space Launch System are also visible in the background. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

51A-39-040 (14 Nov. 1984) --- A 70mm frame of Westar VI retrieval. Astronauts Dale A. Gardner, left, and Joseph P. Allen IV work together with Anna L. Fisher (not pictured, controlling remote manipulator system (RMS) arm from Discovery?s cabin) to bring Westar VI/PAM-D into cargo bay. Allen is on the mobile foot restraint, which is attached to the RMS end effector, while Gardner works to remove a stinger device from the now stabilized satellite. Photo credit: NASA
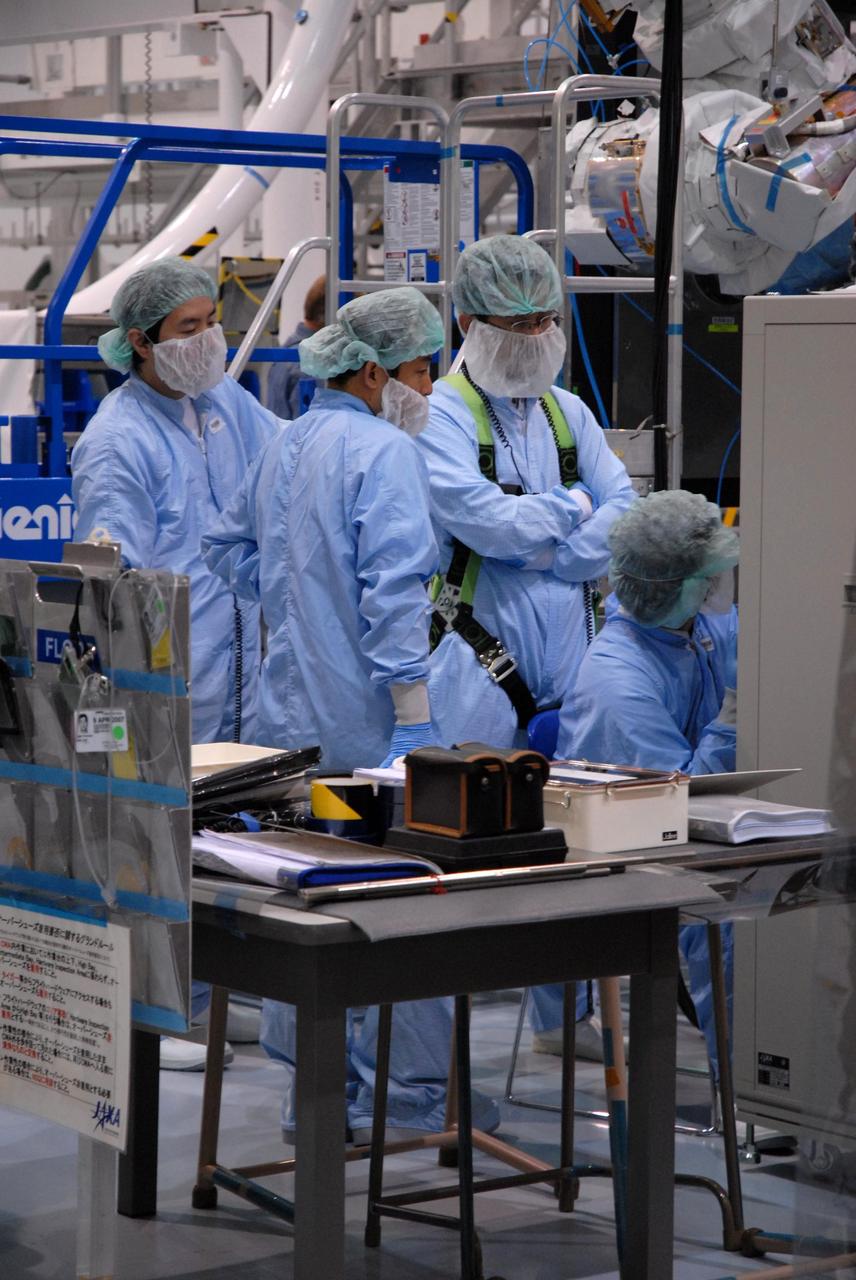

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency watch from a control area as the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, is attached to a hoisting device to prepare it for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
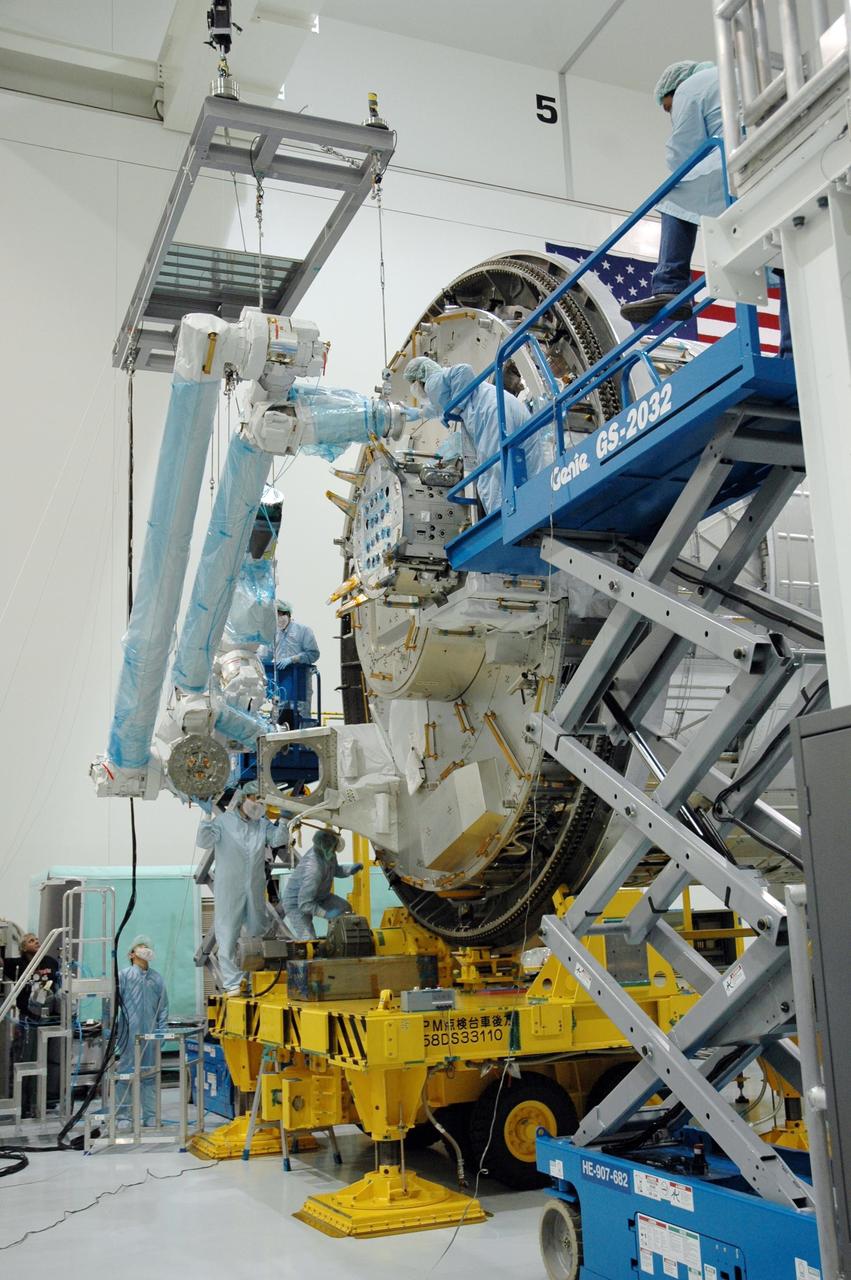
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers use a hoisting device to move the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, toward the Japanese Experiment Module for installation and testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008.The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
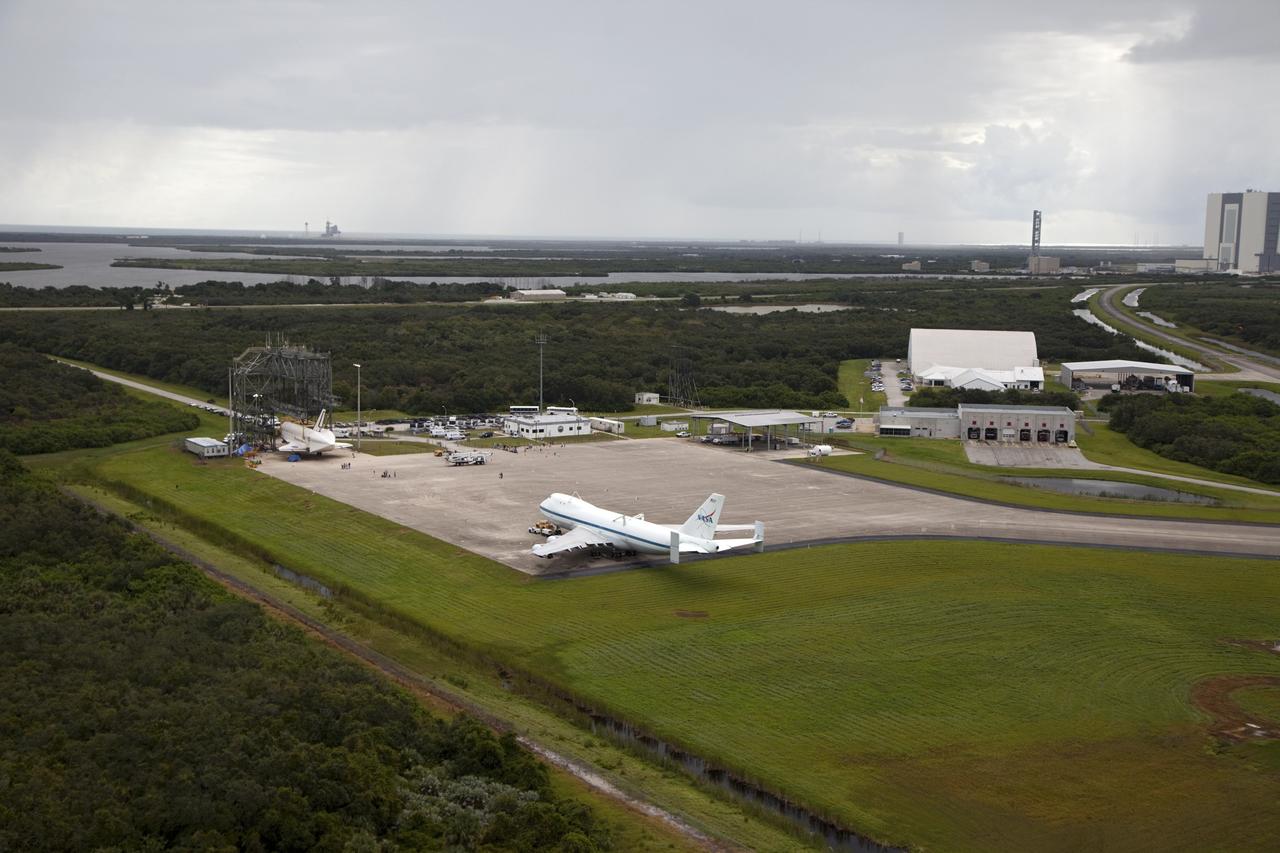

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, is seen on the ramp. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. The center's Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, and the mobile launcher built for the Space Launch System are also visible in the background. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
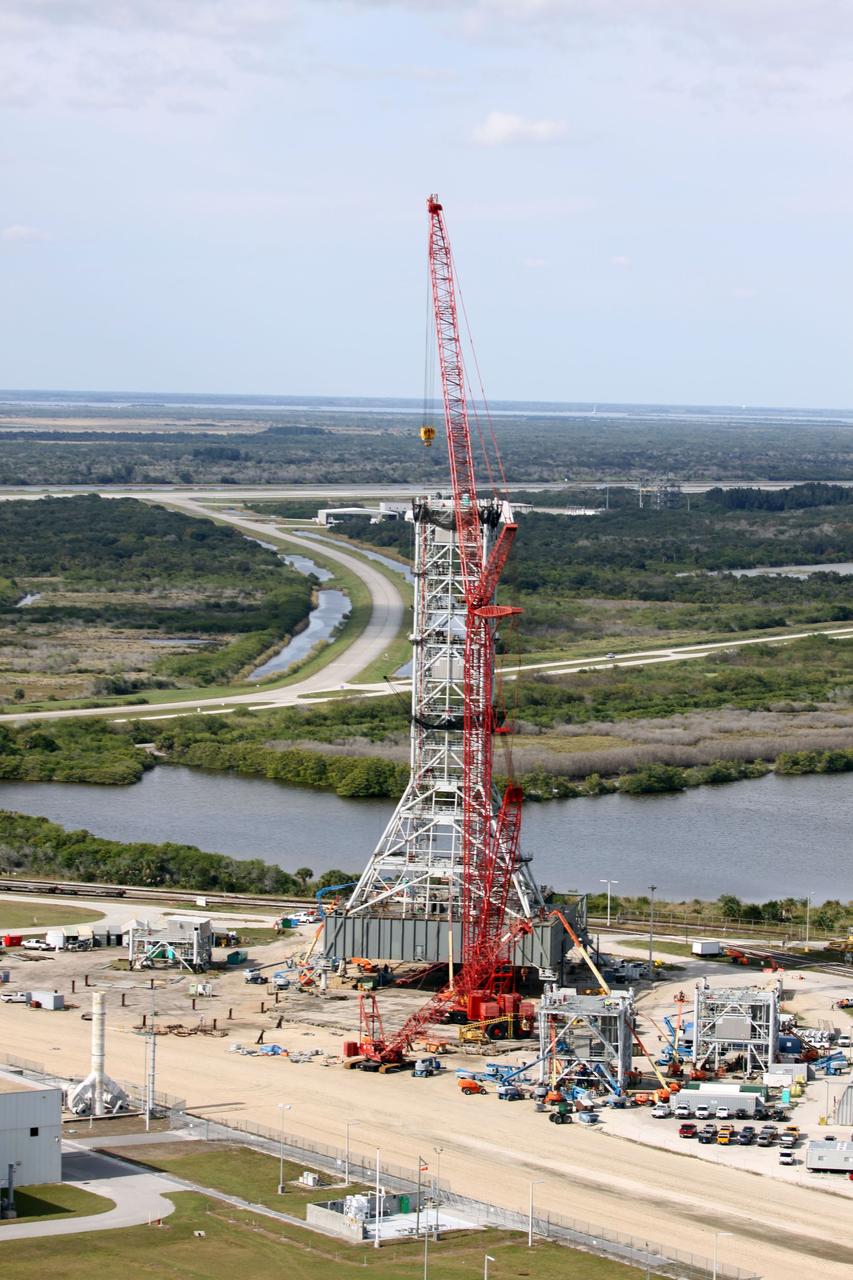

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this aerial view of the mobile launcher park site area north of the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building shows a new mobile launcher, or ML, for the Constellation Program under construction. In the background are the Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the towway and the mate-demate device. When completed, the tower will be approximately 345 feet tall and have multiple platforms for personnel access. Its base is being made lighter than space shuttle mobile launcher platforms so the crawler-transporter can pick up the heavier load of the tower and a taller rocket. For information on the Constellation Program, visit http://www.nasa.gov/constellation. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
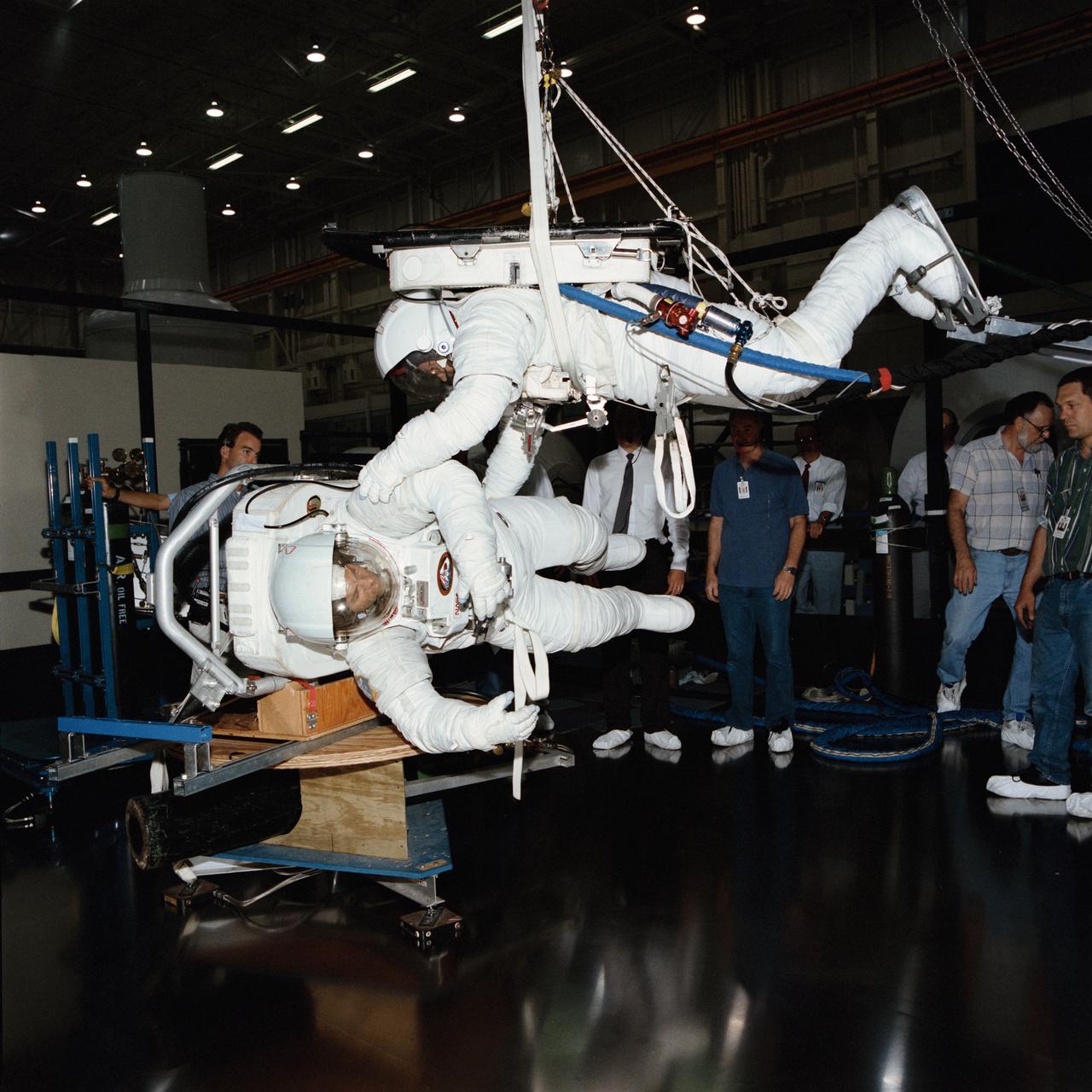

S94-33357 (1994) --- Scott Bleiseth, top, prepares to spin Mike Hess, a fellow EVA engineer, during a test on the air-bearing floor in the Shuttle Mock-up and Integration Laboratory at NASA's Johnson Space Center. The hardware being tested is part of the Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER). The pair was developing techniques by which the non-SAFER equipped spacewalker will impart a rotation to the SAFER-using spacewalker during the STS-64 mission. Once the SAFER astronaut is spinning, the device will be activated and its automatic attitude hold capability will be tested. SAFER is to fly on STS-76 as well. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
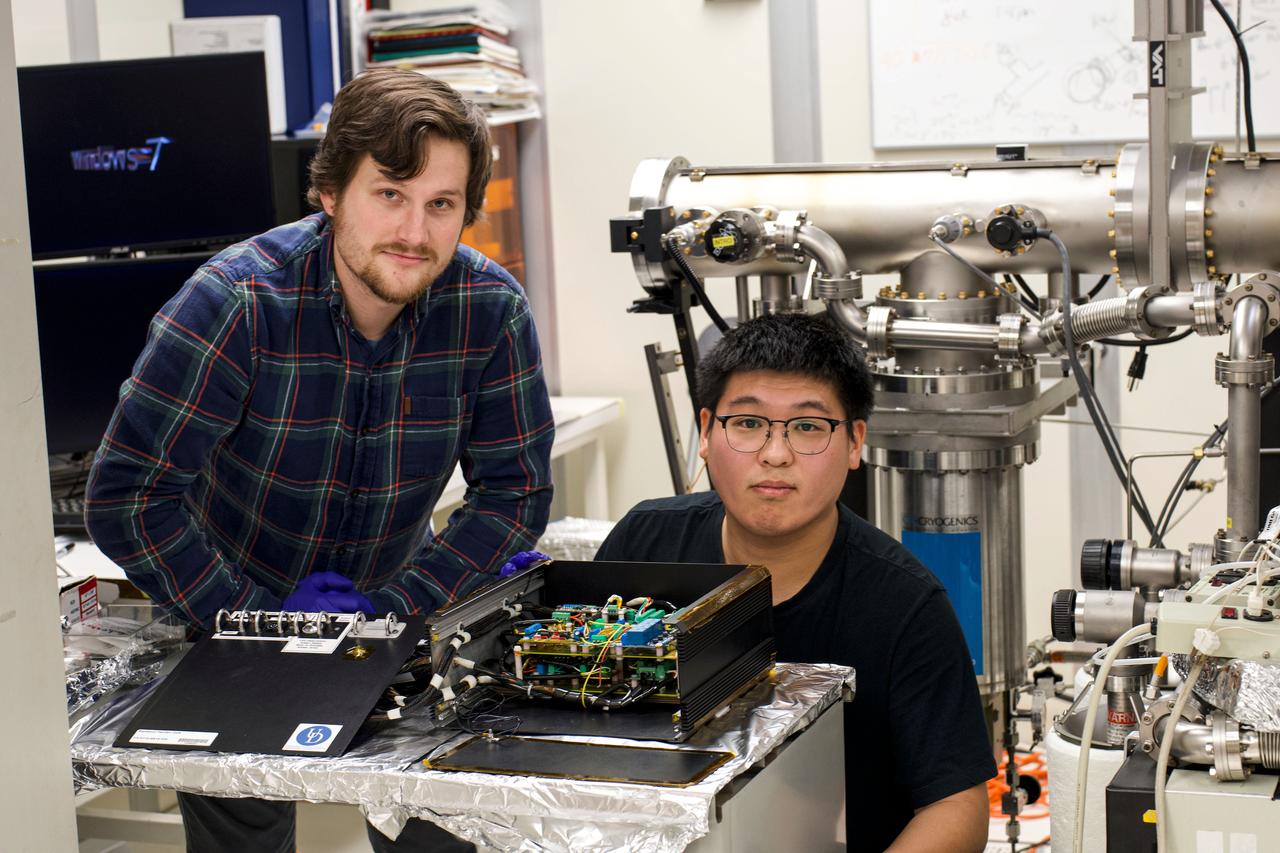
jsc2025e015687 (3/6/2025) --- Alex Katorkas (left) and Haochen Zhao (right) work in front of a prototype as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
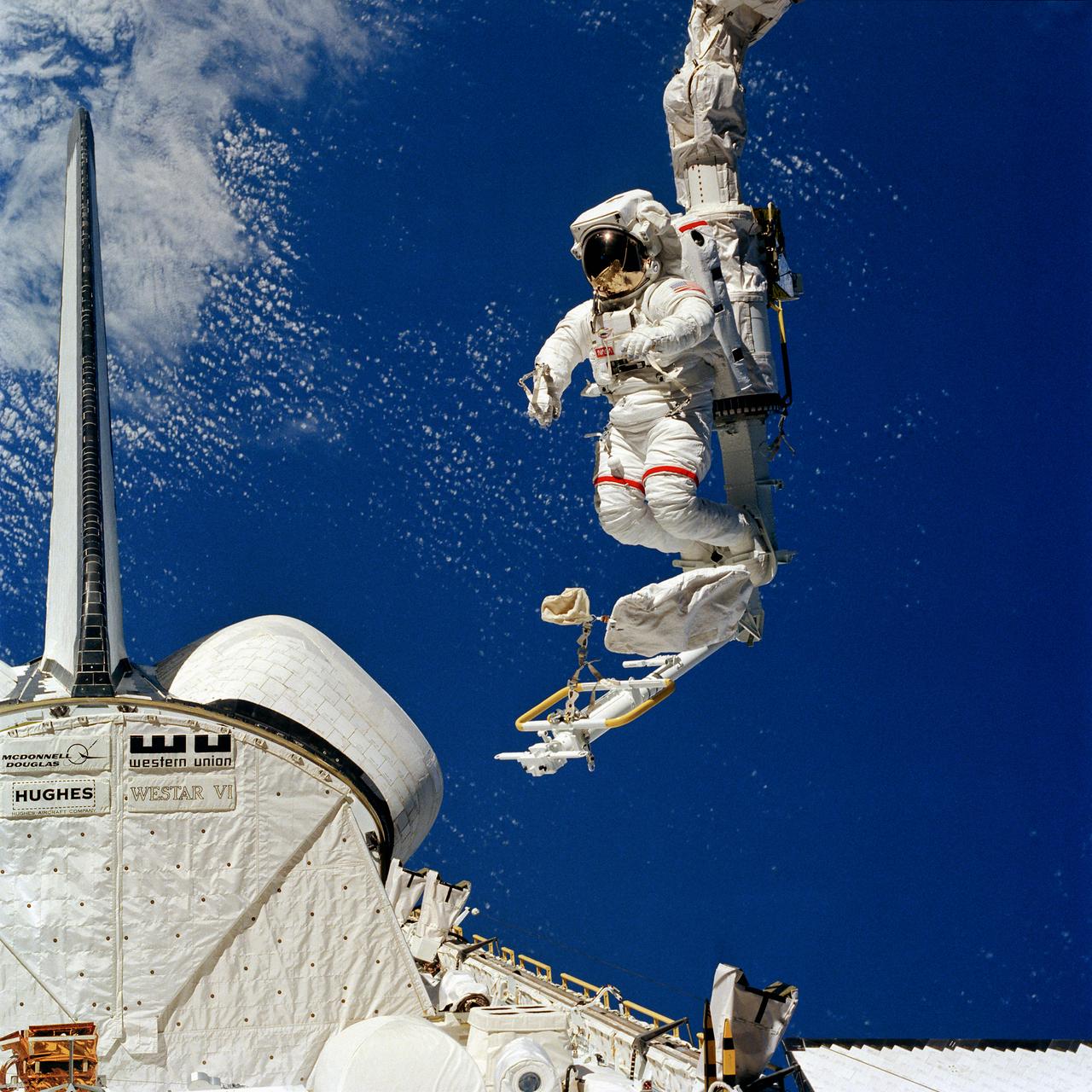

S84-27040 (7 Feb 1984) --- Some have called it NASA's first "cherry picker" in space. Others simply call it the mobile foot restraint (MFR) connected to the remote manipulator system (RMS). Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, pictured leaning out into space as his feet are anchored in the MFR, and moved around by the RMS, calls it a look of things to come. The aft portion of the Challenger, to which the RMS is connected, is seen in lower left corner. This photograph is one of a sequence showing McCandless in the device. On this same EVA, McCandless also initiated use of the manned maneuvering unit (MMU), not pictured here, a nitrogen-propelled back pack apparatus allowing for free movement in space.
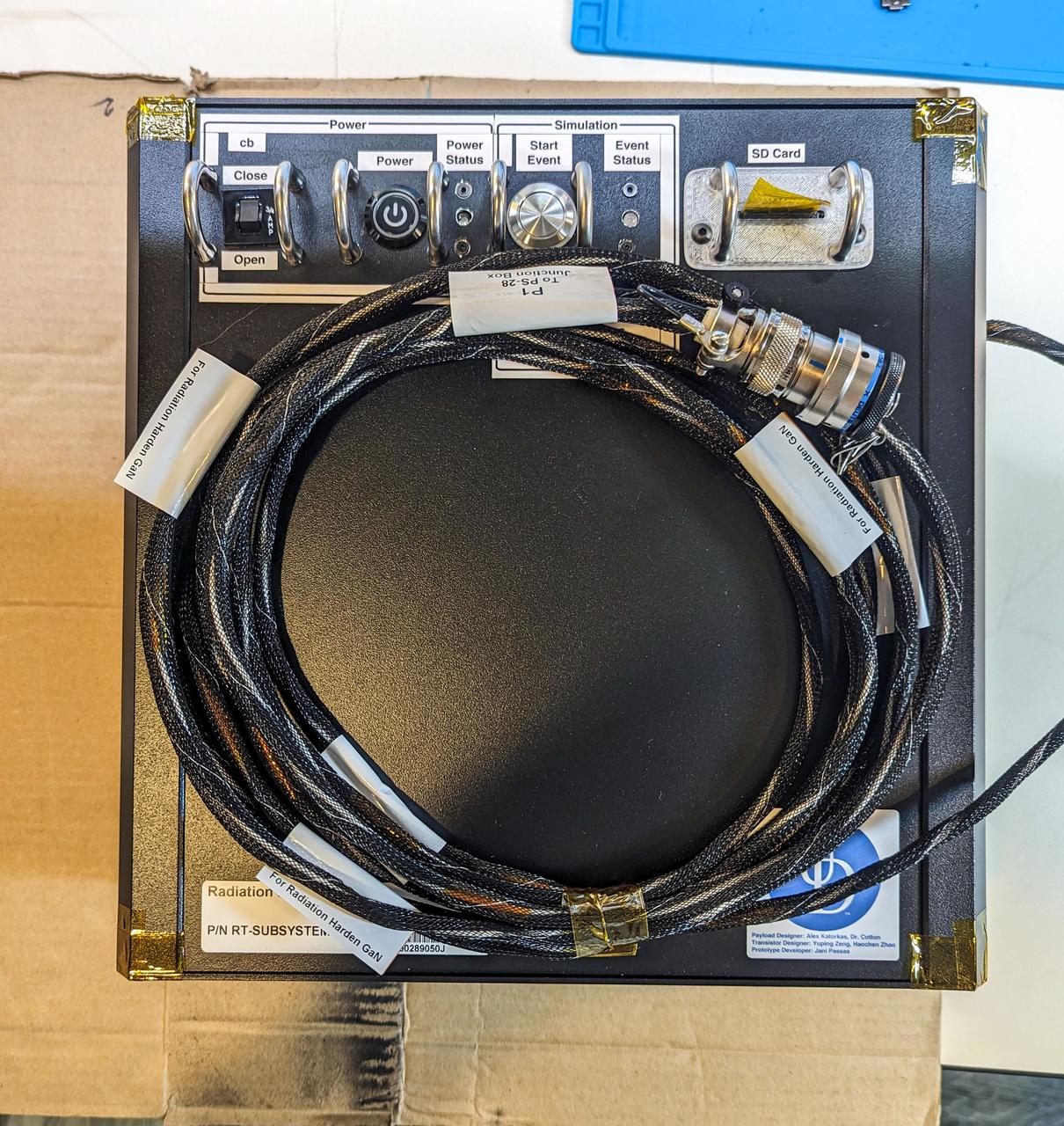

jsc2025e015688 (3/6/2025) --- The GaN radiation testing prototype enclosure faceplate as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
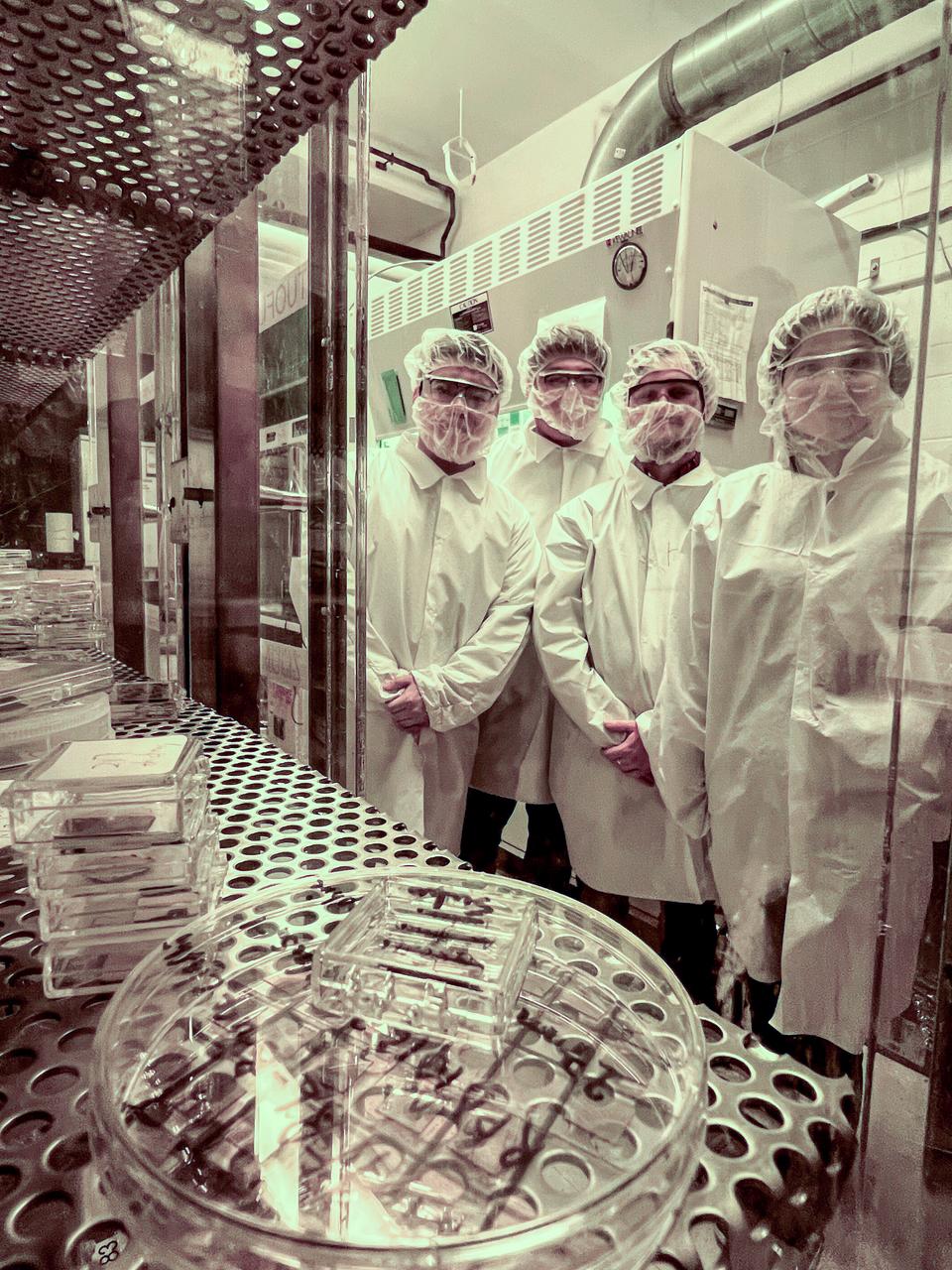

jsc2025e015684 (3/6/2025) --- The Radiation Harden GaN research team in the lithography room where patterning of transistors takes place. The High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
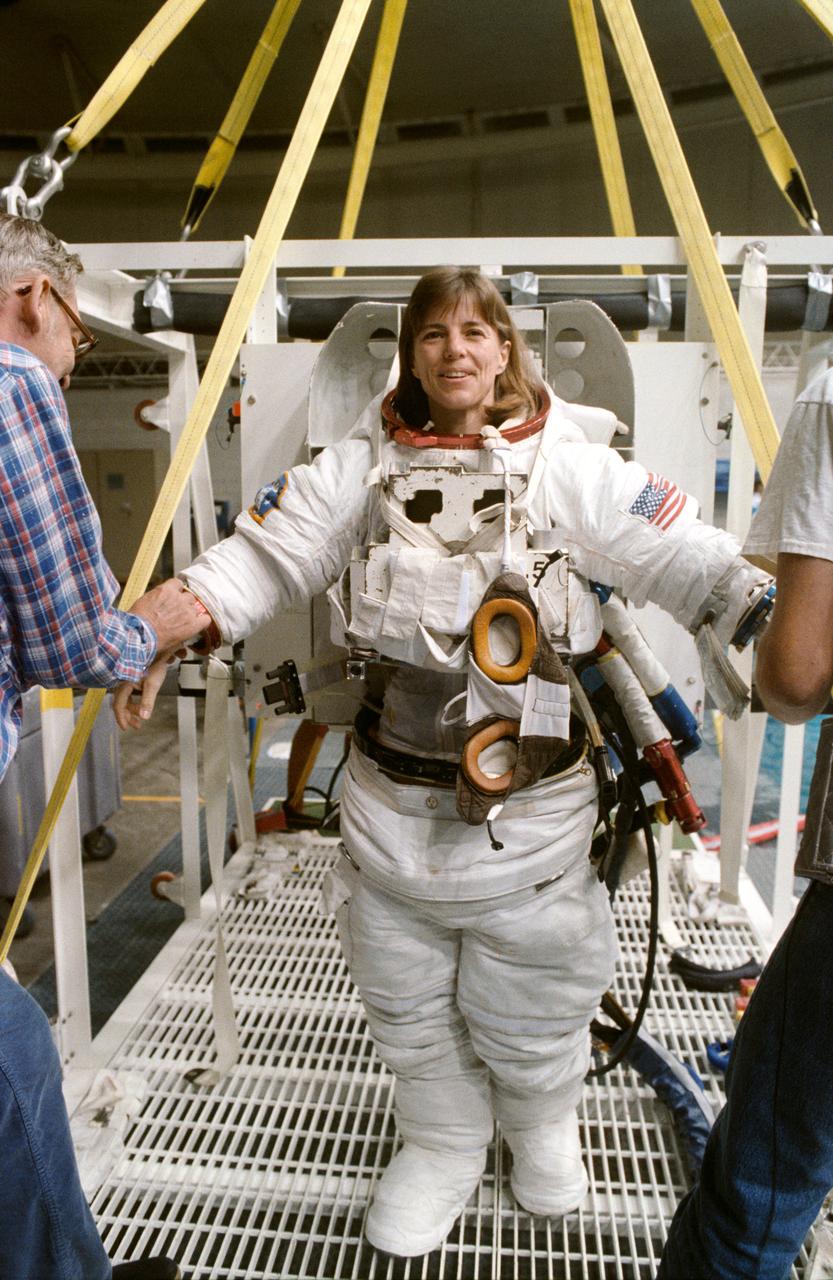

S89-41597 (Nov 1989) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, prepares to don gloves and subsequently a helmet and to be lowered by a hoist device for a session of underwater training in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Minutes later, Astronauts Dunbar and G. David Low, mission specialists, were neutrally buoyant in the nearby 25-ft. deep pool simulating a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the scheduled December 1989 STS-32 mission. There are no scheduled EVAs for the crew, whose main missions are to retrieve the Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) and to deploy a Syncom satellite.
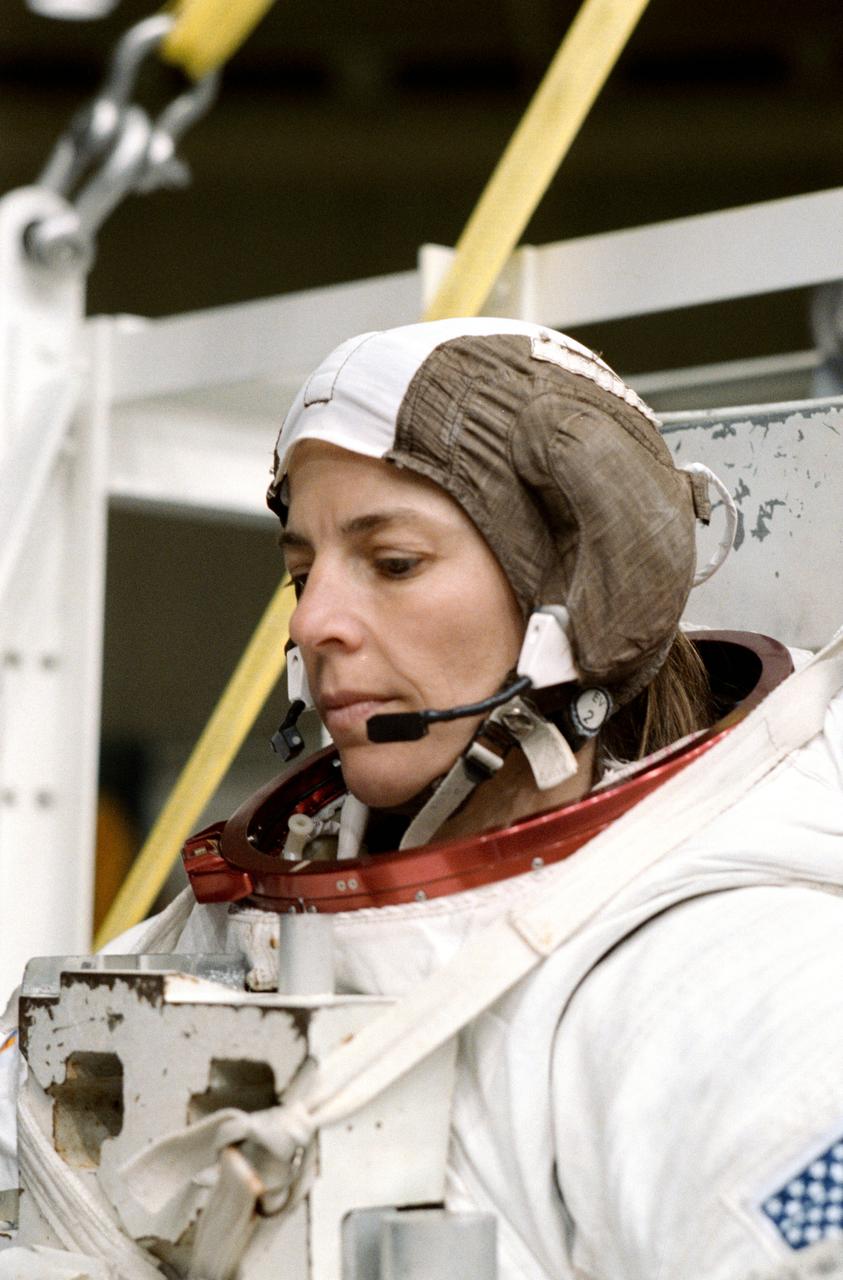

S89-41600 (Nov 1989) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, prepares to don a helmet and be lowered by a hoist device for a session of underwater training in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Minutes later, Astronauts Dunbar and G. David Low, mission specialists, were neutrally buoyant in the nearby 25-ft. deep pool simulating a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the scheduled December 1989 STS-32 mission. There are no scheduled EVAs for the crew, whose main missions are to retrieve the Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) and to deploy a Syncom satellite.
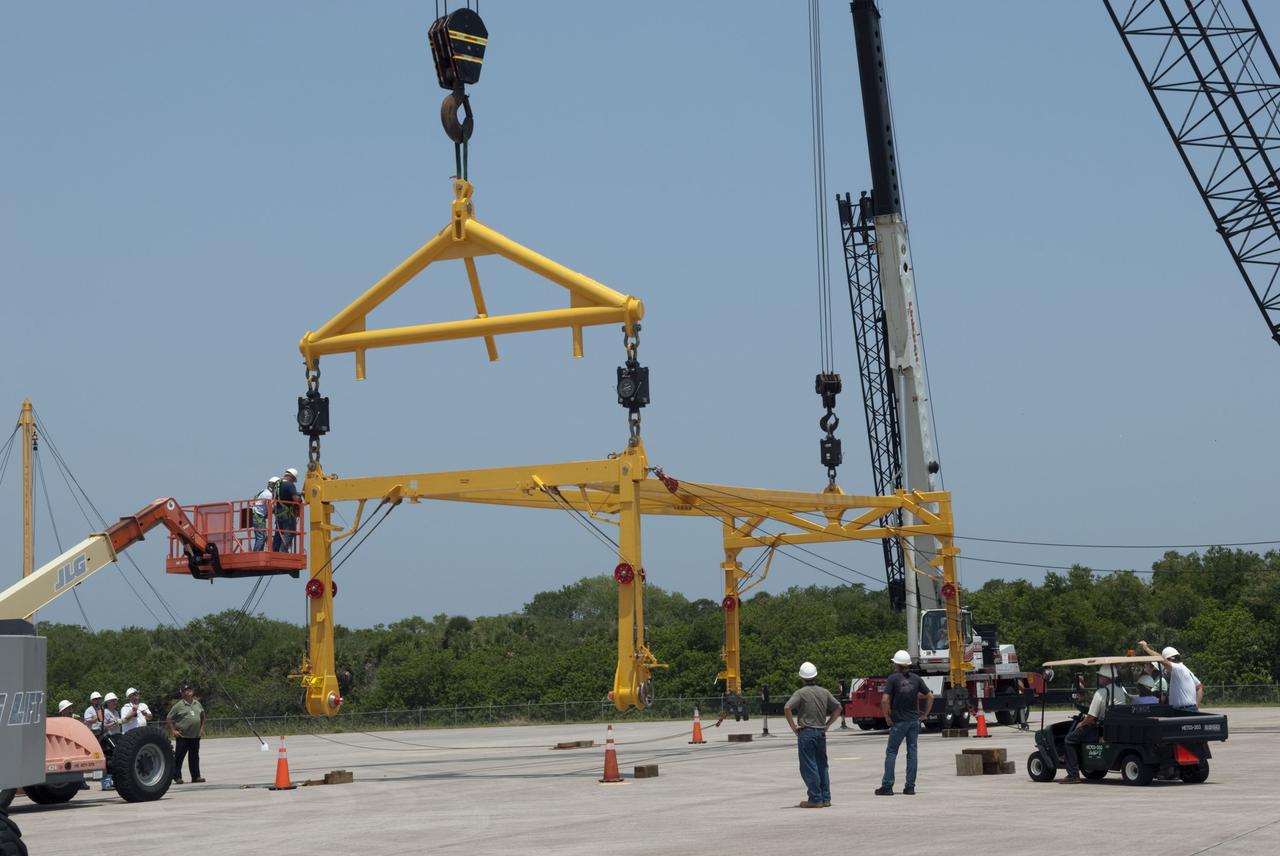

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers practice assembly and disassembling a mobile sling and crane, part of a portable mate-demate device. The portable sling and crane will be used to lift shuttles off their 747 carrier aircraft for delivery to museums next year. Shuttle Discovery will go to the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., Endeavour will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles and Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. Shuttle Atlantis will go to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and won't require use of the portable sling and crane. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
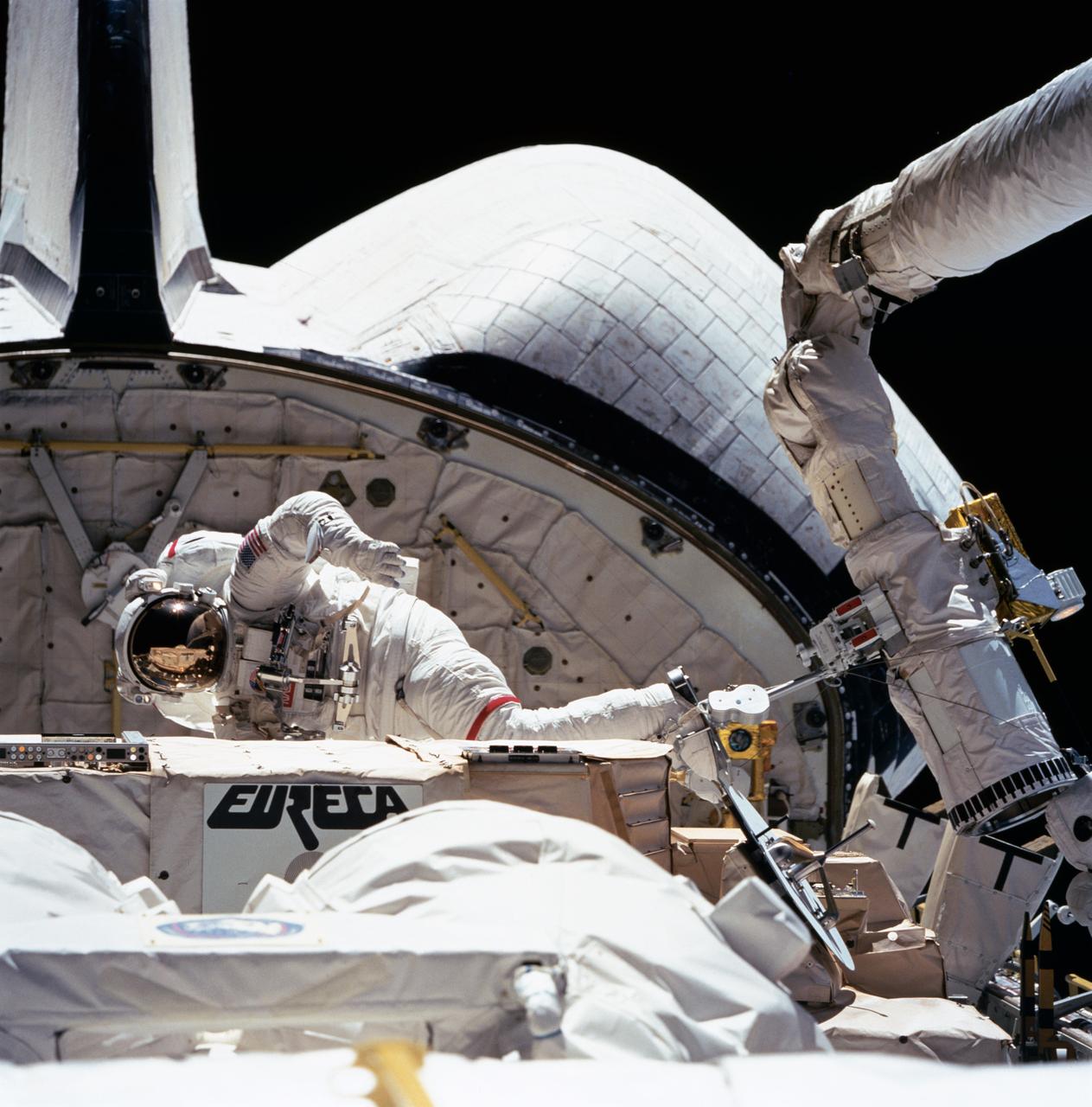

The darkness of space forms the backdrop for this extravehicular activity (EVA) scene captured by one of the STS-57 crewmembers in Endeavour's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105's, crew cabin. Pictured near the recently "captured" European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA) at frame center is Mission Specialist (MS) and Payload Commander (PLC) G. David Low. Suited in an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), Low, anchored to the remote manipulator system (RMS) via a portable foot restraint (PFR) (manipulator foot restraint (MFR)), is conducting Detailed Test Objective (DTO) 1210 procedures. Specifically, this activity will assist in refining several procedures being developed to service the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on mission STS-61 in December 1993. The PFR is attached to the RMS end effector via a PFR attachment device (PAD). Partially visible in the foreground is the Superfluid Helium Onorbit Transfer (SHOOT) payload.
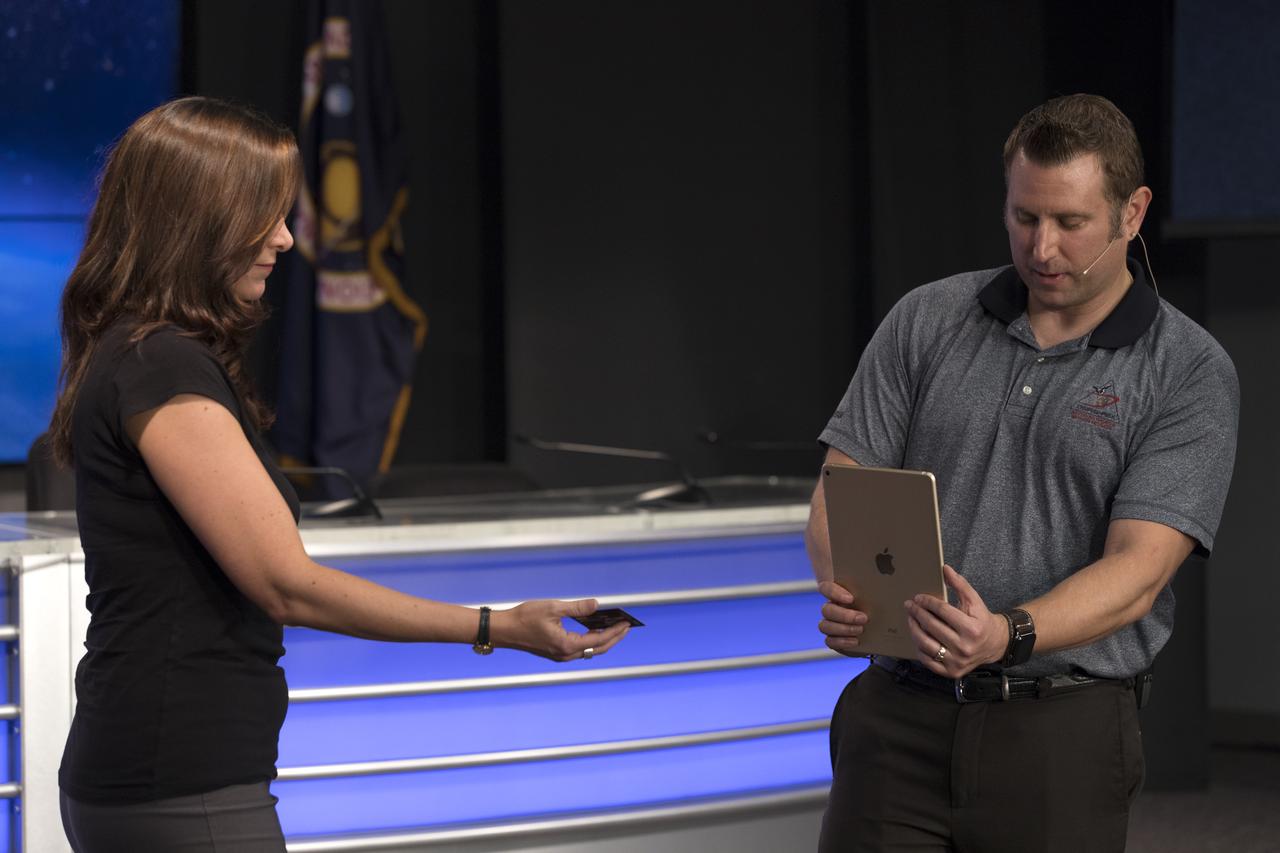

Skip Owen of NASA Launch Services, right, is demonstrating an app that can run on a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet computer. The app is depicting the launch of the TDRS-M satellite on an Atlas V rocket. The demonstration took place during a briefing focused on preparations to launch NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. The latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites, TDRS-M will allow nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 8:03 a.m. EDT Aug. 18.
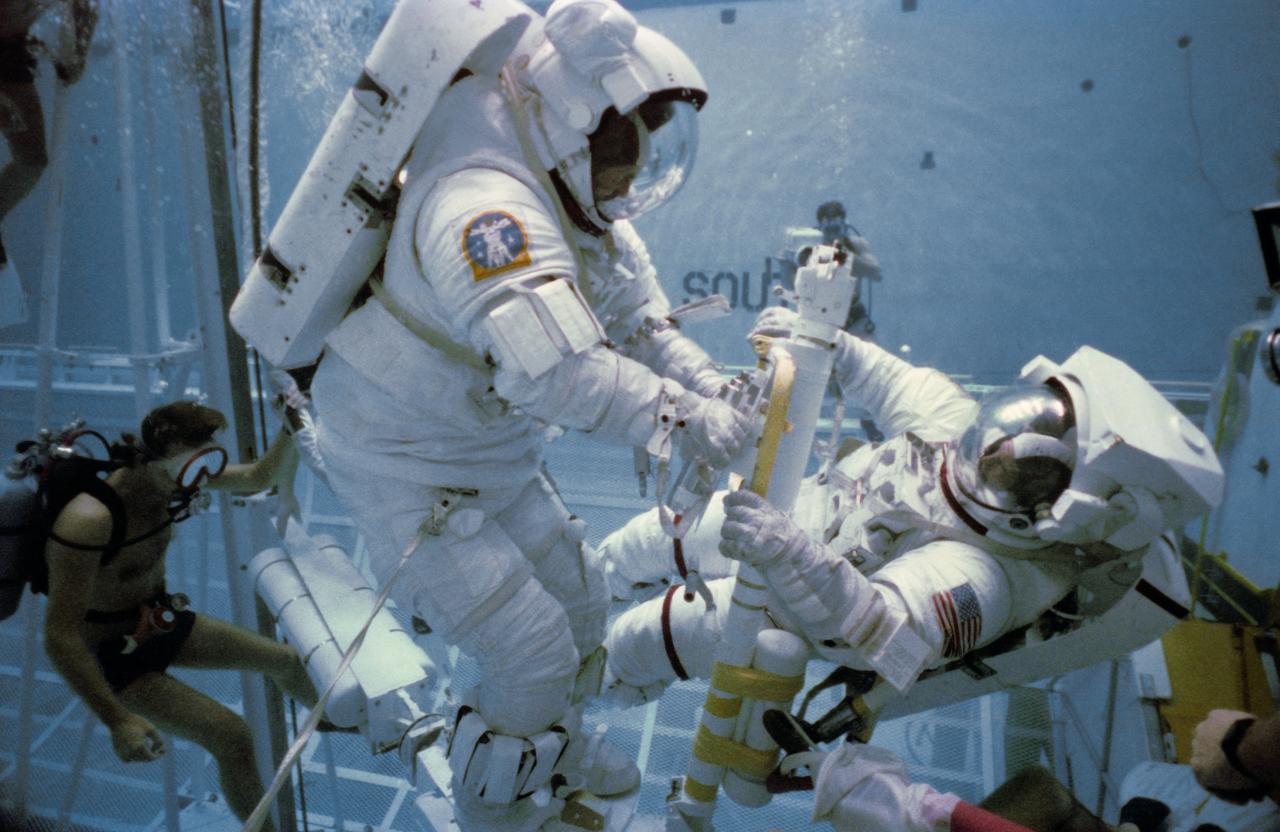

S83-42895 (19 Oct 1983) --- Astronauts George D. Nelson and James D. van Hoften, NASA Flight STS-41C mission specialists, offer an underwater version of a preview of their mission's extravehicular activity (EVA). The April 1984 flight includes as one of its primary objectives a two-person EVA and a visit to the damaged Solar Maximum Satellite (SMS). Van Hoften, left, and Nelson work here with the mobile foot restraint (MFR), which attaches to the remote manipulator system (RMS) arm to form a "cherry-picker" device. Van Hoften is standing on the MFR. The two are making use of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) weightless environment training facility (WET-F). This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
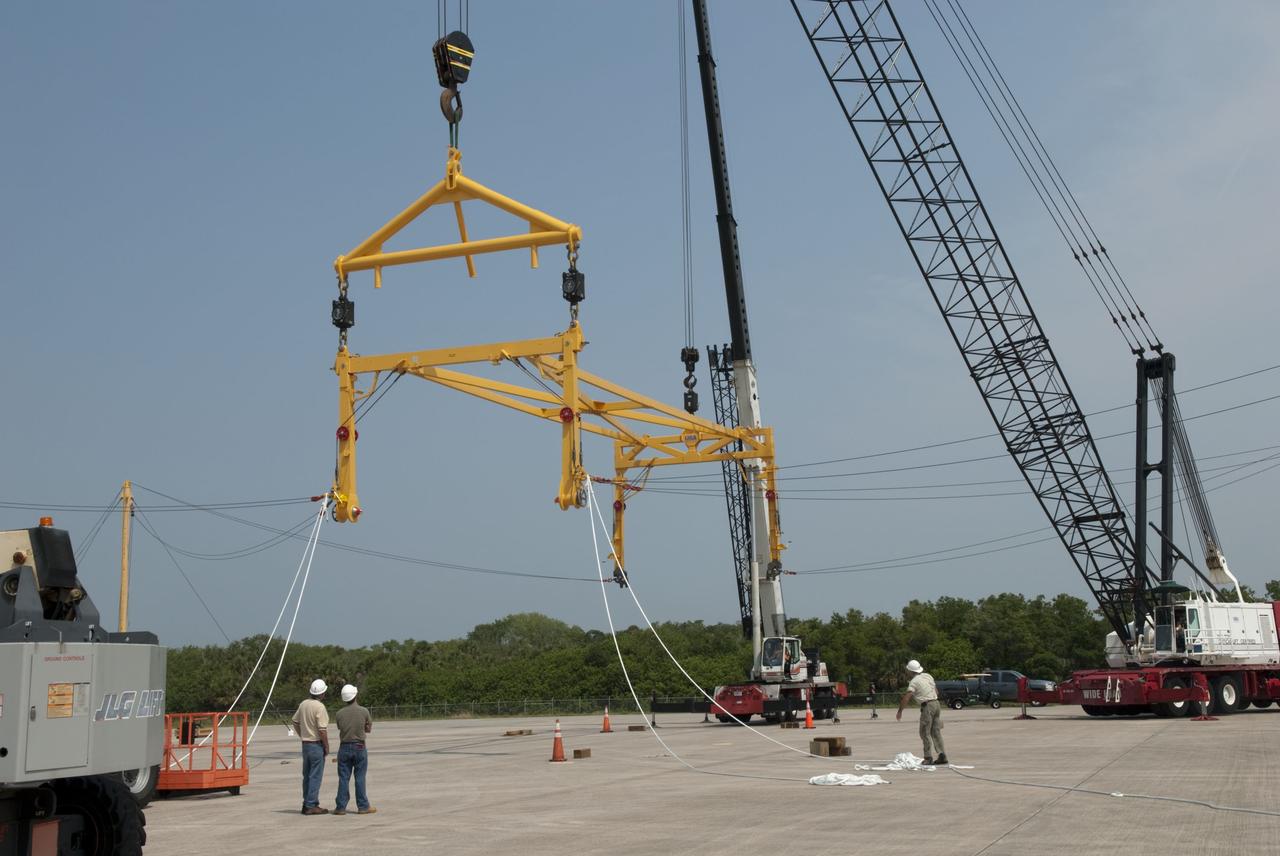

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers practice assembly and disassembling a mobile sling and crane, part of a portable mate-demate device. The portable sling and crane will be used to lift shuttles off their 747 carrier aircraft for delivery to museums next year. Shuttle Discovery will go to the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., Endeavour will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles and Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. Shuttle Atlantis will go to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and won't require use of the portable sling and crane. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
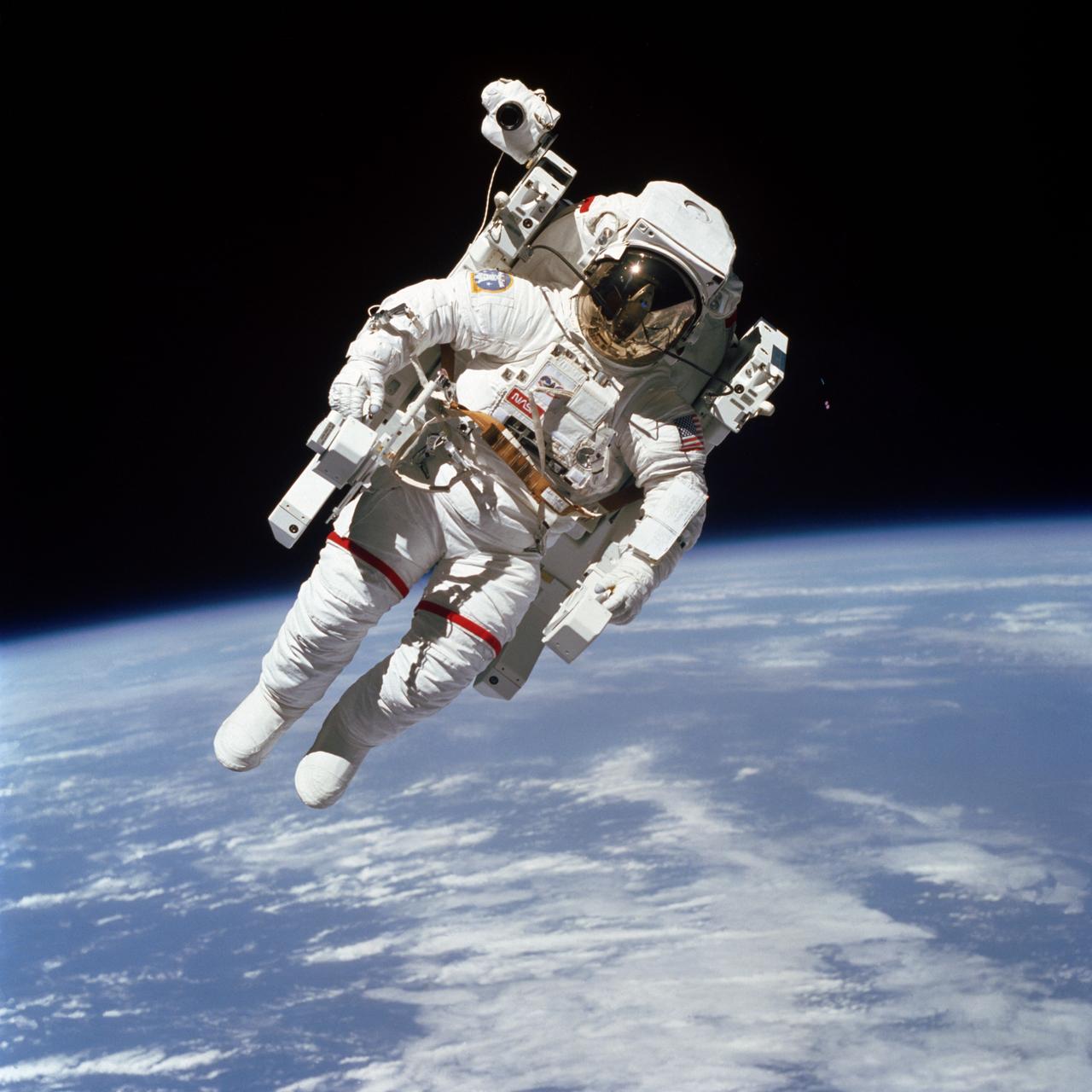

S84-27562 (7 Feb. 1984) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, one of two 41B mission specialists participating in a historical Extravehicular Activity (EVA), is a few meters away from the cabin of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger in this 70mm frame. This Extravehicular Activity (EVA) represented the first use of a nitrogen-propelled, hand-controlled device called the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), which allows for much greater mobility than that afforded previous spacewalkers who had to use restrictive tethers. Robert L. Stewart later tried out the MMU McCandless is using here, and the two of them tested another similar unit two days later. Inside the spacecraft were astronauts Vance D. Brand, commander; Robert L. Gibson, pilot; and Ronald E. McNair, mission specialist. Photo credit: NASA
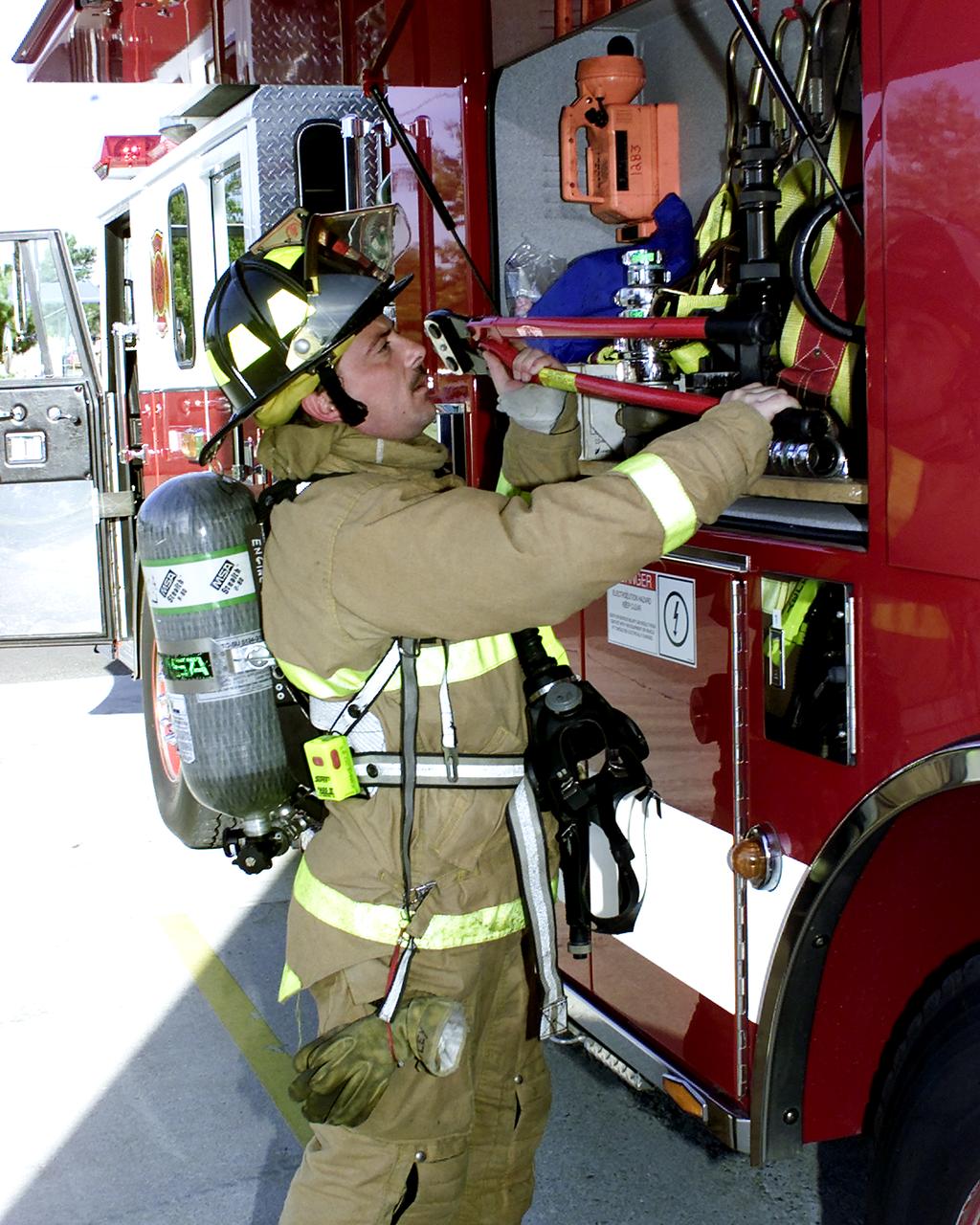

Technology used to provide thermal protection for Apollo astronauts and spacecraft components provides firefighters with better protective clothing and equipment. Spinoffs include a portable firefighting module, protective clothing for workers in hazardous environments, fire-retardant paints and forms, fireblocking coating for outdoor structures, and flame-resistant fabric. Perhaps the farthest reaching is the breathing apparatus worn by firefighters throughout the U.S. for protection against smoke inhalation injury. The breathing system weighs approximately 20 pounds, one-third less than past systems, and it enables the wearer to have improved mobility. It consists of a face mask, frame and harness, a warning device, and an air bottle. The basic air cylinder offers the same 30-minutes of operation time as its predecessor. The result is a drastic reduction in the number of inhalation injuries to firefighters. Though they have made many design modifications and refinements, manufacturers of breathing apparatus still incorporate the original NASA technology.
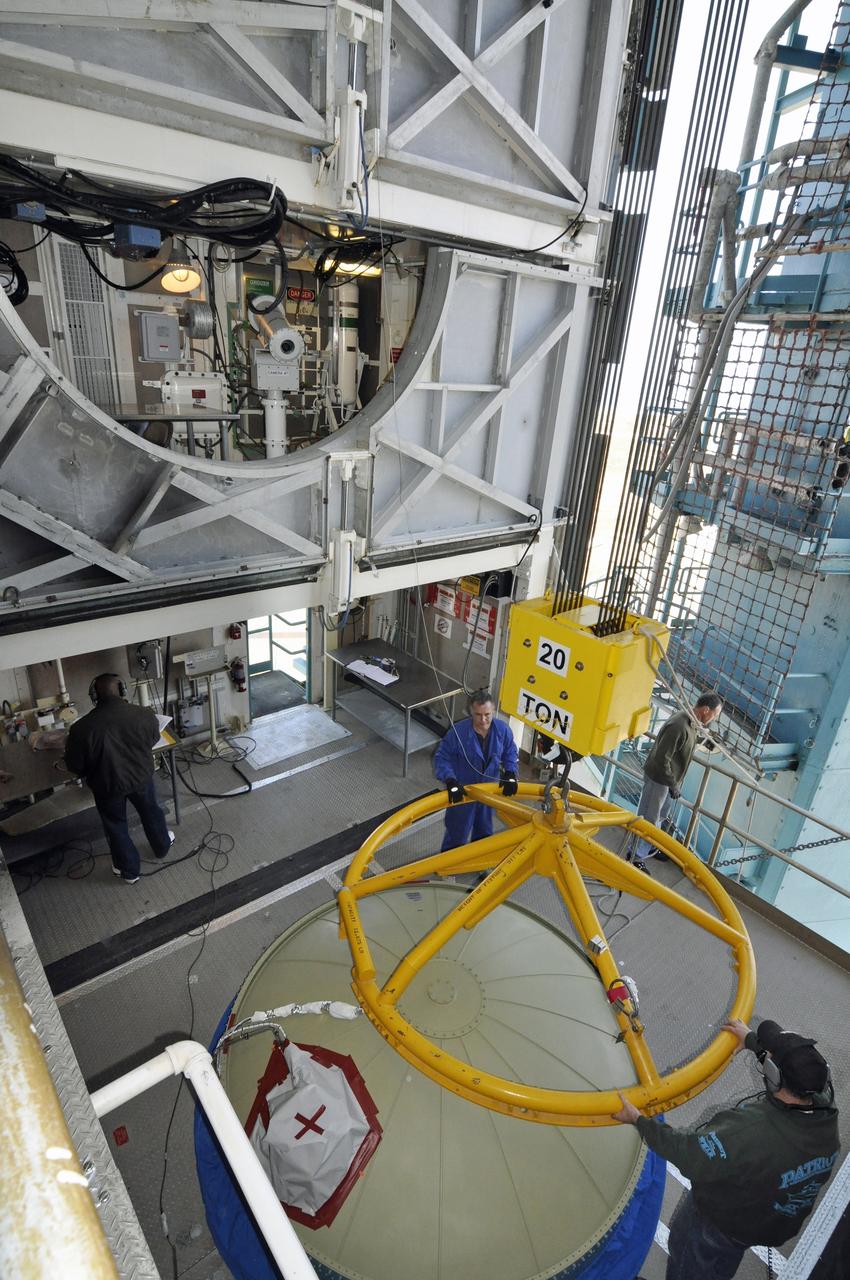

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The lifting device detached and moved away from the upper end of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
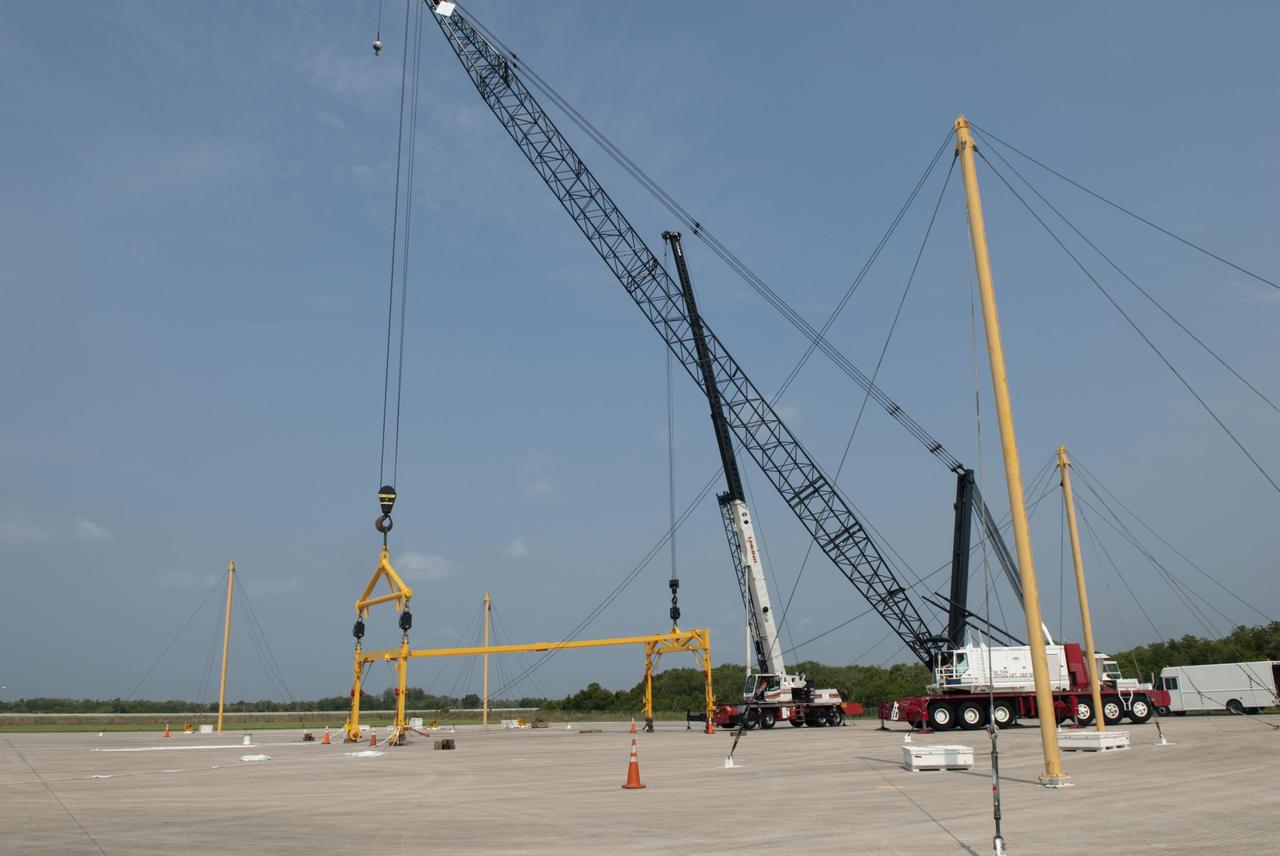

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers practice assembly and disassembling a mobile sling and crane, part of a portable mate-demate device. The portable sling and crane will be used to lift shuttles off their 747 carrier aircraft for delivery to museums next year. Shuttle Discovery will go to the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., Endeavour will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles and Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. Shuttle Atlantis will go to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and won't require use of the portable sling and crane. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
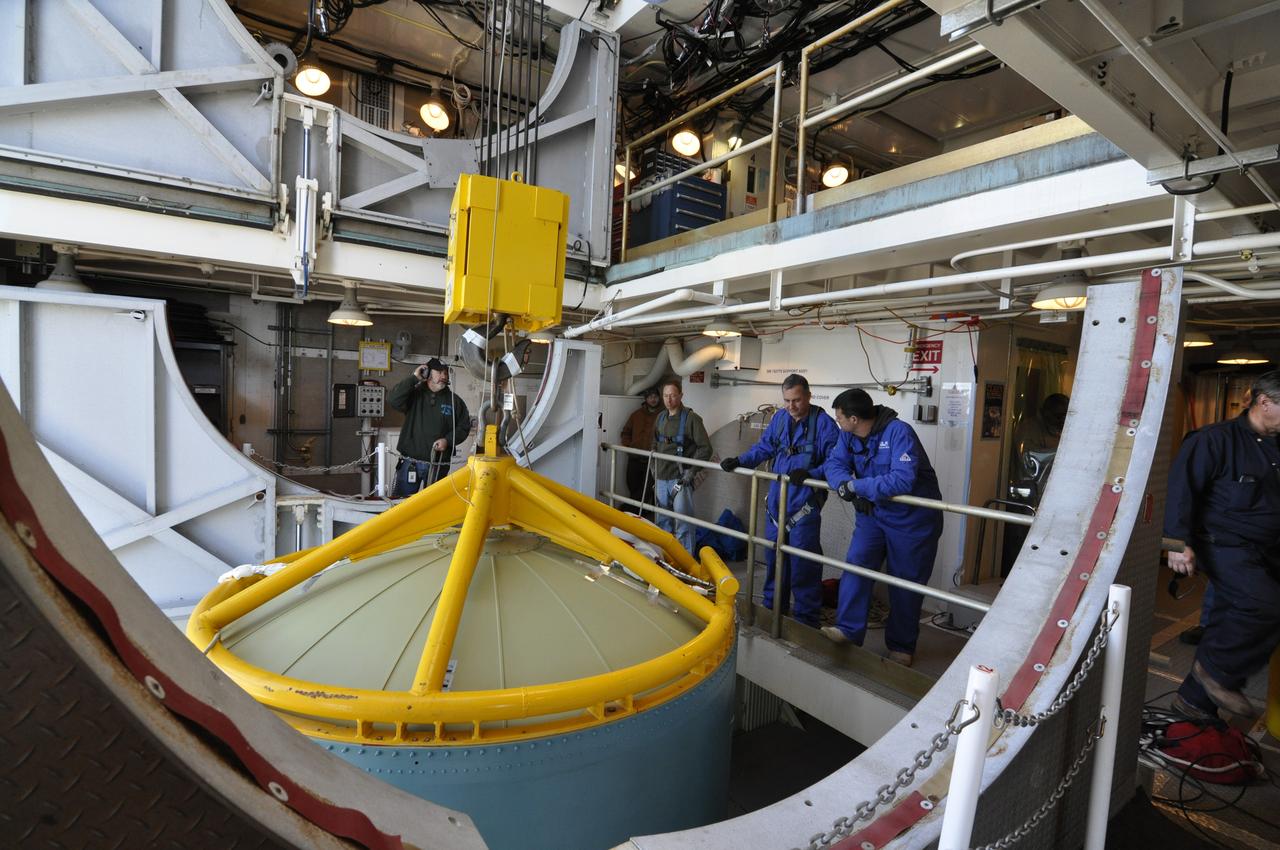

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California prepare to release the upper end of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from the lifting device. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
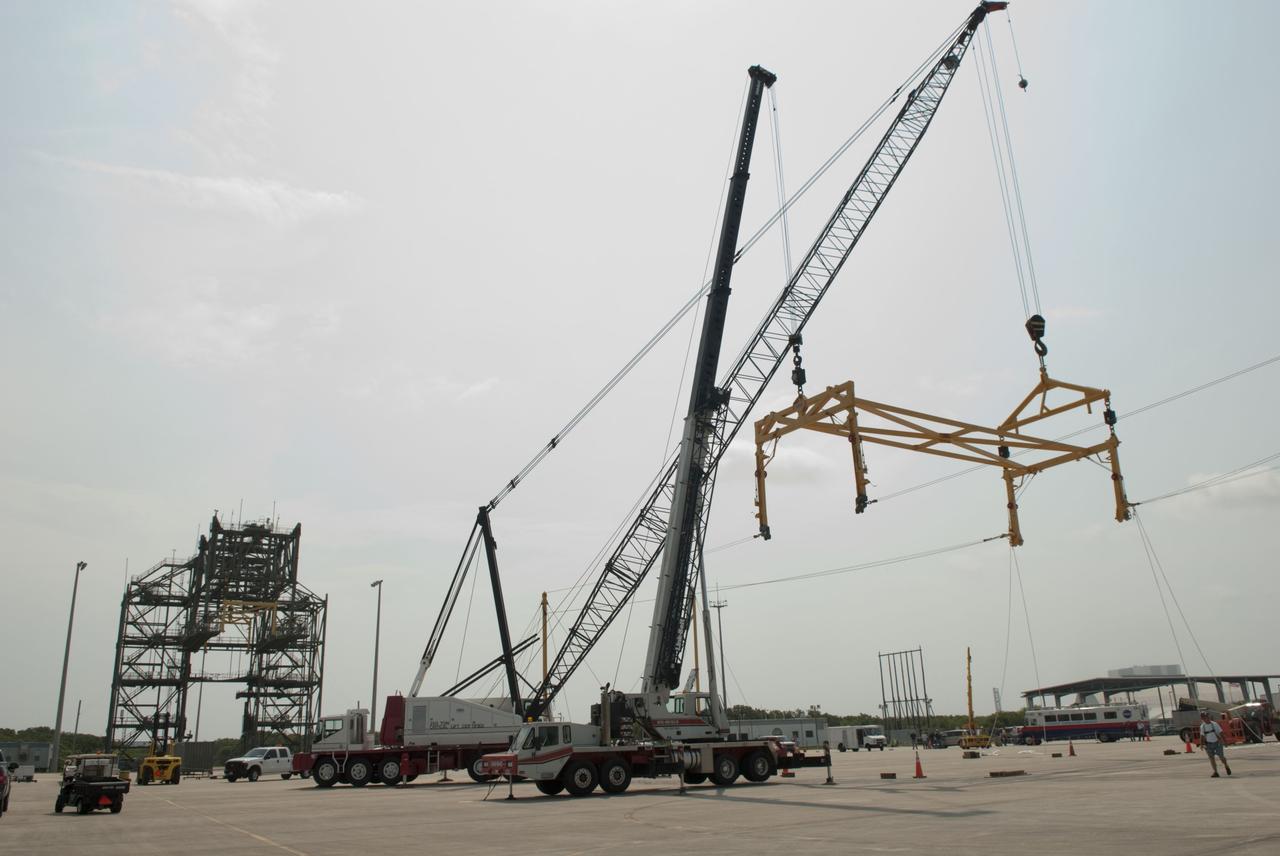

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers practice assembly and disassembling a mobile sling and crane, part of a portable mate-demate device (image left). The portable sling and crane will be used to lift shuttles off their 747 carrier aircraft for delivery to museums next year. Shuttle Discovery will go to the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., Endeavour will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles and Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. Shuttle Atlantis will go to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and won't require use of the portable sling and crane. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
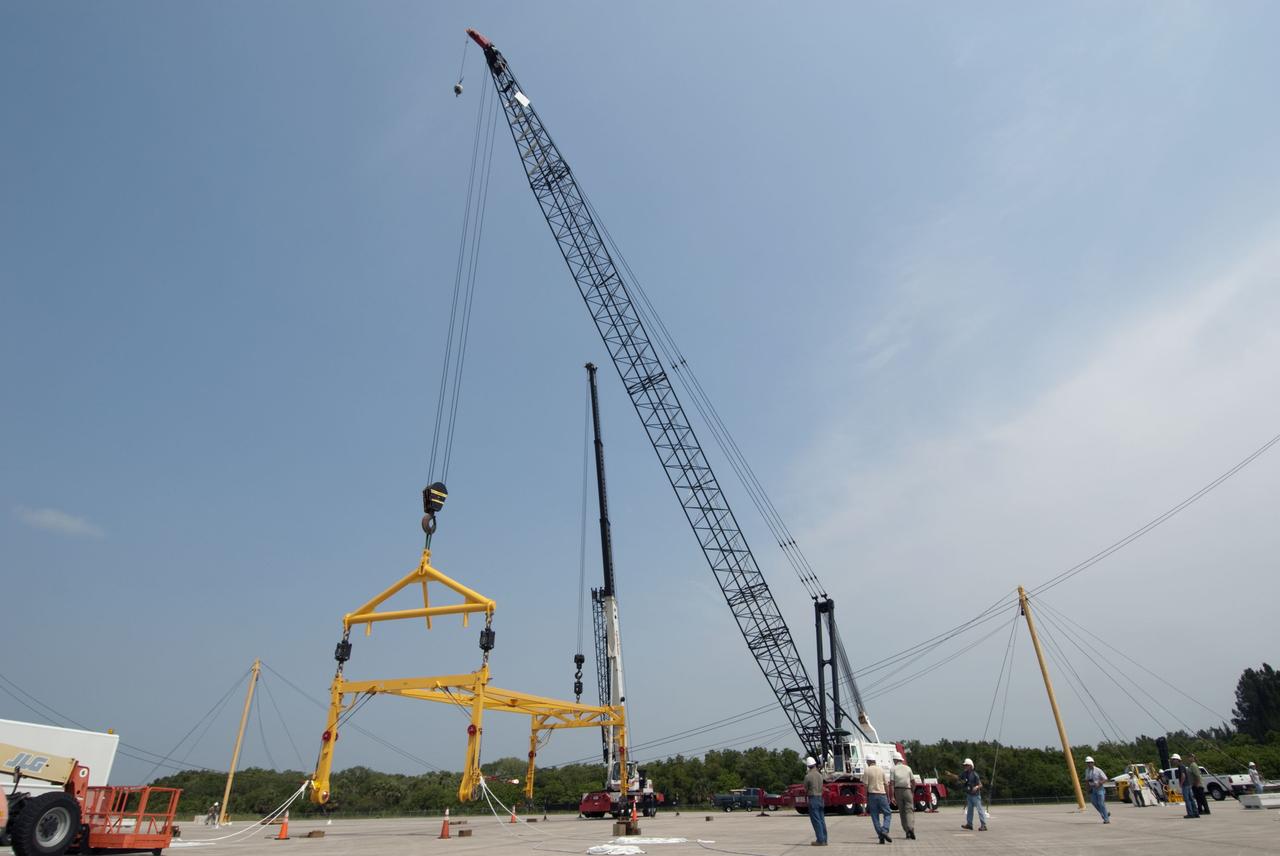

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers practice assembly and disassembling a mobile sling and crane, part of a portable mate-demate device. The portable sling and crane will be used to lift shuttles off their 747 carrier aircraft for delivery to museums next year. Shuttle Discovery will go to the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., Endeavour will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles and Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. Shuttle Atlantis will go to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and won't require use of the portable sling and crane. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
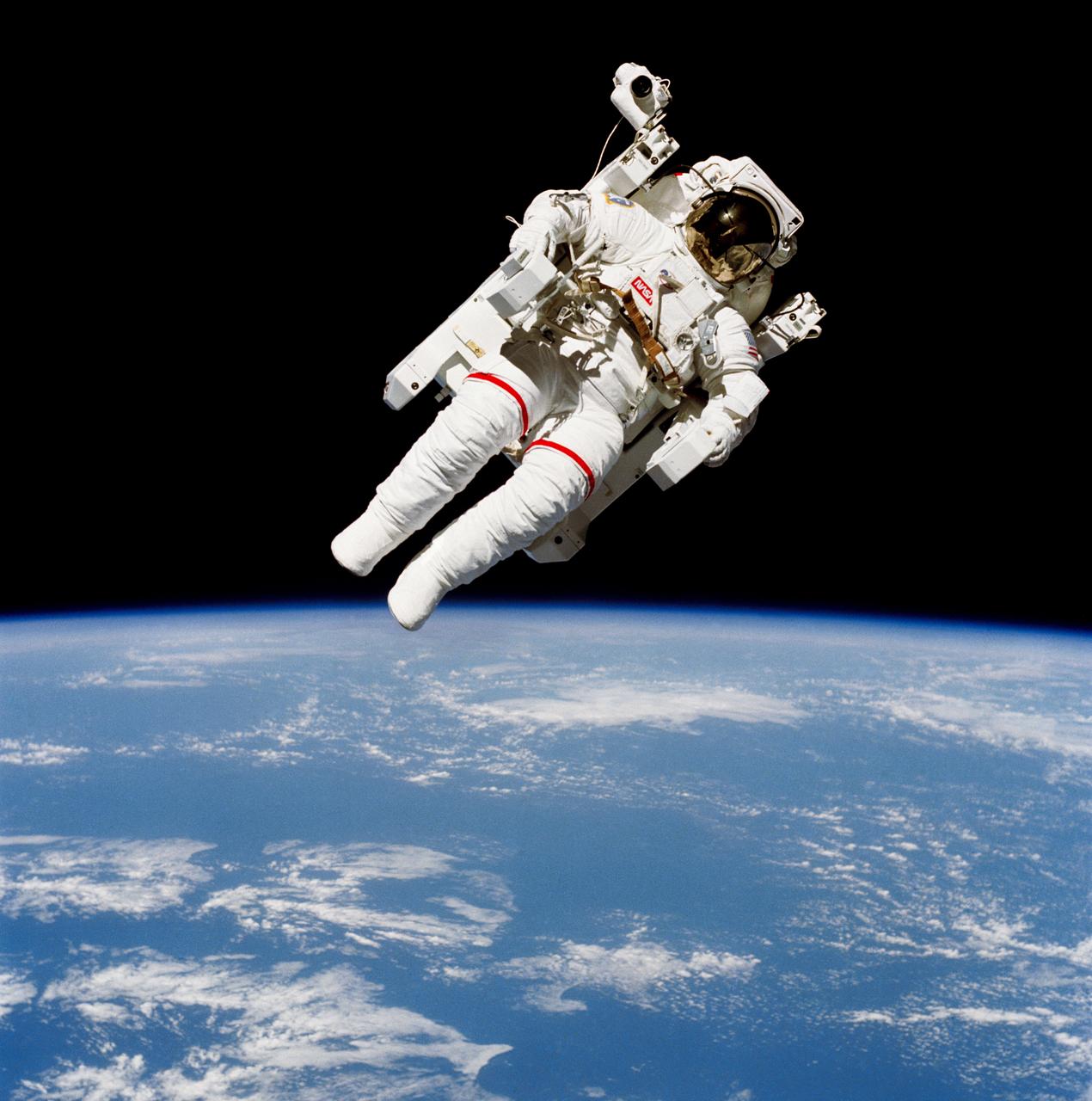

S84-27017 (7 Feb. 1984) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, one of two 41-B mission specialist, participating in a historical Extravehicular Activity (EVA), is a few meters away from the cabin of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger in this 70mm frame. This EVA represented the first use of a nitrogen-propelled, hand-controlled device called the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), which allows for much greater mobility than that afforded previous spacewalkers who had to use restrictive tethers. Robert L. Stewart, mission specialist, later tried out the MMU McCandless is using here. The two of them tested another similar unit two days later. Inside the spacecraft were astronauts Vance D. Brand, commander; Robert L. Gibson, pilot; and Ronald E. McNair, mission specialist. Photo credit: NASA
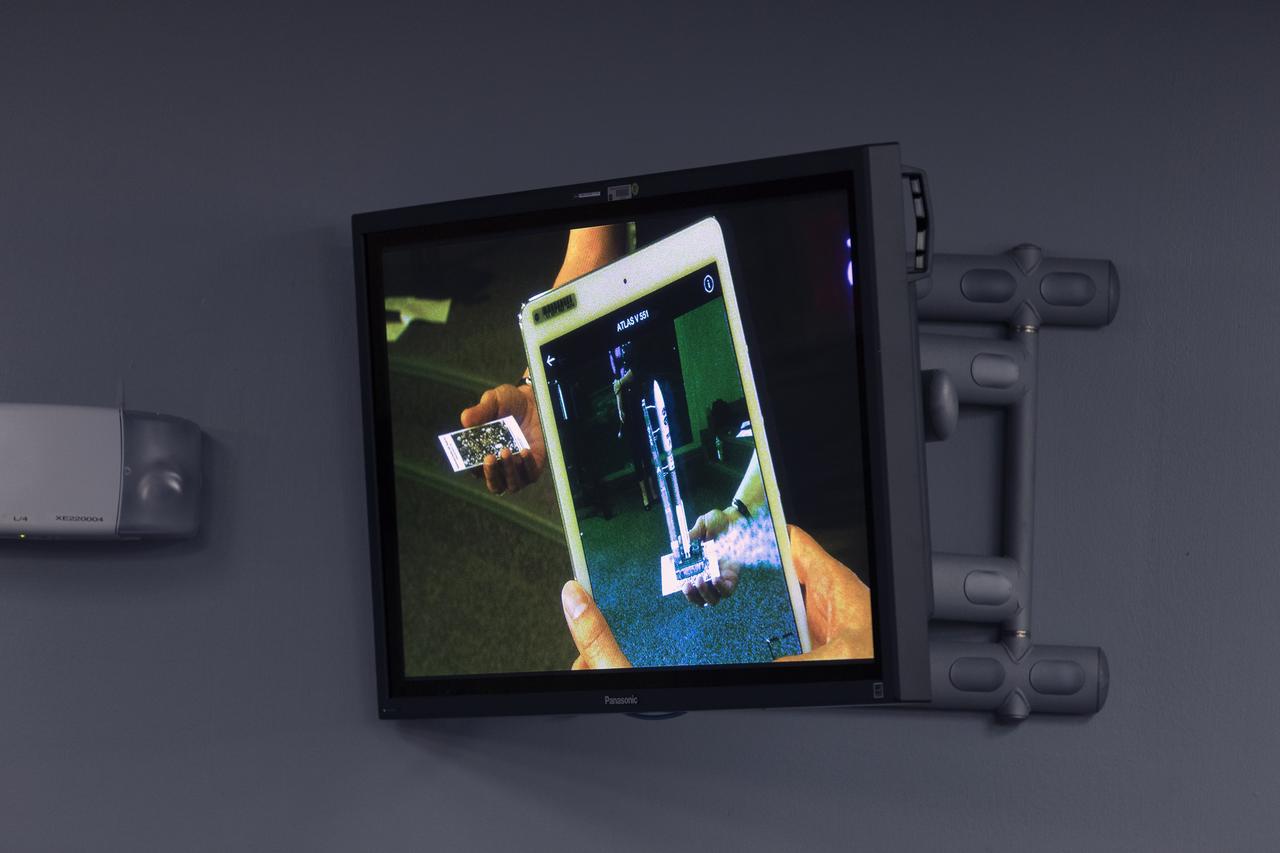

An app is demonstrated that can run on a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet computer. The app is depicting the launch of the TDRS-M satellite on an Atlas V rocket. The demonstration took place during a briefing focused on preparations to launch NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. The latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites, TDRS-M will allow nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 8:03 a.m. EDT Aug. 18.
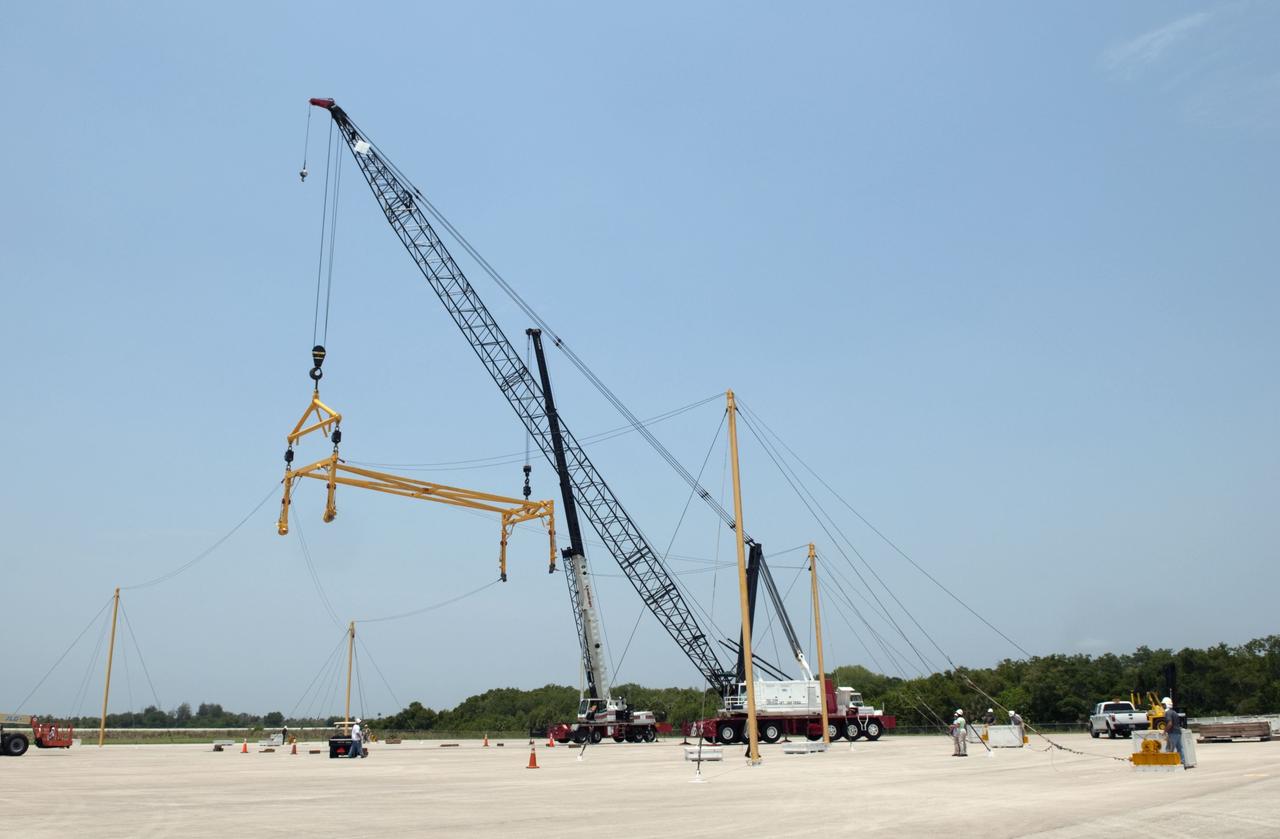

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers practice assembly and disassembling a mobile sling and crane, part of a portable mate-demate device. The portable sling and crane will be used to lift shuttles off their 747 carrier aircraft for delivery to museums next year. Shuttle Discovery will go to the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., Endeavour will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles and Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. Shuttle Atlantis will go to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and won't require use of the portable sling and crane. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
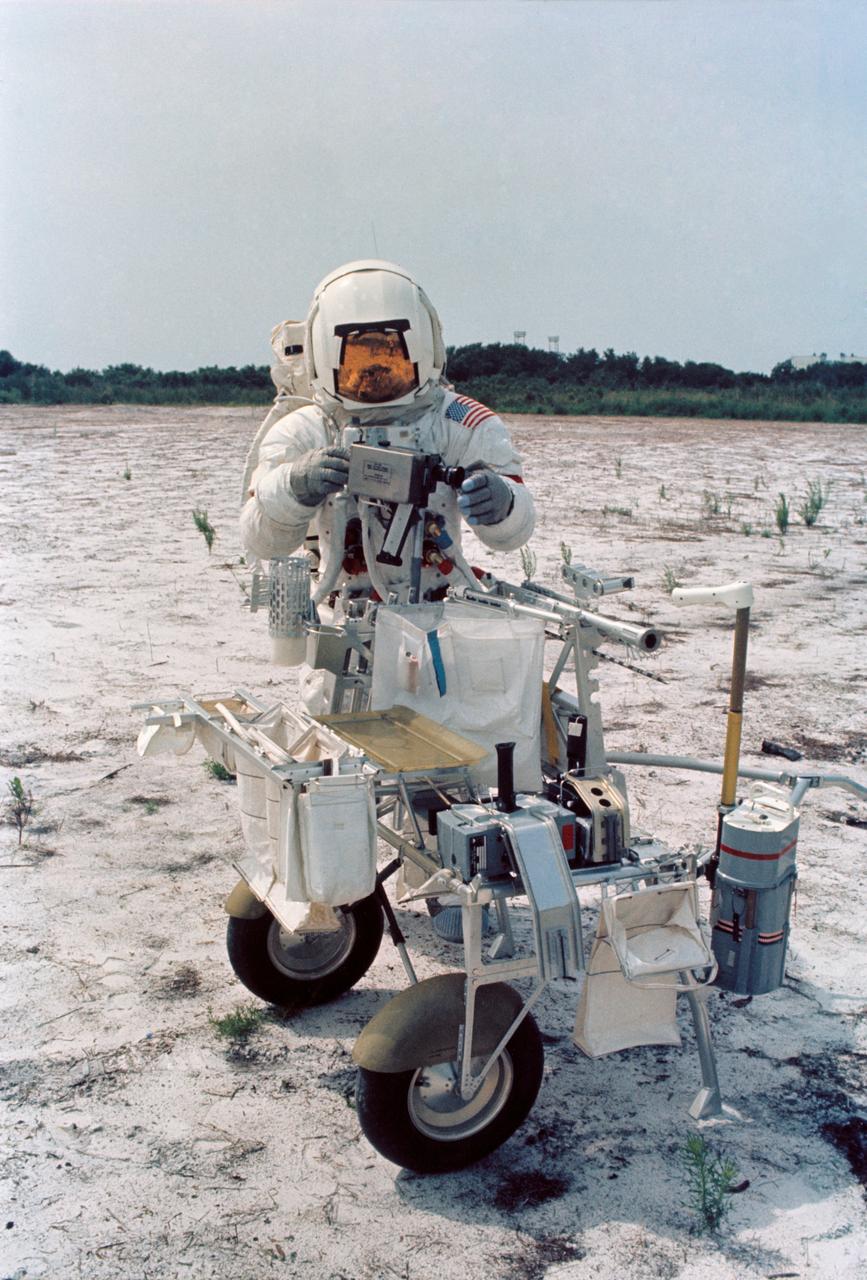

S70-46191 (July 1970) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface training at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Shepard is adjusting a camera mounted to the modular equipment transporter (MET). The MET, nicknamed the "Rickshaw", will serve as a portable work bench with a place for the Apollo lunar hand tools and their carrier, three cameras, two sample container bags, a special environment sample container, spare magazines, and a lunar surface Penetrometer. Shepard is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU).
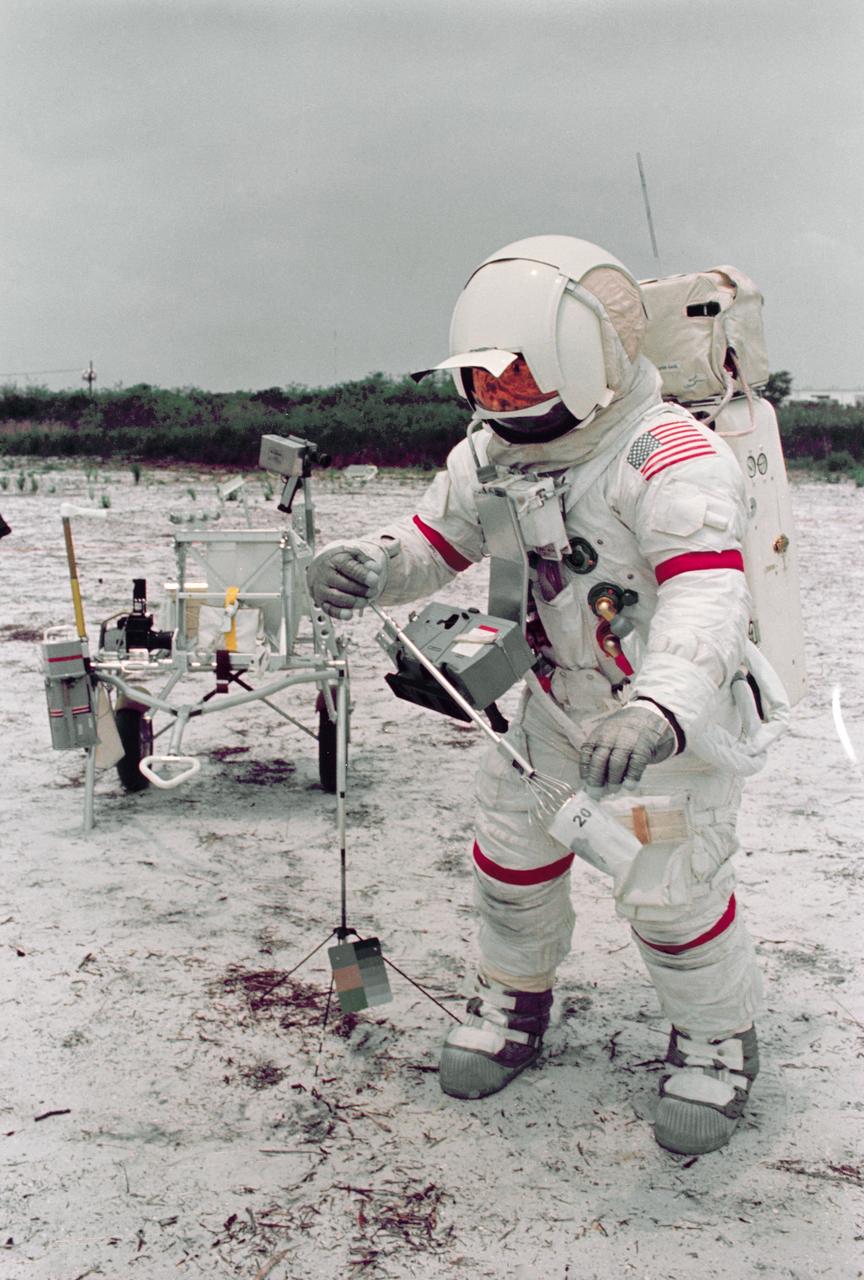
S70-46157 (July 1970) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface simulation training at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The modular equipment transporter (MET) is in the left background, in the center foreground is a gnomon. The MET, nicknamed the "Rickshaw", will serve as a portable work bench with a place for the Apollo lunar hand tools and their carrier, three cameras, two sample container bags, a special environment sample container, spare magazines, and a lunar surface Penetrometer. Shepard is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU).
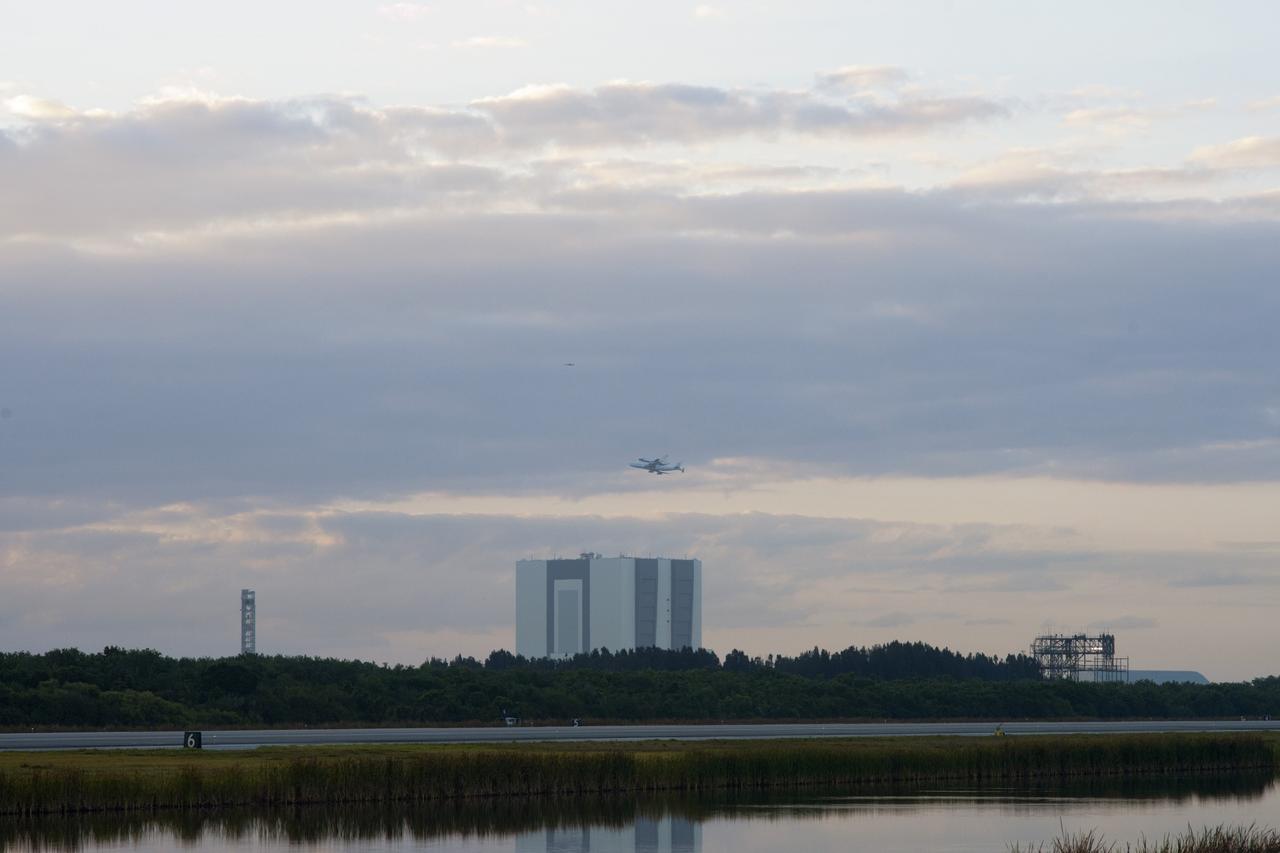

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft transporting space shuttle Discovery to its new home takes off from the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7 a.m. EDT. The facilities beneath the aircraft are, from left, NASA’s new mobile launcher, the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building and the mate/demate device at the landing facility. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Powers and Rick Wetherington
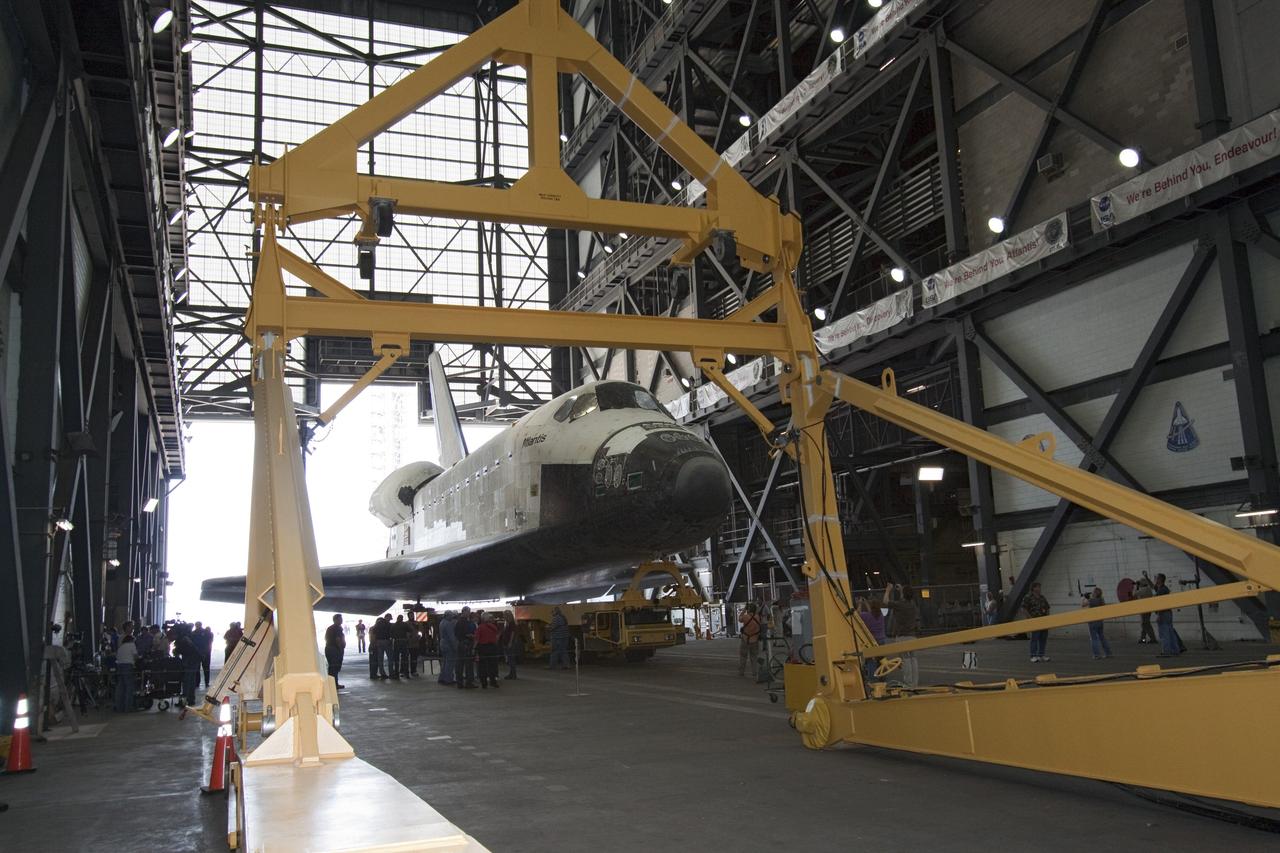

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Shuttle Atlantis is parked in the transfer aisle in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A large yellow sling device (foreground) will be used to lift Atlantis into a high bay for joining to the solid rocket boosters and external tank already installed on a mobile launcher platform. The move called "rollover" is a major milestone in processing for the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are expected to launch mid July, taking with them the Raffaello multipurpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
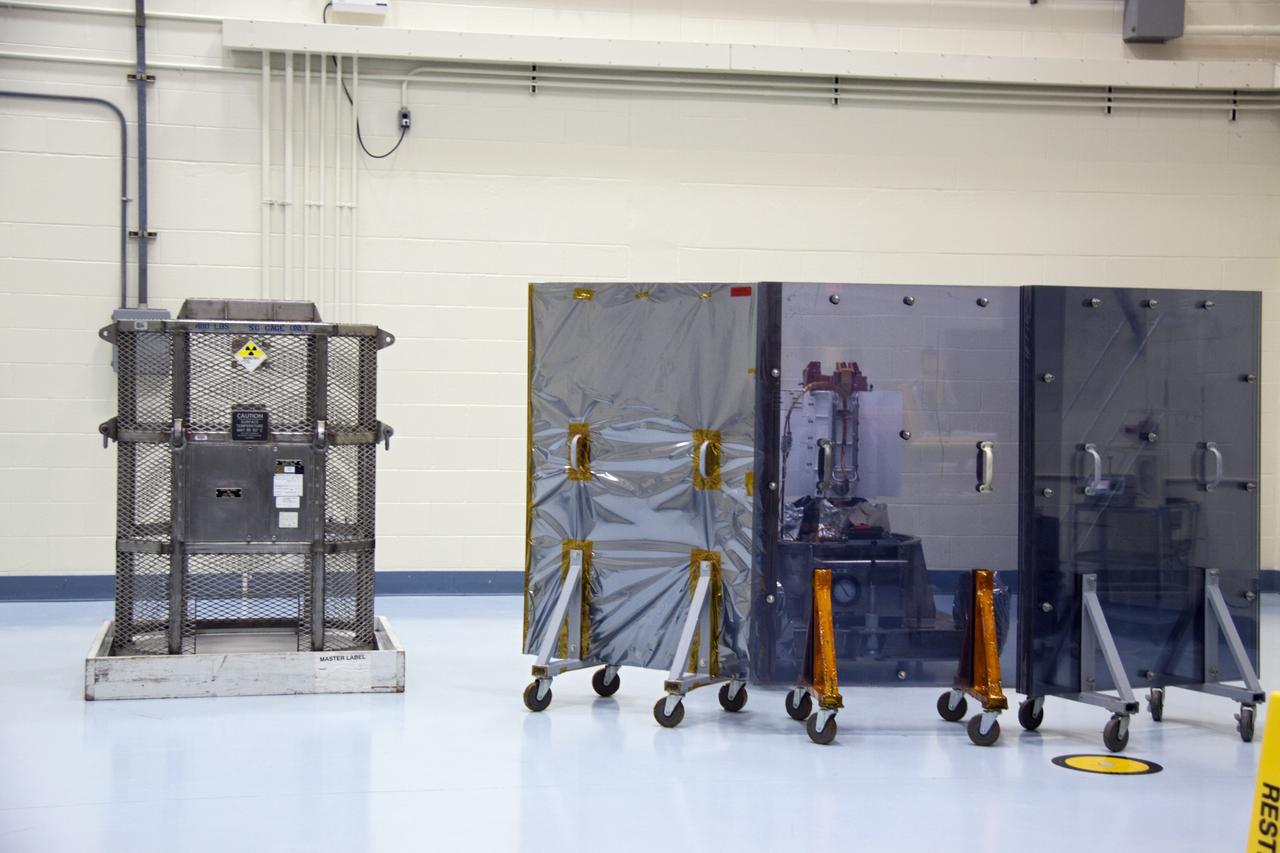

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is position behind mobile plexiglass radiation shields in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG was returned to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The generator will remain in the RTGF until is moved to the pad for integration on the rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
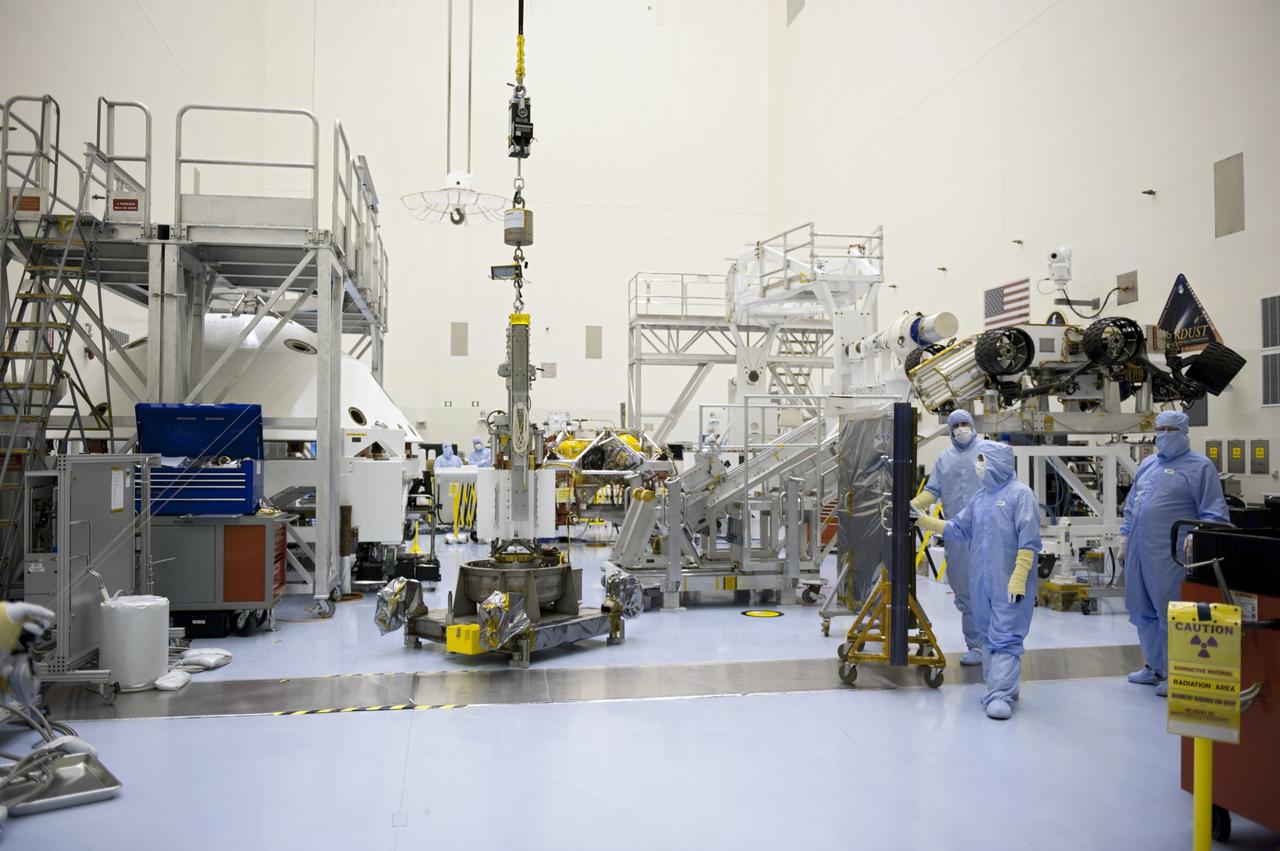

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, still connected to the turning fixture, rests on a support base following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. A mobile plexiglass radiation shield is in place between the MMRTG and the spacecraft technicians, at right, to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
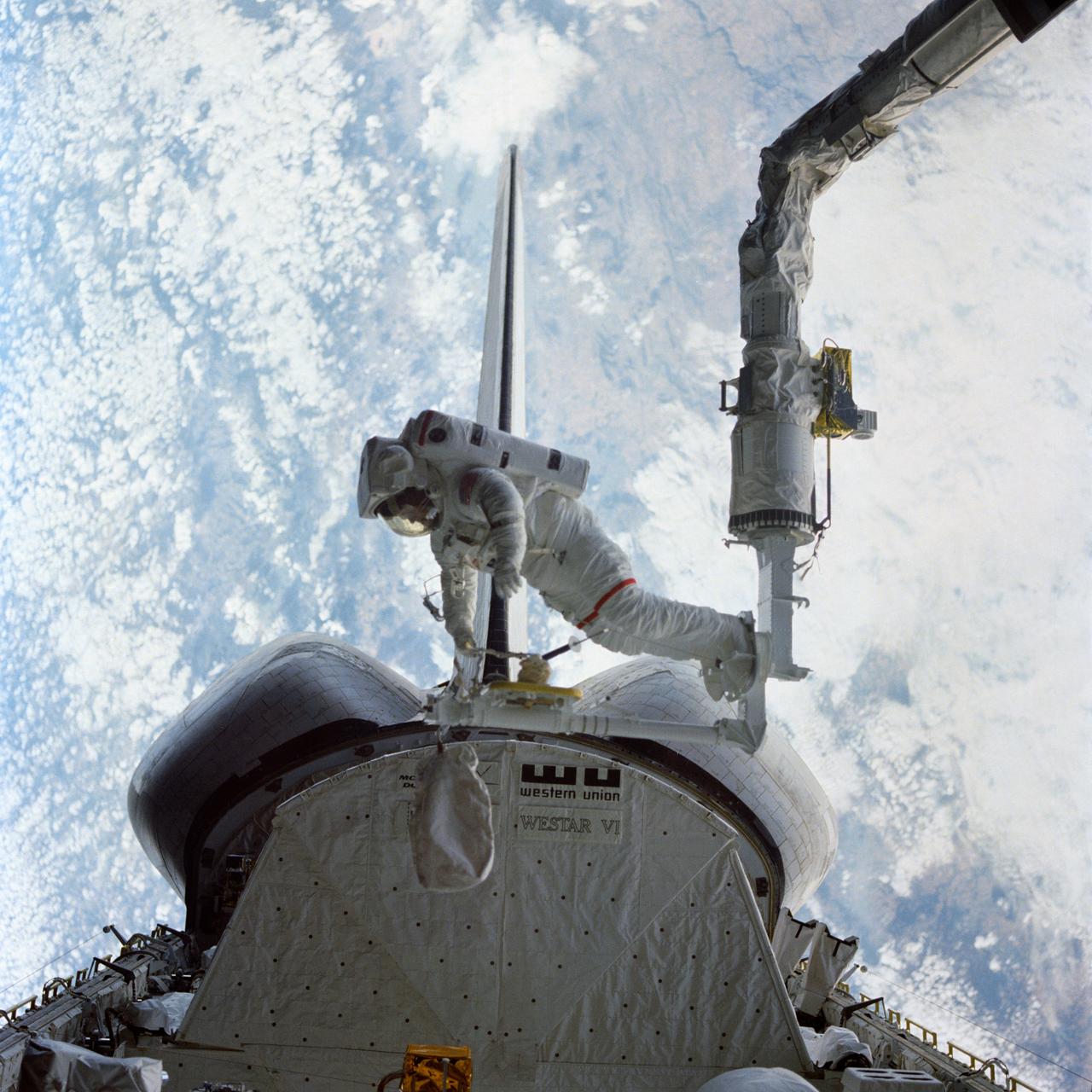

S84-27021 (7 Feb 1984) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, 41B mission specialist tests a "cherry-picker" type device during February 7 historical Extravehicular Activity (EVA). The EVA, in which Astronauts McCandless and Robert L. Stewart, two of three STS-41B mission specialists, participated, marked two firsts--initial use of both the Mobile Foot Restraint (MFR) attached to the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm here, and the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU) backpack (not seen in this frame). The Challenger was flying with its aft end aimed toward the Earth. This photograph clearly shows where the MFR connects to the end effector of the Canadian-built RMS arm. The two spacewalkers were monitored and photographed by their fellow crewmembers, astronauts Vance D. Brand, commander; Robert L. Gibson, pilot; and Ronald E. McNair, mission specialist. The three remained in the cabin for another EVA session two days later. Photo Credit: NASA
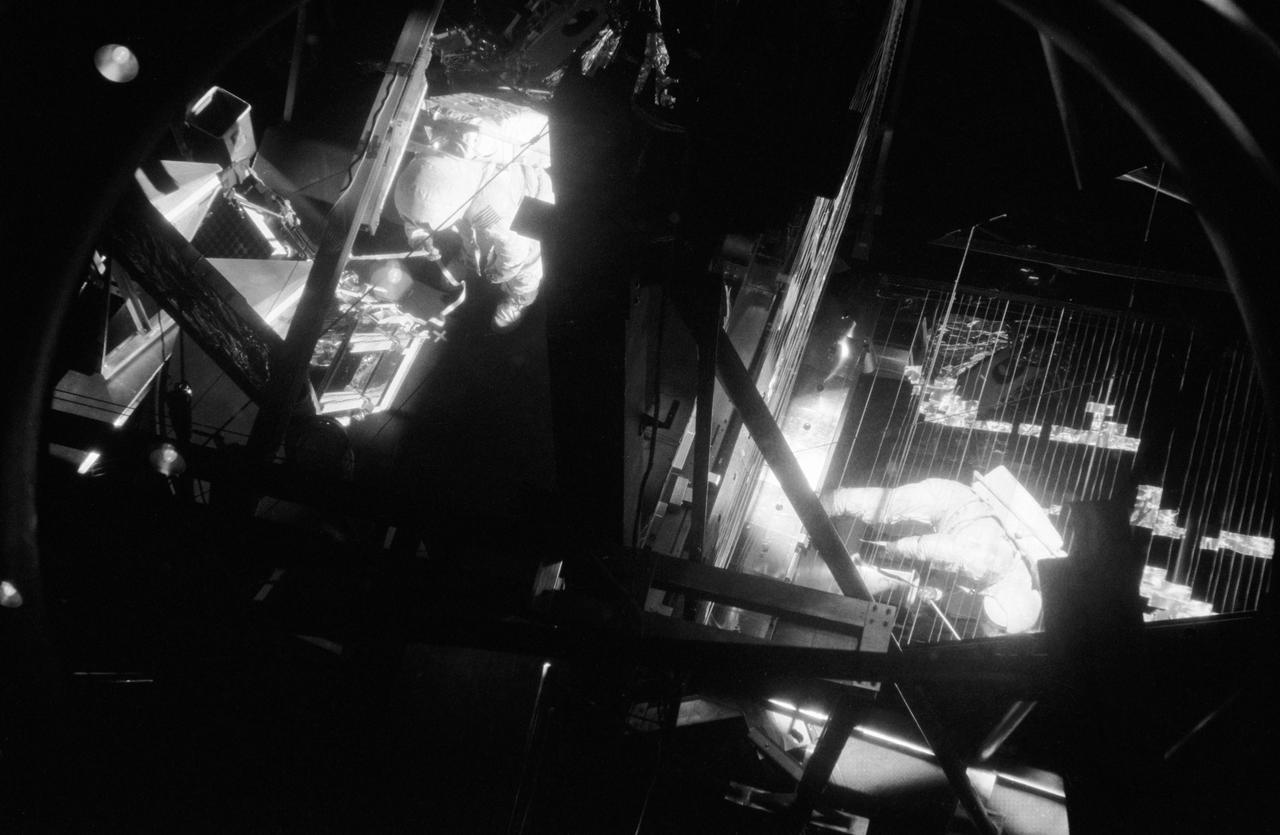

Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, is photographed during thermovacuum training in Chamber B of the Space Environment Simulation Laboratory, Building 32, Manned Spacecraft Center. He is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit. The training simulated lunar surface vacuum and thermal conditions during astronaut operations outside the Lunar Module on the moon's surface. The mirror was used to reflect solar light.
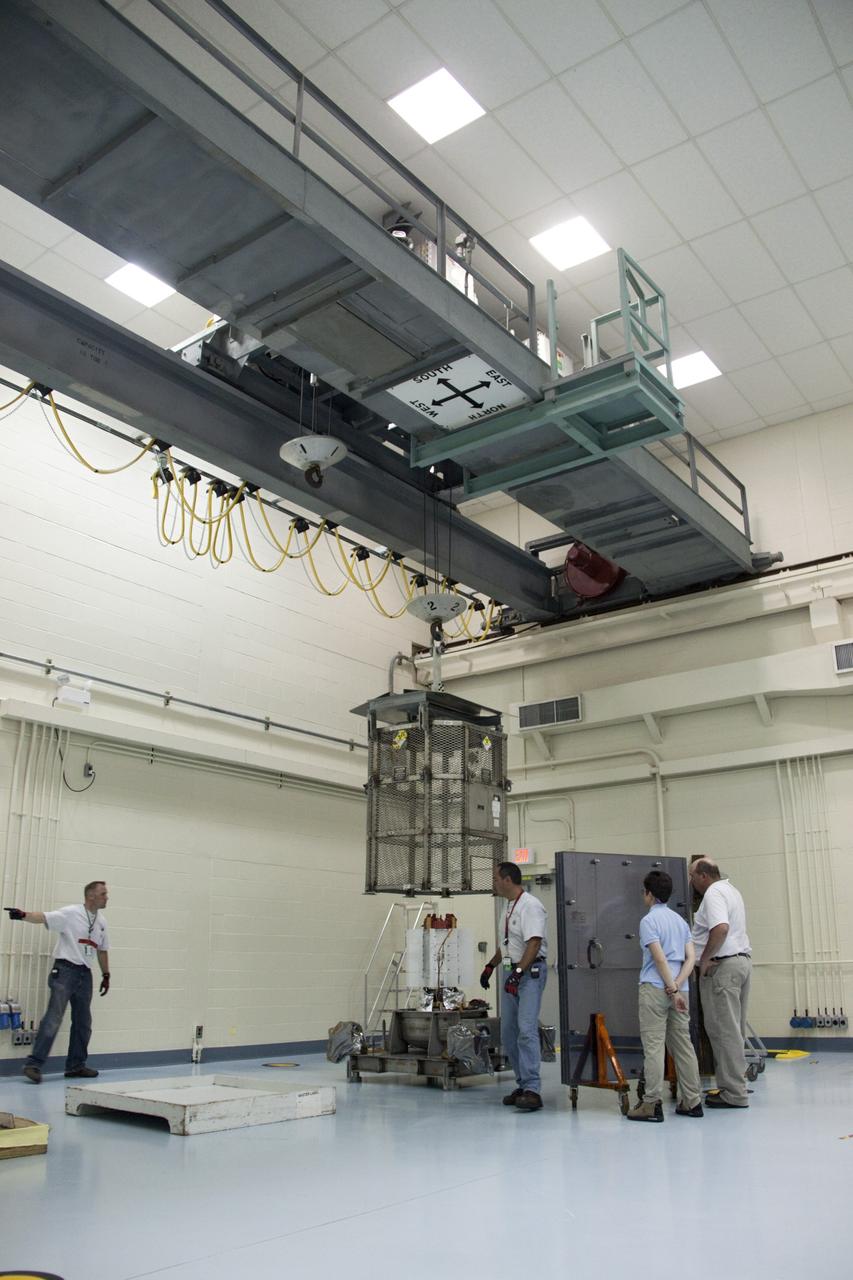

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted from around the MMRTG. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The cage is being removed following the return of the MMRTG to the RTGF from a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The workers at right are observing the operation from behind a mobile plexiglass radiation shield to minimize their radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
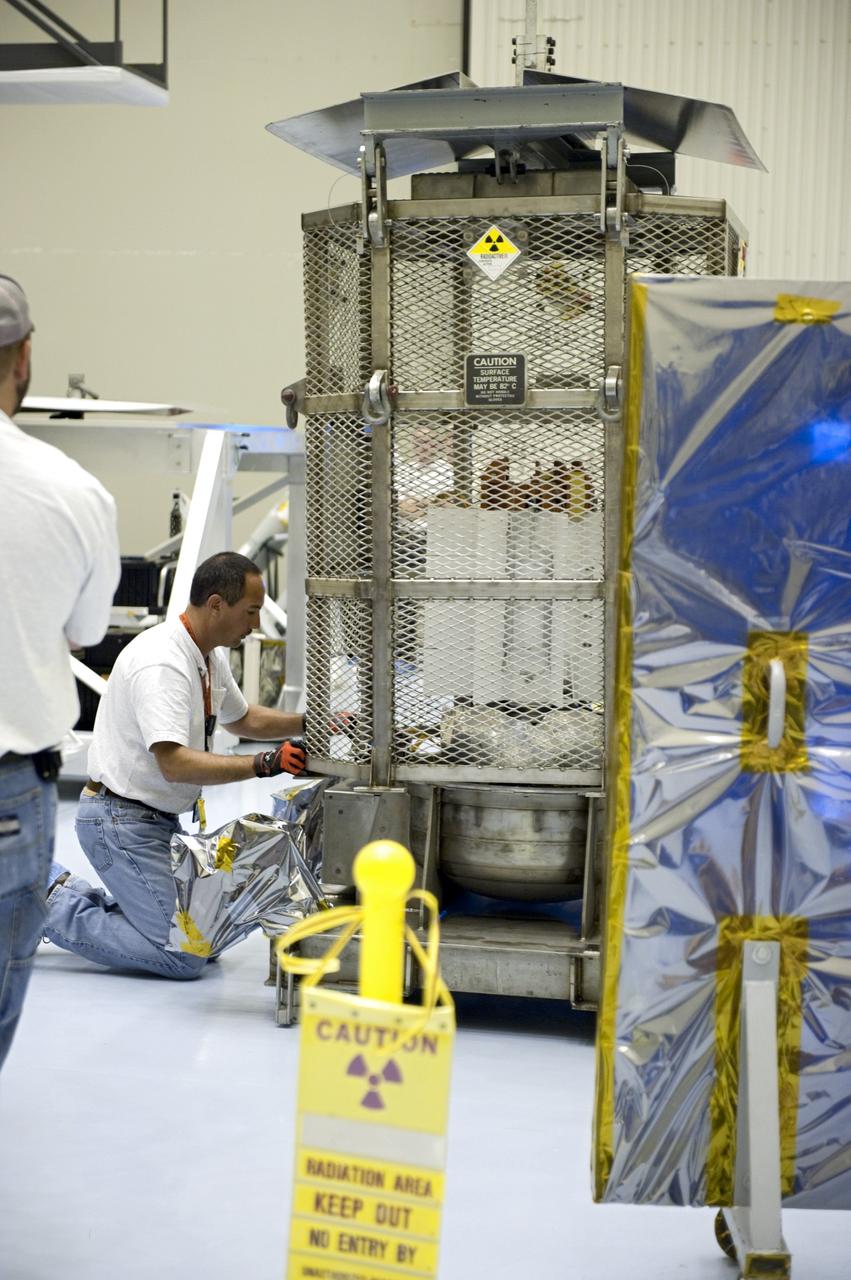

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Department of Energy employee positions the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," on the support base of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The mobile plexiglass radiation shields, in the foreground at right, helps minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy employees lower the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," toward the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The employees are standing behind mobile plexiglass radiation shields to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
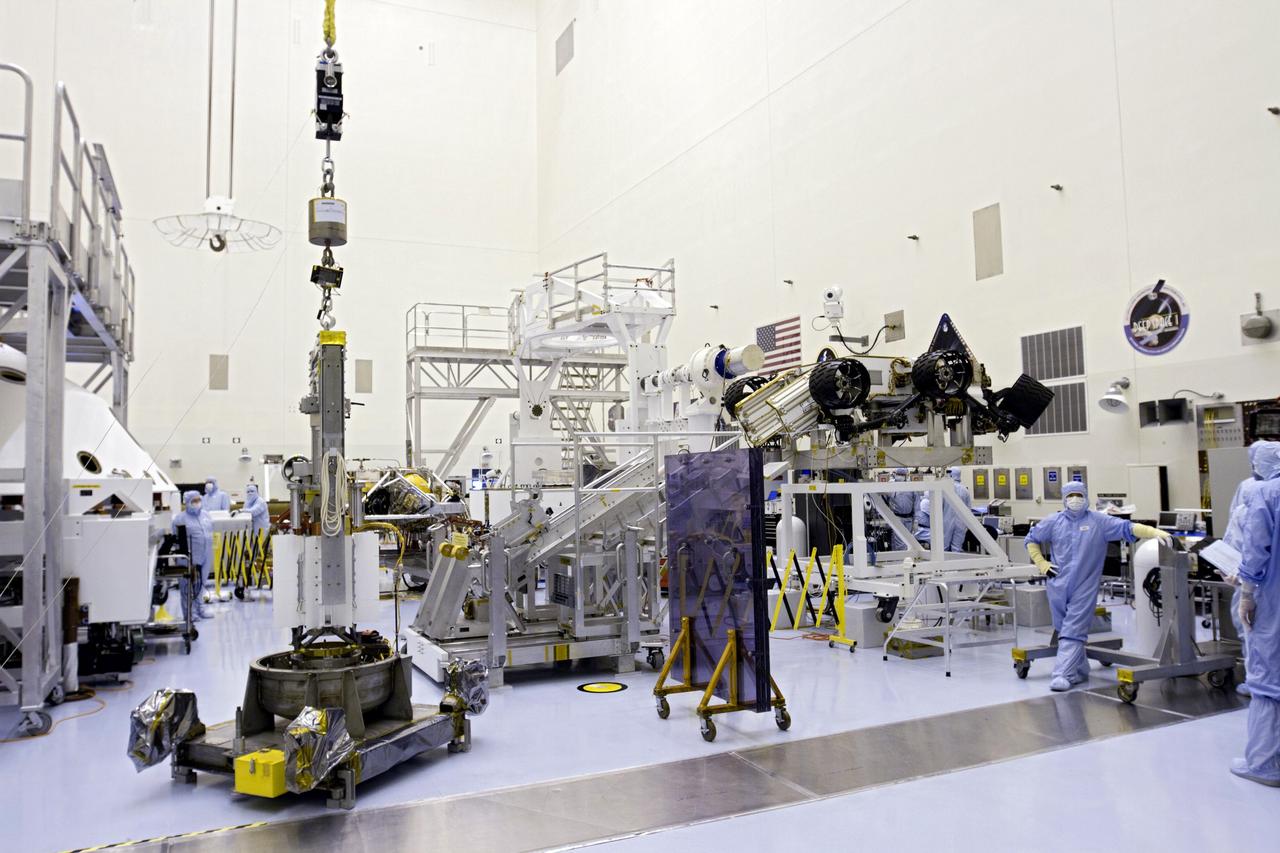

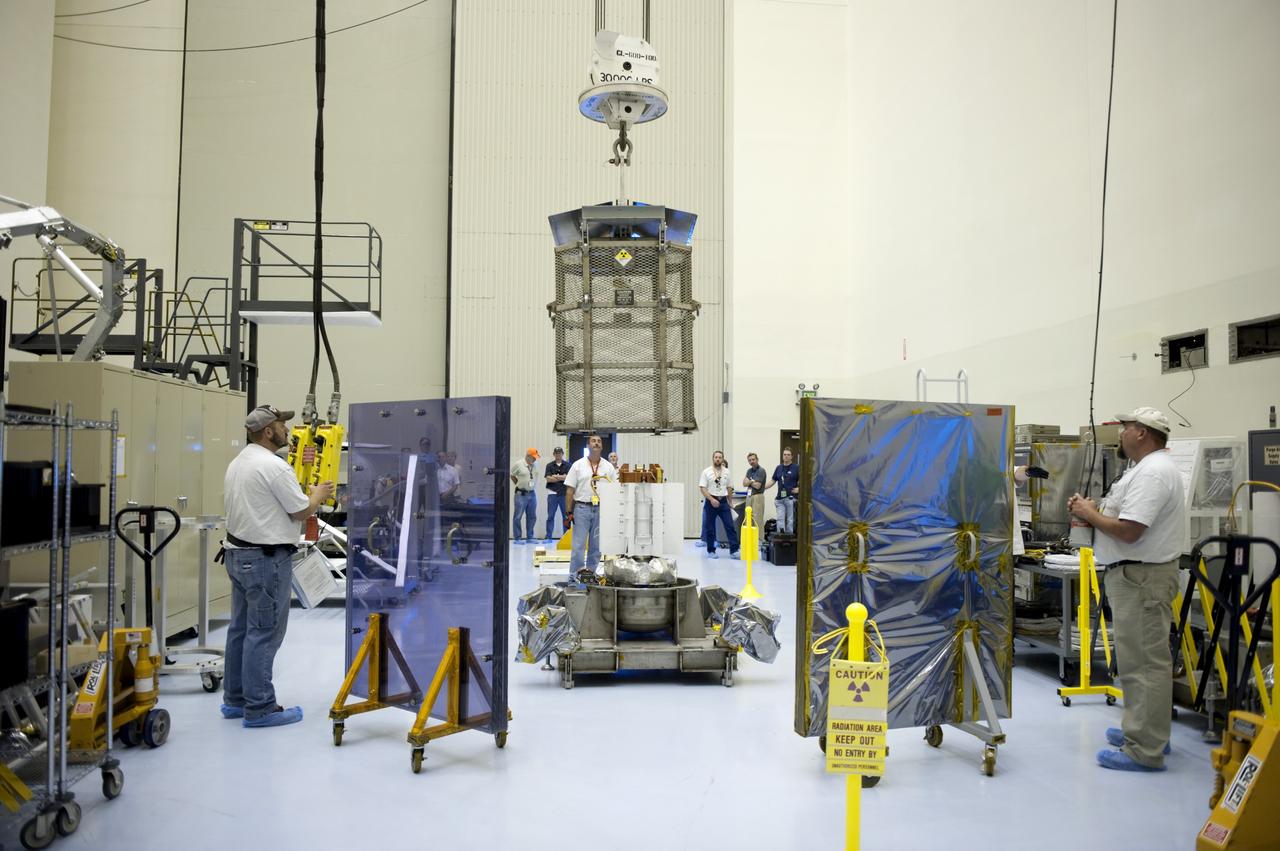
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way for a crane to lift the turning fixture connected to the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission from its support base. Between the MMRTG and the spacecraft technicians at right is a mobile plexiglass radiation shield to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The turning fixture will lift and lower the MMRTG onto the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on Curiosity for a fit check. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

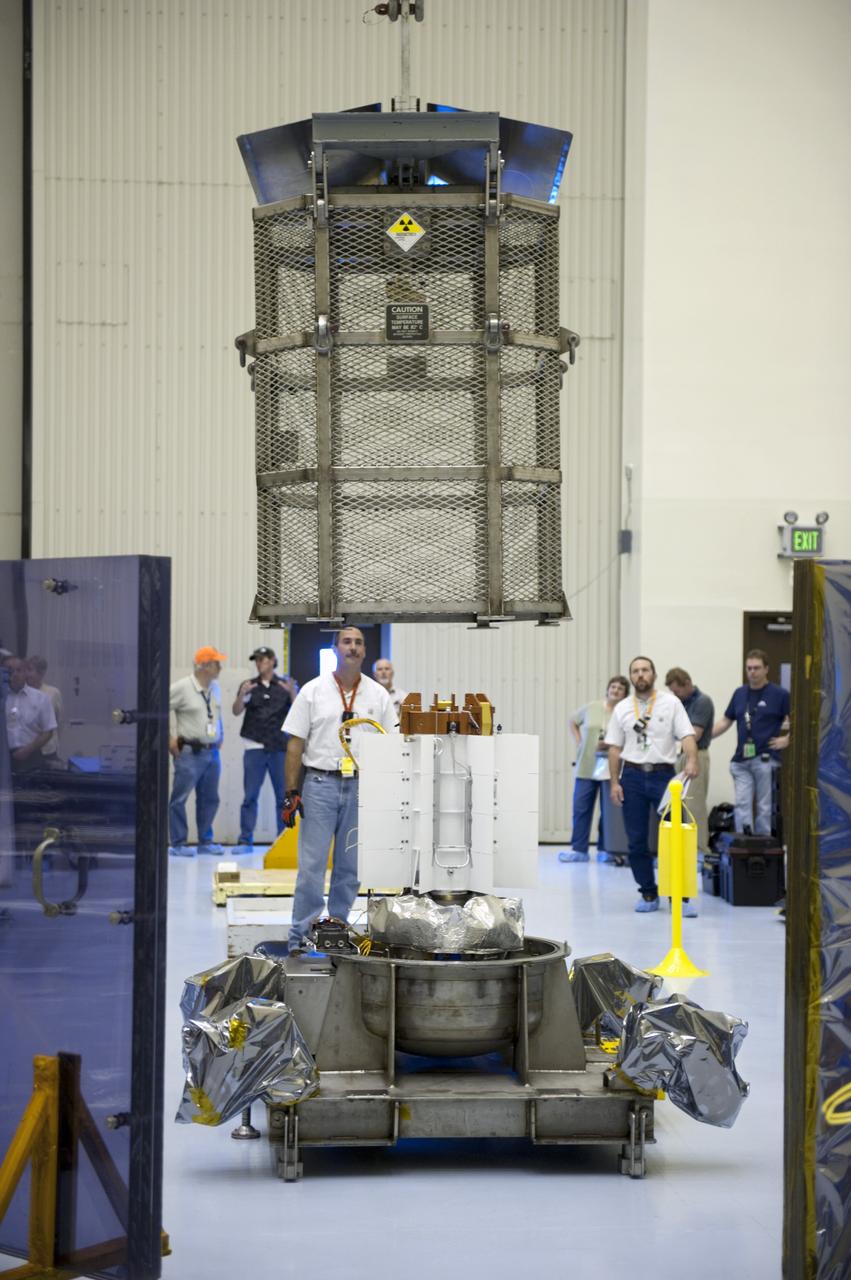
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy workers guide the mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission as it is lifted by a crane. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The cage is being removed from around the MMRTG following it return to the RTGF from a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The workers at right are observing the operation from behind a mobile plexiglass radiation shield to minimize their radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
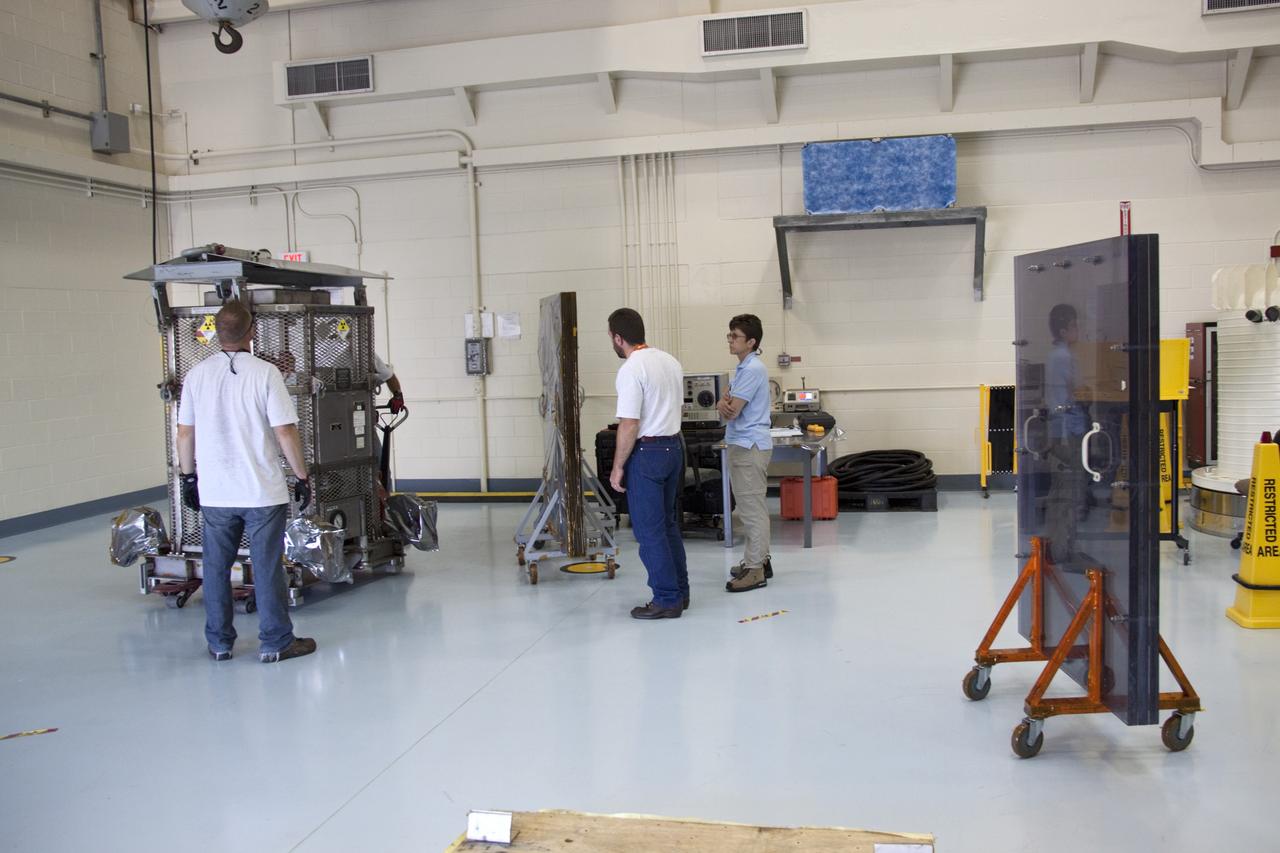

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Department of Energy workers position mobile plexiglass radiation shields around the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission upon its arrival in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The shields are designed to minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The MMRTG is enclosed in a mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," which protects it during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

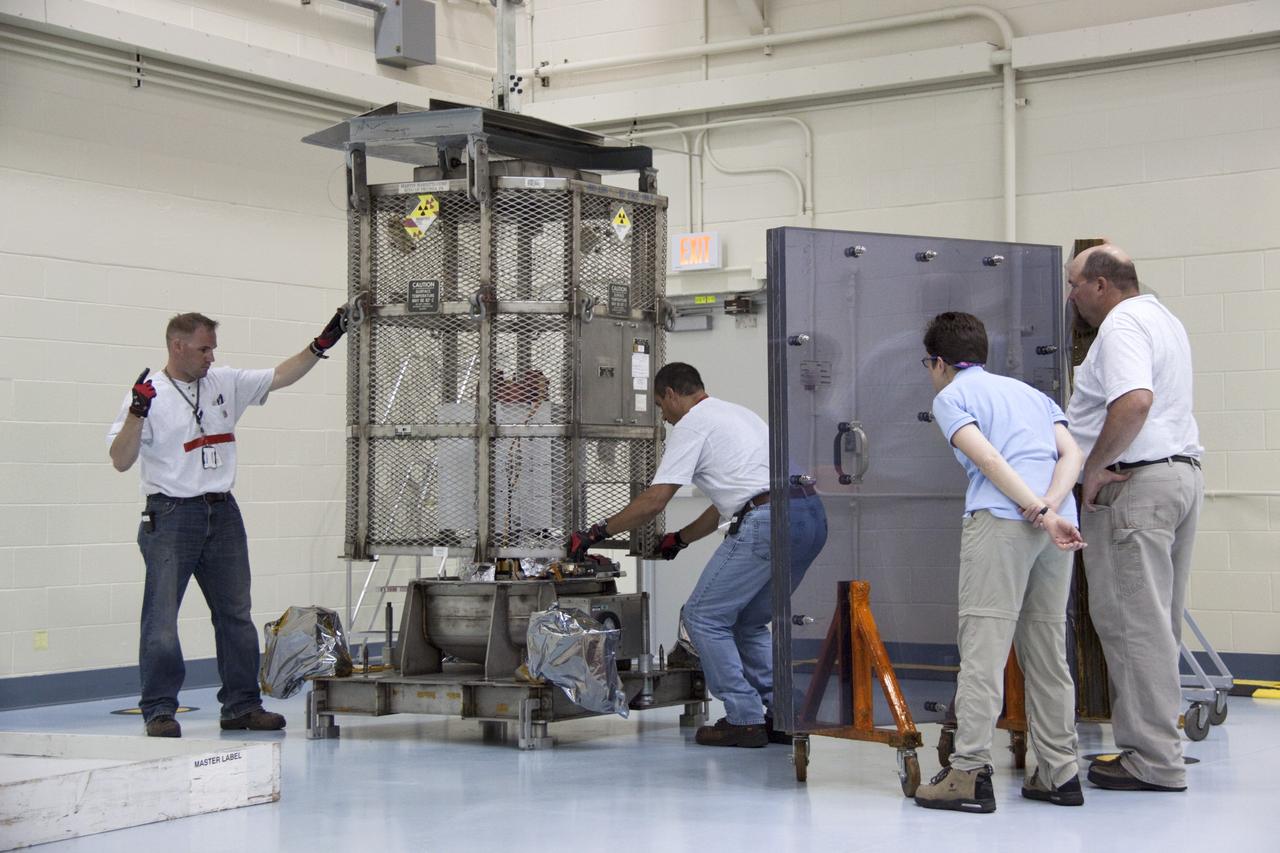
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy employees lower the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," toward the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The mobile plexiglass radiation shields in the foreground help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett