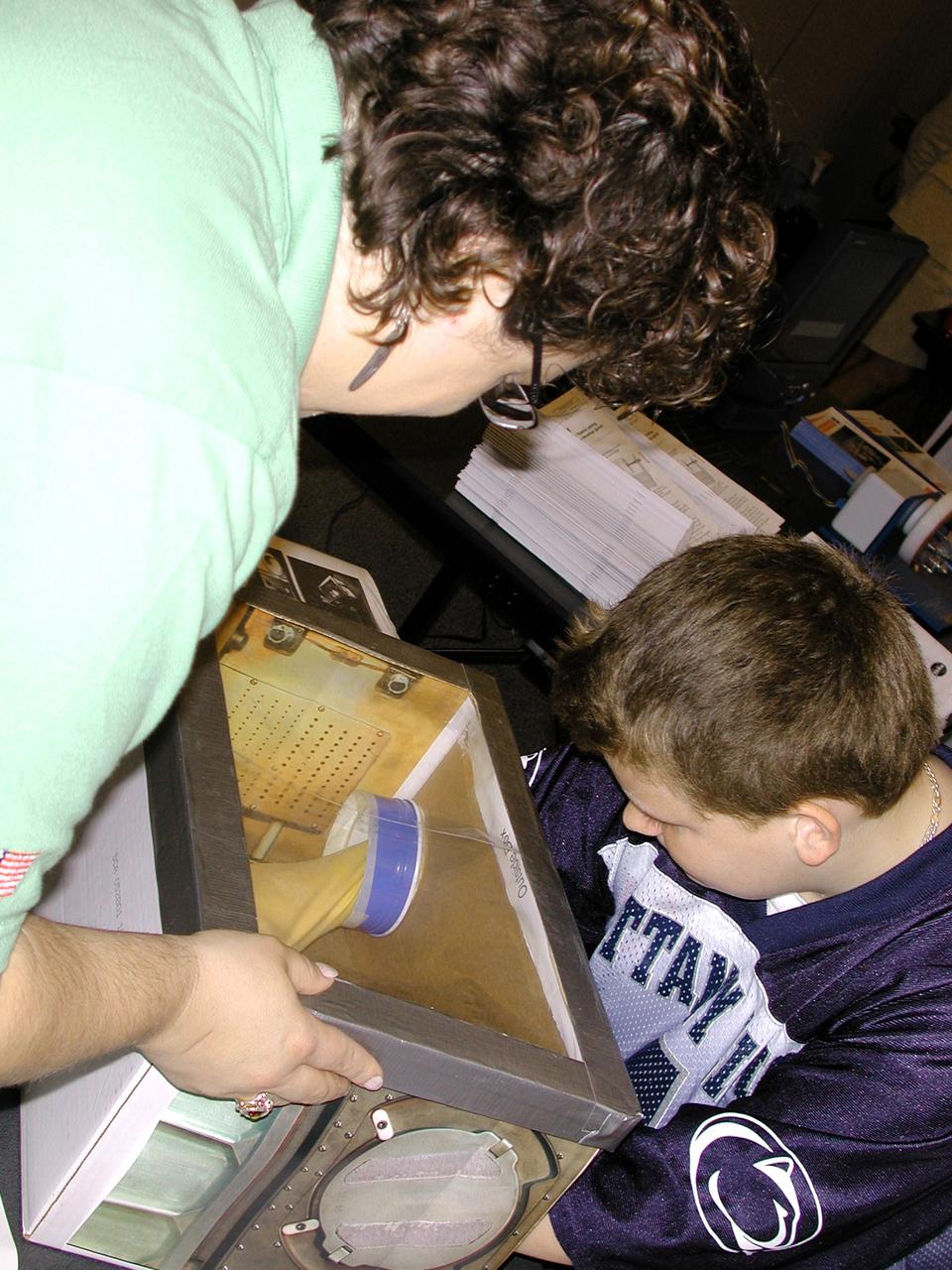

Carla Rosenberg of the National Center for Microgravity Research explains the operation of the Middeck Glovebox to a middle school student. The activity was part of the Space Research and You education event held by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research on June 25, 2002, in Arlington, VA, to highlight the research that will be conducted on STS-107.
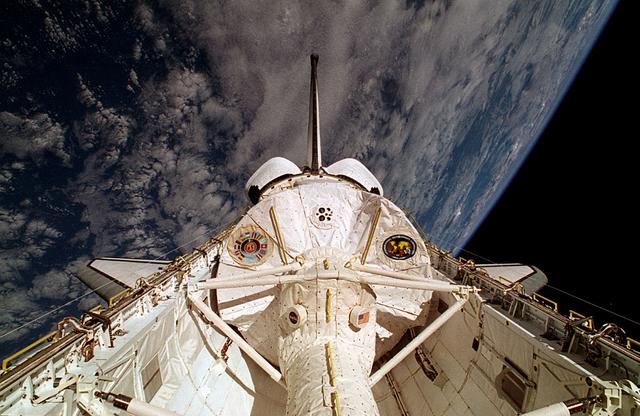

This is a Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) onboard photo of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) in the cargo bay with Earth in the background. Mission objectives of IML-2 were to conduct science and technology investigations that required the low-gravity environment of space, with emphasis on experiments that studied the effects of microgravity on materials processes and living organisms. Materials science and life sciences are two of the most exciting areas of microgravity research because discoveries in these fields could greatly enhance the quality of life on Earth. If the structure of certain proteins can be determined by examining high-quality protein crystals grown in microgravity, advances can be made to improve the treatment of many human diseases. Electronic materials research in space may help us refine processes and make better products, such as computers, lasers, and other high-tech devices. The 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (SCA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DARA/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) participated in developing hardware and experiments for the IML missions. The missions were managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. The Orbiter Columbia was launched from the Kennedy Space Center on July 8, 1994 for the IML-2 mission.
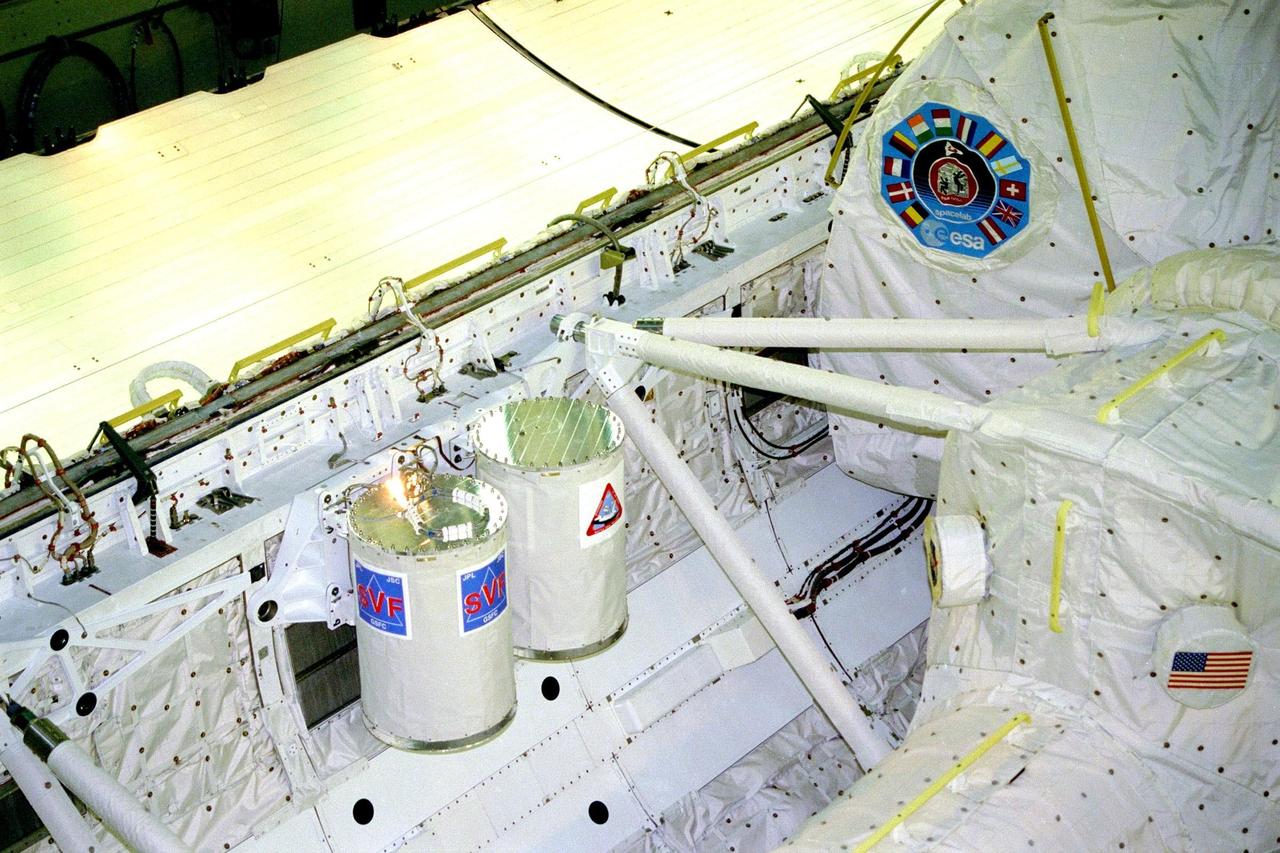
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-90 Neurolab payload and two of the four Getaway Specials (GAS) await payload bay door closure in the orbiter Columbia today in Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3. Investigations during the Neurolab mission will focus on the effects of microgravity on the nervous system. The mission is a joint venture of six space agencies and seven U.S. research agencies. Investigator teams from nine countries will conduct 31 studies in the microgravity environment of space. Other agencies participating in this mission include six institutes of the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, and the Office of Naval Research, as well as the space agencies of Canada, France, Germany, and Japan, and the European Space Agency (ESA)
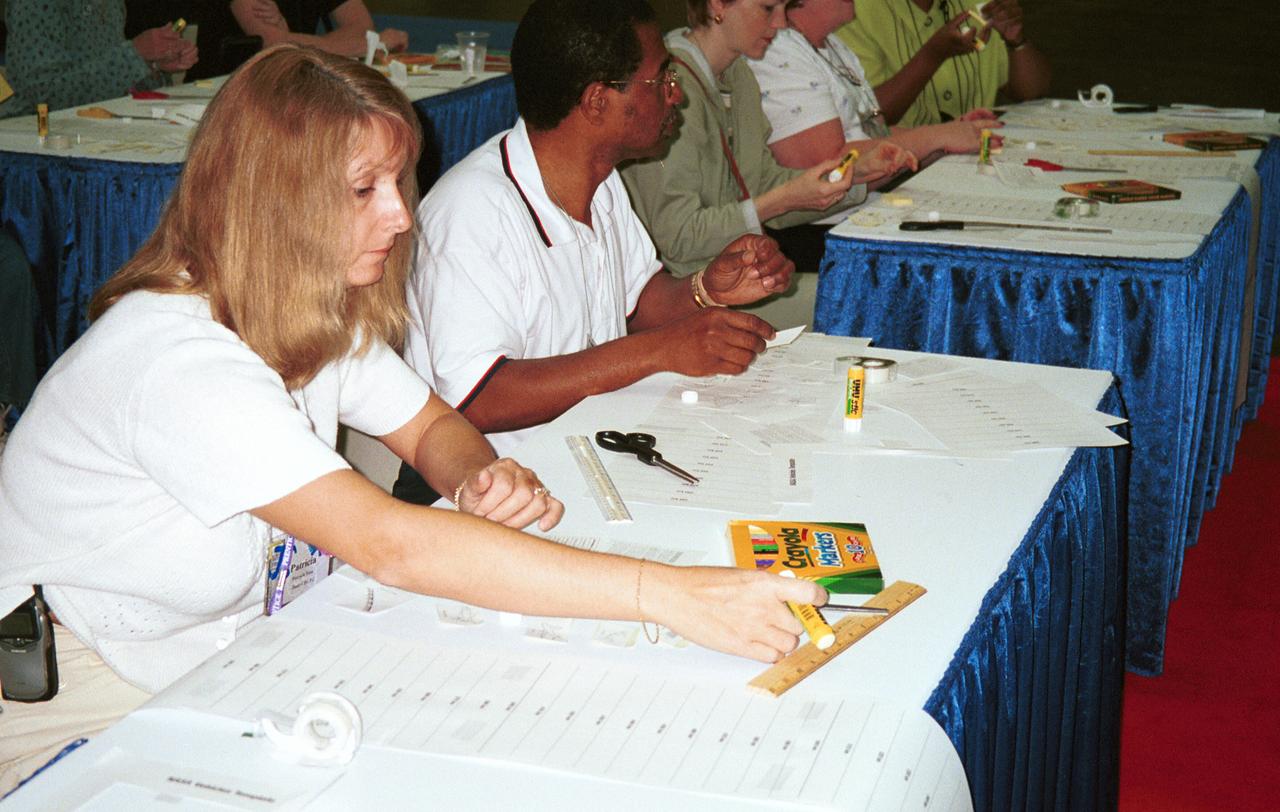

One of NASA's newest education publications made its debut at the arnual National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) conference held in Orlando, Florida April 5-7. How High Is It? An Educator's Guide with Activities Focused on Scale Models of Distances was presented by Carla Rosenberg of the National Center for Microgravity Research at Glenn Research Center. Rosenberg, an author of the Guide, led teachers in several hands-on activities from the Guide. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

One of NASA's newest education publications made its debut at the arnual National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) conference held in Orlando, Florida April 5-7. How High Is It? An Educator's Guide with Activities Focused on Scale Models of Distances was presented by Carla Rosenberg of the National Center for Microgravity Research at Glenn Research Center. Rosenberg, an author of the Guide, led teachers in several hands-on activities from the Guide. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
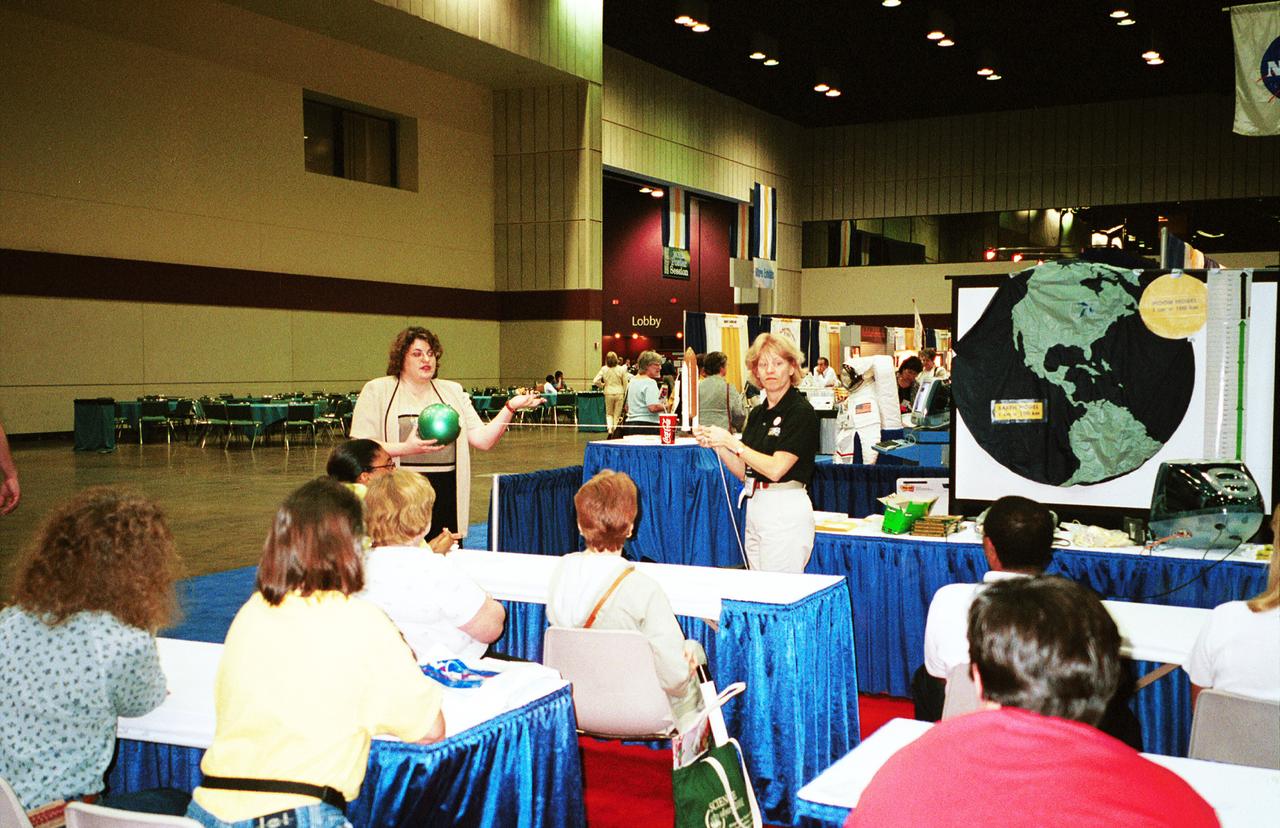

One of NASA's newest education publications made its debut at the arnual National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) conference held in Orlando, Florida April 5-7. How High Is It? An Educator's Guide with Activities Focused on Scale Models of Distances was presented by Carla Rosenberg of the National Center for Microgravity Research at Glenn Research Center. Rosenberg, an author of the Guide, led teachers in several hands-on activities from the Guide. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

One of NASA's newest education publications made its debut at the arnual National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) conference held in Orlando, Florida April 5-7. How High Is It? An Educator's Guide with Activities Focused on Scale Models of Distances was presented by Carla Rosenberg of the National Center for Microgravity Research at Glenn Research Center. Rosenberg, an author of the Guide, led teachers in several hands-on activities from the Guide. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

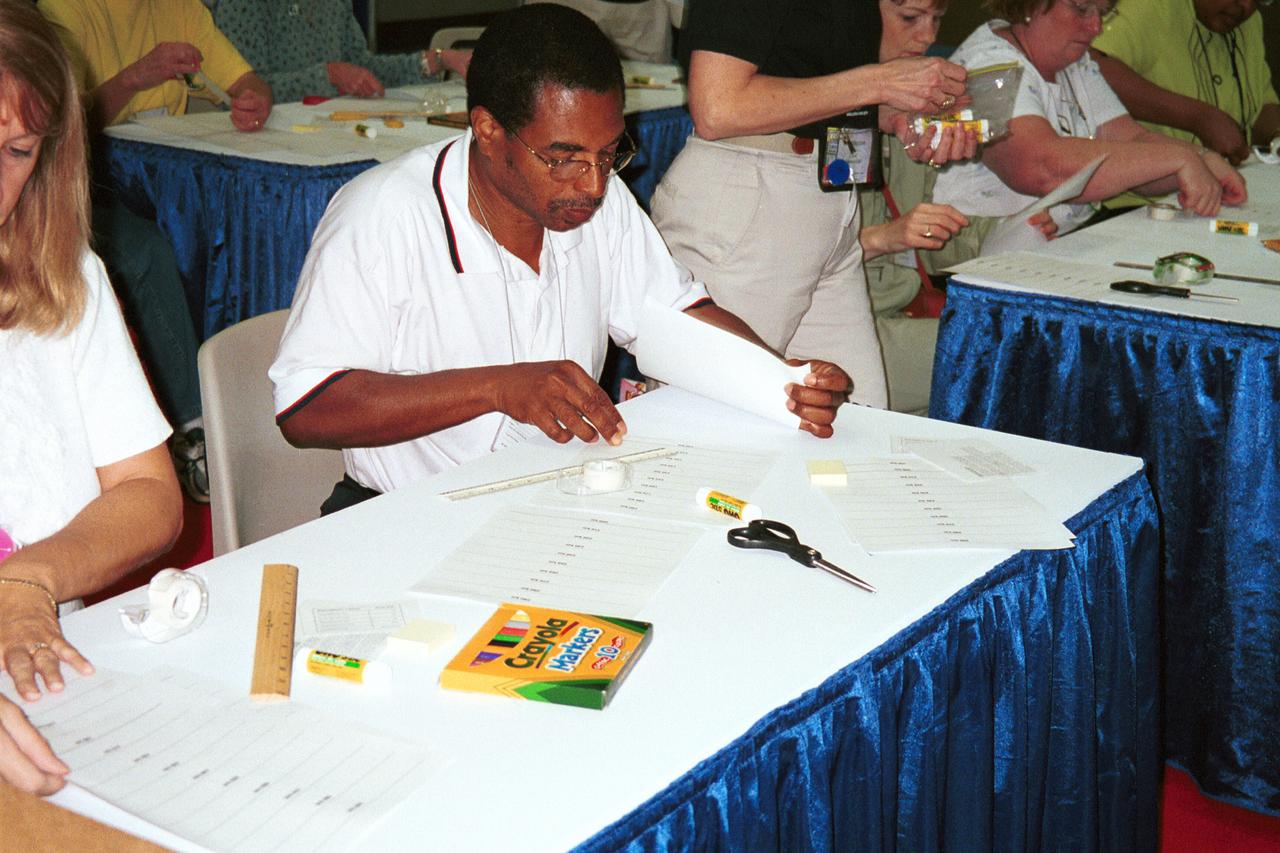
The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Here Carol Hodanbosi of the National Center for Microgravity Research and Jose Carrion, a lab mechanic with AKAC, prepare a student experiment package (inside the silver-colored frame) inside the orange-colored drag shield that encloses all experiment hardware. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Sandi Thompson of the National Center for Microgravity Research GRC makes a final adjustment to the drop package. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
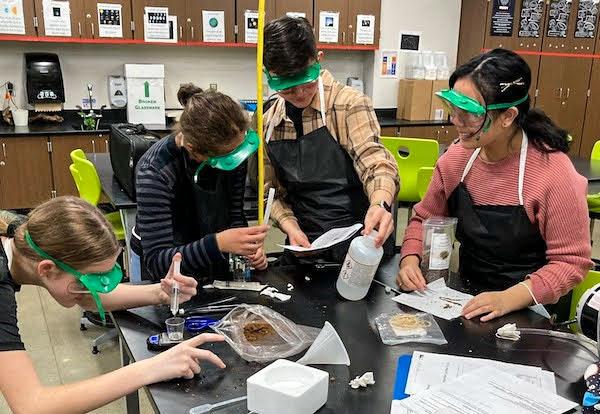

jsc2023e065214 (2/7/2023) --- Eighth grade student researchers work on their experiment, Microgreen Growth in Microgravity Environment, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
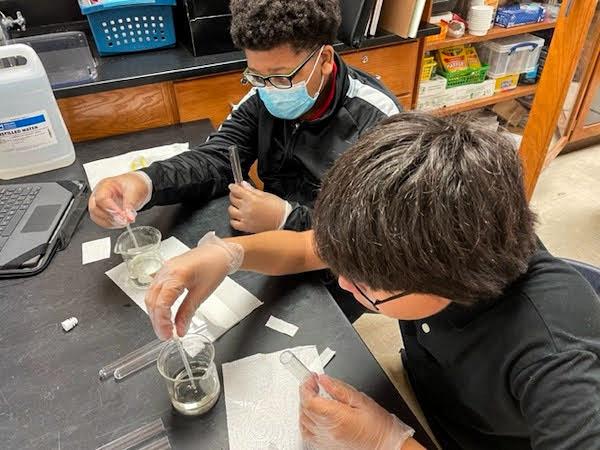

jsc2023e065199 (1/26/2023) --- Mundy's Mill Middle School student researchers work on their experiment, Germination of Mentha spicata in Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
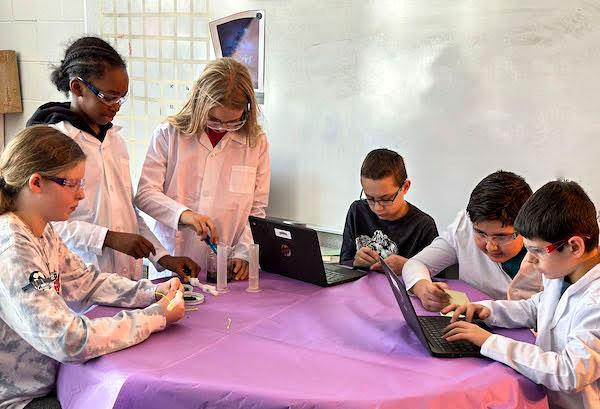

jsc2023e06522 (3/3/2023) --- Fifth grade student researchers from Walker-Winter Elementary School work on their experiment, Mushroom Germination in Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
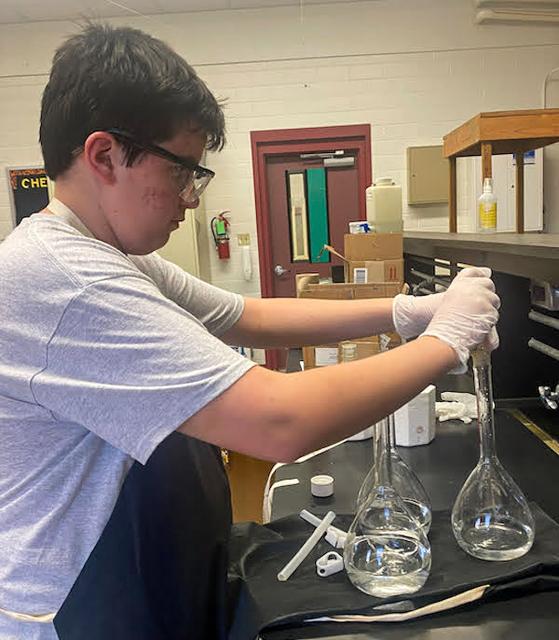

jsc2023e065200 (10/19/2023) --- Student researcher Sam Dondapati work on his experiment, Growth of Spirulina in Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
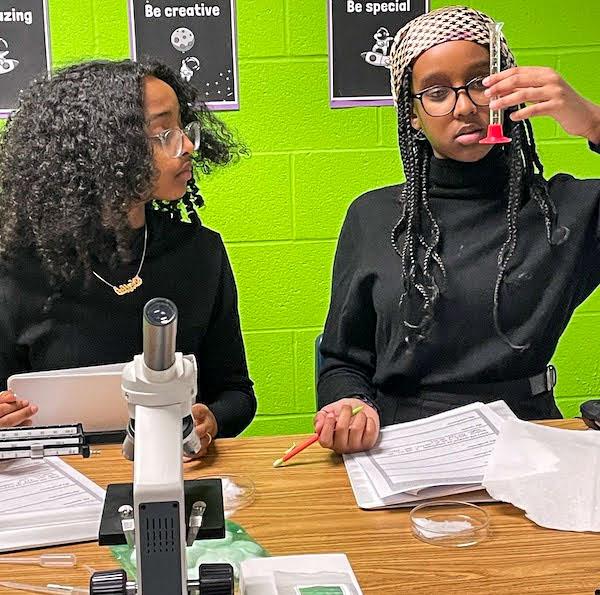

jsc2023e065211 (1/19/2023) --- Harmon Middle School student researchers work on their experiment, Bamboo Growth in Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
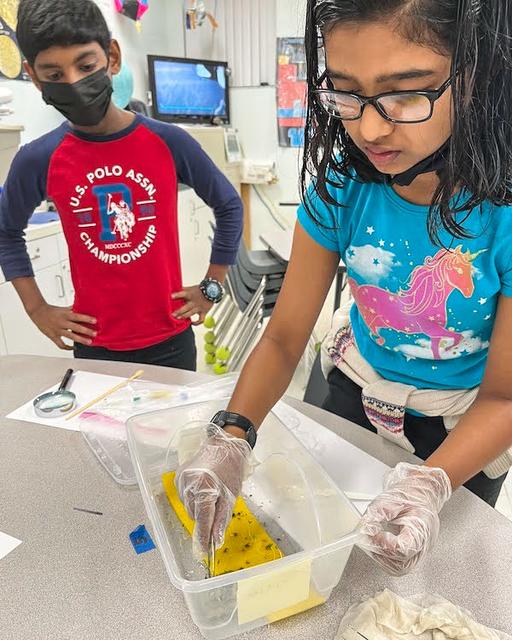

jsc2023e065196 (10/26/2023) --- Student researchers Lonappan John and Aadrita Roywork on their experiment, The Changes of Nutritional and Germination values of Sesame Microgreens in Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).

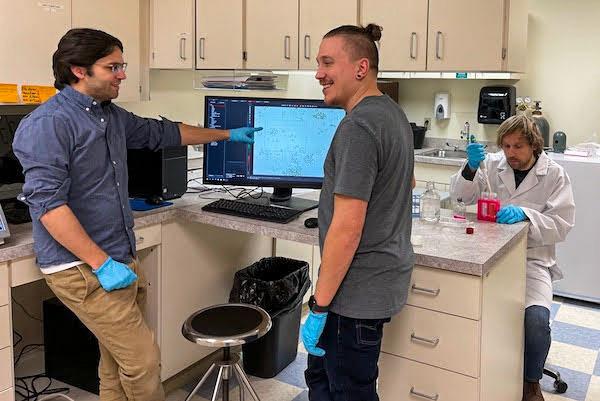
jsc2024e066517 (10/4/2024) --- Young researchers work on their experiment, Production of Biomedical Purpose Hydrogels in Microgravity, part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).

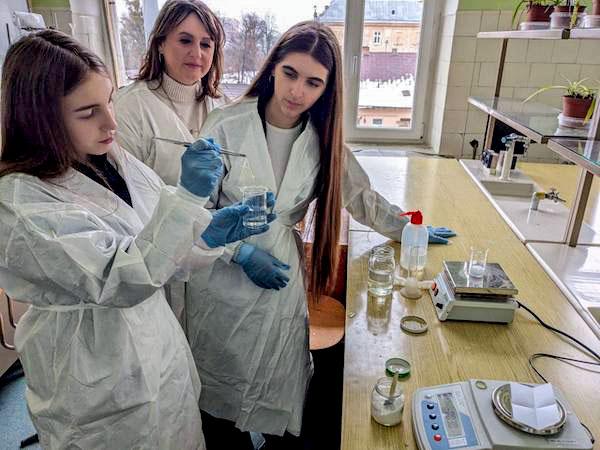
jsc2023e065201 (1/12/2023) --- Pinecrest St. Rose student researchers work on their experiment, Wolffia in Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).

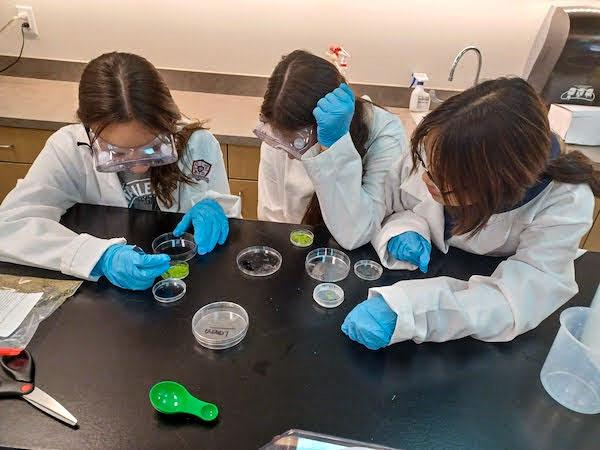
sc2023e065194 (1/20/2023) --- A student researcher works on their The Effects of Microgravity on Cholesterol Lowering Activity by Lactobacillus acidophilus, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).

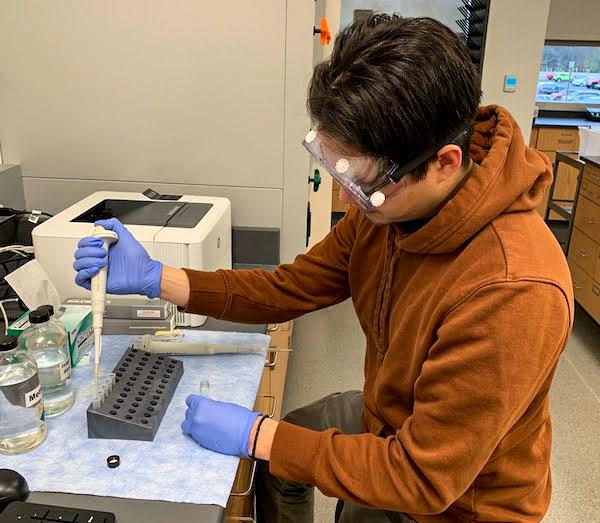
jsc2023e065212 (2/1/2023) --- Student researchers Daniel Roth and Jason Gomes work on their experiment, The Effect(s) of Microgravity on the Dormant State of Cancer Cells, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
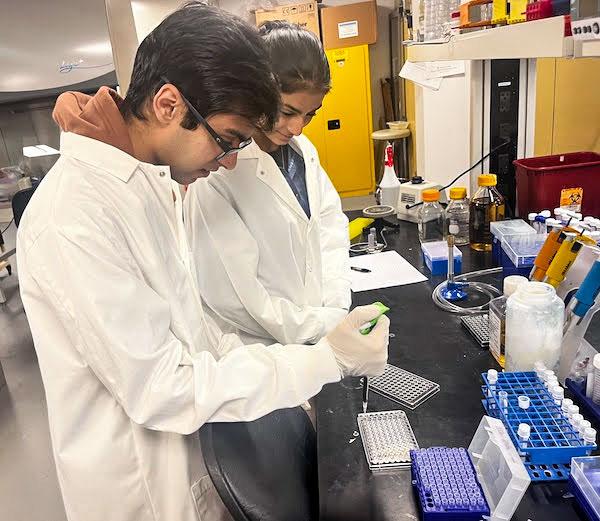

jsc2023e065219 (2/3/2023) --- Student researchers work on their experiment, The Effect of Microgravity on Telomerase Activity and Efficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
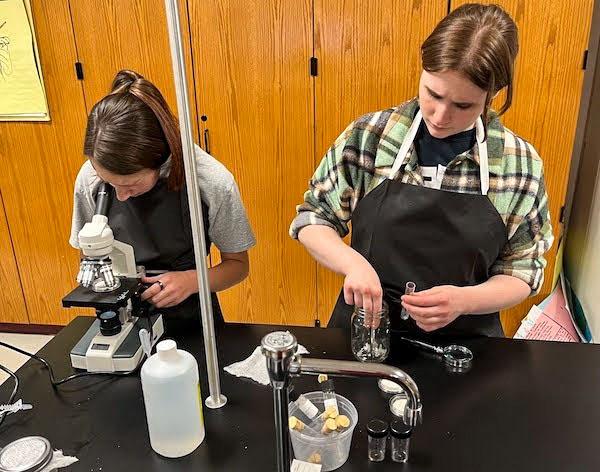

jsc2023e065207 (1/5/2023) --- Student researchers work on their experiment, The Effects of Microgravity on the Reproduction Cycle of Drosophila melanogaster, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).

jsc2023e065202 (10/19/2023) --- Student researchers work on their experiment, How Does Microgravity Affect the Germination of Oyster Mushroom Spawns (Pleurotus Ostreatus), which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
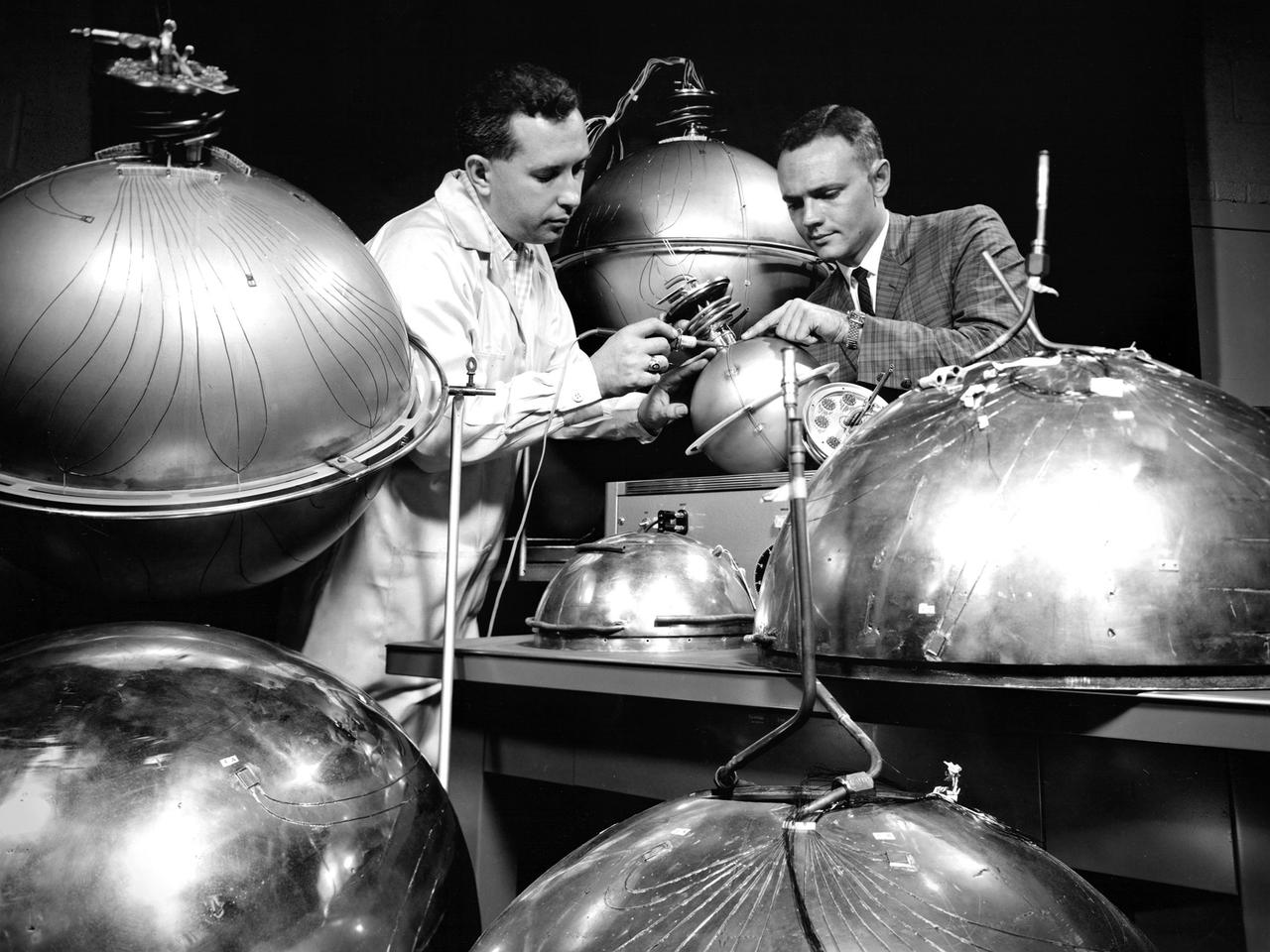

An engineer and technician at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center install the instrumentation on spherical fuel tanks for an investigation of the behavior of liquids in microgravity. Lewis researchers were undertaking a broad effort to study the heat transfer properties of high energy propellants such as liquid hydrogen in microgravity. In the center’s 2.2-Second Drop Tower they investigated the wetting characteristics of liquid and the liquid-vapor configurations, and predicted the equilibrium state in microgravity conditions. Lewis was also conducting a series microgravity investigations which launched 9-inch diameter spherical dewars, seen here, on an Aerobee sounding rocket. A camera inside the rocket filmed the liquid hydrogen’s behavior during its 4 to 7 minutes of freefall. The researchers concluded, however, that they needed to extend the weightlessness period to obtain better results. So they designed an experiment to be launched on an Atlas missile that would provide 21 minutes of weightlessness. The experiment was flight qualified at Lewis. The 36-percent full liquid hydrogen stainless steel dewar was launched on the Atlas on February 25, 1964. The instrumentation measured temperature, pressure, vacuum, and liquid level. Temperature instrumentation indicated wall drying during the freefall. The resultant pressure-rise characteristics were similar to those used for the normal-gravity test.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. NASA and contractor personnel who conducted the DIME activity with the students. Shown (L-R) are: Daniel Dietrich (NASA) mentor for Sycamore High School team), Carol Hodanbosi (National Center for Microgravity Research; DIME staff), Jose Carrion (GRC Akima, drop tower technician), Dennis Stocker (NASA; DIME staff), Richard DeLombard (NASA; DIME staff), Sandi Thompson (NSMR sabbatical teacher; DIME staff), Peter Sunderland (NCMR, mentor for COSI Academy student team), Adam Malcolm (NASA co-op student; DIME staff). This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
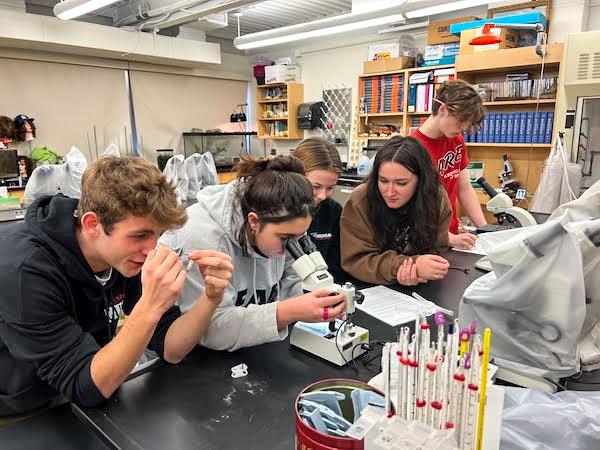

jsc2023e065213 (10/19/2023) --- Student researchers work on their experiment, Examining Artemia salina Hatching in the Presence of Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP). Pictured from left to right: Raphael Senterfit-Sanjuan, Zola Campisi, Avis Roszco, Jessica Amato and Tucker Sheehan.
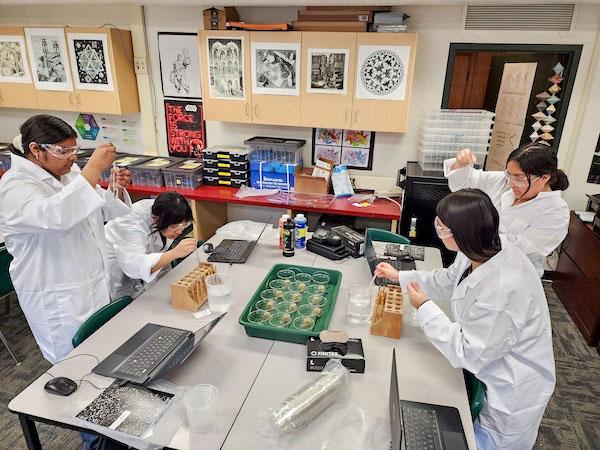

jsc2024e066521 (2/8/2024) --- Lamont Community winners work to cultivate knowledge through Spinacia oleracea seed germination research. Their experiment, Effects of Microgravity on Spinacia oleracea, is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).
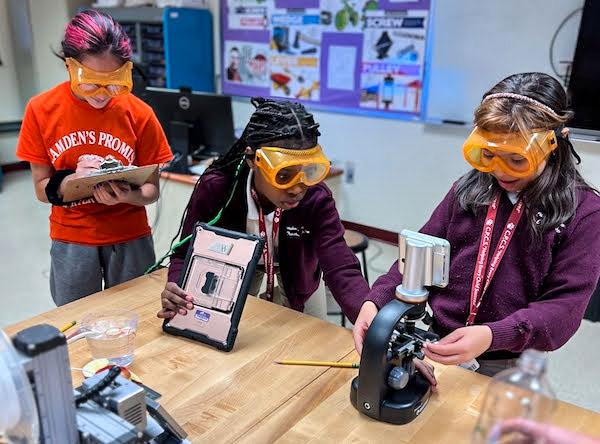

jsc2023e065186 (10/19/2023) --- Student researchers Inari Toledo (left), Sahara Miller (middle), and Siany Lee (right) work on their experiment on how microgravity effects mold growth, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).
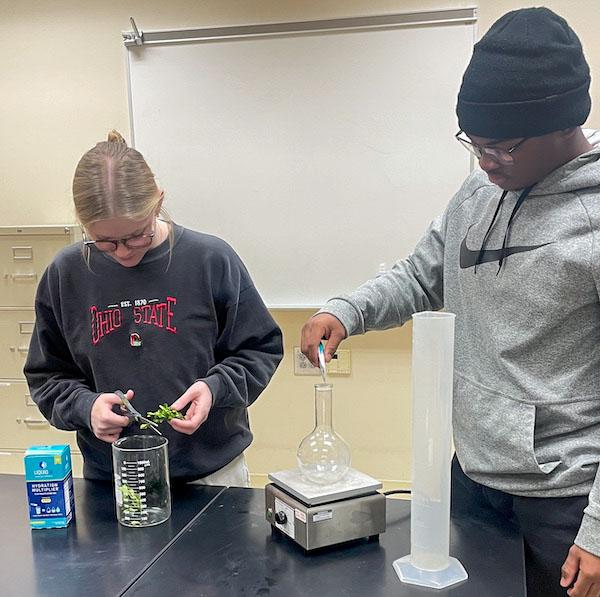

jsc2024e067095 (1/30/2024) --- Pickerington High School North students Macy Erickson and Dorian Hamilton prepard Elodea samples and hydration solution for their research experiment trials. Their experiment, Effects of Microgravity on Liquid I.V. Hydration Multiplier, is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).
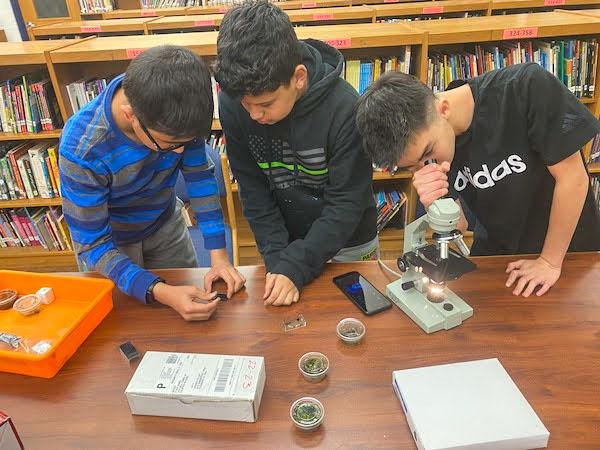

jsc2023e065216 (10/19/2023) --- Seventh grade student researchers Nirav Neupane, Kevontae Espada, and Max Gaylor work on their experiment, Do Tardigrades Develop Properly in Microgravity, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).

jsc2024e066516 (10/4/2024) --- Student researcher Ryan Stewart works to optimize the bacterial growth medium for his experiment, The Impact of Lectins on Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation in Microgravity. The experiment is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).

jsc2023e065189 (1/24/2023) --- Student researchers ( left to right: Scott Erskine, Marcus Li, XiaoLin Liu and Samuel Cullen) work on their experiment examining the Effects of Microgravity on the Statoliths and Statocyst Cells in Lepidium sativum (Garden Cress), which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).

jsc2024e066525 (10/7/2024) --- Seventh grade researchers from Randall Middle School work on optimizing their Taraxacum officinale germination experiment, Handy Dandy Dandelions – Germination of Dandelion in Microgravity, for flight.Their experiment is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).

jsc2023e065215 (2/2/2023) --- Student researchers Isabella Zabinski, Sharlyn Dubey, Aria Molinelli, Avital Kandel, and Taylor Tripet work on their experiment, The Effect of Microgravity on Gray Mold, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP).

jsc2024e067104 (10/15/2024) --- Robbie E. Howard Junior High School student researchers (Cadee Smith, Coralee Holloway, Caiden Holmquist, and Levi Blaise Lewis) take measurements and record data for their experiment, How do microgravity and space conditions affect the growth of Cucumber, Cucumbis sativus? Their experiment is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).

jsc2024e066532 (2/28/2024) --- View of Long Beach, NY student researchers Katrina Casey, Claire Cristallo and Jasmine Davidson-Smith. Their experiment, The Effect of Microgravity on the Germination of Watercress Seeds, is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).
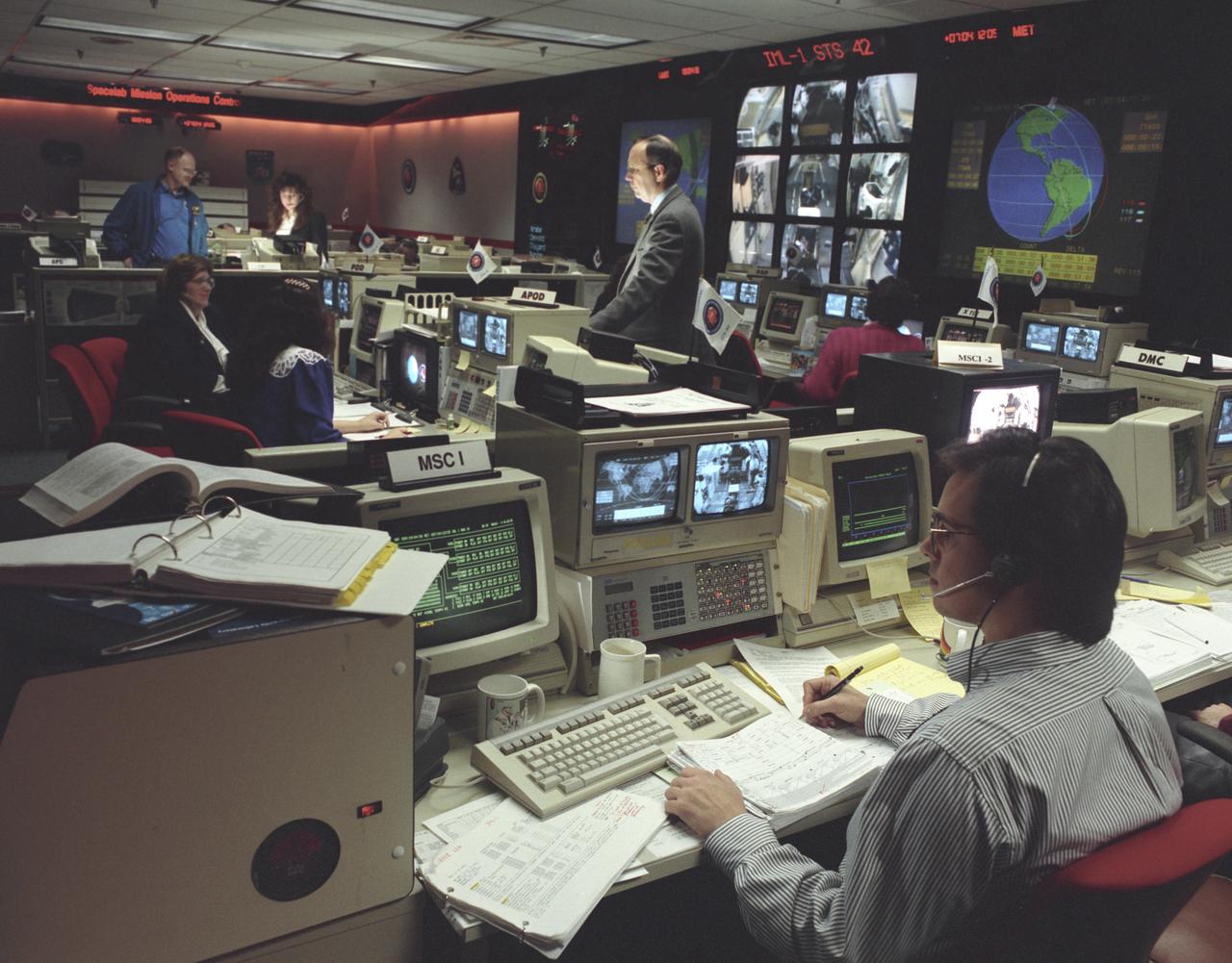

This photograph shows activities during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission (STS-42) in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research. The mission was to explore, in depth, the complex effects of weightlessness on living organisms and materials processing. The crew conducted experiments on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and the effects on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Low gravity materials processing experiments included crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury, iodine, and virus. The International space science research organizations that participated in this mission were: The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, the French National Center for Space Studies, the German Space Agency, and the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The POCC was the air/ground communication charnel used between the astronauts aboard the Spacelab and scientists, researchers, and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The facility made instantaneous video and audio communications possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress and to send direct commands of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew.
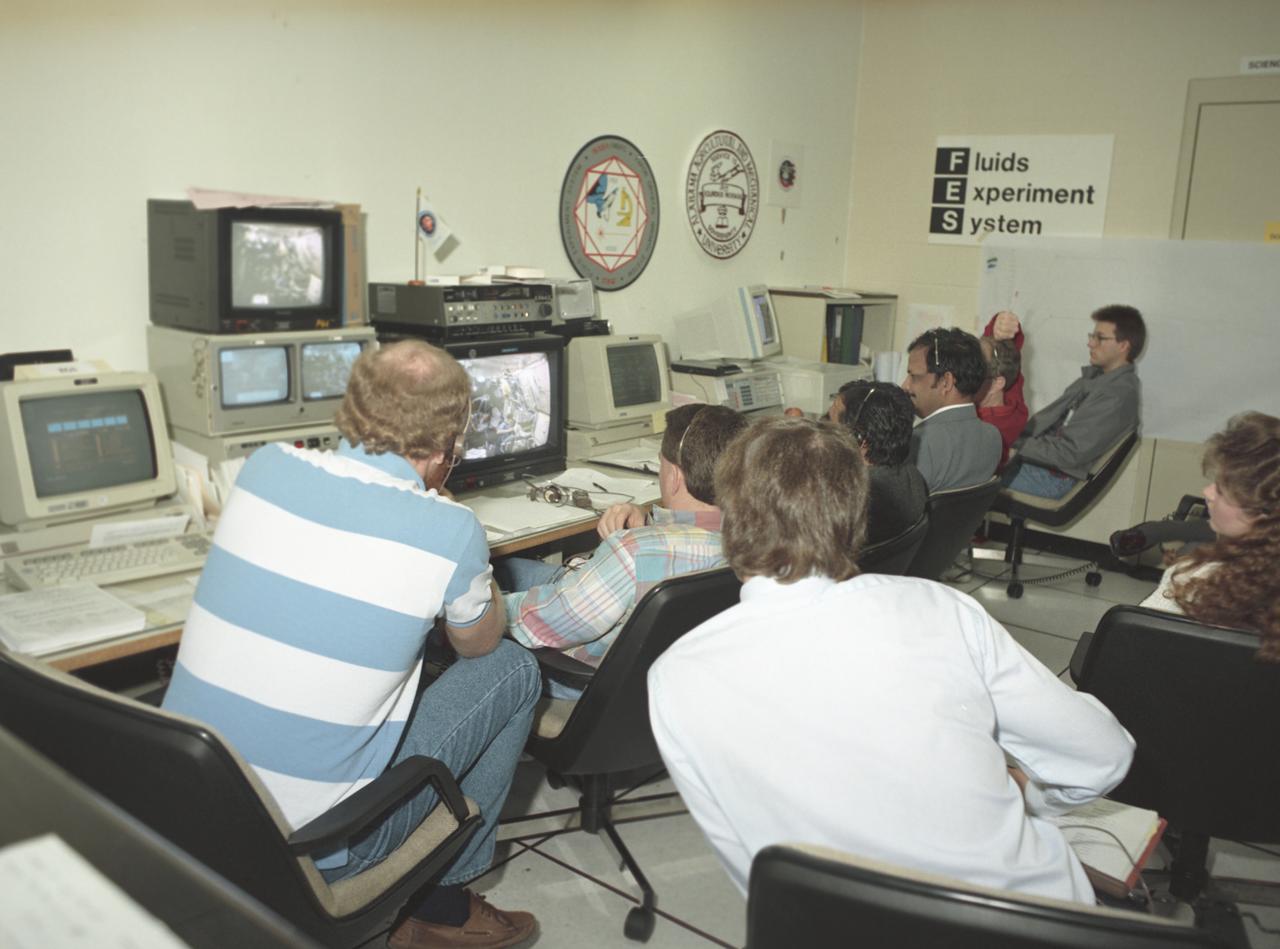

This photograph shows activities during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission (STS-42) in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. Members of the Fluid Experiment System (FES) group monitor the progress of their experiment through video at the POCC. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research. The mission was to explore, in depth, the complex effects of weightlessness on living organisms and materials processing. The crew conducted experiments on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and the effects on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Low gravity materials processing experiments included crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury, iodine, and virus. The International space science research organizations that participated in this mission were: The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administion, the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, the French National Center for Space Studies, the German Space Agency, and the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The POCC was the air/ground communication charnel used between astronauts aboard the Spacelab and scientists, researchers, and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The facility made instantaneous video and audio communications possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress and to send direct commands of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. NASA and contractor personnel who conducted the DIME activity with the students. Shown (L-R) are: Eric Baumann (NASA, 2.2-second Drop Tower Facility manager), Daniel Dietrich (NASA) mentor for Sycamore High School team), Carol Hodanbosi (National Center for Microgravity Research; DIME staff), Richard DeLombard (NASA; DIME staff), Jose Carrion (GRC Akima, drop tower technician), Dennis Stocker (NASA; DIME staff), Peter Sunderland (NCMR, mentor for COSI Academy student team), Sandi Thompson (NSMR sabbatical teacher; DIME staff), Dan Woodard (MASA Microgravity Outreach Program Manager), Adam Malcolm (NASA co-op student; DIME staff), Carla Rosenberg (NCMR; DIME staff), and Twila Schneider (Infinity Technology; NASA Microgravity Research program contractor). This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
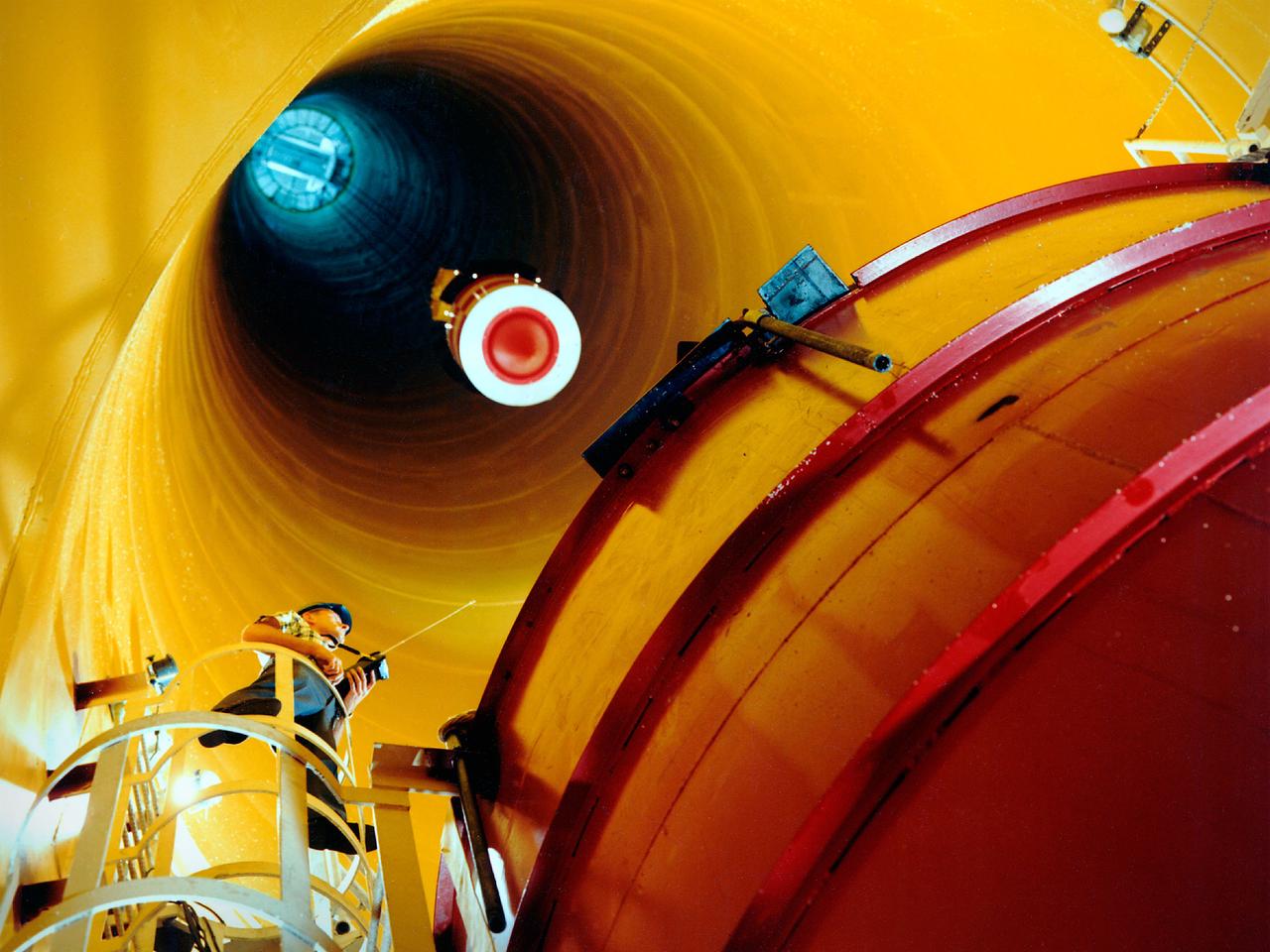

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis researchers had been studying the behavior of liquid in microgravity for several years using ballistic rocket flights, aircraft flying series of parabolas, and in the 2.2-Second Drop Tower. It was easier to control experiments and repeat tests based on almost instantaneous test results in the Zero Gravity Research Facility than missiles or aircraft. It also more than doubled the microgravity time of the original drop tower. The experiments were enclosed in a large experiment package that was suspended inside the chamber. A vacuum was introduced to the chamber before the package was released. The test equipment allowed researchers to film and take measurements of the experiment as it was falling. The 2500‐pound package was slowed by special Styrofoam‐like pellets in a decelerator cart. An experiment, traveling 176 feet per second, was stopped in about 15 feet of deceleration material. The facility’s designers struggled to determine the correct type of deceleration pellets to use. For several years Lewis engineers tested various samples from manufacturers. The final selection was not made until the facility’s completion in May 1966, just before the facility made its public debut at the 1966 Inspection of the Center.
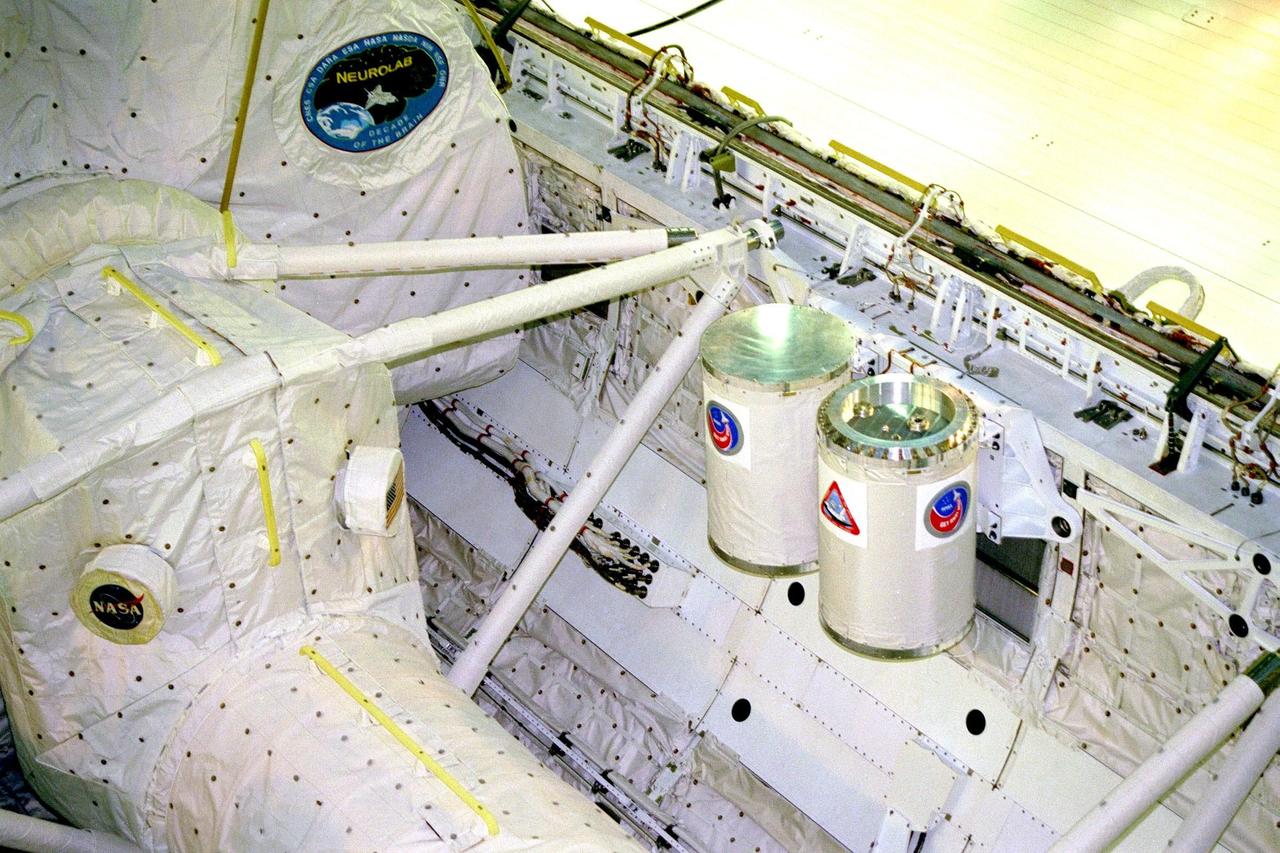

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-90 Neurolab payload and two of the four Getaway Specials (GAS) await payload bay door closure in the orbiter Columbia today in Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3. Investigations during the Neurolab mission will focus on the effects of microgravity on the nervous system. The GAS container on the left contains the COLLisions Into Dust Experiment, or COLLIDE, which will study low velocity collisions between space-borne particles in an attempt to better understand planetary ring dynamics. The STS-90 mission is a joint venture of six space agencies and seven U.S. research agencies. Agencies participating in this mission include six institutes of the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, and the Office of Naval Research, as well as the space agencies of Canada, France, Germany, and Japan, and the European Space Agency (ESA)
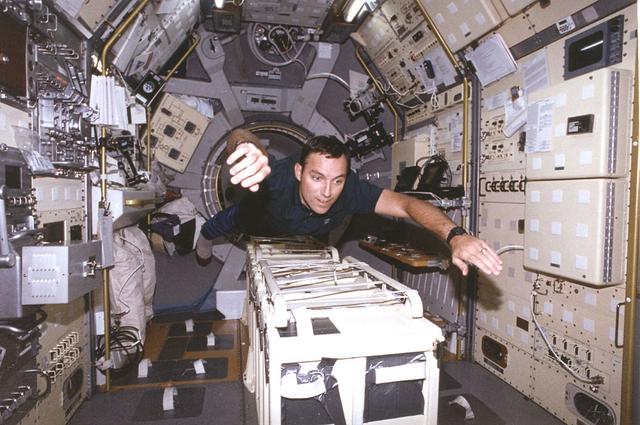

Astronaut Carl E. Walz, mission specialist, flies through the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) science module, STS-65 mission. IML was dedicated to study fundamental materials and life sciences in a microgravity environment inside Spacelab, a laboratory carried aloft by the Shuttle. The mission explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. The IML program gave a team of scientists from around the world access to a unique environment, one that is free from most of Earth's gravity. Managed by the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (SCA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DARA/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) participated in developing hardware and experiments for the IML missions. The missions were managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. The Orbiter Columbia was launched on July 8, 1994 for the IML-2 mission.
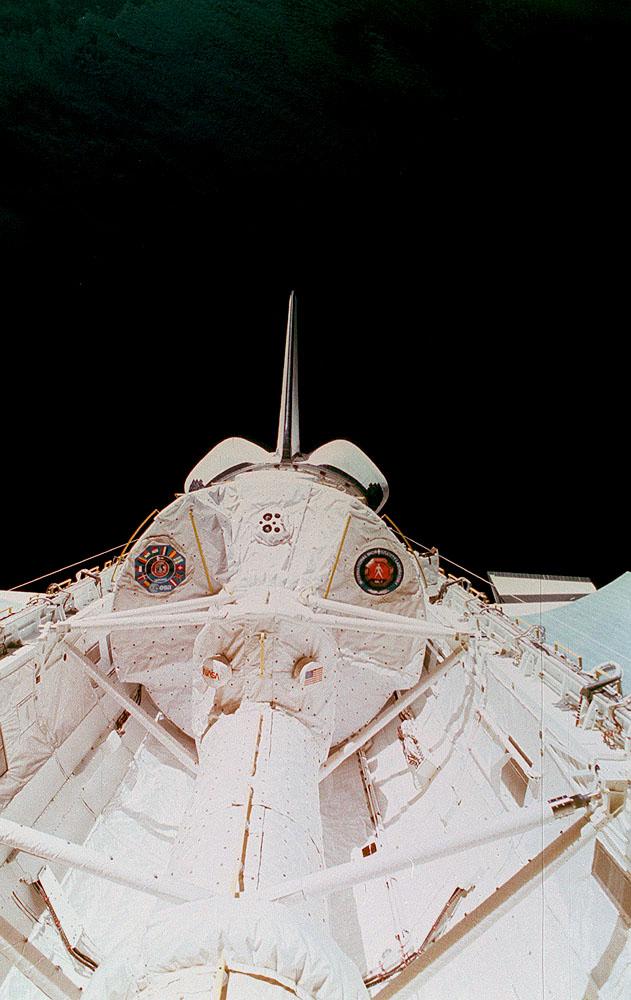
This is the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery, STS-42 mission, with the First International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) module shown in the cargo bay. IML-1, the first in a series of Shuttle flights, was dedicated to study the fundamental materials and life sciences in the microgravity environment inside Spacelab, a laboratory carried aloft by the Shuttle. The mission explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. The IML program gave a team of scientists from around the world access to a unique environment, one that is free from most of Earth's gravity. The 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (SCA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DARA/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) participated in developing hardware and experiments for the IML missions. The missions were managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. The Orbiter Discovery was launched on January 22, 1992 for the IML-1 mission.
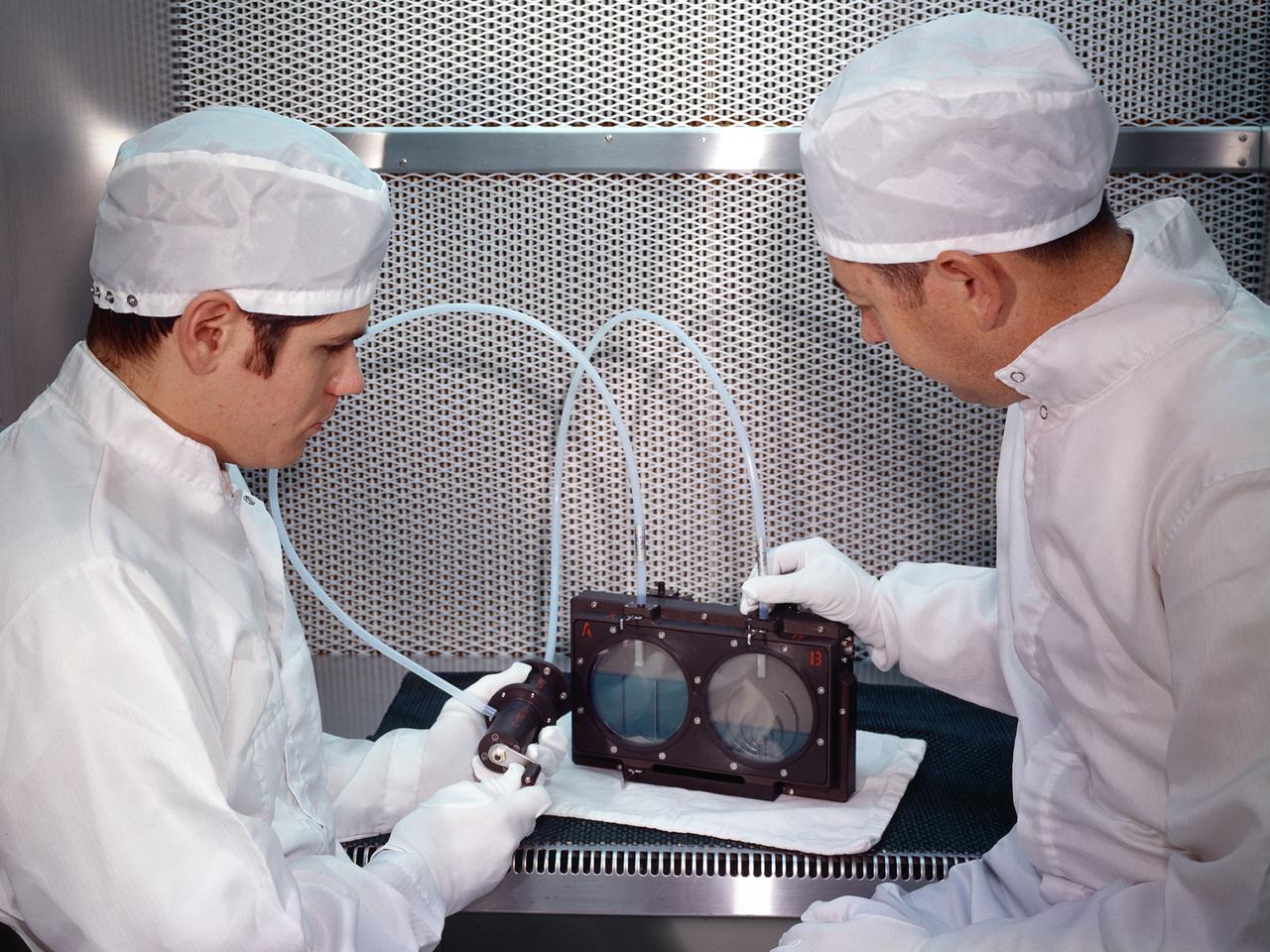
Two researchers at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center demonstrate the test equipment they devised to study the transfer of liquid in microgravity onboard the Apollo 14 mission. The test was an early step in developing the ability to transfer liquids from a tanker vehicle to spacecraft in space. Researchers needed to know the tank’s outflow characteristics, the fluid’s behavior when entering new tank, and the effects of accelerations. Others had performed some calculations and analytical studies, but no one had examined the complete transfer from one tank to another in microgravity. The early calculations concluded that the transfer process was impossible without devices to control the liquid and gas. This investigation specifically sought to demonstrate the effectiveness of two different surface-tension baffle designs. The experiment was an entirely closed system with two baffled-tanks. The researchers also built a similar device without the baffles. The experiment was carried onboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft and conducted during the coast period on the way to the moon. The two surface tension baffle designs in the separate tanks were shown to be effective both as supply tanks and as receiver tanks. The liquid transferred within two percent of the design value with ingesting gas. The unbaffled tanks ingested gas after only 12-percent of the fluid had transferred.
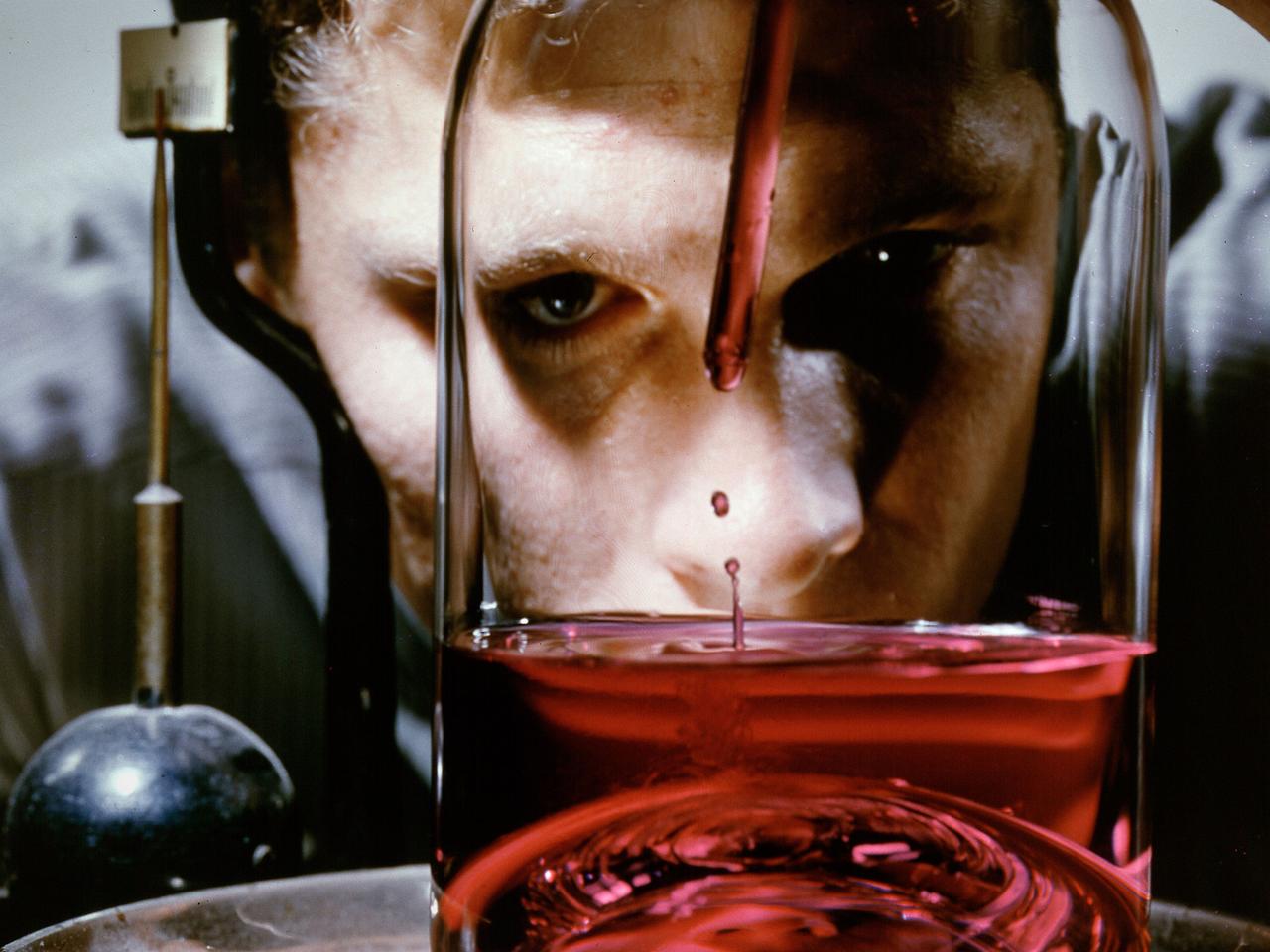

A researcher fills a small container used to represent a liquid hydrogen tank in preparation for a microgravity test in the 2.2-Second Drop Tower at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. For over a decade, NASA Lewis endeavored to make liquid hydrogen a viable propellant. Hydrogen’s light weight and high energy made it very appealing for rocket propulsion. One of the unknowns at the time was the behavior of fluids in the microgravity of space. Rocket designers needed to know where the propellant would be inside the fuel tank in order to pump it to the engine. NASA Lewis utilized sounding rockets, research aircraft, and the 2.2 Second Drop Tower to study liquids in microgravity. The drop tower, originally built as a fuel distillation tower in 1948, descended into a steep ravine. By early 1961 the facility was converted into an eight-floor, 100-foot tower connected to a shop and laboratory space. Small glass tanks, like this one, were installed in experiment carts with cameras to film the liquid’s behavior during freefall. Thousands of drop tower tests in the early 1960s provided an increased understanding of low-gravity processes and phenomena. The tower only afforded a relatively short experiment time but was sufficient enough that the research could be expanded upon using longer duration freefalls on sounding rockets or aircraft. The results of the early experimental fluid studies verified predictions made by Lewis researchers that the total surface energy would be minimized in microgravity.
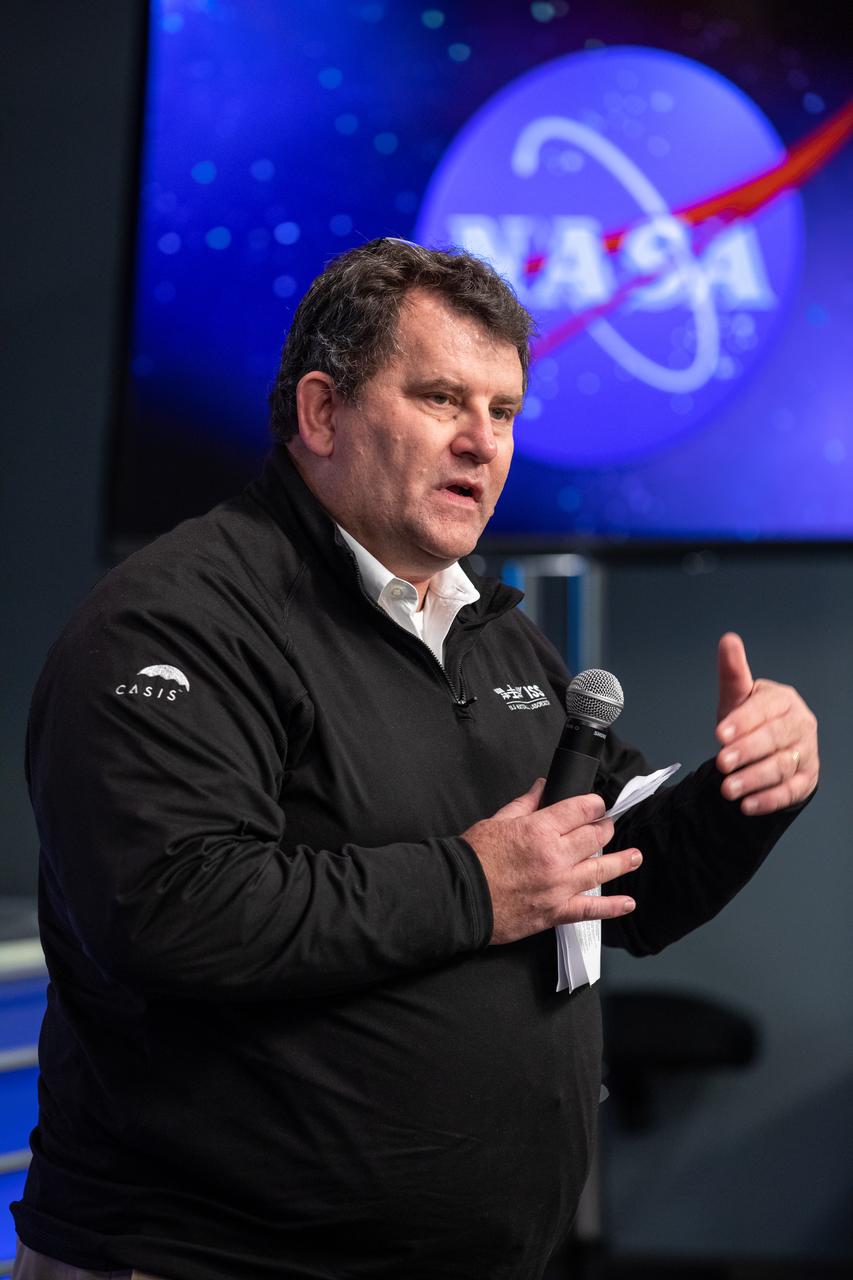

A What’s On Board Briefing for SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-19) mission for NASA to the International Space Station took place on Dec. 3, 2019, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Michael Roberts, interim chief scientist for the International Space Station U.S. National Laboratory, discusses the lab’s work in advancing science in space, and in developing partnerships that drive industrialization through microgravity research. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch on Dec. 4, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
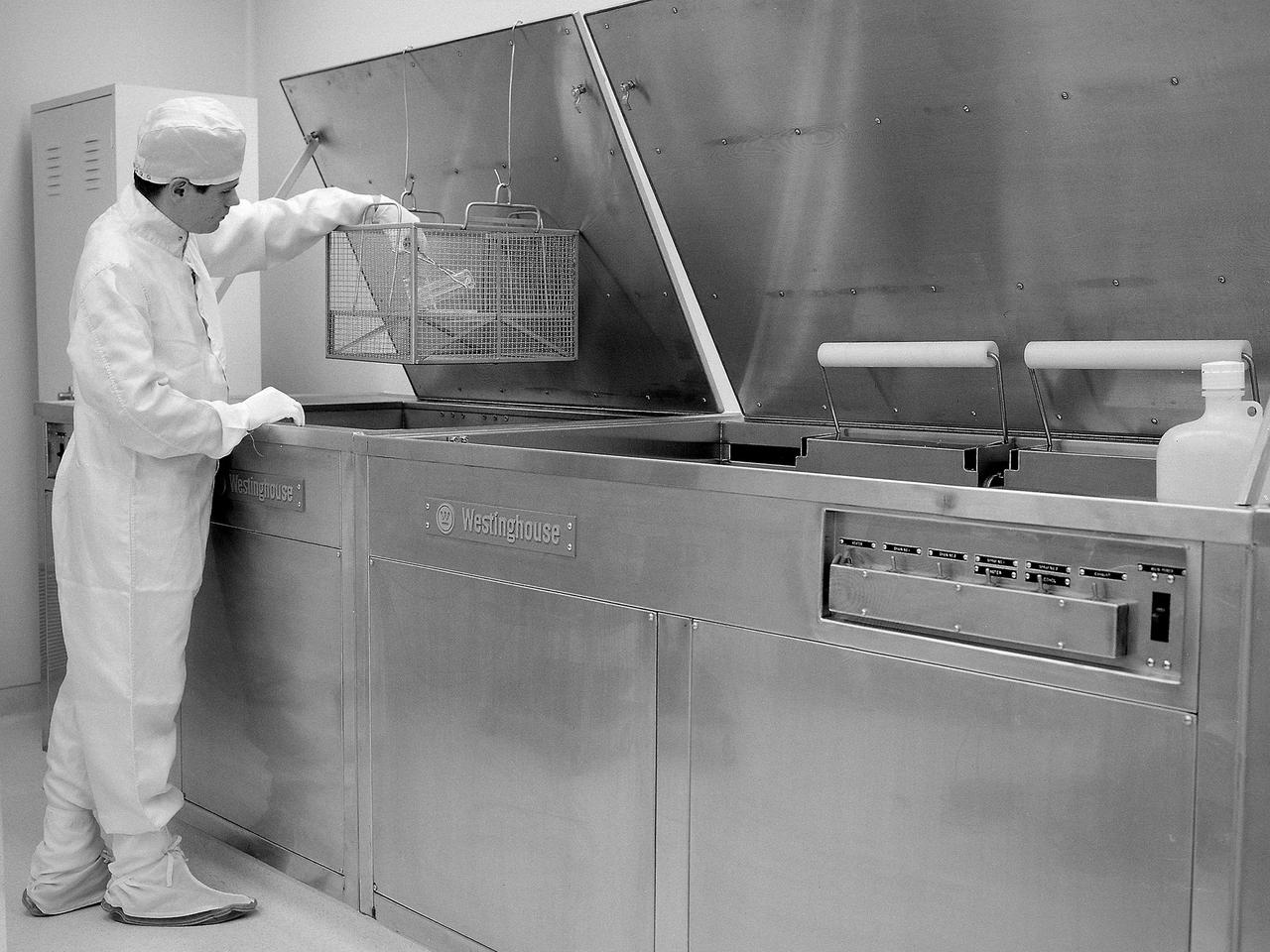

A technician prepares a test sample in the Zero Gravity Research Facility clean room at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Zero Gravity Research Facility contained a drop tower which provided five seconds of microgravity during freefall in its 450-foot deep vacuum chamber. The facility has been used for a variety of studies relating to the behavior of fluids and flames in microgravity. During normal operations, a cylindrical 3-foot diameter and 11-foot long vehicle was used to house the experiments, instrumentation, and high speed cameras. The 4.5-foot long and 1.5-foot wide rectangular vehicle, seen in this photograph, was used less frequently. A 3-foot diameter orb was used for the special ten-second drops in which the package was pneumatically shot to the top of the tower then dropped. The facility also contained a control room, shop offices, tool and equipment rooms, and this clean room. The 242.5-foot long and 19.5-foot wide clean room was equipped with specialized cleaning equipment. In the 1960s the room was rated as a class 10,000 clean room, but I was capable of meeting the class 100 requirements. The room included a fume hood, ultrasonic cleaner, and a laminar flow station which operated as a class 100 environment. The environment in the clean room was maintained at 71° F and a relative humidity of 45- percent.
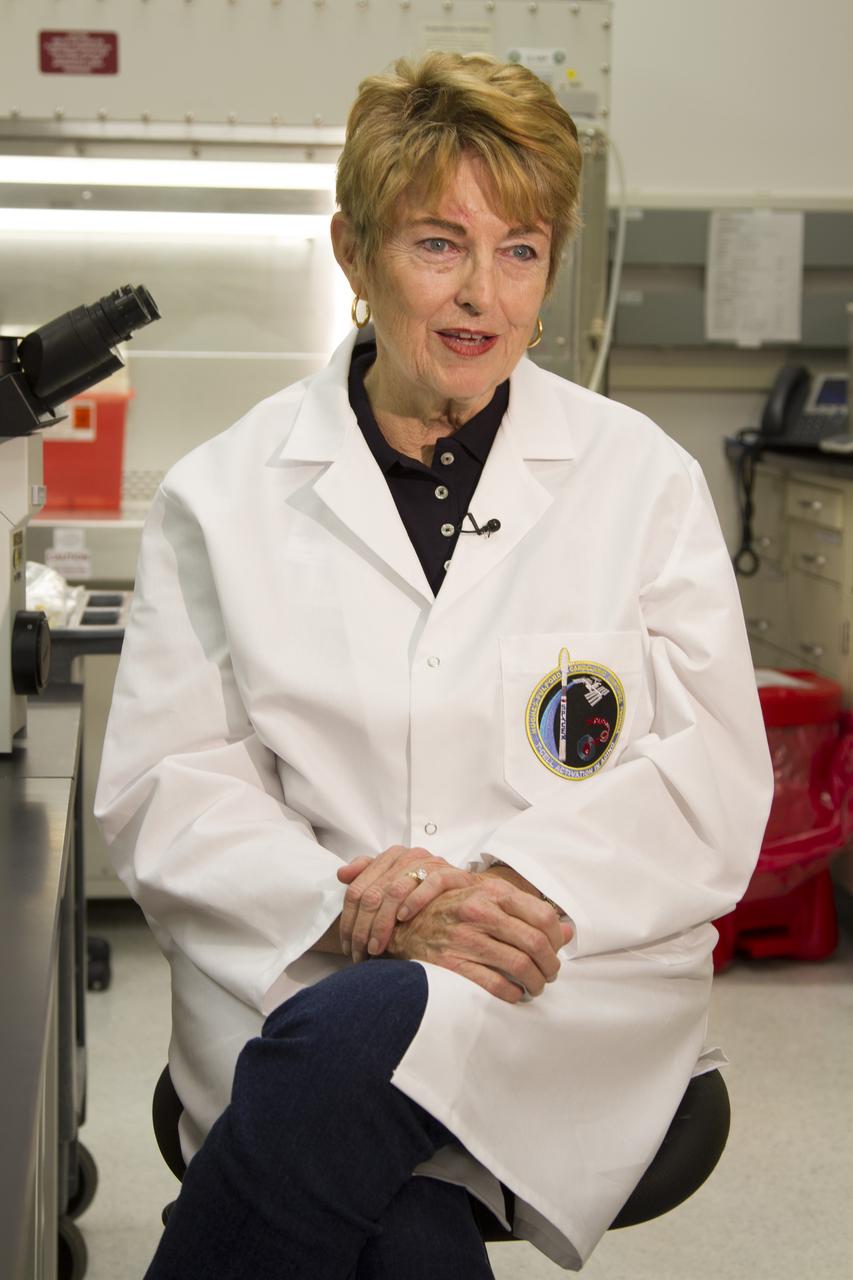

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Researcher and former NASA payload specialist Millie Hughes-Fulford, of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., discusses her laboratory's T-cell experiment and the impact the research may have on aging adults and their immune systems with an interviewer in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
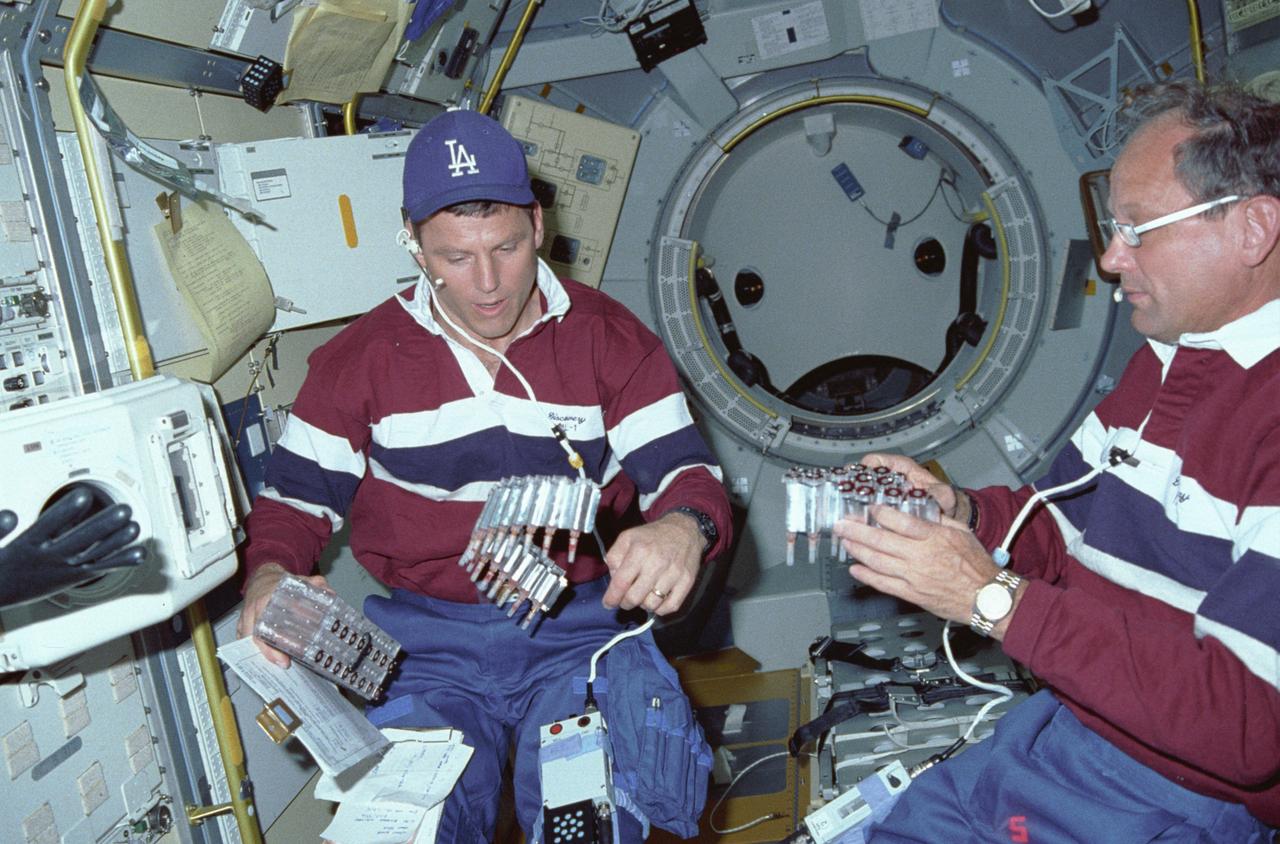

International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. In this photograph, Astronauts Stephen S. Oswald and Norman E. Thagard handle ampoules used in the Mercuric Iodide Crystal Growth (MICG) experiment. Mercury Iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their exceptional electronic properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature rather than at the extremely low temperatures usually required by other materials. Because a bulky cooling system is urnecessary, these crystals could be useful in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and astronomical observation. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).
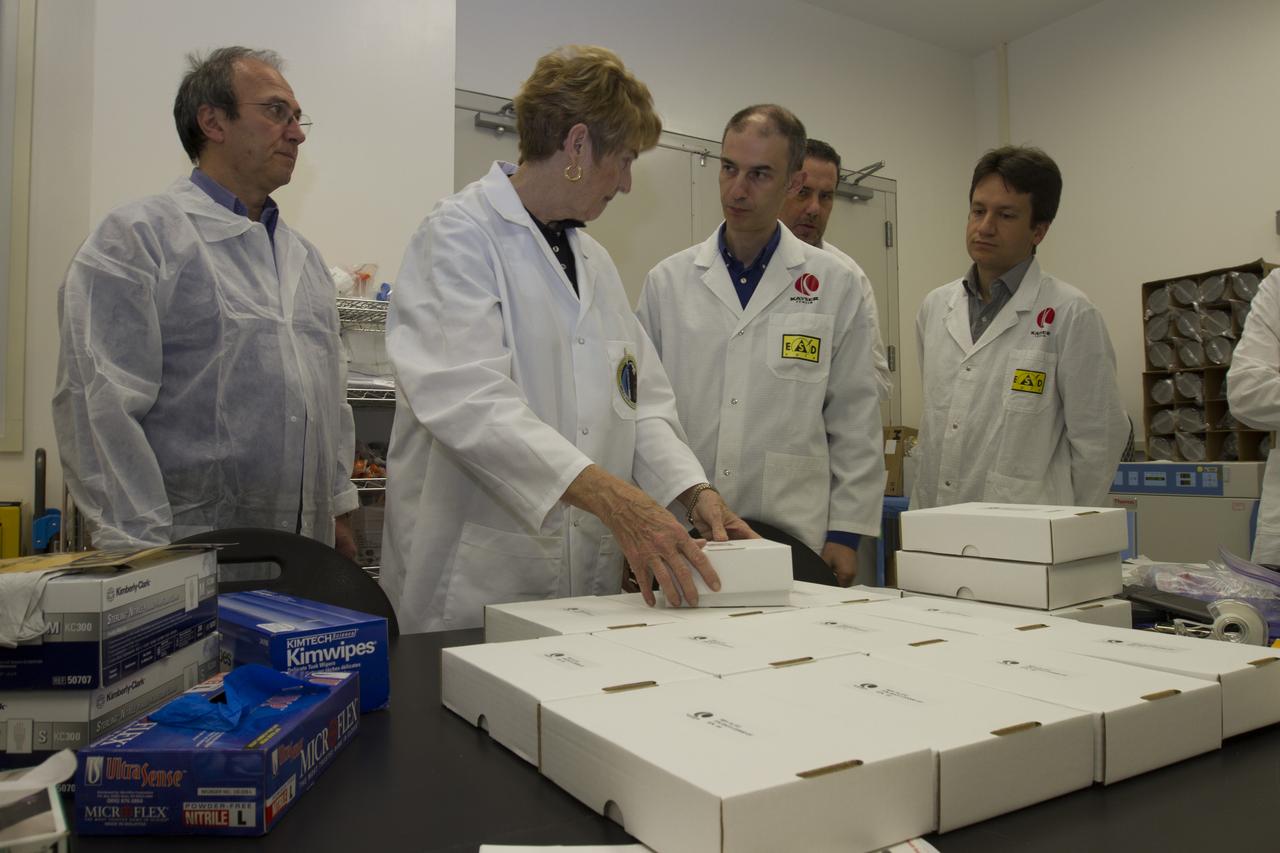

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Researcher and former NASA payload specialist Millie Hughes-Fulford, of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., accepts the European Space Agency ESA T-cell experiment flight units being handed over in a Space Station Processing Facility laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Raimondo Fortezza of ESA, Hughes-Fulford, and Pier Luigi Ganga, Marco Vukich and Fabio Creati of Kayser Italia, manufacturer of the hardware. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

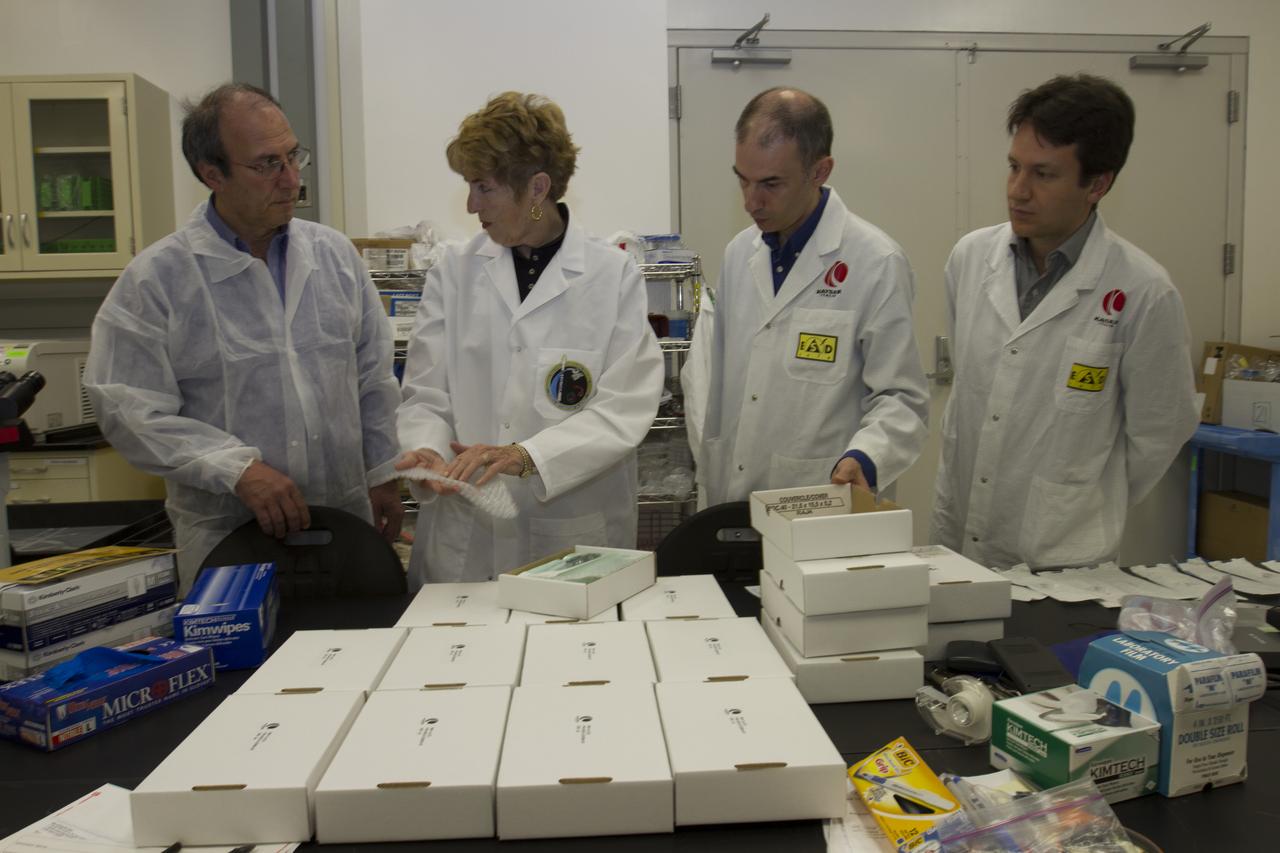
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Researcher and former NASA payload specialist Millie Hughes-Fulford, of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., accepts the European Space Agency ESA T-cell experiment flight units being handed over in a Space Station Processing Facility laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Hughes-Fulford shaking hands with Pier Luigi Ganga of Kayser Italia, manufacturer of the hardware, with Raimondo Fortezza of ESA looking on. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
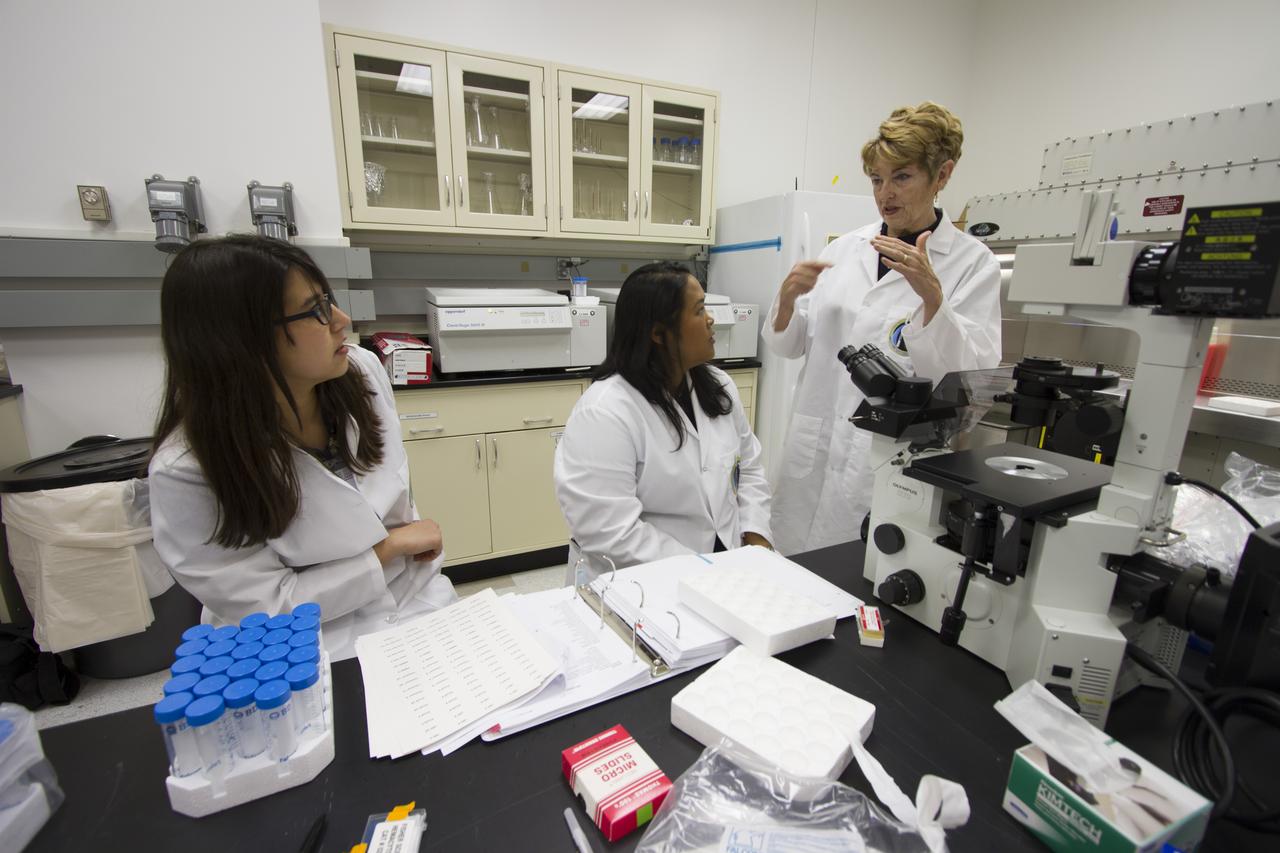

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Researcher and principal investigator Dr. Millie Hughes-Fulford of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., at right, plans preflight and post-flight experiment operations with T-cell science team members Emily Martinez, left, and Tara Candelario in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
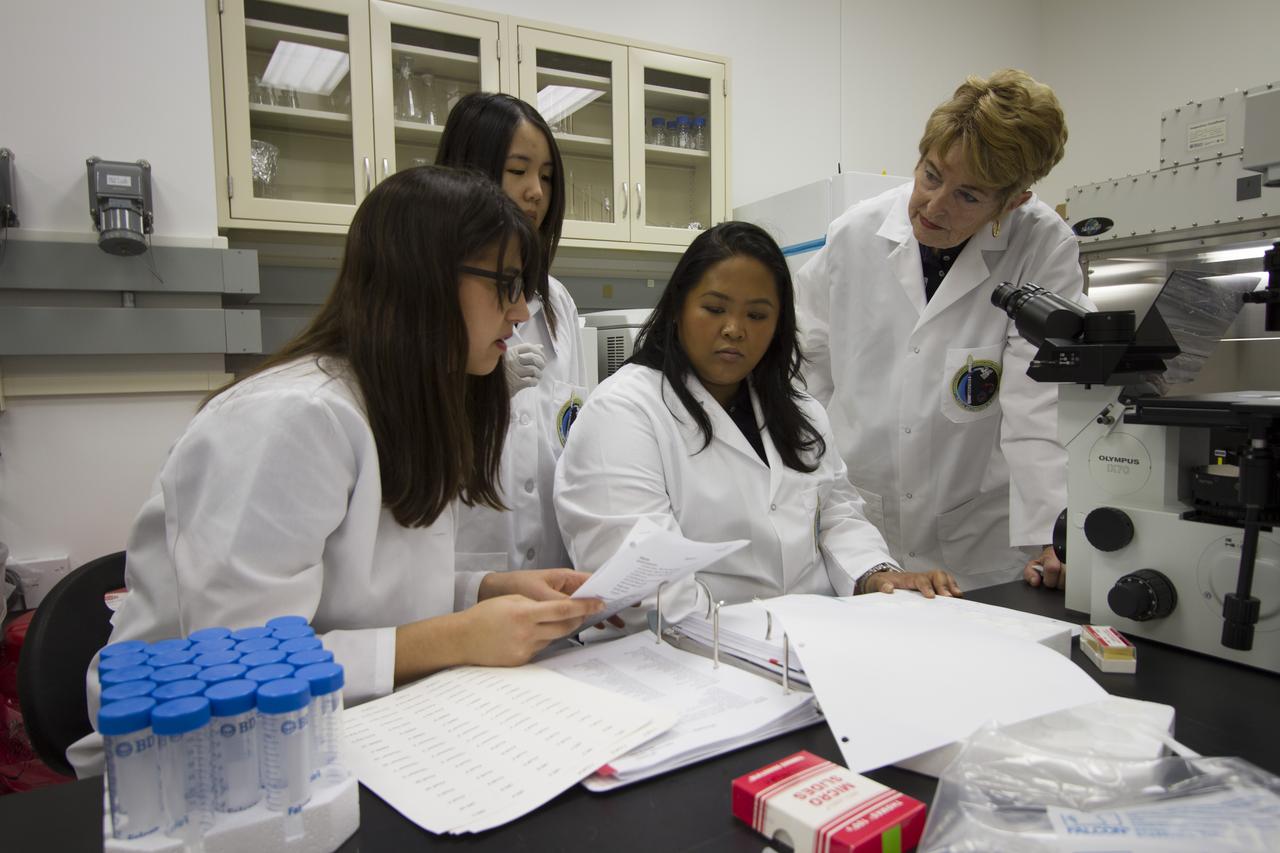

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - From left, T-cell science team members Emily Martinez, Miya Yoshida and Tara Candelario, of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., discuss preflight and post-flight experiment operations with researcher and principal investigator Dr. Millie Hughes-Fulford in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

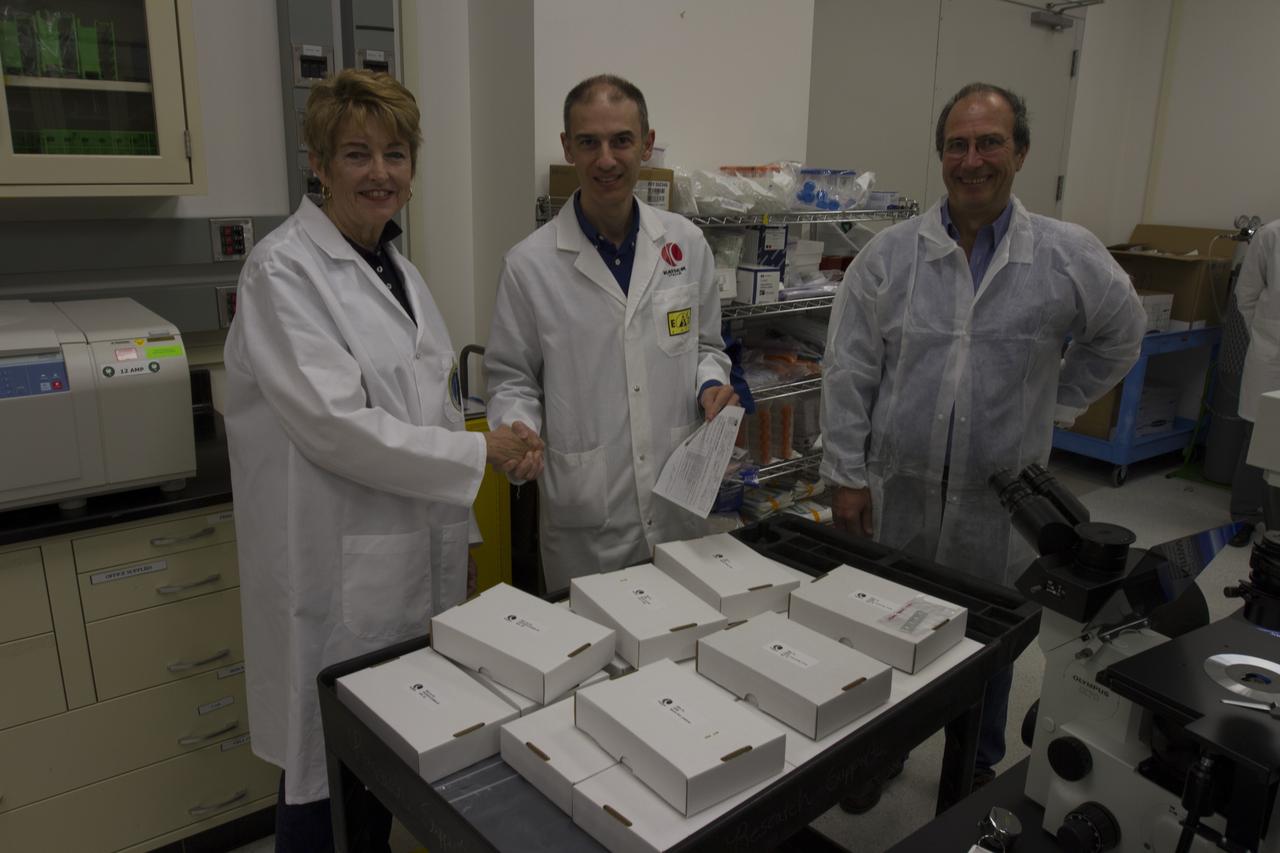
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Researcher and former NASA payload specialist Millie Hughes-Fulford, of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., accepts the European Space Agency ESA T-cell experiment flight units being handed over in a Space Station Processing Facility laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Raimondo Fortezza of ESA, Hughes-Fulford, and Pier Luigi Ganga and Fabio Creati of Kayser Italia, manufacturer of the hardware. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
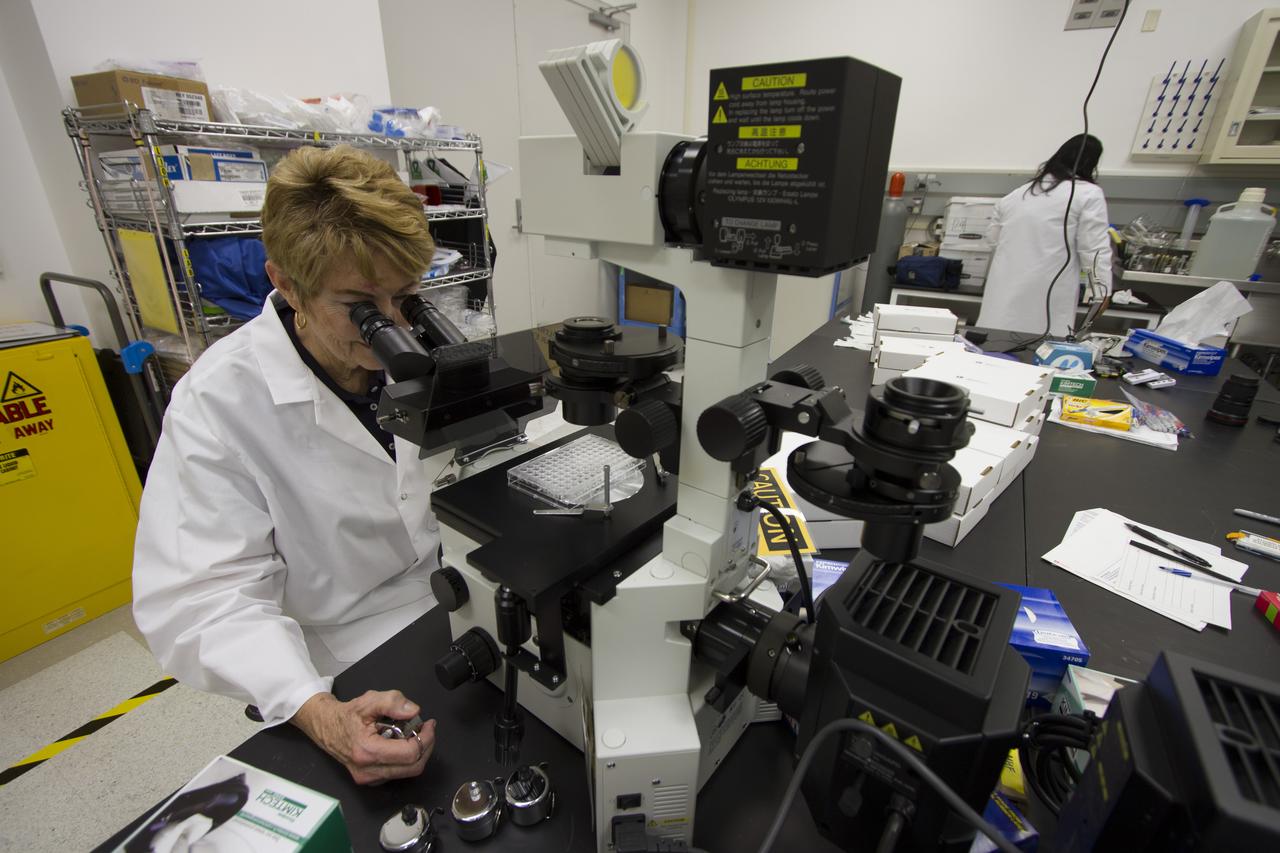

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Researcher and principal investigator Dr. Millie Hughes-Fulford, of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., at the microscope, examines T-cells as part of preflight experiment operations in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
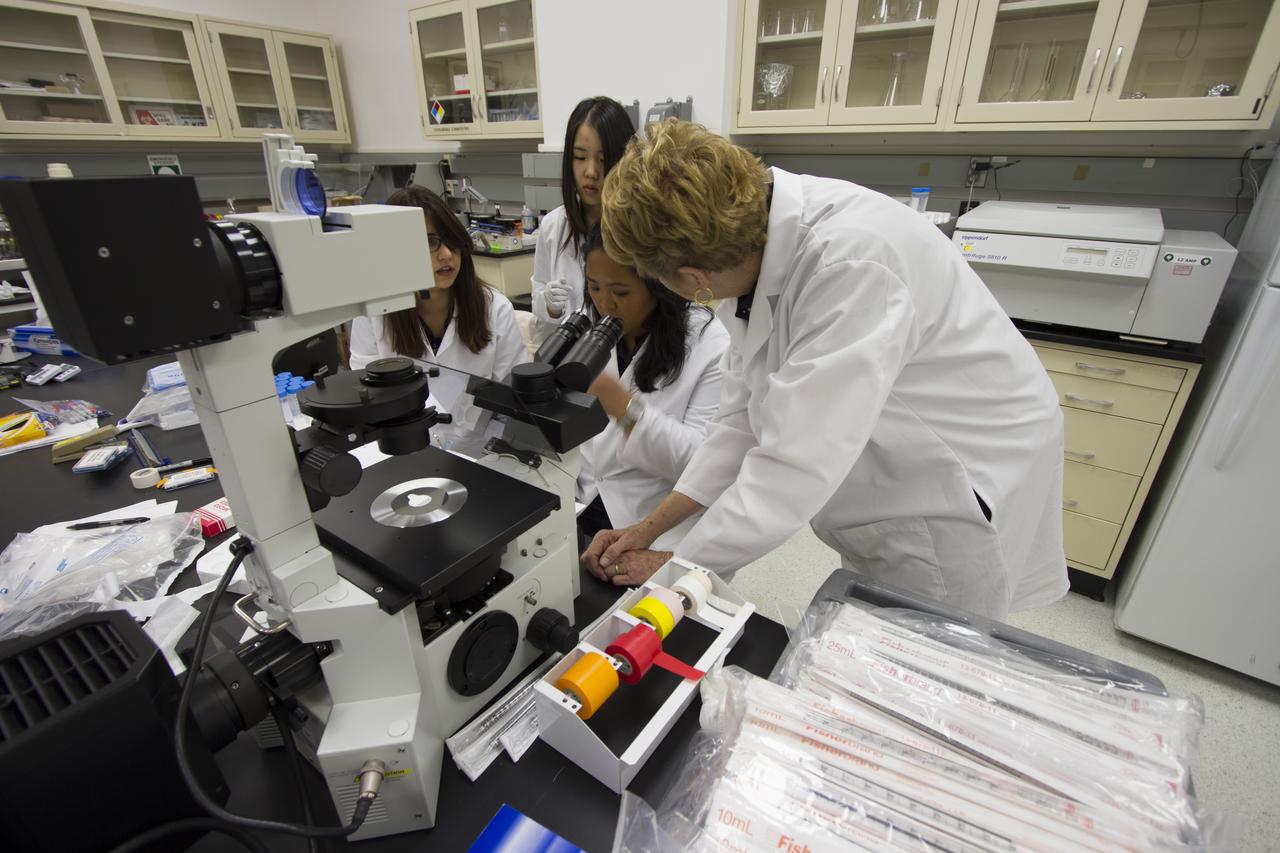

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - T-cell science team member Tara Candelario of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory, San Francisco, Calif., at the microscope, discusses preflight and post-flight experiment operations with researcher and principal investigator Dr. Millie Hughes-Fulford in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida as T-cell science team members Emily Martinez, left, and Miya Yoshida look on. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

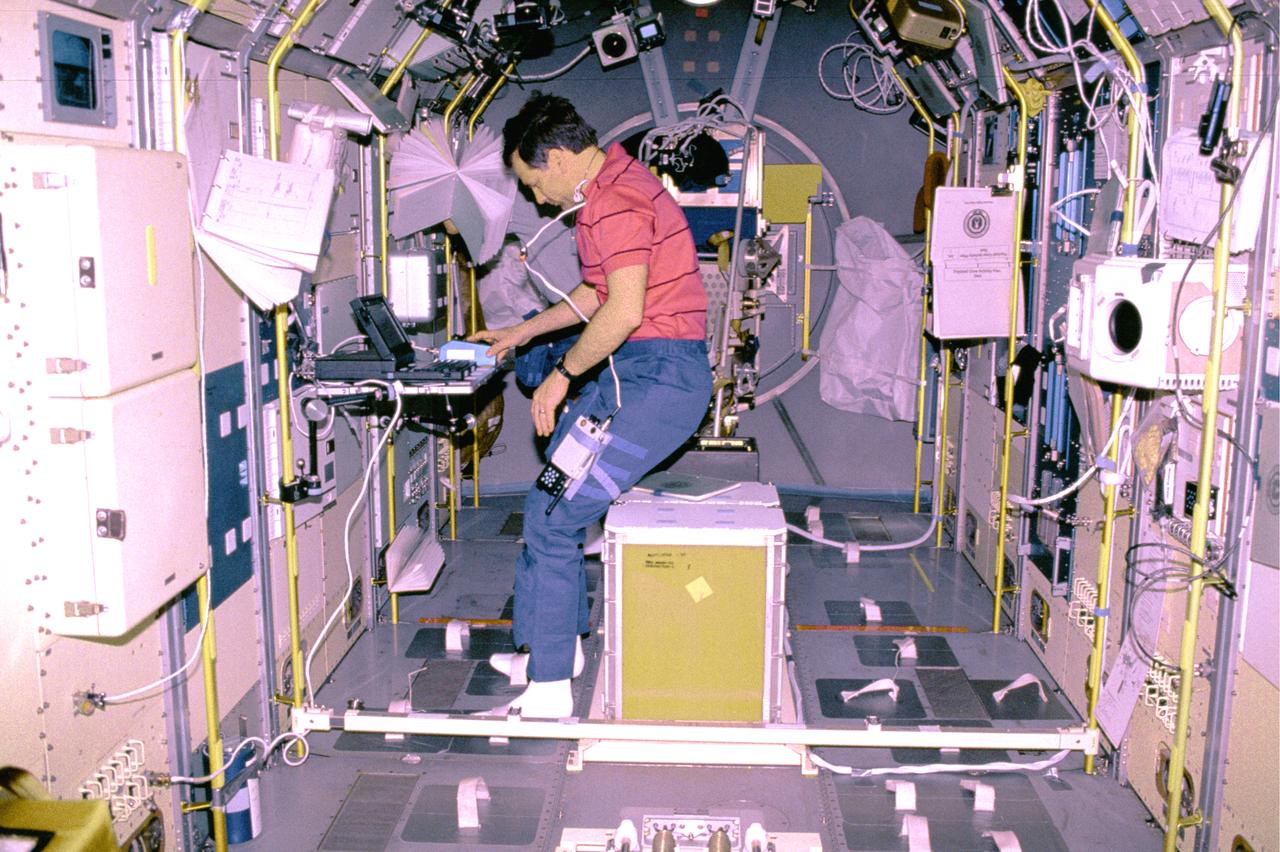
The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), The French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. This photograph shows Astronaut Norman Thagard performing the fluid experiment at the Fluid Experiment System (FES) facility inside the laboratory module. The FES facility had sophisticated optical systems for imaging fluid flows during materials processing, such as experiments to grow crystals from solution and solidify metal-modeling salts. A special laser diagnostic technique recorded the experiments, holograms were made for post-flight analysis, and video was used to view the samples in space and on the ground. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the IML-1 mission was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42).

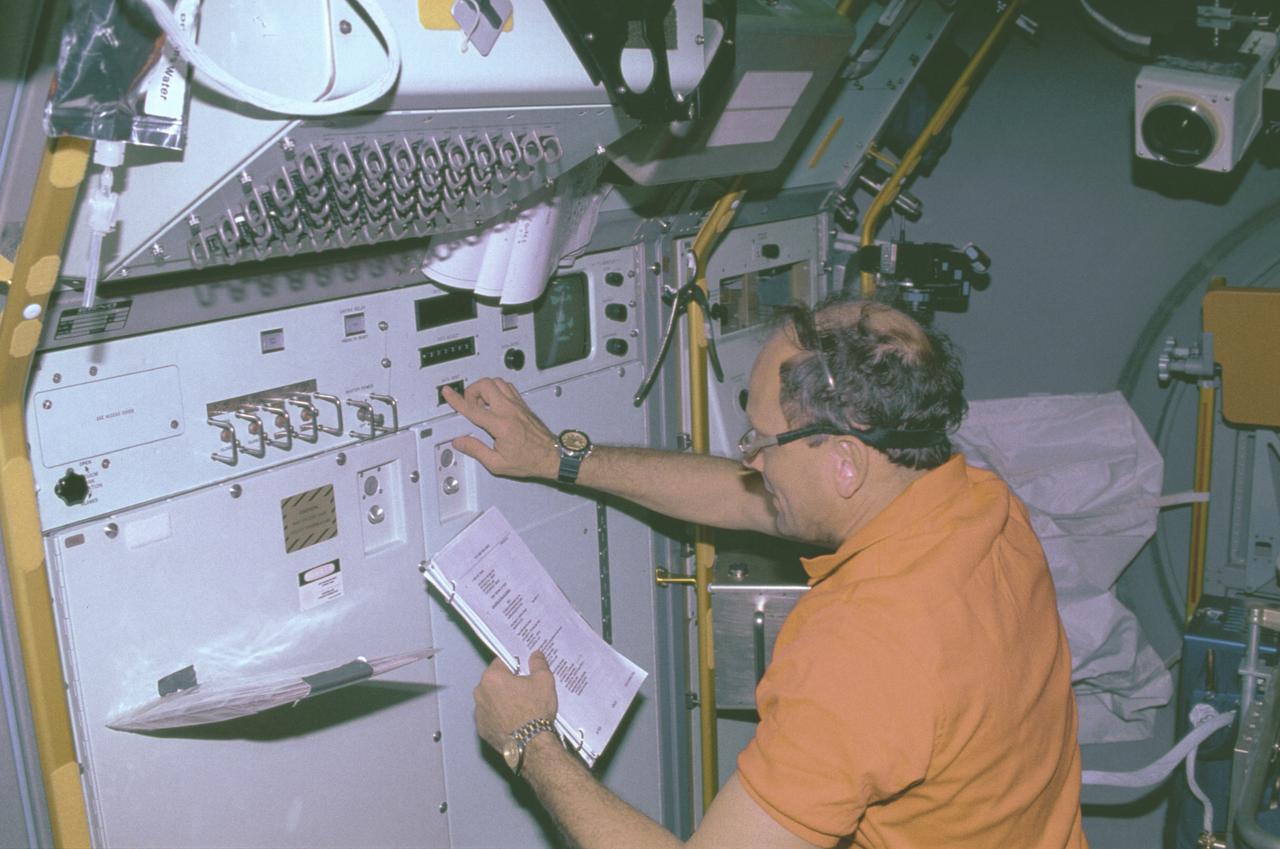
The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. In this photograph, Commander Ronald J. Grabe works with the Mental Workload and Performance Evaluation Experiment (MWPE) in the IML-1 module. This experiment was designed as a result of difficulty experienced by crewmembers working at a computer station on a previous Space Shuttle mission. The problem was due to the workstation's design being based on Earthbound conditions with the operator in a typical one-G standing position. Information gained from this experiment was used to design workstations for future Spacelab missions and the International Space Station. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).
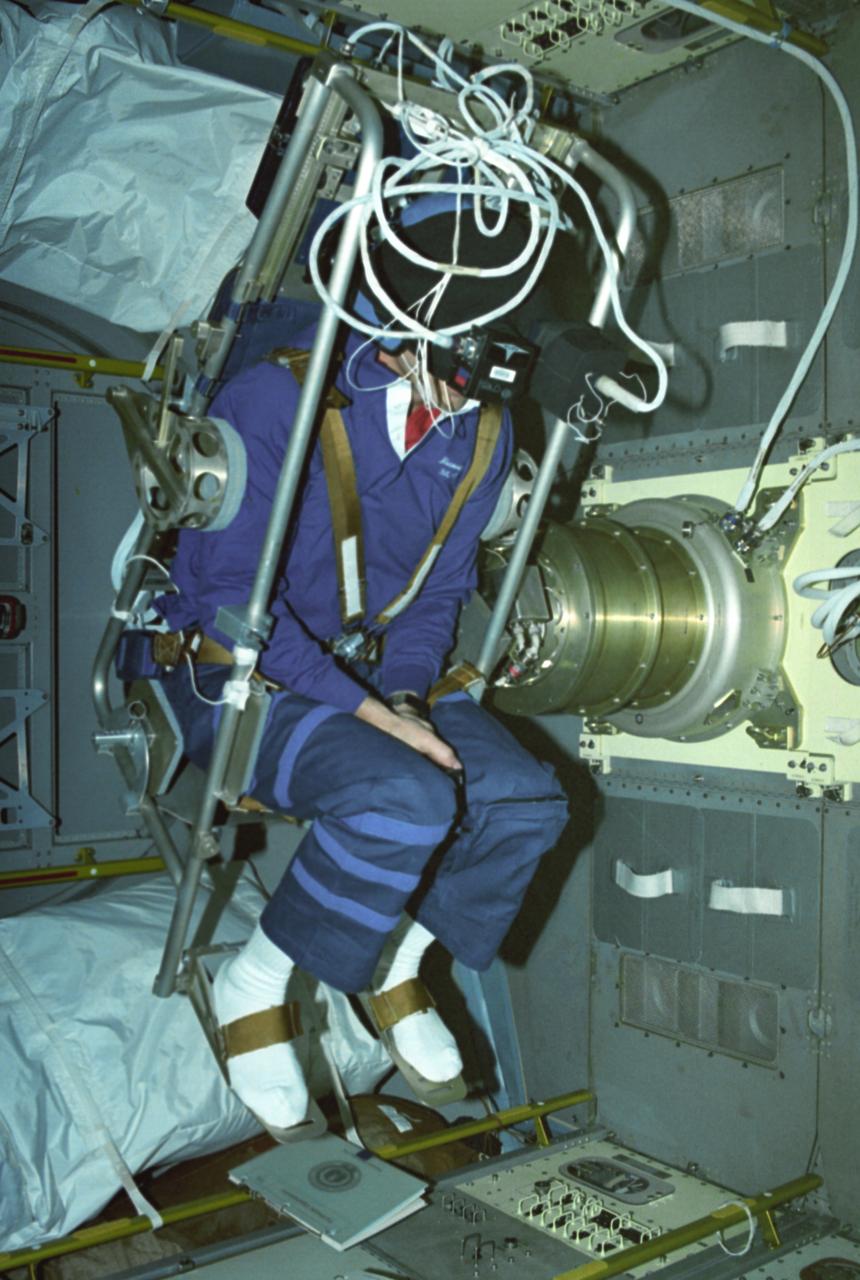

Astronaut David C. Hilmers conducts the Microgravity Vestibular Investigations (MVI) sitting in its rotator chair inside the IML-1 science module. When environmental conditions change so that the body receives new stimuli, the nervous system responds by interpreting the incoming sensory information differently. In space, the free-fall environment of an orbiting spacecraft requires that the body adapts to the virtual absence of gravity. Early in flights, crewmembers may feel disoriented or experience space motion sickness. MVI examined the effects of orbital flight on the human orientation system to obtain a better understanding of the mechanisms of adaptation to weightlessness. By provoking interactions among the vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive systems and then measuring the perceptual and sensorimotor reactions, scientists can study changes that are integral to the adaptive process. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center acquired two North American AJ-2 Savages in the early 1960s to fly microgravity-inducing parabola flight patterns. Lewis was in the midst of an extensive study to determine the behavior of liquid hydrogen in microgravity so that proper fuel systems could be designed. Jack Enders was the primary pilot for the program and future astronaut Fred Haise worked with the cameras and instrumentation in the rear of the aircraft. North American developed the AJ-2 for the Navy in the mid-1940s as a carrier-based bomber. By the 1960s the Savage was no longer considered a modern aircraft, but its performance capabilities made it appealing to the Lewis researchers. The AJ-2 ‘s power, speed, response time, structural robustness, and large interior space were applicable to the microgravity flights. The AJ-2 could also accommodate a pilot, flight engineer, and two observers. Lewis engineers installed a 100-litre liquid hydrogen dewar, cryogenic cooling system, and cameras in the bomb bay. The AJ-2 was flown on a level course over western Lake Erie then went into a 20-degree dip to generate 375 knot. At 13,000 feet the pilot pulled the nose up by 40 degrees. The speed decreased and both latitudinal and longitudinal accelerations were nullified. Upon reaching 17,000 feet, the pilot turned the aircraft into a 45-degree dive. As the speed reached 390 knots the pilot pulled the aircraft up again. Each maneuver produced approximately 27 seconds of microgravity.
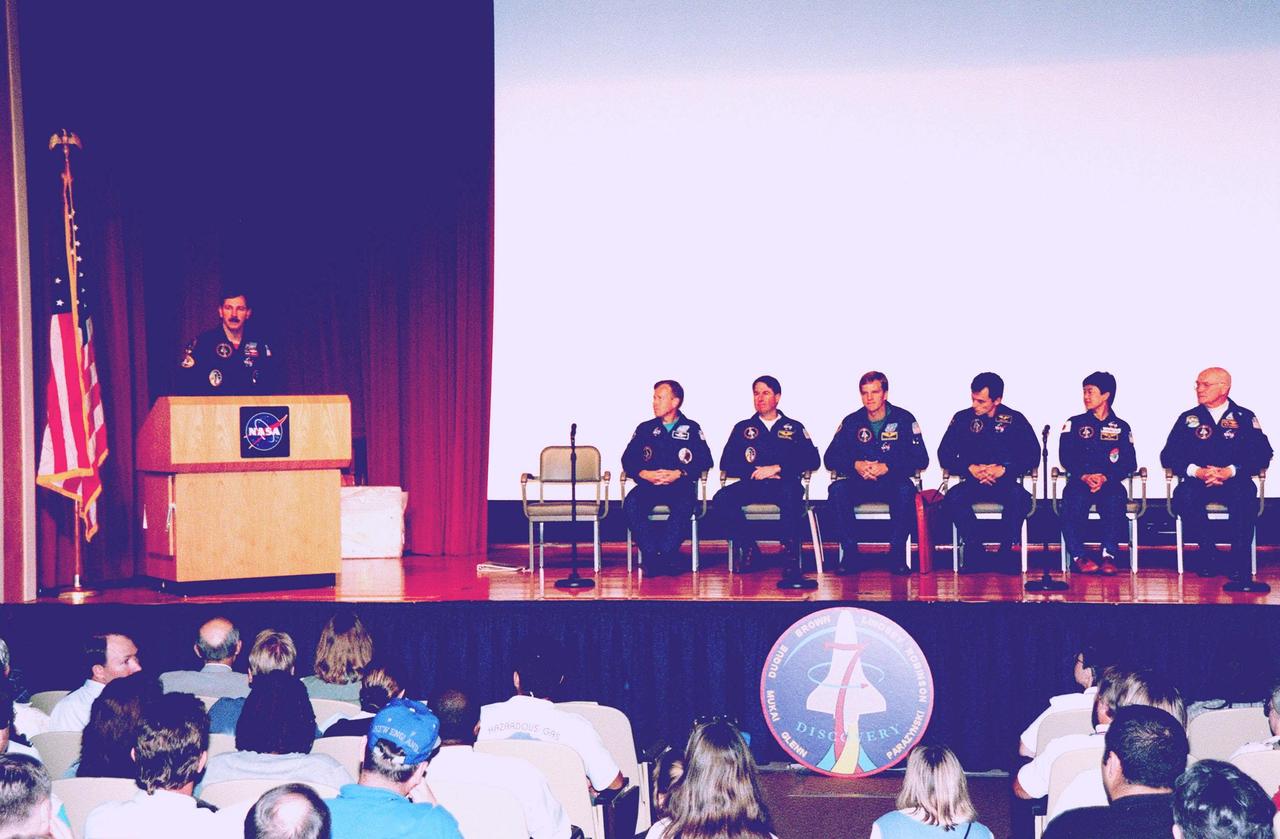

In the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Training Auditorium, STS-95 Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. (at podium) addresses KSC employees who were invited to hear the STS-95 crew describe their experiences during their successful mission dedicated to microgravity research and to view a videotape of the highlights of the mission. The other STS-95 crew members are (seated, from left to right) Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist and Payload Commander Stephen K. Robinson; Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski and Pedro Duque, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialists Chiaki Mukai, with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio and one of the original seven Project Mercury astronauts. Later in the afternoon, the crew will participate in a parade down State Road A1A in nearby Cocoa Beach, reminiscent of those held after missions during the Mercury Program
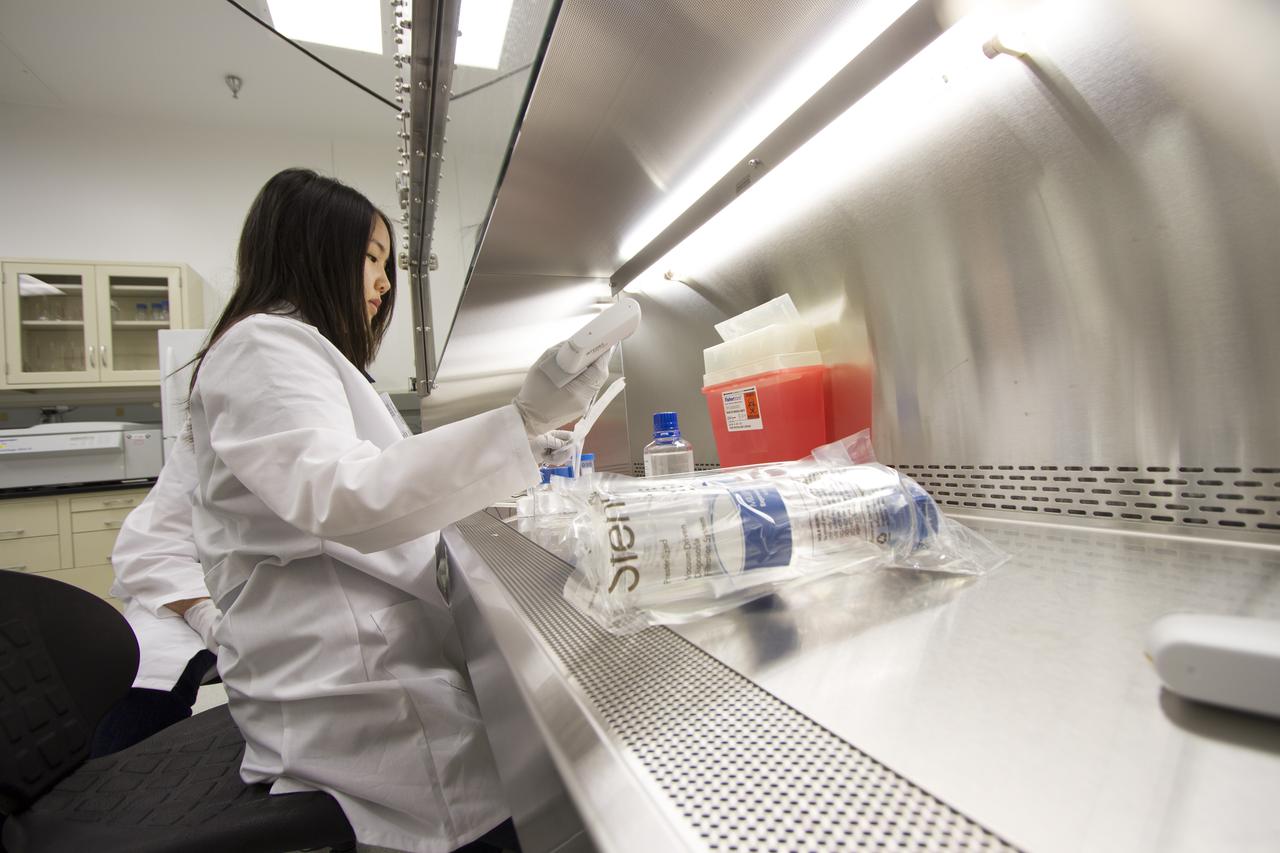

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - T-cell science team member Miya Yoshida, of the Hughes-Fulford Laboratory in San Francisco, Calif., works in a biosafety hood during preflight experiment preparations in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The immunology experiment will launch on SpaceX-3 and focus on the effects of microgravity on early T-cell signaling pathways. Current work aims to identify and compare the gene expression of microRNAs miRNAs during T-cell activation under normal gravity and in microgravity, and compare those patterns to changes seen in aging populations. The experiment will be the first flown on SpaceX funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hughes-Fulford flew aboard space shuttle mission STS-40 in June 1991, the first Spacelab mission dedicated to biomedical studies. For more information on the T-cell experiment, visit http://hughesfulfordlab.com and http://www.nasa.gov/ames/research/space-biosciences/t-cell-activation-in-aging-spacex-3/. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Dr. Freya Shephard is interviewed by the media in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during prelaunch activities for the SpaceX demonstration test flight. Shephard is a researcher from the University of Nottingham in the United Kingdom and mentor to Paul Warren, an eleventh-grade student investigator from Henry E. Lackey High School in Charles County, Md. Warren’s experiment “Physiological Effects of Microgravity and Increased Levels of Radiation on Wild Type and Genetically Engineered Caenorhabditis elegans,” is one of 15 in the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program, or SSEP, being ferried to the International Space Station inside the Dragon capsule. The launch will be the second demonstration test flight for SpaceX for NASA's Commercial Orbital Transportation Services program, or COTS. SSEP, which began operation in June 2010 through a partnership of the National Center for Earth and Space Science Education with NanoRacks LLC, is a U.S. national science, technology, engineering and mathematics STEM education initiative that gives students across a community the opportunity to propose and design real experiments to fly in low Earth orbit. SSEP experiments flew on space shuttle missions STS-134 and STS-135 in 2011, the final flights of space shuttles Endeavour and Atlantis. For more information on SSEP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/audience/foreducators/station-here-we-come.html. Photo credit: NASA/Gianni Woods
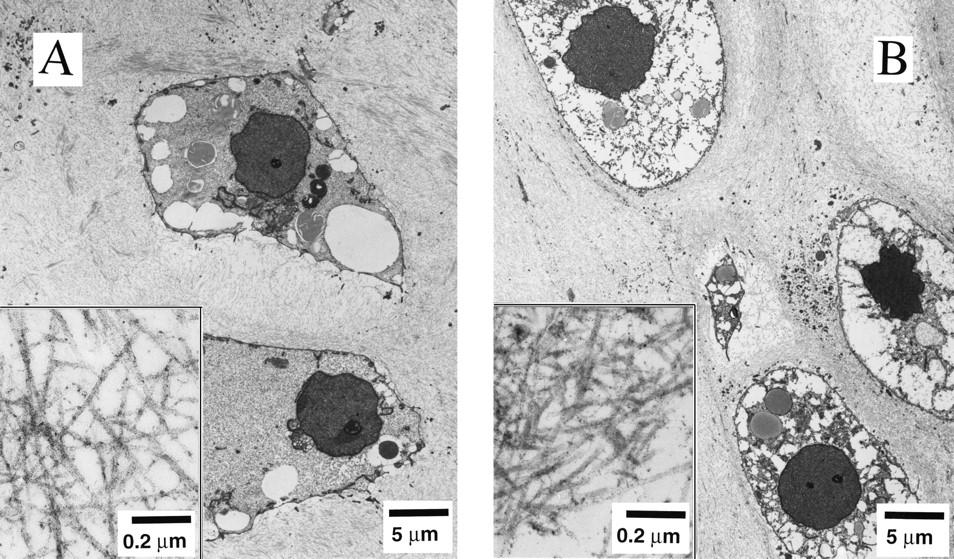
Dr. Lisa E. Freed of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and her colleagues have reported that initially disc-like specimens tend to become spherical in space, demonstrating that tissues can grow and differentiate into distinct structures in microgravity. The Mir Increment 3 (Sept. 16, 1996 - Jan. 22, 1997) samples were smaller, more spherical, and mechanically weaker than Earth-grown control samples. These results demonstrate the feasibility of microgravity tissue engineering and may have implications for long human space voyages and for treating musculoskeletal disorders on earth. Final samples from Mir and Earth appeared histologically cartilaginous throughout their entire cross sections (5-8 mm thick), with the exception of fibrous outer capsules. Constructs grown on Earth (A) appeared to have a more organized extracellular matrix with more uniform collagen orientation as compared with constructs grown on Mir (B), but the average collagen fiber diameter was similar in the two groups (22 +- 2 nm) and comparable to that previously reported for developing articular cartilage. Randomly oriented collagen in Mir samples would be consistent with previous reports that microgravity disrupts fibrillogenesis. These are transmission electron micrographs of constructs from Mir (A) and Earth (B) groups at magnifications of x3,500 and x120,000 (Inset). The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Credit: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
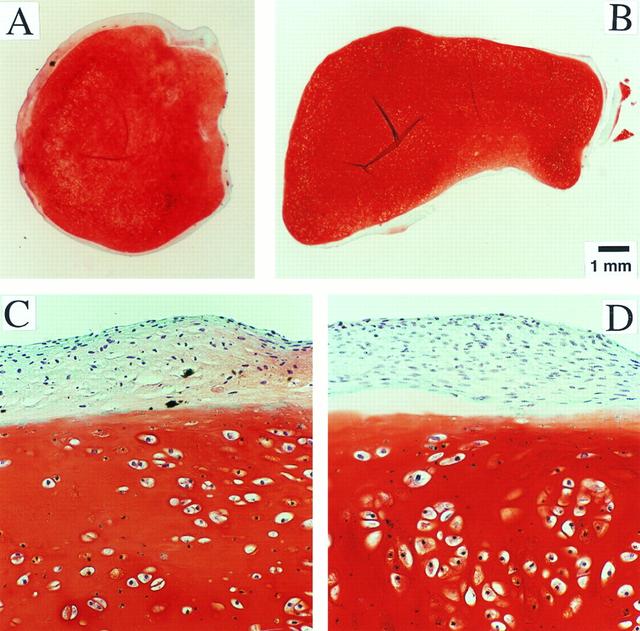
Dr. Lisa E. Freed of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and her colleagues have reported that initially disc-like specimens of cartilage tend to become spherical in space, demonstrating that tissues can grow and differentiate into distinct structures in microgravity. The Mir Increment 3 (Sept. 16, 1996 - Jan. 22, 1997) samples were smaller, more spherical, and mechanically weaker than Earth-grown control samples. These results demonstrate the feasibility of microgravity tissue engineering and may have implications for long human space voyages and for treating musculoskeletal disorders on earth. Constructs grown on Mir (A) tended to become more spherical, whereas those grown on Earth (B) maintained their initial disc shape. These findings might be related to differences in cultivation conditions, i.e., videotapes showed that constructs floated freely in microgravity but settled and collided with the rotating vessel wall at 1g (Earth's gravity). In particular, on Mir the constructs were exposed to uniform shear and mass transfer at all surfaces such that the tissue grew equally in all directions, whereas on Earth the settling of discoid constructs tended to align their flat circular areas perpendicular to the direction of motion, increasing shear and mass transfer circumferentially such that the tissue grew preferentially in the radial direction. A and B are full cross sections of constructs from Mir and Earth groups shown at 10-power. C and D are representative areas at the construct surfaces enlarged to 200-power. They are stained red with safranin-O. NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). Photo credit: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
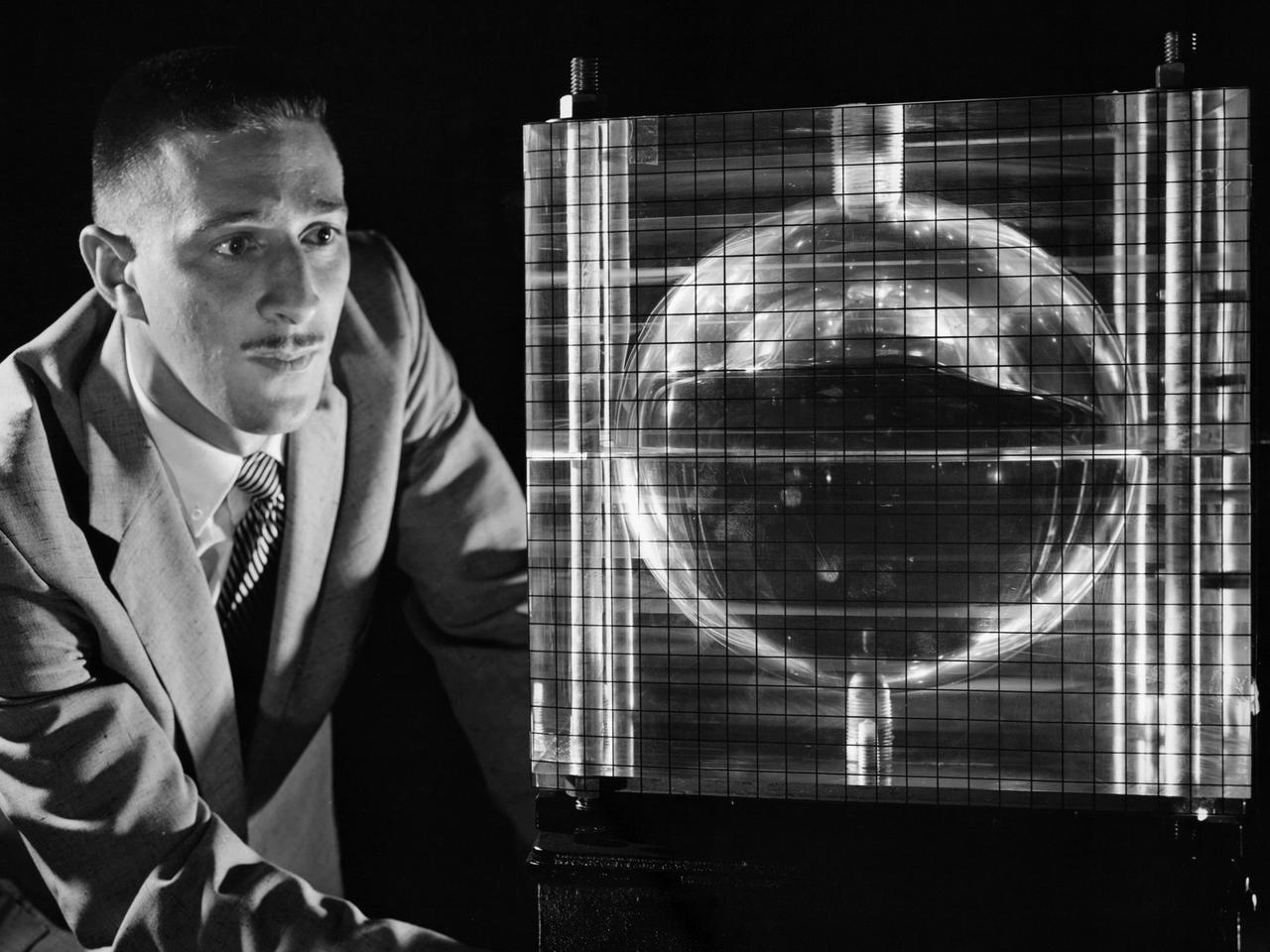

Andy Stofan views a small-scale tank built to study the sloshing characteristics of liquid hydrogen at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Stofan was tasked with the study of propellant motion, or sloshing, in space vehicle propellant tanks. At the time, there was little knowledge of the behavior of fluids in microgravity or the effects of the launch on the propellant’s motion. Sloshing in the tank could alter a spacecraft’s trajectory or move the propellant away from the turbopump. Stofan became an expert and authored numerous technical reports on the subject. Stofan was assigned to the original Centaur Project Office in 1962 as a member of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan was instrumental in solving a dynamic instability problem on the Centaur vehicle and served as the systems engineer for the development of the Centaur propellant utilization system. The solution was also applied to the upper-stages of Saturn. In 1966, Stofan was named Head of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan continued rising through the managerial ranks at Lewis. In 1967 he became Project Manager of a test program that successfully demonstrated the use of a pressurization system for the Centaur vehicle; in 1969 the Assistant Project Manager on the Improved Centaur project; in 1970 Manager of the Titan/Centaur Project Office; in 1974 Director of the Launch Vehicles Division. In 1978, Stofan was appointed Deputy Associate Administrator for the Headquarters Office of Space Science. In 1982, he was named Director of Lewis Research Center.
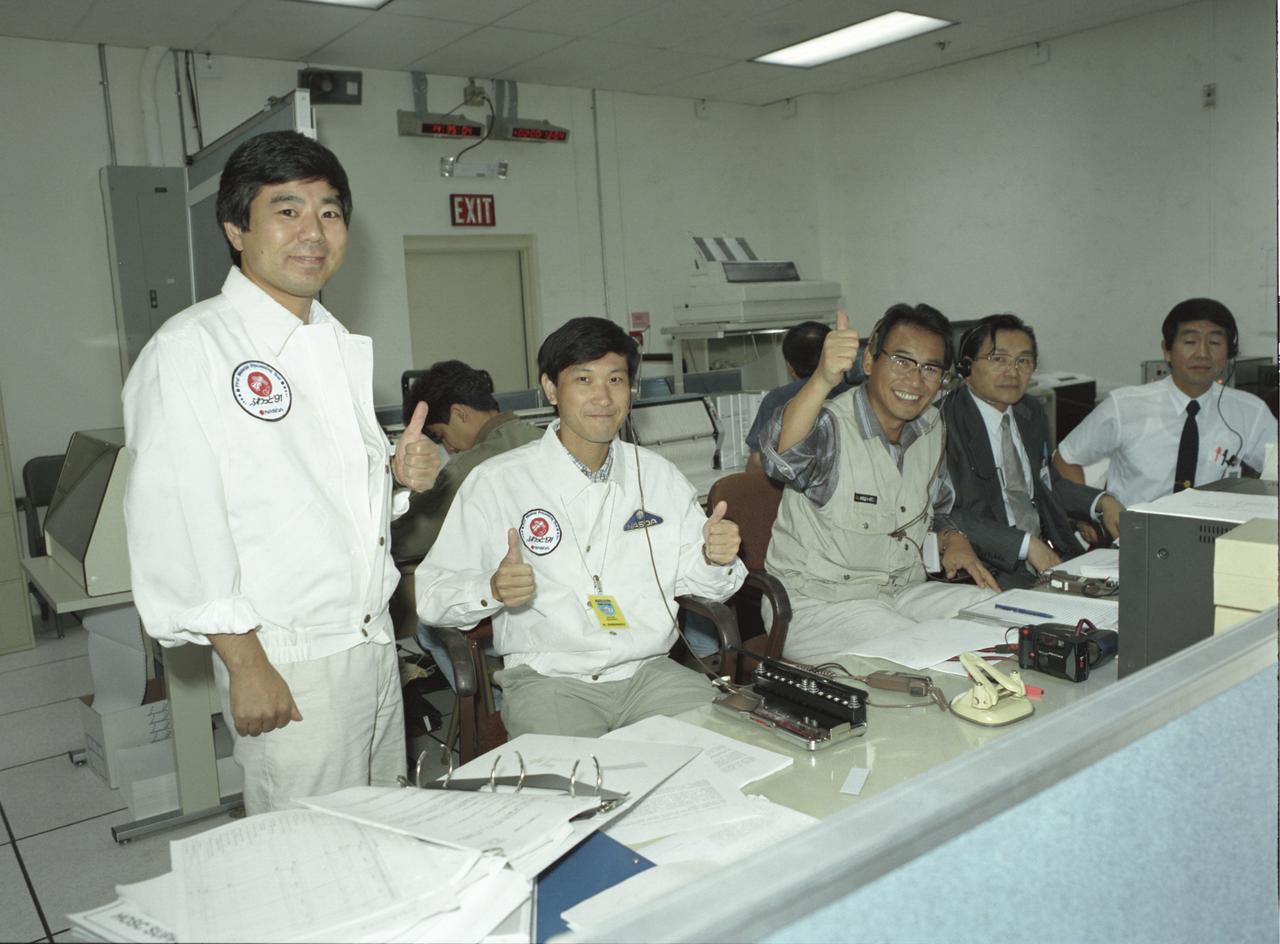

The group of Japanese researchers of the Spacelab-J (SL-J) were thumbs-up in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center after the successful launch of Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour that carried their experiments. The SL-J was a joint mission of NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted microgravity investigations in materials and life sciences. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, frogs, and frog eggs. The POCC was the air/ground communications channel between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The Spacelab science operations were a cooperative effort between the science astronaut crew in orbit and their colleagues in the POCC. Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
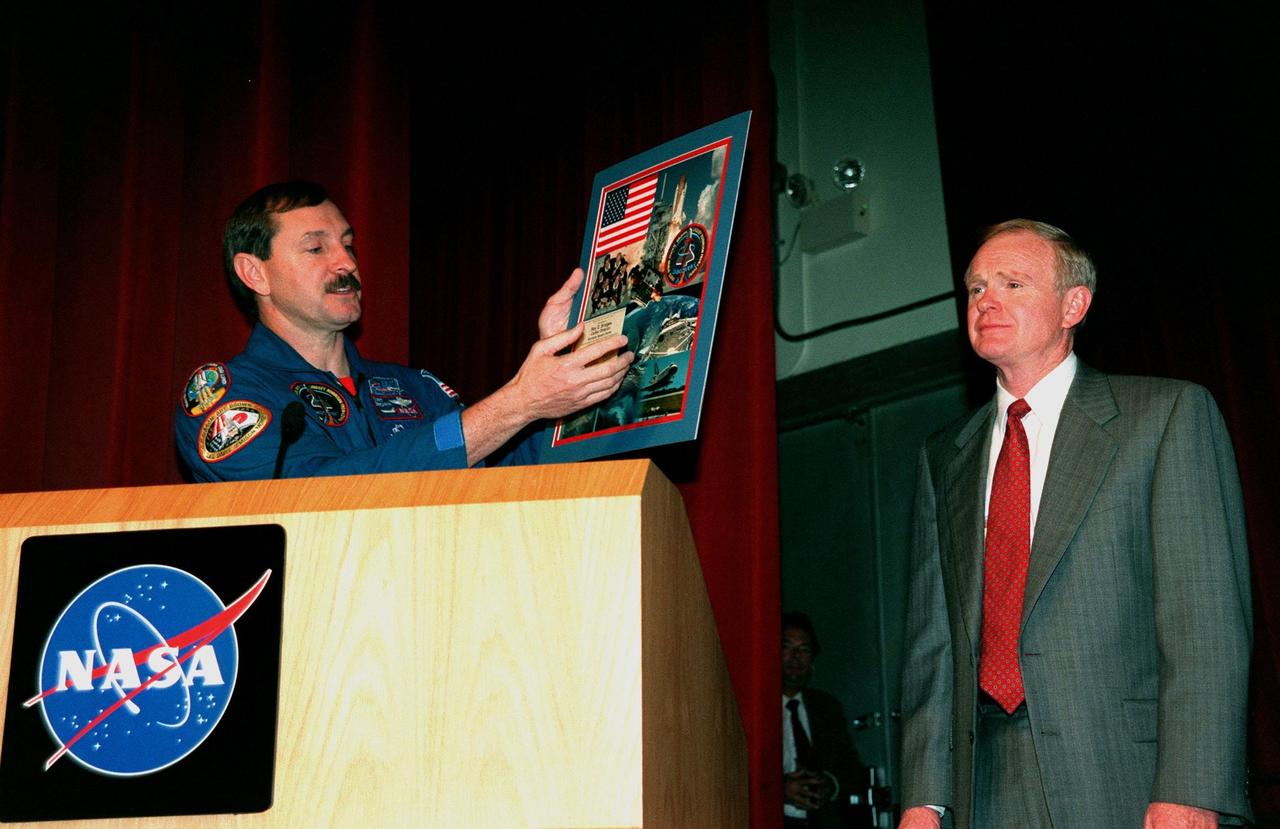

STS-95 Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. (left) presents a composite photograph of images taken during the STS-95 mission to Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Director Roy Bridges in the Training Auditorium. The auditorium is filled with KSC employees who were invited to hear the crew describe their experiences during their successful mission dedicated to microgravity research and to view a videotape of the highlights of the mission. The other crew members are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist and Payload Commander Stephen K. Robinson; Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski and Pedro Duque, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialists Chiaki Mukai, with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio and one of the original seven Project Mercury astronauts. Later in the afternoon, the crew will participate in a parade down State Road A1A in nearby Cocoa Beach, reminiscent of those held after missions during the Mercury Program
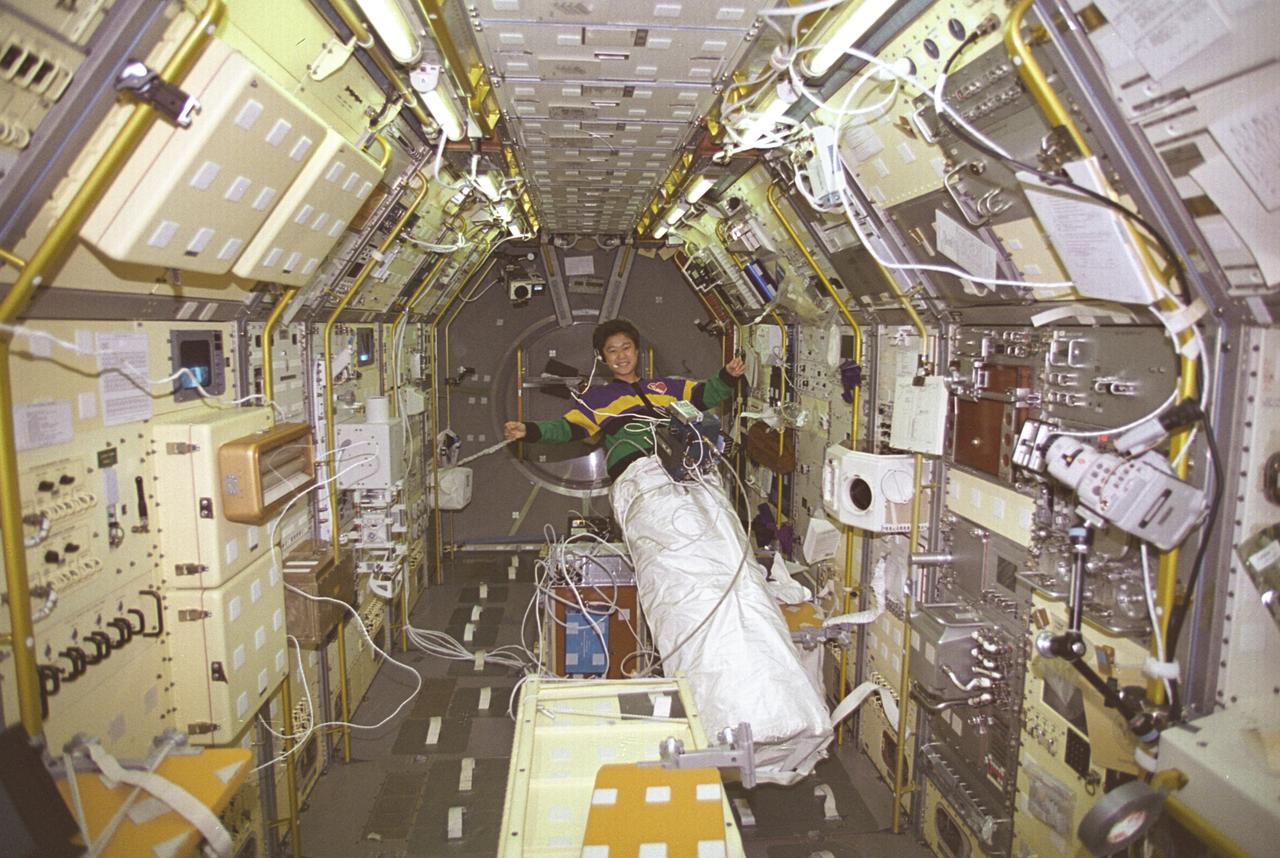

Astronaut Chiaki Mukai conducts the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment inside the International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) mission science module. Dr. Chiaki Mukai is one of the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) astronauts chosen by NASA as a payload specialist (PS). She was the second NASDA PS who flew aboard the Space Shuttle, and was the first female astronaut in Asia. When humans go into space, the lack of gravity causes many changes in the body. One change is that fluids normally kept in the lower body by gravity shift upward to the head and chest. This is why astronauts' faces appear chubby or puffy. The change in fluid volume also affects the heart. The reduced fluid volume means that there is less blood to circulate through the body. Crewmembers may experience reduced blood flow to the brain when returning to Earth. This leads to fainting or near-fainting episodes. With the use of the LBNP to simulate the pull of gravity in conjunction with fluids, salt tablets can recondition the cardiovascular system. This treatment, called "soak," is effective up to 24 hours. The LBNP uses a three-layer collapsible cylinder that seals around the crewmember's waist which simulates the effects of gravity and helps pull fluids into the lower body. The data collected will be analyzed to determine physiological changes in the crewmembers and effectiveness of the treatment. The IML-2 was the second in a series of Spacelab flights designed by the international science community to conduct research in a microgravity environment Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-2 was launched on July 8, 1994 aboard the STS-65 Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia mission.
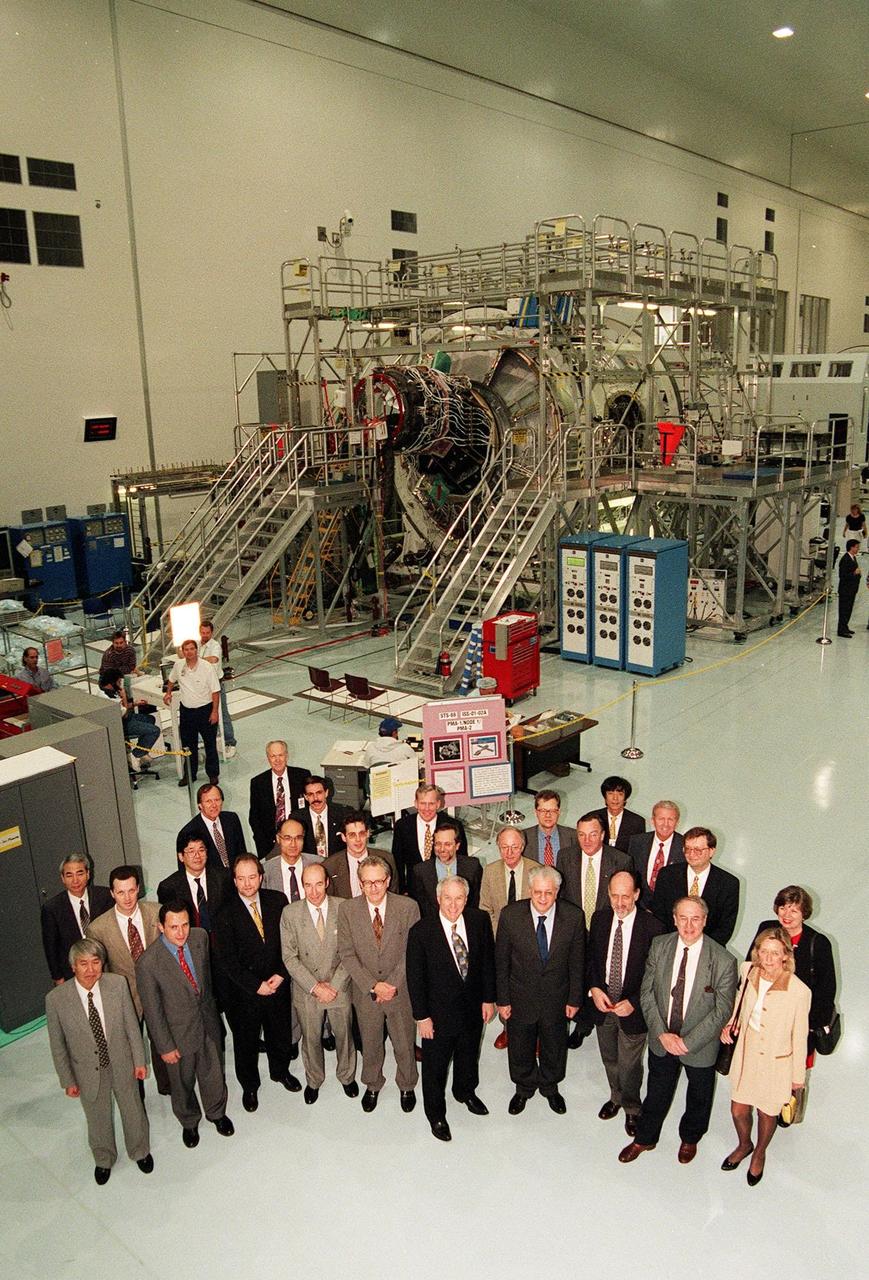
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the International Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, senior government officials from 15 countries participating in the space station program signed agreements in Washington D.C. on Jan. 29 to establish the framework of cooperation among the partners on the design, development, operation and utilization of the space station. Acting Secretary of State Strobe Talbott signed the 1998 Intergovernmental Agreement on Space Station Cooperation with representatives of Russia, Japan, Canada, and participating countries of the European Space Agency ESA -- Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. Some of these officials then toured Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility SSPF with NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin, at front, sixth from the left. They are, left to right, front to back: Hidetoshi Murayama, National Space Development Agency of Japan NASDA Louis Laurent, Embassy of France Haakon Blankenborg, Norwegian Parliament Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs His Excellency Joris Vos, ambassador of the Netherlands His Excellency Tom Vraalsen, ambassador of Norway Goldin Luigi Berlinguer, Italian minister for education, scientific, and technological research Antonio Rodota, director general, ESA Yvan Ylieff, Belgian minister of science and chairman of the ESA Ministerial Council Jacqueline Ylieff Masaaki Komatsu, Kennedy local NASDA representative and interpreter Serge Ivanets, space attache, Embassy of Russia Hiroshi Fujita, Science and Technology Agency of Japan Akira Mizutani, Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs Peter Grognard, science attache', Royal Embassy of Belgium Michelangelo Pipan, Italian diplomatic counselor to the minister His Excellency Gerhard Fulda, German Federal Foreign Office Jorg Feustel-Buechl, ESA director of manned space flight and microgravity A. Yakovenko, Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs JoAnn Morgan, Kennedy associate director for Advanced Development and Shuttle Upgrades Steve Francois, director, International Space Station and Shuttle Processing Roy Tharpe, Boeing launch site manager Jon Cowart, ISS elements manager John Schumacher, NASA associate administrator for external relations Didier Kechemair, space advistor to the French minister for education, research, and technology Yoshinori Yoshimura, NASDA and Loren Shriver, Kennedy deputy director for launch and payload processing. Node 1 of the ISS is in the background. Photo Credit: NASA