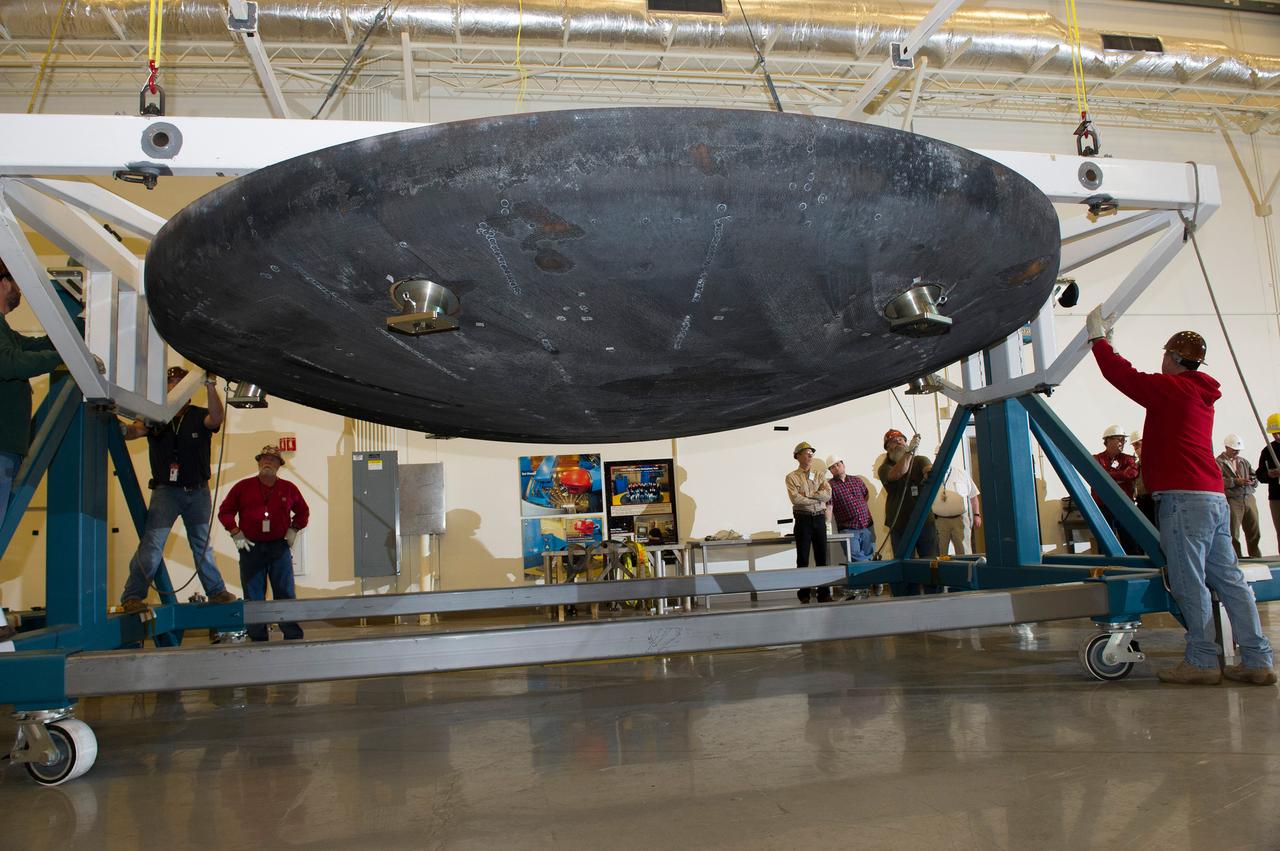

ORION HEAT SHIELD

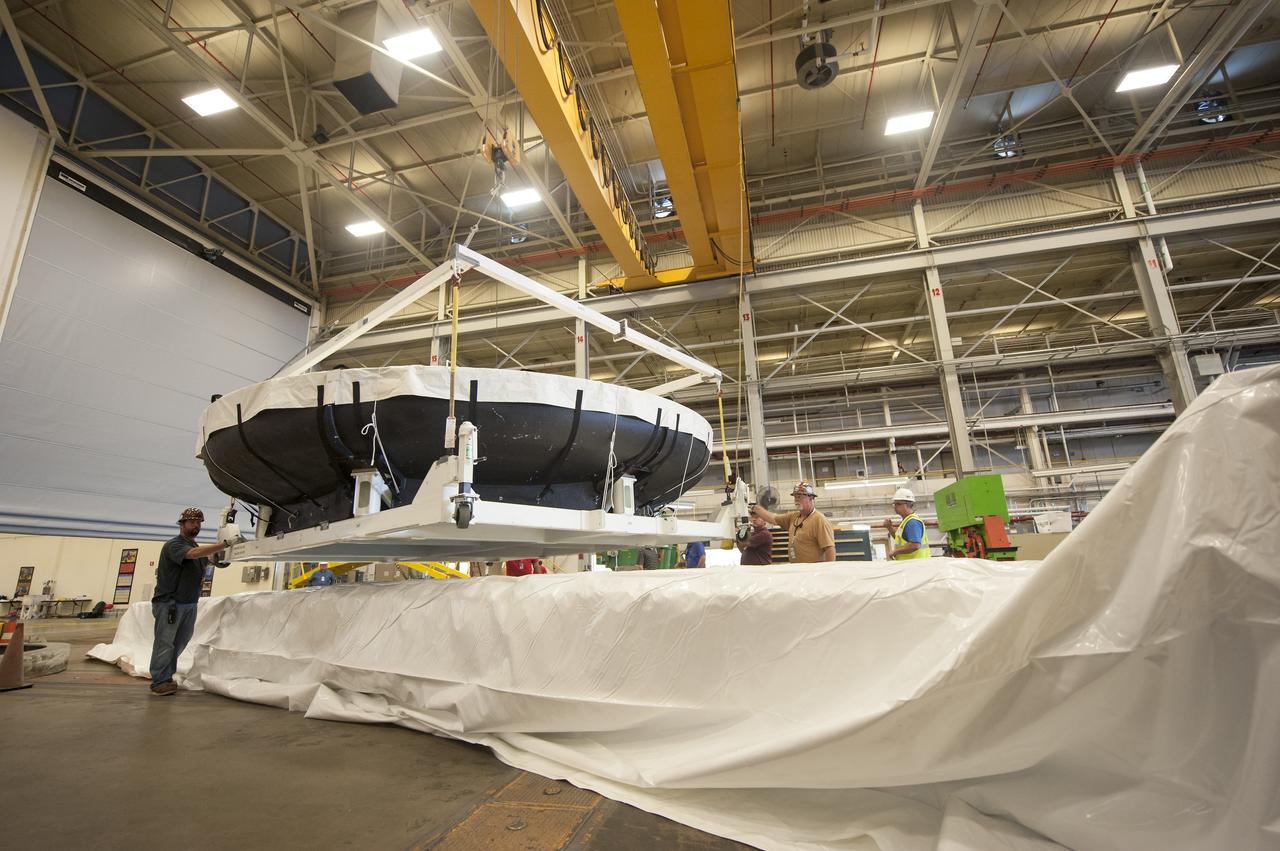
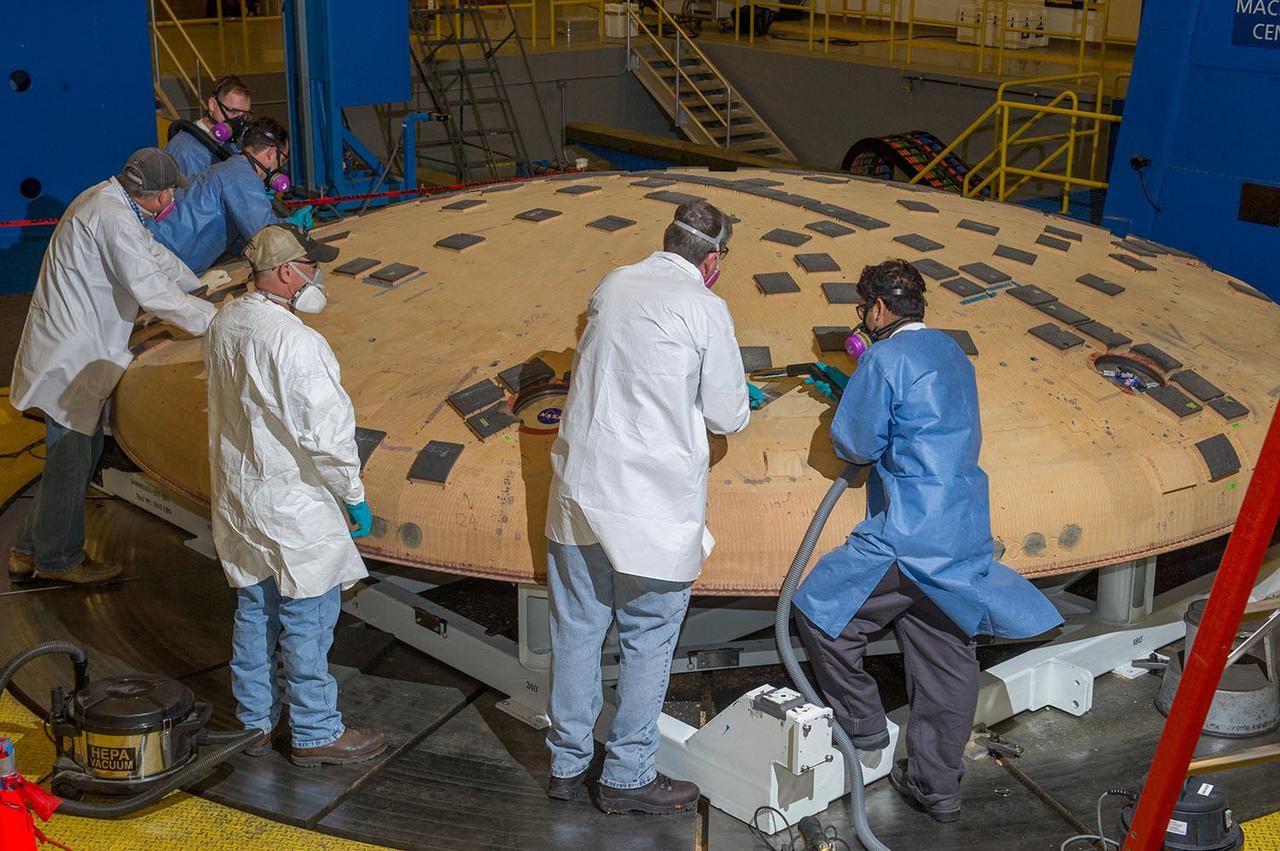
THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.

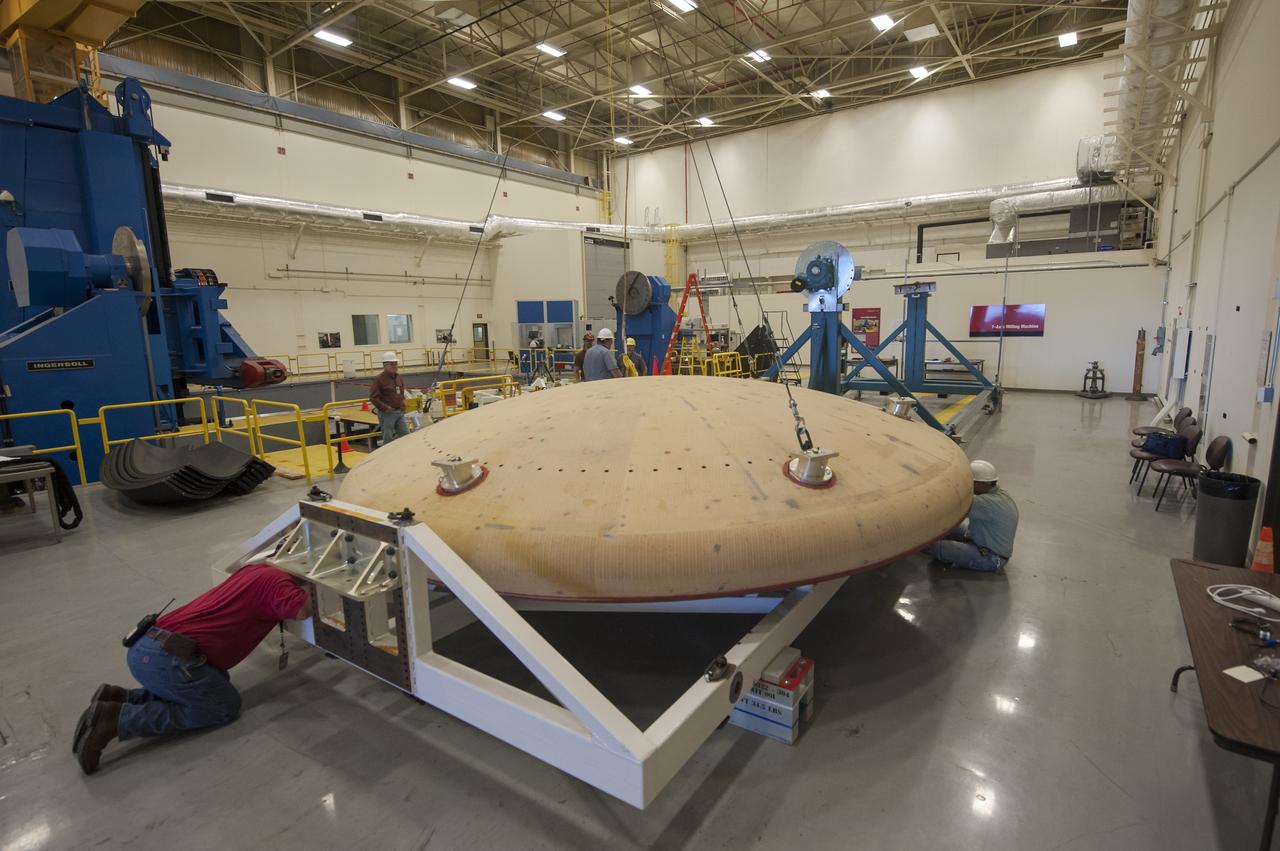
THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.

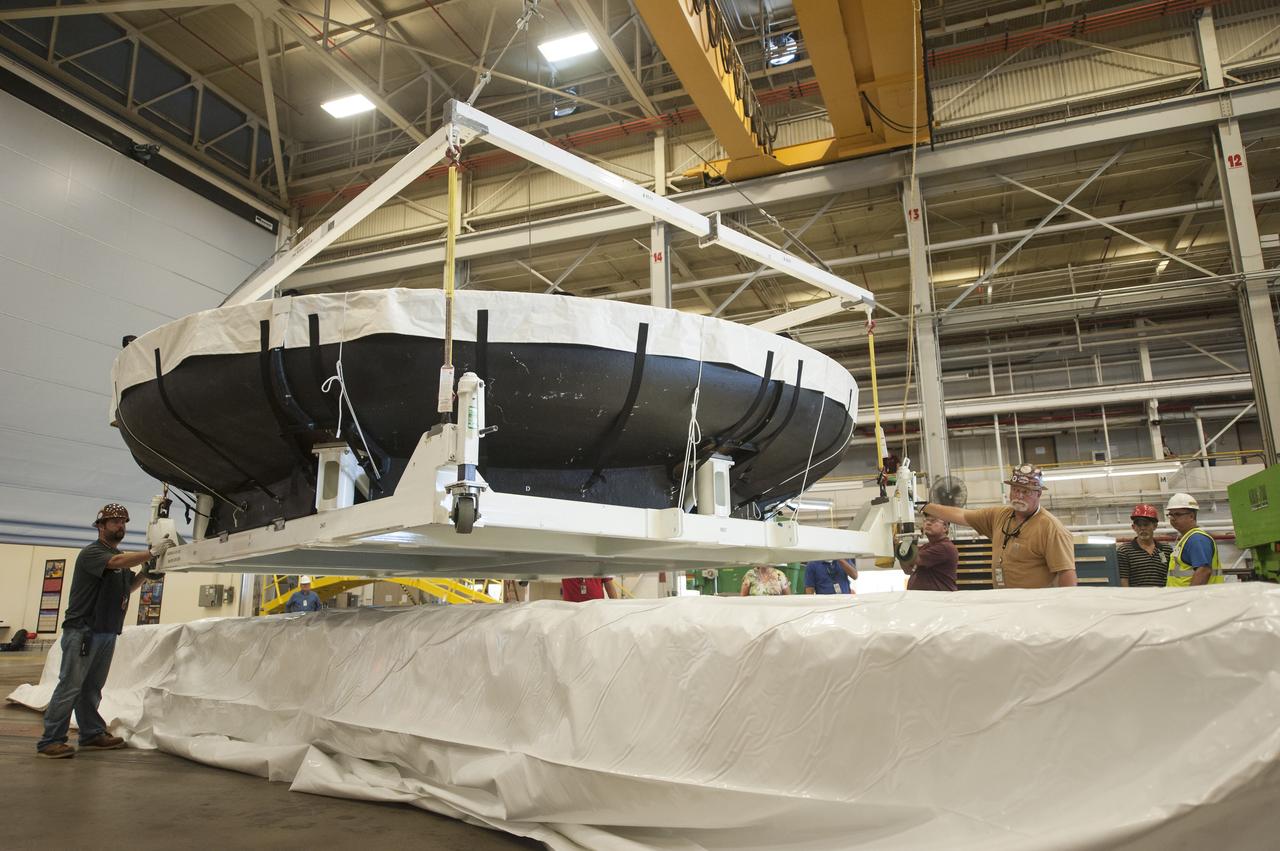
THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
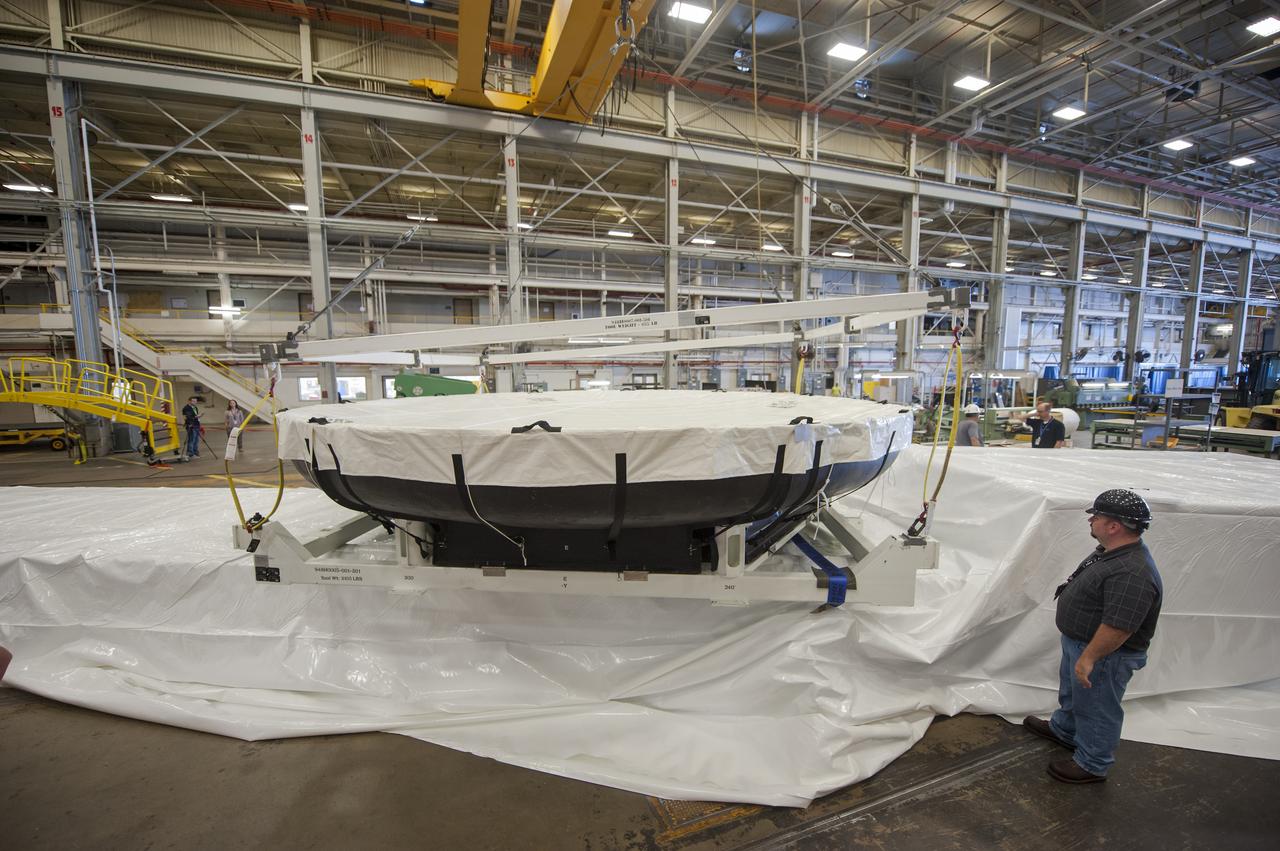

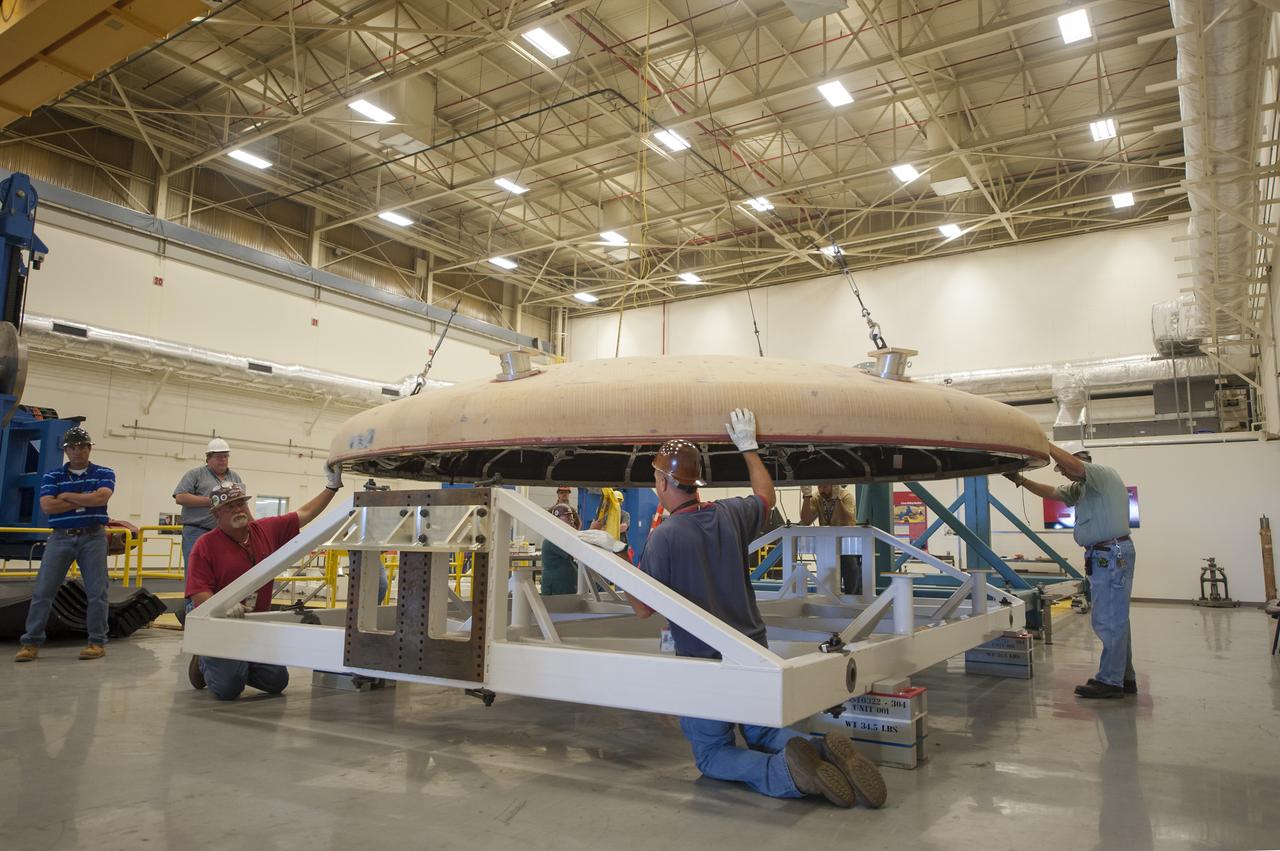
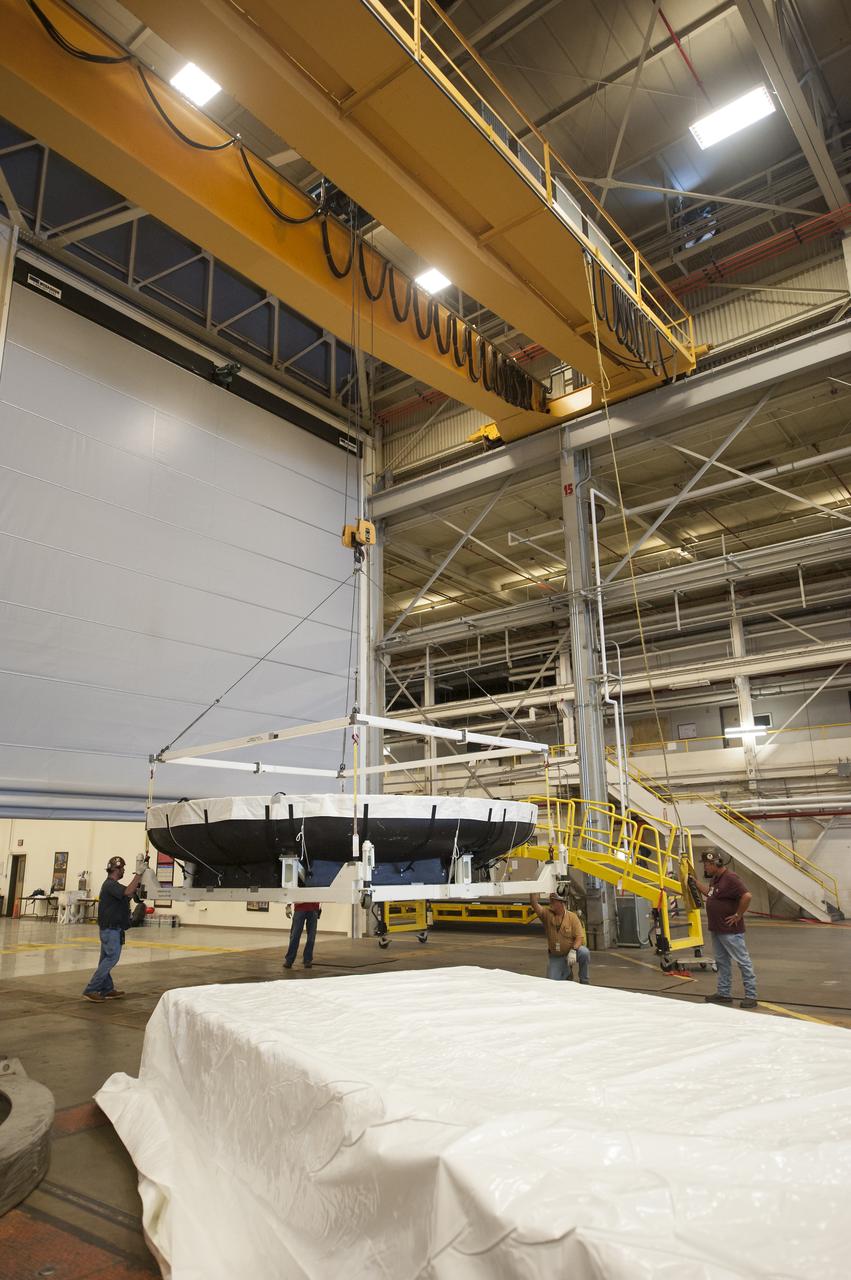
THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
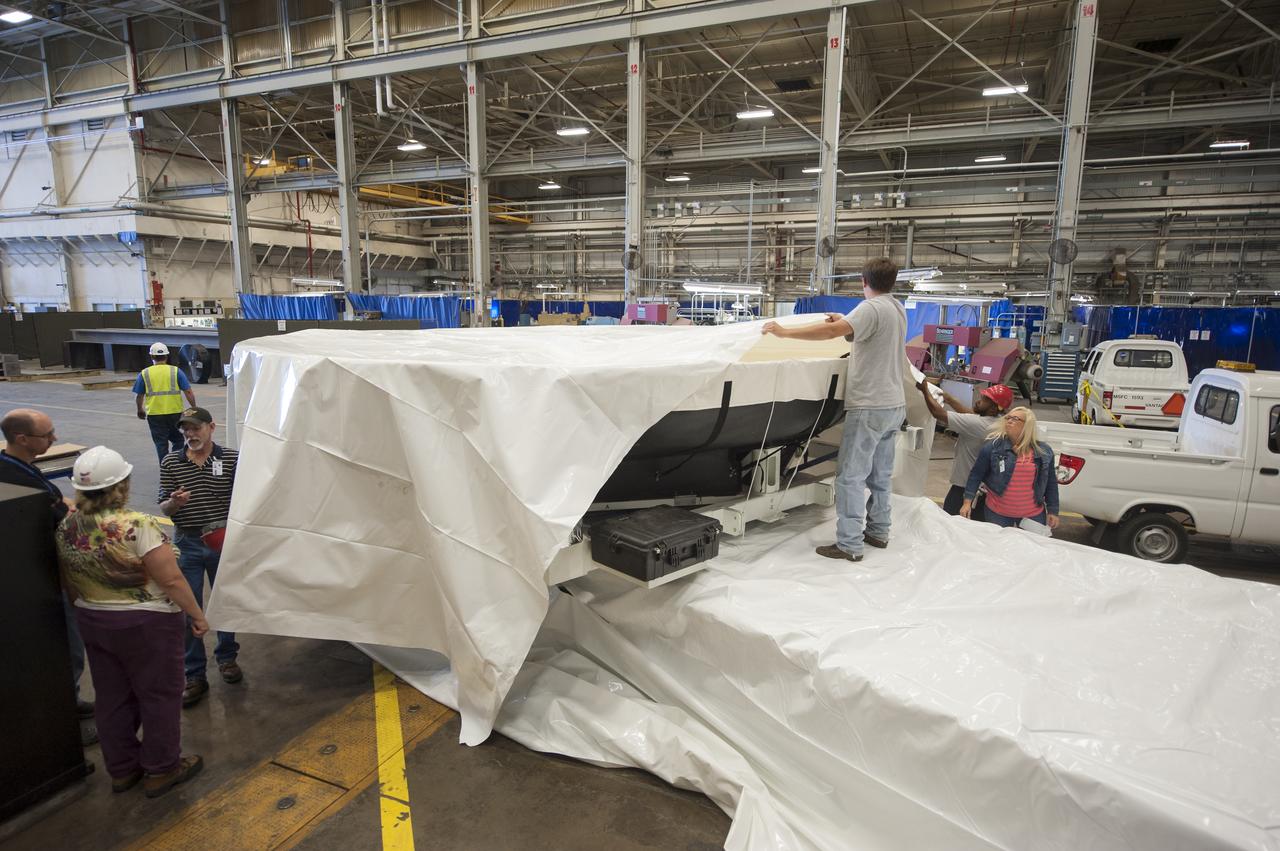

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
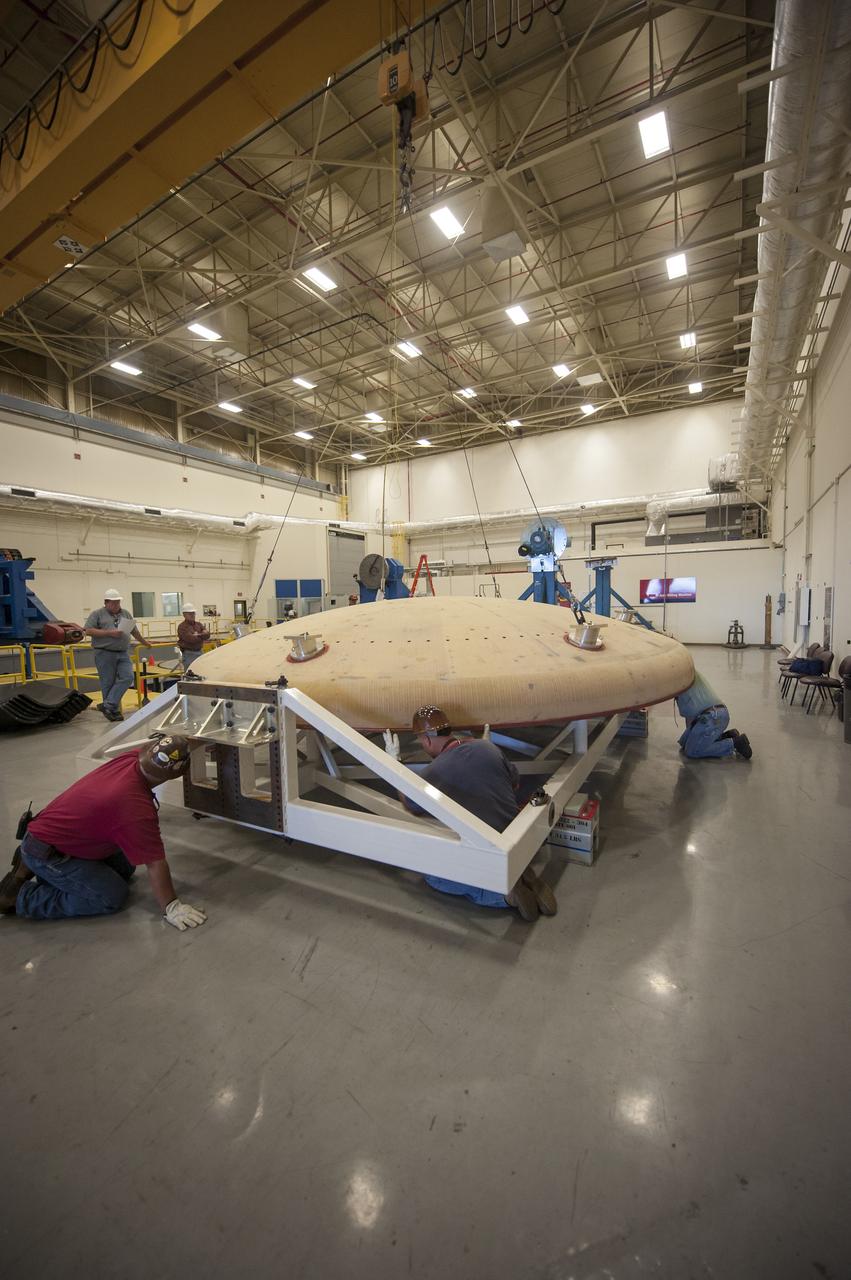

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
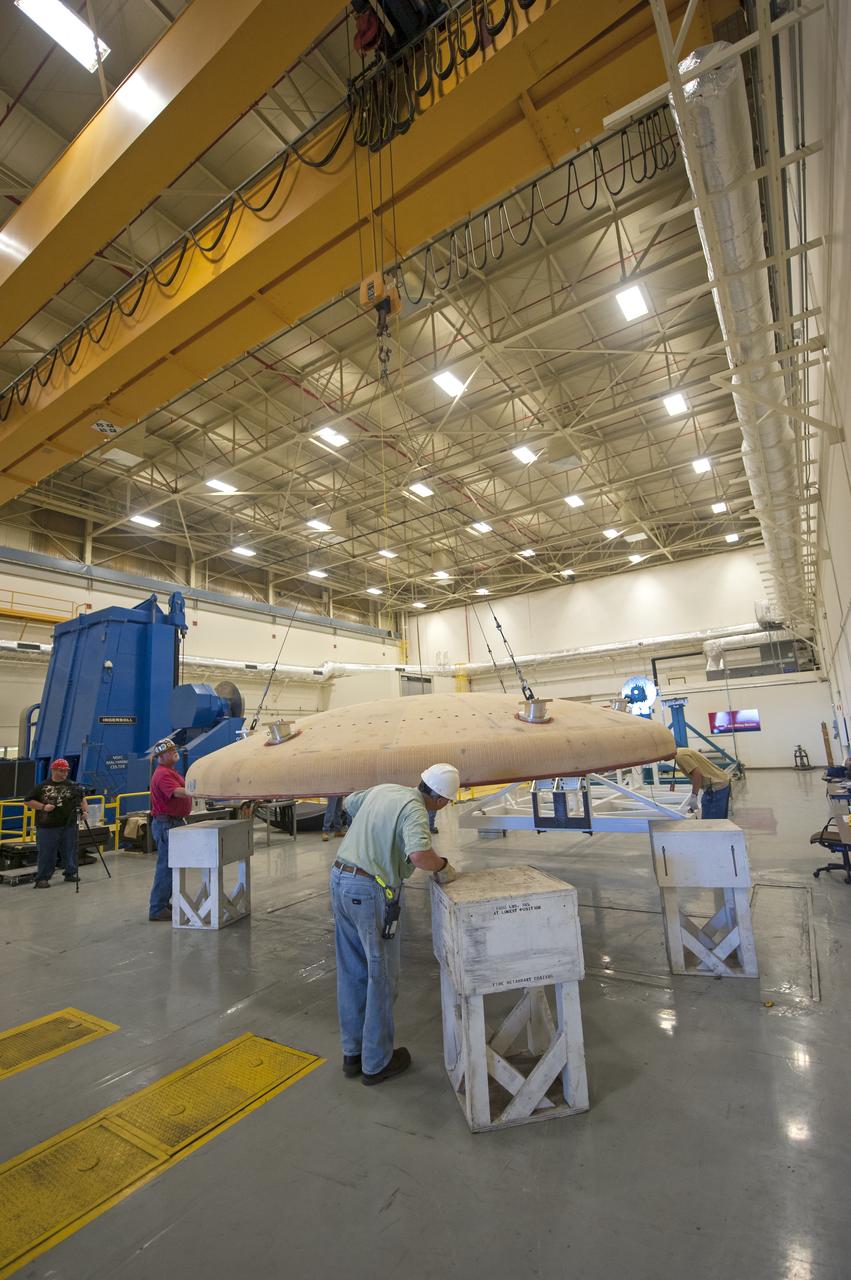

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
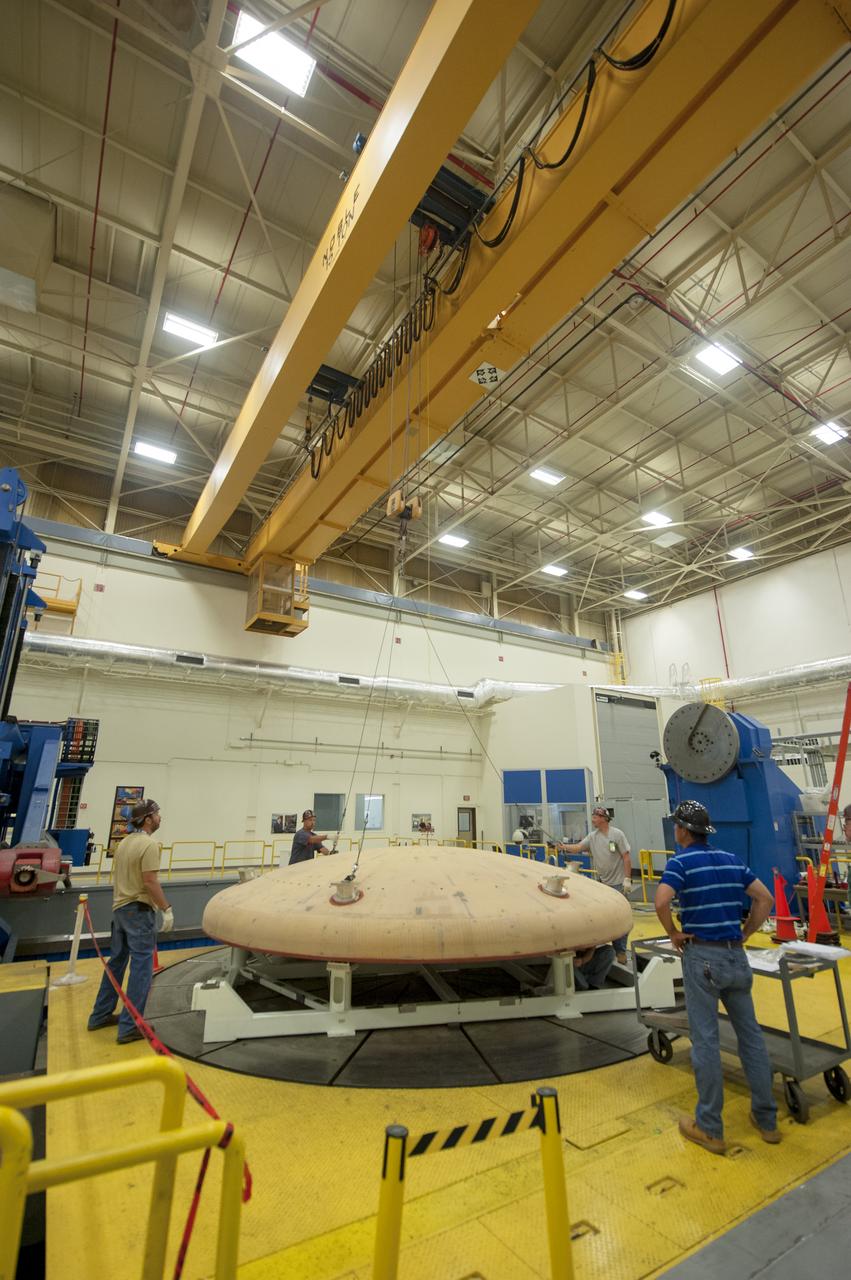

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
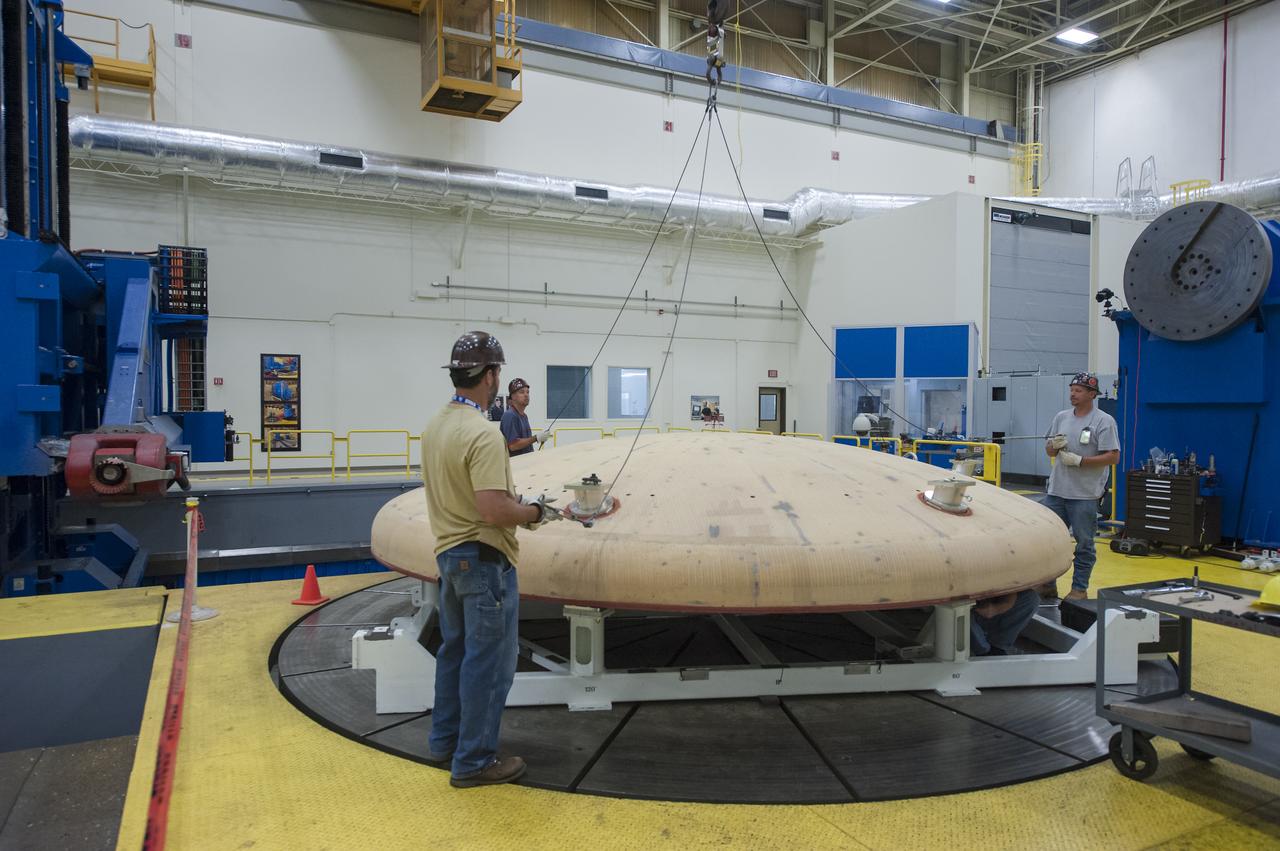

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
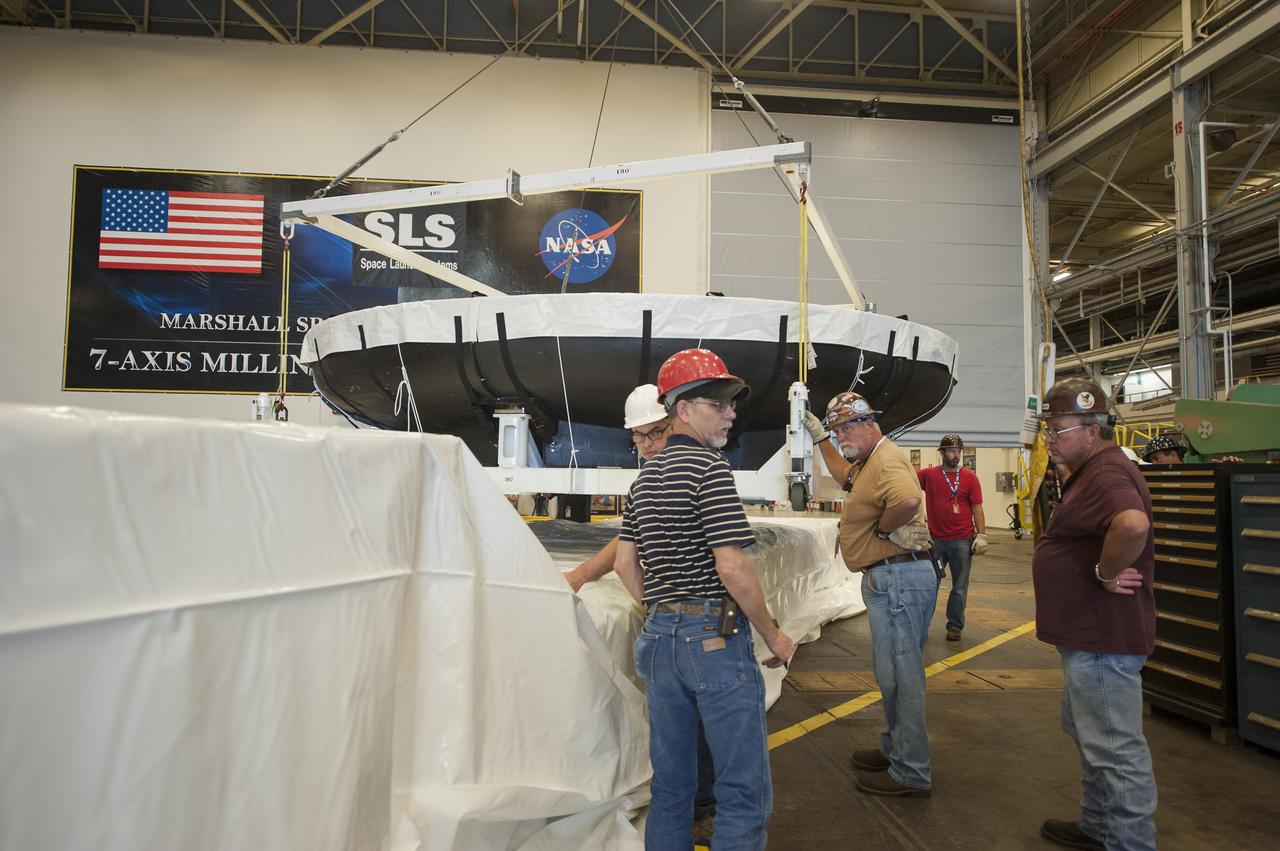

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
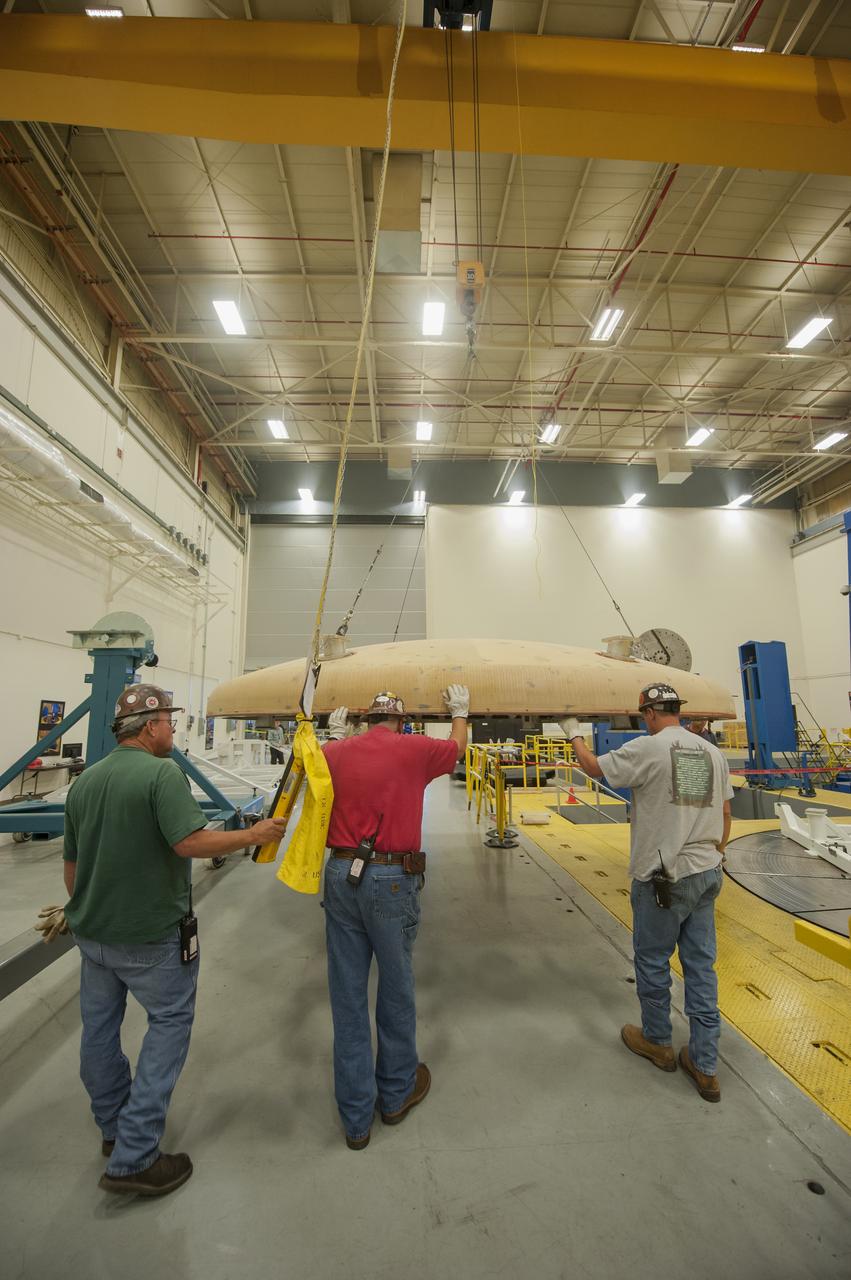

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
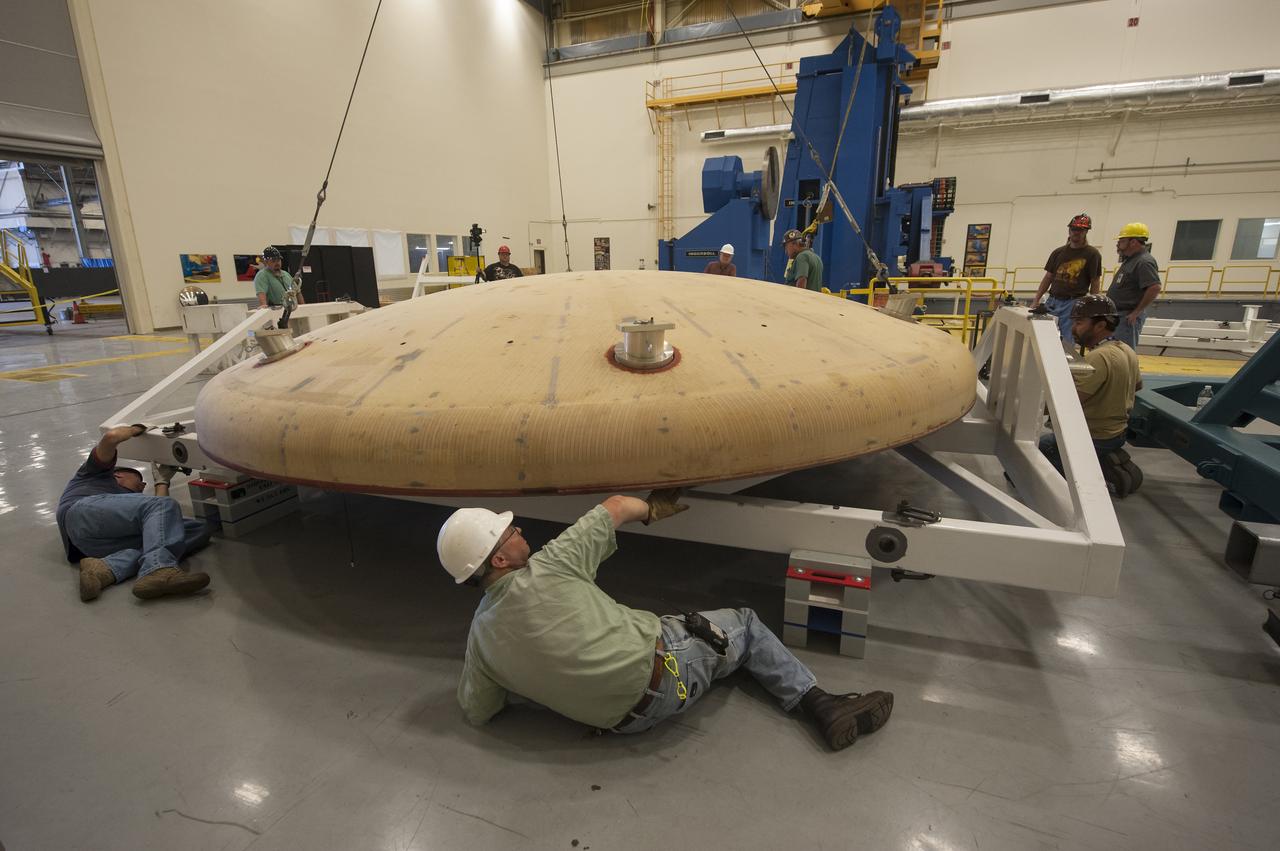

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
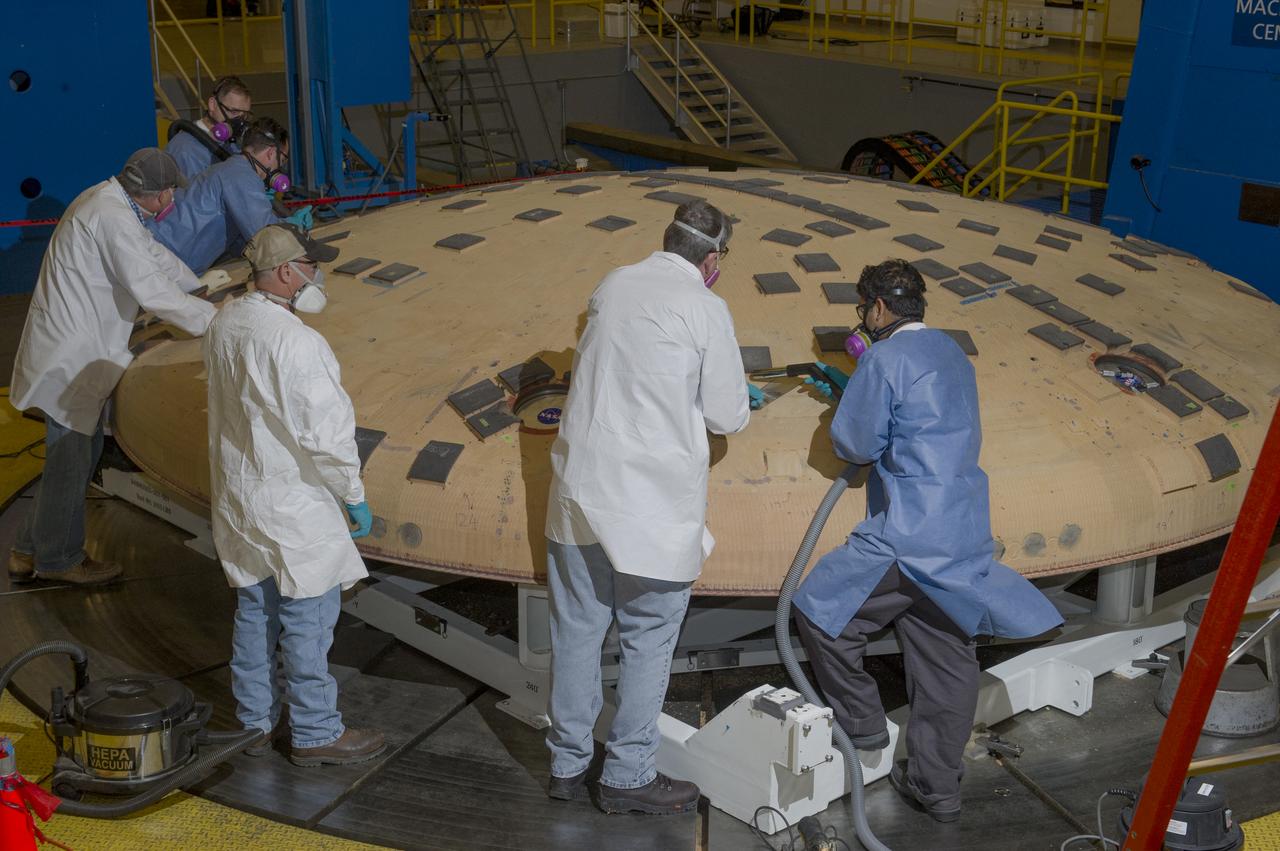

ENGINEERS FROM AMES RESEARCH CENTER AND MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER REMOVE AVCOAT SEGMENTS FROM THE SURFACE OF THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, THE PROTECTIVE SHELL DESIGNED TO HELP THE NEXT GENERATION CREW MODULE WITHSTAND THE HEAT OF ATMOSPHERIC REENTRY. THE HEAT SHIELD FLEW TO SPACE DURING THE EFT-1 FULL SCALL FLIGHT TEST OF ORION IN DECEMBER 2014
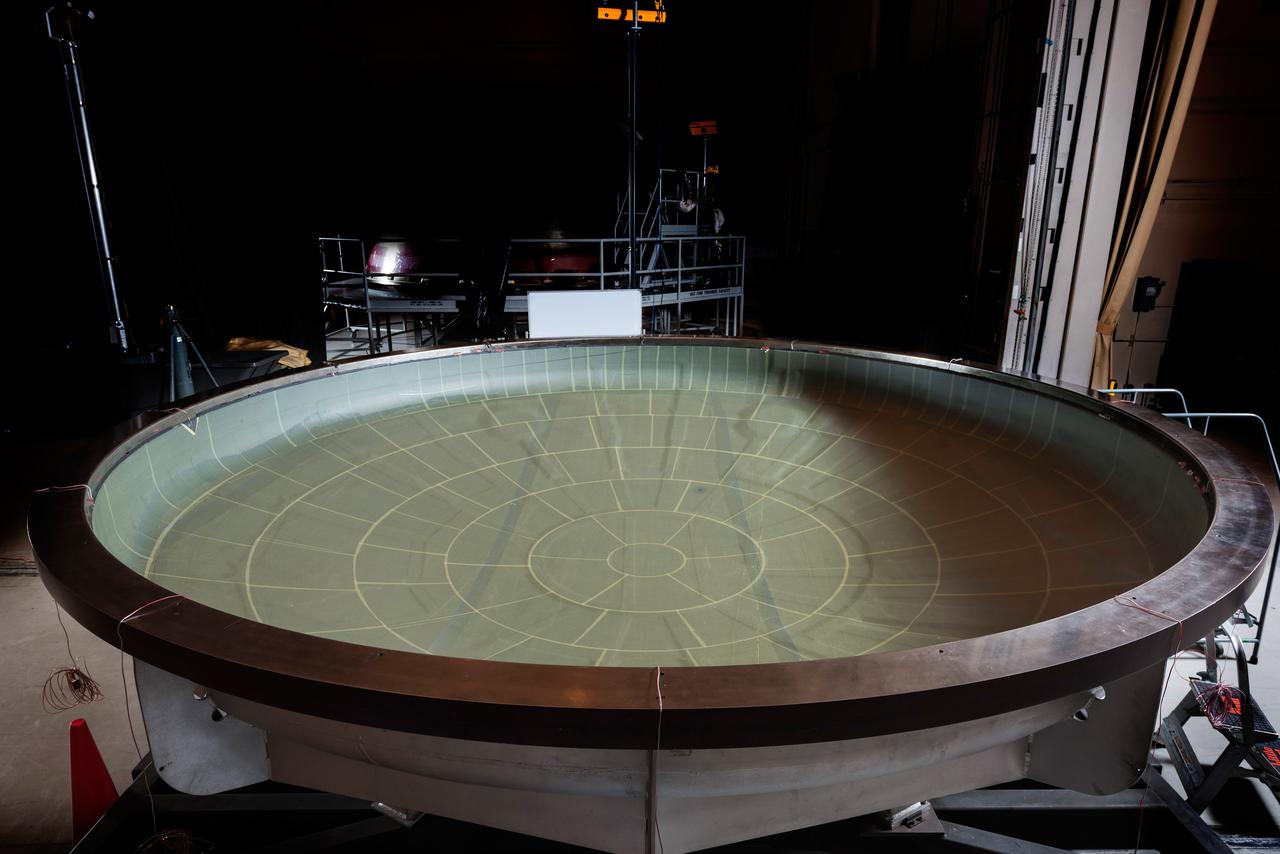
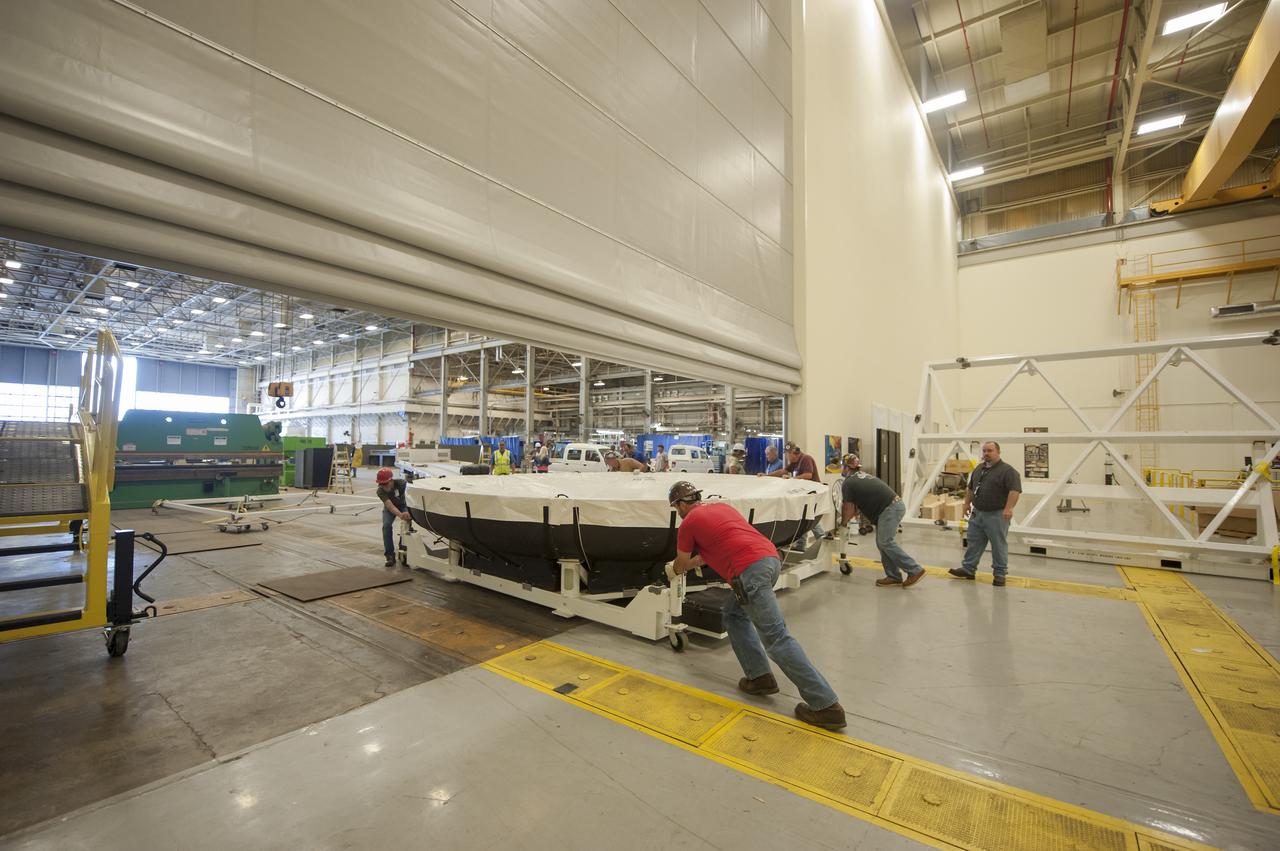
The NASA Super Guppy arrived at Moffett Field on Jan. 7, 2016, carrying the Artemis I Orion heat shield skin. The heat shield is being primarily built at Lockheed Martin’s Littleton, Colo. facility, and it was temporarily sent to Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, Calif. facility for an autoclave cure (shown here). The heat shield is a stiffened skin design, and this cure process is the last step prior to attaching titanium stiffeners to the interior surface. Once the skin and stiffeners are attached, ablative material is applied to the exterior. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
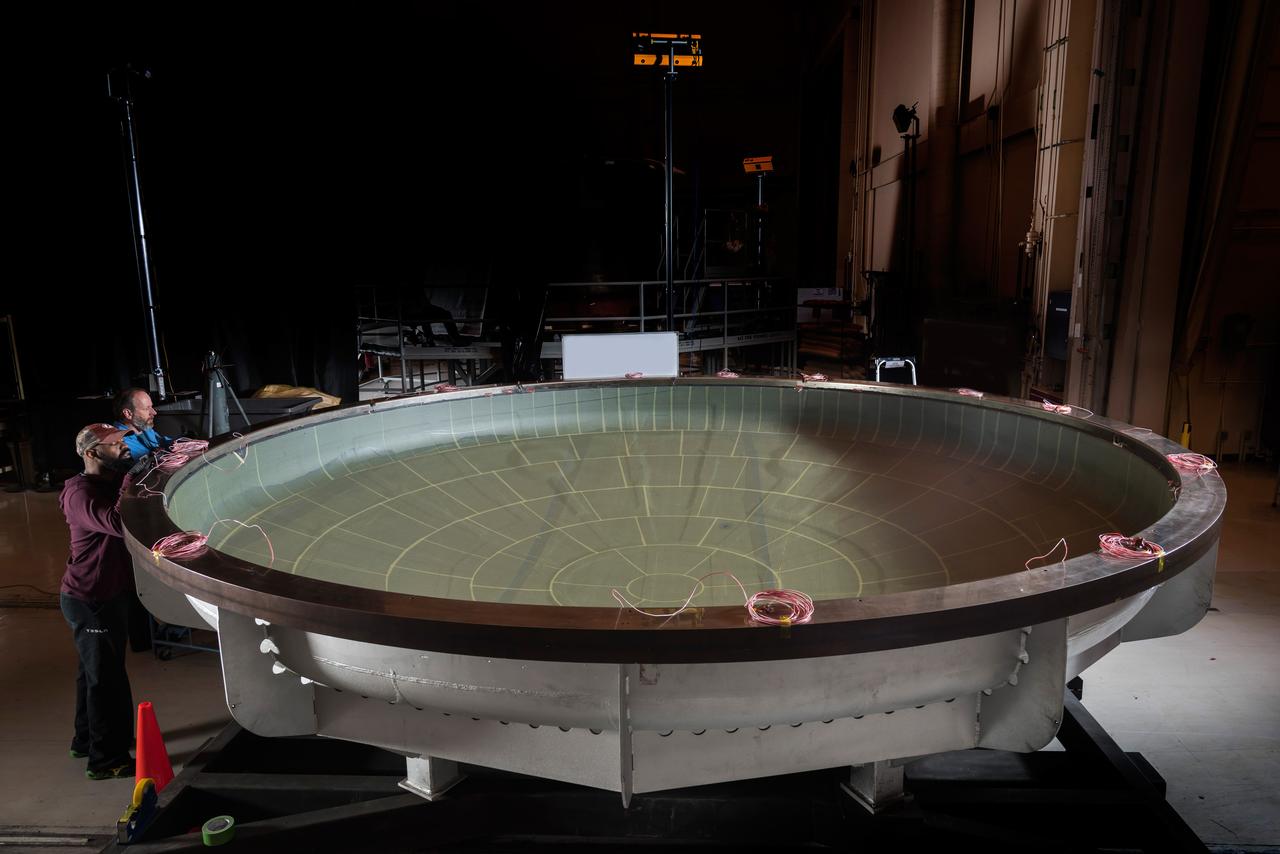

The NASA Super Guppy arrived at Moffett Field on Jan. 7, 2016, carrying the Artemis I Orion heat shield skin. The heat shield is being primarily built at Lockheed Martin’s Littleton, Colo. facility, and it was temporarily sent to Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, Calif. facility for an autoclave cure (shown here). The heat shield is a stiffened skin design, and this cure process is the last step prior to attaching titanium stiffeners to the interior surface. Once the skin and stiffeners are attached, ablative material is applied to the exterior. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
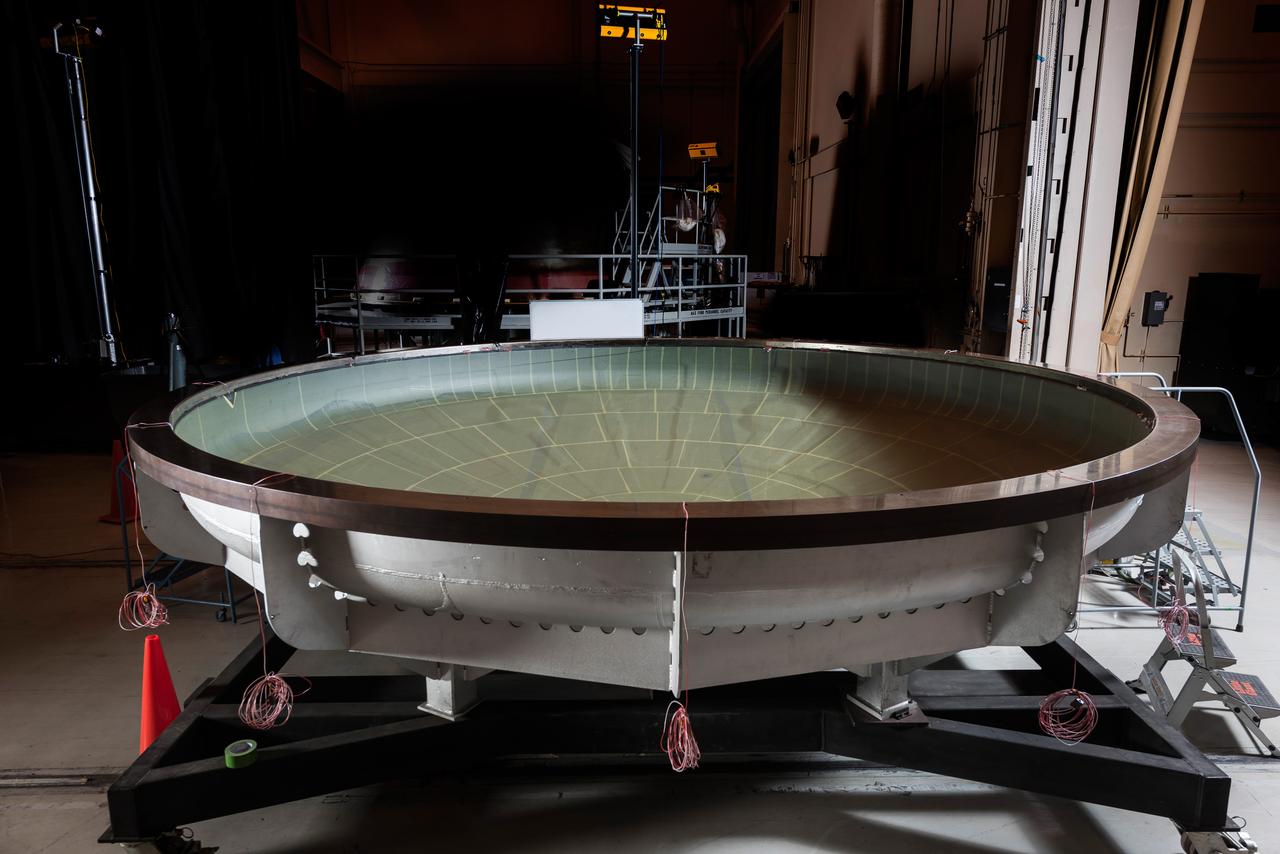

The NASA Super Guppy arrived at Moffett Field on Jan. 7, 2016, carrying the Artemis I Orion heat shield skin. The heat shield is being primarily built at Lockheed Martin’s Littleton, Colo. facility, and it was temporarily sent to Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, Calif. facility for an autoclave cure (shown here). The heat shield is a stiffened skin design, and this cure process is the last step prior to attaching titanium stiffeners to the interior surface. Once the skin and stiffeners are attached, ablative material is applied to the exterior. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
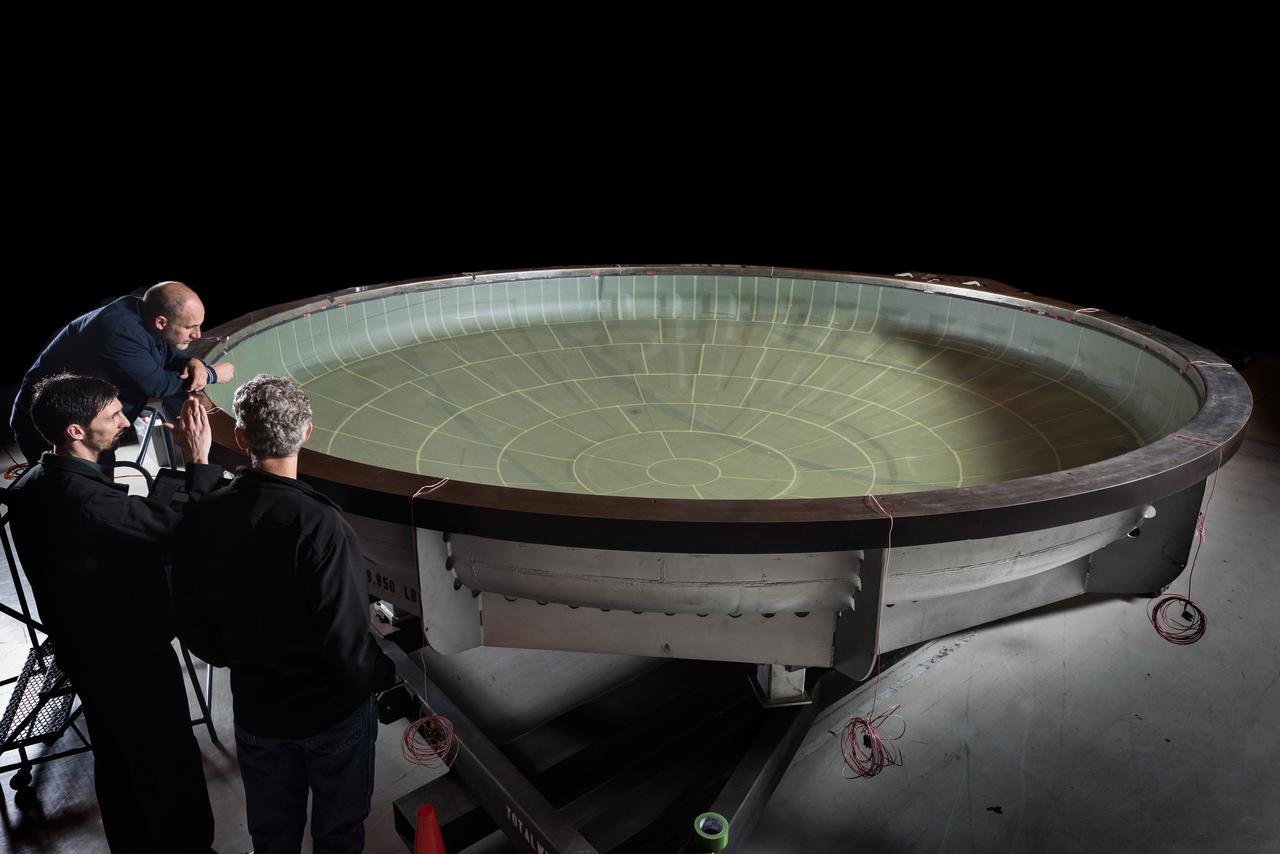

The NASA Super Guppy arrived at Moffett Field on Jan. 7, 2016, carrying the Artemis I Orion heat shield skin. The heat shield is being primarily built at Lockheed Martin’s Littleton, Colo. facility, and it was temporarily sent to Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, Calif. facility for an autoclave cure (shown here). The heat shield is a stiffened skin design, and this cure process is the last step prior to attaching titanium stiffeners to the interior surface. Once the skin and stiffeners are attached, ablative material is applied to the exterior. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
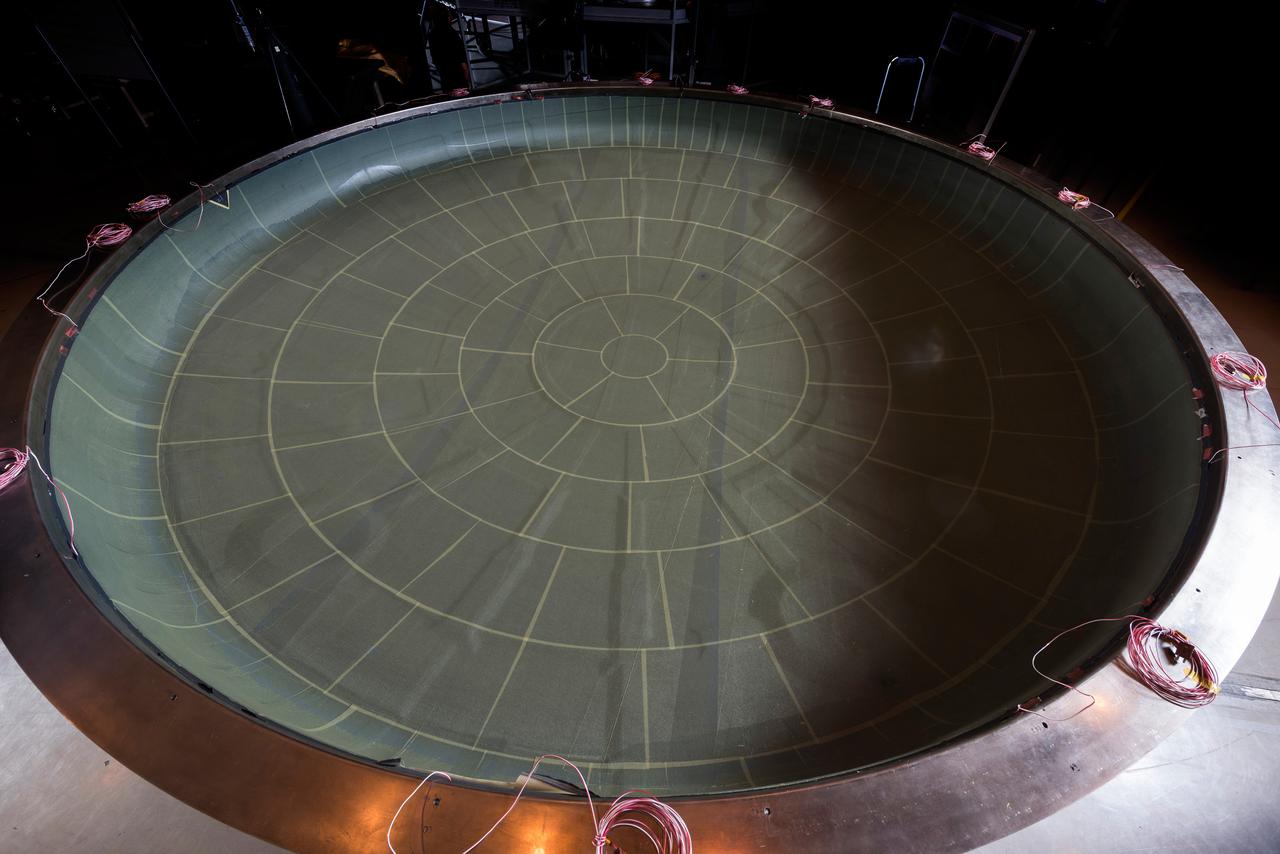
The NASA Super Guppy arrived at Moffett Field on Jan. 7, 2016, carrying the Artemis I Orion heat shield skin. The heat shield is being primarily built at Lockheed Martin’s Littleton, Colo. facility, and it was temporarily sent to Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, Calif. facility for an autoclave cure (shown here). The heat shield is a stiffened skin design, and this cure process is the last step prior to attaching titanium stiffeners to the interior surface. Once the skin and stiffeners are attached, ablative material is applied to the exterior. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
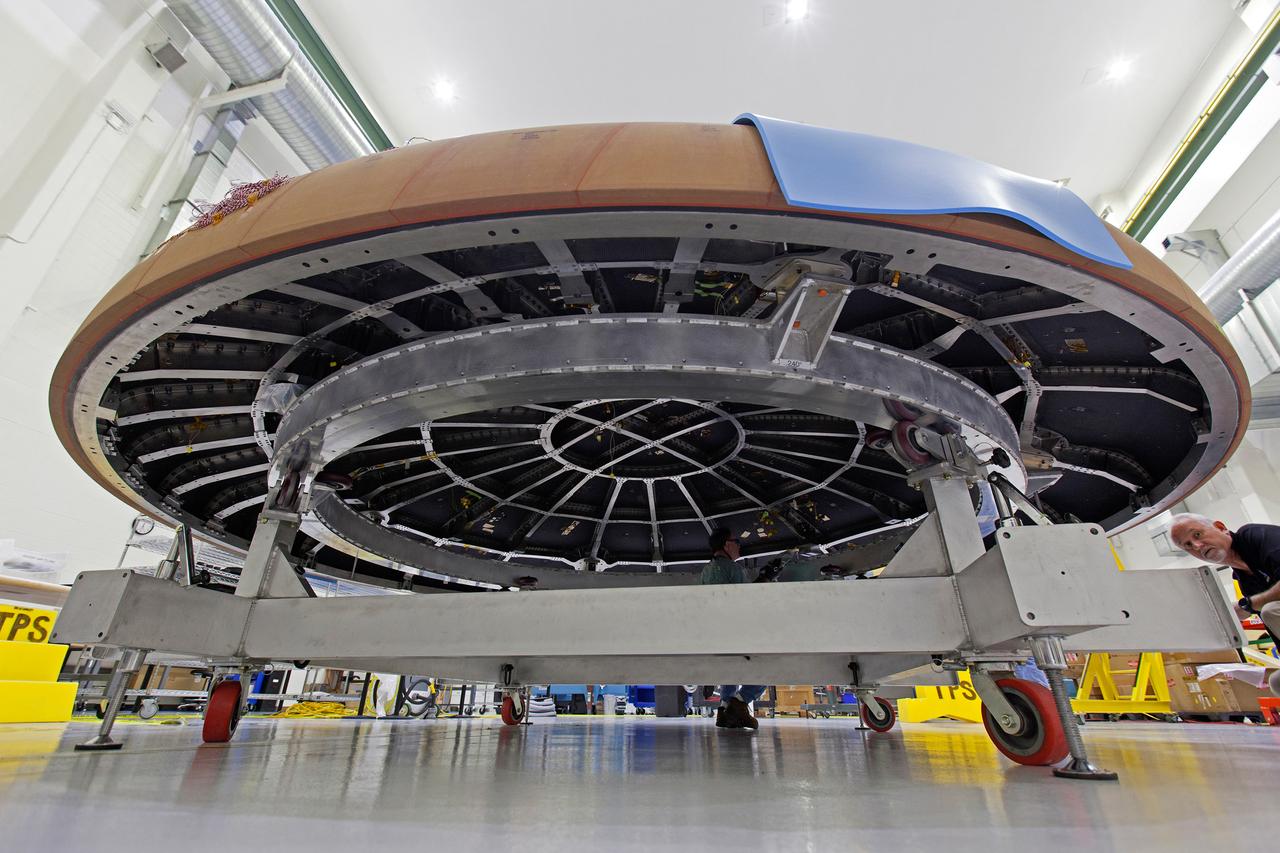

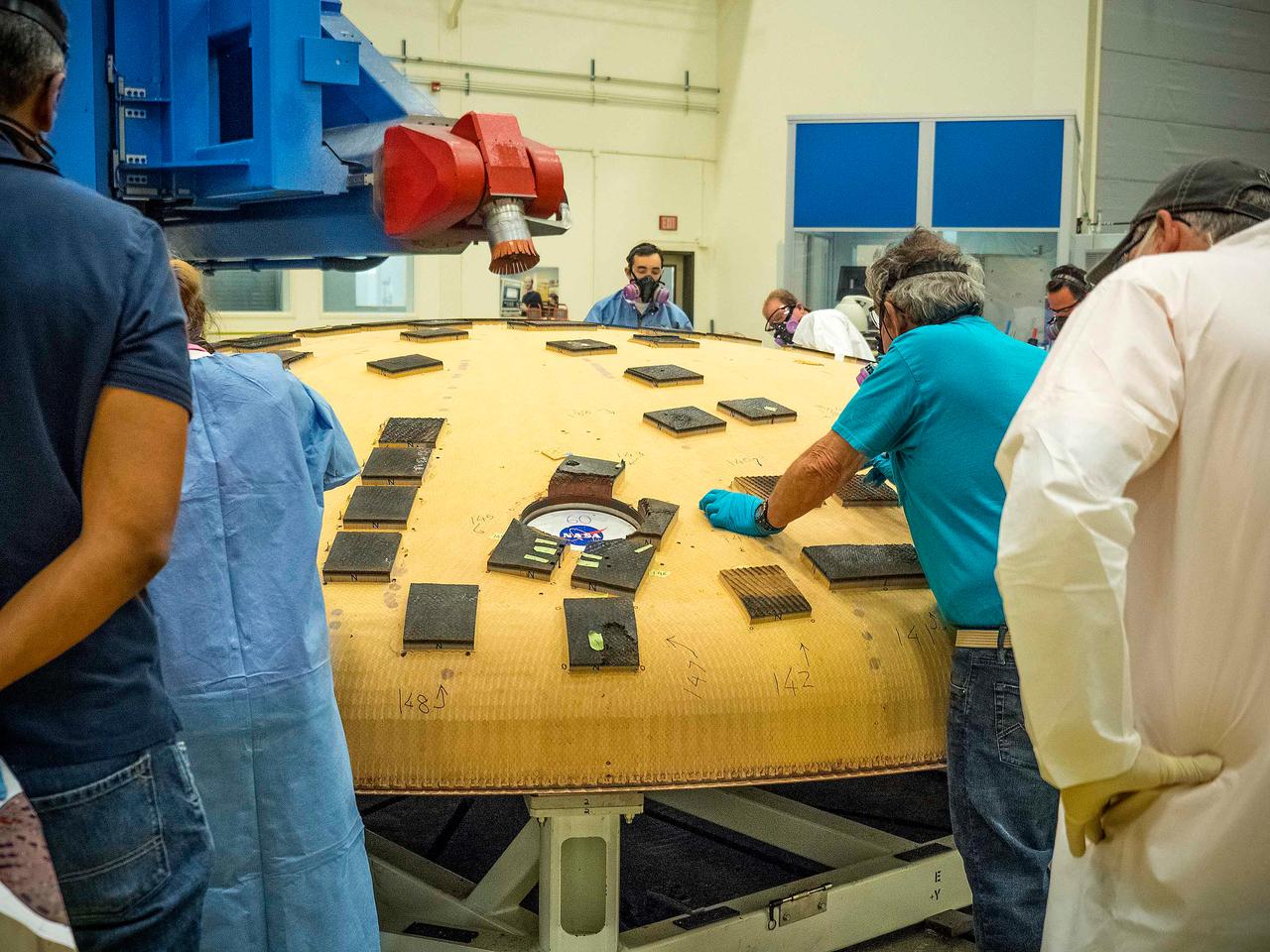
The Orion heat shield for Artemis I is being prepared for its move to the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2017. Protective pads are being attached to the heat shield surface. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test also serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight.
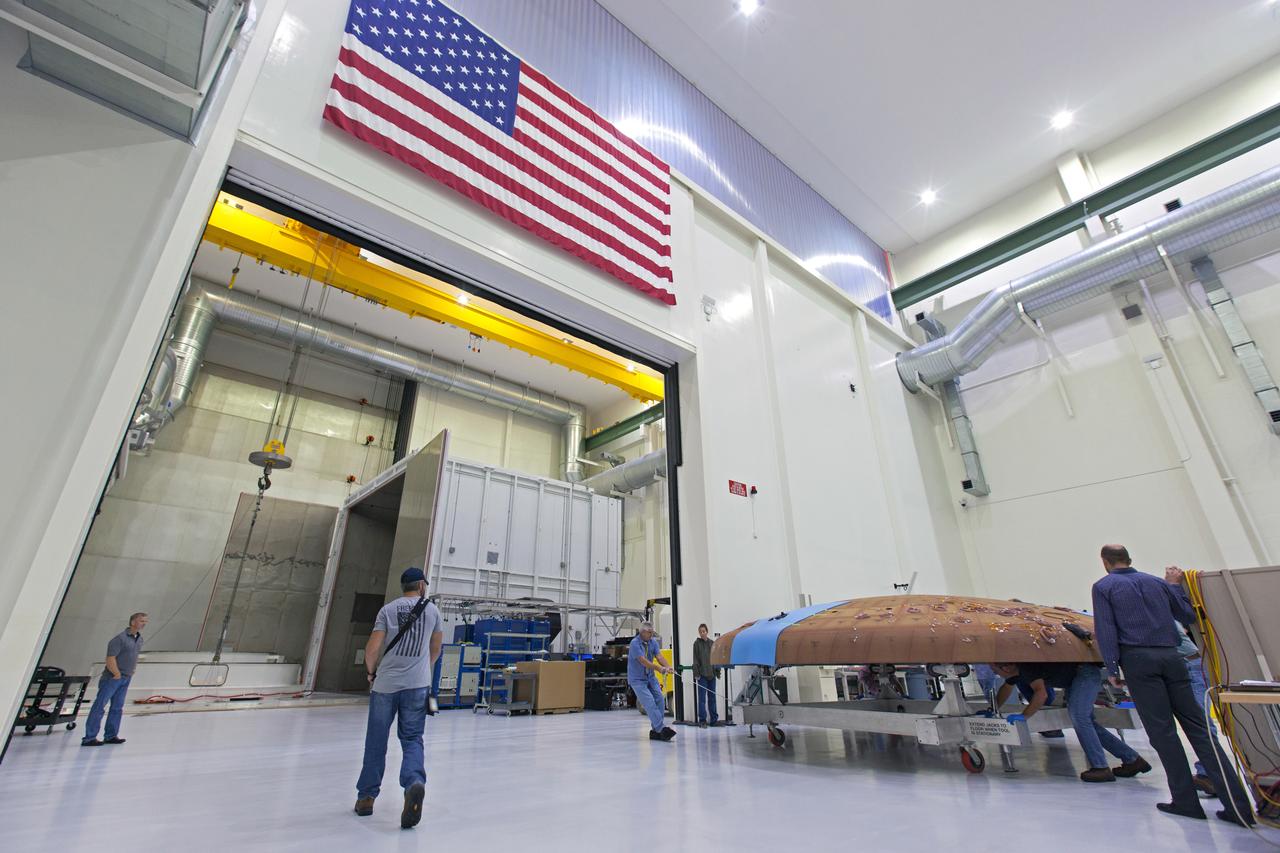

Technicians move the Orion heat shield for Artemis I toward the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2017. Protective pads were attached to the heat shield surface. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test also serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on it first uncrewed integrated flight.
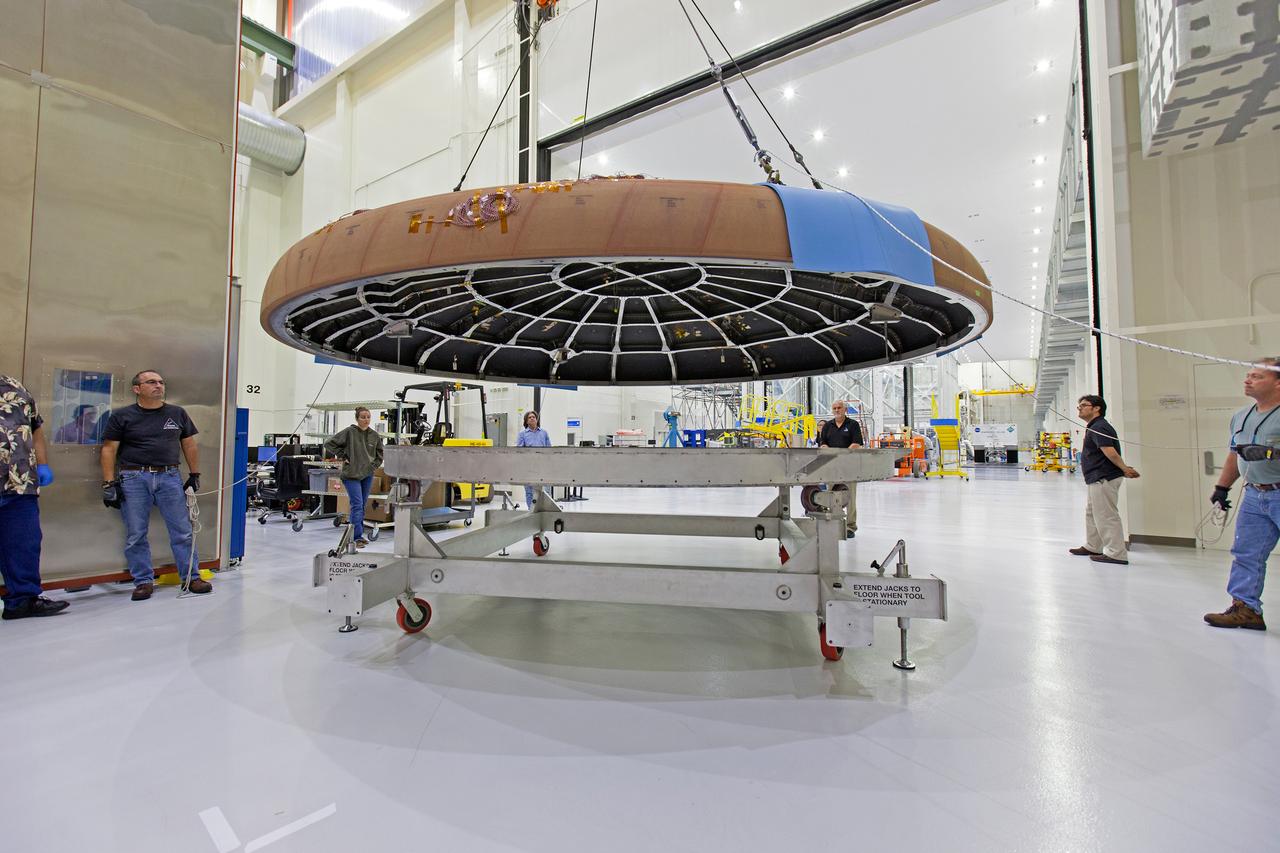

A crane attached to the Orion heat shield for Artemis I moves it toward the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2017. Protective pads were attached to the heat shield surface. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test also serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on it first uncrewed integrated flight.
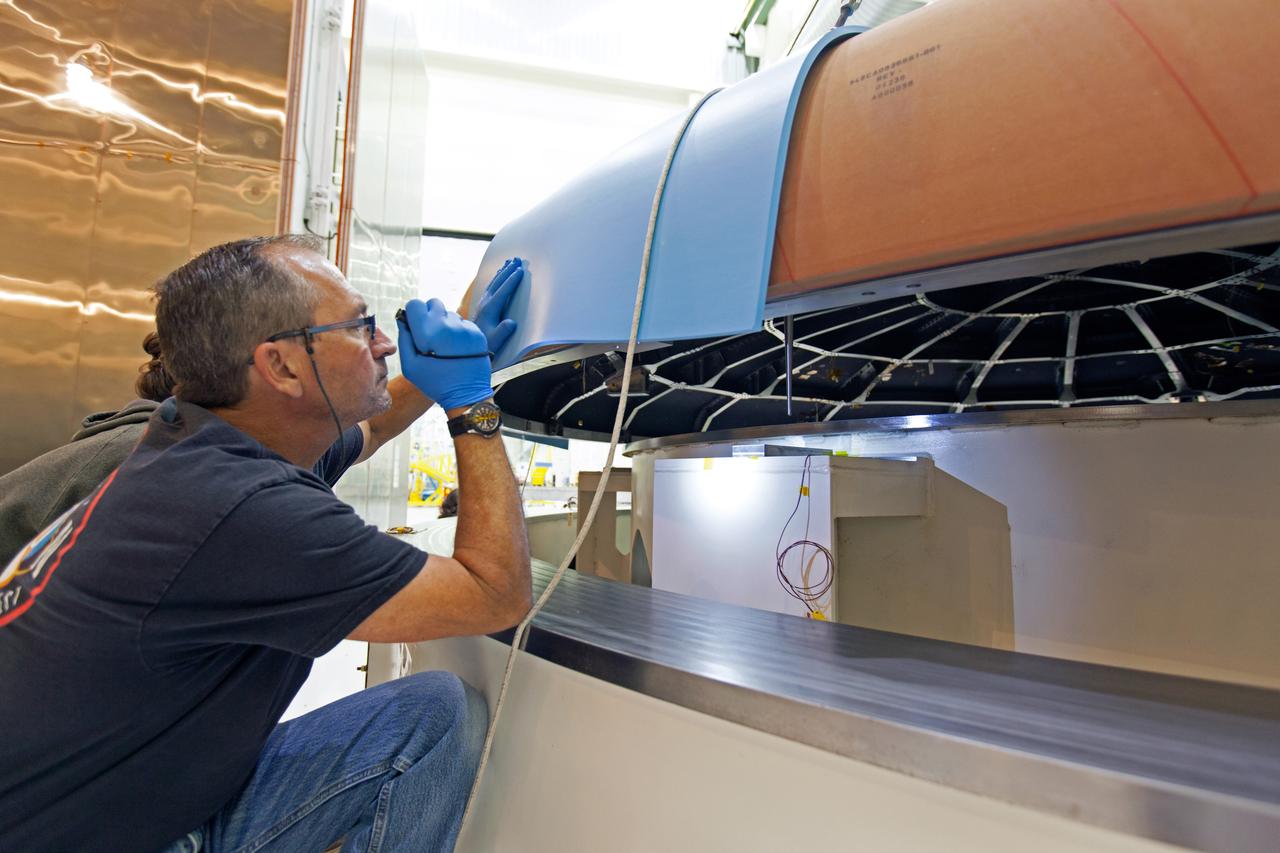

A technician checks the Orion heat shield for Artemis I before it is moved into the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2017. Protective pads were attached to the heat shield surface. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test also serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on it first uncrewed integrated flight.
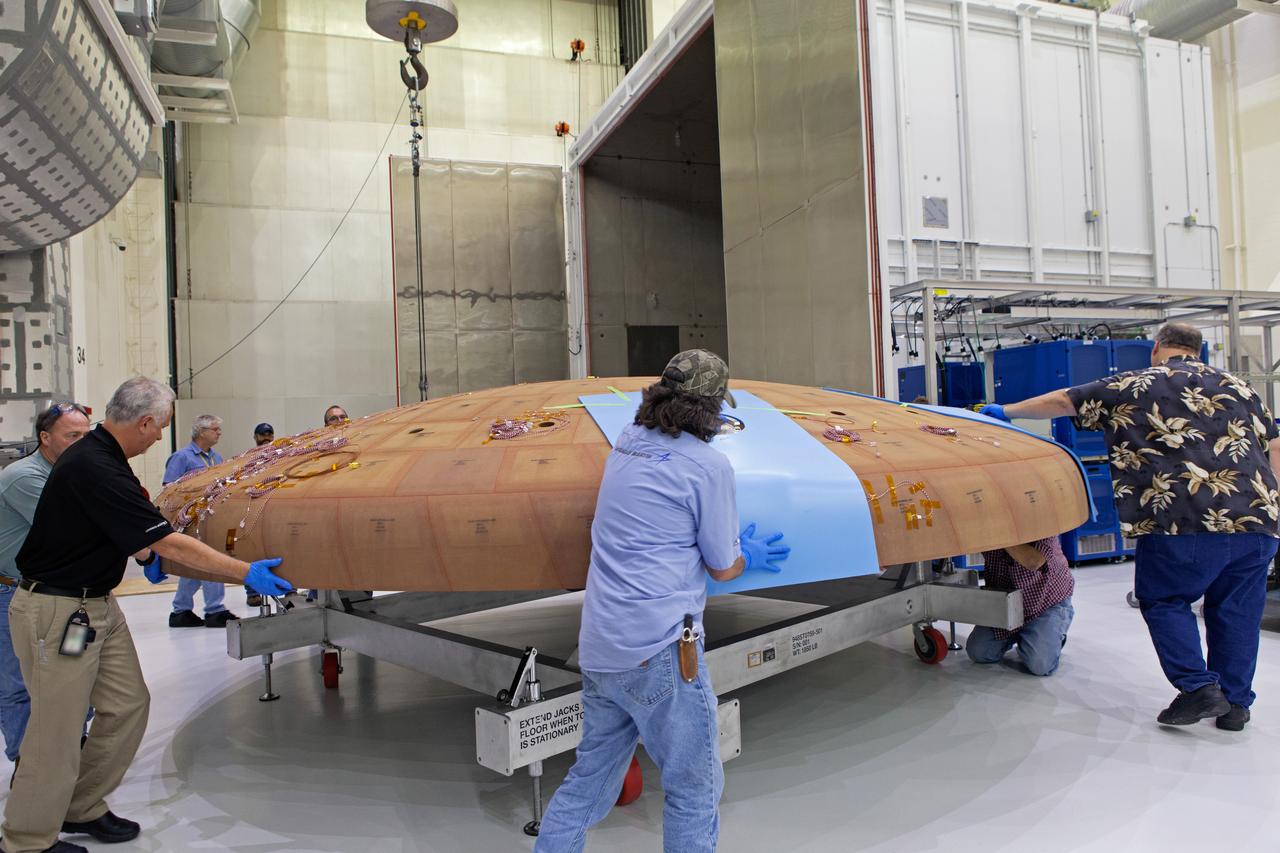

Technicians move the Orion heat shield for Artemis I toward the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2017. Protective pads were attached to the heat shield surface. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test also serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on it first uncrewed integrated flight.
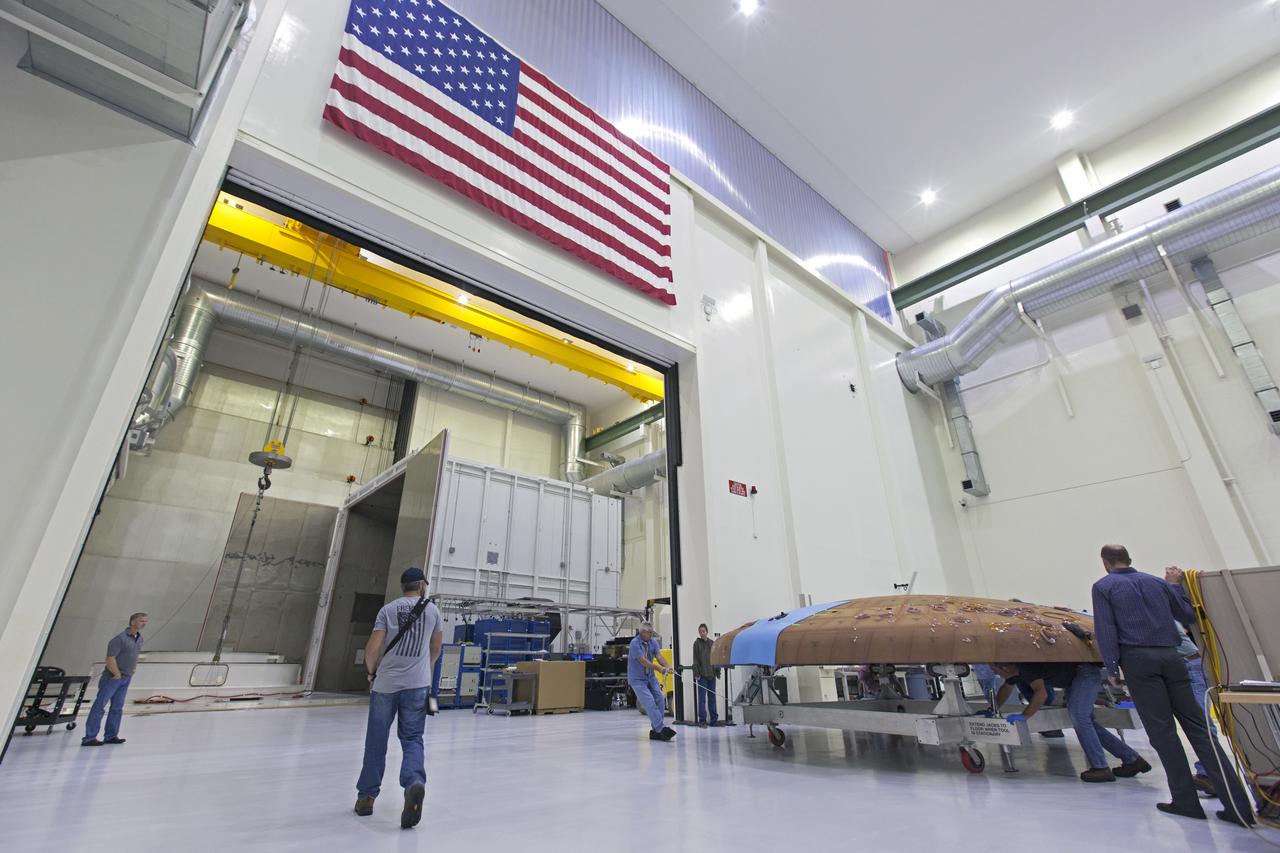

Technicians move the Orion heat shield for Exploration Mission-1 toward the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Protective pads are being attached to the heat shield surface. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test also serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight.
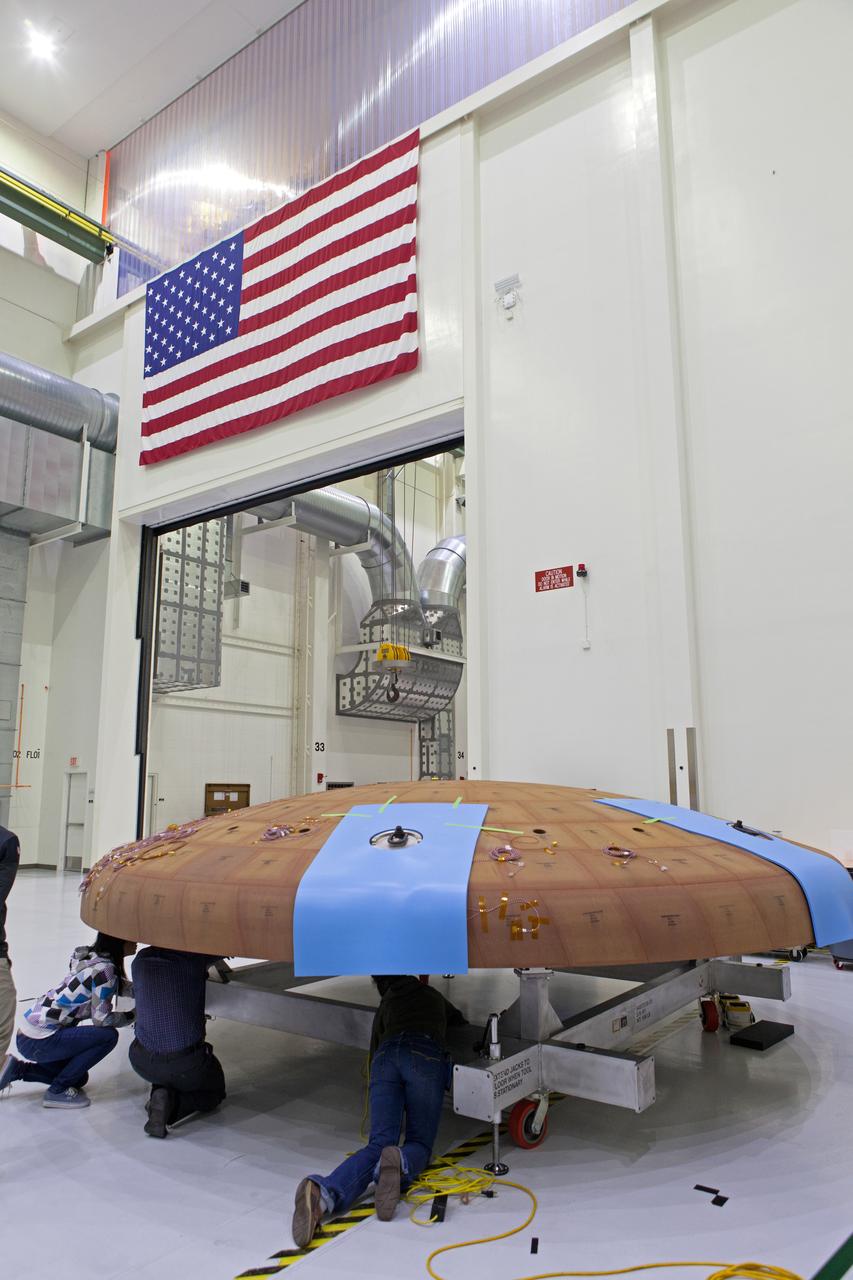

Lockheed Martin engineers and technicians prepare the Orion heat shield for Artemis I for its move to the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2017. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight.
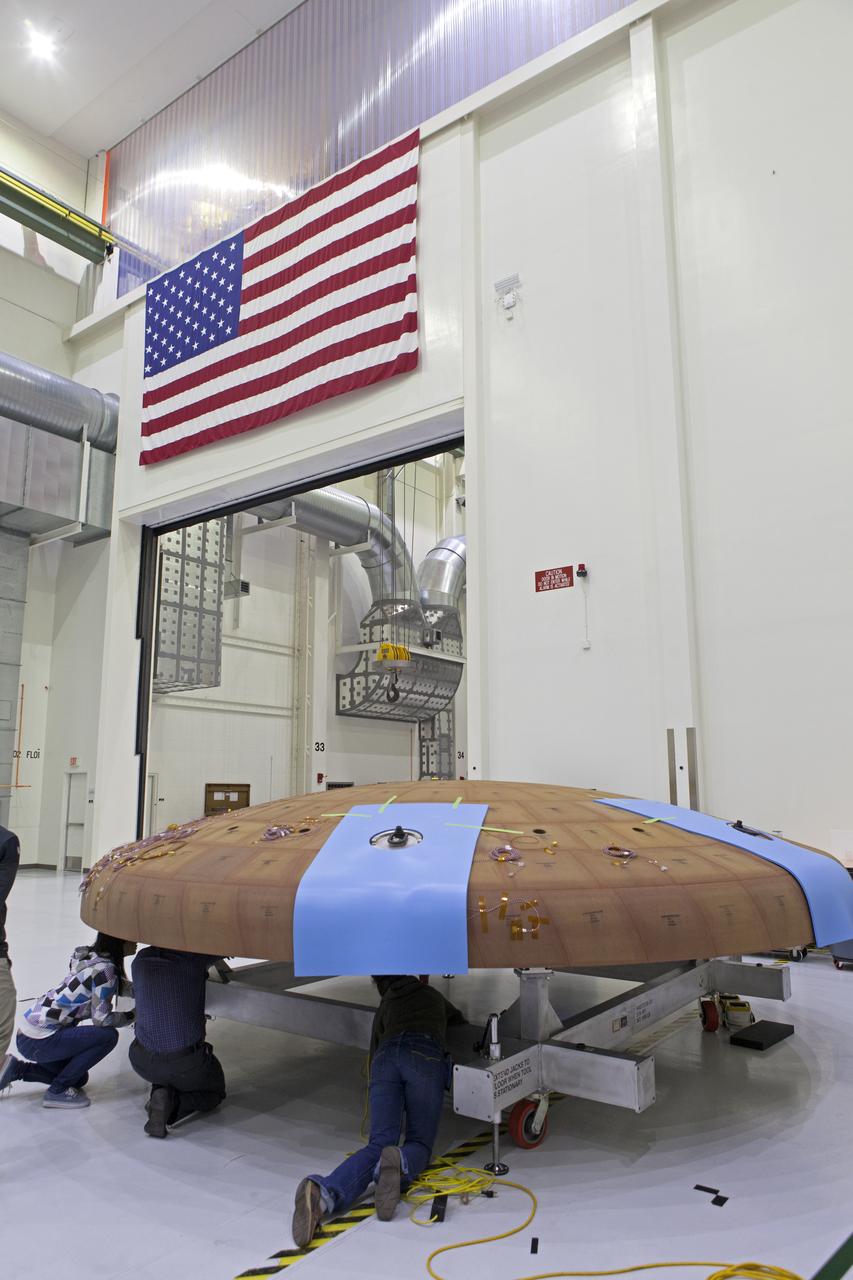

Lockheed Martin engineers and technicians prepare the Orion heat shield for Exploration Mission-1 for its move to the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield will undergo a thermal cycle test to verify acceptable workmanship and material quality. The test serves to verify the heat shield's thermal protection systems have been manufactured and assembled correctly. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight.
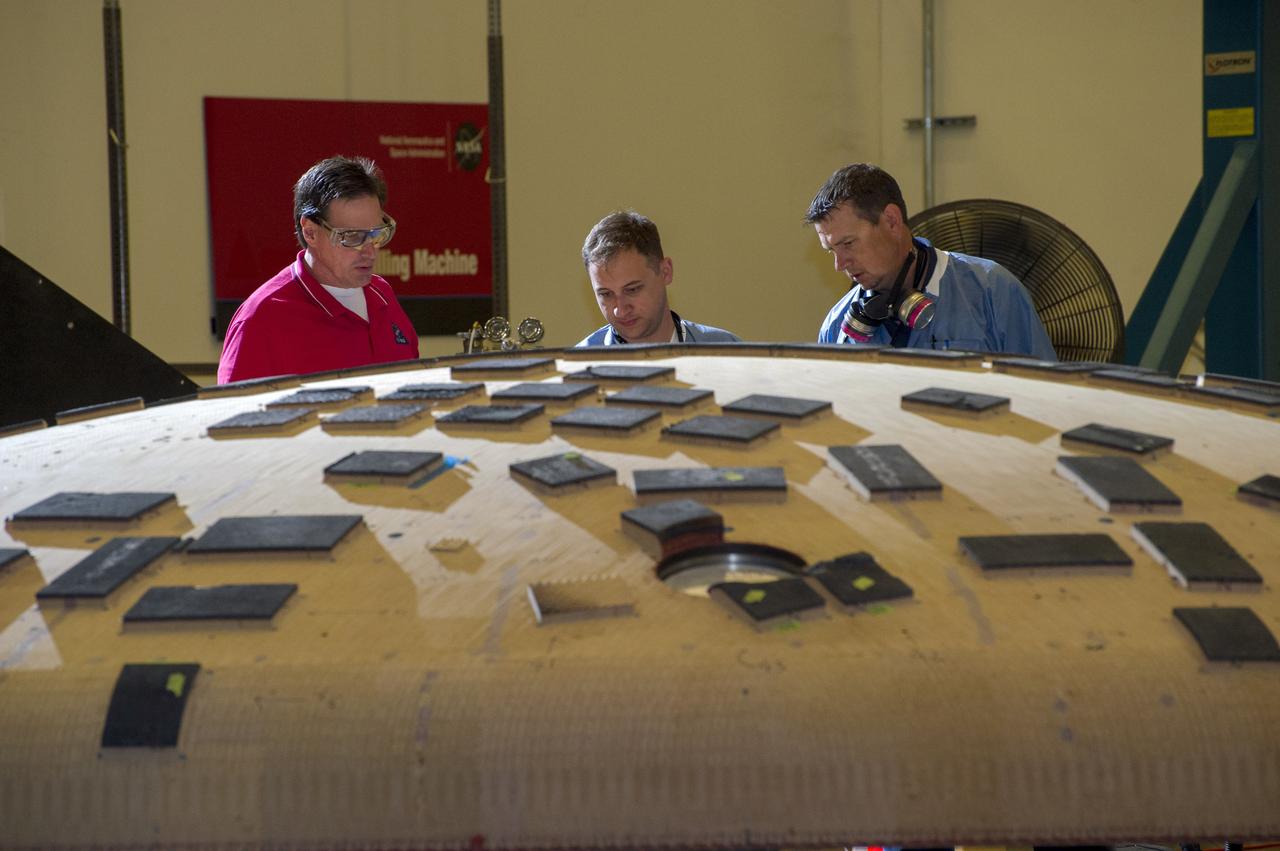

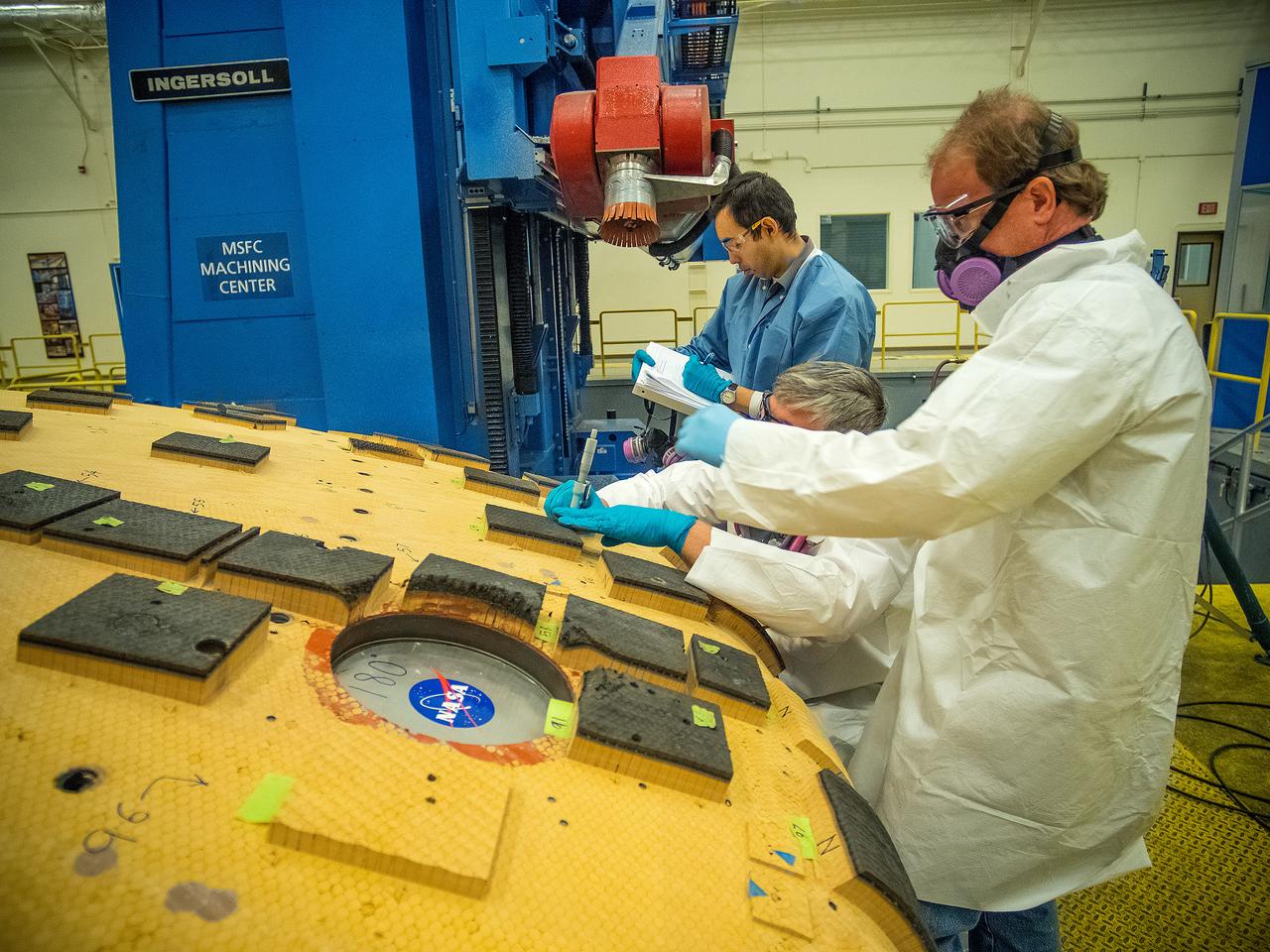
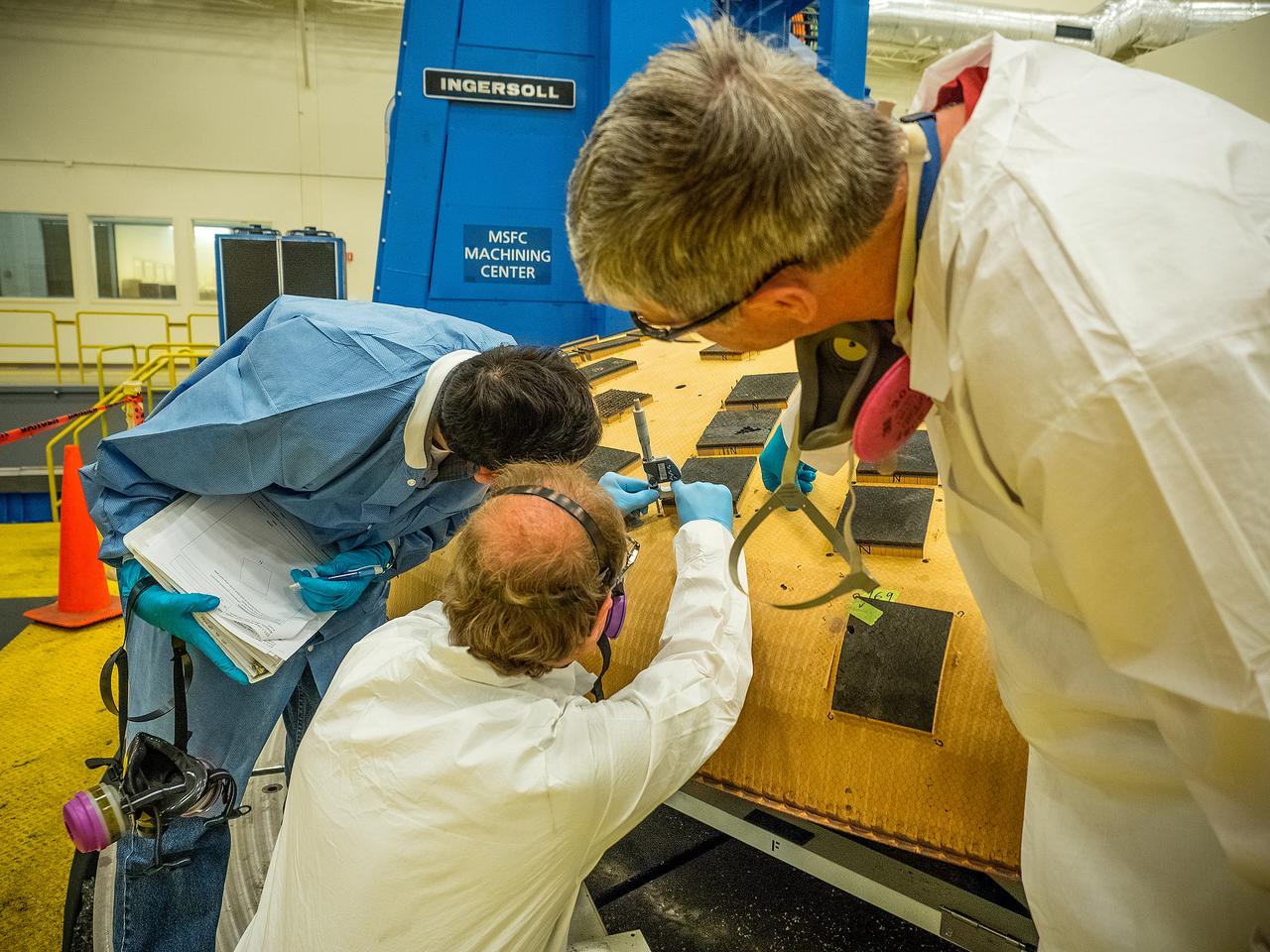
OVERSEEING ORION HEAT SHIELD WORK IN MARSHALL'S SEVEN-AXIS MILLING AND MACHINING FACILITY ARE, FROM LEFT, JOHN KOWAL, MANAGER OF ORION'S THERMAL PROTECTION SYSTEM AT JOHNSON SPACE CENTER; NICHOLAS CROWLEY, AN AMES ENGINEERING TECHNICIAN; AND ROB KORNIENKO, AMES ENGINEERING BRANCH CHIEF. THE HEAT SHIELD FLEW TO SPACE DURING THE EFT-1 FULL SCALE FLIGHT TEST OF ORION IN DECEMBER, 2014

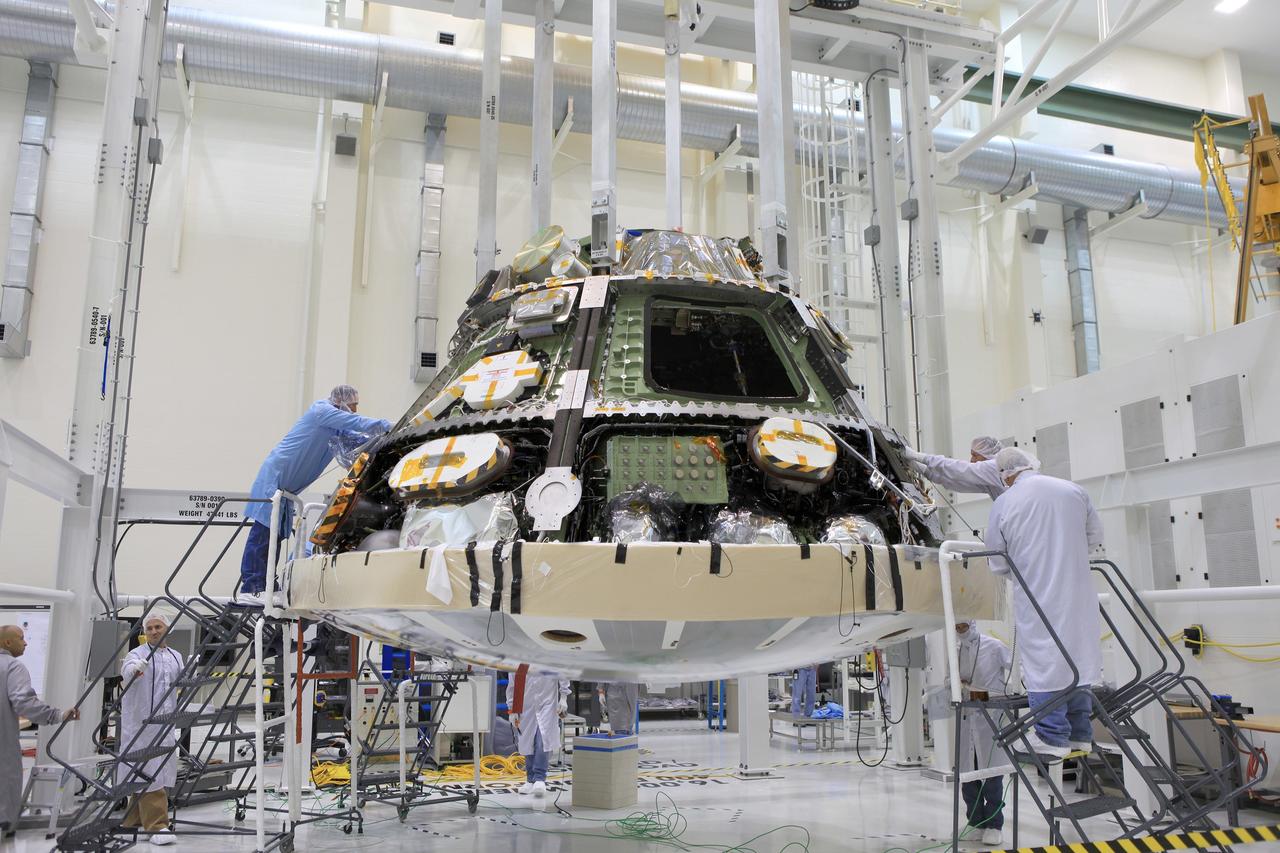
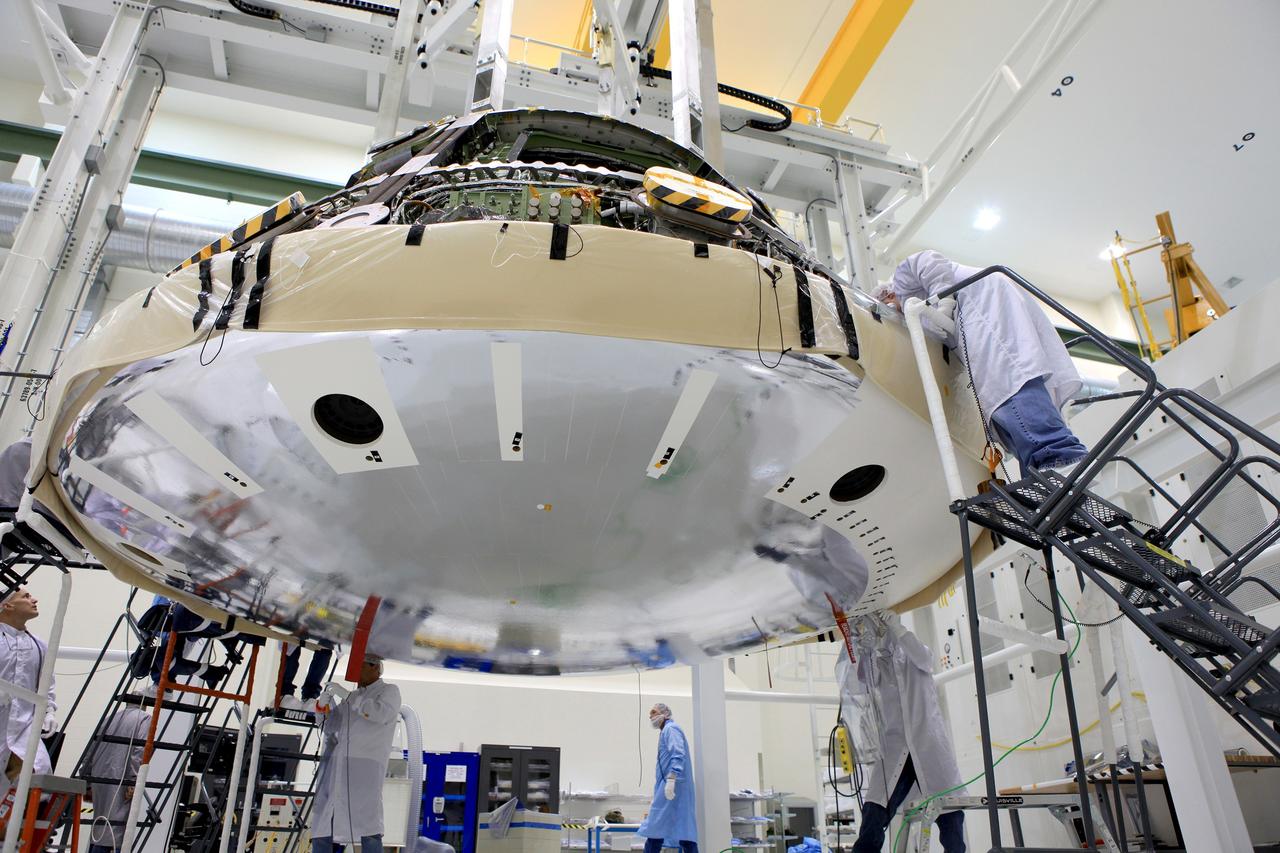
Lockheed Martin engineers and technicians are installing the heat shield to the Orion crew module July 25, 2018, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion is being prepared for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight. The heat shield will need to withstand temperatures of up to 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit during Orion's descent and re-entry through the Earth's atmosphere before it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean.
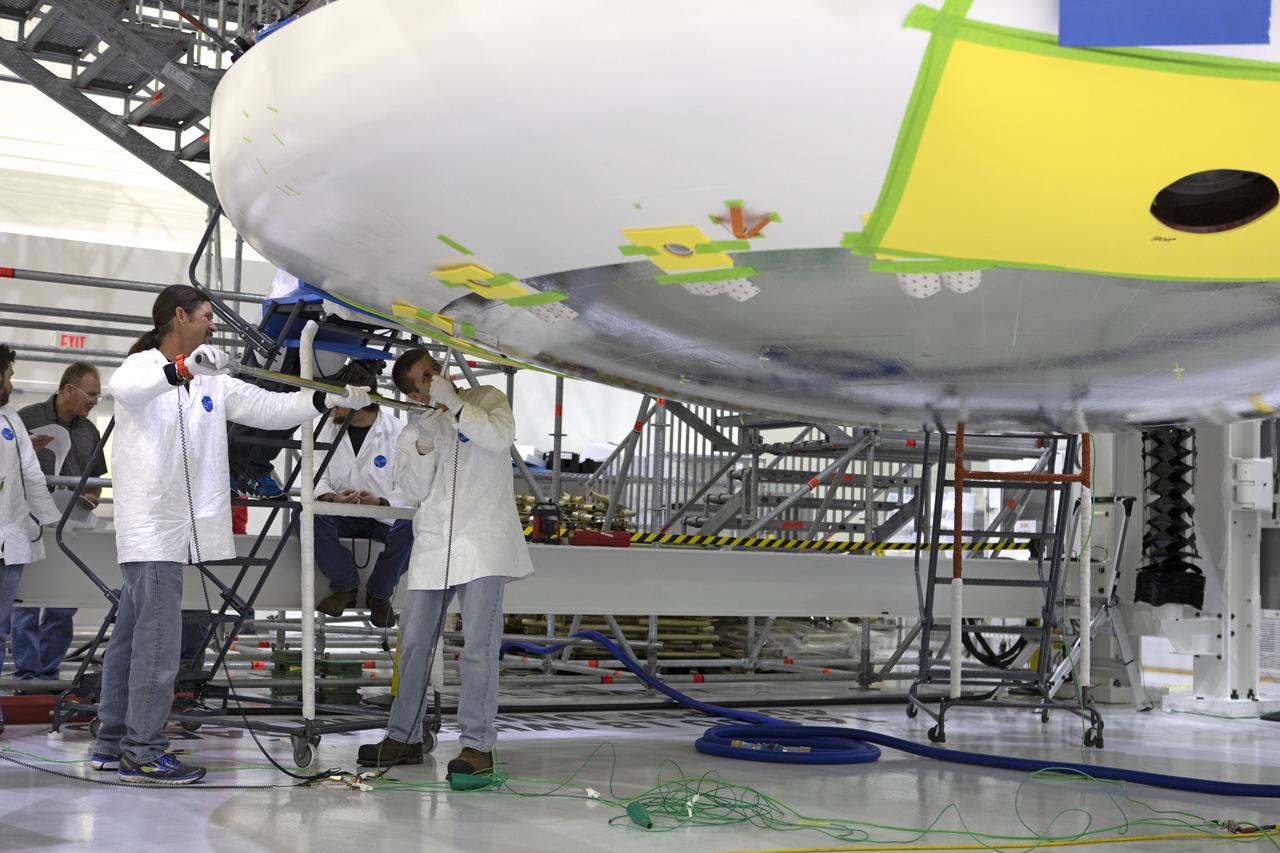

Lockheed Martin engineers and technicians are installing the heat shield to the Orion crew module July 25, 2018, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion is being prepared for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight. The heat shield will need to withstand temperatures of up to 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit during Orion's descent and re-entry through the Earth's atmosphere before it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean.
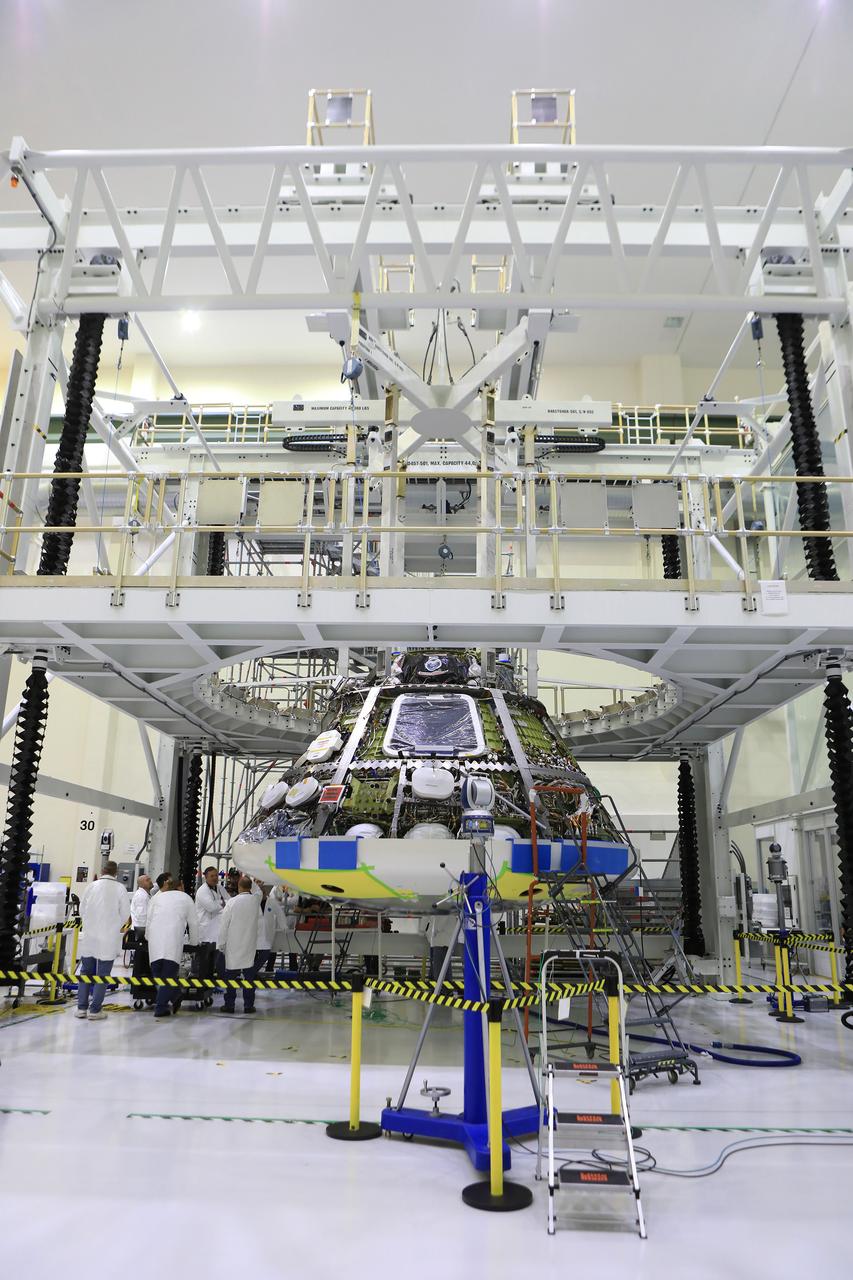

Lockheed Martin engineers and technicians are installing the heat shield to the Orion crew module July 25, 2018, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion is being prepared for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight. The heat shield will need to withstand temperatures of up to 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit during Orion's descent and re-entry through the Earth's atmosphere before it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean.
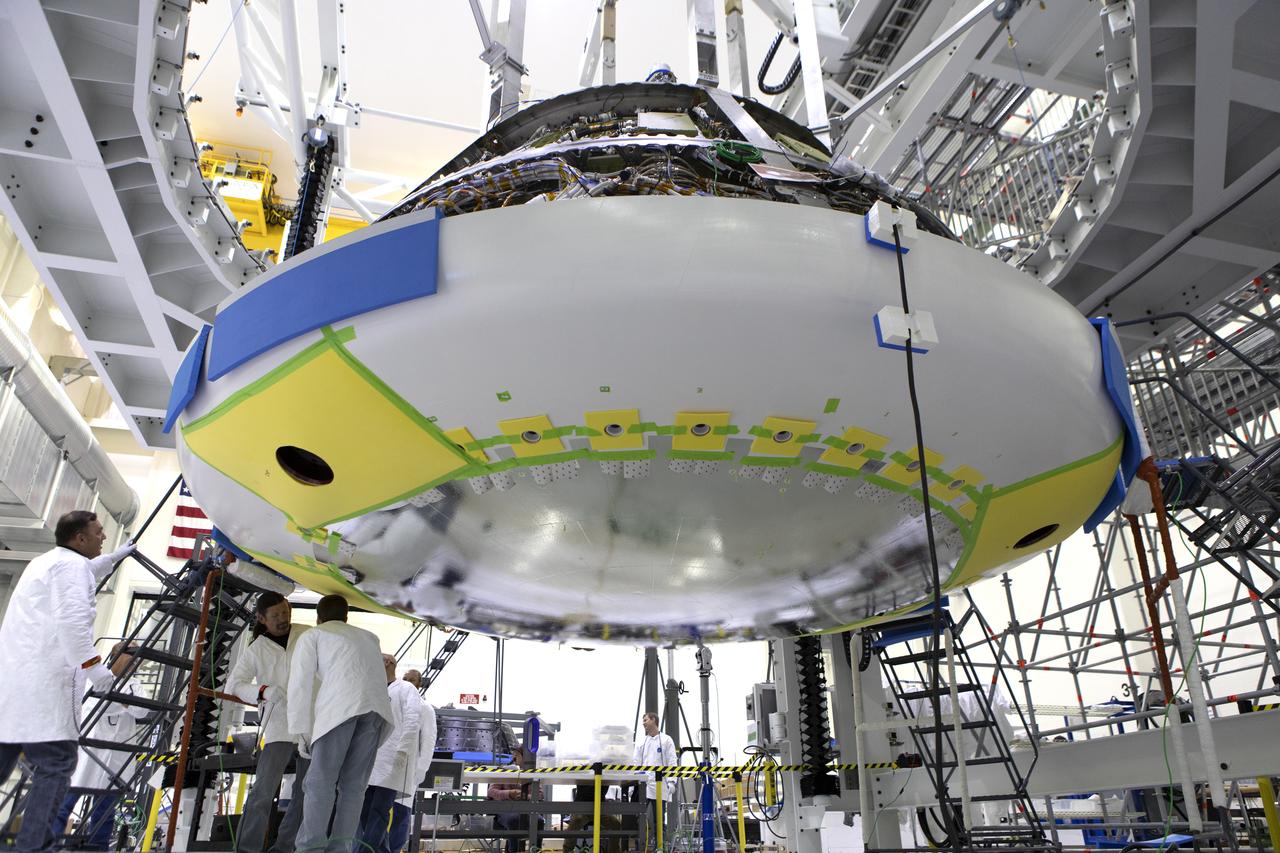

Lockheed Martin engineers and technicians are installing the heat shield to the Orion crew module July 25, 2018, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion is being prepared for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), the first unscrewed integrated flight test atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket. The heat shield will need to withstand temperatures of up to 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit during Orion's descent and re-entry through the Earth's atmosphere before it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean.
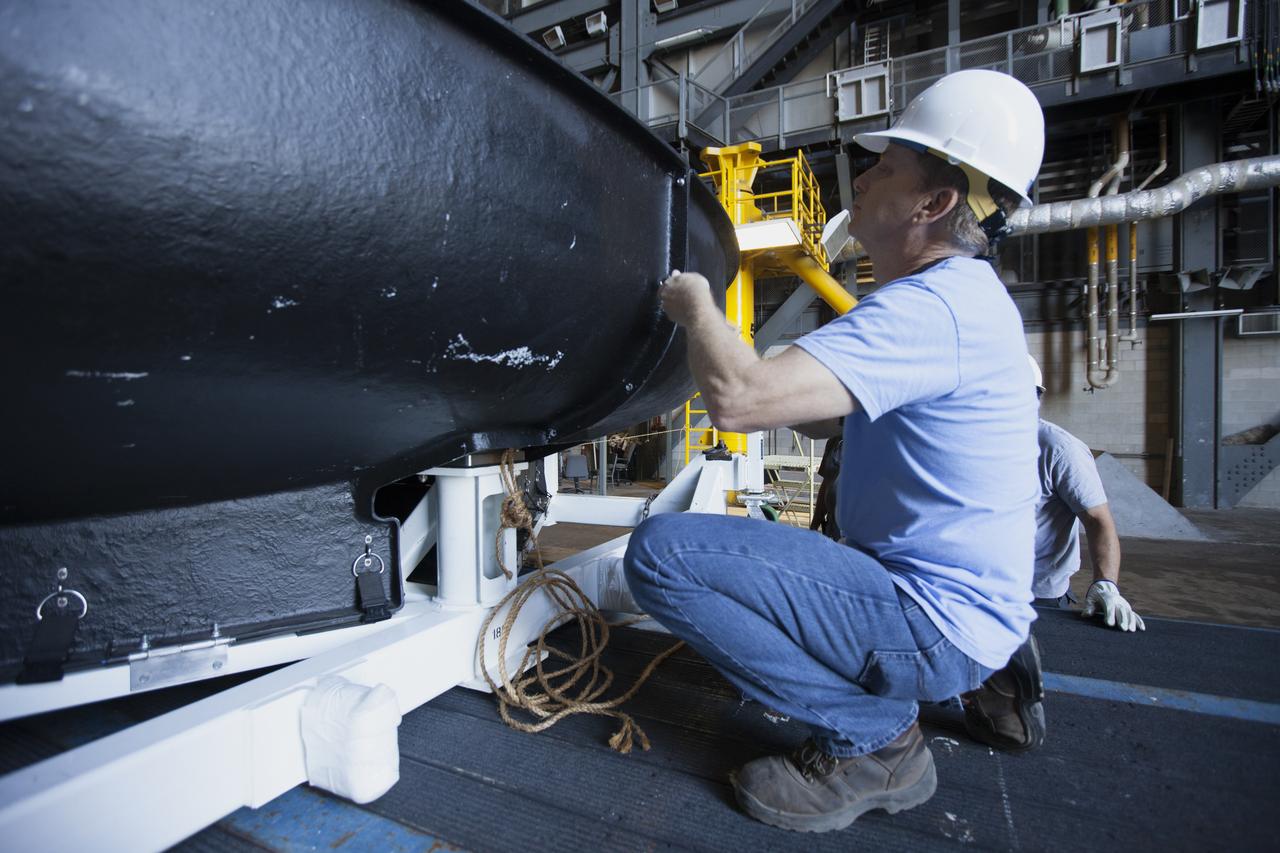

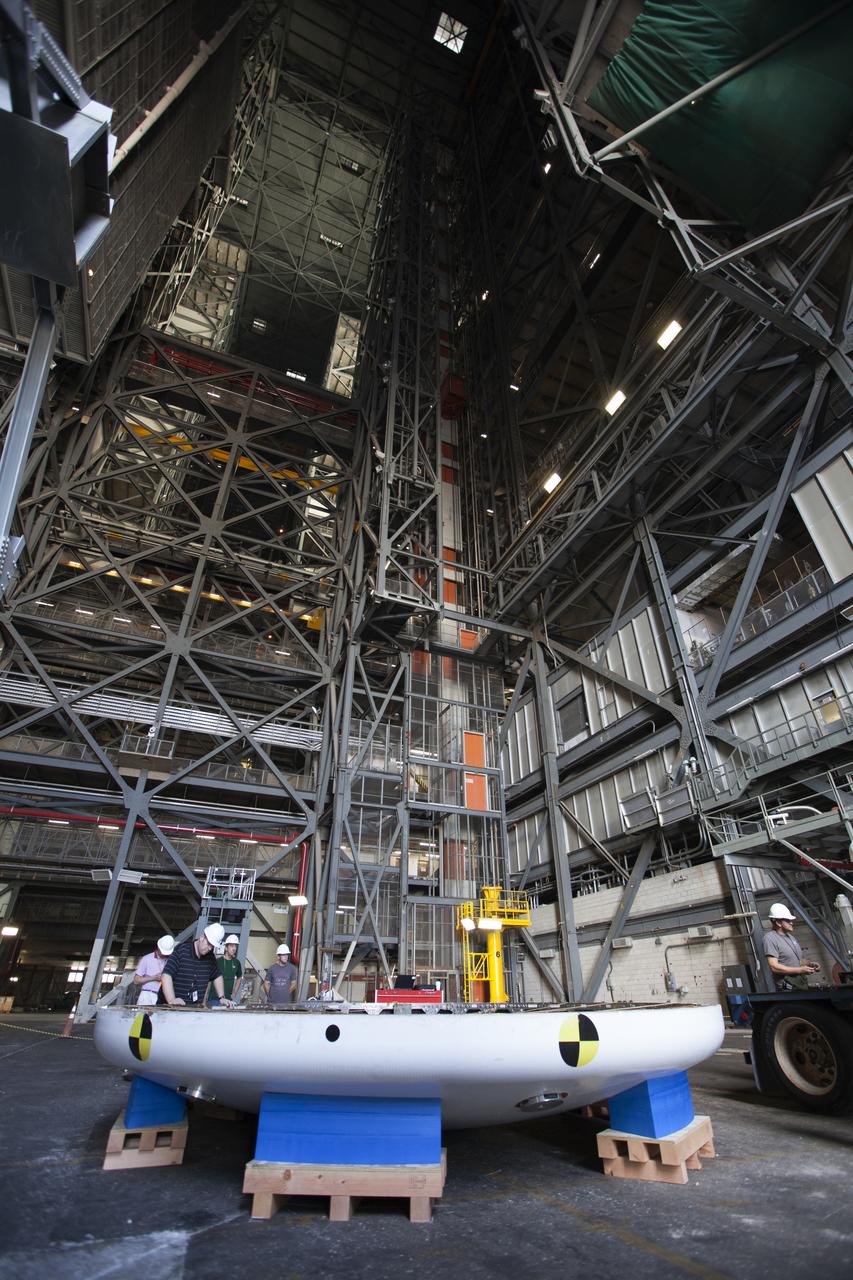
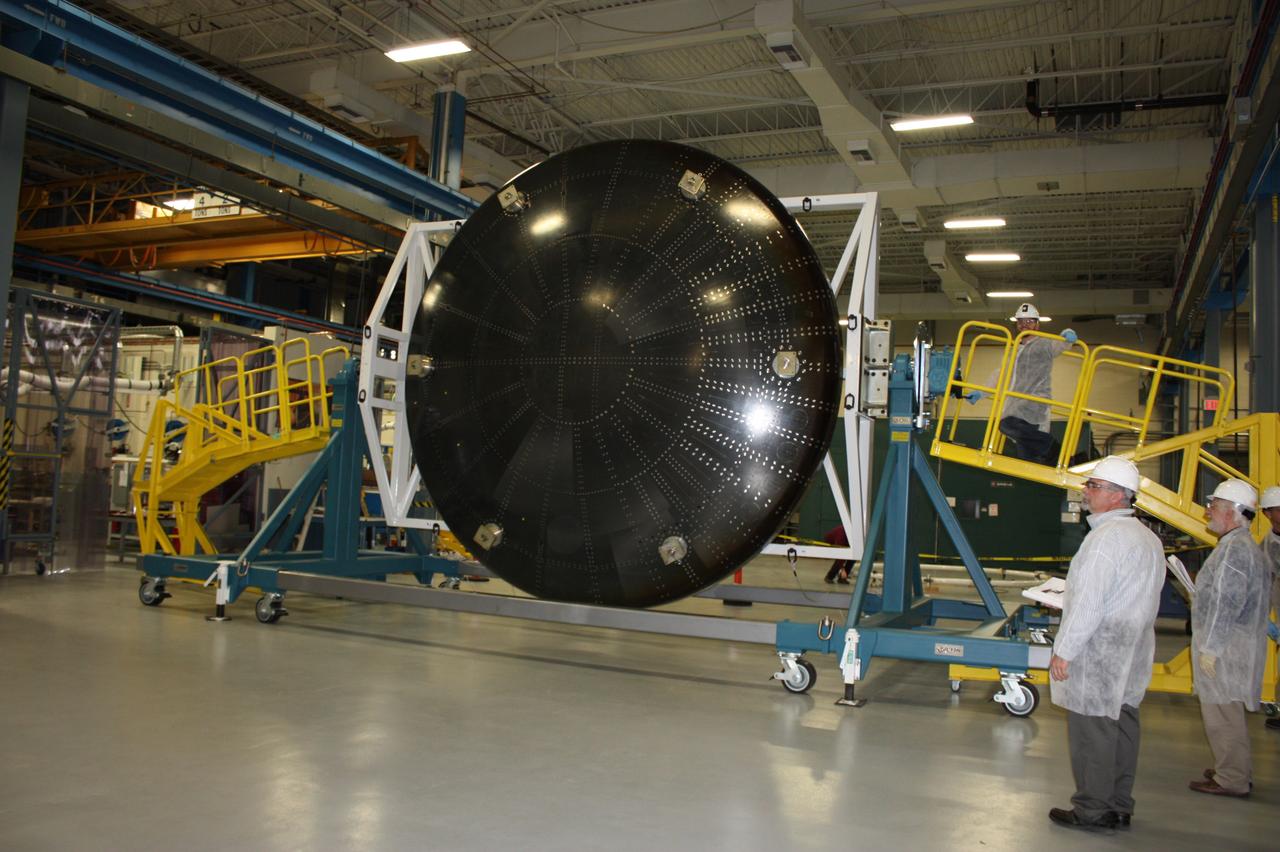
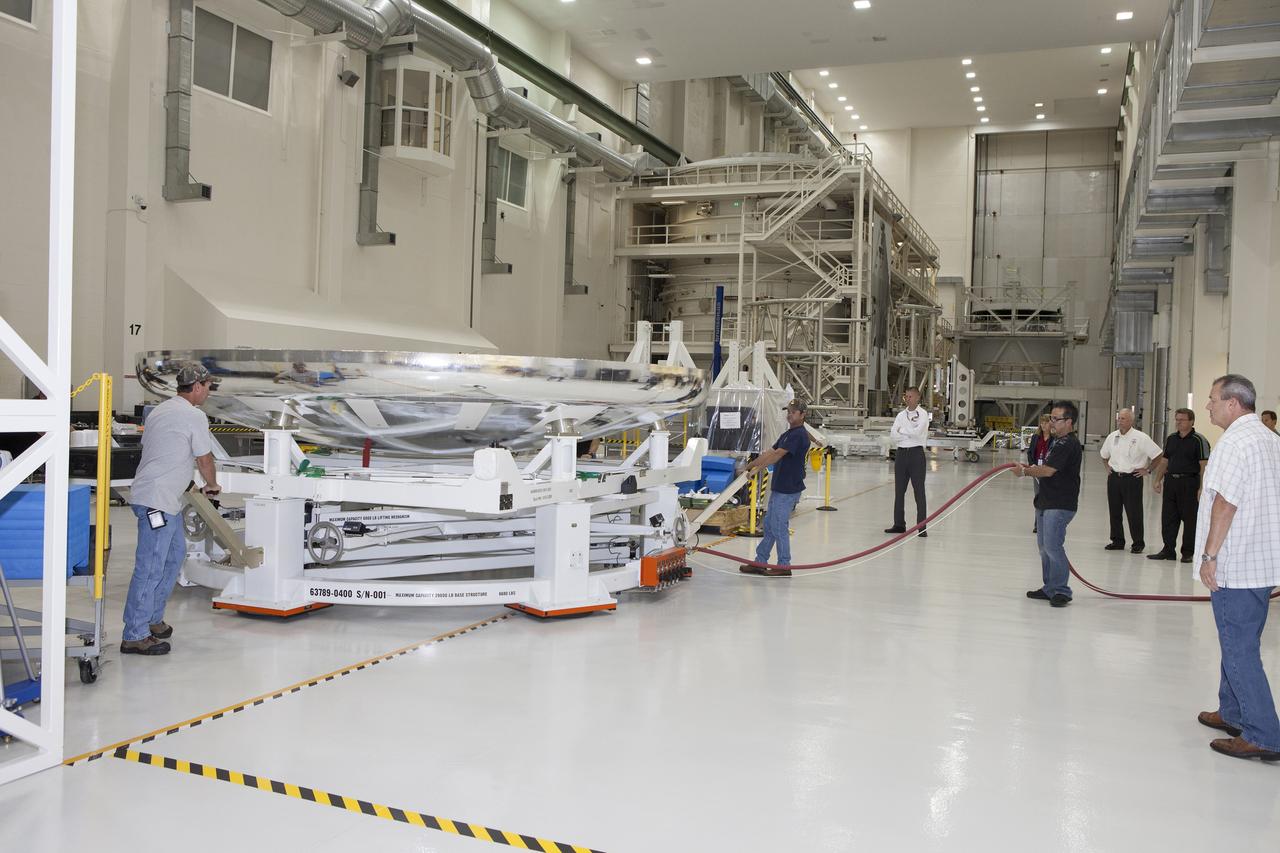
Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers help prepare the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 for unloading off its transporter. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.

Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker monitors the progress as a crane lowers the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 onto foam blocks. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.

Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is attached to the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 for unloading off its transporter. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.

Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers help prepare the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 for unloading off its transporter. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
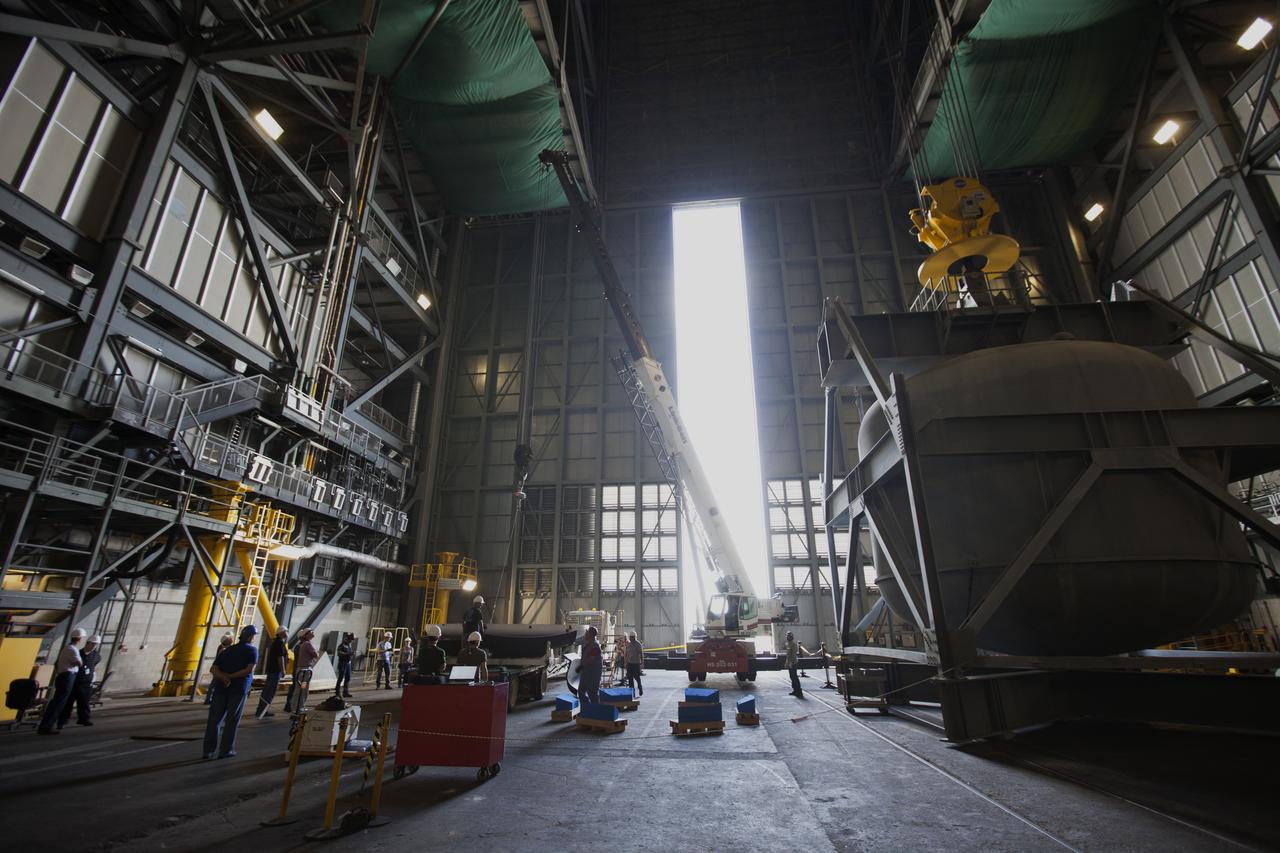

Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is attached to the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 for unloading off its transporter. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
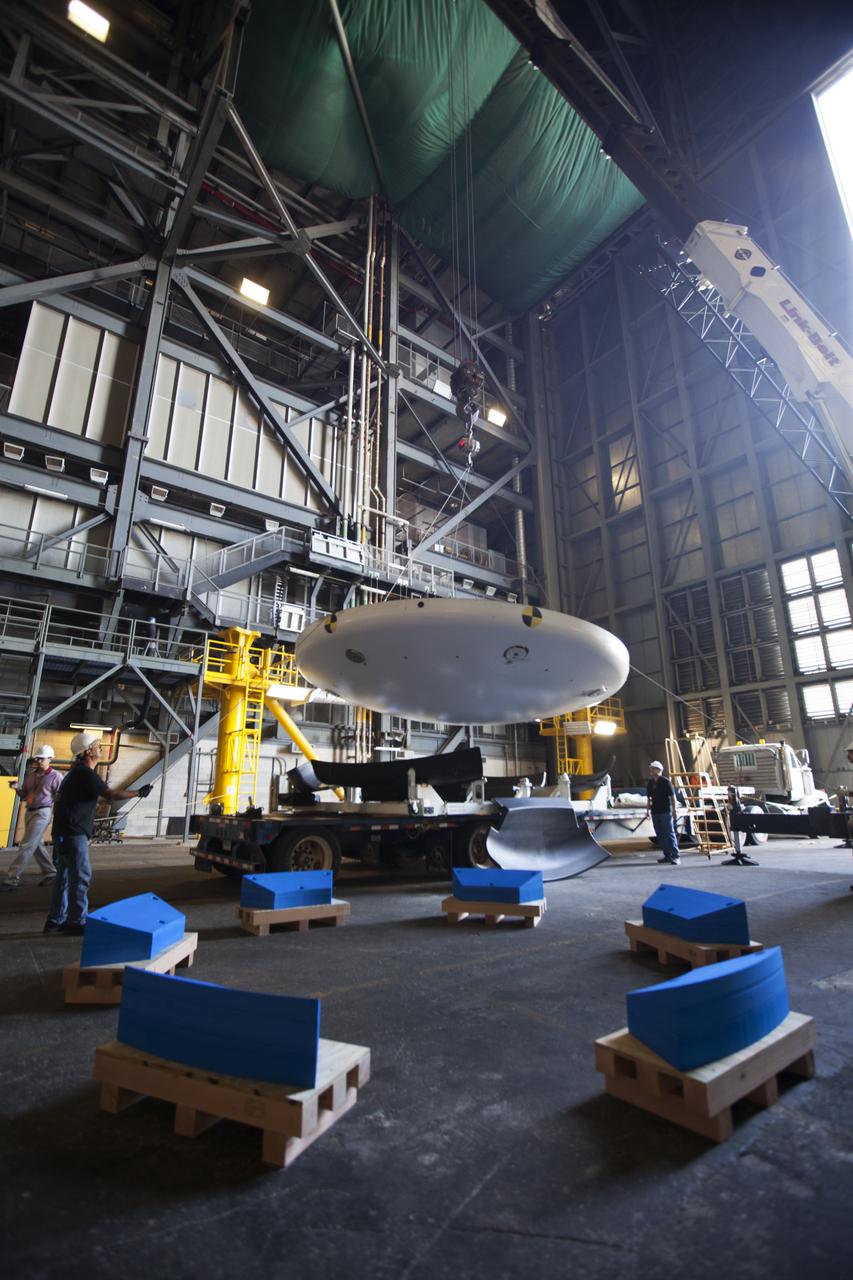

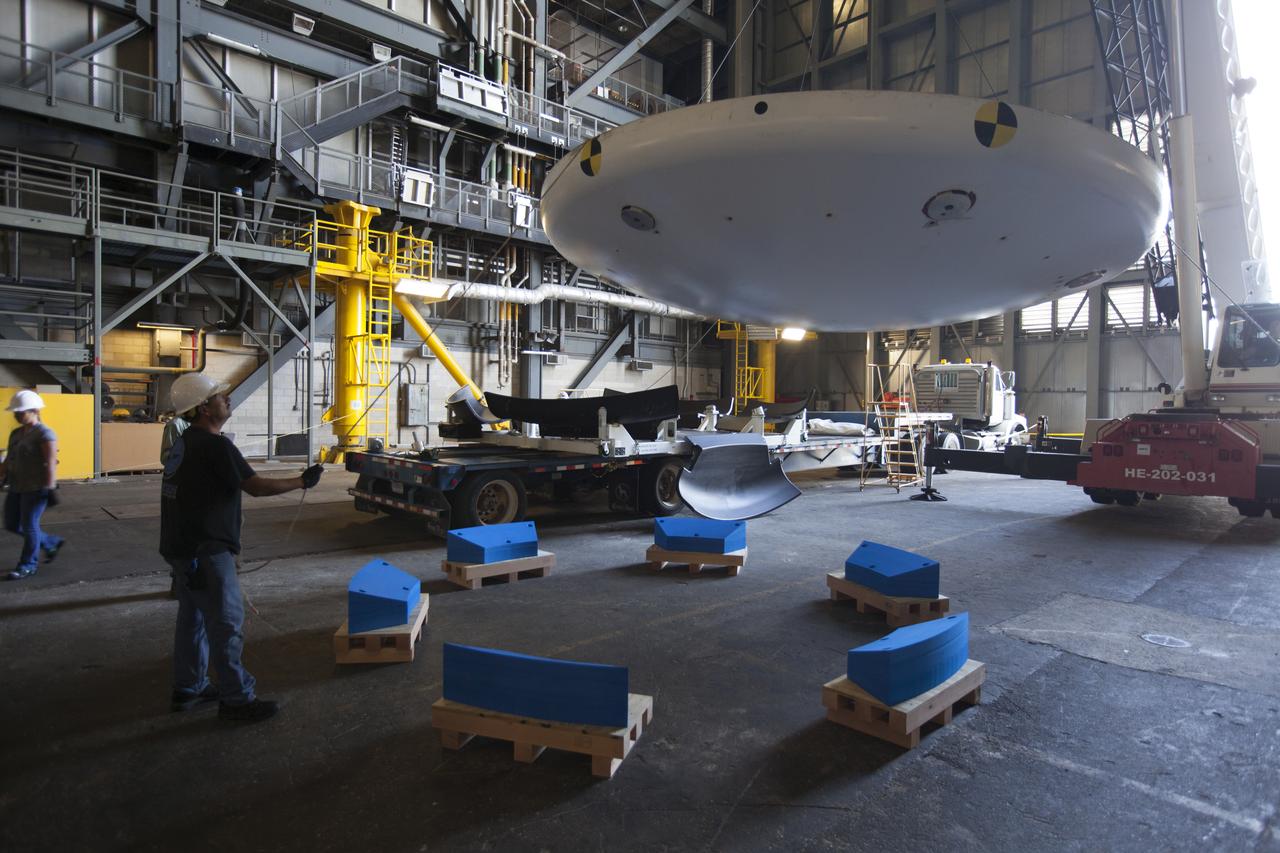
Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 up off its transporter. It will be lowered onto foam blocks. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
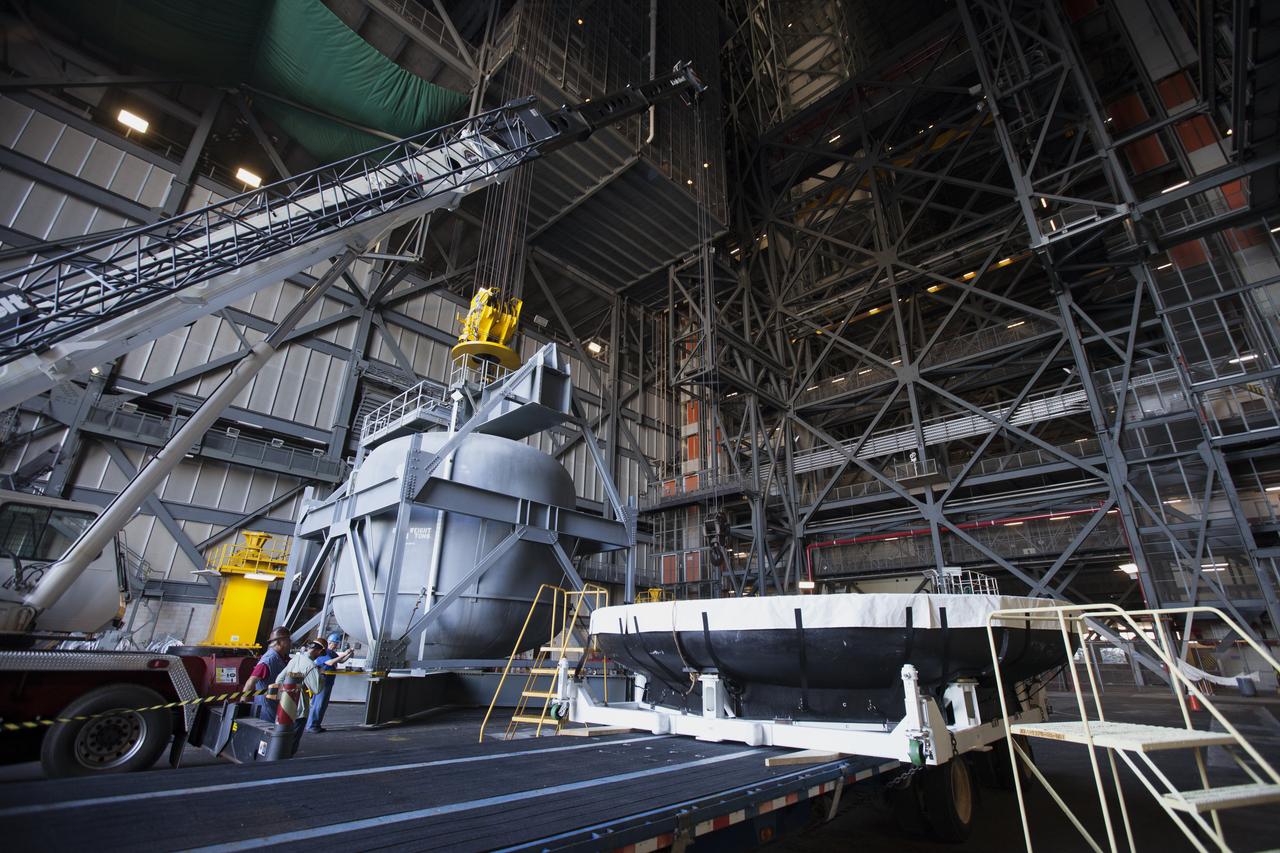

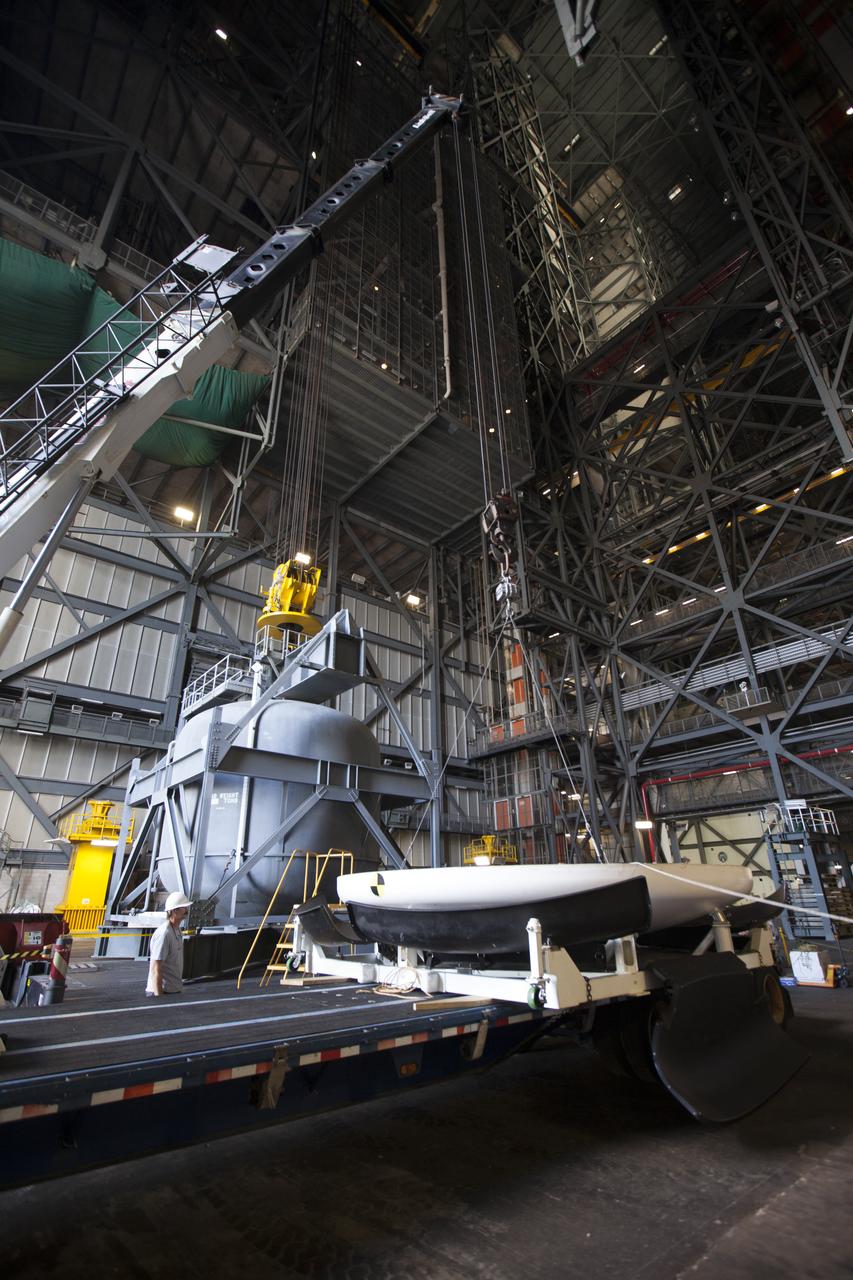
The Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 has arrived in High Bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
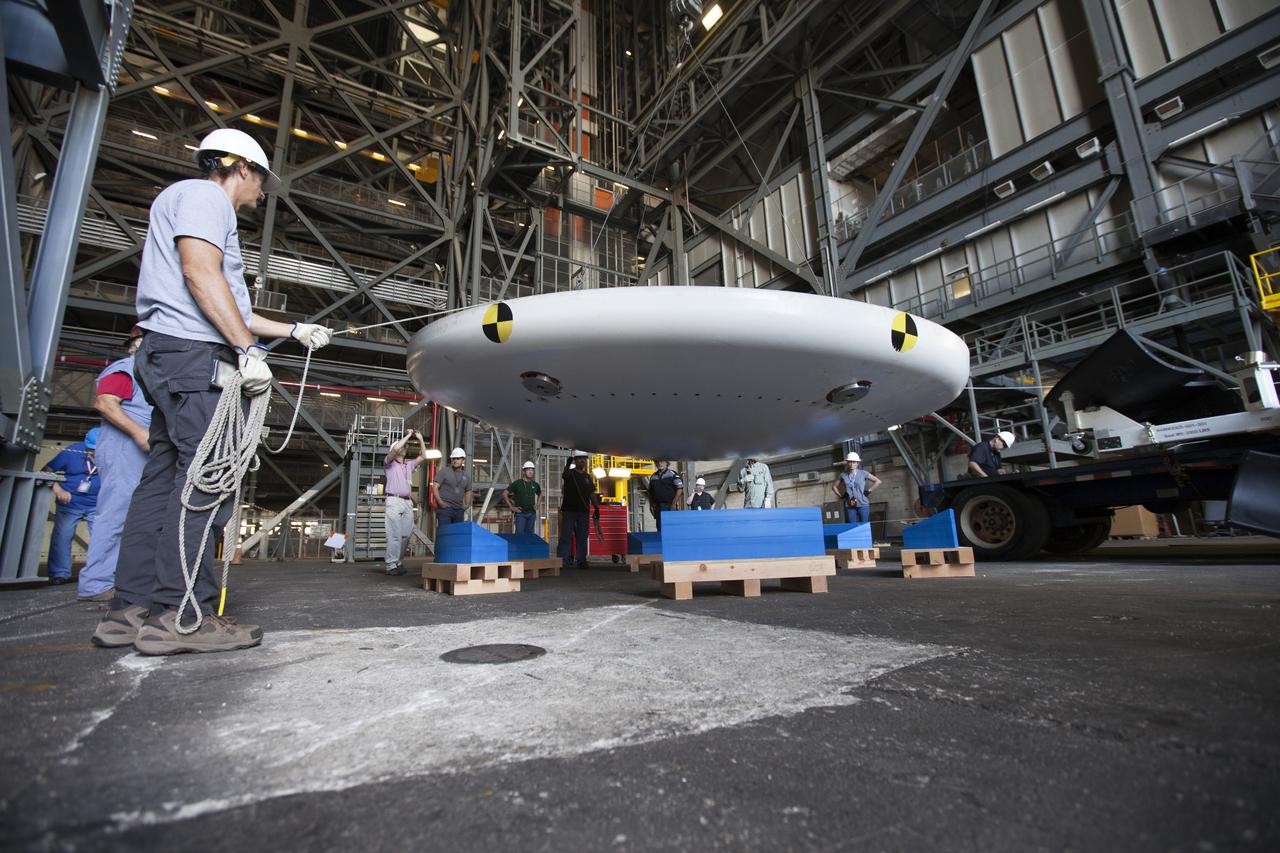

Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress as a crane lowers the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 onto foam blocks. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.

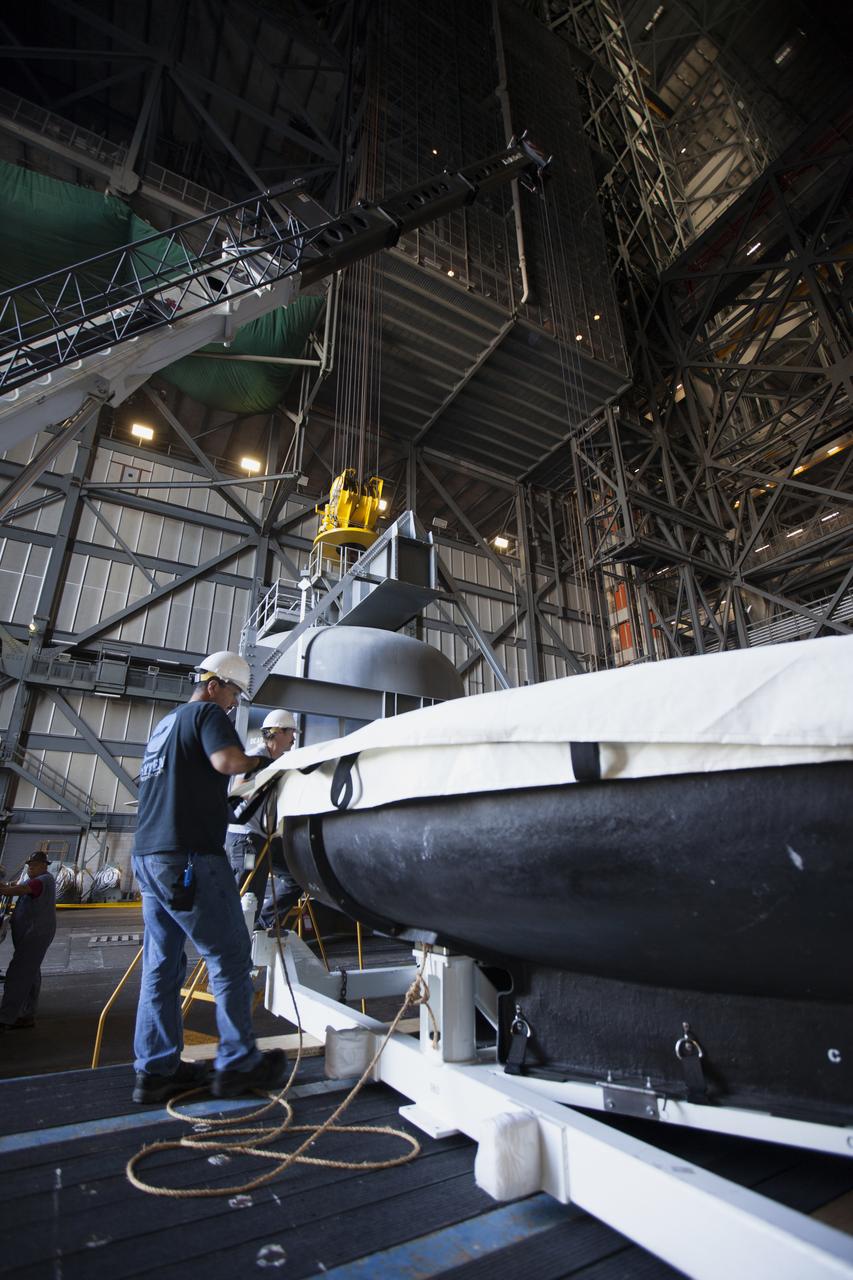
Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker helps prepare the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 for unloading off its transporter. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.

Inside High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is secured on foam blocks. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
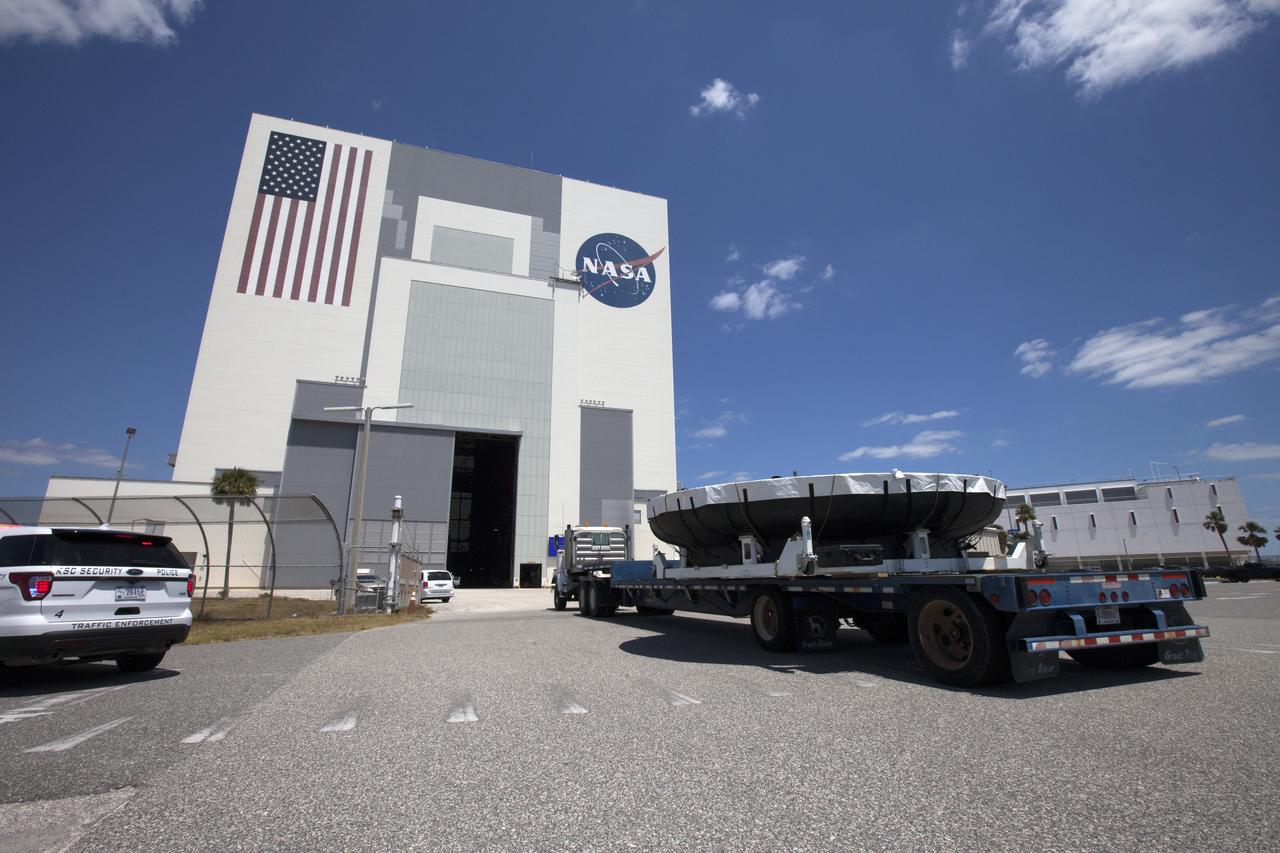

The Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, secured on a transporter, arrives at the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.

A flatbed truck carrying the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, prepares to back into High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
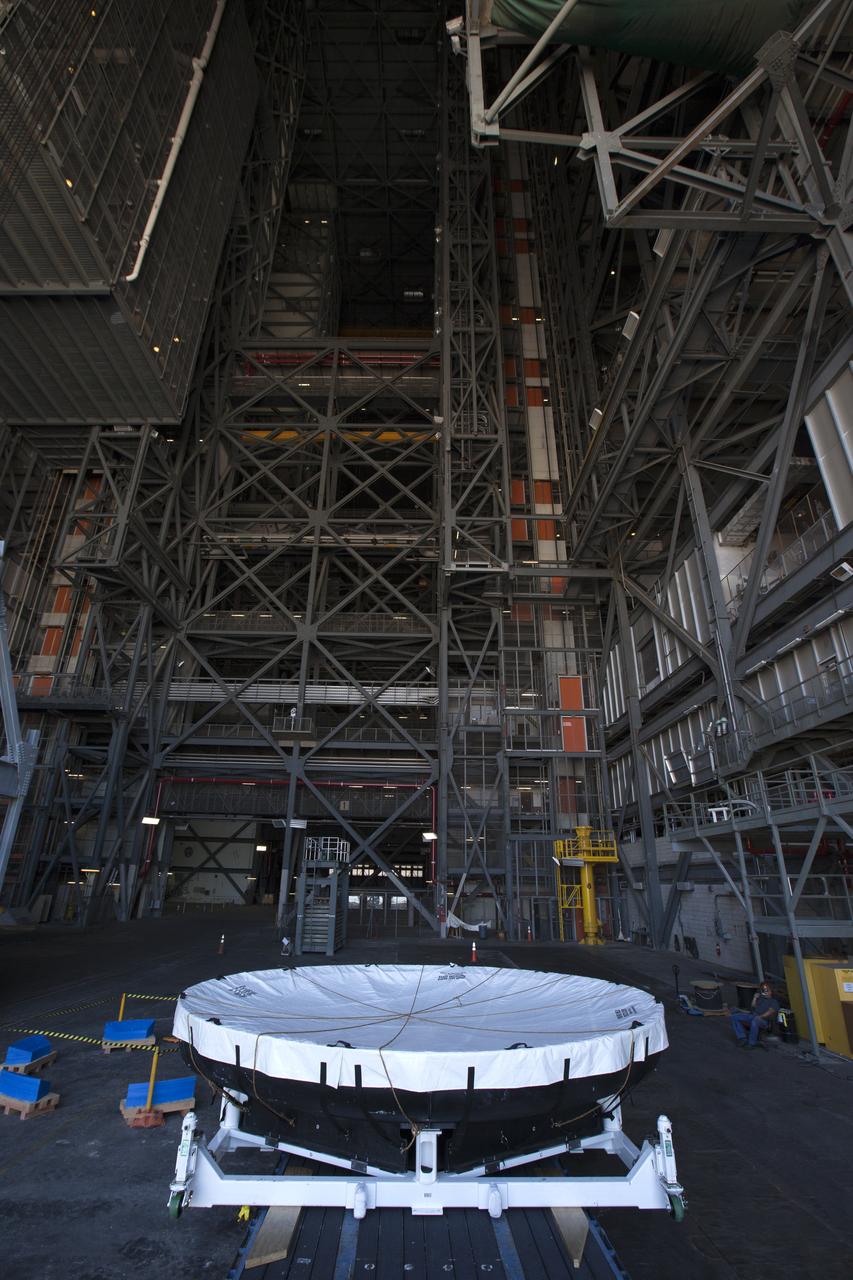

The Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 has arrived in High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
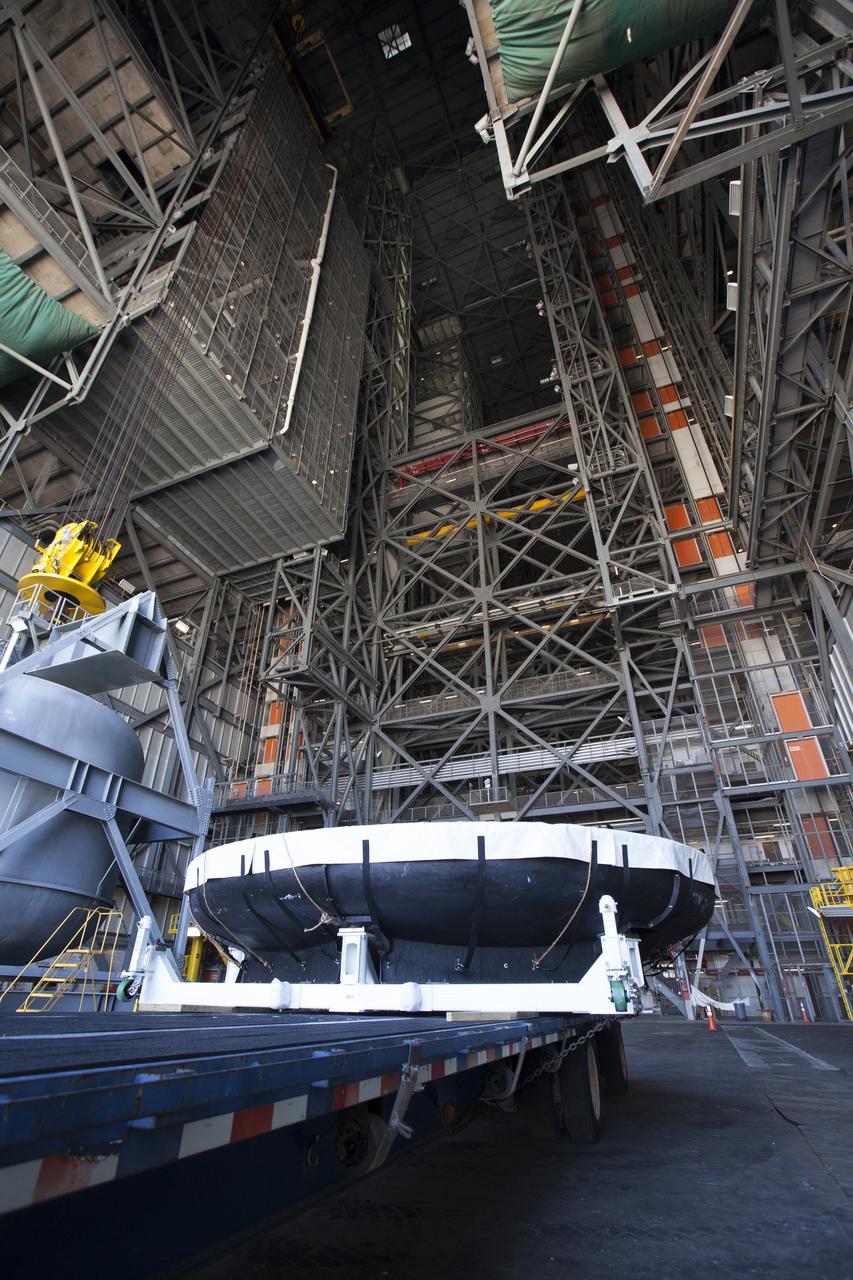

A flatbed truck carrying the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, backs into High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
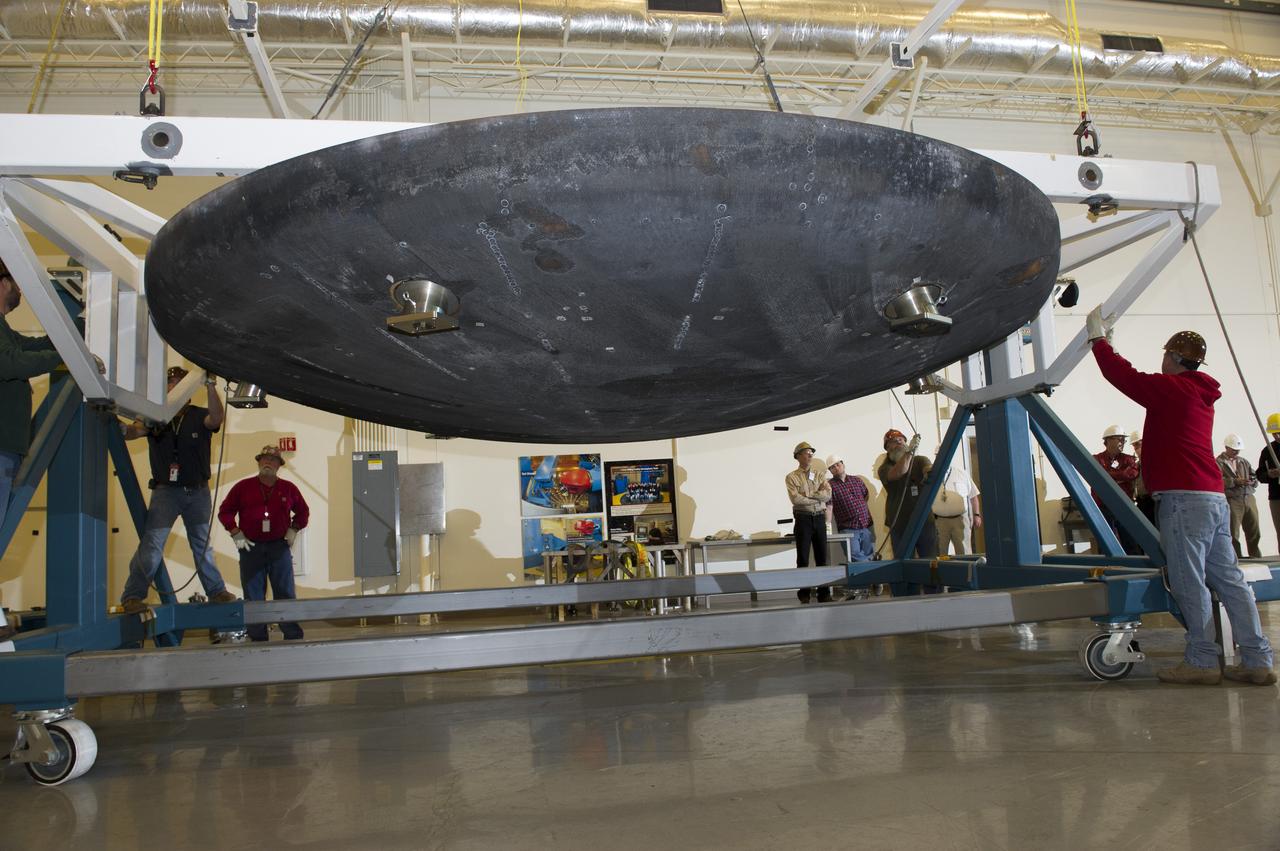

THE HEAT SHIELD ARRIVED MARCH 9 AT MARSHALL, WHERE EXPERTS FROM THE CENTER AND NASA’S AMES RESEARCH CENTER WILL EXTRACT SAMPLES OF THE ABLATIVE MATERIAL, OR AVCOAT
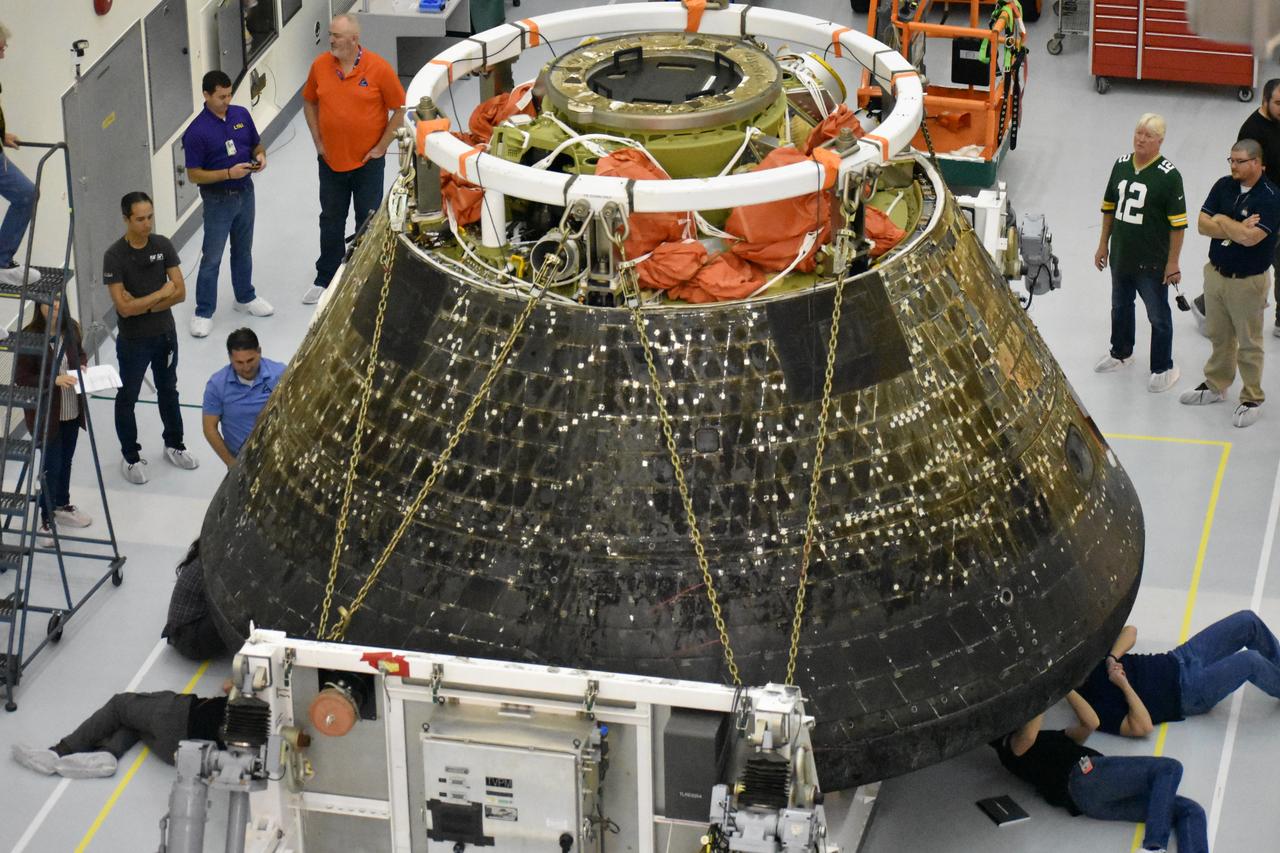

Inside the Multi Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engineers and technicians conduct inspections of the heat shield on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission. Orion returned to Kennedy on Dec. 30, 2022, after splashing down in the Pacific Ocean on Dec. 11 following a 25-day mission around the Moon.
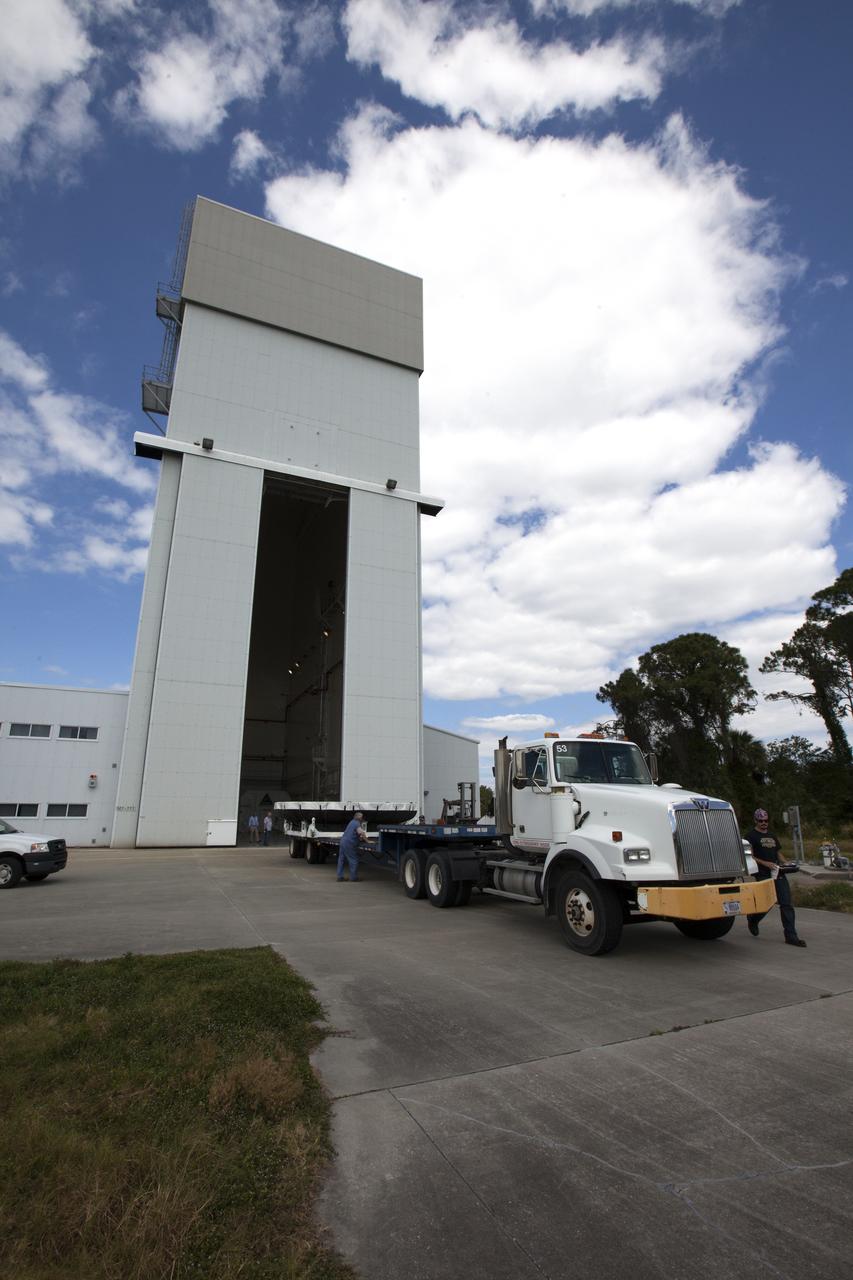

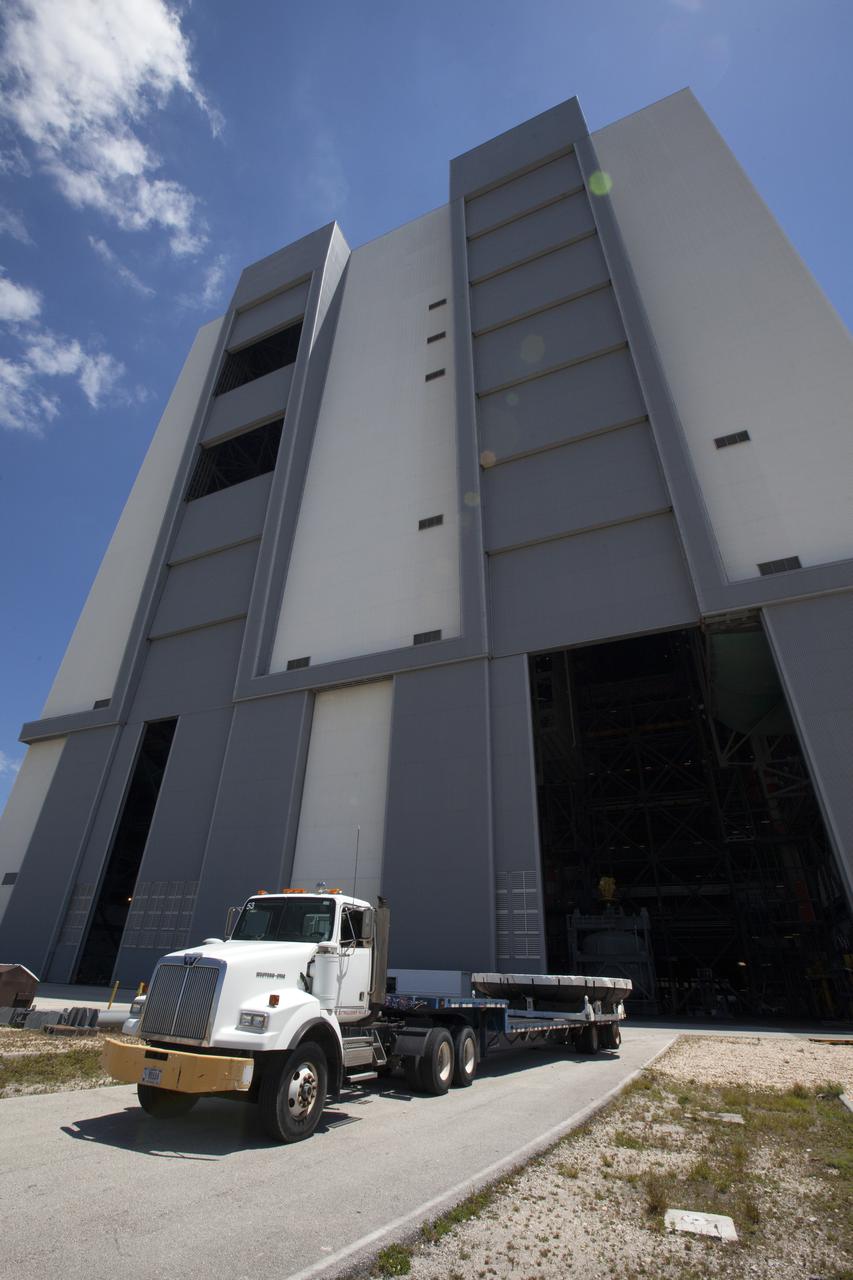
The Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, secured on a transporter, departs the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
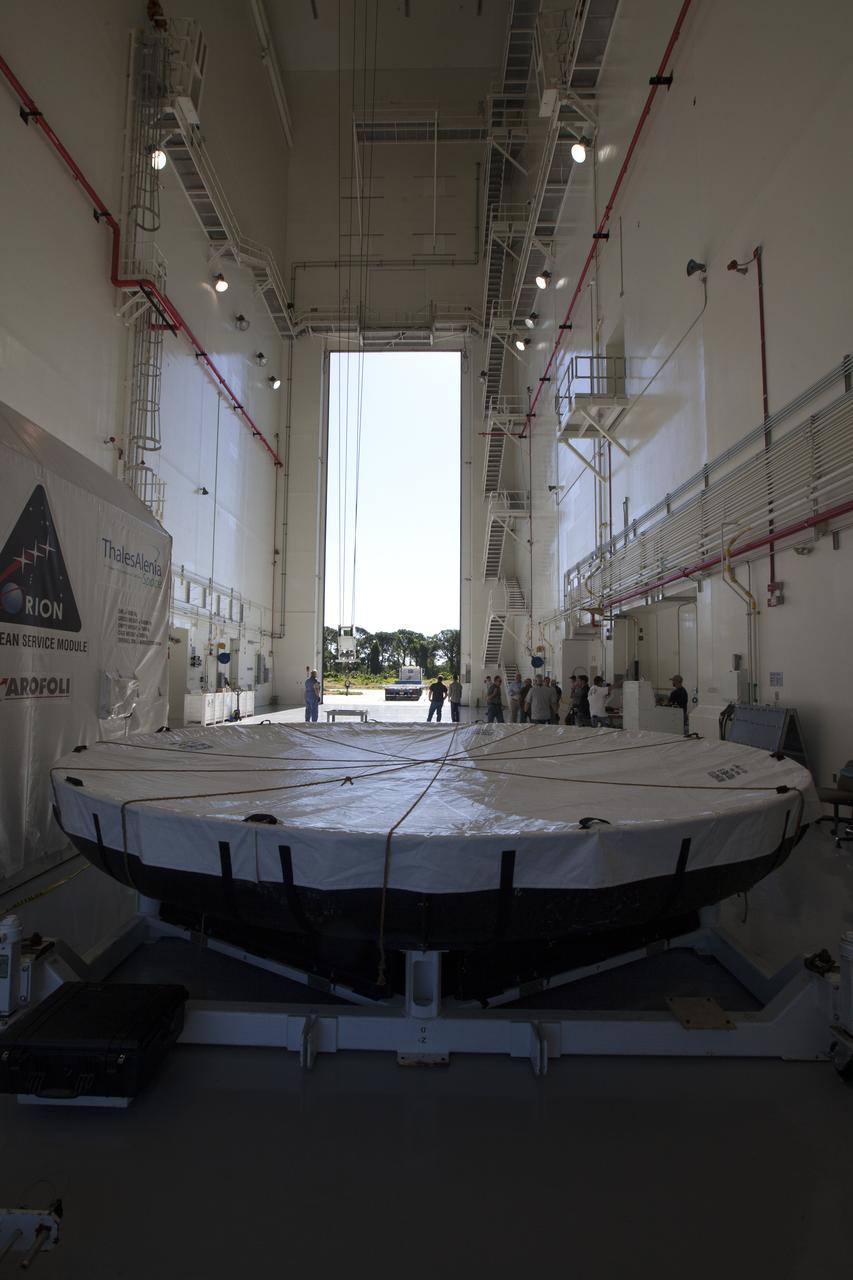

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is being prepared for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
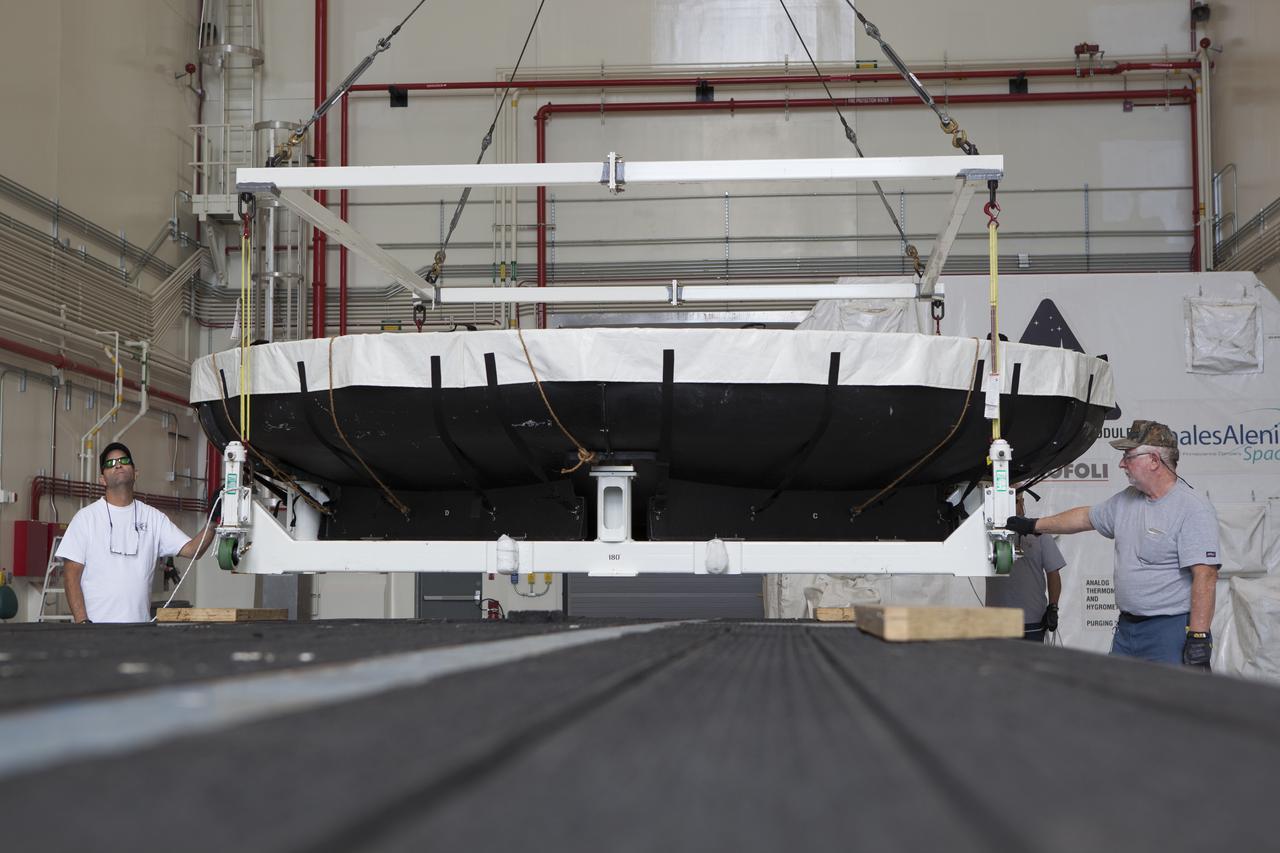

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is being loaded onto a transporter for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
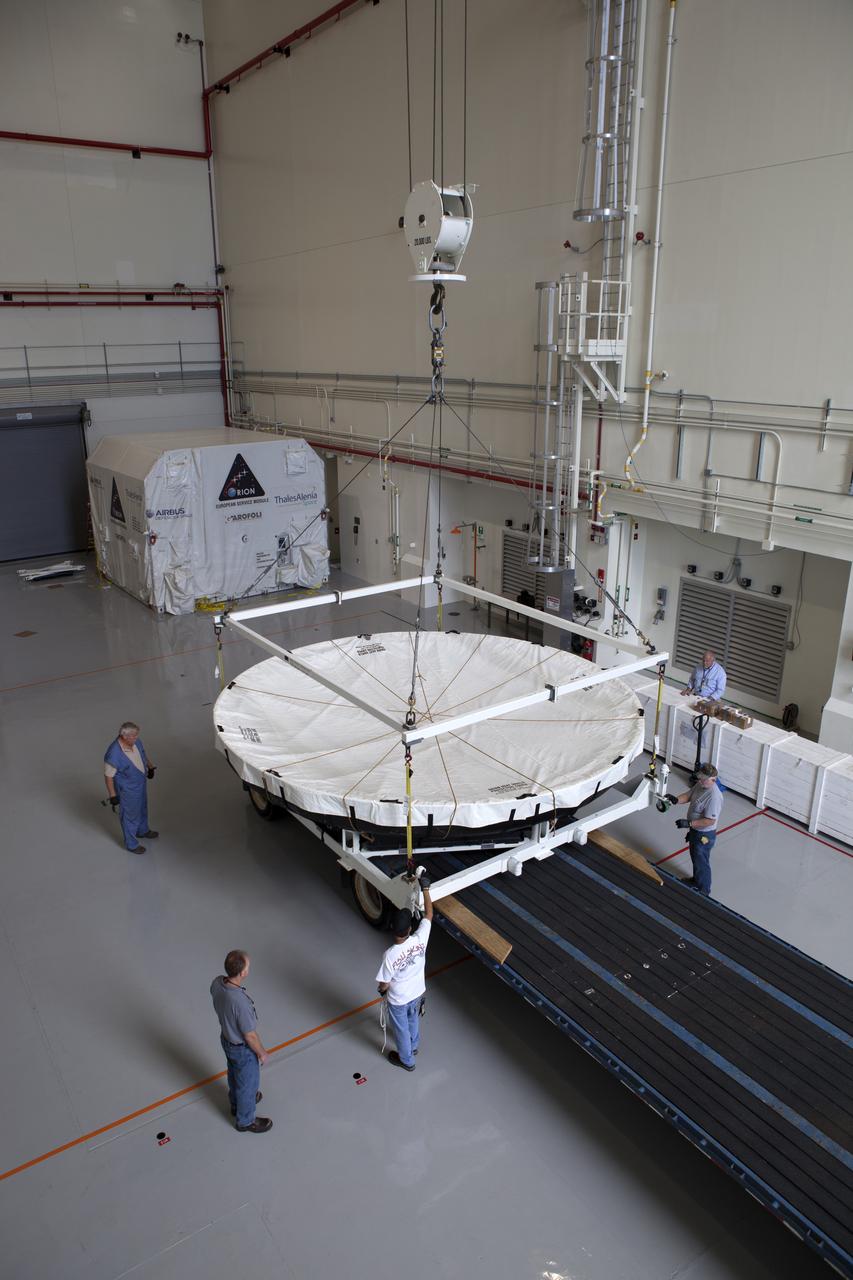

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 onto a transporter for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
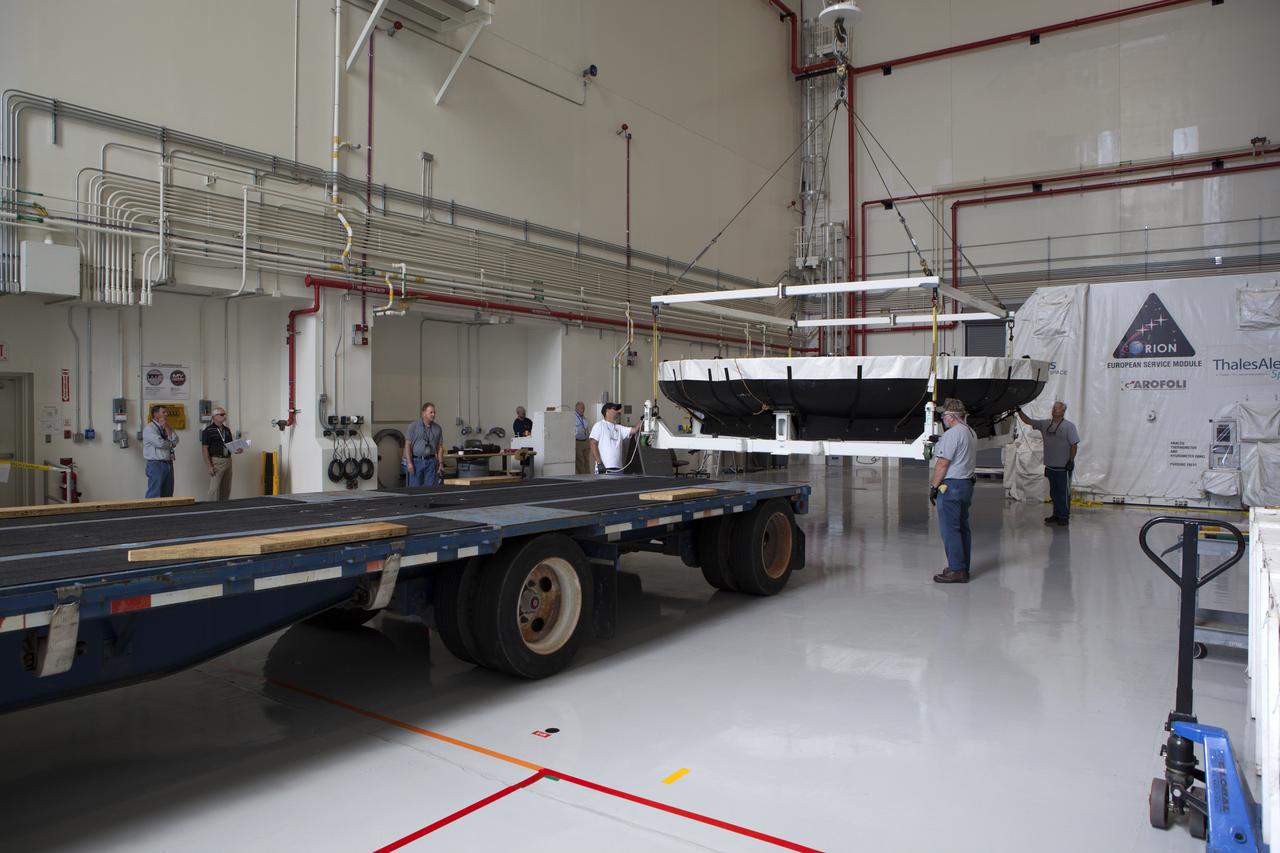

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is being loaded onto a transporter for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
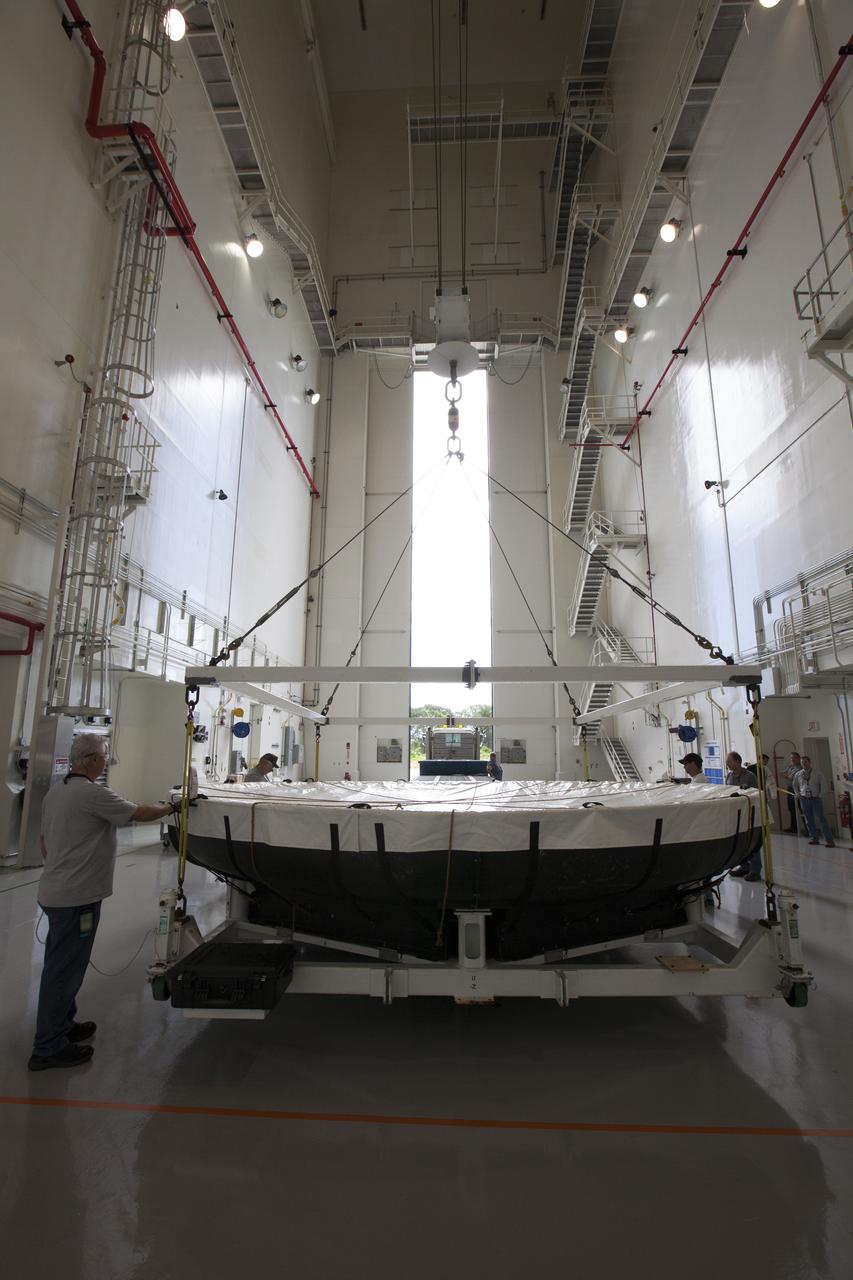

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is secured on a transporter and ready for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
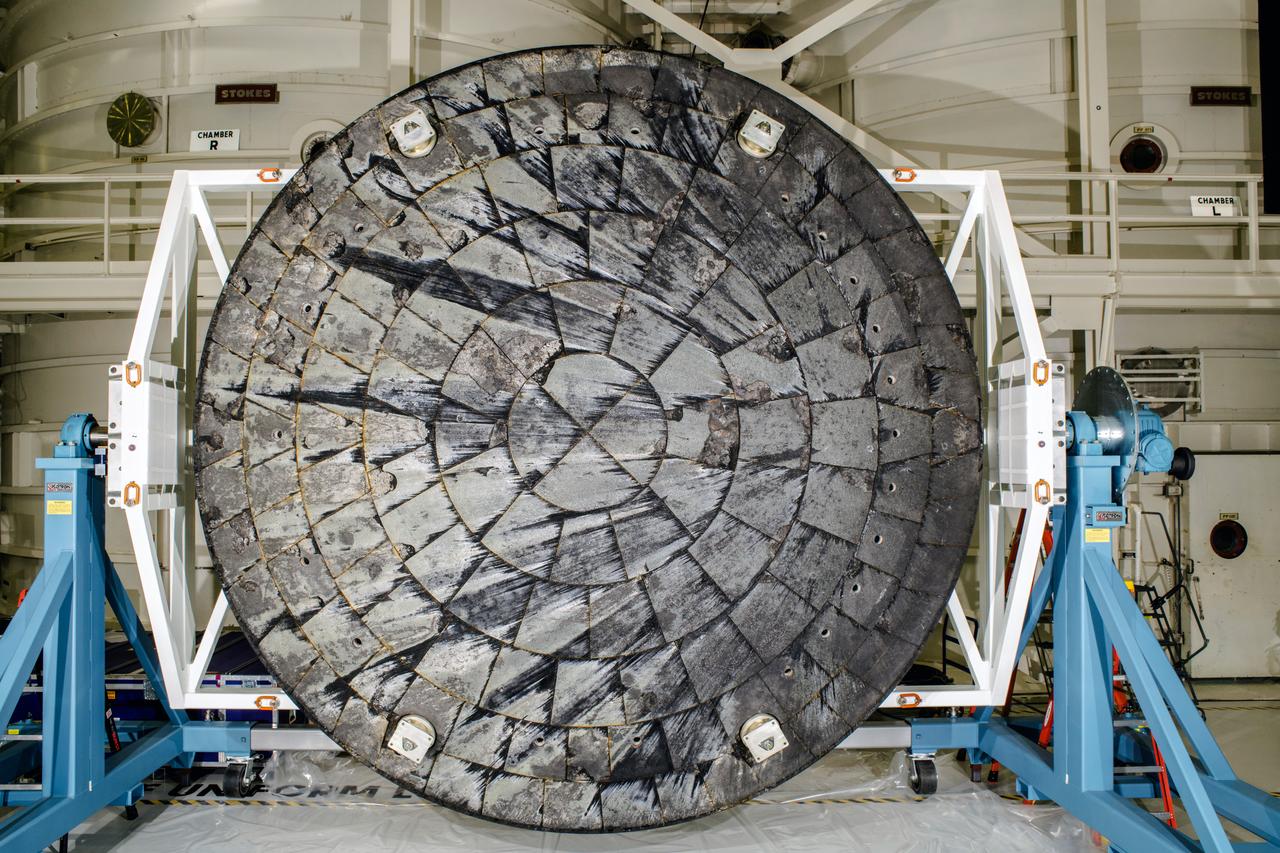

After NASA’s Orion spacecraft was recovered at the conclusion of the Artemis I test flight and transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, its heat shield was removed from the crew module inside the Operations and Checkout Building and rotated for inspection.
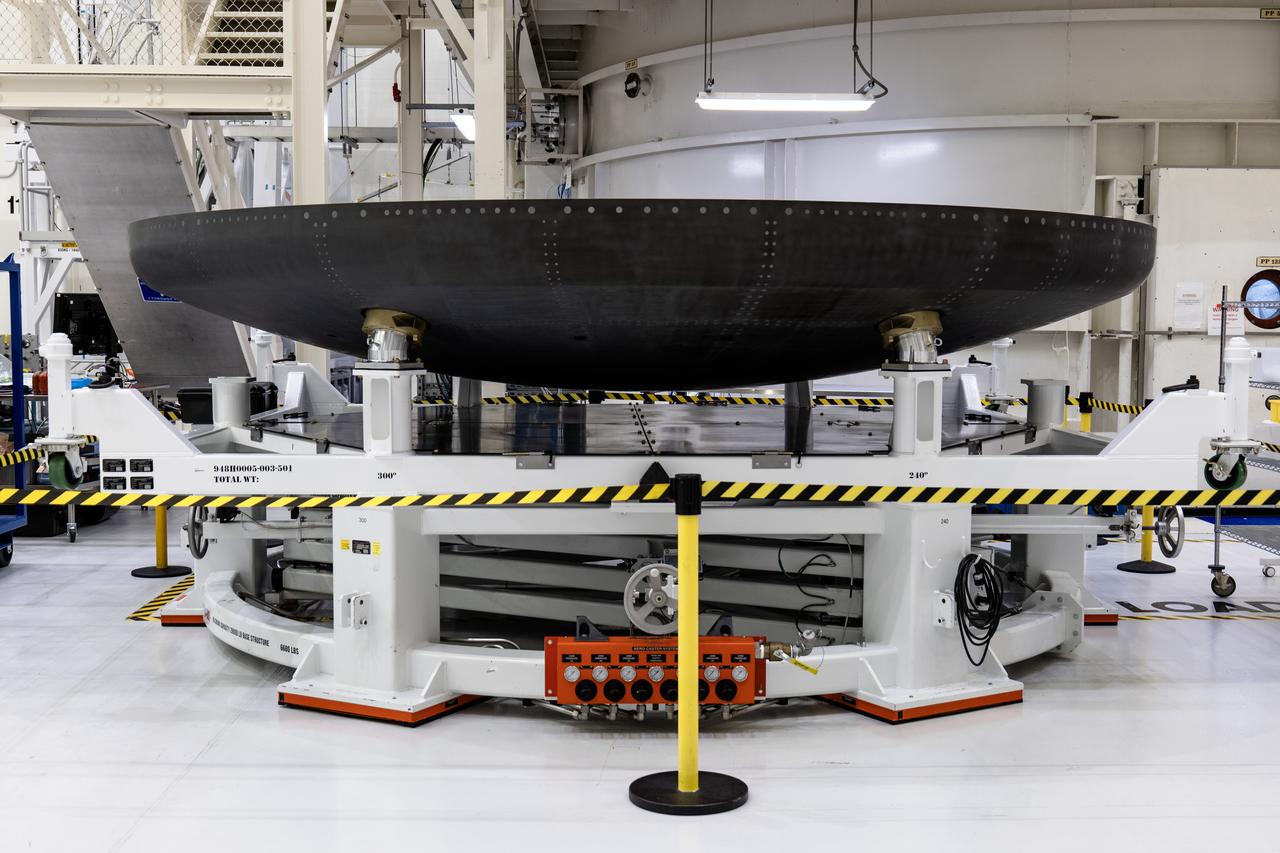

The heat shield carrier for Orion’s Artemis IV mission is in view secured on a work stand in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The carrier structure holds the thermal protection system heat shield securely to the Orion crew module while facing launch, reentry, and splashdown impact loads.

The heat shield carrier for Orion’s Artemis IV mission is in view secured on a work stand in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The carrier structure holds the thermal protection system heat shield securely to the Orion crew module while facing launch, reentry, and splashdown impact loads.

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.

THE ORION HEAT SHIELD, WHICH WAS AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER FROM MARCH-MAY 2015 FOR ENGINEERING AND ANALYSIS, IS READIED FOR DEPARTURE AT THE END OF ITS STAY. THE HEAT SHIELD’S ABLATED SURFACE MATERIAL WAS REMOVED AT MARSHALL FOR ANALYSIS, USING THE CENTER’S STATE-OF-THE-ART SEVEN-AXIS MILLING MACHINE. IT NEXT WILL GO TO NASA’S LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER FOR WATER-IMPACT TESTING. NASA’S JOHNSON SPACE CENTER LEADS THE ORION PROGRAM FOR NASA.
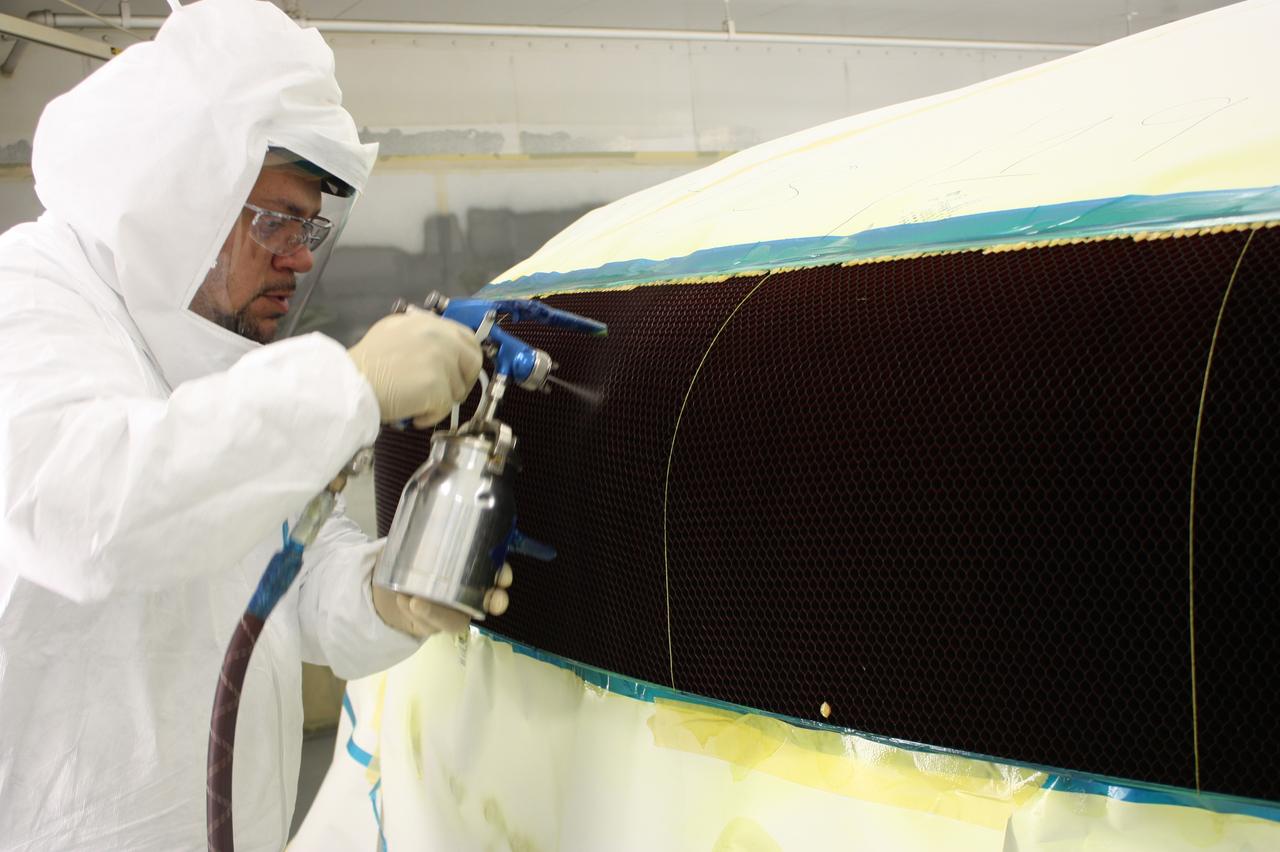

Technicians at Textron in Wimington, MA, work on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion heat shield carrier structure on May 8, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Technicians work on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion heat shield at Textron in Wimington, MA on June 7, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
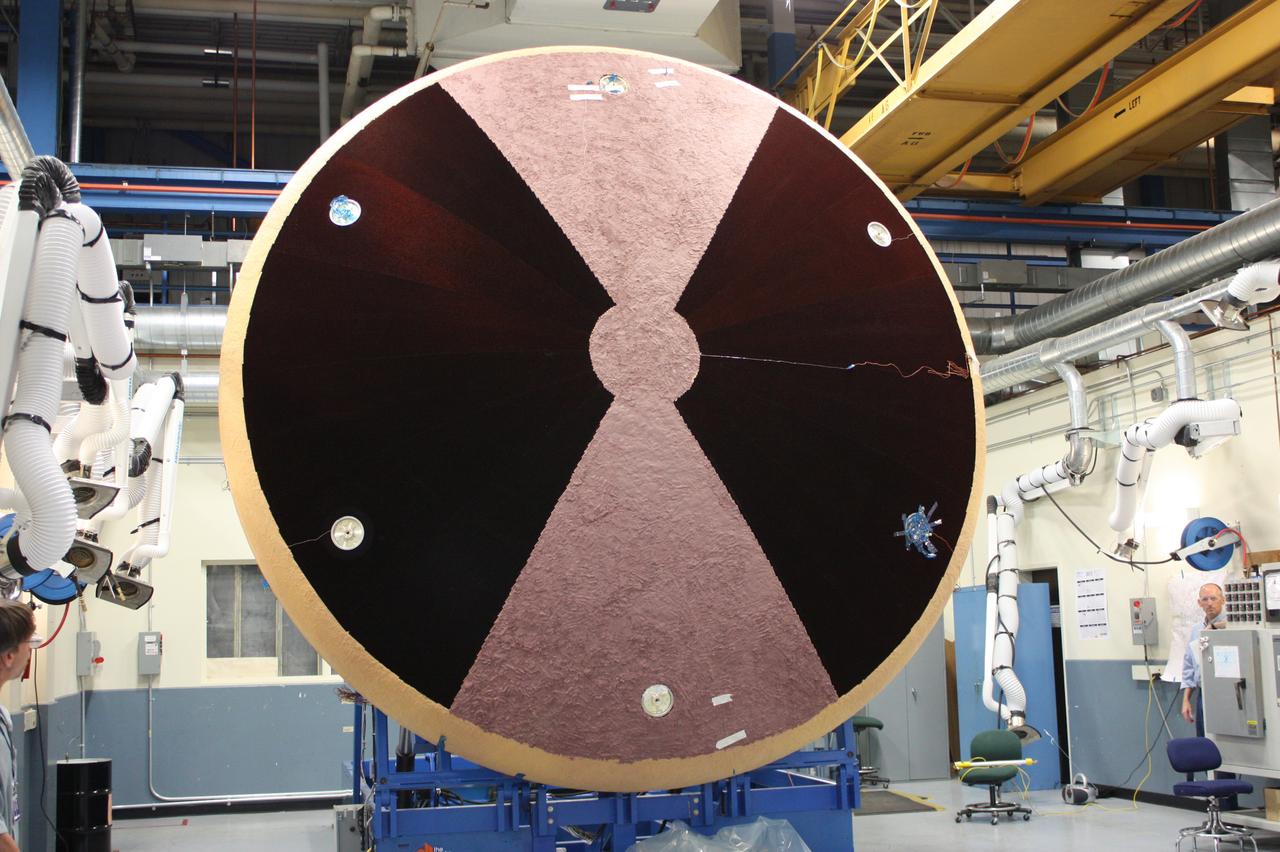
Technicians work on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion heat shield at Textron in Wimington, MA on June 7, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
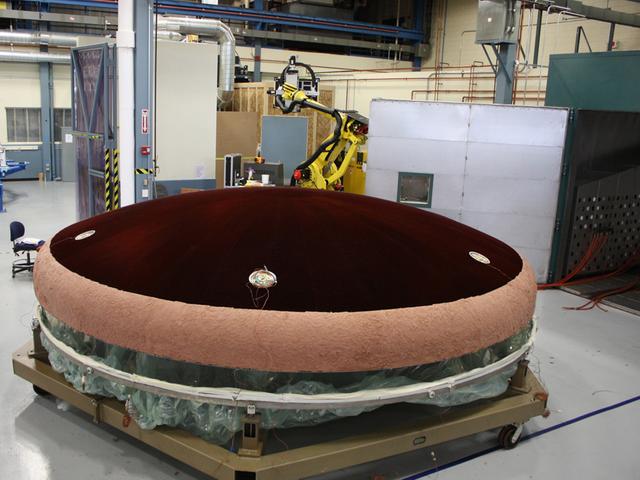

Technicians work on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion heat shield at Textron in Wimington, MA on June 7, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
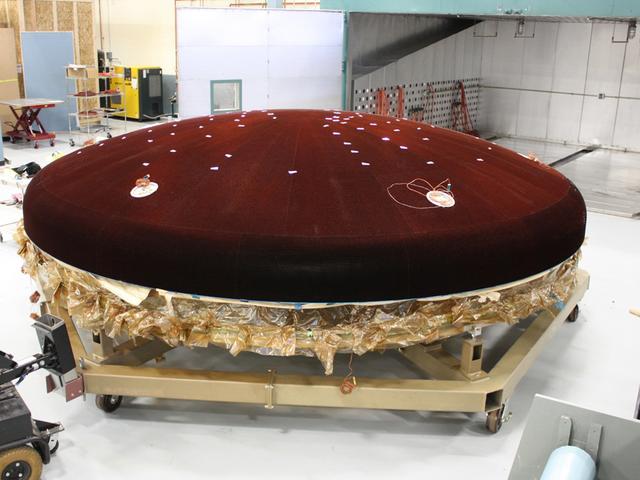

Technicians work on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion heat shield at Textron in Wimington, MA on June 7, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Technicians work on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion heat shield at Textron in Wimington, MA on June 7, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

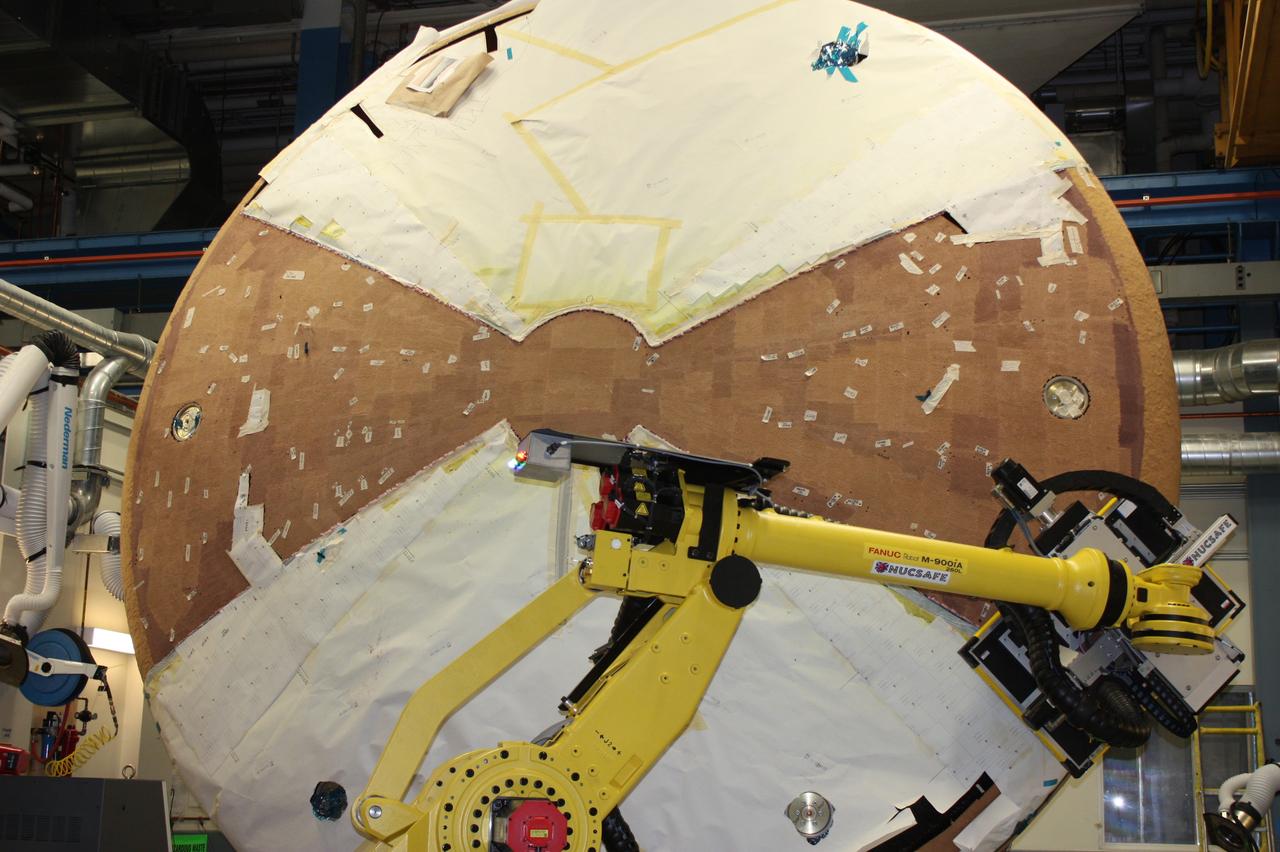
Work continues on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion heat shield at Textron in Wimington, MA on March 28, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
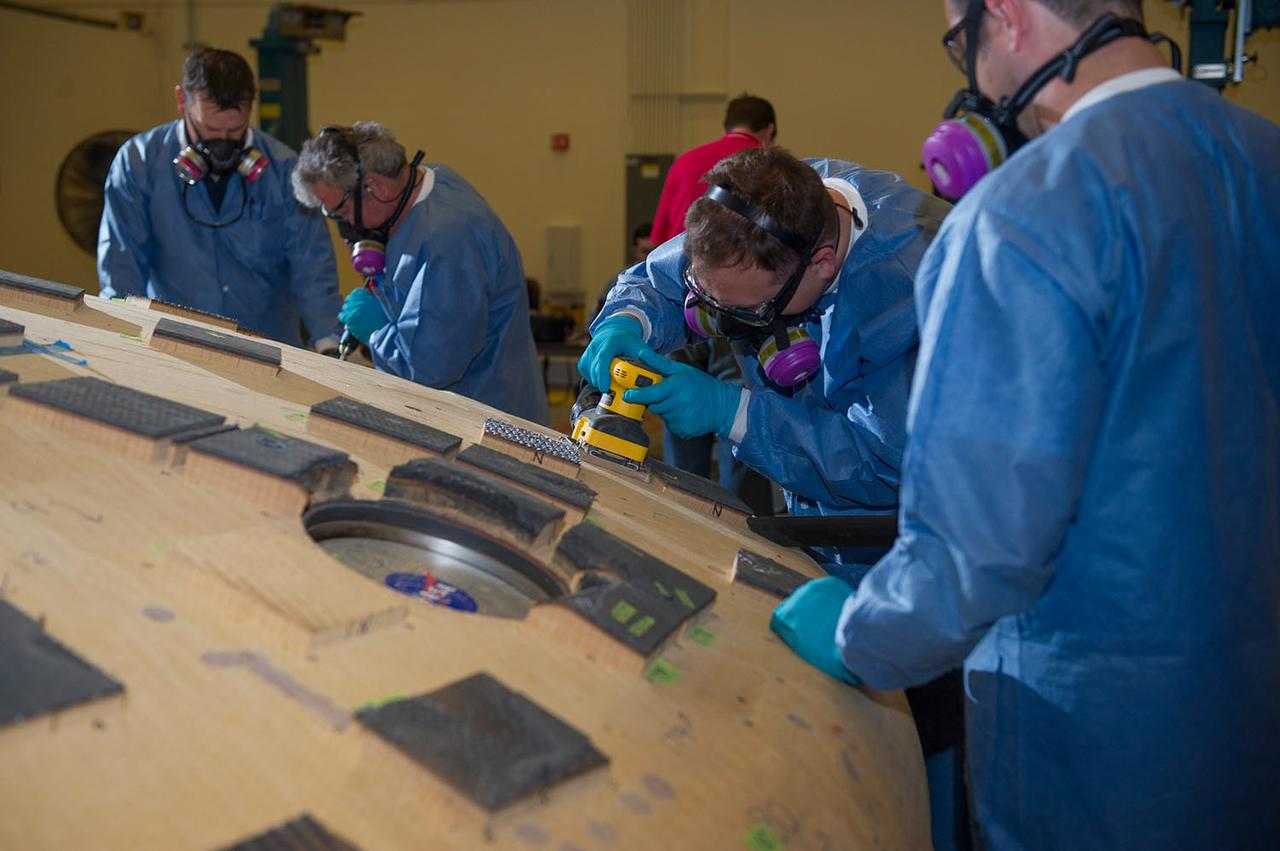

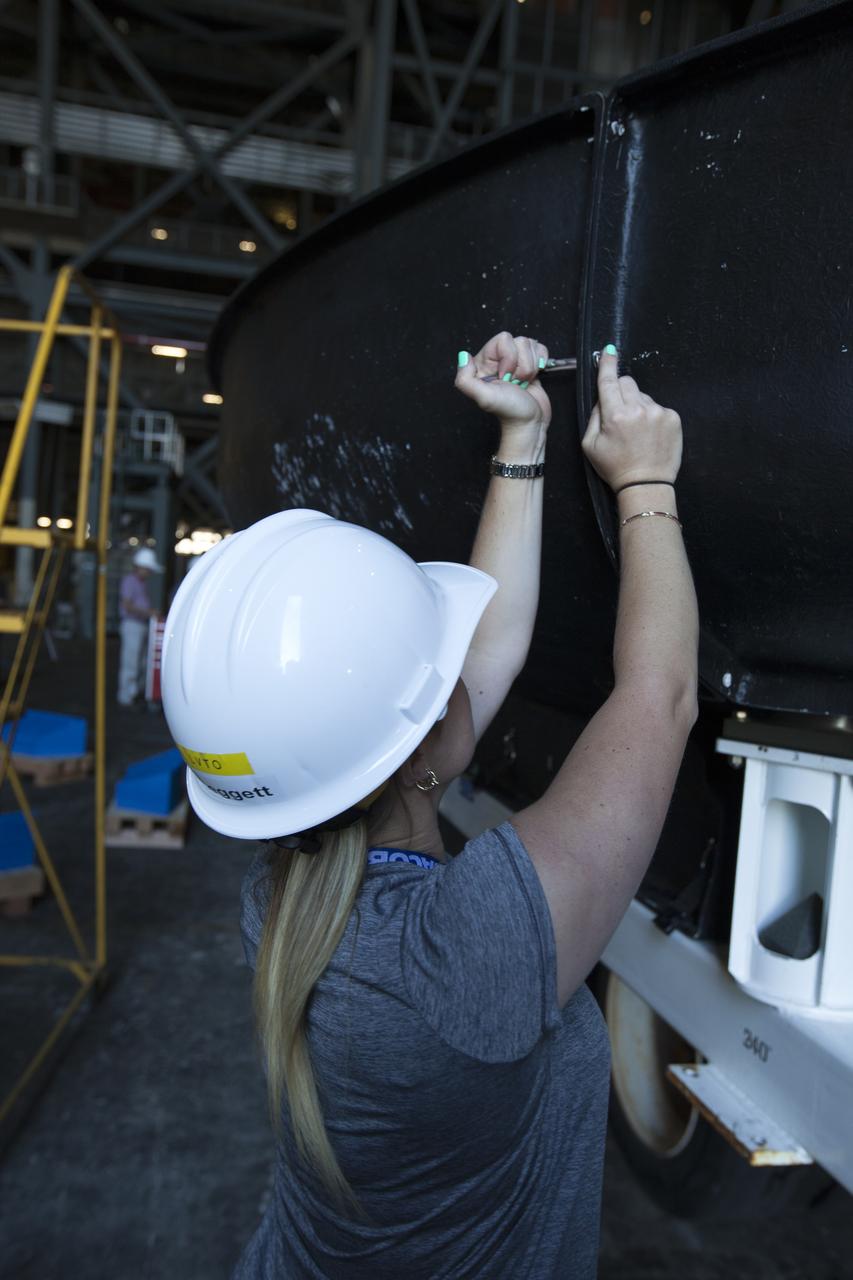
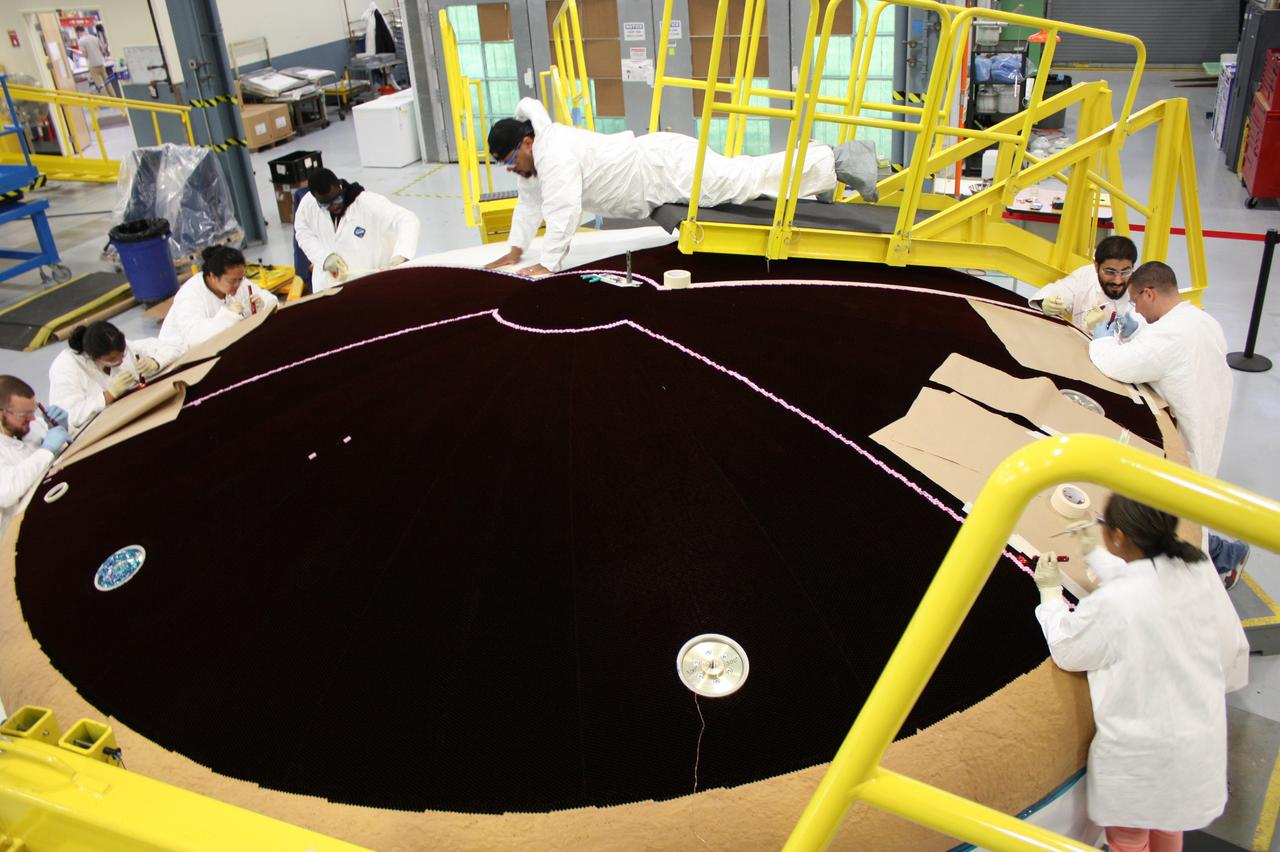
Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
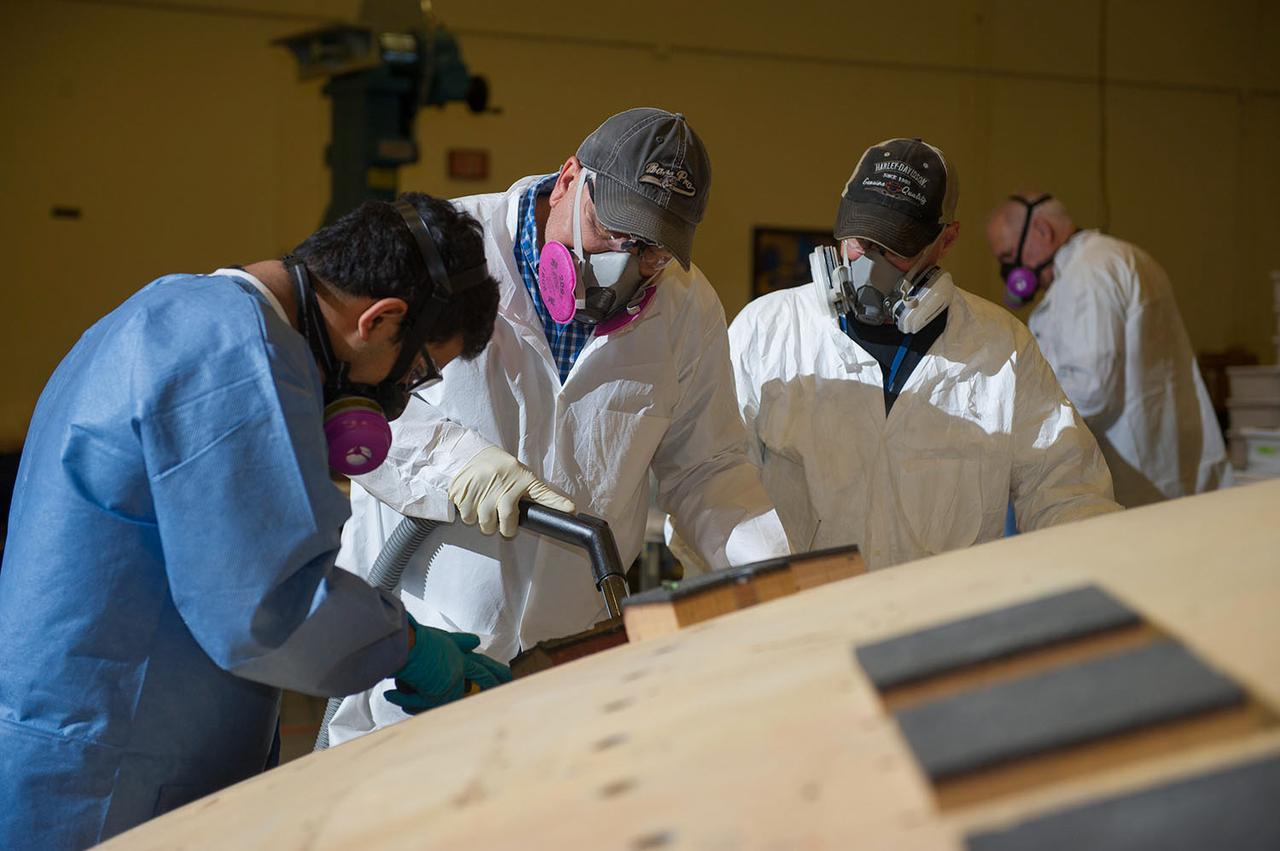

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
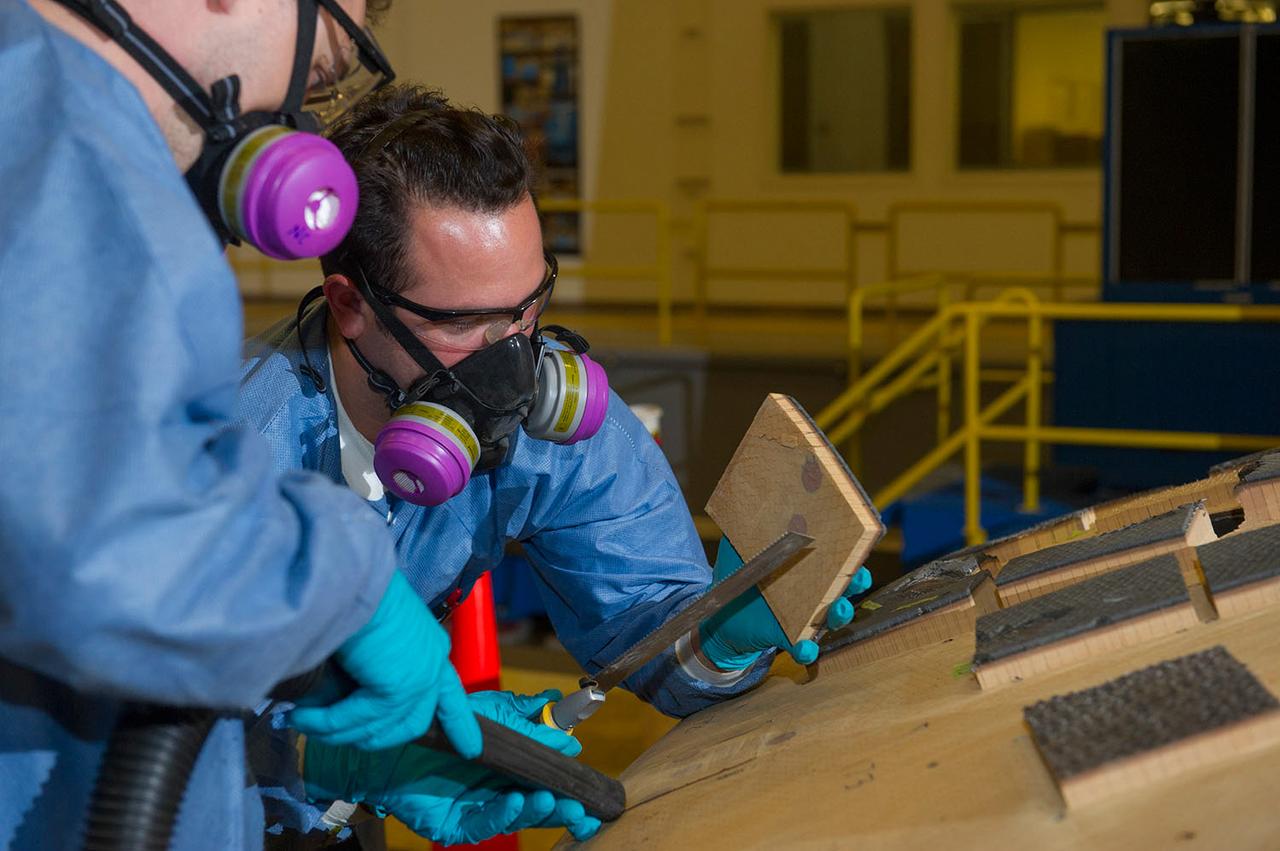

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
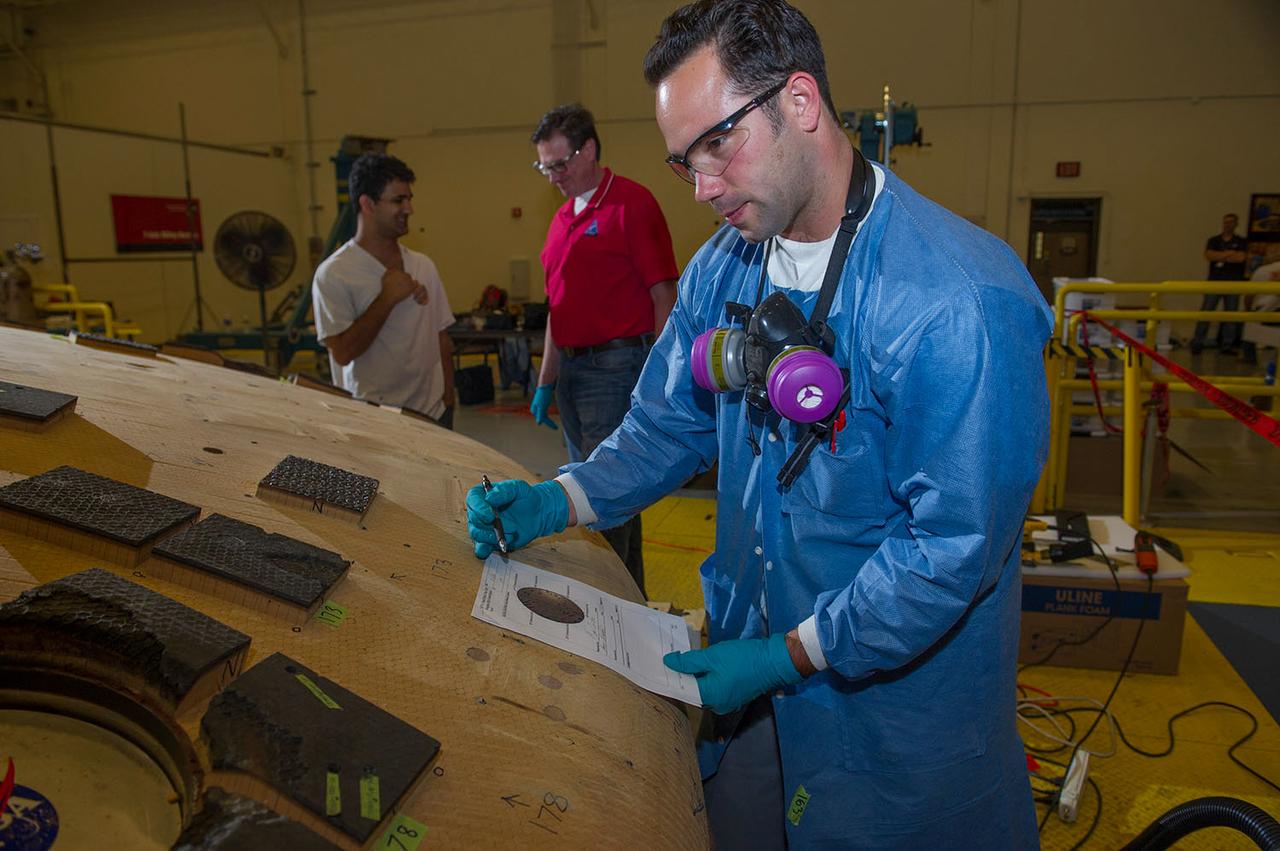

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
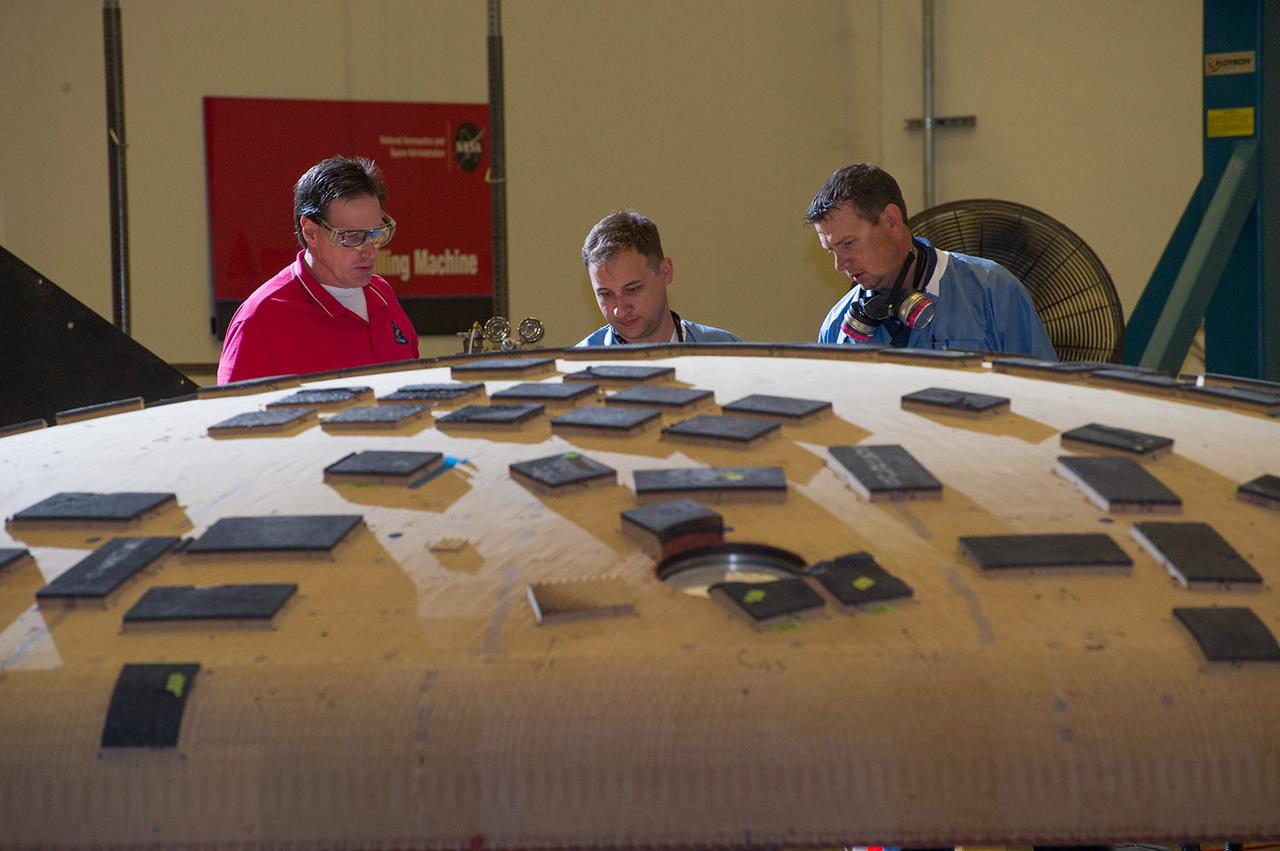

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, California, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, remove samples on May 4, 2015, from Orion's heat shield which flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in 2014. The heat shield protected the spacecraft from temperatures reaching 4000 degrees F. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield for the Orion crew module has been secured in a special work stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians prepare to move the heat shield for a fit check with the crew module. More than 200 instrumentation sensors have been installed on the heat shield. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers attach the heat shield to the Orion crew module inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield for Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1. The flight test will provide engineers with data about the heat shield's ability to protect Orion and its future crews from the 4,000-degree heat of reentry and an ocean splashdown following the spacecraft’s 20,000-mph reentry from space. Data gathered during the flight will inform decisions about design improvements on the heat shield and other Orion systems, and authenticate existing computer models and new approaches to space systems design and development. This process is critical to reducing overall risks and costs of future Orion missions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers attach the heat shield to the Orion crew module inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield for Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1. The flight test will provide engineers with data about the heat shield's ability to protect Orion and its future crews from the 4,000-degree heat of reentry and an ocean splashdown following the spacecraft’s 20,000-mph reentry from space. Data gathered during the flight will inform decisions about design improvements on the heat shield and other Orion systems, and authenticate existing computer models and new approaches to space systems design and development. This process is critical to reducing overall risks and costs of future Orion missions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
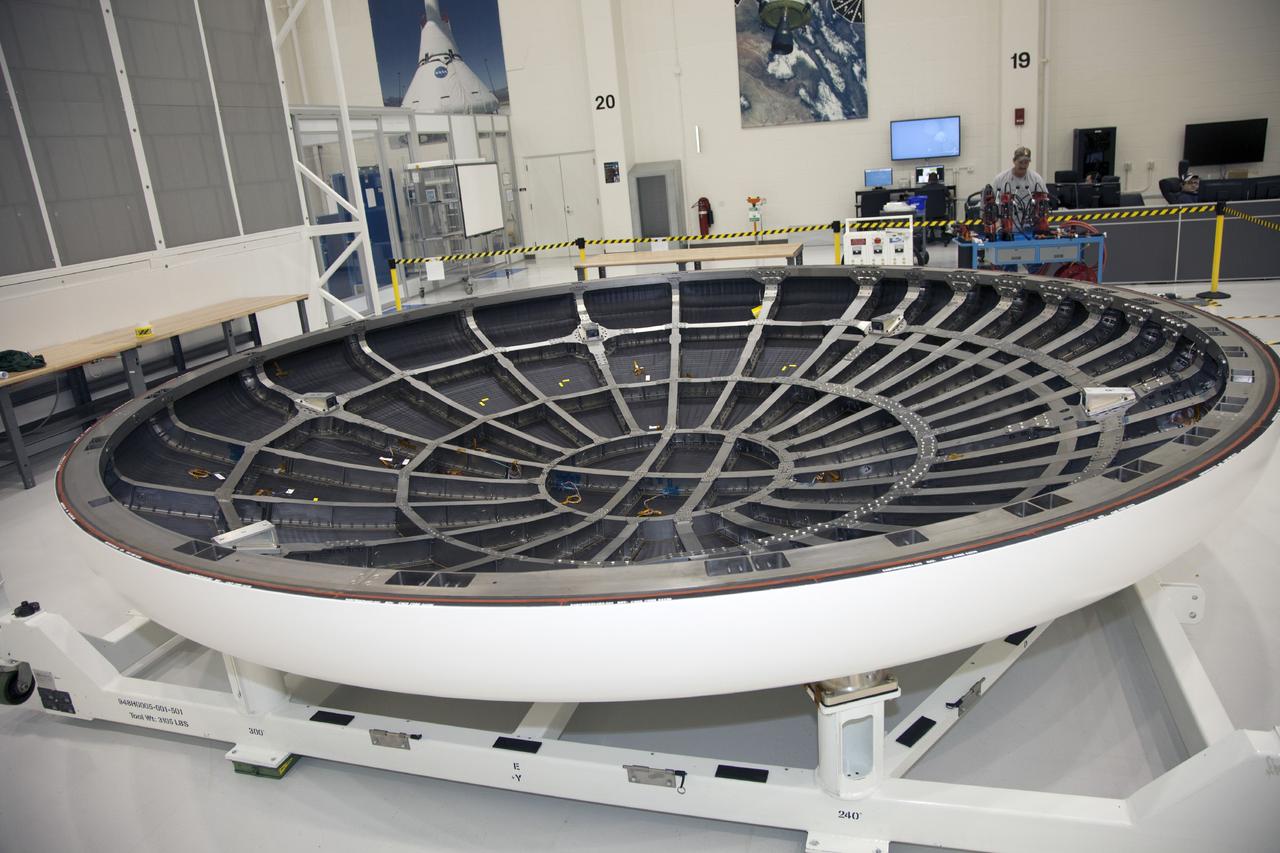

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield for the Orion spacecraft has been placed on a work stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield arrived at Kennedy’s Shuttle Landing Facility on Dec. 5 on NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft. The largest of its kind ever built, the heat shield is planned for installation on the Orion crew module in March 2014. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its first unpiloted flight test, Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1, scheduled for launch atop a Delta IV rocket in September 2014. The Orion spacecraft is designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in 2017. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Mike Chambers
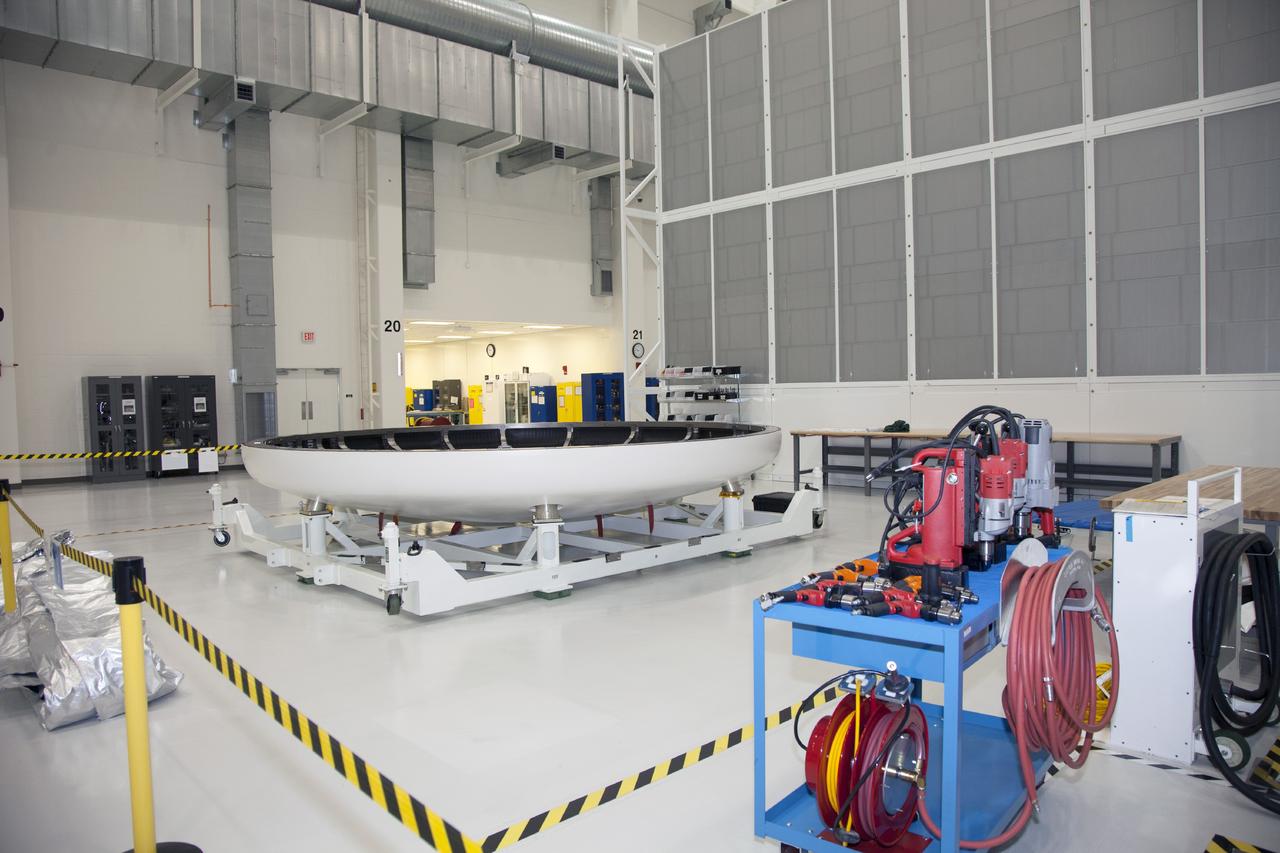

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield for the Orion spacecraft has been placed on a work stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield arrived at Kennedy’s Shuttle Landing Facility on Dec. 5 on NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft. The largest of its kind ever built, the heat shield is planned for installation on the Orion crew module in March 2014. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its first unpiloted flight test, Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1, scheduled for launch atop a Delta IV rocket in September 2014. The Orion spacecraft is designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in 2017. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Mike Chambers
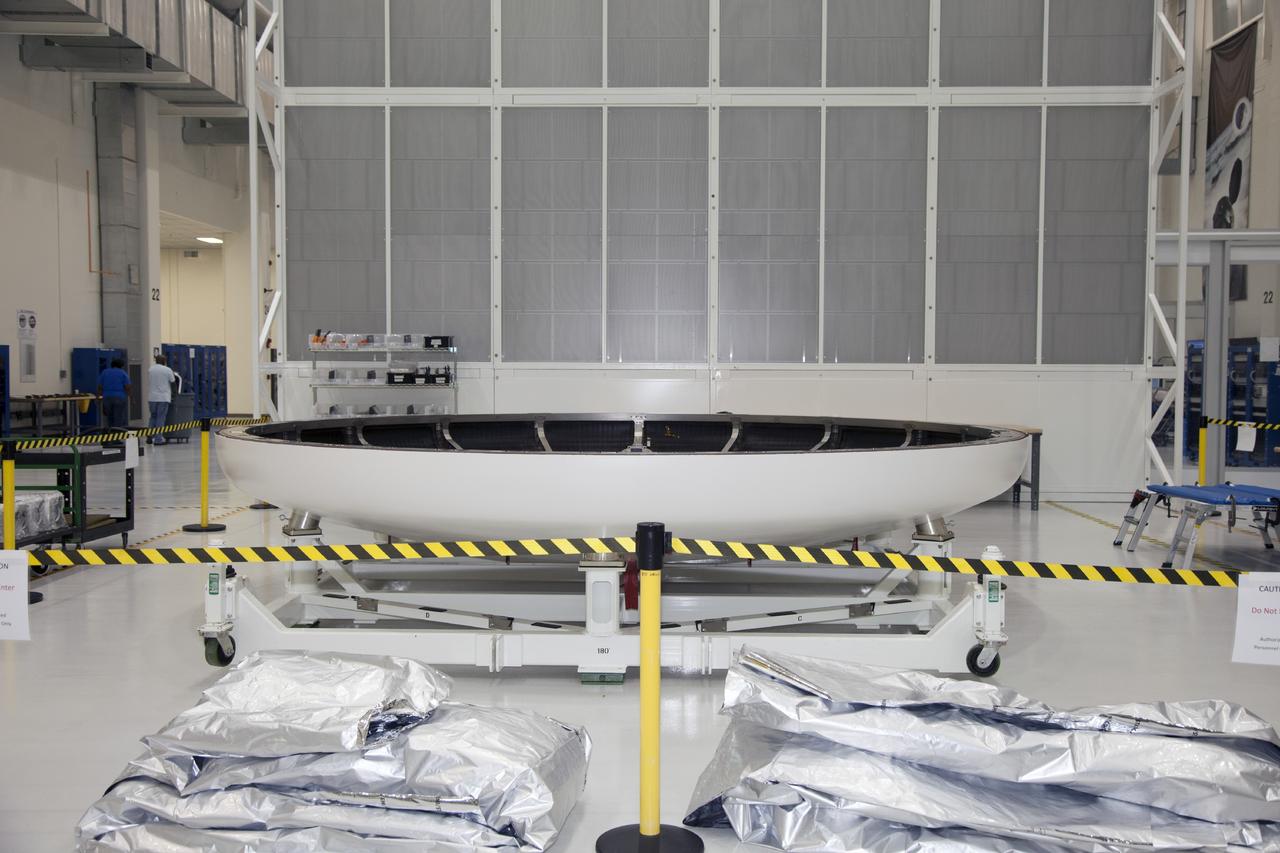

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield for the Orion spacecraft has been placed on a work stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield arrived at Kennedy’s Shuttle Landing Facility on Dec. 5 on NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft. The largest of its kind ever built, the heat shield is planned for installation on the Orion crew module in March 2014. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its first unpiloted flight test, Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1, scheduled for launch atop a Delta IV rocket in September 2014. The Orion spacecraft is designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in 2017. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Mike Chambers
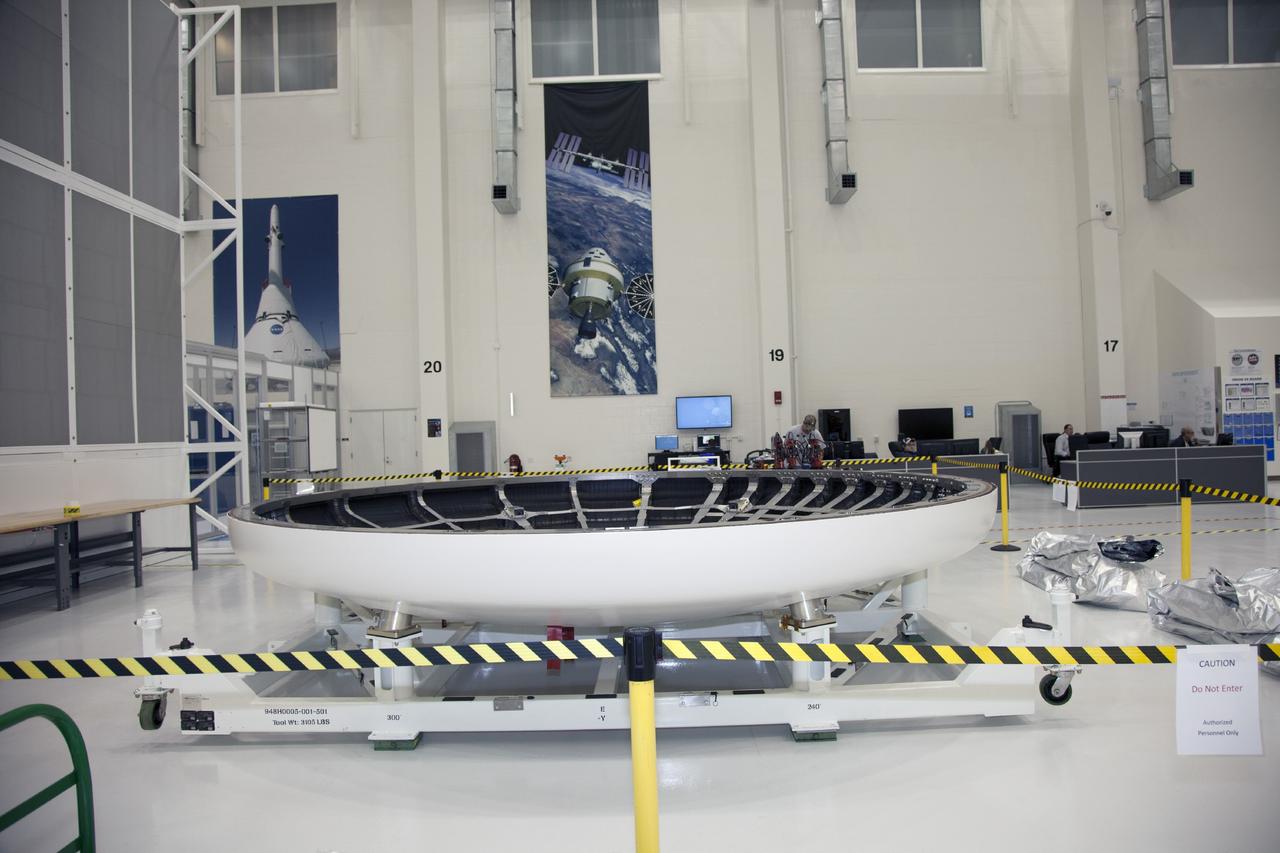

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield for the Orion spacecraft has been placed on a work stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield arrived at Kennedy’s Shuttle Landing Facility on Dec. 5 on NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft. The largest of its kind ever built, the heat shield is planned for installation on the Orion crew module in March 2014. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its first unpiloted flight test, Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1, scheduled for launch atop a Delta IV rocket in September 2014. The Orion spacecraft is designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in 2017. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Mike Chambers
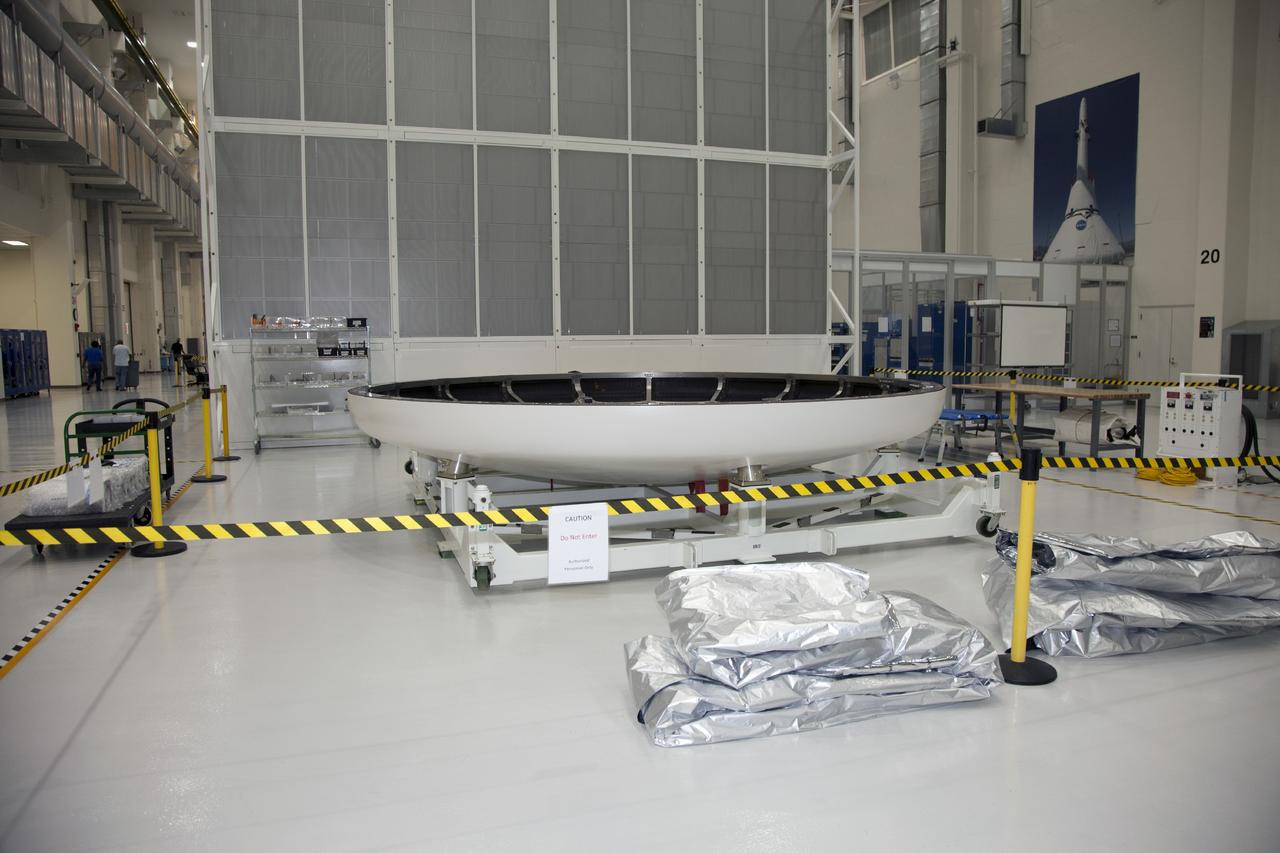

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield for the Orion spacecraft has been placed on a work stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield arrived at Kennedy’s Shuttle Landing Facility on Dec. 5 on NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft. The largest of its kind ever built, the heat shield is planned for installation on the Orion crew module in March 2014. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for its first unpiloted flight test, Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1, scheduled for launch atop a Delta IV rocket in September 2014. The Orion spacecraft is designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in 2017. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Mike Chambers

The Orion heat shield that flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in December 2014, arrives at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama for machining and post-flight evaluation on March 9, 2015. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
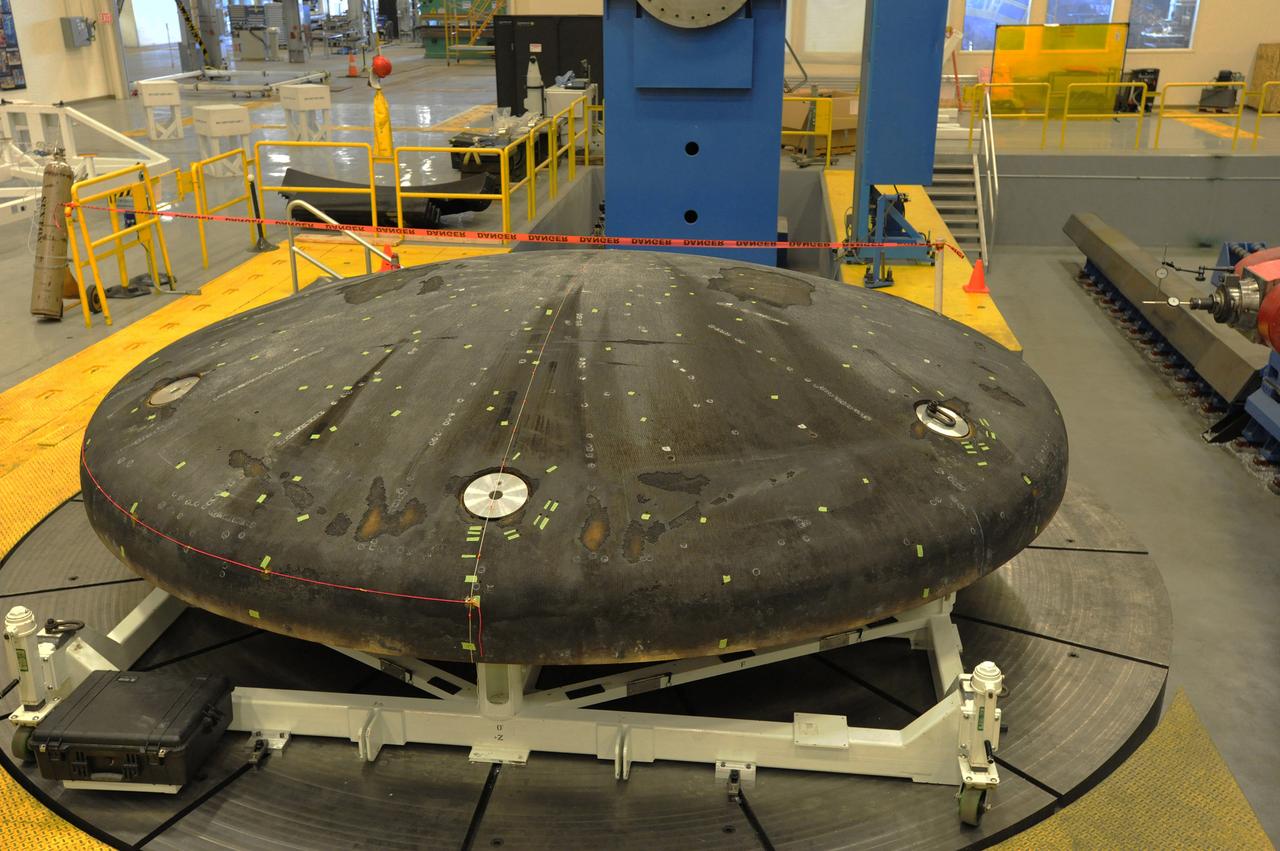

The Orion heat shield that flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in December 2014, arrives at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL for machining and post-flight evaluation on March 24, 2015. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
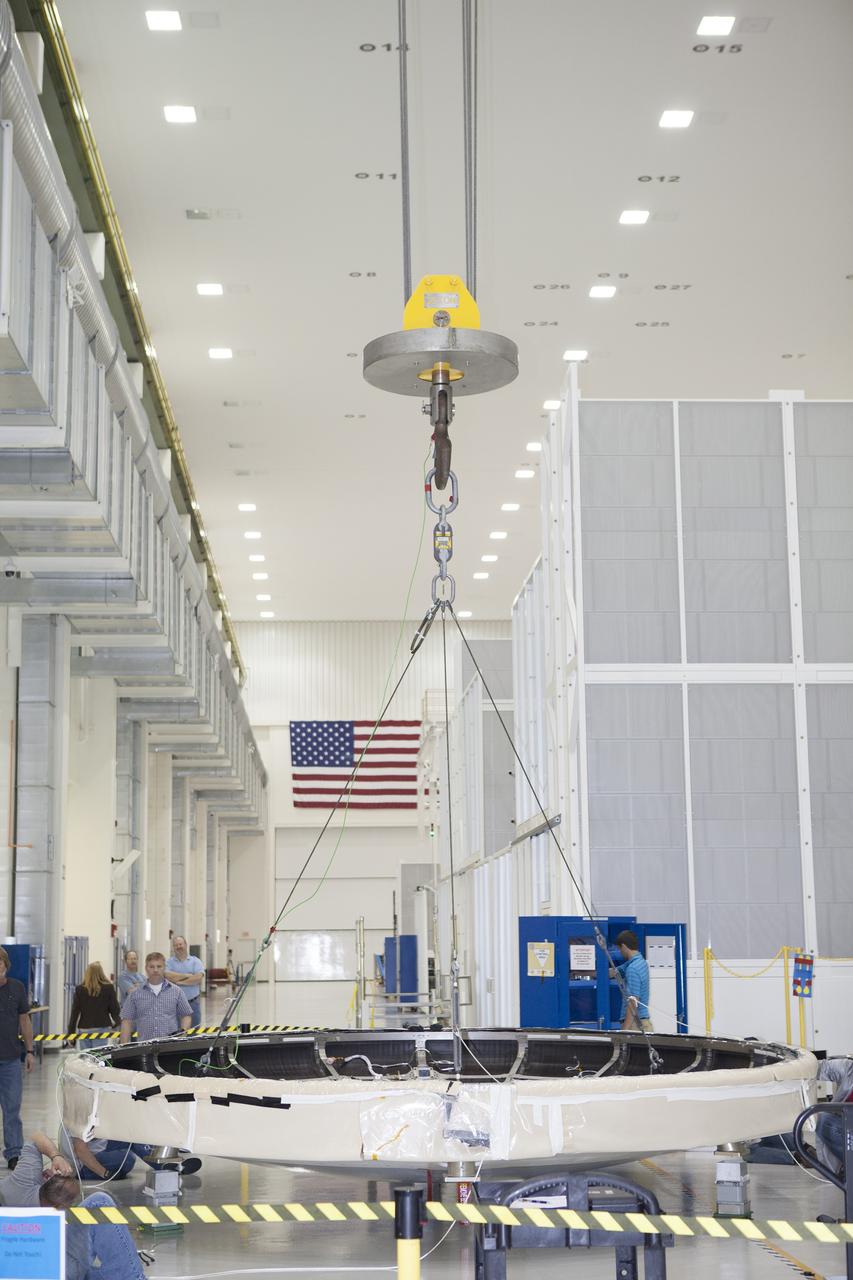

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane has lowered the Orion heat shield onto a stand. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
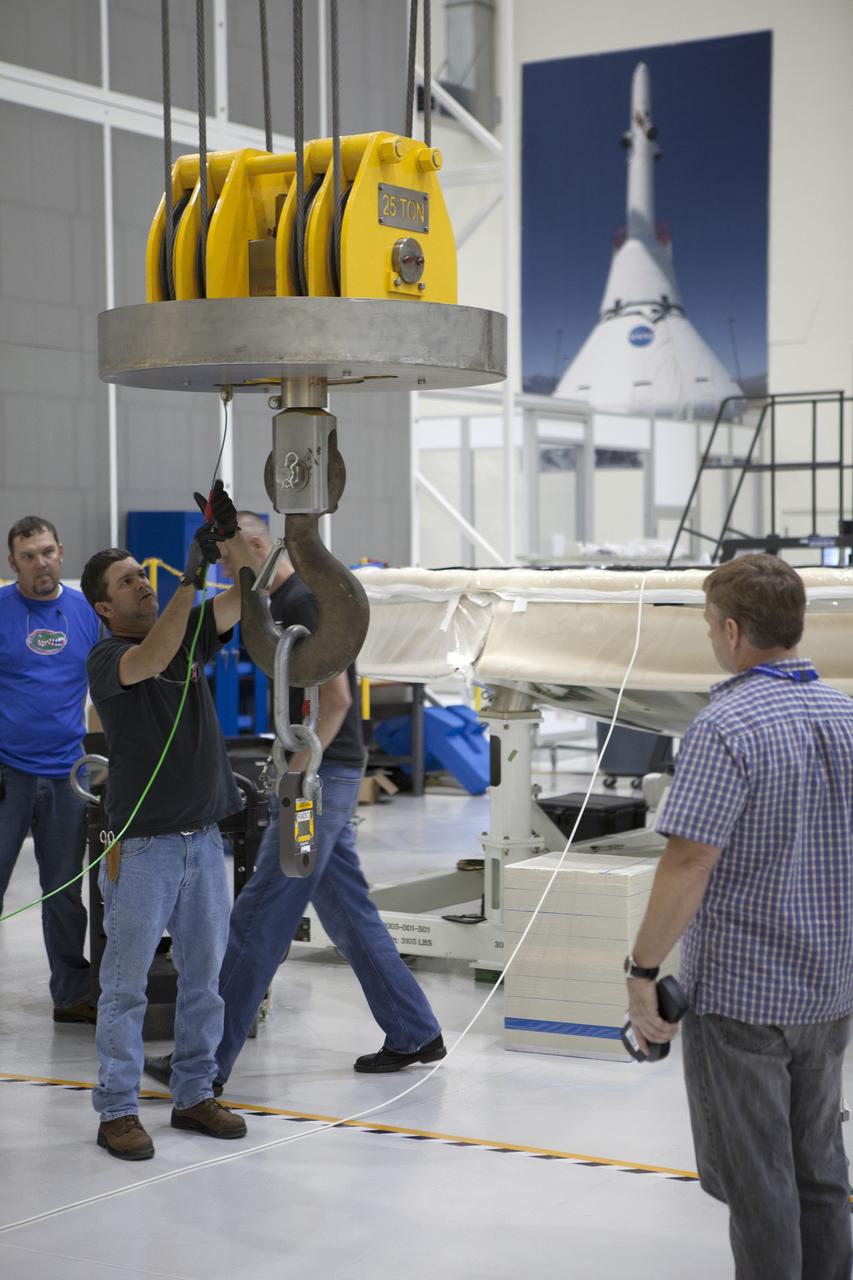

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers prepare a crane that will be used to lift the Orion heat shield inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
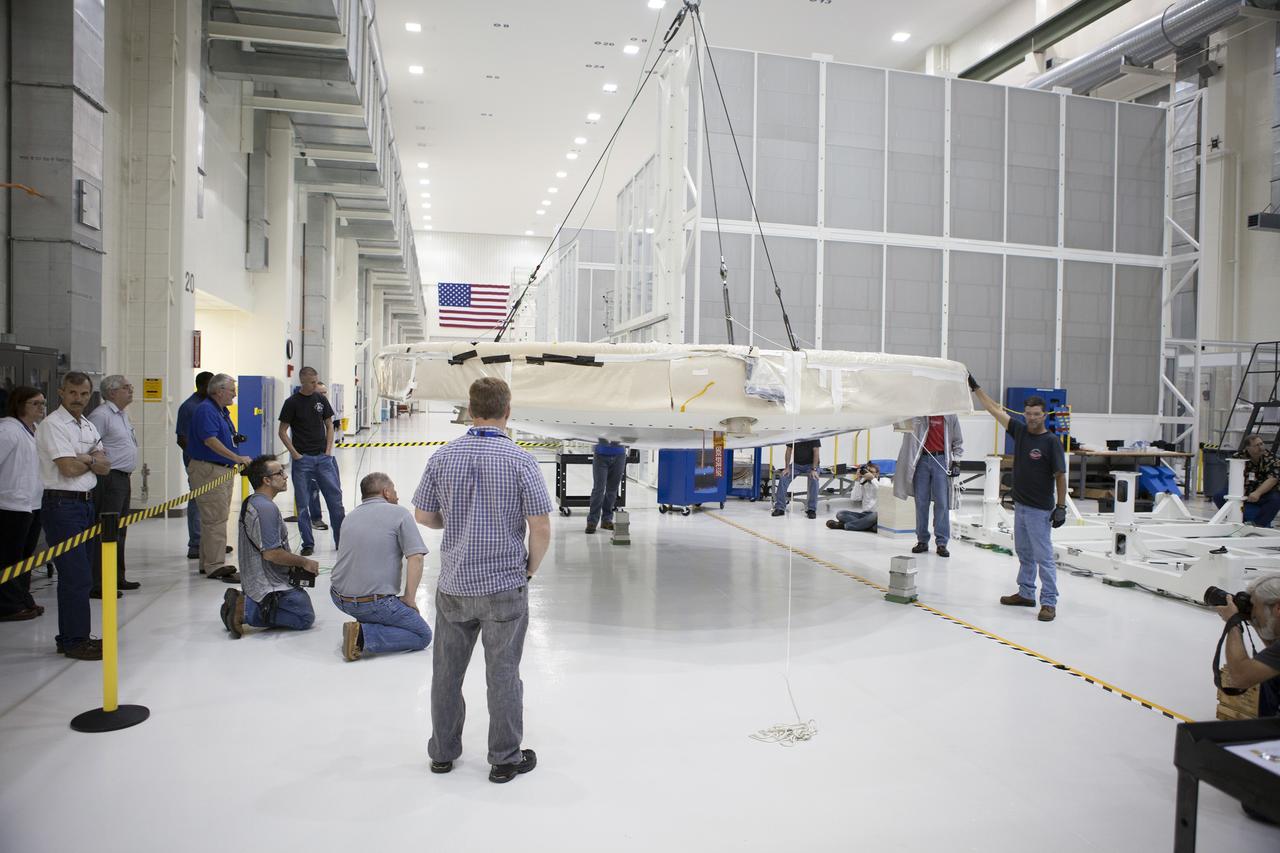

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers monitor the progress as a crane positions the Orion heat shield near the crew module in the high bay. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
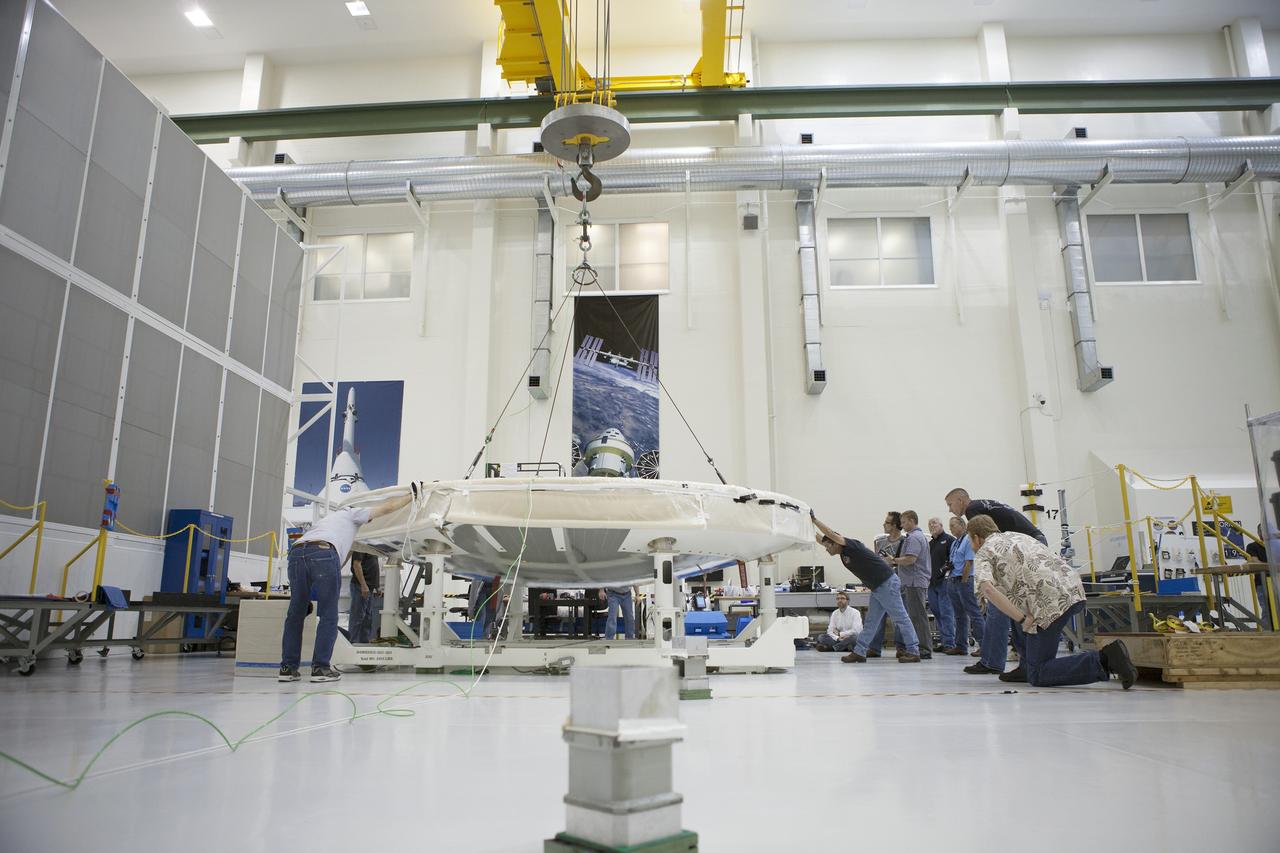

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers monitor the progress and assist as needed as a crane begins to lift the Orion heat shield away from a stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
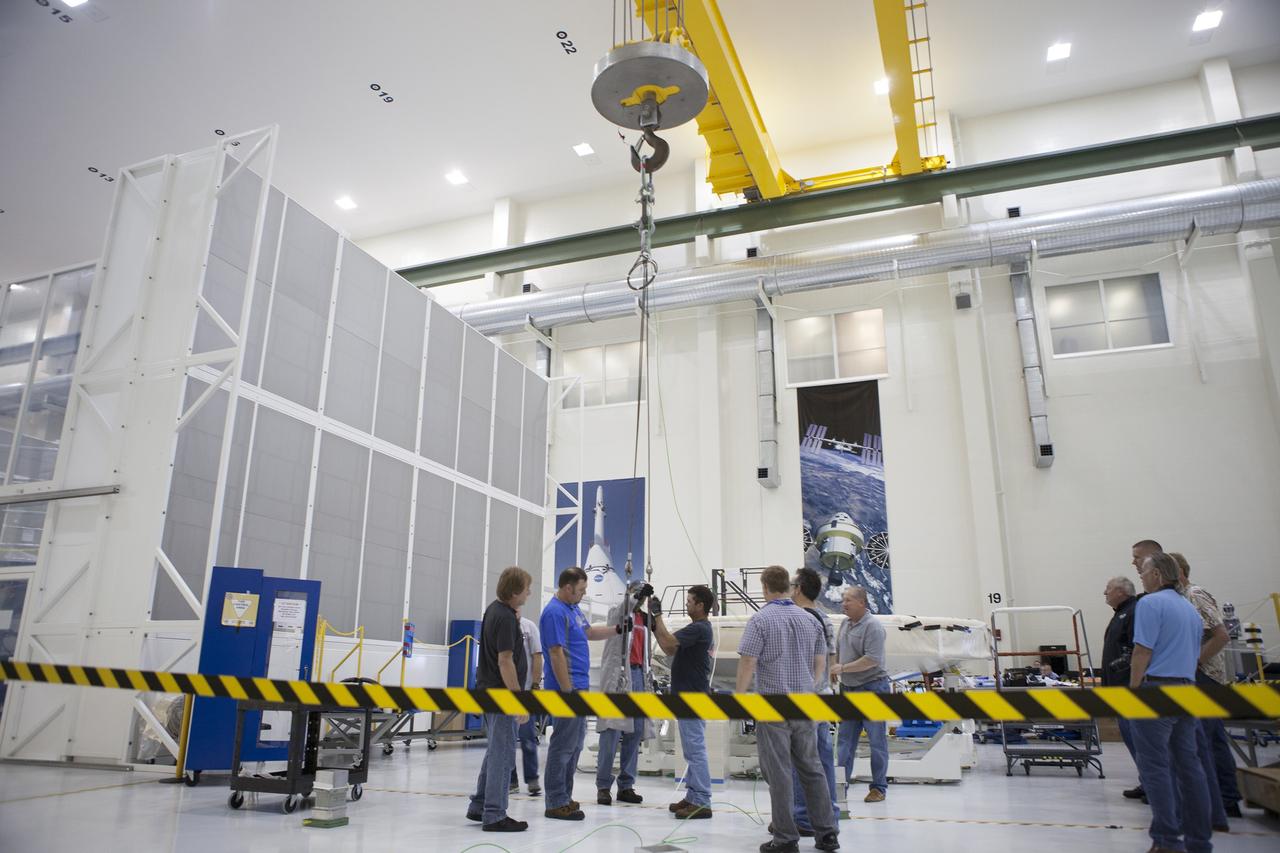

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians attach a crane to the Orion heat shield to prepare to move it away from a stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
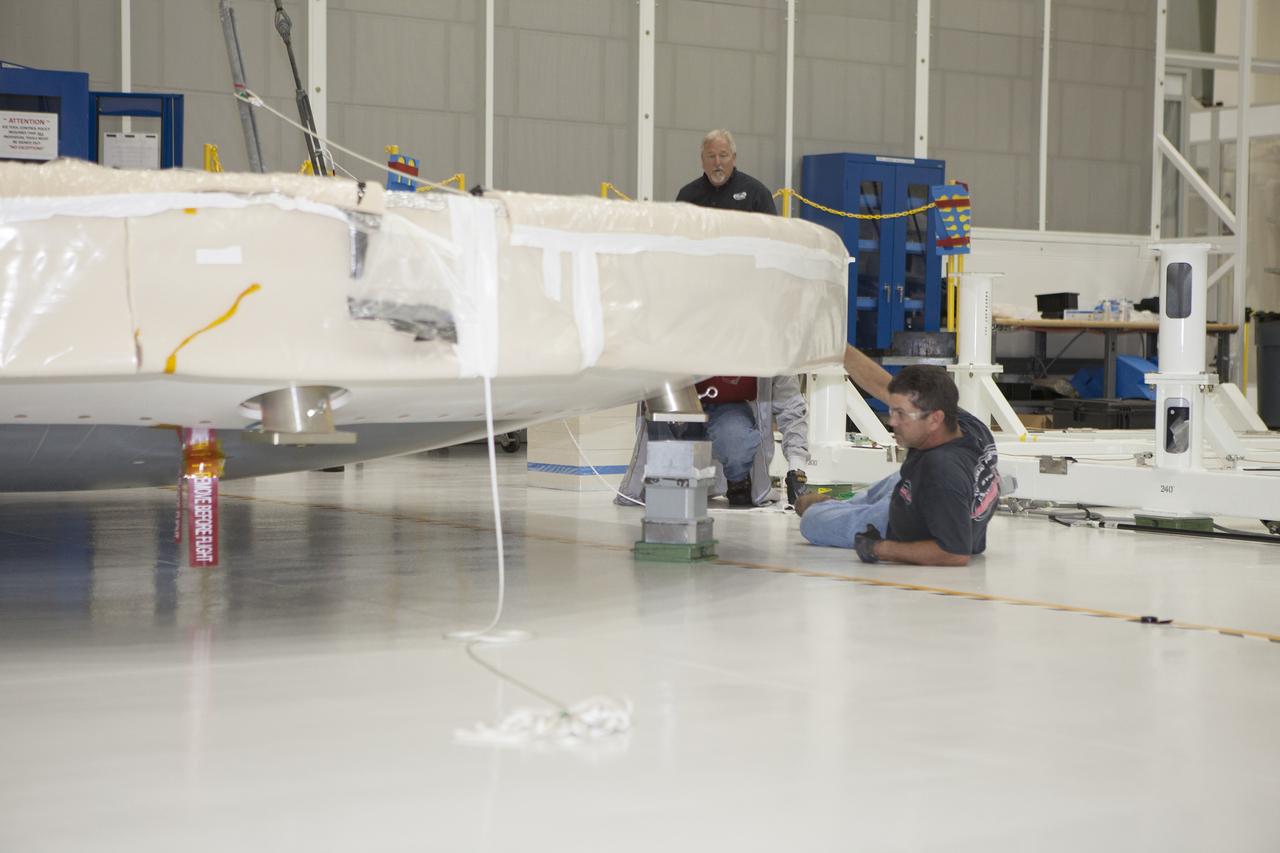

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers closely monitor the progress as a crane lowers the Orion heat shield onto a stand. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
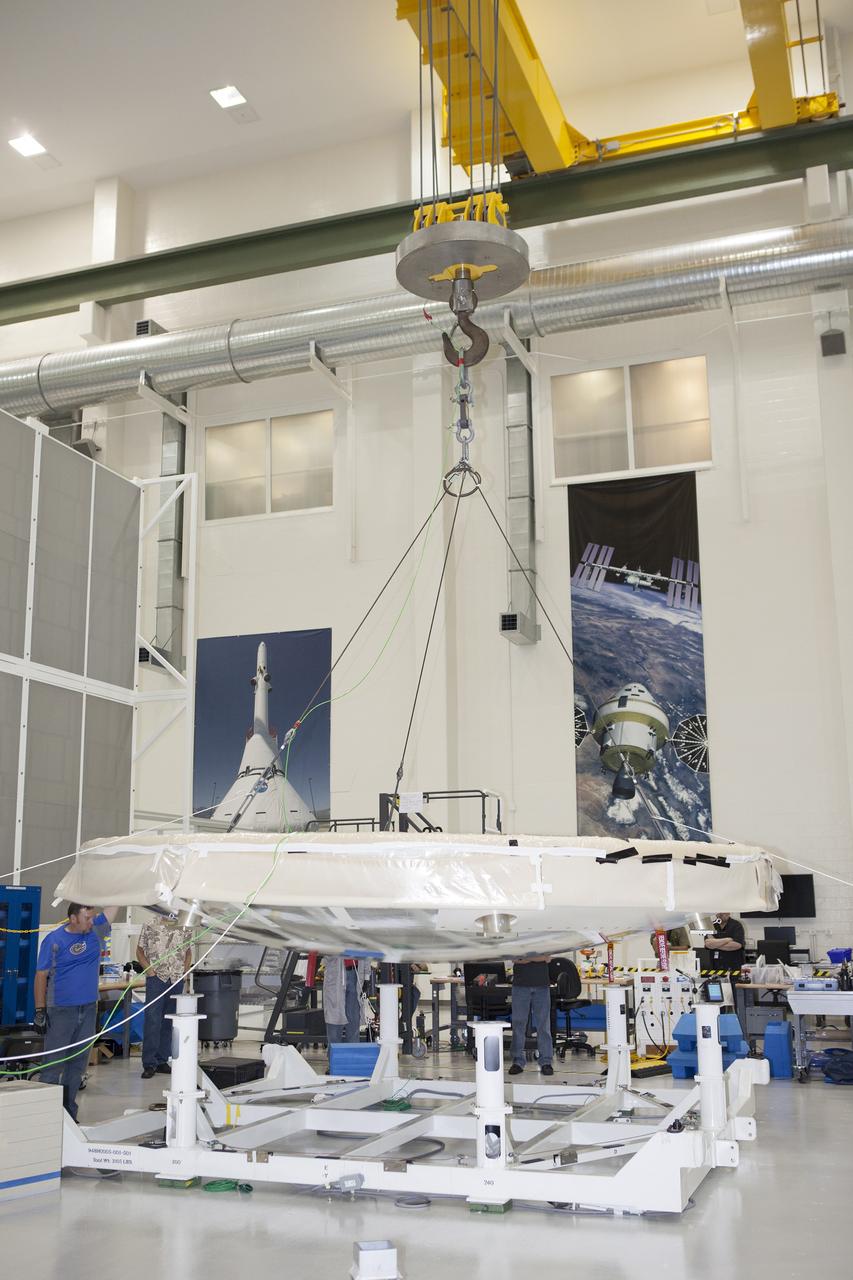

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers monitor the progress as a crane lifts the Orion heat shield away from a stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
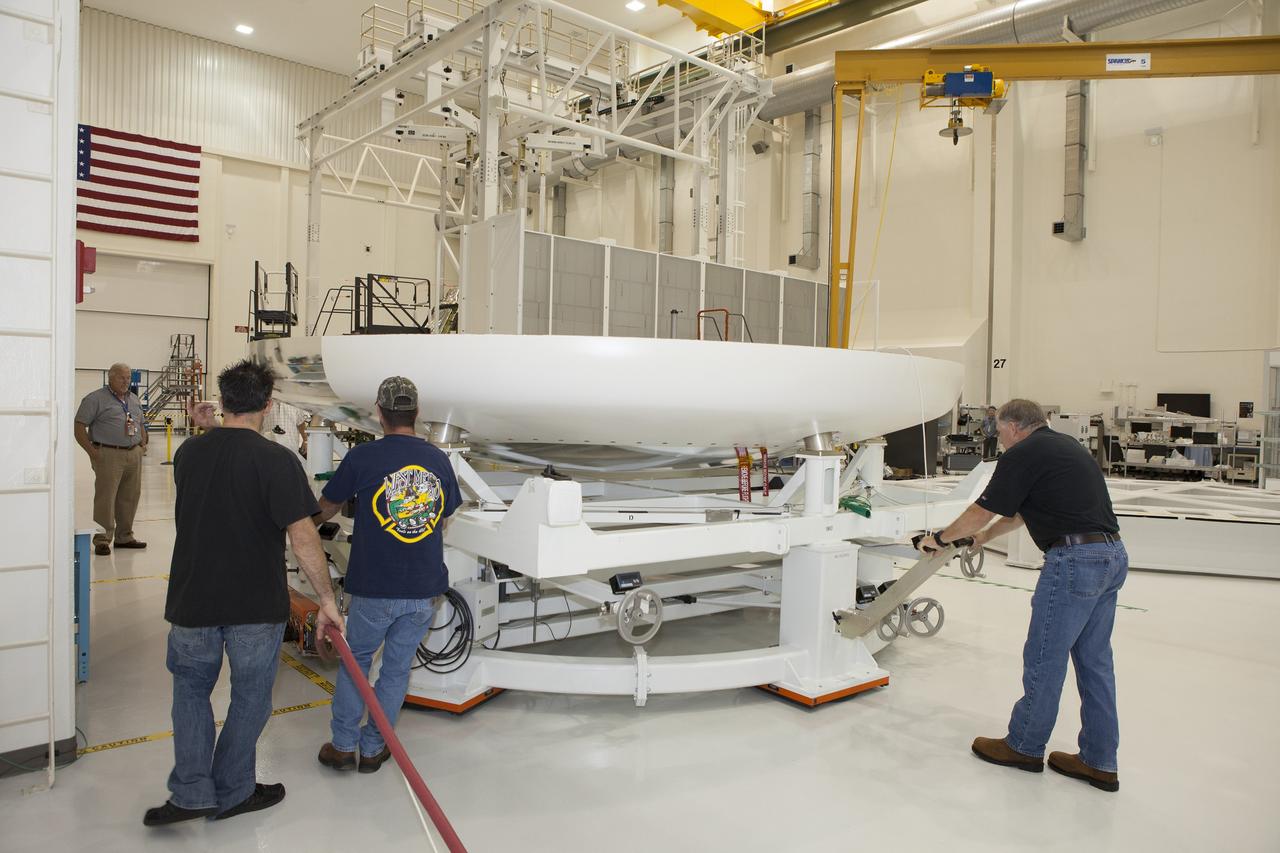

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers move the heat shield for the Orion crew module down the aisle inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
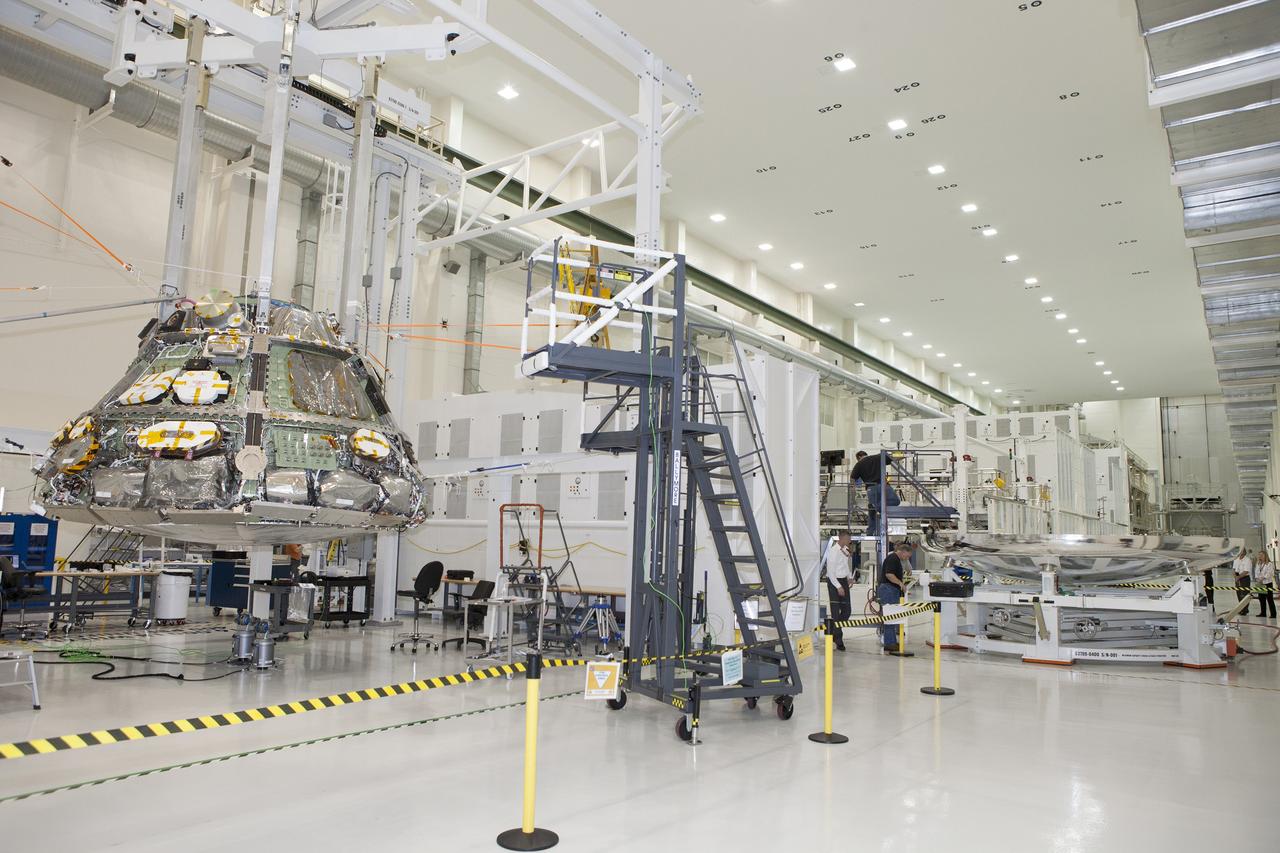

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers have positioned the heat shield near the Orion crew module. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
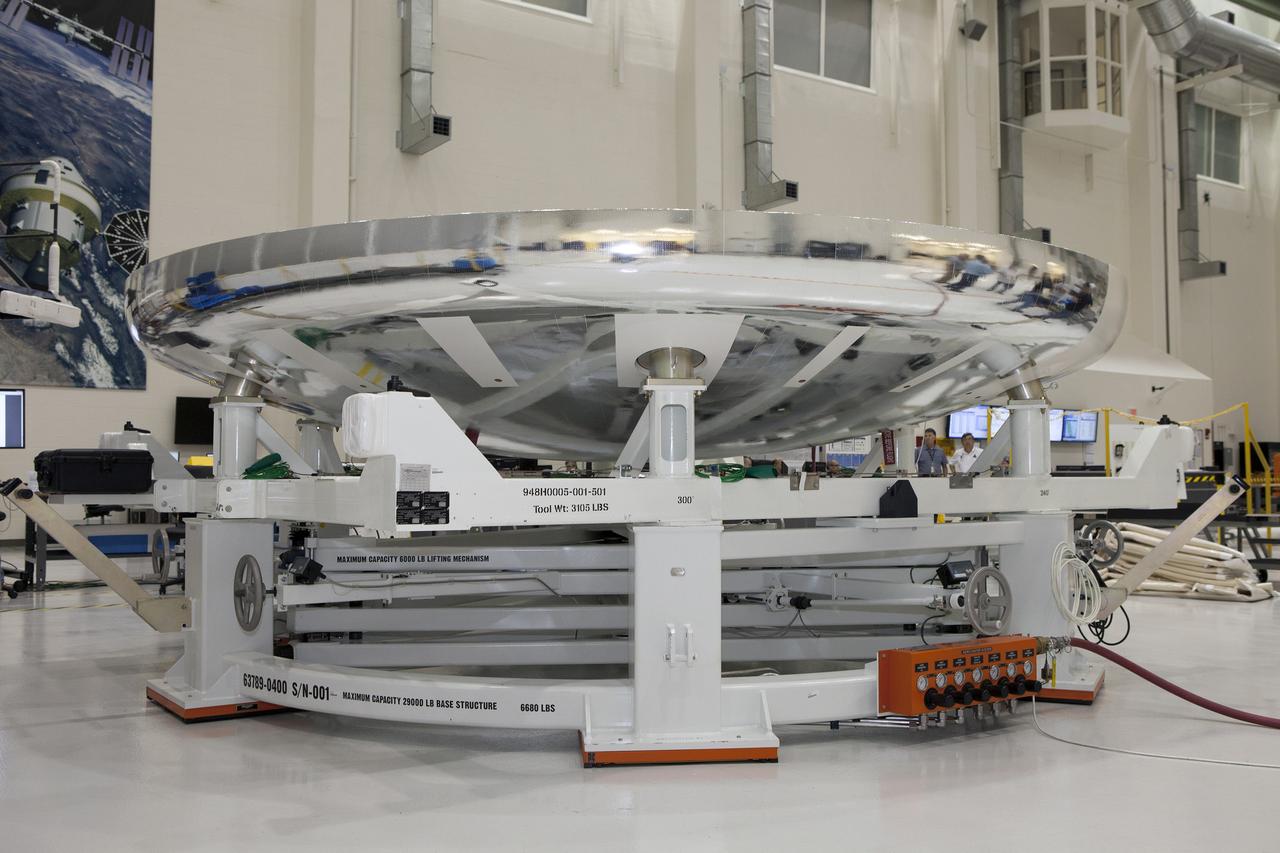

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield for the Orion crew module has been secured in a special work stand inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
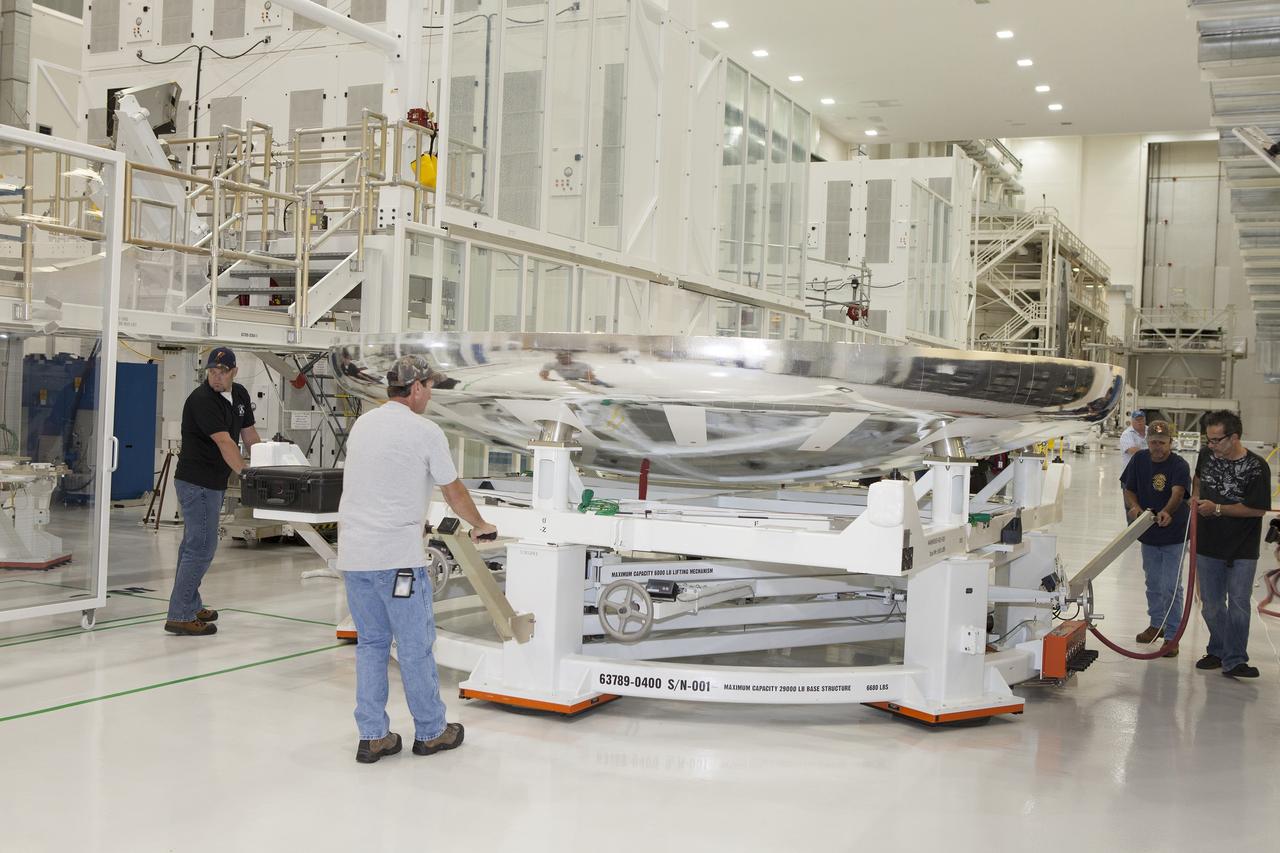

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers move the heat shield for the Orion crew module down the aisle inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation on the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
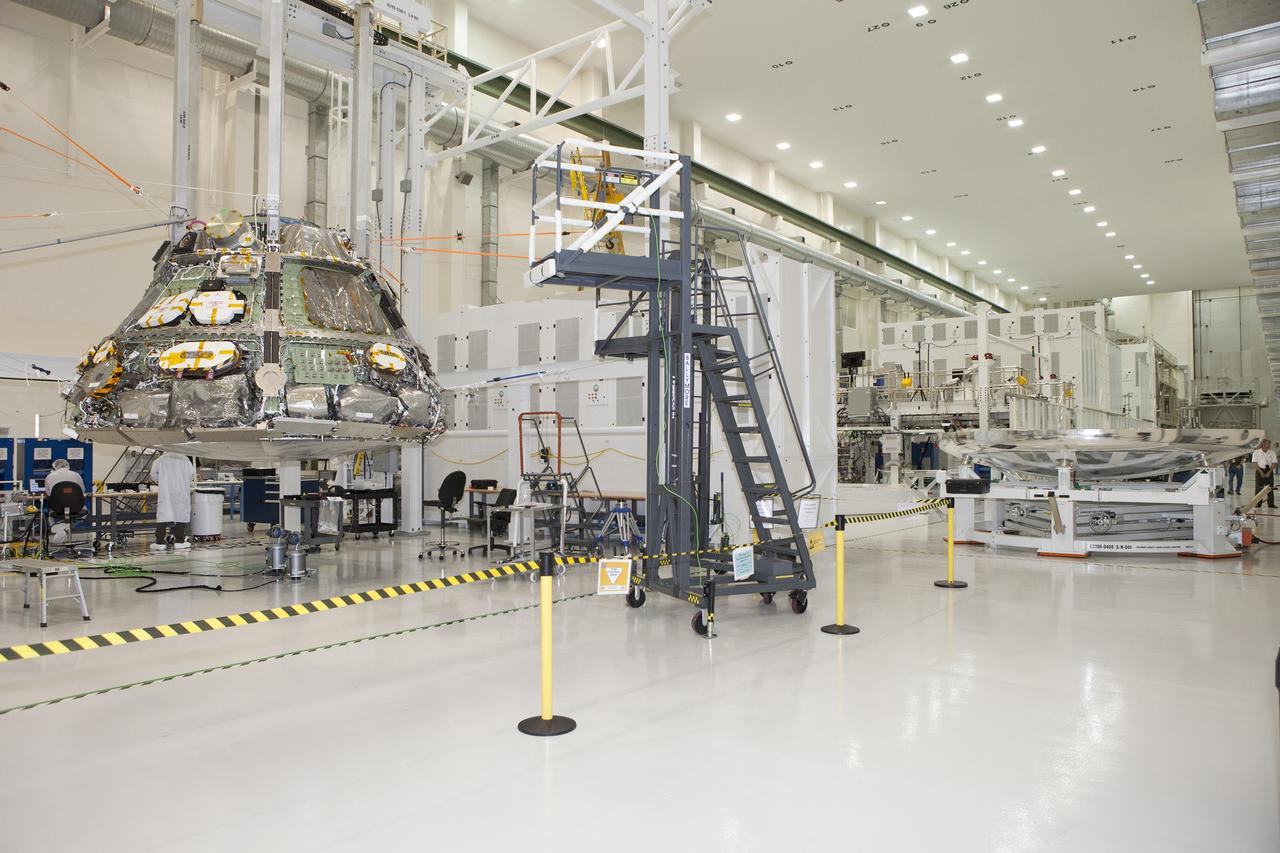

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers have positioned the heat shield near the Orion crew module. Technicians have installed more than 200 instrumentation sensors on the heat shield and are preparing it for installation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
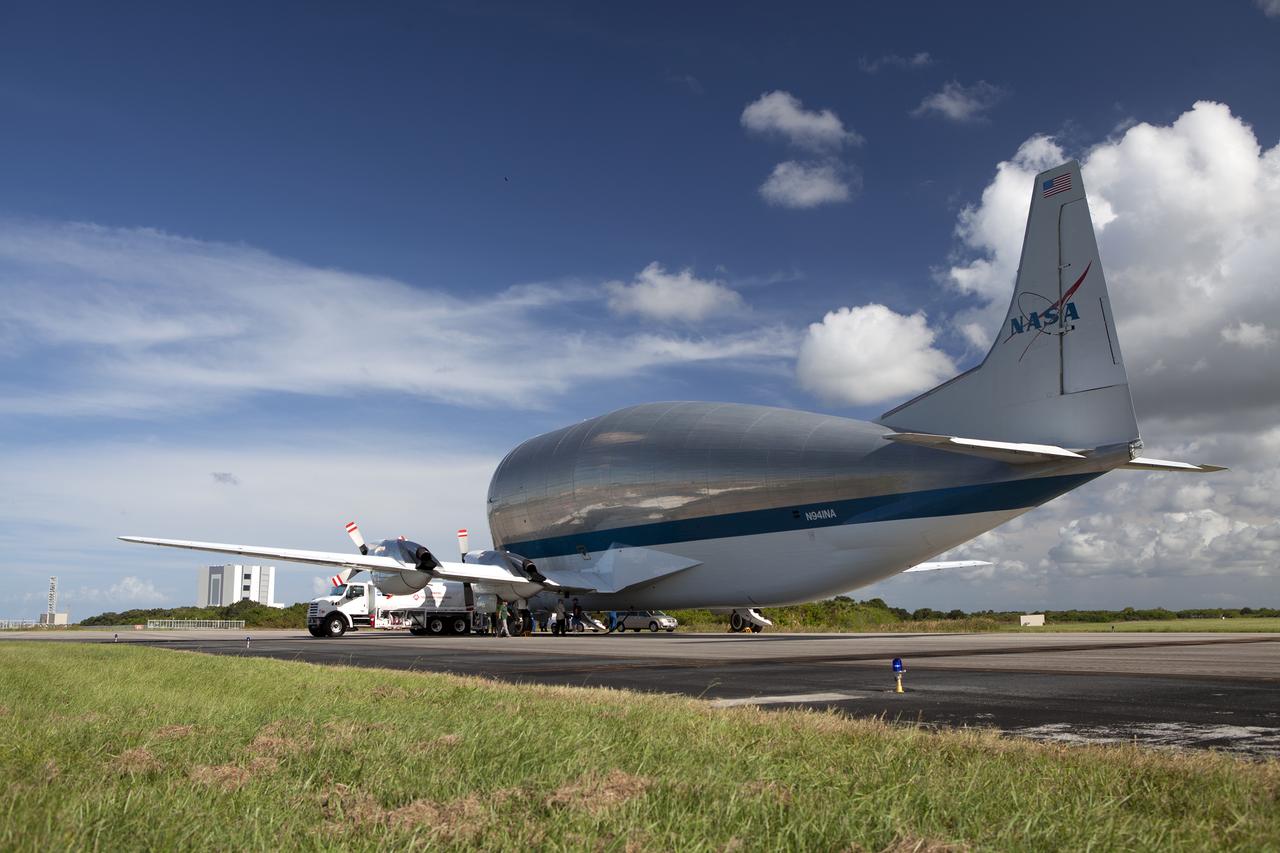

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft touched and came to a stop at the Shuttle Landing Facility, managed and operated by Space Florida, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the heat shield for Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1). The heat shield will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for processing. The heat shield arrived from manufacturer Lockheed Martin in Denver. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, an uncrewed test flight, in 2018.
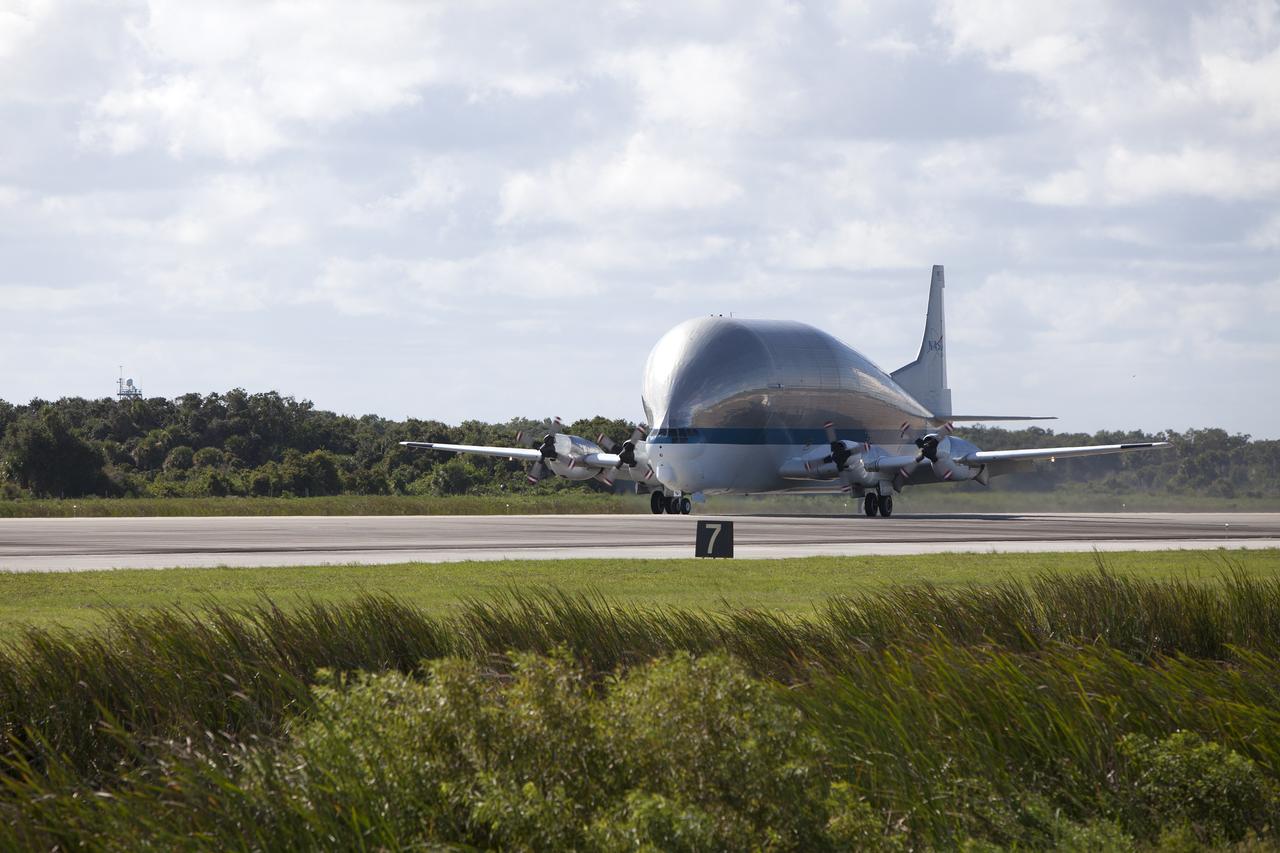

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft touched down at the Shuttle Landing Facility, managed and operated by Space Florida, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the heat shield for Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1). The heat shield will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for processing. The heat shield arrived from manufacturer Lockheed Martin in Denver. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, an uncrewed test flight, in 2018.