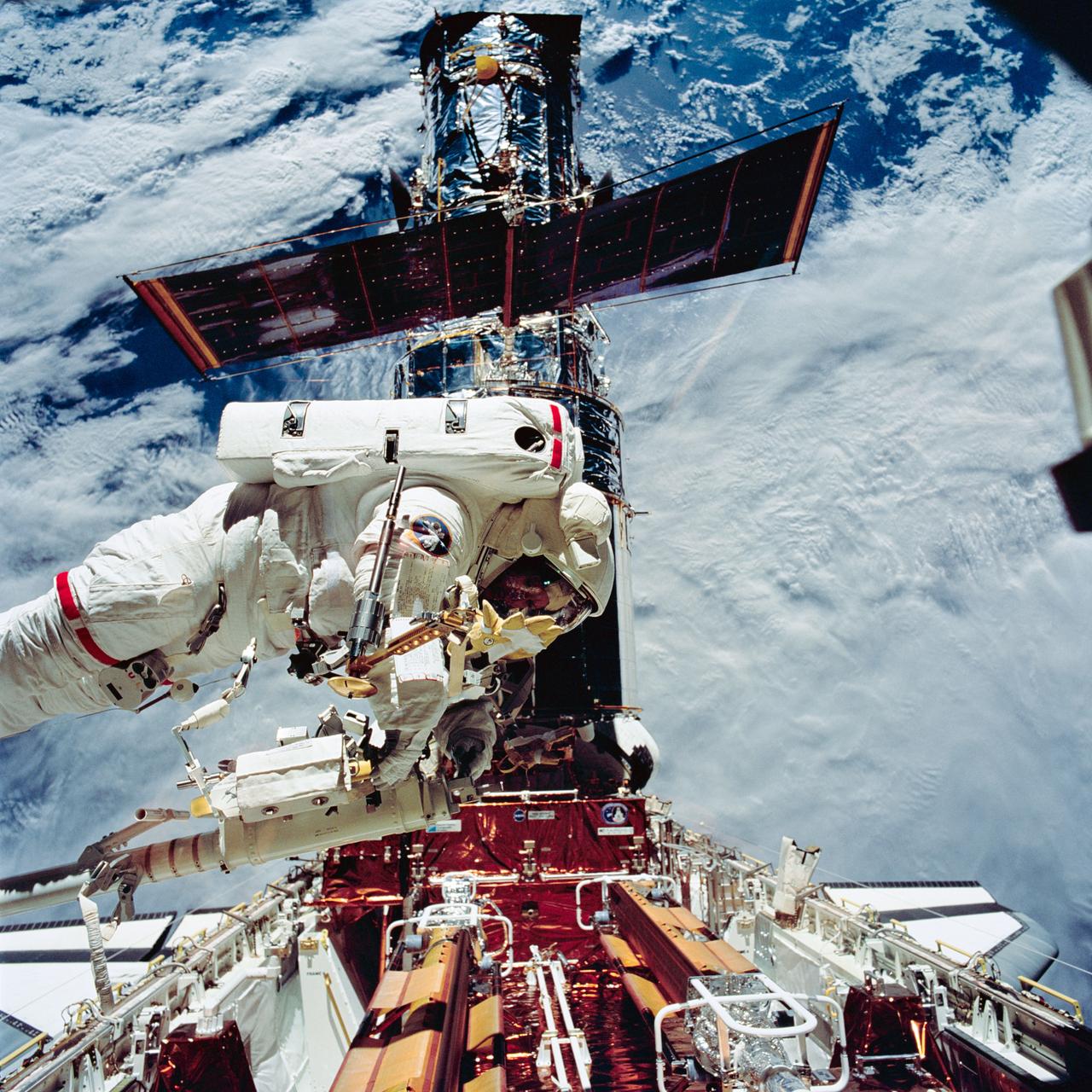

STS061-95-028 (6 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, hovers over equipment associated with servicing chores on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during the second extravehicular activity (EVA) on the eleven-day mission. Astronauts Thornton and Thomas D. Akers changed out the solar array panels during this EVA.
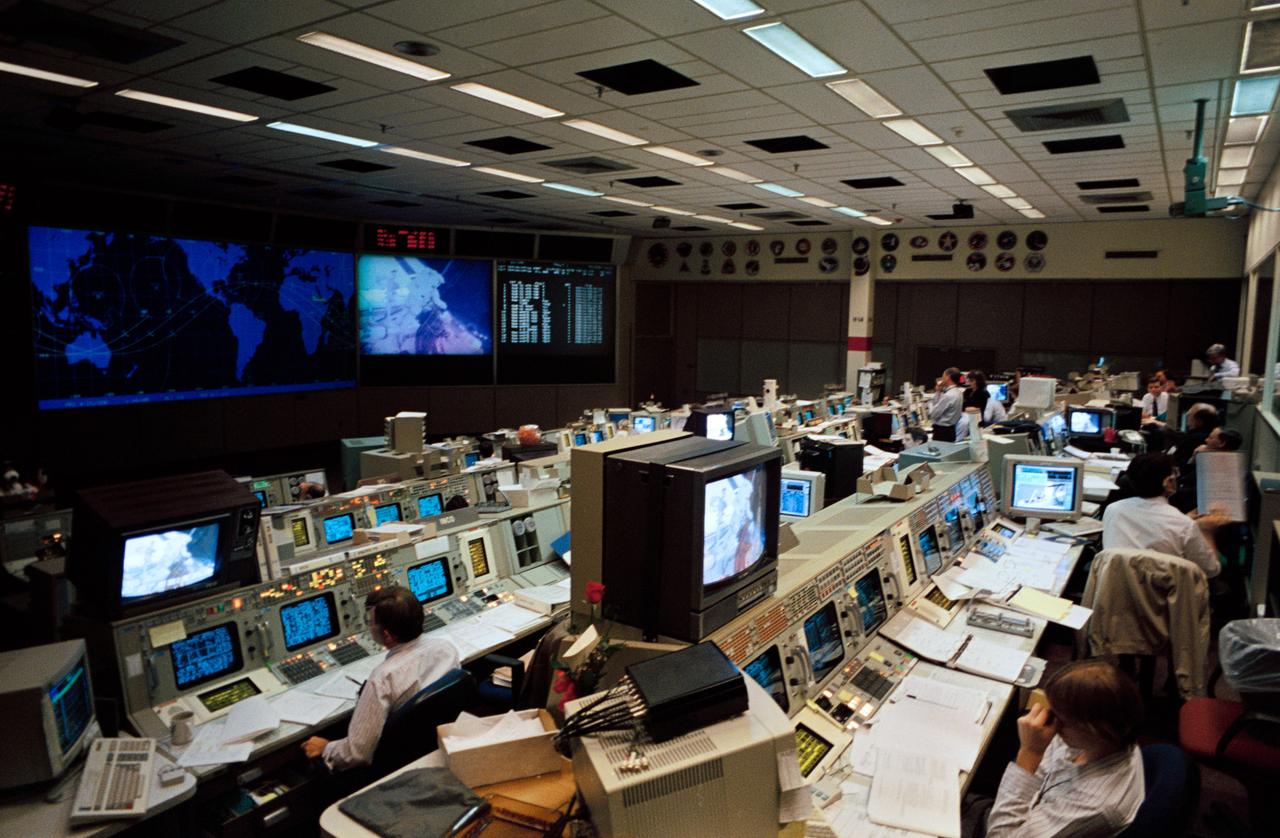

STS61-S-093 (5 Dec 1993) --- Flight controller Kevin McCluney monitors the televised activity of astronauts F. Story Musgrave and Jeffrey A. Hoffman. The veteran astronauts were performing the first extravehicular activity (EVA-1) of the STS-61 Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. McCluney's duties deal with maintenance, mechanical, arm and crew systems, meaning that he and his colleagues will be exceptionally busy for the next five days. Four astronauts in alternating pairs will perform a variety of tasks on the giant telescope during that period.
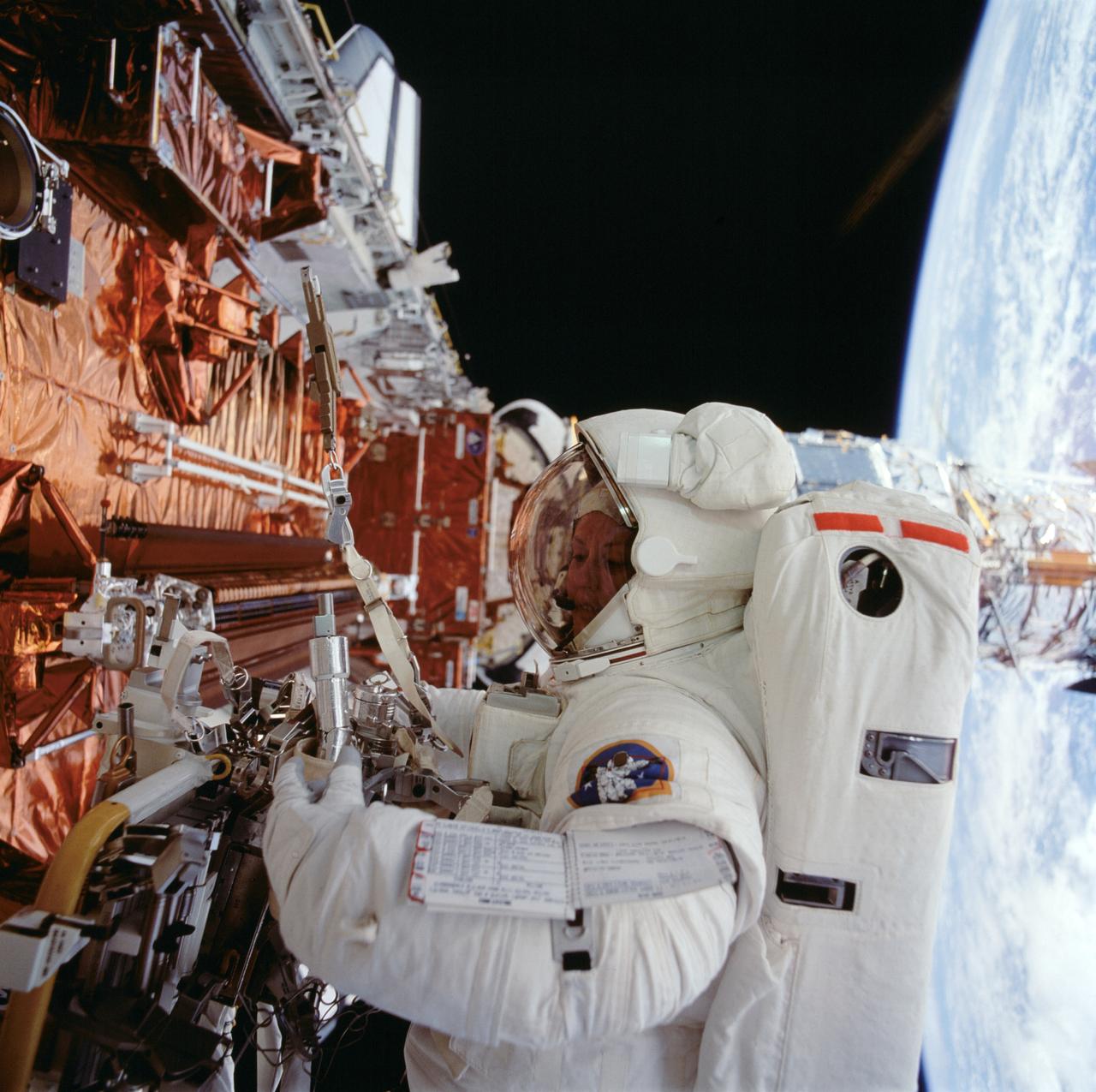

STS061-098-000K (8 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton works with equipment associated with servicing chores on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during the fourth extravehicular activity (EVA) on the eleven-day mission.
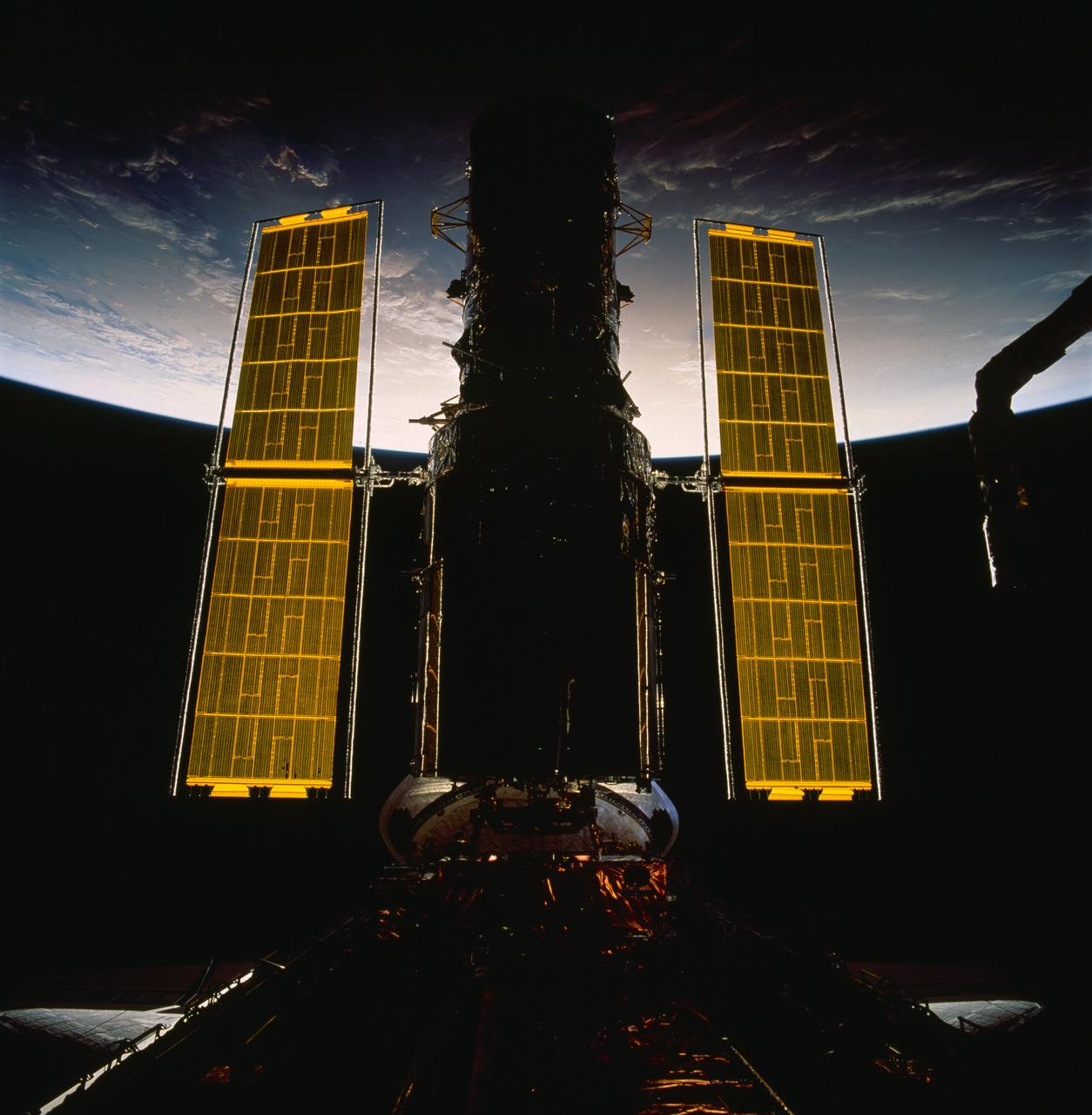

STS061-99-002 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- The new set of solar array panels deployed on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is backdropped against the blackness of space and a widely cloud-covered area on Earth. The 70mm frame was exposed by one of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's seven crew members on the aft flight deck.
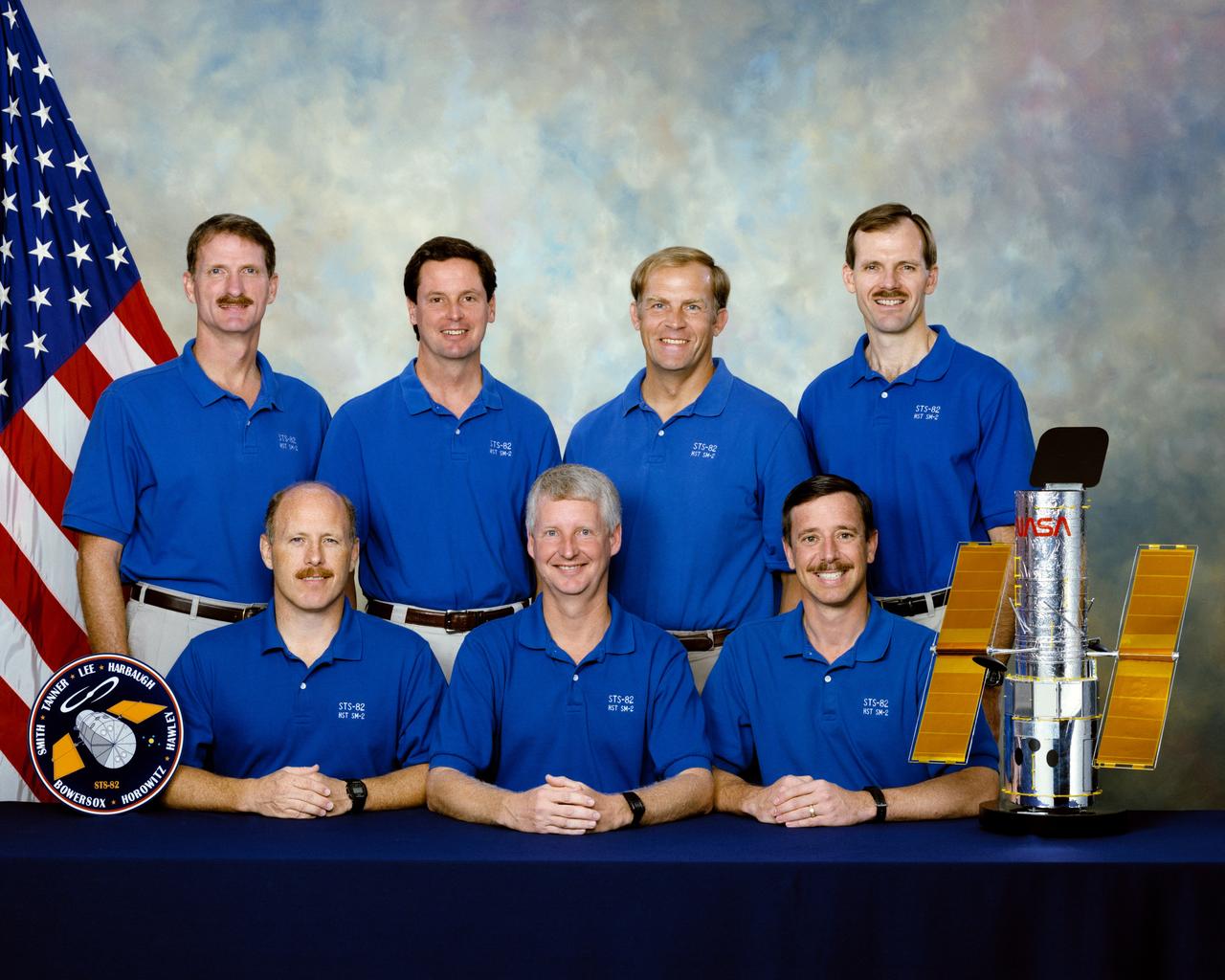

STS082-S-002 (December 1996) --- These seven astronauts are prime crew members for NASA’s STS-82 mission. They are, on the front row, from the left, Kenneth D. Bowersox, Steven A. Hawley and Scott J. Horowitz. On the back row are Joseph R. Tanner, Gregory J. Harbaugh; Mark C. Lee and Steven L. Smith. Bowersox and Horowitz are commander and pilot, respectively, with Lee assigned as payload commander. Hawley, Harbaugh, Smith and Tanner are mission specialists. The seven are pictured with a small model of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), which they will be paying a visit representing the second HST maintenance mission. Bowersox was pilot for the STS-61 mission, which performed the first maintenance on HST. Hawley was a mission specialist on STS-31, the mission whose astronauts originally deployed the HST.

STS061-77-094 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, anchored to the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, prepares to stow the Wide Field\Planetary Camera (WF\PC I) for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), during their extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, stationed at the stowage area at bottom of frame, assists. WF/PC II is in place on the HST.
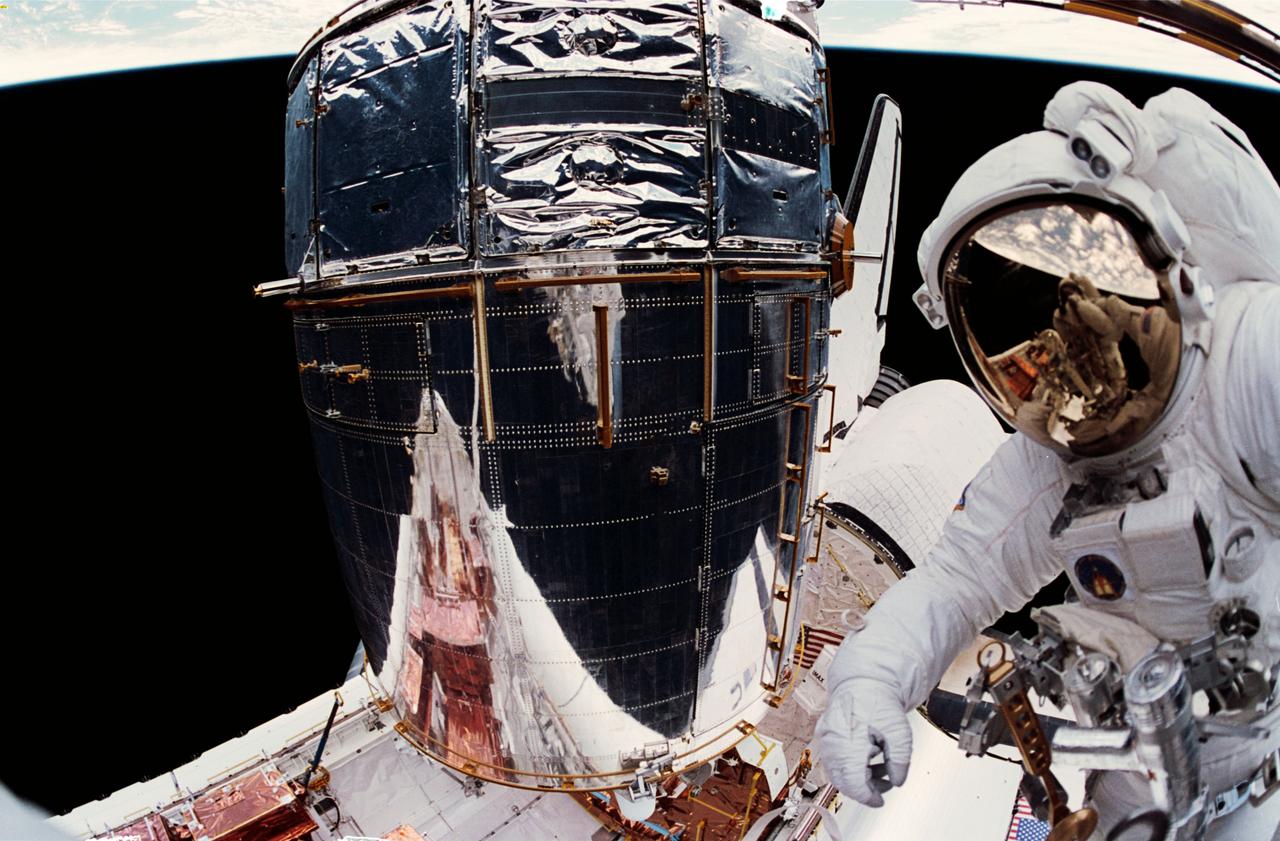

STS061-65-009 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman is reflected in the helmet visor of F. Story Musgrave as he photographs the veteran astronaut during one of the pair's three-shared extravehicular activity?s (EVA).

STS061-77-078 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is pictured with the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC I) during the third of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA). Astronauts Hoffman and F. Story Musgrave, seen near the stowage area for the WF/PC, had earlier installed the new camera (note white rectangle) on lower portion of telescope.
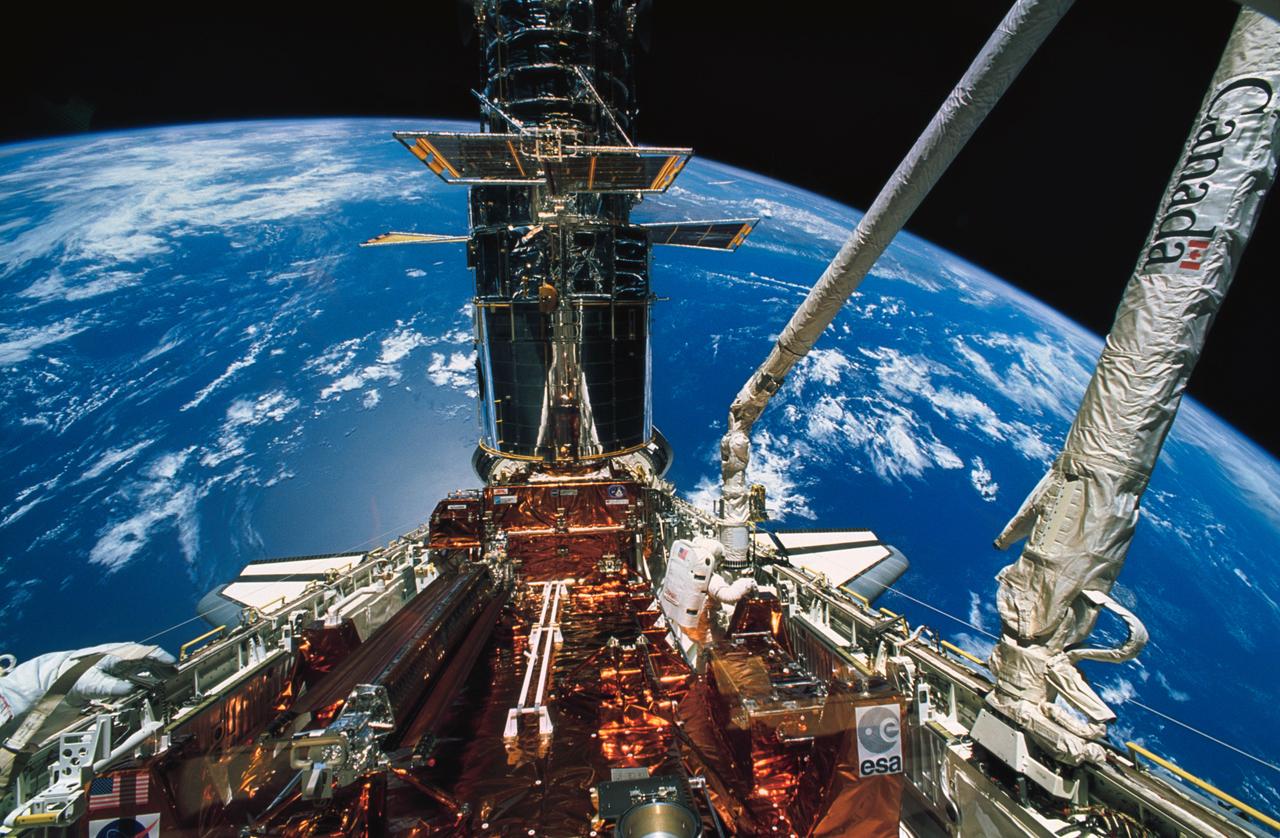

STS061-48-027 (9 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave moves about in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay during the deployment of the solar array panels on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during the final of five STS-61 space walks. The left hand of astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman appears at lower left corner.
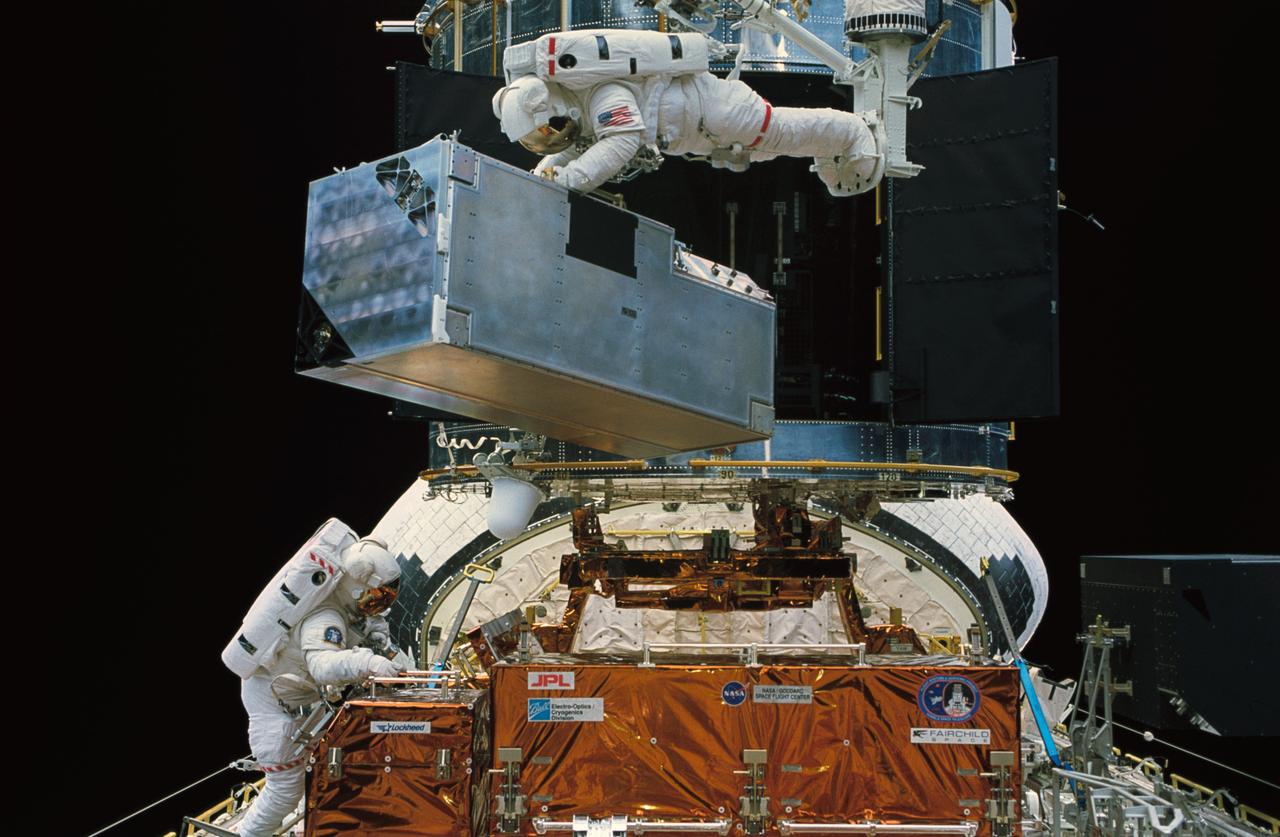
STS061-47-014 (8 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton lifts the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) prior to its installation on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Thornton is anchored to a foot restraint on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. Astronaut Thomas D. Akers, who assisted in the COSTAR installation, is at lower left.
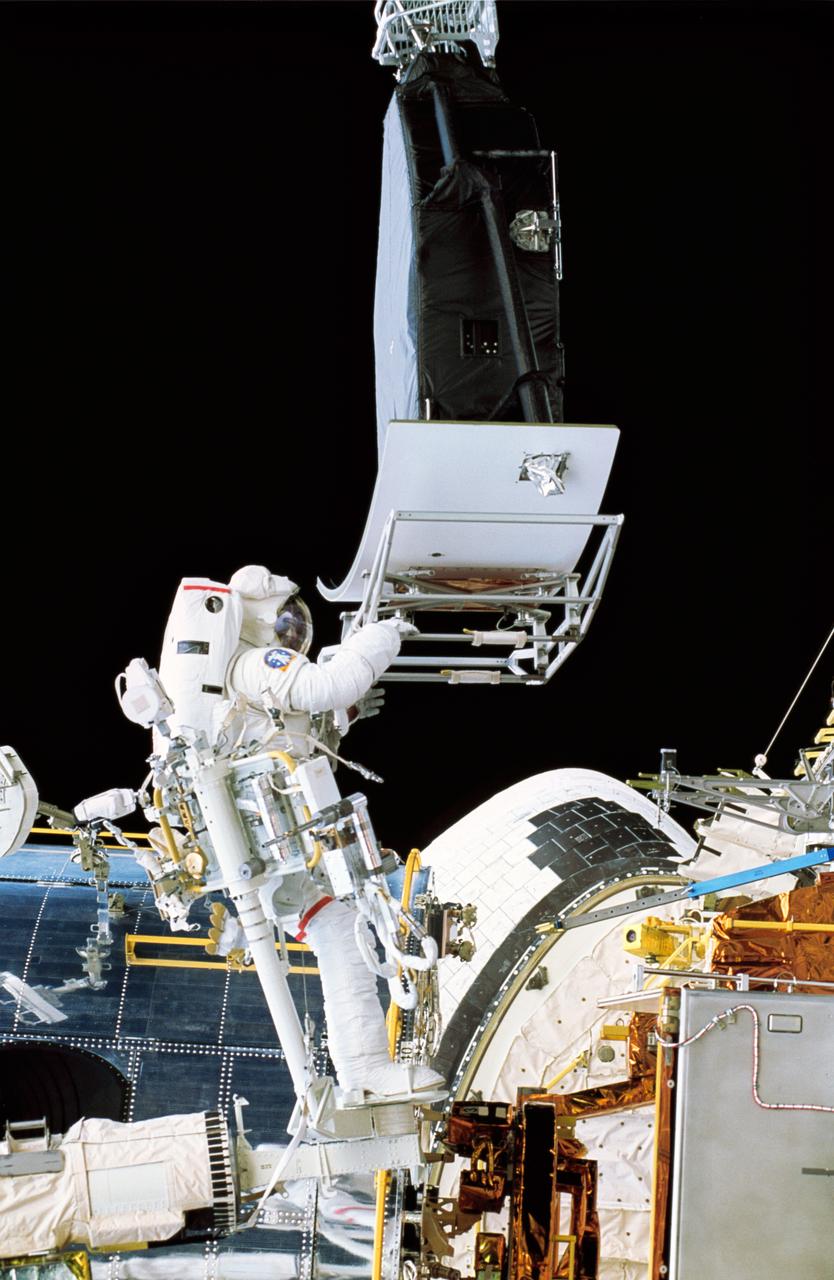

STS061-37-011 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman with Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC 1) during changeout operations. WF/PC-2 has already been installed in cavity (out of frame). Astronauts Hoffman and Story Musgrave are performing Extravehicular Activities (EVA) to repair the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
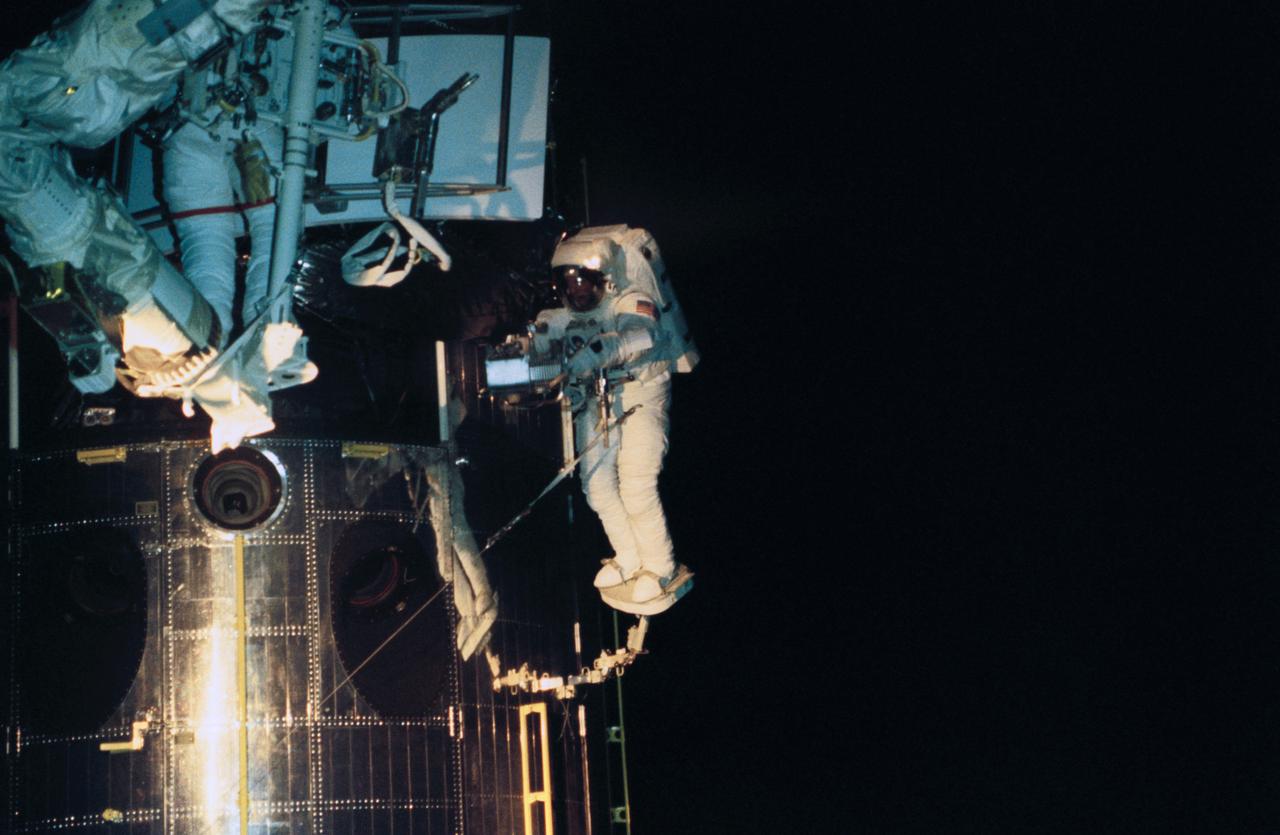

STS061-58-033 (7 Dec 1993) --- Anchored to the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman works with the replacement Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC II) for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during the third of five space walks. Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, who joined Hoffman for three of the five space walks, helps with alignment at center frame.
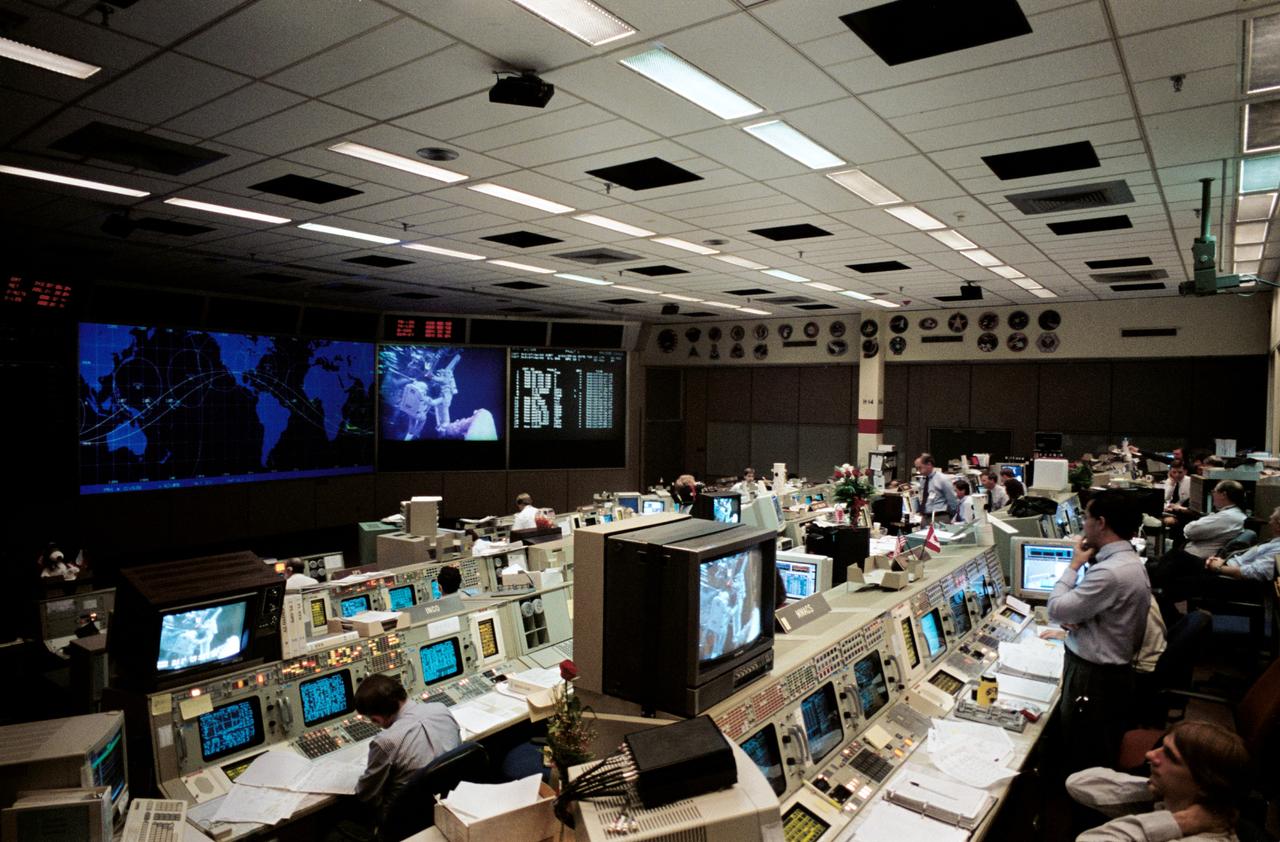

STS061-S-102 (5 Dec. 1993) --- Flight controllers Harry Black (left foreground) and Kevin McCluney (right foreground) monitor the televised activity of two space walkers during the first STS-61 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts F. Story Musgrave and Jeffrey A. Hoffman were performing a variety of equipment replacements. At the Integrated Communications Officer Console (INCO) Black plays a roill in controlling the TV while McLuney's duties deal with maintenance, mechanical, arm and crew systems, meaning that they and their colleagues will be busy for the next five days. Four astronauts in alternating pairs will perform a variety of tasks on the giant telescope during that period.
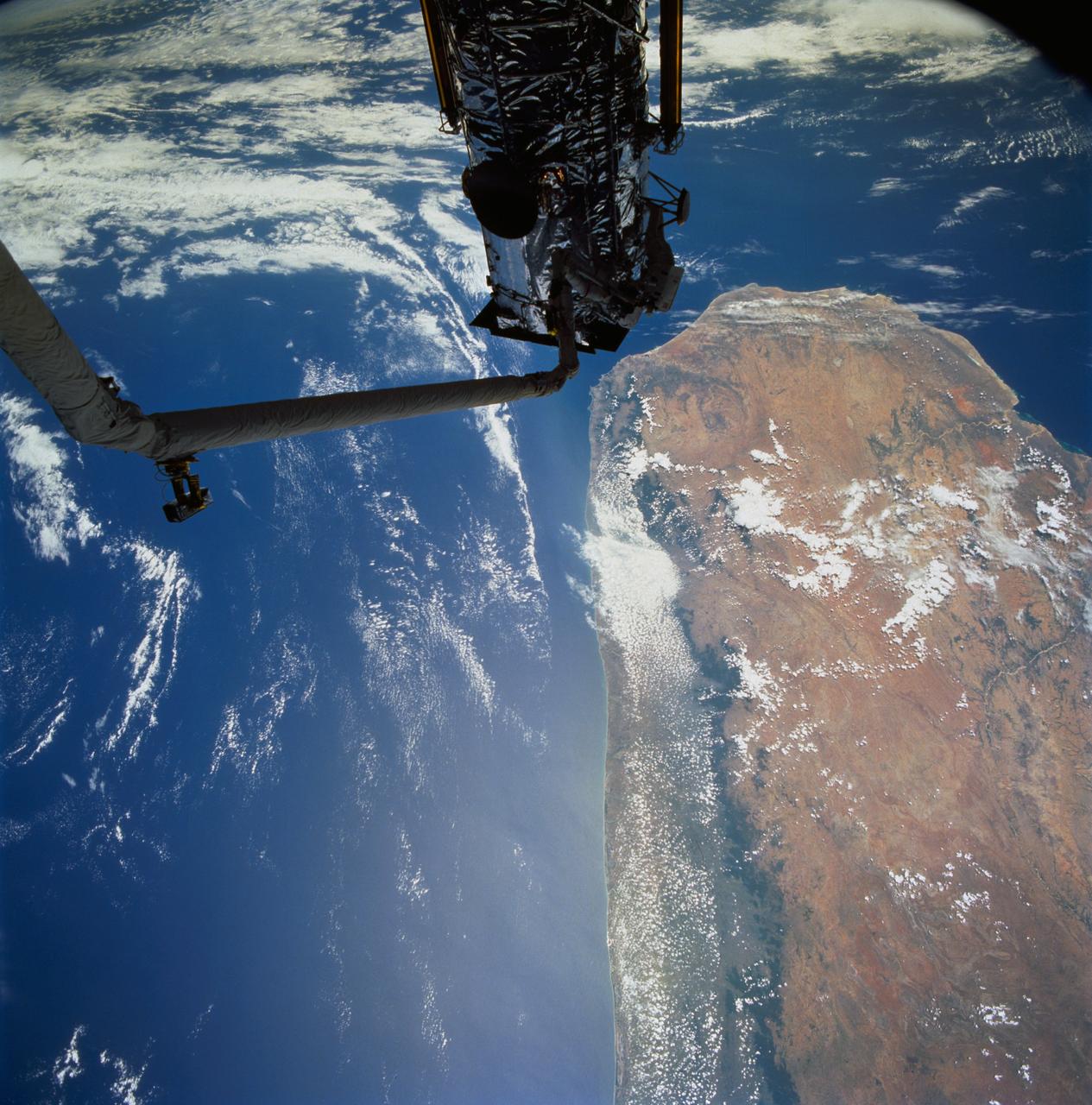

STS061-77-102 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (left) and F. Story Musgrave are partially silhouetted against the Indian Ocean as they work to install the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Musgrave is anchored to the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The HST is positioned along the southern end of Madagascar, 325 nautical miles away. Visible on the western coast are the sediment laden Onilahy and Fiherenana Rivers which empty into Saint Augustin Bay. North of Fiherenana River is the Mangoky River. The circular feature on the southern end of Madagascar and to the right of HST is the L'ivakoany Mountains. The eastern coast is relatively straight compared to the western coast.
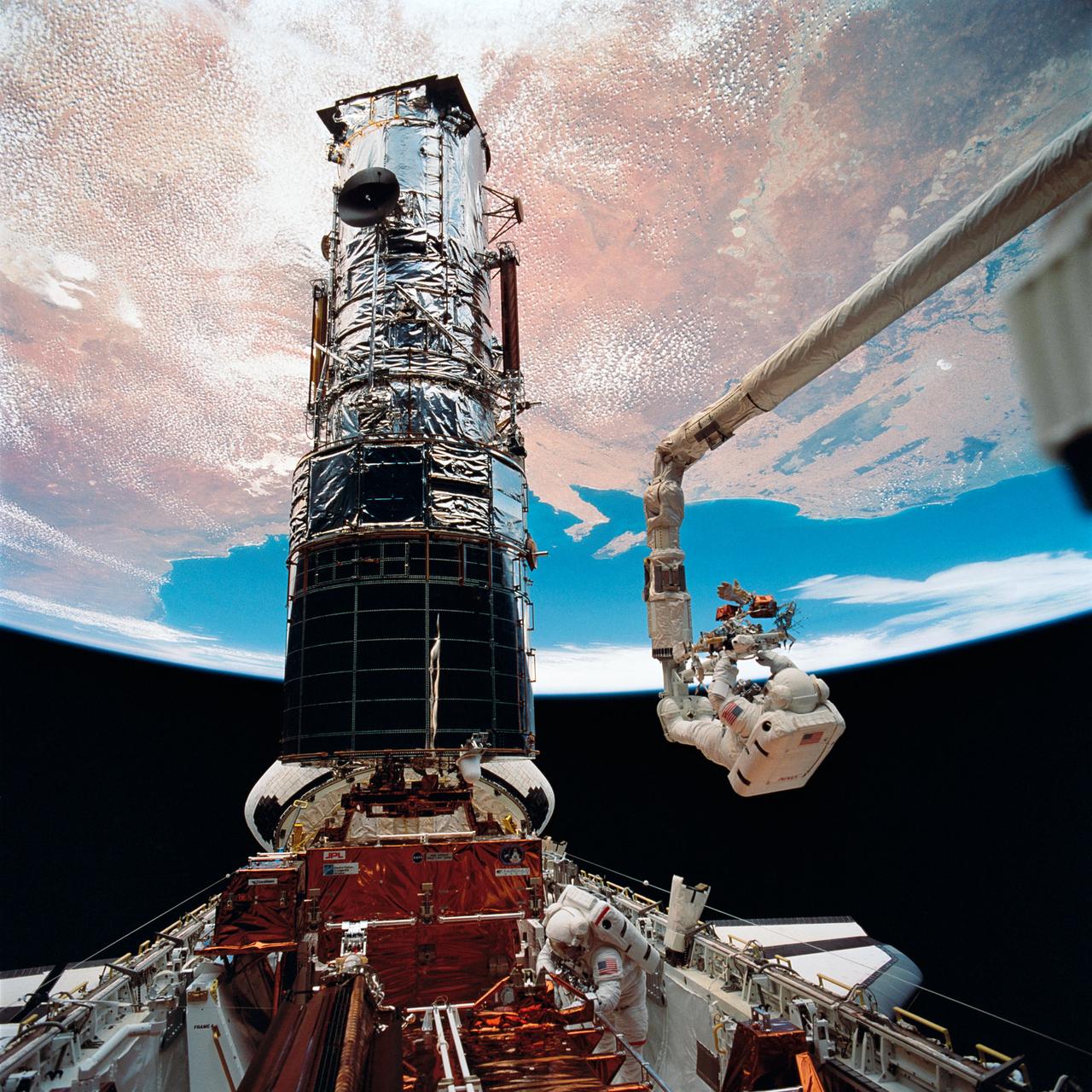

STS061-98-050 (9 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, prepares to be elevated to the top of the towering Hubble Space Telescope (HST) to install protective covers on magnetometers. Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman (bottom of frame) assisted Musgrave with final servicing tasks on the telescope, wrapping up five days of extravehicular activities (EVA).
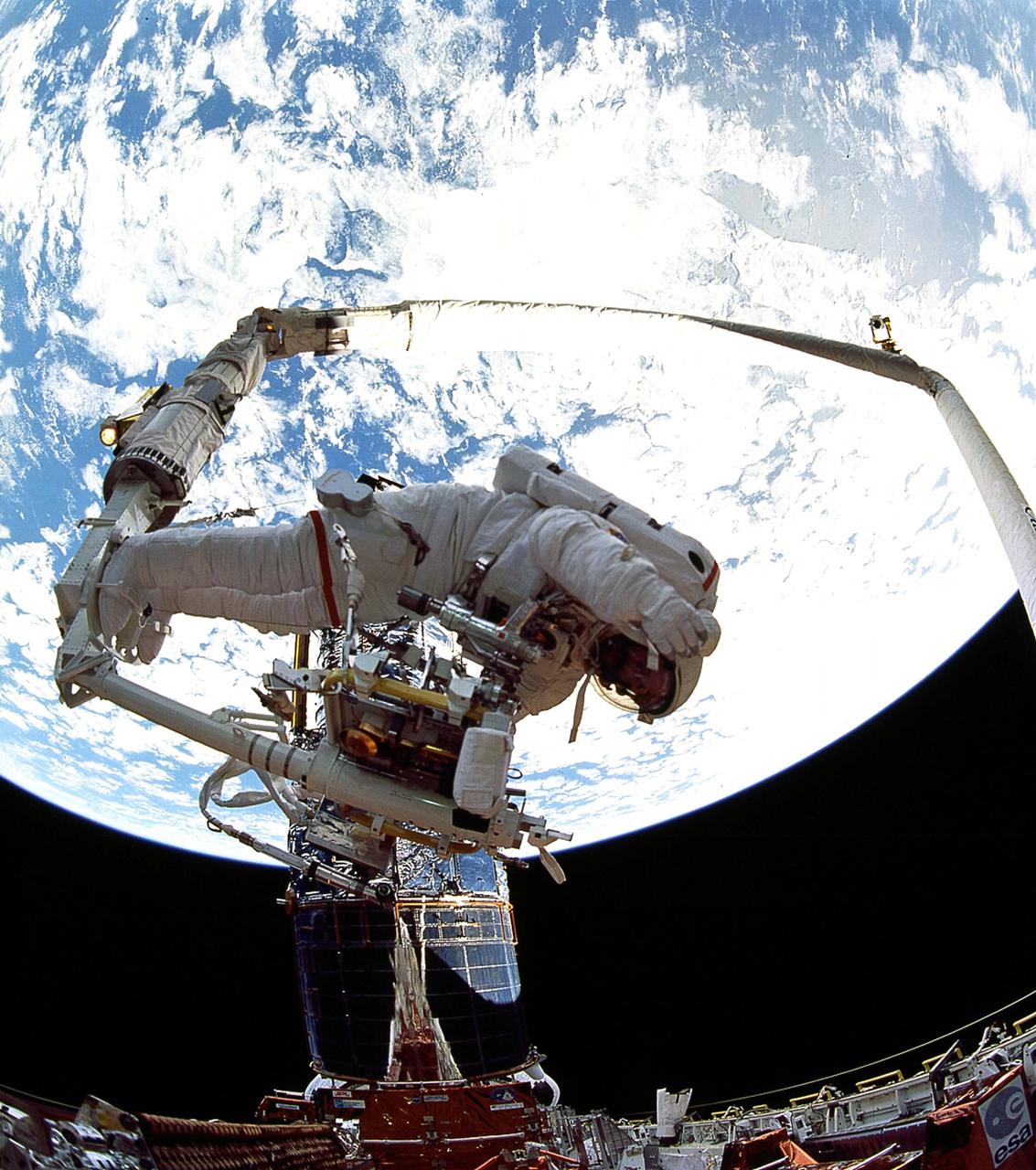

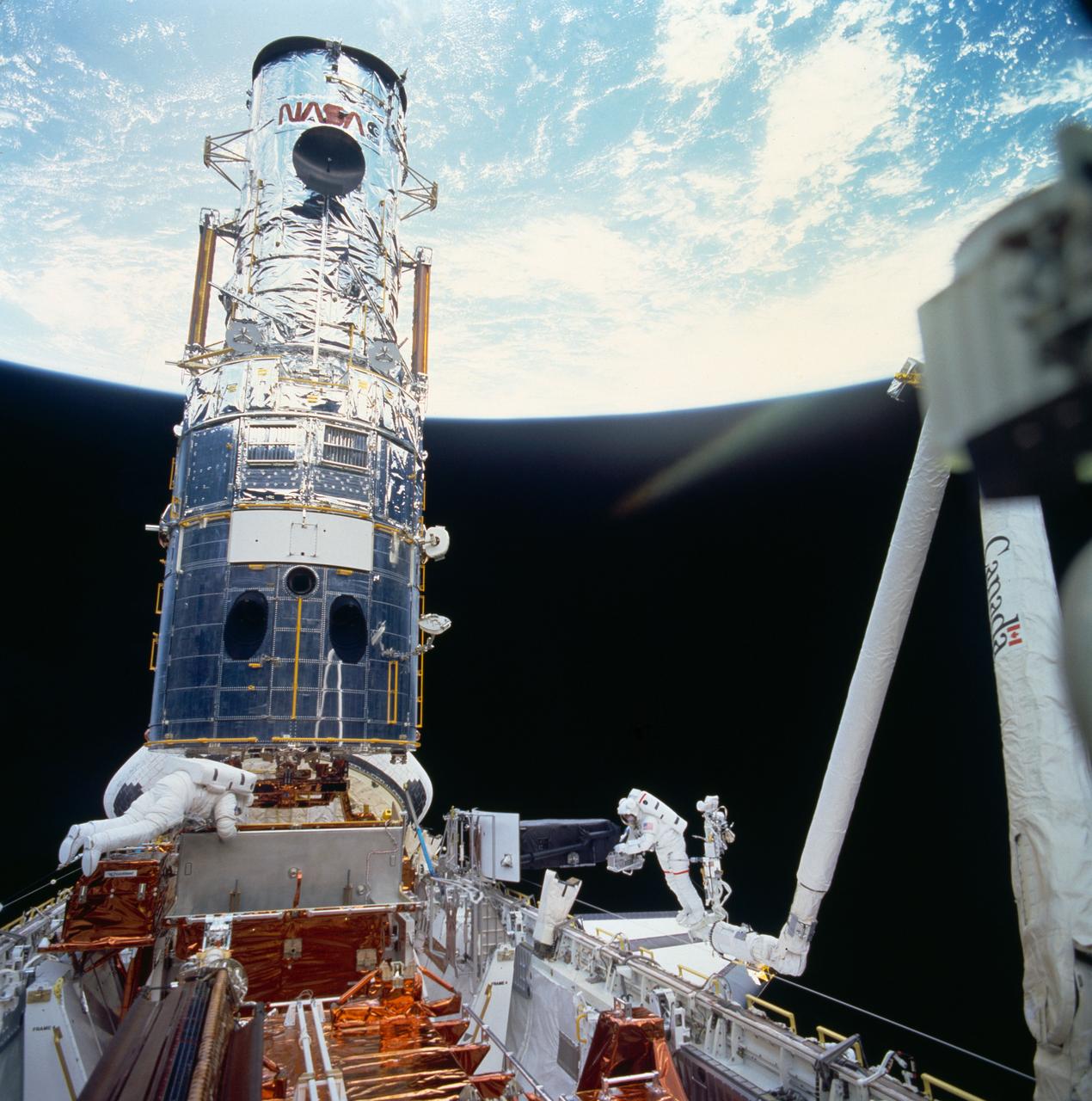
STS061-105-026 (7 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman signals directions to European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Claude Nicollier, as the latter controls the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm during the third of five Extravehicular Activities (EVA) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. Astronauts Hoffman and F. Story Musgrave earlier changed out the Wide Field\Planetary Camera (WF\PC).
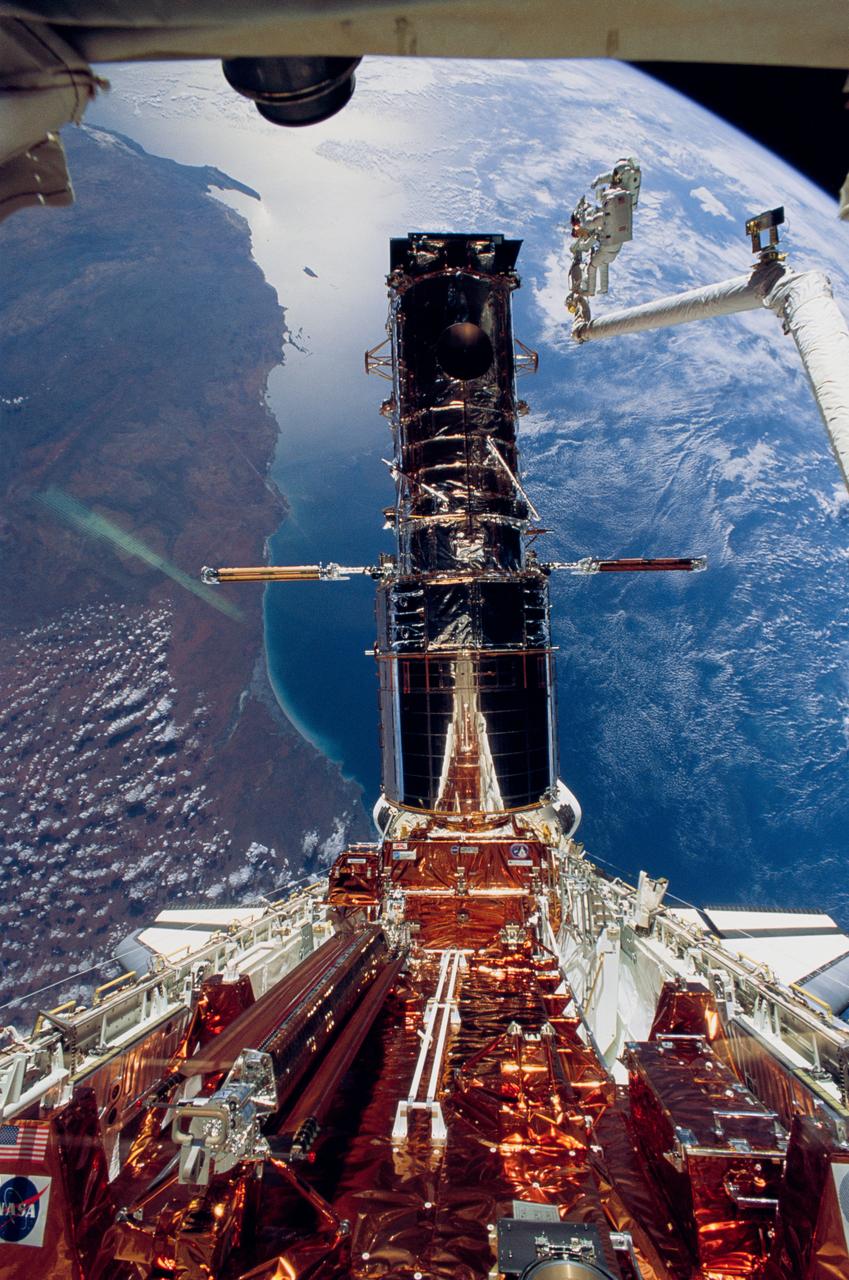

STS061-48-001 (9 Dec 1993) --- Orbiting Earth at an altitude of 356 nautical miles perched atop a foot restraint on the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, astronauts F. Story Musgrave (top) and Jeffrey A. Hoffman wrap up the final of five Extravehicular Activities (EVA). The west coast of Australia forms the backdrop for the 35mm frame.
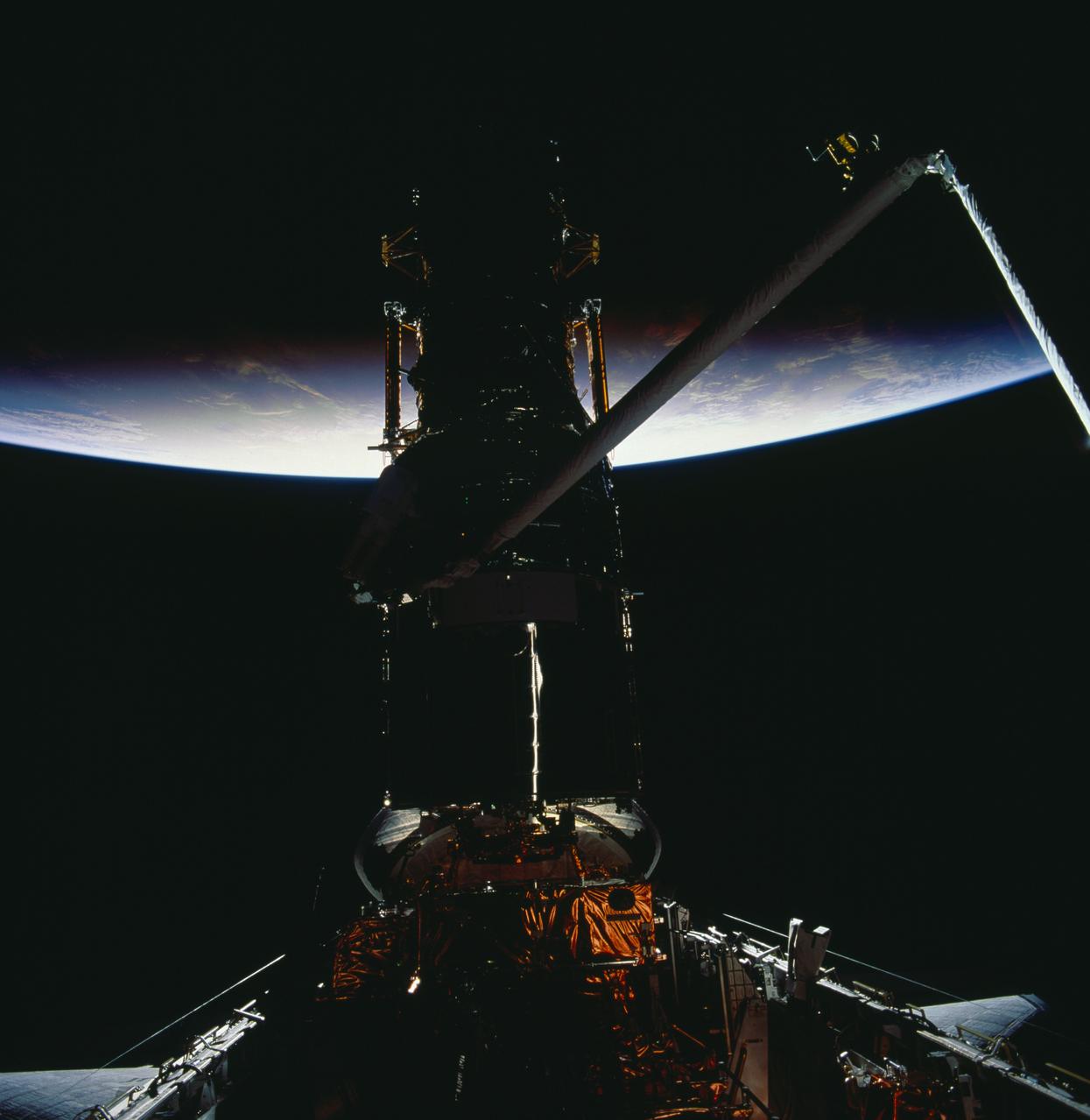

STS061-98-0AR (8 Dec 1993) --- Earth is partially illuminated but the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Space Shuttle Endeavour are still mostly in darkness, in this 70mm frame photographed during the fourth of five space walks. Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, barely visible above left center in the frame, works to install the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR).
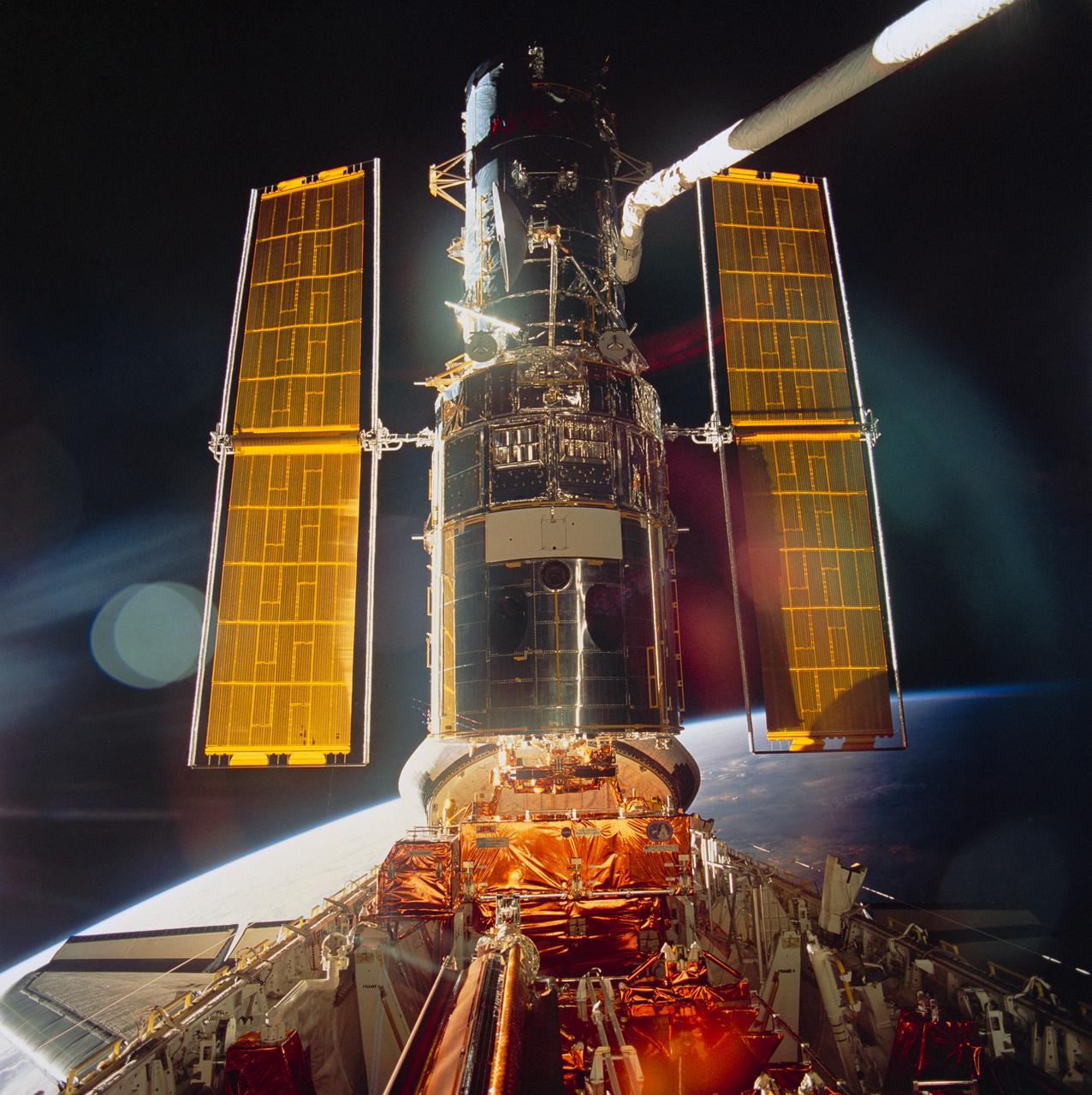

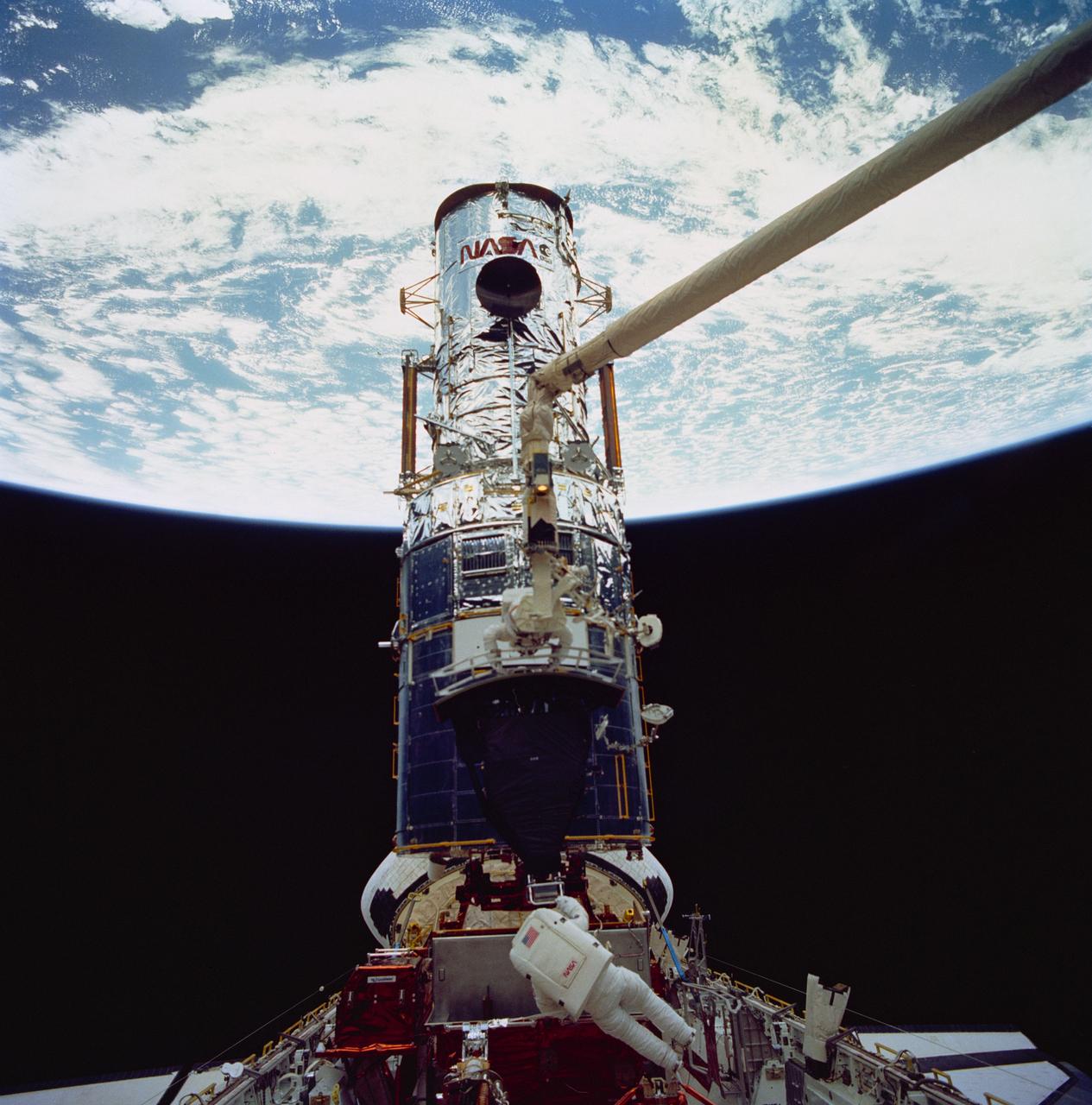
STS061-99-009 (9 Dec 1993) --- Sunlight reflects off the Space Shuttle Endeavour's aft windows and the shiny Hubble Space Telescope (HST) prior to its post-servicing deployment near the end of the eleven-day mission. A handheld Hasselblad camera was used inside Endeavour's cabin to record the image.
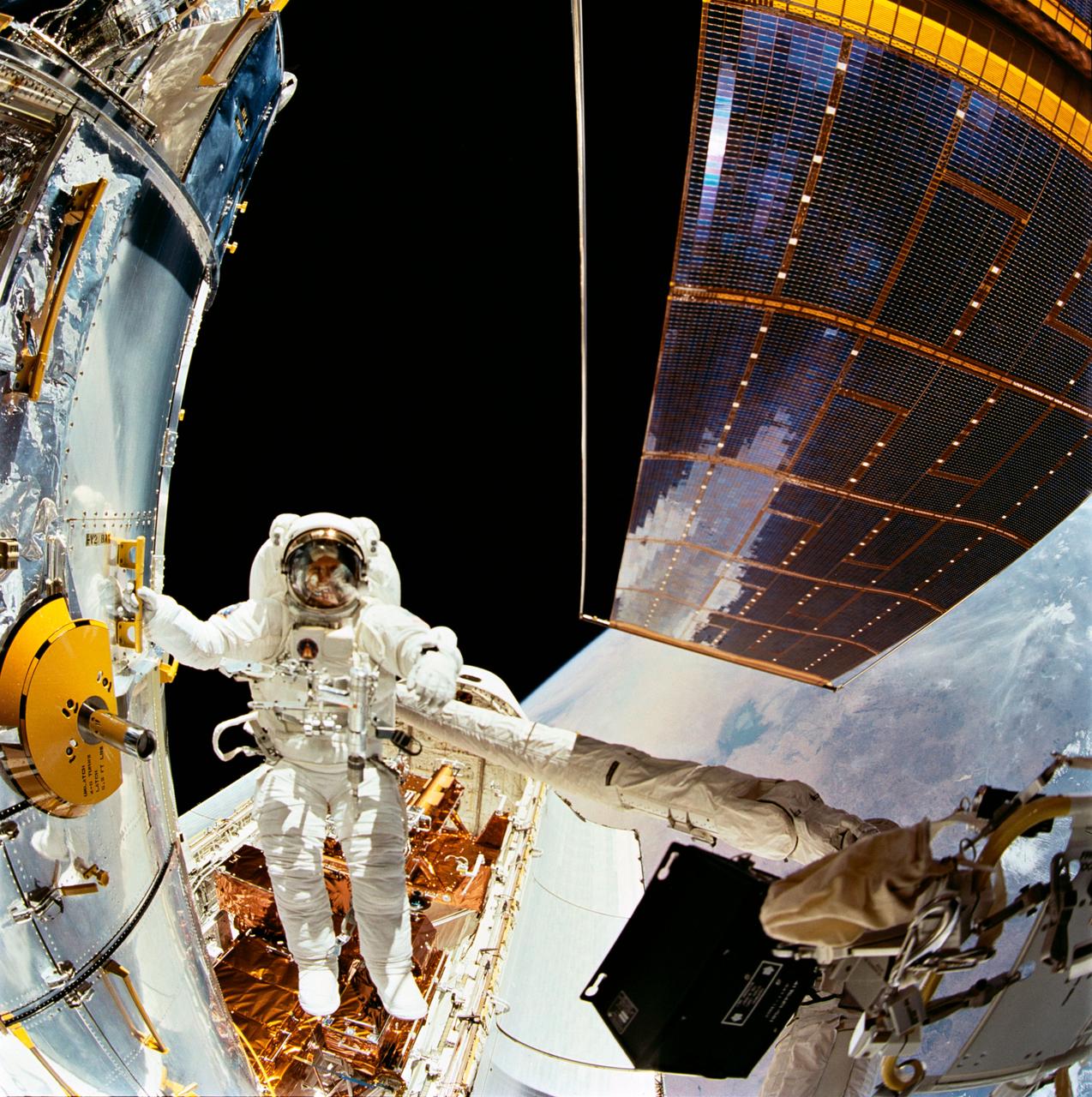

STS061-104-007 (5 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, holding to one of many strategically placed handrails on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), is photographed during the first of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA) on the HST-servicing mission, aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour.
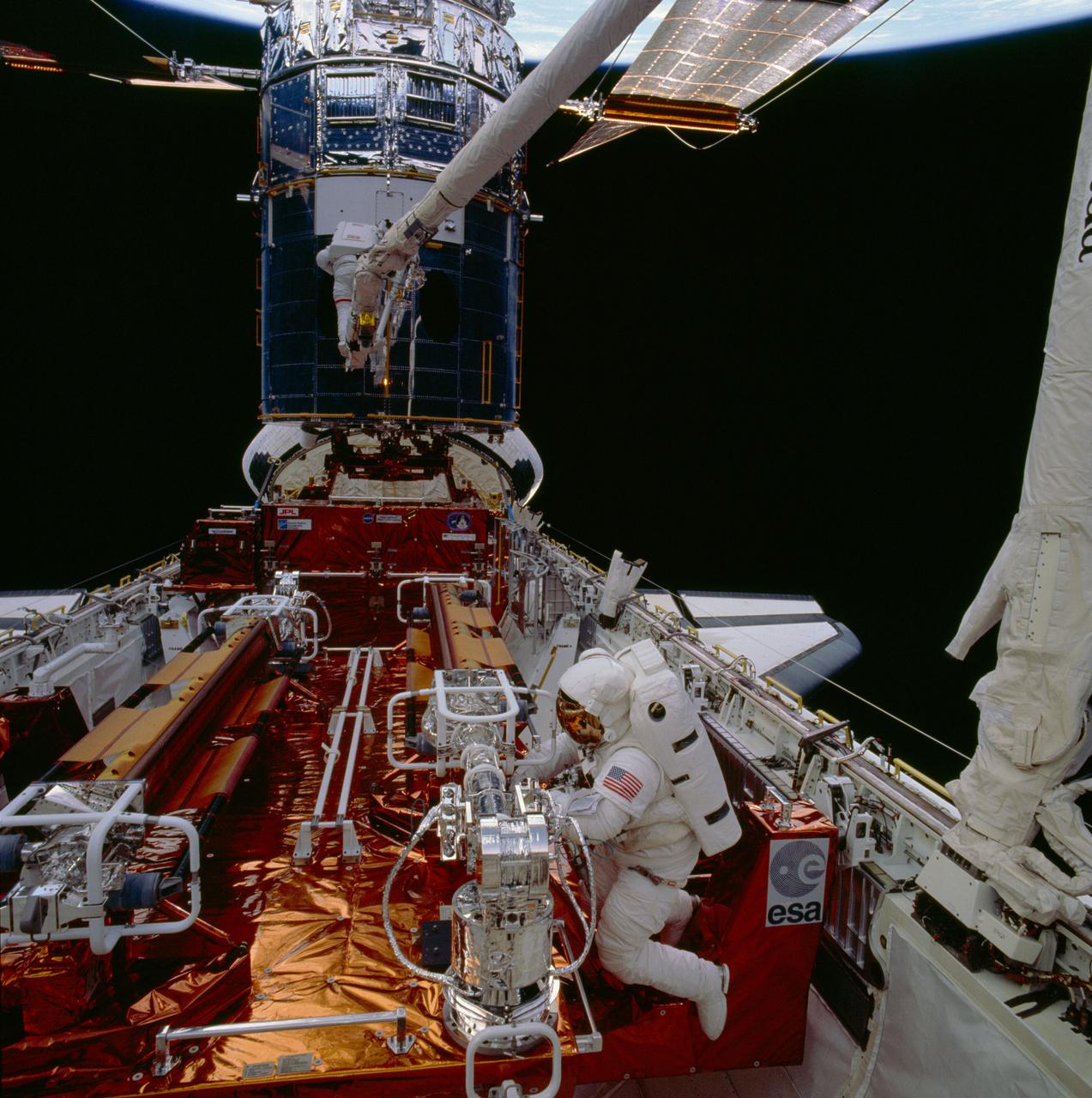
STS061-86-048 (5 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts F. Story Musgrave (foreground) and Jeffrey A. Hoffman are pictured near the end of the first of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA). Musgrave works at the Solar Array Carrier (SAC) in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. Hoffman, anchored to a foot restraint mounted on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, waits to be maneuvered to the forward payload bay. The original solar array panels are partially visible at top, while their replacements remain stowed in foreground. The crew's second pair of space walkers -- astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers -- later changed the solar arrays on the mission's second EVA.
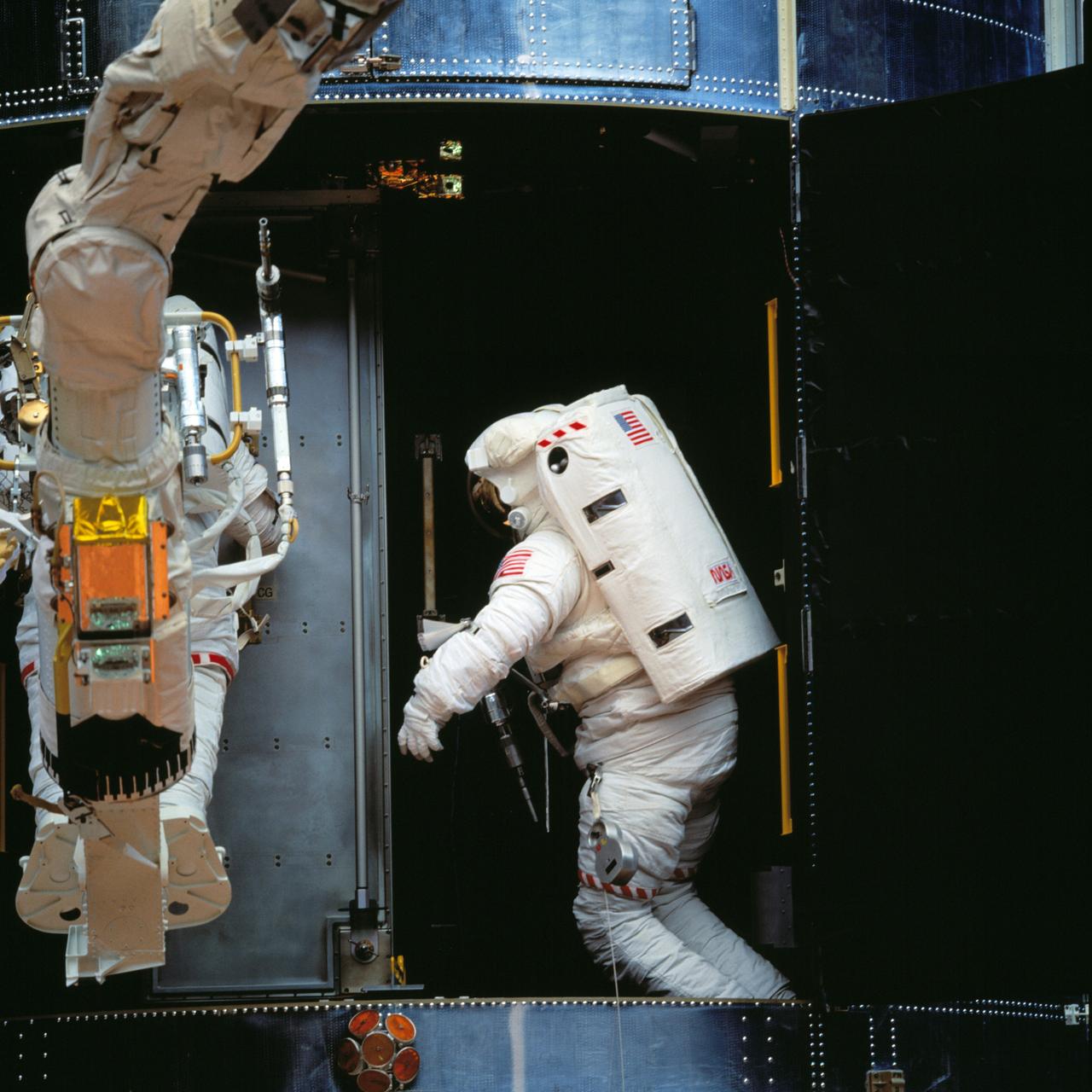
STS061-94-059 (8 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers maneuvers inside the bay which will house the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) while assisting astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton with the installation of the 640-pound instrument. Thornton, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is partially visible as she prepares to install the COSTAR.
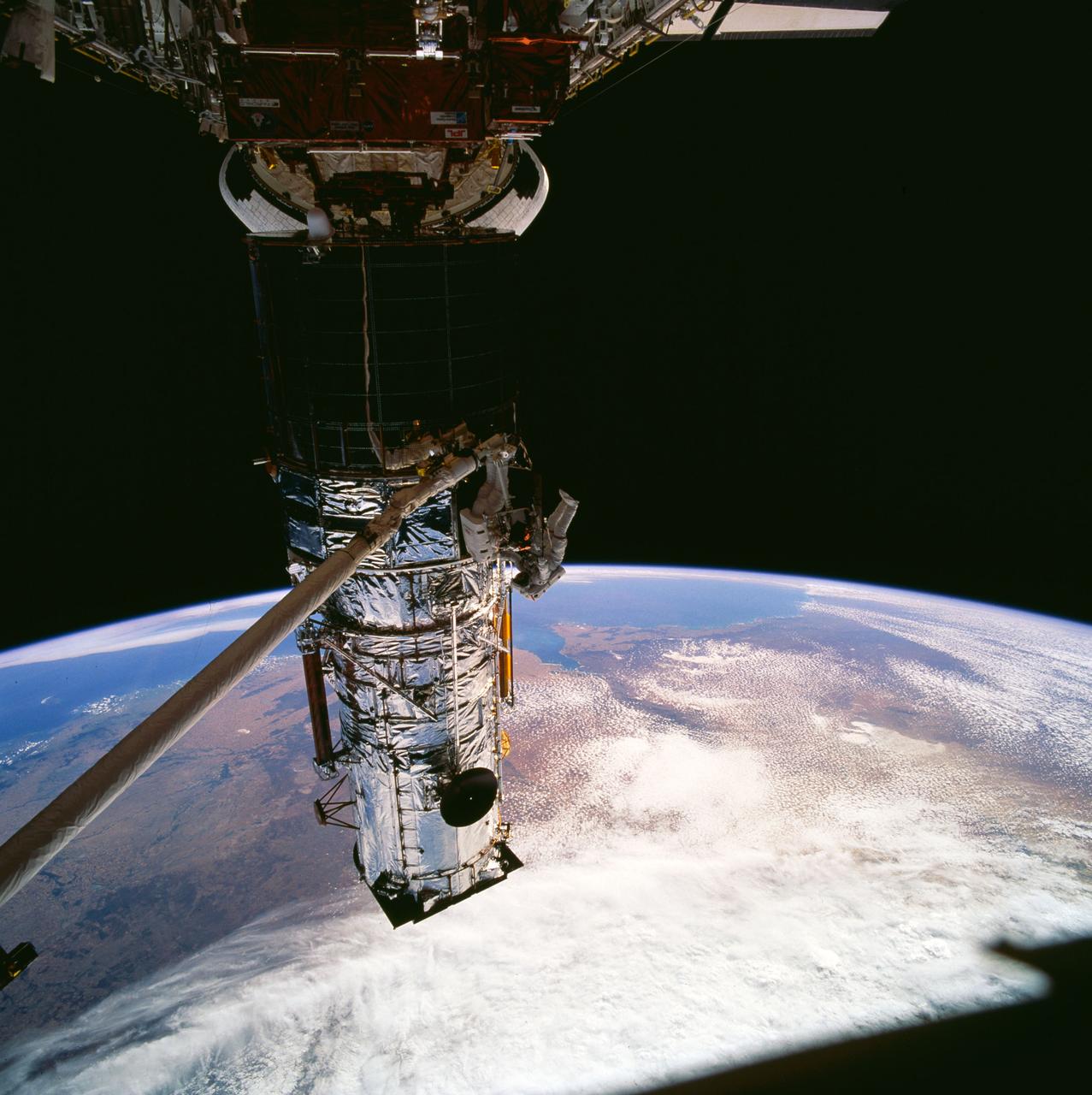

STS061-102-010 (9 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (left) and F. Story Musgrave team to replace one of two Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) units on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Musgrave is standing on a foot restraint mounted on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The black object, in upper left corner, is part of the window frame, through which this 70mm frame was exposed, inside Endeavour's cabin.
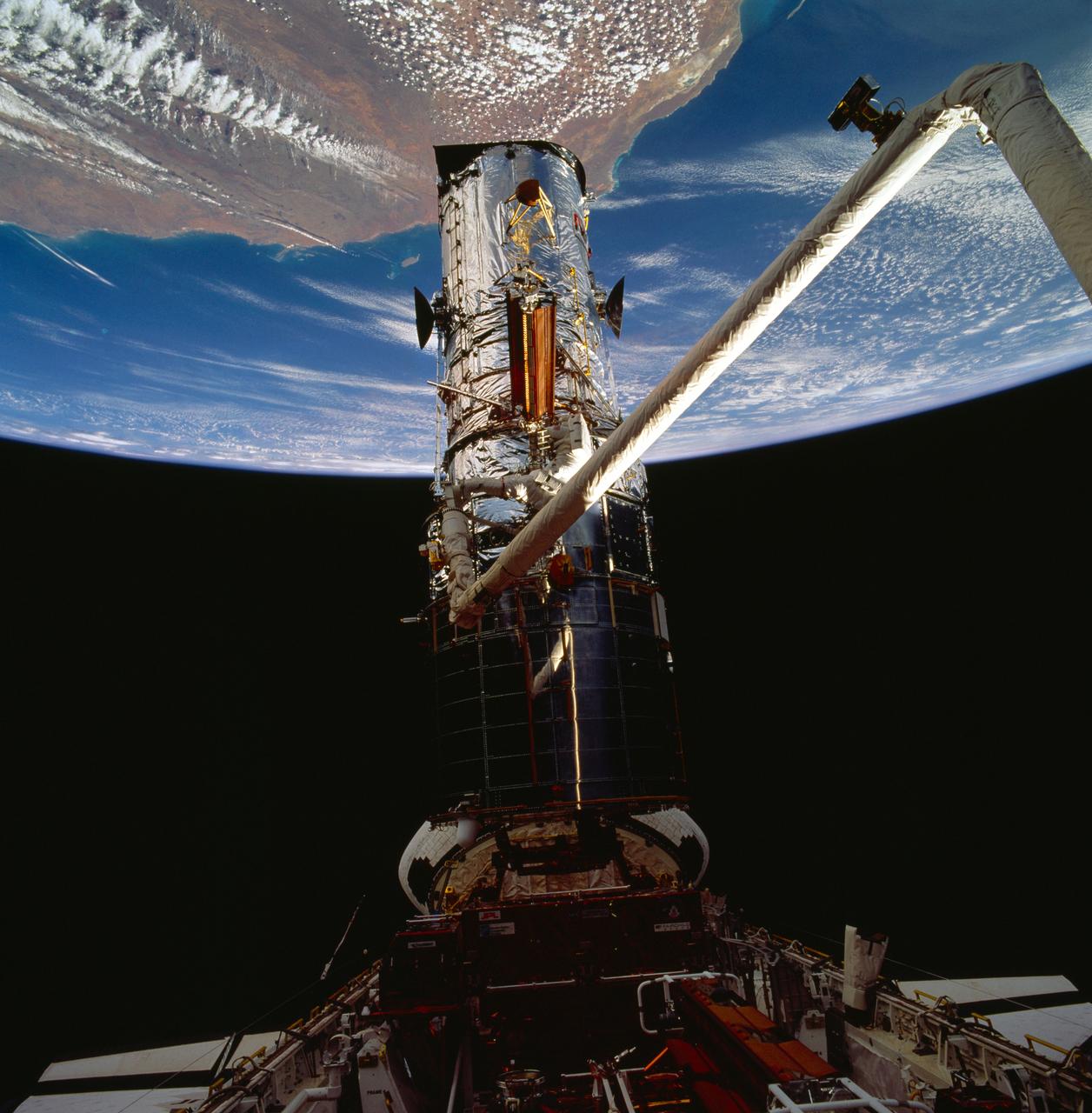

STS061-95-075 (6 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers work to remove one of the solar arrays on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on the second of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA). The two space walkers later replaced both solar array panels. Part of Australia is in the background.
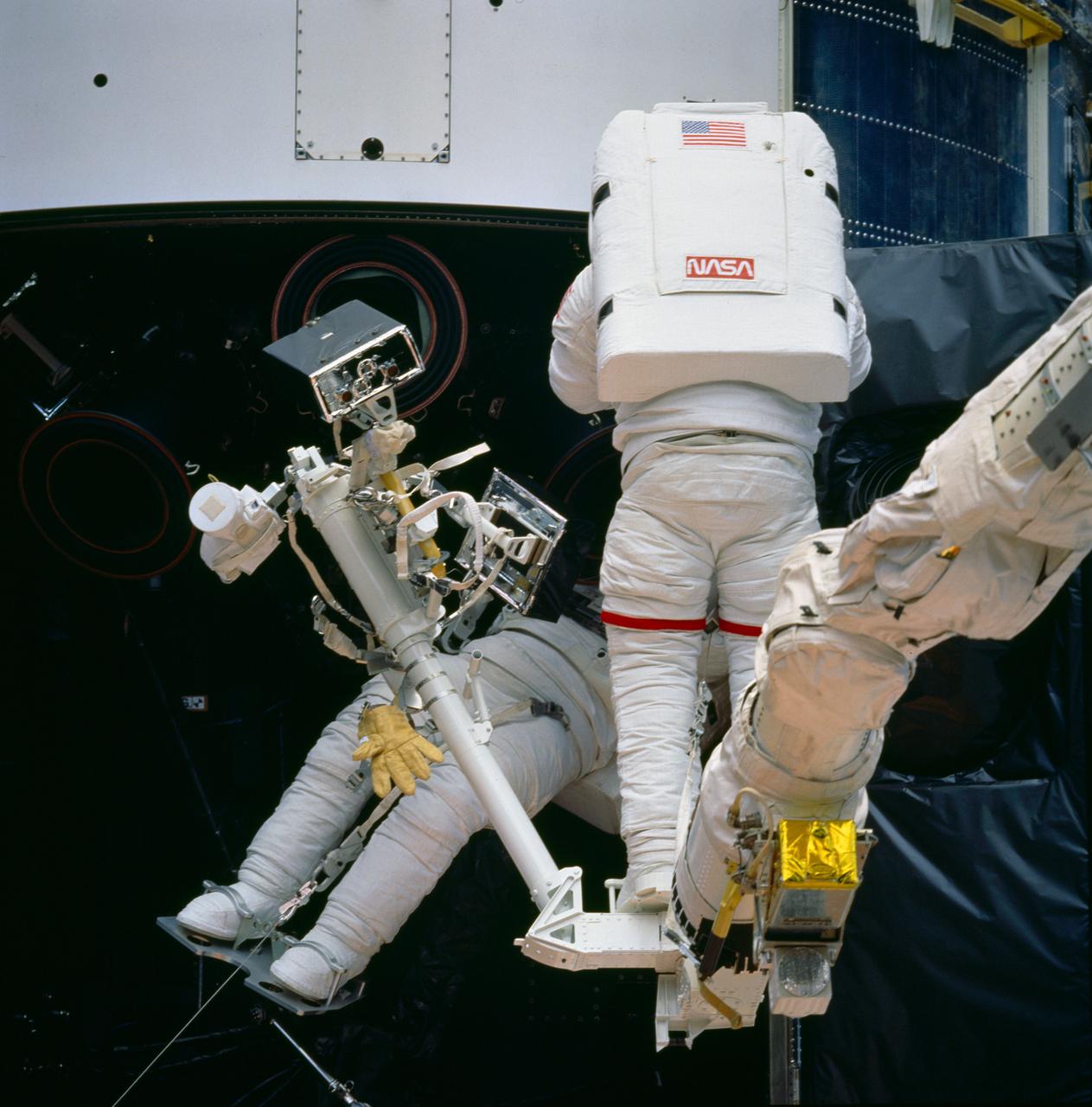

STS061-87-046 (5 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (right) and F. Story Musgrave work near the base of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on the first of five spacewalks. Their particular mission here is to replace failed Rate Sensor Units (RSU) inside the telescope's housing. Hoffman is anchored to a foot restraint, mounted on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, while Musgrave is standing on a foot restraint attached to a support structure in the cargo bay.
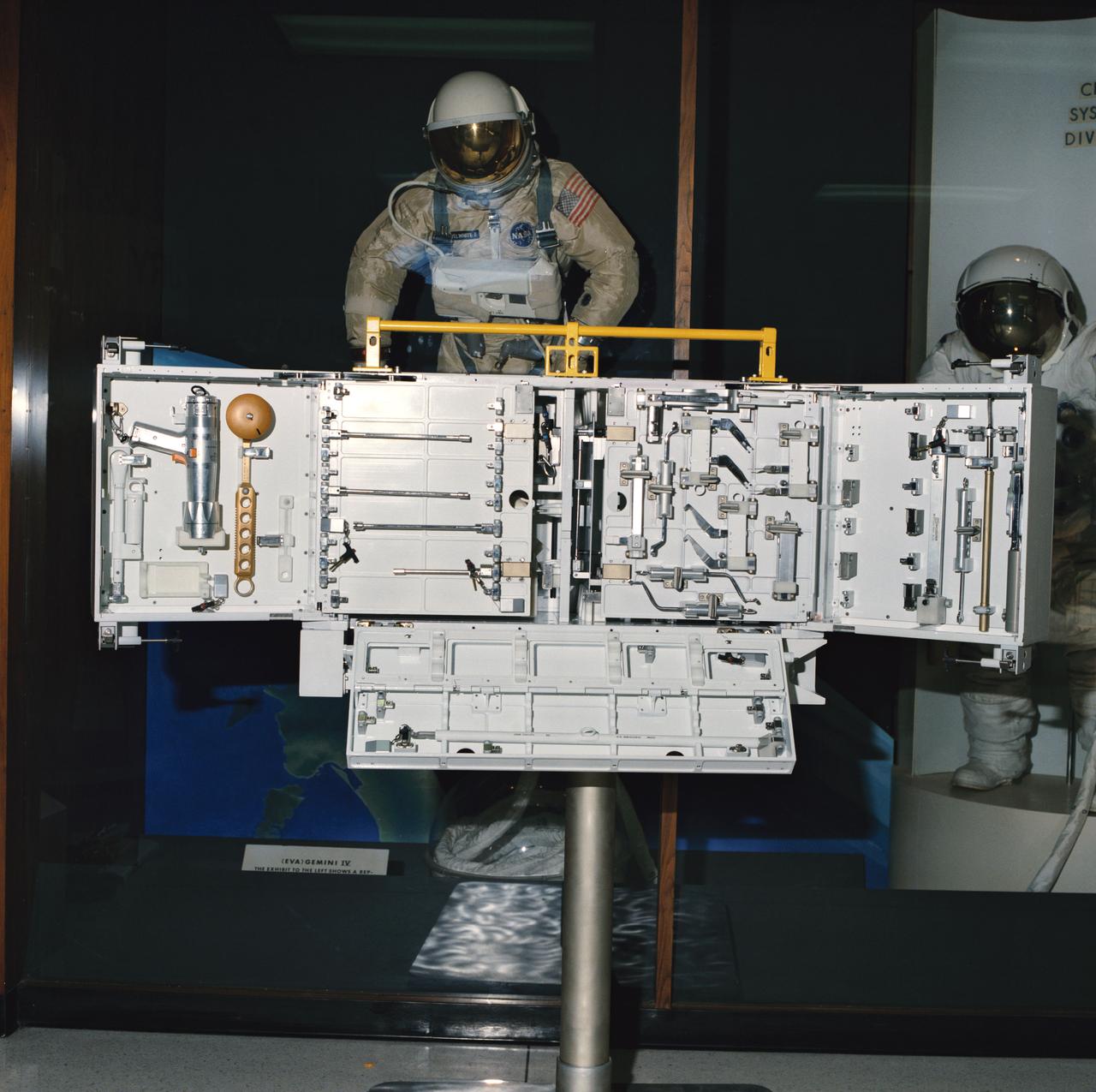
S87-49426 (1987) --- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) tool box provides stowage of individual tools, tool boards and tool caddies required for maintenance of the telescope. The basic box design was revised from the LEASAT (U.S. Navy) equipment stowage container. It can be mounted to a base plate or back plate depending on the mission location requirements. A four-point latching system secured with pip pins is used to latch the tool box doors for launch. Various other latches are designed into the door panels and tool mounting locations for tool retention. The box consists of aluminum sides and base, a dividing wall and deep doors. Along three sides there are handrails by which STS-61 extravehicular activity (EVA) crew members can translate themselves or brace themselves when stowing and unstowing equipment.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility for a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station are (kneeling) STS-96 Mission Specialists Julie Payette and Ellen Ochoa, Pilot Rick Husband, and (standing at right) Mission Specialist Dan Barry. At the left is James Behling, with Boeing, explaining some of the equipment that will be on board STS-96. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
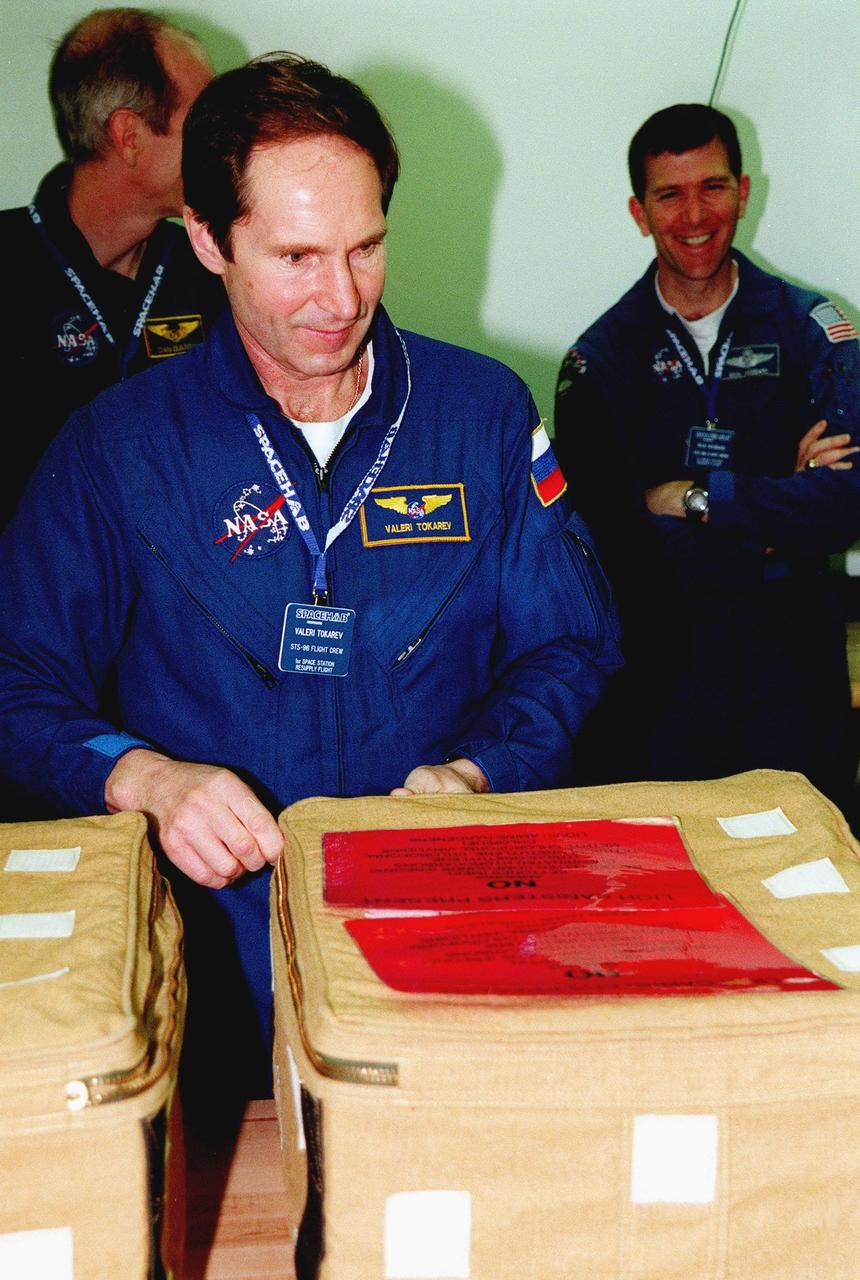

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Valery Tokarev (in foreground) of the Russian Space Agency closes a container, part of the equipment that will be in the SPACEHAB module on mission STS-96. Behind Tokarev are Mission Specialist Dan Barry (left) and Pilot Rick Husband right). Other crew members at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Tamara Jernigan and Julie Payette. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
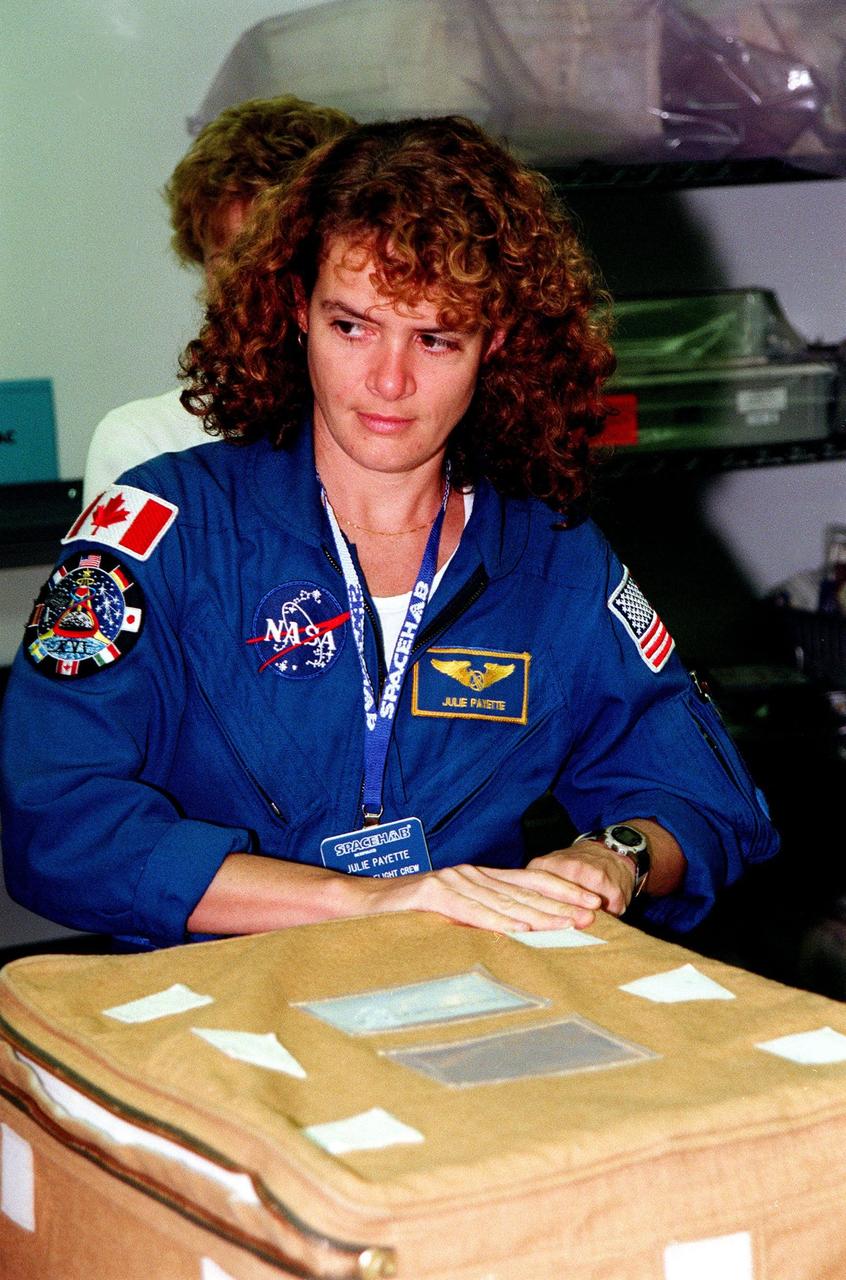

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Julie Payette closes a container, part of the equipment to be carried on the SPACEHAB and mission STS-96. She and other crew members Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband, and Mission Speciaists Ellen Ochoa, Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Valery Tokarev of Russia are at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station . Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
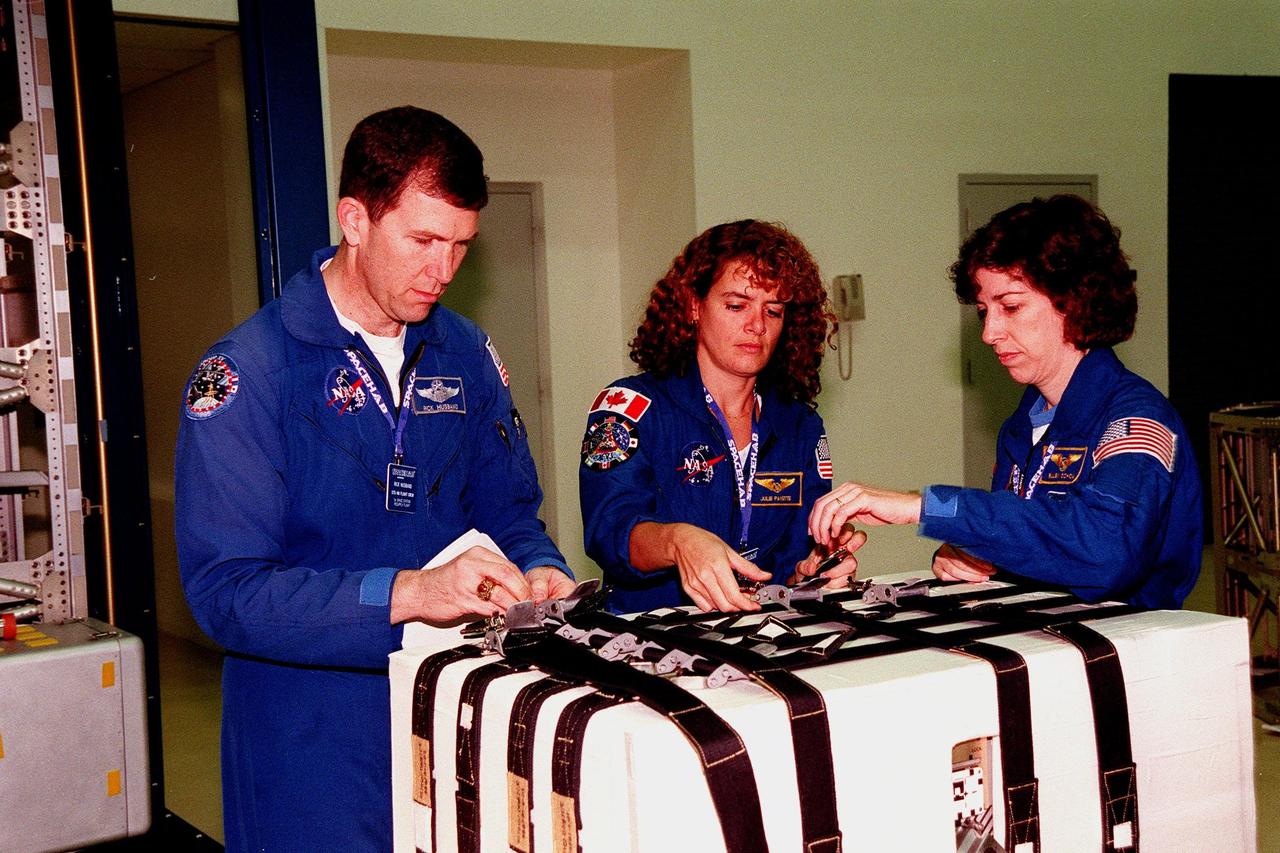

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, (left to right) STS-96 Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Julie Payette and Ellen Ochoa work the straps on the Sequential Shunt Unit (SSU) in front of them. The STS-96 crew is at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for its upcoming mission to the International Space Station . Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Valery Tokarev of Russia. The SSU is part of the cargo on Mission STS-96, which carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, with equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
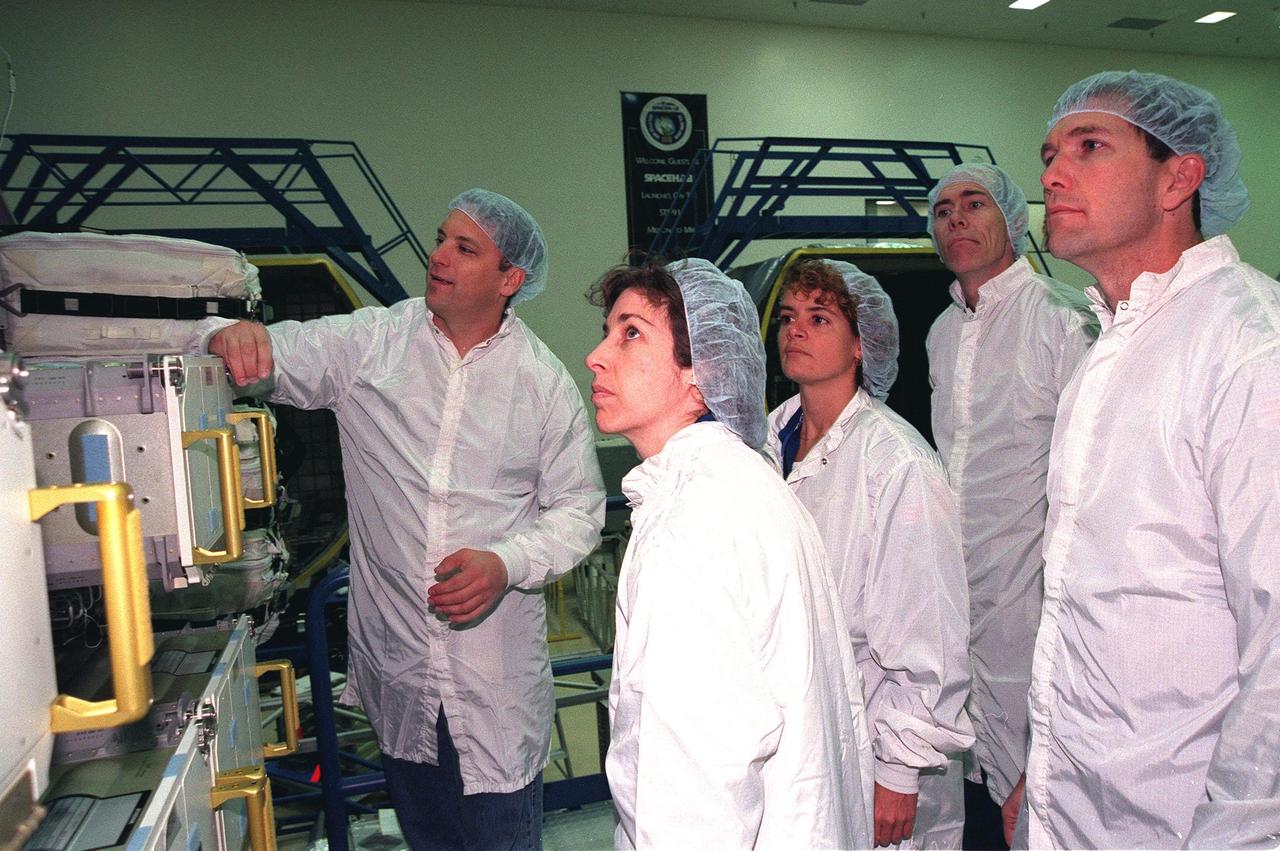

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, James Behling, with Boeing, talks about equipment for mission STS-96 during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT). Watching are (from left) Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Julie Payette and Dan Berry, and Pilot Rick Husband. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m

In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialists Dan Barry and Tamara Jernigan discuss procedures during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
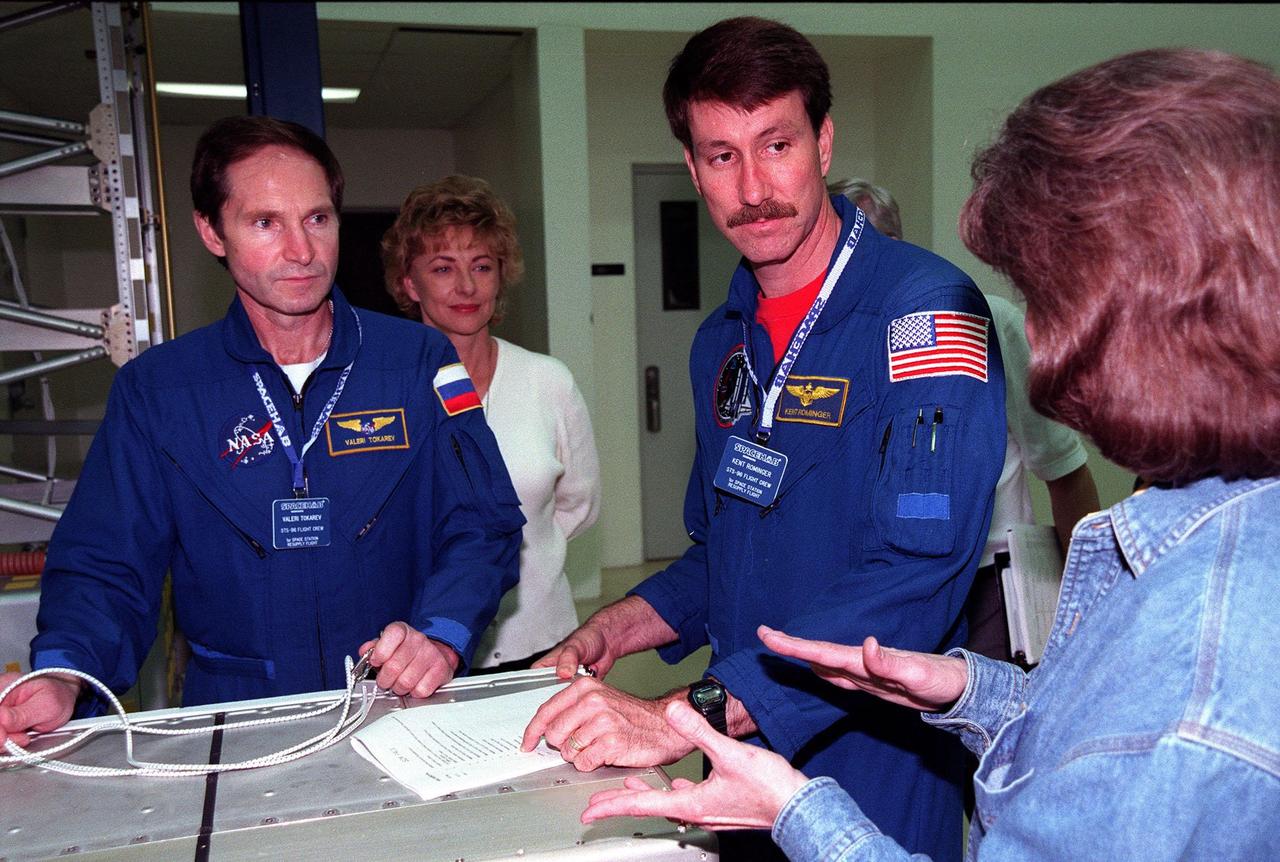

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Valery Tokarev of Russia (left) and Commander Kent Rominger (second from right) listen to Lynn Ashby (far right), with JSC, talking about the SPACEHAB equipment in front of them during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT). In the background behind Tokarev is TTI interpreter Valentina Maydell. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Dan Barry, Ellen Ochoa, Tamara Jernigan and Julie Payette. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
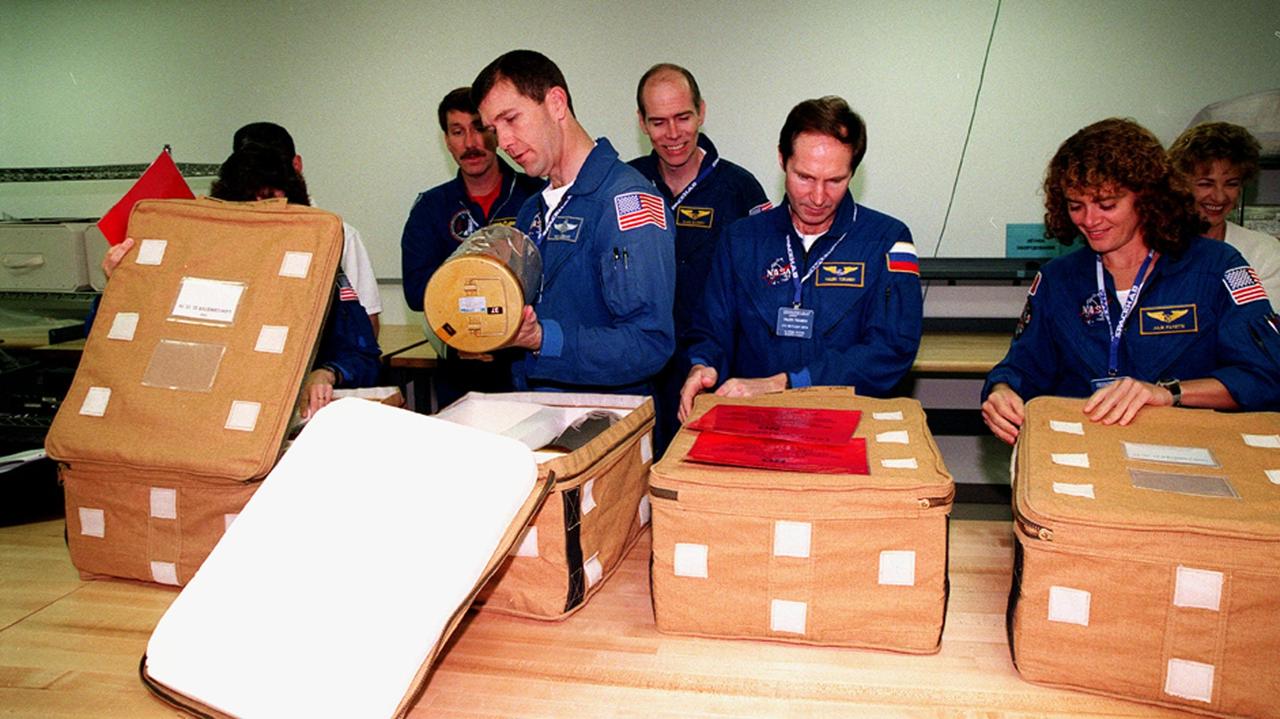

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, the STS-96 crew looks at equipment as part of a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station . From left are Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa (behind the opened storage cover ), Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband (holding a lithium hydroxide canister) and Mission Specialists Dan Barry, Valery Tokarev of Russia and Julie Payette. In the background is TTI interpreter Valentina Maydell. The other crew member at KSC for the IVT is Mission Specialist Tamara Jernigan. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
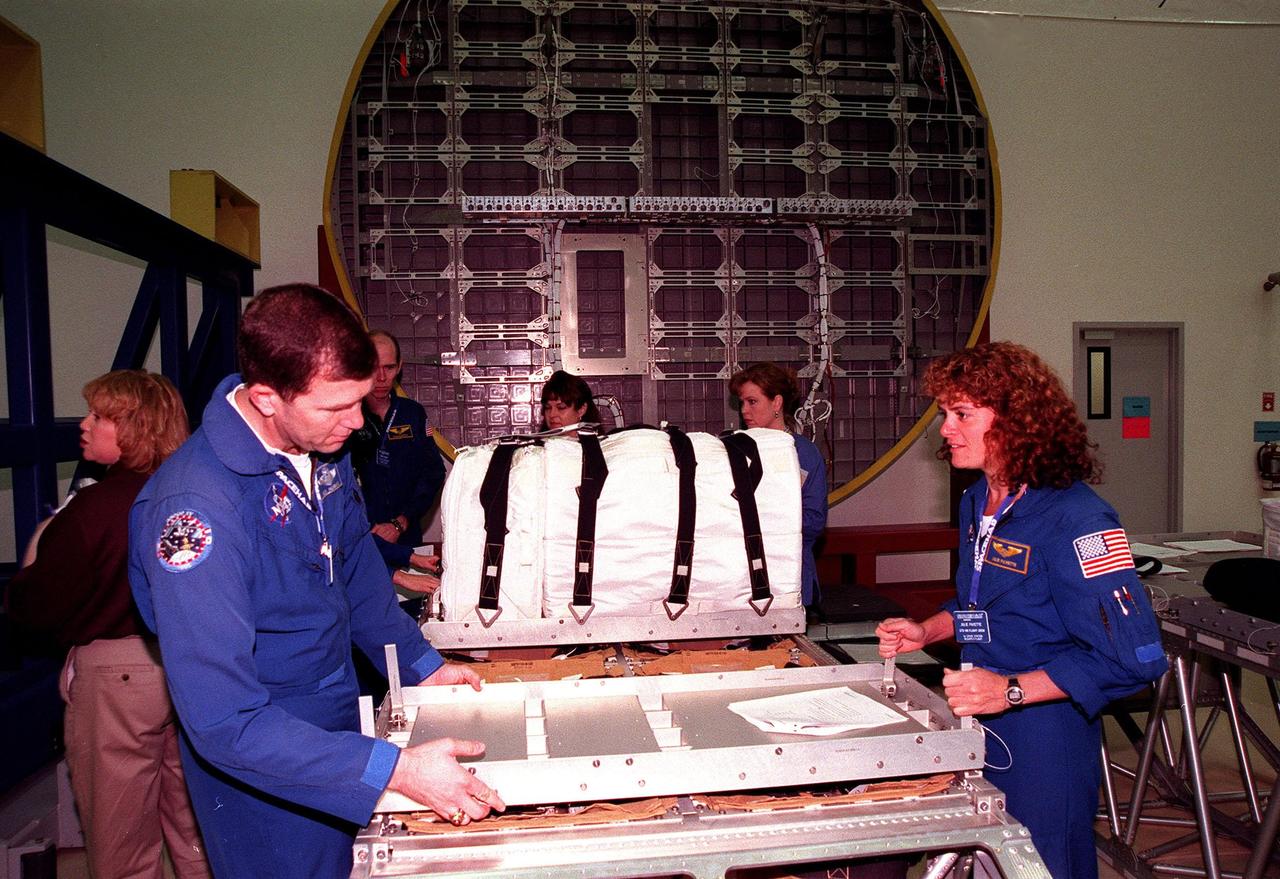

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 crew members look over equipment during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. From left are Khristal Parker, with Boeing; Mission Specialist Dan Barry, Pilot Rick Husband, Mission Specialist Tamara Jernigan, and at the far right, Mission Specialist Julie Payette. An unidentified worker is in the background. Also at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station, STS-96 Mission Specialists Julie Payette, Dan Barry, and Valery Tokarev of Russia, look at a Sequential Shunt Unit in the SPACEHAB Facility. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband, and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Tamara Jernigan. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, the STS-96 crew looks over equipment during a payload Interface Verification Test for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. From left are Commander Kent Rominger, Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan and Valery Tokarev of Russia, Pilot Rick Husband, and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Julie Payette (backs to the camera). They are listening to Chris Jaskolka of Boeing talk about the equipment. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
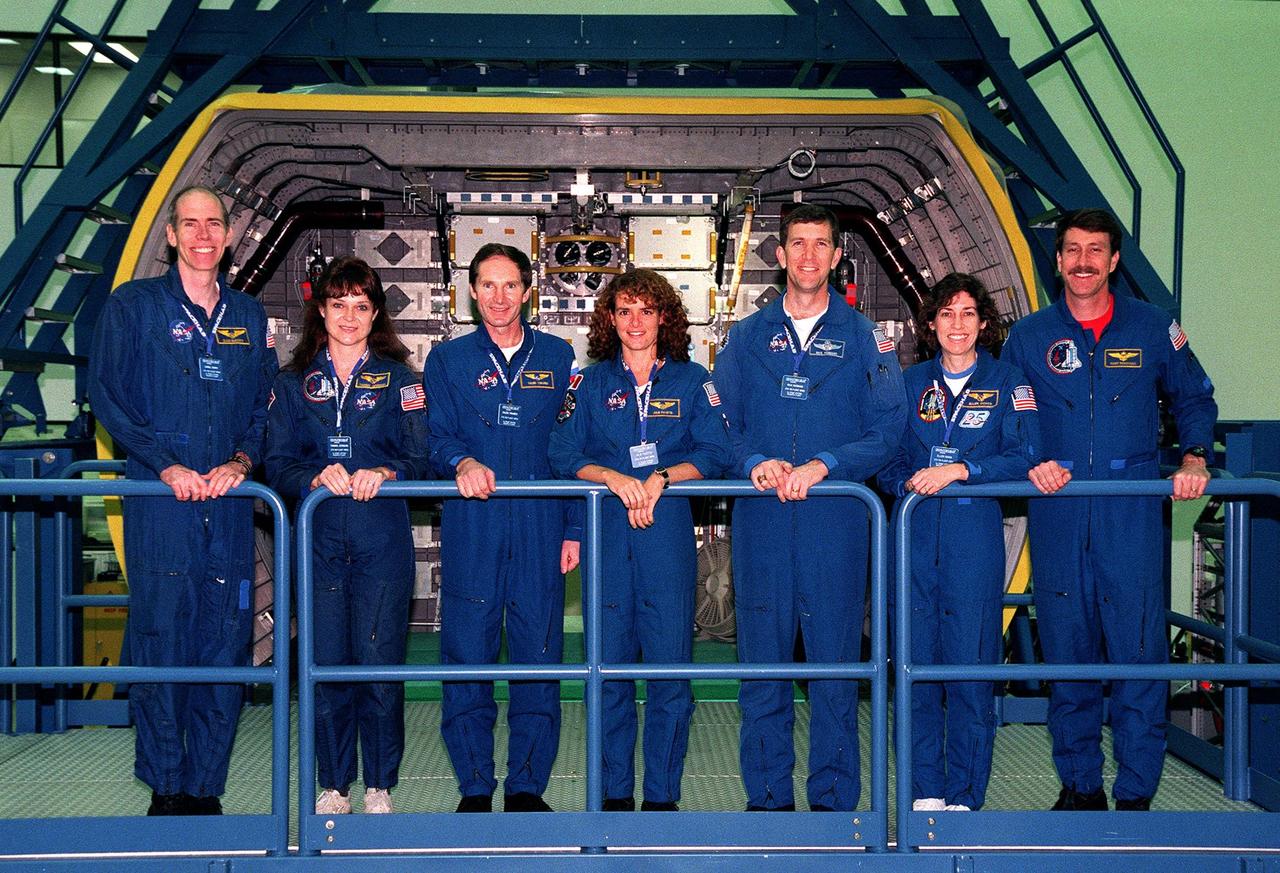

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Posing on the platform next to the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module in the SPACEHAB Facility are the STS-96 crew (from left) Mission Specialists Dan Barry, Tamara Jernigan, Valery Tokarev of Russia, and Julie Payette; Pilot Rick Husband; Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa; and Commander Kent Rominger. The crew is at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
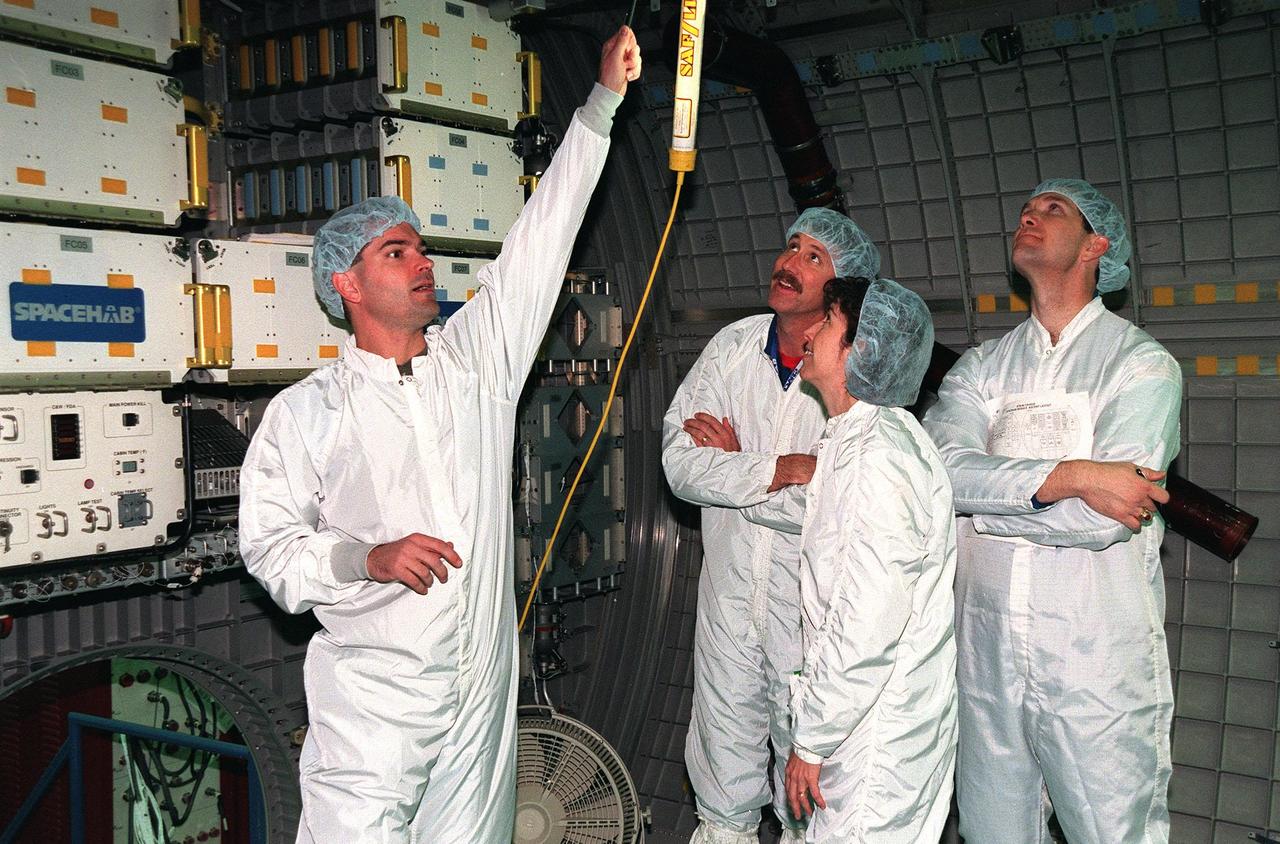

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station , Chris Jaskolka of Boeing points out a piece of equipment in the SPACEHAB module to STS-96 Commander Kent Rominger, Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa and Pilot Rick Husband. Other crew members visiting KSC for the IVT are Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
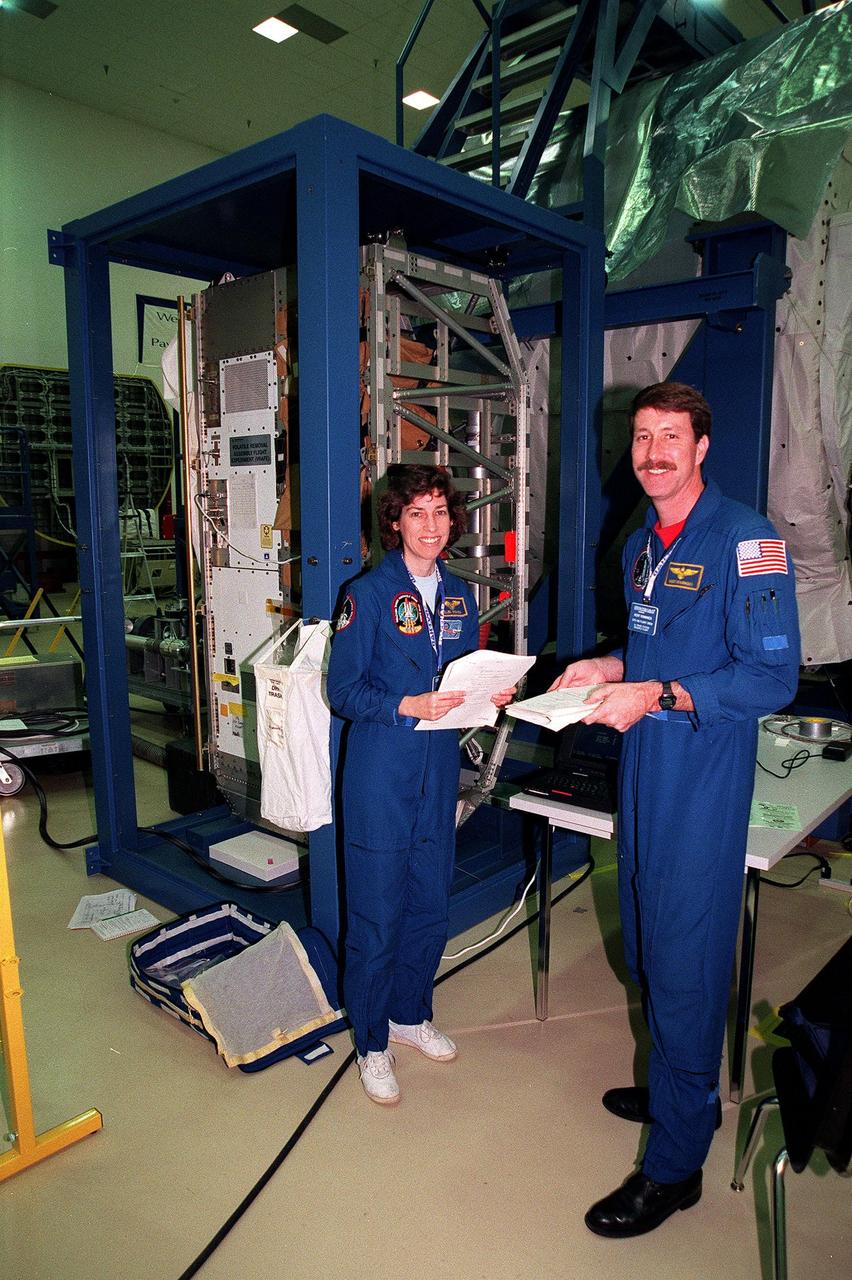

At the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa and Commander Kent Rominger pause during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
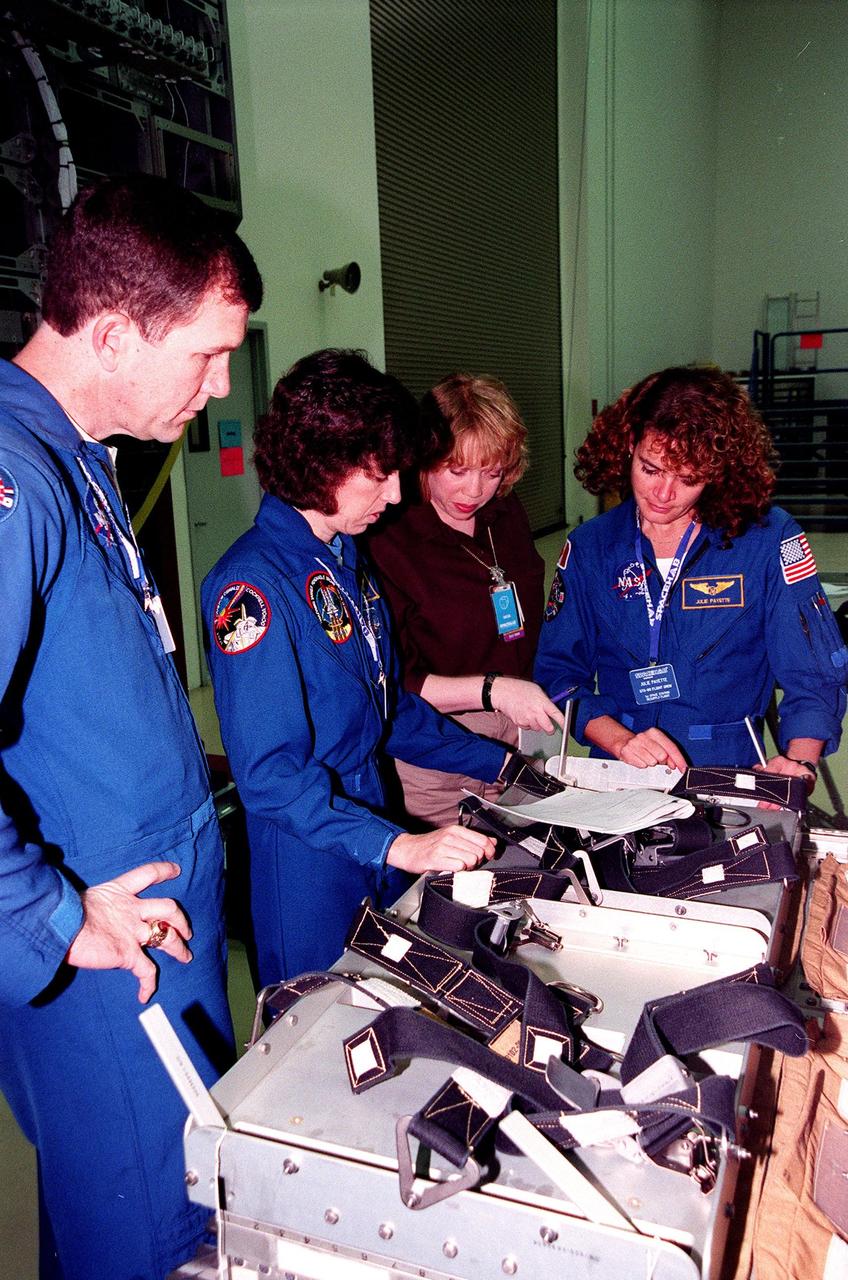

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) in the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa (on the left) and Mission Specialist Julie Payette (on the far right) listen to Khristal Parker (second from right), with Boeing, explain about the equipment in front of them. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Valery Tokarev of Russia. The SSU is part of the cargo on Mission STS-96, which carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, with equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
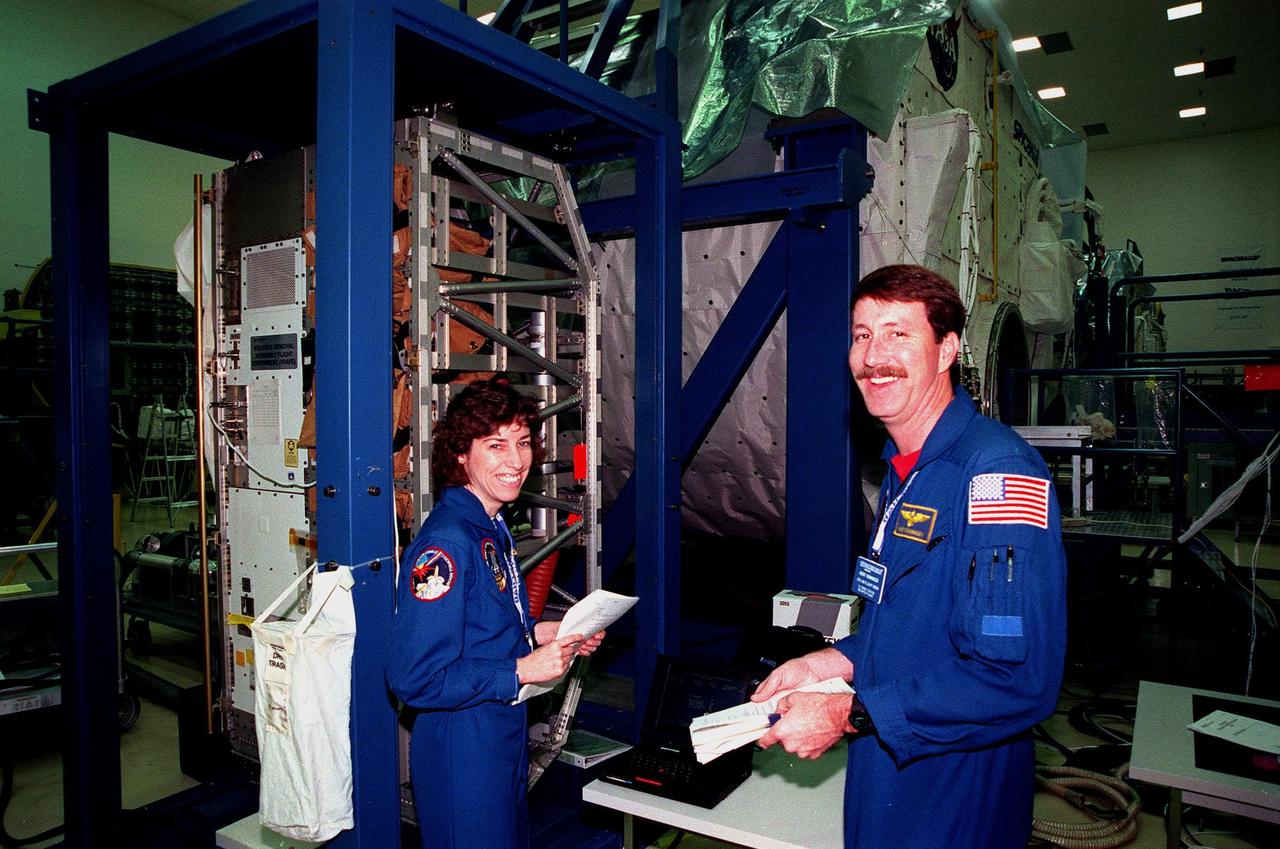

At the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa and Commander Kent Rominger smile for the camera during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
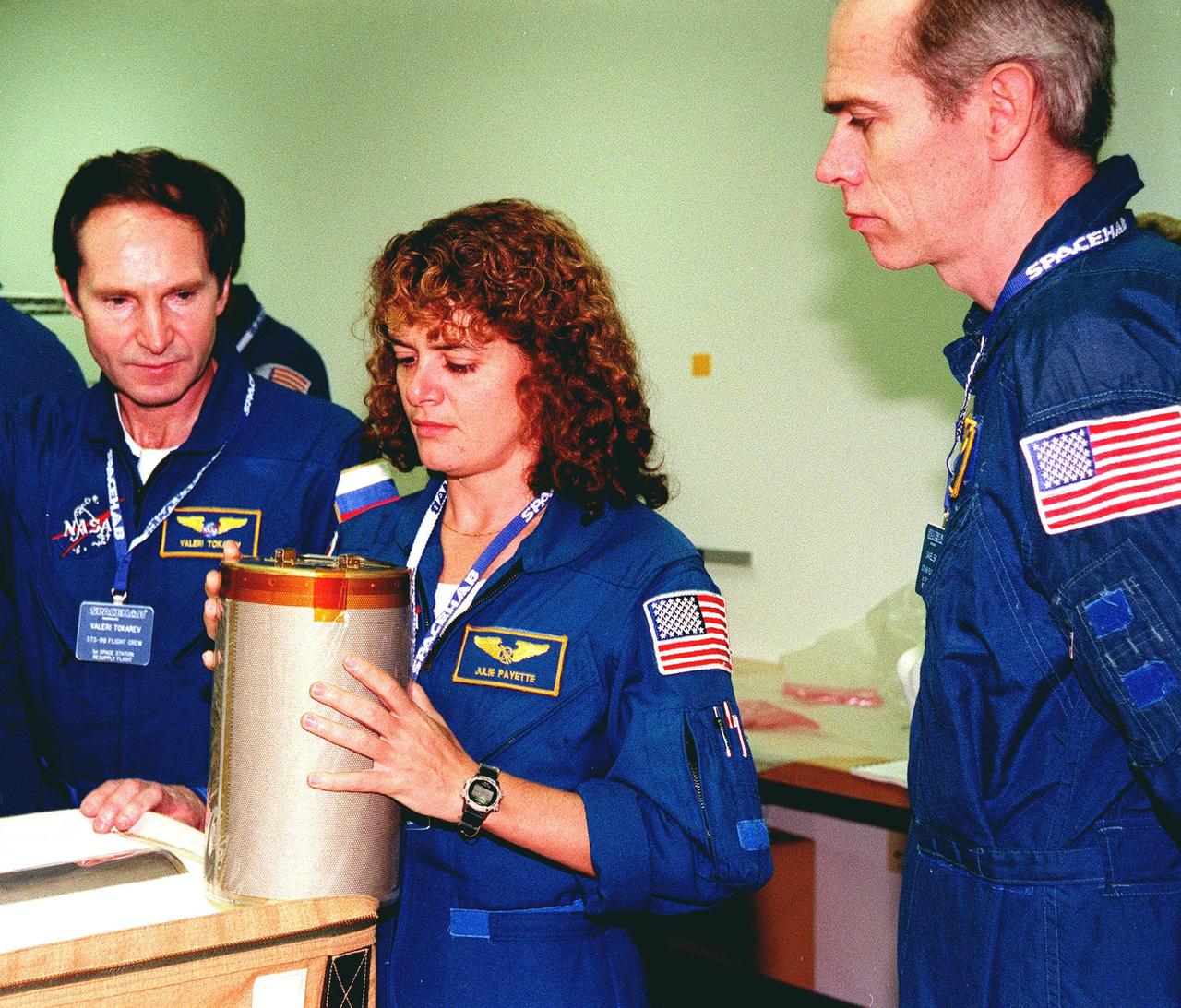

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility for a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station are (left to right) Mission Specialists Valery Tokarev, Julie Payette (holding a lithium hydroxide canister) and Dan Barry. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Tamara Jernigan. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
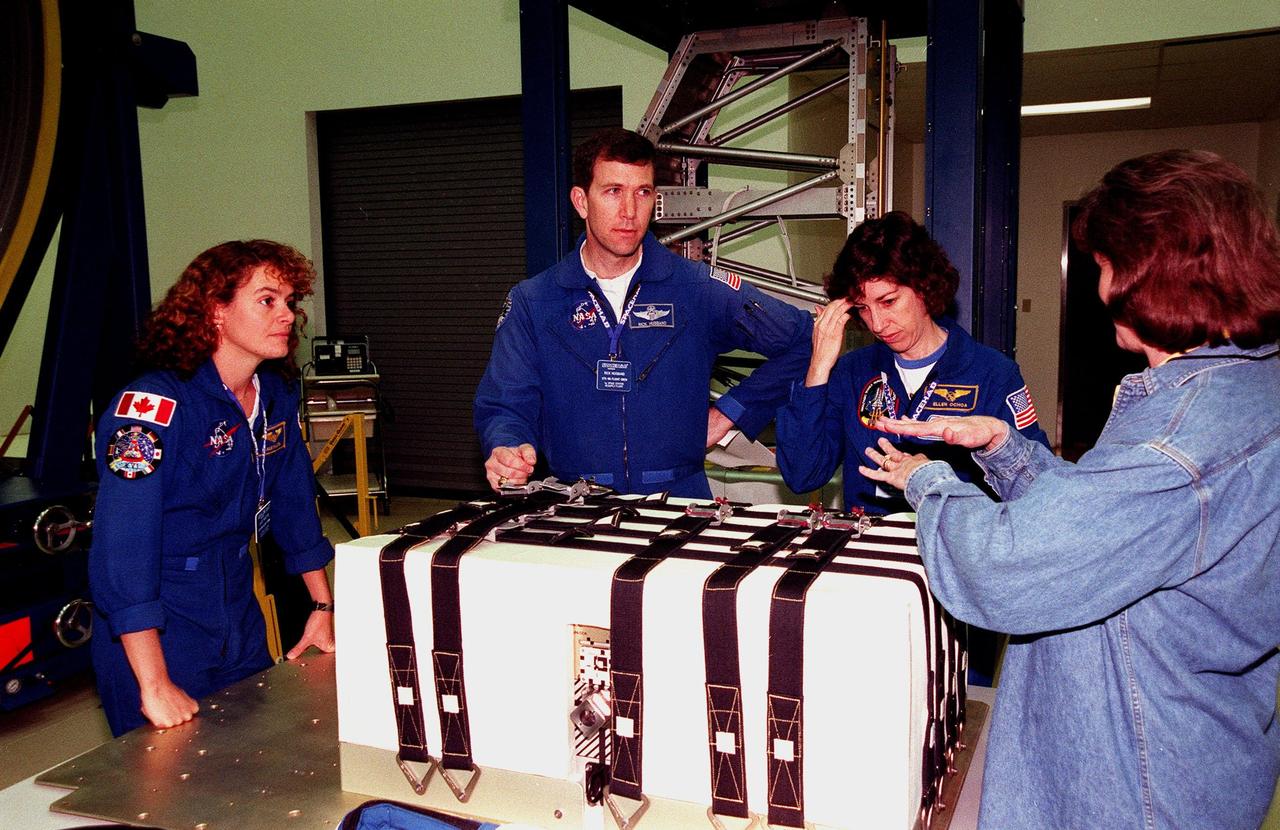

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, (from left) STS-96 Mission Specialist Julie Payette, Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa learn about the Sequential Shunt Unit (SSU) in front of them from Lynn Ashby (far right), with Johnson Space Center. The STS-96 crew is at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station . Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Valery Tokarev of Russia. The SSU is part of the cargo on Mission STS-96, which carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, with equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
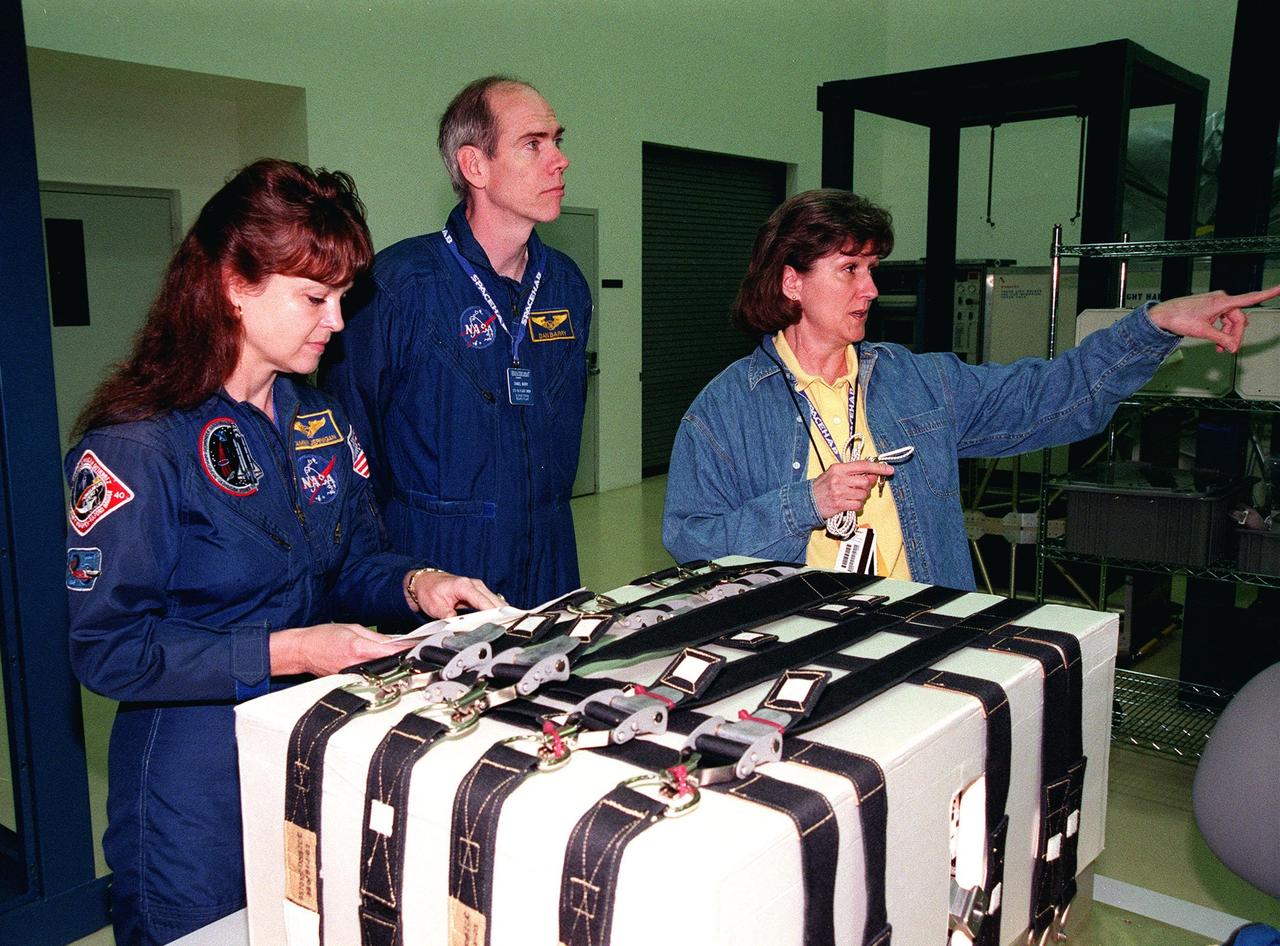

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) in the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Tamara Jernigan checks over instructions while Mission Specialist Dan Barry looks up from the Sequential Shunt Unit (SSU) in front of him to other equipment Lynn Ashby (right), with Johnson Space Center, is pointing at. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband, and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. The SSU is part of the cargo on Mission STS-96, which carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, with equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
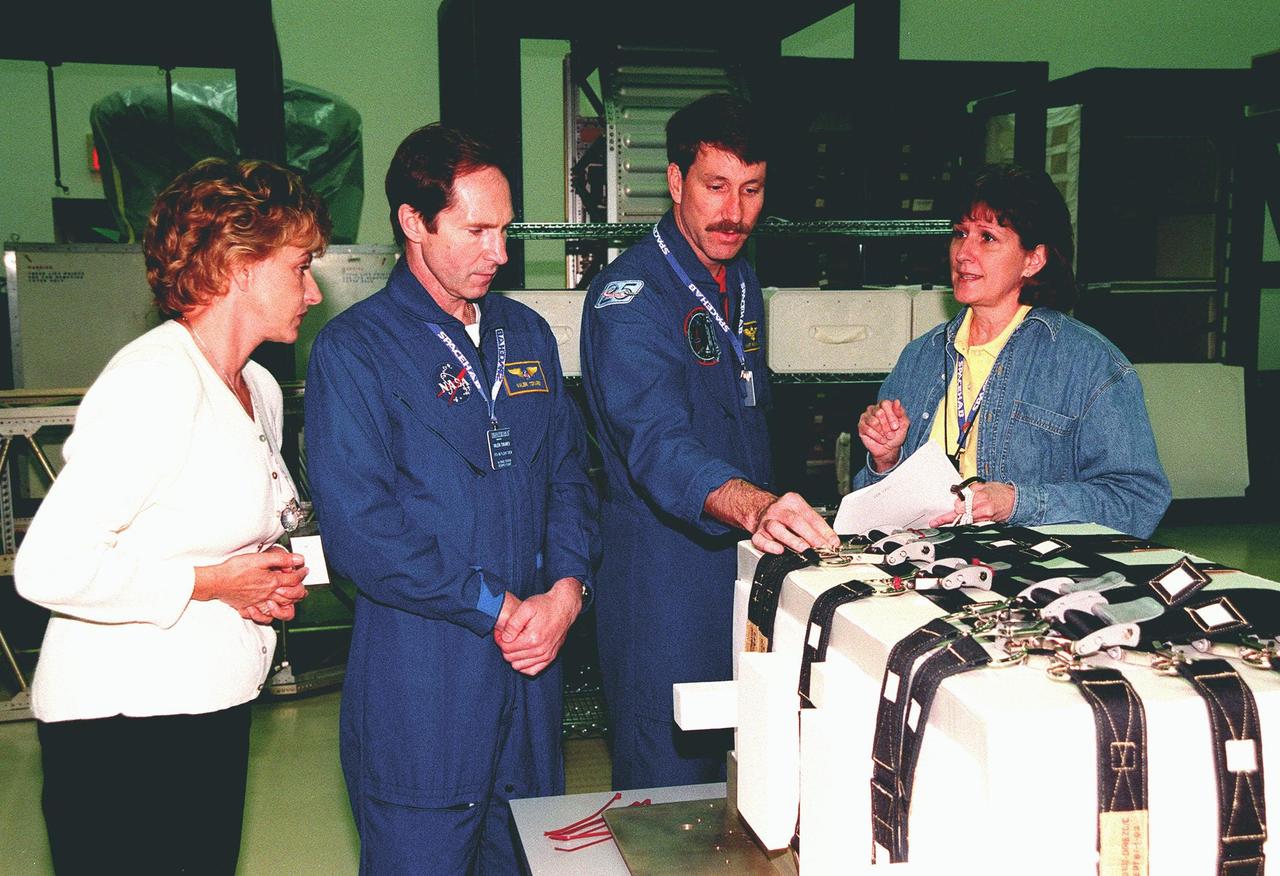

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) in the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Valery Tokarev of Russia (second from left) and Commander Kent Rominger learn about the Sequential Shunt Unit (SSU) in front of them from Lynn Ashby (far right), with Johnson Space Center. At the far left looking on is TTI interpreter Valentina Maydell. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Julie Payette. The SSU is part of the cargo on Mission STS-96, which carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, with equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m