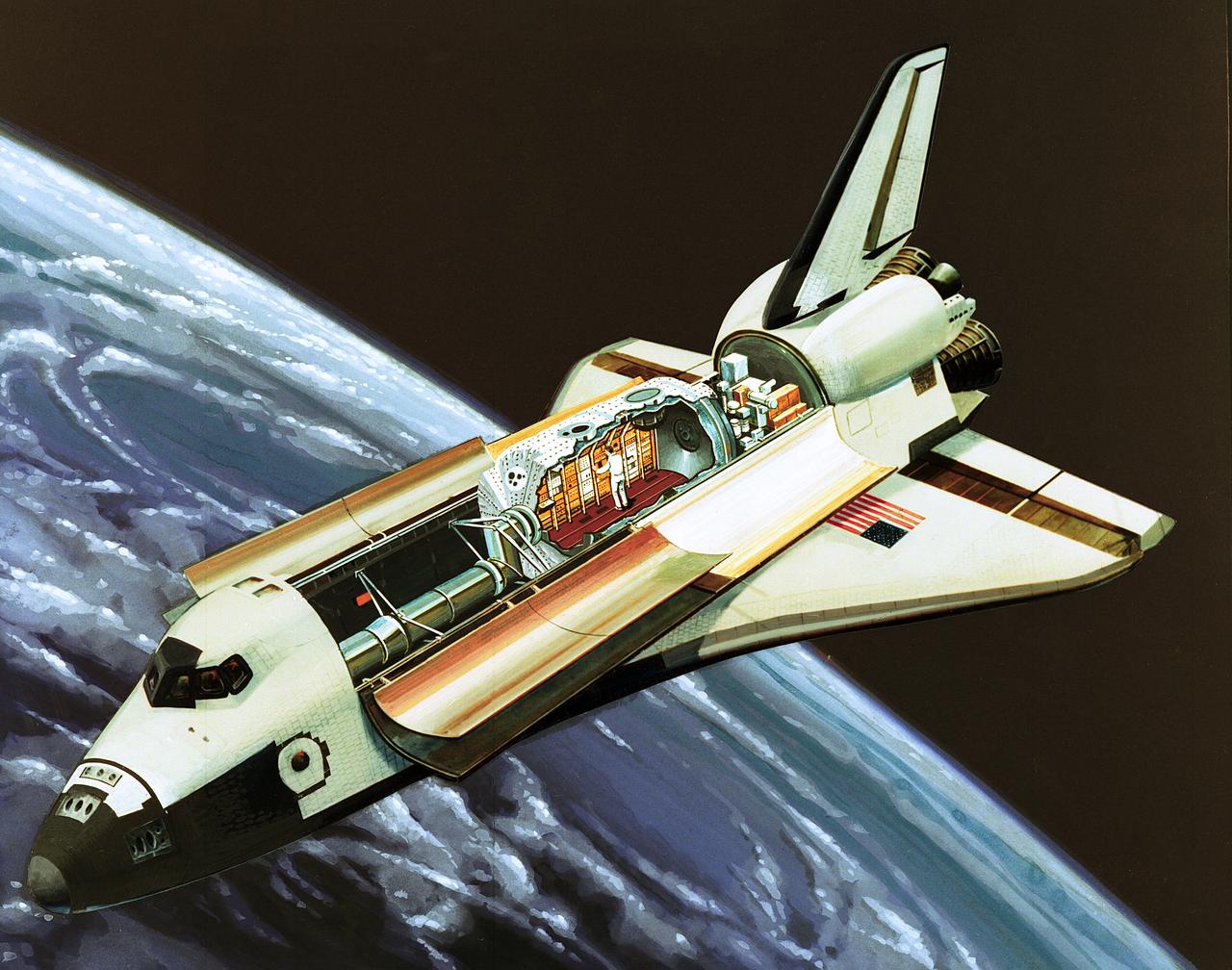
Spacelab was a versatile laboratory carried in the Space Shuttle's cargo bay for special research flights. Its various elements could be combined to accommodate the many types of scientific research that could best be performed in space. Spacelab consisted of an enclosed, pressurized laboratory module and open U-shaped pallets located at the rear of the laboratory module. The laboratory module contained utilities, computers, work benches, and instrument racks to conduct scientific experiments in astronomy, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, and engineering. Equipment, such as telescopes, anternas, and sensors, was mounted on pallets for direct exposure to space. A 1-meter (3.3-ft.) diameter aluminum tunnel, resembling a z-shaped tube, connected the crew compartment (mid deck) to the module. The reusable Spacelab allowed scientists to bring experiment samples back to Earth for post-flight analysis. Spacelab was a cooperative venture of the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA. ESA was responsible for funding, developing, and building of Spacelab, while NASA was responsible for the launch and operational use of Spacelab. Spacelab missions were cooperative efforts between scientists and engineers from around the world. Teams from NASA centers, universities, private industry, government agencies and international space organizations designed the experiments. The Marshall Space Flight Center was NASA's lead center for monitoring the development of Spacelab and managing the program.

Spacelab was a versatile laboratory carried in the Space Shuttle's cargo bay for special research flights. Its various elements could be combined to accommodate the many types of scientific research that could best be performed in space. Spacelab consisted of an enclosed, pressurized laboratory module and open U-shaped pallets located at the rear of the laboratory module. The laboratory module contained utilities, computers, work benches, and instrument racks to conduct scientific experiments in astronomy, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, and engineering. Equipment, such as telescopes, anternas, and sensors, was mounted on pallets for direct exposure to space. A 1-meter (3.3-ft.) diameter aluminum tunnel, resembling a z-shaped tube, connected the crew compartment (mid deck) to the module. The reusable Spacelab allowed scientists to bring experiment samples back to Earth for post-flight analysis. Spacelab was a cooperative venture of the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA. ESA was responsible for funding, developing, and building of Spacelab, while NASA was responsible for the launch and operational use of Spacelab. Spacelab missions were cooperative efforts between scientists and engineers from around the world. Teams from NASA centers, universities, private industry, government agencies and international space organizations designed the experiments. The Marshall Space Flight Center was NASA's lead center for monitoring the development of Spacelab and managing the program.
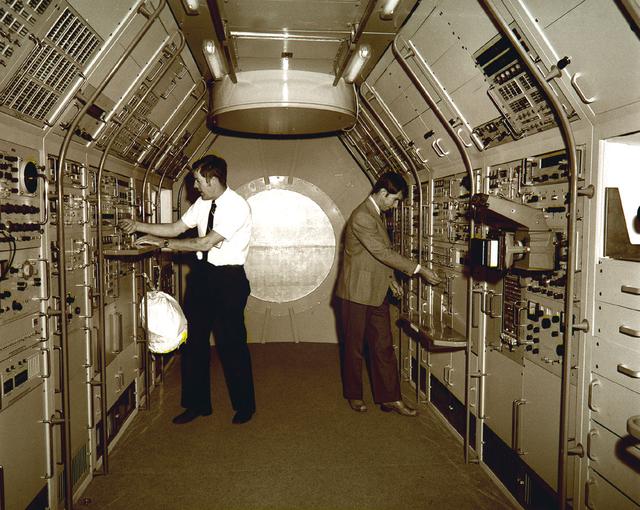

Astronauts Joseph Kerwin (left) and William Lenoir familiarize themselves with equipment aboard the Spacelab mockup during a 1976 visit to the Marshall Space Flight Center. Kerwin and Lenoir were part of an astronaut group briefed on Spacelab subsystems and crew activities by Marshall scientists and engineers. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility for Spacelab.

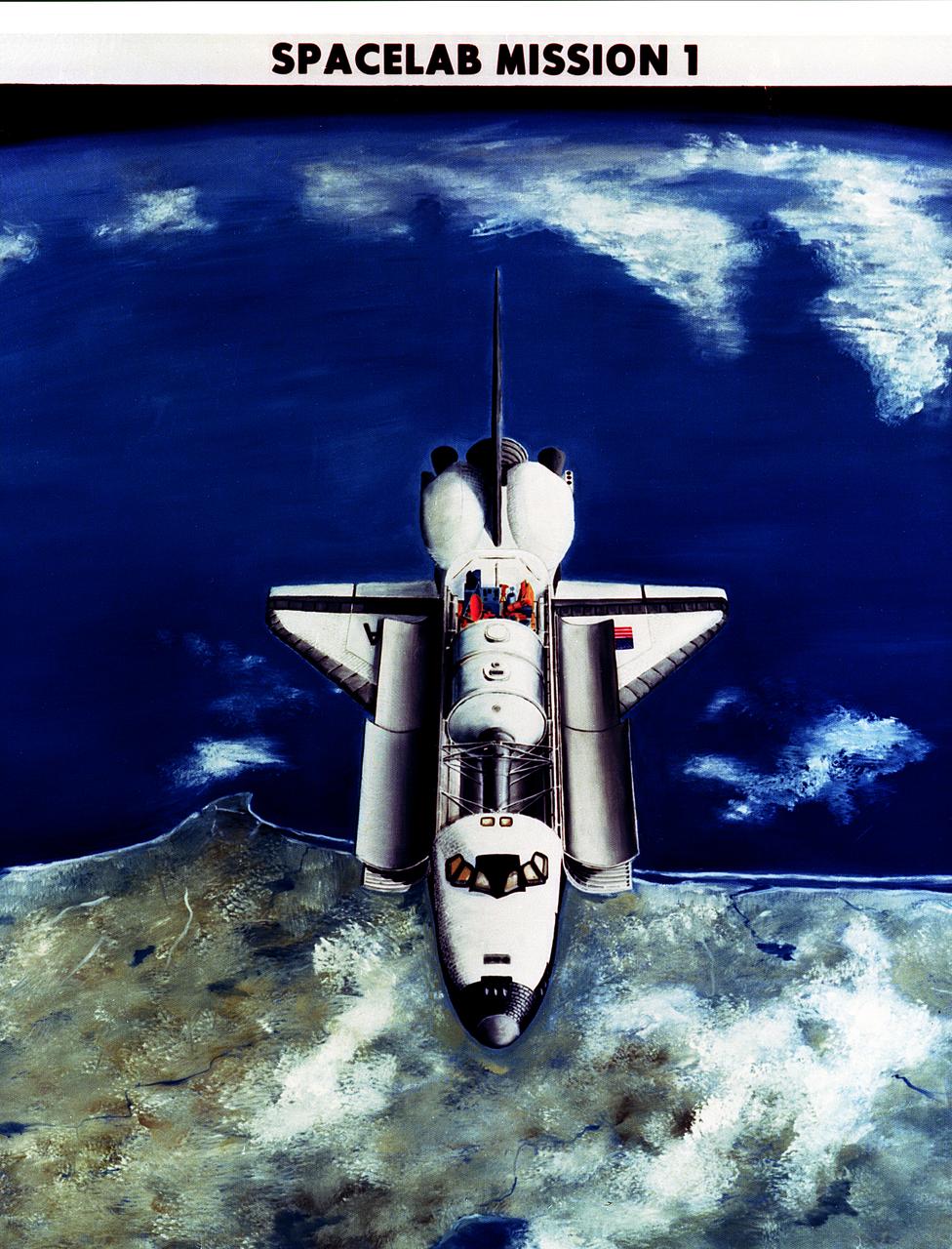
This photograph shows the Spacelab 1 module and pallet ready to be installed in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia at the Kennedy Space Center. The overall goal of the first Spacelab mission was to verify its Space performance through a variety of scientific experiments. The investigation selected for this mission tested the Spacelab hardware, flight and ground systems, and crew to demonstrate their capabilities for advanced research in space. However, Spacelab 1 was not merely a checkout flight or a trial run. Important research problems that required a laboratory in space were scheduled for the mission. Spacelab 1 was a multidisciplinary mission; that is, investigations were performed in several different fields of scientific research. These fields were Astronomy and Solar Physics, Space Plasma Physics, Atmospheric Physics and Earth Observations, Life Sciences, and Materials Science. Spacelab 1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-9 mission) on November 28, 1983.
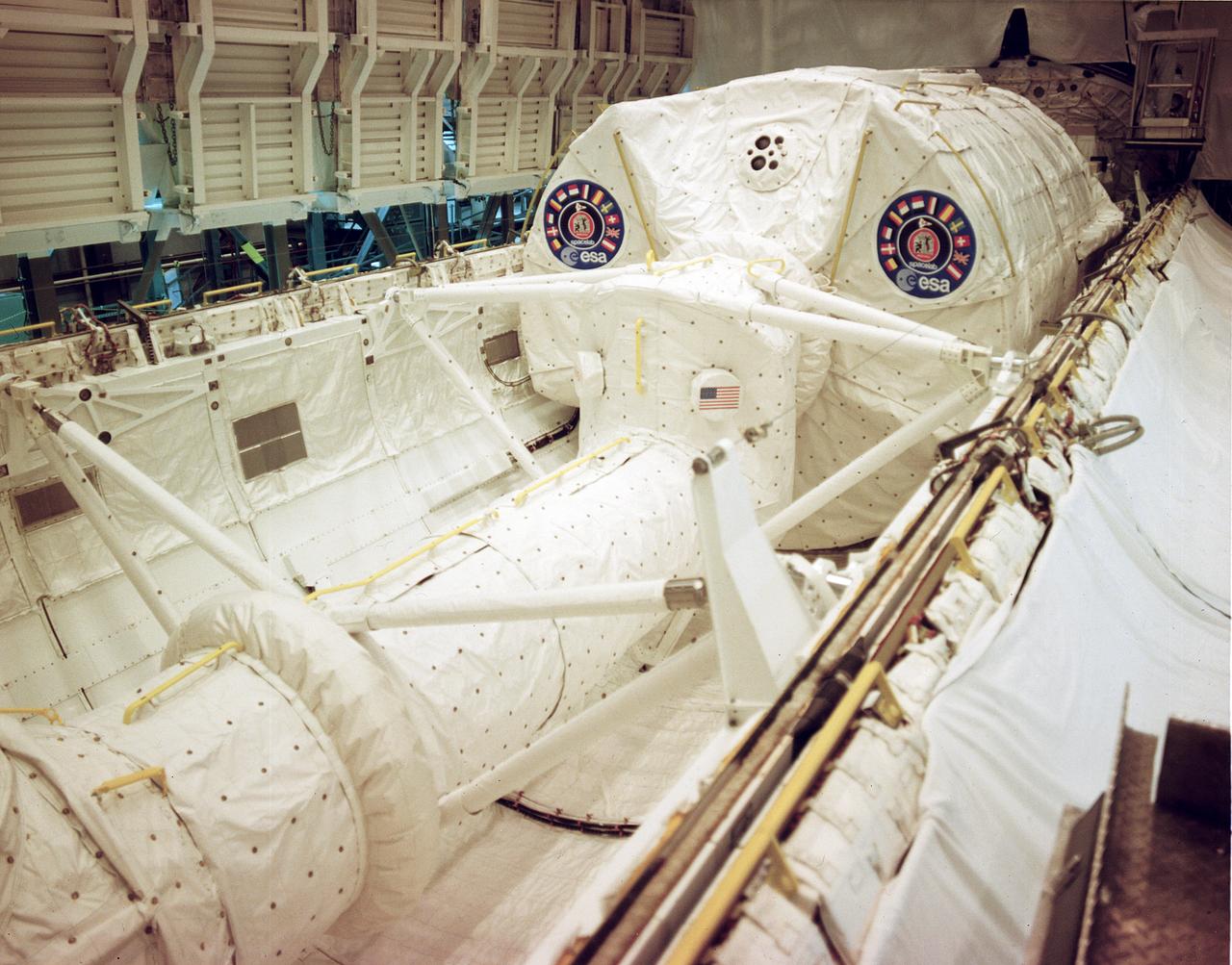
This photograph shows the Spacelab-1 module and Spacelab access turnel being installed in the cargo bay of orbiter Columbia for the STS-9 mission. The oribiting laboratory, built by the European Space Agency, is capable of supporting many types of scientific research that can best be performed in space. The Spacelab access tunnel, the only major piece of Spacelab hardware made in the U.S., connects the module with the mid-deck level of the orbiter cabin. The first Spacelab mission, Spacelab-1, sponsored jointly and shared equally by NASA and the European Space Agency, was a multidisciplinary mission; that is, investigations were performed in several different fields of scientific research. The overall goal of the mission was to verify Spacelab performance through a variety of scientific experiments. The disciplines represented by these experiments were: astronomy and solar physics, earth observations, space plasma physics, materials sciences, atmospheric physics, and life sciences. International in nature, Spacelab-1 conducted experiments from the United States, Japan, the Netherlands, United Kingdom, Beluga, France, Germany, Italy, and Switzerland. Spacelab-1, was launched from the Kennedy Space Center on November 28, 1983 aboard the orbiter Columbia (STS-9). The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for managing the Spacelab missions.
This double exposure image shows Spacelab-1 in the cargo bay of orbiter Columbia. From top to bottom inside the cargo bay are the Spacelab Access Turnel, which is connected to the mid-deck of the orbiter; the Spacelab module, a pressurized module in which scientists conduct experiments not possible on Earth; and Spacelab pallets, which can hold instruments for the experiments requiring direct exposure to space. The first Spacelab mission, Spacelab-1, sponsored jointly and shared equally by NASA and the European Space Agency, was a multidisciplinary mission; that is, investigations were performed in several different fields of scientific research. The overall goal of the mission was to verify Spacelab performance through a variety of scientific experiments. The disciplines represented by these experiments were astronomy and solar physics, earth observations, space plasma physics, materials sciences, atmospheric physics, and life sciences. International in nature, Spacelab-1 conducted experiments from the United States, Japan, the Netherlands, United Kingdom, Beluga, France, Germany, Italy, and Switzerland. Spacelab-1 was launched from the Kennedy Space Center on November 28, 1983 aboard the orbiter Columbia (STS-9). The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for managing the Spacelab missions.
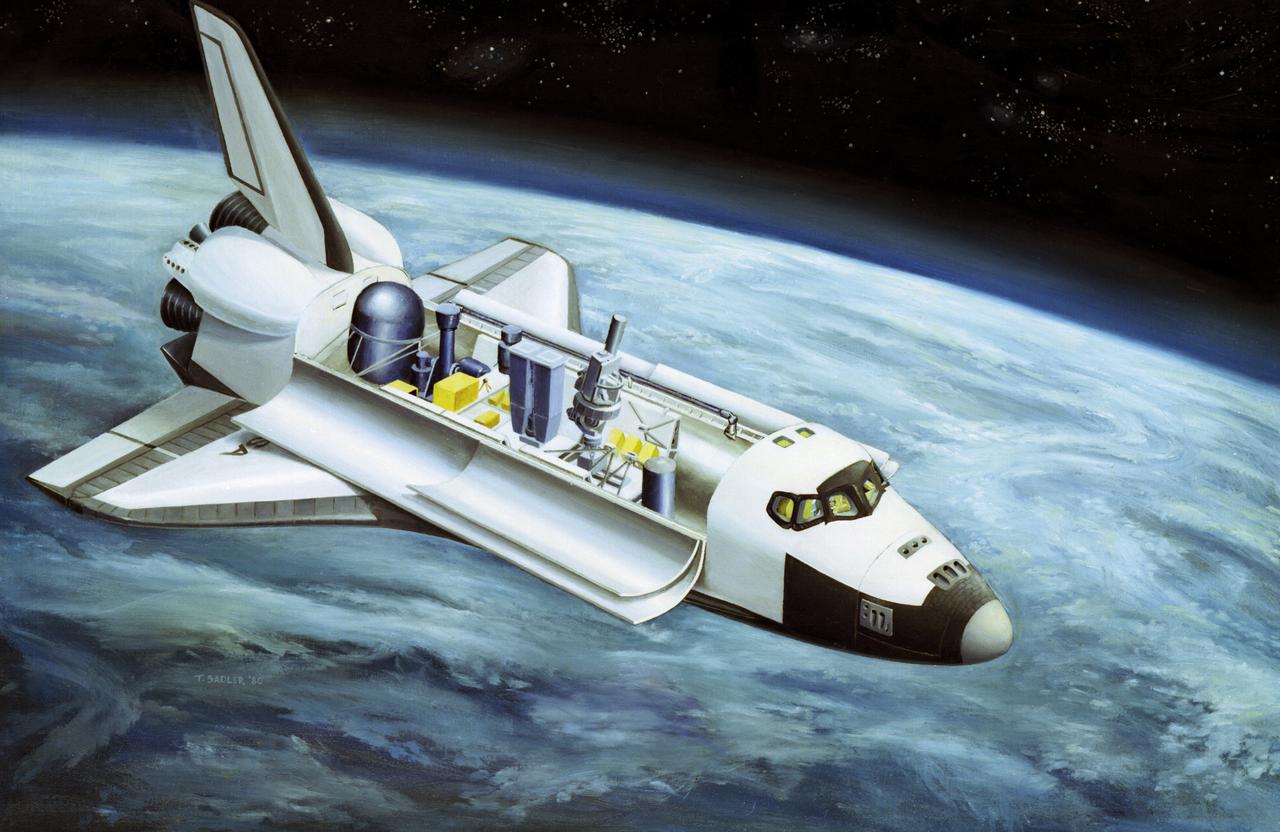
This illustration depicts the configuration of the Spacelab-2 in the cargo bay of the orbiter. Spacelab was a versatile laboratory carried in the Space Shuttle's cargo bay for scientific research flights. Each Spacelab mission had a unique design appropriate to the mission's goals. A number of Spacelab configurations could be assembled from pressurized habitation modules and exposed platforms called pallets. Spacelab-2 was the first pallet-only mission. One of the goals of the mission was to verify that the pallets' configuration was satisfactory for observations and research. Except for two biological experiments and an experiment that used ground-based instruments, the Spacelab-2 scientific instruments needed direct exposure to space. On the first pallet, three solar instruments and one atmospheric instrument were mounted on the Instrument Pointing System, which was being tested on its first flight. The second Spacelab pallet held a large double x-ray telescope and three plasma physics detectors. The last pallet supported an infrared telescope, a superfluid helium technology experiment, and a small plasma diagnostics satellite. The Spacelab-2 mission was designed to capitalize on the Shuttle-Spacelab capabilities, to launch and retrieve satellites, and to point several instruments independently with accuracy and stability. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched aboard Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on July 29, 1985. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall management responsibilities of the Spacelab missions.
The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew did research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new mini-labs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. The instruments requiring direct exposure to space were mounted outside in the open payload bay of the Shuttle. Spacelab represented the merger of science and marned spaceflight. It opened remarkable opportunities to push the frontiers of knowledge beyond the limits of research on Earth. Scientists in space performed experiments in close collaboration with their colleagues on the ground. On the Spacelab-3 mission, managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, this versatile laboratory entered routine operation service for the next two decades. Spacelab-3 (STS-51B mission) was launched aboard Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on April 29, 1985.
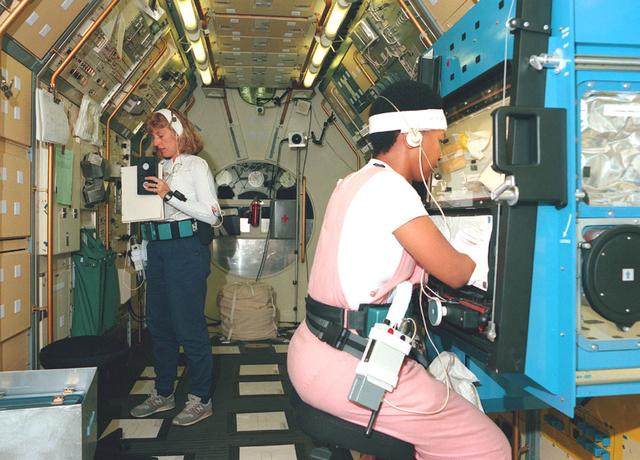

Female astronauts Jan Davis and Mae Jemison undergo training at Marshall's Spacelab-J Crew Training facility.
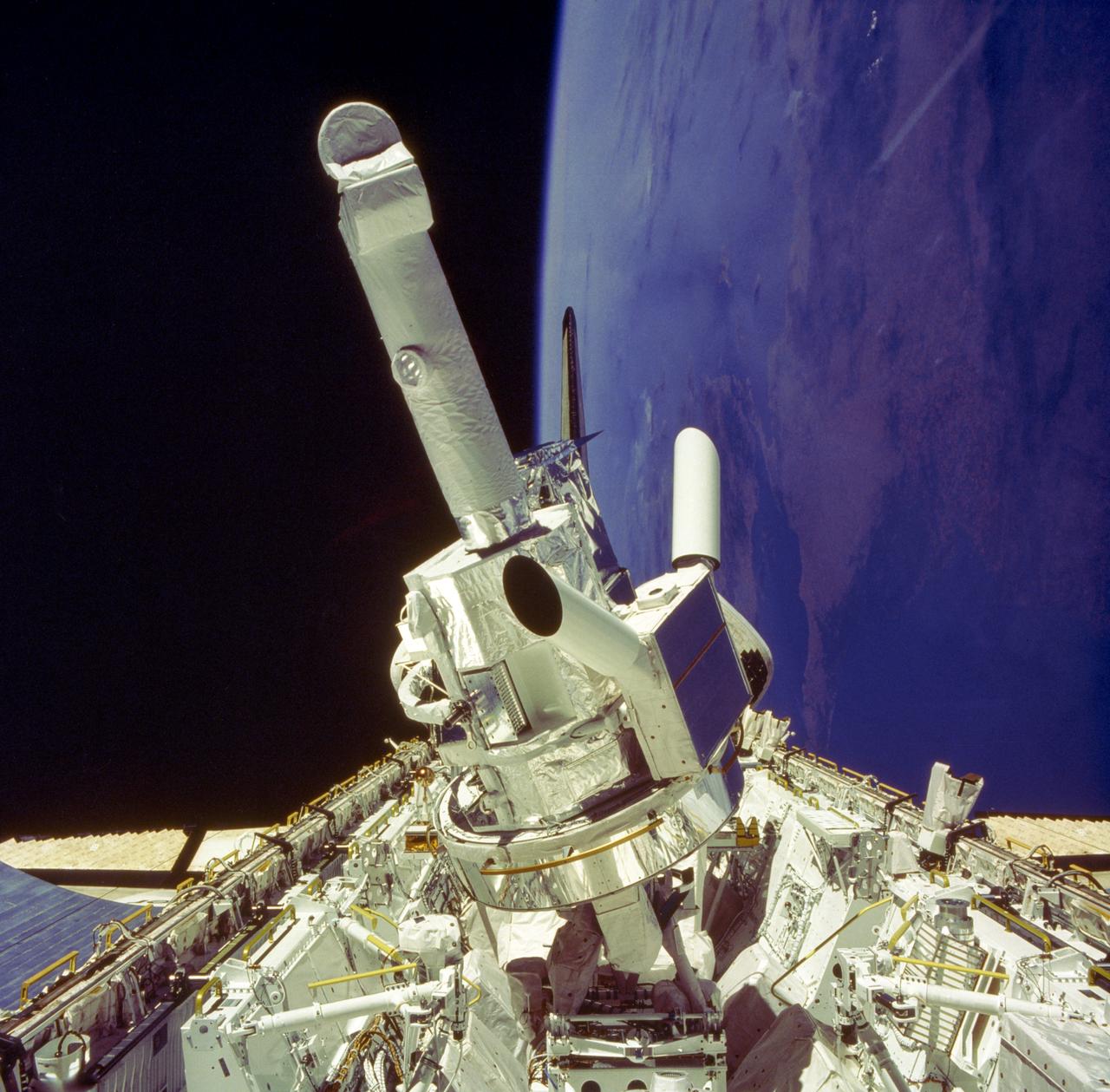

This photograph shows the Instrument Pointing System (IPS) for Spacelab-2 being deployed in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. The European Space Agency (ESA) developed this irnovative pointing system for the Spacelab program. Previously, instruments were pointed toward particular celestial objects or areas by maneuvering the Shuttle to an appropriate attitude. The IPS could aim instruments more accurately than the Shuttle and kept them fixed on a target as the Shuttle moved. On the first pallet, three solar instruments and one atmospheric instrument were mounted on the IPS. Spacelab-2 was the first pallet-only mission. One of the goals of the mission was to verify that the pallets' configuration was satisfactory for observations and research. Except for two biological experiments and an experiment that used ground-based instruments, the Spacelab-2 scientific instruments needed direct exposure to space. The Spacelab-2 mission was designed to capitalize on the Shuttle-Spacelab capabilities to carry very large instruments, launch and retrieve satellites, and point several instruments independently with accuracy and stability. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched on July 29, 1985 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall management responsibilities of the Spacelab missions.
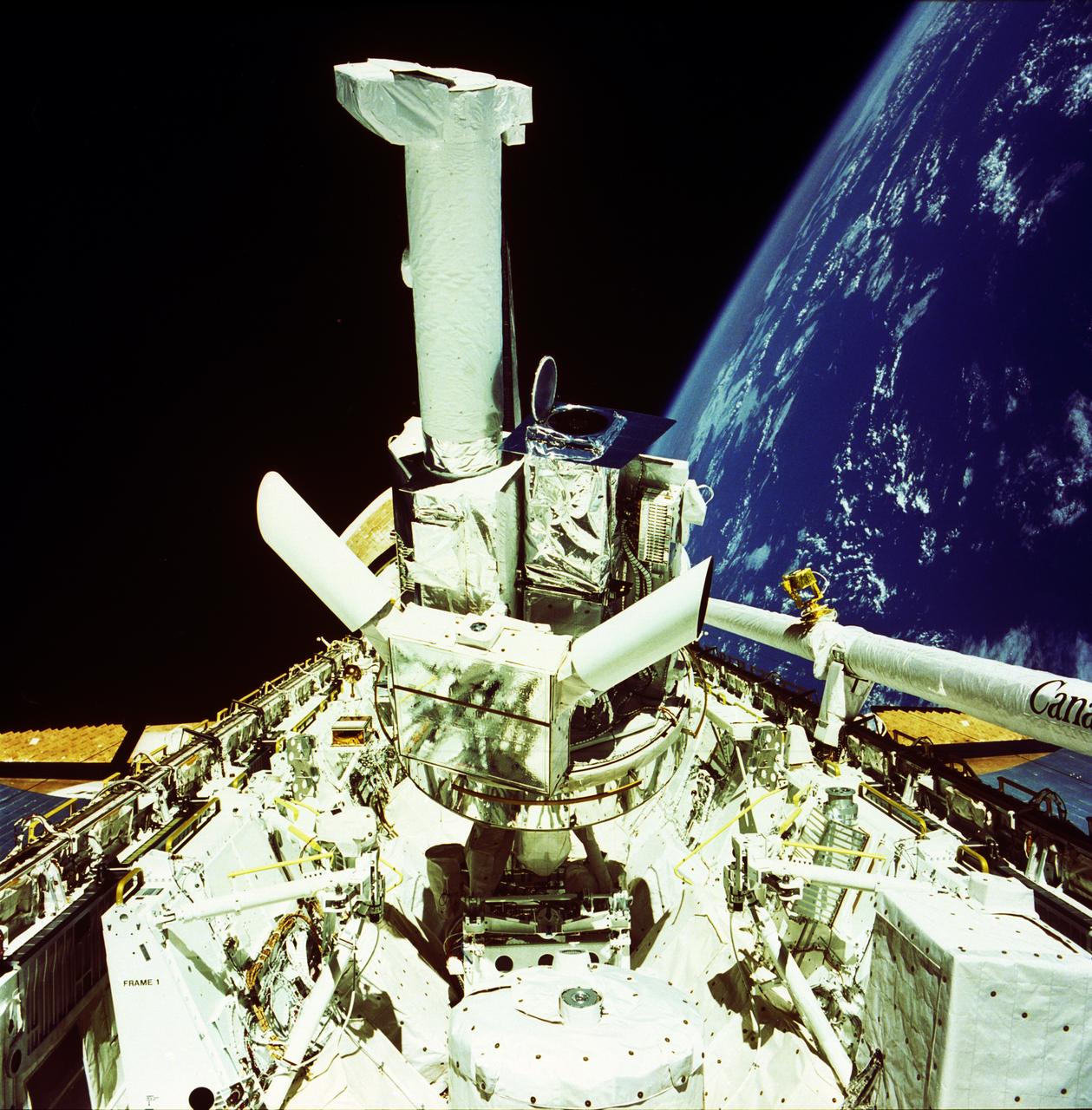

This photograph shows the Instrument Pointing System (IPS) for Spacelab-2 being deployed in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. The European Space Agency (ESA) developed this irnovative pointing system for the Spacelab program. Previously, instruments were pointed toward particular celestial objects or areas by maneuvering the Shuttle to an appropriate attitude. The IPS could aim instruments more accurately than the Shuttle and kept them fixed on a target as the Shuttle moved. On the first pallet, three solar instruments and one atmospheric instrument were mounted on the IPS. Spacelab-2 was the first pallet-only mission. One of the goals of the mission was to verify that the pallets' configuration was satisfactory for observations and research. Except for two biological experiments and an experiment that uses ground-based instruments, the Spacelab-2 scientific instruments needed direct exposure to space. The Spacelab-2 mission was designed to capitalize on the Shuttle-Spacelab capabilities to carry very large instruments, launch and retrieve satellites, and point several instruments independently with accuracy and stability. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched on July 29, 1985 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall management responsibilities of the Spacelab missions.
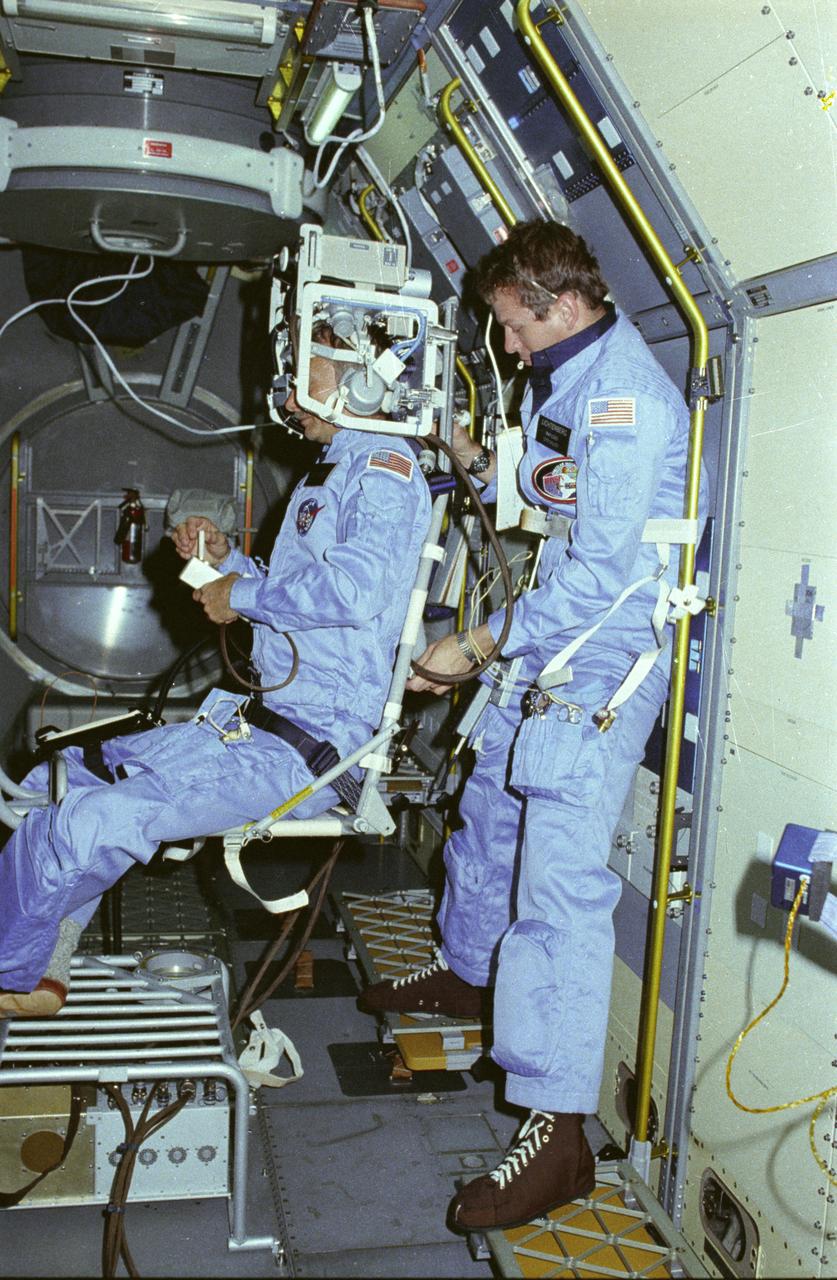

In this photograph, astronauts Owen Garriott on the body restriant system and Byron Lichtenberg prepare for a Vestibular Experiment during the Spacelab-1 mission. The Vestibular Experiments in Space were the study of the interaction among the otoliths, semicircular canals, vision, and spinal reflexes in humans. The main objective was to determine how the body, which receives redundant information for several sensory sources, interprets this information in microgravity. Another objective was to record and characterize the symptoms of space sickness experienced by crewmembers. The body restraint system was a rotating chair with a harness to hold the test subject in place. The crewmember wore an accelerometer and electrodes to record head motion and horizontal and vertical eye movement as the body rotated. The first Spacelab mission, Spacelab-1, sponsored jointly and shared equally by NASA and the European Space Agency, was a multidisciplinary mission; that is, investigations were performed in several different fields of scientific research. The overall goal of the mission was to verify Spacelab performance through a variety of scientific experiments. The Spacelab-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia for the STS-9 mission on November 28, 1983. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibilities for the mission.
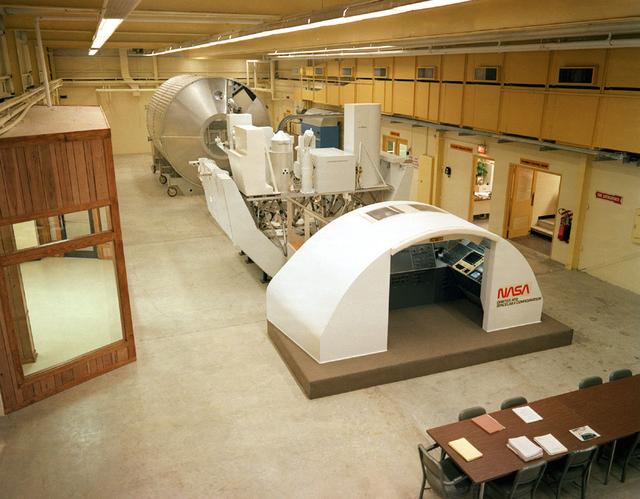

A mockup of the Spacelab II configuration was built at Marshall's Completed Payload Crew Training Complex (PCTC) located at Building 4612.

Spacelab-3 launched aboard STS-51B, with the major science objective being to perform engineering tests on two new facilities: the rodent animal holding facility and the primate animal holding facility. In addition, scientists observed the animals to obtain first hand knowledge of the effects of launch and reentry stresses and behavior. The need for suitable animal housing to support research in space led to the development of the Research Animal Holding Facility at the Ames Research Center. Scientists often study animals to find clues to human physiology and behavior. Rats, insects, and microorganisms had already been studied aboard the Shuttle on previous missions. On Spacelab-3, scientists had a chance to observe a large number of animals living in space in a specially designed and independently controlled housing facility. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had management responsibility for the Spacelab 3 mission. This photograph depicts activities during the mission at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC.

Spacelab-3 launched aboard STS-51B, with the major science objective being to perform engineering tests on two new facilities: the rodent animal holding facility and the primate animal holding facility. In addition, scientists observed the animals to obtain first hand knowledge of the effects of launch and reentry stresses and behavior. The need for suitable animal housing to support research in space led to the development of the Research Animal Holding Facility at the Ames Research Center. Scientists often study animals to find clues to human physiology and behavior. Rats, insects, and microorganisms had already been studied aboard the Shuttle on previous missions. On Spacelab-3, scientists had a chance to observe a large number of animals living in space in a specially designed and independently controlled housing facility. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had management responsibility for the Spacelab-3 mission. This photograph depicts activities during the mission at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC.

Spacelab-3 launched aboard STS-51B, with the major science objective being to perform engineering tests on two new facilities: the rodent animal holding facility and the primate animal holding facility. In addition, scientists observed the animals to obtain first hand knowledge of the effects of launch and reentry stresses and behavior. The need for suitable animal housing to support research in space led to the development of the Research Animal Holding Facility at the Ames Research Center. Scientists often study animals to find clues to human physiology and behavior. Rats, insects, and microorganisms had already been studied aboard the Shuttle on previous missions. On Spacelab-3, scientists had a chance to observe a large number of animals living in space in a specially designed and independently controlled housing facility. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had management responsibility for the Spacelab-3 mission. This photograph depicts activities during the mission at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC.

Spacelab-3 launched aboard STS-51B, with the major science objective being to perform engineering tests on two new facilities: the rodent animal holding facility and the primate animal holding facility. In addition, scientists observed the animals to obtain first hand knowledge of the effects of launch and reentry stresses and behavior. The need for suitable animal housing to support research in space led to the development of the Research Animal Holding Facility at the Ames Research Center. Scientists often study animals to find clues to human physiology and behavior. Rats, insects, and microorganisms had already been studied aboard the Shuttle on previous missions. On Spacelab-3, scientists had a chance to observe a large number of animals living in space in a specially designed and independently controlled housing facility. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had management responsibility for the Spacelab 3 mission. This photograph depicts activities during the mission at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC.

Spacelab-3 launched aboard STS-51B, with the major science objective being to perform engineering tests on two new facilities: the rodent animal holding facility and the primate animal holding facility. In addition, scientists observed the animals to obtain first hand knowledge of the effects of launch and reentry stresses and behavior. The need for suitable animal housing to support research in space led to the development of the Research Animal Holding Facility at the Ames Research Center. Scientists often study animals to find clues to human physiology and behavior. Rats, insects, and microorganisms had already been studied aboard the Shuttle on previous missions. On Spacelab-3, scientists had a chance to observe a large number of animals living in space in a specially designed and independently controlled housing facility. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had management responsibility for the Spacelab-3 mission. This photograph depicts activities during the mission at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC.
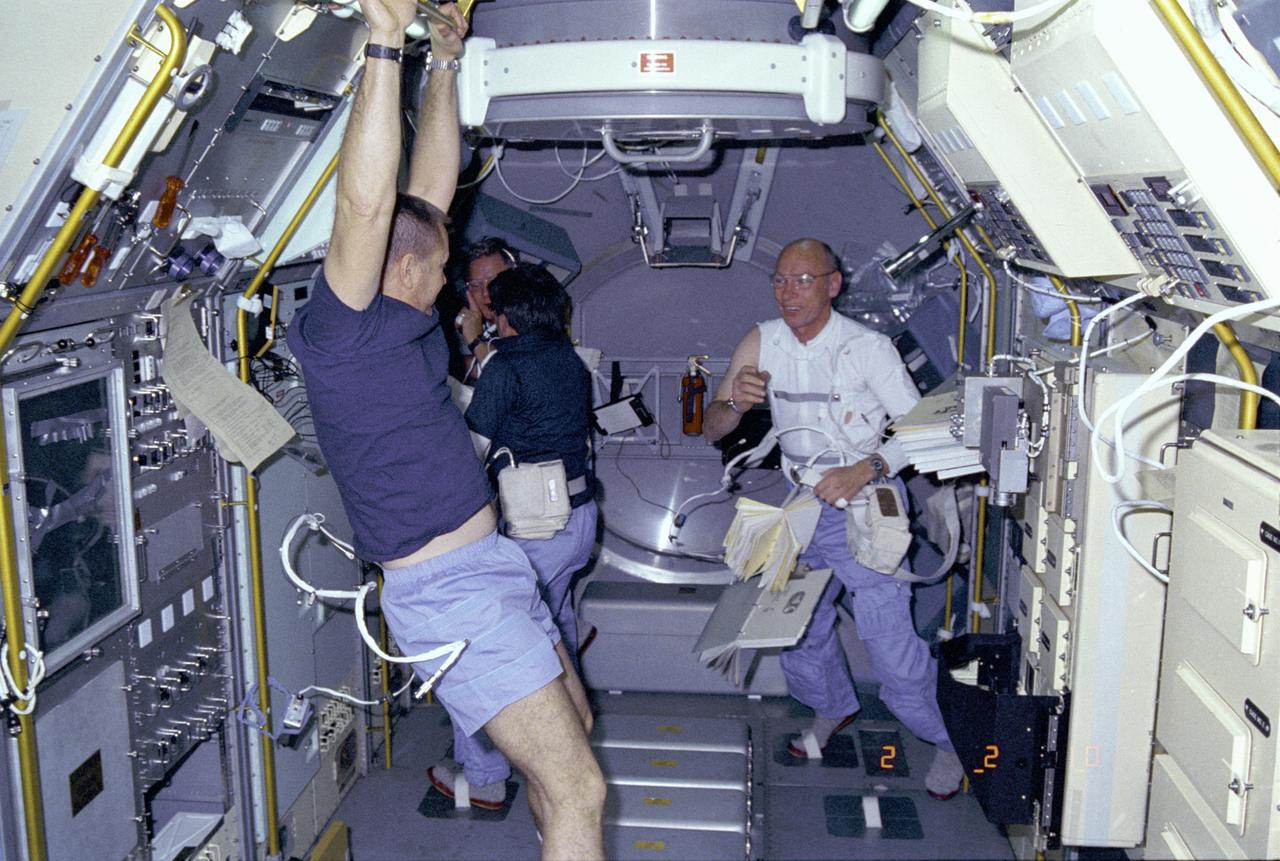

Activities inside the laboratory module during the Spacelab-3 mission are shown in this photograph. Left to right are astronauts Robert Overmyer, Commander of the mission; Don Lind, Mission Specialist; Lodewijk van den Berg, Payload Specialist; and William Thornton, Mission Specialist. The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew did research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new minilabs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. Spacelab-3 (STS-51B) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger on April 29, 1985. The Marshall Space Flight Center had managing responsibilities of the mission.
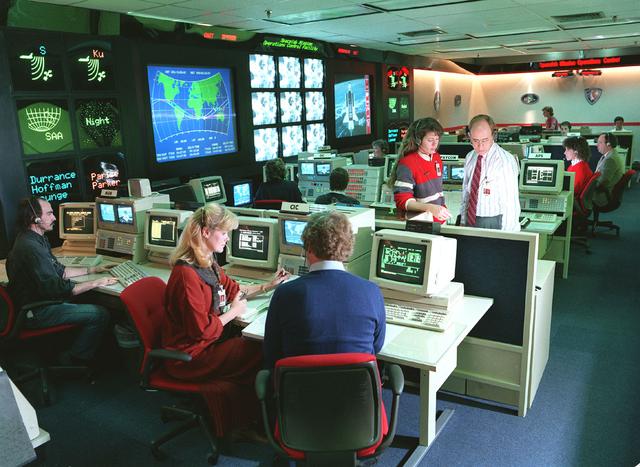

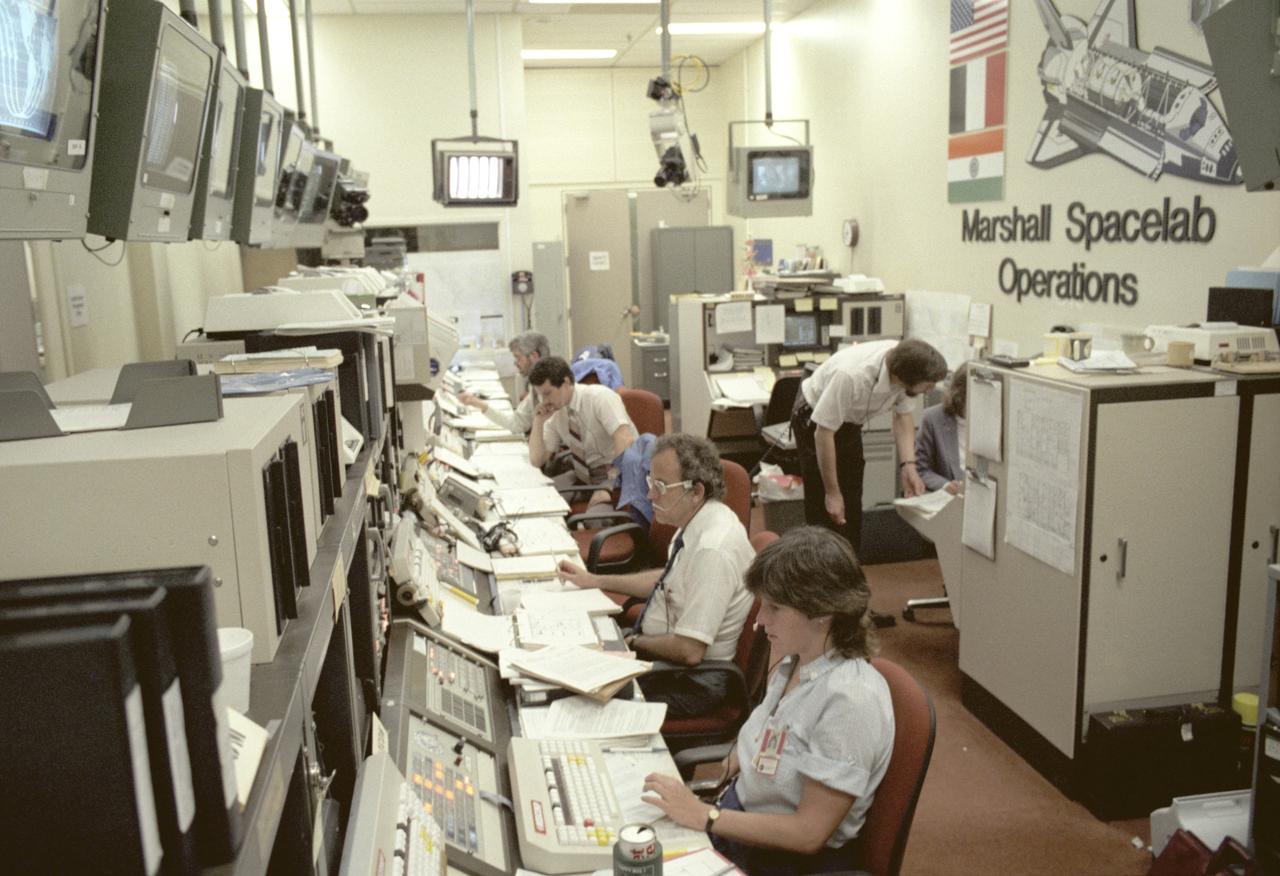
Activities in the Spacelab Mission Operations Control facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) are shown in this photograph. All NASA Spacelab science missions were controlled from and the science astronauts were supported by this facility during the missions. Teams of flight controllers and researchers at the MSFC Space Mission Operations Control Center directed all NASA science operations, sent commands directly to the crew of Spacelab, and received and analyzed data from experiments on board the Spacelab. The facility used the air/ground communications charnels between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Spacelab science operations were a cooperative effort between the science astronaut crew in orbit and their colleagues in the Space Mission Operations Control Center. Though the crew and the instrument science teams were separated by many miles, they interacted with one another to evaluate observations and solve problems in much the same way as they would when working side by side in a ground-based laboratory. Most of the action was centered in two work areas: The payload control area from which the overall payload was monitored and controlled and the science operations area where teams of scientists monitored their instruments and direct experiment activities. This facility is no longer operational since the last Spacelab mission, U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 in December 1997, and has become one of the historical sites at MSFC. The facility was reopened as the International Space Station Payload Operations Center in March 2001.
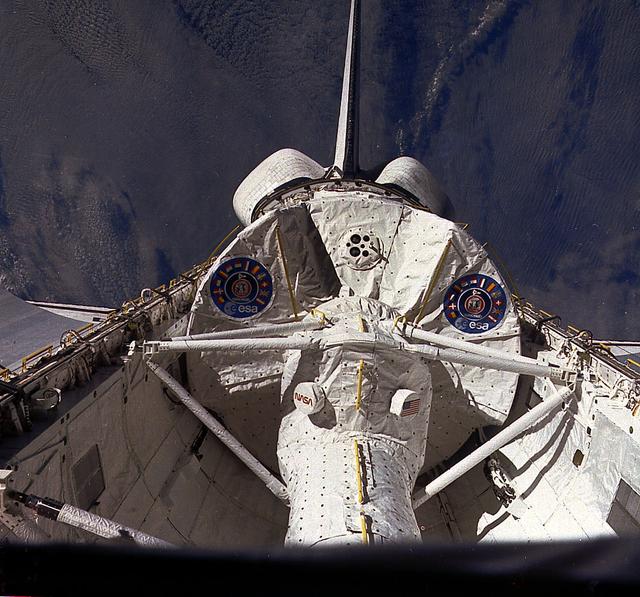

A Space Shuttle mission STS-9 onboard view show's Spacelab-1 (SL-1) module in orbiter Columbia's payload bay. Spacelab-1 was a cooperative venture of NASA and the European Space Agency. Scientists from eleven European nations plus Canada, Japan and the U.S. provided instruments and experimental procedures for over 70 different investigations in five research areas of disciplines: astronomy and solar physics, space plasma physics, atmospheric physics and Earth observations, life sciences and materials science.
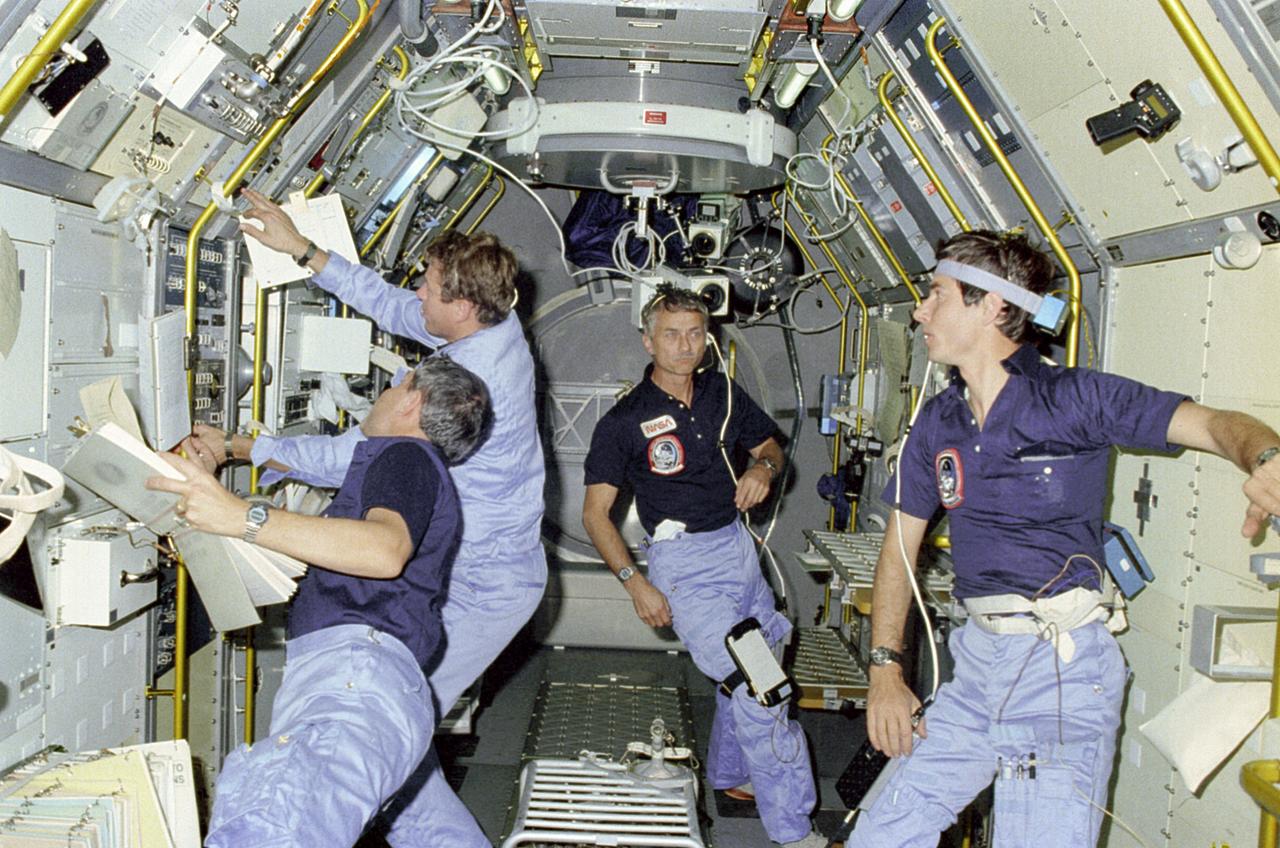

This photograph shows activities inside the science module during the Spacelab-1 (STS-9) mission. Left to right are Mission Specialist Robert Parker, Payload Specialist Byron Lichtenberg, Mission Specialist Owen Garriott, and Payload Specialist Ulf Merbold. The overall goal of the Spacelab-1 mission, the first mission of the Spacelab facility, were: (1) To verify the Spacelab system capability, (2) to obtain valuable scientific, applications, and technology data from a U.S./European multidisciplinary payload, and (3) to demonstrate the broad capability of Spacelab for scientific research. More than 70 experiments in 5 disciplines from 14 nations were conducted during the mission. The mission marked the the entry of non-astronaut persornel, called Payload Specialists, into space as working members of the crew. They are fellow scientists representing the international group of investigators using the mission. Mission Specialists are NASA astronauts who have broad scientific training. They operate various Orbiter-Spacelab systems, perform any required activity outside the spacecraft, and support investigations as needed. The Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia that carried Spacelab-1 was operated by two other NASA astronauts serving as commander and pilot. The STS-9 mission, managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was launched on November 28, 1983.
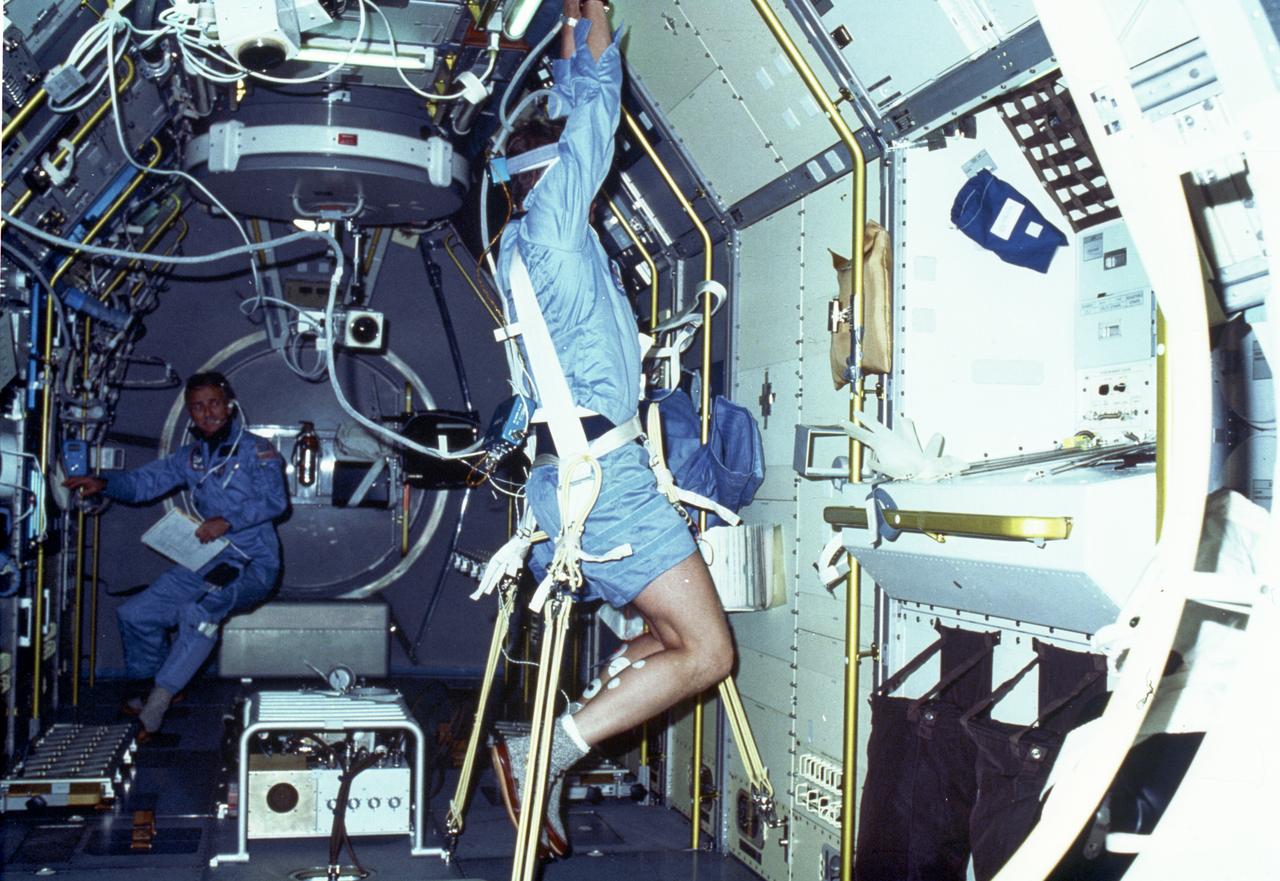
In this Spacelab-1 mission onboard photograph, astronaut Byron Lichtenberg performs a drop experiment, one of the Vestibular Experiments in Space investigations. The experiment examined spinal reflexes to determine whether they changed in microgravity. In Earth's environment, the otoliths signal the muscles to prepare for jolts associated with falling. During the flight, the normal reflex between the otoliths and the muscles was partially inhibited early in flight, declined further as the flight progressed, and returned to normal immediately after landing, suggesting that the brain ignored or reinterpreted otolith signals during space flight. Crewmembers reported a lack of awareness of position and location of feet, difficulty in maintaining balance, and a perception that falls were more sudden, faster, and harder than similar drops experienced in preflight. Crewmembers experienced illusions as they performed prescribed movement tests. When crew members viewed various targets and then pointed at them while blindfolded, their perception of target location and position of their own limbs was inaccurate in flight compared with similar tests on the ground. The Spacelab-1 was a multidisciplinary mission; that is, investigations were performed in several different fields of scientific research. The overall goal of the mission was to verify Spacelab performance through a variety of scientific experiments. The Spacelab-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia for the STS-9 mission on November 28, 1983. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibilities for the mission.
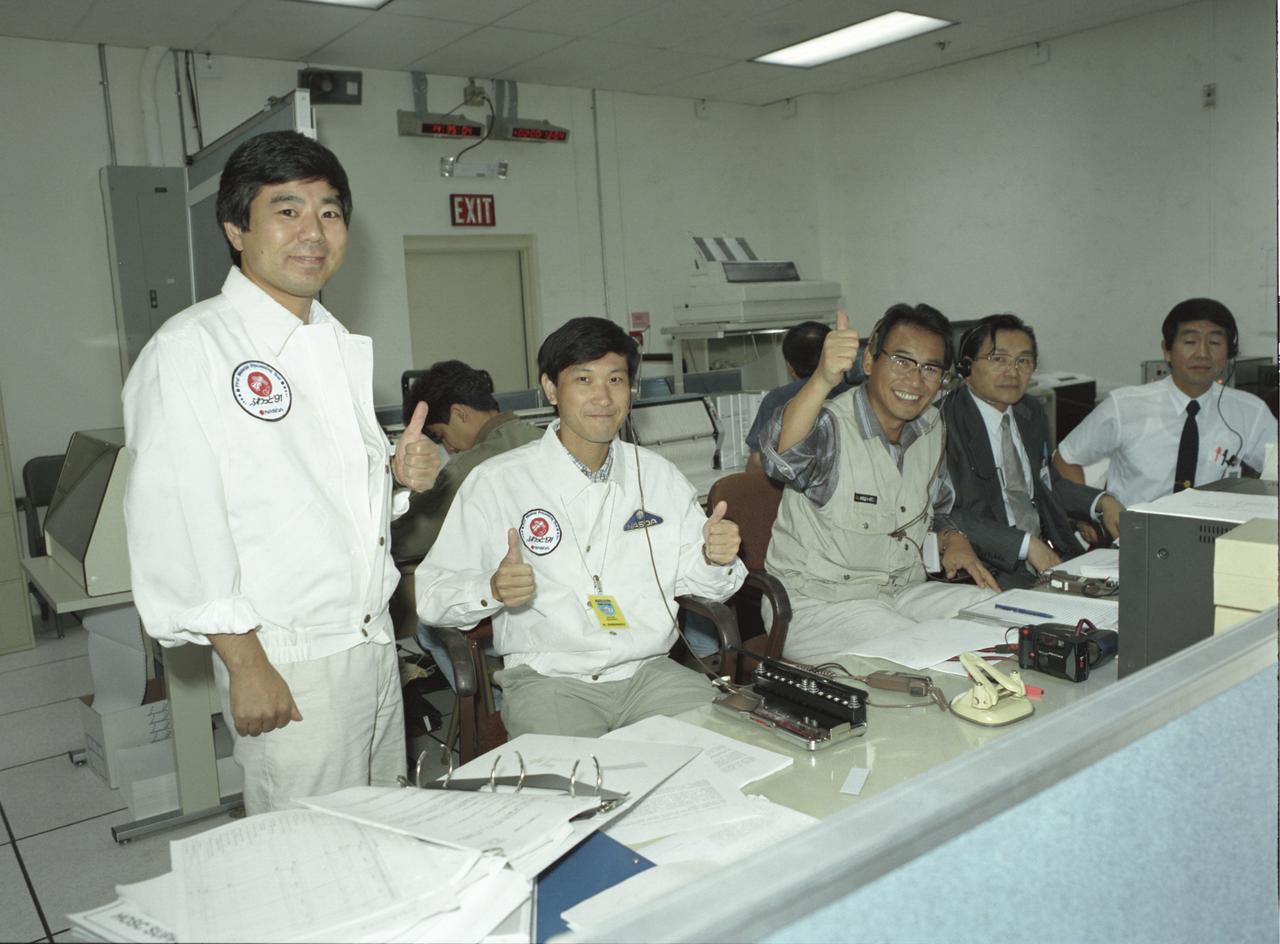

The group of Japanese researchers of the Spacelab-J (SL-J) were thumbs-up in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center after the successful launch of Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour that carried their experiments. The SL-J was a joint mission of NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted microgravity investigations in materials and life sciences. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, frogs, and frog eggs. The POCC was the air/ground communications channel between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The Spacelab science operations were a cooperative effort between the science astronaut crew in orbit and their colleagues in the POCC. Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
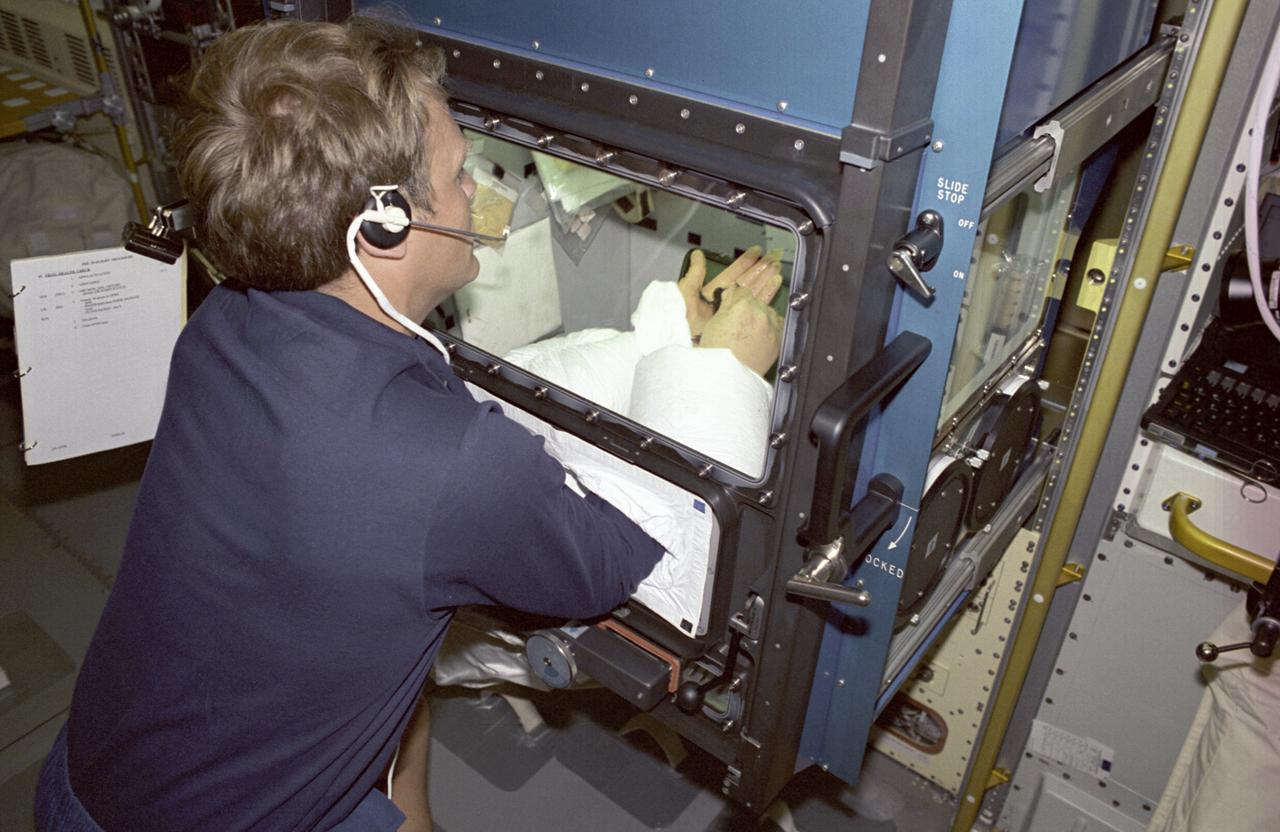

The Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Before long-term space ventures are attempted, numerous questions must be answered: how will gravity play in the early development of an organism, and how will new generations of a species be conceived and develop normally in microgravity. The Effects of Weightlessness on the Development of Amphibian Eggs Fertilized in Space experiment aboard SL-J examined aspects of these questions. To investigate the effect of microgravity on amphibian development, female frogs carried aboard SL-J were induced to ovulate and shed eggs. These eggs were then fertilized in the microgravity environment. Half were incubated in microgravity, while the other half were incubated in a centrifuge that spins to simulate normal gravity. This photograph shows astronaut Mark Lee working with one of the adult female frogs inside the incubator. The mission also examined the swimming behavior of tadpoles grown in the absence of gravity. The Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
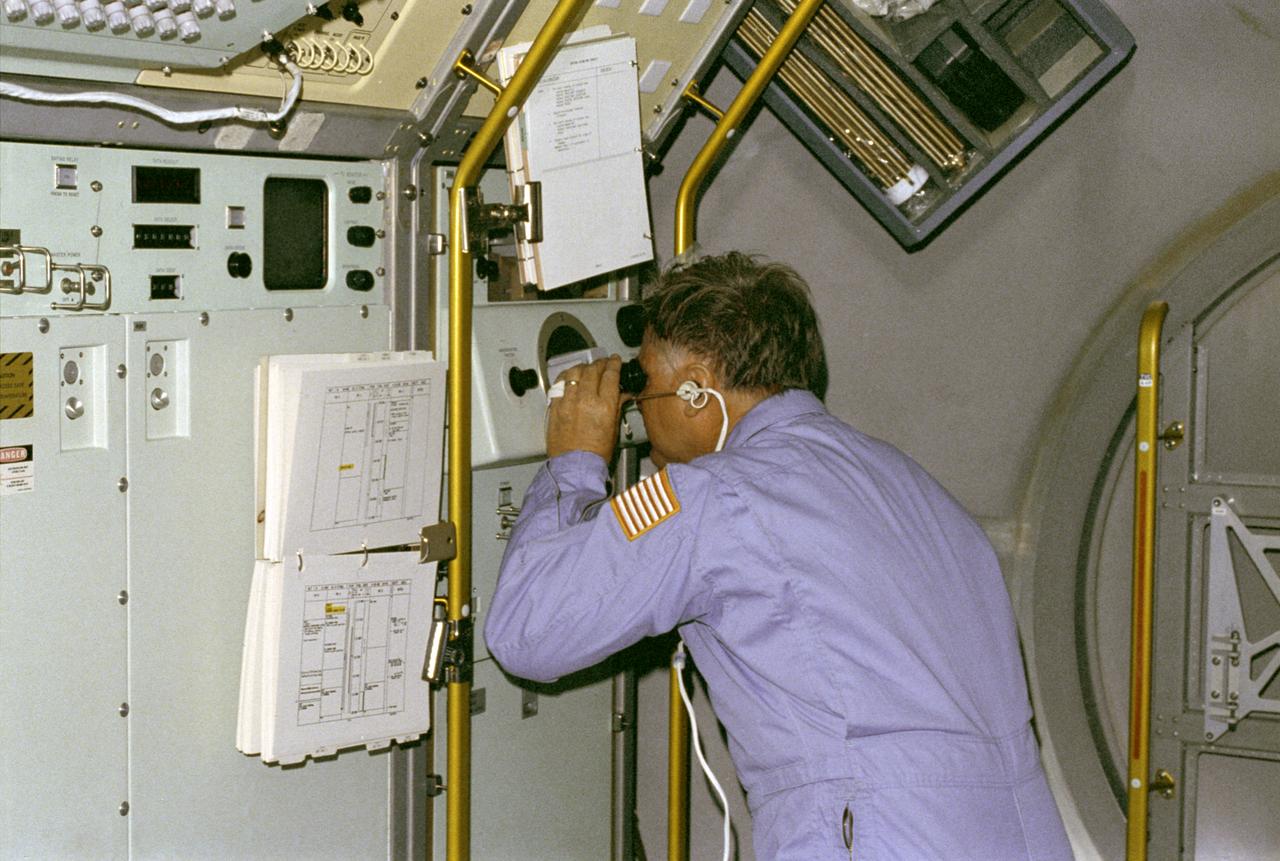

The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew performed research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new minilabs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. In this photograph, astronaut Don Lind observes the mercuric iodide growth experiment through a microscope at the vapor crystal growth furnace. The goals of this investigation were to grow near-perfect single crystals of mercuric iodide and to gain improved understanding of crystal growth by a vapor process. Mercuric iodide crystals have practical use as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors, and in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and in astronomical instruments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, Spacelab-3 (STS-51B) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on April 29, 1985.
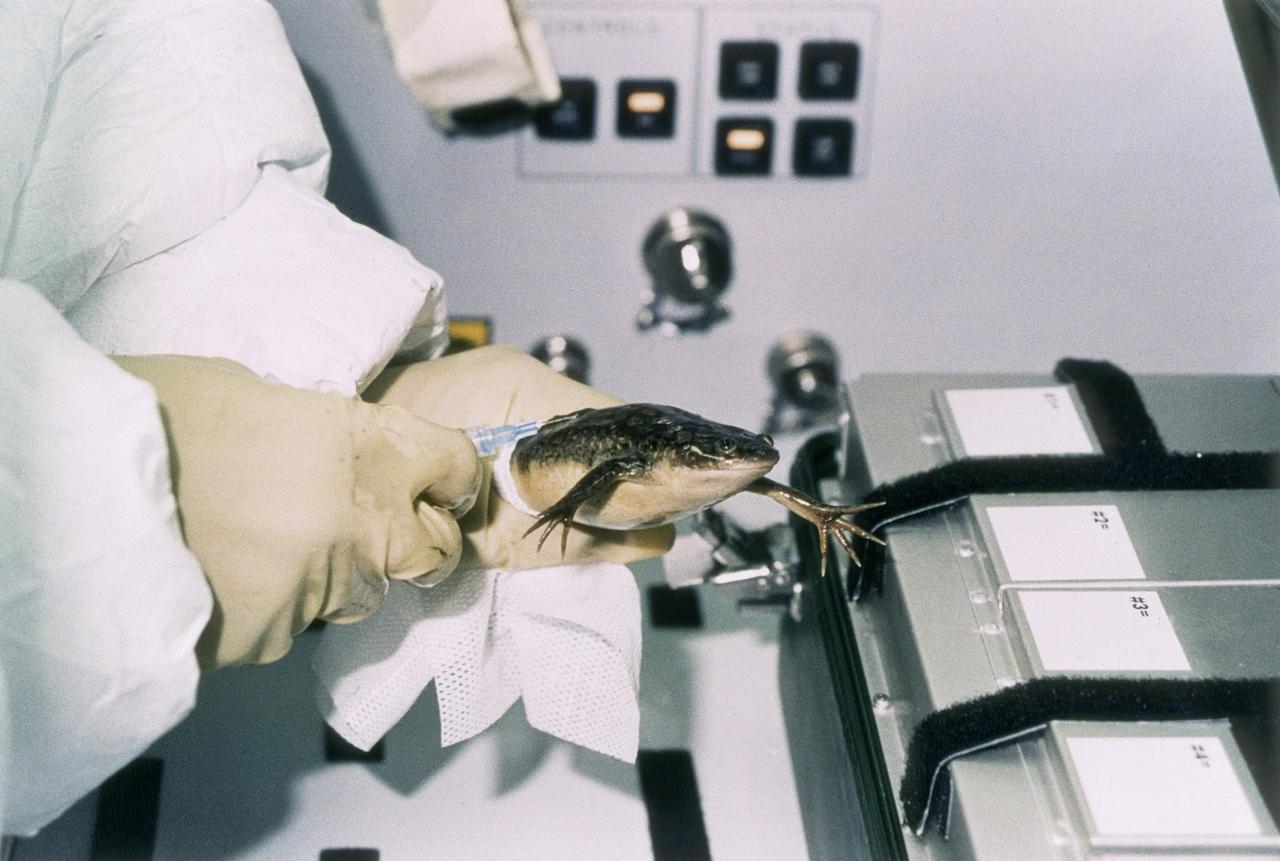
The Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Before long-term space ventures are attempted, numerous questions must be answered: how will gravity play in the early development of an organism, and how will new generations of a species be conceived and develop normally in microgravity. The Effects of Weightlessness on the Development of Amphibian Eggs Fertilized in Space experiment aboard SL-J examined aspects of these questions. To investigate the effect of microgravity on amphibian development, female frogs carried aboard SL-J were induced to ovulate and shed eggs. These eggs were then fertilized in the microgravity environment. Half were incubated in microgravity, while the other half were incubated in a centrifuge that spins to simulate normal gravity. This photograph shows an astronaut working with one of the adult female frogs inside the incubator. The mission also examined the swimming behavior of tadpoles grown in the absence of gravity. The Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
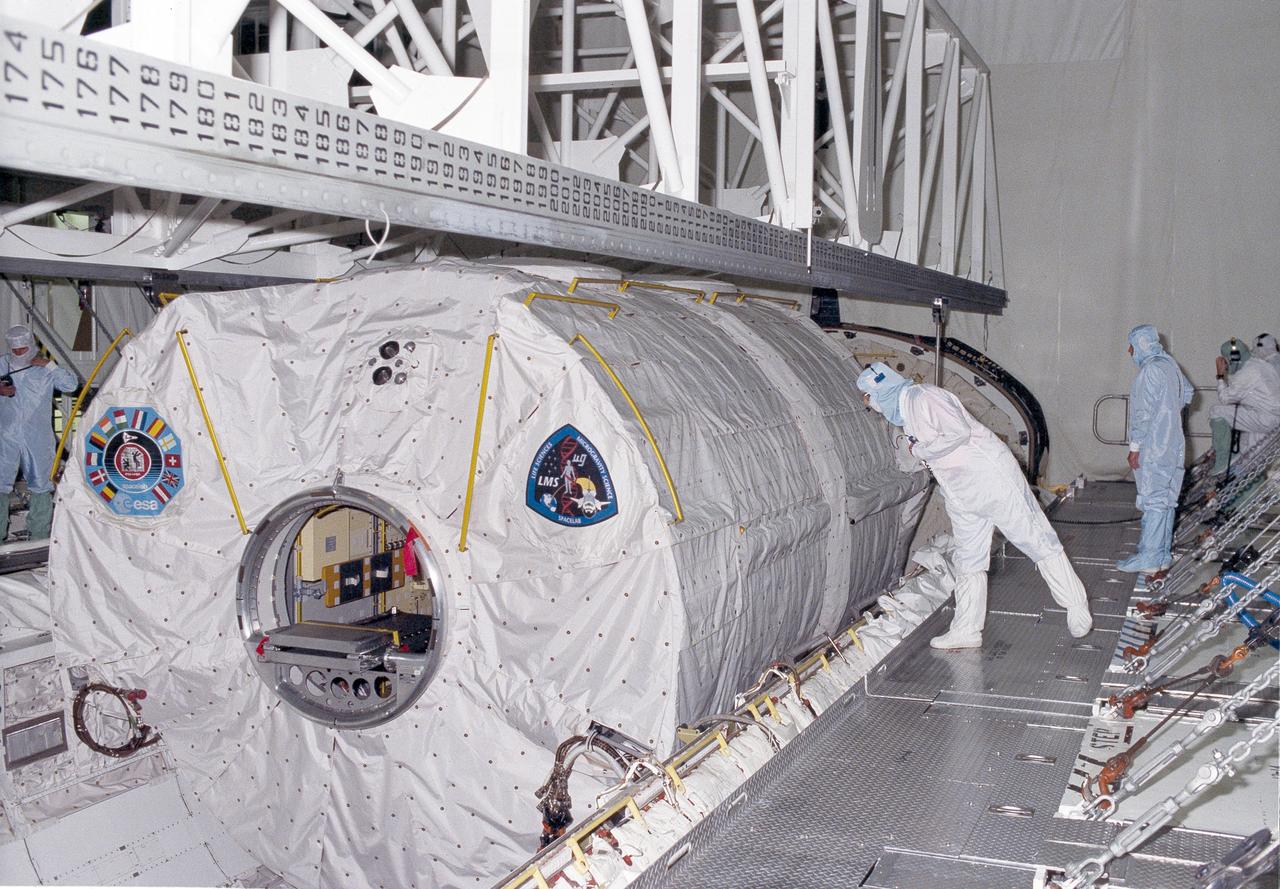

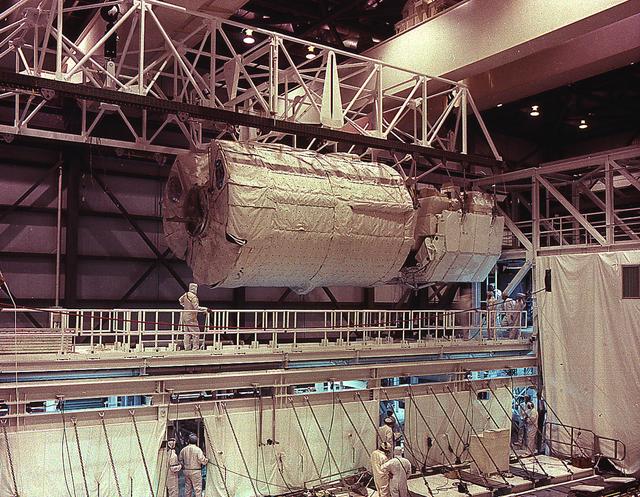
Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This photo shows the LMS spacelab being installed in the payload bay of the orbiter Columbia during preflight preparations.
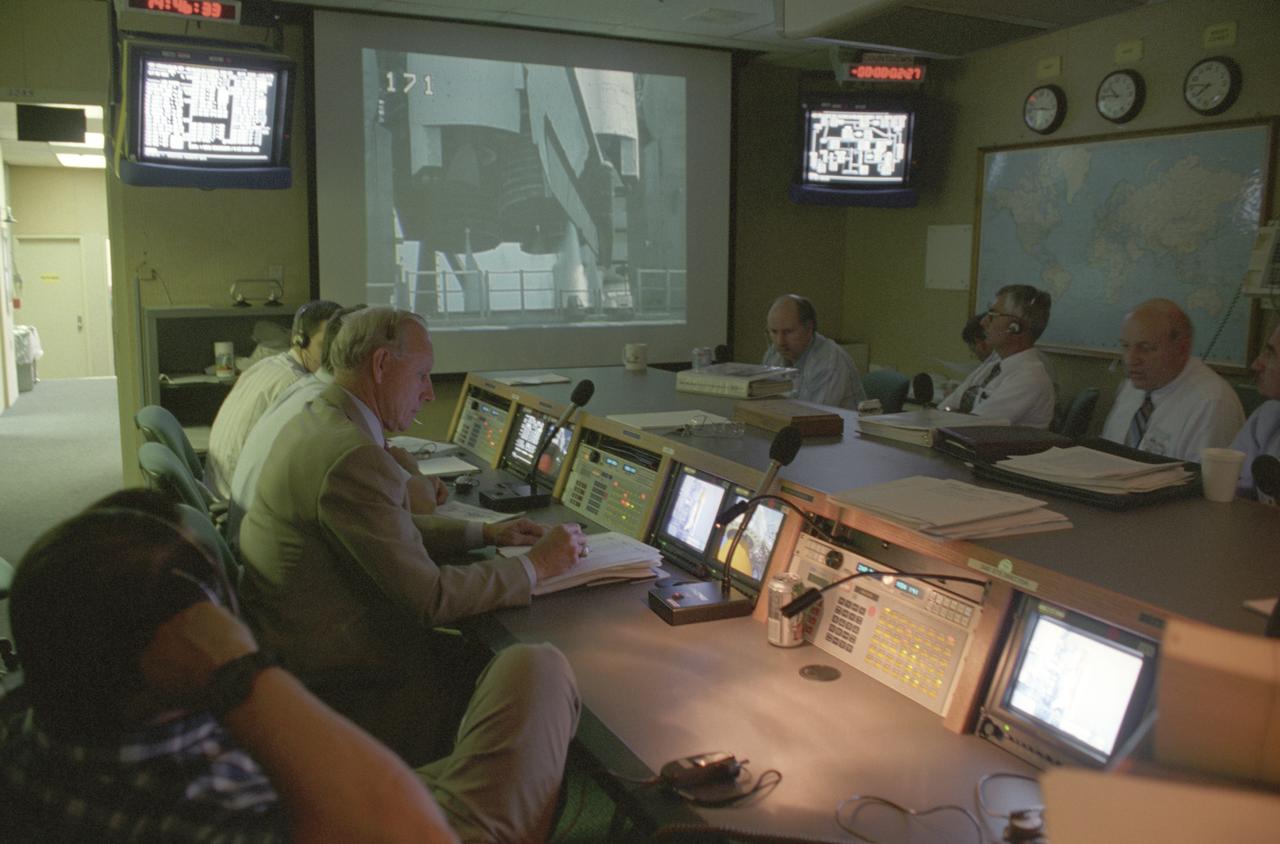

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This photo was taken in the Shuttle Action Center (SAC) of the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC during the mission.
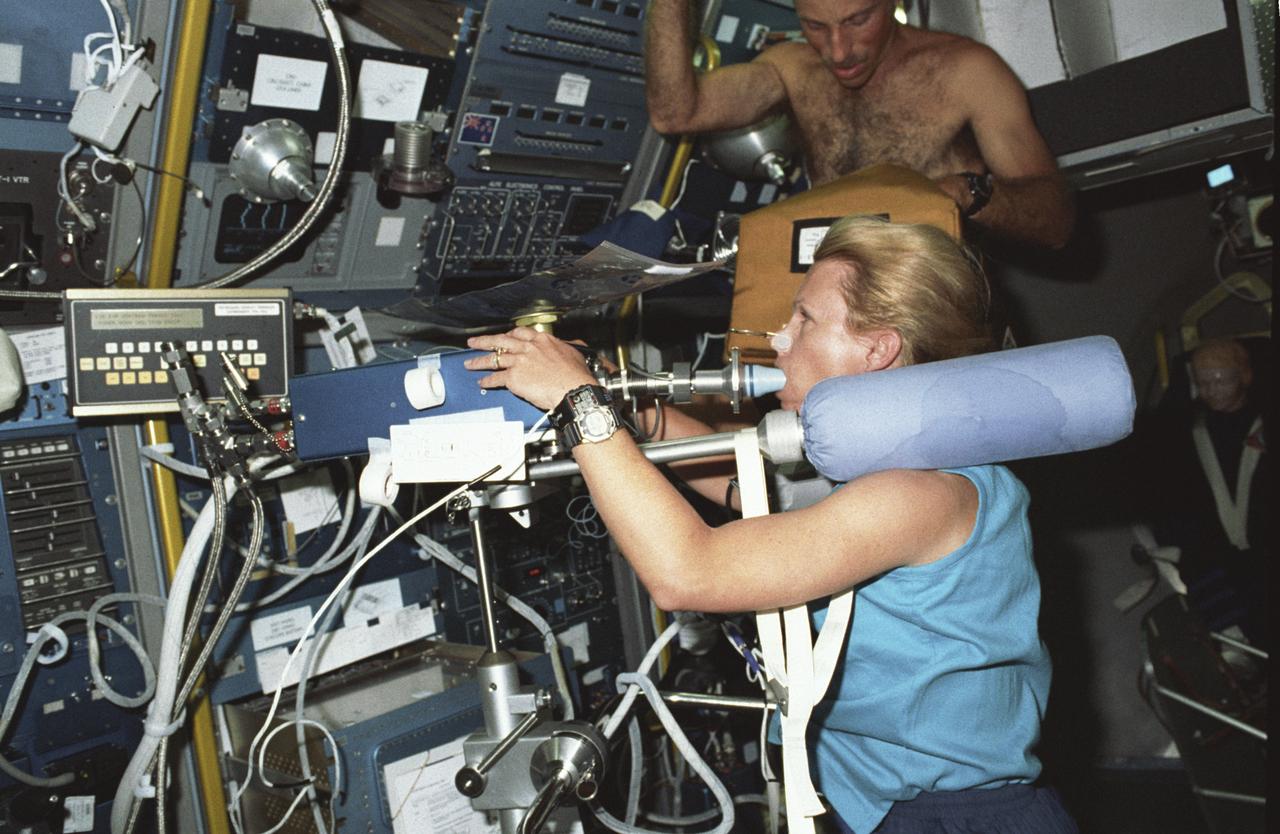
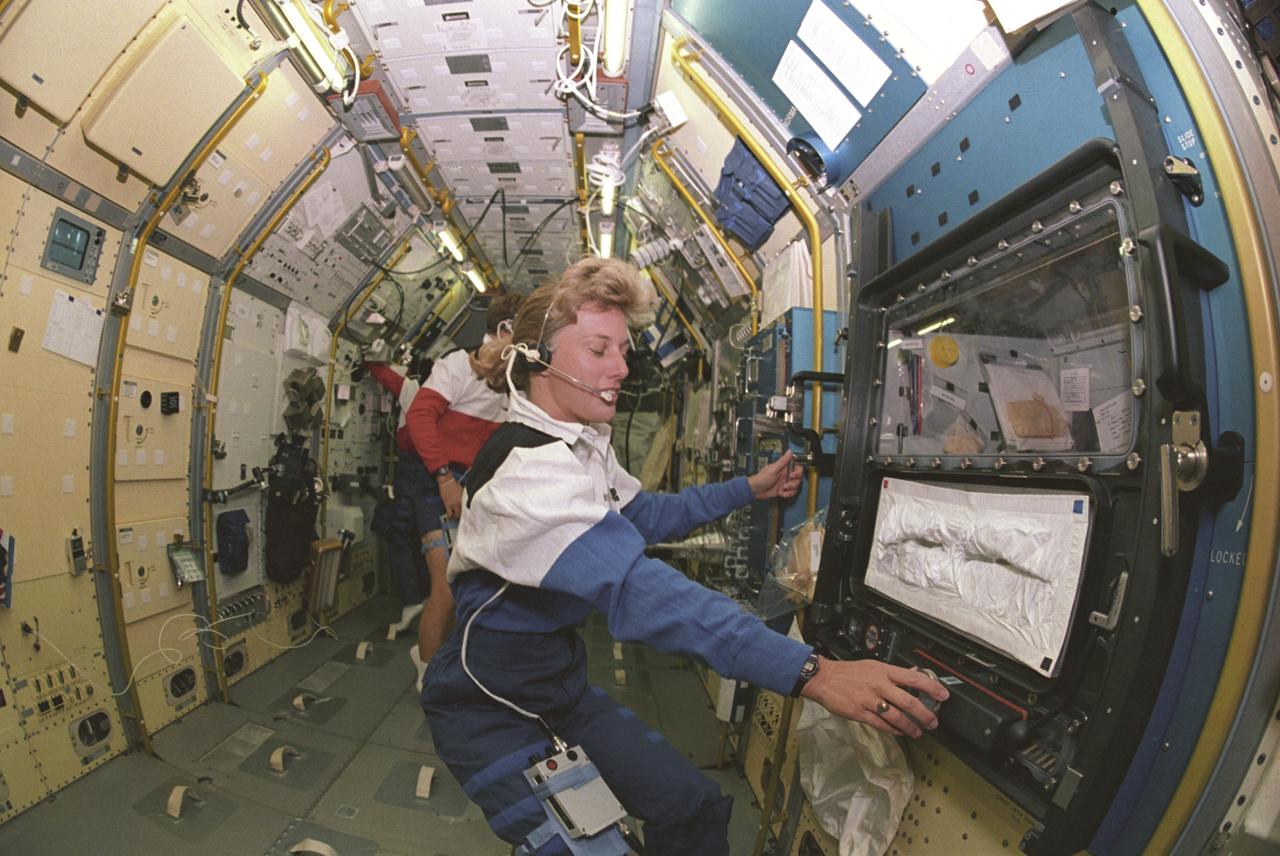
Spacelab Life Science -1 (SLS-1) was the first Spacelab mission dedicated solely to life sciences. The main purpose of the SLS-1 mission was to study the mechanisms, magnitudes, and time courses of certain physiological changes that occur during space flight, to investigate the consequences of the body's adaptation to microgravity and readjustment to Earth's gravity, and bring the benefits back home to Earth. The mission was designed to explore the responses of the heart, lungs, blood vessels, kidneys, and hormone-secreting glands to microgravity and related body fluid shifts; examine the causes of space motion sickness; and study changes in the muscles, bones, and cells. This photograph shows astronaut Rhea Seddon conducting an inflight study of the Cardiovascular Deconditioning experiment by breathing into the cardiovascular rebreathing unit. This experiment focused on the deconditioning of the heart and lungs and changes in cardiopulmonary function that occur upon return to Earth. By using noninvasive techniques of prolonged expiration and rebreathing, investigators can determine the amount of blood pumped out of the heart (cardiac output), the ease with which blood flows through all the vessels (total peripheral resistance), oxygen used and carbon dioxide released by the body, and lung function and volume changes. SLS-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-40) on June 5, 1995.
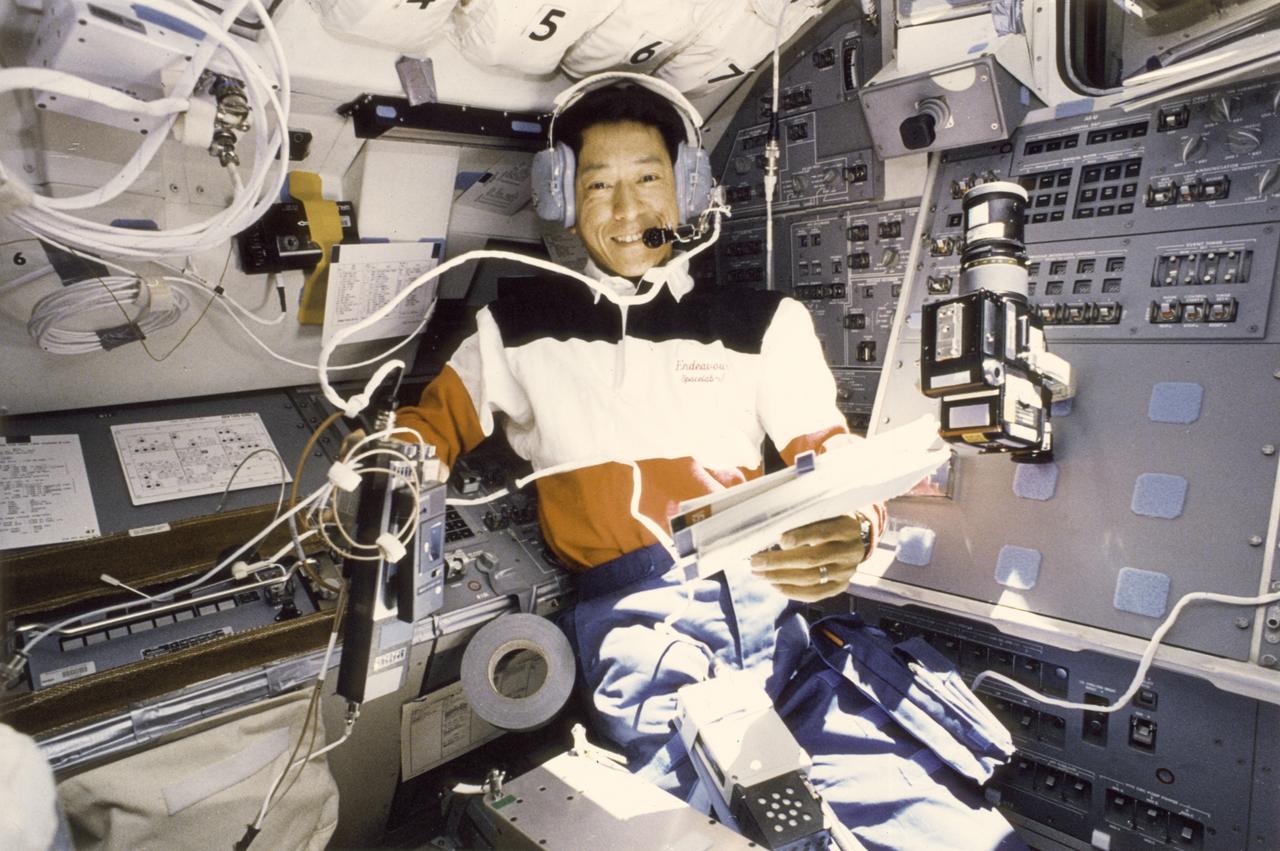

Japanese astronaut, Mamoru Mohri, talks to Japanese students from the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour during the Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission. The SL-J mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
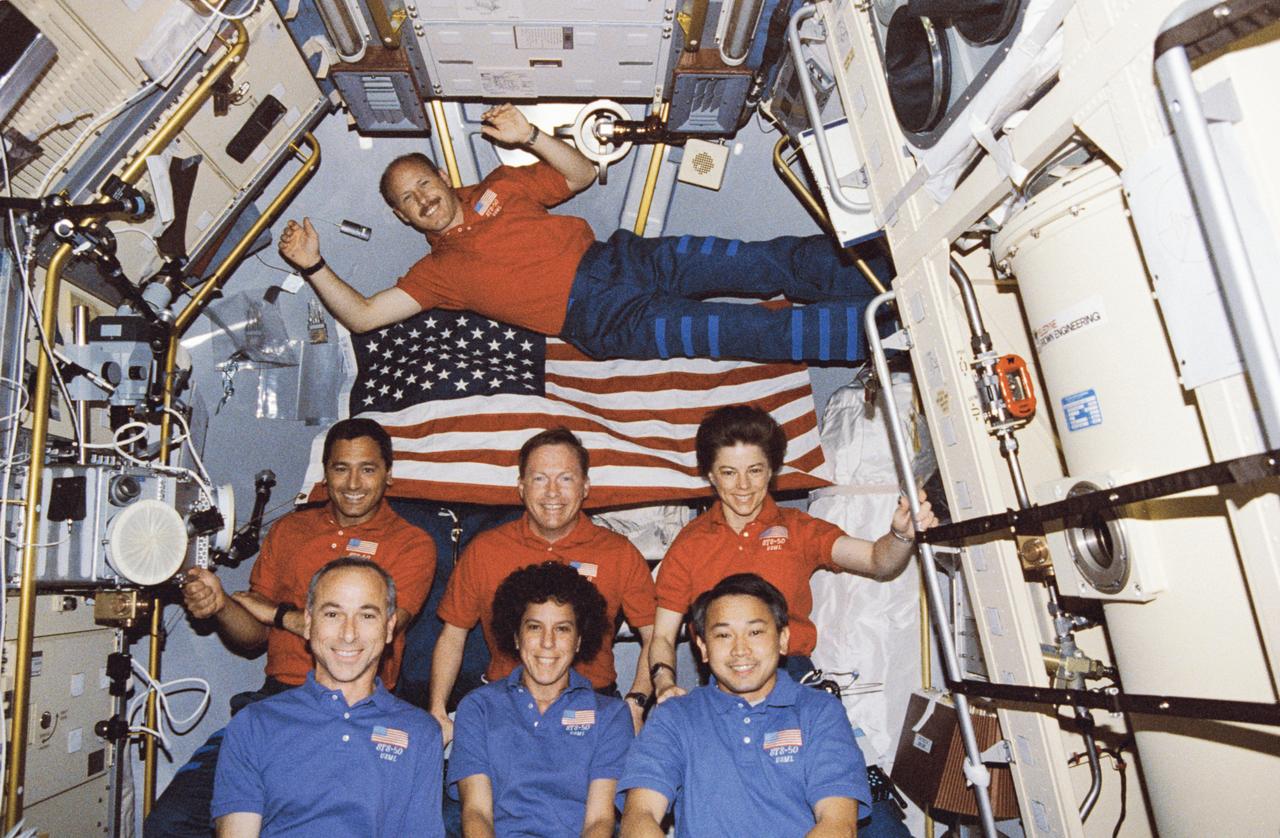

STS050-291-006 (9 July 1992) --- In orbit crew portrait of STS-50 crewmembers in the Spacelab.
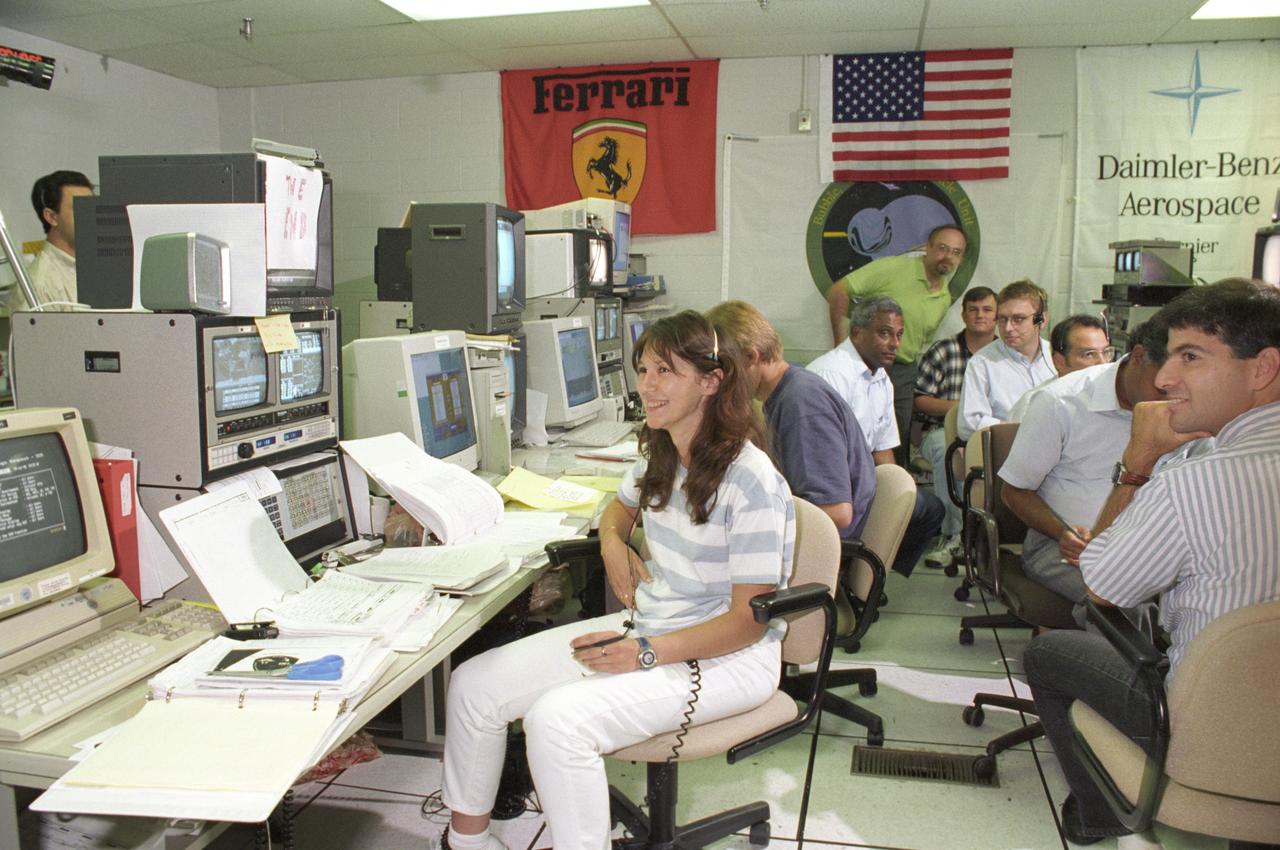

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This photo represents members of the Bubble Drop and Particle Unit team expressing satisfaction with a completed experiment run at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC.
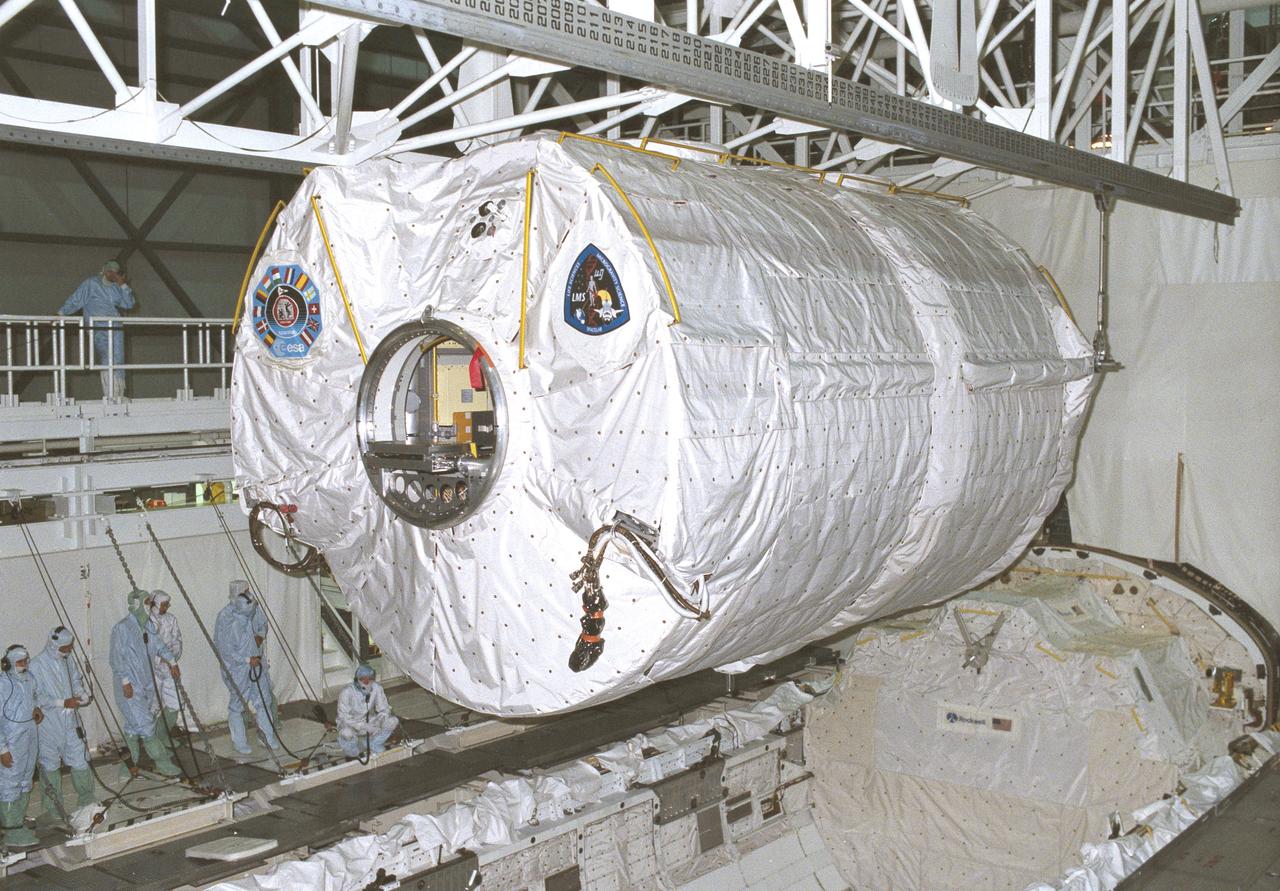

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This photo shows the LMS being installed in the payload bay of the orbiter Columbia during preflight preparations.
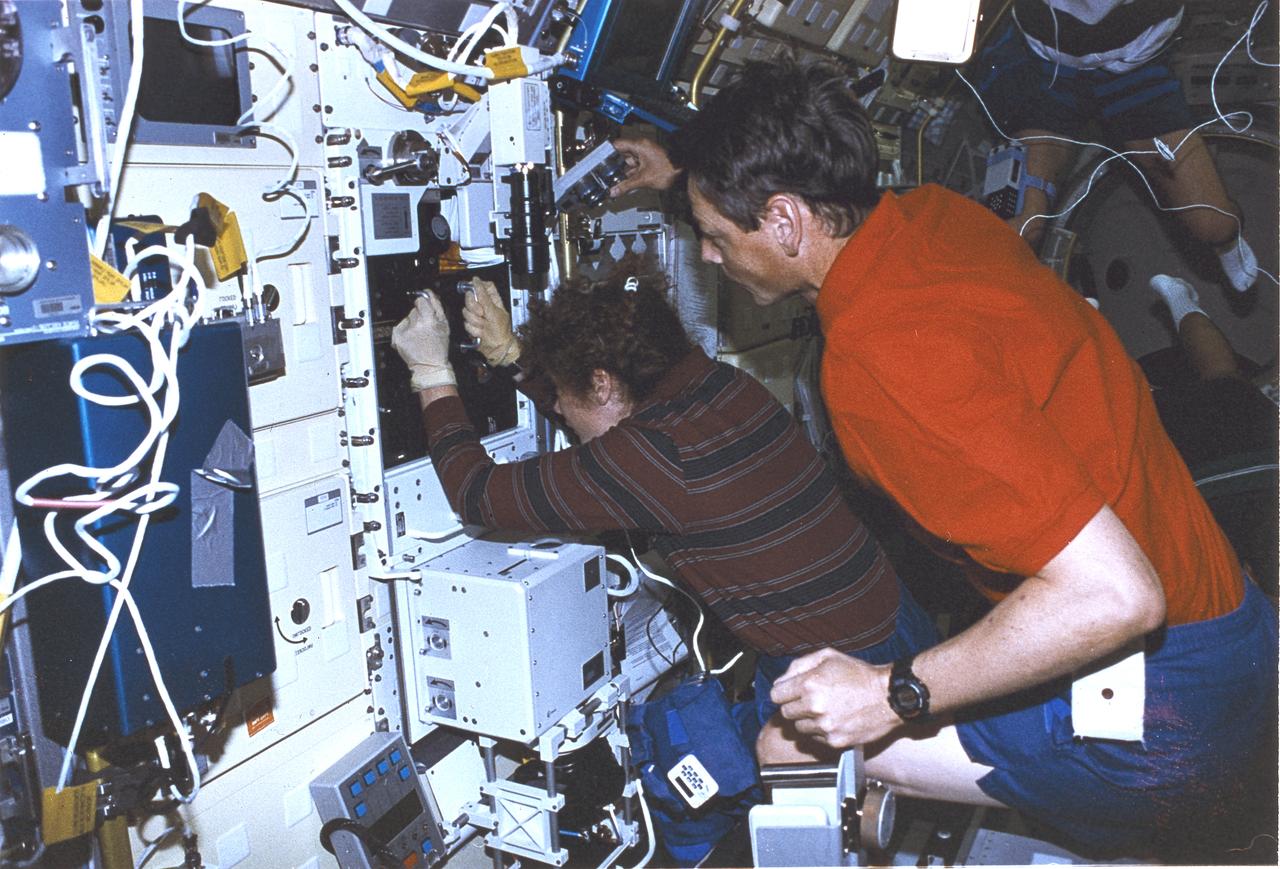

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This onboard photo represents payload commander Susan Helms and fellow astronaut in the LMS.
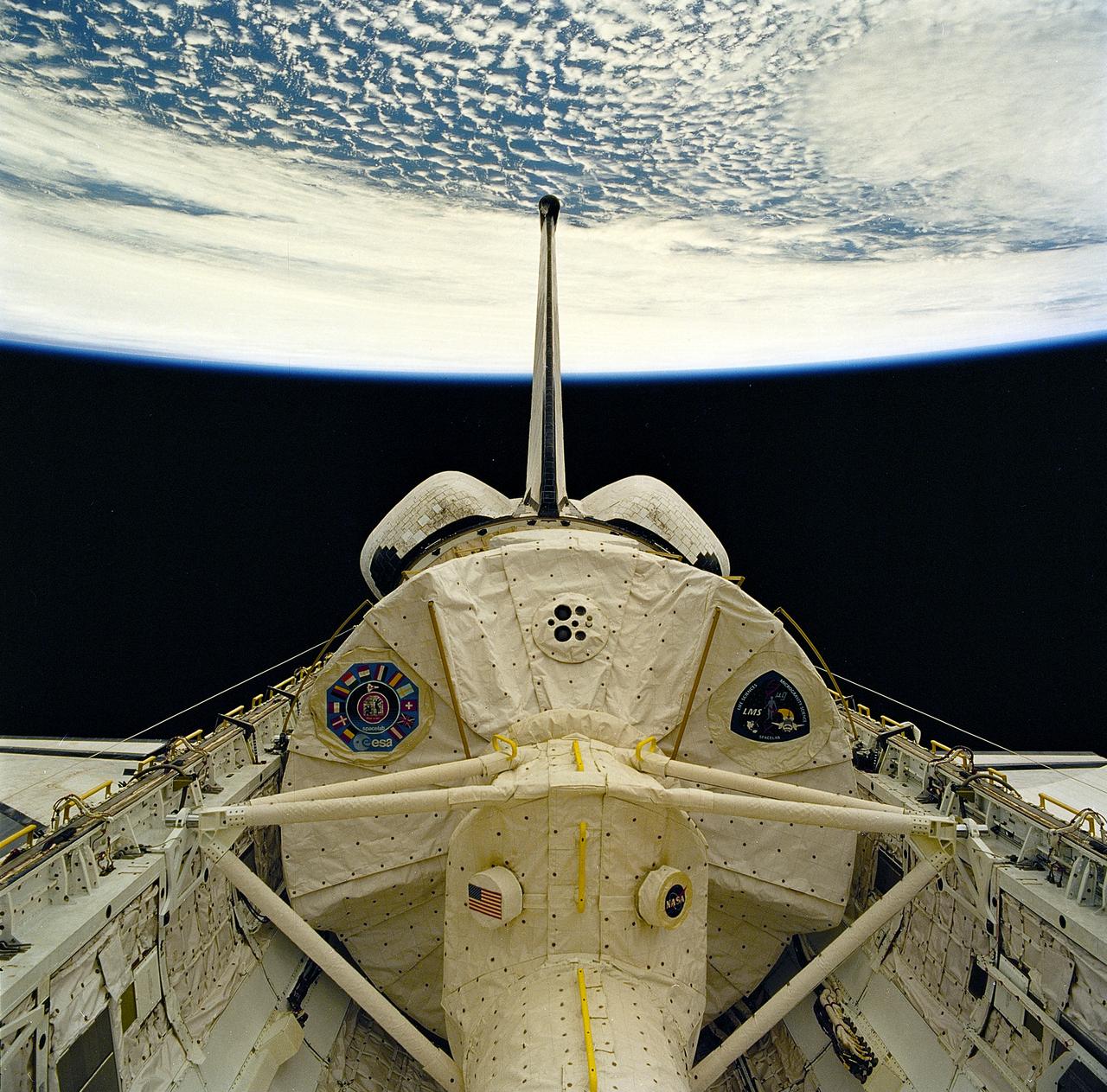

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This onboard photo represents a view of the LMS Module in the Cargo Bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia.

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This photo represents payload specialist, Robert Thirsk, involved in an onboard experiment.
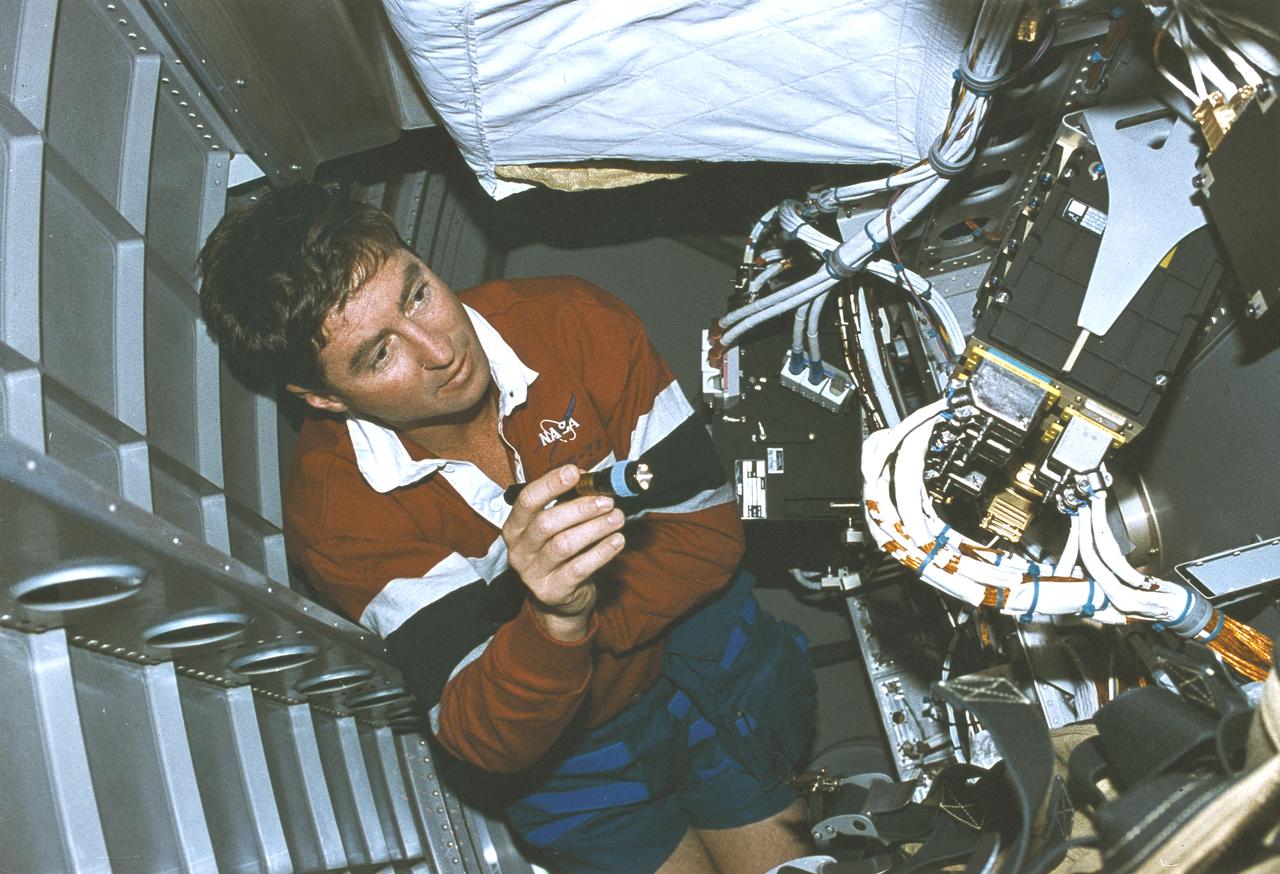

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. In this onboard photograph, mission commander Terence Henricks is checking out equipment.
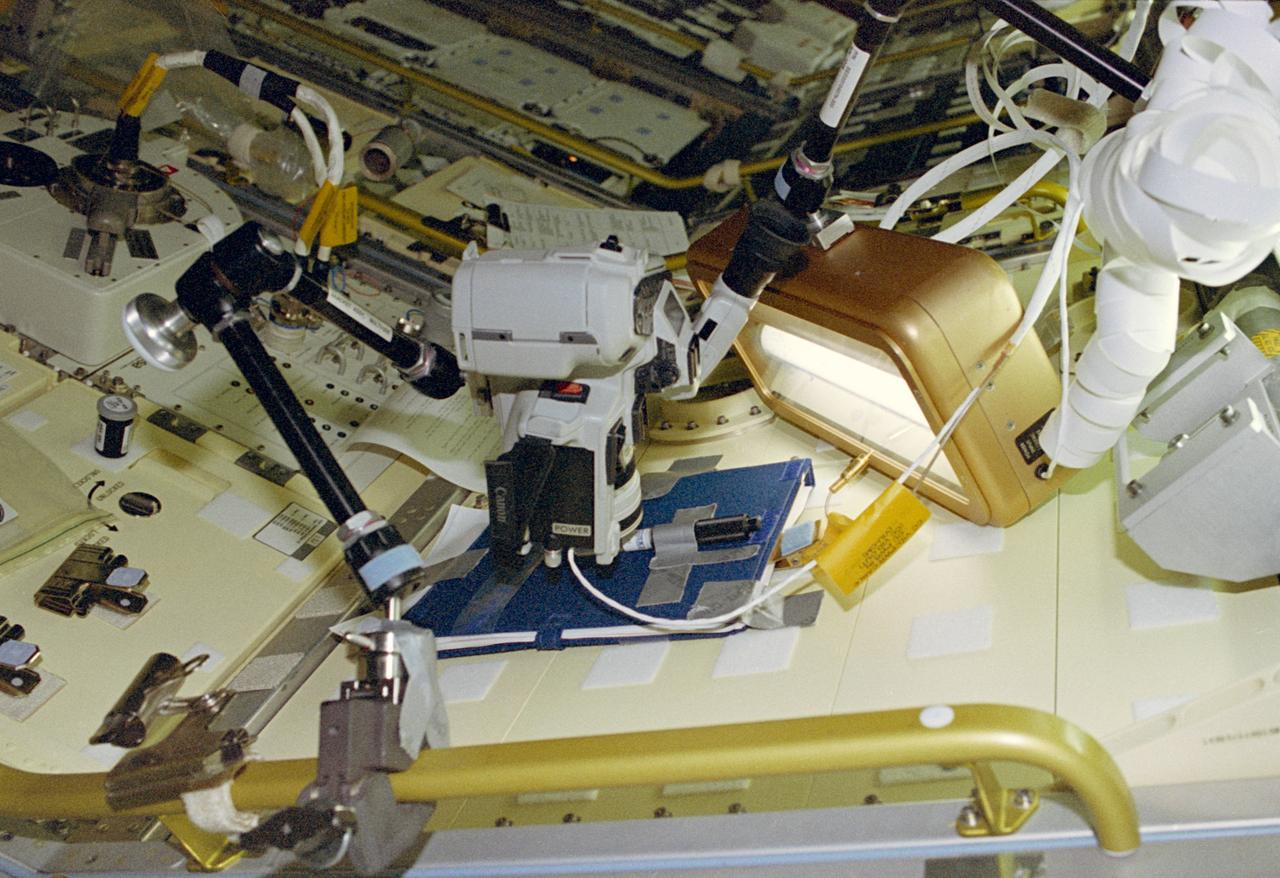

Video camcorder up close to a clyinder attached to a Spacelab locker.
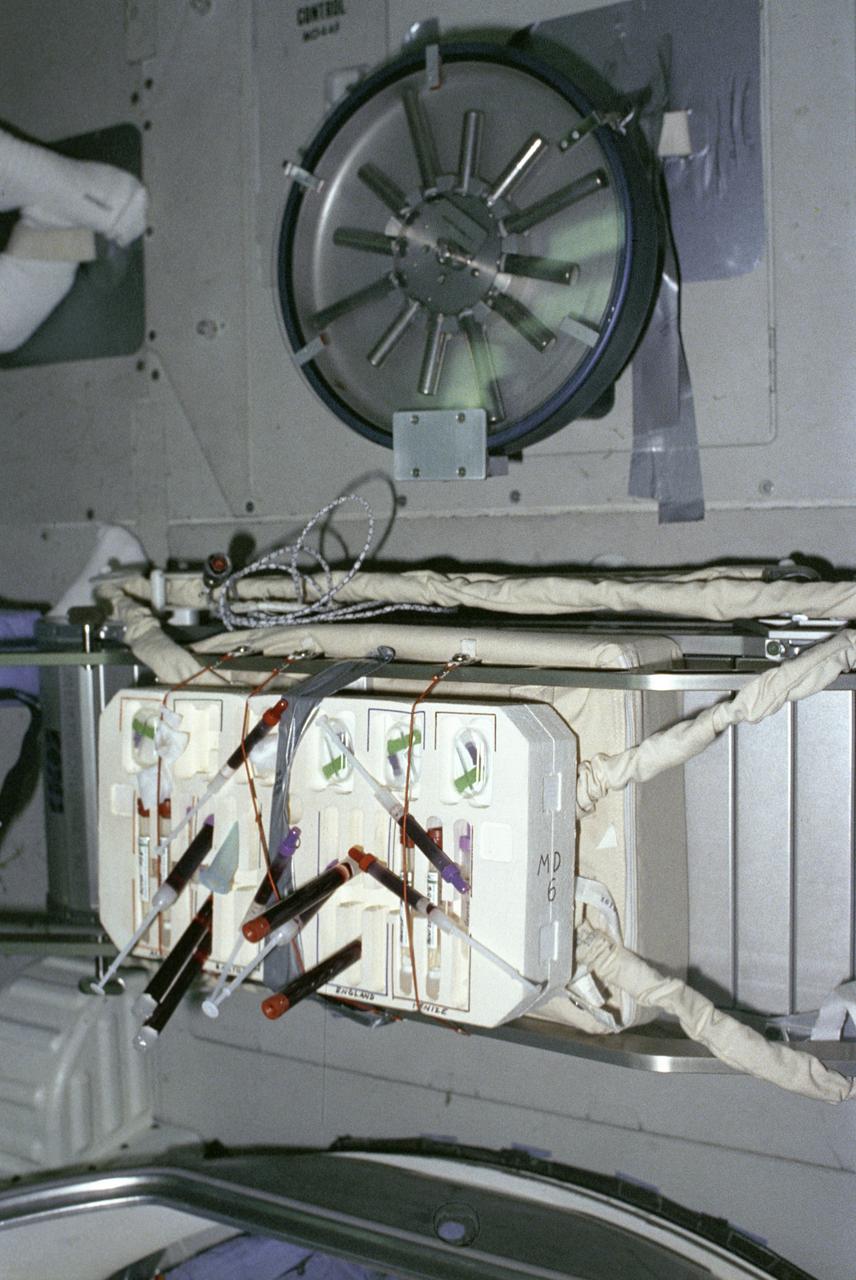
While instruments on the pallets in the payload bay observed the universe, biological experiments were performed in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. Studying life processes in a microgravity environment can shed new light on the functioning of biological systems on Earth. These investigations can also help us understand how living organisms react to prolonged weightlessness. One such experiment was the vitamin D metabolites and bone demineralization experiment. This investigation measured the vitamin d metabolite levels of crew members to gain information on the cause of bone demineralization and mineral imbalance that occur during prolonged spaceflight as well as on Earth. Research into the biochemical nature of vitamin D has shown that the D-metabolites play a major role in regulating the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. One major function of the most biologically active vitamin D metabolite is to regulate the amount of calcium absorbed from the diet and taken out of bones. This investigation had two phases. The first was the developmental phase, which included extensive testing before flight, and the second, or final phase, involved the postflight analysis of the crew's blood samples. This photograph shows a blood draw test kit and centrifuge used for the experiment aboard the Spacelab-2. Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibilities of all Spacelab missions.
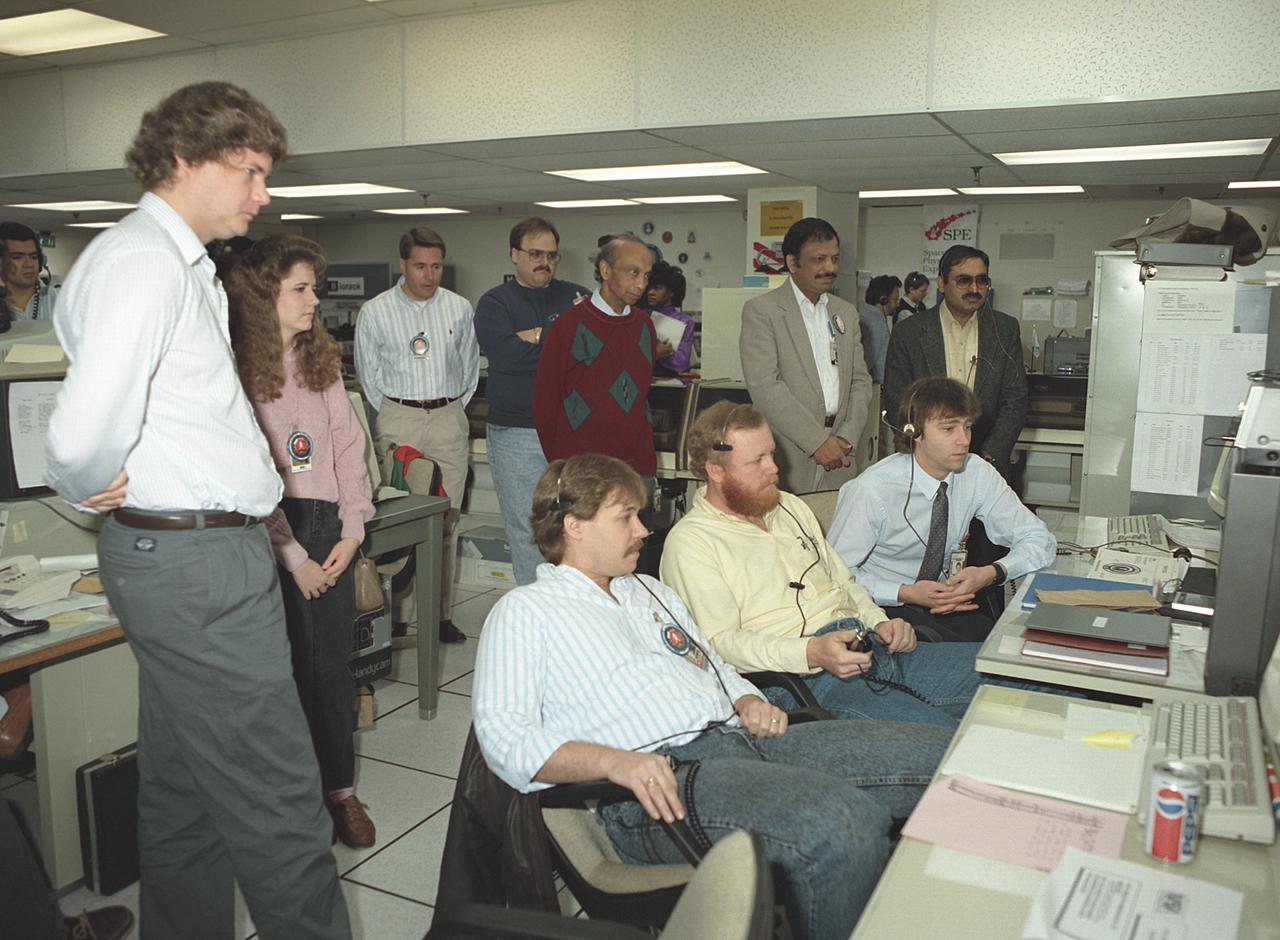

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured is the Crystal Growth team in the SL POCC during STS-42, IML-1 mission.
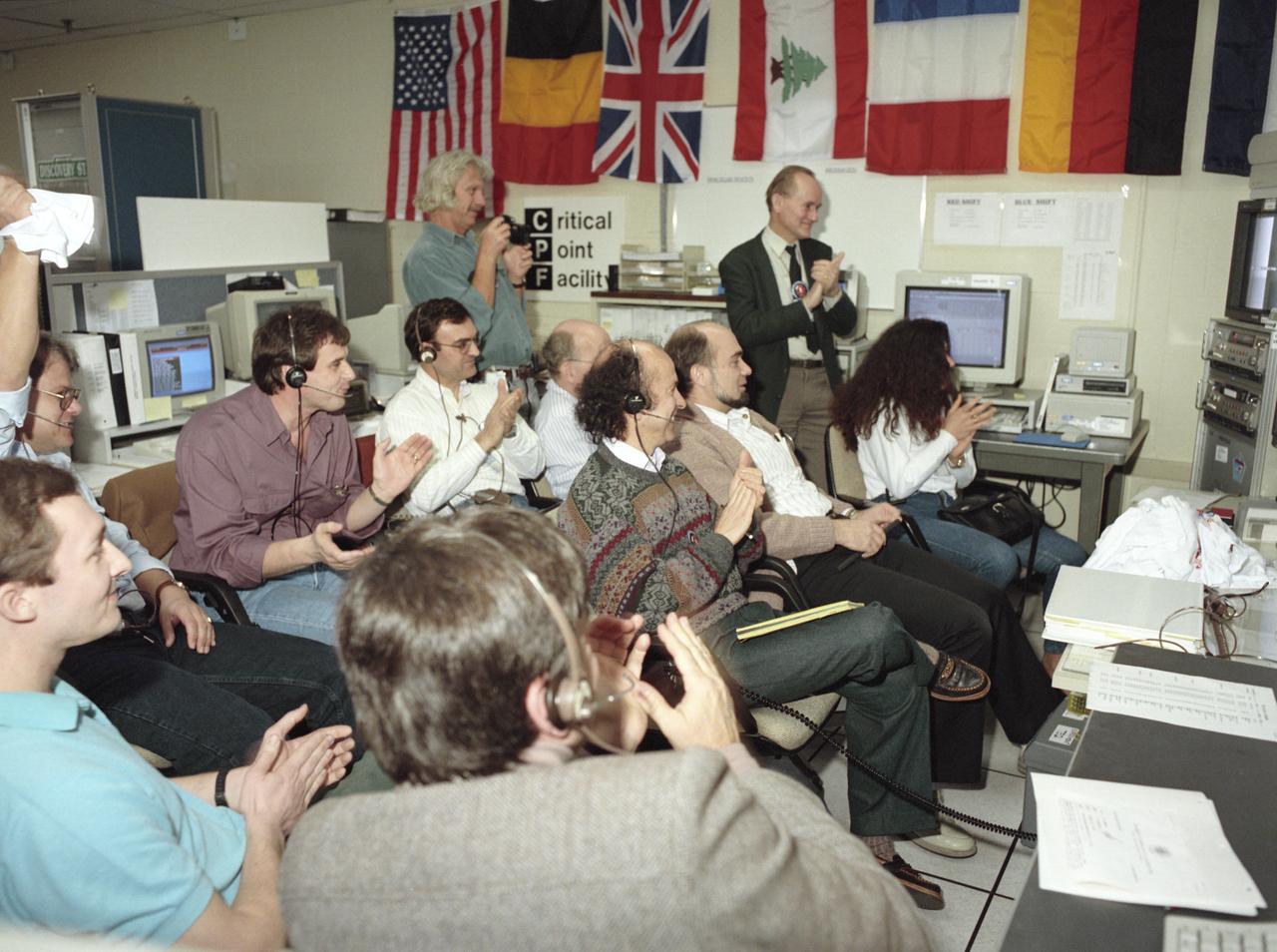

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured is the Critical Point Facility (CPE) group in the SL POCC during STS-42, IML-1 mission.
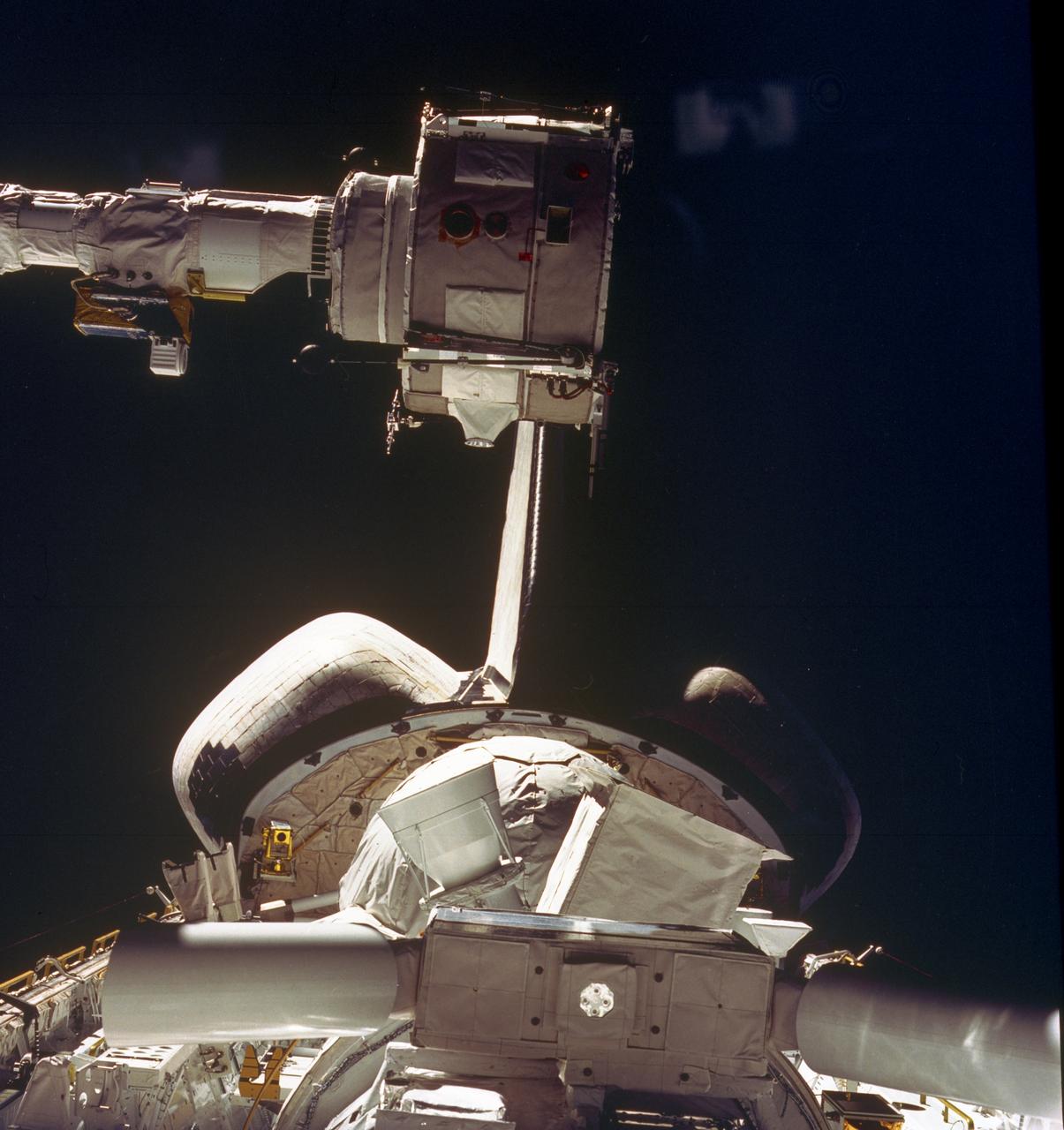

This STS-51F mission onboard Photograph shows some of the Spacelab-2 instruments in the cargo bay of the Orbiter Challenger. The Plasma Diagnostics Package (PDP). shown at the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), used instruments on a subsatellite to study natural plasma processes, orbiter-induced plasma processes, and beam plasma physics. Fourteen instruments were mounted on the PDP for measurements of various plasma characteristics. The X-ray Telescope (XRT), is at the front. The goal of this investigation was to image and examine the X-ray emissions from clusters of galaxies in order to study the mechanisms that cause high-temperature emissions and to determine the weight of galactic clusters. The Small Helium-Cooled Infrared Telescope (IRT) is at the right behind the XRT. The objective of this investigation was to measure and map diffused and discrete infrared astronomical sources while evaluating the Space Shuttle as a platform for infrared astronomy. At the same time, a new large superfluid helium dewar system for cooling the telescope was evaluated. The egg-shaped Cosmic Ray Nuclei experiment (CRNE) is shown at the rear. This investigation was to study the composition of high-energy cosmic rays by using a large instrument exposed to space for a considerable period of time. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on July 29, 1985.
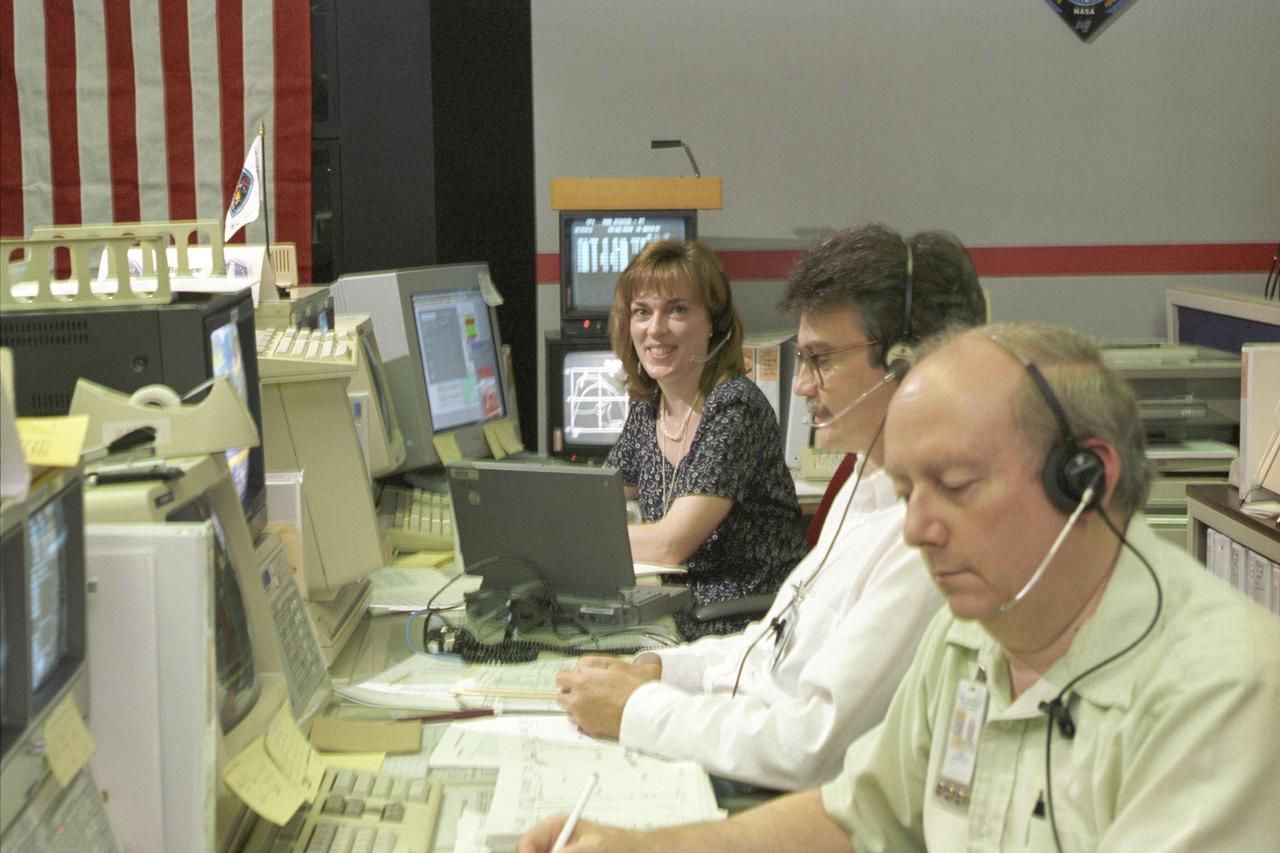

Launched on June 20, 1996, the STS-78 mission’s primary payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS), which was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). During the 17 day space flight, the crew conducted a diverse slate of experiments divided into a mix of life science and microgravity investigations. In a manner very similar to future International Space Station operations, LMS researchers from the United States and their European counterparts shared resources such as crew time and equipment. Five space agencies (NASA/USA, European Space Agency/Europe (ESA), French Space Agency/France, Canadian Space Agency /Canada, and Italian Space Agency/Italy) along with research scientists from 10 countries worked together on the design, development and construction of the LMS. This photo represents Data Management Coordinators monitoring the progress of the mission at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC. Pictured are assistant mission scientist Dr. Dalle Kornfeld, Rick McConnel, and Ann Bathew.
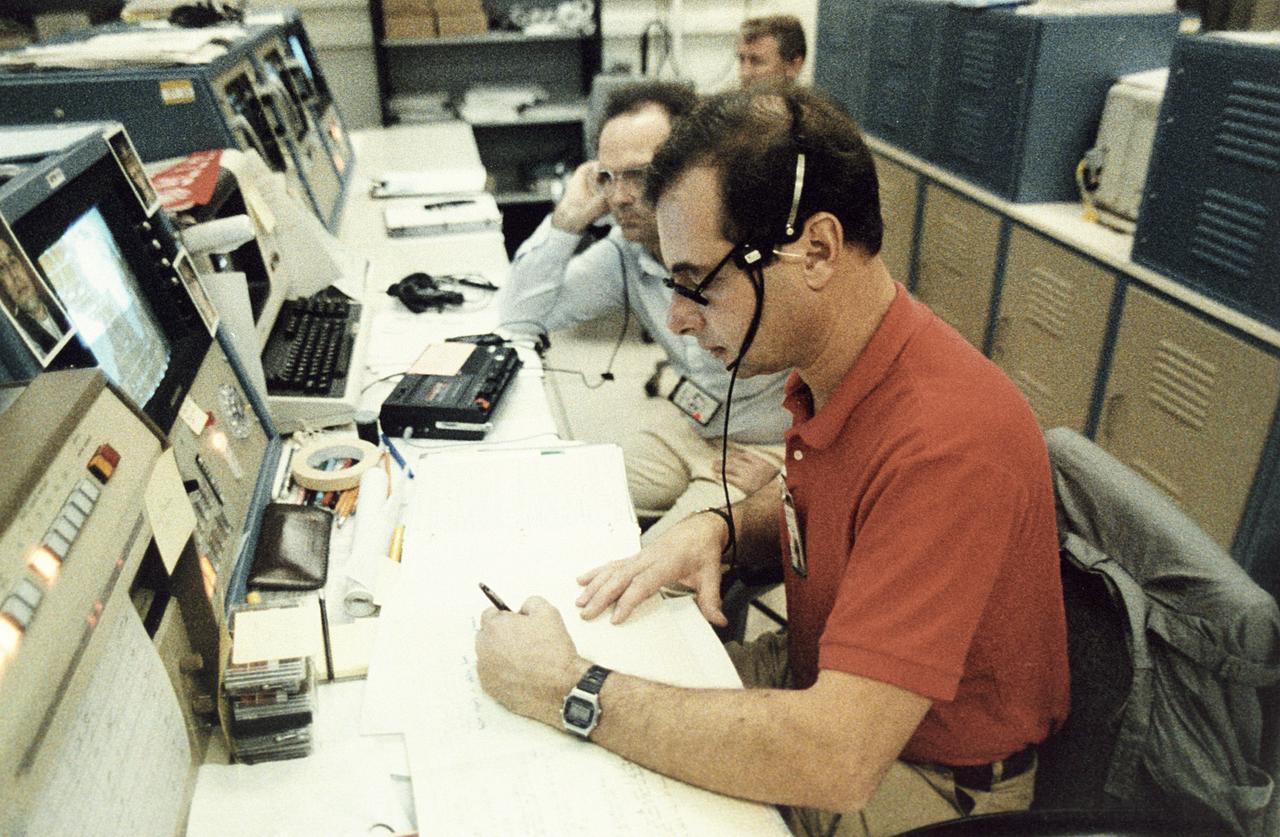

During a Spacelab flight, the hub of activity was the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Johnson Space Flight Center (JSC) in Houston, Texas. The POCC became home to the management and science teams who worked around the clock to guide and support the mission. All Spacelab principal investigators and their teams of scientists and engineers set up work areas in the POCC. Through the use of computers, they could send commands to their instruments and receive and analyze experiment data. Instantaneous video and audio communications made it possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew. This real-time interaction between investigators on the ground and the crew in space was probably the most exciting of Spacelab's many capabilities. As principal investigators talked to the payload specialists during the mission, they consulted on experiment operations, made decisions, and shared in the thrill of gaining new knowledge. In December 1990, a newly-established POCC at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) opened its door for the operations of the Spacelab payloads and experiments, while JSC monitored the Shuttle flight operations. MSFC had managing responsibilities for the Spacelab missions.
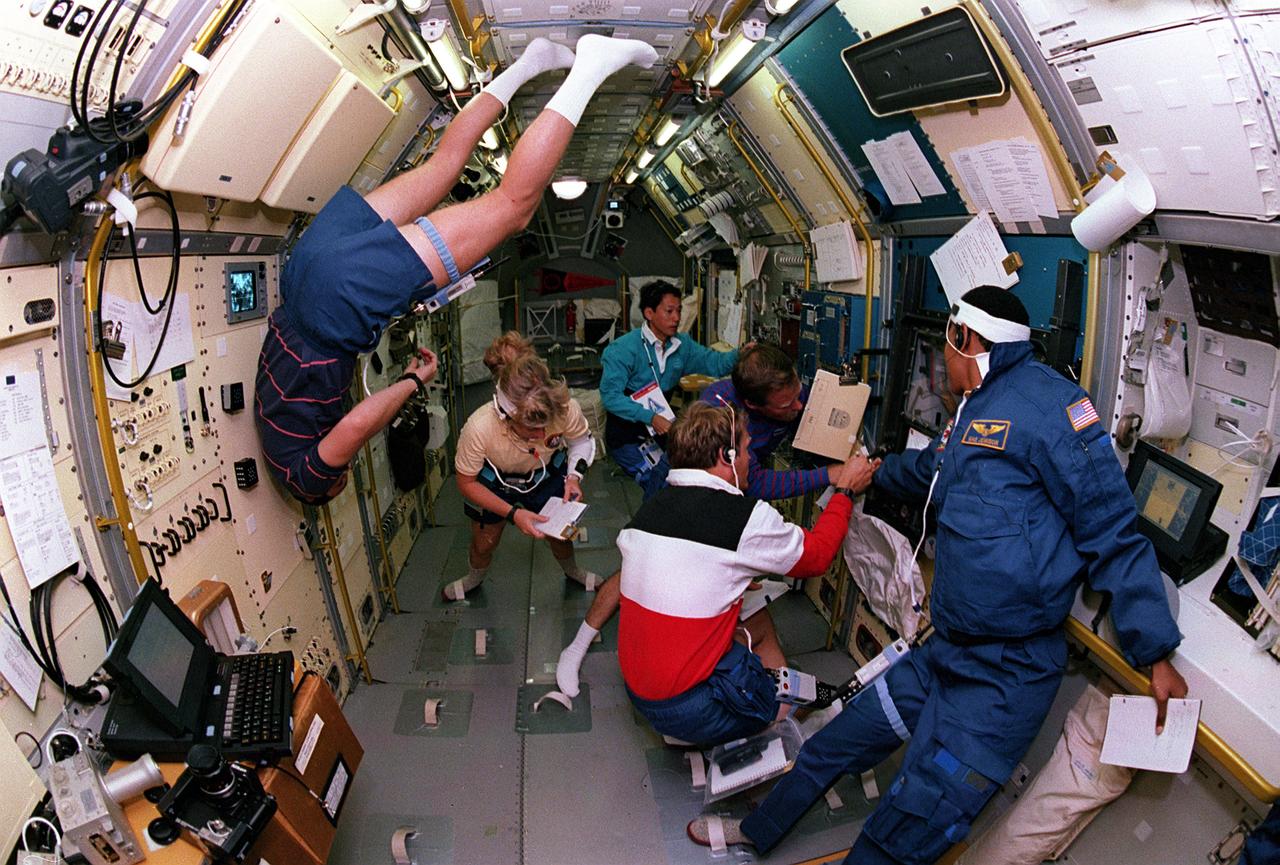

Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) onboard photo of crew members working in the Spacelab-J module.
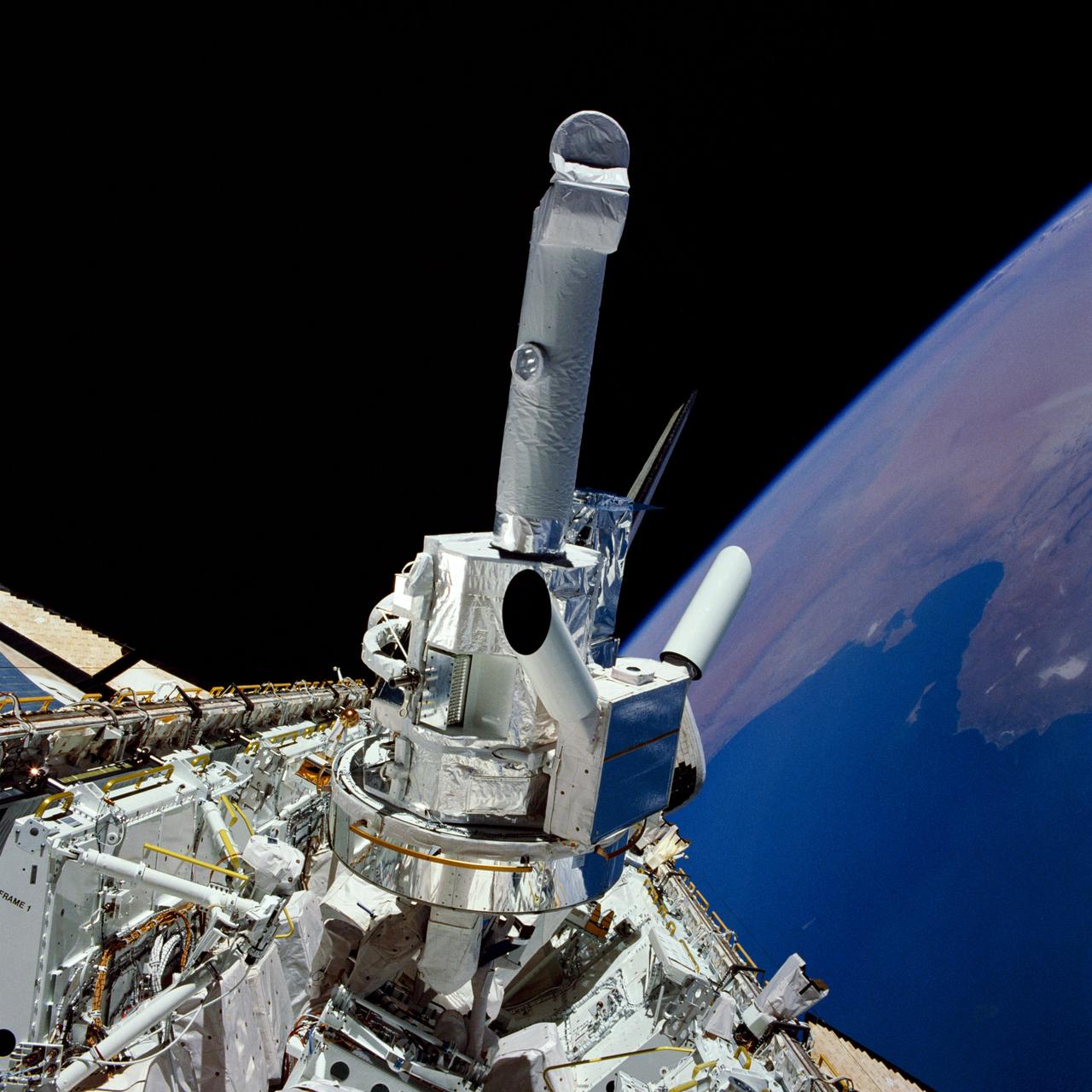

51F-33-005 (29 July - 6 August 1985) --- Experiments and the instrument pointing system (IPS) for Spacelab 2 are backdropped against the Libya/Tunisia Mediterranean coast and black space in this 70mm view photographed through the aft flight deck windows of the Space Shuttle Challenger. Also partially visible among the cluster of Spacelab 2 hardware are the solar optical universal polarimeter (SOUP) experiment and the coronal helium abundance experiment (CHASE).
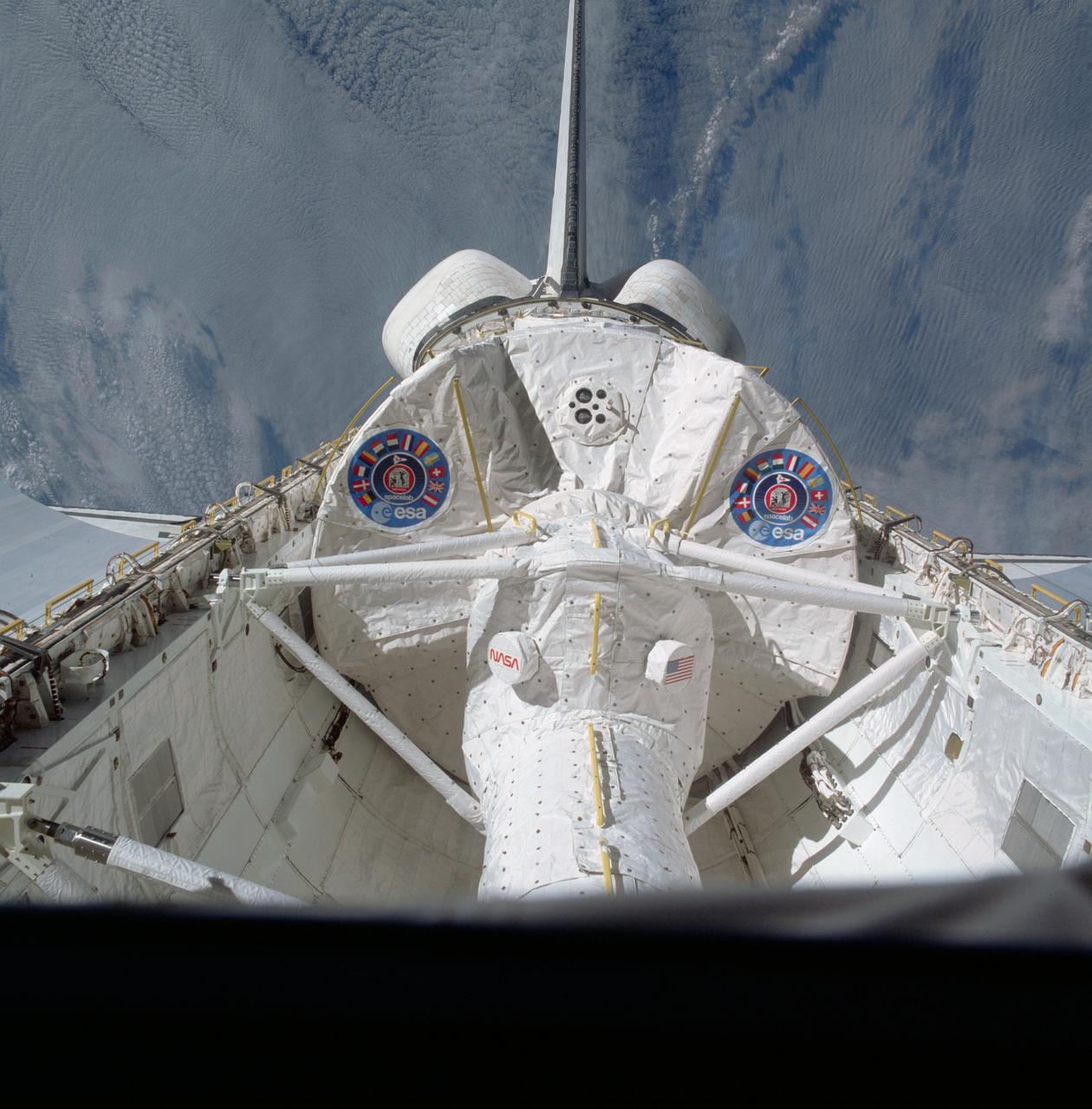

STS009-32-1112 (28 Nov-8 Dec 1983) --- A handheld Hasselblad camera was aimed through the aft windows on the flight deck of Columbia for this initially released scene of the active Spacelab module in the cargo bay. The docking tunnel, leading from the shirt-sleeve environment of the orbiter to the equally comfortable environment of Spacelab, is in the foreground.
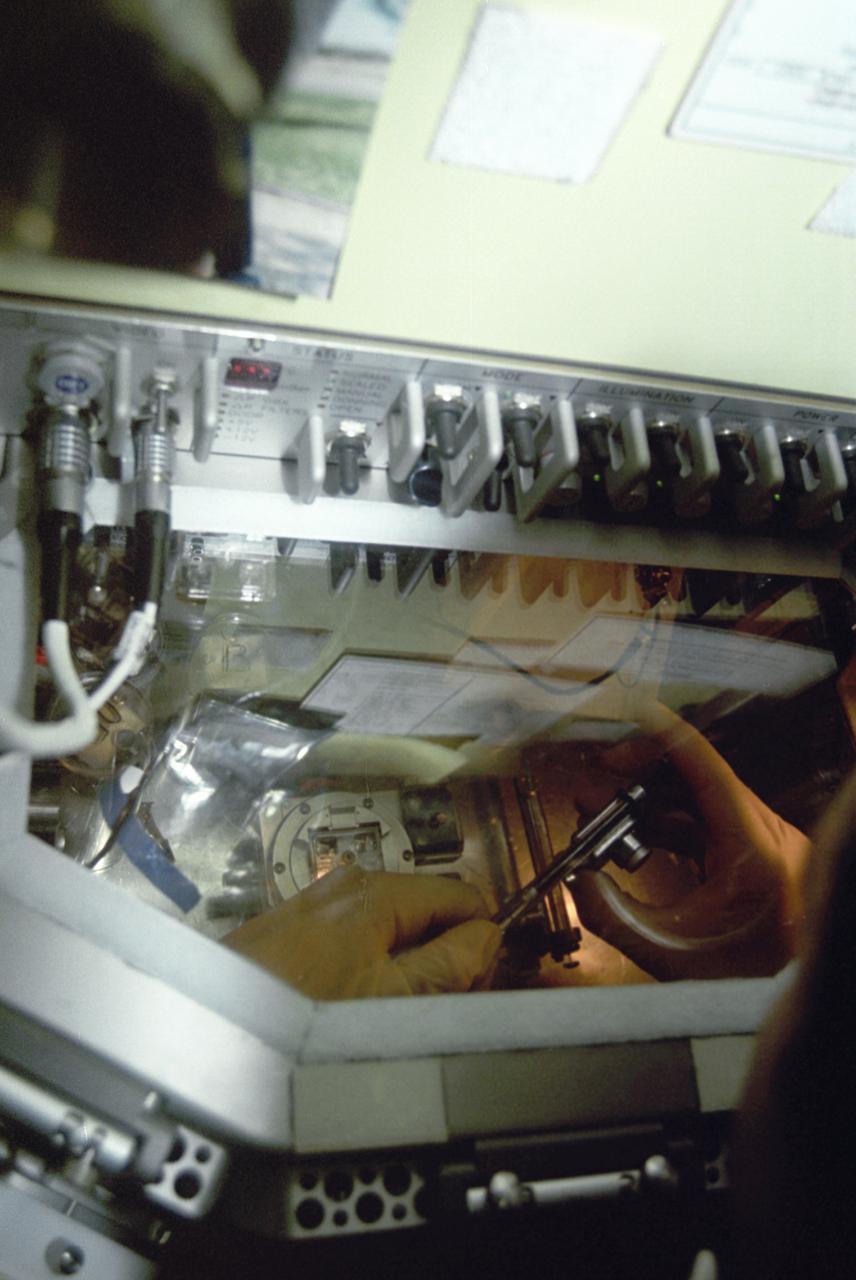

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) provided scientific research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology, and combustion science in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. This photograph is a close-up view of the Glovebox in operation during the mission. The Spacelab Glovebox, provided by the European Space Agency, offers experimenters new capabilities to test and develop science procedures and technologies in microgravity. It enables crewmembers to handle, transfer, and otherwise manipulate materials in ways that are impractical in the open Spacelab. The facility is equipped with three doors: a central port through which experiments are placed in the Glovebox and two glovedoors on both sides with an attachment for gloves or adjustable cuffs and adapters for cameras. The Glovebox has an enclosed compartment that offers a clean working space and minimizes the contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. Although fluid containment and ease of cleanup are major benefits provided by the facility, it can also contain powders and bioparticles; toxic, irritating, or potentially infectious materials; and other debris produced during experiment operations. The facility is equipped with photographic/video capabilities and permits mounting a microscope. For the USML-1 mission, the Glovebox experiments fell into four basic categories: fluid dynamics, combustion science, crystal growth, and technology demonstration. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission in June 1992.
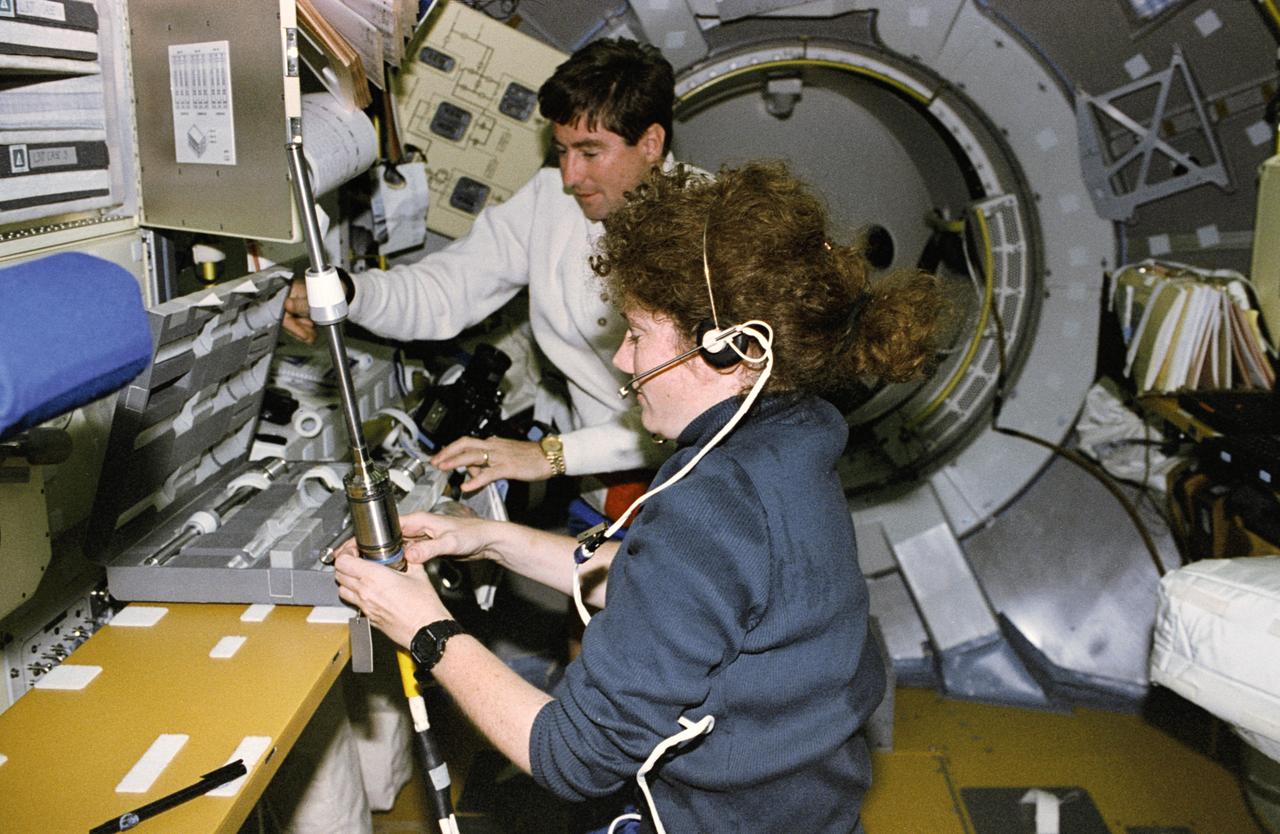

STS078-368-022 (20 June - 7 July 1996) --- Astronauts Susan J. Helms, payload commander, and Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, mission commander, prepare a sample cartridge containing semiconductor crystals for Spacelab research. The crystals were later placed in the Advanced Gradient Heating Furnace (AGHF) in the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS-1) Science Module. The AGHF is designed for directional solidification of the crystals in the sample cartridges. The microgravity of space allows the crystals to grow in a perfect state that can not be accomplished in Earth's gravity.
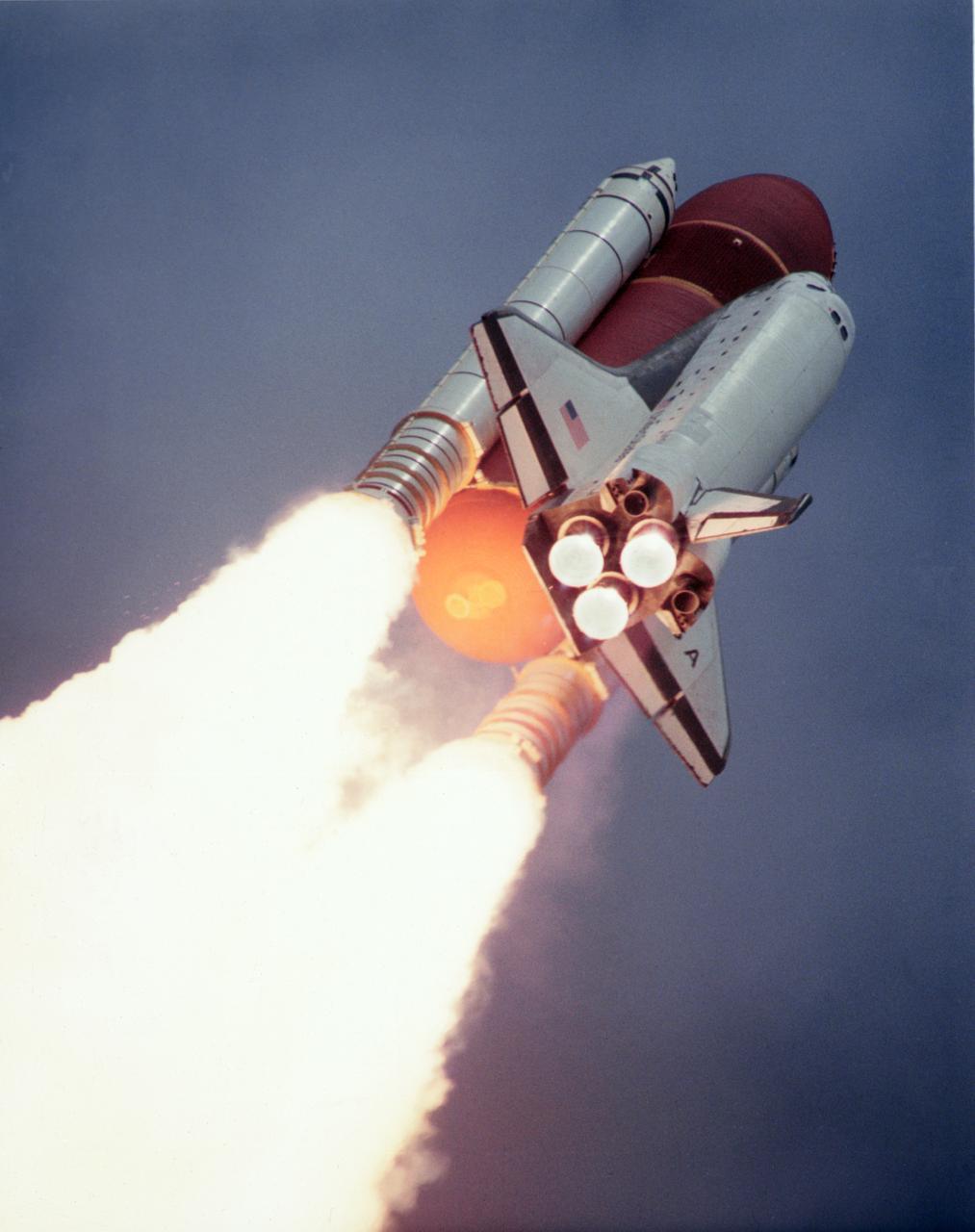

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on June 5, 1991 at 9:24; am (EDT), the STS-40 mission was the fifth dedicated Spacelab Mission, Spacelab Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1), and the first mission dedicated solely to life sciences. The STS-40 crew included 7 astronauts: Bryan D. O’Connor, commander; Sidney M. Gutierrez, pilot; F. Drew Gaffney, payload specialist 1; Milli-Hughes Fulford, payload specialist 2; James P. Bagian, mission specialist 1; Tamara E. Jernigan, mission specialist 2; and M. Rhea Seddon, mission specialist 3.
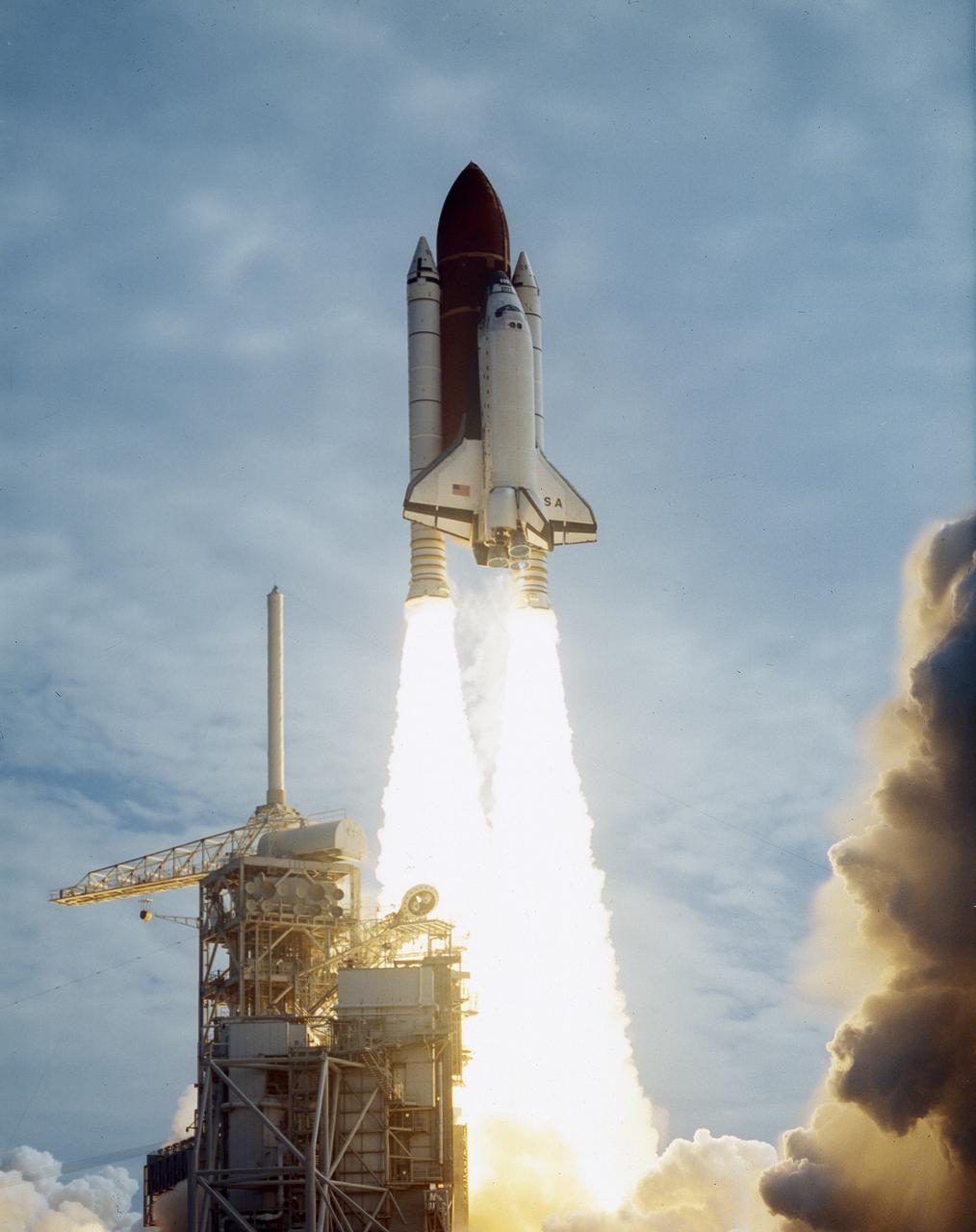

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on June 5, 1991 at 9:24; am (EDT), the STS-40 mission was the fifth dedicated Spacelab Mission, Spacelab Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1), and the first mission dedicated solely to life sciences. The STS-40 crew included 7 astronauts: Bryan D. O’Connor, commander; Sidney M. Gutierrez, pilot; F. Drew Gaffney, payload specialist 1; Milli-Hughes Fulford, payload specialist 2; James P. Bagian, mission specialist 1; Tamara E. Jernigan, mission specialist 2; and M. Rhea Seddon, mission specialist 3.

Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) onboard photo of Astronaut Jan Davis inside the Spacelab-J module. Spacelab-J is a combined National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) and NASA mission. The objectives included life sciences, microgravity and technology research.
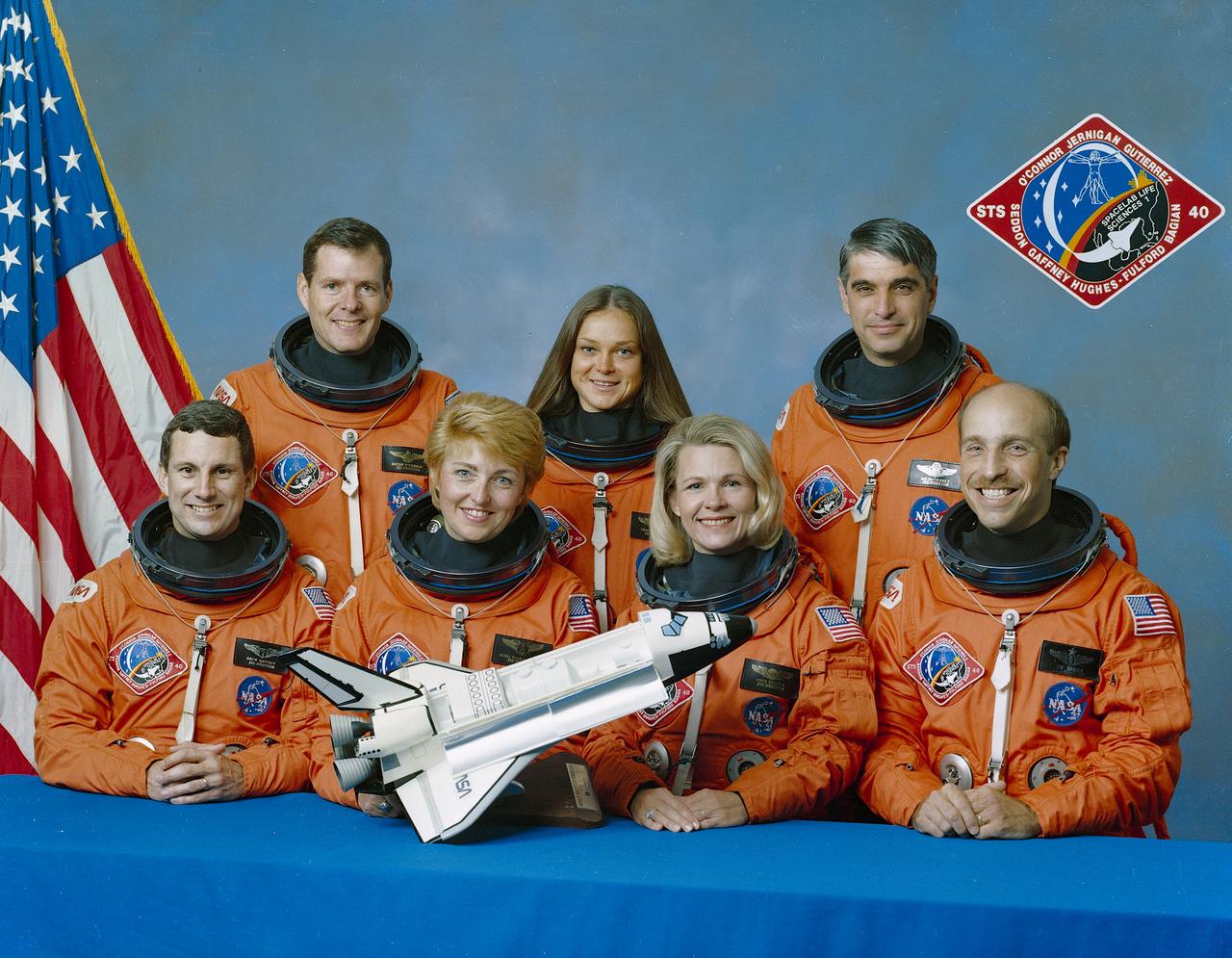

The STS-40 crew portrait includes 7 astronauts. Pictured on the front row from left to right are F. Drew Gaffney, payload specialist 1; Milli-Hughes Fulford, payload specialist 2; M. Rhea Seddon, mission specialist 3; and James P. Bagian, mission specialist 1. Standing in the rear, left to right, are Bryan D. O’Connor, commander; Tamara E. Jernigan, mission specialist 2; and Sidney M. Gutierrez, pilot. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on June 5, 1991 at 9:24; am (EDT), the STS-40 mission was the fifth dedicated Spacelab Mission, Spacelab Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1), and the first mission dedicated solely to life sciences.
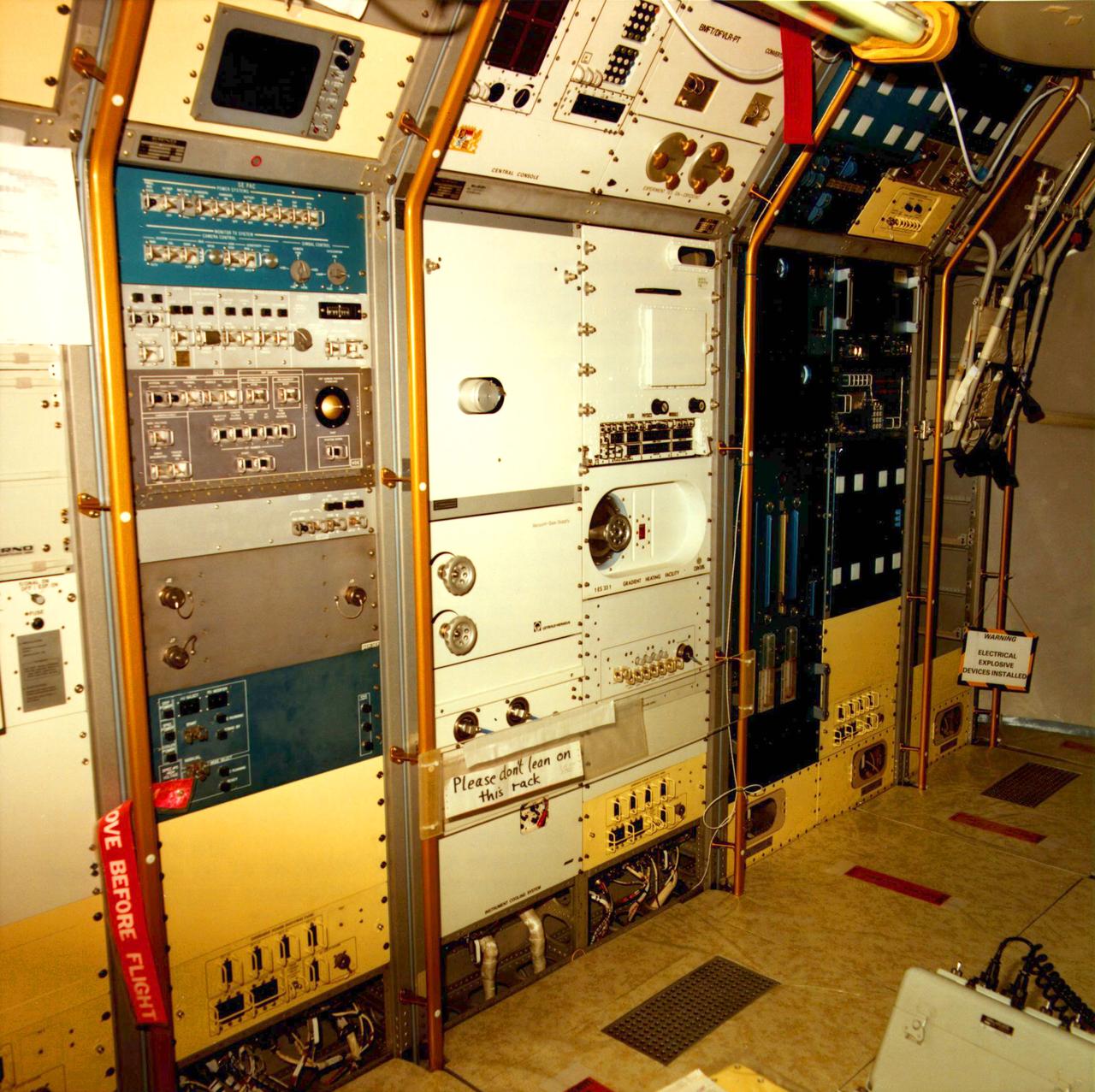

Interior view of Spacelab 1 to show layout of equipment and astronauts testing tools. Operations Checkout (O C) Building located at KSC.
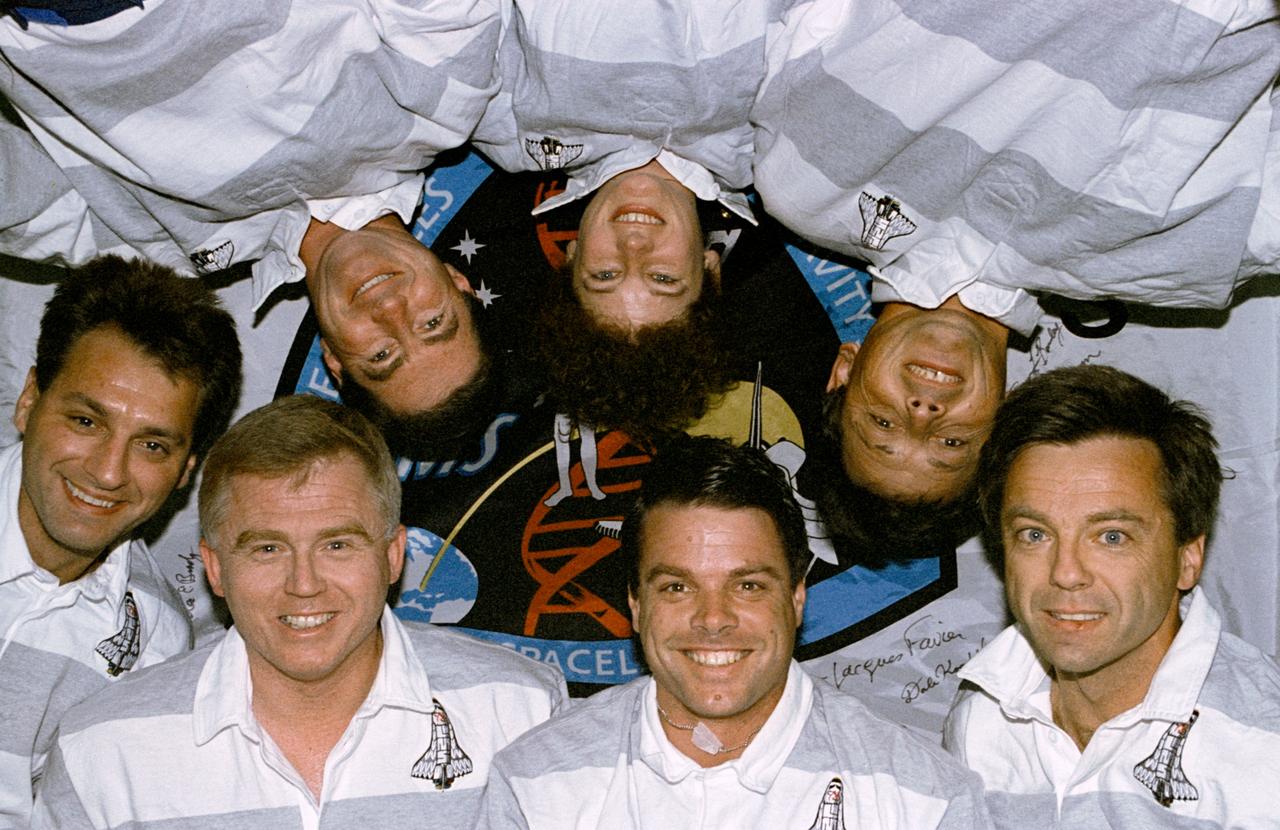

STS078-397-030 (20 June - 7 July 1996) --- Five NASA astronauts and two international payload specialists take a break from a Shuttle duration record-breaker flight to pose for the traditional inflight crew portrait. The photograph should be oriented with payload commander Susan J. Helms at bottom center. Others, clockwise, are French payload specialist Jean-Jacques Favier, Canadian payload specialist Robert B. Thirsk; and astronauts Kevin R. Kregel, pilot; and Charles J. (Chuck) Brady and Richard M. Linnehan, both mission specialists, and Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, mission commander. The crew chose the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS-1) Science Module, situated in the Space Shuttle Columbia's cargo bay, for the portrait setting.
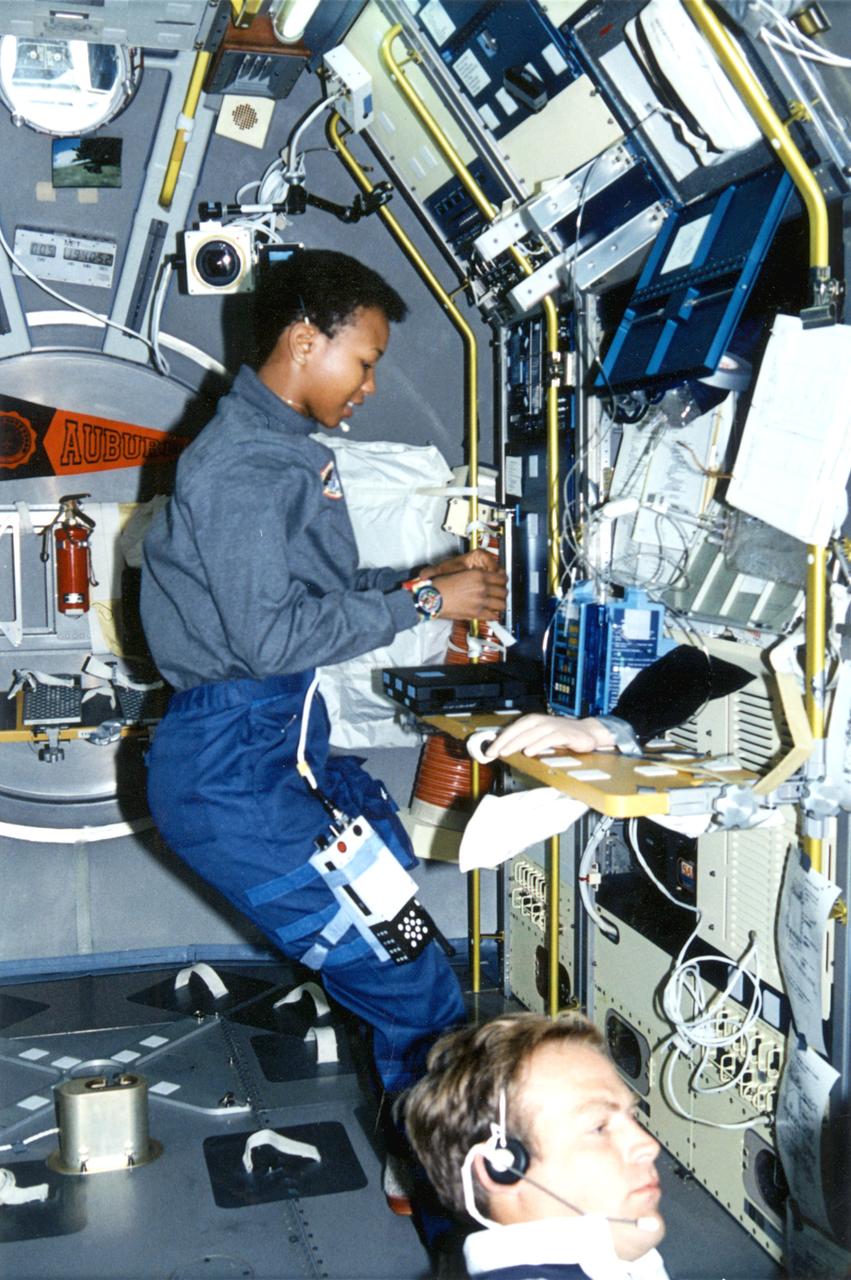

Astronaut Mae Jemison on Spacelab-J.
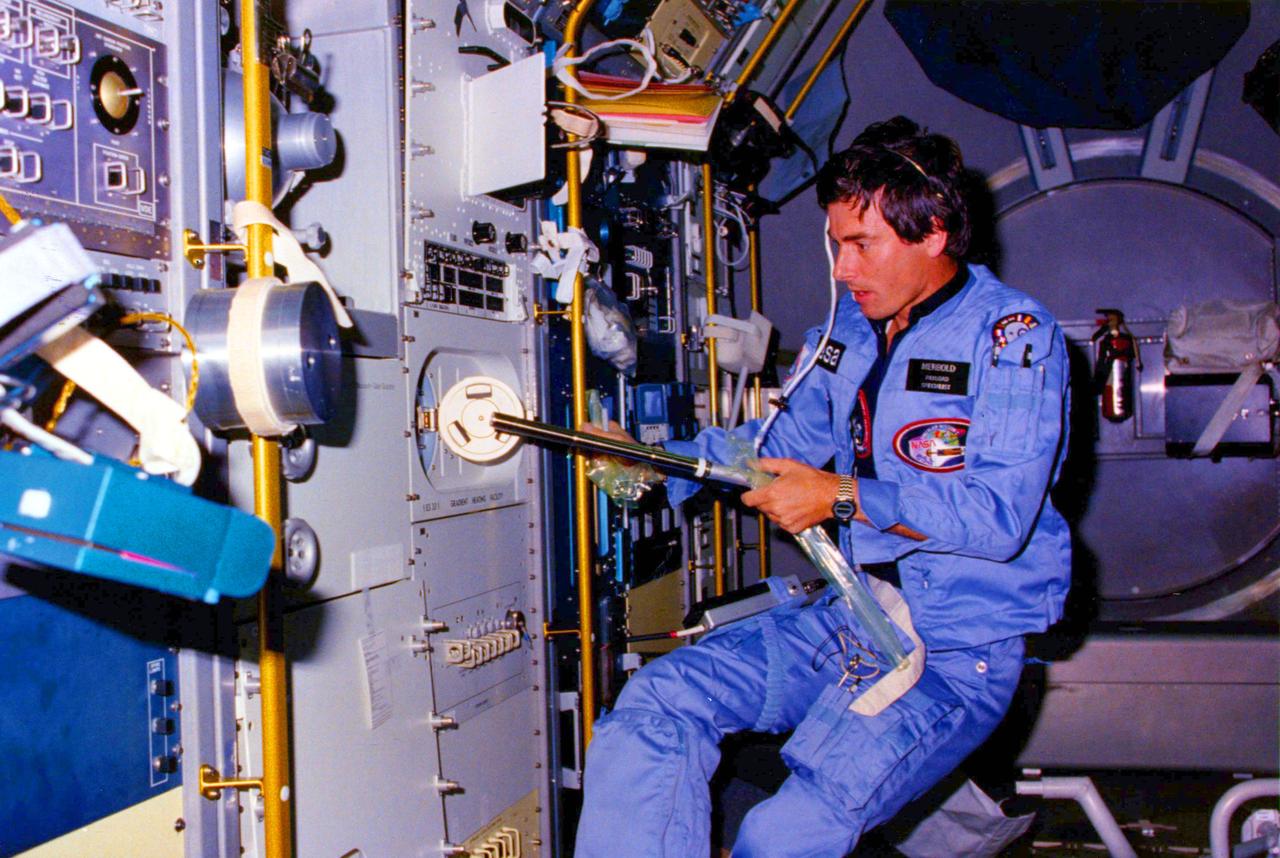

The Space Shuttle was designed to carry large payloads into Earth orbit. One of the most important payloads is Spacelab. The Spacelab serves as a small but well-equipped laboratory in space to perform experiments in zero-gravity and make astronomical observations above the Earth's obscuring atmosphere. In this photograph, Payload Specialist, Ulf Merbold, is working at Gradient Heating Facility on the Materials Science Double Rack (MSDR) inside the science module in the Orbiter Columbia's payload bay during STS-9, Spacelab-1 mission. Spacelab-1, the joint ESA (European Space Agency)/NASA mission, was the first operational flight for the Spacelab, and demonstrated new instruments and methods for conducting experiments that are difficult or impossible in ground-based laboratories. This facility performed, in extremely low gravity, a wide variety of materials processing experiments in crystal growth, fluid physics, and metallurgy. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall management responsibilities.

This photograph was taken during the integration of the Astro-1 mission payloads at the Kennedy Space Center on March 20, 1990, showing the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT) at the left, as three telescopes for the Astro-1 Observatory are settled into the Orbiter Columbia payload bay. Above Earth's atmospheric interference, Astro-1 would make precise measurements of objects such as planets, stars, and galaxies in relatively small fields of view and would observe and measure ultraviolet radiation from celestial objects. The Astro-1 used a Spacelab pallet system with an instrument pointing system and a cruciform structure for bearing the three ultraviolet instruments mounted in a parallel configuration. The three instruments were: The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), which was designed to obtain far-ultraviolet spectroscopic data from white dwarfs, emission nebulae, active galaxies, and quasars; the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE) which was to study polarized ultraviolet light from magnetic white dwarfs, binary stars, reflection nebulae, and active galaxies; and the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), which was to record photographic images in ultraviolet light of galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. The star trackers that supported the instrument pointing system, were also mounted on the cruciform. Also in the payload bay was the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT), which was designed to obtain high-resolution x-ray spectra from stellar corona, x-ray binary stars, active galactic nuclei, and galaxy clusters. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the Astro-1 observatory was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35) on December 2, 1990.
STS050-255-027 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Payload specialist Eugene H. Trinh, left, and astronaut Carl J. Meade, mission specialist, go to work in the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) science module as the blue shift crew takes over from the red. Trinh is working with an experiment at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) and Meade prepares to monitor an experiment in the Glovebox. The two joined four other astronauts and a second scientist from the private sector for 14-days of scientific data-gathering.

S93-26894 (March 1993) --- Spacelab Life Sciences 2, scheduled to fly as the major payload on the STS-58 mission, is represented with this logo. As in the case of SLS-1, which flew in space in June of 1991, this Spacelab mission will be devoted to life sciences and will carry a crew of experts in the associated disciplines.
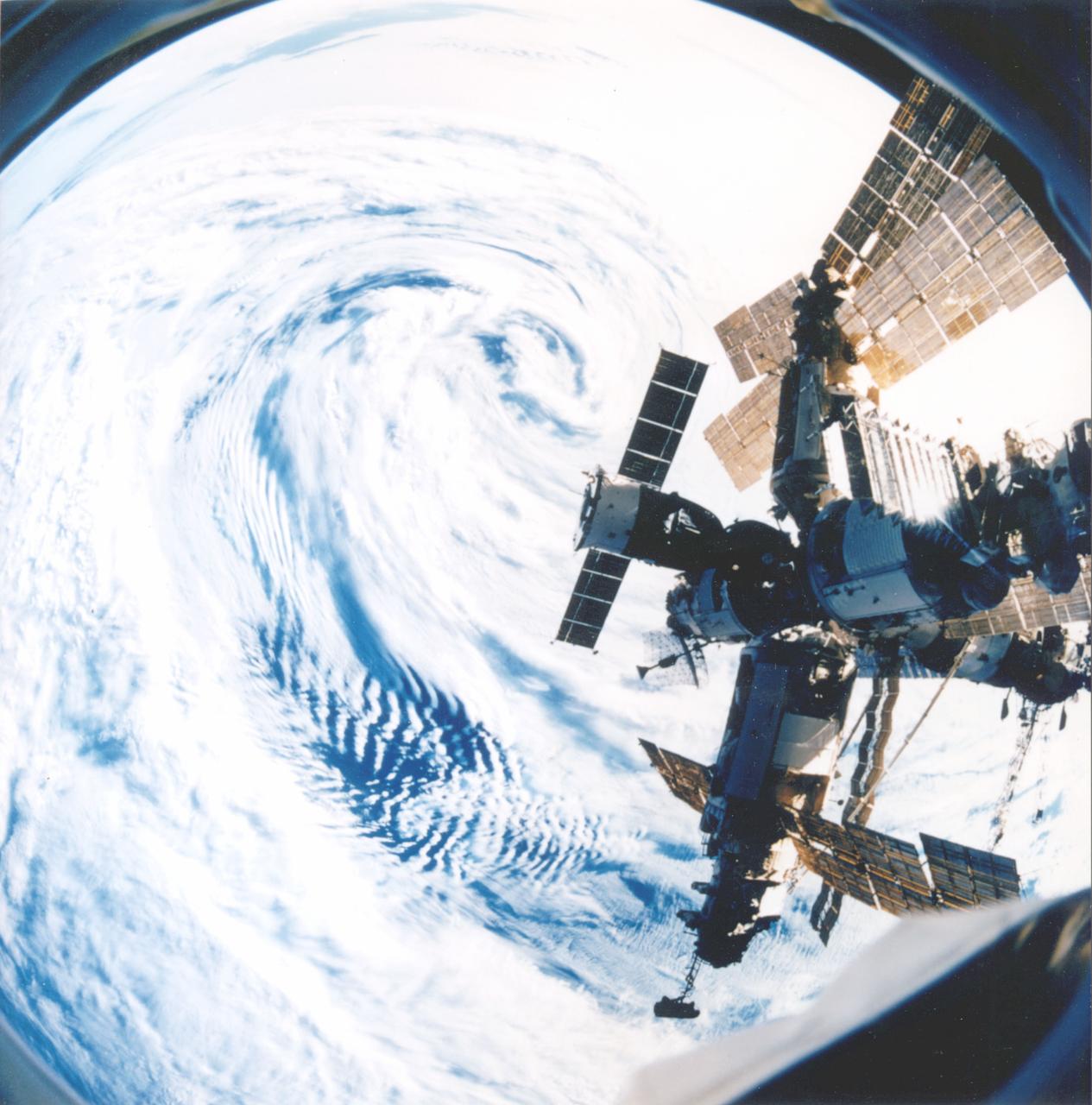

STS-79, Spacelab DM, Mir-docking-4, Shuttle and Mir Docking
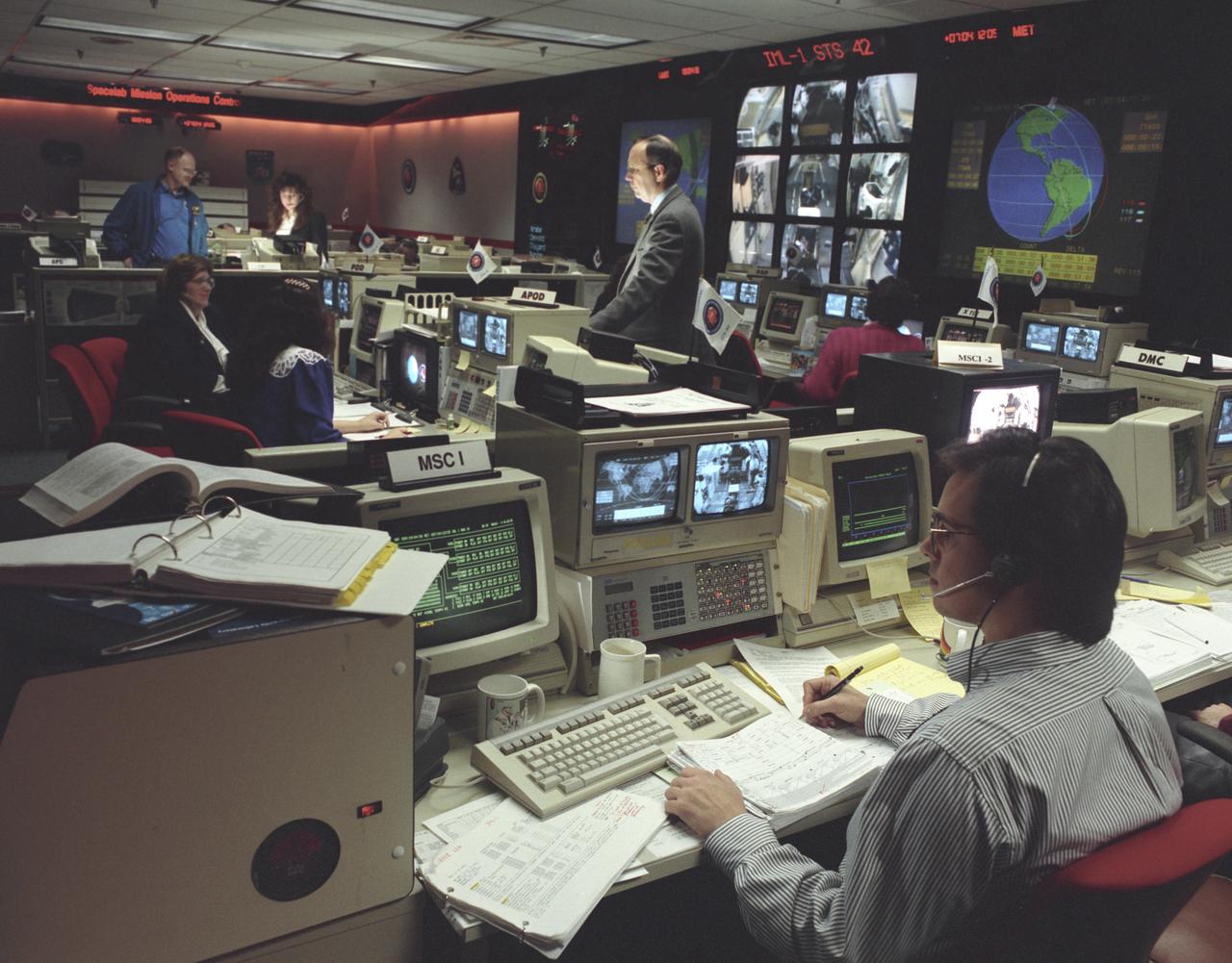

This photograph shows activities during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission (STS-42) in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research. The mission was to explore, in depth, the complex effects of weightlessness on living organisms and materials processing. The crew conducted experiments on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and the effects on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Low gravity materials processing experiments included crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury, iodine, and virus. The International space science research organizations that participated in this mission were: The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, the French National Center for Space Studies, the German Space Agency, and the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The POCC was the air/ground communication charnel used between the astronauts aboard the Spacelab and scientists, researchers, and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The facility made instantaneous video and audio communications possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress and to send direct commands of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew.
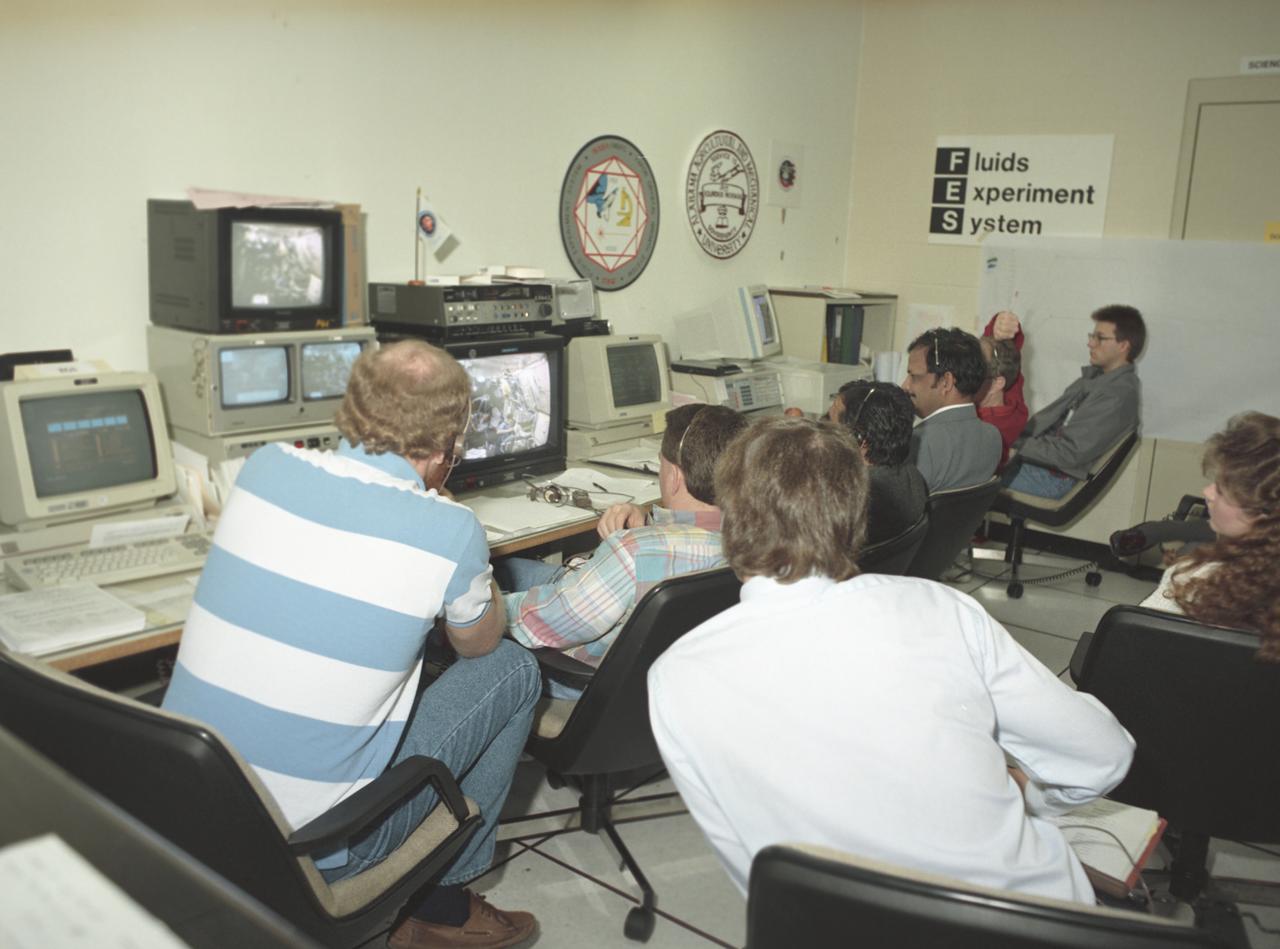

This photograph shows activities during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission (STS-42) in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. Members of the Fluid Experiment System (FES) group monitor the progress of their experiment through video at the POCC. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research. The mission was to explore, in depth, the complex effects of weightlessness on living organisms and materials processing. The crew conducted experiments on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and the effects on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Low gravity materials processing experiments included crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury, iodine, and virus. The International space science research organizations that participated in this mission were: The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administion, the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, the French National Center for Space Studies, the German Space Agency, and the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The POCC was the air/ground communication charnel used between astronauts aboard the Spacelab and scientists, researchers, and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The facility made instantaneous video and audio communications possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress and to send direct commands of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew.
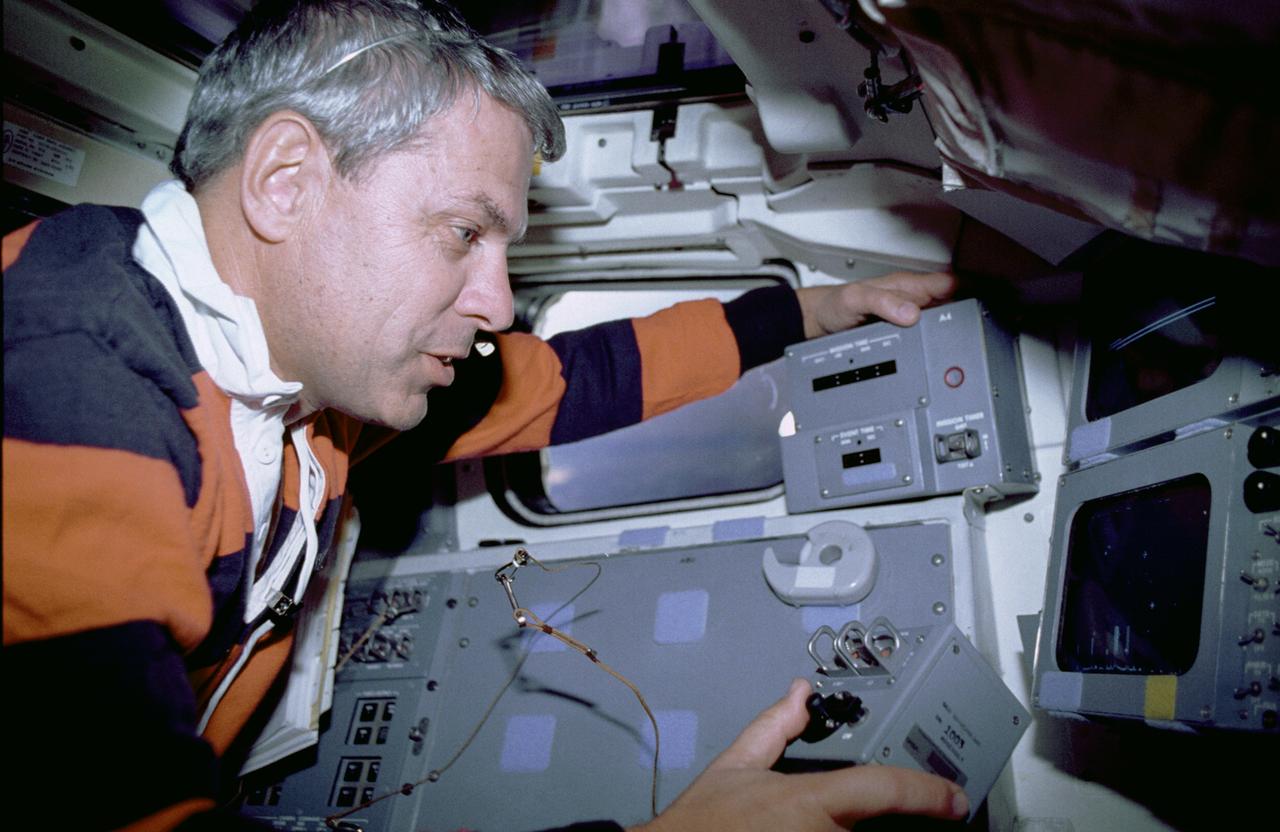

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. Pictured onboard the shuttle is astronaut Robert Parker using a Manual Pointing Controller (MPC) for the ASTRO-1 mission Instrument Pointing System (IPS).
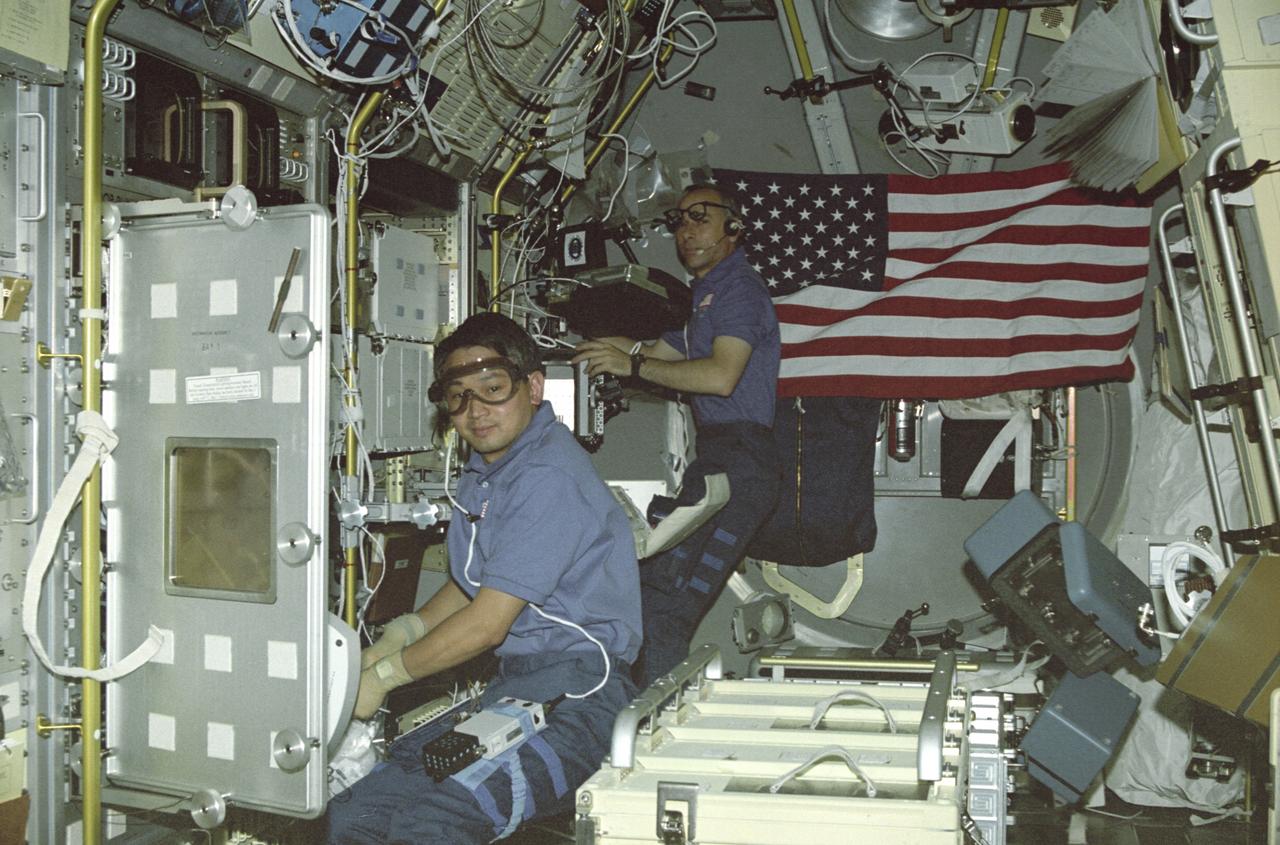

In this photograph, astronaut Eugene Trinh, a payload specialist for this mission, is working at the Drop Physics Module (DPM), and mission specialist Carl Meade is working on the experiment at the Glovebox inside the first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) Science Module. The USML-1 was one of NASA's missions dedicated to scientific investigations in a microgravity environment inside the Spacelab module. Investigations aboard the USML-1 included: materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. The DPM is dedicated to the detailed study of the dynamics of fluid drops in microgravity. The Glovebox offers experimenters new capabilities and technologies in microgravity with a clean working space and minimizes contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. Payload specialists are professional scientists or engineers whose only assignment on a space flight is to carry out scientific and technological experiments. Their specific training for a space flight is usually limited to a short period of learning how to live and work in weightlessness. Mission Specialists are both professional scientists and career astronauts. Thus they are a link or bridge between the other crew members, and combine the functions of resident maintenance engineers, in-space counterparts of flight engineers in aircraft, and fully qualified scientists. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992, and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
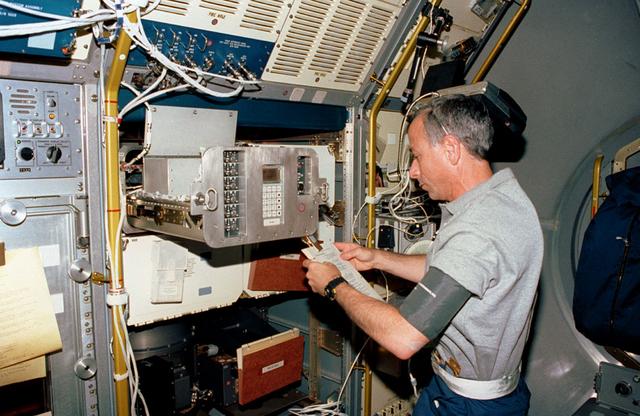

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs and provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology, and combustion science. In this photograph, astronaut Carl Meade is reviewing the manual to activate the Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (GBA) inside the Spacelab module. The GBA for the USML-1 mission was a multipurpose facility that could help us answer important questions about the relationship between gravity and biology. This unique facility allowed scientists to study biological processes in samples ranging from molecules to small organisms. For example, scientists would examine how collagen, a protein substance found in cornective tissue, bones, and cartilage, forms fibers. In microgravity, it might be possible to alter collagen fiber assembly so that this material could be used more effectively as artificial skin, blood vessels, and other parts of the body. The USML-1 was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and waslaunched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
This is a photograph of the Spacelab module for the first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) mission, showing logos of the Spacelab mission on the left and the USML-1 mission on the right. The USML-1 was one part of a science and technology program that opened NASA's next great era of discovery and established the United States' leadership in space. From investigations designed to gather fundamental knowledge in a variety of areas to demonstrations of new equipment, USML-1 forged the way for future USML missions and helped prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. Thirty-one investigations comprised the payload of the first USML-1 mission. The experiments aboard USML-1 covered five basic areas: fluid dynamics, the study of how liquids and gases respond to the application or absence of differing forces; crystal growth, the production of inorganic and organic crystals; combustion science, the study of the processes and phenomena of burning; biological science, the study of plant and animal life; and technology demonstrations. The USML-1 was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
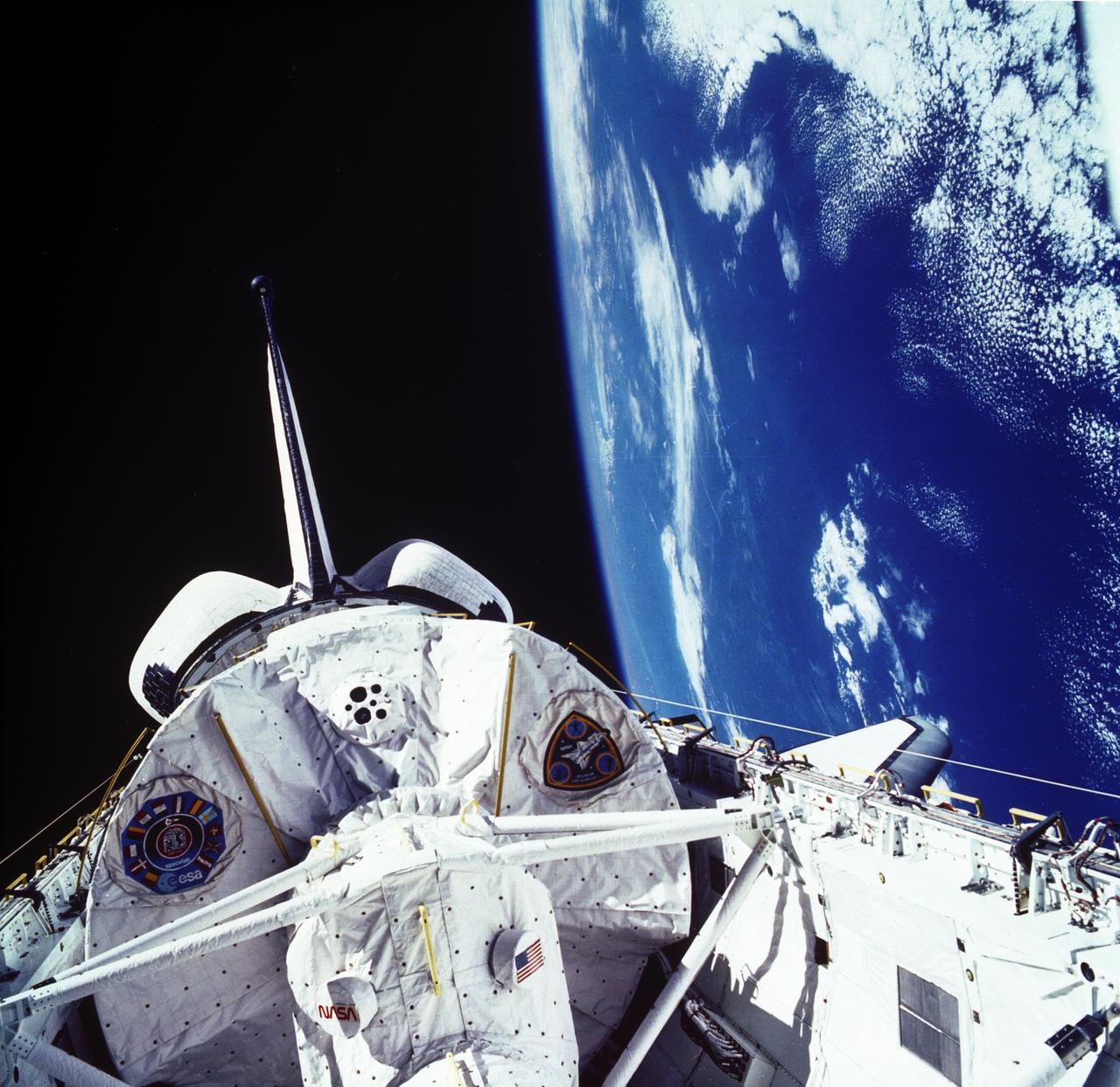

The laboratory module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia was photographed during the Spacelab Life Science-1 (SLS-1) mission. SLS-1 was the first Spacelab mission dedicated solely to life sciences. The main purpose of the SLS-1 mission was to study the mechanisms, magnitudes, and time courses of certain physiological changes that occur during space flight, to investigate the consequences of the body's adaptation to microgravity and readjustment to Earth's gravity, and to bring the benefits back home to Earth. The mission was designed to explore the responses of the heart, lungs, blood vessels, kidneys, and hormone-secreting glands to microgravity and related body fluid shifts; examine the causes of space motion sickness; and study changes in the muscles, bones and cells. The five body systems being studied were: The Cardiovascular/Cardiopulmonary System (heart, lungs, and blood vessels), the Renal/Endocrine System (kidney and hormone-secreting organs), the Immune System (white blood cells), the Musculoskeletal System (muscles and bones), and the Neurovestibular System (brain and nerves, eyes, and irner ear). The SLS-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-40) on June 5, 1995.
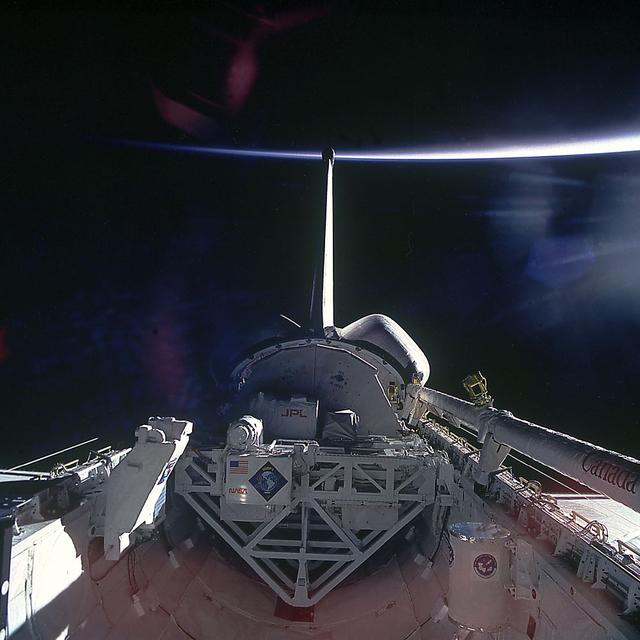

This is a Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-52) onboard photograph of the United States Microgravity Payload-1 (USMP-1) in the cargo bay. The USMP program is a series of missions developed by NASA to provide scientists with the opportunity to conduct research in the unique microgravity environment of the Space Shuttle's payload bay. The USMP-1 mission was designed for microgravity experiments that do not require the hands-on environment of the Spacelab. Science teams on the ground would remotely command and monitor instruments and analyze data from work stations at NASA's Spacelab Mission Operation Control facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The USMP-1 payload carried three investigations: two studied basic fluid and metallurgical processes in microgravity, and the third would characterize the microgravity environment onboard the Space Shuttle. The three experiments that made up USMP-1 were the Lambda Point Experiment, the Space Acceleration Measurement System, and the Materials for the Study of Interesting Phenomena of Solidification Earth and in Orbit (MEPHISTO). The three experiments were mounted on two cornected Mission Peculiar Equipment Support Structures (MPESS) mounted in the orbiter's cargo bay. The USMP program was managed by the MSFC and the MPESS was developed by the MSFC.
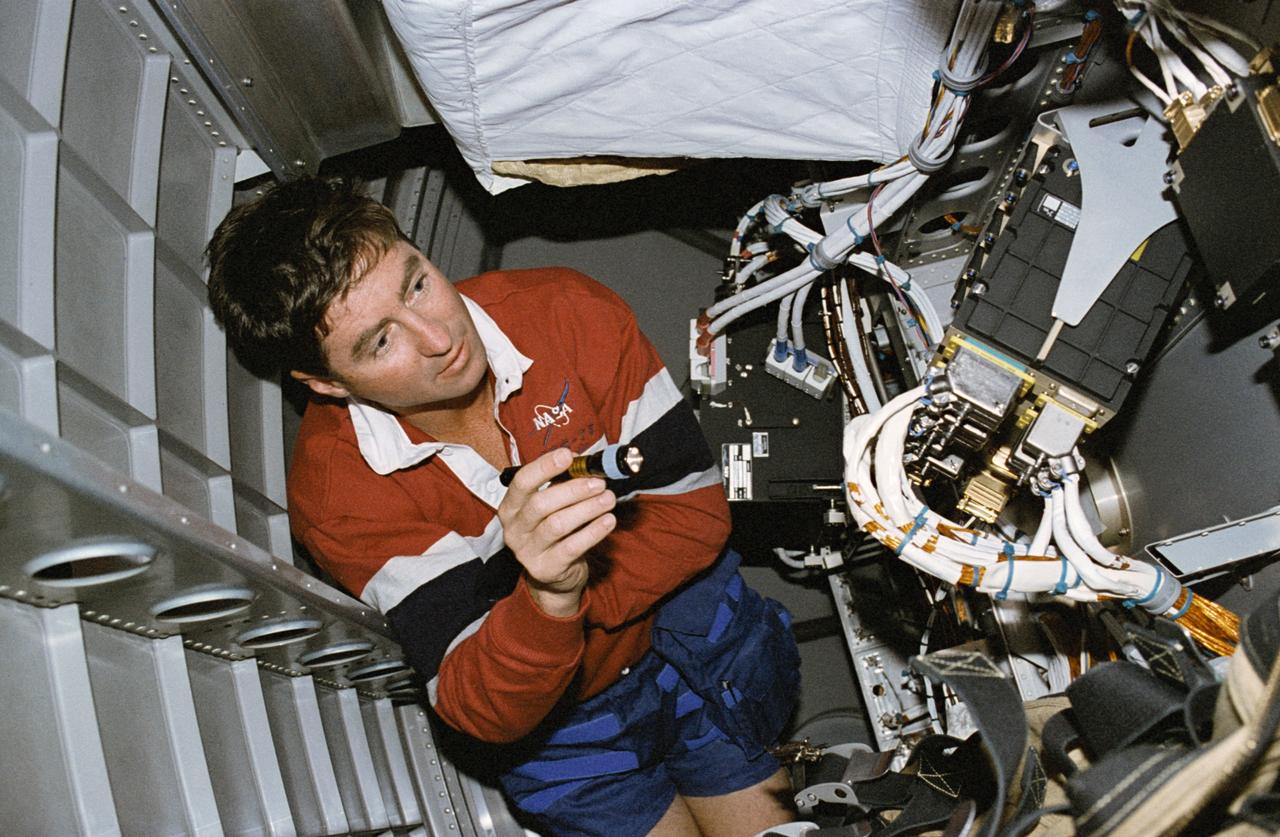

STS078-432-009 (20 June-7 July 1996) --- Among the inflight maintenance (IFM) chores that were handled by the crew members during their almost 17 days in space aboard the space shuttle Columbia was one that involved going into the bay beneath the floor of the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS-1) Science Module. Astronaut Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, mission commander, shines a tiny flashlight onto some cables related to LMS-1 supported computer systems. As in the case of the other IFM chores, Henricks' efforts were successful. He was joined by four other NASA astronauts and two international payload specialists for the space shuttle duration record-setting mission.
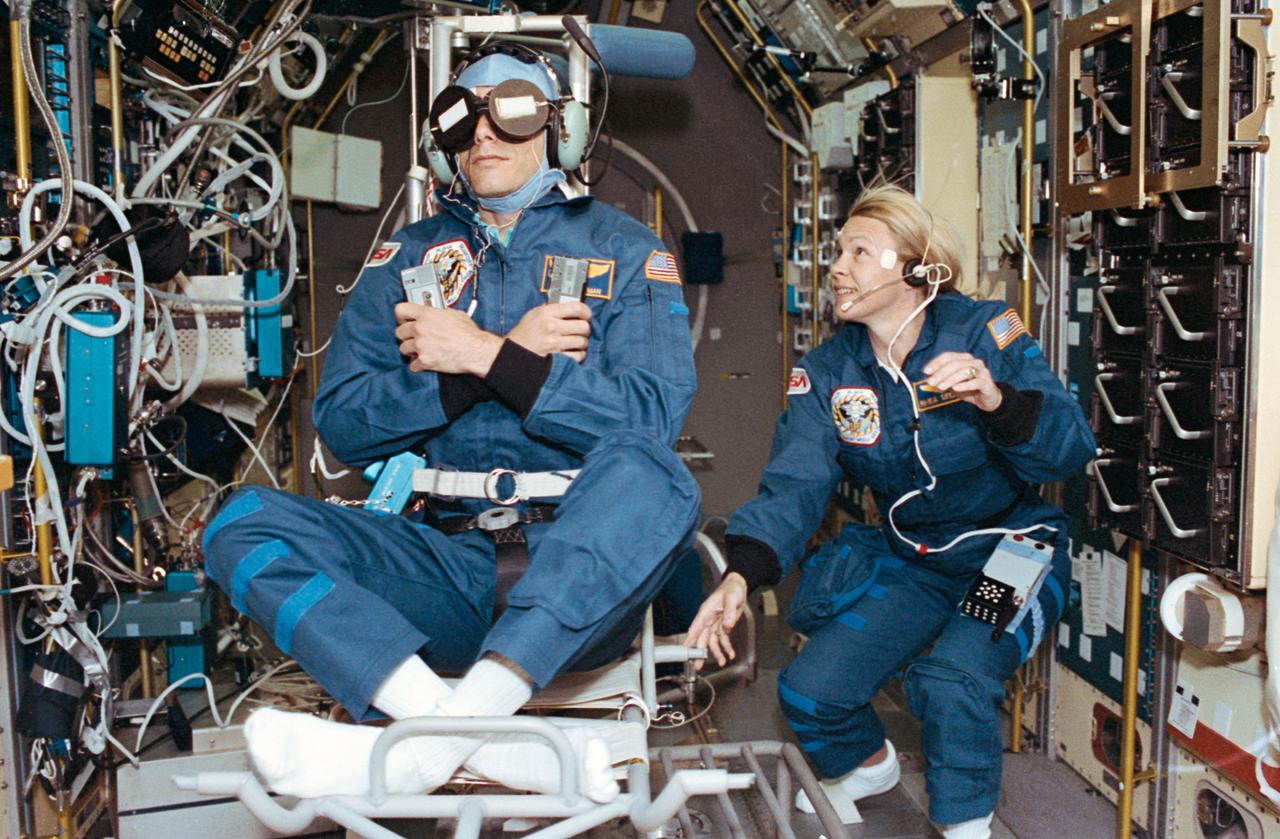

STS058-202-002 (18 Oct.-1 Nov. 1993) --- Astronaut Rhea Seddon, STS-58 payload commander, spins the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) rotating chair as payload specialist Martin J. Fettman serves as test subject. The two joined five NASA astronauts for fourteen days of medical research aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia. Photo credit: NASA
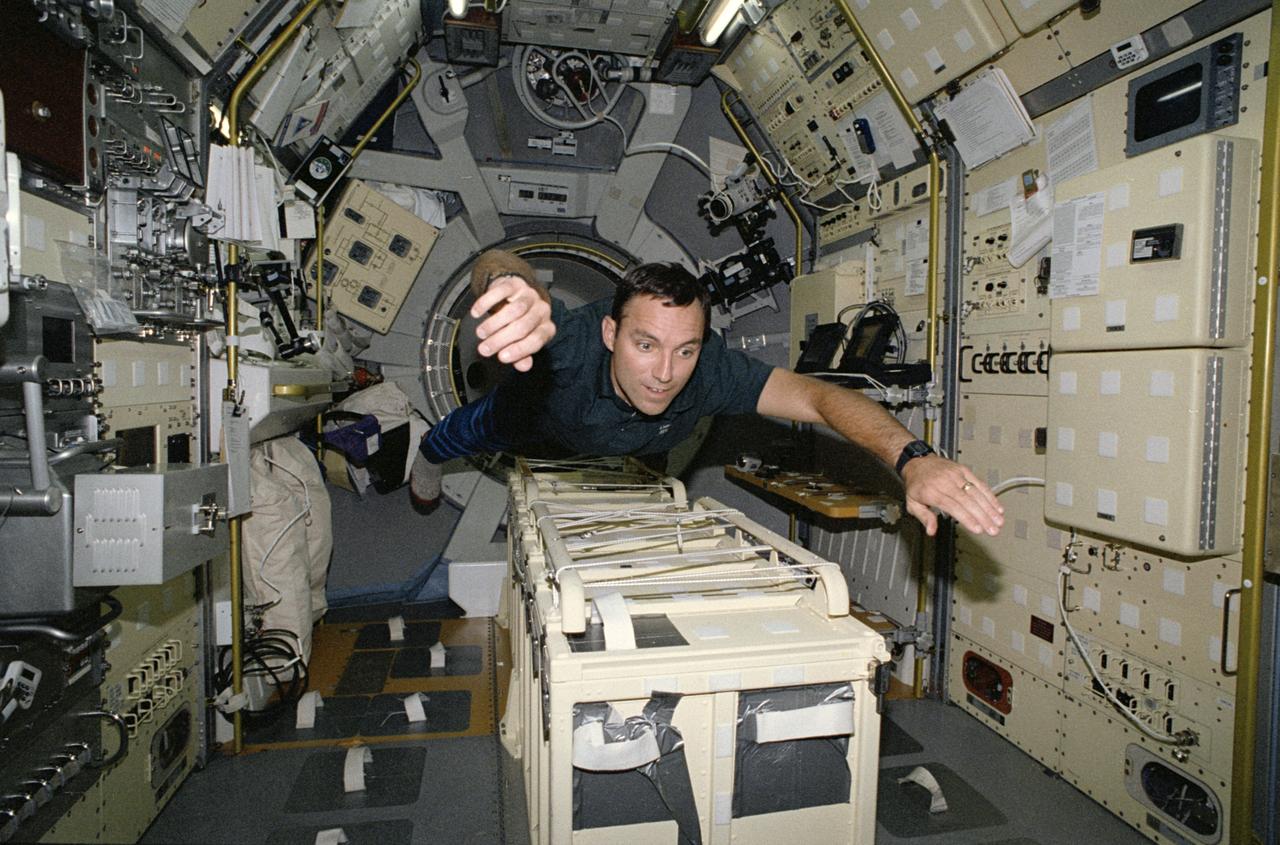

STS-65 Mission Specialist Carl E. Walz floats above center aisle equipment in the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) spacelab science module. Walz has just entered the IML-2 module via the spacelab tunnel (note hatch opening behind him). The tunnel connects the IML-2 module with Columbia's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102's, crew compartment. Walz along with five other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist spent more than two weeks in Earth orbit conducting IML-2 experiments. This photo was among the first released by NASA following IML-2.
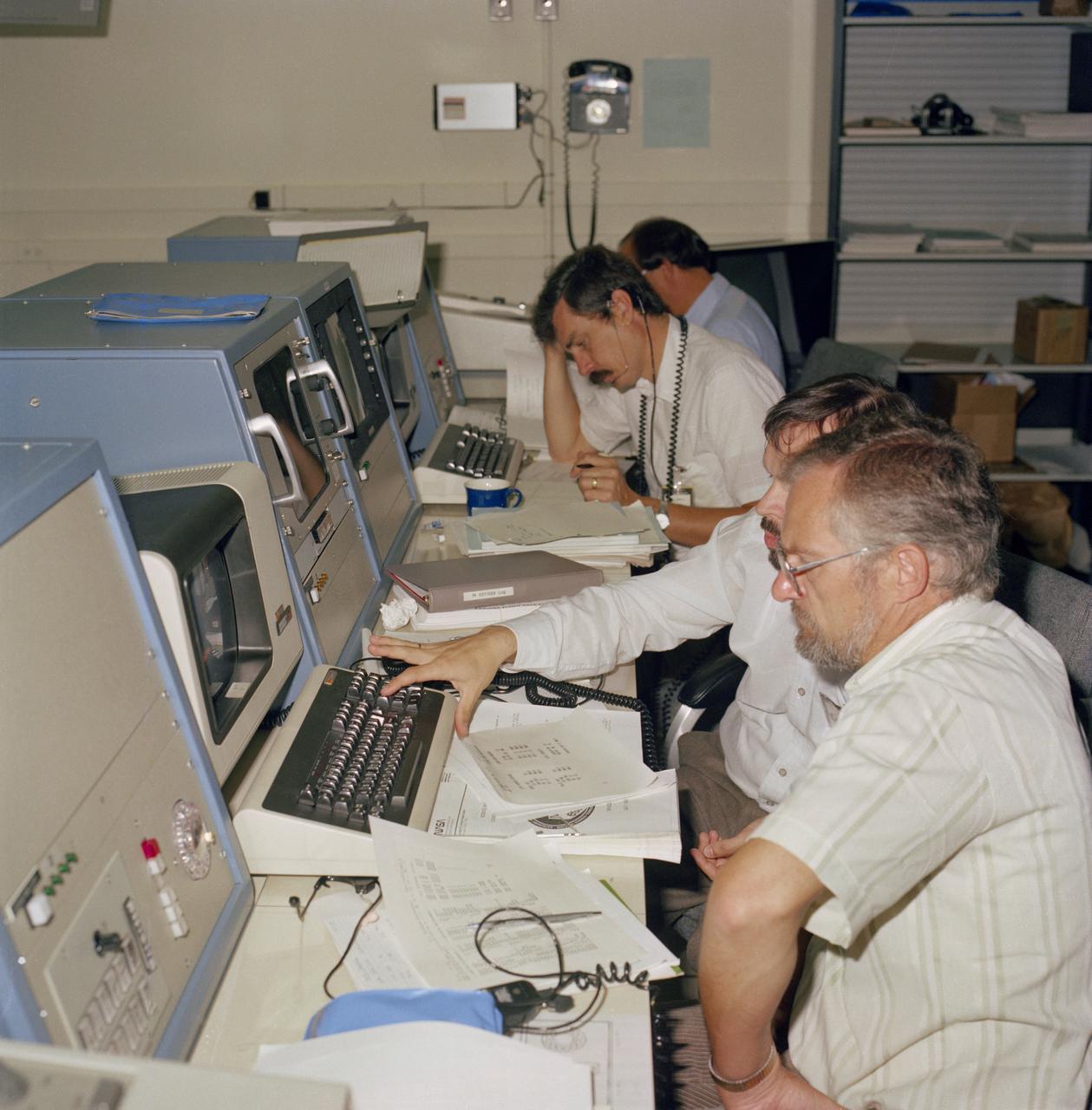

S83-40845 (Dec 1983) --- Principal investigators and their ground support teams follow Spacelab 1 activities in the Science Monitoring Area of the Johnson Space Center's mission control center. NOTE: This area will be manned for the Spacelab Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1) mission, currently scheduled for May of 1991.
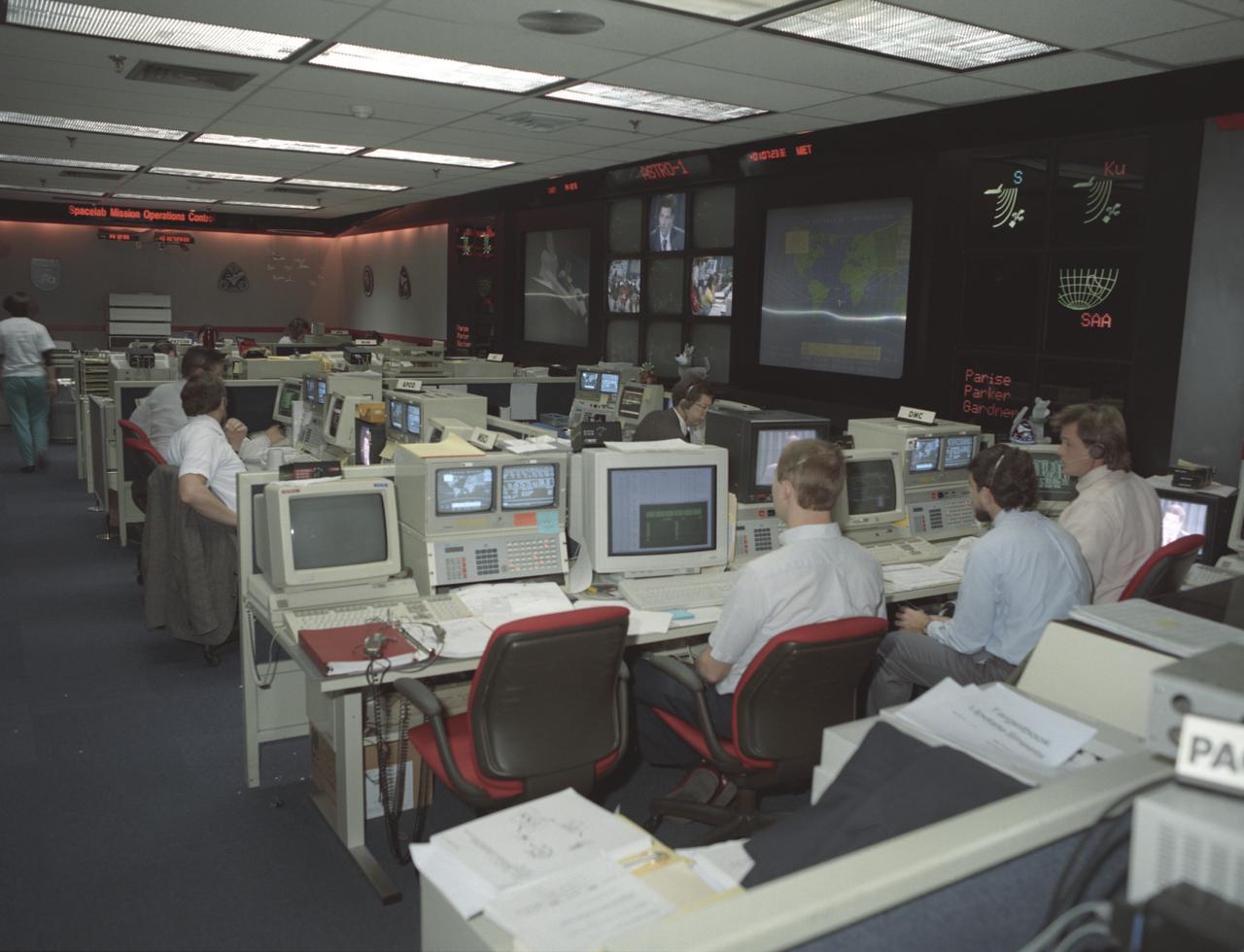

This photograph was taken during the Astro-1 mission (STS-35) showing activities at NASA's new Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The POCC was the air/ground communication charnel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crewmembers to resolve problems with their experiments.
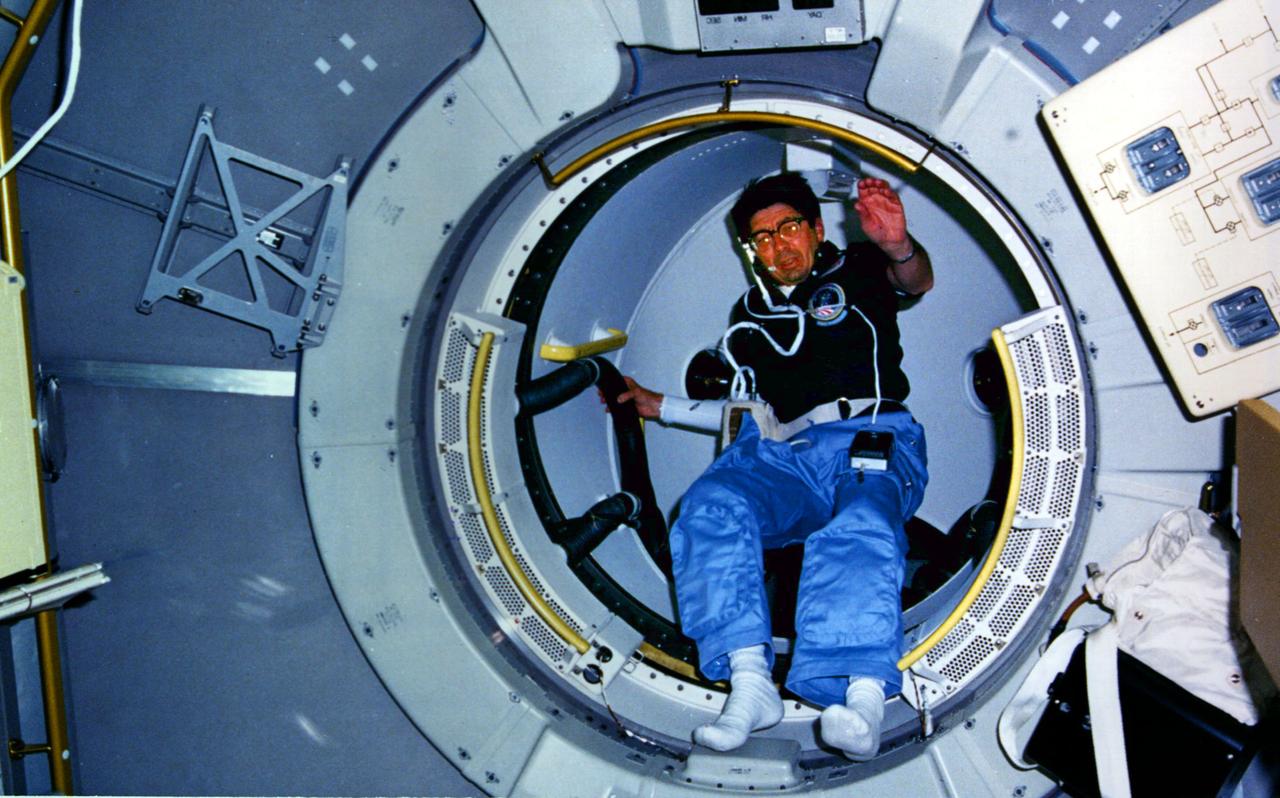

STS-51B, Spacelab 3, Lodewijk van den Berg coming through the turnel.
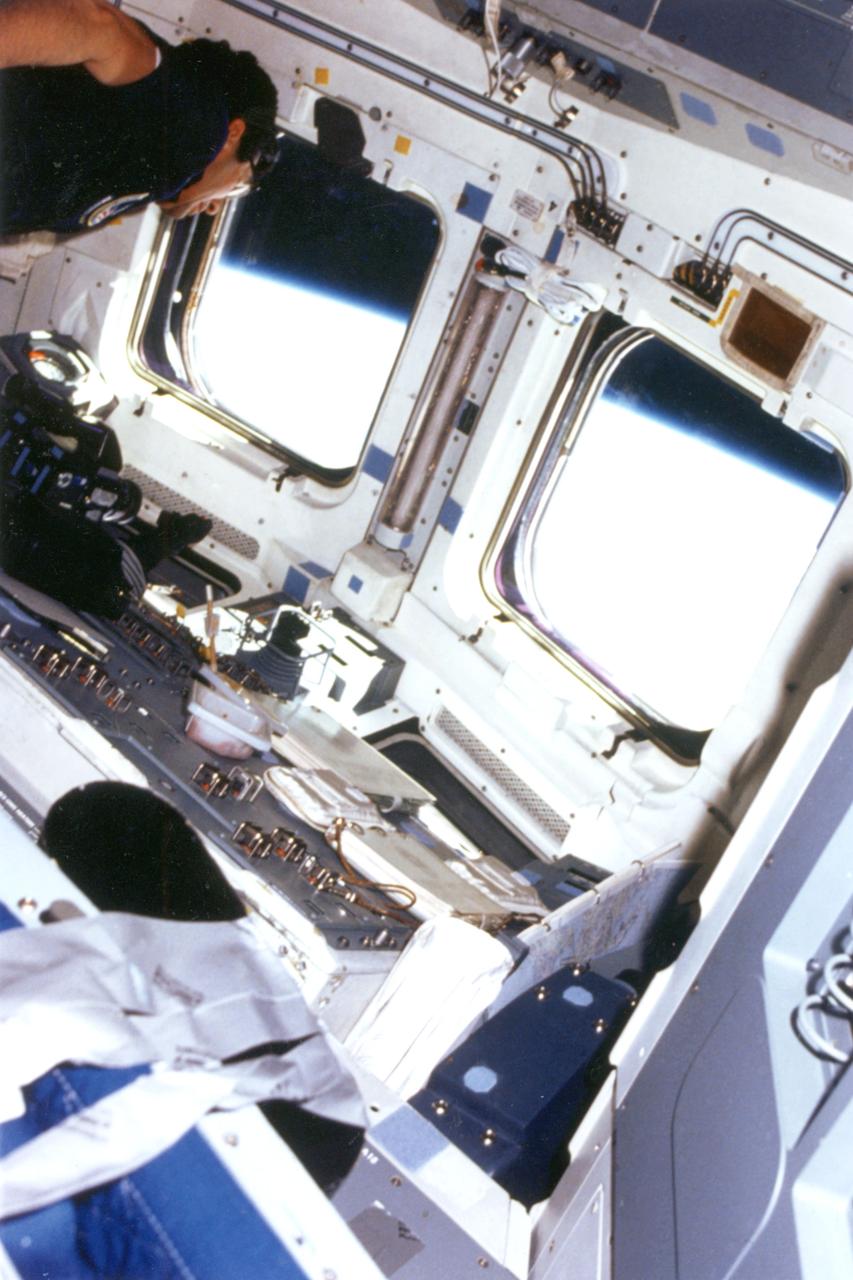

STS-51B, Spacelab-3, Payload Specialist Lodewijk van den Berg on flight deck with earth view out window.
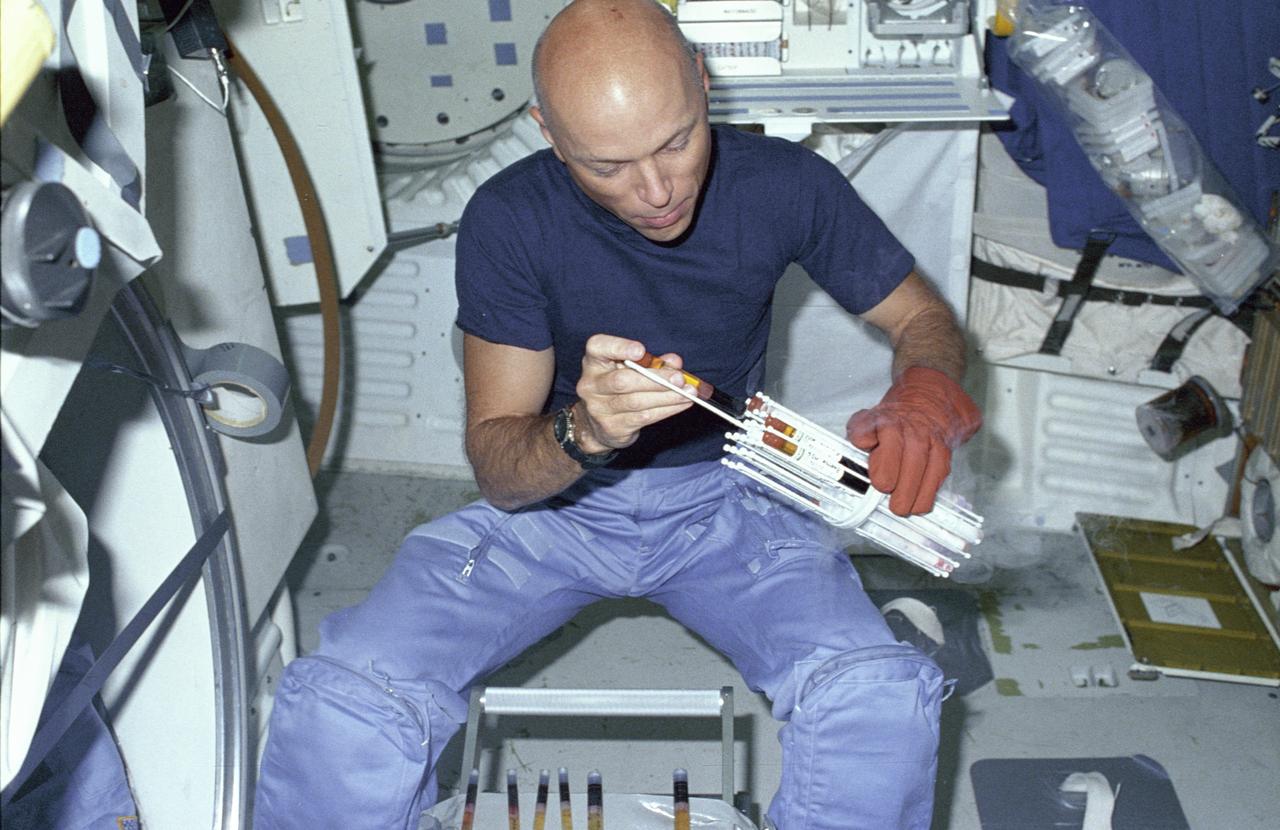

While instruments on the pallets in the payload bay observed the universe, biological experiments were performed in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. Studying life processes in a microgravity environment can shed new light on the functioning of biological systems on Earth. These investigations can also help us understand how living organisms react to prolonged weightlessness. One such experiment was the vitamin D metabolites and bone demineralization experiment. This investigation measured the vitamin D metabolite levels of crew members to gain information on the cause of bone demineralization and mineral imbalance that occur during prolonged spaceflight as well as on Earth. Research into the biochemical nature of vitamin D has shown that the D-metabolites play a major role in regulating the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. One major function of the most biologically active vitamin D metabolite is to regulate the amount of calcium absorbed from the diet and taken out of bones. This investigation had two phases. The first was the developmental phase, which included extensive testing before flight, and the second, or final phase, involved the postflight analysis of the crew's blood samples. This photograph shows astronaut Story Musgrave in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger, attending to the blood samples he collected from crew members for the experiment.

S82-31408 (May 1983) --- The Spacelab 2 emblem is a symbolic representation of the scientific objectives of the mission. The emblem is in the shape of a triangular shield with convexly curved edges. Across the top of a black out border are the words ?SPACELAB 2?. Within the black border is a sky blue border carryhing the words: ?ASTRONOMY?, ON TOP? ?PHYSICS?, on the left; and ?BIOLOGY?, on the right. Within the blue border is a schematic view of the sun, the earth, and the orbiter with Spacelab 2. The sun appears in the upper right background as a white disc surrounded by six concentric rings ranging grom bright yellow near the disc through yellow-red to a dark red out ring. A sector of the earth with blue ocean and a black portion of North America is in the upper left corner. The black and white Orbiter is seen from directly overhead in the foreground, the right side illuminated by the sun, the left side in shadow. Although the payload bay doors are not open, the Spacelab 2 payload is seen as if the doors were open. In black on white are seen the three pallets, and the separately mounted cosmic ray experiment at the aft end of the bay.
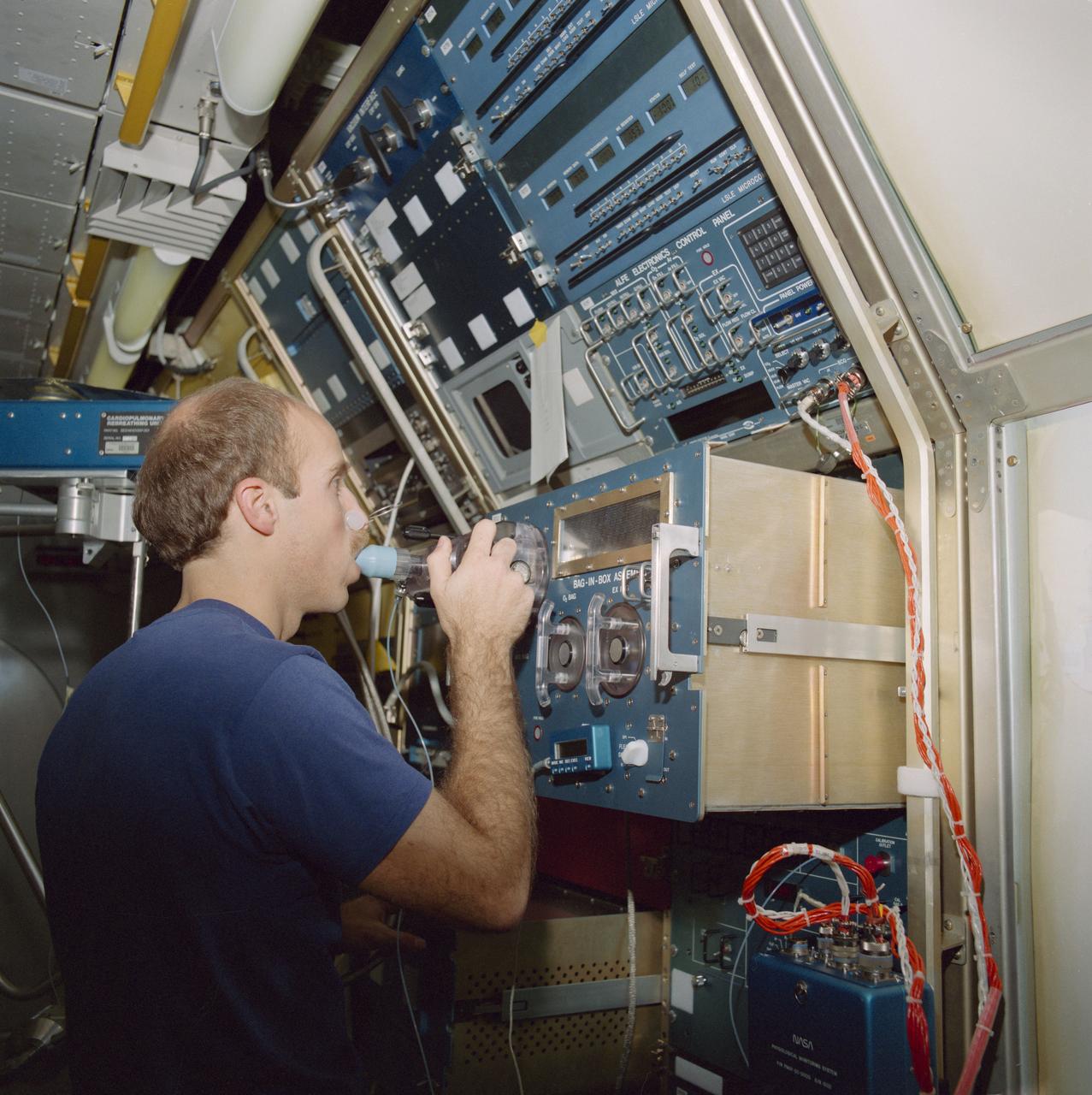

S85-26582 (Feb 1985) --- Training on the rebreathing assembly, astronaut James P. Bagian, STS-40 mission specialist, inhales a predetermined gas composition. A gas analyzer mass spectrometer determines the composition of the gases he exhales. The rebreathing assembly and gas analyzer system are part of an investigation that explores how lung function is altered. Dr. Bagian will be joined by two other mission specialists, the mission commander, the pilot and two payload specialists for the scheduled 10-day Spacelab Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1) mission. The flight is totally dedicated to biological and medical experimentation.
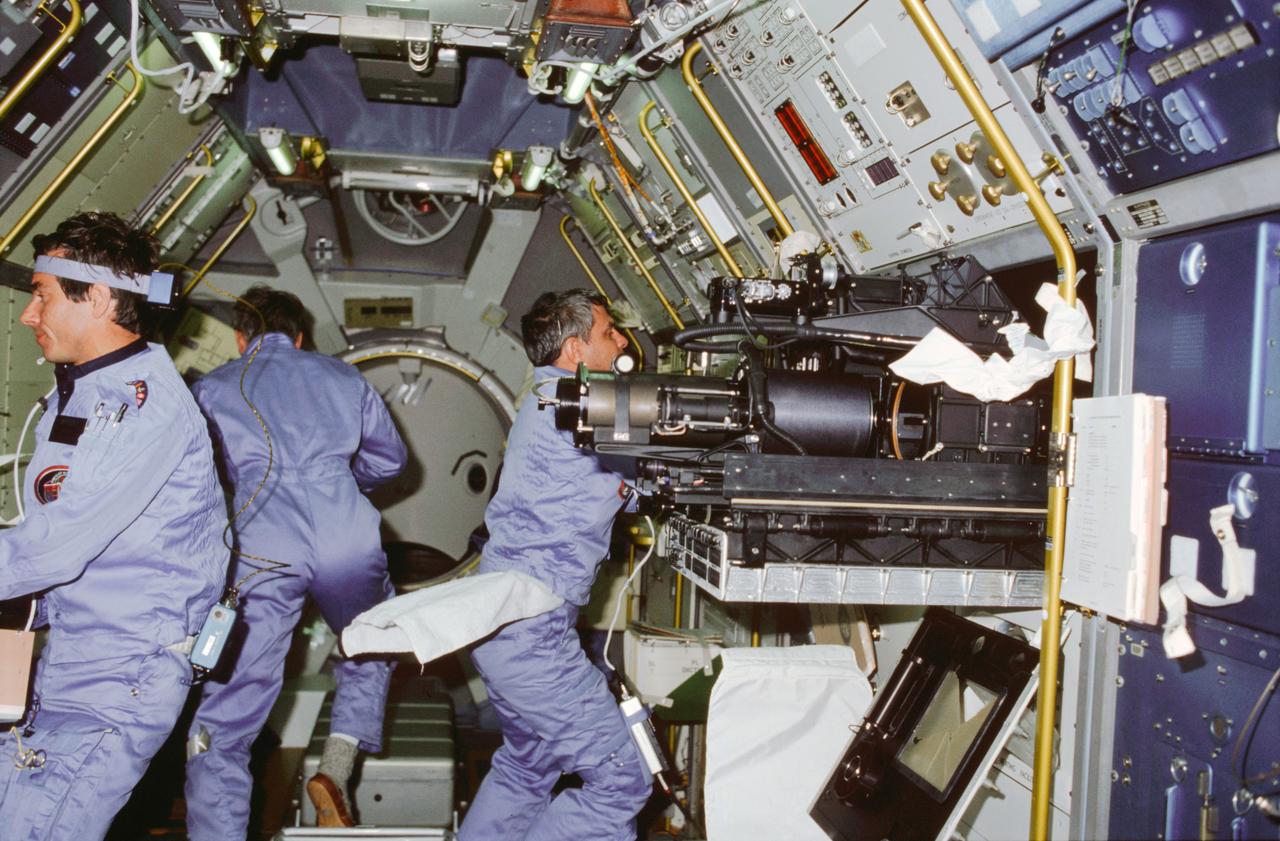

STS009-03-093 (28 Nov-8 Dec 1983) --- A mission specialist and two payload specialists busy themselves in the Spacelab 1 module aboard the Earth orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Left to right are Payload Specialist Robert A. R. Parker. Parker is partially obscured by a deployed instrument of the fluid physics module at the materials sciences double rack. Merbold, a physicist from Max-Planck Institute in the Federal Republic of Germany, wears a head band-like device and a recorder as part of an overall effort to learn more about space adaptation. Both Space lab 1 payload specialists wore the devices during most of their waking hours on this 10-day flight. The frame was exposed with a 35mm camera.
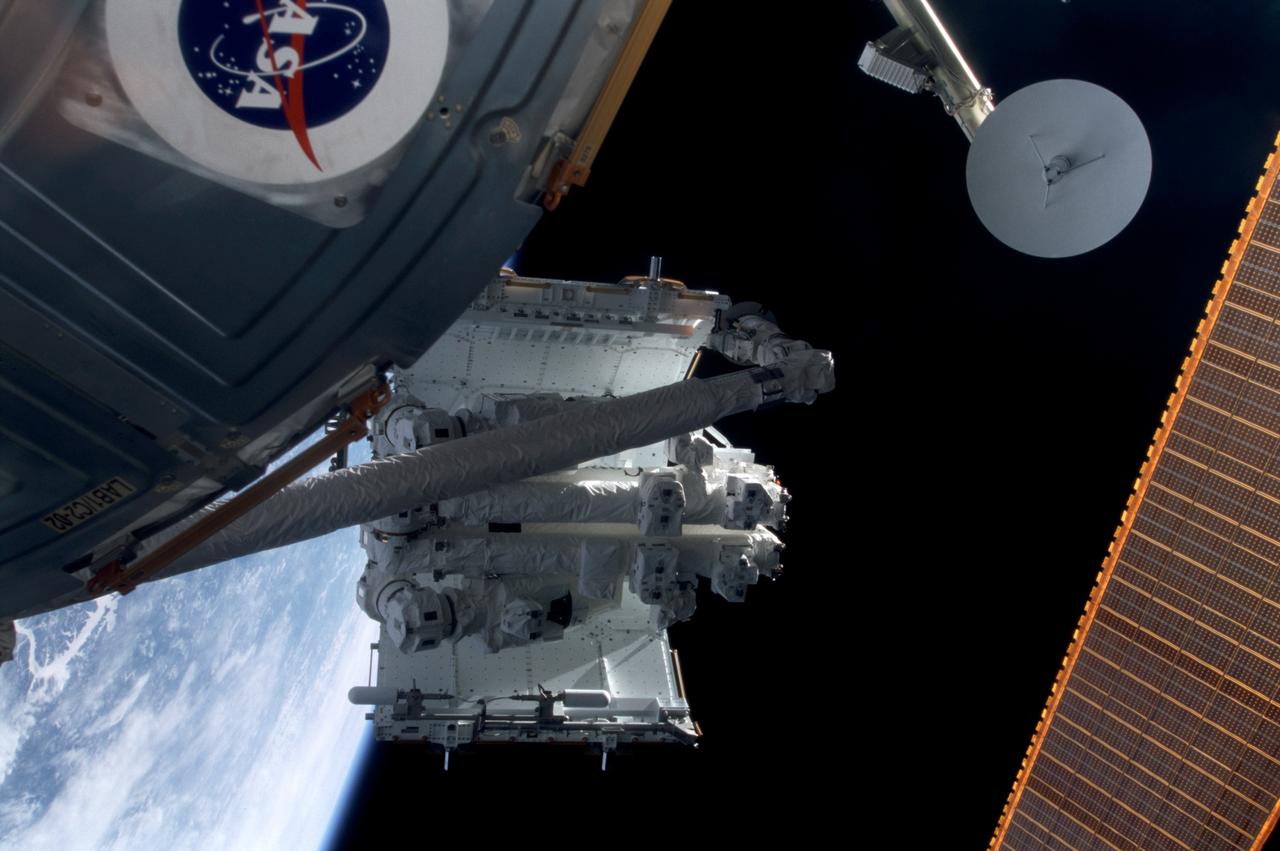

STS100-388-010 (19 April-1 May 2001) --- In the grasp of the shuttle's remote manipulator system (RMS) robot arm, the Spacelab pallet is installed on the Lab Cradle Assembly (LCA) on the International Space Station (ISS).
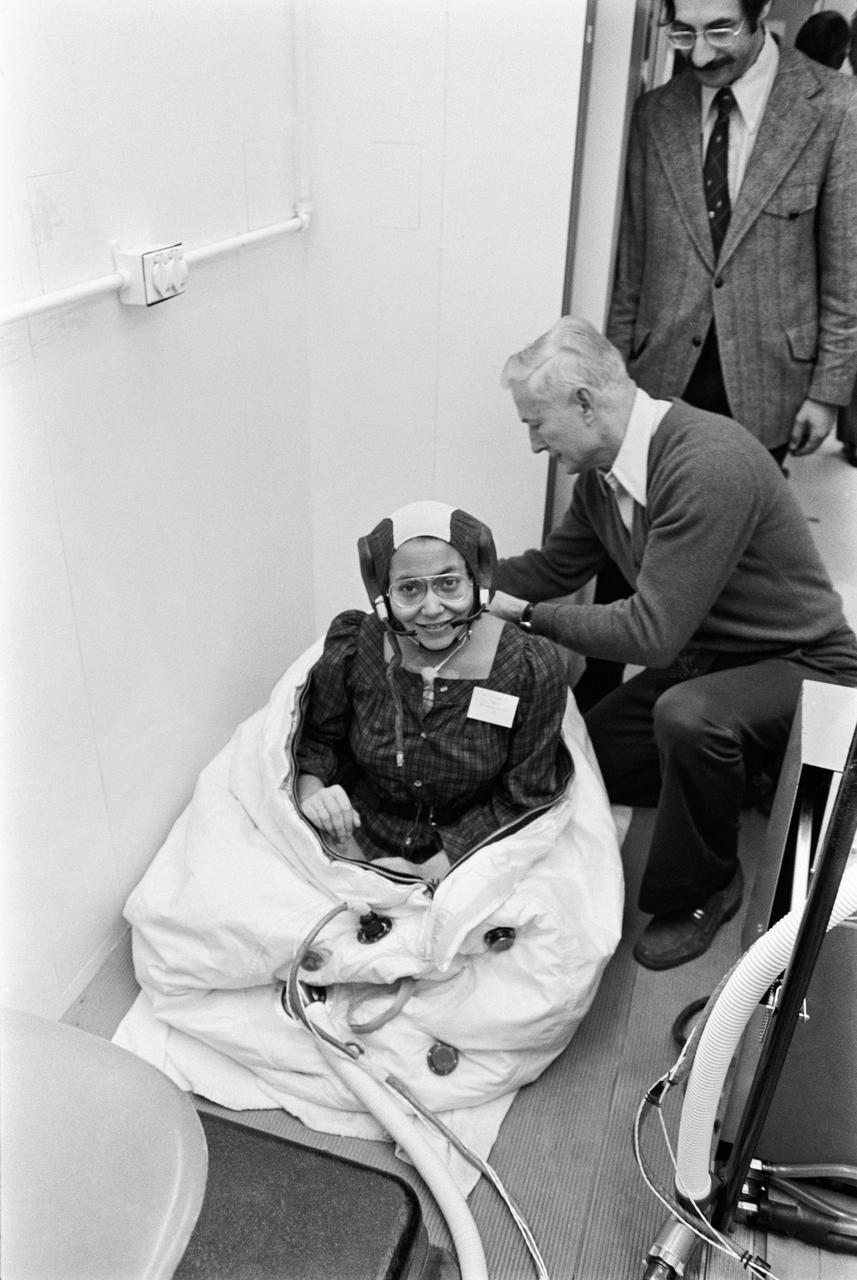
Spacelab simulations crew members during medical testing. Photo is of Patricia Cowings being zipped into the one-meter-diameter rescue ball during physical tests. Assisting her is Joe Schmitt, a suit technician.
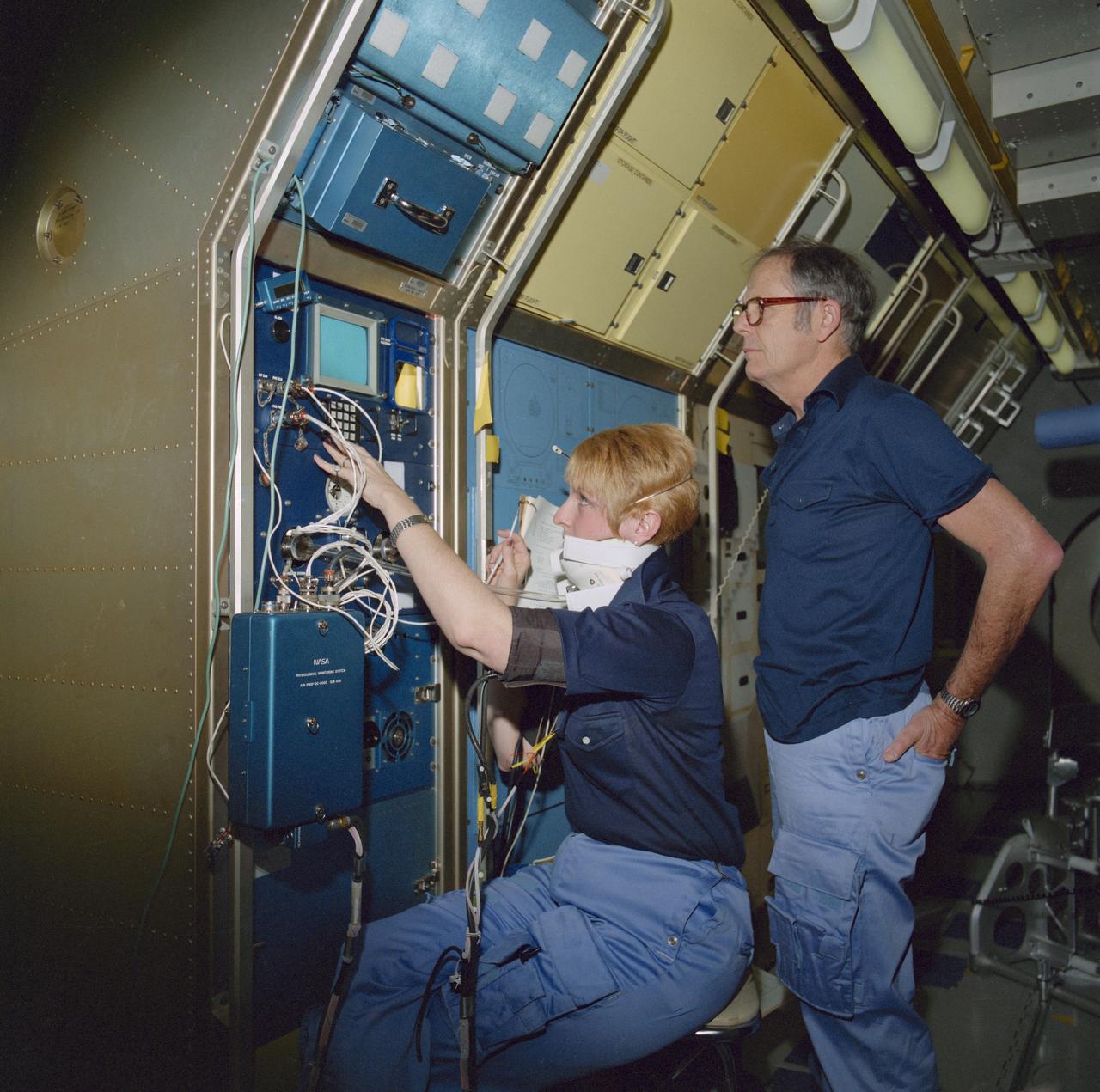

S85-26571 (Feb 1985) --- Wearing a special collar, Millie Hughes-Fulford, payload specialist, practices medical test operations scheduled for the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) mission. Robert Ward Phillips, backup payload specialist, looks on. The collar, called the baroflex neck pressure chamber, is designed to stimulate the bioceptors in the carotid artery, one of the two main arteries that supply blood to the head.
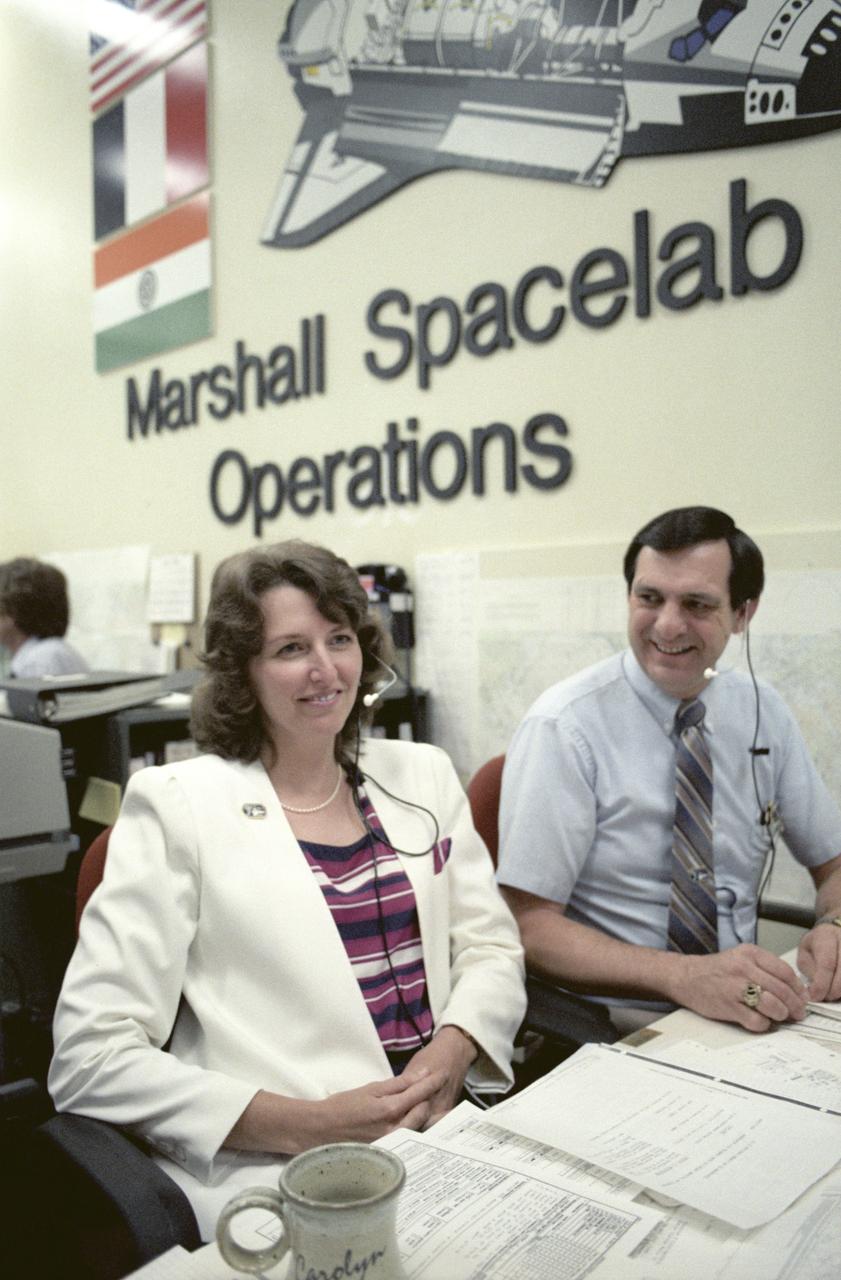

Spacelab-3 launched aboard STS-51B, with the major science objective being to perform engineering tests on two new facilities: the rodent animal holding facility and the primate animal holding facility. In addition, scientists observed the animals to obtain first hand knowledge of the effects of launch and reentry stresses and behavior. The need for suitable animal housing to support research in space led to the development of the Research Animal Holding Facility at the Ames Research Center. Scientists often study animals to find clues to human physiology and behavior. Rats, insects, and microorganisms had already been studied aboard the Shuttle on previous missions. On Spacelab-3, scientists had a chance to observe a large number of animals living in space in a specially designed and independently controlled housing facility. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had management responsibility for the Spacelab-3 mission. This photograph depicts activities during the mission at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at MSFC.
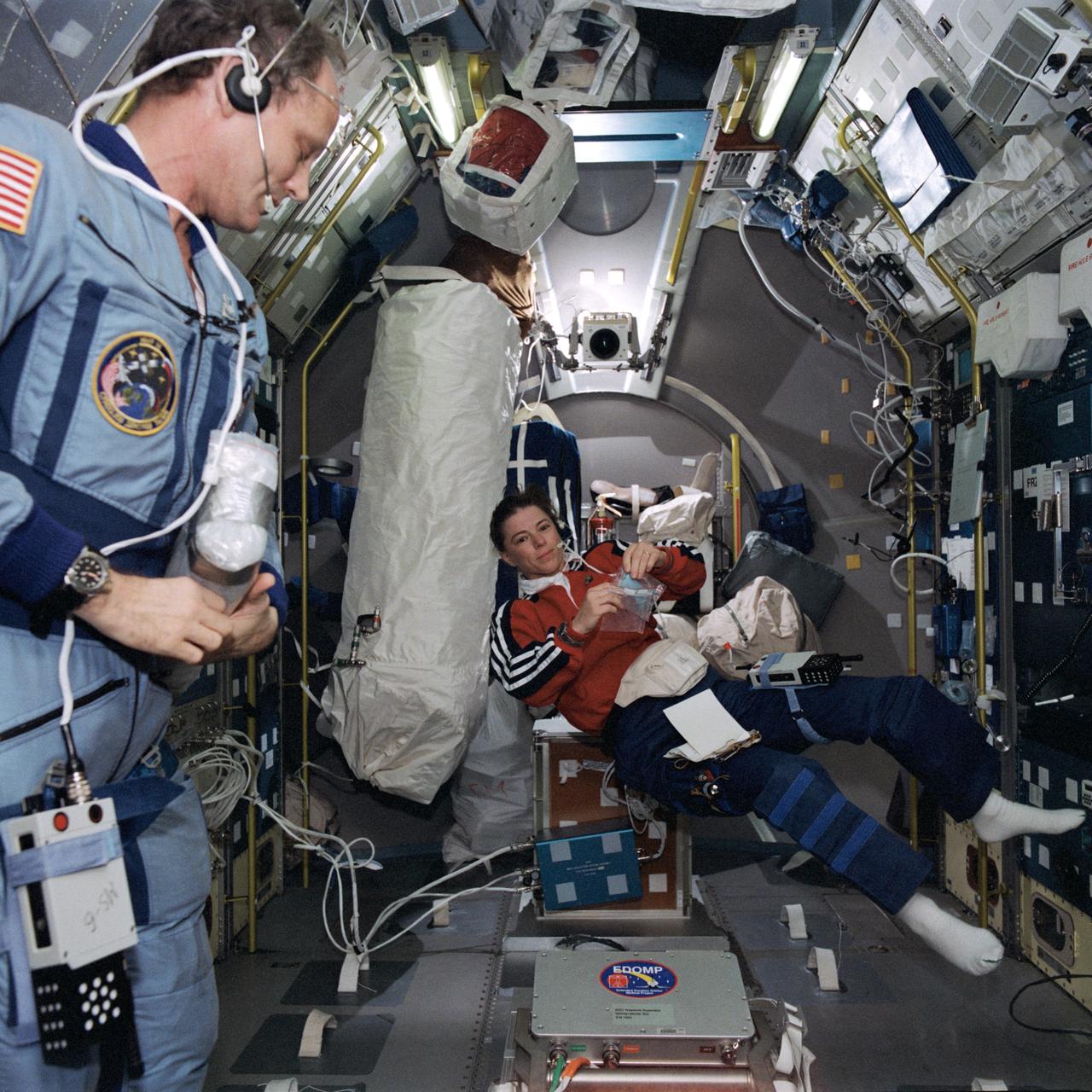

STS071-758-009 (27 June - 7 July 1995) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, mission specialist, floats about in the Spacelab Science Module as astronaut Norman E. Thagard looks on. Thagard, Mir-18 guest cosmonaut researcher, had completed four months in space aboard Russia's Mir Space Station. When this photograph was taken he was undergoing a battery of tests and data collection exercises on Spacelab, onboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis. Dunbar had served as his Mir-18 backup, during a year's training in Russia.

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) flew in orbit inside the Spacelab science module for extended periods, providing scientists and researchers greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This photograph shows Astronaut Larry De Lucas wearing a stocking plethysmograph during the mission. Muscle size in the legs changes with exposure to microgravity. A stocking plethysmograph, a device for measuring the volume of a limb, was used to help determine these changes. Several times over the course of the mission, an astronaut will put on the plethysmograph, pull the tapes tight and mark them. By comparing the marks, changes in muscle volume can be measured. The USML-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.

After completion of a seven-day flight mission, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour (STS-47) landed at Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility. Spacelab-J, a joint research venture between NASA and NASDA (National Space Development Agency of Japan) completed a successful mission.
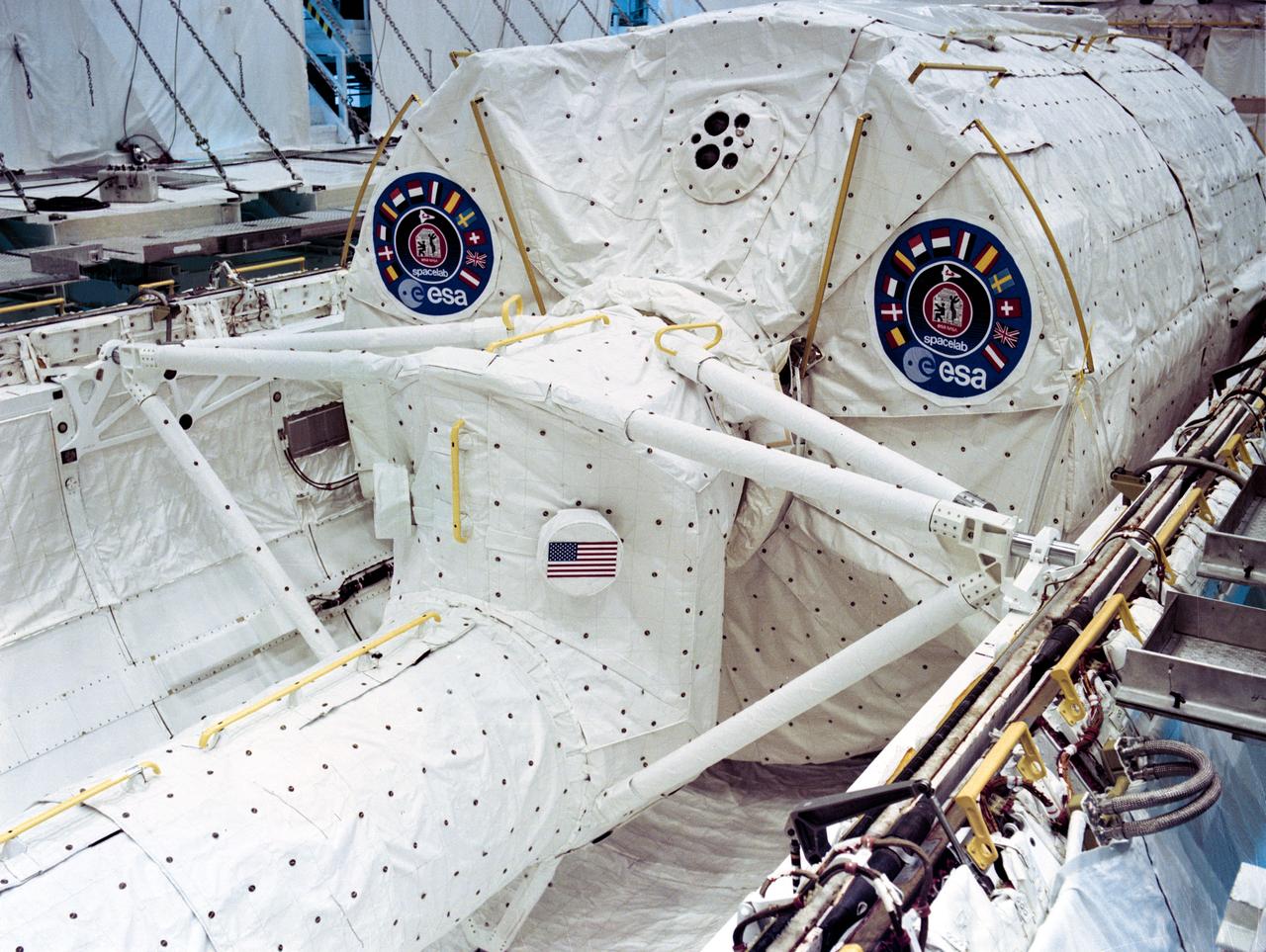

Spacelab I is installed in the Orbiter Columbia and connected to the Orbiter Crew Compartment by the Crew Access Tunnel. The tunnel allows the Astronauts to travel between the Orbiter Crew Compartment and the Spacelab in "shirt-sleeve" conditions. KSC, FL Also available in 4x5 B&W
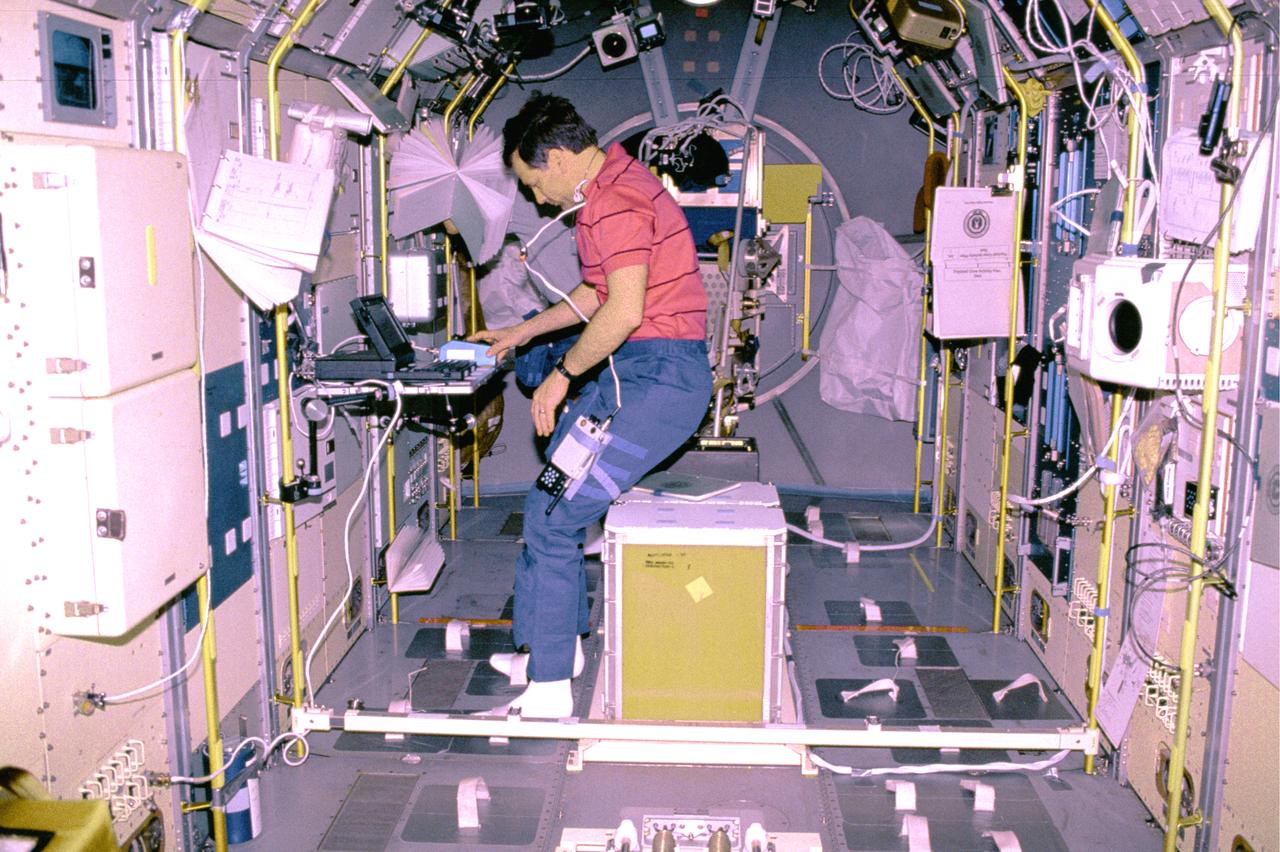

The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. In this photograph, Commander Ronald J. Grabe works with the Mental Workload and Performance Evaluation Experiment (MWPE) in the IML-1 module. This experiment was designed as a result of difficulty experienced by crewmembers working at a computer station on a previous Space Shuttle mission. The problem was due to the workstation's design being based on Earthbound conditions with the operator in a typical one-G standing position. Information gained from this experiment was used to design workstations for future Spacelab missions and the International Space Station. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).

This image of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis, with cargo bay doors open showing Spacelab Module for the Spacelab Life Science and the docking port, was photographed from the Russian Mir Space Station during STS-71 mission. The STS-71 mission performed the first docking with the Russian Mir Space Station to exchange crews. The Mir 19 crew, cosmonauts Anatoly Solovyev and Nikolai Budarin, replaced the Mir 18 crew, cosmonauts Valdamir Dezhurov and Gernady Strekalov, and astronaut Norman Thagard. Astronaut Thagard was launched aboard a Soyuz spacecraft in March 1995 for a three-month stay on the Mir Space Station as part of the Mir 18 crew. The Orbiter Atlantis was modified to carry a docking system compatible with the Mir Space Station. The Orbiter also carried a Spacelab module for the Spacelab Life Science mission in the payload bay in which various life science experiments and data collection took place throughout the 10-day mission.

This photograph of aurora borealis, northern aurora, was taken during the Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission (STS-47). People who live in the northernmost areas like Alaska or work in the southernmost regions like Antarctica often see colorful lights produced by Earth's natural electromagnetic generator; these shimmering expanses of light are auroras, commonly called the northern and southern lights. Charged particles from the magnetosphere follow magnetic fields and are accelerated toward Earth at the magnetic poles where they strike molecules in the upper atmosphere, staining the sky with the red and green lights of oxygen and hydrogen, and the purples and pinks of nitrogen. The altitude and inclination of the Spacelab will give scientists unique views of auroras, which occur at altitudes ranging from about 90 to 300 kilometers (56 to 186 miles). Most views of the auroras have been from the ground where only limited parts can be seen. These Spacelab views will give scientists information on their complex structure and chemical composition. The Spacelab-J was a joint mission of NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted microgravity investigations in materials and life sciences. The SL-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour (STS-47) on September 12, 1992.

Portrait of STS 51-F Spacelab backup payload specialist George Simon, in blue flight suit
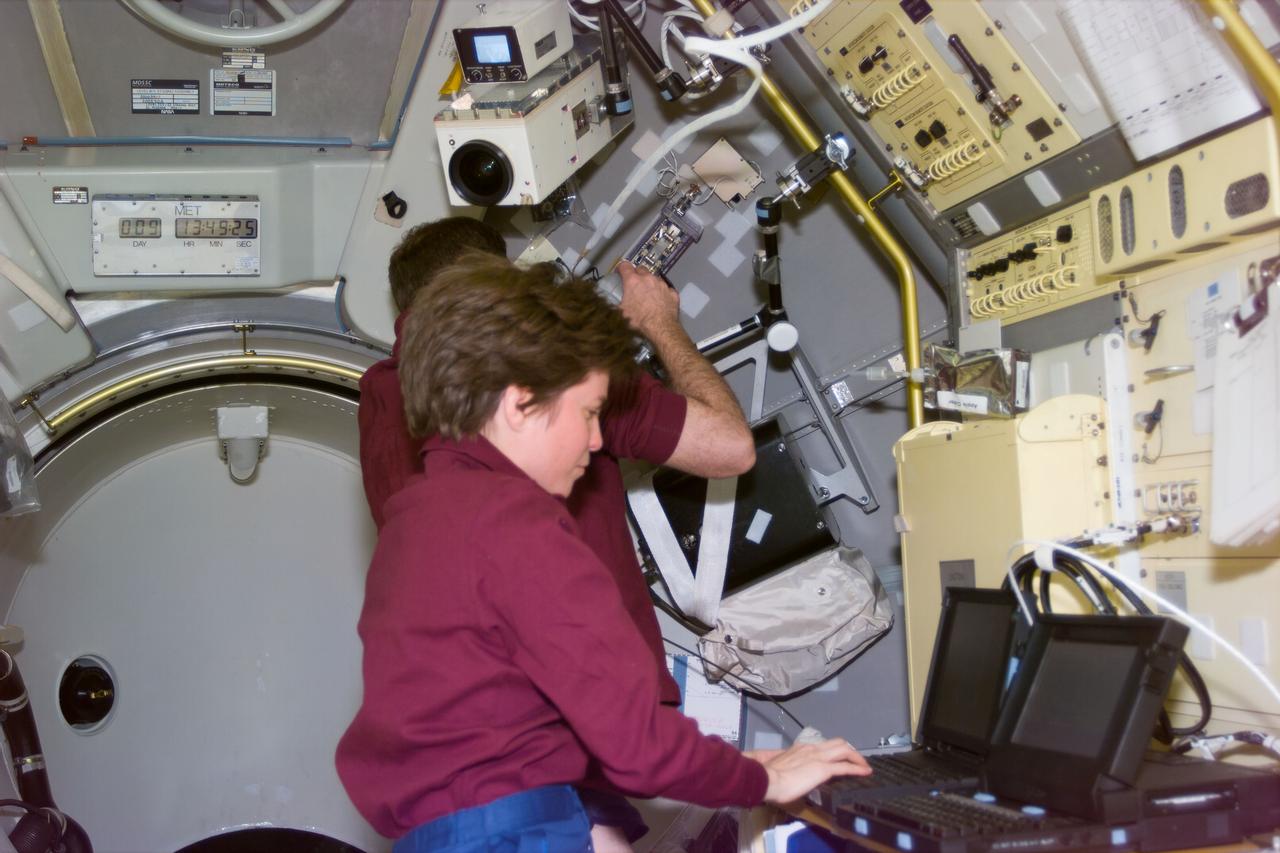

S94-E-5047 (July 1997) --- Astronaut Janice E. Voss, mission specialist, works at a lap top computer in the Spacelab science module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia.
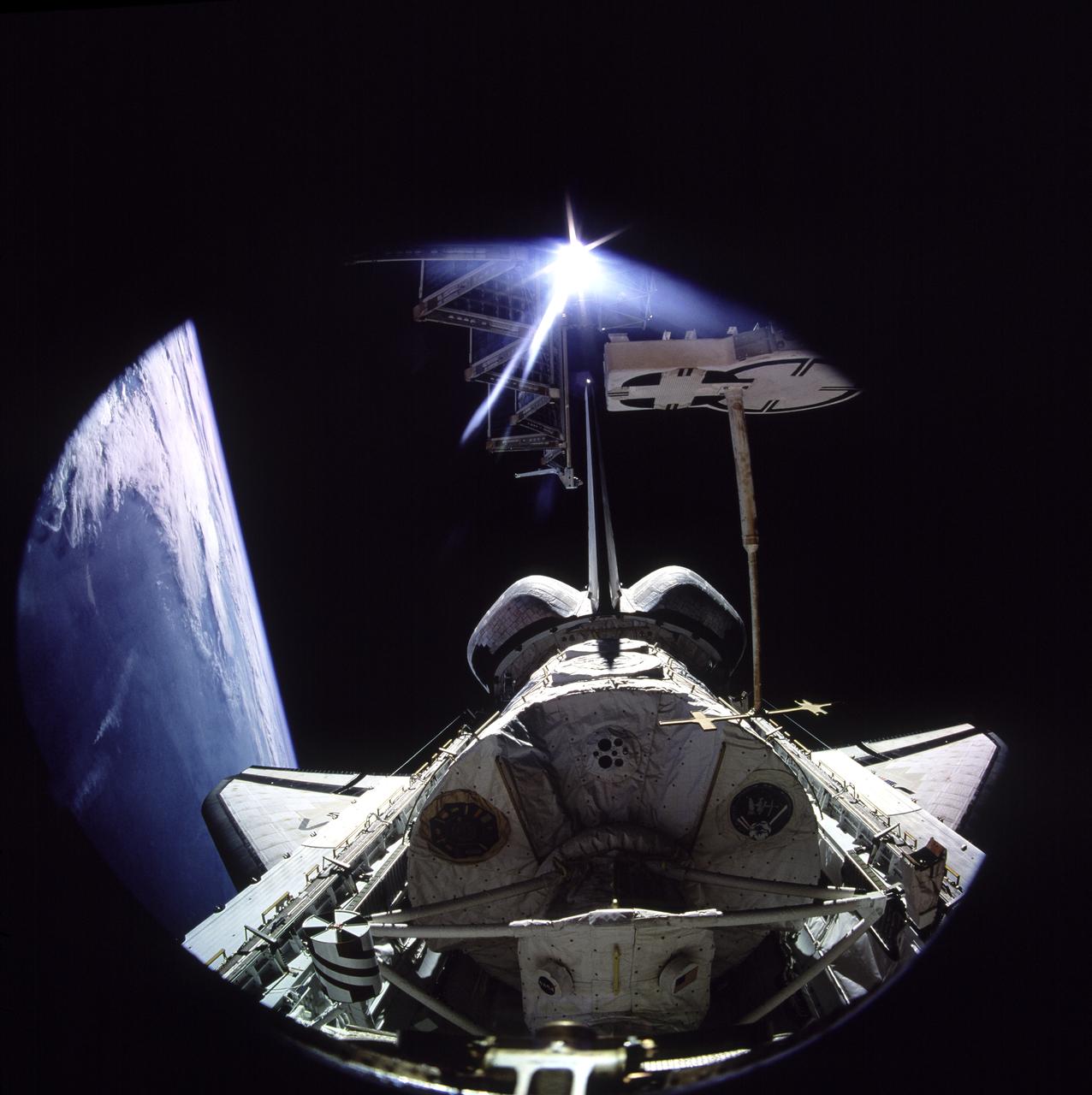

STS071-741-057 (27 June-7 July 1995) --- Docked already with Russia's Mir Space Station, the space shuttle Atlantis' aft cargo bay and Spacelab science module are visible through a window on the Mir Space Station. A 70mm camera, carried into space by the STS-71 crew aboard Atlantis, was used to expose the image. The linkup enabled the seven STS-71 crew members to visit Mir and it allowed the three Mir-18 crew members, in space since March of this year, access to Spacelab. That module was quite busy with tests and data collection involving the three until Atlantis brought them home on July 7, 1995.
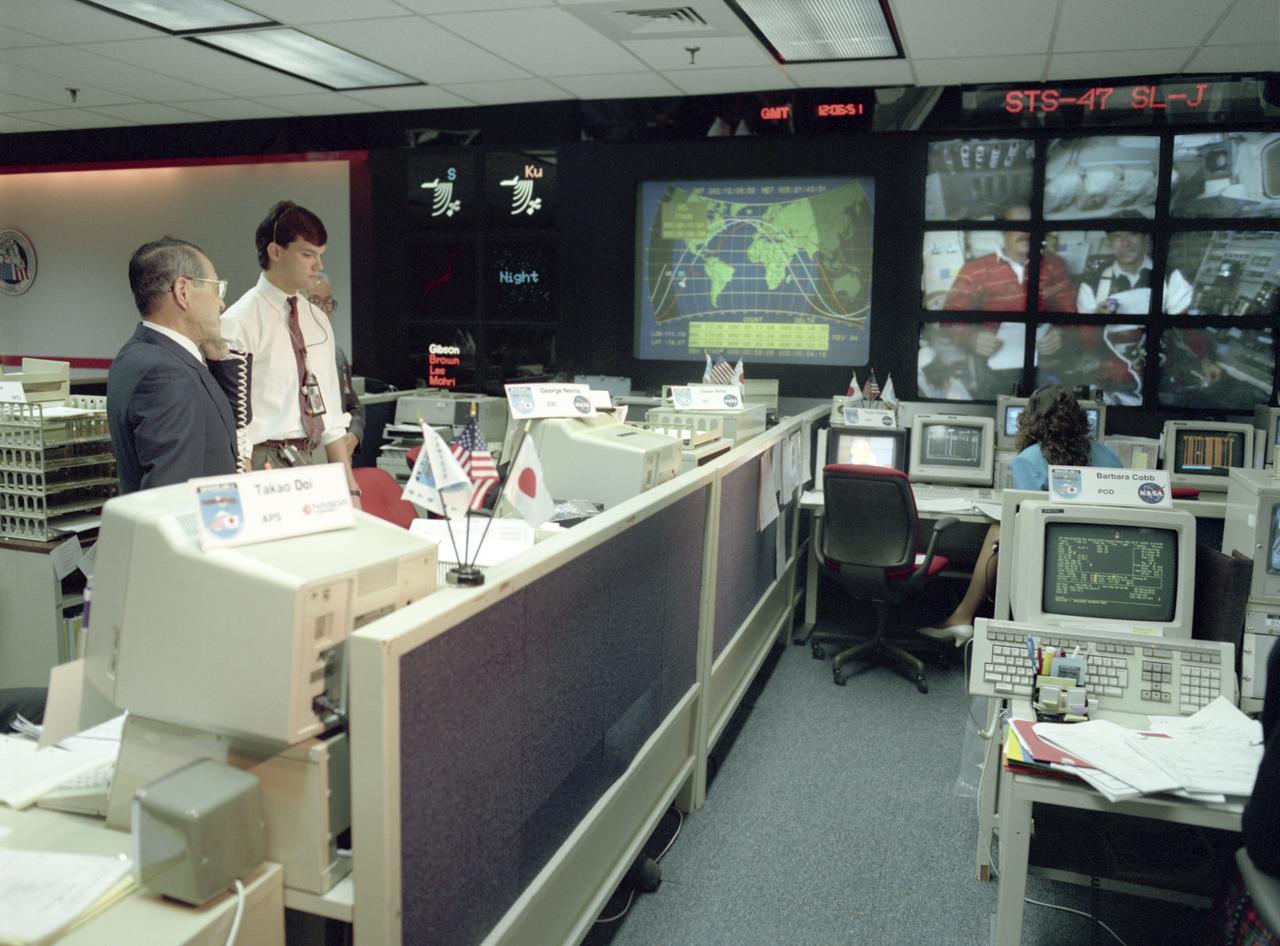

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. From the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC), NASDA President, Mr. Yamano, speaks to Payload Specialist Mamoru Mohri, a Japanese crew member aboard the STS-47 Spacelab J mission.
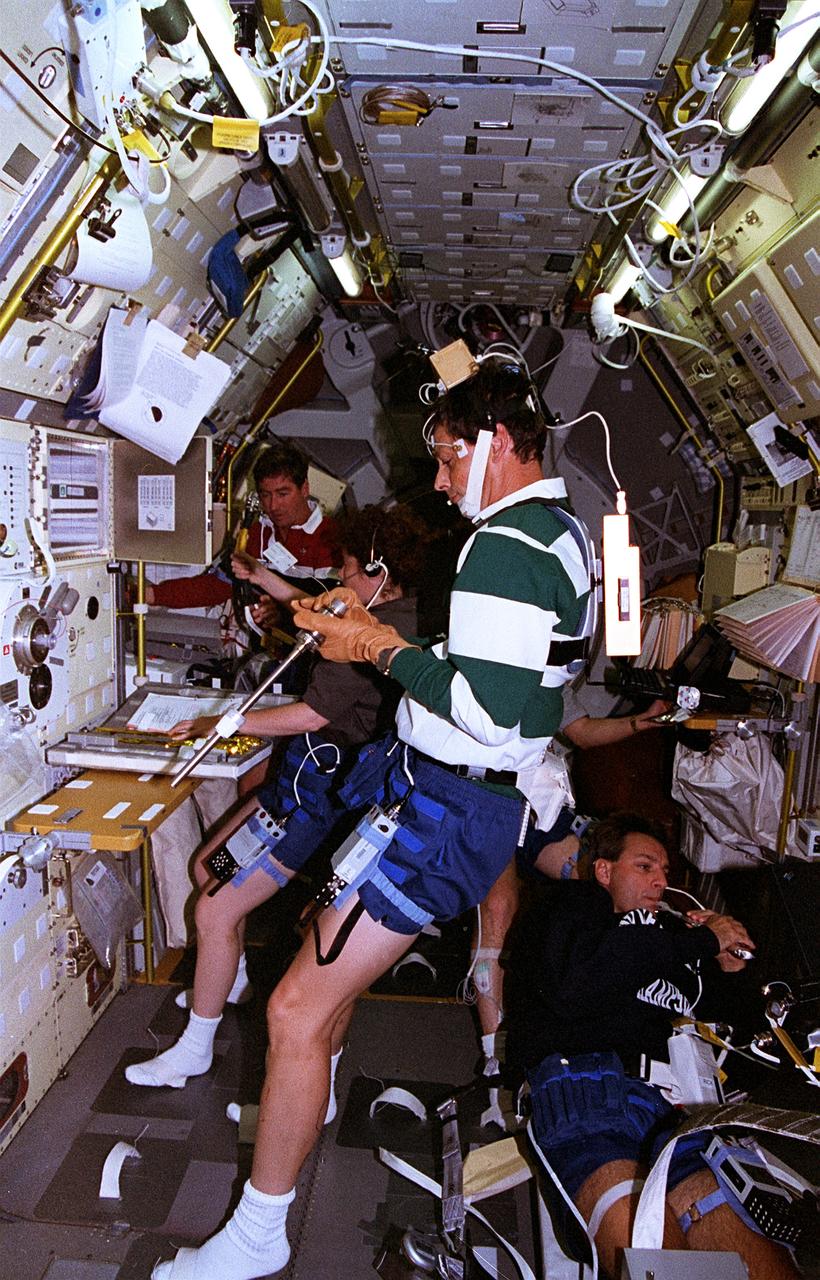

STS078-396-015 (20 June - 7 July 1996) --- Payload specialist Jean-Jacques Favier, representing the French Space Agency (CNES), prepares a sample for the Advanced Gradient Heating Facility (AGHF) while wearing instruments that measure upper body movement. The Torso Rotation Experiment (TRE) complements other vestibular studies that measure differences in the way human beings react physically to their surroundings in microgravity. This is a typical Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS-1) mission scene, with several experiments being performed. Astronaut Susan J. Helms, payload commander, assists Favier in the AGHF preparations. Astronaut Richard M. Linnehan (bottom right), mission specialist, tests his muscle response with the Handgrip Dynamometer. Astronaut Thomas T. (Tom) Henricks (far background), mission commander, offers assistance.
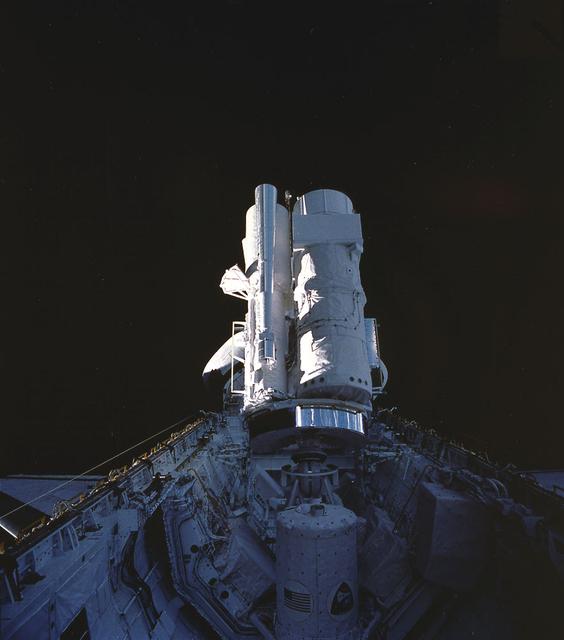

Onboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35), the various components of the Astro-1 payload are seen backdropped against dark space. Parts of the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), and the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimetry Experiment (WUPPE) are visible on the Spacelab pallet. The Broad-Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT) is behind the pallet and is not visible in this scene. The smaller cylinder in the foreground is the igloo. The igloo was a pressurized container housing the Command Data Management System, that interfaced with the in-cabin controllers to control the Instrument Pointing System (IPS) and the telescopes. The Astro Observatory was designed to explore the universe by observing and measuring the ultraviolet radiation from celestial objects. Astronomical targets of observation selected for Astro missions included planets, stars, star clusters, galaxies, clusters of galaxies, quasars, remnants of exploded stars (supernovae), clouds of gas and dust (nebulae), and the interstellar medium. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the Astro-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35) on December 2, 1990.
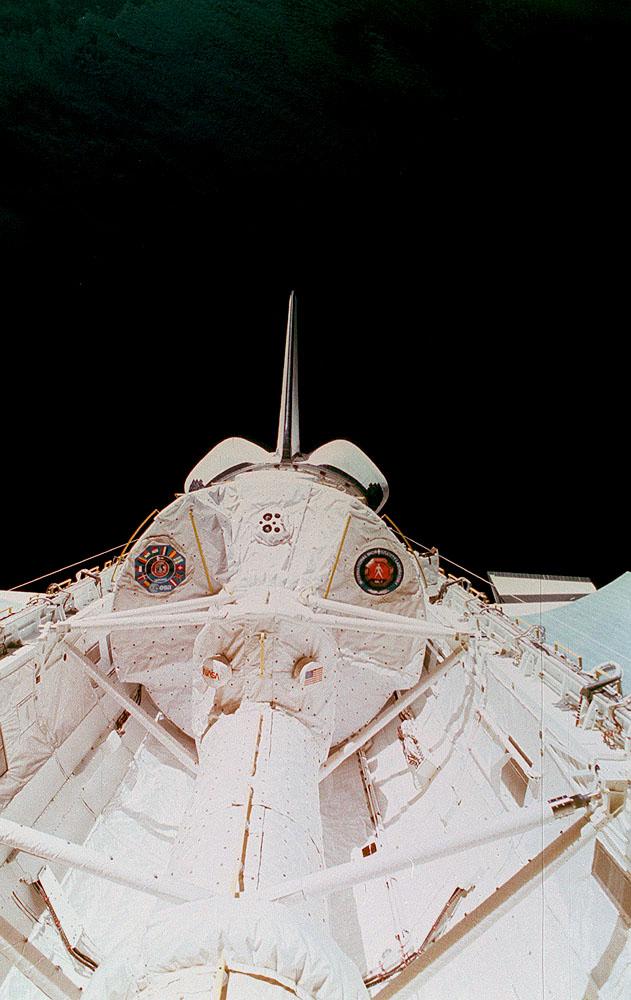
This is the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery, STS-42 mission, with the First International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) module shown in the cargo bay. IML-1, the first in a series of Shuttle flights, was dedicated to study the fundamental materials and life sciences in the microgravity environment inside Spacelab, a laboratory carried aloft by the Shuttle. The mission explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. The IML program gave a team of scientists from around the world access to a unique environment, one that is free from most of Earth's gravity. The 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (SCA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DARA/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) participated in developing hardware and experiments for the IML missions. The missions were managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. The Orbiter Discovery was launched on January 22, 1992 for the IML-1 mission.
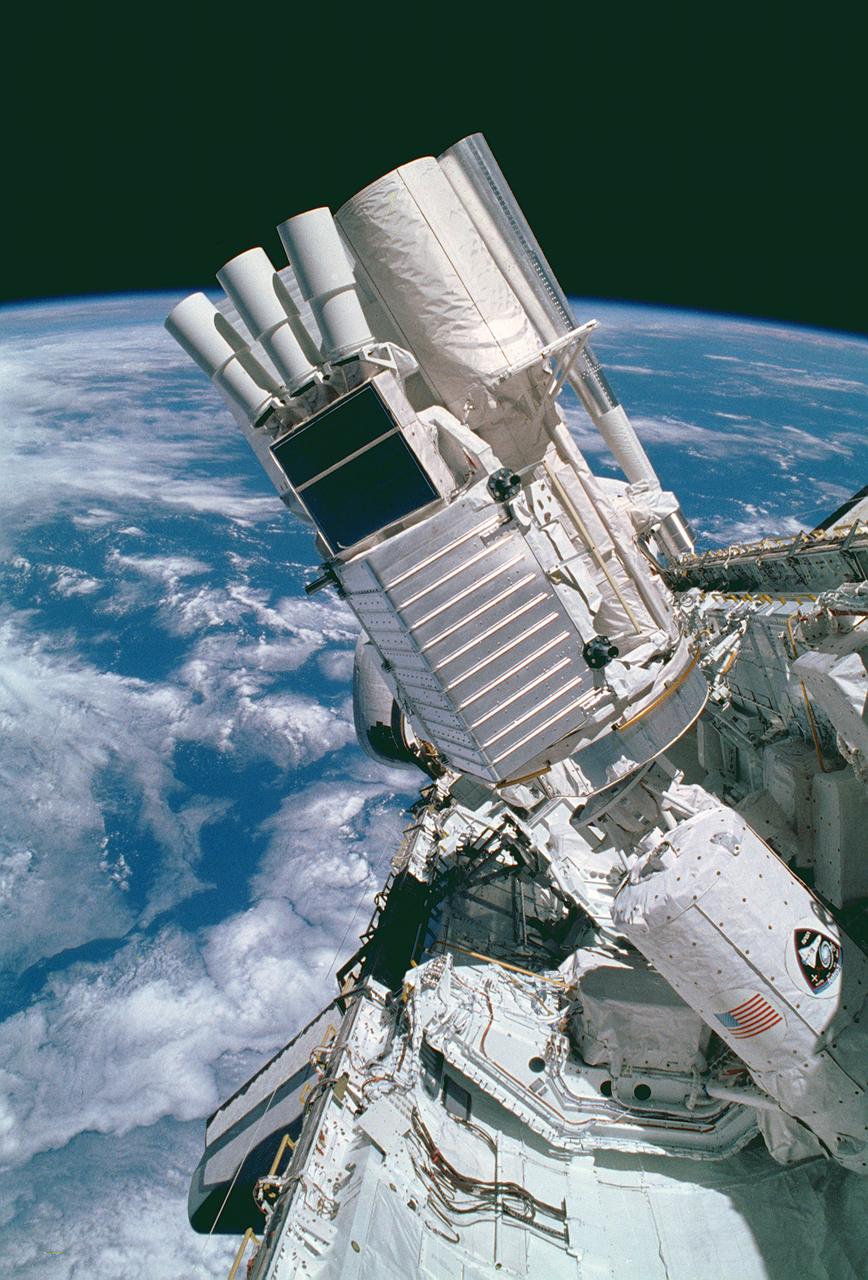

Onboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35), the various components of the Astro-1 payload are seen backdropped against a blue and white Earth. Parts of the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), and the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimetry Experiment (WUPPE) are visible on the Spacelab pallet. The Broad-Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT) is behind the pallet and is not visible in this scene. The smaller cylinder in the foreground is the igloo. The igloo was a pressurized container housing the Command Data Management System, that interfaced with the in-cabin controllers to control the Instrument Pointing System (IPS) and the telescopes. The Astro Observatory was designed to explore the universe by observing and measuring the ultraviolet radiation from celestial objects. Astronomical targets of observation selected for Astro missions included planets, stars, star clusters, galaxies, clusters of galaxies, quasars, remnants of exploded stars (supernovae), clouds of gas and dust (nebulae), and the interstellar medium. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the Astro-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35) on December 2, 1990.