
The mission patch for STS-85 is designed to reflect the broad range of science and engineering payloads on the flight. The primary objectives of the mission were to measure chemical constituents in Earth’s atmosphere with a free-flying satellite and to flight-test a new Japanese robotic arm designed for use on the International Space Station (ISS). STS-85 was the second flight of the satellite known as Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 CRISTA-SPAS-02. CRISTA, depicted on the right side of the patch pointing its trio of infrared telescopes at Earth’s atmosphere, stands for Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere. The high inclination orbit is shown as a yellow band over Earth’s northern latitudes. In the Space Shuttle Discovery’s open payload bay an enlarged version of the Japanese National Space Development Agency’s (NASDA) Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) robotic arm is shown. Also shown in the payload bay are two sets of multi-science experiments: the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-02) nearest the tail and the Technology Applications and Science (TAS-01) payload. Jupiter and three stars are shown to represent sources of ultraviolet energy in the universe. Comet Hale-Bopp, which was visible from Earth during the mission, is depicted at upper right. The left side of the patch symbolizes daytime operations over the Northern Hemisphere of Earth and the solar science objectives of several of the payloads.

STS085-S-001 (May 1997) --- The mission patch for STS-85 is designed to reflect the broad range of science and engineering payloads on the flight. The primary objectives of the mission are to measure chemical constituents in Earth?s atmosphere with a free-flying satellite and to flight-test a new Japanese robotic arm designed for use on the International Space Station (ISS). STS-85 is the second flight of the satellite known as CRISTA-SPAS-02. CRISTA, depicted on the right side of the patch pointing its trio of infrared telescopes at Earth?s atmosphere, stands for Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere. The high inclination orbit is shown as a yellow band over Earth?s northern latitudes. In the space shuttle Discovery?s open payload bay an enlarged version of the Japanese National Space Development Agency?s (NASDA) Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) robotic arm is shown. Also shown in the payload bay are two sets of multi-science experiments: the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-02) nearest the tail and the Technology Applications and Science (TAS-01) payload. Jupiter and three stars are shown to represent sources of ultraviolet energy in the universe. Comet Hale-Bopp, which will be visible from Earth during the mission, is depicted at upper right. The left side of the patch symbolizes daytime operations over the Northern Hemisphere of Earth and the solar science objectives of several of the payloads. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
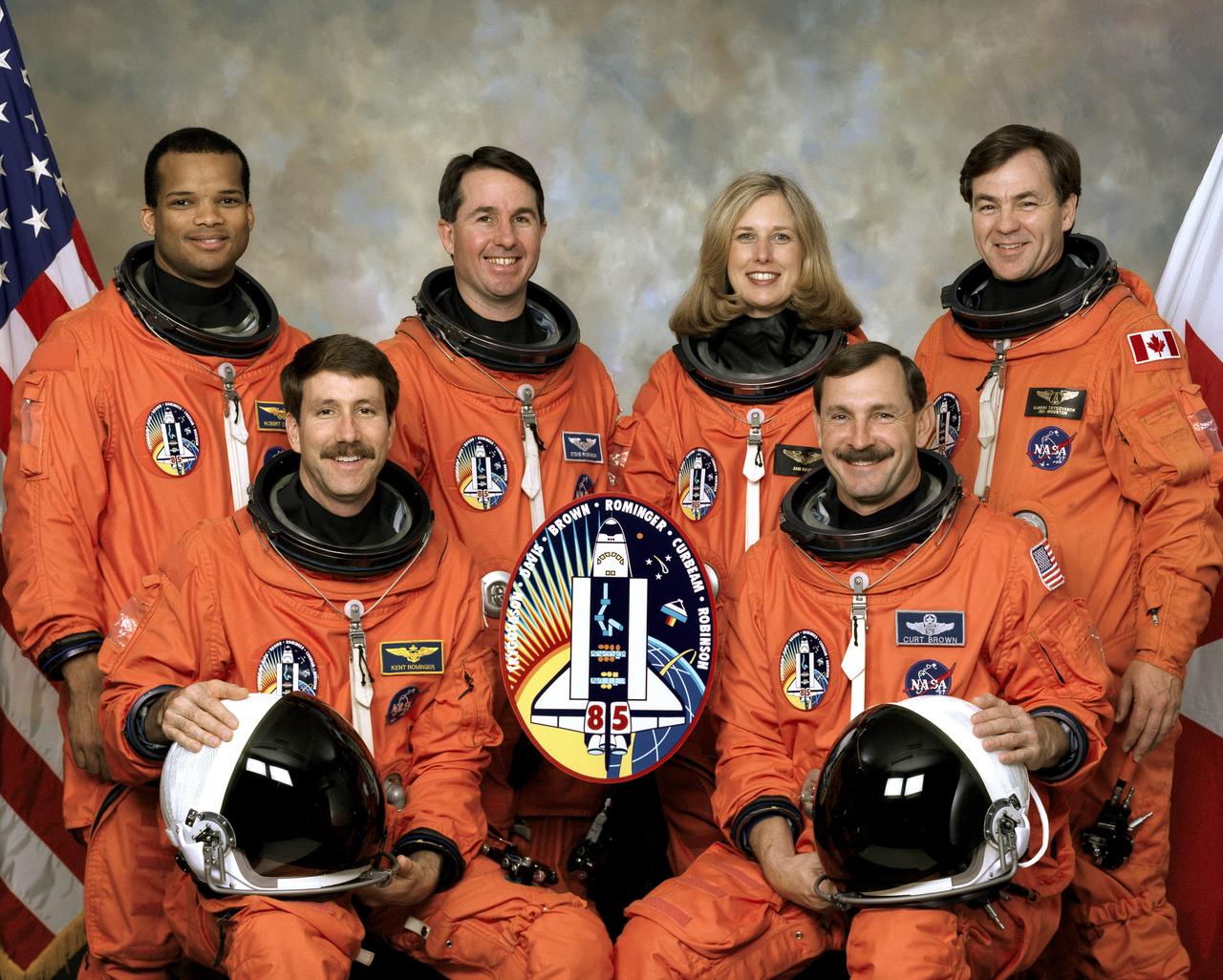

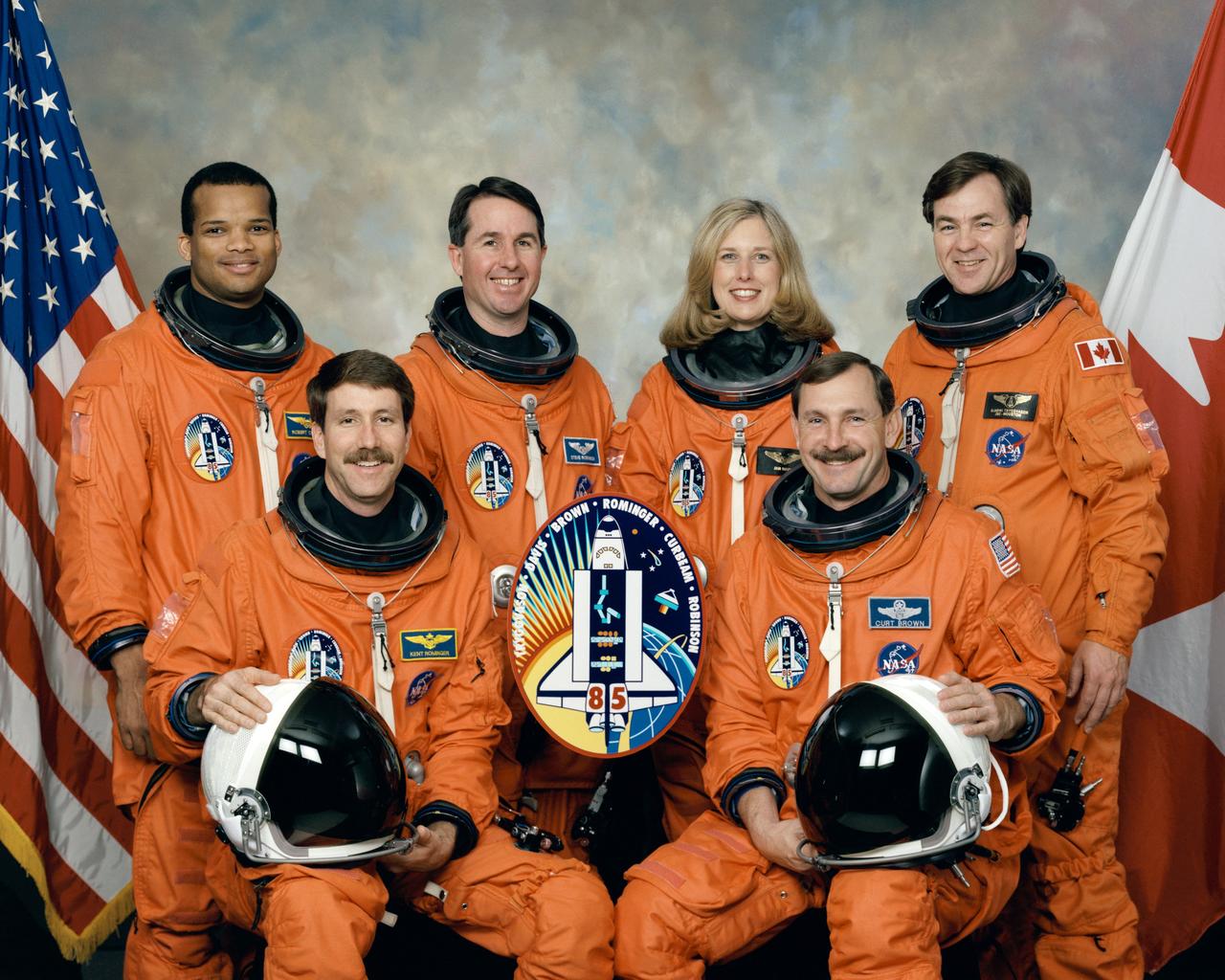
Five NASA astronauts and a Canadian payload specialist pause from their training schedule to pose for the traditional crew portrait for their mission, STS-85. In front are astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr. (right), mission commander, and Kent V. Rominger, pilot. On the back row, from the left, are astronauts Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., Stephen K. Robinson, and N. Jan Davis, all mission specialists, along with the Canadian Space Agency’s (CSA) payload specialist, Bjarni Tryggvason. The five launched into space aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on August 7, 1997 at 10:41:00 a.m. (EDT). Major payloads included the satellite known as Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 CRISTA-SPAS-02. CRISTA; a Japanese Manipulator Flight Development (MFD); the Technology Applications and Science (TAS-01); and the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-02).
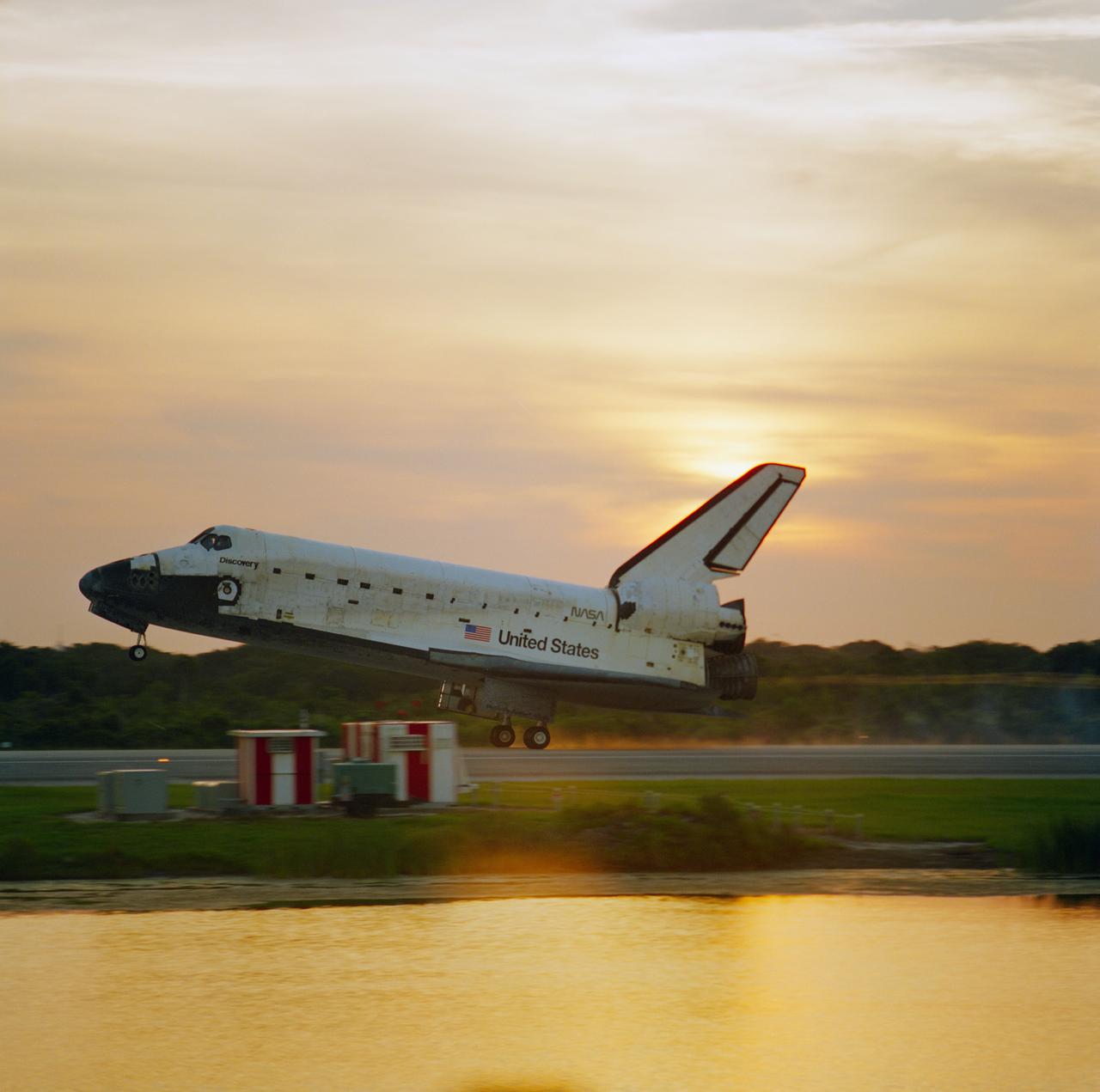

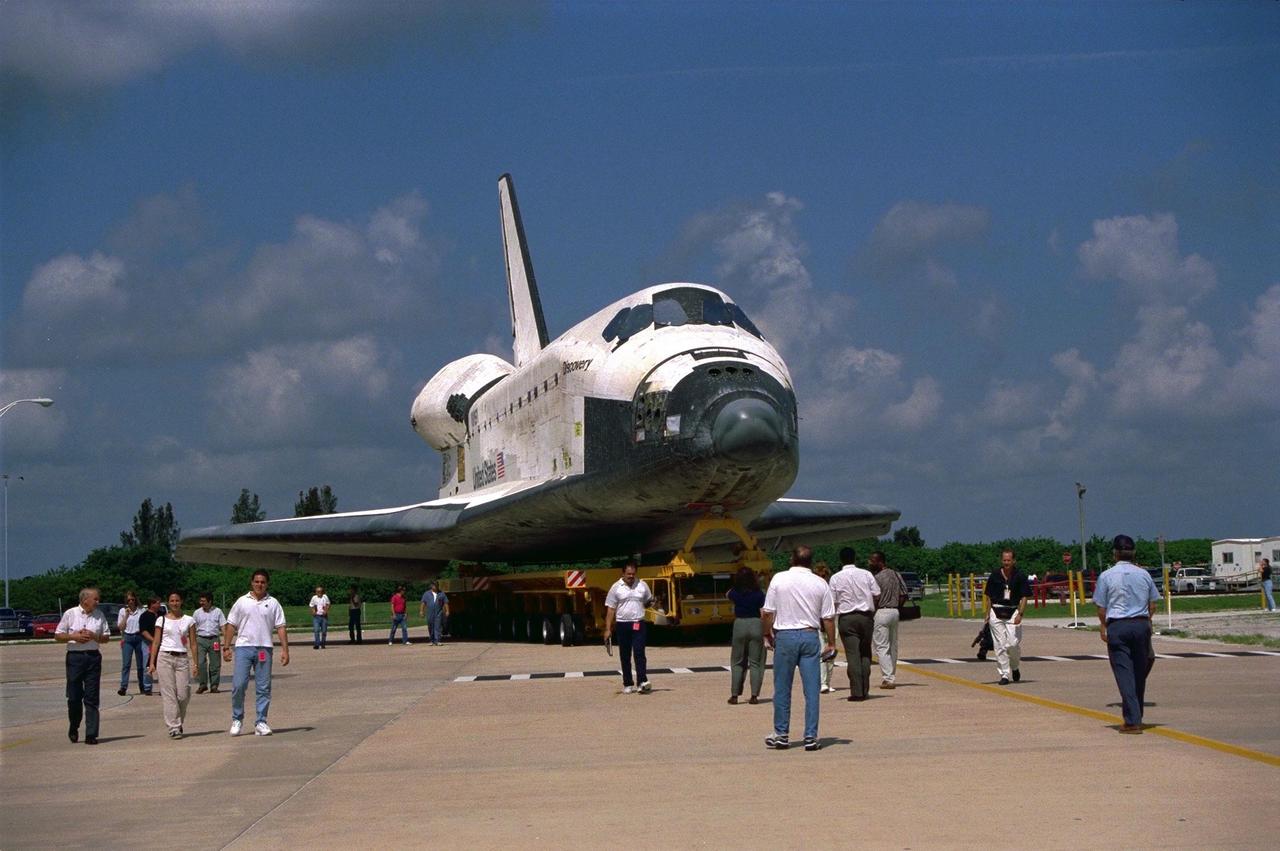
STS085-S-014 (19 Aug. 1997) --- The main landing gear of the space shuttle Discovery touches down on Runway 33 at the Kennedy Space Center to mark the successful completion of 12-day STS-85 mission. Landing occurred at 7:08 a.m. (EDT) on Aug. 19, 1997. Onboard were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; N. Jan Davis, payload commander; and Robert L. Curbeam and Stephen K. Robinson, both mission specialists; along with payload specialist Bjarni Tryggvason, representing the Canadian Space Agency. Photo credit: NASA
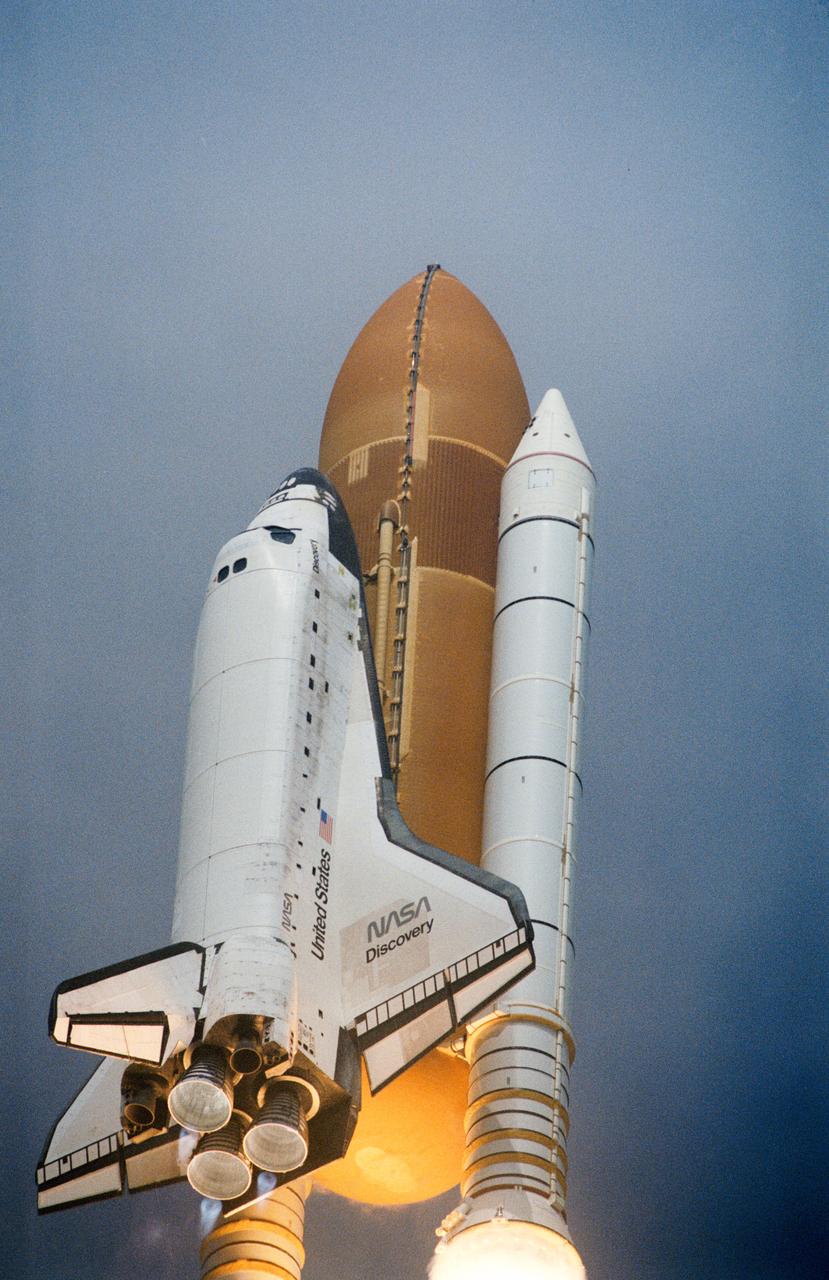
STS085-S-006 (7 August 1997) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery has cleared the launch tower at Pad 39A, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), in this low-angle, 35mm frame, and is headed toward an eleven-day mission in Earth-orbit in support of the STS-85 mission. Launch occurred at 10:41 a.m. (EDT), August 7, 1997. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; N. Jan Davis, payload commander; and Stephen K. Robinson and Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., both mission specialists; along with payload specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason, a Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut.
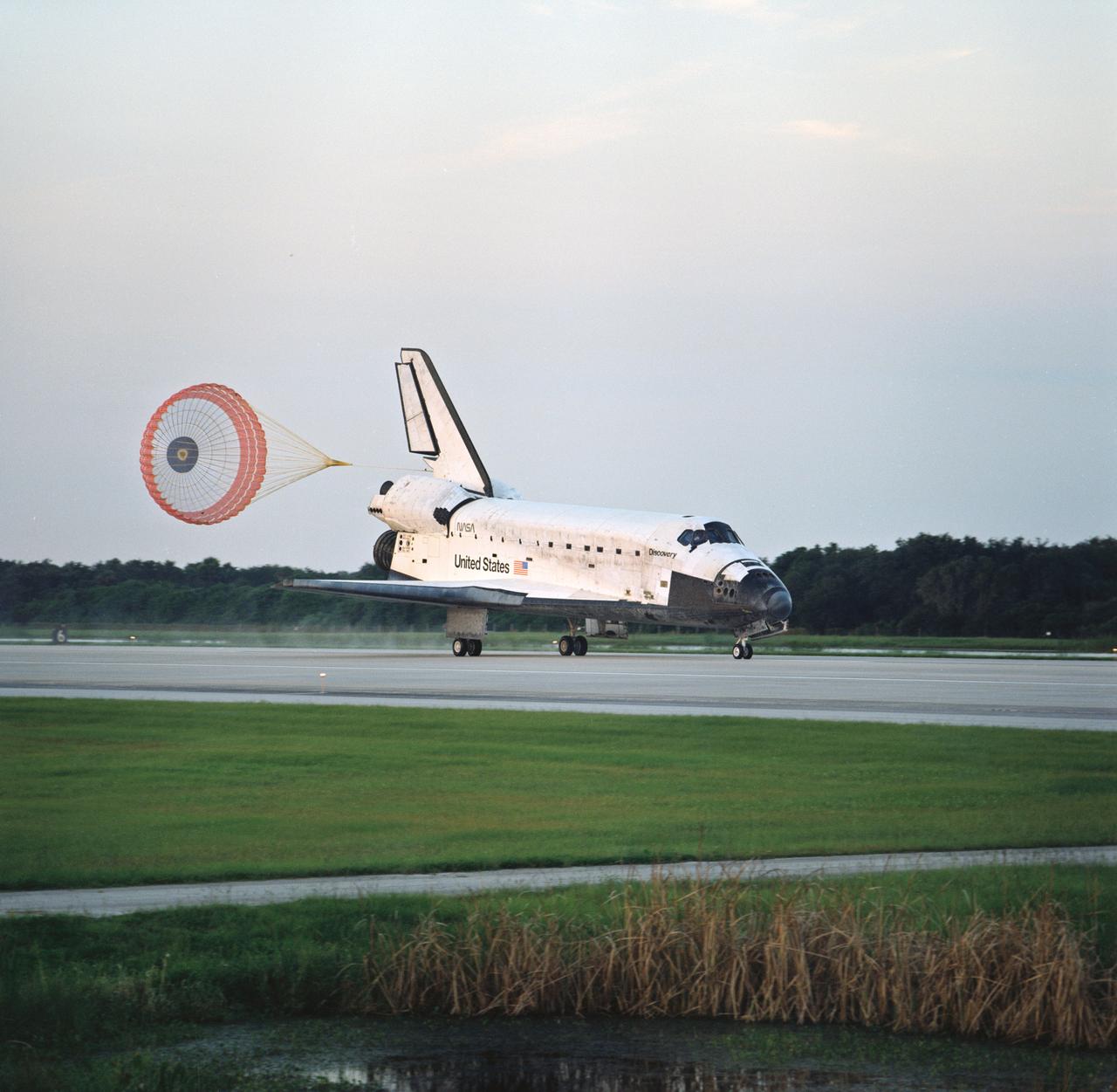

STS085-S-013 (19 August 1997) --- The drag chute of the Space Shuttle Discovery is fully deployed in this scene of the spacecraft's landing on runway 33 at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The landing, at 7:08 a.m. (EDT), August 19, 1997, marked the completion of a successful 12-day STS-85 mission. Onboard were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; N. Jan Davis, payload commander; and Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., and Stephen K. Robinson, both mission specialists; along with payload specialist Bjarni Tryggvason, representing the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
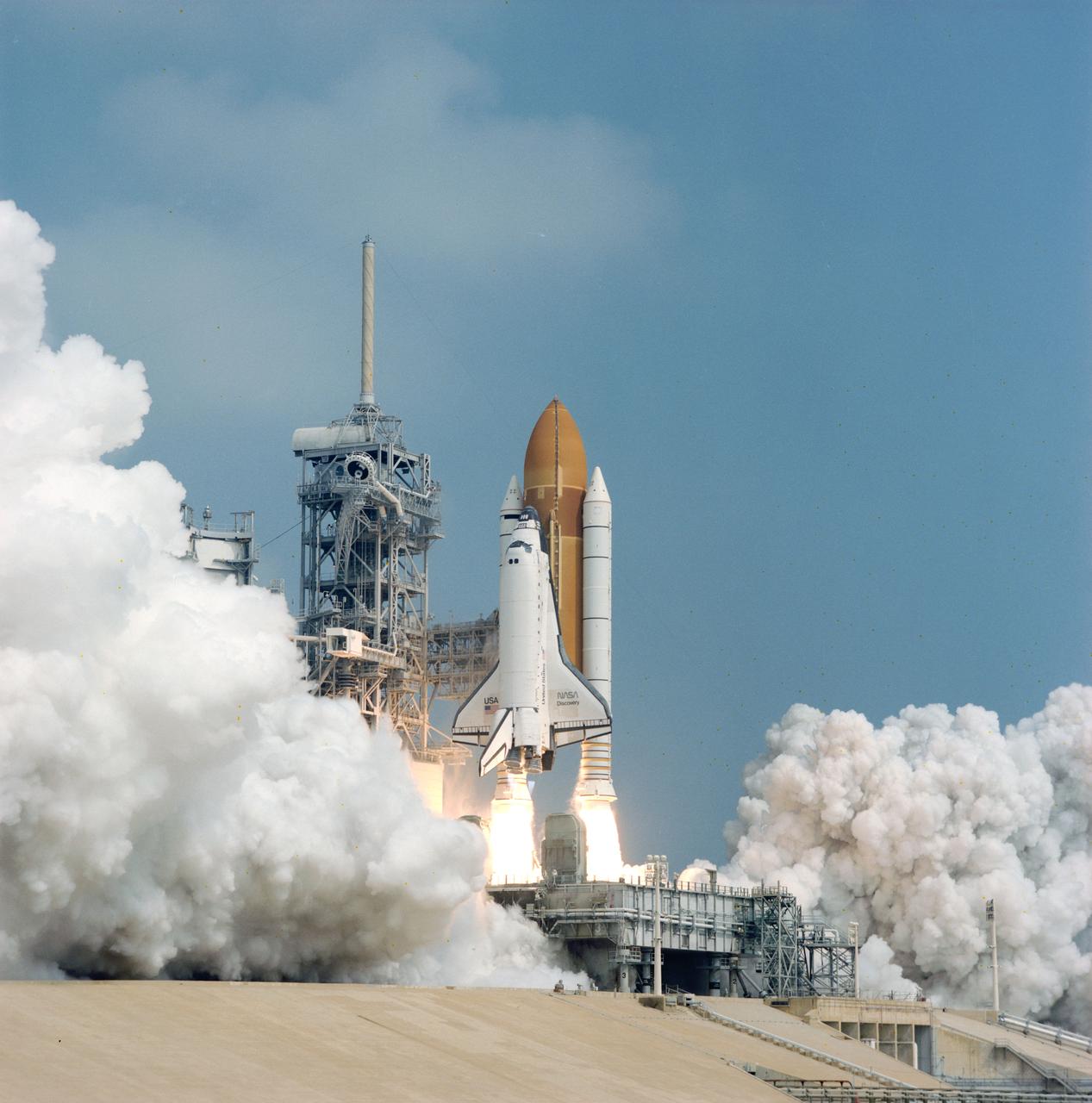

STS085-S-005 (7 August 1997) --- In this scene moments after ignition at Launch Pad 39A, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), the Space Shuttle Discovery heads toward an eleven-day mission in Earth-orbit in support of the STS-85 mission. Launch occurred at 10:41 a.m. (EDT), August 7, 1997. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; N. Jan Davis, payload commander; and Stephen K. Robinson and Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., both mission specialists; along with payload specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason, a Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut.
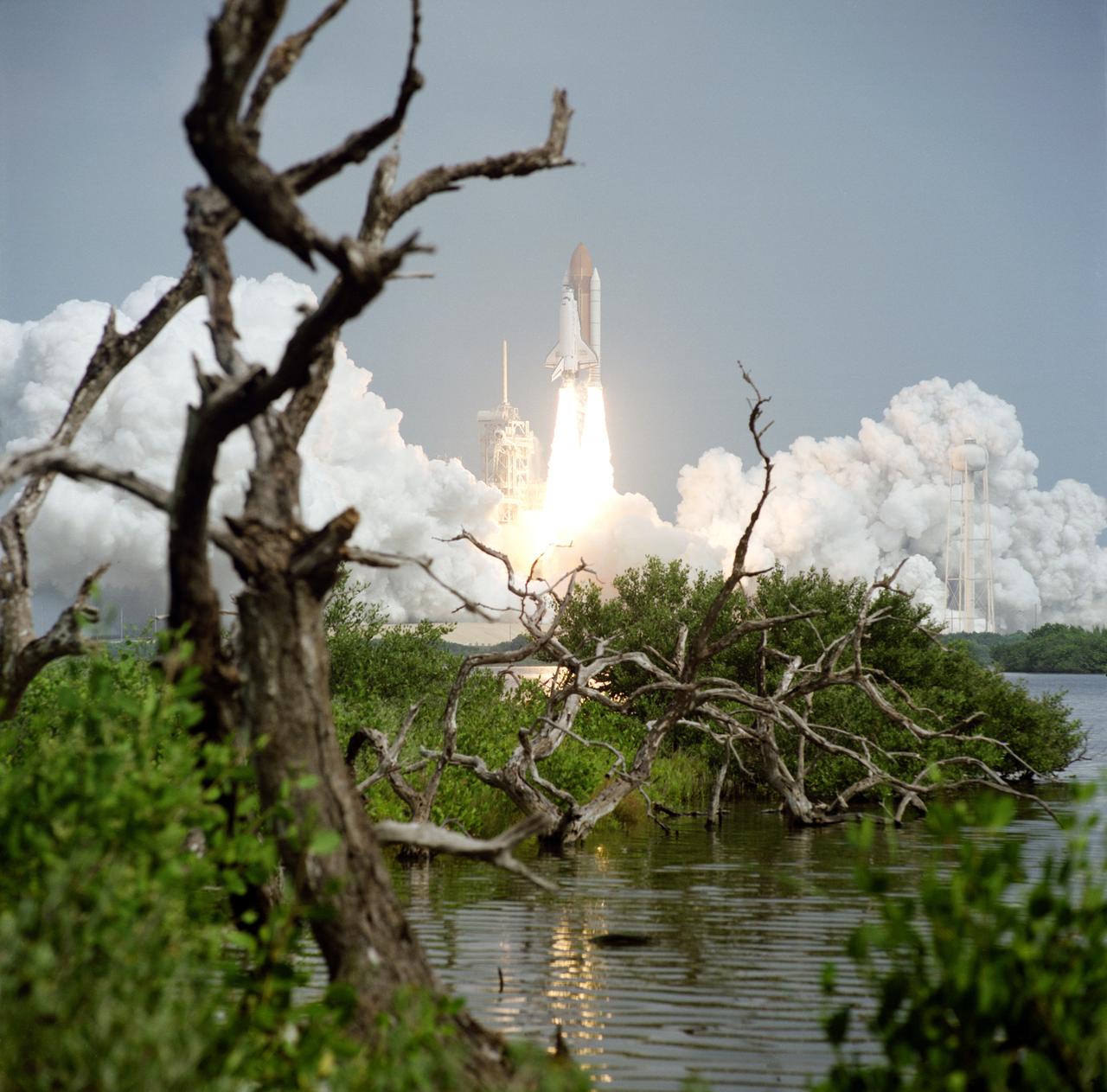

STS085-S-009 (7 August 1997) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery has cleared the launch tower in this low-angle, 35mm frame, and is headed toward an eleven-day mission in Earth-orbit in support of the STS-85 mission. Launch from Pad 39A, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), occurred at 10:41 a.m. (EDT), August 7, 1997. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; N. Jan Davis, payload commander; and Stephen K. Robinson and Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., both mission specialists; along with payload specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason, a Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut.
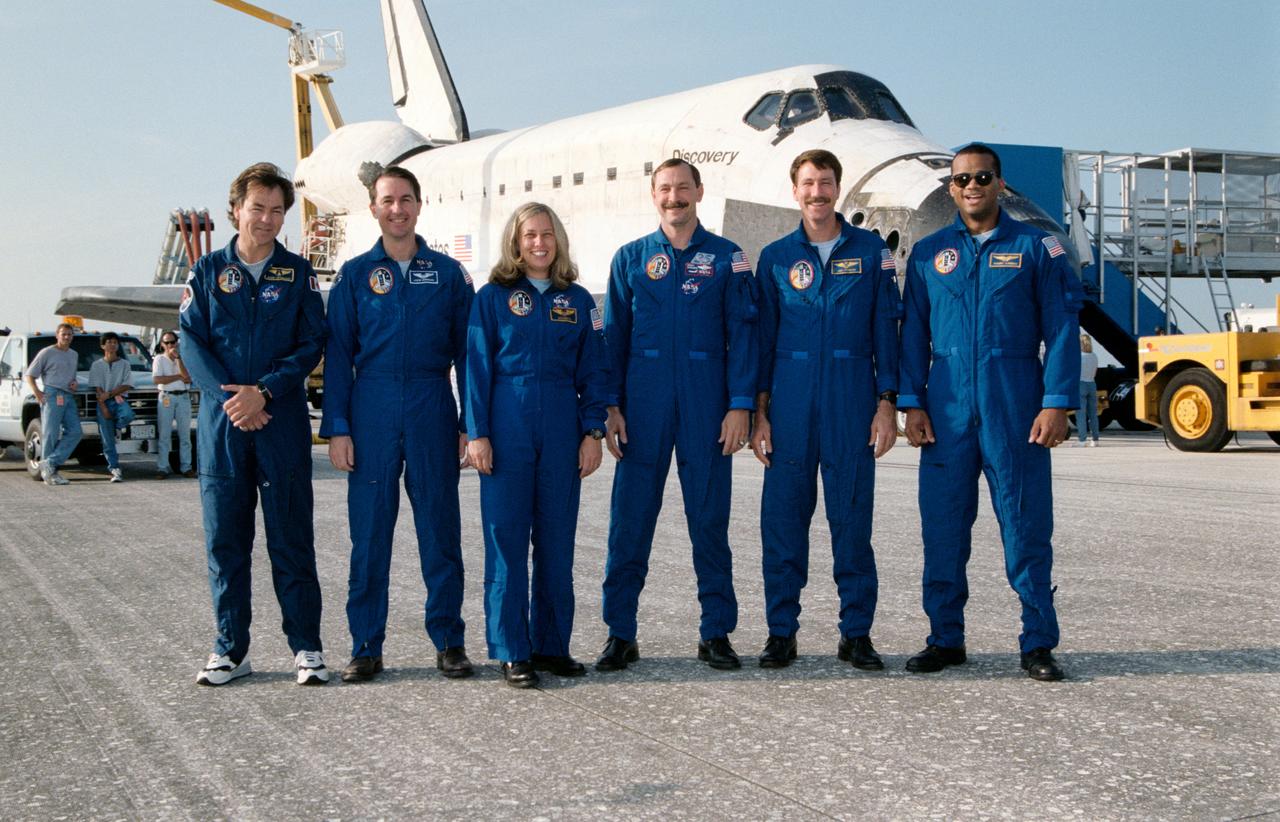

STS085-S-011 (19 August 1997) --- Following the landing of the Space Shuttle Discovery on runway 33 at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), the six member crew poses for a final crew portrait. The landing, at 7:08 a.m. (EDT), August 19, 1997, marked the completion of a successful 12-day STS-85 mission. Left to right are payload specialist Bjarni Tryggvason of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), along with astronauts Stephen K. Robinson, mission specialist; N. Jan Davis, payload commander; Curtis L. Brown, Jr., mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; and Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., mission specialist.
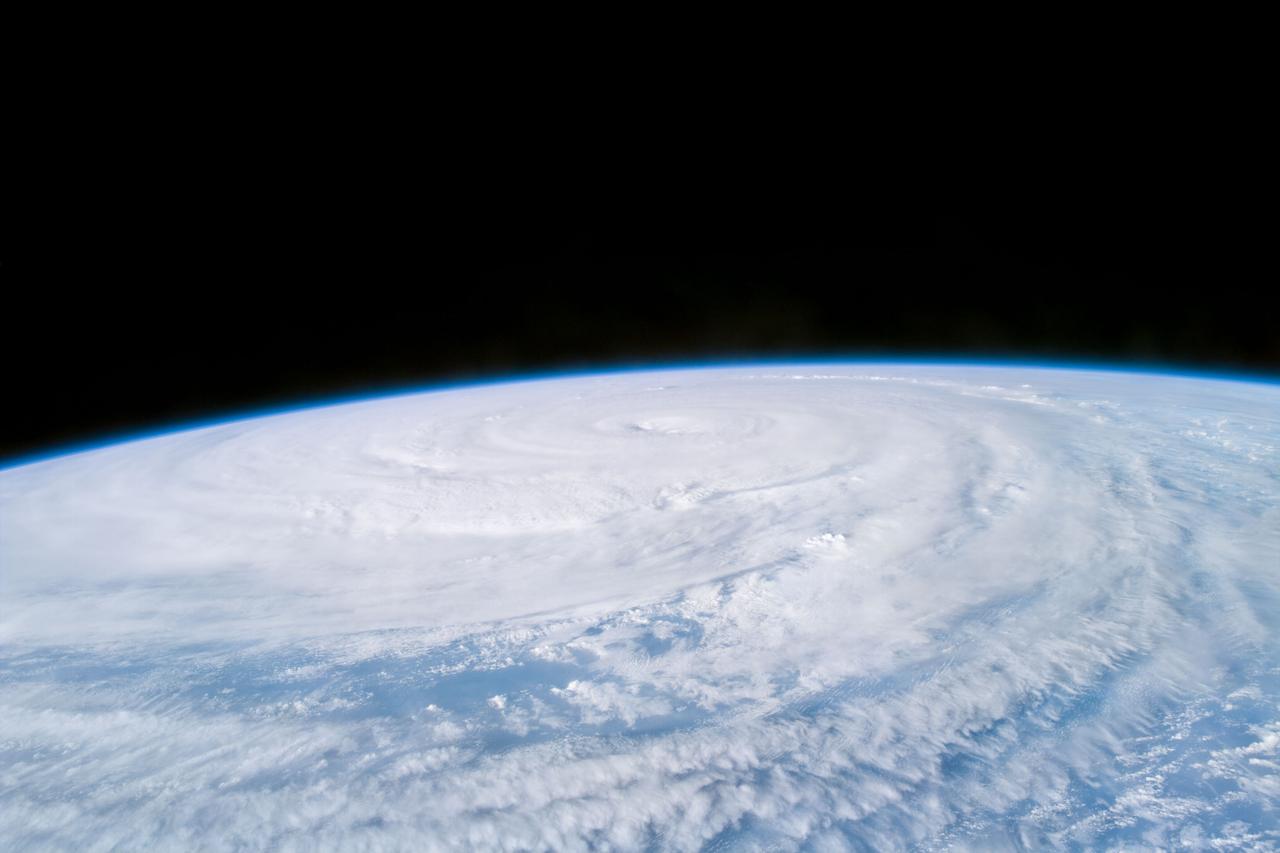

S85-E-5071 (13 August 1997) --- The STS-85 crew members aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery downlinked this oblique, Electronic Still Camera (ESC) view of the Super Typhoon Winnie about halfway between New Guinea and Japan in the Pacific Ocean late evening, August 13, 1997. Maximum sustained winds of 105 knots, gusts up to 130 knots. This photo was taken 14 1/2 hours after STS085-E-5069 was recorded with the same ESC.

S85-E-5092 (14 August 1997) --- Flying directly over the eye just before 3 p.m. (EST), Aug. 15, the STS-85 crew members captured this image of Super Typhoon Winnie. The massive typhoon is located about half way between Japan and New Guinea in the Pacific Ocean. The Canadian-built robot arm of Discovery, being used in operations with CRISTA-SPAS on this mission, is partially visible in left foreground.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Discovery, targeted for launch on August 7, 1997, on mission <a href="http://www.ksc.nasa.gov/shuttle/missions/sts-85/mission-sts-85.html">STS-85</a>, rolls out to <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/pads.htm">Launch Complex 39A</a>. STS-85 will feature the second flight of the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (<a href="http://www.crista.uni-wuppertal.de">CRISTA-SPAS</a>)
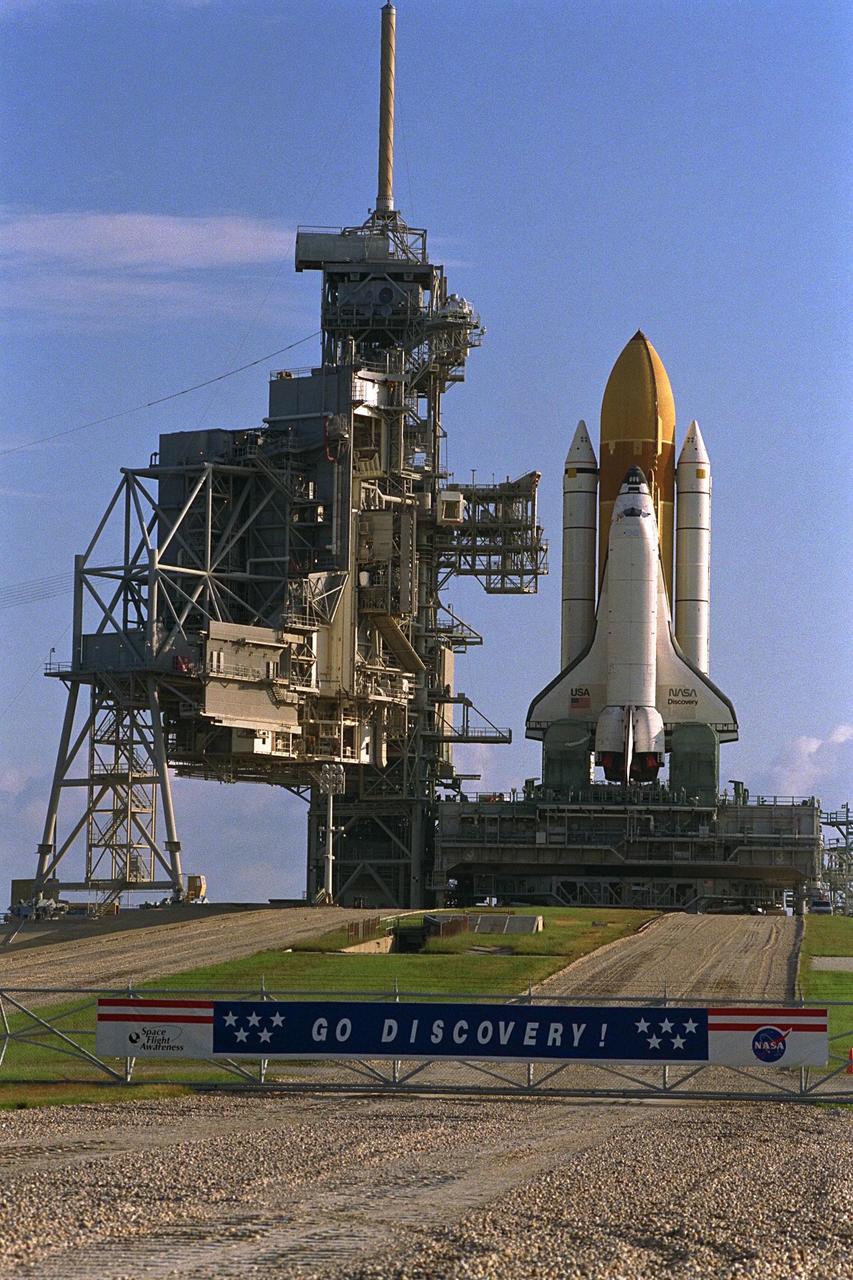

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Discovery, targeted for launch on August 7, 1997, on mission <a href="http://www.ksc.nasa.gov/shuttle/missions/sts-85/mission-sts-85.html">STS-85</a>, rolls out to <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/pads.htm">Launch Complex 39A</a>. STS-85 will feature the second flight of the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (<a href="http://www.crista.uni-wuppertal.de">CRISTA-SPAS</a>)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Discovery, targeted for launch on August 7, 1997, on mission <a href="http://www.ksc.nasa.gov/shuttle/missions/sts-85/mission-sts-85.html">STS-85</a>, rolls out to <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/pads.htm">Launch Complex 39A</a>. STS-85 will feature the second flight of the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (<a href="http://www.crista.uni-wuppertal.de">CRISTA-SPAS</a>)
STS-85 Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT
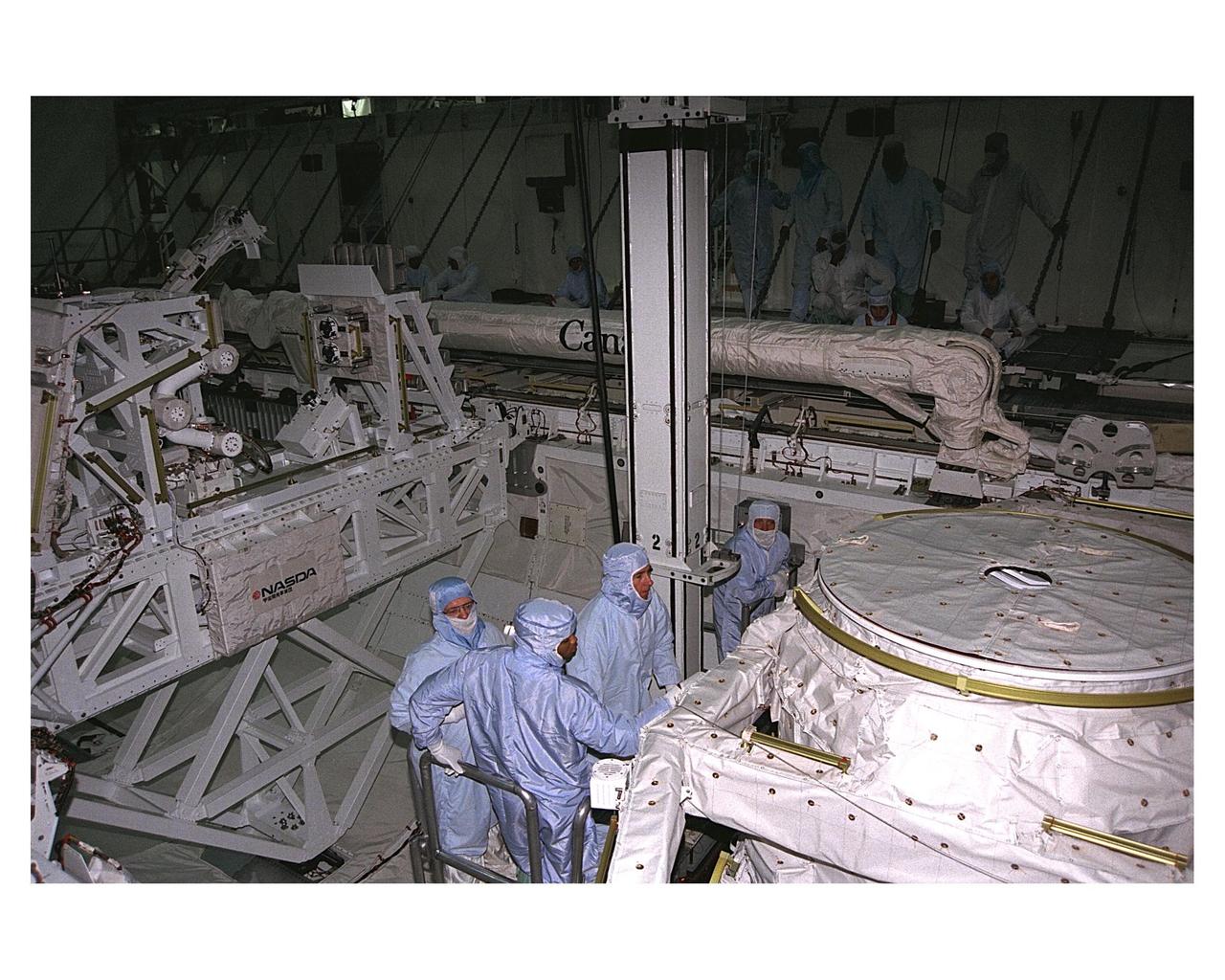

STS-85 Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT
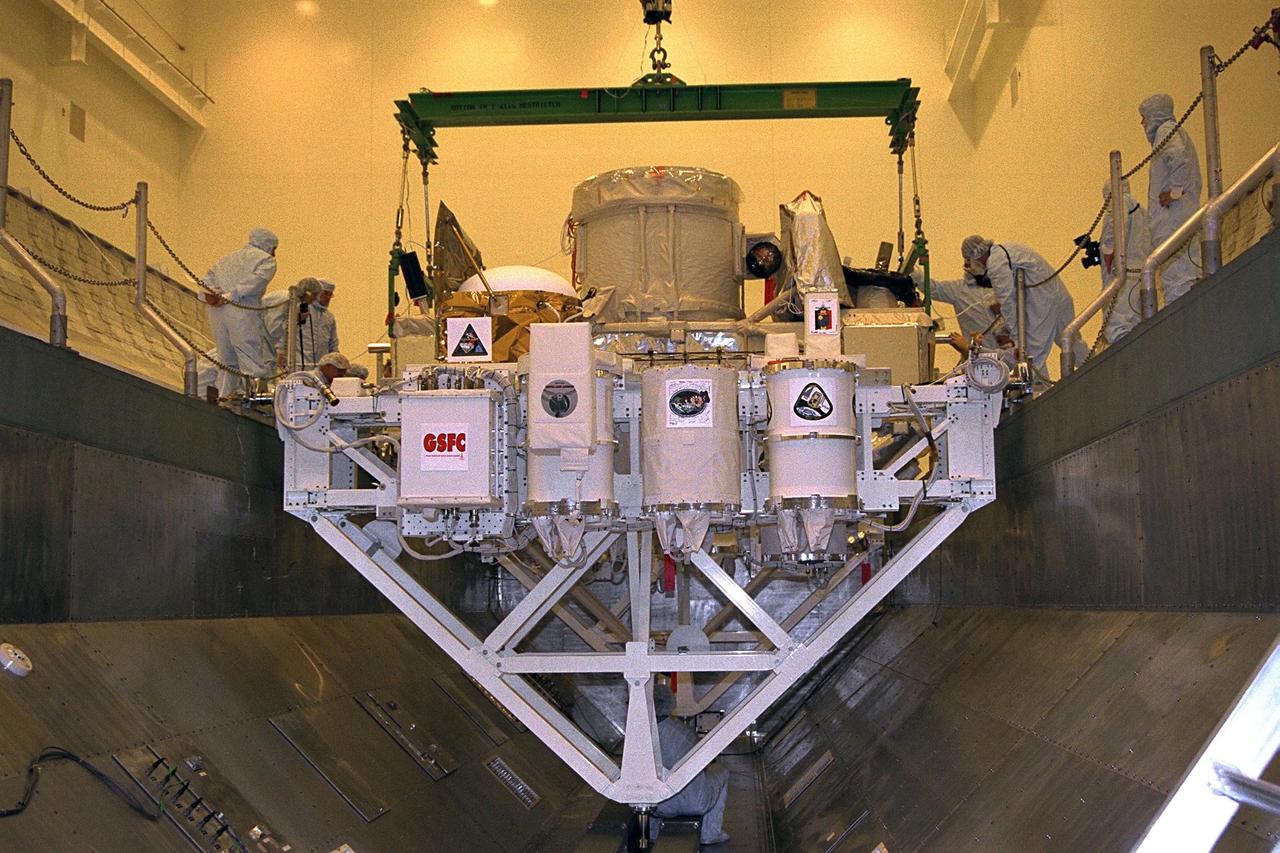

The CRISTA-SPAS payload, manifested on Space Shuttle Mission STS-85, is placed in the transport canister

The CRISTA-SPAS payload, manifested on Space Shuttle Mission STS-85, is placed in the transport canister
The CRISTA-SPAS payload, manifested on Space Shuttle Mission STS-85, is placed in the transport canister
The CRISTA-SPAS payload, manifested on Space Shuttle Mission STS-85, is placed in the transport canister
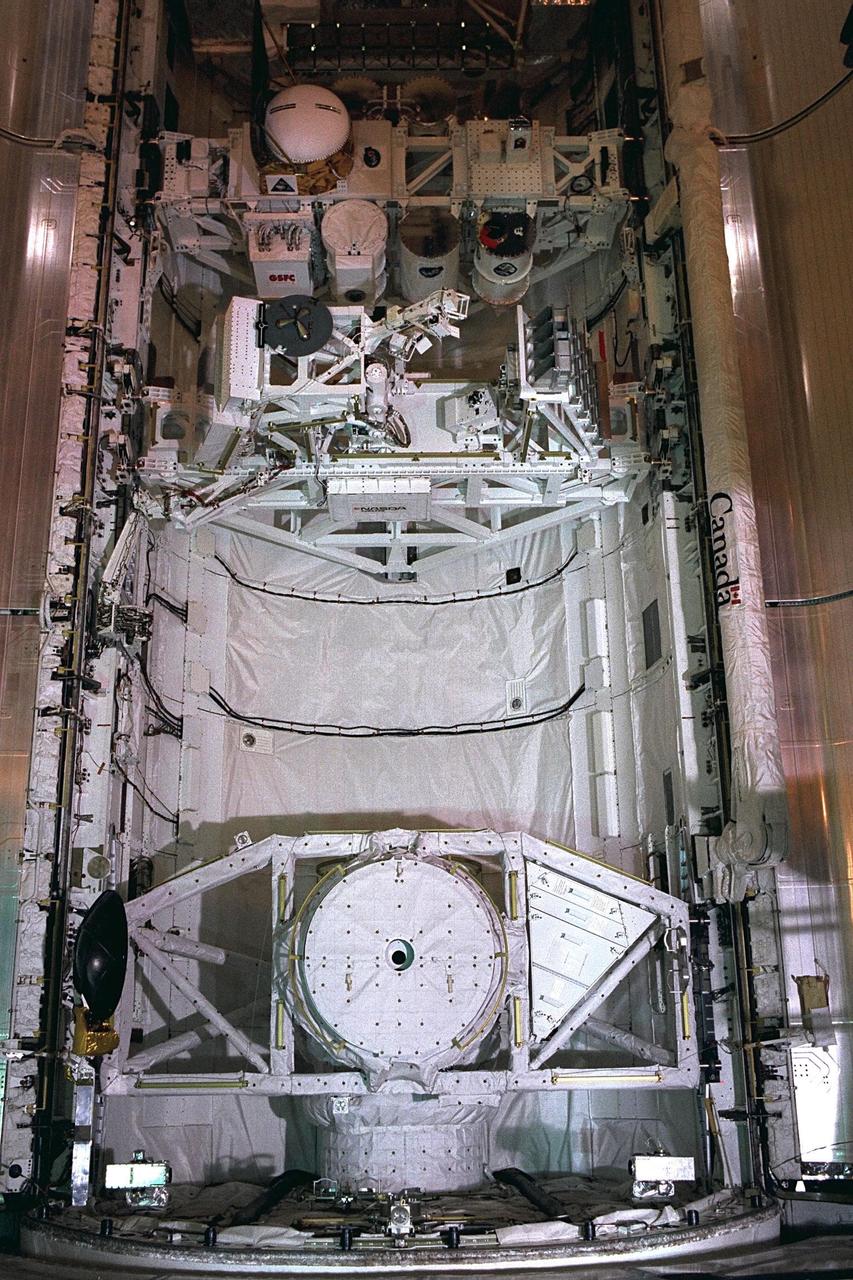
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery's payload bay doors are closed in preparation for the flight of mission STS-85

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery's payload bay doors are closed in preparation for the flight of mission STS-85

STS085-S-002 (May 1997) --- Five NASA astronauts and a Canadian payload specialist pause from their training schedule to pose for the traditional crew portrait for their mission. In front are astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr. (right), mission commander, and Kent V. Rominger, pilot. On the back row, from the left, are astronauts Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., Stephen K. Robinson and N. Jan Davis, all mission specialists, along with the Canadian Space Agency’s (CSA) payload specialist Bjarni Tryggvason.

STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason poses in the cockpit of his T-38 jet trainer aircraft at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) after his arrival with the rest of the flight crew from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin final preparations for the STS-85 mission. The other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Pilot Kent V. Rominger, Payload Commander N. Jan Davis, Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery for the 11-day space flight is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
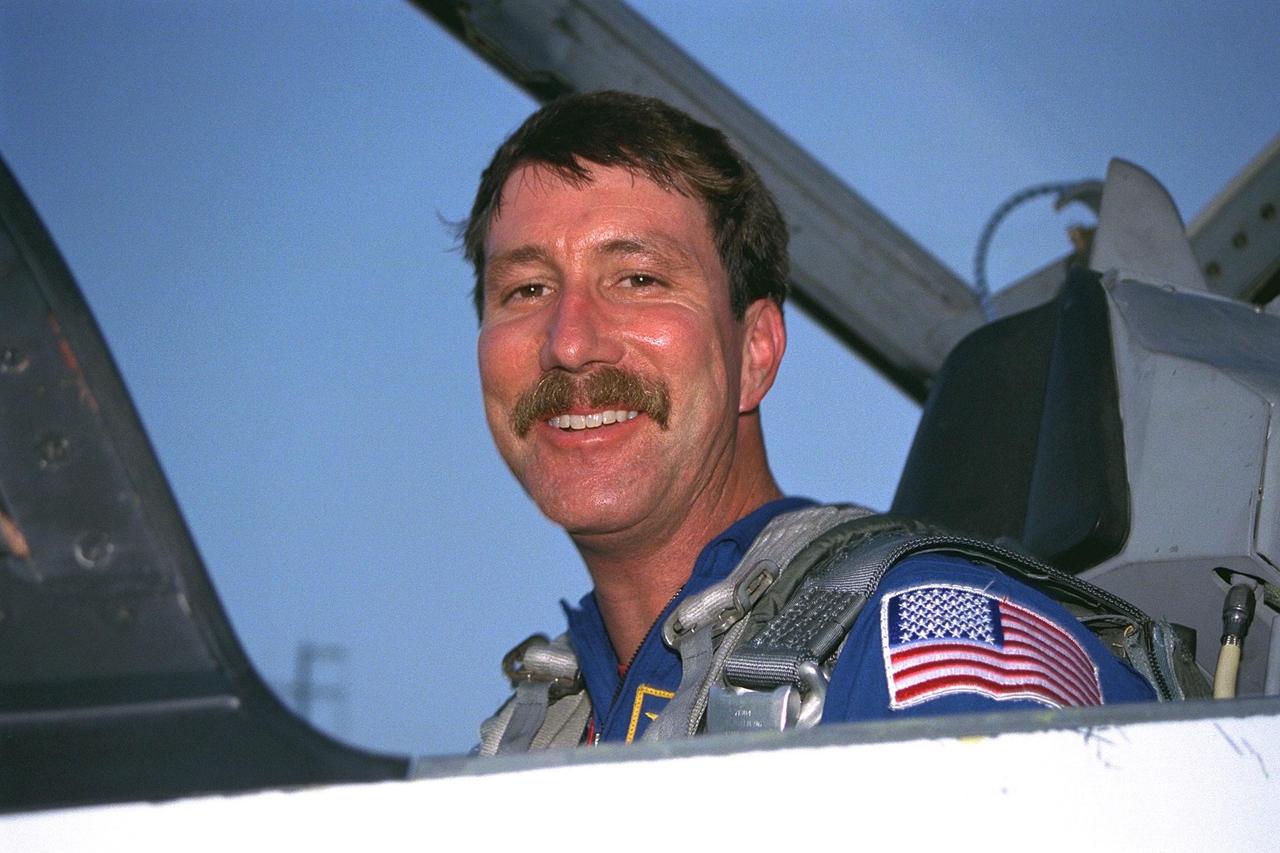

STS-85 Pilot Kent V. Rominger poses in his T-38 jet trainer after landing with other members of the flight crew at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a dress rehearsal of the launch countdown. The STS-85 mission is now targeted for Aug. 7. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), nd Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
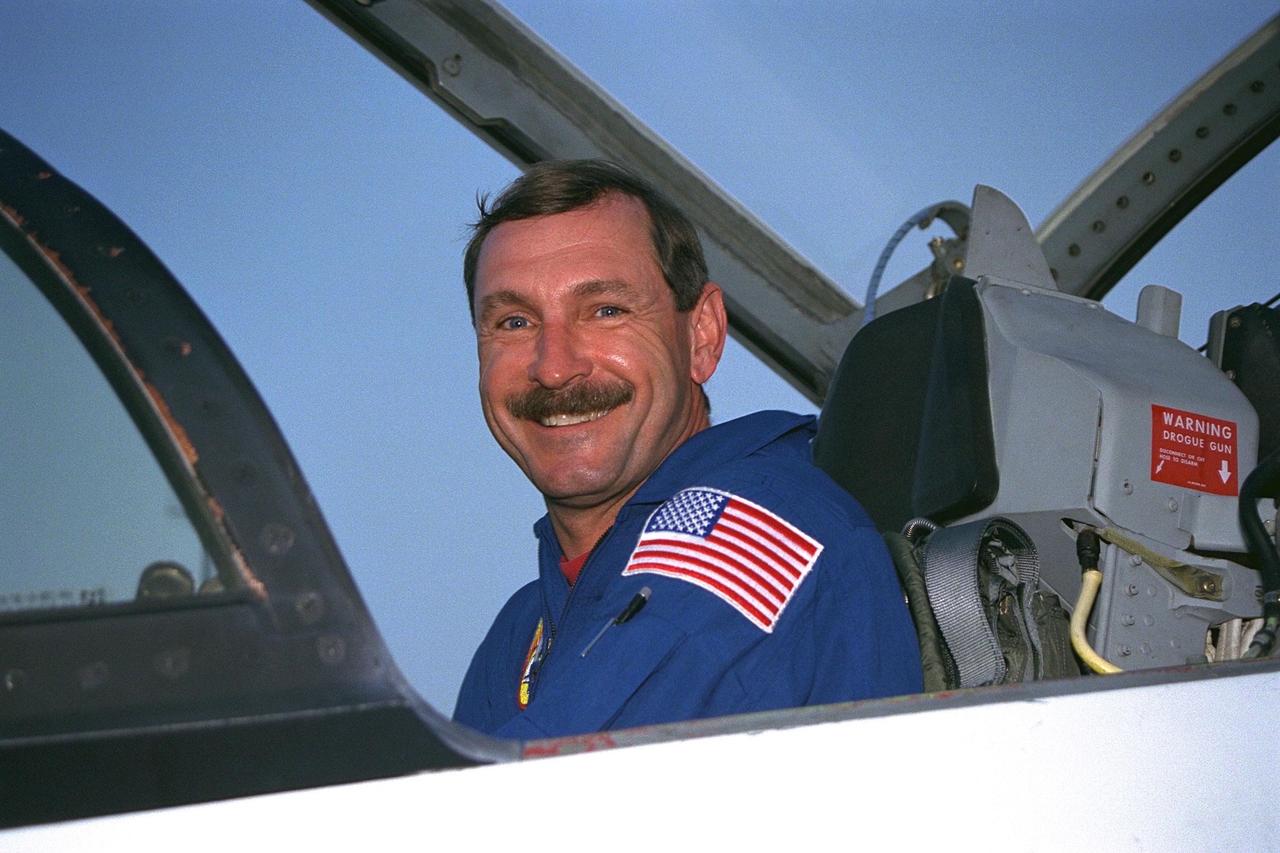

STS-85 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., poses in his T-38 jet trainer after landing with his crew at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a dress rehearsal of the launch countdown. The STS-85 mission is now targeted for Aug. 7. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Rotating Service Structure is rolled back at Launch Complex 39A to reveal the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery, scheduled to launch on mission STS-85 at 10:41 a.m. EDT on August 7. The STS-85 flight crew members are Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Pilot Kent V. Rominger; Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery for the 11-day space flight is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
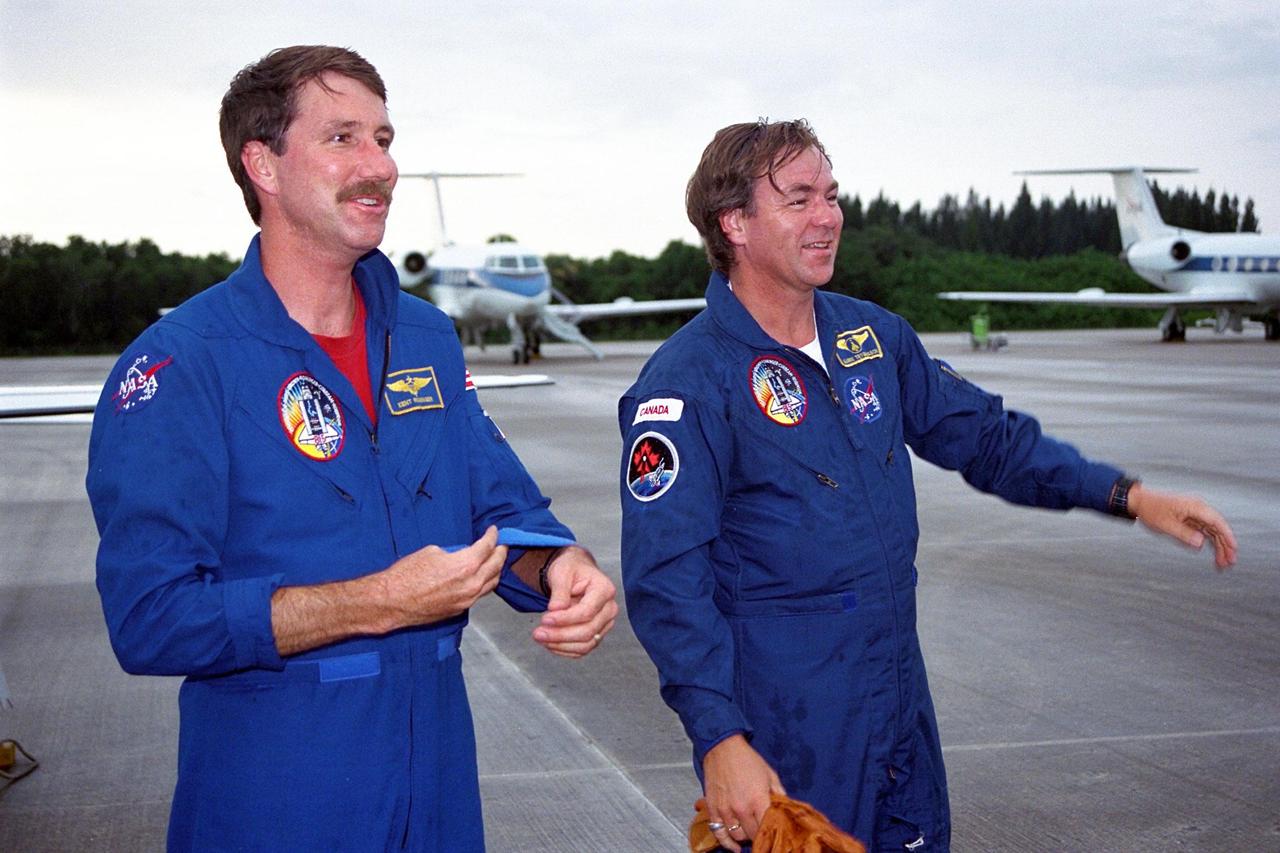

STS-85 Pilot Kent V. Rominger (left) and Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason prepare to greet the rest of the flight crew at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) after their arrival from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin final preparations for the STS-85 mission. The other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Payload Commander N. Jan Davis, Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery for the 11-day space flight is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
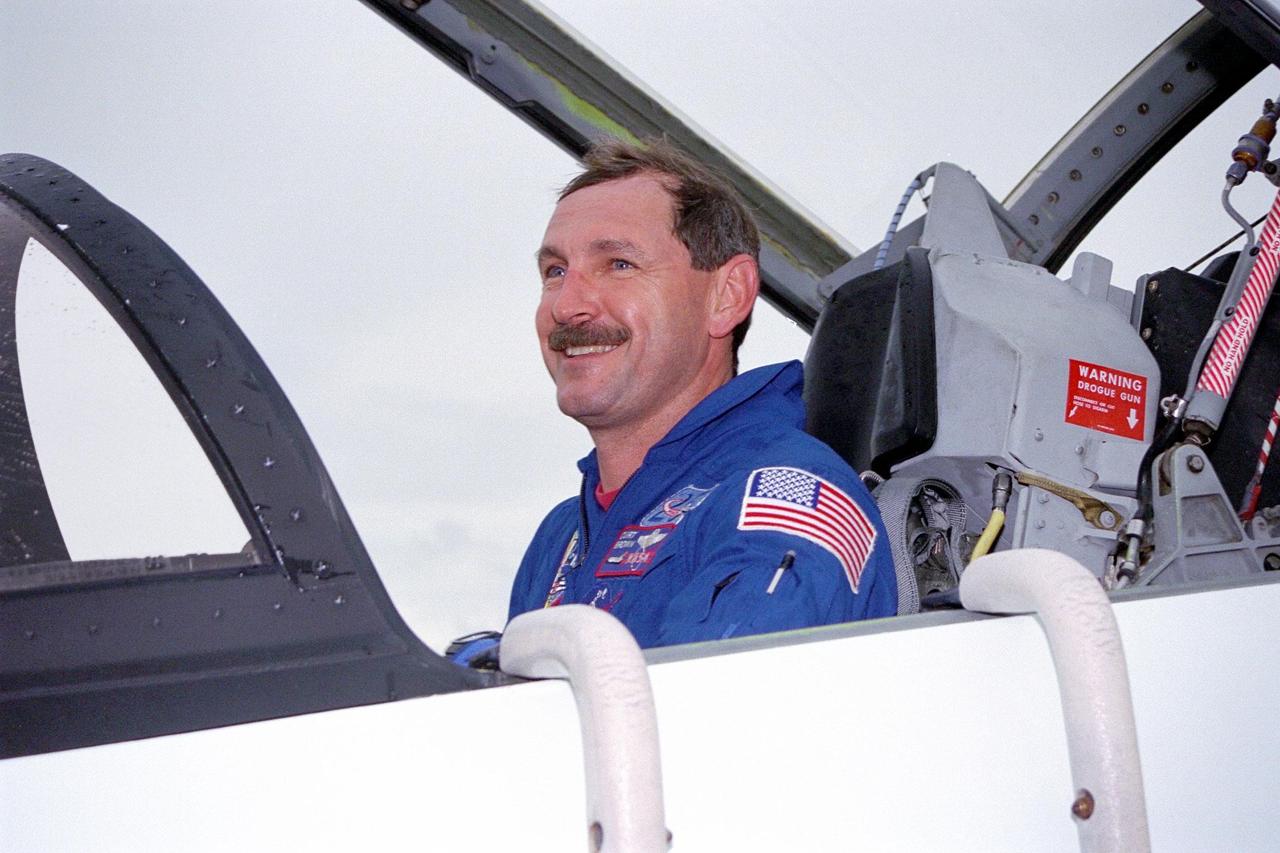

STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr. poses in the cockpit of his T-38 jet trainer aircraft at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) after his arrival with the rest of the flight crew from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin final preparations for the STS-85 mission. The other crew members are Pilot Kent V. Rominger, Payload Commander N. Jan Davis, Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson and Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery for the 11-day space flight is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
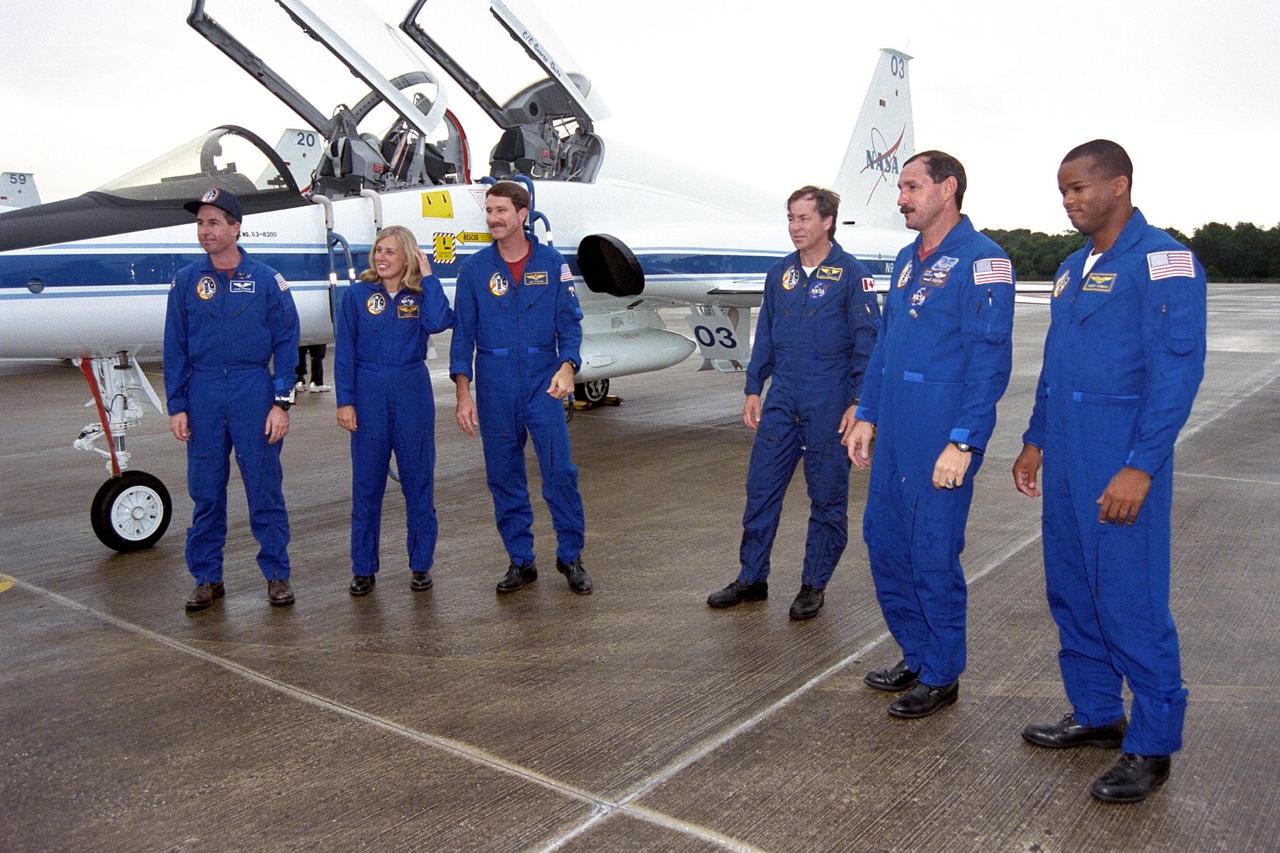

The STS-85 flight crew members pose with their T-38 jet trainer aircraft at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) after their arrival from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin final preparations for the STS-85 mission. They are (from left): Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Pilot Kent V. Rominger; Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery for the 11-day space flight is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-85 flight crew members address the news media at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) after their arrival from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin final preparations for the STS-85 mission. They are (from left): Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; Pilot Kent V. Rominger; Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr.; and Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery for the 11-day space flight is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments.
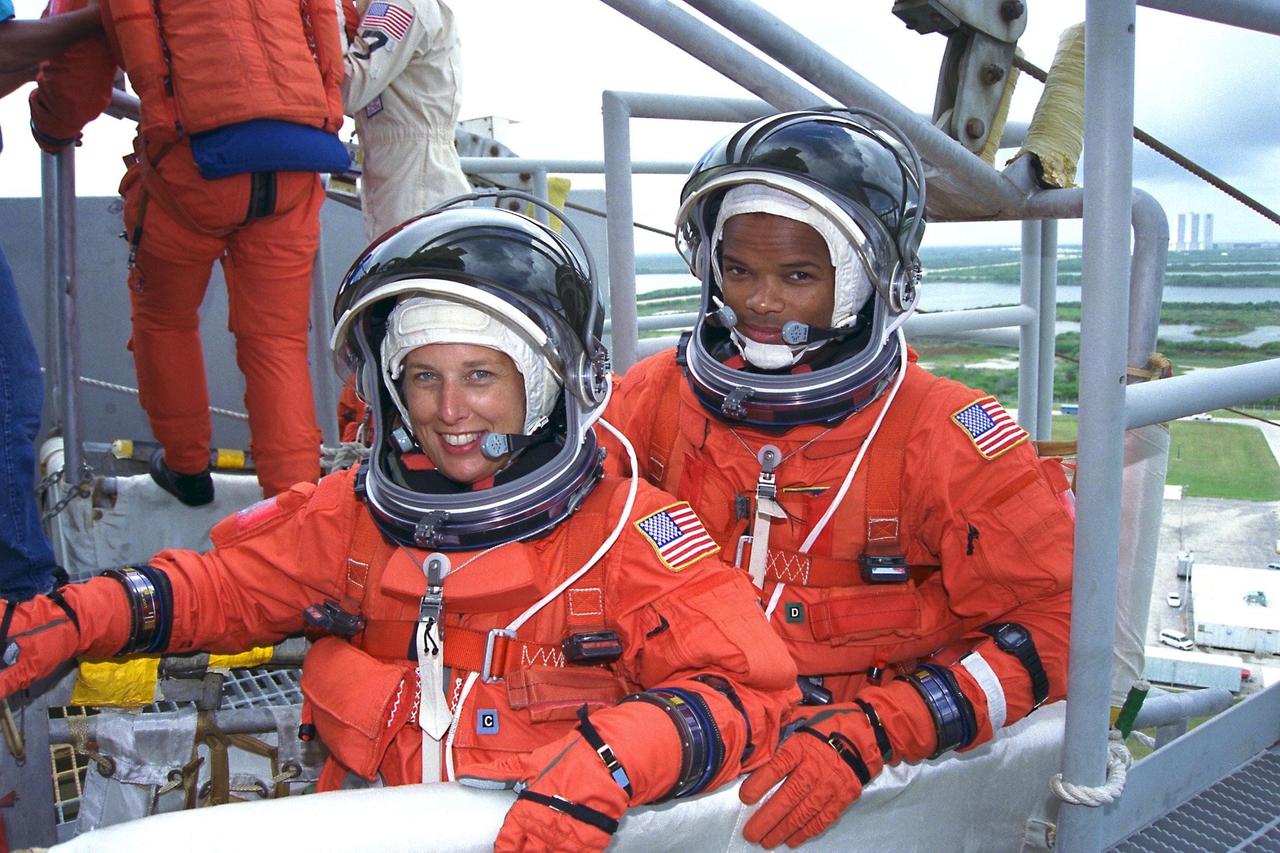

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Payload Commander N. Jan Davis (left) and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., check out an emergency egress slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2)
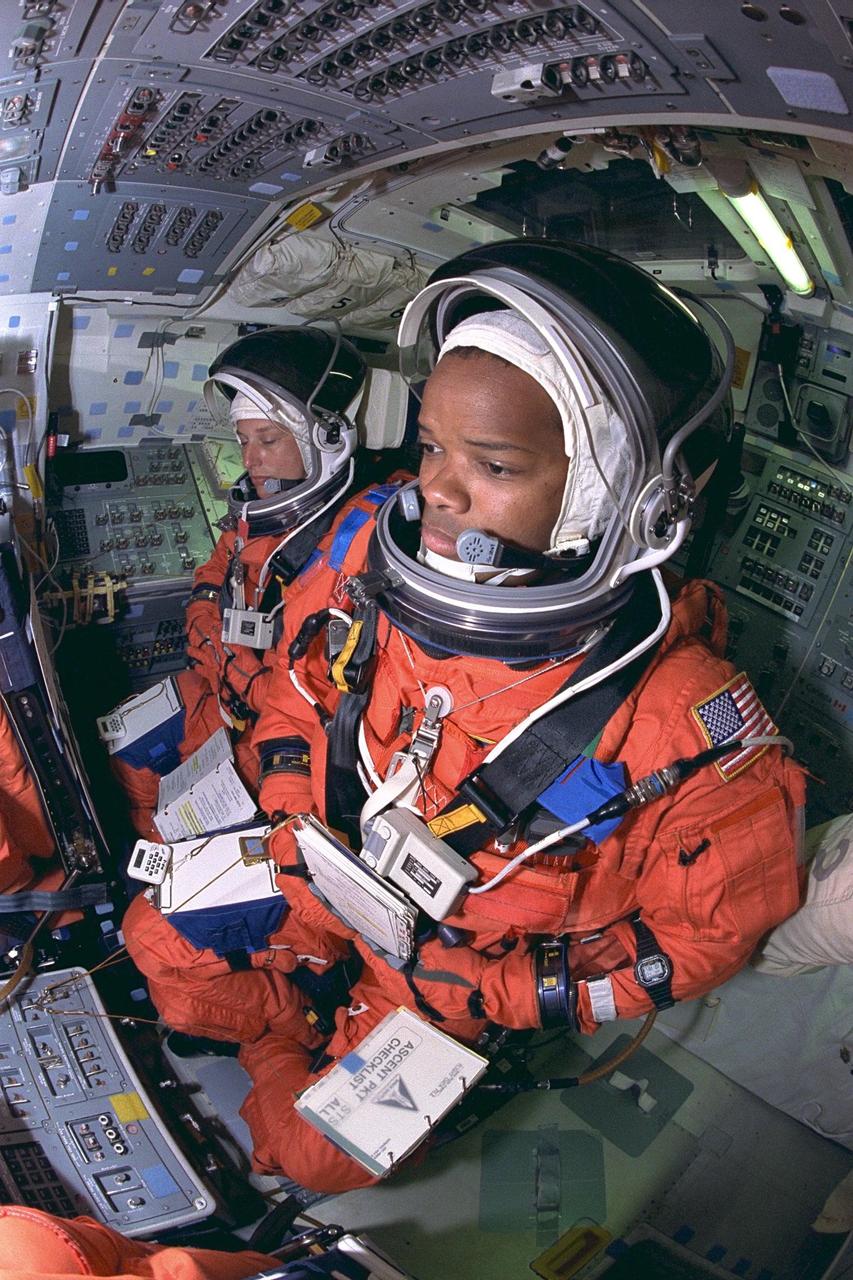

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Payload Commander N. Jan Davis (left) and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., go through countdown procedures aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
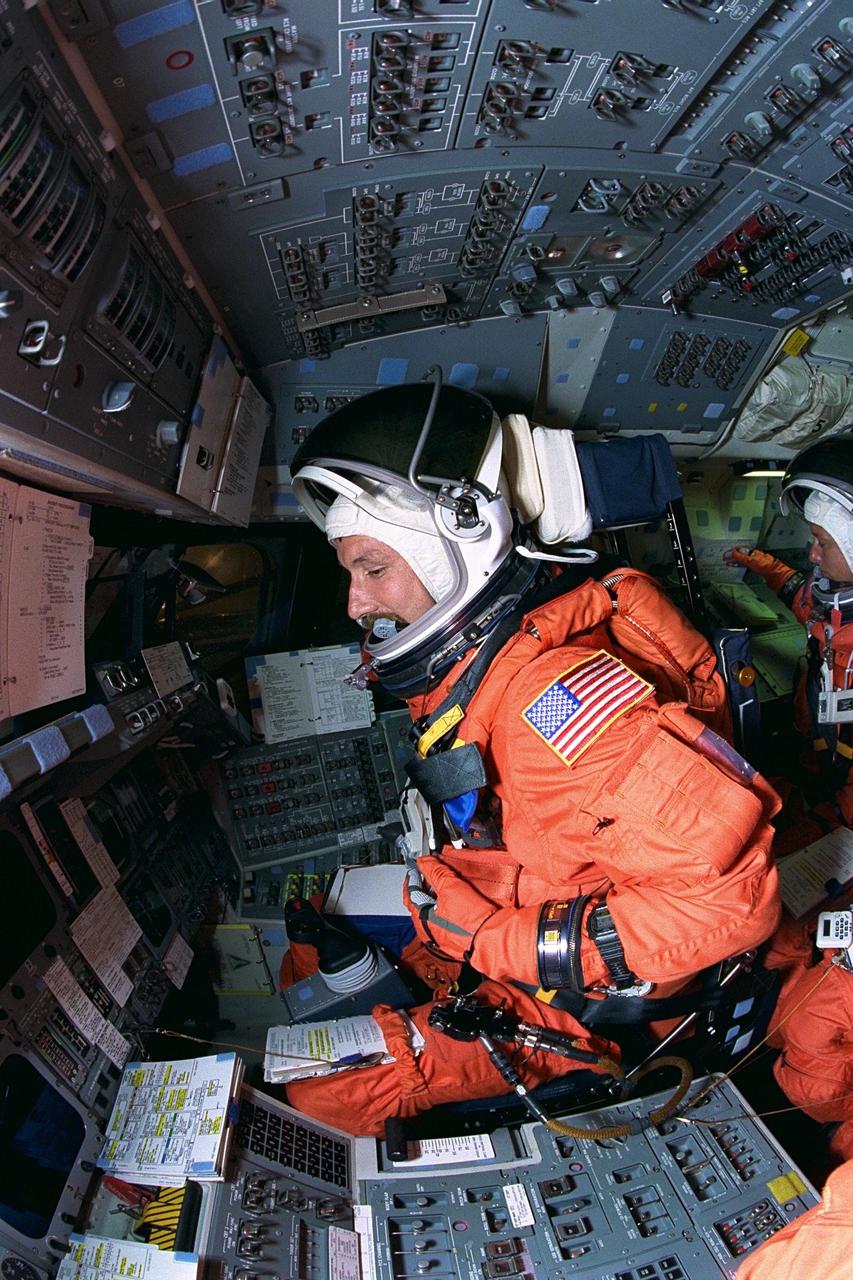

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Pilot Kent V. Rominger goes through countdown procedures on the flight deck aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson (left) and Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason check out an emergency egress slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2)
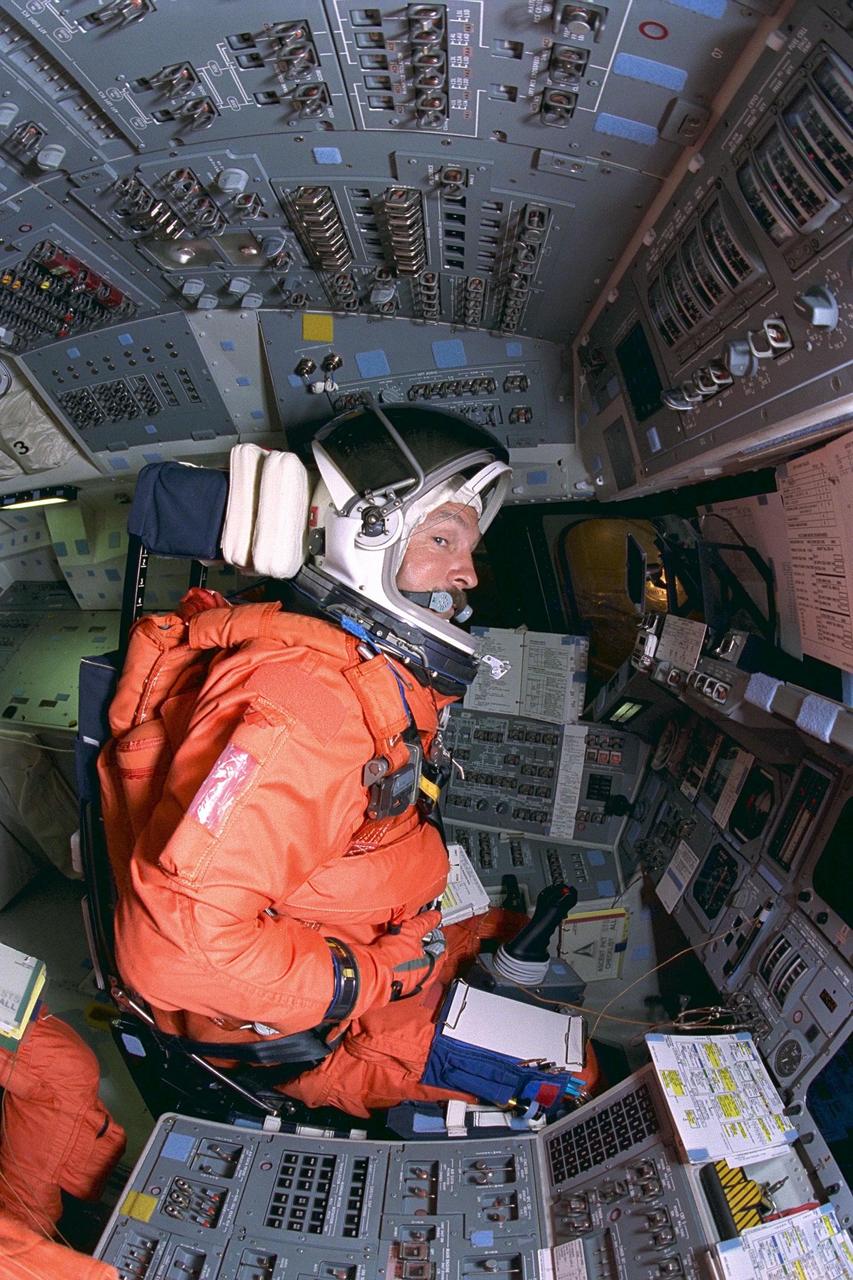

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., goes through countdown procedures on the flight deck aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson go through countdown procedures aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS- 2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
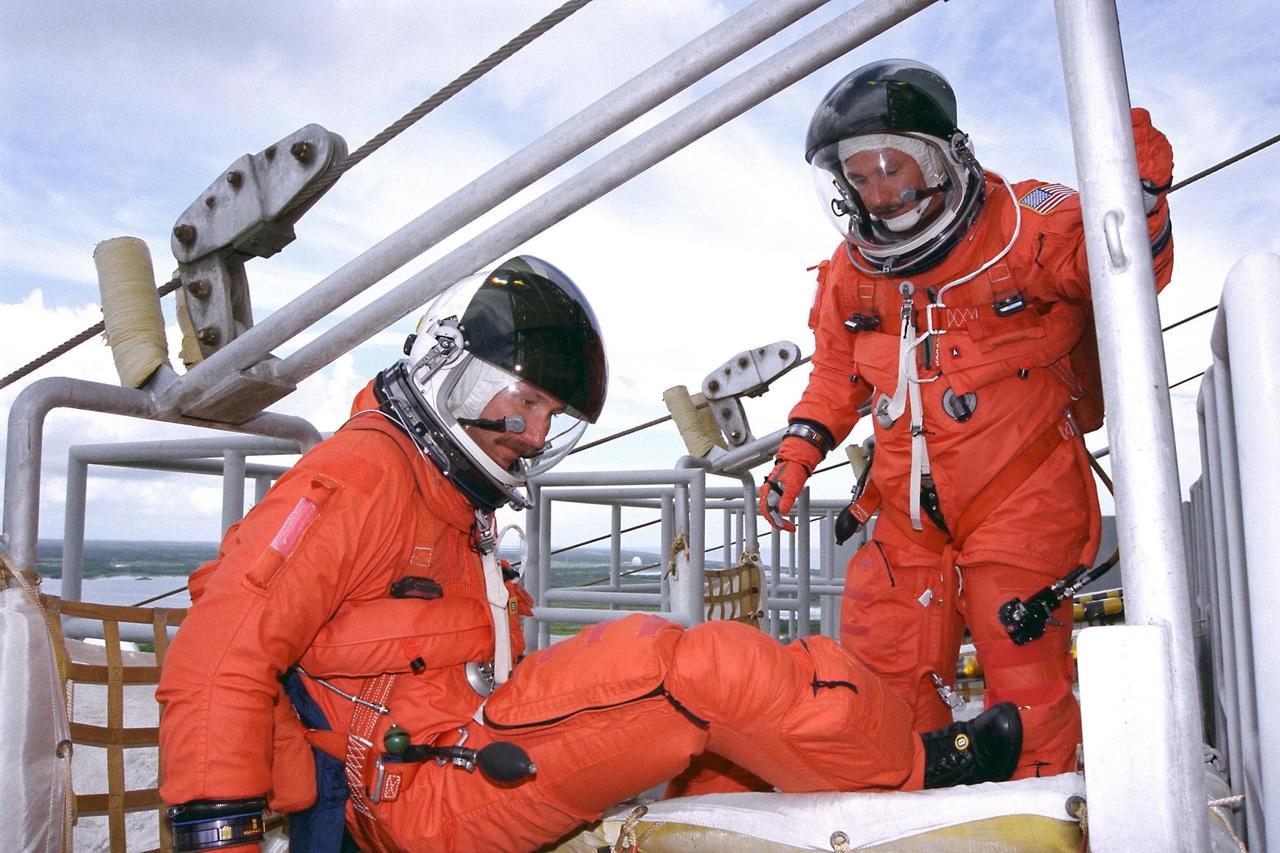

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Pilot Kent V. Rominger (left) and Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr. exit an emergency egress slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2)
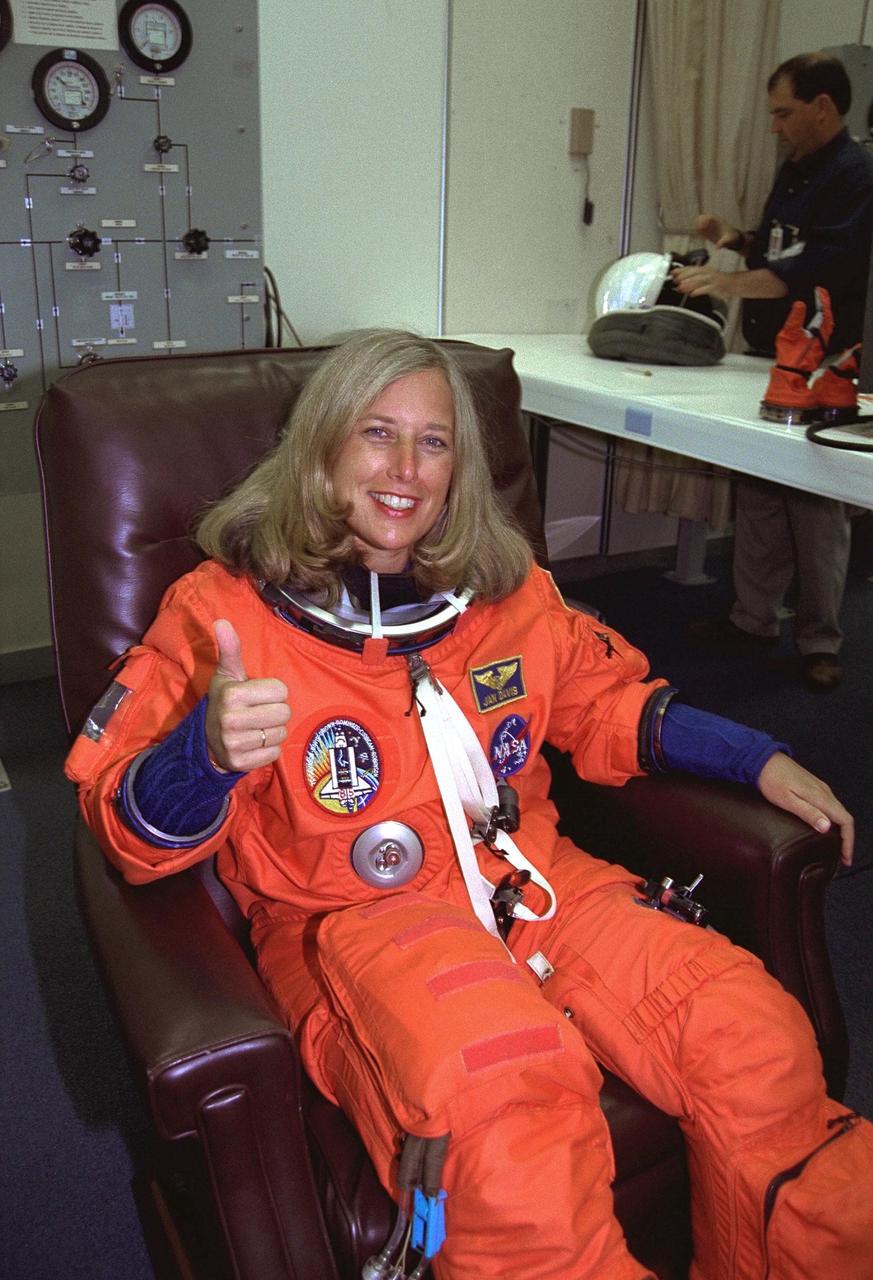

STS-85 Payload Commander N. Jan Davis gives a thumbs up as she is assisted with her ascent/reentry flight suit in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building. She has logged nearly 400 hours in space on the STS-47 and STS-60 missions and holds a doctorate in mechanical engineering. Davis will have overall responsibility for the experiments conducted on STS-85. She will also deploy and retrieve the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the AtmosphereShuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) free-flyer and operate the prototype Japanese robotic arm. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the CRISTA-SPAS-2. Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
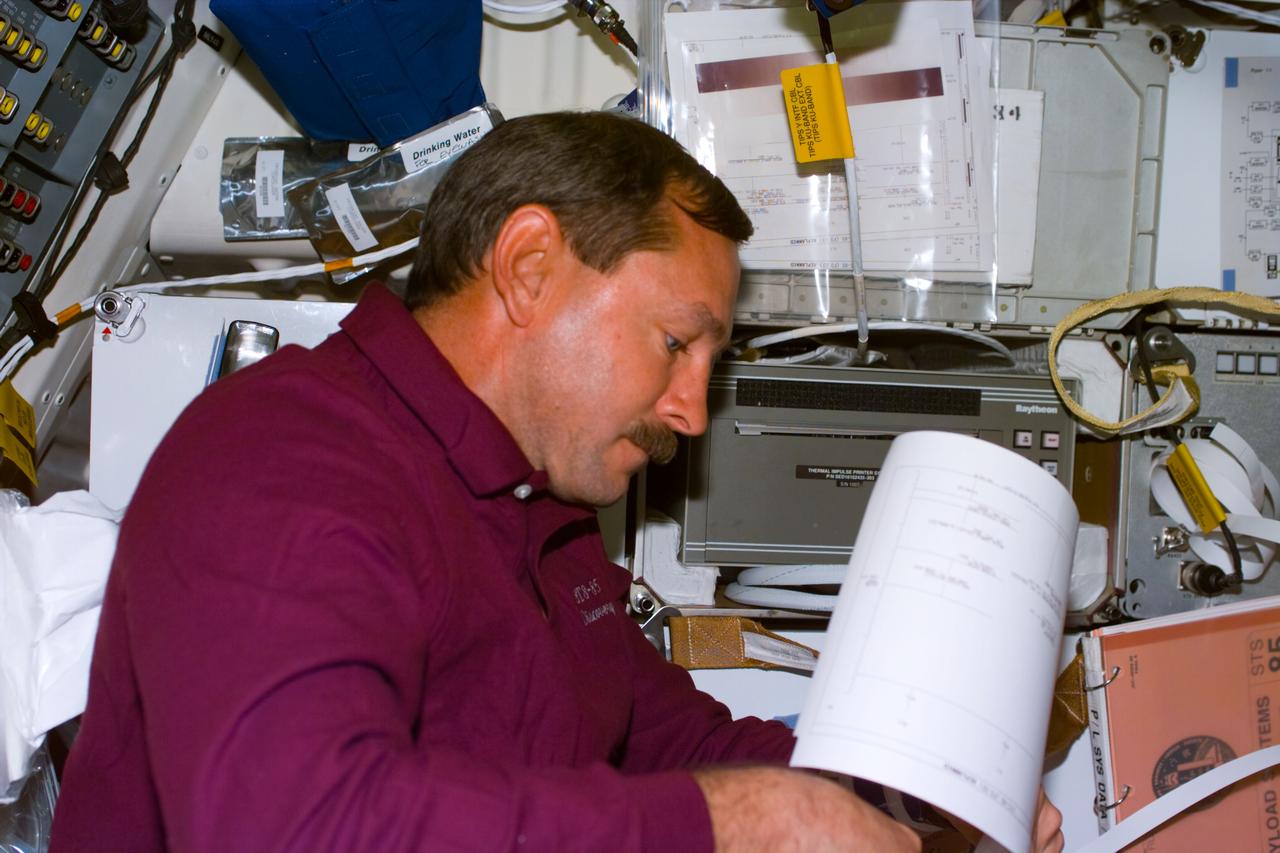

S85-E-5038 (11 August 1997) --- Astronaut Curtis L. Brown, Jr., commander, checks over the most recent send-up of mail from flight controllers in Houston, Texas. The Thermal Imaging Printing System (TIPS) station is on the mid-deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery.
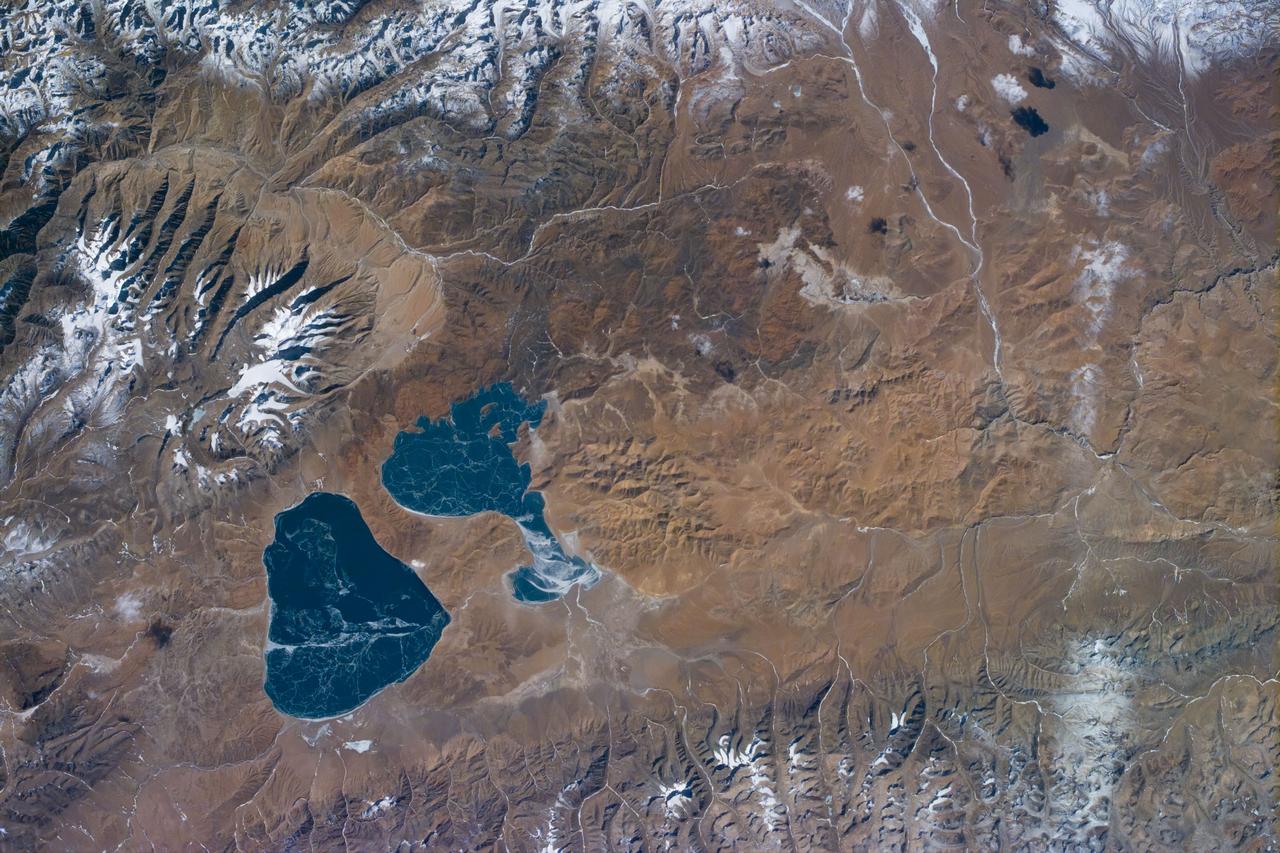

S81E5015 (13 January 1997) --- An Electronic Still Camera (ESC), mounted in the Space Shuttle Atlantis' aft flight deck overhead window, recorded this view of China, featuring two large lakes, Mapam Yumco and Langa Co. Once a year, NASA flies aboard its Shuttle fleet a student project called Kidsat, which enables students on Earth to have hands-on interface with Earth observations from a space perspective.
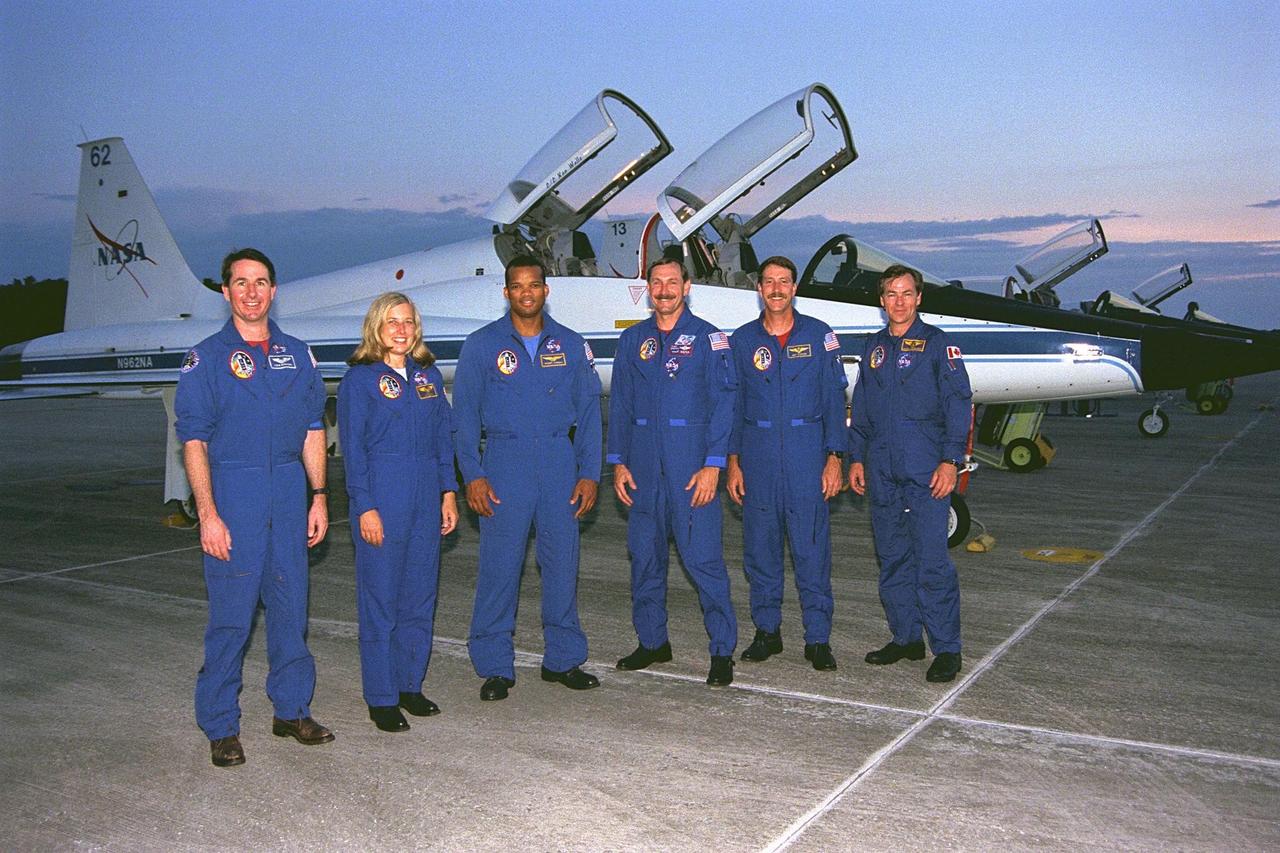

The STS-85 mission crew members pose in front of their T-38 jet trainers after they arrived at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a dress rehearsal of the launch countdown. They are (front row, from left): Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr.; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; Pilot Kent V. Rominger; and Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason. The STS-85 mission is now targeted for Aug. 7. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
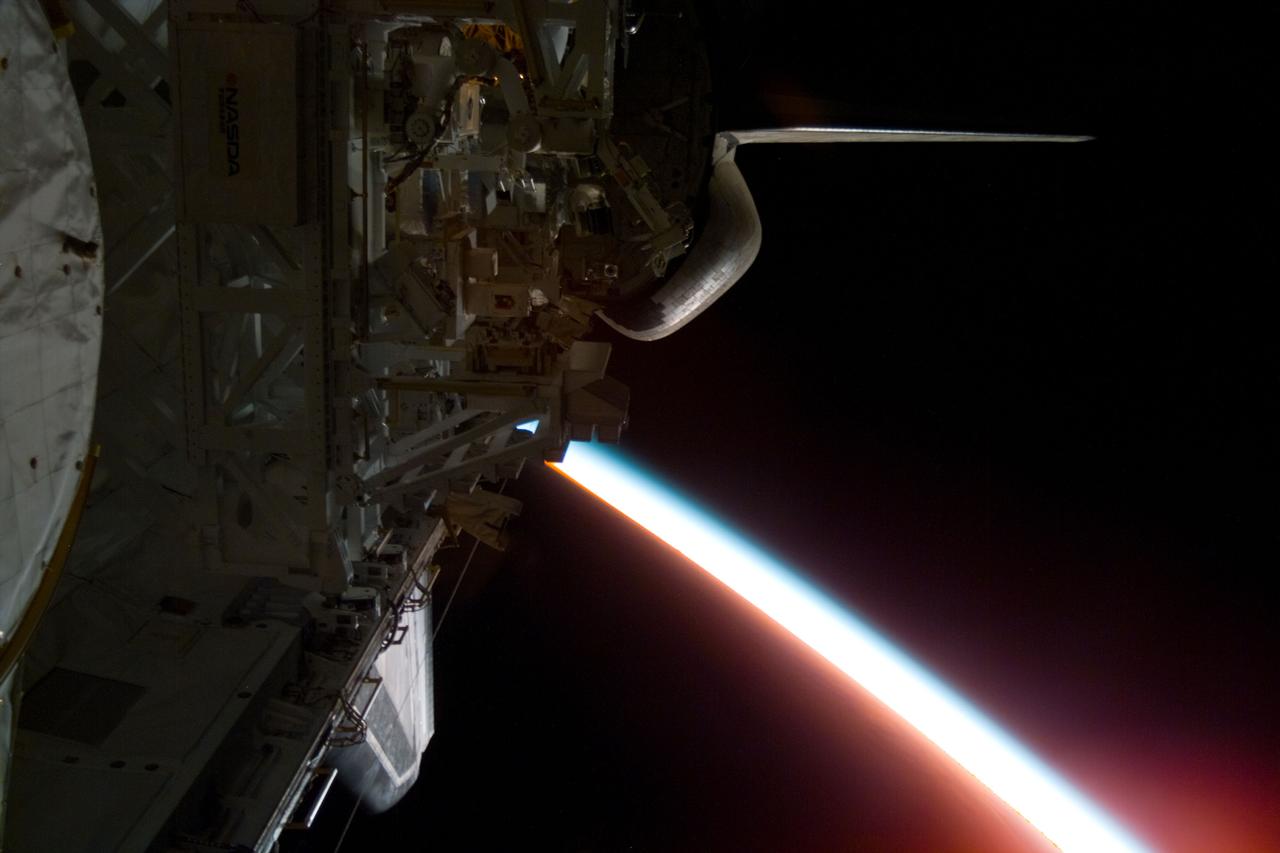

S85-E-5089 (14 August 1997) --- The sun sets on Earth's horizon in this electronic still camera's view photographed on STS-85 flight day 8 aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. The portside wing of Discovery is pointed toward Earth in the view, captured through windows on the aft flight deck.
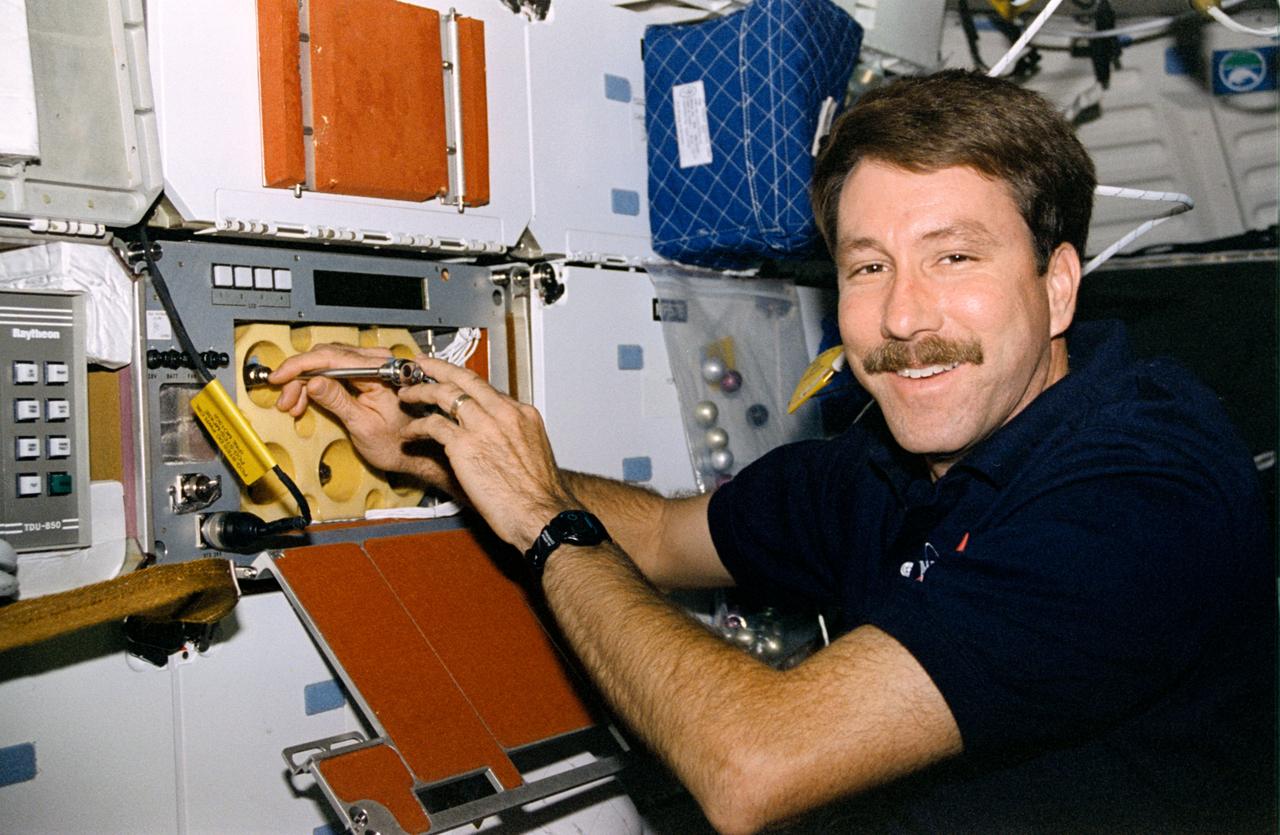

STS085-324-007 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- Astronaut Kent V. Rominger, pilot, uses a tool to deactivate the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment on the mid-deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery near the end of the 12-day STS-85 flight.
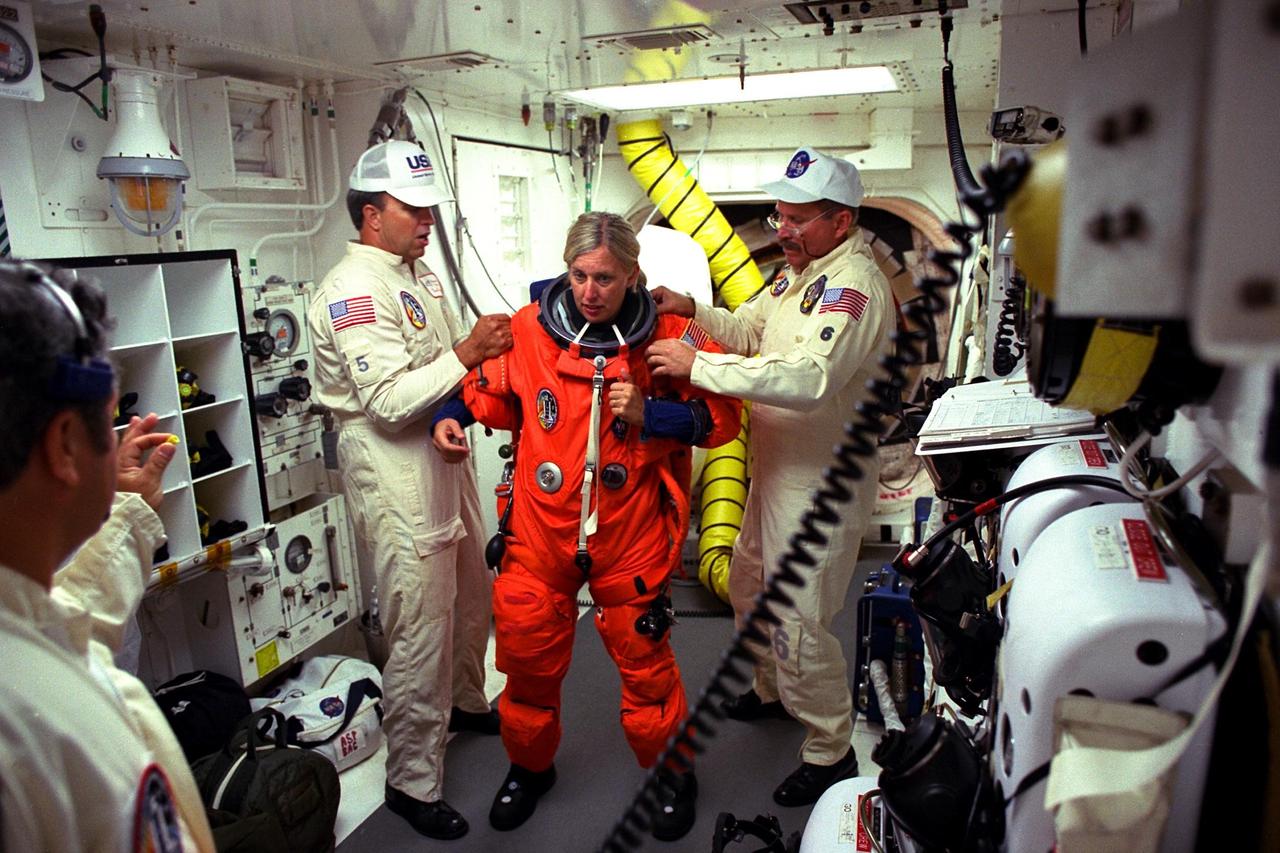

STS-85 Payload Commander N. Jan Davis is assisted with her ascent/reentry flight suit by white room closeout crew members Dave Law (left) and Jack Burritt at Launch Pad 39A before she enters the crew cabin of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery
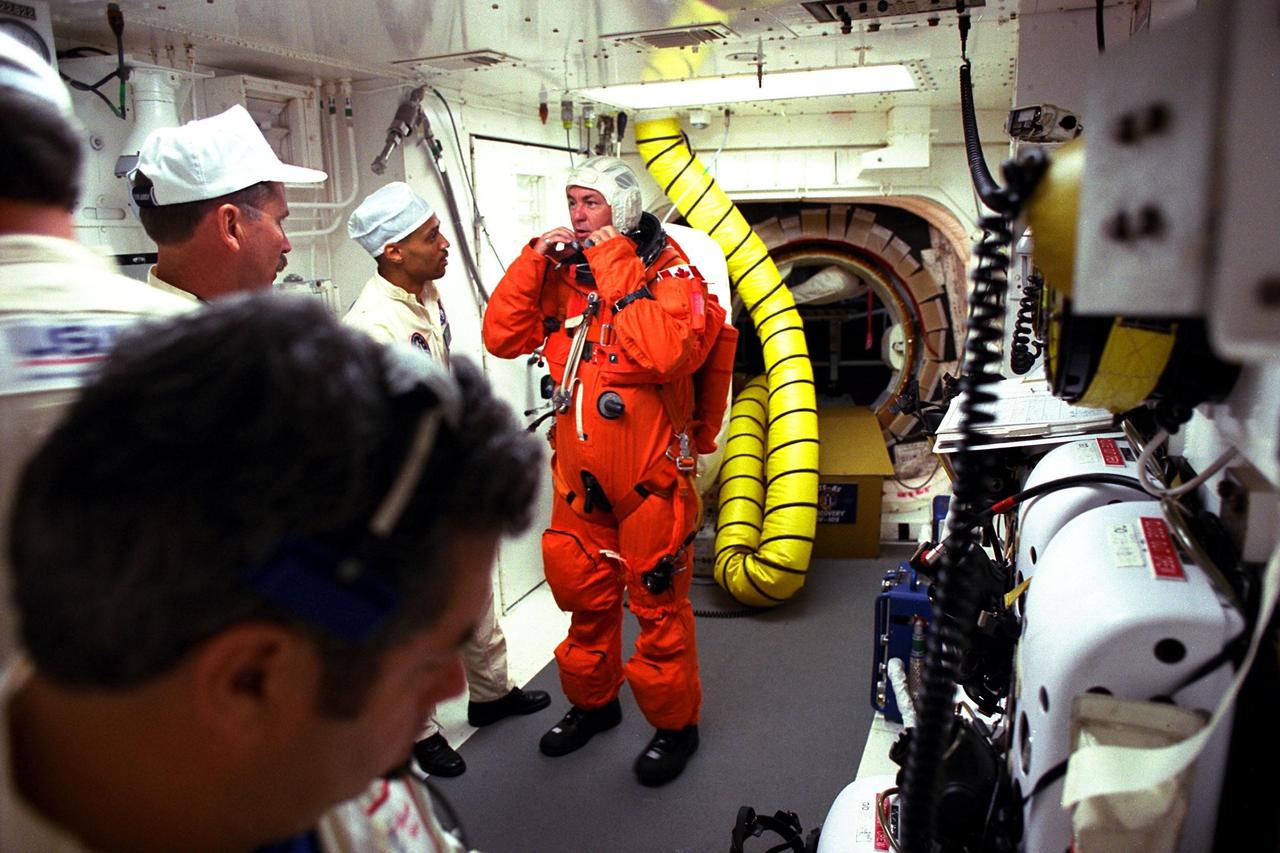

STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason is assisted with his ascent/reentry flight suit by white room closeout crew members Jack Burritt and Carlos Gillis at Launch Pad 39A before he enters the crew cabin of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery
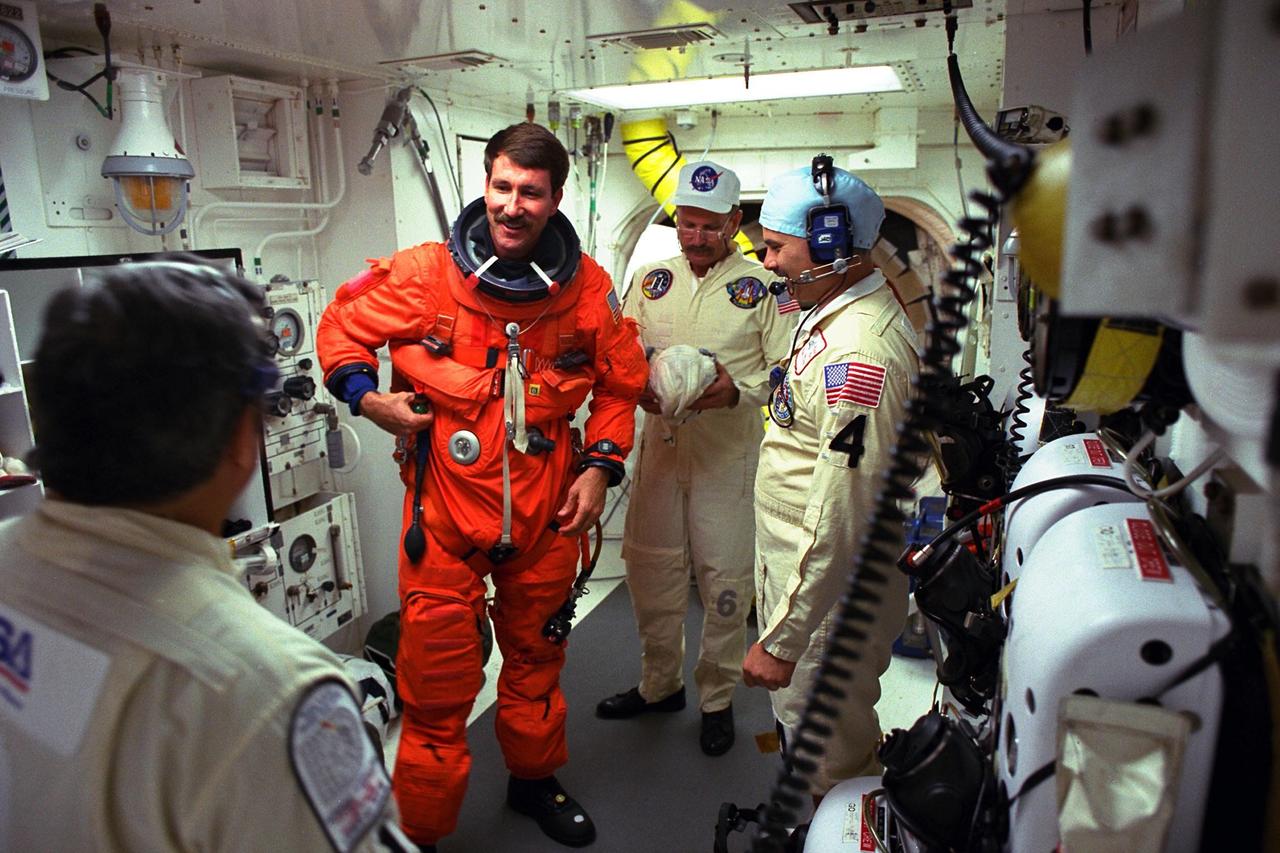

STS-85 Pilot Kent V. Rominger visits with white room closeout crew members Mike Mangione (left foreground), Jack Burritt (center), and Chris Meinert at Launch Pad 39A as they assist him with his ascent/reentry flight suit before he enters the crew cabin of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery
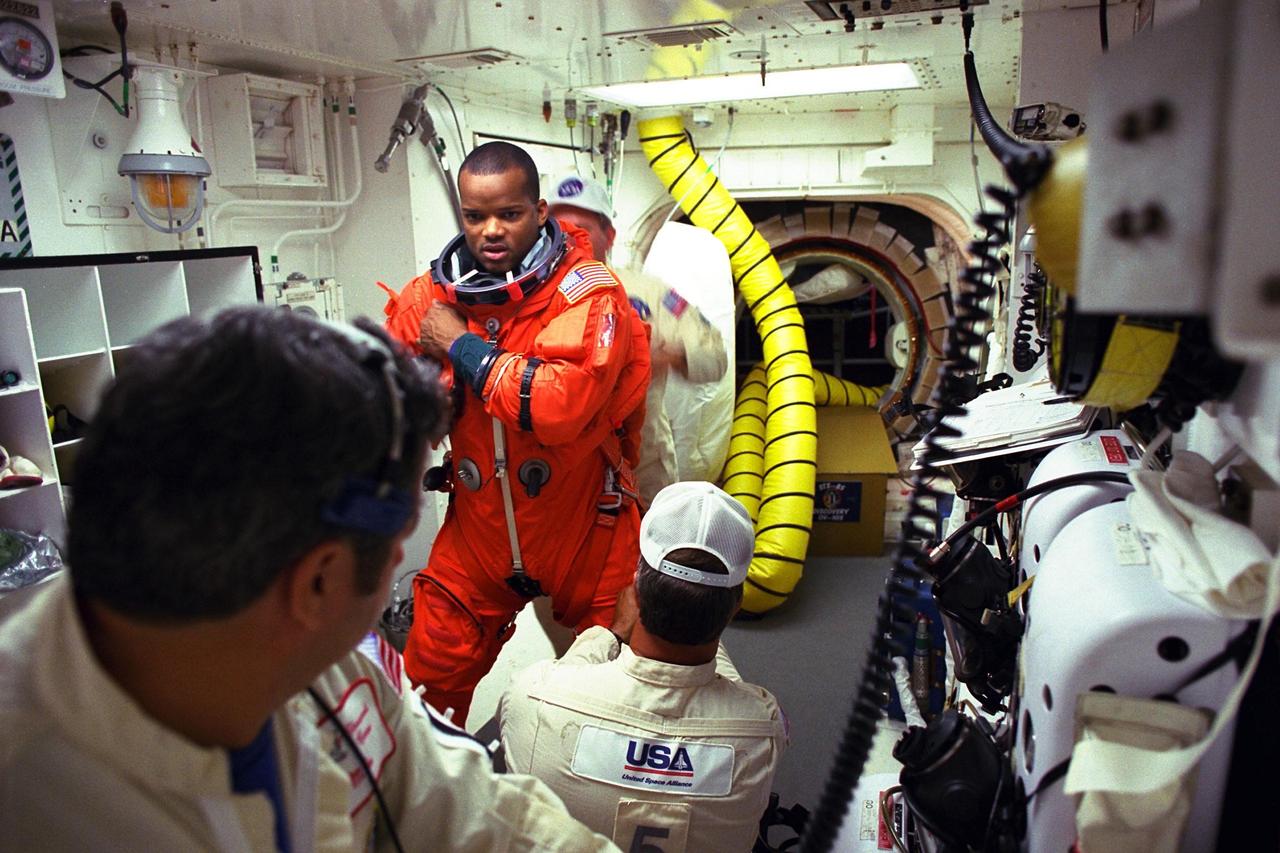

STS-85 Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. is assisted with his ascent/reentry flight suit by white room closeout crew members Mike Mangione (left foreground) and Dave Law at Launch Pad 39A before he enters the crew cabin of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery
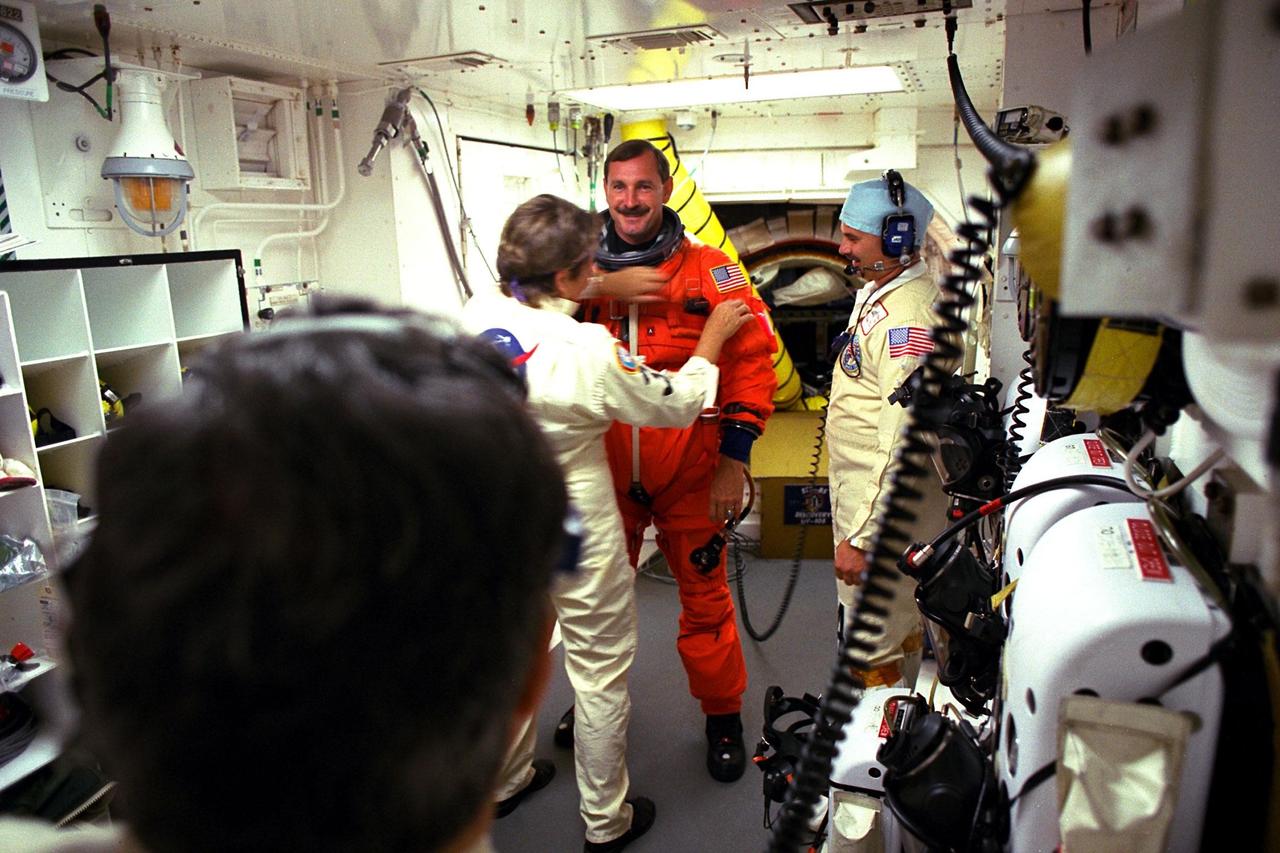

STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr. is assisted with his ascent/reentry flight suit by white room closeout crew members Jean Alexander (left) and Chris Meinert at Launch Pad 39A before he enters the crew cabin of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery
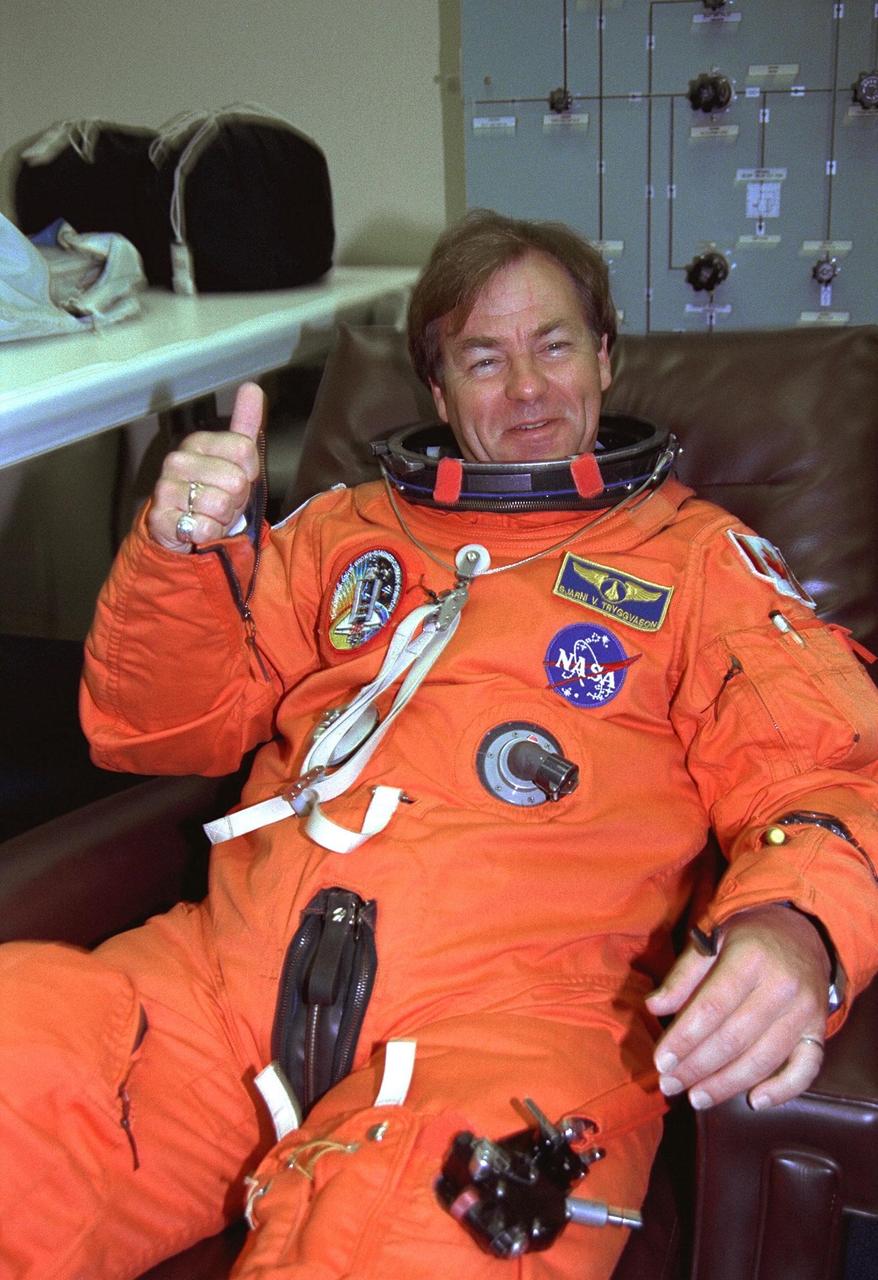

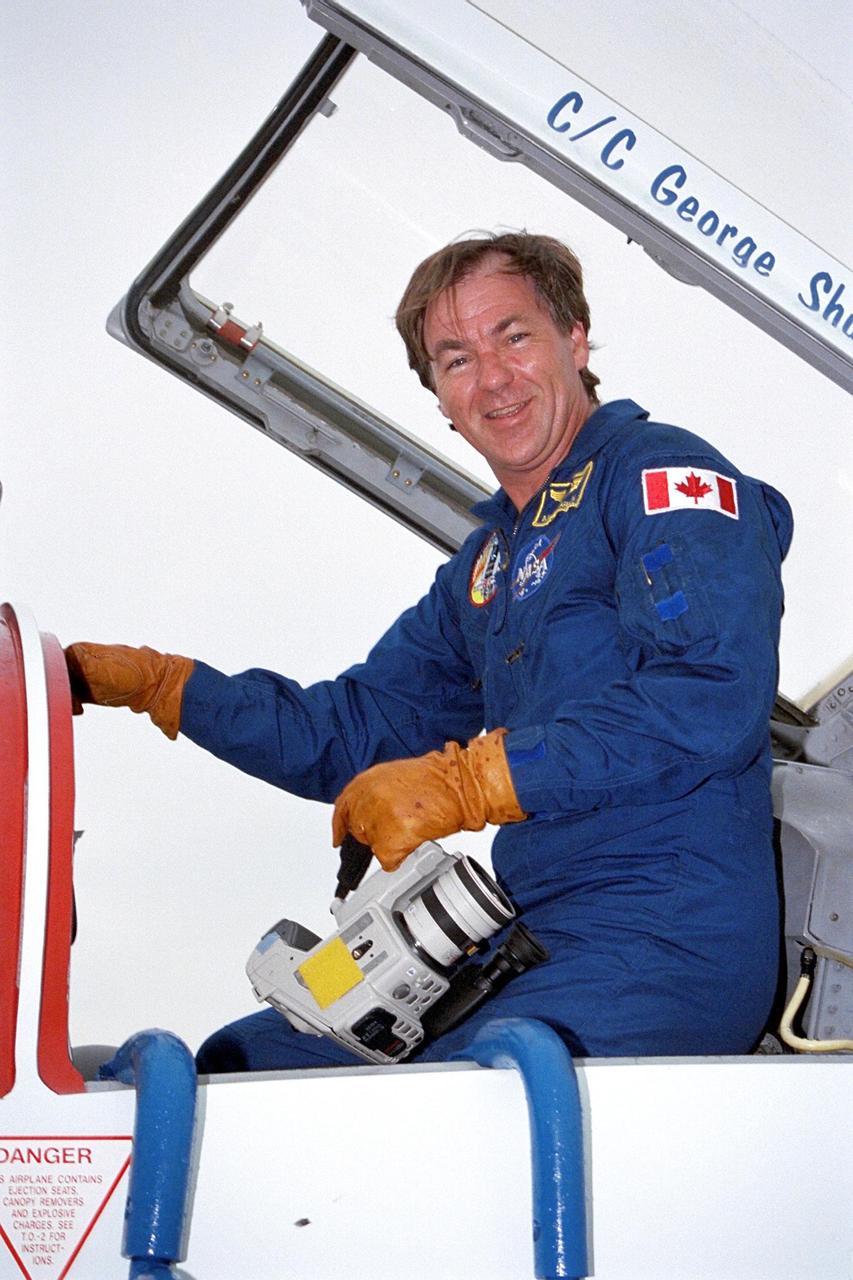
STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason gives a thumbs up as he is assisted with his ascent/reentry flight suit in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building. He is a Canadian Space Agency astronaut and was born in Iceland. Tryggvason has also been a flight instructor for the Canadian Air Force. Tryggvason is the principal investigator of the Microgravity Vibration Isolation Mount now flying on the Russian Mir space station. During STS-85, Tryggvason will conduct vibration isolation mount and fluid physics investigations. His work to study how Shuttle vibrations affect the results of experiments will be valuable to the International Space Station program, since this experiment is planned for use on that space platform. Tryggvason will also conduct Bioreactor experiments and assist Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson with photography
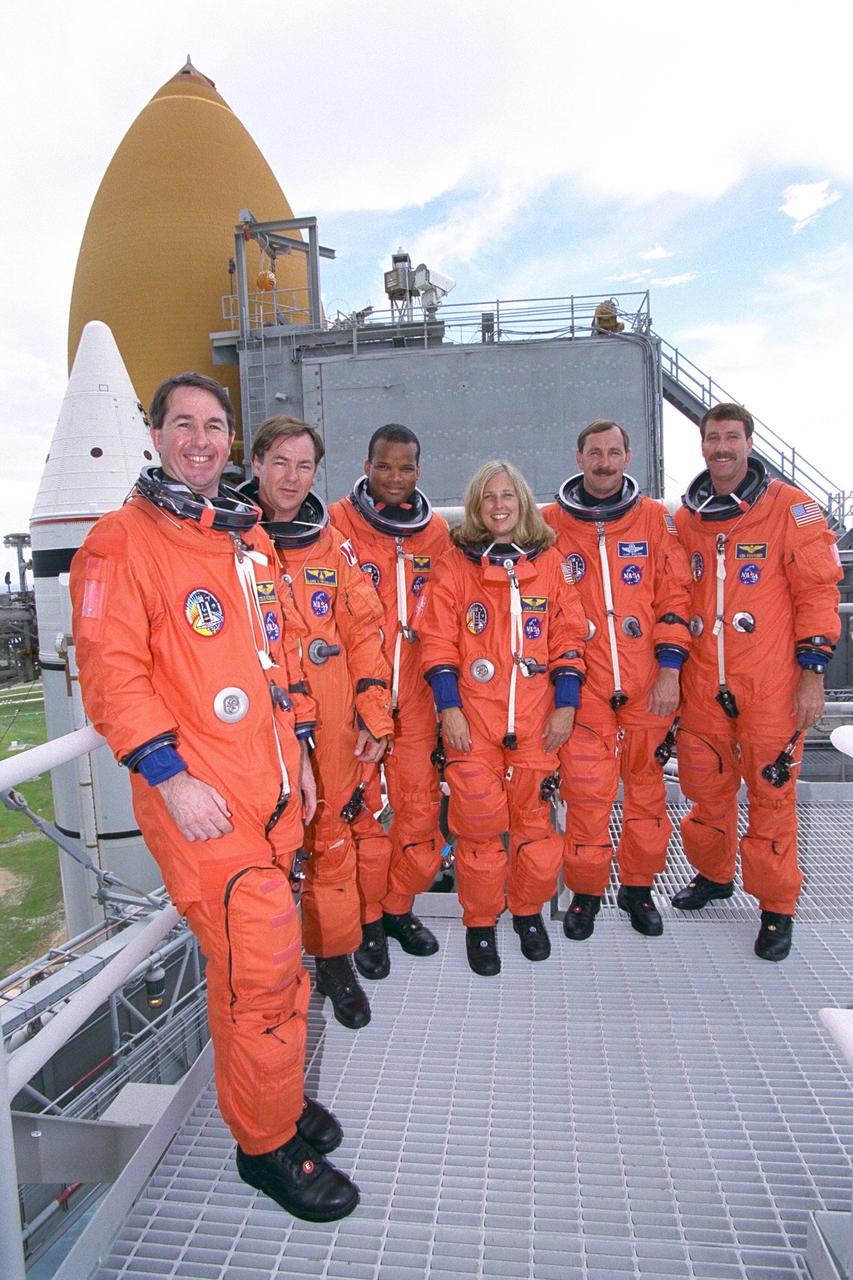

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-85 flight crew members pose at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A with the Space Shuttle Discovery in the background during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. They are (from left): Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason; Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr.; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; and Pilot Kent V. Rominger. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
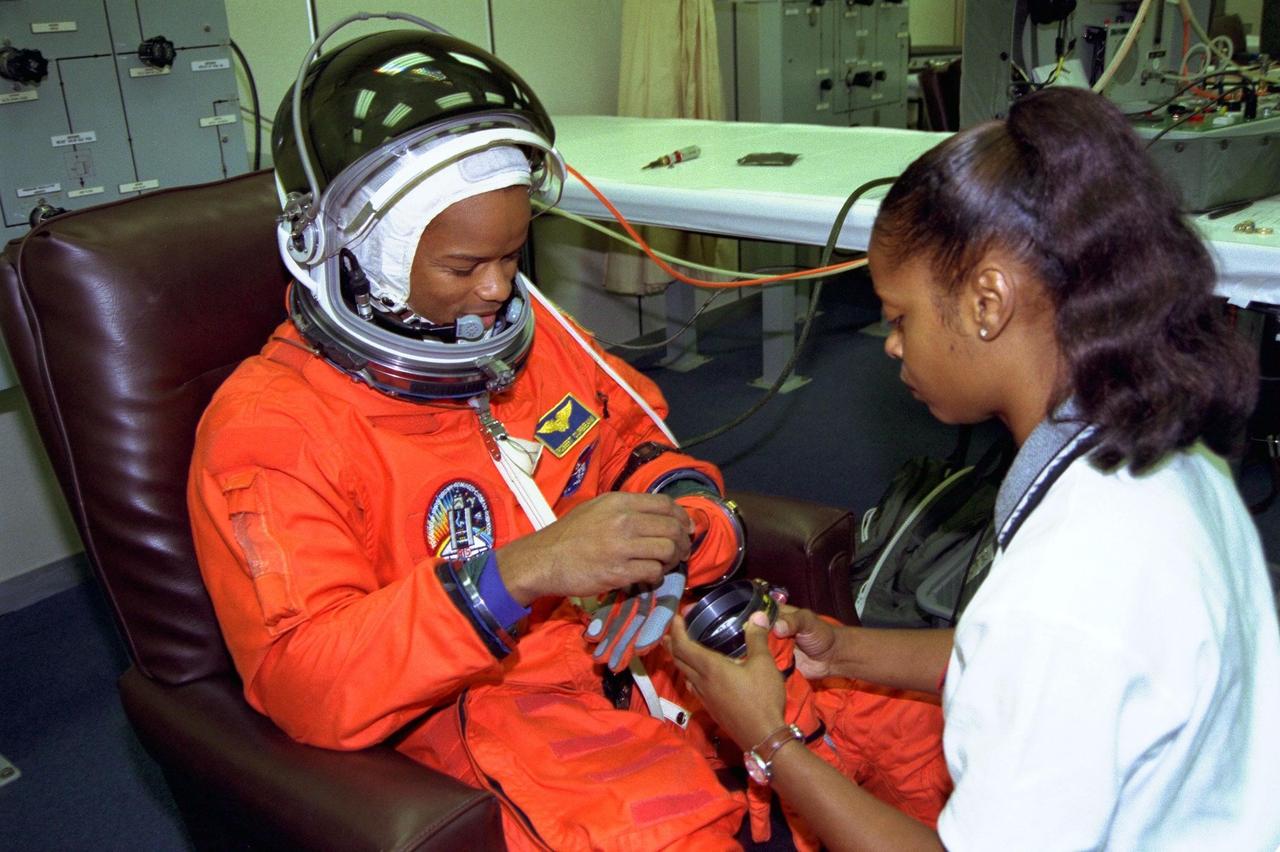

STS-85 Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. looks down at his glove as a suit technician helps him with the other as he undergoes suitup in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building. He is a lieutenant commander in the Navy and is a former radar intercept officer. Curbeam holds a master’s degree in aeronautical engineering and was selected as an astronaut in 1994. On TS-85, Curbeam will serve as the expert for the operation of the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) free-flyer, Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and science, and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 payloads. He will also serve as the flight engineer during ascent and reentry operations
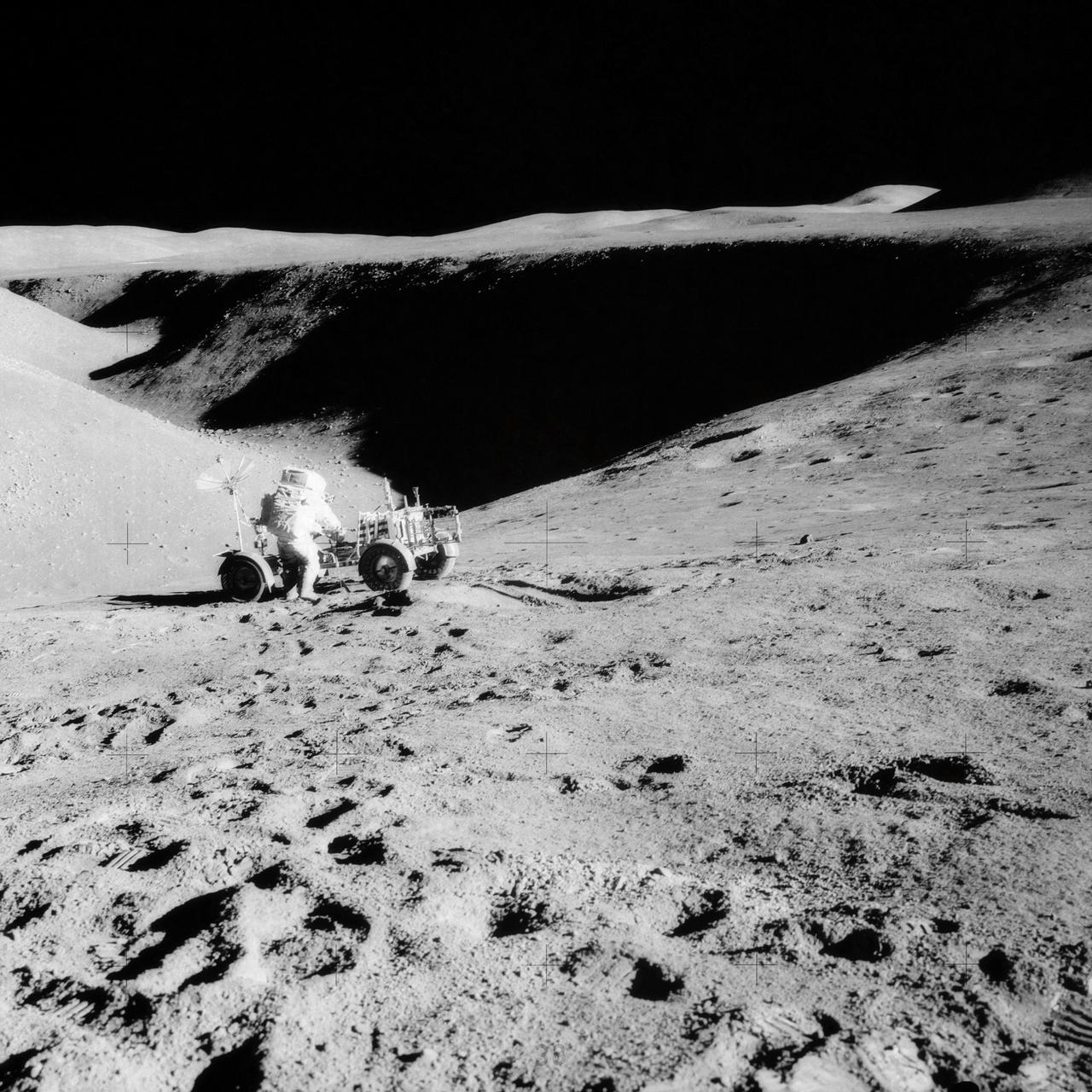

AS15-85-11451 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, mission commander, performs a task at the Lunar Roving Vehicle parked on the edge of Hadley Rille during the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). This photograph was taken by astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, from the flank of St. George Crater. The view is looking north along the rille.
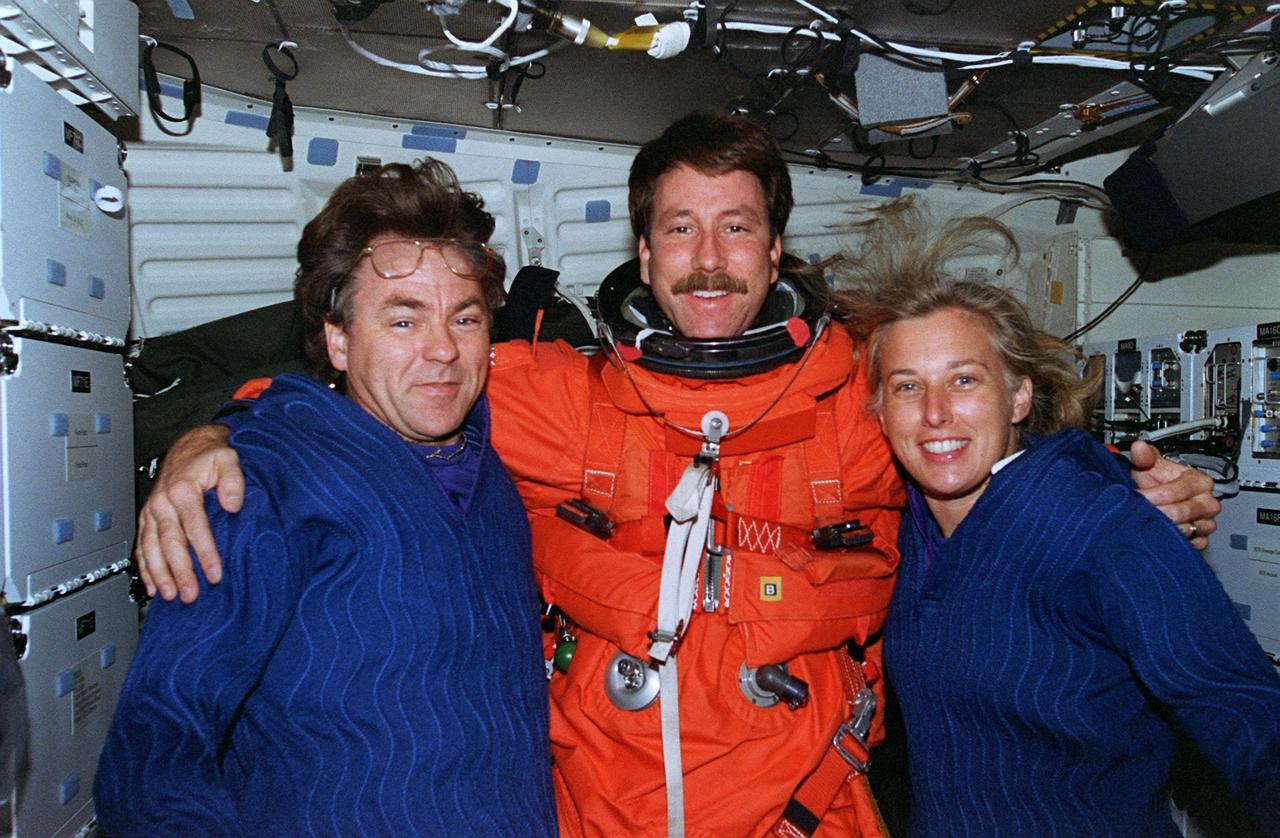

STS085-364-008 (19 August 1997) --- One of the final pictures taken during the STS-85 mission was this frame, exposed on the mid-deck during preparations for the August 19, 1997 entry. Left to right are payload specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason, with astronauts Kent V. Rominger, pilot, and N. Jan Davis, payload commander. Rominger has already donned his partial pressure launch and entry suit, while Tryggvason and Davis have put on their blue under garments but have yet to don their escape suits.
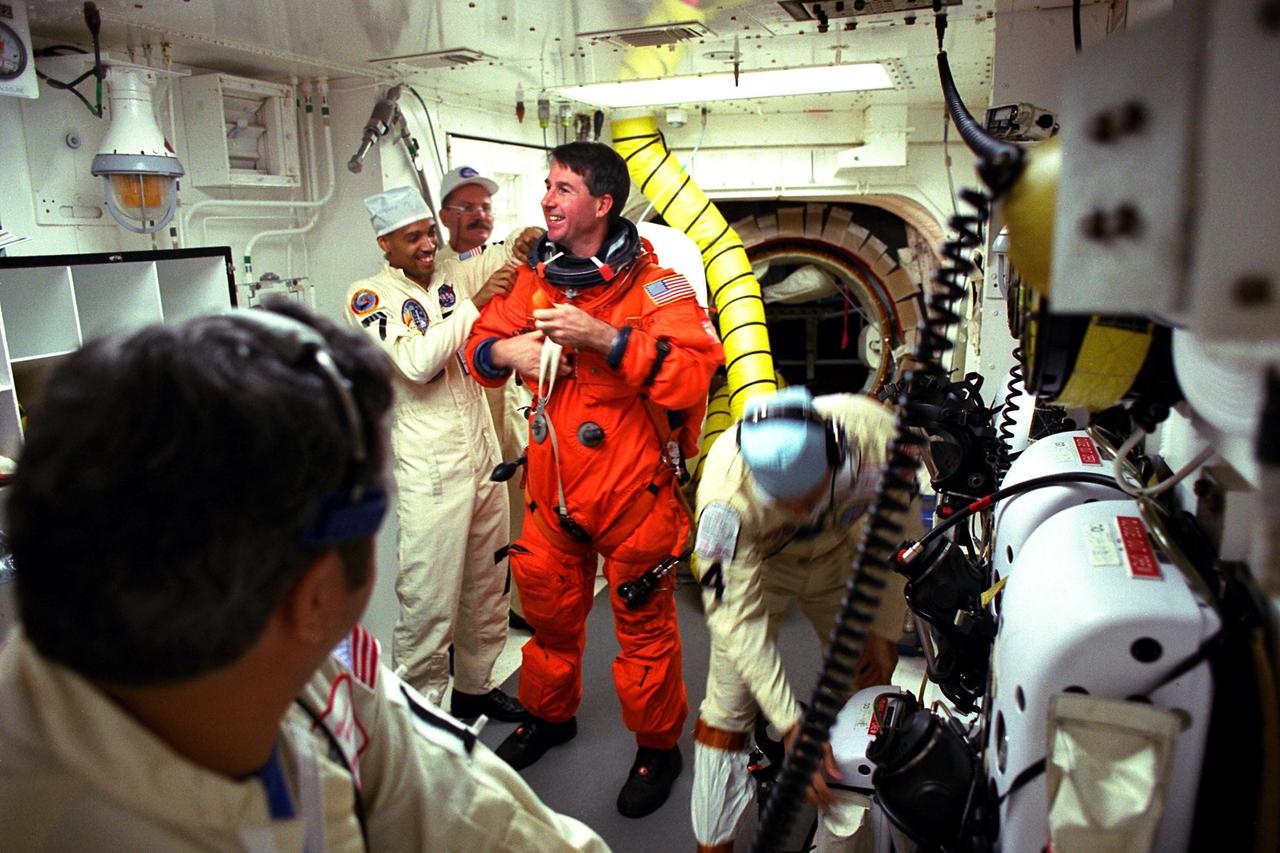

STS-85 Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson visits with white room closeout crew members Mike Mangione (left foreground), Carlos Gillis, Jack Burritt (center), and Chris Meinert at Launch Pad 39A as they assist him with his ascent/reentry flight suit before he enters the crew cabin of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery

S96-12924 (14 February 1996) --- astronaut Stephen K. Robinson stands on a platform connected to a hoist that will lower him and astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. (view obscured, other side of platform) into Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Test Facility (WET-F) pool. The two were about to participate in an underwater simulation of contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) that might be needed to support the scheduled 11-day August 1997 STS-85 mission.
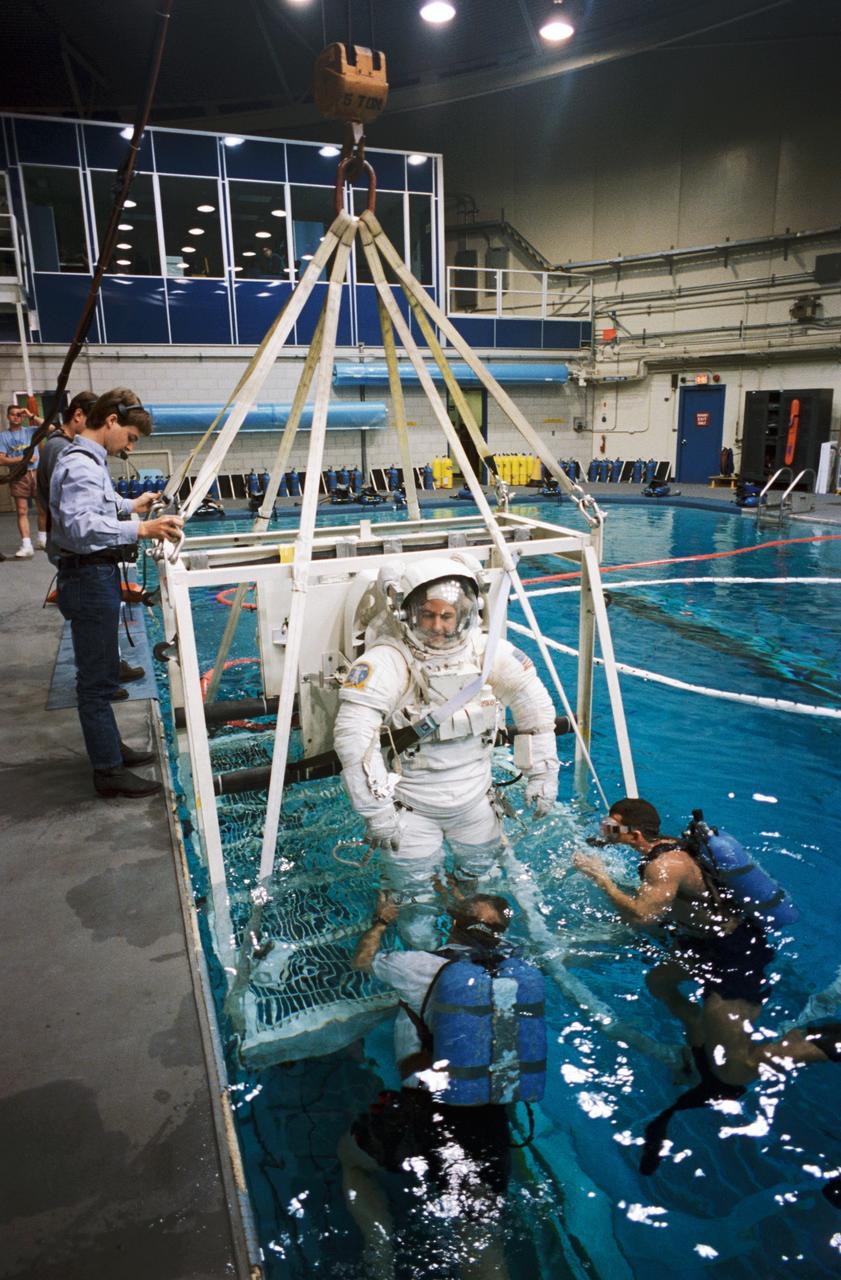

S96-12935 (14 Feb. 1996) --- Attired in a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Stephen K. Robinson is lowered into Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Test Facility (WET-F) pool. Astronauts Robinson and Robert L. Curbeam were about to participate in an underwater simulation of contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) that might be needed to support the scheduled 11-day August 1997 STS-85 mission.

S96-12948 (14 February 1996) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. stands on a platform connected to a hoist that will lower him and astronaut Stephen L. Robinson (out of frame) into Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Test Facility (WET-F) pool. The two, attired in training versions of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), were about to participate in an underwater simulation of contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) for the scheduled 11-day August 1997 STS-85 mission.
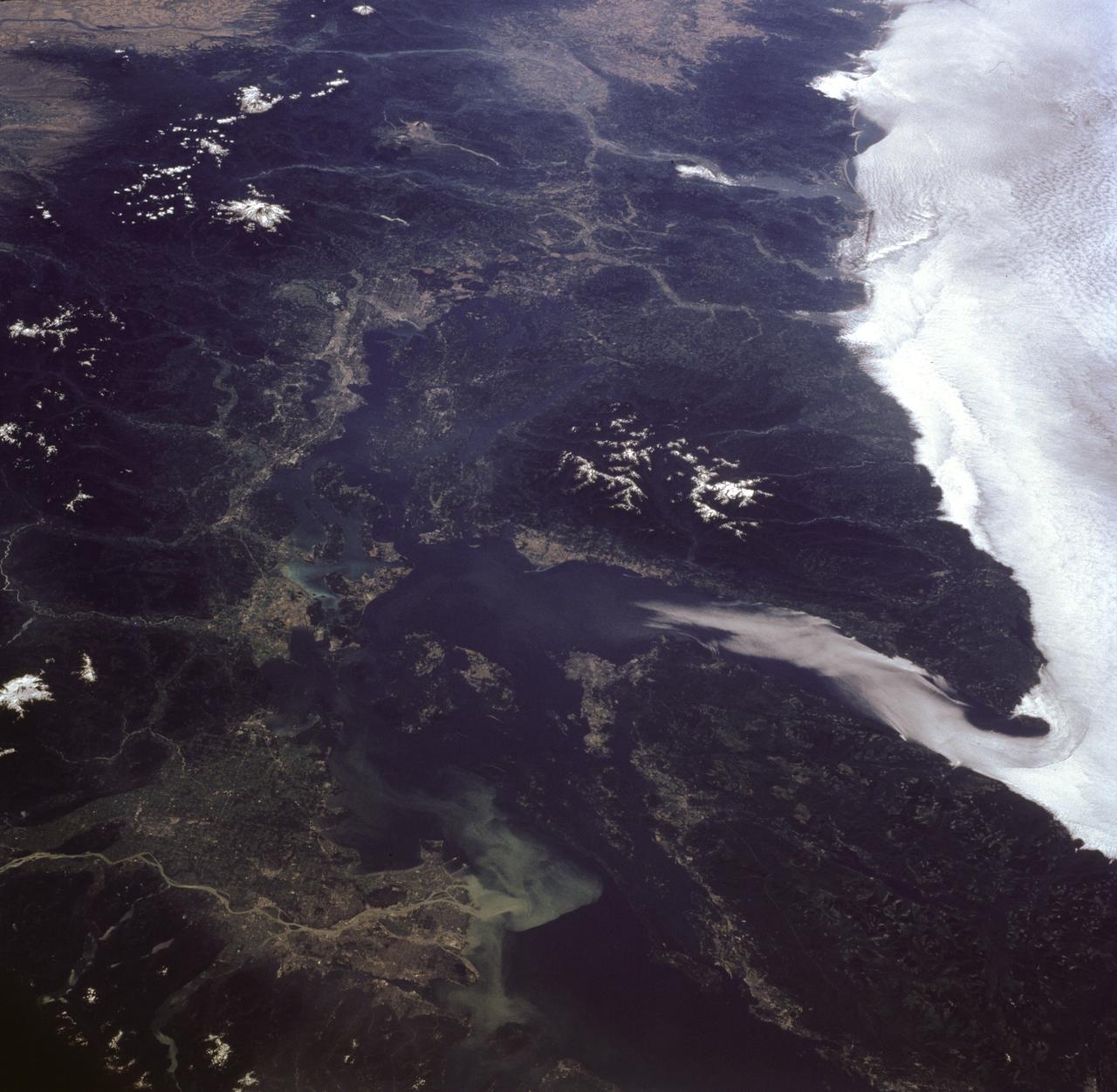

STS085-716-081 (7-19 August 1997) --- This photograph provides a southerly view from Vancouver, B. C. in the foreground, to Portland, Oregon near the top. Coastal stratus, a common occurrence, hugs the Pacific coastline and laps into Puget sound. The silty Fraser River cuts through Vancouver and empties into Puget Sound with a large, milky plume of sediment (bottom). Near the top of the image, the Columbia River runs across the Cascades (between Mt. Adams and Mt. Hood) and the Coast Ranges to the Pacific Ocean. Snow caps the highest peaks of the Olympic Mountains (near center), and the Cascade volcanoes of Rainier (closest to Seattle), Adams and Hood (top). The smaller, gray mountain just south (above and right) of Rainier is Mt. St. Helens.
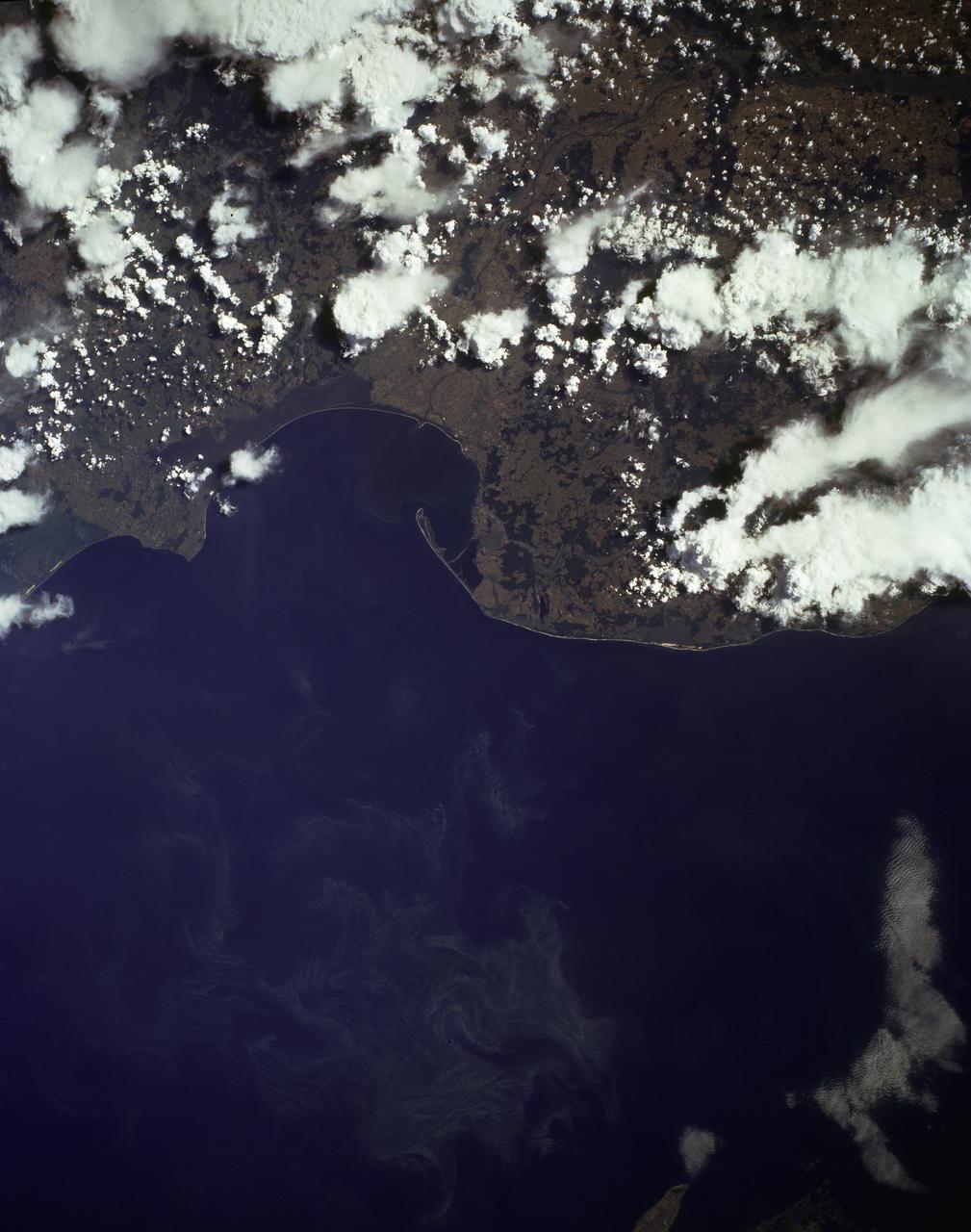

STS085-502-104 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- The abundant plankton, microscopic organisms, are taking the shape of the currents in the Baltic Sea offshore from Gdansk, Poland. Plankton blooms occur when there is enough nutrient in the water to support rapid growth and reproduction of the microorganisms. Gdansk is situated at the mouth of the Vistula River on the north coast of Poland. It is a major industrial center for shipyards, metallurgical and chemical plants, timber mills, food-processing facilities and more recently (since 1975) for coal exports and petroleum imports.
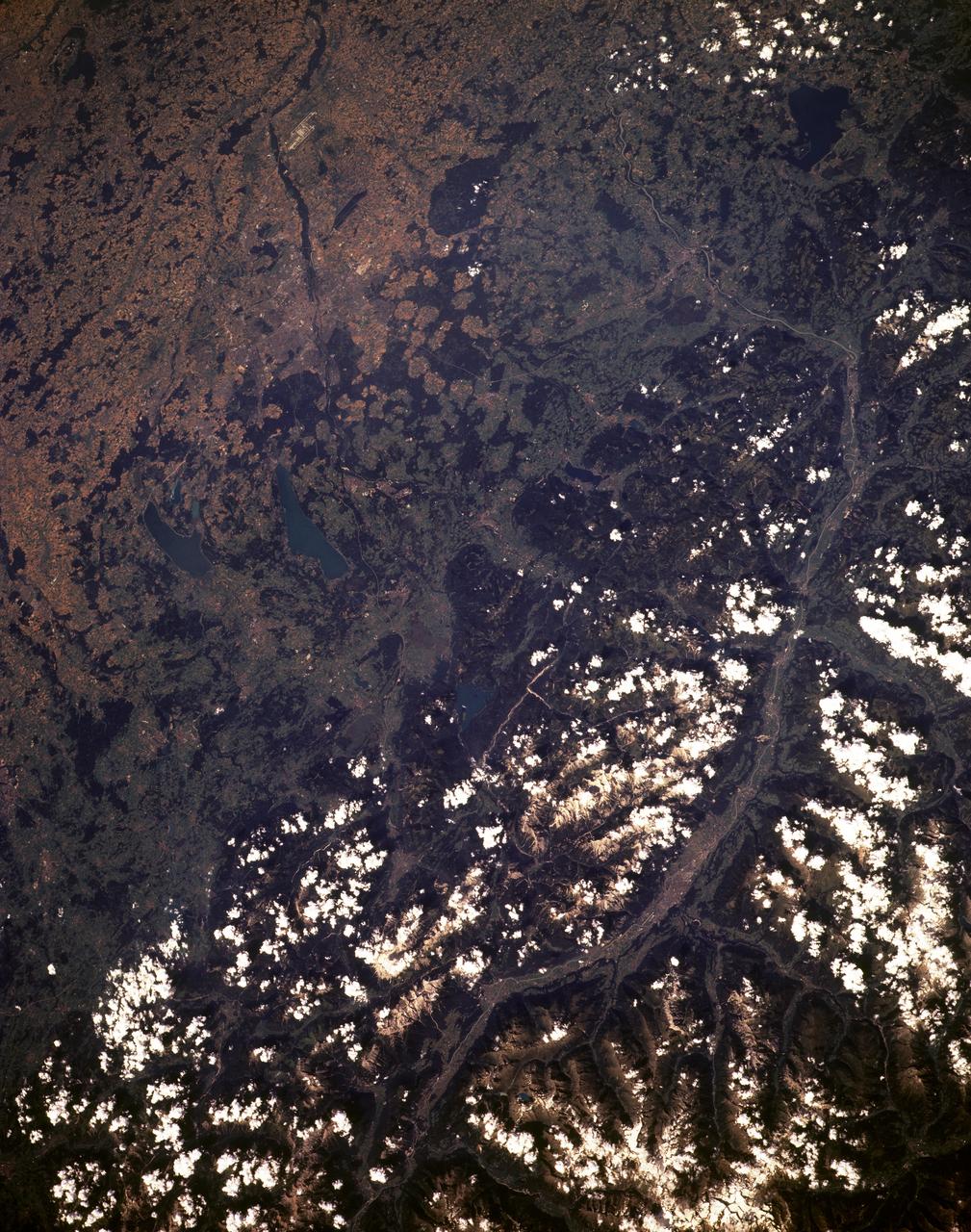

STS085-501-069 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- This 70mm frame was photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery during the mission. Bare, brown rock and snow-capped Alpine summits in Austria contrast with dark, heavily-wooded upper slopes, the patchy silviculture of lower slopes, and completely farmed plains of Bavaria to the north. The large river is the Inn; Innsbruck is visible within the flat-bottomed, formerly glaciated valley. The new and old airports of Munich are prominent on the flat land to the north. Oberpfaffenhofen, the home of the German Space Agency (DARA), can be picked out west of Munich, south of an autobahn.

STS085-503-061 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- Lakes Balkhash and Alakol, southern uplands of Kazakhstan, central Asia. The long, 600 kilometers arc of Lake Balkhash occupies the center of this clear west-looking view. The left of the view shows clearly the westernmost Dzungarian Basin in the autonomous region of Xinjiang Uygur (Sinkiang), China. Kazakhstan's capital city Almaty (Alma-Ata) lies out of sight behind the boom. The Dzungarian Gate is the straight, fault-bounded valley cutting through the Dzhungarskiy Alatau Range. The Gate has acted as a major pass for centuries, allowing access between east Asia and central Asia (the valley floor is about 1,500 feet, whereas peaks reach 15,000 feet on the west and about 10,000 feet on the east side) -- it was one of the routes used by the Mongols when they began their invasion of central Asia and Europe in the 13th century. Lake Ebinur is the bright area beneath the dust plume (left center); strong north winds from the steppes of Kazakhstan and Russia are funneled through the Dzungarian Gate where they pick up sediment from dry lakebeds and blow it into China. The Ili River flows westward, parallel to the Dzhungarskiy Alatau Range, through Kapchagay Lake (partially visible beneath boom), then northwest across a large delta plain and into Lake Balkhash.
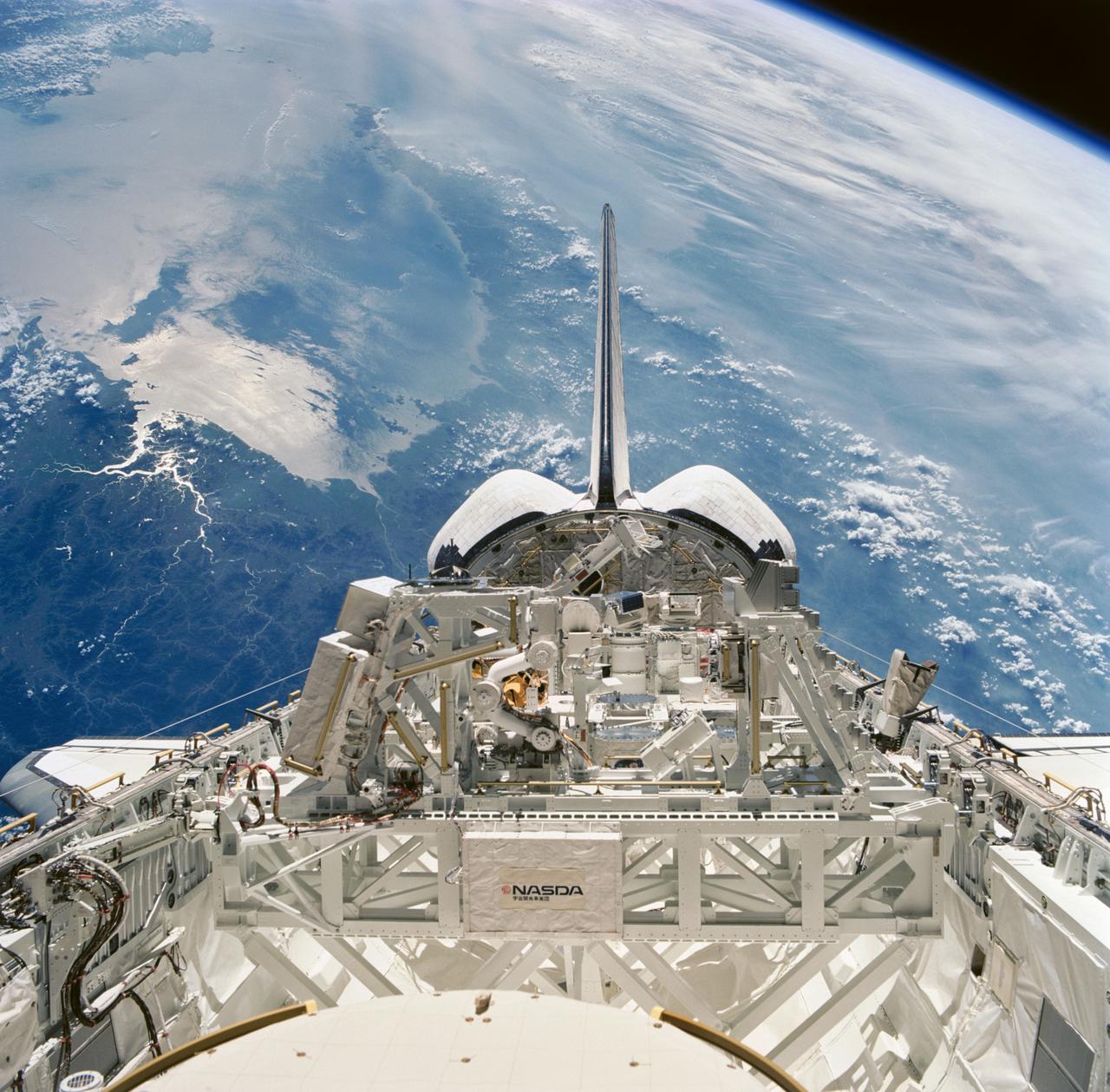

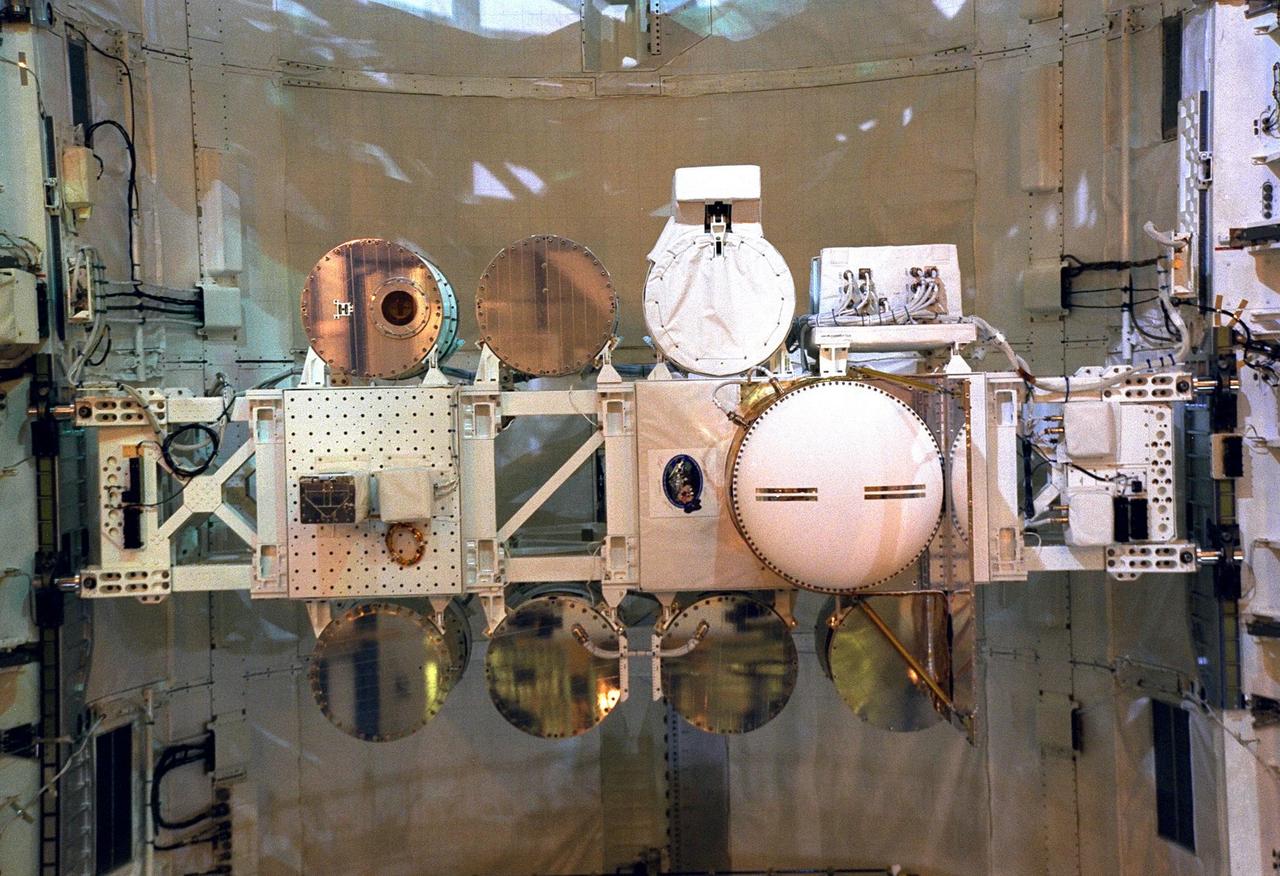
STS085-751-039 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- This 70mm frame, exposed through aft flight deck windows of the Space Shuttle Discovery, shows experiments in the cargo bay, as the spacecraft was flying over the Sea of Japan. In center foreground is the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD). The MFD, sponsored by National Space Development Agency (NASDA), will evaluate the use of the Small Fine Arm (SFA) that is planned to be part of the future Japanese Experiment Module's (JEM) Remote Manipulator System (RMS) on the International Space Station (ISS).
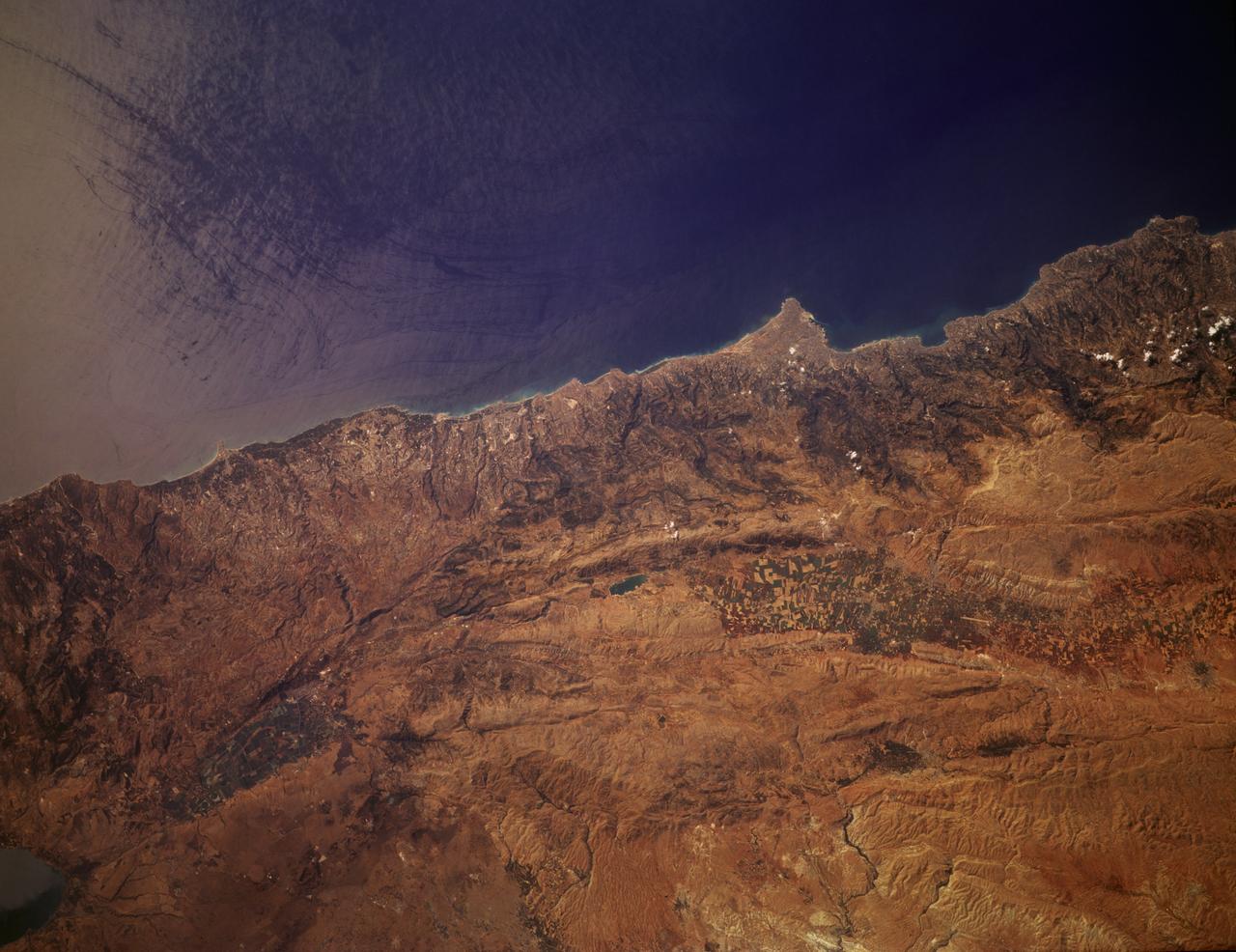

STS085-505-078 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- This large-format photograph, taken from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery with a 250mm lens, shows most of Lebanon, from the Israeli border to just south of Tripoli. The main distinction is that between the forested coastal mountain ranges which receive rainfall regularly off the Mediterranean, and the yellow-brown "rainshadow" deserts inland (east) of the mountains. Damascus, capital of Syria lies just outside the view bottom right. The biblical and classical cities of Acre (bottom), Tyre, Sidon and Beirut (top, on promontory) all lie on the coast. The Bekaa valley and the Litani River lie inland of the Lebanon Mountains east of Beirut. The agricultural area in the south of the photograph is part of Israel and borders the Golan Heights.
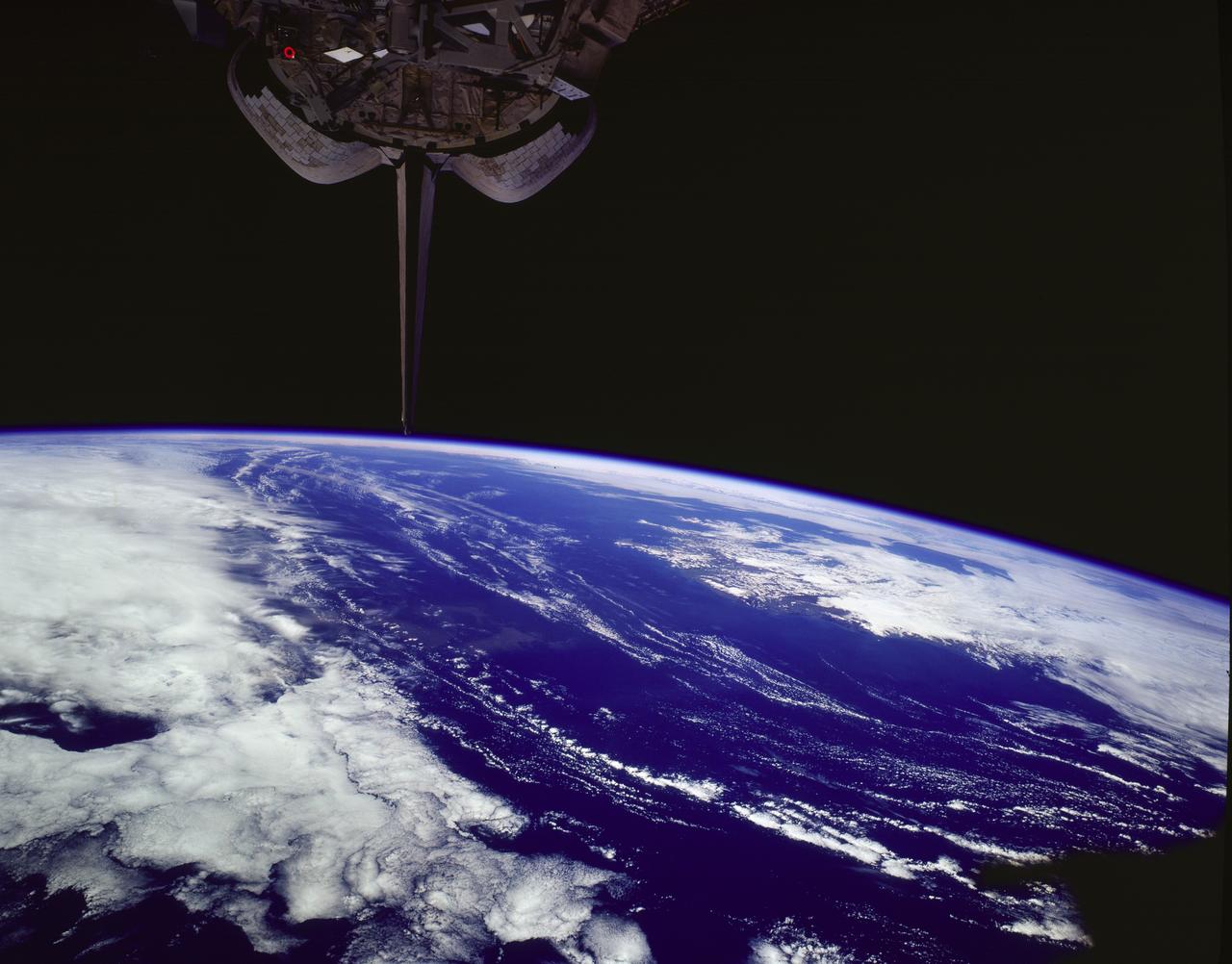

STS085-502-078 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- The southern coastline of seldom-seen Iceland can be detected under cloud, top right in this dramatic west-looking view. Iceland's capital city, Reykjavik, lies on the cape that projects furthest left (i.e. southwest) in this view. Along the southeast margin (nearest to the viewer), Iceland's largest icecap, Vatnajškull, appears as a white mass with a texture different to the spotty cumulus cloud. At the closest point, Greenland only lies 170 miles to the northwest of Iceland -- and under a hand lens, hundreds of miles of the east coast of Greenland can be seen stretching across the top of this view. Taken with the large format Linhof camera, the enormous clarity of the air on this day allowed the crew to photograph Iceland which lies 400 miles and more north of the northernmost point which the Space Shuttle Discovery attained (57.5 degrees north latitude). Greenland lies more than 700 miles from the orbiter. The nature of the light brown feature in the ocean (middle of the view under the tailfin) is unclear. Part is a reflection off the window, but part shows details characteristic of a plankton bloom.
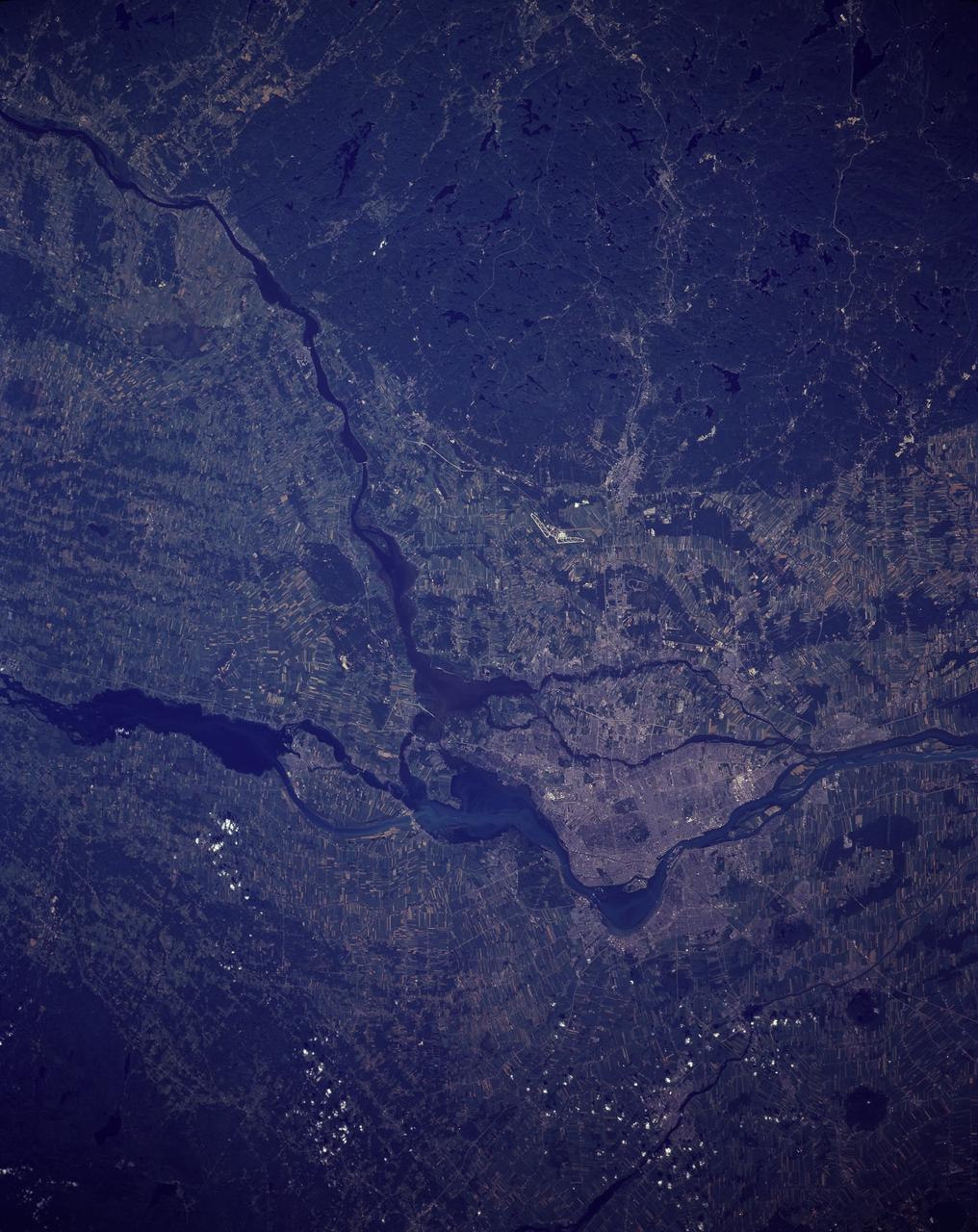

STS085-506-081 (7-19 August 1997) --- Montreal is a city on an island that grew up around the mountain -- in 1535 Jacques Cartier landed on an island in the St. Lawrence River and named a 233 meter-high mountain Mount Royal. It was not until 1642 that Ville Marie, founded by missionaries, would officially become the city of Montreal. The cityscape contrasts well with the farmland and natural forests in this summer view. Today Montreal is the largest city in the province of Quebec, and is the second most populous metropolitan area in Canada -- in 1991 the population was just more than one million in the city and 3,127,242 in the metropolitan area. While owing its early growth to the fur trade, the city is a leading producer of aircraft, chemical and pharmaceutical products, and is a major petroleum production center. Nearly half of Canada's .8 billion aerospace industry is located in the Montreal area. In the image captured by the astronauts, the lighter blue, wide river is the St. Lawrence. The city of Montreal is located on the Ile de Montreal to the northwest of the St. Lawrence river. The Ottawa River enters the St. Lawrence near the center of the view. Mirabel International Airport stands out well, on the north side of the city. The long, narrow strips of land in the image are indicative of French agricultural land use. The narrow ends of farmlands are oriented perpendicular to rivers so that more farmers will have access to water resources.
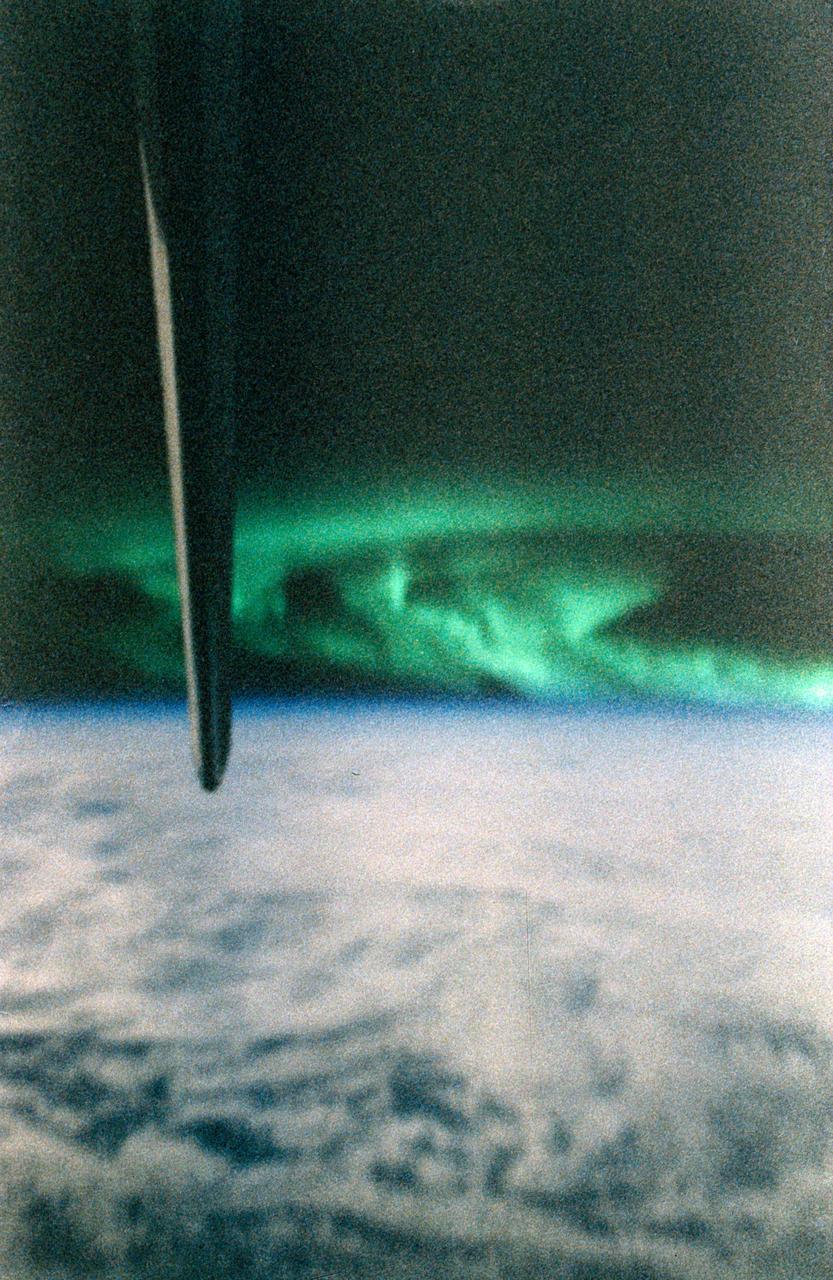

STS085-365-006 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- A 35mm camera with a time exposure was used to record this image of the southern lights or the aurora Australis. The vertical stabilizer of the Space Shuttle Discovery appears in the foreground.
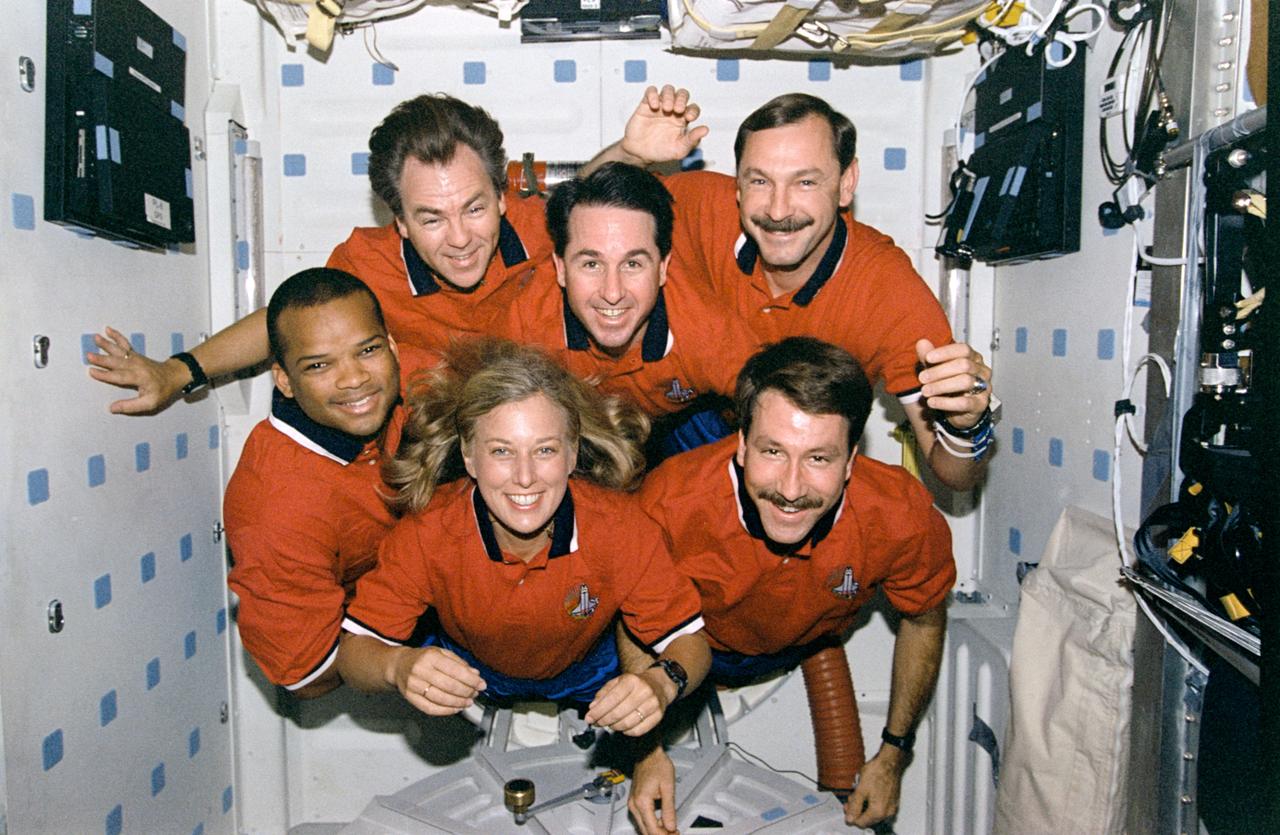

STS085-320-020 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- For their traditional in-flight crew portrait, the six crew members for this mission float on the mid-deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery. On top, left to right, are Bjarni Tryggvason, payload specialist of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA); along with astronauts Stephen K. Robinson, mission specialist; and Curtis L. Brown, Jr., mission commander. On bottom, from the left, are astronauts Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., mission specialist; N. Jan Davis, payload commander; and Kent V. Rominger, pilot.
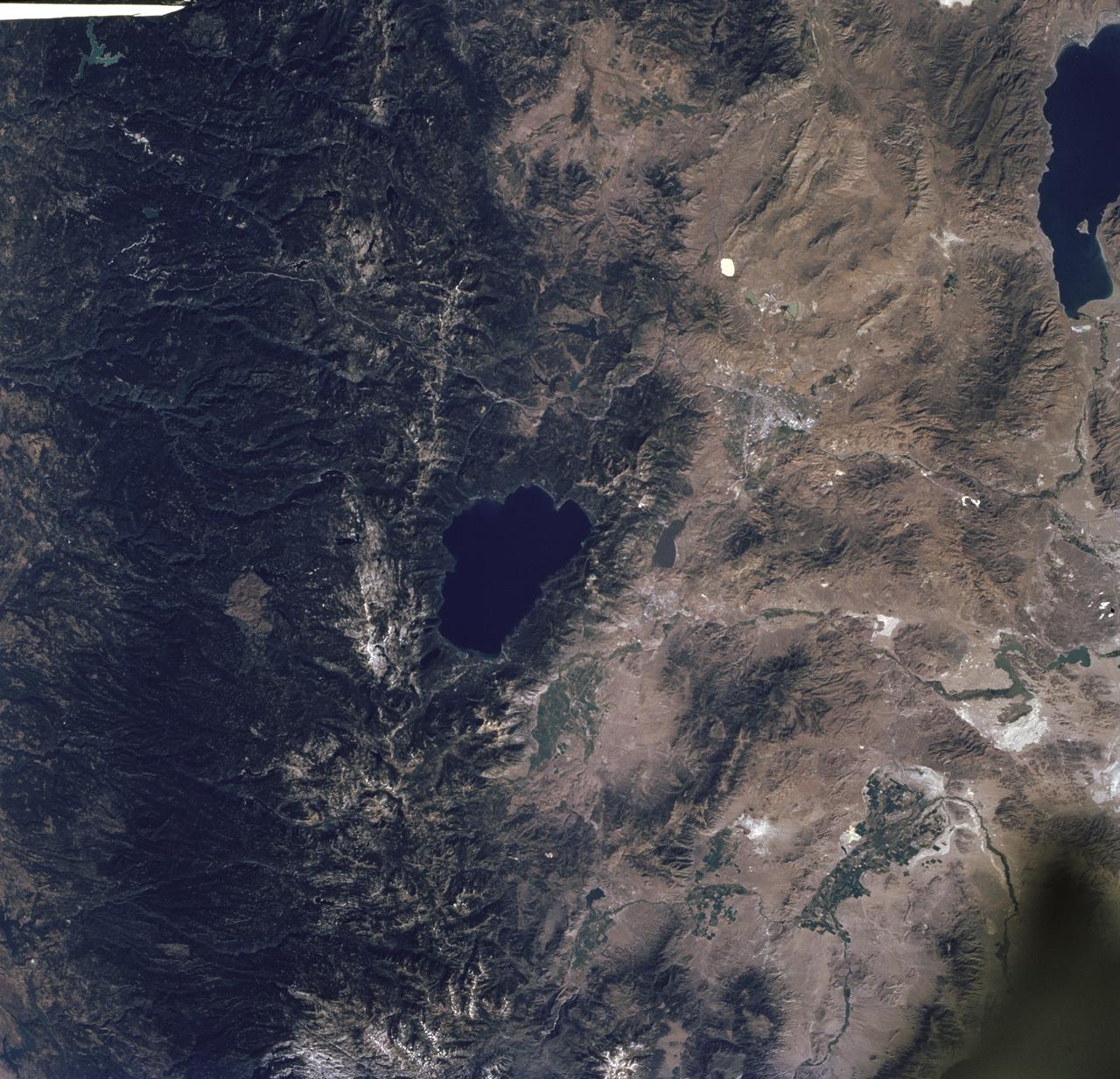

STS085-716-061 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- The dark green forests of the Sierra Nevada Mts. occupy the left side of the picture. Reno lies between Lake Tahoe (center) and Pyramid Lake (top right). Lake Tahoe, is a clear, deep alpine lake (over 505 meters deep), surrounded by Montane forest, ski resorts and casinos. Although Tahoe is known as one of the clearest lakes in the world, water quality in the lake has been declining due to soil erosion from development. Since 1968, it has lost about 30 feet of clarity. A partnership was recently formed between environmentalists and resort owners to protect their common interest in keeping the lake as clear as possible. Over the last five years they have slowed the erosion and the growth of algae that it causes so that clarity is now "only" lost at a rate of roughly one foot per year. Pyramid Lake (on the upper right of the photo) is as different from Tahoe as a lake could be. The sagebrush desert around the lake and is owned by the Pyramid Lake Paiute tribe who manage it as a fishery for an endangered sucker (fish), the cui-cui. The tribe has added modern fisheries' biology methods to their traditional management and chooses not to develop the lake as a recreation destination. Anaho Island, in the lower half of the lake, is a wildlife refuge managed for American White Pelicans which fly hundreds of miles each day to get from this safe breeding area to the shallow marshes where they feed. Directly above Lake Tahoe is Donner pass, near the site where the beleaguered Donner Party spent the winter of 1846 - 1847 trapped in the mountains. Several shallow ephemeral lakes can be seen in Lemmon Valley north of Reno's core urban area. These lakes would normally have dried up by August when this photo was taken, but are still wet because of the extremely wet winter and floods of January 1997.
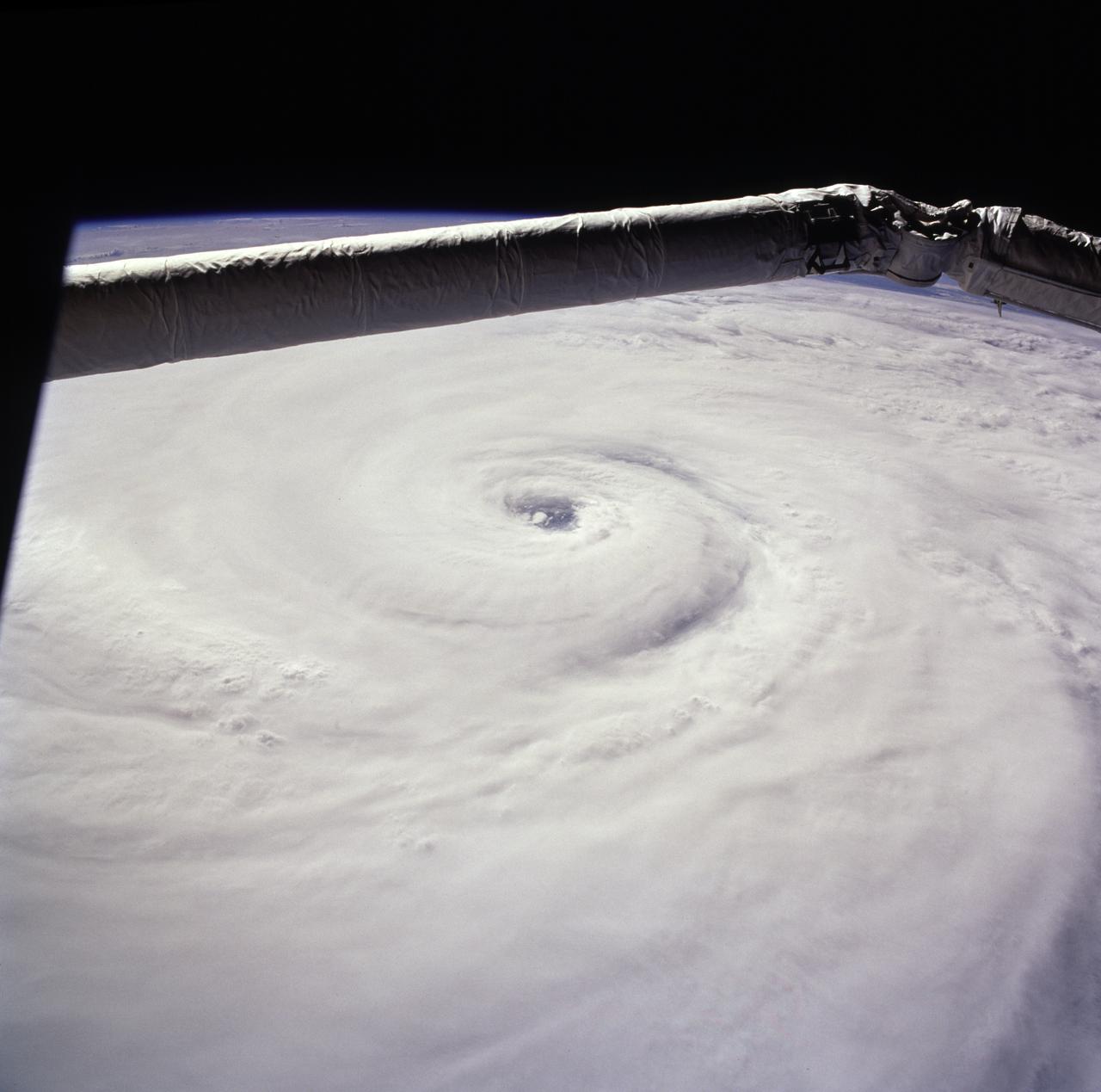

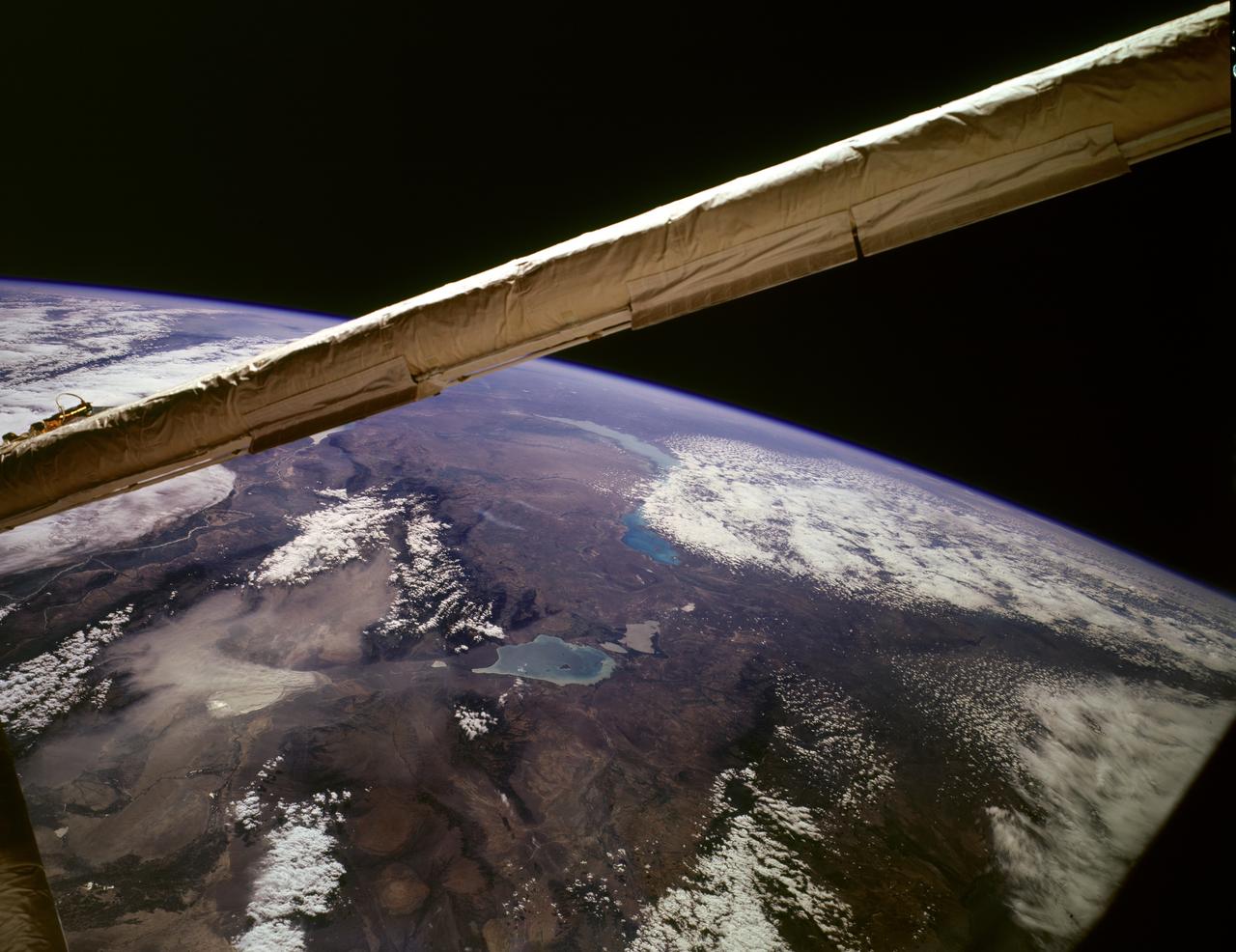
STS085-722-019 (15 August 1997) --- This view of supertyphoon Winnie was taken on August 15, 1997, as the storm swirled about 400 miles south of the southern tip of Japan. Sustained winds were 105 knots, gusting to 130 knots. This photo was shot on the Space Shuttle Discovery's twenty-third flight, as it glided by 170 miles above the sea surface on Orbit 123. On one pass the Discovery flew right over the eye; the commander commented that the eye was so large that it completely filled the window. The robotic arm crosses the top of the view. The cloud mass associated with Winnie covered thousands of square miles as this storm grew to supertyphoon status in the previous days, and raked across the Marianas Islands. A few days after this shot was taken, Winnie ploughed ashore on the coast of China, a bit south of the major metropolis of Shanghai, reportedly killing at least 100 people.
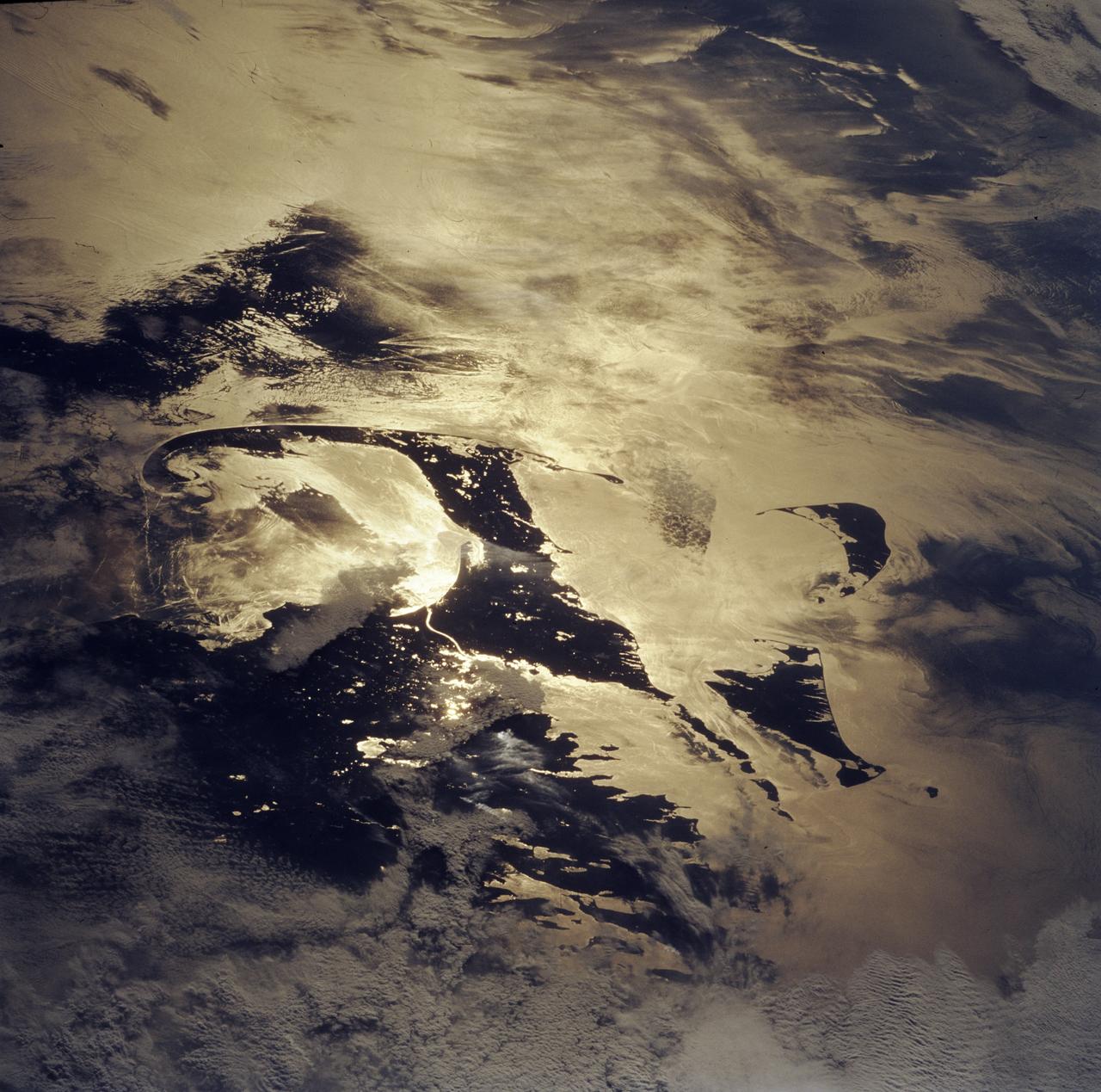

STS085-743-000D (7 - 19 August 1997) --- Cape Cod almost looks like an elf's slipper with this orientation in the sunglint. The sunglint also reveals other features such as shipwakes, calmer sea surfaces (the darker areas) and internal waves which are waves traveling along a layer of denser water many tens of feet below the surface.
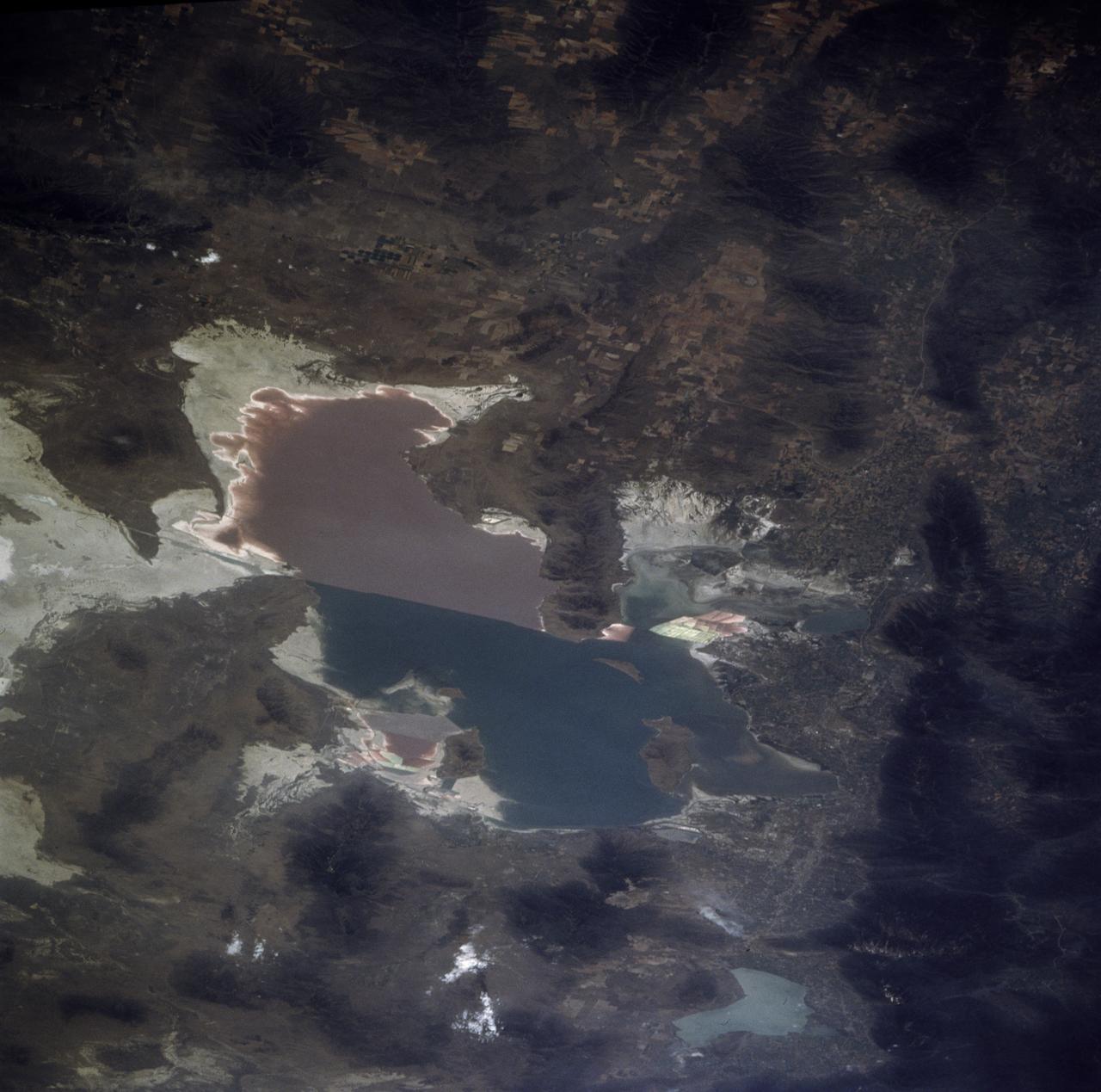

STS085-705-062 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- The Great Salt is one of the most saline inland bodies of water in the world and is the largest inland body of salt water in the Western Hemisphere. The lake is fed by three rivers (Bear, Weber and Jordon) and has no outlet. The water level varies with the amount of rainfall and evaporation in the basin. The distinct line across the center of the lake is the Lucin Cutoff. It is a 30 mile (48 kilometers), east-west causeway built in 1959 to support a rail line. The causeway connects the cities of Ogden and Lucin and affects the water level of the lake. Because the lake's main tributaries enter from the south, the water level of the southern section is several inches higher than that of the northern part. The Great Salt Lake's record high levels in the mid-1980's threatened the Lucin Cutoff, highways and sewage-treatment plants along the shore -- in 1987 pumps were installed that began draining some of the excess water into the Great Salt Lake Desert to the west. The resulting new body of water was called the Newfoundland Evaporation Basin -- it contains dissolved minerals, primarily sodium and chloride along with sulfate, magnesium, and potassium. The dissolved minerals, turbidity and microorganisms which can survive in saline water give the lake its varying colors. In this photo the north portion is dark red. The crew said that it looked like dirt when they first saw it. Crews can not remember the north portion ever looking so red -- it is usually a light blue color.
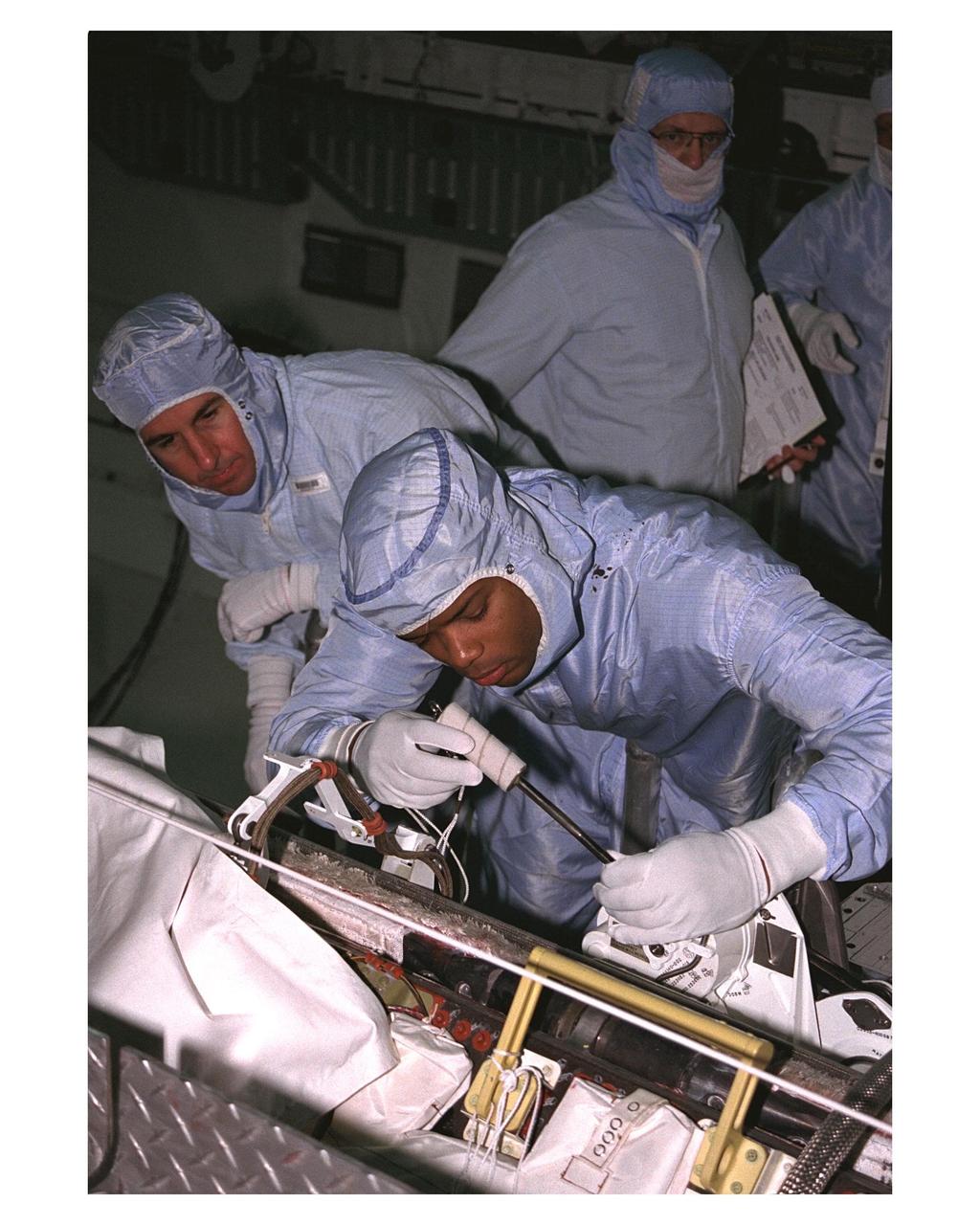
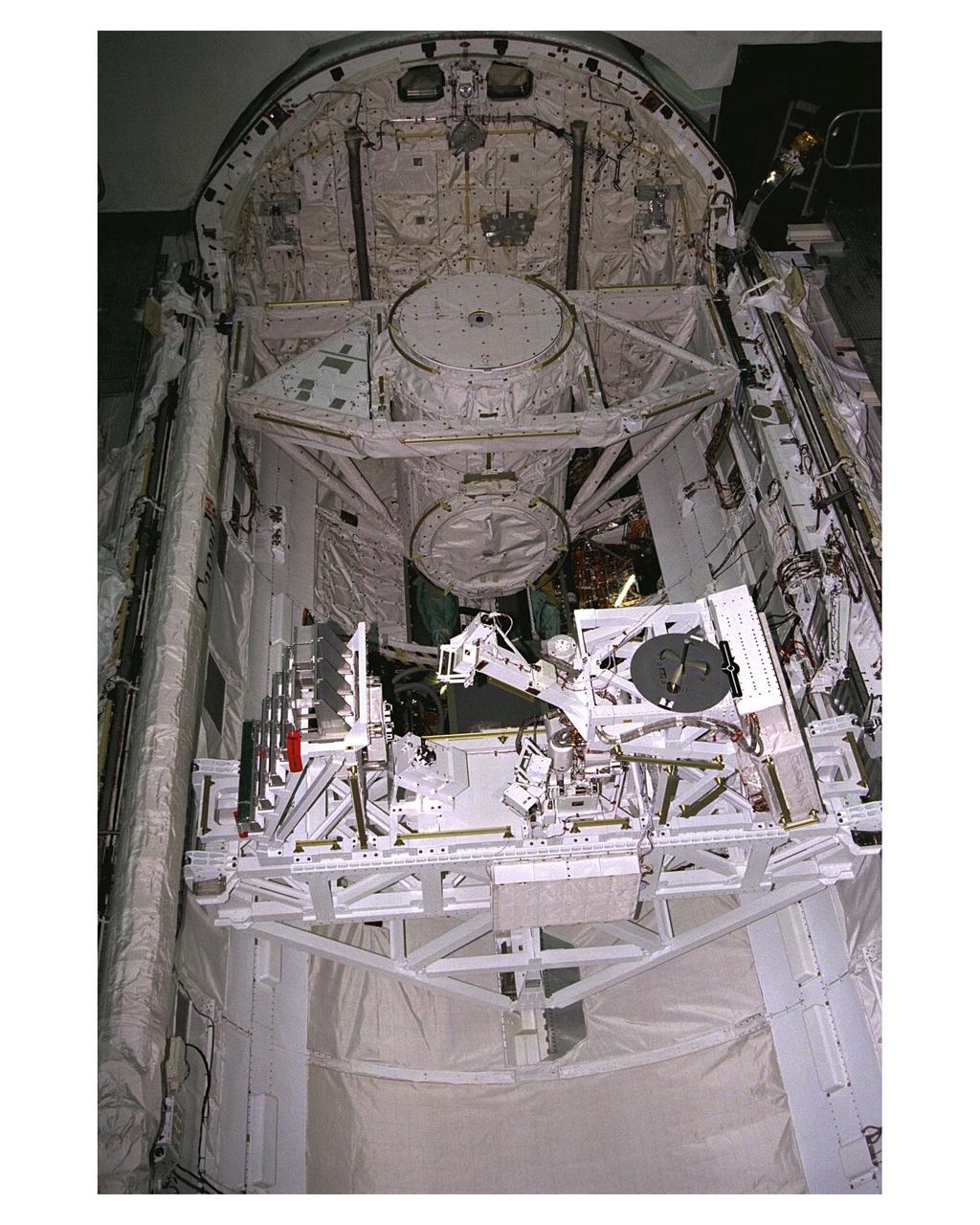
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-85 flight crew perform a sharp-edge inspection in the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery in the space plane's payload bay during Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities for that mission. They are (from left, foreground) Mission Specialists Stephen K. Robinson and Robert L. Curbeam Jr. (right). They are accompanied by a United Space Alliance (USA) payload technician. The Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) payload is one of several that will fly on the STS-85 mission. This payload is designed to test the operational capability of the Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System (JEM RMS) Small Fine Arm (SFA). The arm, which will be a part of the JEM element of the Interntional Space Station, will be operated from the orbiter's aft flight deck during the 11-day mission. Other payloads that will be aboard Discovery on this space flight include the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhhiker (IEH-2) experiments.
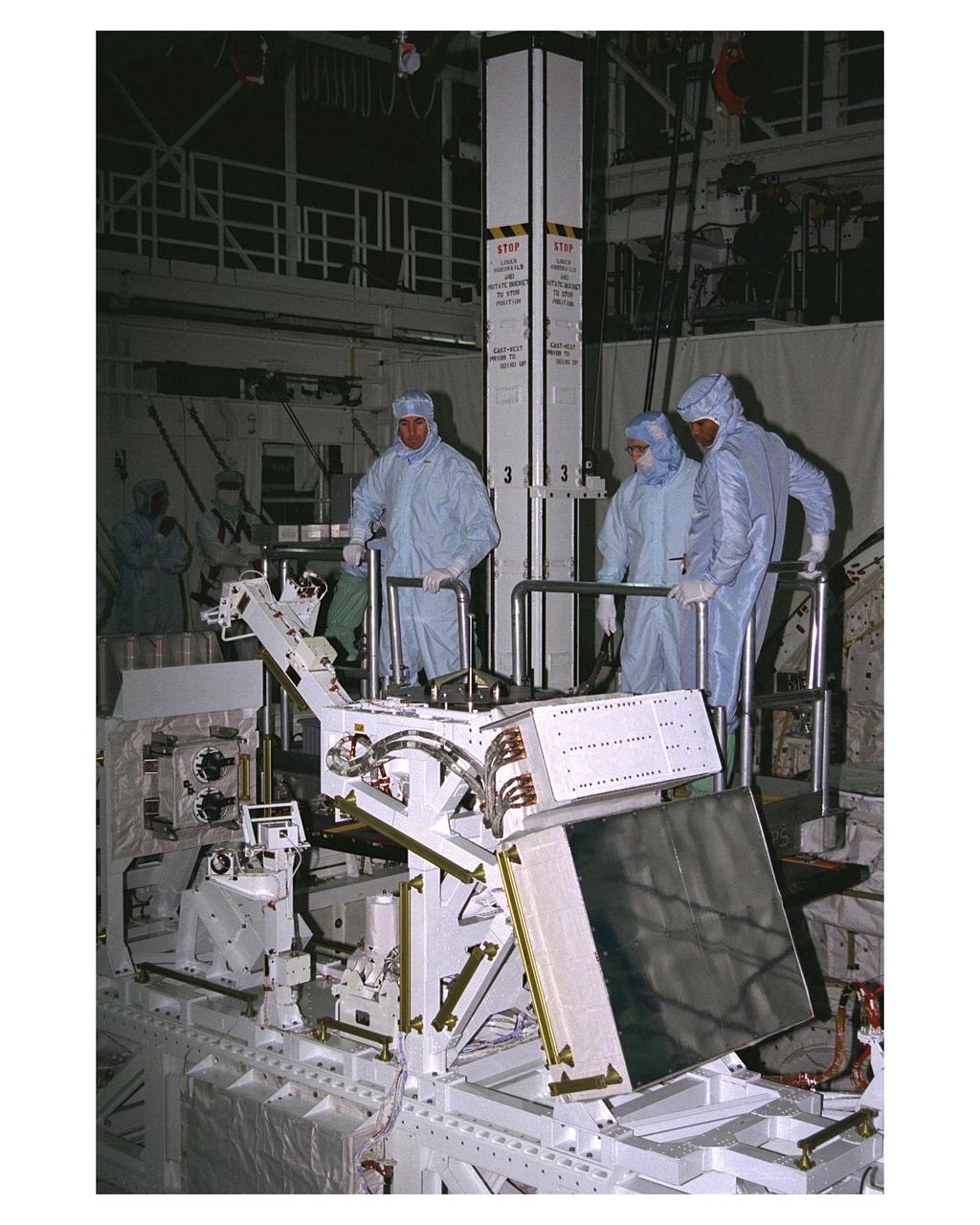

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-85 flight crew examine the Manipulator Flight Demonstraton (MFD) payload in the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery during Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities for that mission. They are (left) Mission Specialists Stephen K. Robinson and Robert L. Curbeam Jr. (right). They are accompanied by a United Space Alliance (USA) payload technician. The MFD is one of several payloads that will fly on the STS-85 mission. This payload is designed to test the operational capability of the Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System (JEM RMS) Small Fine Arm (SFA), which can be seen atop its Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure (MPES) carrier that will serve as a platform in the payload bay for the robotic arm experiment. The arm, which will be a part of the JEM element of the Interntional Space Station, will be operated from the orbiter's aft flight deck during the 11-day mission. Other payloads that will be aboard Discovery on this space flight include the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhhiker (IEH-2) experiments.
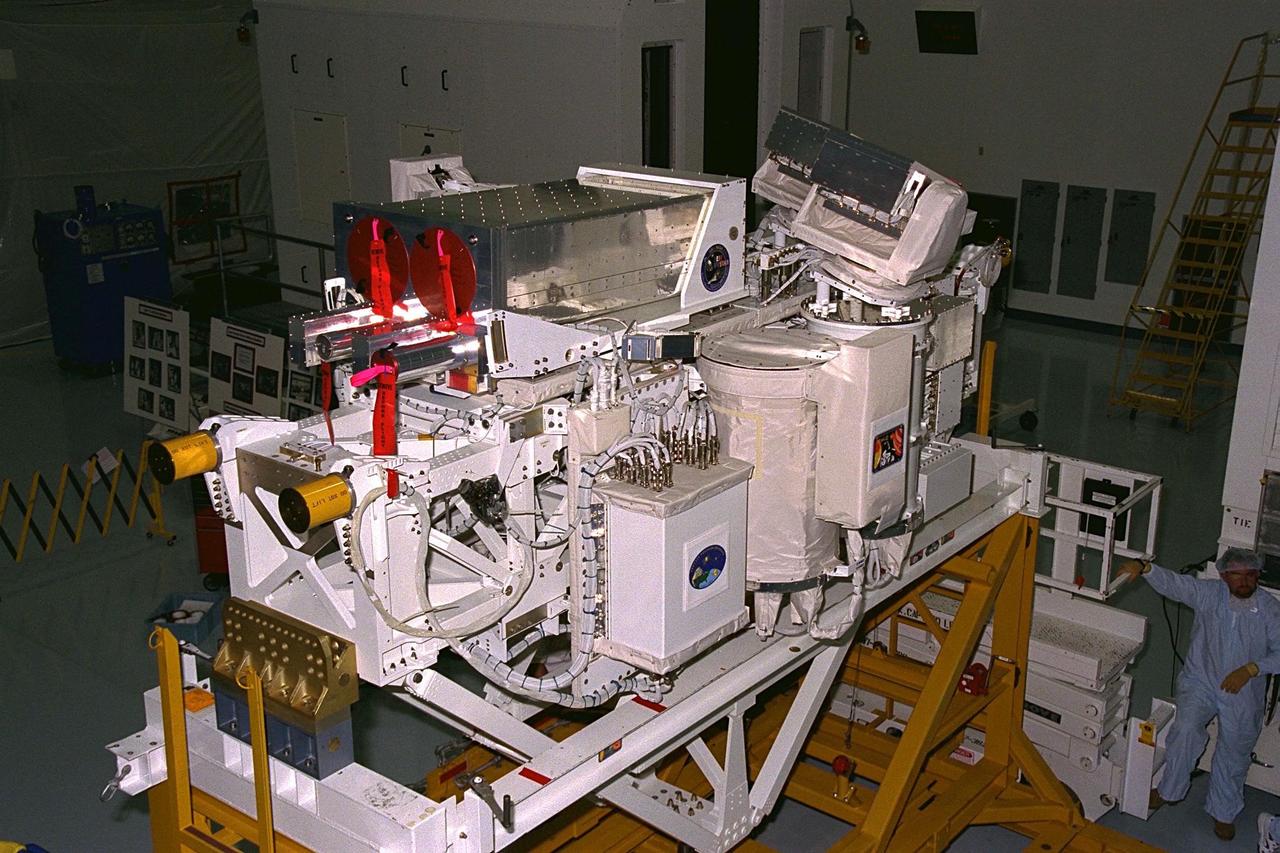
The International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) payload rests in a work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility prior to its trip out to Launch Pad 39A for installation into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the STS-85 mission. The IEH-2 experiments will study ultraviolet radiation from stars, the sun and in the solar system. The Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) payload is another series of experiments that will be conducted during the 11-day mission in Discovery’s payload bay. The TAS-1 holds seven separate experiments that will provide data on the Earth’s topography and atmosphere, study the sun’s energy, and test new thermal control devices, as well as several student-developed experiments. Other STS-85 payloads include the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. The CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere
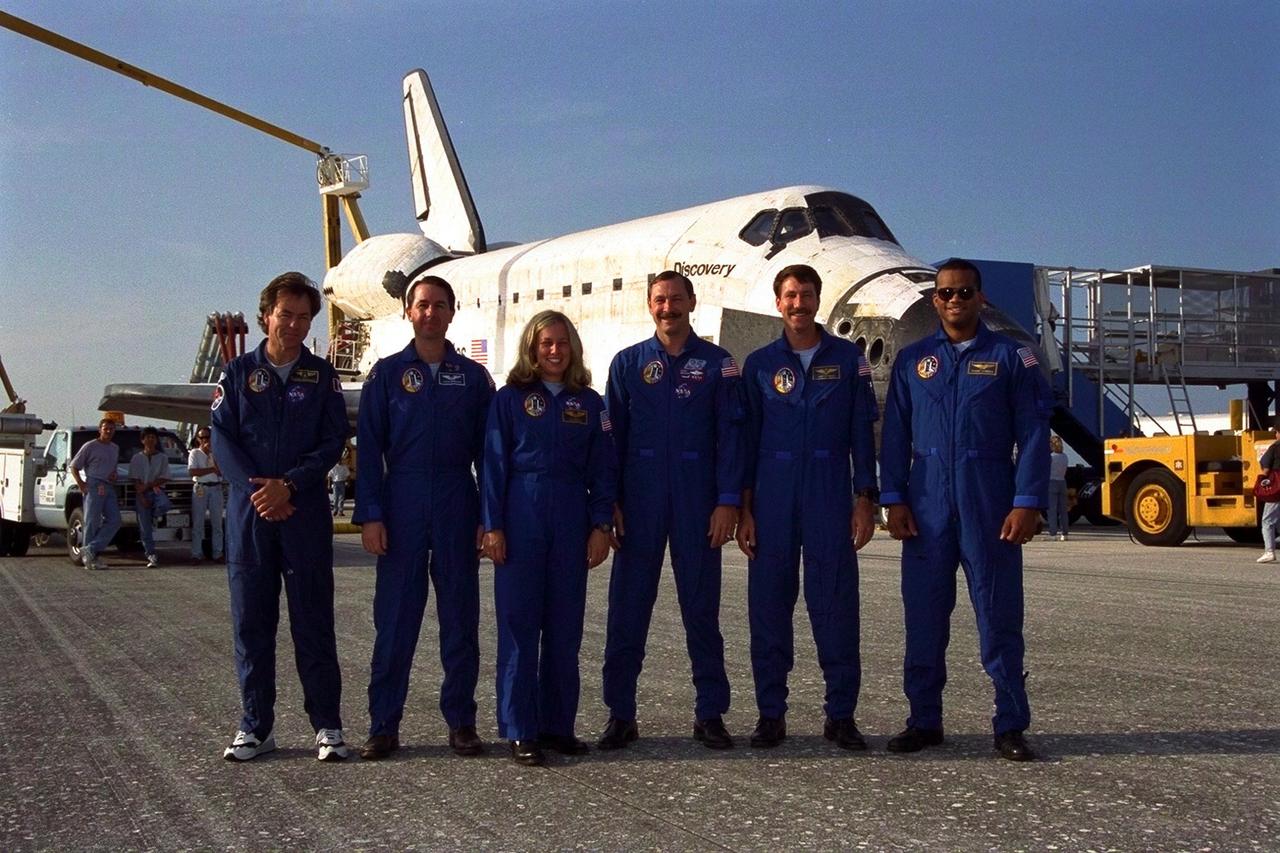

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-85 crew poses in front of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery after the space plane landed on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility Aug. 19 to complete the 11-day, 20-hour and 27-minute-long STS-85 mission. They are (from left): Payload Specialist and Canadian Space Agency astronaut Bjarni V. Tryggvason; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; Pilot Kent V. Rominger, and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. During the 86th Space Shuttle mission, the crew deployed the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the AtmosphereShuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) free-flyer to conduct research on the Earth’s middle atmosphere, retrieving it on flight day 9. The crew also conducted investigations with the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments. This was the 39th landing at KSC in the history of the Space Shuttle program and the 11th touchdown for Discovery at the space center
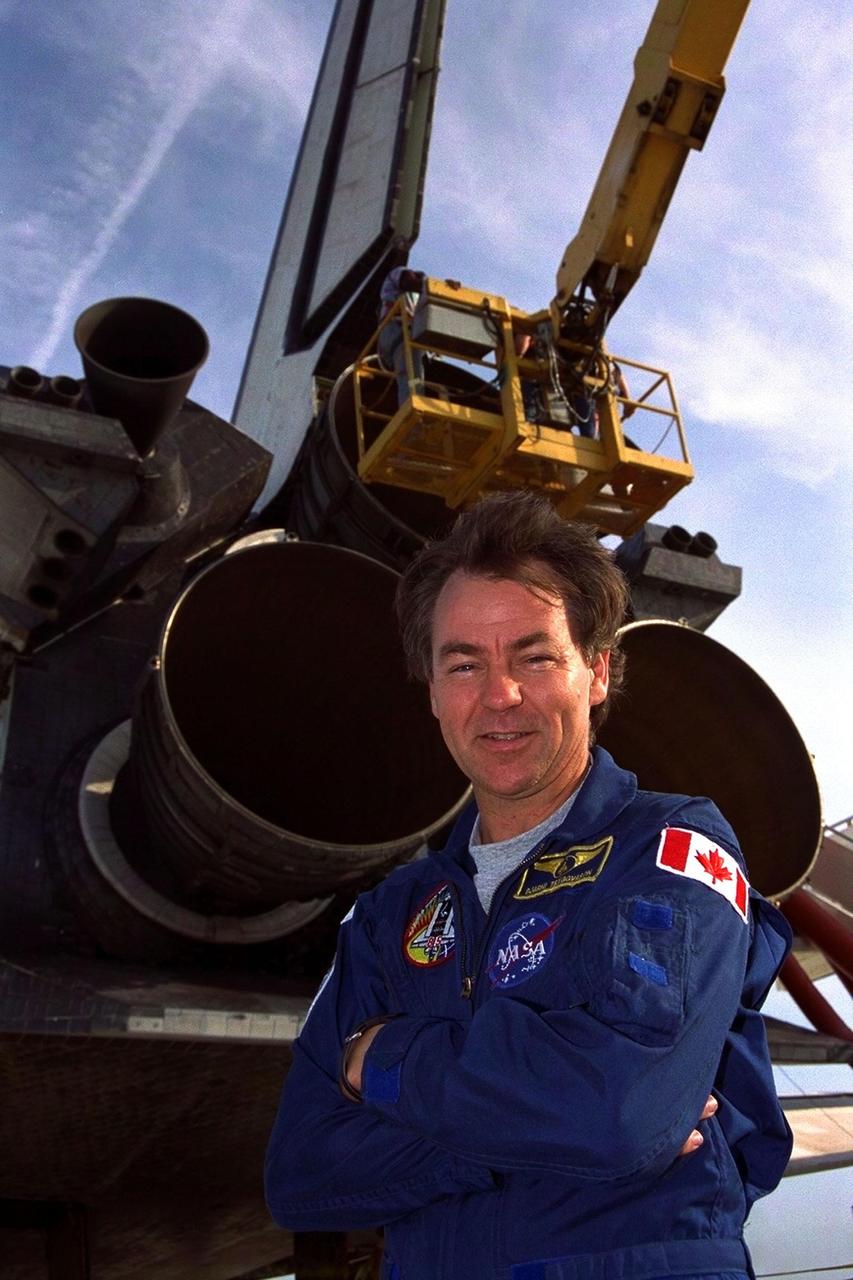

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Payload Specialist and Canadian Space Agency astronaut Bjarni V. Tryggvason poses under the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery after the space plane landed on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility Aug. 19 to complete the 11-day, 20-hour and 27-minute-long STS-85 mission. Also on board were Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Pilot Kent V. Rominger, Payload Commander N. Jan Davis, Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson During the 86th Space Shuttle mission, the crew deployed the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) free-flyer to conduct research on the Earth’s middle atmosphere, retrieving it on flight day 9. The crew also conducted investigations with the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments. This was the 39th landing at KSC in the history of the Space Shuttle program and the 11th touchdown for Discovery at the space center
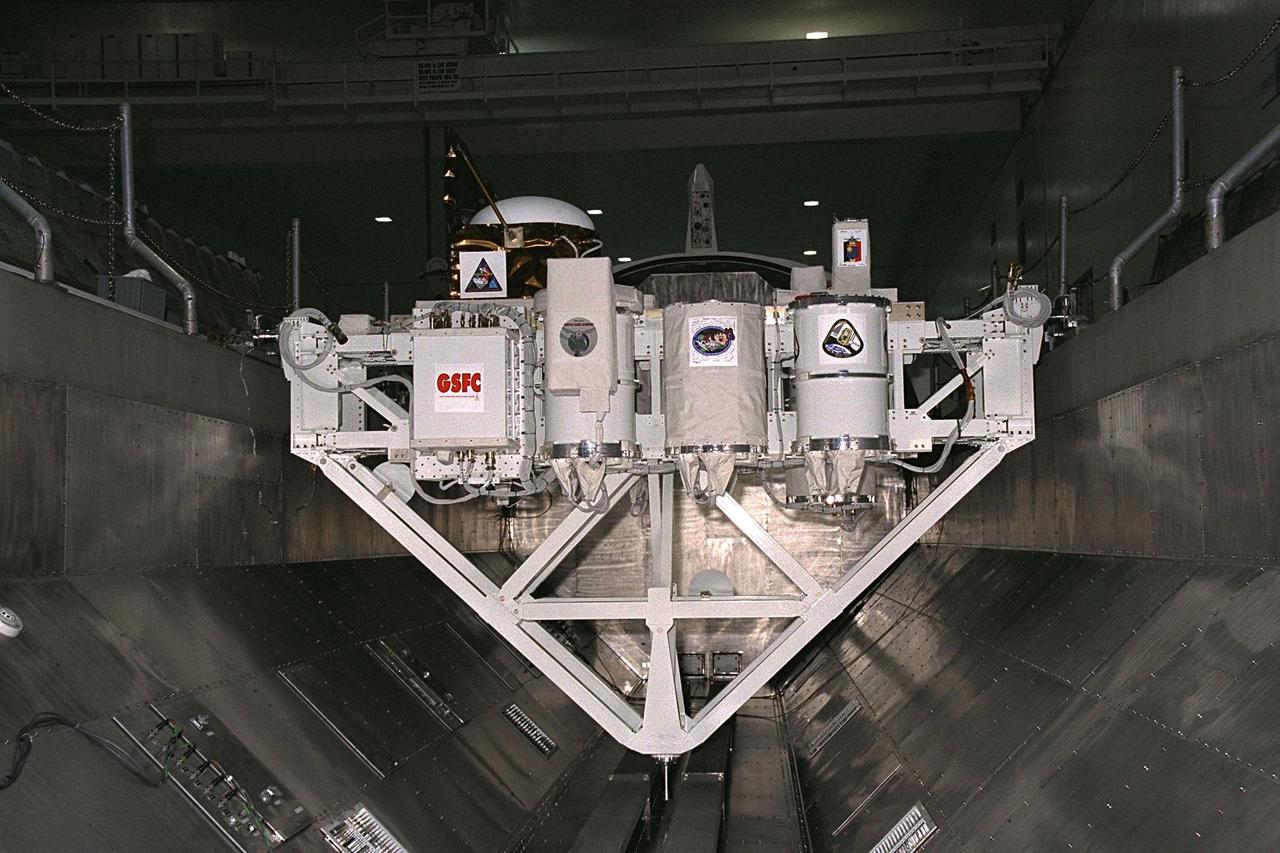
The Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) payload for the STS-85 mission rests in a payload canister in the Space Station Processing Facility prior to its trip out to Launch Pad 39A for installation into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery. The TAS-1 holds seven separate experiments that will provide data on the Earth’s topography and atmosphere, study the sun’s energy, and test new thermal control devices, as well as several student-developed experiments. Other STS-85 payloads include the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11-day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere. The International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) will also be in the payload bay. The IEH-2 experiments will study ultraviolet radiation from stars, the sun and in the solar system
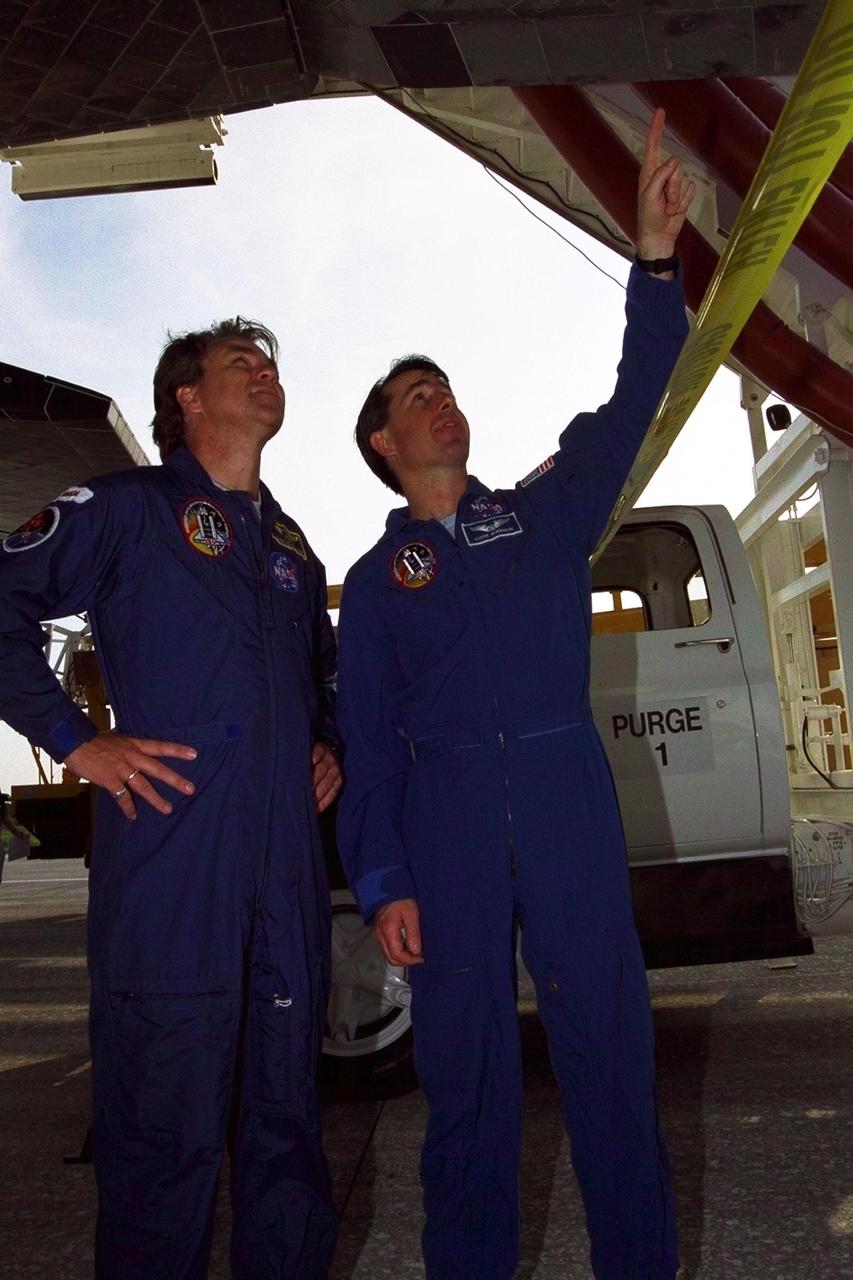

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Payload Specialist and Canadian Space Agency astronaut Bjarni V. Tryggvason (left) and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson examine the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery after the space plane landed on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility Aug. 19 to complete the 11-day, 20-hour and 27-minute-long STS-85 mission. Also on board were Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Pilot Kent V. Rominger, Payload Commander N. Jan Davis and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. During the 86th Space Shuttle mission, the crew deployed the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) free-flyer to conduct research on the Earth’s middle atmosphere, retrieving it on flight day 9. The crew also conducted investigations with the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments. This was the 39th landing at KSC in the history of the Space Shuttle program and the 11th touchdown for Discovery at the space center
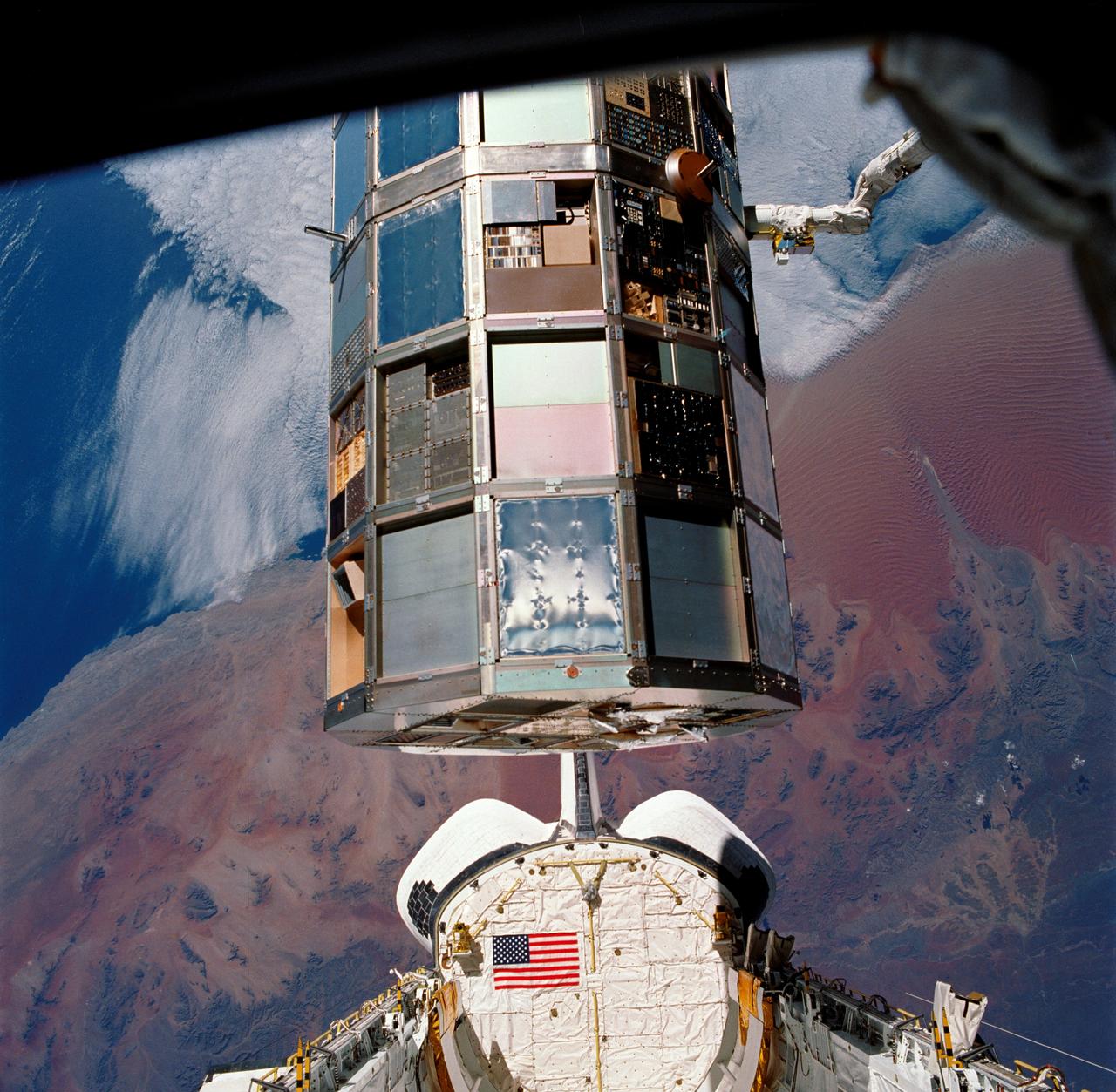

STS032-85-029 (12 Jan. 1990) --- (ORIENT PHOTO WITH COLUMBIA'S CARGO BAY IN LOWER CENTER). This 70mm frame was taken during a battery of documentary photographs of the recently-recaptured Long Duration Exposure Facility (LEDF). The Atlantic Coast of Namibia serves as a backdrop for the colorful scene. After five-and-one half years orbiting Earth, LDEF was retrieved by STS-32 crewmembers and brought back home at the end of the eleven-day mission for scientific observation. The bus-sized spacecraft was held in the grasp of Columbia's remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector during the survey.
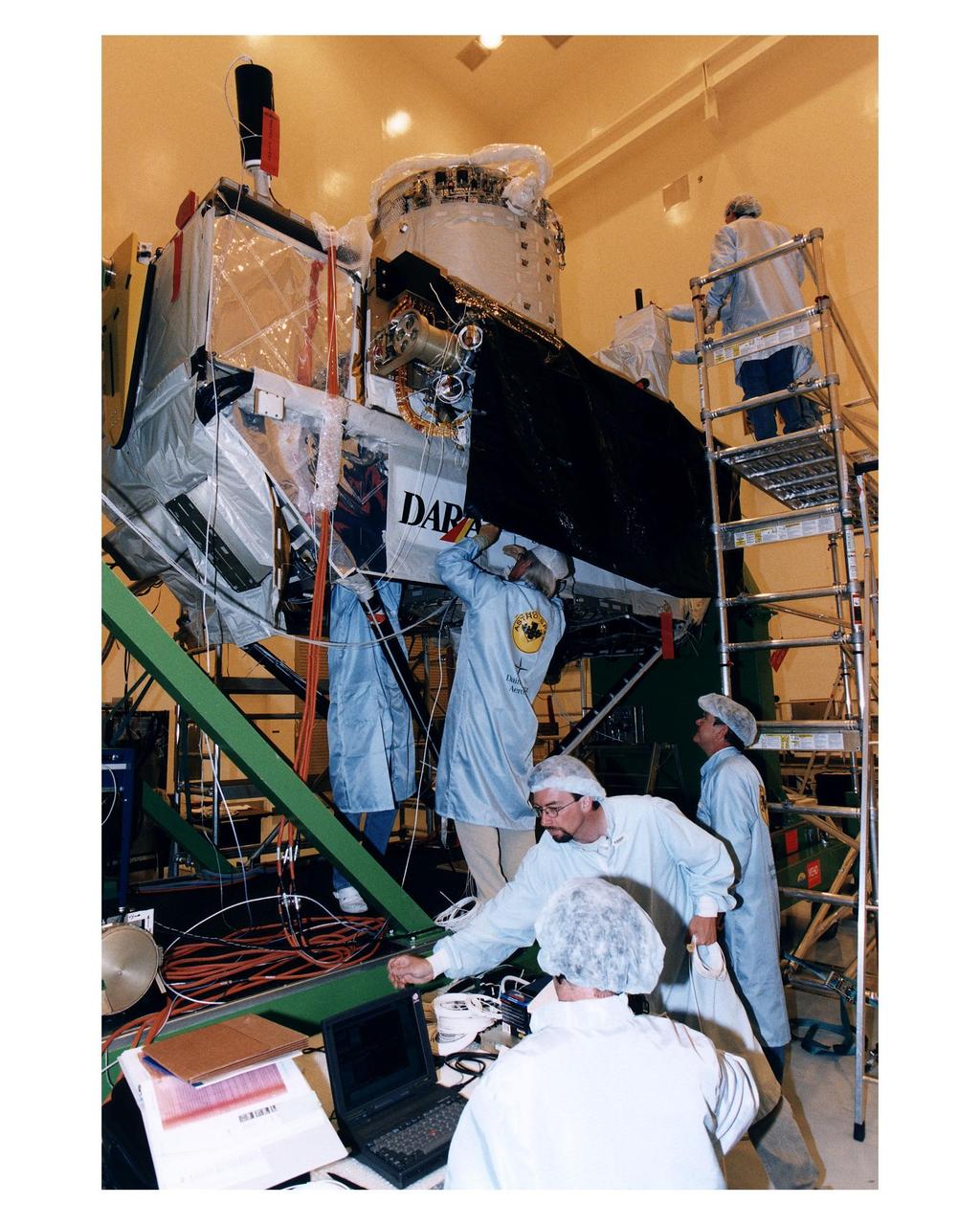

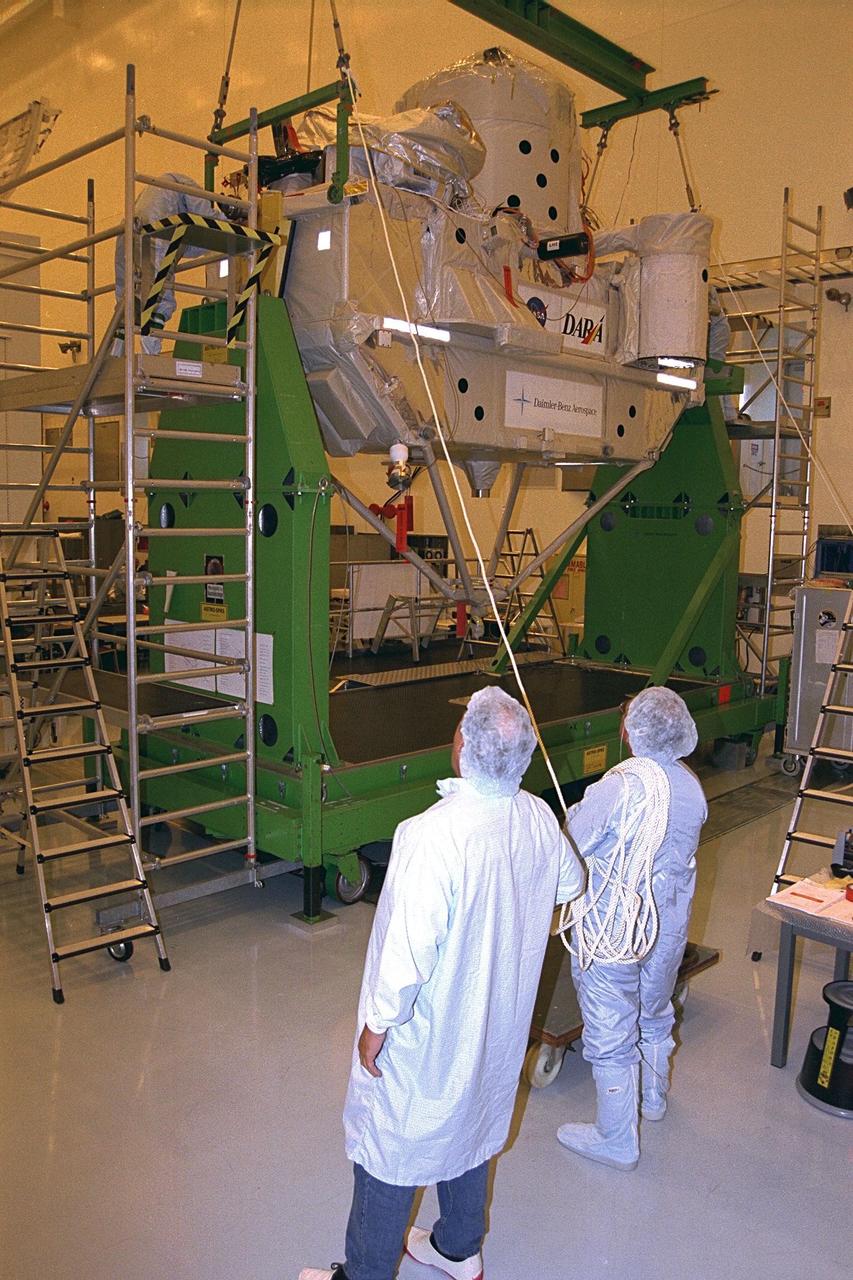
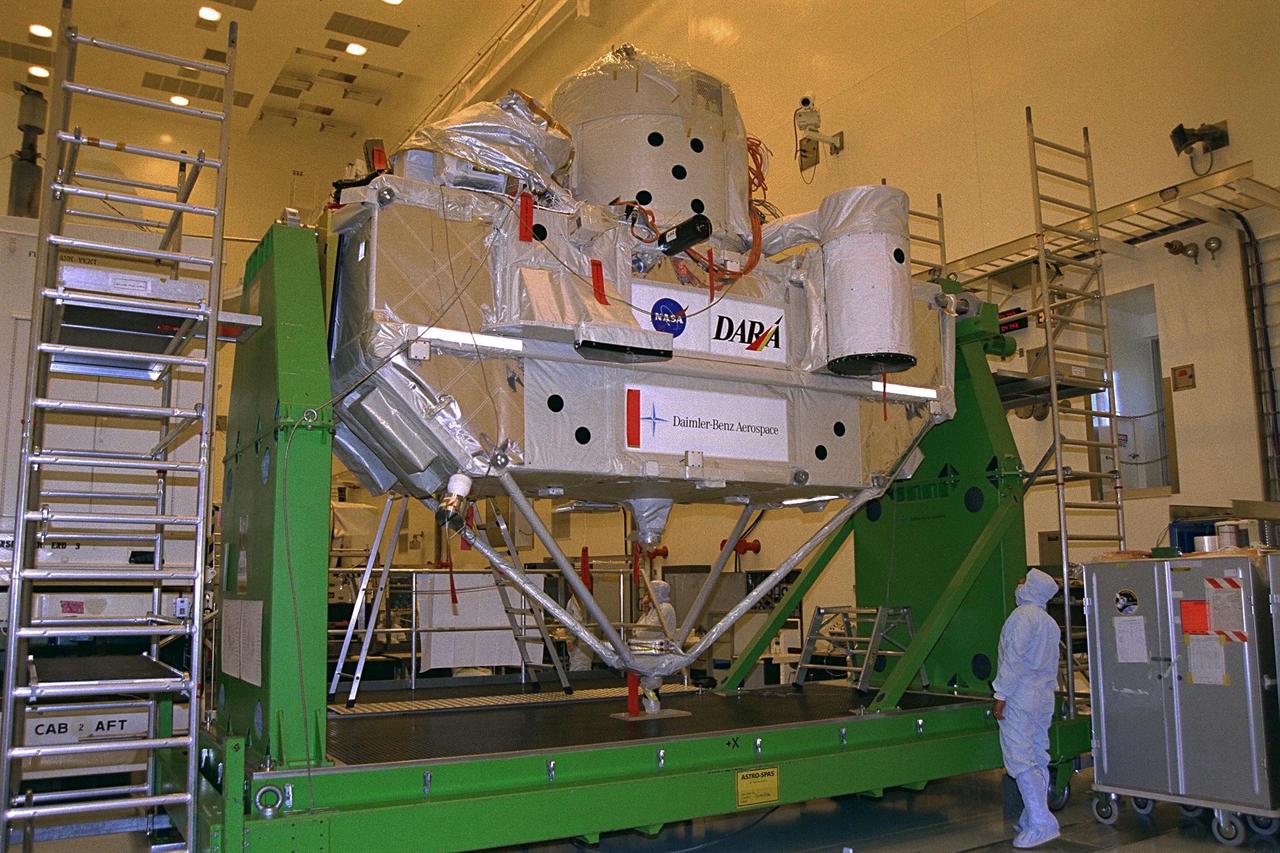
Employees of Daimler-Benz Aerospace in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility install insulation on the Cryogenic Infrared Spectro-meters and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11- day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere
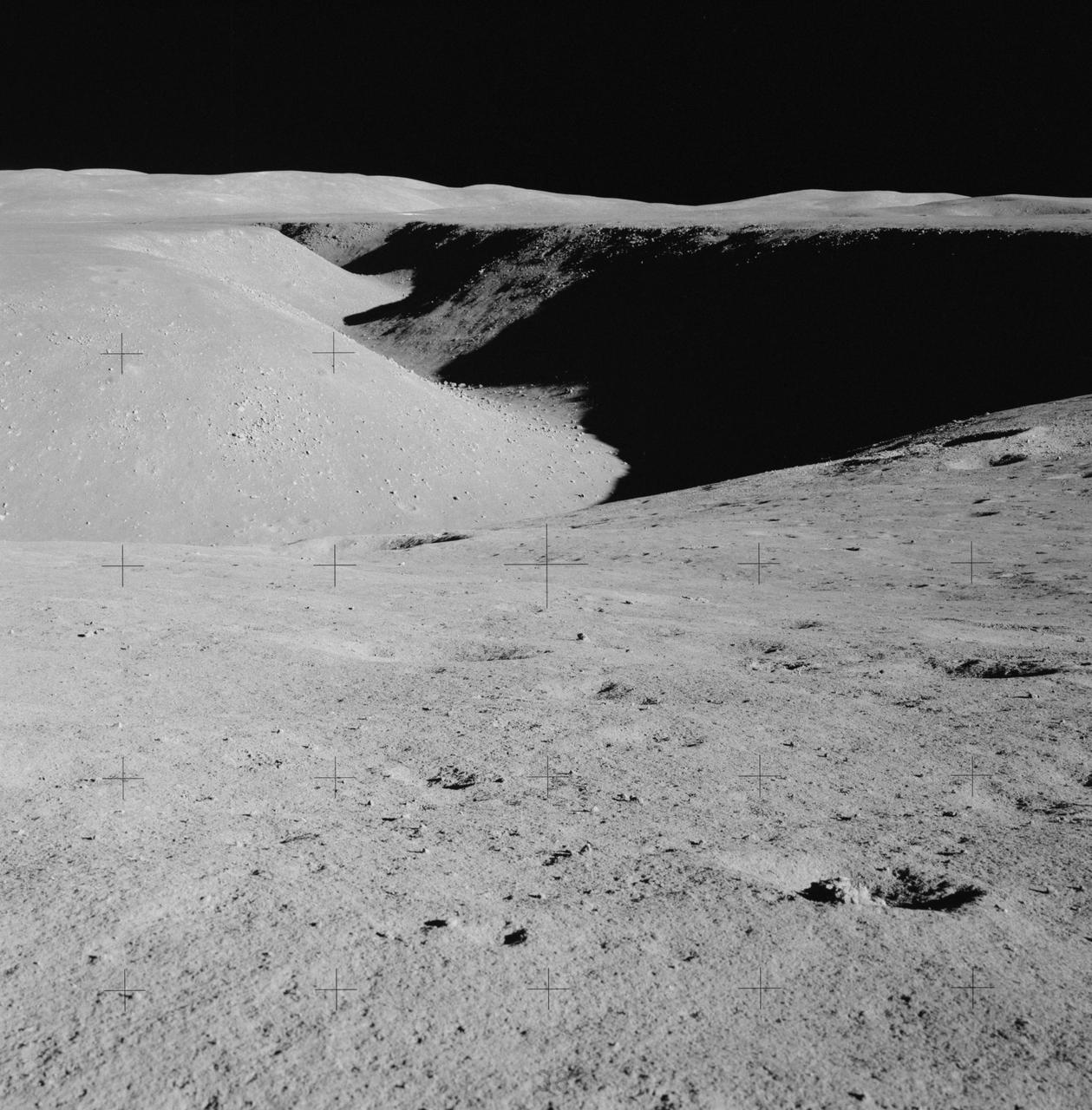

AS15-85-11425 (31 July 1971) --- A view of Hadley Rille, looking northwest, as photographed from near Station No. 2 (St. George Crater) during the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). This picture shows layering in the rille wall and blocks on the floor of the rille. The feature referred to as the "Terrace" is visible on the right (east) side of the rille. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Module's (CSM) in lunar orbit.
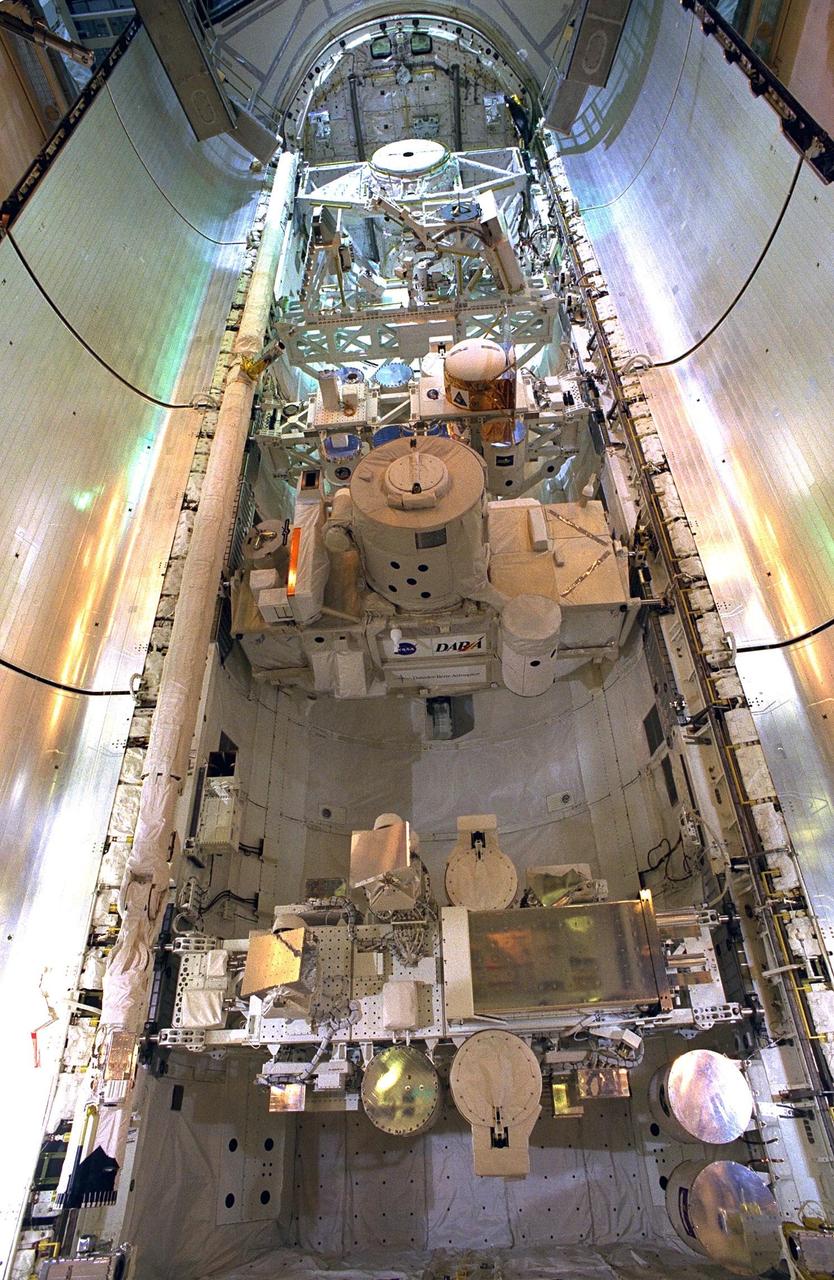
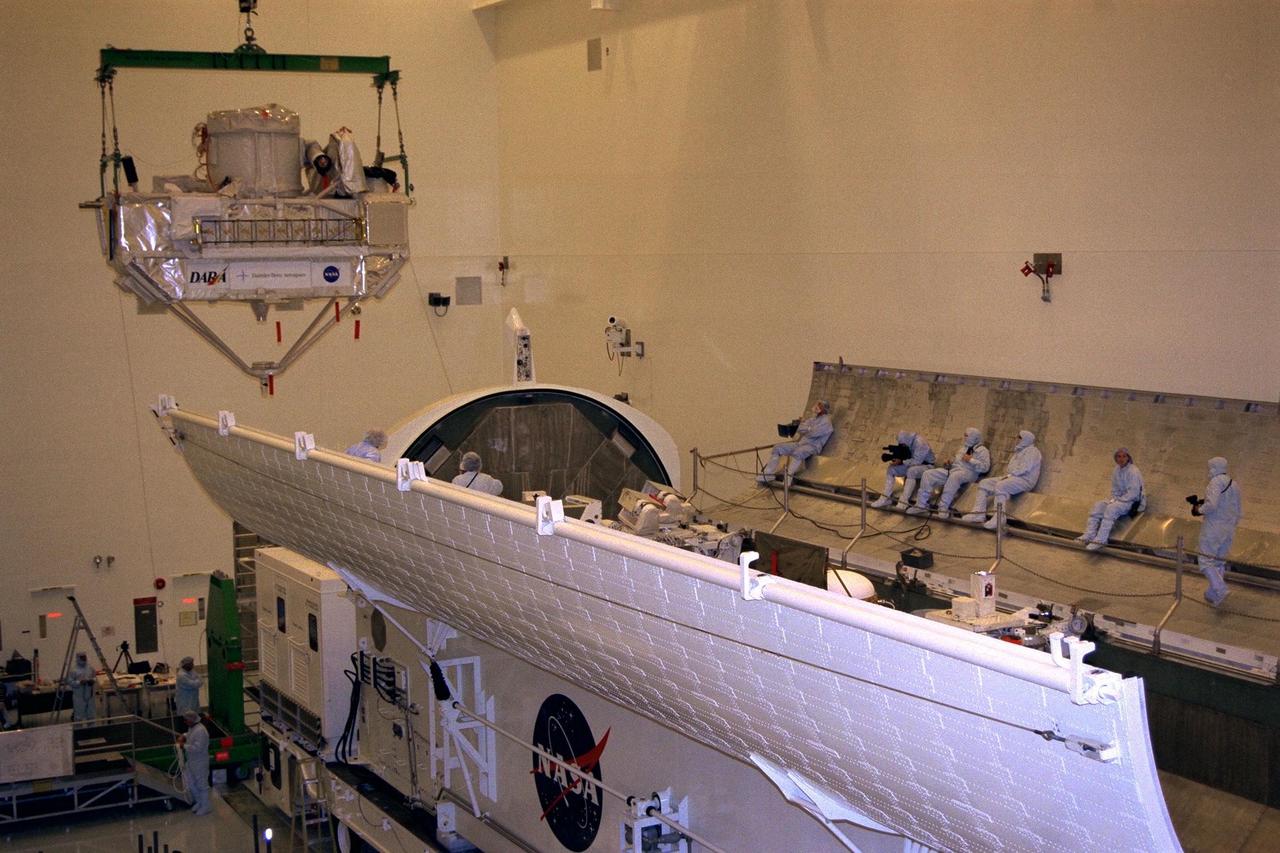
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The final tasks to prepare the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission are completed aboard Discovery at Launch Complex 39A. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11-day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere.
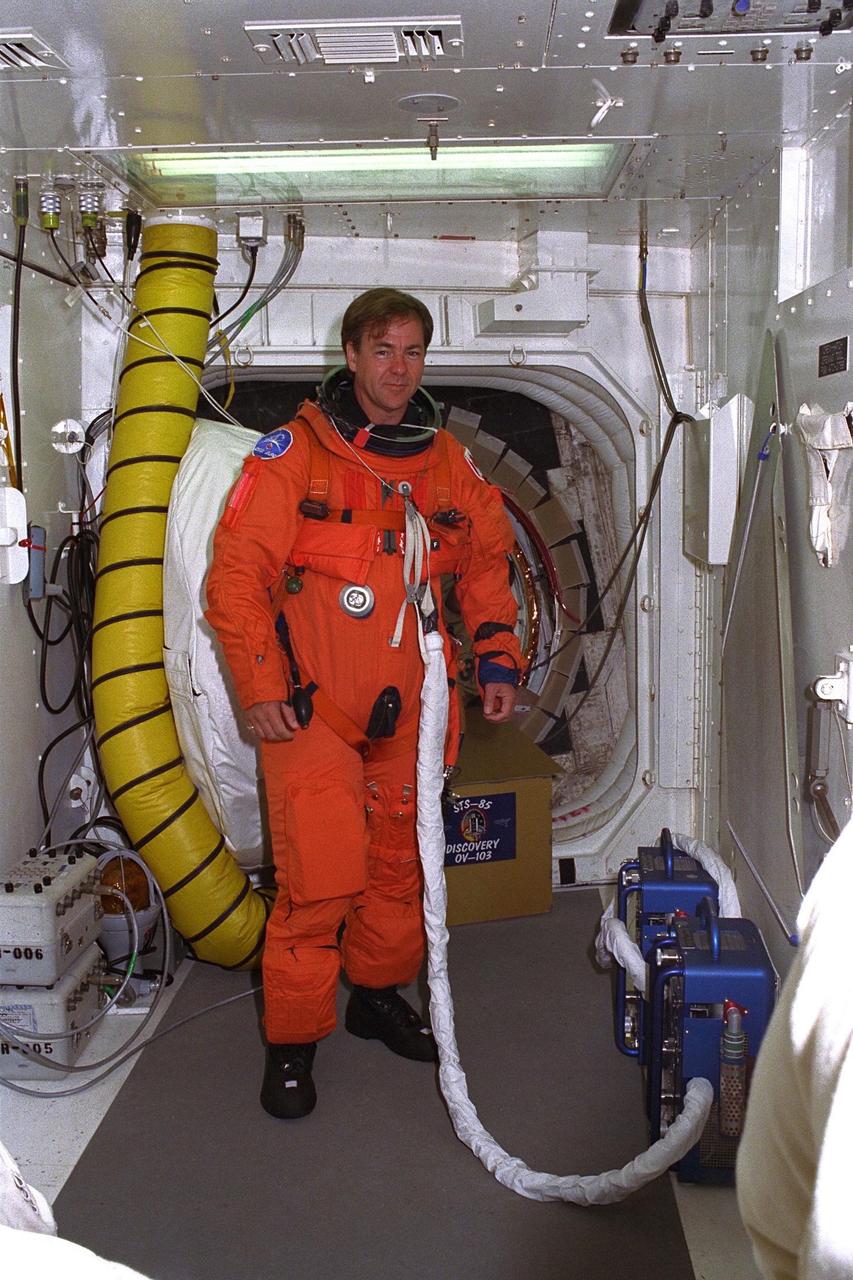

STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason poses in the white room at Launch Pad 39A with his ascent/reentry flight suit as he prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery at Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
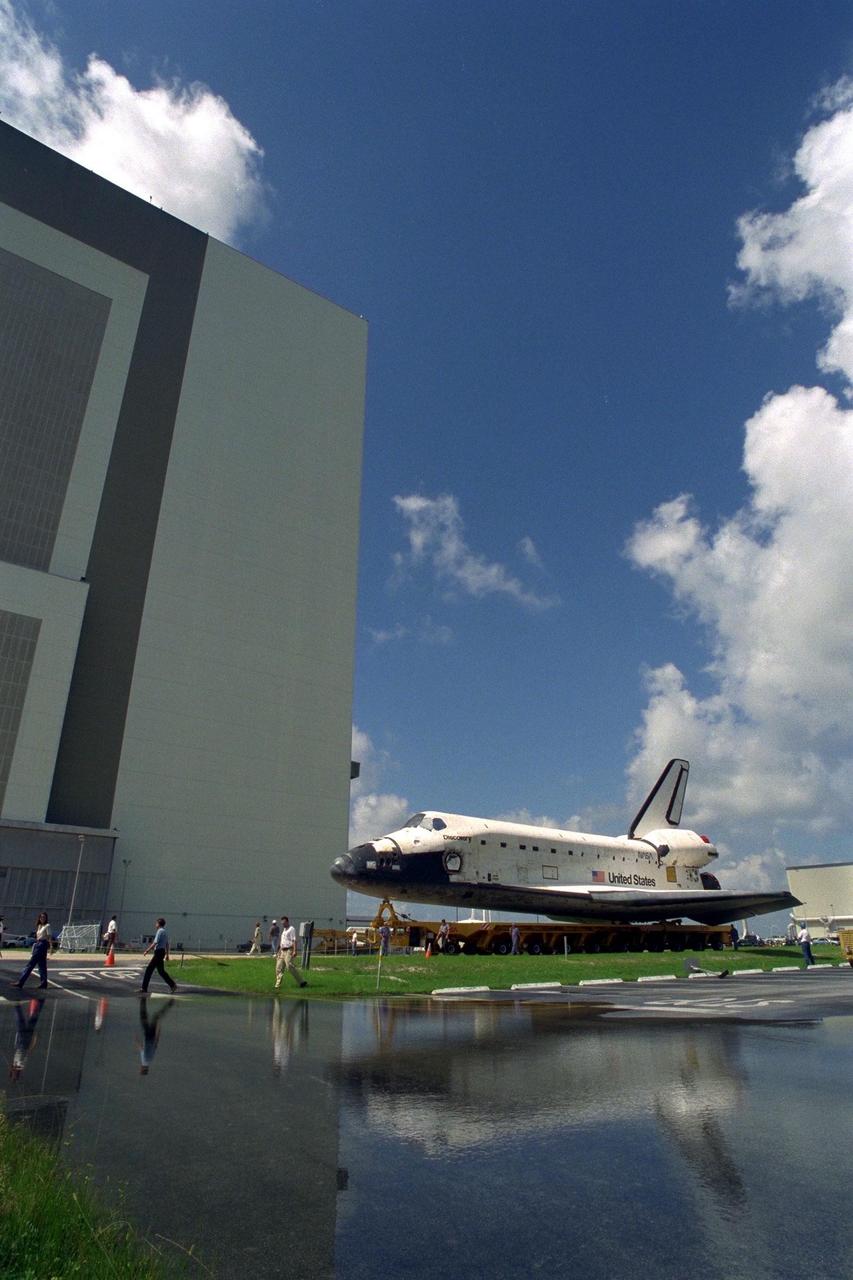

The Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery rolls over from Orbiter Processing Facility 2 on top of the orbiter transporter to the Vehicle Assembly Building for mating with its external tank and solid rocket boosters in preparation for the STS-85 mission. Several payloads will be aboard Discovery during the 11-day mission, including the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) and the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2), as well as the Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-2) experiments
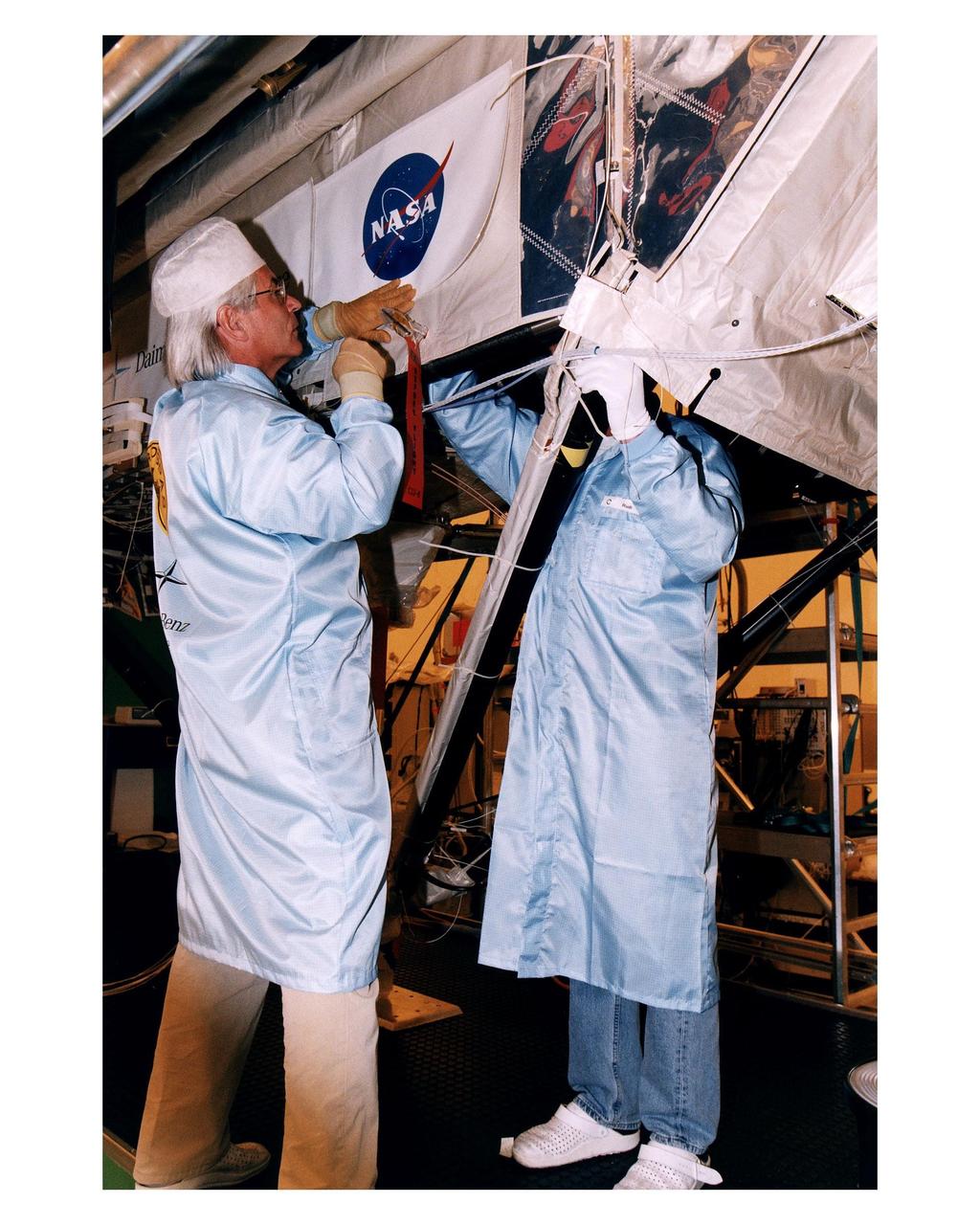

Employees of Daimler-Benz Aerospace in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility install insulation on the Cryogenic Infrared Spectro-meters and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11- day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere
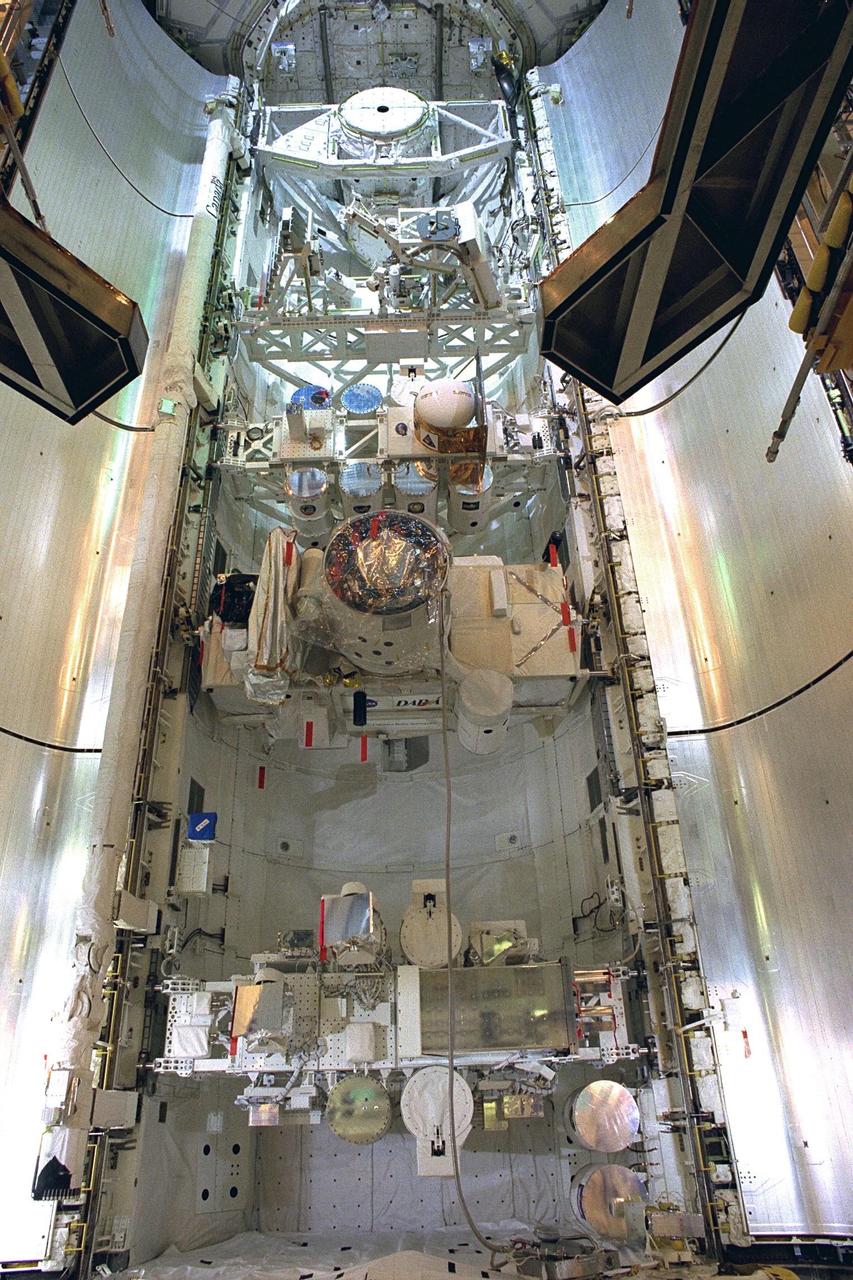

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery's payload bay doors are closed in preparation for the flight of mission STS-85. The payload includes the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11-day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason stands ready for questions at a news briefing at Launch Pad 39A during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
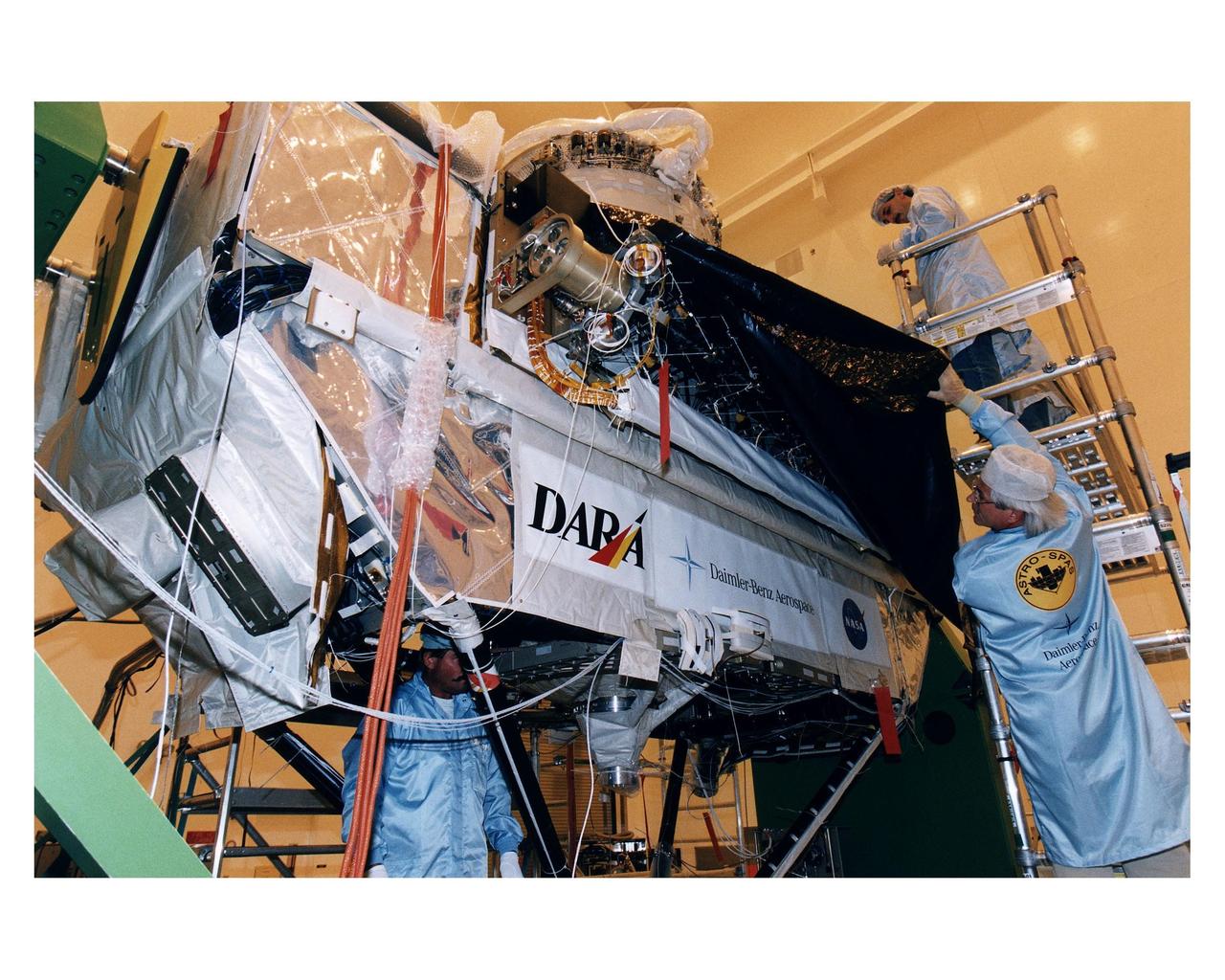
Employees of Daimler-Benz Aerospace in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility install insulation on the Cryogenic Infrared Spectro-meters and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11- day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere
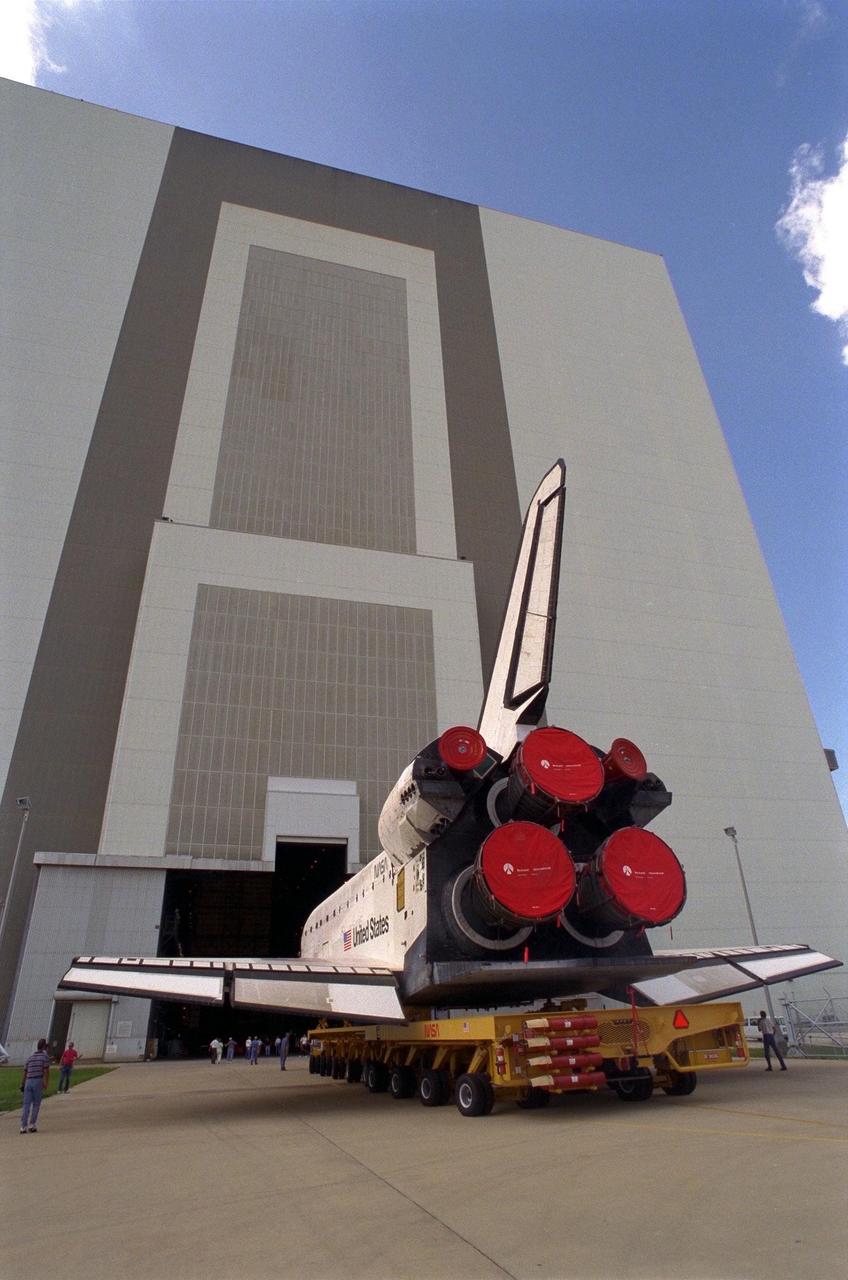

The Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery rolls over from Orbiter Processing Facility 2 on top of the orbiter transporter to the Vehicle Assembly Building for mating with its external tank and solid rocket boosters in preparation for the STS-85 mission. Several payloads will be aboard Discovery during the 11-day mission, including the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) and the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2), as well as the Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-2) experiments

The Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery rolls over from Orbiter Processing Facility 2 on top of the orbiter transporter to the Vehicle Assembly Building for mating with its external tank and solid rocket boosters in preparation for the STS-85 mission. Several payloads will be aboard Discovery during the 11-day mission, including the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) and the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2), as well as the Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-2) experiments
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The final tasks to prepare the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission are completed aboard Discovery at Launch Complex 39A. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11-day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere.
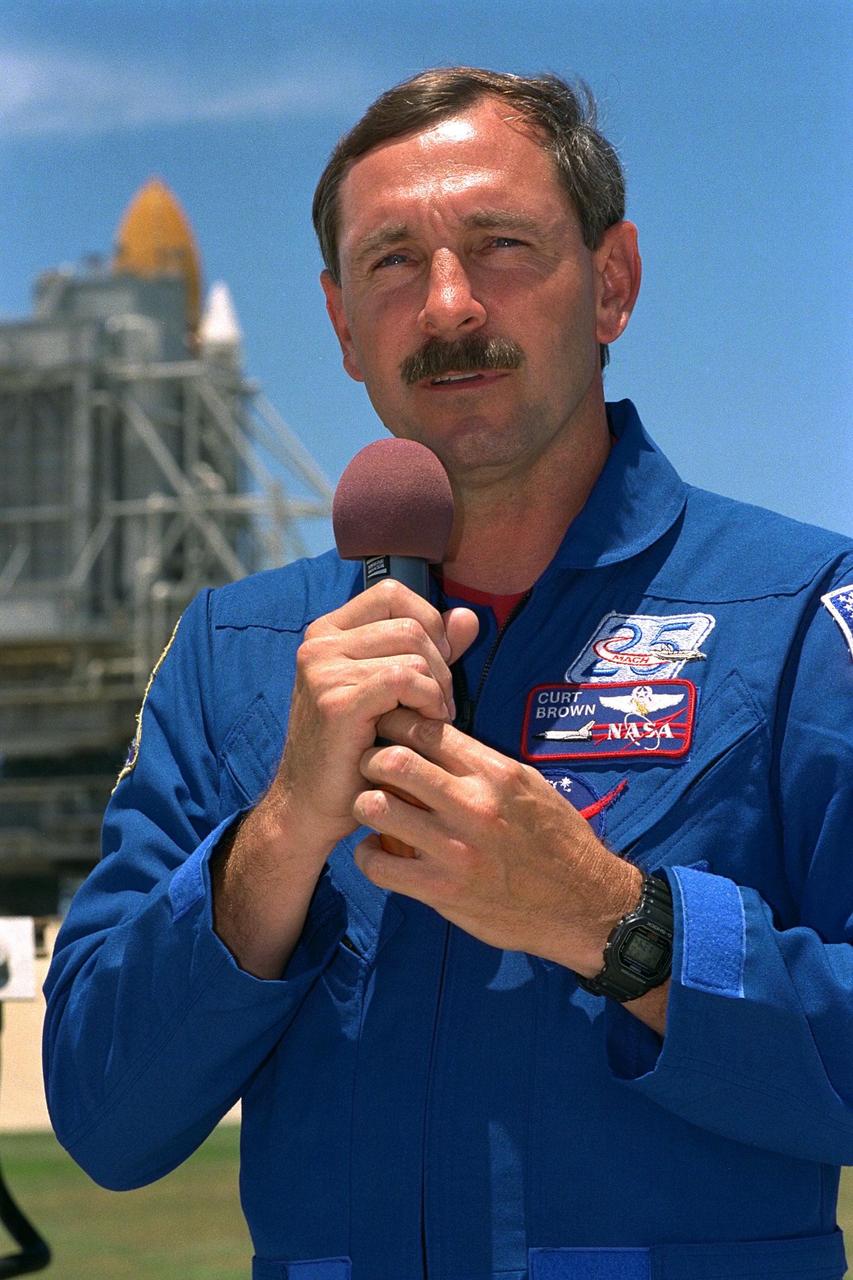

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., addresses the news media at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
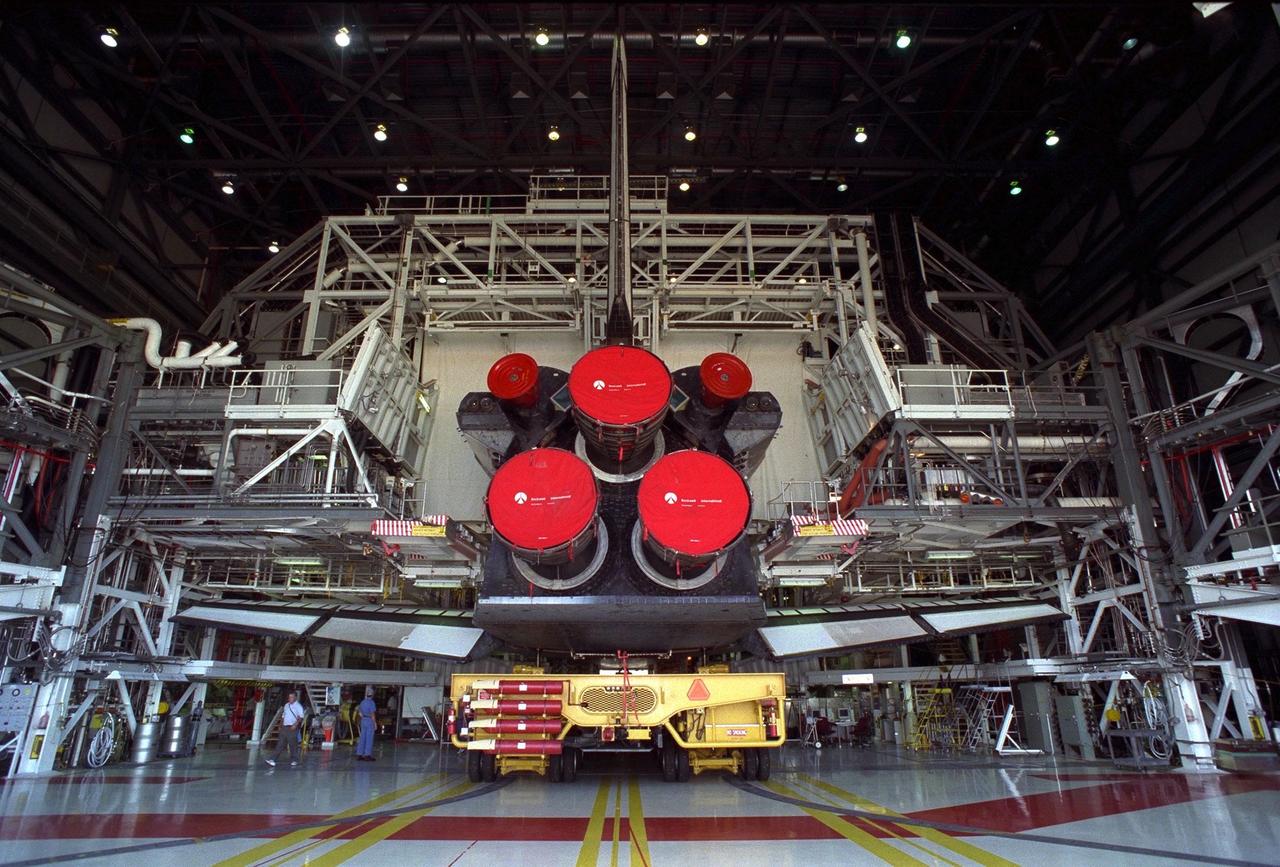
The Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery in Orbiter Processing Facility 2 begins its rollover on top of the orbiter transporter to the Vehicle Assembly Building for mating with its external tank and solid rocket boosters in preparation for the STS-85 mission. Several payloads will be aboard Discovery during the 11-day mission, including the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) and the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2), as well as the Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-2) experiments
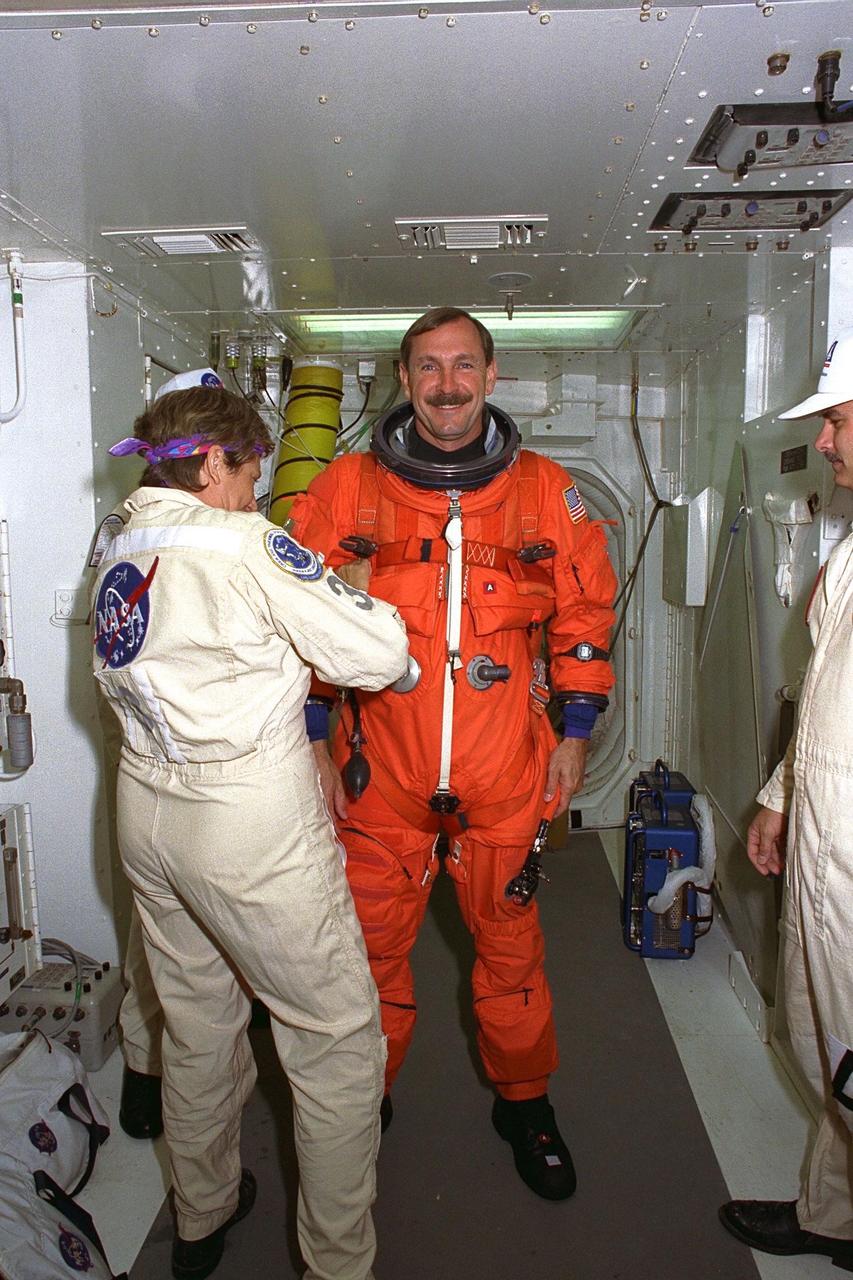

STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., is assisted with his ascent/reentry flight suit by a white room crew member as he prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery at Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
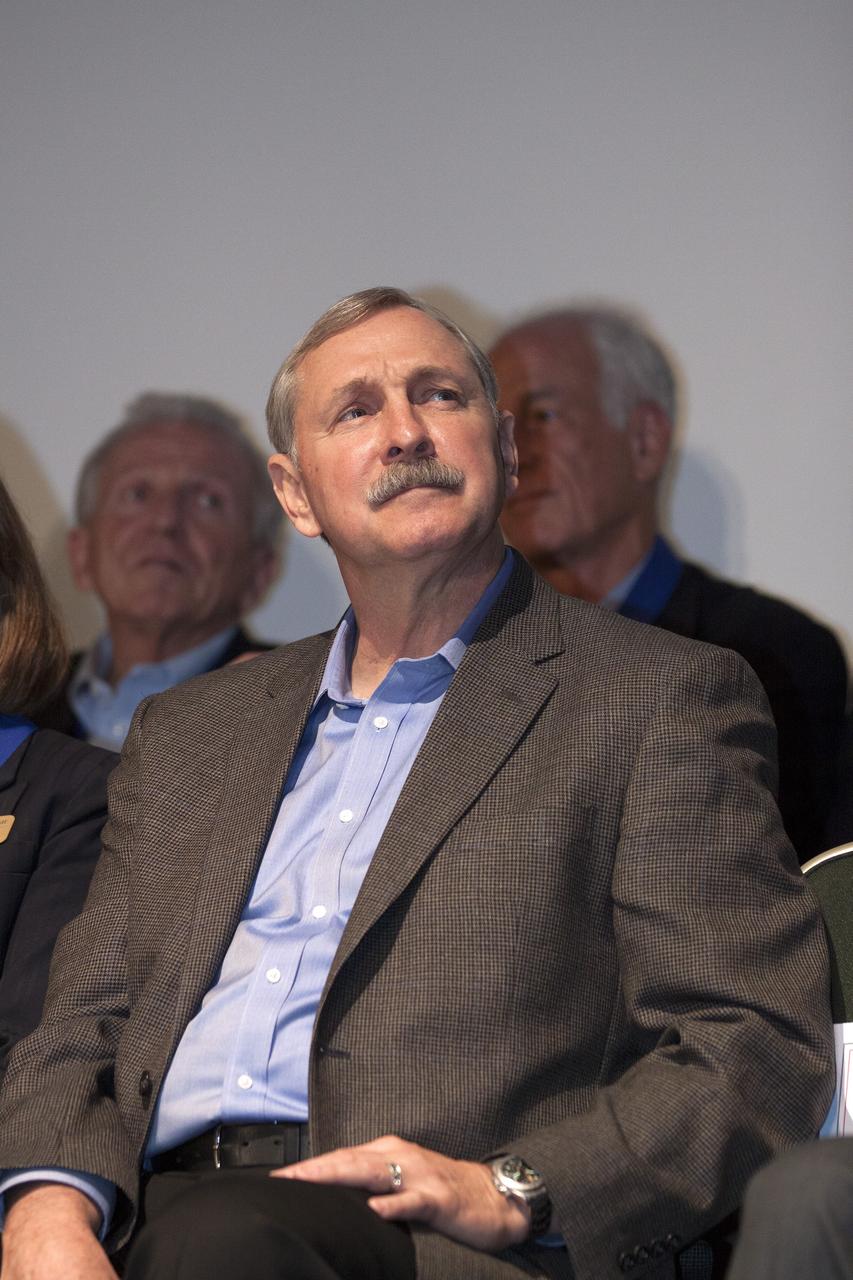

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, shuttle astronaut Curt Brown listens as he is being introduced for induction into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame AHOF. Brown, a veteran of six spaceflights, began his career with NASA in 1987 as a pilot and has logged more than 1,383 hours in space. Brown’s missions aboard the space shuttle include STS-47, STS-66, STS-77, STS-85, STS-95 and STS-103. Shuttle astronauts Eileen Collins and Bonnie Dunbar also were inducted into the AHOF. This induction is the twelfth group of space shuttle astronauts named to the AHOF, and the first time two women are inducted at the same time. The year’s inductees were selected by a committee of current Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, historians and journalists. The selection process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. For more on the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, go to http://www.kennedyspacecenter.com/astronaut-hall-of-fame.aspx For more on the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, go to http://astronautscholarship.org/ Photo credit: NASA/ Kim Shiflett
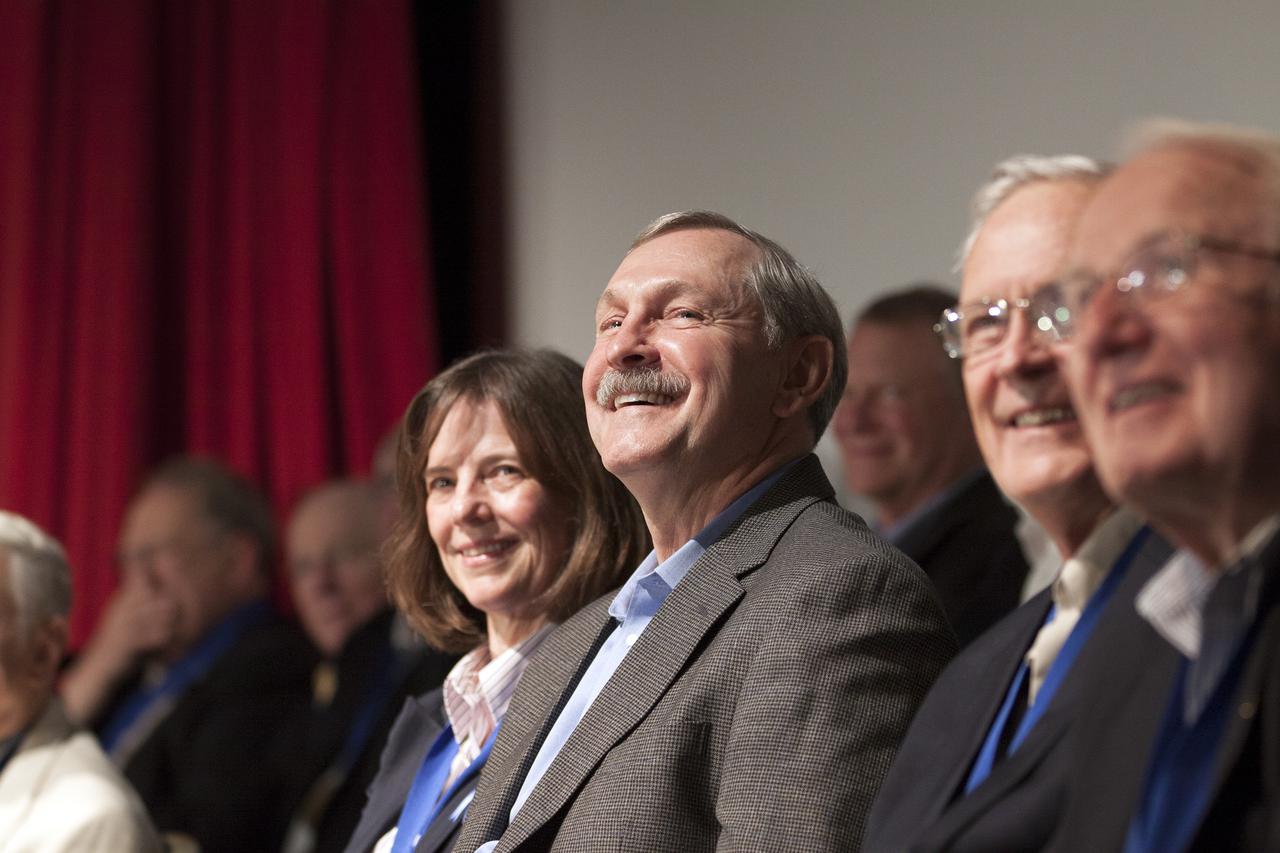

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, shuttle astronaut Curt Brown listens as he is being introduced for induction into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame AHOF. Brown, a veteran of six spaceflights, began his career with NASA in 1987 as a pilot and has logged more than 1,383 hours in space. Brown’s missions aboard the space shuttle include STS-47, STS-66, STS-77, STS-85, STS-95 and STS-103. Shuttle astronauts Eileen Collins and Bonnie Dunbar also were inducted into the AHOF. This induction is the twelfth group of space shuttle astronauts named to the AHOF, and the first time two women are inducted at the same time. The year’s inductees were selected by a committee of current Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, historians and journalists. The selection process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. For more on the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, go to http:__www.kennedyspacecenter.com_astronaut-hall-of-fame.aspx For more on the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, go to http:__astronautscholarship.org_ Photo credit: NASA_ Kim Shiflett
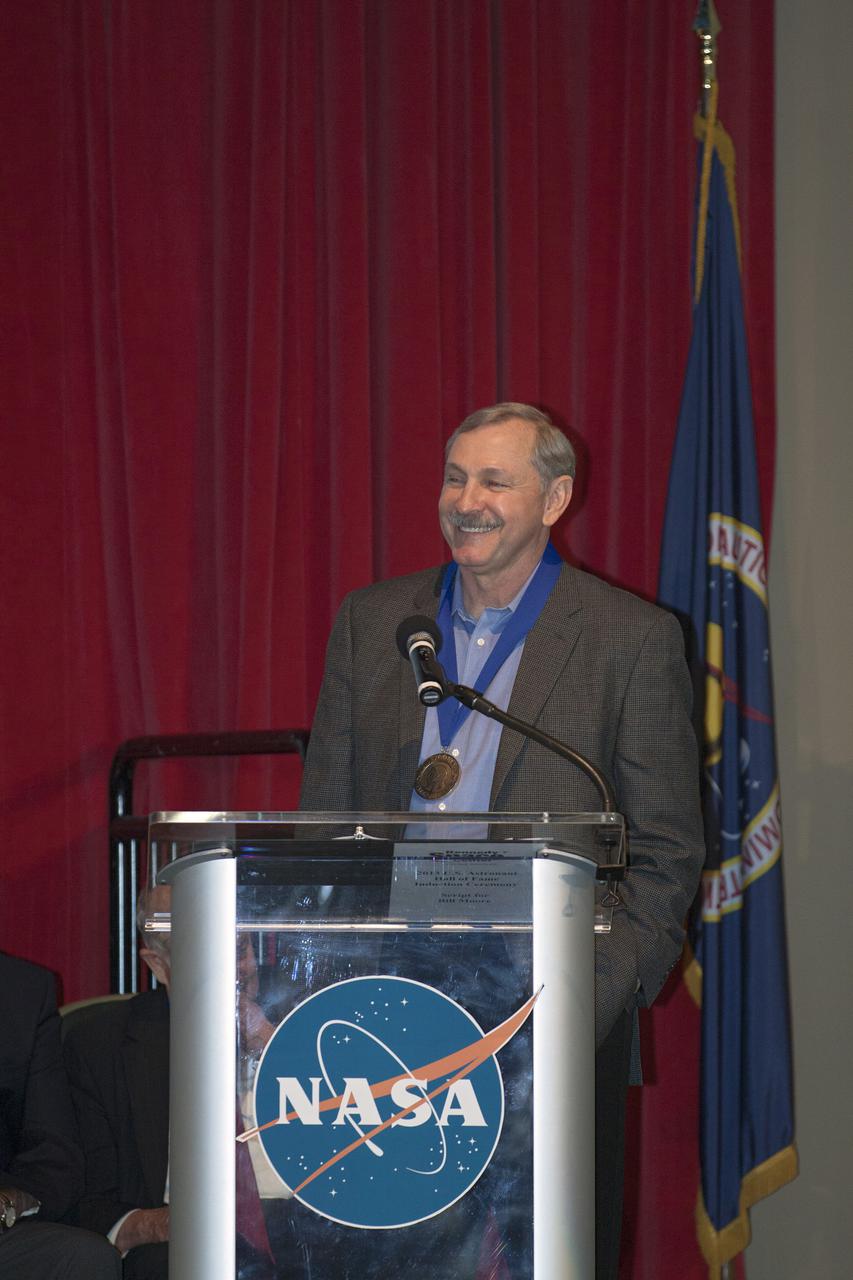

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, shuttle astronaut Curt Brown speaks after being inducted into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame AHOF. Brown, a veteran of six spaceflights, began his career with NASA in 1987 as a pilot and has logged more than 1,383 hours in space. Brown’s missions aboard the space shuttle include STS-47, STS-66, STS-77, STS-85, STS-95 and STS-103. Shuttle astronauts Eileen Collins and Bonnie Dunbar also were inducted into the AHOF. This induction is the twelfth group of space shuttle astronauts named to the AHOF, and the first time two women are inducted at the same time. The year’s inductees were selected by a committee of current Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, historians and journalists. The selection process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. For more on the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, go to http:__www.kennedyspacecenter.com_astronaut-hall-of-fame.aspx For more on the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, go to http:__astronautscholarship.org_ Photo credit: NASA_ Kim Shiflett
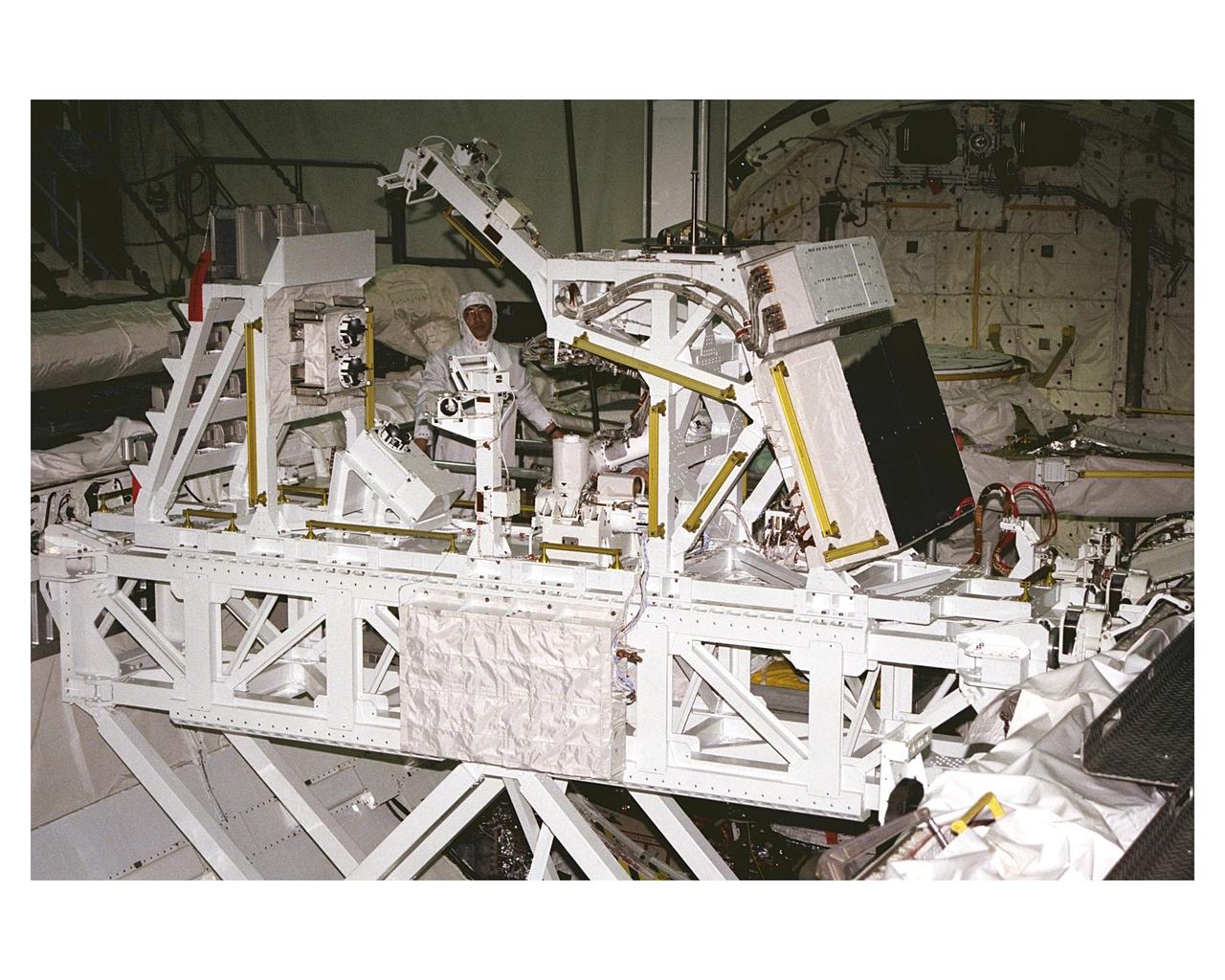
The Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD) payload is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery in Orbiter Processing Facility 2. The MFD is one of several payloads that will fly on the STS-85 mission. This payload is designed to test the operational capability of the Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System (JEM RMS) Small Fine Arm (SFA), which can be seen atop its Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure (MPESS) carrier that will serve as a platform in the payload bay for the robotic arm experiment. The arm, which will be a part of the JEM element of the International Space Station, will be operated from the orbiter’s aft flight deck during the 11-day mission. Other payloads that will be aboard Discovery on this space flight include the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA- SPAS-2), Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-2) experiments
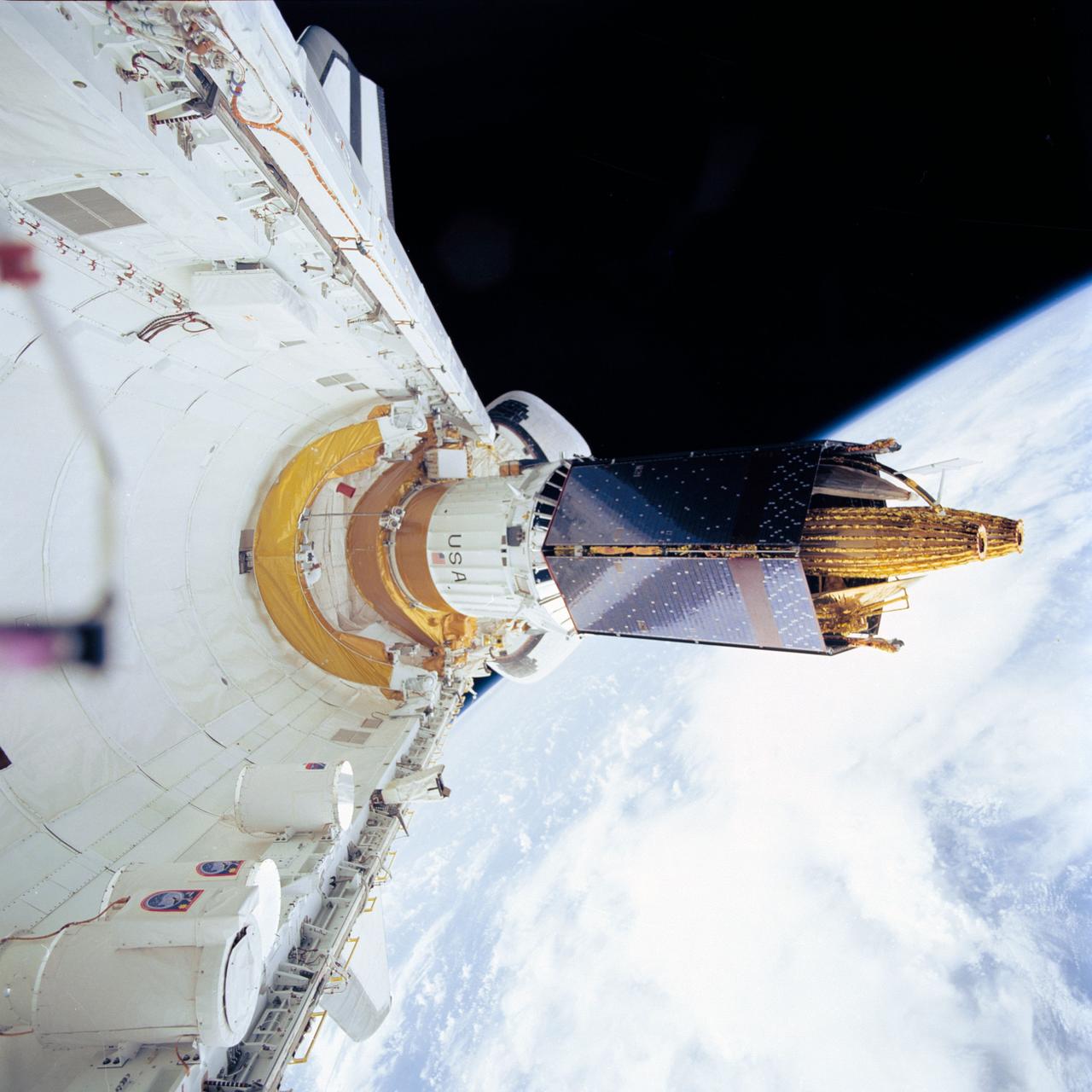

STS043-72-002 (2 Aug 1991) --- The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-E), leaves the payload bay of the earth-orbiting Atlantis a mere six hours after the Space Shuttle was launched from Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. TDRS, built by TRW, will be placed in a geosynchronous orbit and after on-orbit testing, which requires several weeks, will be designated TDRS-5. The communications satellite will replace TDRS-3 at 174 degrees West longitude. The backbone of NASA's space-to-ground communications, the Tracking and Data Relay satellites have increased NASA's ability to send and receive data to spacecraft in low-earth orbit to more than 85 percent of the time. The five astronauts of the STS 43 mission are John E. Blaha, mission commander, Michael A. Baker, pilot, and Shannon W. Lucid, G. David Low, and James C. Adamson, all mission specialists.