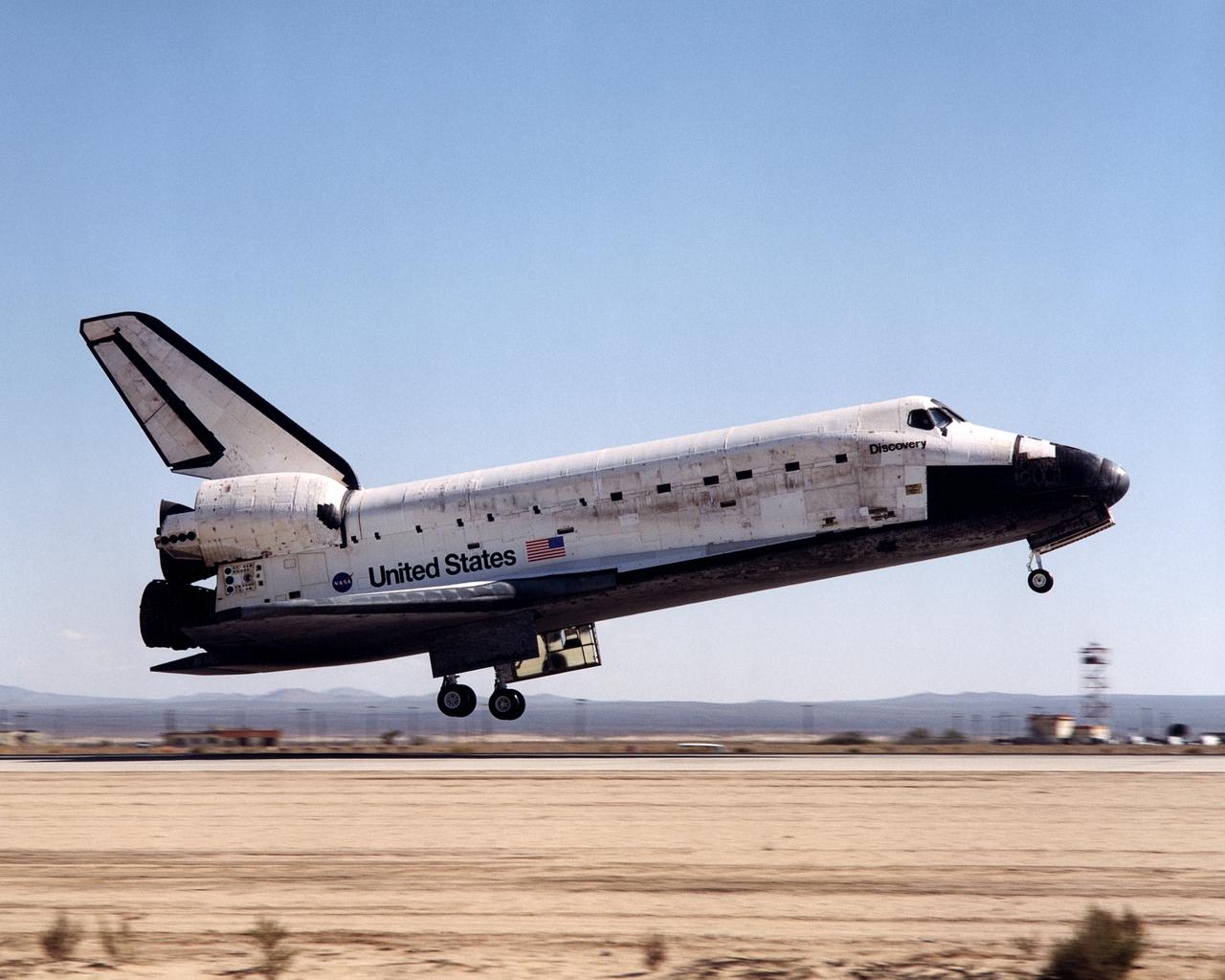

The Space Shuttle Discovery glides in for landing at Edwards Air Force Base in Southern California at the conclusion of mission STS-92 on October 24, 2000.
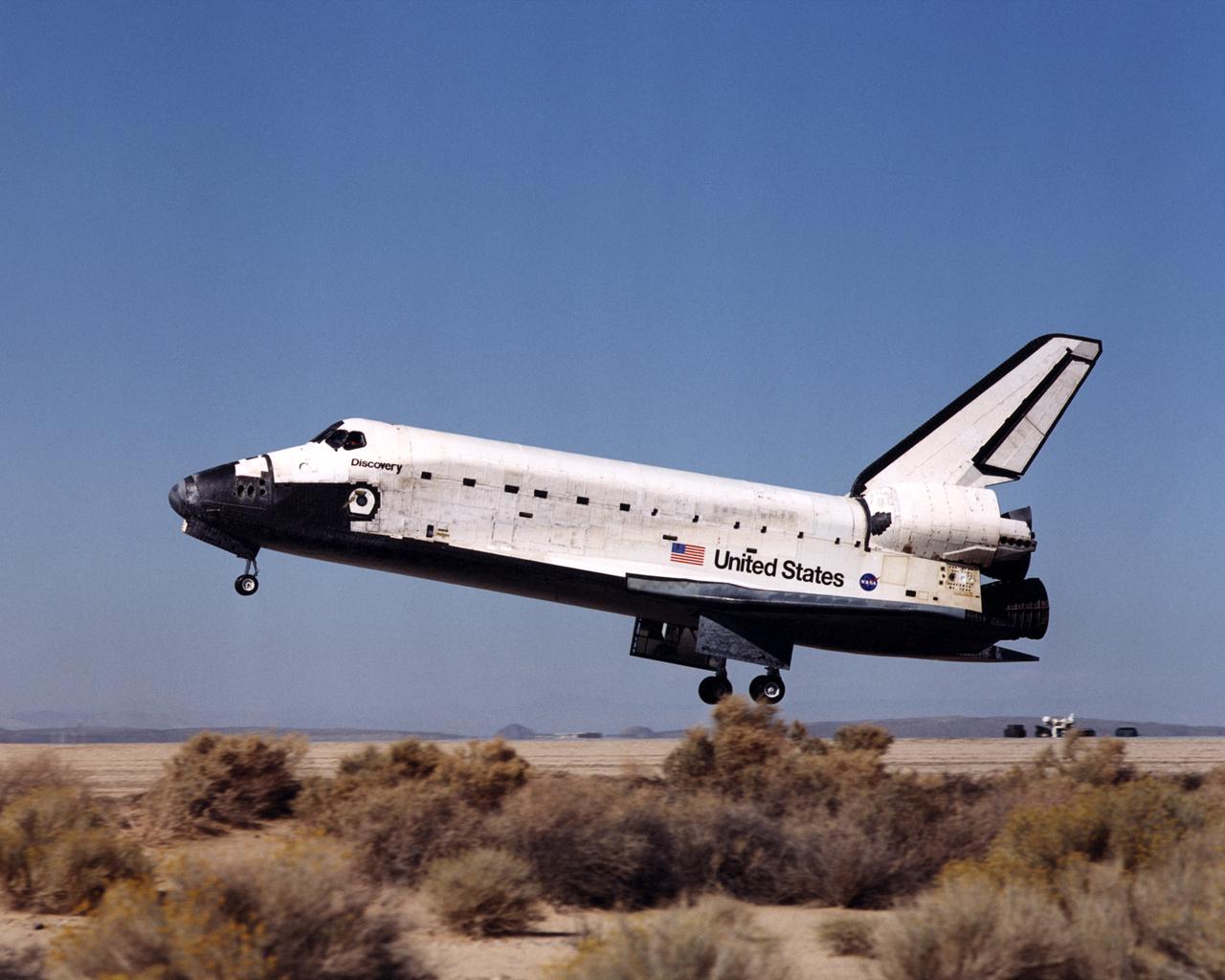

The Space Shuttle Discovery glides in for landing at Edwards Air Force Base in Southern California at the conclusion of mission STS-92 on October 24, 2000.
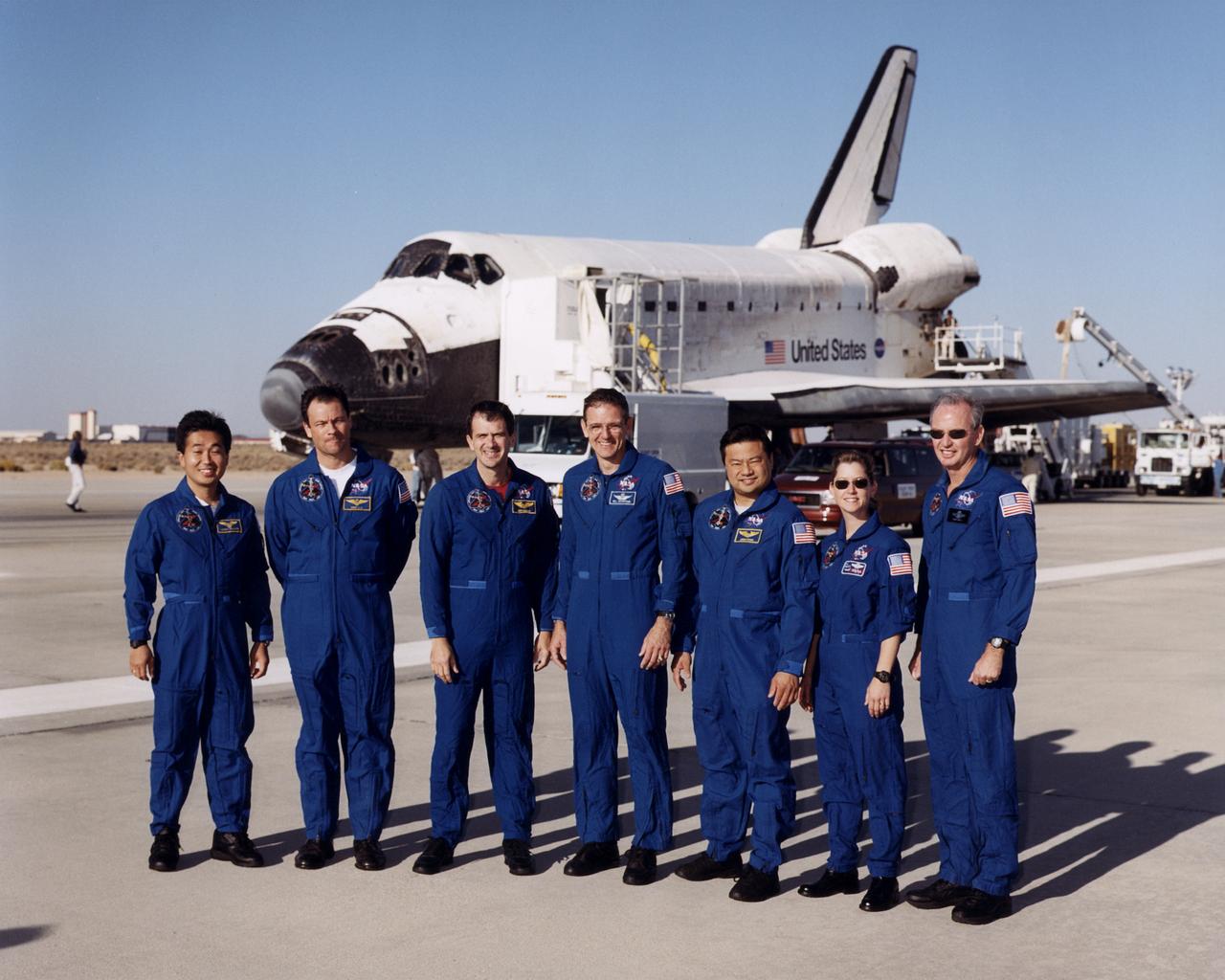

The seven-member crew of the Space Shuttle mission STS-92 gathered in front of the Shuttle Discovery shortly after landing at Edwards Air Force Base in Southern California October 24, 2000. From left are mission specialists Koichi Wakata, Michael Lopez-Alegria, Jeff Wisoff, Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao, pilot Pam Melroy and mission commander Brian Duffy.
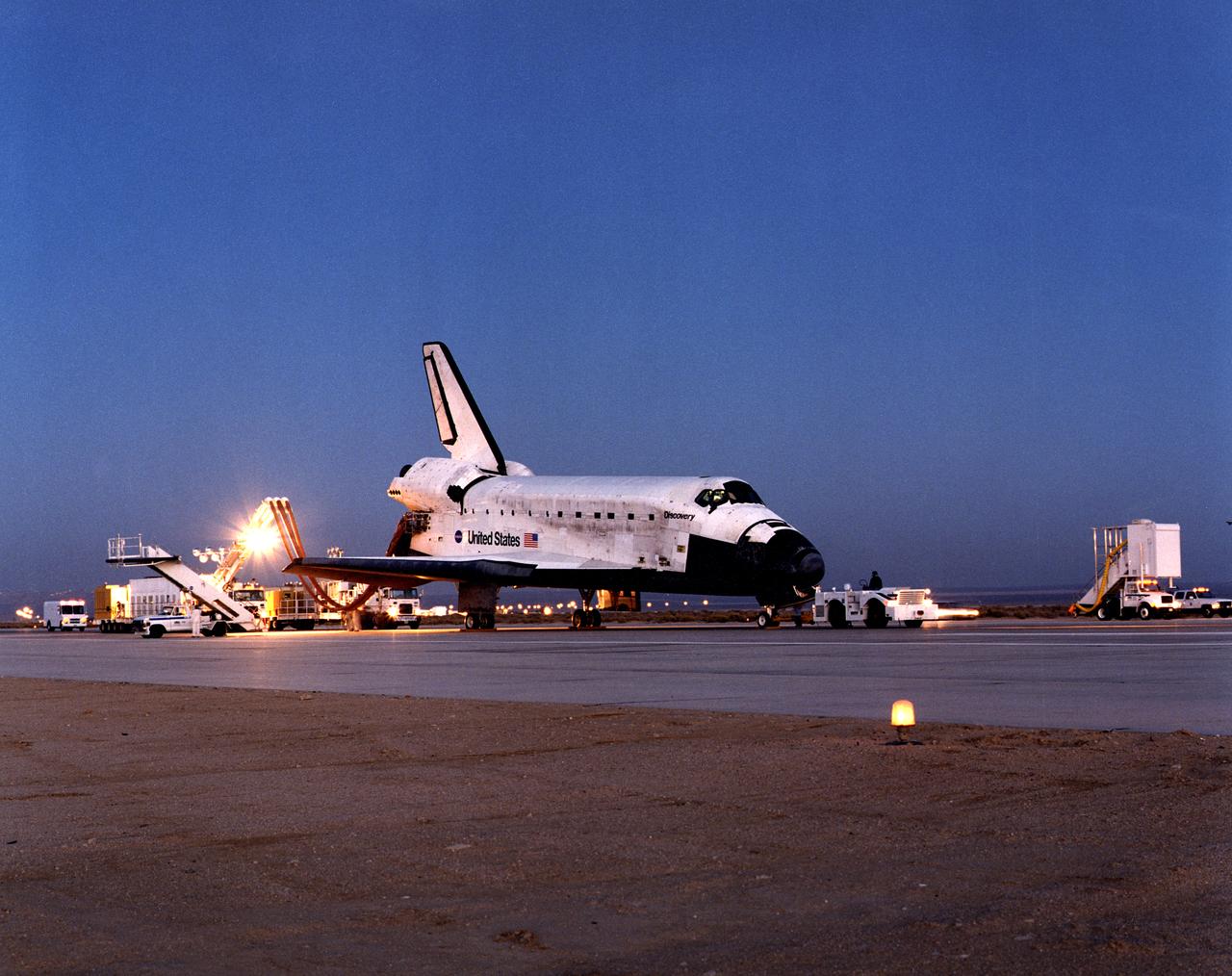

Ground crews worked into the evening to prepare the Space Shuttle Discovery for towing back to NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center after its landing at Edwards Air Force Base on October 24, 2000. The landing marked the end of the STS-92 mission.
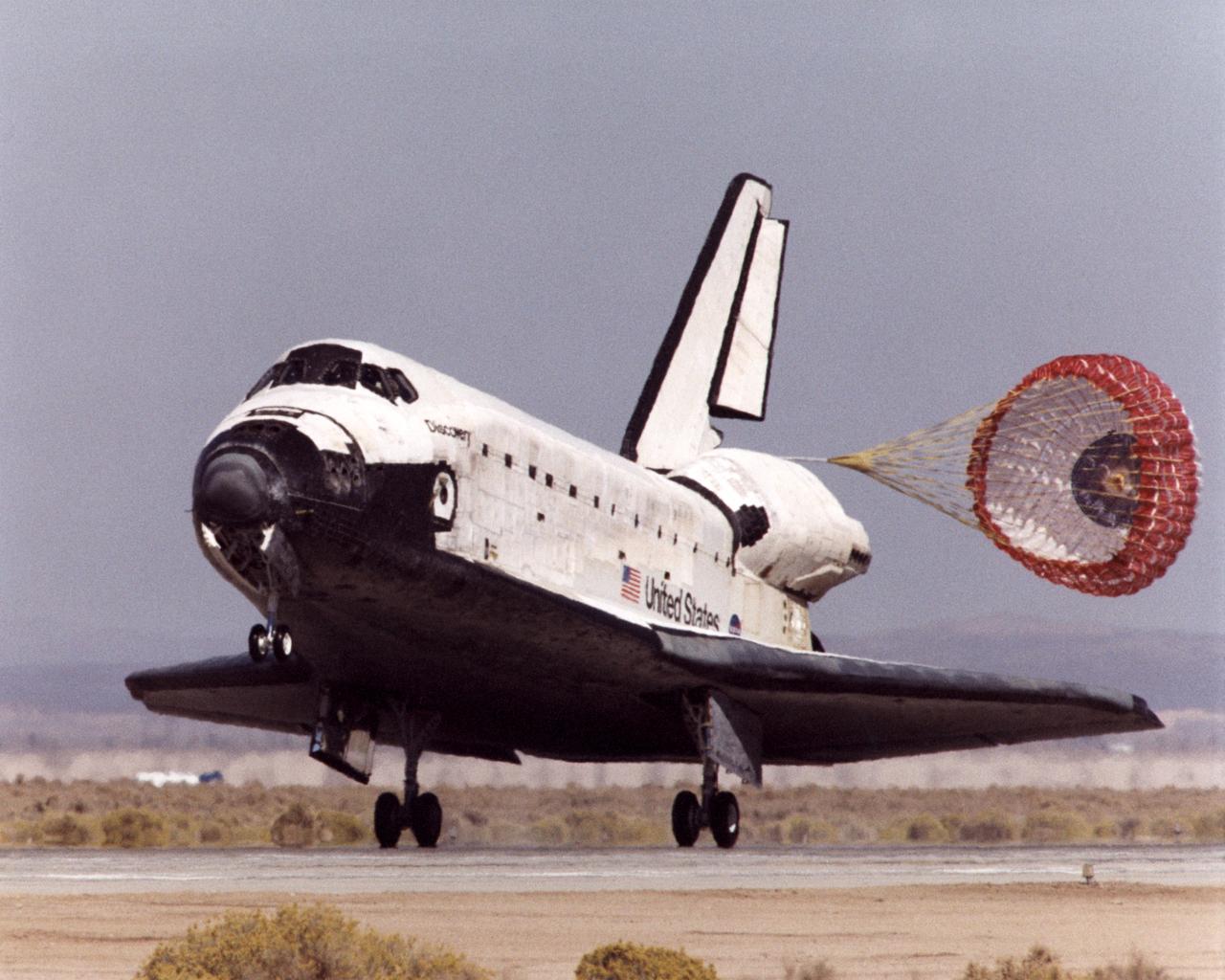

With its drag parachute deployed to help slow it down, the Space Shuttle Discovery rolls down the runway after landing at Edwards Air Force Base in Southern California at the conclusion of mission STS-92 on October 24, 2000.
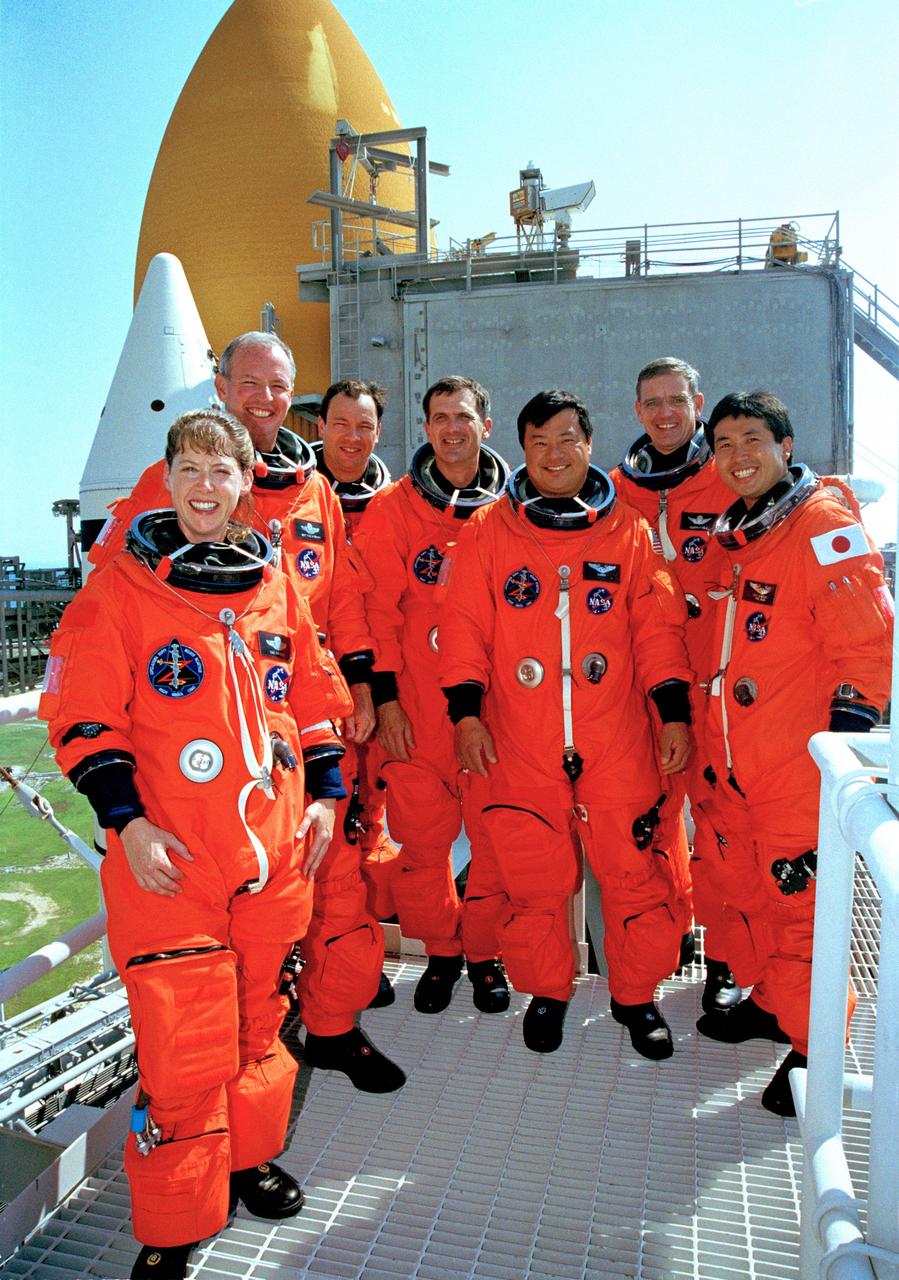

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After completing emergency egress training at Launch Pad 39A, the STS-92 crew poses for a photo. Standing, left to right, are Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy, Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr. and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The training is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated countdown. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the space station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program. Photo credit: NASA

Designed by the crew members, the STS-92 patch symbolizes the second mission to carry U.S. built elements to the International Space Station (ISS) for assembly. The black silhouette of the Space Shuttle Discovery stands out against the deep blue background of space in low Earth orbit. In the foreground, in gray, is a profile view of the ISS as it appears when the shuttle and crew arrive, with the station consisting of the Unity node, its two Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMA), the Zarya functional cargo block, the Zvezda service module, and the Progress cargo vehicle. Following the shuttle's rendezvous and docking, the ISS configuration now augmented by the two elements delivered by Discovery, the Z1 truss and PMA-3. These two elements, depicted in red, were installed using the shuttle's robot arm and connected to ISS during four space walks. The multinational nature of both the STS-92 crew and the ISS are reflected in the multi-colored Astronaut Office symbol.
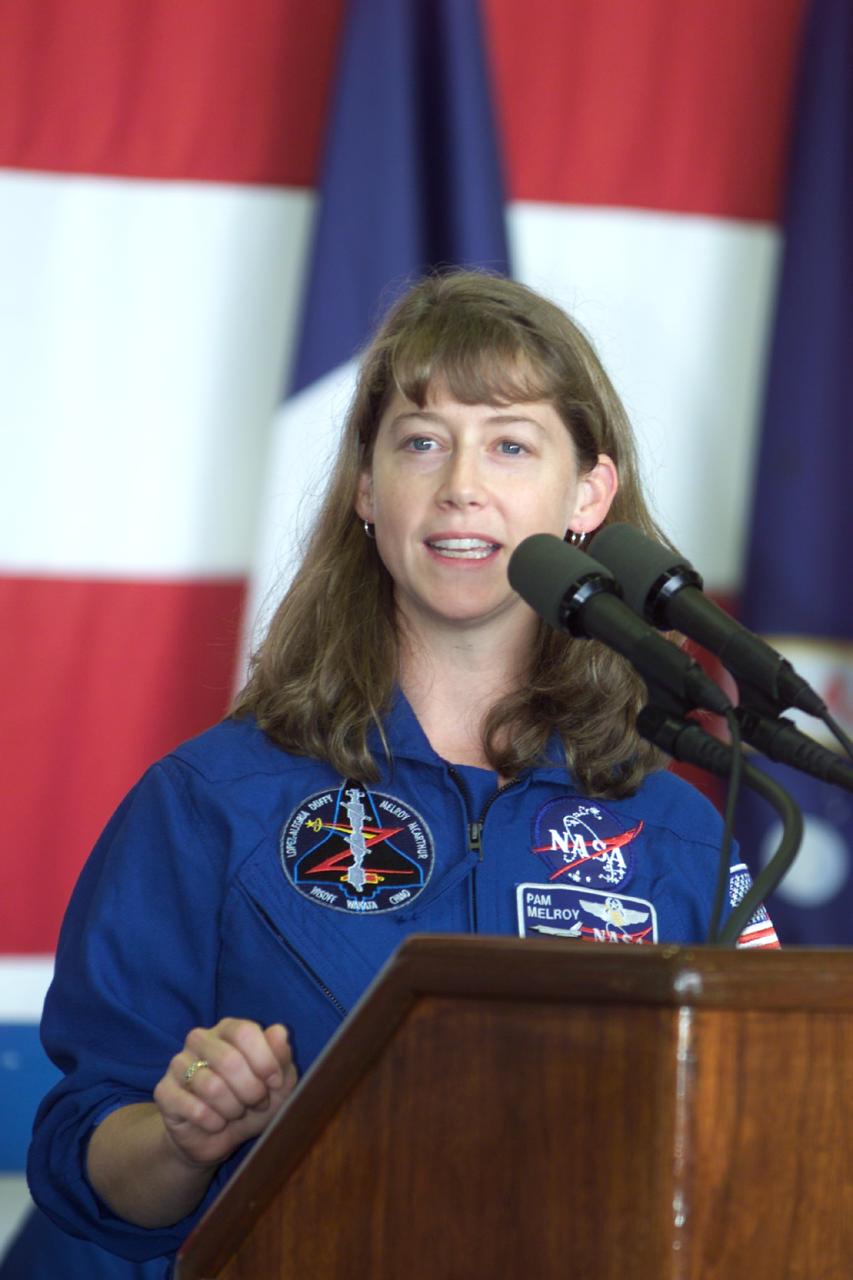

JSC2000-E-27052 (27 October 2000) --- Astronaut Pamela Melroy, STS-92 pilot, addresses crowd at Ellington Field during crew return ceremonies.
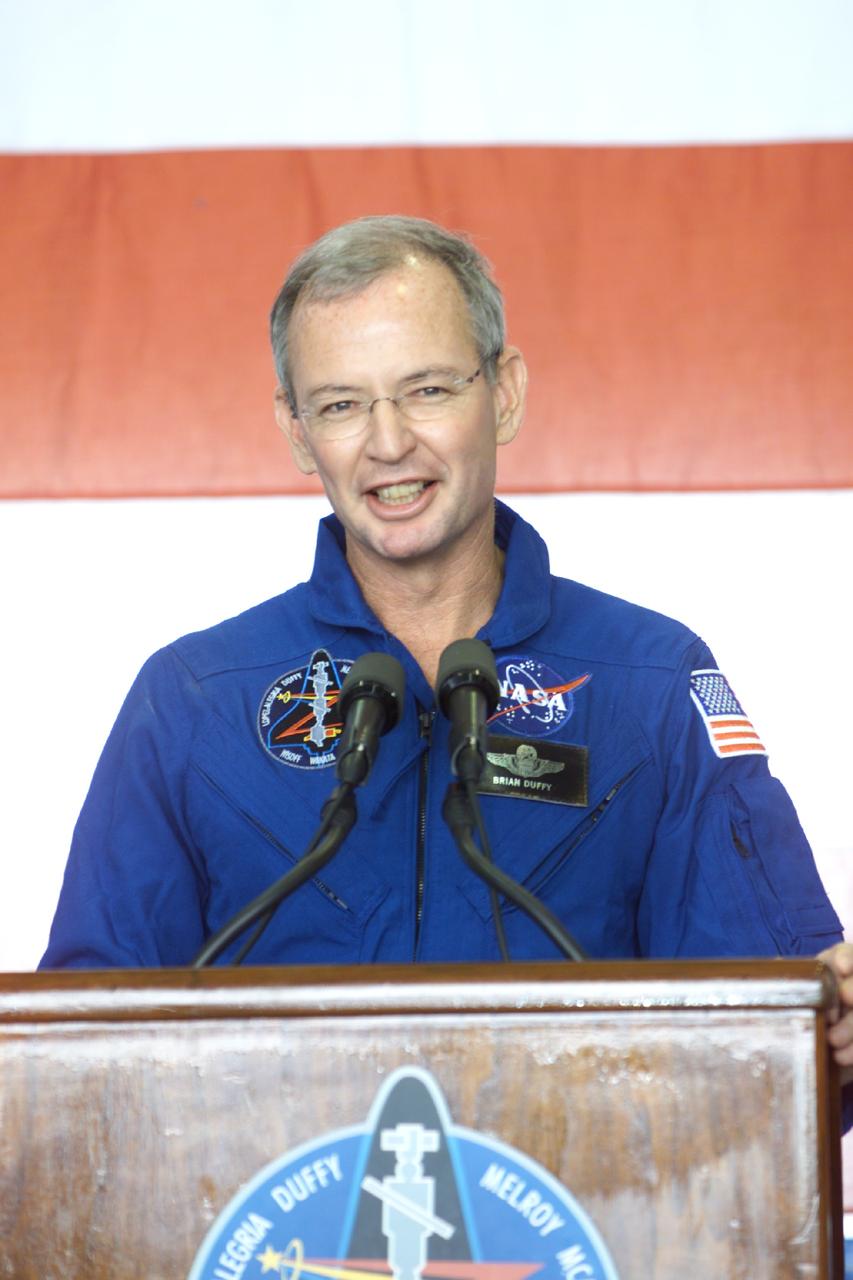

JSC2000-E-27051 (27 October 2000) --- Astronaut Brian Duffy, STS-92 commander, addresses crowd at Ellington Field during crew return ceremonies.
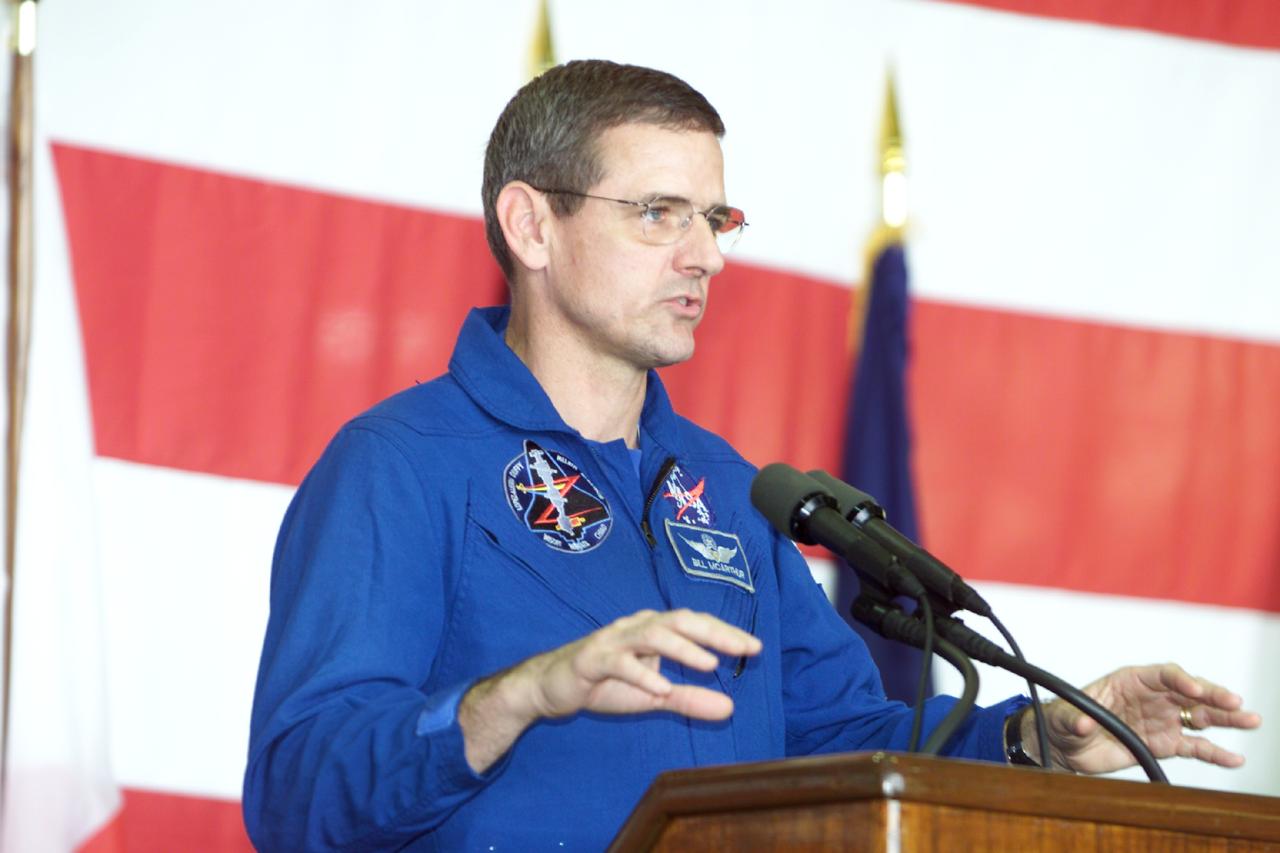

JSC2000-E-27054 (27 October 2000) --- Astronaut William (Bill) McArthur, STS-92 mission specialist, addresses crowd at Ellington Field during crew return ceremonies.
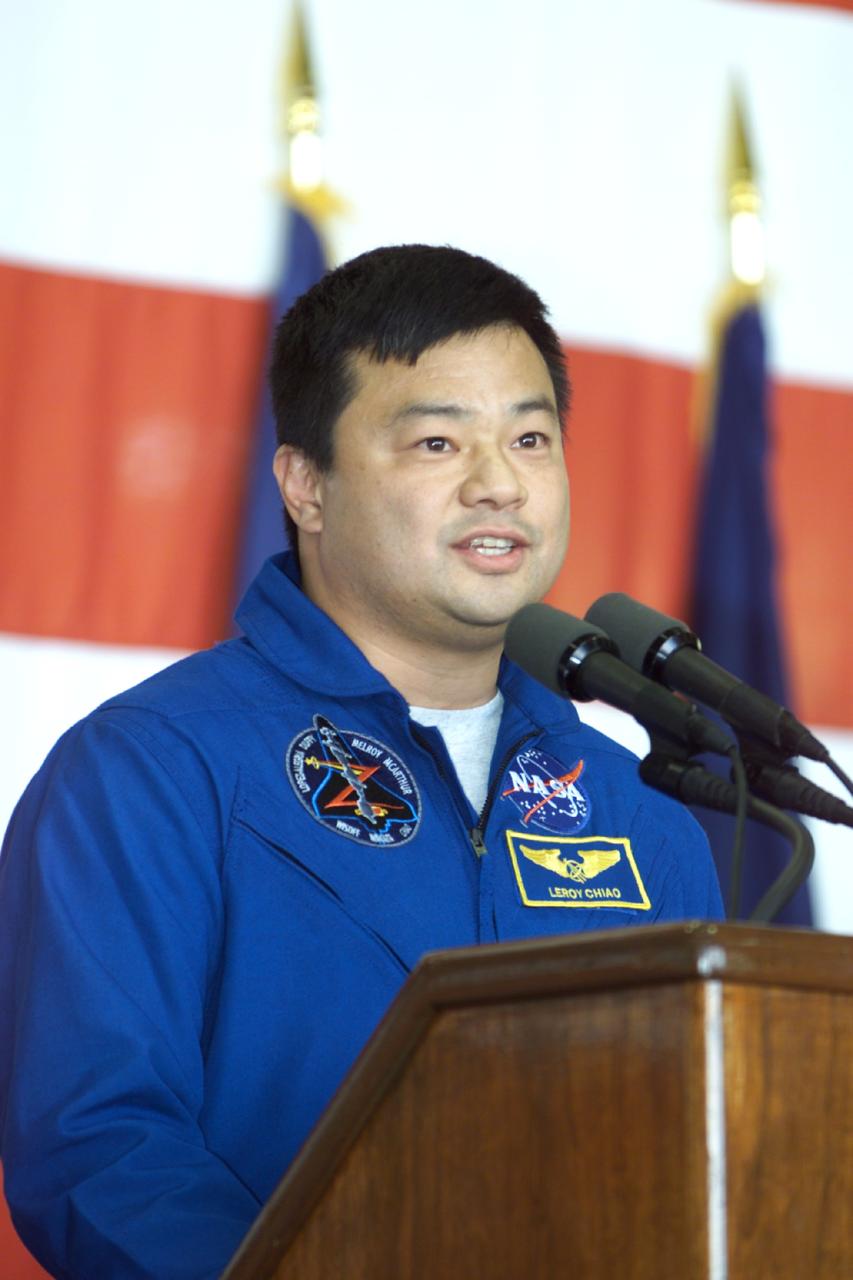

JSC2000-E-27053 (27 October 2000) --- Astronaut Leroy Chiao, STS-92 mission specialist, addresses crowd at Ellington Field during crew return ceremonies.
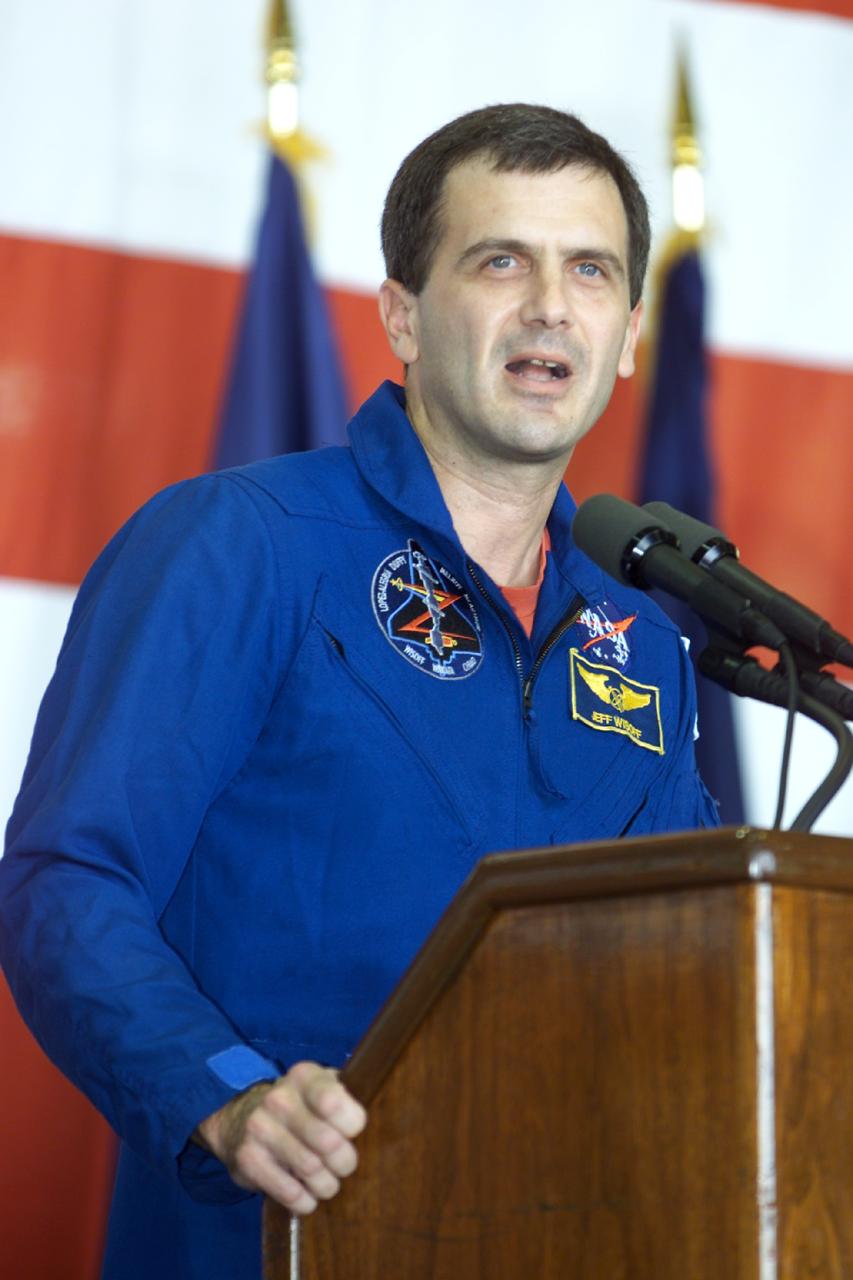

JSC2000-E-27055 (27 October 2000) --- Astronaut Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff, STS-92 mission specialist, addresses crowd at Ellington Field during crew return ceremonies.
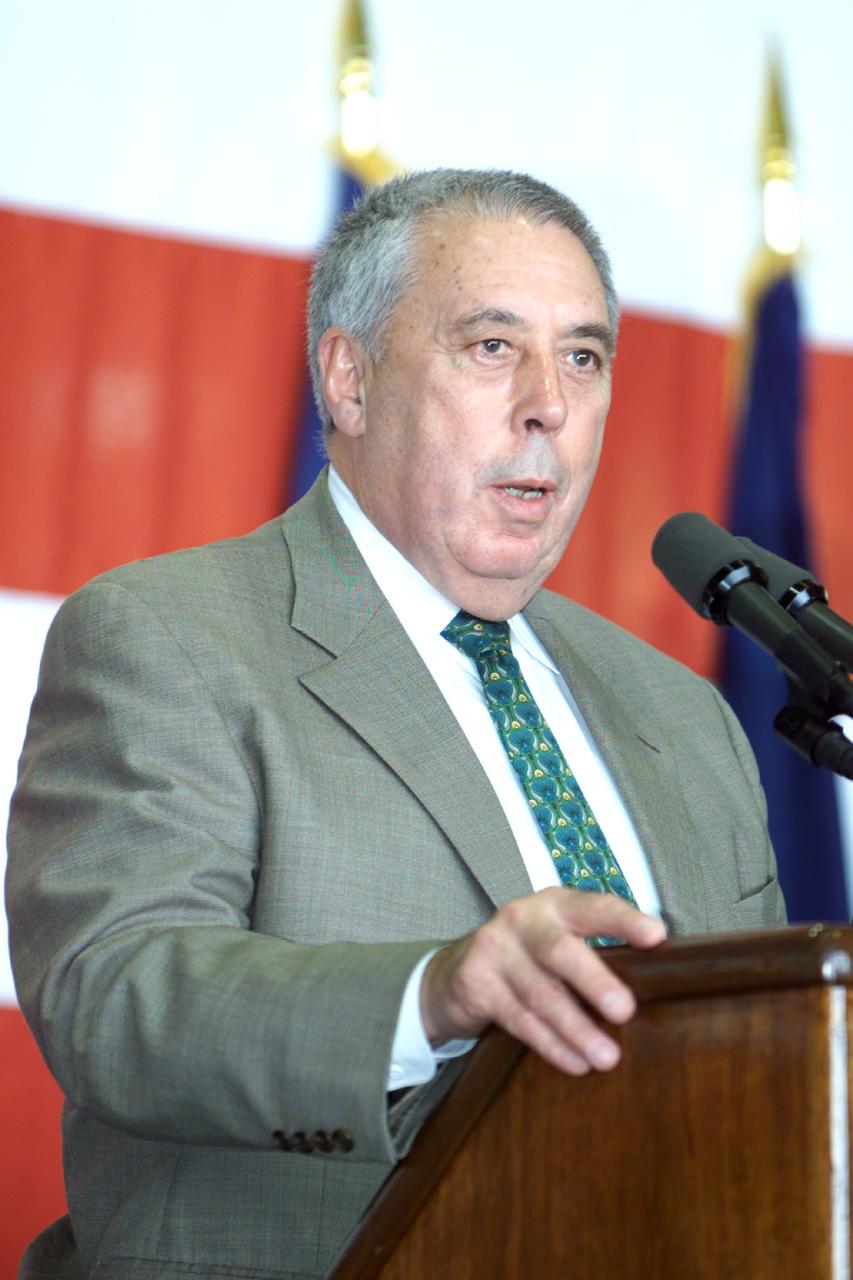

JSC2000-E-27059 (26 October 2000) --- JSC Director George W.S. Abbey speaks to crowd in Ellington Field's Hangar 990 during STS-92 crew return ceremonies.
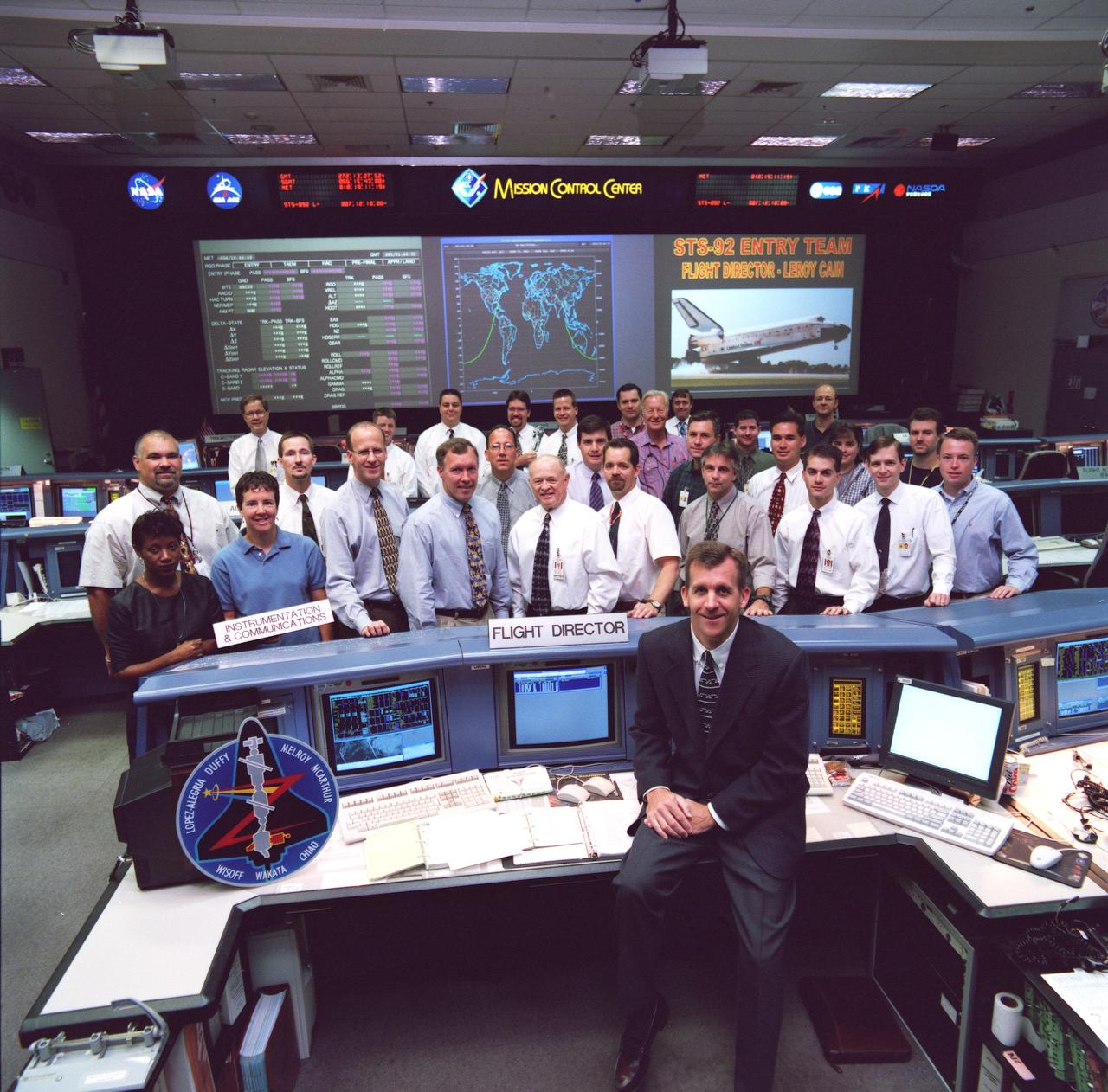

JSC2000-06401 (October 2000) --- LeRoy Cain (foreground), entry flight director for the STS-92 mission, poses with the 30-odd flight controllers who support his shift.
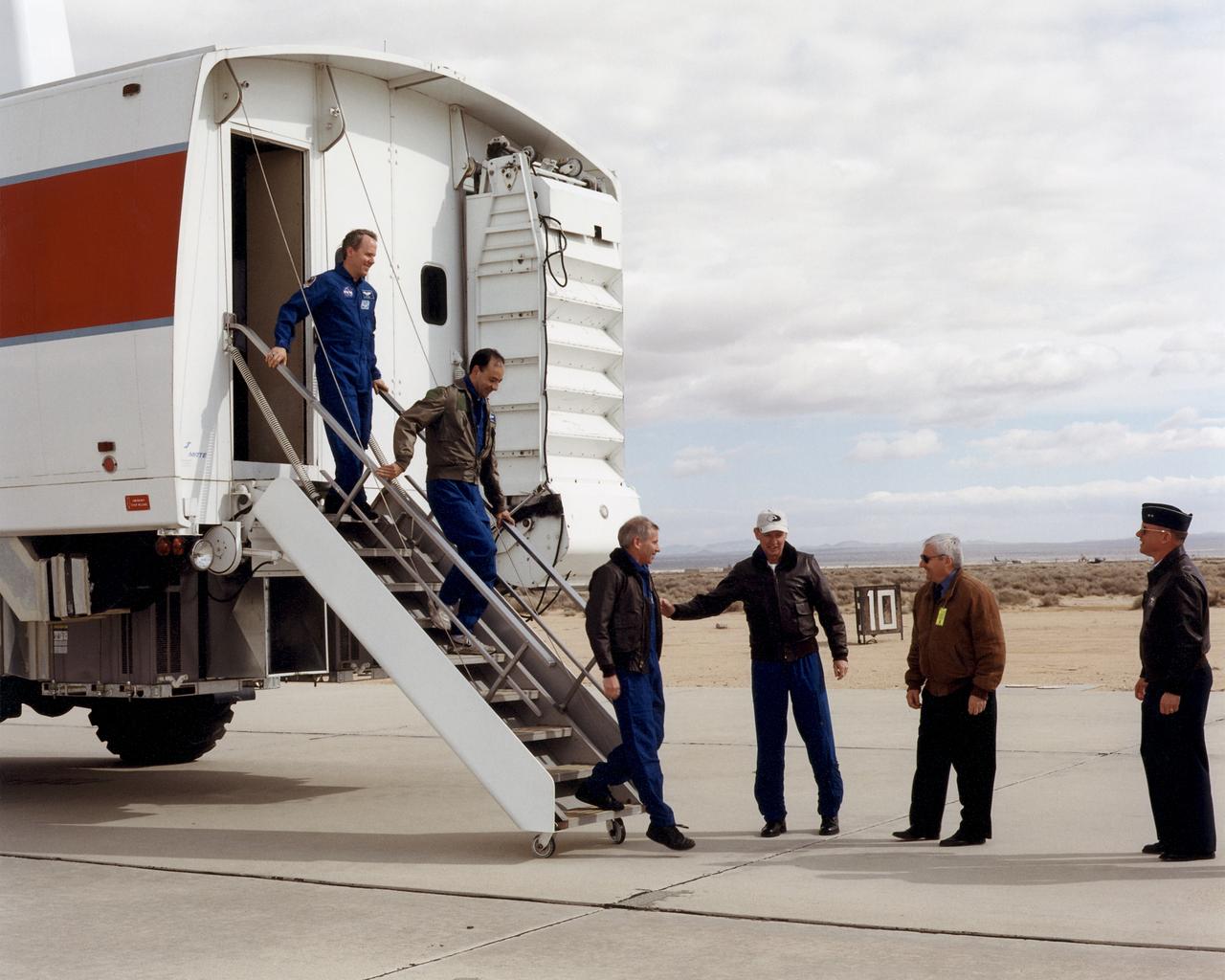

L to R: STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky, and Commander Kenneth Cockrell greet STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy, Dryden Center Director Kevin Petersen, and AFFTC Commander Major General Richard Reynolds after landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, where NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center is located.
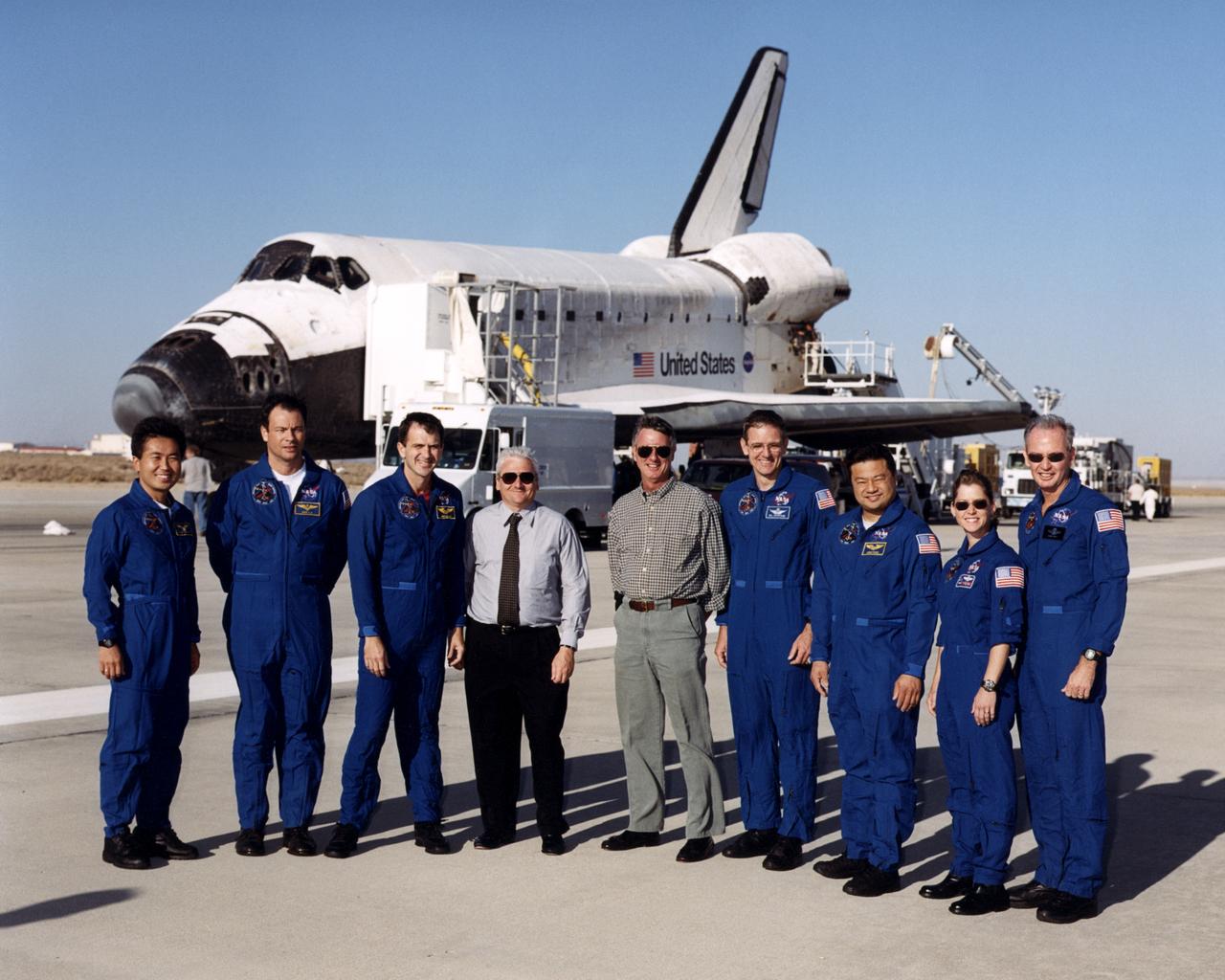

The seven-member crew of the Space Shuttle mission STS-92 gathered in front of the Shuttle Discovery shortly after landing at Edwards Air Force Base in Southern California October 24, 2000. They are seen here with NASA Dryden Fight Research Center Director Kevin Petersen and Deputy Director Wallace Sawyer. From left are mission specialists Koichi Wakata, Michael Lopez-Alegria, Jeff Wisoff, Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao, pilot Pam Melroy and mission commander Brian Duffy. Between Jeff Wisoff and Brian McArthur are Kevin Petersen and Wally Sawyer, wearing ordinary civilian clothing.

While early morning light spotlights Space Shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A, storm clouds roll in from the east. Launch Pad 39B can be seen in the distance. At right is the 300,000-gallon water tank that provides the water for sound suppression during launch.
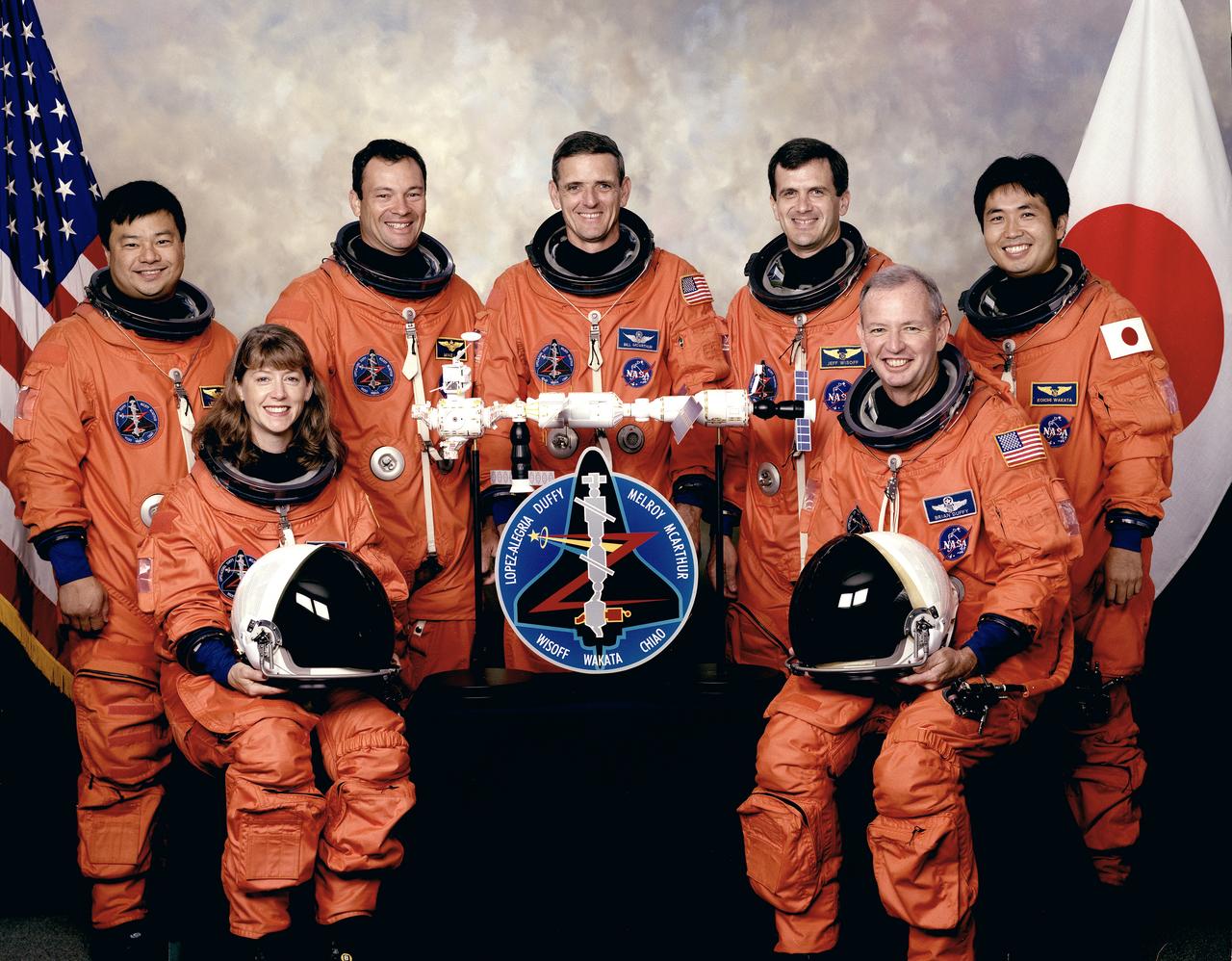

These seven astronauts composed the crew for the STS-92 mission. In front are astronauts Pamela A. Melroy, pilot; and Brian Duffy, mission commander. In the rear, from the left, are astronauts Leroy Chiao, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, William S. McArthur, Jr., Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff, and Koichi Wakata, all mission specialists. Wakata represents Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA). Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on October 11, 2000, the 100th shuttle flight was the second to deliver hardware to the International Space Station (ISS). During Four space walks, the crew installed the Z1 truss and the Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA) 3.
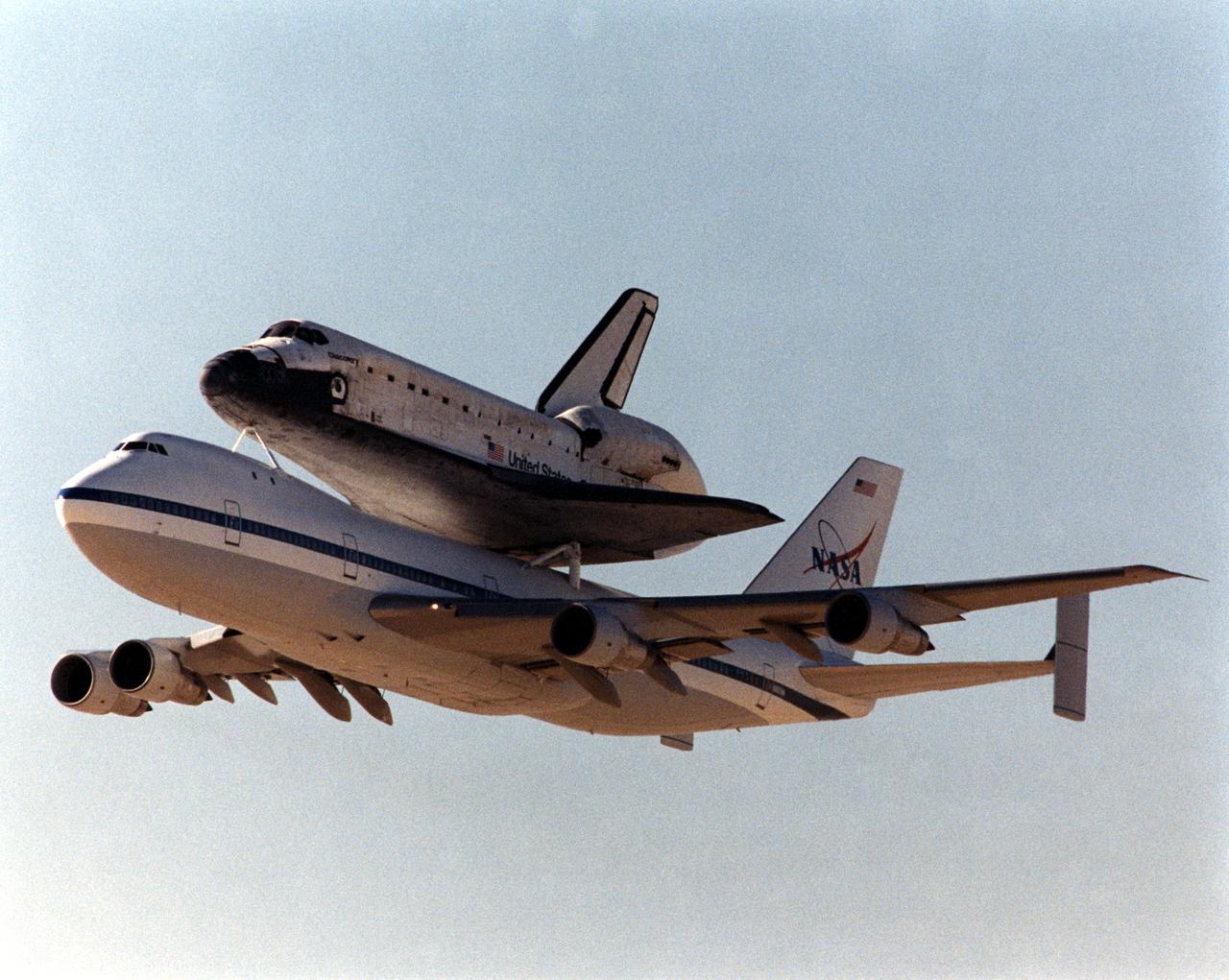

One of NASA’s two modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery on its back climbs out after takeoff from Edwards Air Force Base, California. The Discovery was ferried from NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 2, 2000, after extensive post-landing servicing and ferry flight preparations.
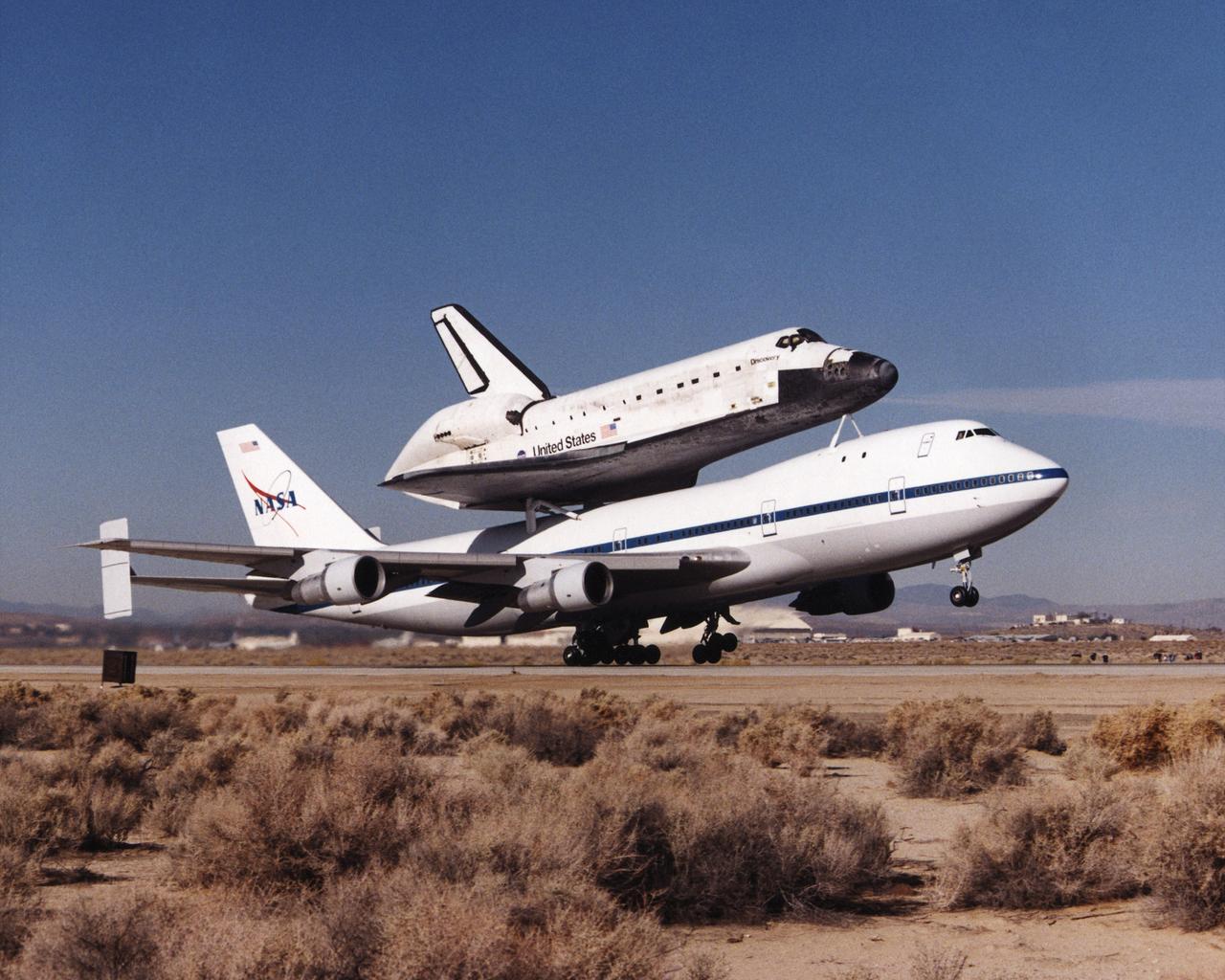

Carrying the Space Shuttle Discovery piggyback, one of NASA’s modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft lifts off the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California. The Discovery was ferried from NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 2, 2000, after extensive post-landing servicing and ferry flight preparations.
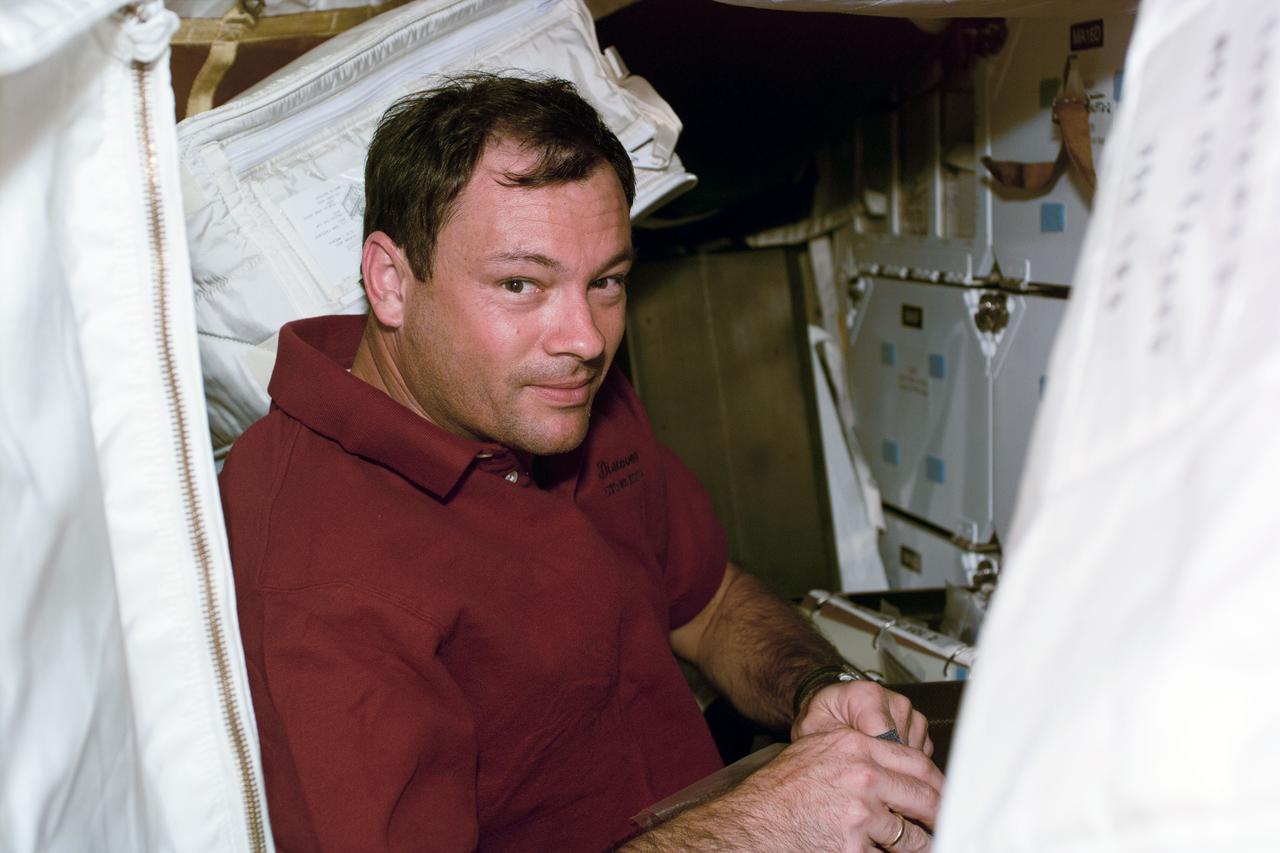

S92-E-5026 (12 October 2000) --- Astronaut Michael Lopez-Alegria, one of four STS-92 crew members who are participating in the four scheduled space walks designed to put final touches on the current ISS configuration for its first occupancy, was recorded by an electronic still camera (ESC) on Flight Day 2.
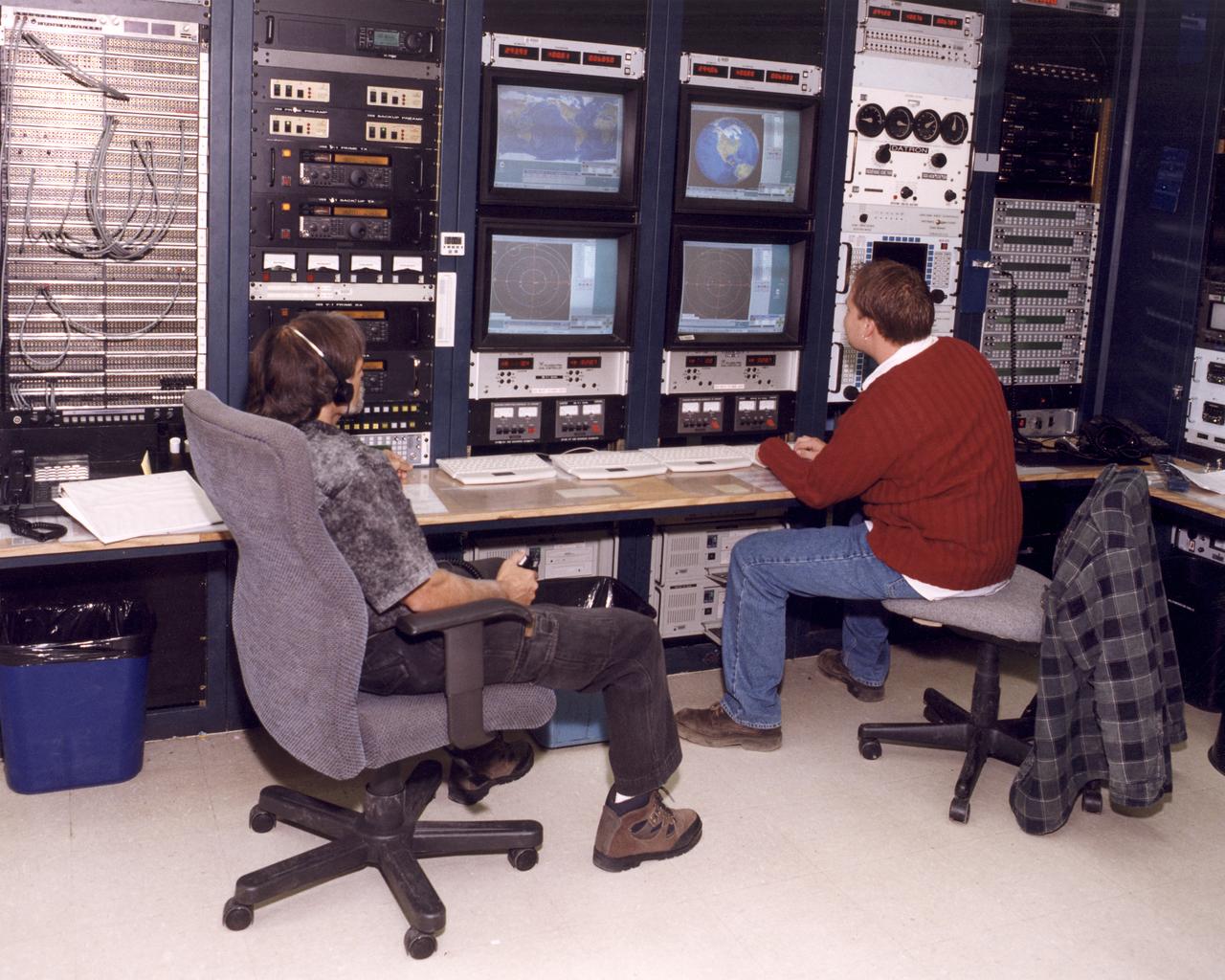

Mike Yettaw and Donavon Hoover providing air-to-ground communications to the Johnson Space Center during STS-92.
![STS092-S-023 [EC00-0311-4] (24 October 2000)--- The seven astronauts for the STS-92 flight, having just returned from a mission in Earth orbit aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery, pose near that vehicle at Edwards Air Force Base in the Mojave Desert of California. From the left are astronauts Koichi Wakata of Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA), Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff, William S. McArthur, Jr., Leroy Chiao, Pamela A. Melroy and Brian Duffy. Discovery touched down at 2 p.m. (PDT), October 24, and rolled to a stop on Edward's concrete runway at 2:0l, for a mission elapsed time of 12 days, 21 hours and 43 minutes.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/sts092-s-023/sts092-s-023~medium.jpg)
STS092-S-023 [EC00-0311-4] (24 October 2000)--- The seven astronauts for the STS-92 flight, having just returned from a mission in Earth orbit aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery, pose near that vehicle at Edwards Air Force Base in the Mojave Desert of California. From the left are astronauts Koichi Wakata of Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA), Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff, William S. McArthur, Jr., Leroy Chiao, Pamela A. Melroy and Brian Duffy. Discovery touched down at 2 p.m. (PDT), October 24, and rolled to a stop on Edward's concrete runway at 2:0l, for a mission elapsed time of 12 days, 21 hours and 43 minutes.
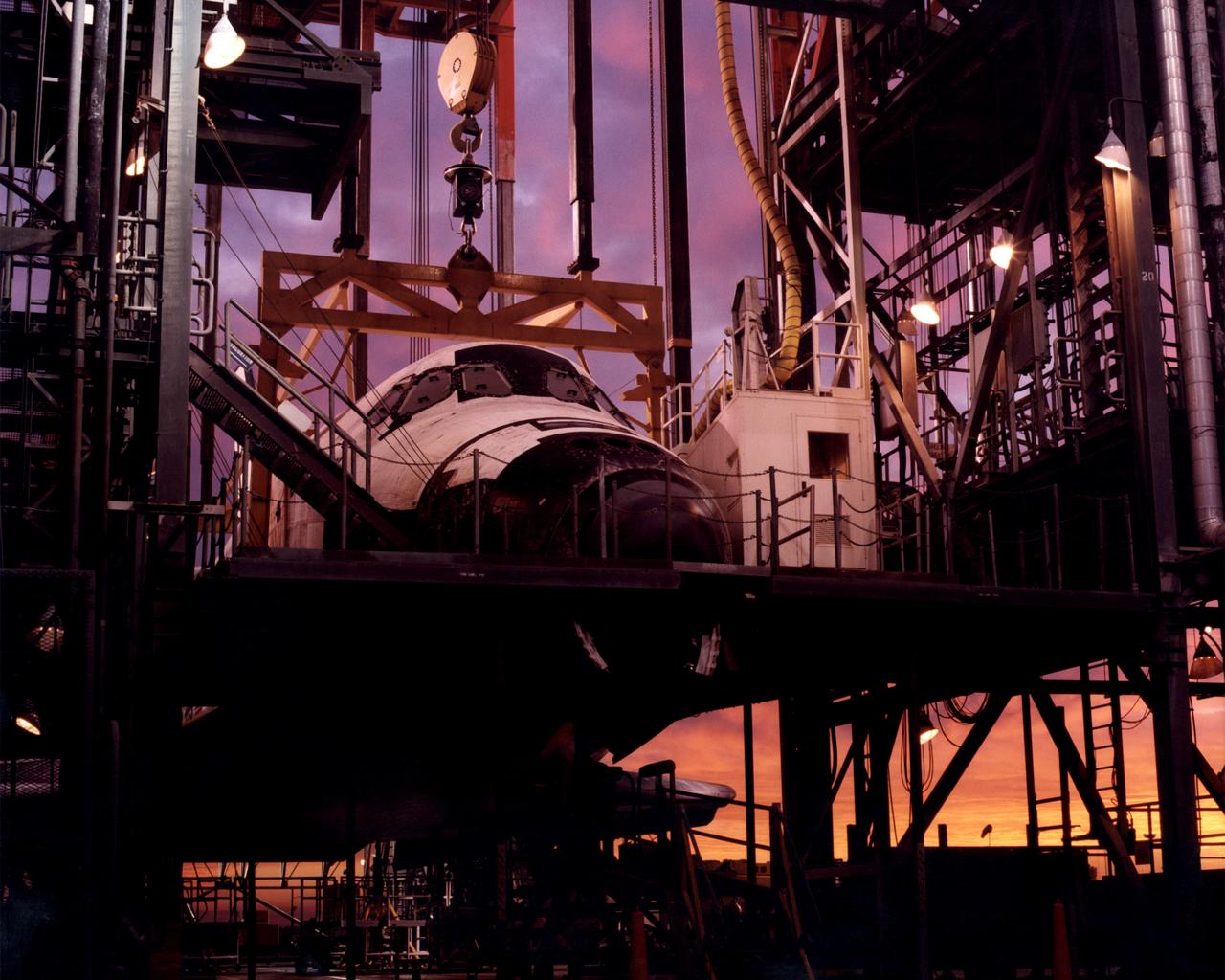

The early-morning Sun bathes the Space Shuttle Discovery in hues of purple, pink and gold as it is encased in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used to prepare the shuttle for its ferry flight back to the Kennedy space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA’s modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.
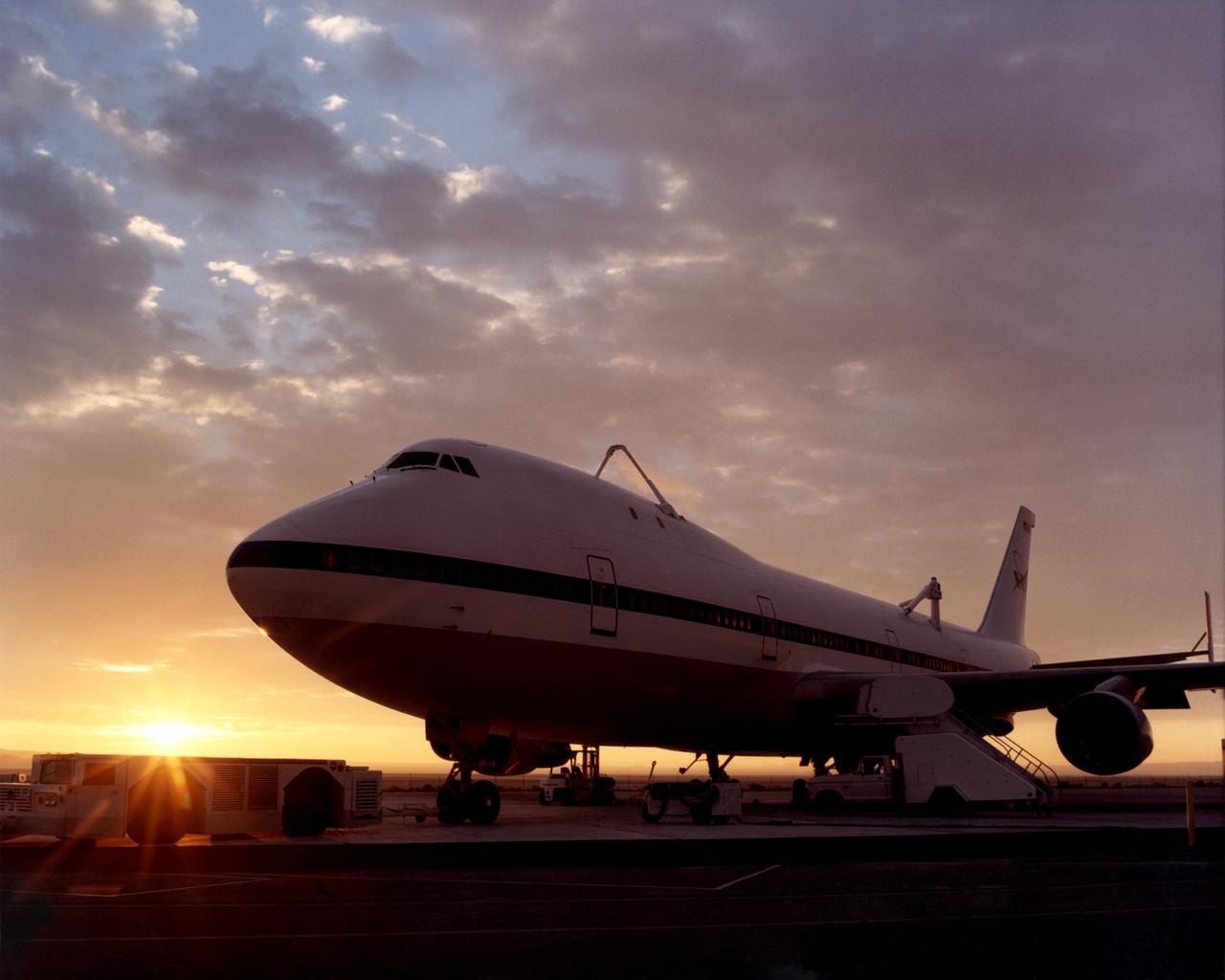

One of NASA’s two modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft is bathed in the morning Sun at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. The modified jumbo jetliners are used to ferry the Space Shuttle orbiters between Dryden and the Kennedy Space Center in Florida and Boeing’s Reusable Space Systems modification facility at Palmdale, California. Features which distinguish the two SCAs from standard 747 jetliners are three struts, with associated interior structural strengthening, which protrude from the top of the fuselage (two aft, one forward) on which the orbiter is attached, and two additional vertical stabilizers, one on each end of the standard horizontal stabilizer, to enhance directional stability. All interior furnishings and equipment aft of the forward No. 1 doors have also been removed to reduce weight. The two SCAs are under the operational control of NASA's Johnson Space Center, Houston, Texas.
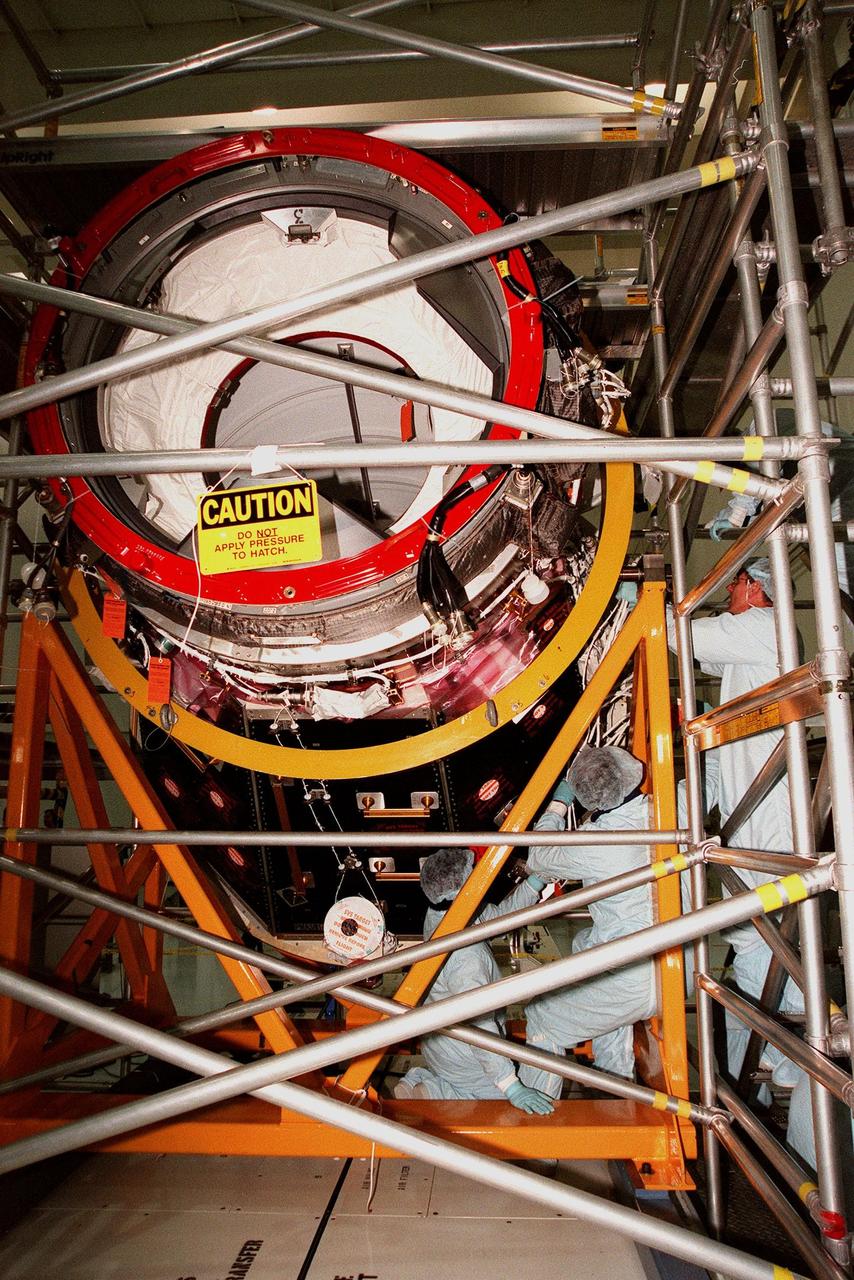
In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew practice working with the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3, part of the payload for their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). STS-92 is targeted for launch in December 1999. STS-92 crew members visiting KSC are Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Jeff Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria and Bill McArthur. STS-92 is the fourth U.S. flight for construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes an integrated truss structure
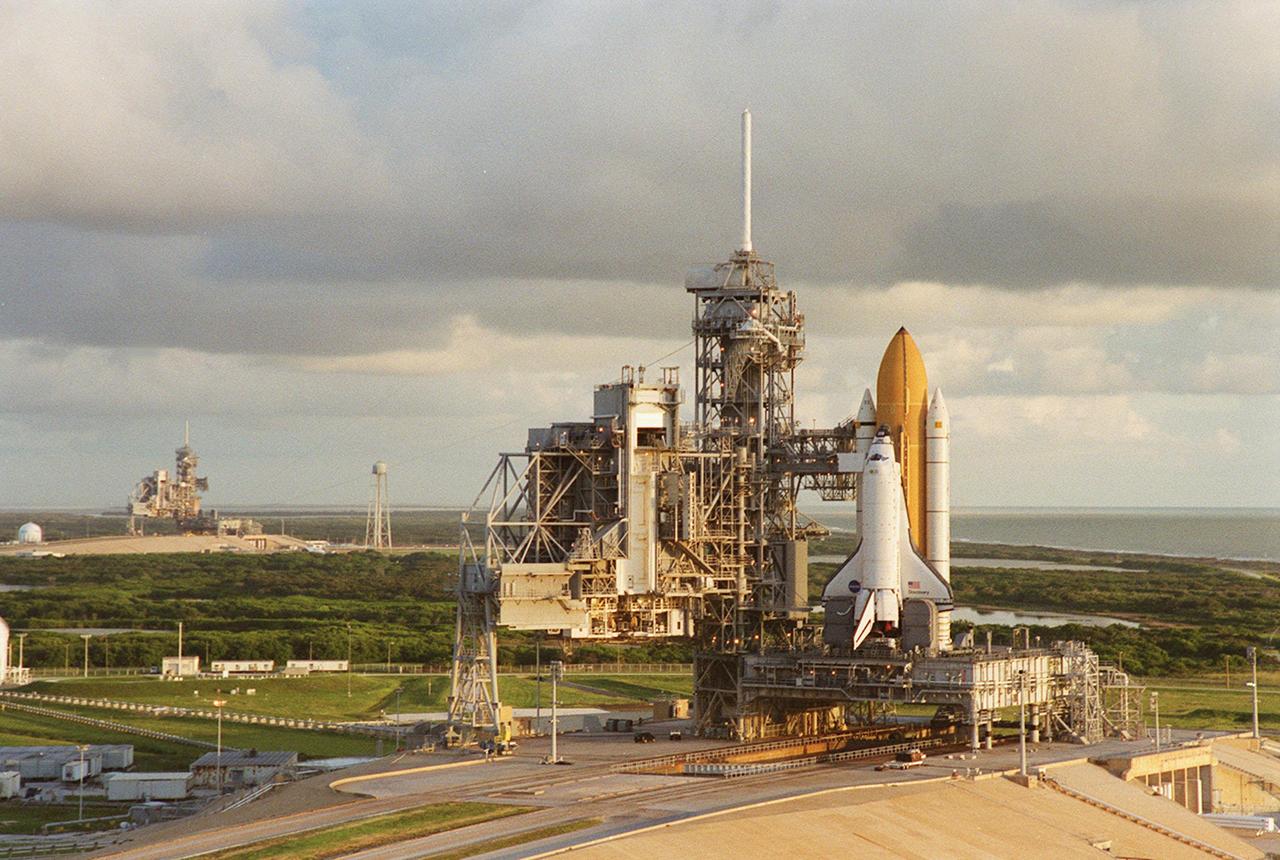

Cloudy skies form a backdrop for Launch Pads 39B (left) and 39A (foreground). Space Shuttle Discovery waits on top of the pad for its launch Oct. 5 to the International Space Station. Between the pads can be seen the 300,000-gallon water tank that provides water for the sound suppression system during launch.
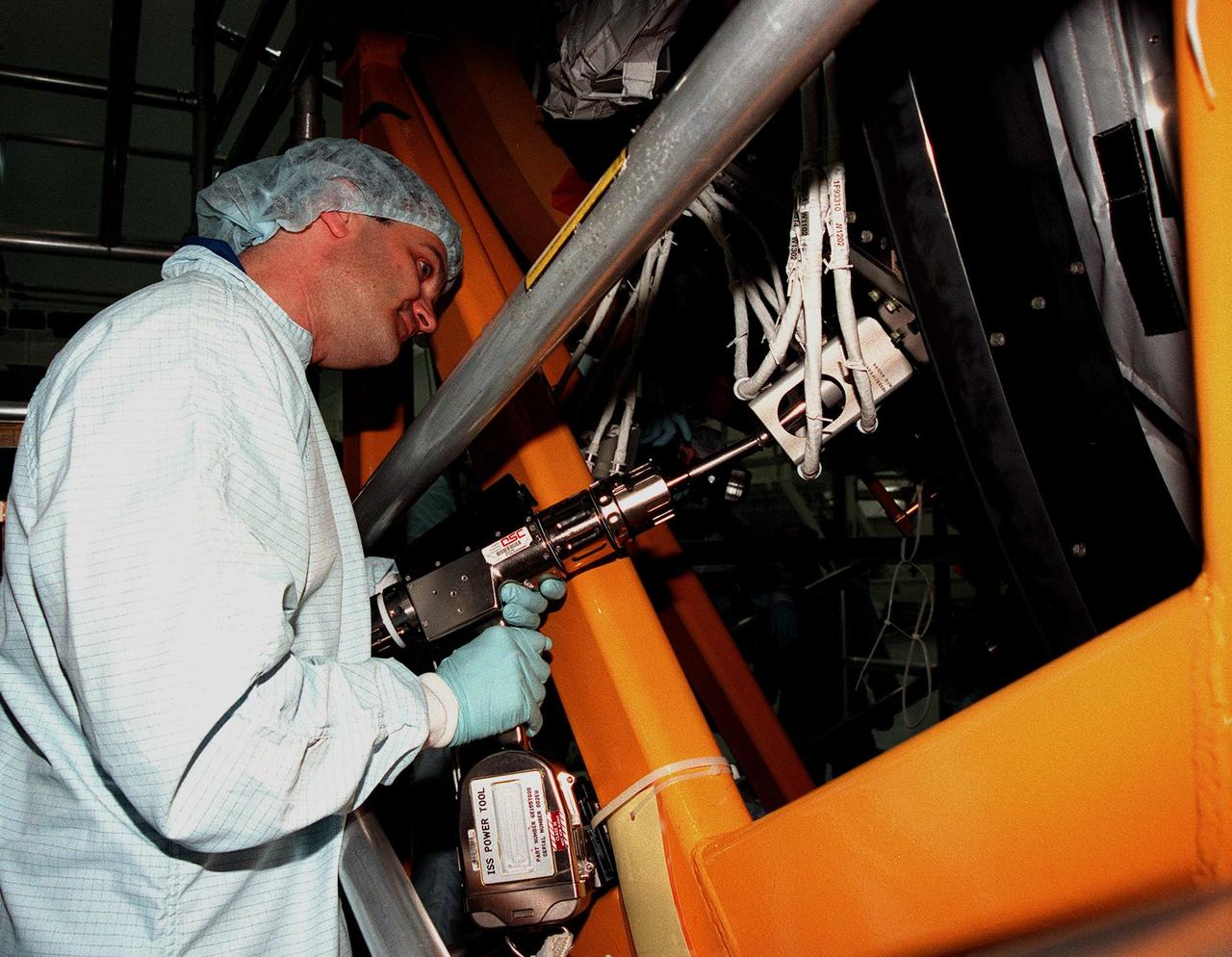

In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-92 Mission Specialist Jeff Wisoff practices removing a wire harness from the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3, part of the payload on the STS-92 mission to the International Space Station (ISS). STS-92 is targeted for launch in December 1999. Other crew members visiting KSC are Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Michael Lopez-Alegria and Bill McArthur. STS-92 is the fourth U.S. flight for construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes an integrated truss structure
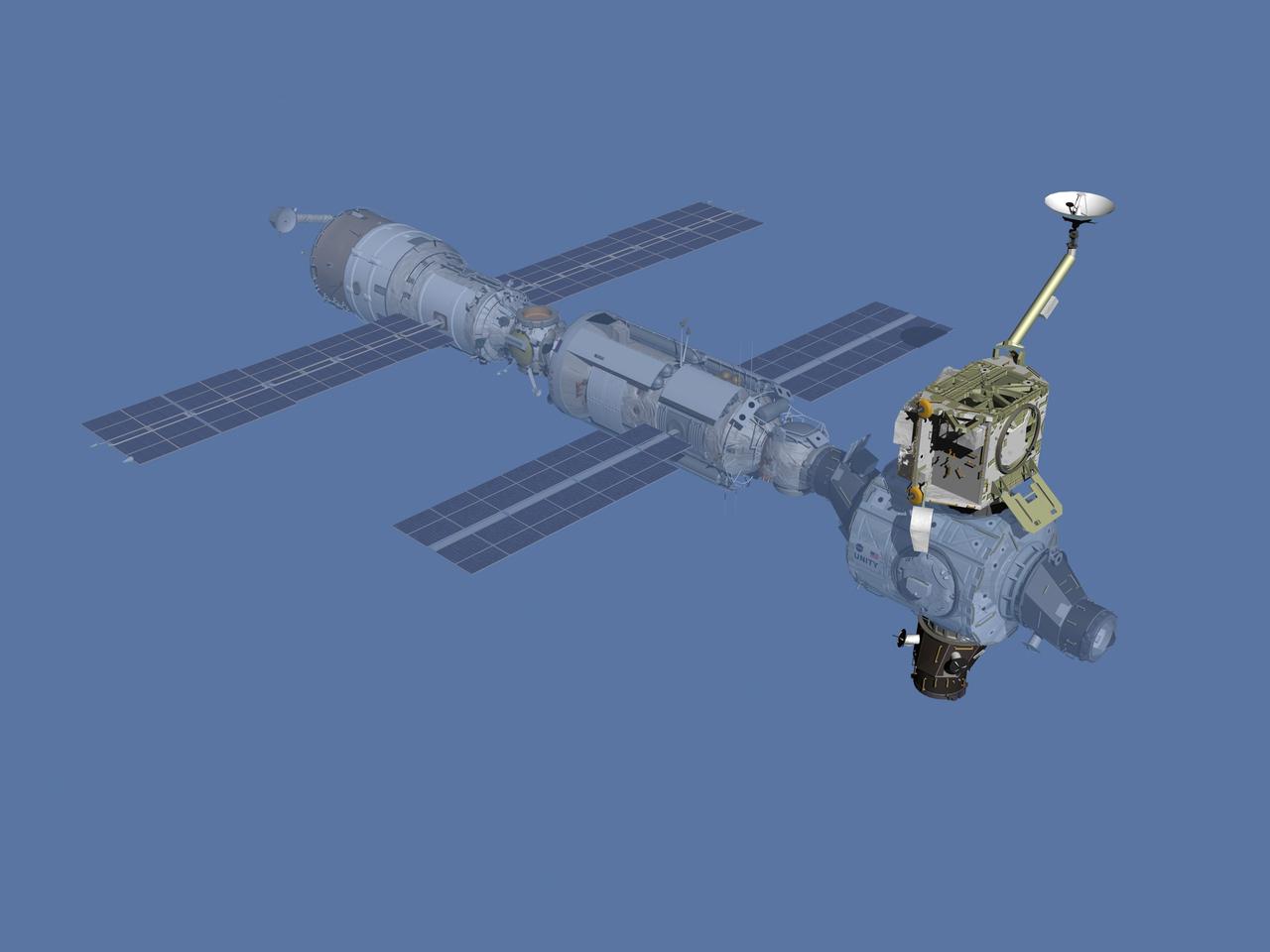
JSC2006-E-43482 (October 2000) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight STS-92/3A. Arriving aboard Space Shuttle Discovery, the STS-92 crew installed the Z1 truss, a third pressurized mating adapter and a Ku-band antenna.
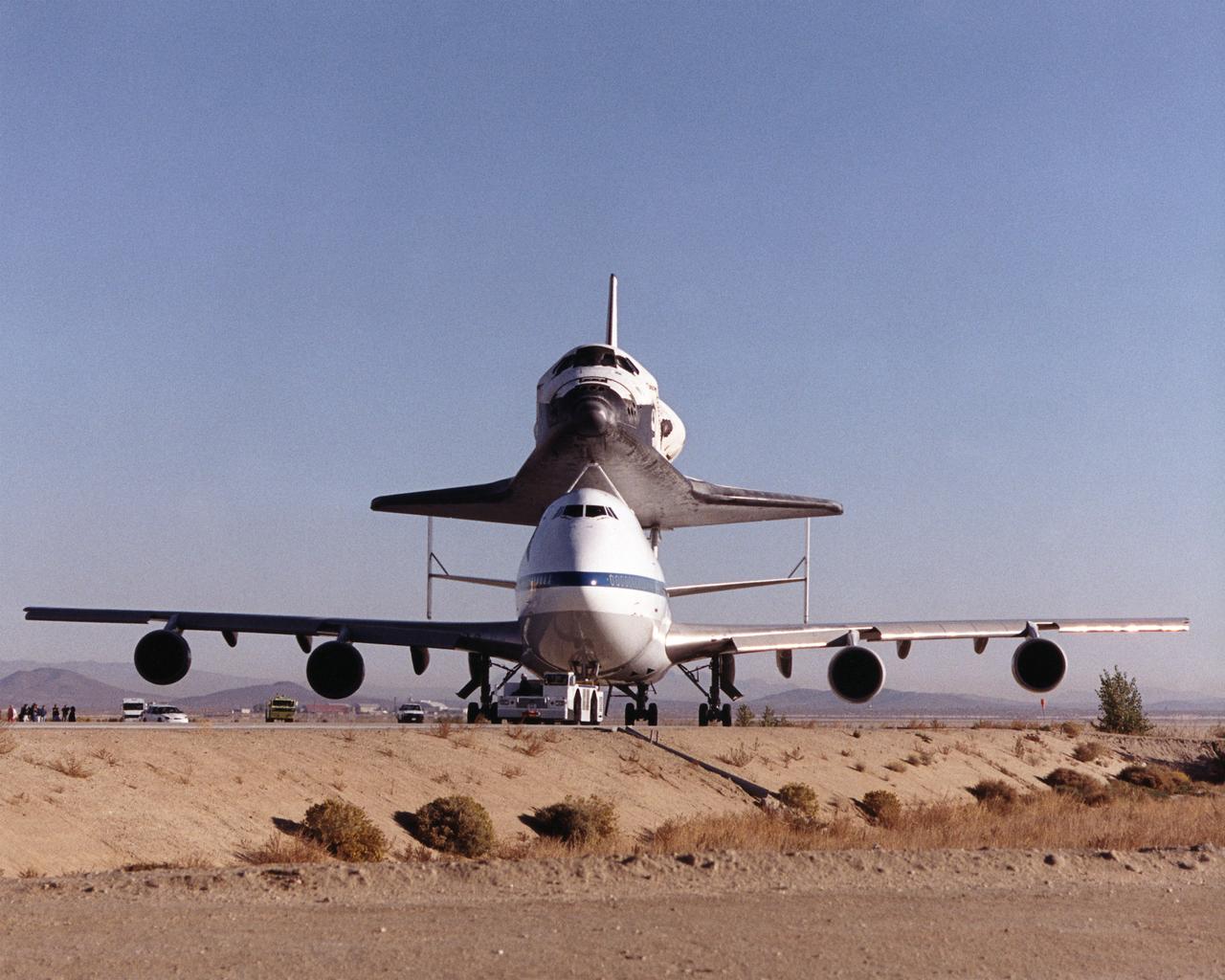

The Space Shuttle Discovery sits atop one of NASA’s modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft as the unusual piggyback duo is towed along a taxiway at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. The Discovery was ferried from NASA Dryden to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 2, 2000, after extensive pre-ferry servicing and preparations.
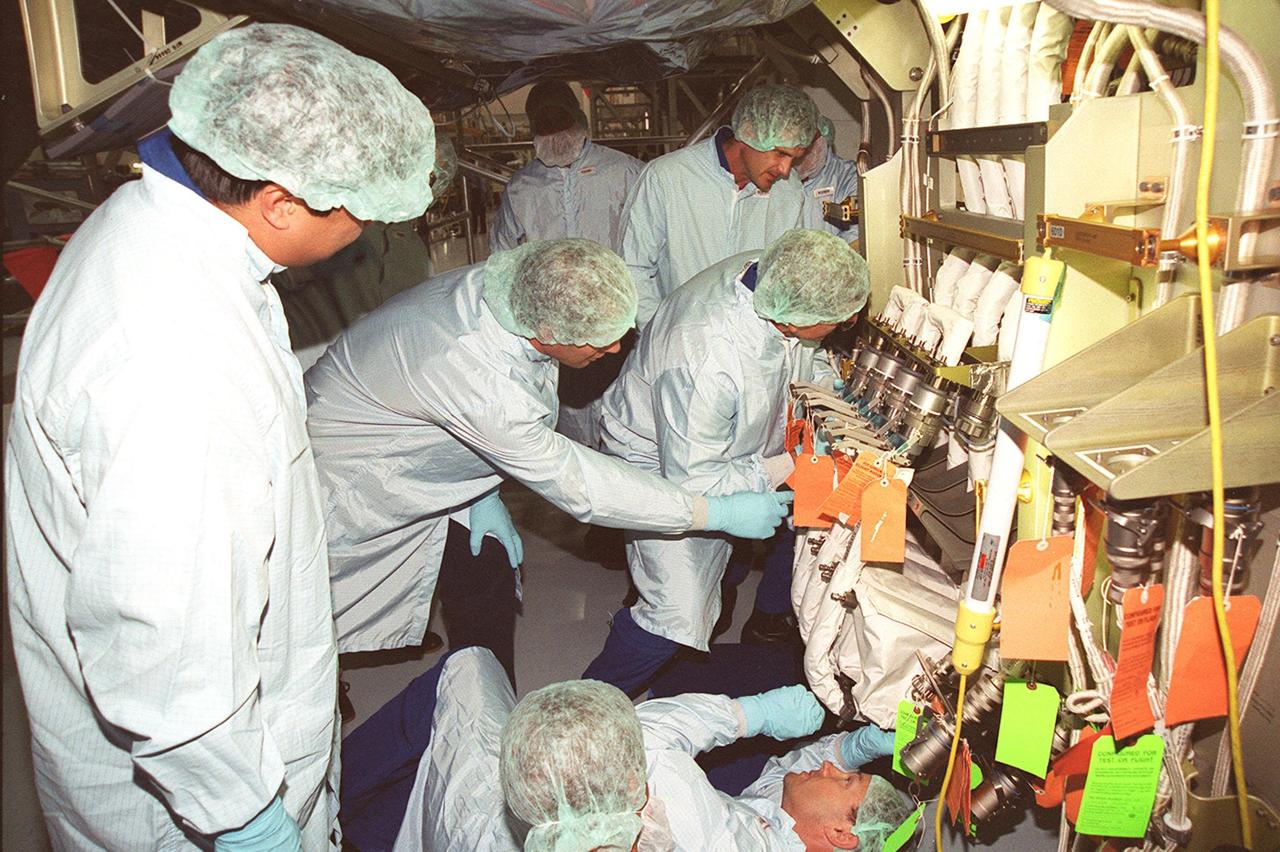
As part of Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities, members of the STS-92 crew check out equipment they will be using on the mission to the International Space Station. At left is Mission Specialist Leroy Chiao, looking at part of the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the Station and payload on STS-92. Others seen in the photo are Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria (on his back, lower right); Jeff Wisoff (standing in back); and Bill McArthur (bending closer to the Z1 truss). Also taking part in the CIET are Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pam Melroy, and Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
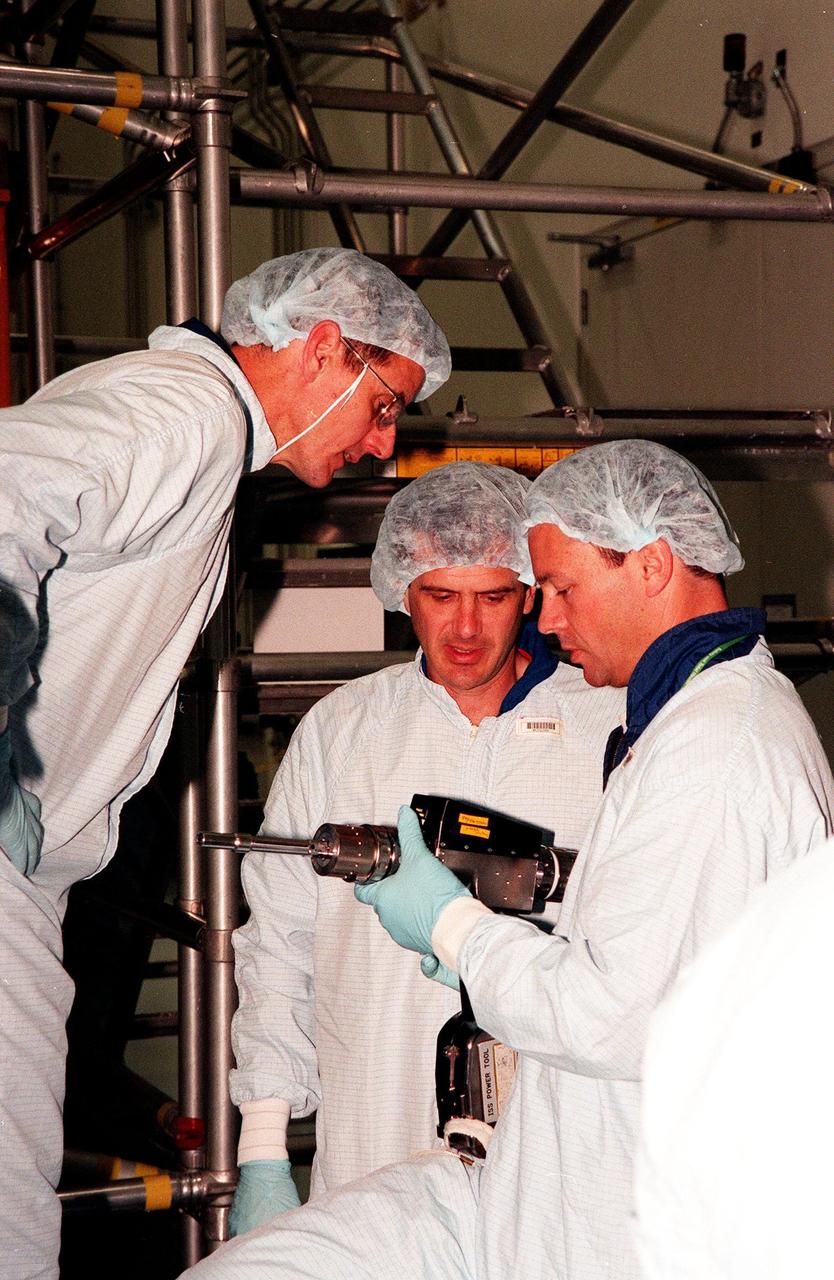

In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew become familiar with equipment in preparation for their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). STS-92 is targeted for launch in December 1999. From left are Mission Specialists Bill McArthur, Jeff Wisoff and Michael Lopez-Alegria, holding an ISS power tool. Other crew members visiting KSC are Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata and Leroy Chiao. STS-92 is the fourth U.S. flight for construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes an integrated truss structure and a pressurized mating adapter
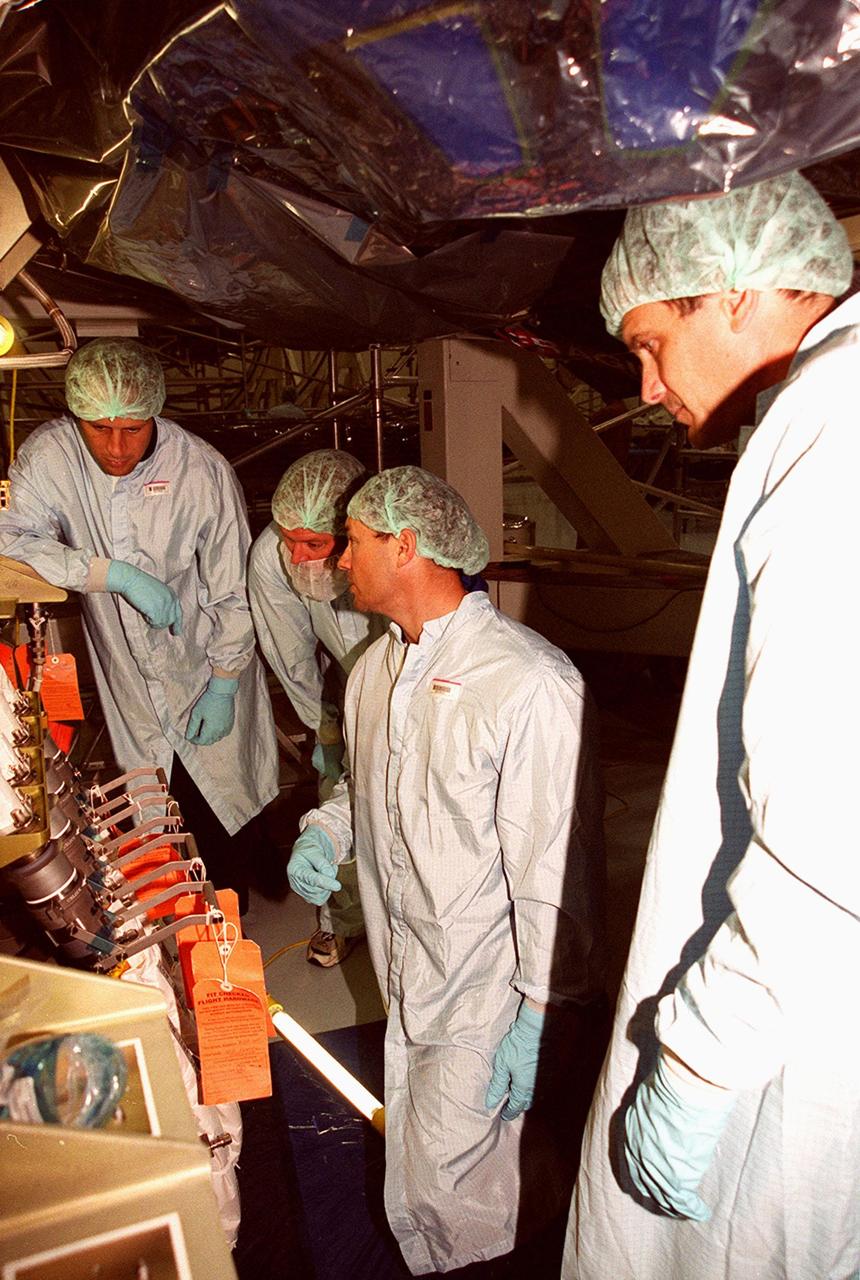

As part of Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities, members of the STS-92 crew check out equipment they will be using on the mission to the International Space Station. Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria (center) and Jeff Wisoff (right) talk with Boeing technicians about the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the Station and payload on STS-92, in front of them. The Z1 truss is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
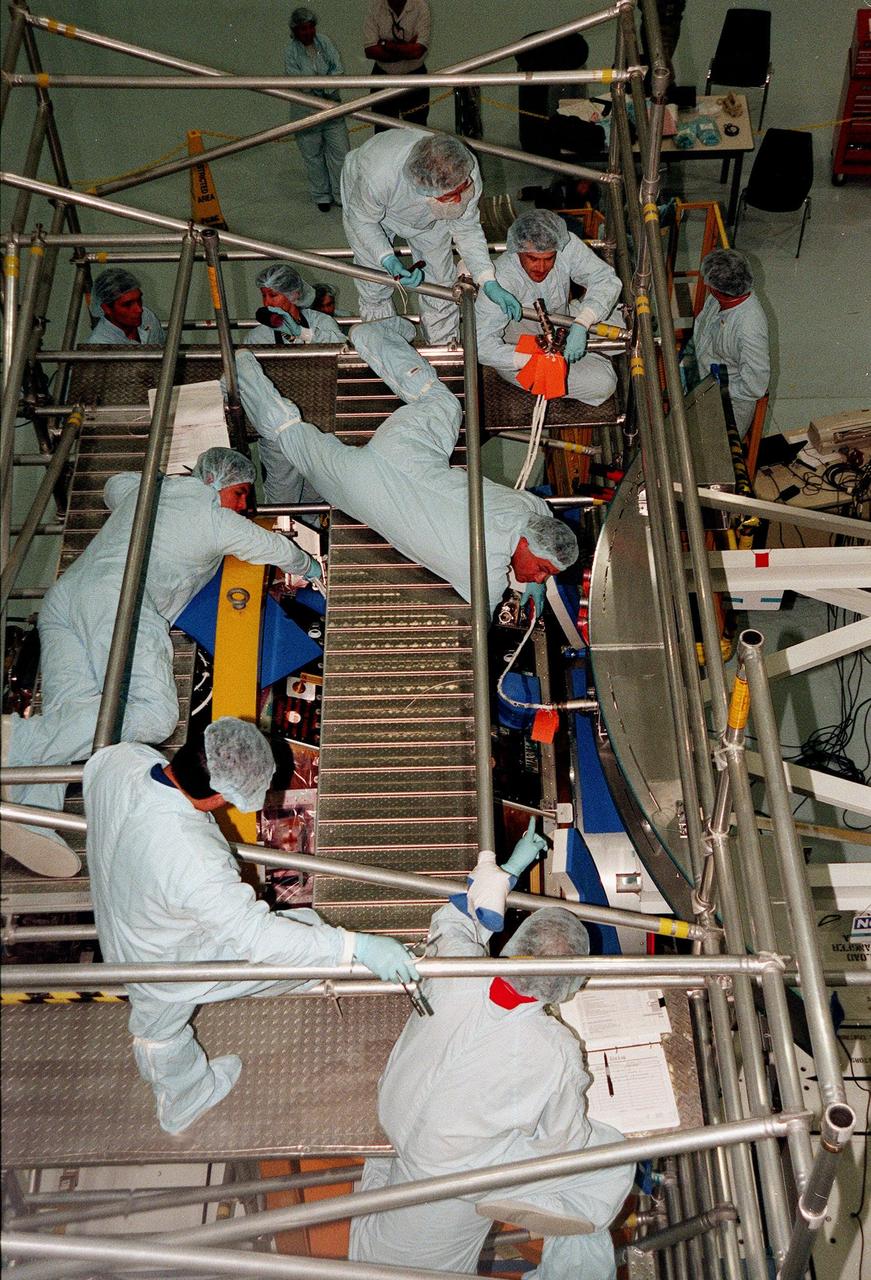

In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew fill scaffolding to look over the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3, part of the payload for their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). STS-92 is targeted for launch in December 1999. From lower left are Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, Michael Lopez-Alegria (center), Bill McArthur and Jeff Wisoff (top). Other crew members visiting KSC are Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata. STS-92 is the fourth U.S. flight for construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes an integrated truss structure
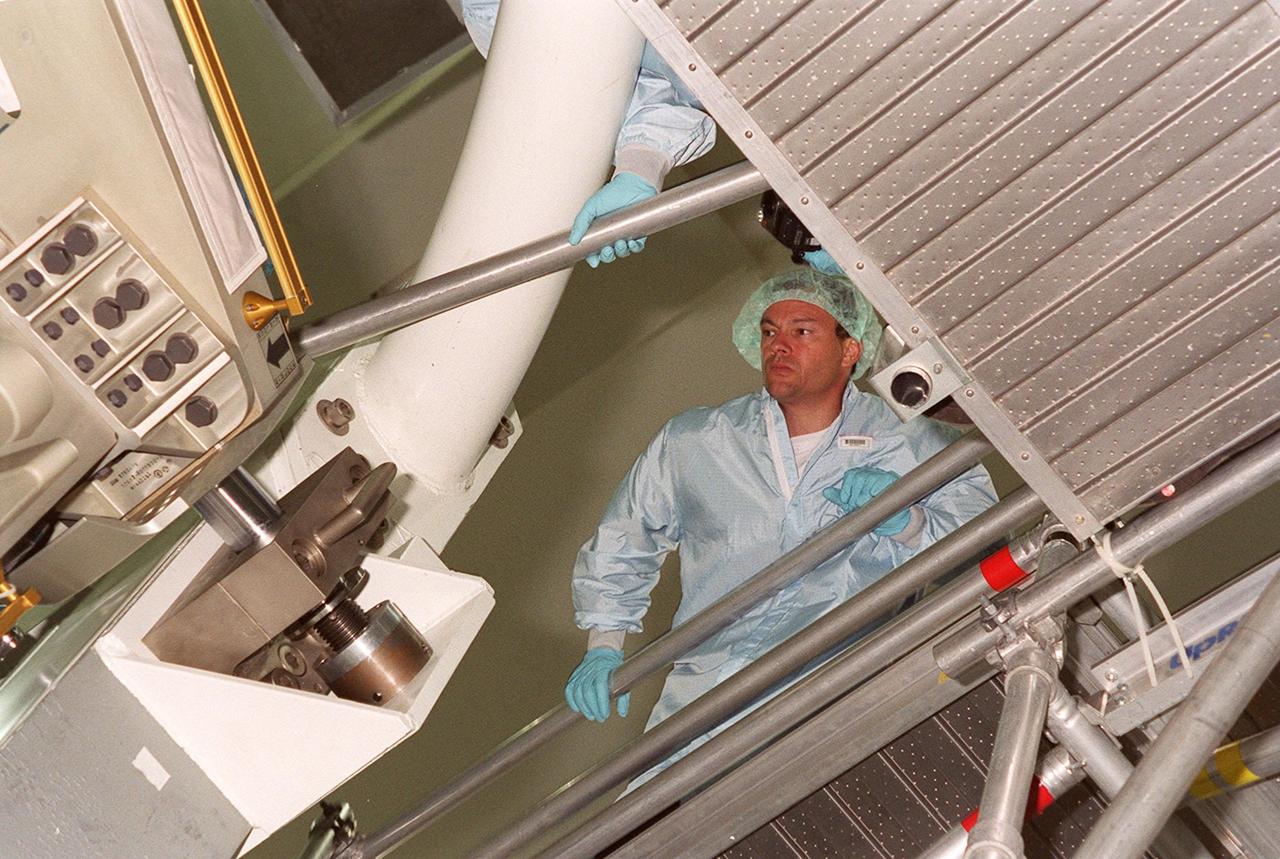

On the scaffolding in the Space Shuttle Processing Facility (SSPF), STS-92 Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria leans over to get a better look at the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1 below. The Z1 is a payload scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall. The Z1 is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station, and will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
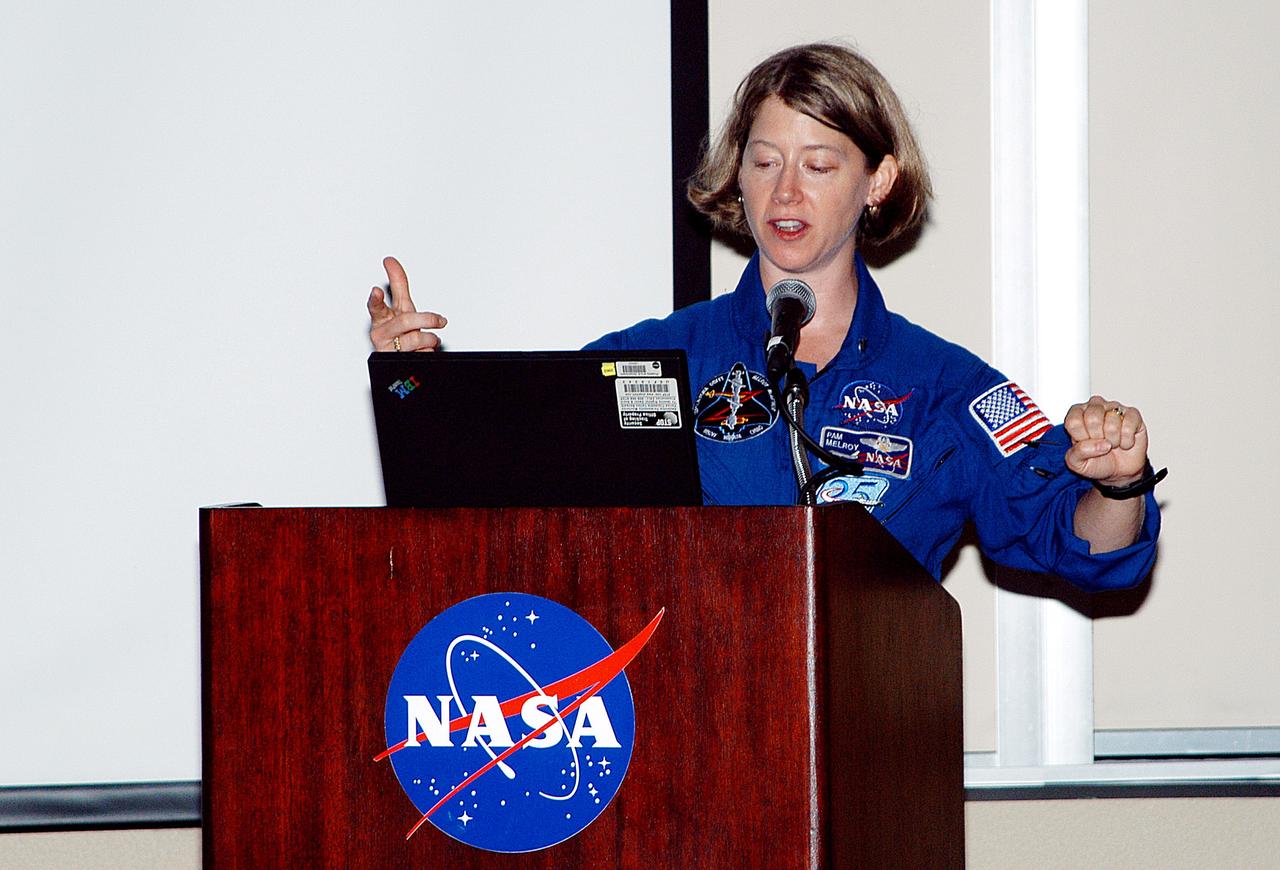

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Florida Commission on the Status of Women held June 7 at the Debus Conference Facility, astronaut Pamela Melroy speaks to attendees. Melroy has served as pilot on two Shuttle flights (STS-92 in 2000 and STS-112 in 2002), and has logged more than 562 hours in space. The commission, through coordinating, researching, communicating, and encouraging legislation, is dedicated to empowering women from all walks of life in achieving their fullest potential, to eliminating barriers to that achievement, and to recognizing women’s accomplishments.
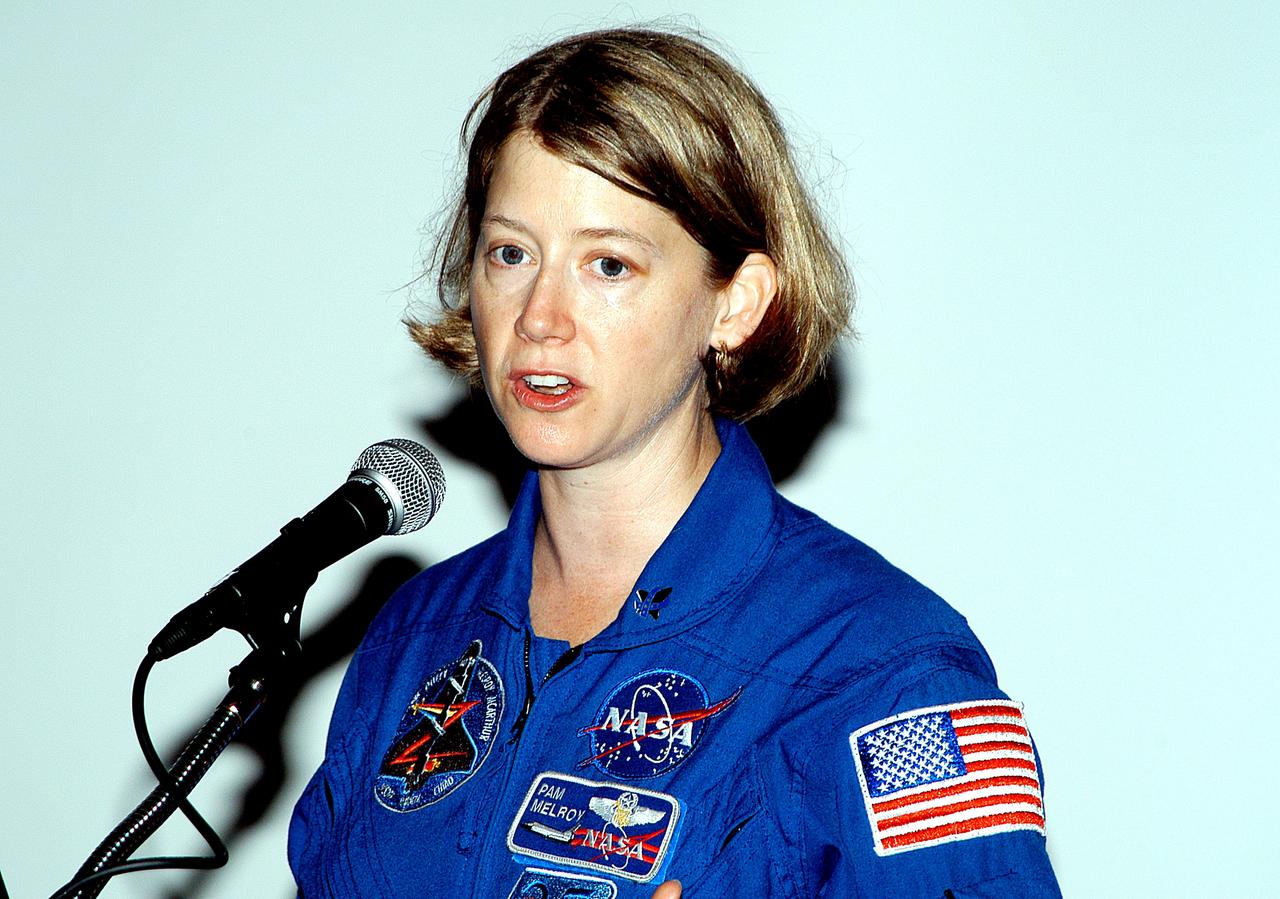

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Florida Commission on the Status of Women held June 7 at the Debus Conference Facility, astronaut Pamela Melroy speaks to attendees. Melroy has served as pilot on two Shuttle flights (STS-92 in 2000 and STS-112 in 2002), and has logged more than 562 hours in space. The commission, through coordinating, researching, communicating, and encouraging legislation, is dedicated to empowering women from all walks of life in achieving their fullest potential, to eliminating barriers to that achievement, and to recognizing women’s accomplishments.
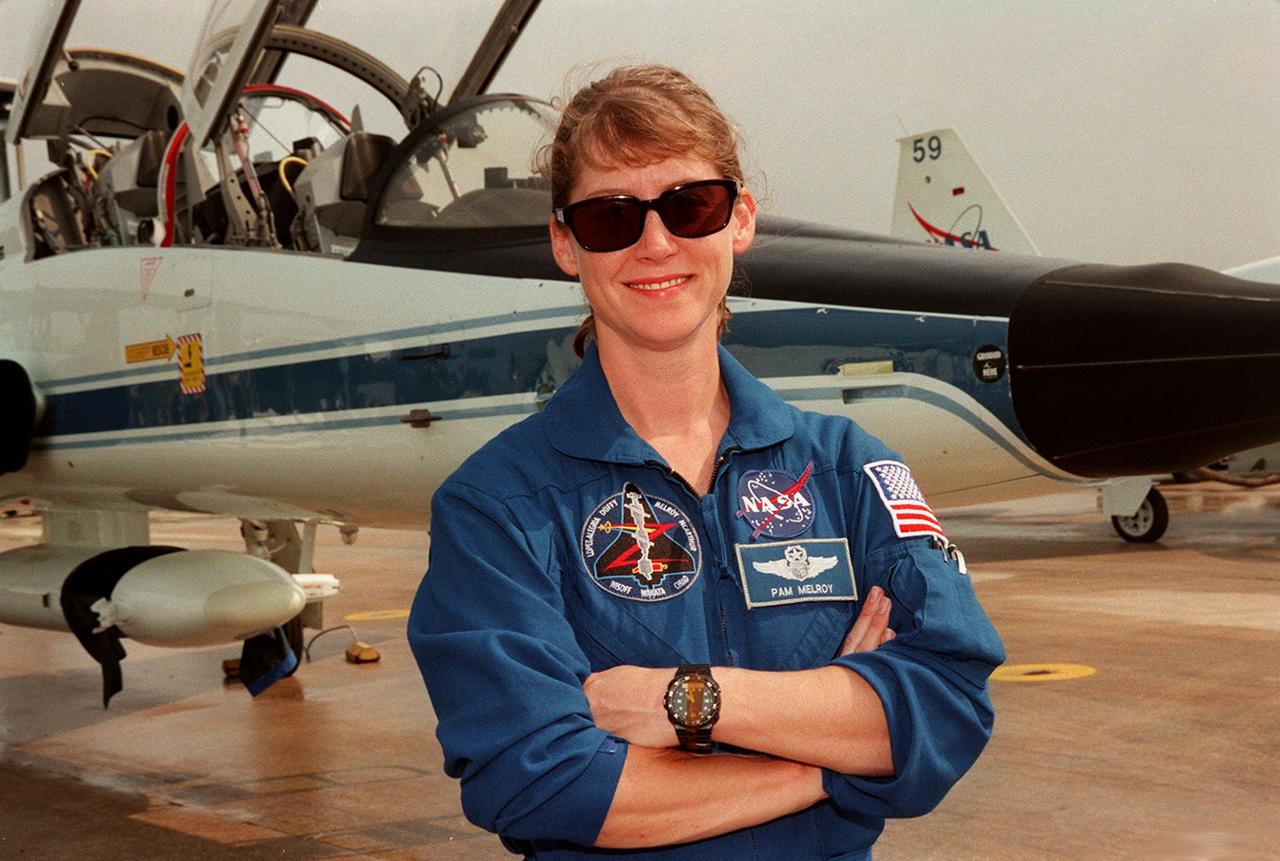

STS-92 Pilot Pam Melroy poses at the Shuttle Landing Facility before flying back to Houston. She and other crew members completed their Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, looking over their mission payload and related equipment. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 on Shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. Discovery will carry the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, the PMA-3, Ku-band Communications System, and Control Moment Gyros (CMGs)
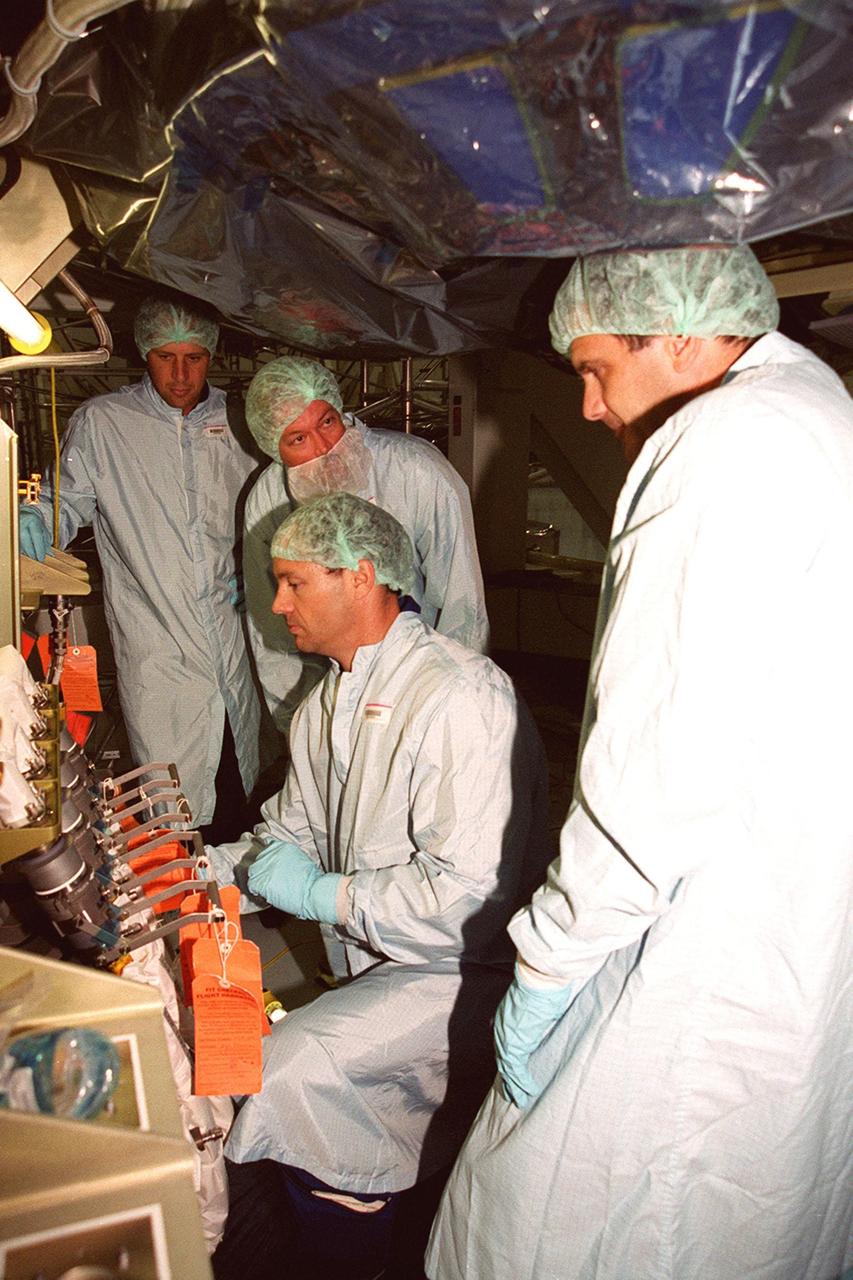

STS-92 Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria (center) and Jeff Wisoff (right) check out the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the International Space Station and payload on their mission. They and other crew members are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities while at KSC. The Z1 truss is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
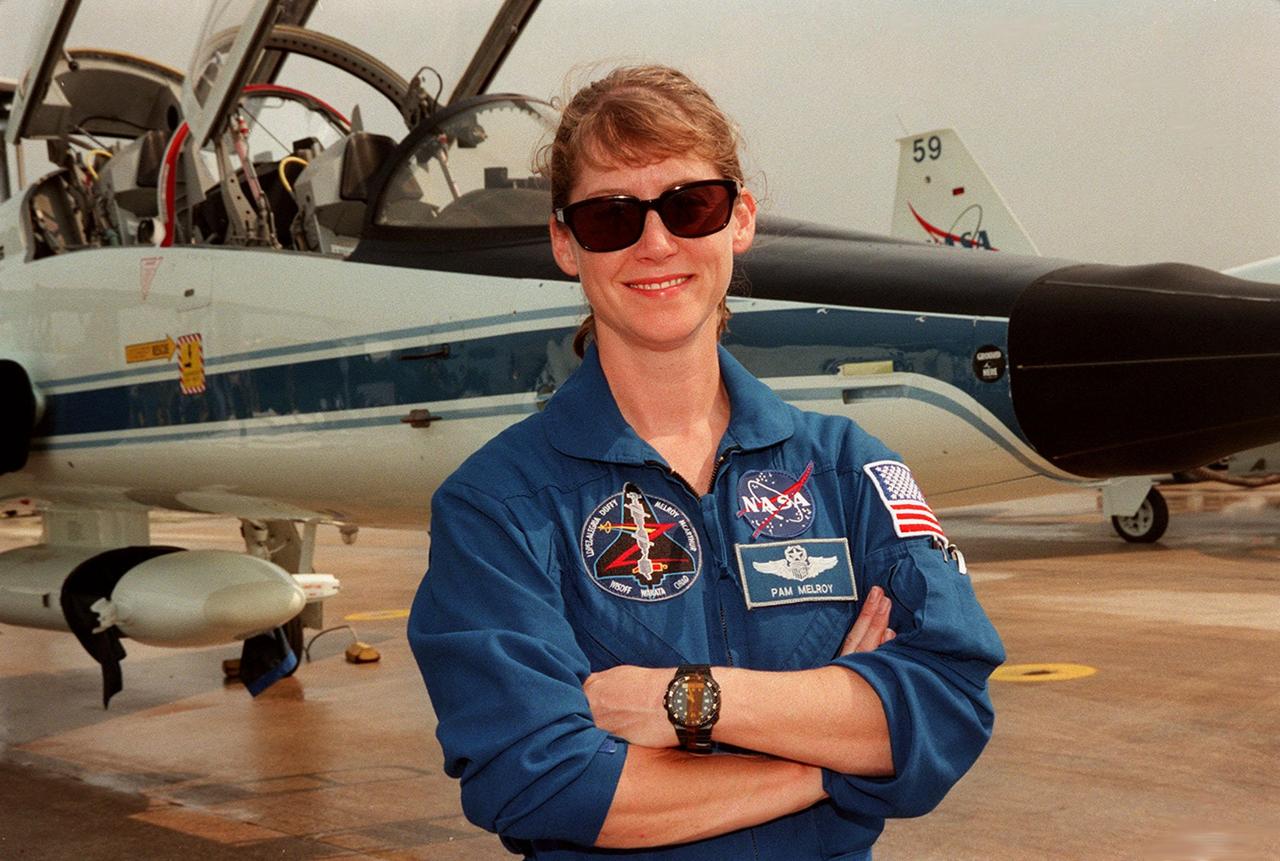

STS-92 Pilot Pam Melroy poses at the Shuttle Landing Facility before flying back to Houston. She and other crew members completed their Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, looking over their mission payload and related equipment. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 on Shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. Discovery will carry the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, the PMA-3, Ku-band Communications System, and Control Moment Gyros (CMGs)
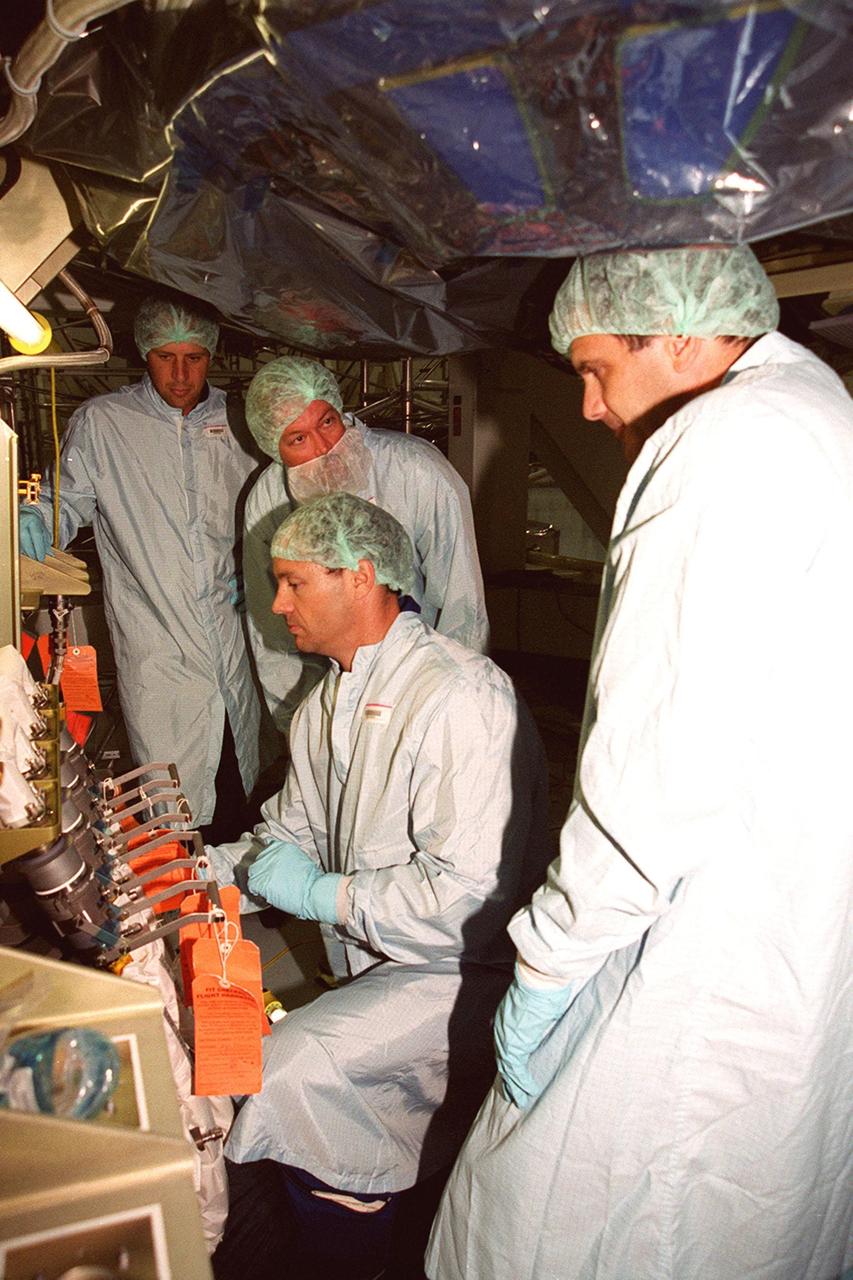

STS-92 Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria (center) and Jeff Wisoff (right) check out the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the International Space Station and payload on their mission. They and other crew members are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities while at KSC. The Z1 truss is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
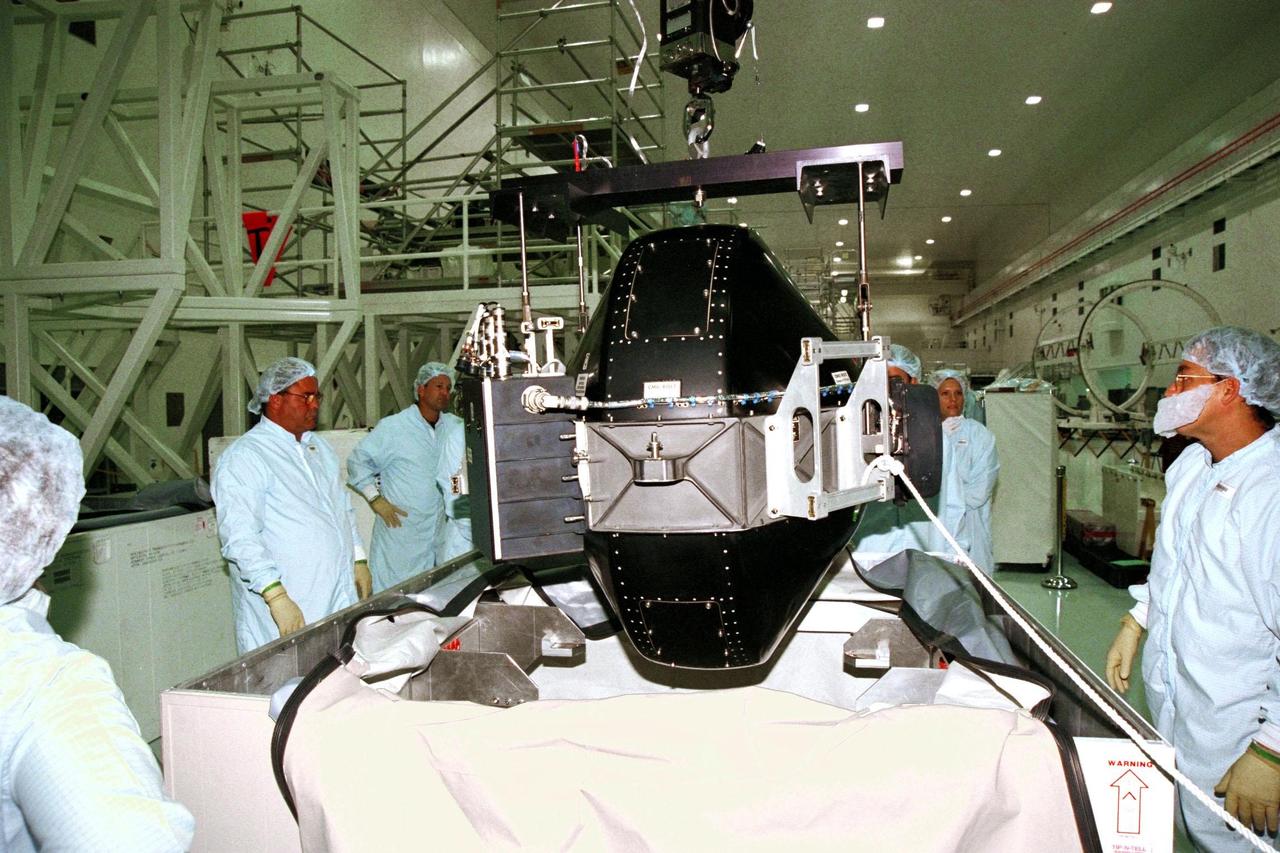

Boeing technicians remove the cover from a Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG) in the Space Station Processing Facility at KSC. The CMG will be attached to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1. Gyroscopes are used for stabilization of the International Space Station (ISS). The CMG and Z1, part of the construction of the ISS, will be carried on STS-92, the third U.S. flight planned for on-orbit construction of the ISS. STS-92 is scheduled for liftoff on June 17, 1999, aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis
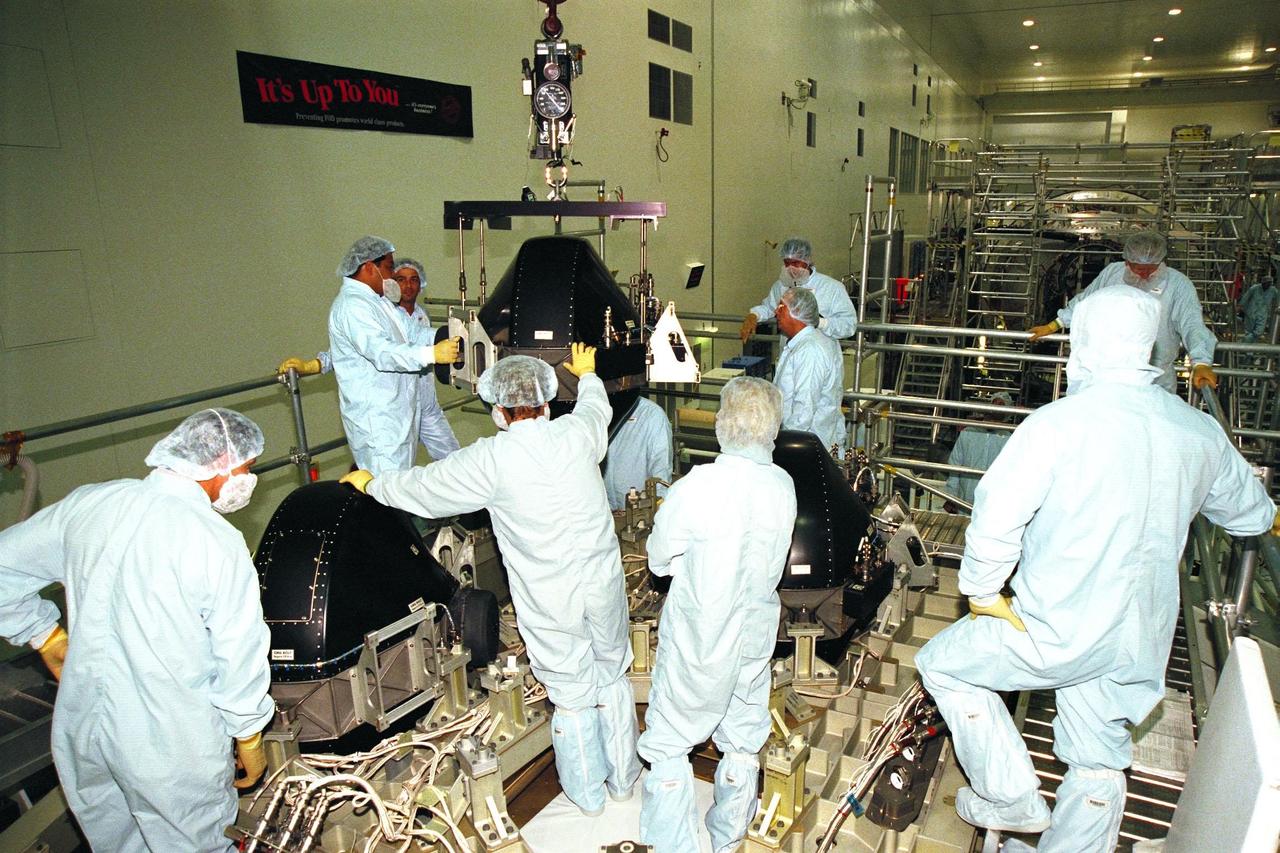

Boeing technicians lower a Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG) into place on the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1 in the Space Station Processing Facility at KSC. Gyroscopes are used for stabilization of the International Space Station (ISS). The CMG and Z1, part of the construction of the ISS, will be carried on STS-92, the third U.S. flight planned for on-orbit construction of the ISS. STS-92 is scheduled for liftoff on June 17, 1999, aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis
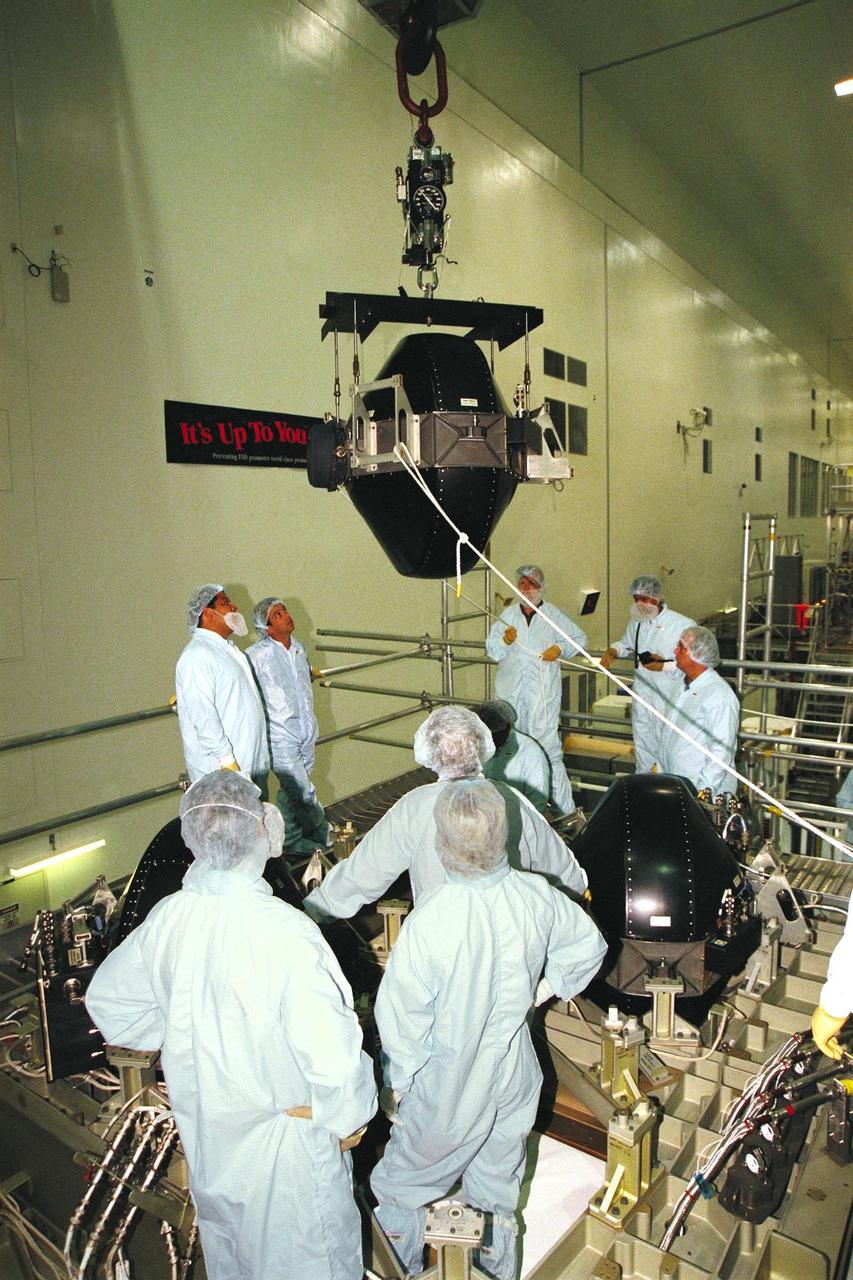

Boeing technicians move a Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG) to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1 in the Space Station Processing Facility at KSC. Gyroscopes are used for stabilization of the International Space Station (ISS). The CMG and Z1, part of the construction of the ISS, will be carried on STS-92, the third U.S. flight planned for on-orbit construction of the ISS. STS-92 is scheduled for liftoff on June 17, 1999, aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis
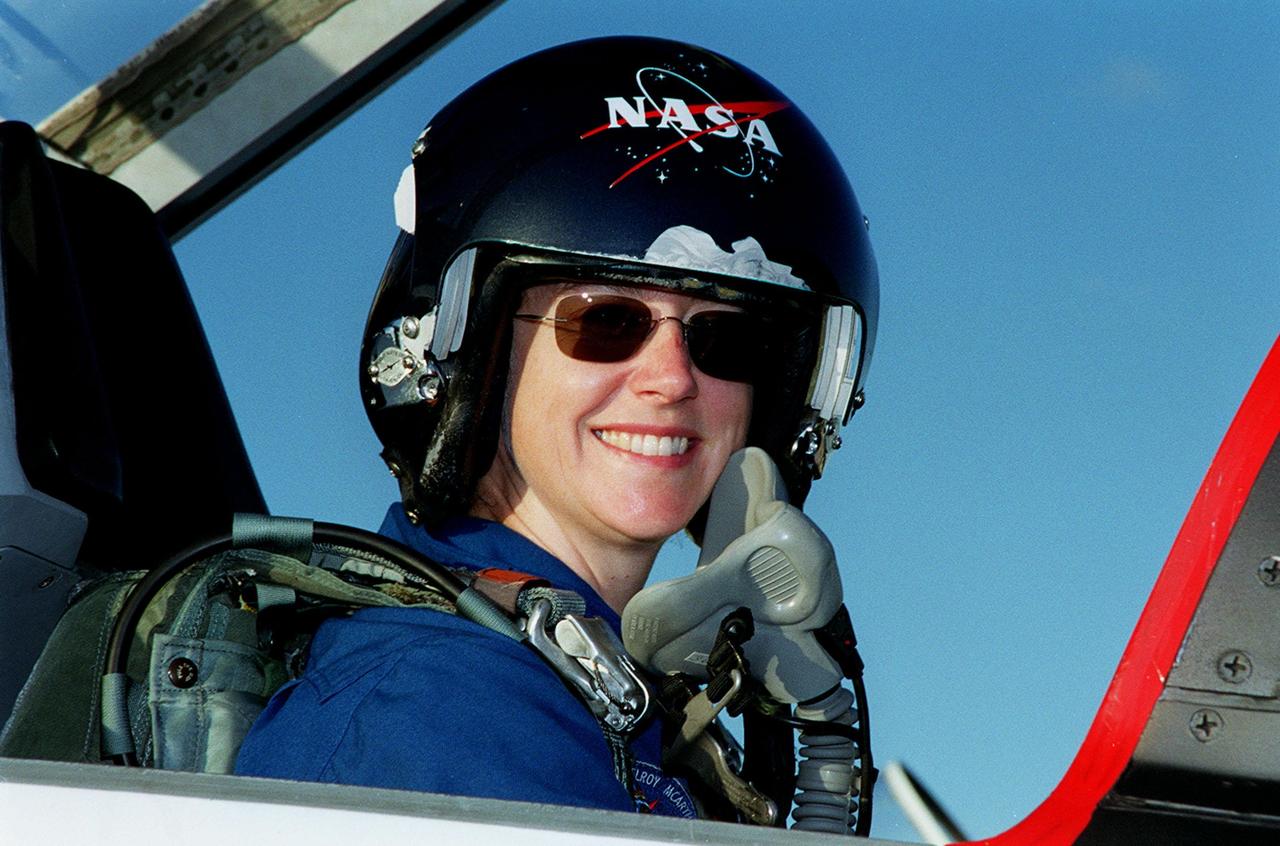

STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy is happy to arrive at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility after a flight from Houston. She and the rest of the crew are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, and a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
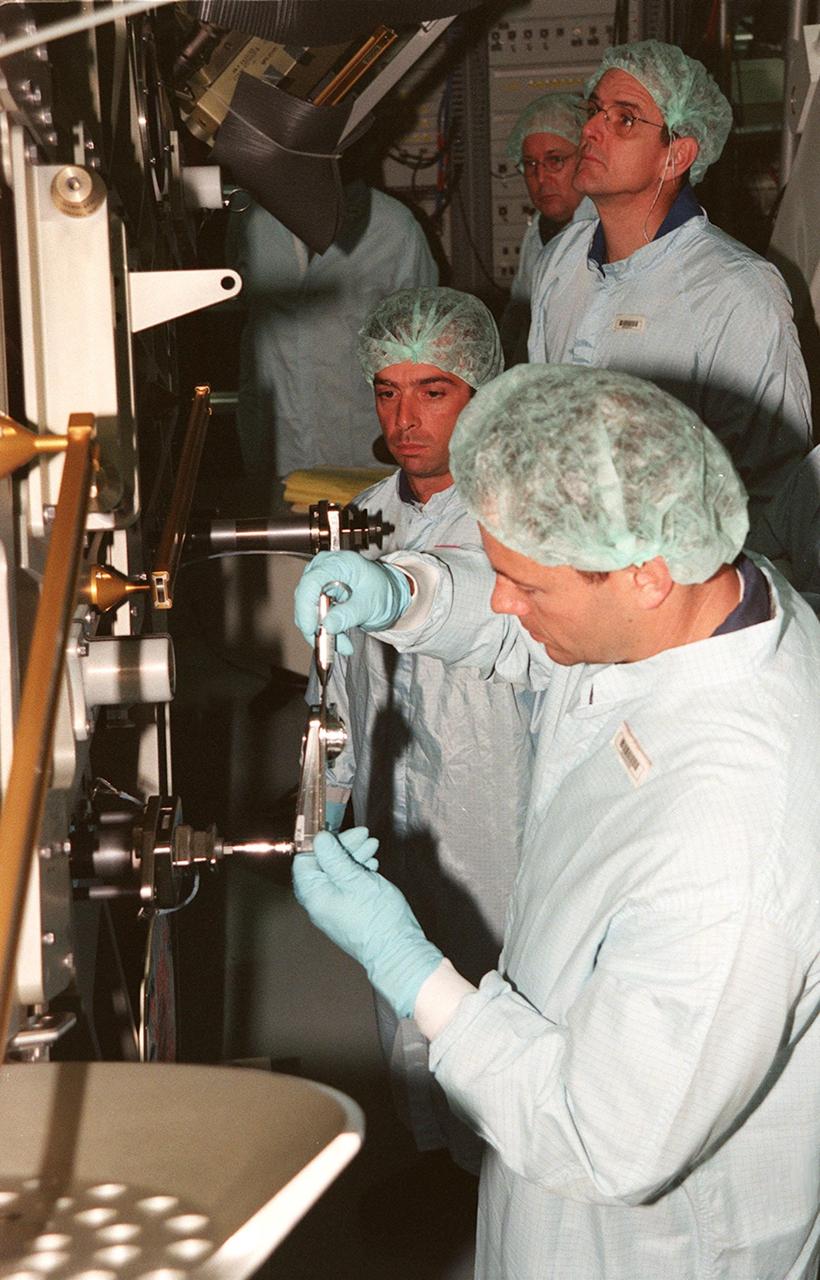

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get hands-on experience with some of the equipment, such as the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, to fly on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
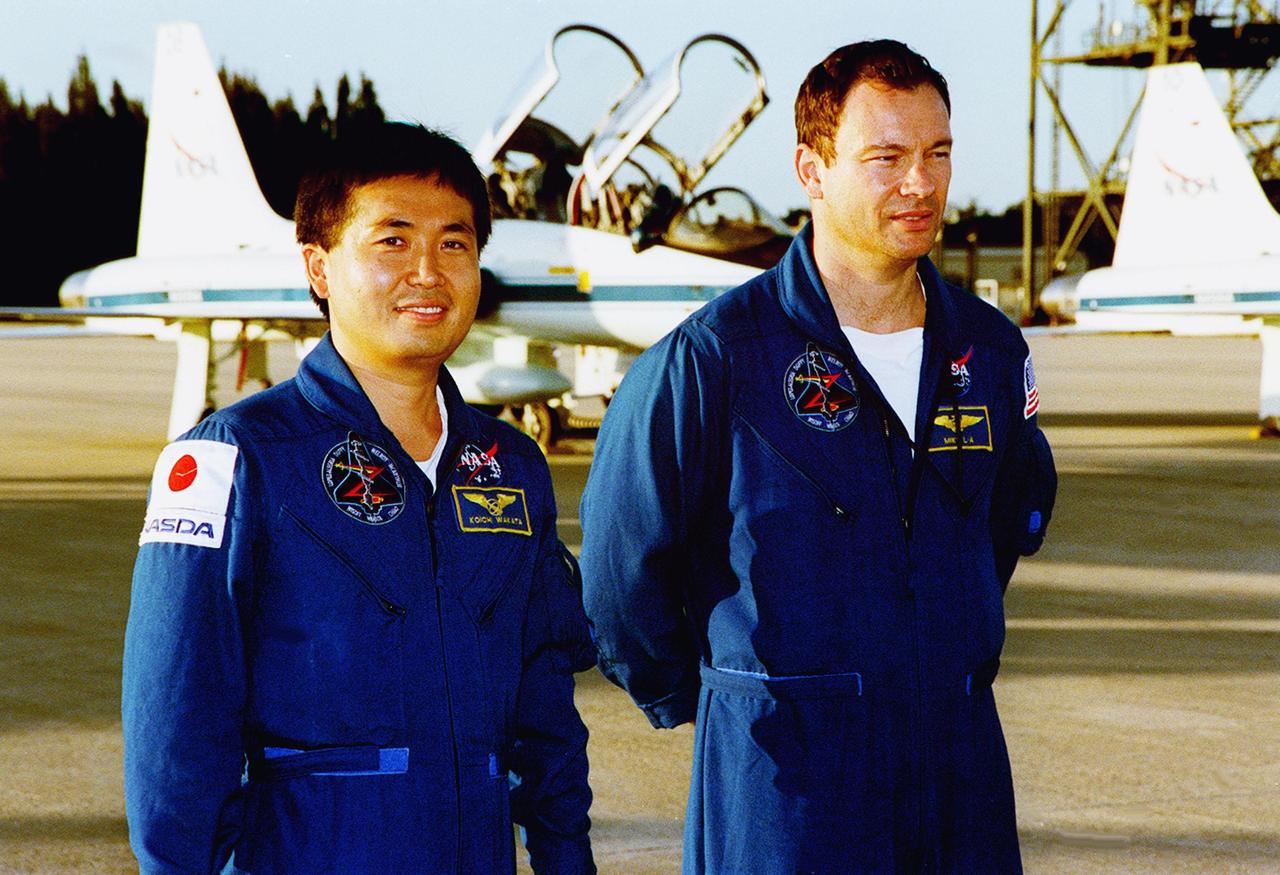
STS-92 Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata and Michael Lopez-Alegria pause on the tarmac after their arrival aboard the T-38 jet aircraft in the background. They and the rest of the crew are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT includes emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, plus a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
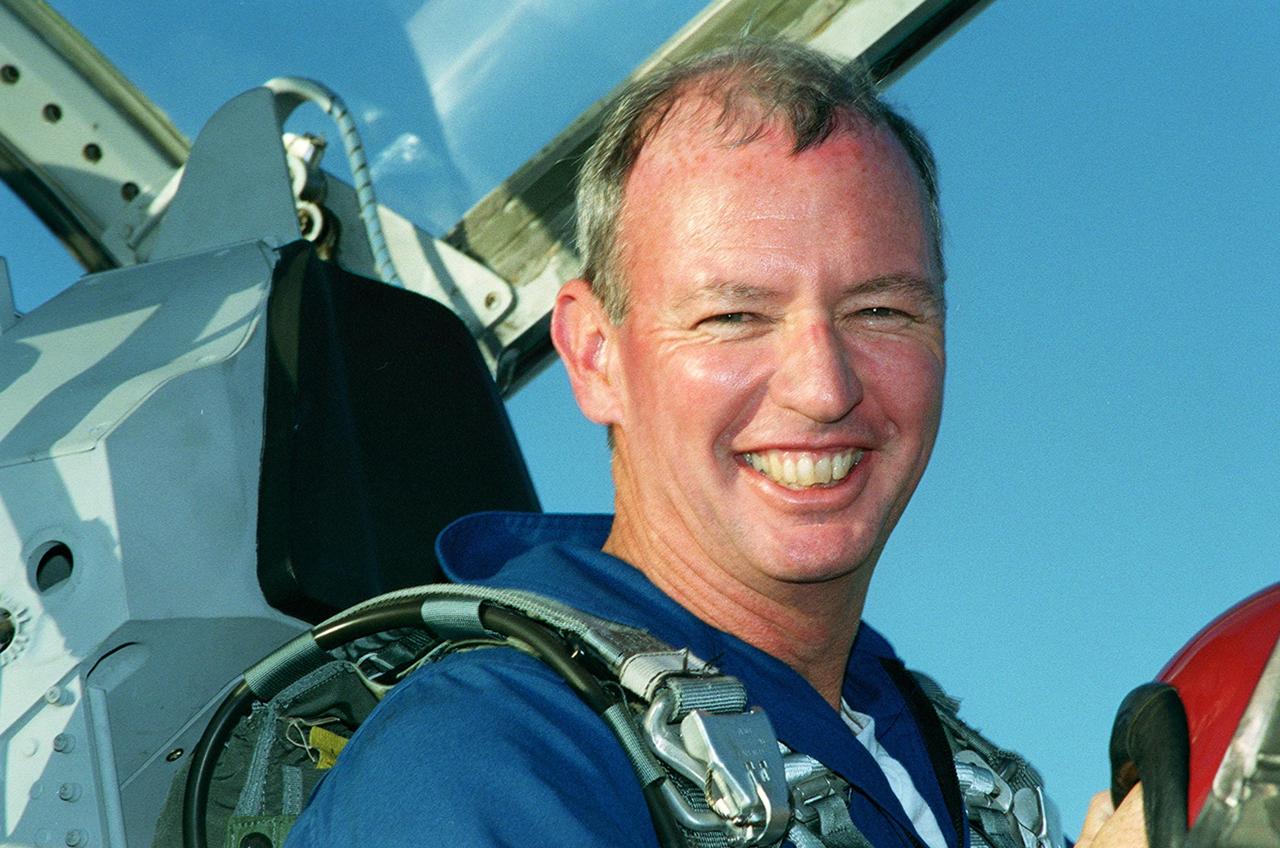

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy smiles after landing at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility in a T-38 training jet aircraft. He and the rest of the crew are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, and a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
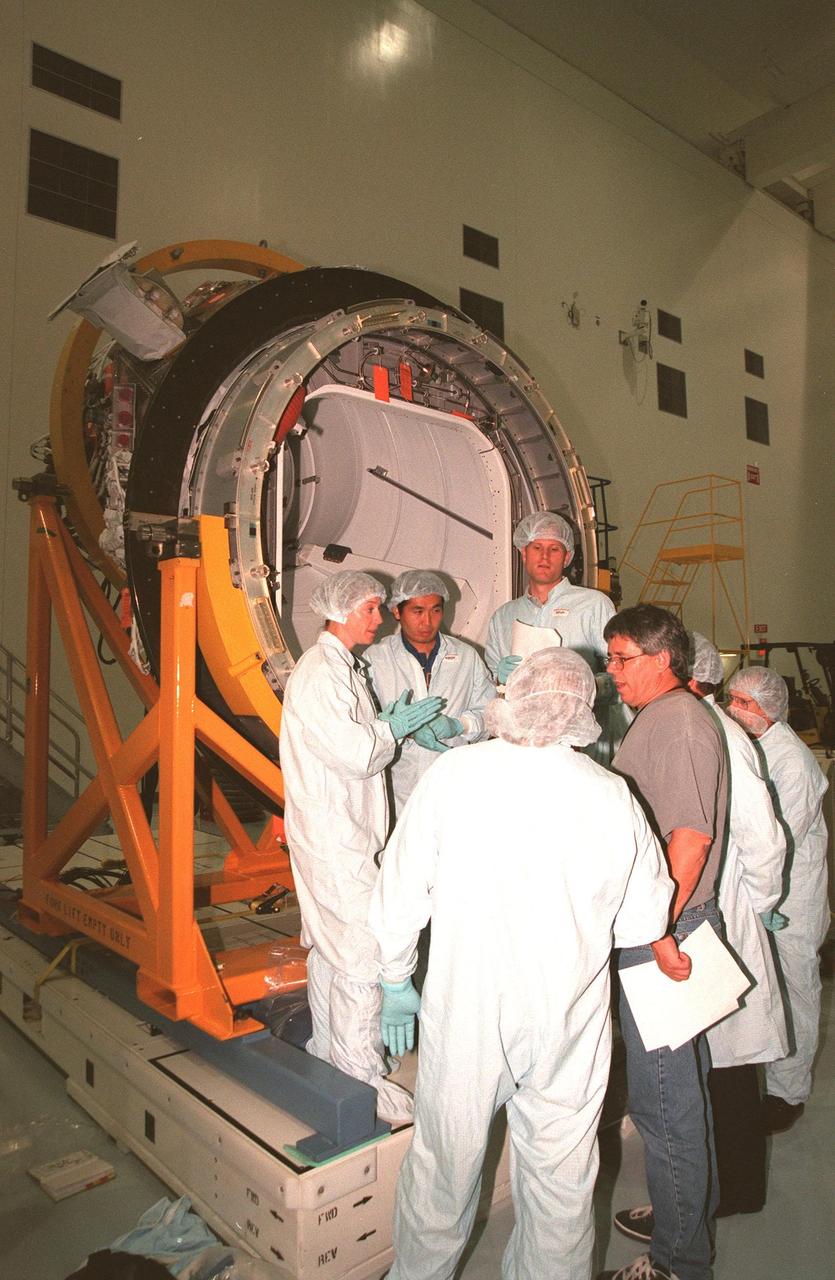

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-92 crew members discuss the Pressurized Mating Adapter -3 (PMA-3) in the background with Boeing workers. From left are Pilot Pamela A. Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, who represents the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Peter J.K. "Jeff" Wisoff (Ph.D.). The STS-92 crew are taking part in a Leak Seal Kit Fit Check in connection with the PMA-3. Other crew members participating are Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao (Ph.D.), Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William Surles "Bill" McArthur Jr. The mission payload also includes an integrated truss structure (Z-1 truss). Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Feb. 24, 2000
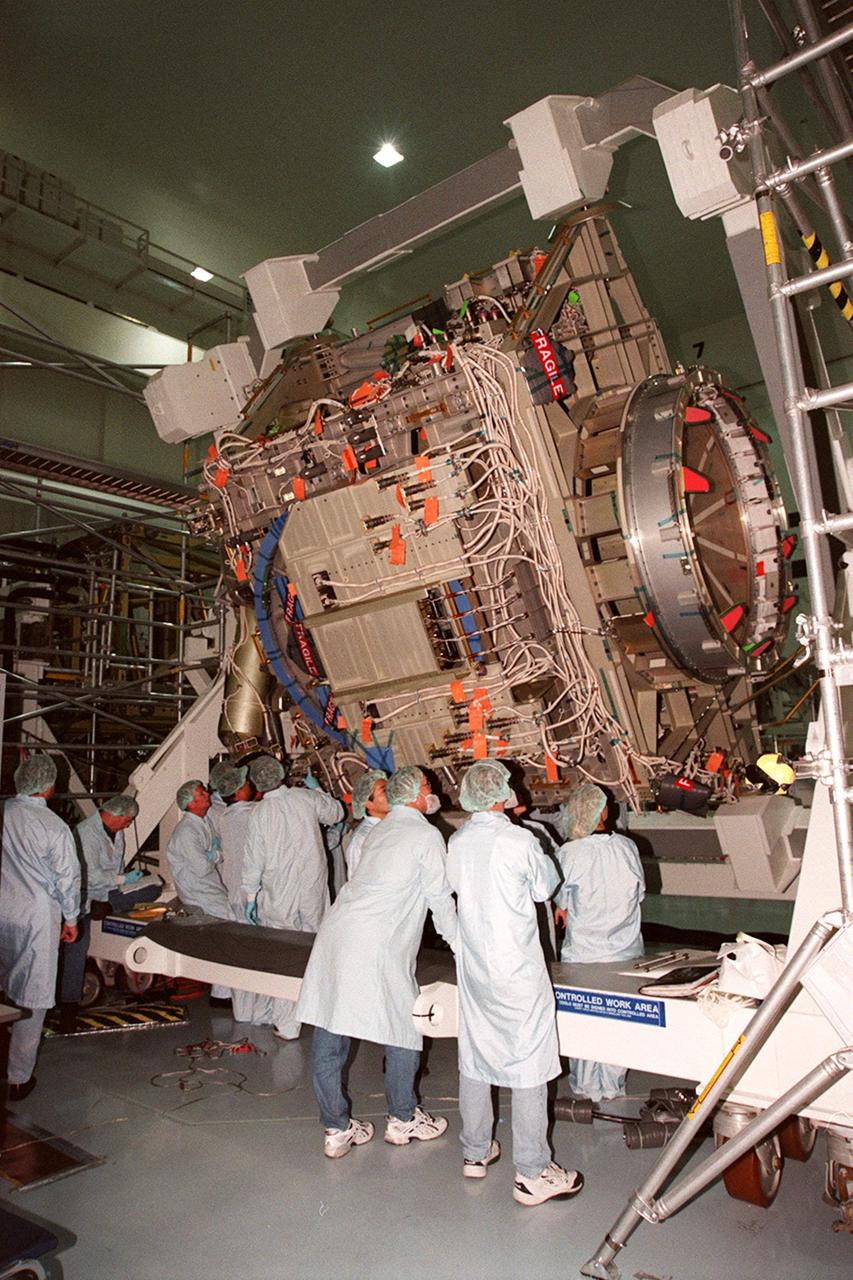

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get a close look at the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, part of the payload on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
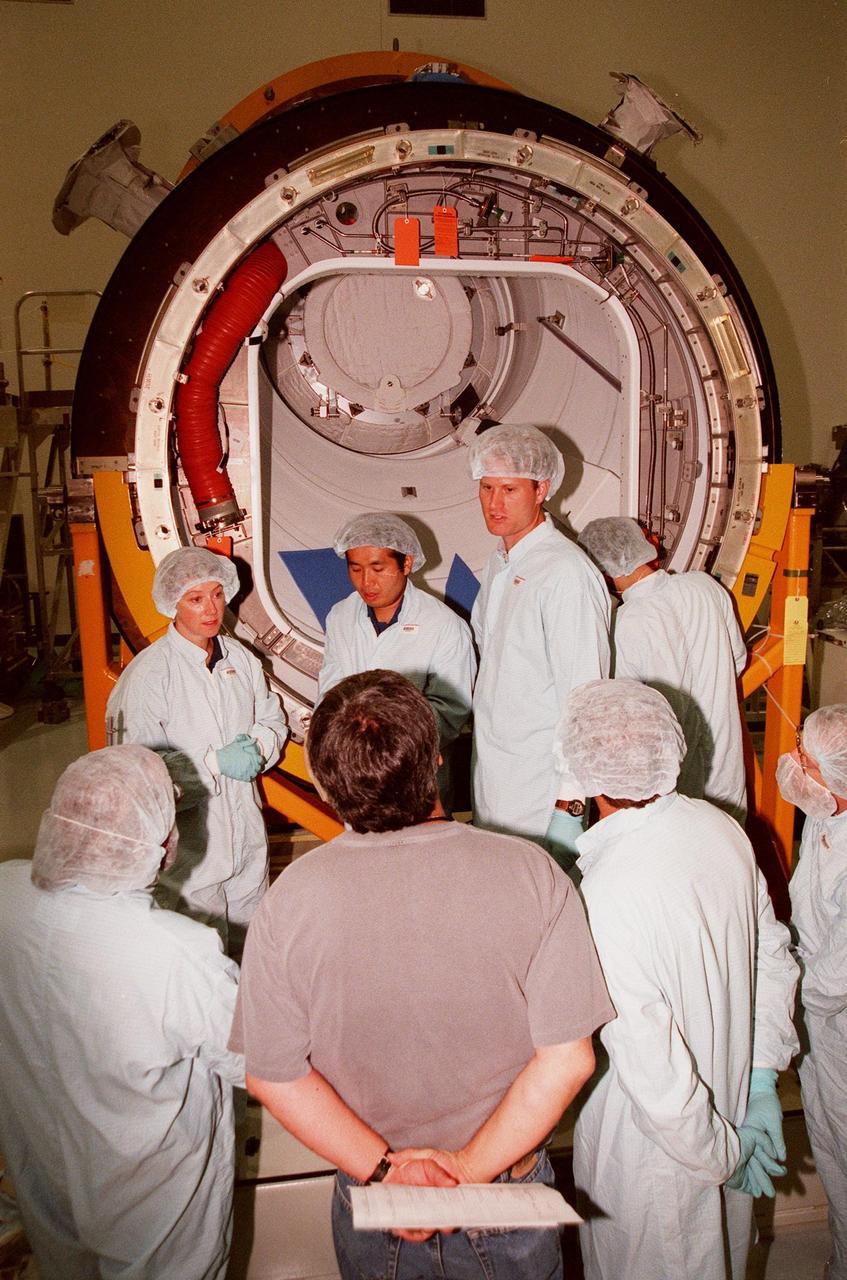

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-92 crew members discuss the Pressurized Mating Adapter -3 (PMA-3), in the background, with Boeing workers. From left are Pilot Pamela A. Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, who represents the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Peter J.K. "Jeff" Wisoff (Ph.D.). The STS-92 crew are taking part in a Leak Seal Kit Fit Check in connection with the PMA-3. Other crew members participating are Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao (Ph.D.), Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William Surles "Bill" McArthur Jr. The mission payload also includes an integrated truss structure (Z-1 truss). Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Feb. 24, 2000
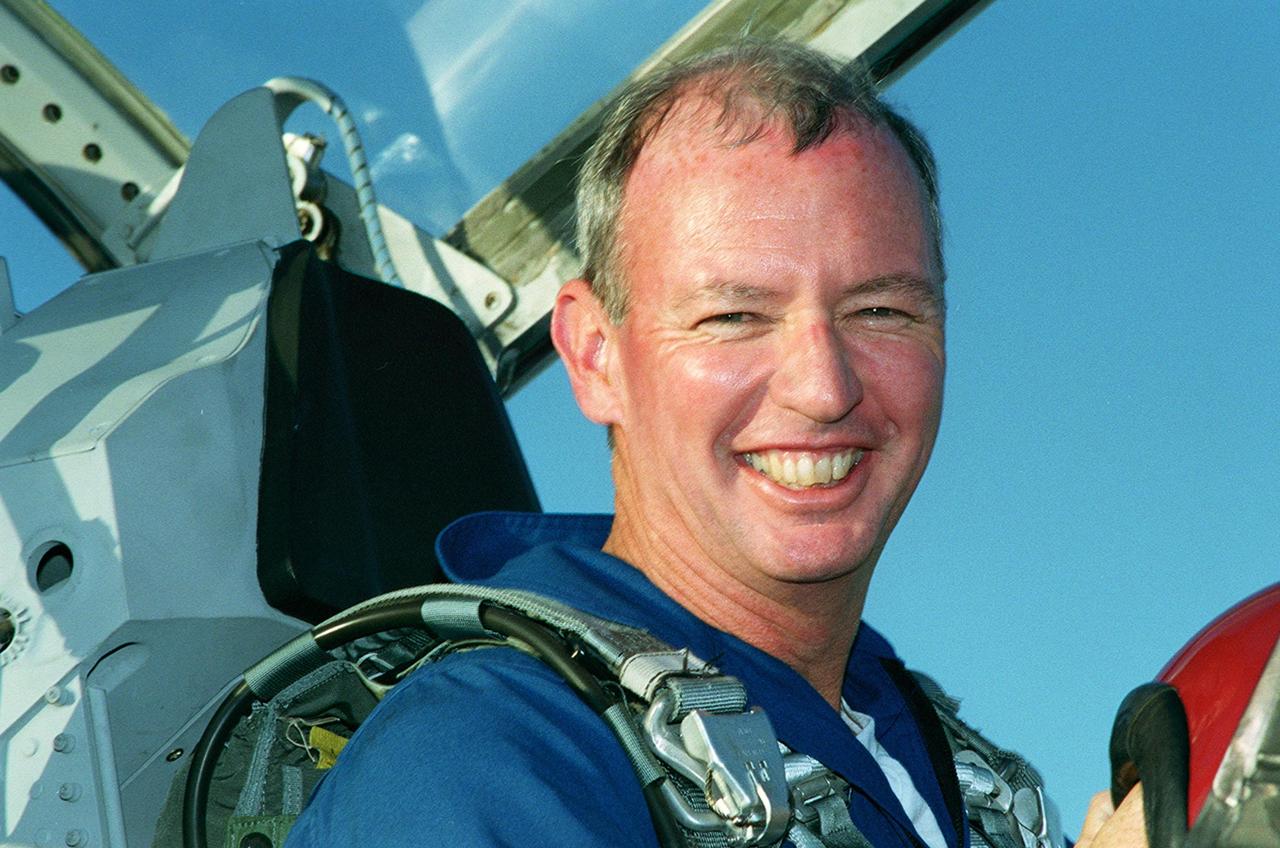

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy smiles after landing at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility in a T-38 training jet aircraft. He and the rest of the crew are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, and a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
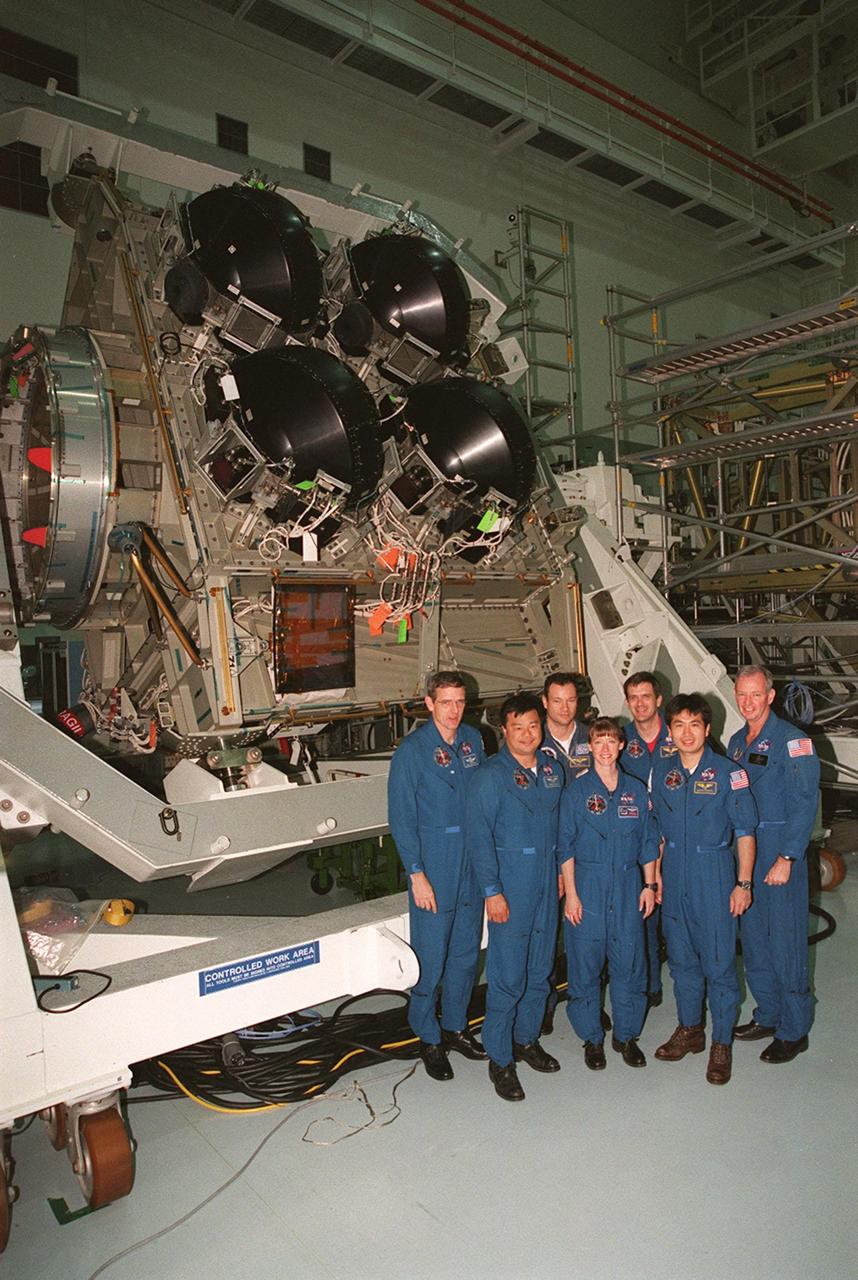

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-92 crew pose in front of the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an element of the International Space Station that will be part of the mission payload. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. Standing left to right are Mission Specialists William S. McArthur Jr., Leroy Chiao, and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria; Pilot Pamela A. Melroy; Mission Specialists Peter J.K. Wisoff and Koichi Wakata; and Commander Brian Duffy. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
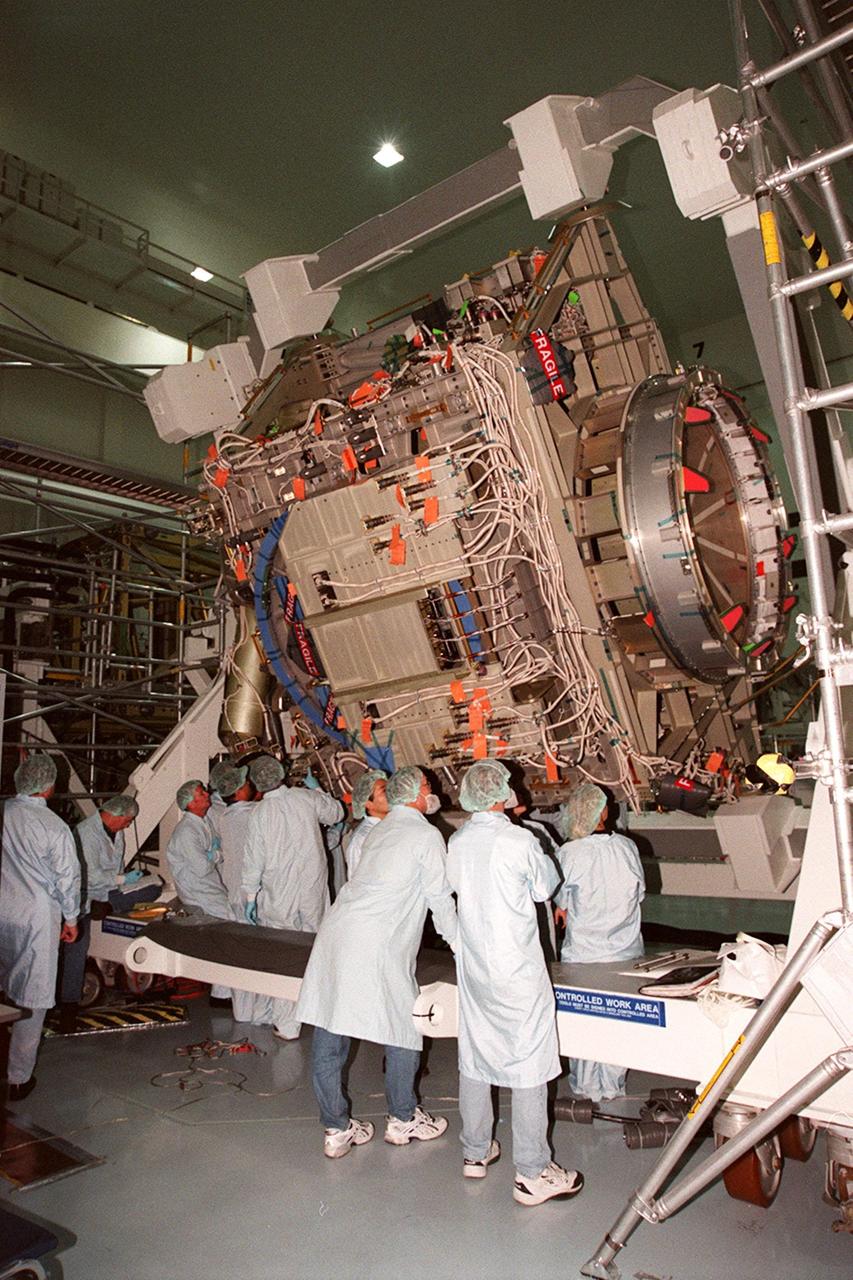

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get a close look at the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, part of the payload on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get hands-on experience with some of the equipment, such as the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, to fly on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
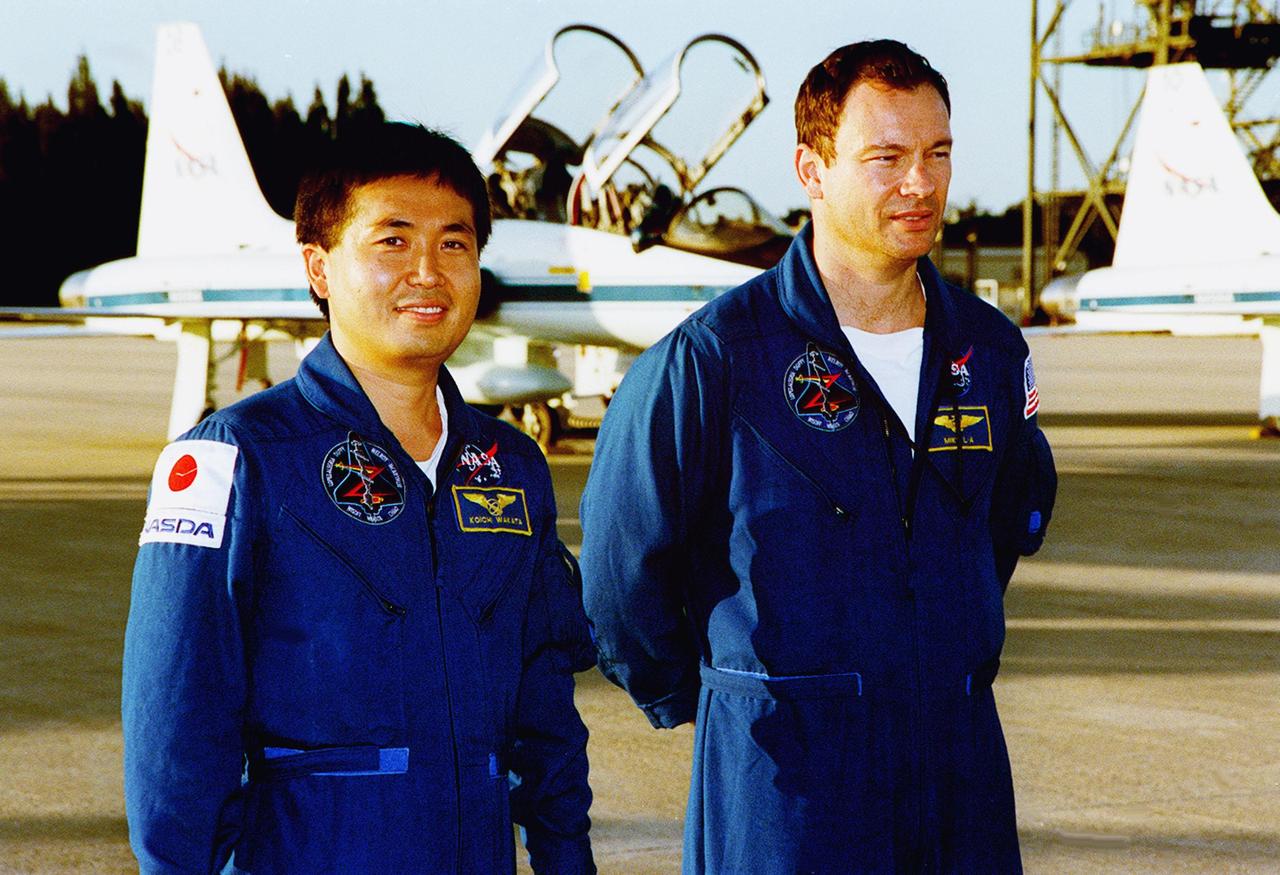
STS-92 Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata and Michael Lopez-Alegria pause on the tarmac after their arrival aboard the T-38 jet aircraft in the background. They and the rest of the crew are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT includes emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, plus a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program

STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy is happy to arrive at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility after a flight from Houston. She and the rest of the crew are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, and a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
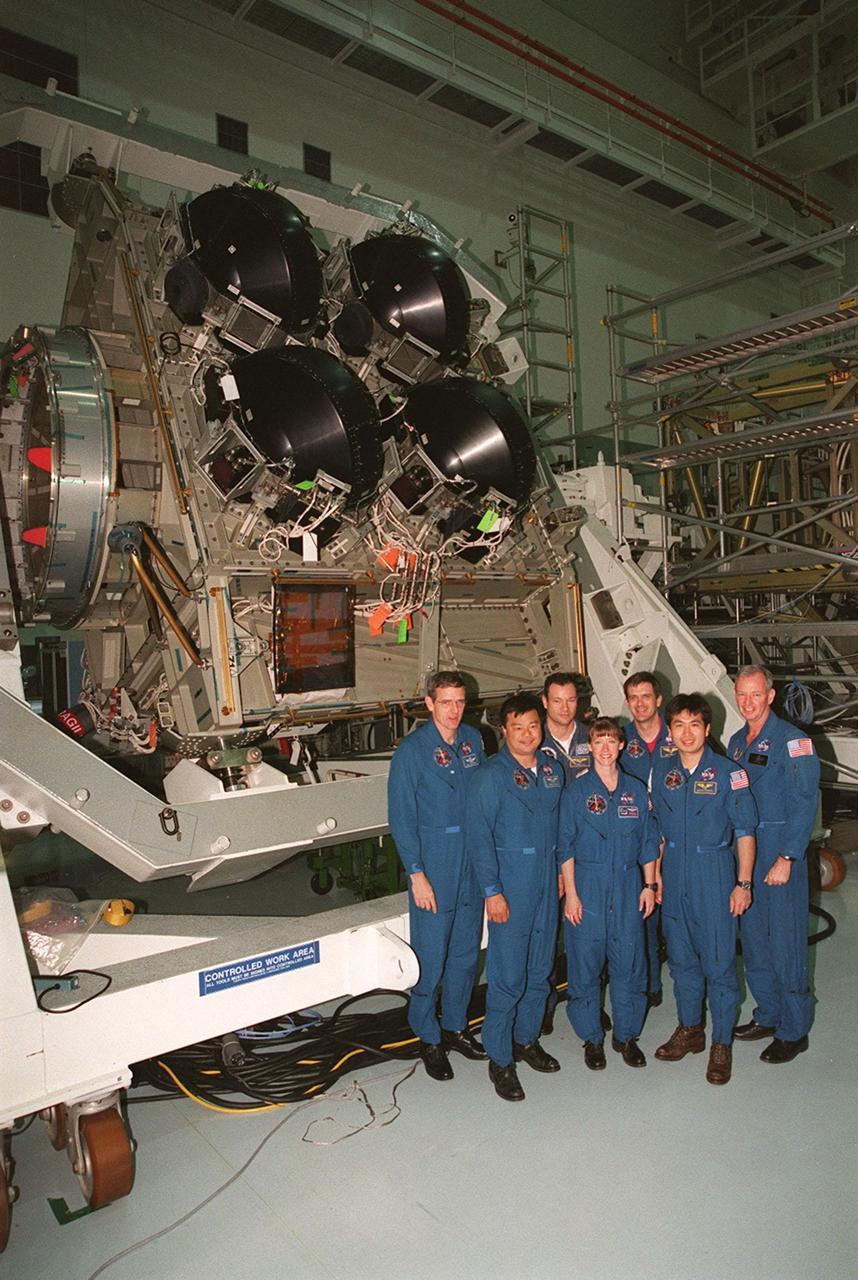

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-92 crew pose in front of the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an element of the International Space Station that will be part of the mission payload. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. Standing left to right are Mission Specialists William S. McArthur Jr., Leroy Chiao, and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria; Pilot Pamela A. Melroy; Mission Specialists Peter J.K. Wisoff and Koichi Wakata; and Commander Brian Duffy. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
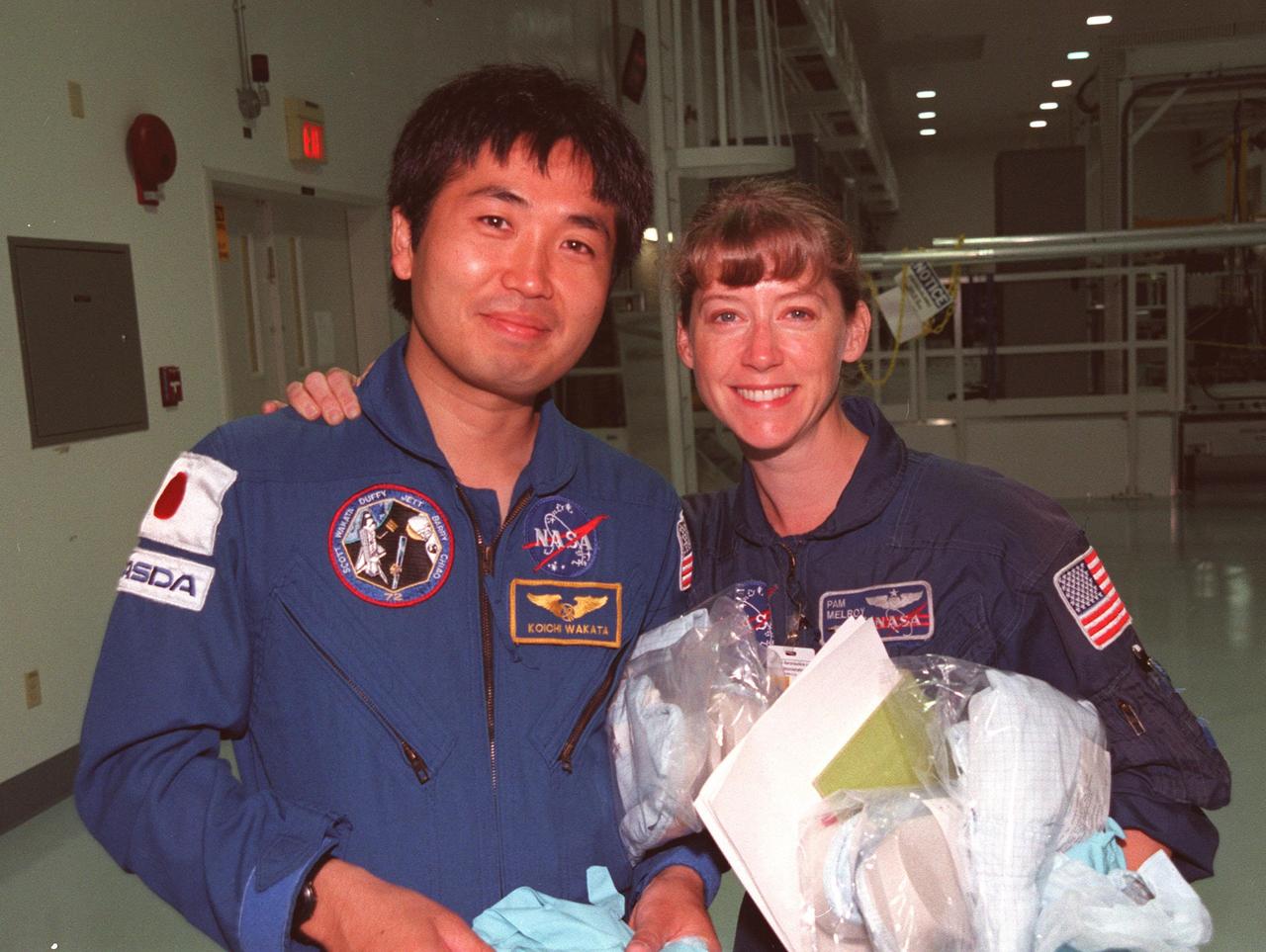

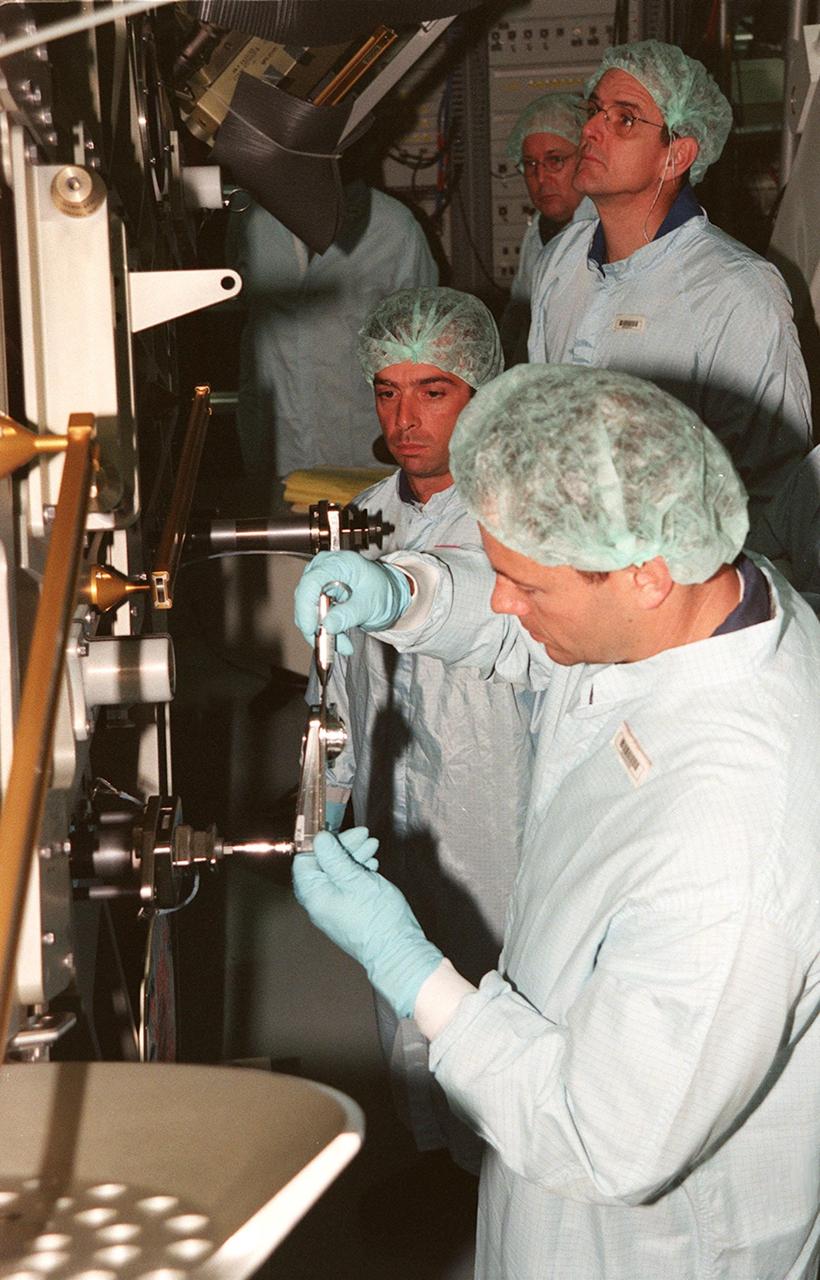
STS-92 Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata, with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Pilot Pamela A. Melroy take a break during a Leak Seal Kit Fit Check of the Pressurized Mating Adapter -3 in the Space Station Processing Facility. Also participating are the other crew members Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao (Ph.D.), Peter J.K. "Jeff" Wisoff (Ph.D.), Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William Surles "Bill" McArthur Jr. STS-92 is the fourth U.S. flight for construction of the International Space Station. The mission payload also includes an integrated truss structure (Z-1 truss). Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Feb. 24, 2000
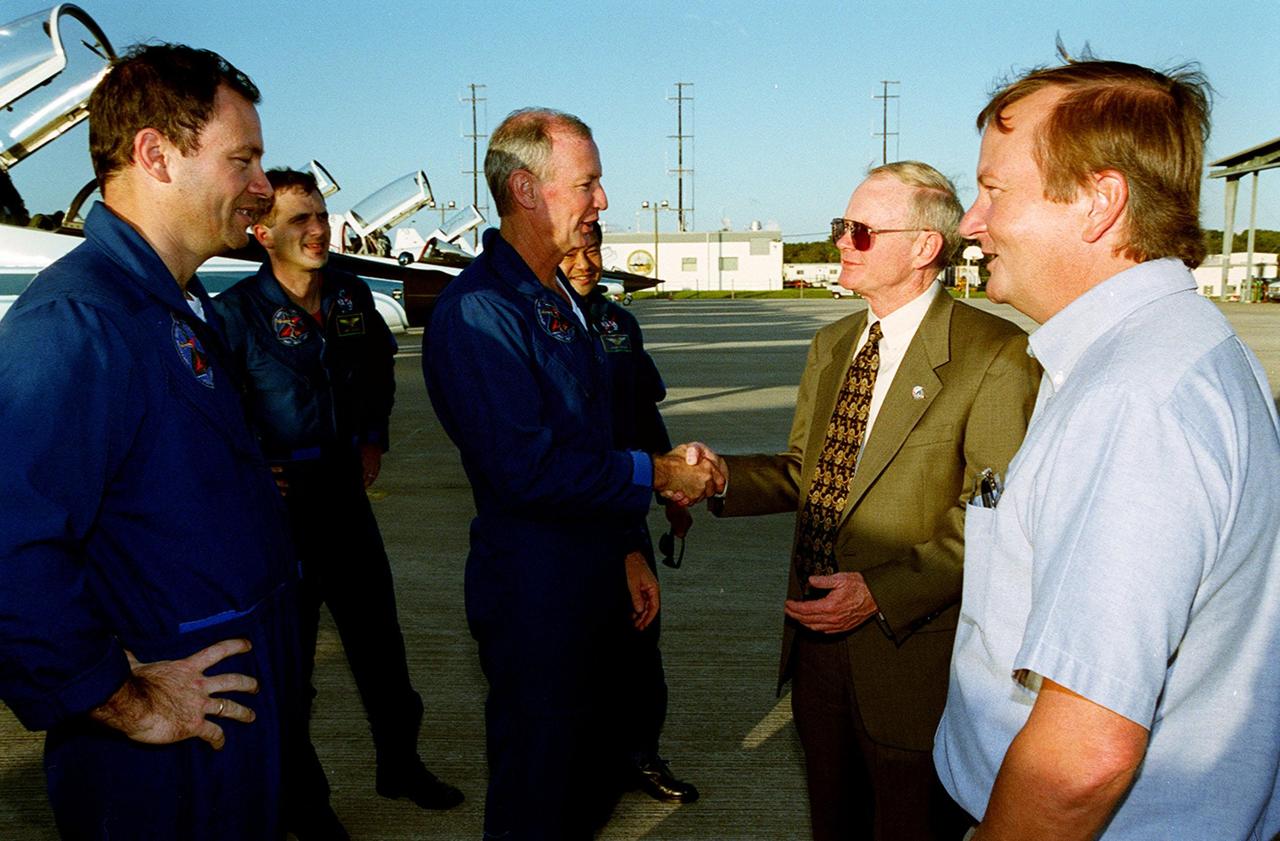

Center Director Roy Bridges greets STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy after the crew’s arrival at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Behind Duffy are Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria, Jeff Wisoff and Koichi Wakata (NASDA). Next to Bridges is Michael Leinbach, the new KSC launch director. The STS-92 crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT includes emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, plus a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
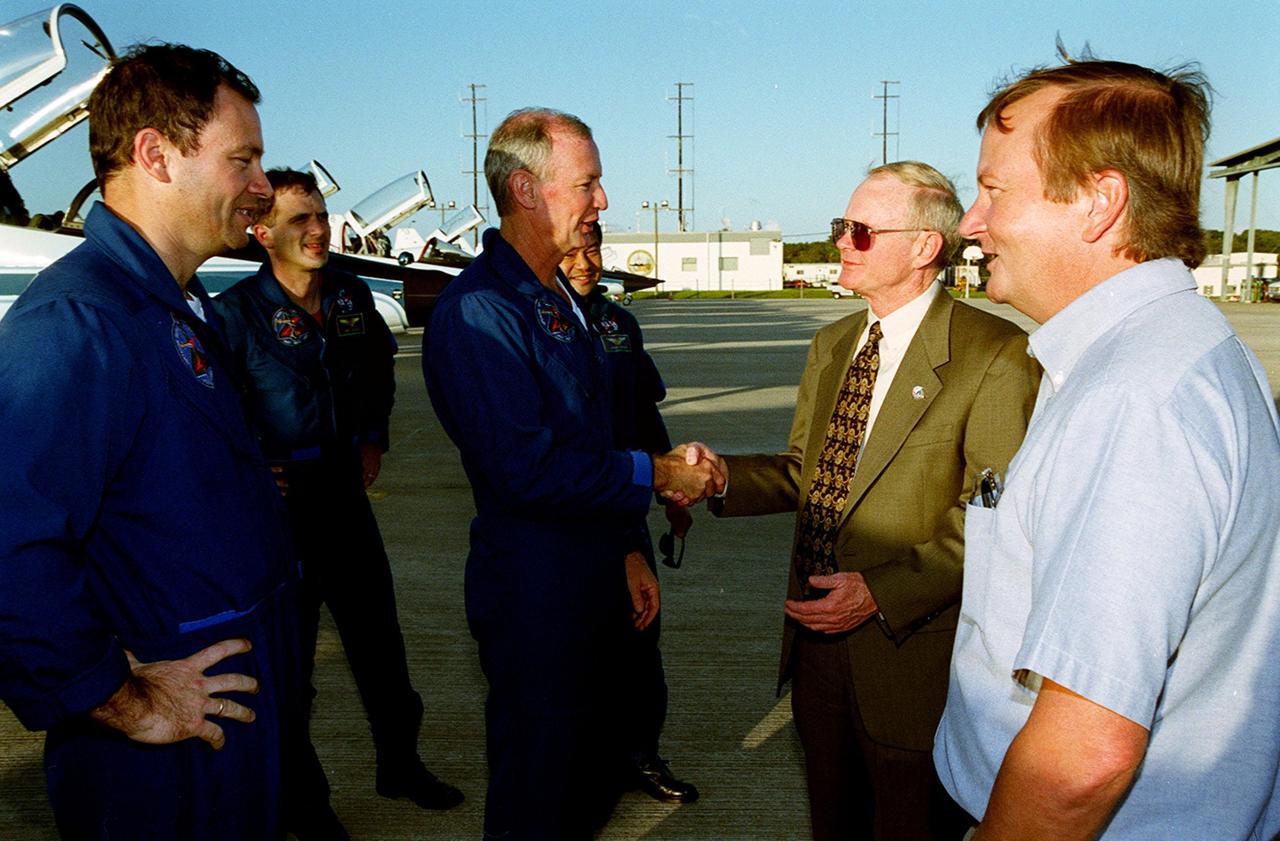

Center Director Roy Bridges greets STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy after the crew’s arrival at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Behind Duffy are Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria, Jeff Wisoff and Koichi Wakata (NASDA). Next to Bridges is Michael Leinbach, the new KSC launch director. The STS-92 crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT includes emergency egress training from the orbiter and pad, plus a simulated countdown. The fifth mission to the International Space Station, STS-92 will carry the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, the first of the planned 10 trusses on the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for the solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A. It will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
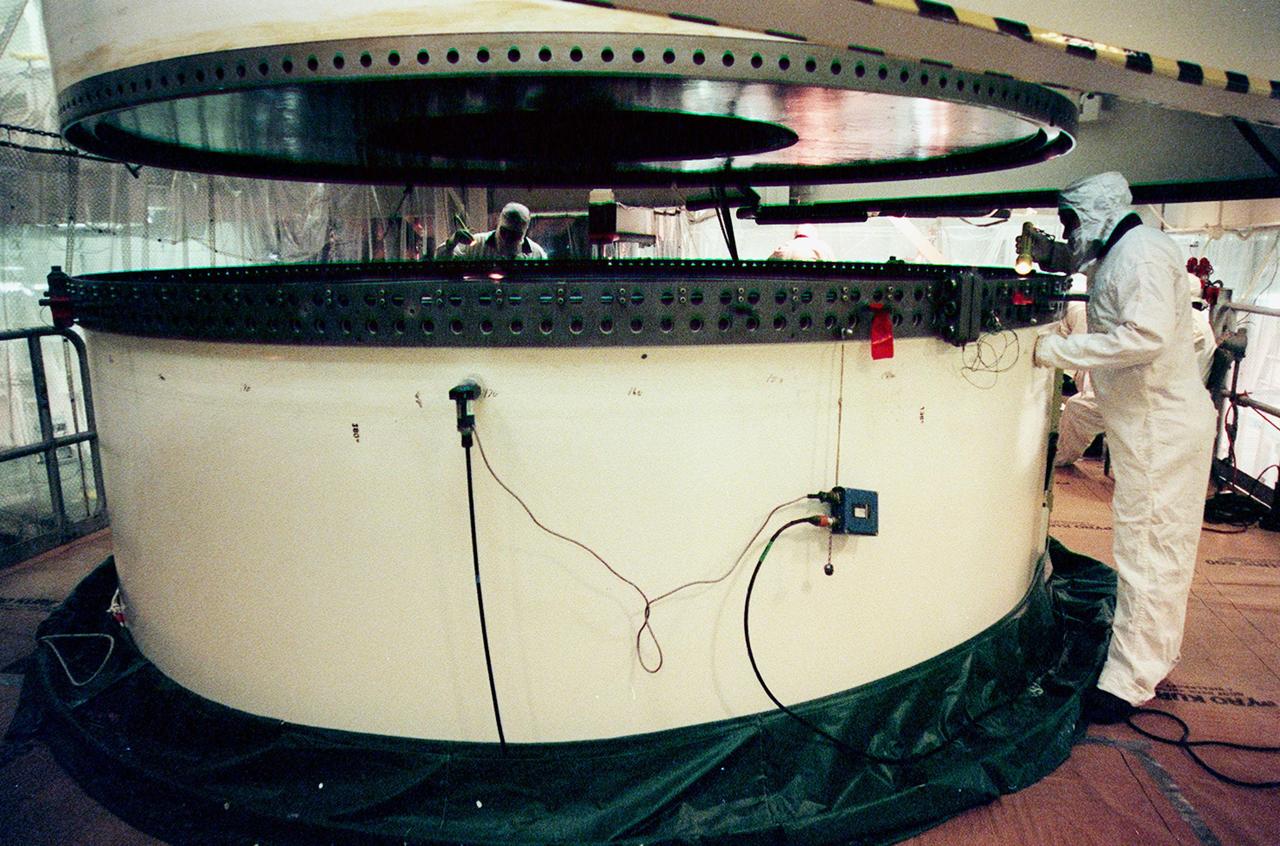
In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check the lower segment of a solid rocket booster (SRB) to be mated to the one above. The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A

In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check two segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB) to be mated. The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
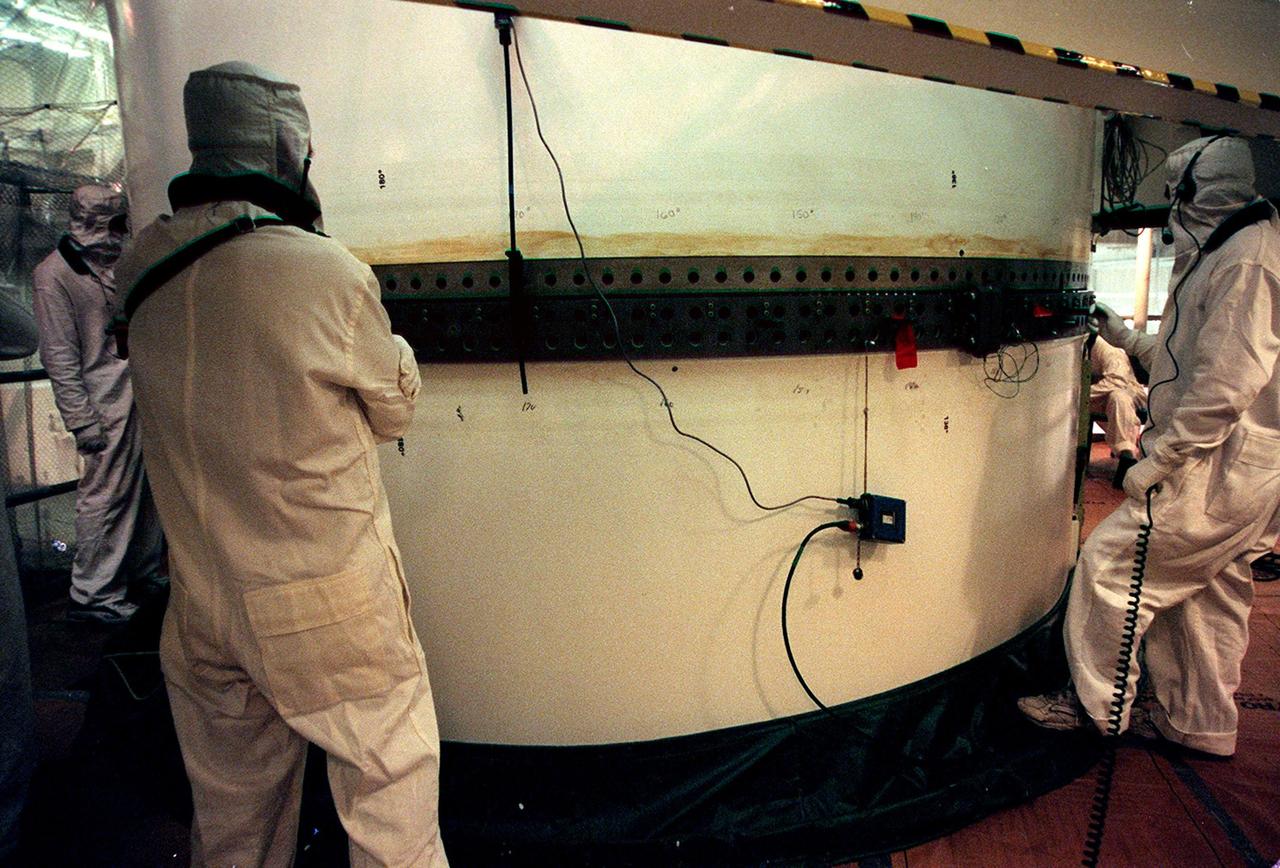

In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check the rings on the segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB) after mating them. The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
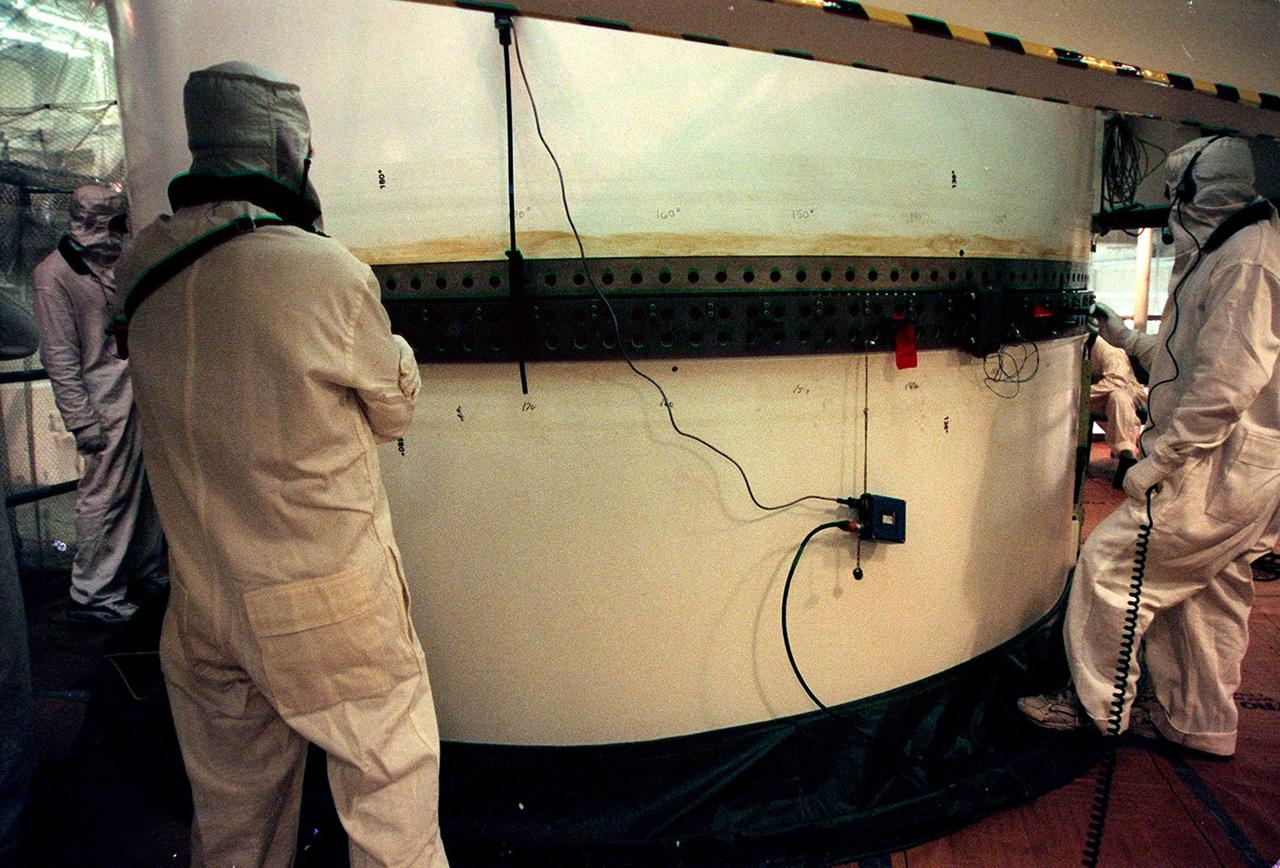

In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check the rings on the segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB) after mating them. The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
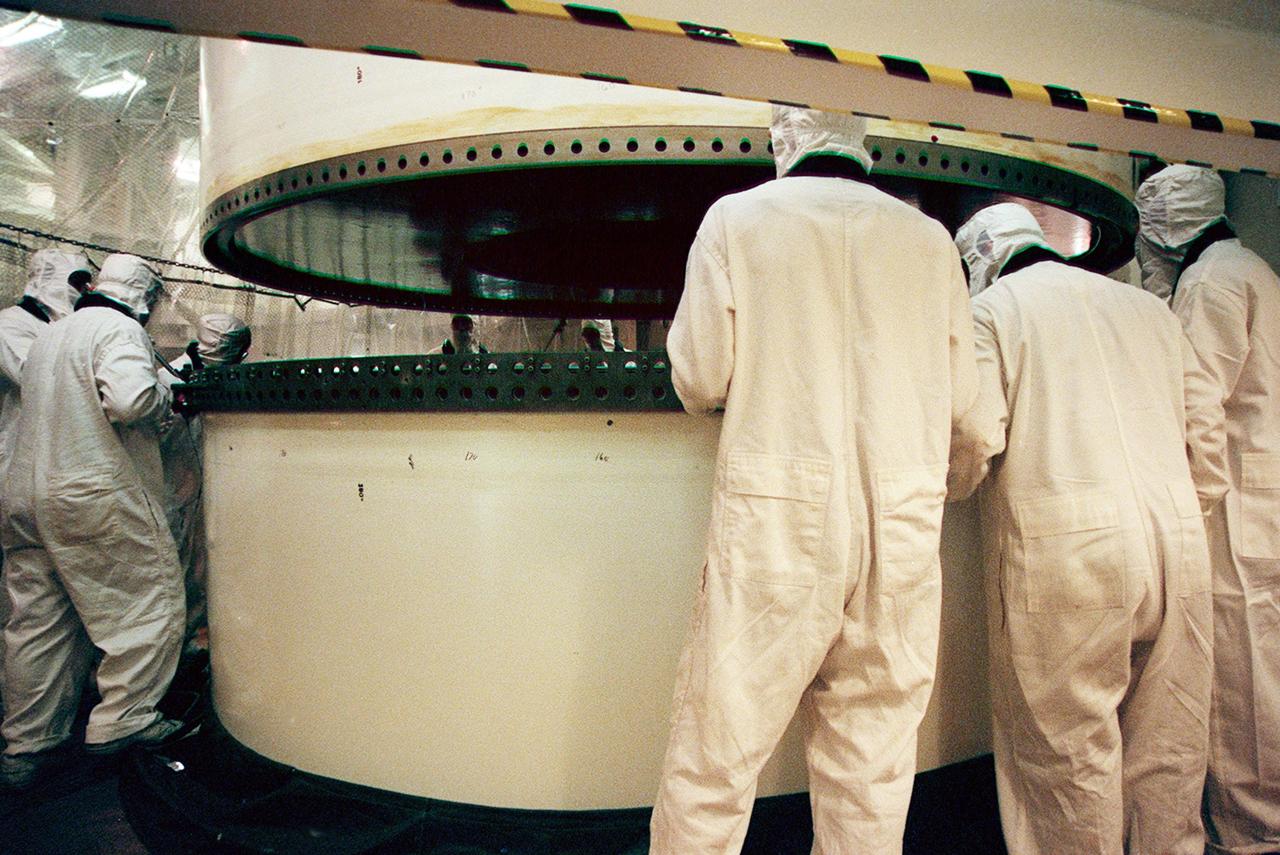

In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers prepare to mate two segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB). The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
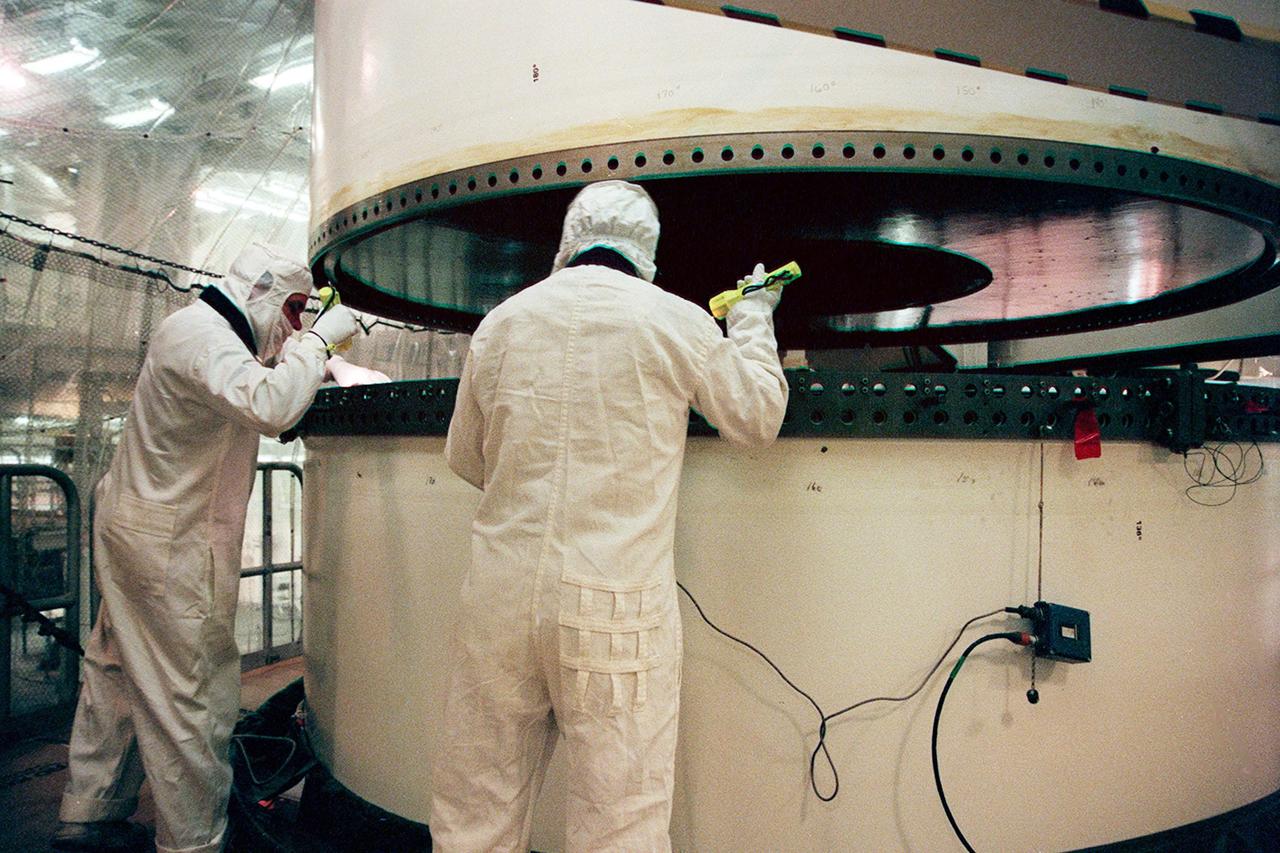

In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check two segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB) to be mated. The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
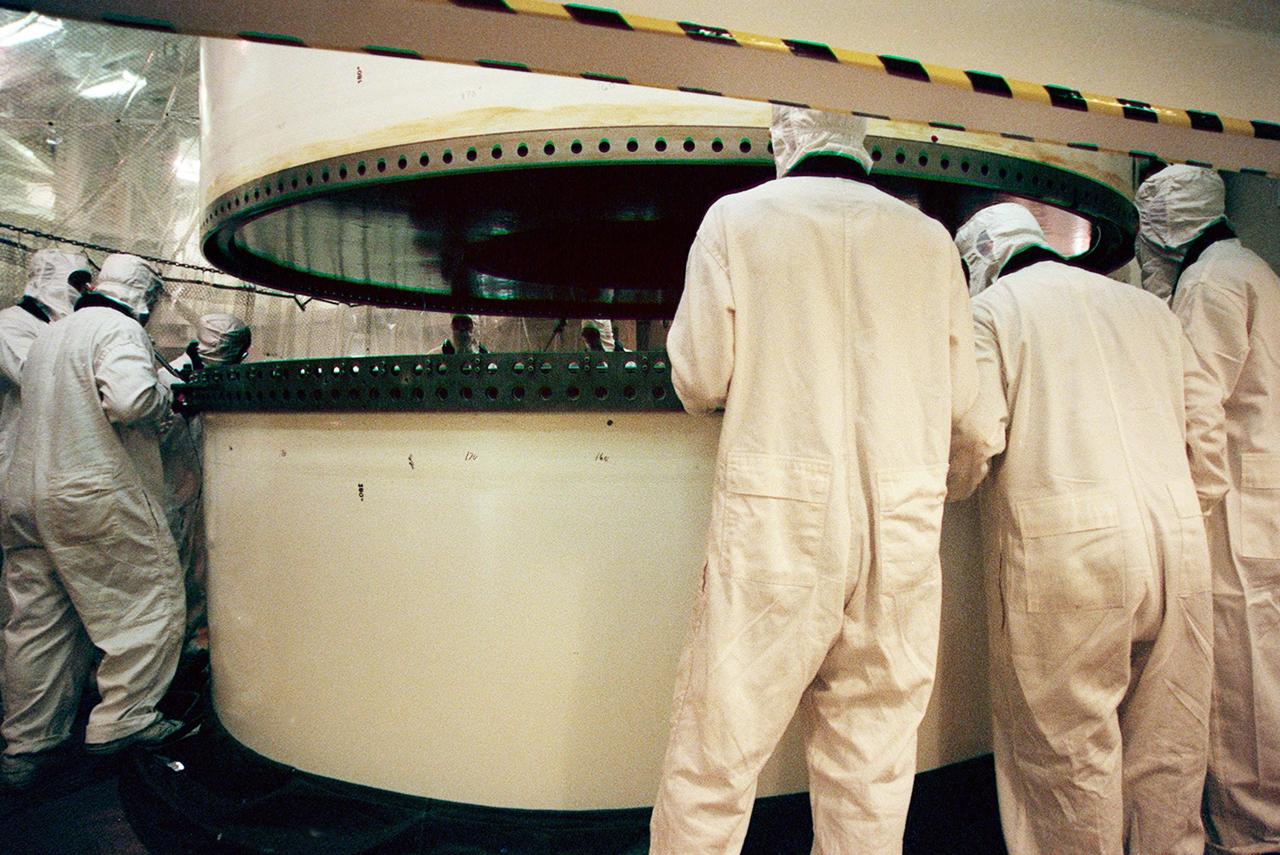

In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers prepare to mate two segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB). The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
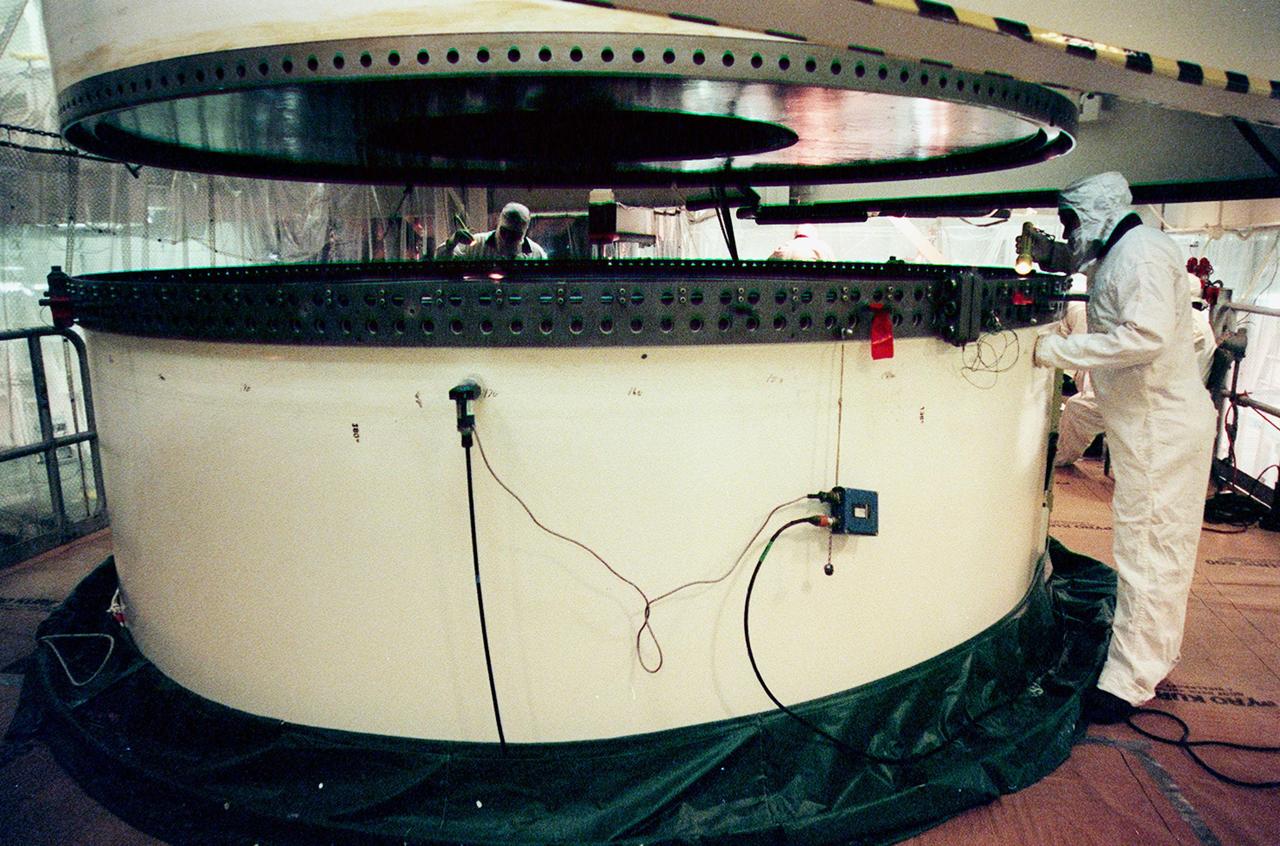
In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check the lower segment of a solid rocket booster (SRB) to be mated to the one above. The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
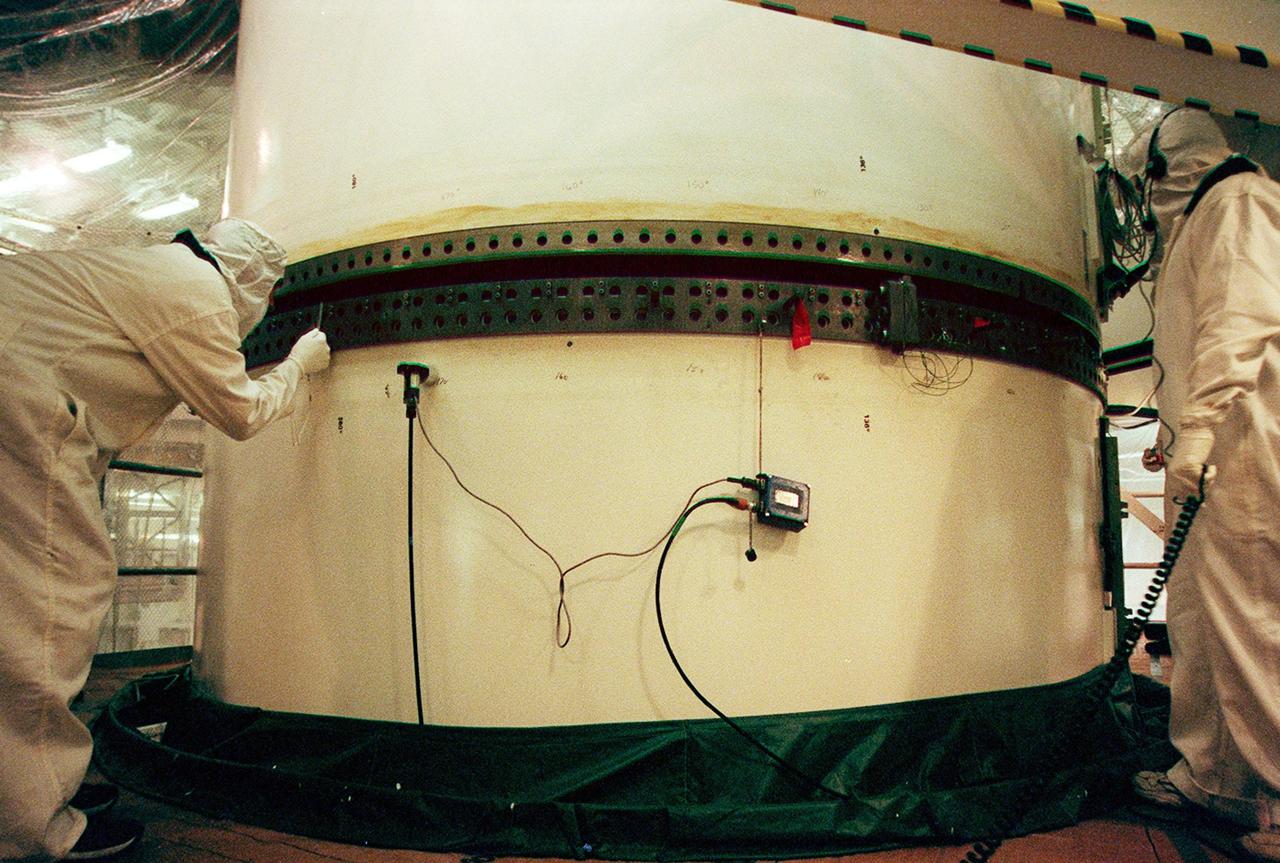
In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check the rings on the segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB) before mating them.; The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
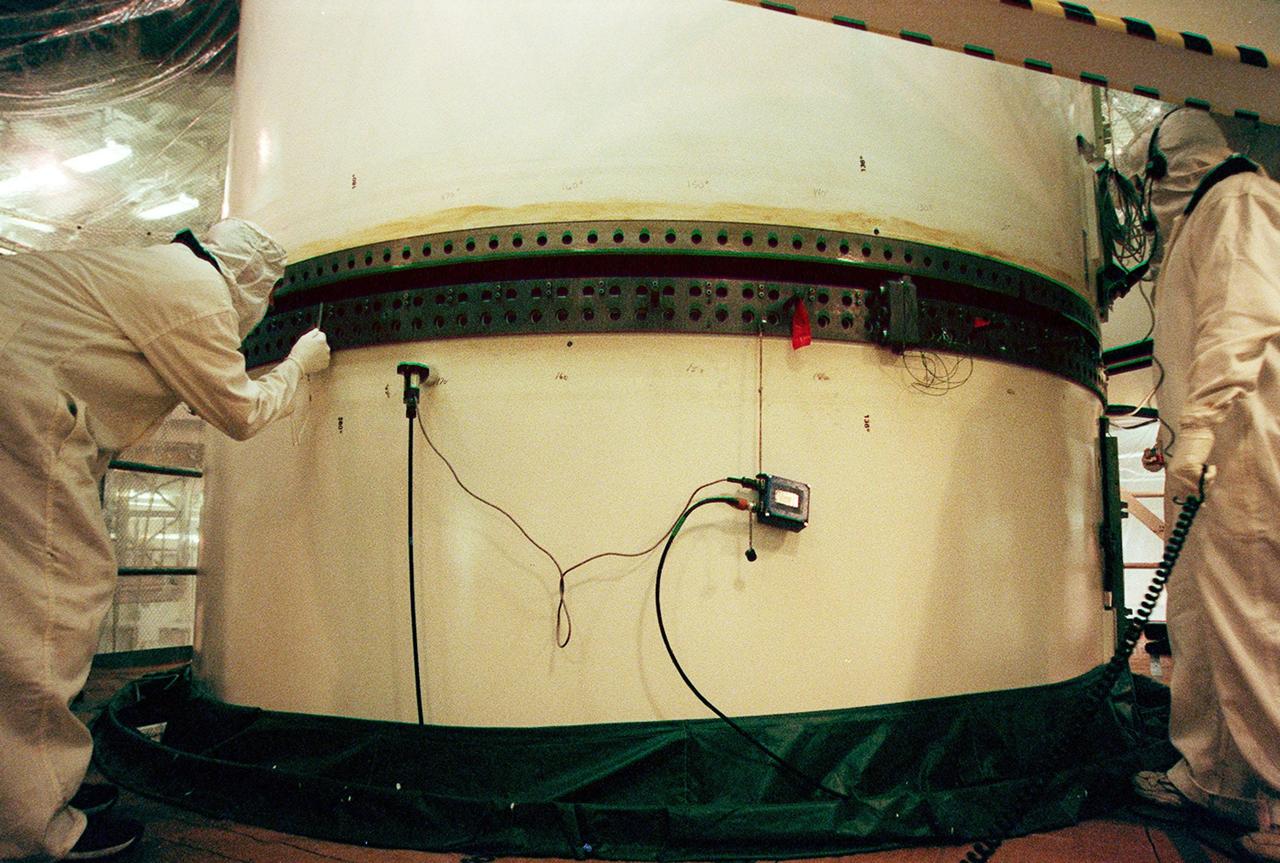
In the Vehicle Assembly Building, workers check the rings on the segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB) before mating them.; The SRB is part of the stack for the STS-92 mission, scheduled for launch Oct. 5 from Launch Pad 39A
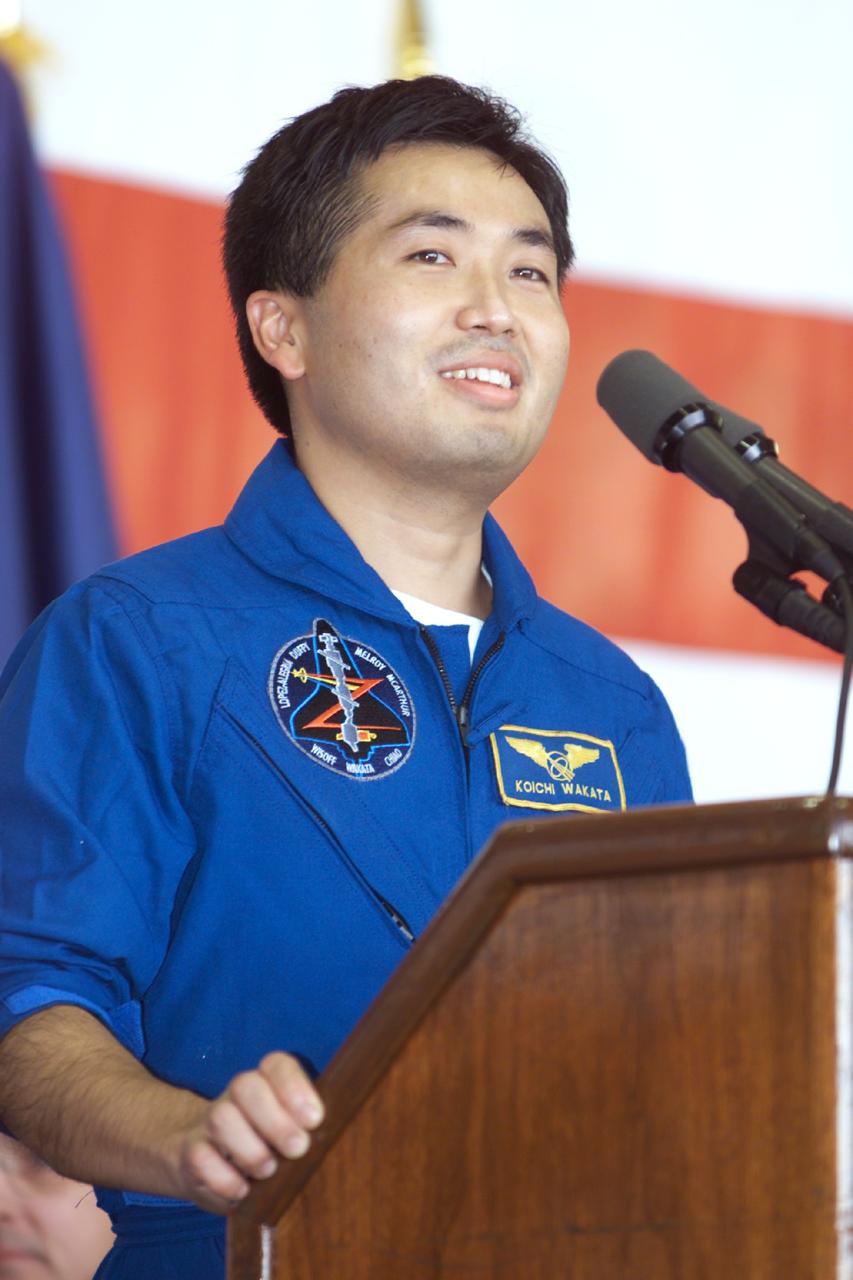

JSC2000-E-27058 (27 October 2000) --- Astronaut Koichi Wakata, mission specialist, addresses crowd at Ellington Field during crew return ceremonies. Wakata represents Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA).
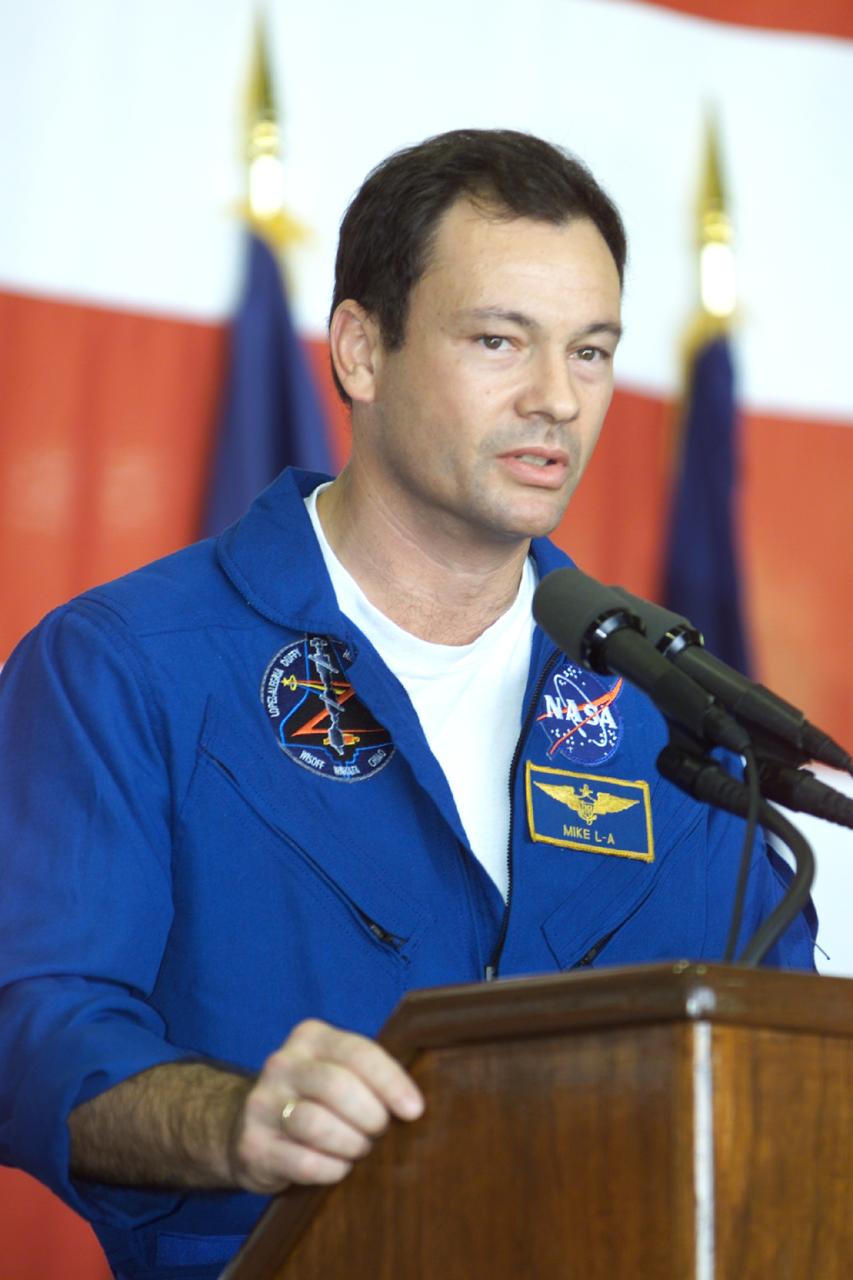

JSC2000-E-27056 (27 October 2000) --- Astronaut Michael Lopez-Alegria, mission specialist, addresses crowd at Ellington Field during crew return ceremonies.
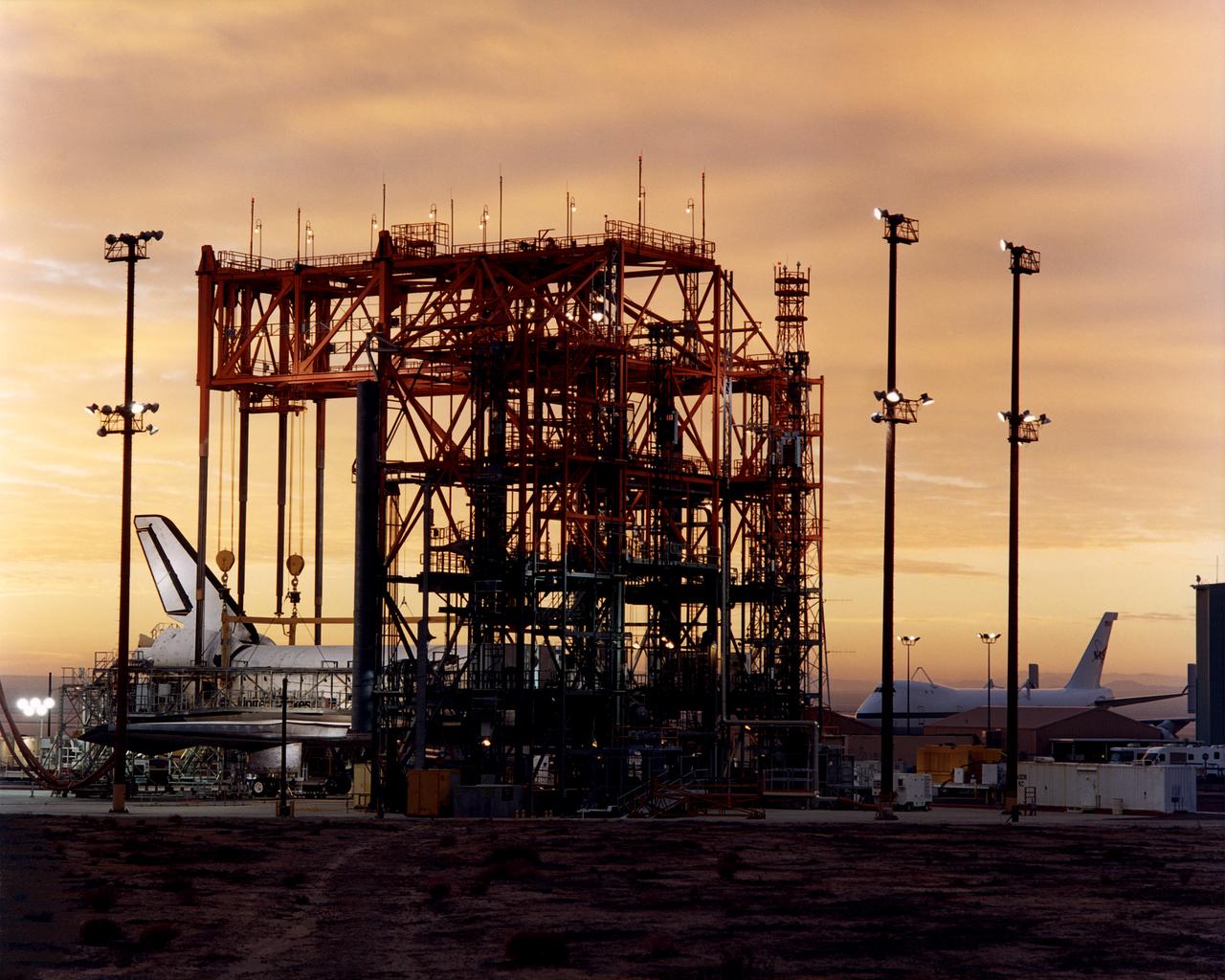

The early-morning Sun provides a golden backdrop to the Space Shuttle Discovery encased in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used to prepare the shuttle for its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA’s modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.
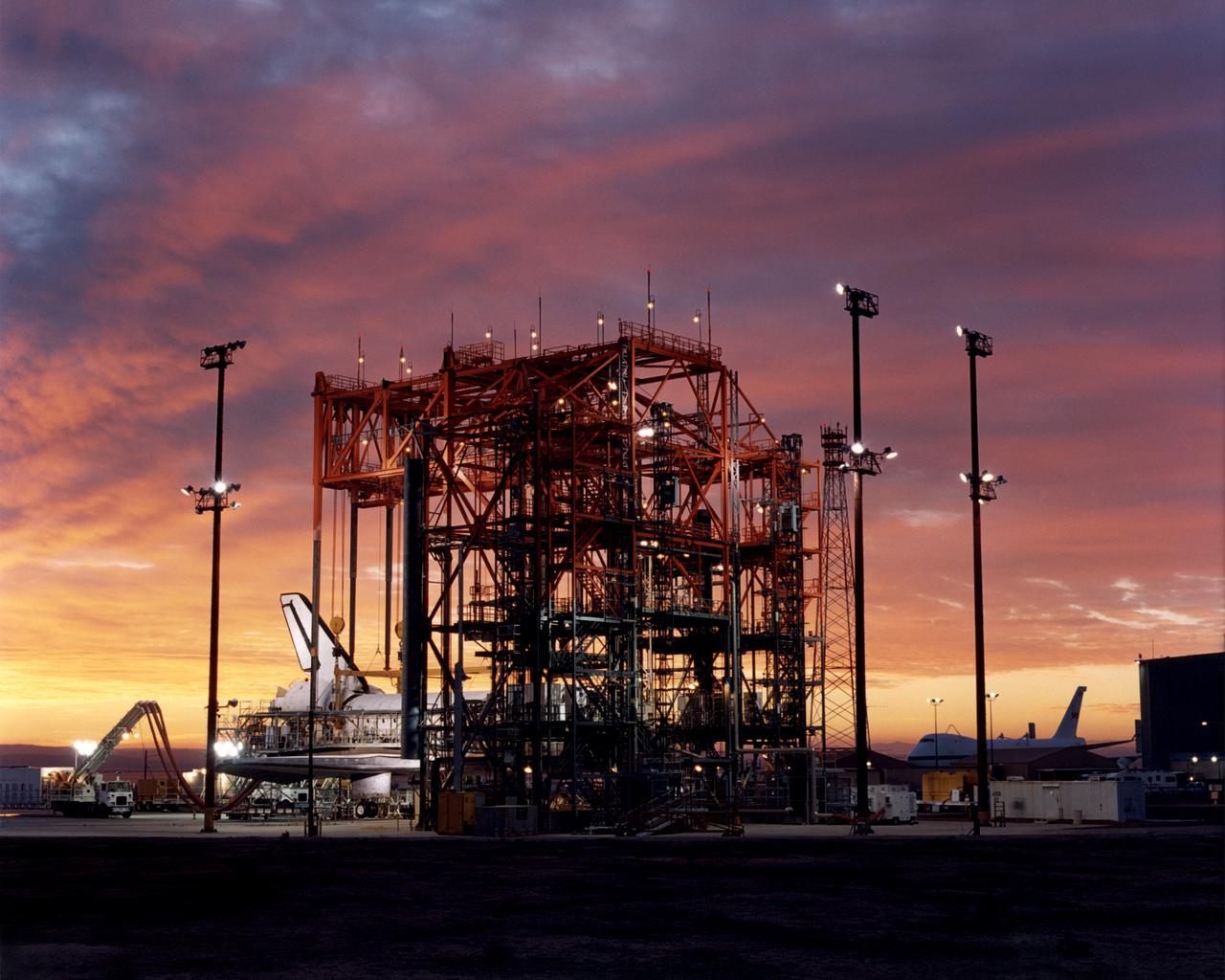

The early-morning Sun bathes the Space Shuttle Discovery in hues of purple, pink and gold as it is encased in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used to prepare the shuttle for its ferry flight back to the Kennedy space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA’s modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.
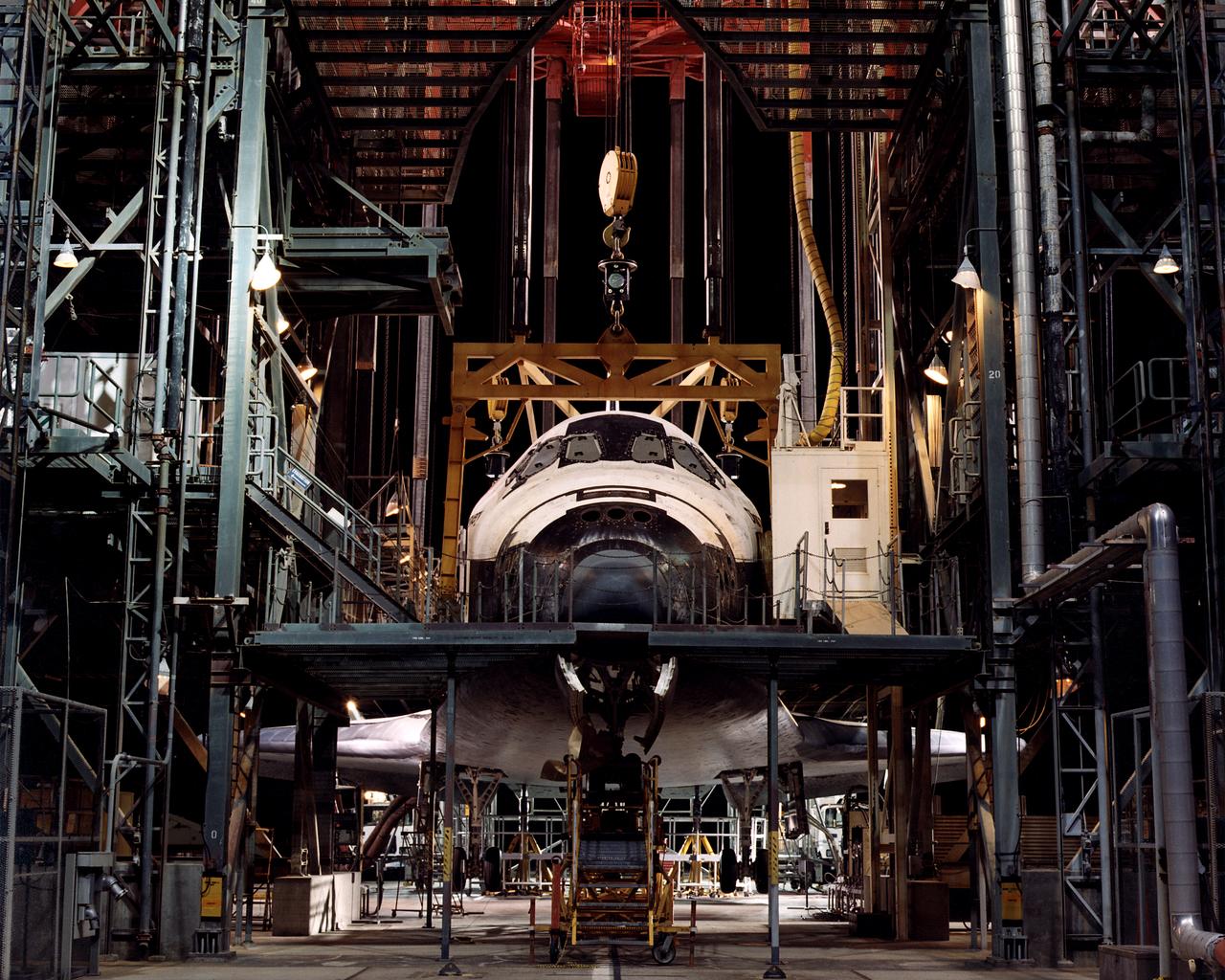
The Space Shuttle Discovery is centered in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA’s modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.
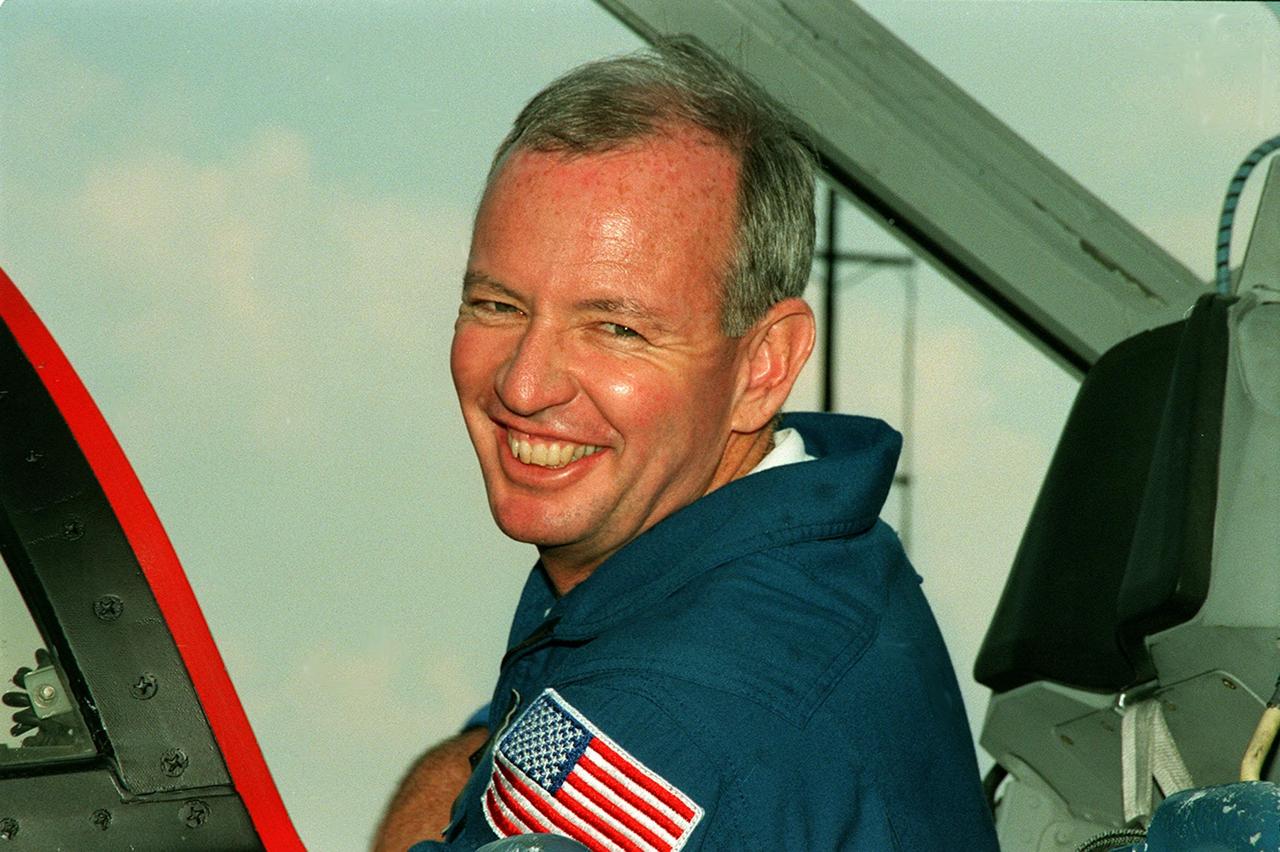

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy climbs into a T-38 jet aircraft at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility for a flight back to Houston. He and other crew members were at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities, looking over their mission payload and related equipment. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 on Shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. Discovery will carry the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, the PMA-3, Ku-band Communications System, and Control Moment Gyros (CMGs)
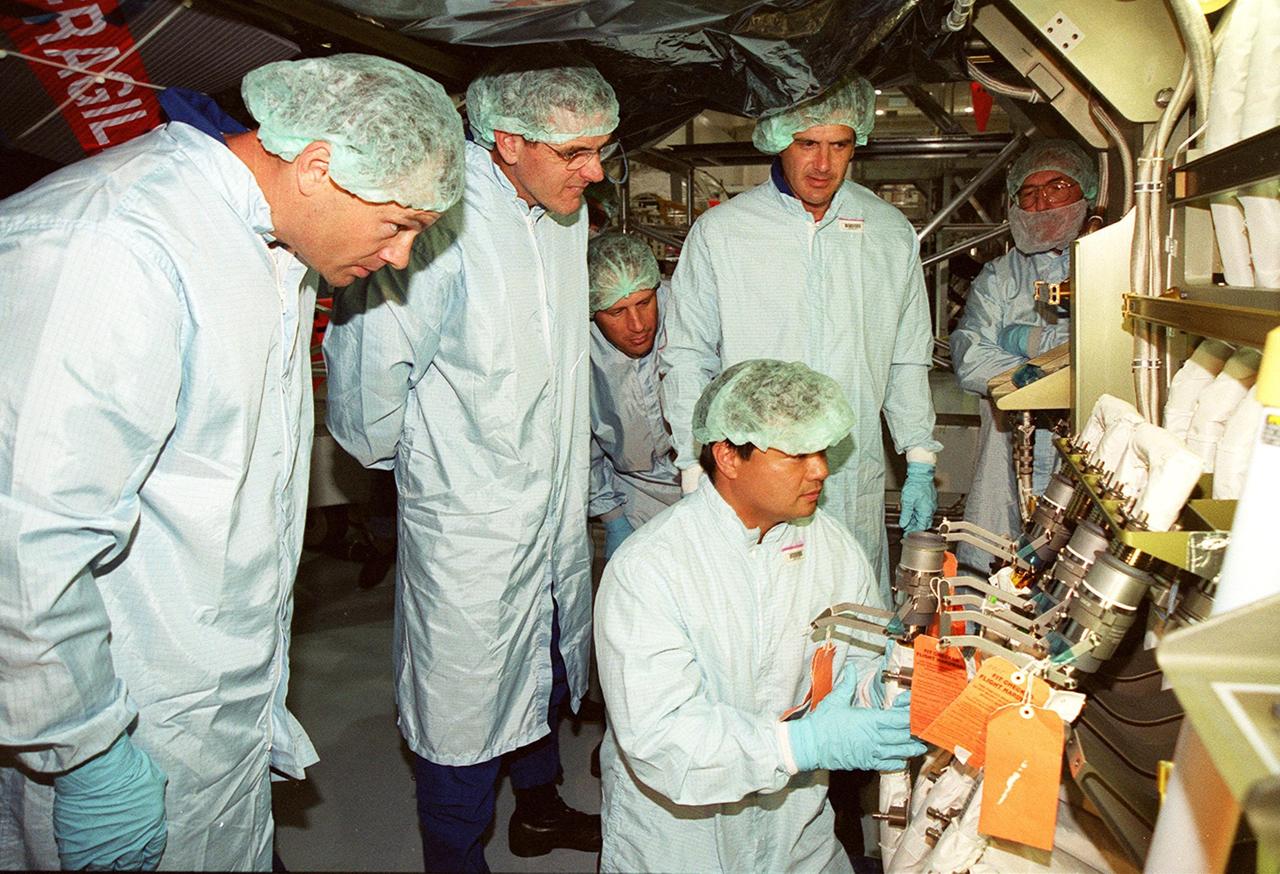

Members of the STS-92 crew check out the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the International Space Station and payload on their mission. From left are Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria, Bill McArthur, Jeff Wisoff and (kneeling) Leroy Chiao. They and other crew members are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities while at KSC. The Z1 truss is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
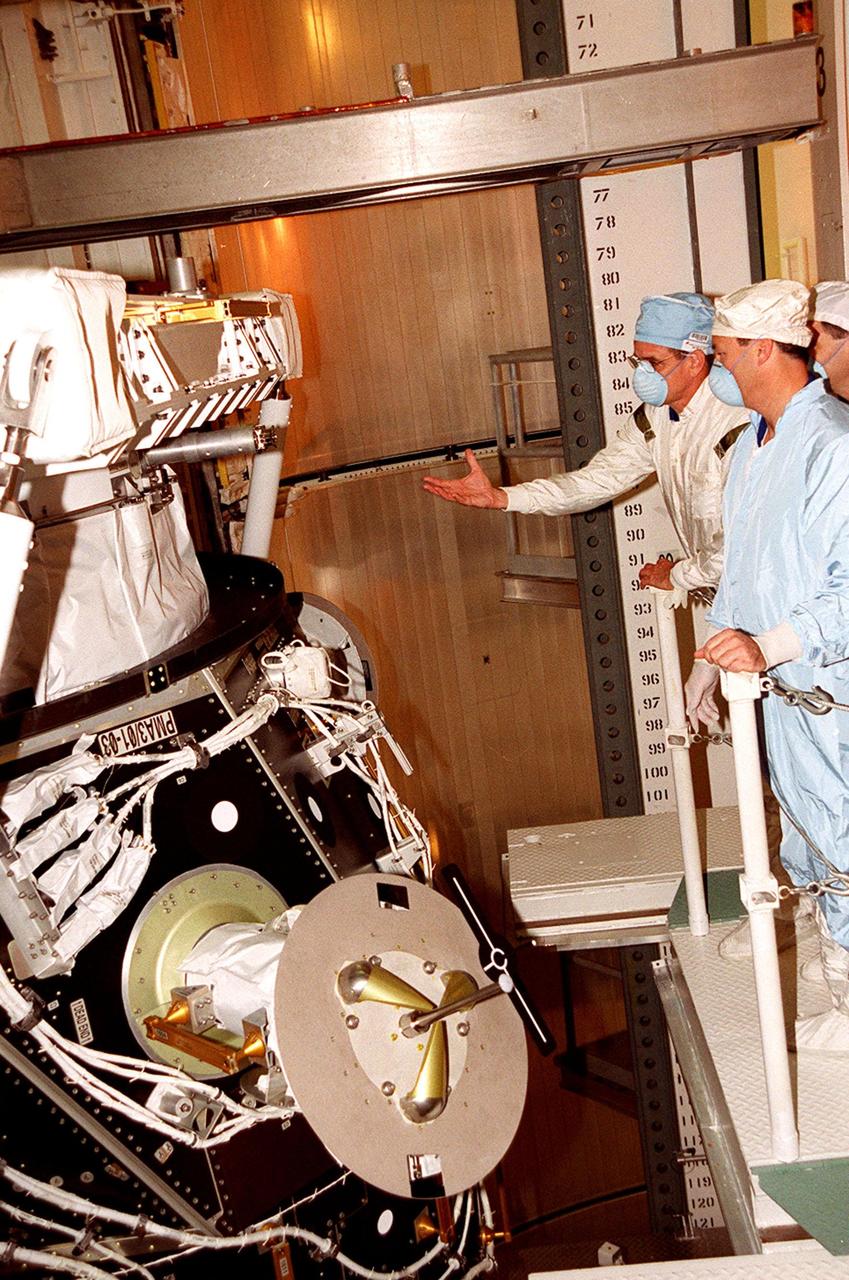

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay, STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. explains something about the Pressurized Mating Adapter in front of him to other Mission Specialists Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Peter J.K. Wisoff. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
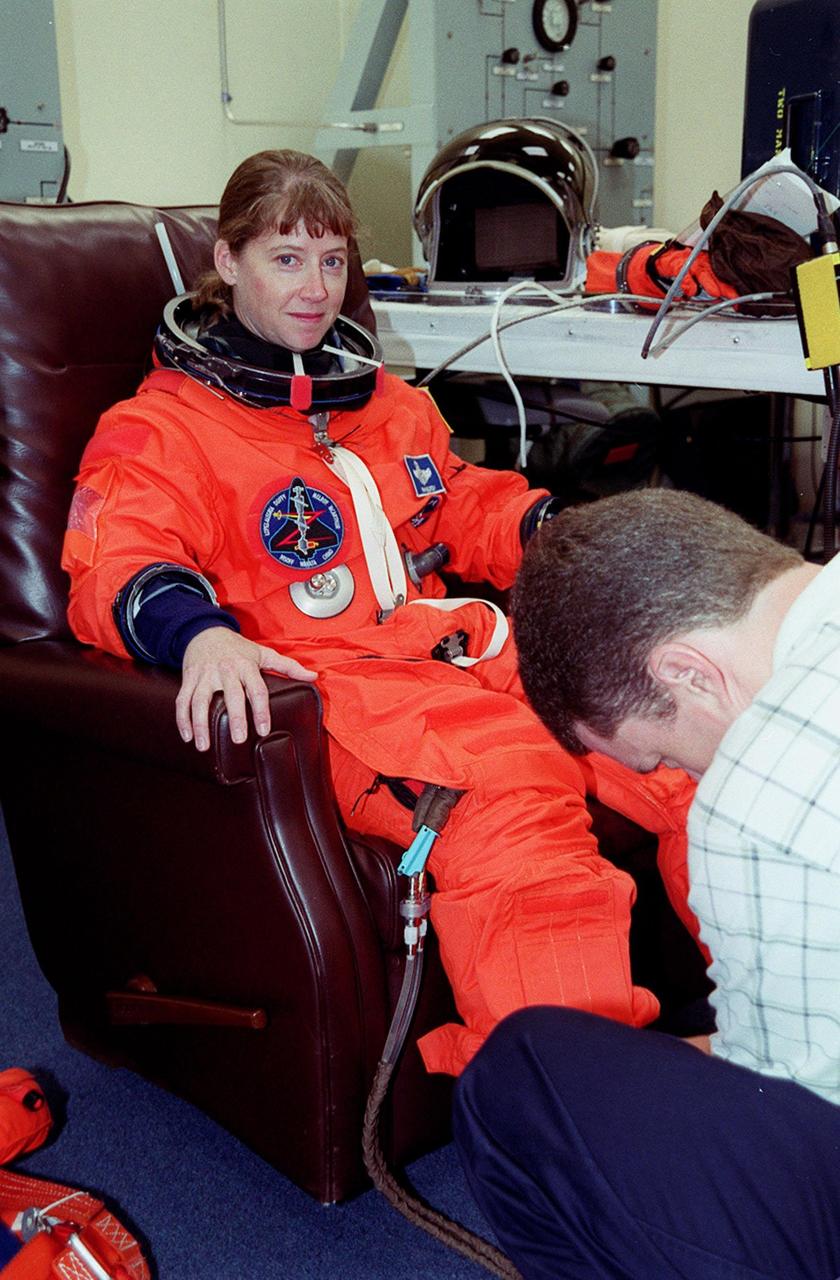

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy has her new launch and entry suit adjusted during fit check. Melroy and the rest of the crew are at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. The TCDT provides emergency egress training, simulated countdown exercises and opportunities to inspect the mission payload. This mission will be Melroy’s first Shuttle flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
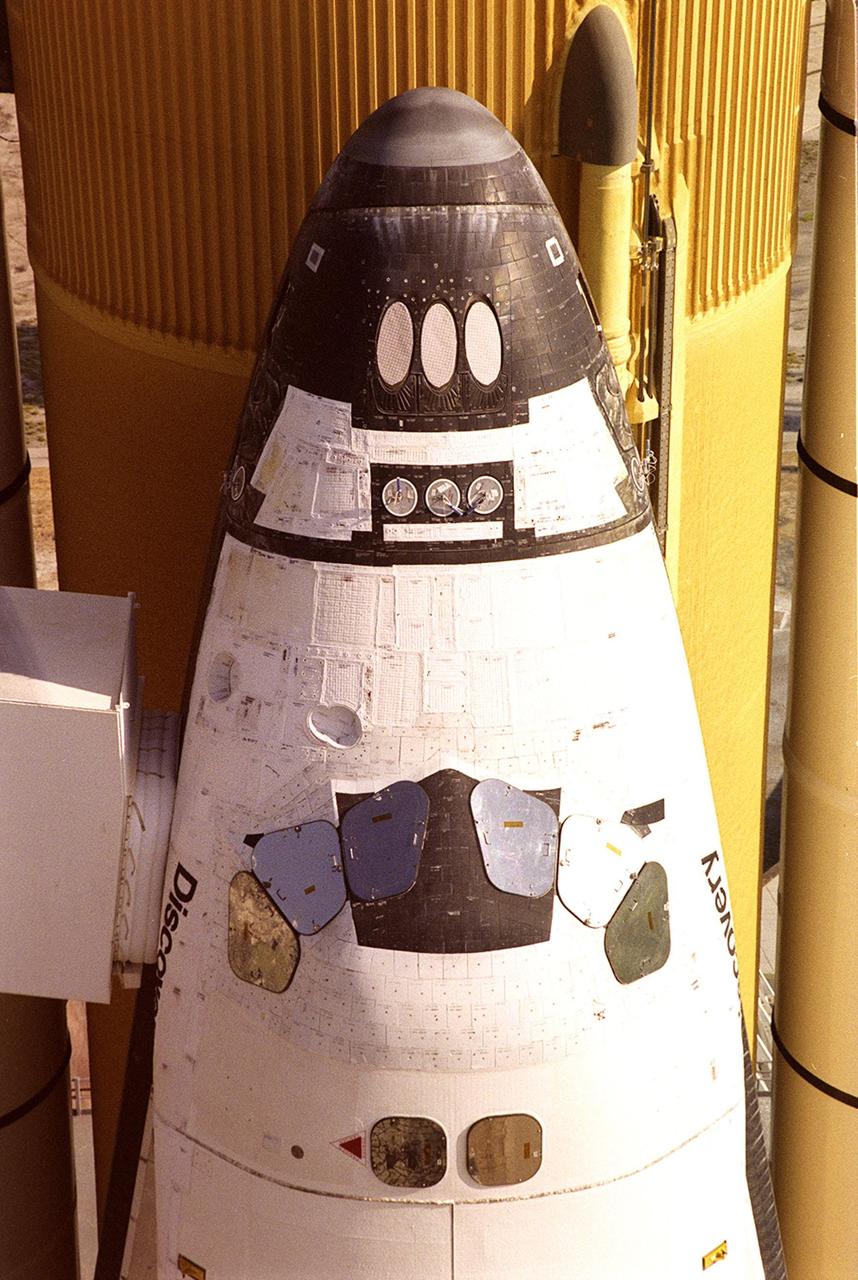
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A closeup of Space Shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A shows the White Room (left) extended to the side of the orbiter, at the entrance to the crew compartment. Discovery is undergoing final launch preparations of STS-92. Scheduled to lift off Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT, Discovery will be making the 100th Space Shuttle mission launched from Kennedy Space Center. Discovery also will be making its 28th flight into space, more than any of the other orbiters to date. STS-92 is a mission to the International Space Station, carrying the Z1 truss, which is the first of 10 trusses on the Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter
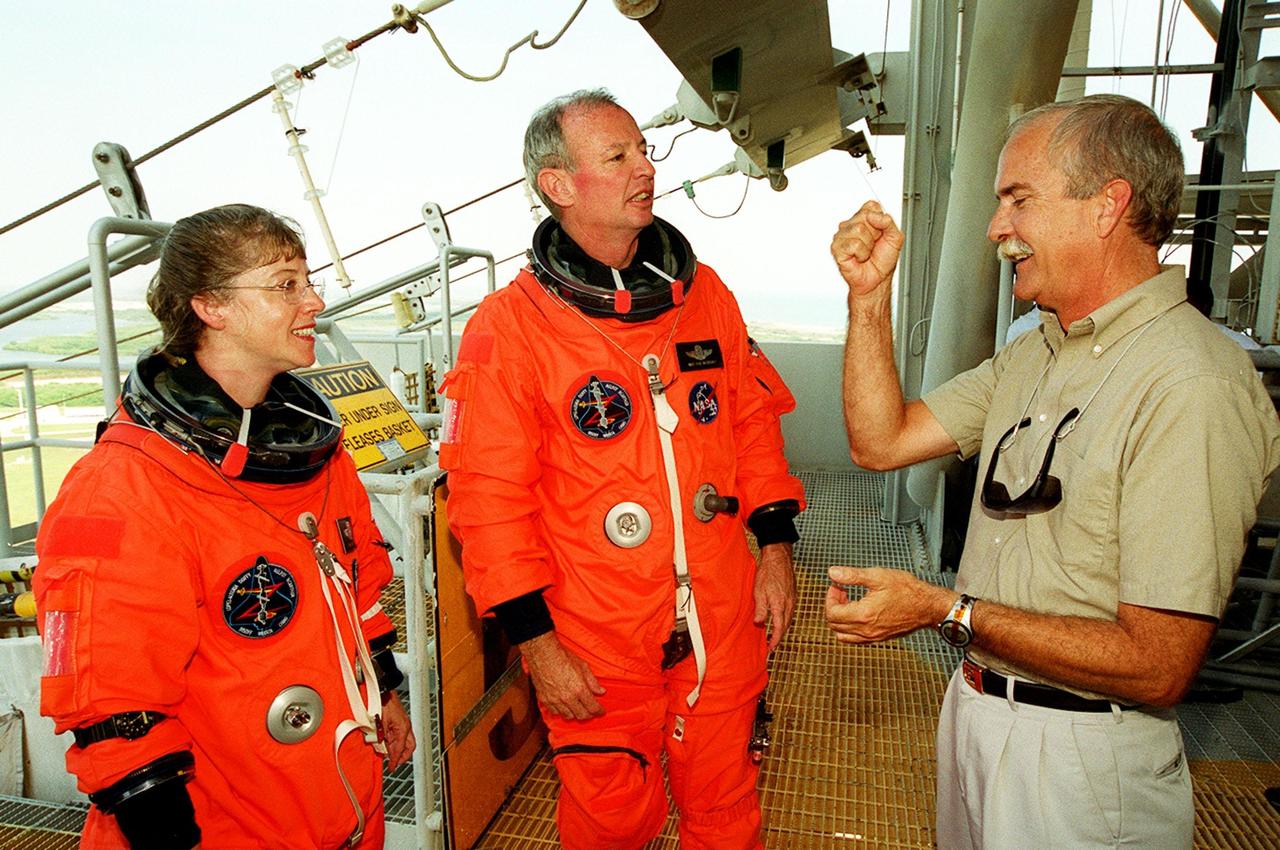

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Pad 39A, STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Commander Brian Duffy learn more about the emergency egress training they and the rest of the crew have received. The training is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated countdown. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
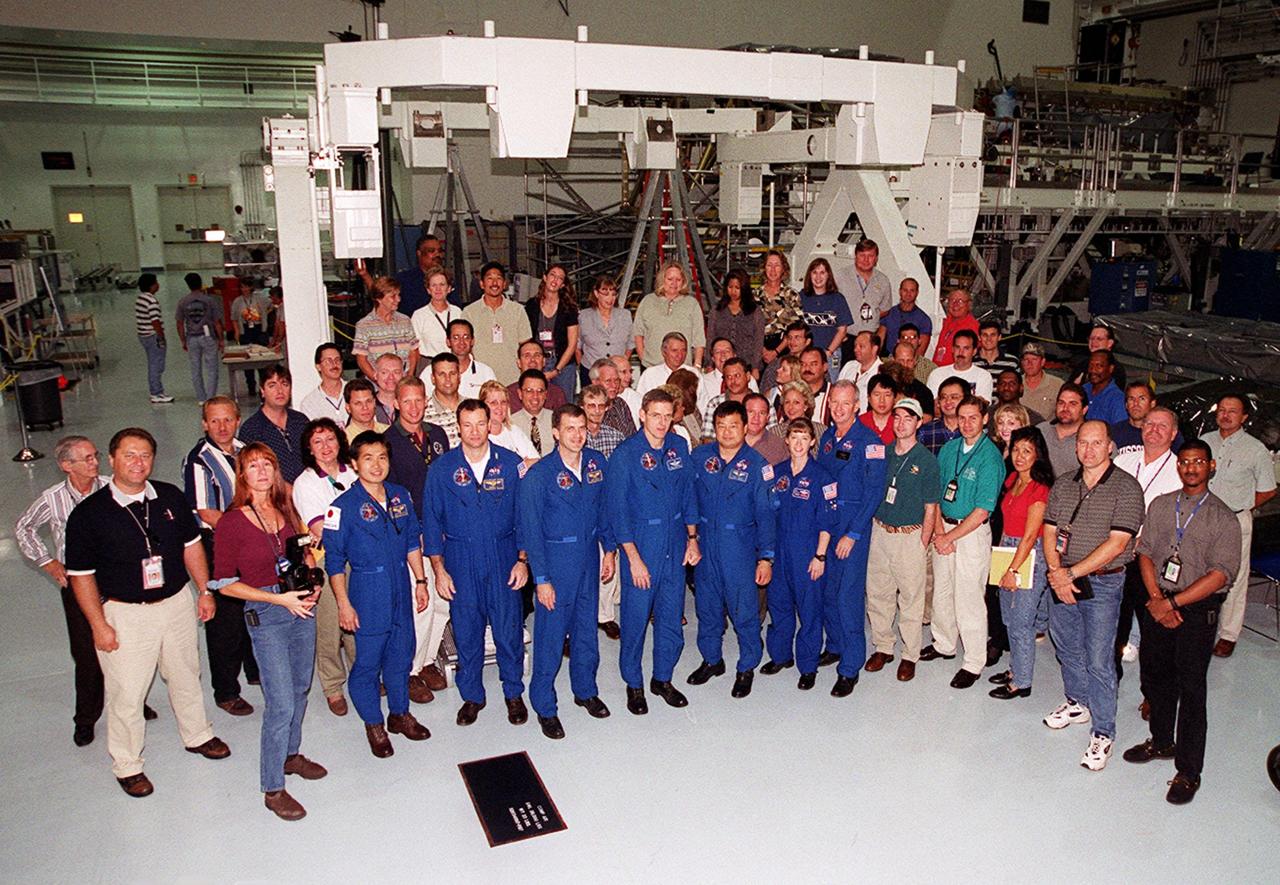

In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers who have supported mission STS-92 gather for a photo with the crew: (left to right) Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan, Michael Lopez-Alegria, Jeff Wisoff, Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao; Pilot Pam Melroy; and Commander Brian Duffy. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:30 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
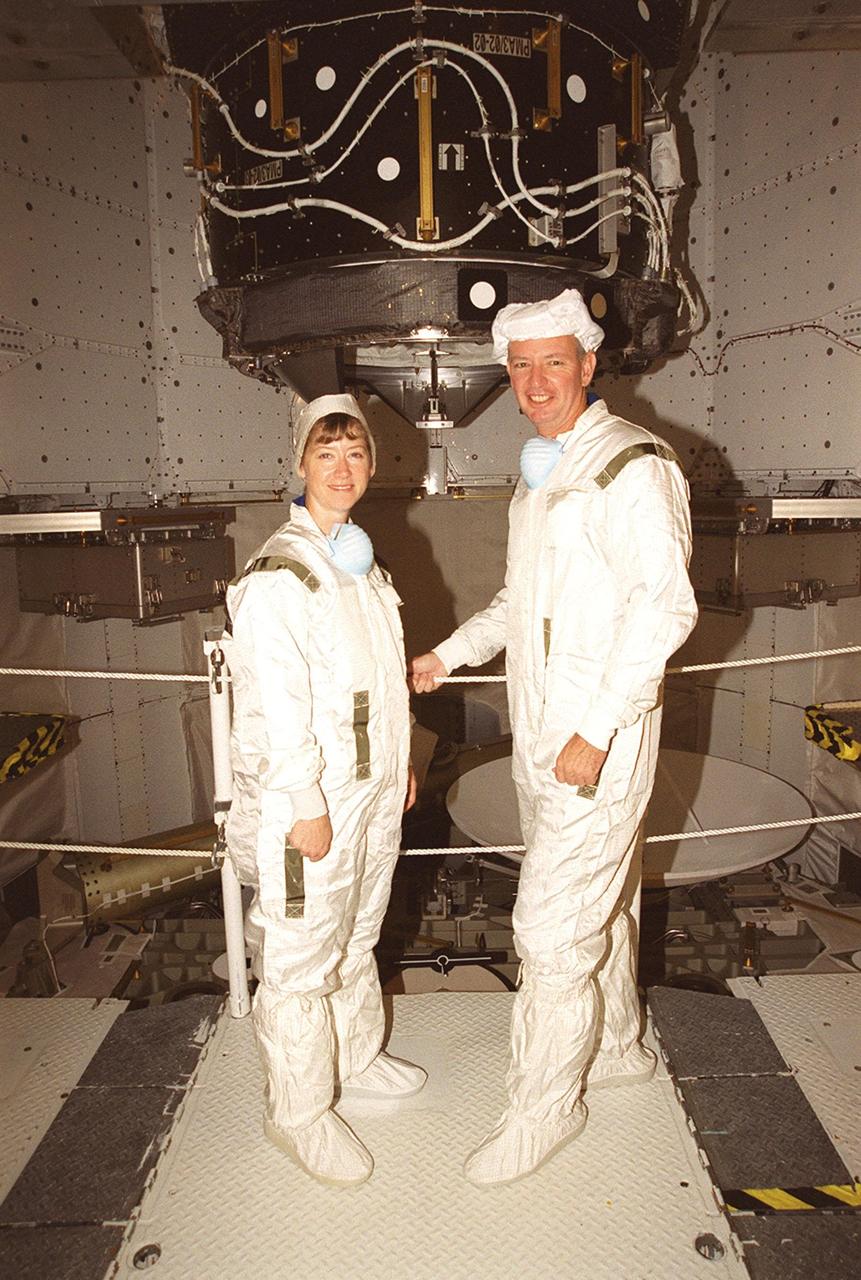

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy (left) and Commander Brian Duffy pose for a photo during payload inspection in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Behind them is the Pressurized Mating Adapter. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
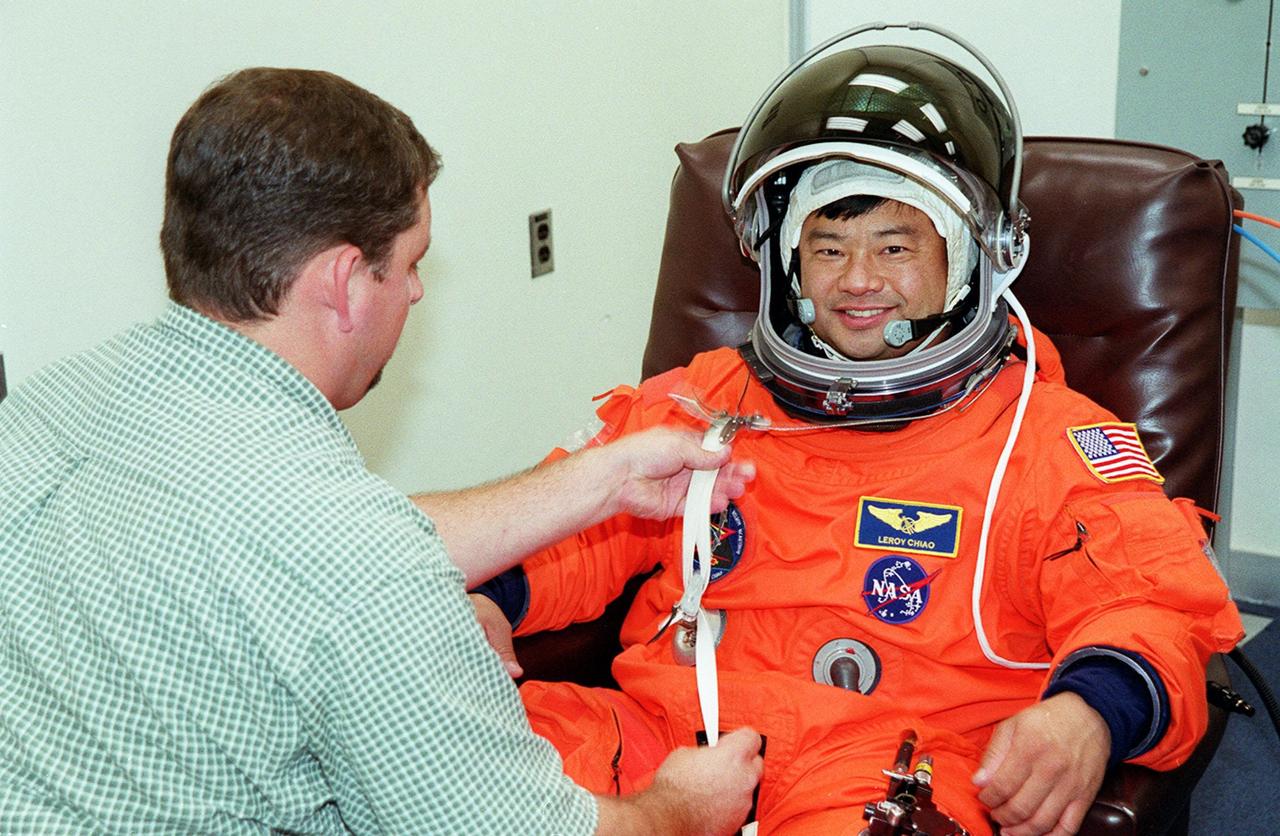

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-92 Mission Specialist Leroy Chiao has his launch and entry suit adjusted during fit check. Chiao and the rest of the crew are at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. The TCDT provides emergency egress training, simulated countdown exercises and opportunities to inspect the mission payload. This mission will be Chiao’s third Shuttle flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
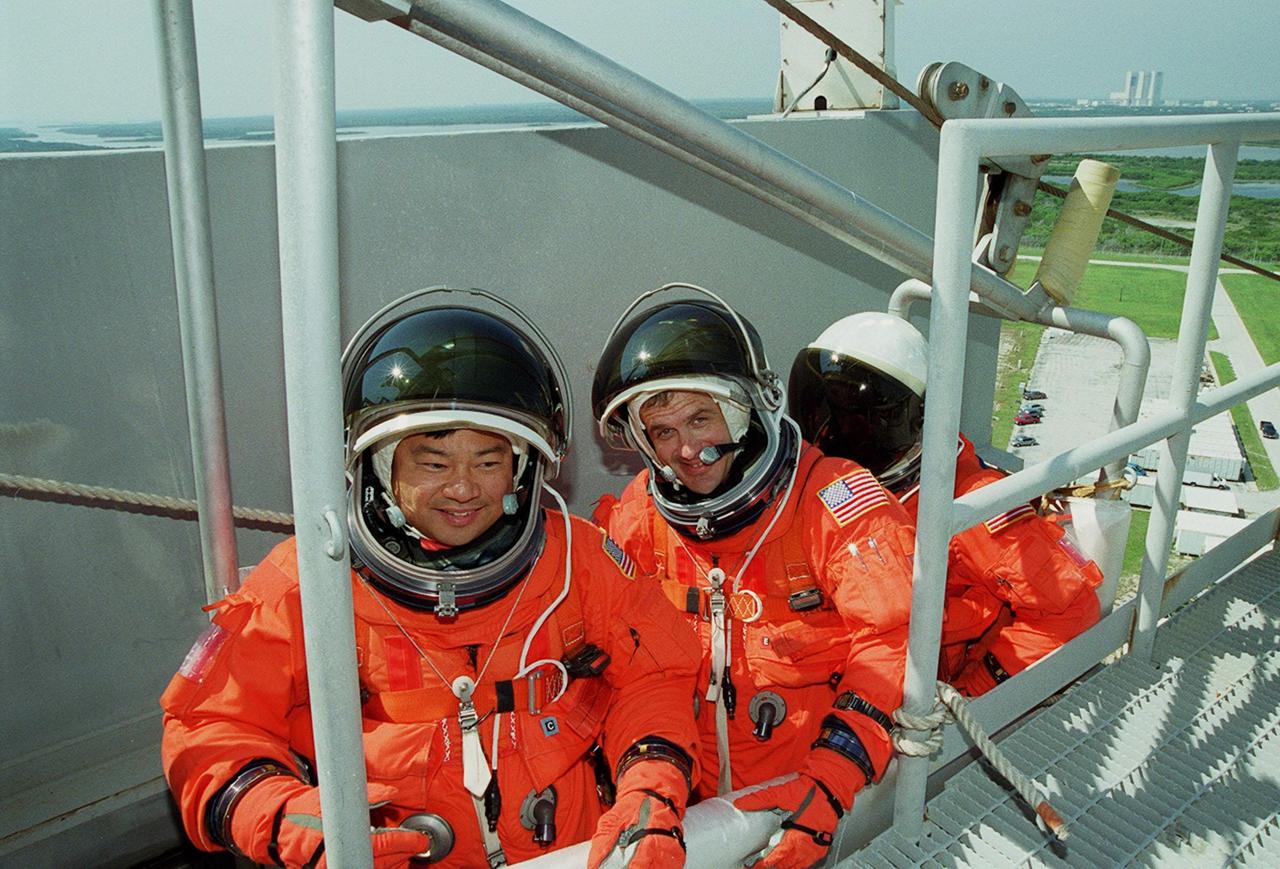

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seated in the slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Pad 39A, STS-92 Mission Specialists Leroy Chaio, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria take part in emergency egress training, one of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated countdown. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
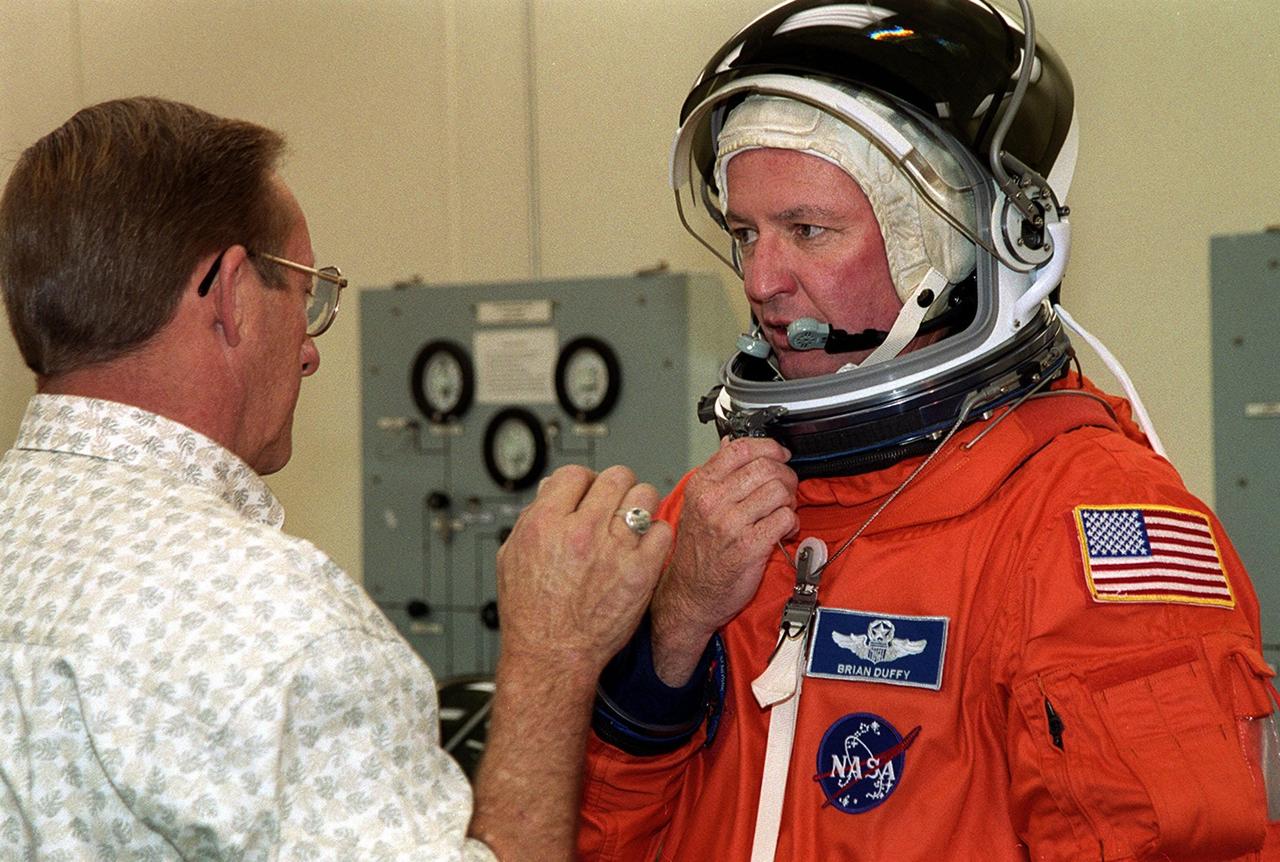

During pre-pack and fit check on his launch and entry suit, STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy adjusts his helmet. Duffy and the rest of the crew are at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. The TCDT provides emergency egress training, simulated countdown exercises and opportunities to inspect the mission payload. This mission will be Duffy’s fourth Shuttle flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
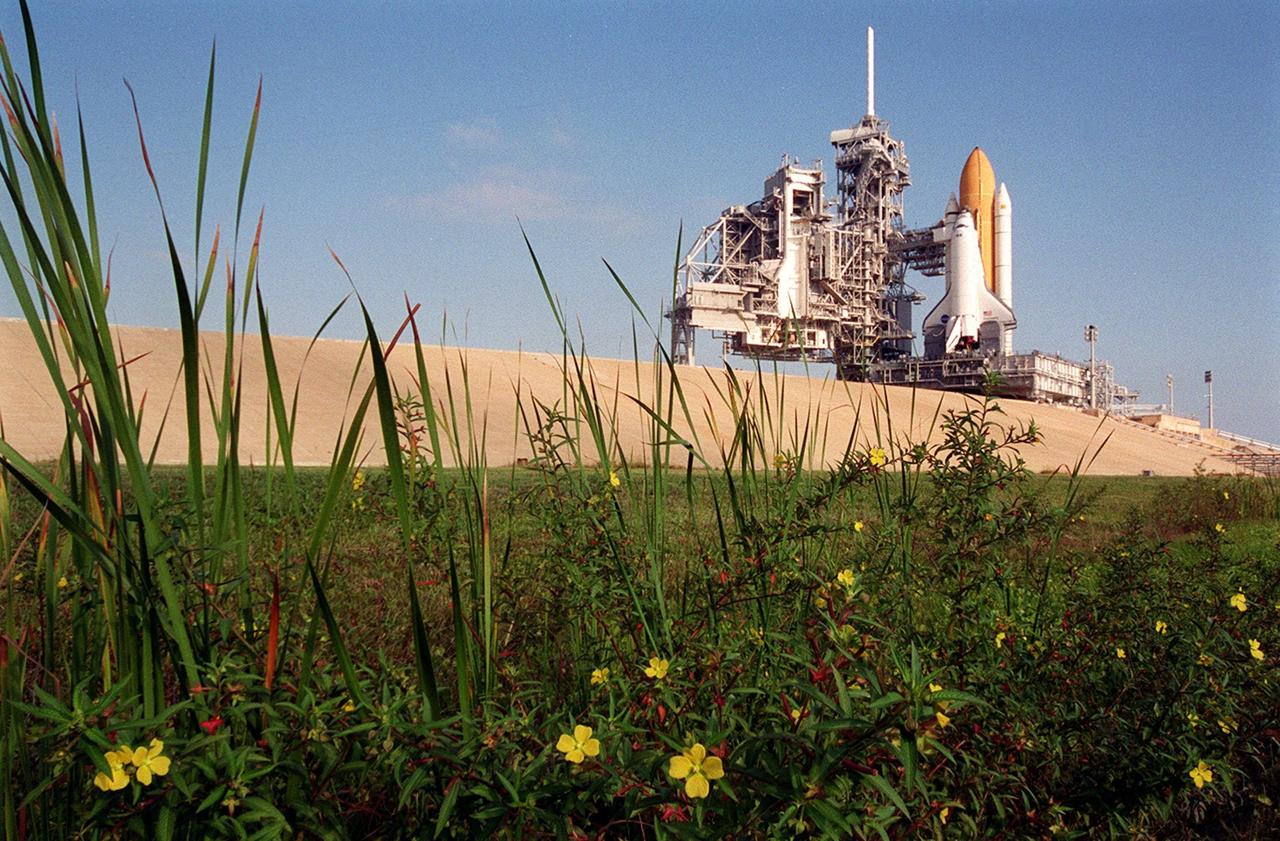

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Viewed across a field of wildflowers and other greenery, Space Shuttle Discovery rises above them on Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is undergoing final launch preparations of STS-92. Scheduled to lift off Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT, Discovery will be making the 100th Space Shuttle mission launched from Kennedy Space Center. Discovery also will be making its 28th flight into space, more than any of the other orbiters to date. STS-92 is a mission to the International Space Station, carrying the Z1 truss, which is the first of 10 trusses on the Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter
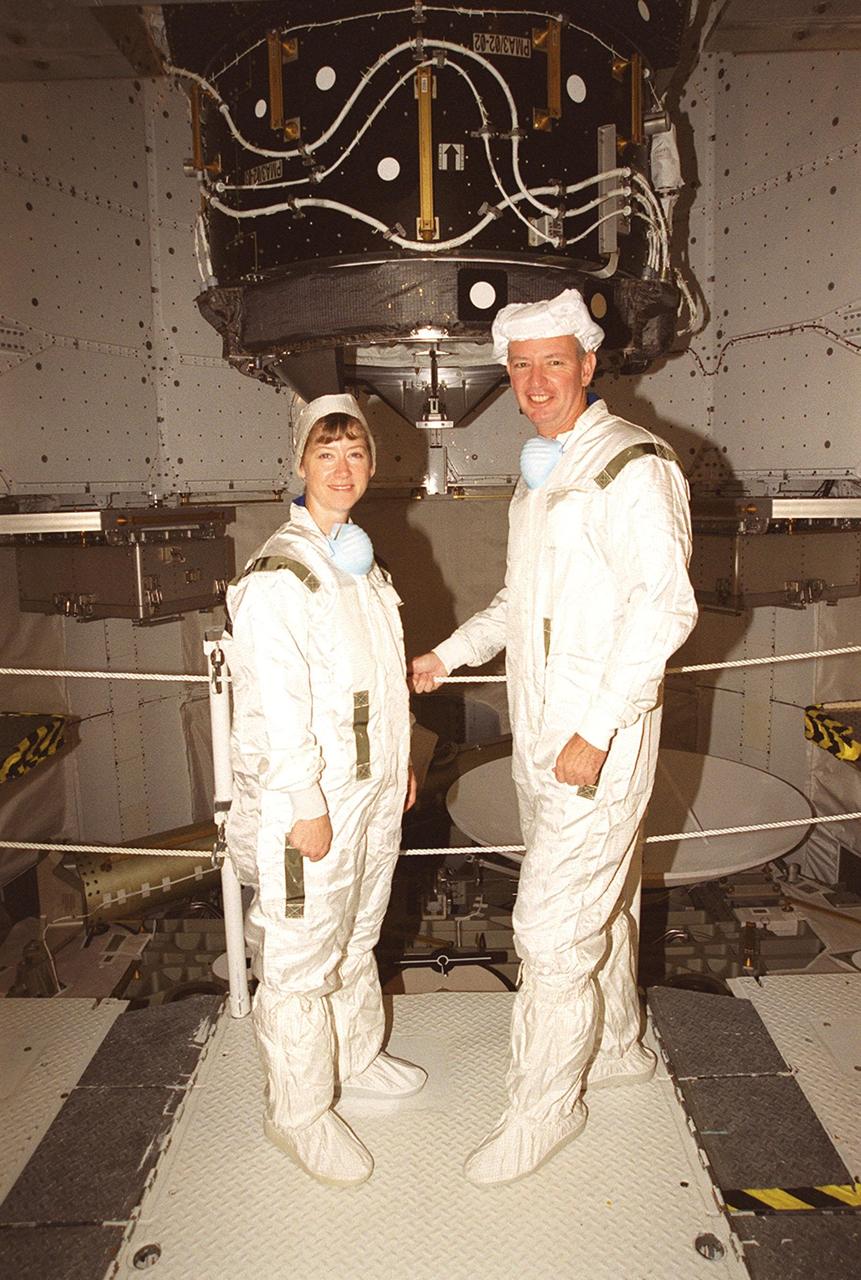

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy (left) and Commander Brian Duffy pose for a photo during payload inspection in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Behind them is the Pressurized Mating Adapter. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned

STS-92 Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata of Japan (center) gets help from United Space Alliance Mechanical Technician Vinny Difranzo (left) and NASA Quality Assurance Specialist Danny Wyatt (right) in suiting up in the White Room. Wakata and other crew members are taking part in a simulated countdown KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
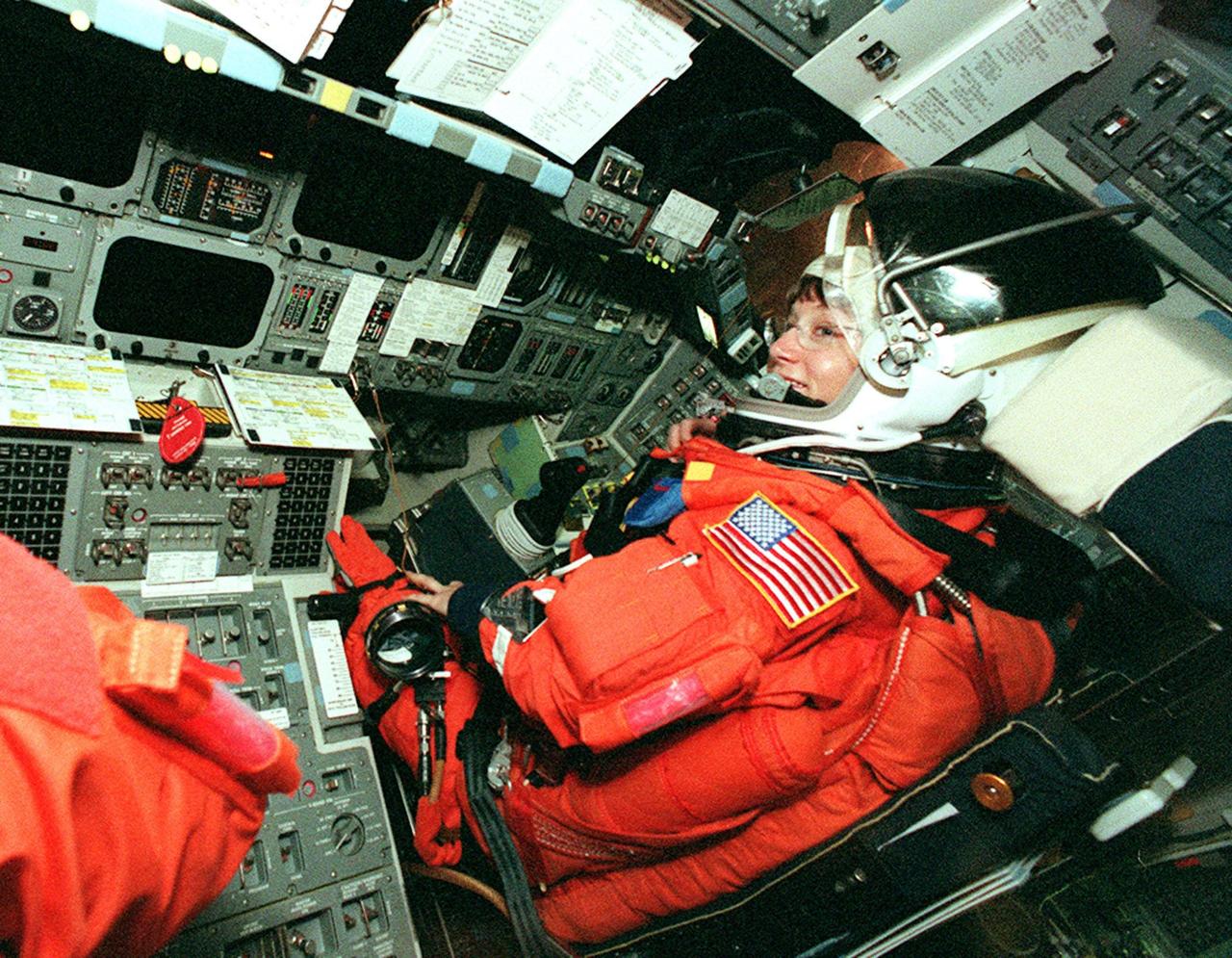

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy gets settled in her seat in Discovery to take part in a simulated countdown. The countdown is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that she and other crew members have been performing. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
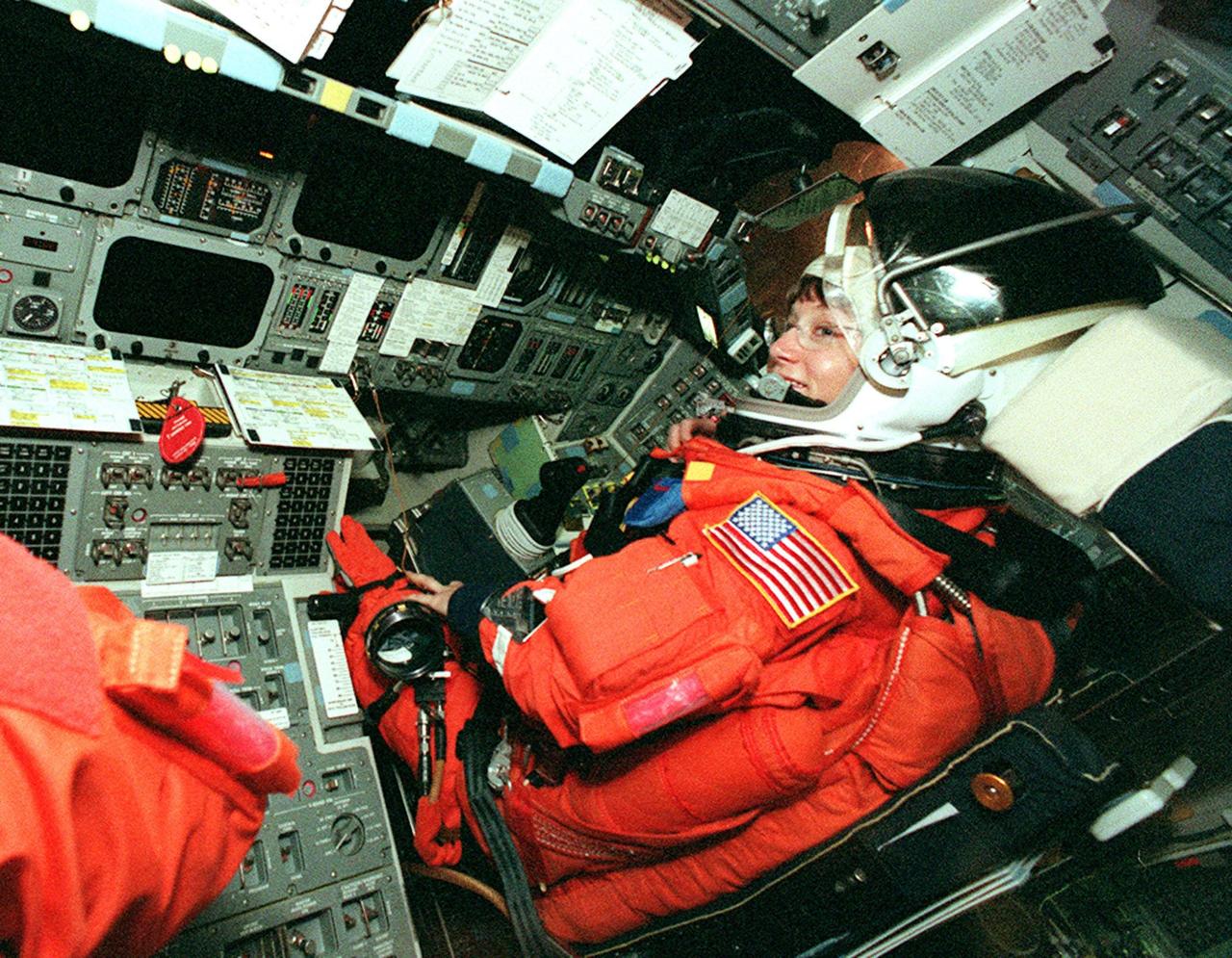

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy gets settled in her seat in Discovery to take part in a simulated countdown. The countdown is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that she and other crew members have been performing. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
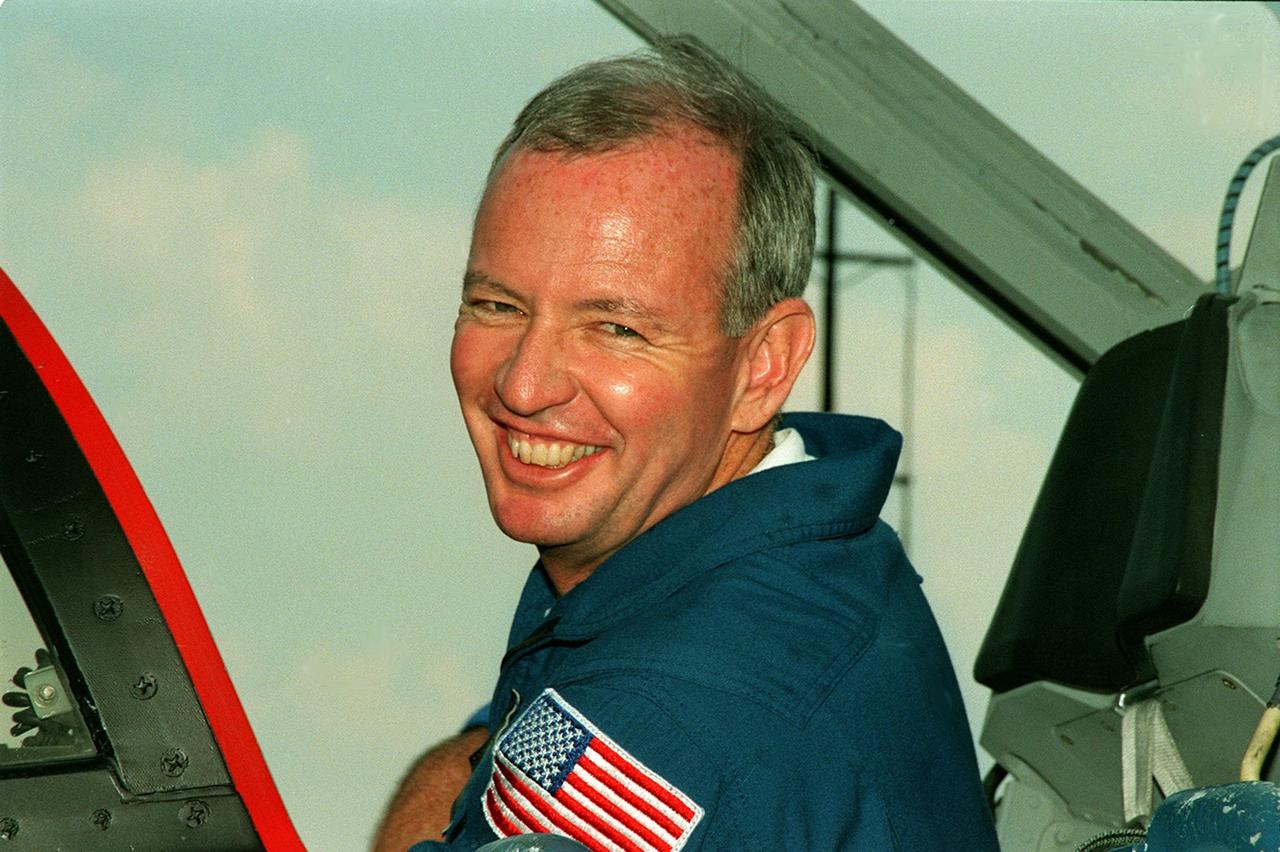

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy climbs into a T-38 jet aircraft at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility for a flight back to Houston. He and other crew members were at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities, looking over their mission payload and related equipment. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 on Shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. Discovery will carry the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, the PMA-3, Ku-band Communications System, and Control Moment Gyros (CMGs)
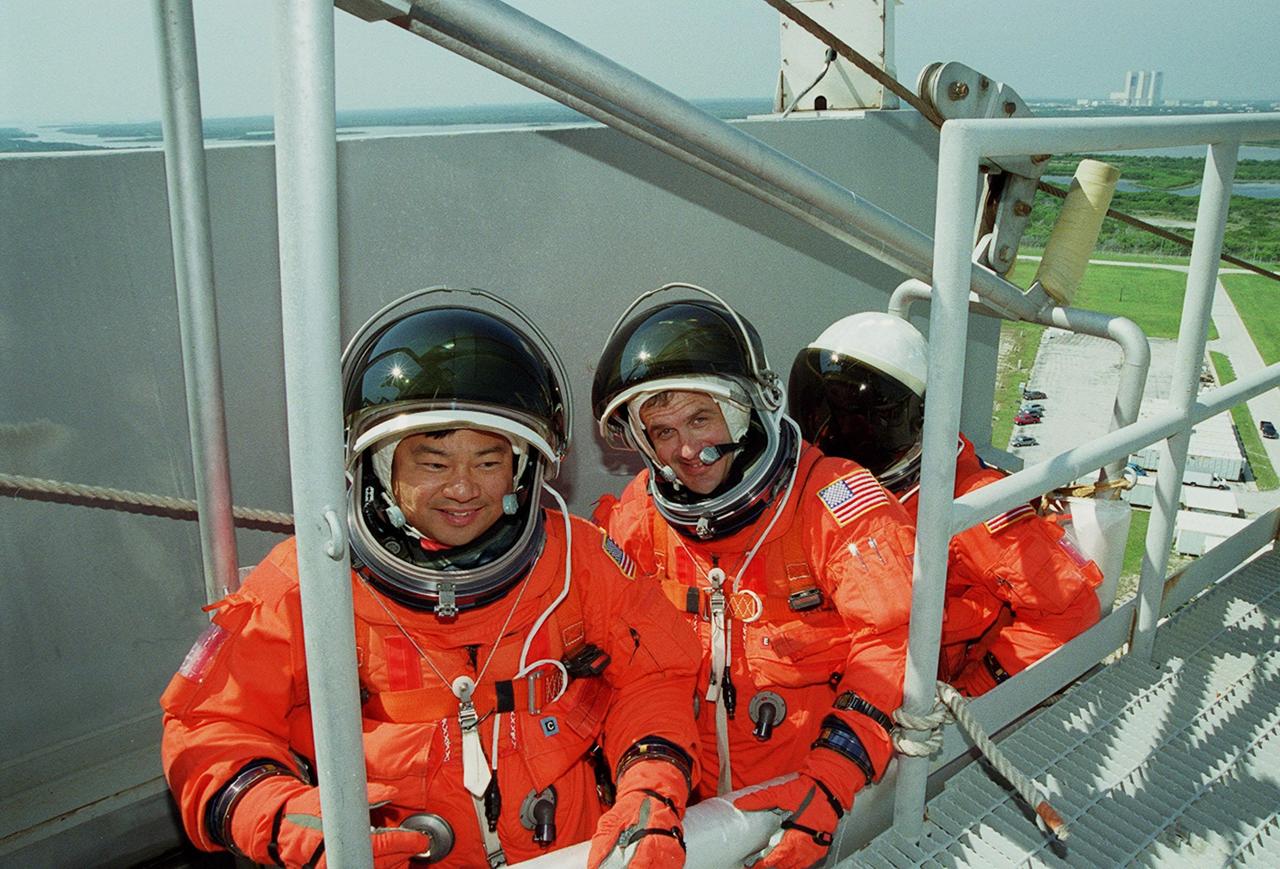

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seated in the slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Pad 39A, STS-92 Mission Specialists Leroy Chaio, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria take part in emergency egress training, one of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated countdown. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
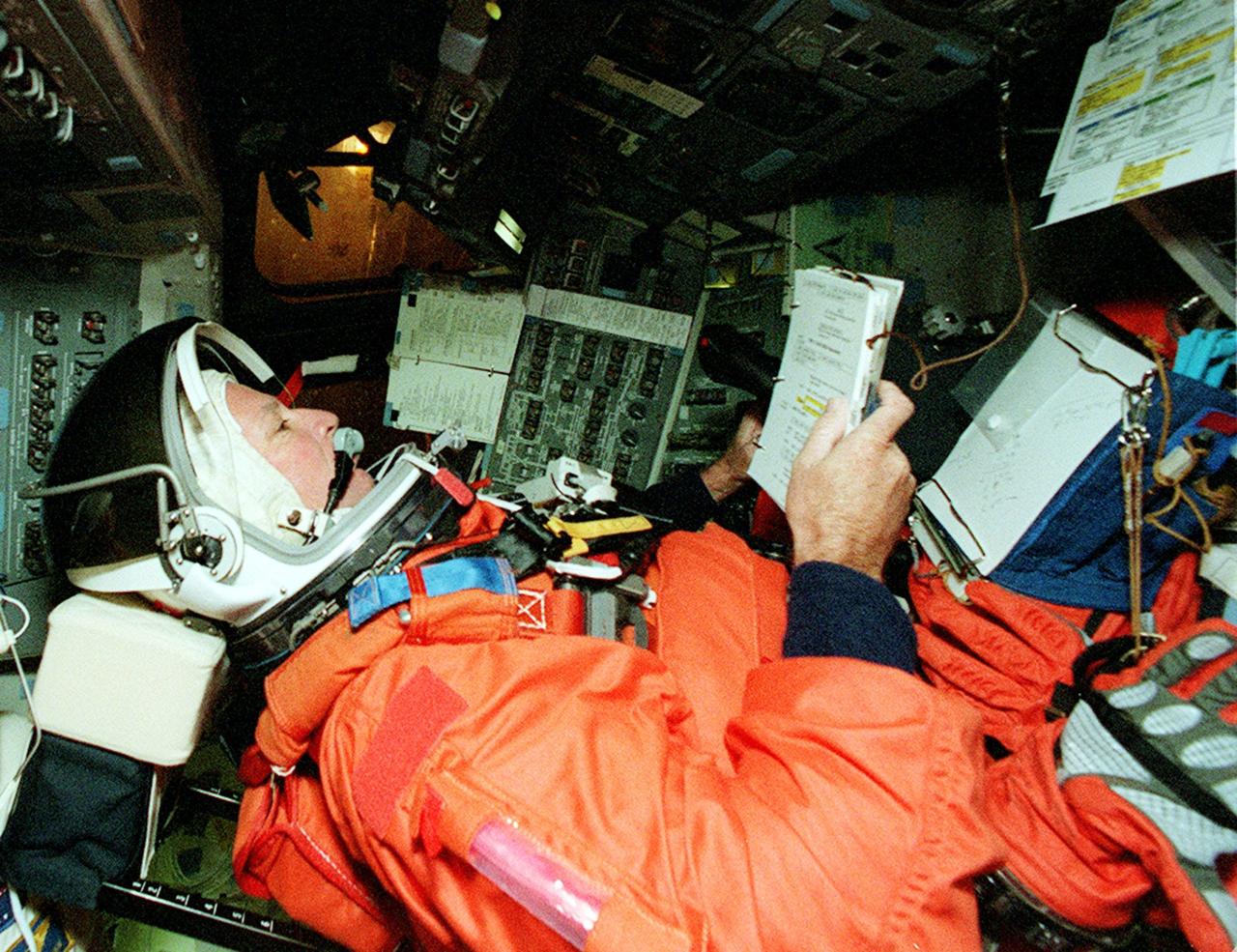

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy is seated at the controls of Discovery to take part in a simulated countdown. The countdown is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that he and other crew members have been performing. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
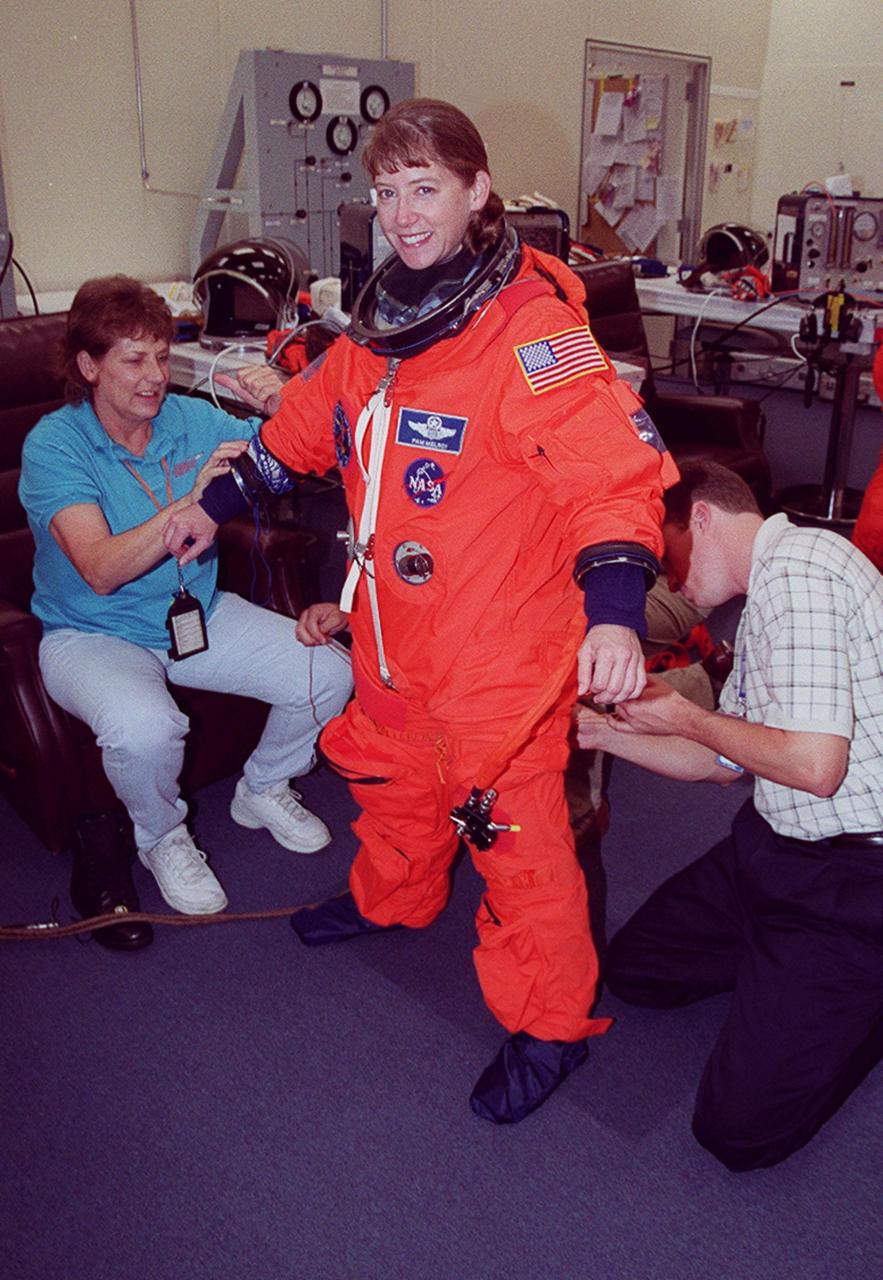

The “rookie” on the STS-92 mission, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy has her new launch and entry suit adjusted during pre-pack and fit check in the Operations and Checkout Building. Melroy and the rest of the crew are at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. The TCDT provides emergency egress training, simulated countdown exercises and opportunities to inspect the mission payload. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
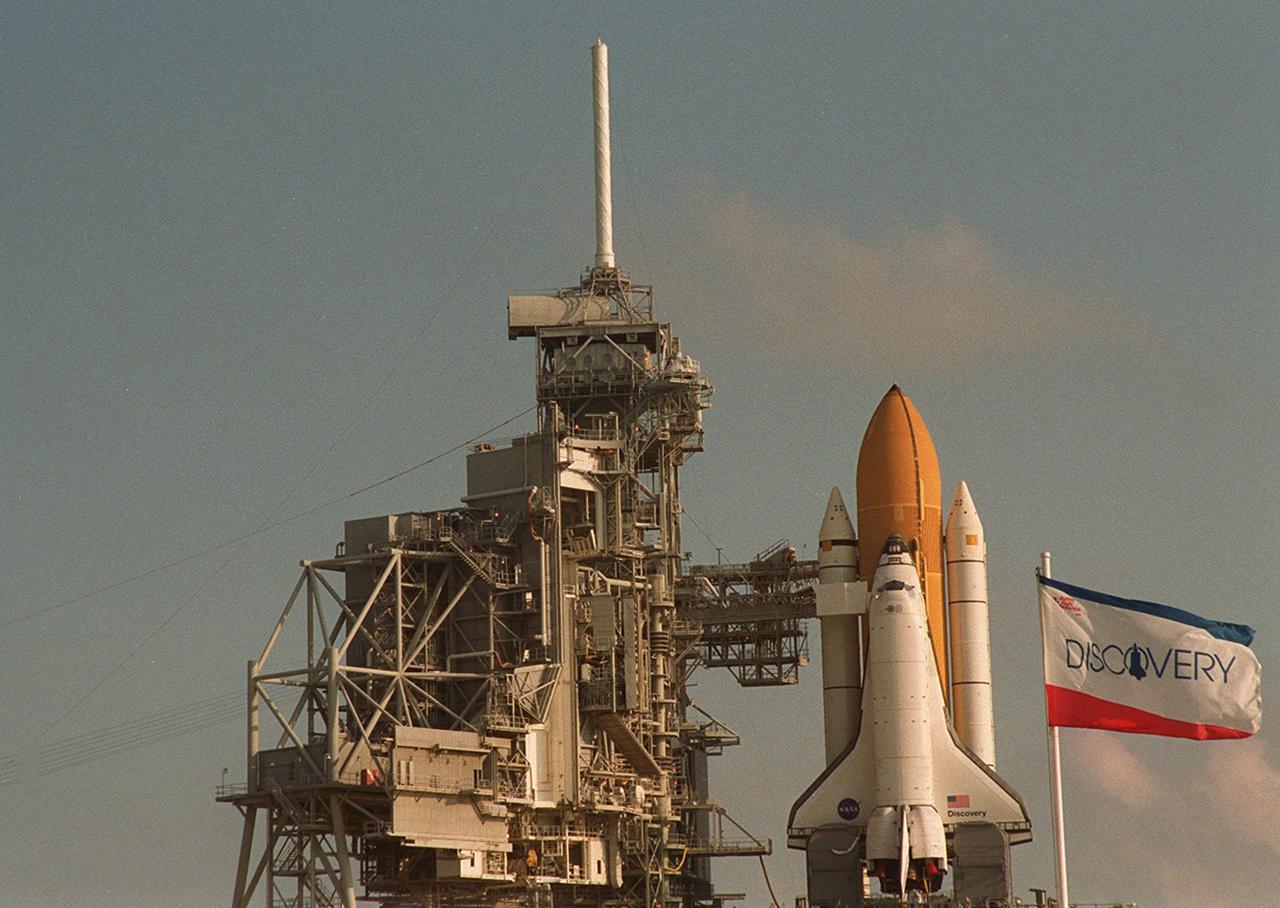

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The flag at right identifies Space Shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A after its rollout and before the Rotating Service Structure is moved around it. Scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on mission STS-92, Discovery will be making the 100th Space Shuttle mission launched from Kennedy Space Center. Discovery also will be making its 28th flight into space, more than any of the other orbiters to date. STS-92 is a mission to the International Space Station, carrying the Z1 truss, which is the first of 10 trusses on the Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter
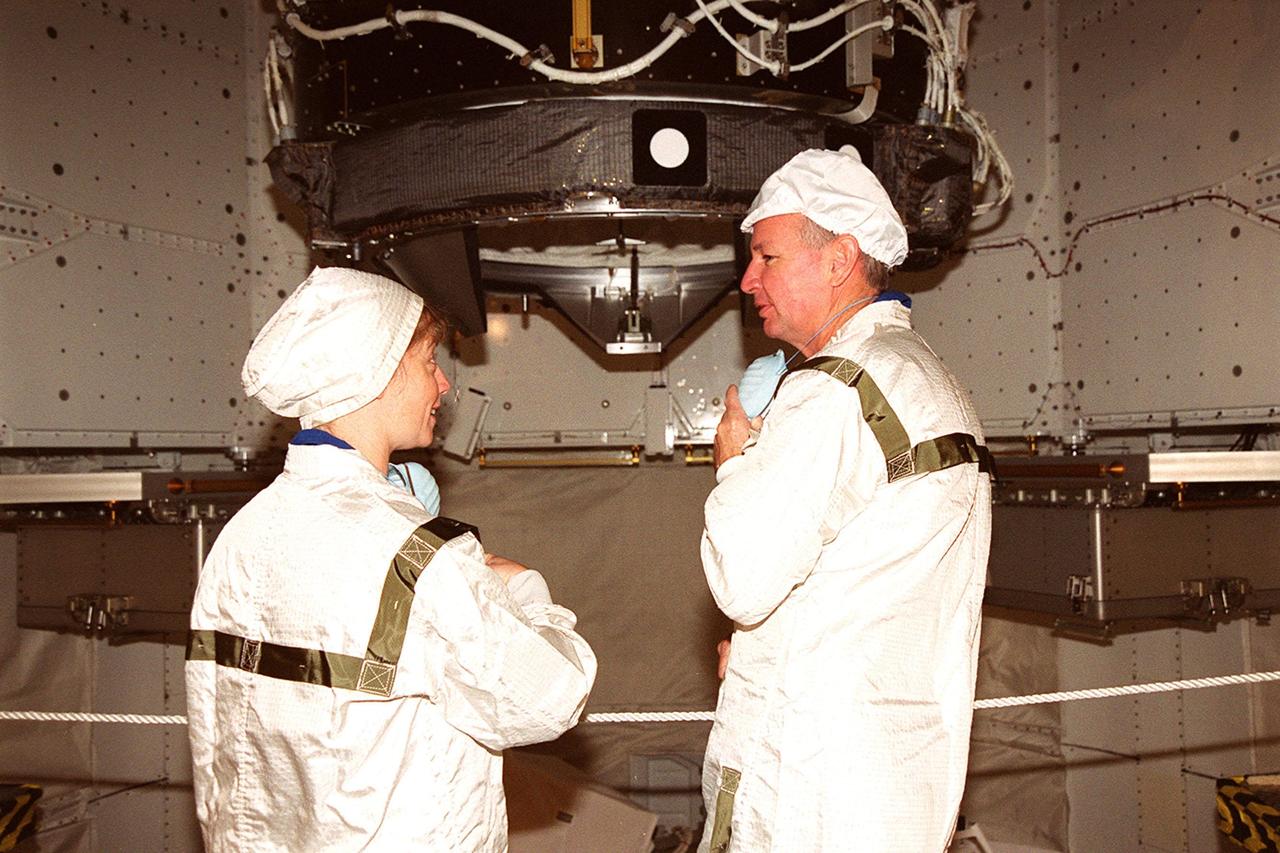

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay, STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy (left) and Commander Brian Duffy share thoughts about the mission as they inspect part of the payload (behind them), the Pressurized Mating Adapter. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
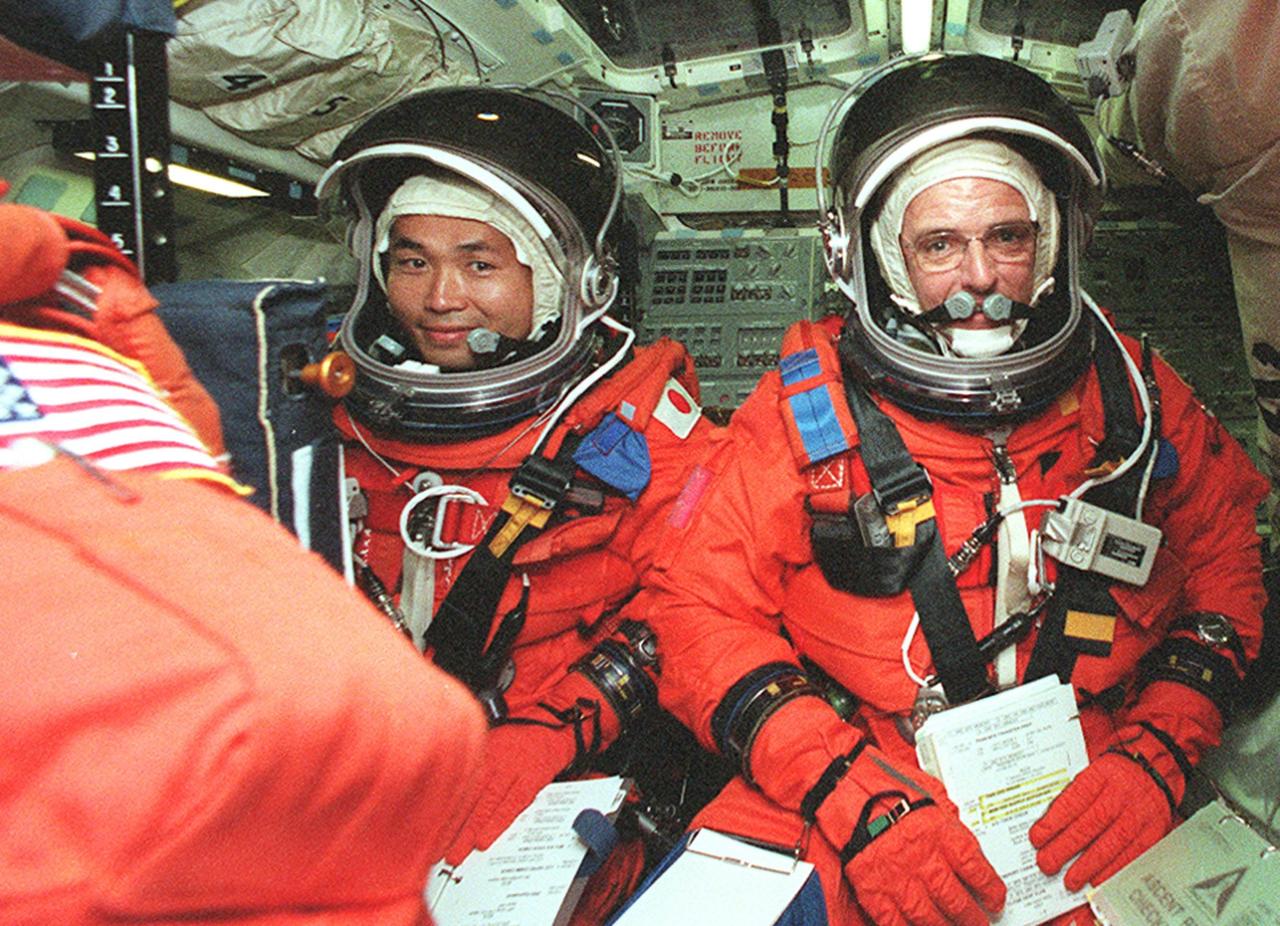

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan (left) and William S. McArthur Jr. (right) get settled in their seats in Discovery for a simulated countdown. The countdown is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that he and other crew members have been performing. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
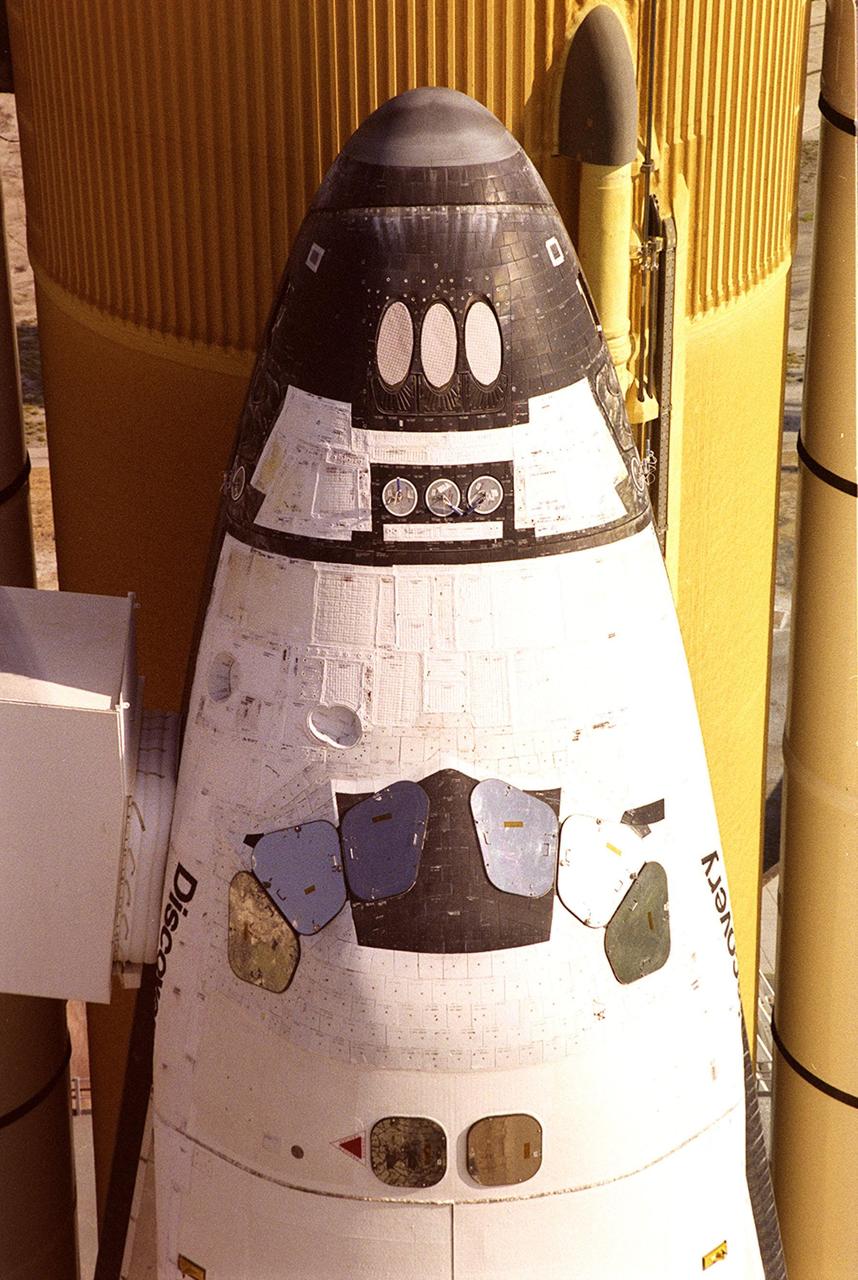
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A closeup of Space Shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A shows the White Room (left) extended to the side of the orbiter, at the entrance to the crew compartment. Discovery is undergoing final launch preparations of STS-92. Scheduled to lift off Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT, Discovery will be making the 100th Space Shuttle mission launched from Kennedy Space Center. Discovery also will be making its 28th flight into space, more than any of the other orbiters to date. STS-92 is a mission to the International Space Station, carrying the Z1 truss, which is the first of 10 trusses on the Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter