
Safety Week 2007 kick off - Steve Zornetzer, Associate Director for institutions and Research Ames Research Center
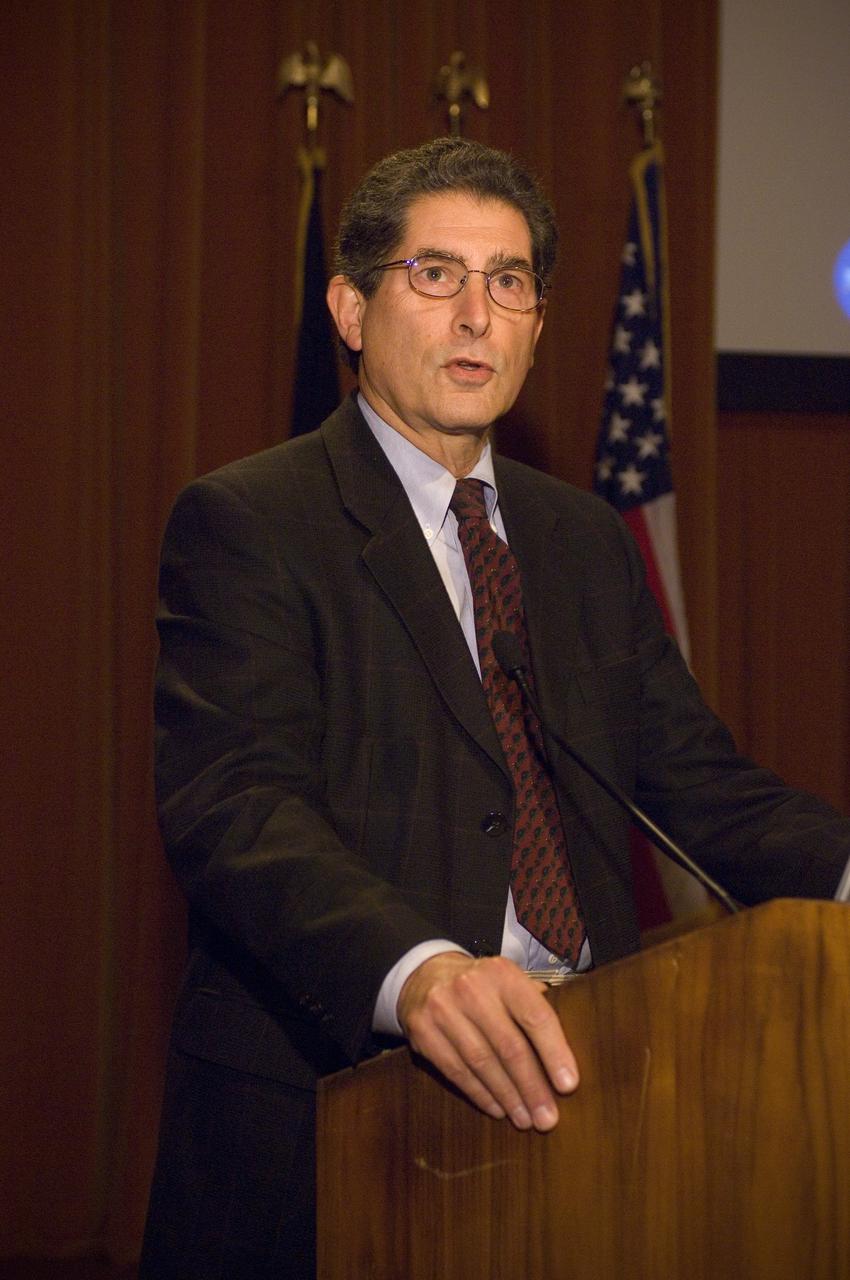

Safety Week 2007 kick off - Steve Zornetzer, Associate Director for institutions and Research Ames Research Center
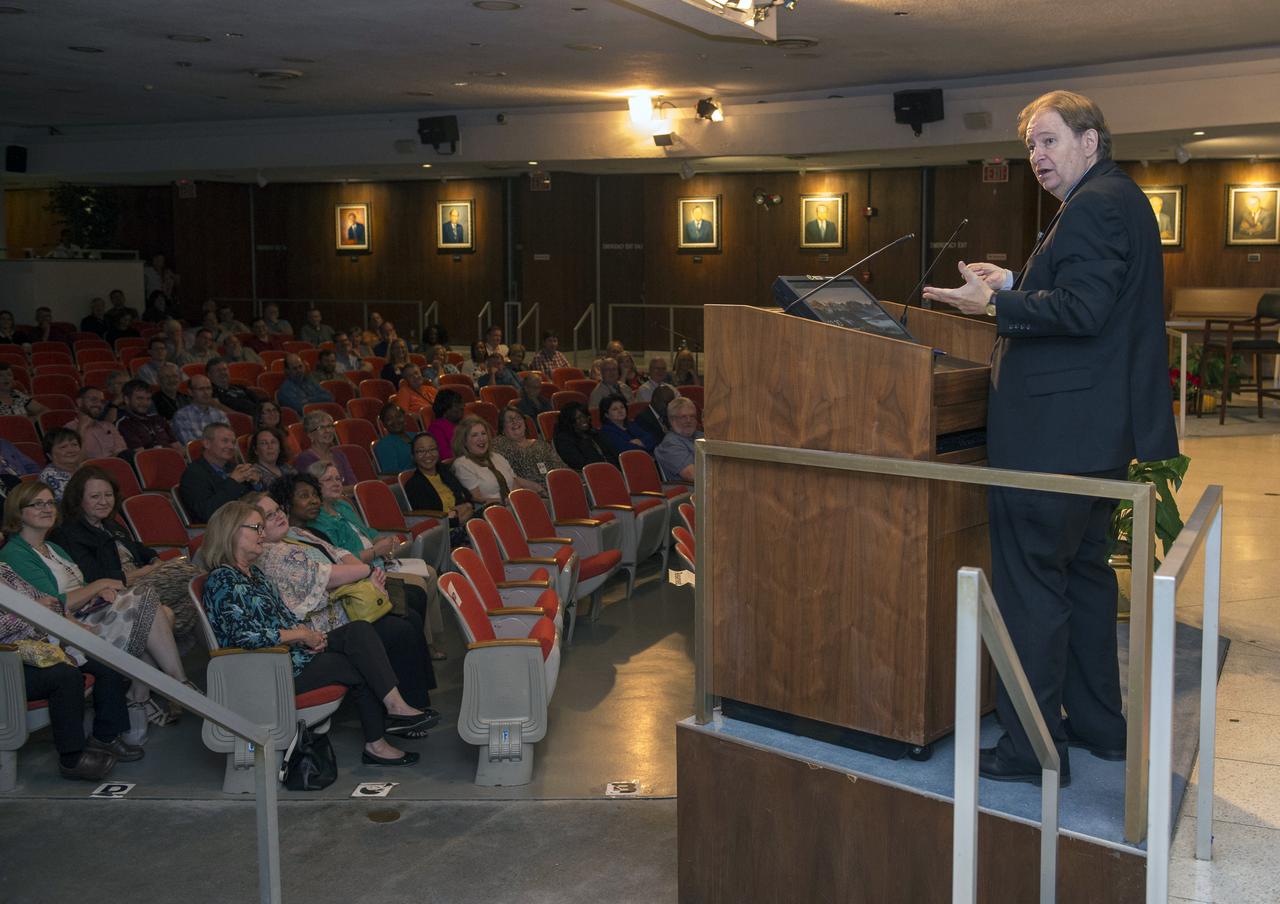

Kickoff speaker for Safety Week 2017 at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, former news reporter Rick Bragg -- now a journalism professor at the University of Alabama in Tuscaloosa -- speaks to team members Sept. 25, 2017
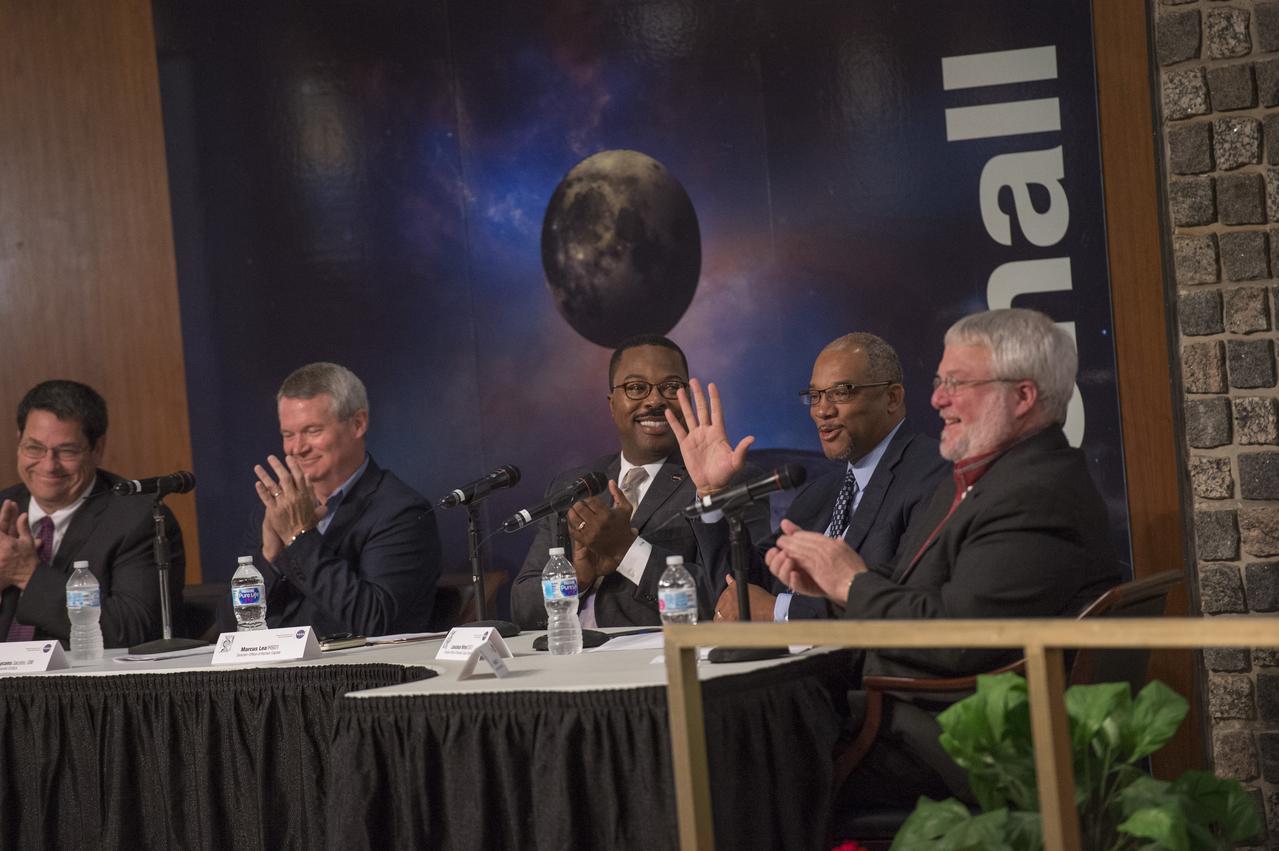

"Just Culture" session panelists Roy Malone, Randy Lycans, Marcus Lea, Loucious Hires, and Pete Allen.
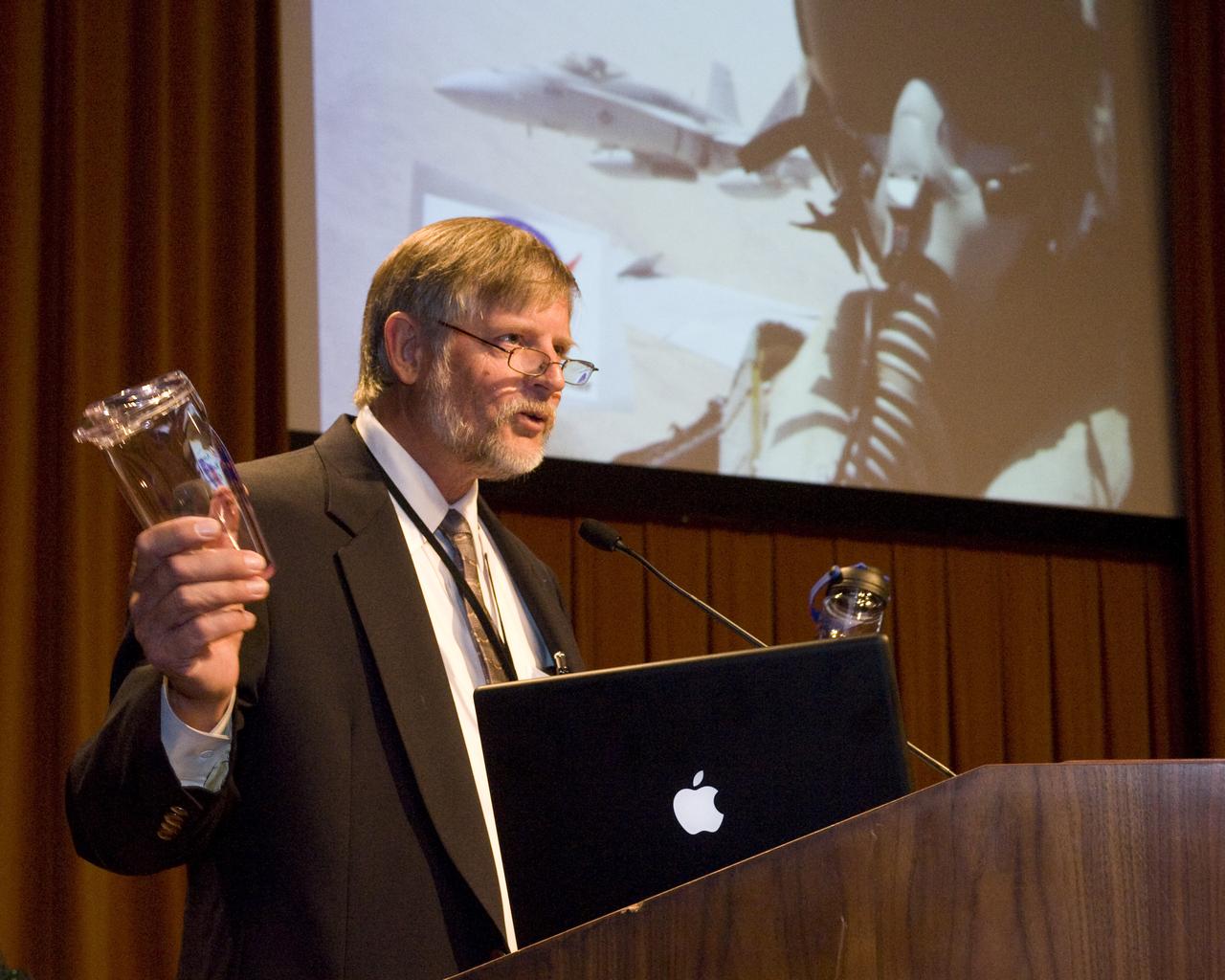

Safety Day Events 2008: Stan Phillips speaks at the open of the 10th annual Safety Awareness Week briefing in N-201.
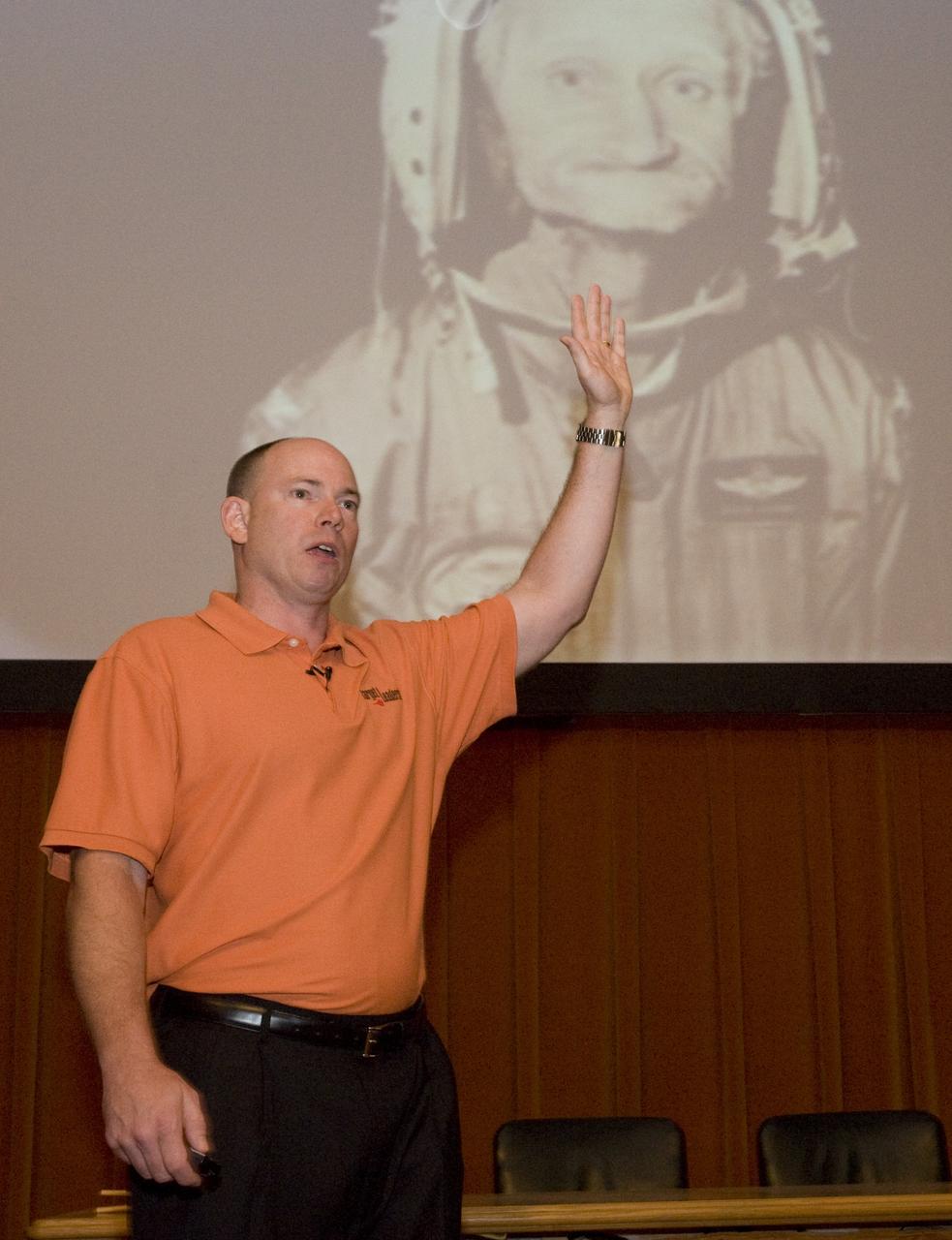

Safety Day Events 2008 Keynote speaker at the !0th Annual Safety Awareness Week Lt Col Wes Sharp shares his reveting account of an F-18 midair collision, his insight into the root cause, lessons he learned and how to excell under pressure to perform.
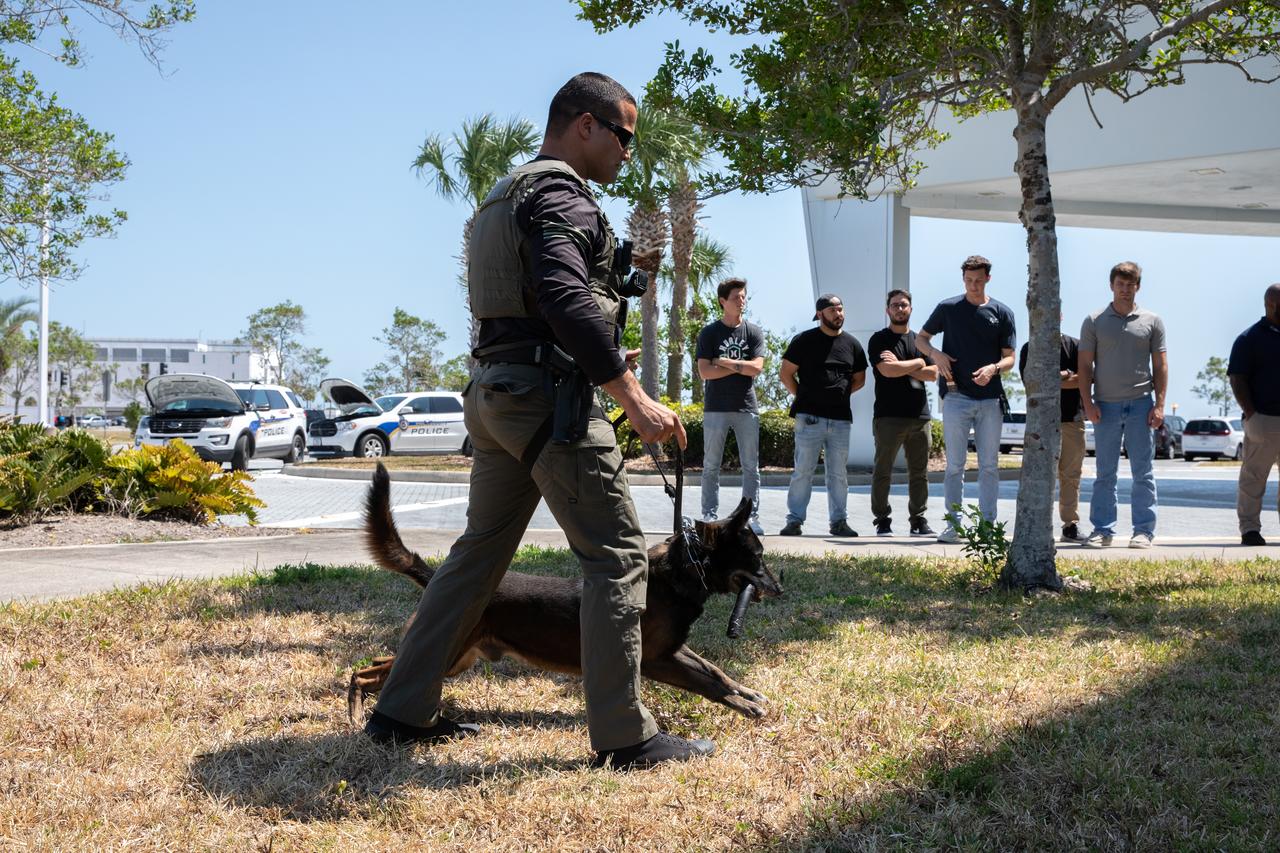

Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida participate in the Safety and Health days activities on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The agency’s Safety and Health days took place the week of May 6-10 to show the NASA’s commitment to the safety and health of the entire workforce, and various organizations provided interactive exhibits and information on a range of safety and health issues.

Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida participate in the Safety and Health days activities on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The agency’s Safety and Health days took place the week of May 6-10 to show the NASA’s commitment to the safety and health of the entire workforce, and various organizations provided interactive exhibits and information on a range of safety and health issues.
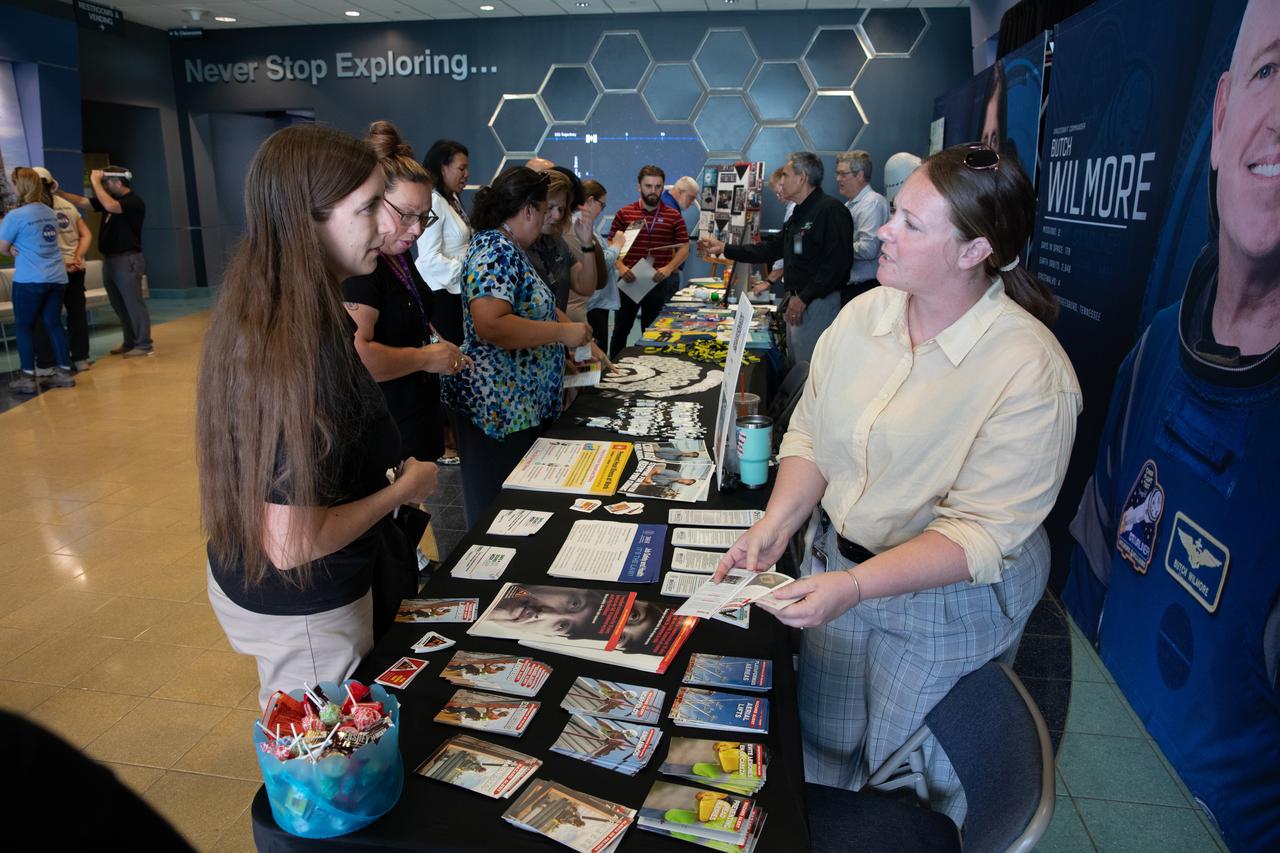

Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida participate in the Safety and Health days activities on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The agency’s Safety and Health days took place the week of May 6-10 to show the NASA’s commitment to the safety and health of the entire workforce, and various organizations provided interactive exhibits and information on a range of safety and health issues.

One of many safety posters produced by NACA artists during World War II. The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory established a Safety Office in 1942 to coordinate and oversee safety-related activities. The lab struggled to maintain a full staff during the war when military research projects were at a peak. NACA management mandated six-day work weeks without overtime and the elimination of holidays. As such, workplace injuries were a serious threat to maintaining productivity needed to sustain the military’s aeronautics efforts.
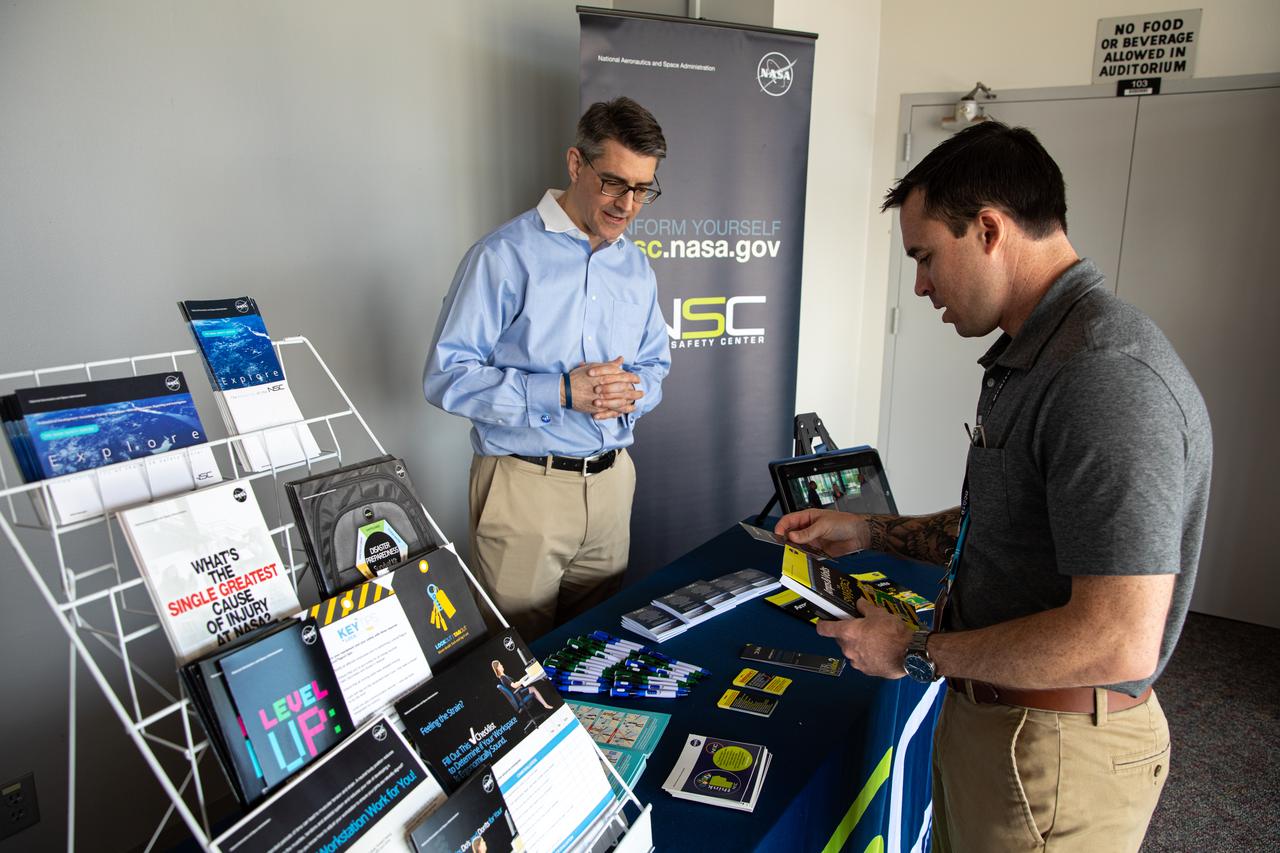

Chas Hoff, a public affairs official from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, provides information on the NASA Safety Center to a Kennedy Space Center employee in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 2, 2020. Hoff had an informational table set up during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.

“I Love Safety” stickers are photographed inside the Training Auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 2, 2020. The stickers were available for Kennedy employees during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
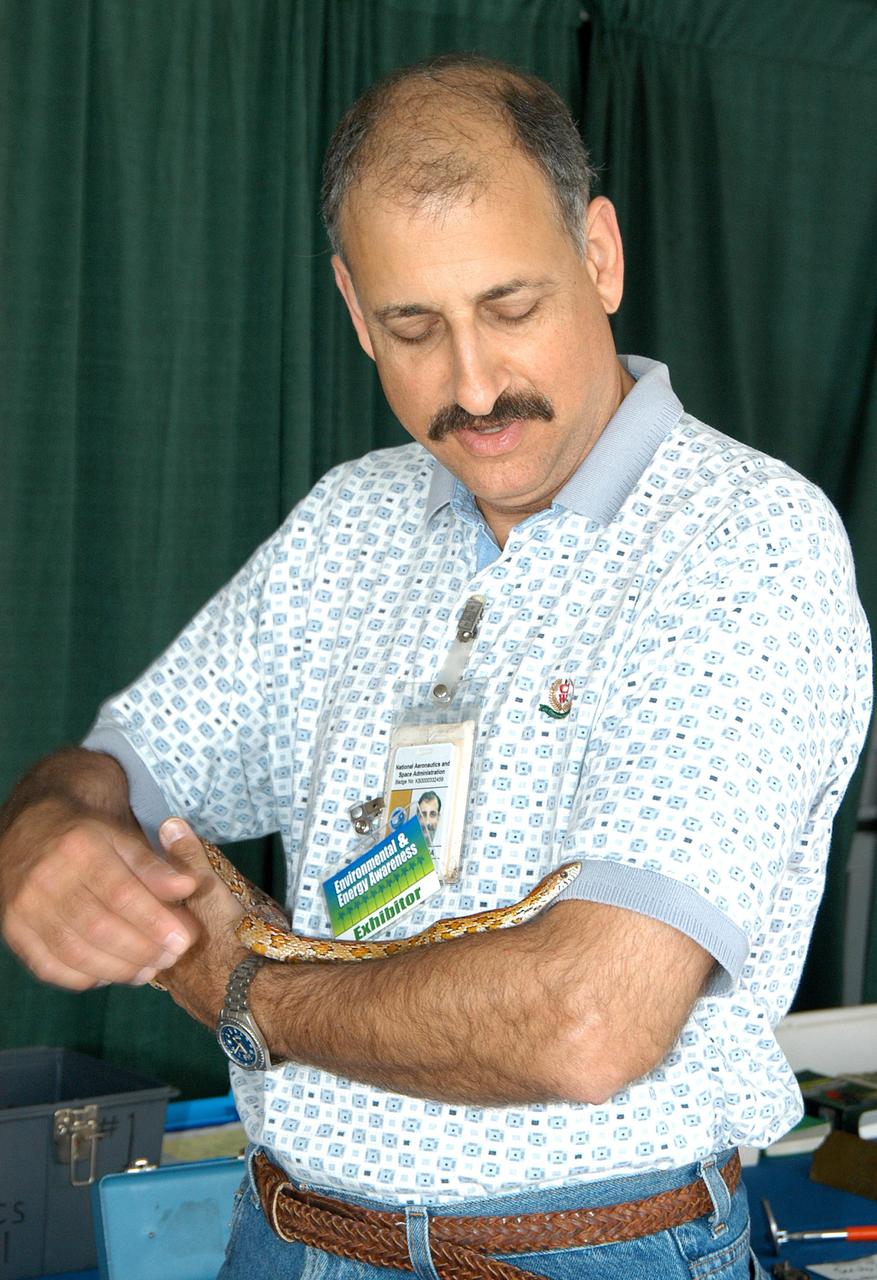
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Mario Busacca, with the Safety, Occupational Health and Environmental Division, handles a snake at one of the exhibits for KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, Energy Efficient Lighting Systems, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.”
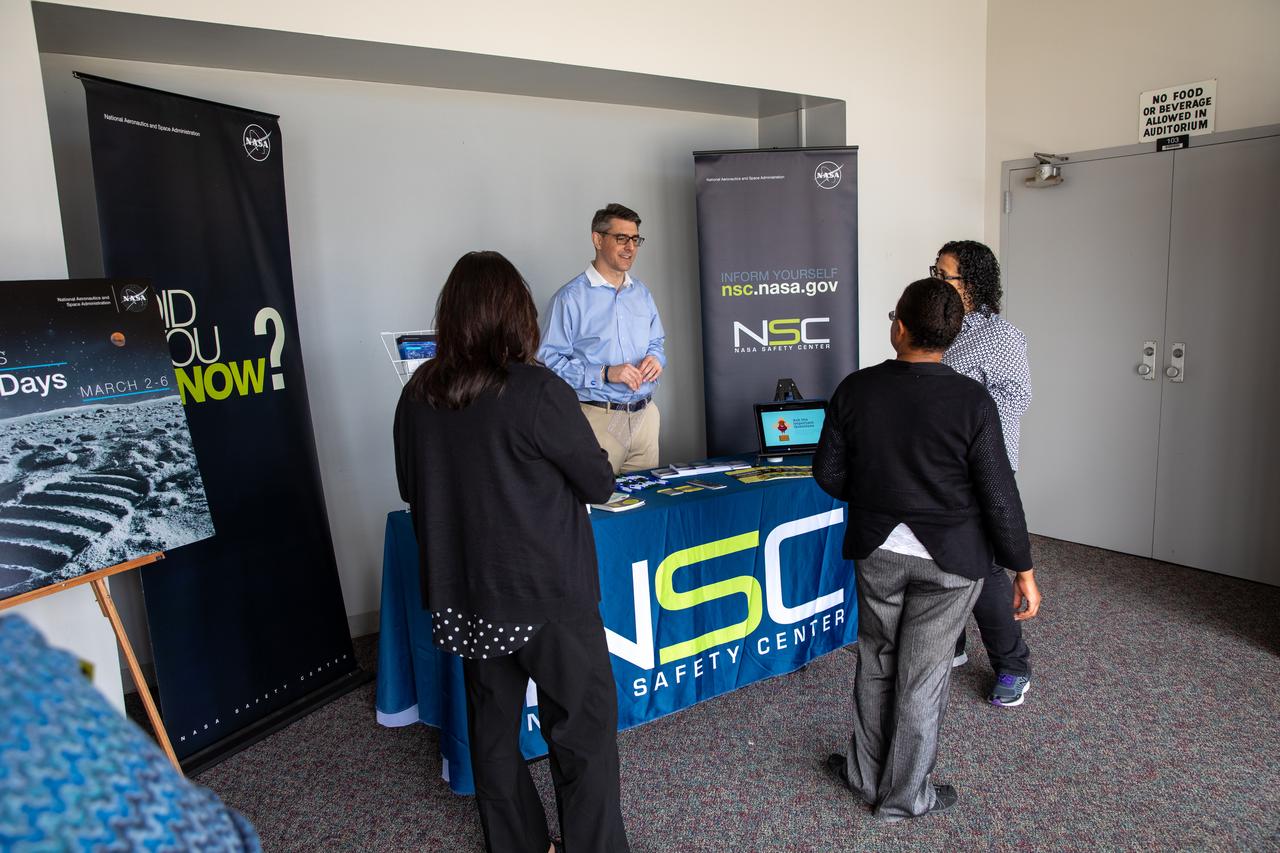

Chas Hoff, a public affairs official from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, provides information on the NASA Safety Center to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 2, 2020. Hoff had an informational table set up during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
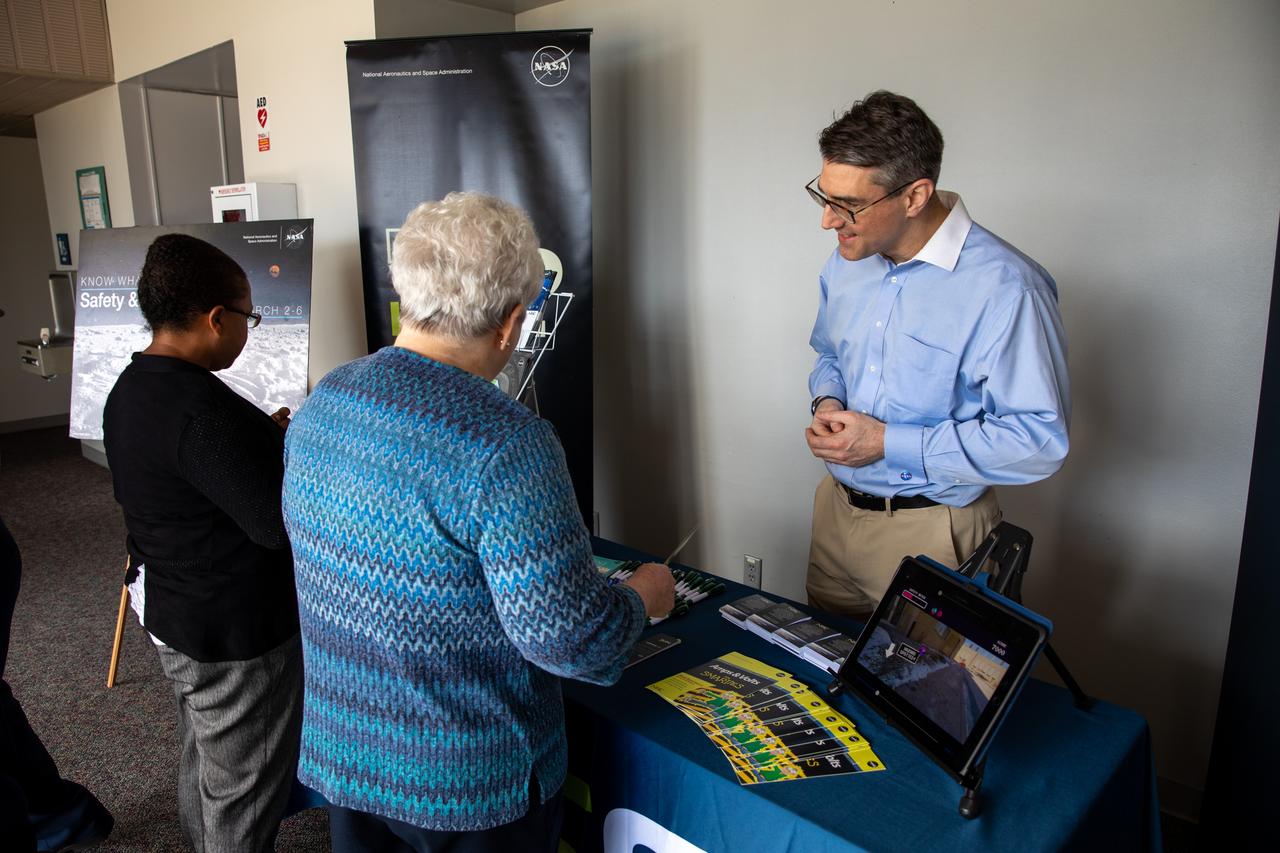

Chas Hoff, a public affairs official from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, provides information on the NASA Safety Center to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 2, 2020. Hoff had an informational table set up during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
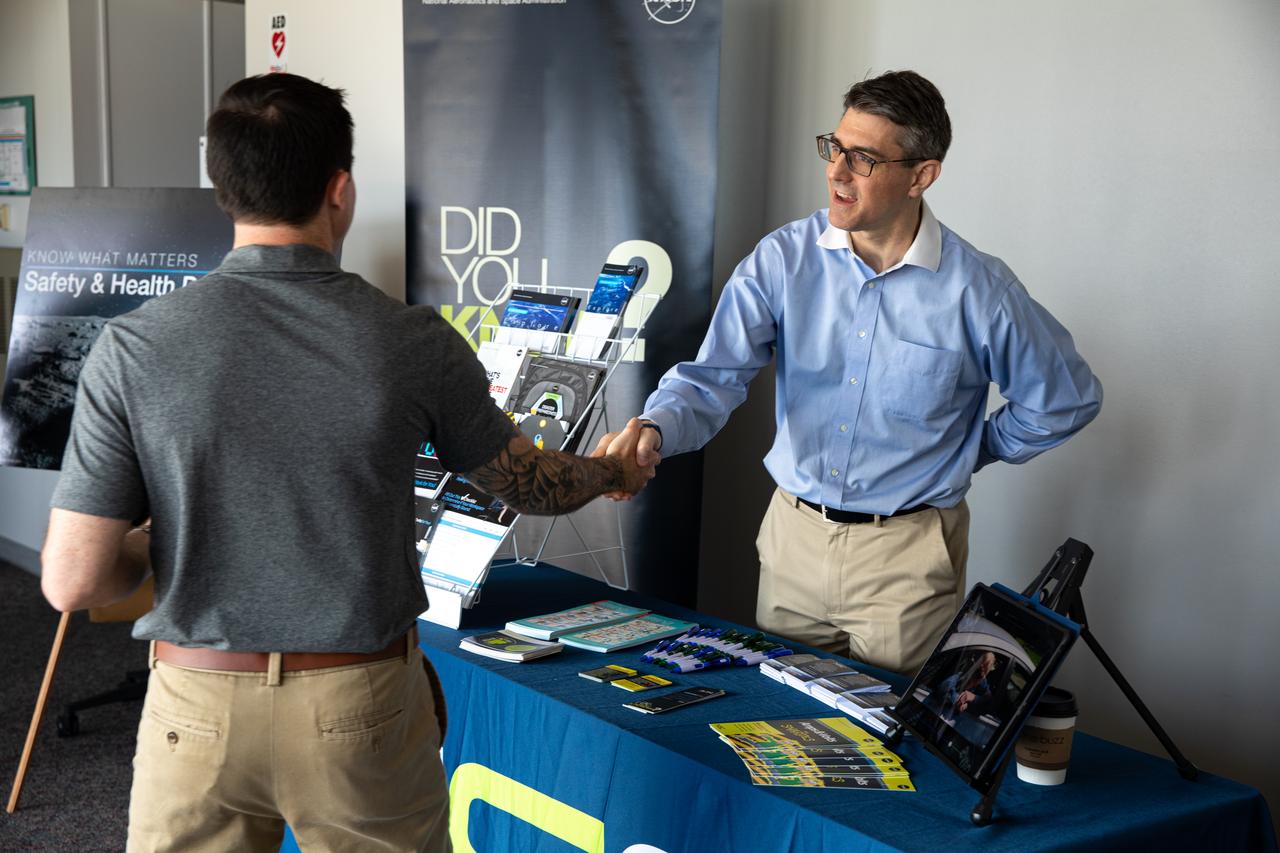

Chas Hoff, a public affairs official from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, provides information on the NASA Safety Center to a Kennedy Space Center employee in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 2, 2020. Hoff had an informational table set up during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
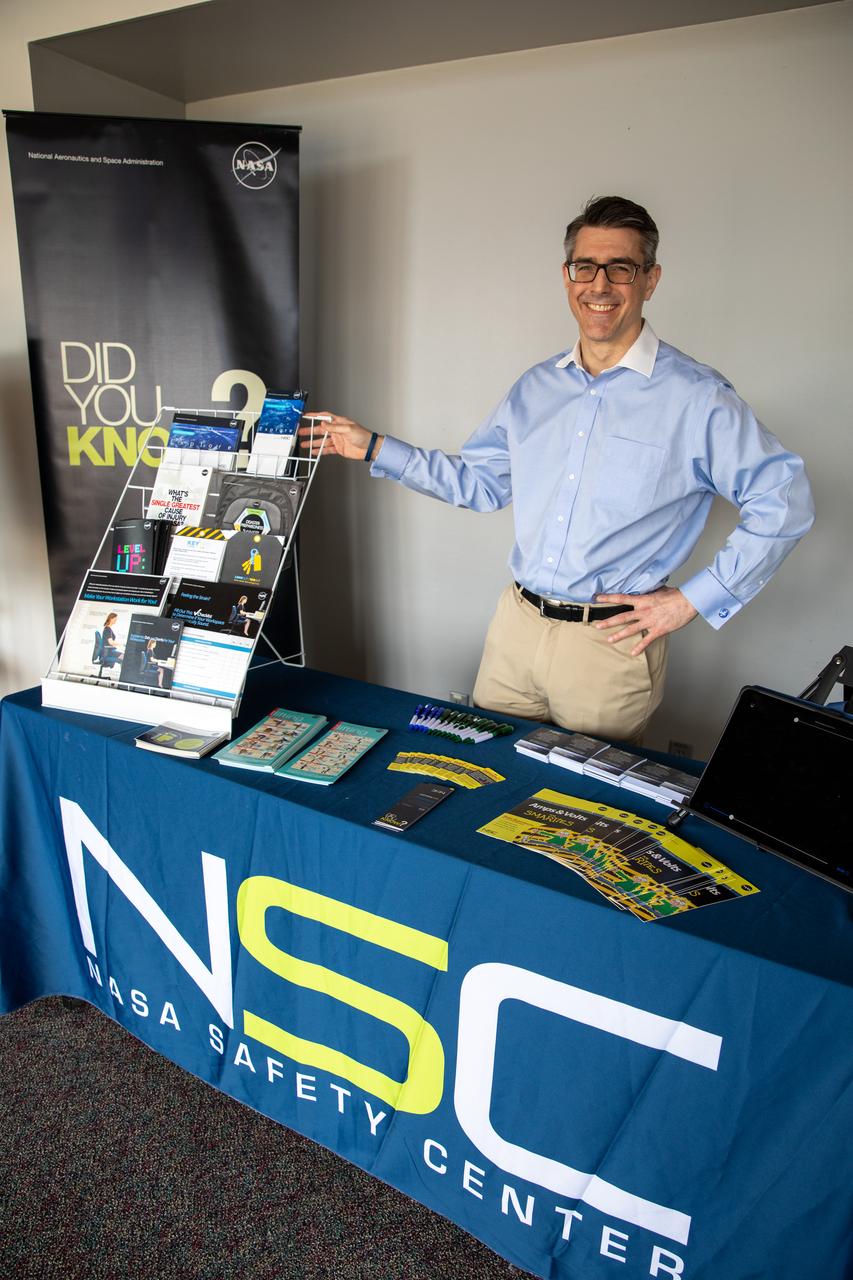

Chas Hoff, a public affairs official from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, stands ready to provide information on the NASA Safety Center to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 2, 2020. Hoff had an informational table set up during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
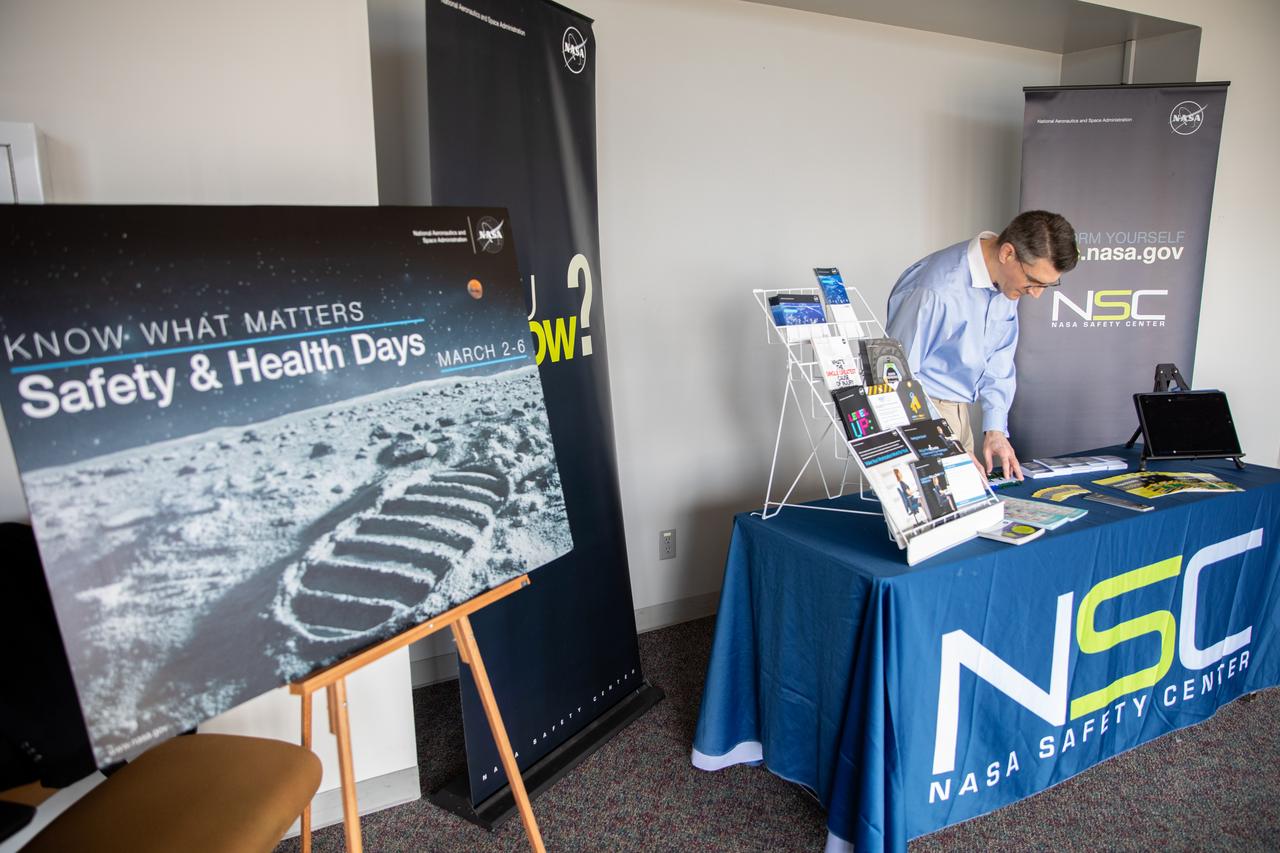

Chas Hoff, a public affairs official from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, stands ready to provide information on the NASA Safety Center to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 2, 2020. Hoff had an informational table set up during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
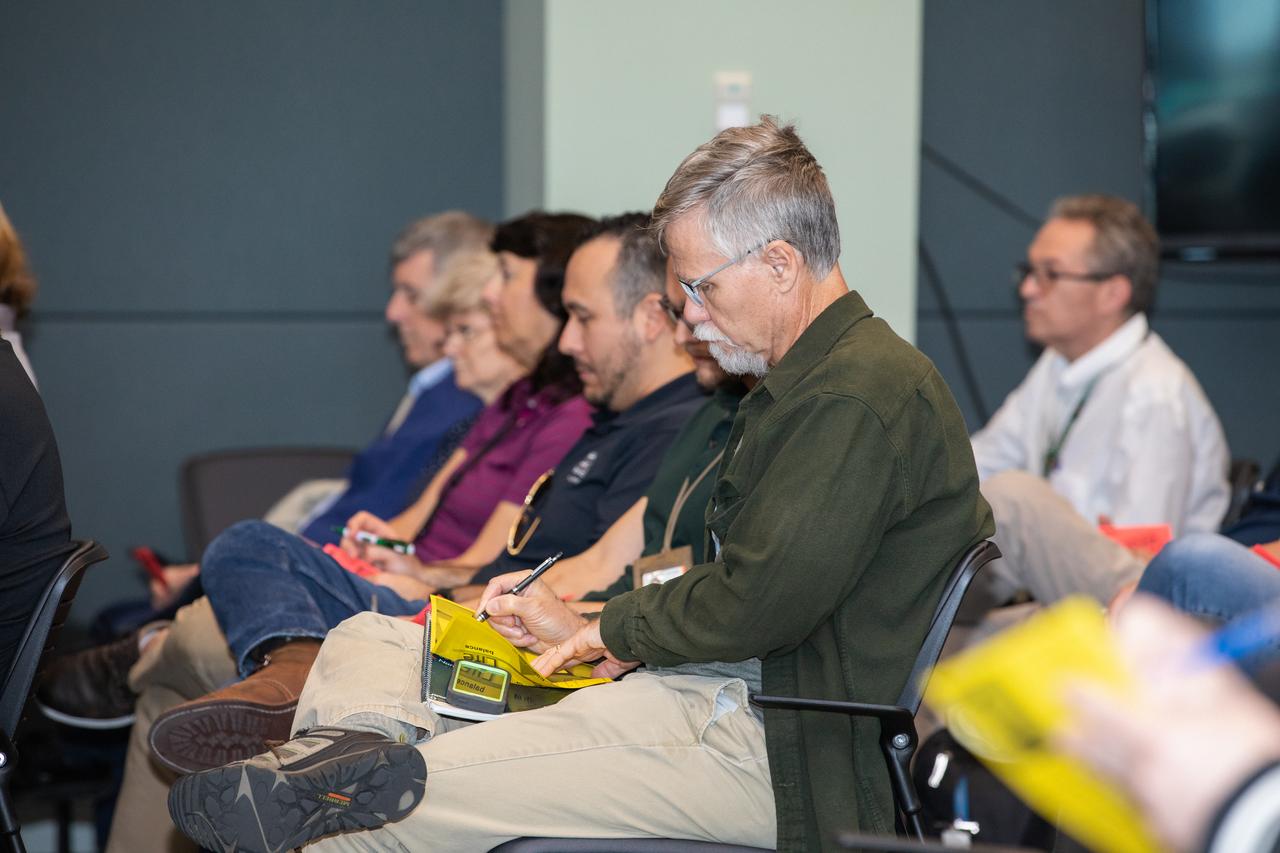

Kennedy Space Center employees attend a presentation on reducing stress and improving focus inside the Florida spaceport’s Operations Support Building II on March 3, 2020. The presentation, led by guest speaker Eliz Greene, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
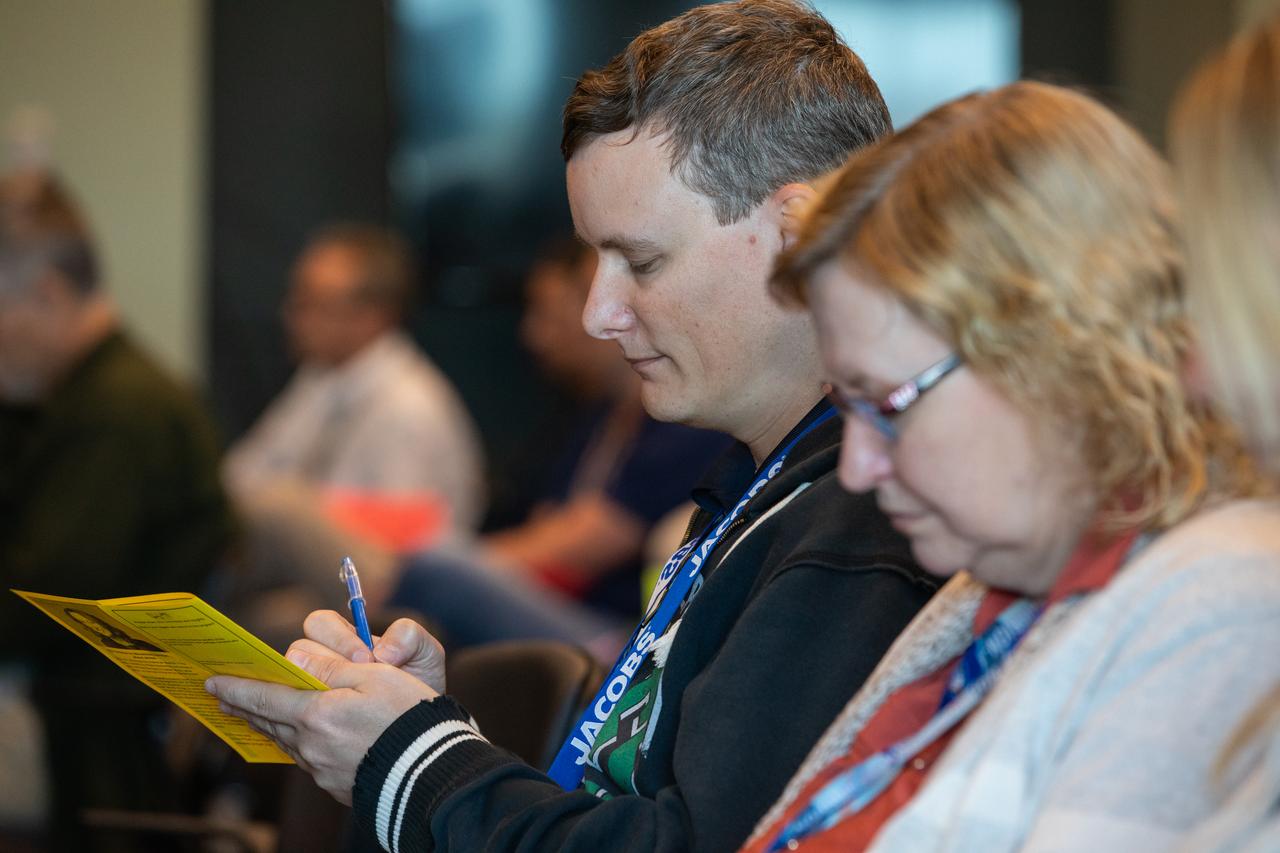

Kennedy Space Center employees attend a presentation on reducing stress and improving focus inside the Florida spaceport’s Operations Support Building II on March 3, 2020. The presentation, led by guest speaker Eliz Greene, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
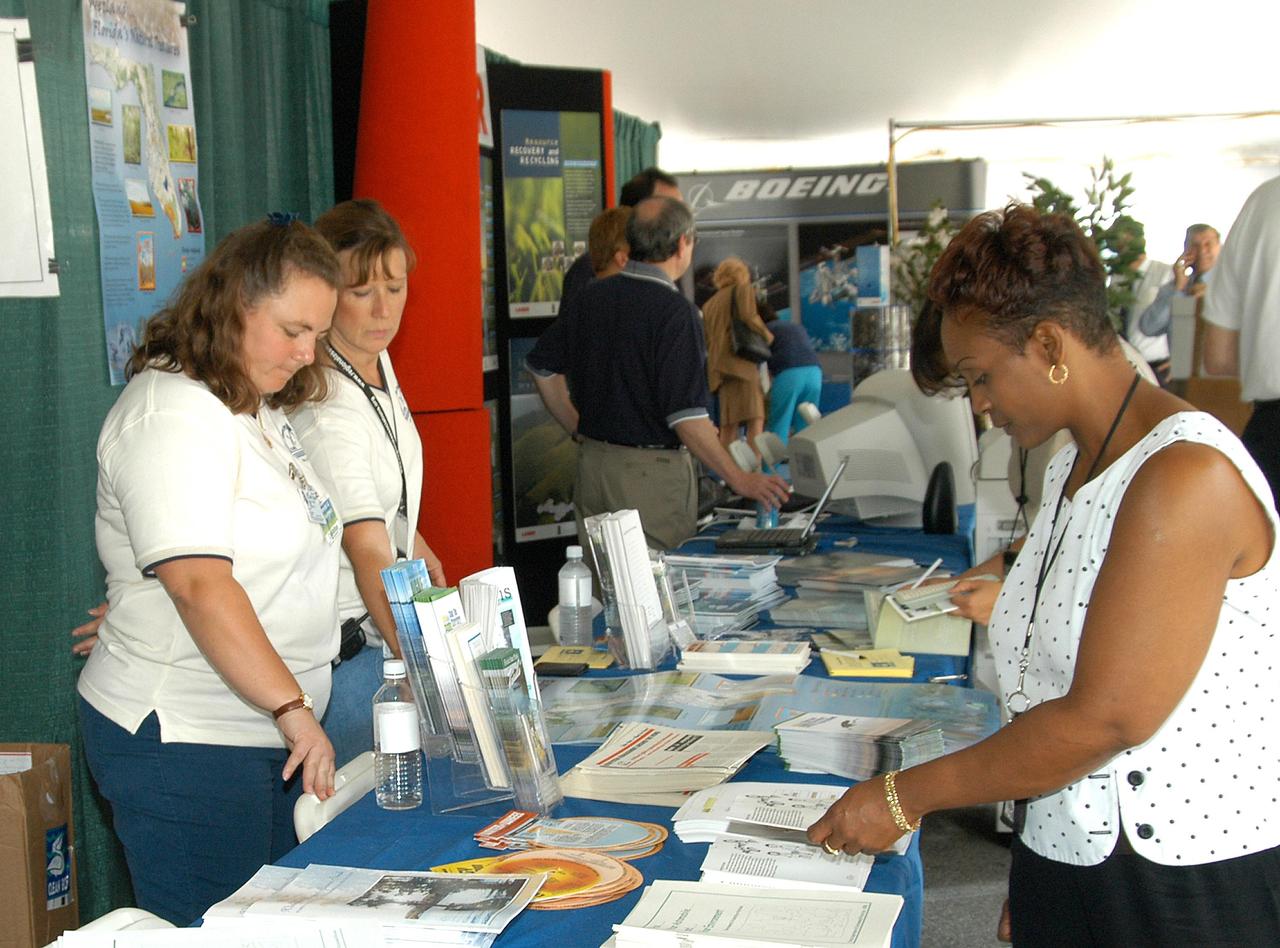

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC employees stop at display tables set up in a tent near the Operations and Checkout Building for KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.” Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, Energy Efficient Lighting Systems, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems.
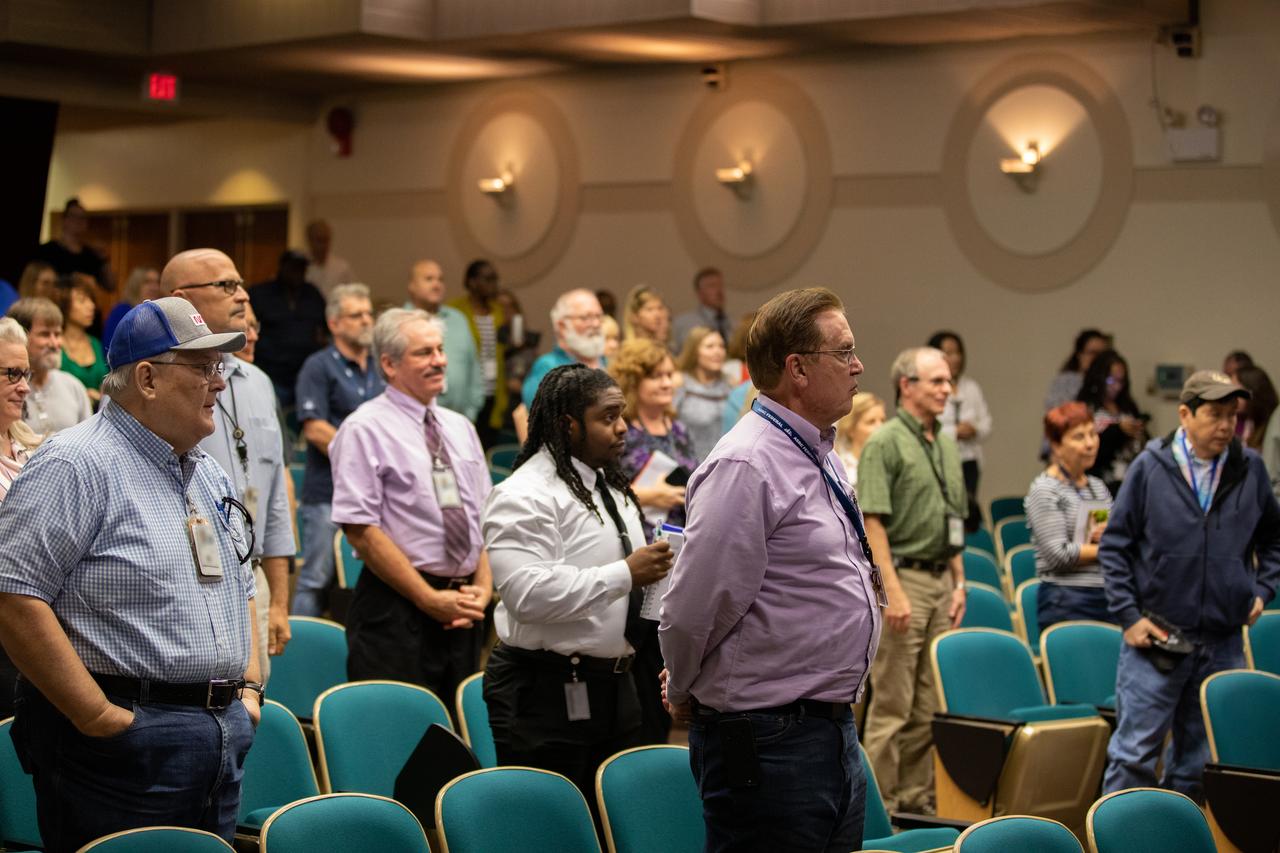

Kennedy Space Center employees attend a presentation on fatigue management inside the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 4, 2020. The presentation, led by guest speaker Cassie Hilditch from the San Jose State University Research Foundation, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
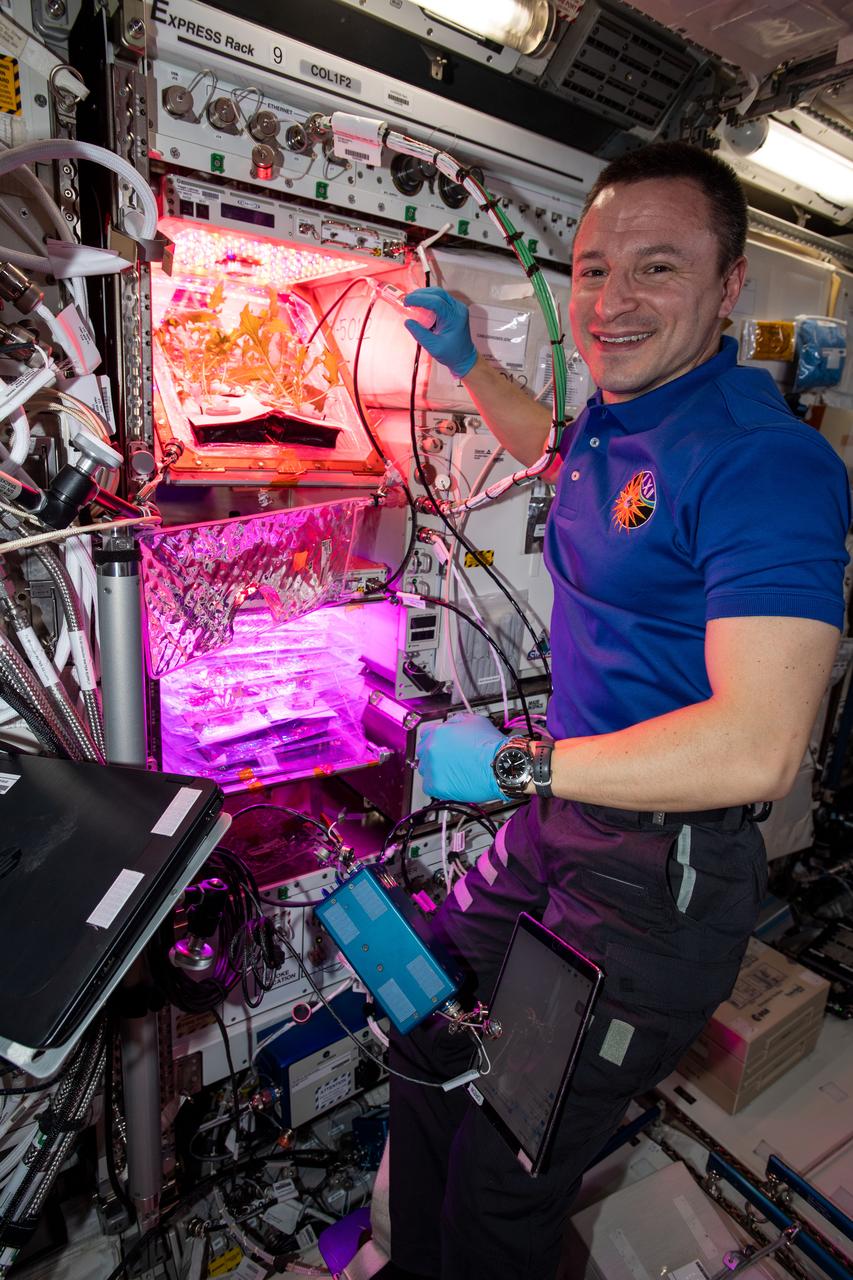

iss061e012956 (Oct. 23, 2019) --- This past week NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan watered the plant pillows in which Mizuna mustard greens are growing for the Veg-04B experiment. Veg-04B focuses on the effects of light quality and fertilizer on the leafy Mizuna crop, microbial food safety, nutritional value and the taste acceptability by the crew. The space botany research is also informing NASA how to provide fresh food for crews on long-term space missions.
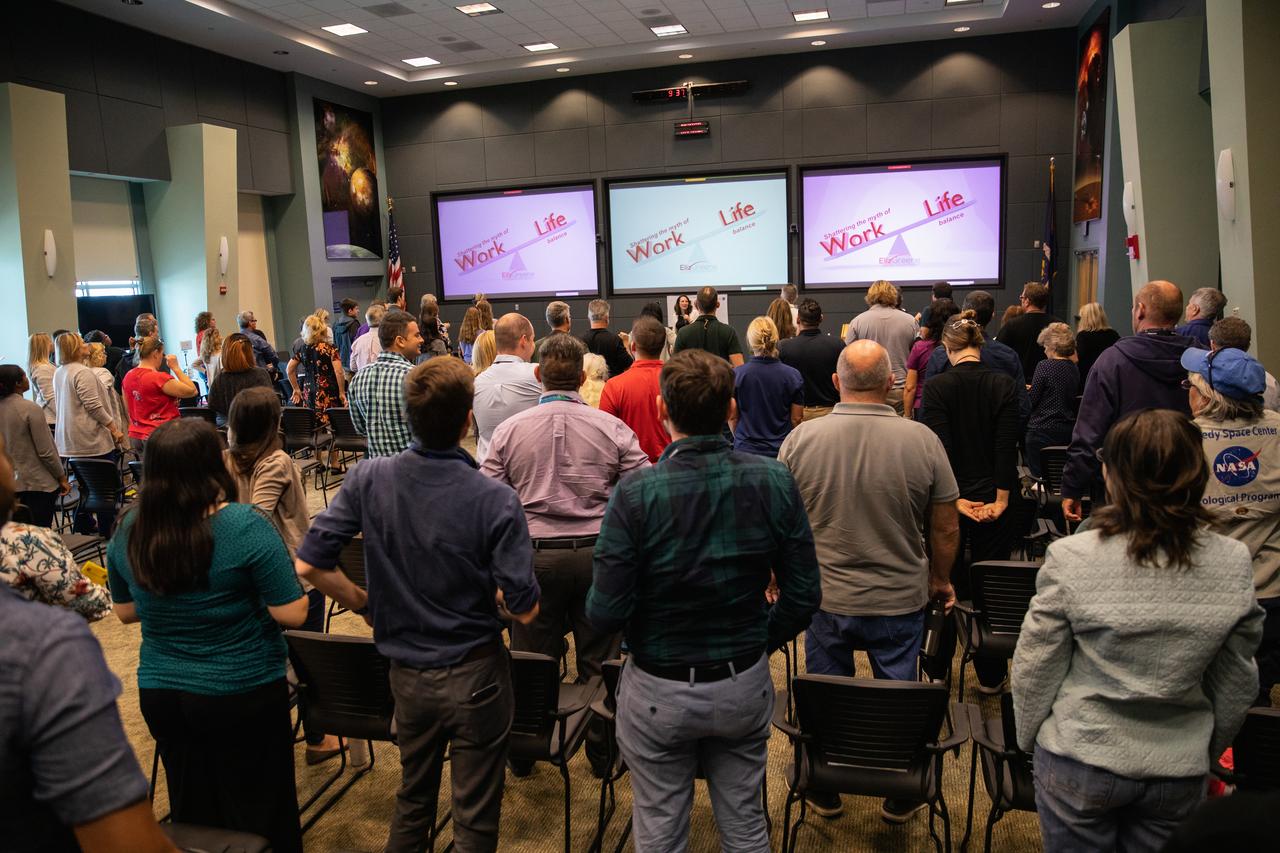

Kennedy Space Center employees attend a presentation on reducing stress and improving focus inside the Florida spaceport’s Operations Support Building II on March 3, 2020. The presentation, led by guest speaker Eliz Greene, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
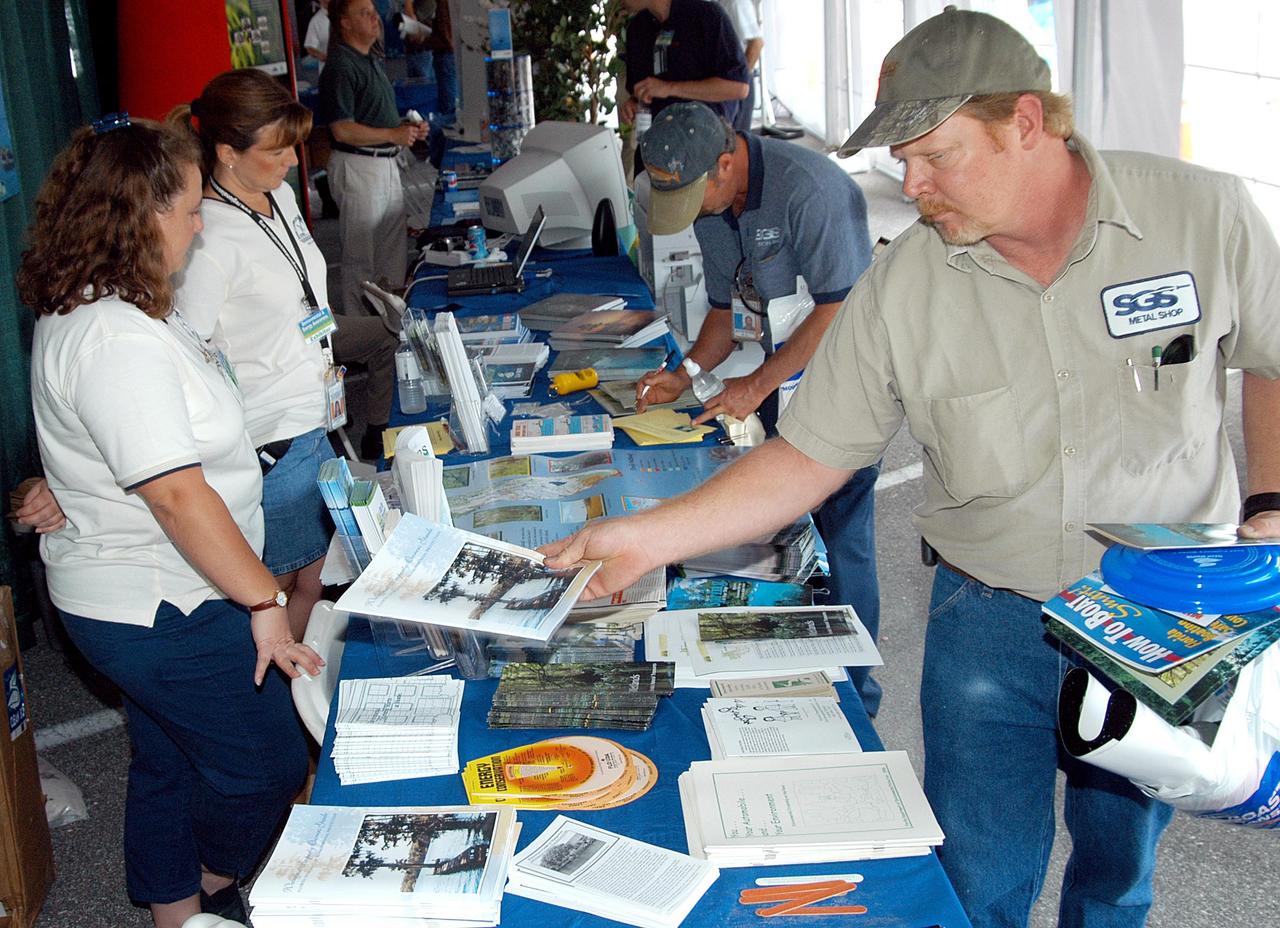

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC employees stop at display tables set up in a tent near the Operations and Checkout Building for KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.” Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, Energy Efficient Lighting Systems, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems.
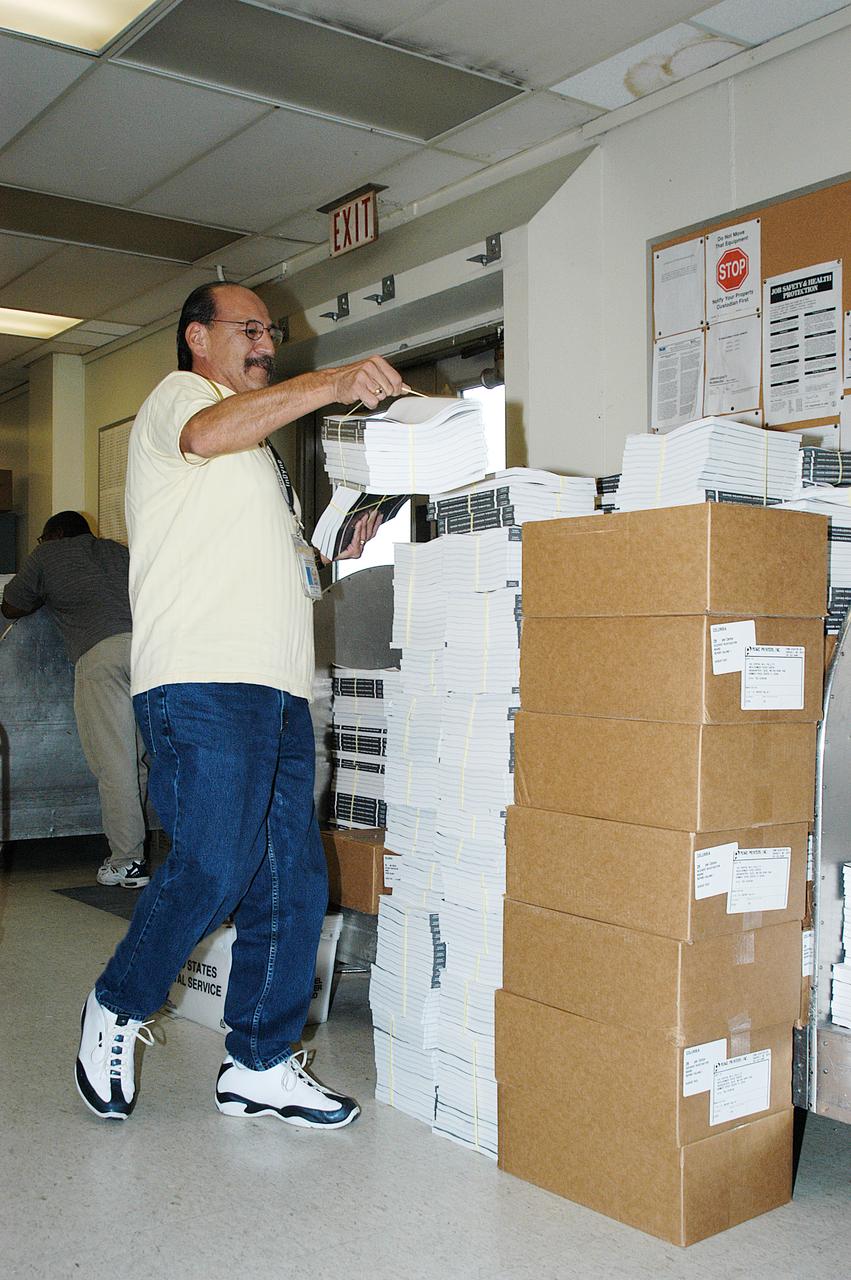

Richard Alonzo, in the Mail Room at KSC, prepares stacks of the Columbia Accident Investigation Report, which are being distributed to all employees. The delivery is a prelude to NASA Safety and Mission Success Week Nov. 17-21, during which all employees are being encouraged to consider ways they can support and enhance recommendations for improvement stated in the report.
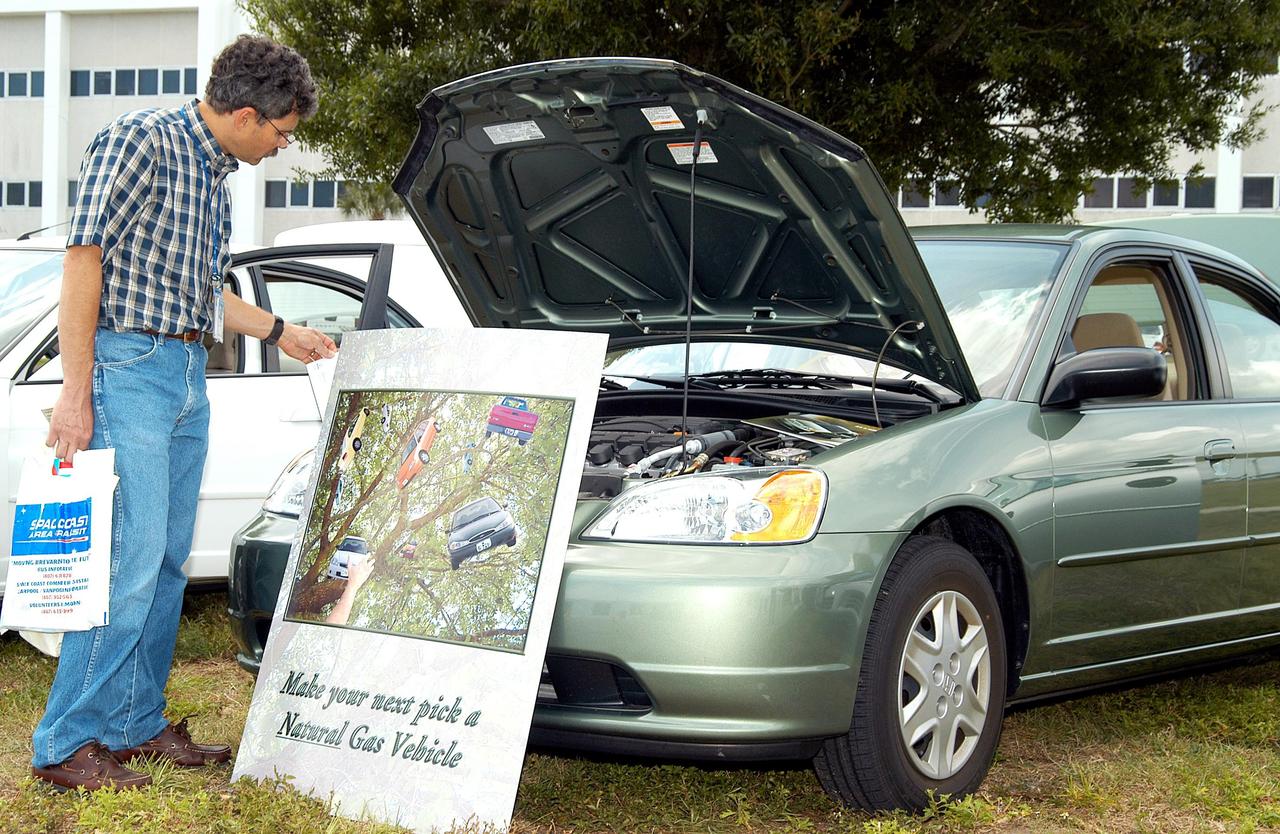

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A KSC employee stops to look at a car equipped to use natural gas as fuel. Several cars using alternative fuel technology were part of an exhibit during KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.” Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, Energy Efficient Lighting Systems, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC employees stop at a display table about energy set up in a tent near the Operations and Checkout Building for KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.” Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems.

Kennedy Space Center employees attend a SafeTALK suicide awareness and intervention training on March 2, 2020, inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. The training, hosted by the KSC Employee Assistance Program, was offered as part of the center’s annual Safety and Health days, taking place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which placed a focus on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
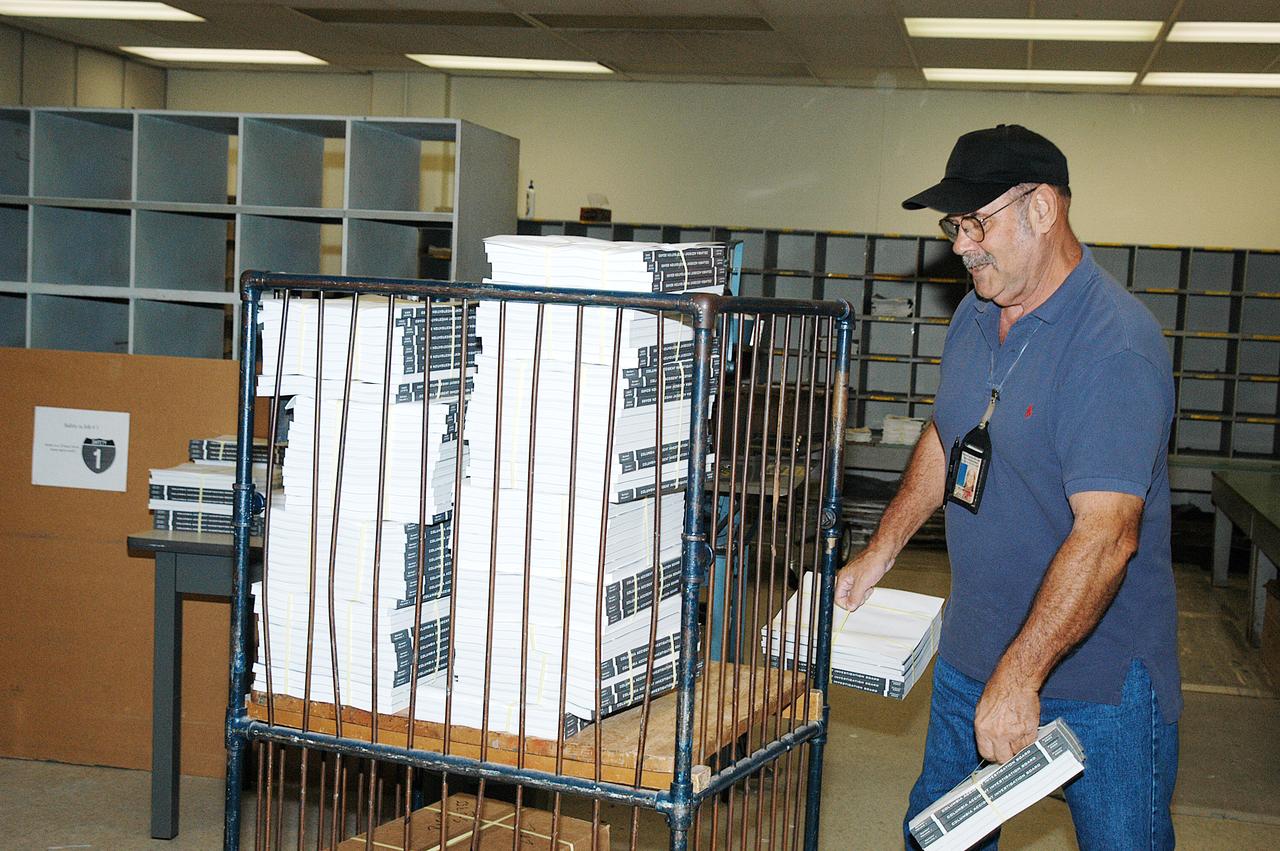

Bill White, in the Mail Room at KSC, stacks copies of the Columbia Accident Investigation Report, which are being distributed to all employees. The delivery is a prelude to NASA Safety and Mission Success Week Nov. 17-21, during which all employees are being encouraged to consider ways they can support and enhance recommendations for improvement stated in the report.
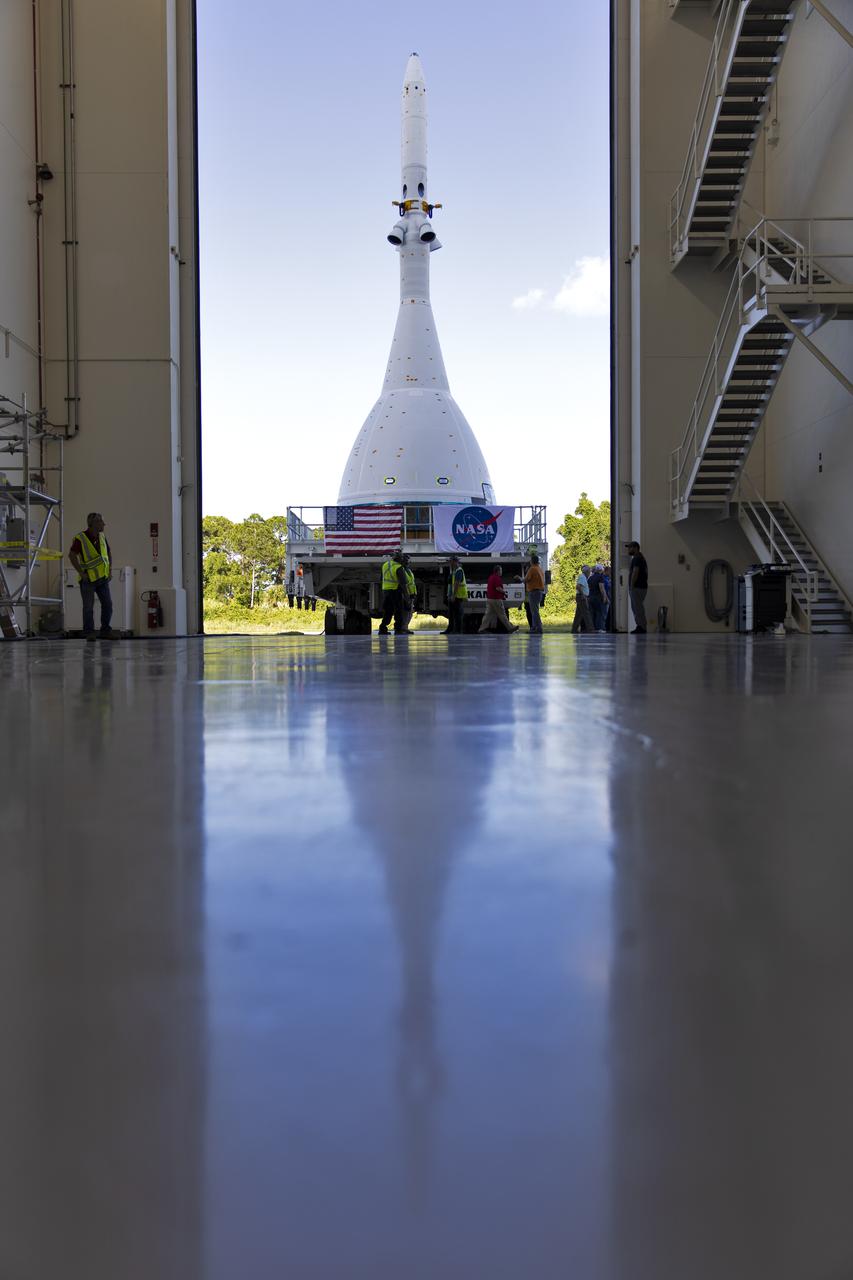

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exits the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
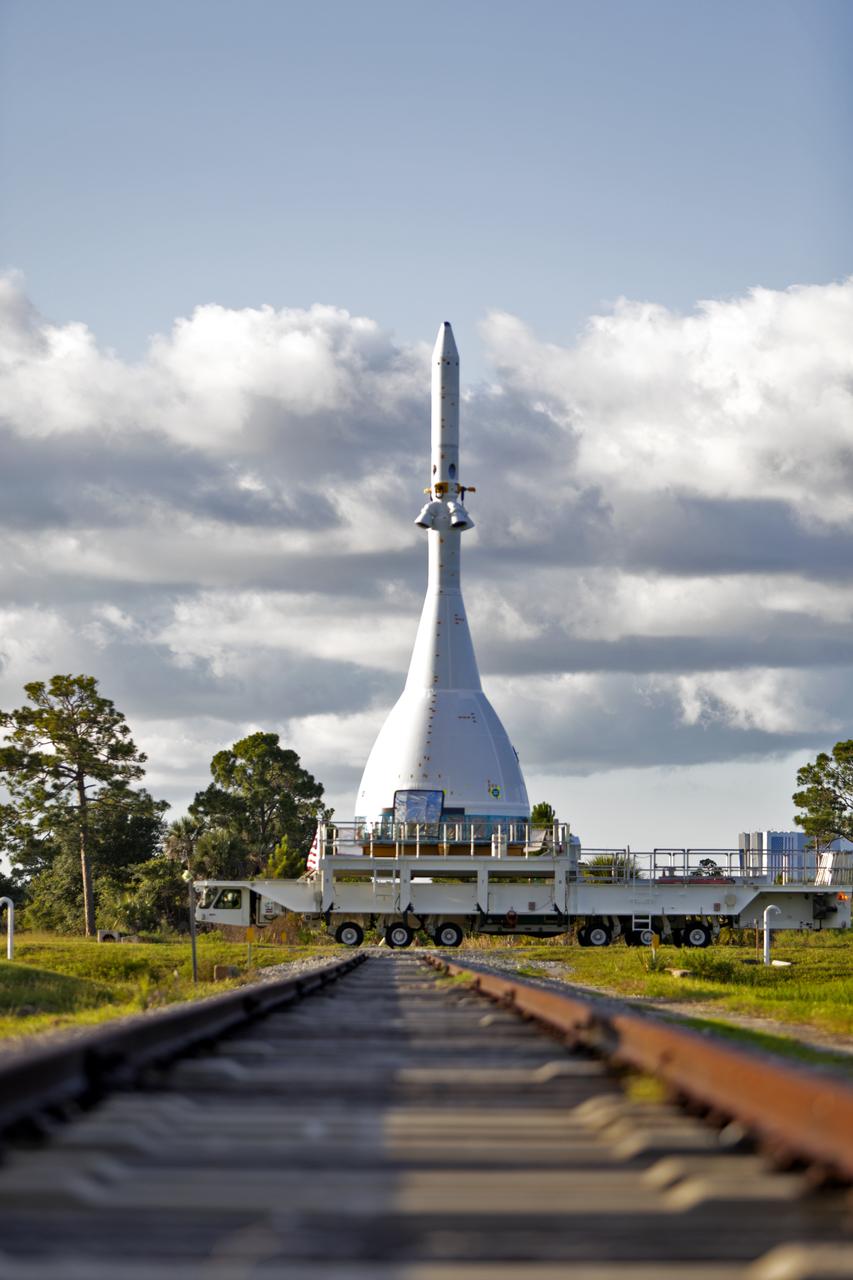

After exiting the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019, the test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is moved on a transport along the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
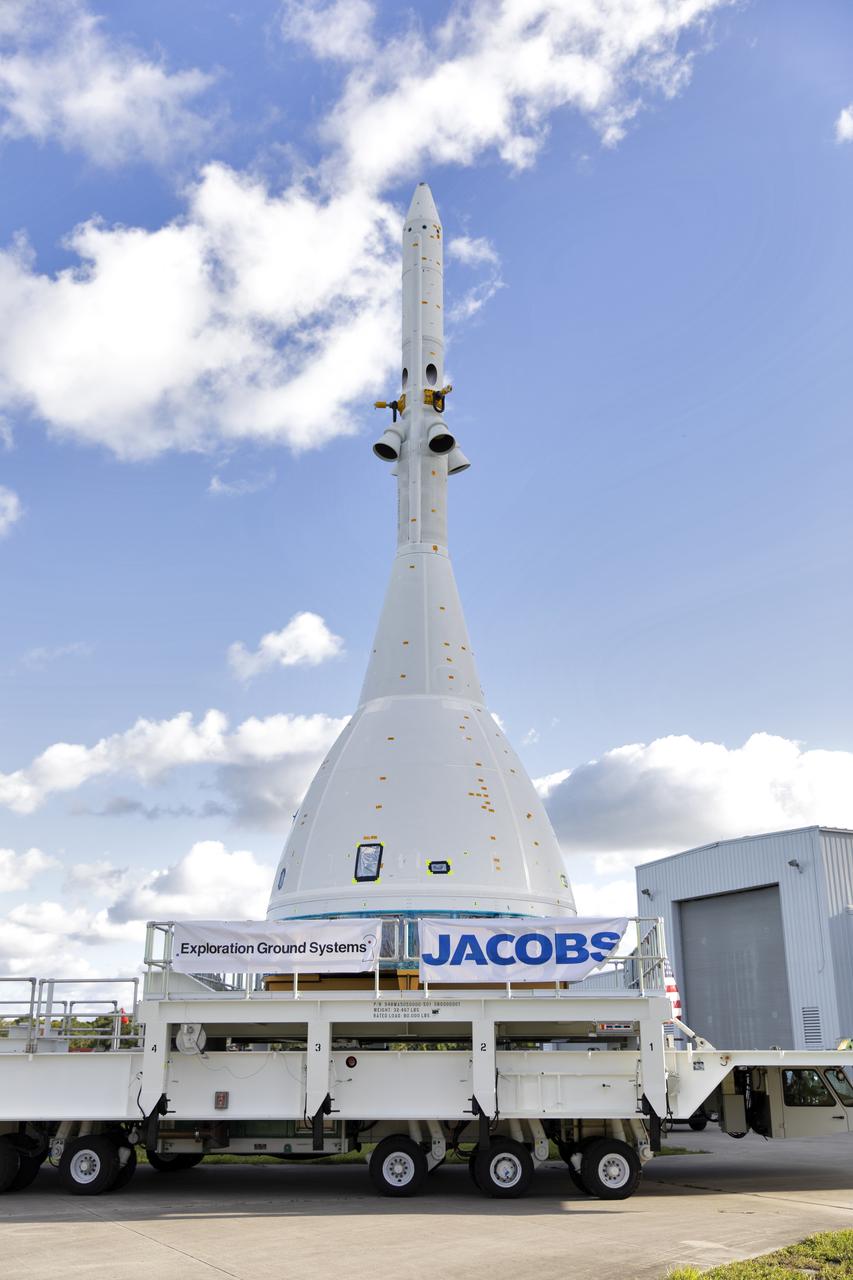

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exited the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
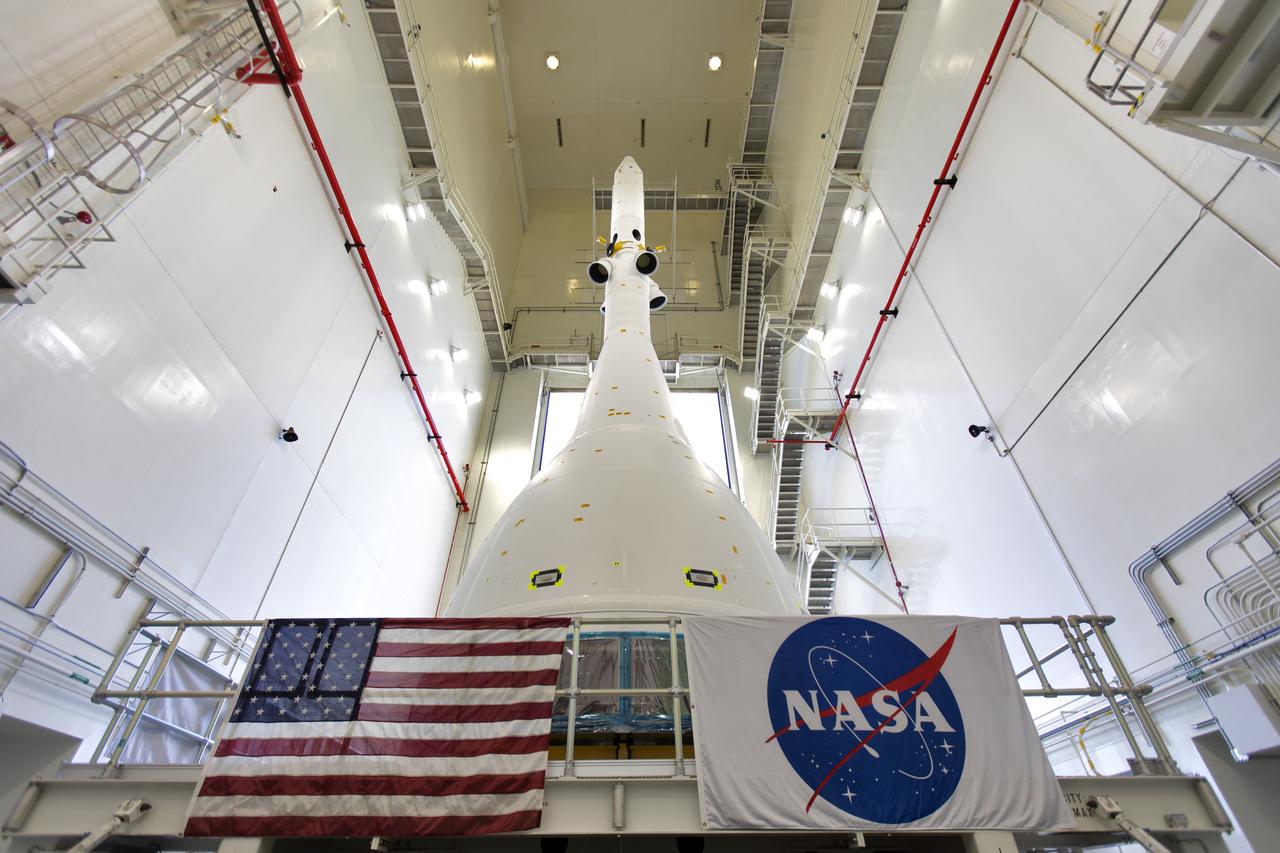

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exits the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
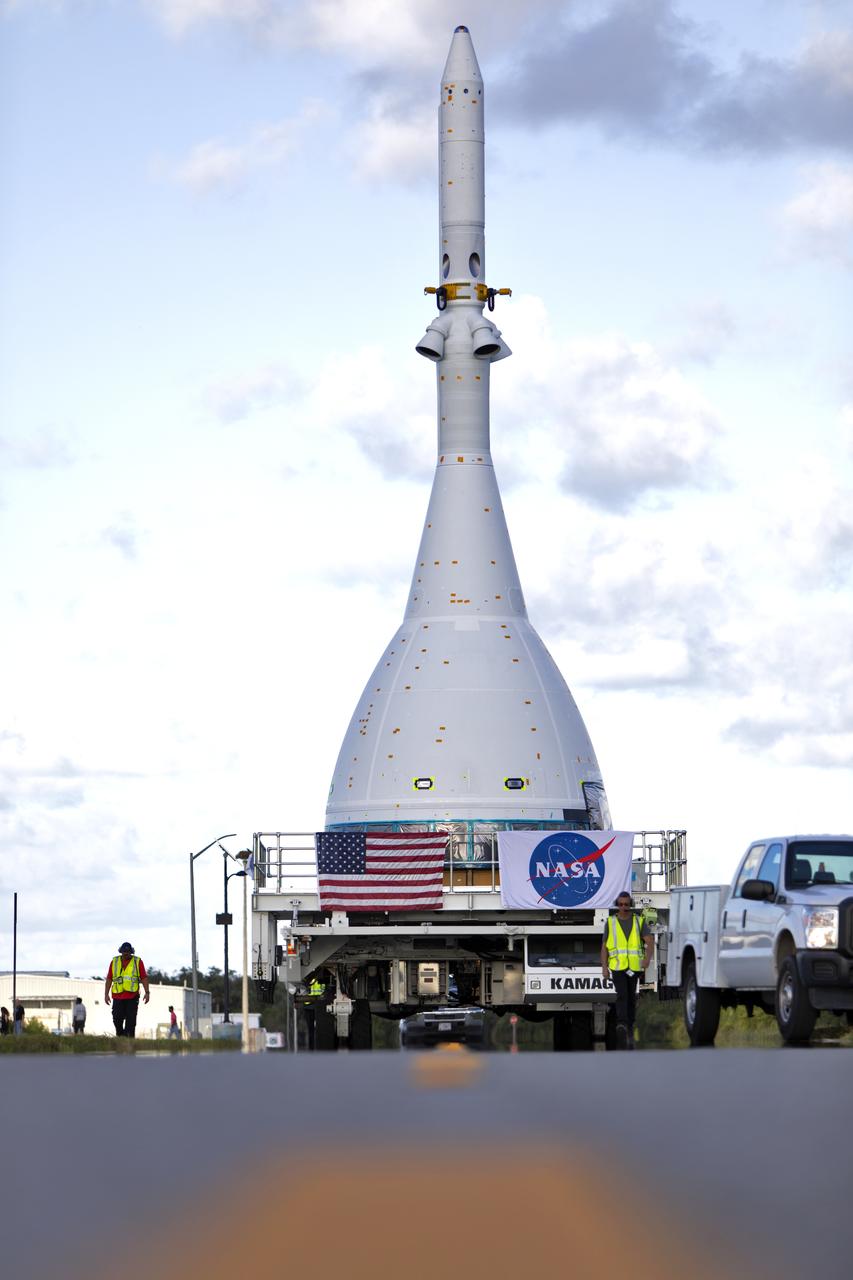

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exited the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
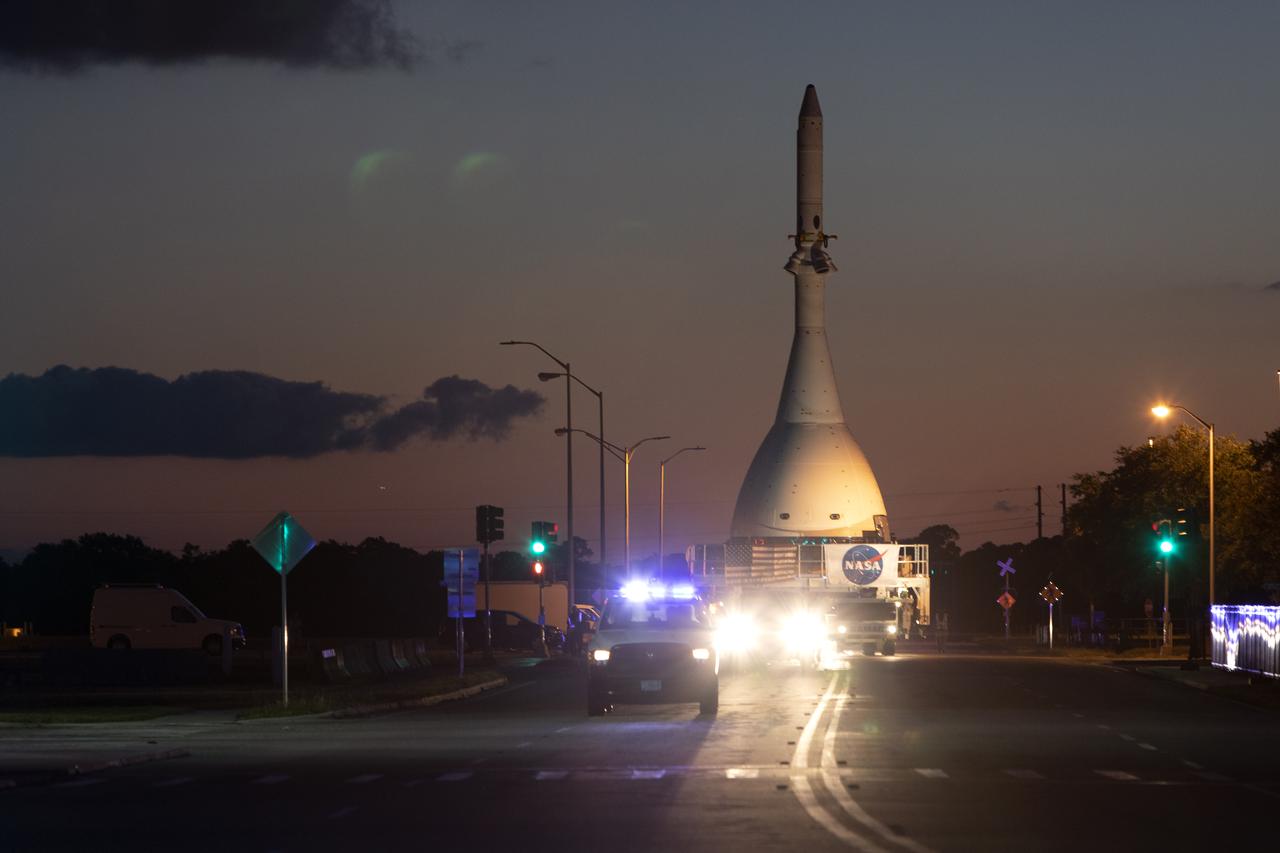

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is moved on a transport at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019, along the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. In the background is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
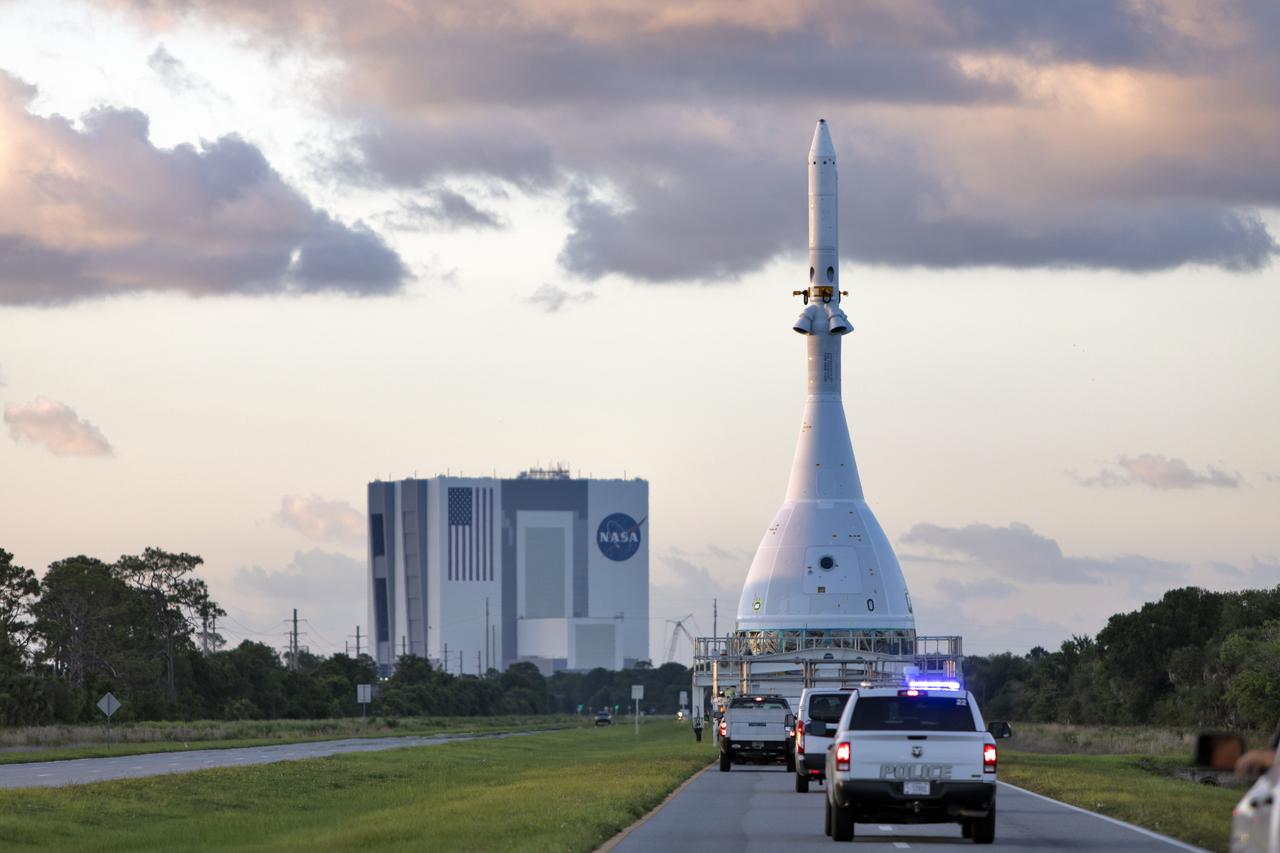

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is moved on a transport at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019, along the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. In the background is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
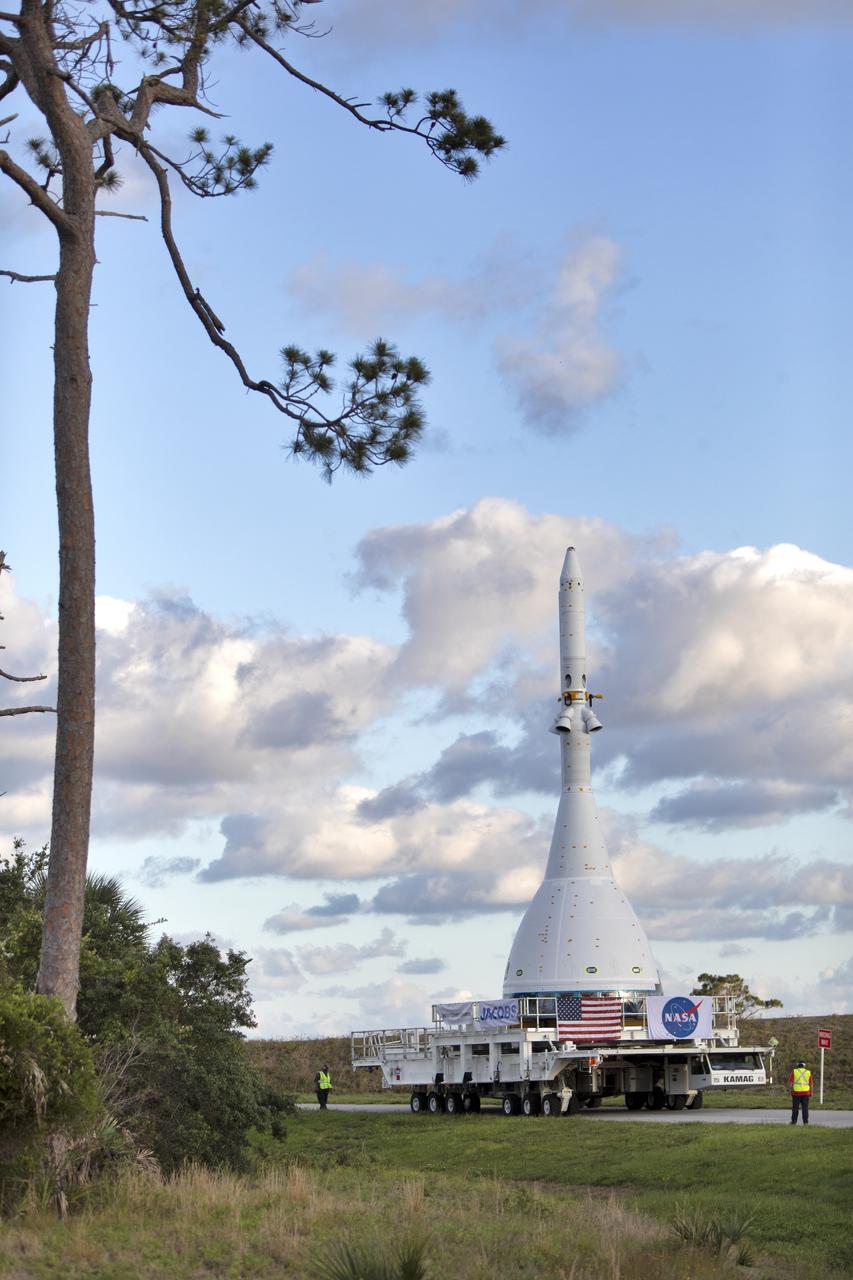

After exiting the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019, the test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is moved on a transport along the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
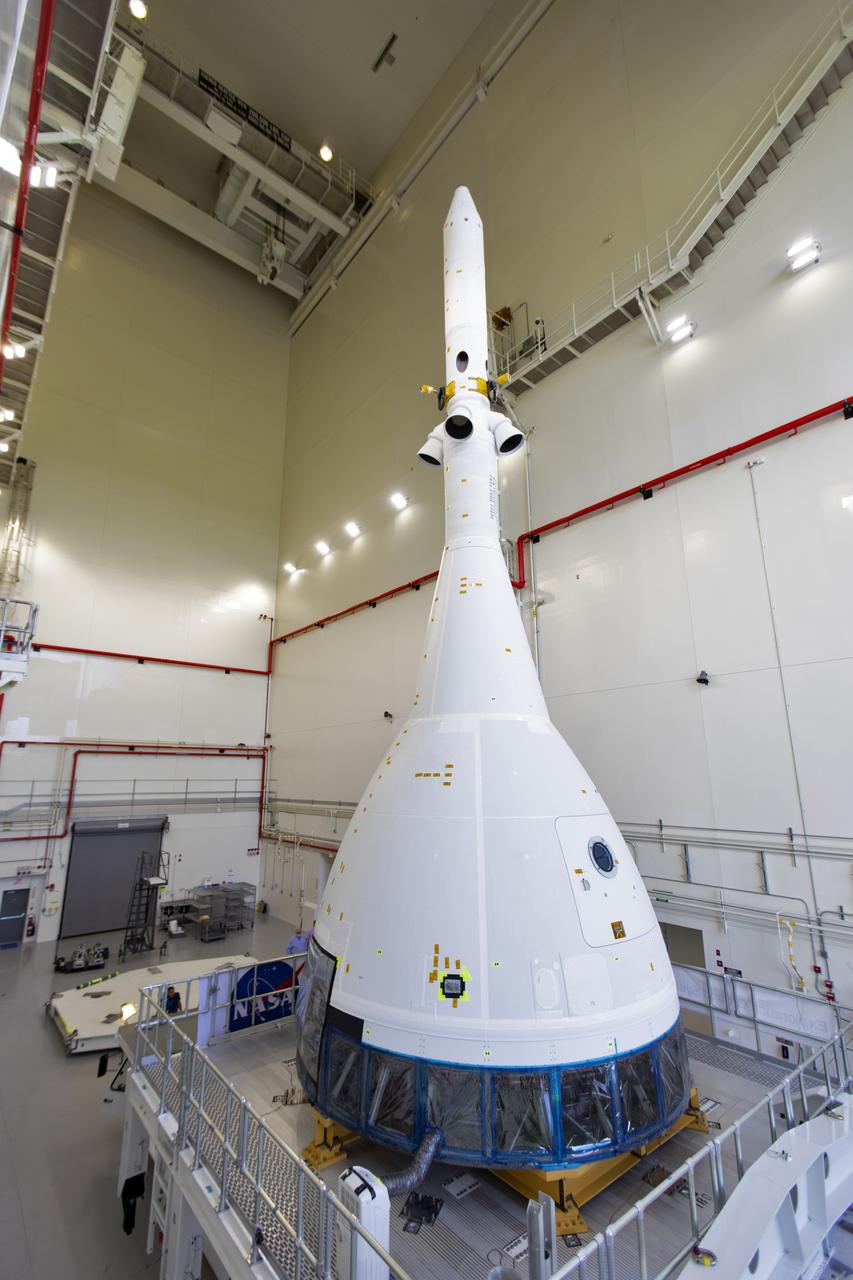

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is ready to exit the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exits the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exits the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
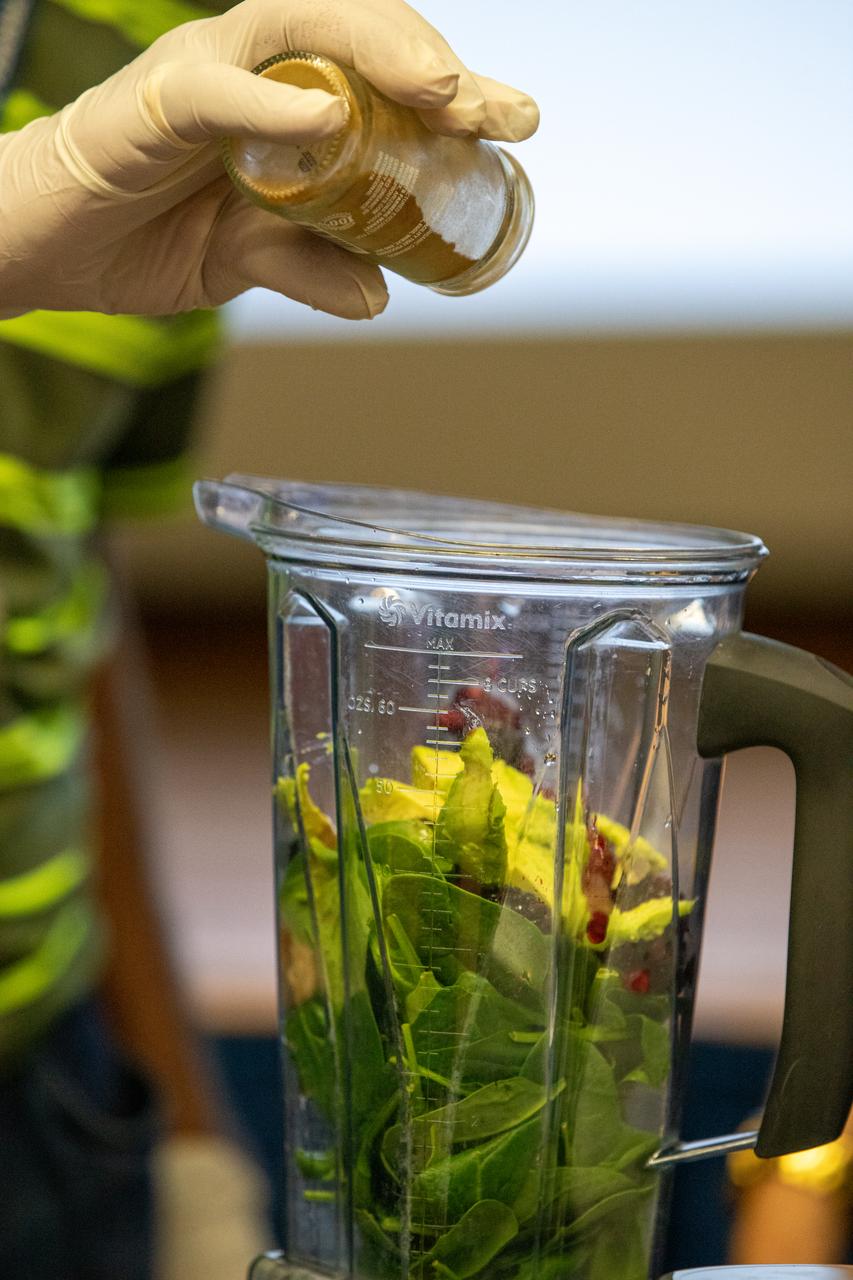
A Kennedy Space Center employee, following instructions from guest speaker Carly Paige, an integrative nutrition health coach and chef, demonstrates how to make a smoothie inside the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 5, 2020. The demonstration was part of a presentation given by Paige during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce. Paige’s presentation included information on simple swaps that can be made to incorporate healthier habits on a daily basis.
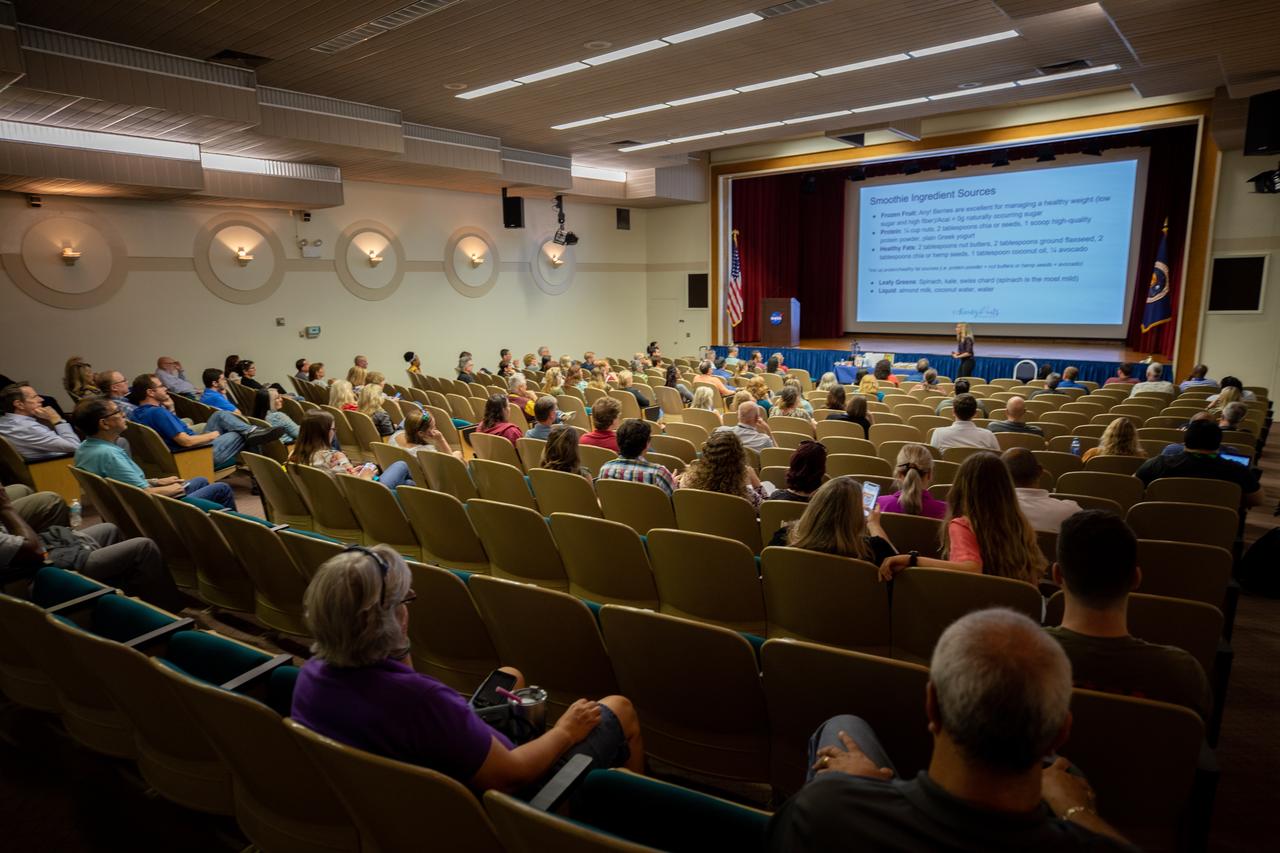

NASA Kennedy Space Center employees attend a presentation on simple swaps that can be made to lead to a healthier lifestyle inside the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 5, 2020. The presentation, led by guest speaker Carly Paige, an integrative nutrition health coach and chef, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
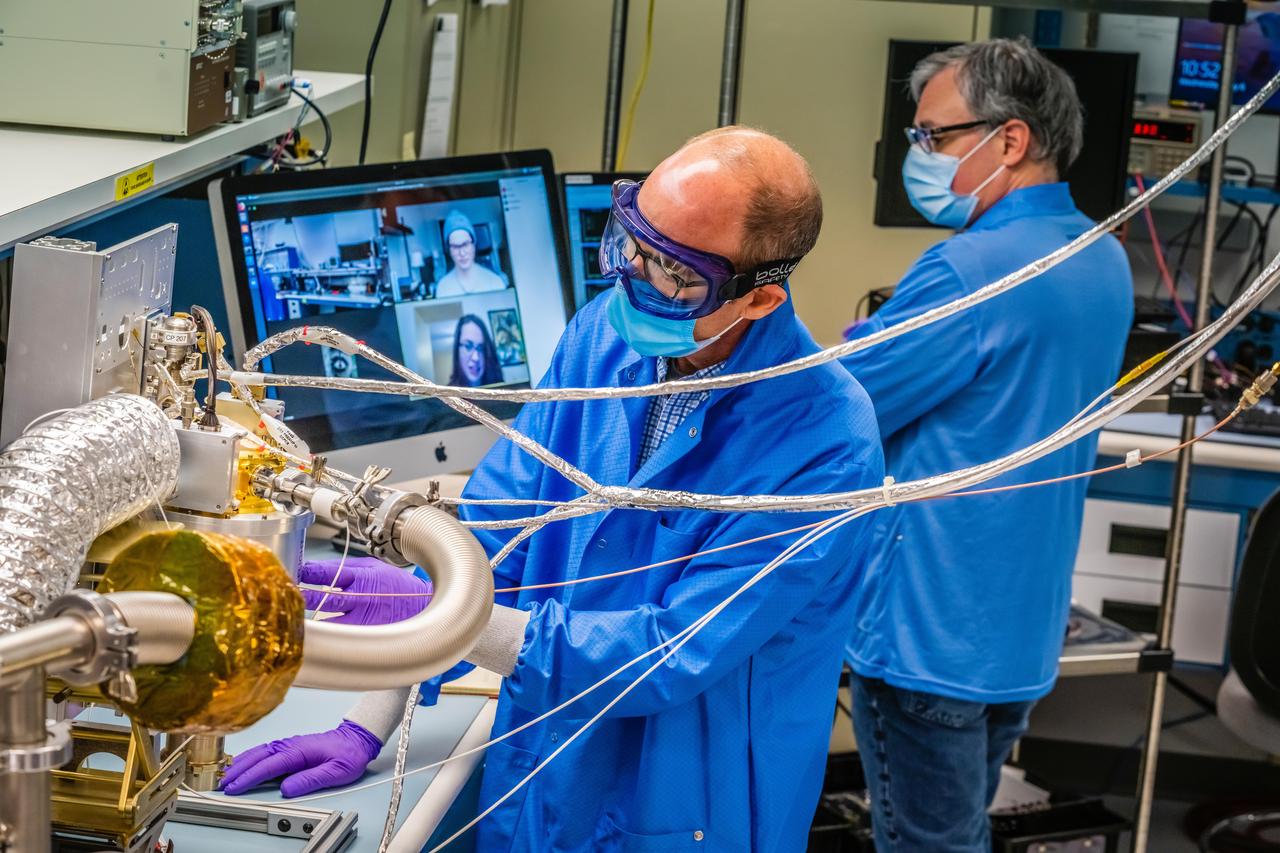

Engineers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, continue to make progress on Psyche's spectrometer while observing COVID-19 safety procedures. Engineers John Goldsten (left) and Sam Fix work on the Gamma Ray/Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS) instrument that will launch aboard the Psyche spacecraft in 2022 to detect, measure and map the asteroid Psyche's elemental composition. The instrument's team at APL moved the majority of its work to video conferencing, which has enabled the team to whittle operations down to requiring just one or two staff members on campus once or twice a week. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23880
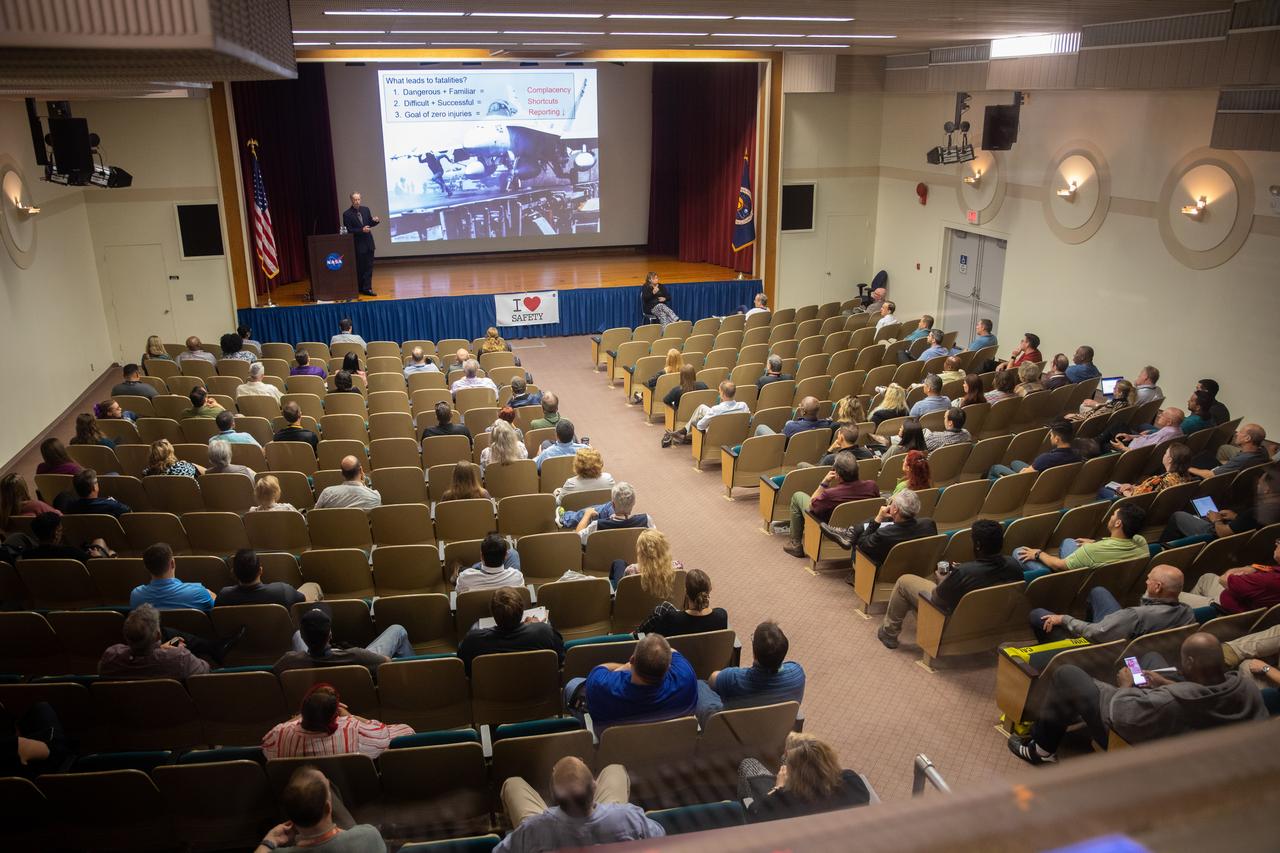

NASA Kennedy Space Center employees attend a presentation on techniques and principles that can help optimize performance in high-risk businesses inside the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on March 4, 2020. The presentation, led by guest speaker and former NASA astronaut Jim Wetherbee, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce.
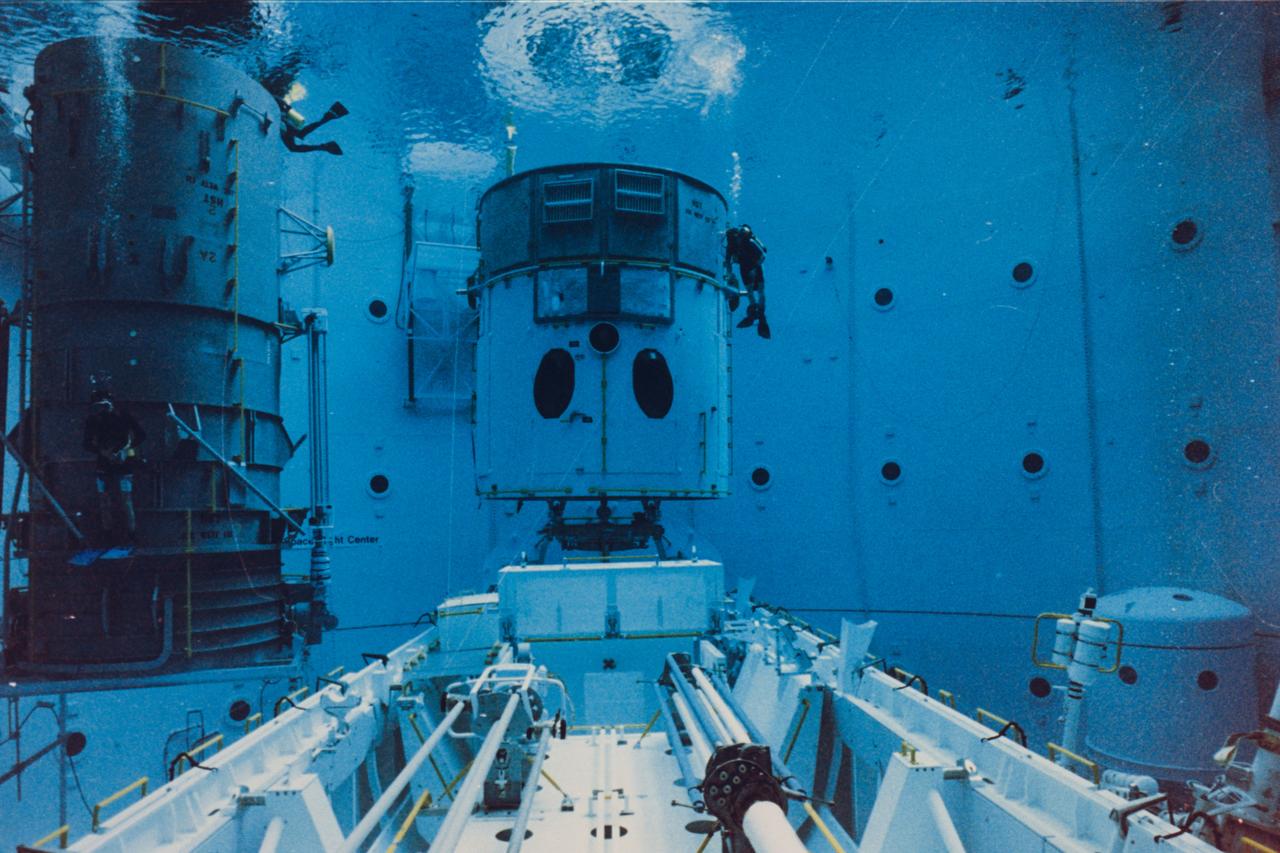
Safety divers in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) prepare a mockup of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) for one of 32 separate training sessions conducted by four of the STS-61 crew members in June. The three-week process allowed mission trainers to refine the timelines for the five separate spacewalks scheduled to be conducted on the actual mission scheduled for December 1993. The HST is separated into two pieces since the water tank depth cannot support the entire structure in one piece. The full length payload bay mockup shows the Solar Array Carrier in the foreground and the various containers that will house replacement hardware that will be carried on the mission.
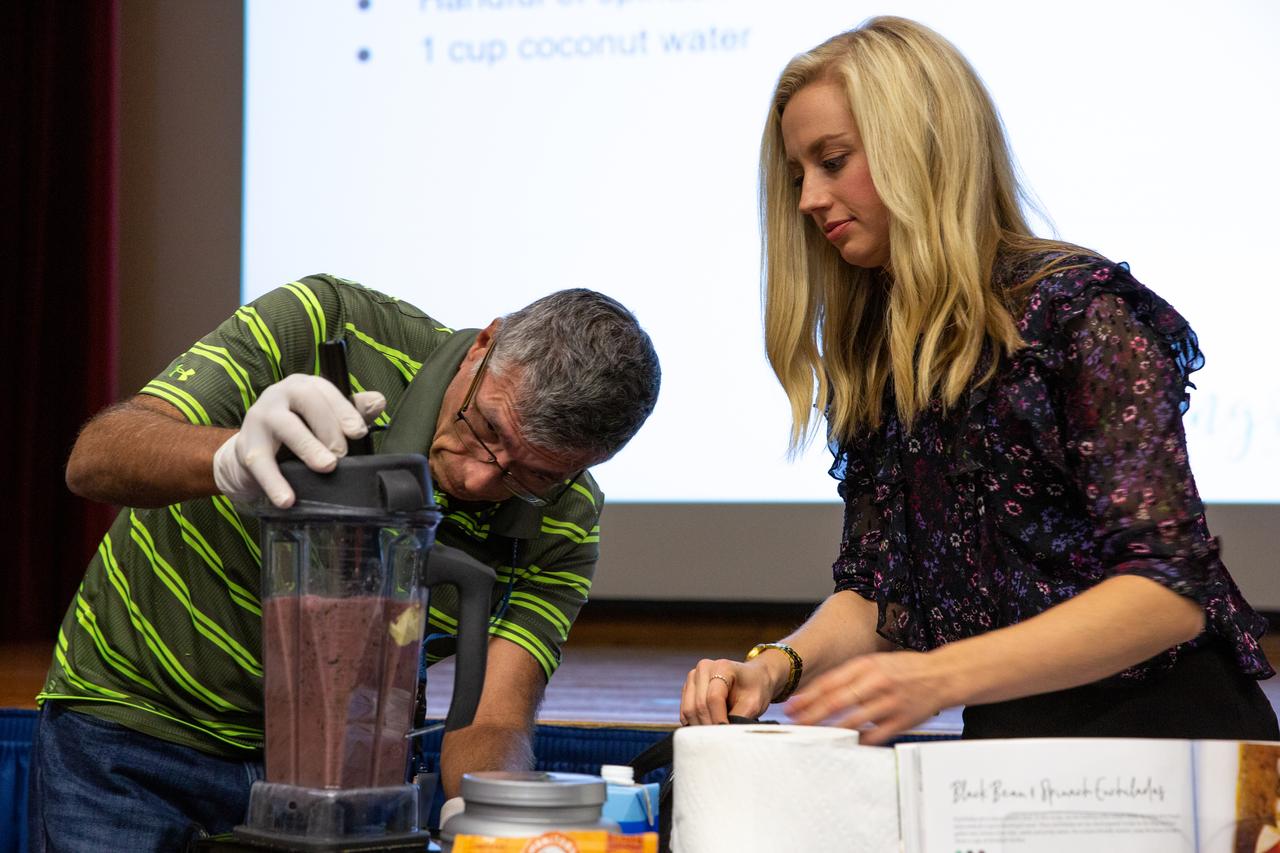

Carly Paige, right, an integrative nutrition health coach and chef, along with help from a Kennedy Space Center employee, demonstrates how to make a smoothie during a presentation inside the Training Auditorium on March 5, 2020. The presentation, led by Paige, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce. Paige’s presentation included information on simple swaps that can be made to incorporate healthier habits on a daily basis.

Carly Paige, right, an integrative nutrition health coach and chef, along with help from a Kennedy Space Center employee, demonstrates how to make a smoothie during a presentation inside the Training Auditorium on March 5, 2020. The presentation, led by Paige, was offered during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days, which took place March 2 through March 6. Throughout the week, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend a variety of presentations – all of which focused on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce. Paige’s presentation included information on simple swaps that can be made to incorporate healthier habits on a daily basis.
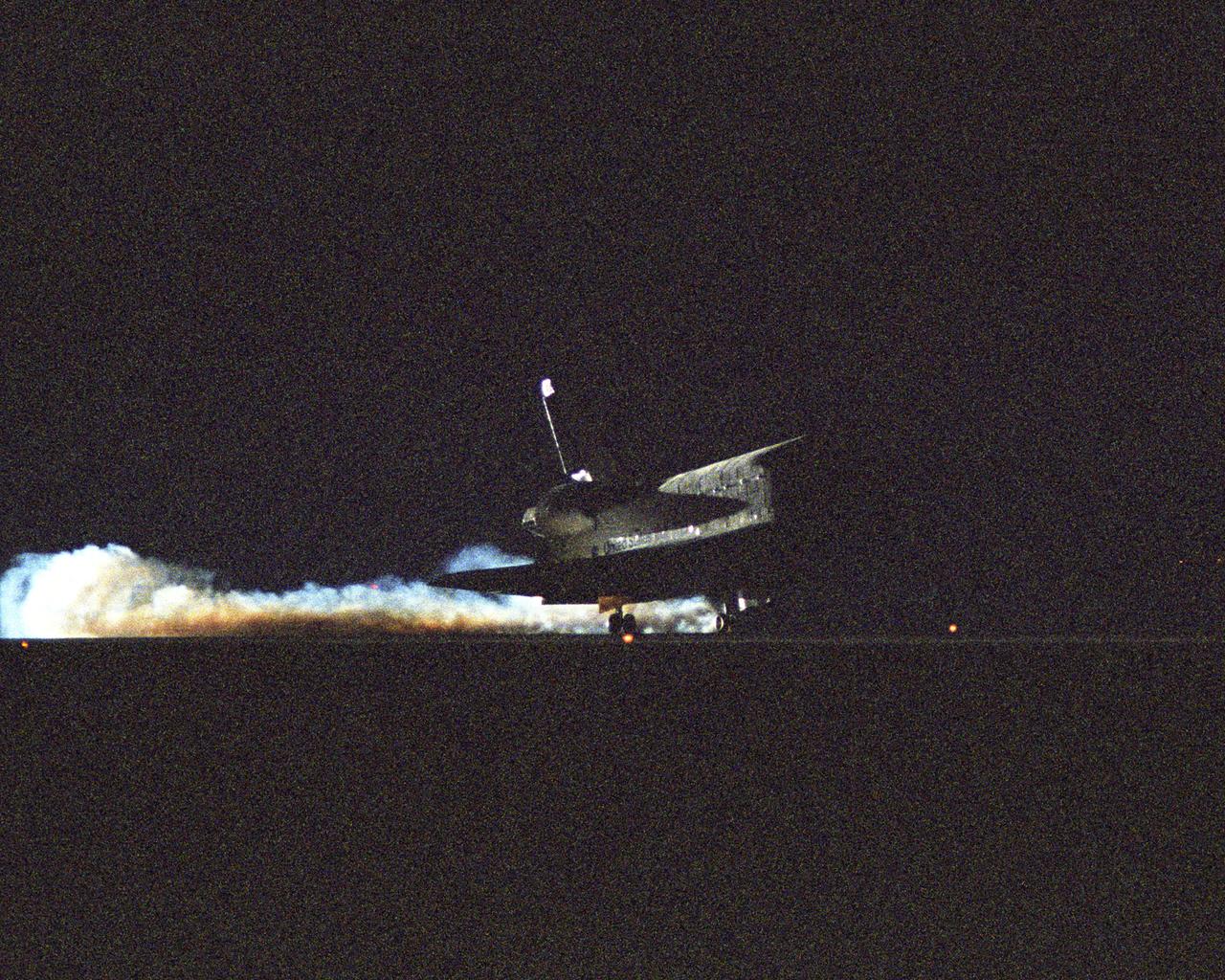

Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in Calif. at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.

Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in Calif. at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.

Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in Calif. at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
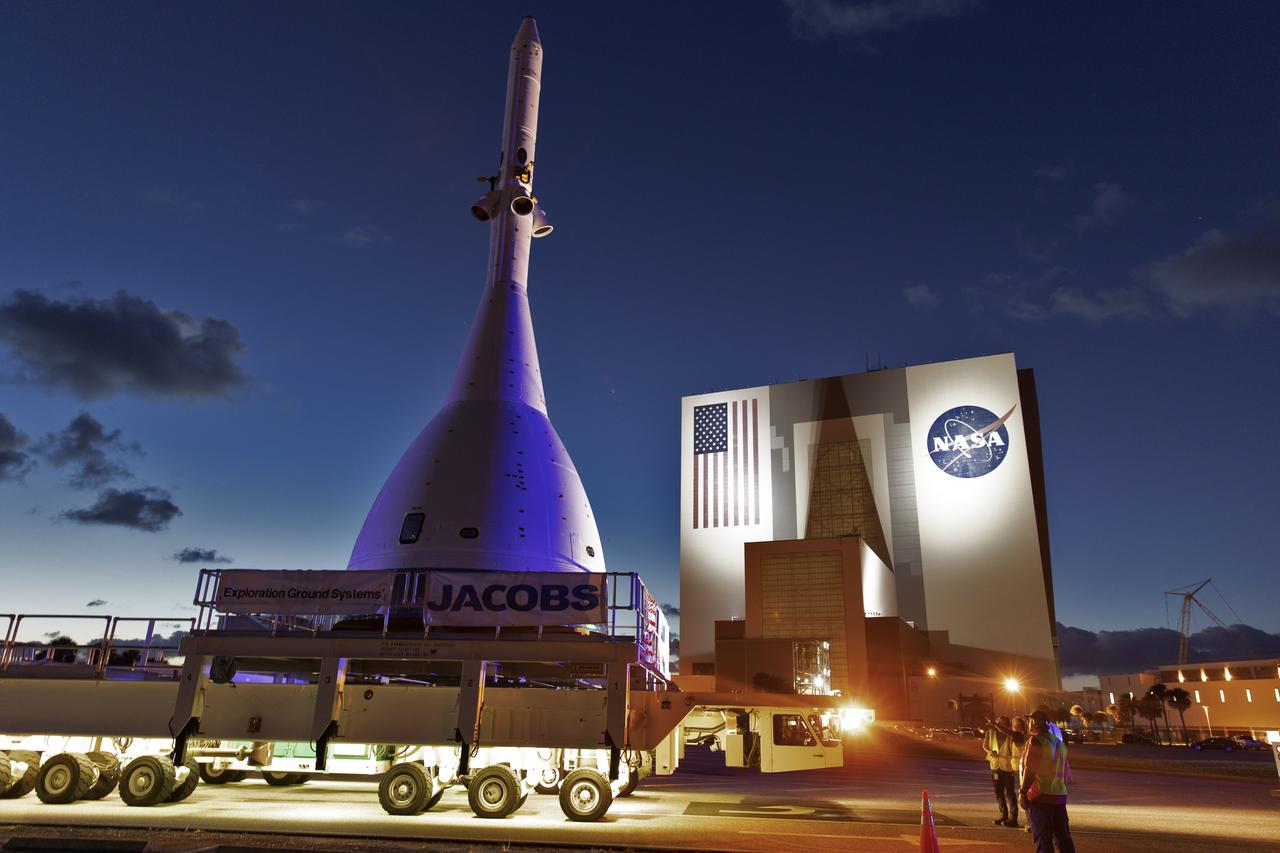

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test passes by the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019, during its 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. In the background is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
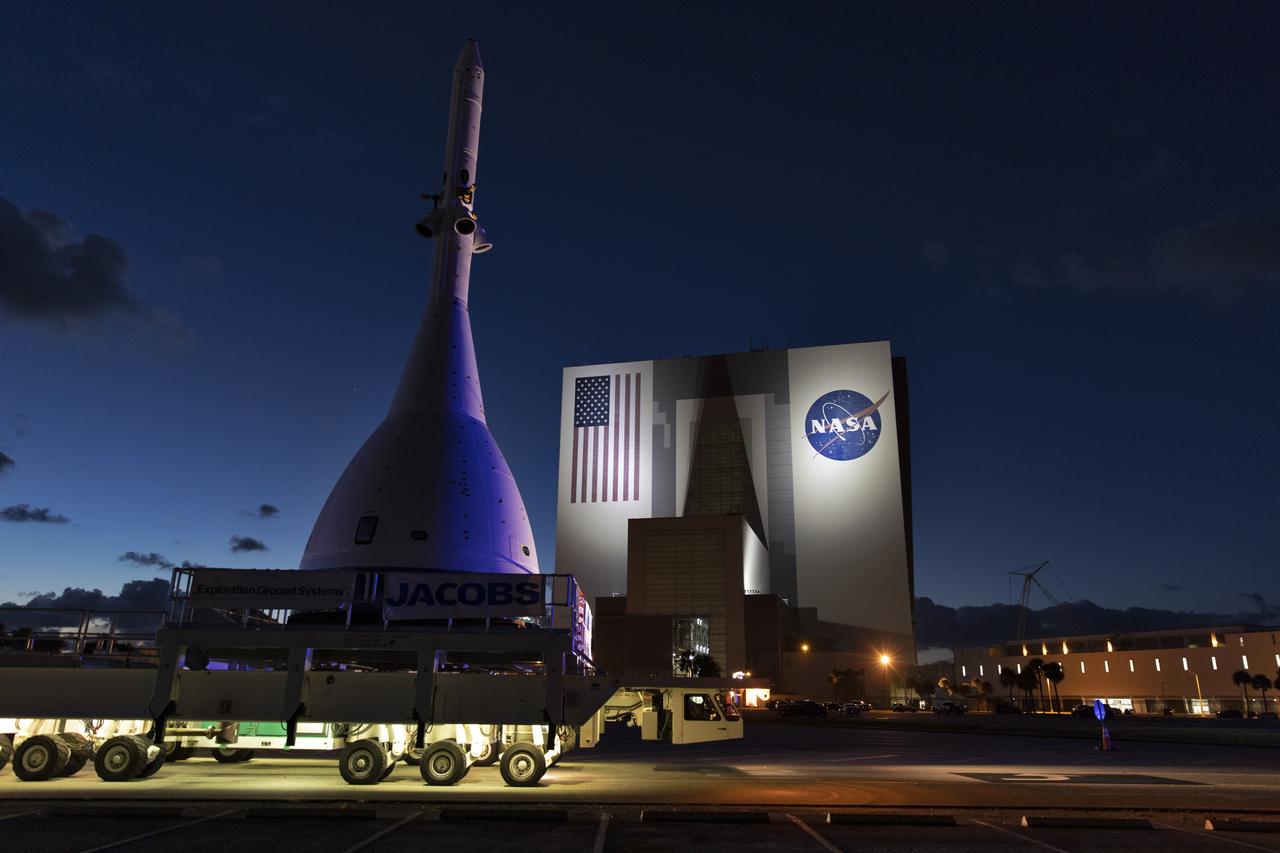

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test passes by the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019, during its 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. In the background is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
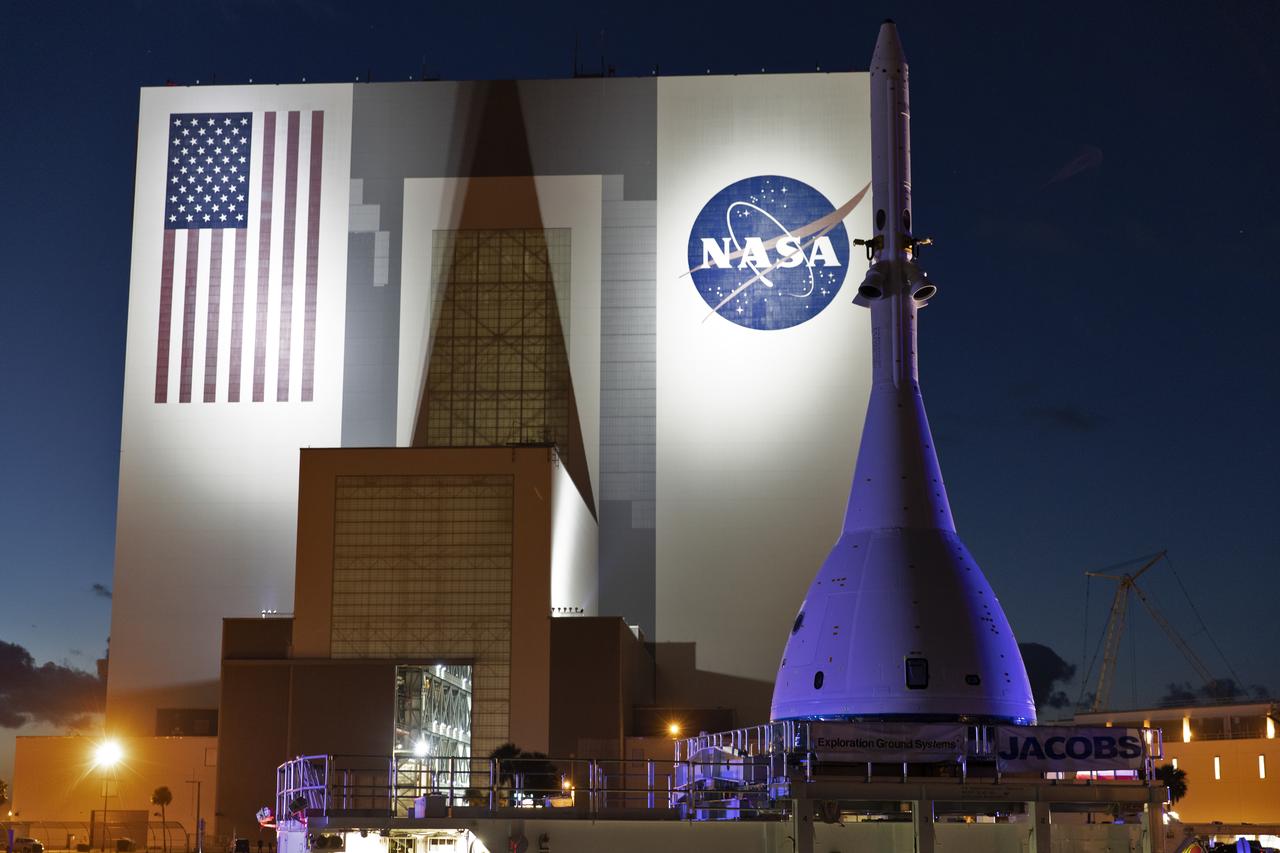

The test version of Orion attached to the Launch Abort System for the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test passes by the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019, during its 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. In the background is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
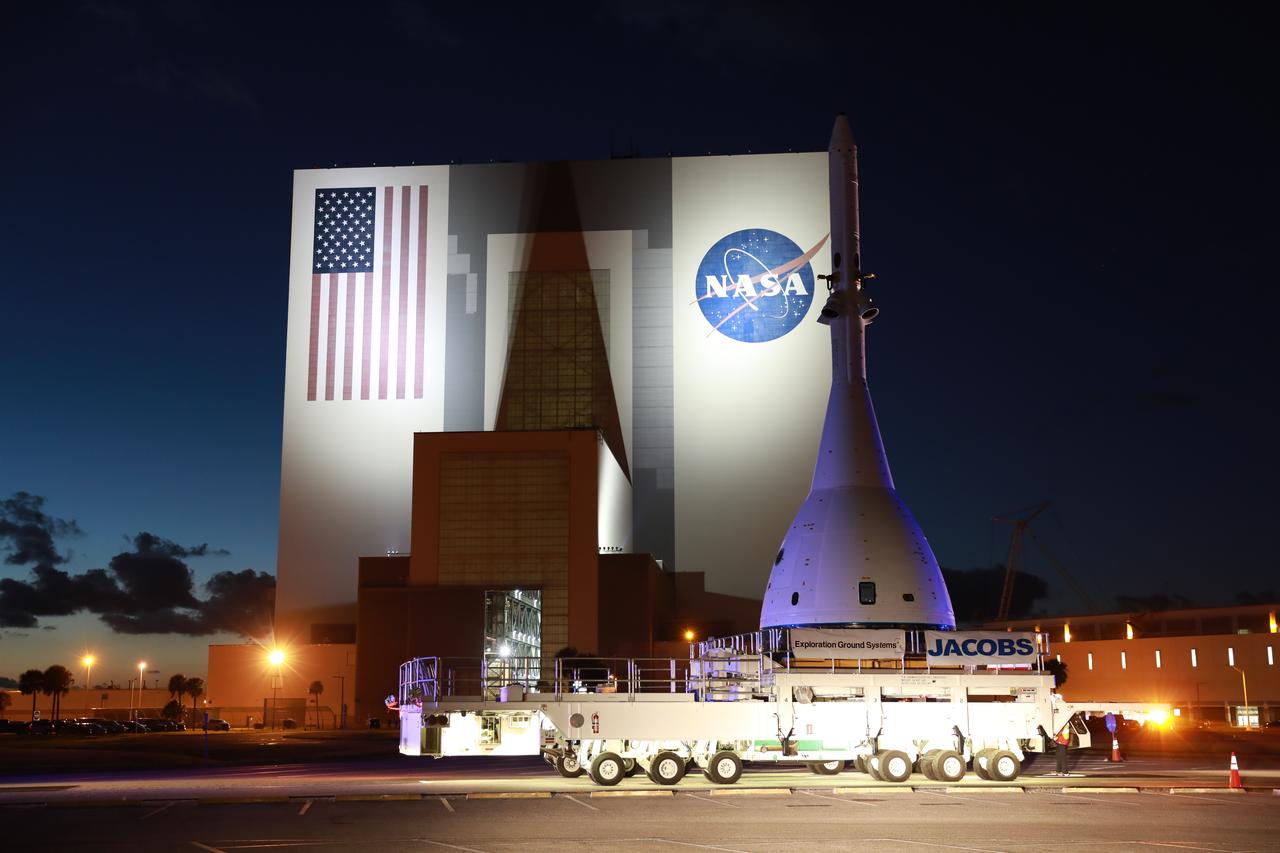

The vehicle for Orion’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) fight test passes by the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on its 21.5-mile-trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on May 22, 2019. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule away to demonstrate it can keep a future crew inside safe if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
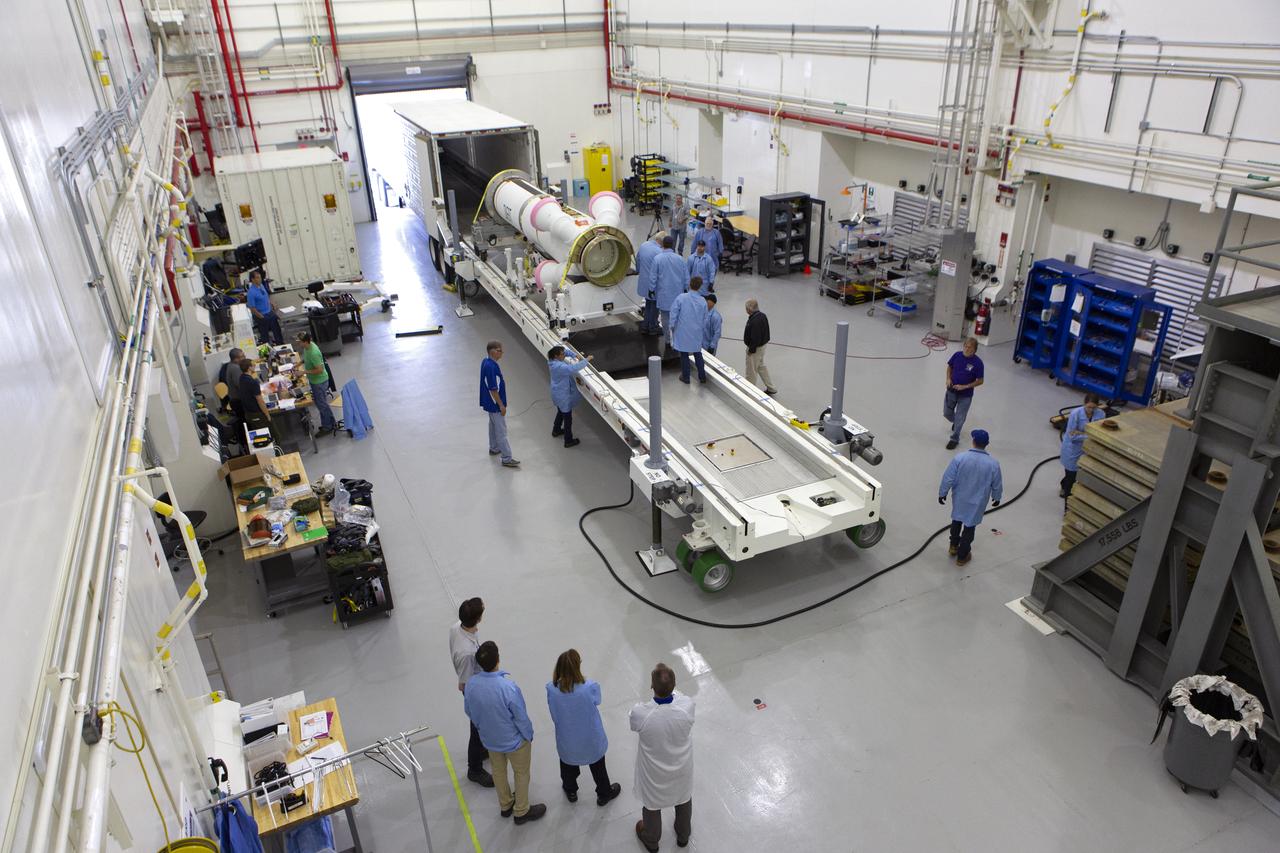

Workers have offloaded the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
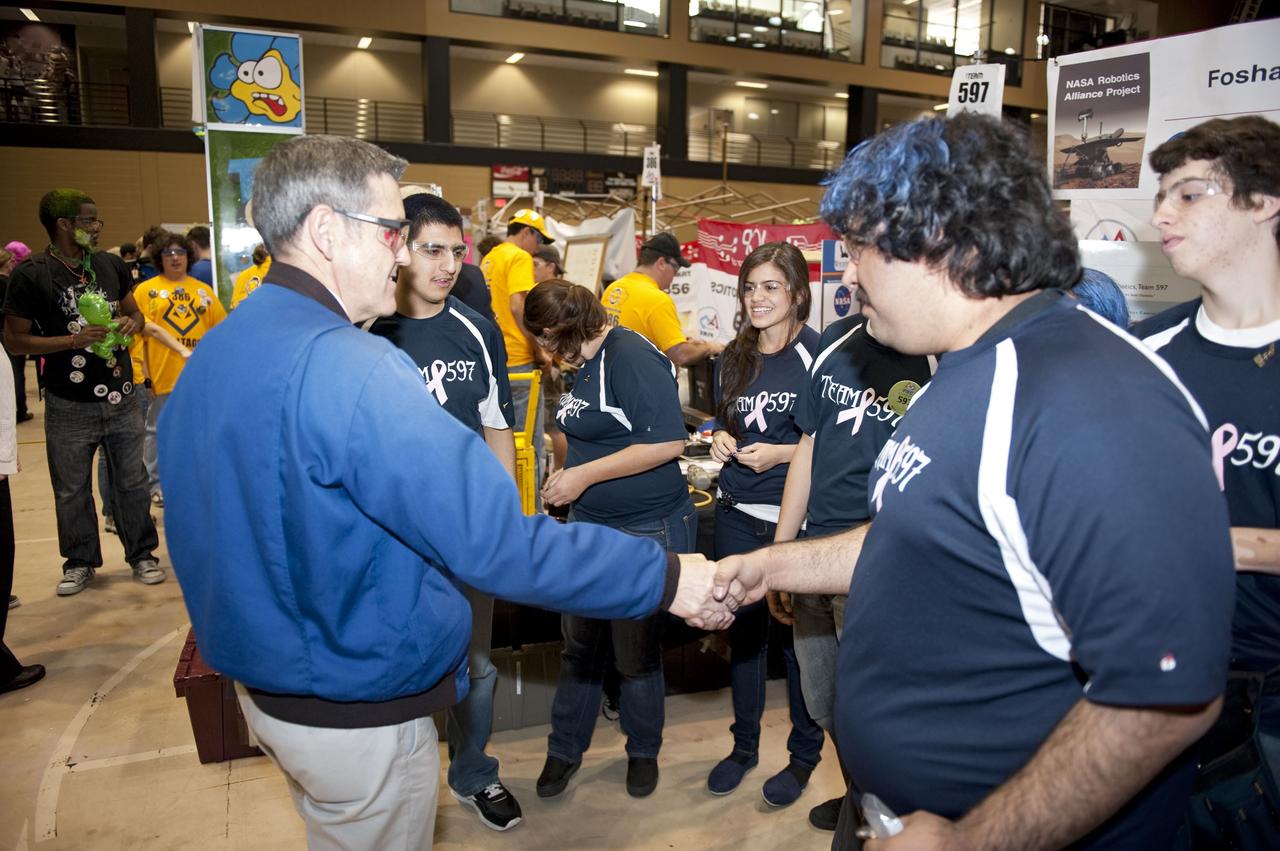

ORLANDO, Fla. – NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana talks to The Wolverines team at the regional FIRST robotics competition at the University of Central Florida in Orlando. The team is made up of students from the Foshay Learning Center located in Los Angeles. NASA is a sponsor of the team. About 60 high school teams took part in the competition called "For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology," or FIRST, in hopes of advancing to the national robotics championship. The team took home the Industrial Safety Award sponsored by Underwriters Laboratories. FIRST, founded in 1989, is a non-profit organization that designs accessible, innovative programs to build self-confidence, knowledge and life skills while motivating young people to pursue academic opportunities. The robotics competition challenges teams of high school students and their mentors to solve a common problem in a six-week timeframe using a standard kit of parts and a common set of rules. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
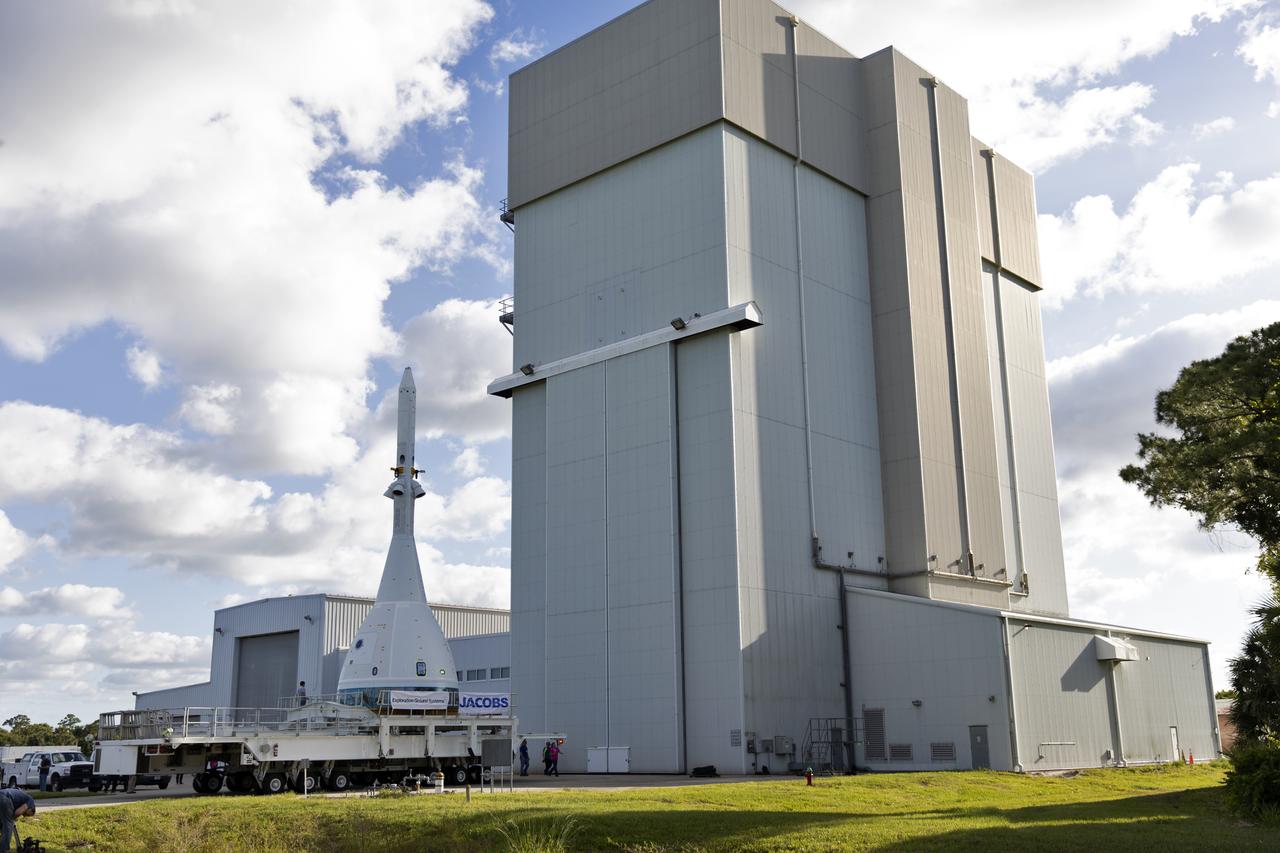

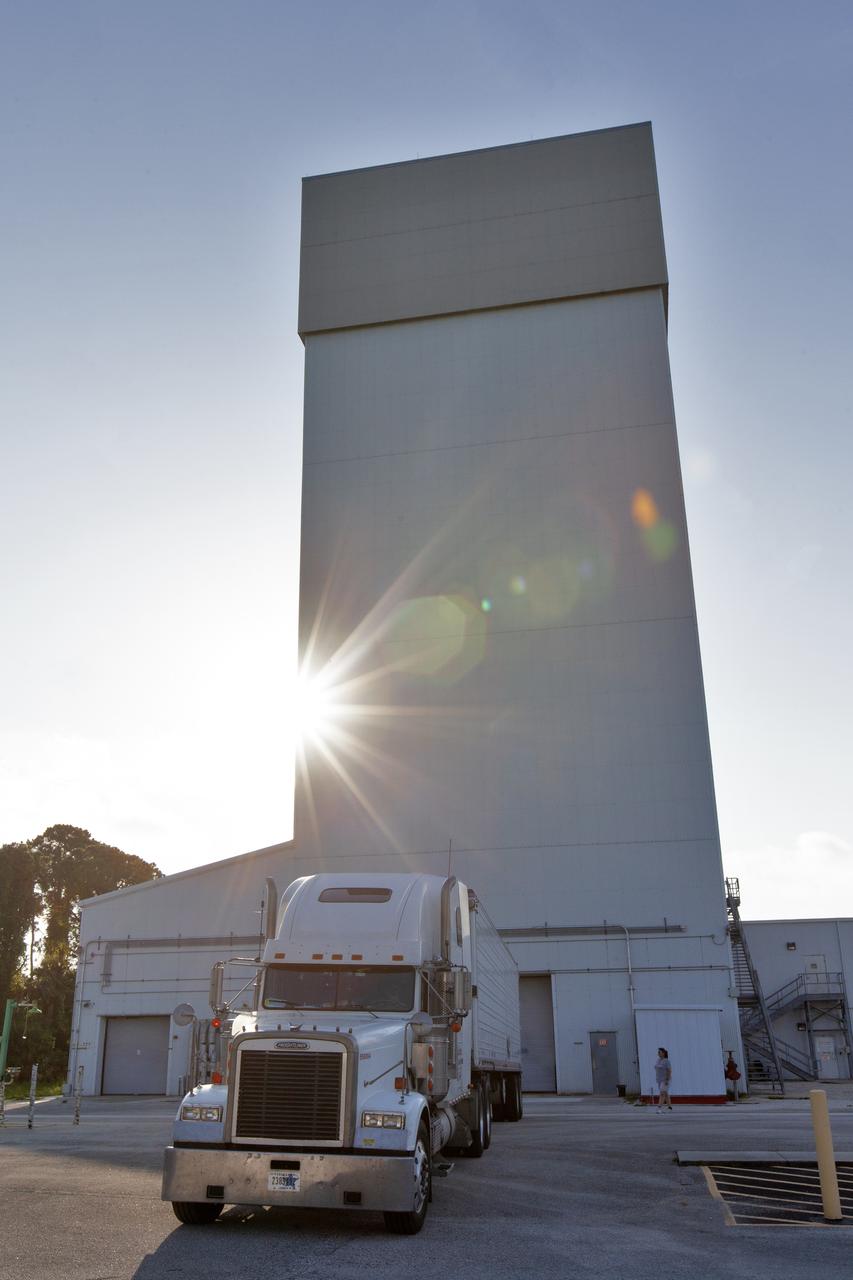
The vehicle for Orion’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exits the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule away to demonstrate it can keep a future crew inside safe if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.
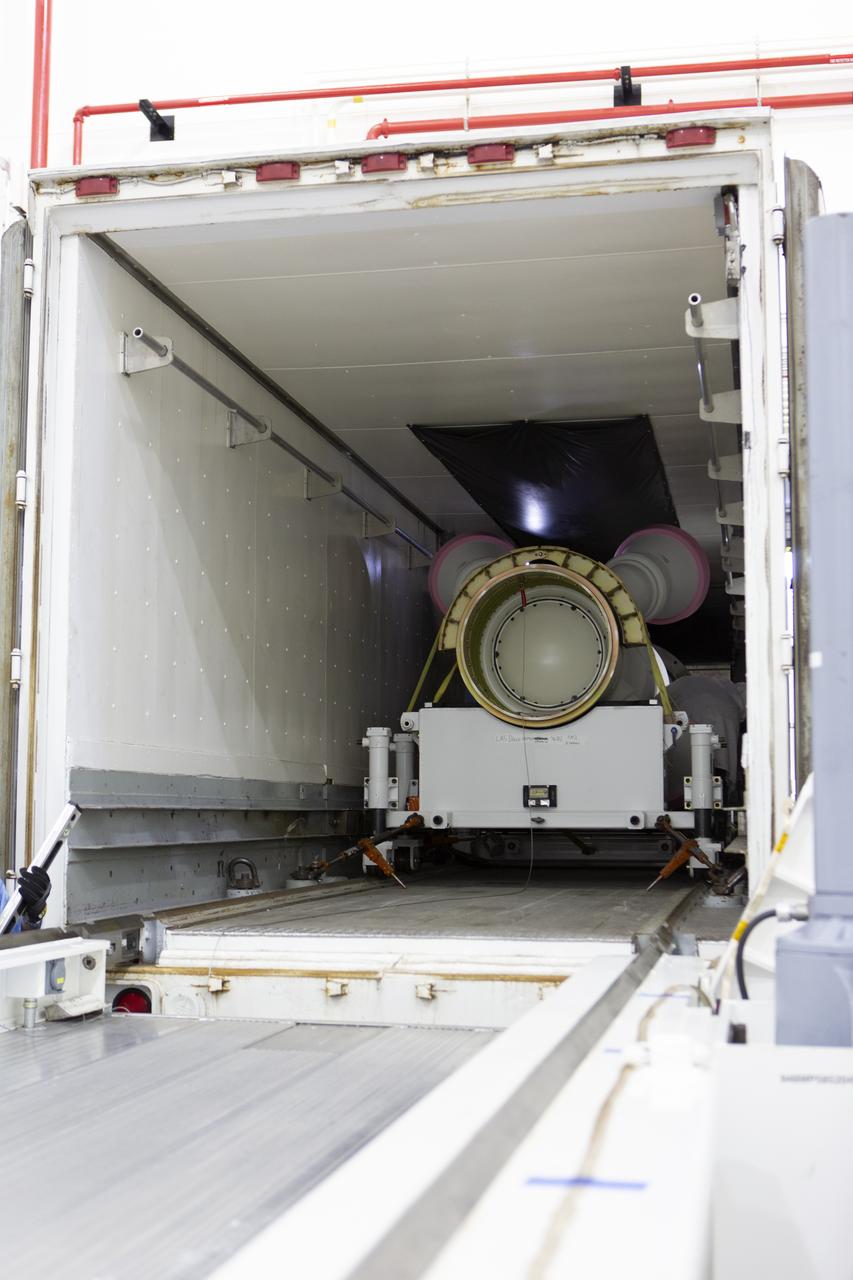

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, is offloaded from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
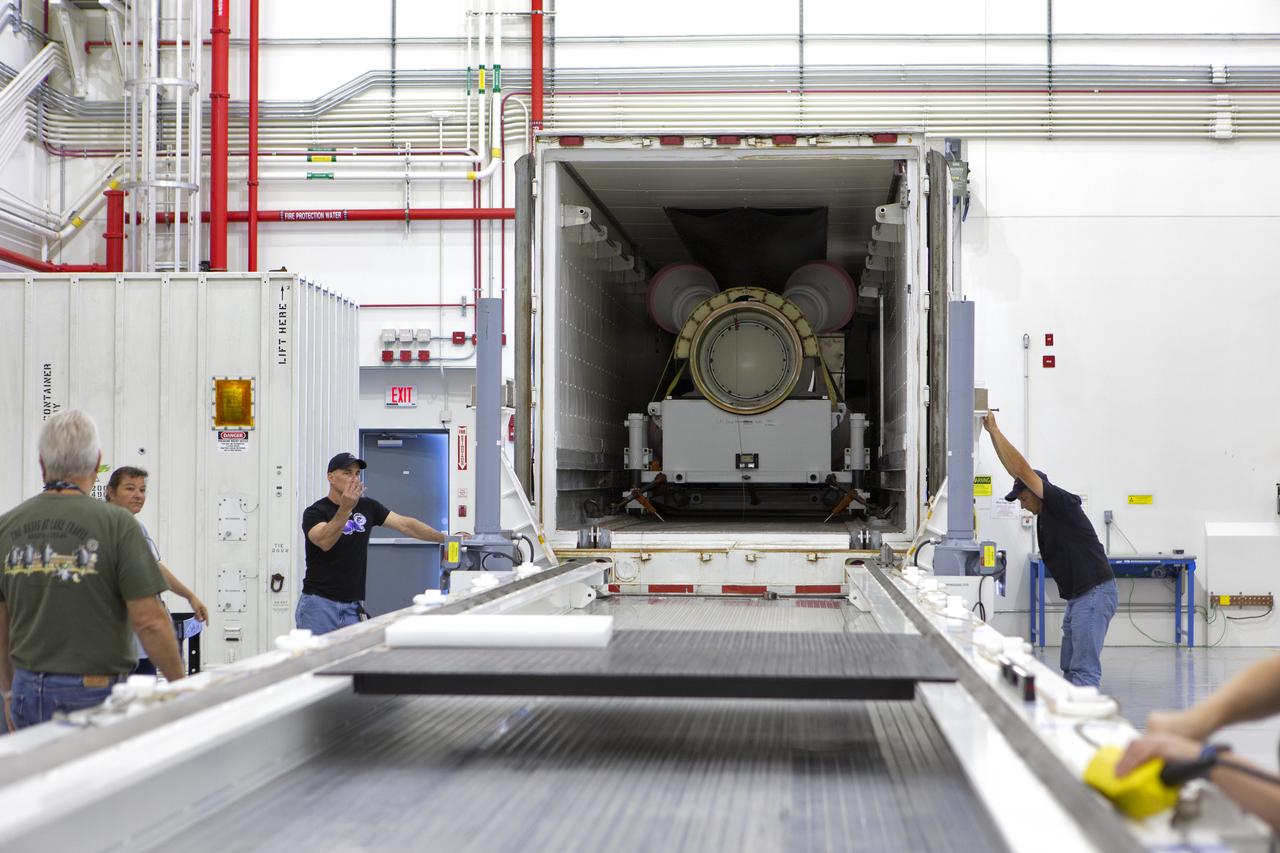

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, is offloaded from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
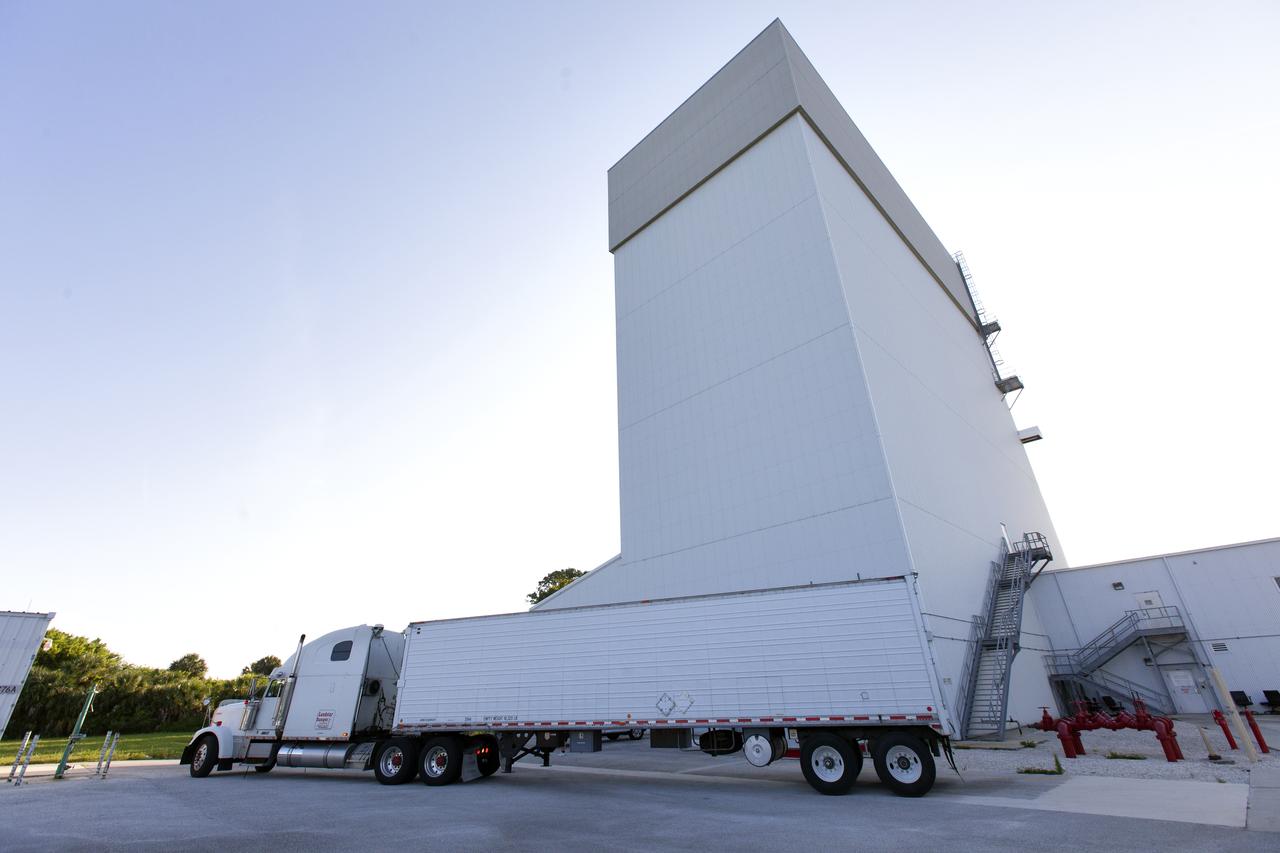

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be offloaded and moved into the LASF where it will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
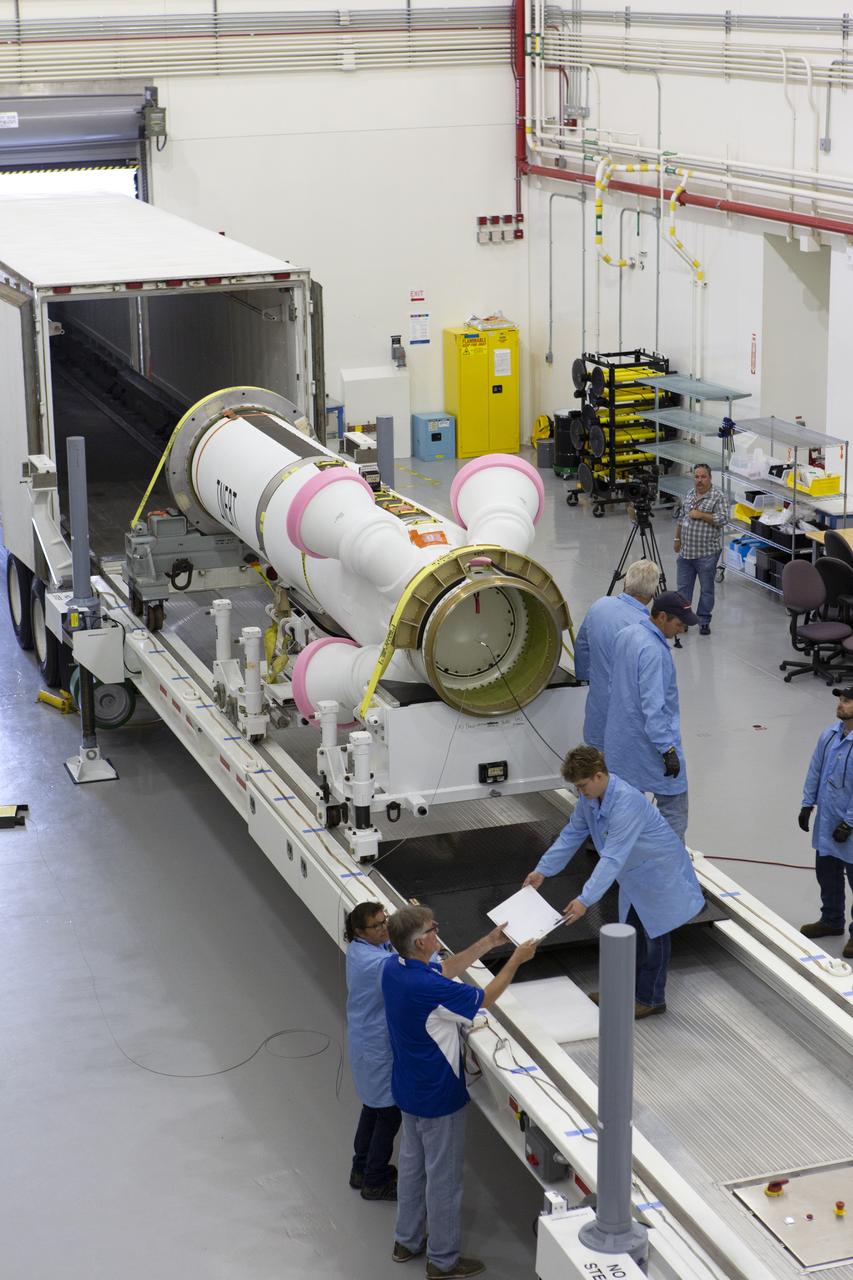

Workers have offloaded the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
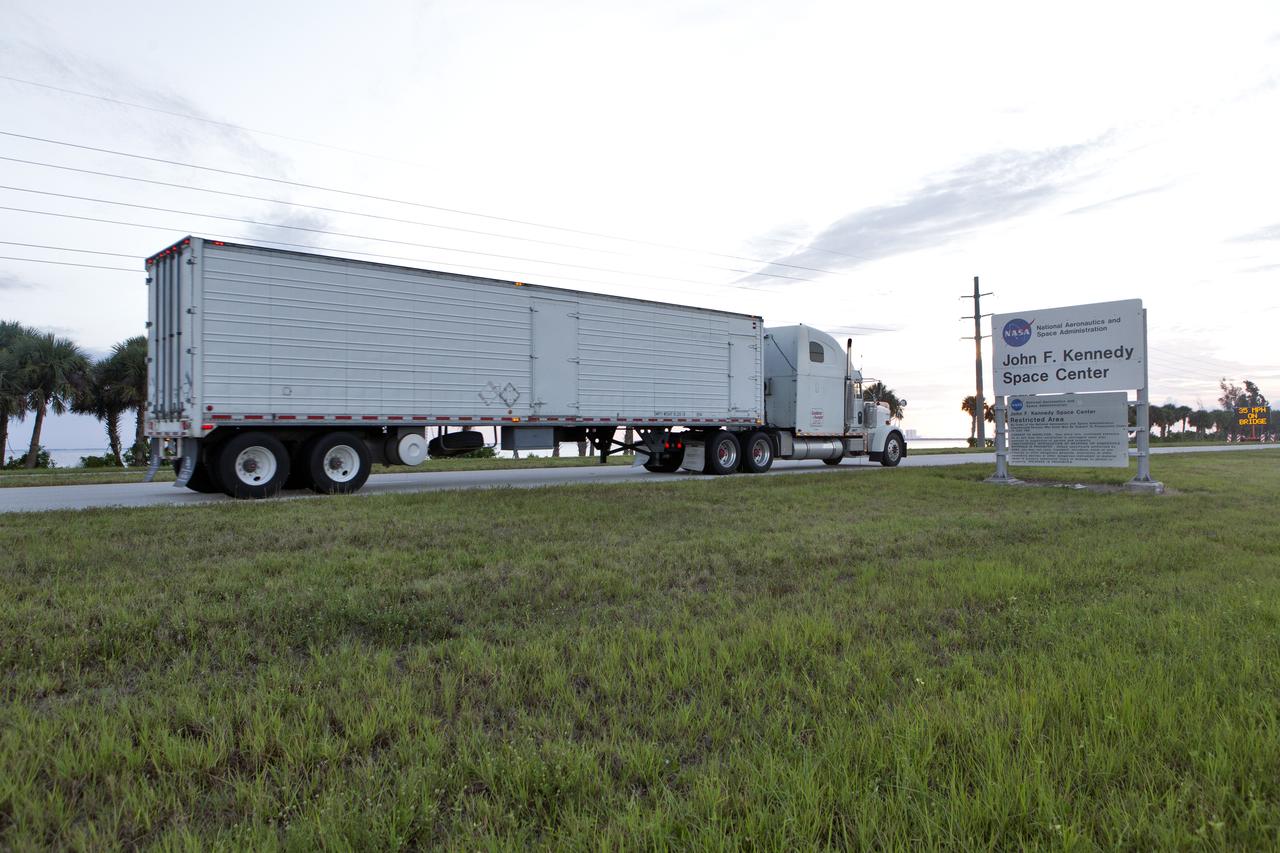

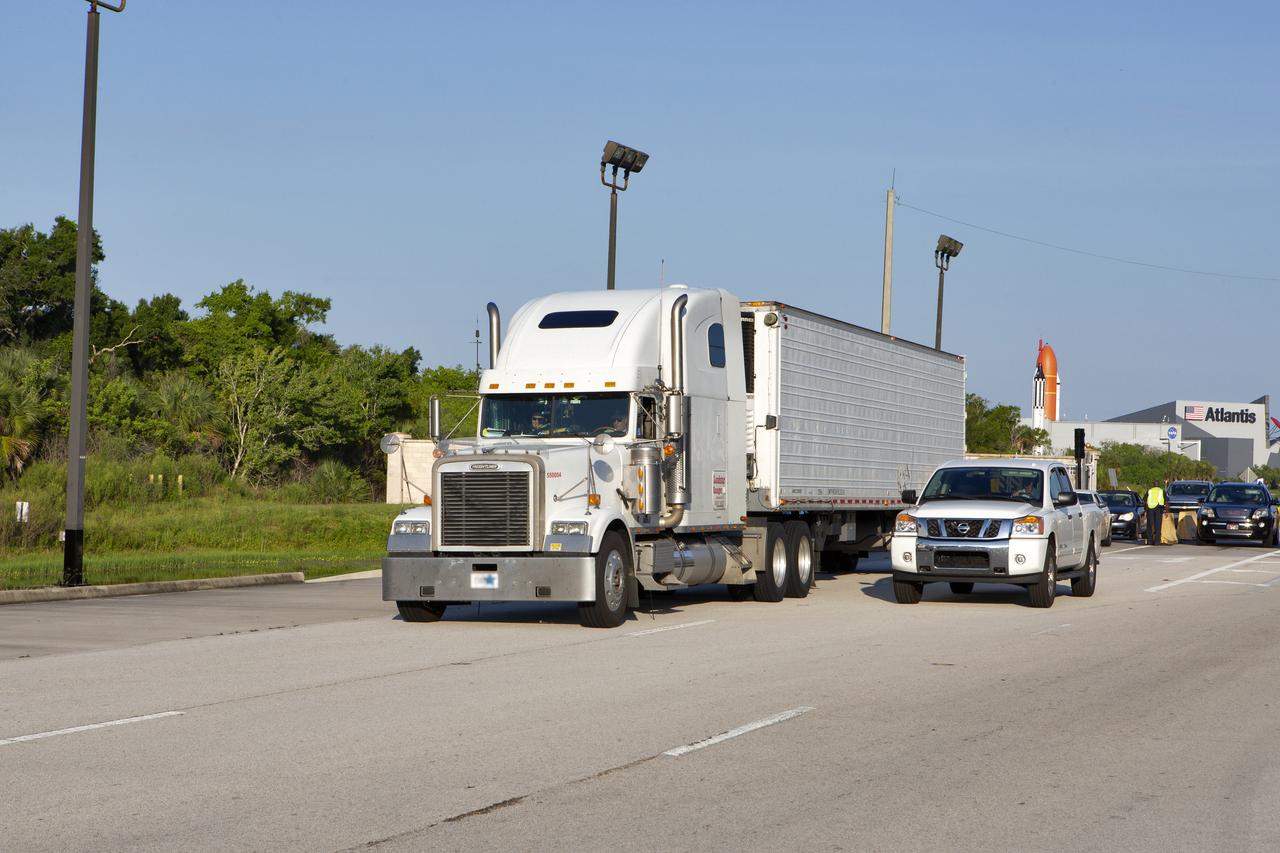
The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the entrance to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be delivered to the Launch Abort System Facility and integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. It is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
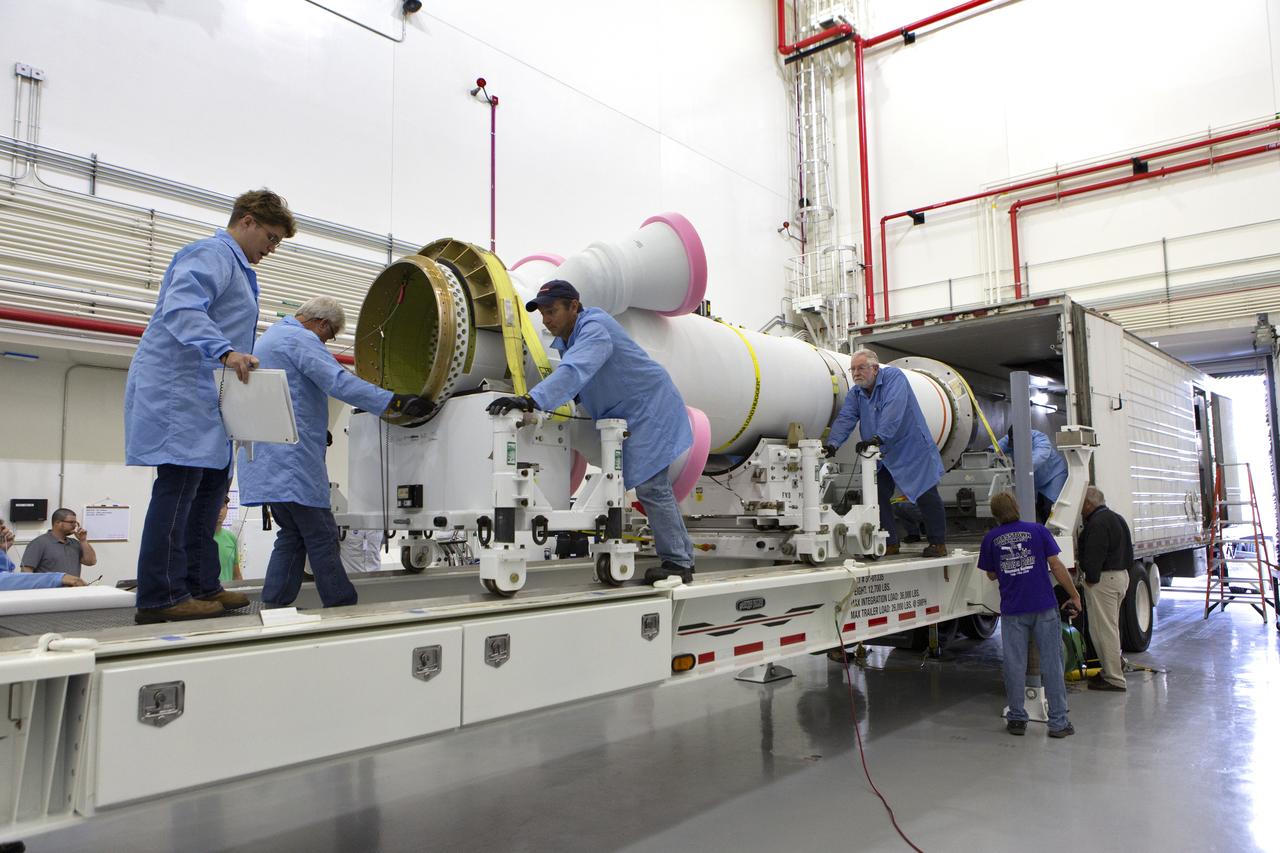

Workers offload the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
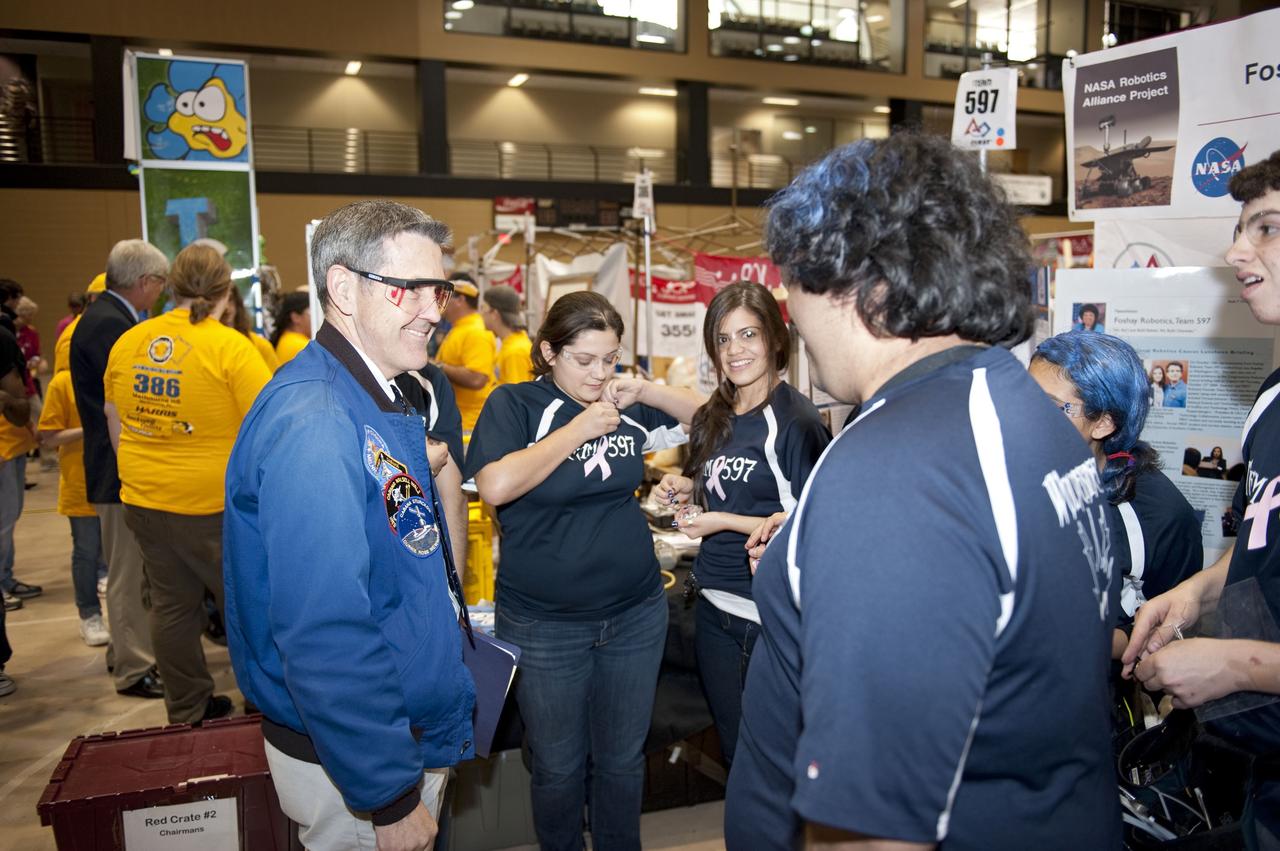

ORLANDO, Fla. – NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana talks to The Wolverines team at the regional FIRST robotics competition at the University of Central Florida in Orlando. The team is made up of students from the Foshay Learning Center located in Los Angeles. NASA is a sponsor of the team. About 60 high school teams took part in the competition called "For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology," or FIRST, in hopes of advancing to the national robotics championship. The team took home the Industrial Safety Award sponsored by Underwriters Laboratories. FIRST, founded in 1989, is a non-profit organization that designs accessible, innovative programs to build self-confidence, knowledge and life skills while motivating young people to pursue academic opportunities. The robotics competition challenges teams of high school students and their mentors to solve a common problem in a six-week timeframe using a standard kit of parts and a common set of rules. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
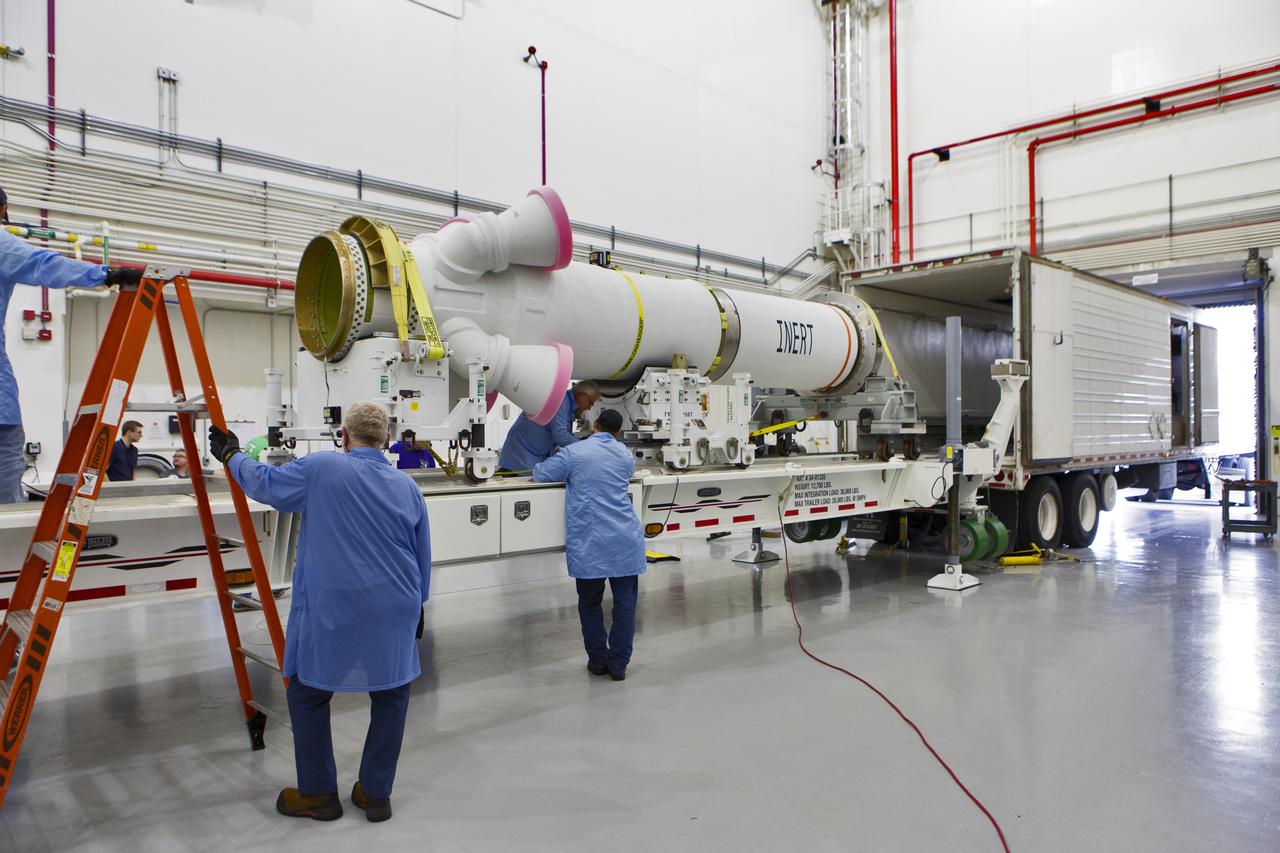

Workers begin checkouts of the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
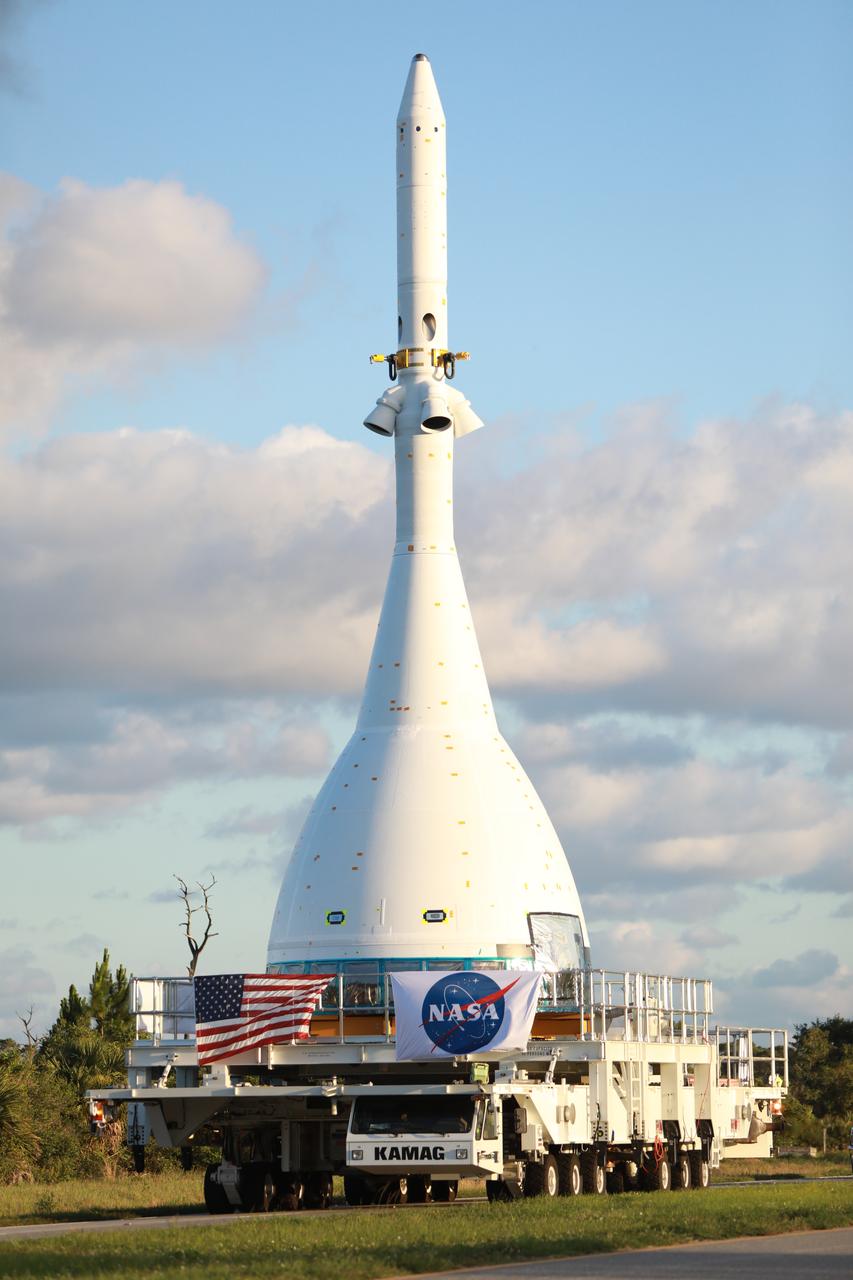

The vehicle for Orion’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is moved along a route from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on May 22, 2019, in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule away to demonstrate it can keep a future crew inside safe if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission is offloaded from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the entrance to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be delivered to the Launch Abort System Facility and integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. It is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
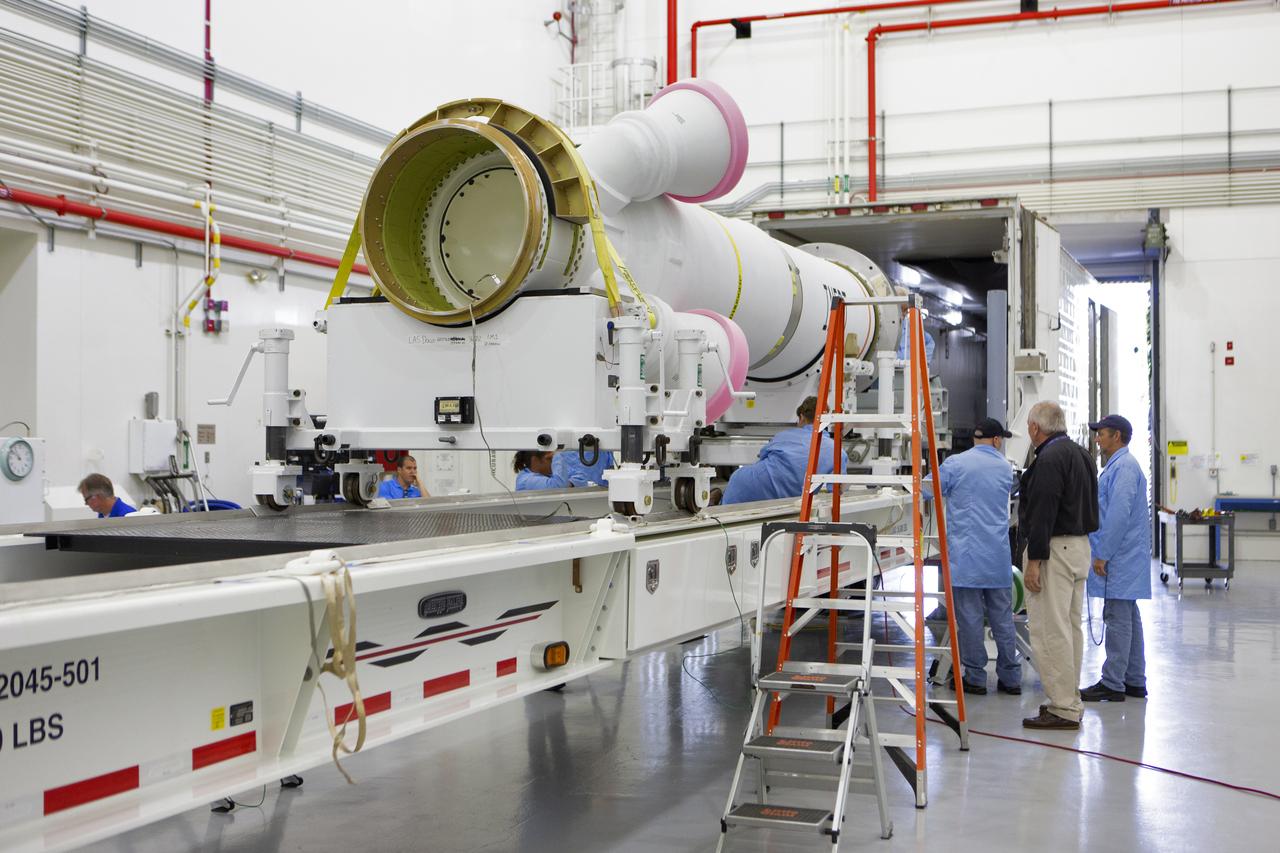

Workers help offload the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
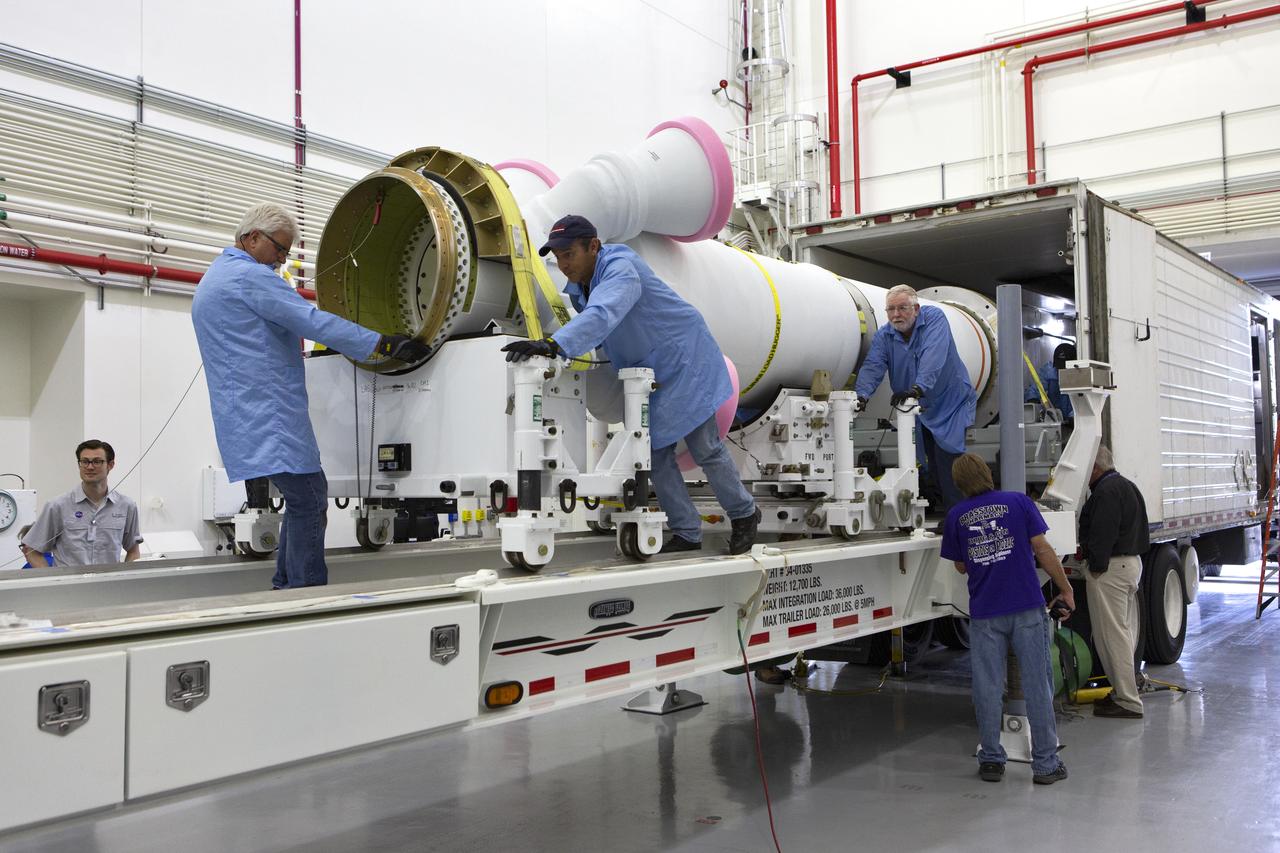

Workers offload the abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission from a heavy transport truck inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS). During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.

The abort motor for NASA’s Artemis 1 mission, secured in a heavy transport truck, arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 6, 2019. The abort motor, manufactured by Northrop Grumman, will be offloaded and moved into the LASF where it will be integrated with Orion subcomponents and prepared for Artemis 1. The abort motor is one of three motors located on the tower of the Launch Abort System (LAS). The LAS is designed to pull the Orion capsule and its crew away to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During Artemis 1, the uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy. Orion will embark on an approximately three-week mission that will take the spacecraft thousands of miles past the Moon. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
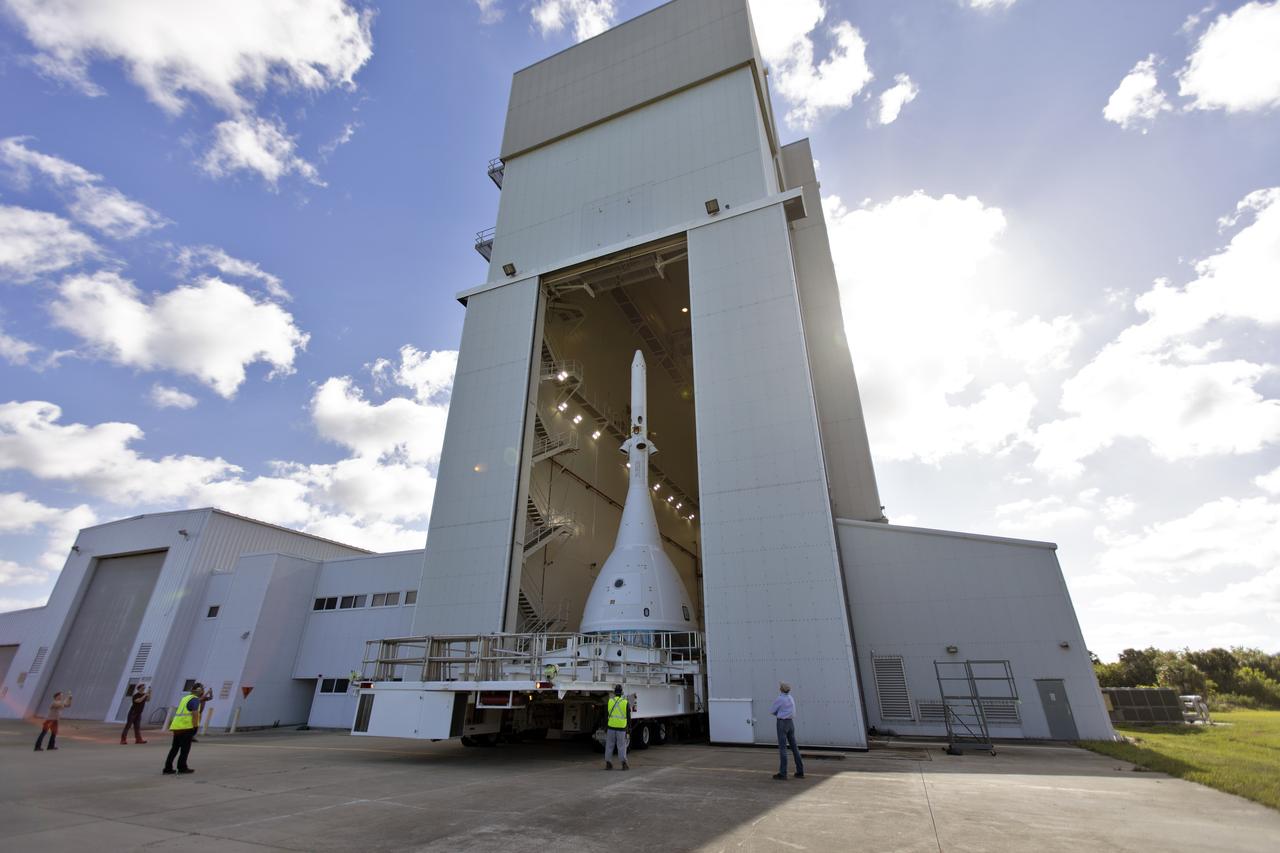

The vehicle for Orion’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test exits the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 22, 2019. The flight test article will make the 21.5 mile trek to Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for its launch this summer. During AA-2, a test version of Orion will launch on a booster to more than six miles in altitude, where Orion’s launch abort system will pull the capsule away to demonstrate it can keep a future crew inside safe if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System rocket. The AA-2 elements will be stacked together at the launch pad over the next several weeks. The launch is planned for July 2 and is a critical safety test that helps pave the way for Artemis missions near the Moon, and will enable astronauts to set foot on the lunar surface by 2024.

At a Sept. 26 all-hands meeting, NASA Marshall Space Flight Center Director Todd May highlights some of the key moments from Vice President Mike Pence's visit to Marshall Sept. 25. "I'd like to thank all the people that prepared for the vice president's visit. I think it was a great day for the center," said May. "We were able to talk to him about NASA's Space Launch System as well as some other projects. As the chairman of the U.S. Space Council, he is going to be very influential in space policy and I think this was a great opportunity for us." May also commented on the nomination of U.S. Rep. Jim Bridenstine, President Donald Trump's selection for NASA Administrator, and spoke about continuing to advance Marshall's Plan to Thrive – a strategic management agenda that focuses on human capital, organizational efficiency and bi-modal operations. Marshall Deputy Director Jody Singer updated the workforce on the results of the recent employee viewpoint survey. Singer also provided an overview of NASA's outreach during the Aug. 21 total solar eclipse, mentoring opportunities and the activities associated with the ongoing Safety Week 2017.
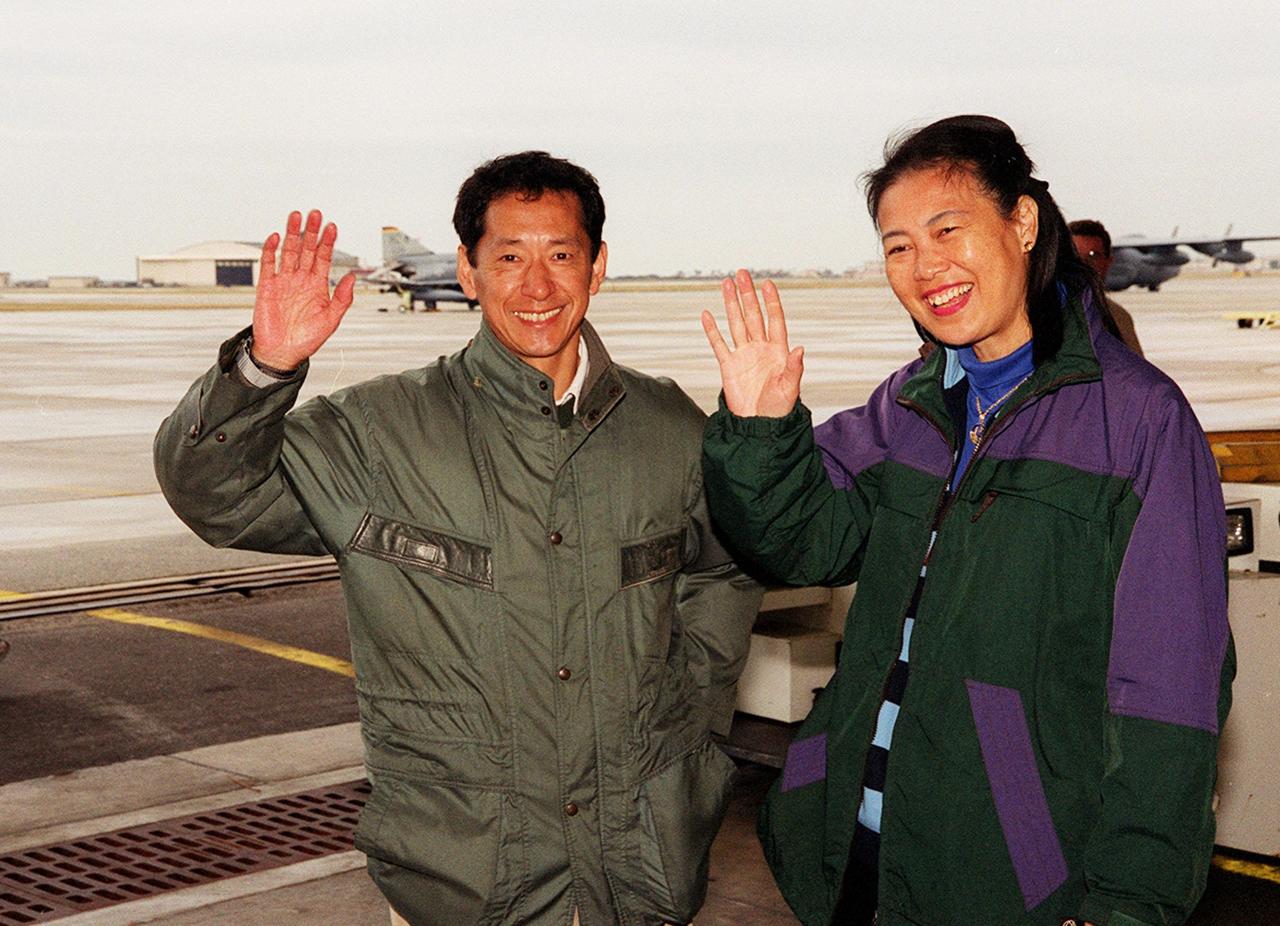

STS-99 Mission Specialist Mamoru Mohri of Japan and his wife, Akiko, wave before their departure from Patrick Air Force Base and return to Houston. With the postponement of the launch of STS-99 on Jan. 31, the crew have an opportunity for more training and time with their families. During the launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety

On the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 crew members Mission Specialists Gerhard Thiele and Janice Voss, Commander Kevin Kregel and Pilot Dominic Gorie briefly talk to the media about their imminent departure to Houston. Kregel and Gorie will be piloting T-38 jets with Voss and Thiele as passengers. During the Jan. 31 launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. The postponed launch gives the crew an opportunity for more training and time with their families. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
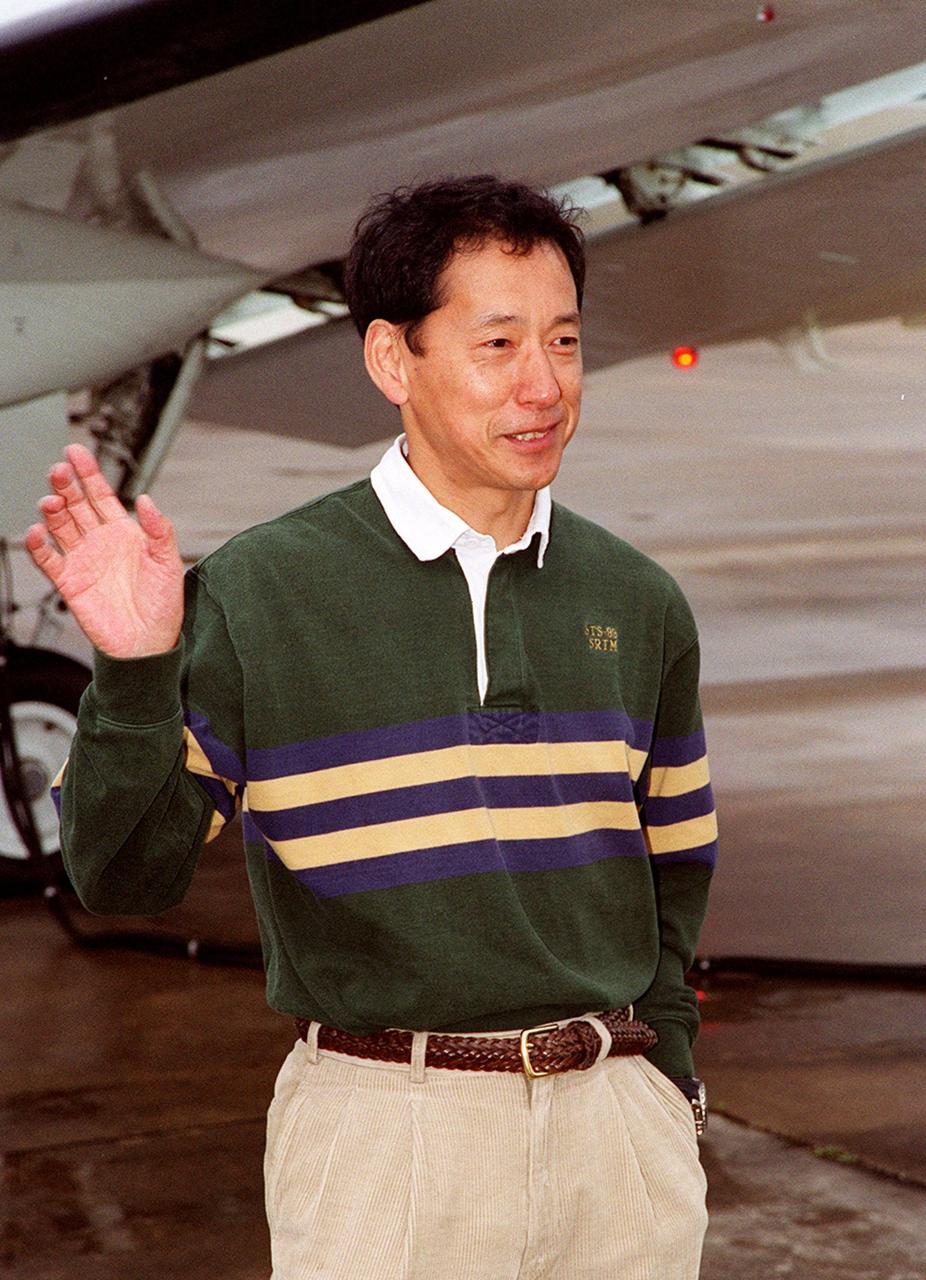

STS-99 Mission Specialist Mamoru Mohri of Japan waves before his departure from Patrick Air Force Base and return to Houston. With the postponement of the launch of STS-99 on Jan. 31, the crew have an opportunity for more training and time with their families. During the launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
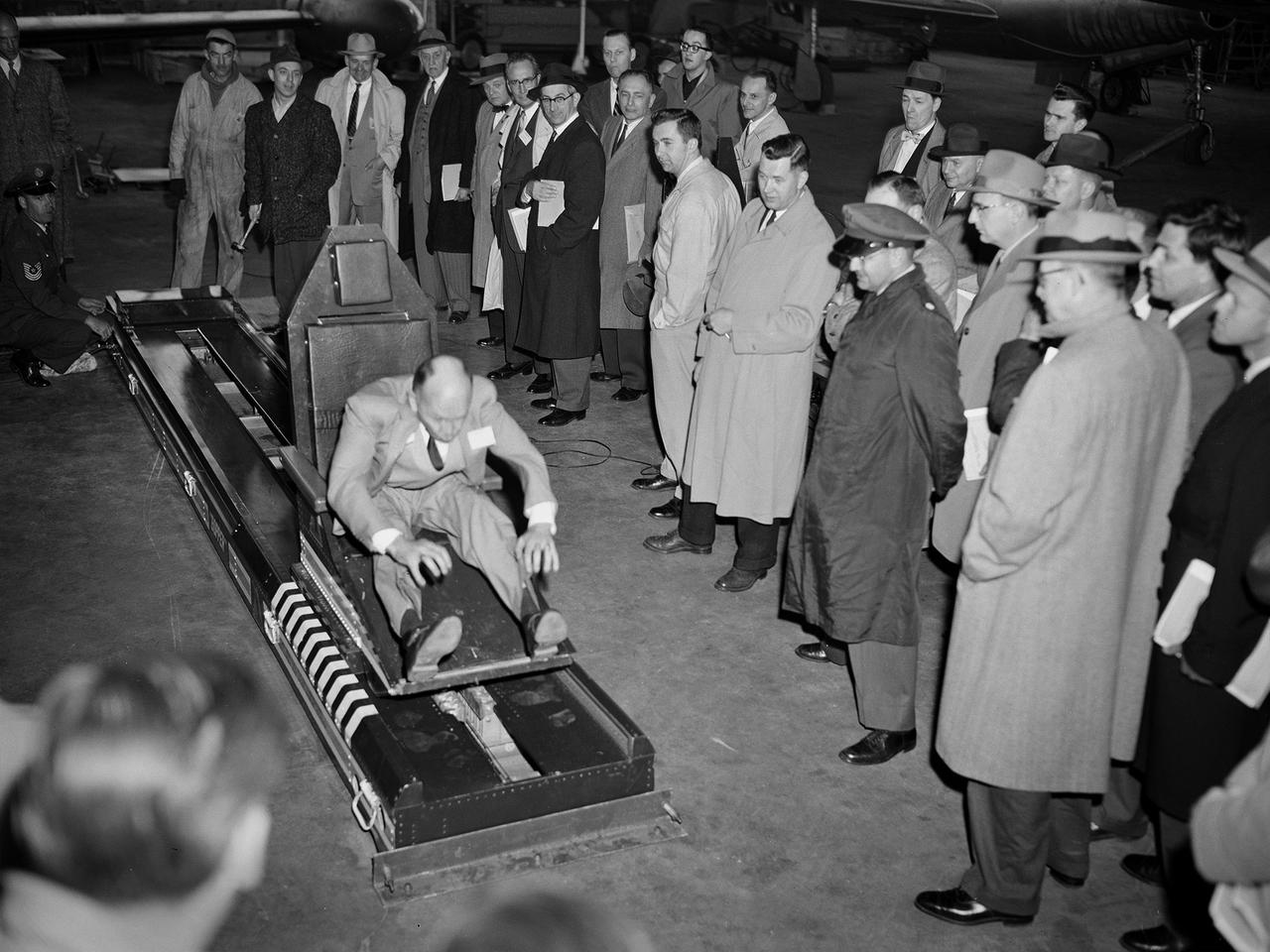

Howard Hasbrook volunteers for a demonstration of a scaled-down version of Lieutenant Colonel John Stapp’s rocket sled set up in the hangar at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In 1945 Stapp, an Air Force medical doctor, volunteered to participate in a deceleration program to study the human body’s tolerance to aircraft crash forces. A 1500-pound sled powered by rockets was installed in 1947 on a section of railroad track in the California desert. Stapp participated in 29 experiments over the next seven years and broke land and deceleration records. These tests studied the effects of acceleration, G-force, deceleration, and wind blast on humans. Stapp suffered broken bones and retinal hemorrhages, but suffered no permanent damage. NACA Lewis was conducting a series of crash impact studies in the mid-1950s using dummies in actual aircraft. Irving Pinkel, the director of the program, and Stapp became friends through their mutual interest in this field. In April 1956 Stapp visited the Cleveland lab to give a talk to the local section of the American Rocket Society that discussed issues relating to the escape of pilots from the cockpit of supersonic jet aircraft. That same week, NACA Lewis’ Pinkel, Gerard Pesman, Merritt Preston, and Dugald Black received the annual Laura Taber Barbour Air Safety Award for their work on the Crash Fire Program. Black and Preston are visible in the crowd in this photograph.
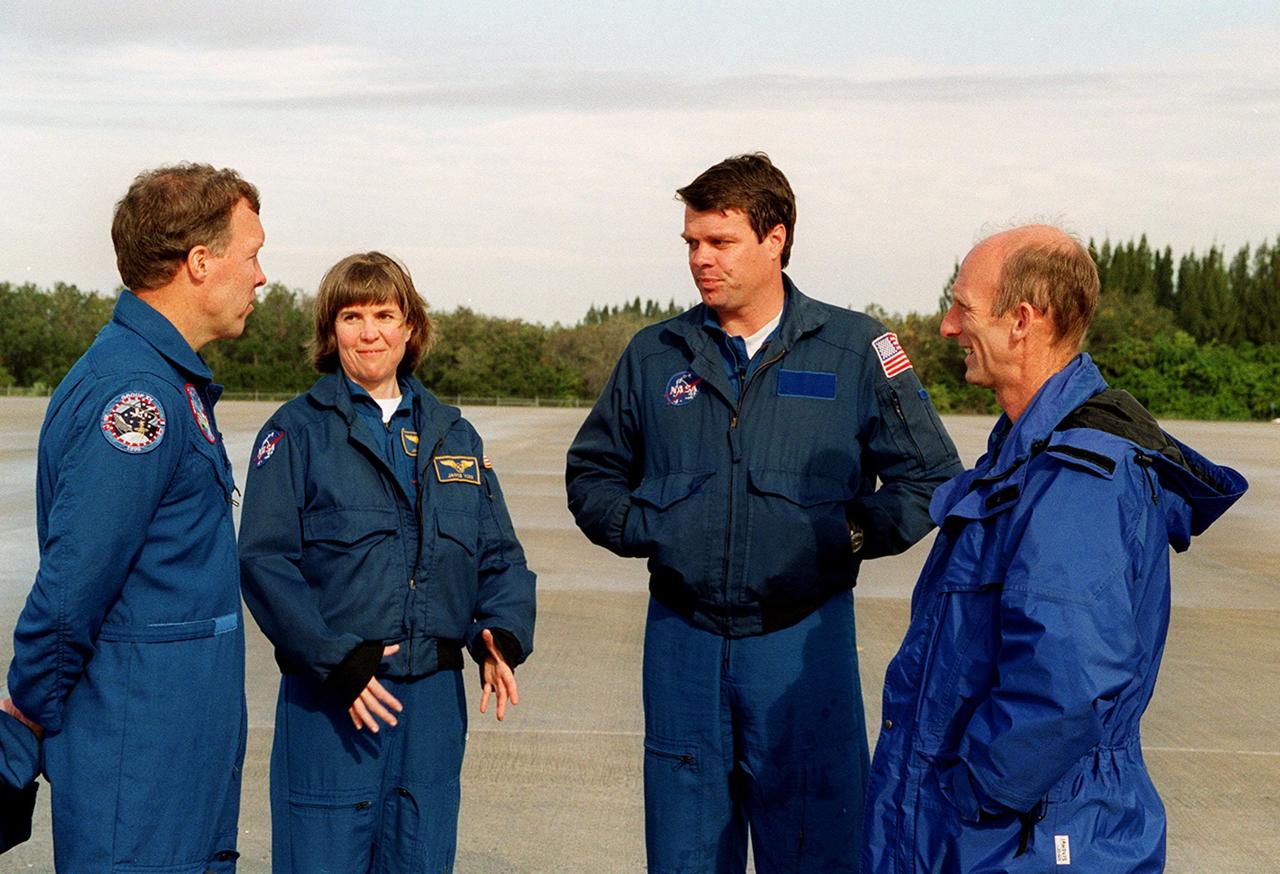

On the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 crew members Pilot Dominic Gorie, Mission Specialist Janice Voss, Commander Kevin Kregel and Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele discuss departure plans to Houston. Kregel and Gorie will be piloting T-38 jets with Voss and Thiele as passengers. During the Jan. 31 launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto latenext week pending availability of the Eastern Range. The postponed launch gives the crew an opportunity for more training and time with their families. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
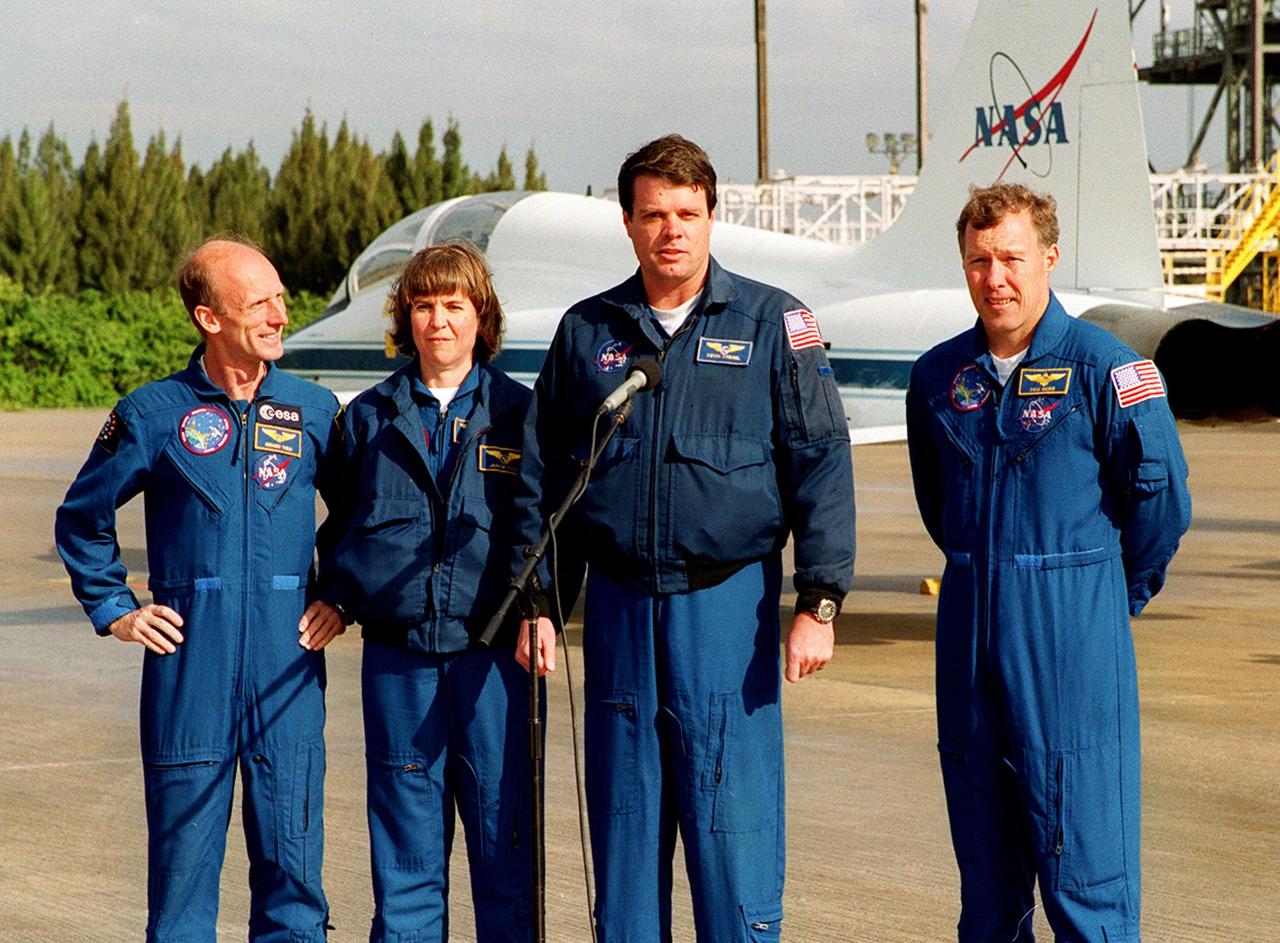

On the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 crew members Mission Specialists Gerhard Thiele and Janice Voss, Commander Kevin Kregel and Pilot Dominic Gorie briefly talk to the media about their imminent departure to Houston. Kregel and Gorie will be piloting T-38 jets with Voss and Thiele as passengers. During the Jan. 31 launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. The postponed launch gives the crew an opportunity for more training and time with their families. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
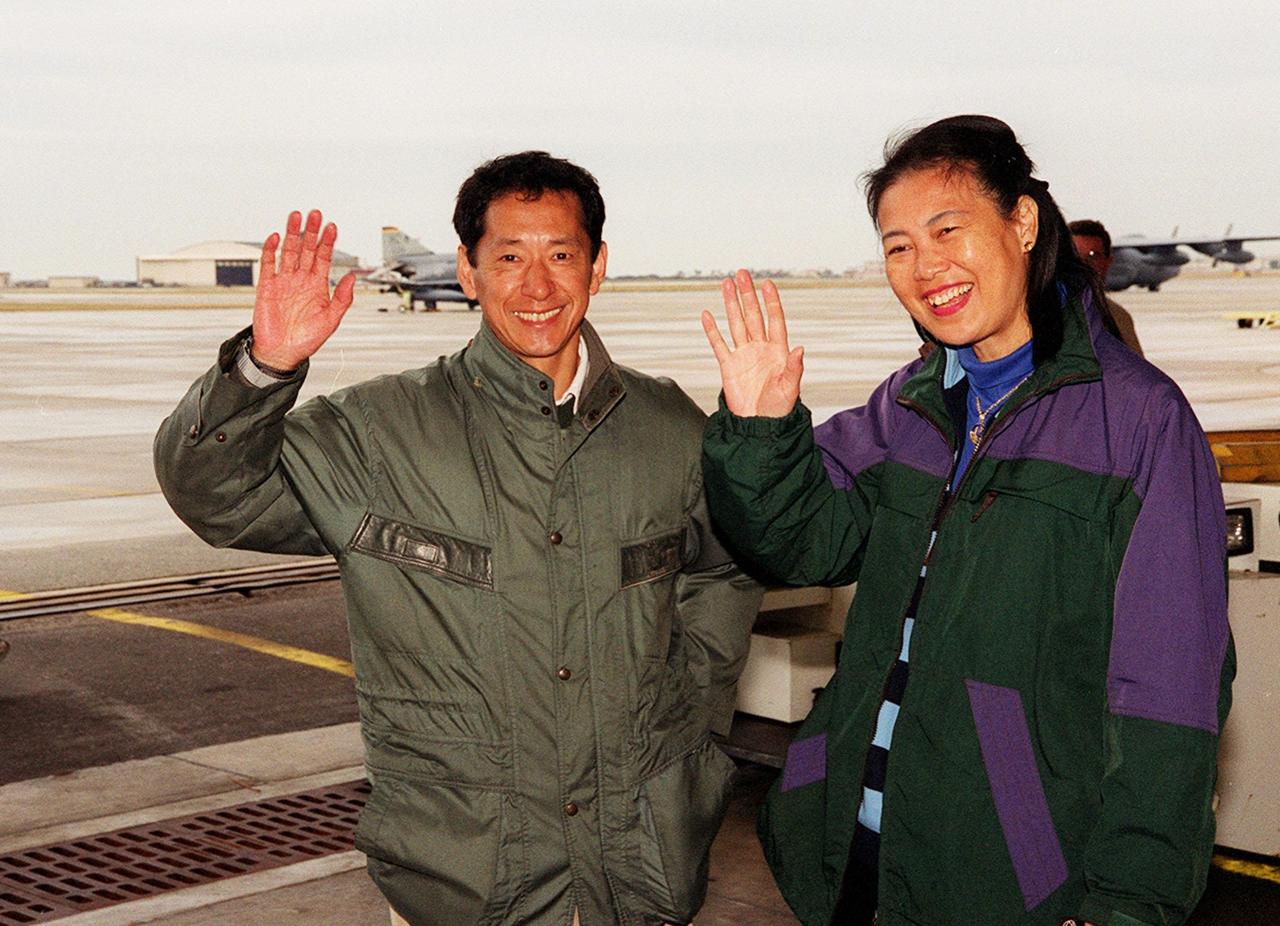

STS-99 Mission Specialist Mamoru Mohri of Japan and his wife, Akiko, wave before their departure from Patrick Air Force Base and return to Houston. With the postponement of the launch of STS-99 on Jan. 31, the crew have an opportunity for more training and time with their families. During the launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
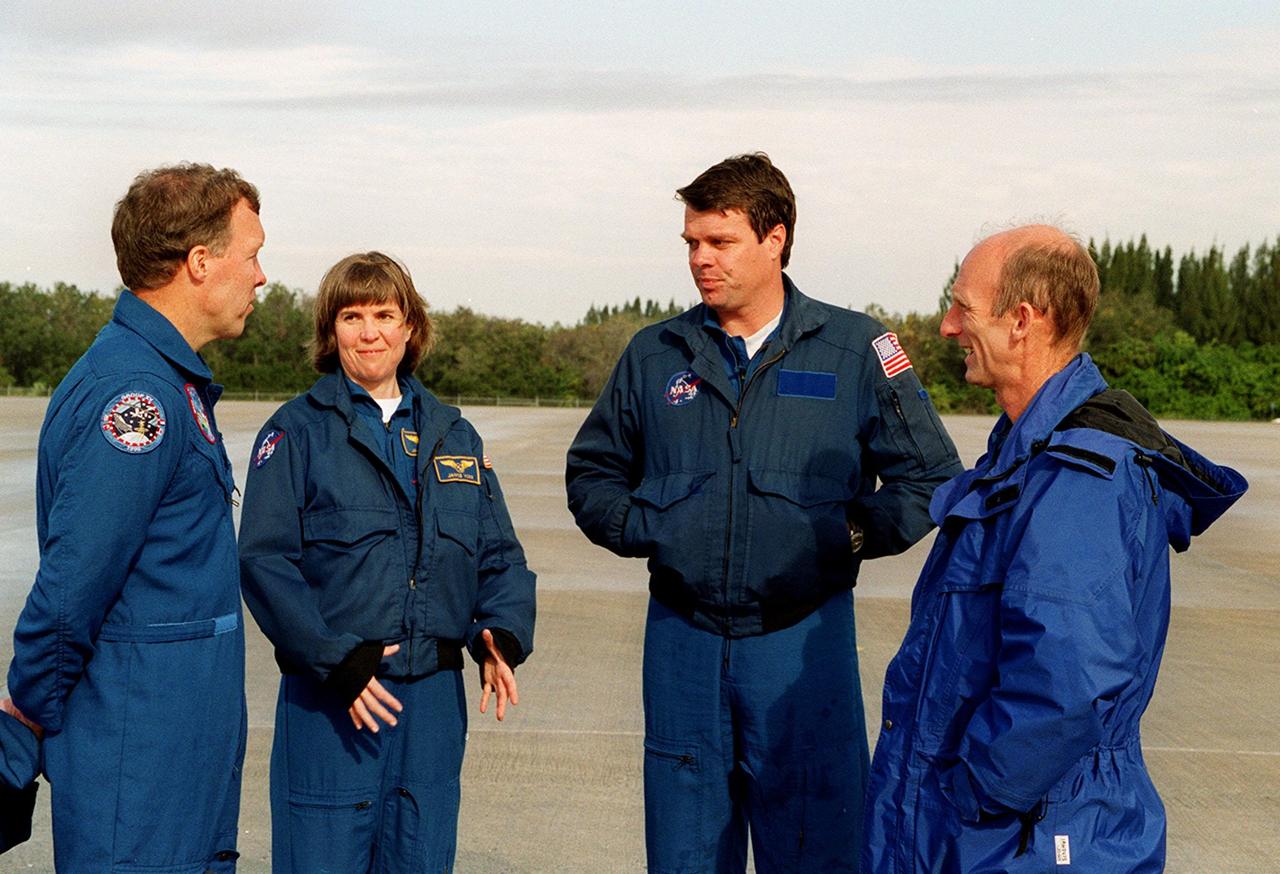

On the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 crew members Pilot Dominic Gorie, Mission Specialist Janice Voss, Commander Kevin Kregel and Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele discuss departure plans to Houston. Kregel and Gorie will be piloting T-38 jets with Voss and Thiele as passengers. During the Jan. 31 launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto latenext week pending availability of the Eastern Range. The postponed launch gives the crew an opportunity for more training and time with their families. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
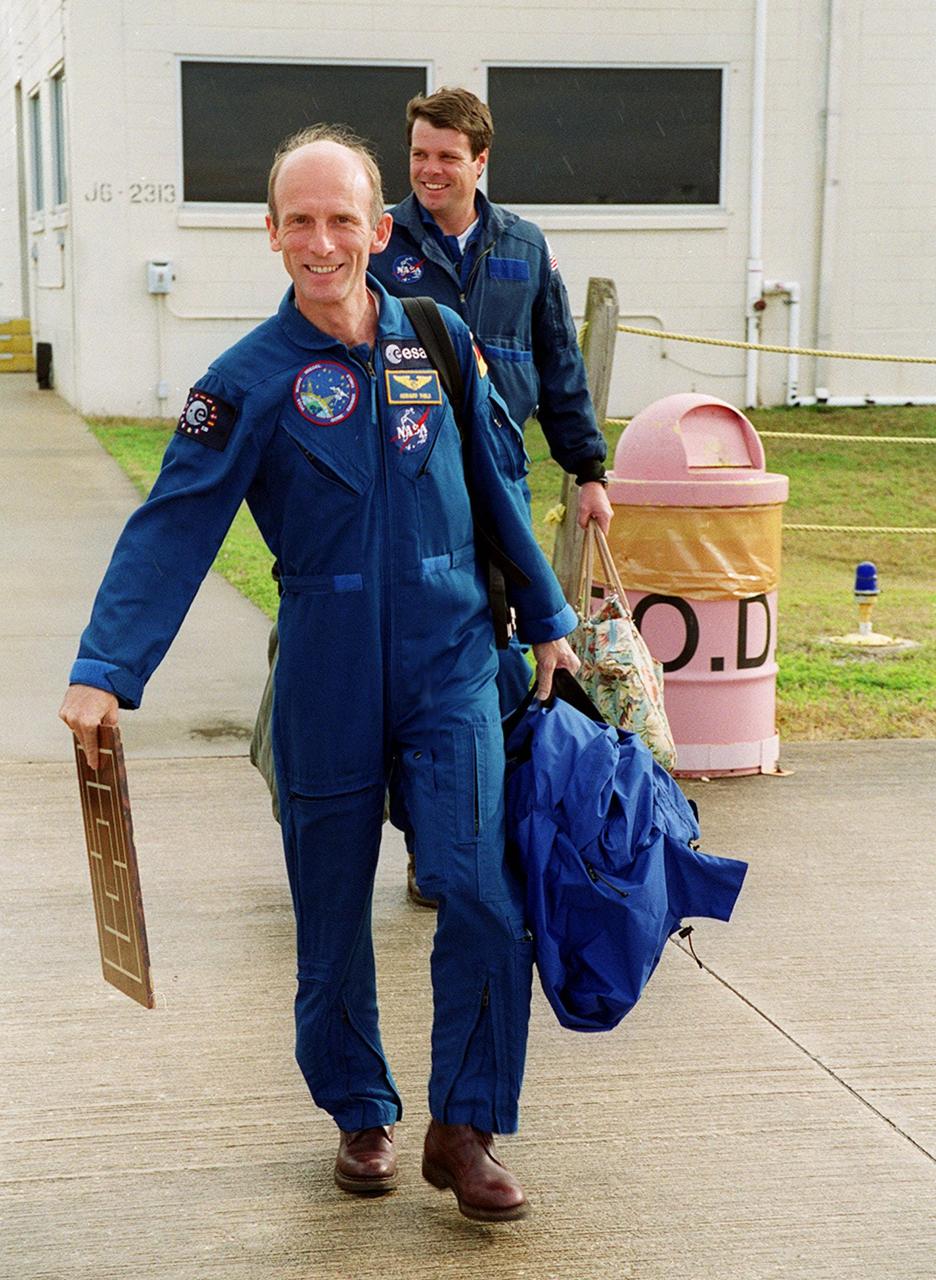

STS-99 Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele (foreground) and Commander Kevin Kregel make their way to the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility for a return flight to Houston. During the Jan. 31 launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. The postponed launch gives the crew an opportunity for more training and time with their families. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
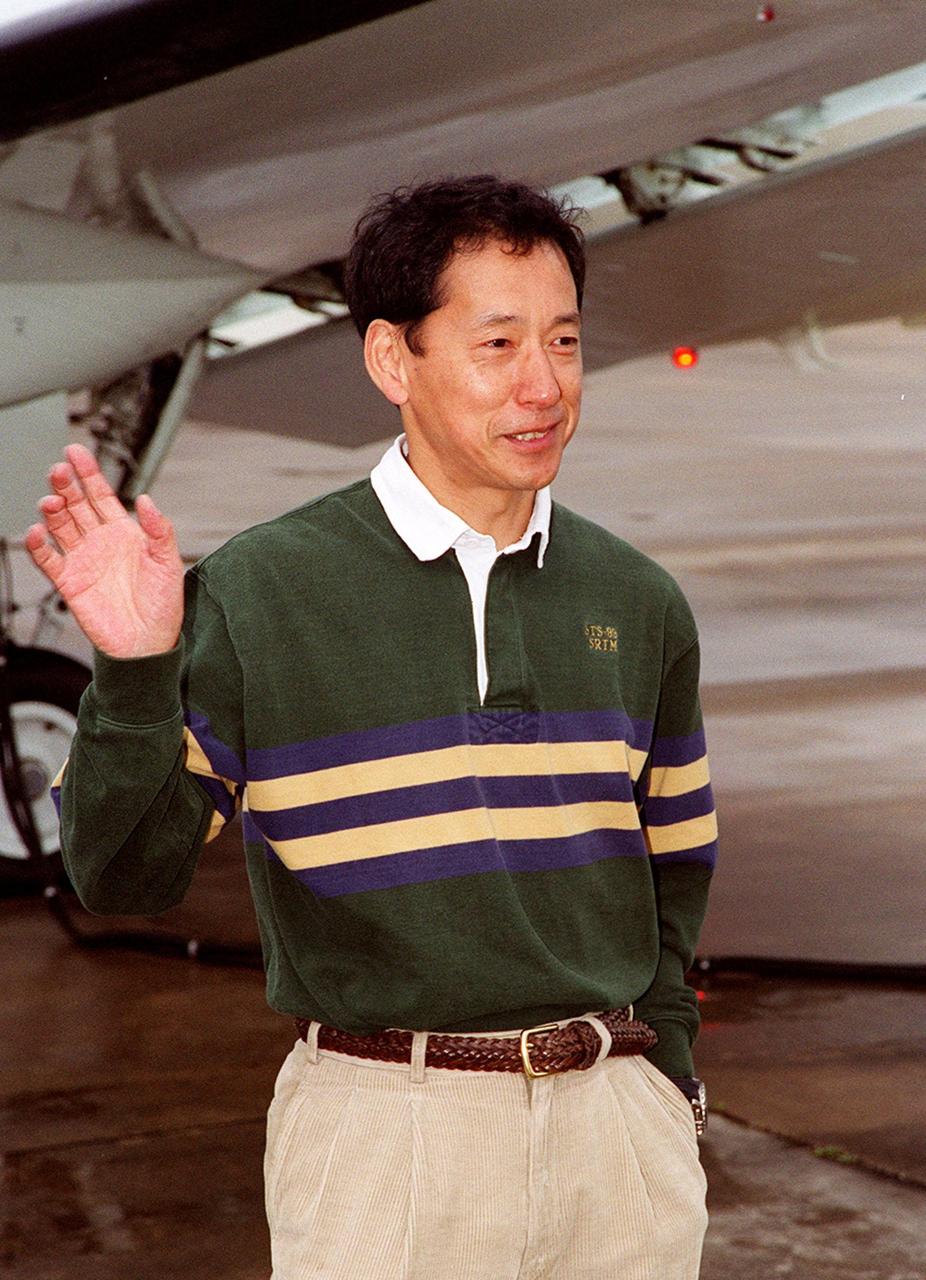

STS-99 Mission Specialist Mamoru Mohri of Japan waves before his departure from Patrick Air Force Base and return to Houston. With the postponement of the launch of STS-99 on Jan. 31, the crew have an opportunity for more training and time with their families. During the launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
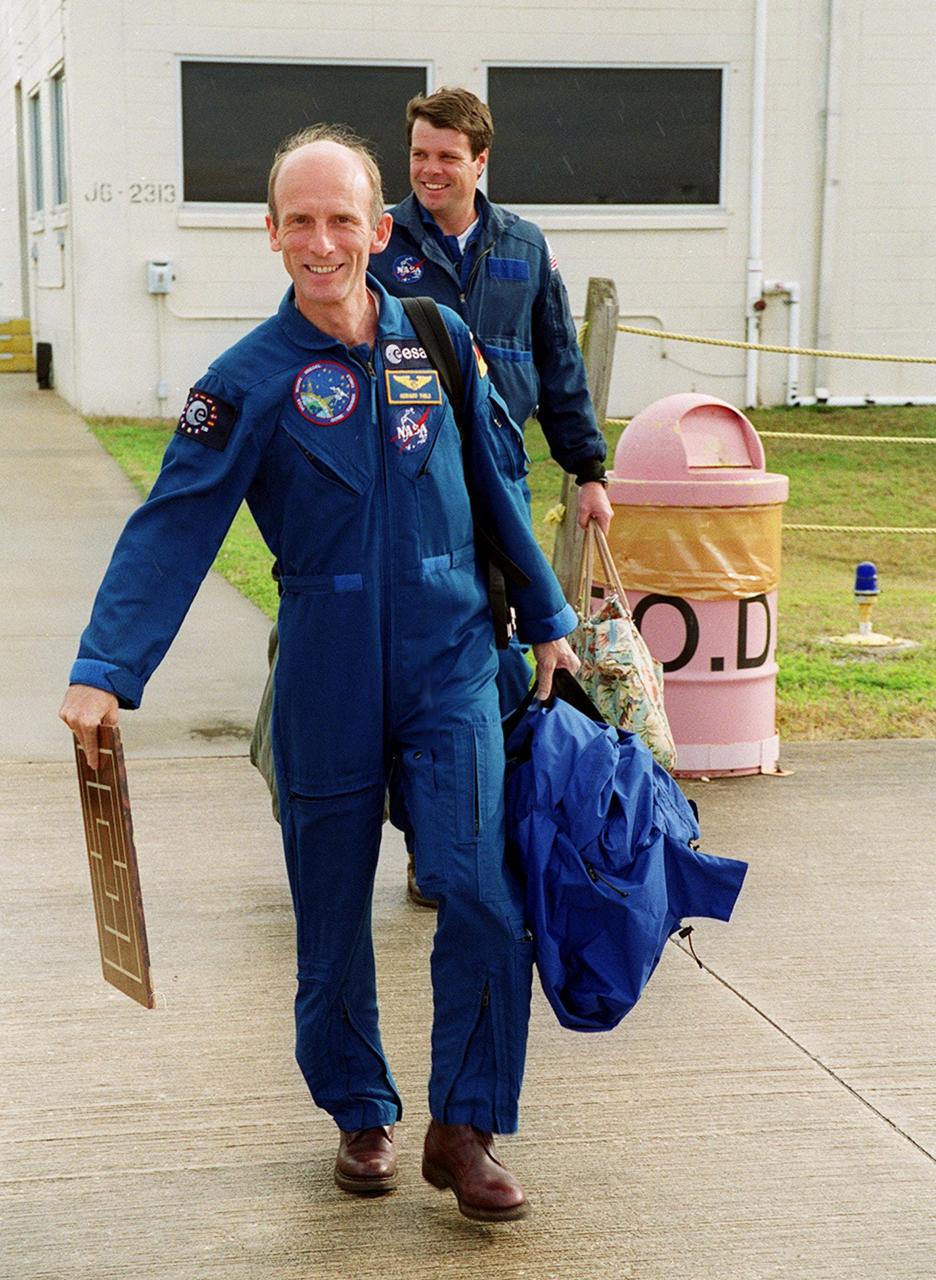

STS-99 Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele (foreground) and Commander Kevin Kregel make their way to the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility for a return flight to Houston. During the Jan. 31 launch countdown, Endeavour's enhanced master events controller (E-MEC) No. 2 failed a standard preflight test. Launch was postponed and Shuttle managers decided to replace the E-MEC located in the orbiter's aft compartment. Launch controllers will be in a position to begin the STS-99 countdown the morning of Feb. 6 and ready to support a launch midto late next week pending availability of the Eastern Range. The postponed launch gives the crew an opportunity for more training and time with their families. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, it will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety
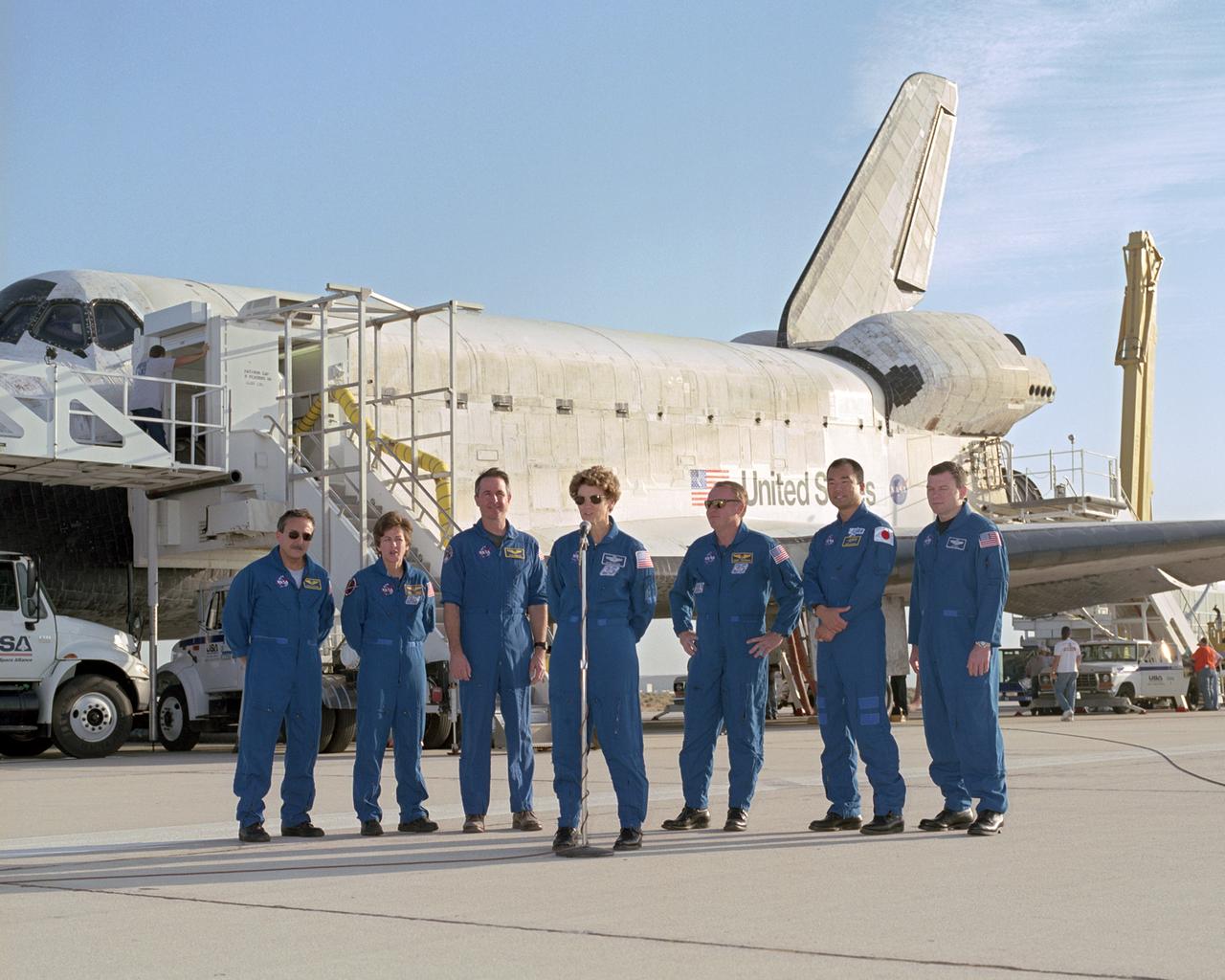

The crew of Space Shuttle mission STS-114 gathered for a press brief following landing at Edwards Air Force Base, California, 5:11 am, August 9, 2005. Left to right: Mission Specialists Charles Camarda, Wendy Lawrence and Stephen Robinson, Commander Eileen Collins at microphone, Mission Specialists Andrew Thomas and Soichi Noguchi, and Pilot James Kelly. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
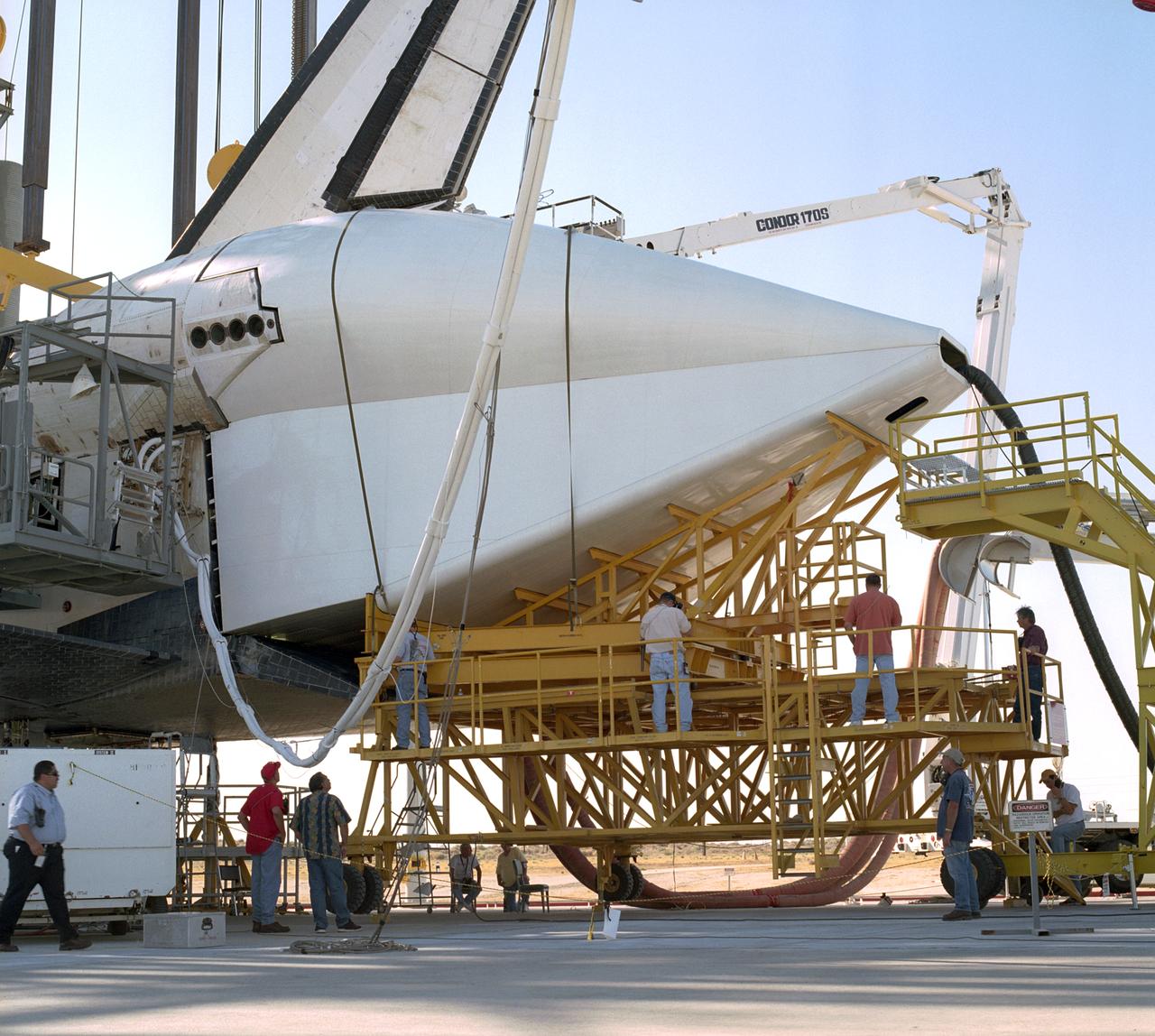

Technicians attach the tail cone, which helps reduce aerodynamic drag and turbulence during its ferry flight, to the Space Shuttle Discovery in preparation for its return to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After the tail-cone is installed, Discovery will be mounted on NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, for the return flight. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
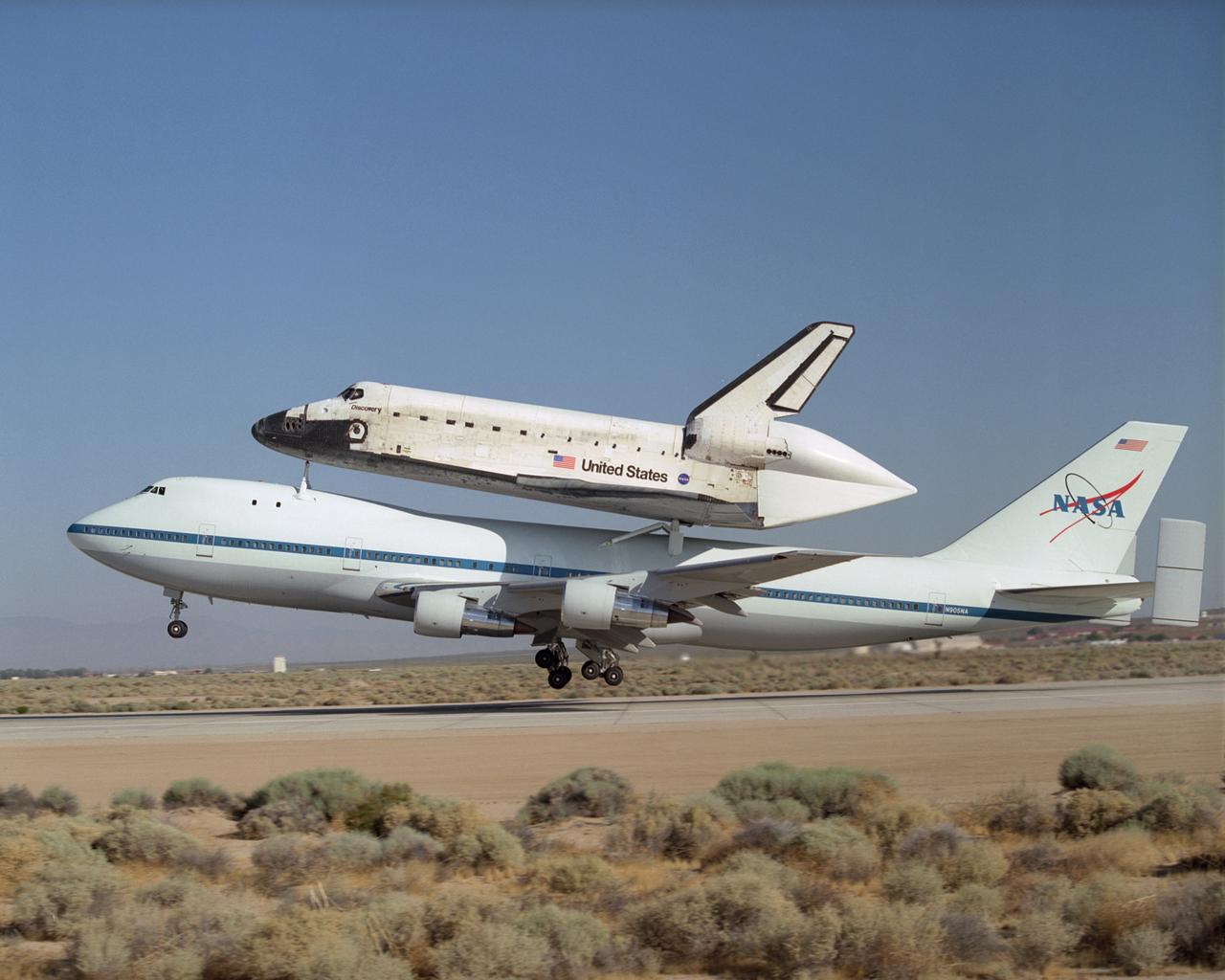

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Discovery on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
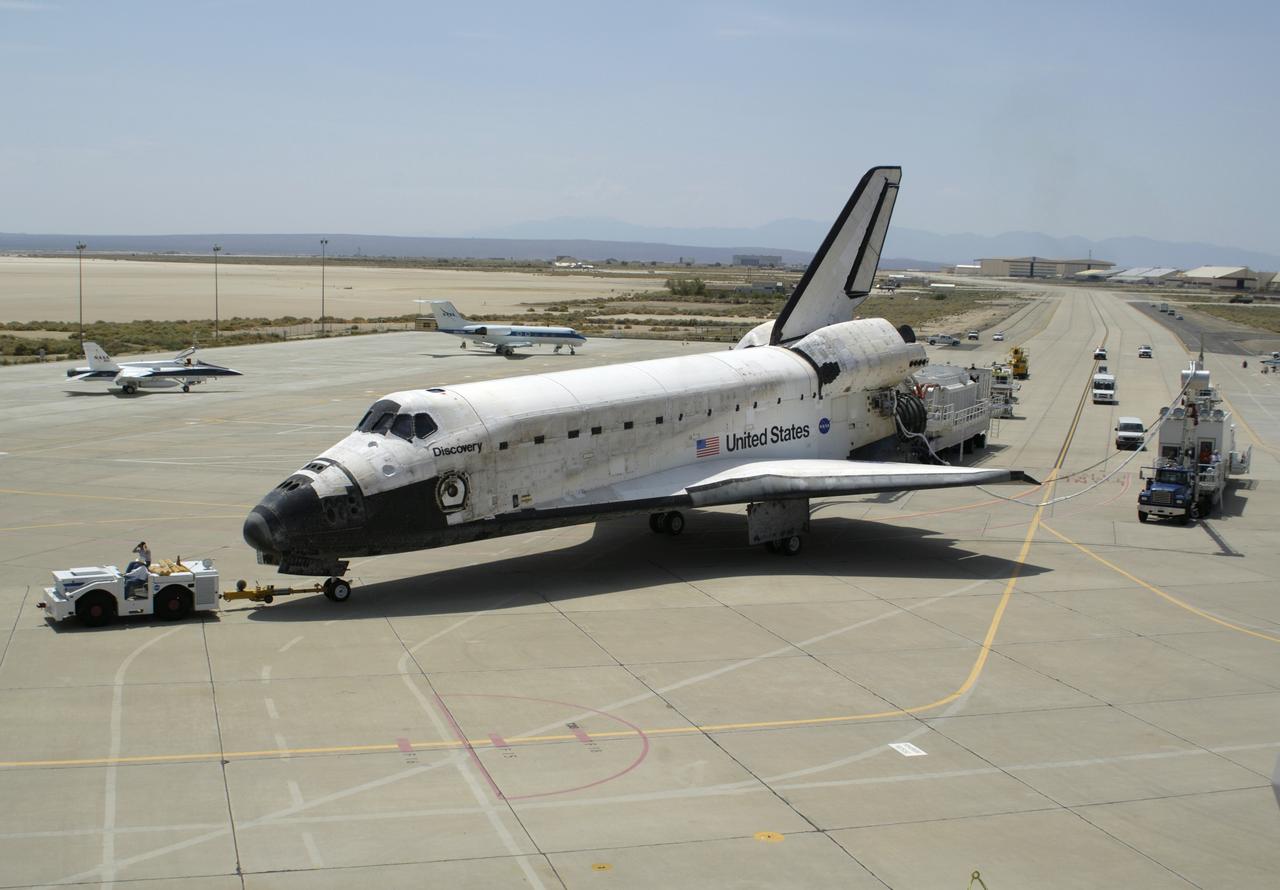

The Space Shuttle Discovery, accompanied by a convoy of recovery vehicles, is towed up the taxiway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, California, following its landing on August 9, 2005. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
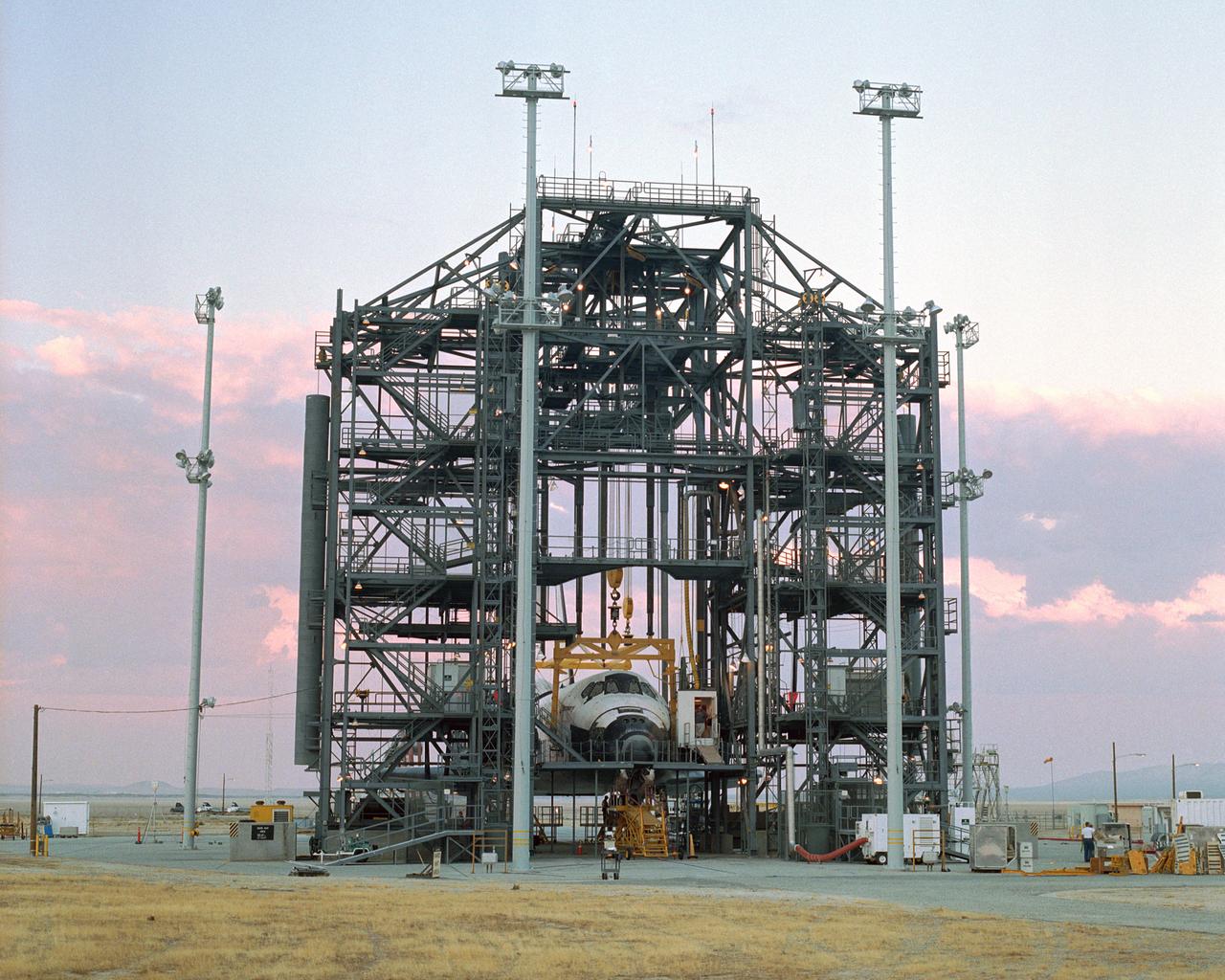
The sun sets on the Space Shuttle Discovery during post-flight processing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD), following its landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
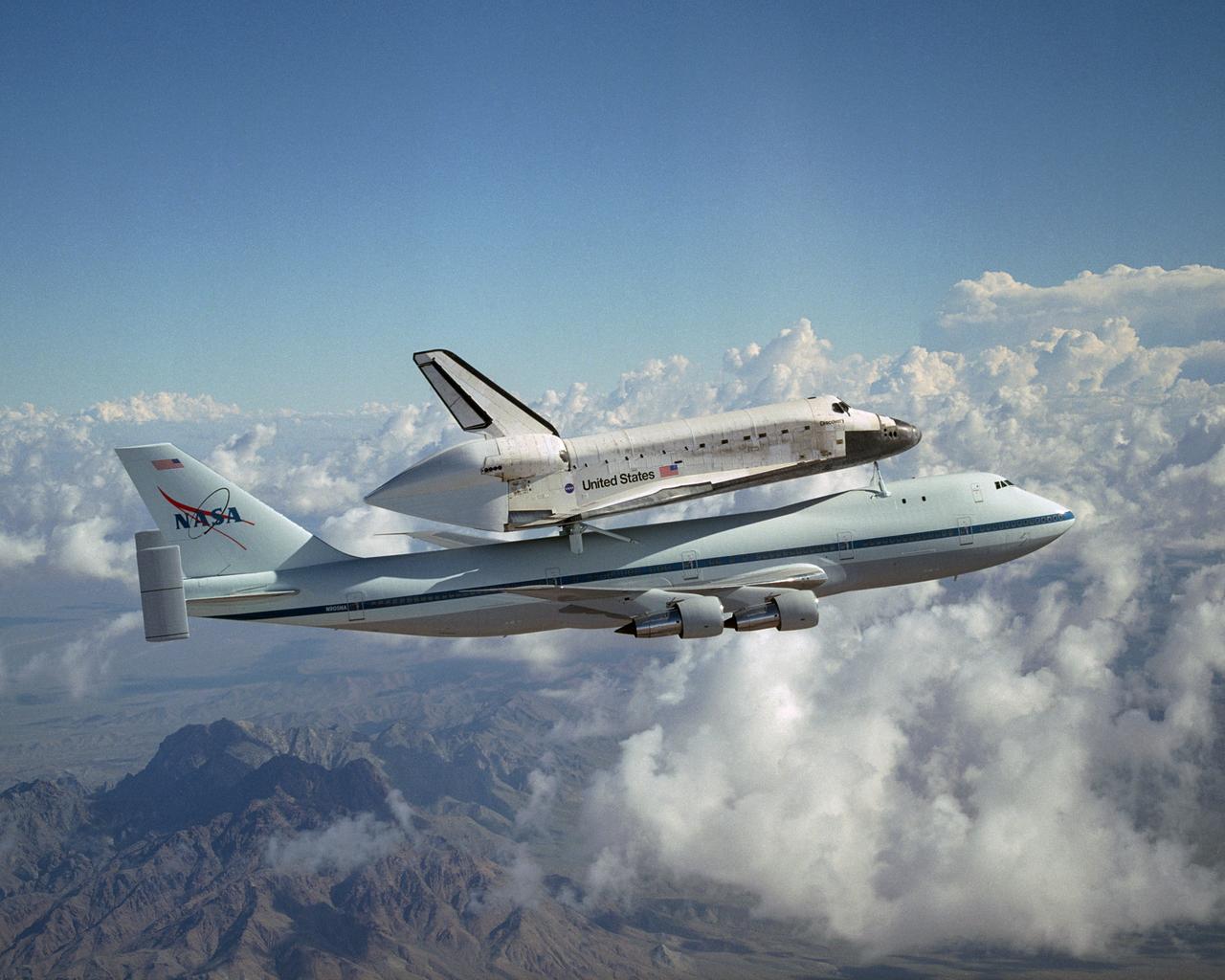

The Space Shuttle Discovery hitched a ride on NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft for the flight from the Dryden Flight Research Center in California, to Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on August 19, 2005. The cross-country ferry flight to return Discovery to Florida after it's landing in California will take two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
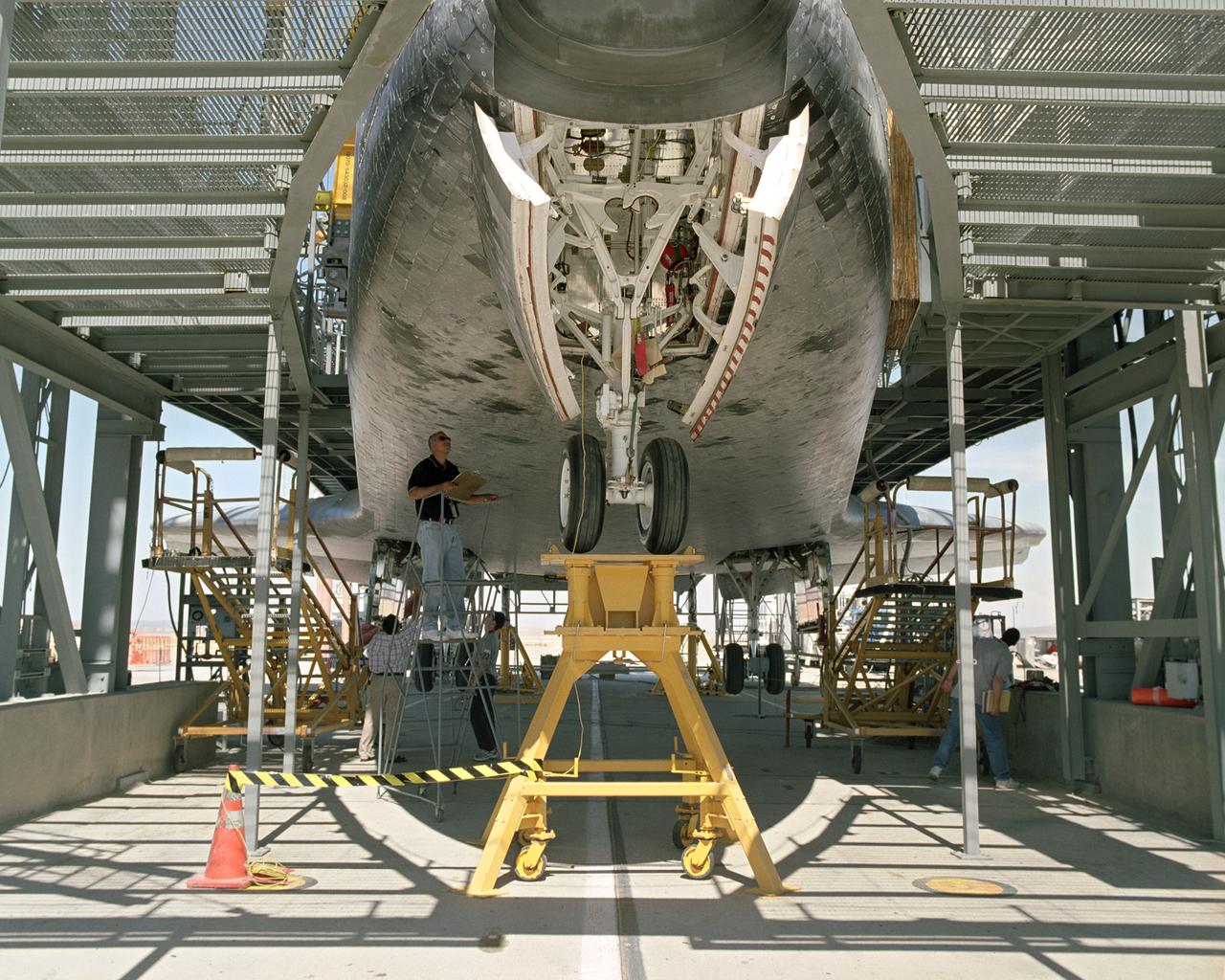

The Space Shuttle Discovery receives post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD), following its landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, August 9, 2005. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
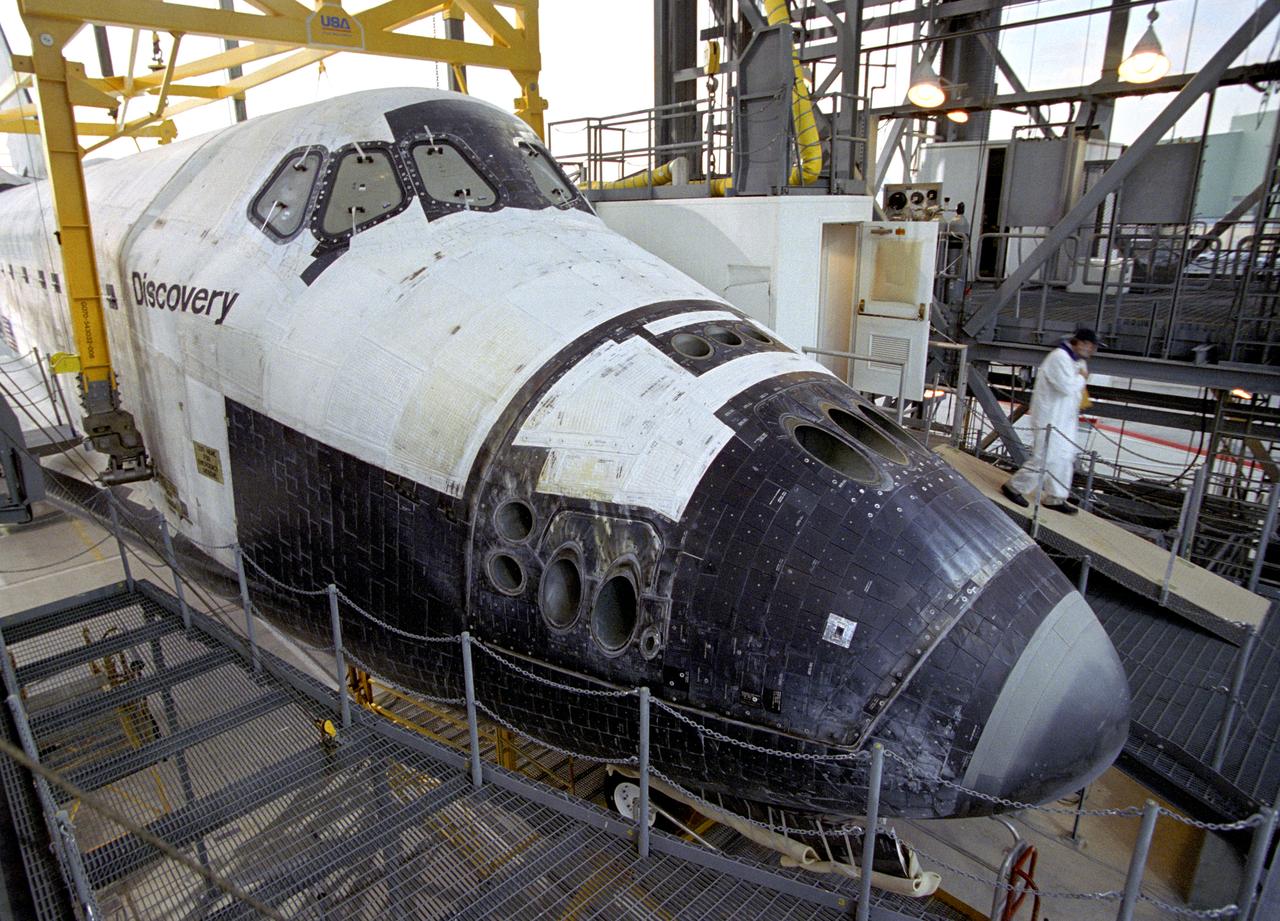

A technician leaves the 'white room', the access point for entering the Space Shuttle Discovery during post-flight processing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
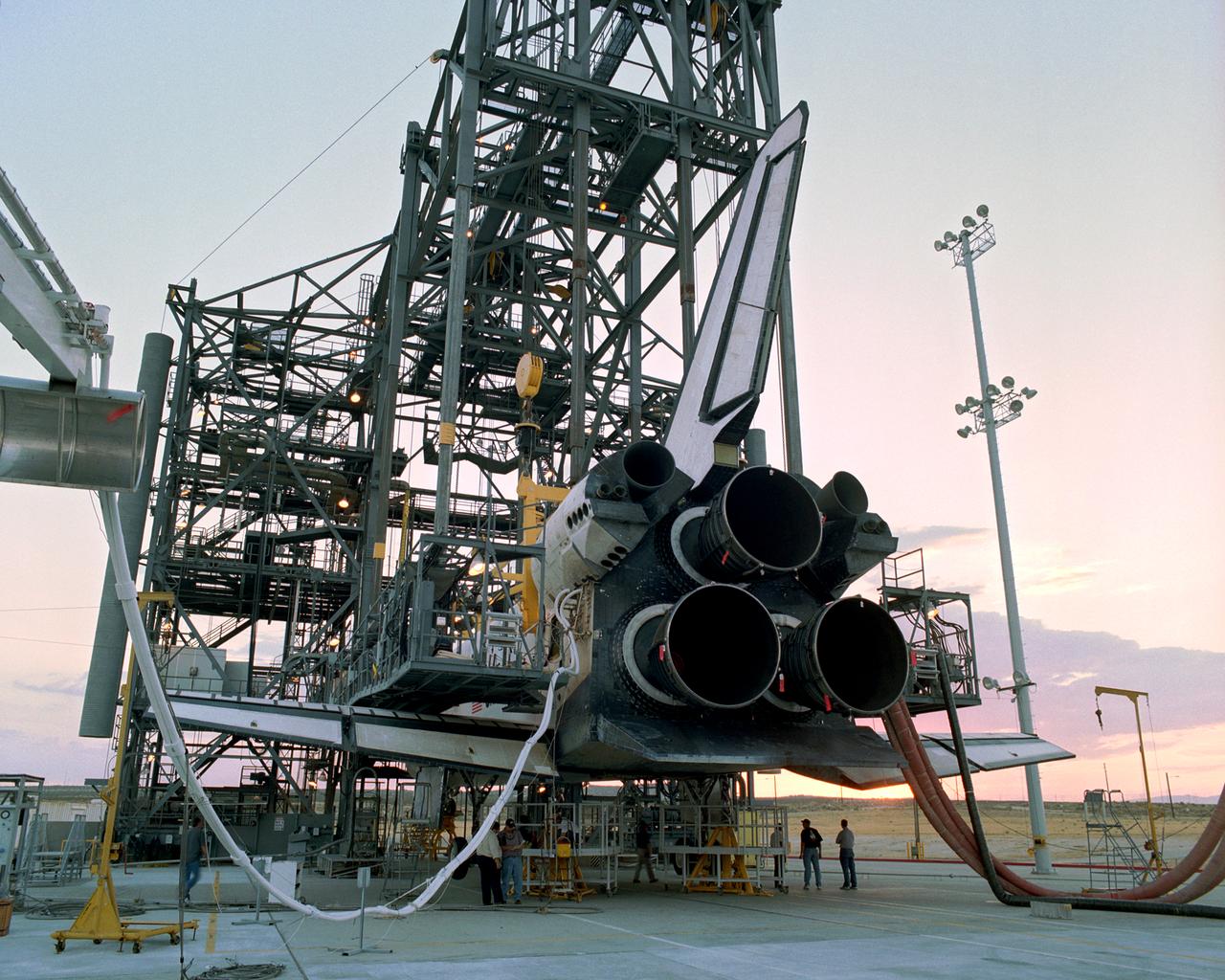
The sun sets on the Space Shuttle Discovery during post-flight processing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD), following its landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
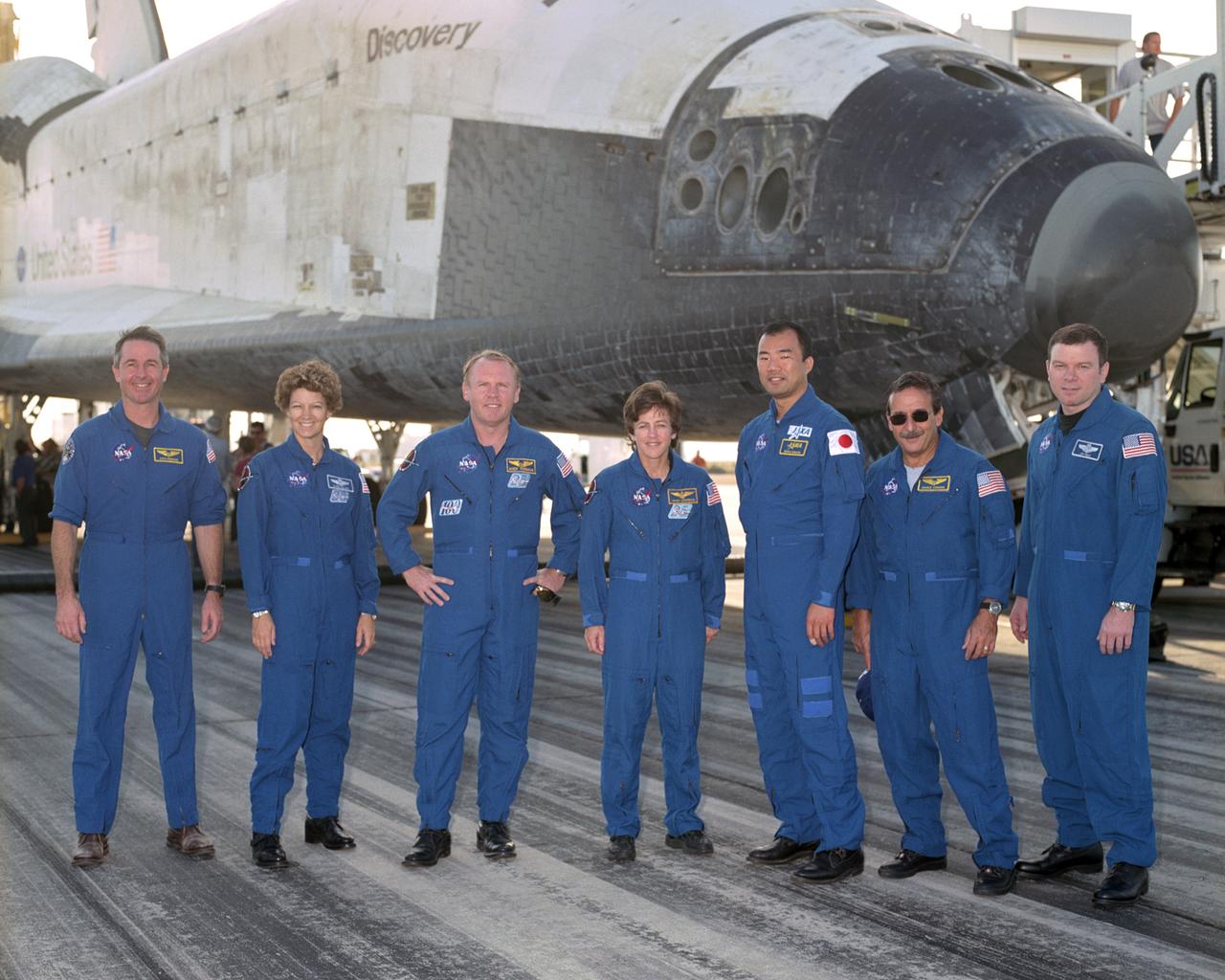

The crew of Space Shuttle mission STS-114 gathered in front of the shuttle Discovery following landing at Edwards Air Force Base, California, August 9, 2005. From left to right: Mission Specialist Stephen Robinson, Commander Eileen Collins, Mission Specialists Andrew Thomas, Wendy Lawrence, Soichi Noguchi and Charles Camarda, and Pilot James Kelly. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
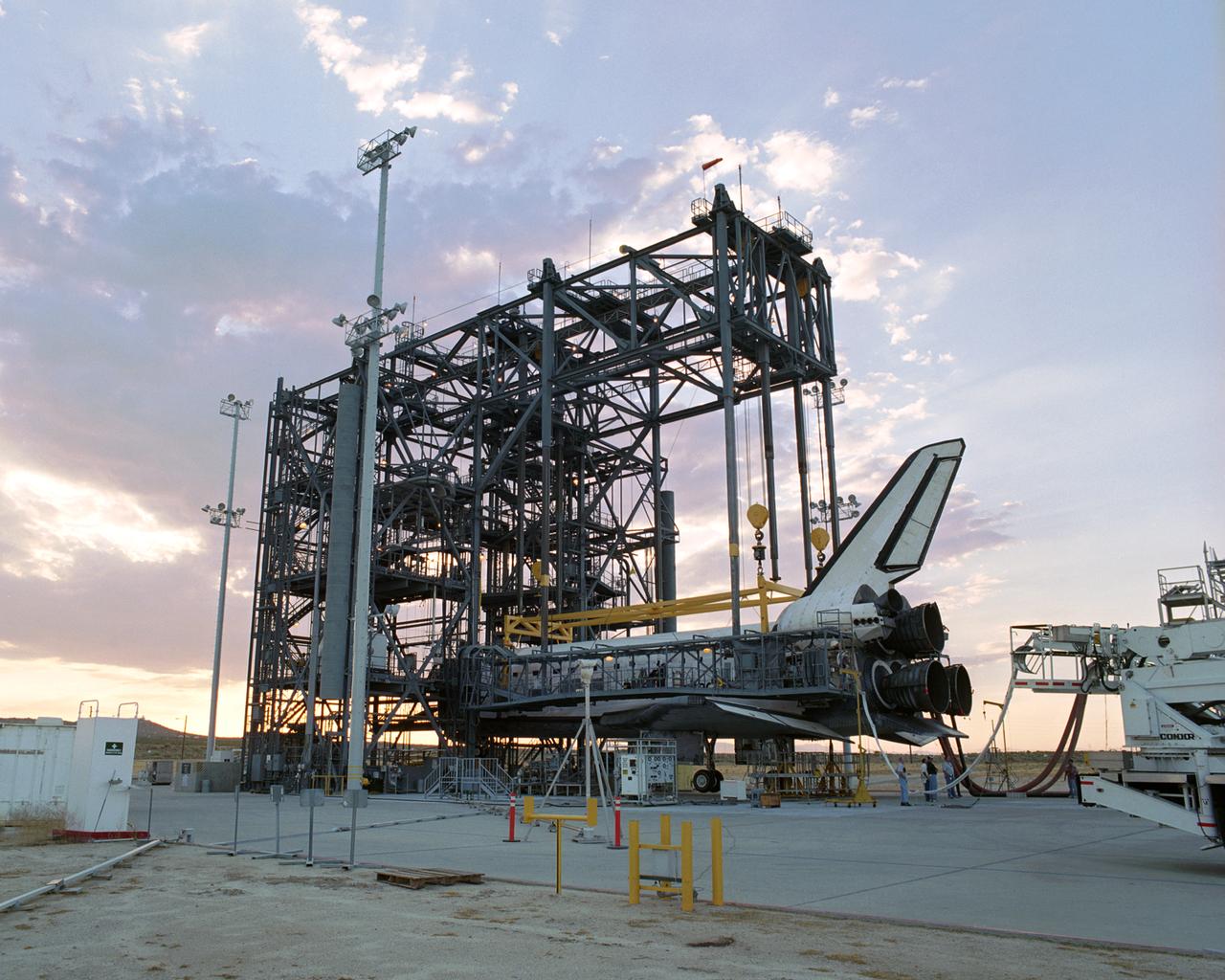

The sun sets on the Space Shuttle Discovery during post-flight processing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD), following its landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
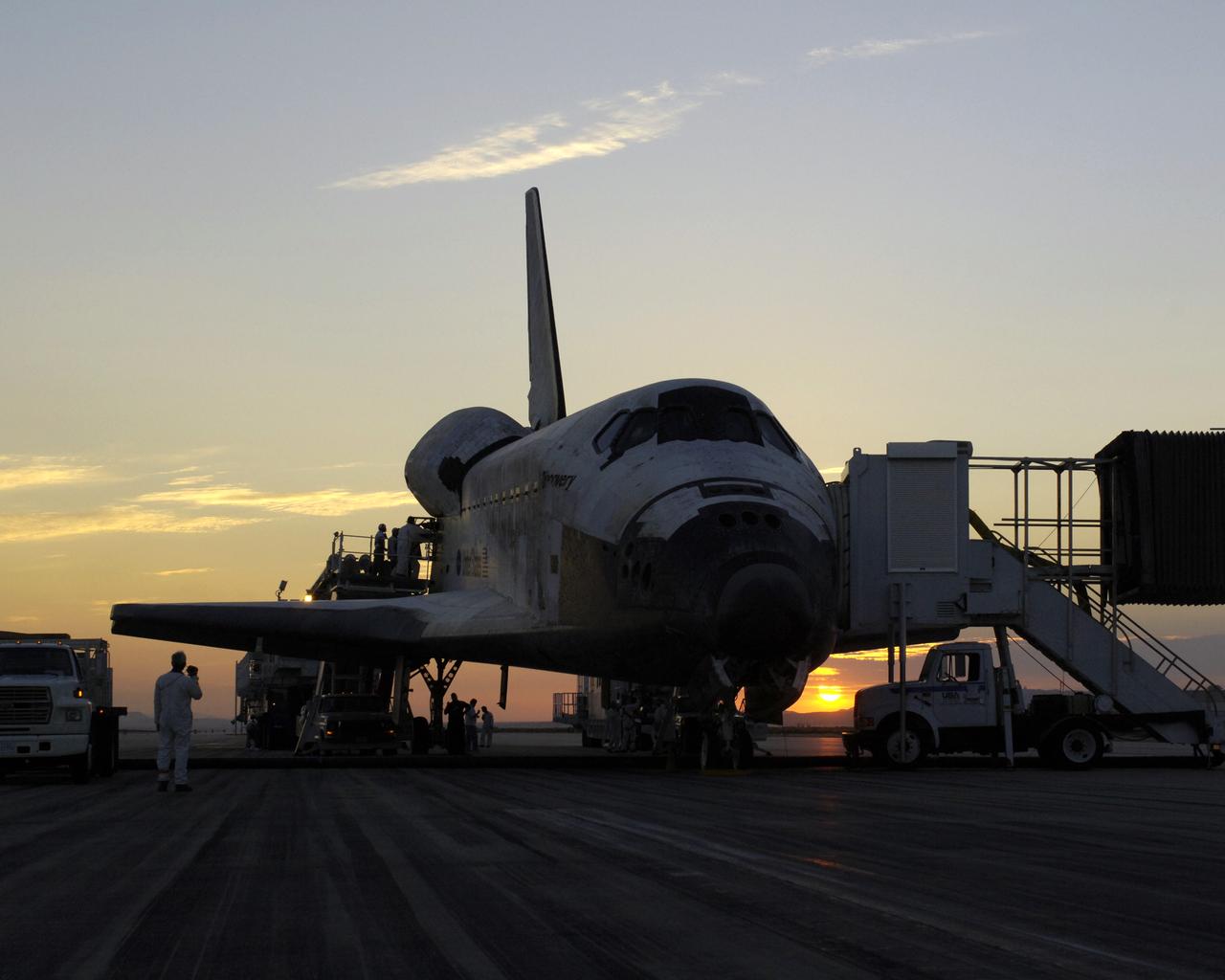

The sun rises on the Space Shuttle Discovery as it rests on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, after a safe landing August 9, 2005 to complete the STS-114 mission. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
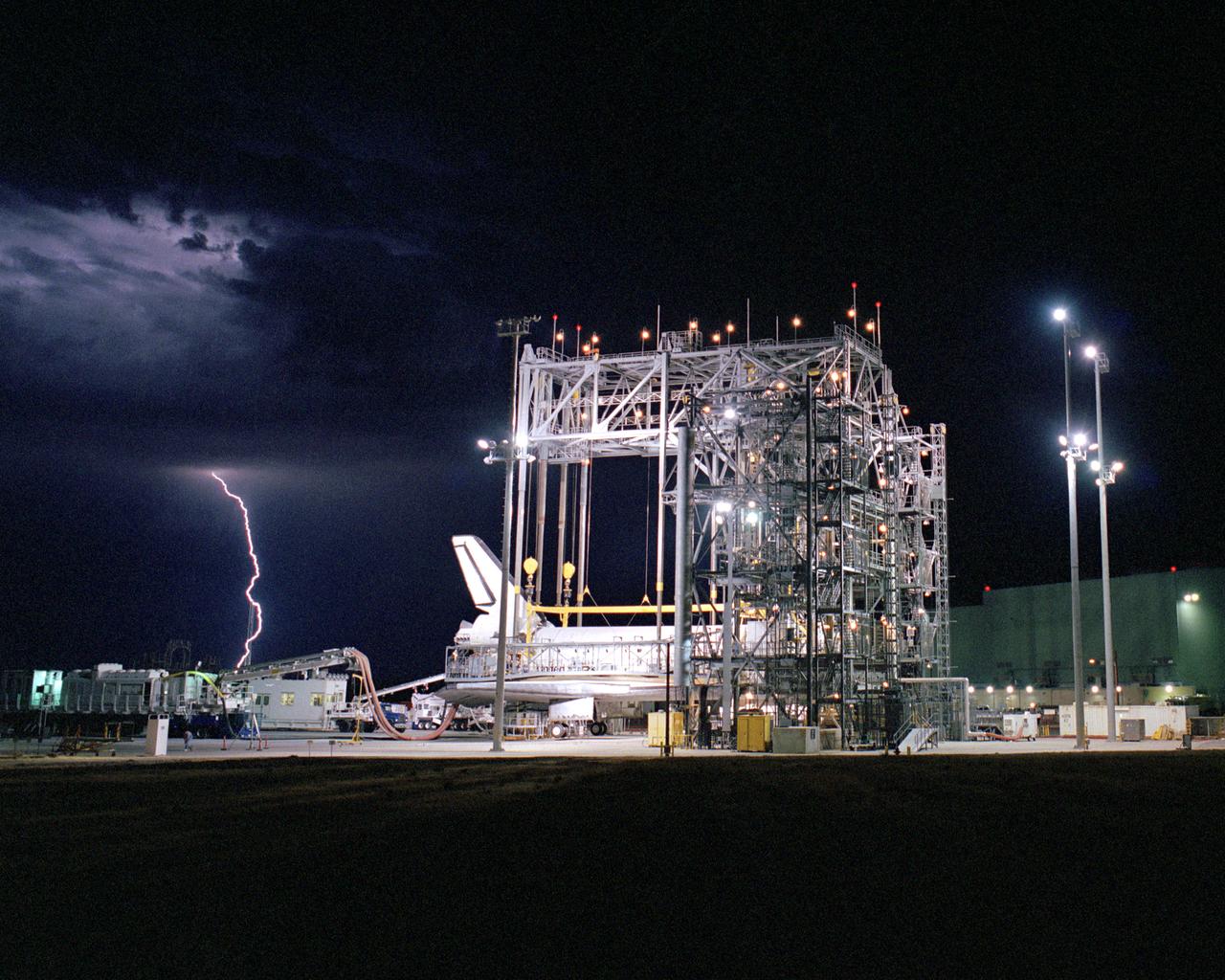

Lightning strikes in the distance as the Space Shuttle Discovery receives post-flight processing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD), following its landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.

Flight Crew Systems Technicians Ray Smith and Raphael Rodriguez remove one of the Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs, from the Space Shuttle Discovery after it's successful landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Space Shuttles receive post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) following landings at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14
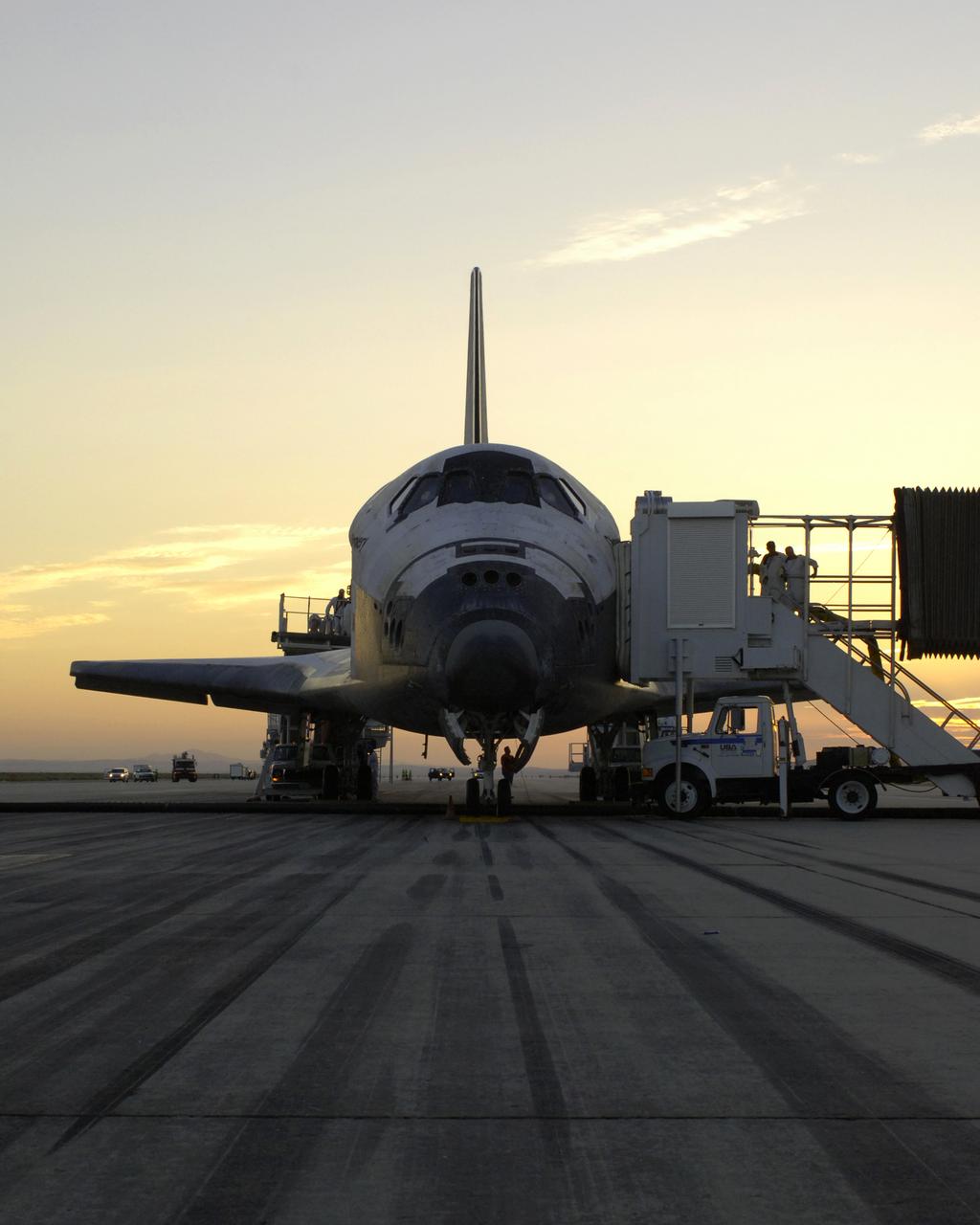

The sun rises on the Space Shuttle Discovery as it rests on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, after a safe landing August 9, 2005 to complete the STS-114 mission. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.