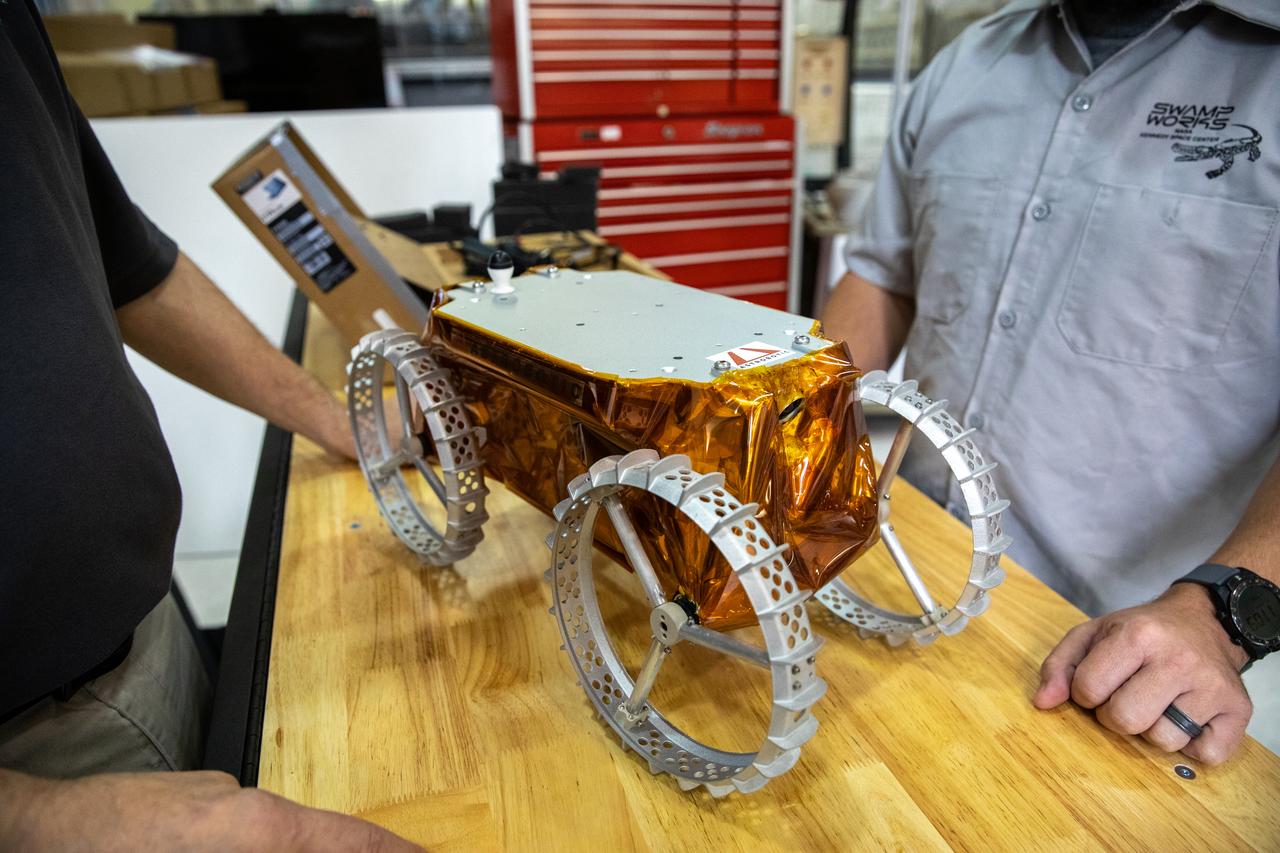

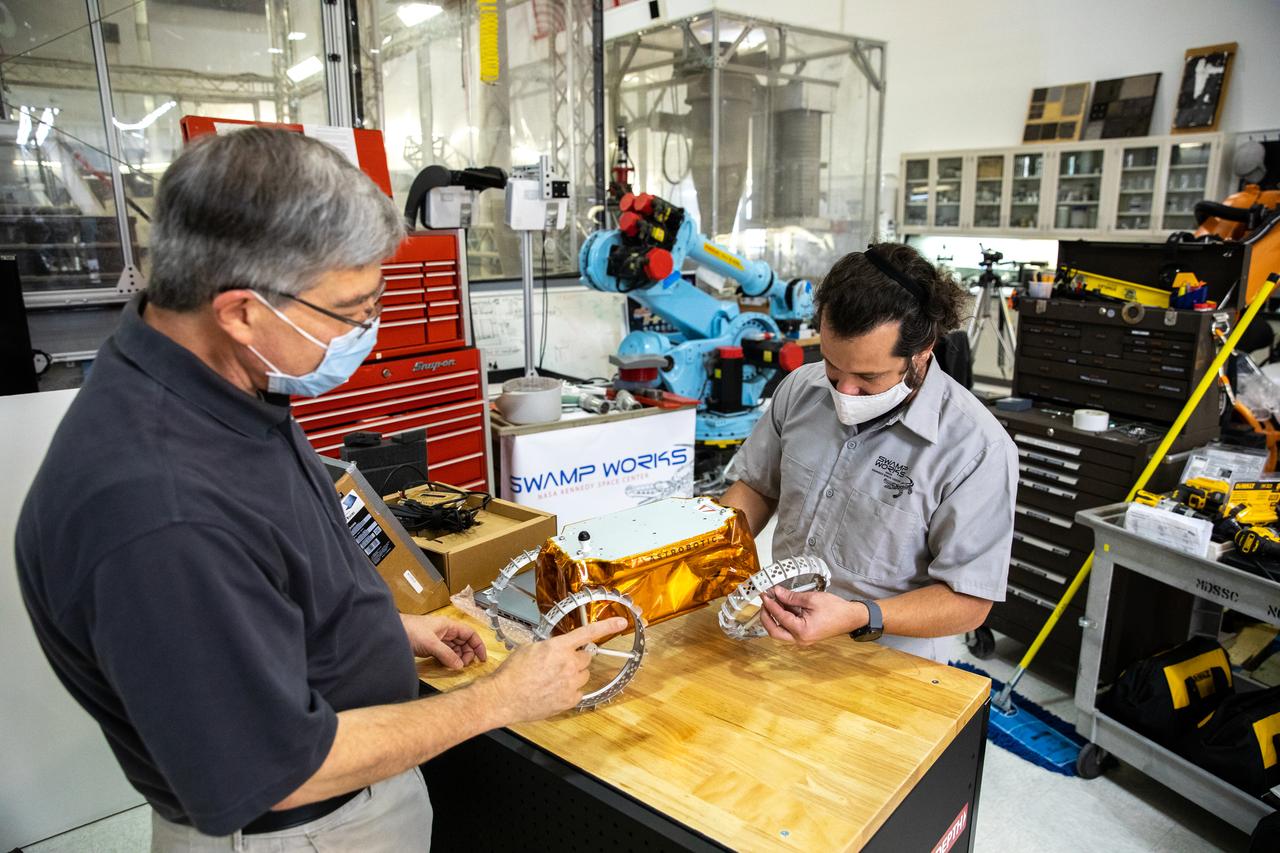
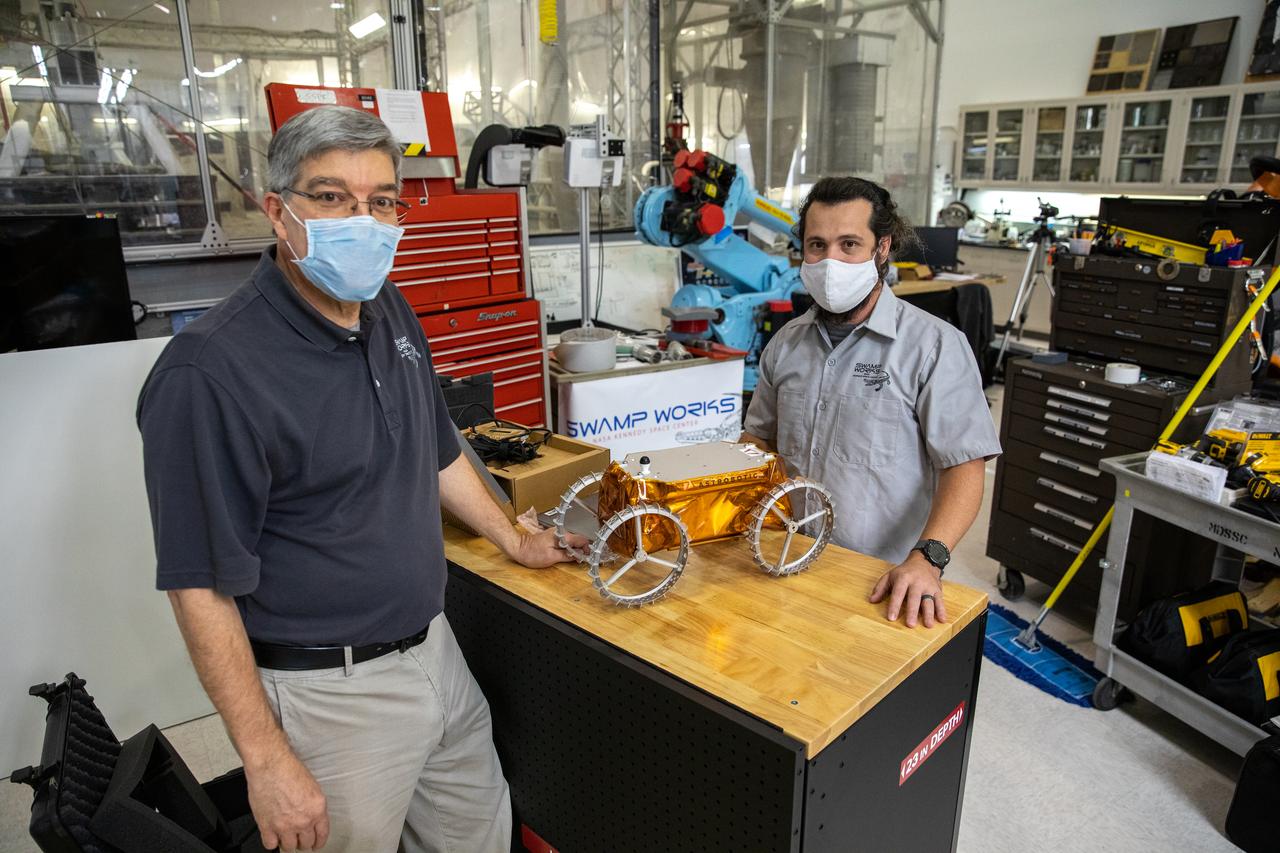
Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
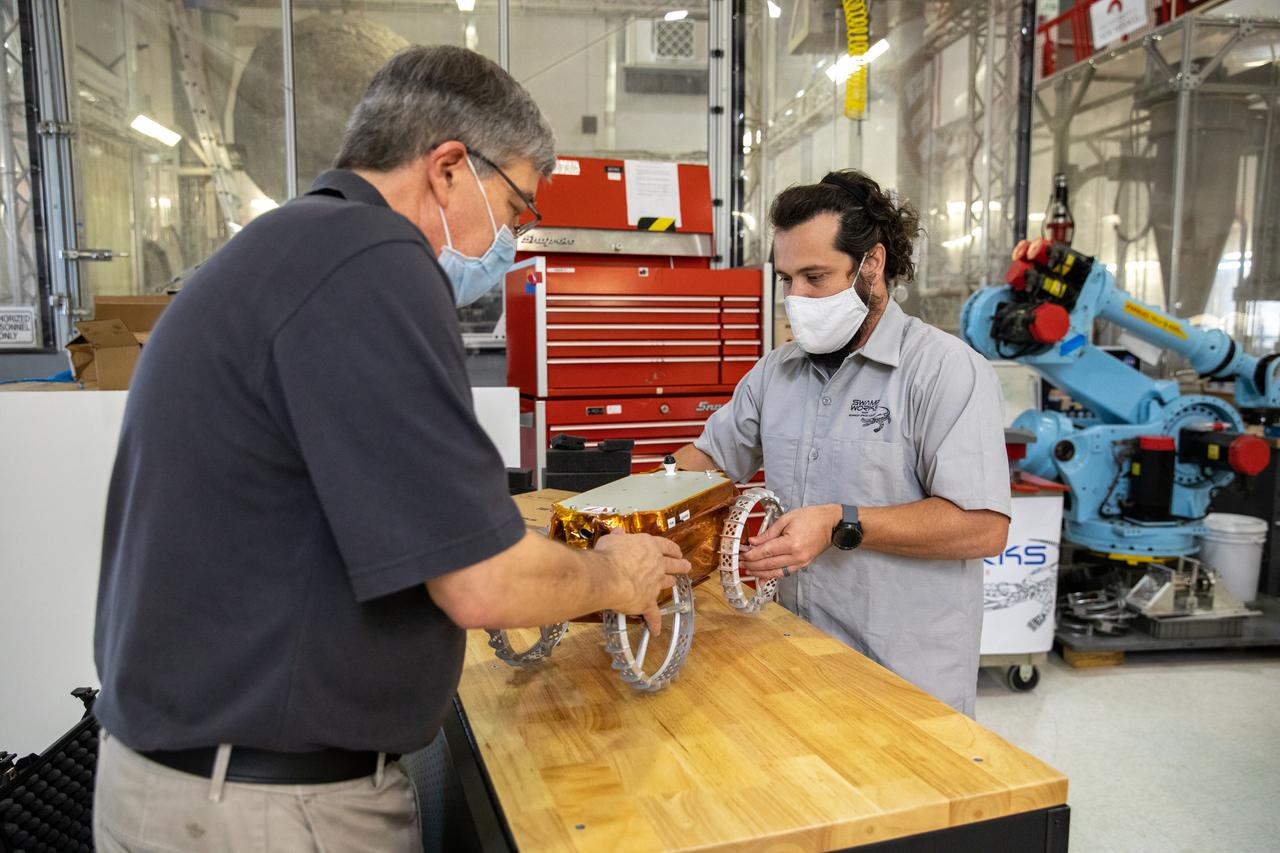

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
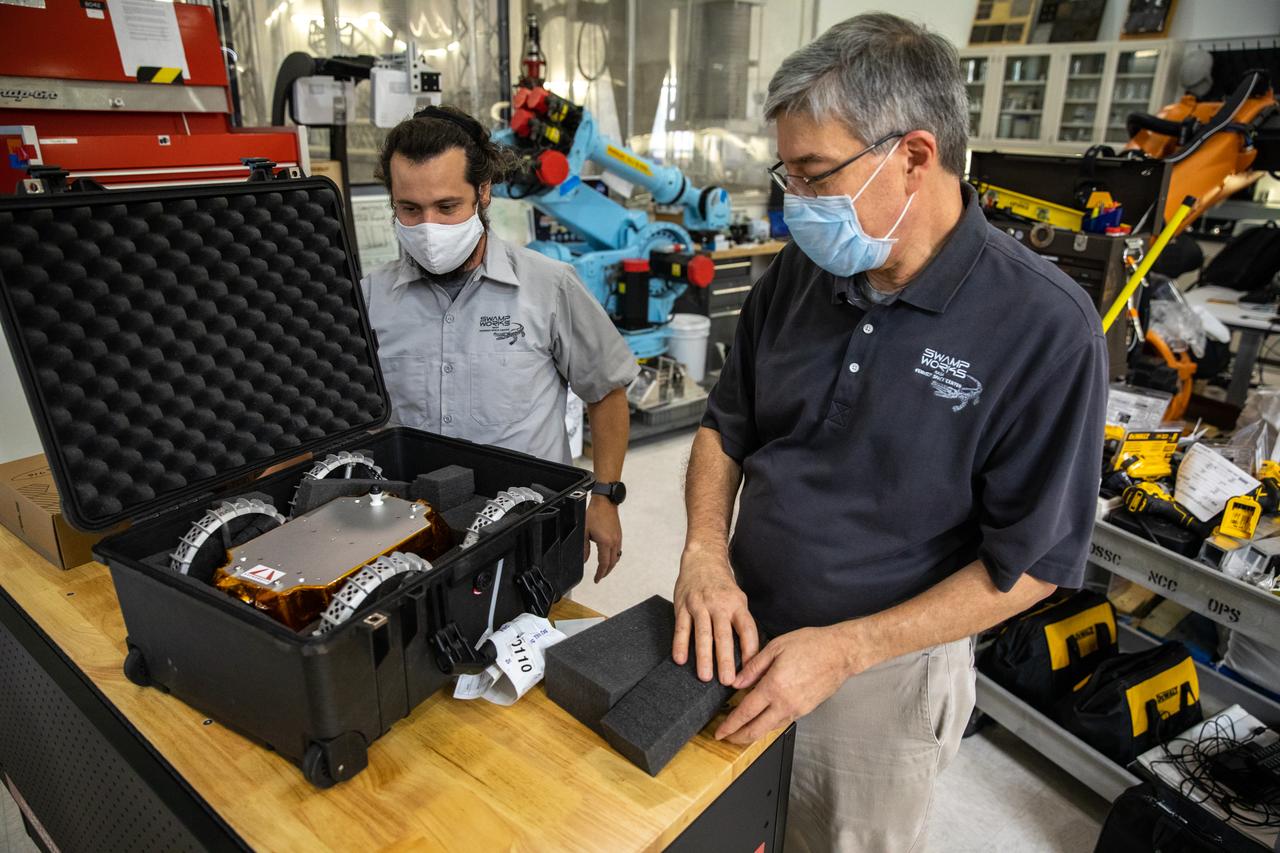

A.J. Nick, left, and Jim Mantovani, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
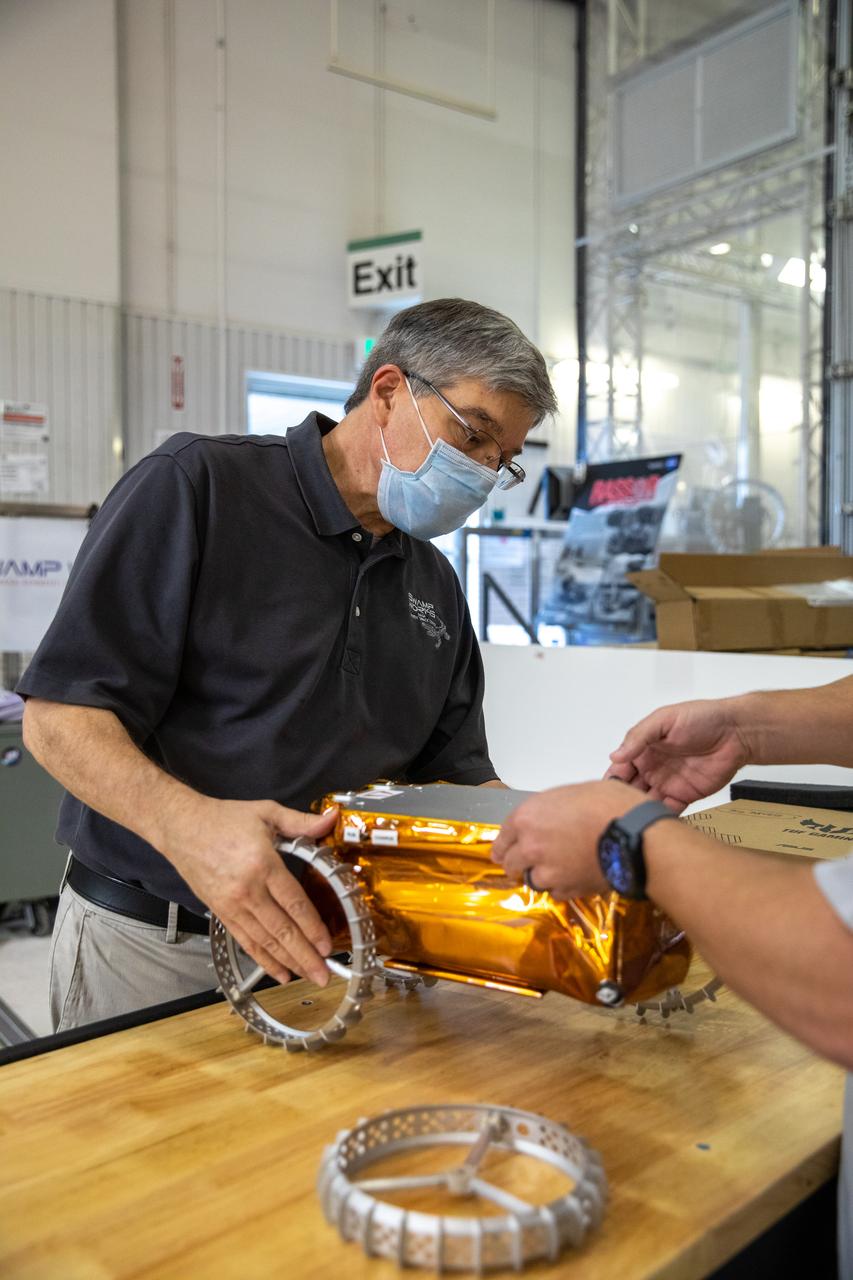

Jim Mantovani, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Kennedy’s A.J. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
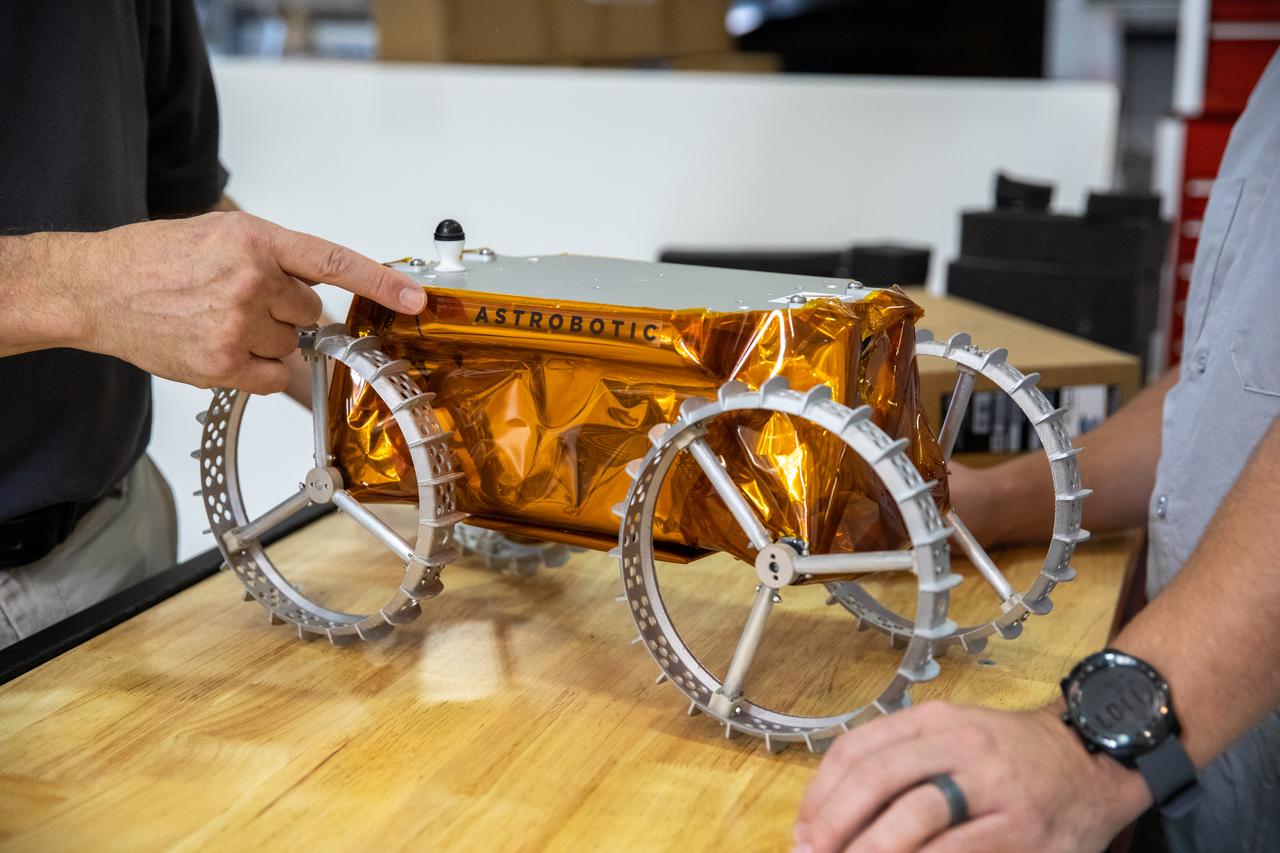

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
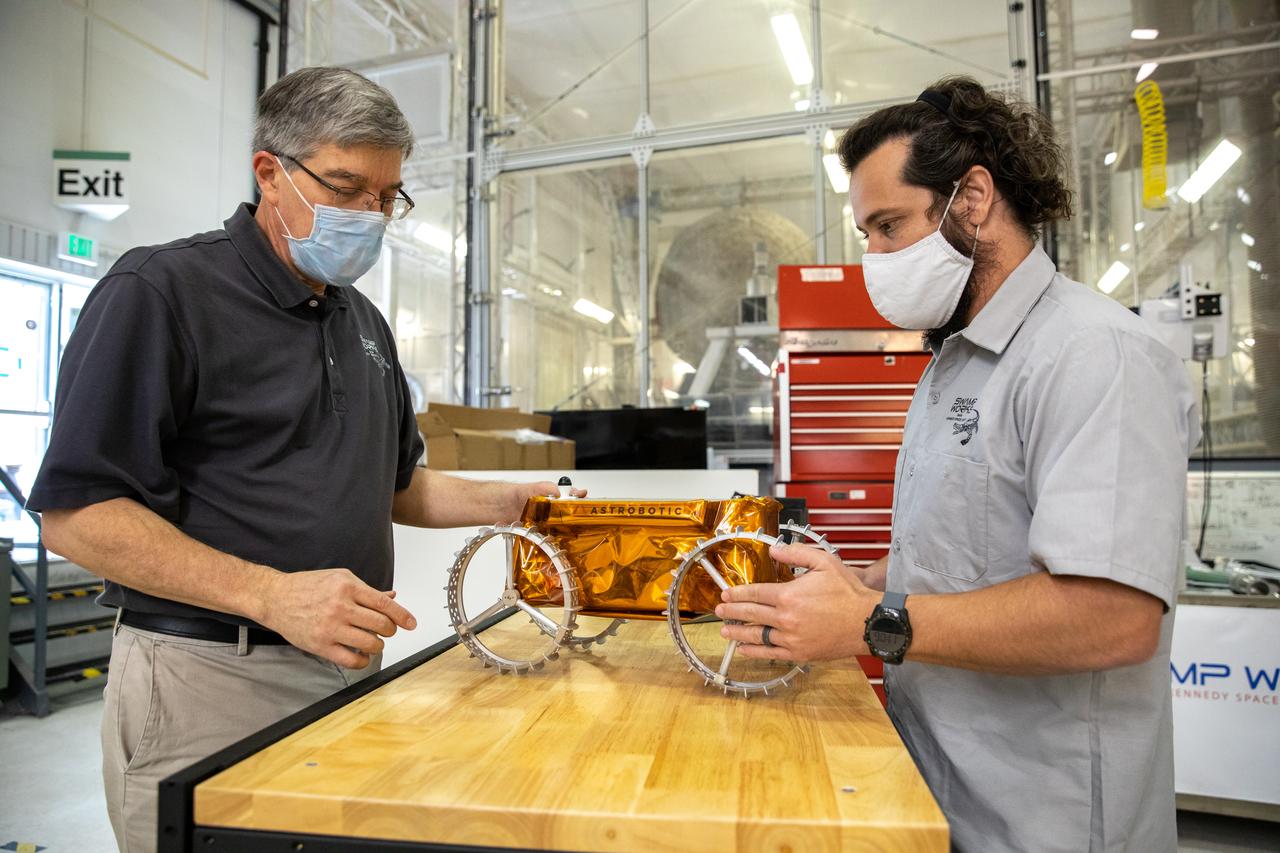

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.

A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
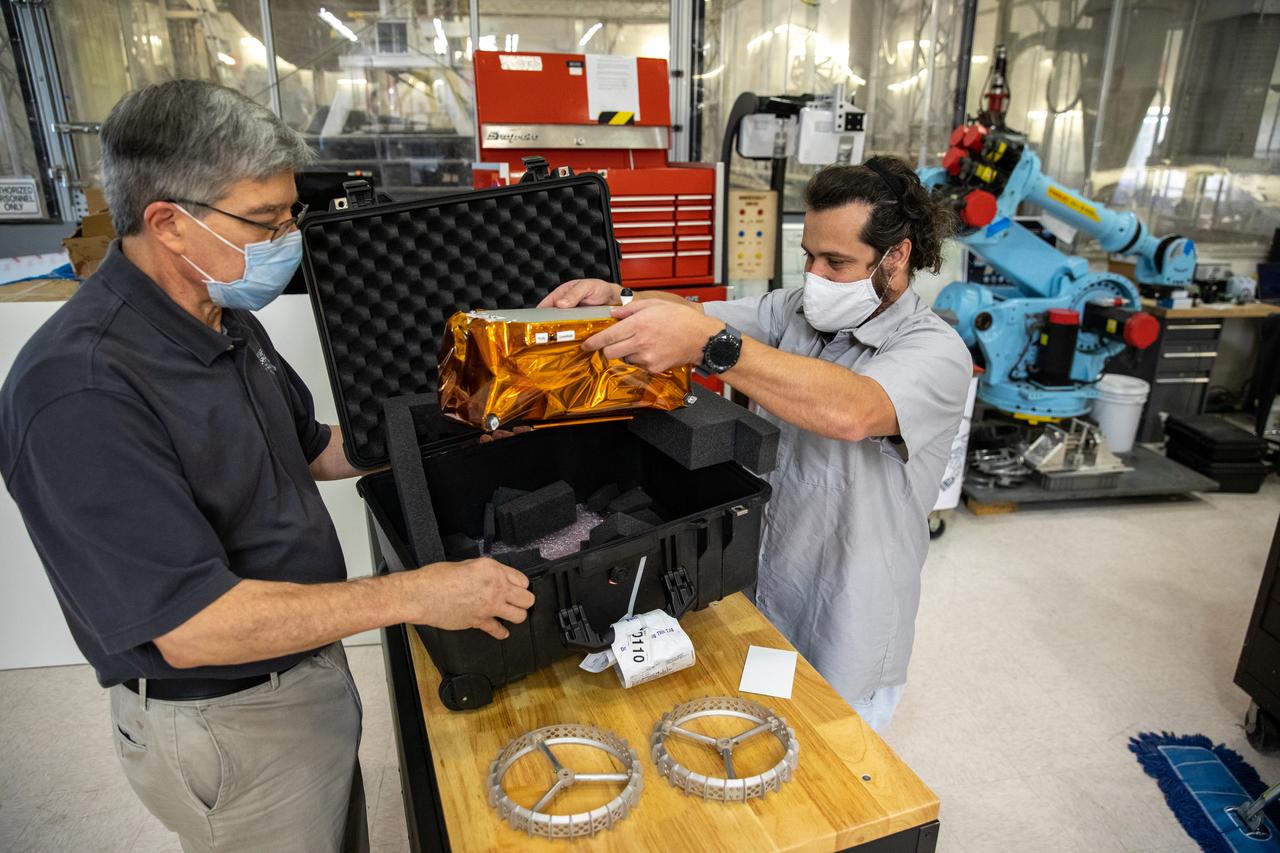

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
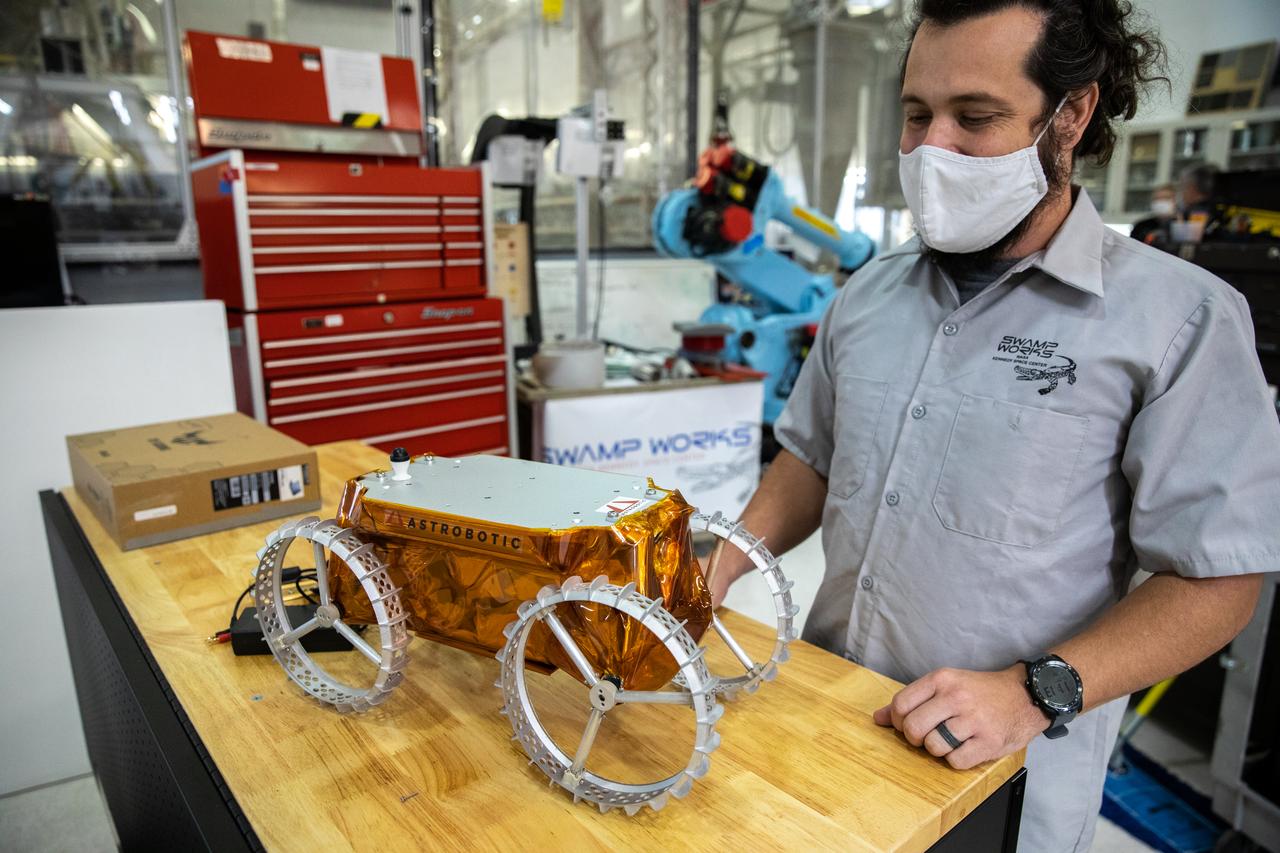

A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
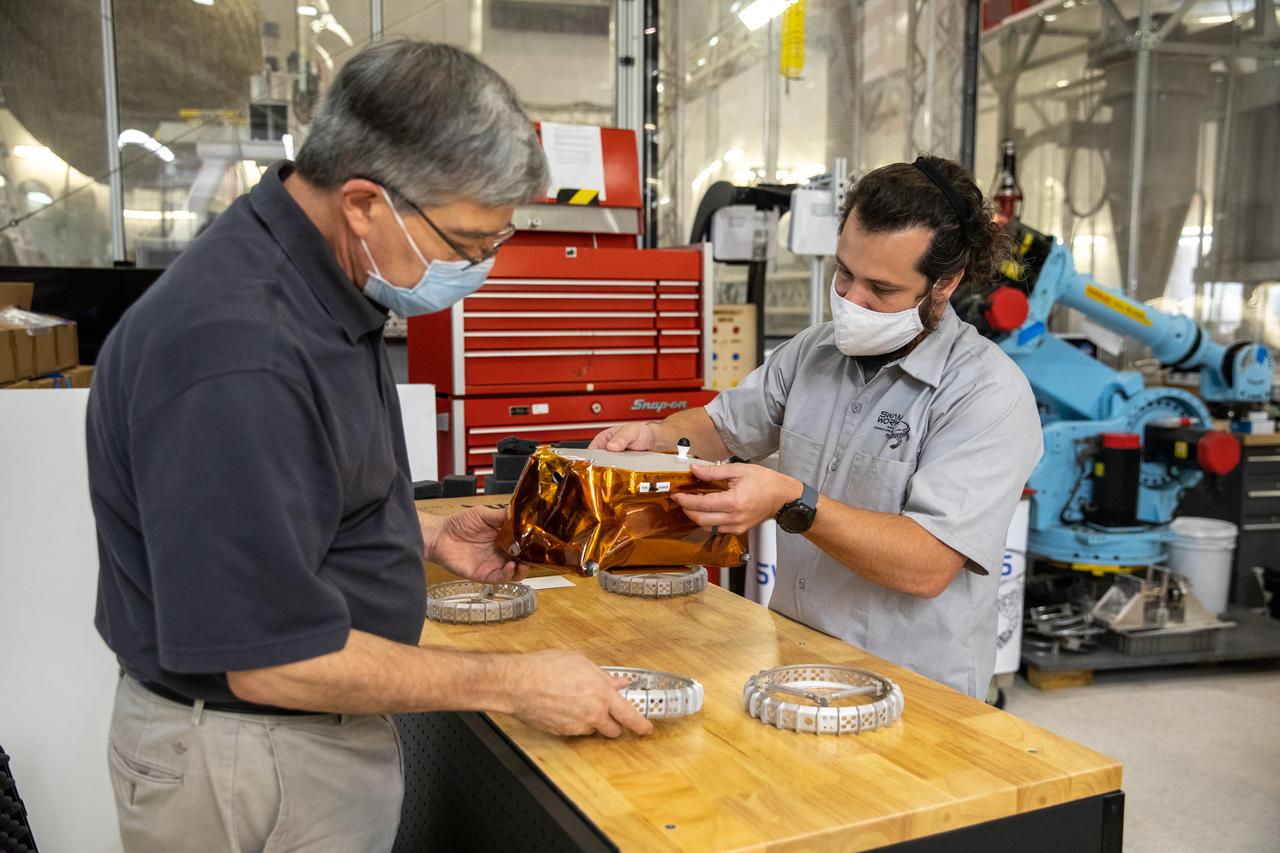

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
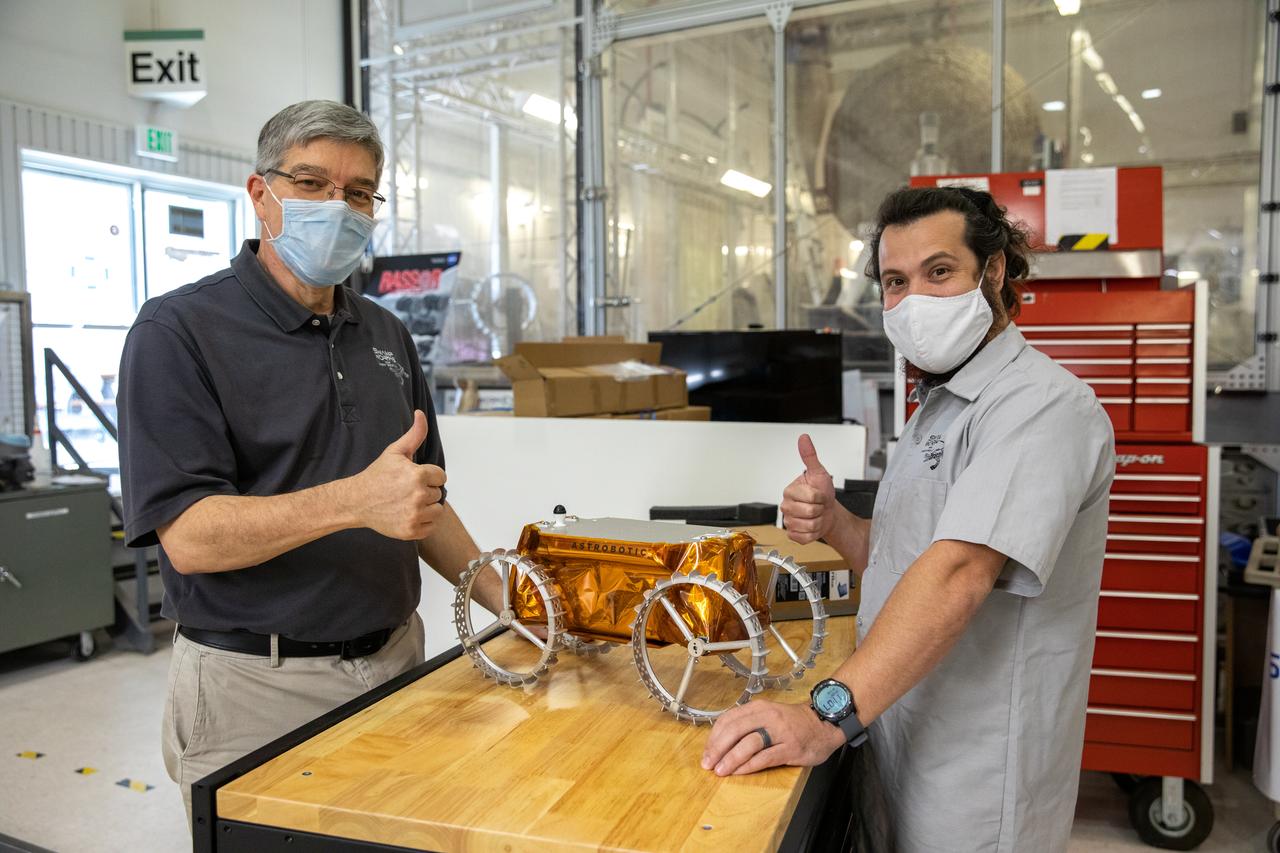

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
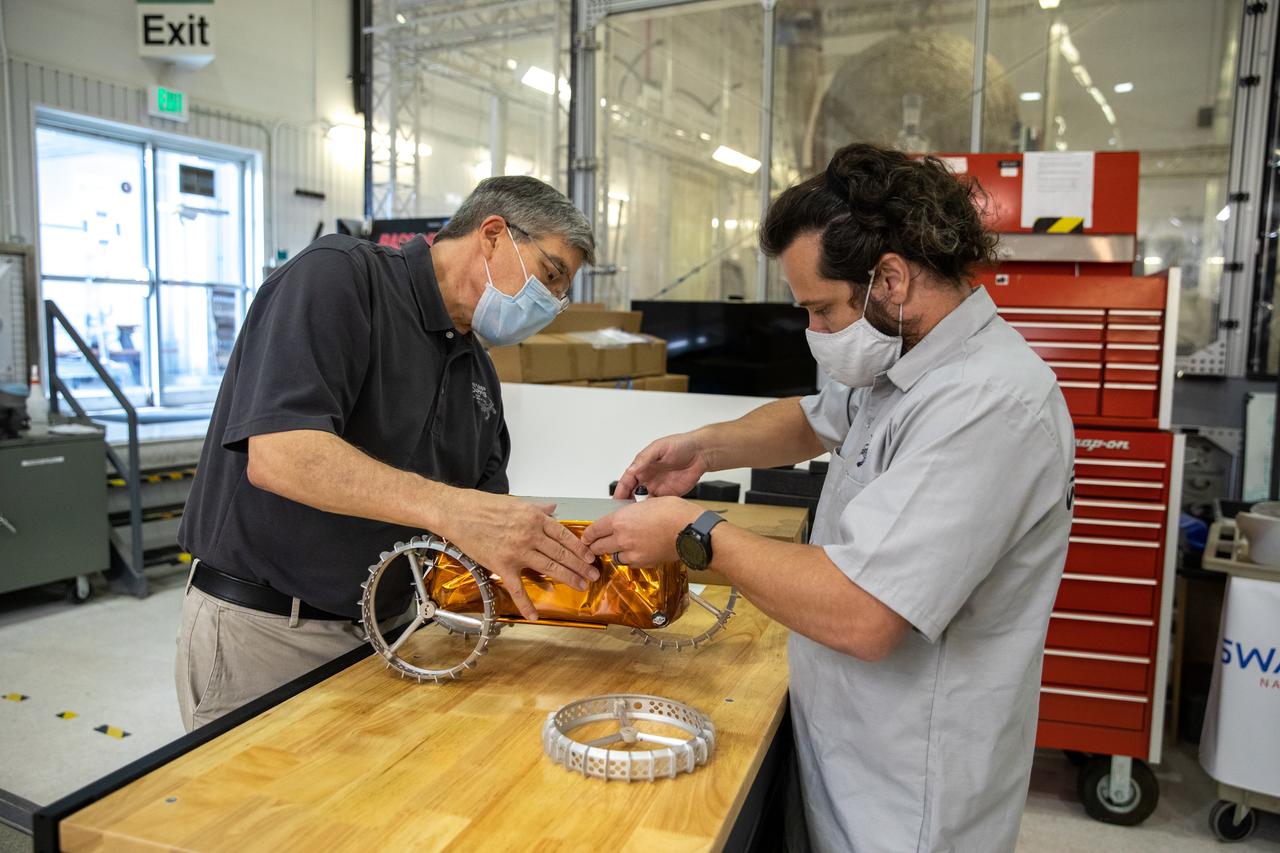

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.

SMALL BUSINESS INNOVATIVE RESEARCH - SBIR - PARTNER DEFORMATION CONTROL TECHNOLOGIES INC

EGC SMALL BUSINESS INNOVATION RESEARCH SBIR PHASE II

MAGNETOSTRICTIVE VALVE ASSEMBLY SMALL BUSINESS INNOVATIVE RESEARCH PROGRAM - MAROTTA INC.

SMALL BUSINESS INNOVATIVE RESEARCH - SBIR - PARTNER TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT INC
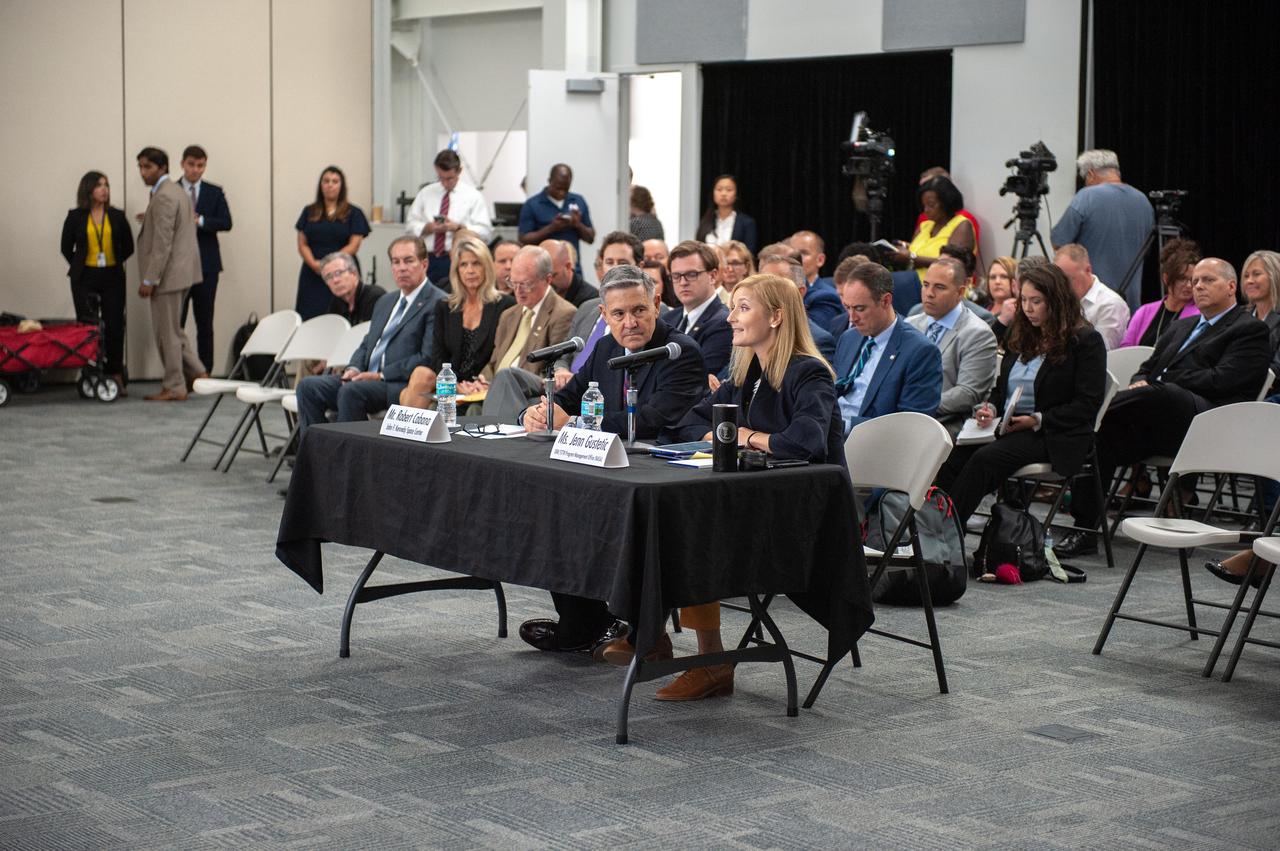

Bob Cabana, director of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and Jenn Gustetic, program executive, NASA Small Business Innovation Research Program (SBIR), speak to Florida legislators participating in the U.S. Senate Committee on Small Business and Entrepreneurship field hearing on July 19, 2019, in the Astronaut Memorial Foundation facility at Kennedy’s Visitor Complex. The topic of the field hearing was “Moon Landings to Mars Exploration: The Role of Small Business Innovation in America’s Space Program.”
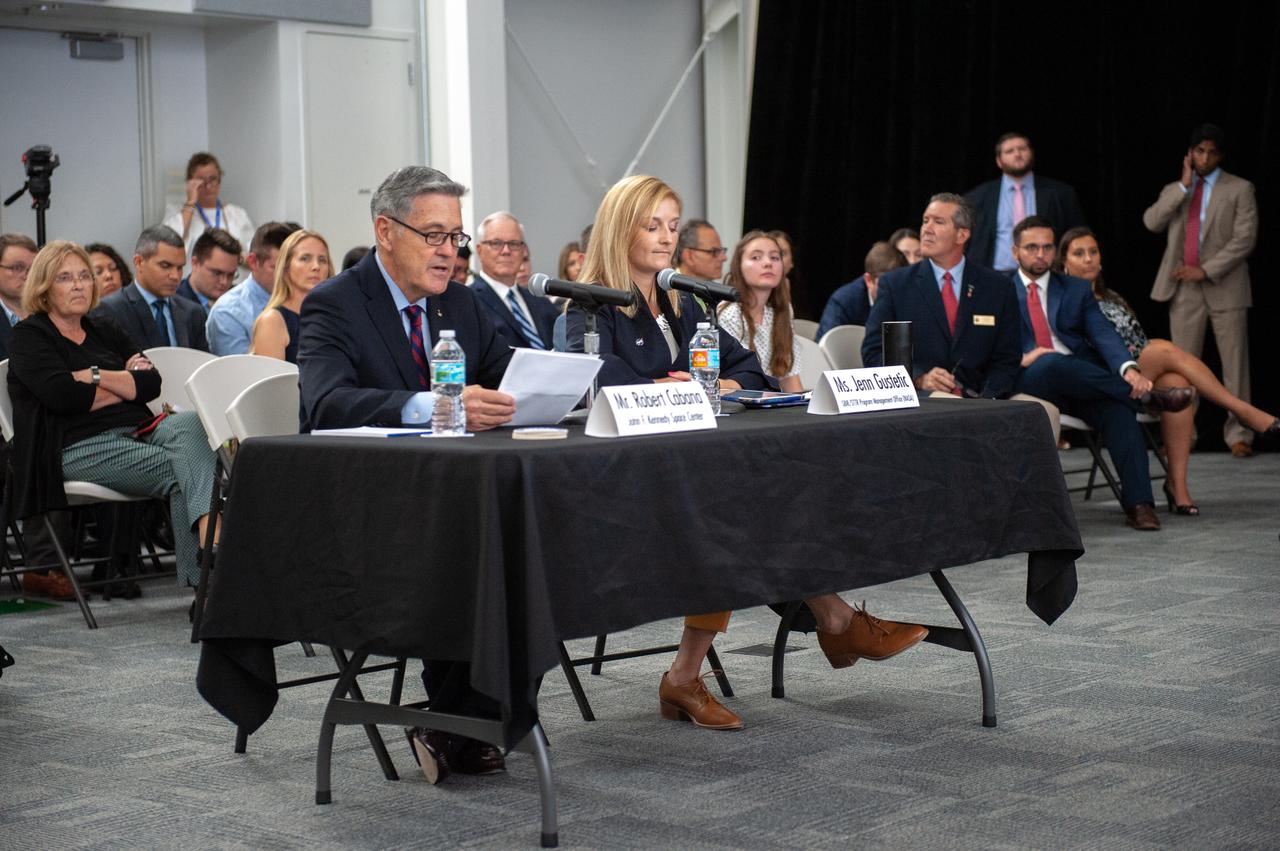

Bob Cabana, left, director of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and Jenn Gustetic, program executive, NASA Small Business Innovation Research Program (SBIR), speak to Florida legislators participating in the U.S. Senate Committee on Small Business and Entrepreneurship field hearing on July 19, 2019, in the Astronaut Memorial Foundation facility at Kennedy’s visitor complex. The topic of the field hearing was “Moon Landings to Mars Exploration: The Role of Small Business Innovation in America’s Space Program.”

Gary Laier, center liaison for the Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) program at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, teaches students about aeronautics during Aero Fair at Tropico Middle School in Rosamond, California, on April 9, 2025.
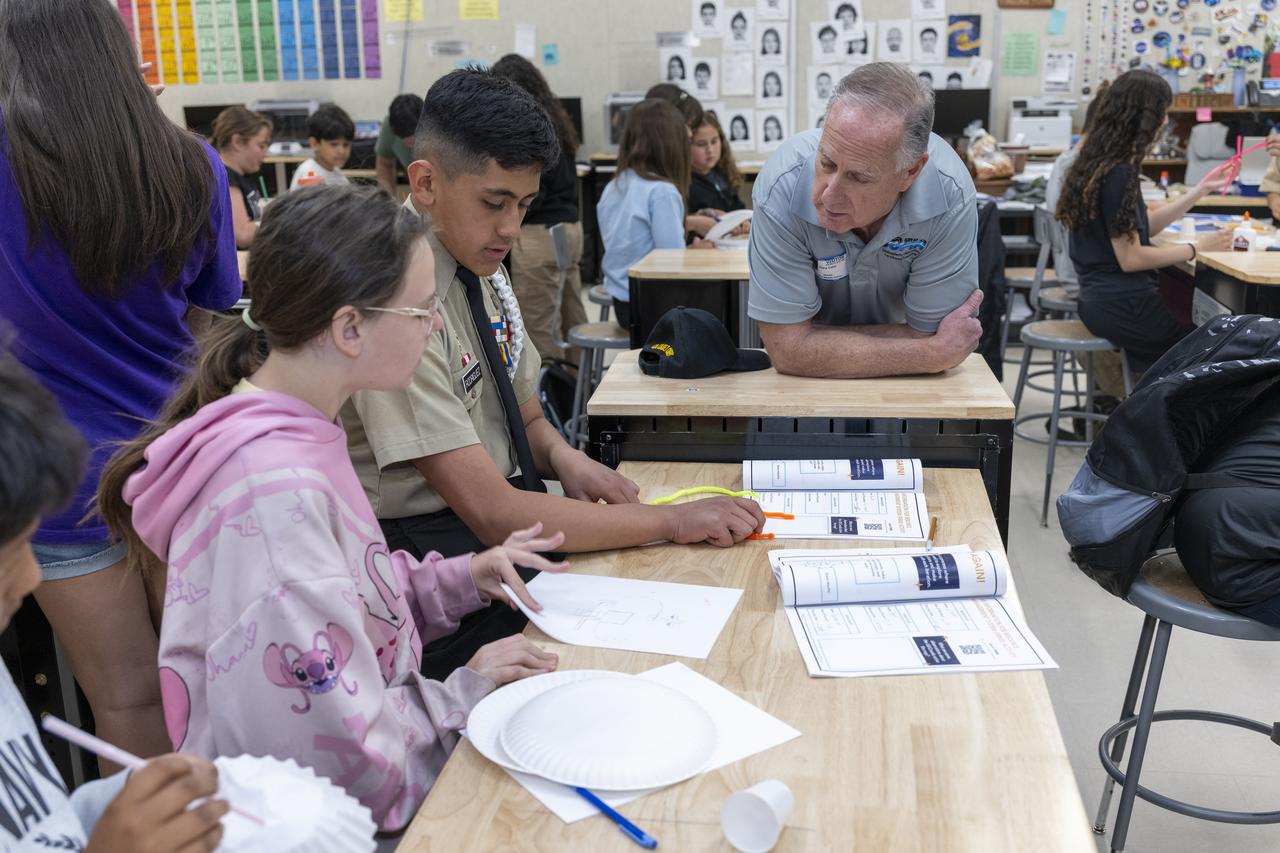

Gary Laier, center liaison for the Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) program at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, teaches students about aeronautics during Aero Fair at Tropico Middle School in Rosamond, California, on April 9, 2025.

Participants in A Day with NASA at The Accelerator in Hattiesburg, Mississippi, included: (left to right) Marc Shoemaker with the NASA Stennis Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer Office; Kay Doane with the NASA Stennis Office of Small Business Programs; Sandy Crist with the Mississippi Manufacturers Association Manufacturing Extension Program; Dr. Monica Tisack with the Mississippi Polymer Institute; Caitlyne Shirley with the Mississippi Polymer Institute; Top Lipski with the NASA Stennis Technology Transfer Expansion Team; Thom Jacks with the NASA Stennis Engineering and Test Directorate; Dawn Davis with the NASA Stennis Engineering and Test Directorate; Kelly McCarthy with the NASA Stennis Office of STEM Engagement; and Janet Parker with Innovate Mississippi.
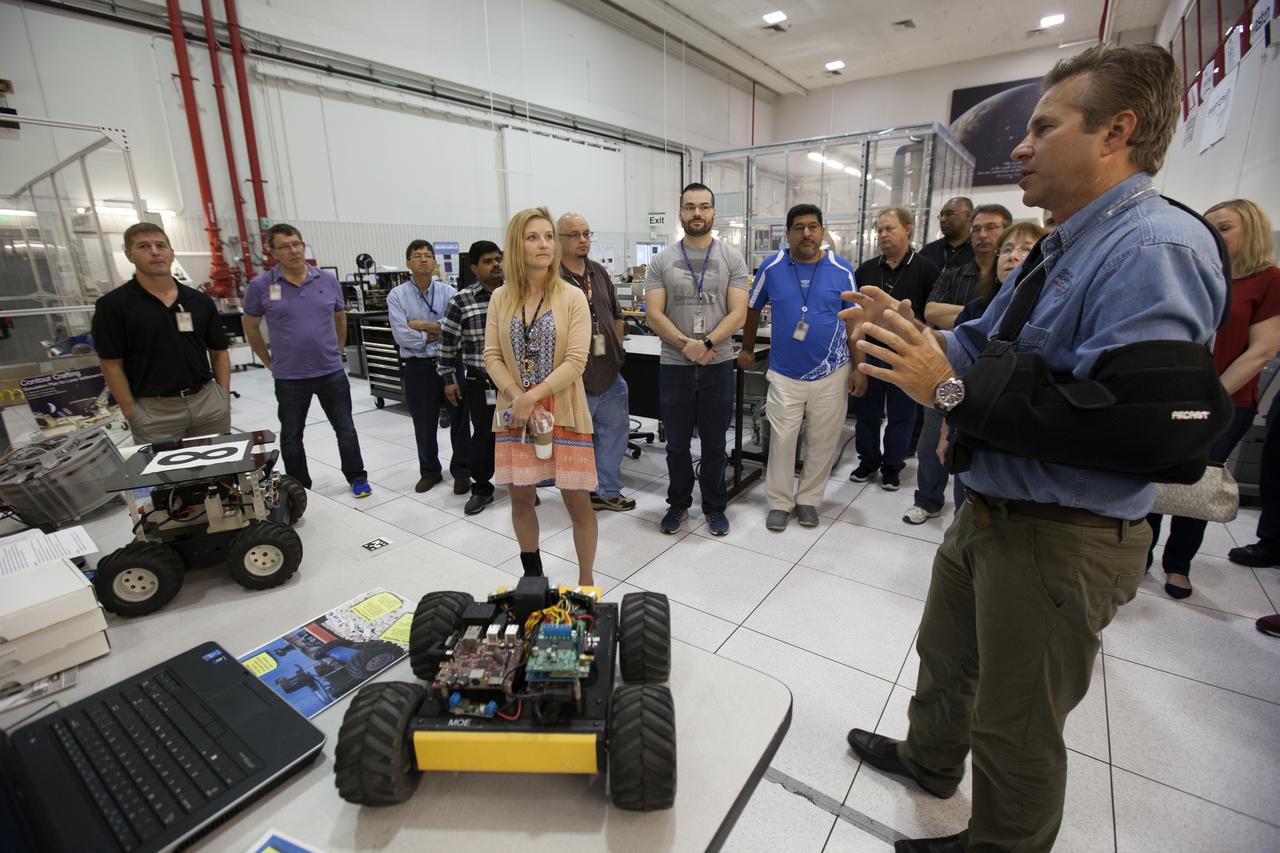

Jenn Gustetic, NASA's Small Business Innovation Research Program executive, talks with Rob Mueller, senior technologist and co-founder of Kennedy Space Center's Swamp Works. Gustetic met team members and viewed many of the pioneering technologies and innovations in development at Kennedy. Swamp Works is a hands-on, lean development environment for innovation following the philosophies pioneered in Kelly Johnson's Skunk Works and Werner von Braun's development shops. The Swamp Works establishes rapid, innovative and cost-effective exploration mission solutions through a highly collaborative, "no walls" approach, leveraging partnerships across NASA, industry and academia.
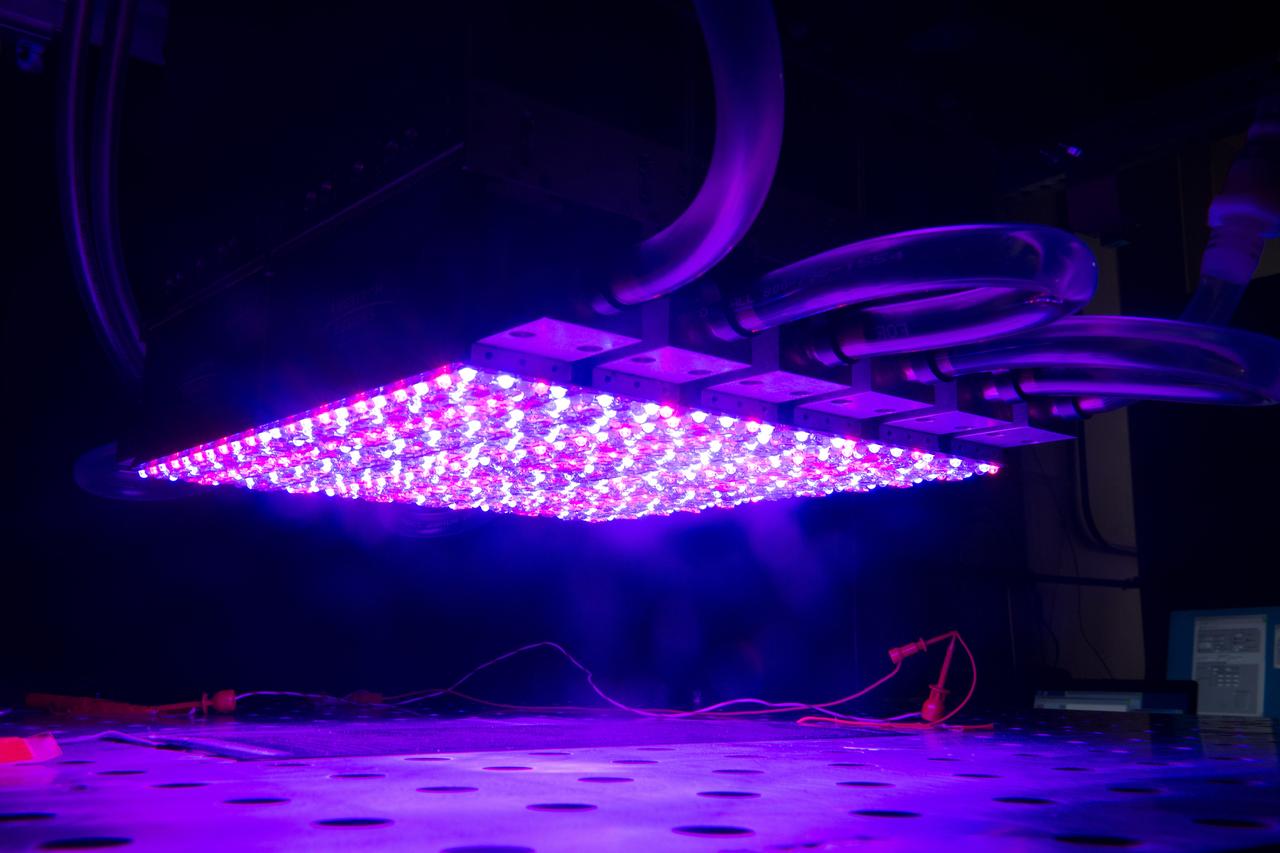

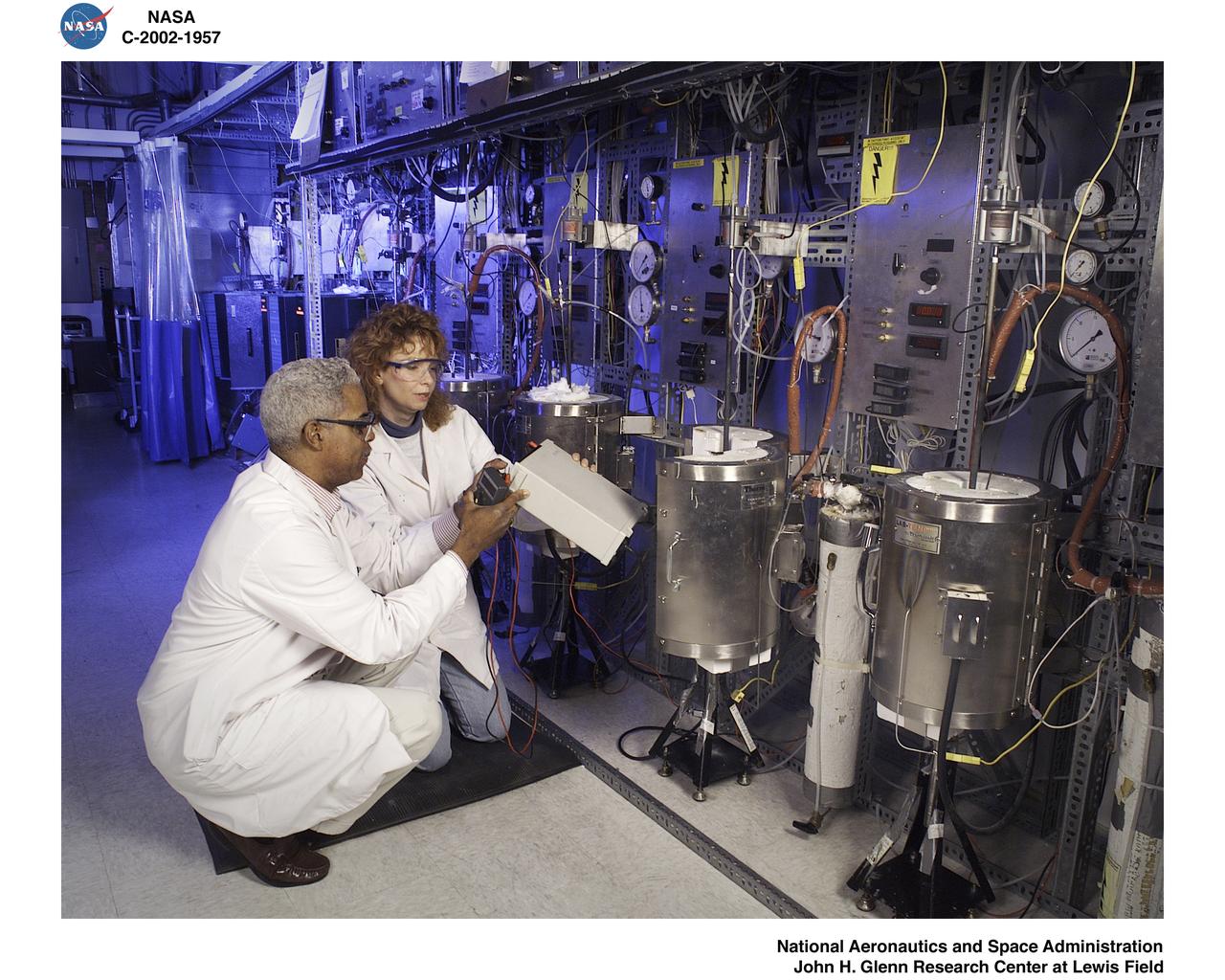
NASA Glenn's new LED solar simulator was developed by Angstrom Designs and UC Santa Barbara under a Small Business Innovative Research program to test the next generation of high-efficiency space solar cells for future missions. The new simulator contains over 1500 individually adjustable light sources, most of which emit light invisible to the human eye, to cover a 10 x10 foot area.
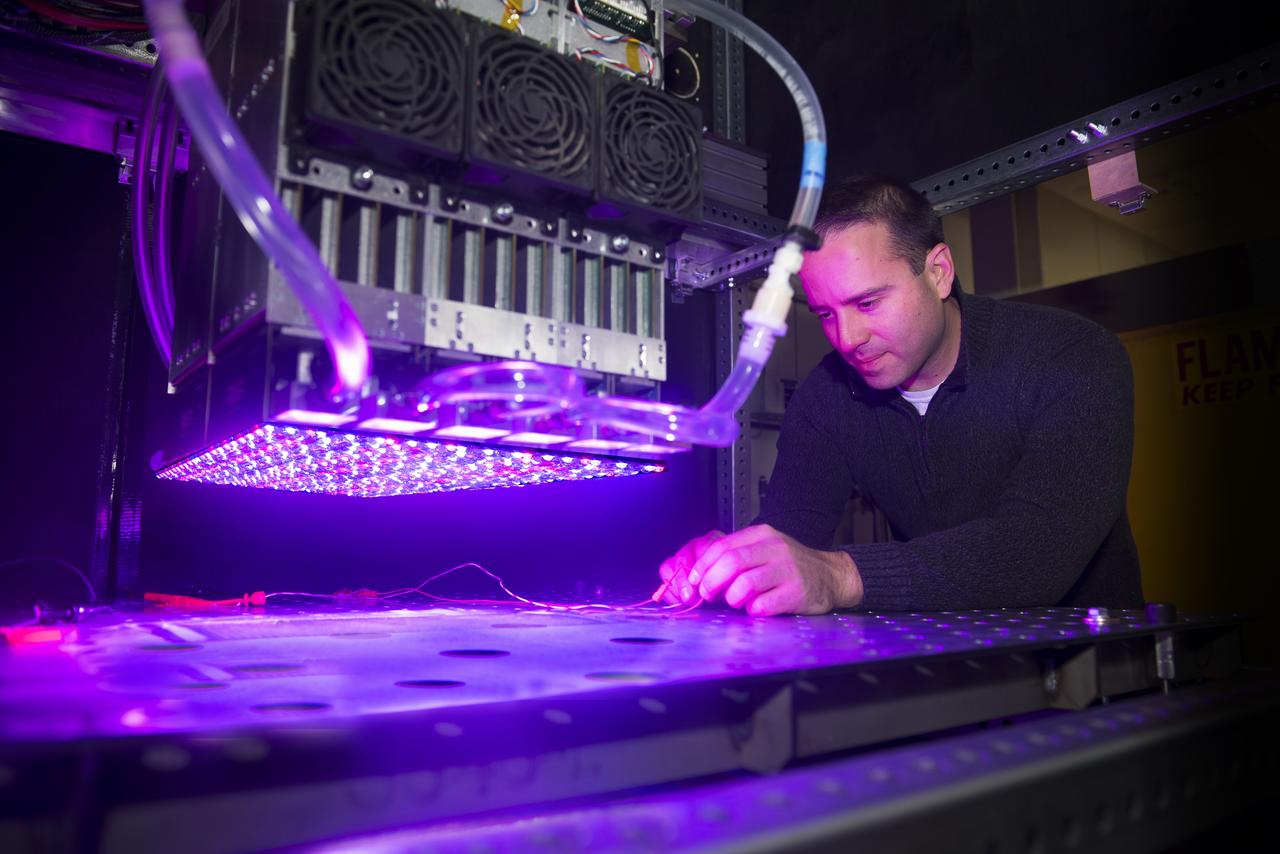

NASA Glenn's new LED solar simulator was developed by Angstrom Designs and UC Santa Barbara under a Small Business Innovative Research program to test the next generation of high-efficiency space solar cells for future missions. The new simulator contains over 1500 individually adjustable light sources, most of which emit light invisible to the human eye, to cover a 10 x10 foot area.

Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker reports the results of a drawbar pull run to Astrobotic staff outside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.

Astrobotic’s mass-offloaded CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – undergoes mobility testing inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
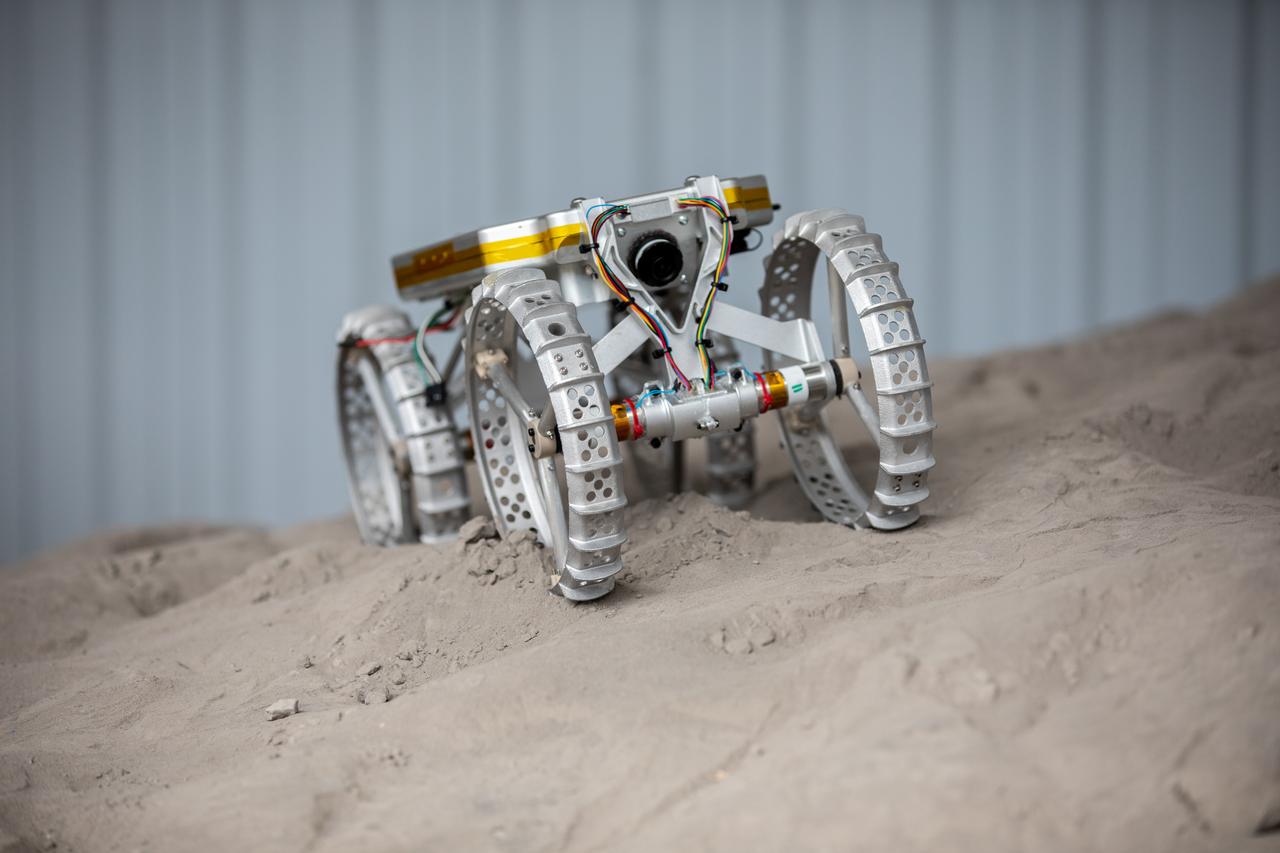
Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – undergoes mobility testing inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.

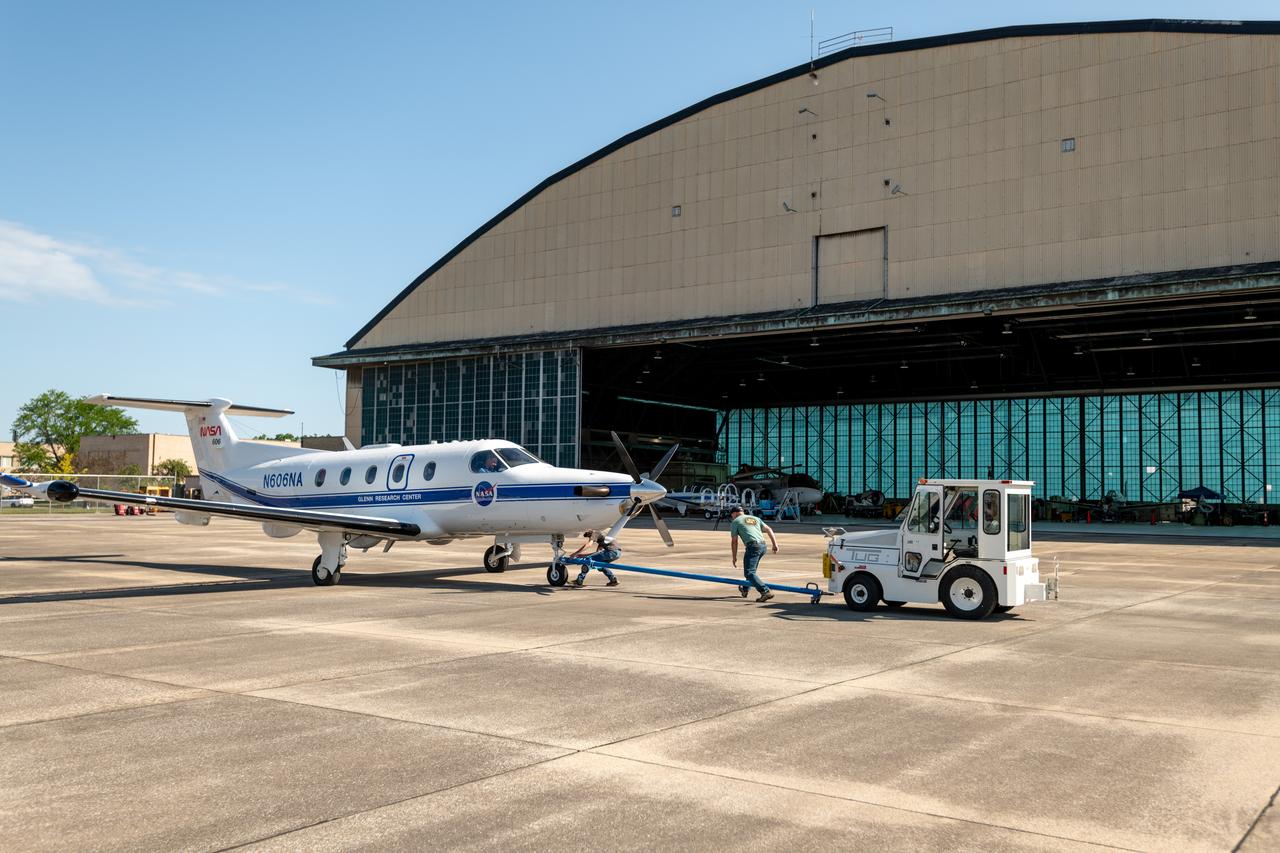
A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Pictured from Left to Right: James Demers, Adam Wroblewski, Shaun McKeehan, Kurt Blankenship. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.
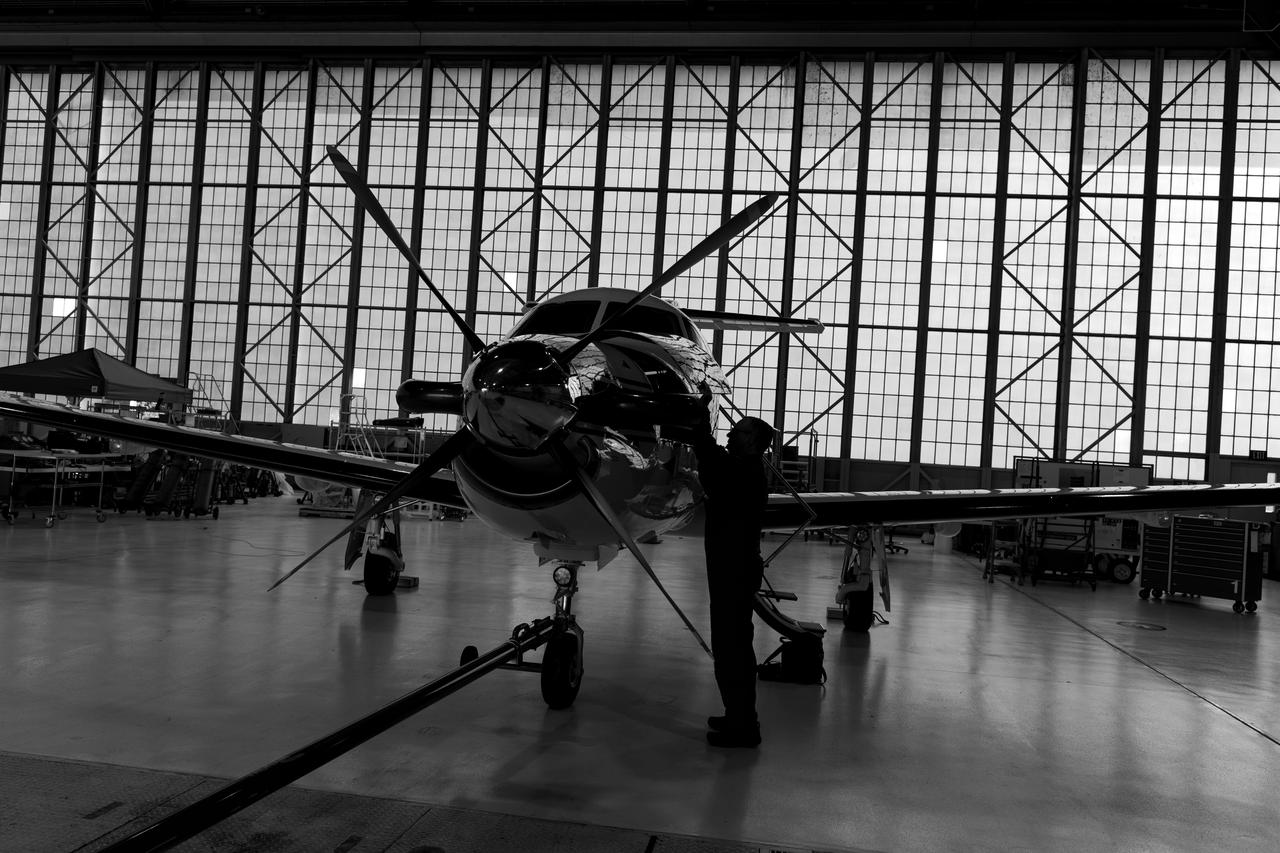

Pilatus PC-12 Aircraft Being Prepped for Takeoff on June 12, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
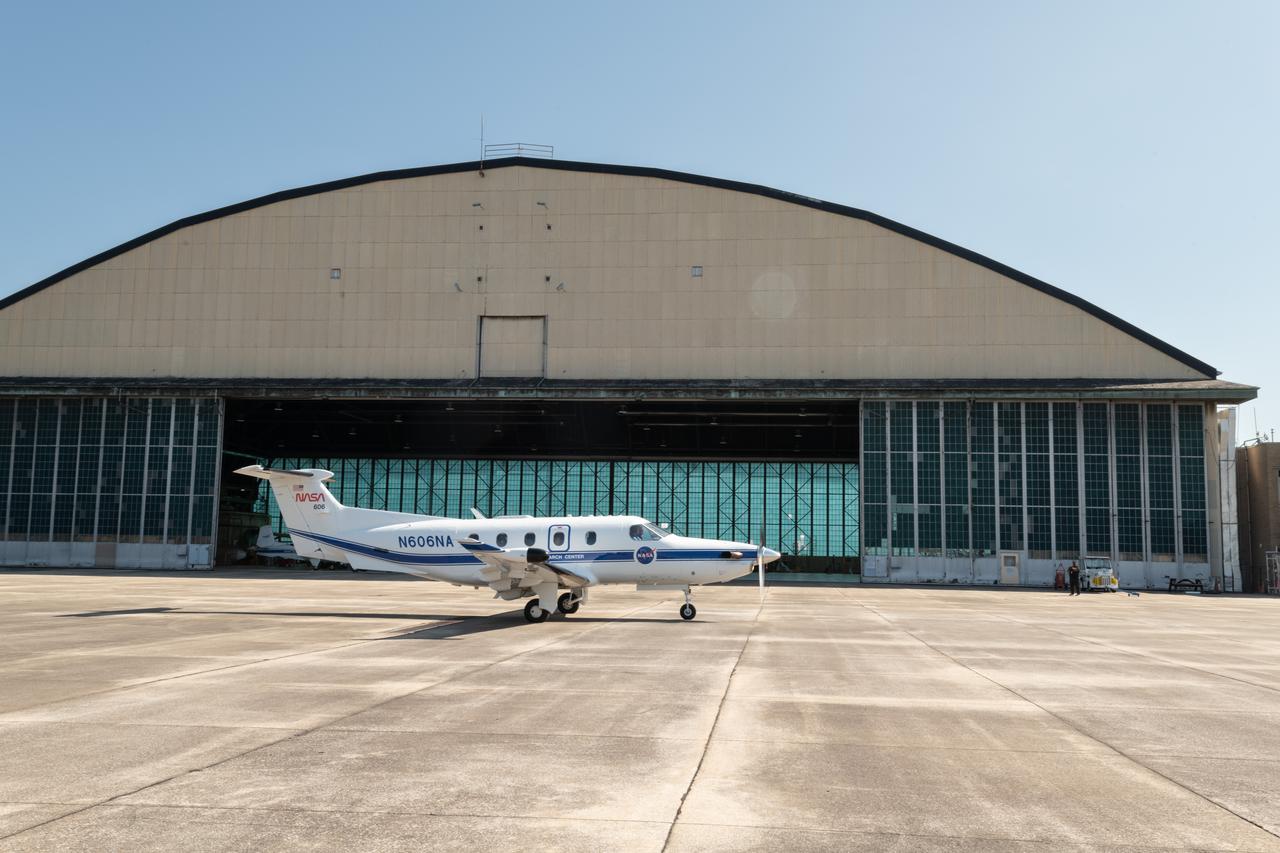

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
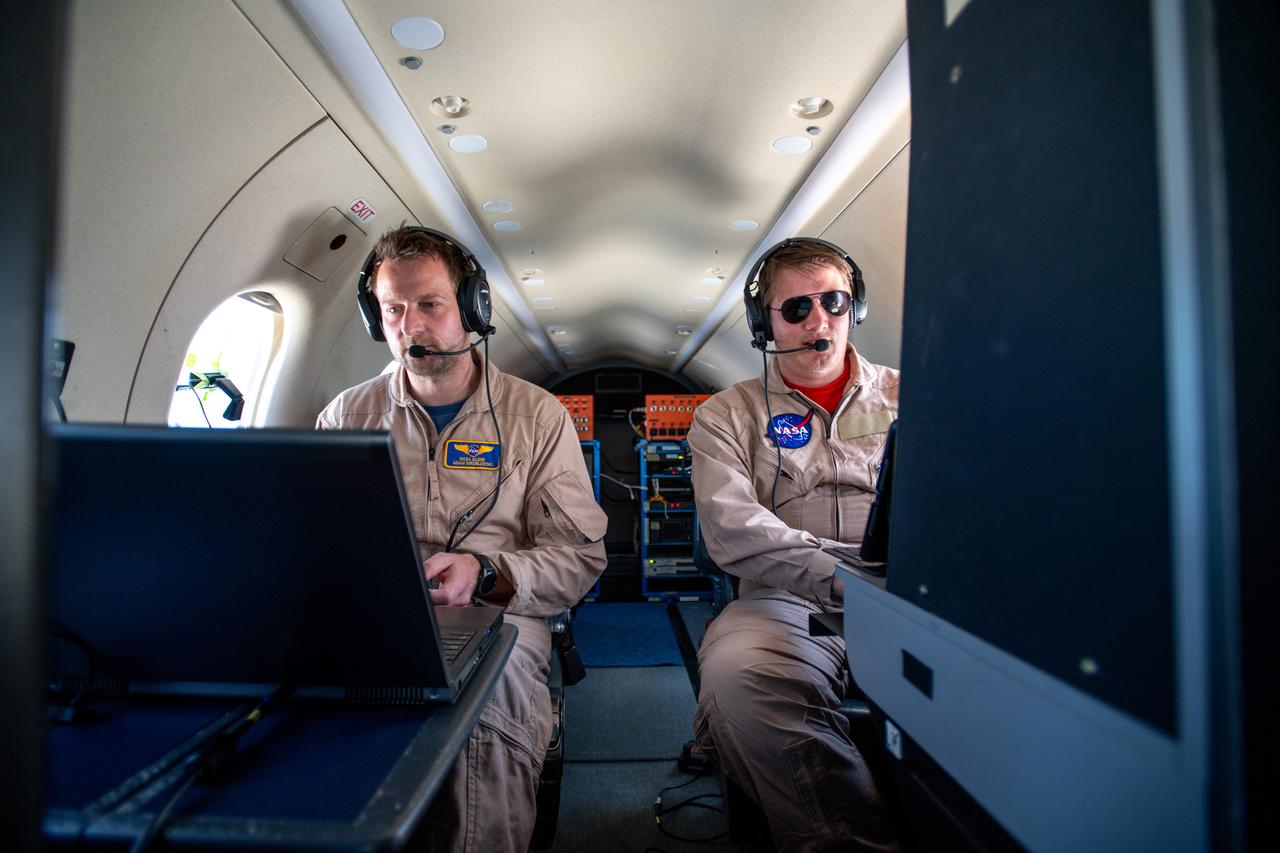

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
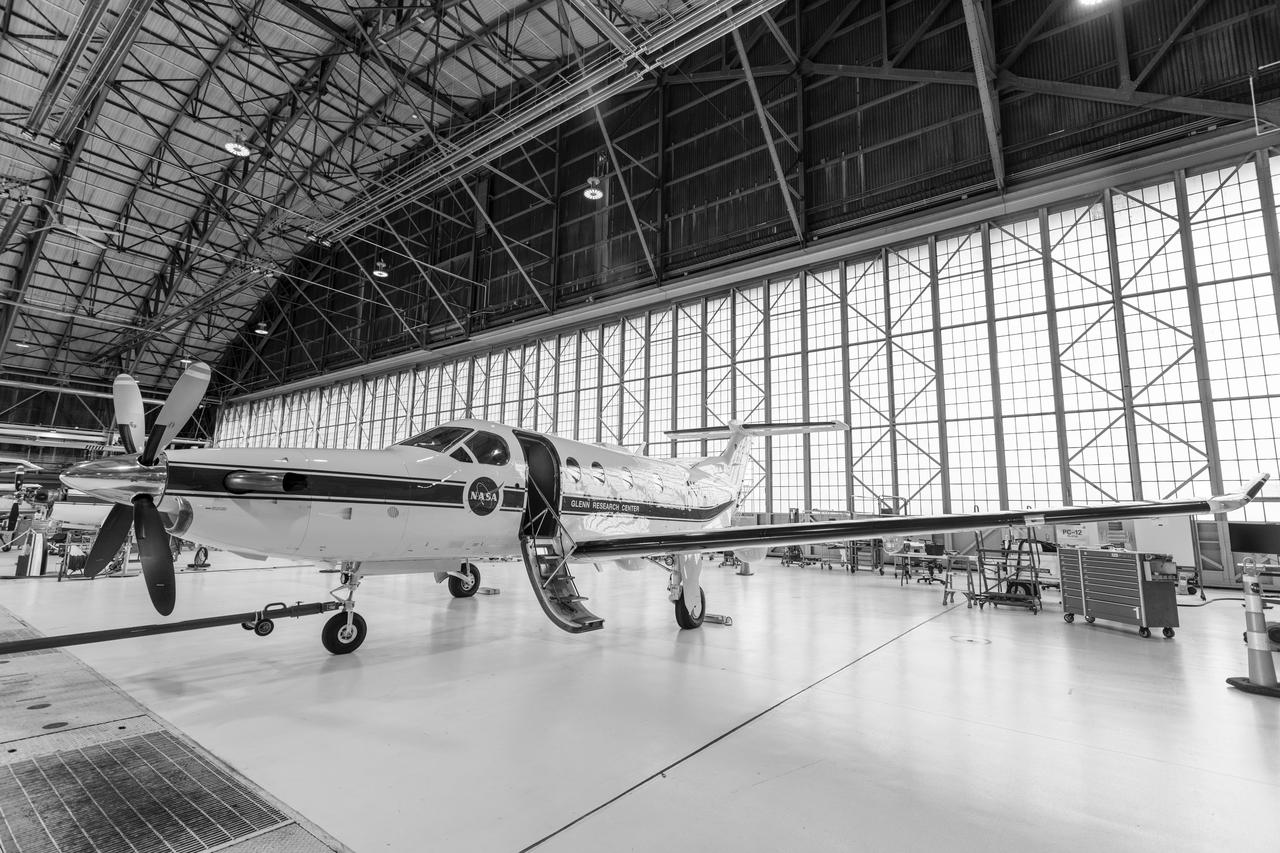

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.
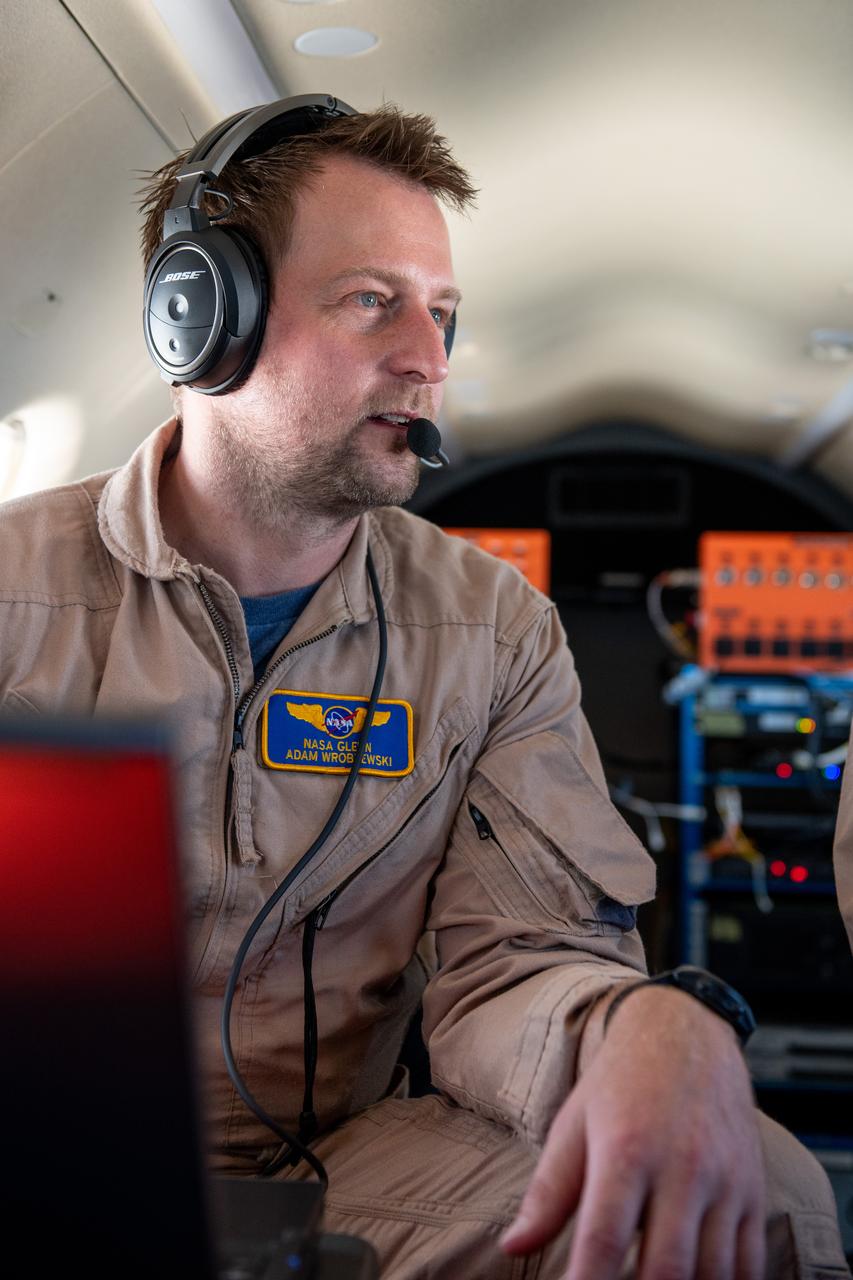

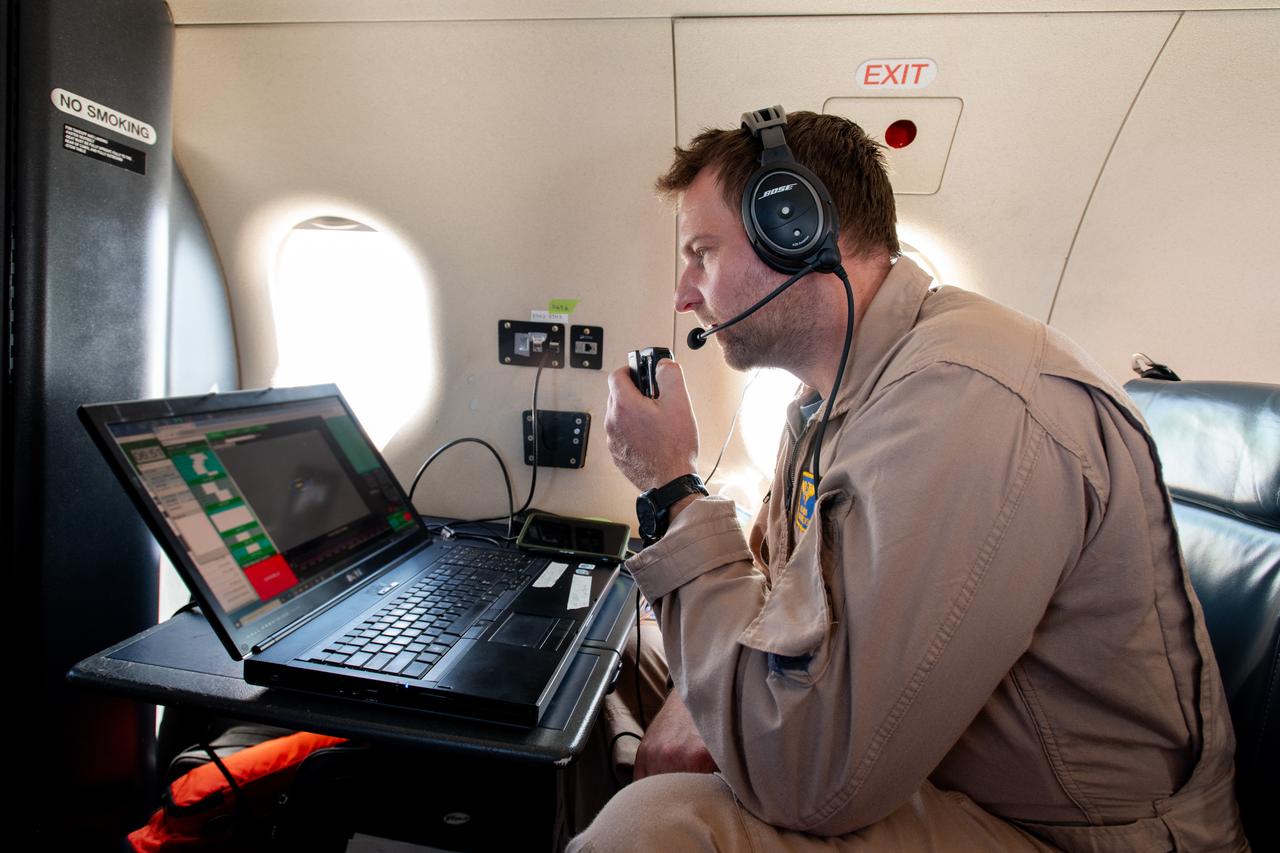
Adam Wroblewski p A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. Adam Wroblewski in the PC-12 over Lake Erie on June 13, 2024 sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
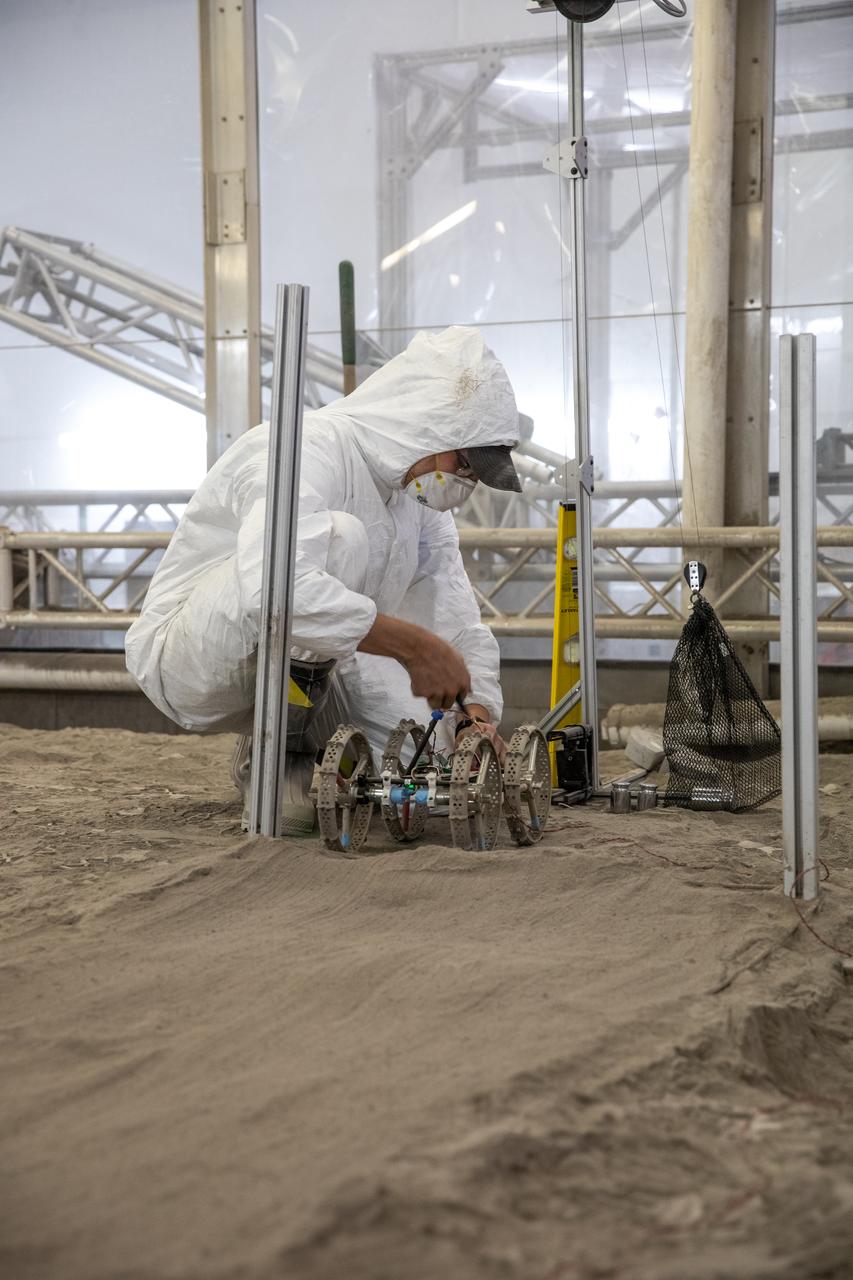

Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker stages Astrobotic’s mass-offloaded CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – for a drawbar pull test inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
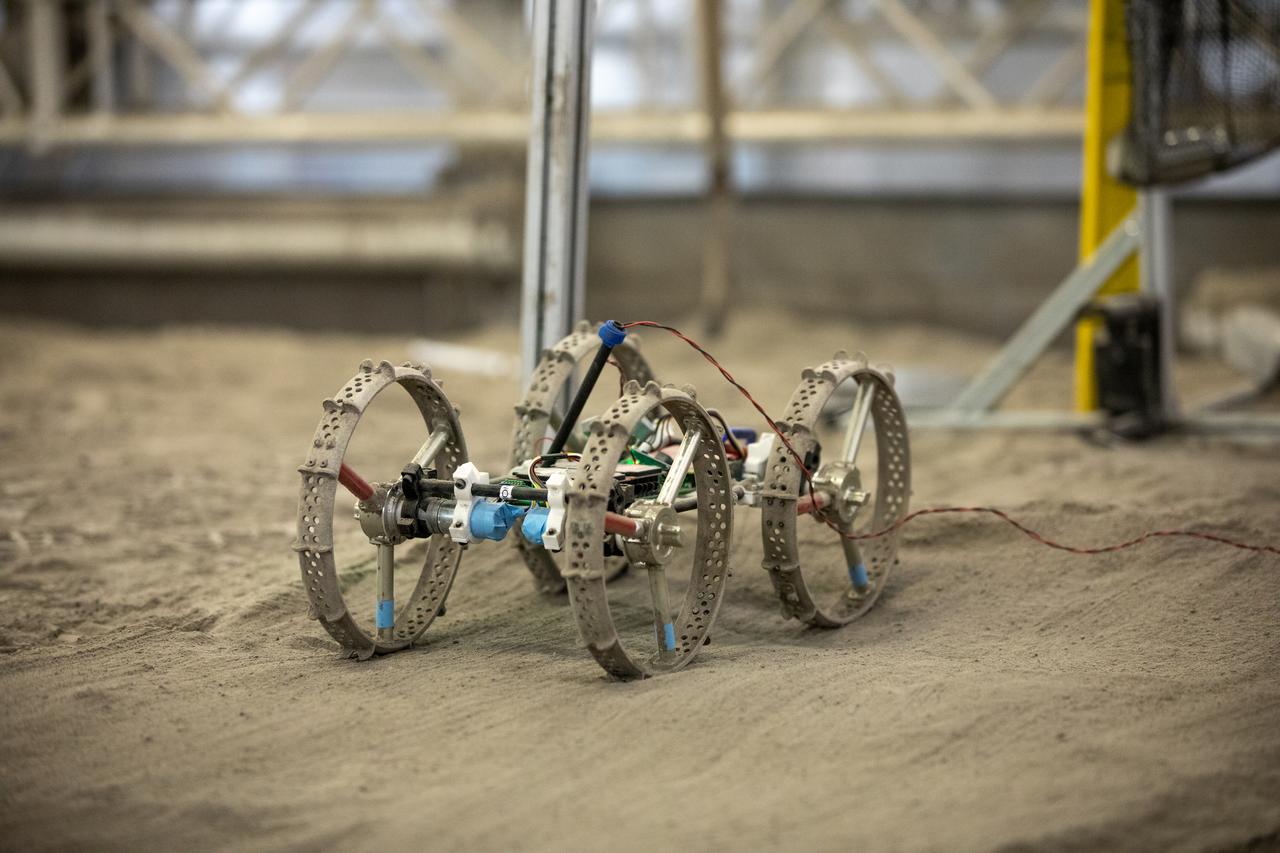
A mass-offloaded version of Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – is used to simulate mobility in low lunar gravity inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
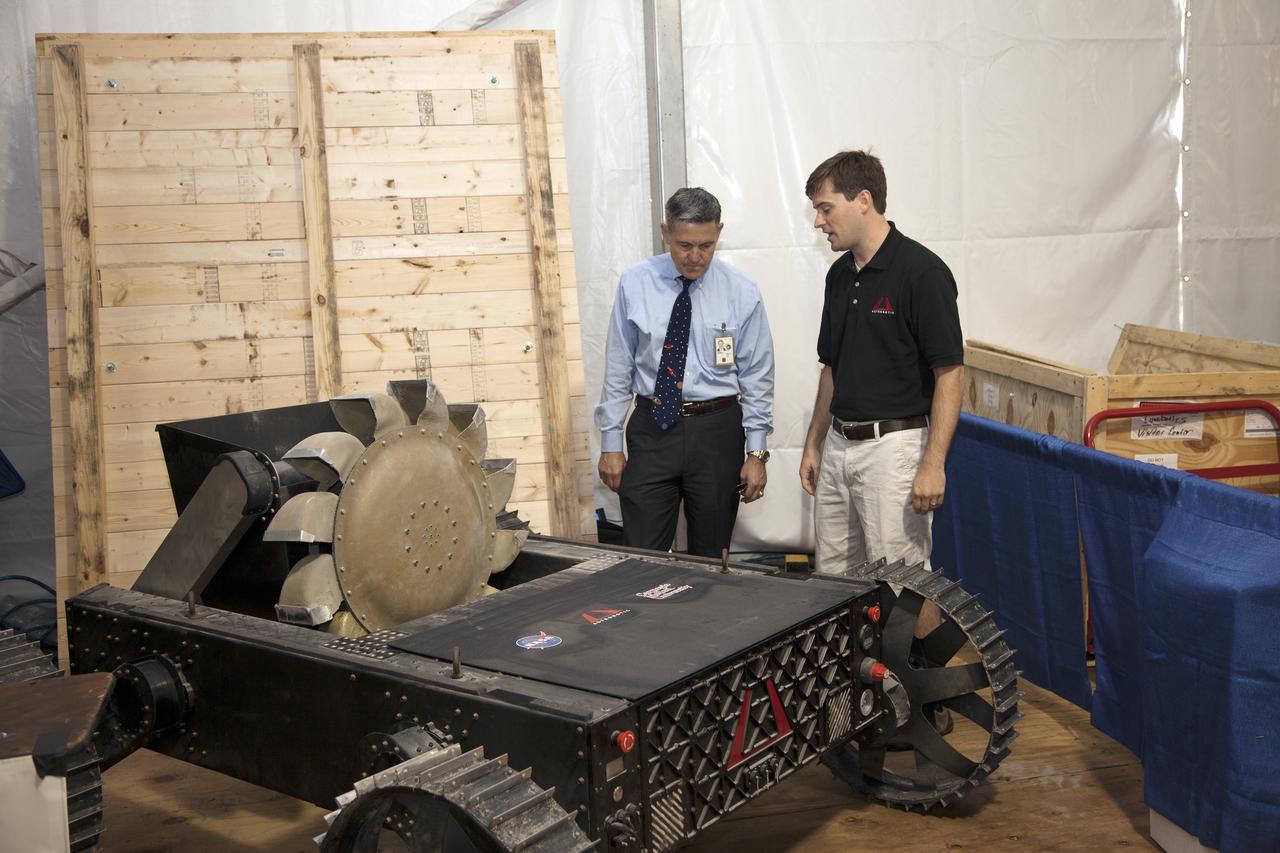

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana looks at the Polaris rover on display at NASA’s Fourth Annual Robotic Mining Competition. Developed by Astrobotic Technologies Inc. under a Small Business Innovative Research contract, Polaris will be demonstrated during the competition that takes place through May 24. The mining competition is coordinated by Kennedy Space Center’s Education Office for the agency’s Exploration Systems Mission Directorate. Undergraduate and graduate students from 50 universities and colleges in the U.S. and eight countries around the world will use their remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material called regolith that has characteristics similar to asteroids, moons of Mars and Mars itself. Photo credit: NASA_Lorne Mathre
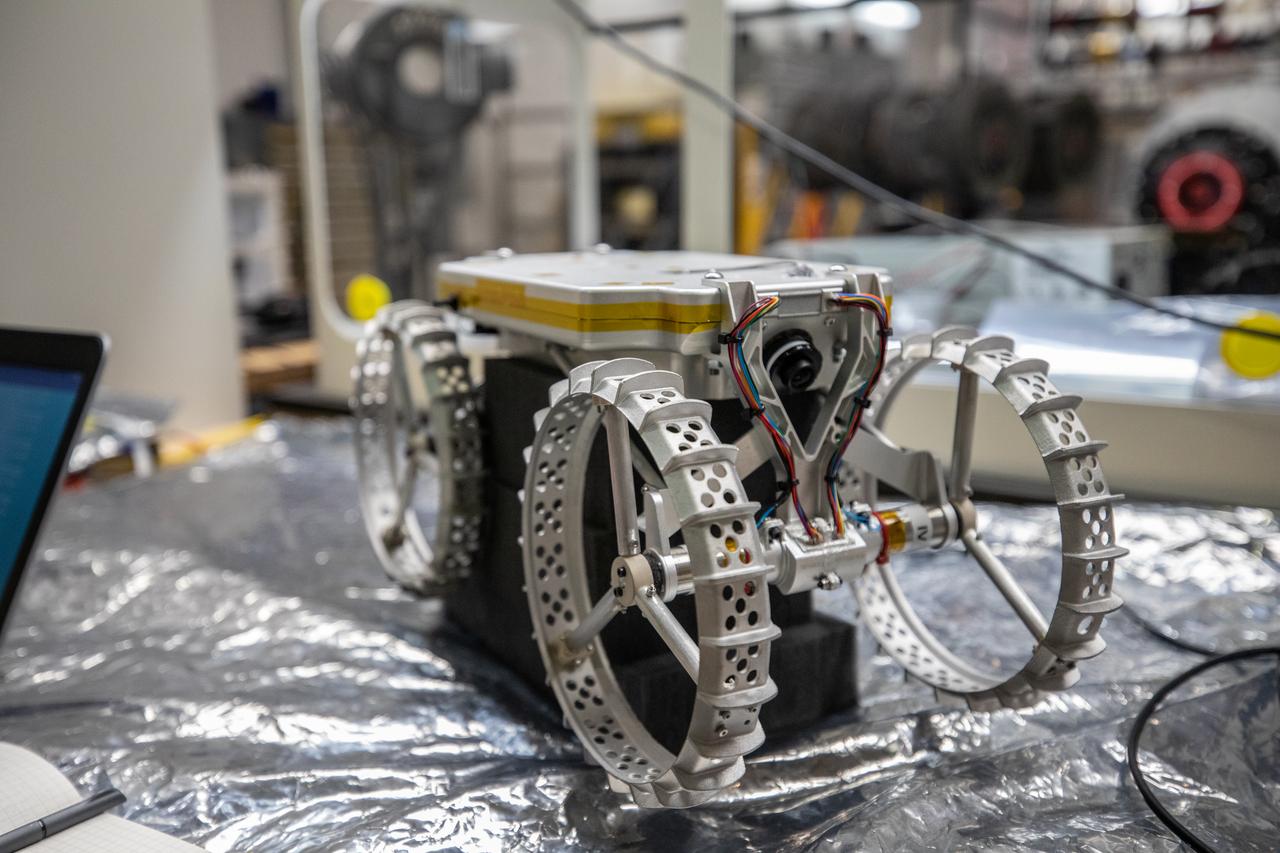
Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – is photographed in its benchtop testing configuration at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is planning to use the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
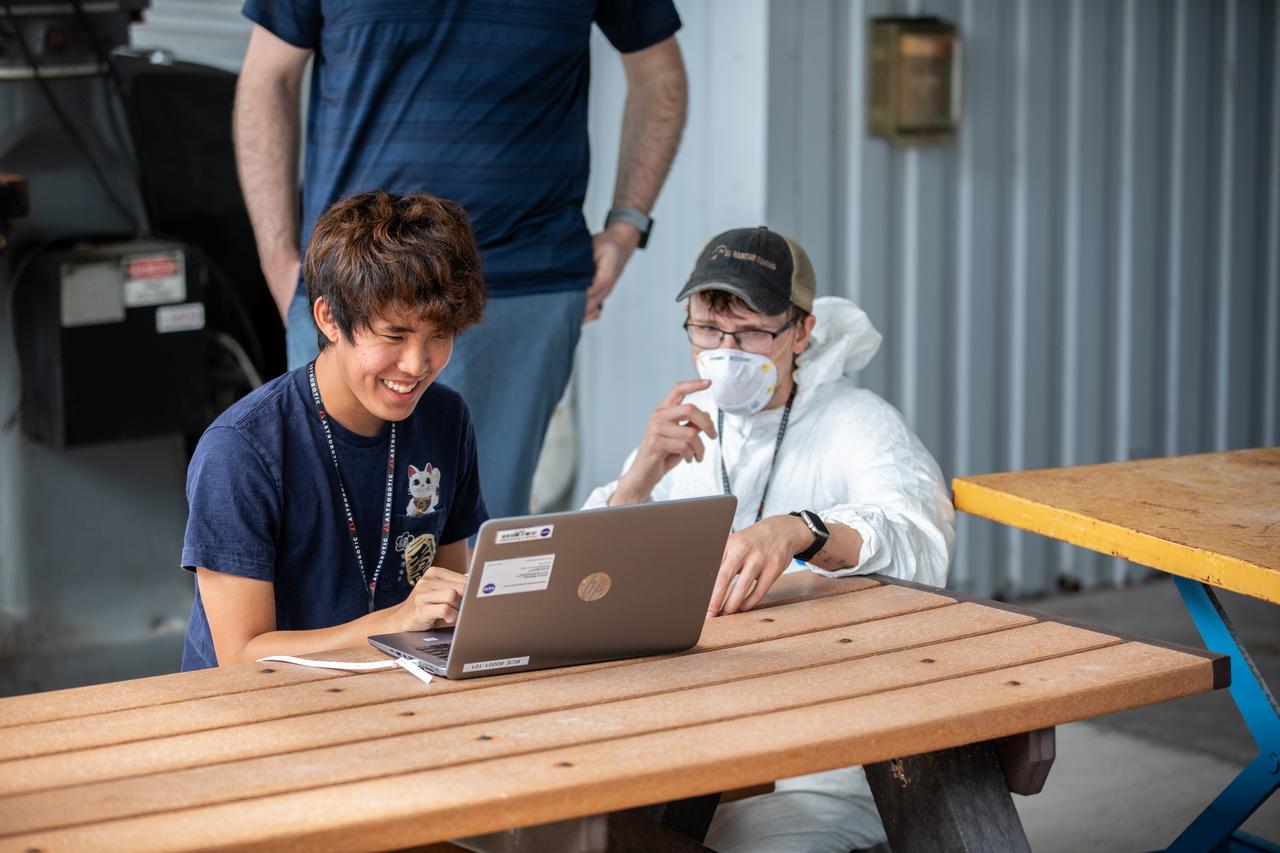

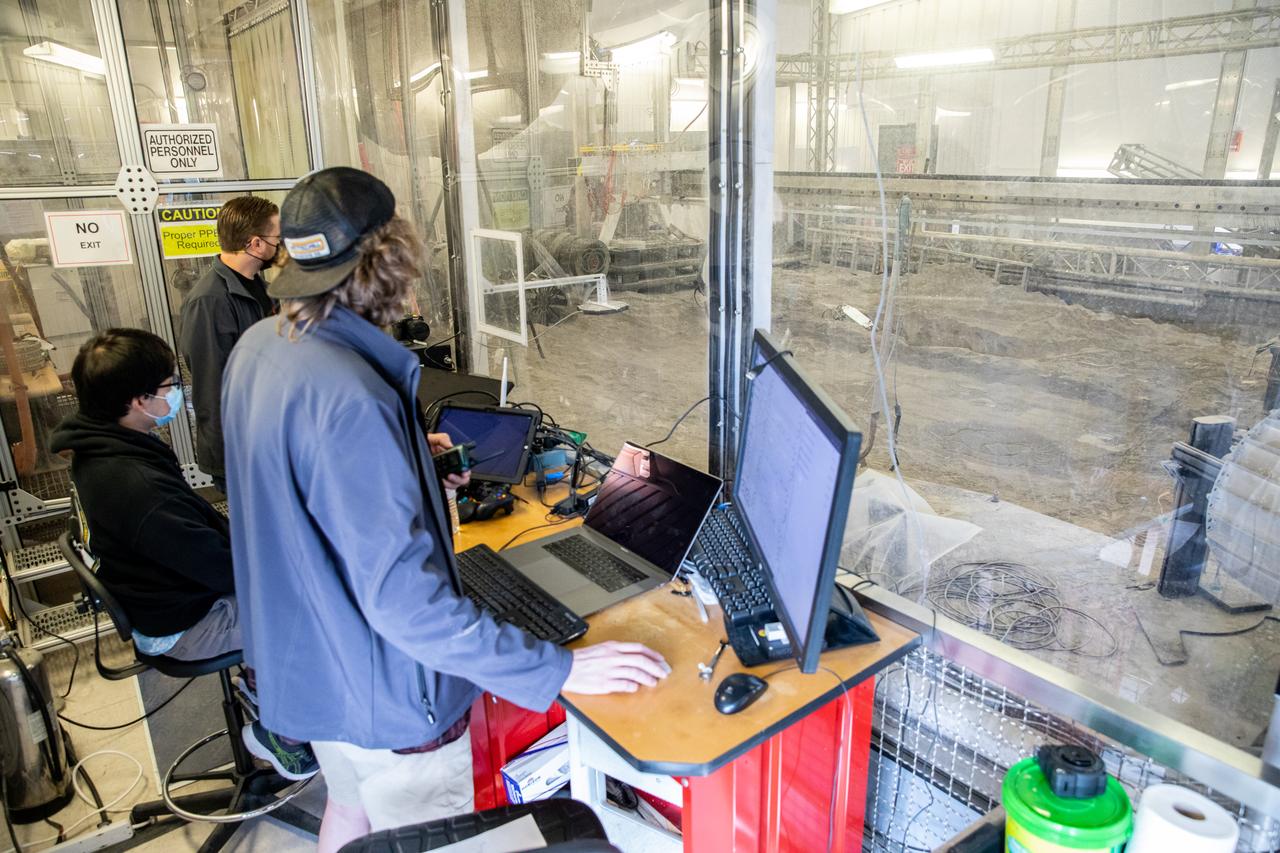
Senior Software Engineer Taylor Whitaker (right) and Software Engineering intern Ashten Akemoto create a mobility routine for Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – using the company’s ground software at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
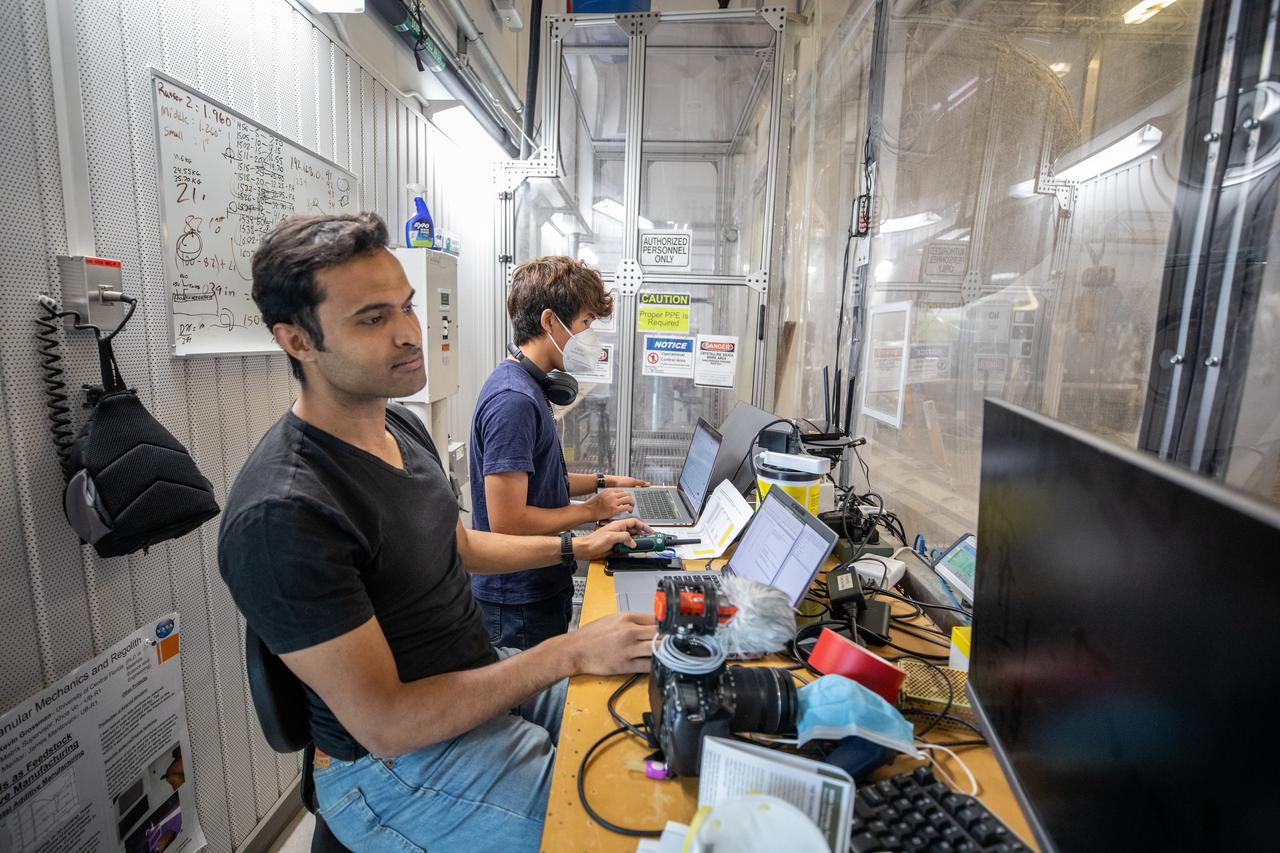

Senior Embedded Software Engineer Aamer Almujahed (left) and Software Engineering intern Ashten Akemoto run the ground software for Astrobotic’s CubeRover drawbar pull test inside the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith pit at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works facility on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the GMRO lab’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.

Robotics Software Engineer II Chris Rampolla (right) and Software Engineering intern Ashten Akemoto issue commands to Astrobotic’s CubeRover using the company’s ground software during mobility testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is using the spaceport’s Swamp Works facility and the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory to conduct mobility testing of their rover. The laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, will help depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
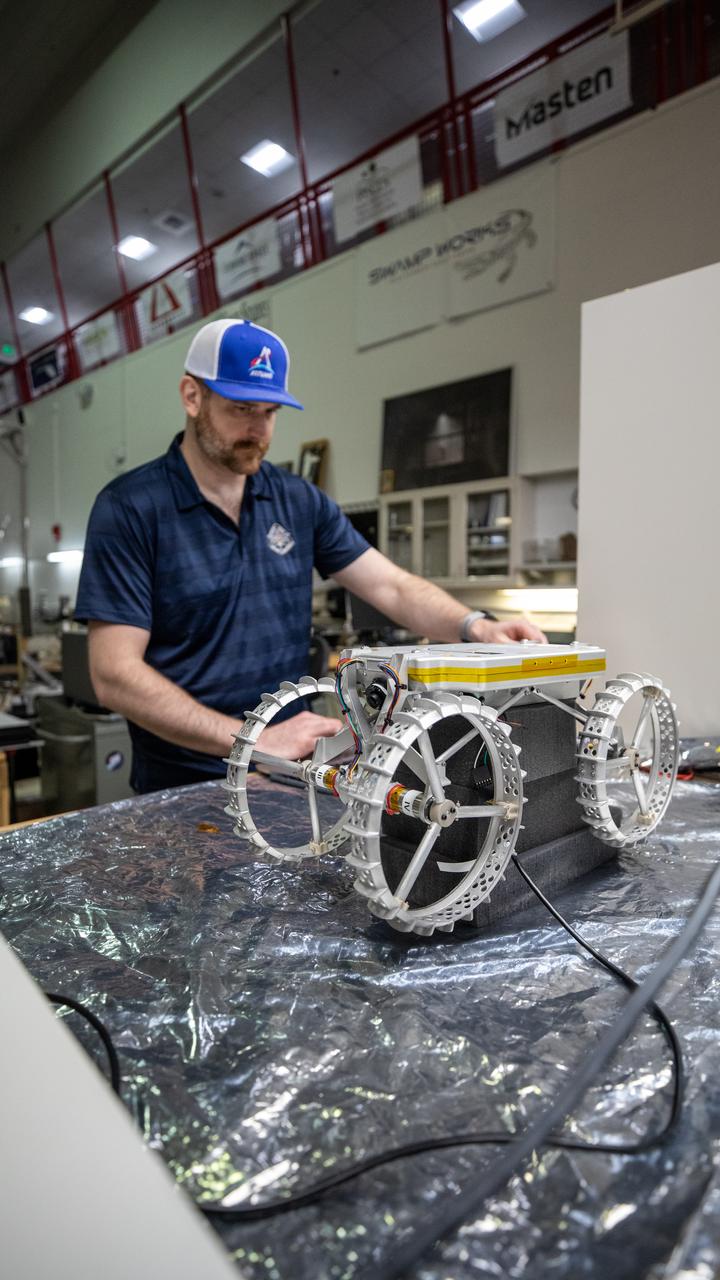

Robotics Software Engineer II Chris Rampolla runs benchtop verifications on Astrobotic’s CubeRover – a lightweight, modular planetary rover – before delivery to Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 30, 2022. Astrobotic – a Pittsburgh-based space robotics company – is planning to use Swamp Work’s Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant, to depict how the company’s CubeRover would perform on the Moon. NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program provided the funding for initial development, and a $2 million Tipping Point award from the agency has provided additional funding for continued development into a more mature rover.
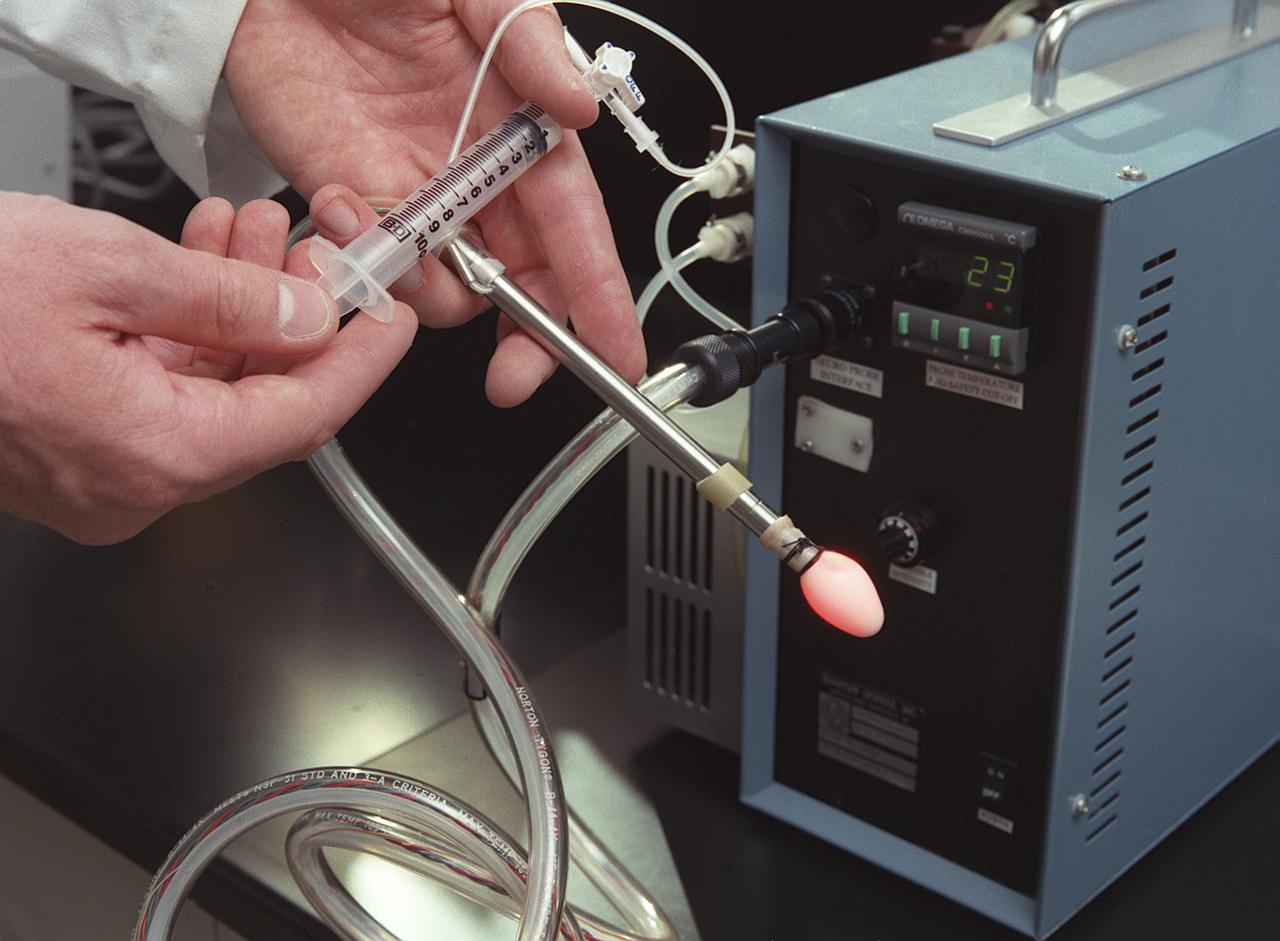

A special lighting technology was developed for space-based commercial plant growth research on NASA's Space Shuttle. Surgeons have used this technology to treat brain cancer on Earth, in two successful operations. The treatment technique called photodynamic therapy, requires the surgeon to use tiny pinhead-size Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) (a source releasing long wavelengths of light) to activate light-sensitive, tumor-treating drugs. Laser light has been used for this type of surgery in the past, but the LED light illuminates through all nearby tissues, reaching parts of a tumor that shorter wavelengths of laser light carnot. The new probe is safer because the longer wavelengths of light are cooler than the shorter wavelengths of laser light, making the LED less likely to injure normal brain tissue near the tumor. It can also be used for hours at a time while still remaining cool to the touch. The LED probe consists of 144 tiny pinhead-size diodes, is 9-inches long, and about one-half-inch in diameter. The small balloon aids in even distribution of the light source. The LED light source is compact, about the size of a briefcase, and can be purchased for a fraction of the cost of a laser. The probe was developed for photodynamic cancer therapy by the Marshall Space Flight Center under a NASA Small Business Innovative Research program grant.
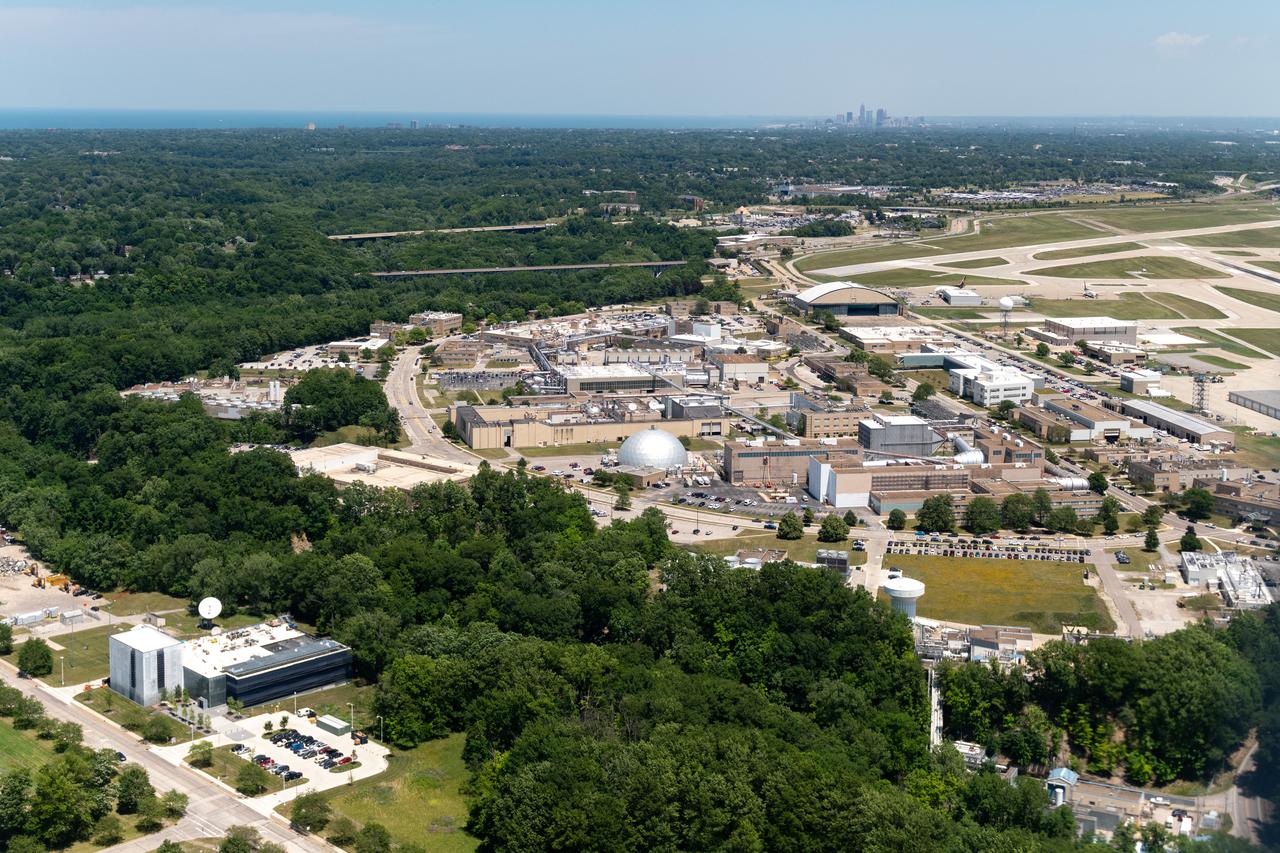

Aerial Photograph of Glenn Research Center With Downtown Cleveland in the Distance taken from the PC-12 on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
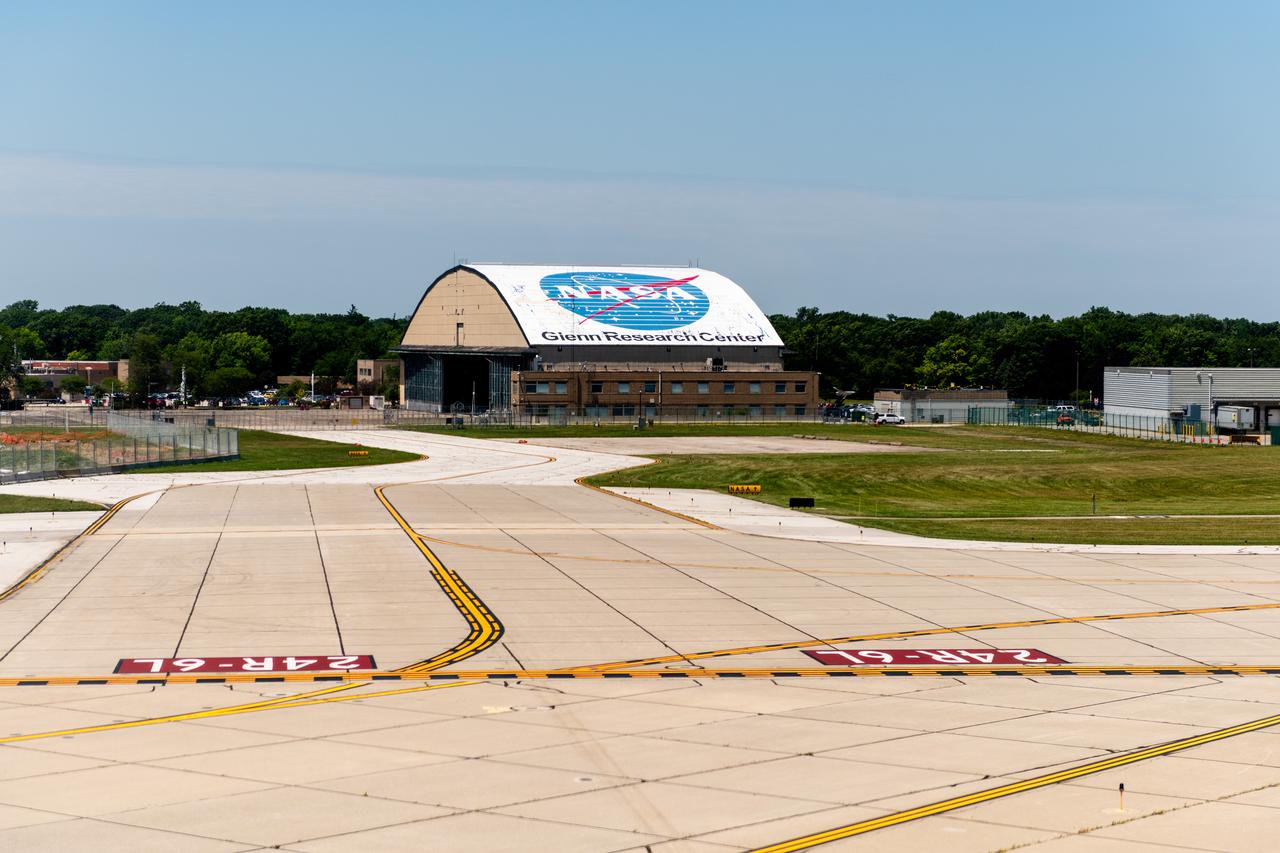

View of the Glenn Research Center Hangar from the Cleveland Hopkins Airport Runway during a testing flight on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
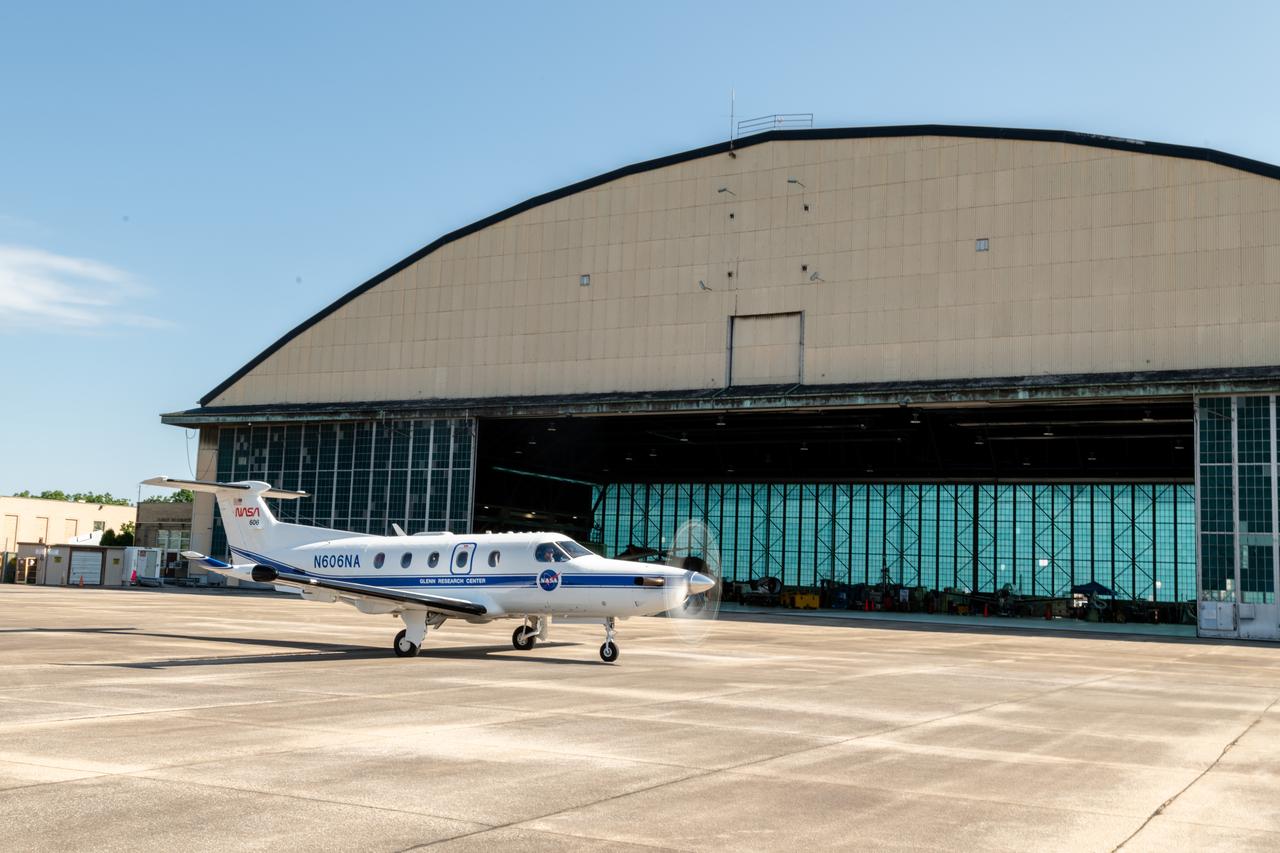

At Glenn Research Center, the PC-12 is Prepped for a flight and ready to takeoff on June 12, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
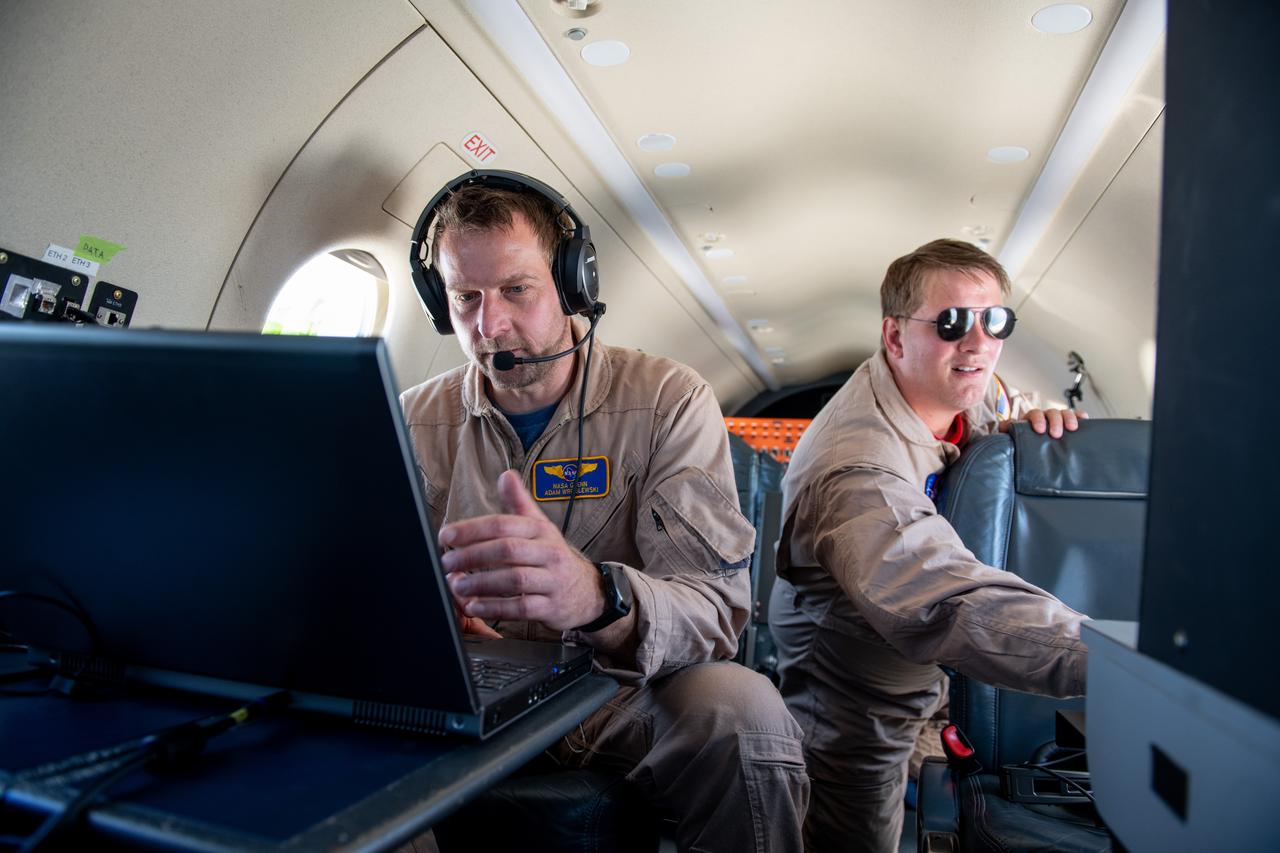

Adam Wroblewski and Shaun McKeehan Working In PC-12 Aircraft during in flight testing on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
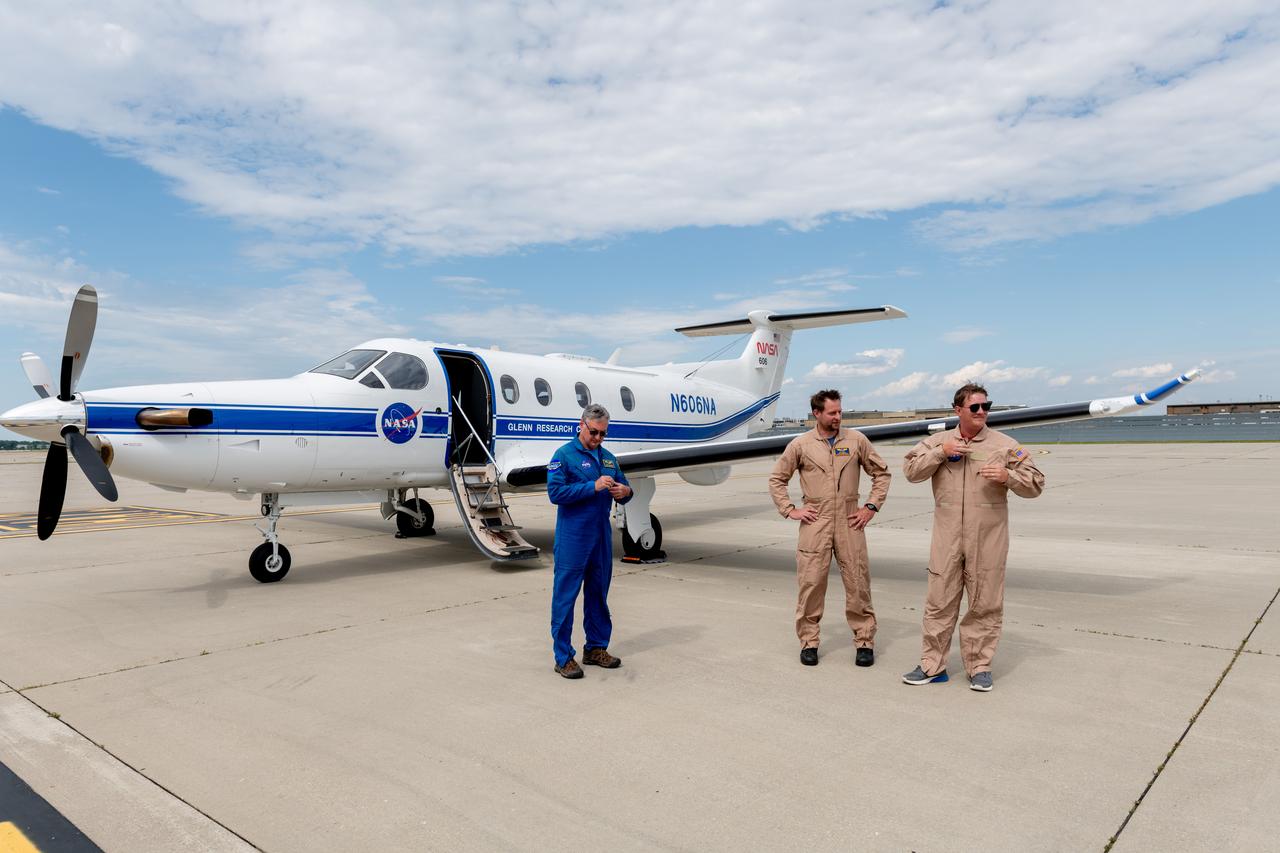

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Pictured here on June 13, 2024 from Left to Right: Kurt Blakenship, Adam Wroblewski, Shaun McKeehan. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
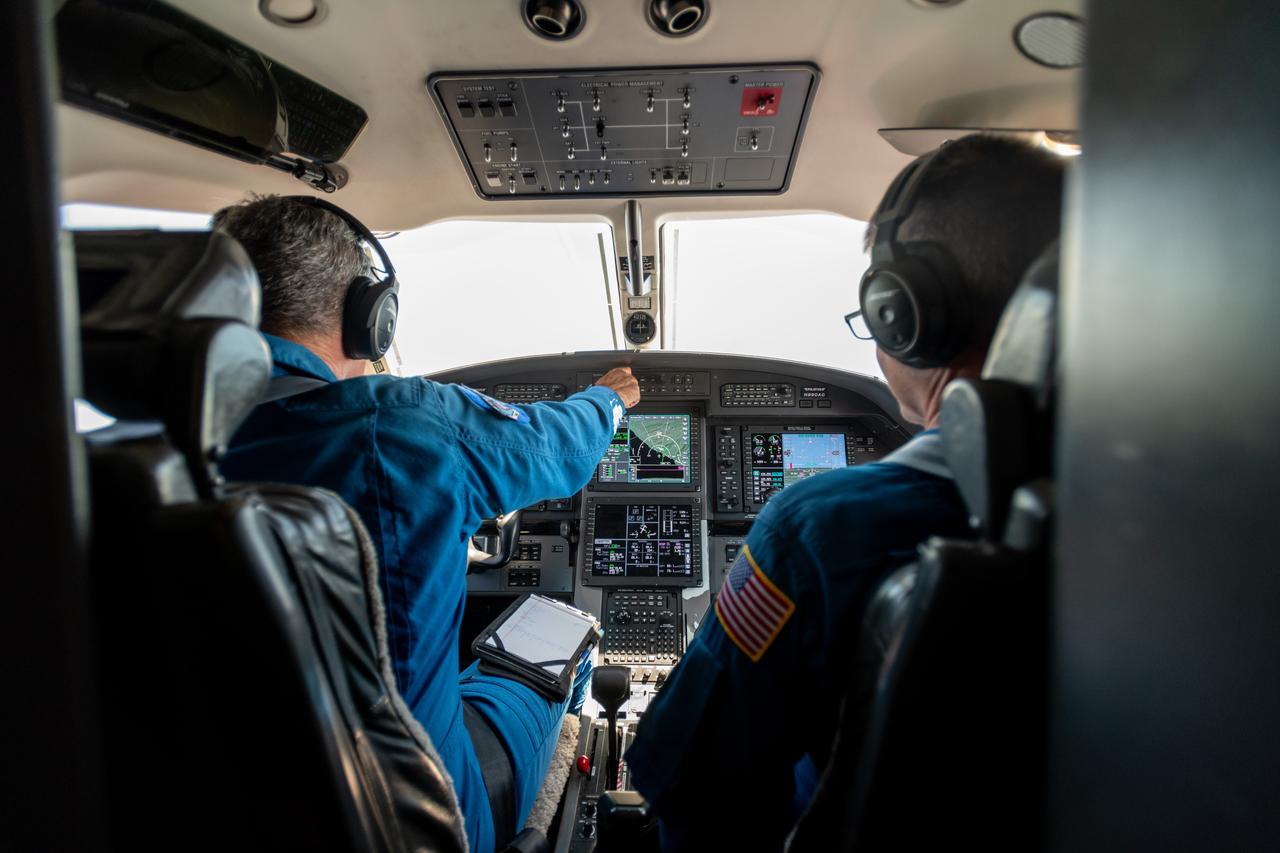

Kurt Blankenship and James Demers Fly PC-12 Aircraft During Testing on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
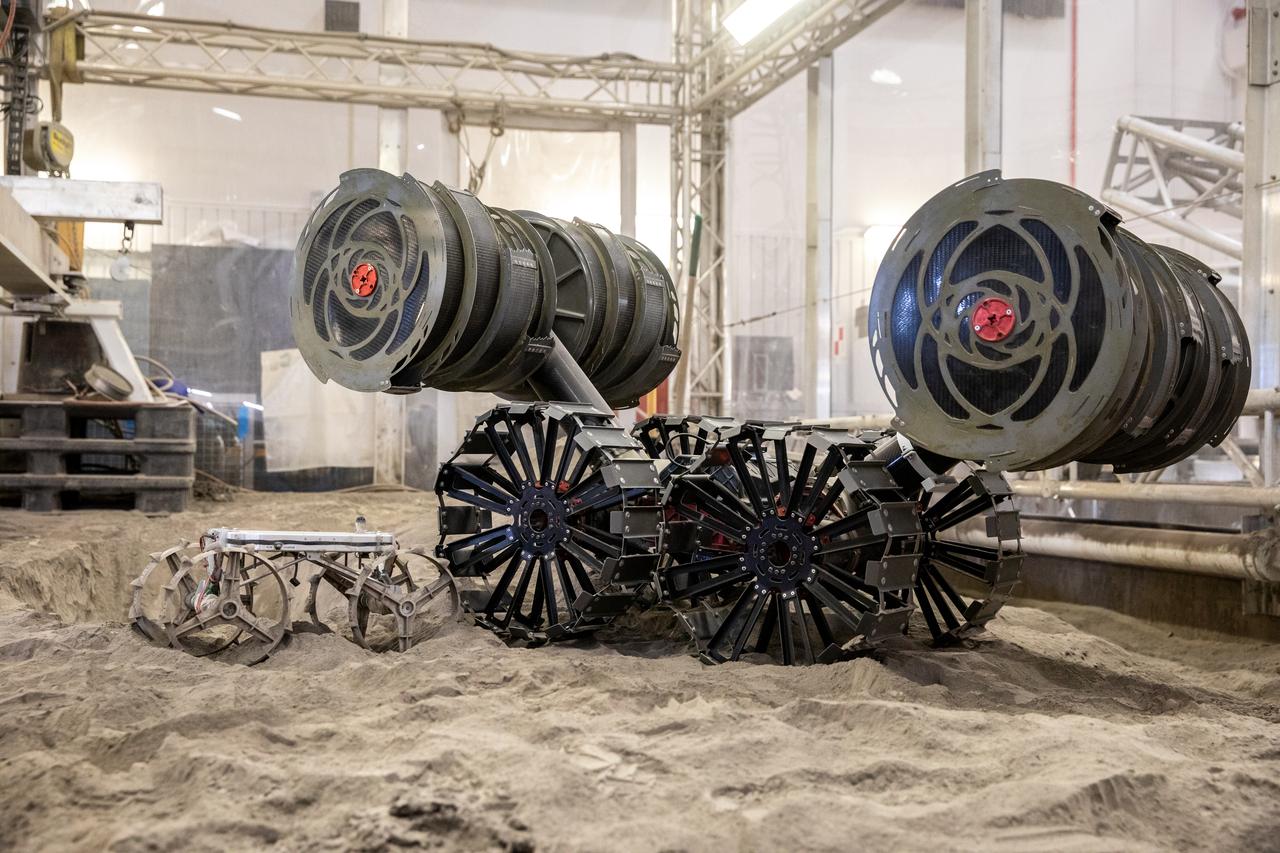

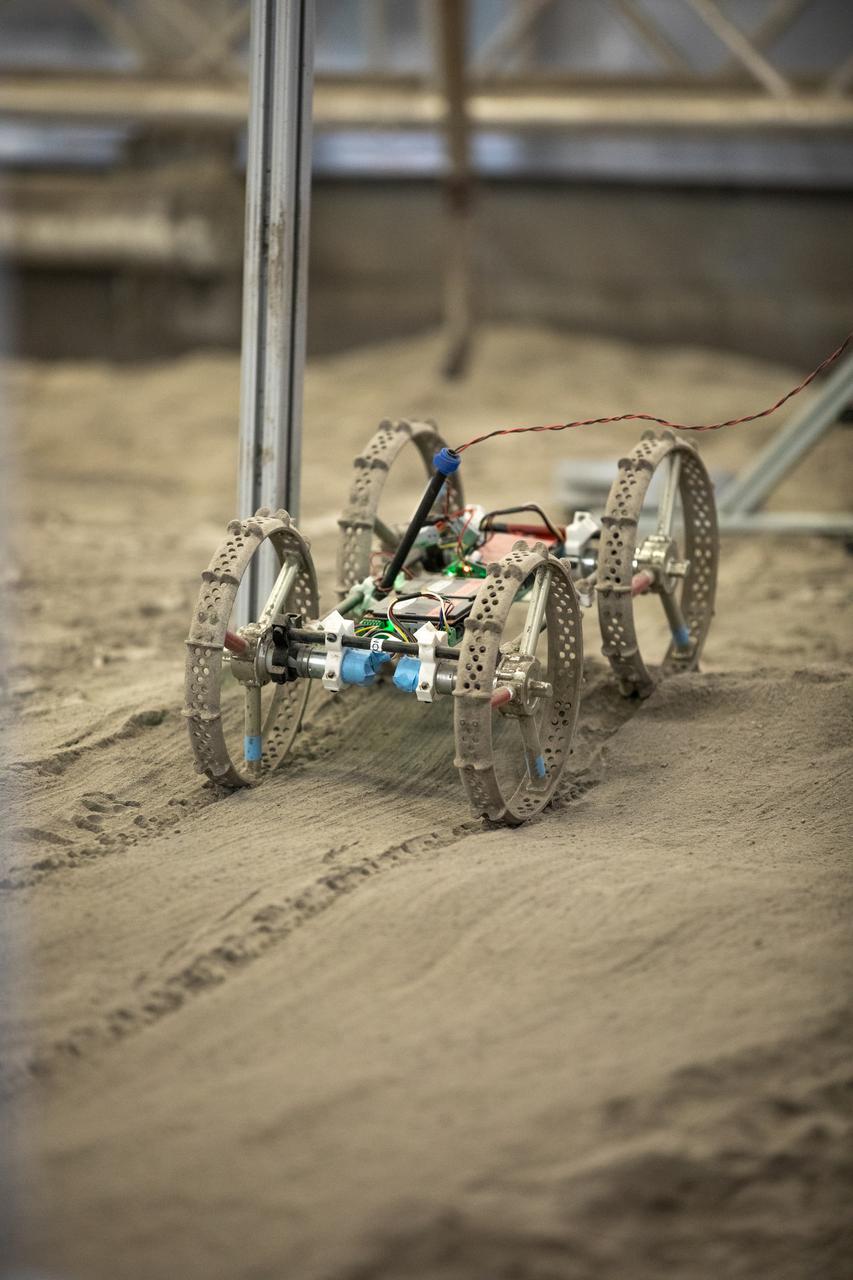
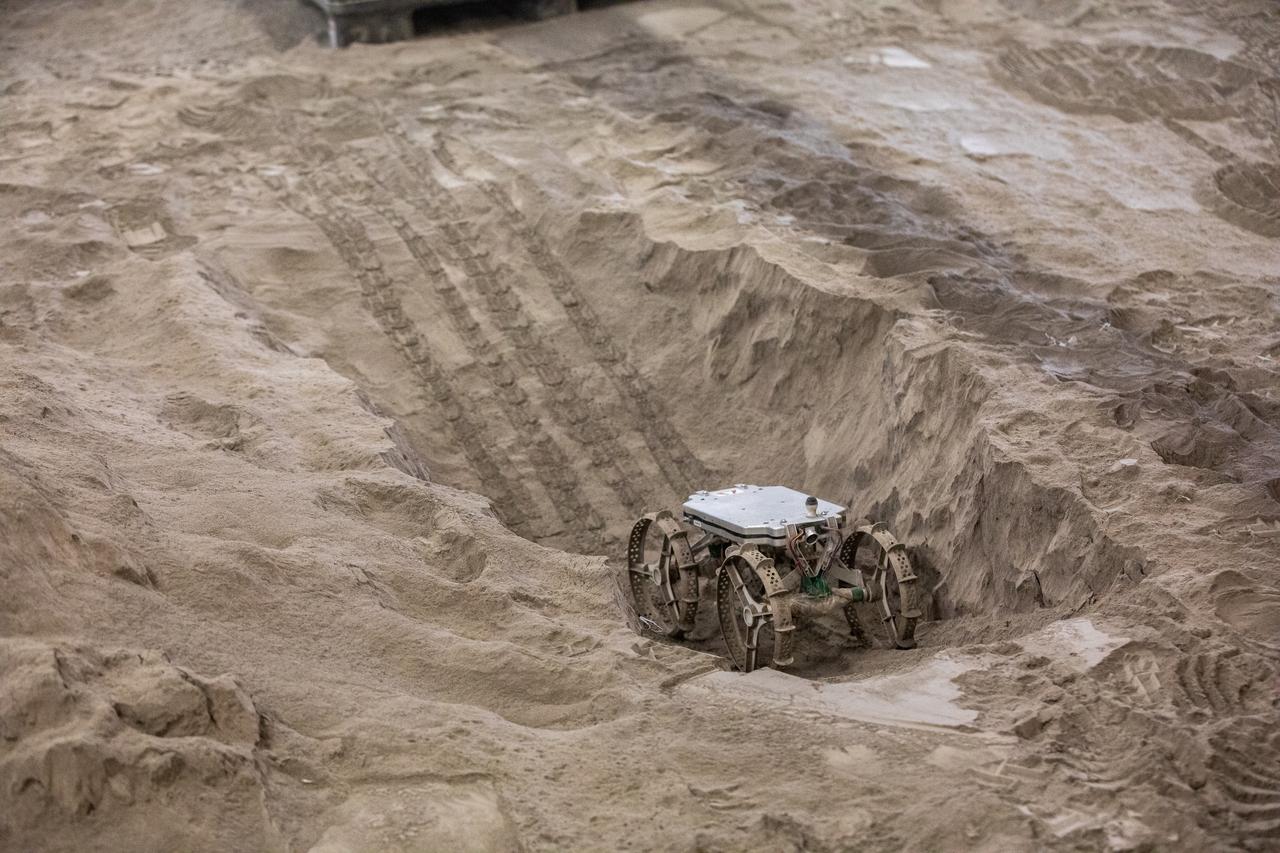
The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design. Also in the bin is NASA’s Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), a robotic platform designed to dig on the Moon. The regolith bin simulates the Moon’s surface.
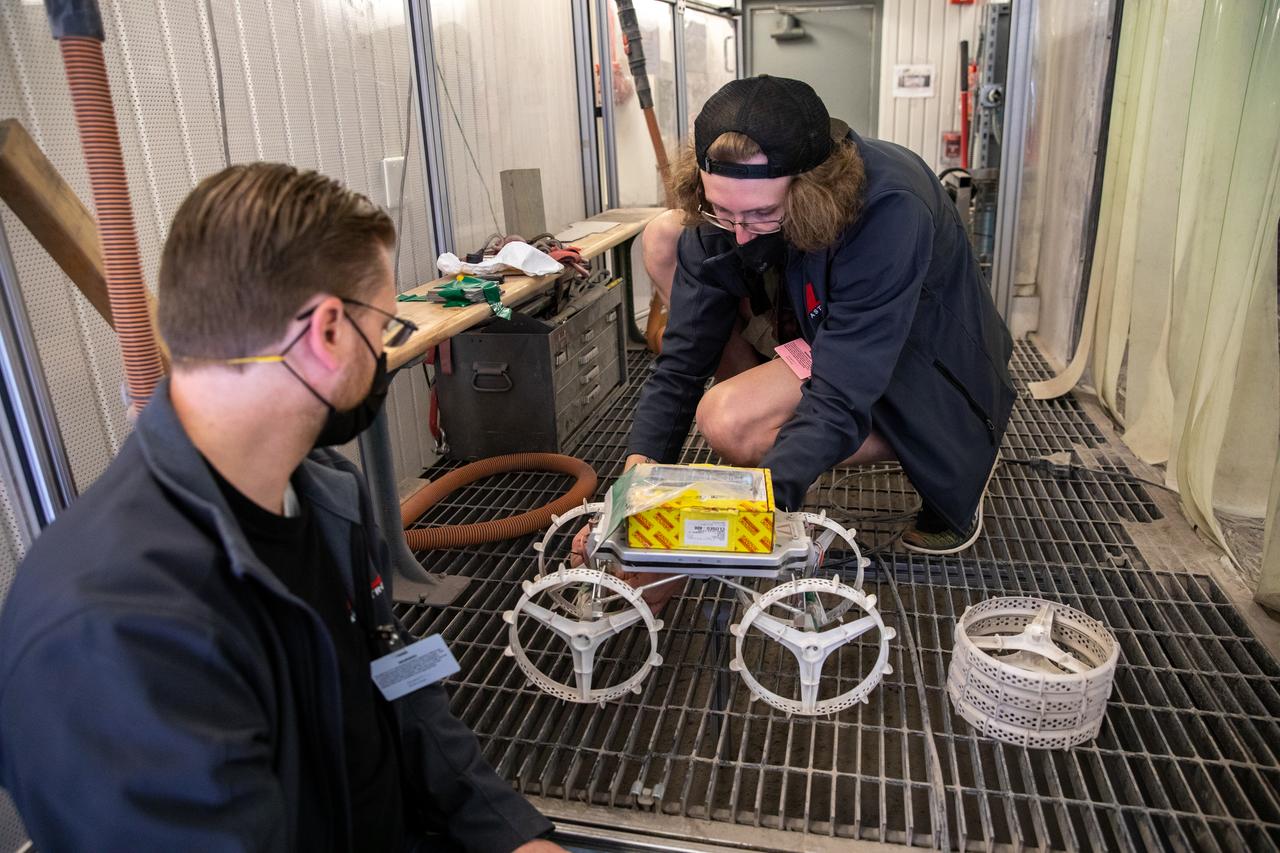

Astrobotic employees Troy Arbuckle, at left, Planetary Mobility lead mechanical engineer, and Taylor Whitaker, flight software engineer, prepare the Astrobotic CubeRover for its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
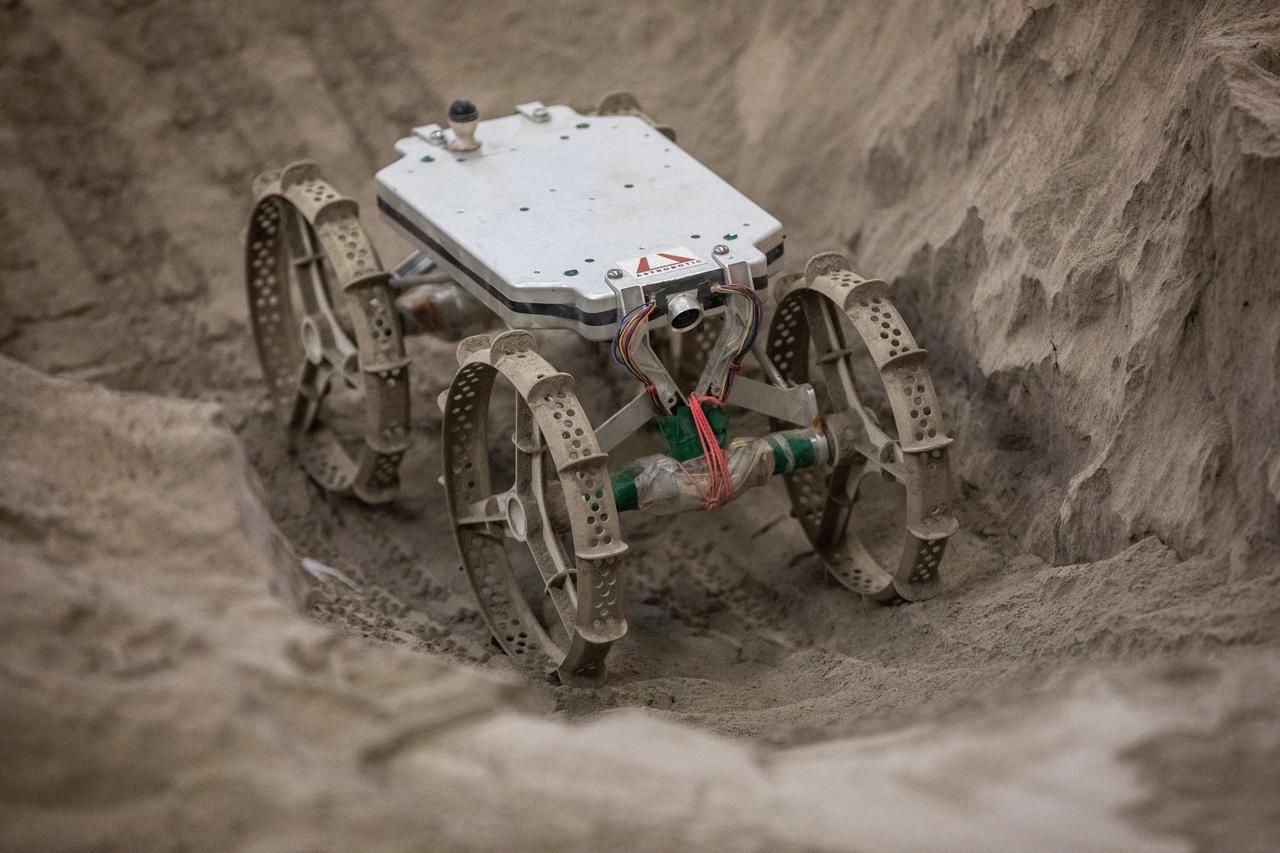

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
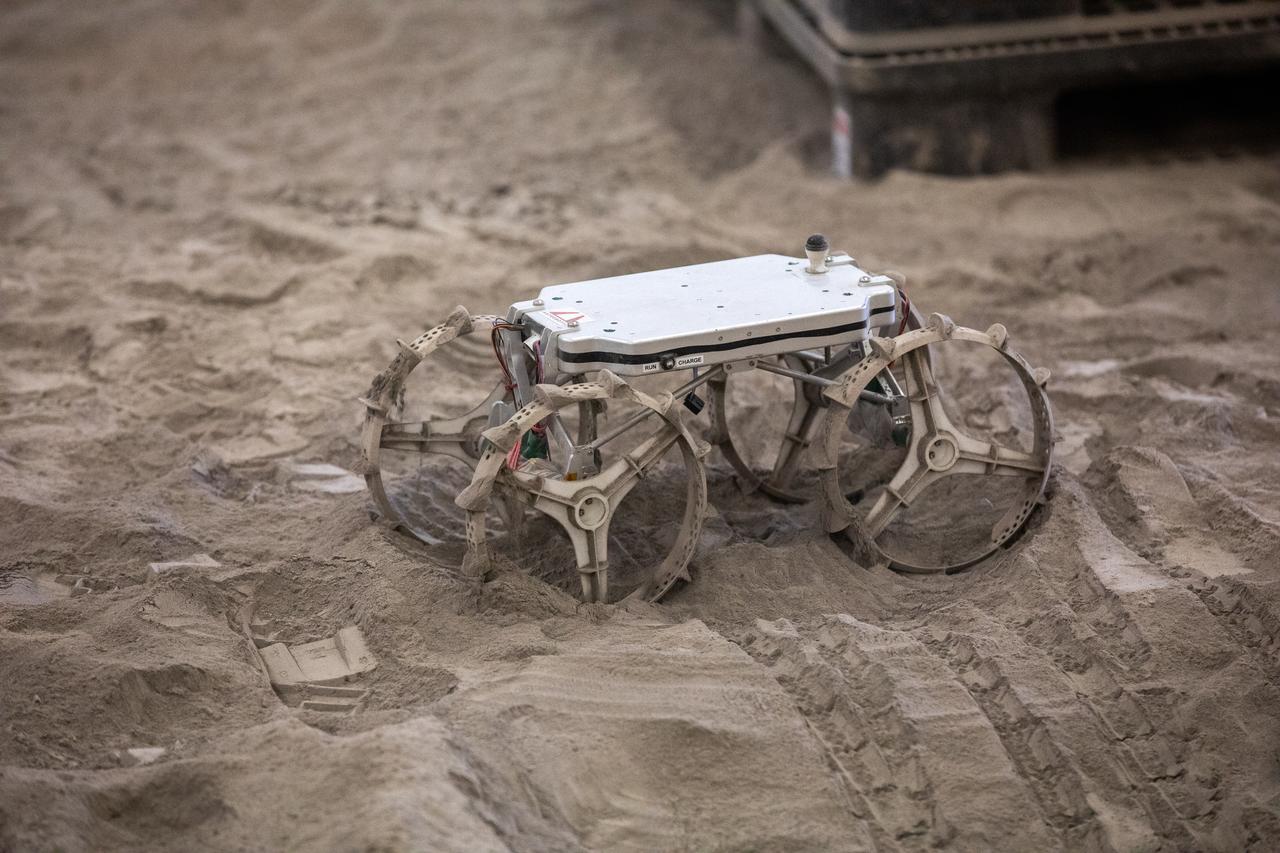

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
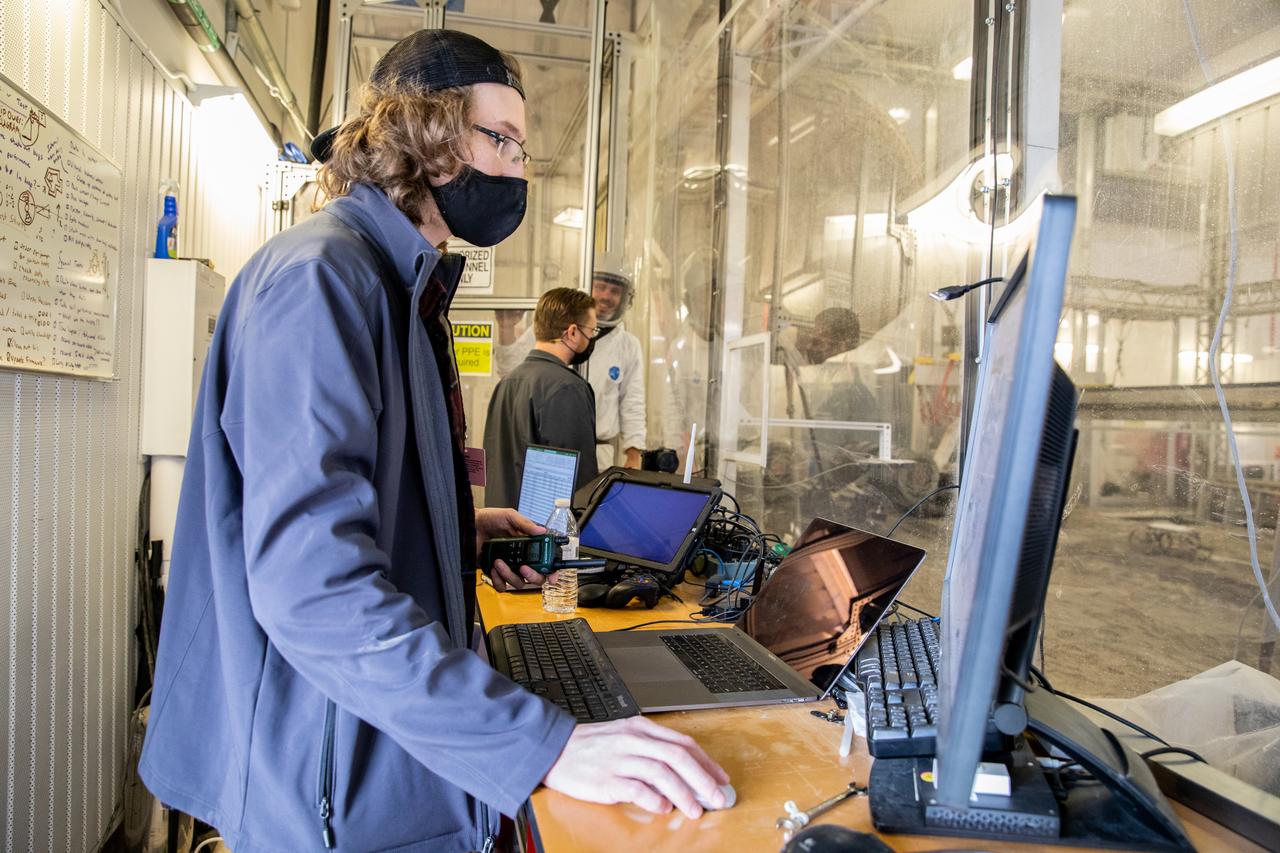

Taylor Whitaker, flight software engineer, monitors the progress of the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
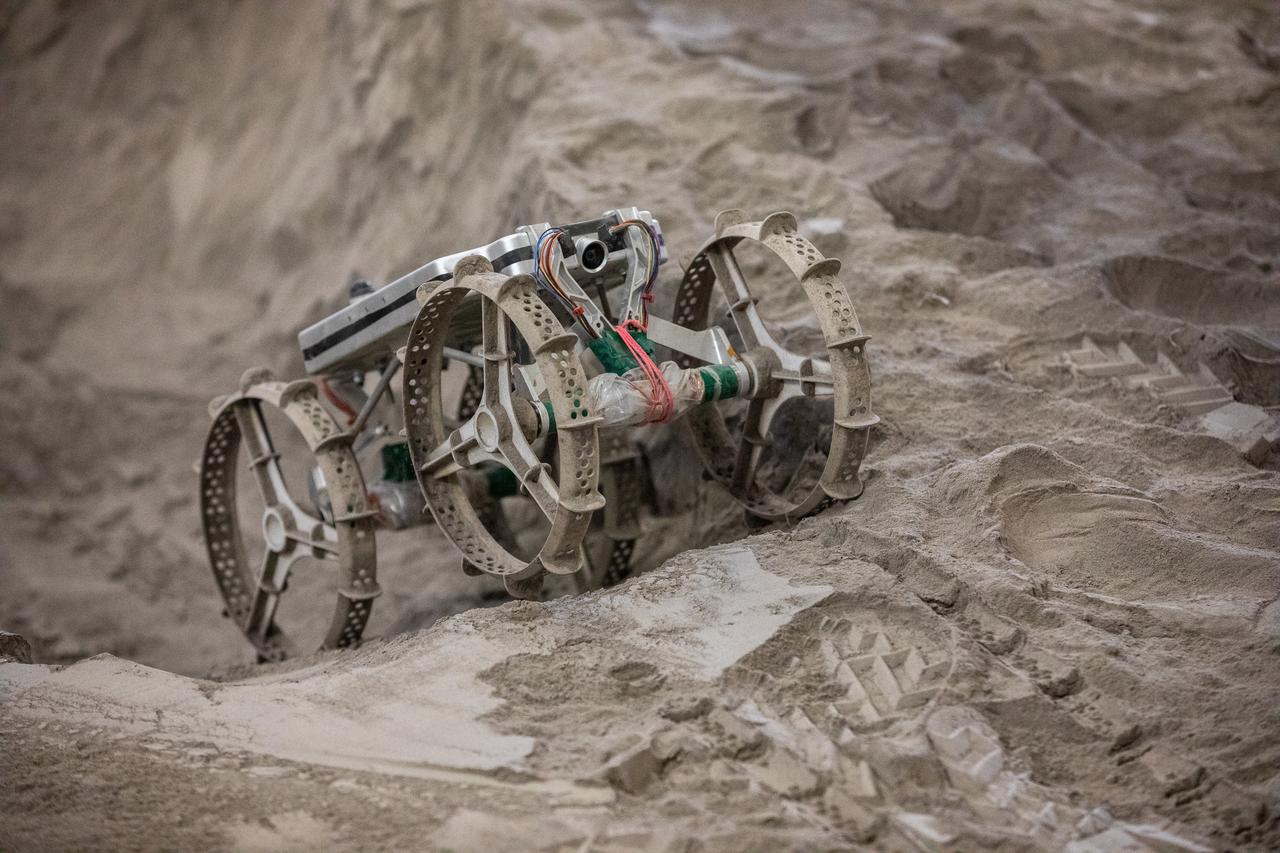

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
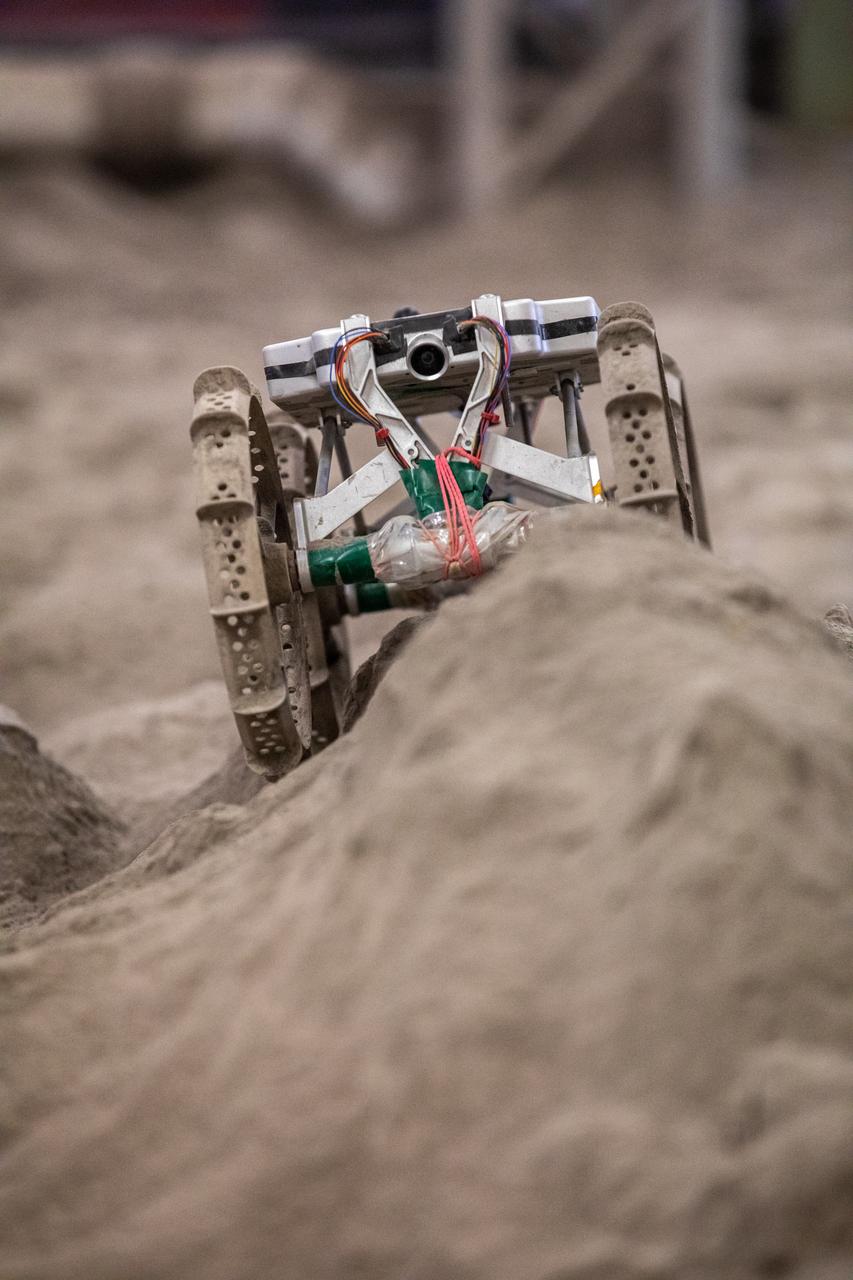

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses obstacles in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

Astrobotic employees Troy Arbuckle, at far left, Planetary Mobility lead mechanical engineer; Takuto Oikawa, mechanical engineer; and Taylor Whitaker, flight software engineer, monitor the progress of the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
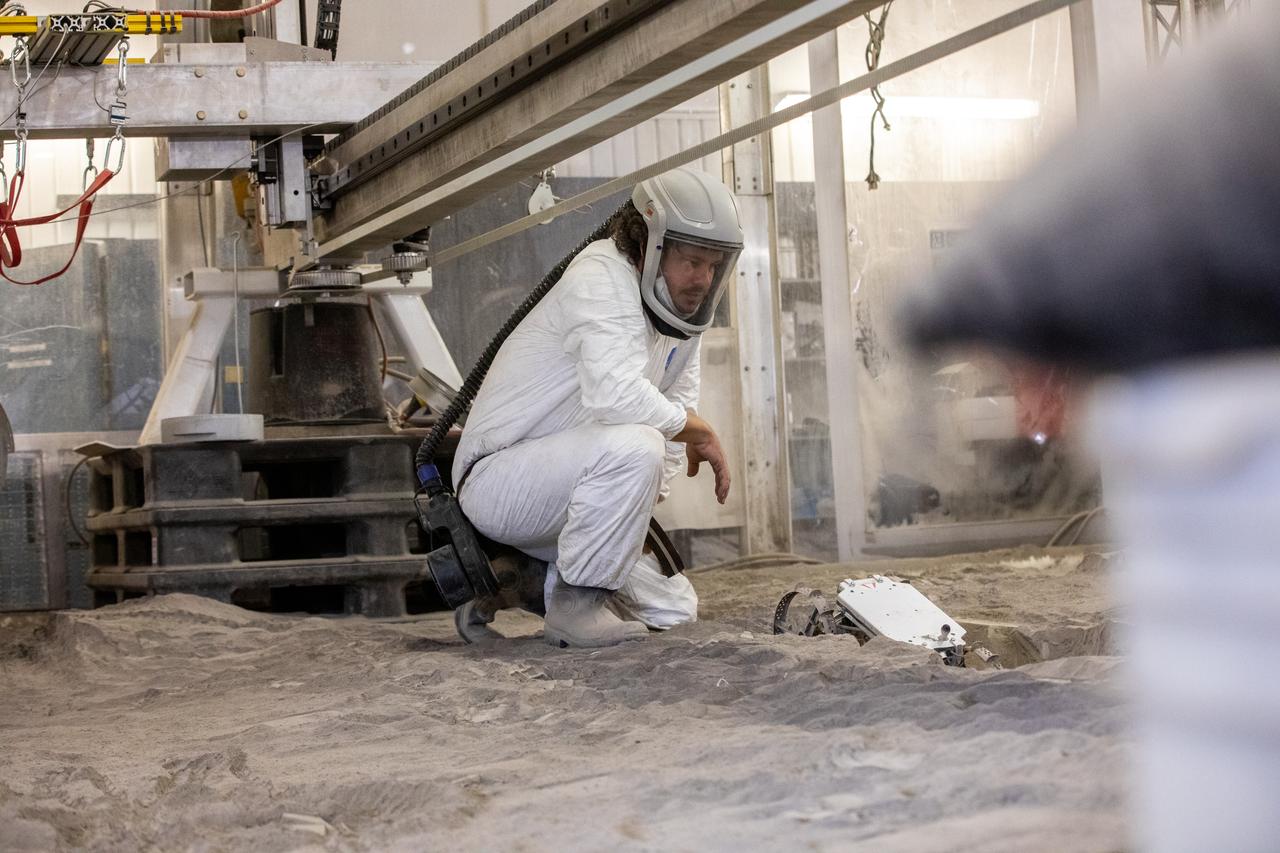

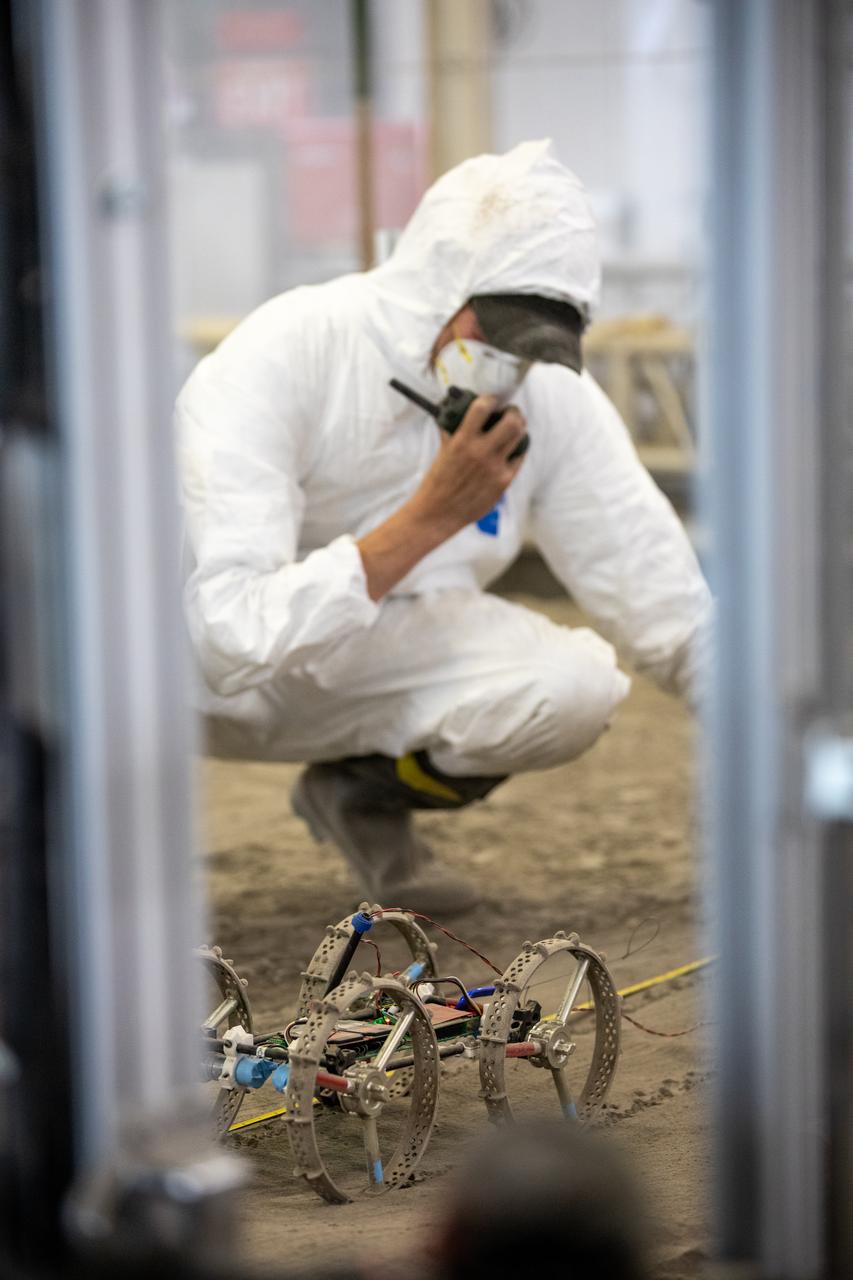
A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, checks the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the regolith bin at Kennedy on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses a trench in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
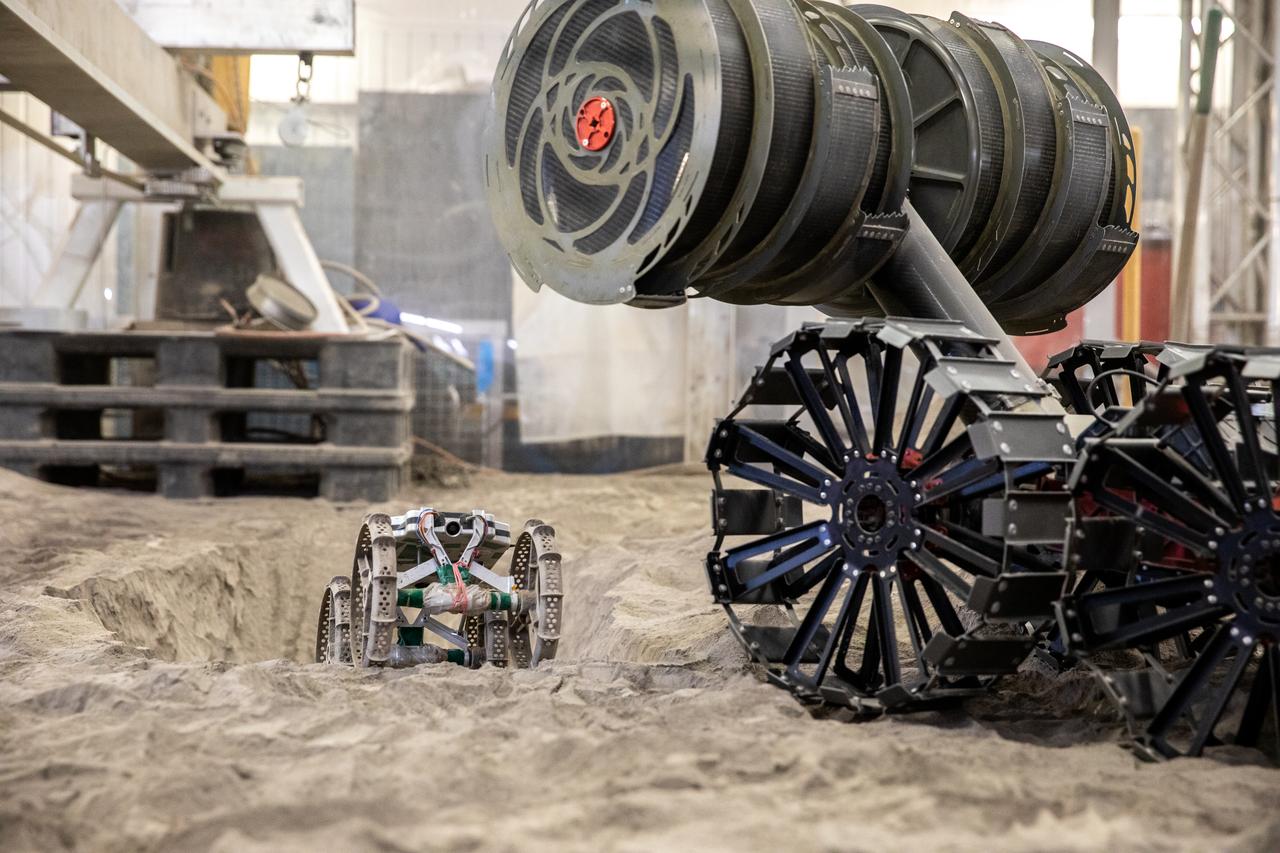

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design. Also in the bin is NASA’s Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), a robotic platform designed to dig on the Moon. The regolith bin simulates the Moon’s surface.
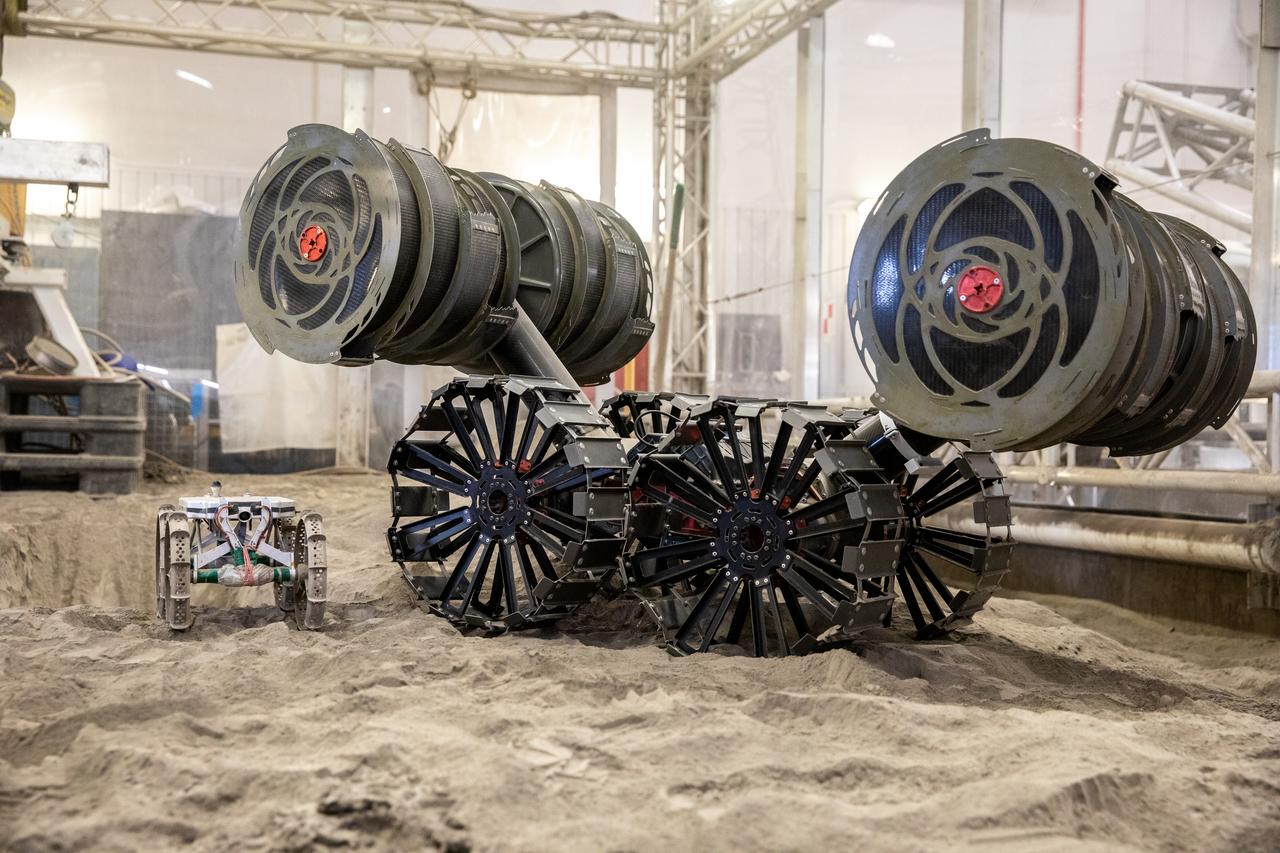

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses the terrain in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design. Also in the bin is NASA’s Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), a robotic platform designed to dig on the Moon. The regolith bin simulates the Moon’s surface.
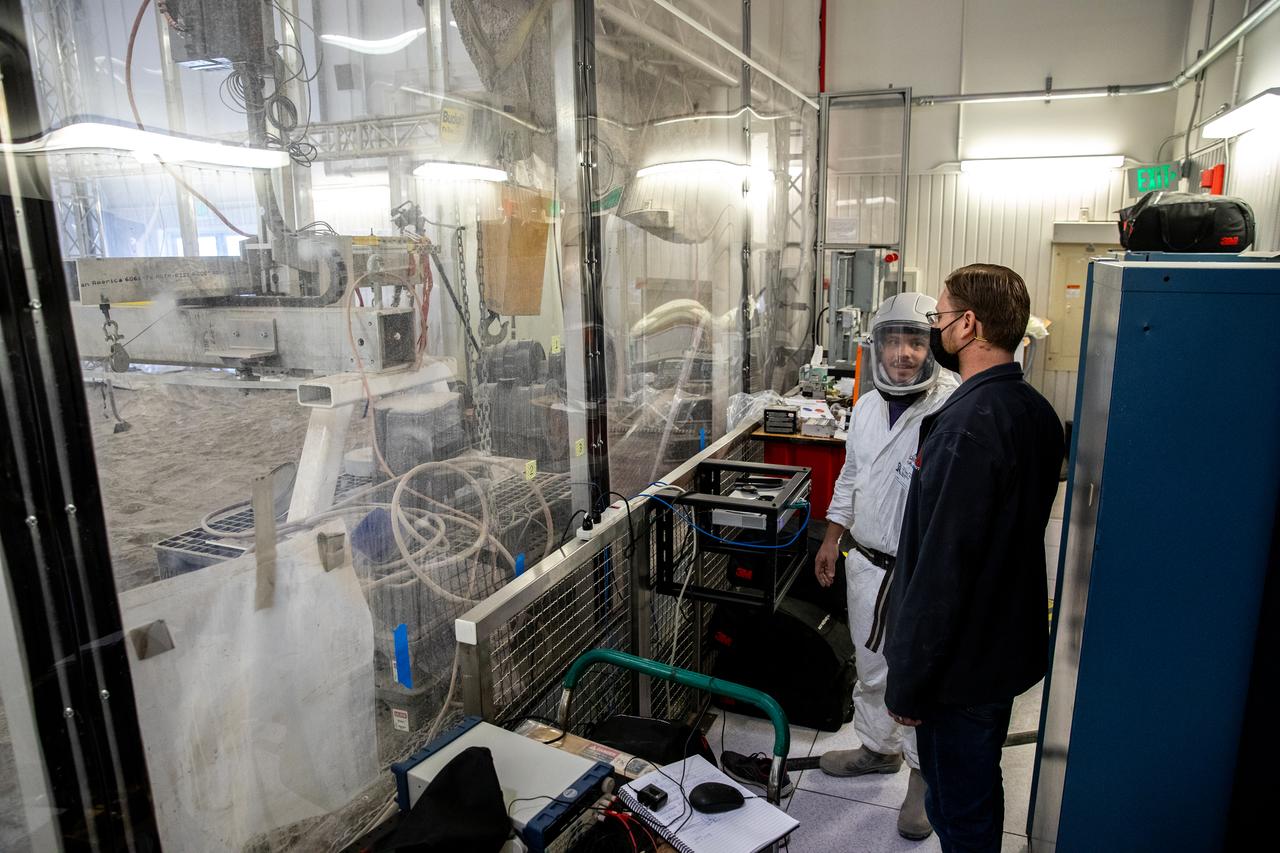

Astrobotic employee Troy Arbuckle, at right, Planetary Mobility lead mechanical engineer, and NASA employee A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, observe the Astrobotic CubeRover during its test run in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
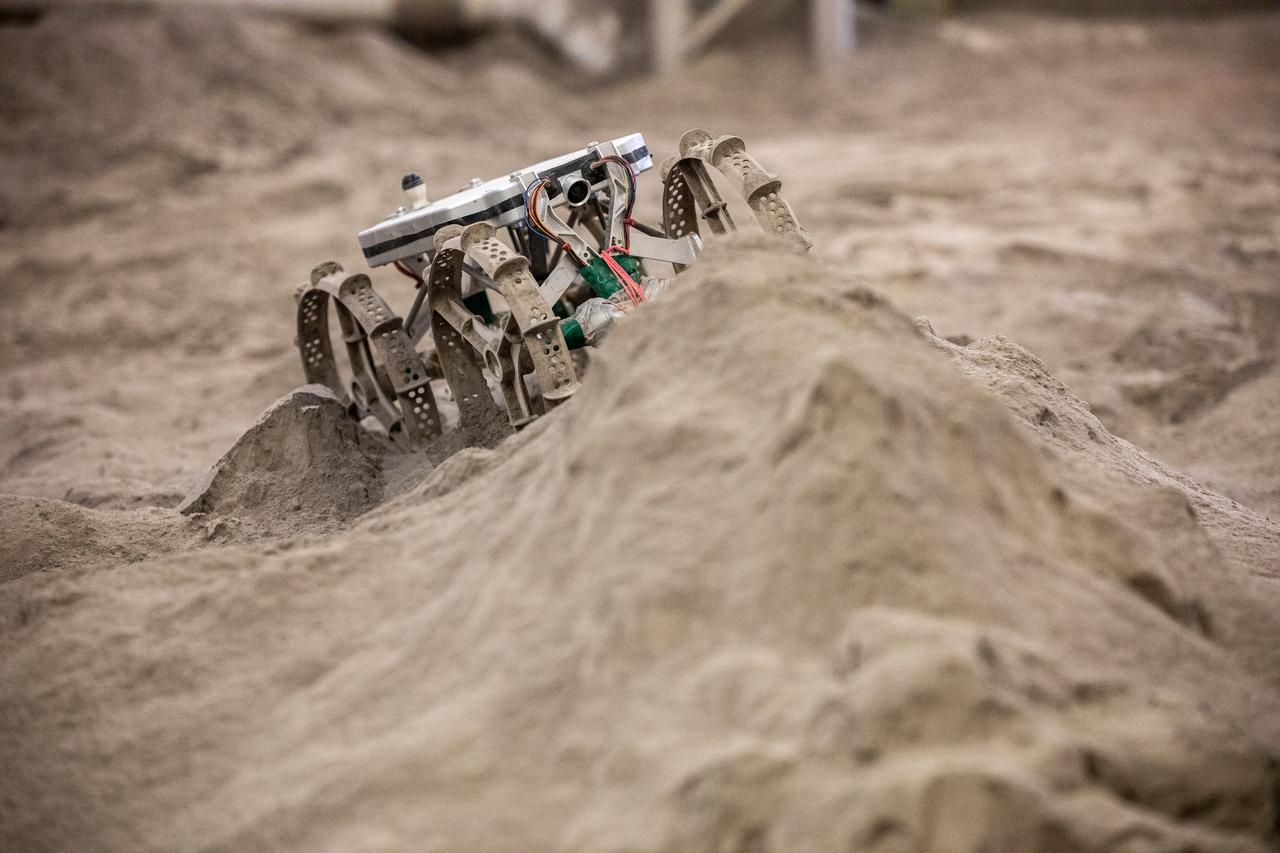

The Astrobotic CubeRover traverses obstacles in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Laboratory regolith bin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 10, 2020. The regolith bin simulates the mechanical properties of the Moon’s surface. NASA and Astrobotic employees put the CubeRover through a series of more than 150 mobility tests over several days to evaluate and improve wheel design.
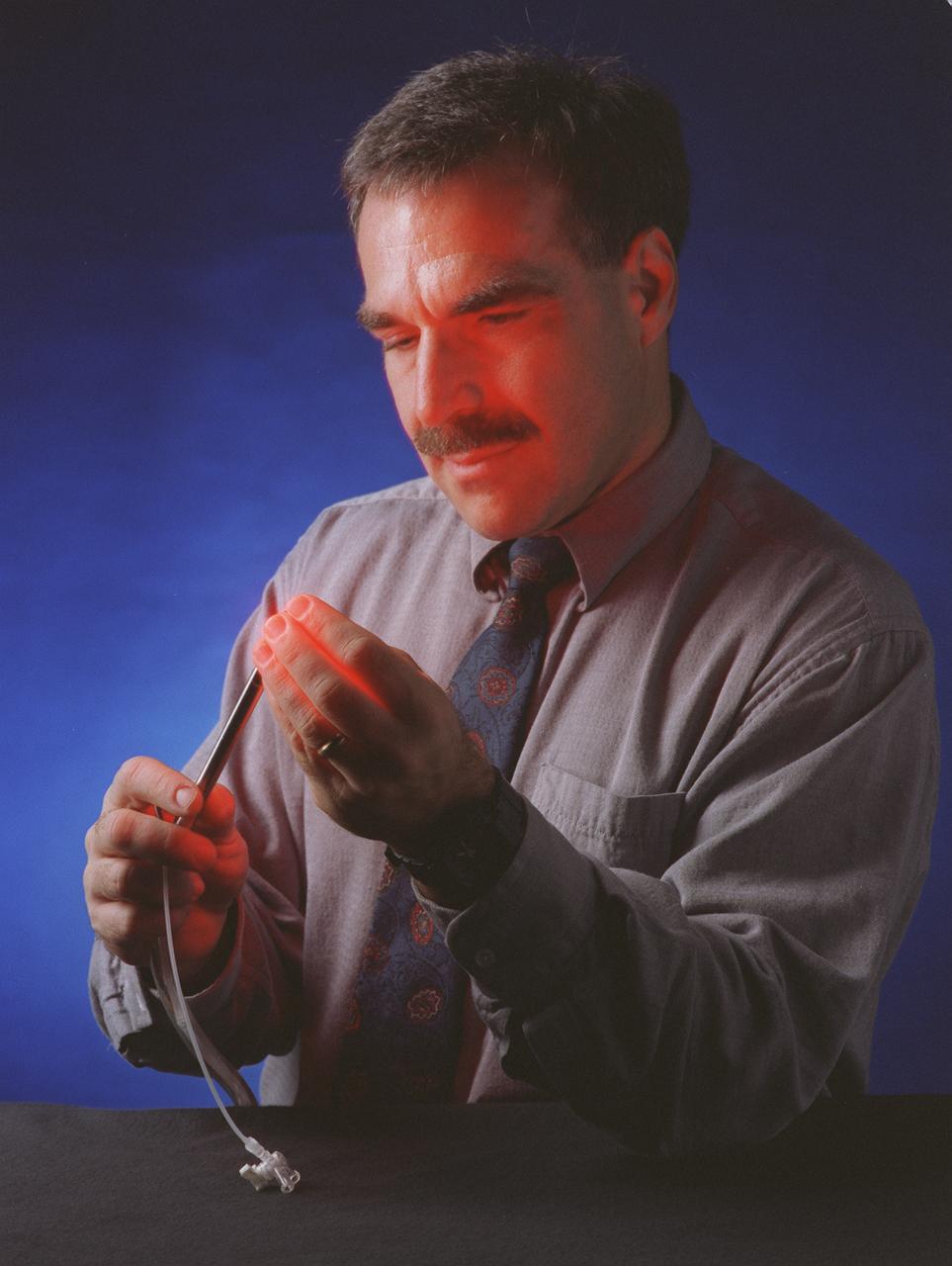
The red light from the Light Emitting Diode (LED) probe shines through the fingers of Dr. Harry Whelan, a pediatric neurologist at the Children's Hospital of Wisconsin in Milwaukee. Dr. Whelan uses the long waves of light from the LED surgical probe to activate special drugs that kill brain tumors. Laser light previously has been used for this type of surgery, but the LED light illuminates through all nearby tissues, reaching parts of tumors that shorter wavelengths of laser light carnot. The new probe is safer because the longer wavelengths of light are cooler than the shorter wavelengths of laser light, making the LED less likely to injure normal brain tissue near the tumor. Also, it can be used for hours at a time while still remaining cool to the touch. The probe was developed for photodynamic cancer therapy under a NASA Small Business Innovative Research Program grant. The program is part of NASA's Technology Transfer Department at the Marshall Space Flight Center.