
Larry DeLucas operating USML-1 Glovebox
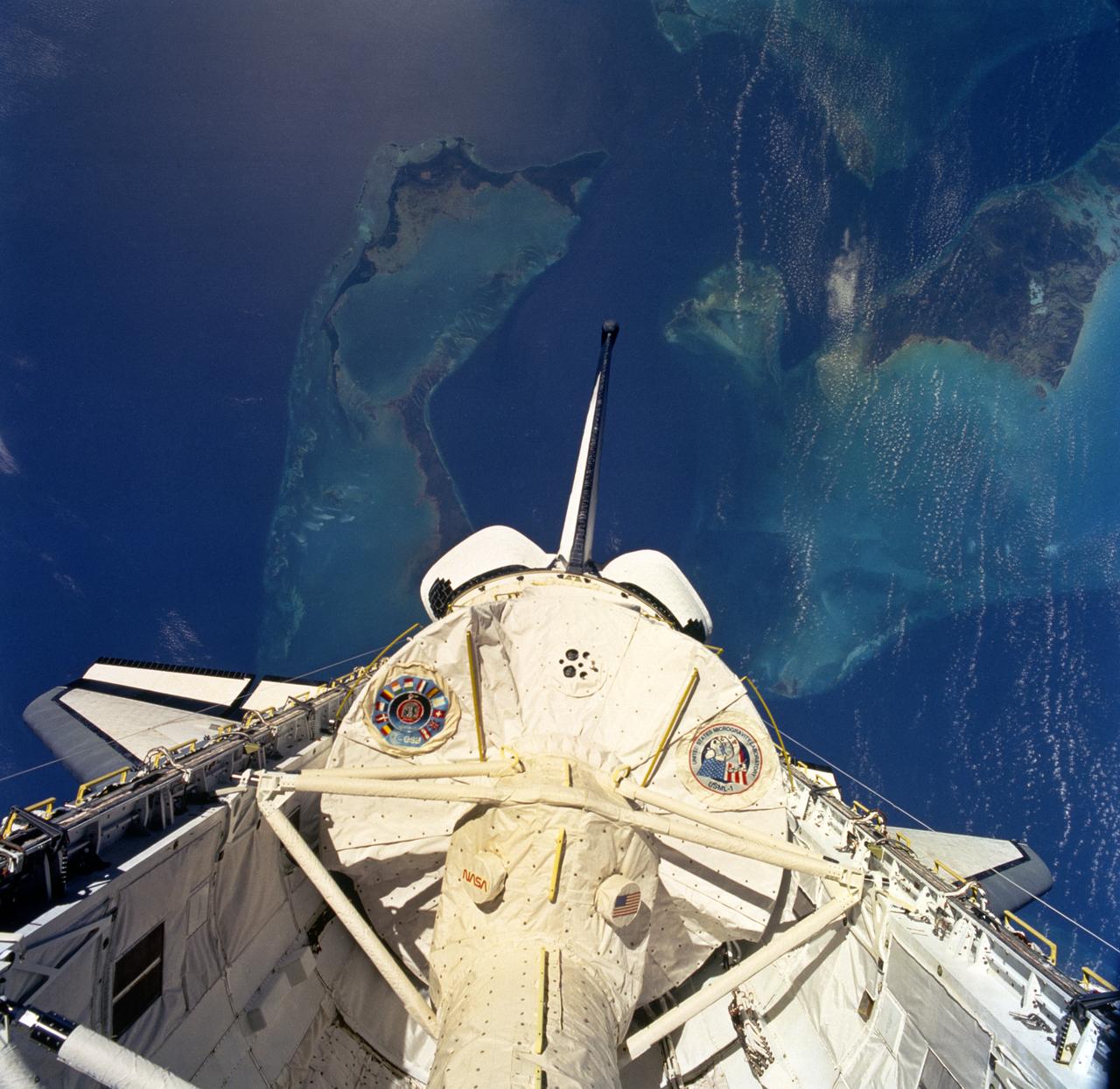

STS-50, USML-1, Spacelab module in cargo bay with earth in background

Experiment sequence test on USML-1 Glovebox equipment and test investigator group.
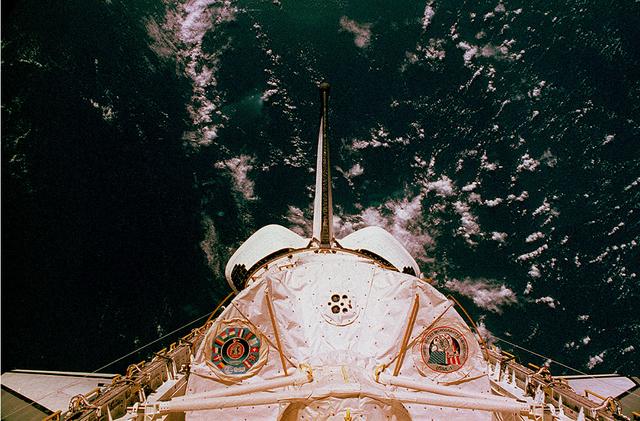
This is a photograph of the Spacelab module for the first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) mission, showing logos of the Spacelab mission on the left and the USML-1 mission on the right. The USML-1 was one part of a science and technology program that opened NASA's next great era of discovery and established the United States' leadership in space. From investigations designed to gather fundamental knowledge in a variety of areas to demonstrations of new equipment, USML-1 forged the way for future USML missions and helped prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. Thirty-one investigations comprised the payload of the first USML-1 mission. The experiments aboard USML-1 covered five basic areas: fluid dynamics, the study of how liquids and gases respond to the application or absence of differing forces; crystal growth, the production of inorganic and organic crystals; combustion science, the study of the processes and phenomena of burning; biological science, the study of plant and animal life; and technology demonstrations. The USML-1 was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) in the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) mission specialist Ellen S. Baker is hard at work.
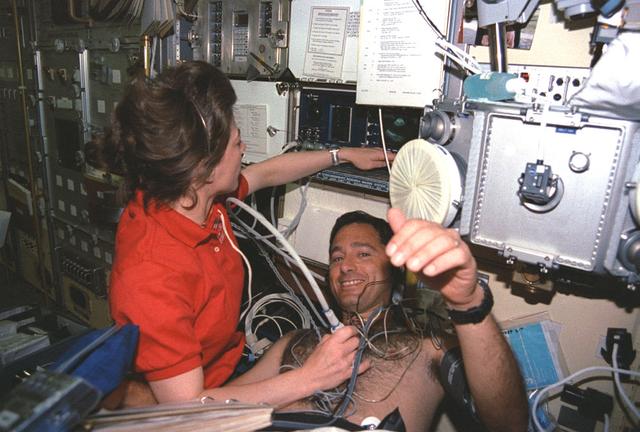
Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) payload commander Bornie Dunbar performs life science experiments on crewmember payload specialist Lawrence Delucas in the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) science module.

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) onboard photo of astronauts working in United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1). USML-1 will fly in orbit for extended periods of time attached to the Shuttle, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology, and combustion science. The scientific data gained from the USML-1 missions will constitute a landmark in space science, pioneering investigations into the role of gravity in a wide array of important processes and phenomena. In addition, the missions will also provide much of the experience in performing research in space and in the design of instruments needed for Space Station Freedom and the programs to follow in the 21st Century.
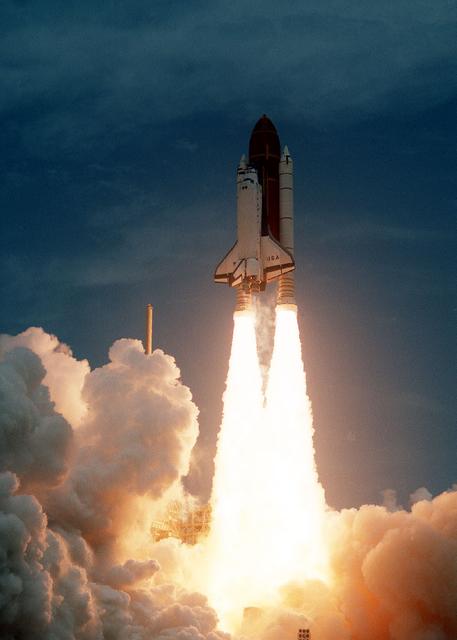

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) launched into history carrying crew of seven and its payload was comprised of the US Microgravity Laboratory 1 (USML-1).The USML-1 was one of NASA's missions dedicated to scientific investigations in a microgravity environment inside the Spacelab module. Investigations aboard the USML-1 included: materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. Managed by Marshall Space Flight Center, the STS-50 mission was plarned for a 13-day duration, the mission ended with 14 days in space, the longest Shuttle mission to date.
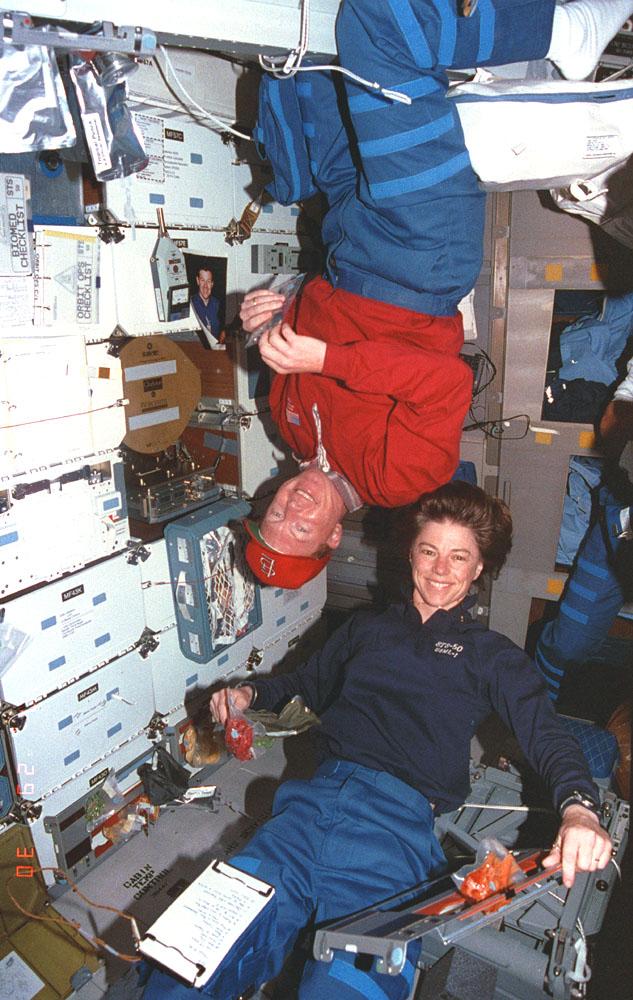

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) all work and no play make commander Richard (Dick) Richards and payload commander Bornie Dunbar take a break from their work in the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) responsibilities.
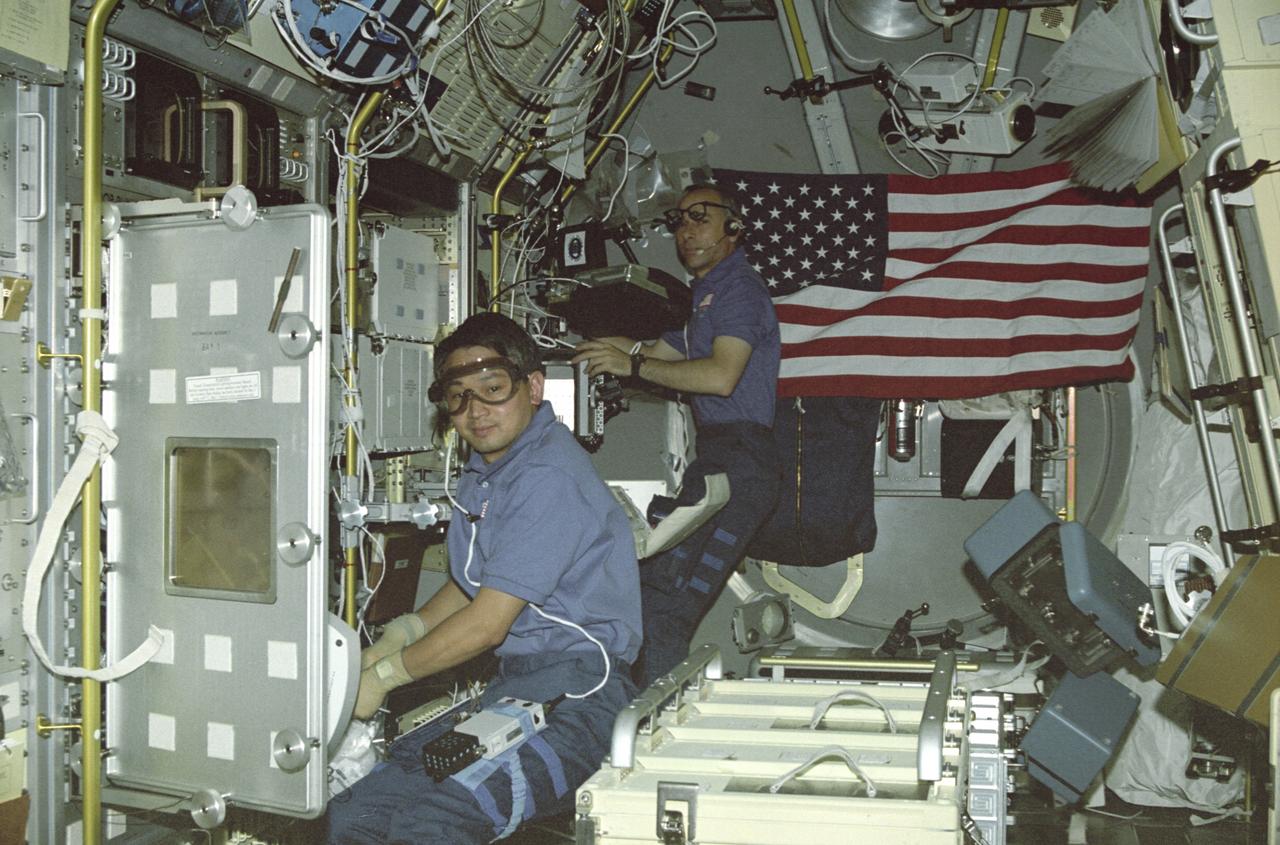

In this photograph, astronaut Eugene Trinh, a payload specialist for this mission, is working at the Drop Physics Module (DPM), and mission specialist Carl Meade is working on the experiment at the Glovebox inside the first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) Science Module. The USML-1 was one of NASA's missions dedicated to scientific investigations in a microgravity environment inside the Spacelab module. Investigations aboard the USML-1 included: materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. The DPM is dedicated to the detailed study of the dynamics of fluid drops in microgravity. The Glovebox offers experimenters new capabilities and technologies in microgravity with a clean working space and minimizes contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. Payload specialists are professional scientists or engineers whose only assignment on a space flight is to carry out scientific and technological experiments. Their specific training for a space flight is usually limited to a short period of learning how to live and work in weightlessness. Mission Specialists are both professional scientists and career astronauts. Thus they are a link or bridge between the other crew members, and combine the functions of resident maintenance engineers, in-space counterparts of flight engineers in aircraft, and fully qualified scientists. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992, and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
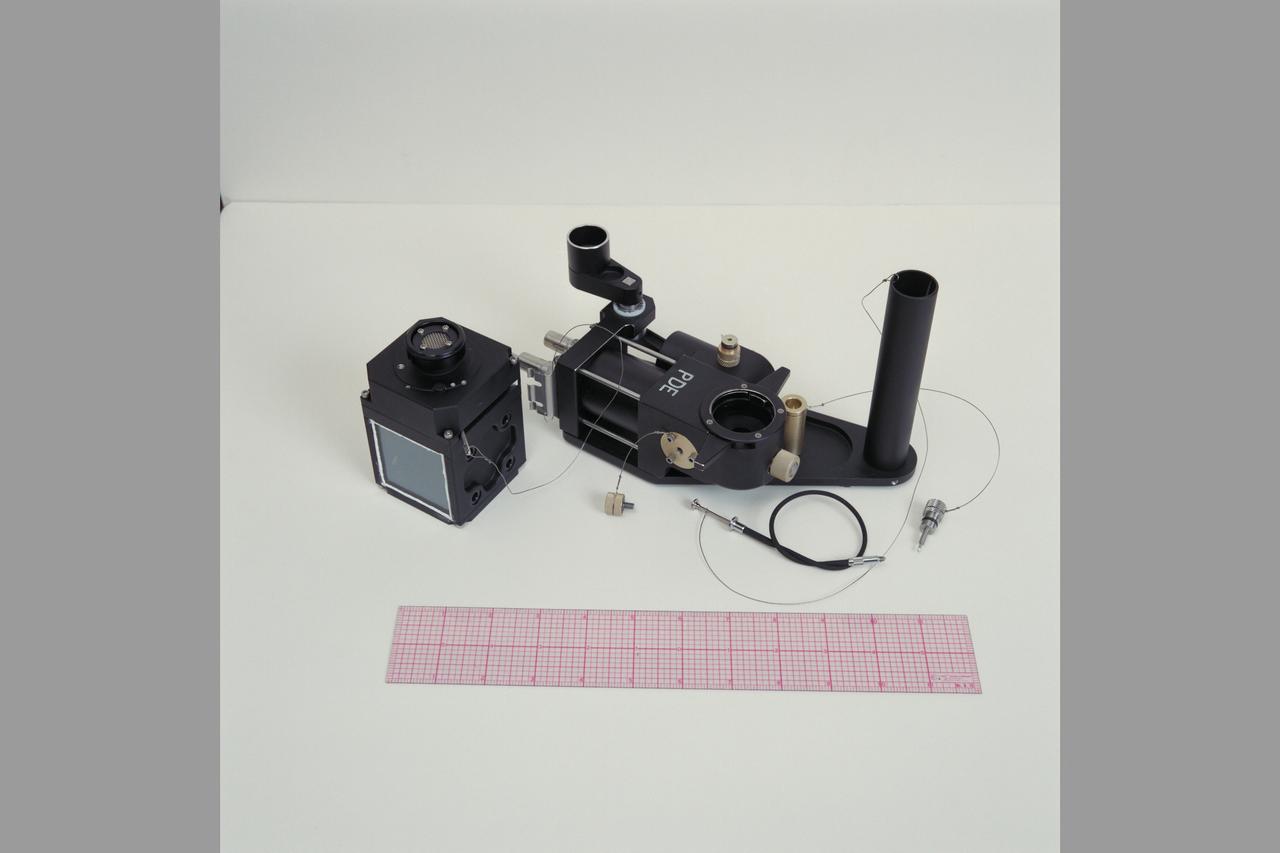
SSE (Solar System Exploration) flight apparatus: PDE (Particle Dispersion Experiement) on-board USML-1 (GEM)
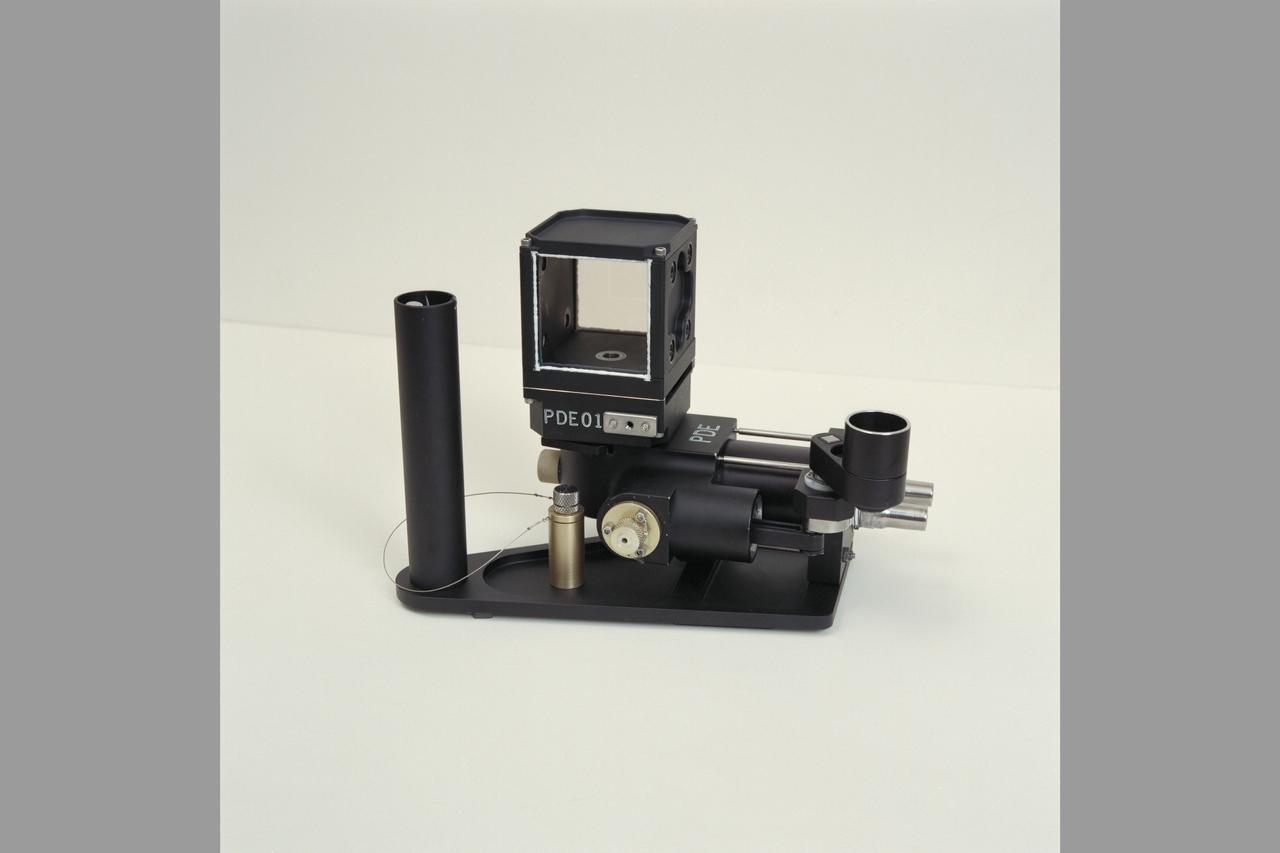

SSE (Solar System Exploration) flight apparatus: PDE (Particle Dispersion Experiement) on-board USML-1 (GEM)
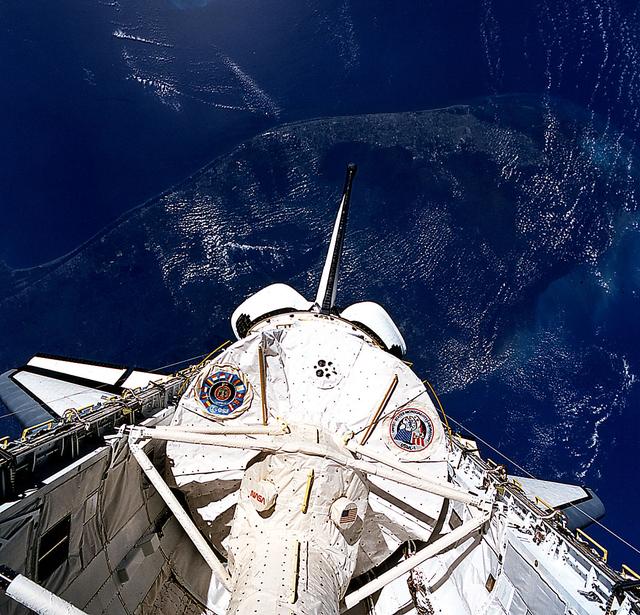

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) onboard photo of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) module in payload bay in this scene over the southern two-thirds of the Florida peninsula. Kennedy Space Center (KSC) can be seen just above Columbia's starboard wing.
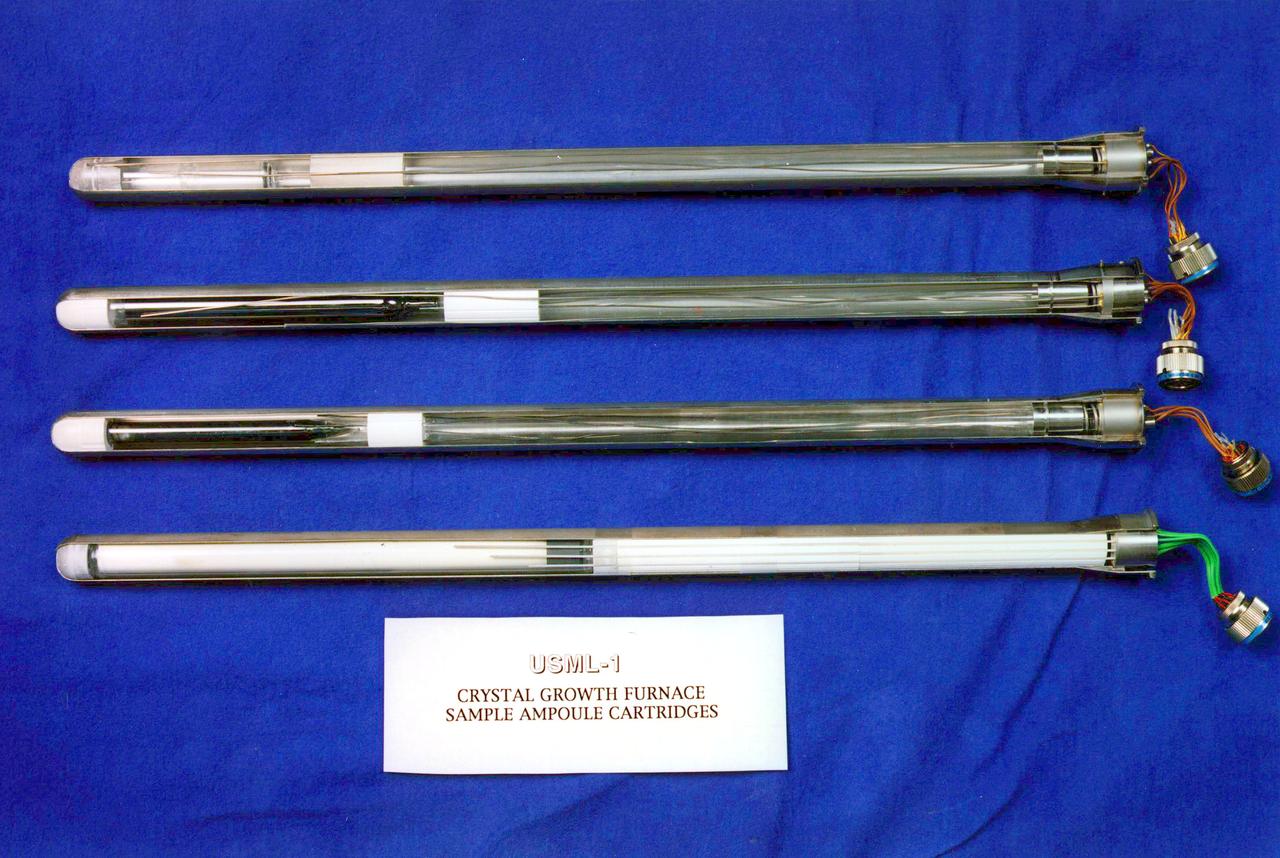

Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) without the EAC internal support structure. Flown on USML-1 and USML-2. The Principal Investigators on these flights were: Larson, Lehoczky, Matthiesen, Wiedemeier. Processed 6 samples on USML-1 and 7 samples on USML-2.
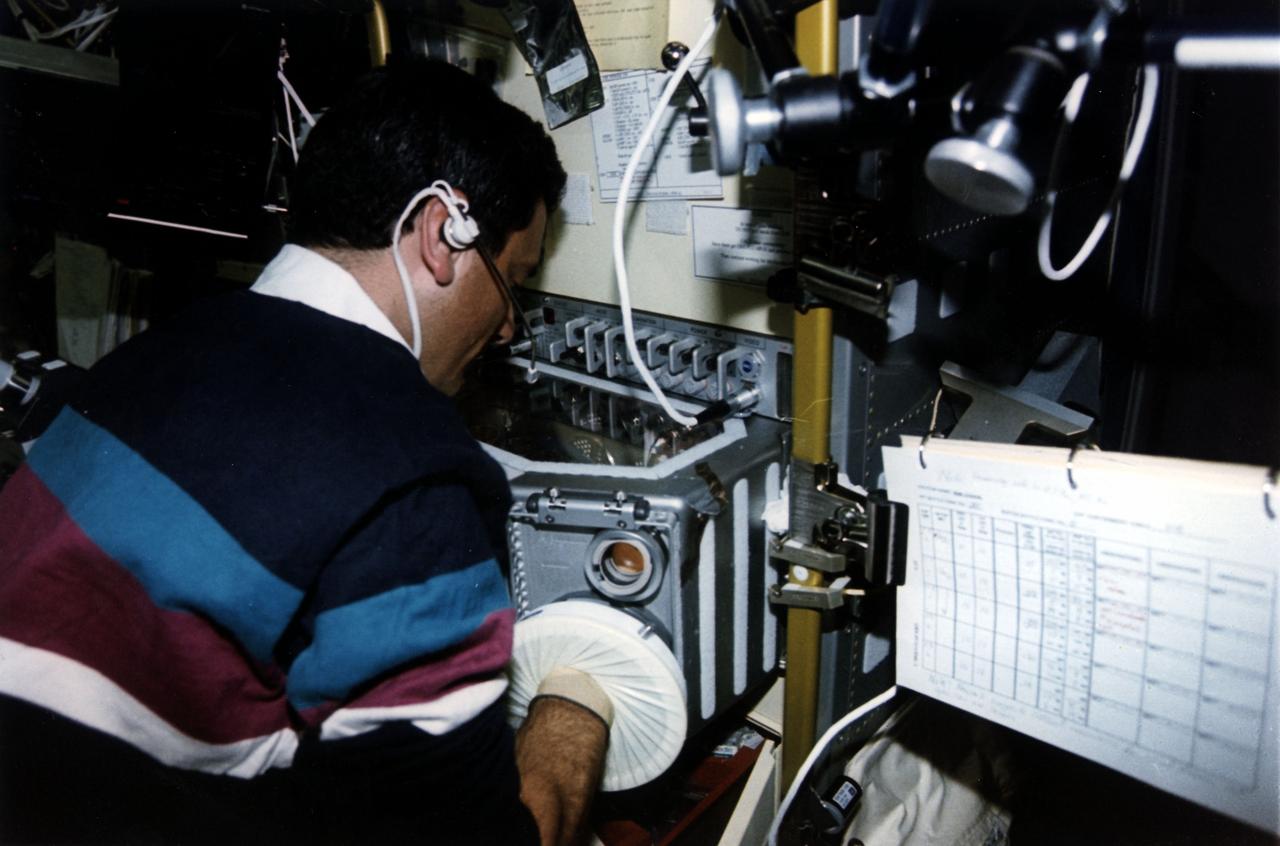

Dr. Larry DeLucas operating the USML-1 Glovebox (GBX) during the USML-1 (STS-50) mission. Dr. DeLucas was a Payload Specialist during the USML-1 mission and is Associate Director of the Center for Macromolecular Crystallography at The University of Alabama at Birmingham.
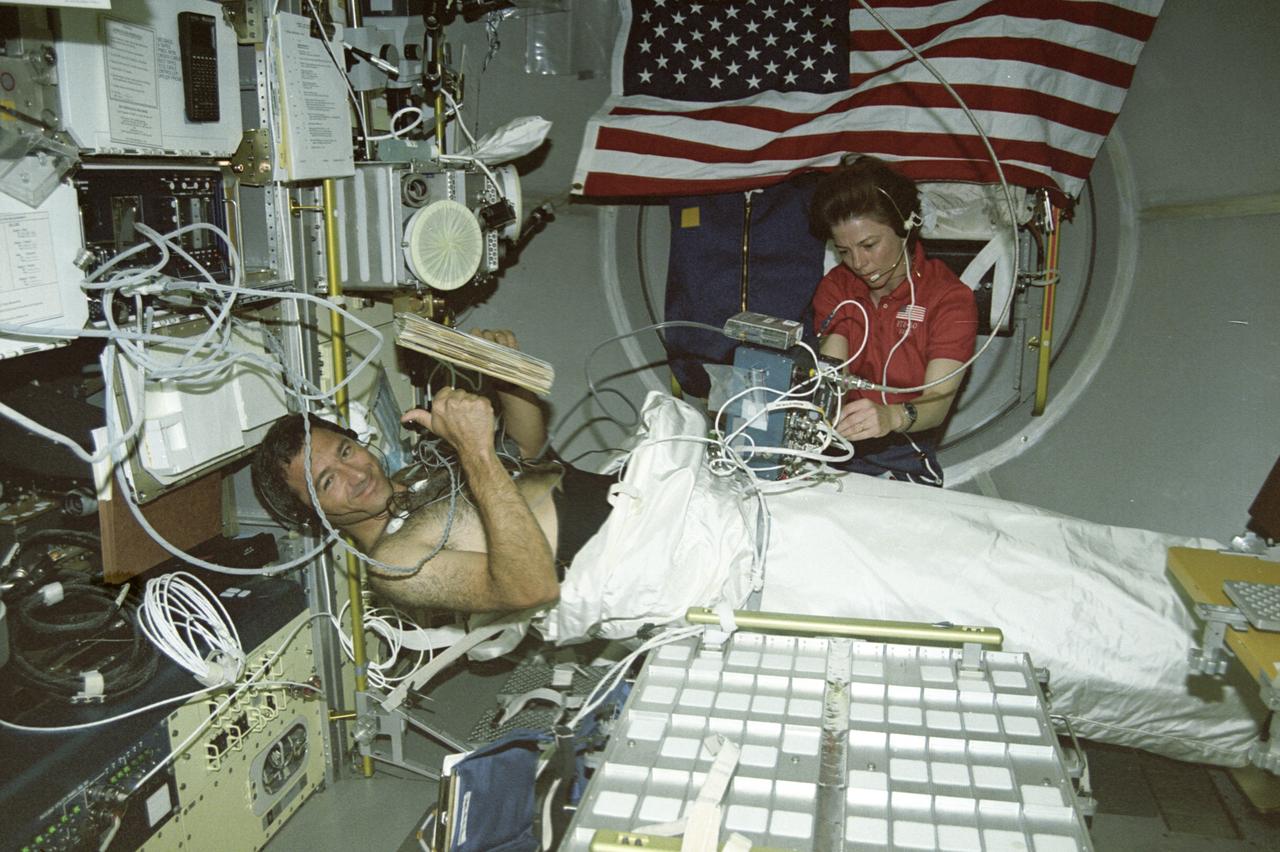

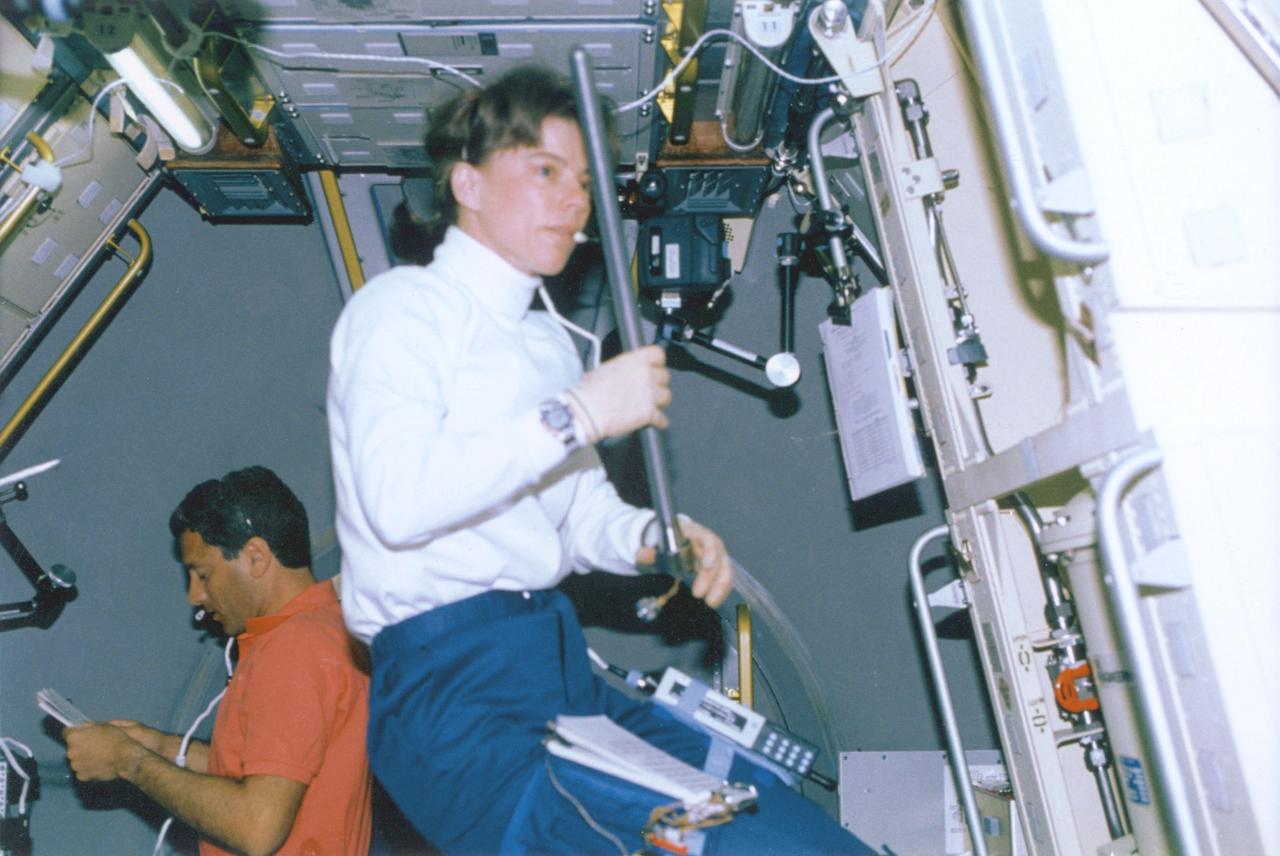
The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) flew in orbit inside the Spacelab science module for extended periods, providing scientists and researchers greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. In this photograph, Astronaut Bornie Dunbar and Astronaut Larry DeLucas are conducting the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment, which is to protect the health and safety of the crew and to shorten the time required to readapt to gravity when they return to Earth. When humans go into space, the lack of gravity causes many changes in the body. One change is that fluids normally kept in the lower body by gravity, shift upward to the head and chest. This is why astronauts' faces appear chubby or puffy. The change in fluid volume also affects the heart. The reduced fluid volume means that there is less blood to circulate through the body. Crewmembers may experience reduced blood flow to the brain when returning to Earth. This leads to fainting or near-fainting episodes. With the use of LBNP to simulate the pull of gravity in conjunction with fluids, salt tablets can recondition the cardiovascular system. This treatment, called "soak," is effective up to 24 hours. The LBNP uses a three-layer collapsible cylinder that seals around the crewmember's waist which simulates the effects of gravity and helps pull fluids into the lower body. The data collected will be analyzed to determine physiological changes in the crewmembers and effectiveness of the treatment. The USML-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
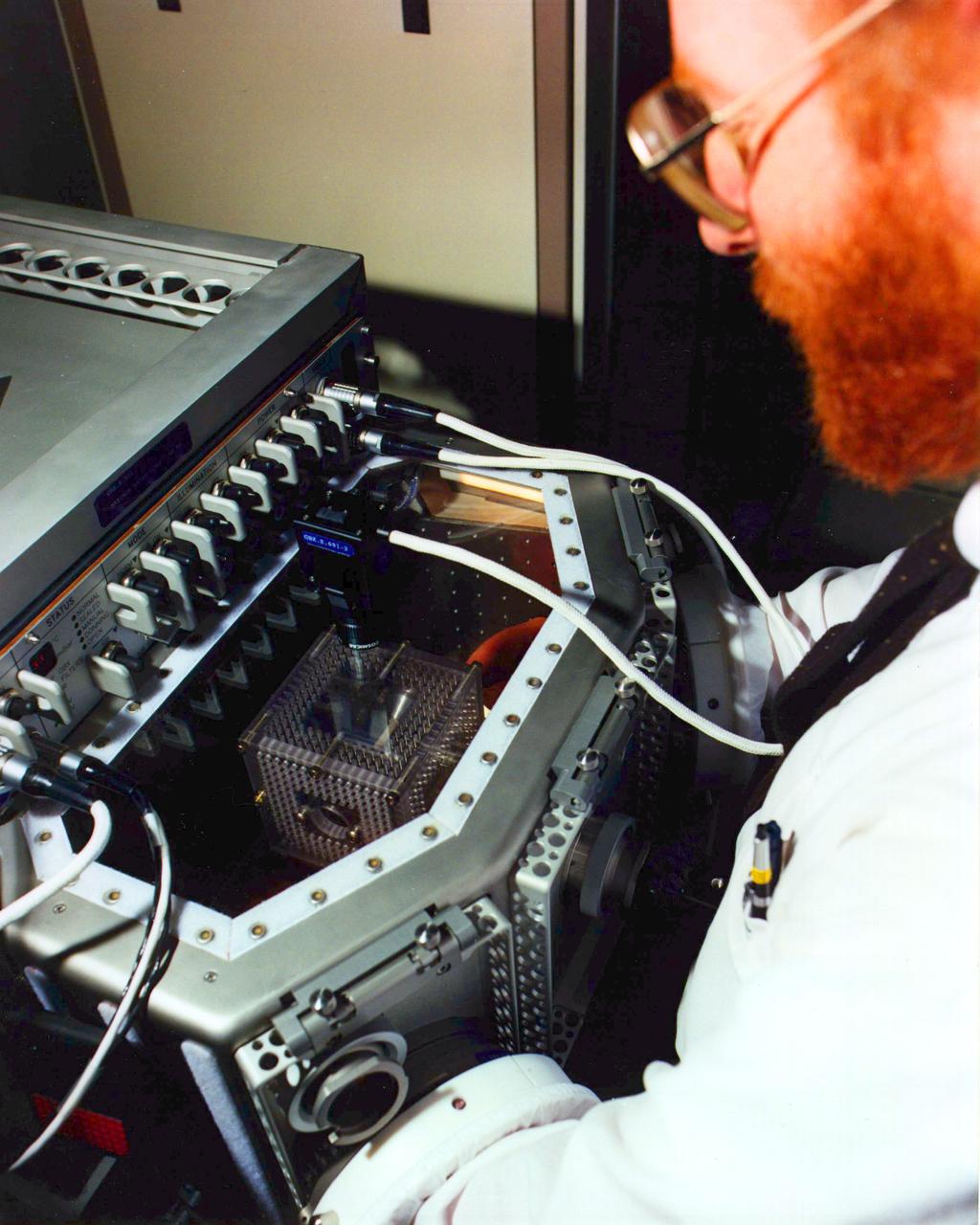

USML-1, Howard Ross working with the Glovebox Module
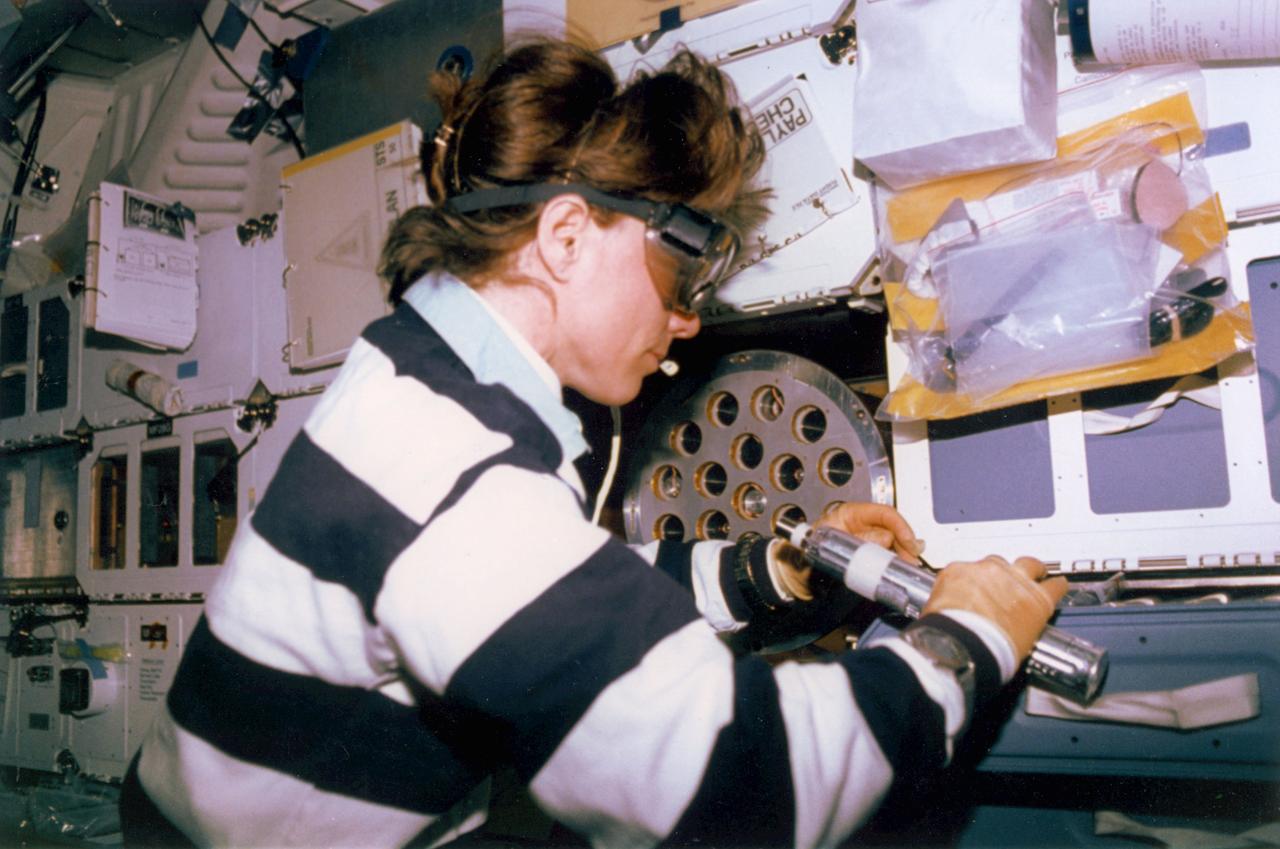

Payload Commander, Bonnie Dunbar working onboard STS-50 USML-1

Payload Commander, Bornie Dunbar loading samples in the CGF onboard STS-50, USML-1.

Payload Commander, Bornie Dunbar activating ZCG autoclave onboard STS-50, USML-1
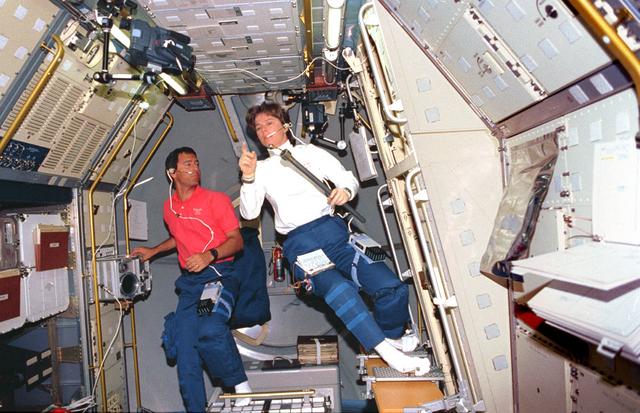

Payload Specialist Larry DeLucas and Payload Commander Bornie Dunbar working in USML-1.
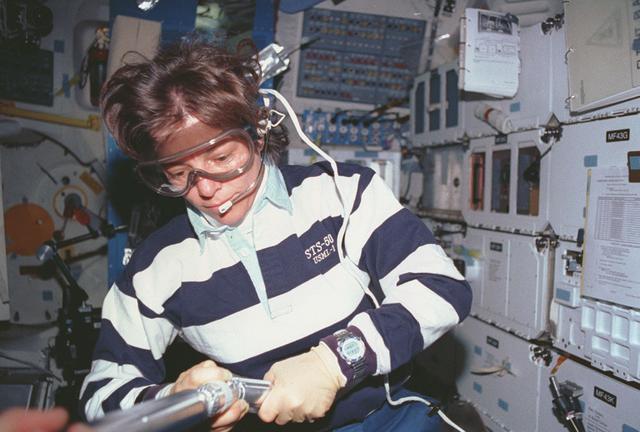

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) astronaut Bornie Dunbar wears protective goggles to assemble a zeolite sample cartridge for the Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) in the United States Microgravity Laboratory-1 (USML-1) science module.
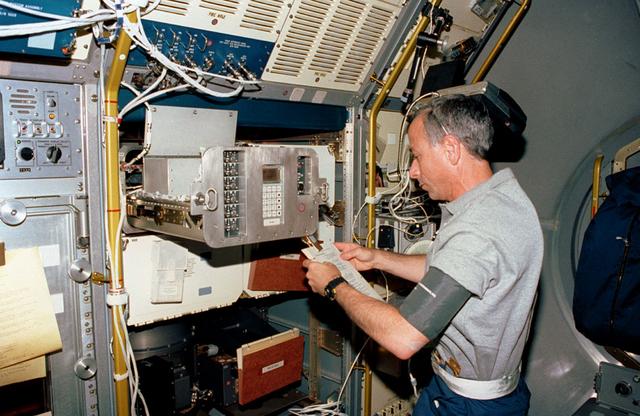

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs and provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology, and combustion science. In this photograph, astronaut Carl Meade is reviewing the manual to activate the Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (GBA) inside the Spacelab module. The GBA for the USML-1 mission was a multipurpose facility that could help us answer important questions about the relationship between gravity and biology. This unique facility allowed scientists to study biological processes in samples ranging from molecules to small organisms. For example, scientists would examine how collagen, a protein substance found in cornective tissue, bones, and cartilage, forms fibers. In microgravity, it might be possible to alter collagen fiber assembly so that this material could be used more effectively as artificial skin, blood vessels, and other parts of the body. The USML-1 was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and waslaunched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
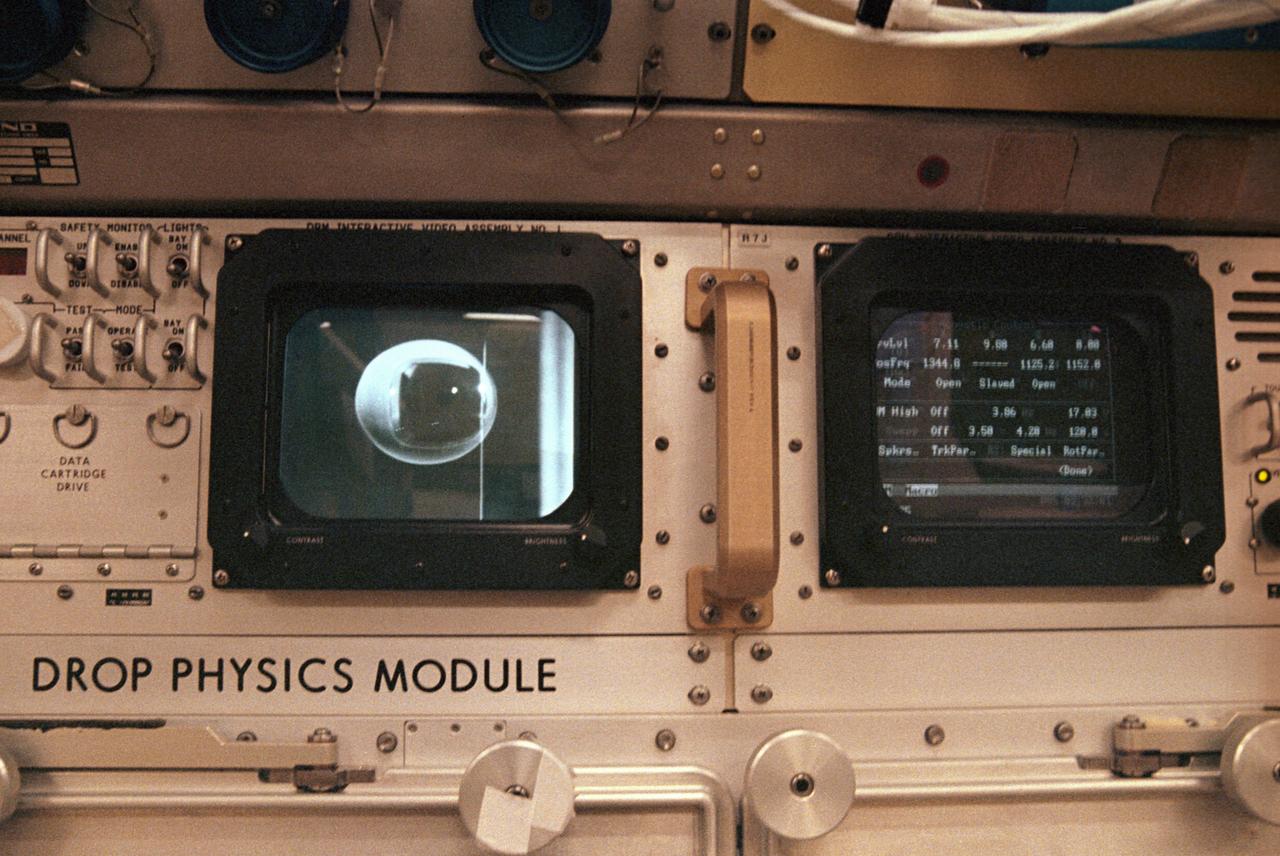
The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs that provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightlessness environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This is a close-up view of the Drop Physics Module (DPM) in the USML science laboratory. The DPM was dedicated to the detailed study of the dynamics of fluid drops in microgravity: their equilibrium shapes, the dynamics of their flows, and their stable and chaotic behaviors. It also demonstrated a technique known as containerless processing. The DPM and microgravity combine to remove the effects of the container, such as chemical contamination and shape, on the sample being studied. Sound waves, generating acoustic forces, were used to suspend a sample in microgravity and to hold a sample of free drops away from the walls of the experiment chamber, which isolated the sample from potentially harmful external influences. The DPM gave scientists the opportunity to test theories of classical fluid physics, which have not been confirmed by experiments conducted on Earth. This image is a close-up view of the DPM. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992, and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
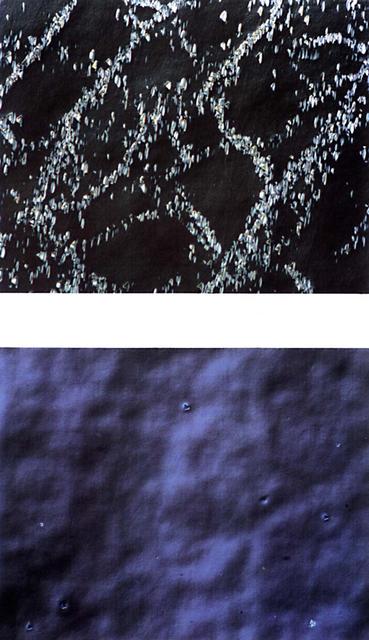
Samples of zinc-alloyed cadmium mercury grown on Earth (1g) and in space (ug) are shown at the same magnification. The space-grown crystal has a more uniform microstructure. Flown on STS-50 USML-1.
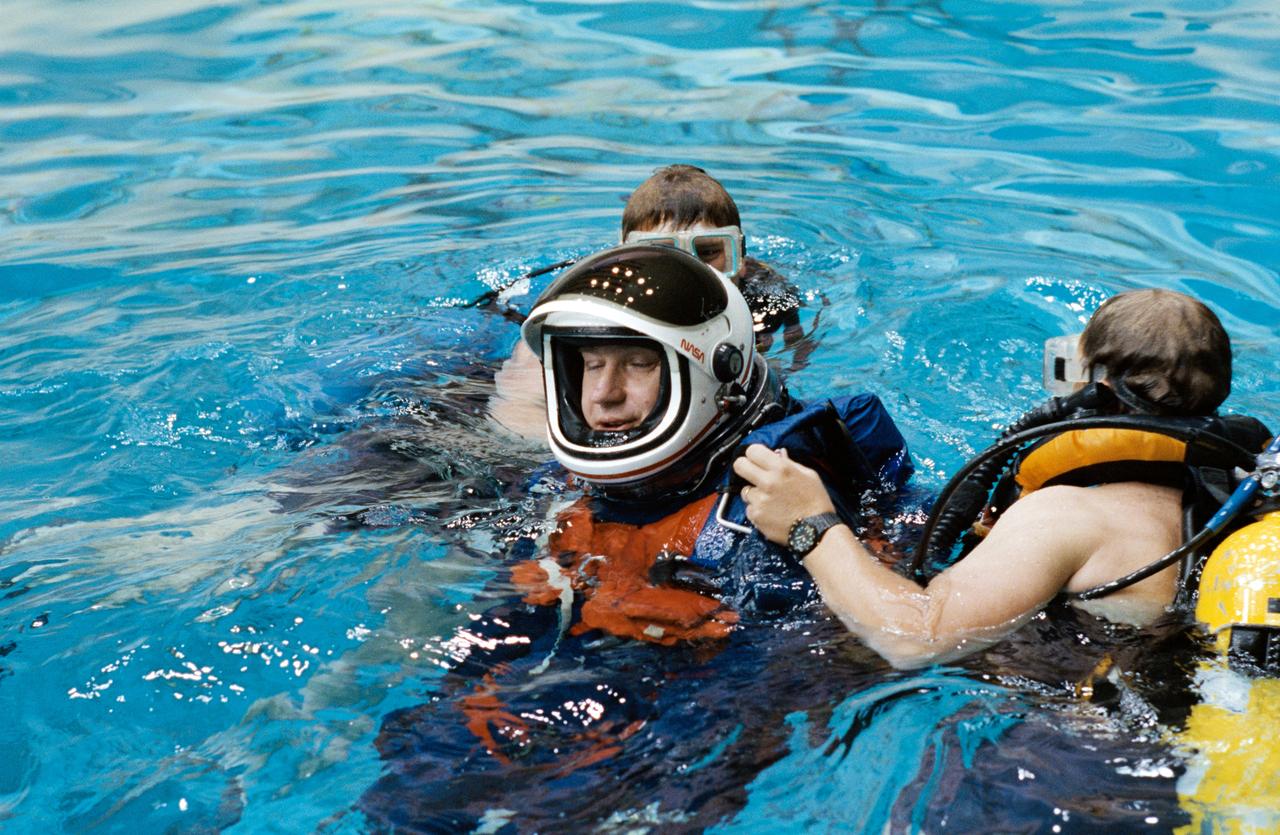

S92-32108 (May 1992) --- Payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. uses a one-person life raft during emergency bailout training exercises in the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Sacco is an alternate payload specialist for the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) mission, scheduled for launch later this year. EDITOR?S NOTE: Sacco was later named as prime crew payload specialist for the USML-2 mission (STS-73), scheduled for 1995.
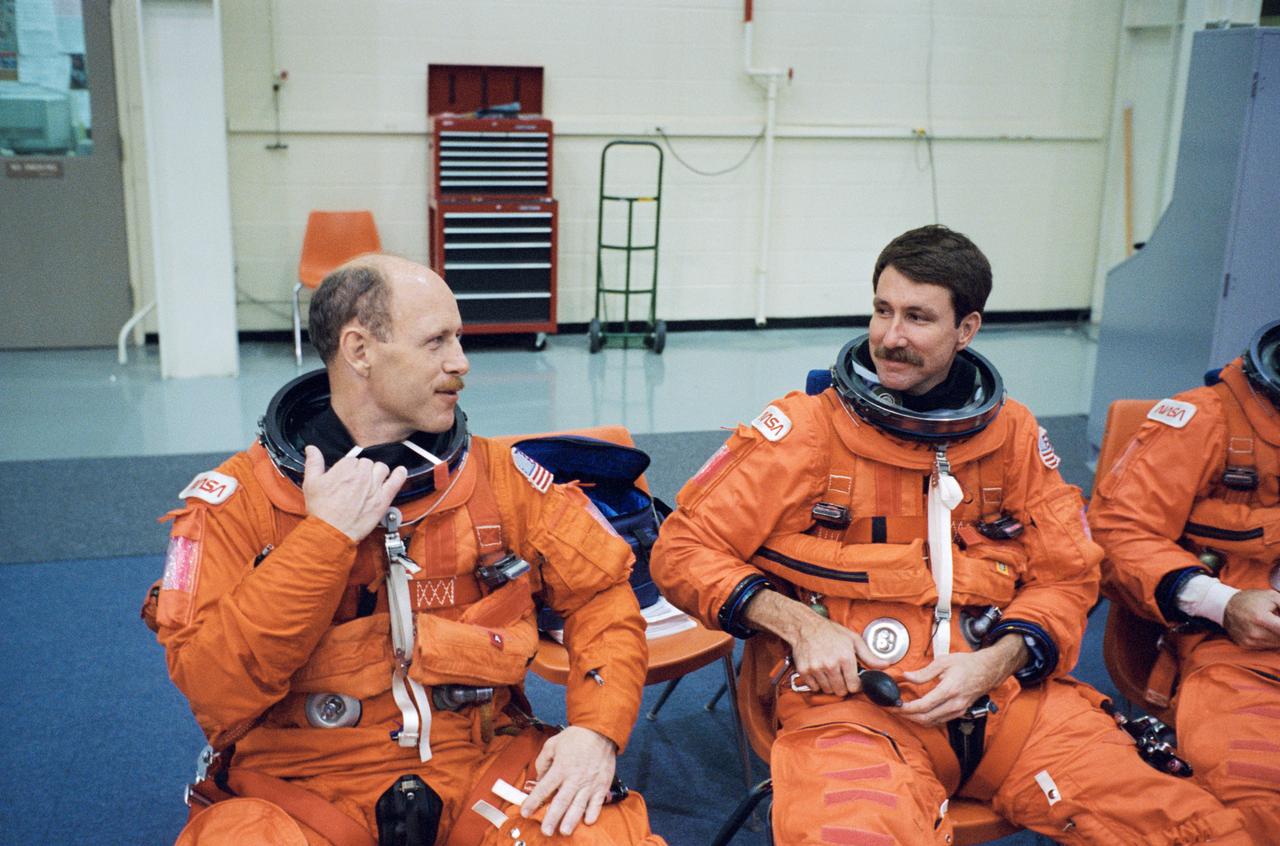

S95-09140 (27 Apr. 1995) --- Attired in training versions of the Space Shuttle partial pressure launch and entry garment, astronauts Kenneth D. Bowersox (left) and Kent V. Rominger prepare to rehearse an emergency situation with the Space Shuttle. The two are commander and pilot, respectively, for the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission. Bowersox was pilot for the USML-1 mission. The emergency egress training exercises took place in the Systems Integration Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC).
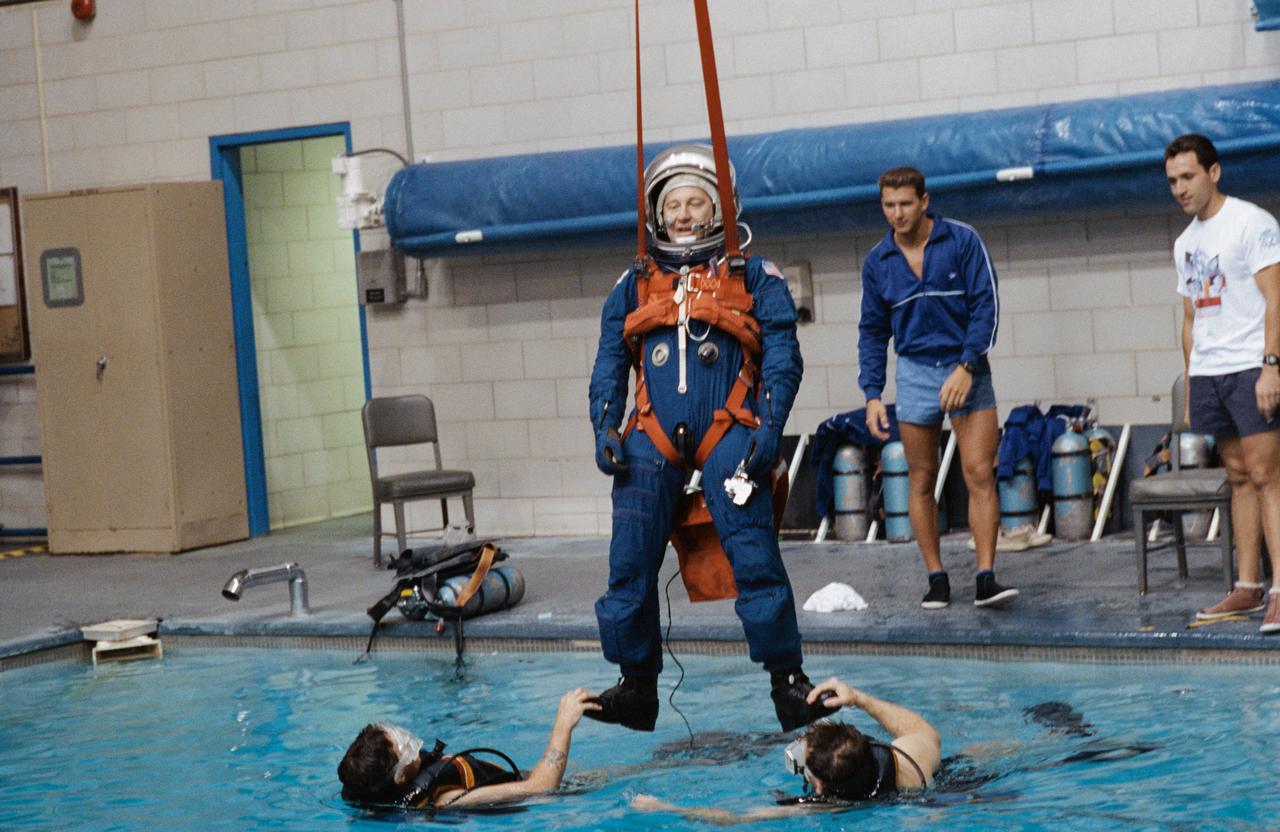

S92-32111 (May 1992) --- Payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. is assisted by two SCUBA-equipped divers as he hangs by his parachute harness during emergency bailout training exercises in the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Sacco is an alternate payload specialist for the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) mission, scheduled for launch later this year. EDITOR?S NOTE: Sacco was later named as prime crew payload specialist for the USML-2 mission (STS-73), scheduled for 1995.

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) provided scientific research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology, and combustion science in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. This photograph is a close-up view of the Glovebox in operation during the mission. The Spacelab Glovebox, provided by the European Space Agency, offers experimenters new capabilities to test and develop science procedures and technologies in microgravity. It enables crewmembers to handle, transfer, and otherwise manipulate materials in ways that are impractical in the open Spacelab. The facility is equipped with three doors: a central port through which experiments are placed in the Glovebox and two glovedoors on both sides with an attachment for gloves or adjustable cuffs and adapters for cameras. The Glovebox has an enclosed compartment that offers a clean working space and minimizes the contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. Although fluid containment and ease of cleanup are major benefits provided by the facility, it can also contain powders and bioparticles; toxic, irritating, or potentially infectious materials; and other debris produced during experiment operations. The facility is equipped with photographic/video capabilities and permits mounting a microscope. For the USML-1 mission, the Glovebox experiments fell into four basic categories: fluid dynamics, combustion science, crystal growth, and technology demonstration. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission in June 1992.
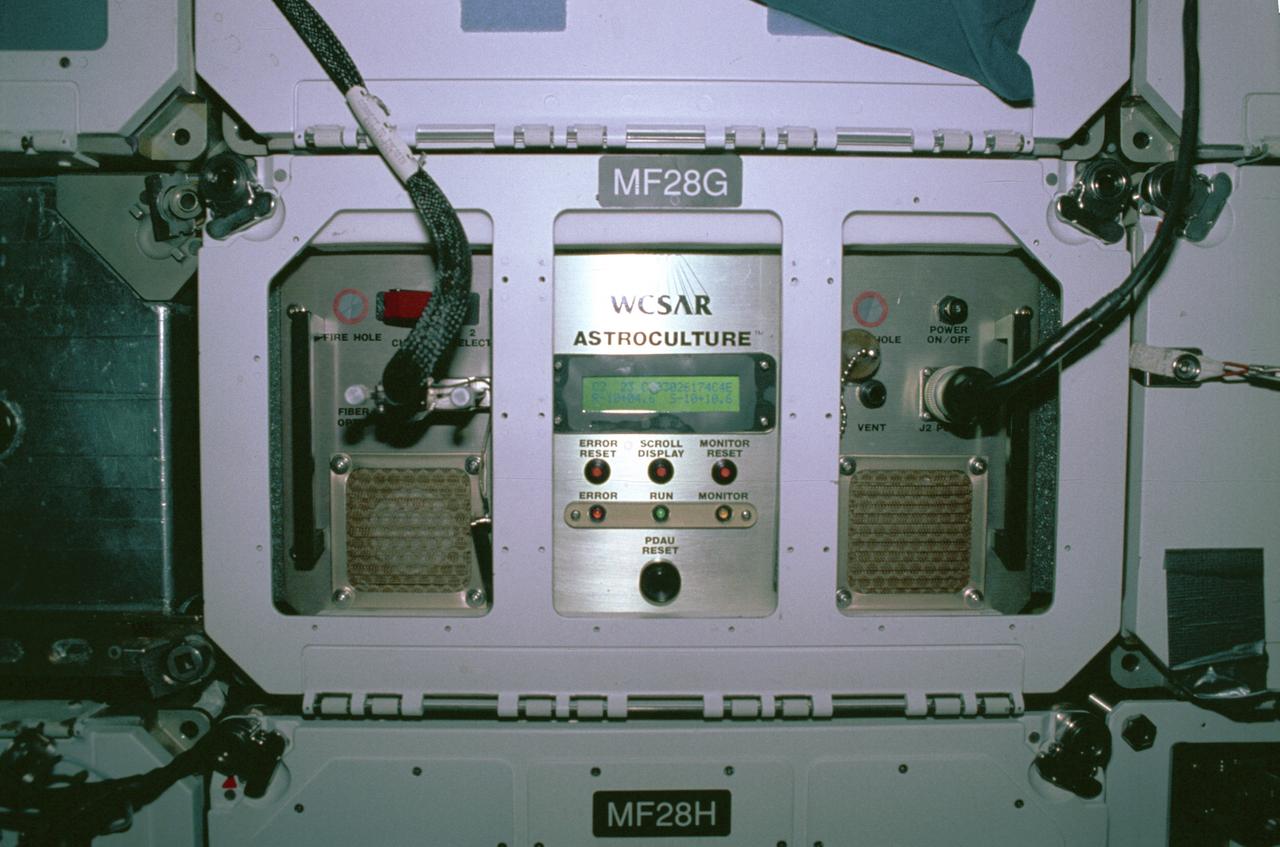

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs that provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This is a close-up view of the Astroculture experiment rack in the middeck of the orbiter. The Astroculture experiment was to evaluate and find effective ways to supply nutrient solutions for optimizing plant growth and avoid releasing solutions into the crew quarters in microgravity. Since fluids behave differently in microgravity, plant watering systems that operate well on Earth do not function effectively in space. Plants can reduce the costs of providing food, oxygen, and pure water, as well as lower the costs of removing carbon dioxide in human space habitats. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992 and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) flew in orbit inside the Spacelab science module for extended periods, providing scientists and researchers greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This photograph shows Astronaut Larry De Lucas wearing a stocking plethysmograph during the mission. Muscle size in the legs changes with exposure to microgravity. A stocking plethysmograph, a device for measuring the volume of a limb, was used to help determine these changes. Several times over the course of the mission, an astronaut will put on the plethysmograph, pull the tapes tight and mark them. By comparing the marks, changes in muscle volume can be measured. The USML-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
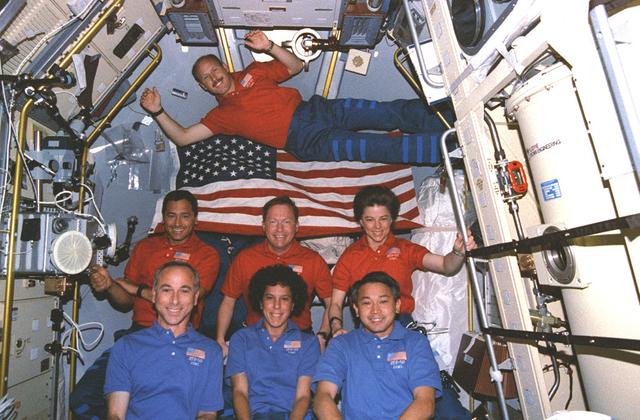

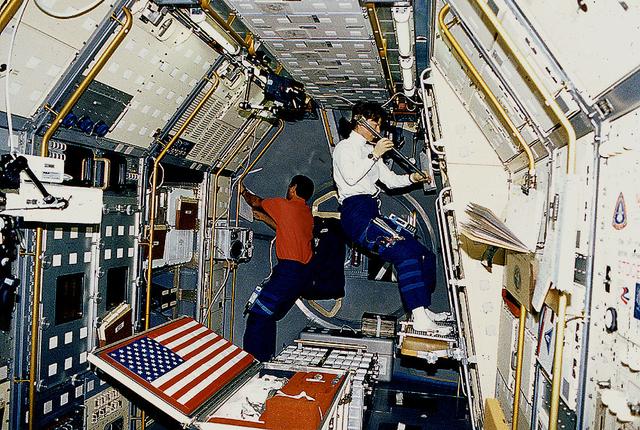
Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) crewmembers rally around the American flag in the United States Microgravity Laboratory-1 (USML-1). Pictured are (from top, left to right) pilot Kerneth D. Bowersox; payload specialist Lawrence J. Delucas; commander Richard N. Richards; payload commander Bonnie J. Dunbar; mission specialists Carl J. Meade and Ellen S. Baker; and payload specialist Eugene H. Trinh.
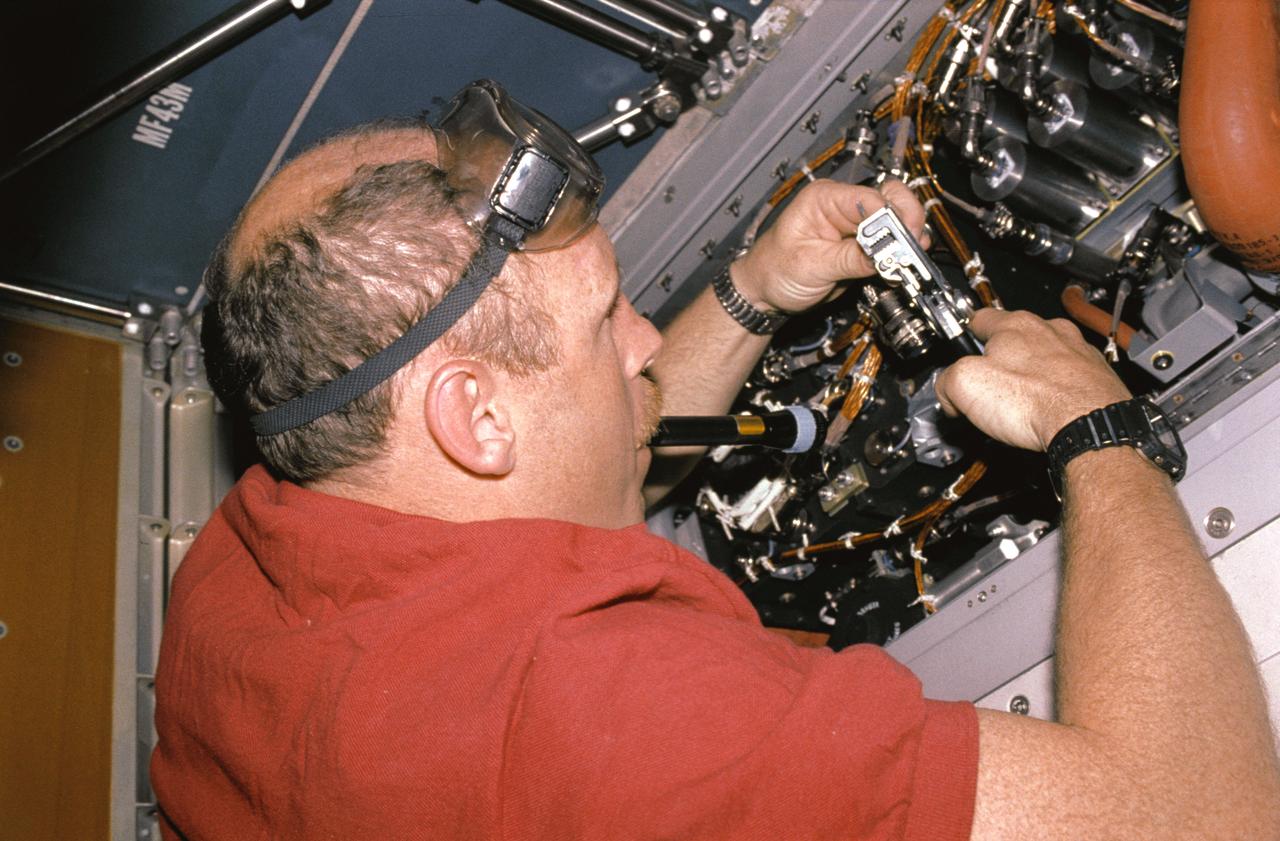
STS050-20-012 (26 June 1992) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot, performs in-flight maintenance (IFM) on the Regenerative Carbon Dioxide Removal System (RCRS) on the mid-deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Bowersox was joined by four other astronauts and two scientists from the private sector for a record-setting 14-day stay aboard the Space Shuttle in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory 1 (USML-1).
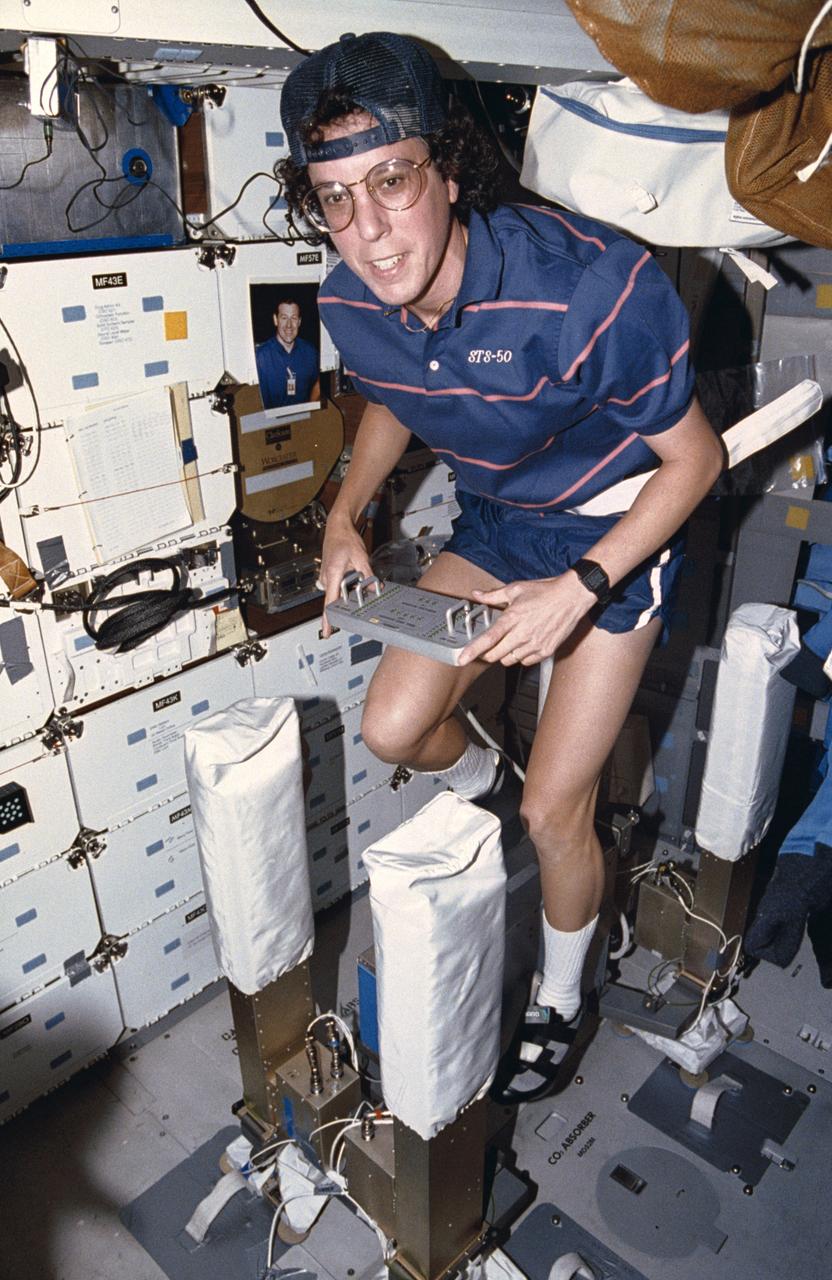

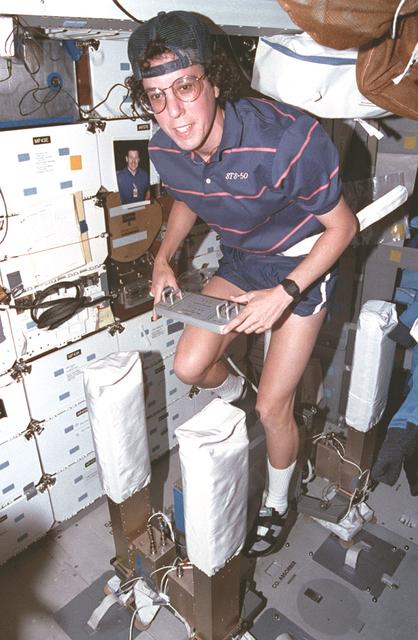
STS050-21-035 (25 June- 9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Ellen S. Baker, mission specialist, works out on the bicycle ergometer on the mid-deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Baker was joined by four other astronauts and two scientists from the private sector for the record-setting 14-day United States Microgravity Laboratory 1 (USML-1) mission.
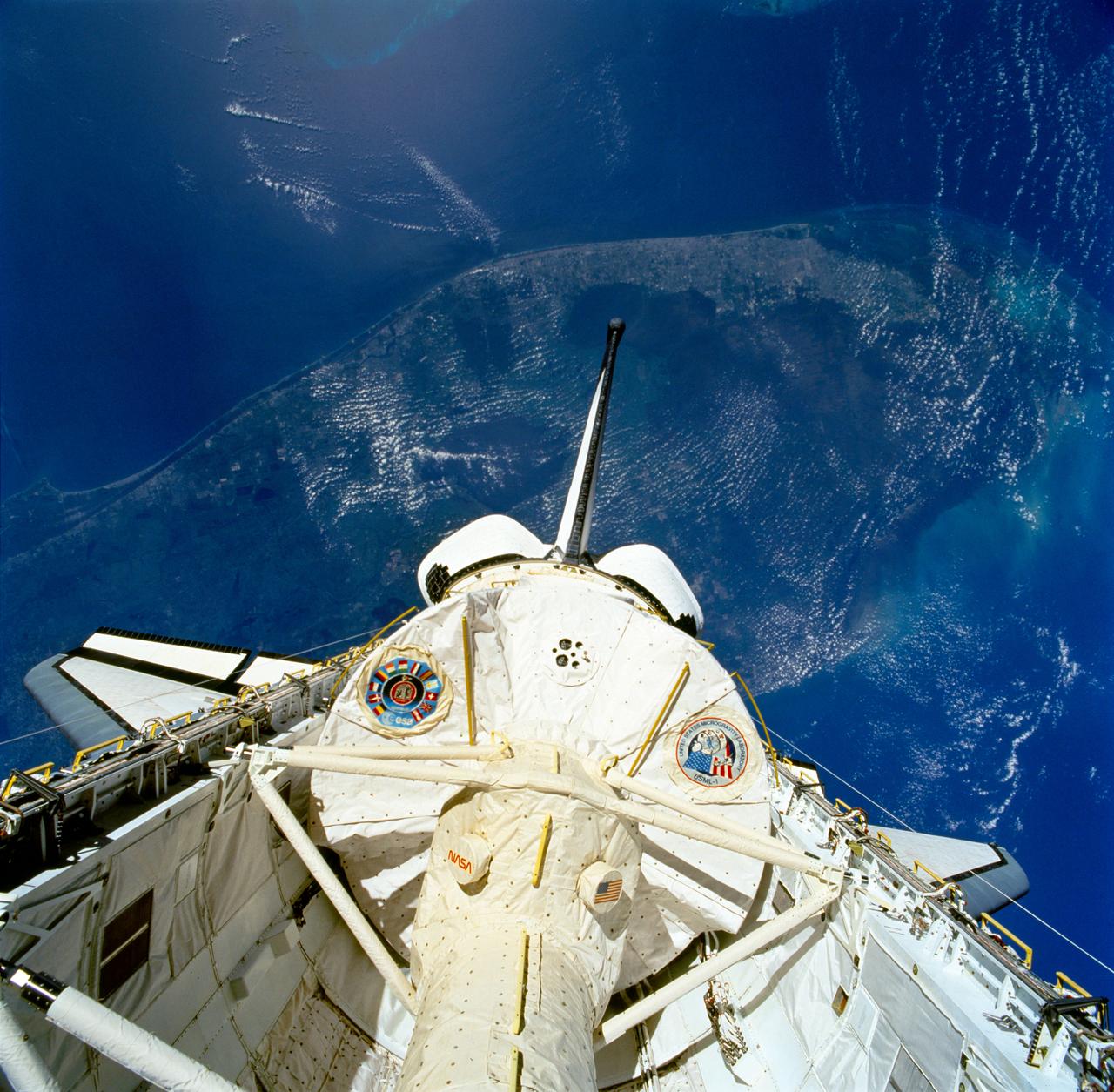

STS050-81-027 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- The first United States Microgravity Laboratory 1 (USML-1) module is pictured in the payload bay of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia in this scene over the southern two-thirds of the Florida peninsula. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC), where the mission began, can be seen just above Columbia's starboard wing. (Hold photo with number at left.)

STS050-02-023 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, payload commander, unstows United States Microgravity Laboratory 1 (USML-1) experiment paraphernalia in early stages of the mission. The Multipurpose Glove Box (MPGB) is at upper left. And, at right center, is the Space Station design foot restraint, making its first flight aboard a Space Shuttle on the record-setting 14-day mission.
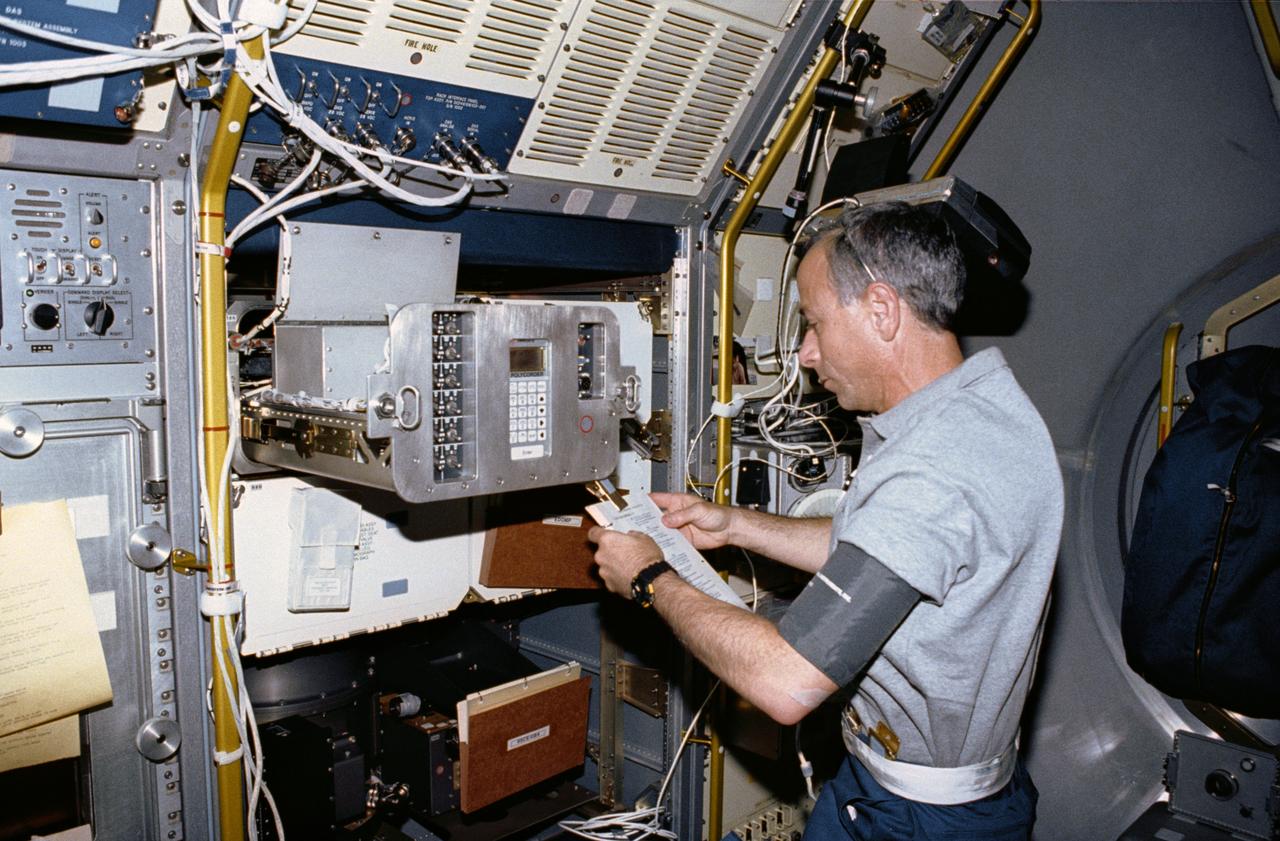

STS050-02-036 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Carl J. Meade, mission specialist, operates the Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (GBA) in the Science Module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. Meade was joined by four astronauts and two scientists from the private sector for the record-setting 14-day United States Microgravity Lab 1 (USML-1) mission.

STS050-S-001 (January 1992) --- Designed by the flight crew, the insignia for the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1), captures a space shuttle traveling above Earth while trailing the USML banner. The orbiter is oriented vertically in a typical attitude for microgravity science and in this position represents the numeral 1 in the mission's abbreviated title. This flight represents the first in a series of USML flights on which the primary objective is microgravity science, planned and executed through the combined efforts of the United States of America's government, industry and academia. Visible in the payload bay are the Spacelab module, and the extended duration orbiter "cryo" pallet which will be making its first flight. The small g and Greek letter mu on the Spacelab module symbolize the microgravity environment being used for research in the areas of materials science and fluid physics. The large block letter U extends outside the patch perimeter, symbolizing the potential for the experiments on this flight to expand the current boundaries of knowledge in microgravity science. The Stars and Stripes of the USML block letters and the United States landmass in the Earth scene below reflect the crew's pride in the United States origin of all onboard experiments. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
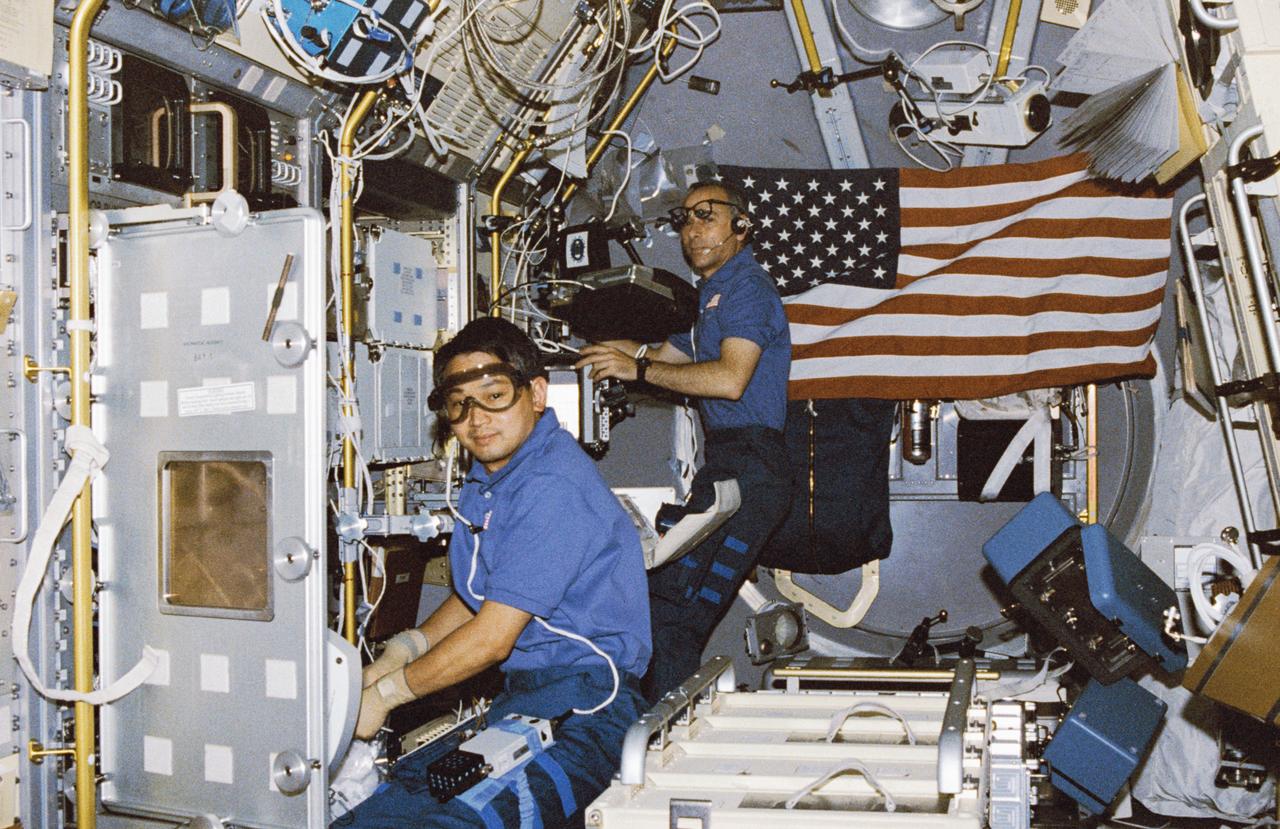
STS050-255-027 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Payload specialist Eugene H. Trinh, left, and astronaut Carl J. Meade, mission specialist, go to work in the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) science module as the blue shift crew takes over from the red. Trinh is working with an experiment at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) and Meade prepares to monitor an experiment in the Glovebox. The two joined four other astronauts and a second scientist from the private sector for 14-days of scientific data-gathering.
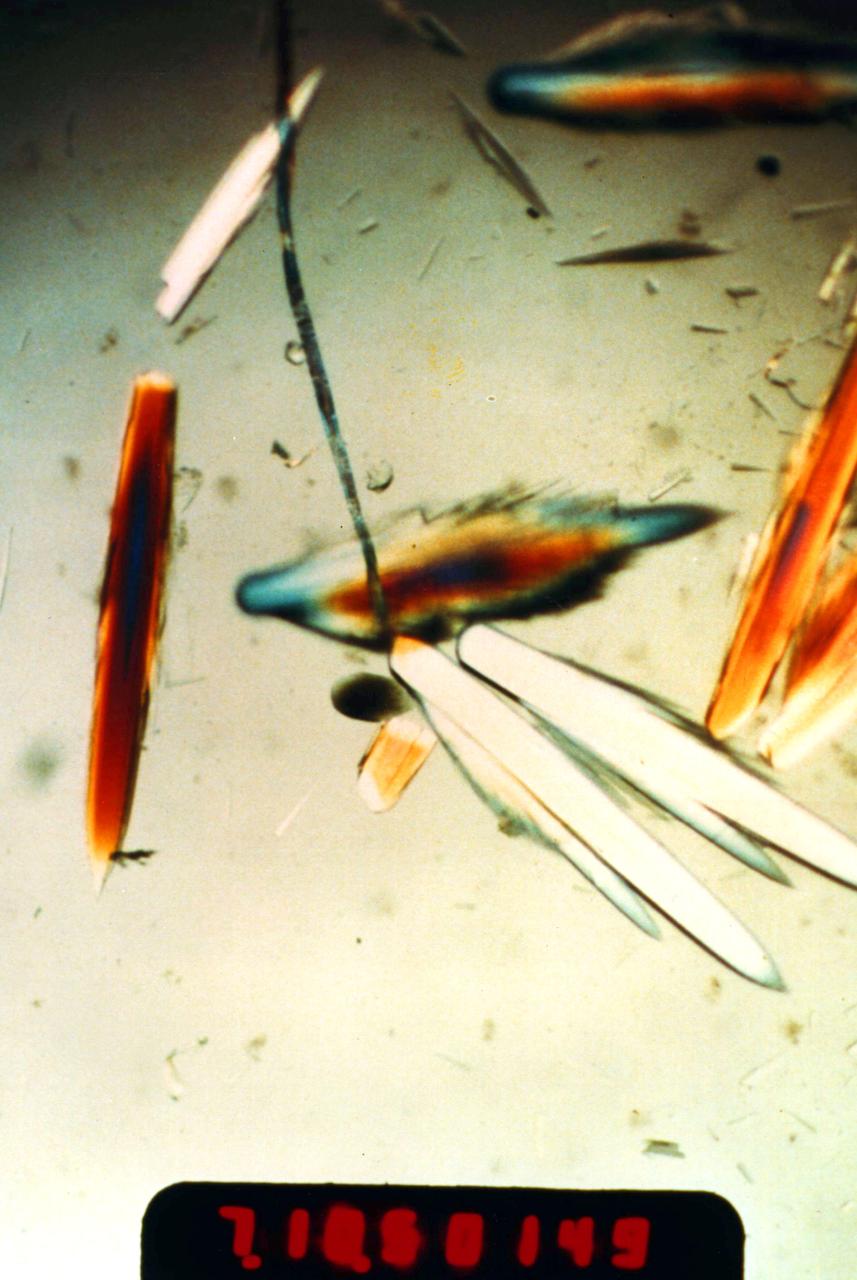
Horse Serum Albumin crystals grown during the USML-1 (STS-50) mission's Protein Crystal Growth Glovebox Experiment. These crystals were grown using a vapor diffusion technique at 22 degrees C. The crystals were allowed to grow for nine days while in orbit. Crystals of 1.0 mm in length were produced. The most abundant blood serum protein, regulates blood pressure and transports ions, metabolites, and therapeutic drugs. Principal Investigator was Edward Meehan.
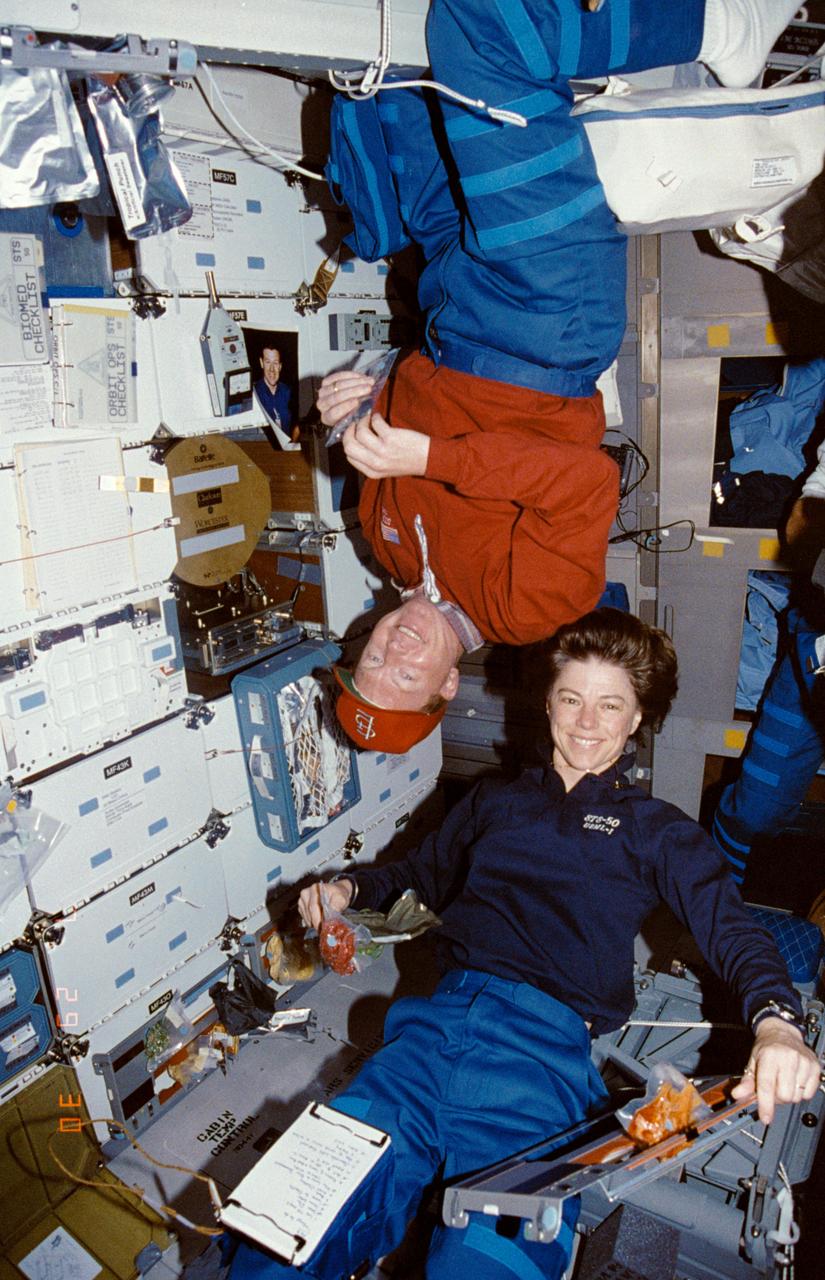

STS050-25-024 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronauts Richard N. Richards and Bonnie J. Dunbar, momentarily on leave from the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) science module, share a meal on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Richards is mission commander, and Dunbar is payload commander on the record-setting 14-day mission. Near Richards' head is the Astroculture experiment.
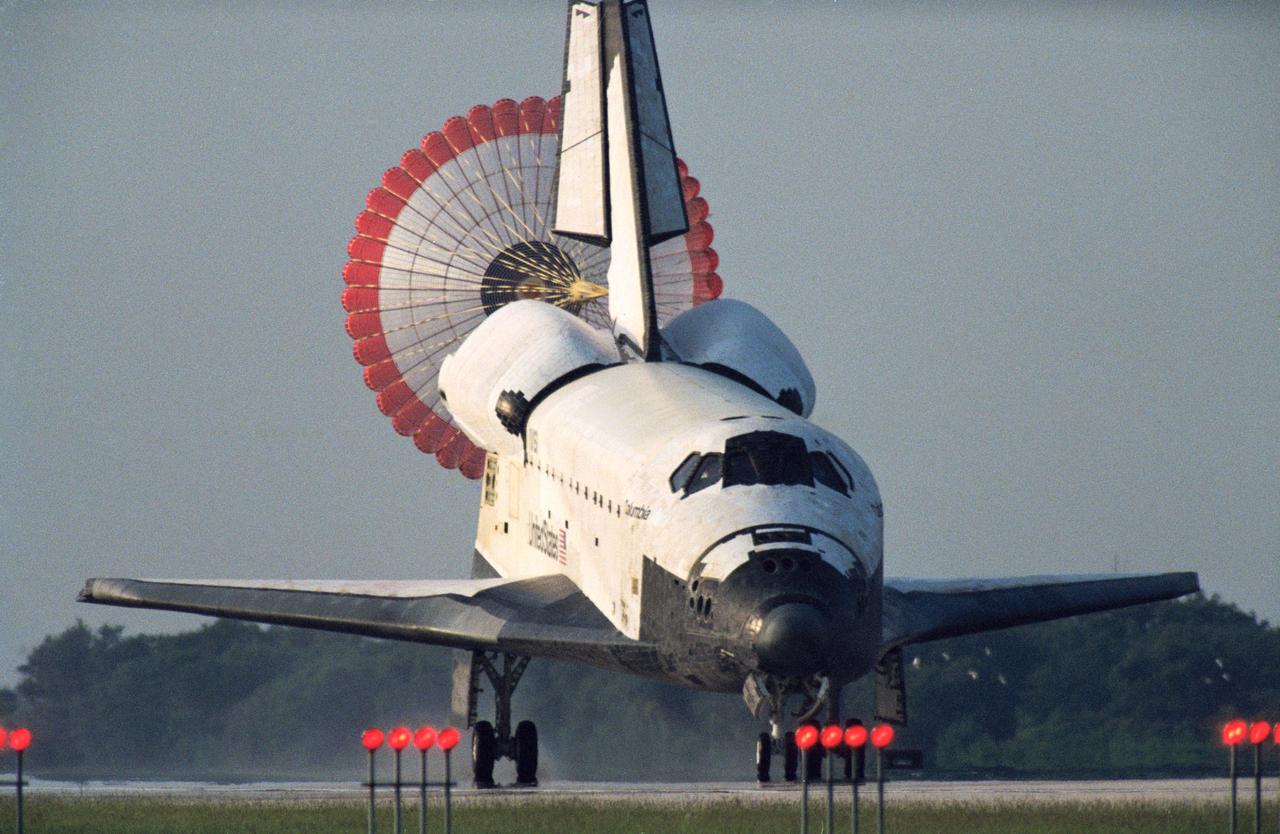

STS050-S-105 (9 July 1992) --- The main drag chute on the Space Shuttle Columbia is fully deployed soon after the Space Shuttle touches down at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) landing facility. Landing occurred at 7:42 a.m. (EDT). Seven crew members, including five astronauts and two scientists from the private sector spent 14 days in space supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1). This marks the first time for usage of the parachute system for a KSC landing and the second occurrence in the program.
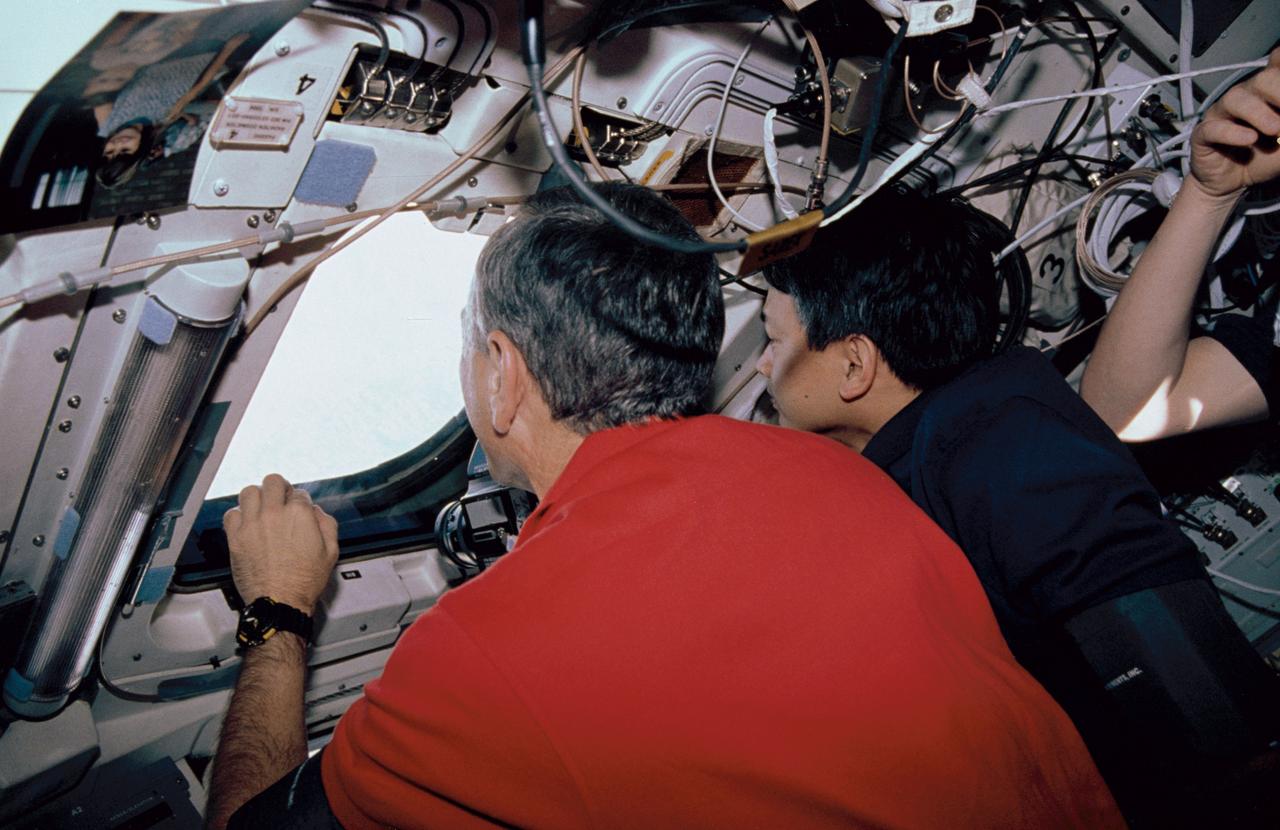

STS050-06-011 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Carl J. Meade (left), mission specialist, and Eugene H. Trinh, payload specialist, share a view through one of the Space Shuttle Columbia's aft flight deck windows during a break in photography of Earth. The two were among seven crew members who shared 14 record-setting days aboard the Space Shuttle supporting the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) mission.
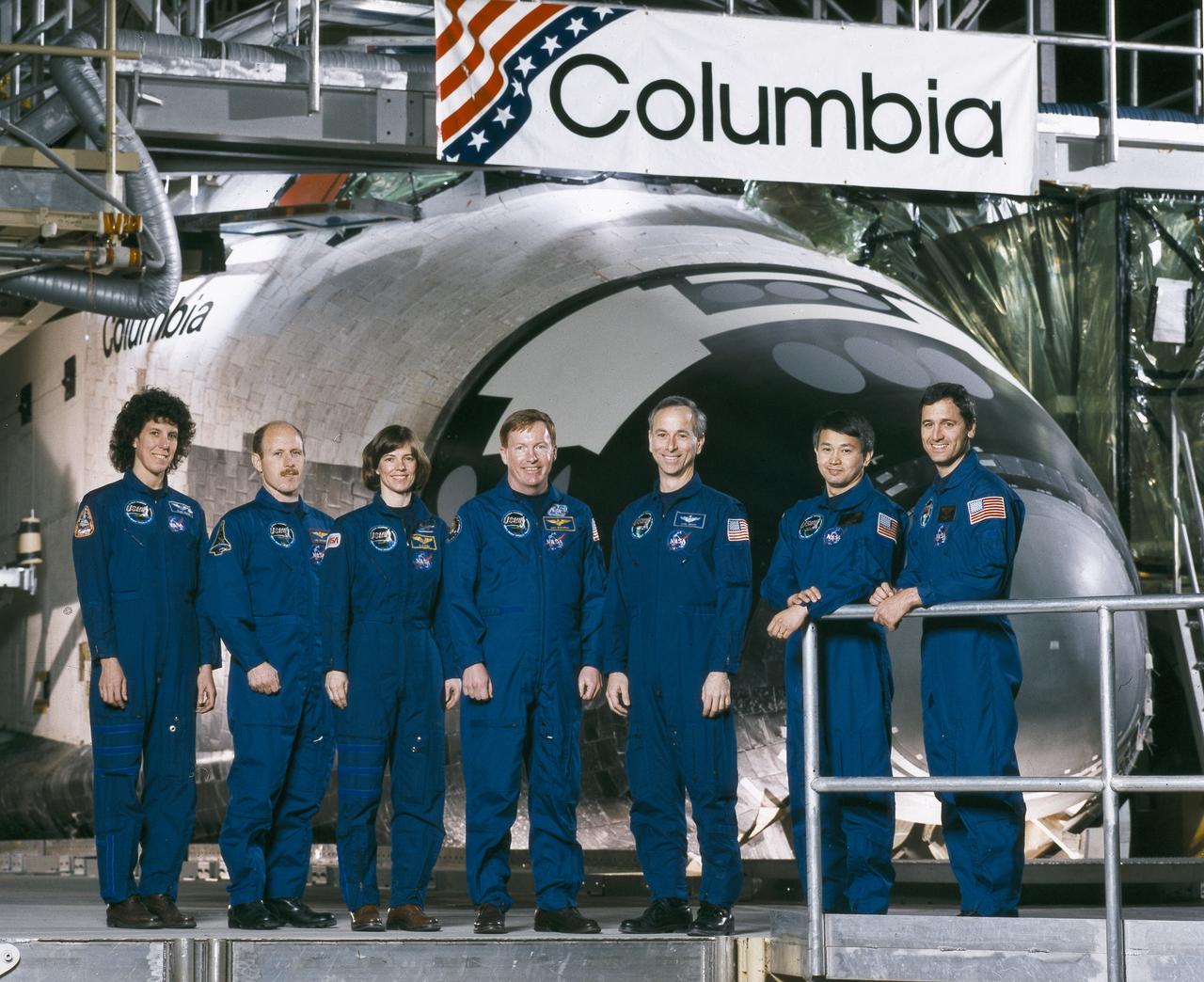

The STS-50 crew portrait includes (from left to right): Ellen S. Baker, mission specialist; Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot; Bonnie J. Dunbar, payload commander; Richard N. Richards, commander; Carl J. Meade, mission specialist; Eugene H. Trinh, payload specialist; and Lawrence J. DeLucas, payload specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on June 25, 1992 at 12:12:23 pm (EDT), the primary payload for the mission was the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-1 (USML-1) featuring a pressurized Spacelab module.

STS050-S-040 (25 June 1992) --- A low-angle perspective captures the Space Shuttle Columbia as it lifts off on its way toward a scheduled record 13-day mission in Earth-orbit. Liftoff occurred at 12:12:23:0534 p.m. (EDT) on June 25, 1992. The modified Columbia is NASA's first Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO). Five NASA astronauts and two scientists/payload specialists are aboard. The seven will divide into two shifts to support United States Microgravity Laboratory 1 (USML-1) research.
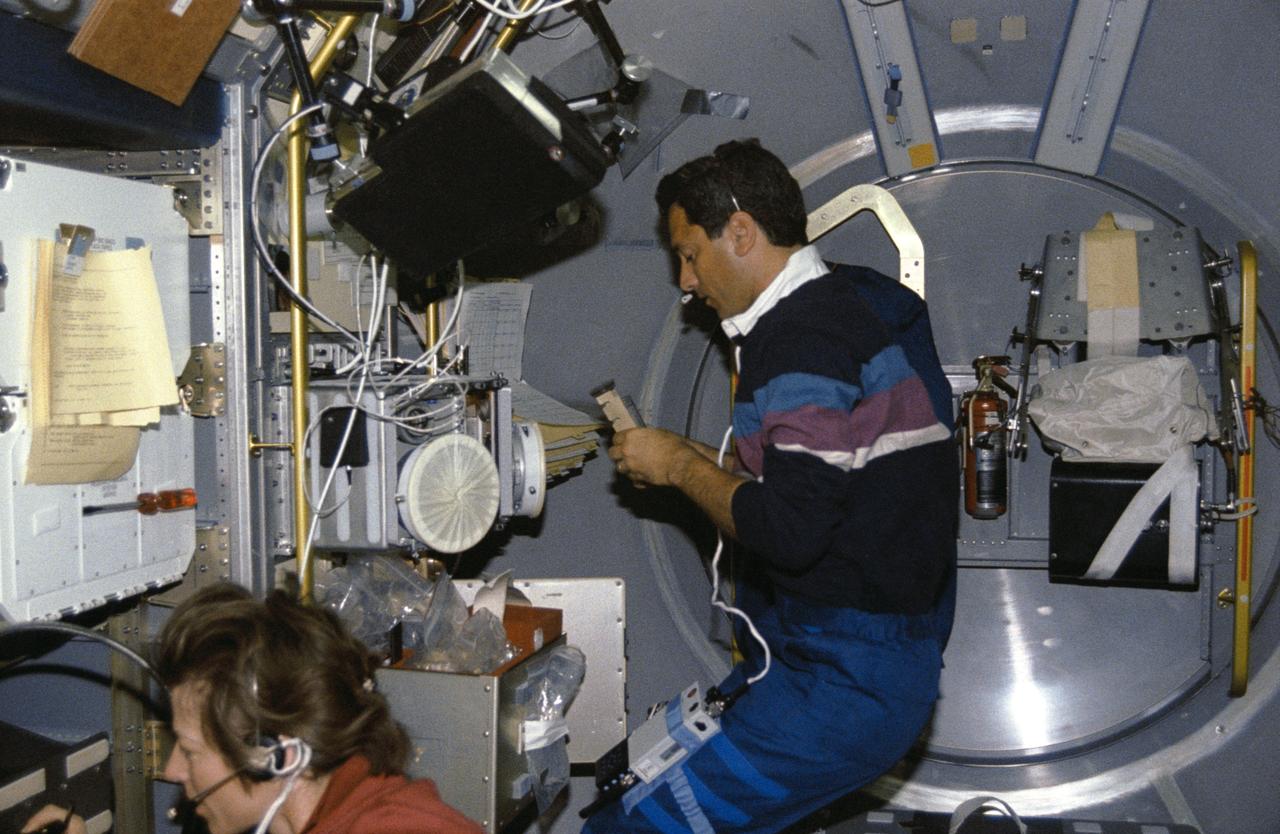

STS050-254-007 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Lawrence J. DeLucas, payload specialist, handles a Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) sample at the multipurpose glovebox aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, payload commander, communicates with ground controllers about the Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE), one of the United States Microgravity Laboratory 1’s (USML-1) three experiments on Rack 10. Five other crew members joined the pair for a record-setting 14-days of scientific data gathering.
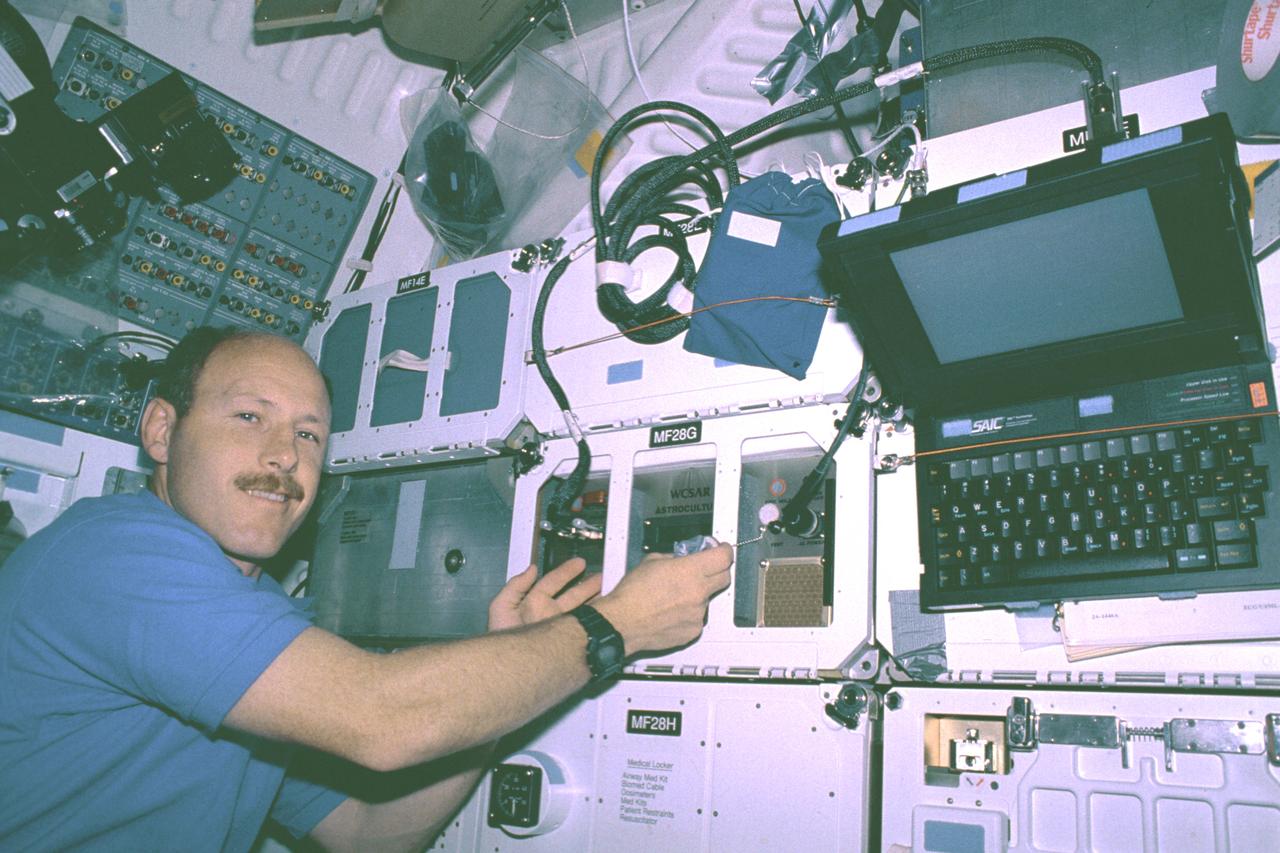

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs that provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This photograph shows astronaut Ken Bowersox conducting the Astroculture experiment in the middeck of the orbiter Columbia. This experiment was to evaluate and find effective ways to supply nutrient solutions for optimizing plant growth and avoid releasing solutions into the crew quarters in microgravity. Since fluids behave differently in microgravity, plant watering systems that operate well on Earth do not function effectively in space. Plants can reduce the costs of providing food, oxygen, and pure water as well as lower the costs of removing carbon dioxide in human space habitats. The Astroculture experiment flew aboard the STS-50 mission in June 1992 and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
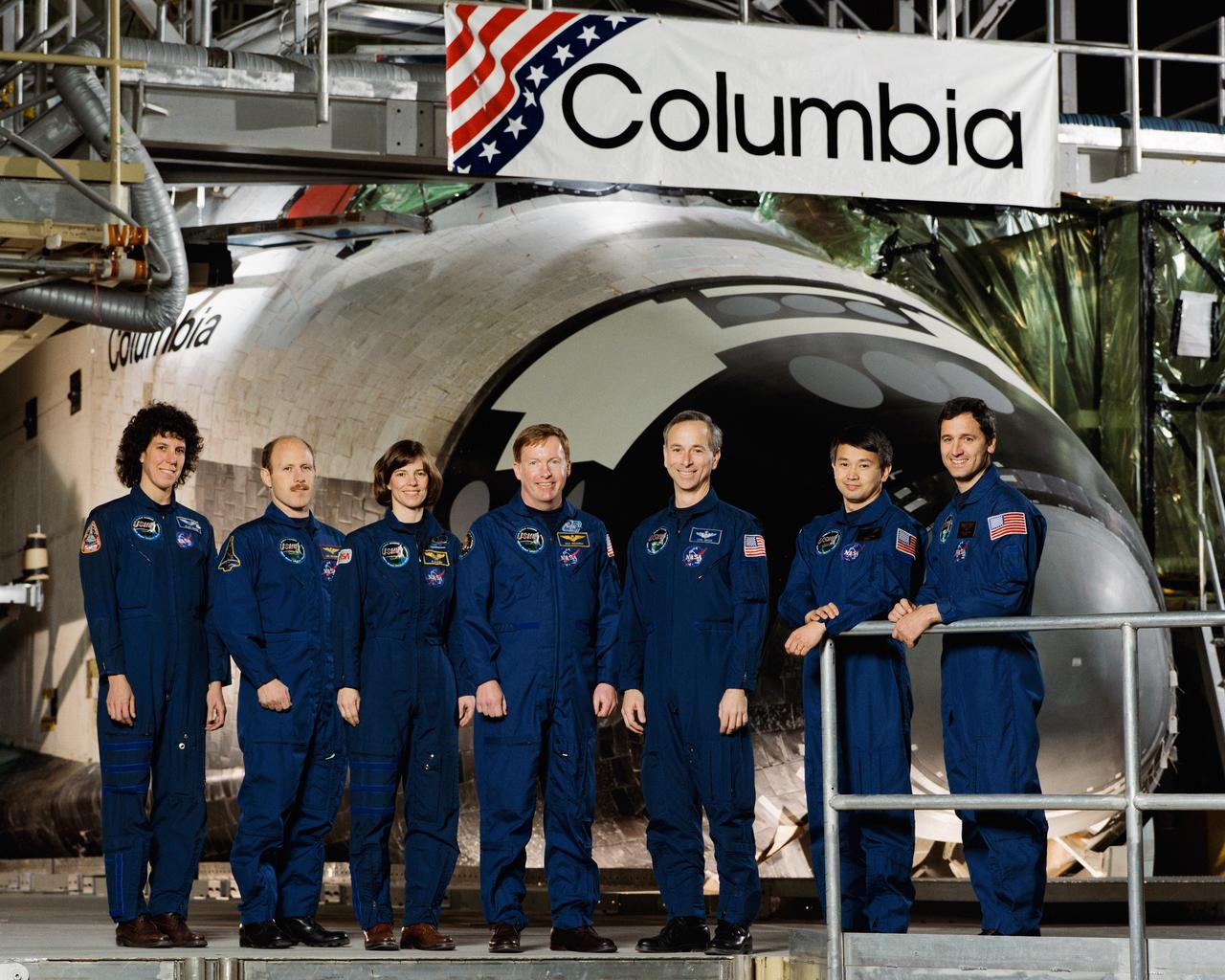

STS050-S-002 (24 Jan. 1992) --- The seven crew members assigned to NASA's mission pose for the traditional crew portrait. The crew was in Palmdale, California for the Space Shuttle Columbia's Extended-Duration Orbiter (EDO) modifications roll-out. Astronaut Richard N. Richards, mission commander, is center. Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot, is second from left. Others, left to right, are astronauts Ellen S. Baker, mission specialist; Bonnie J. Dunbar, payload commander; and Carl J. Meade, mission specialist; Eugene H. Trinh and Lawrence J. DeLucas, payload specialists.
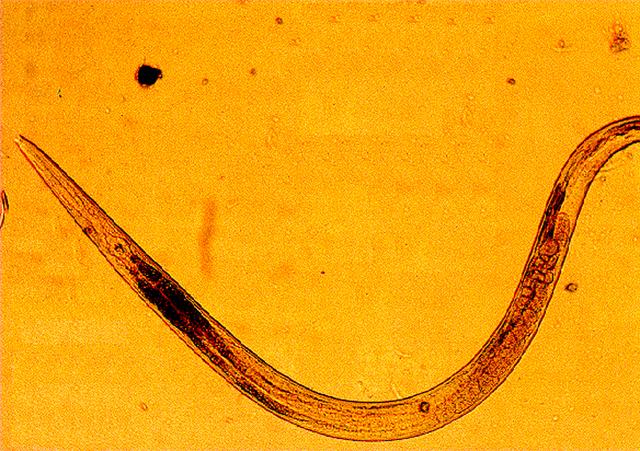
Over a billion of mostly third world people are infected with a roundworm known as ascarids. Ascarids are tiny parasites that infect the intestinal tract of vertebrates. Movement of the larvae into the brain or other parts of the body can prove fatal. Space-based research is providing new hope in combating these parasitic worms. Ascarids are dependent upon a substance known as malic enzyme to regulate certain bodily functions. A new drug designed to interfere with normal functioning of malic enzyme should prove deadly to ascarids. The Center for Macromolecular Crystallography, along with the University of North Texas grew malic enzyme crystals on the USML-1 Spacelab mission. Although these crystals proved to be smaller than ground based ones, they were more perfectly formed, therefore producing better data for drug design.
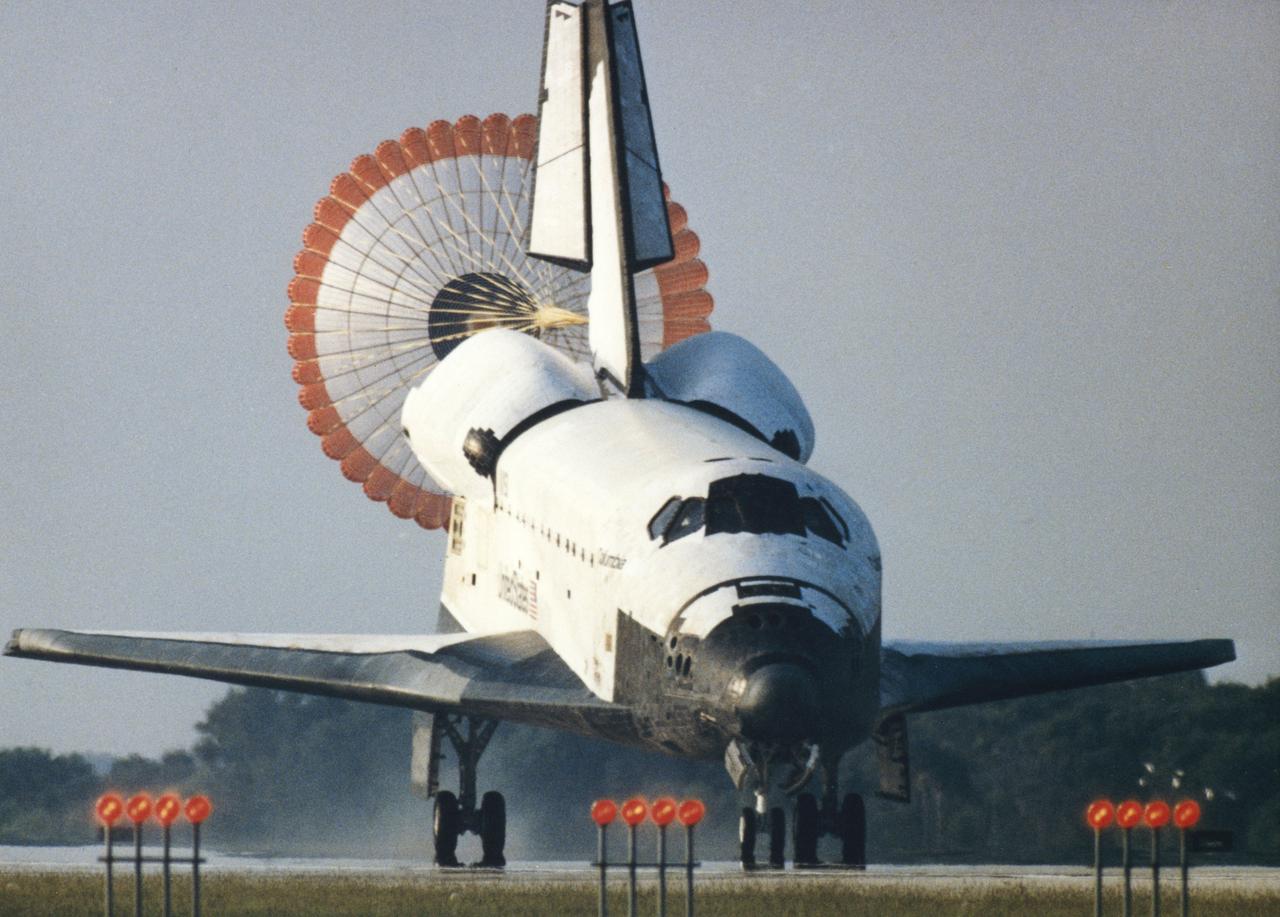

As the orbiter Columbia (STS-50) rolled down Runway 33 of Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility, its distinctively colored drag chute deployed to slow down the spaceship. This landing marked OV-102's first end-of-mission landing at KSC and the tenth in the program, and the second shuttle landing with the drag chute. Edwards Air Force Base, CA, was the designated prime for the landing of Mission STS-50, but poor weather necessitated the switch to KSC after a one-day extension of the historic flight. STS-50 was the longest in Shuttle program historyo date, lasting 13 days, 19 hours, 30 minutes and 4 seconds. A crew of seven and the USML-1 were aboard.
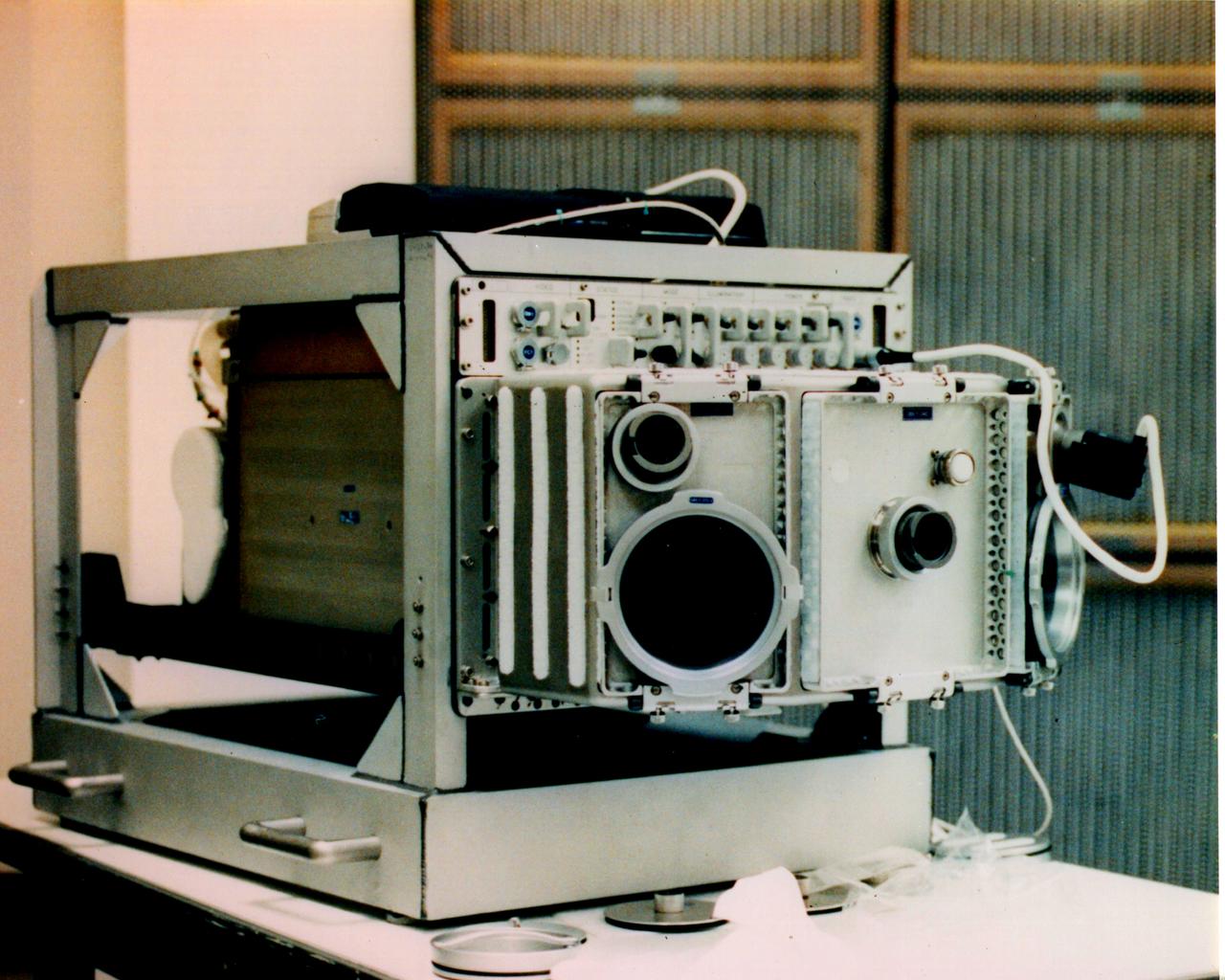
The USML-1 Glovebox (GBX) is a multi-user facility supporting 16 experiments in fluid dynamics, combustion sciences, crystal growth, and technology demonstration. The GBX has an enclosed working space which minimizes the contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. The GBX supports four charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras (two of which may be operated simultaneously) with three black-and-white and three color camera CCD heads available. The GBX also has a backlight panel, a 35 mm camera, and a stereomicroscope that offers high-magnification viewing of experiment samples. Video data can also be downlinked in real-time. The GBX also provides electrical power for experiment hardware, a time-temperature display, and cleaning supplies.
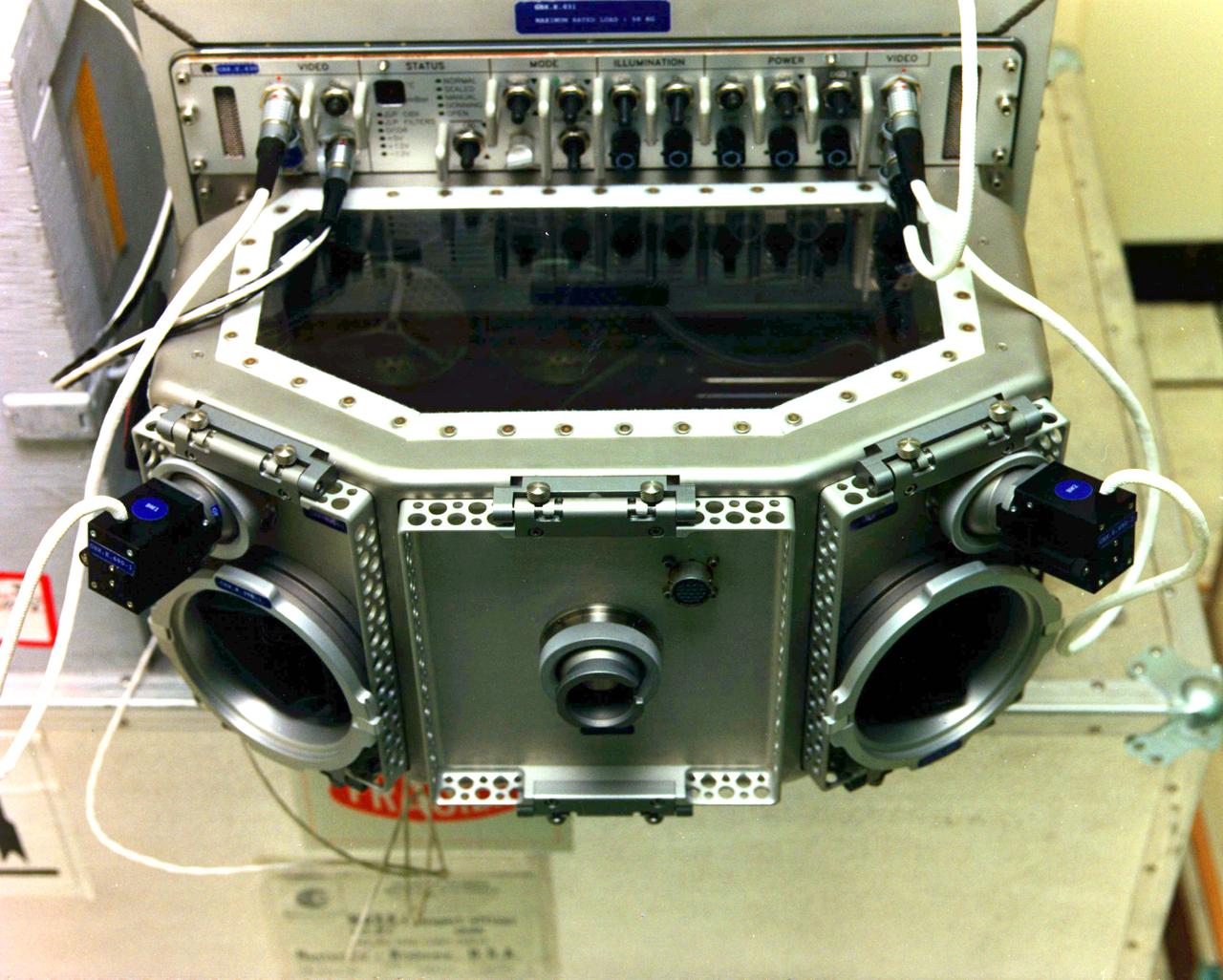

The USML-1 Glovebox (GBX) is a multi-user facility supporting 16 experiments in fluid dynamics, combustion sciences, crystal growth, and technology demonstration. The GBX has an enclosed working space which minimizes the contamination risks to both Spacelab and experiment samples. The GBX supports four charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras (two of which may be operated simultaneously) with three black-and-white and three color camera CCD heads available. The GBX also has a backlight panel, a 35 mm camera, and a stereomicroscope that offers high-magnification viewing of experiment samples. Video data can also be downlinked in real-time. The GBX also provides electrical power for experiment hardware, a time-temperature display, and cleaning supplies.