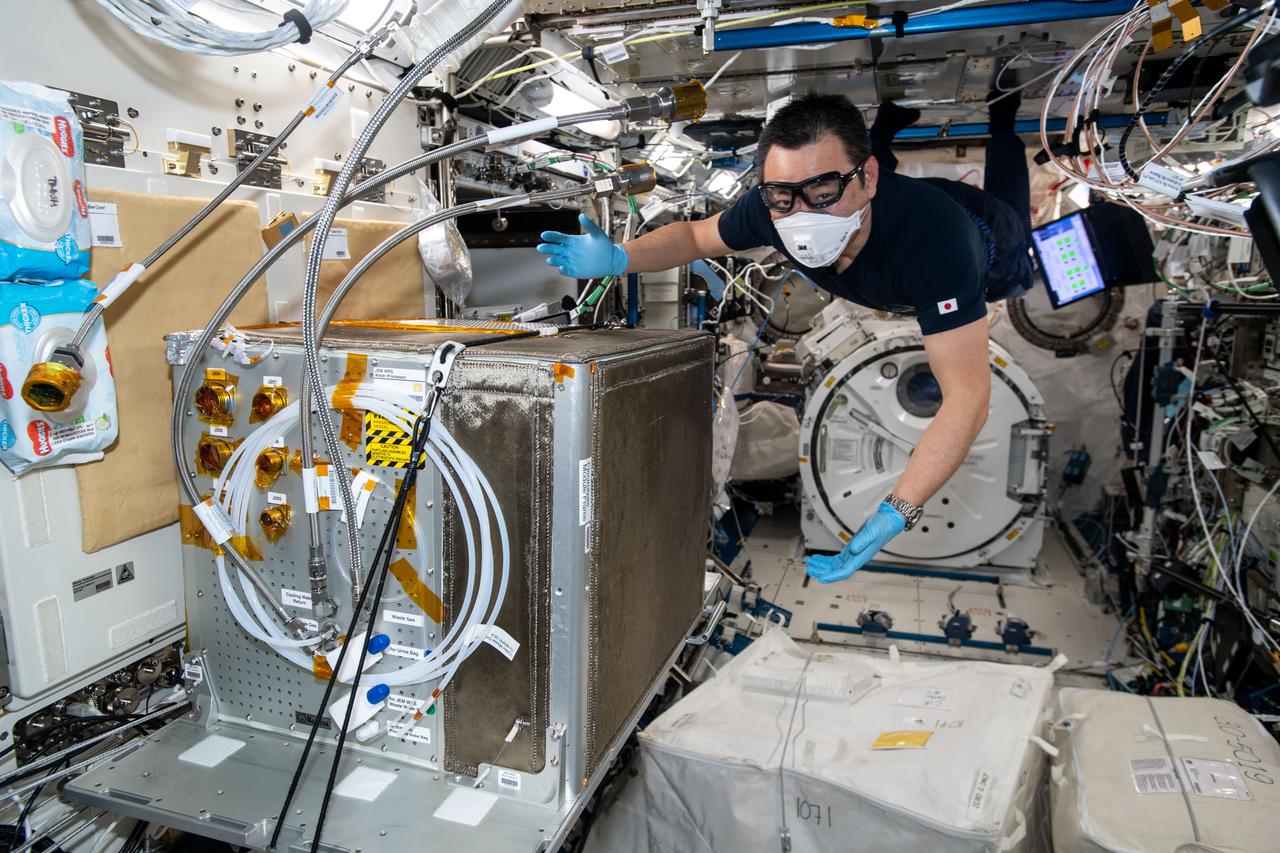

iss065e333421 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.
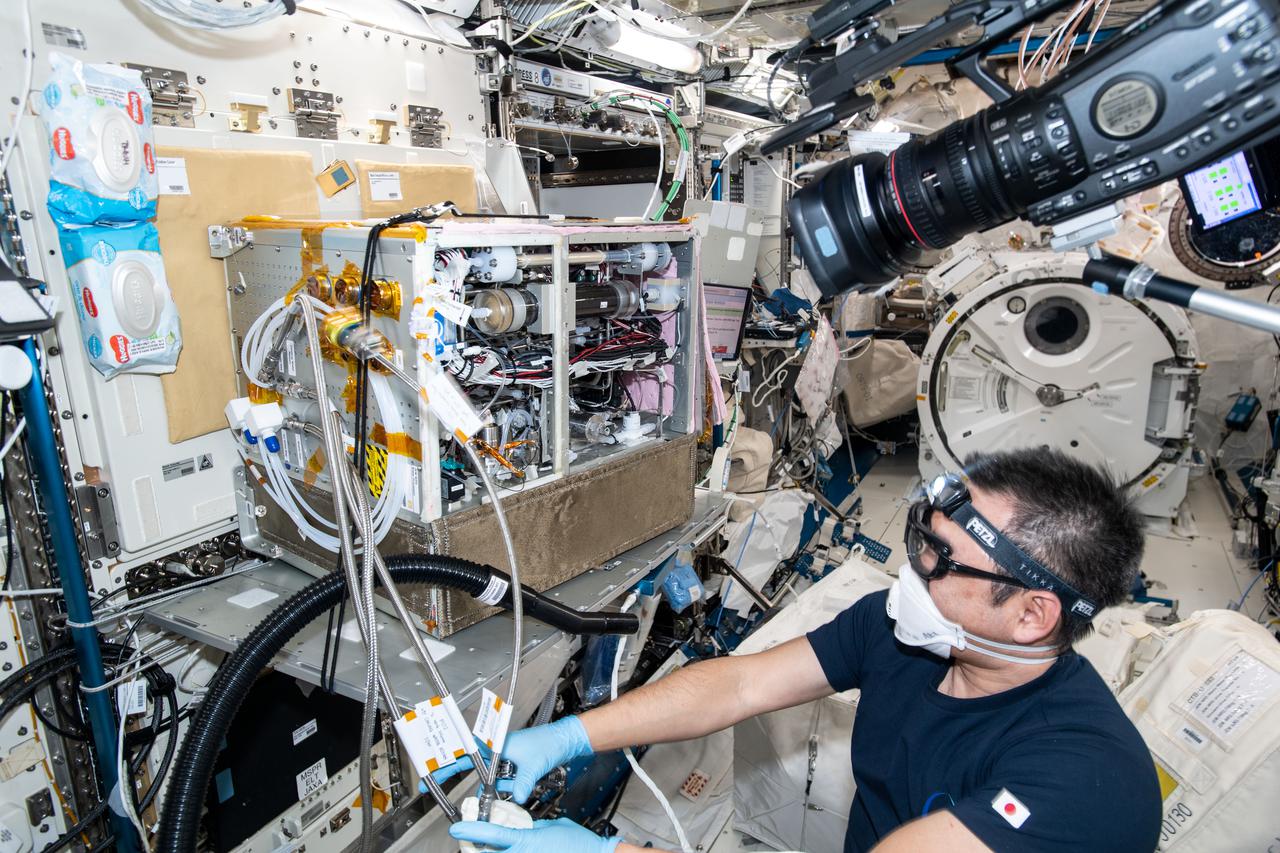

iss065e333427 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.
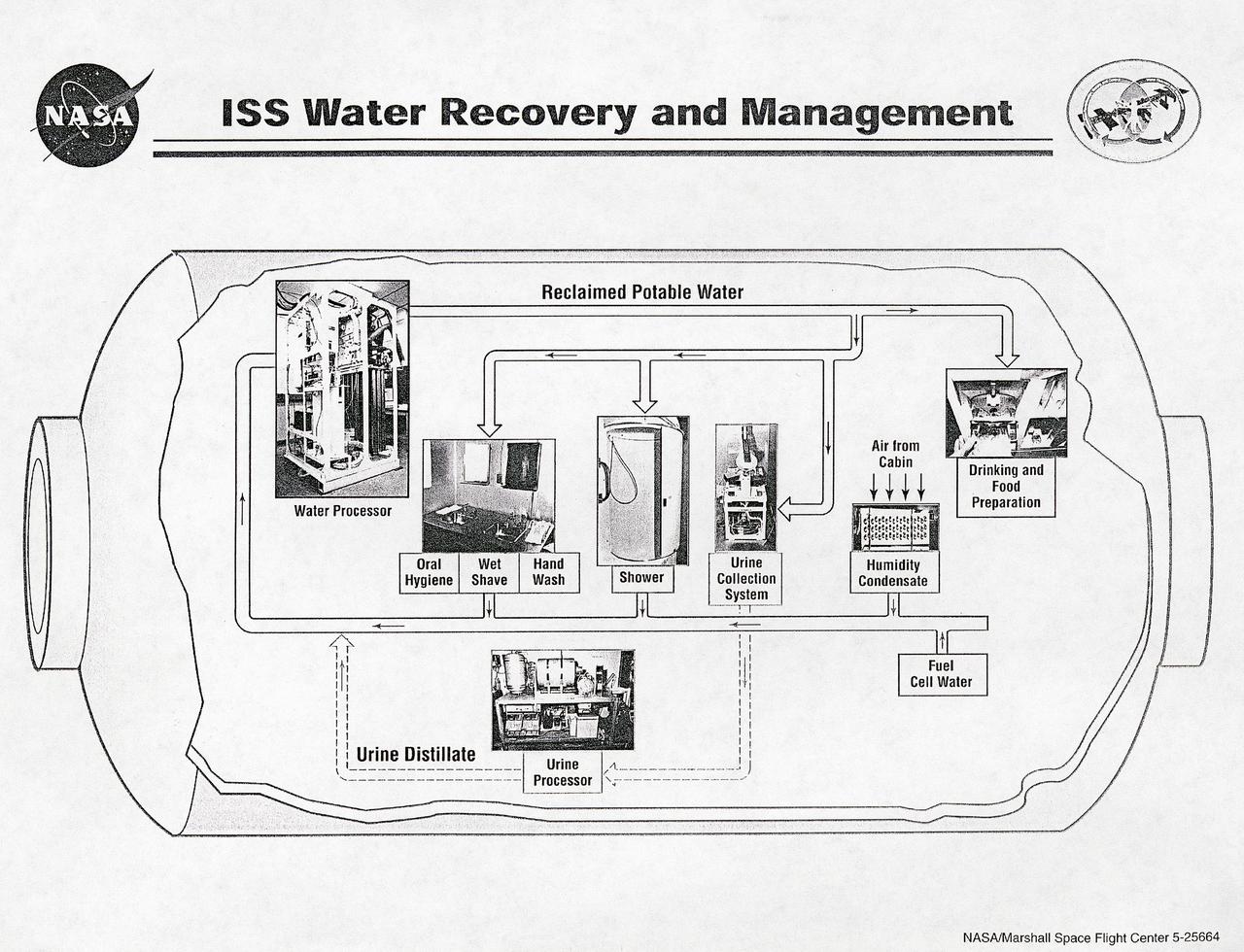
This diagram shows the flow of water recovery and management in the International Space Station (ISS). The Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) Group of the Flight Projects Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center is responsible for the regenerative ECLSS hardware, as well as providing technical support for the rest of the system. The regenerative ECLSS, whose main components are the Water Recovery System (WRS), and the Oxygen Generation System (OGS), reclaims and recycles water oxygen. The ECLSS maintains a pressurized habitation environment, provides water recovery and storage, maintains and provides fire detection/ suppression, and provides breathable air and a comfortable atmosphere in which to live and work within the ISS. The ECLSS hardware will be located in the Node 3 module of the ISS.

ISS018-E-011530 (8 Dec. 2008) --- Astronaut Michael Fincke, Expedition 18 commander, performs a leak check on the Water Recovery System (WRS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
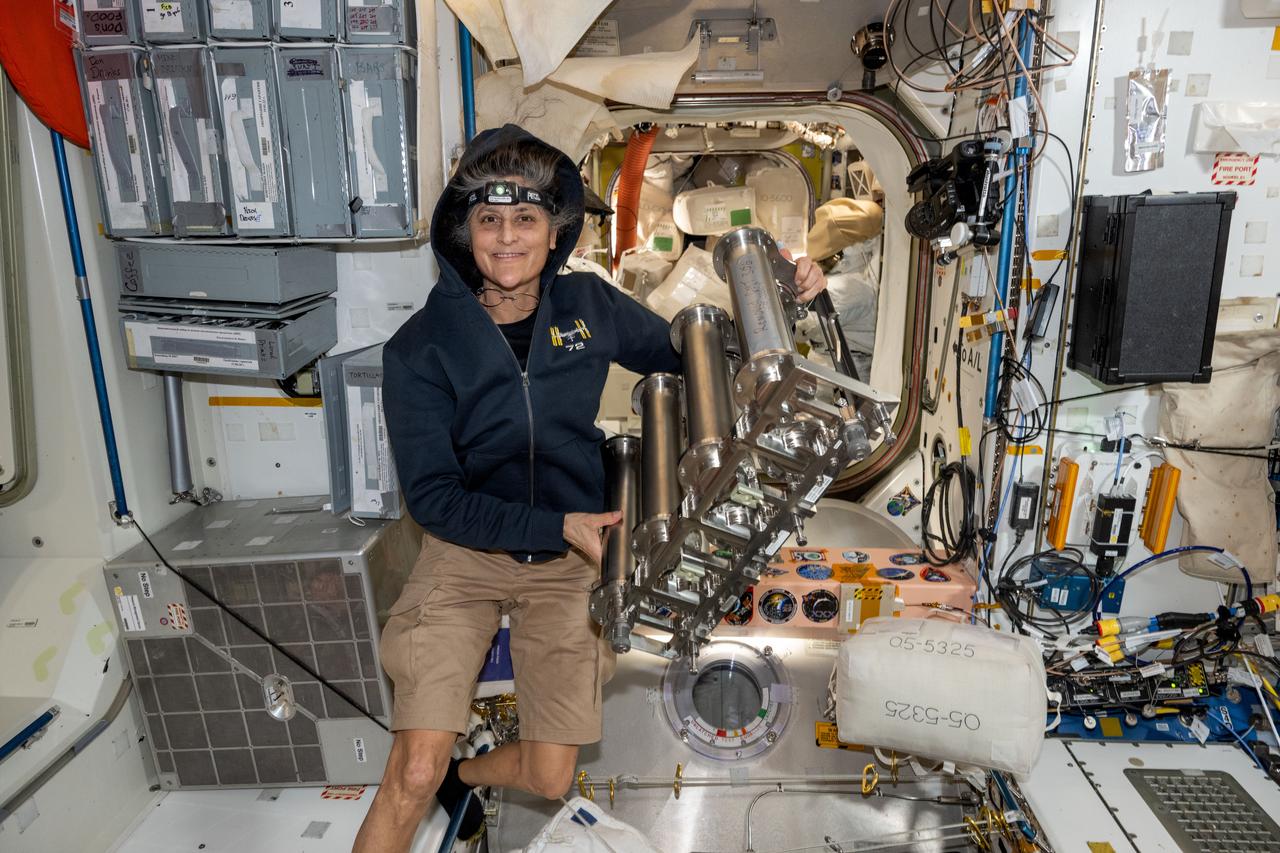

iss072e143163 (Nov. 1, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams replaces particulate filters on the water recovery system, a component of the Tranquility module's waste and hygiene compartment, the International Space Station's bathroom.
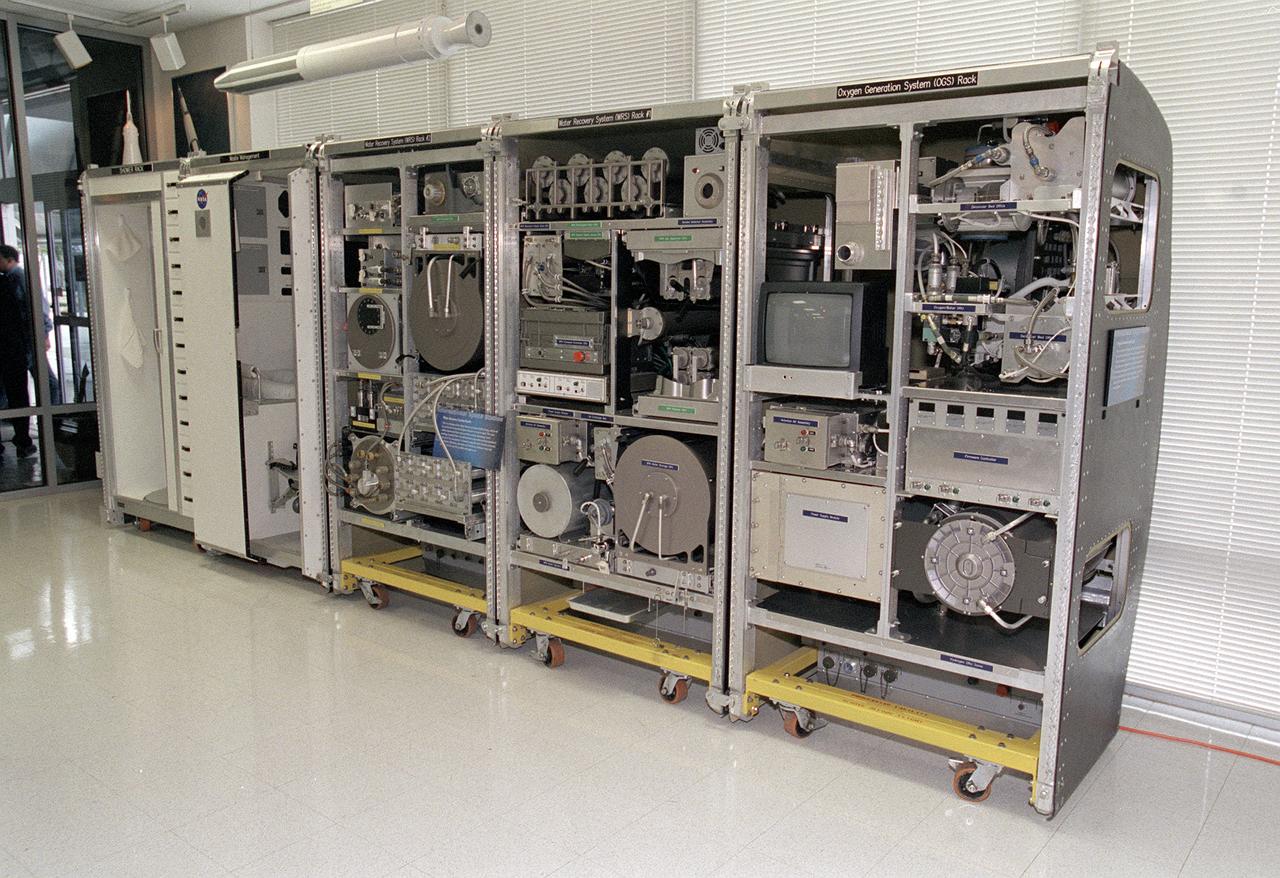

The Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) Group of the Flight Projects Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, is responsible for designing and building the life support systems that will provide the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) a comfortable environment in which to live and work. This photograph shows the mockup of the the ECLSS to be installed in the Node 3 module of the ISS. From left to right, shower rack, waste management rack, Water Recovery System (WRS) Rack #2, WRS Rack #1, and Oxygen Generation System (OGS) rack are shown. The WRS provides clean water through the reclamation of wastewaters and is comprised of a Urine Processor Assembly (UPA) and a Water Processor Assembly (WPA). The UPA accepts and processes pretreated crewmember urine to allow it to be processed along with other wastewaters in the WPA. The WPA removes free gas, organic, and nonorganic constituents before the water goes through a series of multifiltration beds for further purification. The OGS produces oxygen for breathing air for the crew and laboratory animals, as well as for replacing oxygen loss. The OGS is comprised of a cell stack, which electrolyzes (breaks apart the hydrogen and oxygen molecules) some of the clean water provided by the WRS, and the separators that remove the gases from the water after electrolysis.
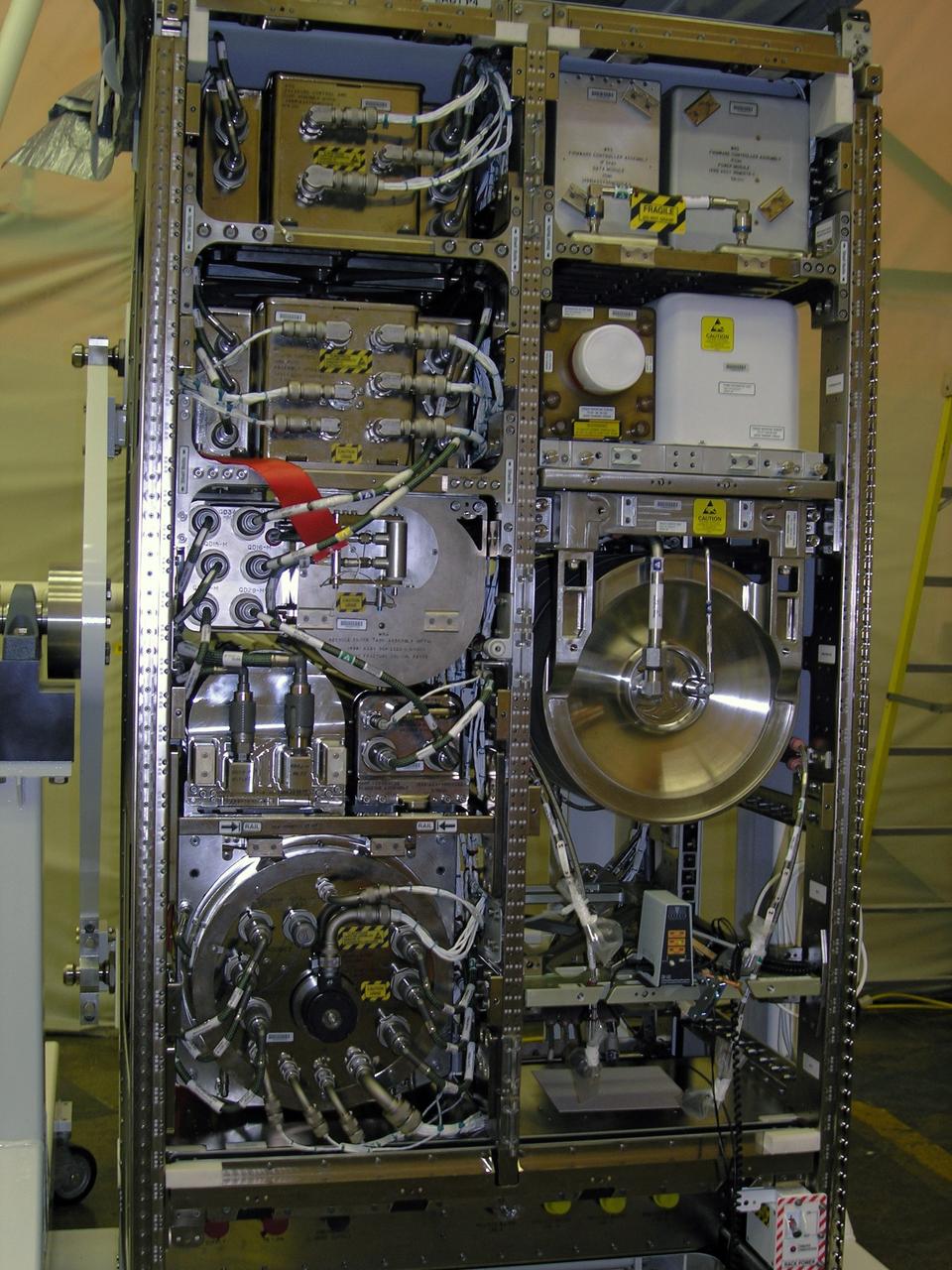

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This photo shows the Water Recovery System's rack 2, that will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission. Its primary purpose is to process urine and waster water so that Waste Recovery System's rack 1 can perform the final cleanup. The two units of the Water Recovery System are designed to provide drinking-quality water through the reclamation of wastewater, including urine and hygiene wastes. The water that’s produced will be used to support the crew and work aboard the station. Endeavour and its crew of seven are scheduled to lift off at 7:55 p.m. Nov. 14 for the 15-day STS-126 mission. Photo credit: NASA

iss069e088358 (9/14/2023) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa is seen processing samples from the JEM Water Recovery System (JWRS) in the KIBO module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The JWRS demonstrates that potable water can be generated from urine. In the past, urine and wastewater were collected and stored, or vented overboard. However, for long-term space missions, water supply could become a limiting factor. Demonstrating the function of this water recovery system on orbit contributes to updating the Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) to support astronauts on the space station and future exploration missions.
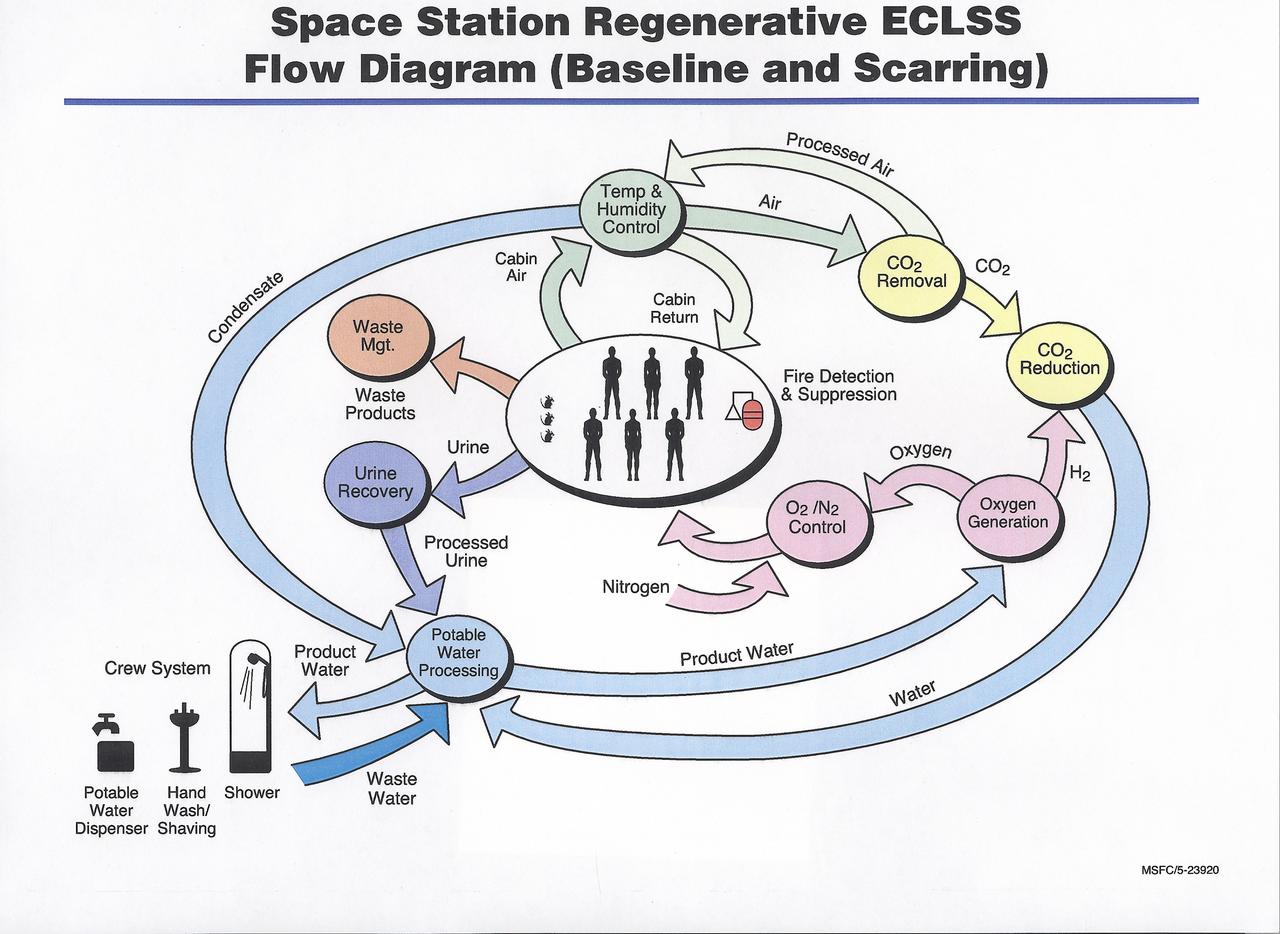
This diagram shows the flow of recyclable resources in the International Space Station (ISS). The Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) Group of the Flight Projects Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center is responsible for the regenerative ECLSS hardware, as well as providing technical support for the rest of the system. The regenerative ECLSS, whose main components are the Water Recovery System (WRS), and the Oxygen Generation System (OGS), reclaims and recycles water and oxygen. The ECLSS maintains a pressurized habitation environment, provides water recovery and storage, maintains and provides fire detection / suppression, and provides breathable air and a comfortable atmosphere in which to live and work within the ISS. The ECLSS hardware will be located in the Node 3 module of the ISS.
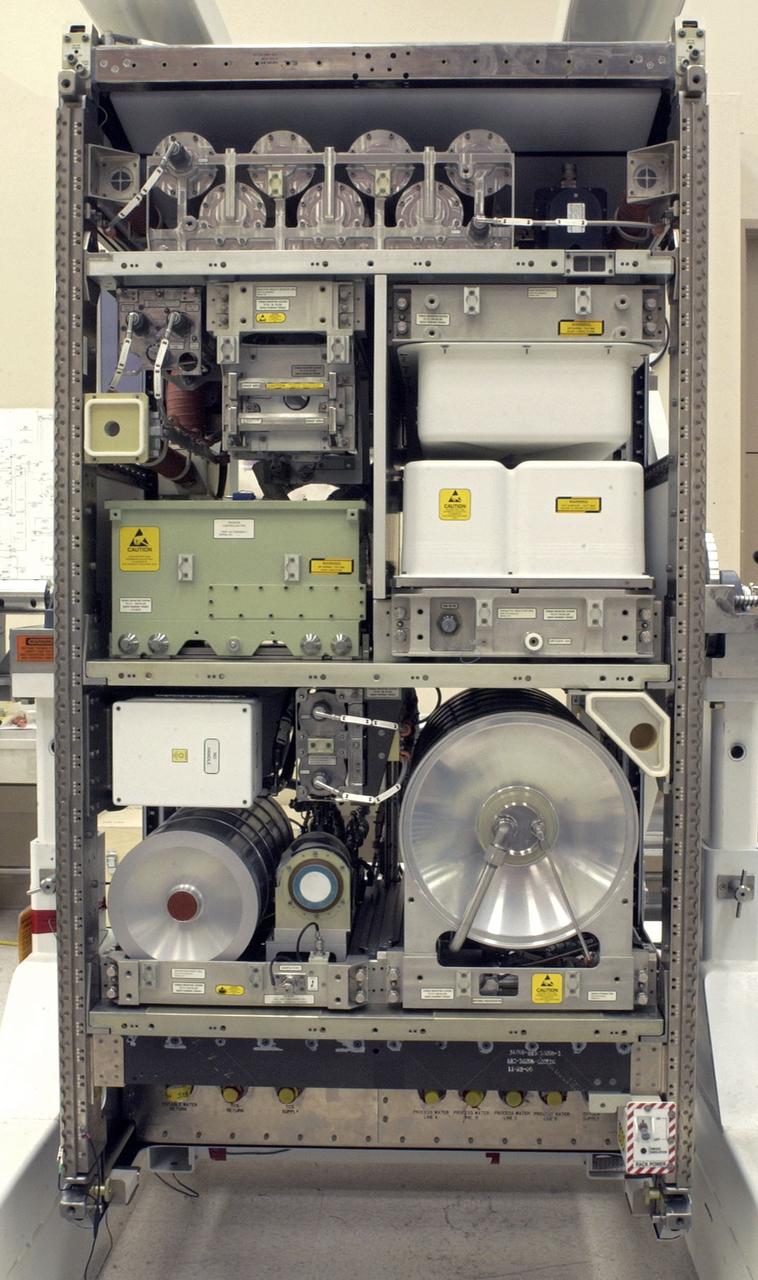

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This photo shows the Water Recovery System's rack 1 that will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission. The two units of the Water Recovery System are designed to provide drinking-quality water through the reclamation of wastewater, including urine and hygiene wastes. The water that’s produced will be used to support the crew and work aboard the station. Endeavour and its crew of seven are scheduled to lift off at 7:55 p.m. Nov. 14 for the 15-day STS-126 mission. Photo credit: NASA
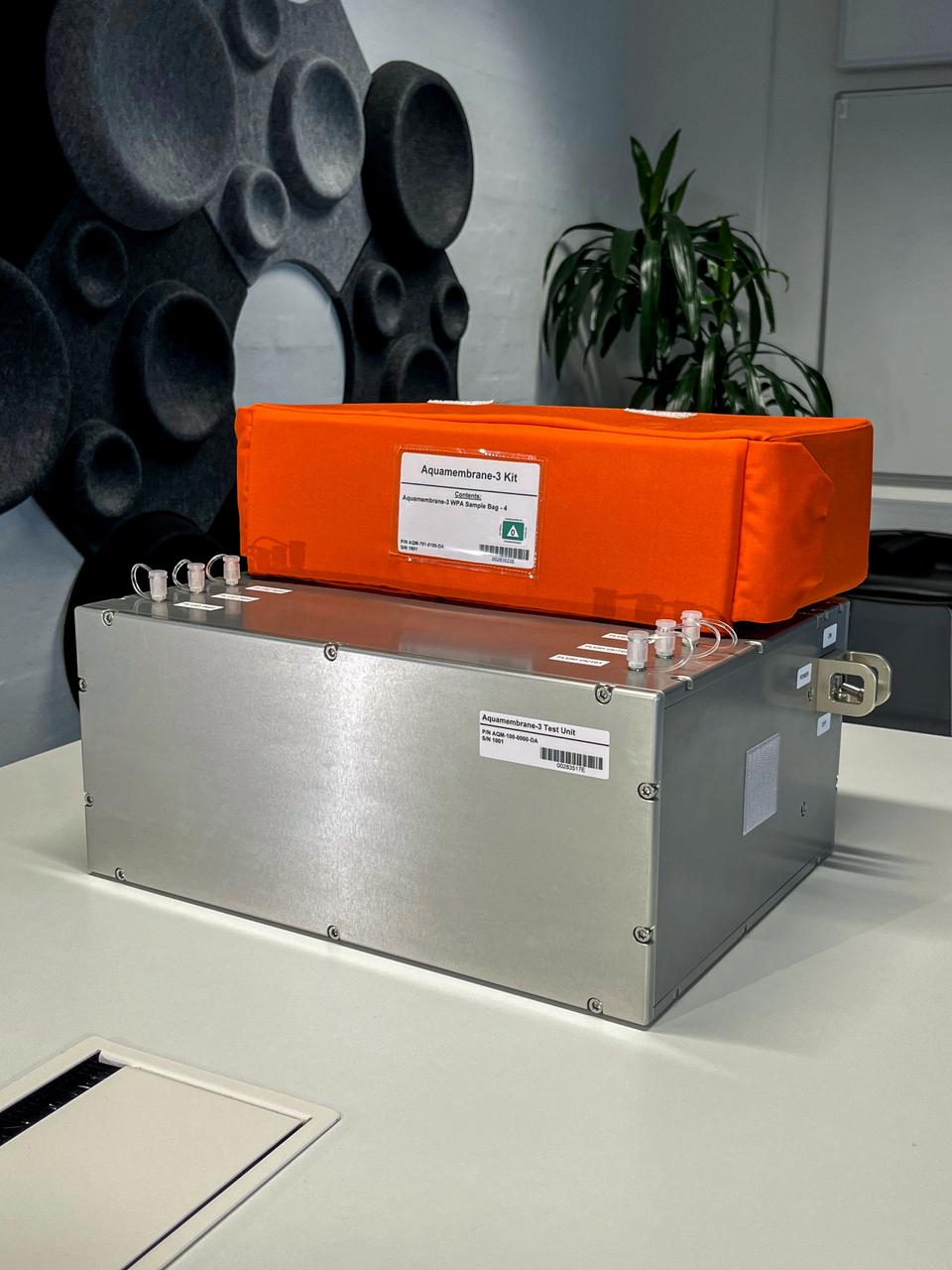

jsc2023e055872 (10/5/2023) --- The Testing Contaminant Rejection of Aquaporin Inside® HFFO Module (Aquamembrane-3) hardware consists of three separate and parallel systems to quantify the membrane's water flux and contamination rejection in microgravity, which are key parameters for a full water recovery system. This image shows the complete experiment hardware.
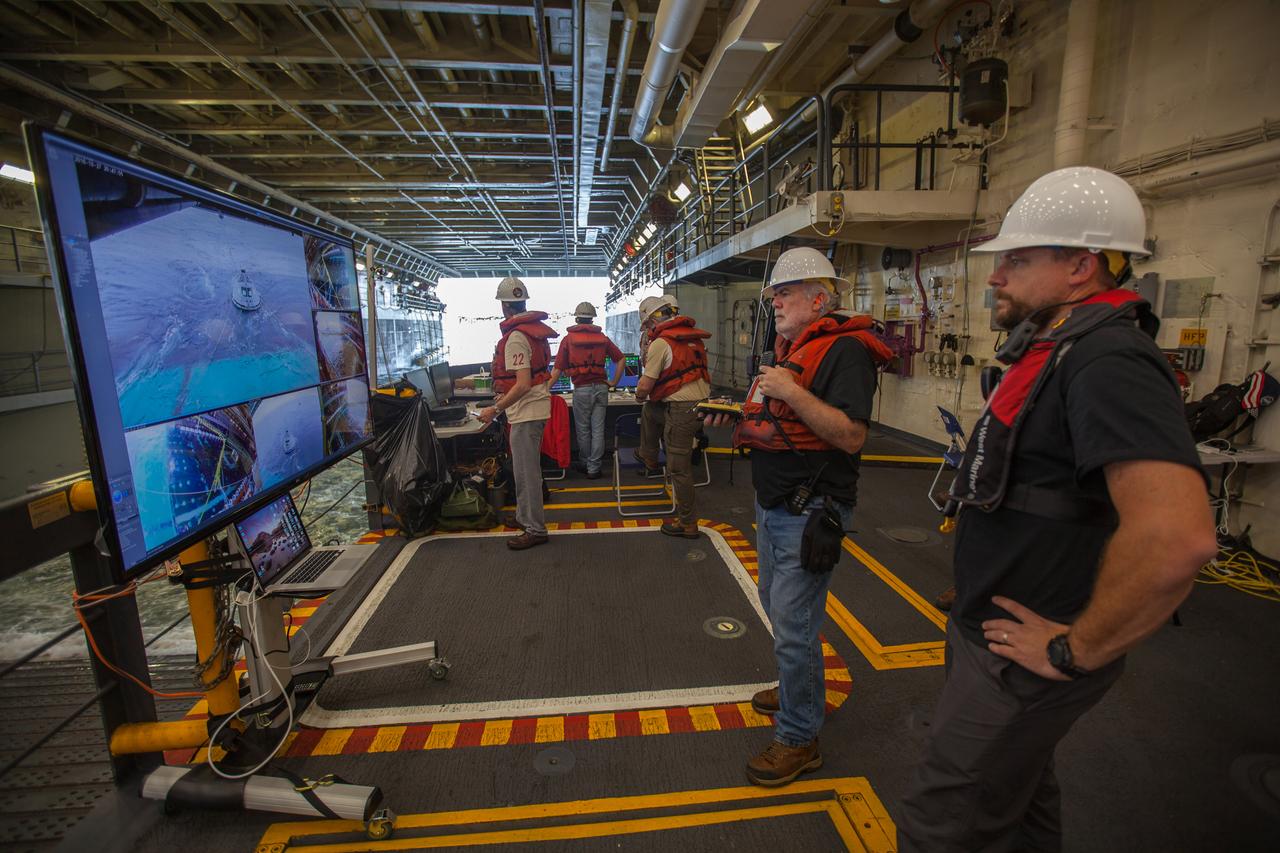

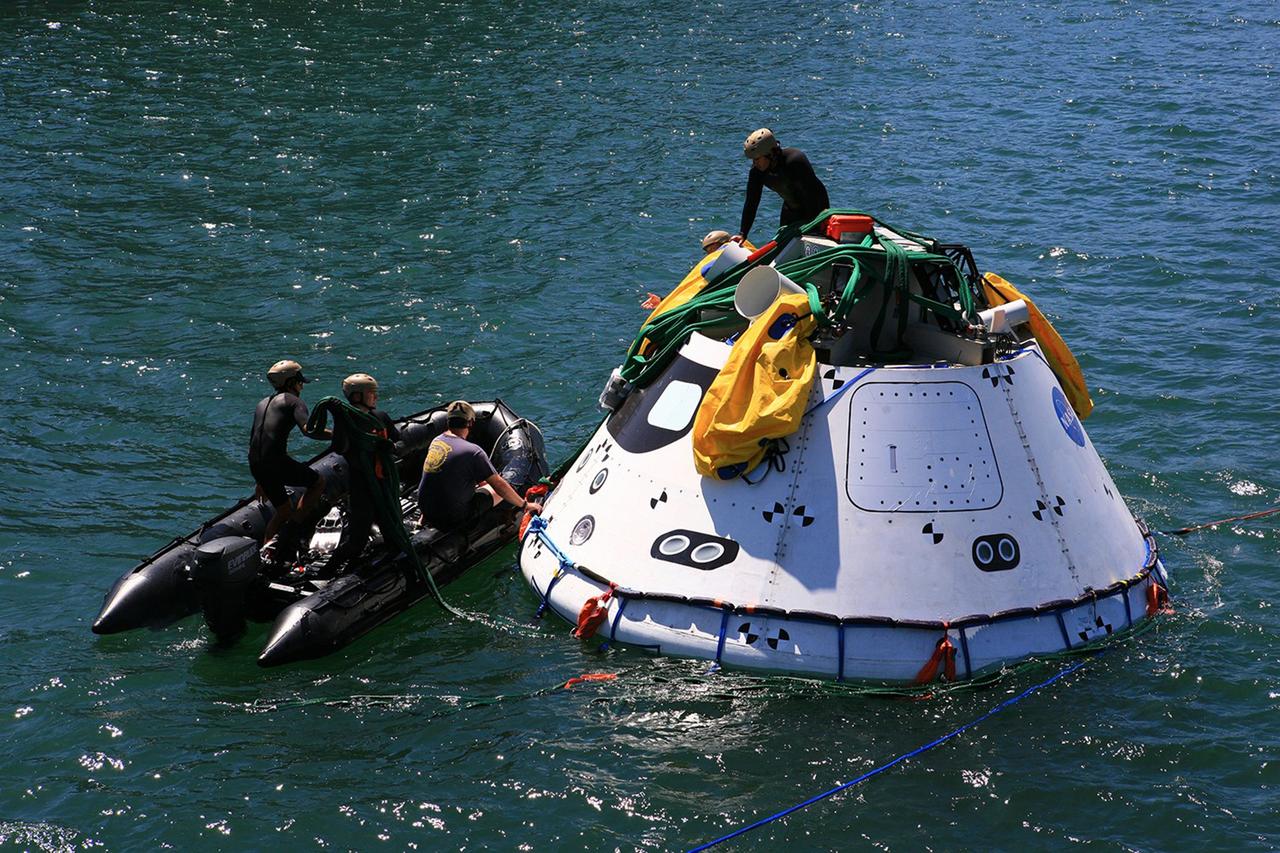
In the well deck of the USS San Diego, recovery team members monitor a portion of Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California on Oct. 27, 2016. A test version of the Orion crew module is floating in open waters. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy are conducting a series of tests using the ship's well deck, the test module, various watercraft and equipment to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
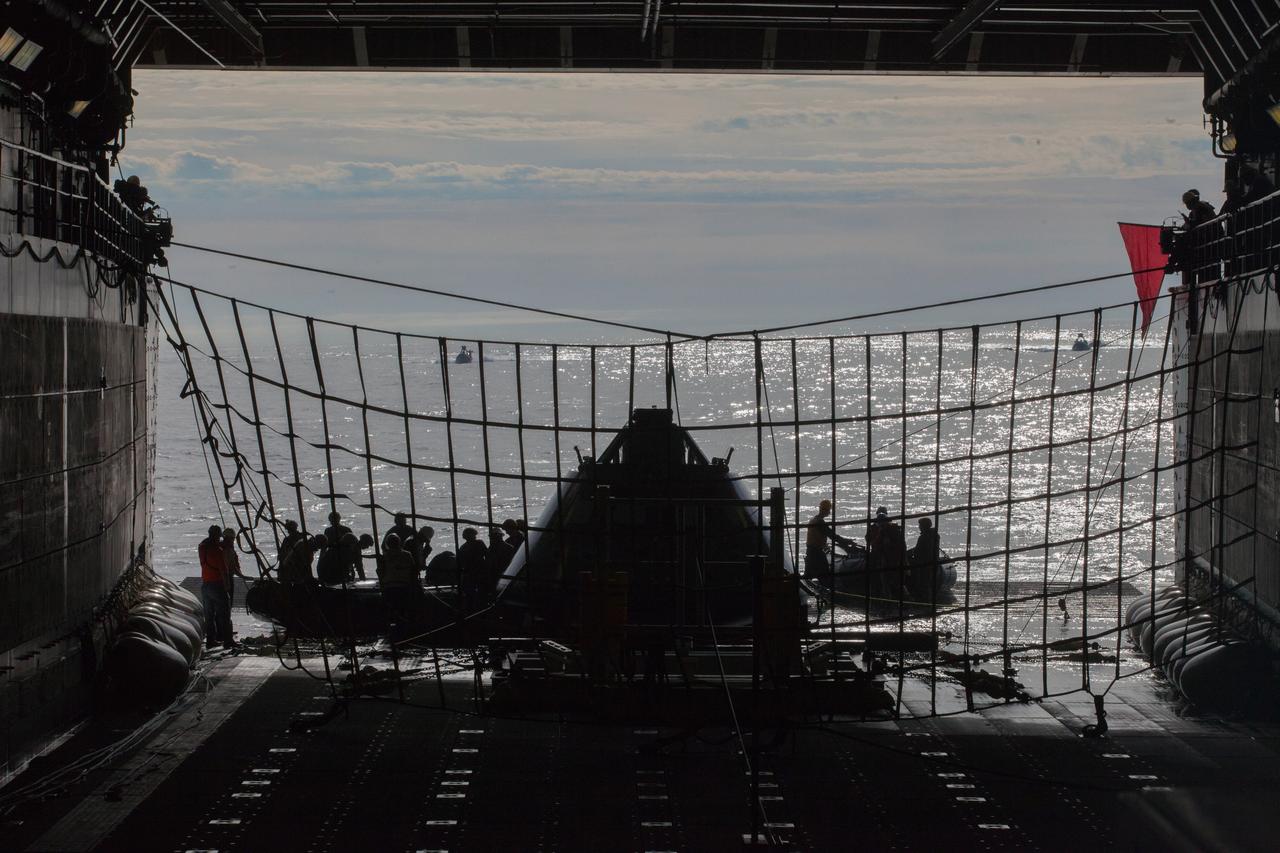

NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy prepare for another day of Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California on Oct. 30, 2016. A test version of the Orion crew module is in the well deck of the ship, and U.S. Navy divers and other personnel are in rigid hull inflatable boats preparing to head out into the open water. The recovery team is conducting a series of tests to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is in the water-filled well deck of the USS Anchorage during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
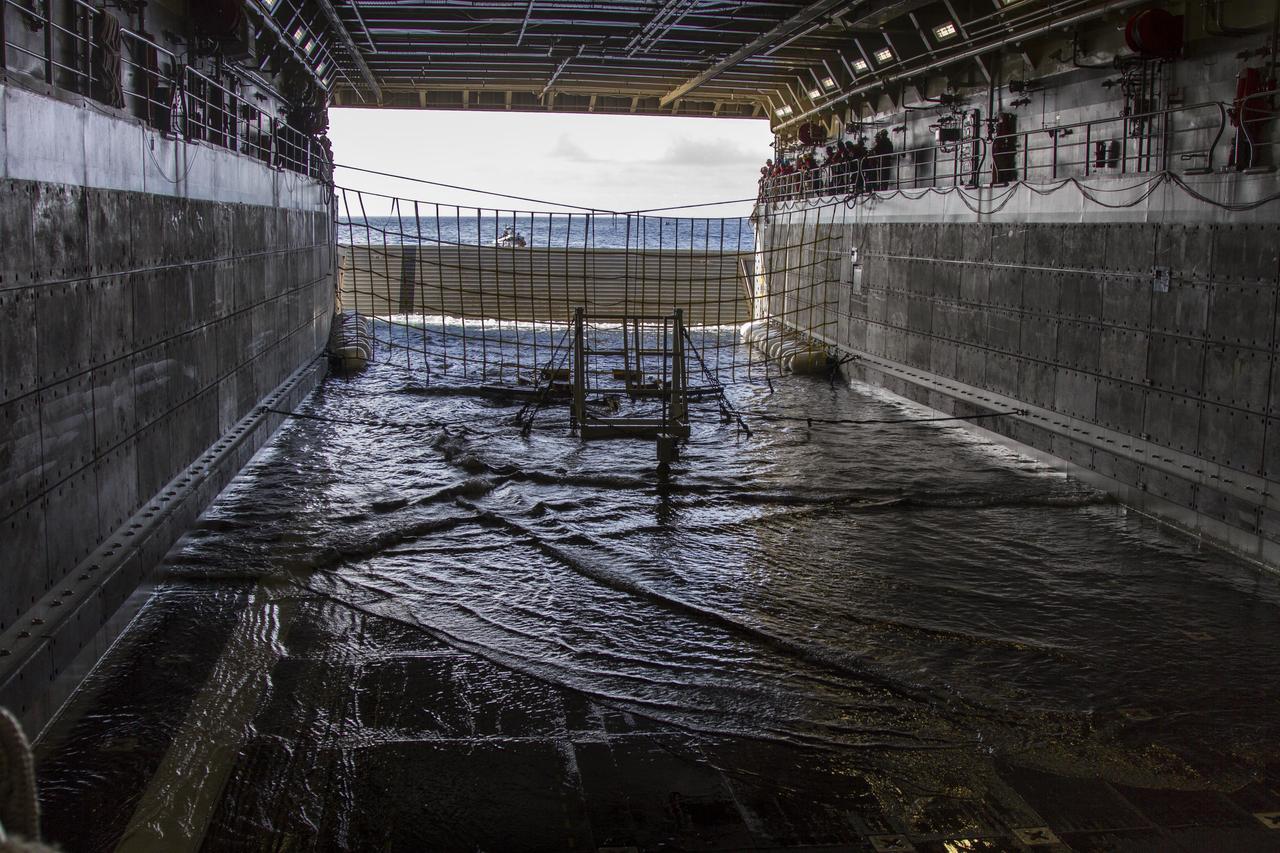

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion after its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, the well deck of the USS Anchorage has been filled with water and recovery hardware is in place. The ship is about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
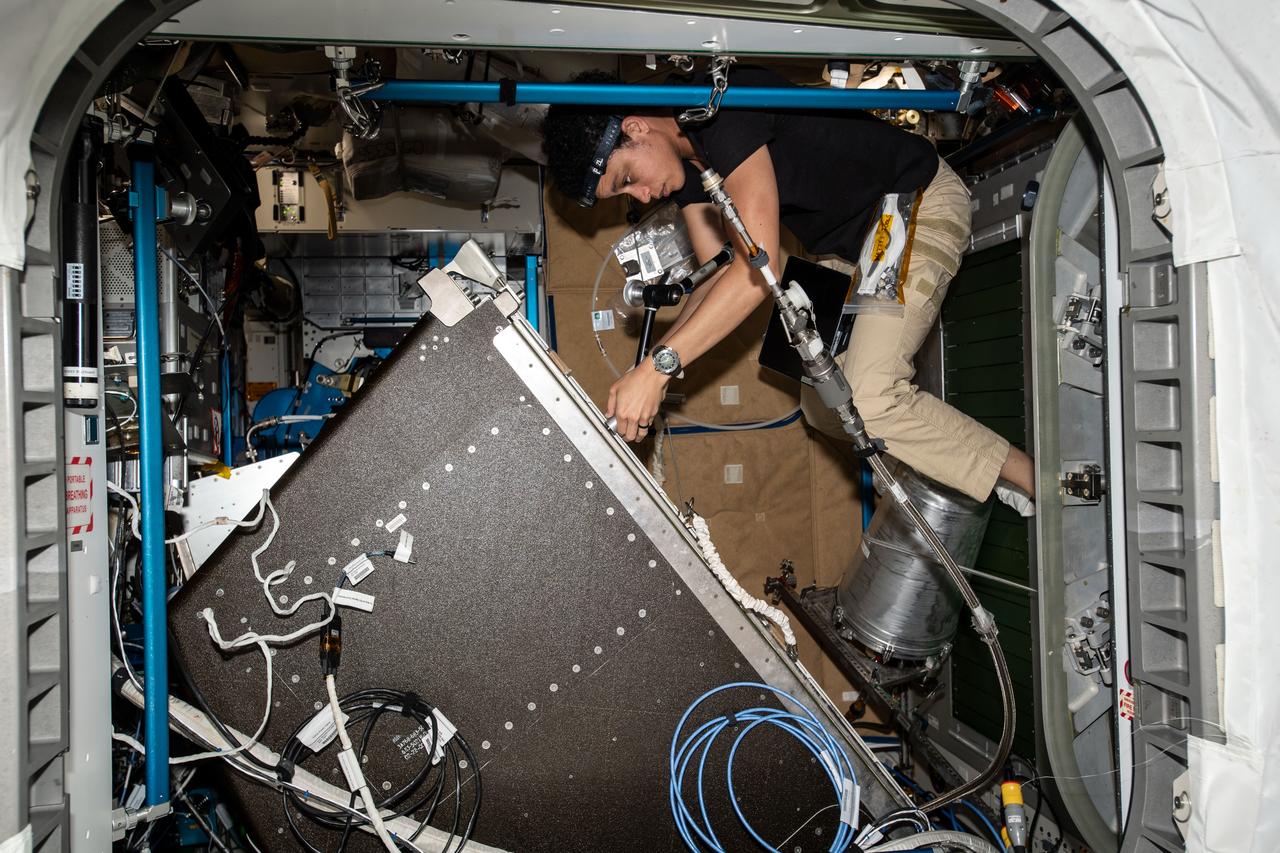

iss067e099373 (June 1, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 67 Flight Engineer Jessica Watkins services life support components inside the Tranquility module's Water Recovery System rack abaord the International Space Station.
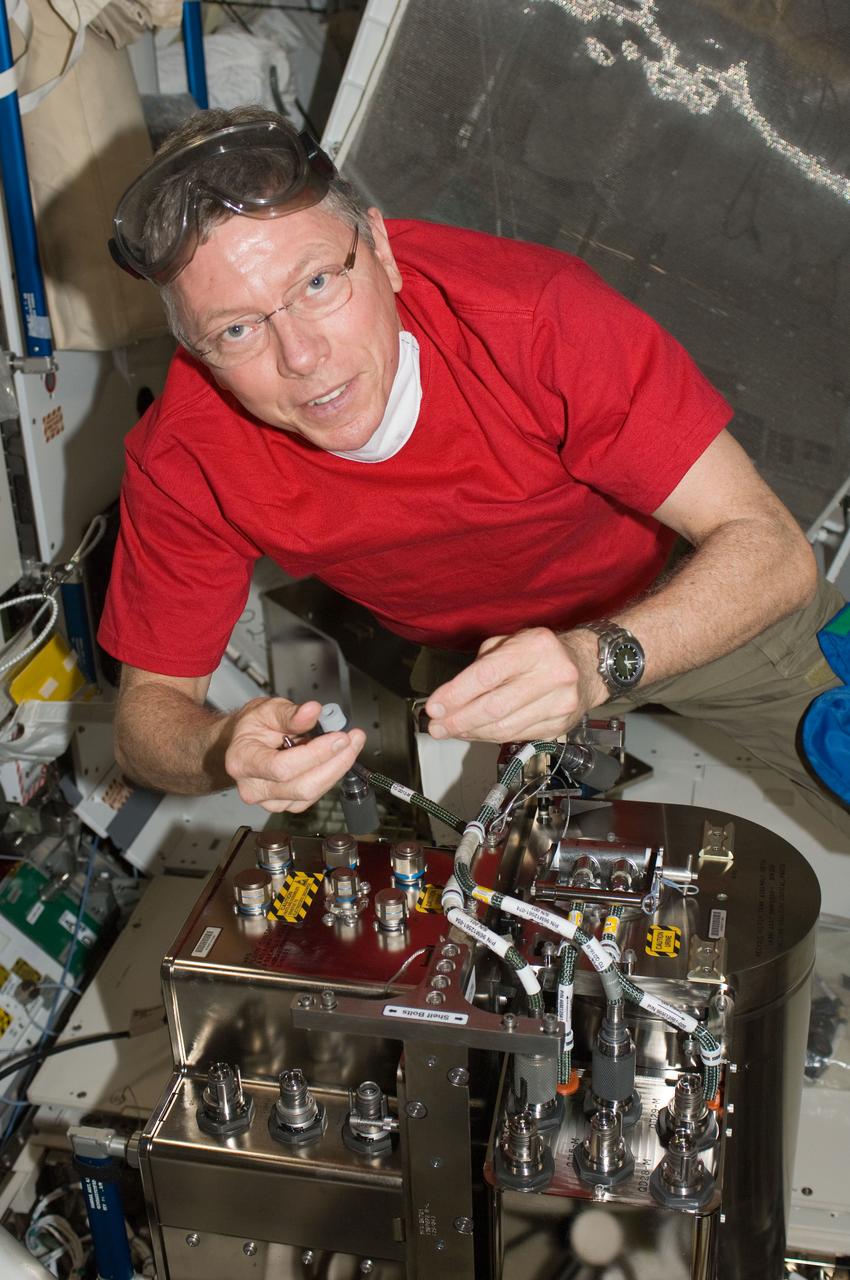

ISS029-E-007893 (23 Sept. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Mike Fossum, Expedition 29 commander, works with the Water Recovery System (WRS) Fluids Control and Pump Assembly (FCPA) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
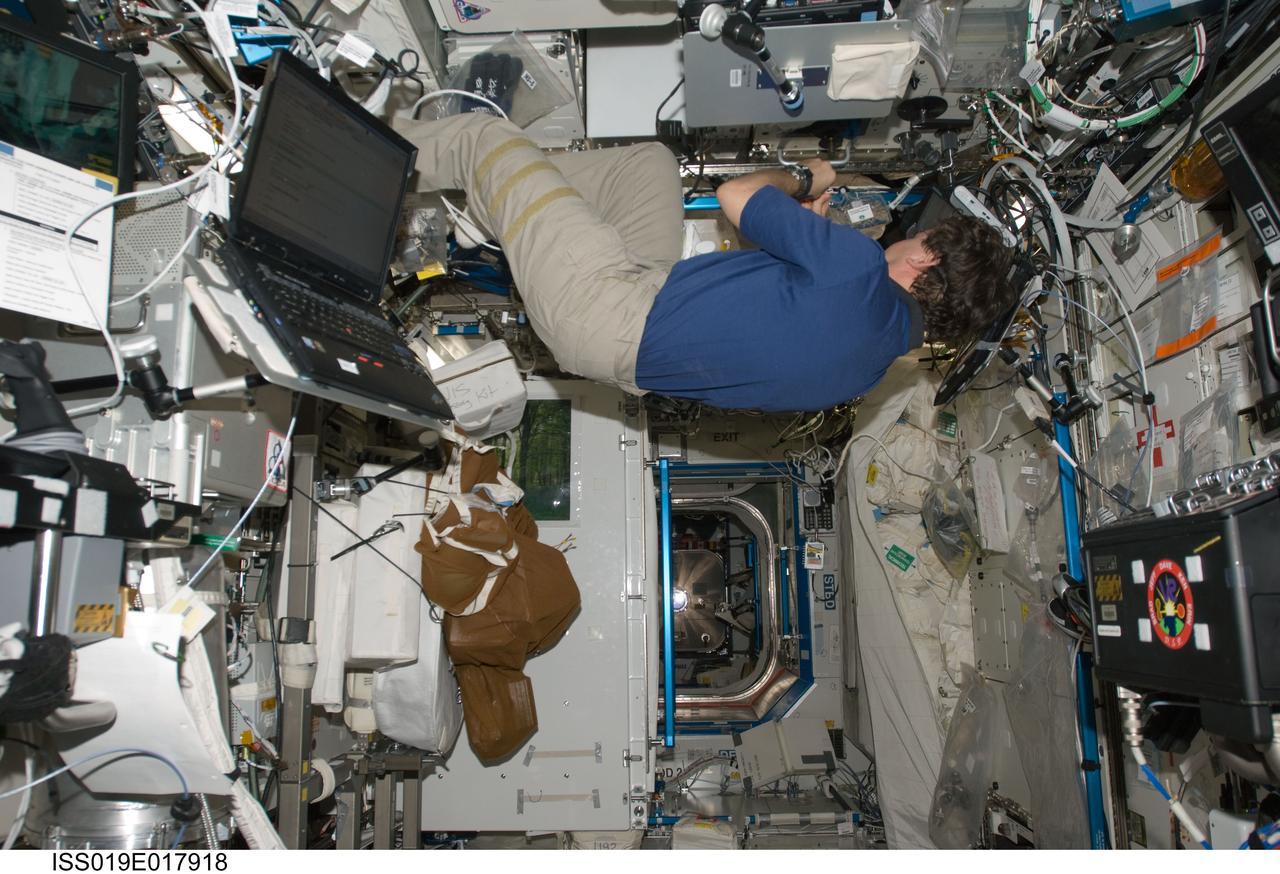

ISS019-E-017918 (19 May 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, collects a sample from the Water Recovery System (WRS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
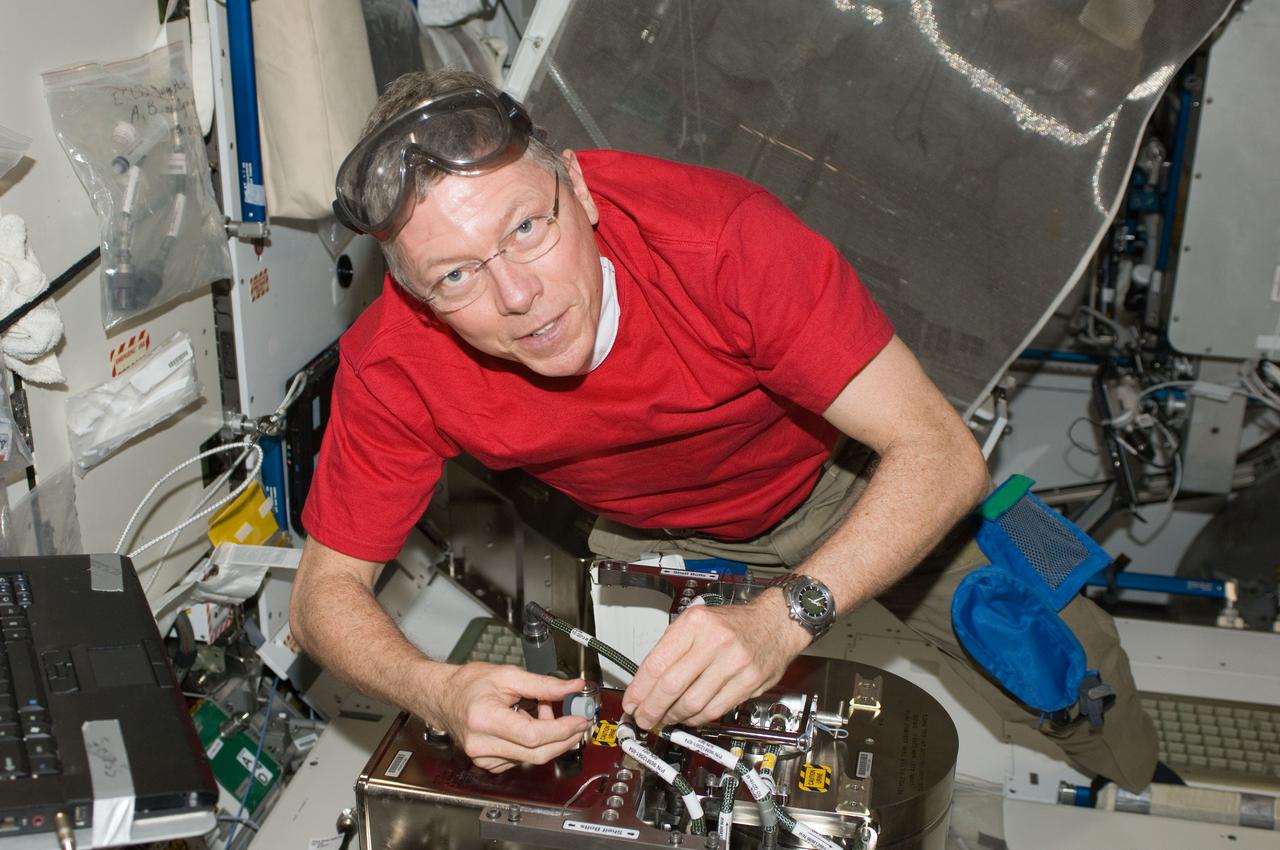

ISS029-E-007892 (23 Sept. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Mike Fossum, Expedition 29 commander, works with the Water Recovery System (WRS) Fluids Control and Pump Assembly (FCPA) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
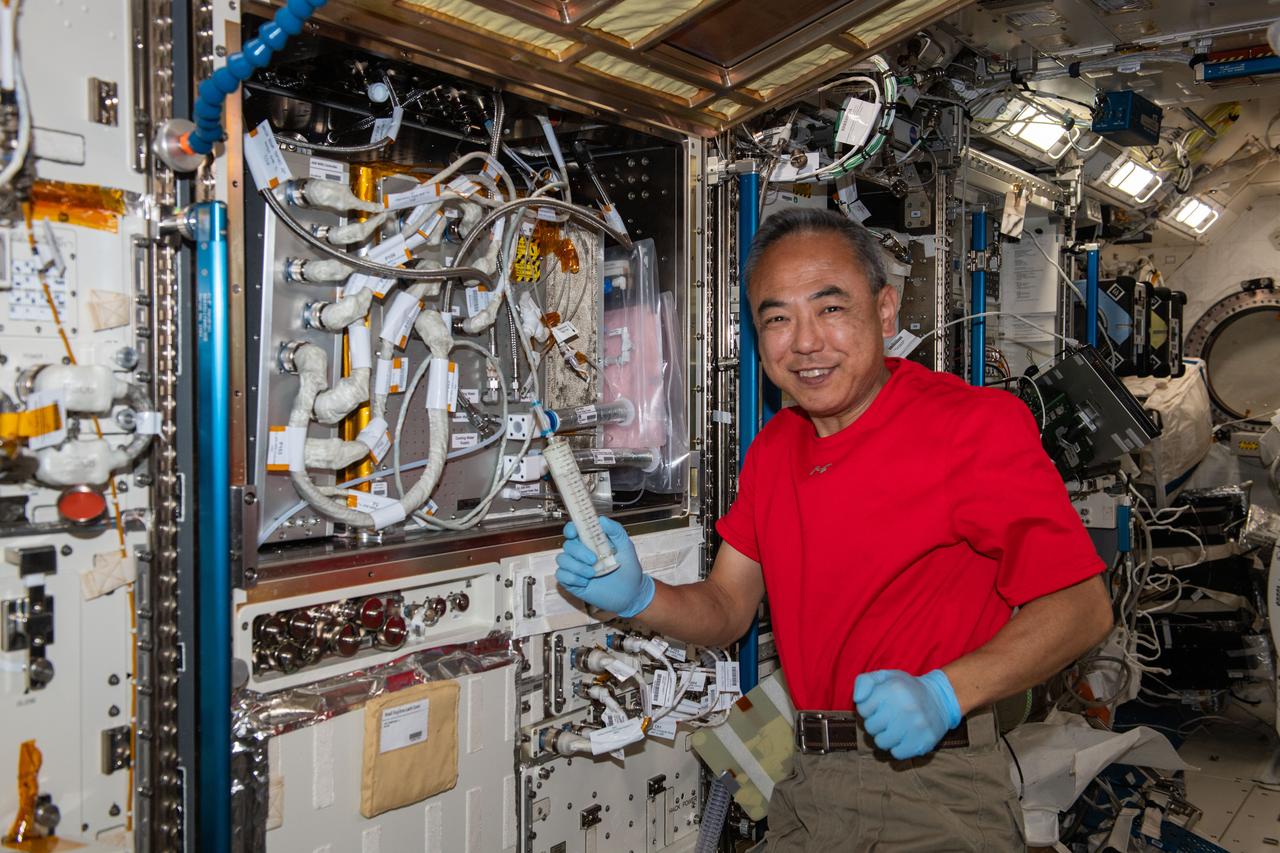

iss069e091003 (Sept. 21, 2023) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Satoshi Furukawa works on the Kibo laboratory module's water recovery system aboard the International Space Station.
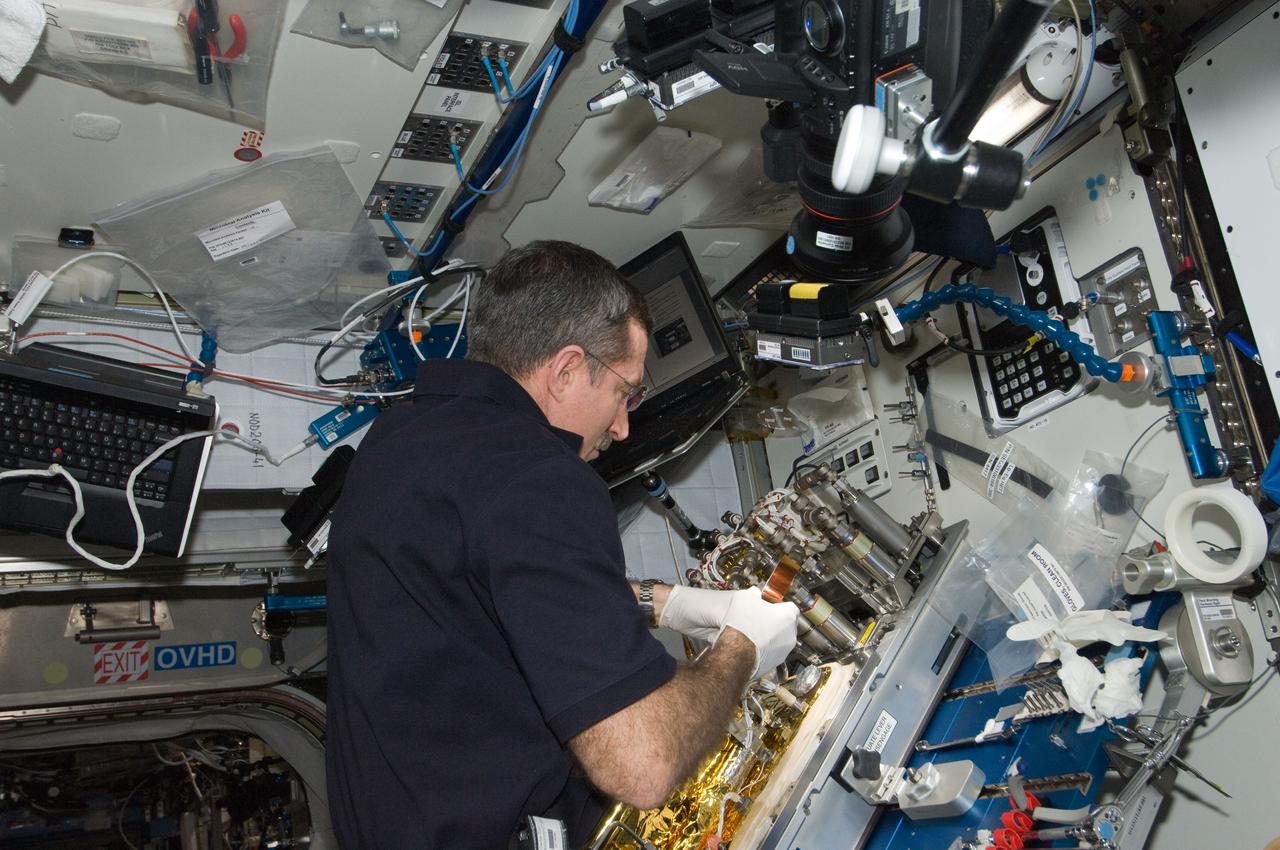

ISS030-E-128878 (9 March 2012) --- At a workstation in the International Space Station?s Harmony node, NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, replaces a Catalytic Reactor in the Water Recovery System.
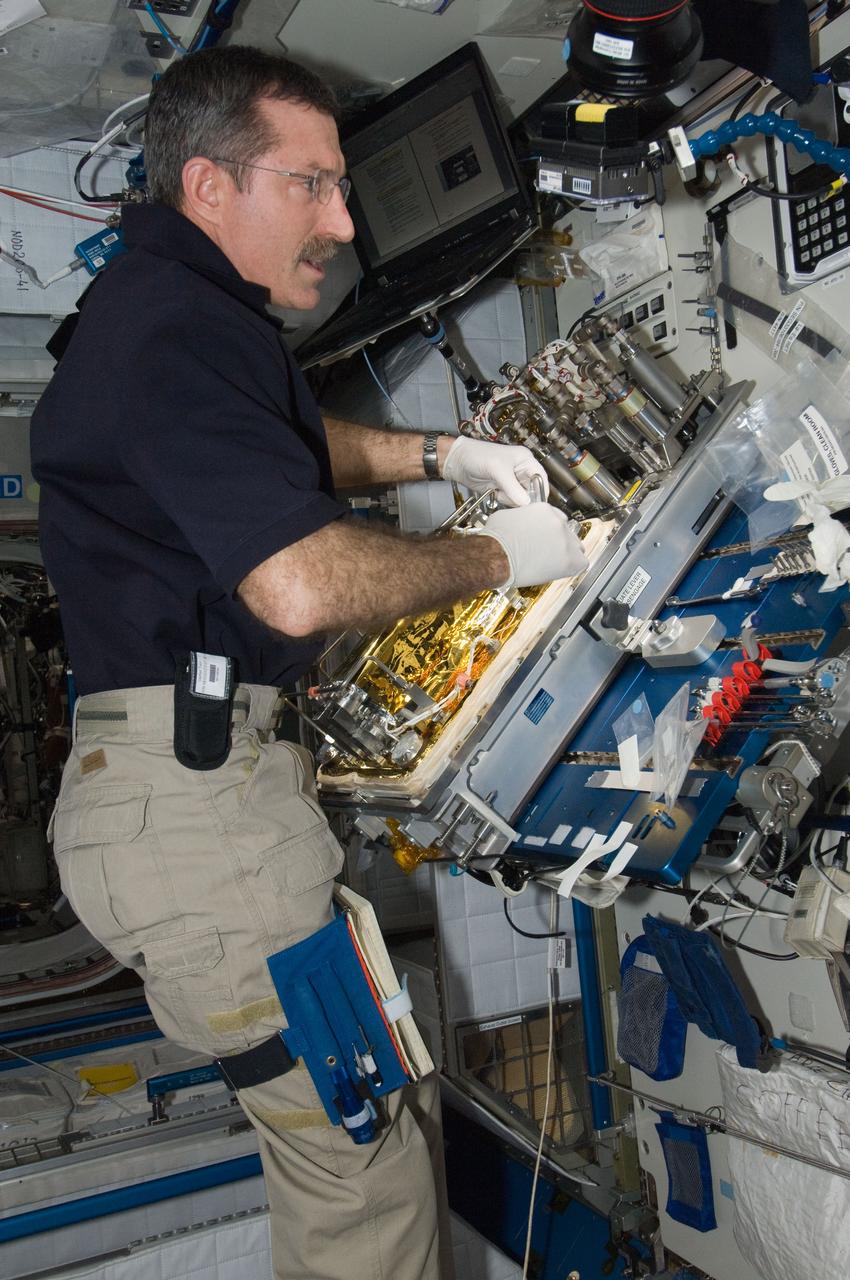

ISS030-E-128877 (9 March 2012) --- At a workstation in the International Space Station?s Harmony node, NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, replaces a Catalytic Reactor in the Water Recovery System.

ISS030-E-051116 (28 Jan. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, performs in-flight maintenance on the Water Recovery System 2 (WRS-2) in the Tranquility node of the International Space Station.
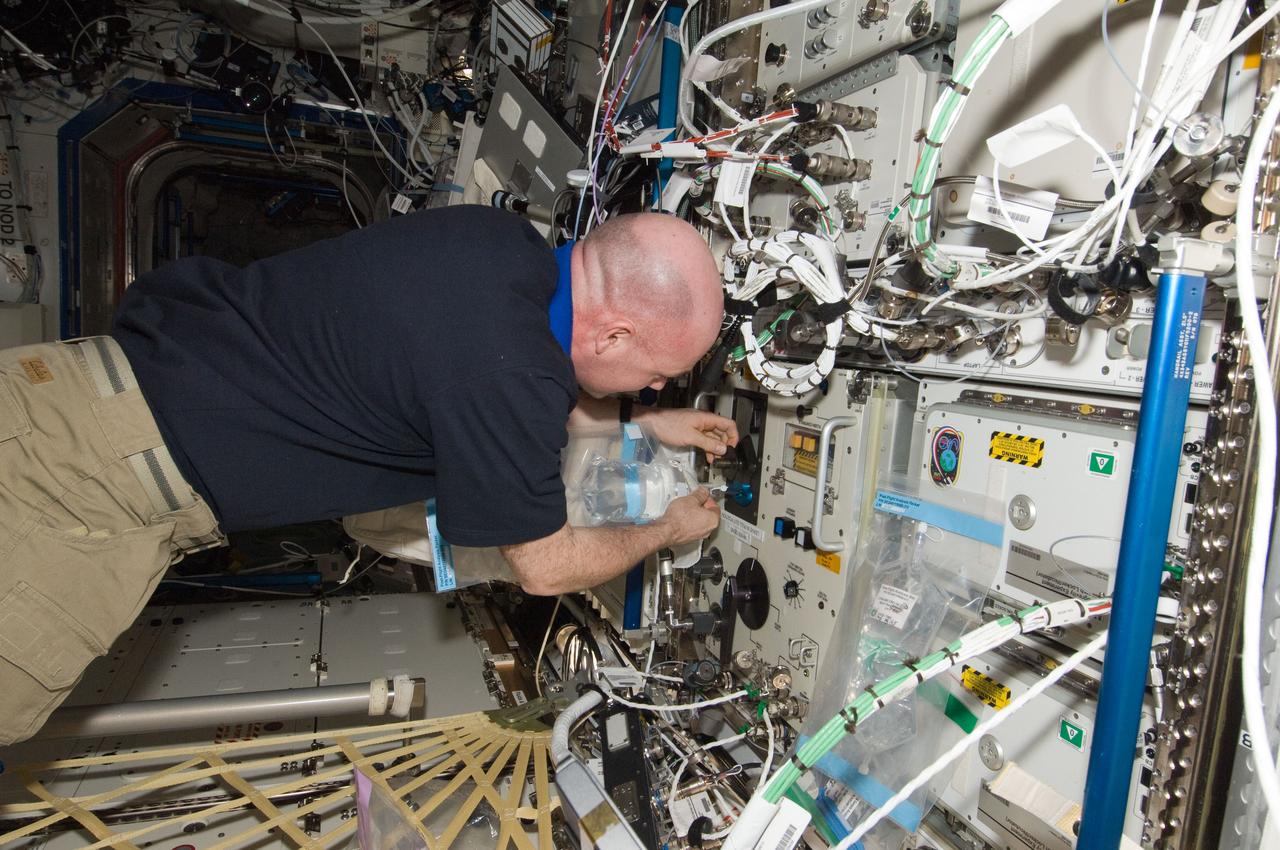

ISS031-E-079015 (15 May 2012) --- European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 31 flight engineer, collects a sample from the Water Recovery System (WRS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
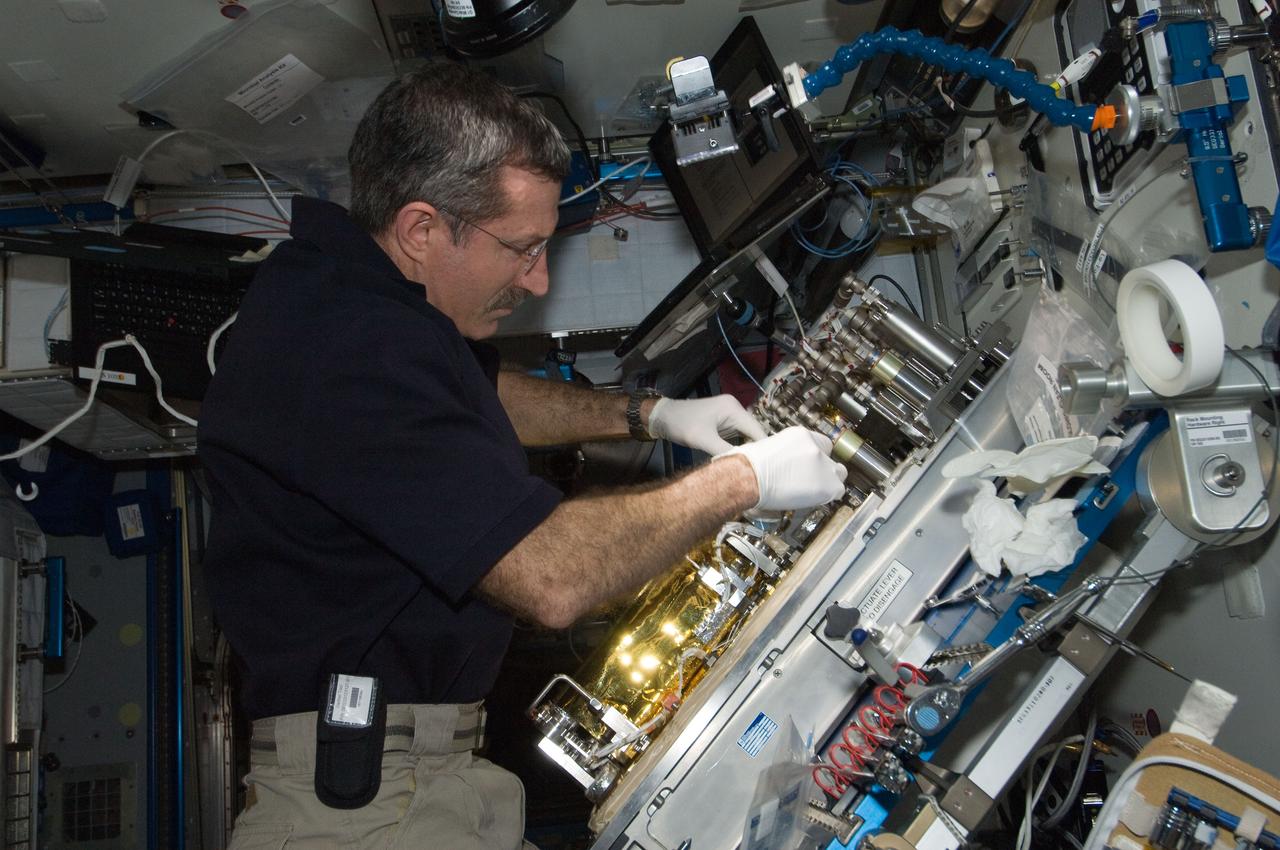

ISS030-E-128879 (9 March 2012) --- At a workstation in the International Space Station?s Harmony node, NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, replaces a Catalytic Reactor in the Water Recovery System.
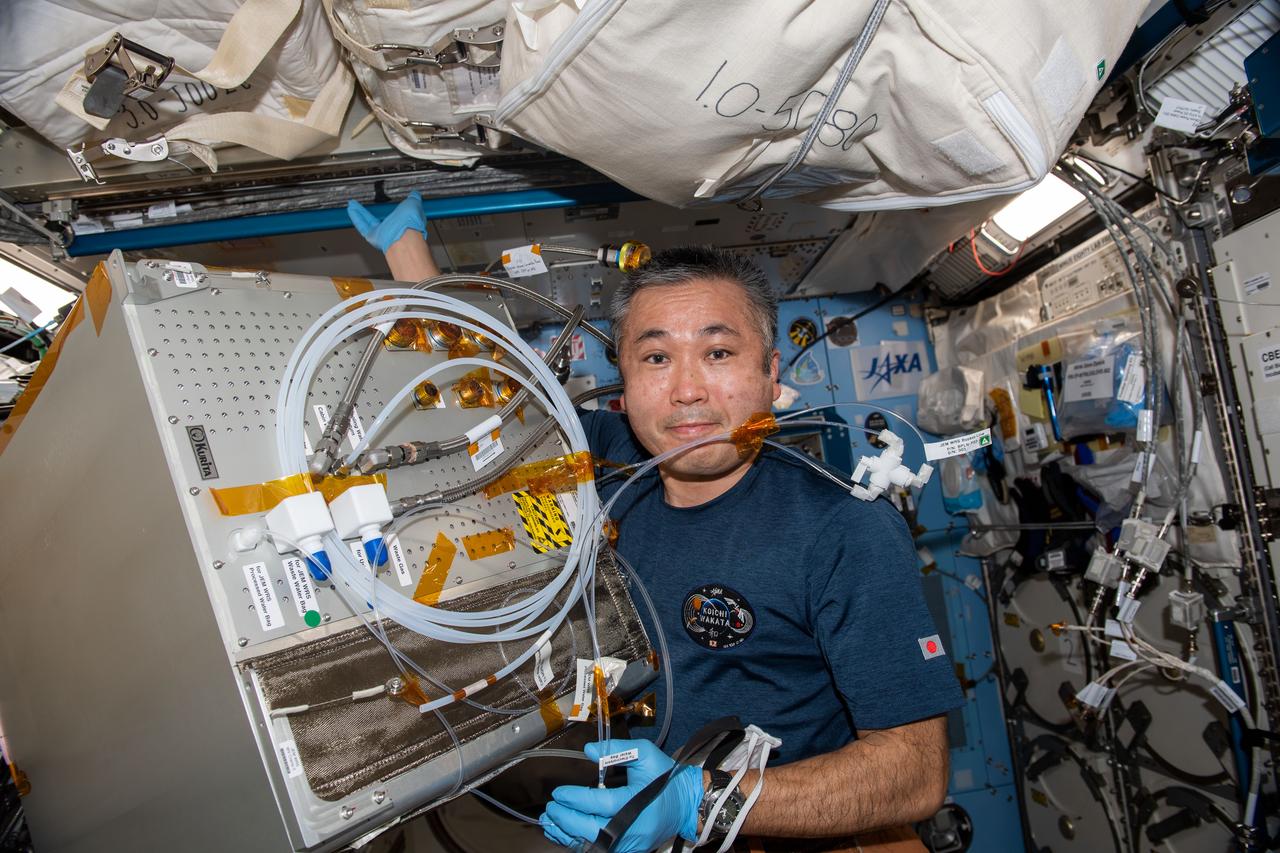

iss068e027924 (Dec. 8, 2022) --- Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) works on water recovery system components inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
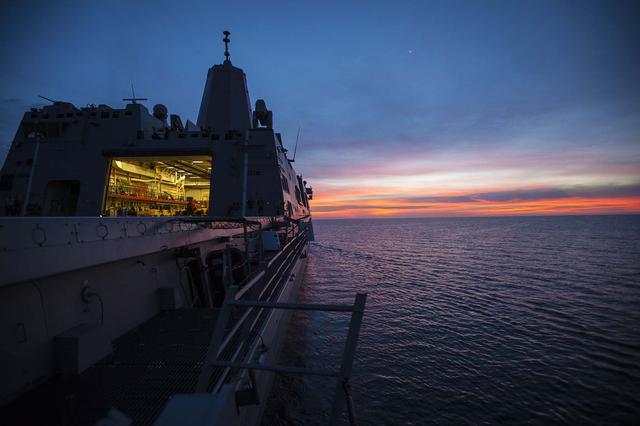

A colorful sunrise illuminates the water on the second day of Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy will practice recovery techniques using the well deck of the USS San Diego and a test version of the Orion crew module to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and NASA's Journey to Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch on NASA's Space Launch System in late 2018. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion.
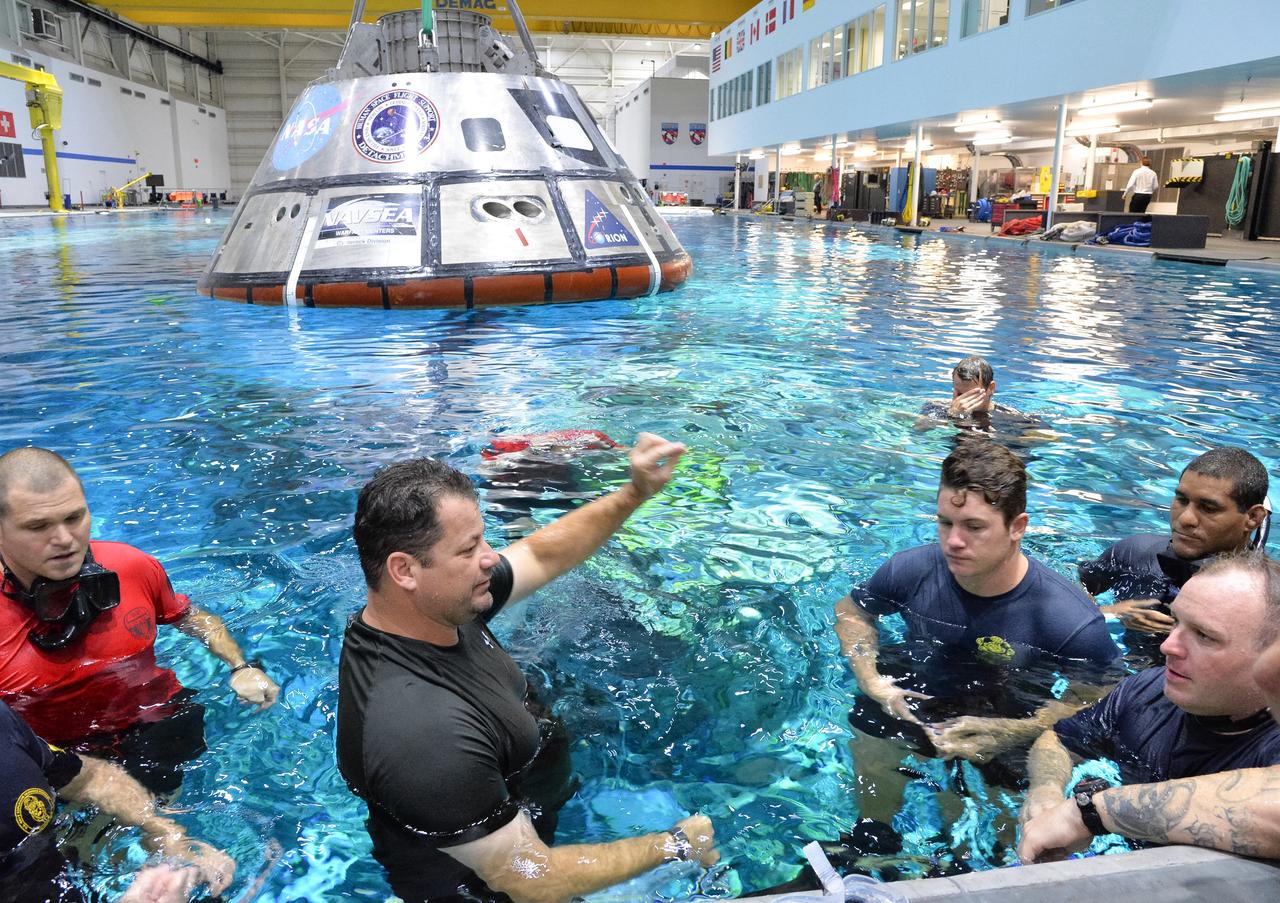

Tim Goddard, center, NASA Open Water Recovery Operations director, reviews recovery procedures with U.S. Navy divers, Air Force pararescuemen and Coast Guard rescue swimmers during training in the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The group is practicing Orion underway recovery techniques using a test version of the Orion spacecraft. Training will help the team prepare for Underway Recovery Test 5 for Exploration Mission 1 aboard the USS San Diego in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California in October. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, along with the U.S. Navy and Lockheed Martin, are preparing the recovery team, hardware and operations to support EM-1 recovery.
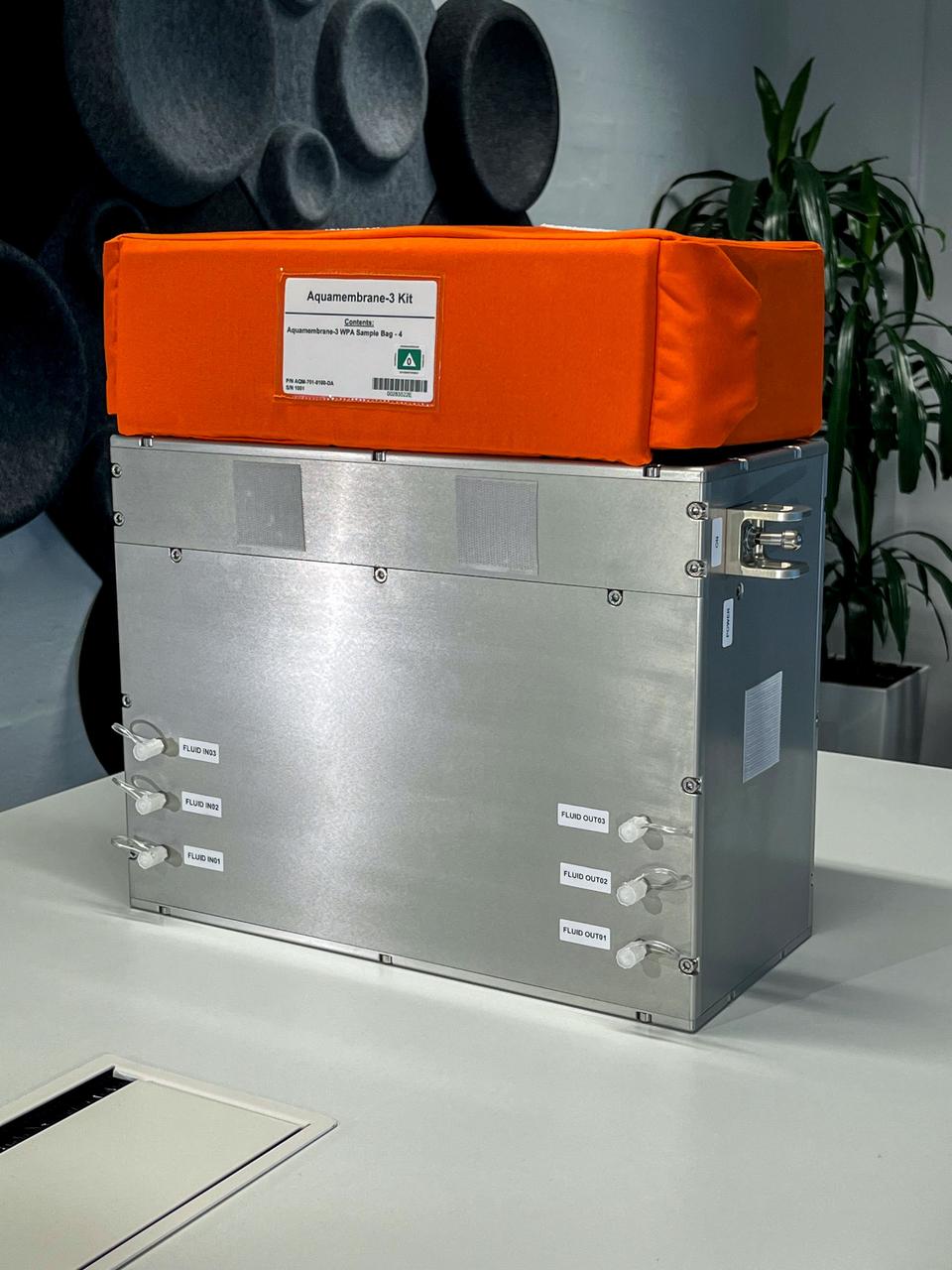

jsc2023e055870 (10/5/2023) --- The Testing Contaminant Rejection of Aquaporin Inside® HFFO Module (Aquamembrane-3) hardware consists of three separate and parallel systems to quantify the membrane's water flux and contamination rejection in microgravity, which are key parameters for a full water recovery system. Aquamembrane-3 tests Aquaporin Inside™ membranes for spacecraft use, a unique water filtration method that mimics fluid transport found in every living cell. Image courtesy of Danish Aerospace Company.
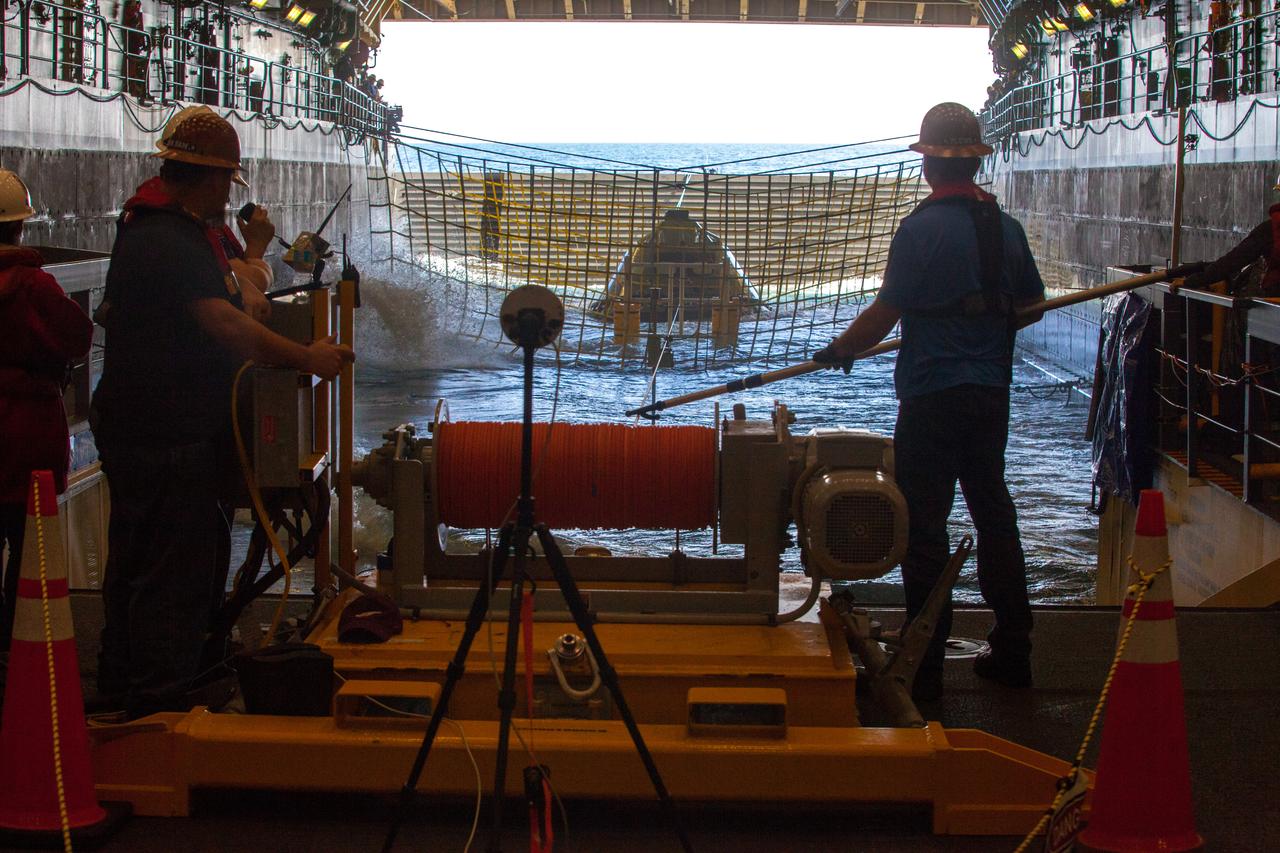

Winch team operators help guide a test version of the Orion crew module into the flooded well deck of the USS San Diego during Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy are conducting a series of tests to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
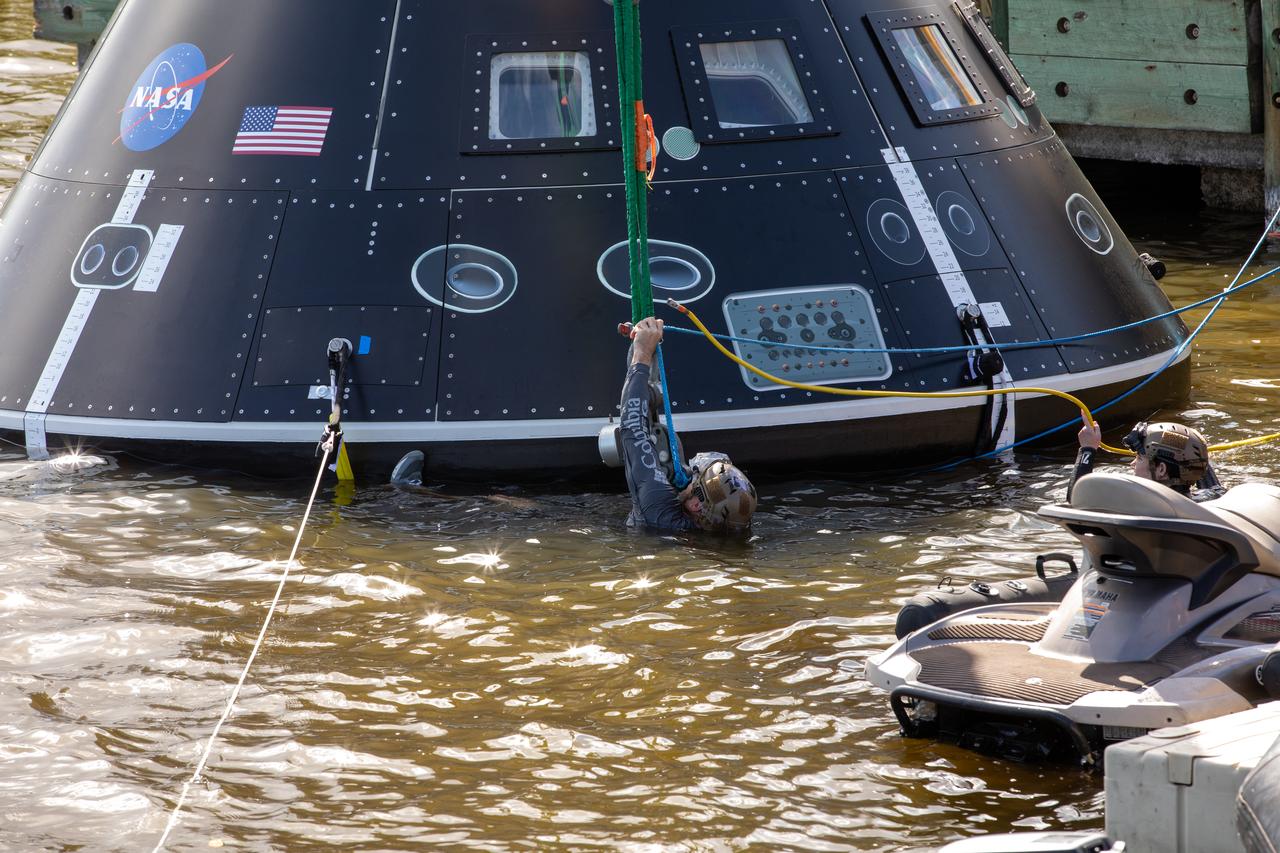

Landing and recovery team members secure the Crew Module Test Article (CMTA) in the water at the turn basin in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2023. The CMTA is being used to practice recovery after splashdown of the Orion spacecraft to prepare for the Artemis II crewed mission. Exploration Ground Systems leads recovery efforts.
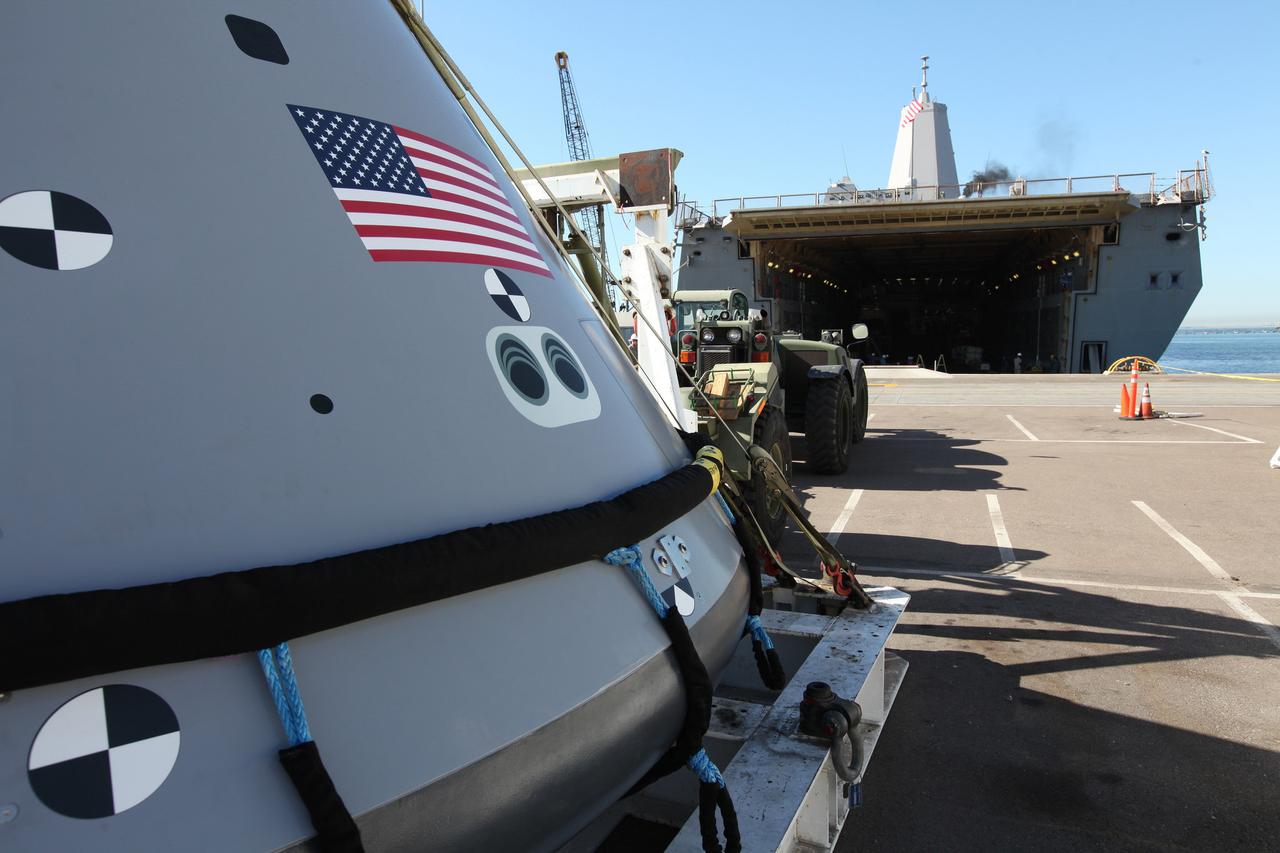

A test version of the Orion crew module seen outside the USS San Diego for Underway Recovery Test 5 on Oct. 27, 2016. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy will conduct a series of tests using the ship's well deck, the test module, various watercraft and equipment to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters.
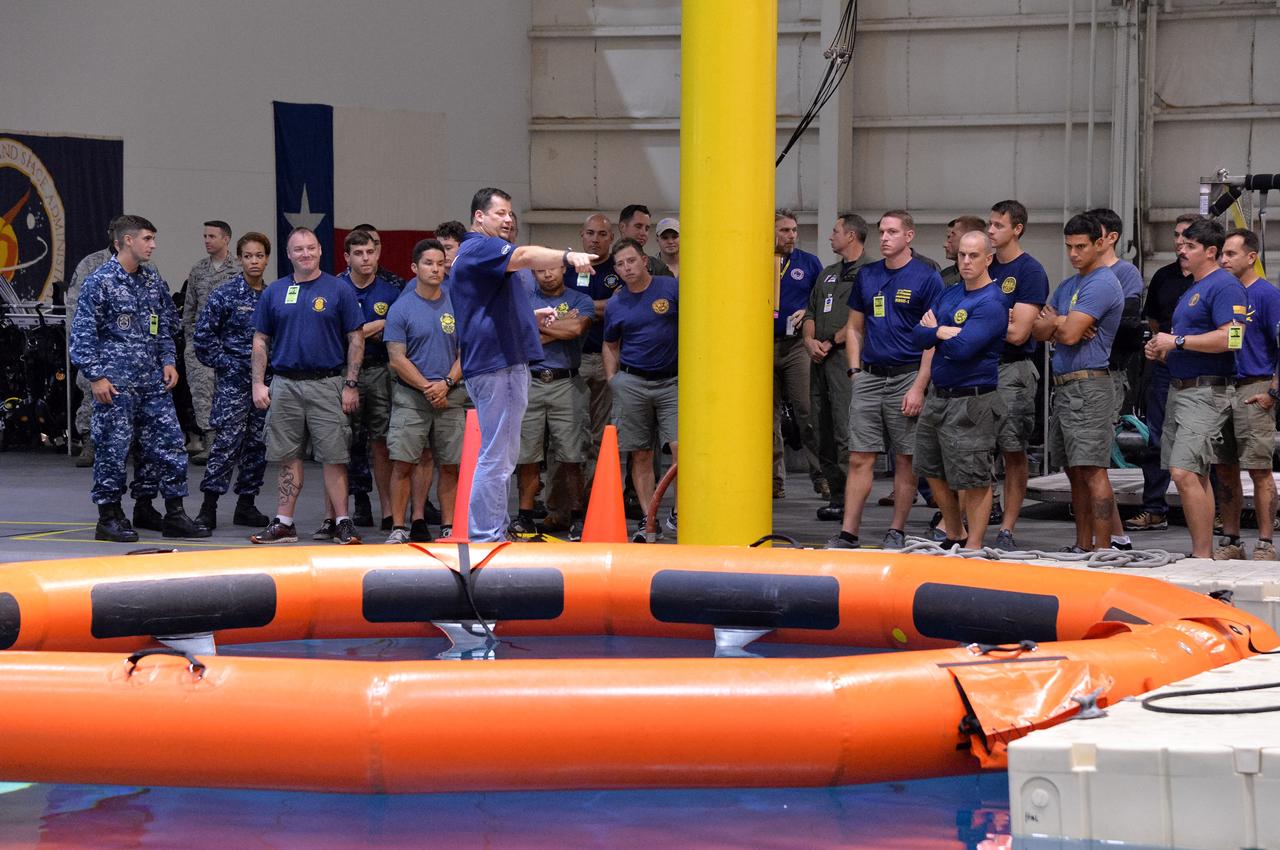

Tim Goddard, NASA Open Water Recovery Operations director, briefs U.S. Navy divers, Air Force pararescuemen and Coast Guard rescue swimmers during training in the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The group is preparing to practice Orion underway recovery techniques using a test version of the Orion spacecraft. Training will help the team prepare for Underway Recovery Test 5 for Exploration Mission 1 aboard the USS San Diego in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California in October. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, along with the U.S. Navy and Lockheed Martin, are preparing the recovery team, hardware and operations to support EM-1 recovery.
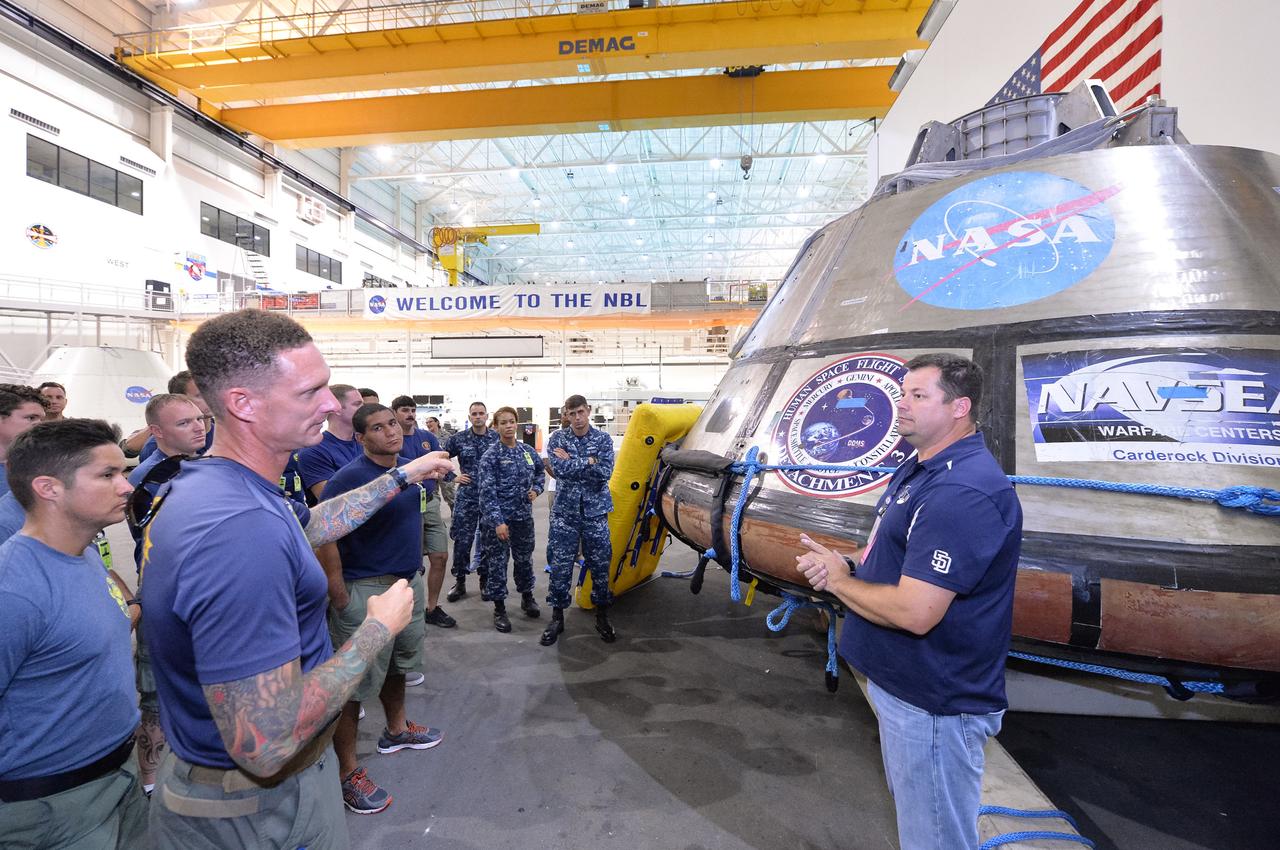

Tim Goddard, far right, NASA Open Water Recovery Operations director, briefs U.S. Navy divers, Air Force pararescuemen and Coast Guard rescue swimmers during training in the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The group is preparing to practice Orion underway recovery techniques using a test version of the Orion spacecraft. Training will help the team prepare for Underway Recovery Test 5 for Exploration Mission 1 aboard the USS San Diego in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California in October. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, along with the U.S. Navy and Lockheed Martin, are preparing the recovery team, hardware and operations to support EM-1 recovery.
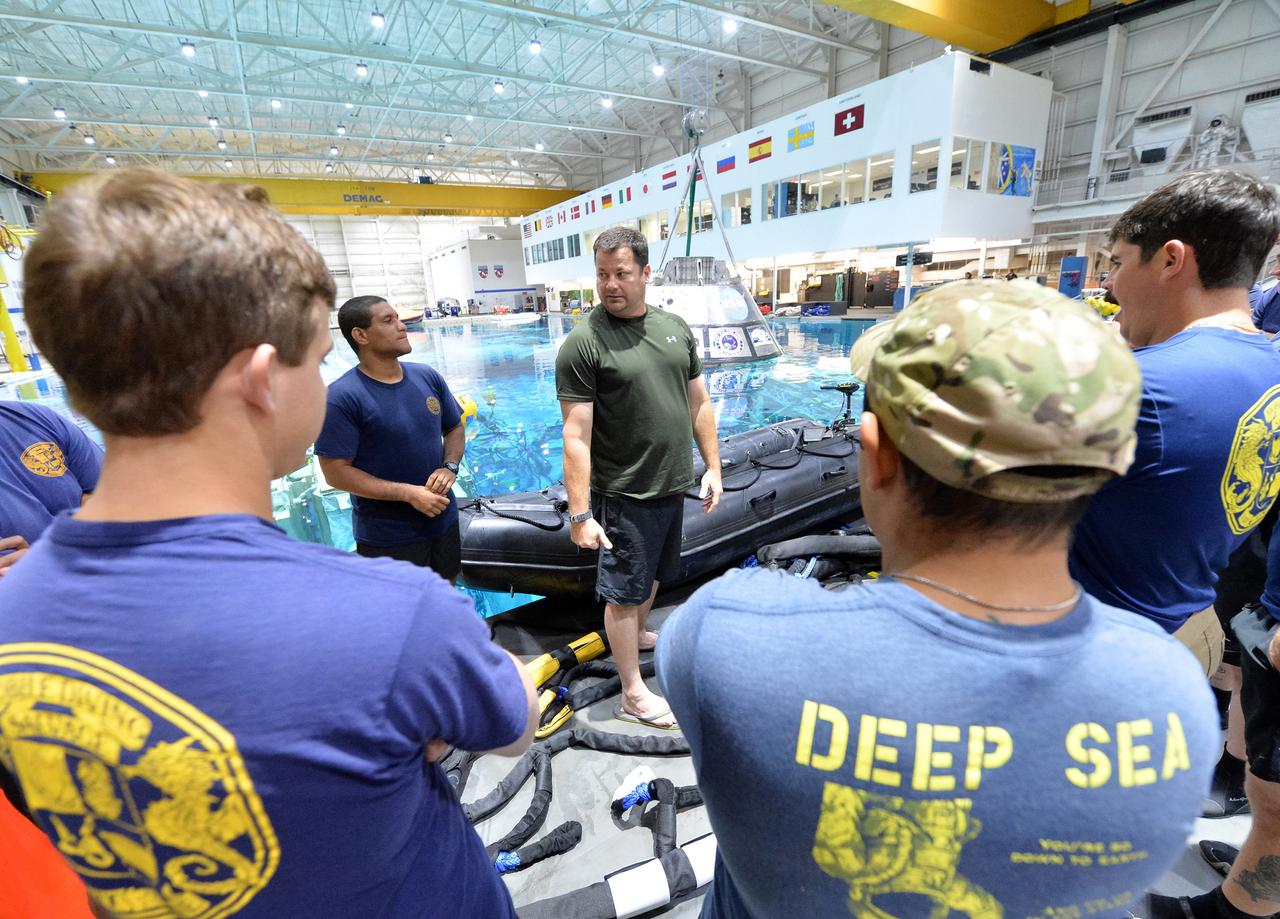

Tim Goddard, center, NASA Open Water Recovery Operations director, briefs U.S. Navy divers, Air Force pararescuemen and Coast Guard rescue swimmers during training in the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The group will practice Orion underway recovery techniques using a test version of the Orion spacecraft. Training will help the team prepare for Underway Recovery Test 5 for Exploration Mission 1 aboard the USS San Diego in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California in October. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, along with the U.S. Navy and Lockheed Martin, are preparing the recovery team, hardware and operations to support EM-1 recovery.
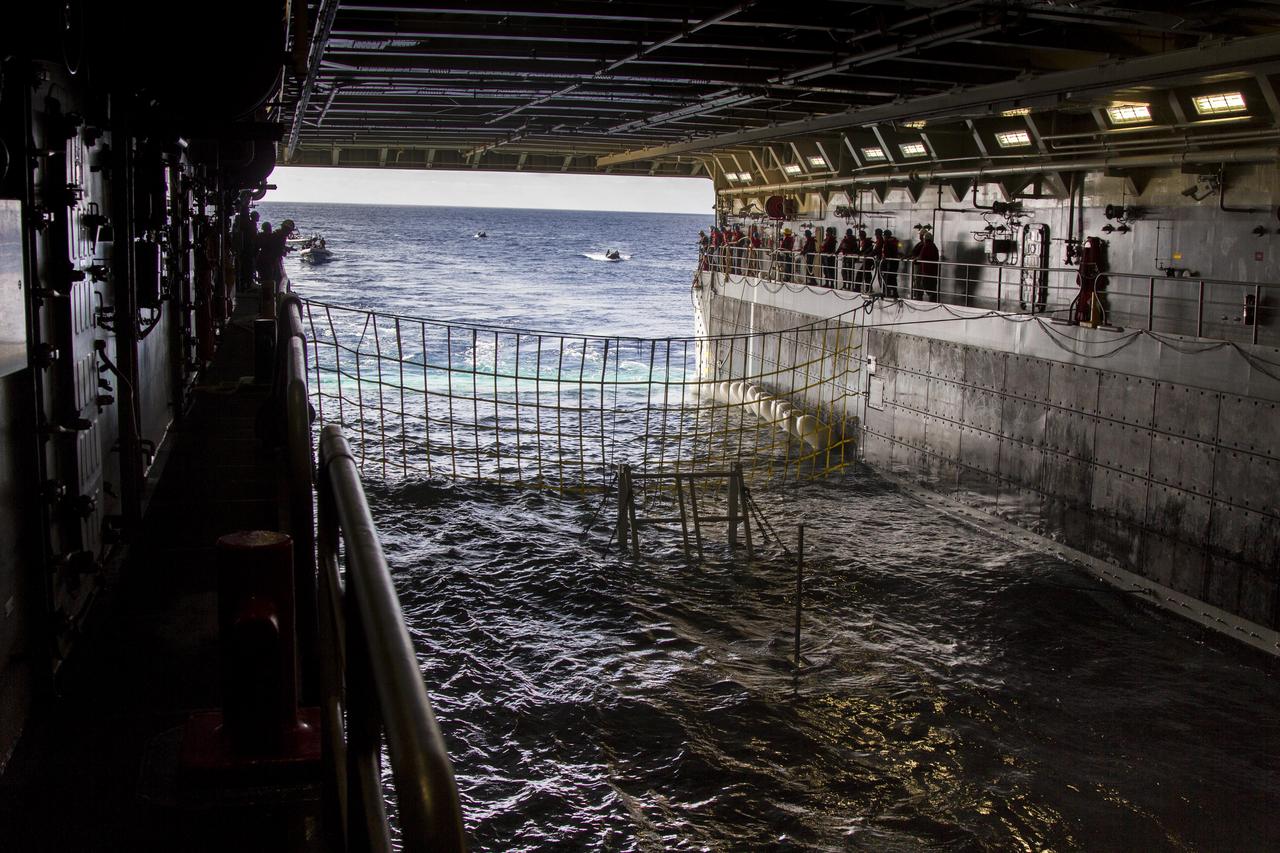

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion after its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, the well deck of the USS Anchorage has been filled with water and recovery hardware is in place. U.S. Navy divers have embarked from ship to practice recovery procedures in rigid hull inflatable boats and Zodiac boats. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
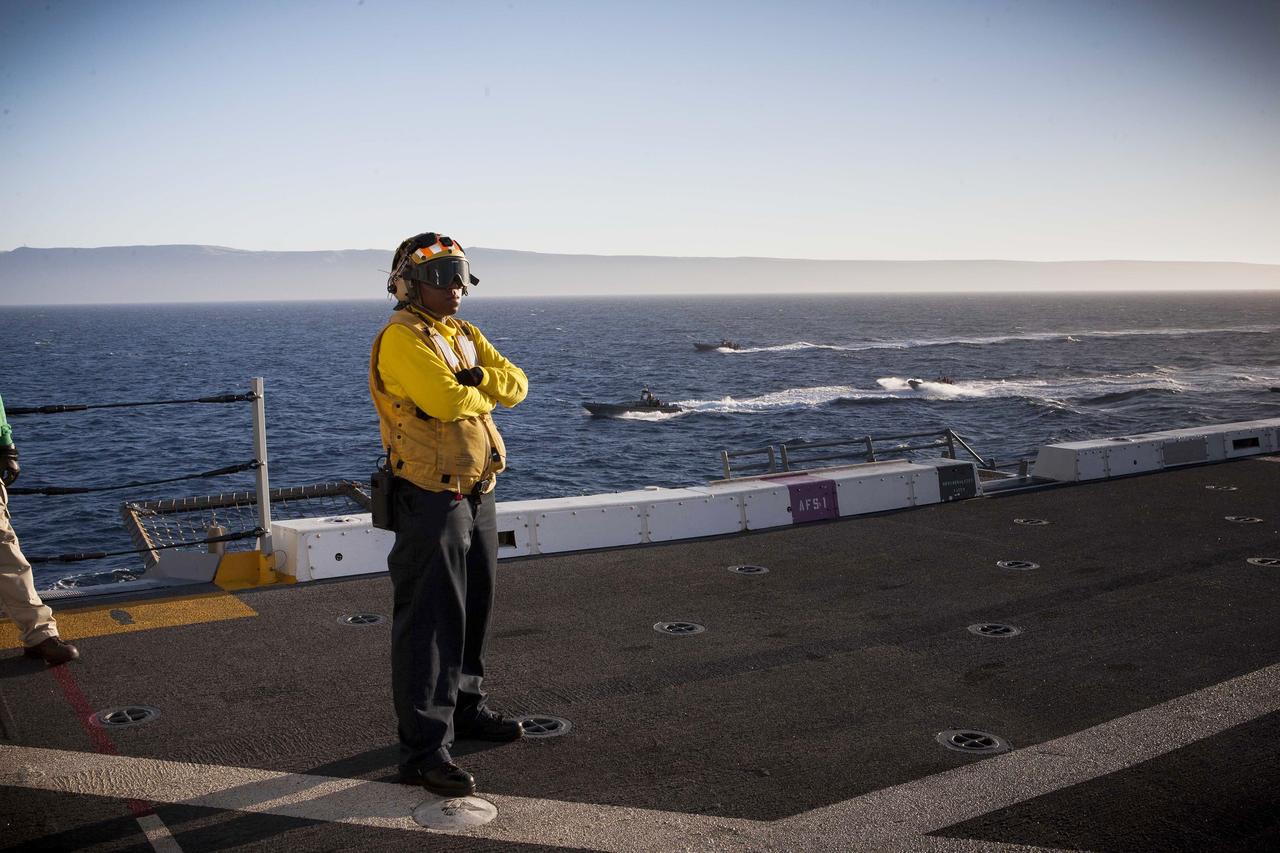

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A member of the U.S. Navy stands on the deck of the USS Anchorage on the first day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. In the water are several Zodiac boats and rigid hull inflatable boats with U.S. Navy personnel and divers that are preparing to recover the Orion boilerplate test vehicle already in the water. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the U.S. Navy’s USS Anchorage, the well deck has filled with water around the Orion boilerplate test vehicle in preparation for a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. Tether lines are being used to control the test vehicle as it floats forward and a safety barrier has been installed to prevent Orion from going further in the well deck. The bright orange stabilizers have been prepared to keep Orion upright in the water. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy will conduct the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
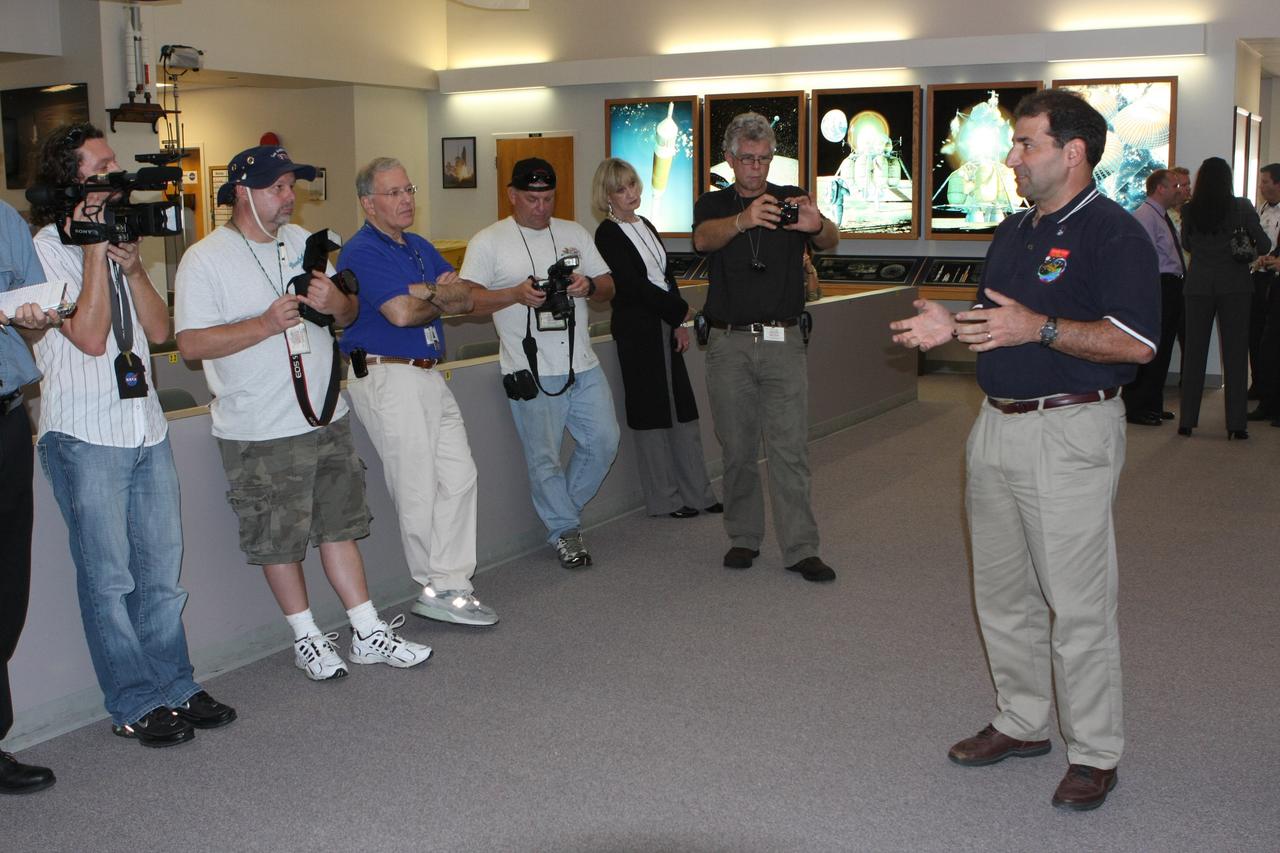

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bob Bagdigian (right) talks to the media about the Water Recovery System being delivered to the International Space Station on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission. The two units of the Water Recovery System are designed to provide drinking-quality water through the reclamation of wastewater, including urine and hygiene wastes. The water that’s produced will be used to support the crew and work aboard the station. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
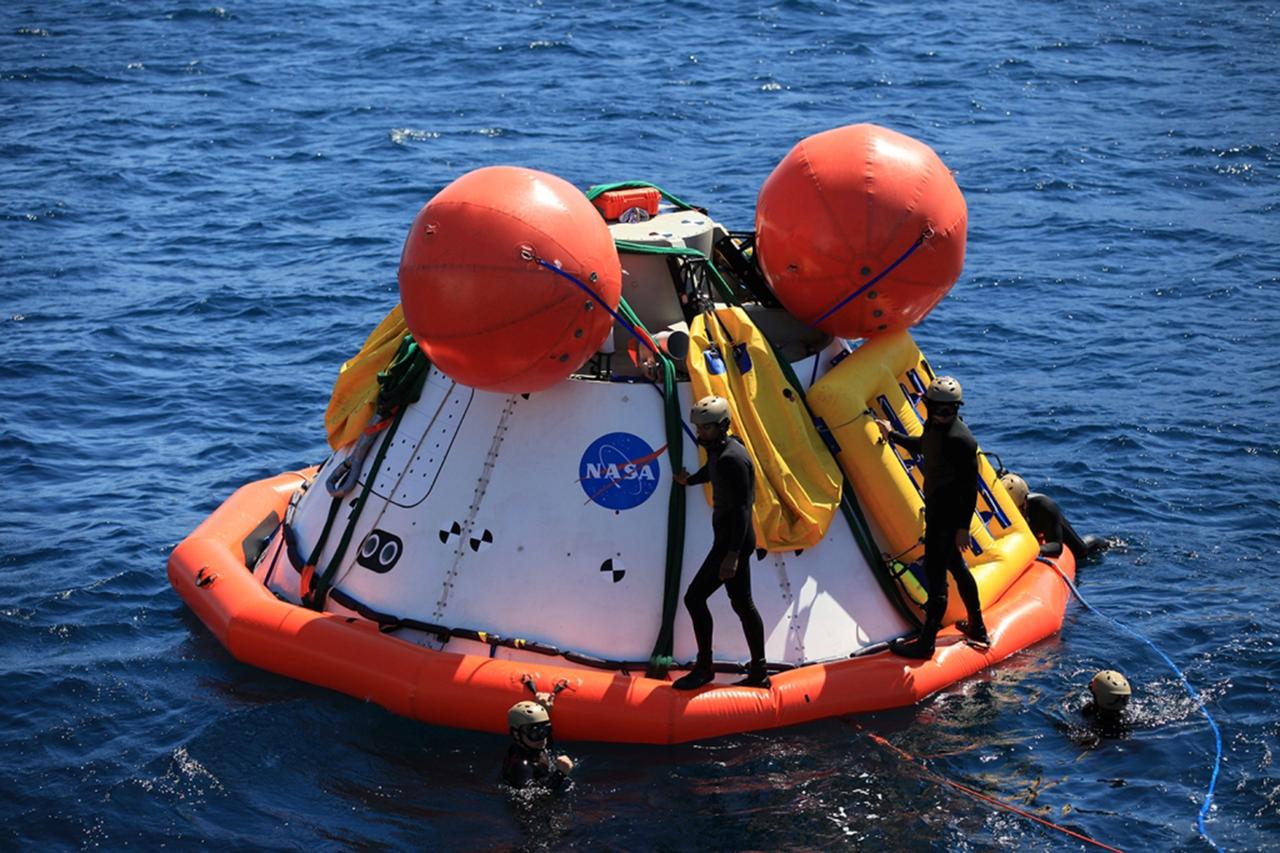

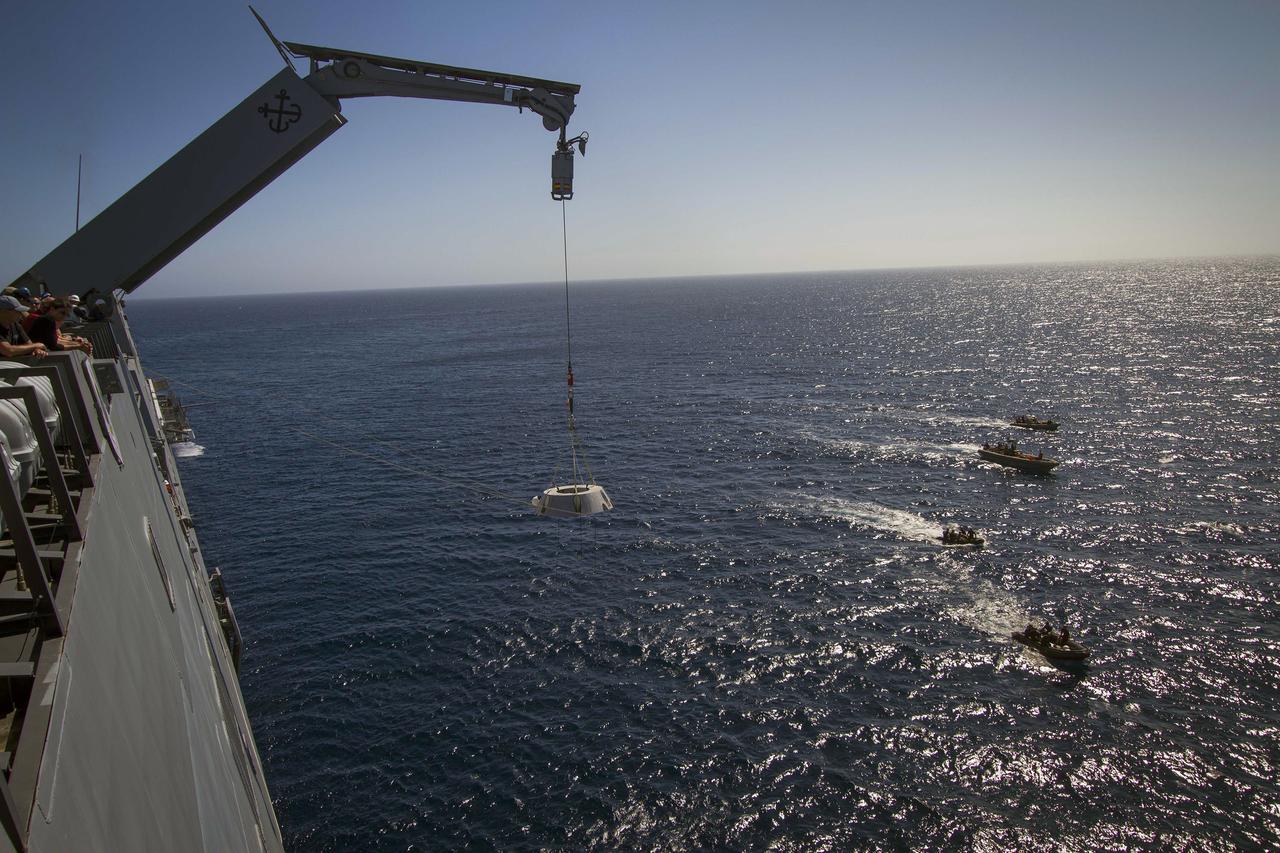
SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship. U.S. Navy divers have attached a flotation collar and tether lines to Orion to prepare for recovery. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting crane recovery tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
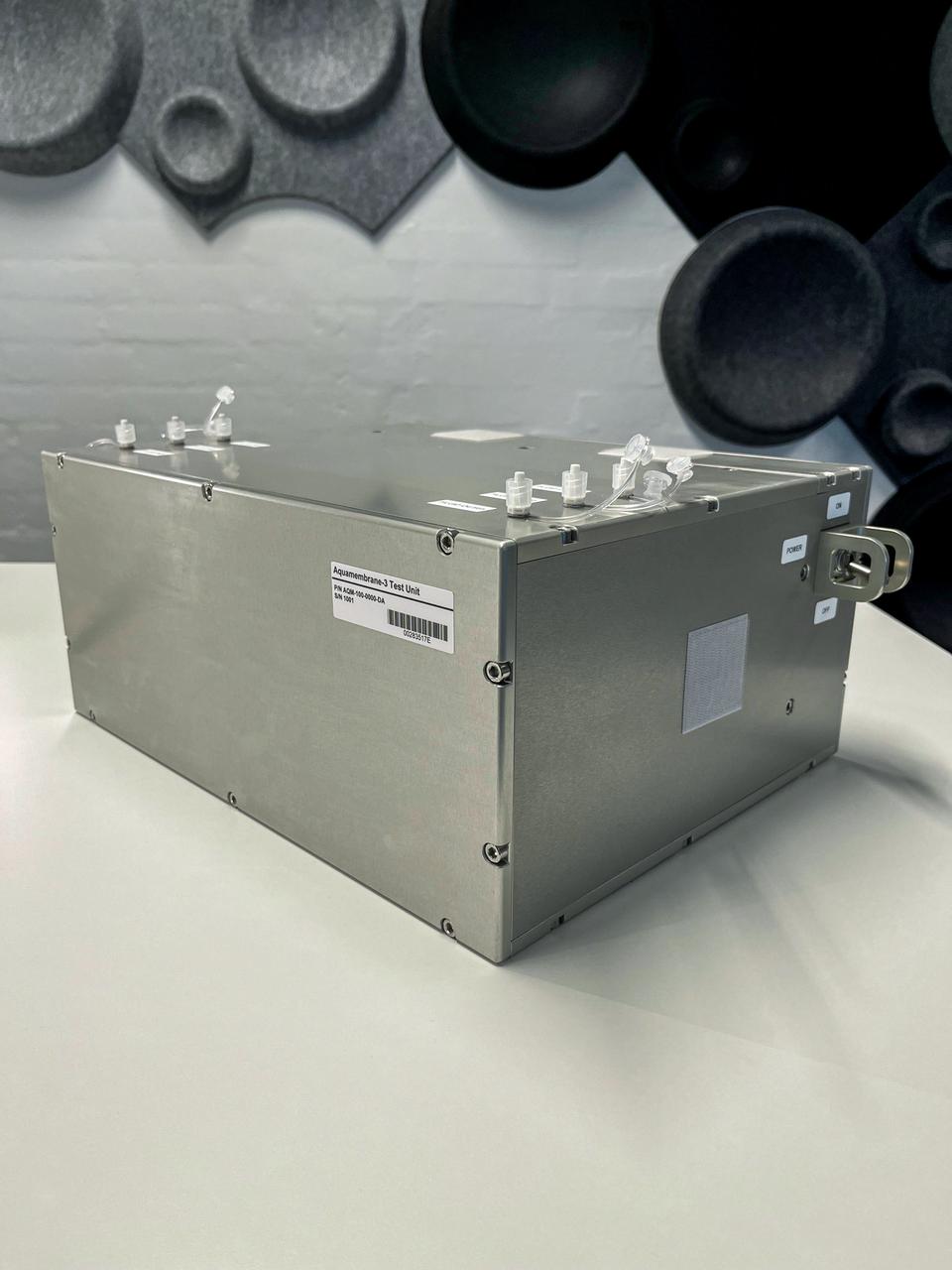

jsc2023e055873 (10/5/2023) --- The Testing Contaminant Rejection of Aquaporin Inside® HFFO Module (Aquamembrane-3) hardware consists of three separate and parallel systems to quantify the membrane's water flux and contamination rejection in microgravity, which are key parameters for a full water recovery system. This image shows the unit containing the forward osmosis membranes and other fluid system components.

A colorful sunset illuminates the water as the USS San Diego prepares for Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California. Using a test version of the Orion crew module, NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy will conduct a series of tests to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and NASA's Journey to Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch on NASA's Space Launch System in late 2018. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion.

Several rigid hull and inflatable Zodiac boats are in the water near a test version of the Orion crew module during the third day of Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy are conducting a series of tests using the USS San Diego, various watercraft and equipment to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and NASA's Journey to Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch on NASA's Space Launch System in late 2018. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion.

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A Zodiac boat containing U.S. Navy divers approaches the Orion boilerplate test vehicle floating in the Pacific Ocean, a distance away from the USS Anchorage, during the third day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3. Orange stabilizers on the top of the test vehicle were inflated to simulate the system that will be used to upright Orion in the water after splashdown. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the test vehicle to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The tethered Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage during the third day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. Orange stabilizers on the top of the test vehicle were inflated to simulate the system that will be used to upright Orion in the water after splashdown. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the test vehicle to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
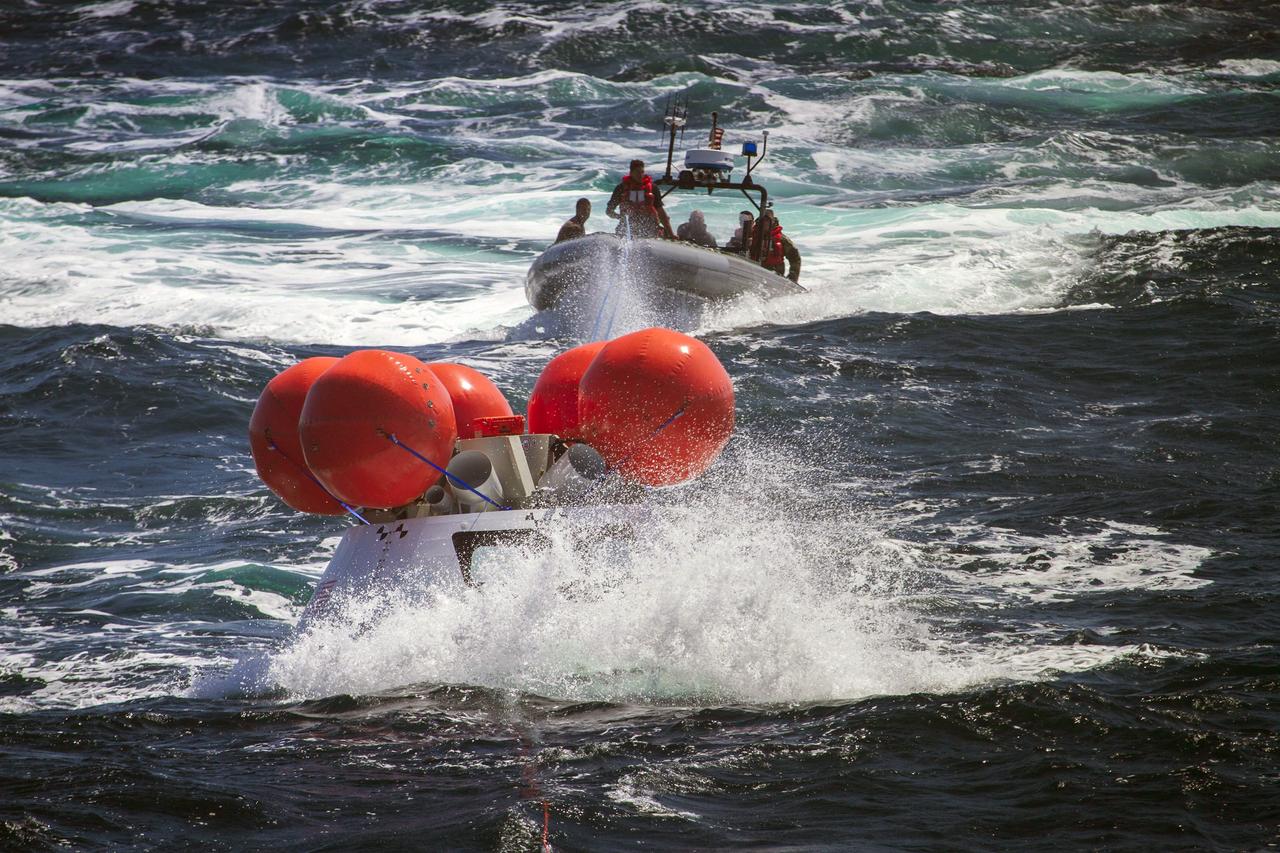

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A rigid hull inflatable boat containing U.S. Navy divers and other personnel approaches the Orion boilerplate test vehicle floating in the Pacific Ocean, a distance away from the USS Anchorage, during the third day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3. Orange stabilizers on the top of the test vehicle were inflated to simulate the system that will be used to upright Orion in the water after splashdown. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the test vehicle to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
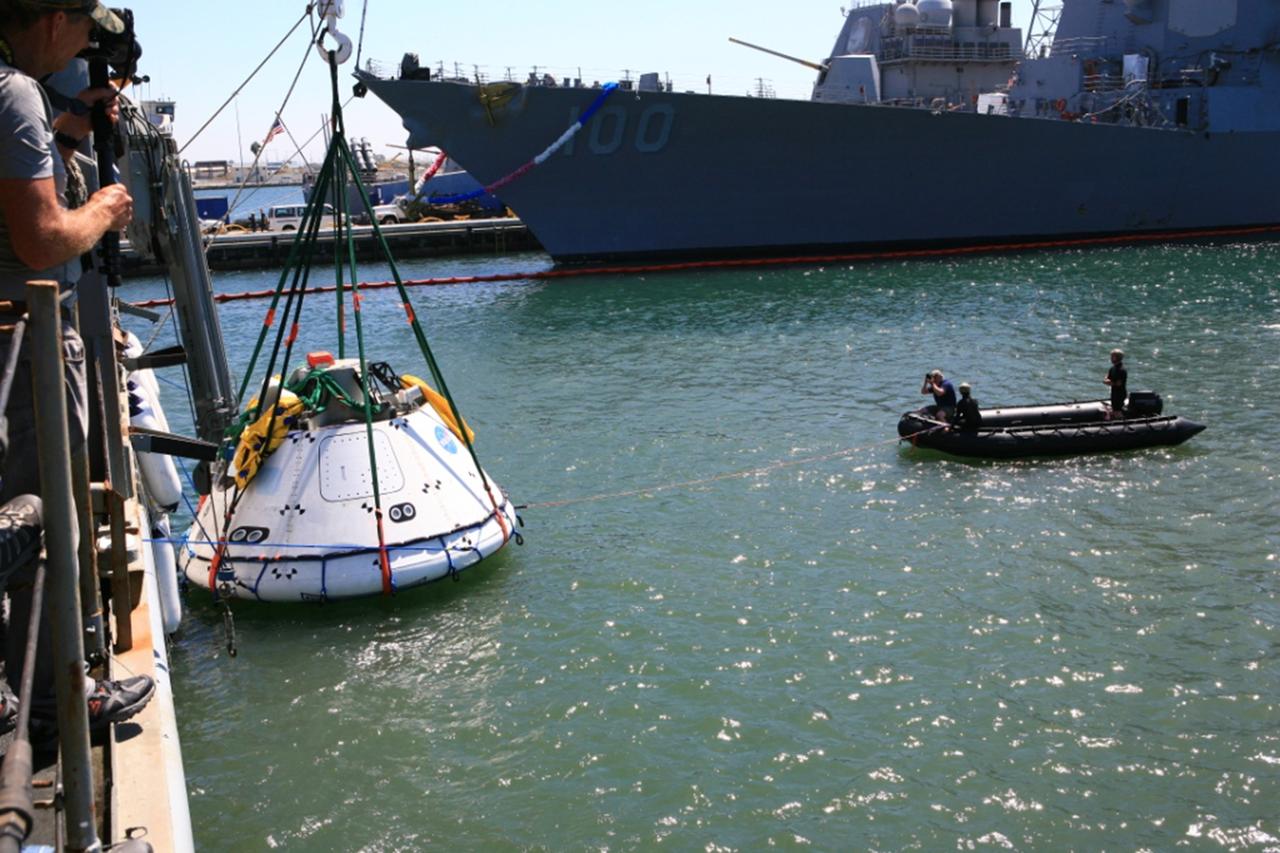

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 4A at Naval Base San Diego in California. U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat practice procedures to tether the test vehicle. The ship will head out to sea for four days to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
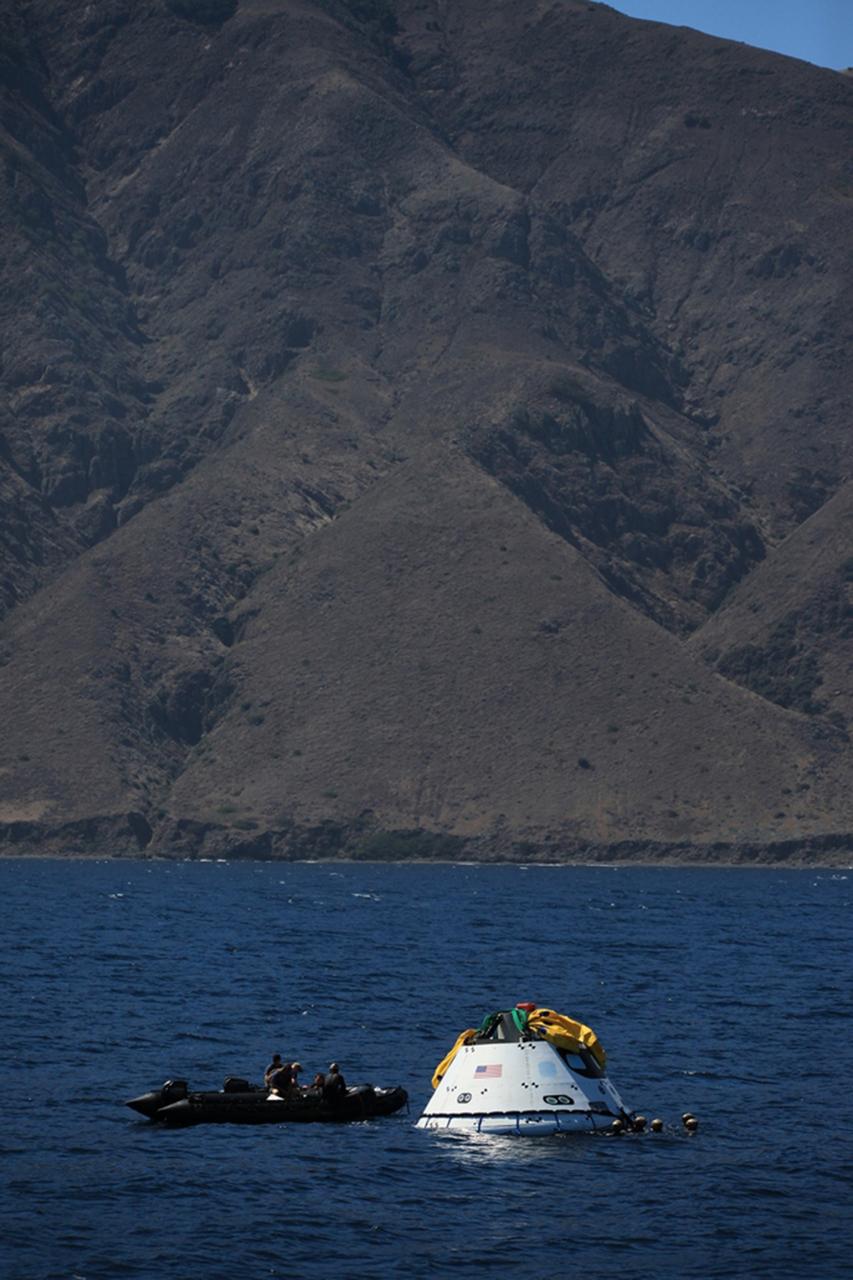

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship. Nearby, U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat prepare to practice procedures to tether and retrieve the test vehicle. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting crane recovery tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
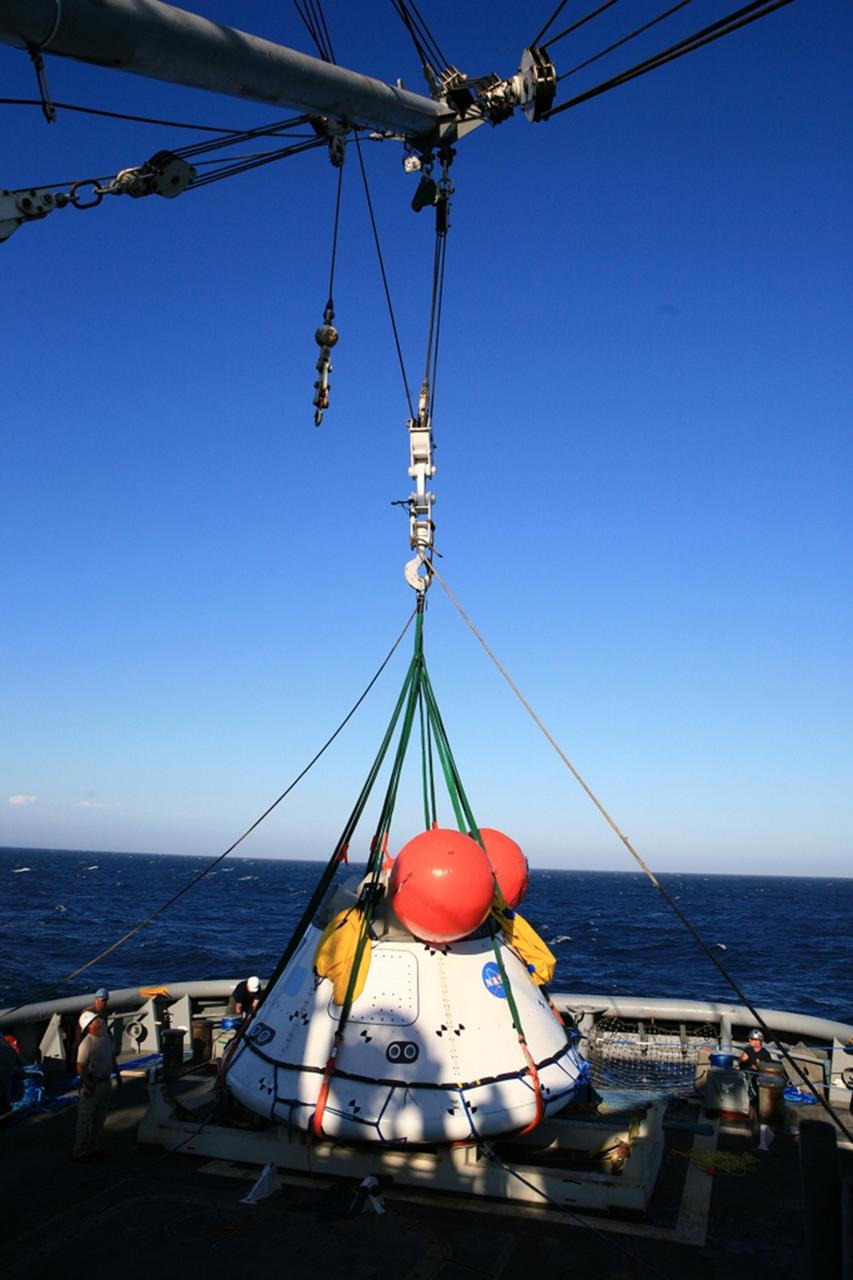

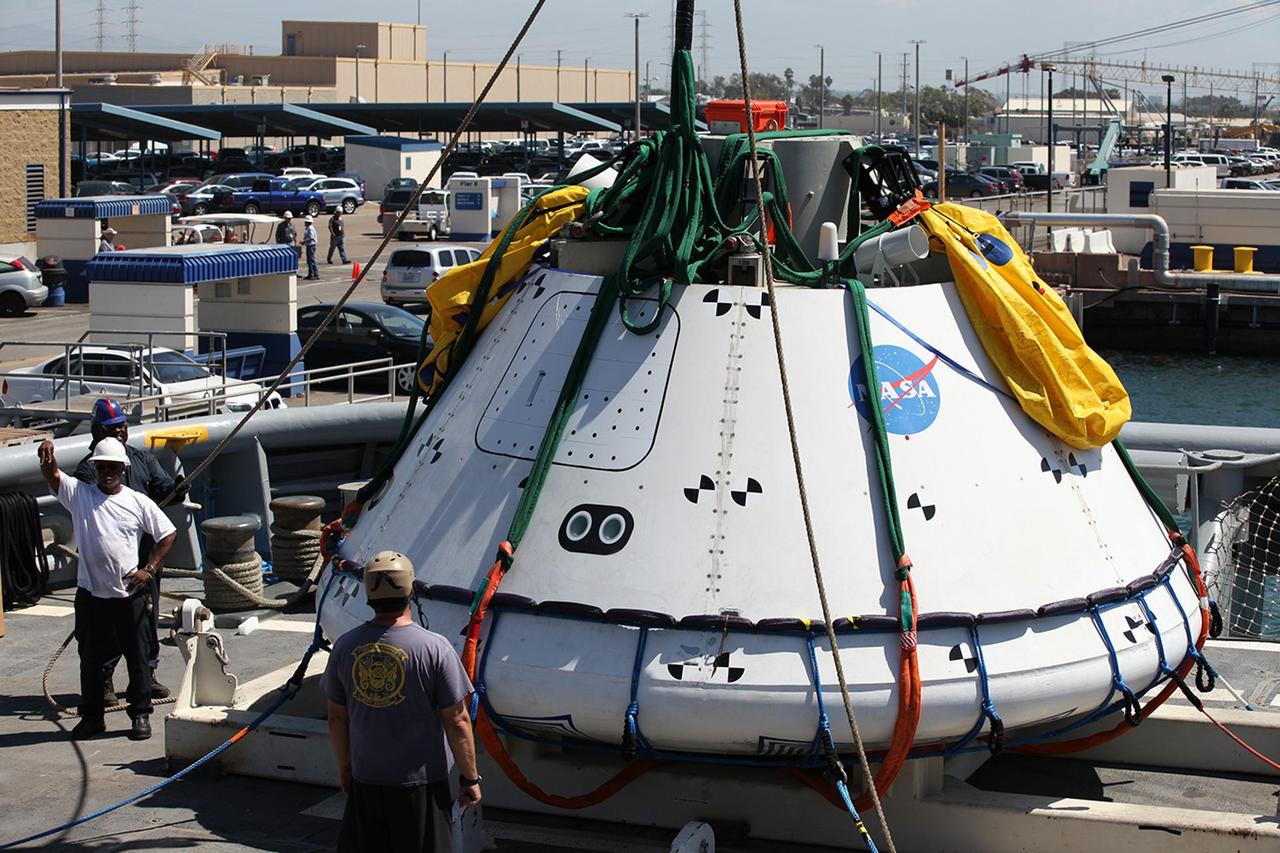
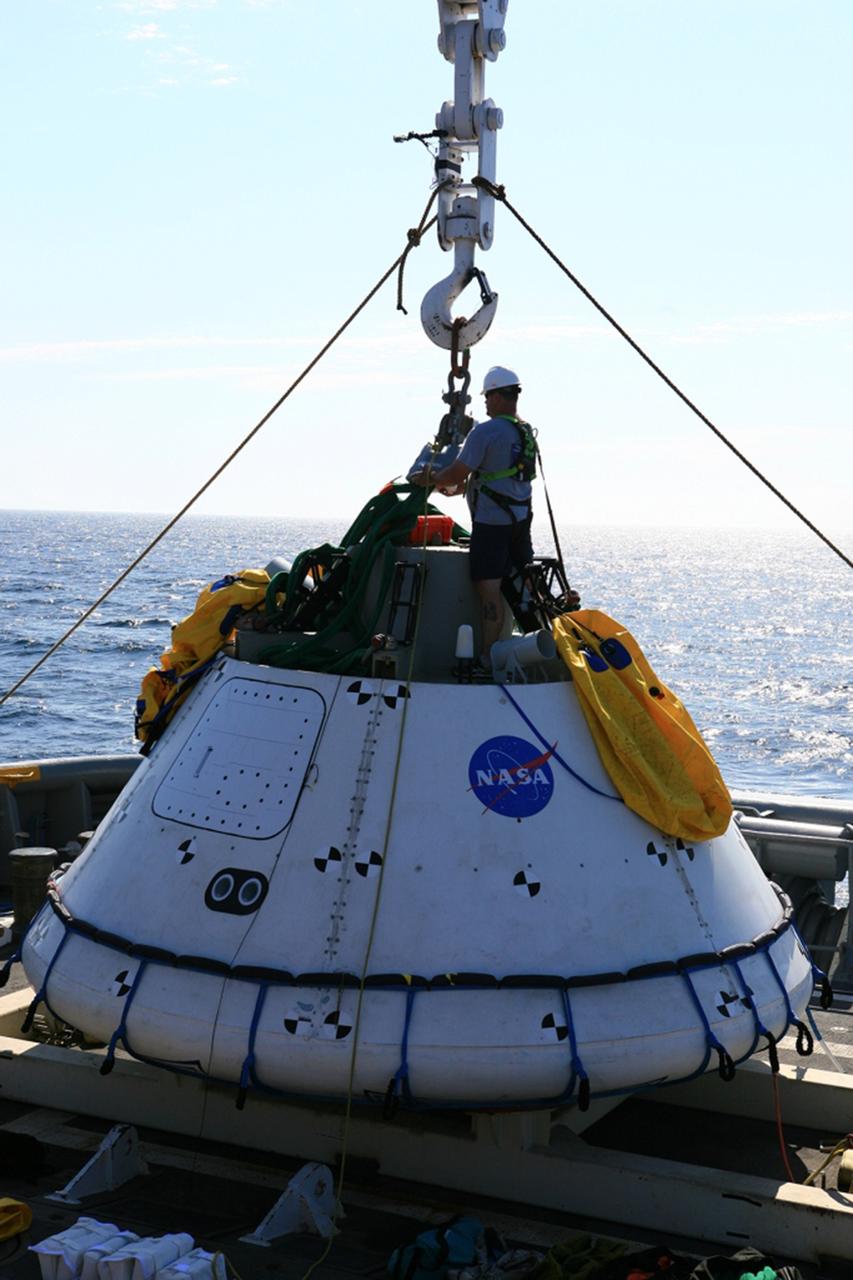
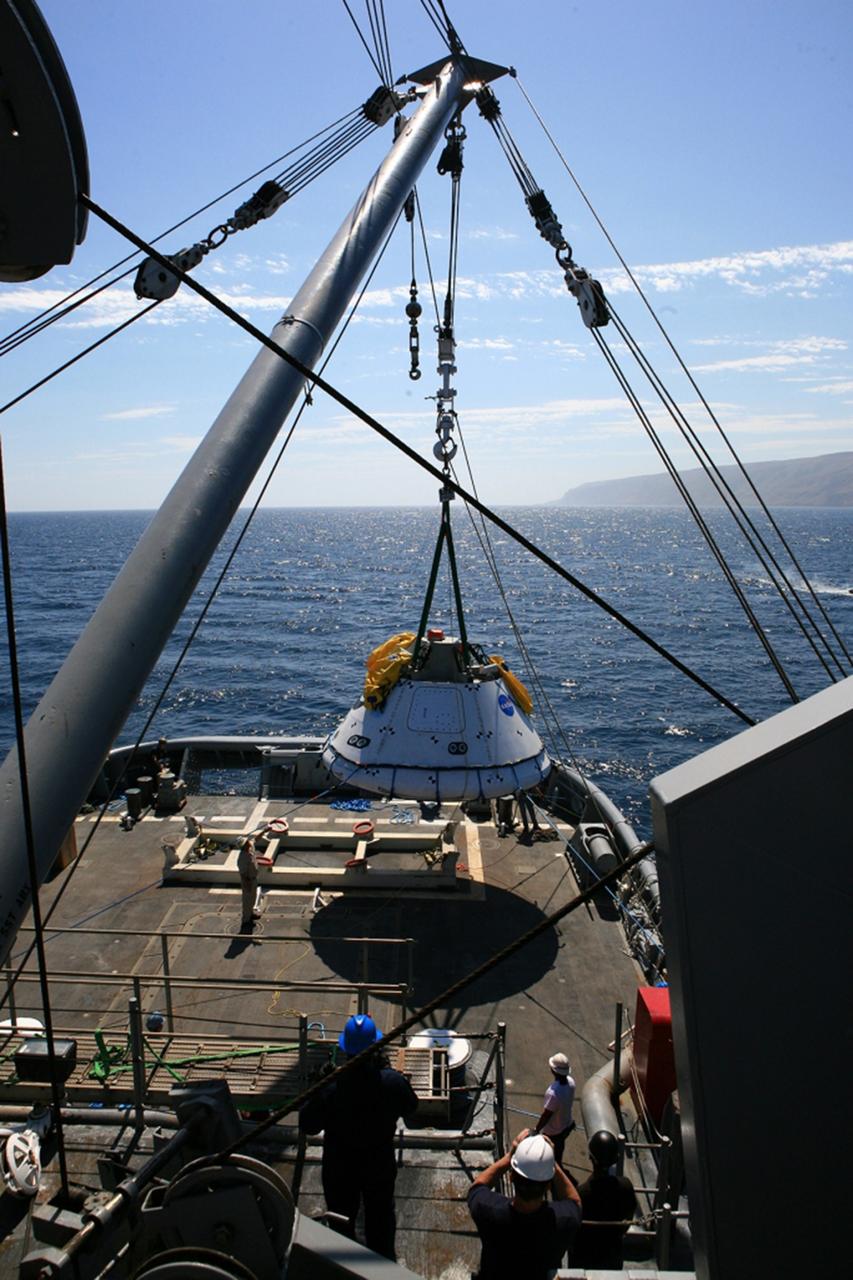
SAN DIEGO, Calif. – On the third day of Underway Recovery Test 4A in the Pacific Ocean, the Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lifted out of the water and placed in a cradle in the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, using a stationary crane. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are testing crane recovery operations to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
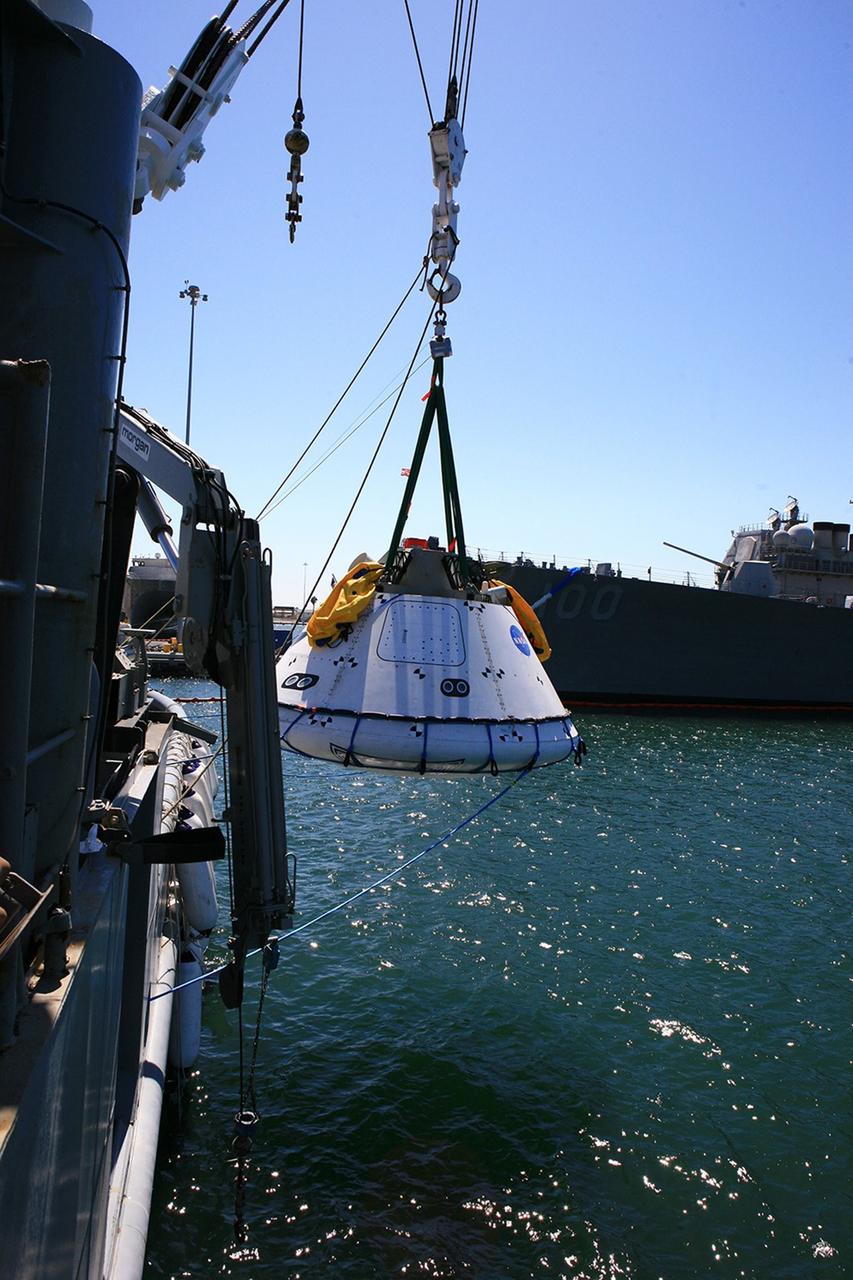

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is slowly lowered by stationary crane toward the water during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 4A aboard the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, at Naval Base San Diego in California. The ship will head out to sea for four days to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
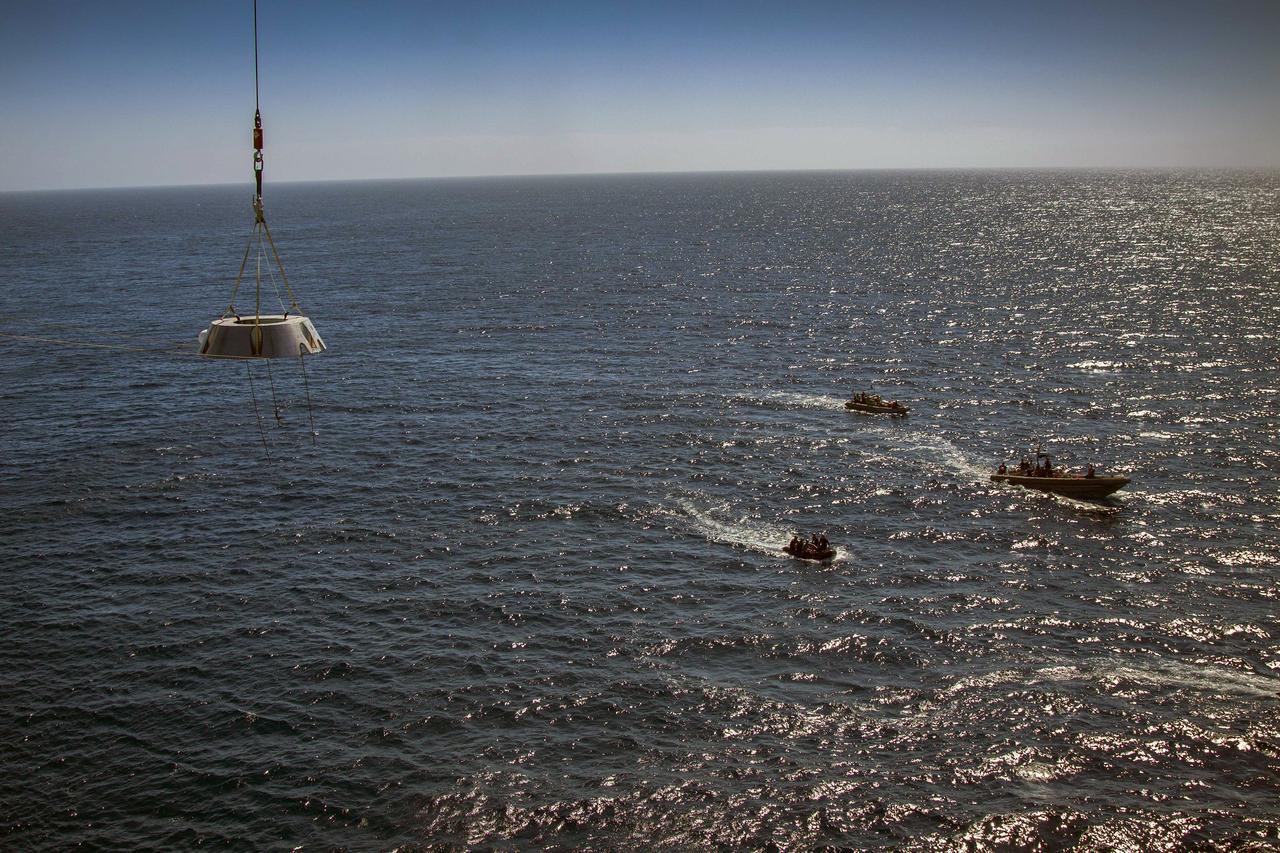

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A mock-up of the Orion forward bay cover is lowered by crane from the USS Anchorage into the water during the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. Nearby, U.S. navy divers in two Zodiac boats and other team members in a rigid hull inflatable boat, wait to practice recovery procedures. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and mock-up forward bay cover to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
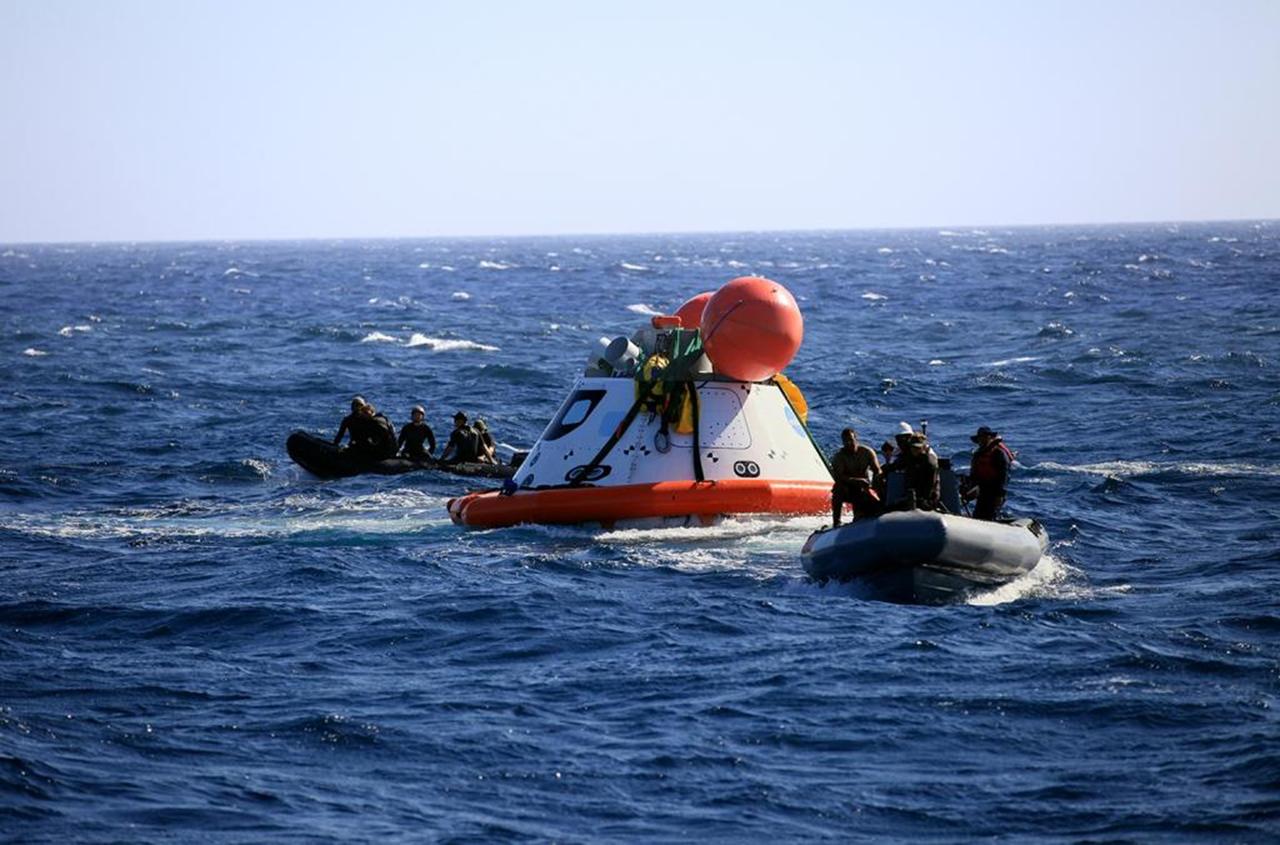

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship. Nearby, Navy divers in two Zodiac boats practice recovery procedures. An orange stabilization collar has been attached around Orion to prepare for lift by stationary crane back onto the USS Salvor. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
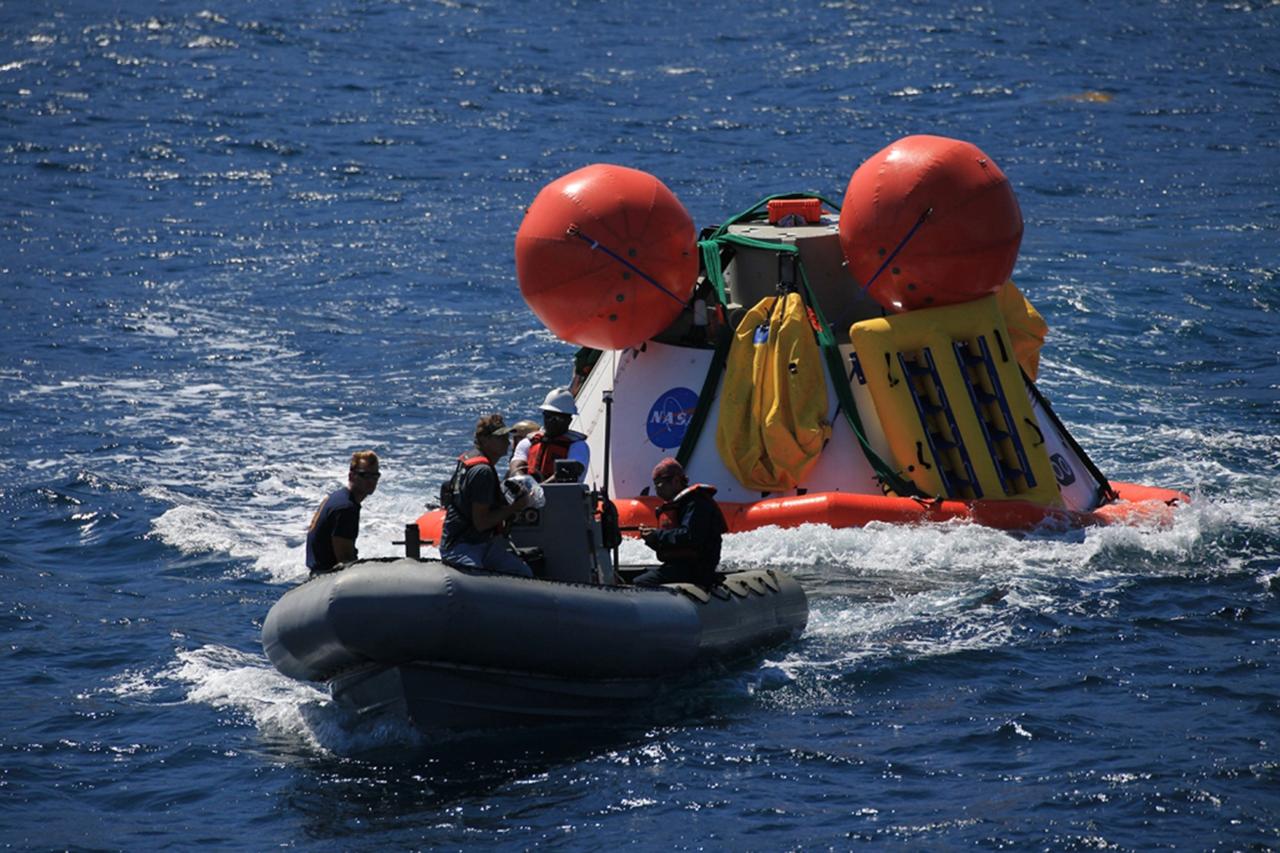

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship. Nearby, U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat have attached a flotation collar and tether lines to Orion to bring the test vehicle closer to the ship. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting crane recovery tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – At Naval Base San Diego in California, U.S. Navy personnel prepare the Orion boilerplate test vehicle to be lifted by stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, and lowered into the water during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 4A. The ship will head out to sea for four days to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 4A at Naval Base San Diego in California. U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat practice procedures to tether and retrieve the test vehicle. The ship will head out to sea for four days to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – On the third day of Underway Recovery Test 4A, the Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean near the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship. Orion was lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the ship. Tether lines from the ship have been attached to Orion for a towing test. Nearby, Navy divers in Zodiac boats monitor Orion and practice recovery procedures. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – On board the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, U.S. Navy personnel check the stationary crane attached to the Orion boilerplate test vehicle during Underway Recovery Test 4A in the Pacific Ocean. The test vehicle will be lifted up and lowered into the water to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – On board the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, U.S. Navy personnel monitor the progress as a stationary crane lifts the Orion boilerplate test vehicle during Underway Recovery Test 4A in the Pacific Ocean. The test vehicle will be lifted up and lowered into the water to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
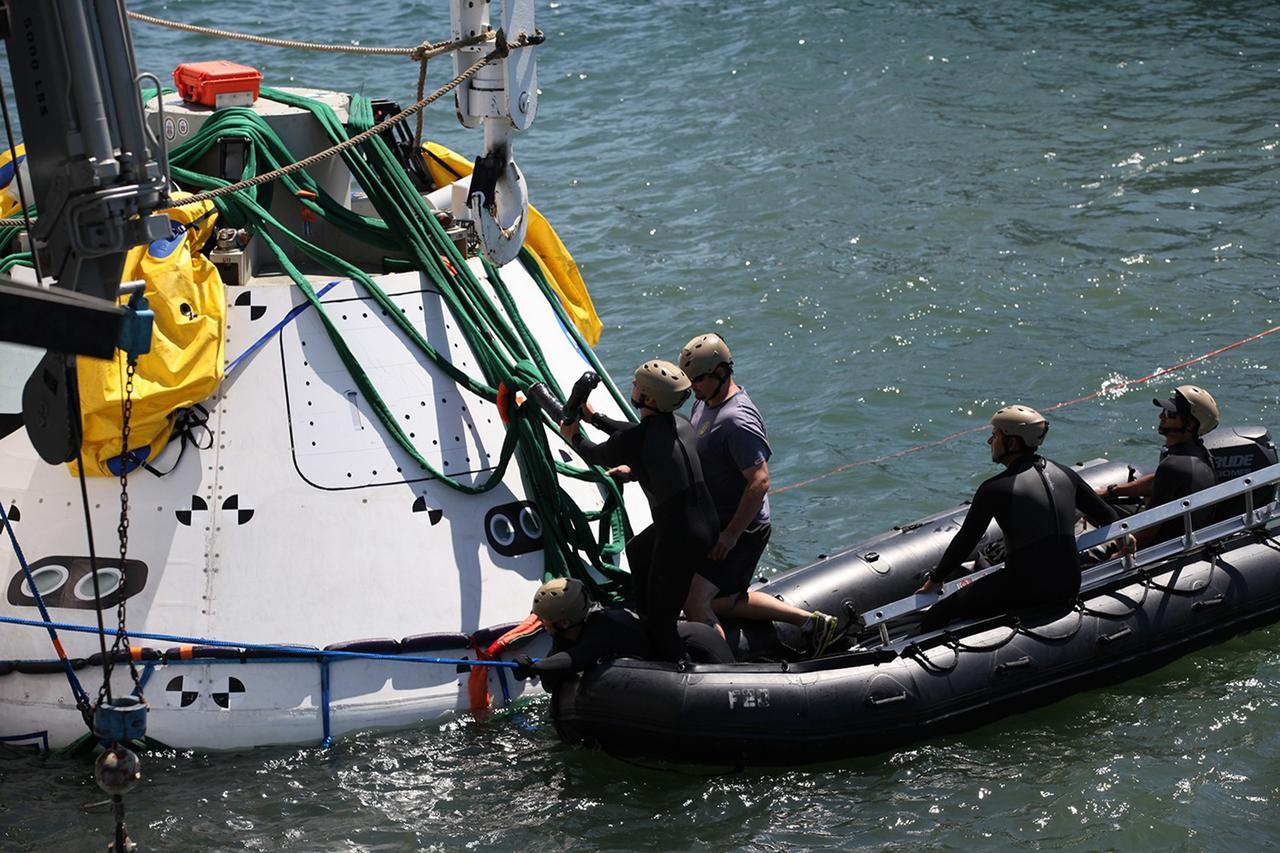

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 4A at Naval Base San Diego in California. U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat practice procedures to tether and retrieve the test vehicle. The ship will head out to sea for four days to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
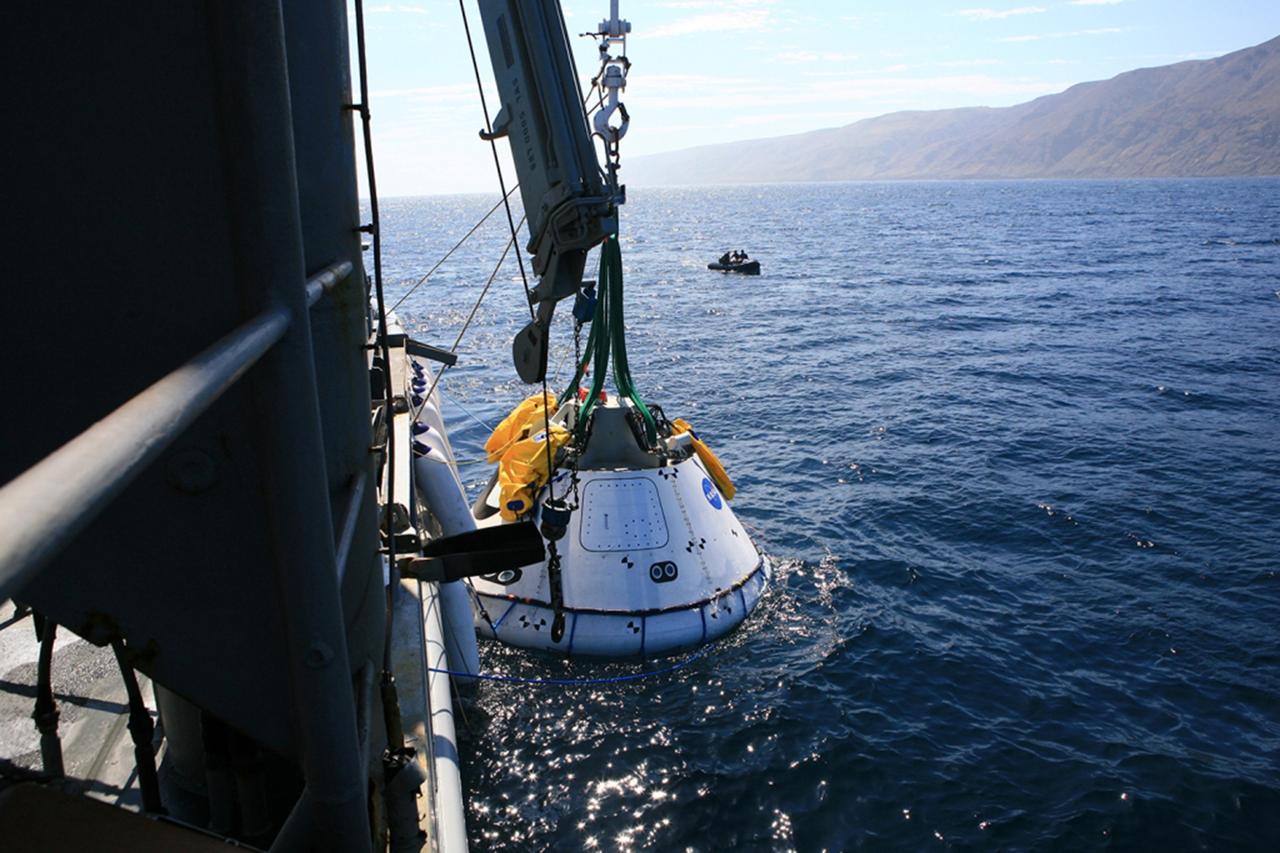

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, during Underway Recovery Test 4A in the Pacific Ocean. Nearby, U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat prepare to practice procedures to tether and retrieve the test vehicle. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are testing crane recovery operations to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
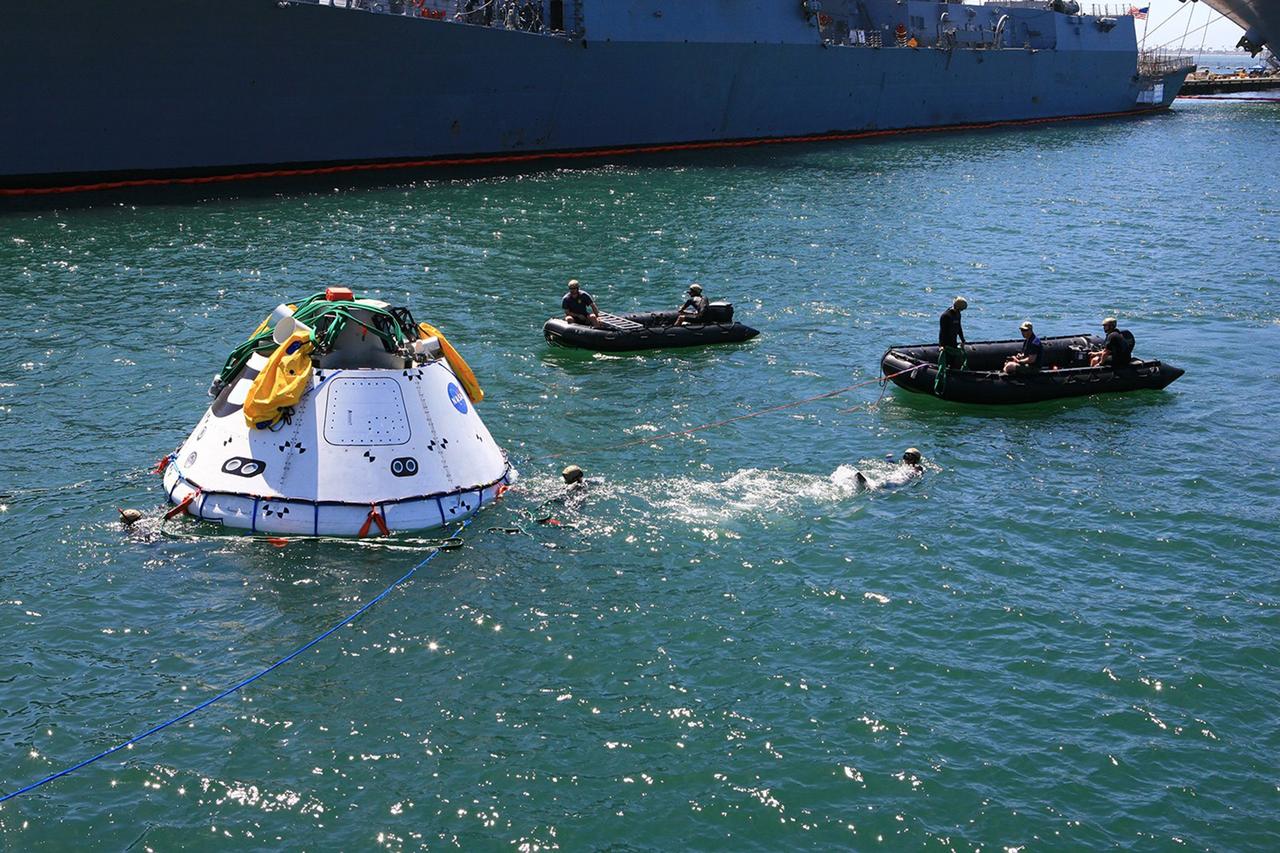

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 4A at Naval Base San Diego in California. U.S. Navy personnel in two Zodiac boats practice procedures to tether and retrieve the test vehicle. The ship will head out to sea for four days to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
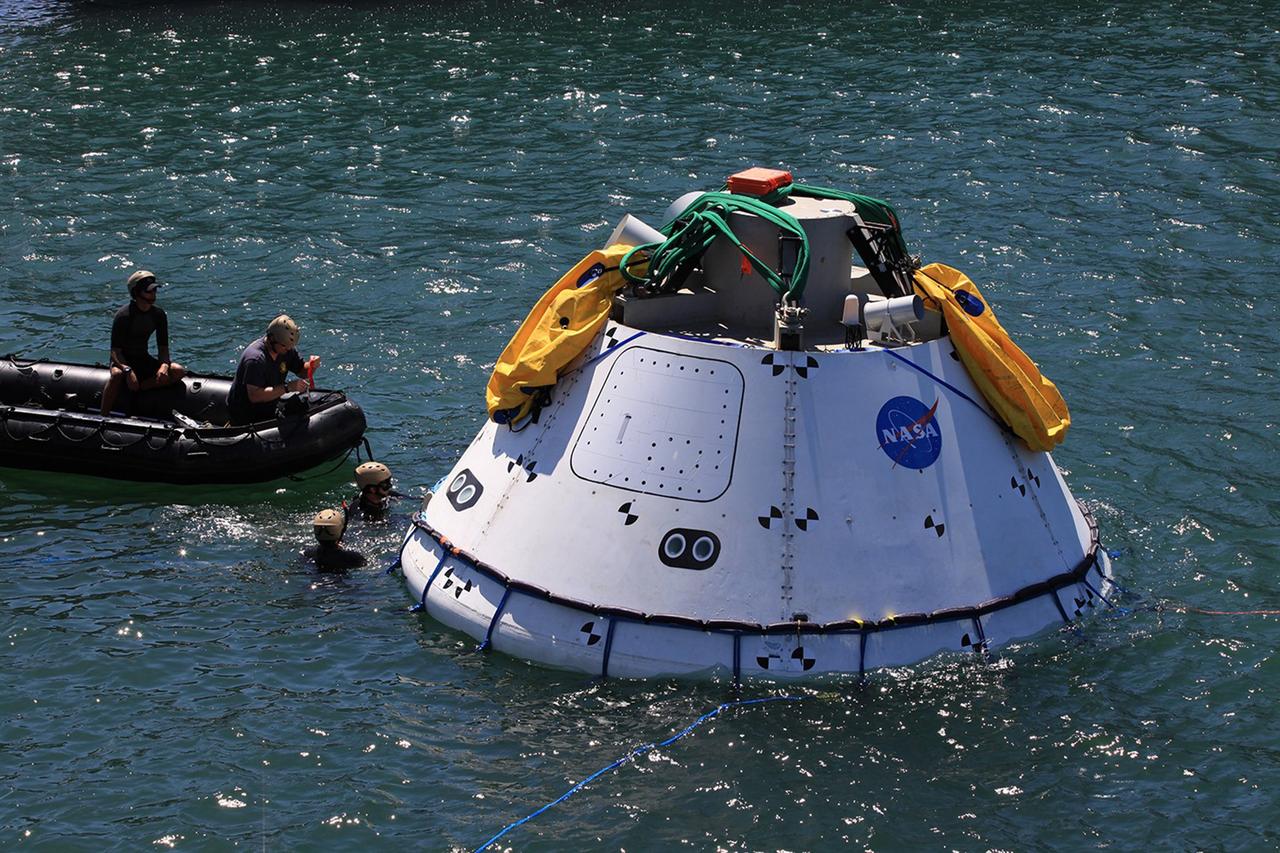

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 4A at Naval Base San Diego in California. U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat practice procedures to tether and retrieve the test vehicle. The ship will head out to sea for four days to test crew module crane recovery operations. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
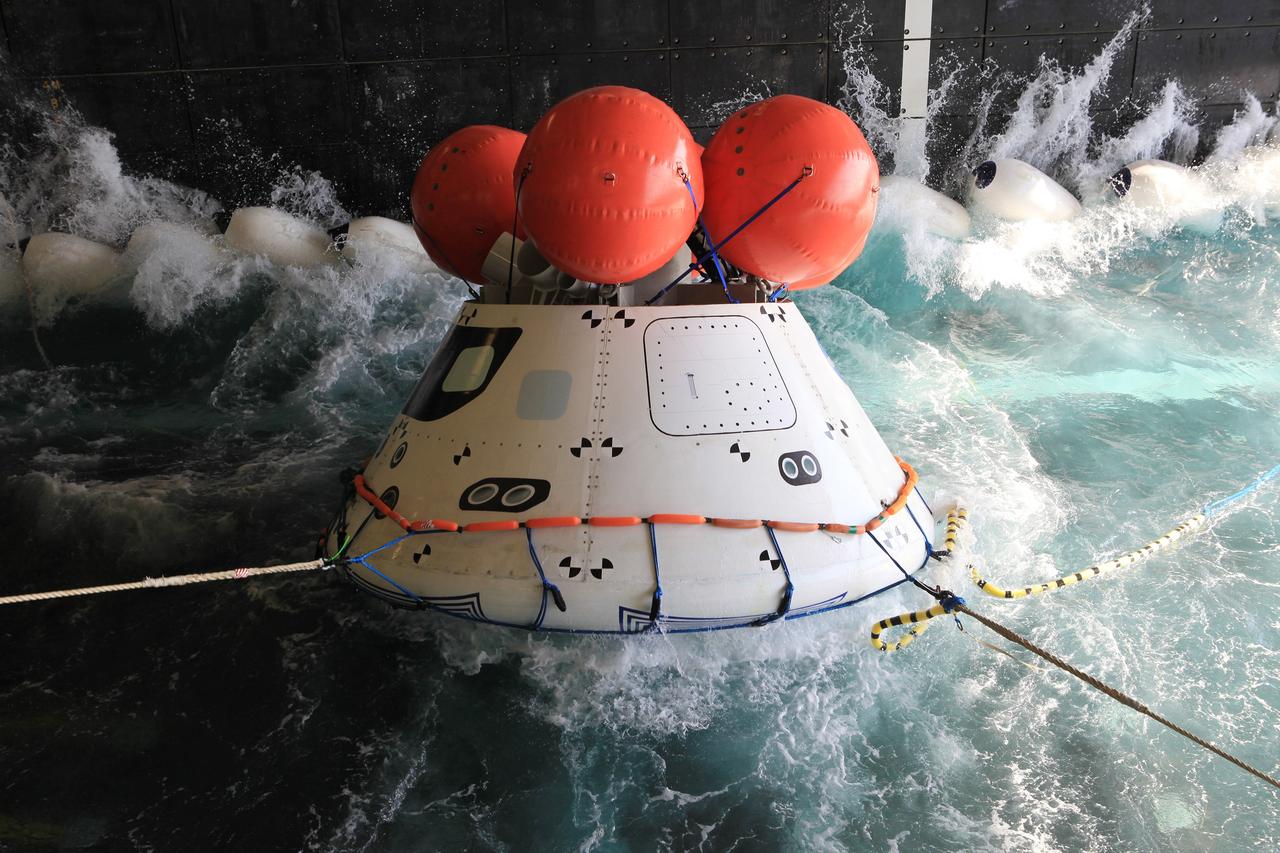

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The well deck of the USS Anchorage fills with water to prepare for recovery of the Orion boilerplate test vehicle during a portion of the Orion Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. The testing is being conducted to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep-space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep-space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

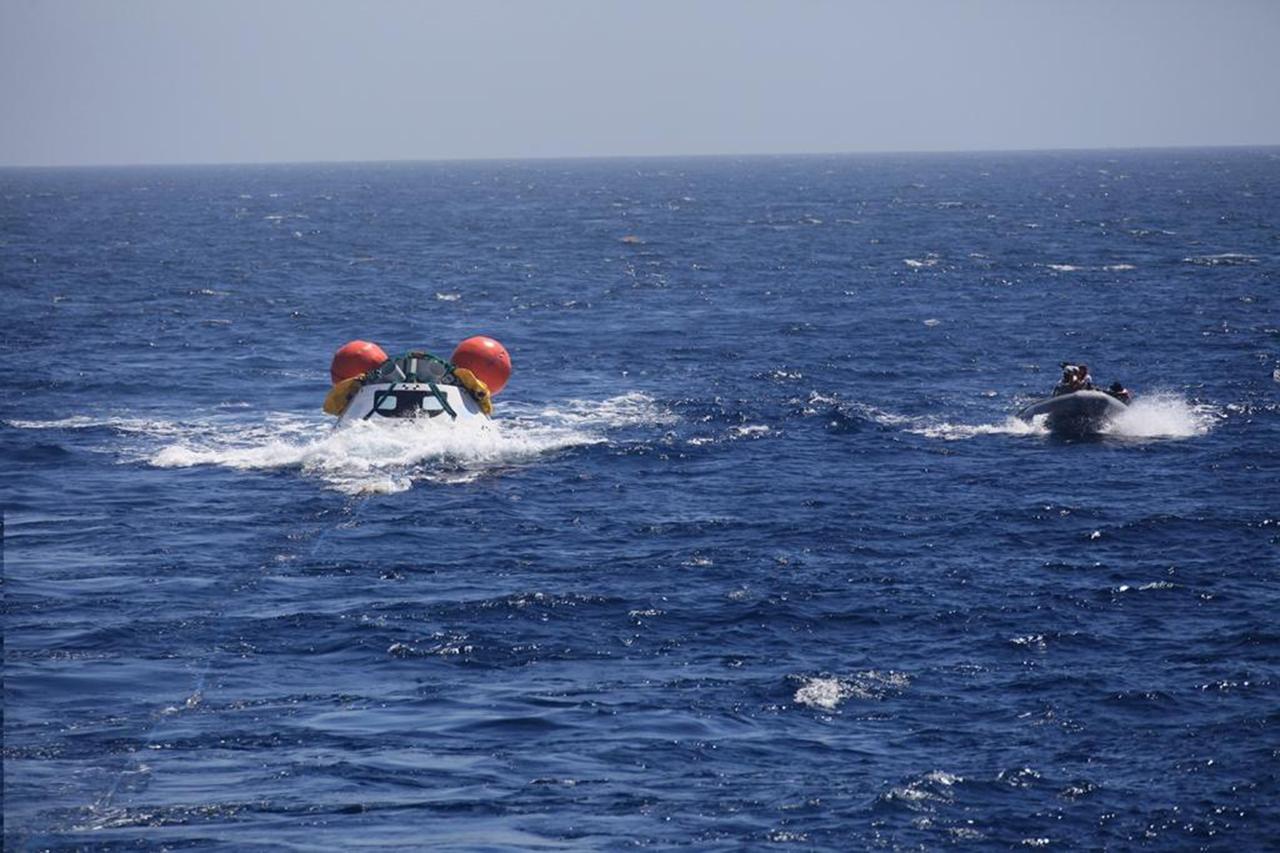
SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship. Nearby, U.S. Navy personnel in a Zodiac boat and rigid hull inflatable boat prepare to practice procedures to tether and retrieve the test vehicle. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting crane recovery tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during the third day of Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, using a stationary crane. Tether lines were attached to the test vehicle from the ship for a towing test. Navy divers in a Zodiac boat practice recovery procedures and monitor Orion. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
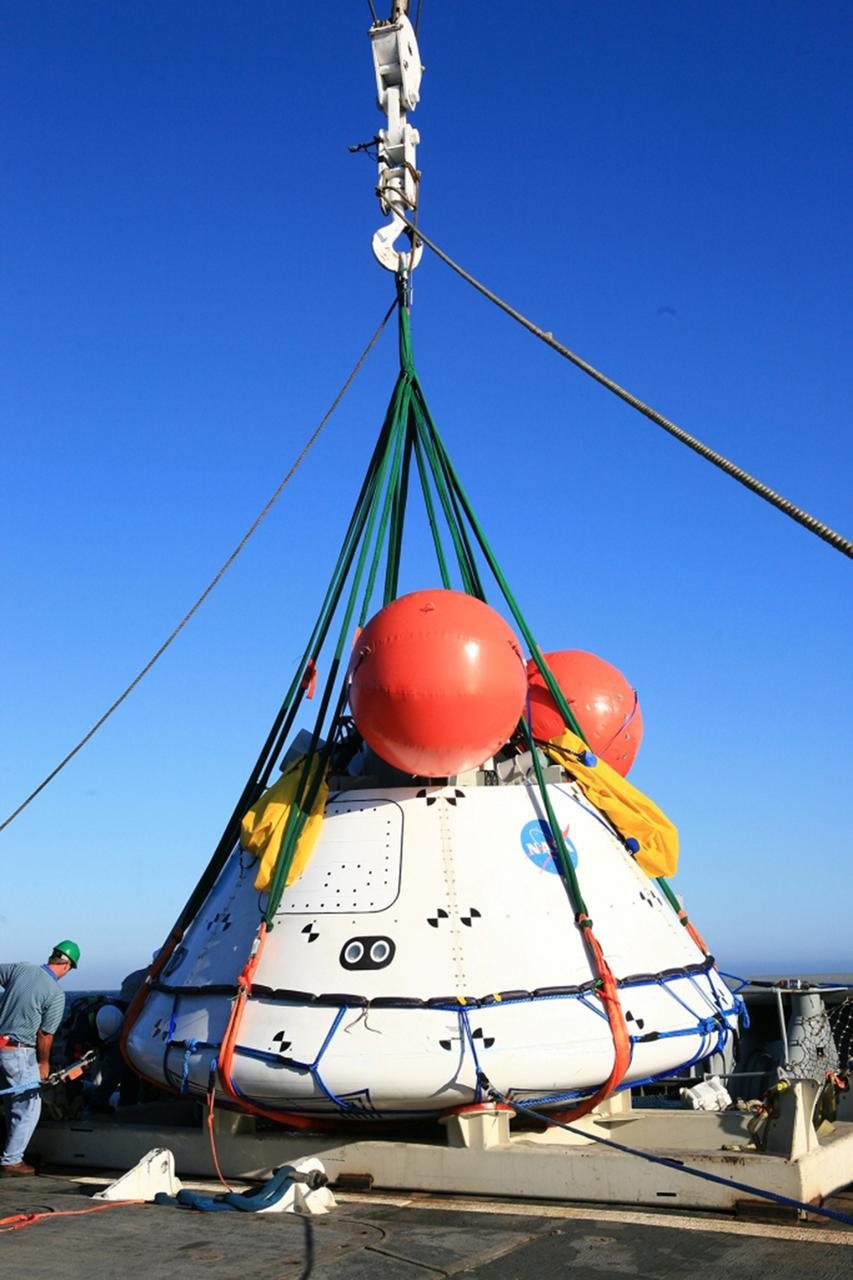

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – On the third day of Underway Recovery Test 4A in the Pacific Ocean, the Orion boilerplate test vehicle has been lifted out of the water and placed in a cradle in the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, using a stationary crane. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are testing crane recovery operations to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
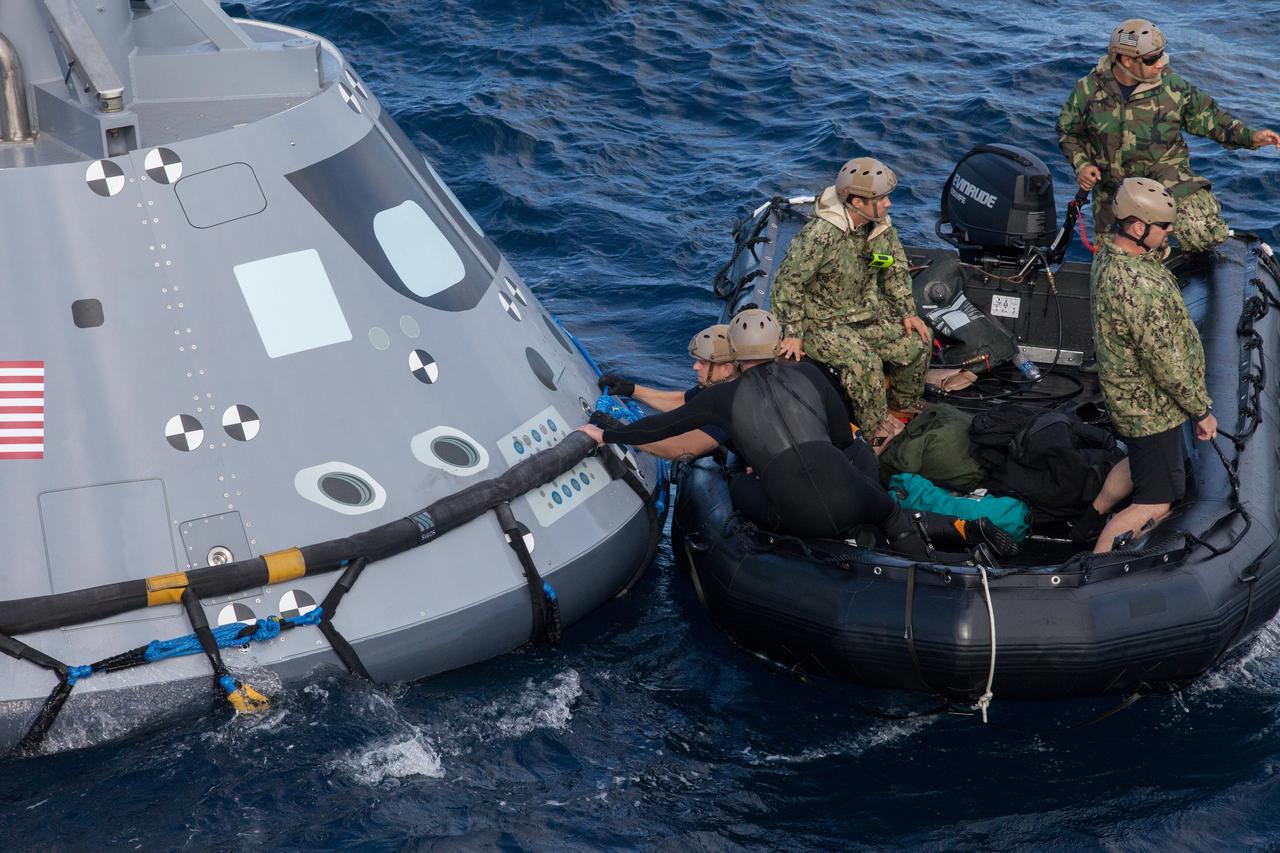

U.S. Navy divers and other personnel in a Zodiac boat secure a harness around a test version of the Orion crew module during Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California on Oct. 28, 2016. Tether lines will be attached to the test module to help guide it back to the well deck of the USS San Diego. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy are practicing recovery techniques to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
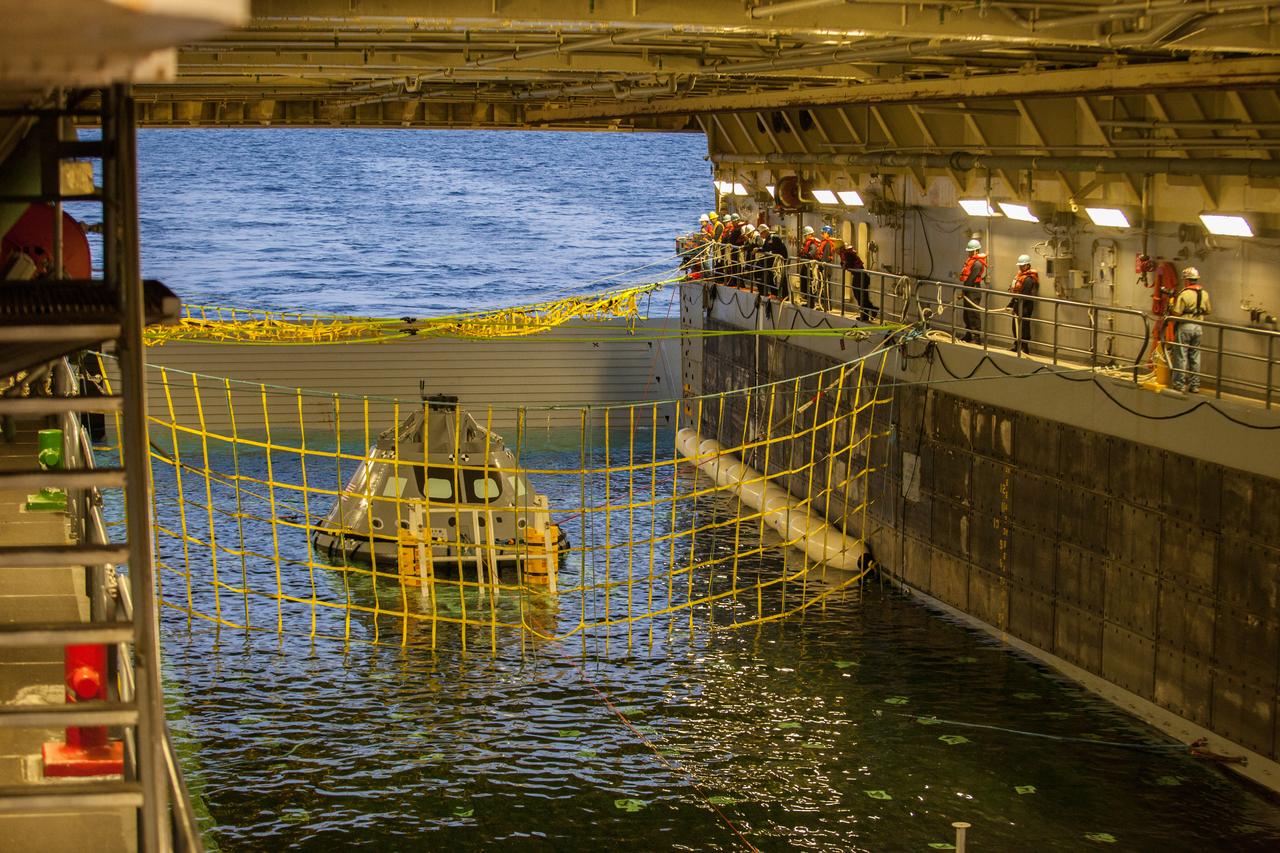

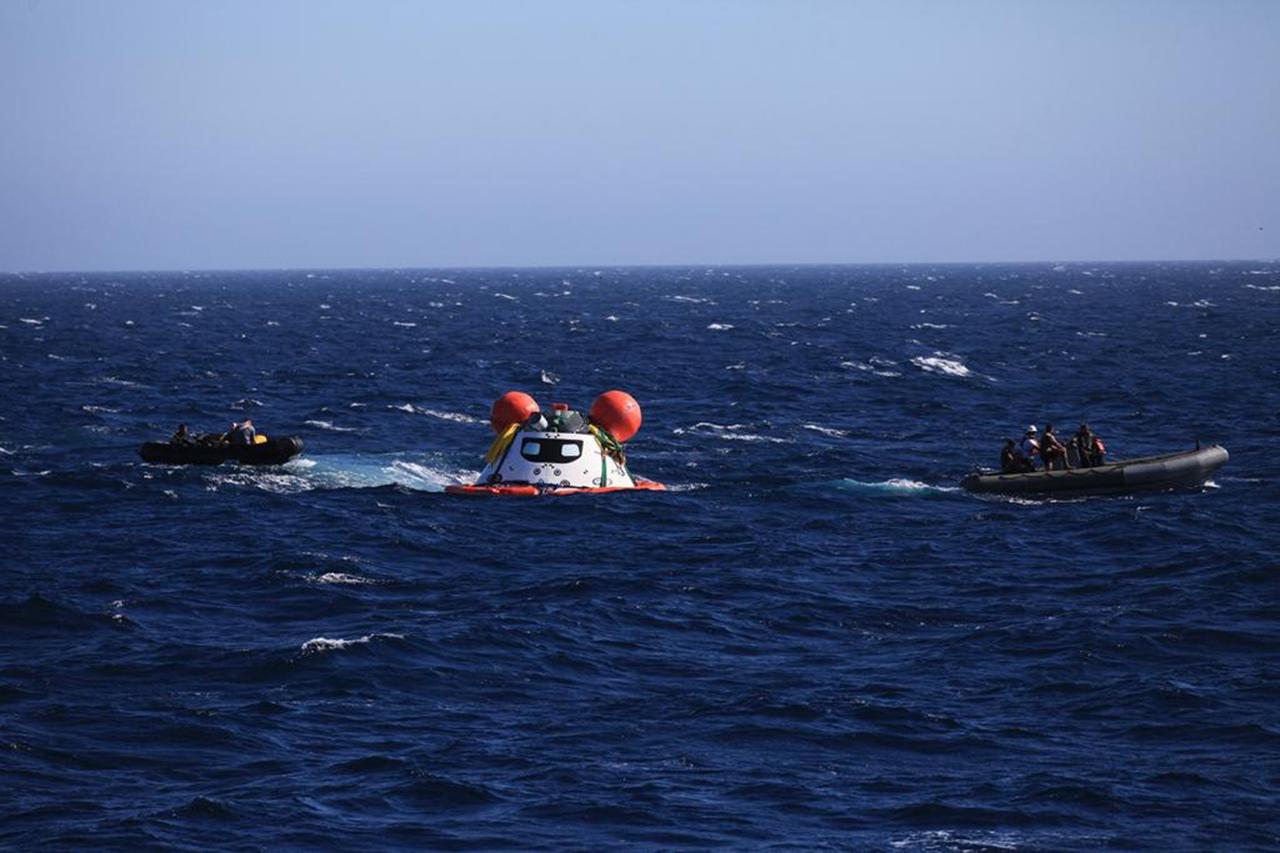
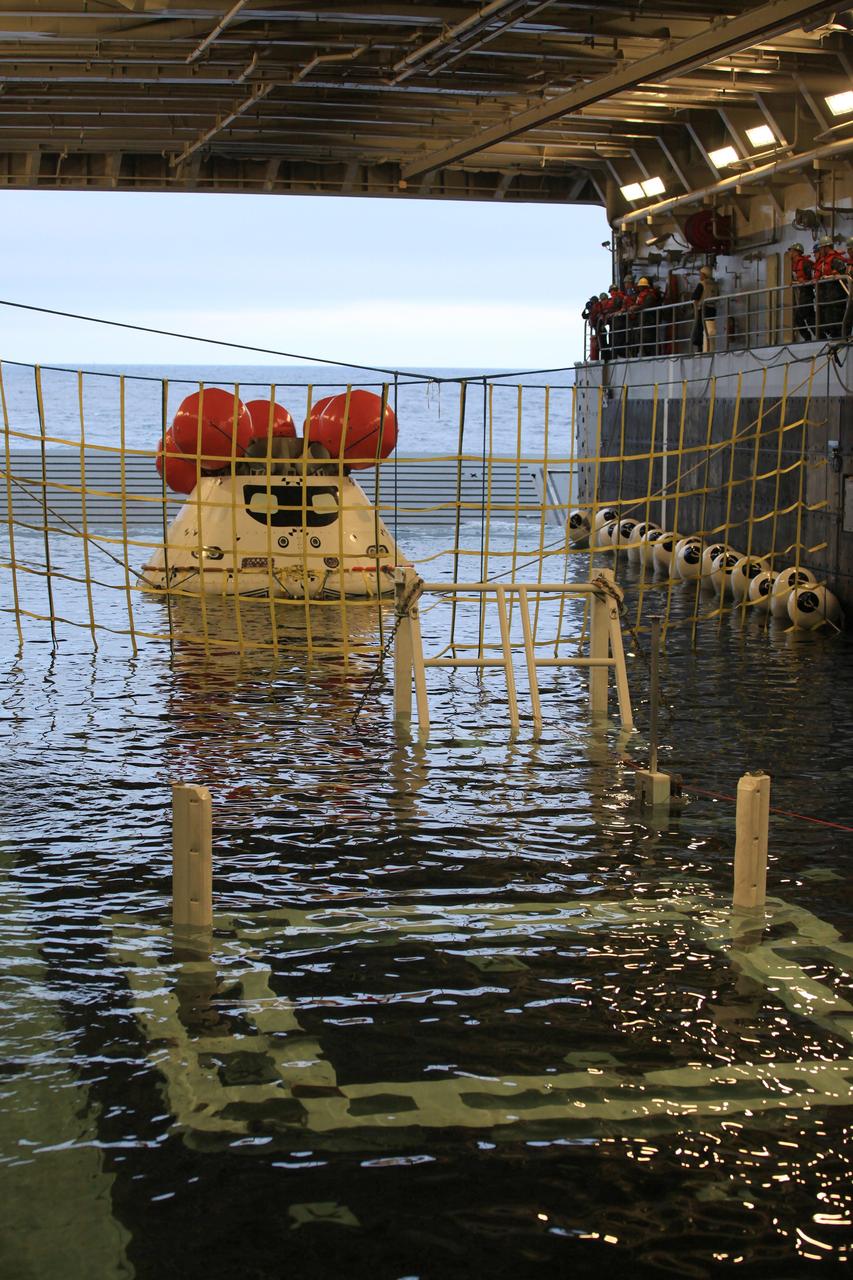
A golden sheen lights up a test version of the Orion crew module in the flooded well deck of the USS San Diego during Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California on Oct. 26, 2016. Recovery team personnel have secured a net around the crew module. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy will conduct a series of tests to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A test version of the Orion crew module floats outside the well deck of the USS San Diego during Orion Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California on Oct. 29, 2016. In the distance are U.S. Navy divers in a rigid hull inflatable boat. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy are practicing recovery techniques using the well deck of the ship and the test version of the crew module to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

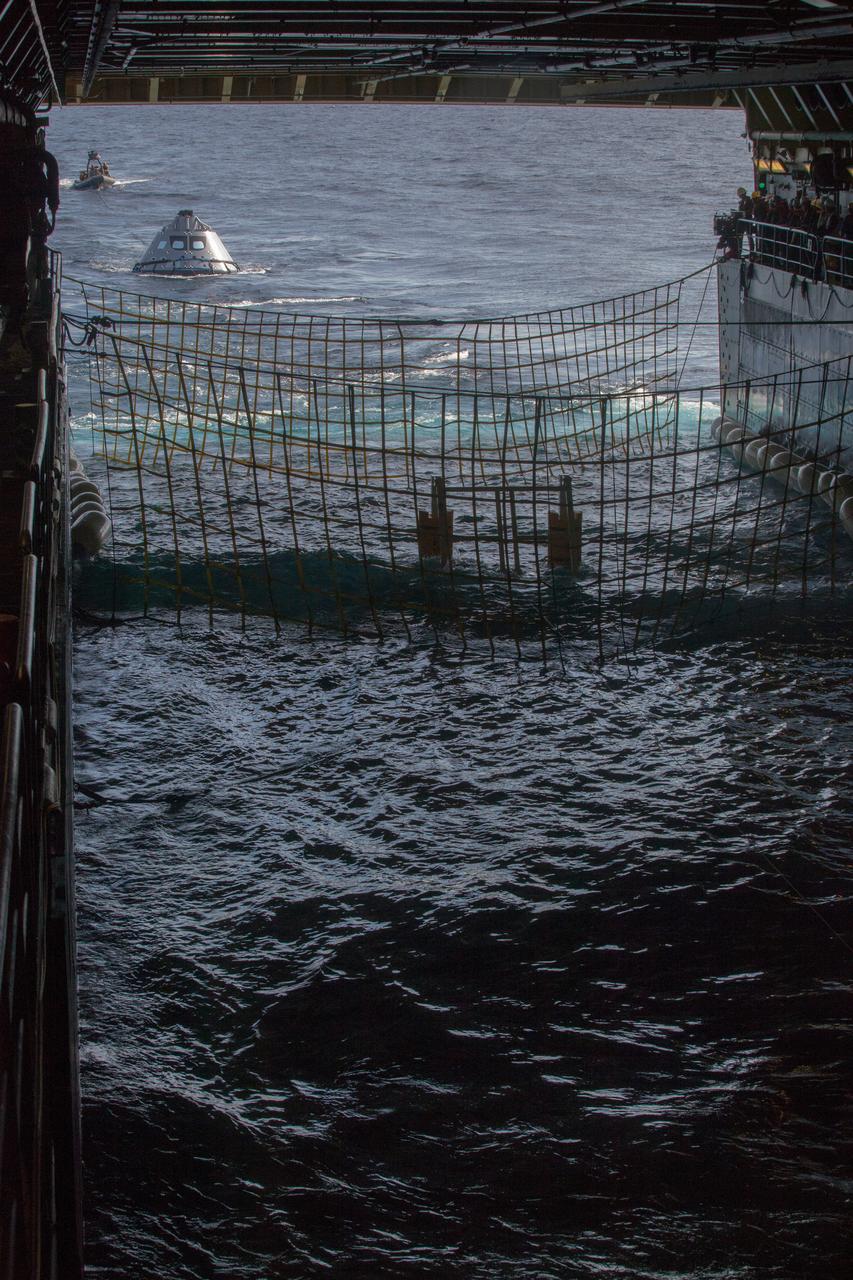
Members of the recovery team watch as the test version of the Orion crew module is guided into the flooded well deck of the USS San Diego during Underway Recovery Test 5 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California on Oct. 30, 2016. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy are conducting a series of tests using the ship's well deck, the test module, various watercraft and equipment to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
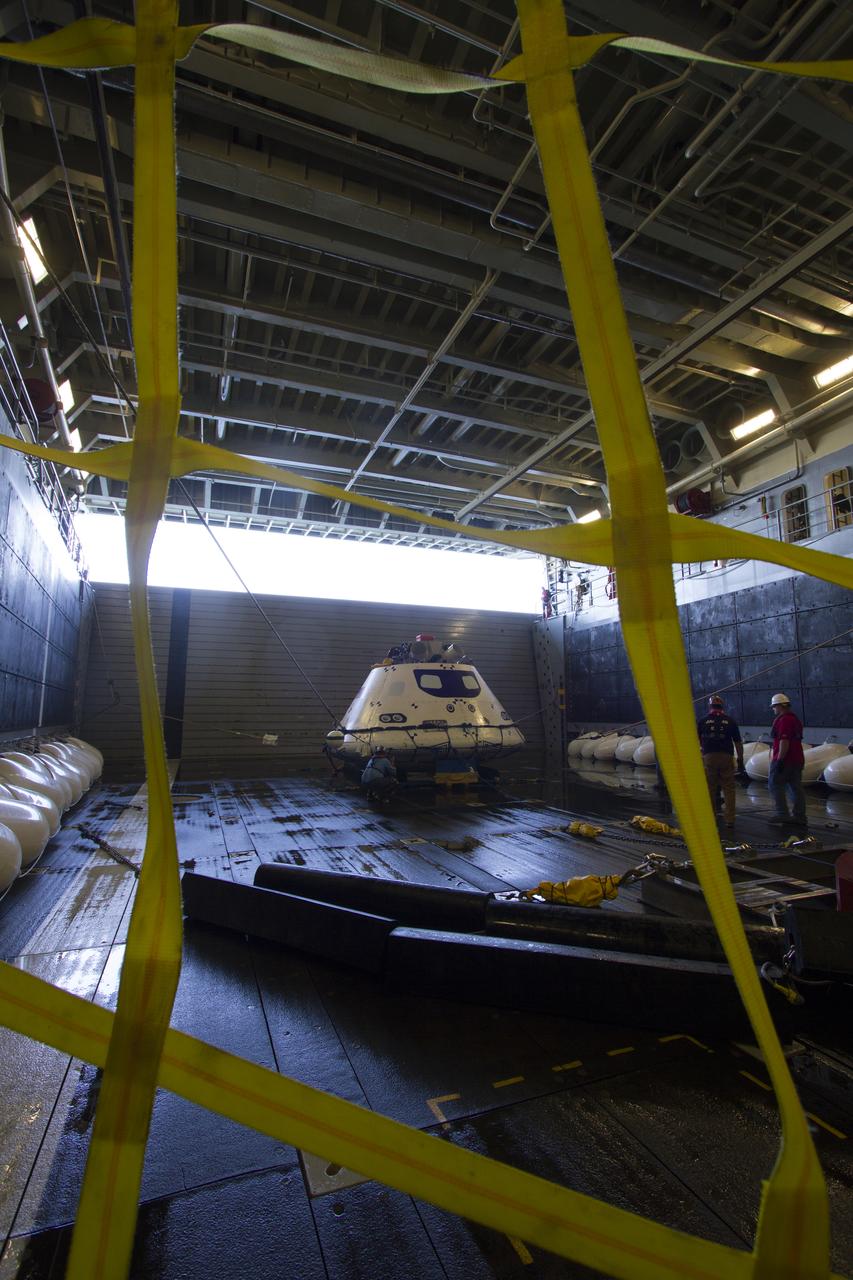

The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage during the first day of Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
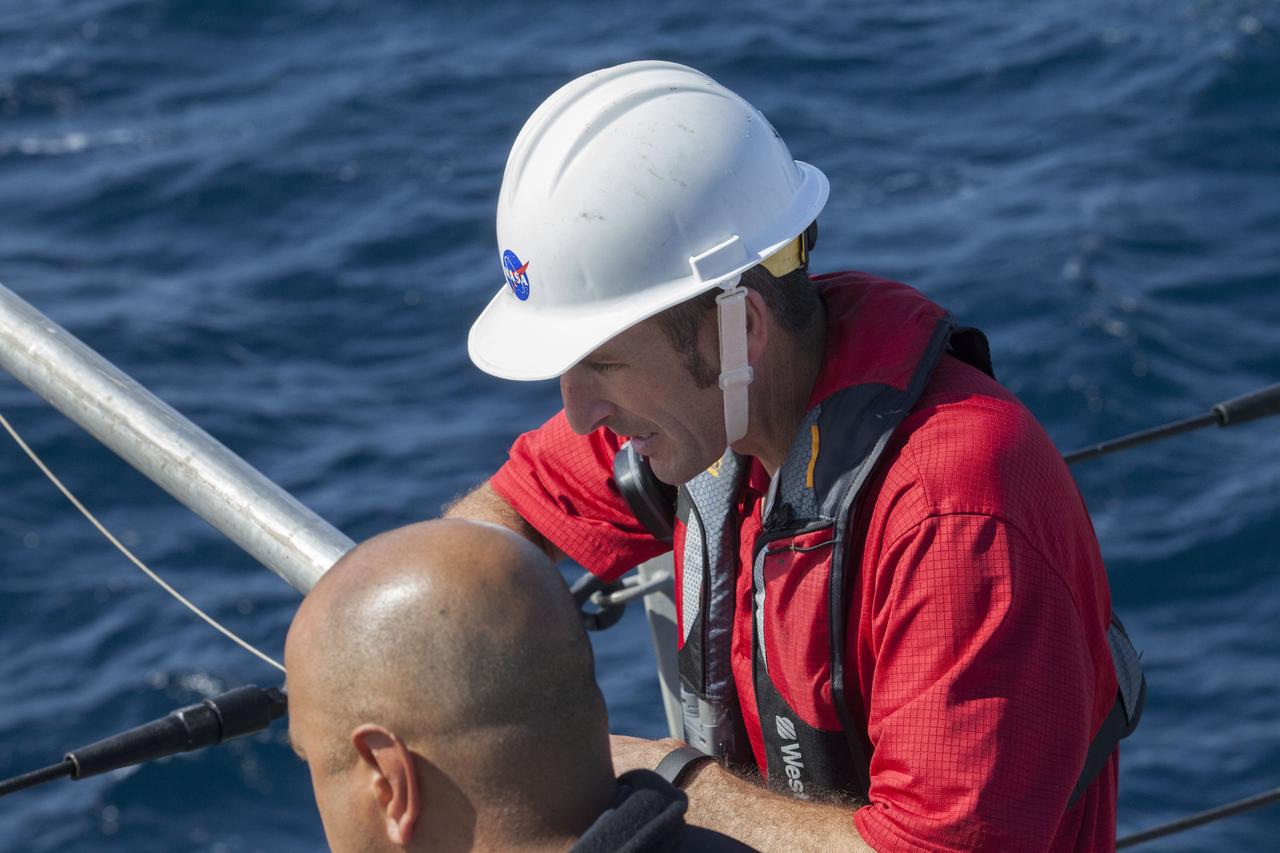

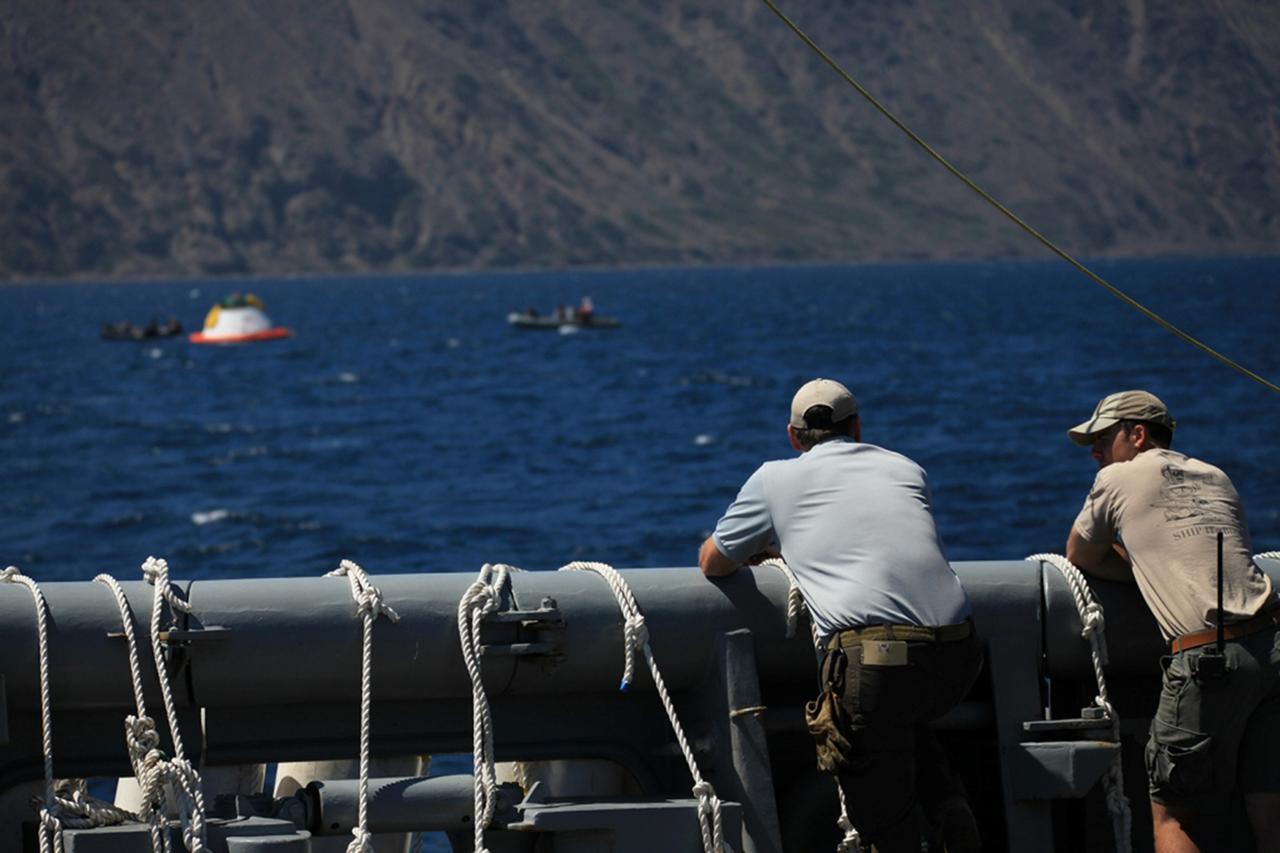
Recovery team members watch Orion Underway Recovery Test 5 activities on the flight deck of the USS San Diego in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program and the U.S. Navy are practicing recovery techniques using the well deck of the ship and a test version of the Orion crew module to prepare for recovery of Orion on its return from deep space missions. The testing will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and NASA's Journey to Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion is scheduled to launch on NASA's Space Launch System in late 2018. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion.
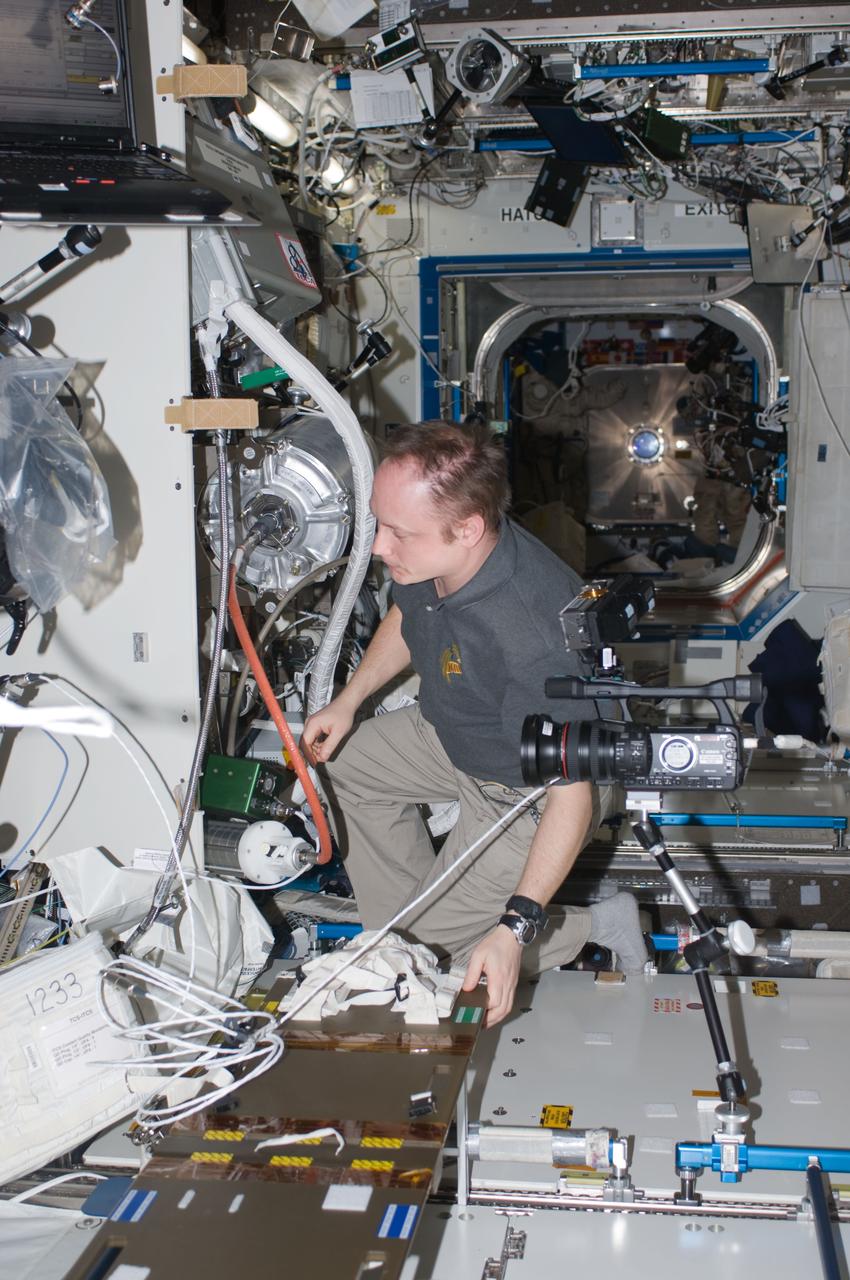

ISS018-E-019723 (9 Jan. 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Fincke, Expedition 18 commander, works on hardware in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
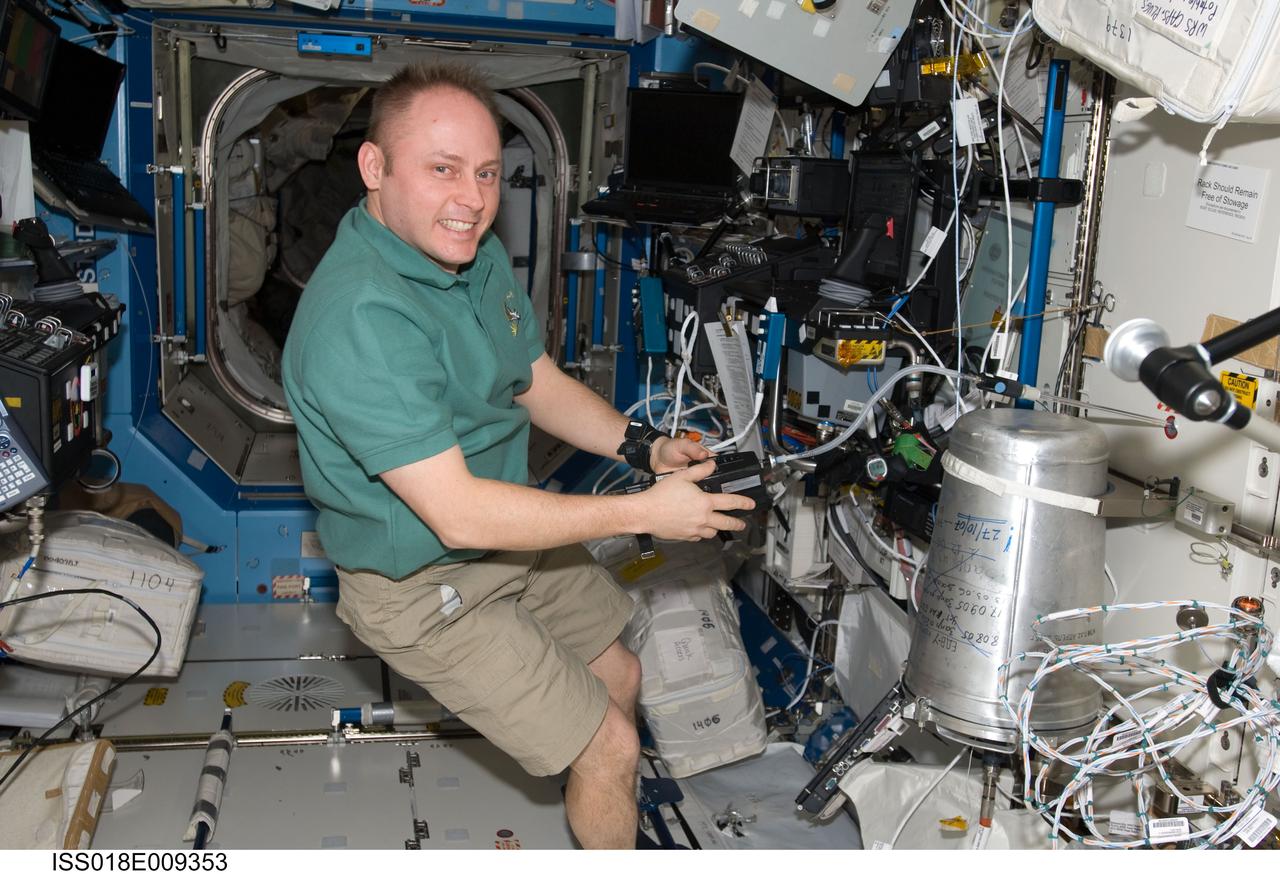

ISS018-E-009353 (20 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Michael Fincke, Expedition 18 commander, works in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-126) remains docked with the station.
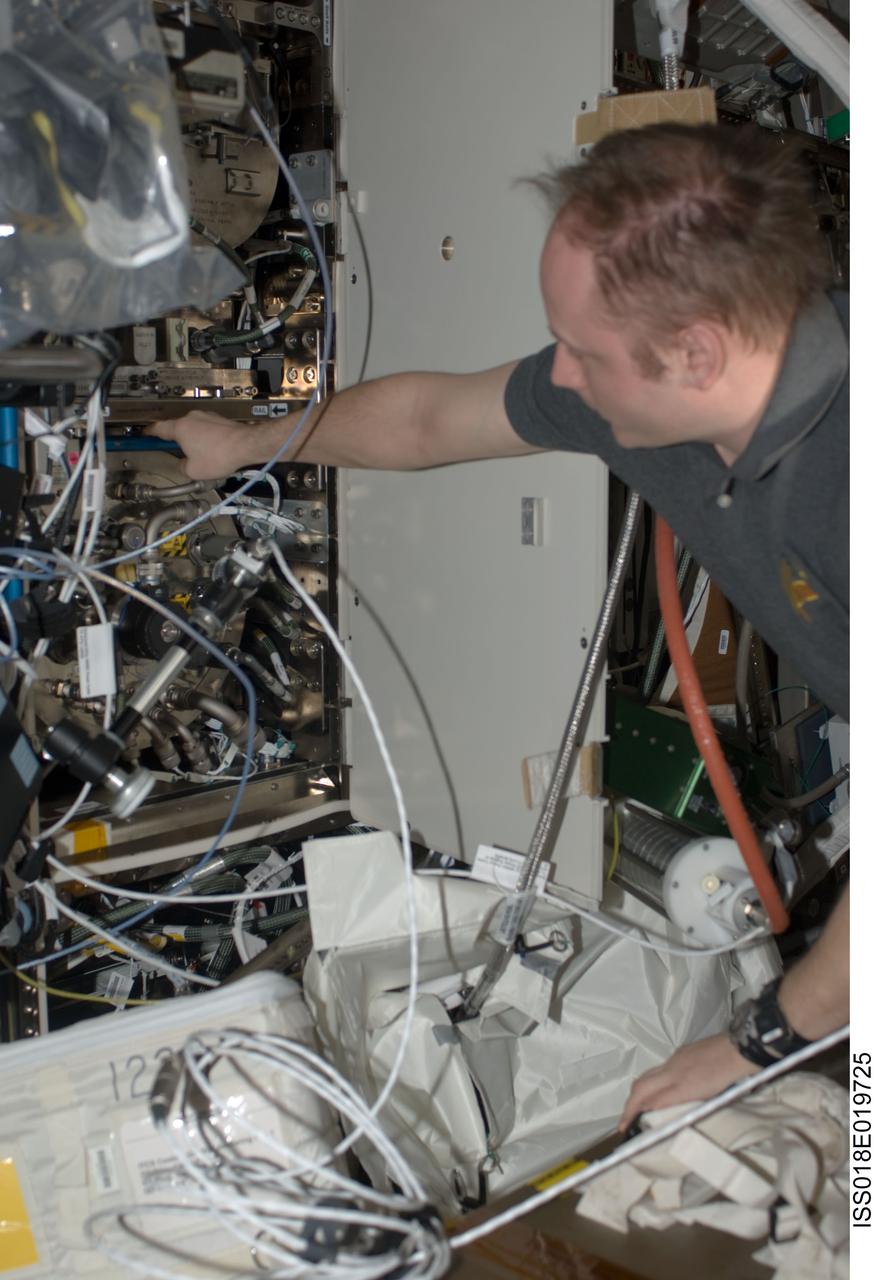

ISS018-E-019725 (9 Jan. 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Fincke, Expedition 18 commander, works on hardware in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
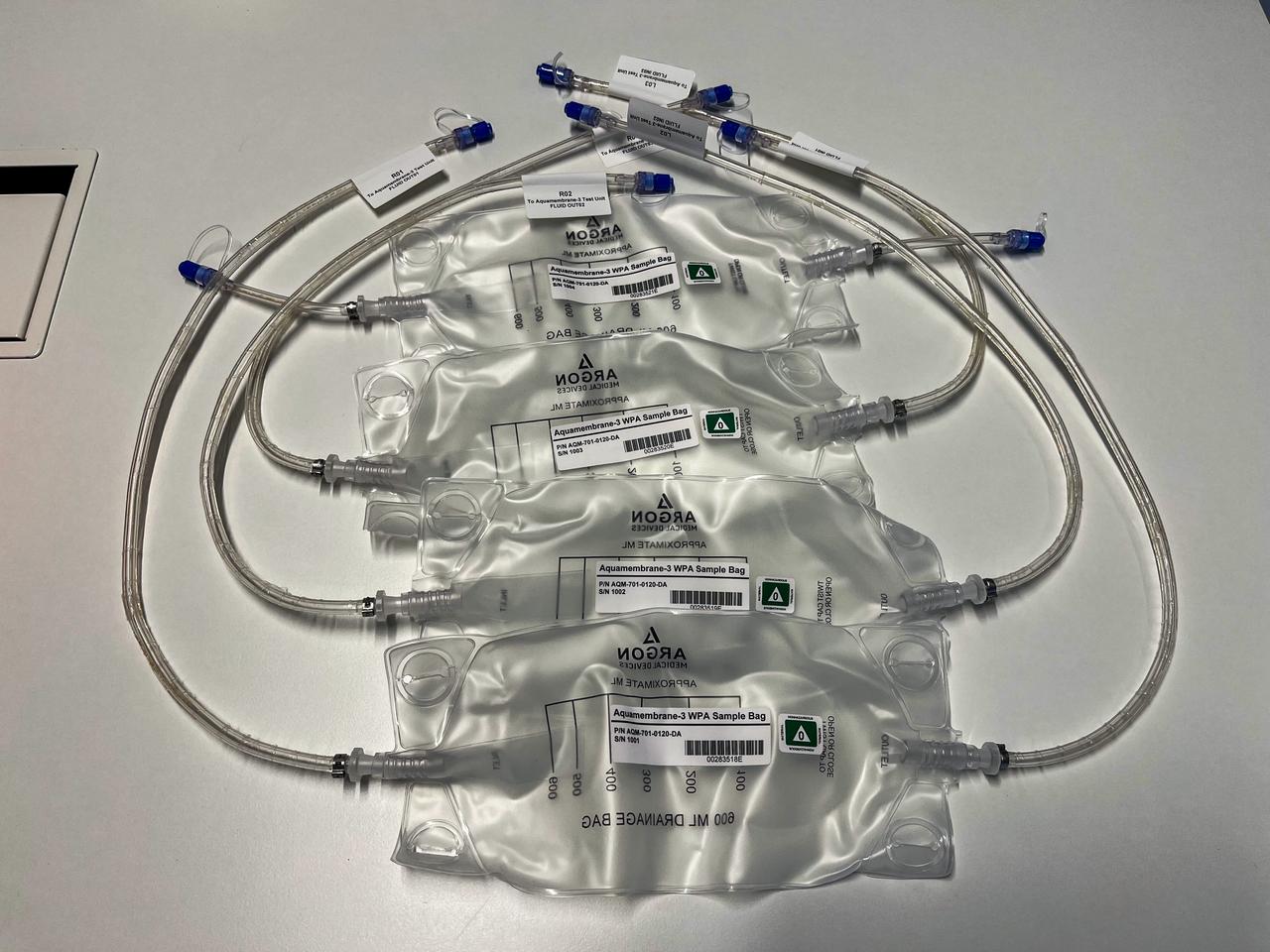
jsc2023e055874 (10/5/2023) --- The Testing Contaminant Rejection of Aquaporin Inside® HFFO Module (Aquamembrane-3) hardware consists of three separate and parallel systems to quantify the membrane's water flux and contamination rejection in microgravity, which are key parameters for a full water recovery system. This image shows the bags in which samples of the ISS WPA are collected for the experiment.
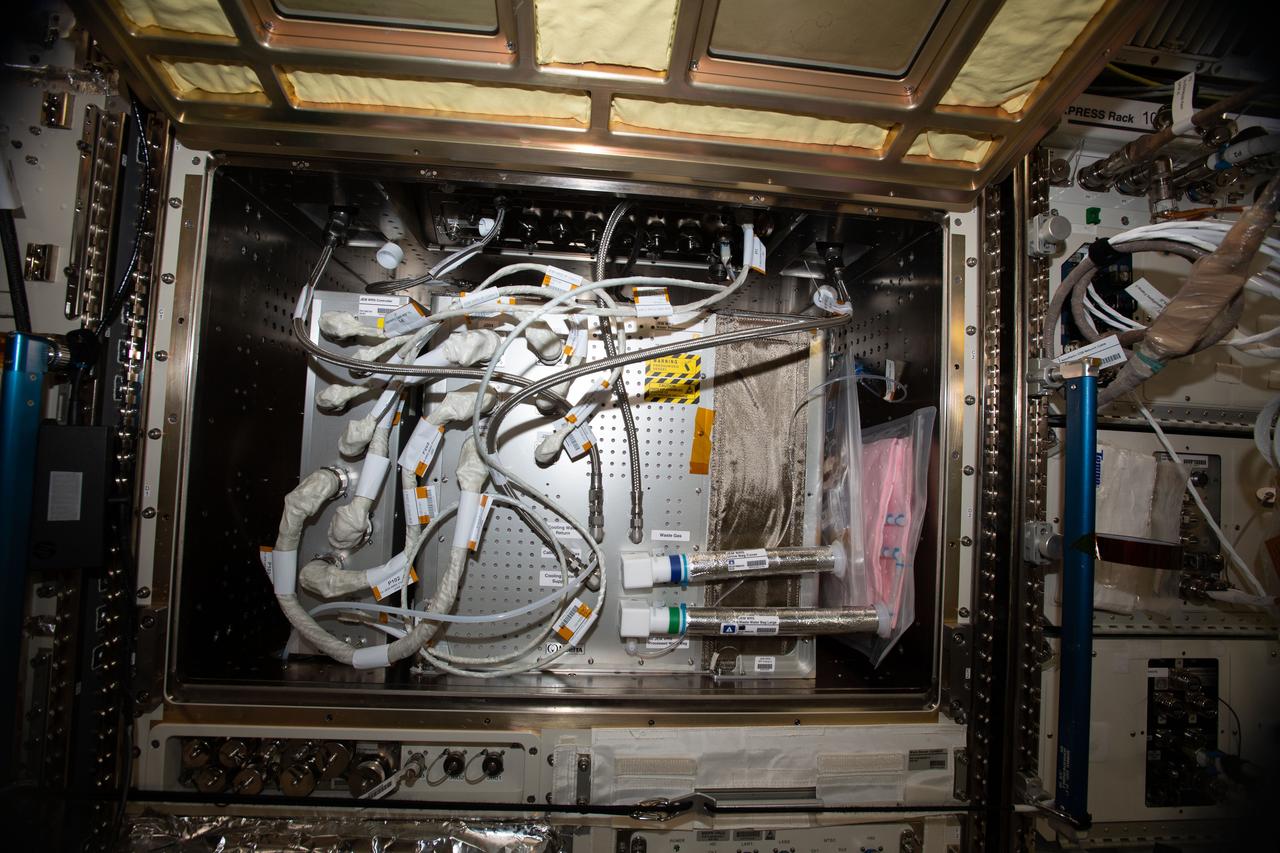

iss061e050296 (11/19/2019) --- A view of the JEM Water Recovery system (JWRS) installed the the Multi-Purpose Small Payload Rack located the the Kibo module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The JWRS contributes to the development of future Life Support Systems to provide basic needs for astronauts on the space station and exploration missions beyond Earth. The technology in the JWRS has potential applications to improve access to potable water in remote and undeveloped locations on Earth.
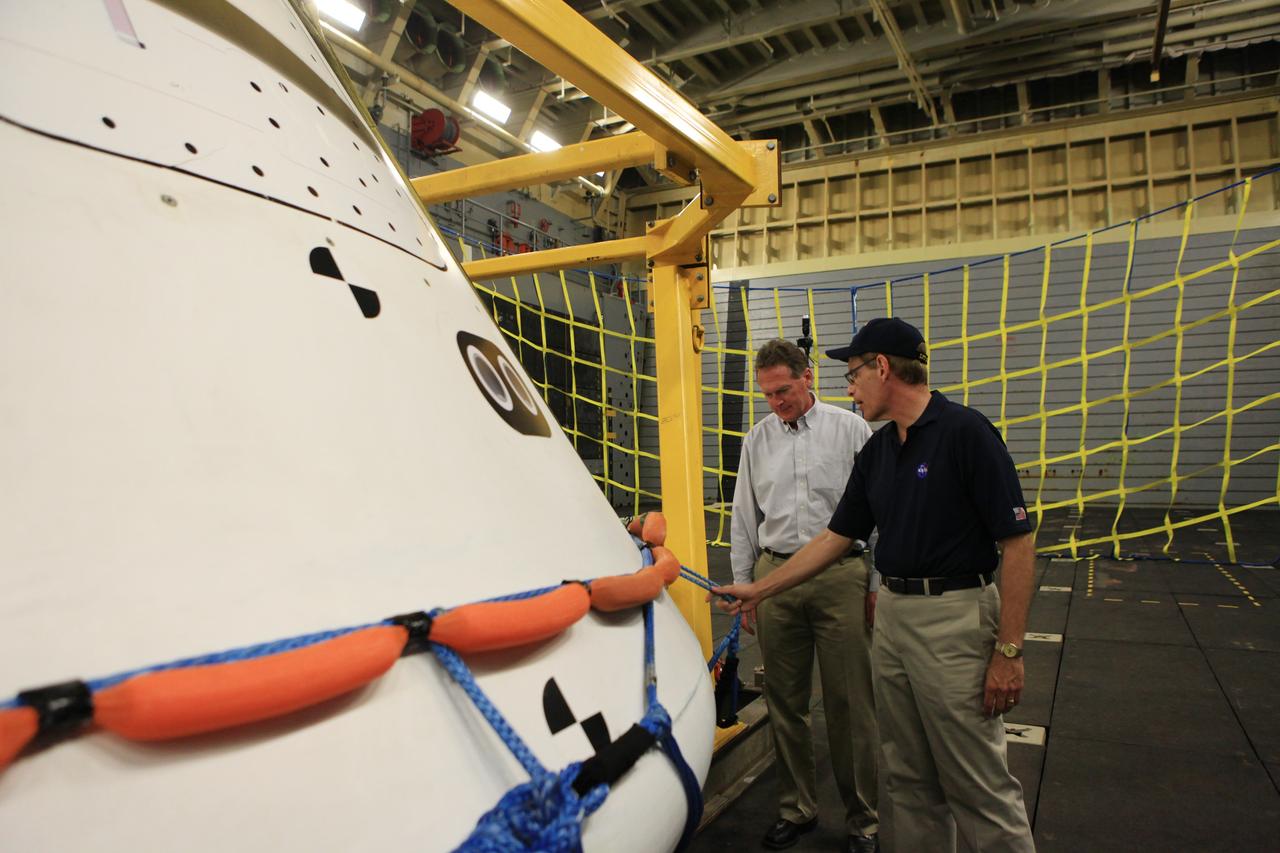

LOS ANGELES, Calif. – Mike Bolger, Ground Systems Development and Operations Program manager, at left, and Mike Generale, Orion Recovery Operations manager and Recovery Test director, both from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, talk about Underway Recovery Test 2 in the well deck of the USS Anchorage. The U.S. Navy ship is in Los Angeles for LA Navy Days. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy completed the recovery test in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test allowed the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
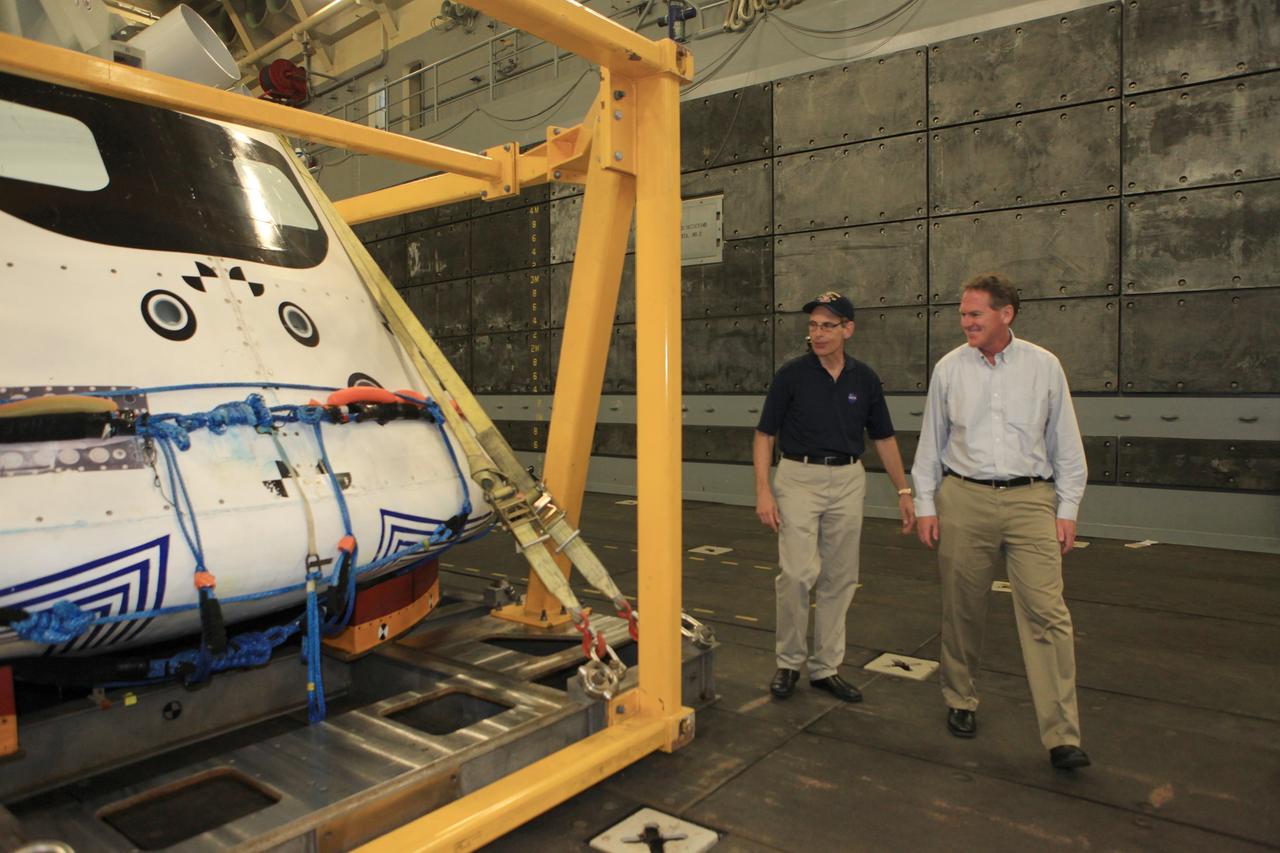

LOS ANGELES, Calif. – Mike Bolger, Ground Systems Development and Operations Program manager, at right, and Mike Generale, Orion Recovery Operations manager and Recovery Test director, both from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, view the Orion boilerplate test vehicle in its recovery cradle in the well deck of the USS Anchorage. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy completed the Orion recovery test in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test allowed the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The U.S. Navy ship is in Los Angeles for LA Navy Days. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
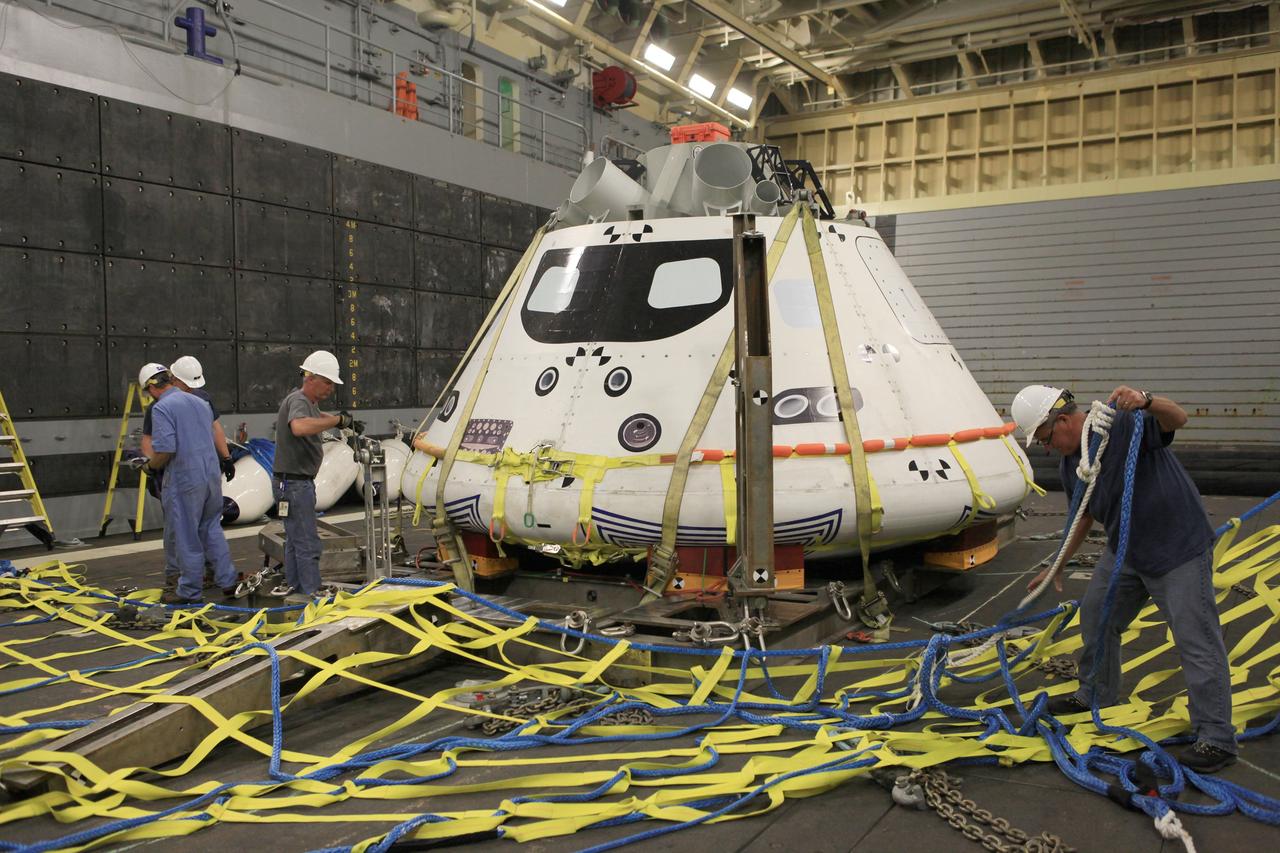

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured on its cradle in the well deck of the U.S. Navy's USS Anchorage in preparation for Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. Workers are installing a safety barrier near the test vehicle to keep it from going further into the well deck as it fills with water. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy will conduct the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
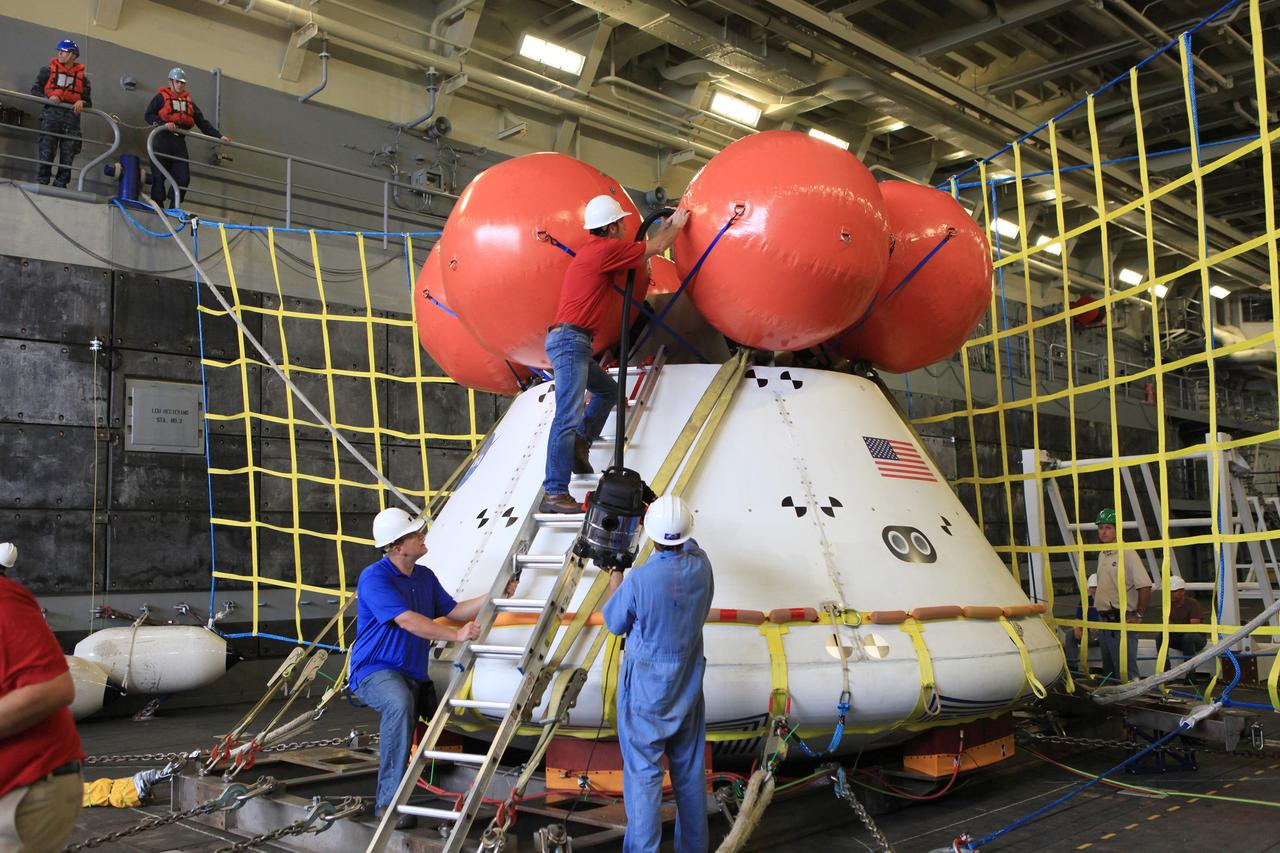

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the well deck of the U.S. Navy's USS Anchorage, the Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured on its cradle before the start of a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2. Tether lines have been attached to the test vehicle and workers check the pressure of the bright orange stabilizers that will keep Orion upright in the water if needed. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
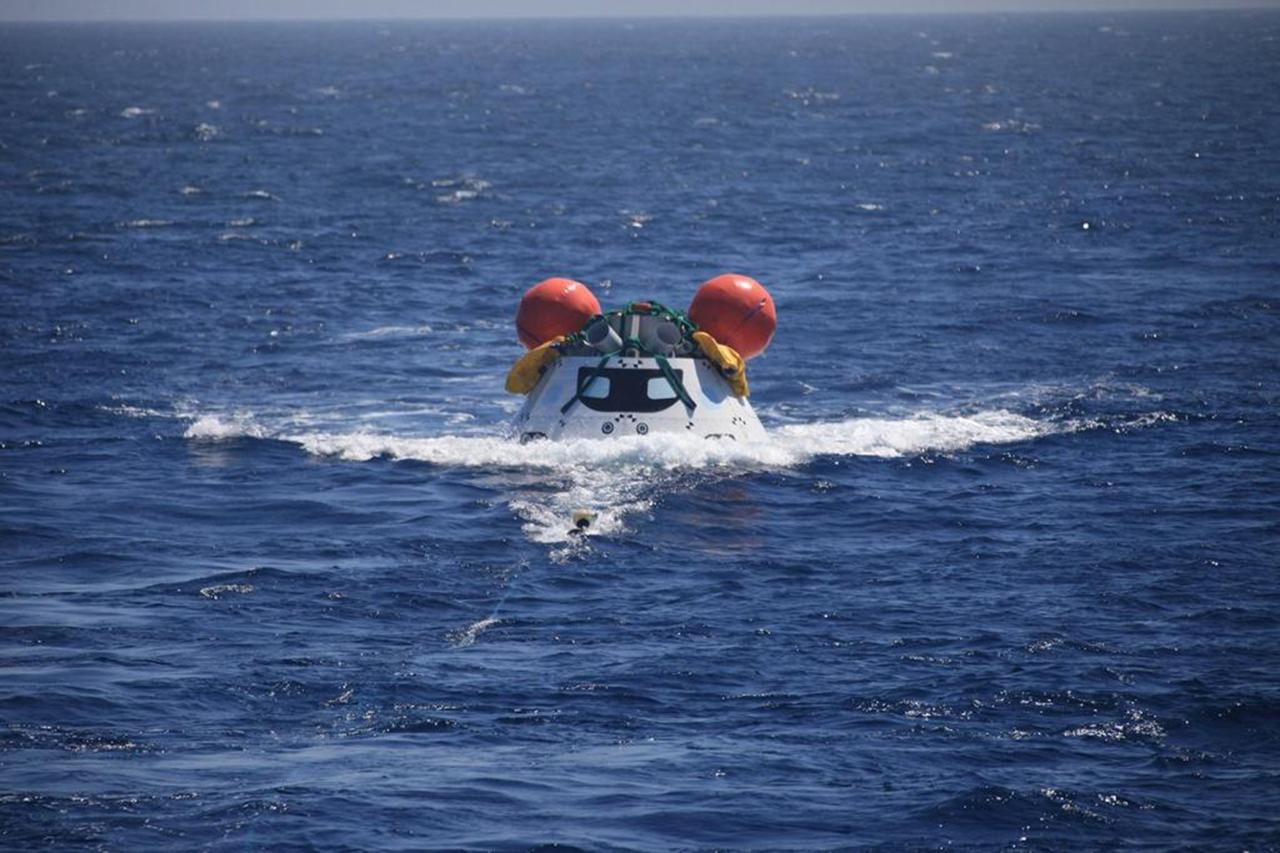

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during the third day of Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, using a stationary crane. Tether lines were attached to the test vehicle from the ship for a towing test. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
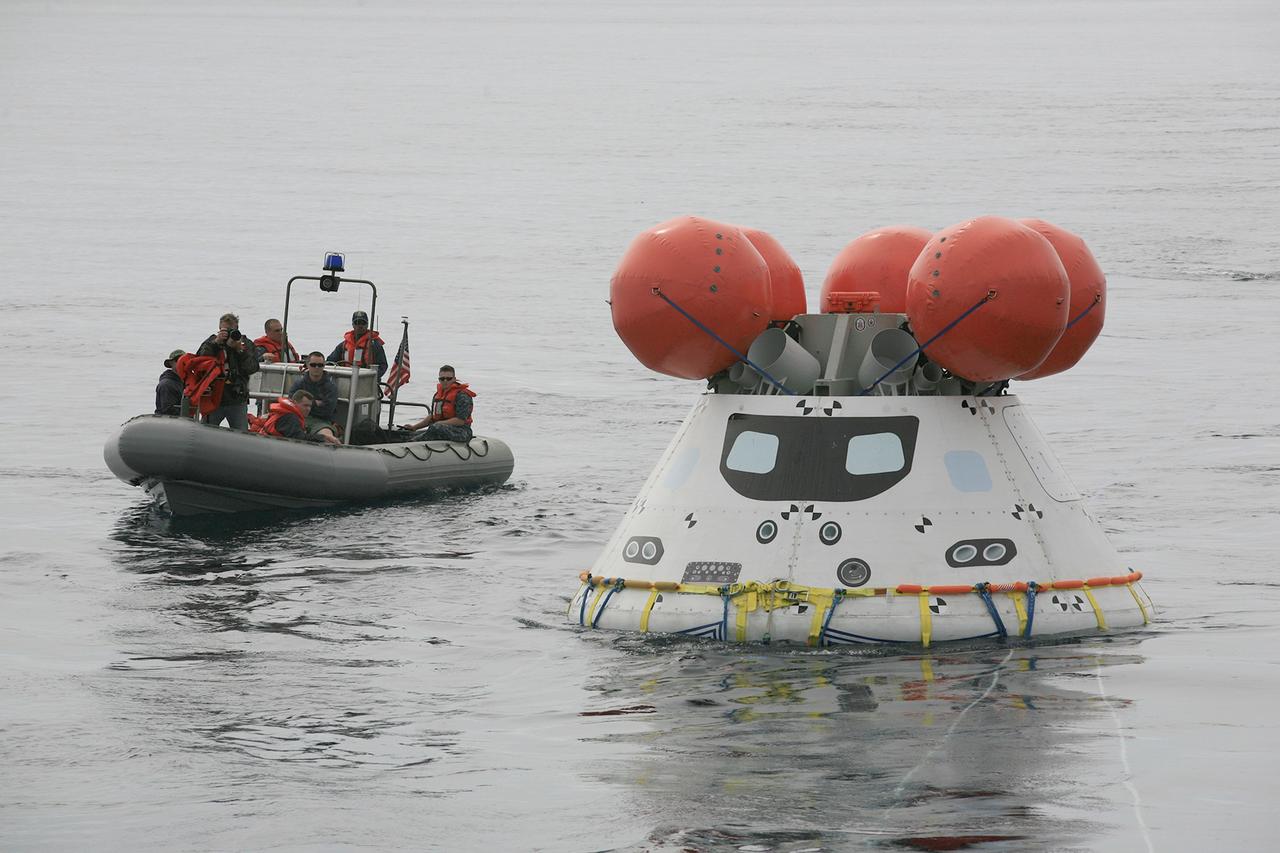

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – U.S. Navy personnel use a rigid hull inflatable boat to approach the Orion boilerplate test article during an evolution of the Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. During the test, the vehicle was released from the well deck of the USS Anchorage and allowed to float freely in the water. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
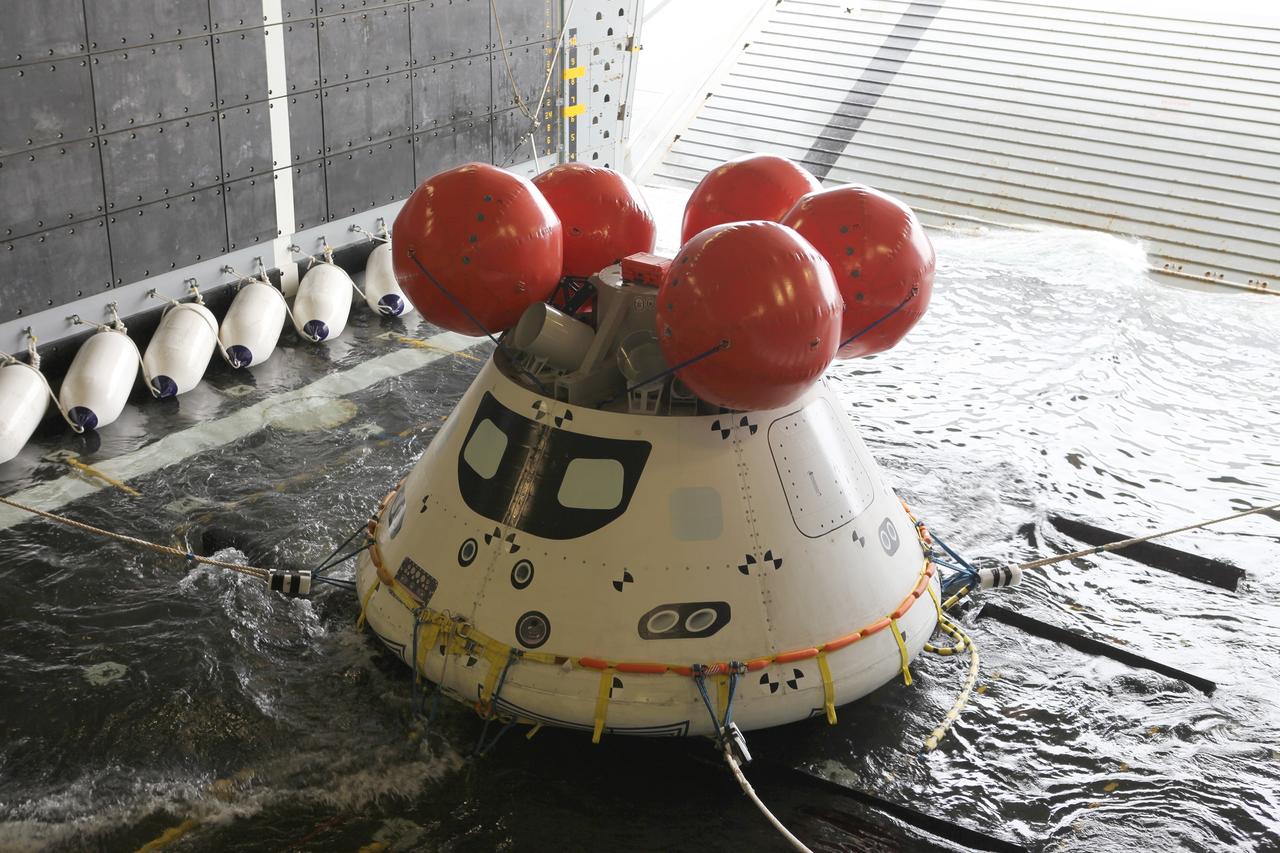

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Water fills the well deck of the U.S. Navy’s USS Anchorage around the Orion boilerplate test vehicle in preparation for a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. The test vehicle has been moved from its cradle onto a set of rubber shock absorbers. Testing of the tether lines attached to Orion is underway. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
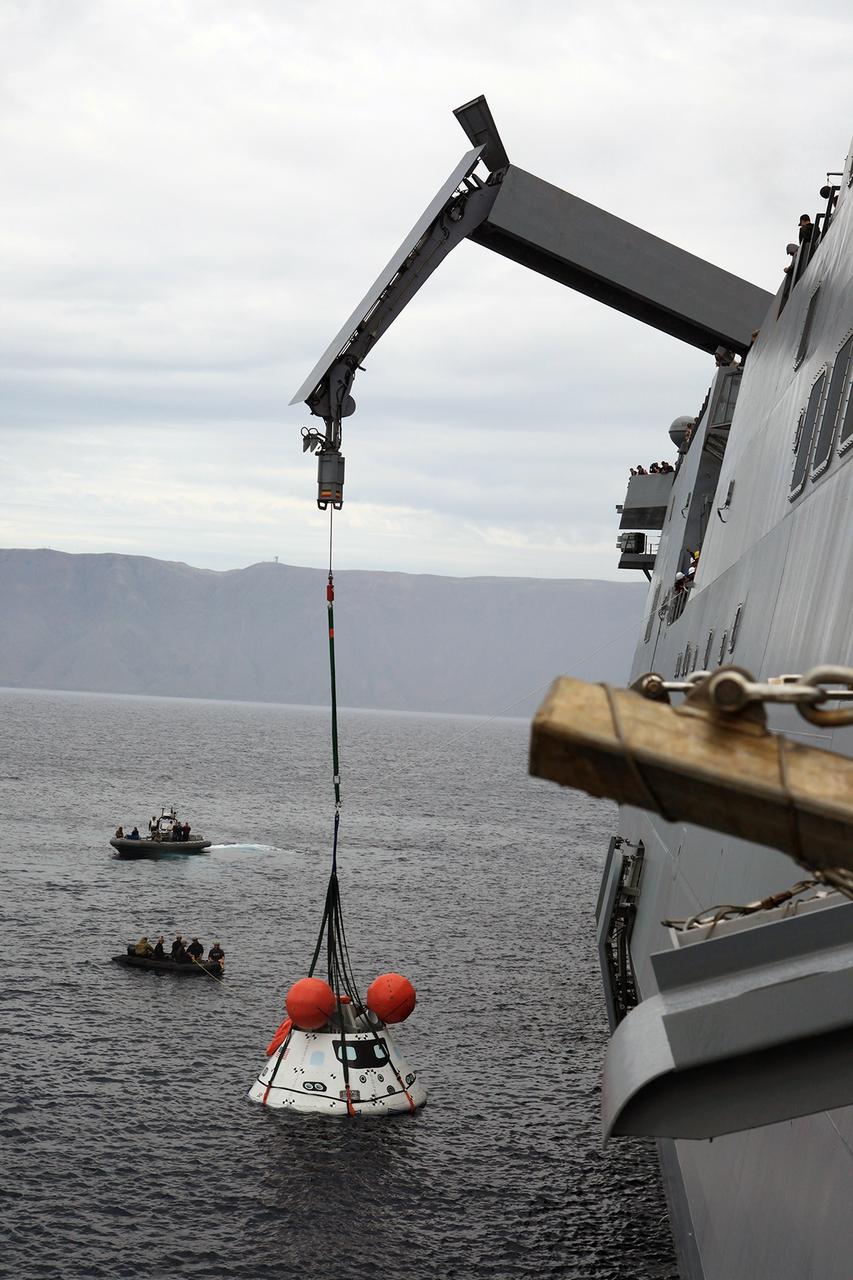

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is slightly lifted by crane from the water to test the proof of concept basket lift method during an evolution of the Underway Recovery Test 2 near the USS Anchorage in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. U.S. Navy personnel are nearby in two rigid hull inflatable boats. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
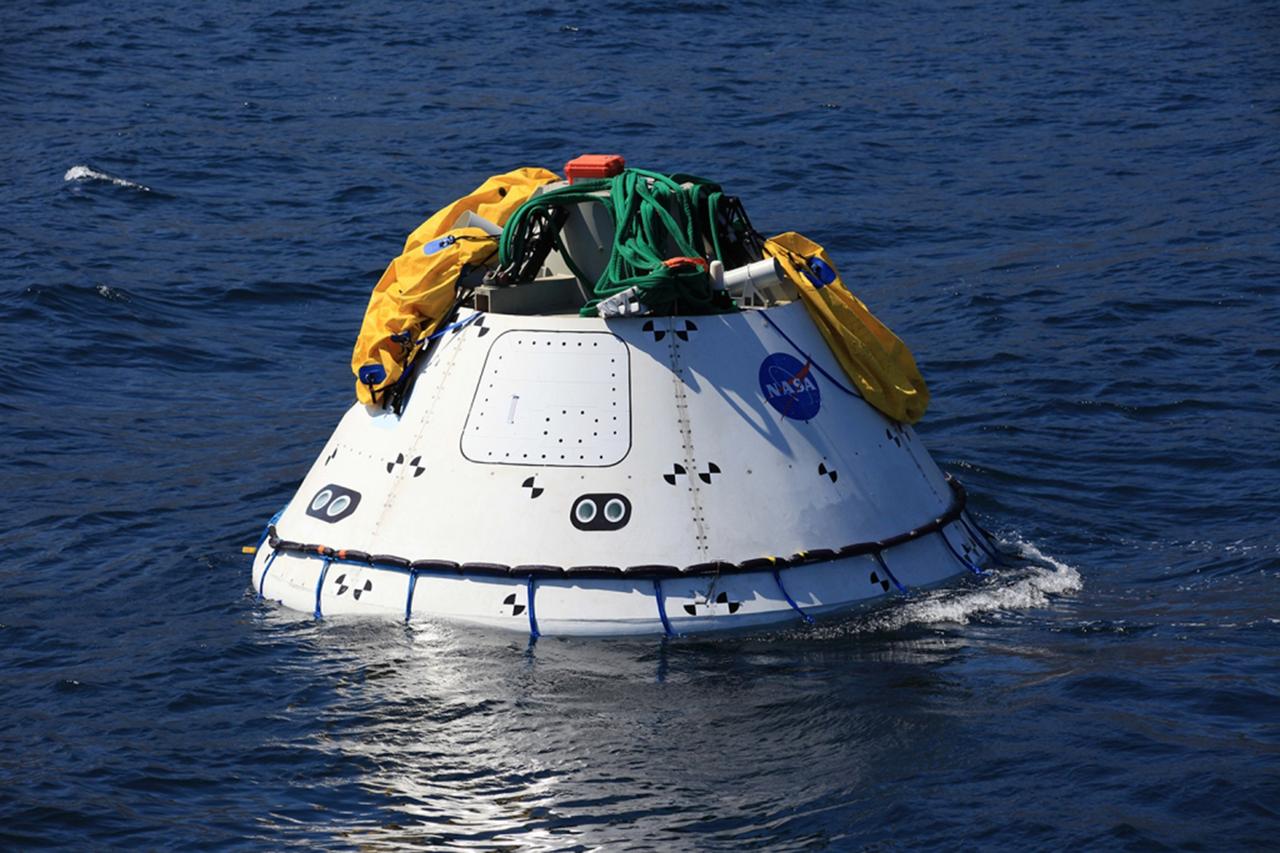

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle floats in the Pacific Ocean during Underway Recovery Test 4A. Orion was lowered into the water with a stationary crane from the USS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
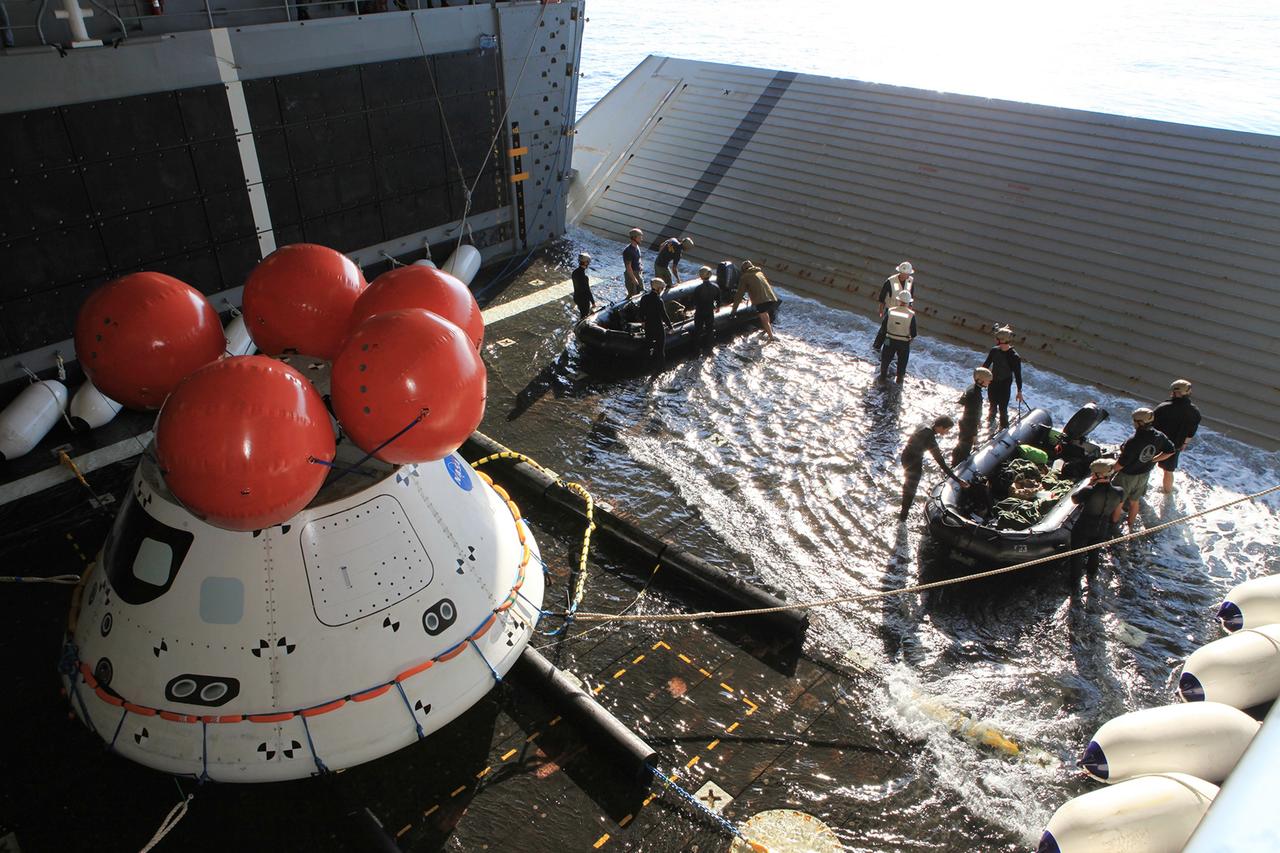

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – U.S. Navy personnel get ready to board two rigid hull inflatable boats in the well deck of the USS Anchorage to prepare for an evolution of the Orion Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. Nearby, tending lines have been attached to the Orion boilerplate test vehicle as the well deck fills with water. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
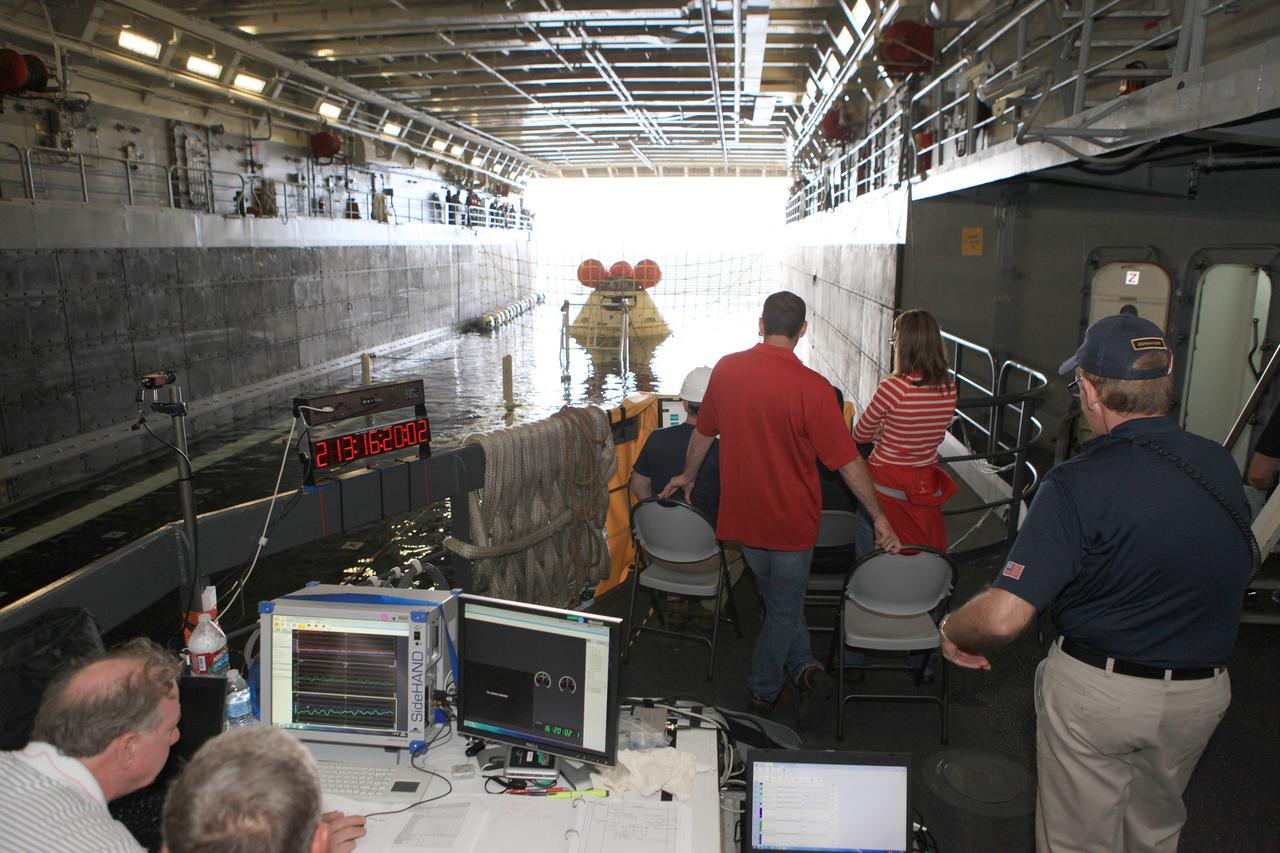

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the U.S. Navy’s USS Anchorage, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel watch as the well deck fills with water around the Orion boilerplate test vehicle in preparation for a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. Tether lines are attached to the test vehicle to control it and a safety barrier has been installed to prevent Orion from going further into the well deck. The test will help the team prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the U.S. Navy’s USS Anchorage, the well deck has filled with water around the Orion boilerplate test vehicle in preparation for a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. Tether lines are attached to the test vehicle to control it and a safety barrier has been installed to prevent Orion from going further in the well deck. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy will conduct the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A mock-up of the Orion forward bay cover is being lowered by crane from the USS Anchorage into the water during the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and mock-up forward bay cover to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
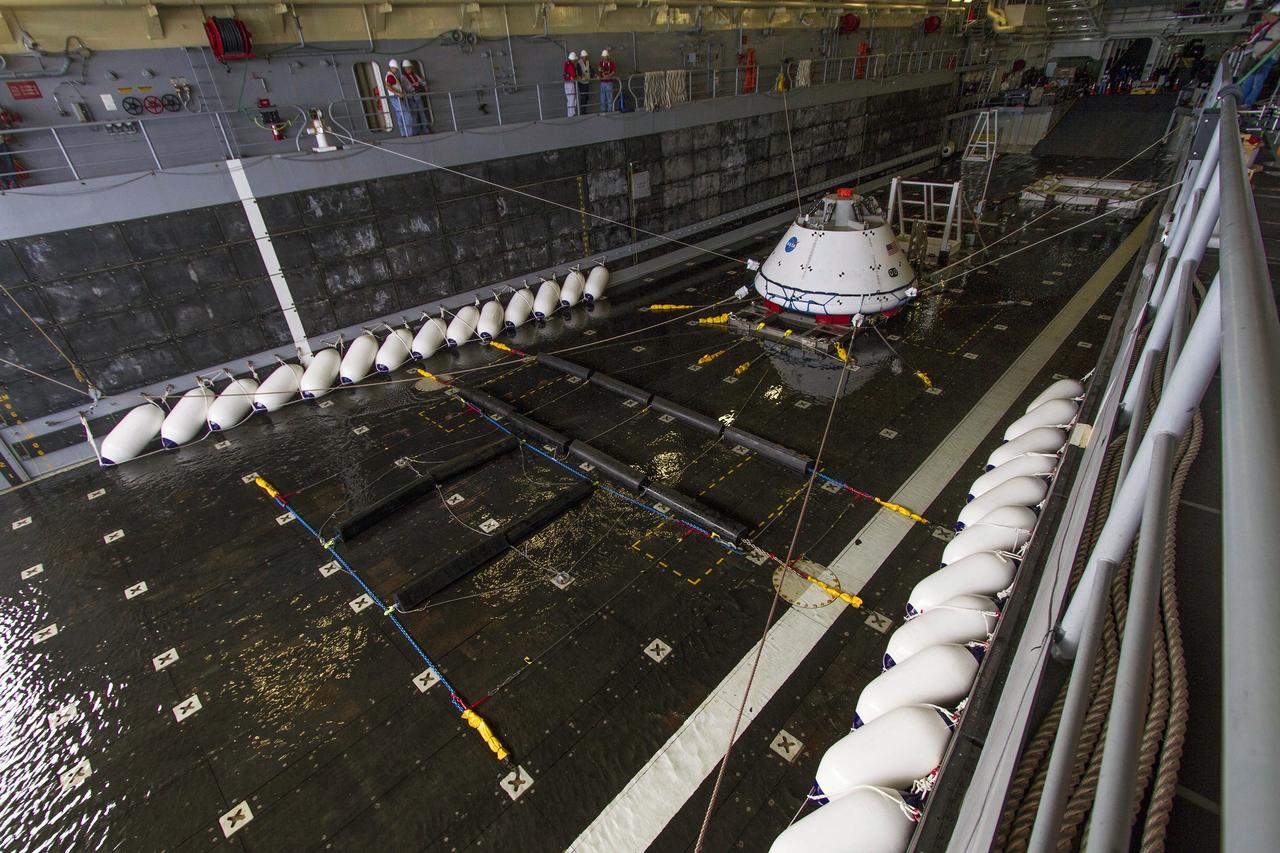

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is tethered in the water-filled well deck of the USS Anchorage during the Underway Recovery Test 3 mission simulation day in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the test vehicle to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
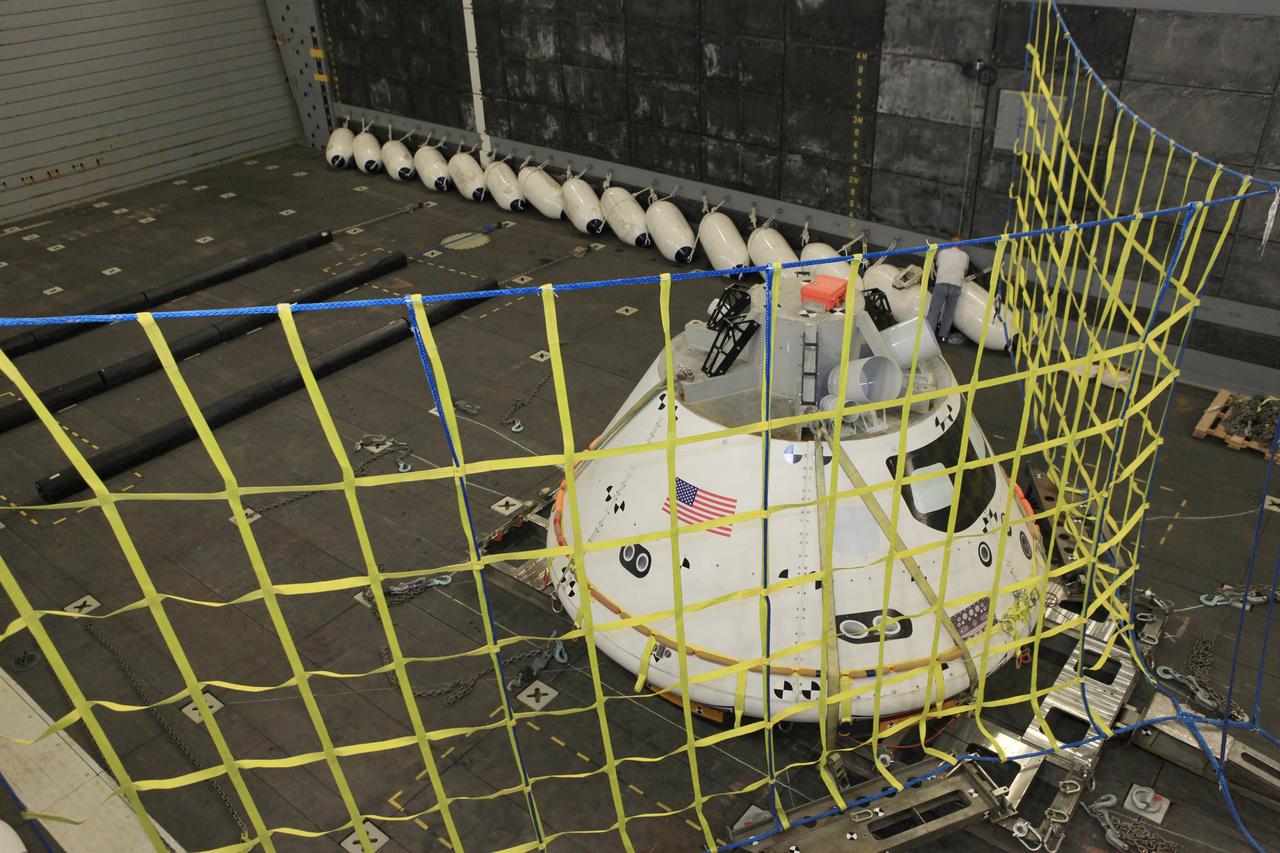

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured on its cradle in the well deck of the U.S. Navy's USS Anchorage in preparation for Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. A safety barrier has been installed near the test vehicle to keep it from going further into the well deck as it fills with water. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy will conduct the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
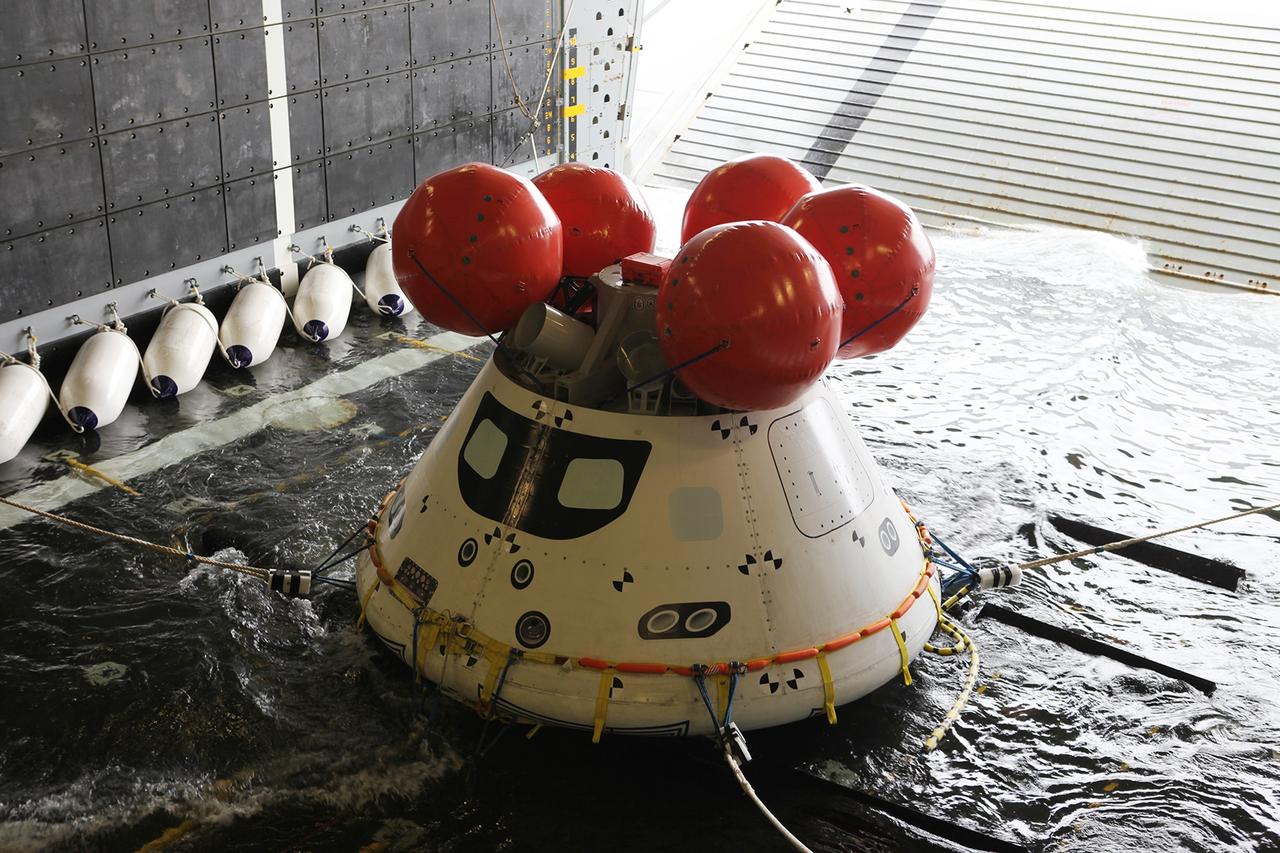

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the well deck of the U.S. Navy's USS Anchorage, the Orion boilerplate test vehicle rests on its cradle as water fills around before the start of an evolution for the Underway Recovery Test 2. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
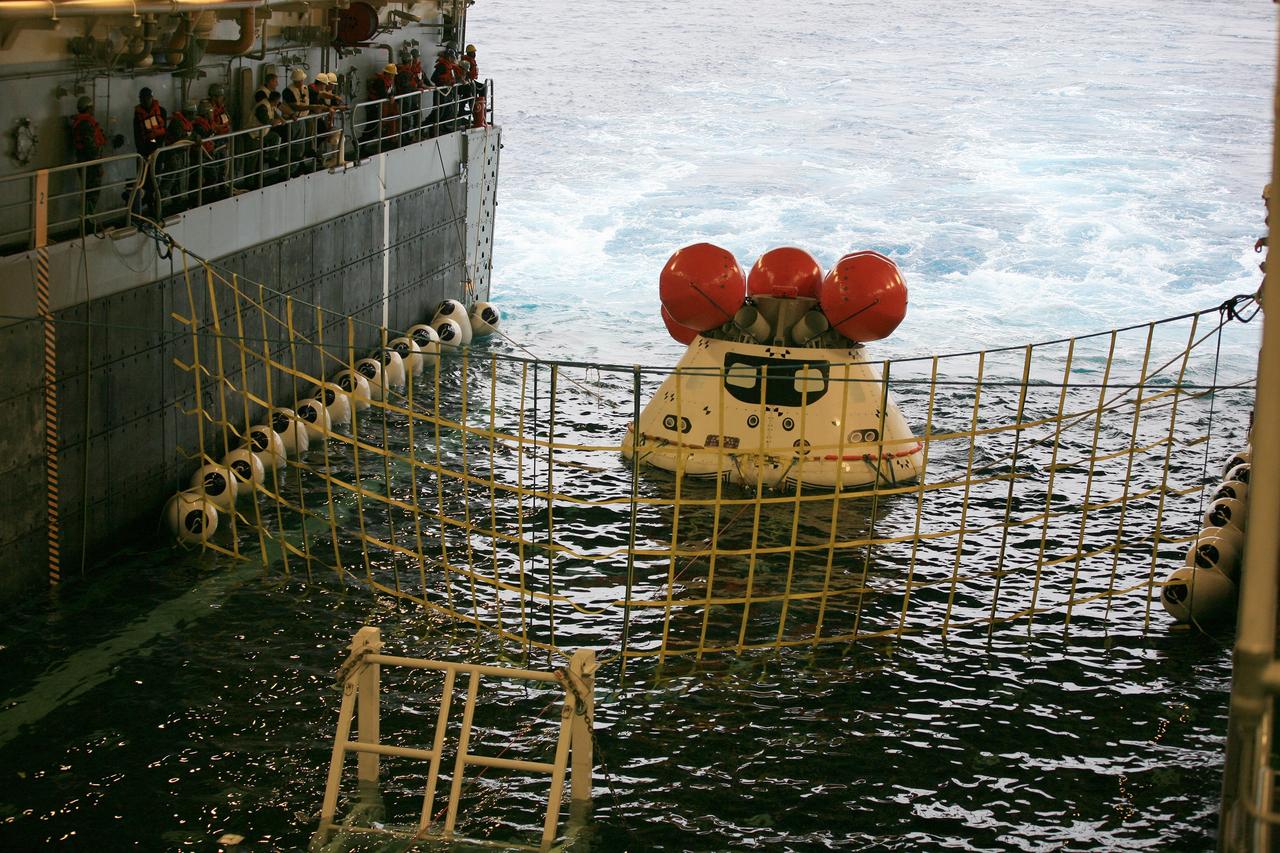

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the U.S. Navy’s USS Anchorage, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel watch as the well deck fills with water around the Orion boilerplate test vehicle during a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. Tether lines are attached to the test vehicle and a safety barrier has been installed to prevent Orion from going further into the well deck. The test will help the team to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the well deck of the U.S. Navy's USS Anchorage, the Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured on its cradle before the start of a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2. A winch line leads to the test vehicle and tether lines have been attached to control Orion. The bright orange stabilizers have been readied to keep Orion upright in the water if needed. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel monitor the Orion boilerplate test vehicle as the well deck of the USS Anchorage fills with water during a portion of the Orion Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. The testing is being conducted to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep-space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep-space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A rigid hull inflatable boat, with U.S. Navy personnel aboard, is being lowered into the water from the USS Anchorage on the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting recovery tests using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
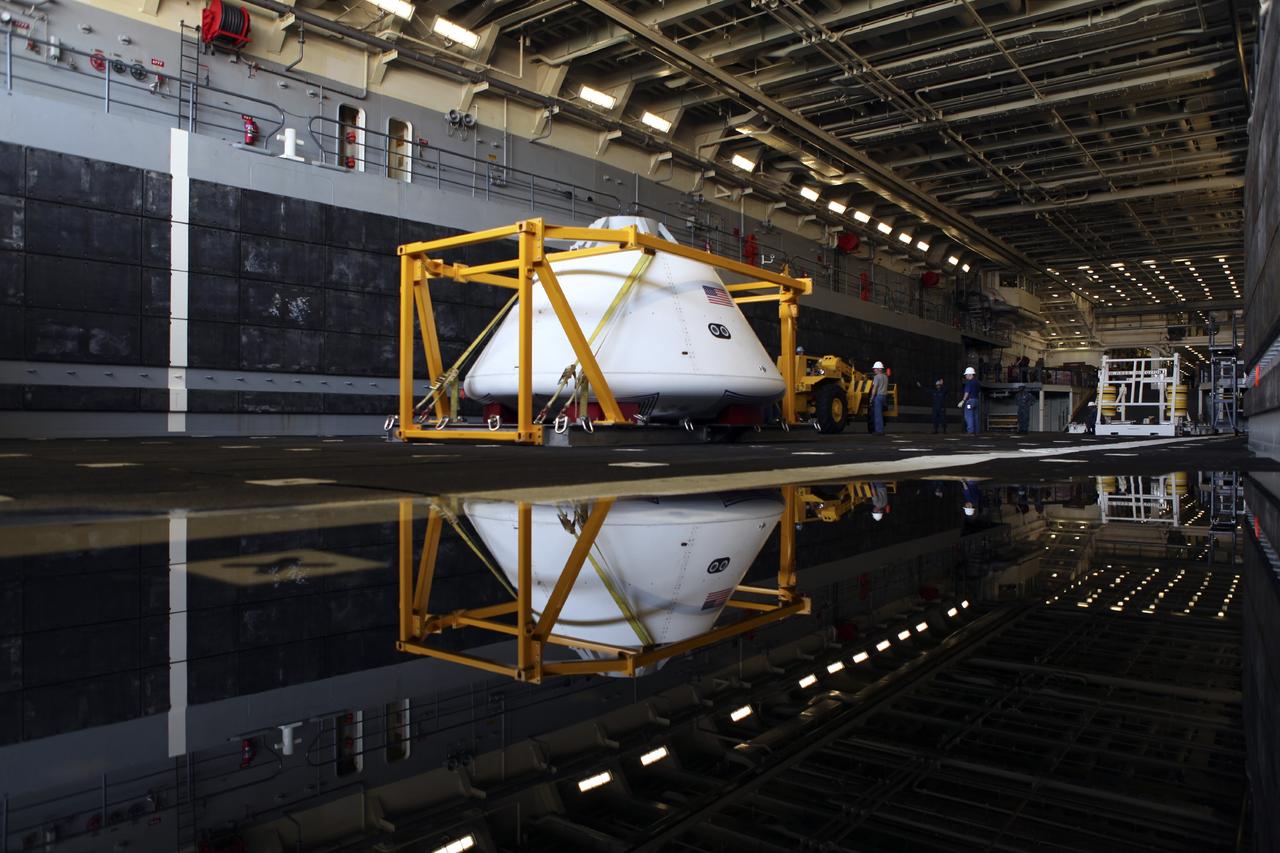

HAMPTON, Va. – At the Naval Station Norfolk near NASA’s Langley Research Center in Virginia, the Orion boilerplate test article is reflected in water on a U.S. Navy ship. The test article and support equipment for a stationary recovery test were transferred to the ship from a floating dock system. NASA and the U.S. Navy are conducting tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module and forward bay cover on its return from a deep space mission. The stationary recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in a controlled environment before conducting a second recovery test next year in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Water fills the well deck of the U.S. Navy’s USS Anchorage around the Orion boilerplate test vehicle in preparation for a portion of Underway Recovery Test 2 in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego. The test vehicle has been moved from its cradle onto a set of rubber shock absorbers. Testing of the tether lines attached to Orion is underway. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Inside the well deck of the U.S. Navy's USS Anchorage, the Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured on its cradle before the start of a portion of the Underway Recovery Test 2. Workers check the pressure of the bright orange stabilizers that will keep Orion upright in the water if needed. NASA, Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy are conducting the test in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the team to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, new hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett