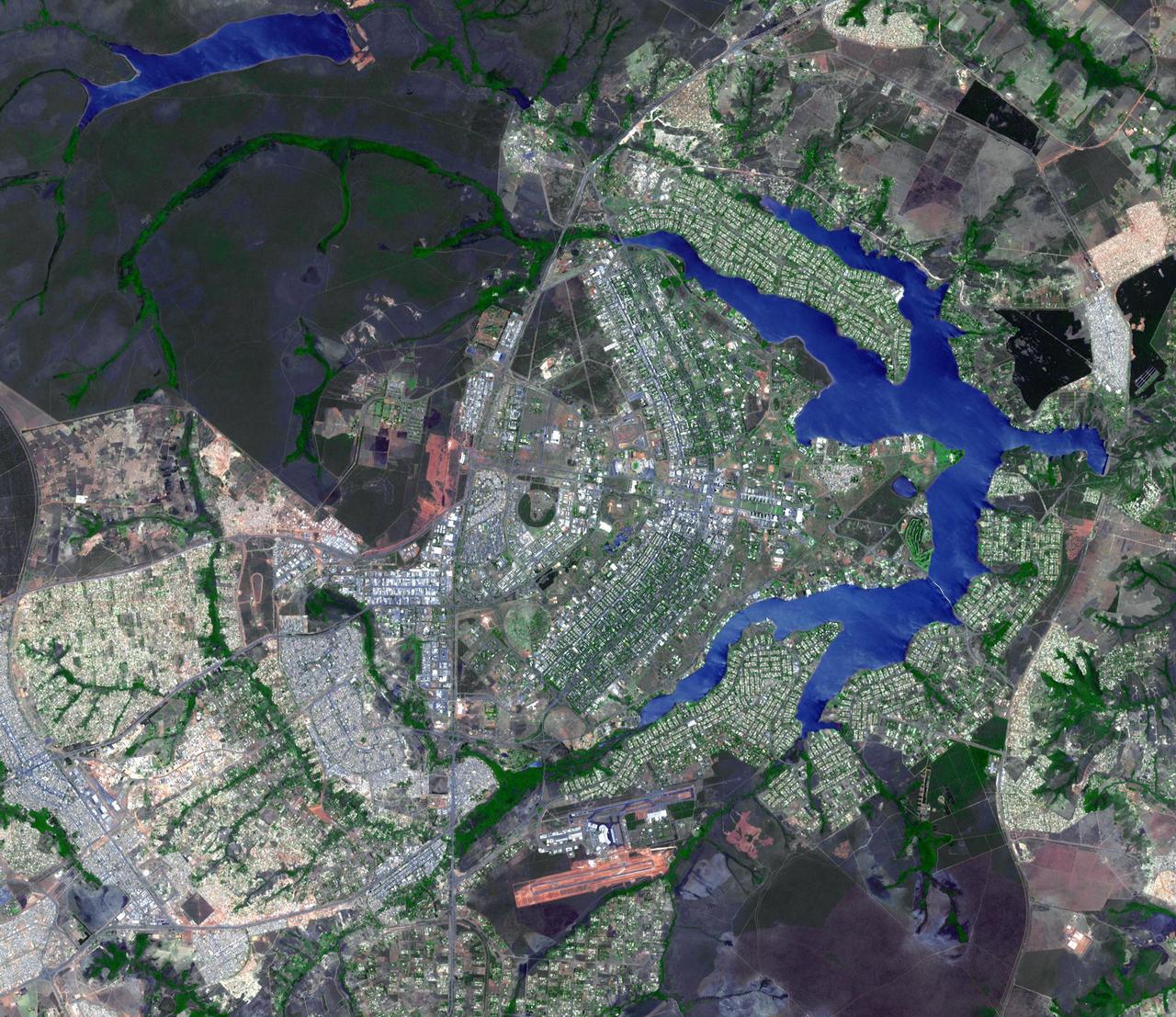

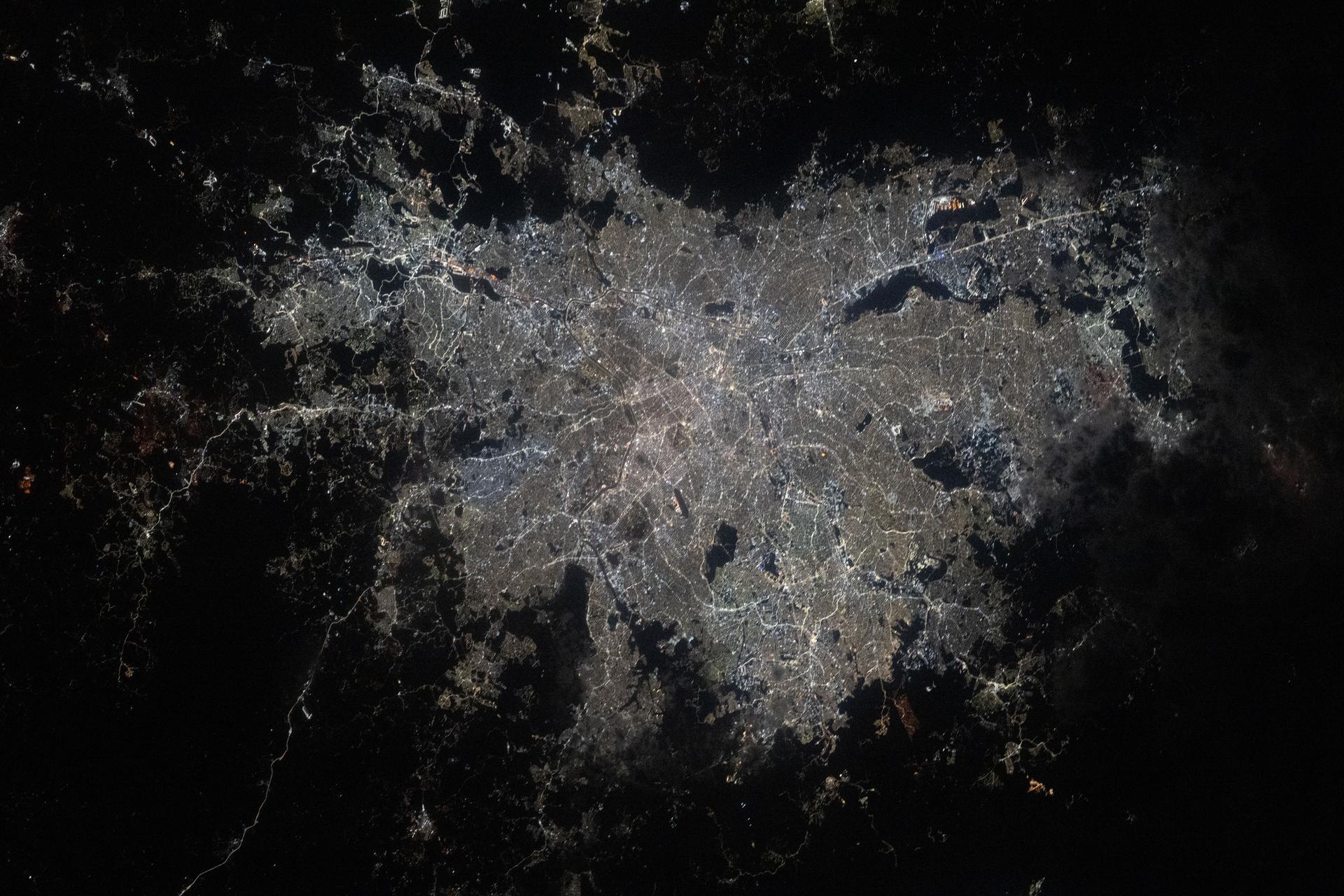
This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the planned city of Brasilia, the capital of Brazil, with a population of about 3.6 million for its metropolitan area.
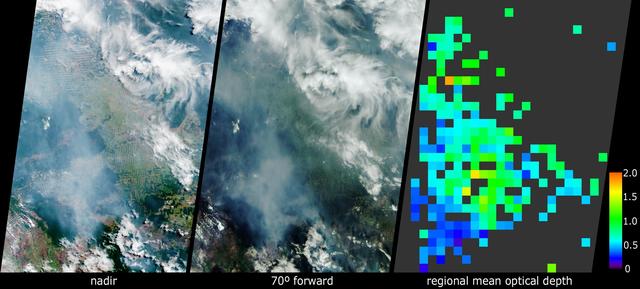
These images acquired in 2002 from NASA Terra satellite show smoke over Rondonia, Brazil.
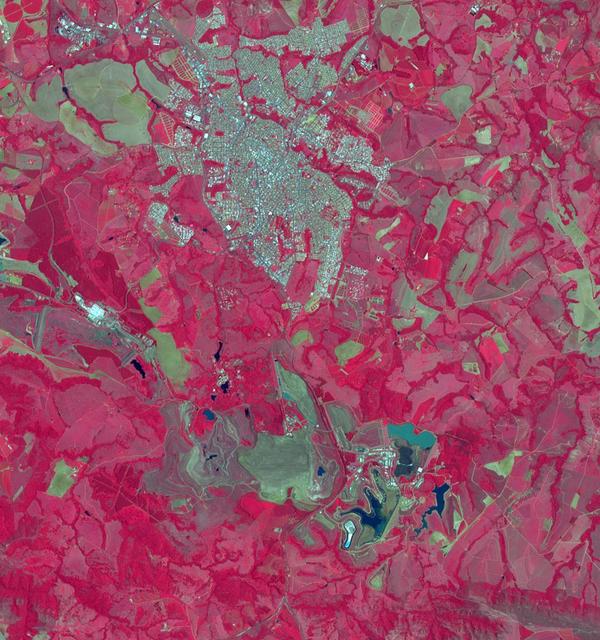

The Araxa mine in southern Brazil produces more than 80% of the world's Niobium. Niobium is used as an alloying agent in steels and in high-tech applications, such as electric car batteries. Brazil currently has 98% of commercial Niobium reserves in the world. The image was acquired November 5, 2023, covers an area of 16 by 17.1 km, and is located at 19.7 degrees south, 46.9 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26395

This view of deforestation in Rondonia, far western Brazil, (10.0S, 63.0W) is part of an agricultural resettlement project which ultimately covers an area about 80% the size of France. The patterns of deforestation in this part of the Amazon River Basin are usually aligned adjacent to highways, secondary roads, and streams for ease of access and transportation. Compare this view with the earlier 51G-37-062 for a comparison of deforestation in the region.

This topographic image acquired in February 2000 by NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM shows an area in the state of Bahia in Brazil.
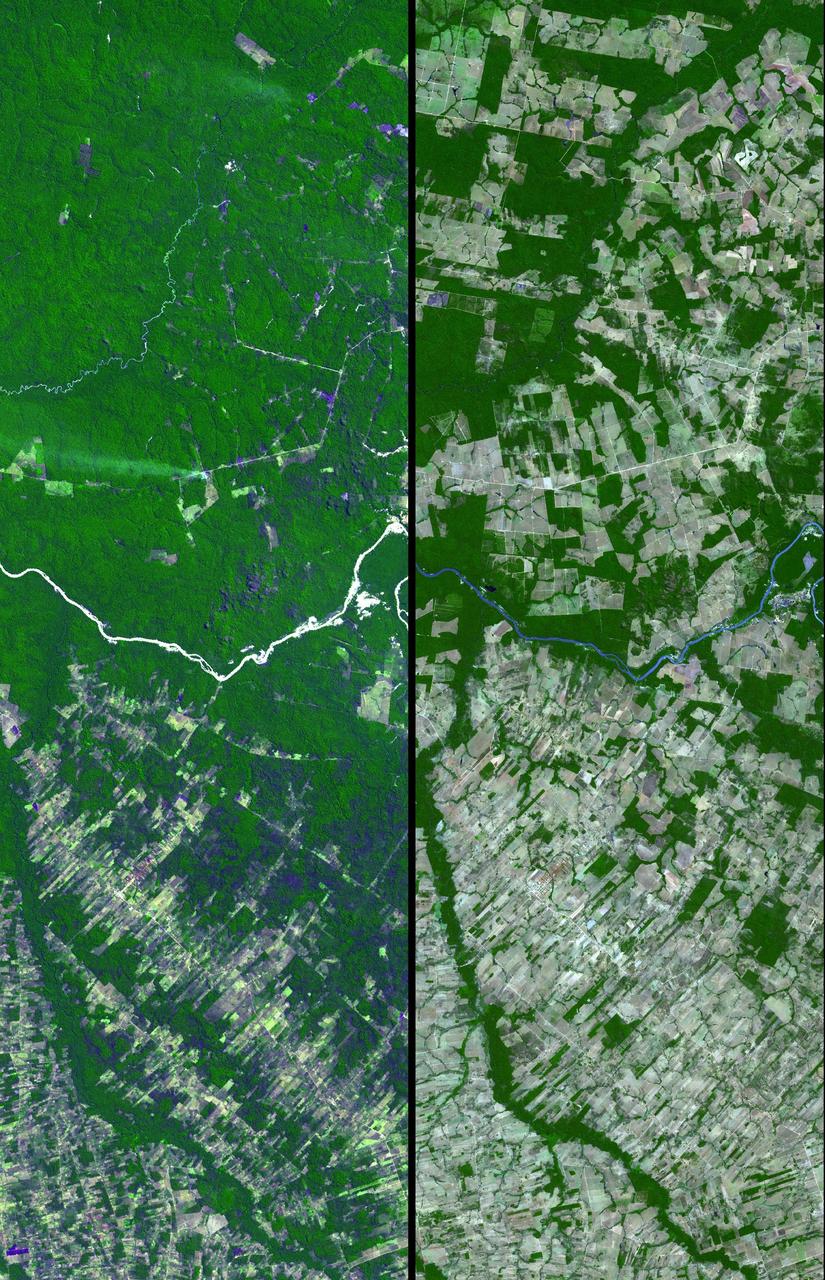
Dense green vegetation gives way to pale fields in these satellite images of deforestation in Brazil Amazon rainforest. This image is from NASA Terra satellite.
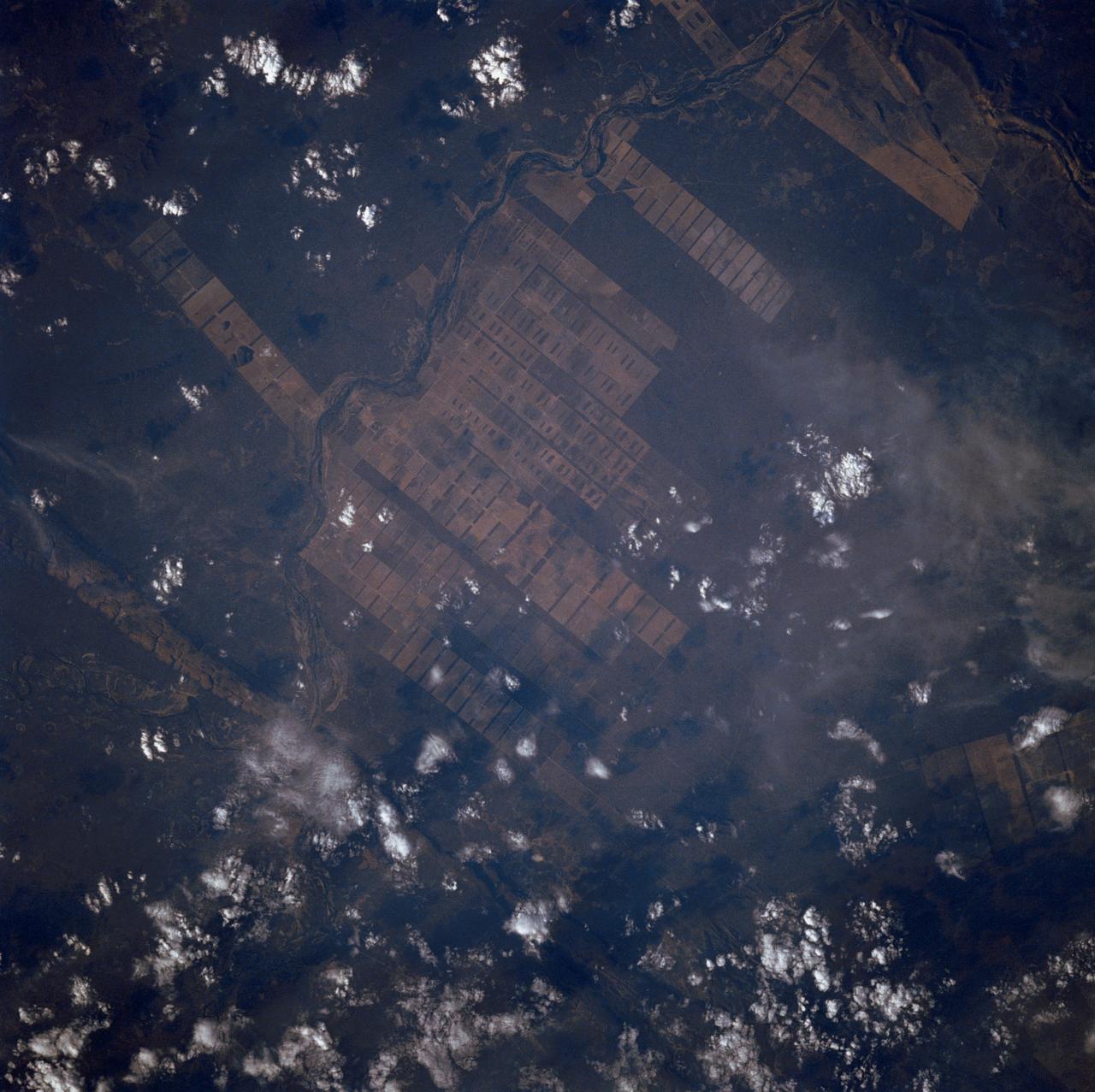

The large field patterns in this view of the Rio Sao Francisco basin, Brazil, South America, (11.5S, 43.5W) indicate a commercial agriculture venture; family subsistence farms are much smaller and laid out in different patterns. Land clearing in Brazil has increased at an alarming rate in recent years and preliminary estimates suggest a 25 to 30% increase in deforestation since 1984. The long term impact on the ecological processes are still unknown.
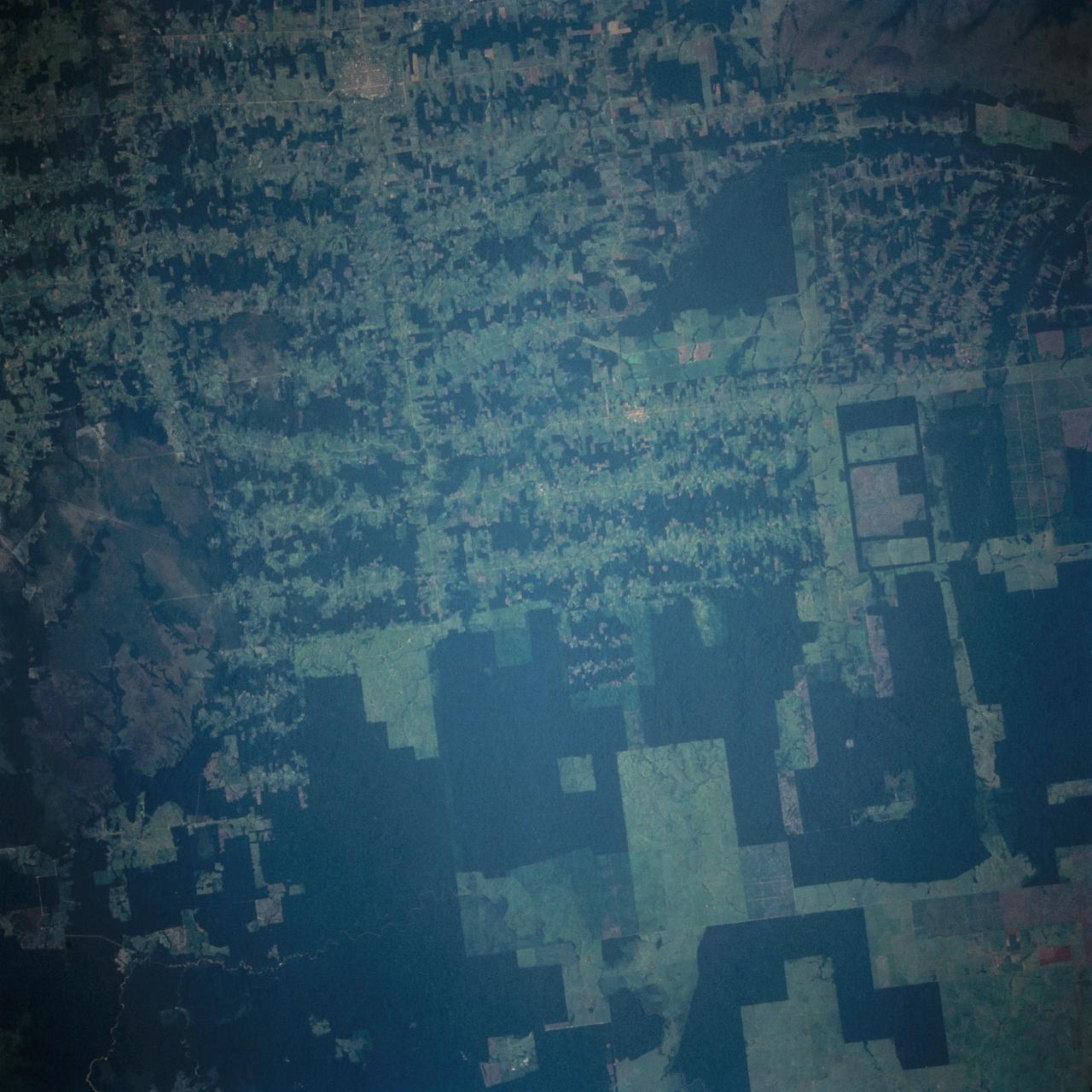

This near vertical photograph illustrates the differences in agricultural land patterns typically seen in many parts of southwestern Brazil, near the Bolivian border. The larger rectangular field patterns reflect a mature, fully developed agricultural environment. The smaller areas are less well defined and indicate new agricultural development.
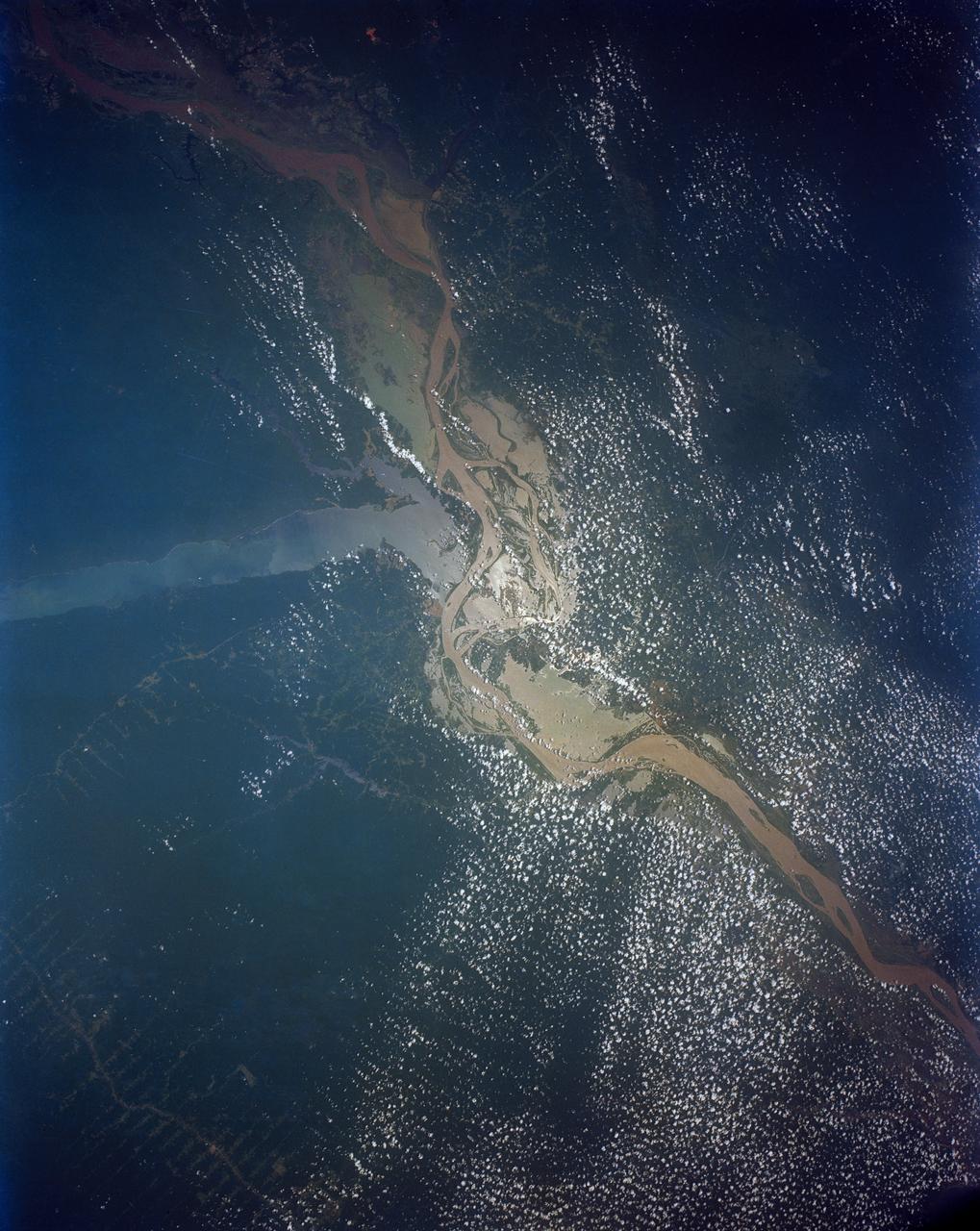

This view shows the confluence of the Amazon and the Topajos Rivers at Santarem, Brazil (2.0S, 55.0W). The Am,azon flows from lower left to upper right of the photo. Below the river juncture of the Amazon and Tapajos, there is considerable deforestation activity along the Trans-Amazon Highway.
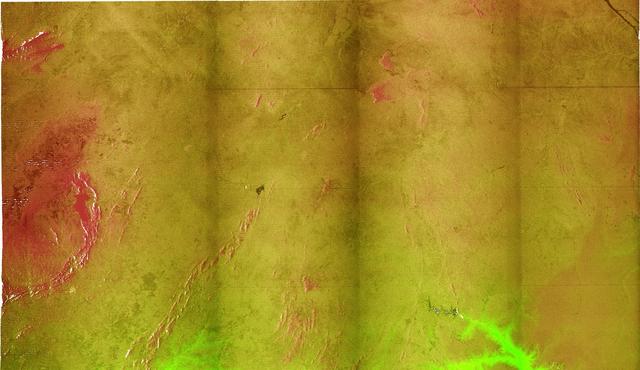
This radar image acquired in February 2000 by NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM shows an area in the state of Bahia in Brazil.
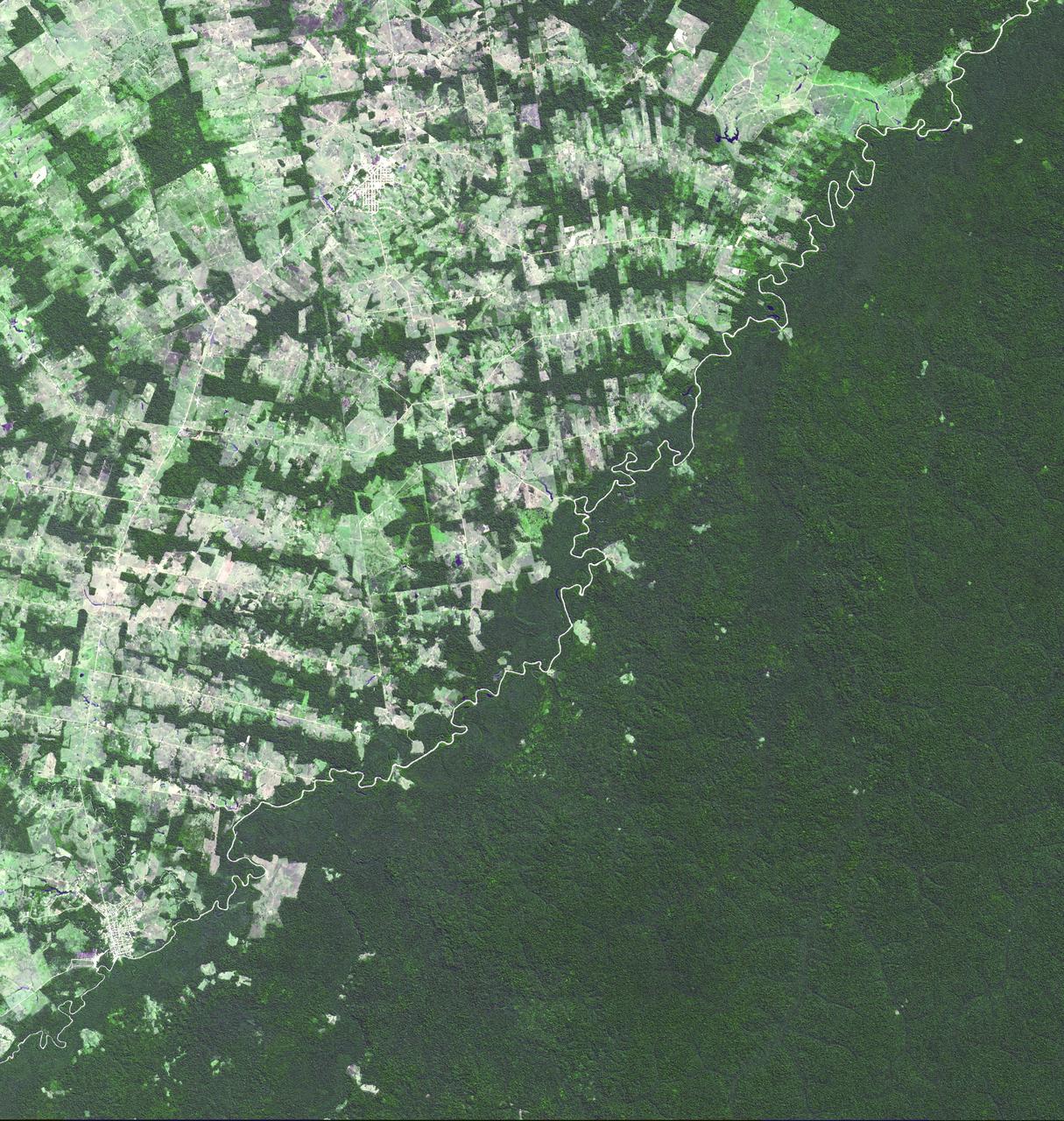

This image of the river-delineated border between western Brazil Acre province, and northwestern Bolivia Pando Department, demarcates a remarkable difference in land use and development practices as seen by NASA Terra spacecraft.

Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation (MCIT) Brazil, and Int'l Astronomical Search Collaboration (IASC) visited Goddard on May 19, 2022. They toured facilities including Hyperwall, Robotics, Spacecraft and Integration, Search and Rescue lab and Earth Sciences
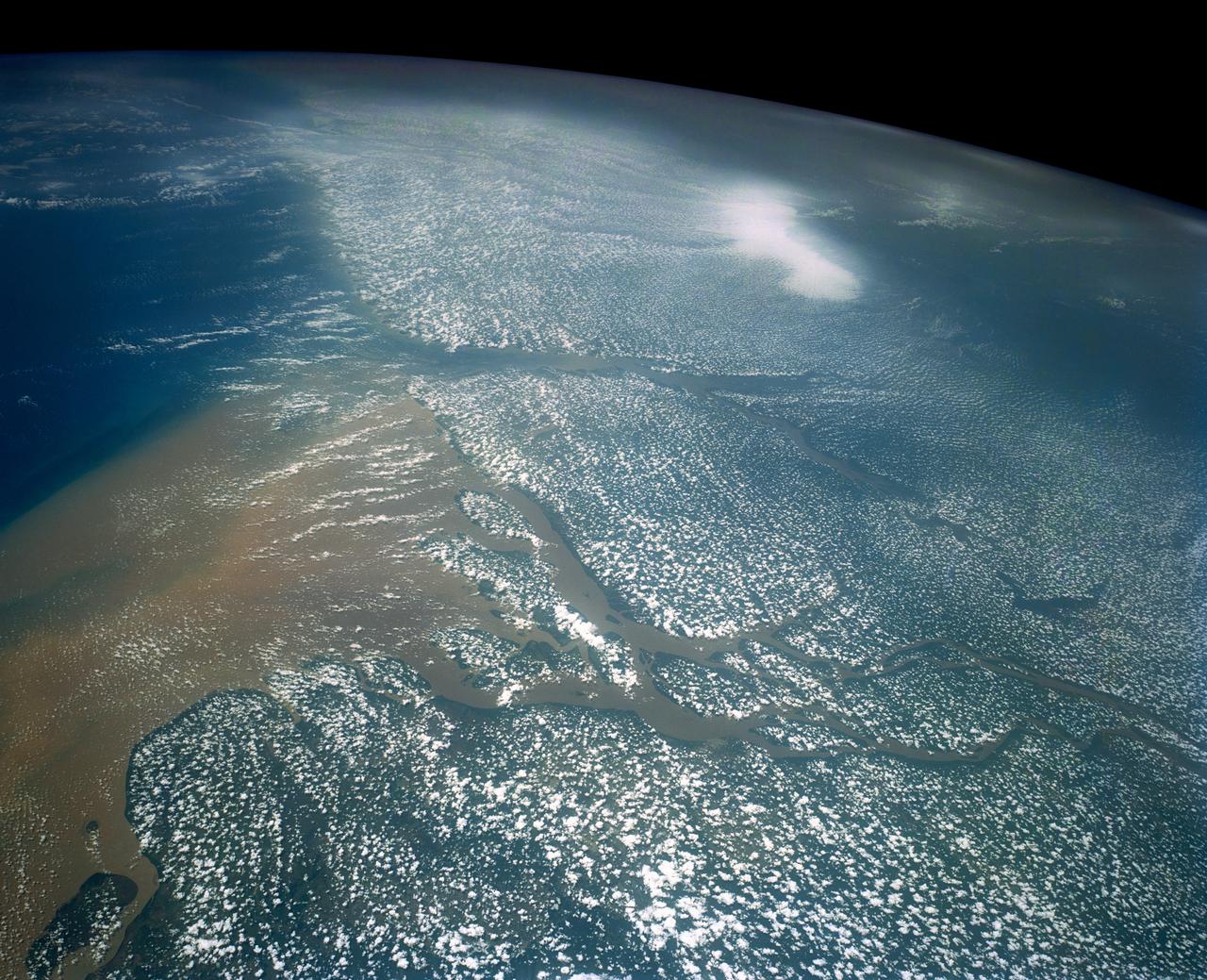

Huge sediment loads from the interior of the country flow through the Mouths of the Amazon River, Brazil (0.5S, 50.0W). The river current carries hundreds of tons of sediment through the multiple outlets of the great river over 100 miles from shore before it is carried northward by oceanic currents. The characteristic "fair weather cumulus" pattern of low clouds over the land but not over water may be observed in this scene.
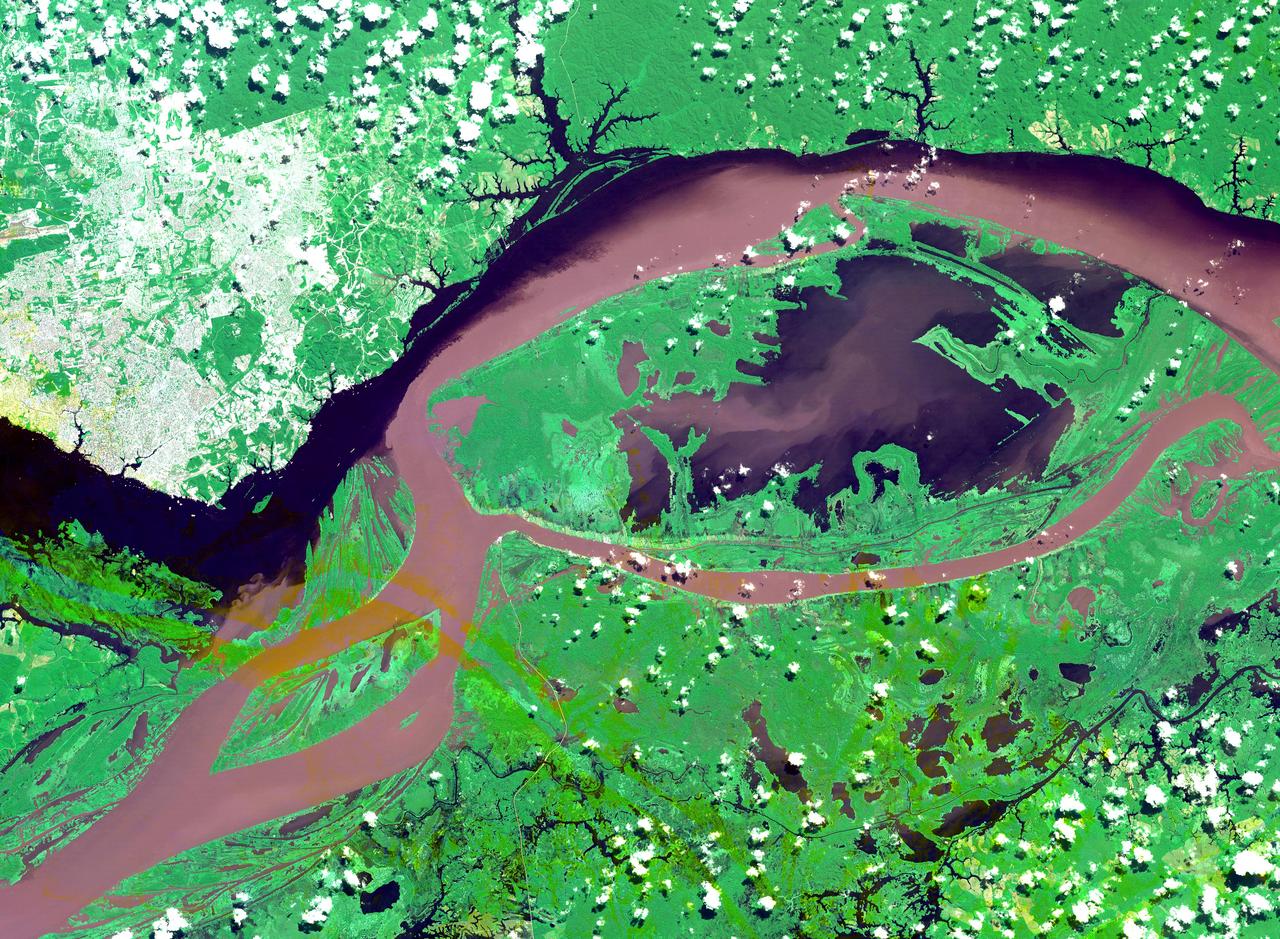

The junctions of the Amazon and the Rio Negro Rivers at Manaus, Brazil. The Rio Negro flows 2300 km from Columbia, and is the dark current forming the north side of the river. It gets its color from the high tannin content in the water. The Amazon is sediment laden, appearing brown in this simulated natural color image. Manaus is the capital of Amazonas state, and has a population in excess of one million. The ASTER image covers an area of 60 x 45 km. This image was acquired on July 16, 2000 by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA's Terra satellite. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region, and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER will image Earth for the next 6 years to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03851

This radar image acquired in February 2000 by NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM shows an area south of the Sao Francisco River in Brazil.
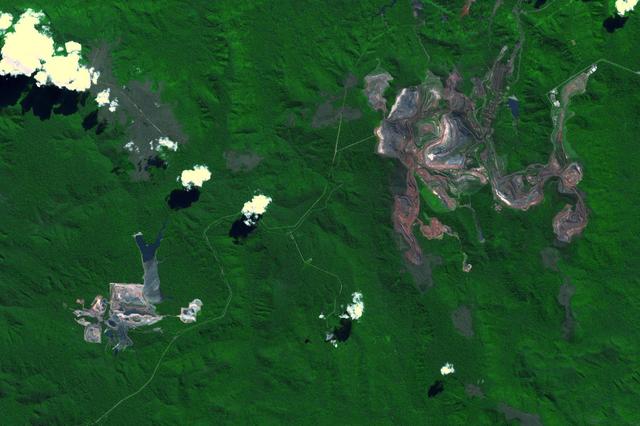

The Carajas Mine is the largest open-pit iron ore mine in the world. It is located in the state of Para, northern Brazil. The mine is estimated to contain over 7 billion tons of iron ore, plus gold, manganese, bauxite, copper and nickel. Ore is loaded into rail cars, and shipped to the Atlantic port city of Sao Luis over 250 kilometers away. The image was acquired June 19, 2017, covers an area of 18 by 27 kilometers, and is located at 6.1 degrees south, 50.2 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22861
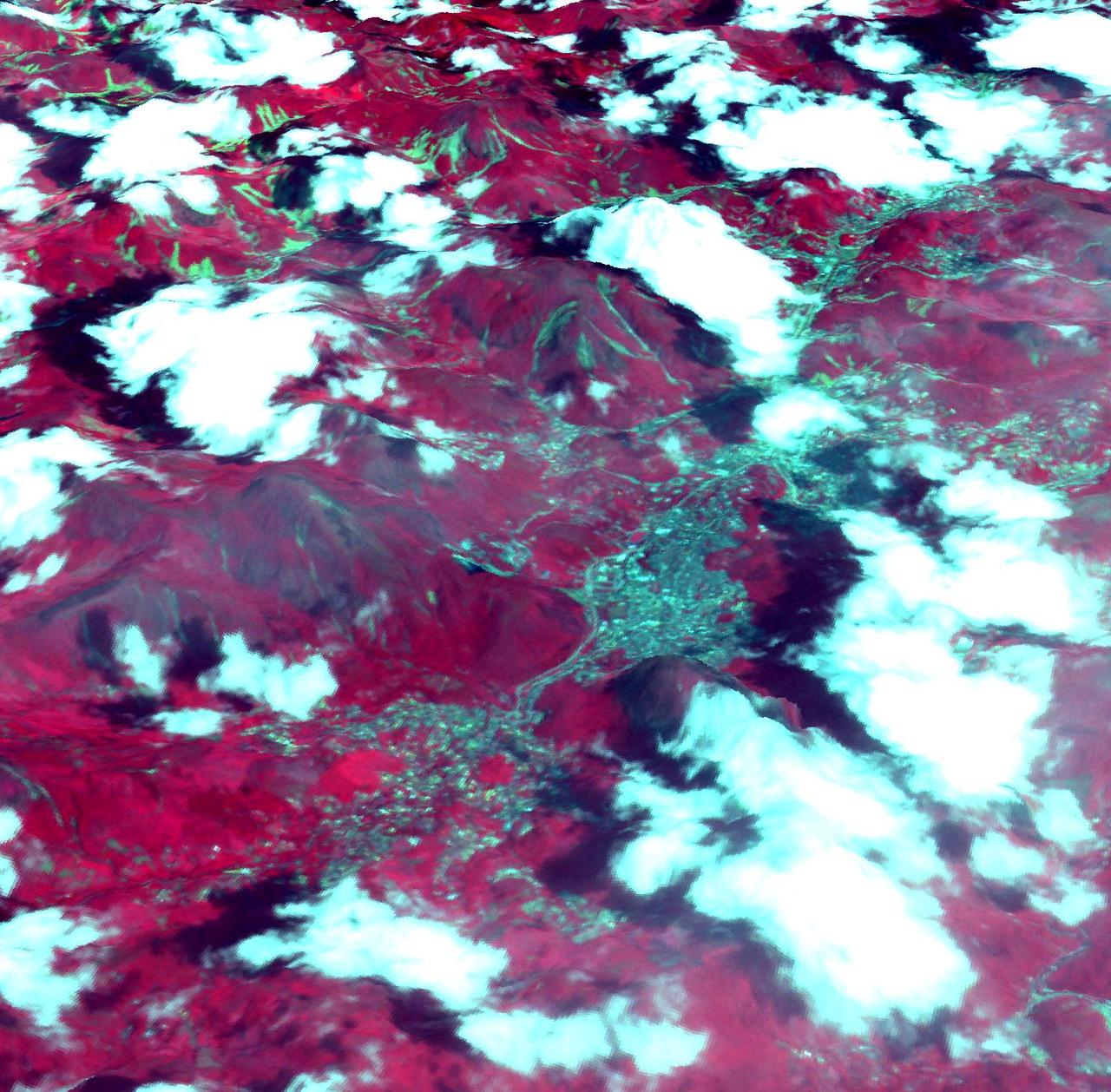
On Jan. 18, 2011, NASA Terra spacecraft captured this 3-D perspective image of the city of Nova Friburgo, Brazil. A week of torrential rains triggered a series of deadly mudslides and floods. More details about this image at the Photojournal.
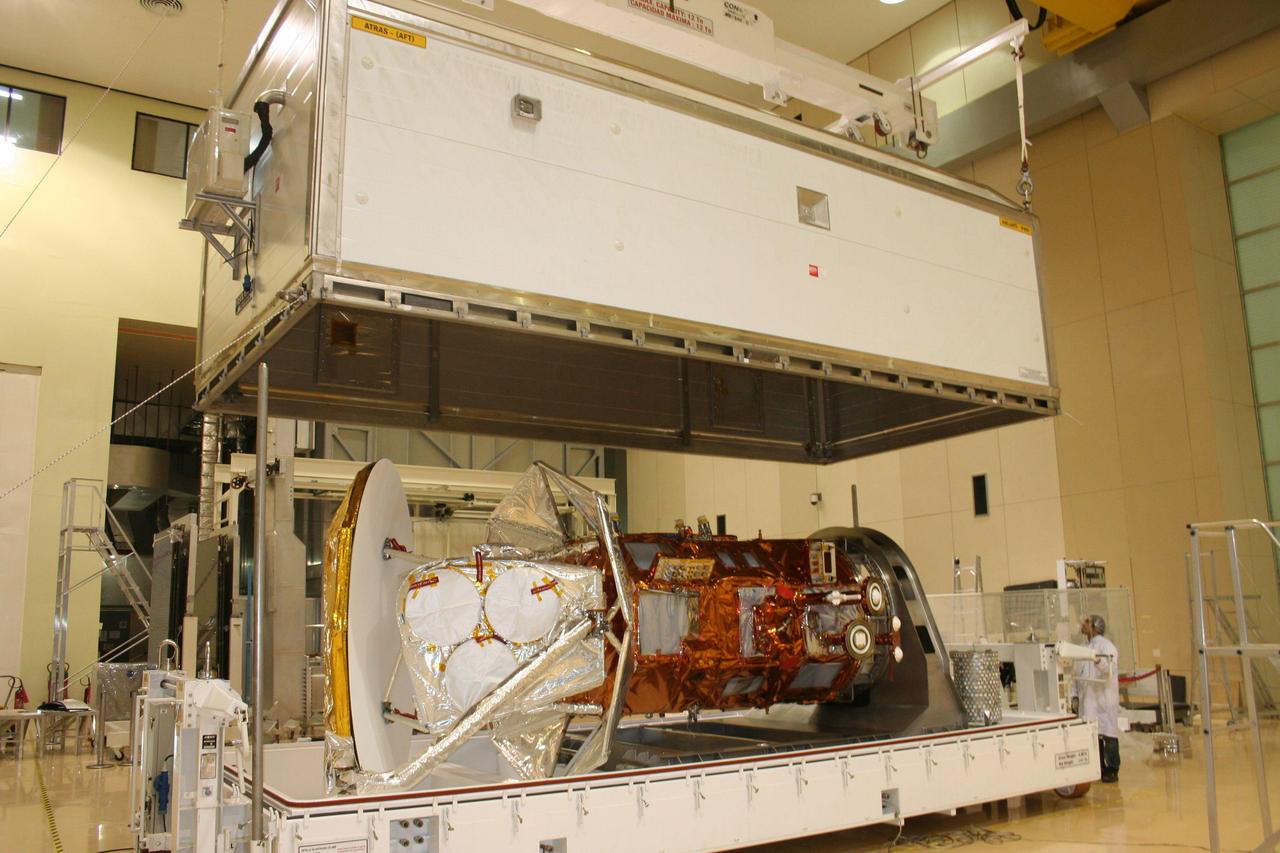

After months of environmental tests at Brazil National Institute for Space Research Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, INPE, NASA Aquarius/SAC-D observatory is loaded into a crate for shipment to Vandenberg Air Force Base.

This false-color L-band image of the Manaus region of Brazil was acquired by NASA Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar SIR-C/X-SAR aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on orbit 46 of the mission.

AS04-01-410 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Coastal Brazil, Atlantic Ocean, West Africa, Sahara, Antarctica, looking west, as photographed from the Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned, Earth-orbital space mission. This picture was taken when the Spacecraft 017 and Saturn S-IVB (third) stage were orbiting Earth at an altitude of 9,745 nautical miles.
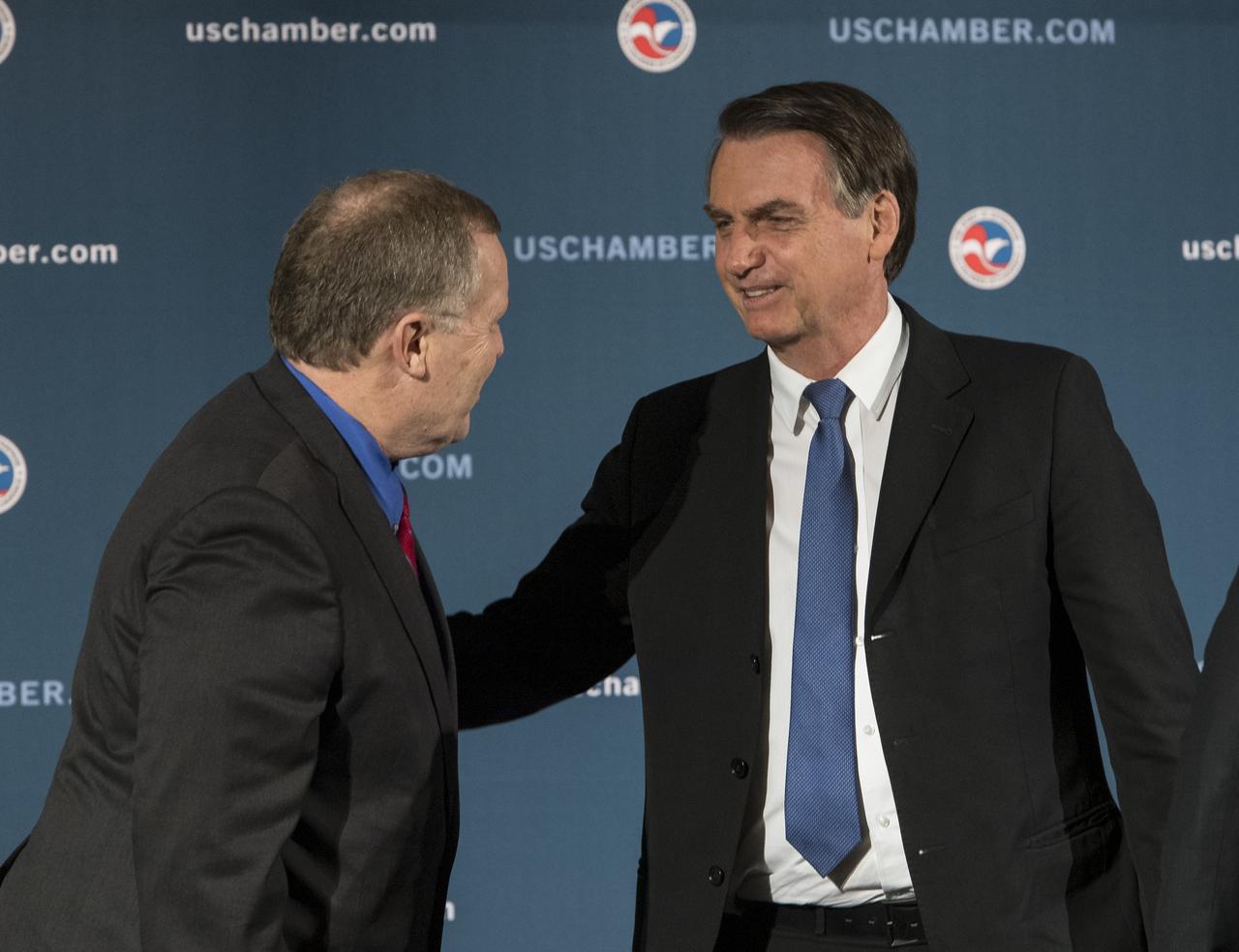

NASA Deputy Administrator James Morhard, left, speaks with H.E. President Jair Bolsonaro of Brazil, just before signing an agreement with President of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB), Carlos Augusto Teixeira de Moura, for cooperation on the Scintillation Prediction Observations Research Task (SPORT), an upcoming NASA-AEB heliophysics CubeSat partnership, Monday, March 18, 2019, at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington. The SPORT CubeSat will investigate two ionospheric phenomena, equatorial plasma bubbles and scintillation, that disrupt radio communication systems, satellite technologies, and Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. SPORT is currently projected to launch in the 2020 timeframe. Photo Credit: (NASA/ Aubrey Gemignani)

AS04-01-580 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Earth as viewed from 10,000 miles. In 1969, the Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned test flight made a great ellipse around Earth as a test of the translunar motors and of the high speed entry required of a manned flight returning from the moon. A 70mm camera was programmed to look out a window toward Earth, and take a series of photographs from "high apogee". Coastal Brazil, Atlantic Ocean, West Africa, Antarctica, looking west. This photograph was made when the Apollo 4 spacecraft, still attached to the S-IVB (third) stage, was orbiting Earth at an altitude of 9,544 miles.
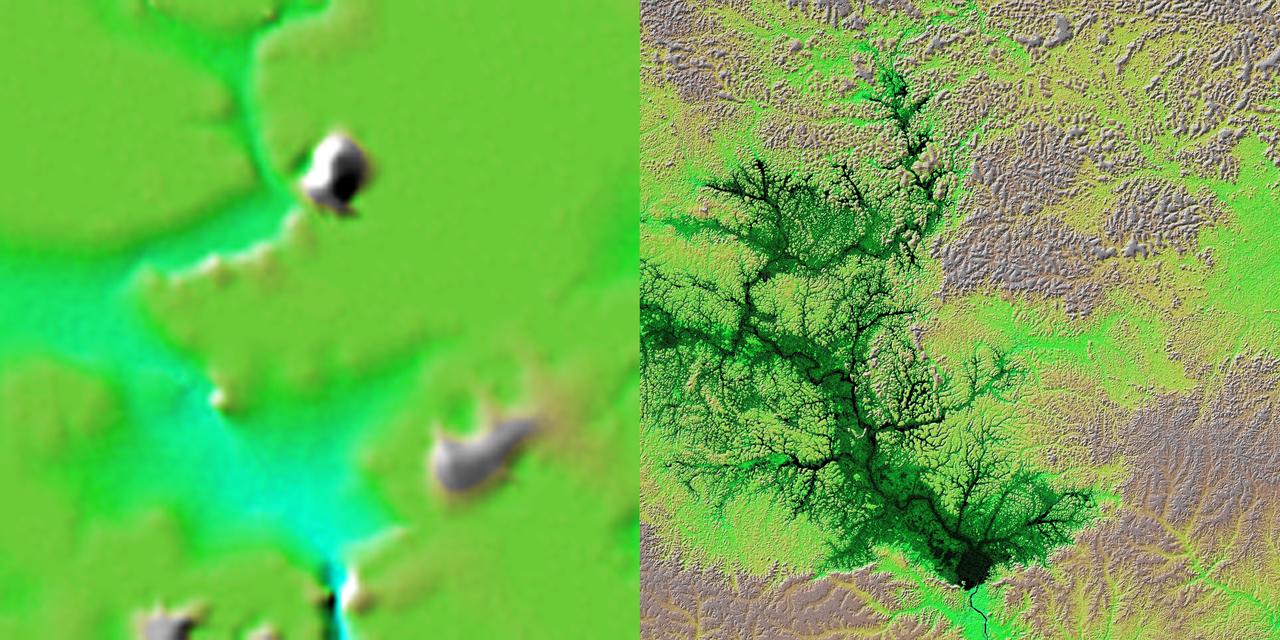
These two images show exactly the same area, Lake Balbina near Manaus, Brazil. The image on the left was created using the best global topographic data set previously available, the U.S. Geological Survey GTOPO30.
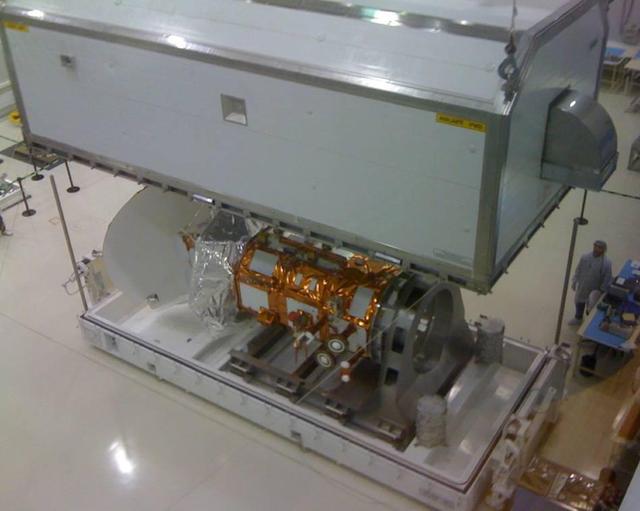

NASA Aquarius/SAC-D being prepared for shipment to Brazil National Institute for Space Research Integration and Testing Lab. At INPE, the Aquarius/SAC-D observatory will undergo its final environmental testing.
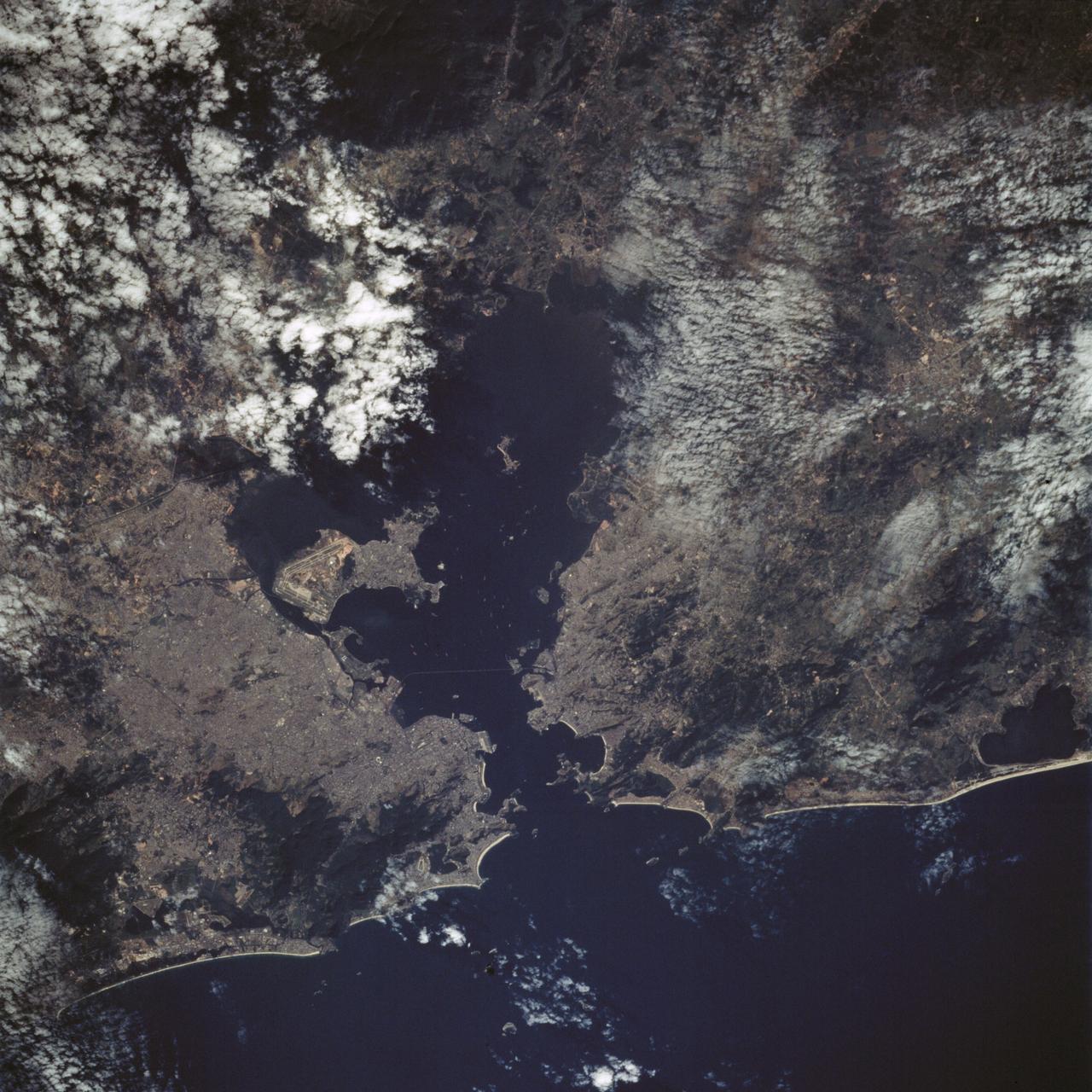

STS065-88-001 (8-23 July 1994) --- Rio de Janeiro, a port city in Brazil with a population of 11.6 million people, can be seen to the left of Governador Island in the Bay of Guanabara. Aeroporto Galeao is visible on the left, or western half of Governador Island. Below Governador Island is the Ponte Rio Niteroi bridge which connects the cities of Rio de Janeiro and Niteroi. Several ships can be seen in the Bay of Guanabara.
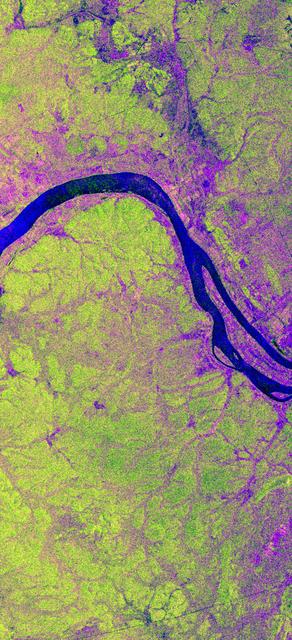
This is an X-band image showing seasonal changes at the hydrological test site of Bebedouro in Brazil. The image is centered at 9 degrees south latitude and 40.2 degrees west longitude. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on April 10, 1994, during the first flight of the radar system, and on October 1, 1994, during the second mission. The swath width is approximately 16.5 kilometers (10.5 miles) wide. The image channels have the following color assignments: red represents data acquired on April 10; green represents data acquired on October 1; blue corresponds to the ratio of the two data sets. Agriculture plays an important economic and social role in Brazil. One of the major problems related to Brazilian agriculture is estimating the size of planting areas and their productivity. Due to cloud cover and the rainy season, which occurs from November through April, optical and infrared Earth observations are seldom used to survey the region. An additional goal of monitoring this region is to watch the floodplains of rivers like Rio Sao Francisco in order to determine suitable locations for additional agricultural fields. This area belongs to the semi-arid northeastern region of Brazil, where estimates have suggested that about 10 times more land could be used for agriculture, including some locations which could be used for irrigation projects. Monitoring of soil moisture during the important summer crop season is of high priority for the future development and productivity of this region. In April the area was covered with vegetation because of the moisture of the soil and only small differences could be seen in X-band data. In October the run-off channels of this hilly region stand out quite clearly because the greenish areas indicated much less soil moisture and water content in plants. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01733
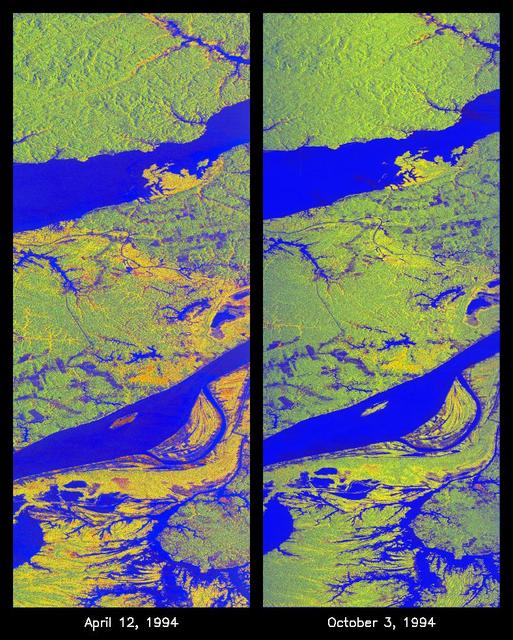
These two false-color images of the Manaus region of Brazil in South America were acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar on board the space shuttle Endeavour. The image at left was acquired on April 12, 1994, and the image at right was acquired on October 3, 1994. The area shown is approximately 8 kilometers by 40 kilometers (5 miles by 25 miles). The two large rivers in this image, the Rio Negro (at top) and the Rio Solimoes (at bottom), combine at Manaus (west of the image) to form the Amazon River. The image is centered at about 3 degrees south latitude and 61 degrees west longitude. North is toward the top left of the images. The false colors were created by displaying three L-band polarization channels: red areas correspond to high backscatter, horizontally transmitted and received, while green areas correspond to high backscatter, horizontally transmitted and vertically received. Blue areas show low returns at vertical transmit/receive polarization; hence the bright blue colors of the smooth river surfaces can be seen. Using this color scheme, green areas in the image are heavily forested, while blue areas are either cleared forest or open water. The yellow and red areas are flooded forest or floating meadows. The extent of the flooding is much greater in the April image than in the October image and appears to follow the 10-meter (33-foot) annual rise and fall of the Amazon River. The flooded forest is a vital habitat for fish, and floating meadows are an important source of atmospheric methane. These images demonstrate the capability of SIR-C/X-SAR to study important environmental changes that are impossible to see with optical sensors over regions such as the Amazon, where frequent cloud cover and dense forest canopies block monitoring of flooding. Field studies by boat, on foot and in low-flying aircraft by the University of California at Santa Barbara, in collaboration with Brazil's Instituto Nacional de Pesguisas Estaciais, during the first and second flights of the SIR-C/X-SAR system have validated the interpretation of the radar images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01735

STS054-86-001 (13-19 Jan. 1993) --- This 70mm view shows a spectacular multiple spit on the coast of Brazil, about halfway between Rio de Janeiro and the mouth of the Amazon River. Over a few thousand years, according to NASA scientists, shifting regimes of wave and current patterns piled up sand onto a series of beach ridges and tidal lagoons. The present swirls of sediment along the coast evidently were derived from beach erosion, because streams flowing into the Atlantic contain dark, clear water. Offshore, reefs and sandbanks parallel the coast. The largest is the Recife da Pedra Grande (Big Rocks Reef).

On Nov. 5, 2015, a dam at an iron-ore mine in southeastern Brazil burst, sending a wall of water, clay-red mud and debris downstream, overwhelming several villages in the path as seen by NASA Terra spacecraft. The Germano mine is near the town of Mariana in Minas Gerais state. The region is seen in this image from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument aboard NASA's Terra spacecraft was acquired Nov. 12, 2015, covers an area of 6.8 by 14.3 miles (11 by 23 kilometers), and is located at 20.2 degrees south, 43.5 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20156
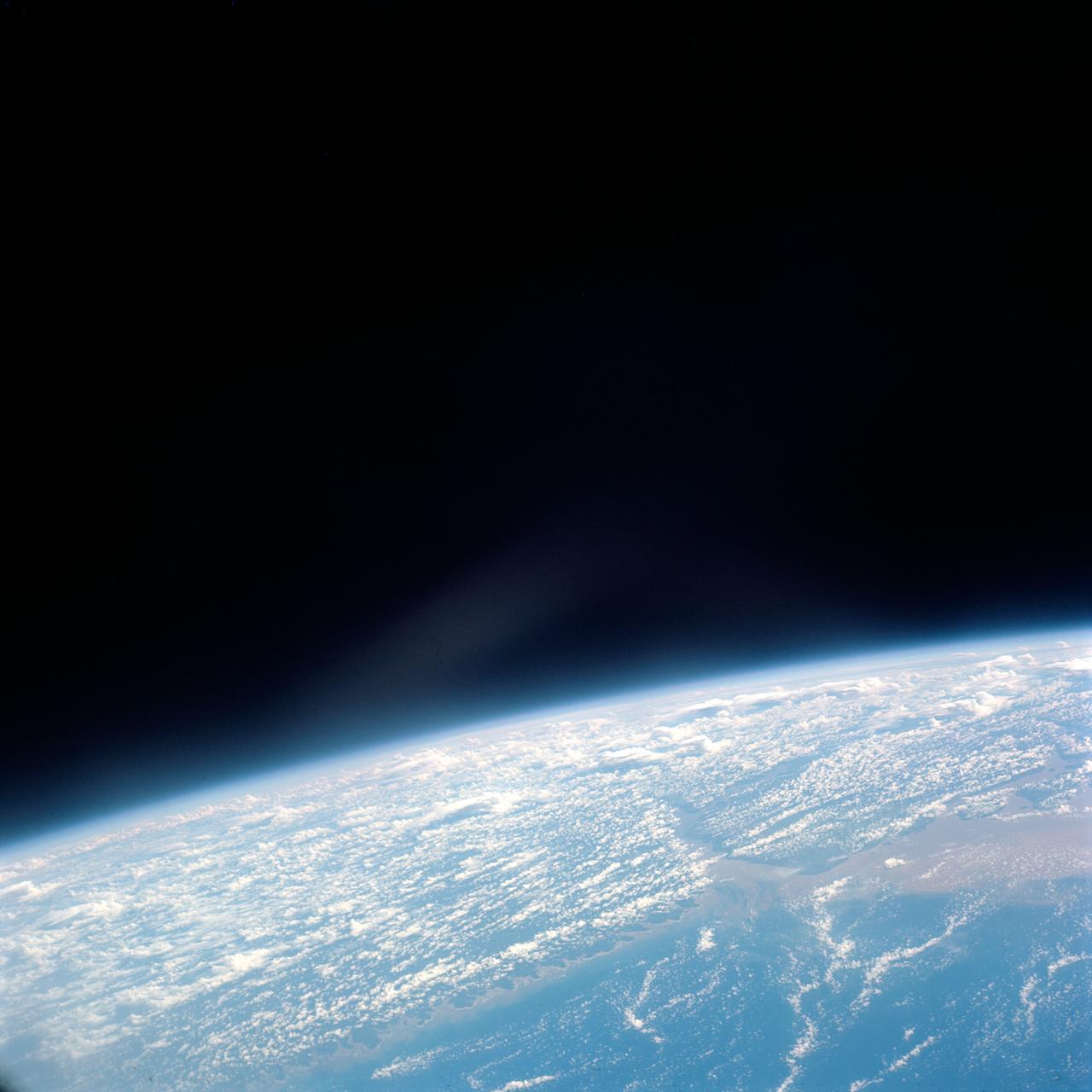

S66-38191 (4 June 1966) --- The mouth of the Amazon River on the northern coast of Brazil, looking southwest, as seen from the Gemini-9A spacecraft during its 18th revolution of Earth. The image was taken with a 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA

iss073e0982063 (Oct. 21, 2025) --- São Paulo, Brazil—with a metropolitan population of about 23 million—is the fifth most populous region in the world. As Brazil's economic powerhouse, São Paulo hosts one of the largest stock exchanges in the world and leads in the automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceutical industries. The city's brighter, more energy-efficient white LED lights reflect the region’s ongoing progress and modernization of its infrastructure. This photograph was taken from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above the Brazilian coast at approximately 2:20 a.m. local time.
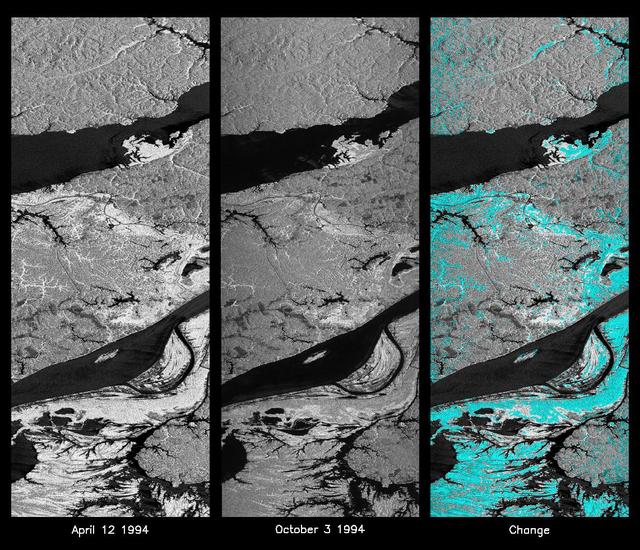
These L-band images of the Manaus region of Brazil were acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour. The left image was acquired on April 12, 1994, and the middle image was acquired on October 3, 1994. The area shown is approximately 8 kilometers by 40 kilometers (5 miles by 25 miles). The two large rivers in this image, the Rio Negro (top) and the Rio Solimoes (bottom), combine at Manaus (west of the image) to form the Amazon River. The image is centered at about 3 degrees south latitude and 61 degrees west longitude. North is toward the top left of the images. The differences in brightness between the images reflect changes in the scattering of the radar channel. In this case, the changes are indicative of flooding. A flooded forest has a higher backscatter at L-band (horizontally transmitted and received) than an unflooded river. The extent of the flooding is much greater in the April image than in the October image, and corresponds to the annual, 10-meter (33-foot) rise and fall of the Amazon River. A third image at right shows the change in the April and October images and was created by determining which areas had significant decreases in the intensity of radar returns. These areas, which appear blue on the third image at right, show the dramatic decrease in the extent of flooded forest, as the level of the Amazon River falls. The flooded forest is a vital habitat for fish and floating meadows are an important source of atmospheric methane. This demonstrates the capability of SIR-C/X-SAR to study important environmental changes that are impossible to see with optical sensors over regions such as the Amazon, where frequent cloud cover and dense forest canopies obscure monitoring of floods. Field studies by boat, on foot and in low-flying aircraft by the University of California at Santa Barbara, in collaboration with Brazil's Instituto Nacional de Pesguisas Estaciais, during the first and second flights of the SIR-C/X-SAR system have validated the interpretation of the radar images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01740
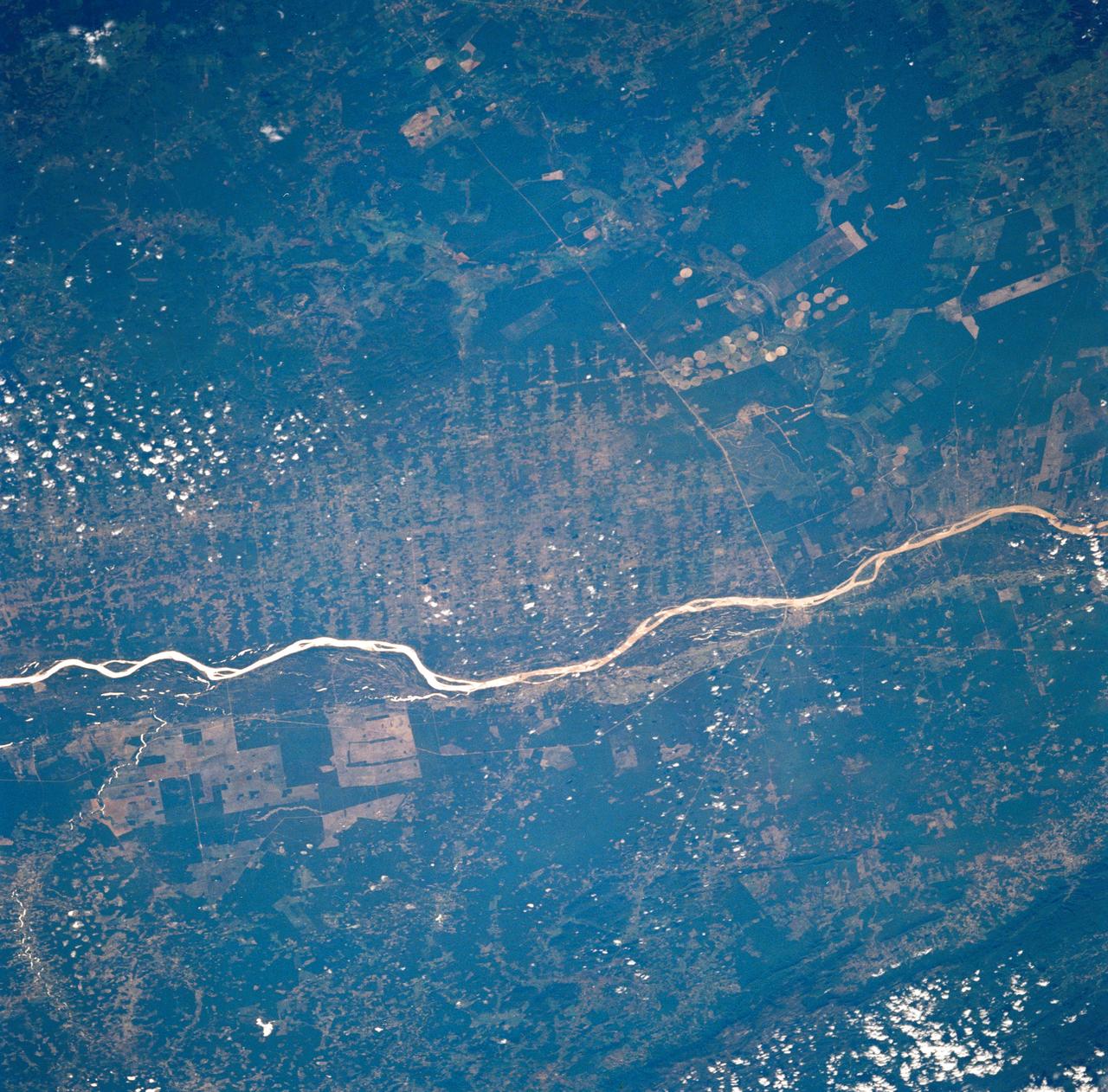

STS035-73-082 (2-10 Dec 1990) --- This agricultural and ranching area, Rio Sao Francisco, Brazil (13.0S, 43.5W) has been under study for several years. See scene STS-31-92-045 for comparison. This area has many small single family subsistence farms, large square and rectangular commercial farms and pastures for livestock grazing. Over the several years of observation, the number and size of farms has increased and center-pivot, swing-arm irrigation systems have been installed.

The First Robotics Rocket City Regional Competition was held at the Von Braun Civic Center in Huntsville, Alabama on March 16, 2018. High school robotics teams from throughout the U.S., as well as a team from Brazil, competed. Pictured is the Brazilian team prior to competition

The First Robotics Rocket City Regional Competition was held at the Von Braun Civic Center in Huntsville, Alabama on March 16, 2018. High school robotics teams from throughout the U.S., as well as a team from Brazil, competed. The Brazilian team sings their national anthem.
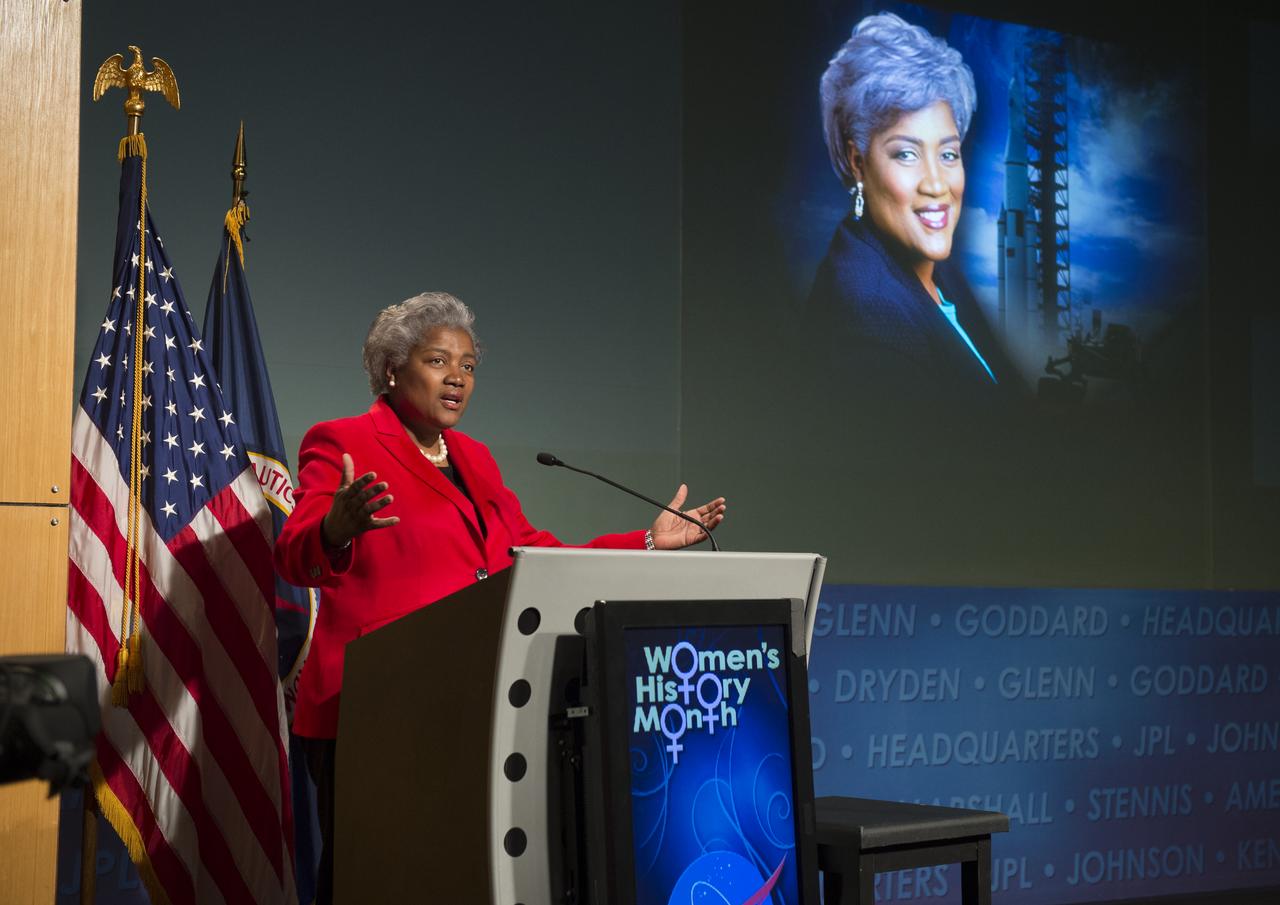

Donna Brazile, adjunct professor at Georgetown University, syndicated newspaper columnist and vice chair of voter registration and participation at the Democratic National Committee (DNC), gives the keynote speech at a program celebrating National Women's History Month at NASA Headquarters, Thursday, March 14, 2013 in Washington. The theme of this year's program was "Women Inspiring Innovation Through Imagination." The program was sponsored by the HQ Equal Opportunity and Diversity Management Division at NASA Headquarters and commemorates the 100th Anniversary of the Women's Suffrage March on Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
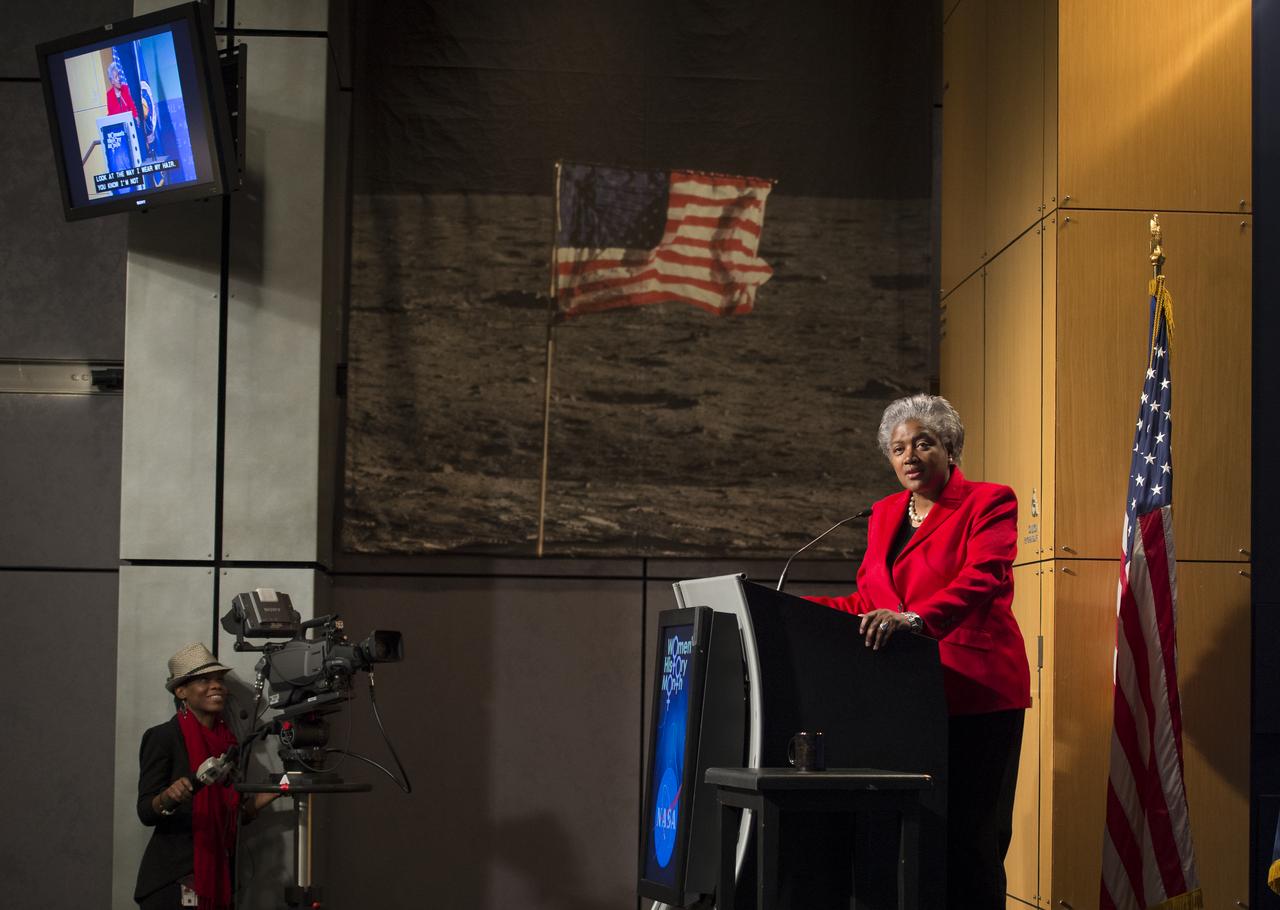

Donna Brazile, adjunct professor at Georgetown University, syndicated newspaper columnist and vice chair of voter registration and participation at the Democratic National Committee (DNC), gives the keynote speech at a program celebrating National Women's History Month at NASA Headquarters, Thursday, March 14, 2013 in Washington. The theme of this year's program was "Women Inspiring Innovation Through Imagination." The program was sponsored by the HQ Equal Opportunity and Diversity Management Division at NASA Headquarters and commemorates the 100th Anniversary of the Women's Suffrage March on Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Donna Brazile, adjunct professor at Georgetown University, syndicated newspaper columnist and vice chair of voter registration and participation at the Democratic National Committee (DNC), gives the keynote speech at a program celebrating National Women's History Month at NASA Headquarters, Thursday, March 14, 2013 in Washington. The theme of this year's program was "Women Inspiring Innovation Through Imagination." The program was sponsored by the HQ Equal Opportunity and Diversity Management Division at NASA Headquarters and commemorates the 100th Anniversary of the Women's Suffrage March on Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Donna Brazile, adjunct professor at Georgetown University, syndicated newspaper columnist and vice chair of voter registration and participation at the Democratic National Committee (DNC), gives the keynote speech at a program celebrating National Women's History Month at NASA Headquarters, Thursday, March 14, 2013 in Washington. The theme of this year's program was "Women Inspiring Innovation Through Imagination." The program was sponsored by the HQ Equal Opportunity and Diversity Management Division at NASA Headquarters and commemorates the 100th Anniversary of the Women's Suffrage March on Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Donna Brazile, adjunct professor at Georgetown University, syndicated newspaper columnist and vice chair of voter registration and participation at the Democratic National Committee (DNC), gives the keynote speech at a program celebrating National Women's History Month at NASA Headquarters, Thursday, March 14, 2013 in Washington. The theme of this year's program was "Women Inspiring Innovation Through Imagination." The program was sponsored by the HQ Equal Opportunity and Diversity Management Division at NASA Headquarters and commemorates the 100th Anniversary of the Women's Suffrage March on Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
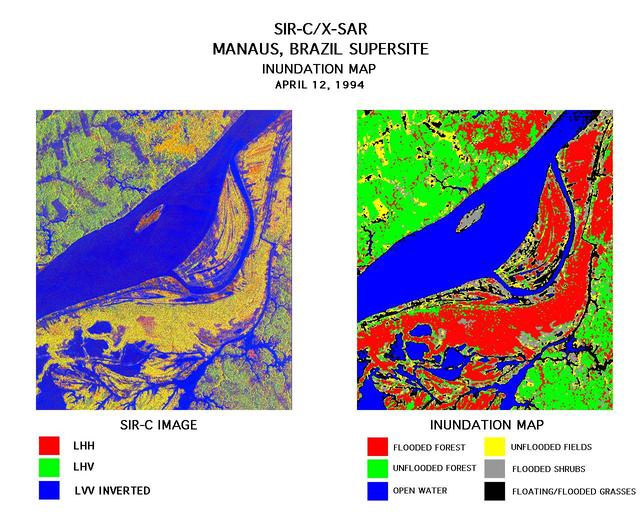
These two images were created using data from the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR). On the left is a false-color image of Manaus, Brazil acquired April 12, 1994, onboard space shuttle Endeavour. In the center of this image is the Solimoes River just west of Manaus before it combines with the Rio Negro to form the Amazon River. The scene is around 8 by 8 kilometers (5 by 5 miles) with north toward the top. The radar image was produced in L-band where red areas correspond to high backscatter at HH polarization, while green areas exhibit high backscatter at HV polarization. Blue areas show low backscatter at VV polarization. The image on the right is a classification map showing the extent of flooding beneath the forest canopy. The classification map was developed by SIR-C/X-SAR science team members at the University of California,Santa Barbara. The map uses the L-HH, L-HV, and L-VV images to classify the radar image into six categories: Red flooded forest Green unflooded tropical rain forest Blue open water, Amazon river Yellow unflooded fields, some floating grasses Gray flooded shrubs Black floating and flooded grasses Data like these help scientists evaluate flood damage on a global scale. Floods are highly episodic and much of the area inundated is often tree-covered. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01712
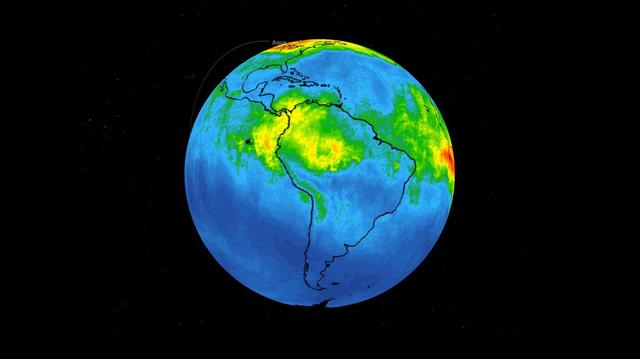
This time series shows carbon monoxide associated with fires from the Amazon region in Brazil from Aug. 8-22, 2019. The images show carbon monoxide at an hPA — a common unit of measurement for atmospheric pressure — of 500, or approximately 18,000 feet (5,500 meters) altitude, made with data collected from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA's Aqua satellite. Each "day" in the series is made by averaging three day's-worth of measurements, a technique used to eliminate data gaps. As the series progresses, the carbon monoxide plume blooms in the northwest Amazon region then drifts south and east in a more concentrated plume toward Sao Paulo. Green indicates concentrations of carbon monoxide at approximately 100 parts per billion by volume (ppbv), yellow at approximately 120 ppbv, and dark red at approximately 160 ppbv. It must be noted that local values can be significantly higher. Carbon monoxide is a pollutant that can be transported large distances and persist in the atmosphere for about one month. It plays a role in both air pollution and climate change. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23356
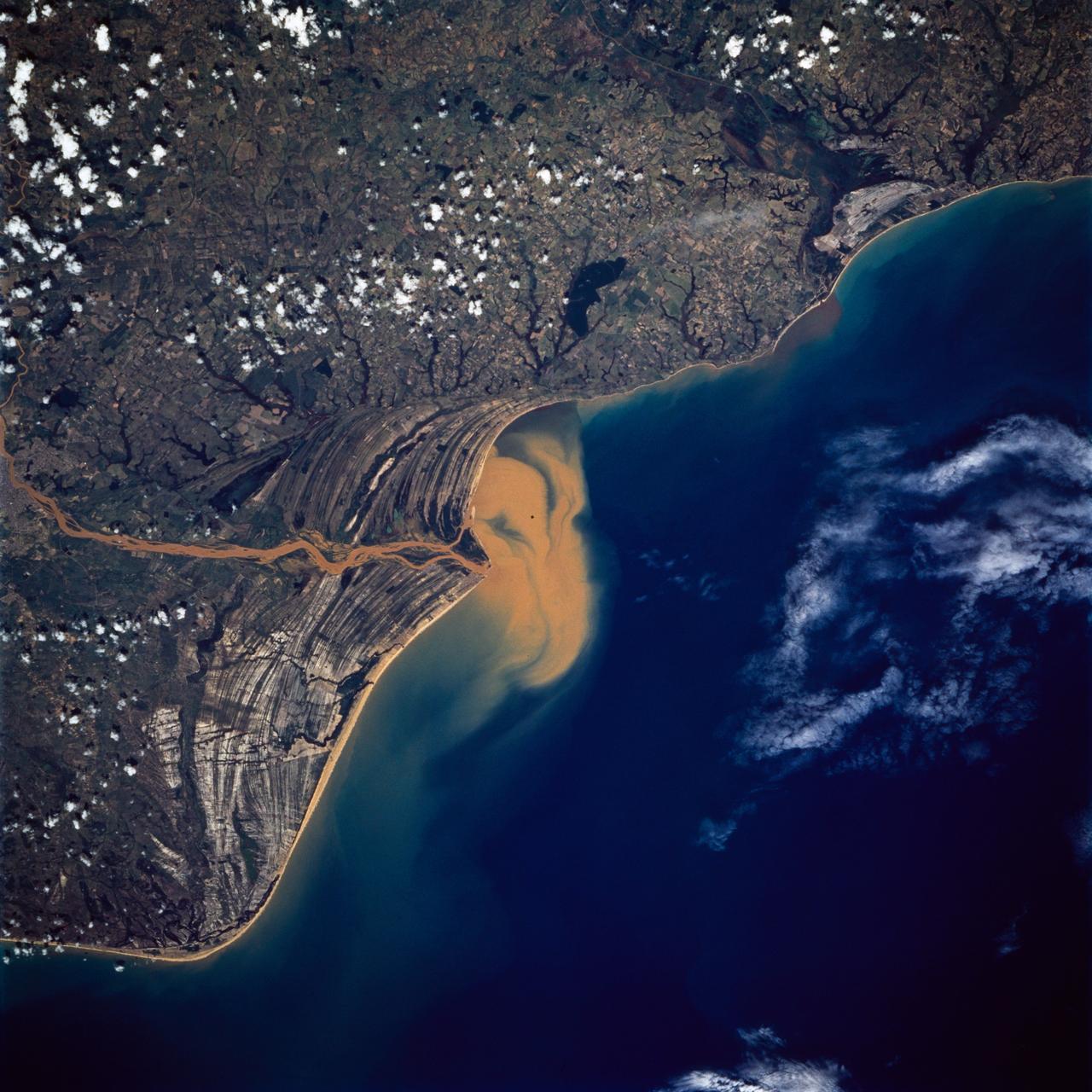

STS072-738-019 (11-20 Jan. 1996) --- The Delta of the Paraiba do Sul River, northeast of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, stands out in this 70mm frame exposed from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. The brown color of the river water and offshore sediment plume show that the river is in flood stage. This delta attracts much attention from orbit because of its prominent beach ridges either side of the river mouth. River sediment from inland supplies the material which is redistributed by coastal currents to form the parallel beach ridges. The lower 20 miles of the river appear in this scene. The river flows into the Atlantic in an easterly direction.
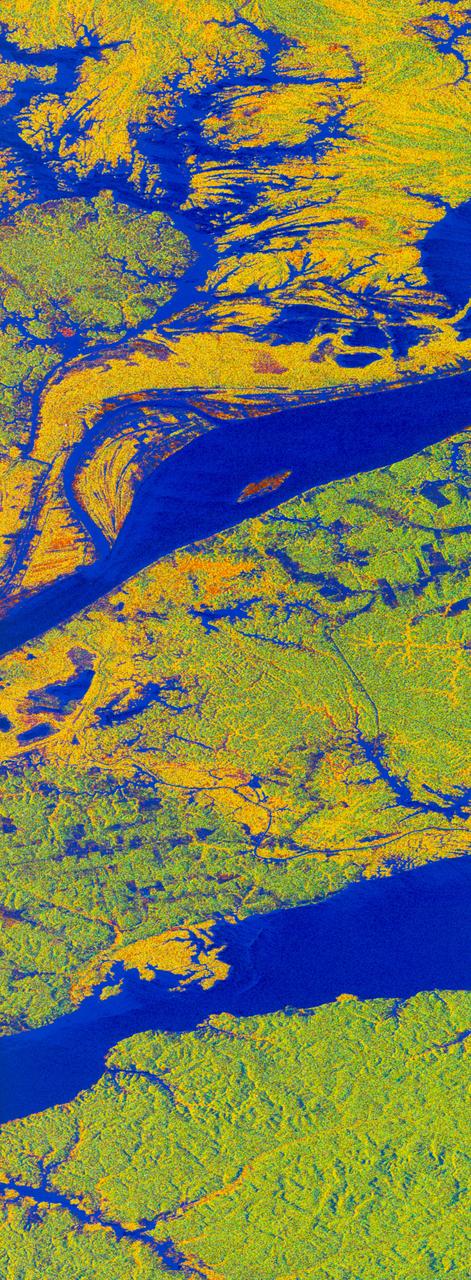

STS059-S-068 (13 April 1994) --- This false-color L-Band image of the Manaus region of Brazil was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on orbit 46 of the mission. The area shown is approximately 8 kilometers by 40 kilometers (5 by 25 miles). At the top of the image are the Solimoes and Rio Negro Rivers just before they combine at Manaus to form the Amazon River. The image is centered at about 3 degrees south latitude, and 61 degrees west longitude. The false colors are created by displaying three L-Band polarization channels; red areas correspond to high backscatter at HH polarization, while green areas exhibit high backscatter at HV polarization. Blue areas show low returns at VV polarization; hence the bright blue colors of the smooth river surfaces. Using this color scheme, green areas in the image are heavily forested, while blue areas are either cleared forest or open water. The yellow and red areas are flooded forest. Between Rio Solimoes and Rio Negro a road can be seen running from some cleared areas (visible as blue rectangles north of Rio Solimoes) north towards a tributary of Rio Negro. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43895
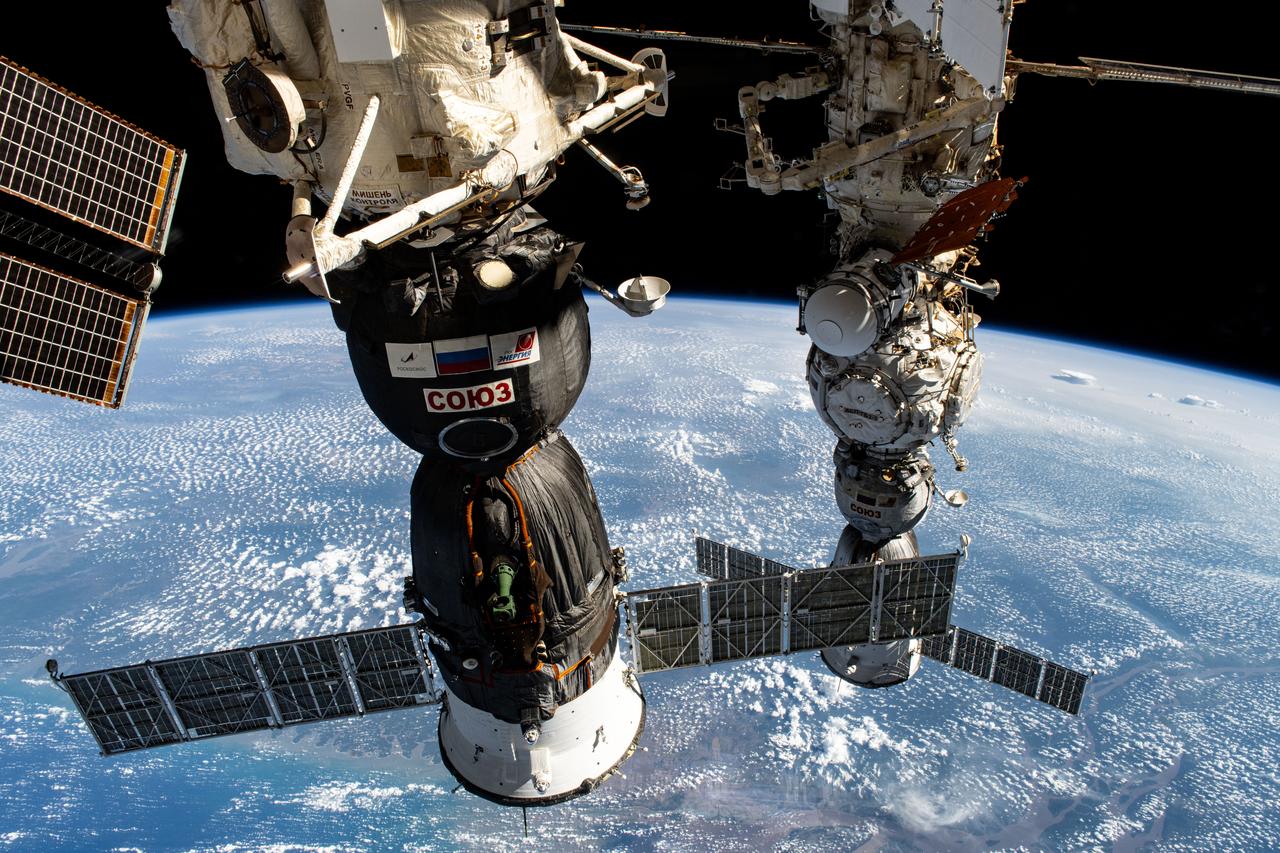

iss071e665075 (Sept. 16, 2024) --- Two Roscosmos crew ships, the Soyuz MS-26 docked to the Rassvet module (foreground) and the Soyuz MS-25 (background) docked to the Prichal docking module, are pictured parked at the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above the Atlantic Ocean near Brazil's Amazon Delta.
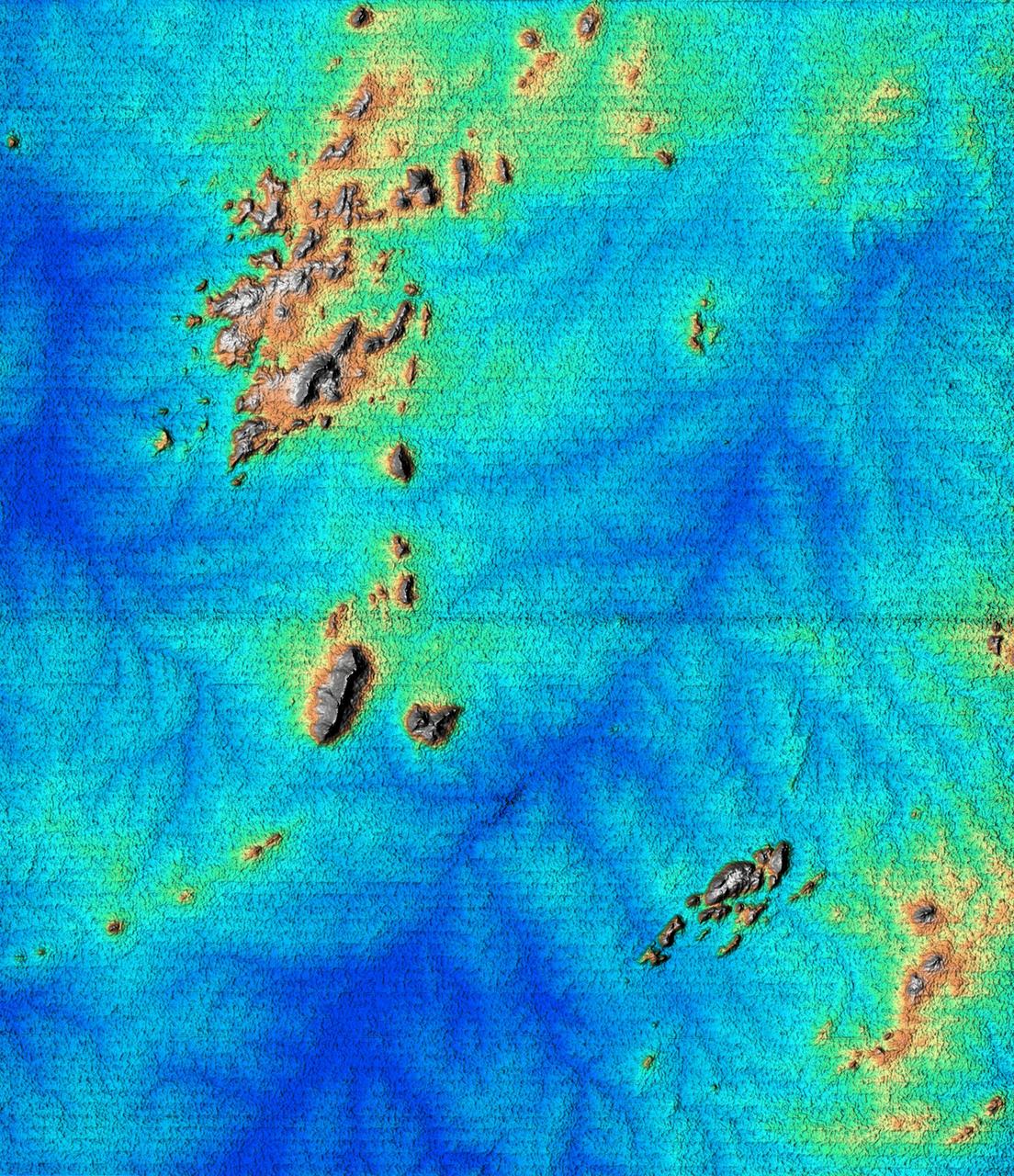
This topographic image acquired by SRTM shows an area south of the Sao Francisco River in Brazil. The scrub forest terrain shows relief of about 400 meters (1300 feet). Areas such as these are difficult to map by traditional methods because of frequent cloud cover and local inaccessibility. This region has little topographic relief, but even subtle changes in topography have far-reaching effects on regional ecosystems. The image covers an area of 57 km x 79 km and represents one quarter of the 225 km SRTM swath. Colors range from dark blue at water level to white and brown at hill tops. The terrain features that are clearly visible in this image include tributaries of the Sao Francisco, the dark-blue branch-like features visible from top right to bottom left, and on the left edge of the image, and hills rising up from the valley floor. The San Francisco River is a major source of water for irrigation and hydroelectric power. Mapping such regions will allow scientists to better understand the relationships between flooding cycles, forestation and human influences on ecosystems. This shaded relief image was generated using topographic data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. A computer-generated artificial light source illuminates the elevation data to produce a pattern of light and shadows. Slopes facing the light appear bright, while those facing away are shaded. On flatter surfaces, the pattern of light and shadows can reveal subtle features in the terrain. Shaded relief maps are commonly used in applications such as geologic mapping and land use planning. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02700
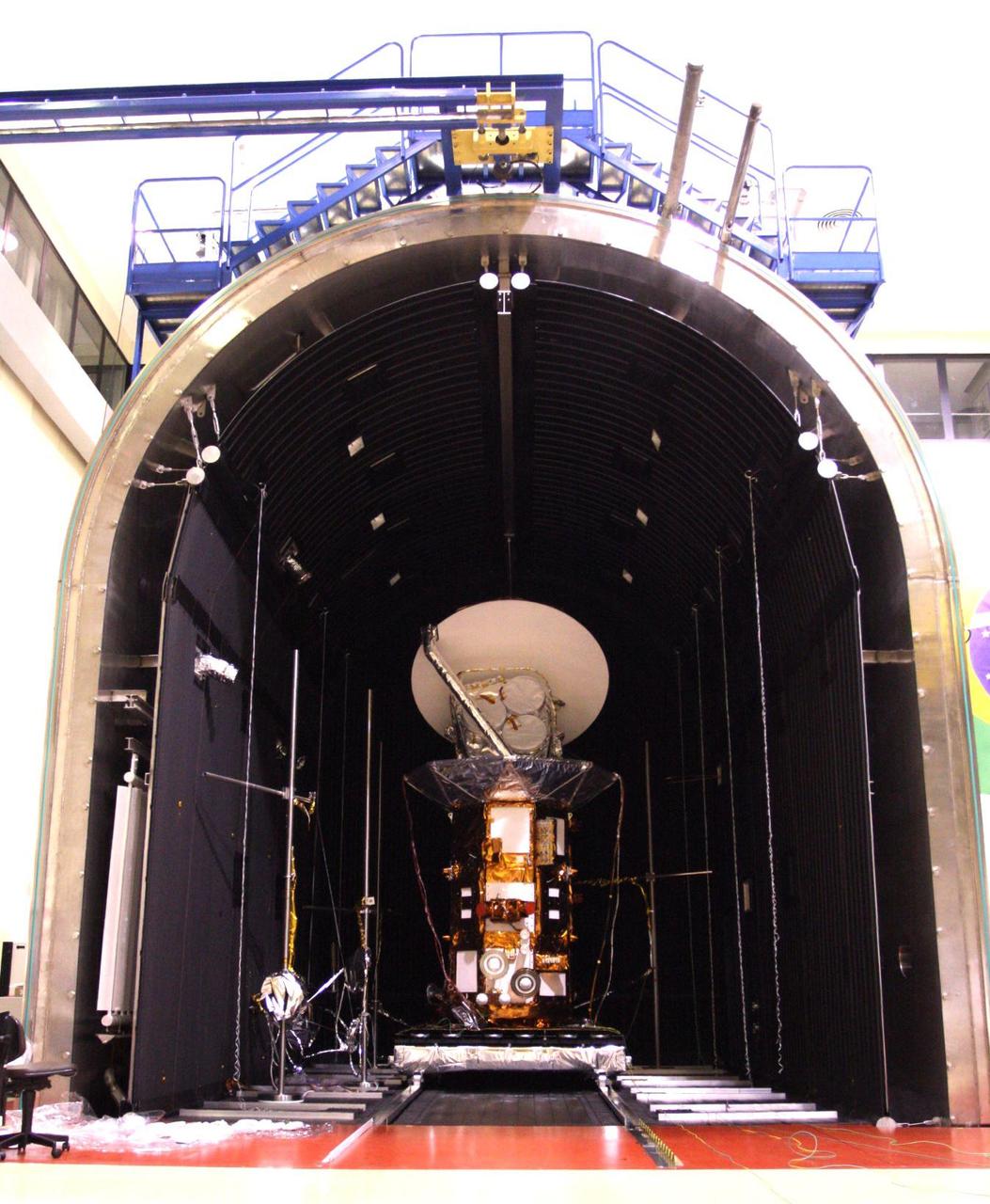

NASA Aquarius/SAC-D observatory is moved into the thermal-vacuum chamber at Brazil National Institute for Space Research.

These two images show exactly the same area in South America, the Guiana Highlands straddling the borders of Venezuela, Guyana and Brazil.
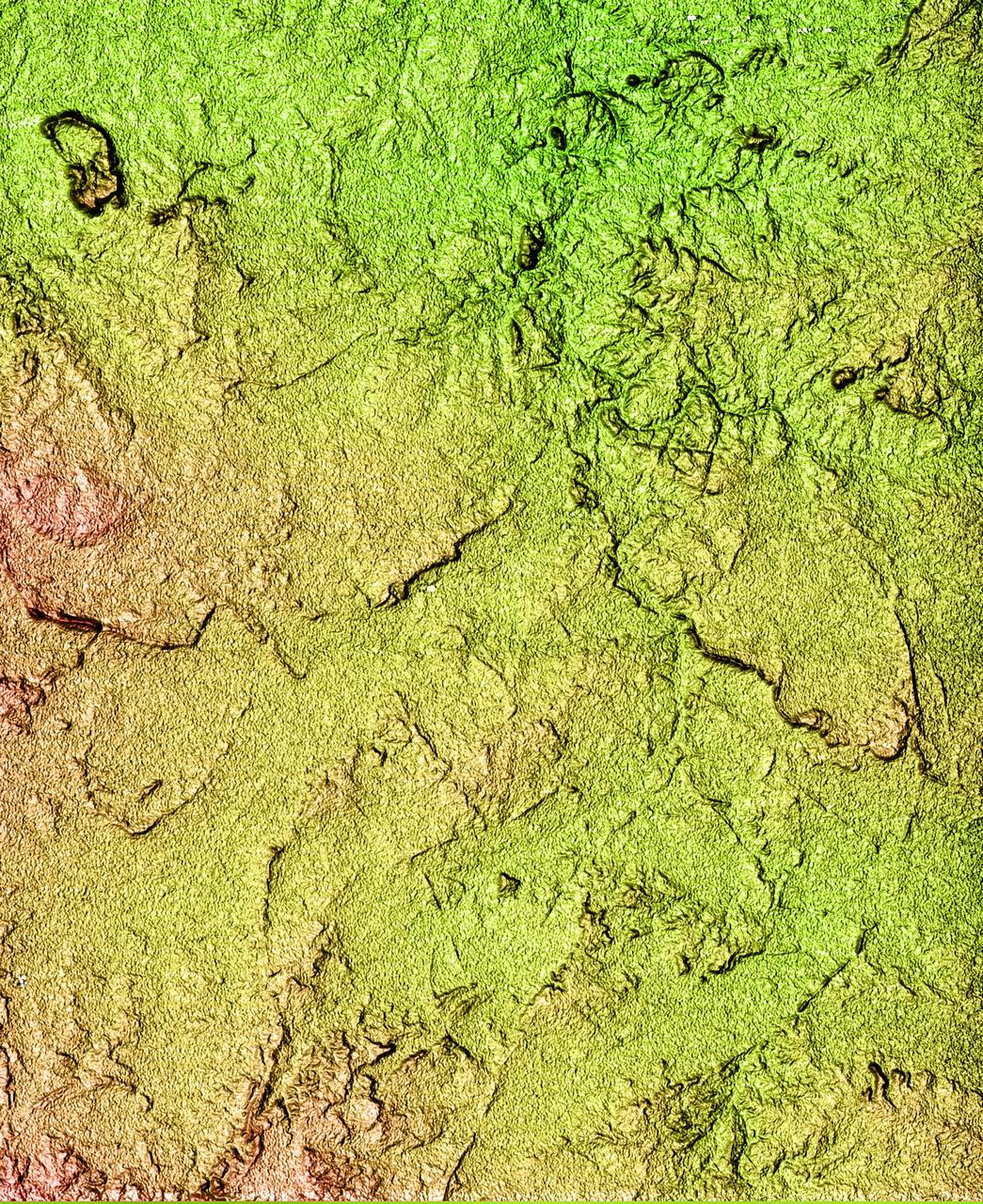
This radar image acquired in February 2000 by NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM shows an area in the state of Bahia in Brazil.
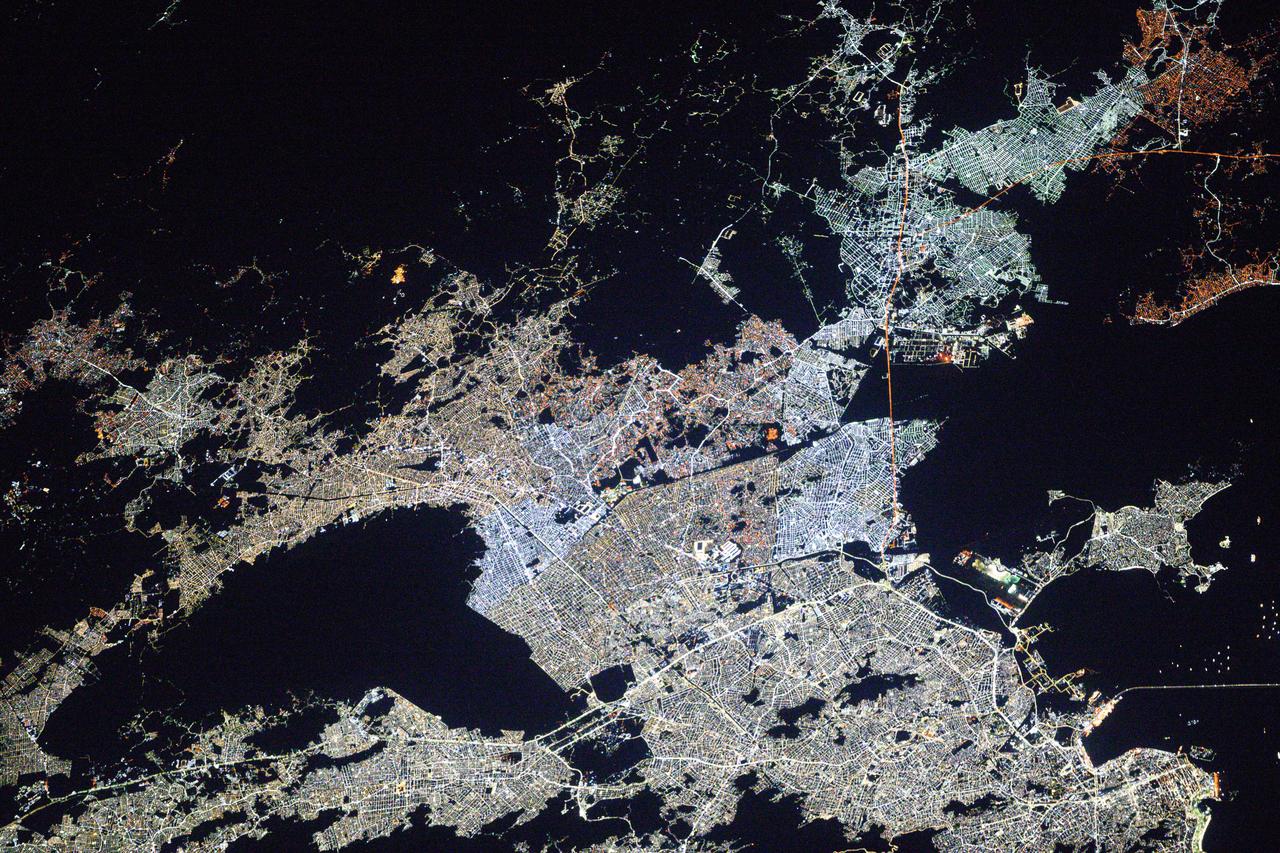

iss073e0119293 (May 20, 2025) --- Rio de Janiero, Brazil's capital and second most-populous city, along with its surrounding suburbs, is pictured in between the dark voids representing Nova Iguaçu Volcano (left) and Guanabara Bay (right) at approximately 3:06 a.m. local time from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above the Atlantic Ocean.
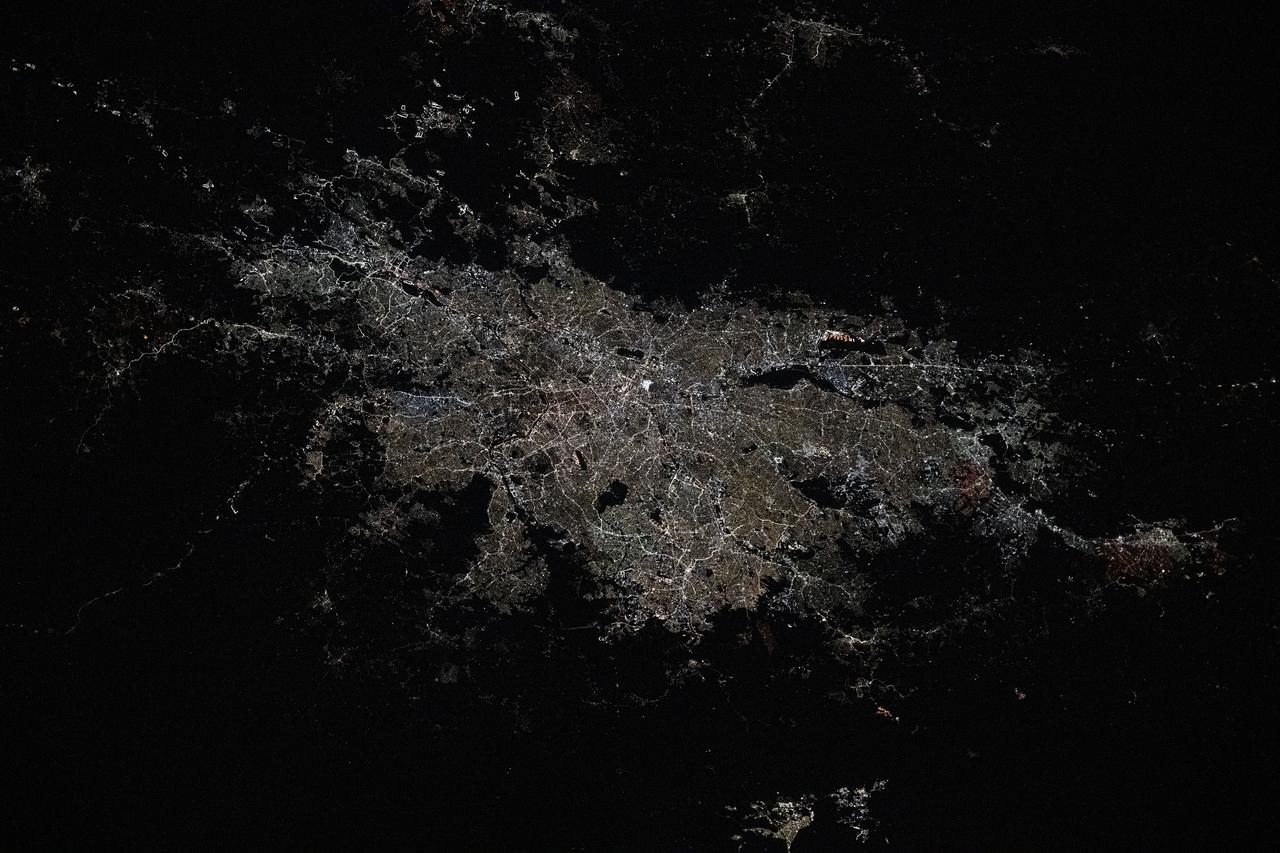

iss073e0120414 (May 19, 2025) --- São Paulo, Brazil, the South American nation's largest city with a population of about 11.9 million, and its surrounding suburbs including Guarulhos, with a population of about 1.29 million, are pictured at approximately 3:54 a.m. local time from the International Space Station as it orbited 265 miles above the Atlantic Ocean.

AS04-01-200 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Coastal Brazil, Atlantic Ocean, West Africa, Sahara, looking northwest, as photographed from the unmanned Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) earth-orbital space mission. This picture was taken when the Spacecraft 017 and the Saturn IVB stage were orbiting Earth at an altitude of 9,060 nautical miles.
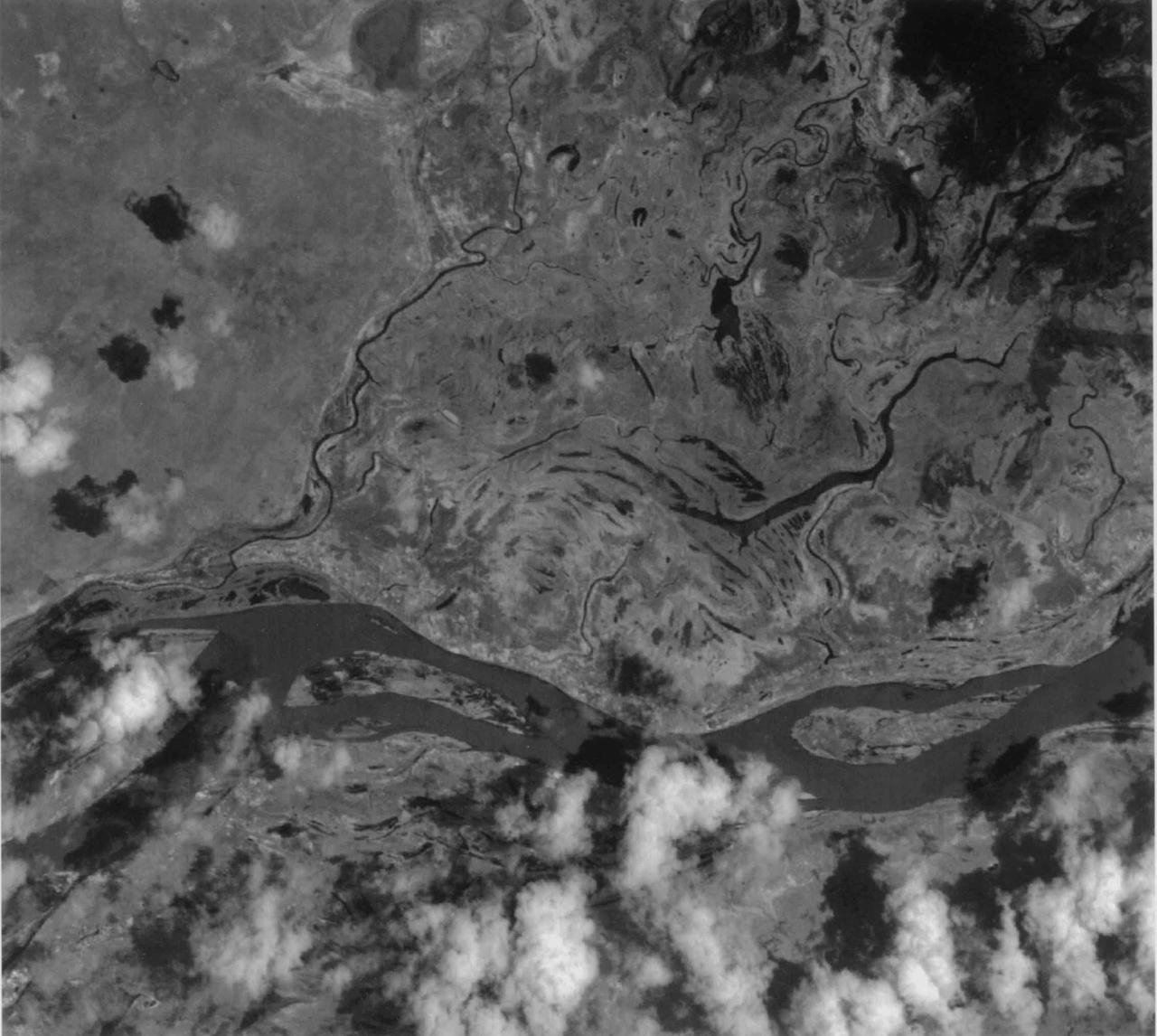

This image of the San Francisco River channel, and its surrounding flood zone, in Brazil was acquired by band 3N of ASTER's Visible/Near Infrared sensor. The surrounding area along the river channel in light gray to white could be covered by dense tropical rain forests. The water surface of the San Francisco River shows rather gray color as compared to small lakes and tributaries, which could indicate that the river water is contaminated by suspended material. The size of image: 20 km x 20 km approx., ground resolution 15 m x 15 m approximately. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02451

Dr. Woodrow Whitlow, Jr. (left), Associate Administrator for Mission Support Directorate at NASA Headquarters presents Donna Brazile, keynote speaker at a program celebrating National Women's History Month, with a framed NASA montage, Thursday, March 14, 2013 in Washington. The theme of theprogram was "Women Inspiring Innovation Through Imagination," and was sponsored by the HQ Equal Opportunity and Diversity Management Division at NASA Headquarters. The event also commemorates the 100th Anniversary of the Women's Suffrage March on Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Technicians lower the cover over the shipping container holding the international Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft at Brazil National Institute for Space Research.

Technicians from NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., install thermal blankets on the Aquarius instrument at Brazil National Institute for Space Research.
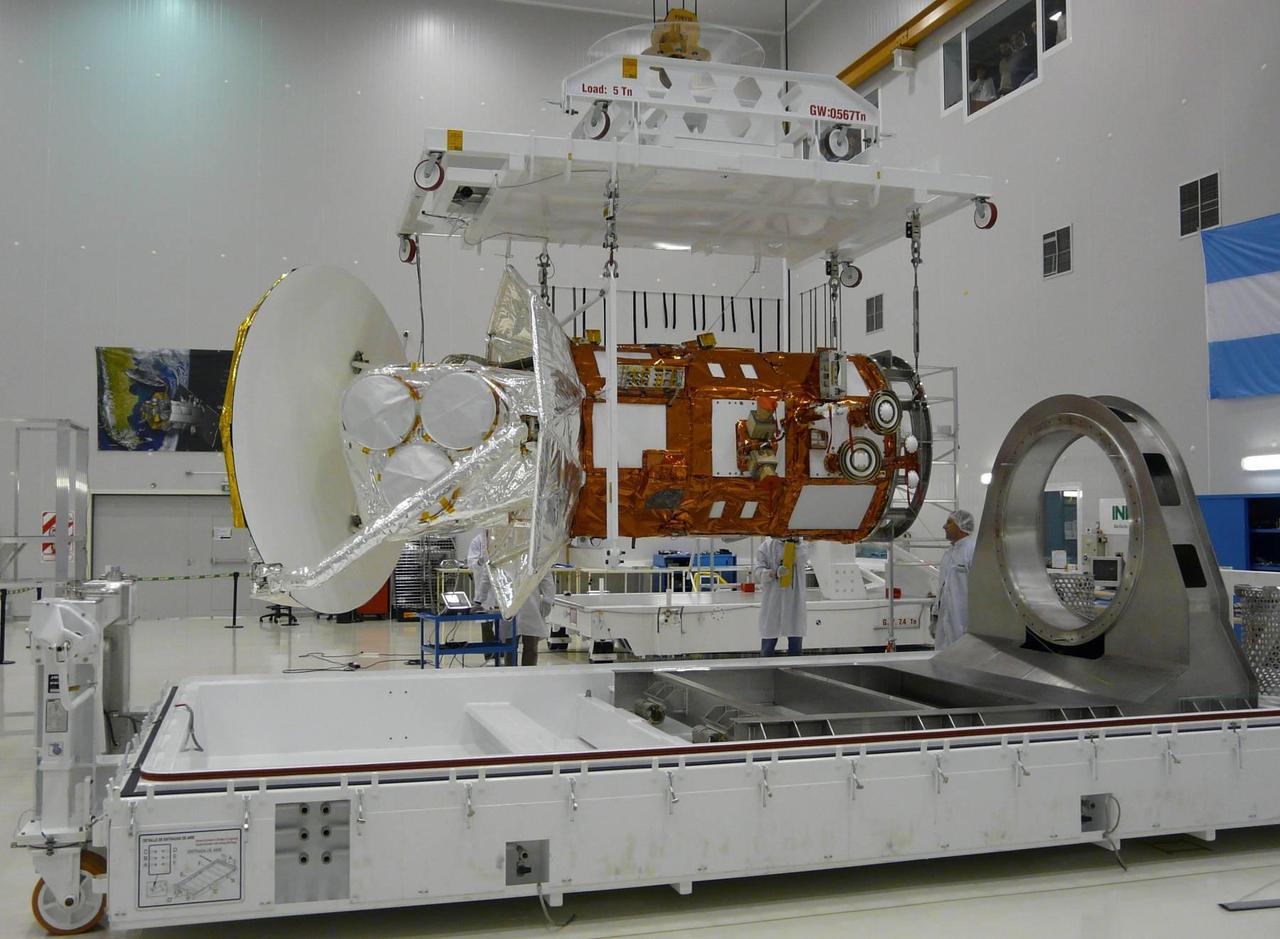

After months of integration and testing at the INVAP facility Bariloche, Argentina, NASA Aquarius/SAC-D is removed from the service platform in preparation for shipping to Brazil.
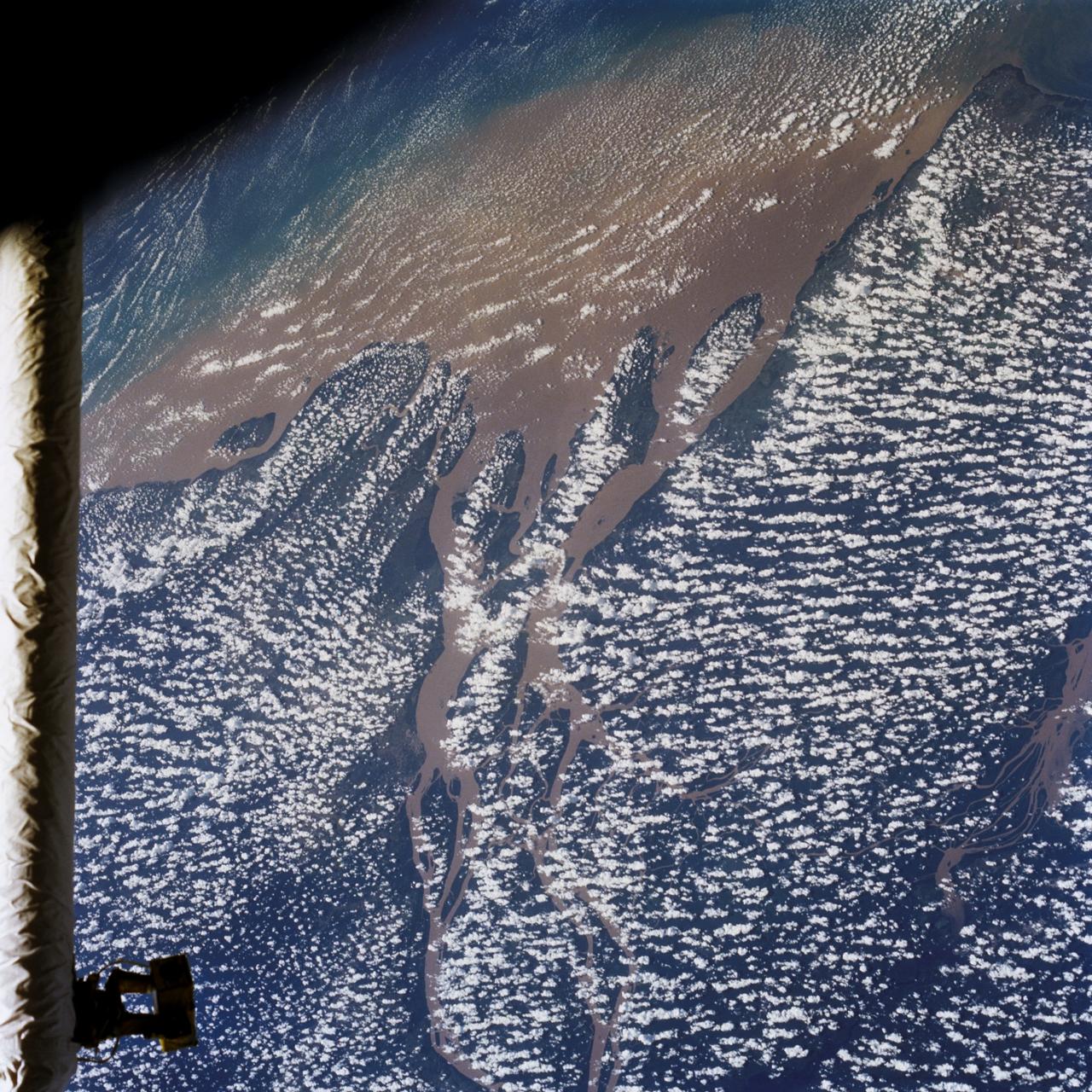

STS046-80-009 (31 July-8 Aug. 1992) --- A view of the mouth of the Amazon River and the Amazon Delta shows a large sediment plume expanding outward into the Atlantic Ocean. The sediment plume can be seen hugging the coast north of the Delta. This is caused by the west-northwest flowing Guyana Current. The large island of Marajo is partially visible through the clouds.
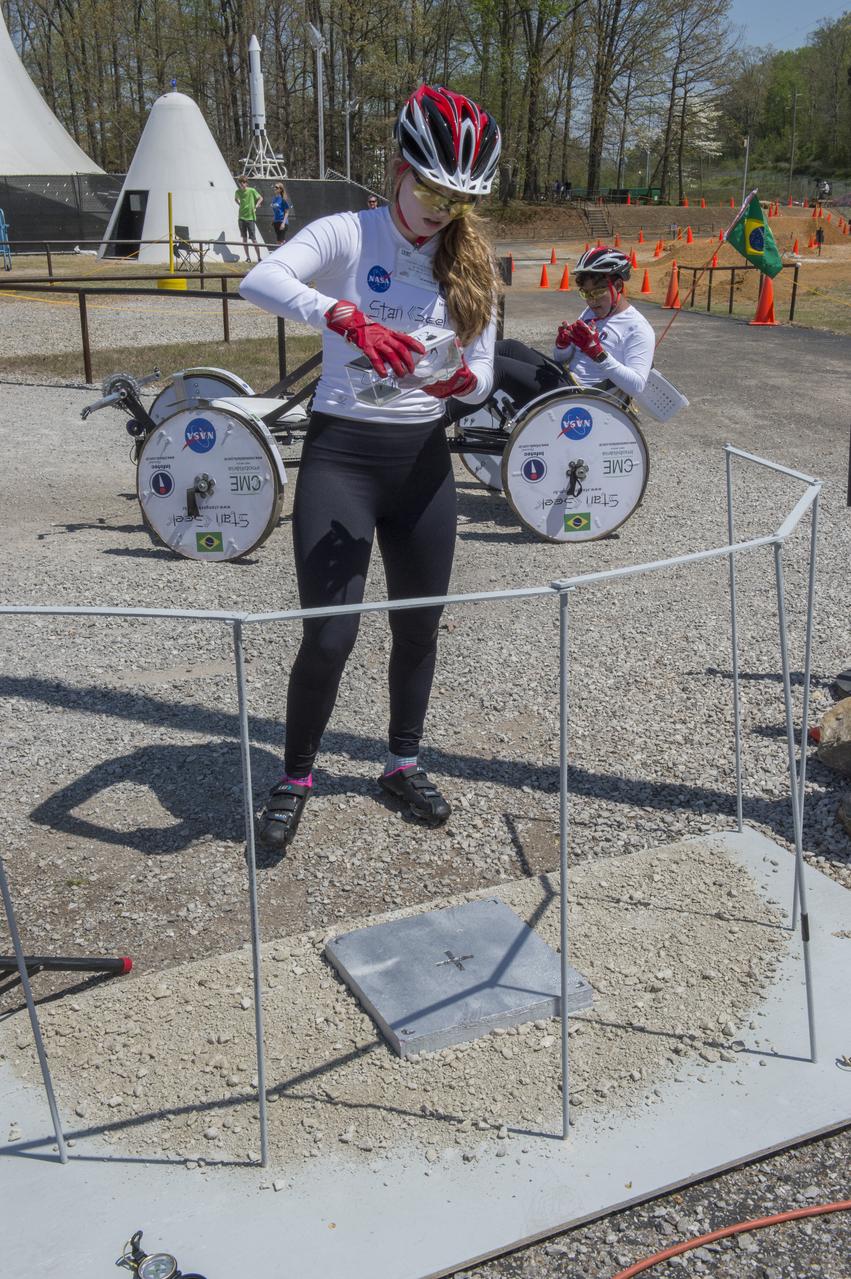

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
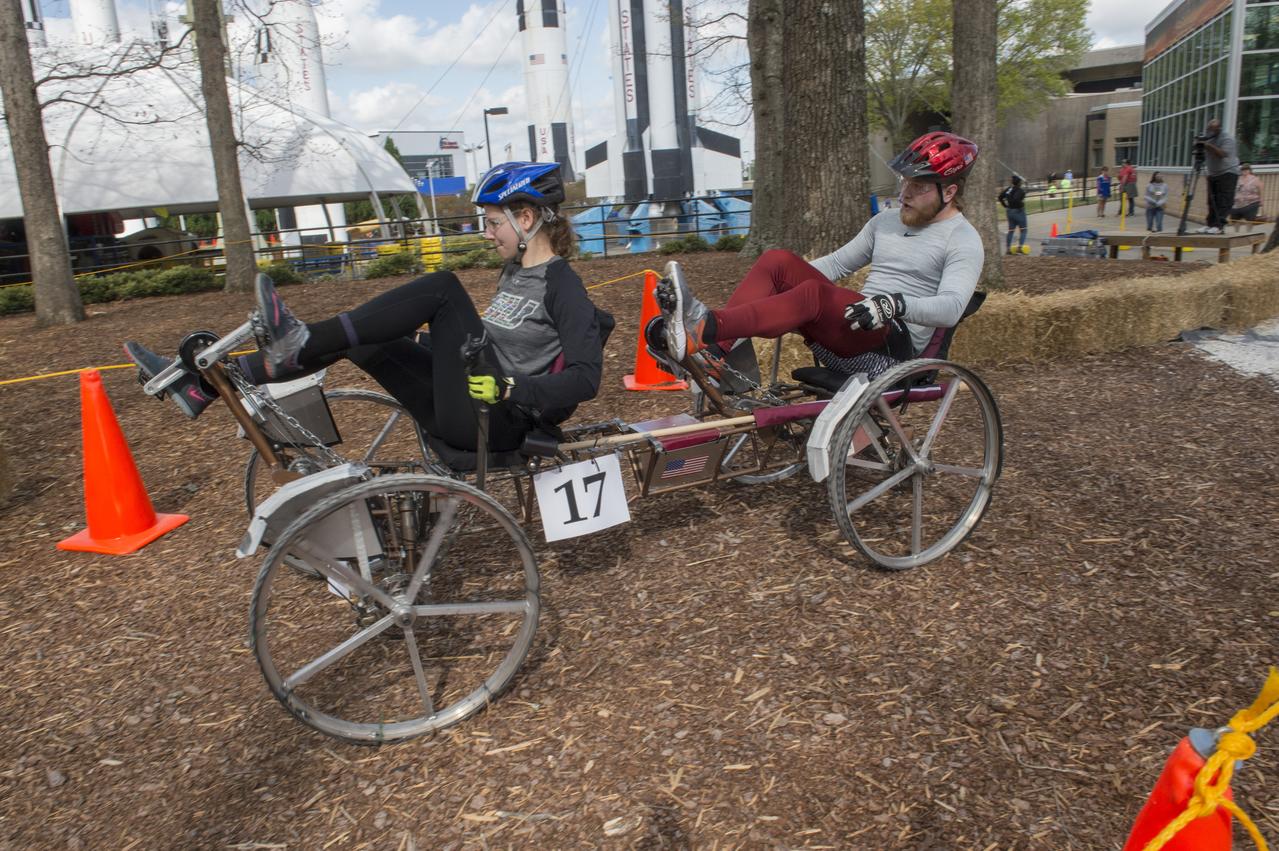

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
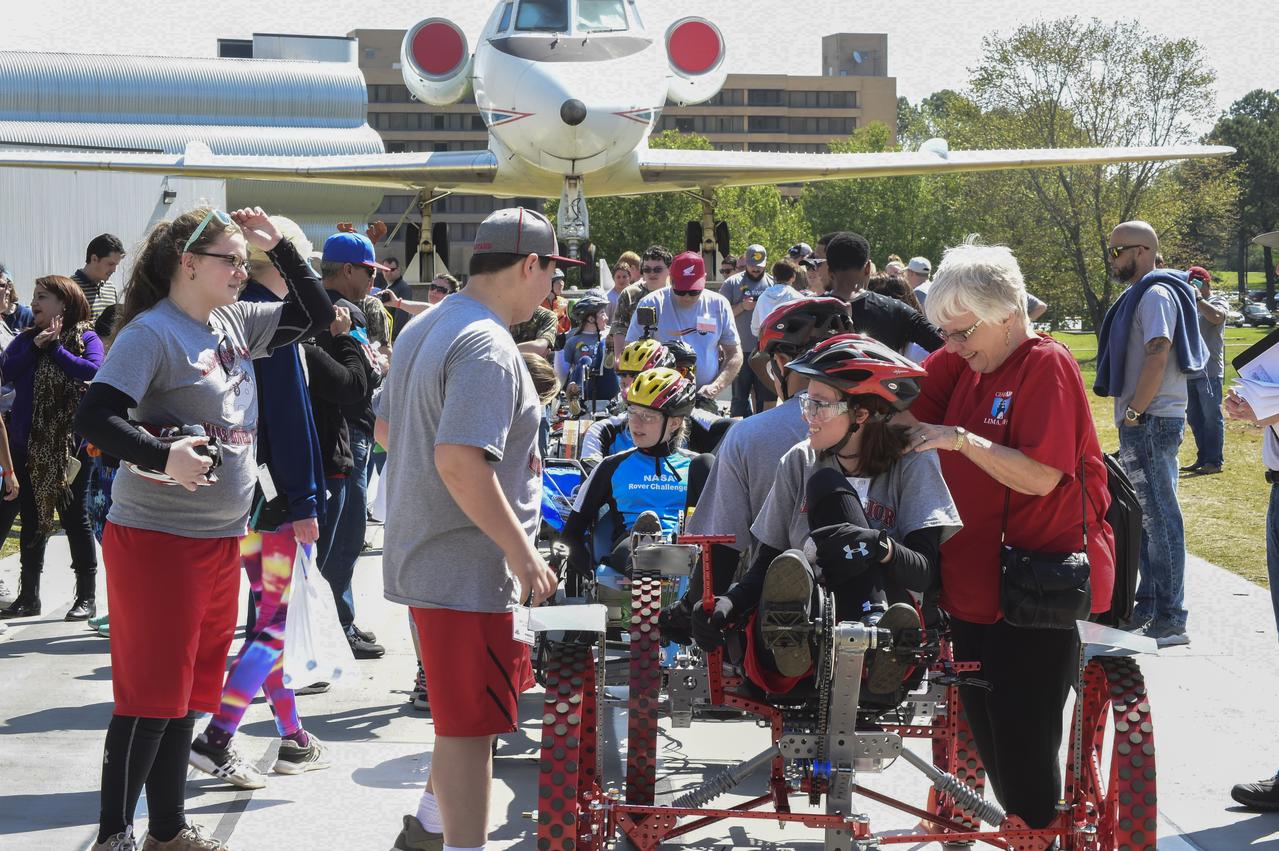

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
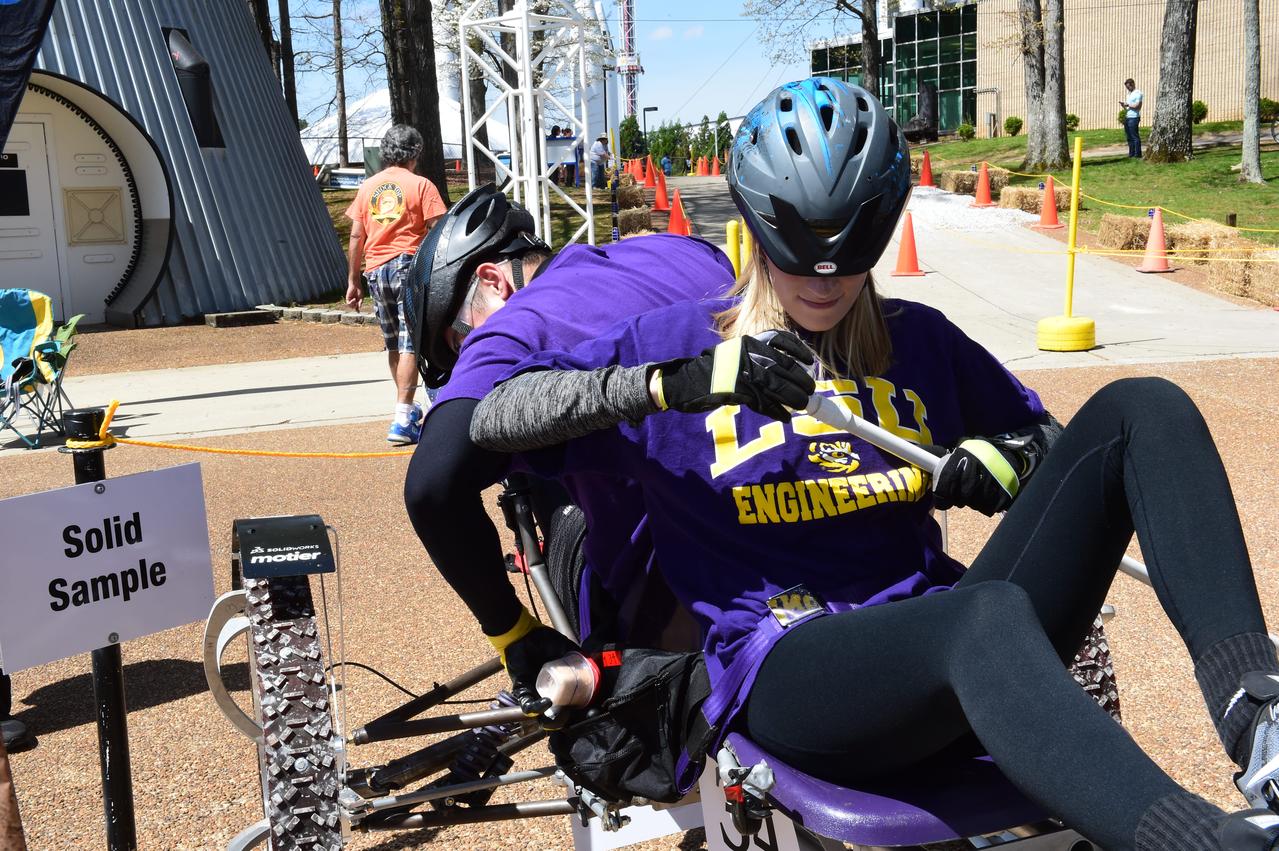

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
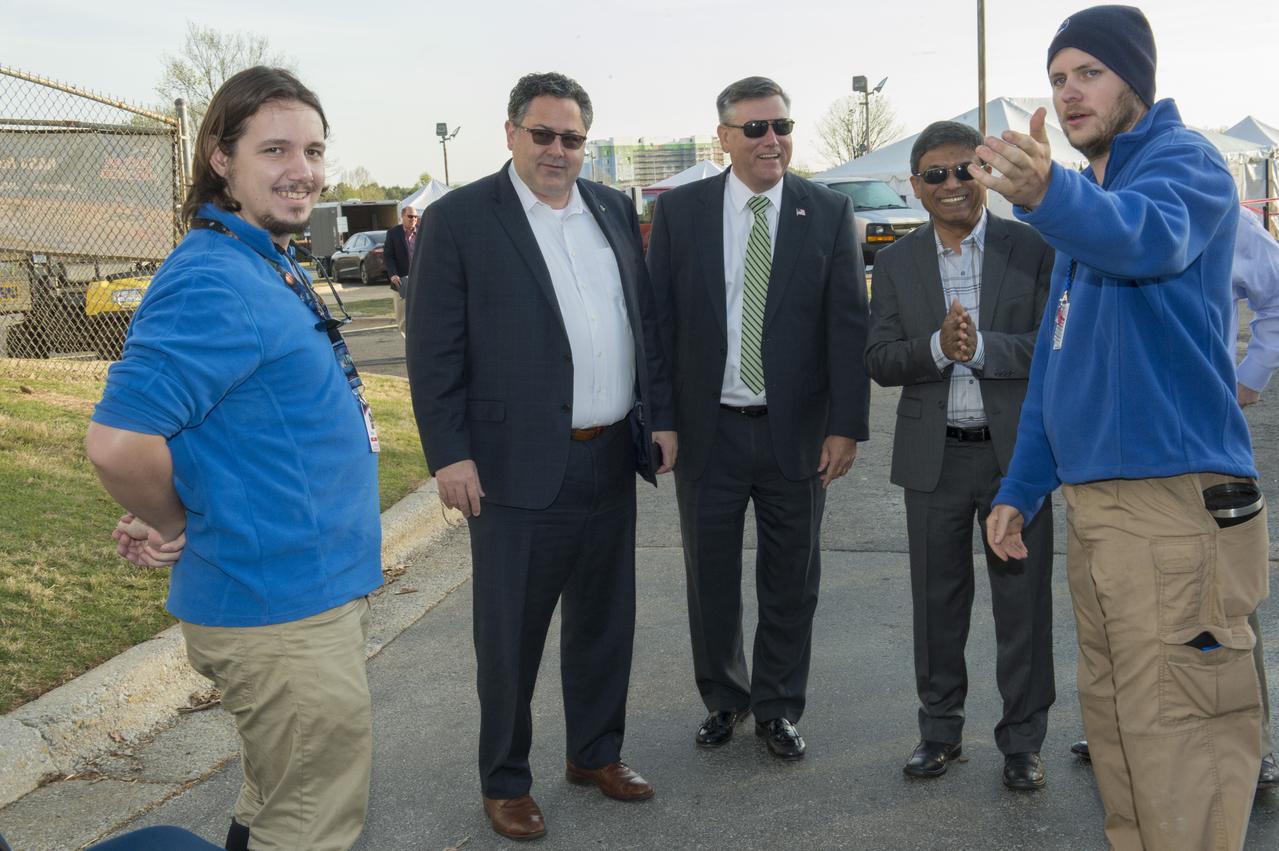

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
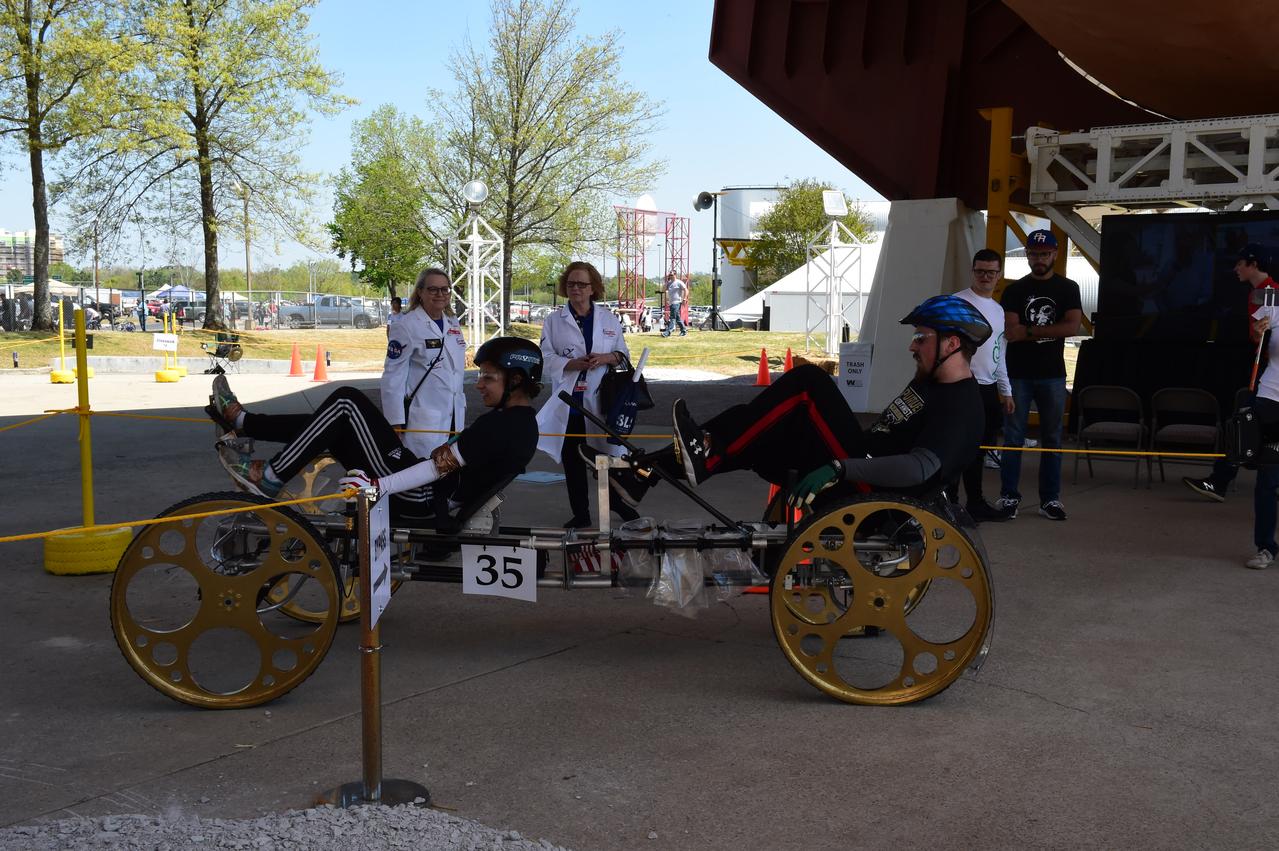

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
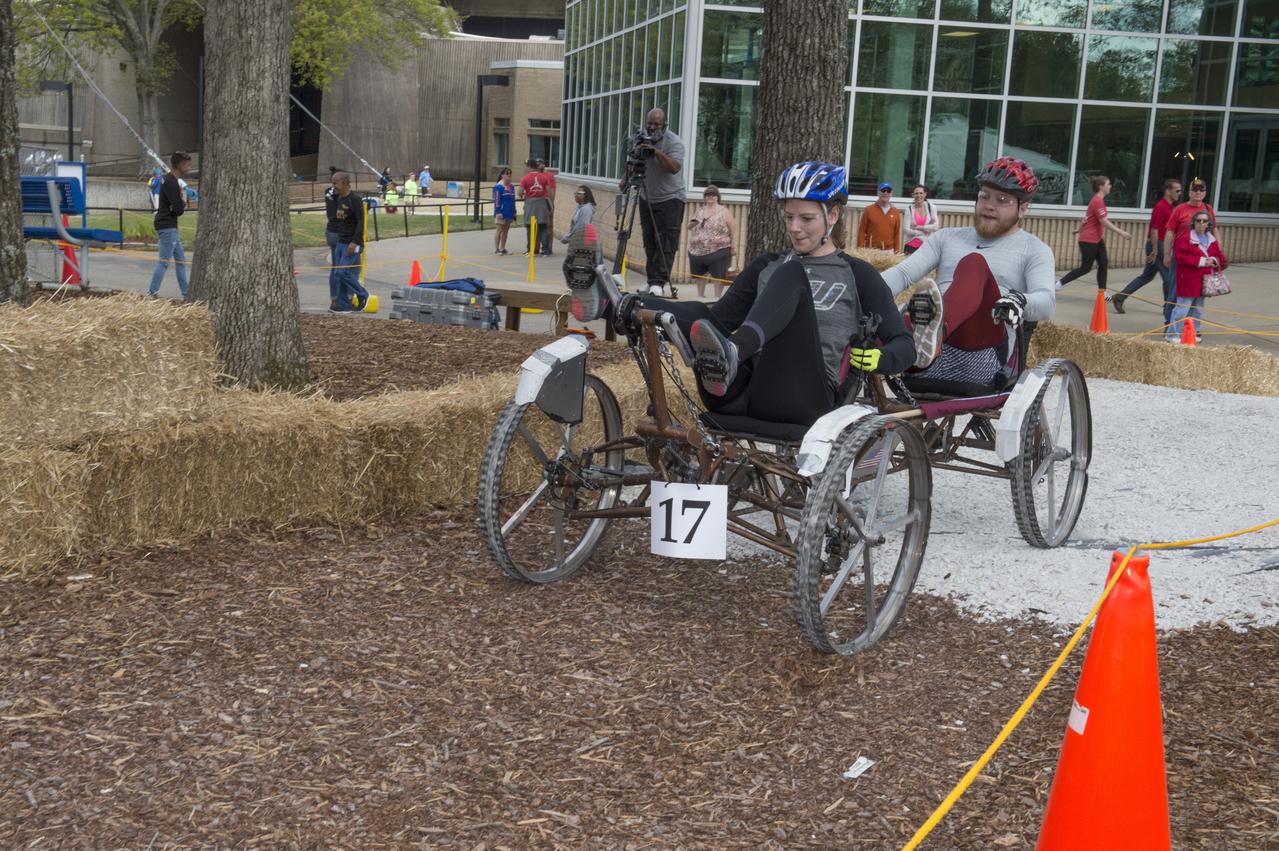

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
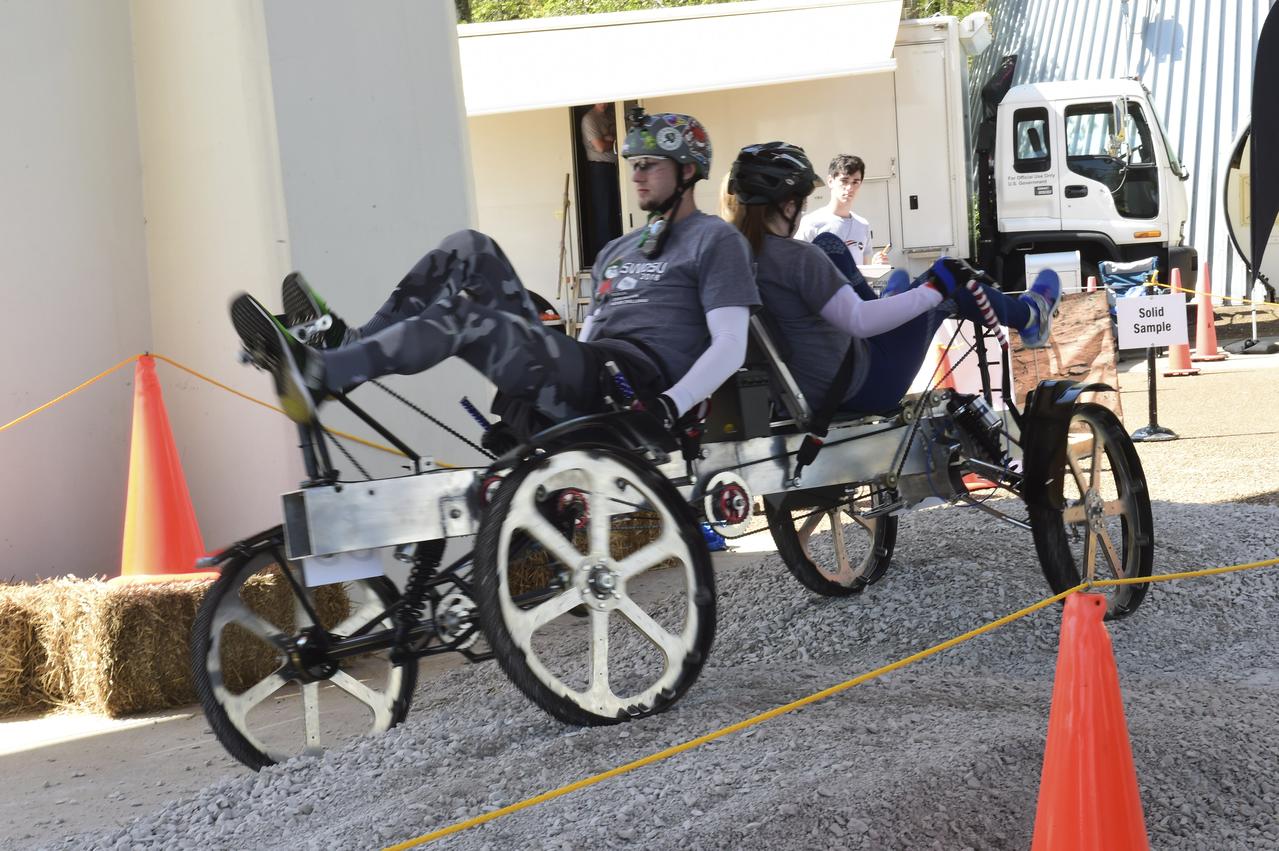

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
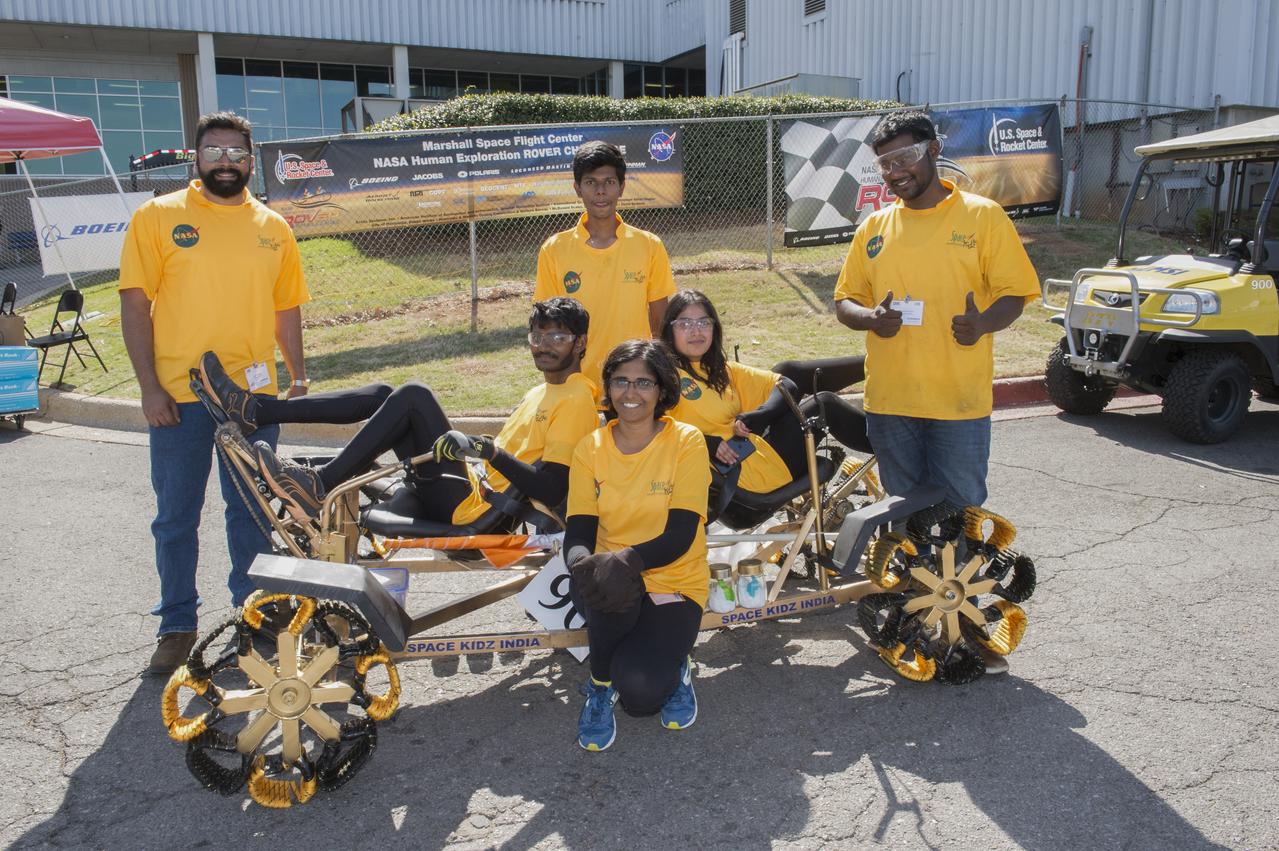

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
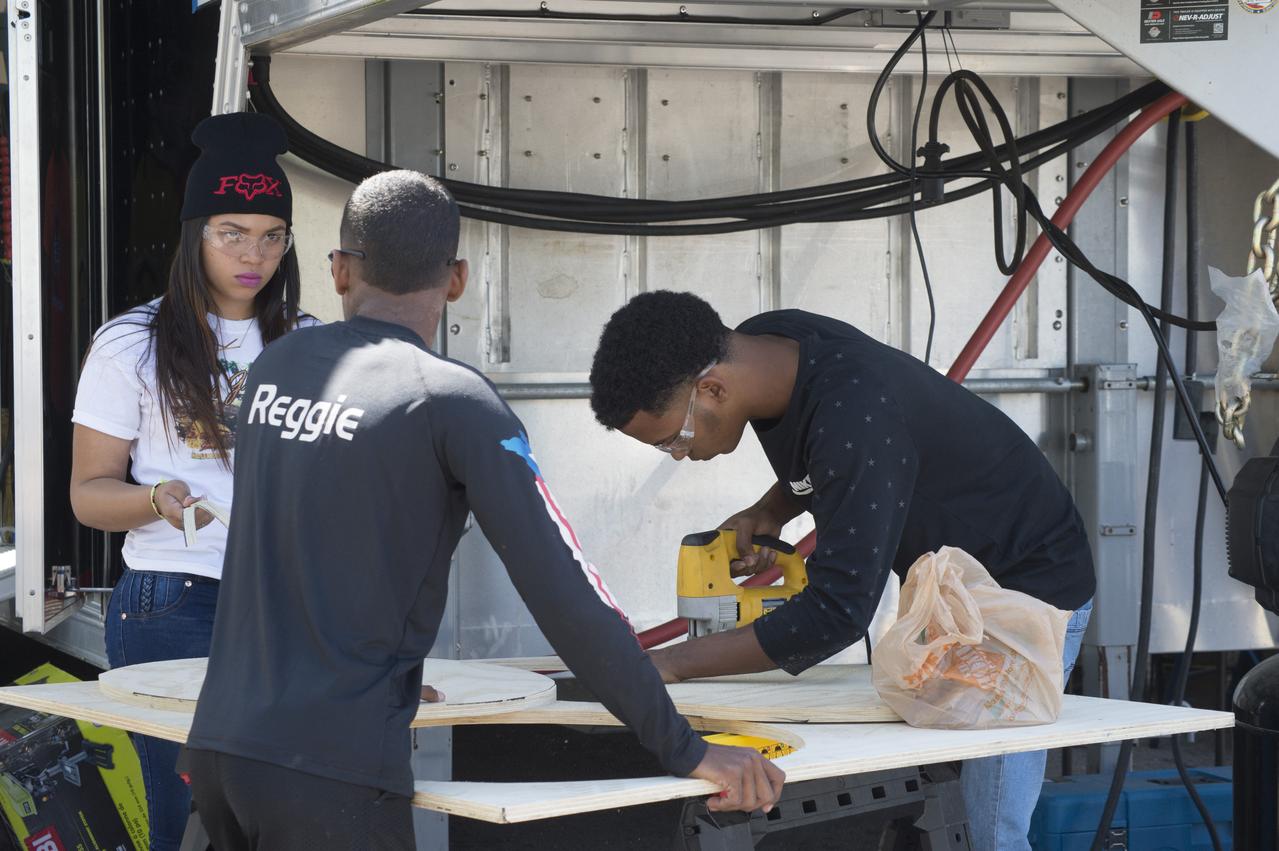

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
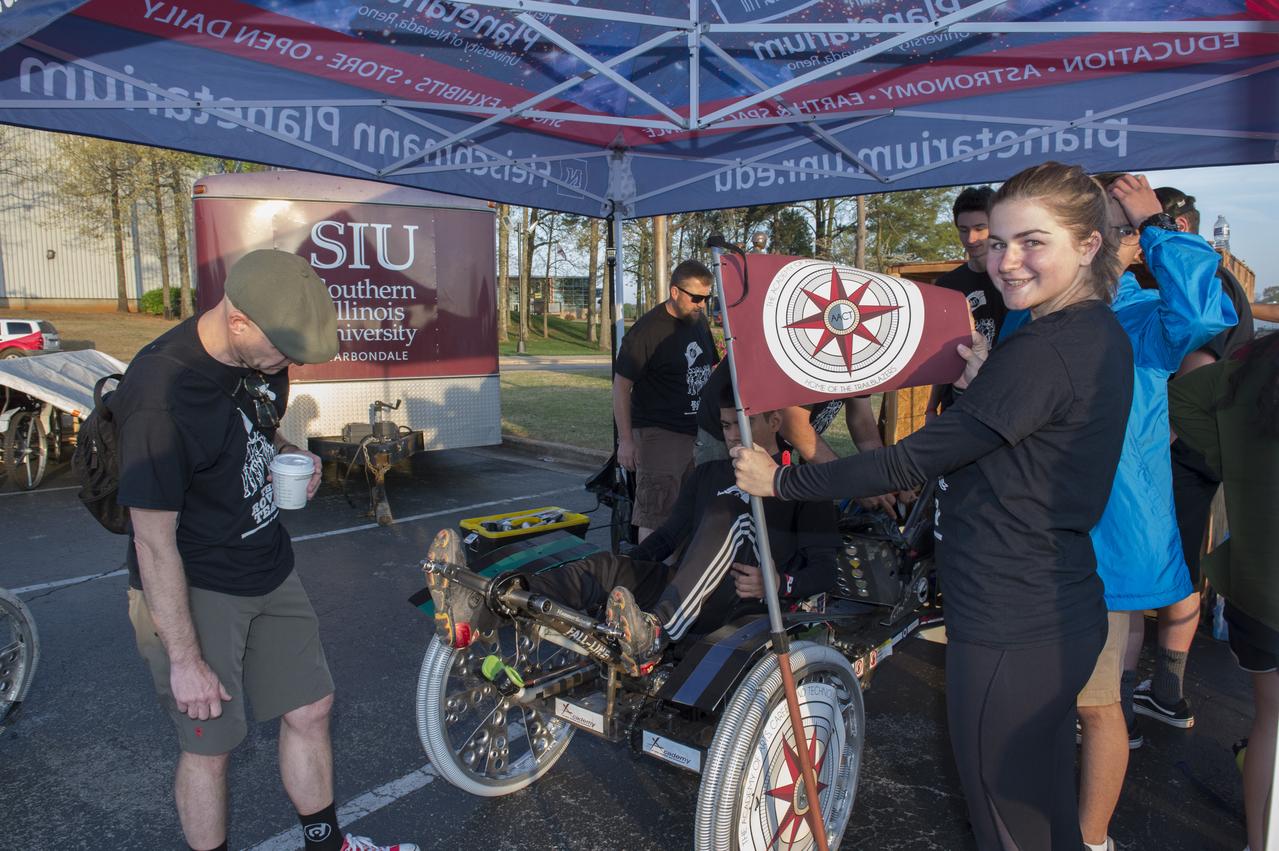

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
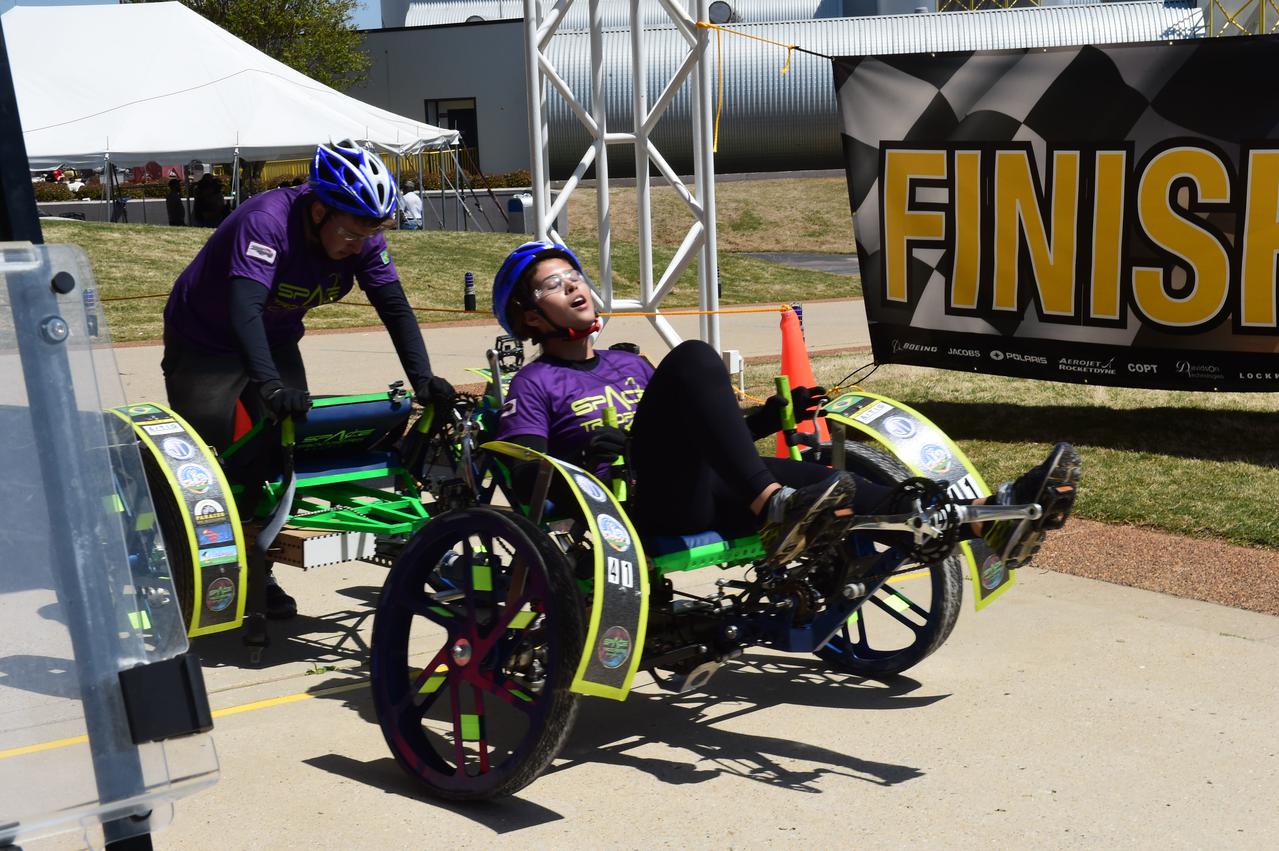

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
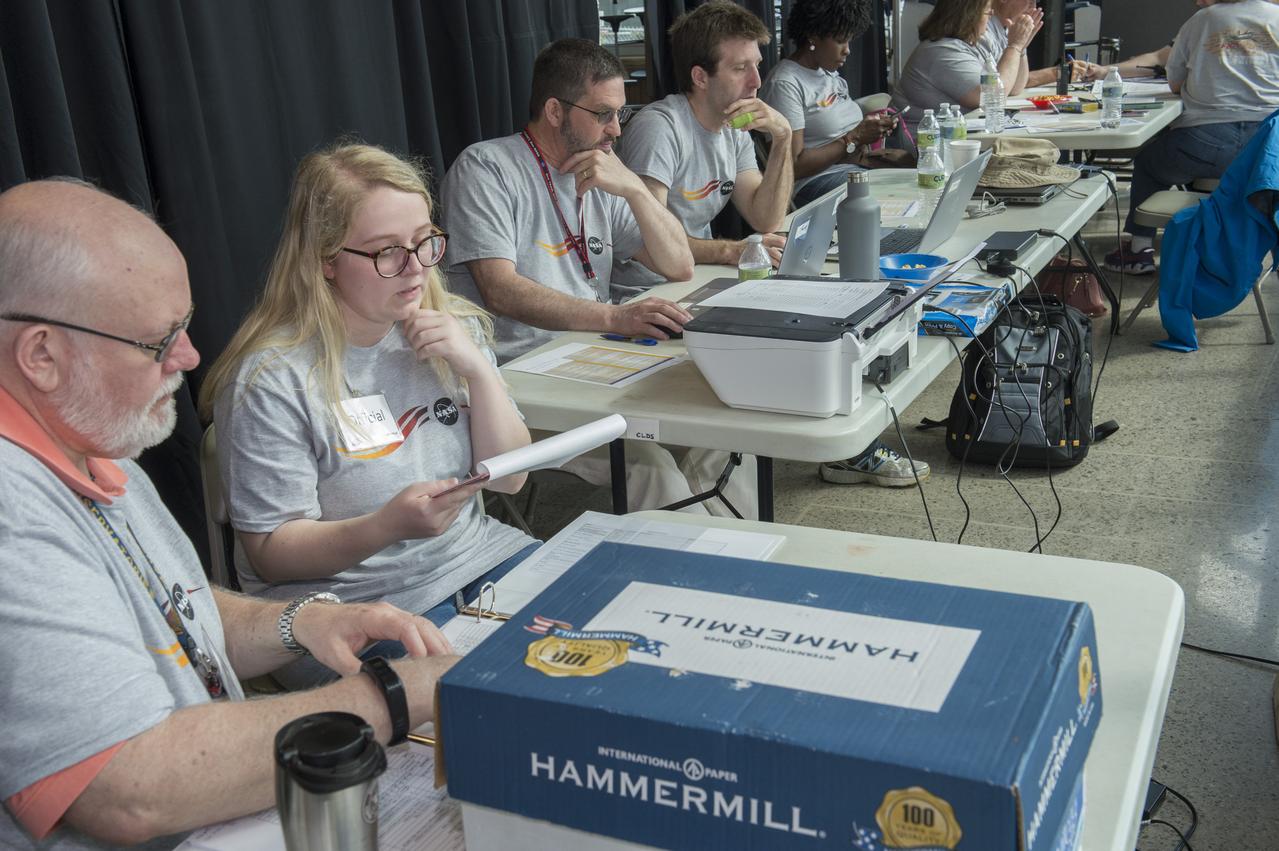

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
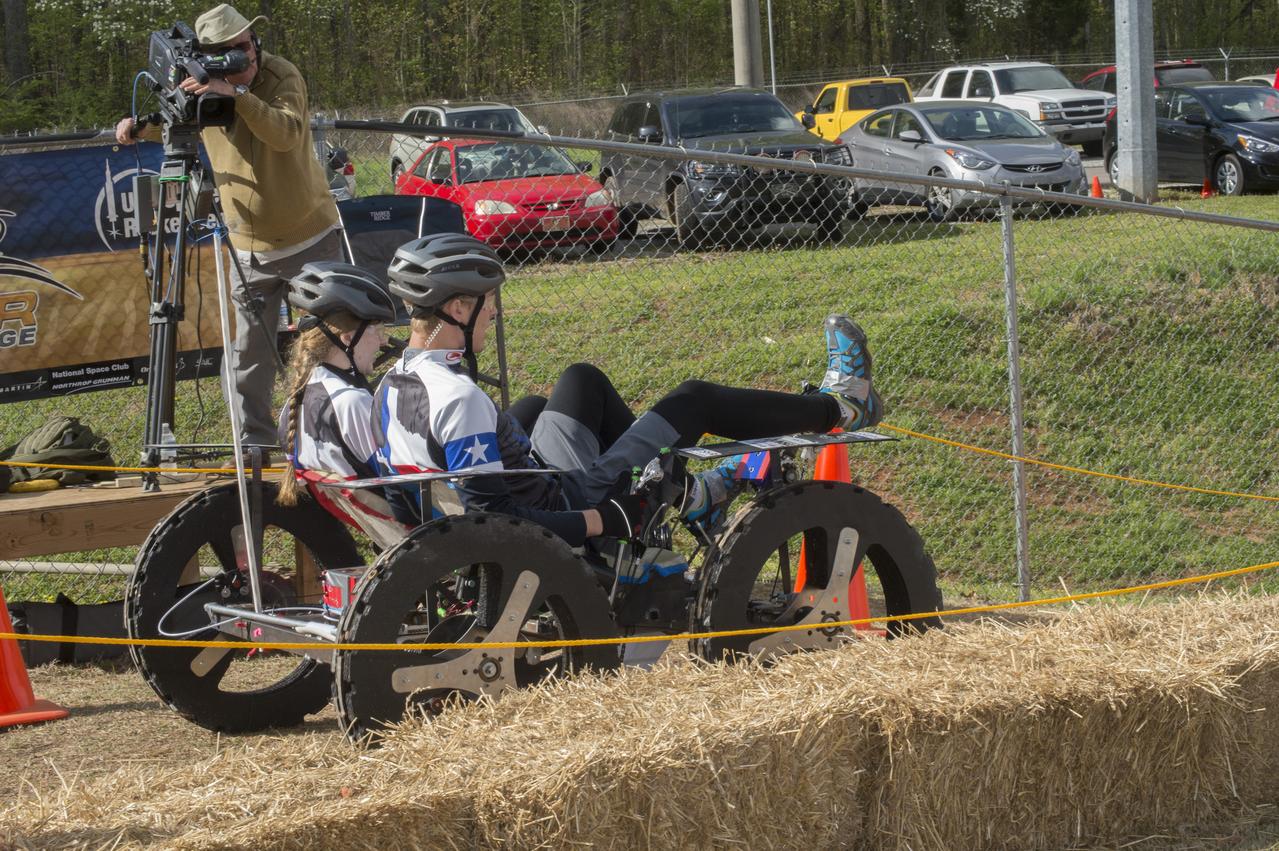

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
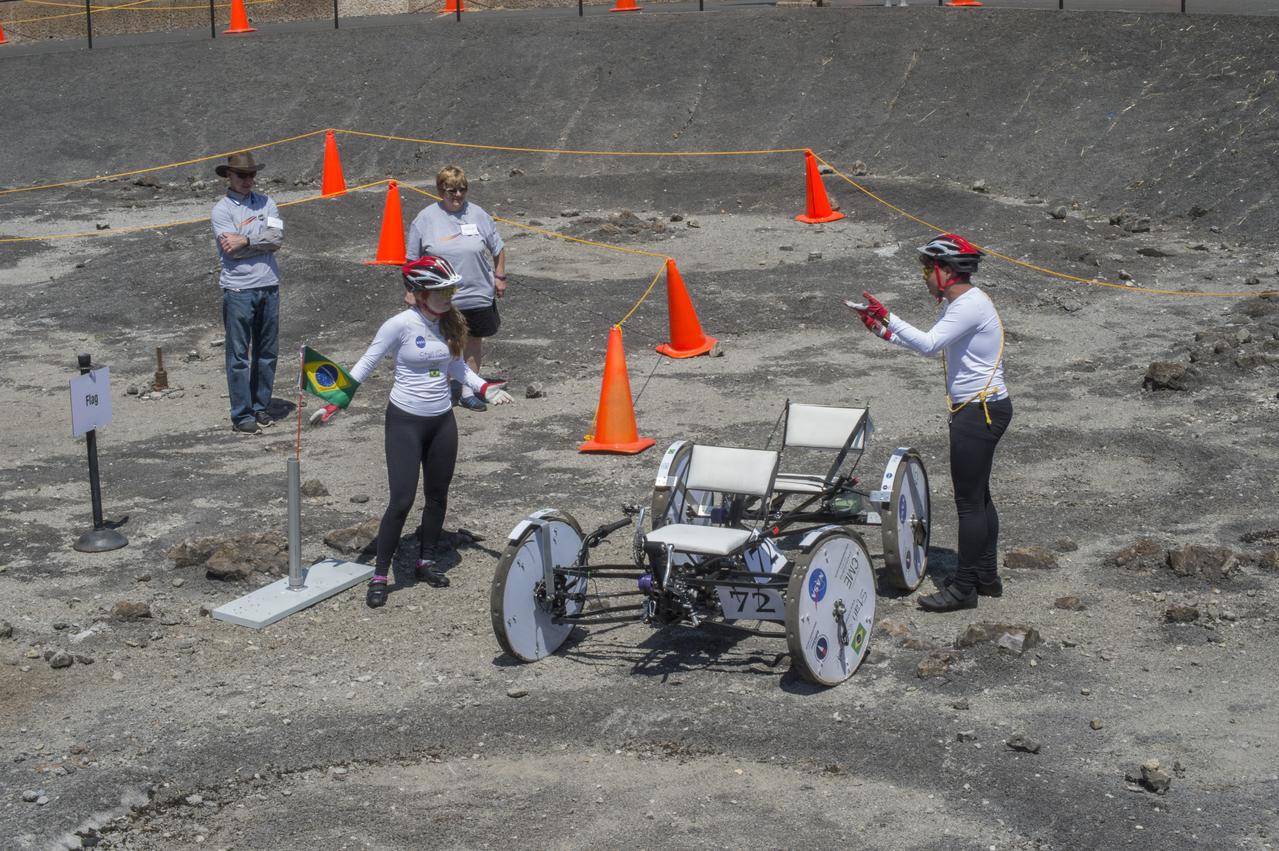

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
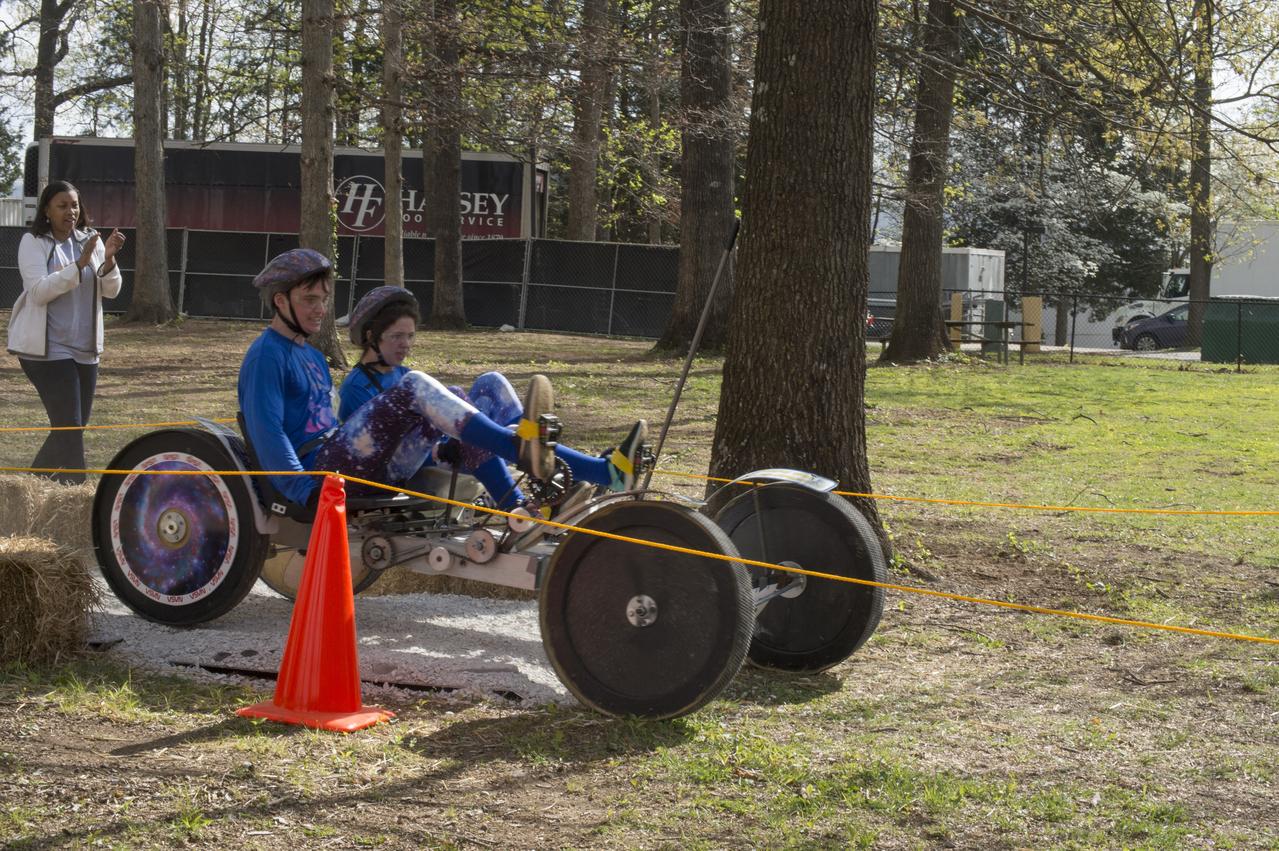

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
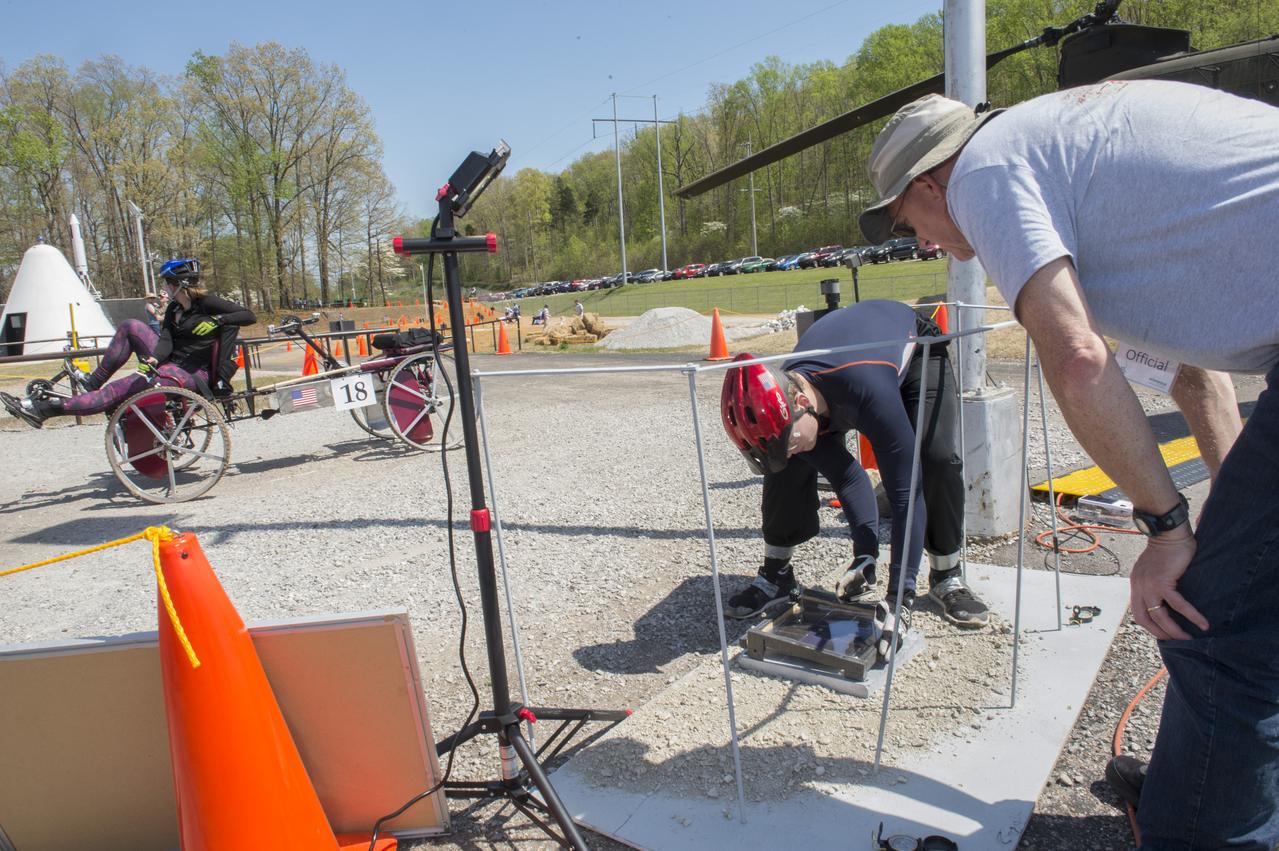

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
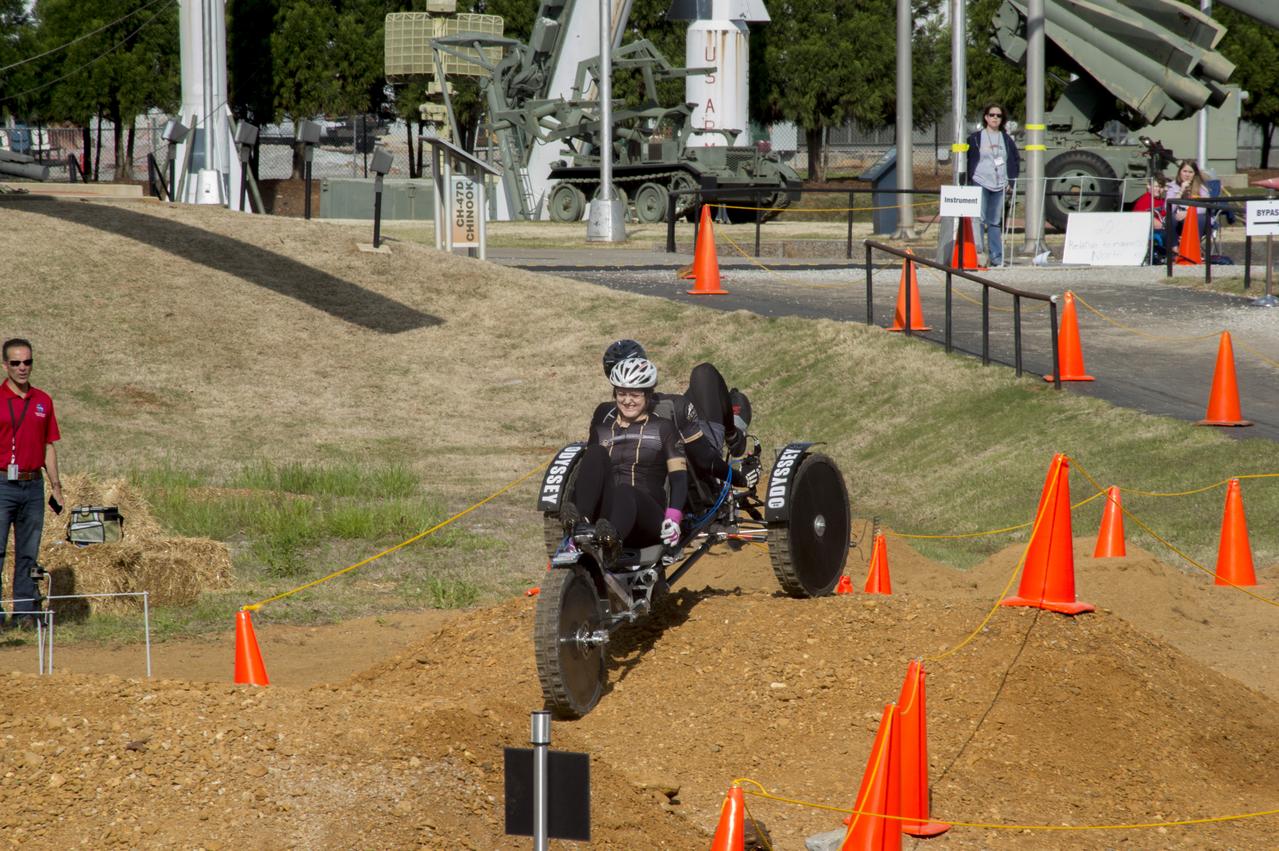

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
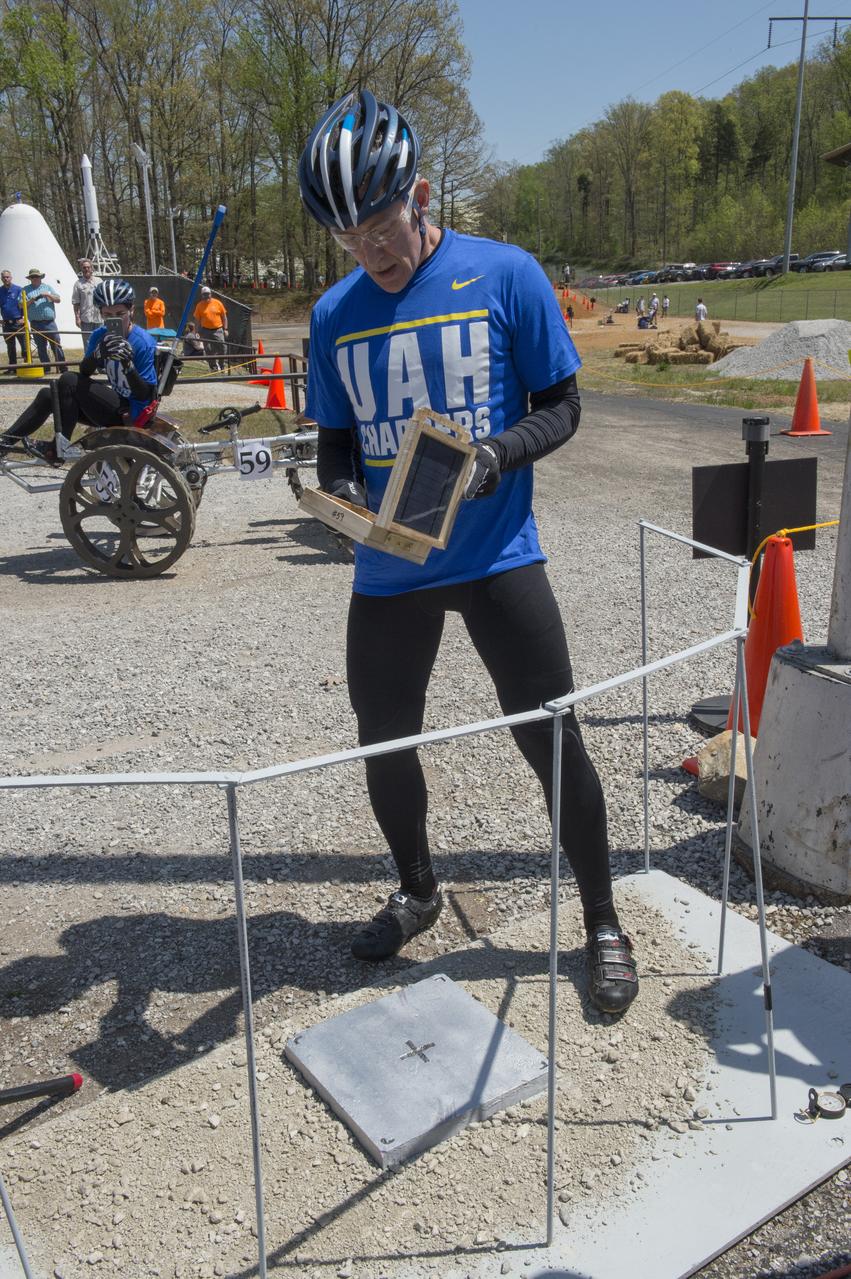

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
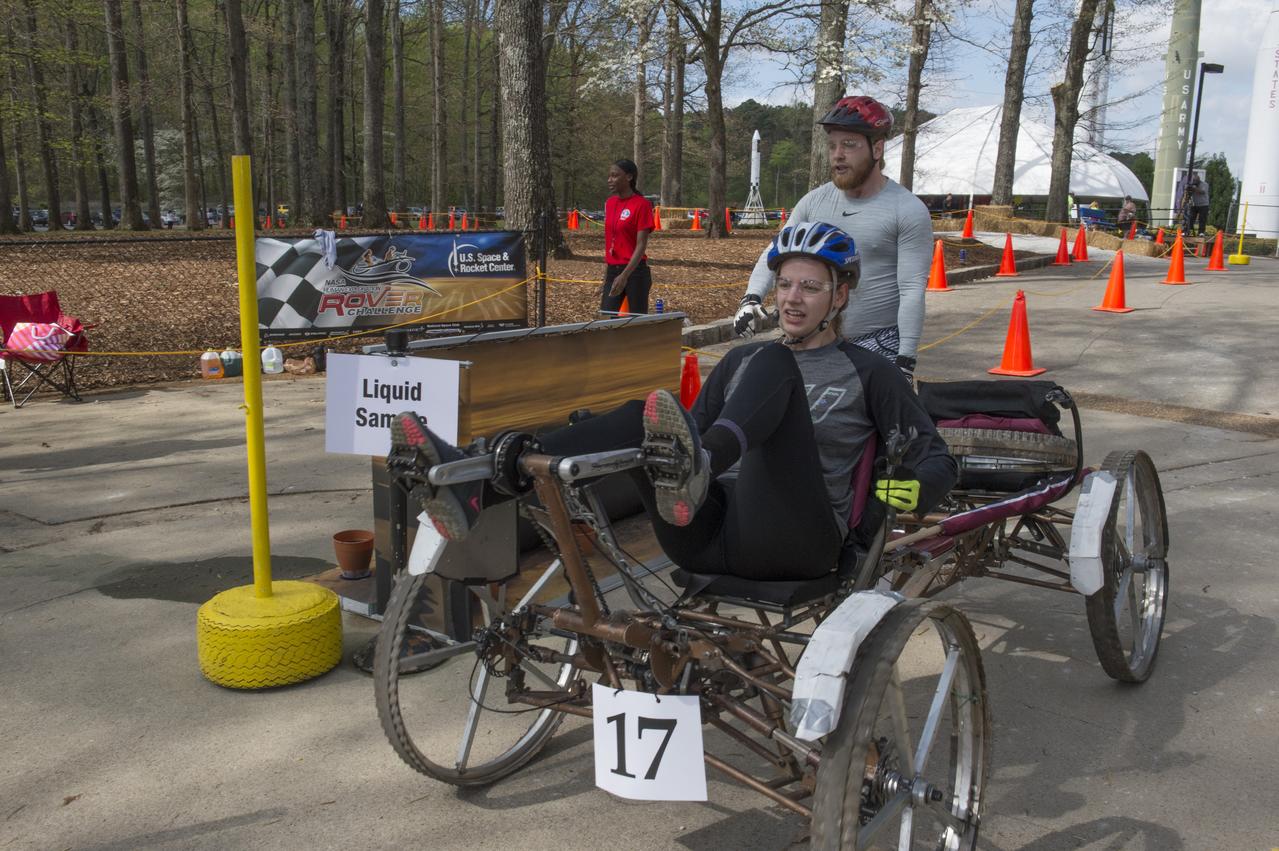

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
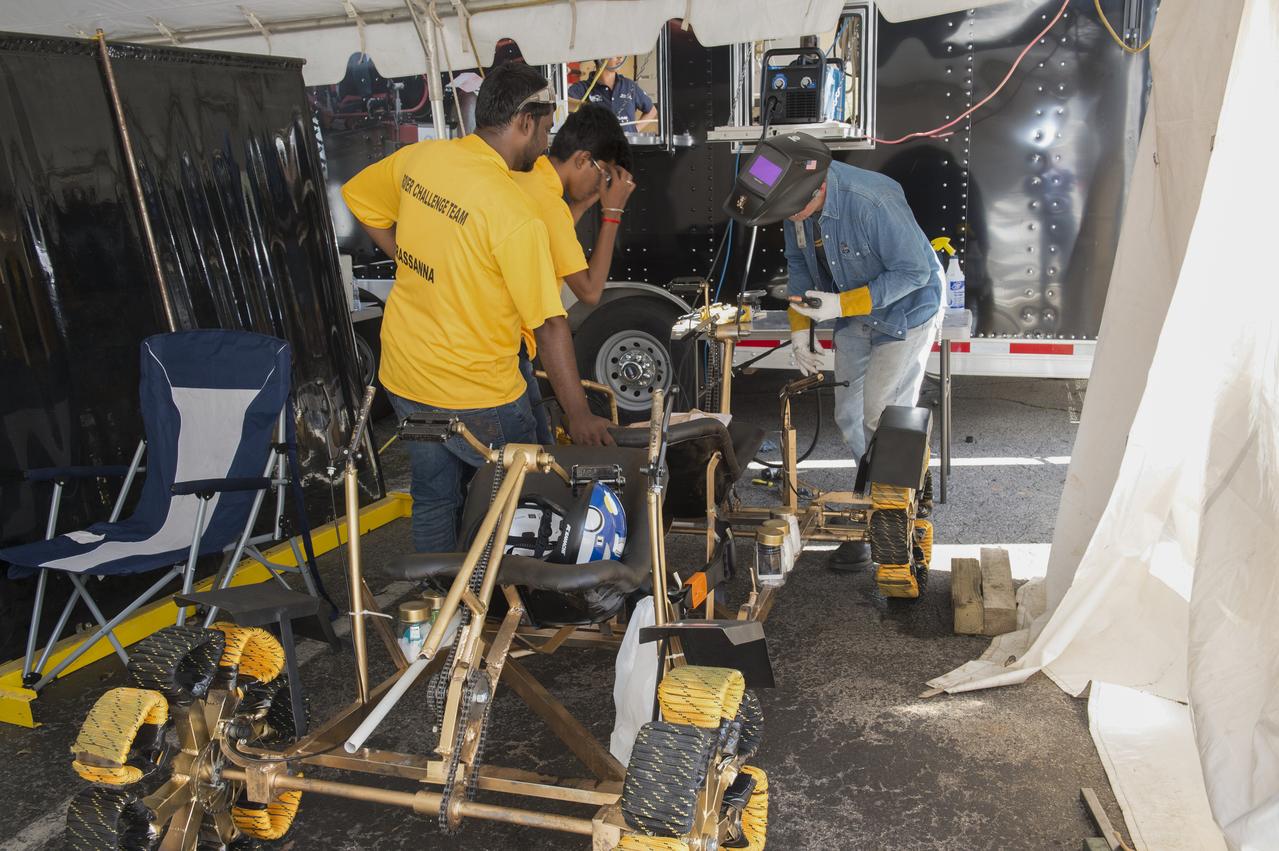

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
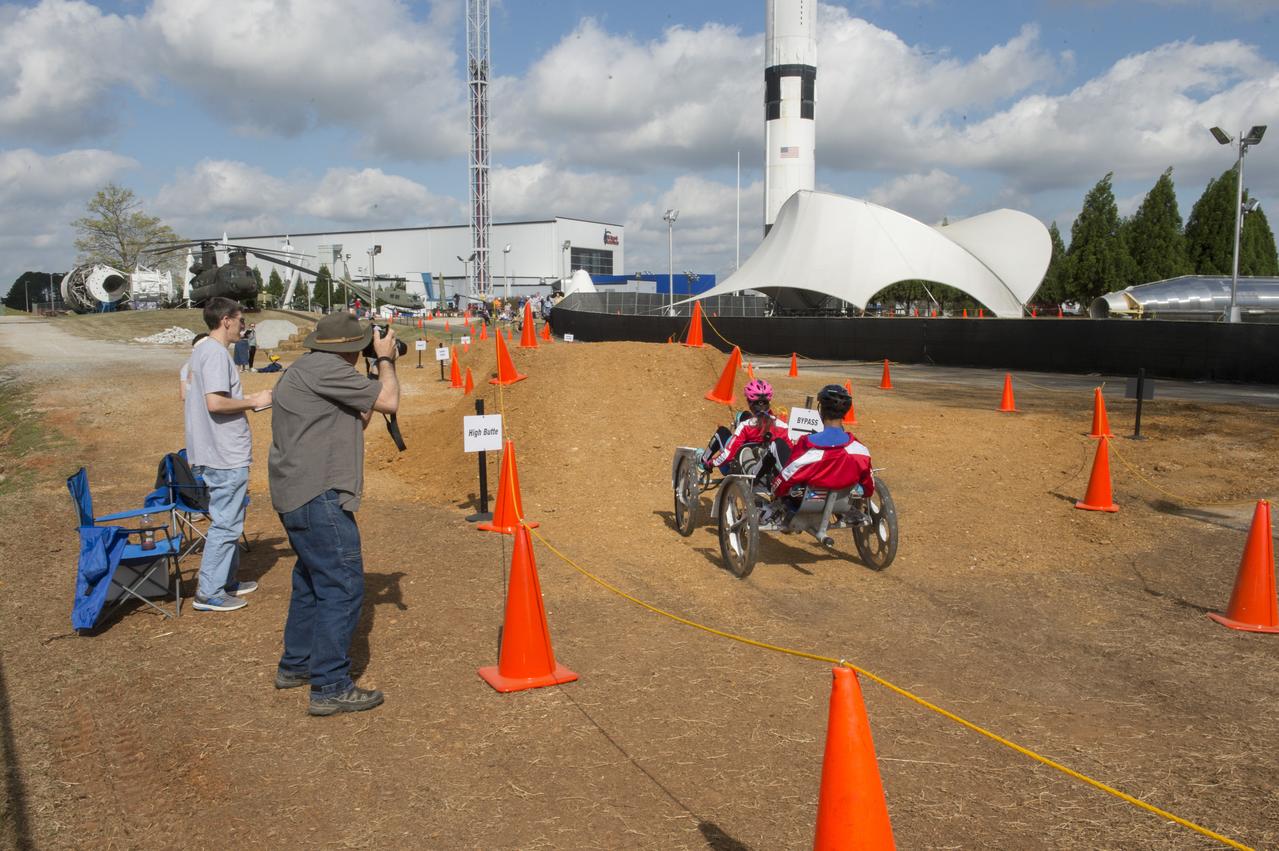

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
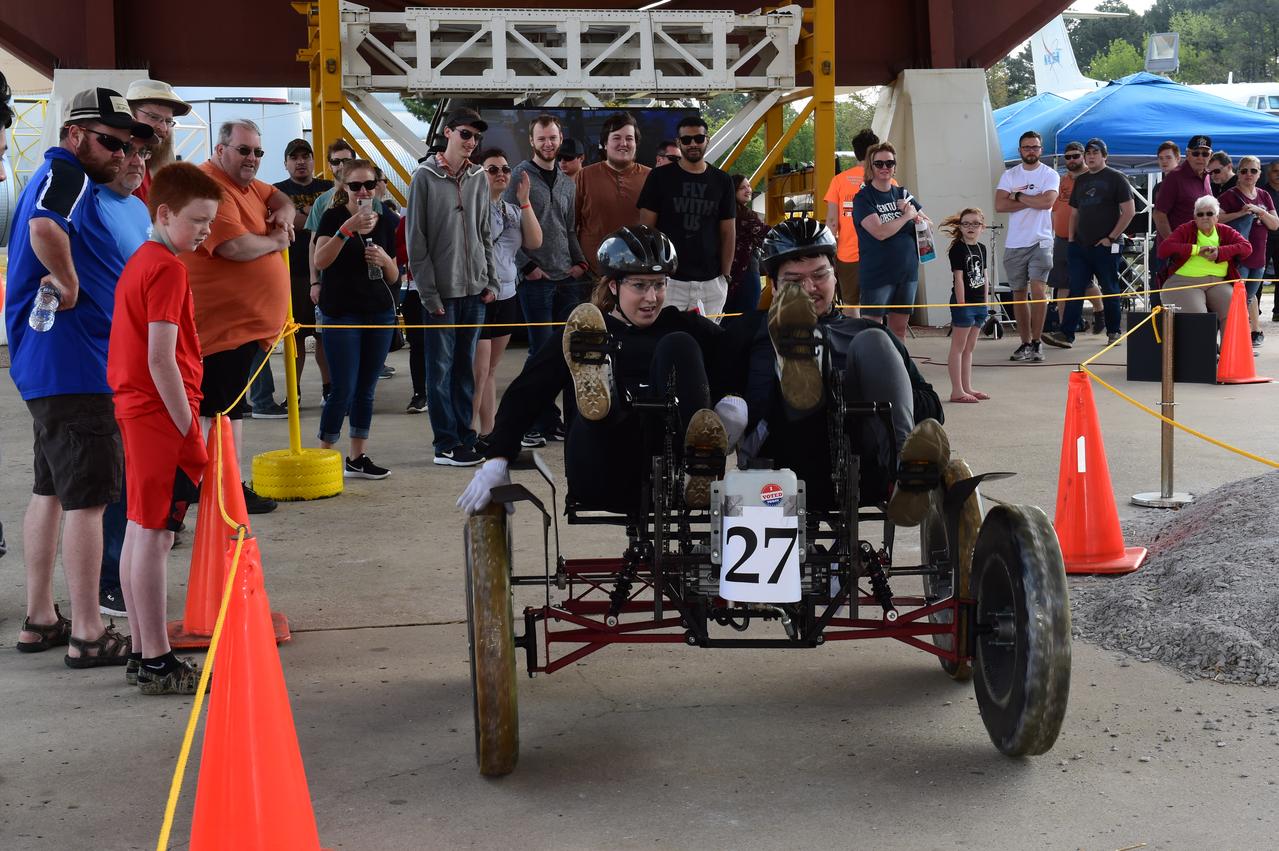

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
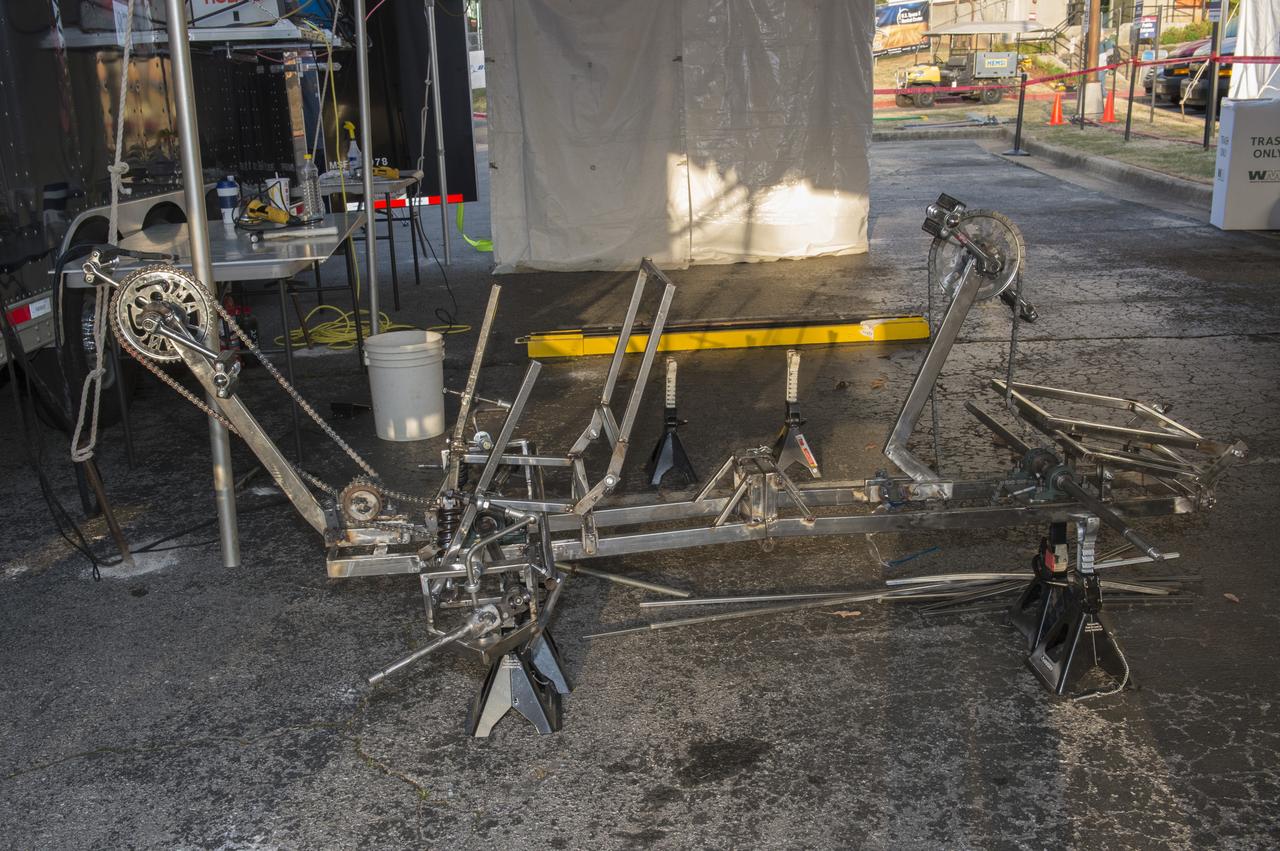

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
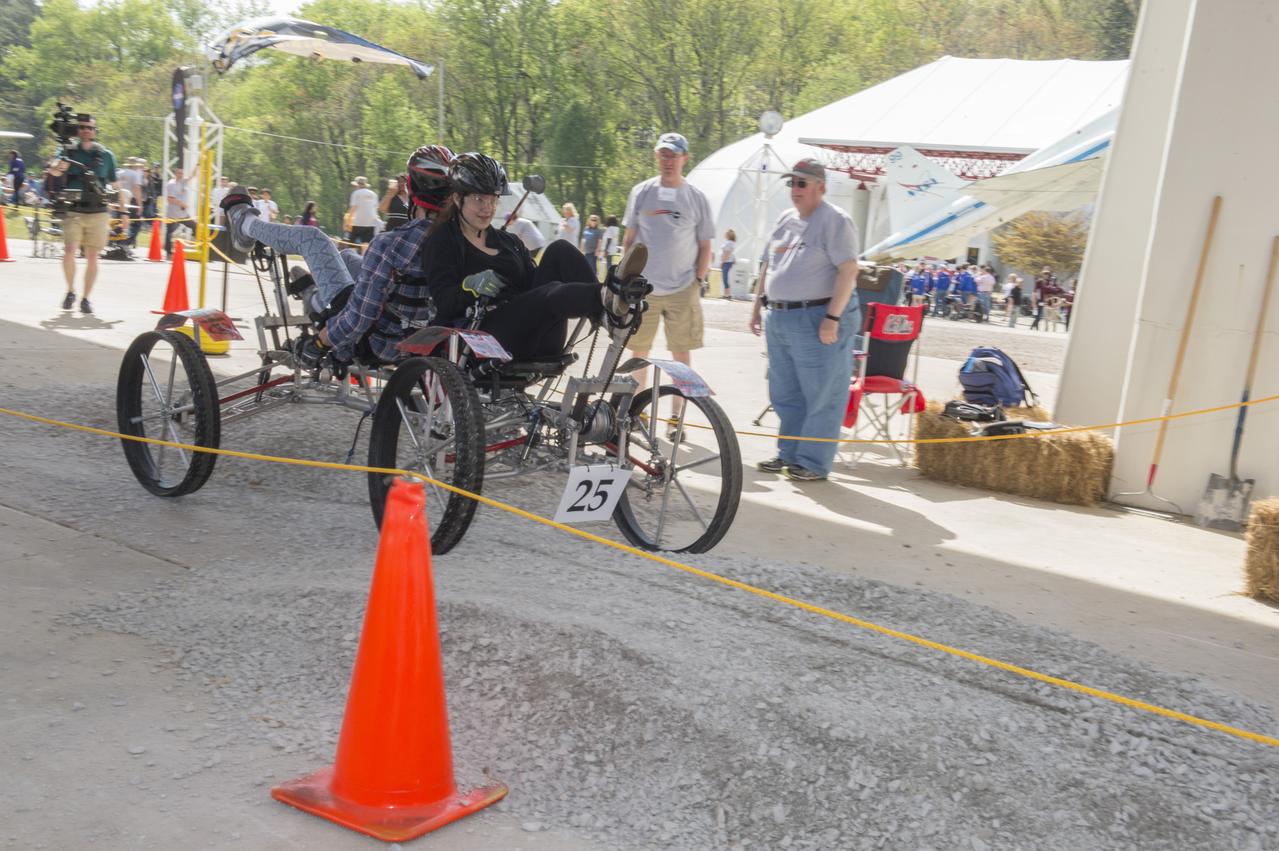

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
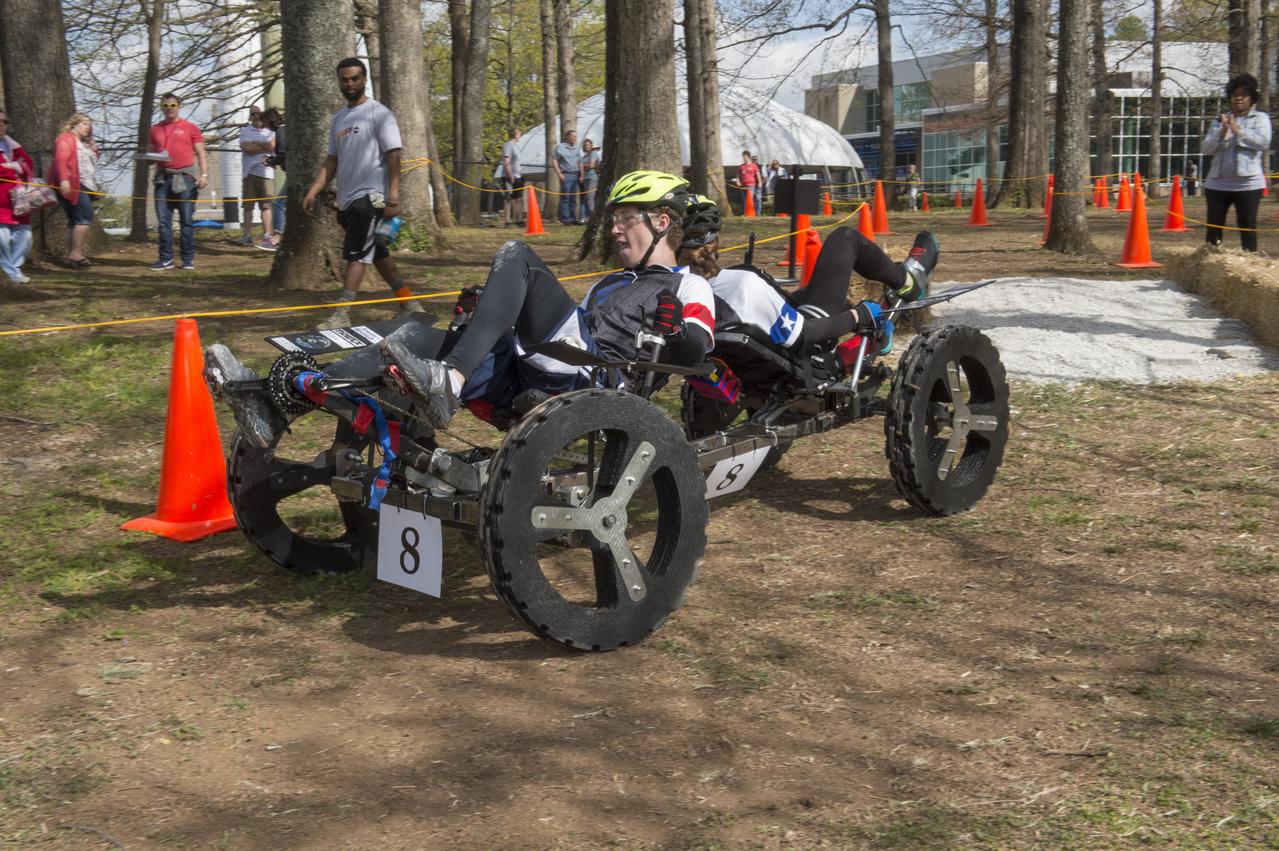

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
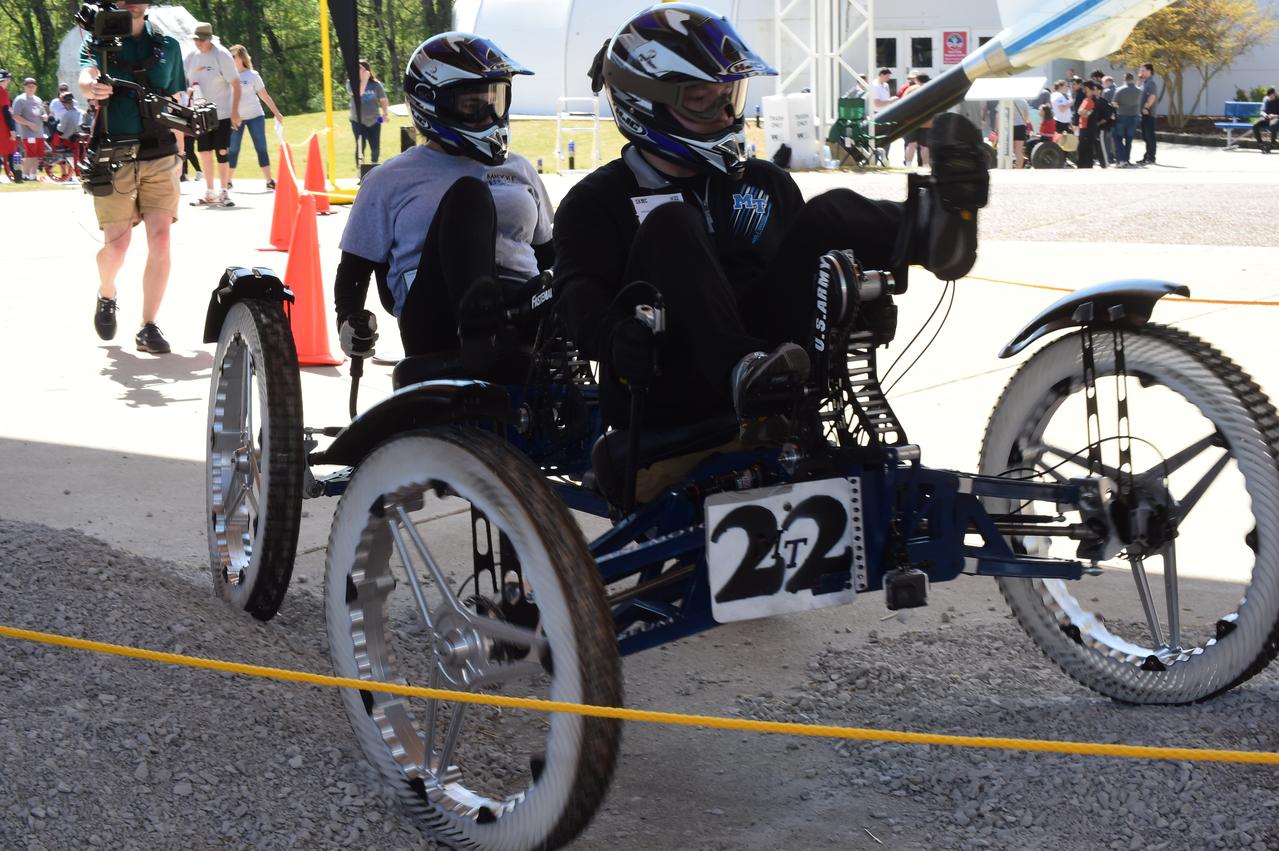

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
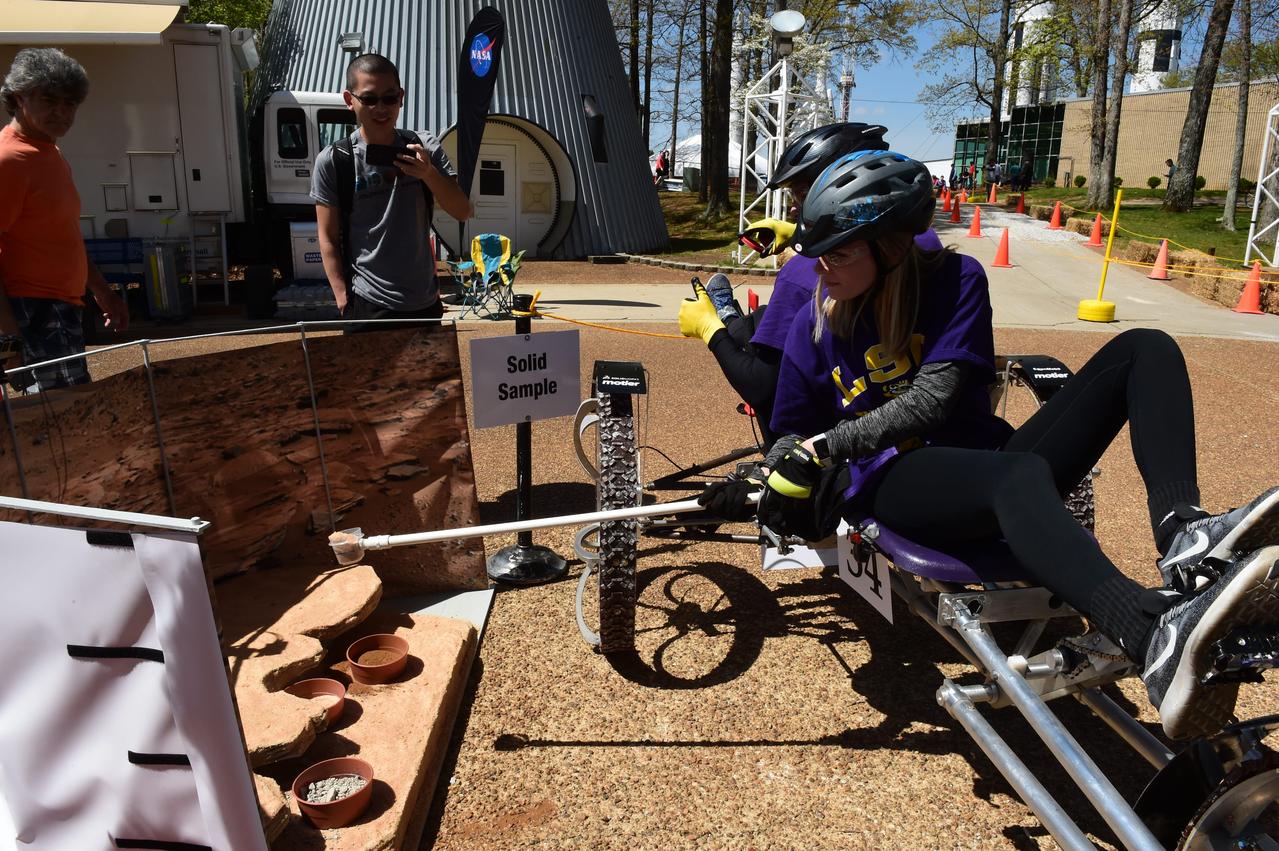

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
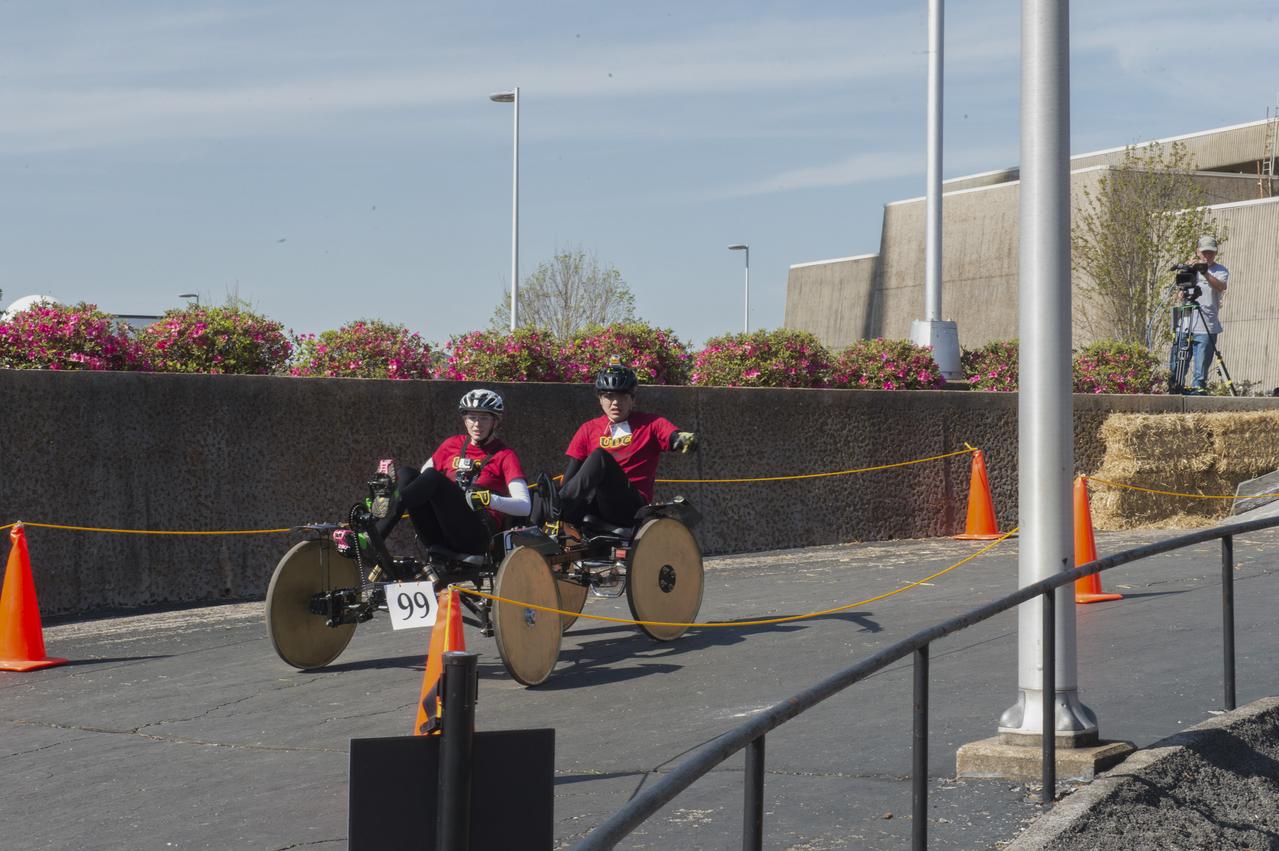

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
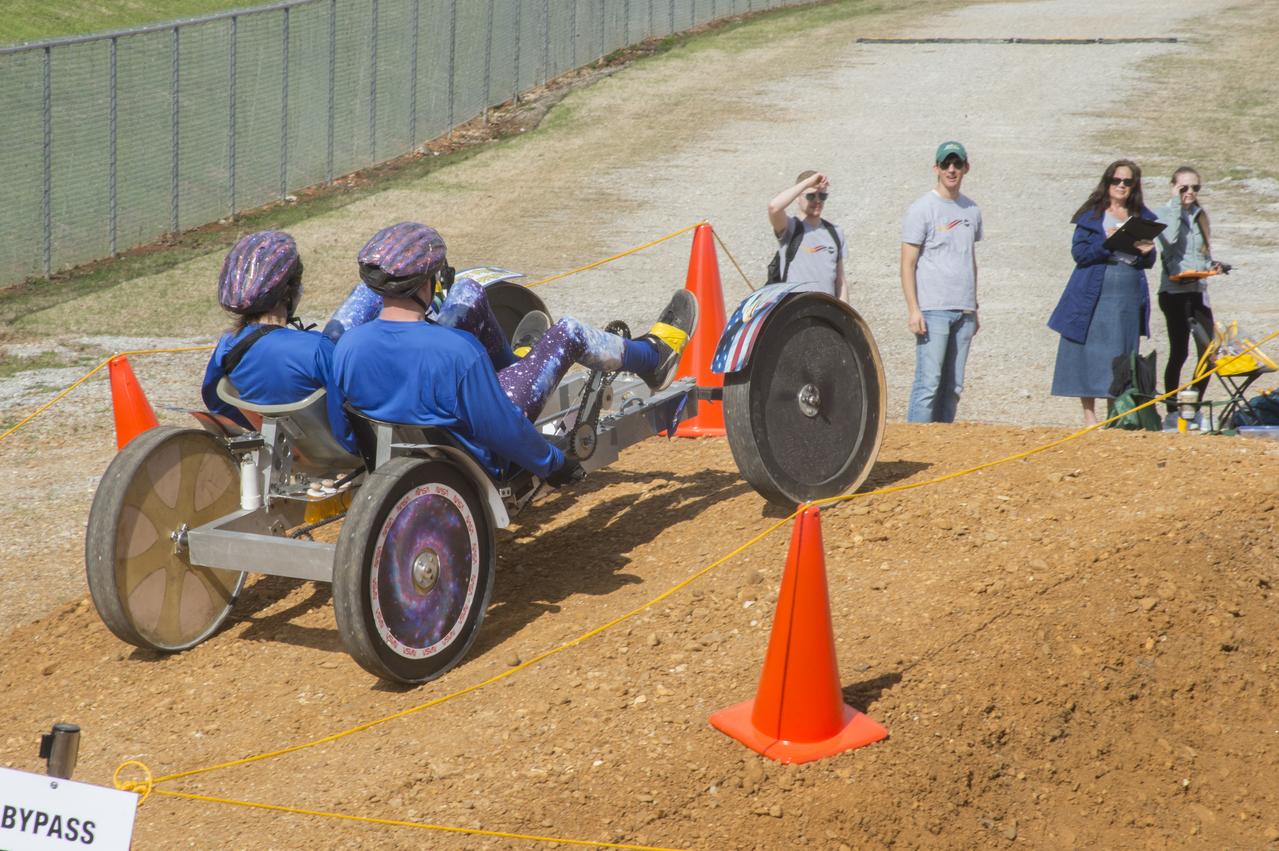

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
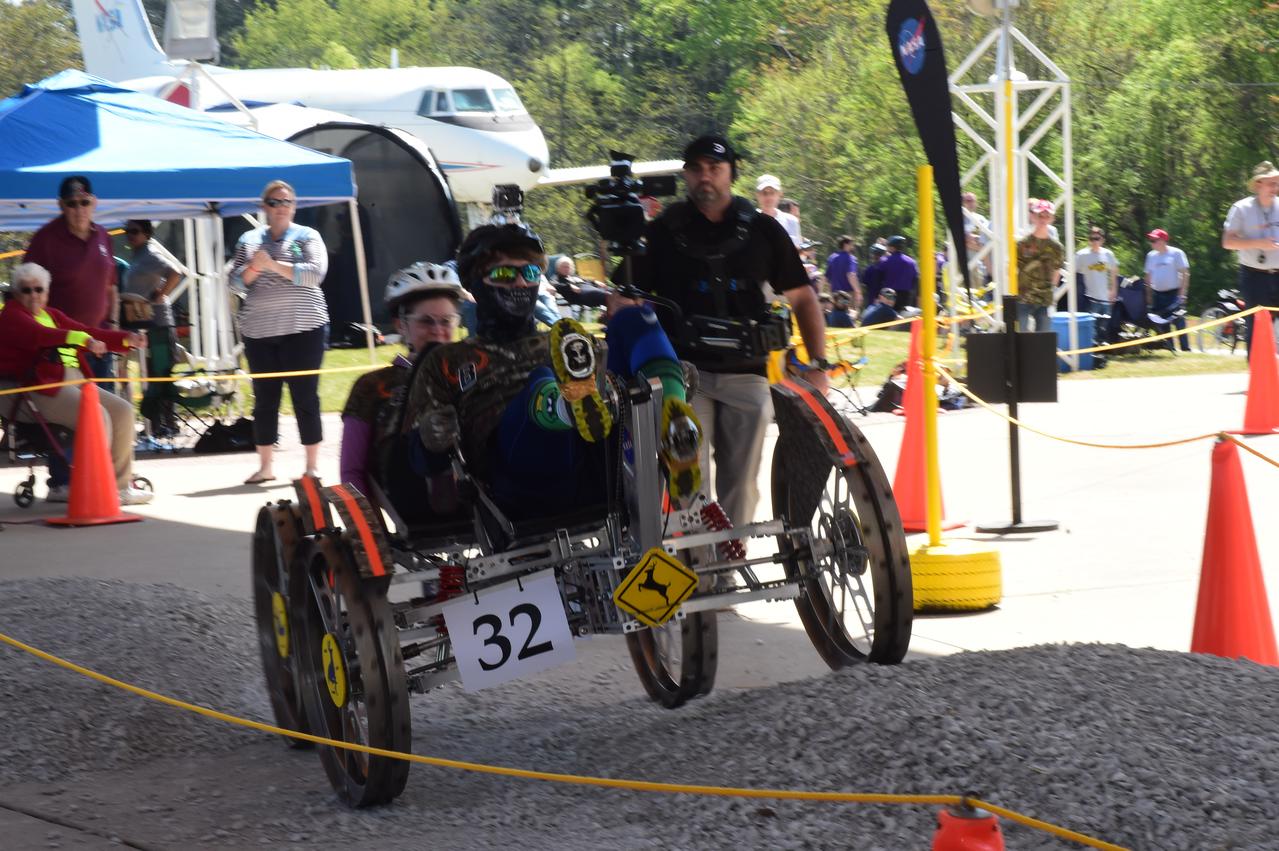

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
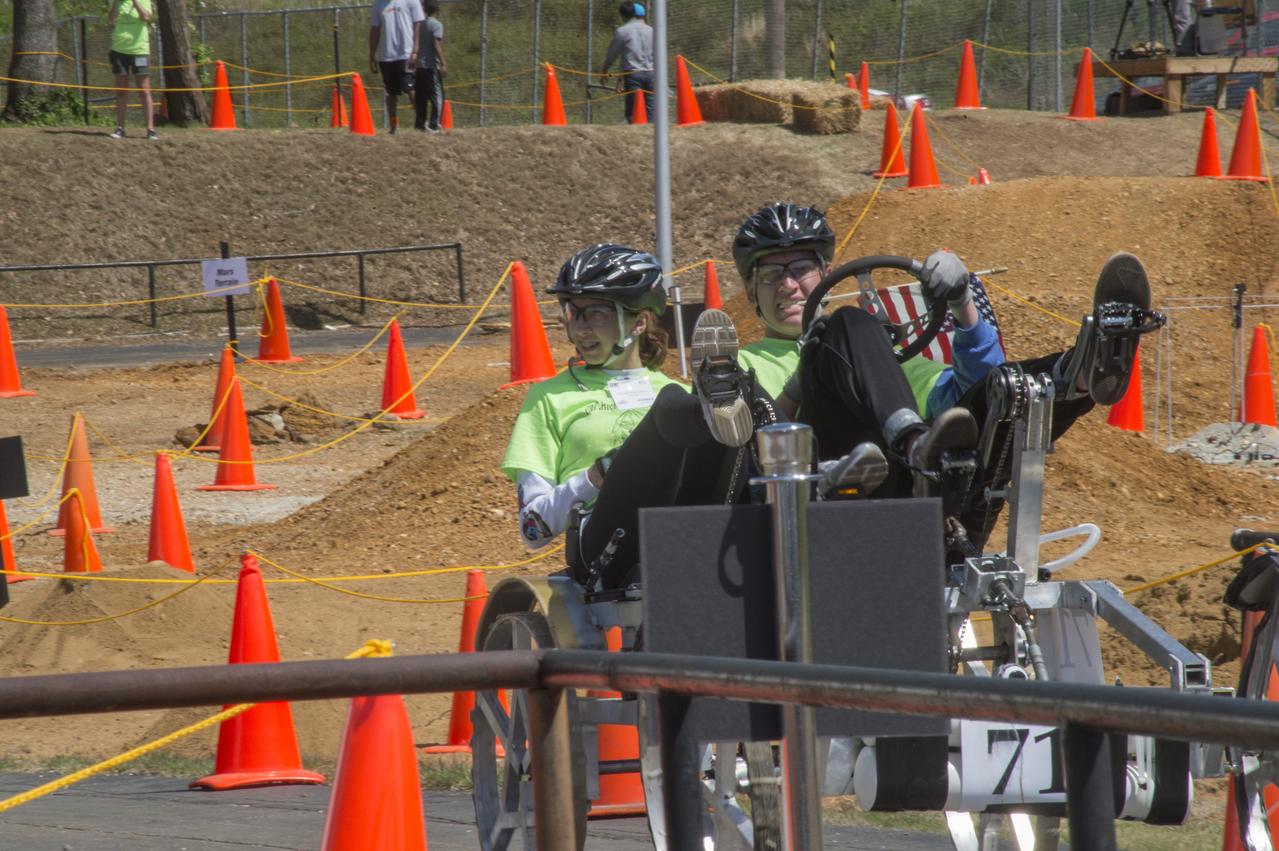

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
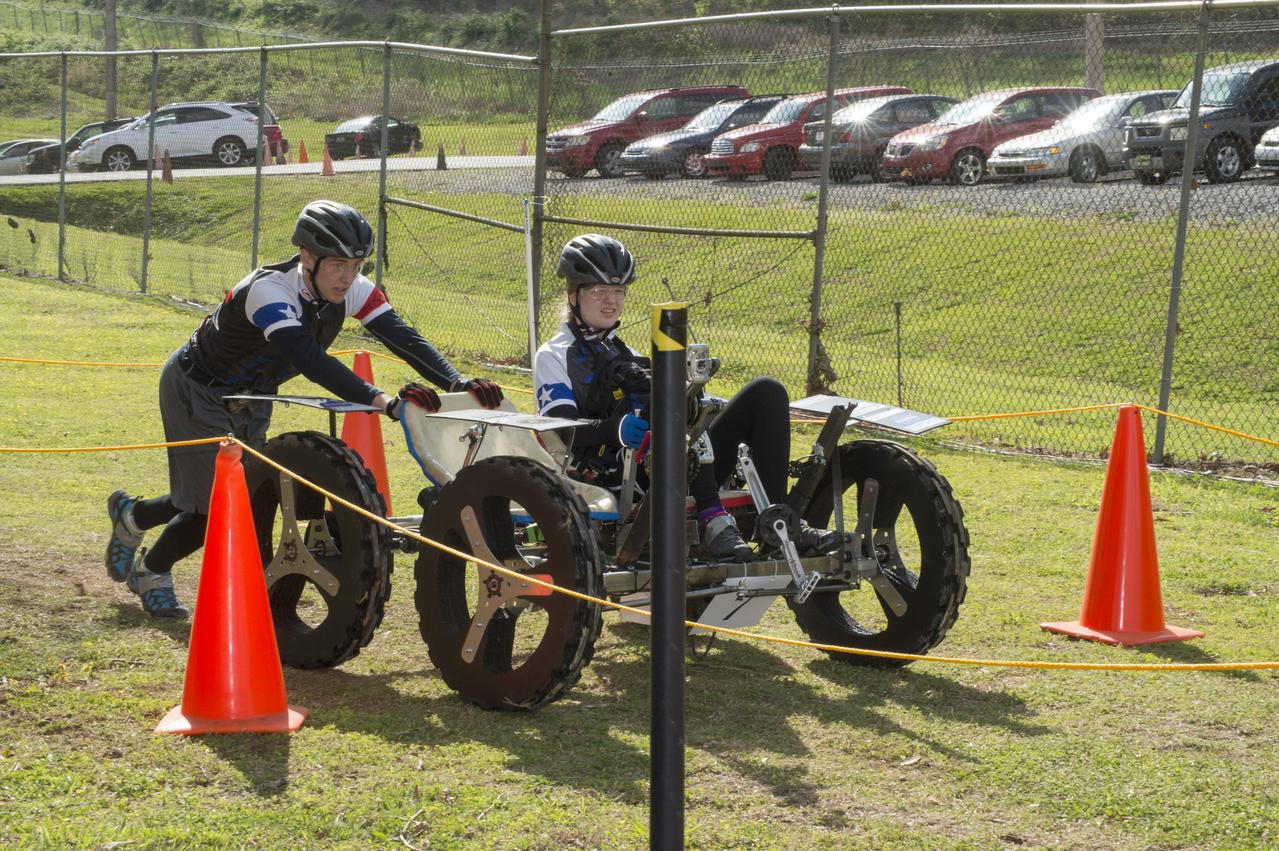

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
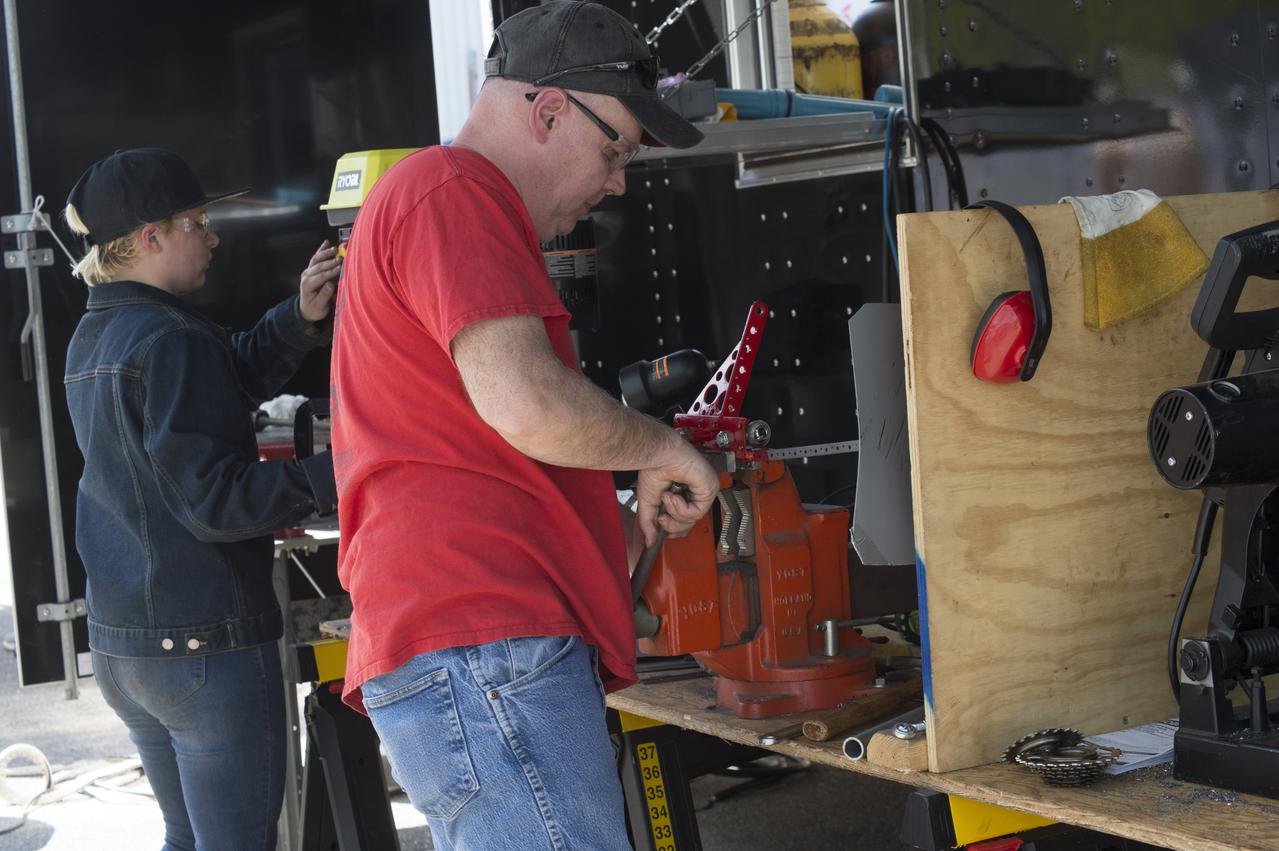

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
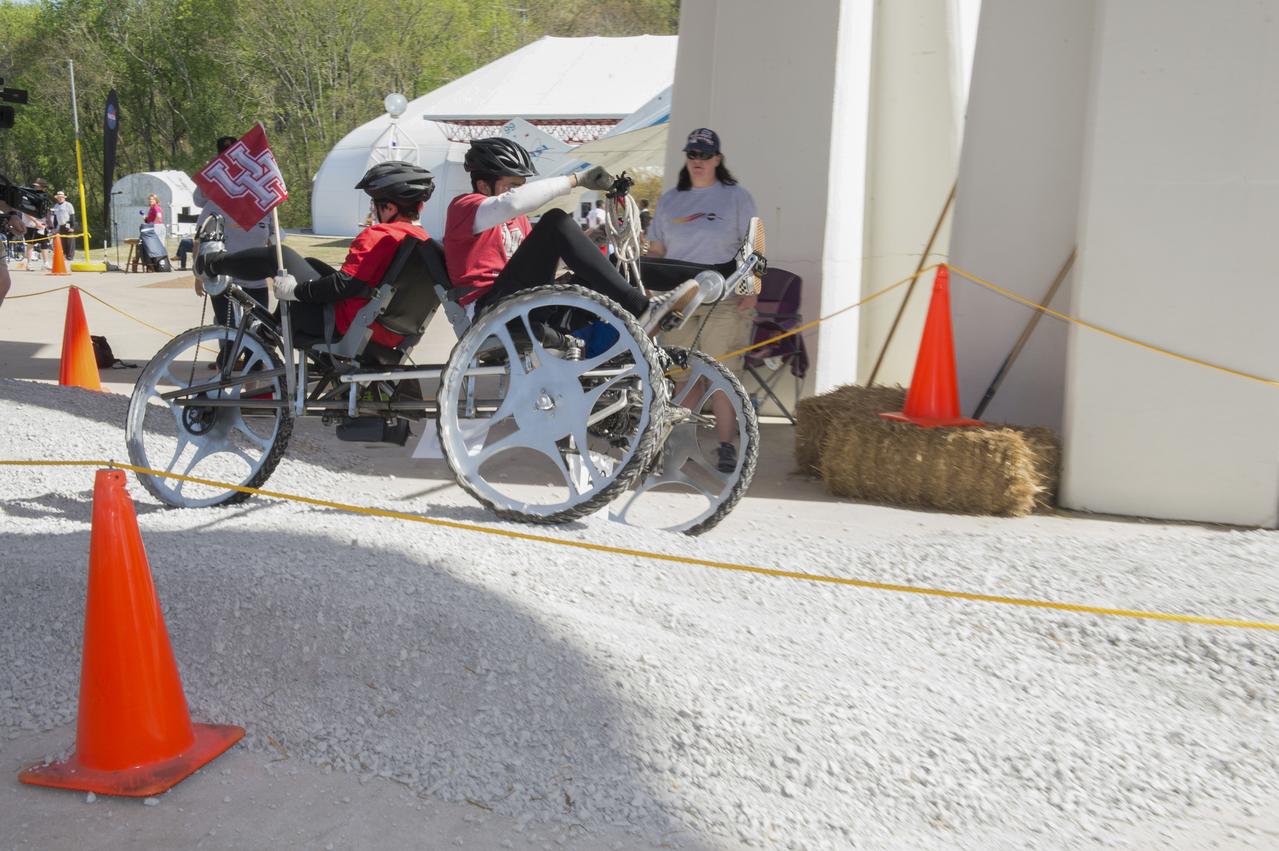

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
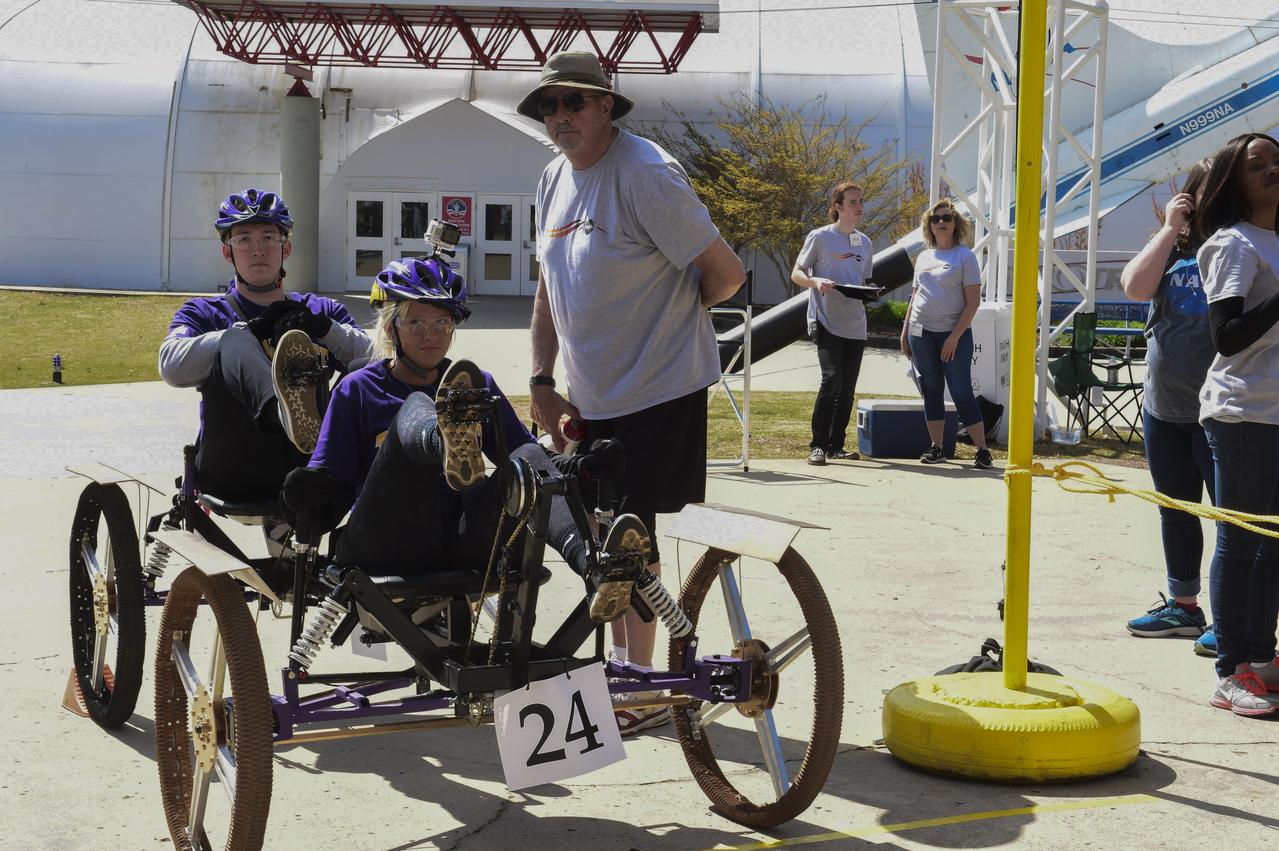

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
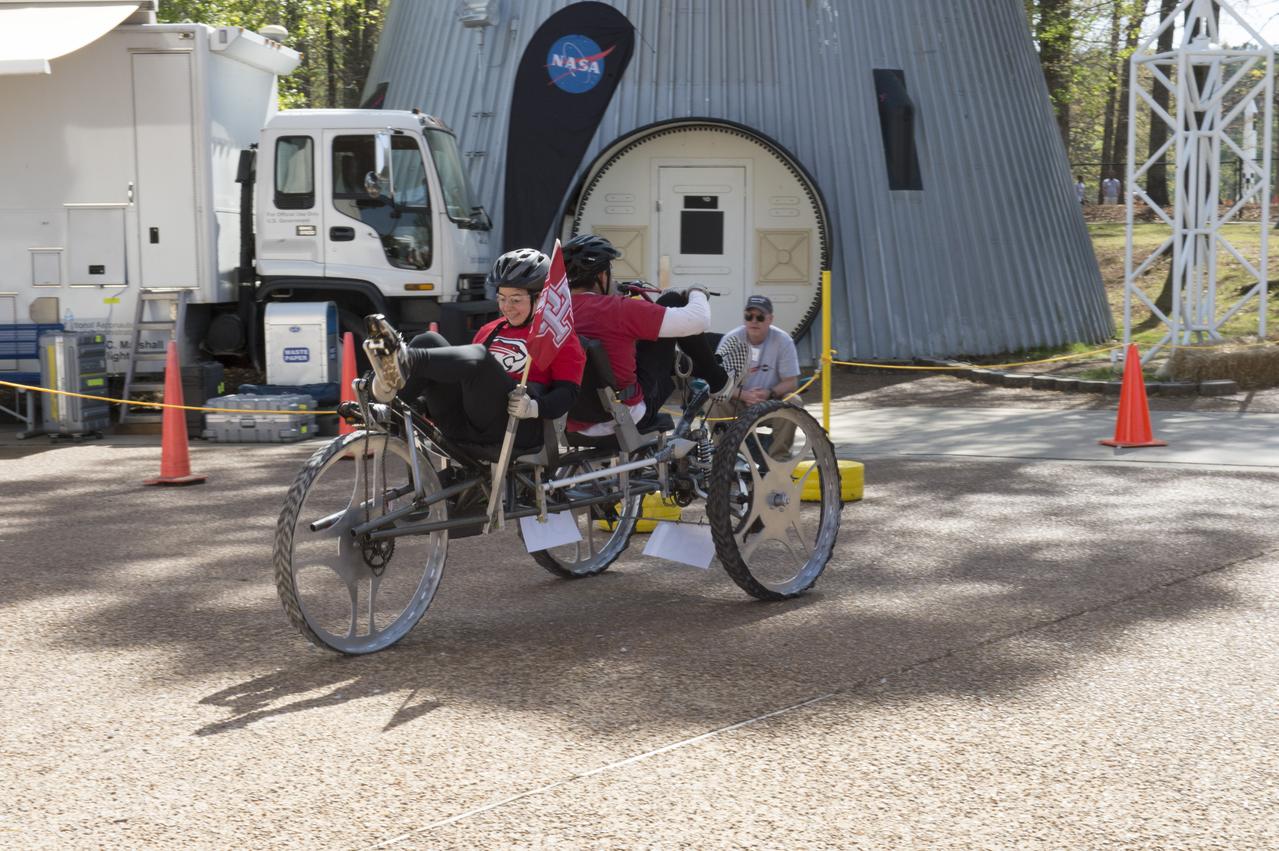

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.