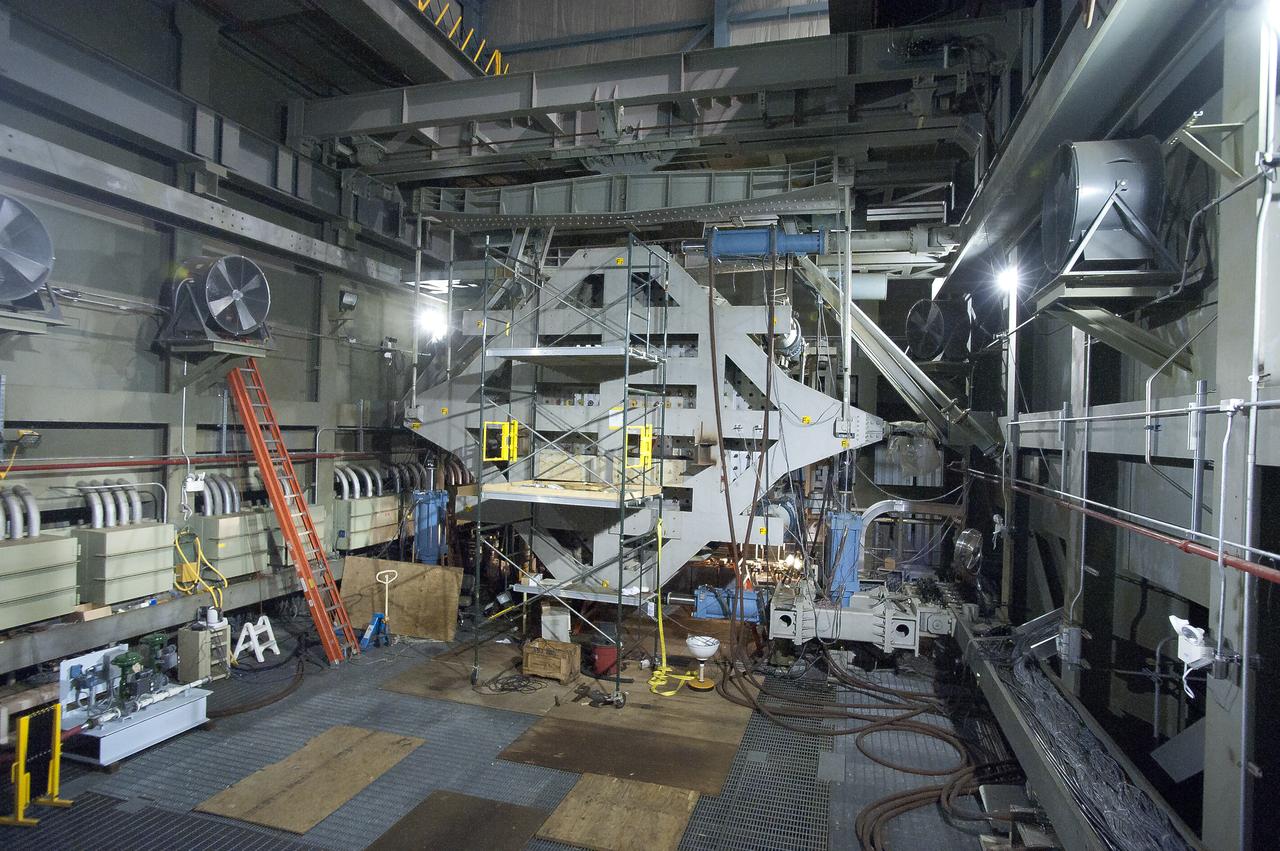

ERA COLTS 30 Toot Checkout Structure Installation: Document relocation of COLTS loading platen 30 Foot Station and installation of 30 Foot Checkout Structure
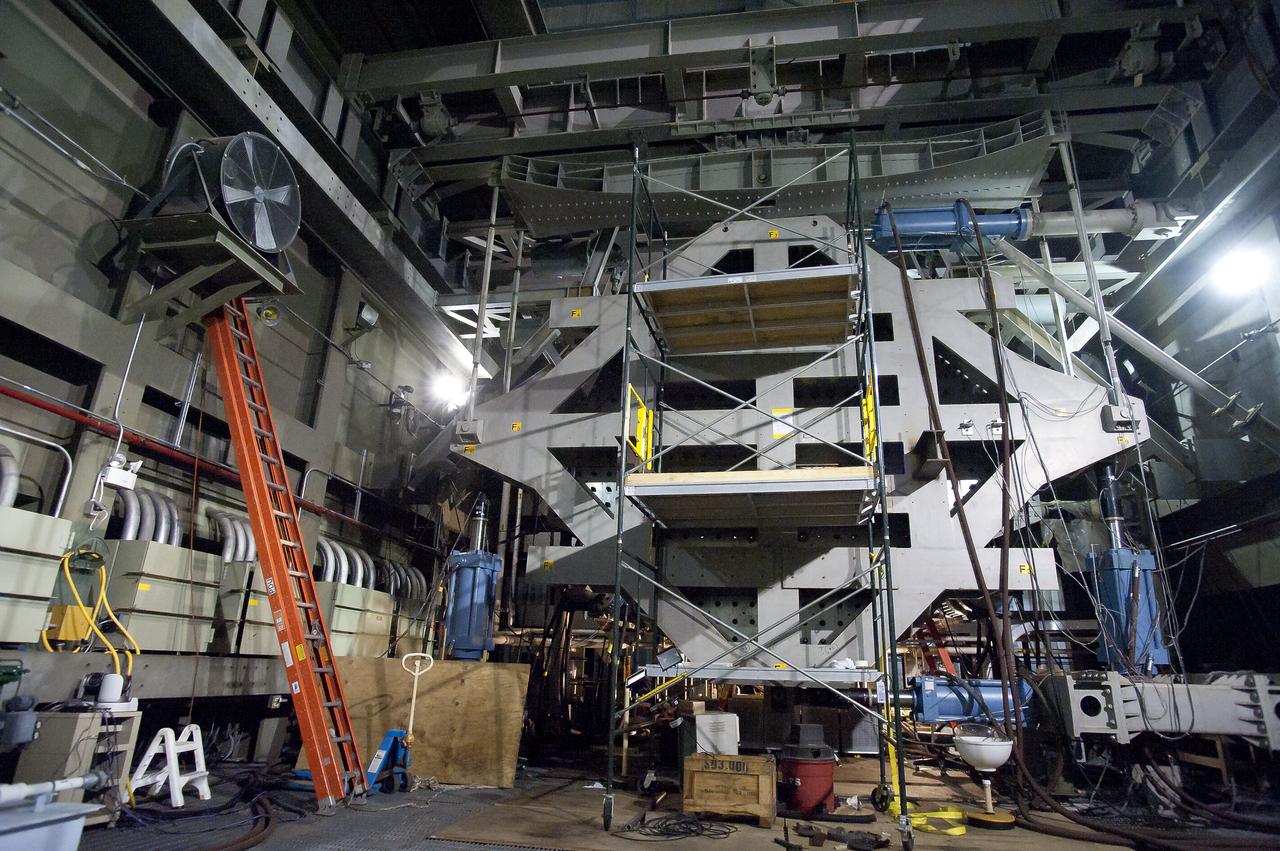

ERA COLTS 30 Toot Checkout Structure Installation: Document relocation of COLTS loading platen 30 Foot Station and installation of 30 Foot Checkout Structure
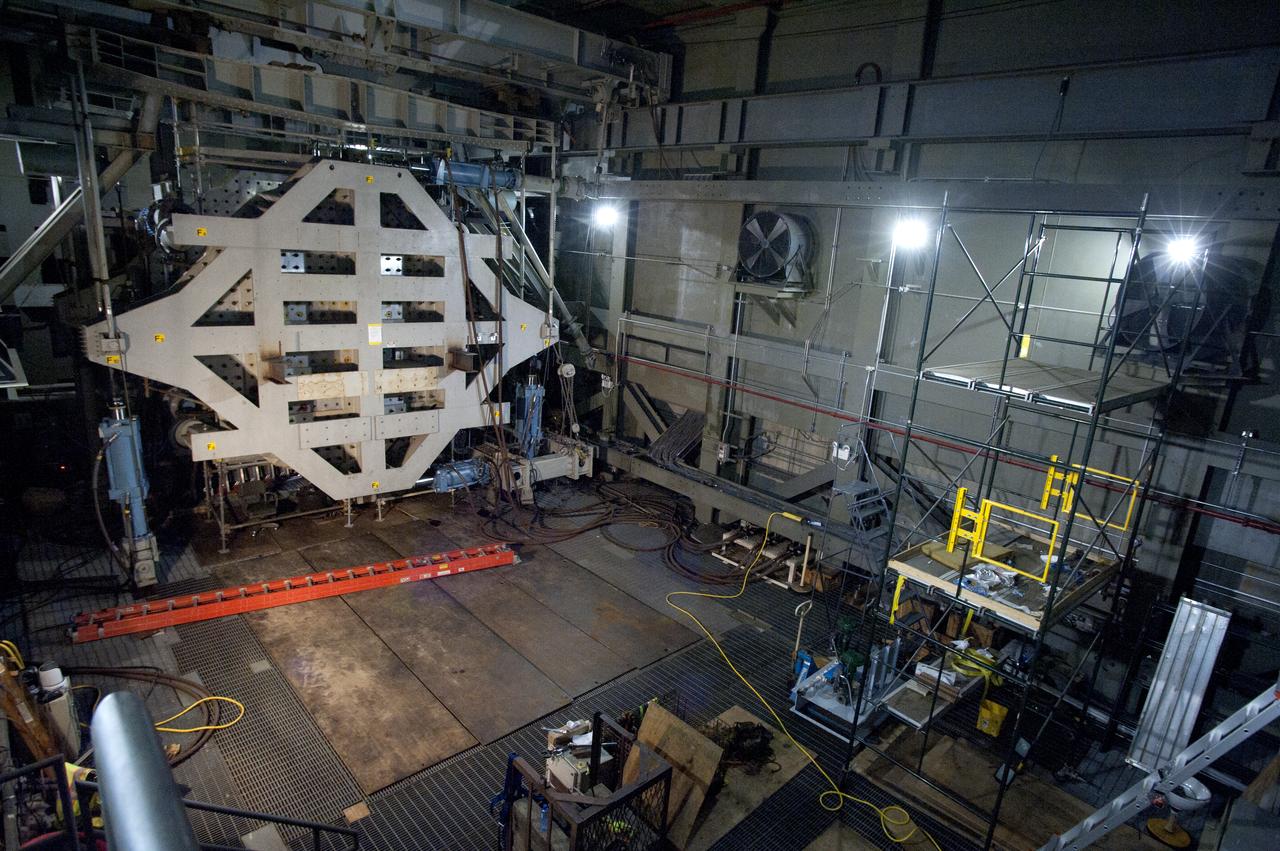
ERA COLTS 30 Toot Checkout Structure Installation: Document relocation of COLTS loading platen 30 Foot Station and installation of 30 Foot Checkout Structure
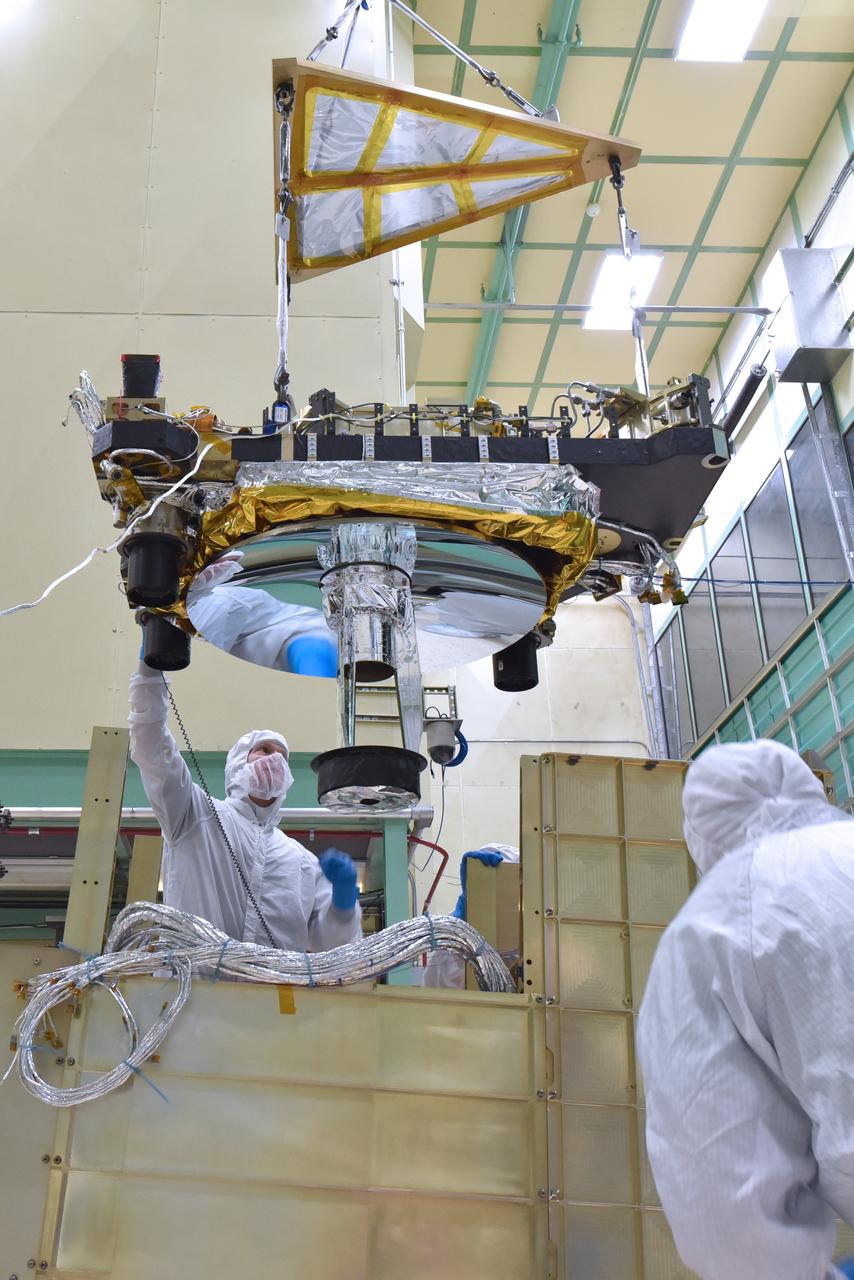

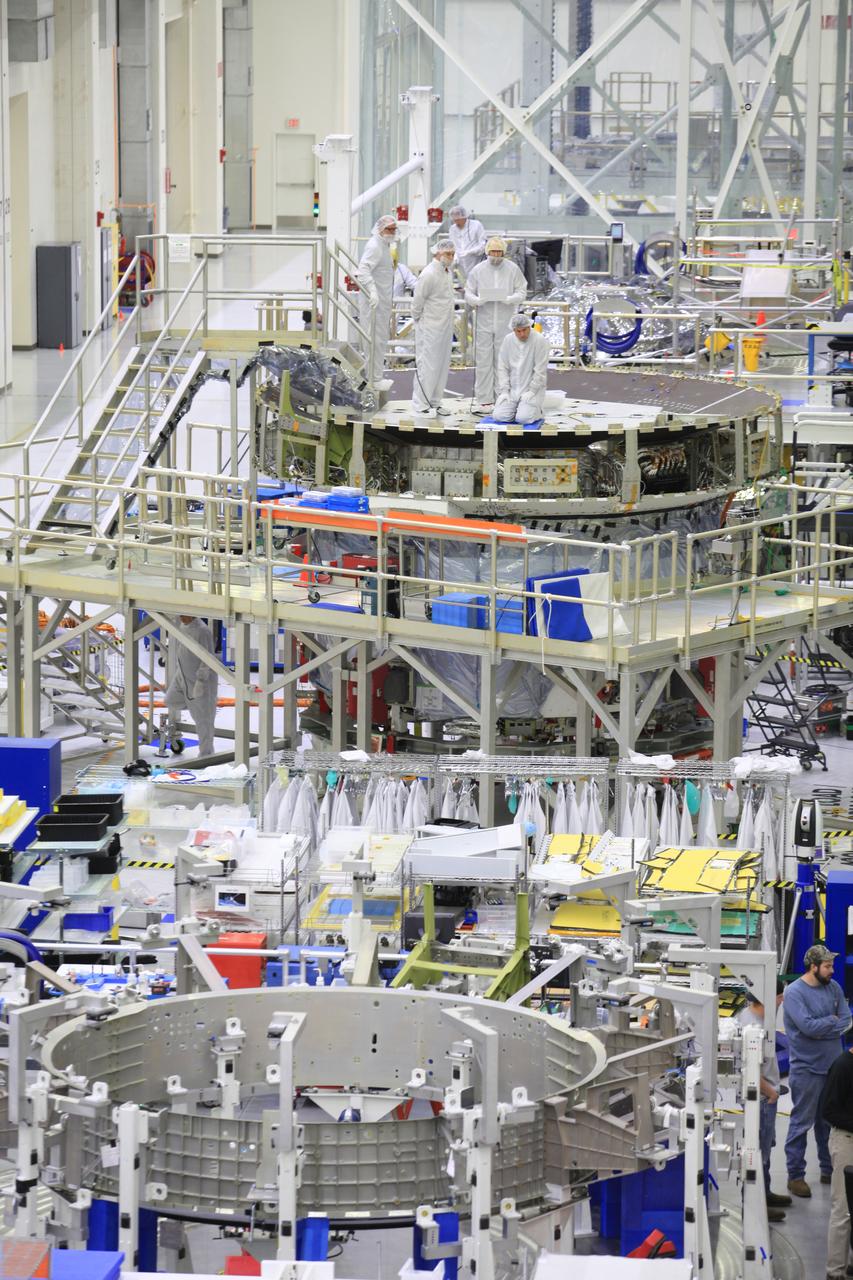
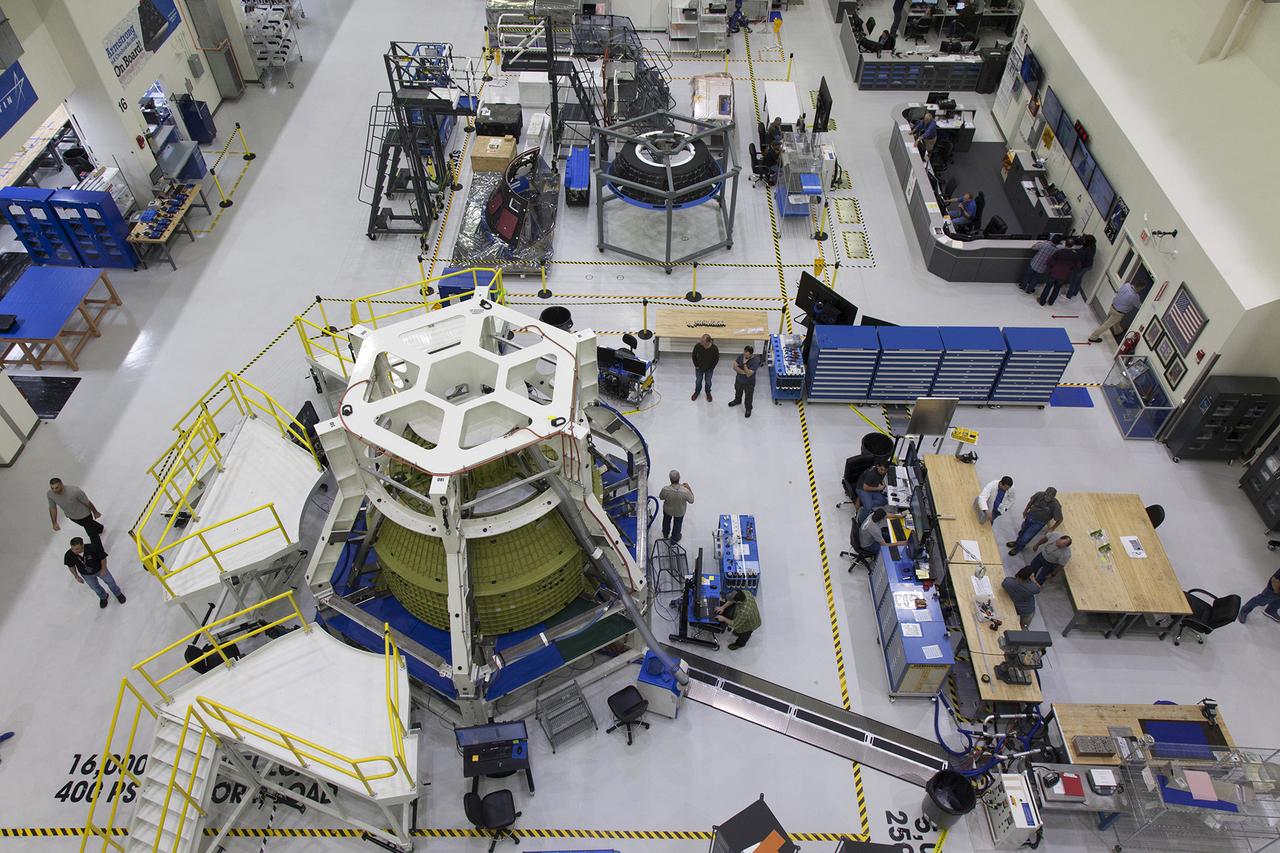
Engineers and technicians from the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) integrate the Optical Bench and the Box Structure in the Spacecraft Checkout and Integration Area (SCA) clean room at Goddard Space Flight Center.

The Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) Optical Bench is suspended from the crane in the Spacecraft Checkout and Integration Area (SCA) clean room at Goddard Space Flight Center. Final cleaning is performed prior to integration into the box structure.
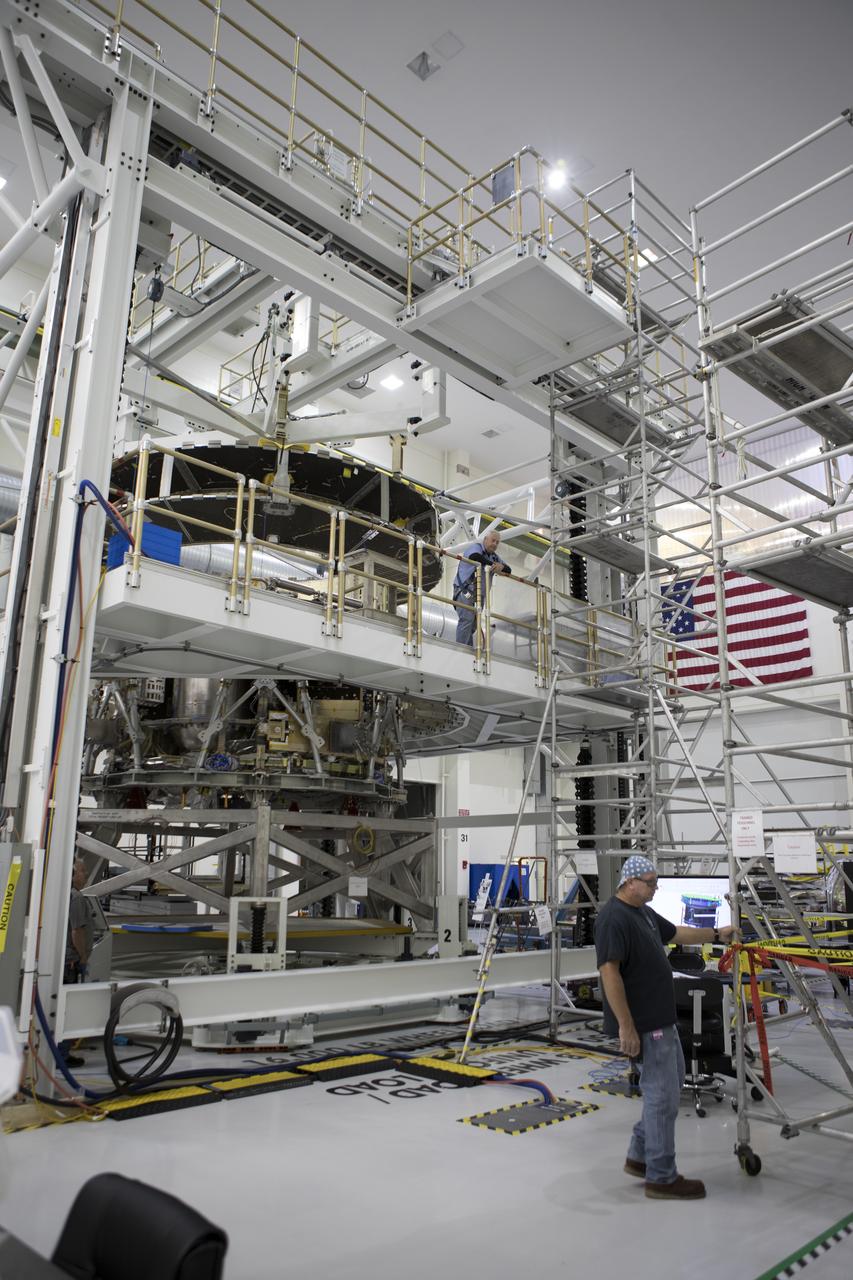

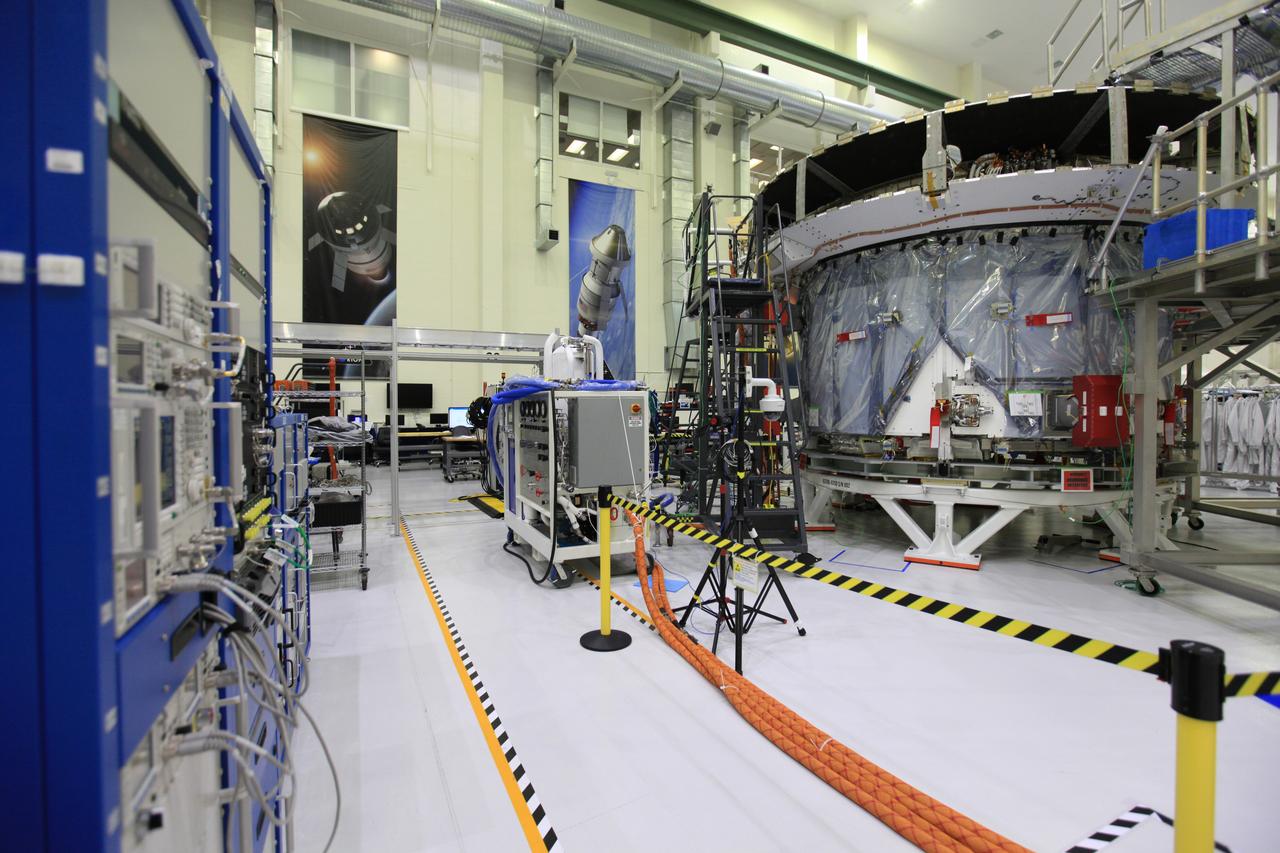
Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, operations are underway to lower the Orion crew module adapter structural test article onto the European Space Agency's service module structural test article. After the hardware is attached, the structure will be packed and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1 in 2019.
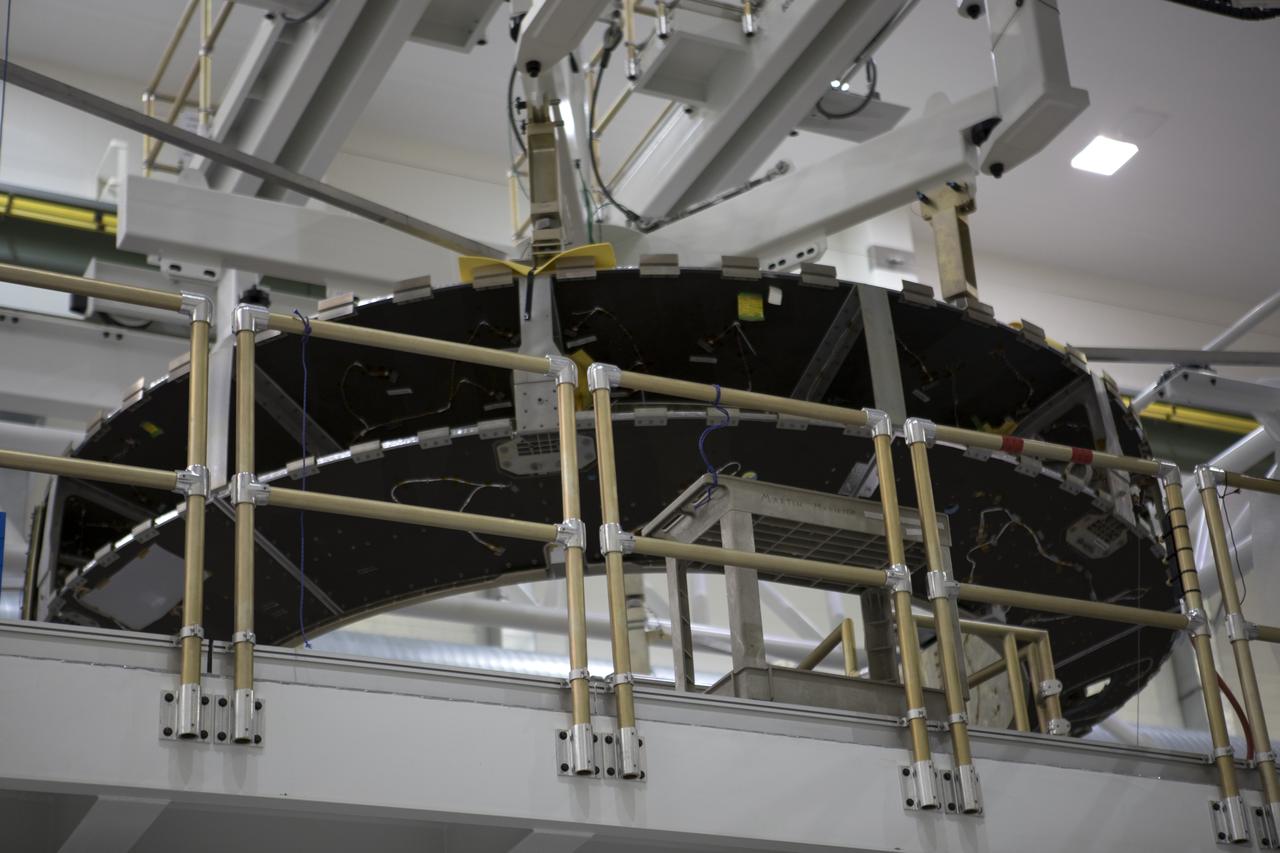

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, operations are underway to lower the Orion crew module adapter structural test article onto the European Space Agency's service module structural test article. After the hardware is attached, the structure will be packed and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1 in 2019.
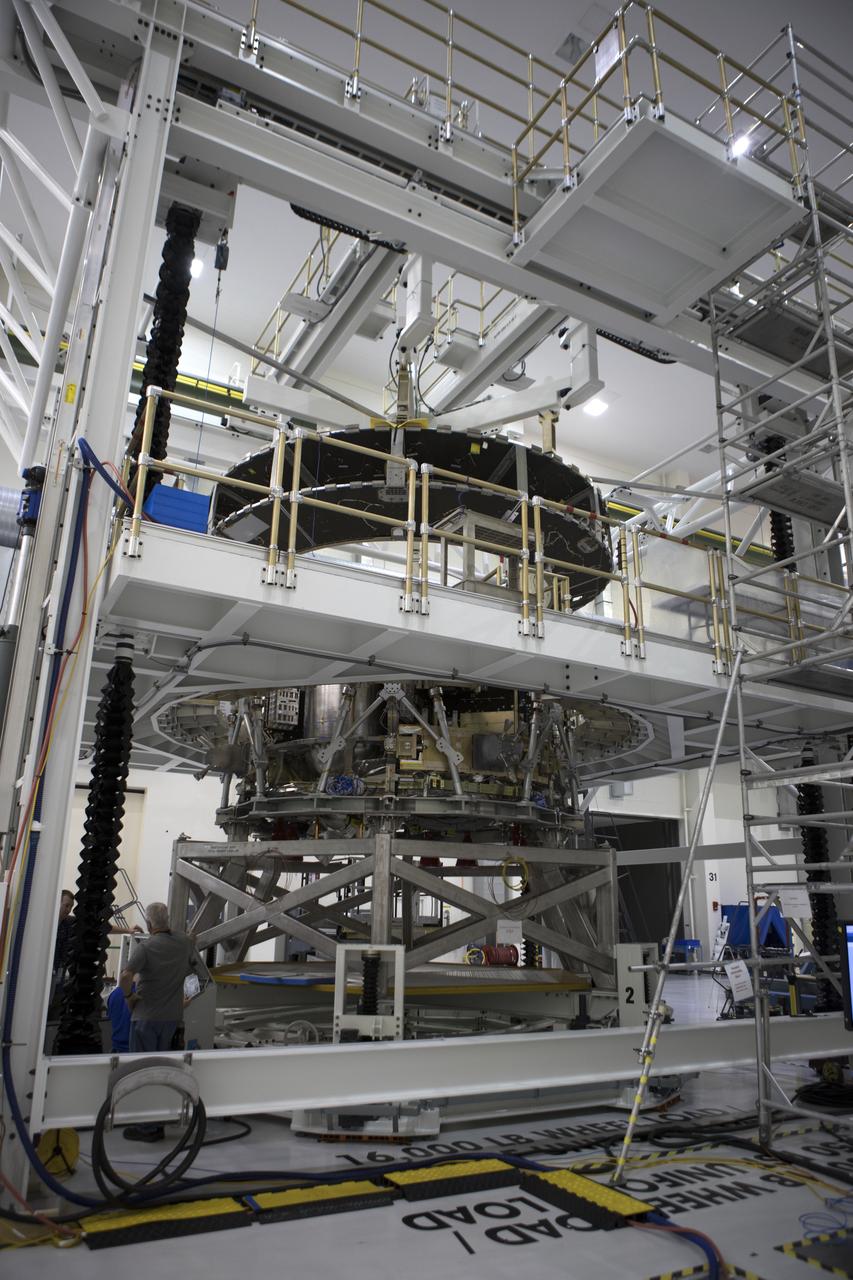

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, operations are underway to lower the Orion crew module adapter structural test article onto the European Space Agency's service module structural test article. After the hardware is attached, the structure will be packed and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1 in 2019.
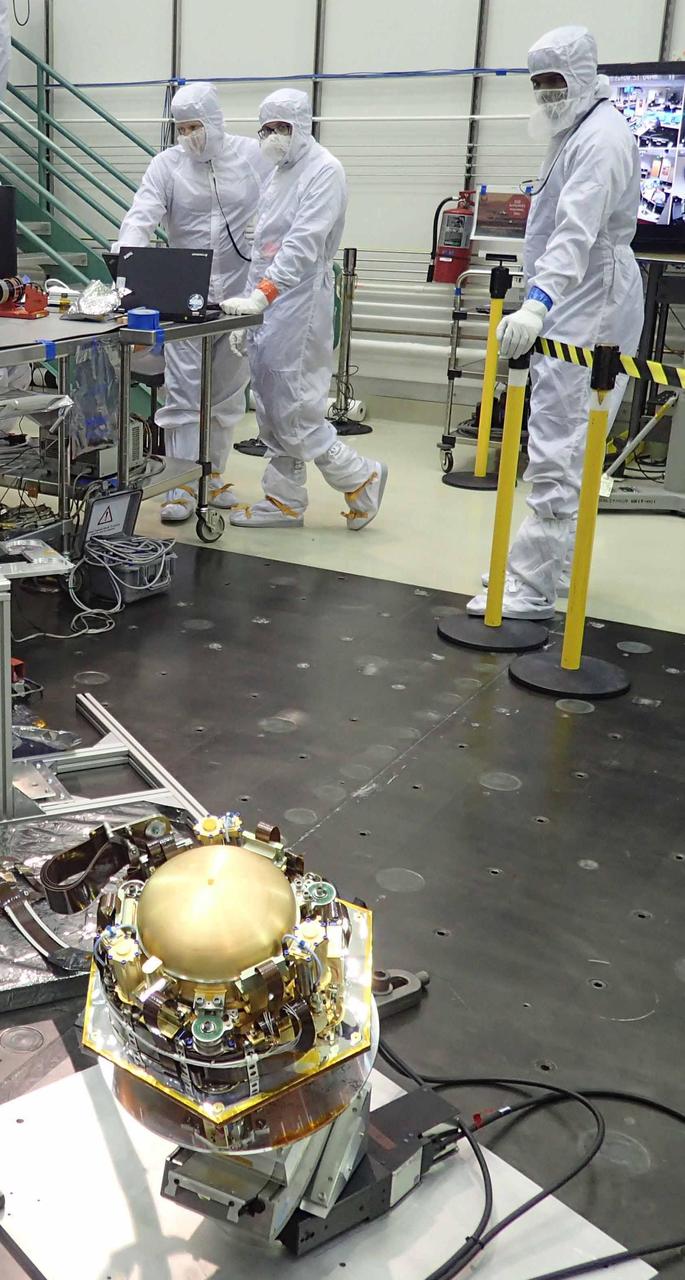

The Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) instrument for NASA's InSight mission to Mars undergoes a checkout for the spacecraft's assembly, test and launch operations (ATLO) in this photo taken July 20, 2017, in a Lockheed Martin clean room facility in Littleton, Colorado. The SEIS was provided by France's national space agency (CNES) with collaboration from the United States, the United Kingdom, Switzerland and Germany. The InSight mission (for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) is scheduled to launch in May 2018 and land on Mars Nov. 26, 2018. It will investigate processes that formed and shaped Mars and will help scientists better understand the evolution of our inner solar system's rocky planets, including Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21846
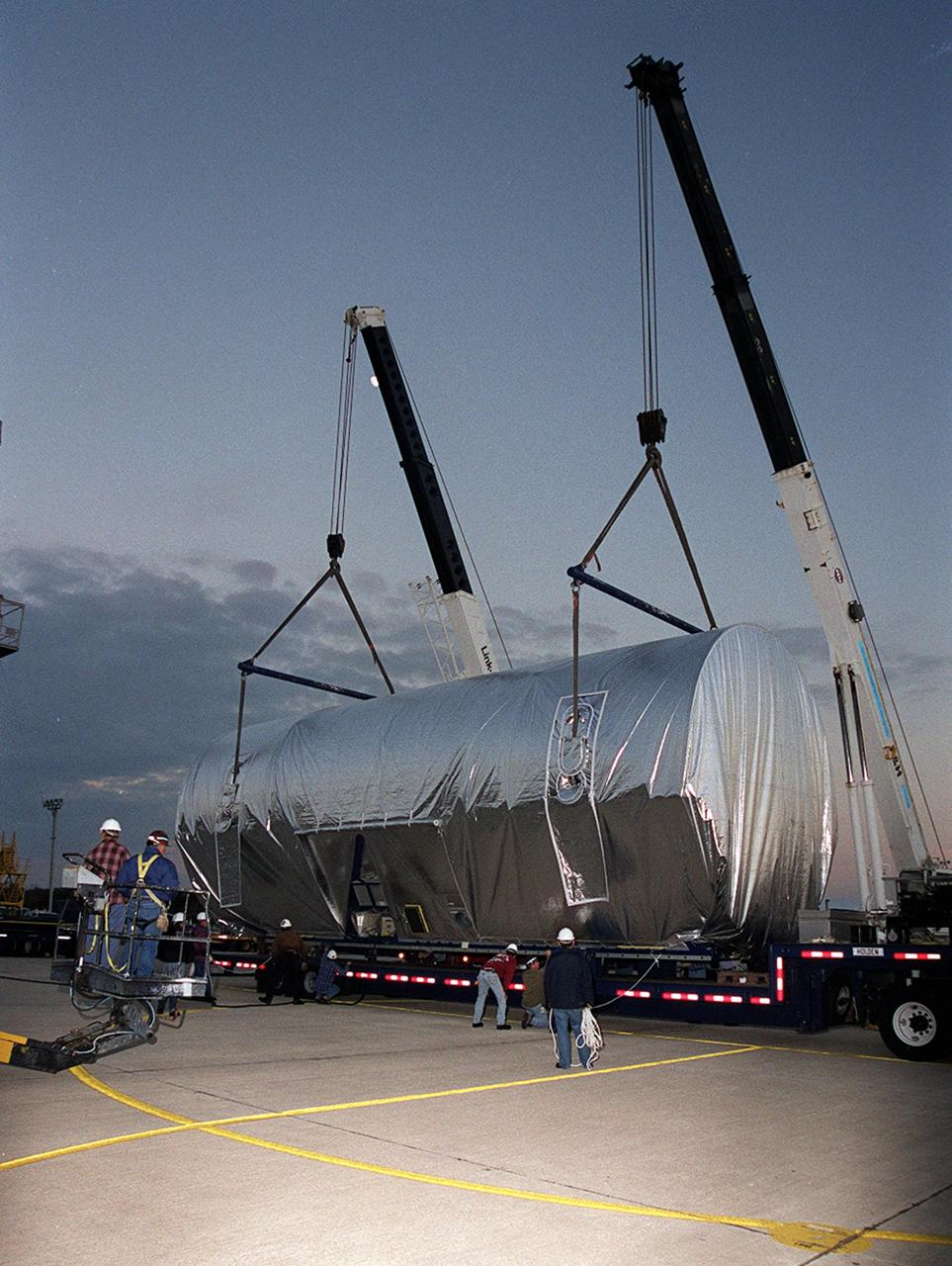

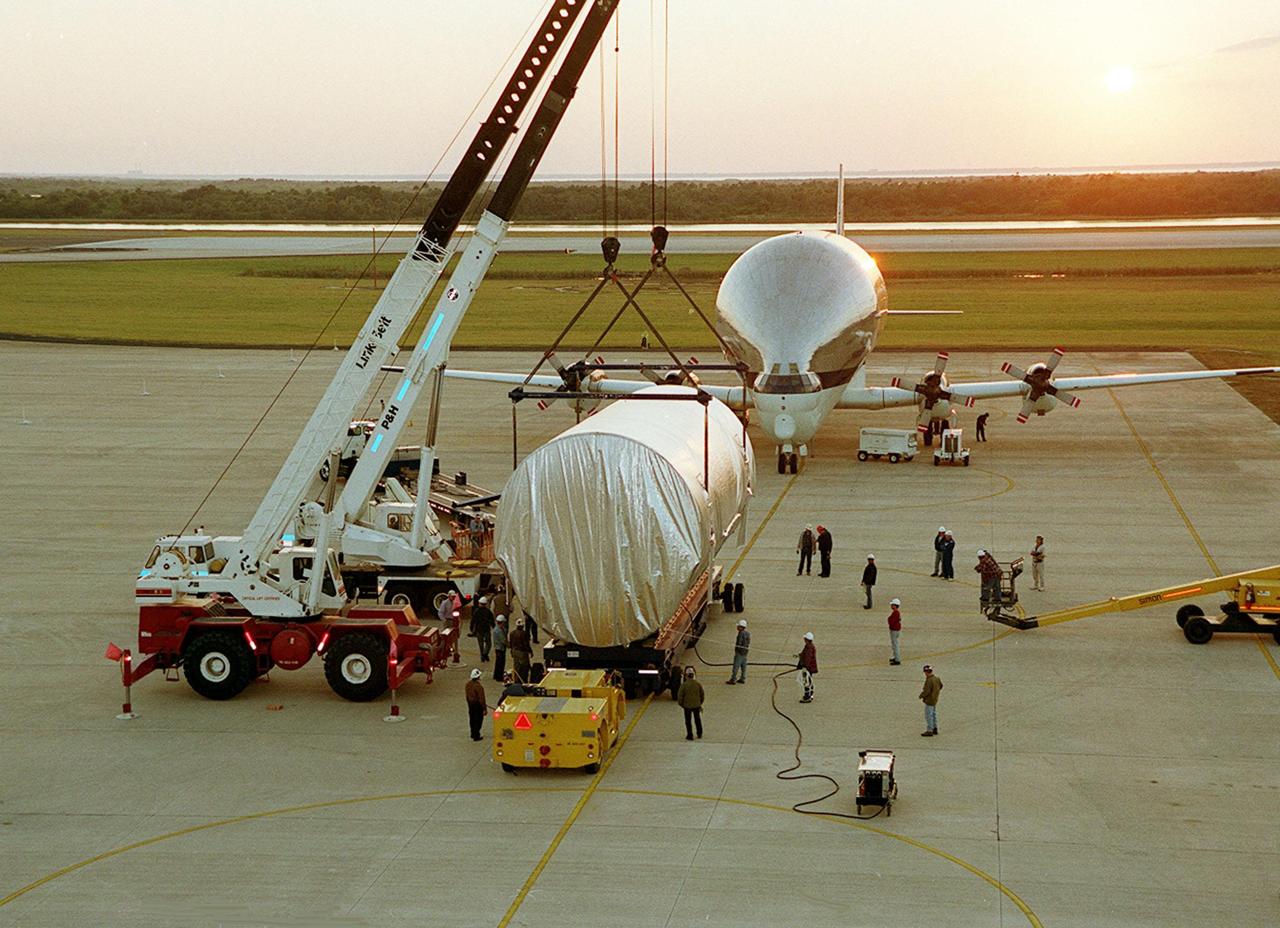
At the Shuttle Landing Facility, cranes position the Integrated Truss Structure S3 onto a flatbed trailer for transport to the Operations and Checkout Building. The S3 arrived aboard a Super Guppy aircraft. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
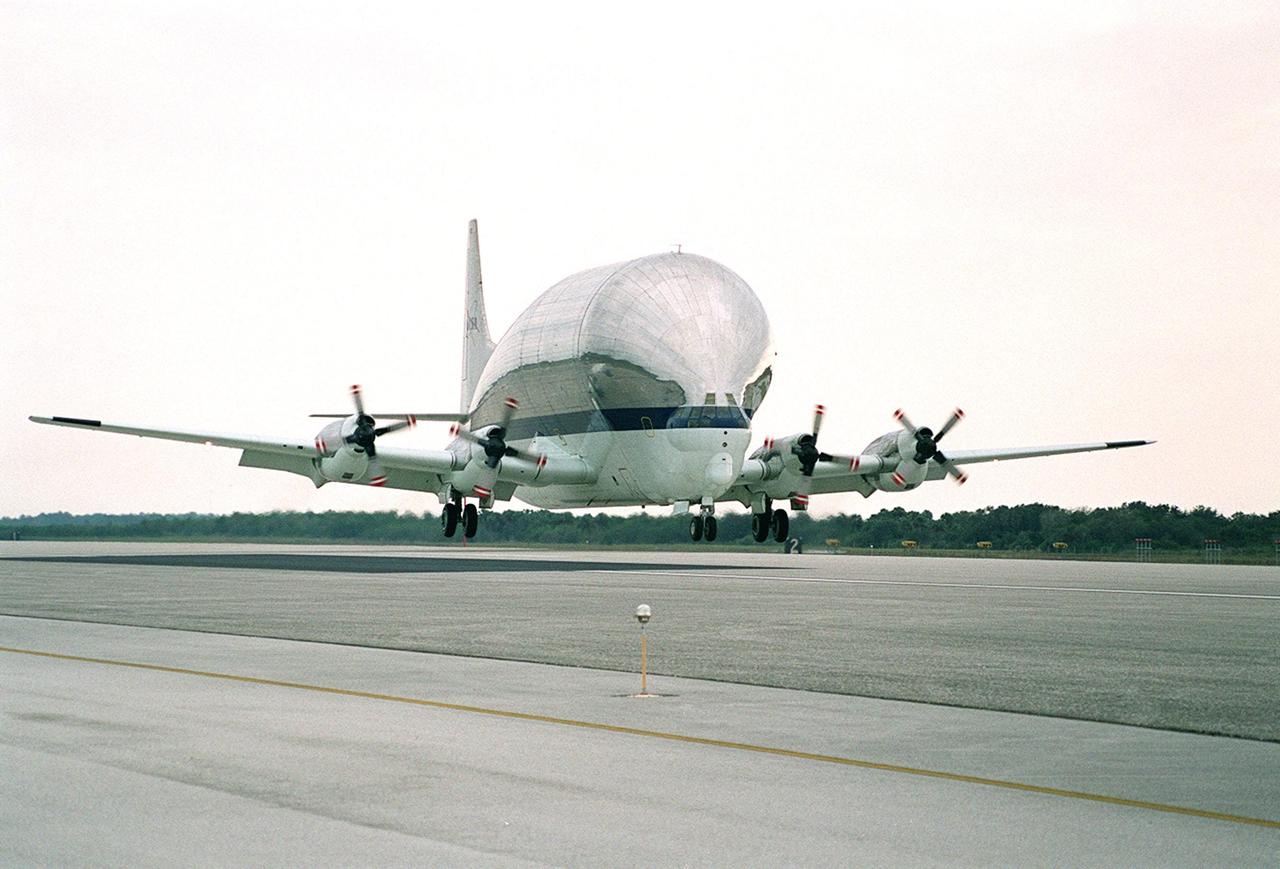

A Super Guppy aircraft arrives at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility with its cargo of Integrated Truss Structure S3, built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
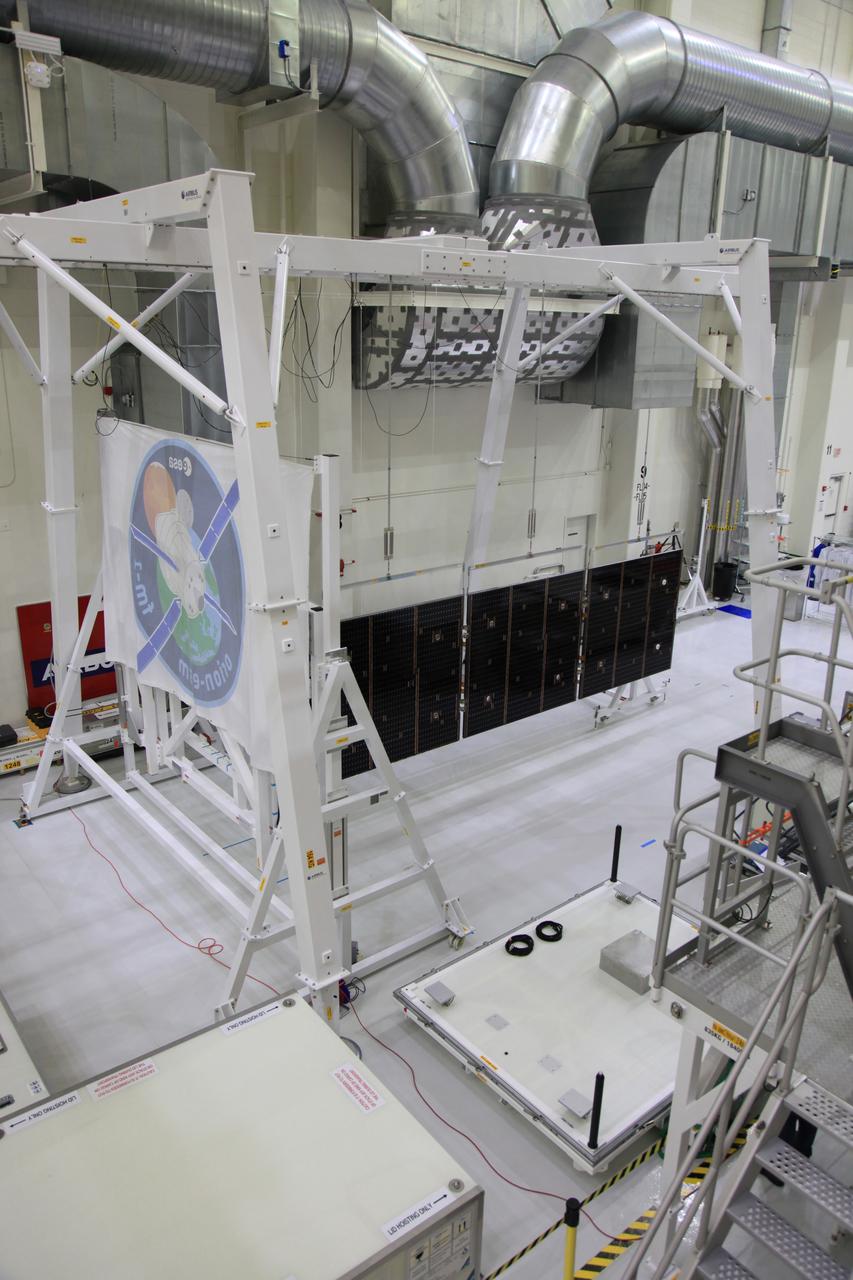

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
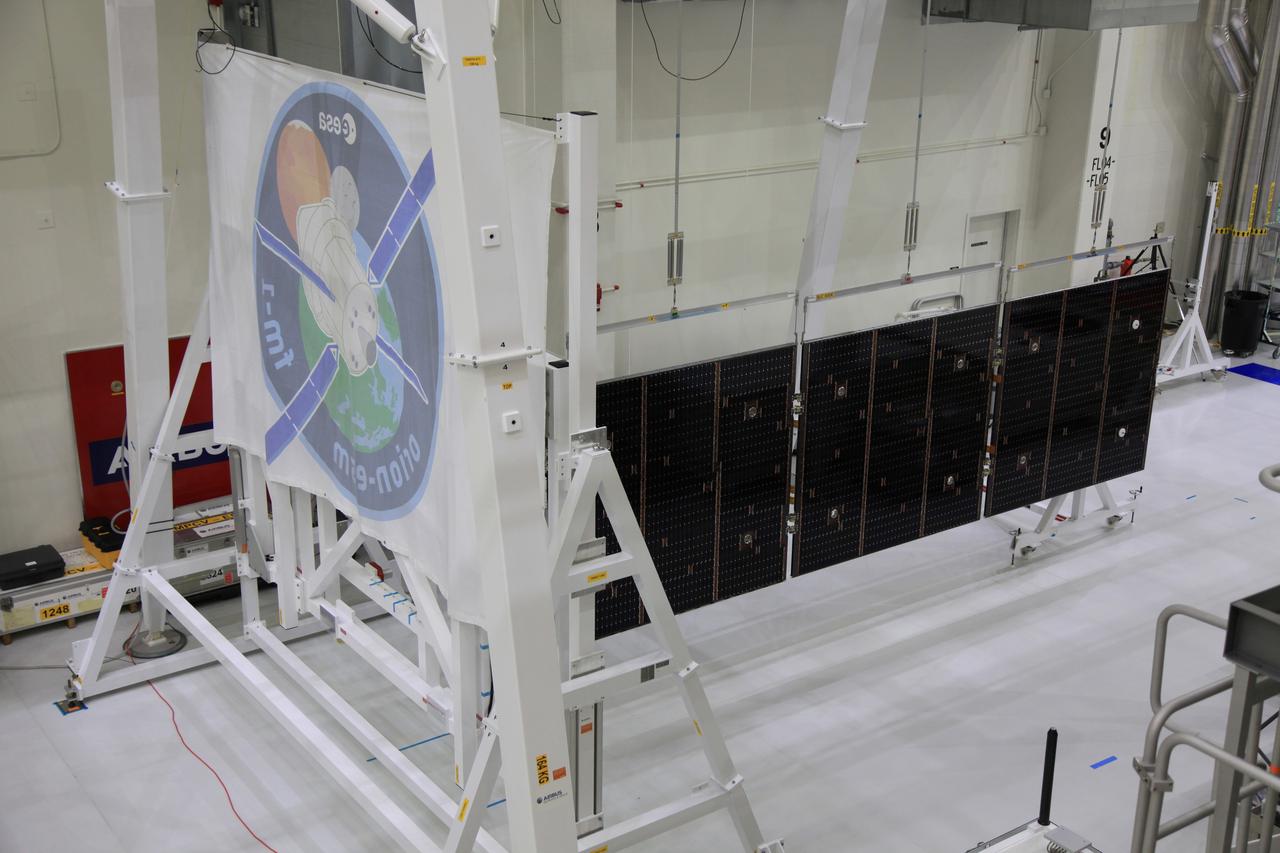

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.

On the parking apron of the Shuttle Landing Facility, workers check the overhead cranes that will move the Integrated Truss Structure S3 to a transporter. The truss will be taken to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
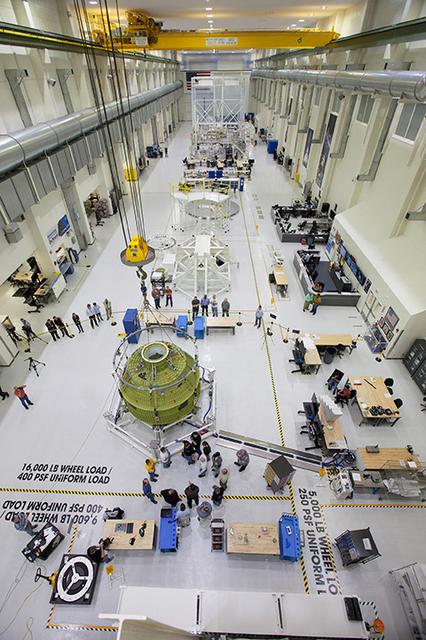

The Orion pressure vessel, which is the underlying structure of the crew module, arrived at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 2, 2016. At Kennedy, engineers will outfit the pressure vessel with Orion's systems and subsystems ahead of Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
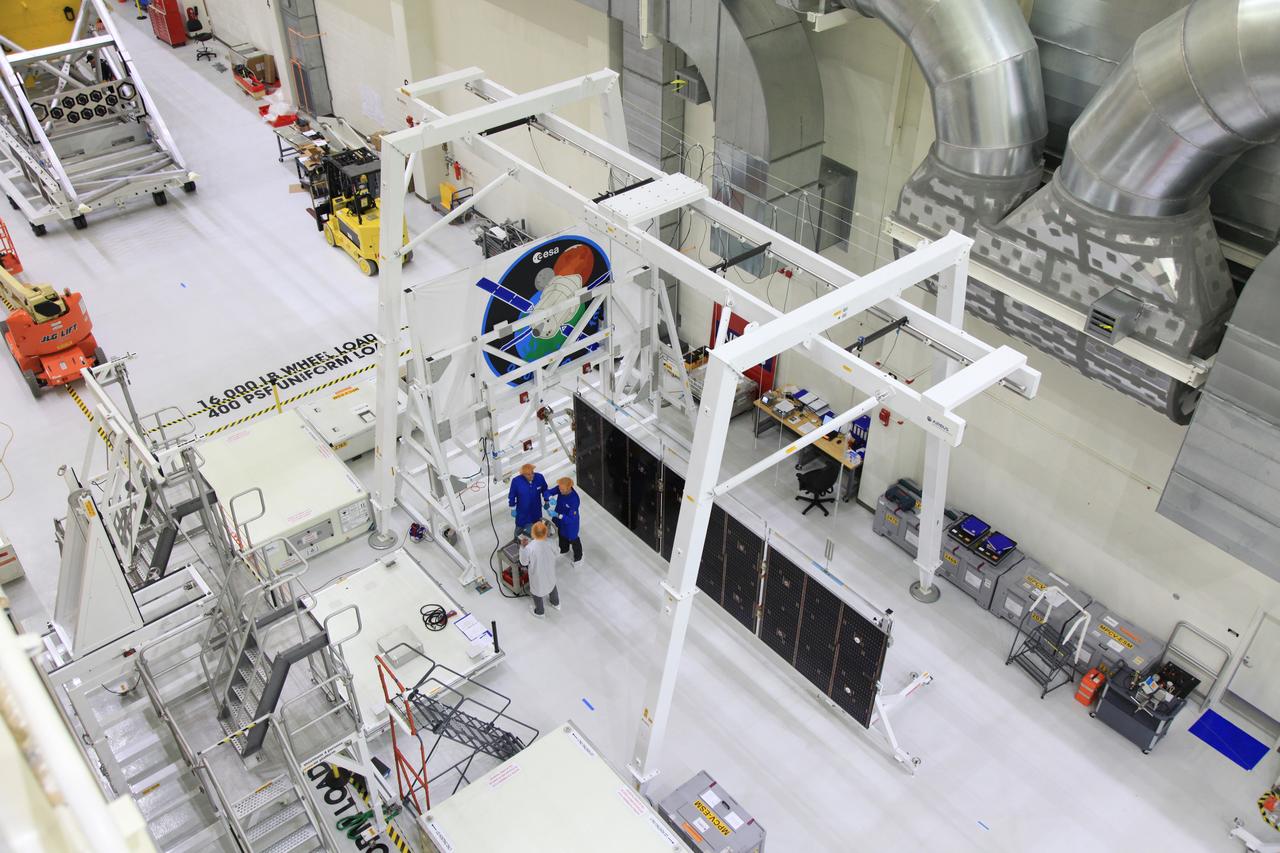

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
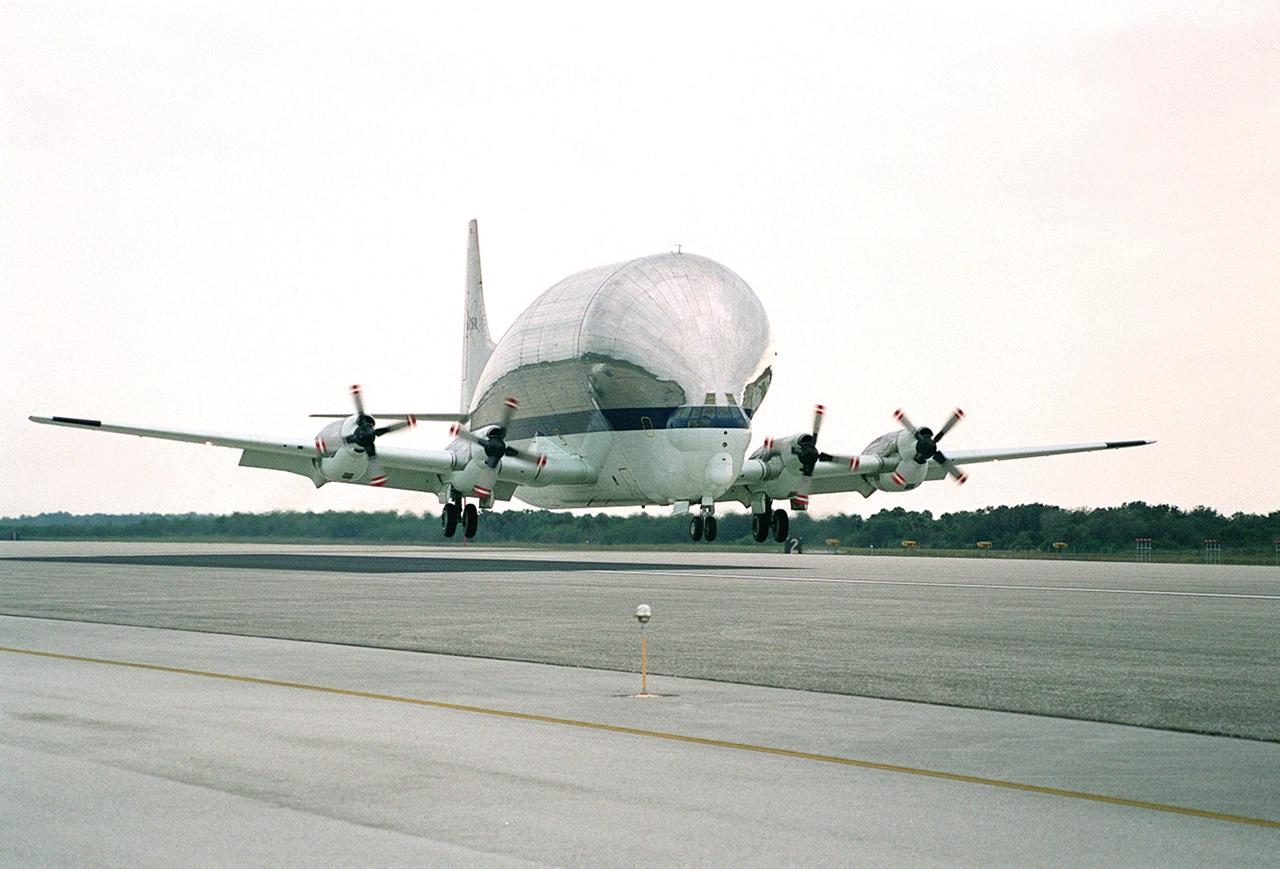

A Super Guppy aircraft arrives at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility with its cargo of Integrated Truss Structure S3, built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
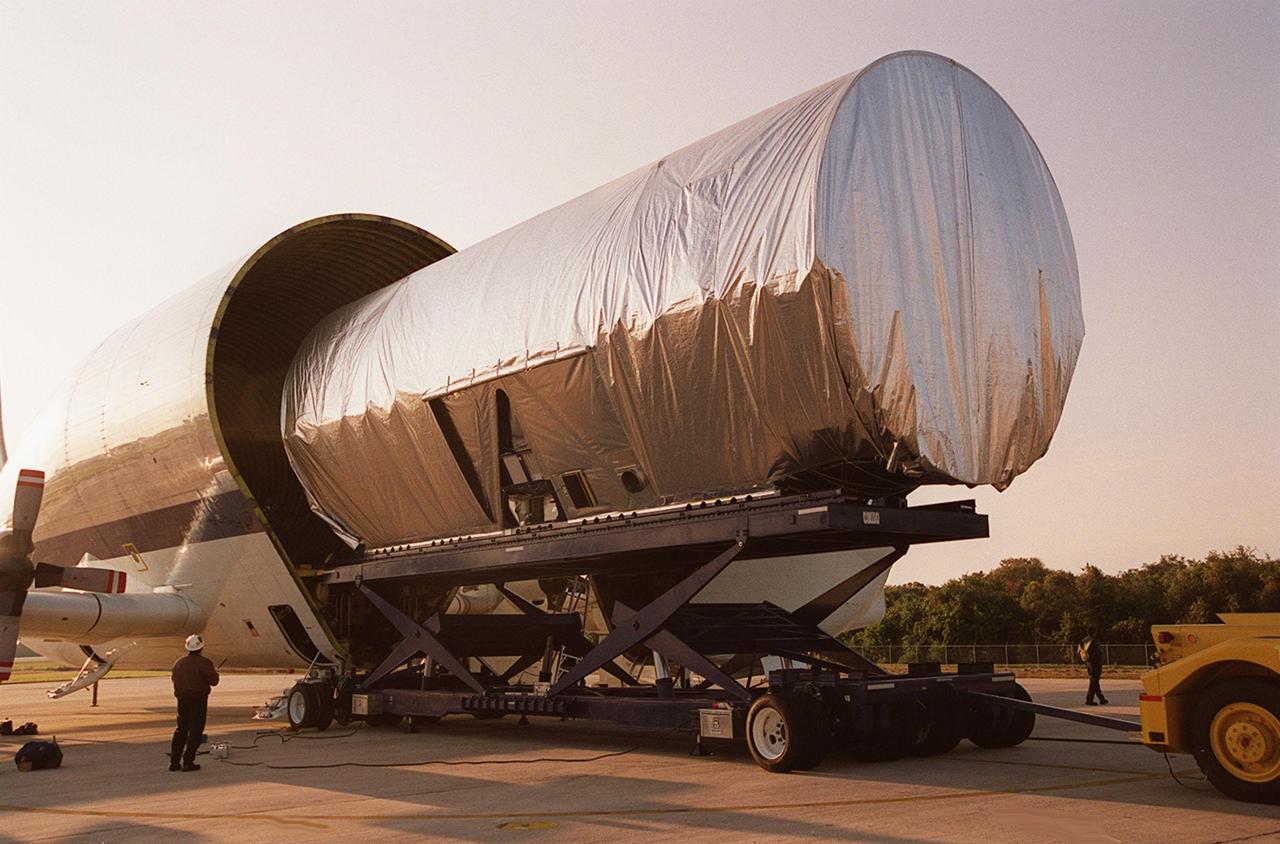

The Integrated Truss Structure S3 is offloaded from the Super Guppy aircraft that brought it to KSC from Tulsa, Okla. The S3 is built by The Boeing Co. The truss will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
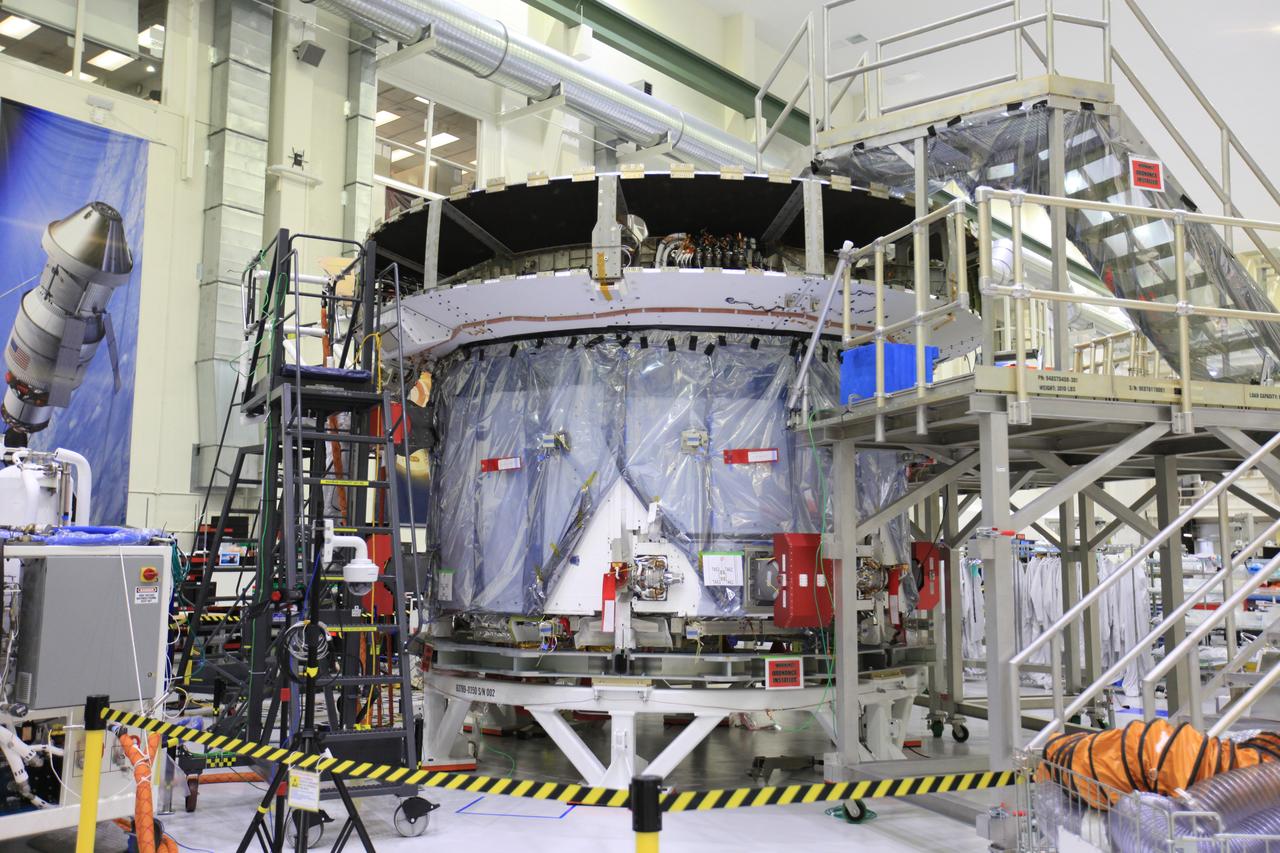

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
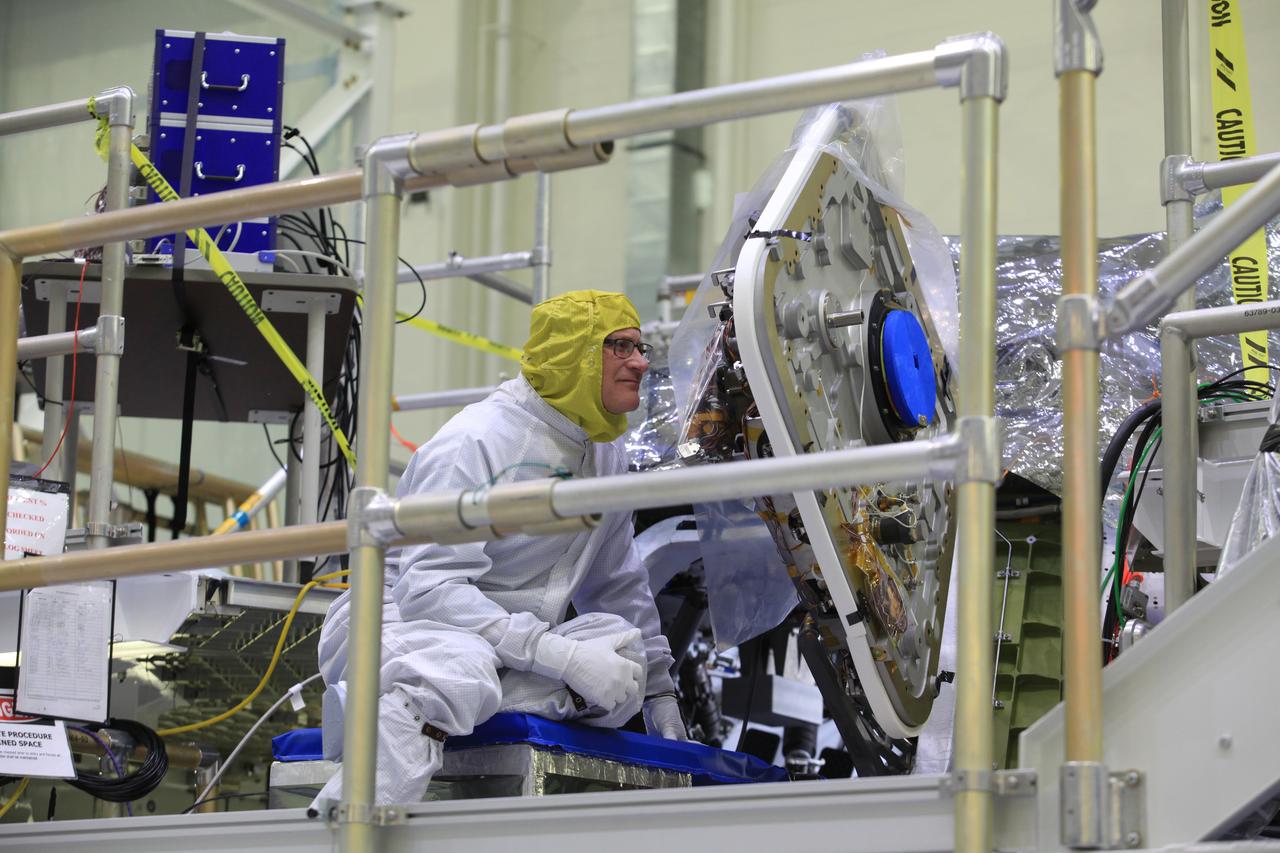

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
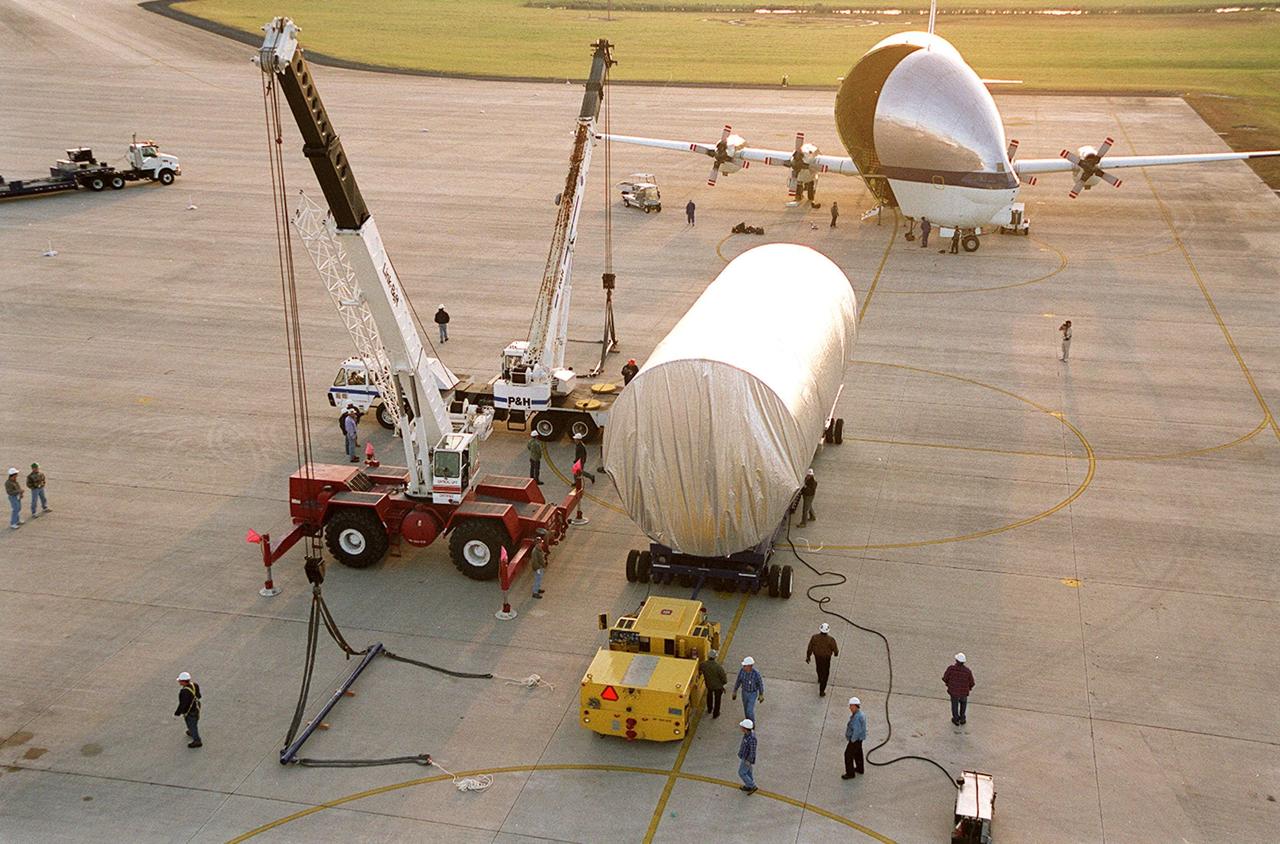

The Integrated Truss Structure S3 waits on the parking apron of the Shuttle Landing Facility after being offloaded from the Super Guppy aircraft in the background. The truss will be moved to a transporter and taken to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
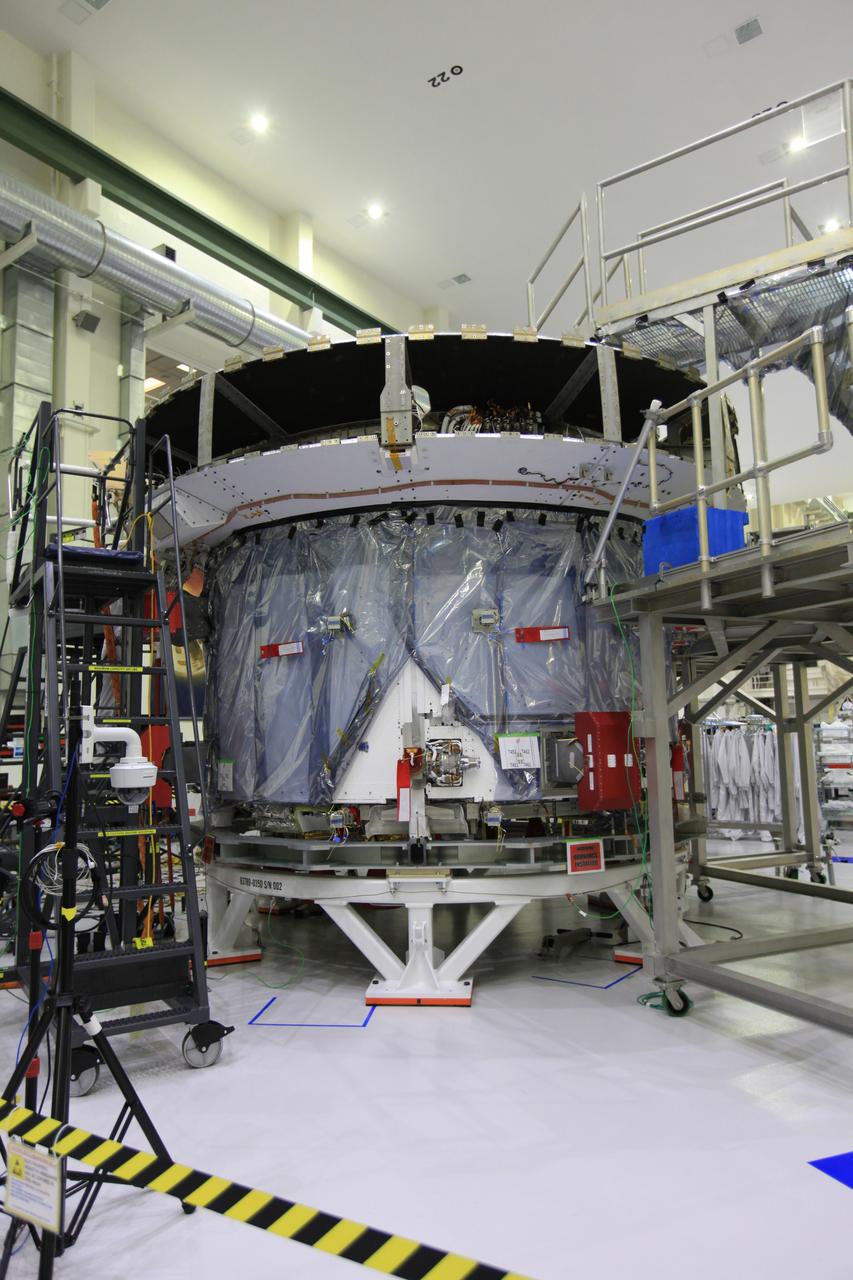

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
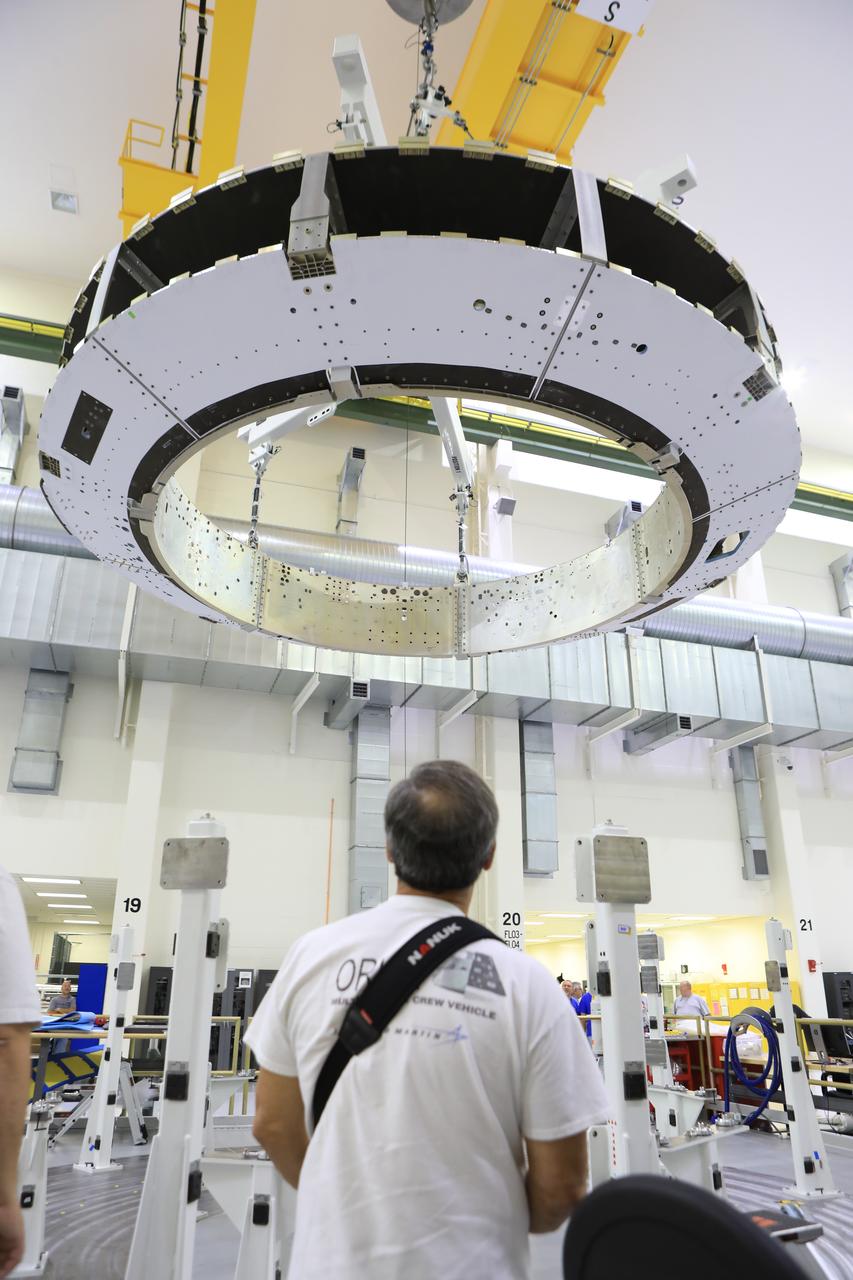

The Orion crew module adapter (CMA) for Exploration Mission 1 was lifted for the first and only time, Nov. 11, during its processing flow inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building high bay at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CMA is now undergoing secondary structure outfitting.

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
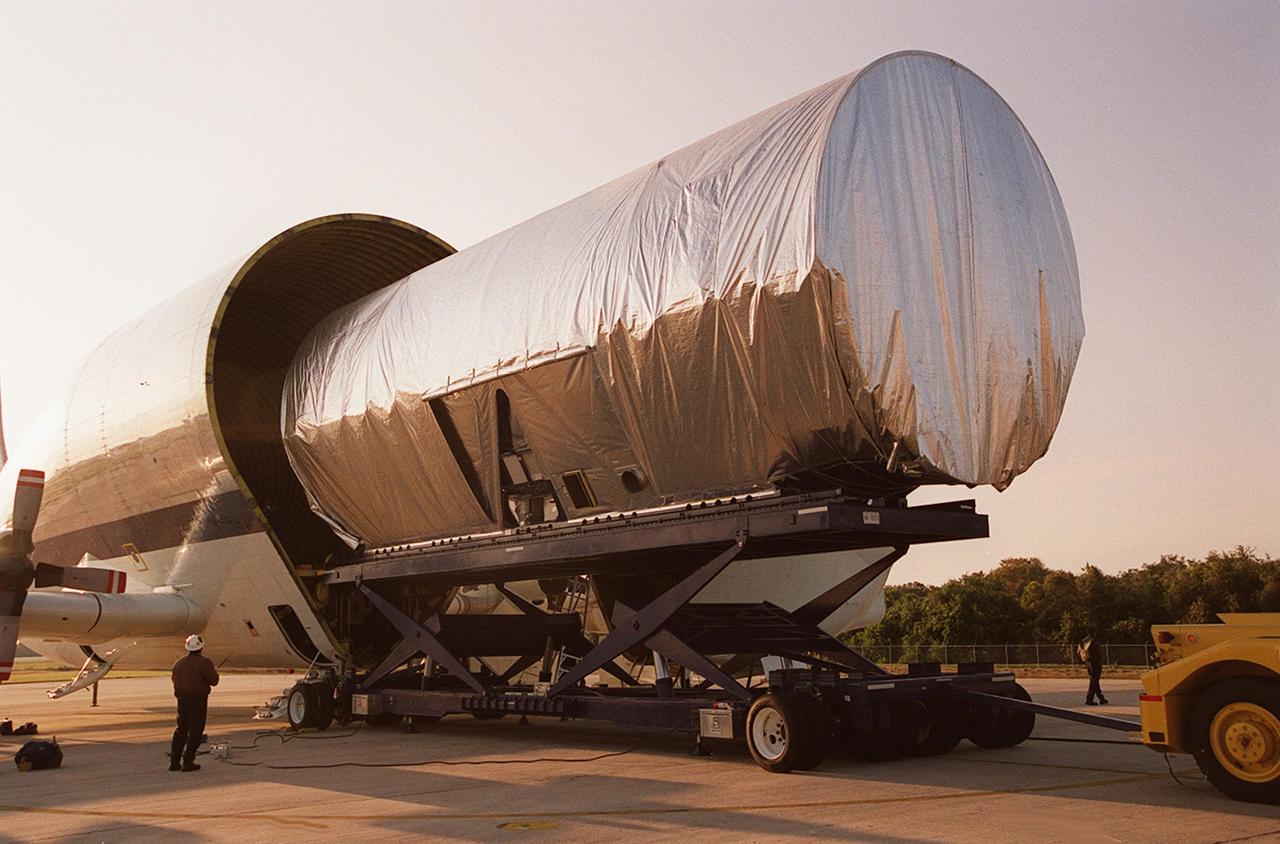

The Integrated Truss Structure S3 is offloaded from the Super Guppy aircraft that brought it to KSC from Tulsa, Okla. The S3 is built by The Boeing Co. The truss will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
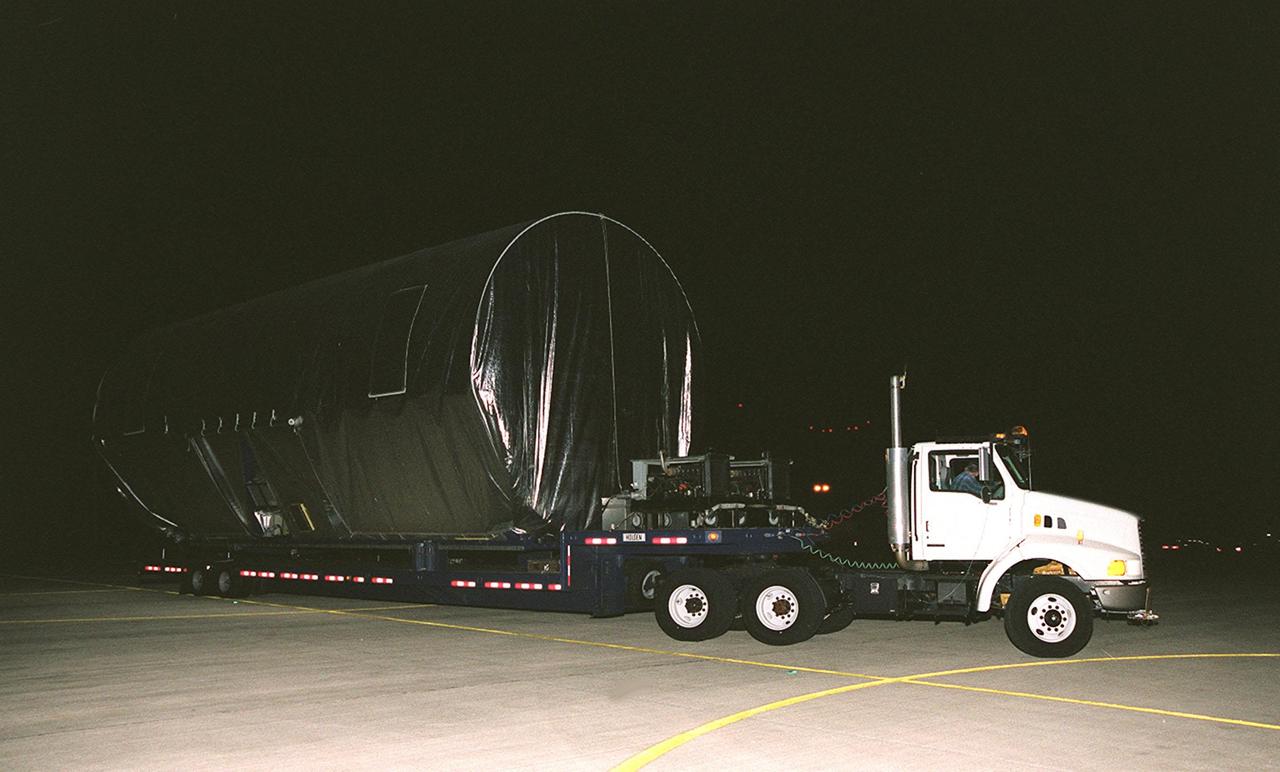

A flatbed trailer begins moving the Integrated Truss Structure S3 from the Shuttle Landing Facility to the Operations and Checkout Building. The S3 arrived aboard a Super Guppy aircraft. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
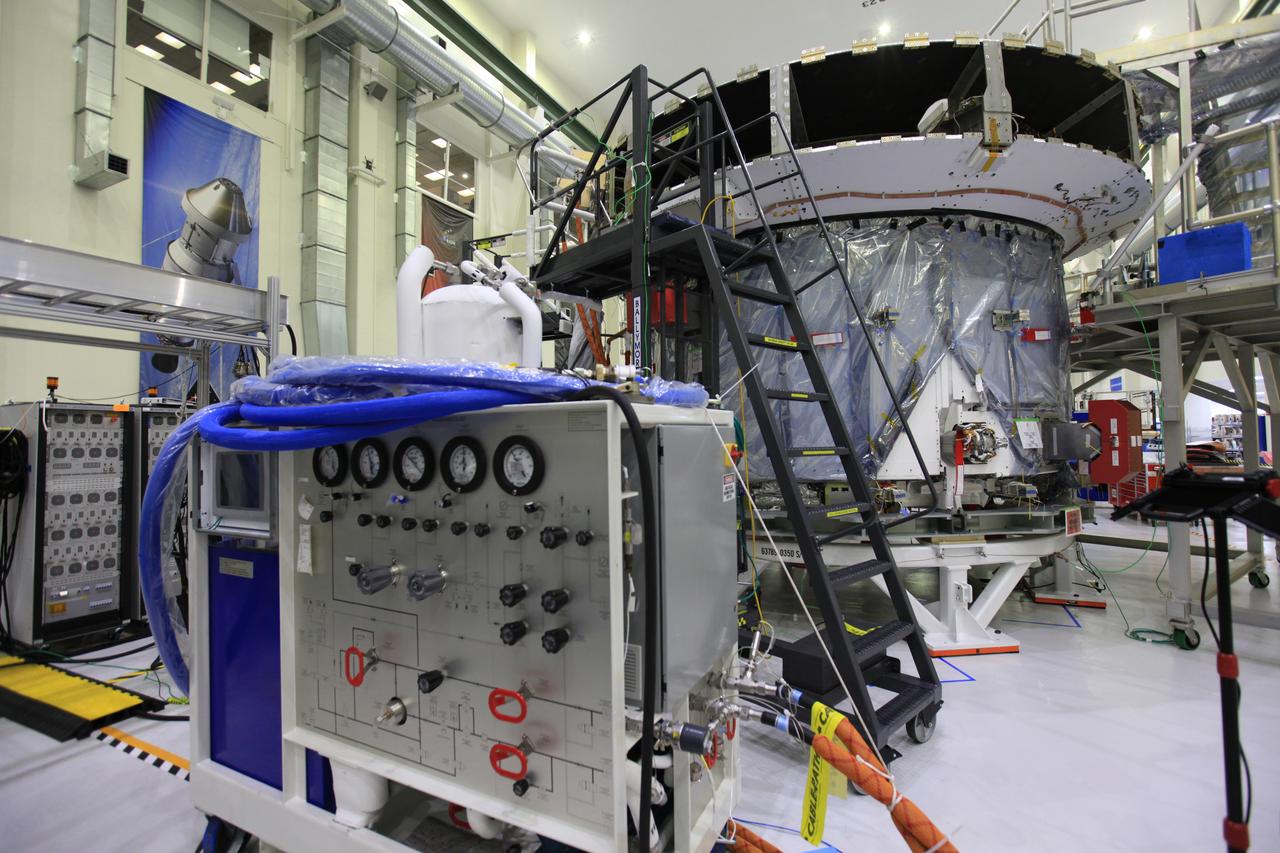
The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
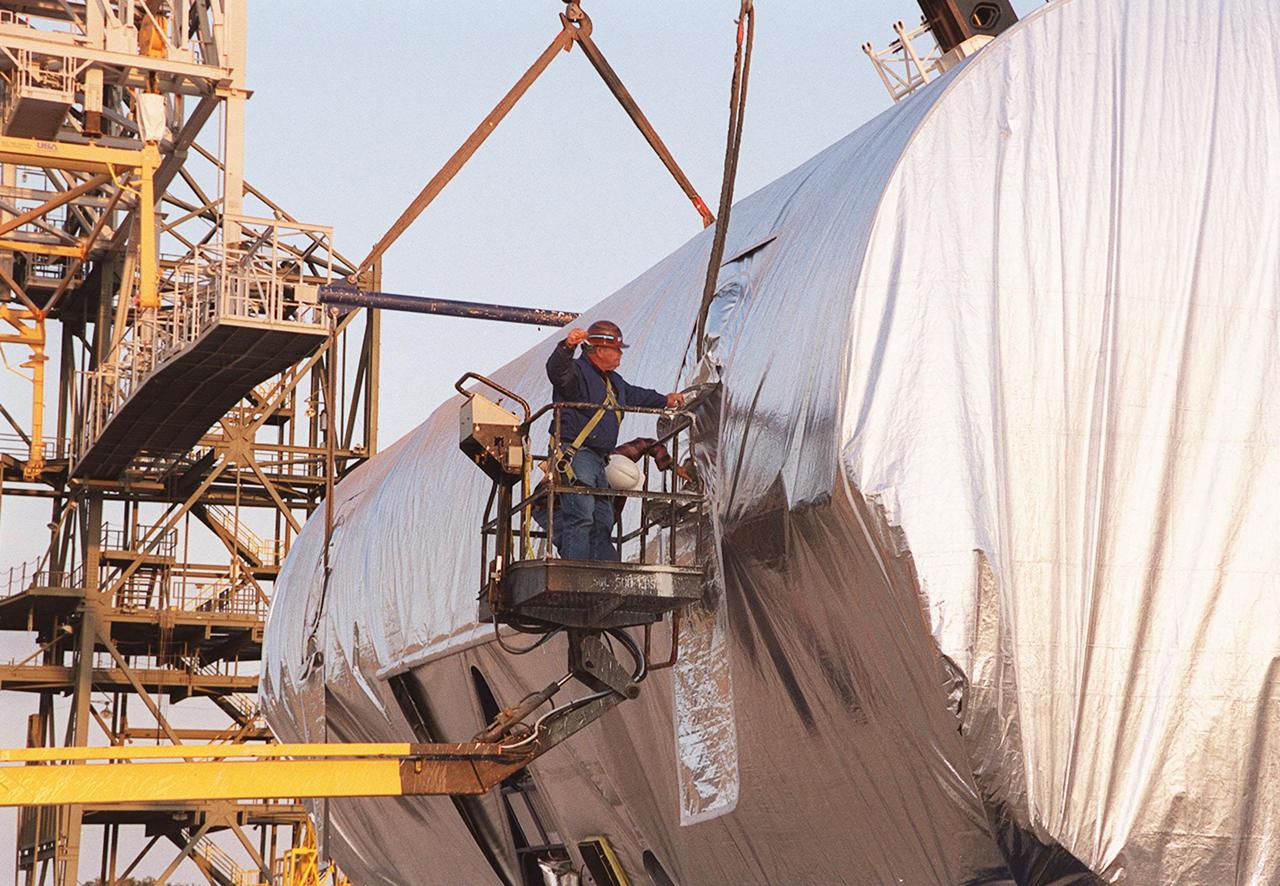

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, a worker attaches one of the cranes to the Integrated Truss Structure S3. Cranes will lift and move the truss to a transporter and take it to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
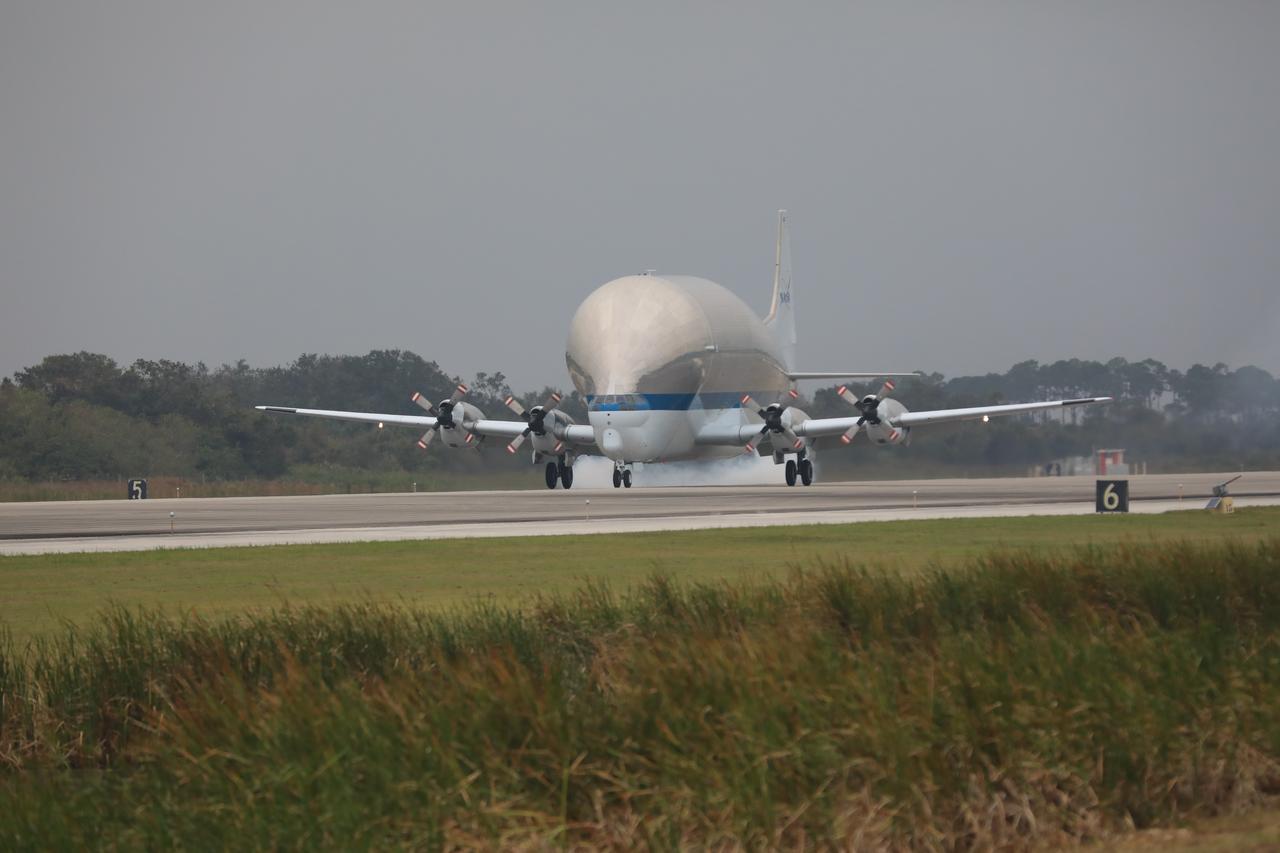

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft touches down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
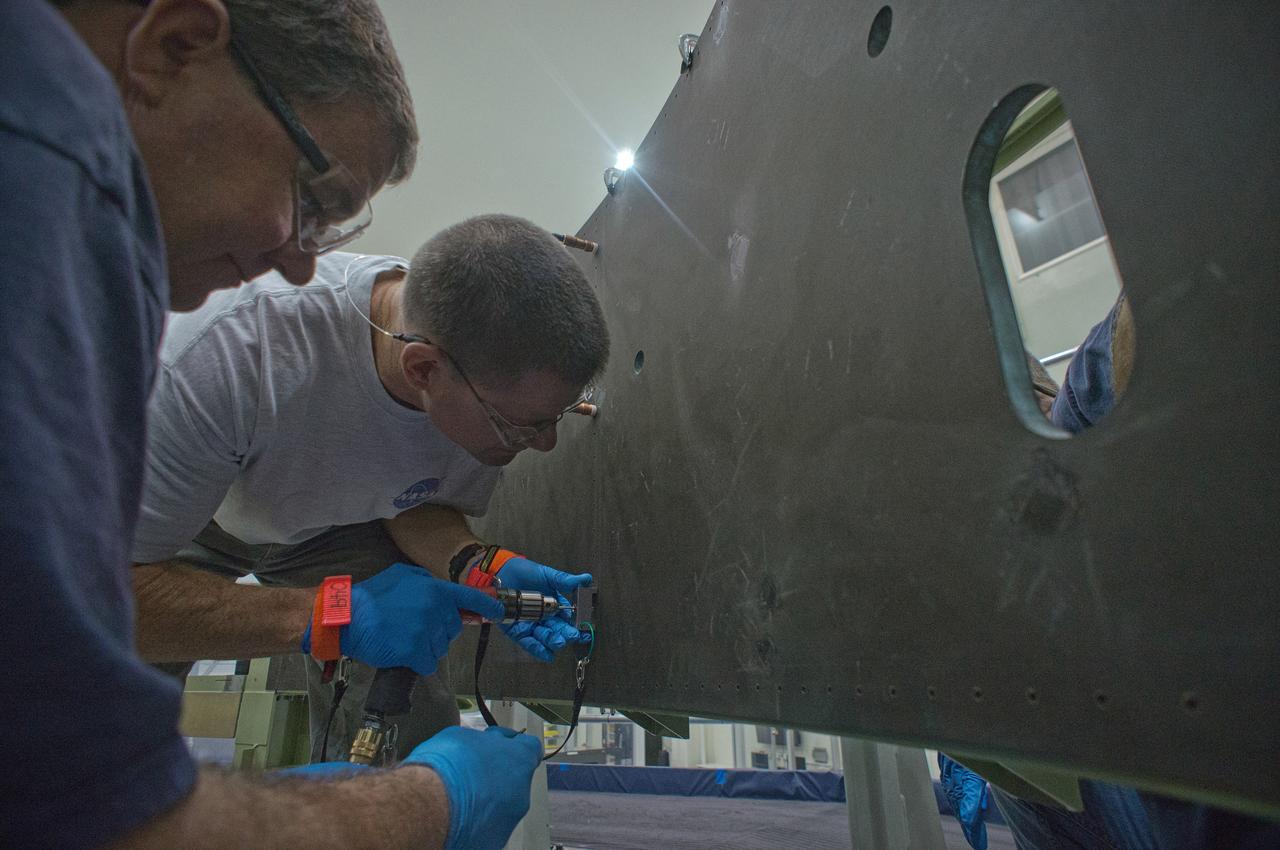

In the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, technicians drill pilot holes into the composite panel clamped to the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion service module structure on Jan. 1, 2012. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
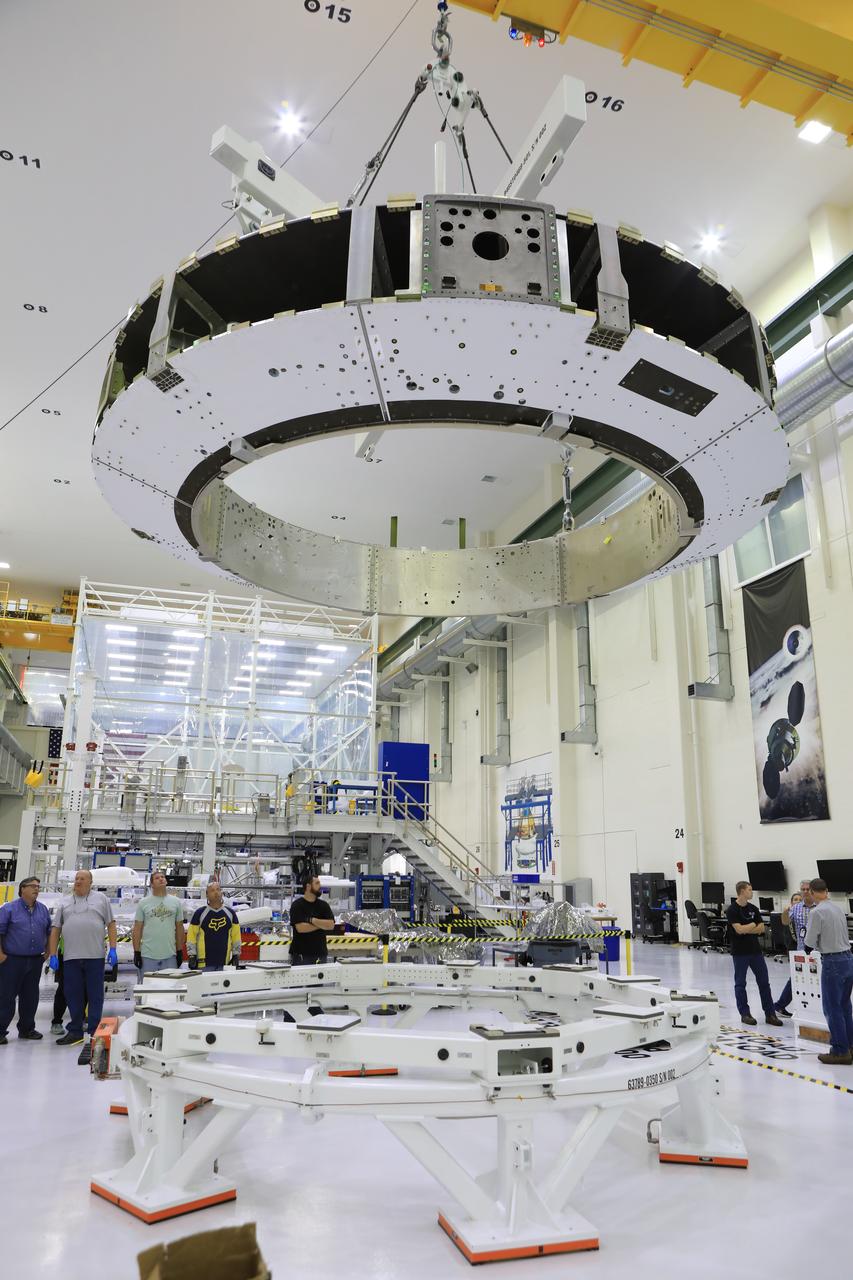

The Orion crew module adapter (CMA) for Exploration Mission 1 was lifted for the first and only time, Nov. 11, during its processing flow inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building high bay at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CMA is now undergoing secondary structure outfitting.
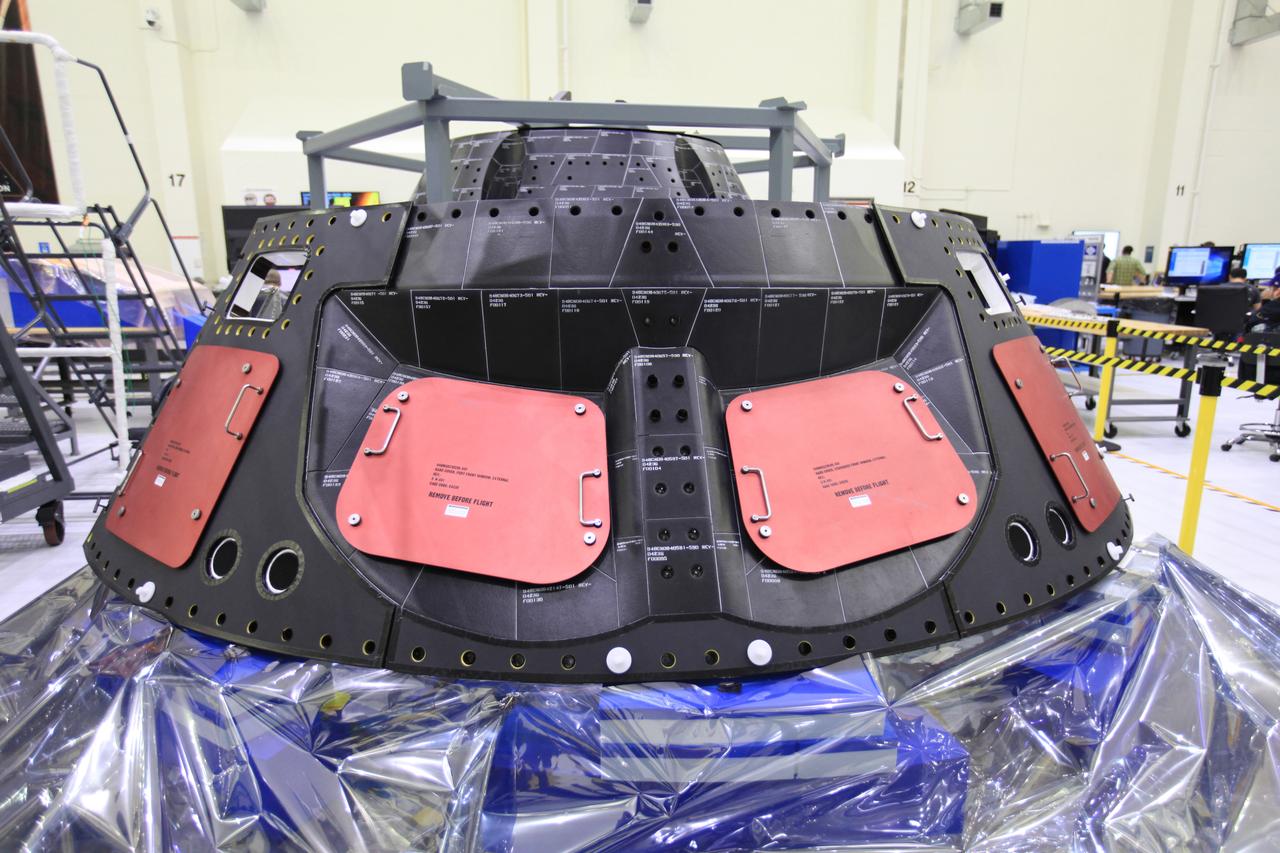
The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
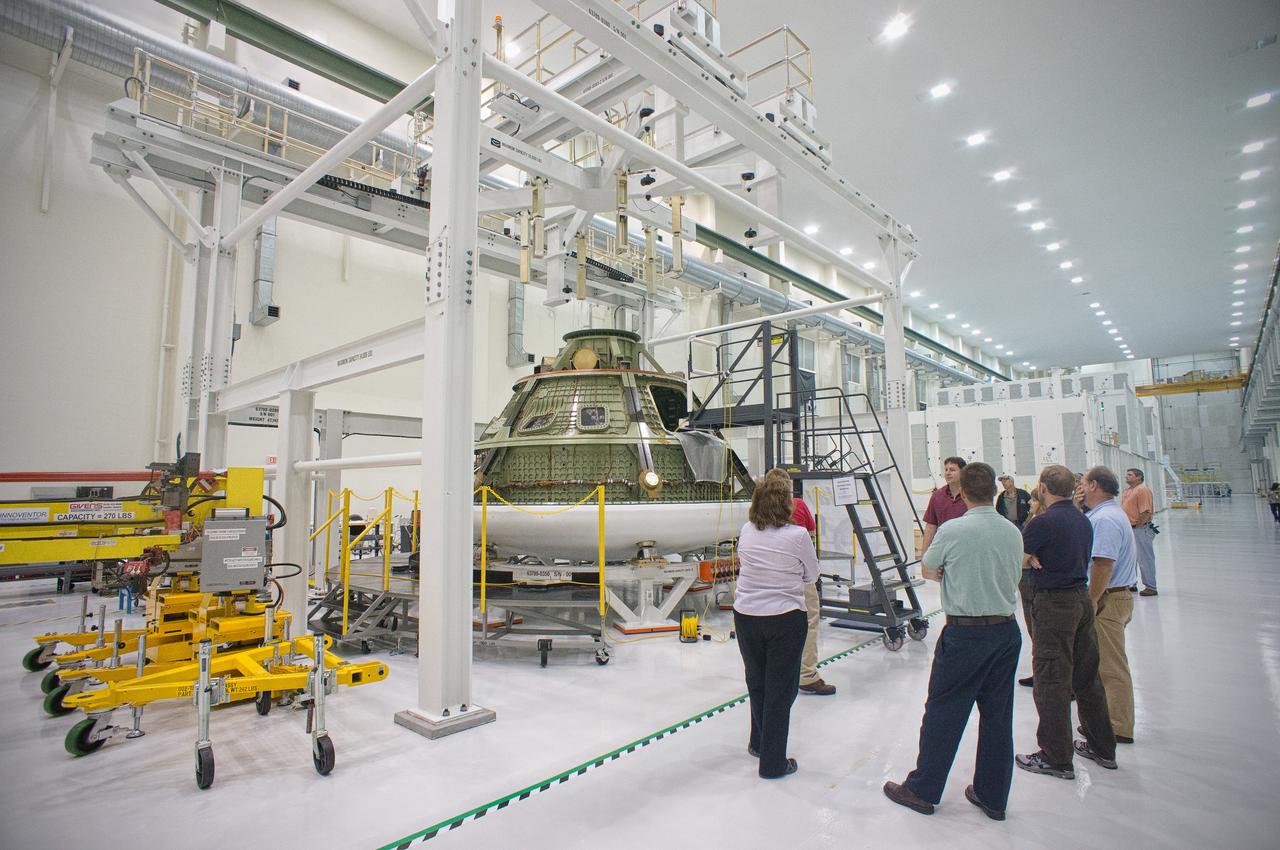

The Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (SPLASH) project team from NASA’s Langley Research Center examines the Orion ground test article in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 31, 2011. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
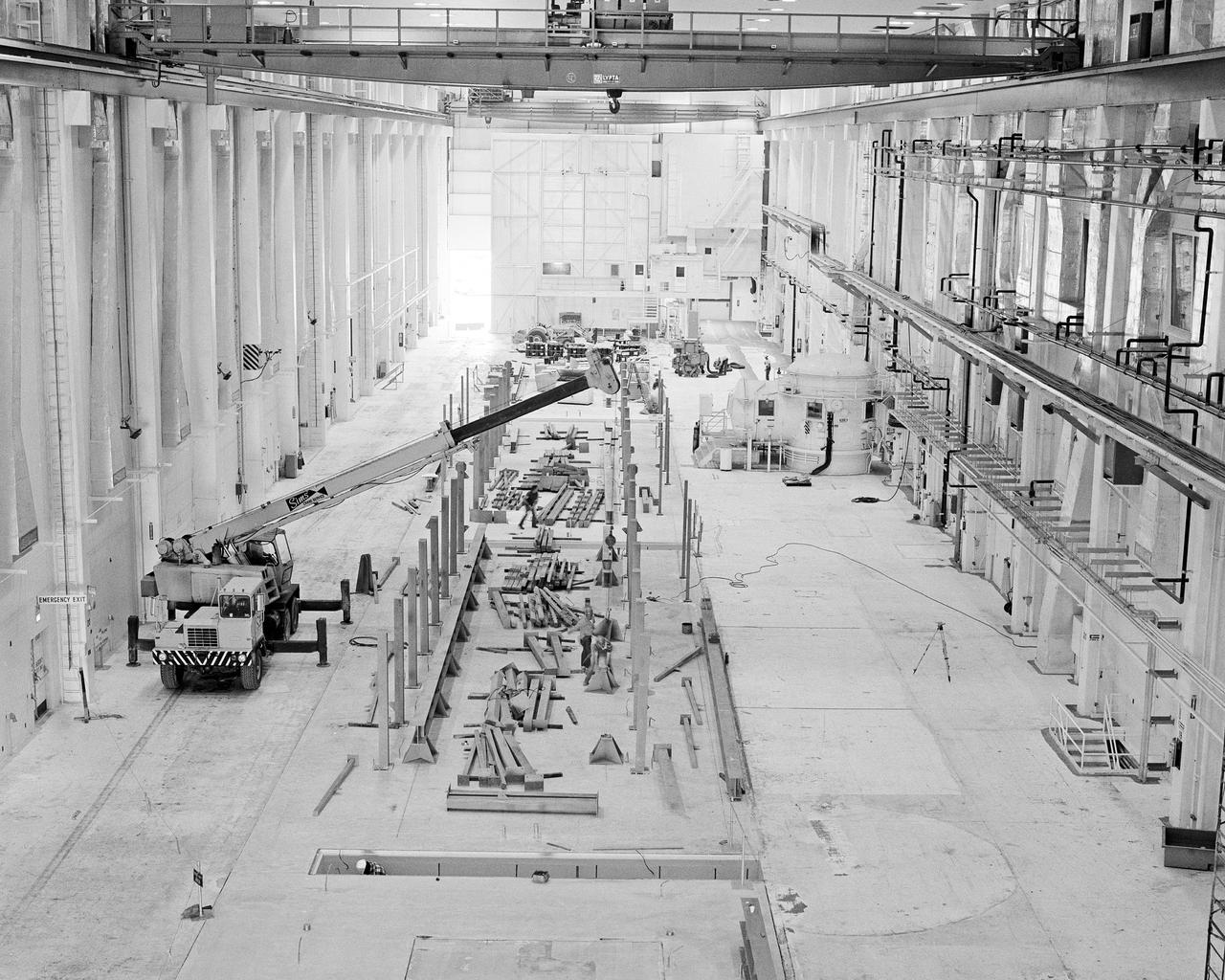

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, structural work is ongoing inside the high bay of the Operations and Checkout Building. The modifications are taking place to configure the facility flight hardware from the Apollo Program and prepare to support payload processing for future space shuttle missions. Photo Credit: NASA
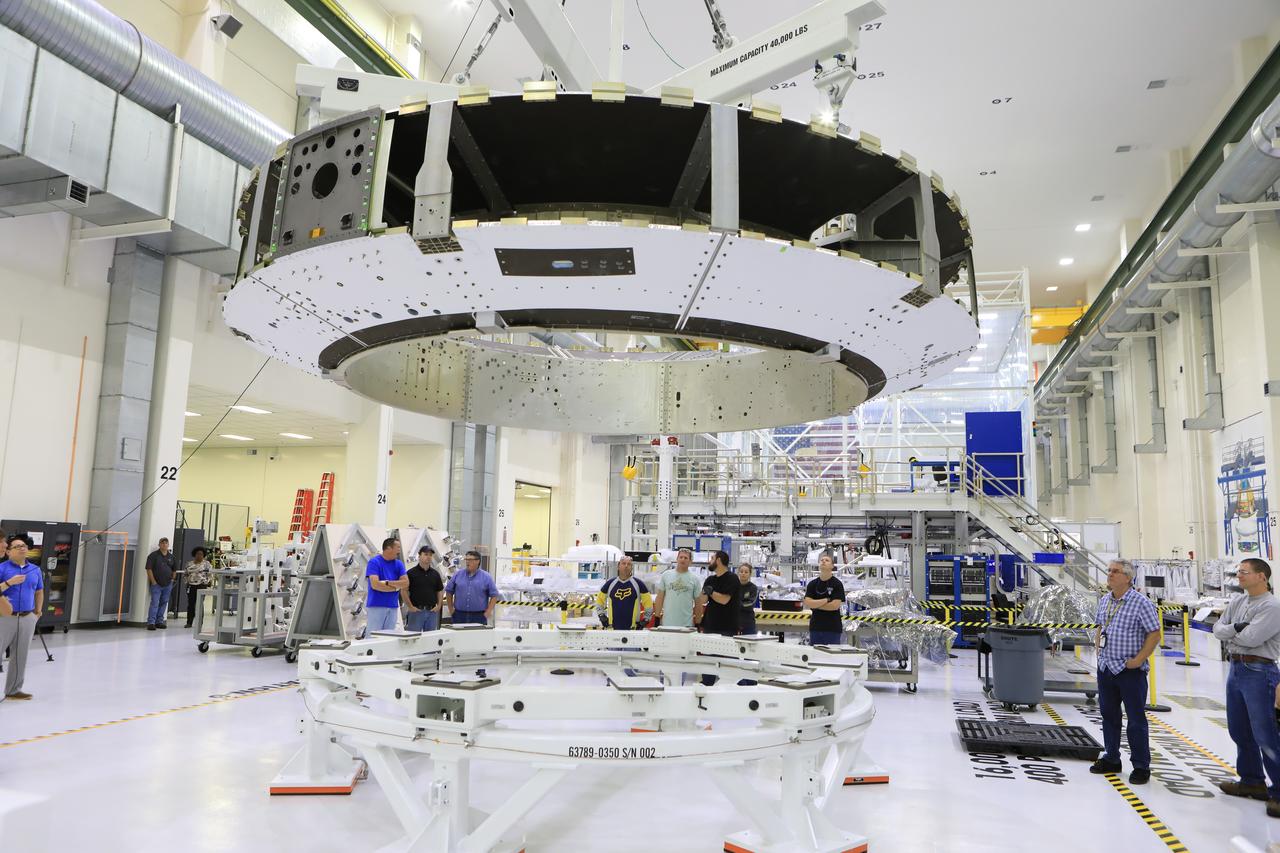

The Orion crew module adapter (CMA) for Exploration Mission 1 was lifted for the first and only time, Nov. 11, during its processing flow inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building high bay at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CMA is now undergoing secondary structure outfitting.
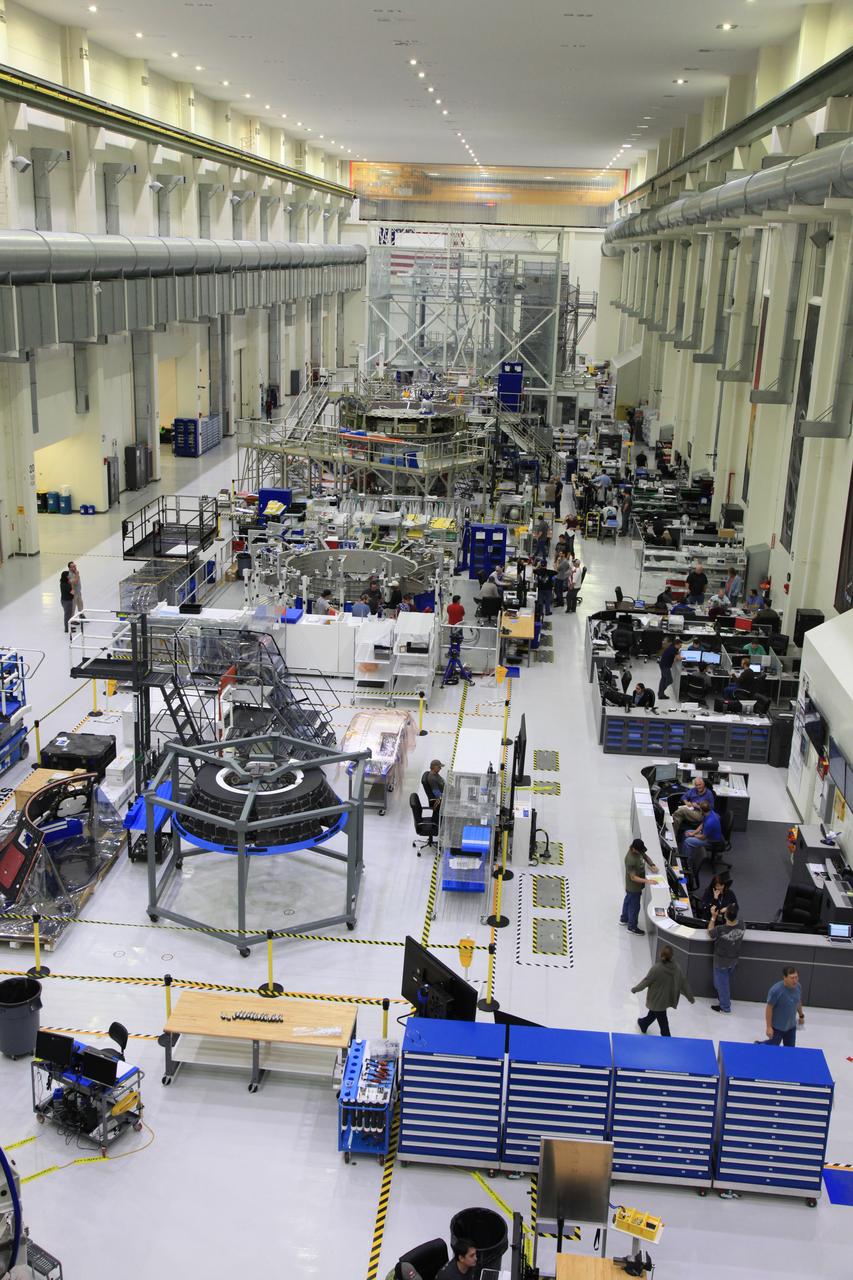

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
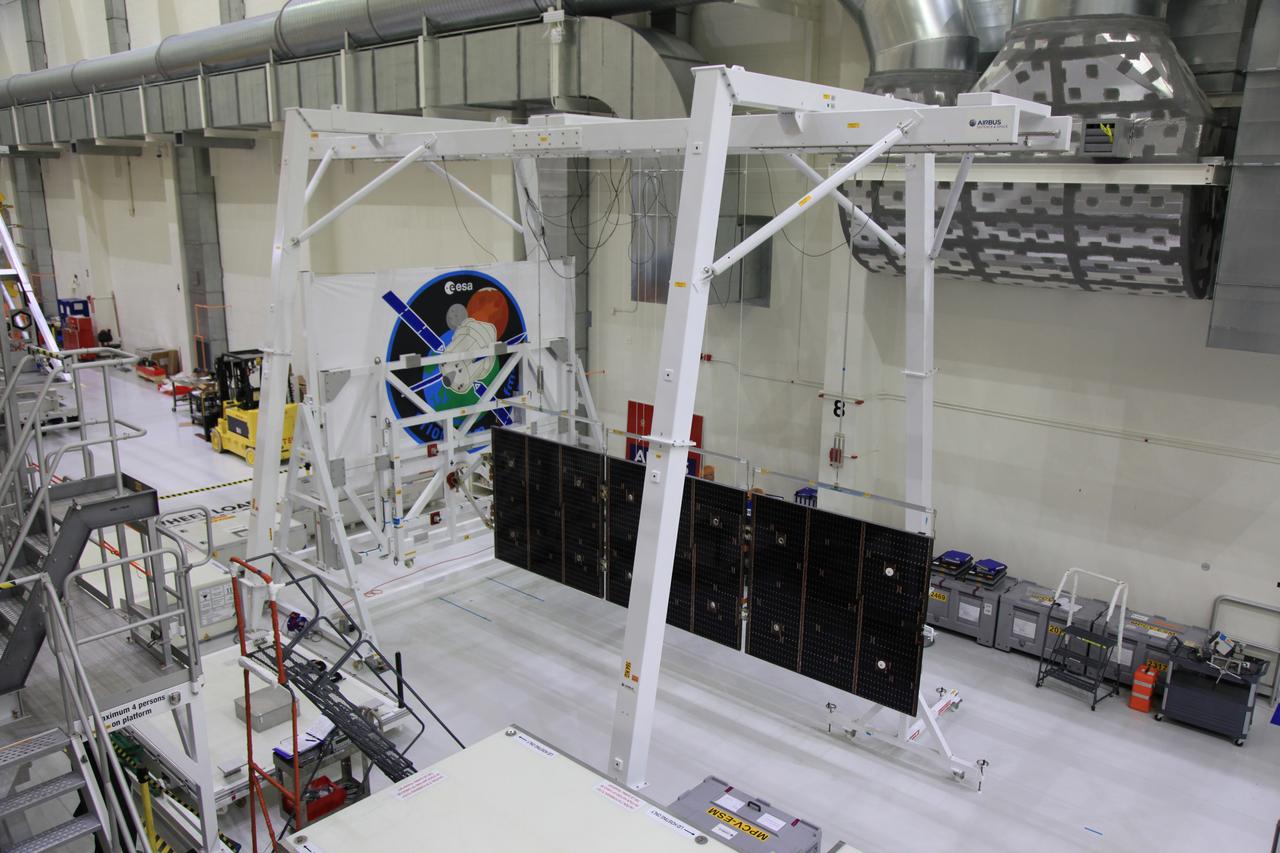

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
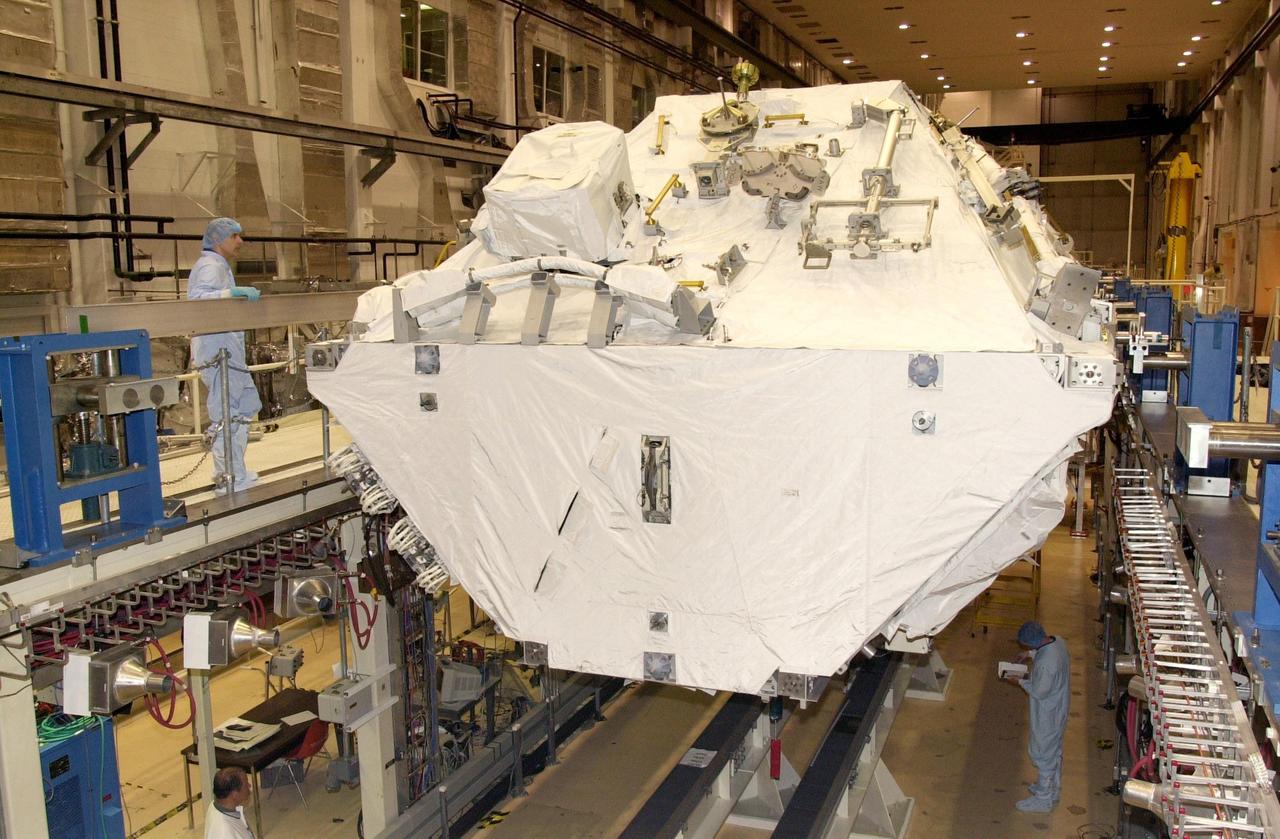
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Integrated Truss Structure S0 is ready for transport to the launch pad on mission STS-110. Scheduled for launch April 4, the 11-day mission will feature Space Shuttle Atlantis docking with the International Space Station (ISS) and delivering the S0 truss, the centerpiece-segment of the primary truss structure that will eventually extend over 300 feet
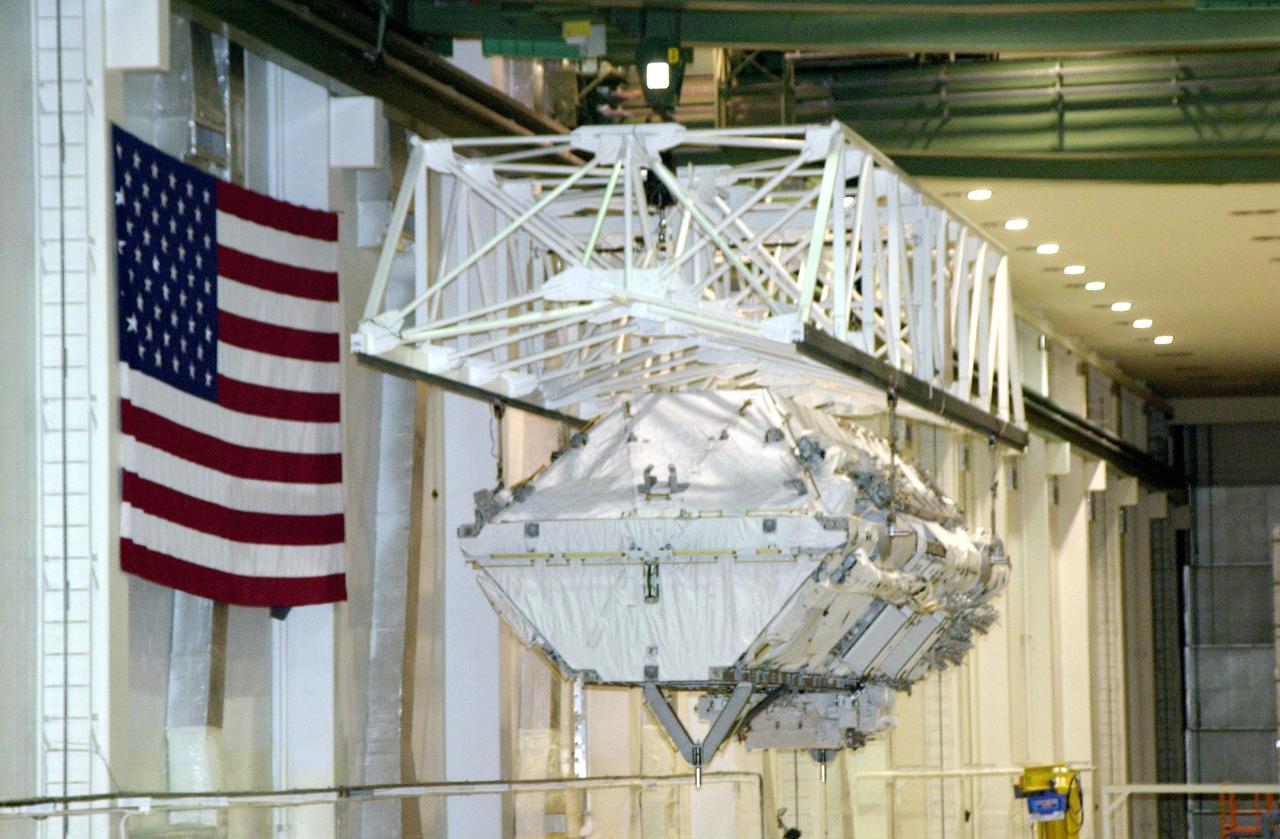
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane carries the Integrated Truss Structure S0 from its workstand toward the payload canister. The S0 truss will be transported to the launch pad for mission STS-110. Part of the payload, the S0 truss will become the backbone of the orbiting International Space Station (ISS), at the center of the 10-truss, girderlike structure that will ultimately extend the length of a football field on the ISS. The S0 truss will be attached to the U.S. Lab, 'Destiny,' on the 11-day mission. Launch is scheduled for April 4
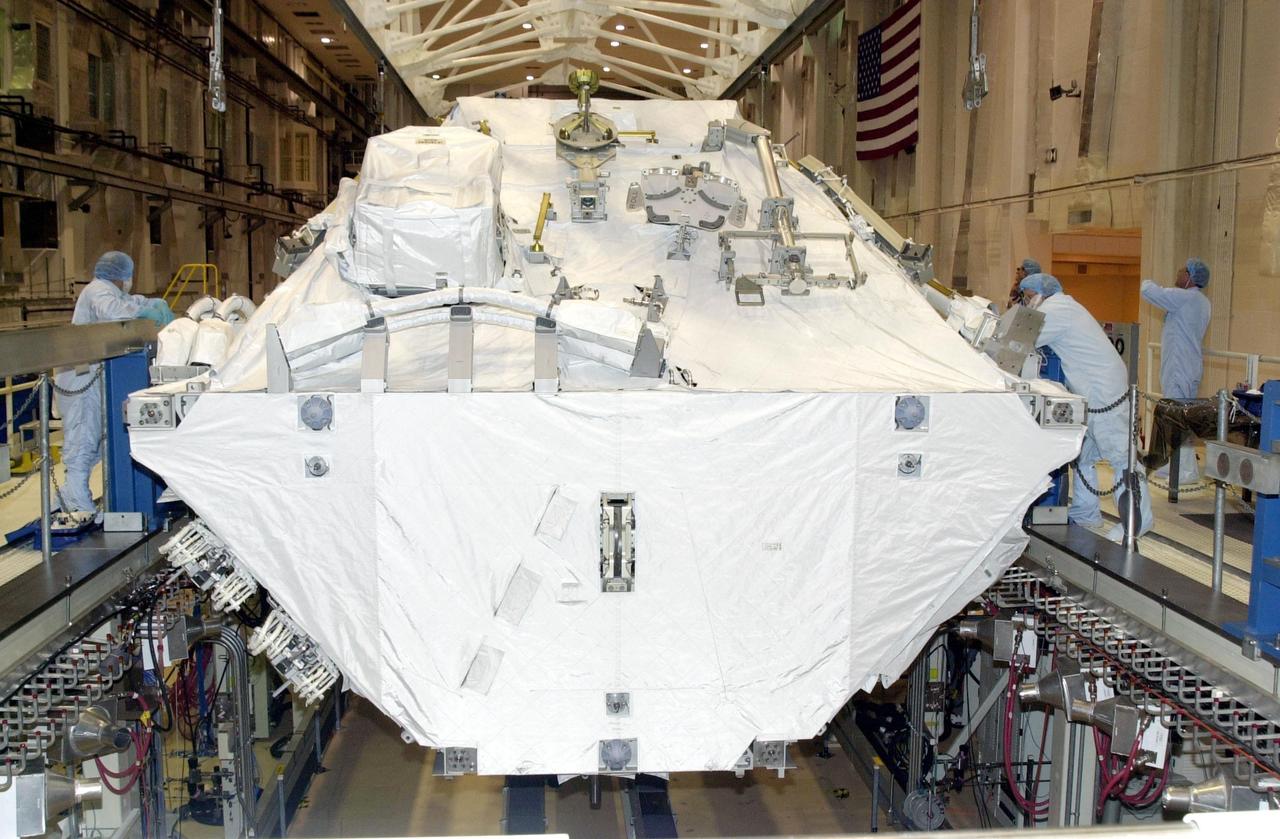

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Integrated Truss Structure S0 is ready to be moved to the payload canister for transport to the launch pad for mission STS-110. Part of the payload, the S0 truss will become the backbone of the orbiting International Space Station (ISS), at the center of the 10-truss, girderlike structure that will ultimately extend the length of a football field on the ISS. The S0 truss will be attached to the U.S. Lab, "Destiny," on the 11-day mission. Launch is scheduled for April 4.
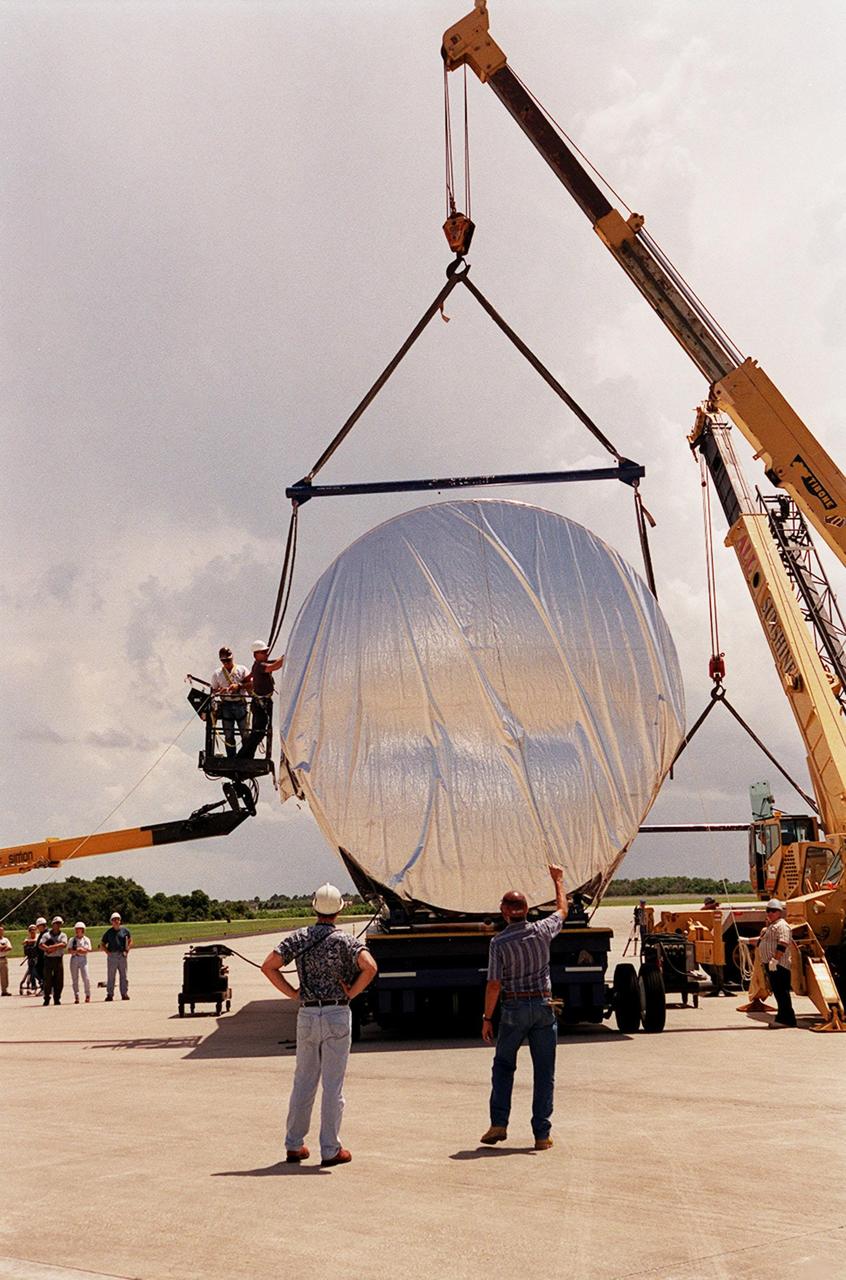

Workers oversee the placement of the P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, onto a flatbed truck that will move it to the Operations and Checkout Building for processing. The P-1 truss, scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
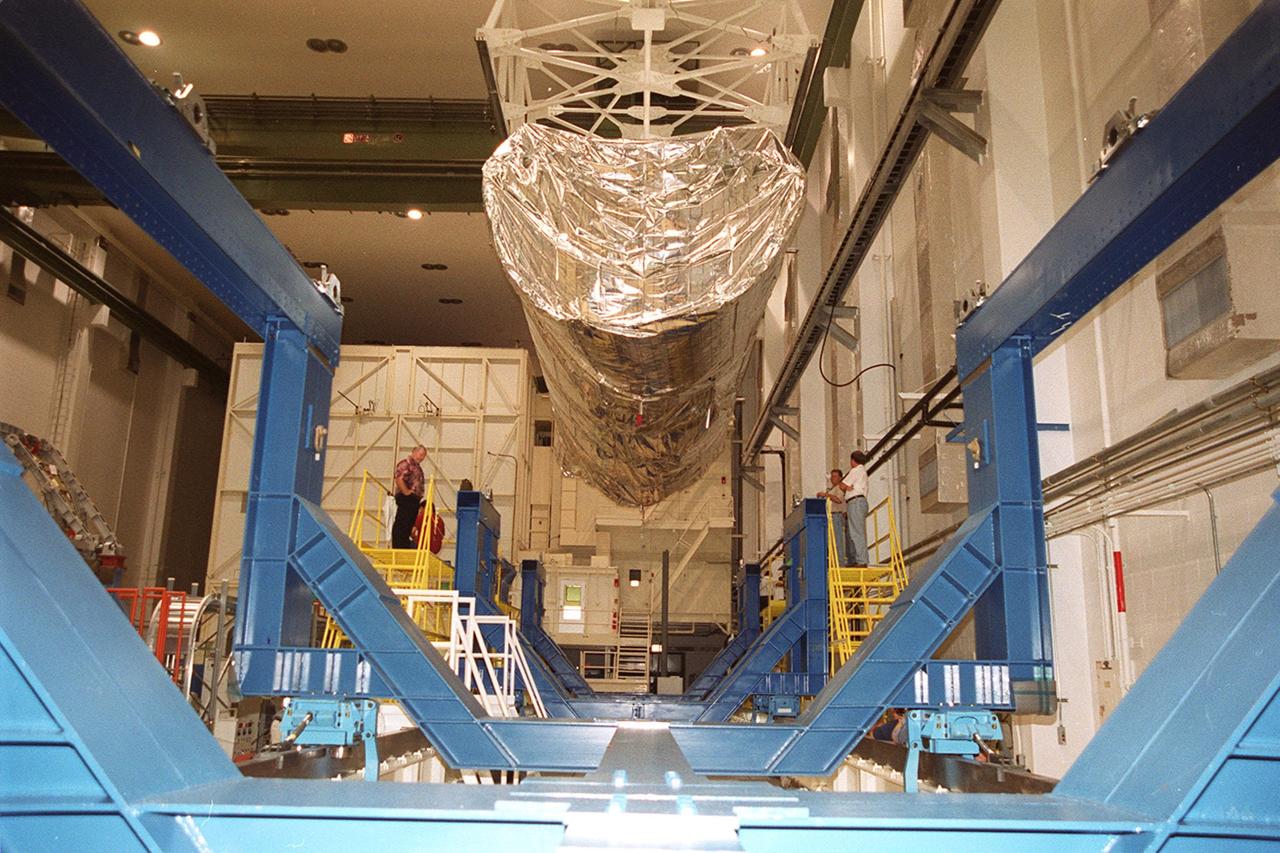

The P-1 truss (top of photo), a component of the International Space Station, nears its work stand in the Operations and Checkout Building where it will undergo processing. Scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, the P-1 is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
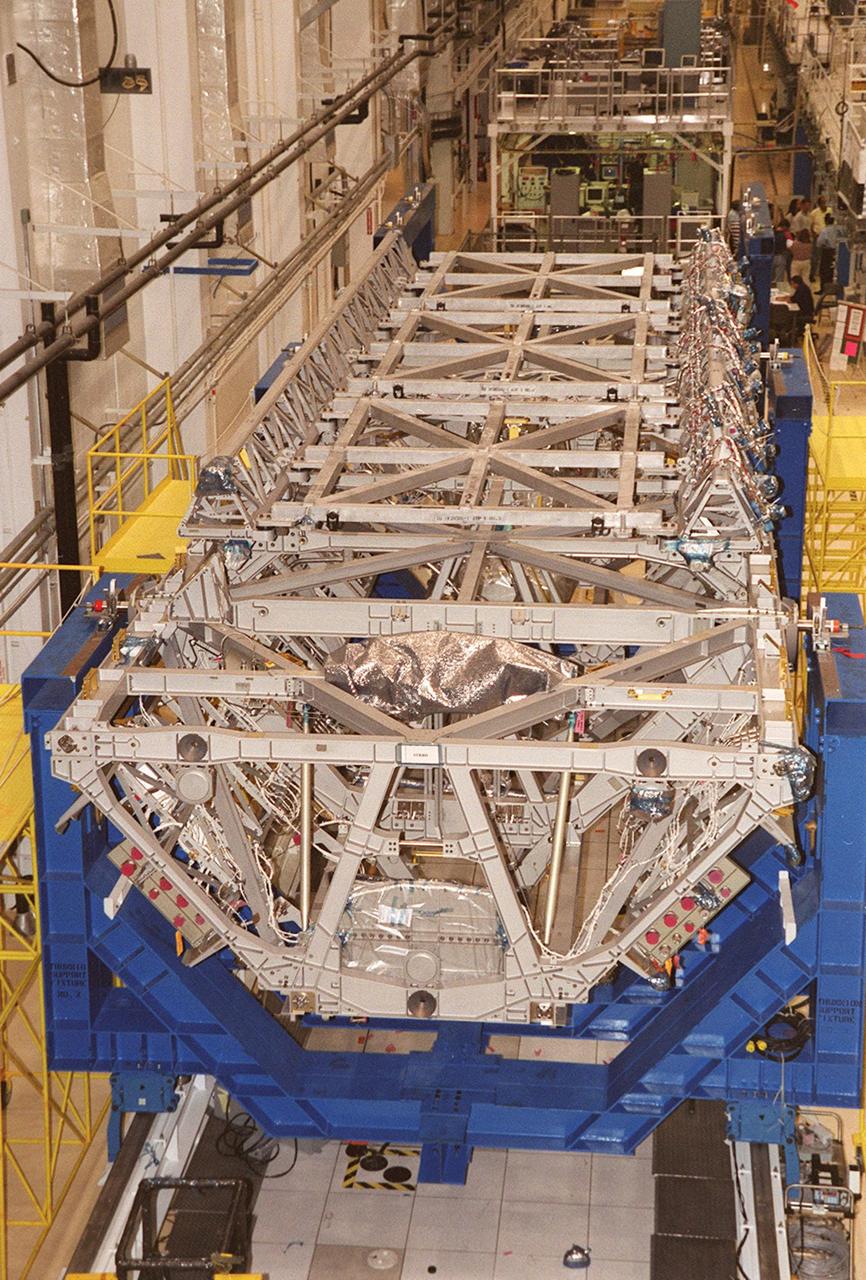
The length of the P-1 truss is seen as it rests in a workstand in the Operations and Checkout Building. Scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, the P-1 is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14by 15-foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the International Space Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency

The P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, is lowered into a work stand in the Operations and Checkout Building where it will undergo processing. Scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, the P-1 is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
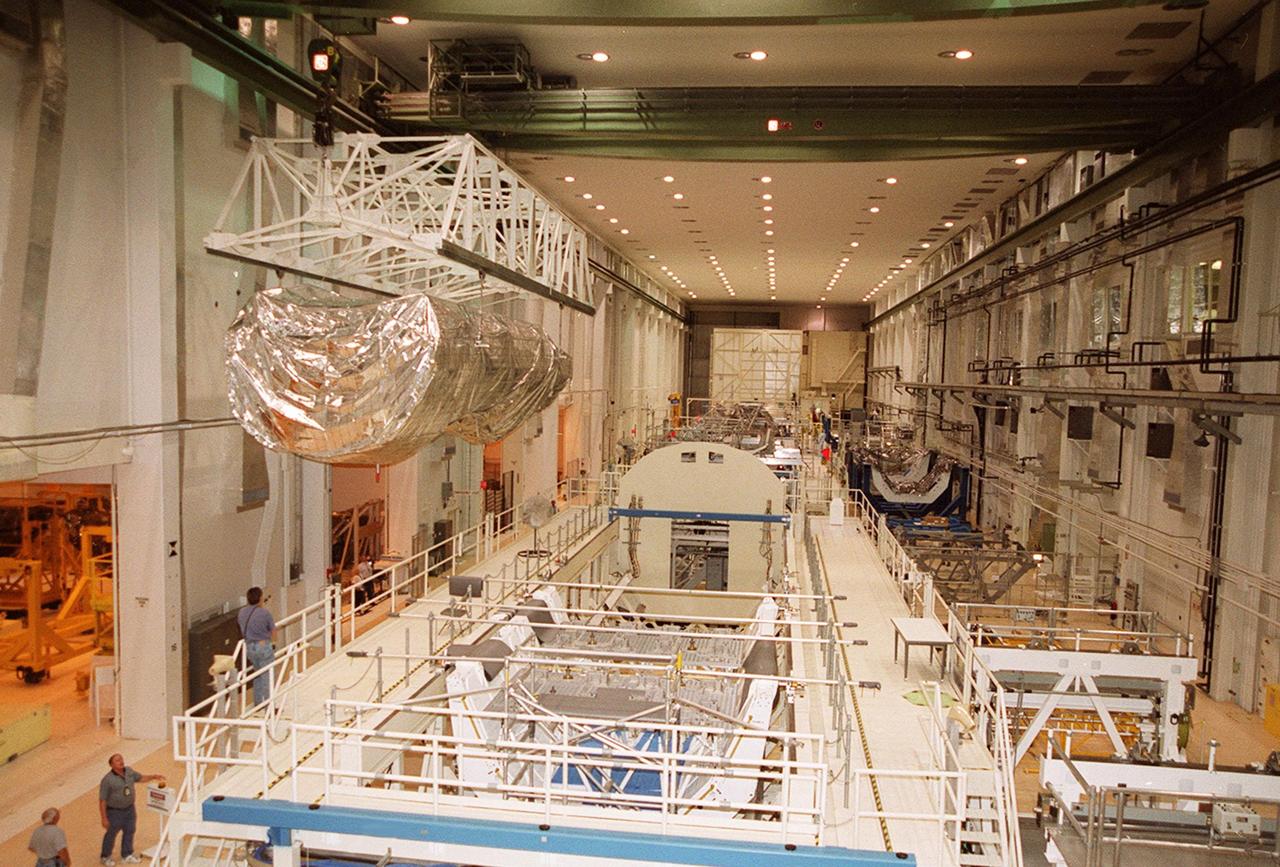

The P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, is moved the length of the Operations and Checkout Building to its work stand where it will undergo processing. Scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, the P-1 is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
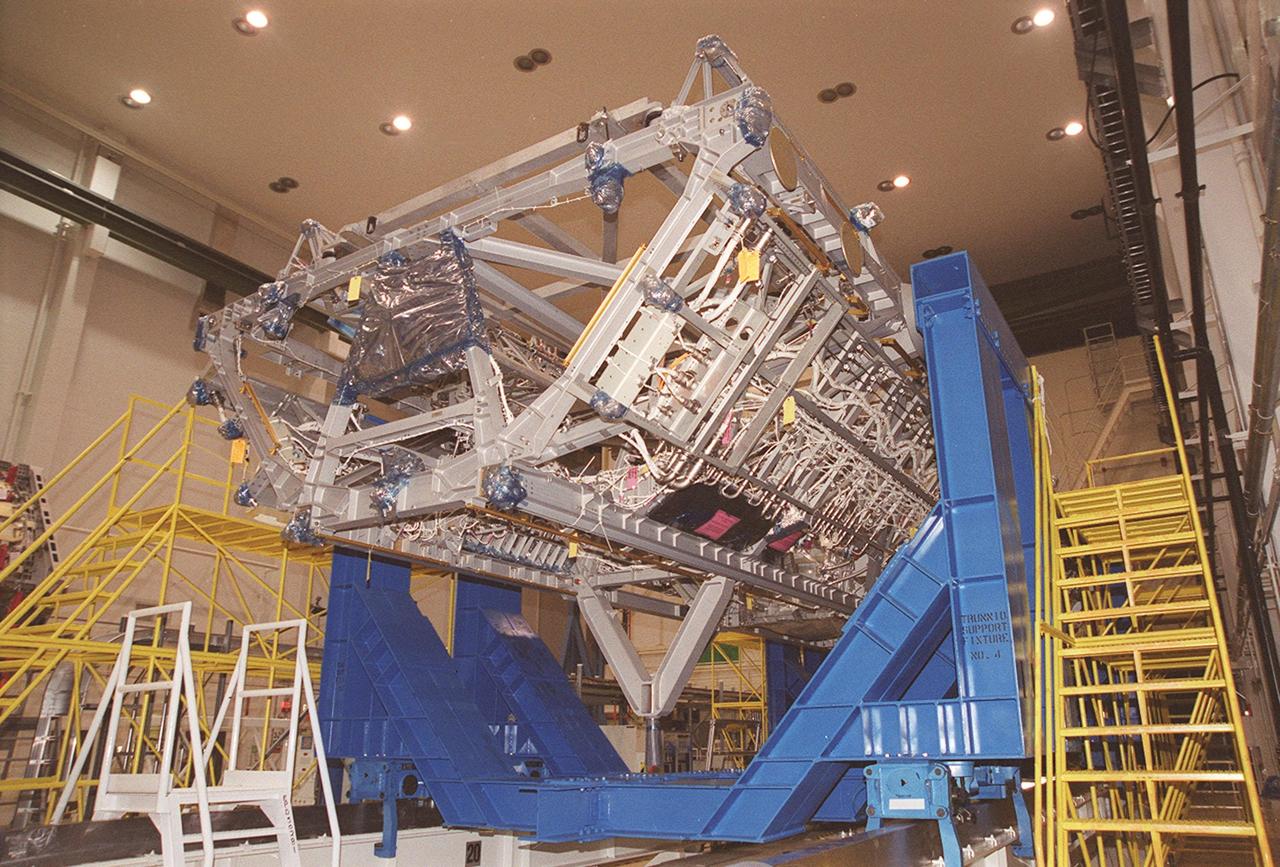
Part of the P-1 truss is seen as it rests in a workstand in the Operations and Checkout Building. Scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, the P-1 is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14by 15-foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the International Space Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
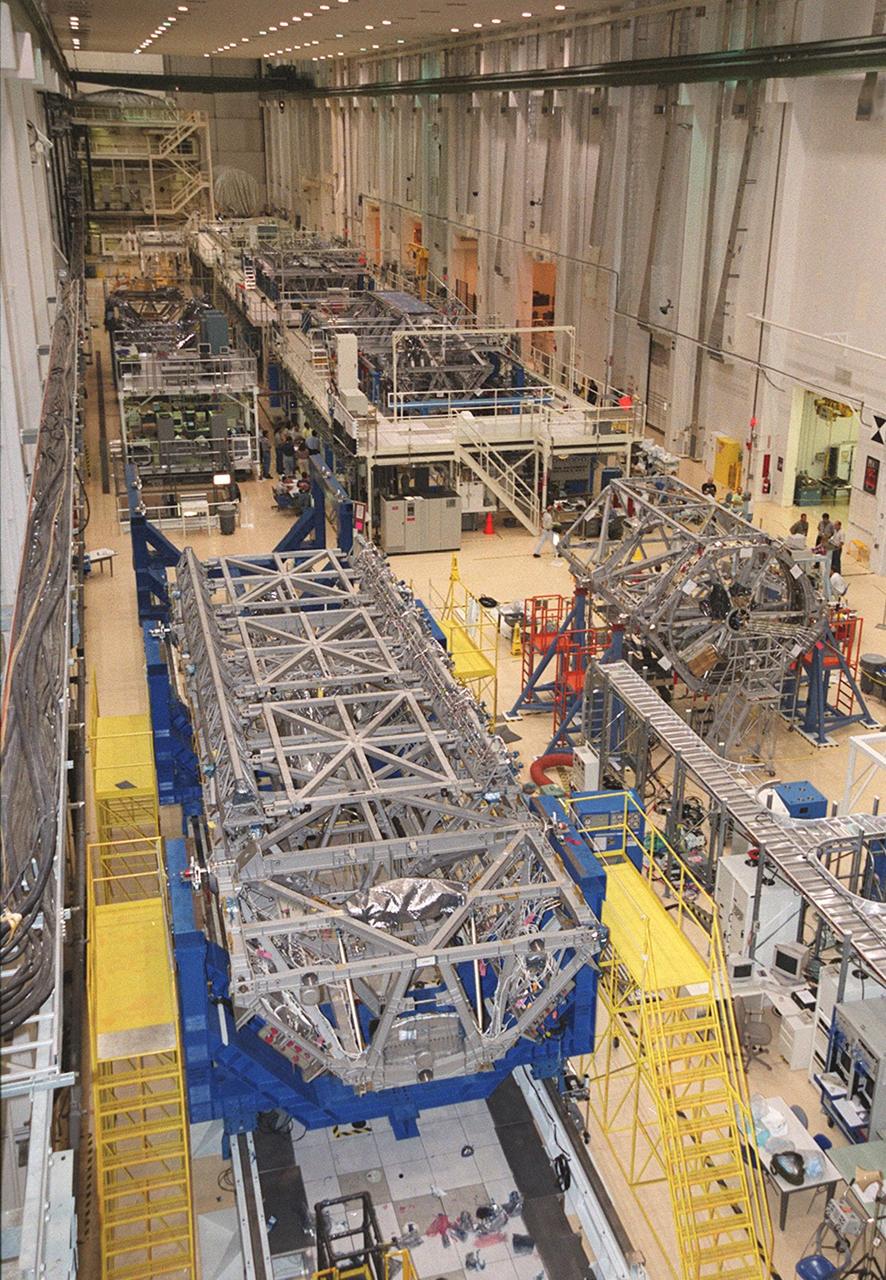

In the foreground is the P-1 truss, resting in a blue workstand in the long, crowded Operations and Checkout Building. Scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, the P-1 is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14by 15-foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the International Space Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
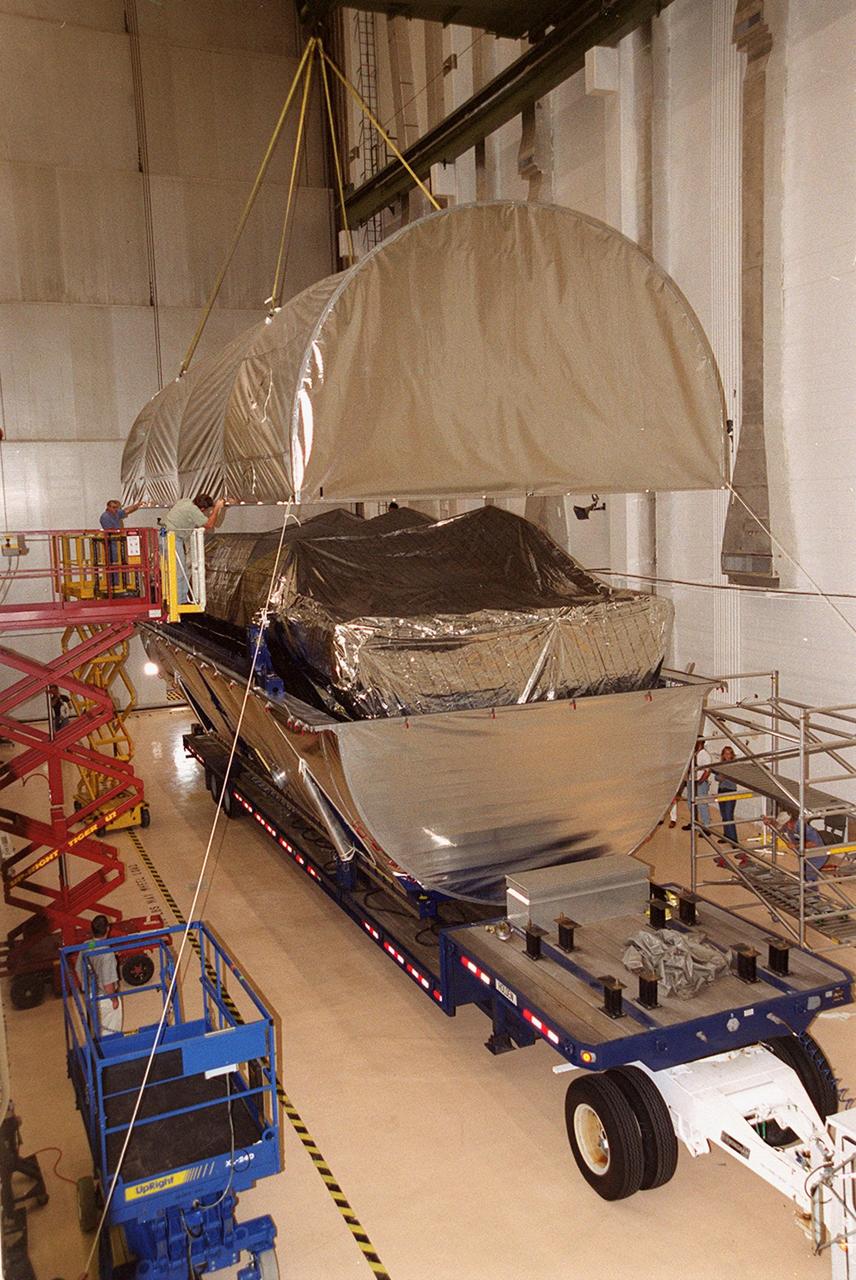

Inside the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the top of the canister containing the P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station. The truss, scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
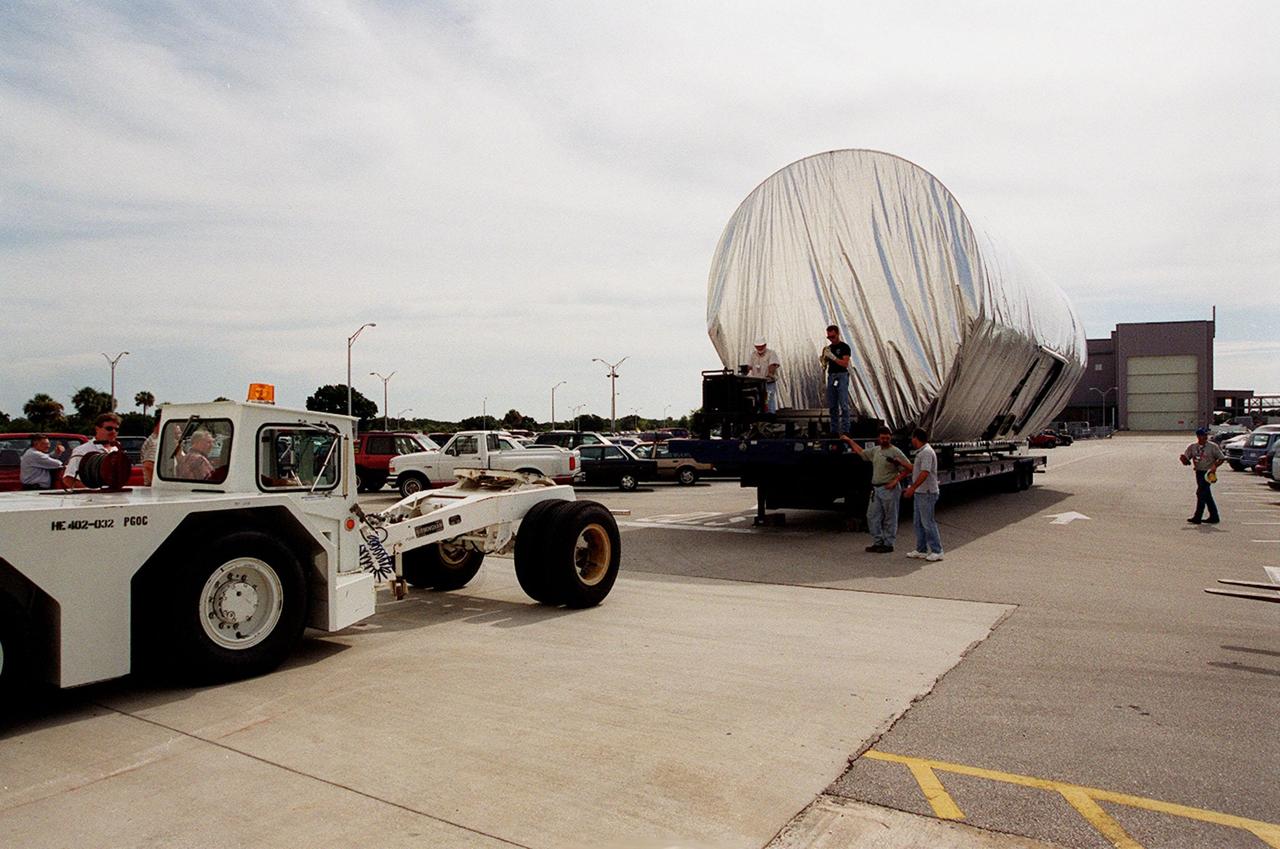

The P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, arrives in the parking lot outside the Operations and Checkout Building where it will undergo processing. The P-1 truss, scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Space Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
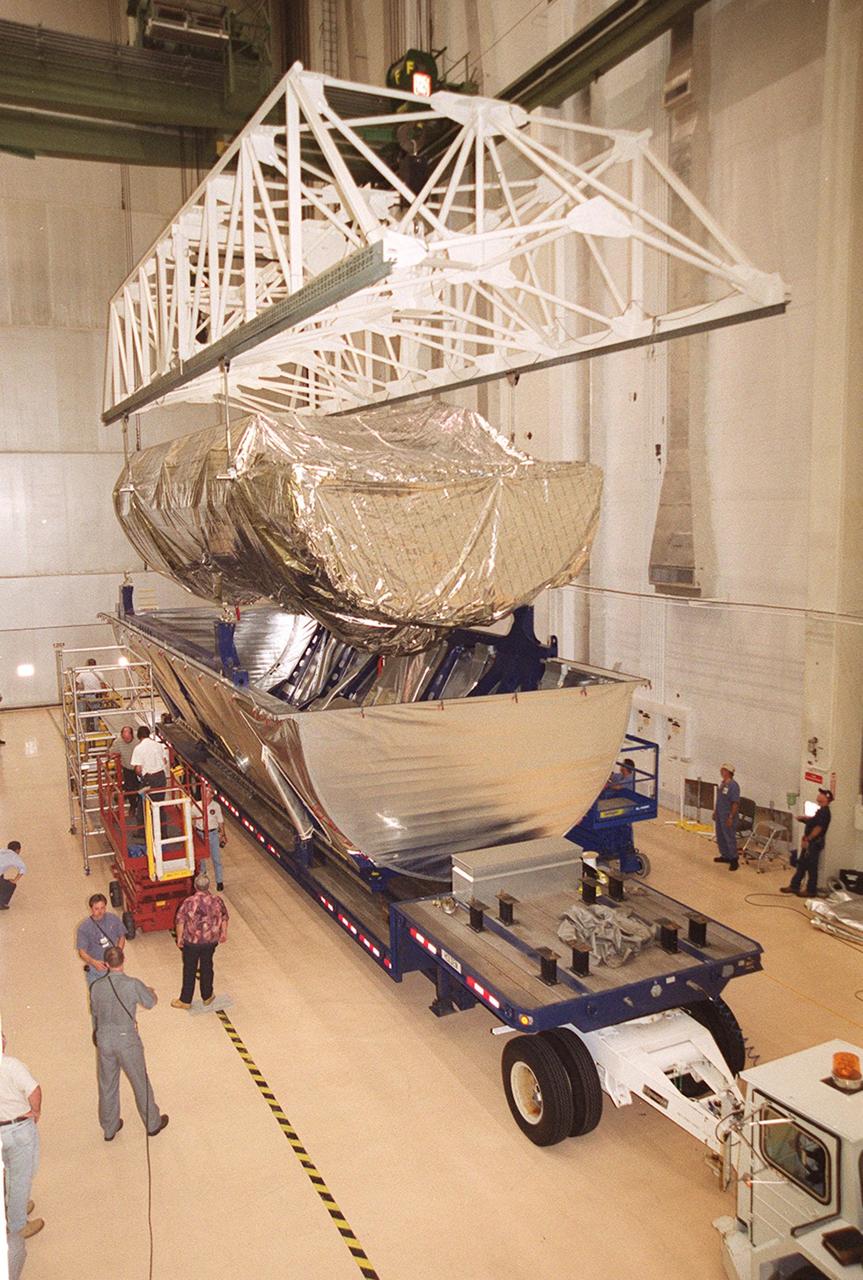

Inside the Operations and Checkout Building, the P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, is lifted out of its canister to move to a work stand where it will undergo processing. Scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, the P-1 is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
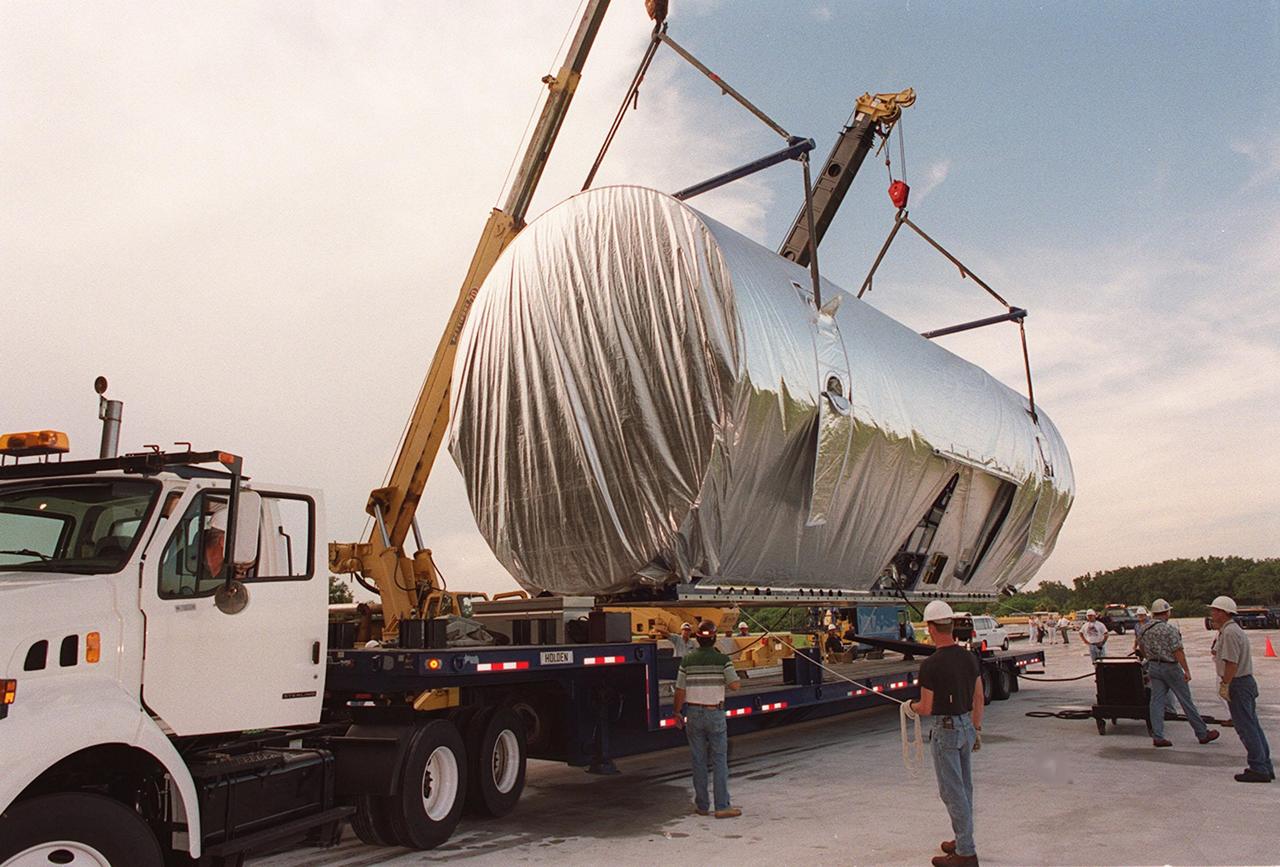

Workers oversee the placement of the P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, onto the bed of a transport vehicle that will move it to the Operations and Checkout Building for processing. The P-1 truss, scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
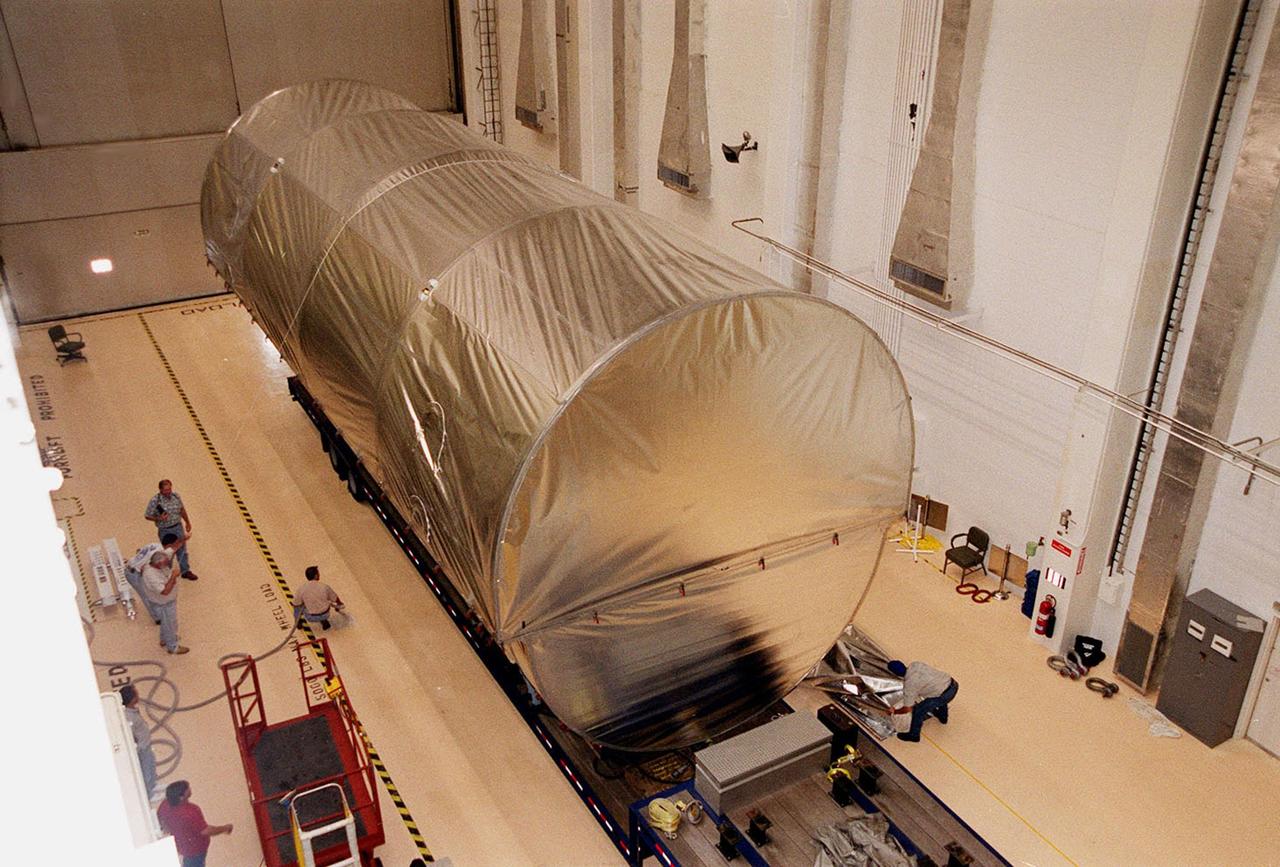

The P-1 truss, a component of the International Space Station, sits inside the Operations and Checkout Building where it will undergo processing. The truss, scheduled to fly in spring of 2002, is part of a total 10-truss, girder-like structure on the Station that will ultimately extend the length of a football field. Astronauts will attach the 14-by-15 foot structure to the port side of the center truss, S0, during the spring assembly flight. The 33,000-pound P-1 will house the thermal radiator rotating joint (TRRJ) that will rotate the Station’s radiators away from the sun to increase their maximum cooling efficiency
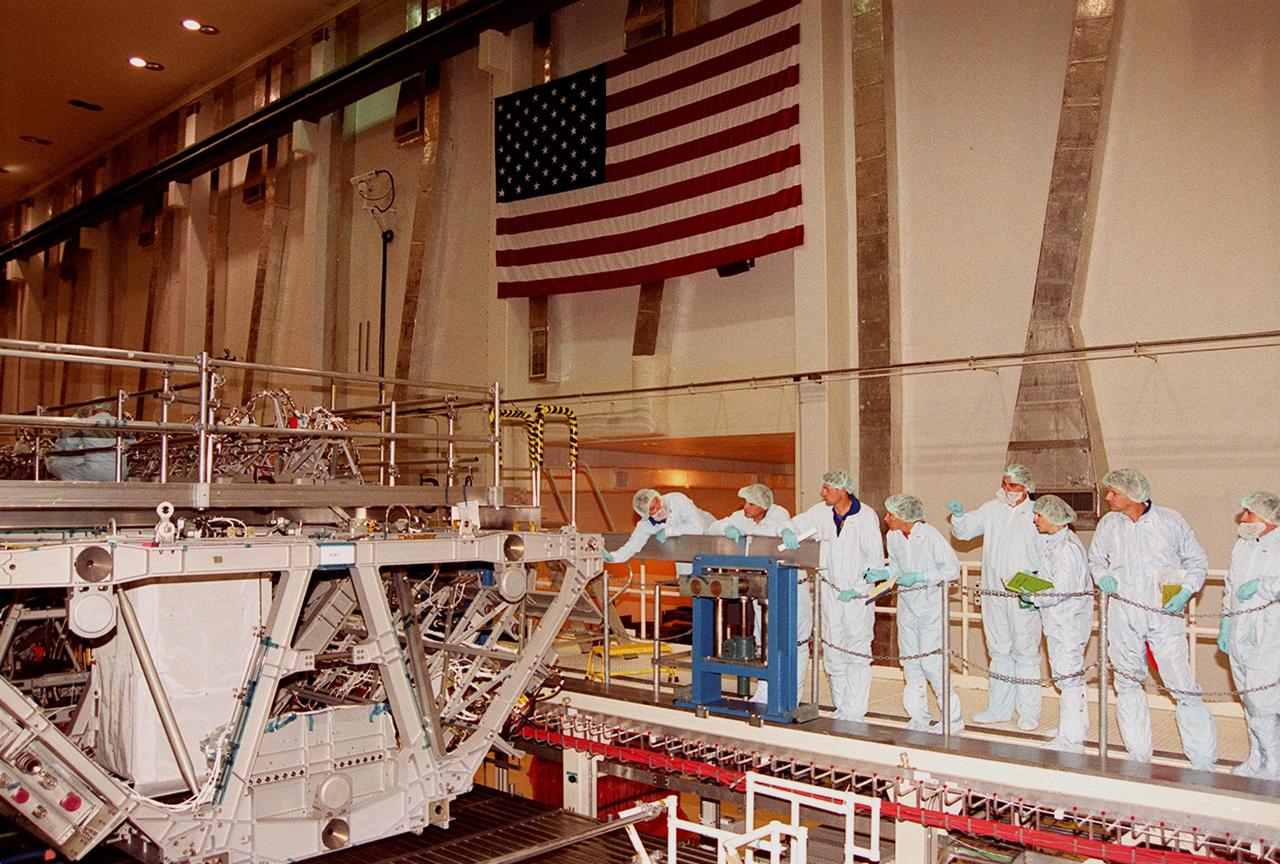

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Operations and Checkout Bldg,, members of the STS-112 crew look over the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) S1 that will be part of the payload on the mission. The crew comprises Commander Jeffrey S. Ashby, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy and Mission Specialists David A. Wolf, Piers J. Sellers, Sandra H. Magnus and Fyodor Nikolayevich Yurchikhin, a cosmonaut with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Mission STS-112 is scheduled for launch in July 2002
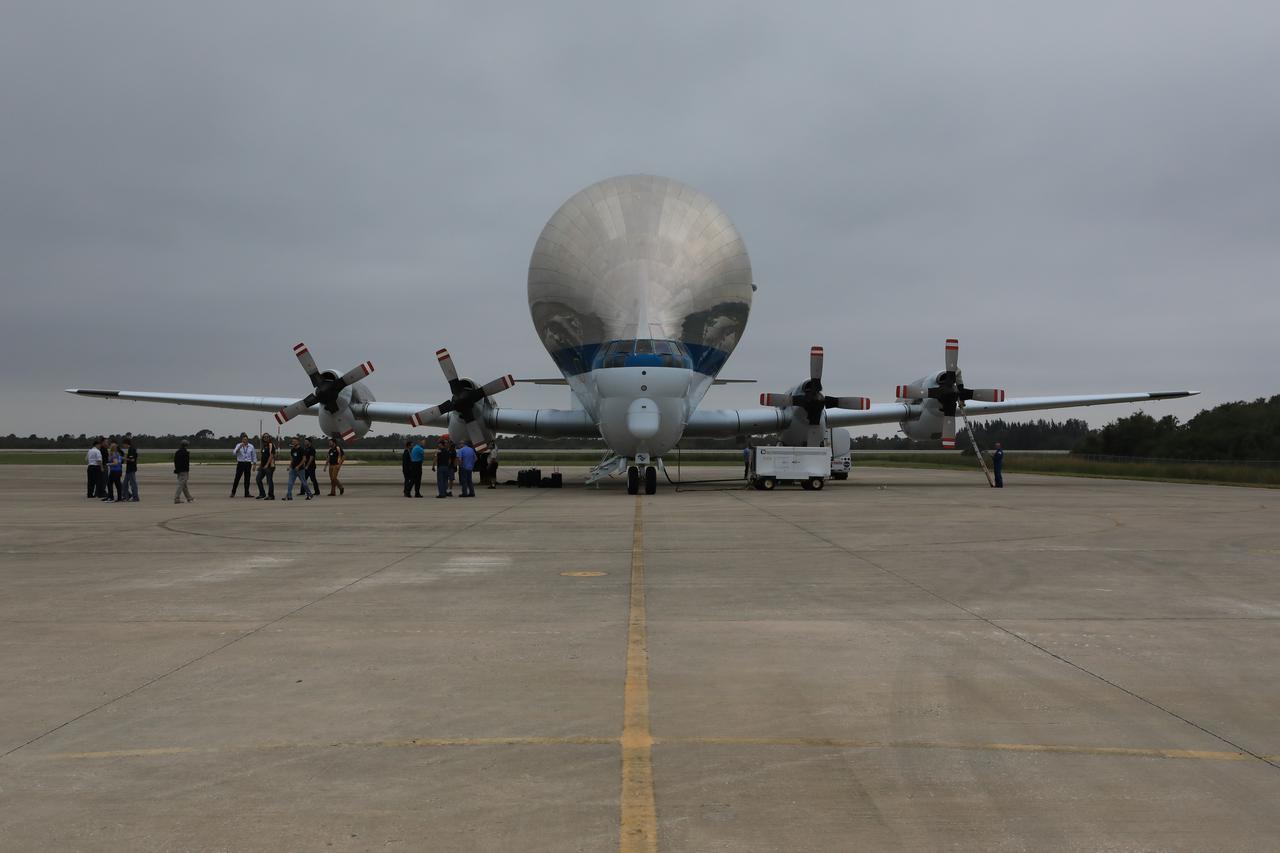

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft arrives on the tarmac after touching down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The guppy is carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
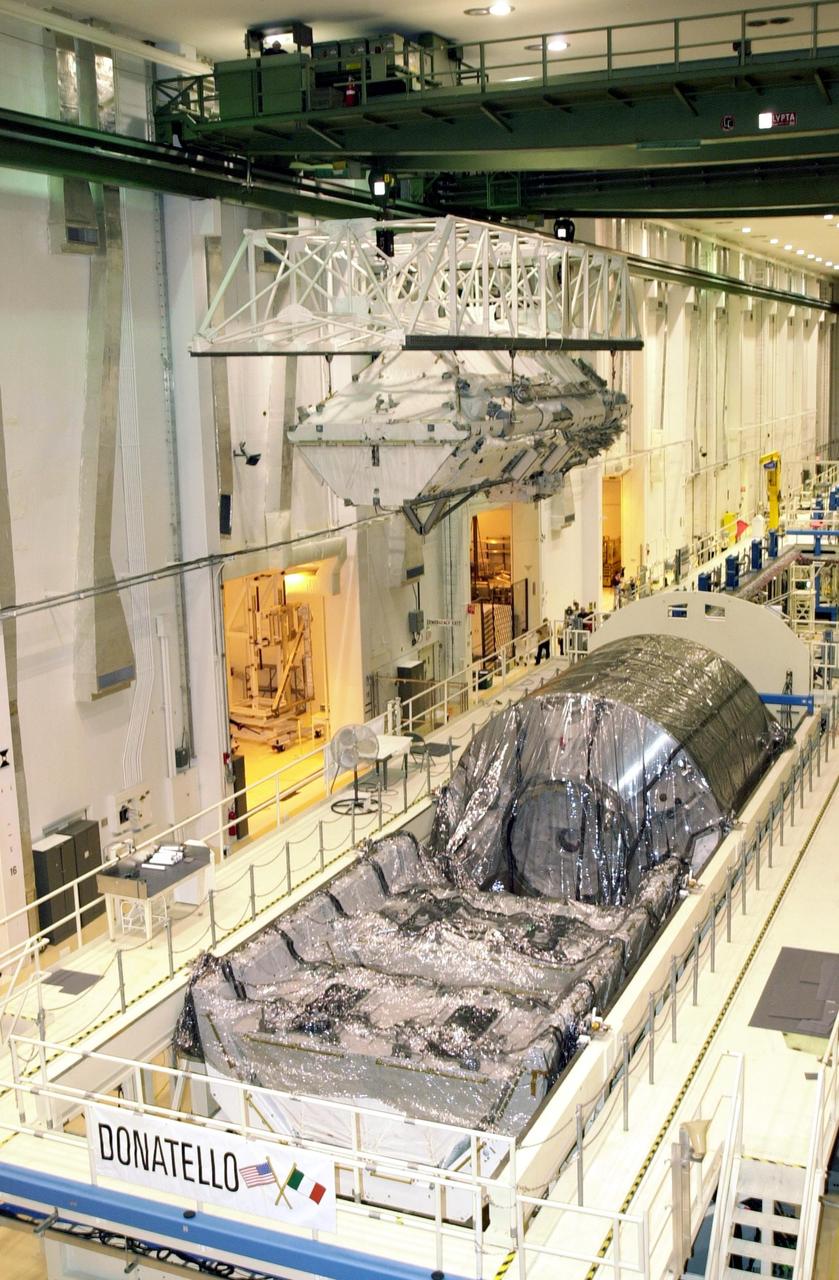

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane carries the Integrated Truss Structure S0 to the payload canister which will transport it to the launch pad for mission STS-110. Seen below the truss is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, currently not in use. The S0 truss will be part of the payload on Space Shuttle Atlantis. The S0 truss will be attached to the U.S. Lab, "Destiny," on the 11-day mission, becoming the backbone of the orbiting International Space Station (ISS). Launch is scheduled for April 4

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) is secured on a test tool called the birdcage. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will undergo further testing in the high bay. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

The Orion crew module for Exploration Mission-1 was moved into the thermal chamber in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew module will undergo a thermal cycle test to assess the workmanship of critical hardware and structural locations. The test also demonstrates crew module subsystem operations in a thermally stressing environment to confirm no damage or anomalous hardware conditions as a result of the test. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA's Space Launch System rocket on its first uncrewed integrated flight.
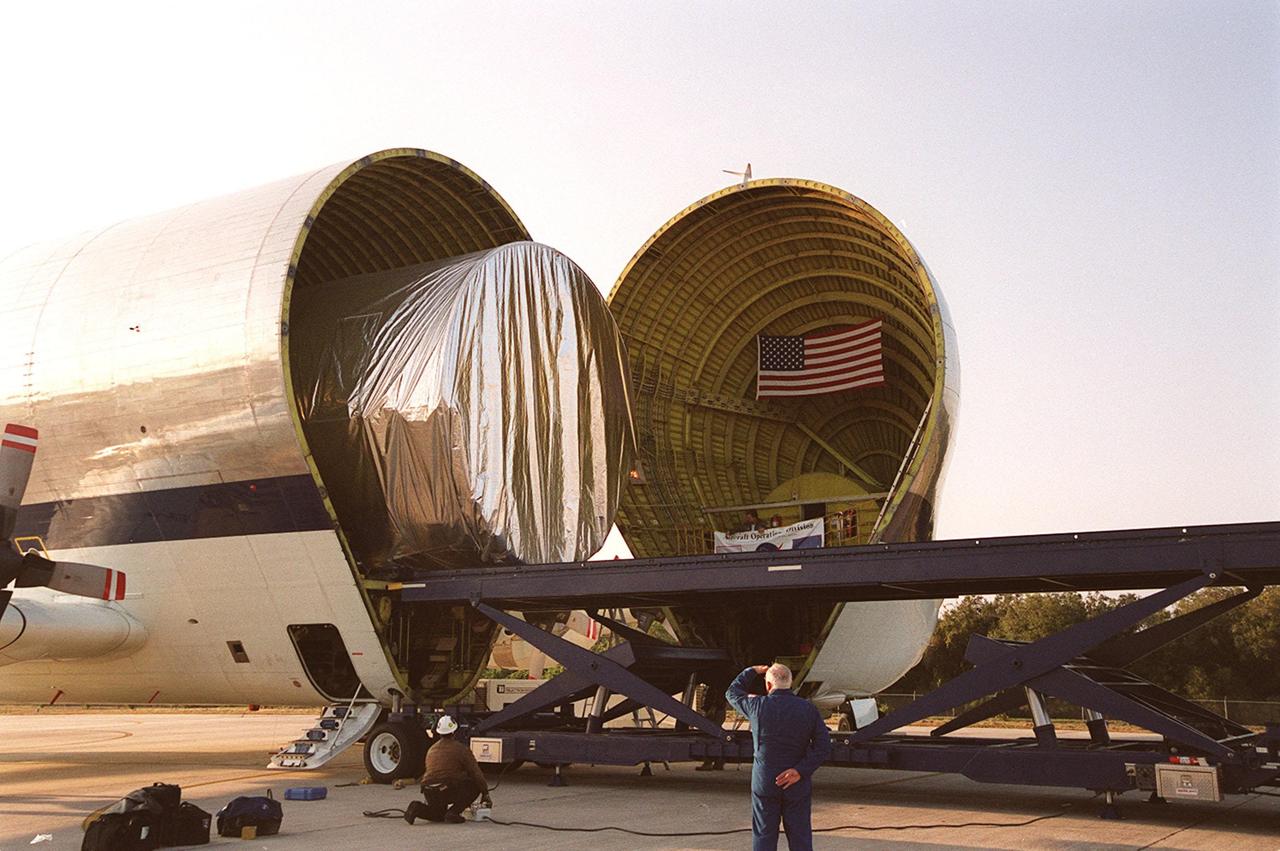

On the parking apron of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the Integrated Truss Structure S3 moves out from inside the Super Guppy aircraft that brought it to KSC from Tulsa, Okla. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
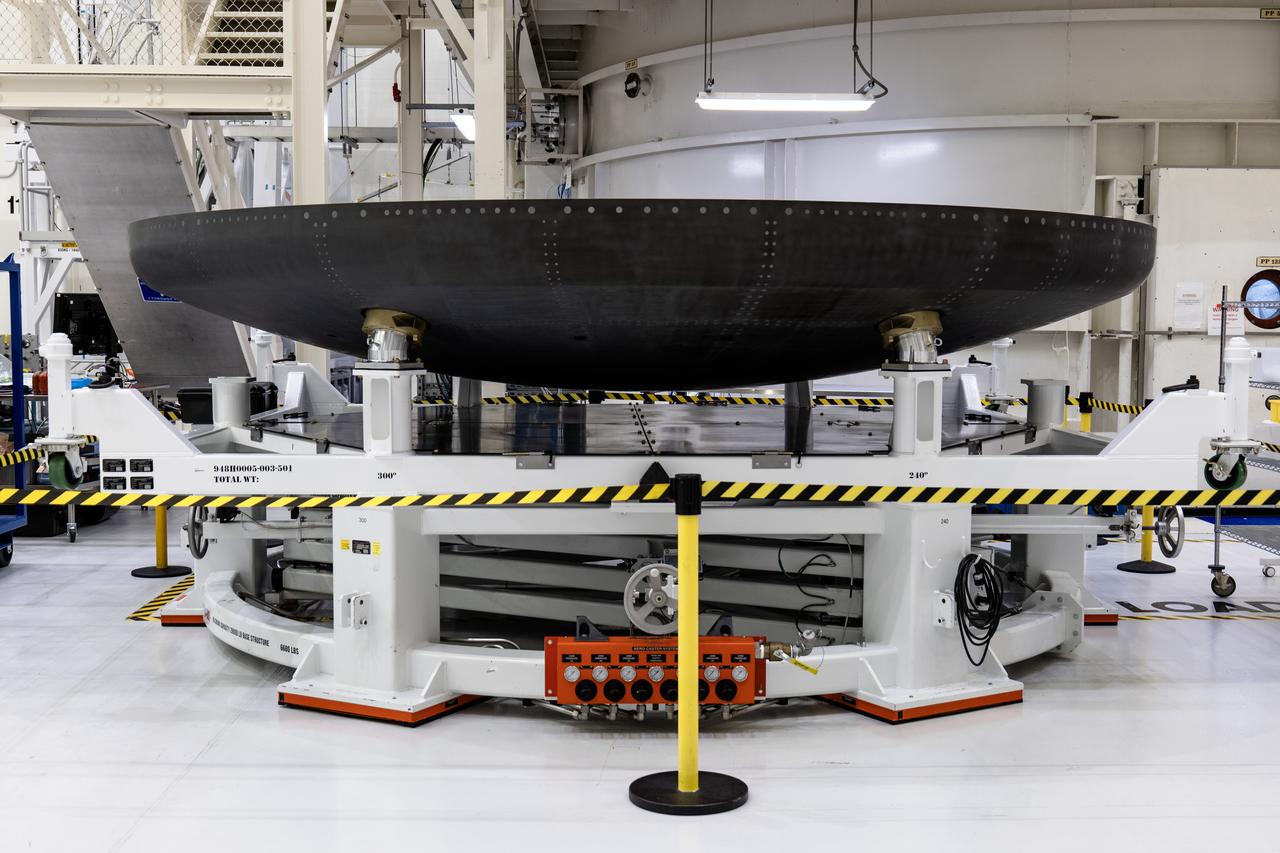

The heat shield carrier for Orion’s Artemis IV mission is in view secured on a work stand in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The carrier structure holds the thermal protection system heat shield securely to the Orion crew module while facing launch, reentry, and splashdown impact loads.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Operations and Checkout Building watch as the Integrated Truss Structure S0 is lowered into the payload canister. The S0 truss will soon be on its way to the launch pad for mission STS-110. Part of the payload on Space Shuttle Atlantis, the S0 truss will be attached to the U.S. Lab, "Destiny," on the 11-day mission, becoming the backbone of the orbiting International Space Station (ISS). Launch is scheduled for April 4
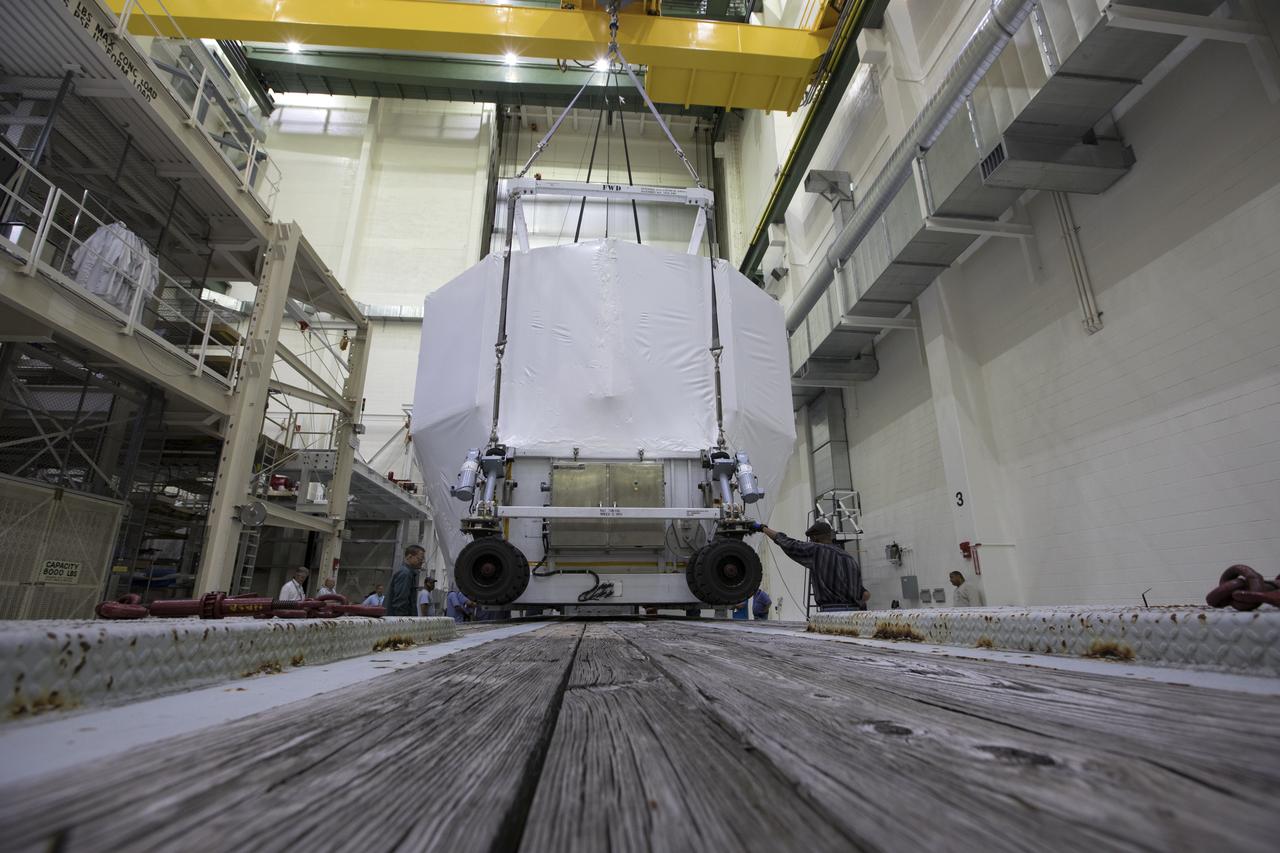

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the module, secured on a stand, for the move to the transport truck. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is secured in a work stand called the bird cage inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on March 21, 2019. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Behind the pressure vessel, secured on a work stand is the Orion bay cover for Exploration Mission-1.
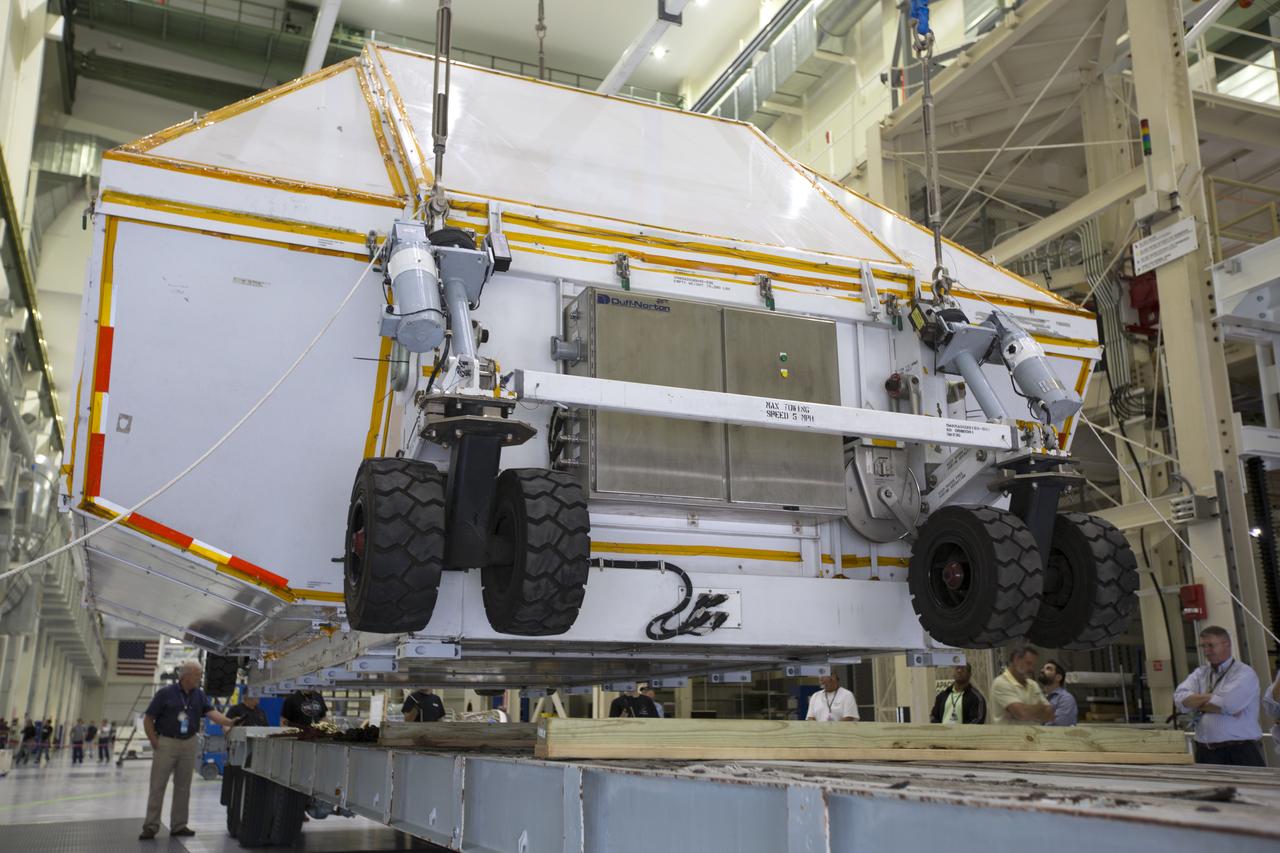

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article, secured inside its transport container, is lowered onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
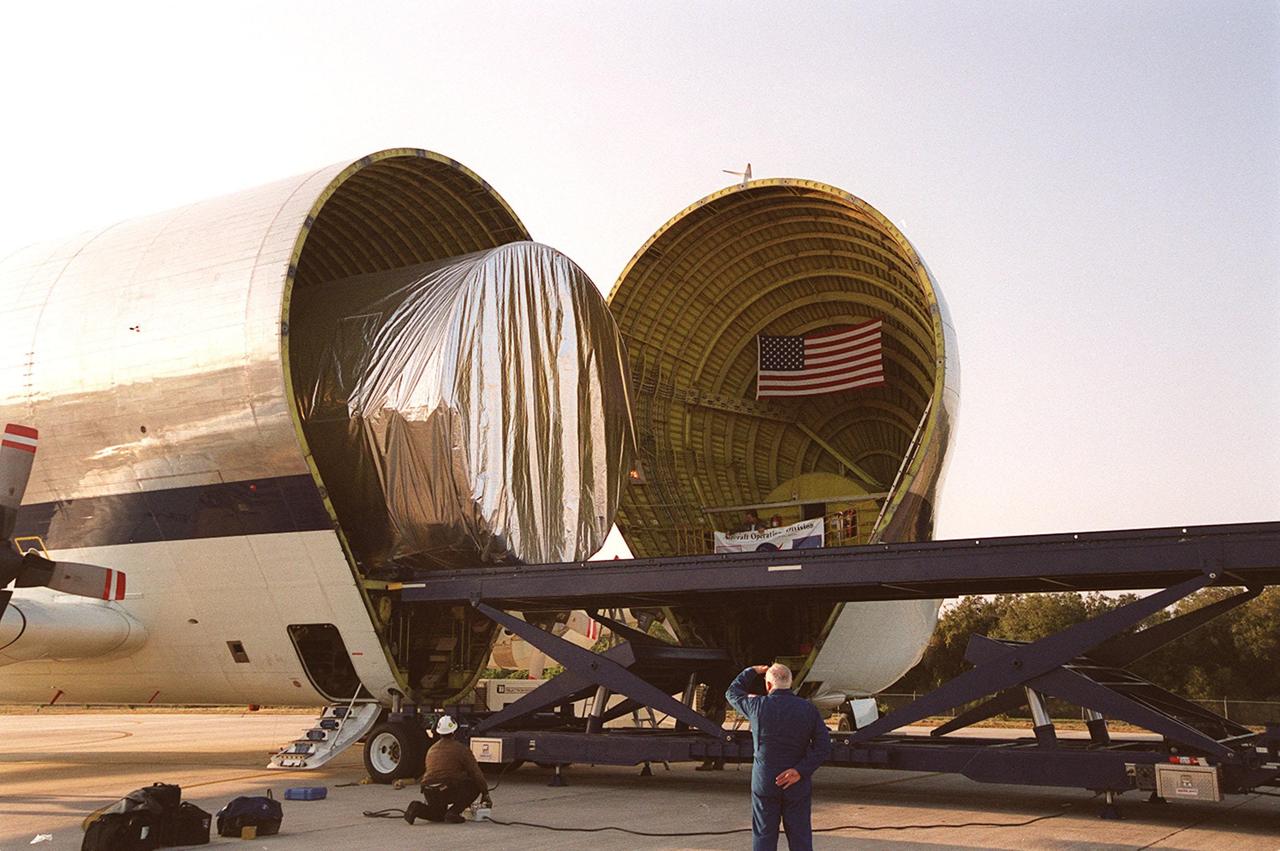

On the parking apron of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the Integrated Truss Structure S3 moves out from inside the Super Guppy aircraft that brought it to KSC from Tulsa, Okla. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
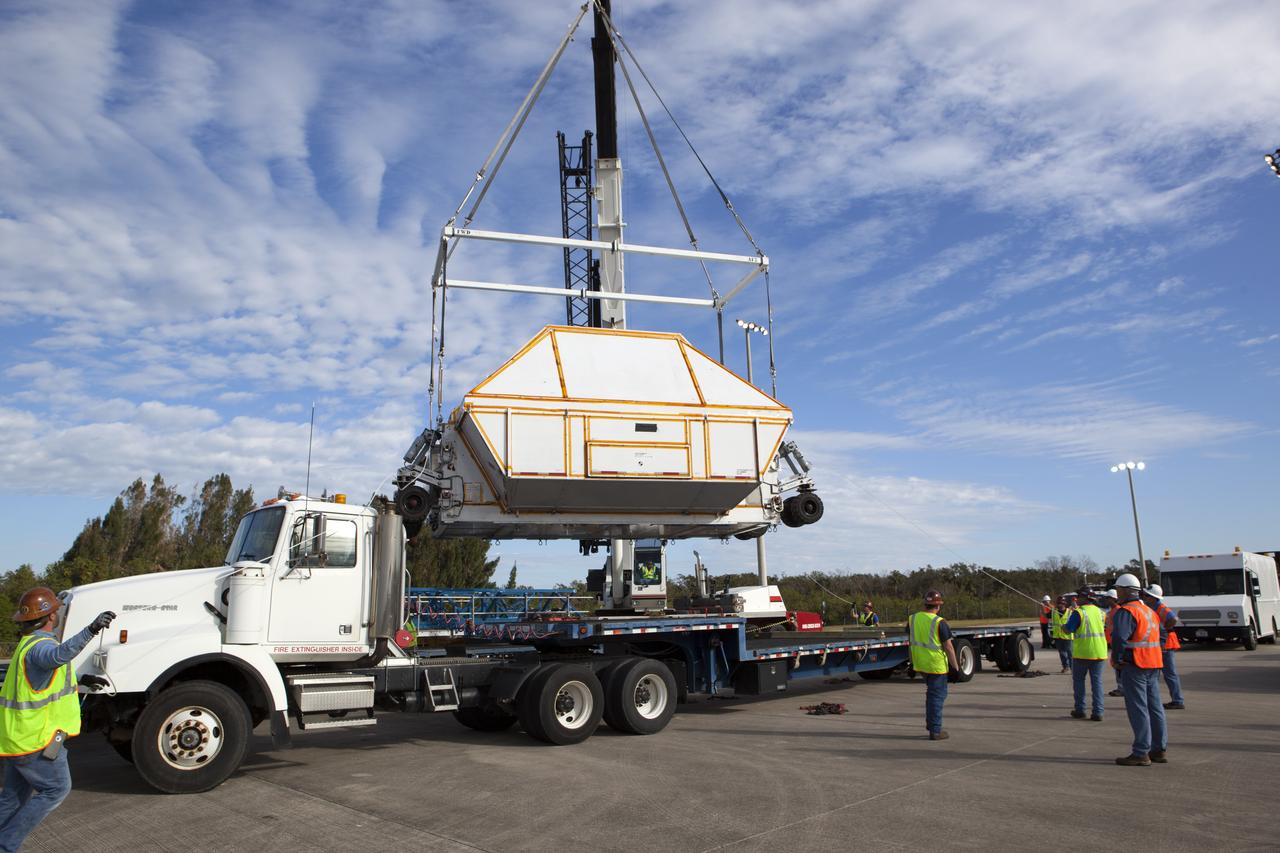

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. A crane is used to lower the container for placement on a transporter. The test article will be moved to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
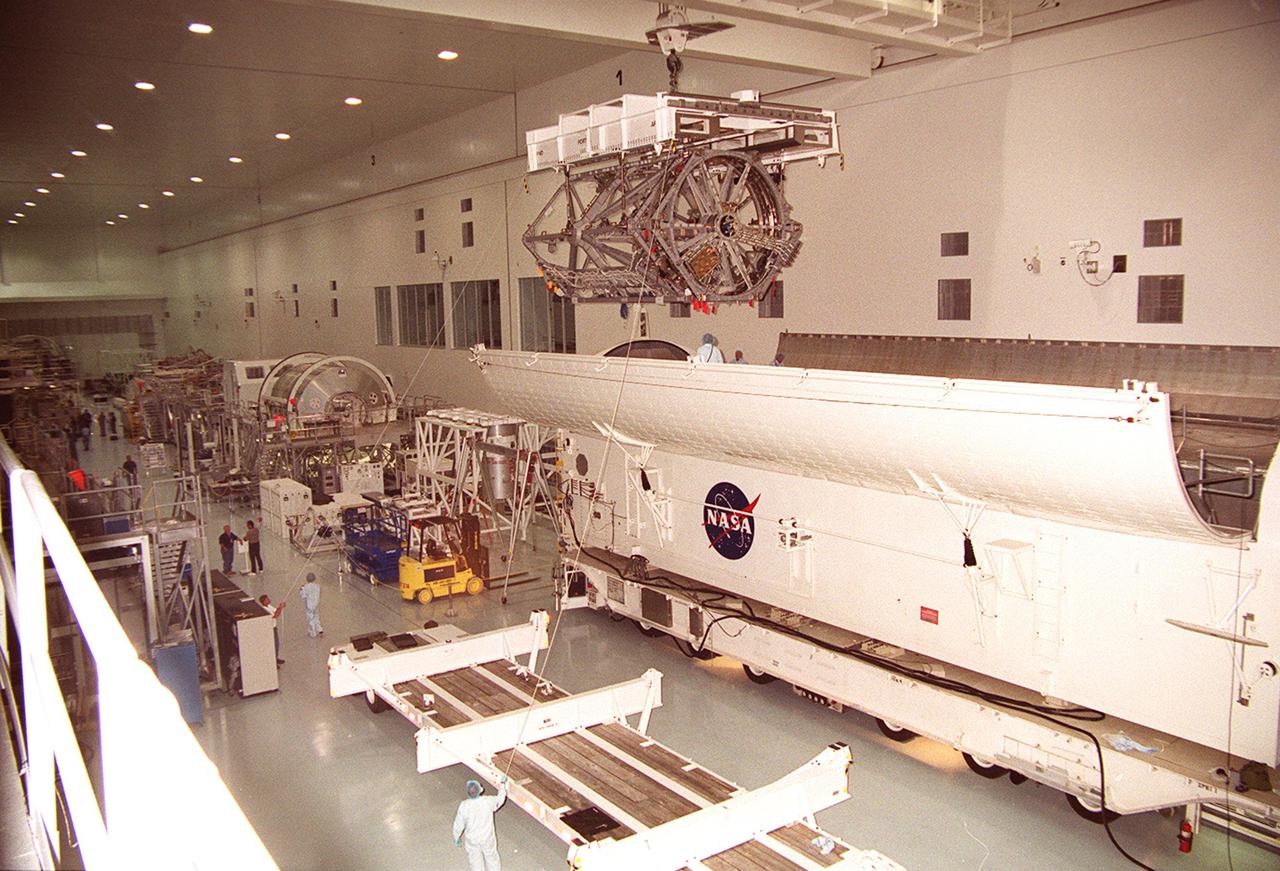
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the P3 Integrated Truss Structure clear of the payload canister that transferred it from the Operations and Checkout Building. The port-side P3 truss is scheduled to be added to the International Space Station on mission STS-115 in 2002 aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis. . The P3 will be attached to the first port truss segment, P1, being installed in an earlier mission
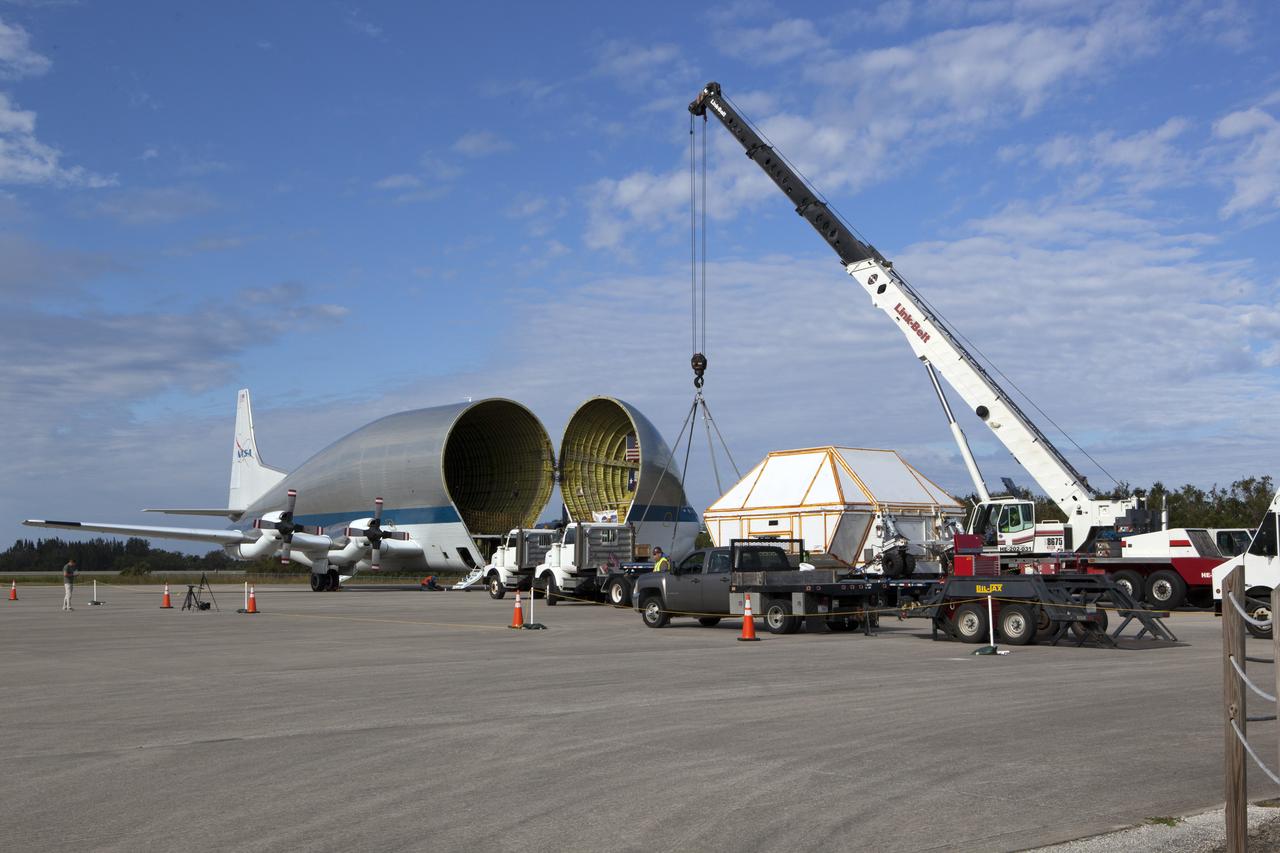

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. A crane was used to lower the container onto a transporter. The test article will be moved to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
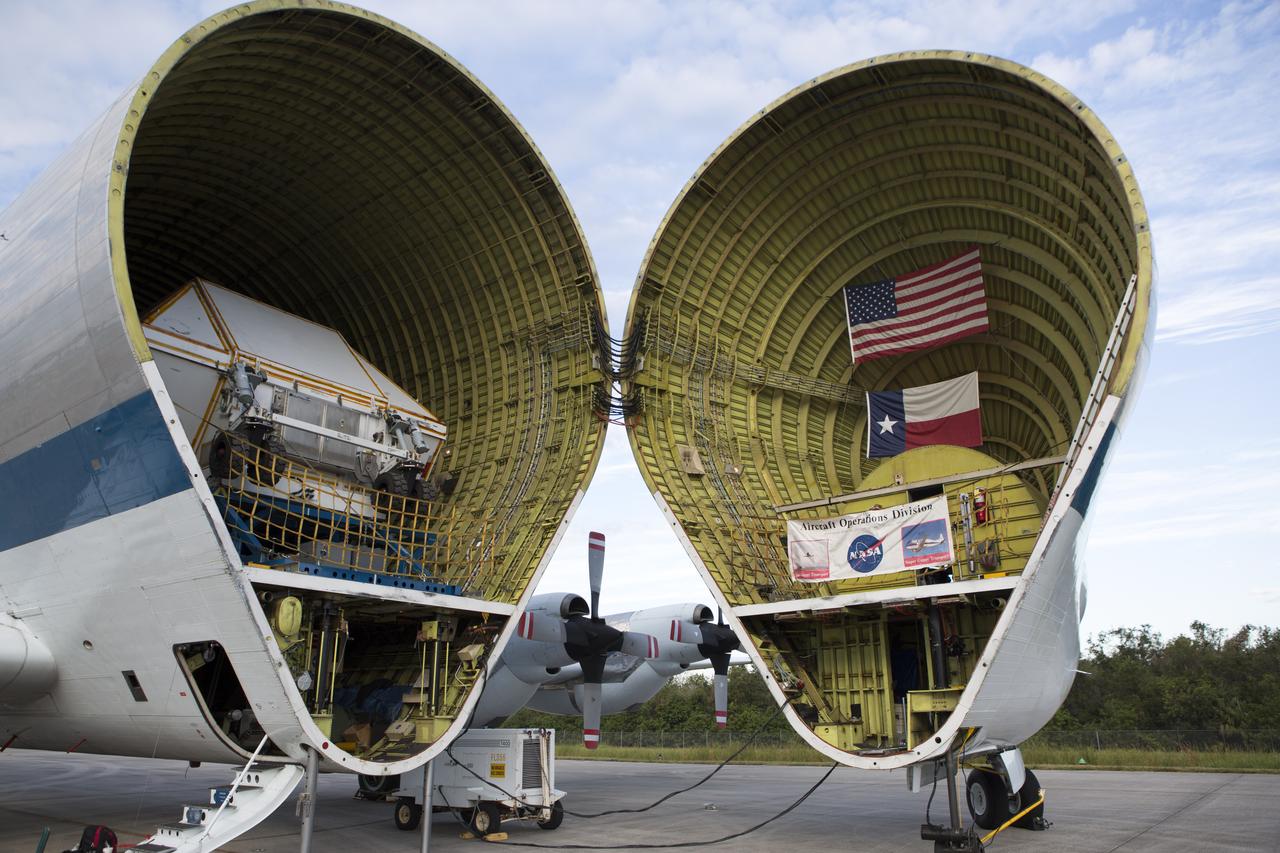

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article, arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The unique aircraft has been opened to reveal the container holding the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
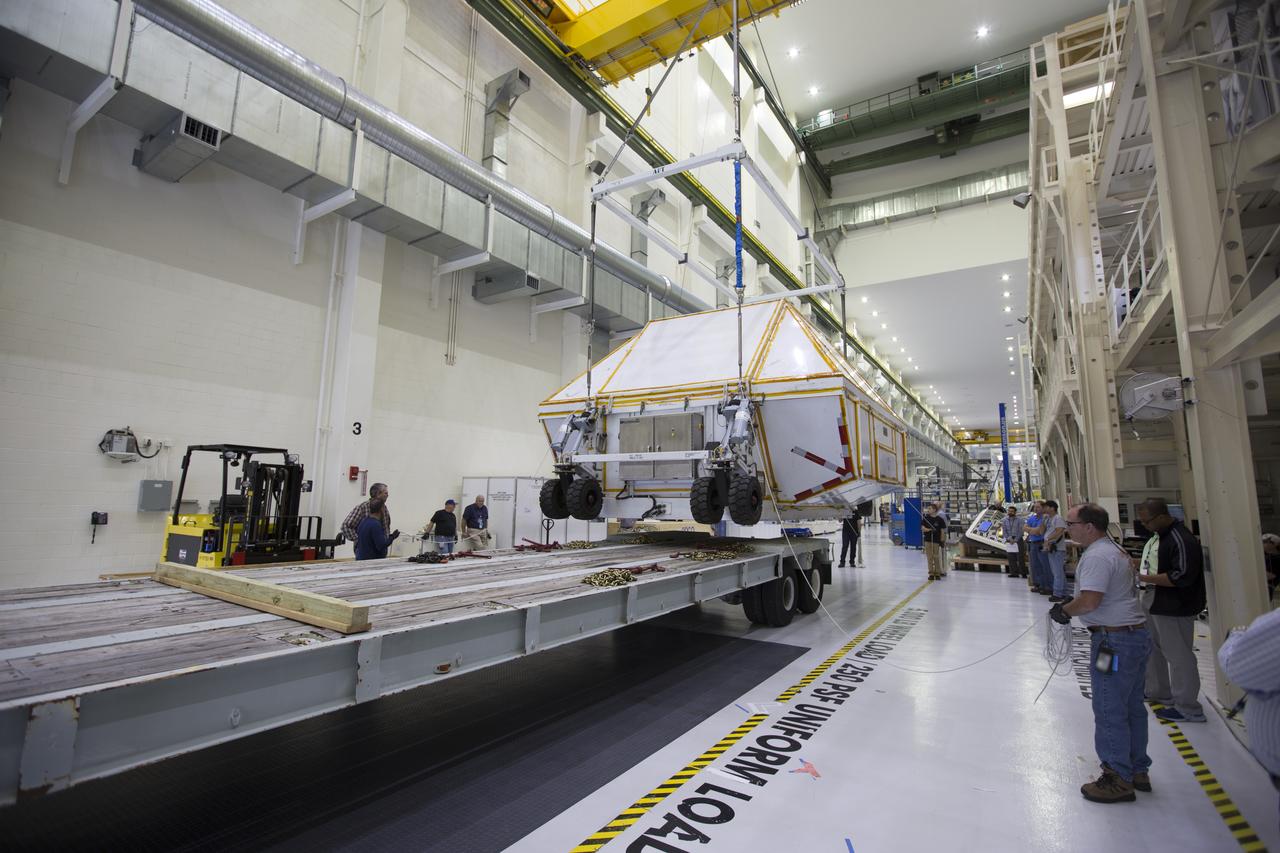

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article, secured inside its transport container, is lowered onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
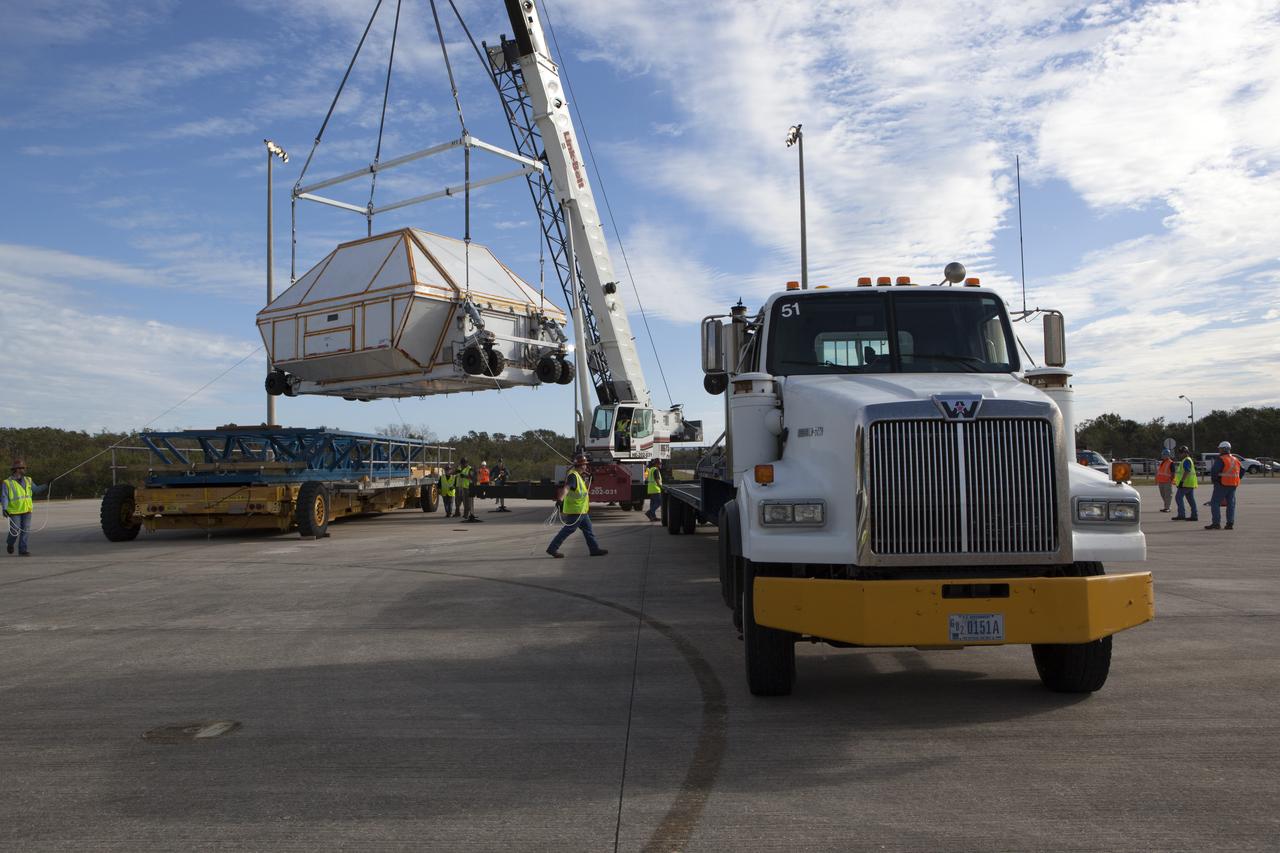

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. A crane has lifted the container for placement on a transporter. The test article will be moved to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
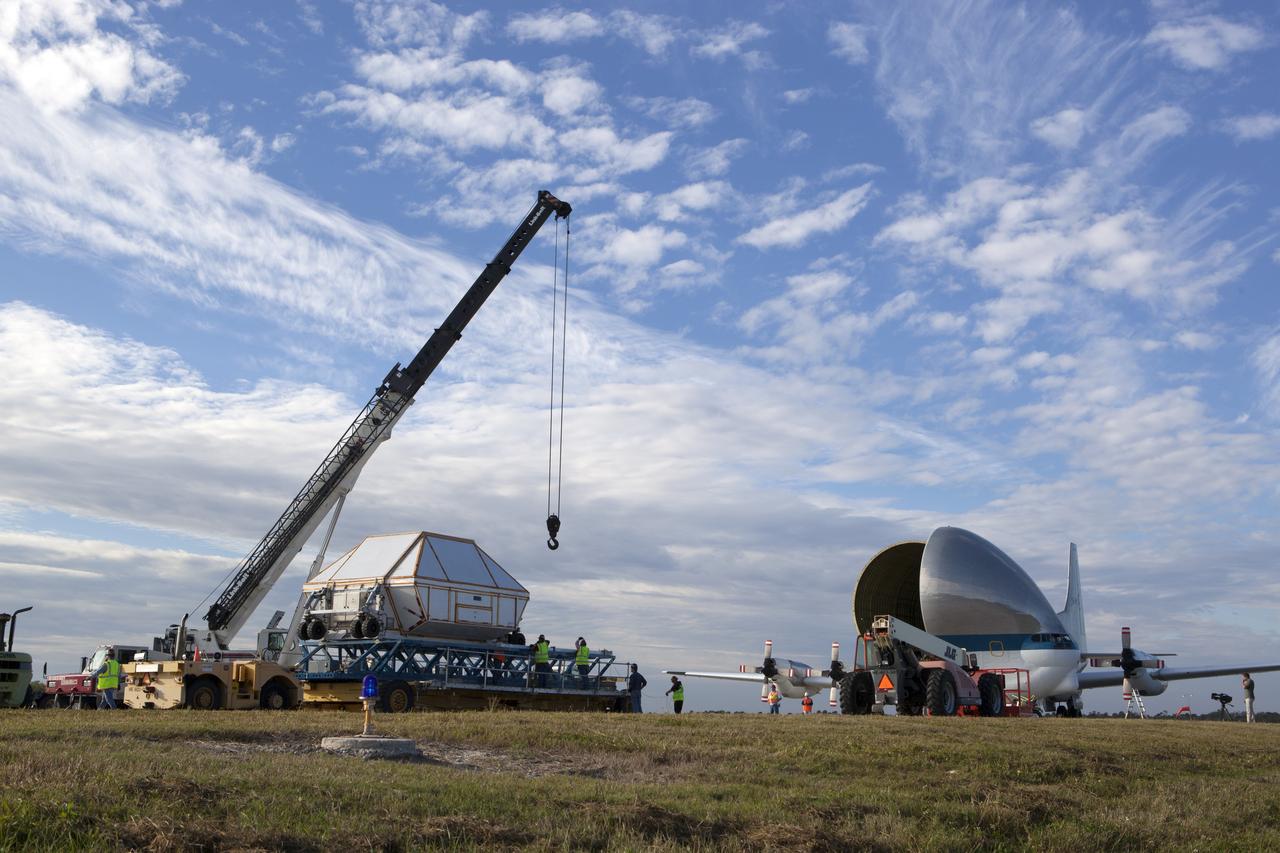

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
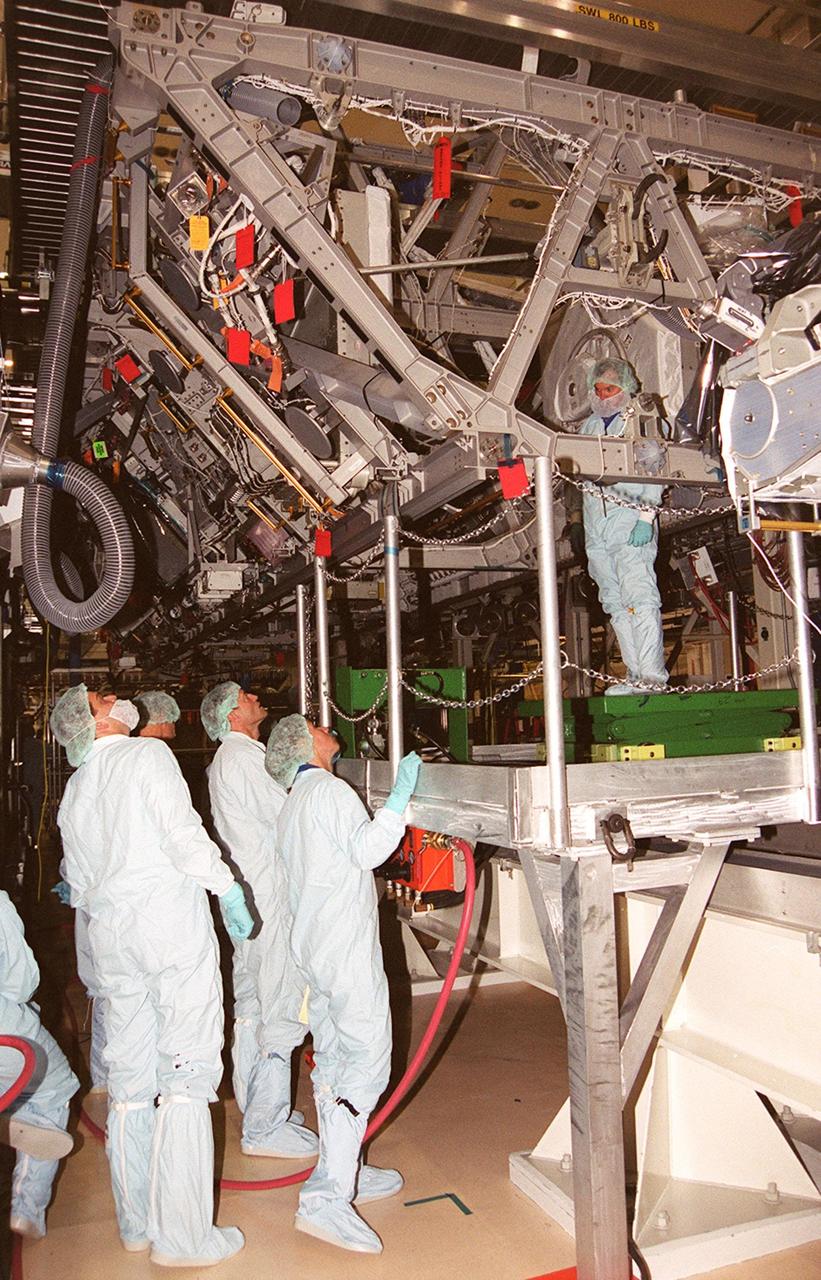

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - From the floor of the Operations and Checkout Bldg,, members of the STS-112 crew look over the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) S1 above them that will be part of the payload on the mission. The crew comprises Commander Jeffrey S. Ashby, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy and Mission Specialists David A. Wolf, Piers J. Sellers, Sandra H. Magnus and Fyodor Nikolayevich Yurchikhin, a cosmonaut with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Mission STS-112 is scheduled for launch in July 2002.
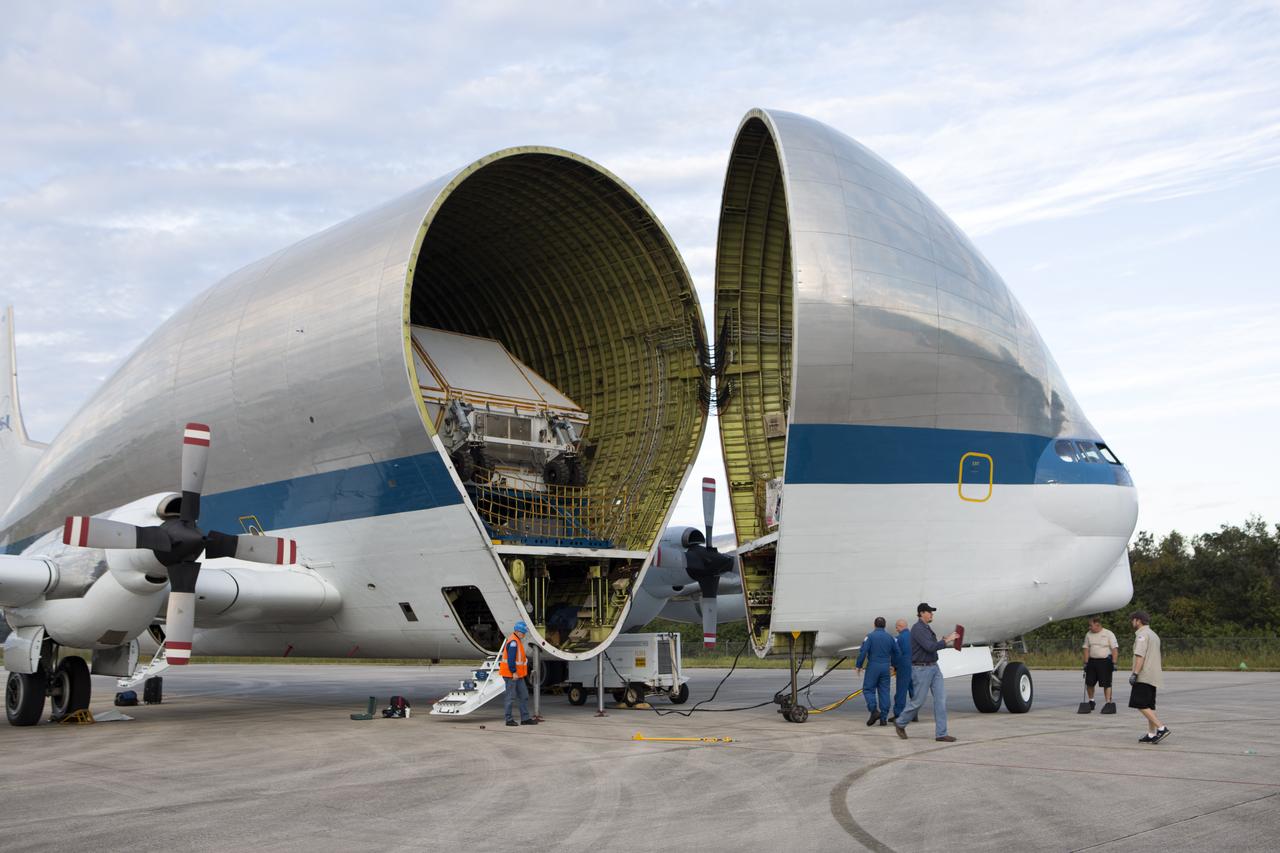

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA), arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The unique aircraft is being opened to offload the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
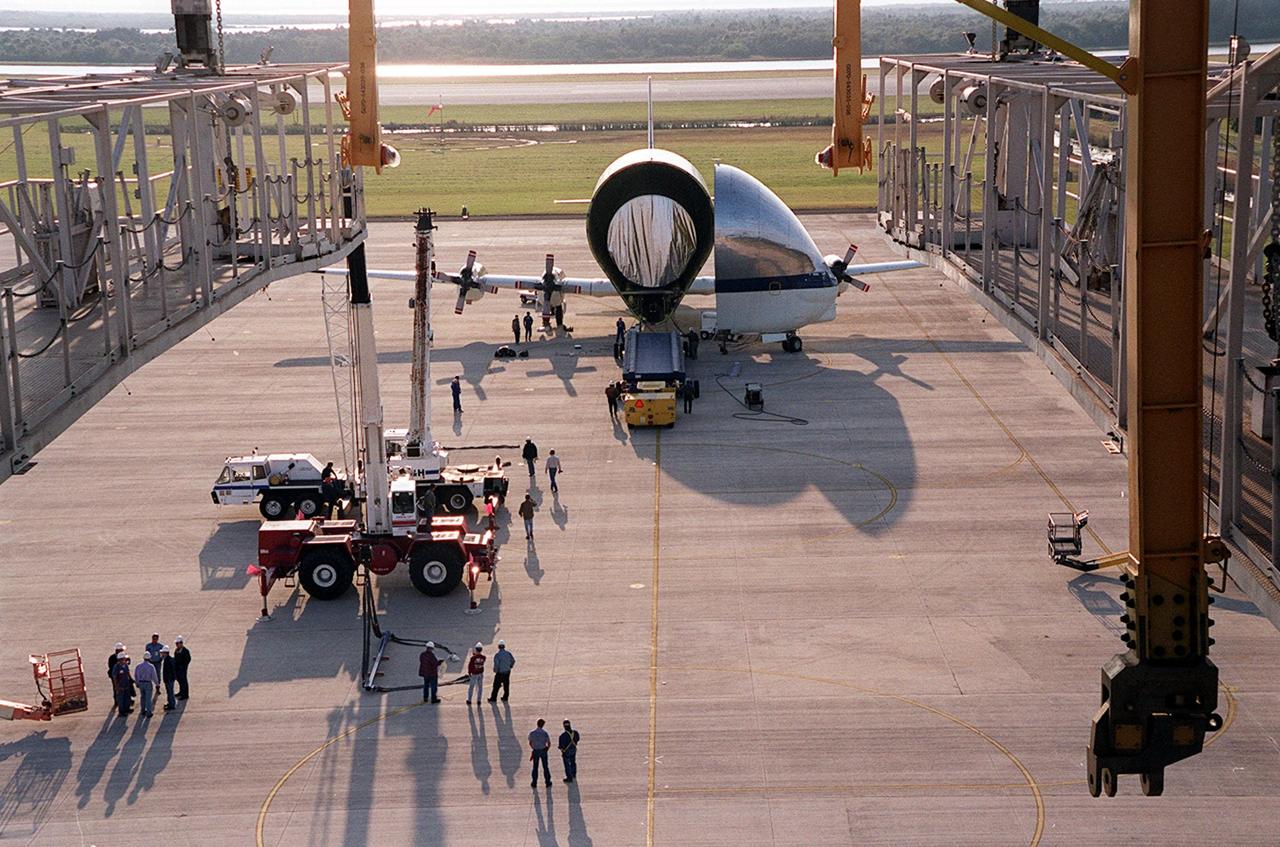

On the parking apron of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, near the Mate/Demate device (seen in the foreground), the opened nose of the Super Guppy aircraft reveals its cargo, the Integrated Truss Structure S3. It was built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
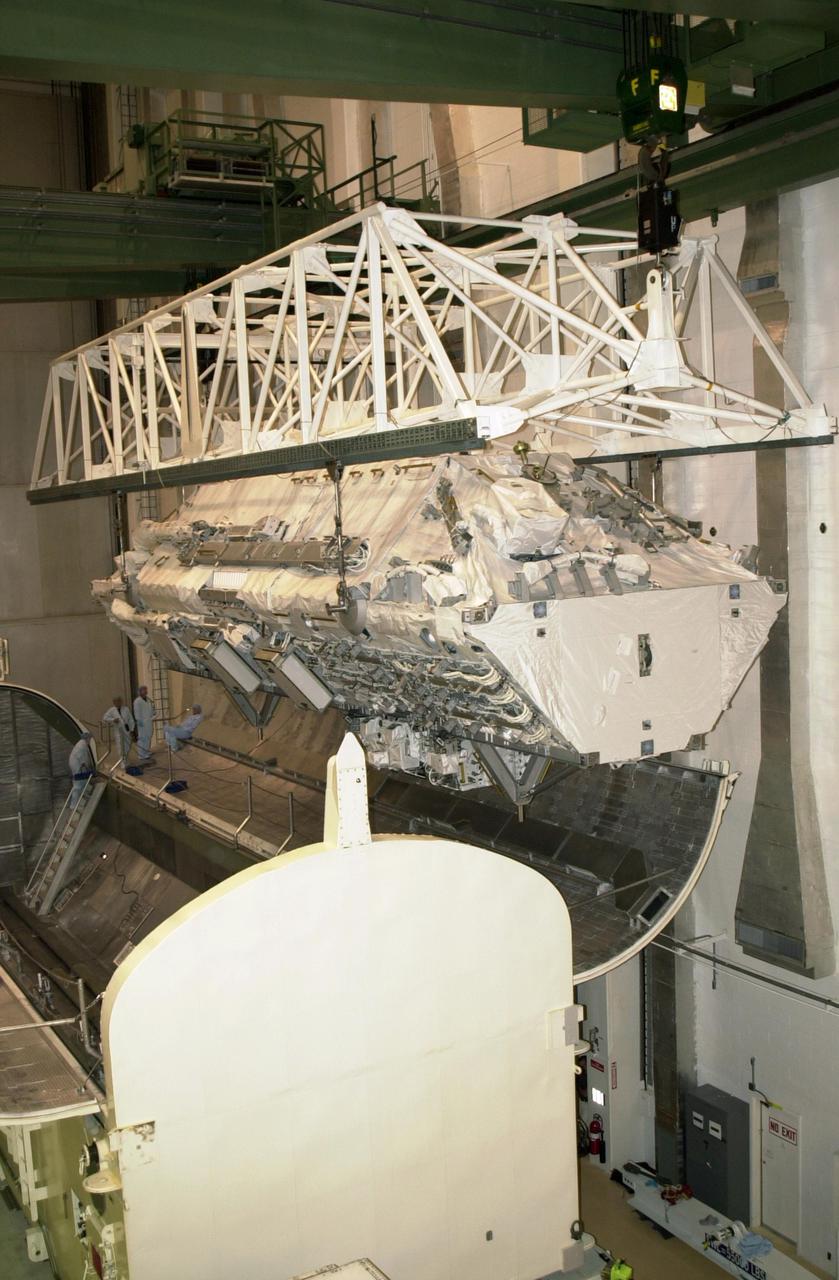
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Integrated Truss Structure S0 arrives at the payload canister in the Operations and Checkout Building for transfer to the launch pad for mission STS-110. Part of the payload on Space Shuttle Atlantis, the S0 truss will be attached to the U.S. Lab, 'Destiny,' on the 11-day mission, becoming the backbone of the orbiting International Space Station (ISS). Launch is scheduled for April 4
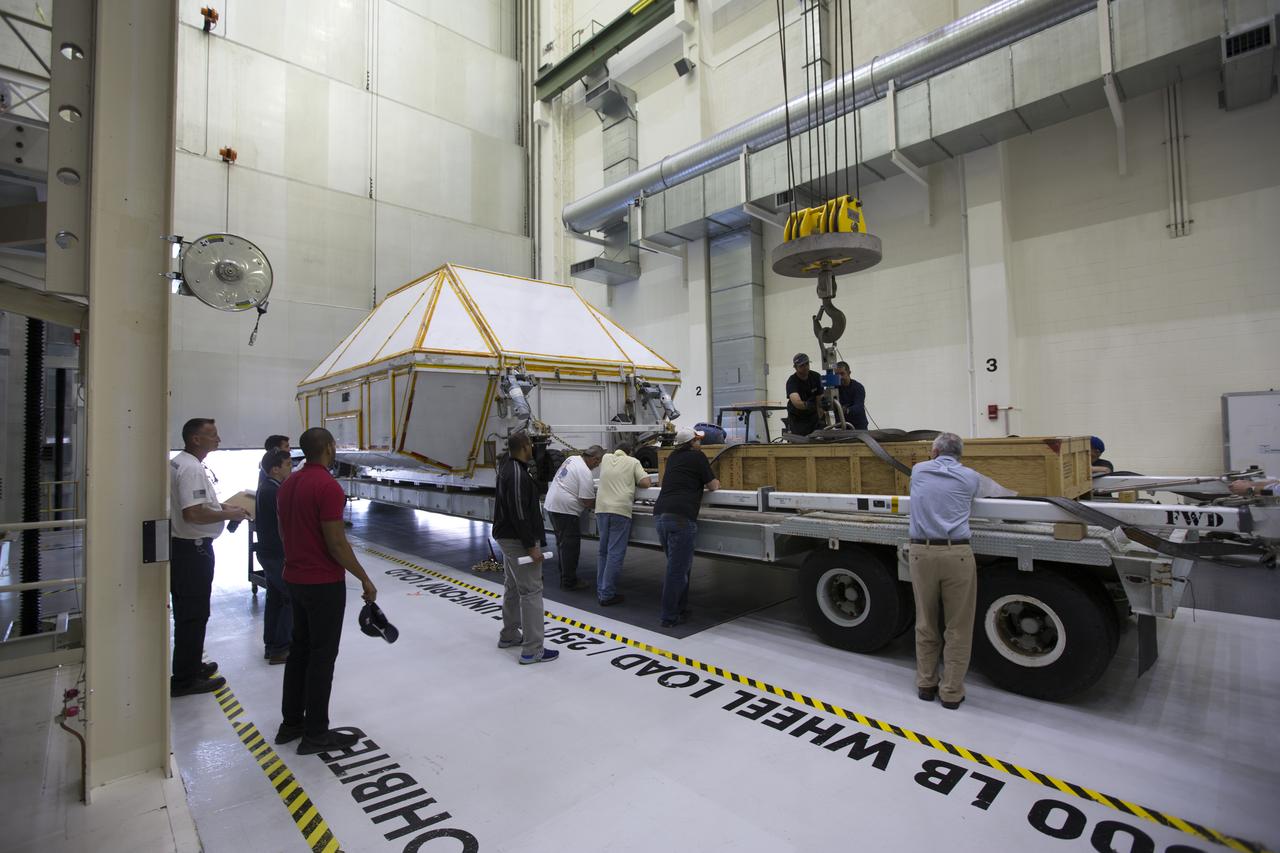

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians secure the transport container with the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
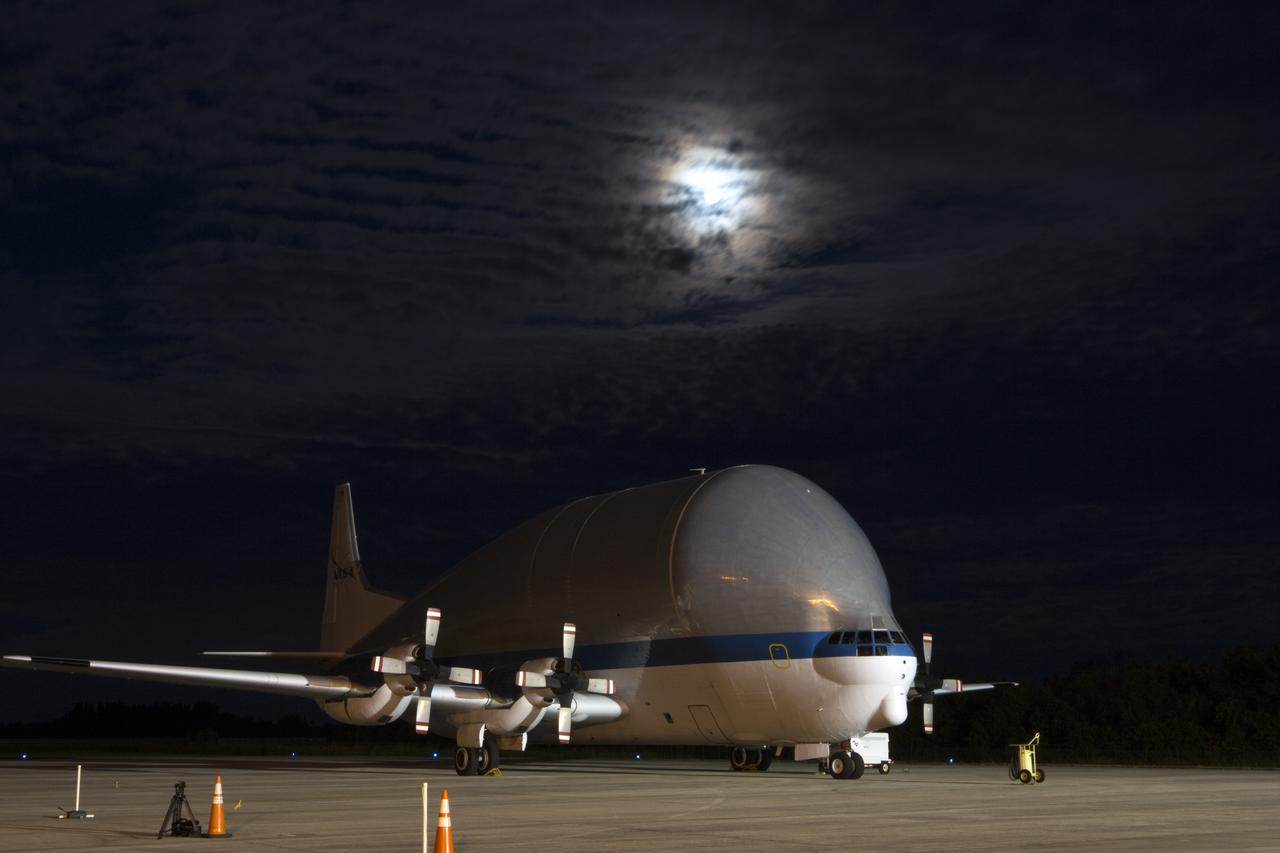

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA), arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
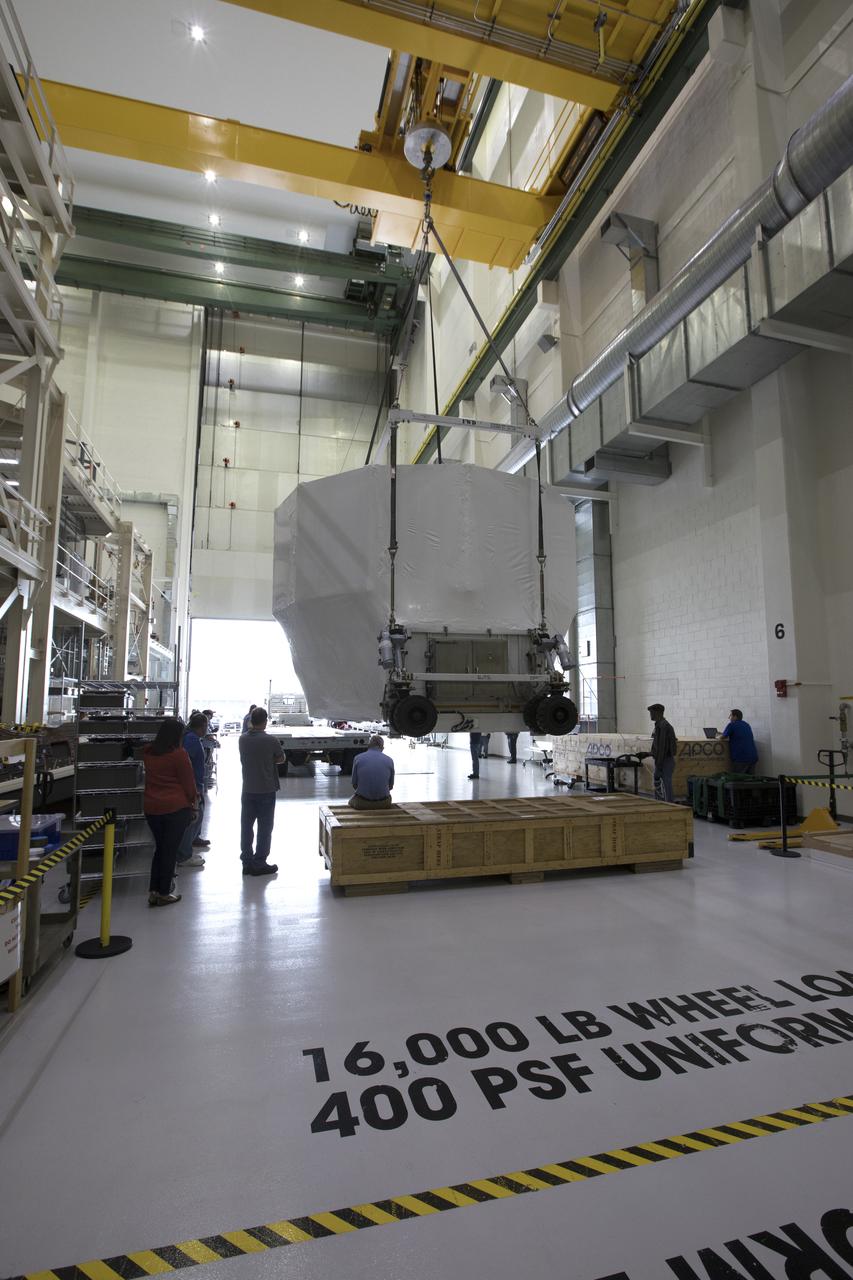

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the module, secured on a stand, for the move to the transport truck. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.

iss073e0000415 (April 21, 2025) --- NASA astronauts Anne McClain (bottom) and Nichole Ayers (top), both Expedition 73 Flight Engineers, checkout spacesuit hardware in the Quest airlock and review procedures for a May 1 spacewalk. The spacewalkers will install a modification kit on the International Space Station’s port side truss structure preparing it for a new rollout solar array and relocate an antenna that communicates with commercial spacecraft.
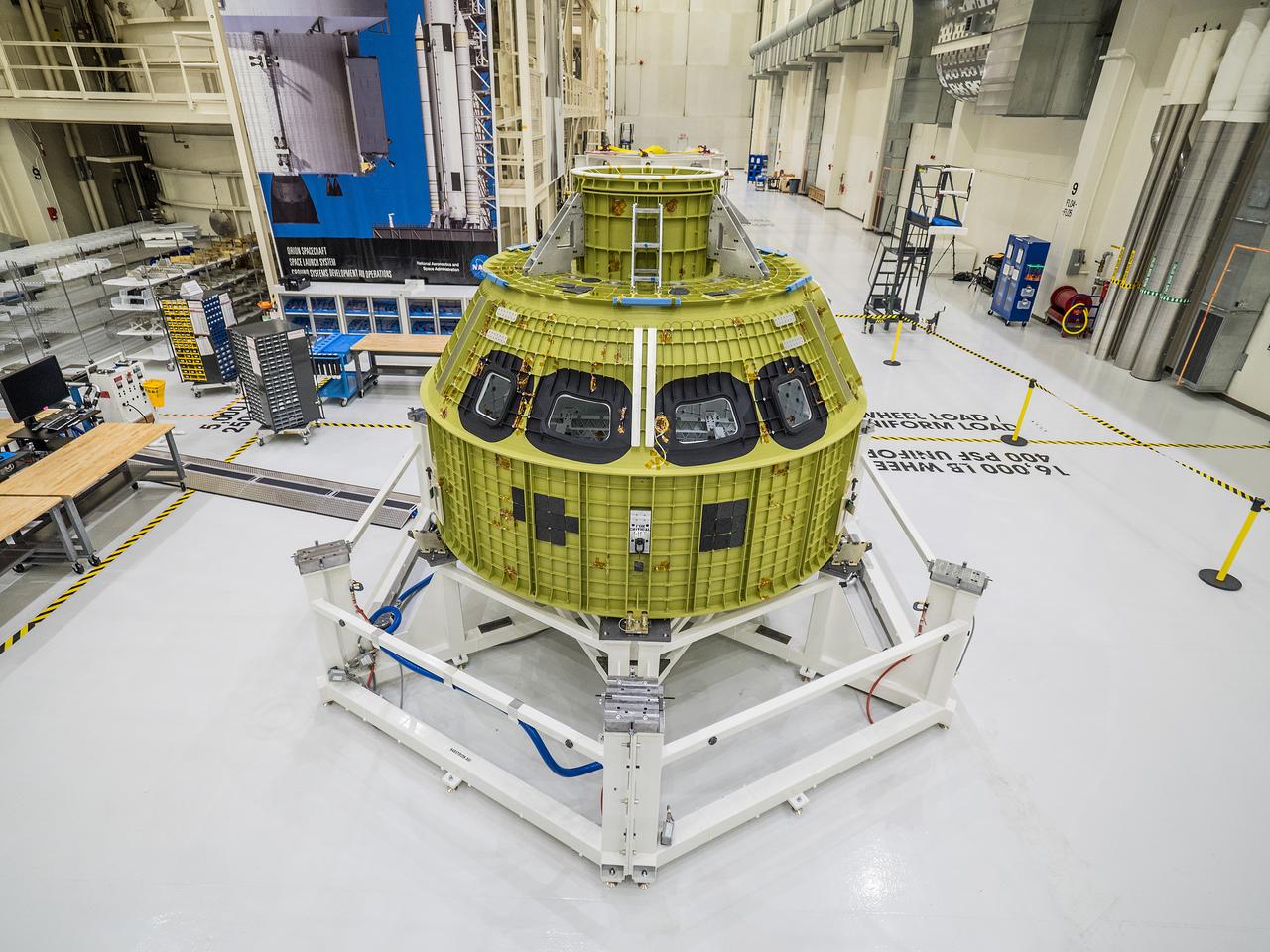

The Orion pressure vessel, which is the underlying structure of the crew module, arrived at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 2, 2016 and was maneuvered into a work stand. At Kennedy, engineers will outfit the pressure vessel with Orion's systems and subsystems ahead of Artemis I. The pressure vessel was welded together at the agency's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
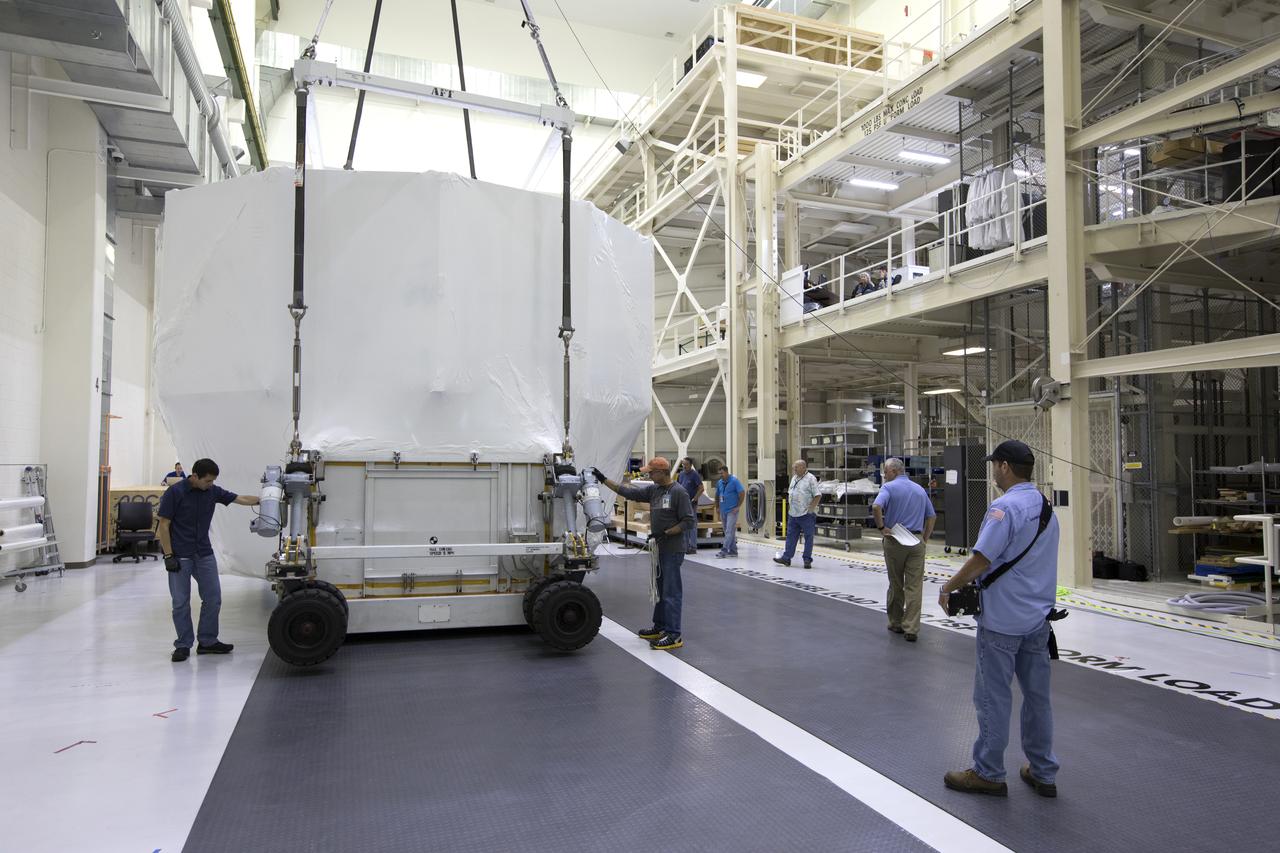

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers secure the protective covering around the module and a crane lifts the module, secured on stand, for the move to the transport truck. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
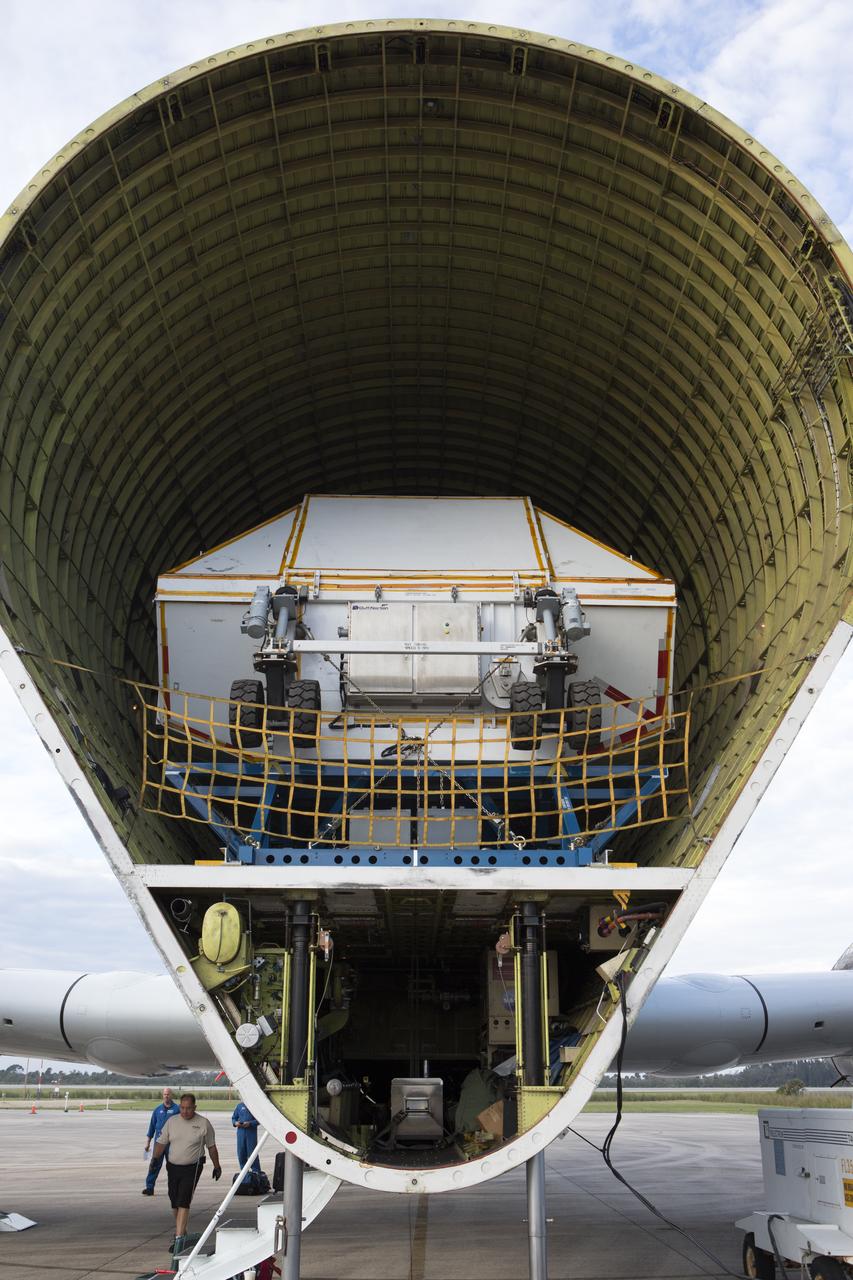

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article, arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The unique aircraft has been opened to reveal the container holding the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
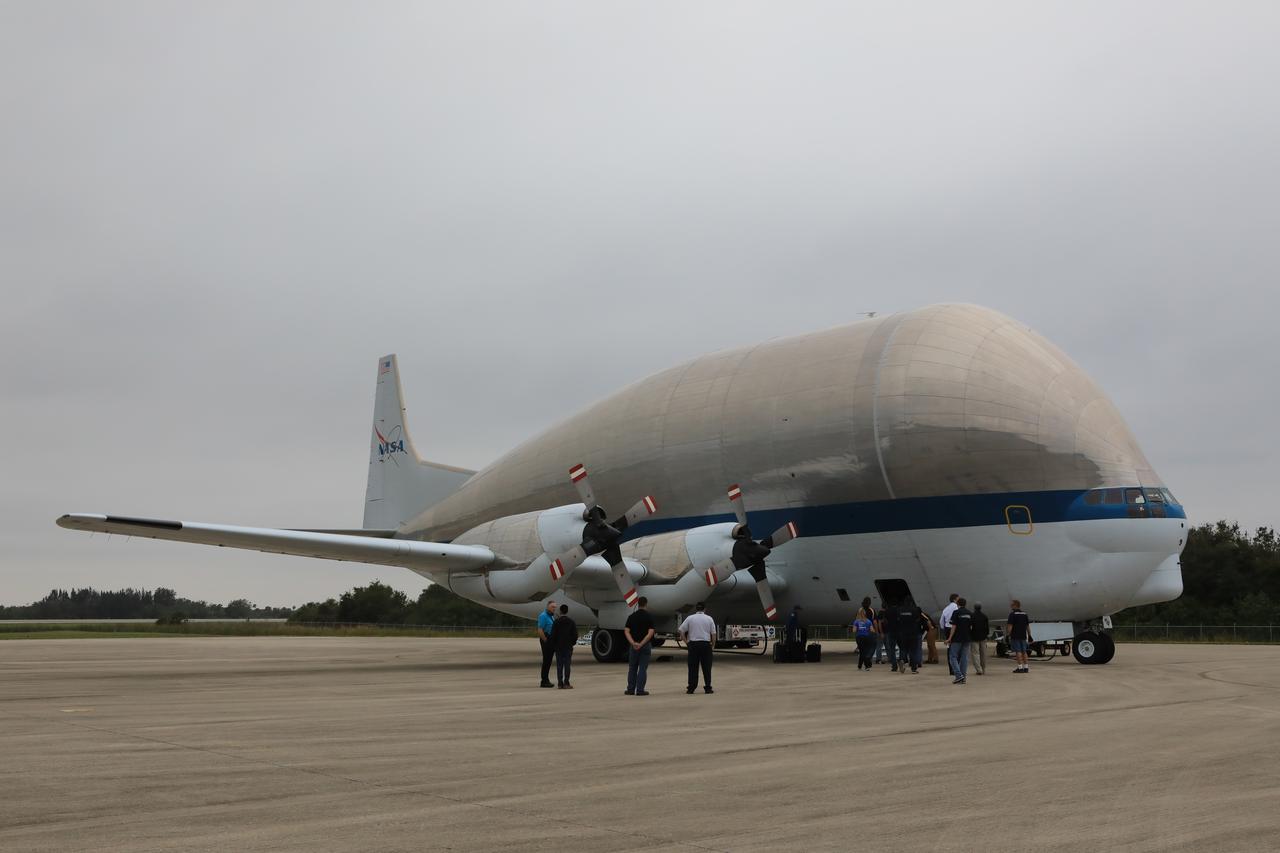

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft arrives on the tarmac after touching down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The guppy is carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

The heat shield carrier for Orion’s Artemis IV mission is in view secured on a work stand in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The carrier structure holds the thermal protection system heat shield securely to the Orion crew module while facing launch, reentry, and splashdown impact loads.
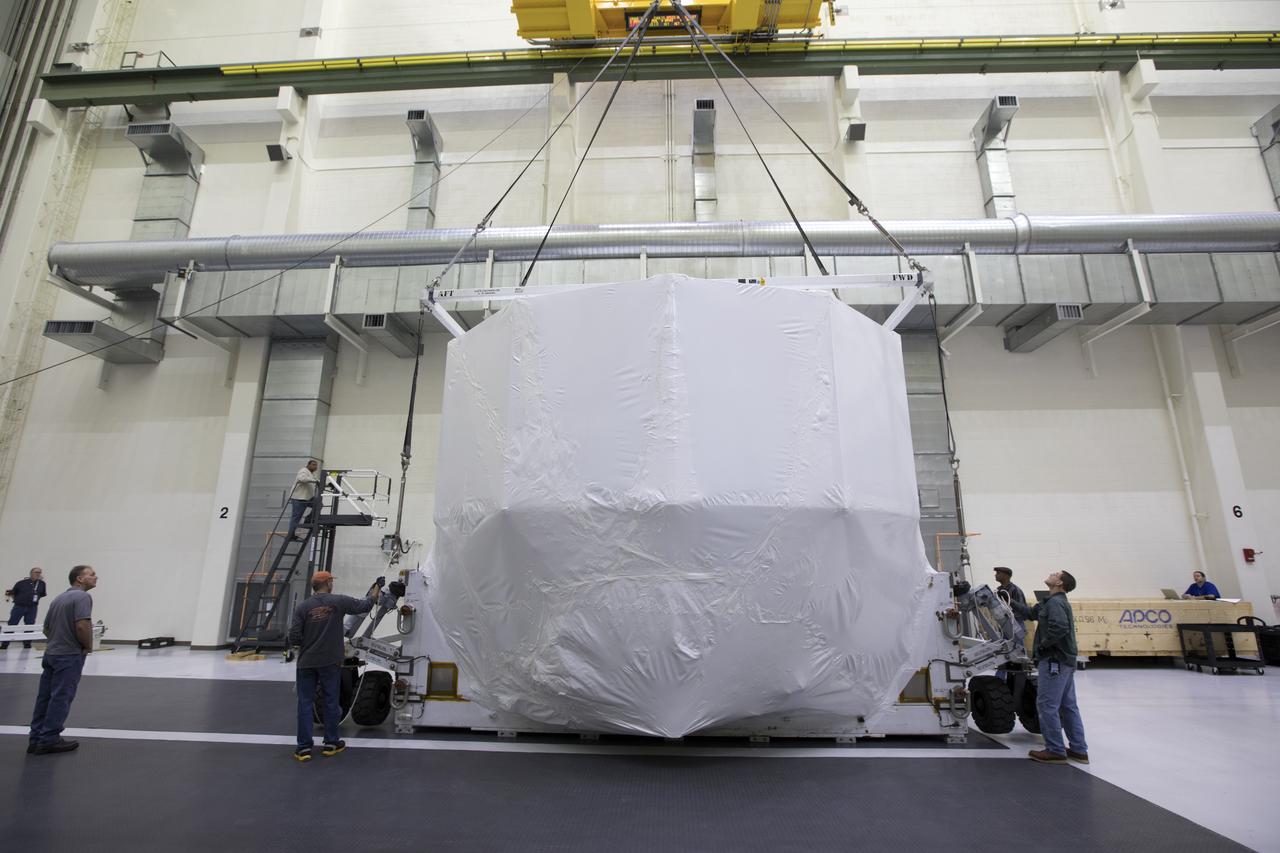

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers secure the protective covering around the module and a crane is used to lower it onto a stand. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
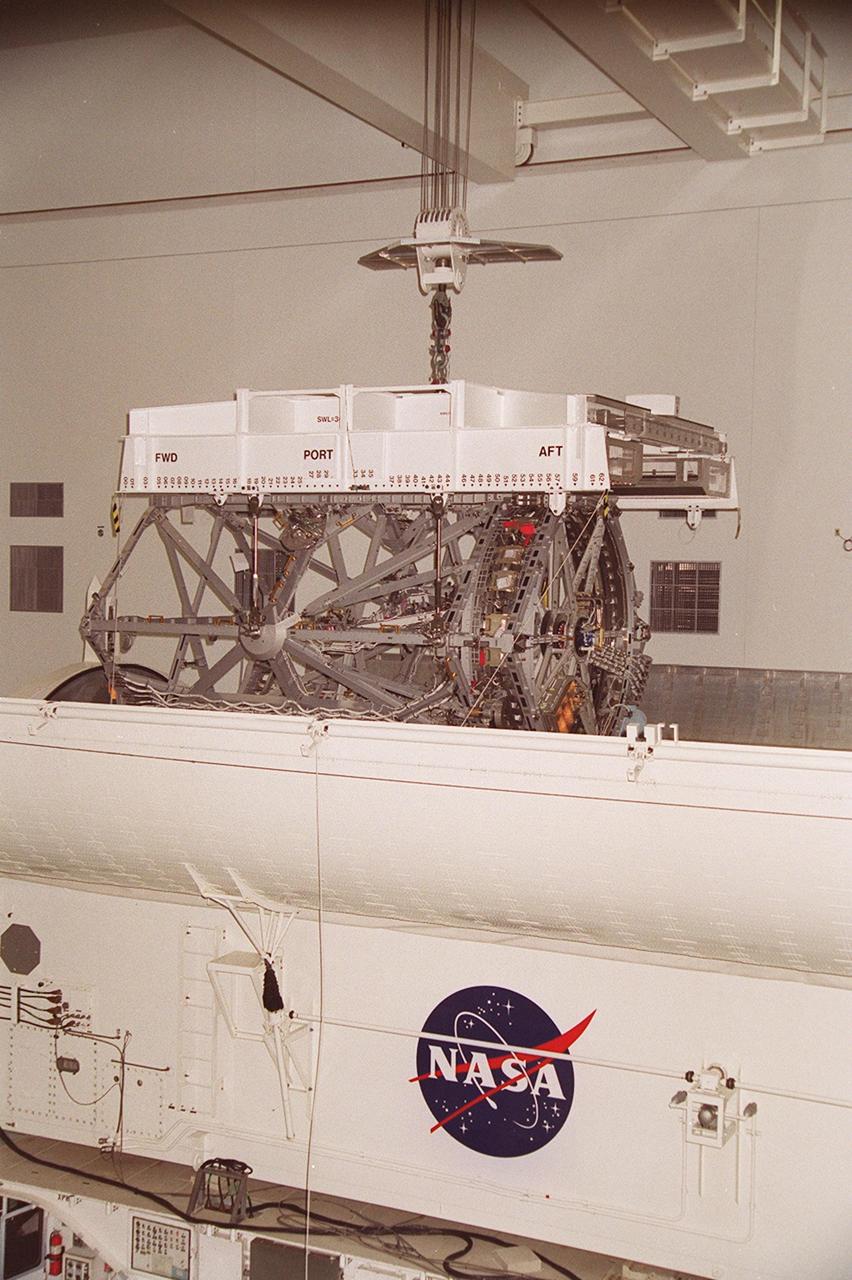
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the P3 Integrated Truss Structure out of the payload canister that transferred it from the Operations and Checkout Building. The port-side P3 truss is scheduled to be added to the International Space Station on mission STS-115 in 2002 aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis. The P3 will be attached to the first port truss segment, P1, being installed in an earlier mission.
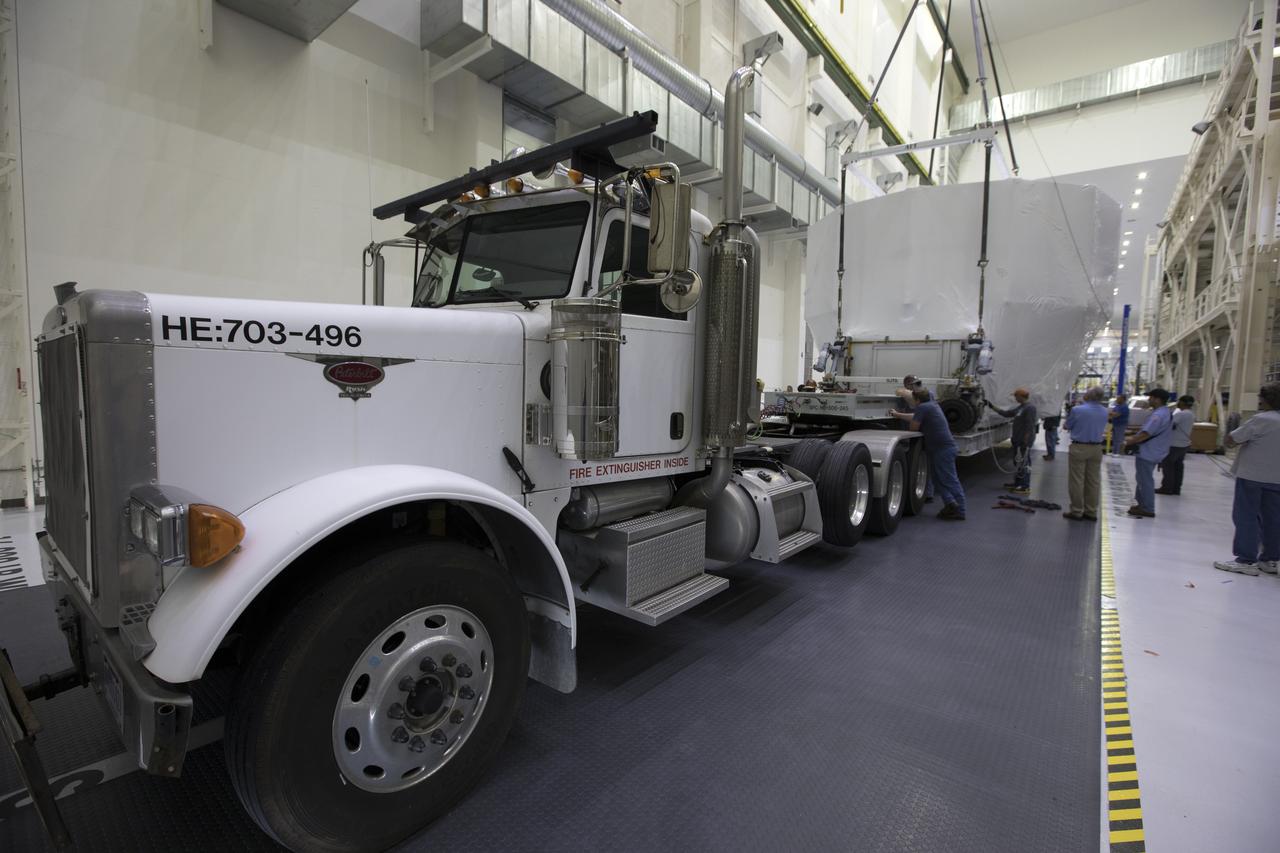

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay, the Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is secured on the flatbed of a transport truck. The service module will be shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
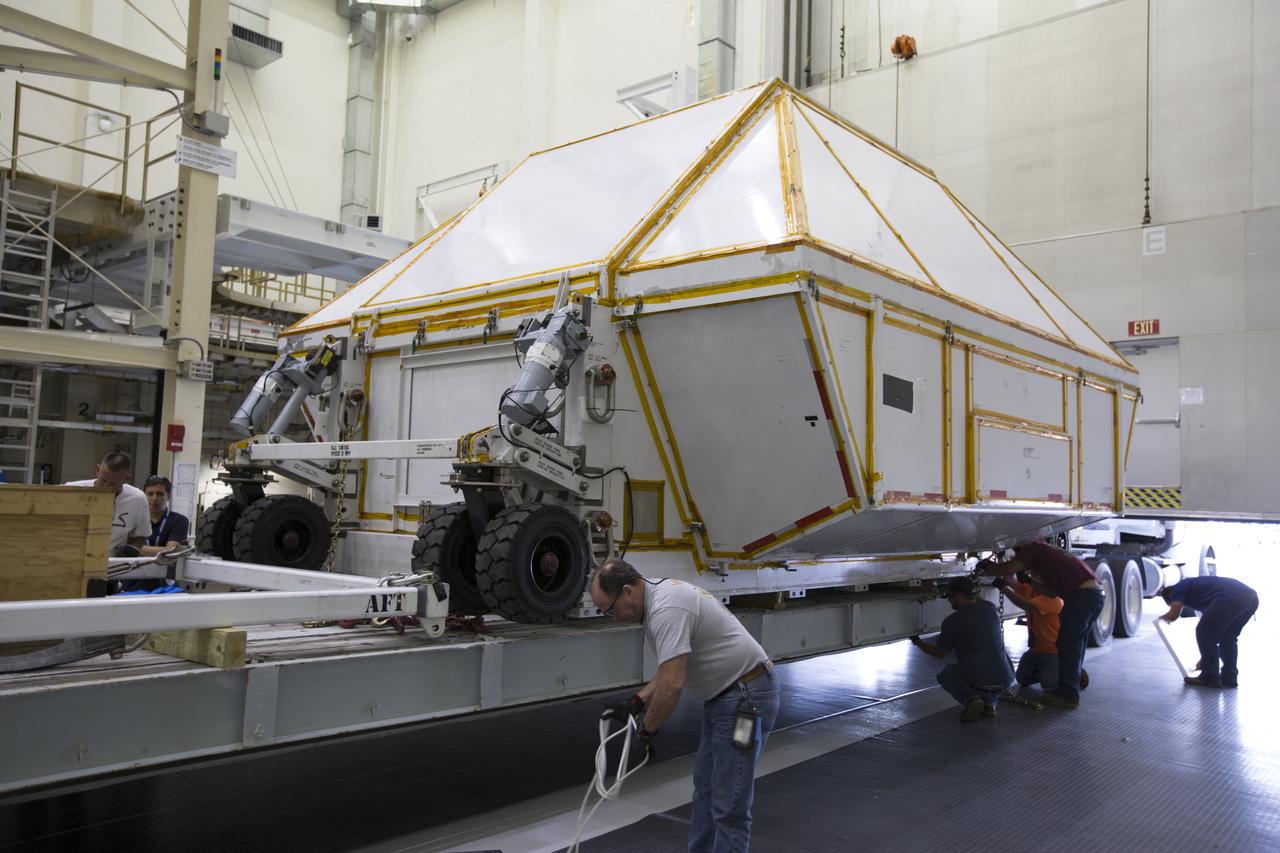

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians secure the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article in its transport container onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
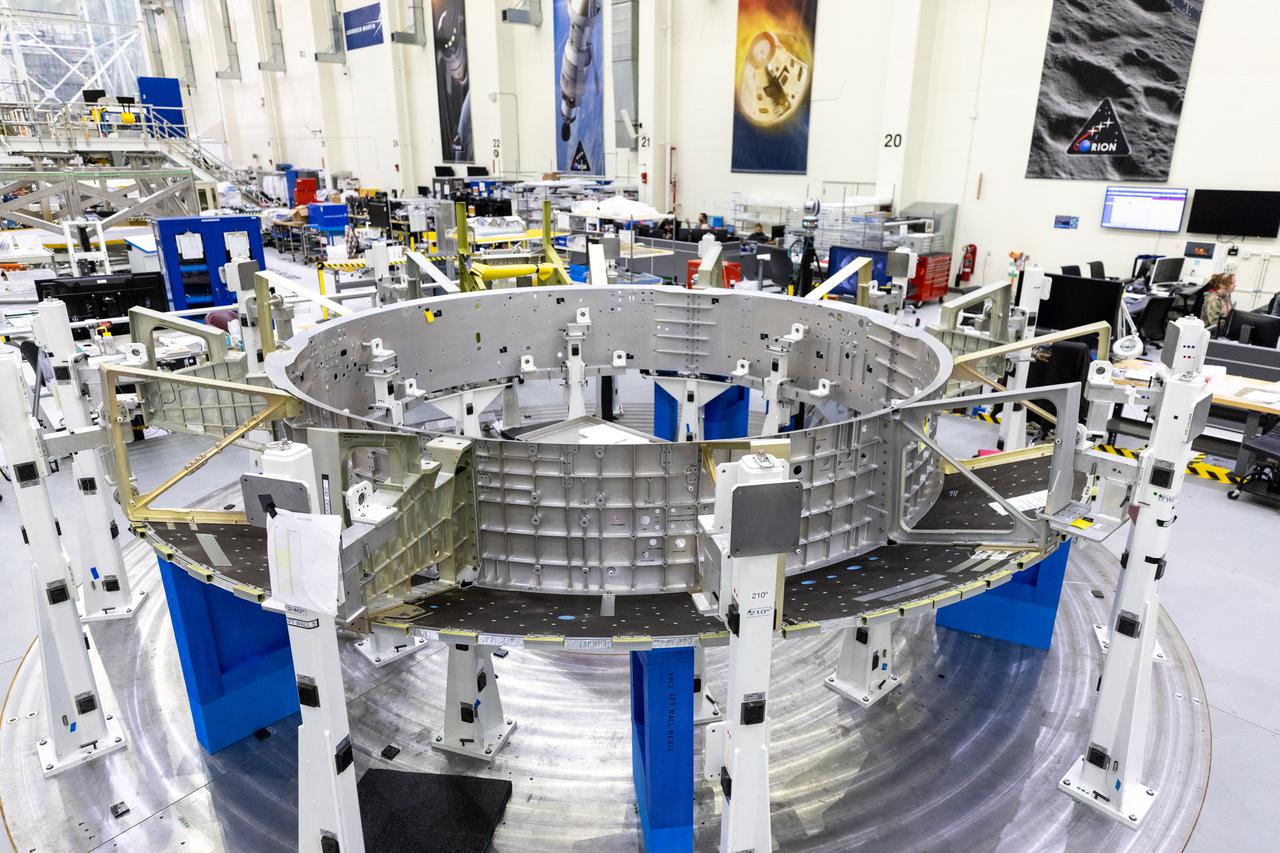

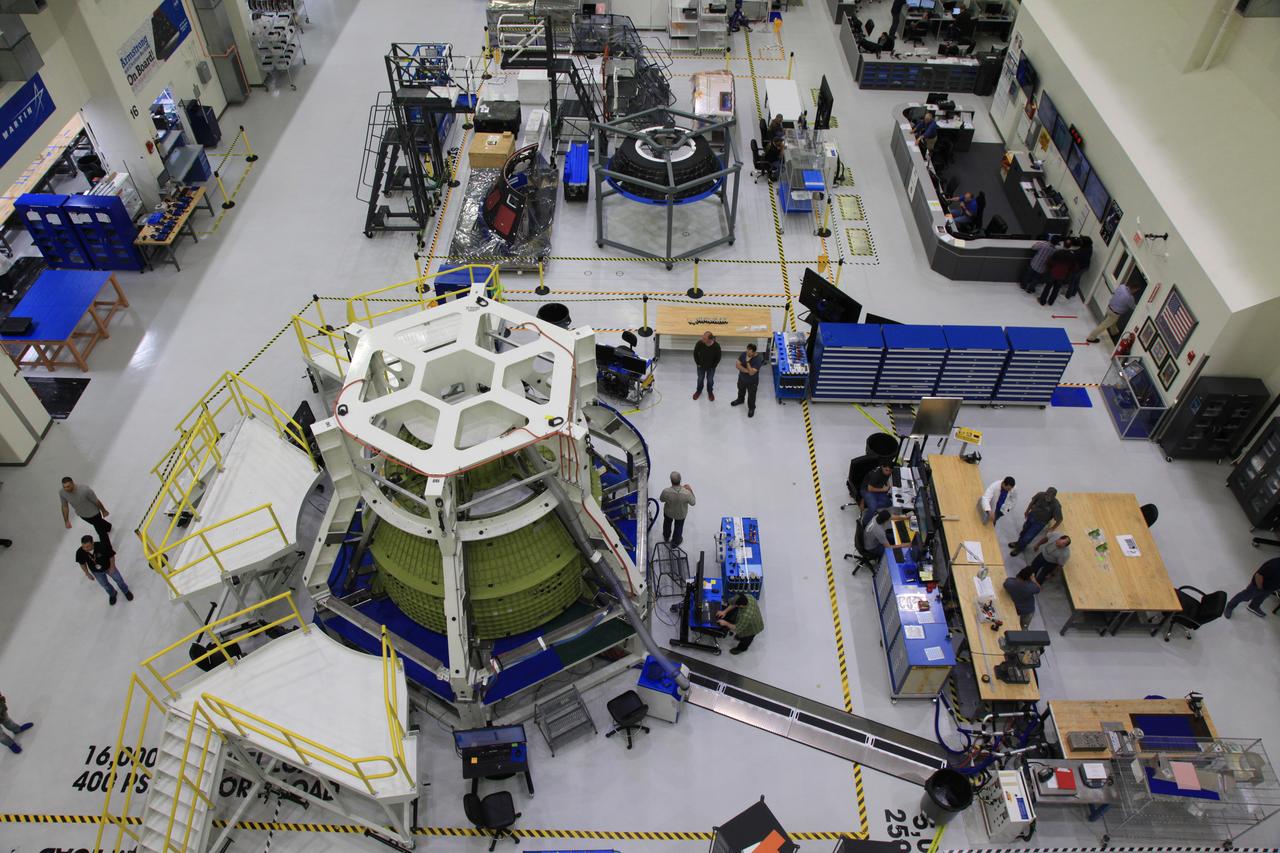
The Orion crew module adapter for NASA’s Artemis III mission is on a work stand inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 20, 2022. Lockheed Martin technicians continue working to install the aft walls as the ring-shaped structure is prepared to ultimately be attached to the European-built service module. Launched atop the Space Launch System rocket, Artemis missions will aim to send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon.
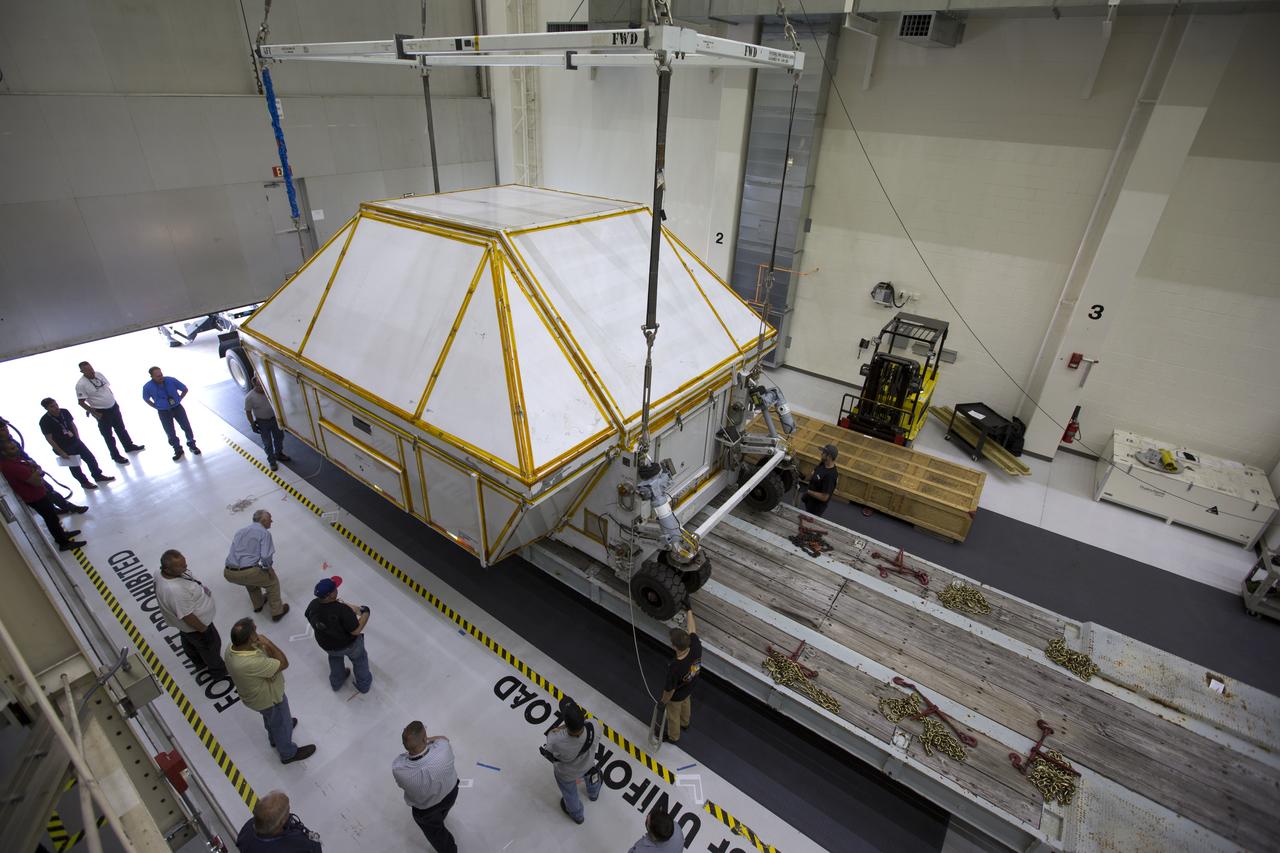

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article inside its transport container, is secured onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
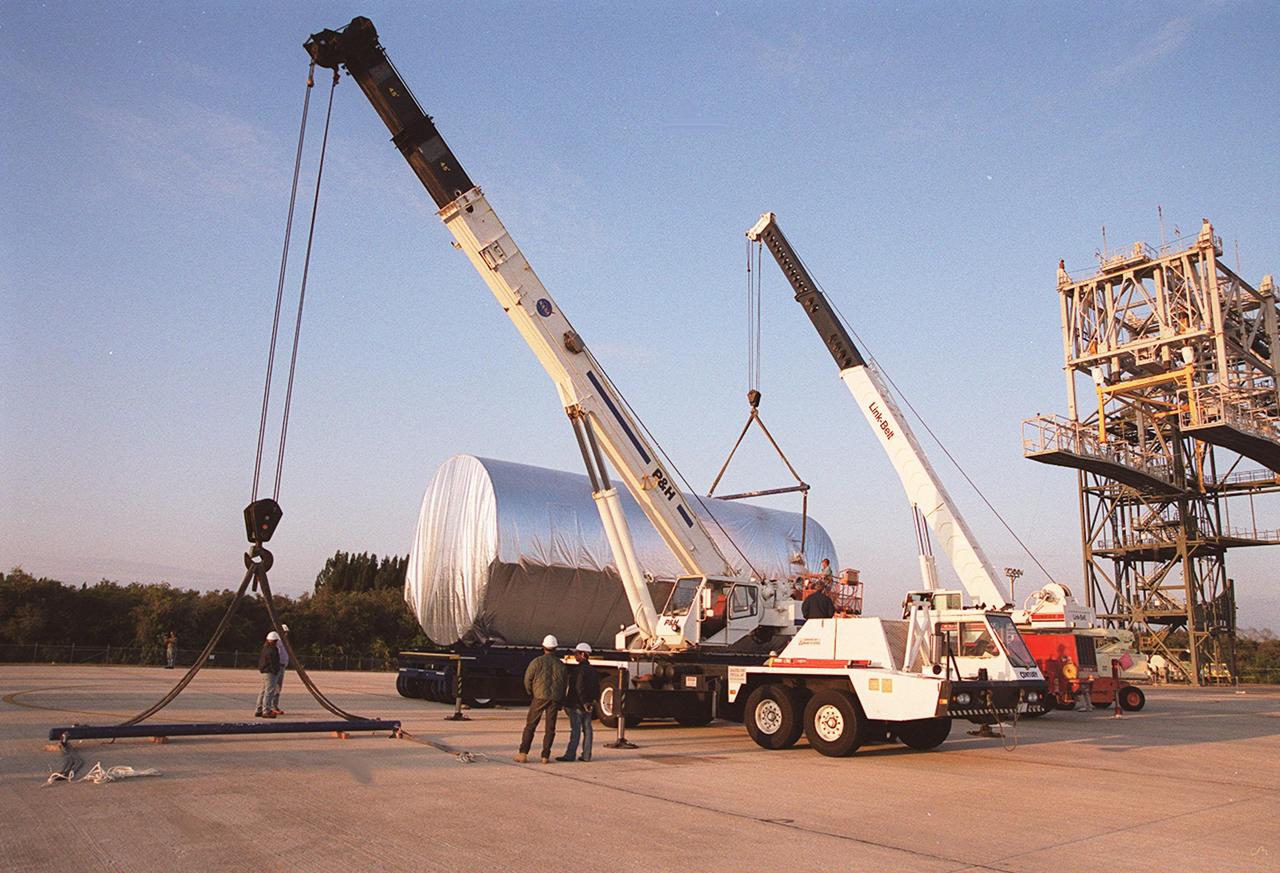

Cranes move toward the Integrated Truss Structure S3 as it sits on the parking apron of the Shuttle Landing Facility after being offloaded from the Super Guppy aircraft. The truss will be moved to a transporter and taken to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
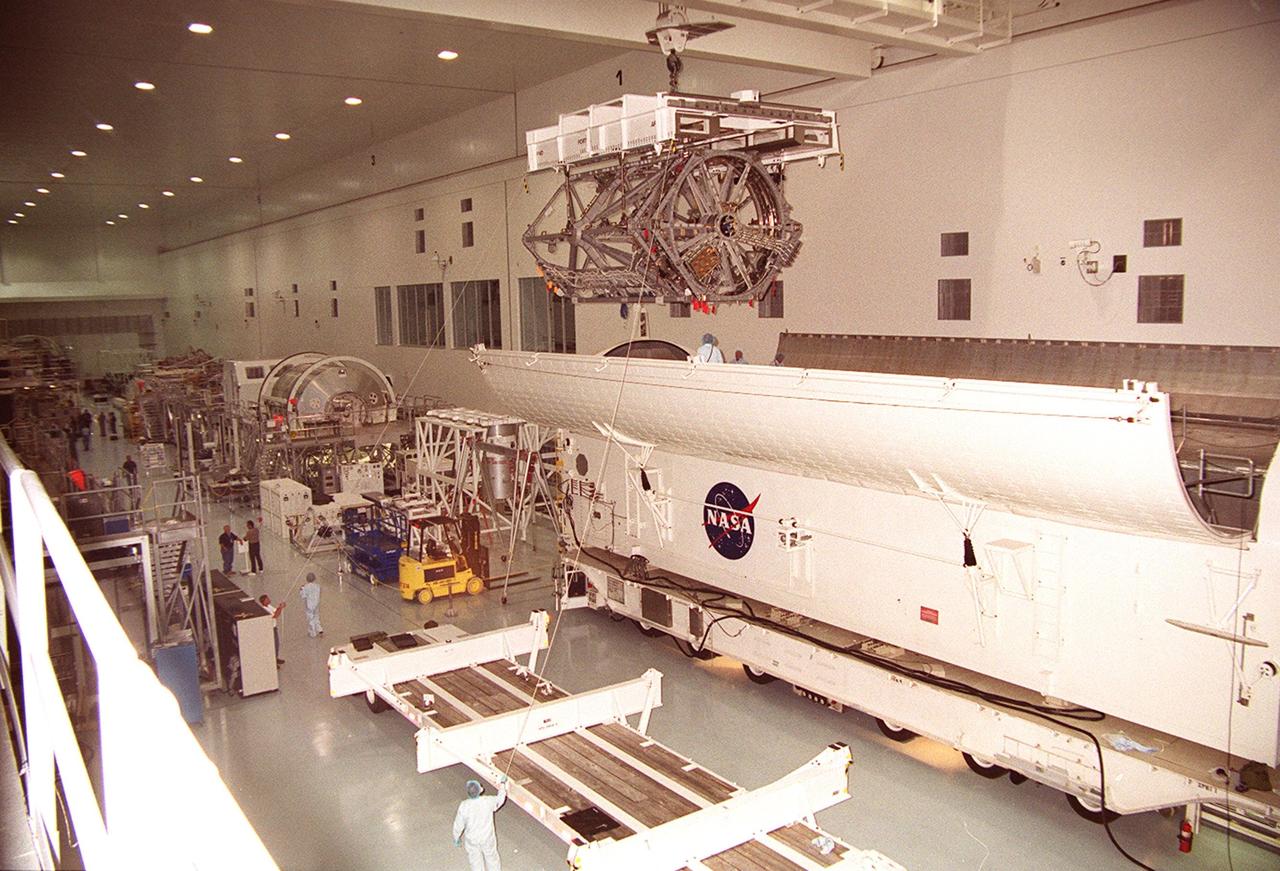
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the P3 Integrated Truss Structure clear of the payload canister that transferred it from the Operations and Checkout Building. The port-side P3 truss is scheduled to be added to the International Space Station on mission STS-115 in 2002 aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis. . The P3 will be attached to the first port truss segment, P1, being installed in an earlier mission
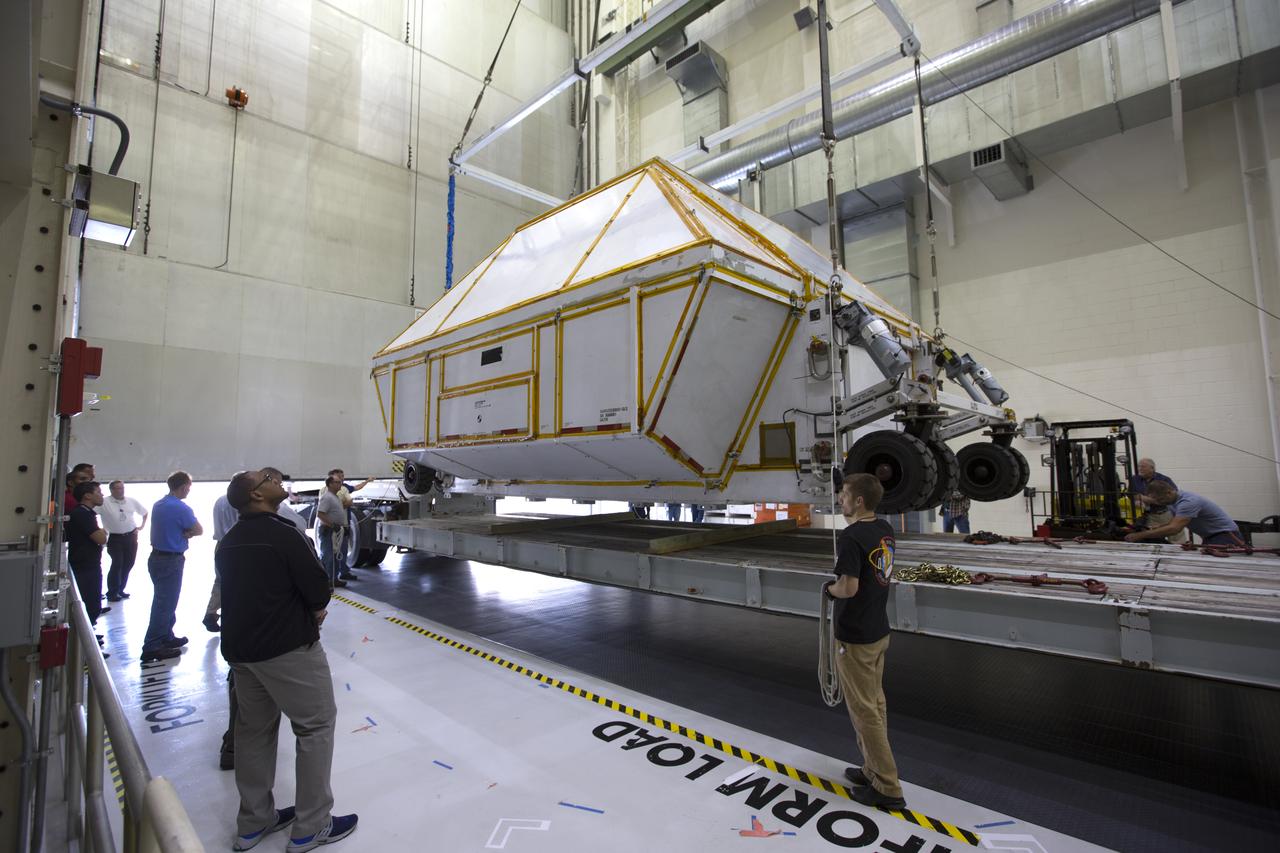

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article, secured inside its transport container, is lowered onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
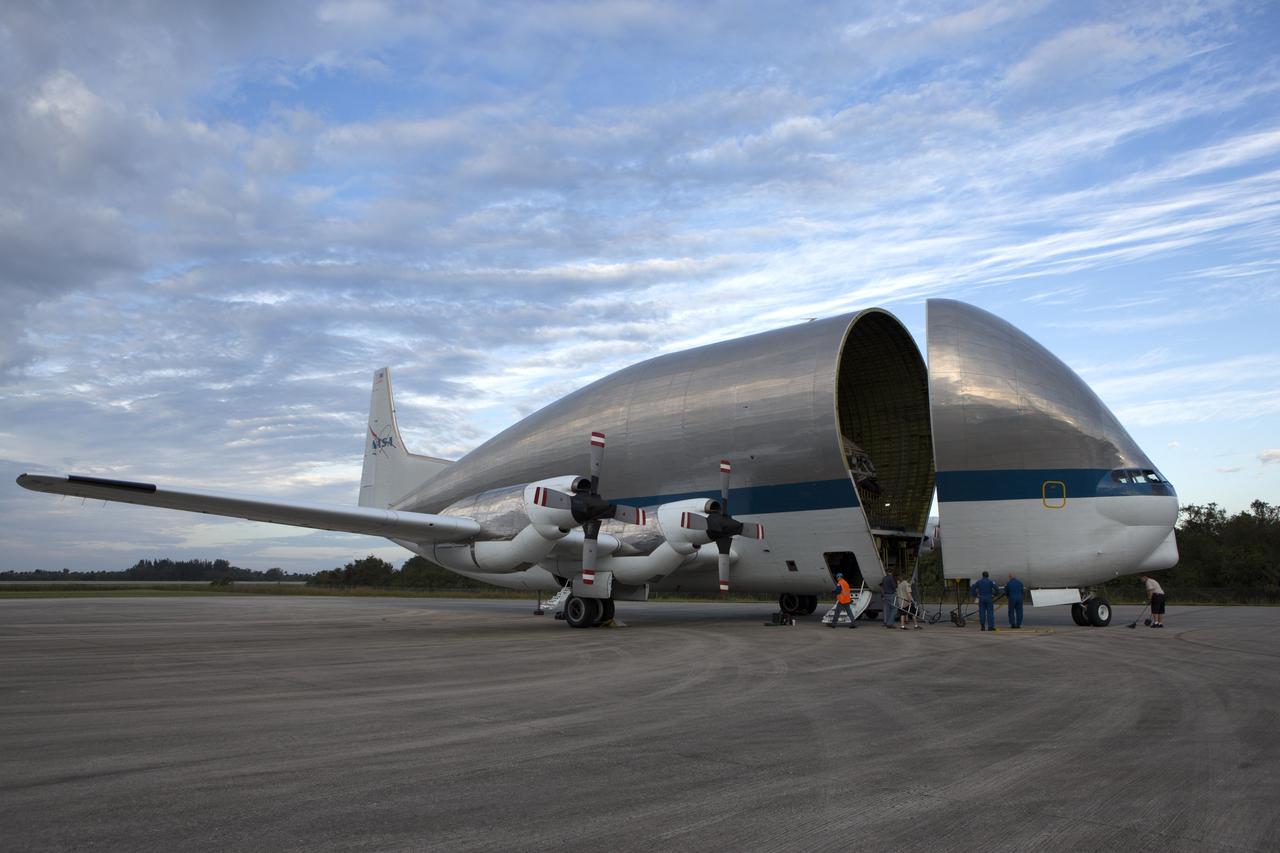

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA), arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The front of the unique aircraft is being opened to offload the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
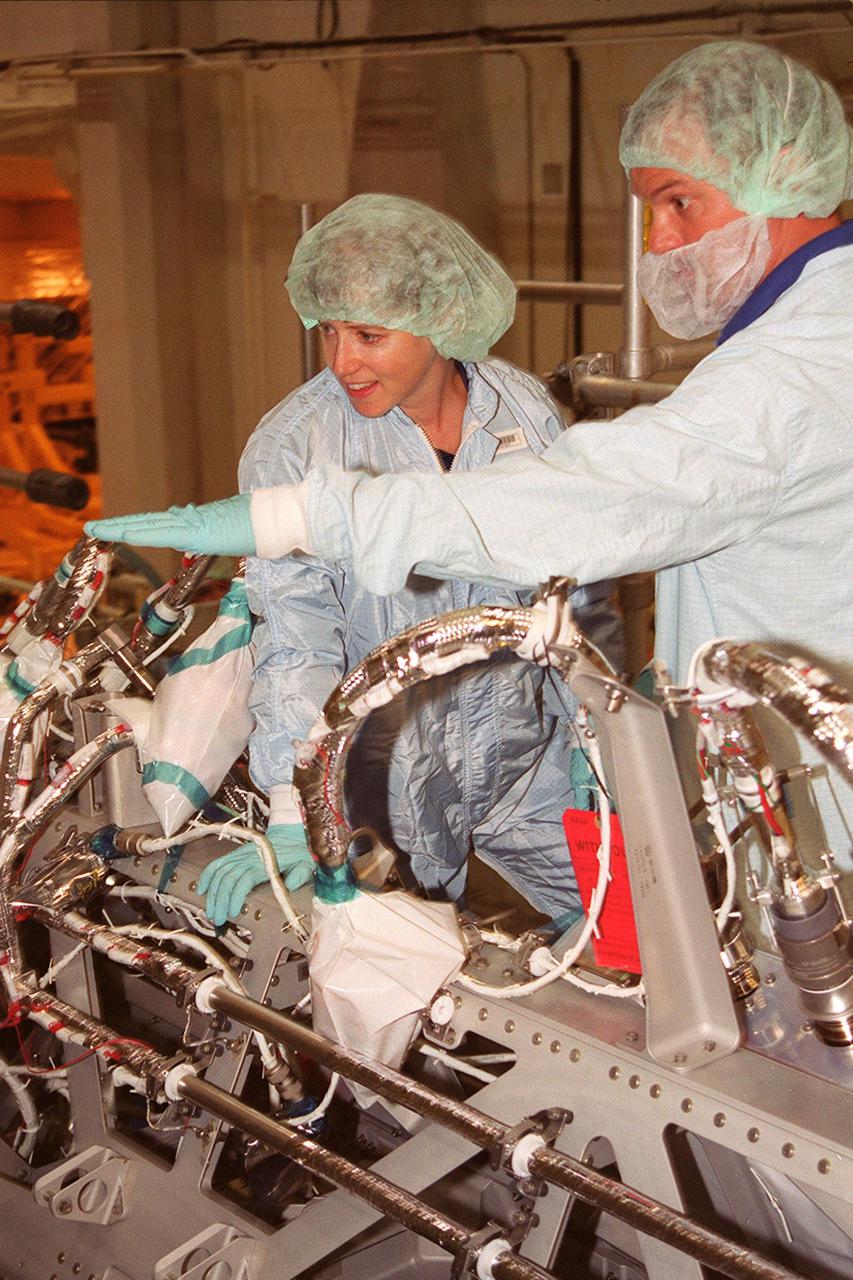

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Operations and Checkout Bldg., STS-112 Pilot Pamela A. Melroy gets a close look at the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) S1 that will be part of the payload on the mission. Other members of the crew are Commander Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists David A. Wolf, Piers J. Sellers, Sandra H. Magnus and Fyodor Nikolayevich Yurchikhin, a cosmonaut with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Mission STS-112 is scheduled for launch in July 2002
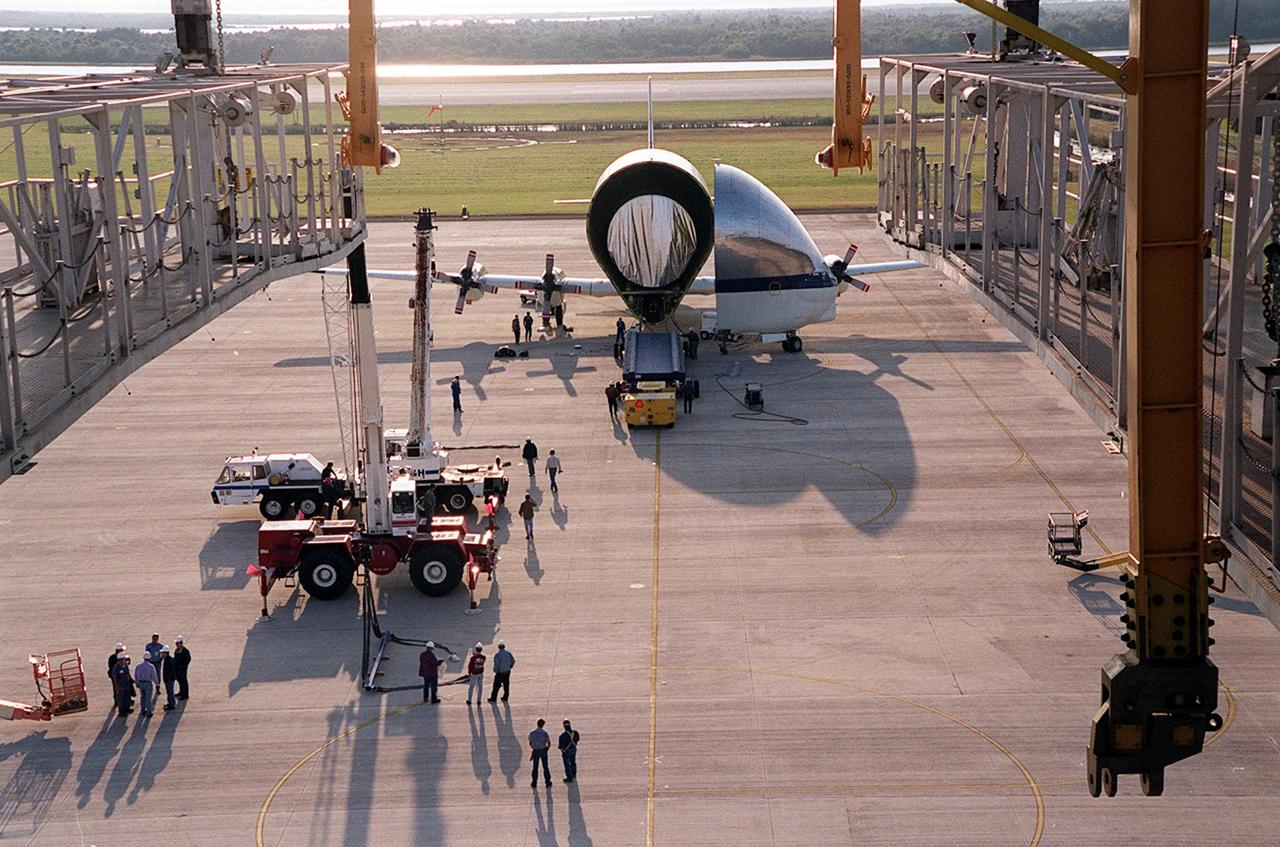

On the parking apron of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, near the Mate/Demate device (seen in the foreground), the opened nose of the Super Guppy aircraft reveals its cargo, the Integrated Truss Structure S3. It was built by The Boeing Co. After offloading, the S3 will be transported to the Operations and Checkout Building. The second starboard truss segment of the International Space Station, the S3 truss is scheduled to be added to the Station in April 2003
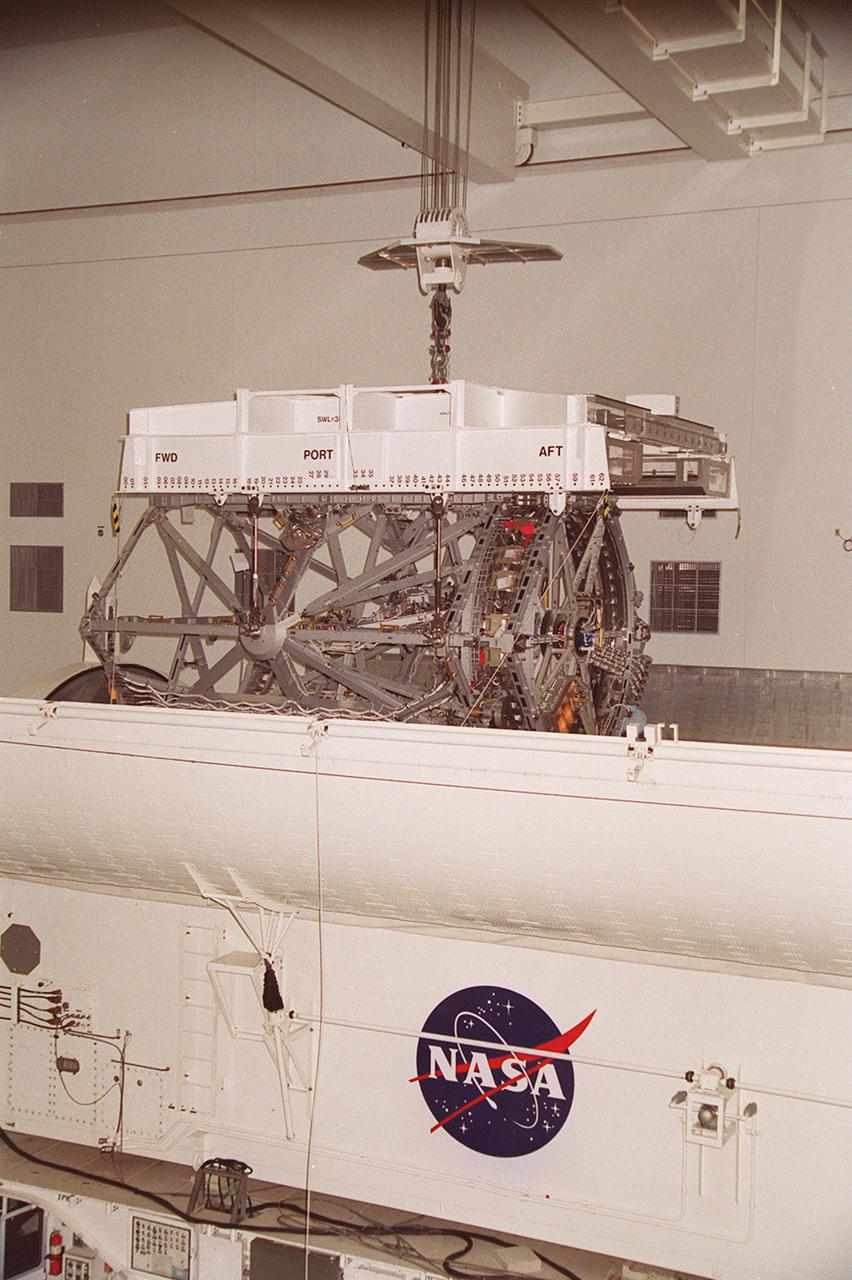
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the P3 Integrated Truss Structure out of the payload canister that transferred it from the Operations and Checkout Building. The port-side P3 truss is scheduled to be added to the International Space Station on mission STS-115 in 2002 aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis. The P3 will be attached to the first port truss segment, P1, being installed in an earlier mission.