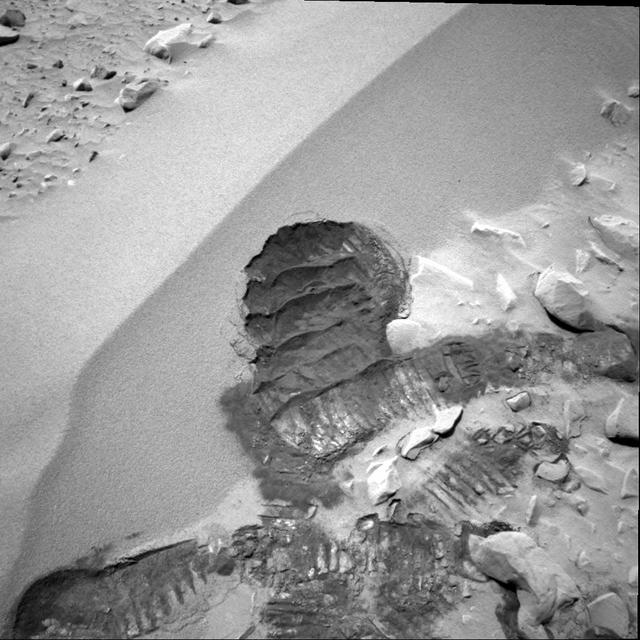

Spirit Digs In

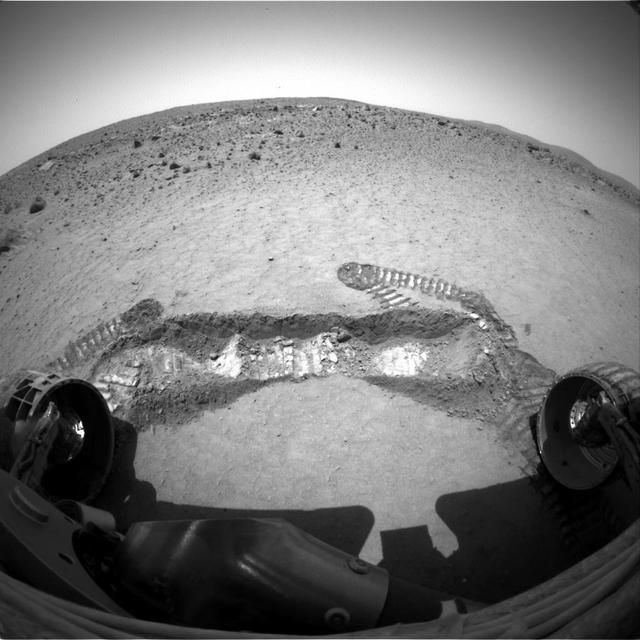
Opportunity Digs

Spirit Digs a Trench
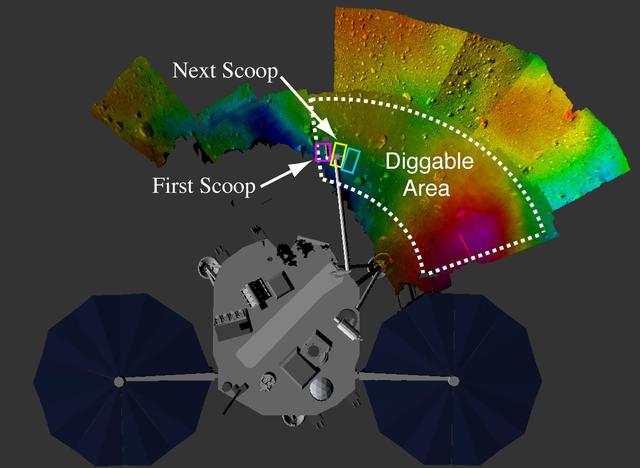
Map of Phoenix Digging Area
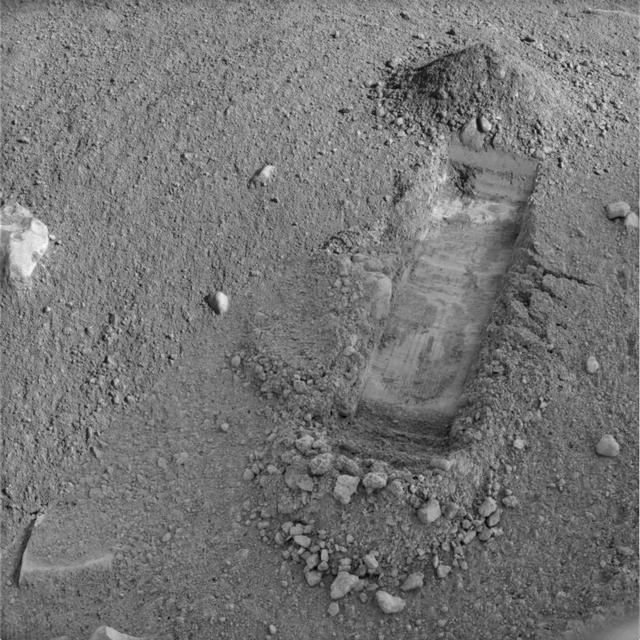

Digging of Snow White Begins

Second Dig and Dump Test

VL1 Digs A Deep Hole On Mars
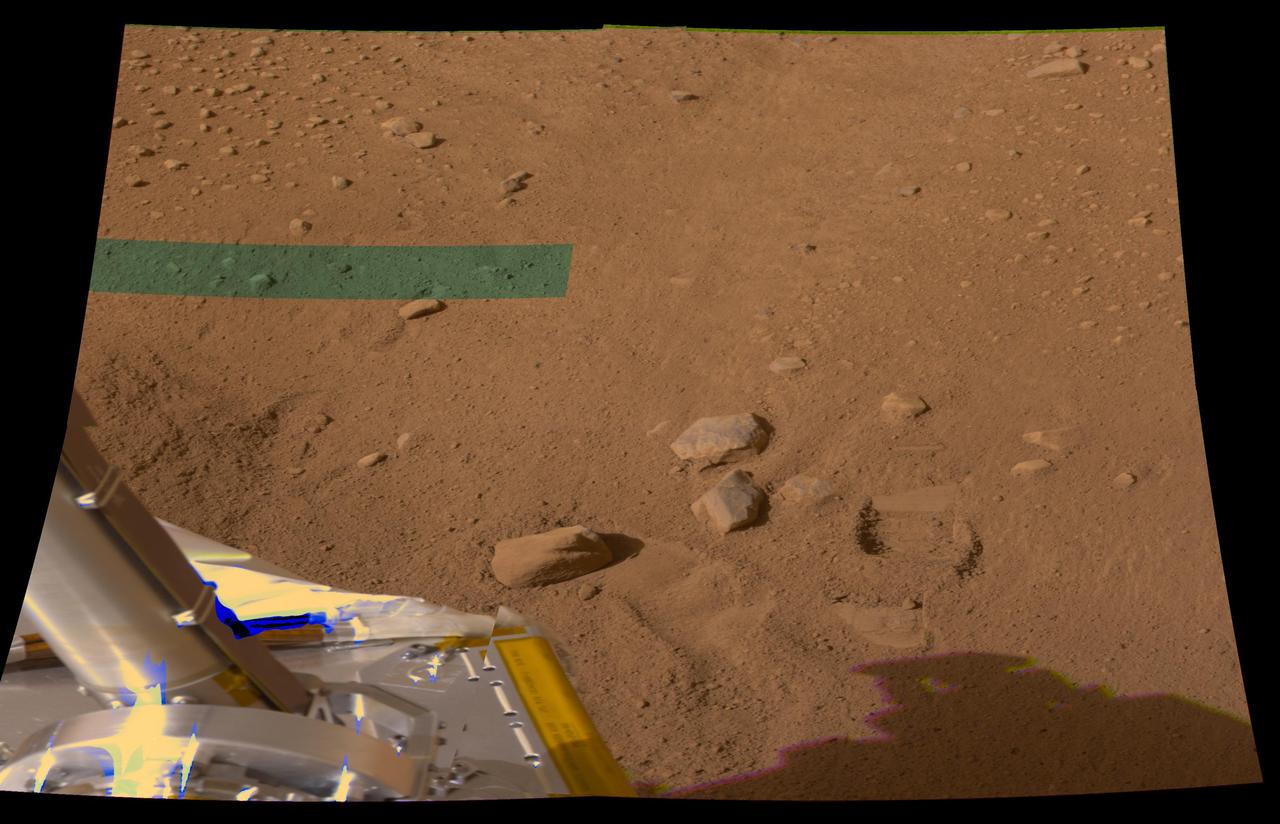

Mark Left by First Dig at Phoenix Site

Digging in Snow

Diane Linne in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPE Lab - Percussive Excavation Bucket reduces reaction forces for extraterrestrial digging of loose and compacted or icy soils.

This image from Sol 1 shows a mosaic of NASA Mars Phoenix digging area in the Martian terrain. Phoenix scientists were very pleased with this view as the terrain features few rocks -- an optimal place for digging.
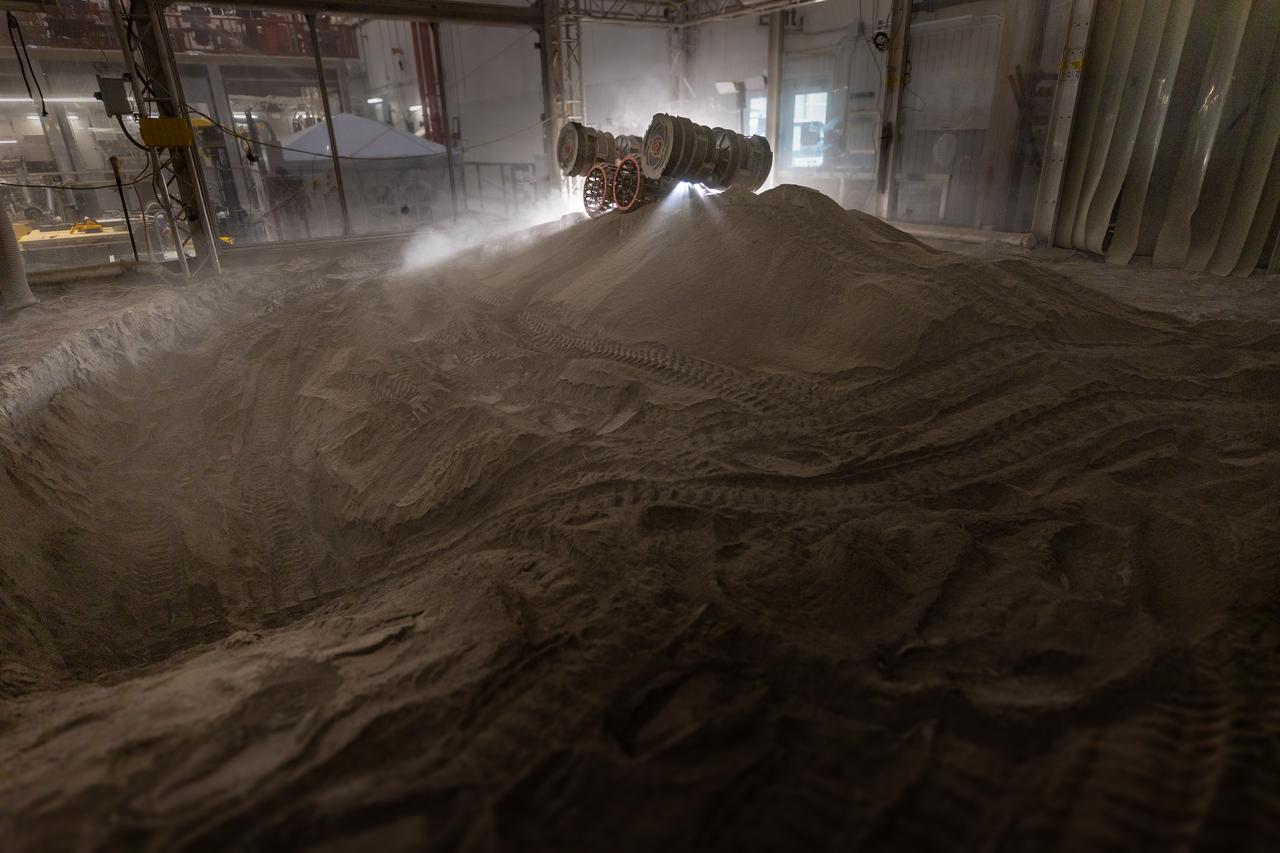

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
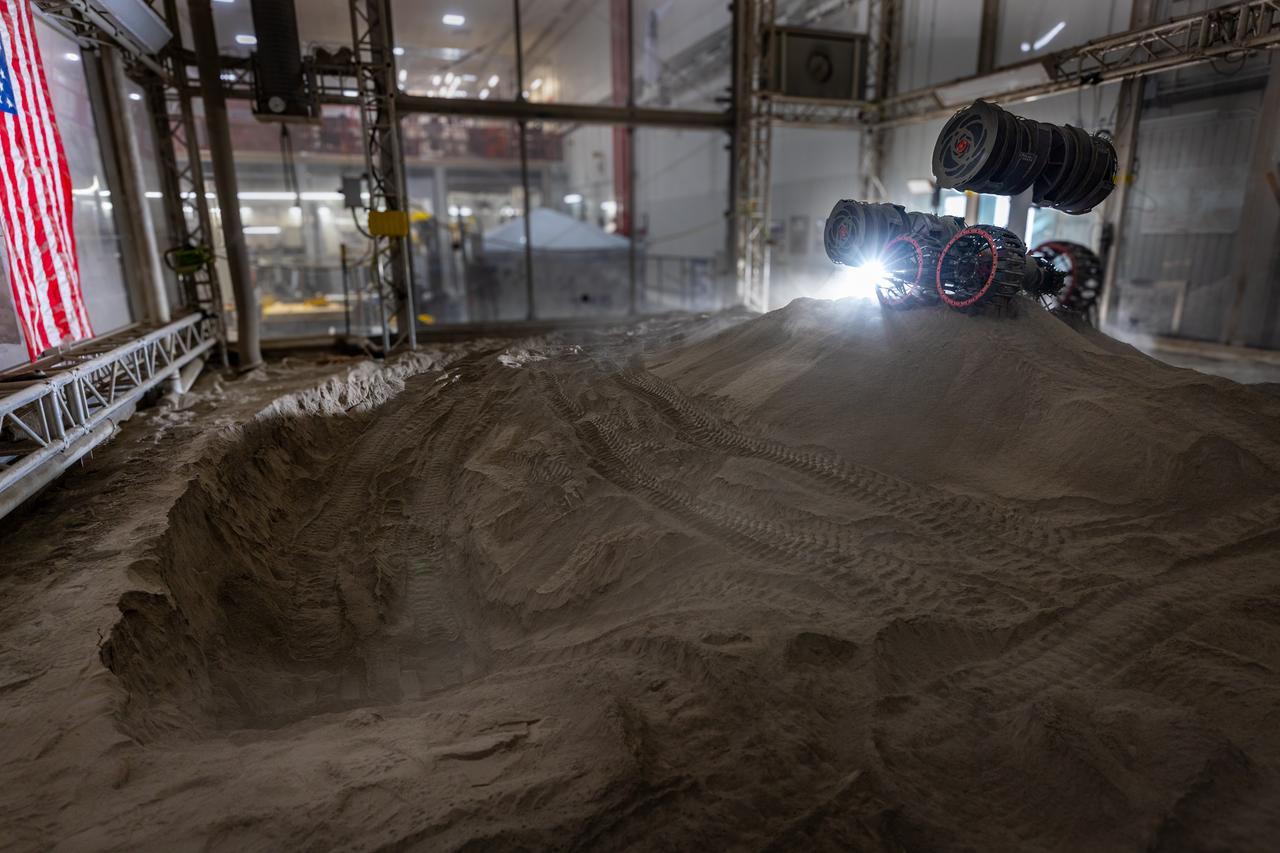

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
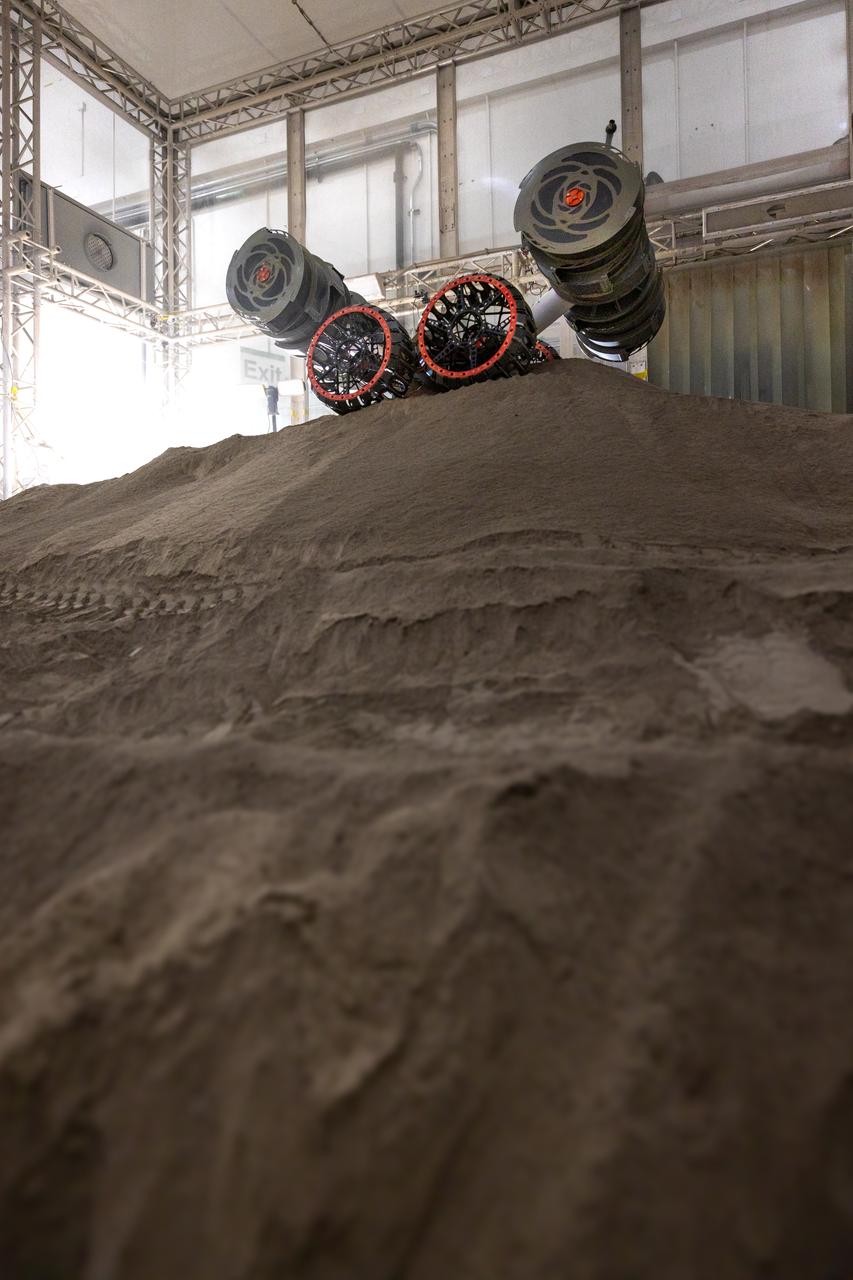

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
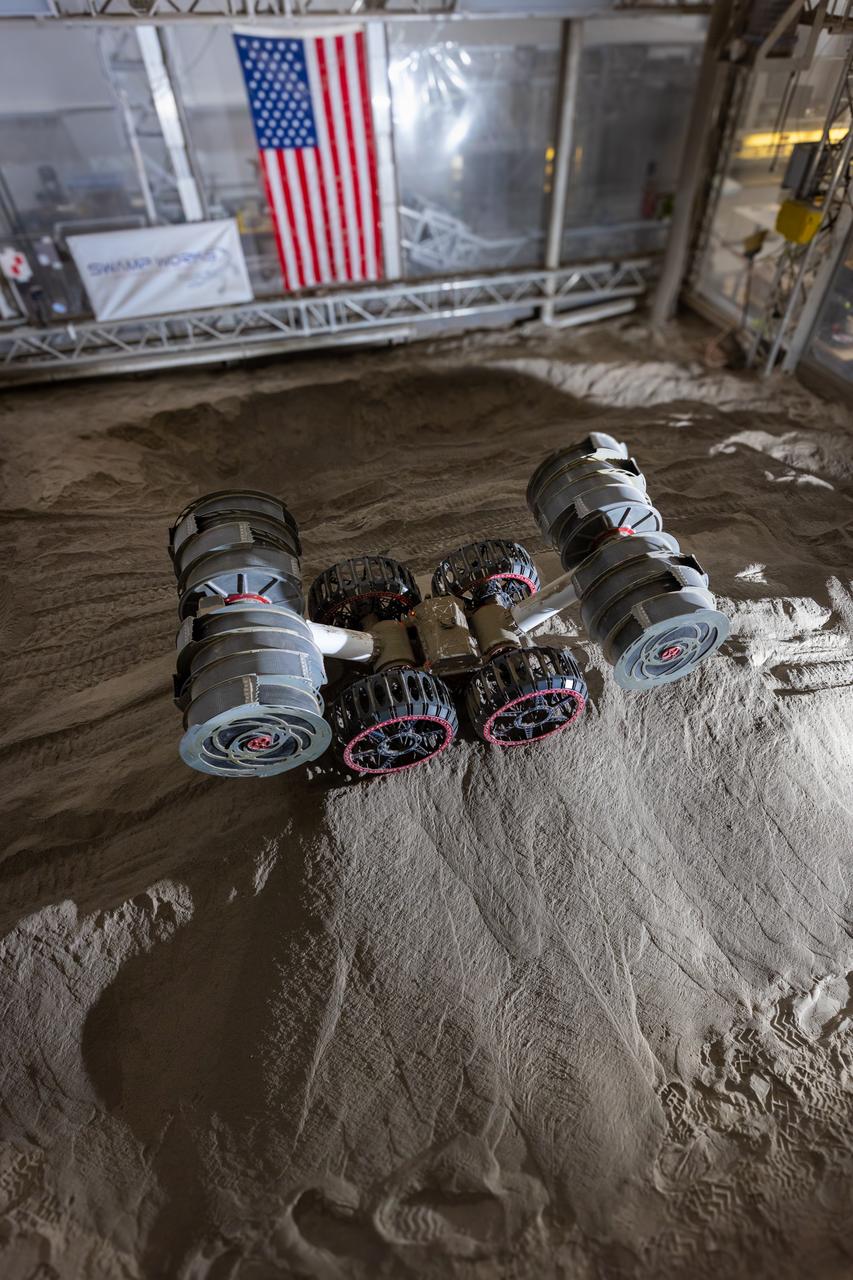

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
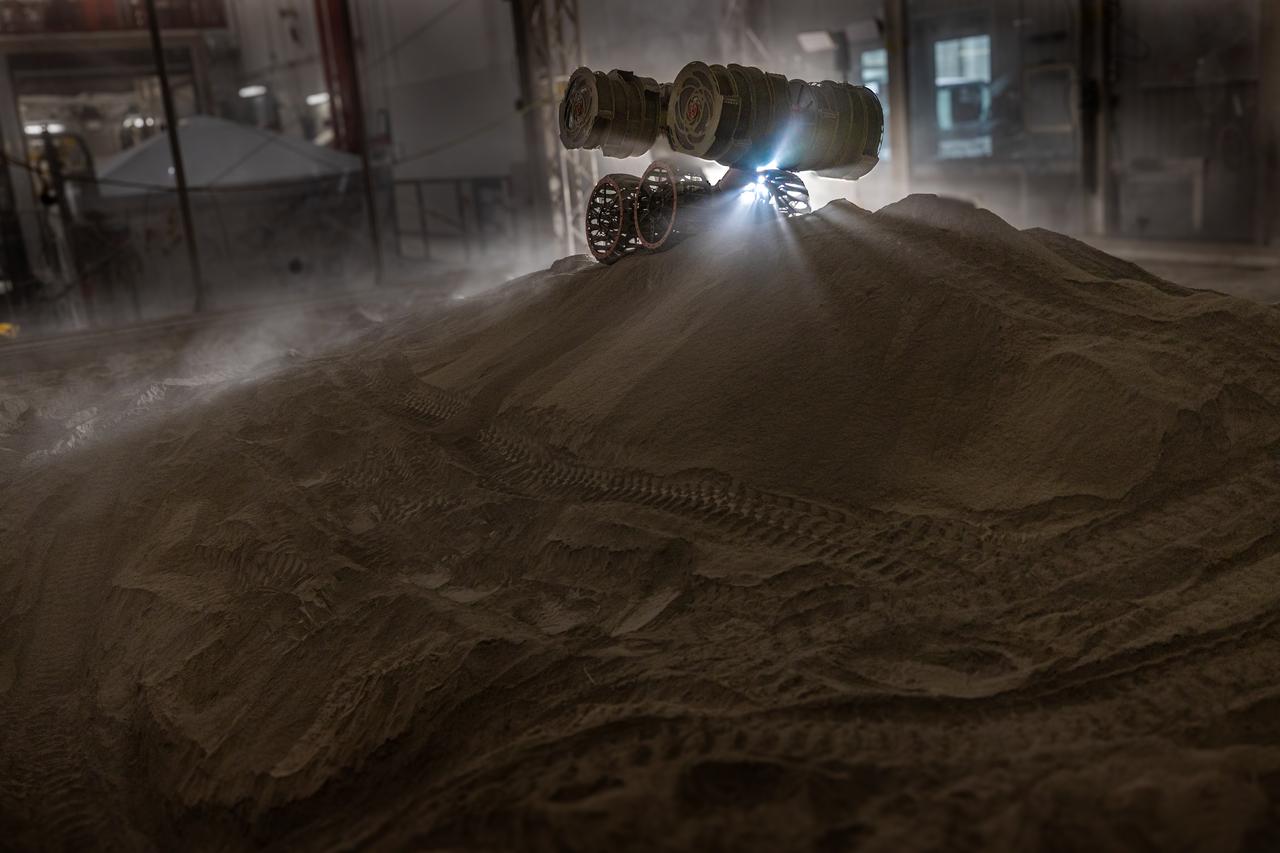

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
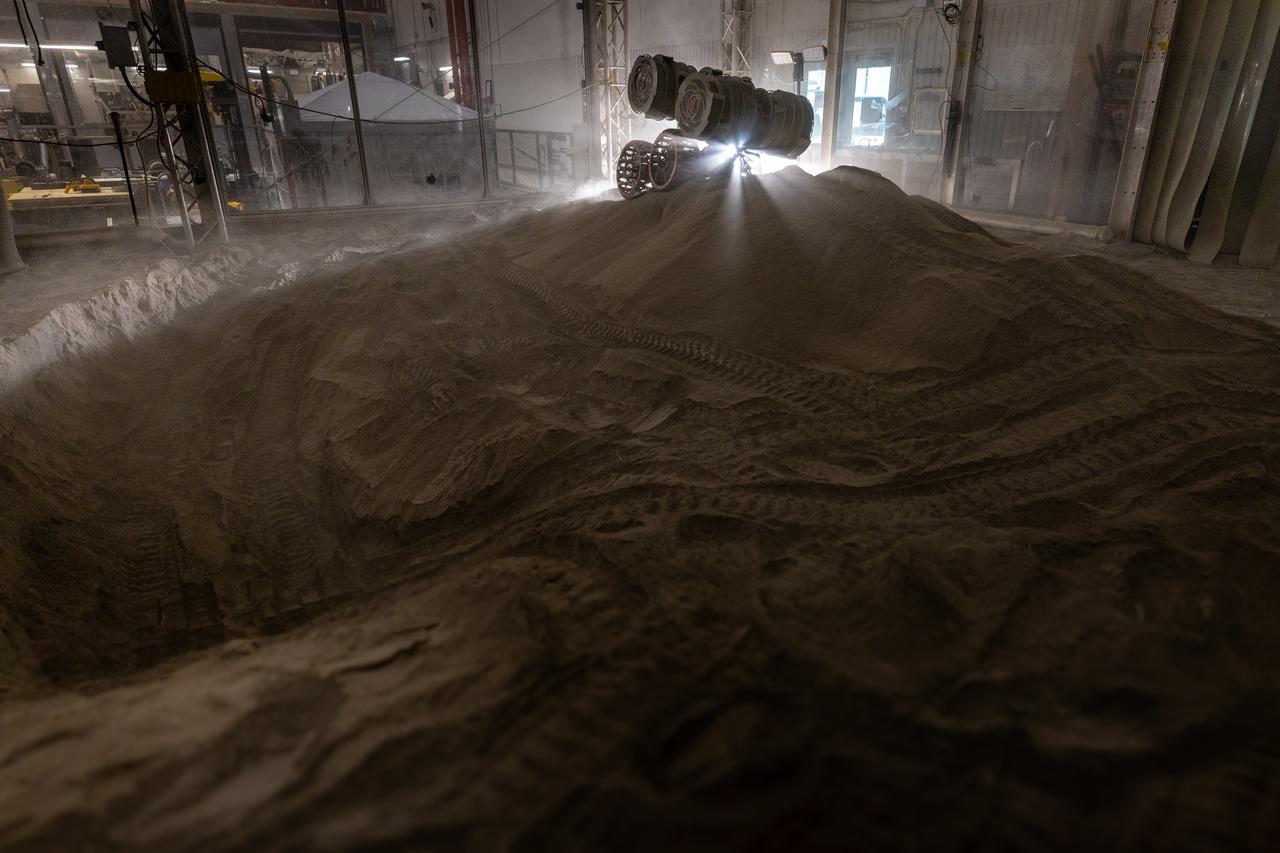

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.

This animation shows NASA InSight's heat probe, or "mole," digging about a centimeter (half an inch) below the surface last week. Using a technique called "pinning," InSight recently pressed against the mole using a scoop on its robotic arm to help the self-hammering heat probe dig so that it can "take the temperature" of Mars. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23379

The Roman Coronagraph Instrument on NASA's upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will test new tools that block starlight, revealing planets hidden by the glare of their parent stars. This graphic shows a test of what engineers call "digging the dark hole." The image shows three computer readouts of real data from the coronagraph's camera. Engineers used lasers and special optics to replicate the light from a star as it would look when observed by the Roman telescope. The image at left shows the amount of starlight that leaks into the coronagraph's field of view when only fixed components called masks are used to block the star at the center of the circle. Using moveable components such as deformable mirrors, the coronagraph can remove more and more of this starlight. The middle and right images show the progression of this process, where red indicates less starlight, and black indicates most or all starlight has been removed. The deformable mirrors are each only 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter and backed by more than 2,000 tiny pistons that move up and down. The pistons work together to change the shape of the mirrors to compensate for the unwanted stray light that spills around the edges of the masks. Though they are too small to affect Roman's other highly precise measurements, the imperfections can send stray starlight into the dark hole. In space, this technique will enable astronomers to observe light directly from planets around other stars, or exoplanets. Once demonstrated on Roman, similar technologies on a future mission could enable astronomers to use that light to identify chemicals in an exoplanet's atmosphere, potentially indicating the presence of life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26279

This pair of images shows a bite mark where NASA Curiosity rover scooped up some Martian soil left, and the scoop carrying soil.

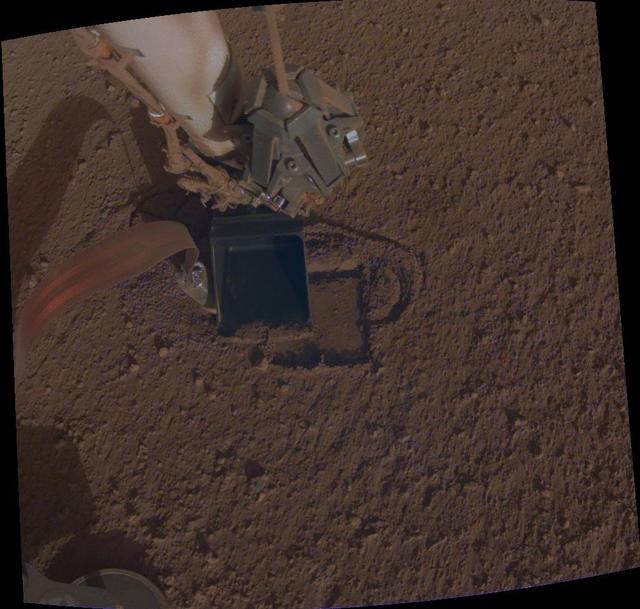
On June 28, 2019, NASA's InSight lander used its robotic arm to move the support structure for its digging instrument, informally called the "mole." This view was captured by the fisheye Instrument Context Camera under the lander's deck. Lifting the support structure had been done in three steps, a little bit at a time, to ensure the mole wasn't pulled out of the soil. Moving the structure out of the way will give the InSight team a better look at the mole and allow them to try to help it dig. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23308
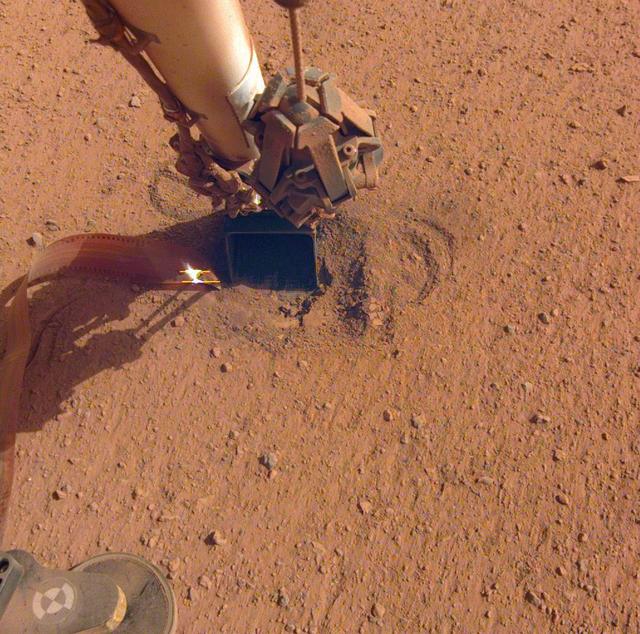

NASA's InSight lander retracted its robotic arm on Oct. 3, 2020, revealing the spot where the self-digging "mole" is attempting to burrow into the planet's surface. Attached to the mole is the copper-colored ribbon, which is laden with temperature sensors designed to measure the heat flow within Mars. In the months to come, the scoop seen on the end of the arm will be used to scrape and tamp down soil on top of the mole, in hopes of helping it dig. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24098

On June 28, 2019, NASA's InSight lander used its robotic arm to move the support structure for its digging instrument, informally called the "mole." This view was captured by the Instrument Deployment Camera on the spacecraft's robotic arm. Lifting the support structure had been done in three steps, a little bit at a time, to ensure the mole wasn't pulled out of the soil. Moving the structure out of the way will give the InSight team a better look at the mole and allow them to try to help it dig. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23309
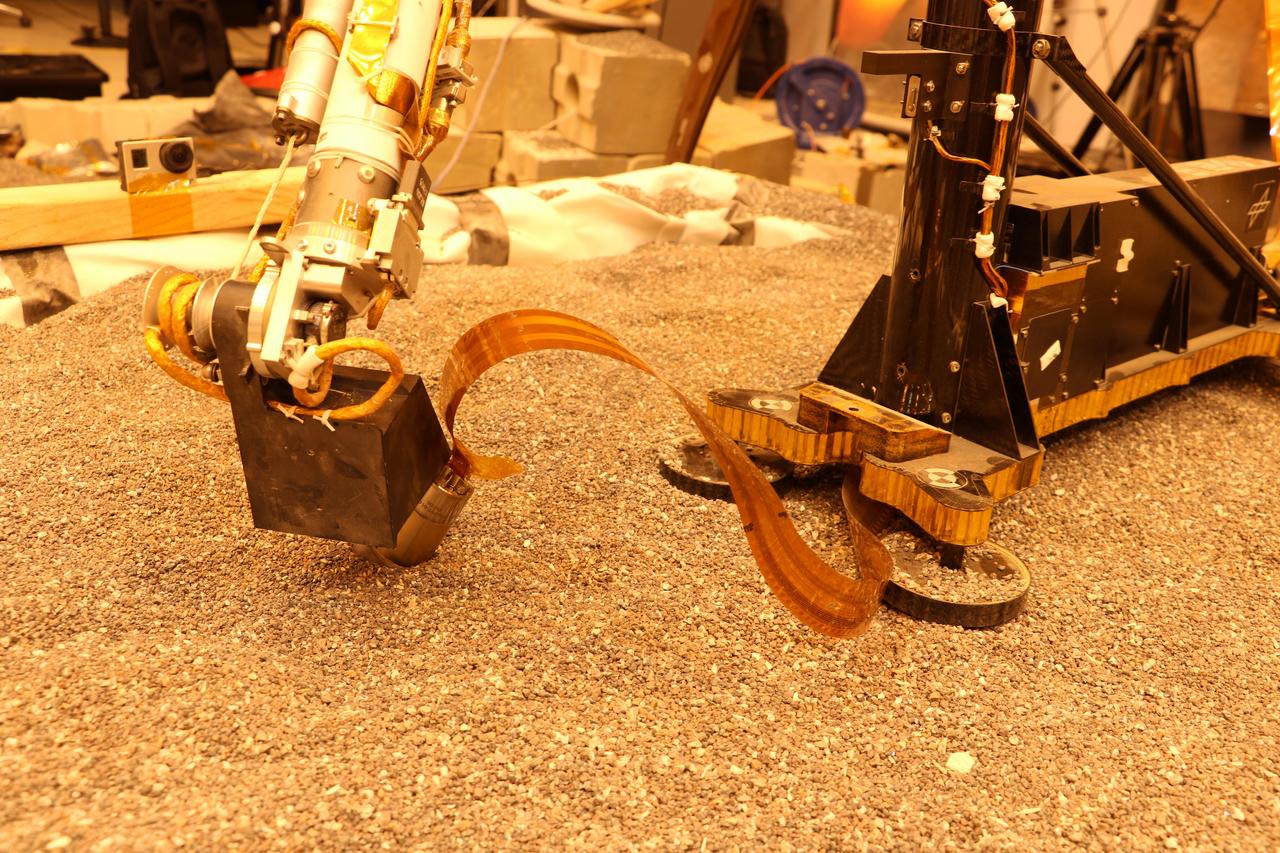

This test using an engineering model of the InSight lander here on Earth shows how the spacecraft on Mars will use its robotic arm to press on a digging device, called the "mole." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23619

This view from the navigation camera on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows tracks left by backing out of a wind-formed ripple after the rover wheels had started to dig too deeply into the dust and sand of the ripple.
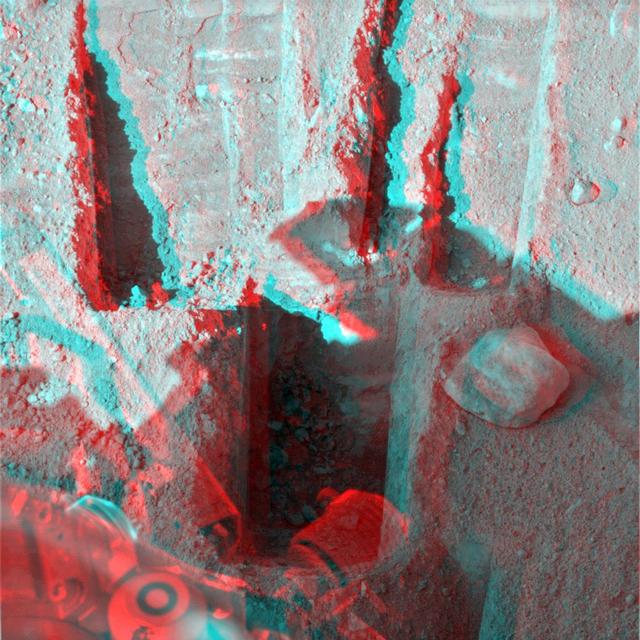
Digging by NASA Phoenix Mars Lander on Aug. 23, 2008, reached a depth about three times greater than in any trench Phoenix has excavated. 3D glasses are necessary.
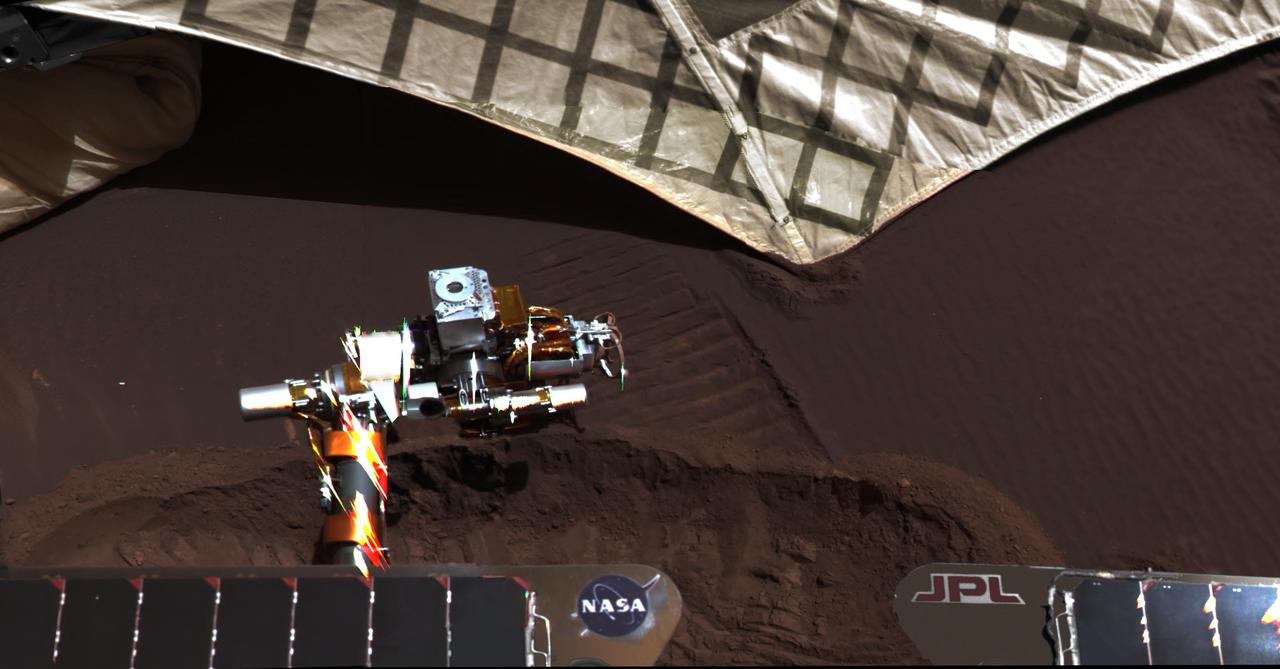

On March 20, 2004, NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity used a wheel to dig a trench revealing subsurface material beside the lander hardware that carried the rover to the surface of Mars 55 Martian days earlier.

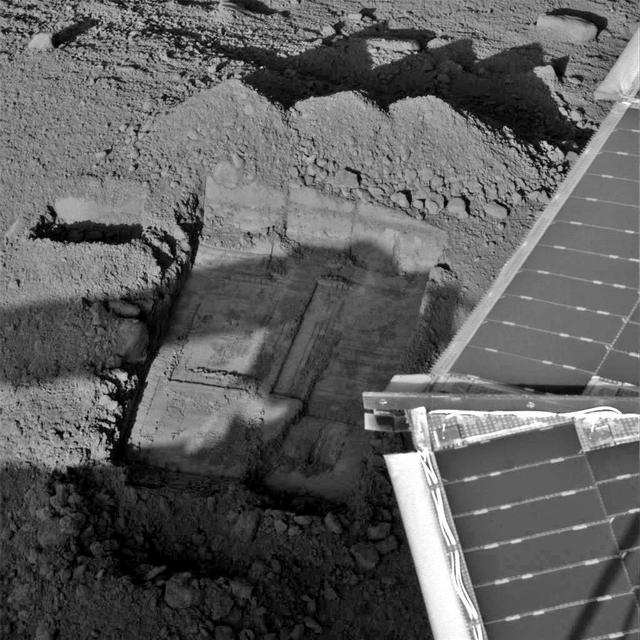
This image shows the evolution of the trench called Snow White that NASA Phoenix Mars Lander began digging on the 22nd Martian day of the mission after the May 25, 2008, landing.

This image was taken by NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander's Robotic Arm Camera (RAC) on the ninth Martian day of the mission, or Sol 9 (June 3, 2008). The center of the image shows a trench informally called "Dodo" after the second dig. "Dodo" is located within the previously determined digging area, informally called "Knave of Hearts." The light square to the right of the trench is the Robotic Arm's Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Probe (TECP). The Robotic Arm has scraped to a bright surface which indicated the Arm has reached a solid structure underneath the surface, which has been seen in other images as well. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10763

The annotated area of Mars in this illustration holds near-surface water ice that would be easily accessible for astronauts to dig up. The water ice was identified as part of a map using data from NASA orbiters. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23515

Two rambunctious young stars are destroying their natal dust cloud with powerful jets of radiation, in an infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
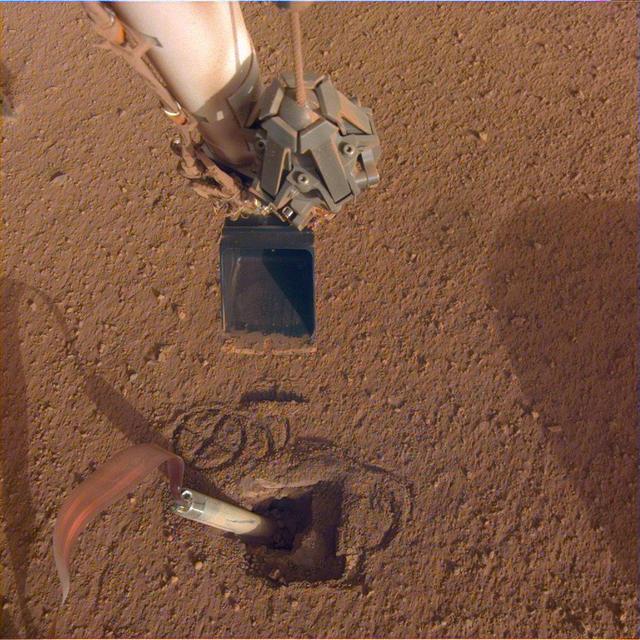
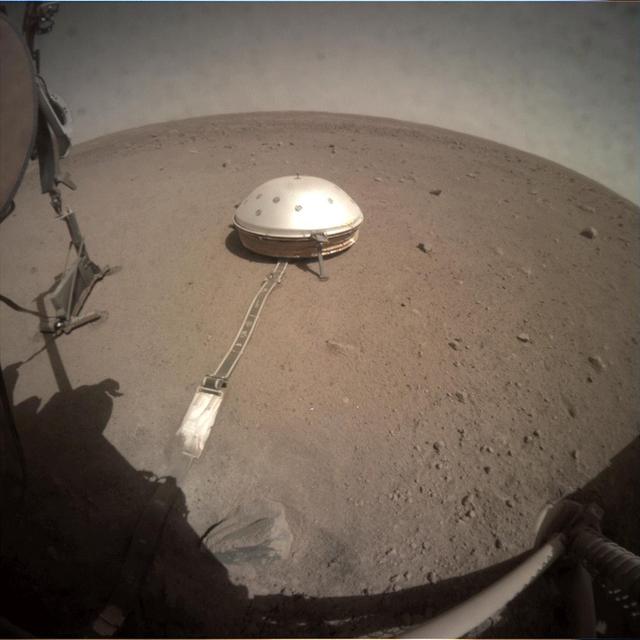
NASA's Mars InSight lander recently moved its robotic arm closer to the heat probe's digging device, called the "mole," in preparation to push on its top, or back cap. The InSight team hopes that pushing on this location will help the mole it bury itself and enable the heat probe to take Mars' temperature. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23622
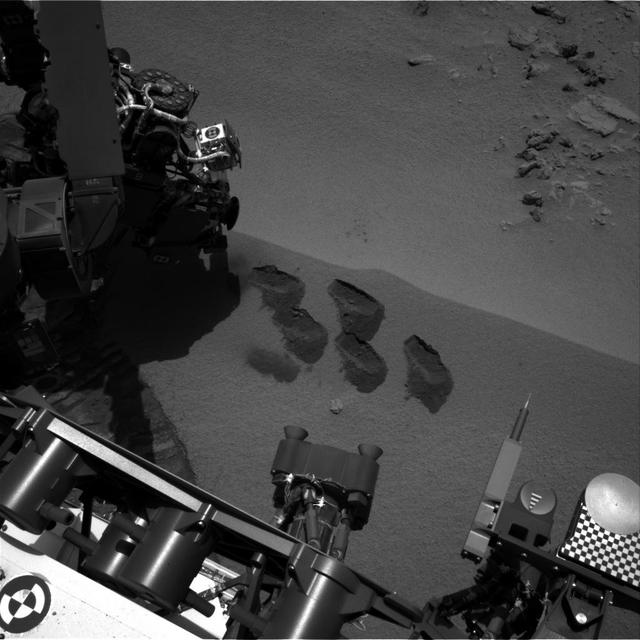

NASA Mars rover Curiosity used a mechanism on its robotic arm to dig up five scoopfuls of material from a patch of dusty sand called Rocknest, producing the five bite-mark pits visible in this image from the rover left Navigation Camera Navcam.
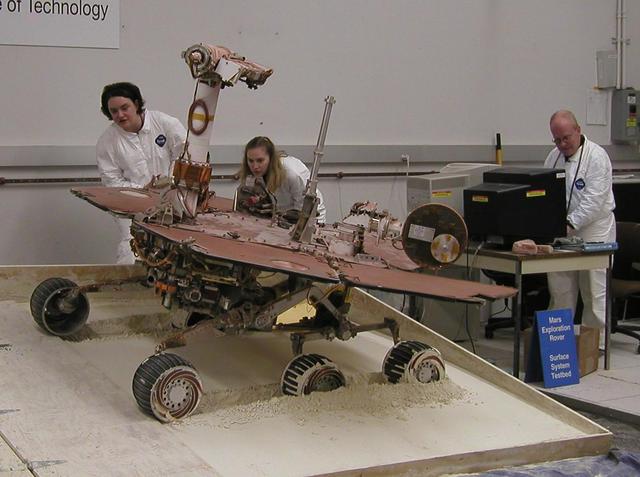

While a test rover rolls off a plywood surface into a prepared bed of soft soil, rover team members Colette Lohr left and Kim Lichtenberg center eye the wheels digging into the soil and Paolo Bellutta enters the next driving command.
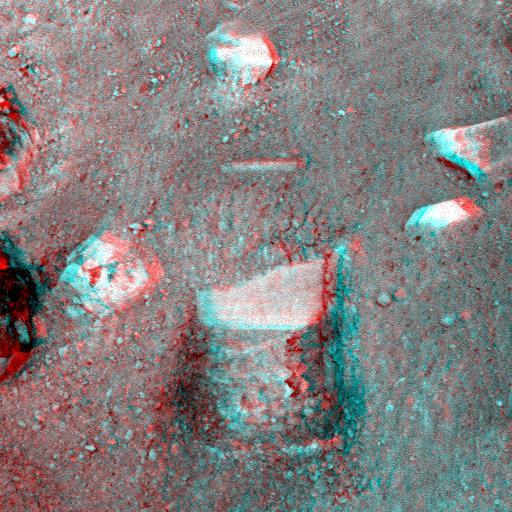
This anaglyph image, acquired by NASA’s Phoenix Lander’s Surface Stereo Imager on June 1, 2008, shows a stereoscopic 3D view of the so-called Knave of Hearts first-dig test area to the north of the lander. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

Mars Exploration Rover team members on July 21, 2009, tested how altering the order in which individual wheels turn for steering affects how those turns dig the wheels deeper into soft soil. From left: Alfonso Herrera, Vandana Verma, Bruce Banerdt.
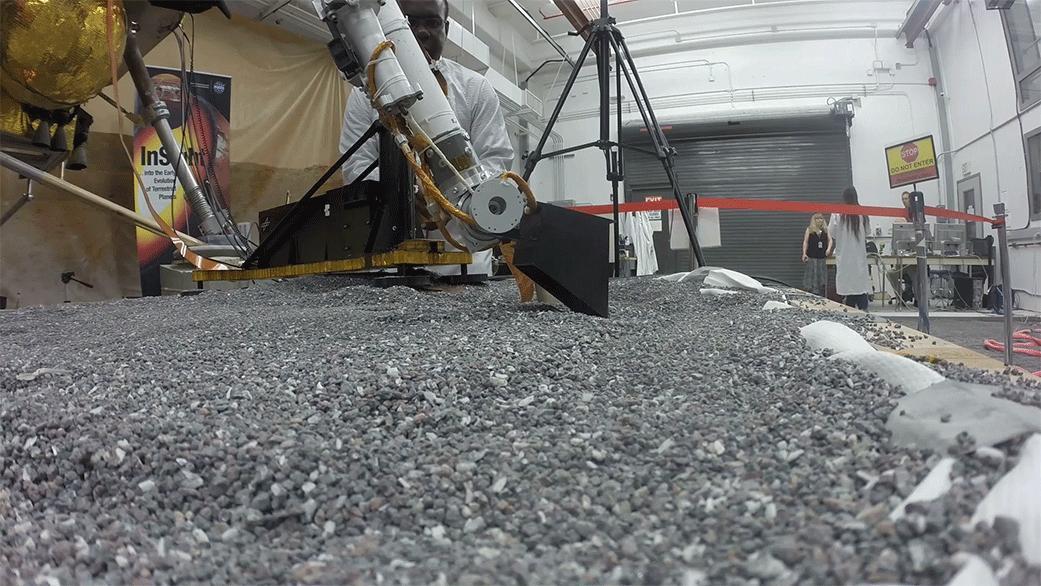

This footage from Aug. 19, 2019, shows a replica of InSight scraping soil with a scoop on the end of its robotic arm in a test lab at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. A replica of the "mole" — the lander's self-hammering heat probe — comes in to view as the scoop moves to the left. On Mars, InSight will use techniques practiced by engineers on Earth in order to scrape and tamp down soil on top of the mole to help it dig. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24099
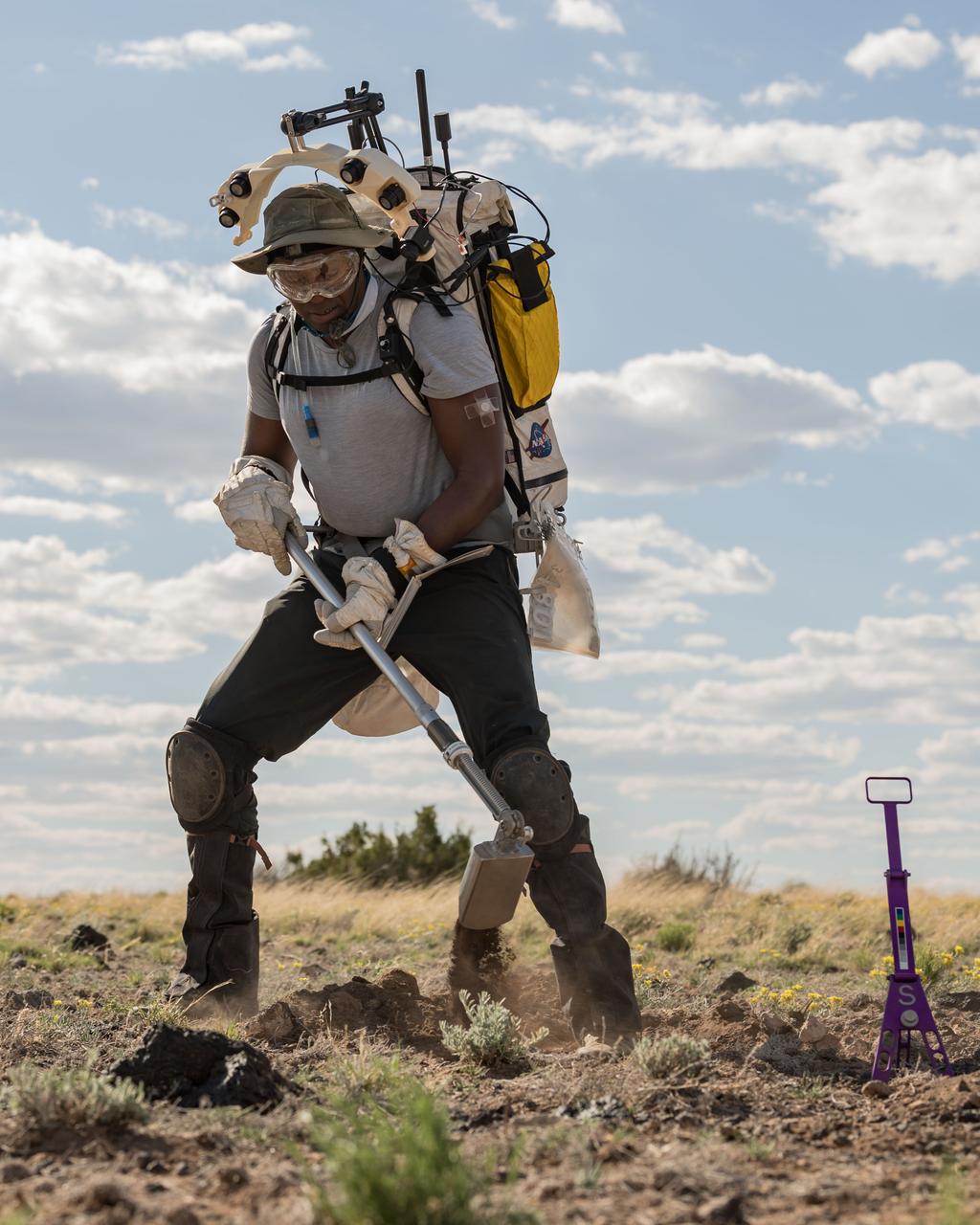

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas uses a scoop to dig into the ground to collect geologic samples during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
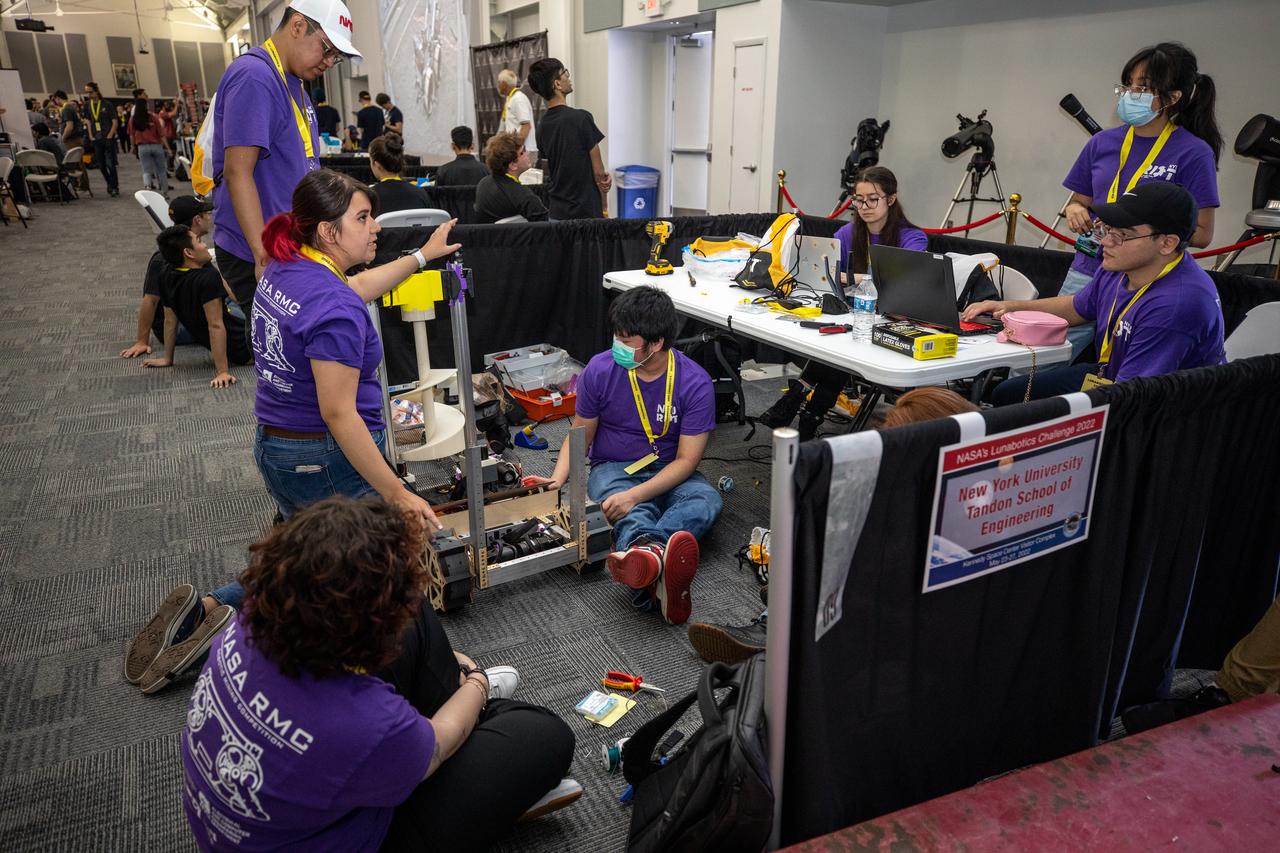

Students from the New York University Tandon School of Engineering prepare their robot for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
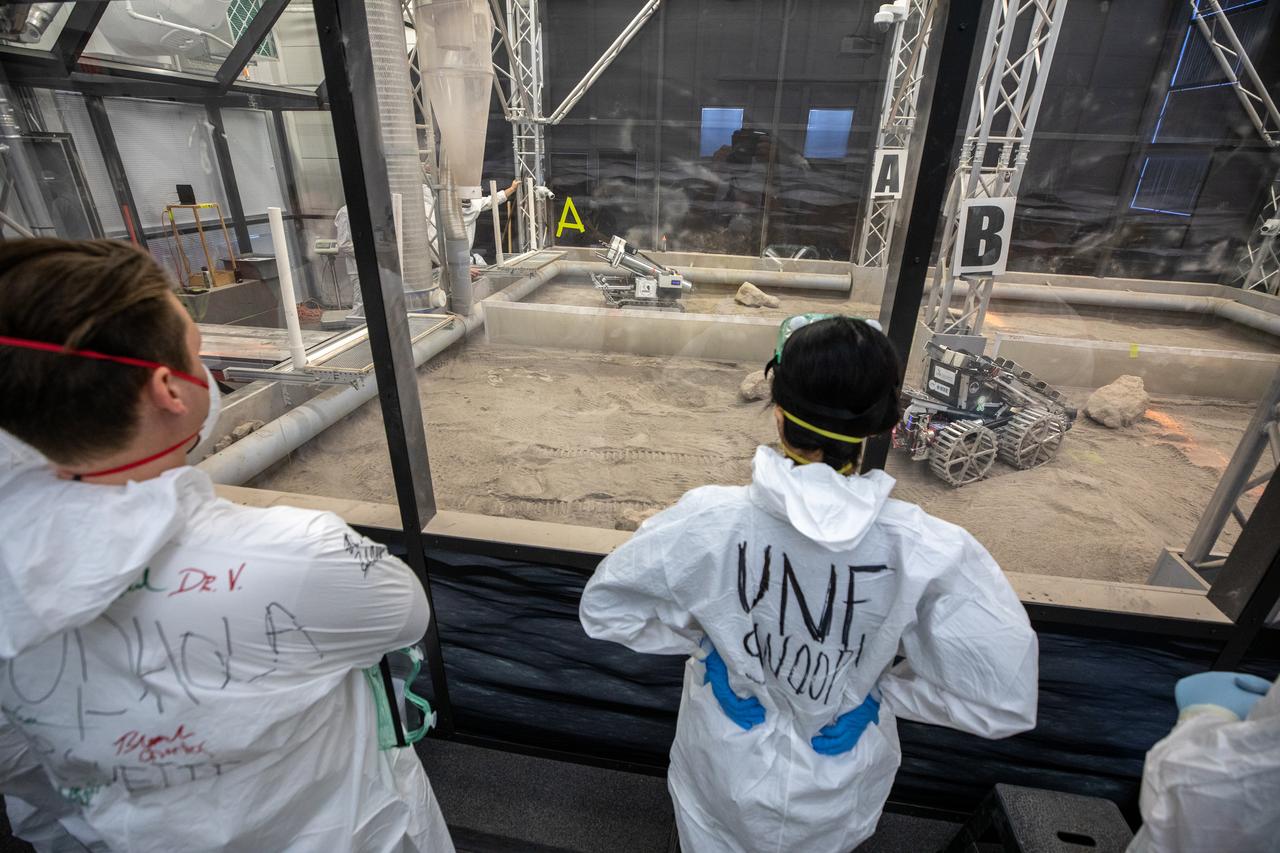

Team members from the University of North Florida watch their robotic miner dig in the mining arena NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 27, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams used their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with lunar simulant and rocks. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
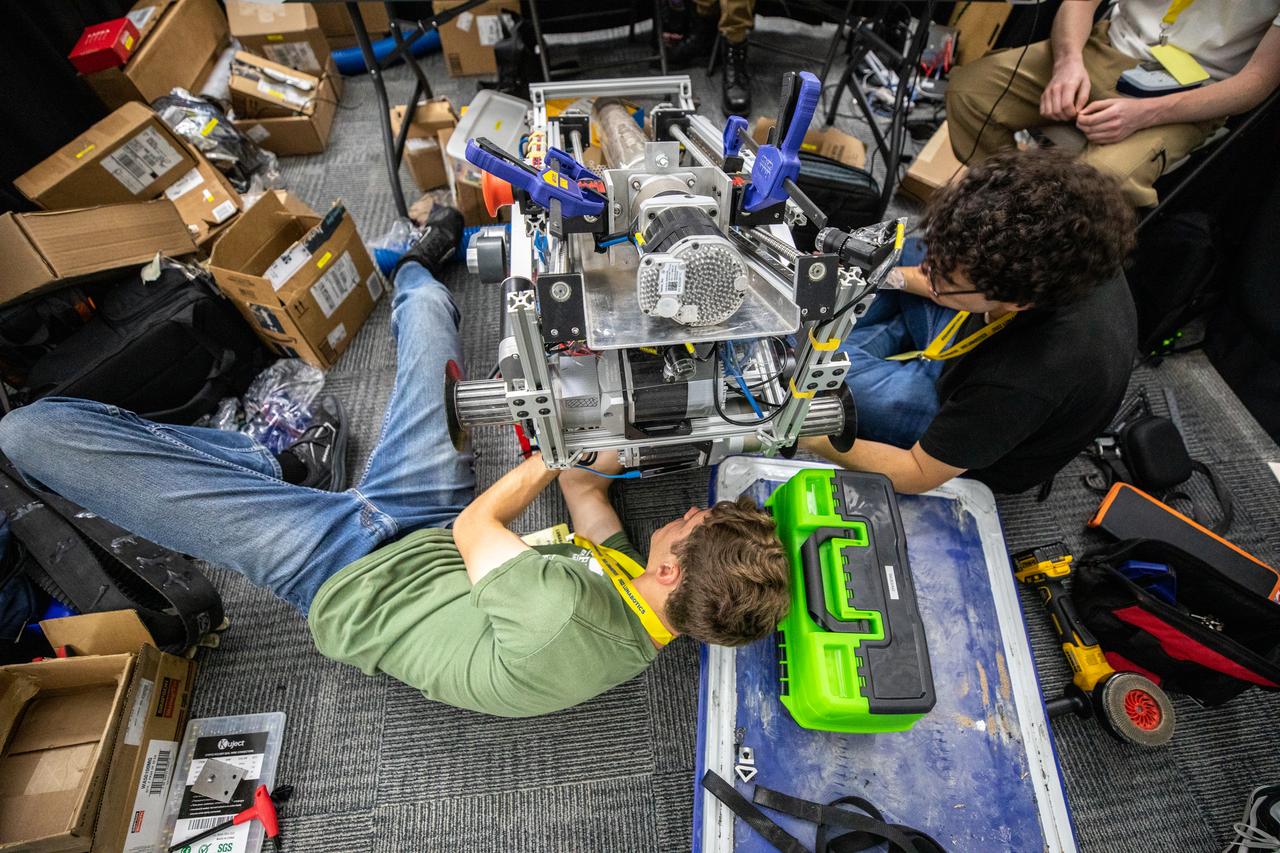

New Mexico Tech students prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
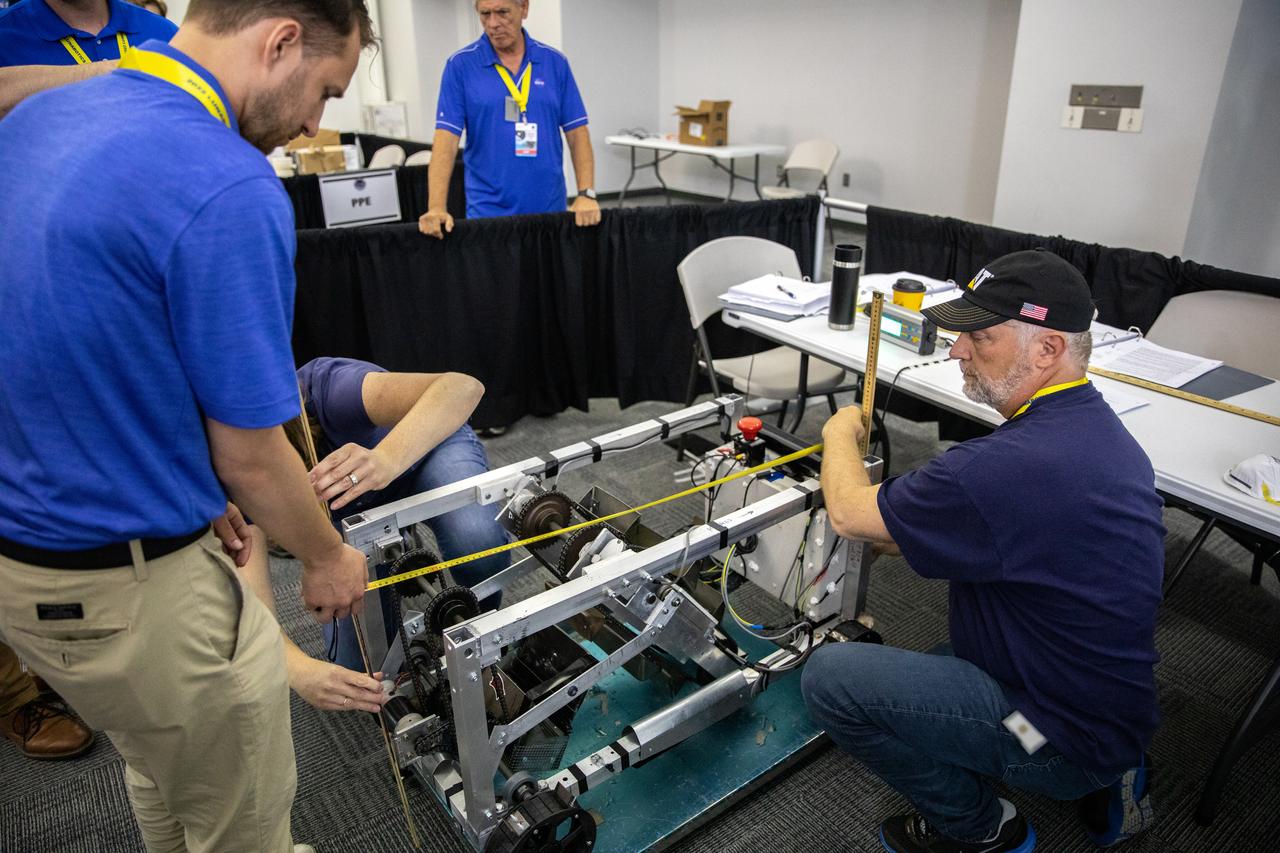

The Saginaw Valley State University team’s robotic miner is being measured and weighed to qualify for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
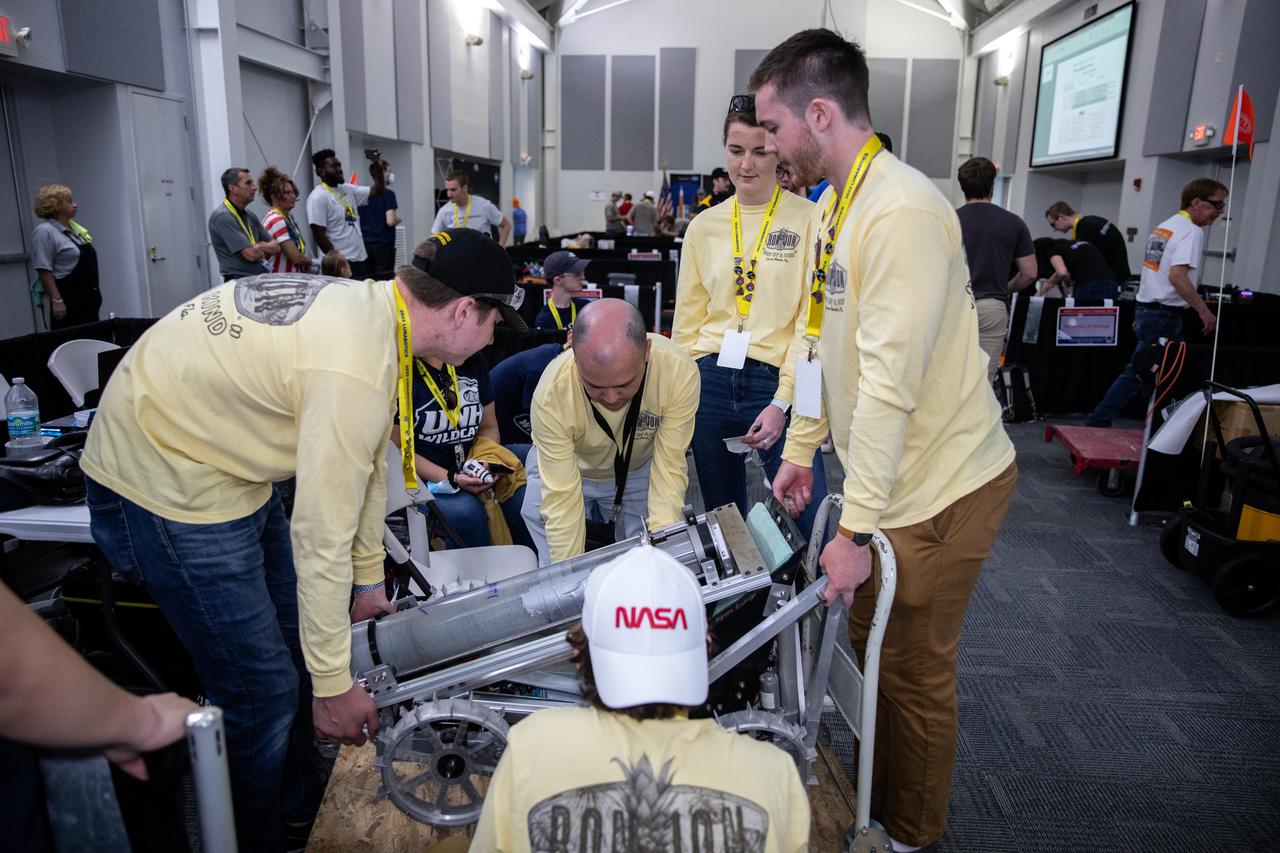

The University of New Hampshire’s robotic miner is placed on a cart to record its measurements and weight before the school’s team prepares it for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 27, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with lunar simulant and rocks. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
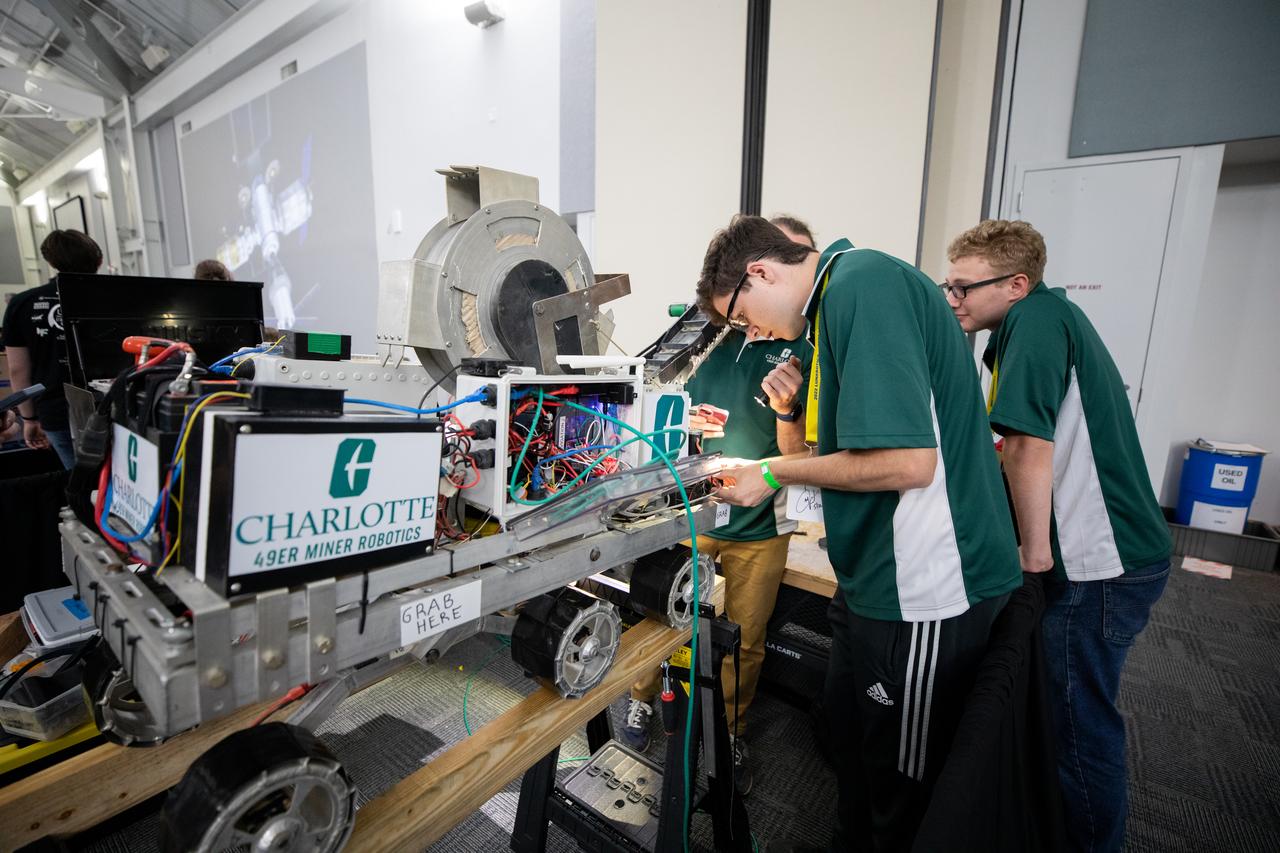

Students from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
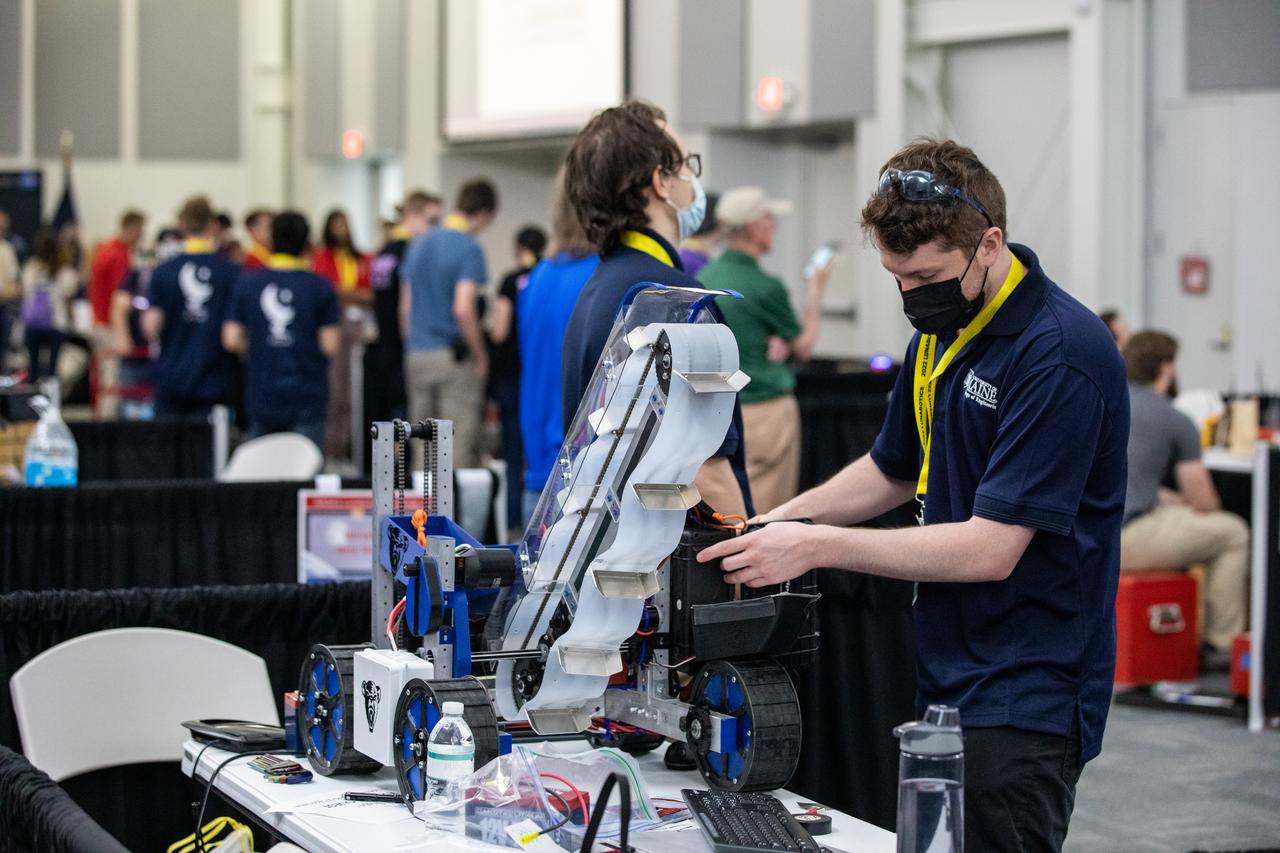

A team member from the University of Maine prepares their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
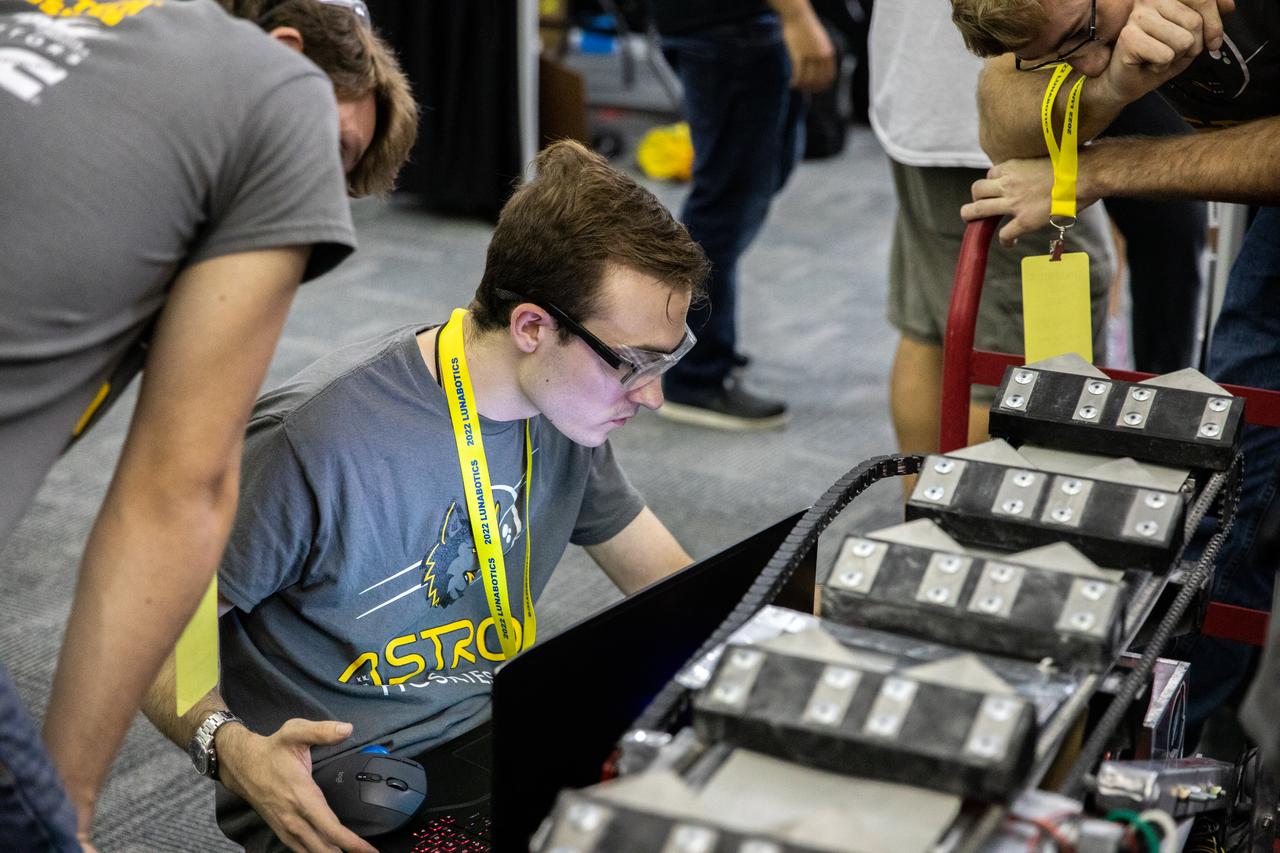

Students from the University of Rochester prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
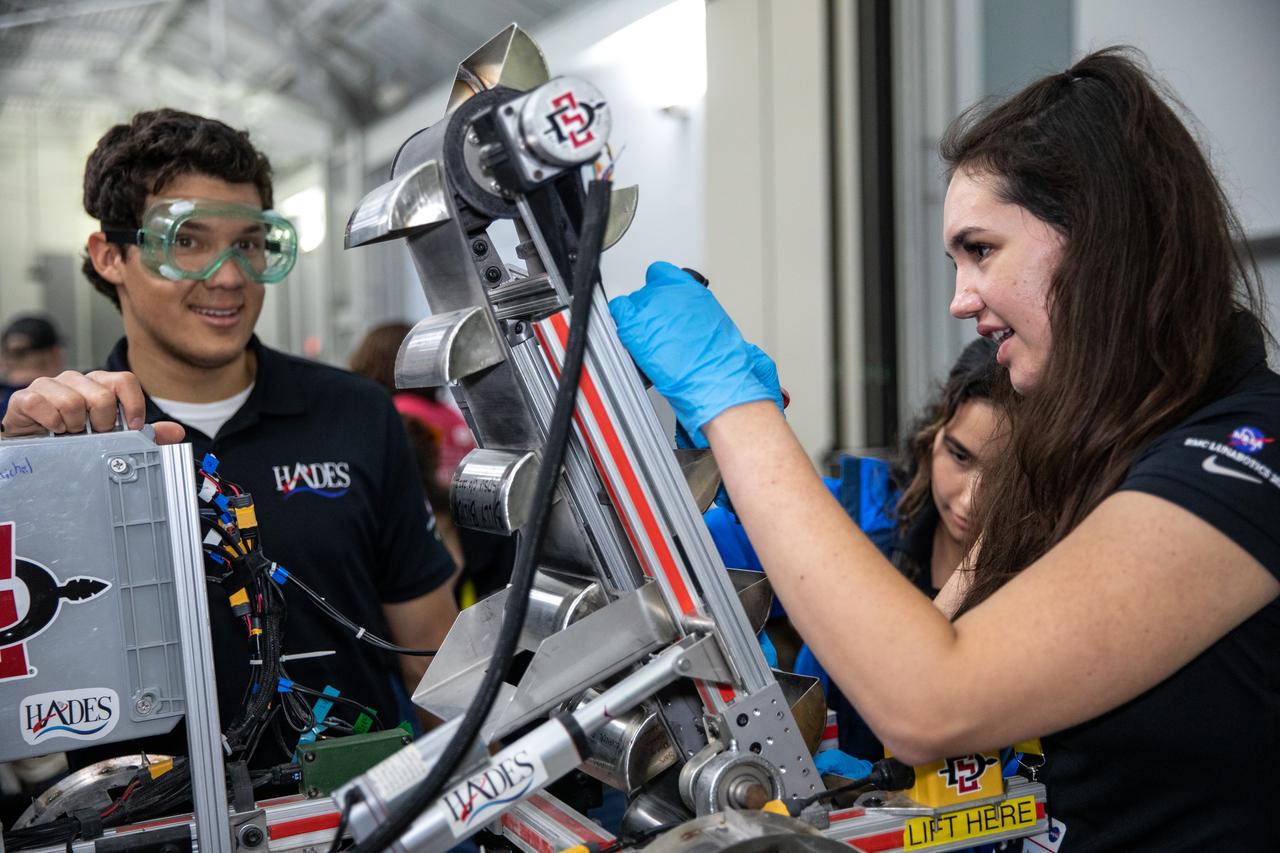

Students from San Diego State College prepare their robotic miner for its second turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 27, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams used their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with lunar simulant and rocks. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
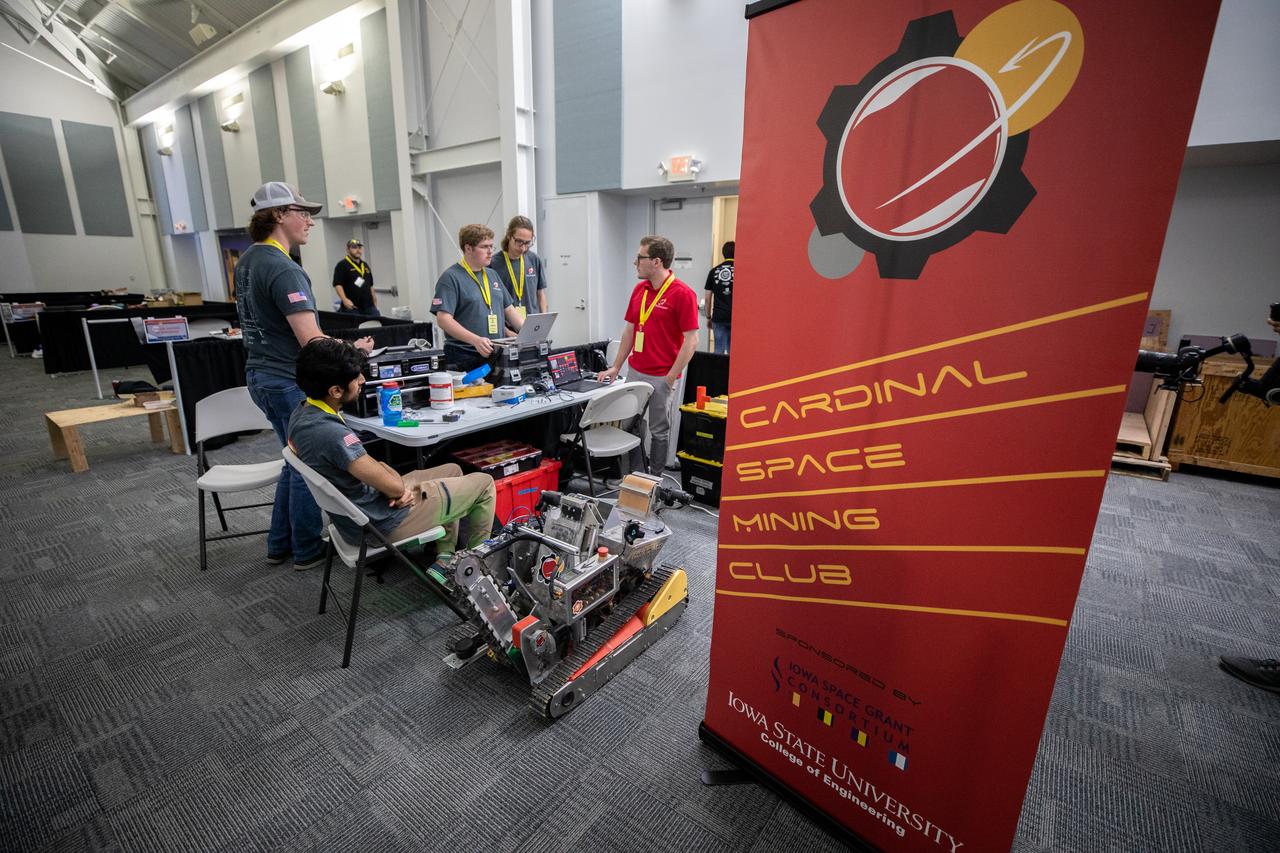

Students from Iowa State University College students prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
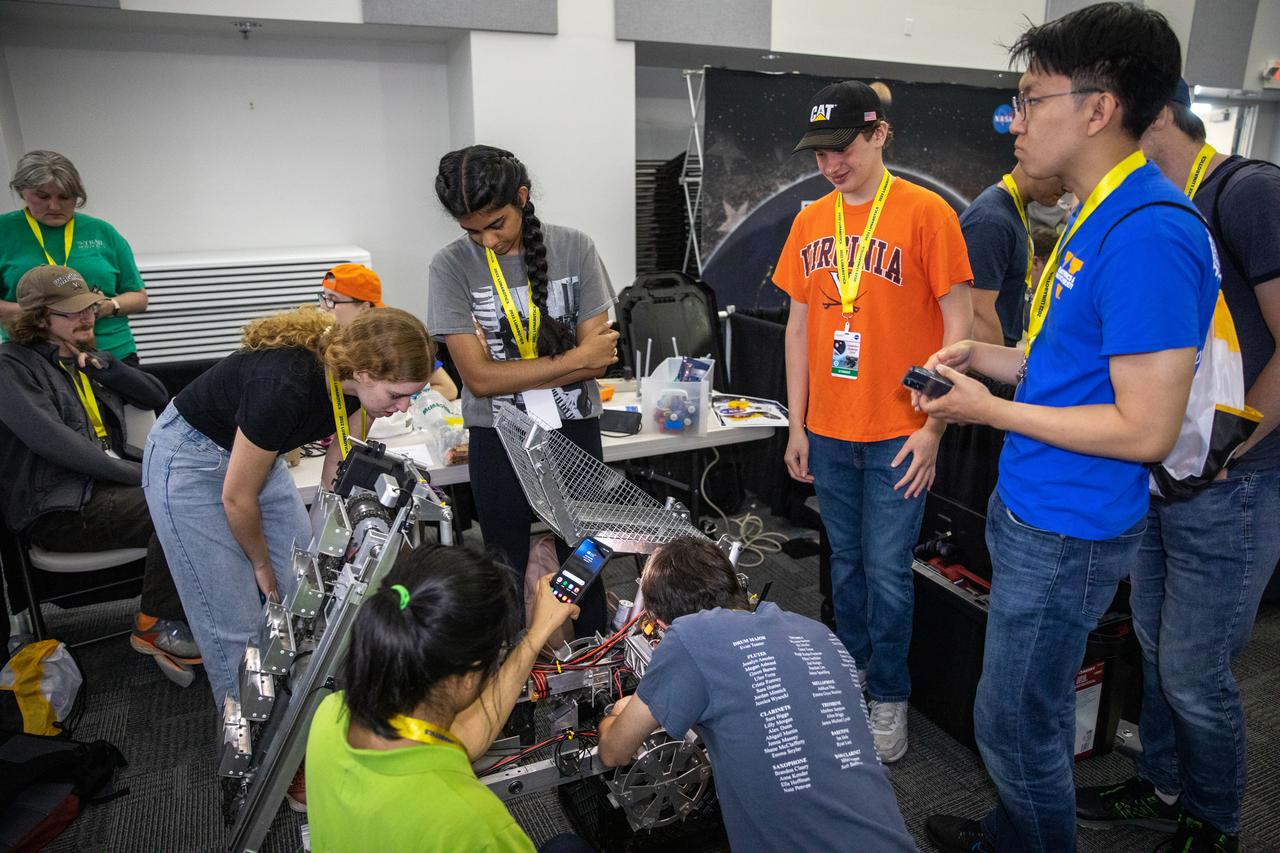

Students from the University of Virginia prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
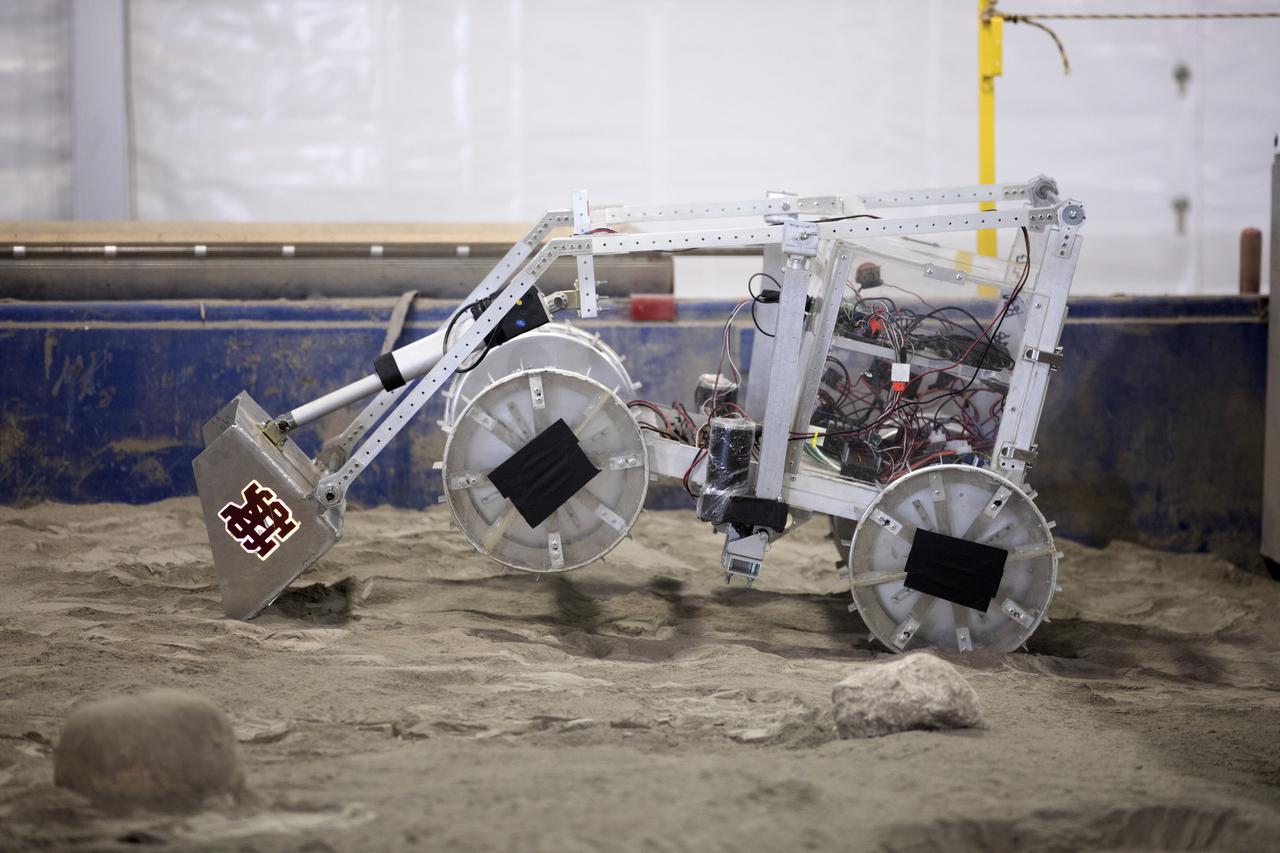
The robotic miner from Mississippi State University digs in the mining arena during NASA's 8th Annual Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. are using their uniquely-designed mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Martian soil, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's Journey to Mars.
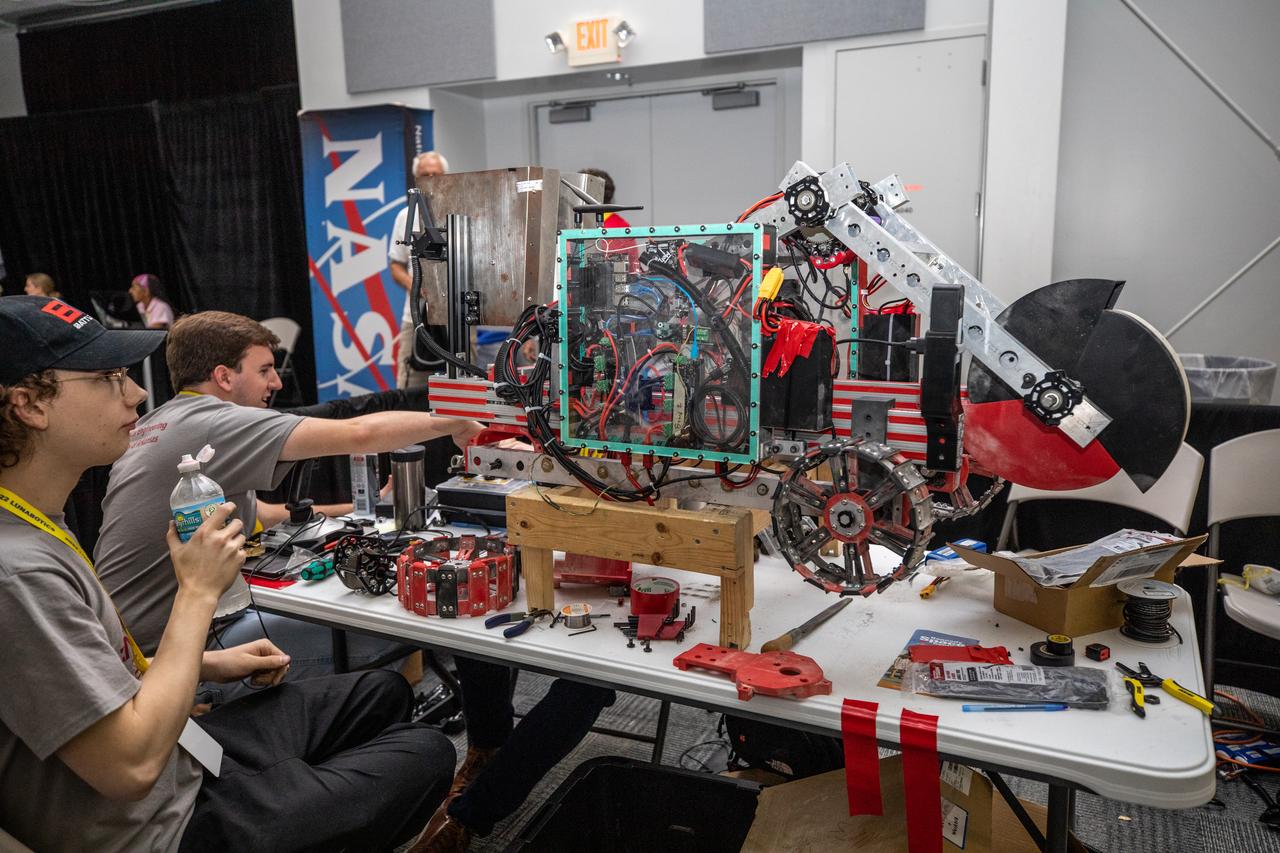

Students from the University of Arkansas prepare their robot for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
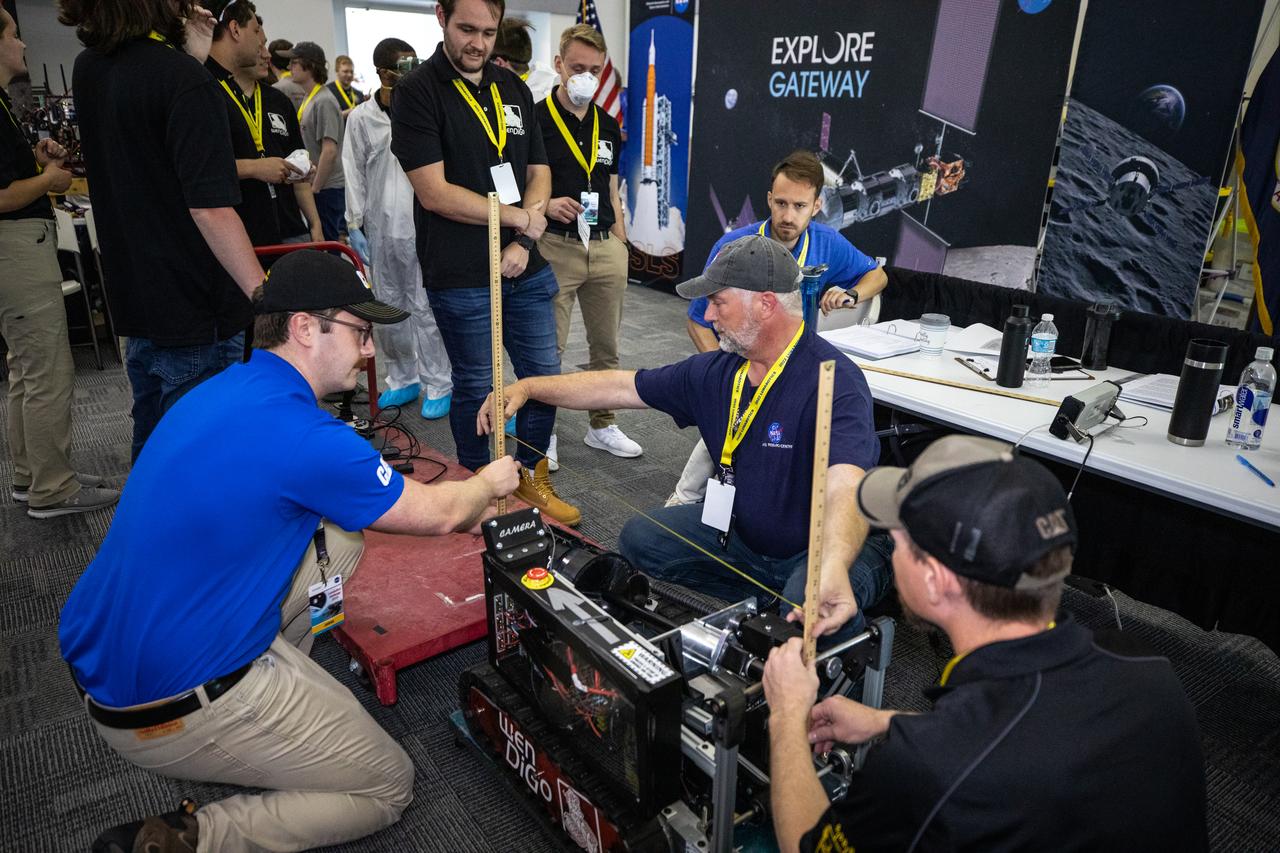

Students from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
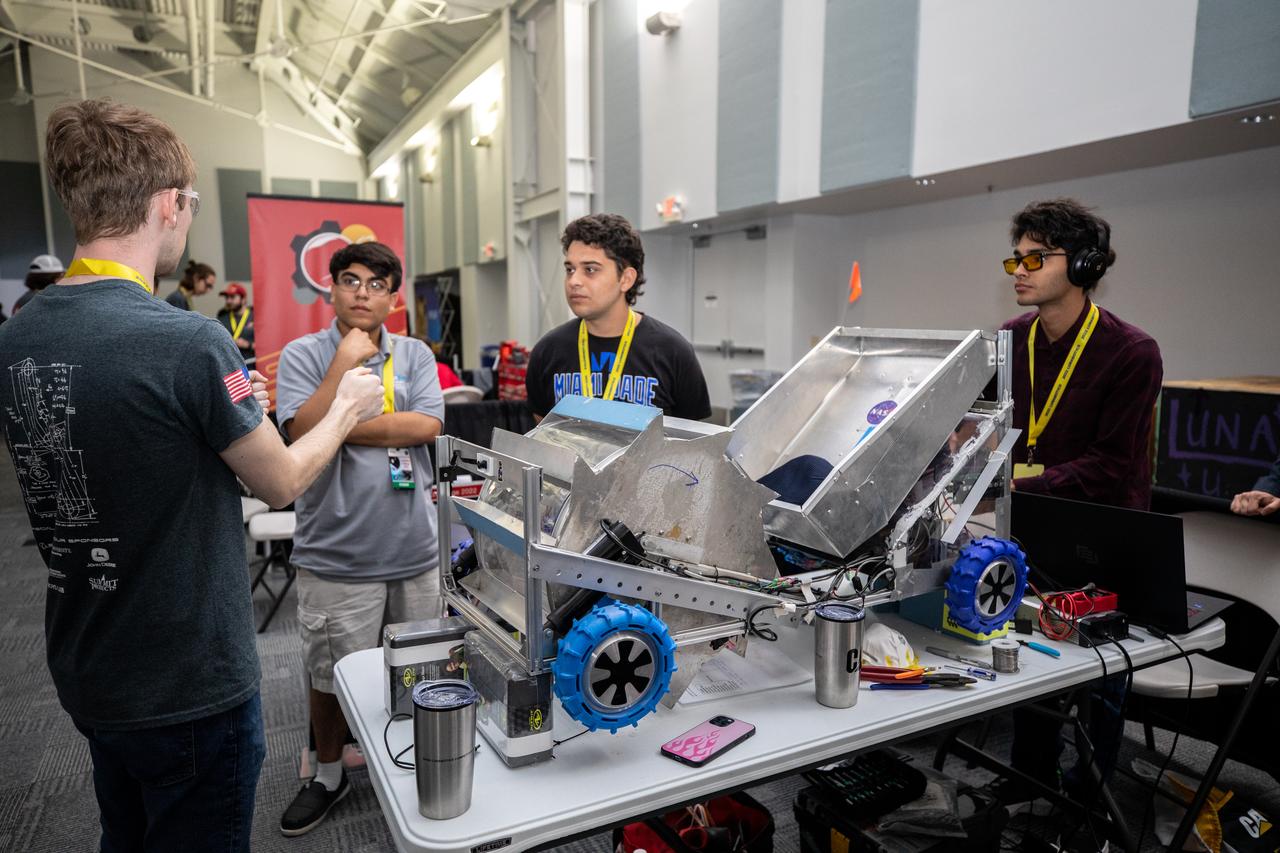

Students from Miami-Dade College at Kendall prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
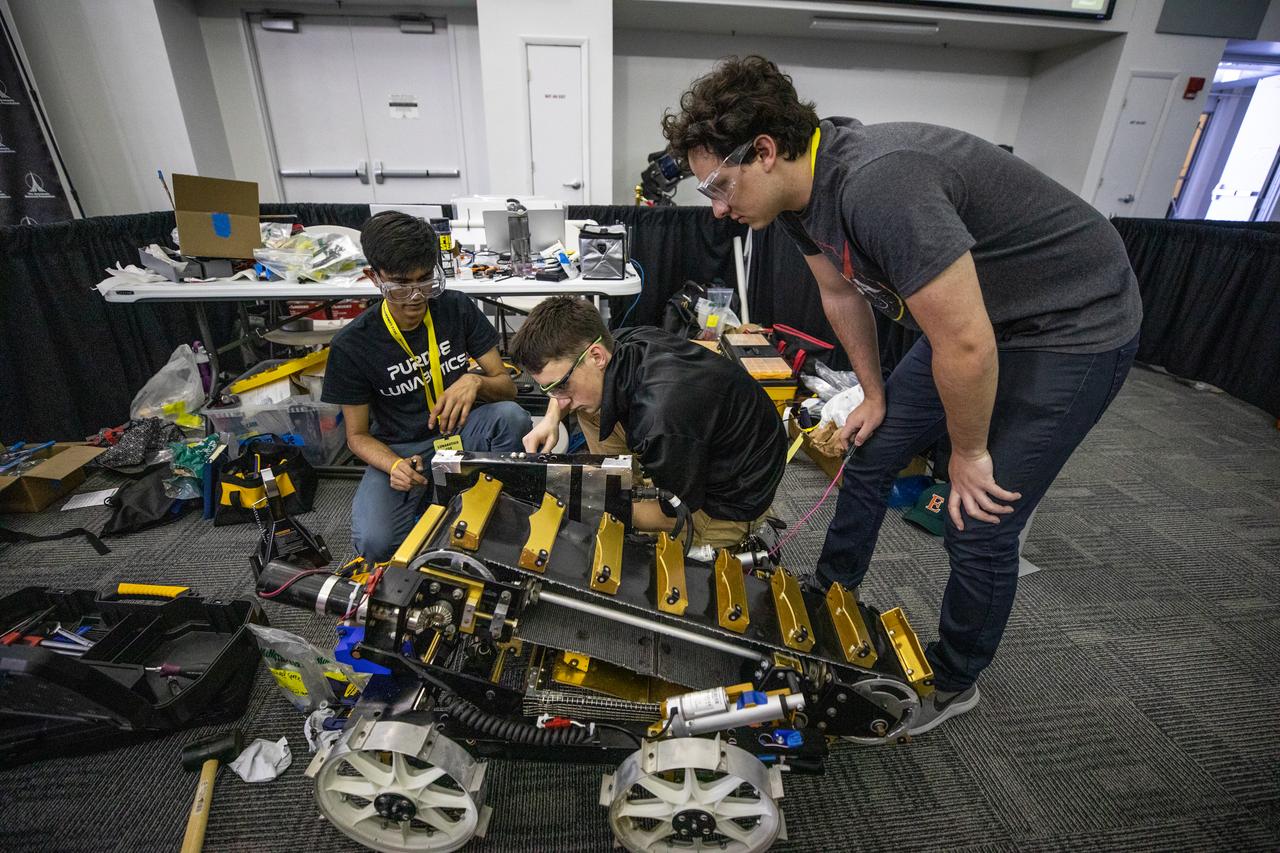

Students from Purdue University prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining pit during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
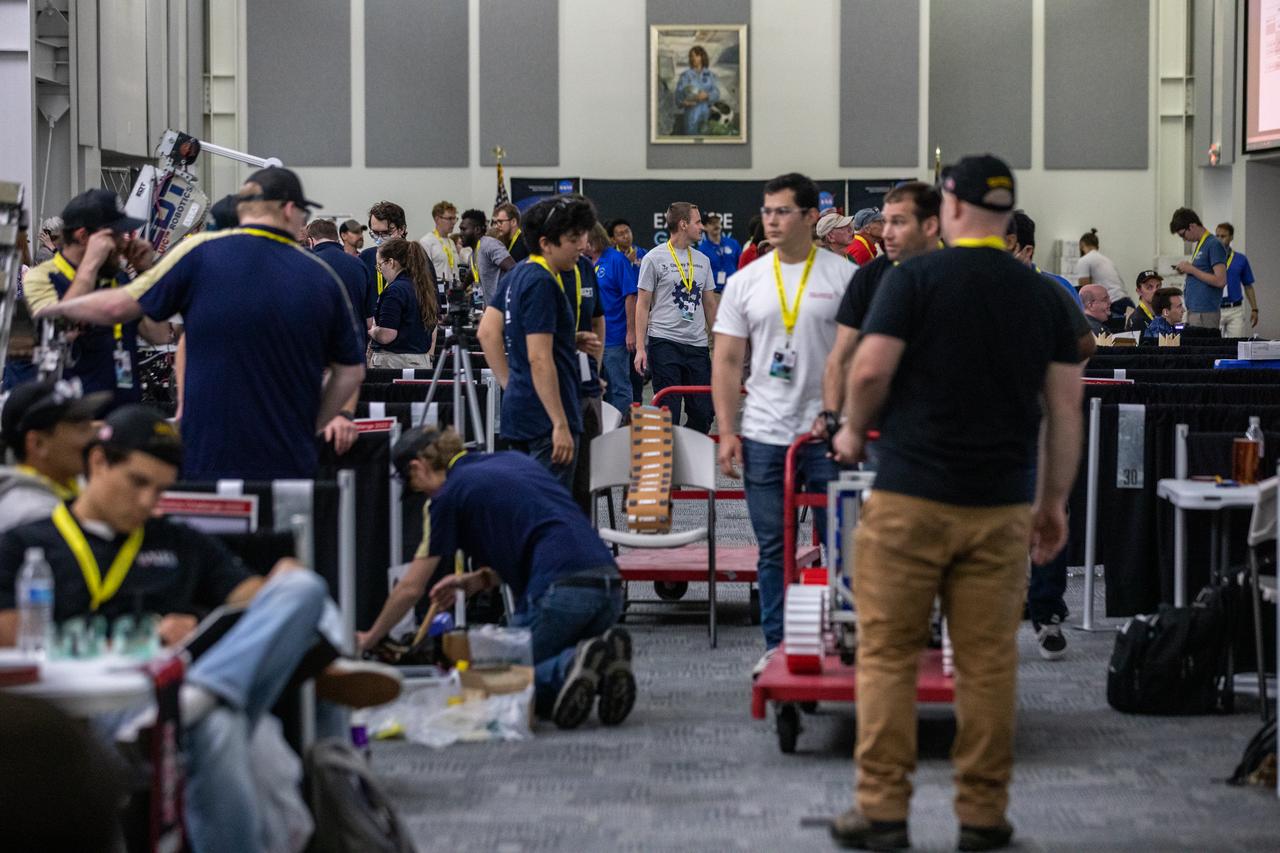

College teams prepare their robotic miners for their turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
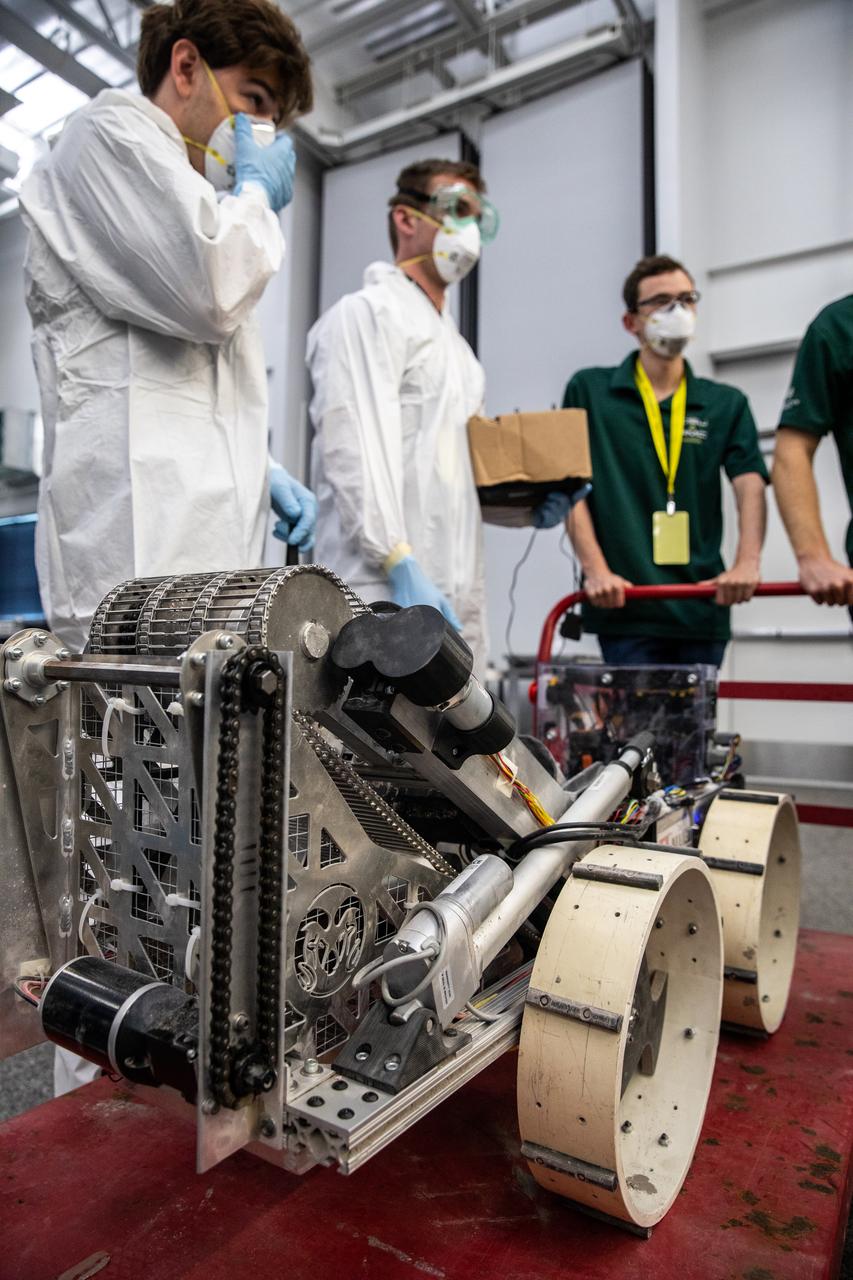
Students from Colorado State University prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.

Students from the University of Illinois at Chicago prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
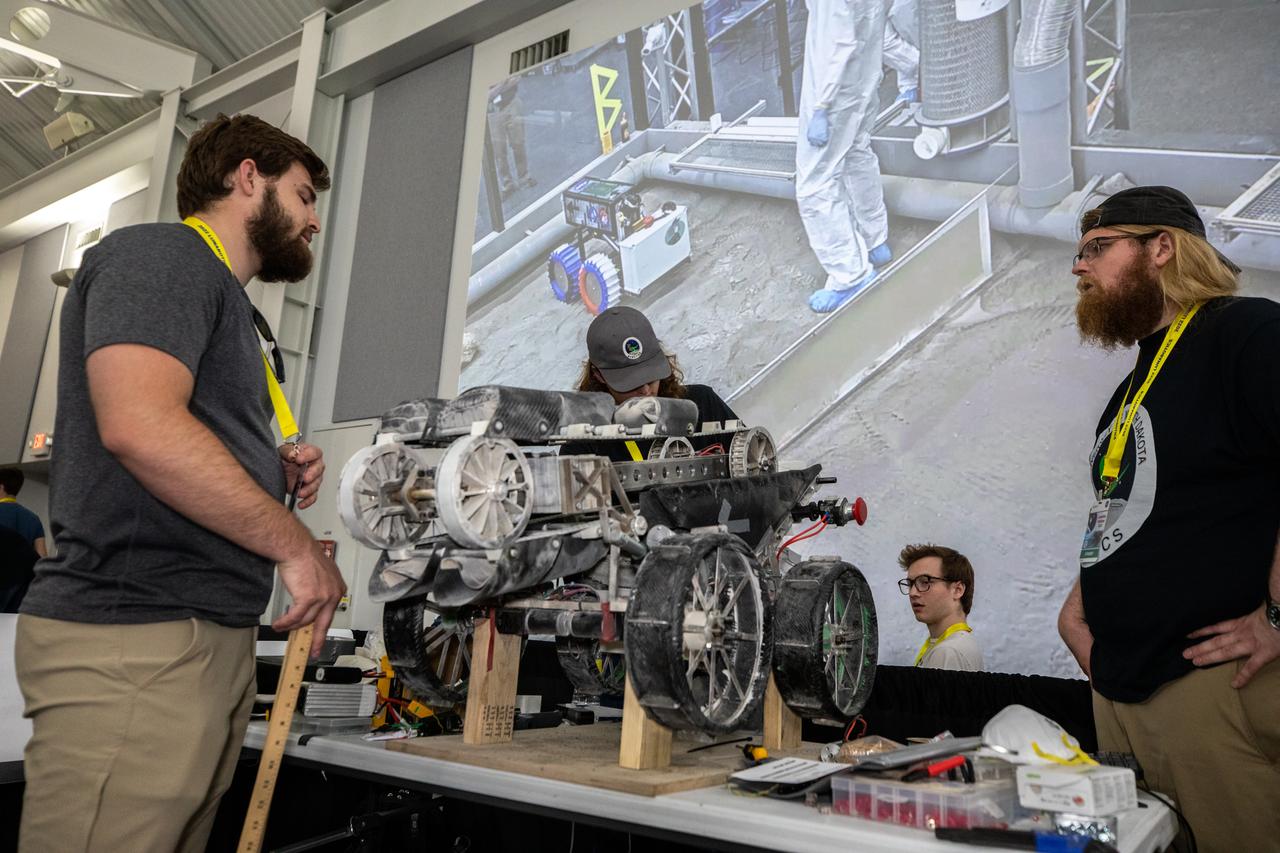
Students from the University of North Dakota prepare their robot miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
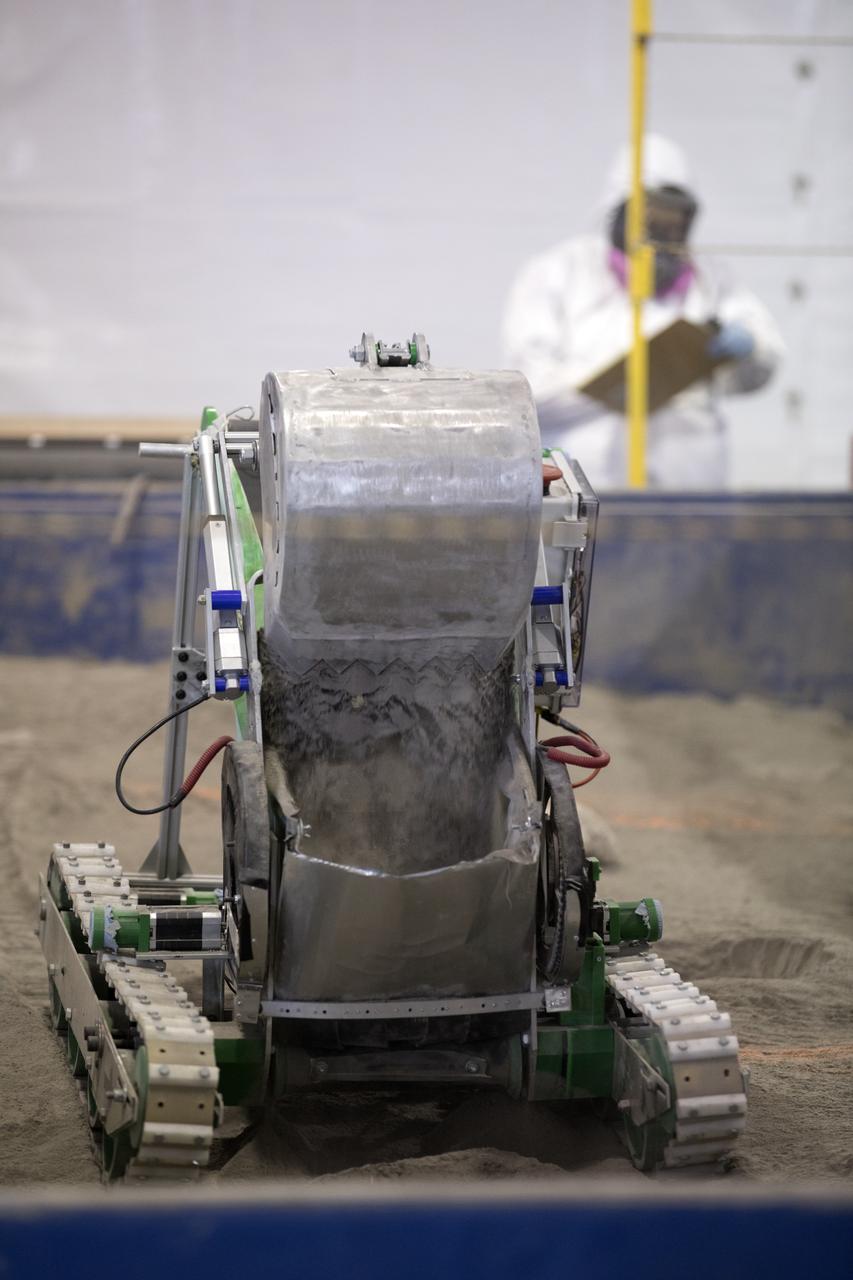

A robotic miner digs in the mining arena during NASA's 8th Annual Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. are using their uniquely-designed mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Martian soil, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's Journey to Mars.
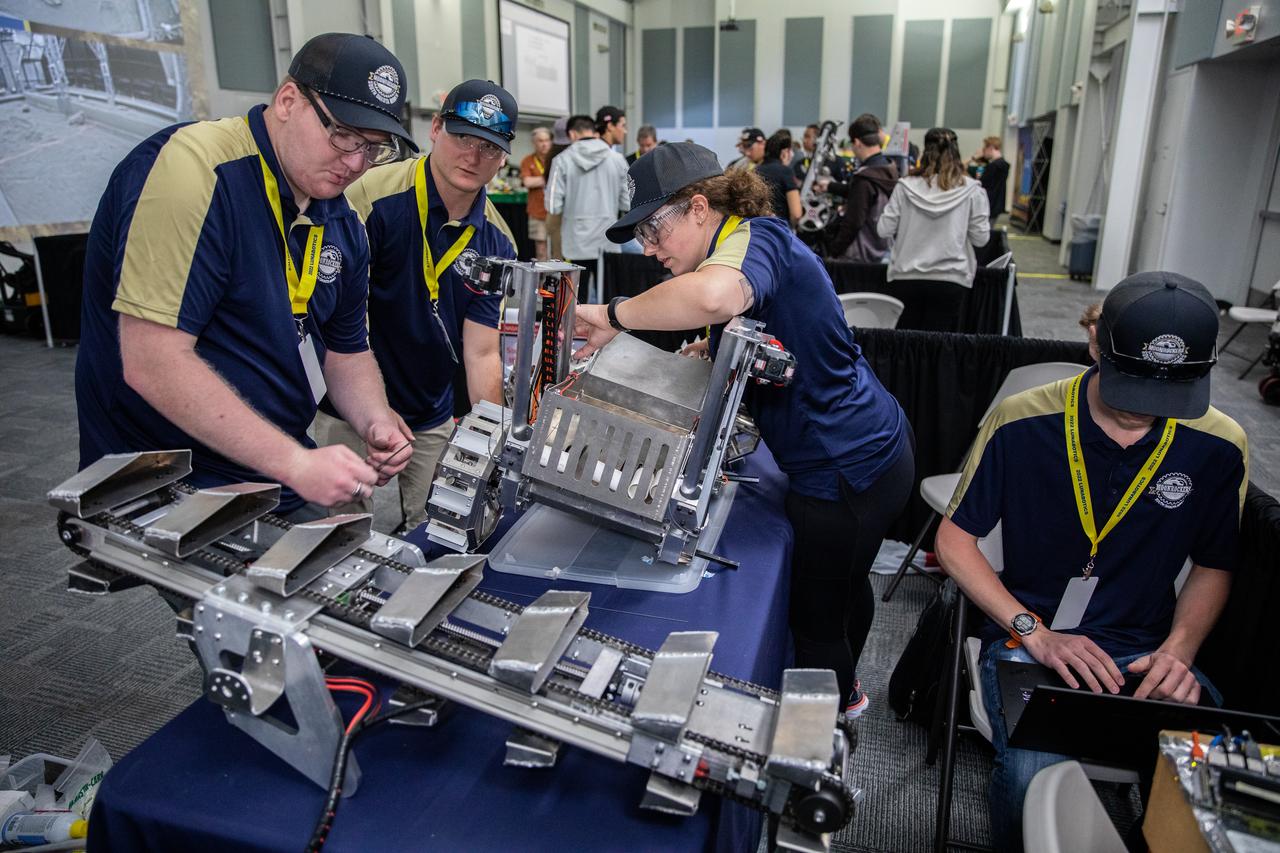

Students from the South Dakota School of Mines and Technology prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
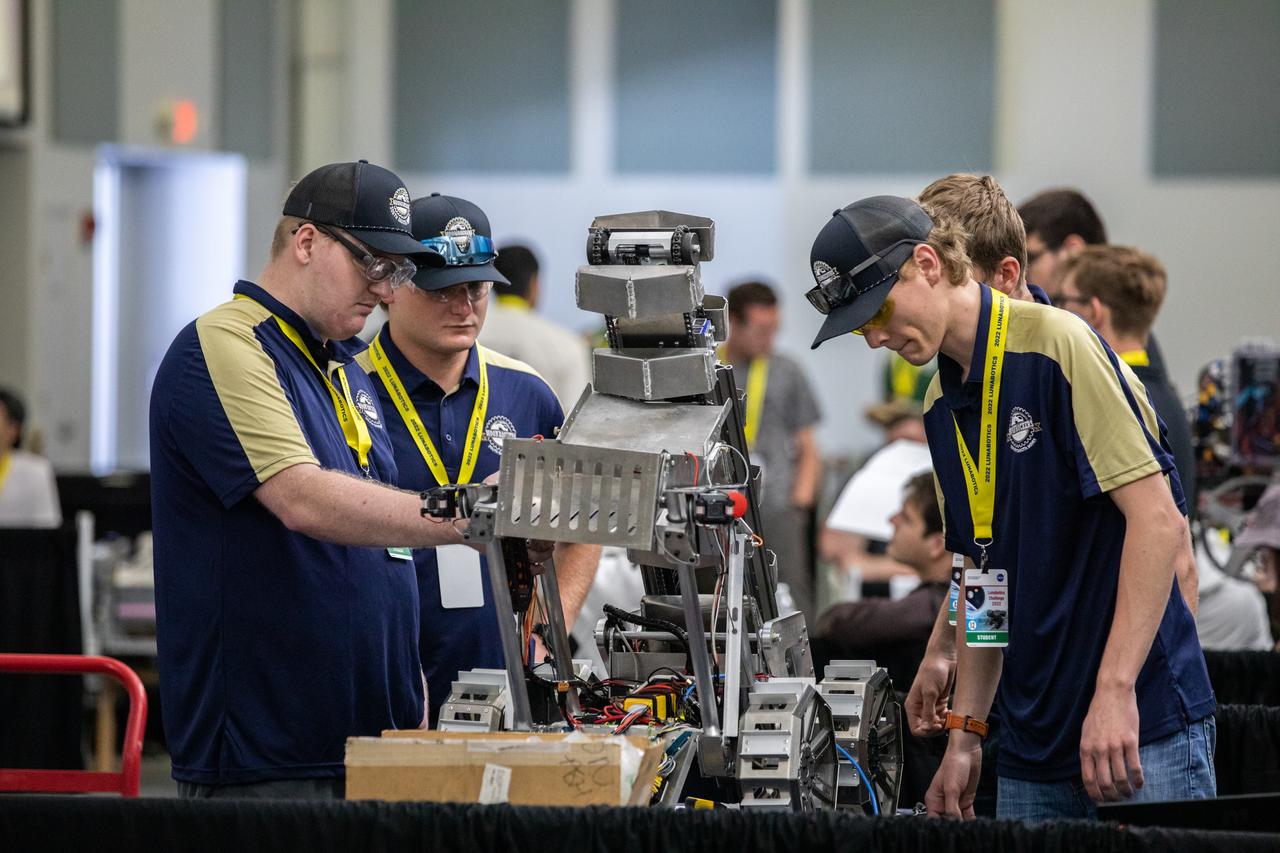

Team members from the South Dakota School of Mines and Technology prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
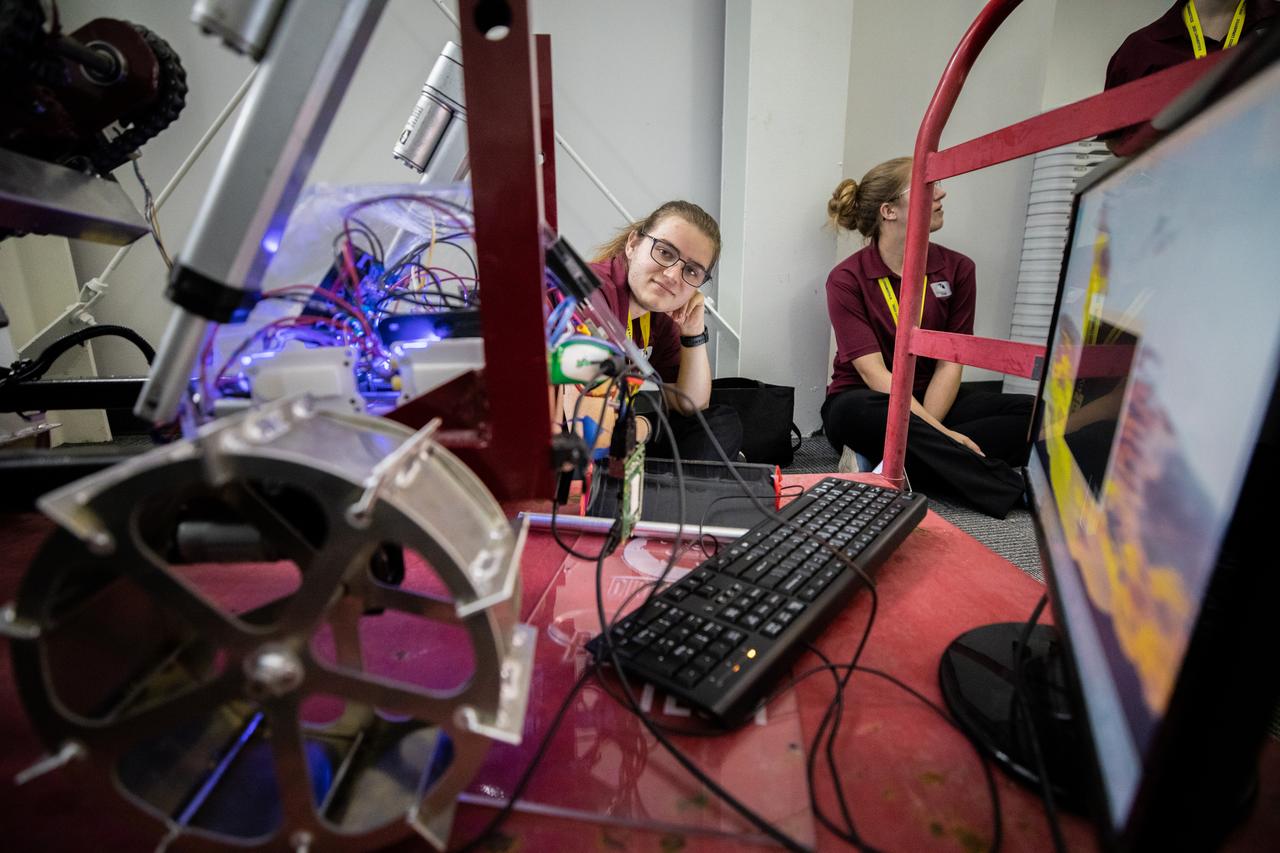

Students with Florida Technological University prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
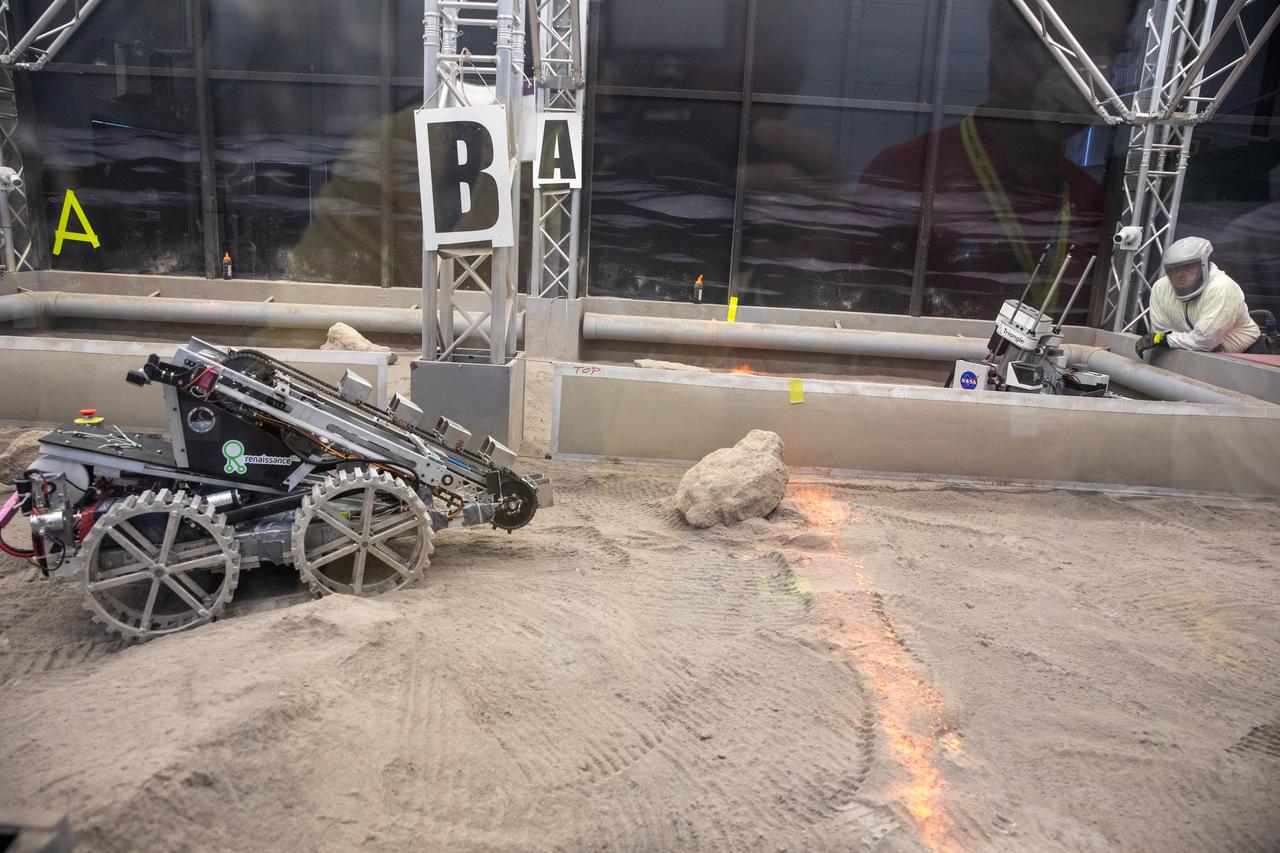
A robotic miner from Marquette University in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, prepares to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 27, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 college and university teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with lunar simulant and rocks. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
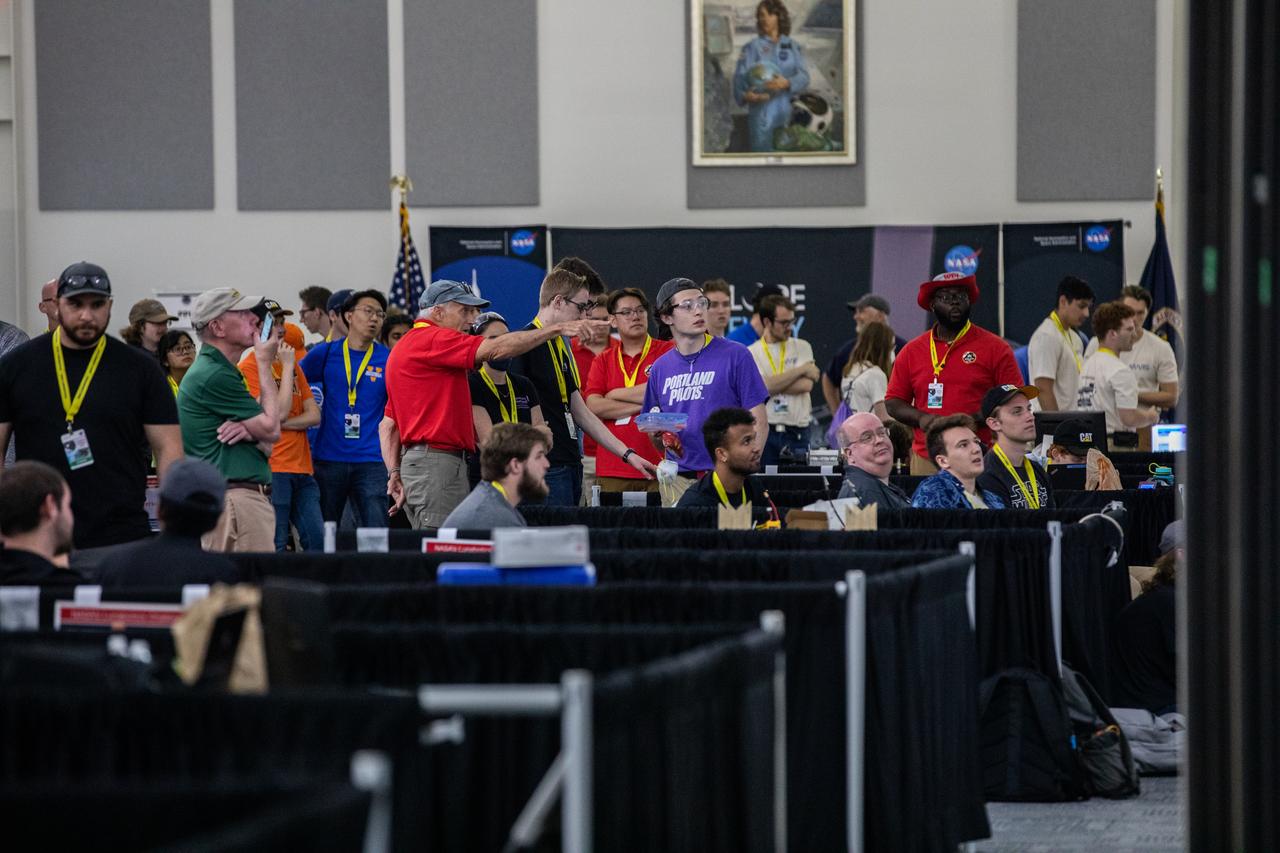

Team members from various colleges and universities watch a jumbo screen as robotic miners dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
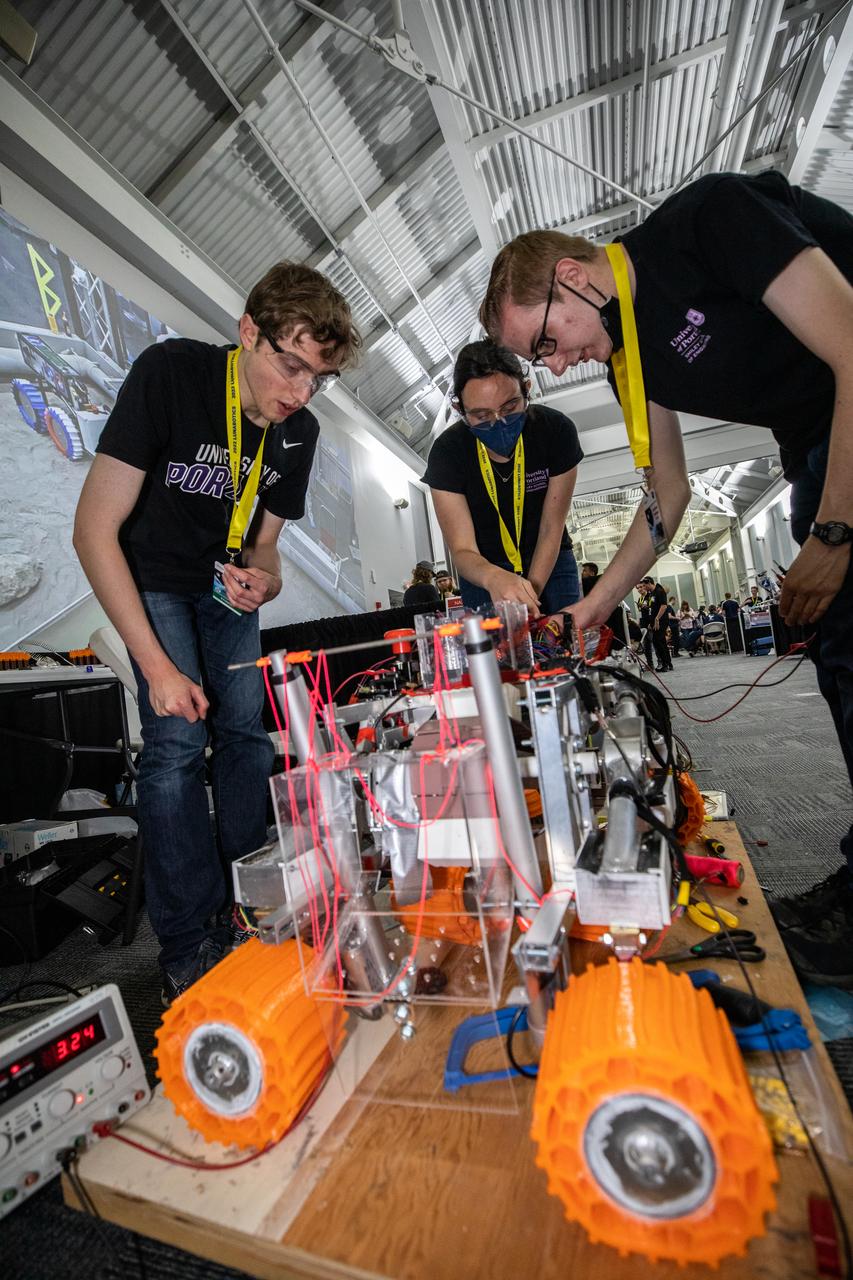
Students from the University of Portland in Oregon prepare their robot miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.

Students from California State University, Long Beach, prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
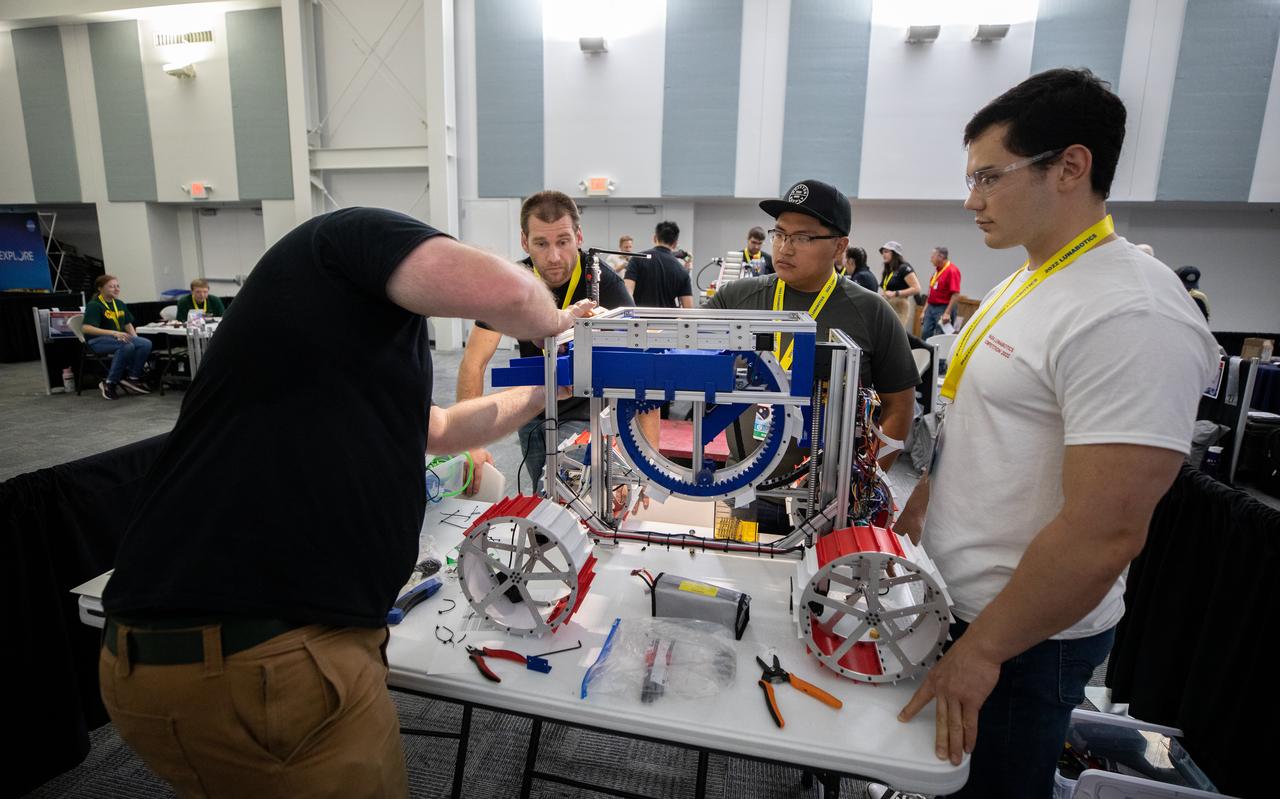

Team members from Sonoma State University in California prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
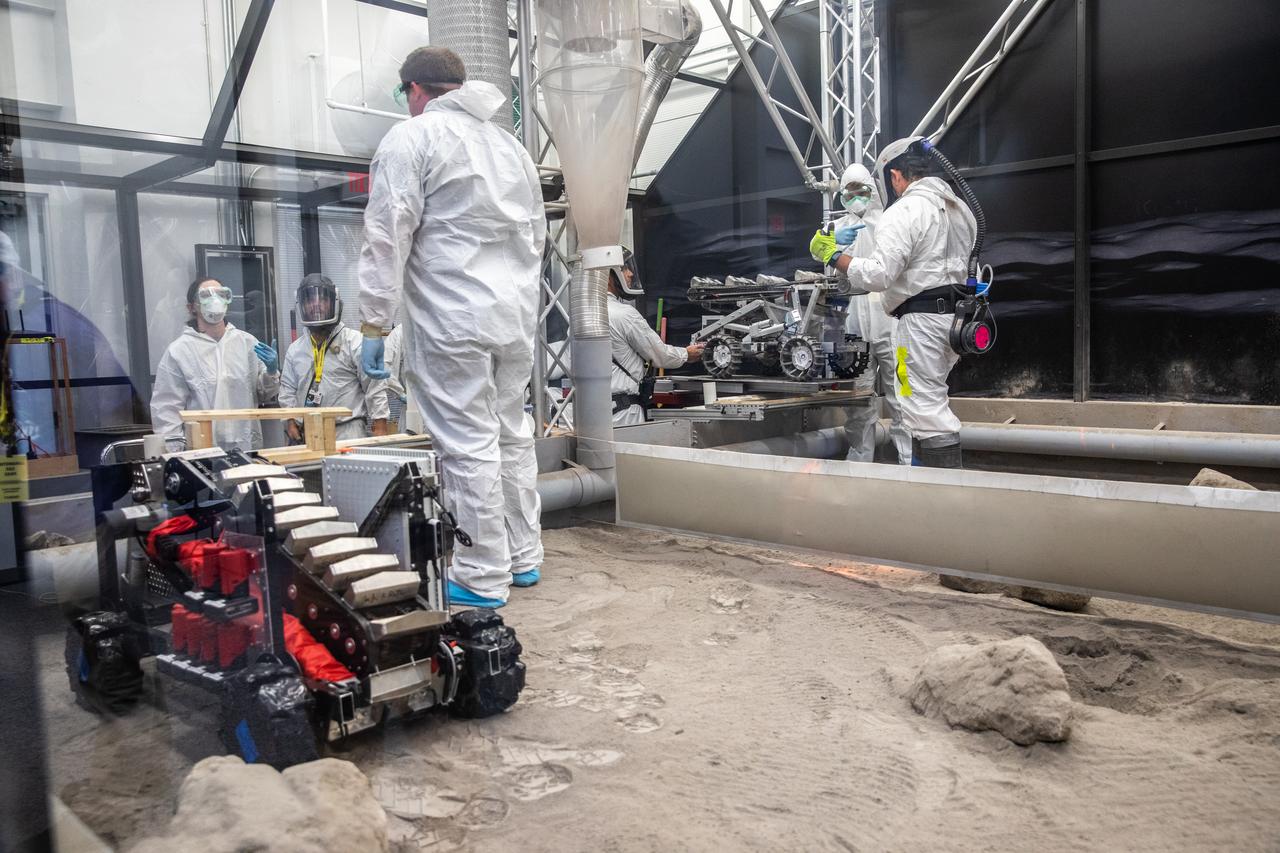

The Milwaukee School of Engineering’s robotic miner is ready for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
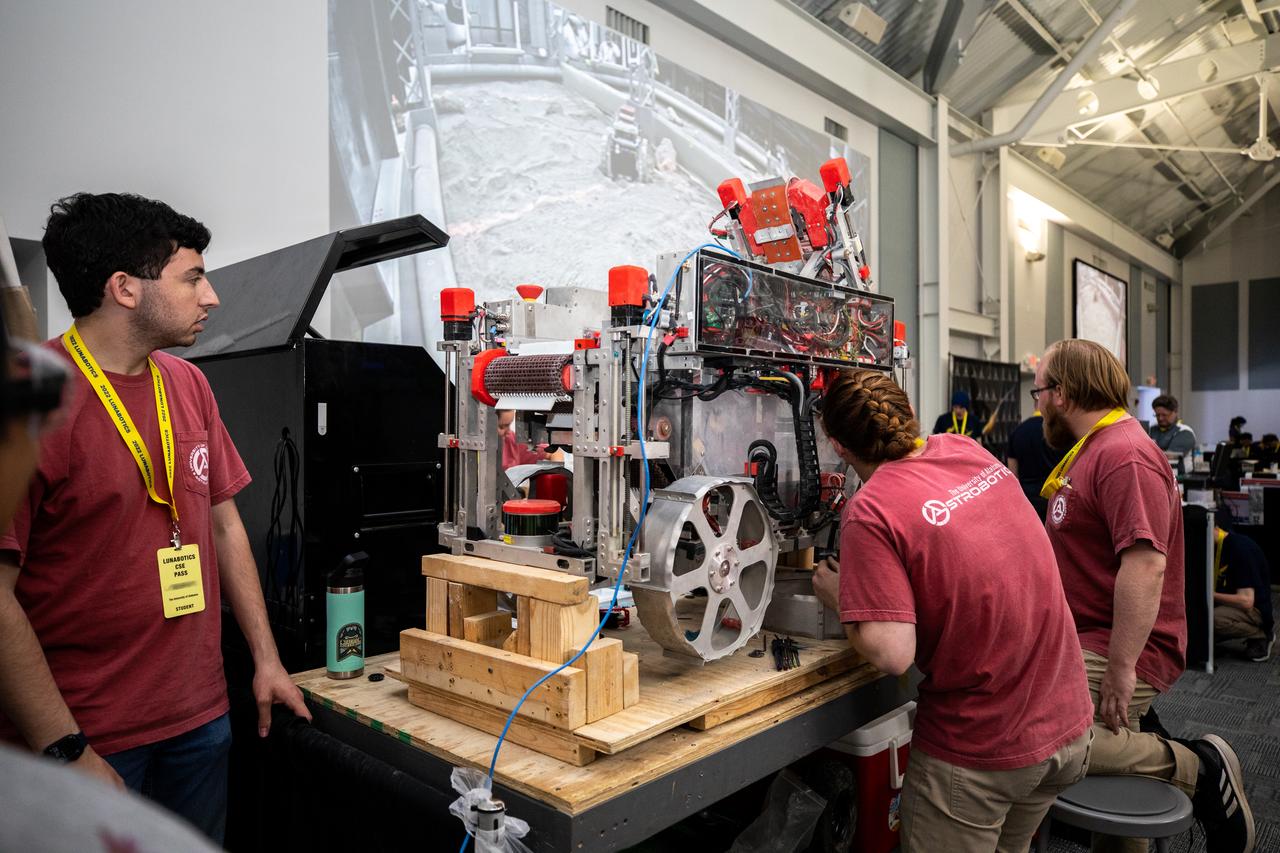
Students from the University of Alabama prepare their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
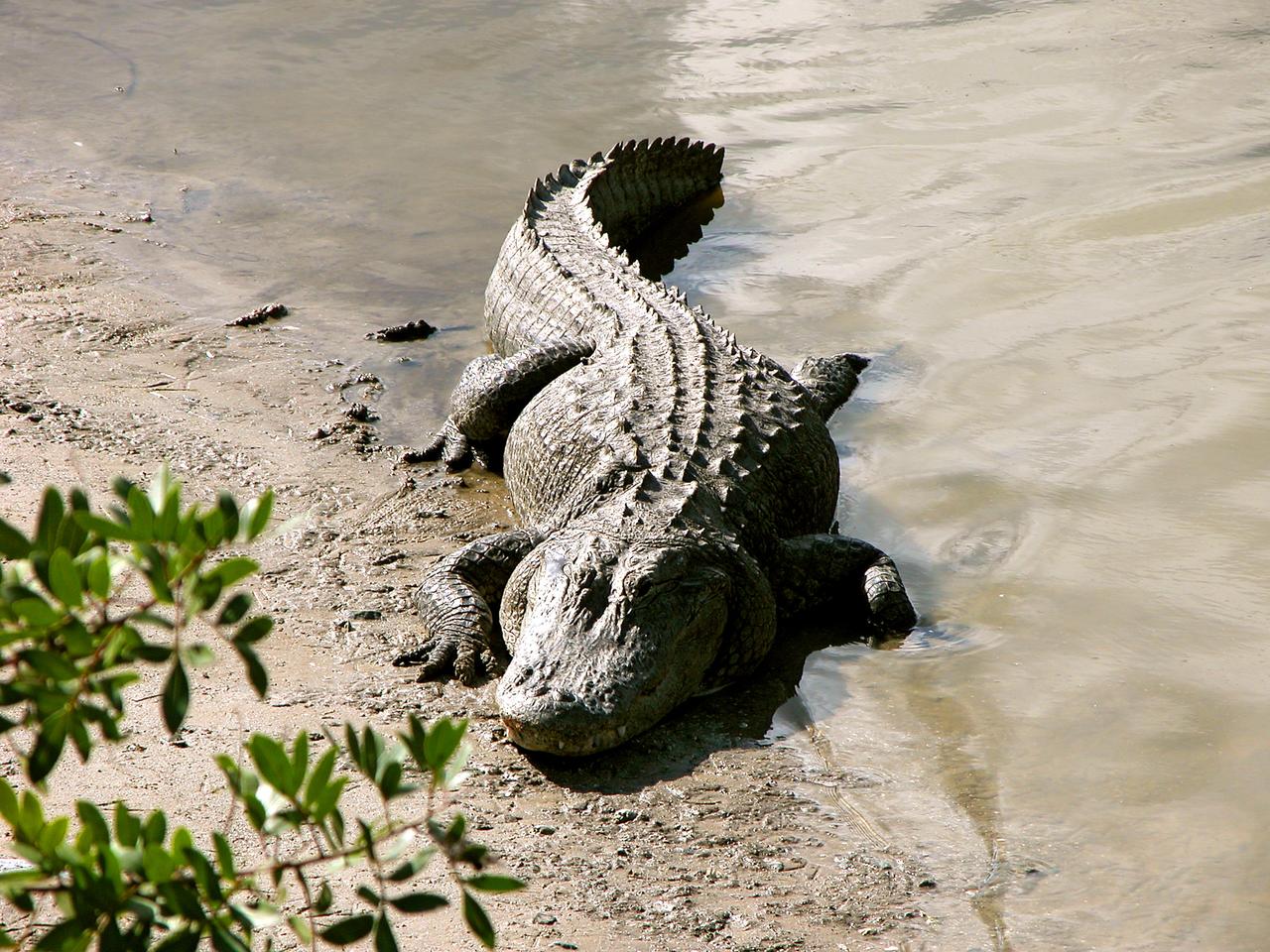

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An alligator is spotted sunning on the muddy bank of a canal in KSC. Nearly 5,000 alligators can be found in canals, ponds, and waterways throughout the Center and the surrounding Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. American alligators feed and rest in the water, and lay their eggs in dens they dig into the banks. The young alligators spend their first several weeks in these dens. The Wildlife Refuge encompasses 92,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An alligator is spotted sunning on the muddy bank of a canal in KSC. Nearly 5,000 alligators can be found in canals, ponds, and waterways throughout the Center and the surrounding Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. American alligators feed and rest in the water, and lay their eggs in dens they dig into the banks. The young alligators spend their first several weeks in these dens. The Wildlife Refuge encompasses 92,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles.
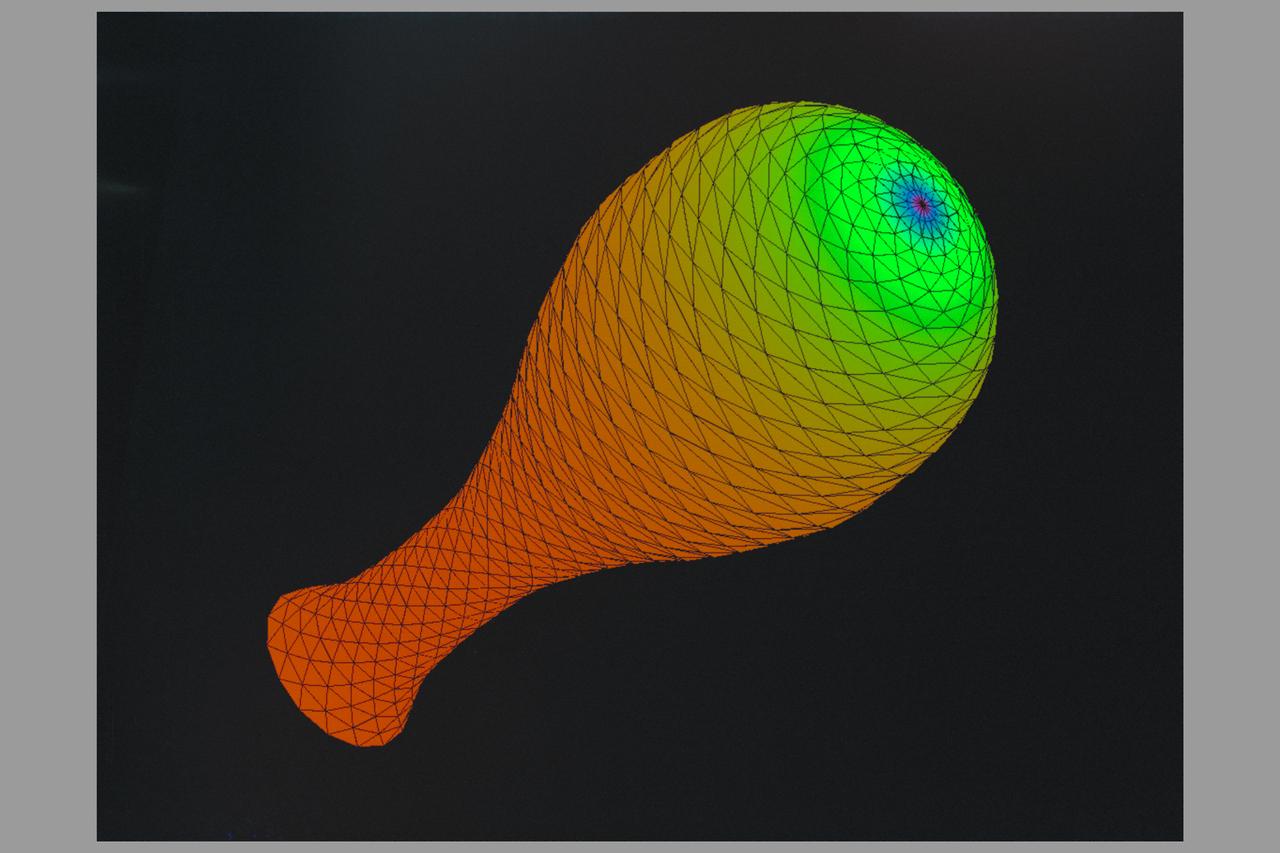
Virtual Reality Application for Neuroscience Research Biocomputation in the study of space motion sickness and balance (inner ear)
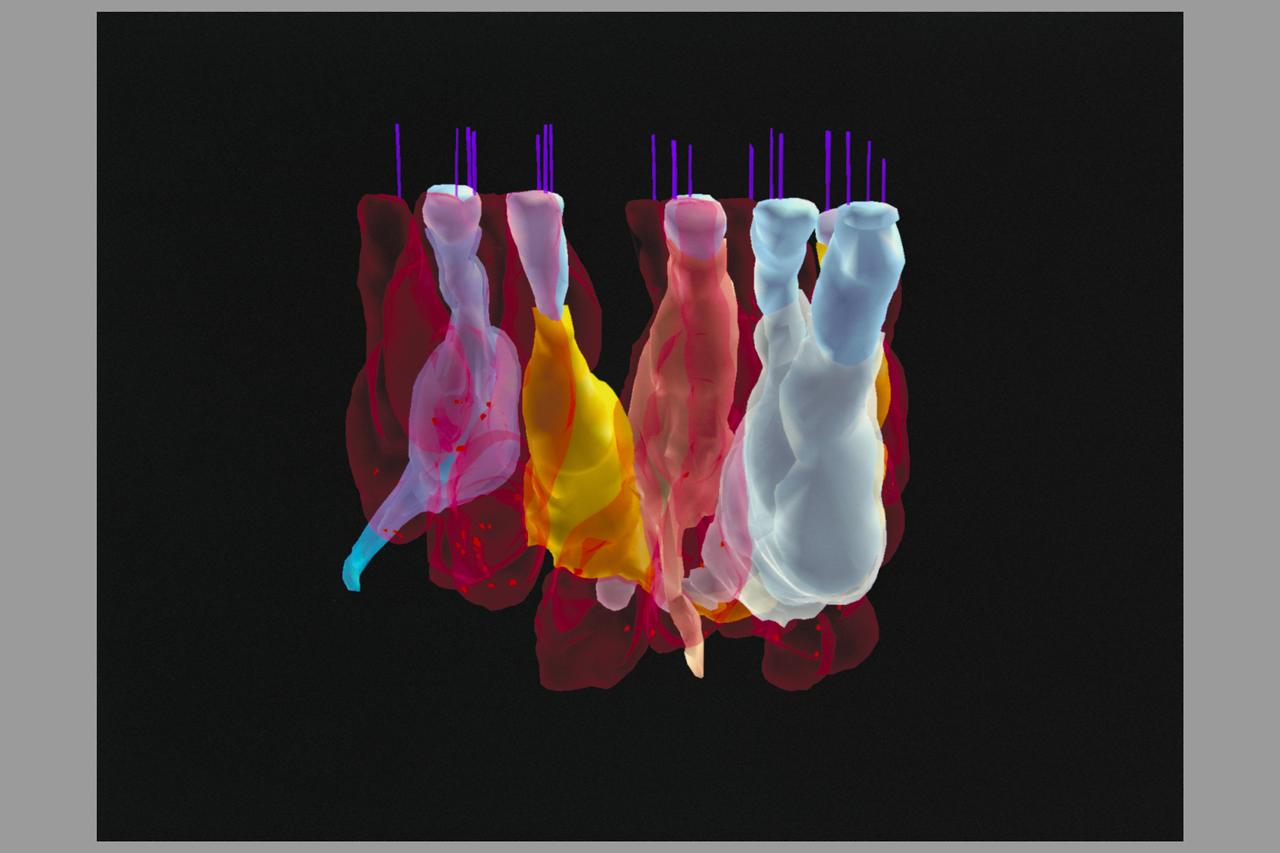

Virtual Reality Application for Neuroscience Research Biocomputation in the study of space motion sickness and balance (inner ear)

The Surface Stereo Imager on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander recorded this image of the lander Robotic Arm enlarging and combining the two trenches informally named Dodo left and Goldilocks.
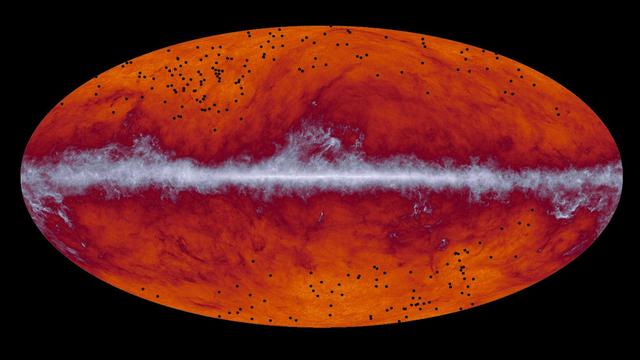
This map of the entire sky was captured by the European Space Agency's Planck mission. The band running through the middle corresponds to dust in our Milky Way galaxy. The black dots indicate the location of galaxy cluster candidates identified by Planck and subsequently observed by the European Space Agency's Herschel mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19330

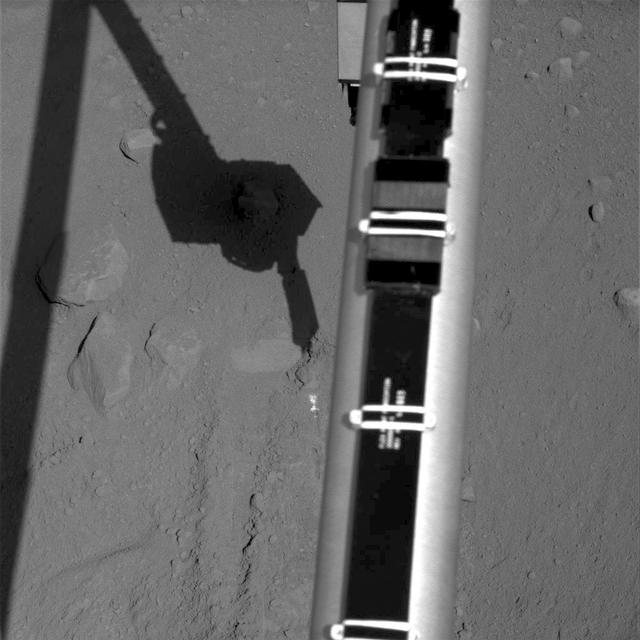
Wheel slippage during attempts to extricate NASA Mars Rover Spirit from a patch of soft ground during the preceding two weeks had partially buried the wheels by the 1,899th Martian day, or sol, of the Spirit mission on Mars May 6, 2009.

Wheel slippage during attempts to extricate NASA's Mars Rover Spirit from a patch of soft ground during the preceding two weeks had partially buried the wheels by the 1,899th Martian day, or sol, of the Spirit's mission on Mars (May 6, 2009). Spirit took this image with its front hazard-avoidance camera on Sol 1899. With Spirit in the position shown here, the rover team temporarily suspended driving attempts while studying the ground around Spirit and planning simulation tests of driving options with a test rover at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Driving attempts between the time Spirit took a similar image (PIA12002) 10 sols earlier and when this image was taken moved the rover a total of about 36 centimeters (14 inches). While driving backwards, the rover drags its right front wheel, which no longer rotates. For scale, the distance between the wheel tracks is about 1 meter (40 inches). This view is looking northward, with Husband Hill on the horizon. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12007

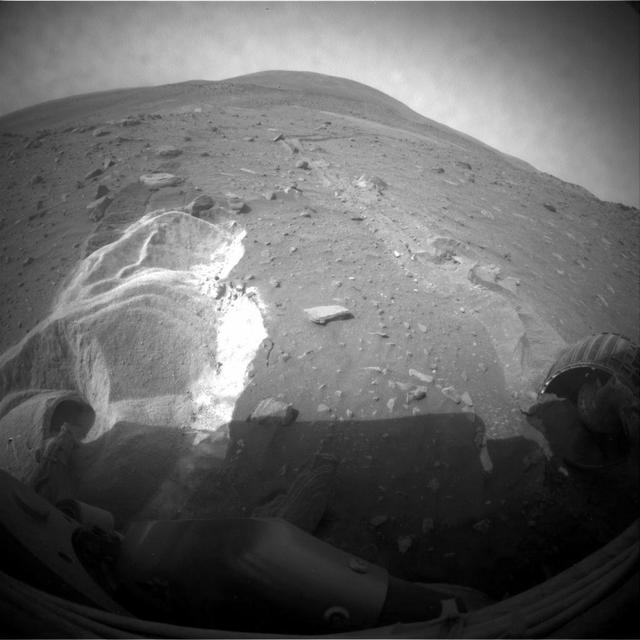
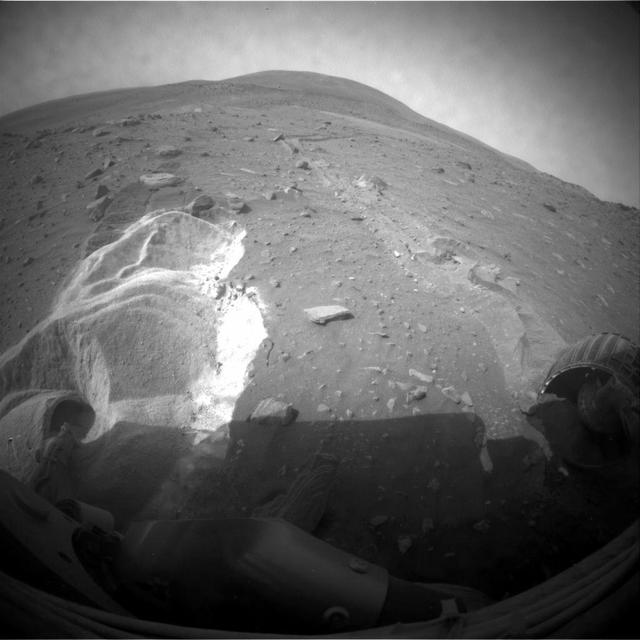
On Earth, geologists can dig holes and pull up core samples to find out what lies beneath the surface. On Mars, geologists cannot dig holes very easily themselves, but a process has been occurring for billions of years that has been digging holes for them: impact cratering. Impact craters form when an asteroid, meteoroid, or comet crashes into a planet's surface, causing an explosion. The energy of the explosion, and the resulting size of the impact crater, depends on the size and density of the impactor, as well as the properties of the surface it hits. In general, the larger and denser the impactor, the larger the crater it will form. The impact crater in this image is a little less than 3 kilometers in diameter. The impact revealed layers when it excavated the Martian surface. Layers can form in a variety of different ways. Multiple lava flows in one area can form stacked sequences, as can deposits from rivers or lakes. Understanding the geology around impact craters and searching for mineralogical data within their layers can help scientists on Earth better understand what the walls of impact craters on Mars expose. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12328
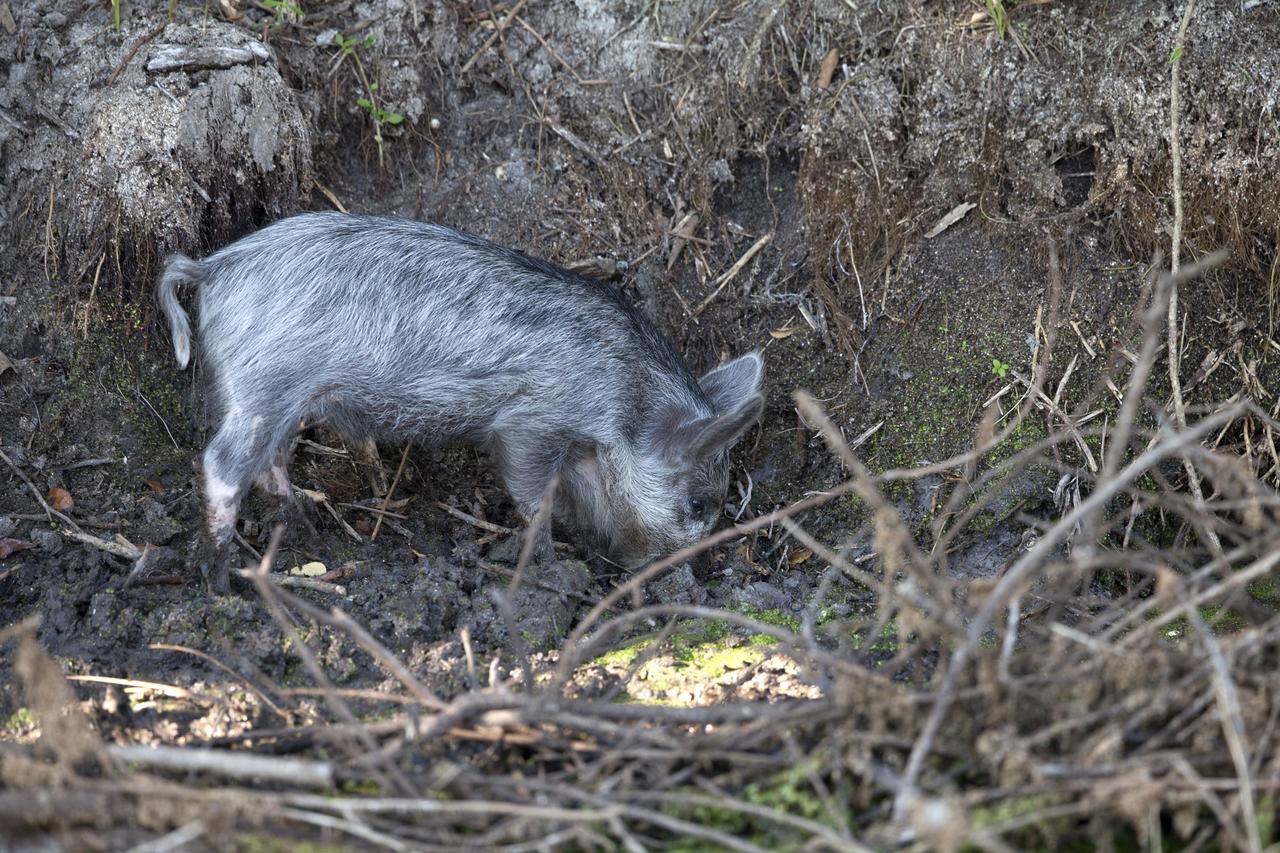

A baby pig digs in the underbrush at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
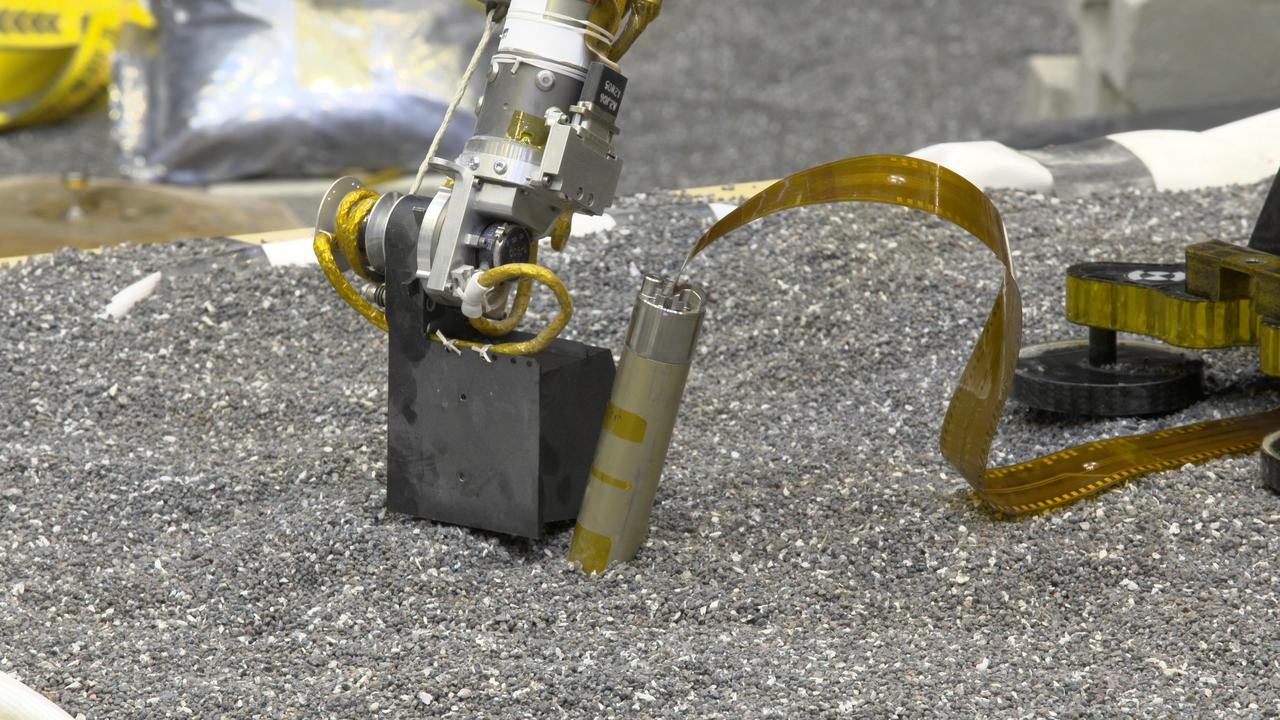

In a JPL lab, a replica of NASA InSight's robotic arm presses with its scoop on crushed garnet near a replica of the spacecraft's self-hammering "mole." Engineers believe pressing like this on Martian soil may help the mole dig by increasing friction of the surrounding soil. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23276
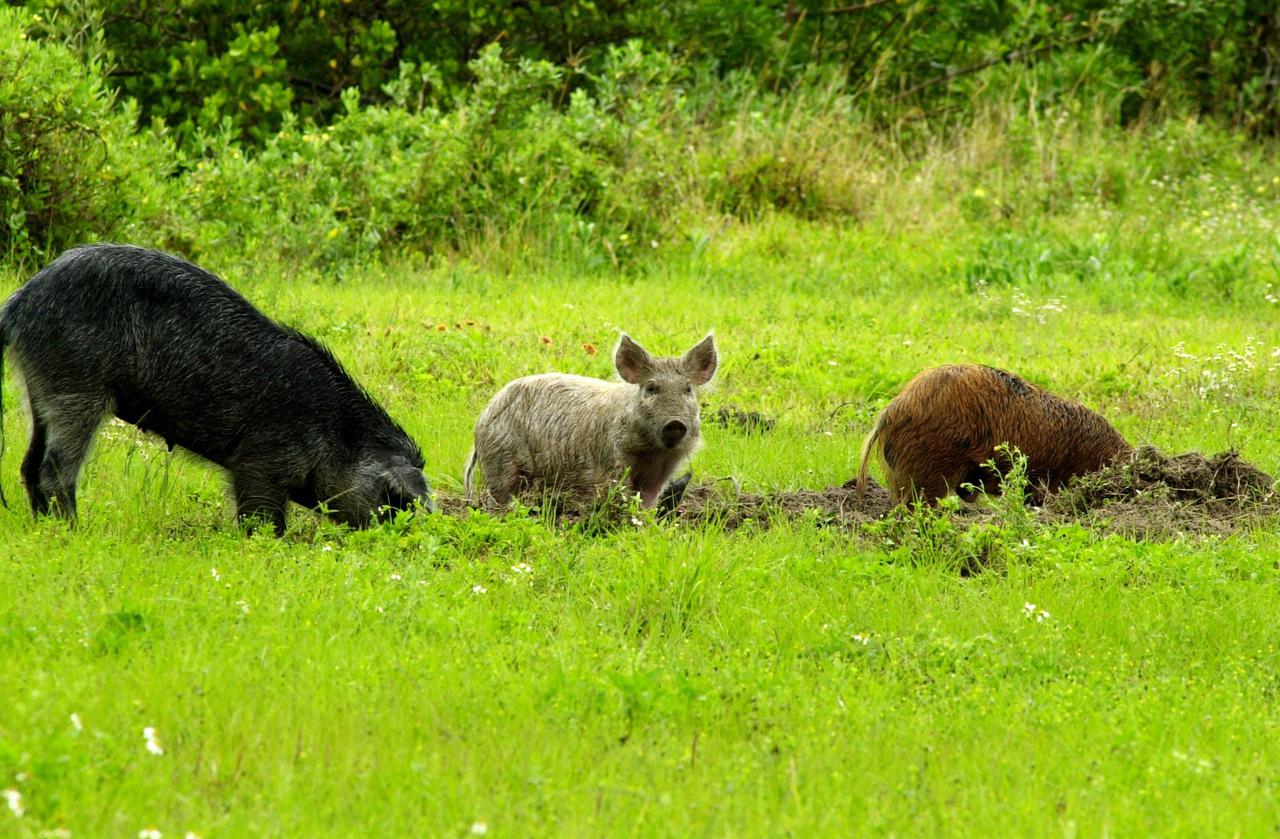

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Feral pigs dig for food on grounds near Kennedy Space Center. Not a native in the environment, the hogs are believed to be descendants from the pigs brought to Florida by the early Spanish explorers. Without many predators other than human, the pigs have flourished
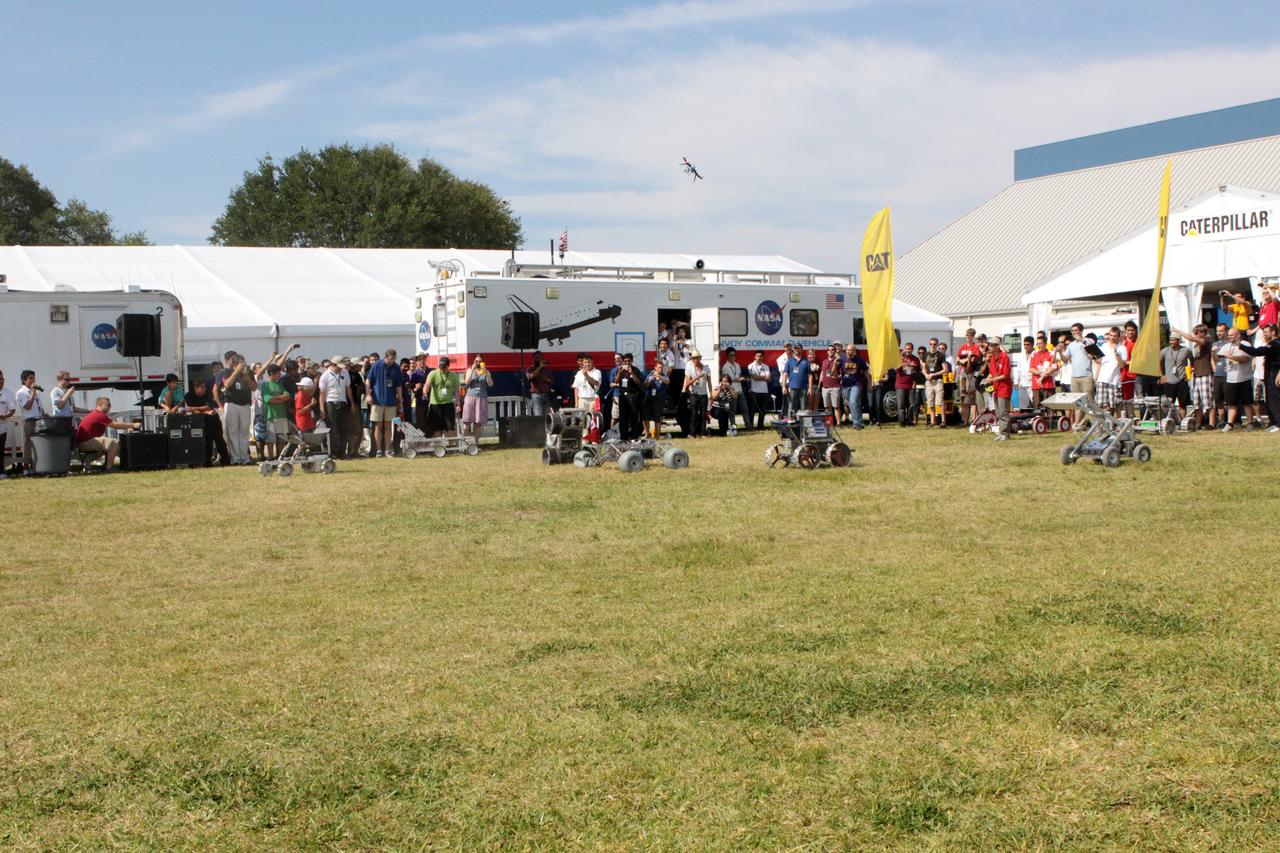

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Robotic vehicles take part in the racing portion of NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Although much of the competition was based on a vehicle's ability to dig soil, the festivities also included head-to-head runs for the robotic craft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
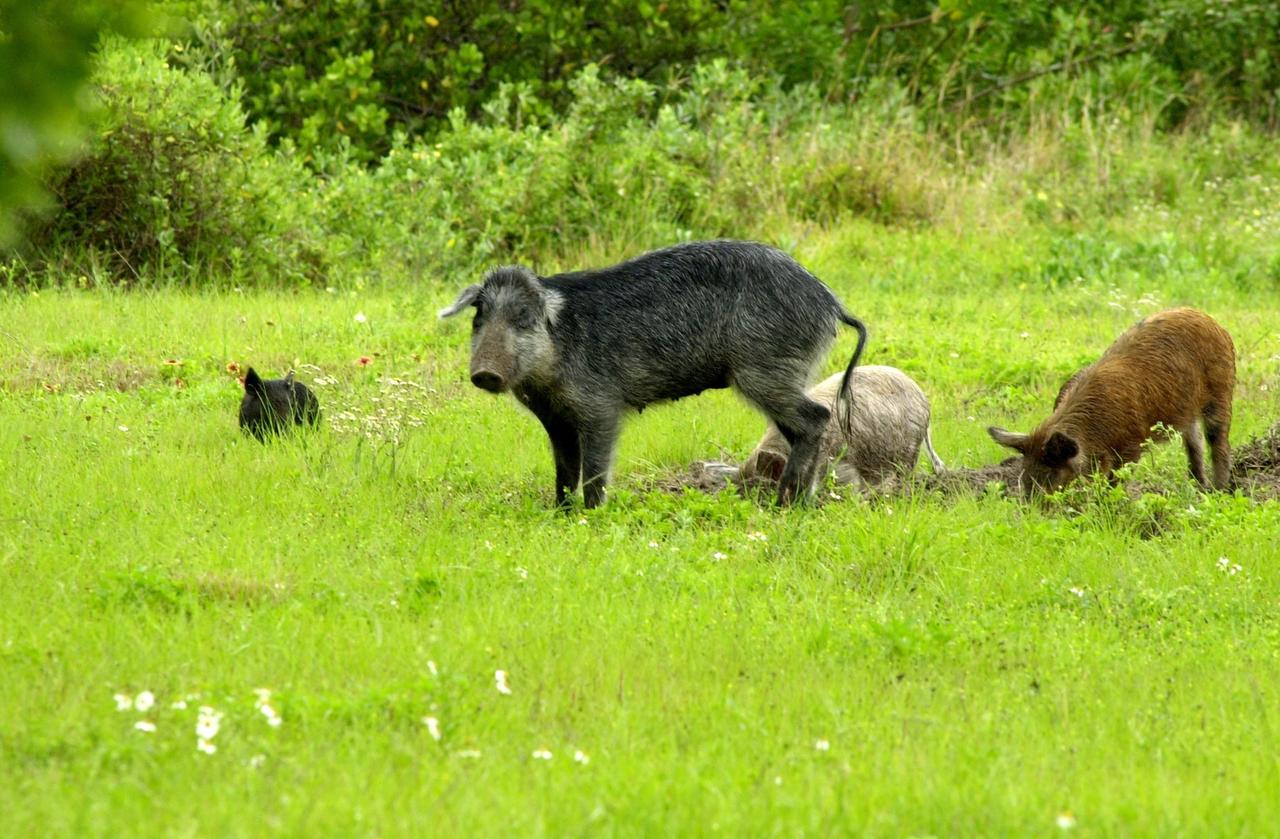

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Feral pigs dig for food on grounds near Kennedy Space Center. Not a native in the environment, the hogs are believed to be descendants from the pigs brought to Florida by the early Spanish explorers. Without many predators other than human, the pigs have flourished
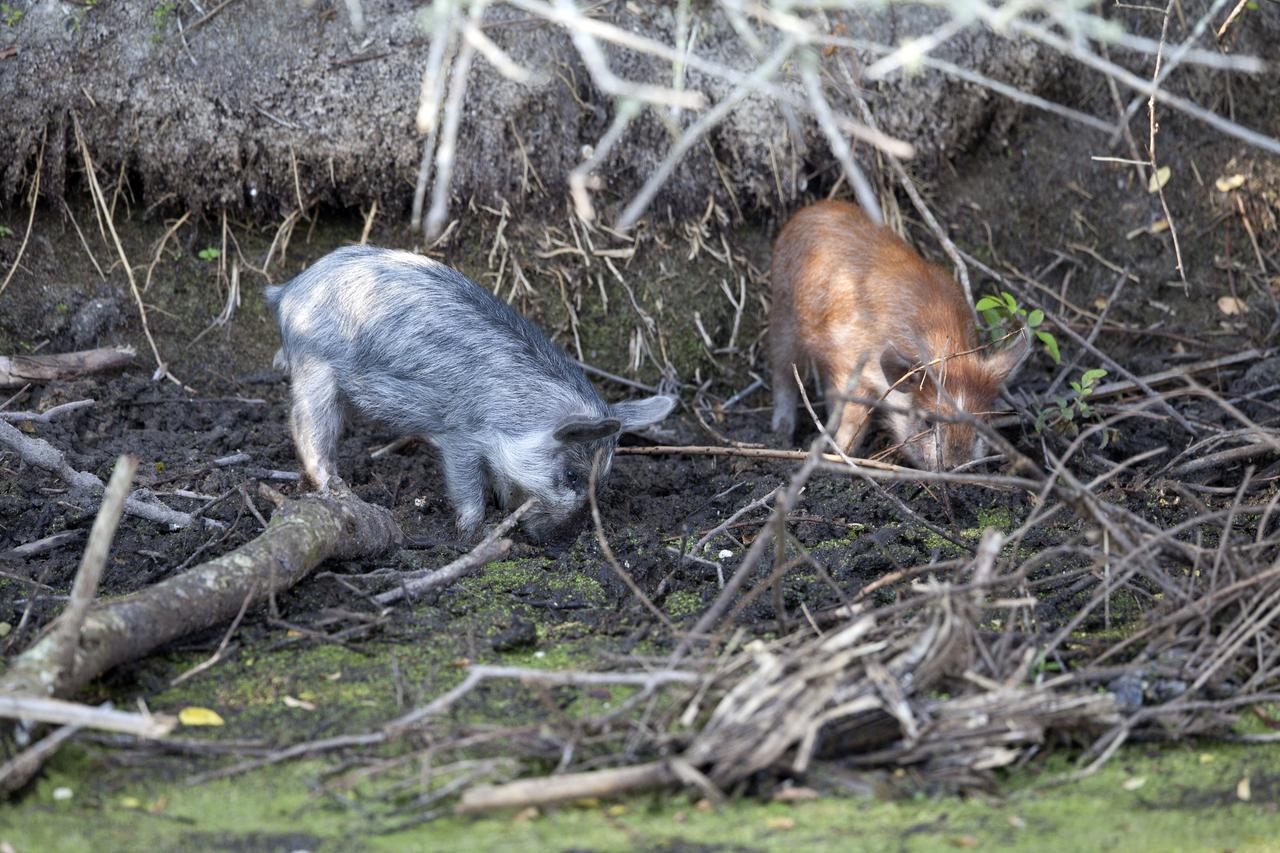

Two baby pigs dig in the underbrush at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

Members of a college team watch on the monitor as their robot miner digs in the mining arena on the third day of NASA's 9th Robotic Mining Competition, May 16, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. will use their mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Lunar soil, gravel and rocks, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's deep space missions.
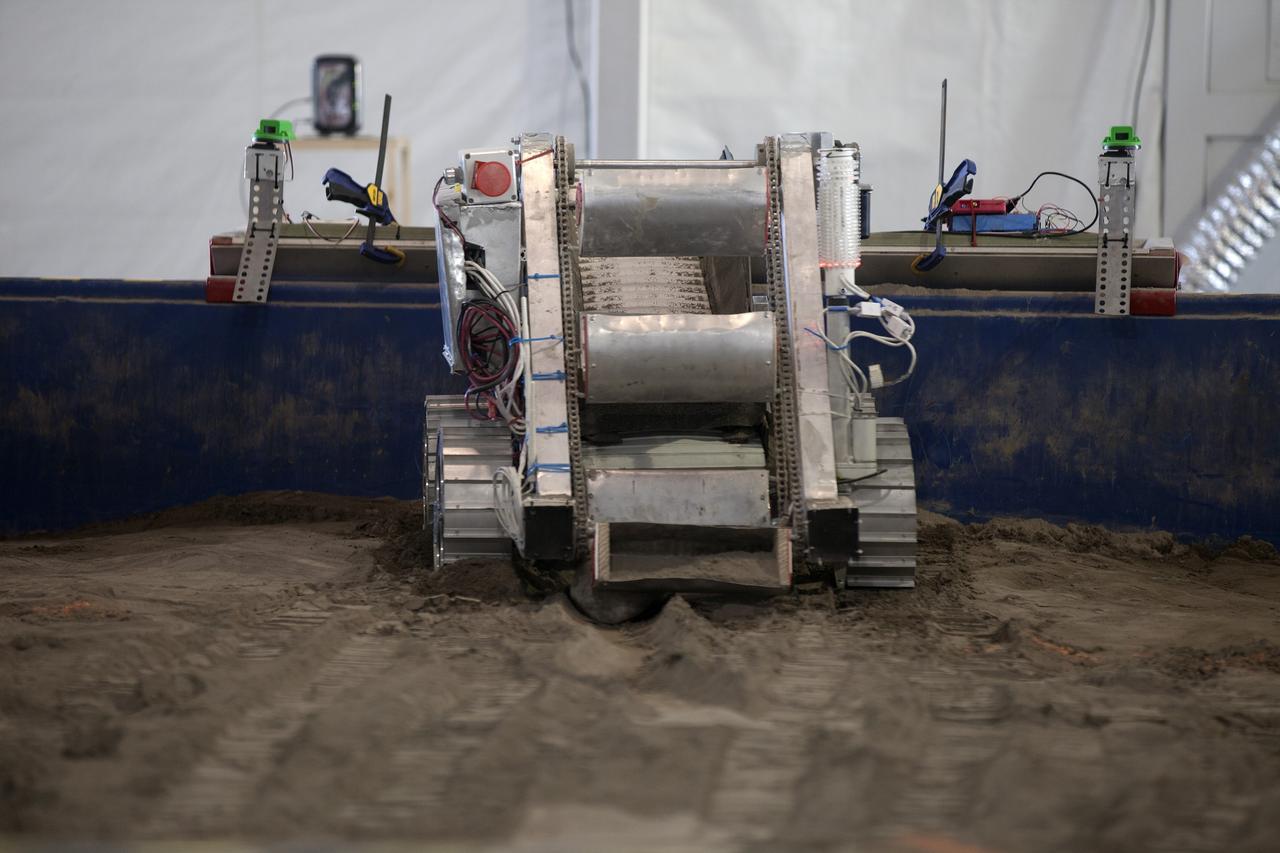

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A robot digs in the simulated Martian soil in the Caterpillar Mining Arena during NASA’s 2014 Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. The competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields by expanding opportunities for student research and design. Teams use their remote-controlled robotics to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material that has characteristics similar to Martian soil. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and move the most regolith within a specified amount of time. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/nasarmc. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
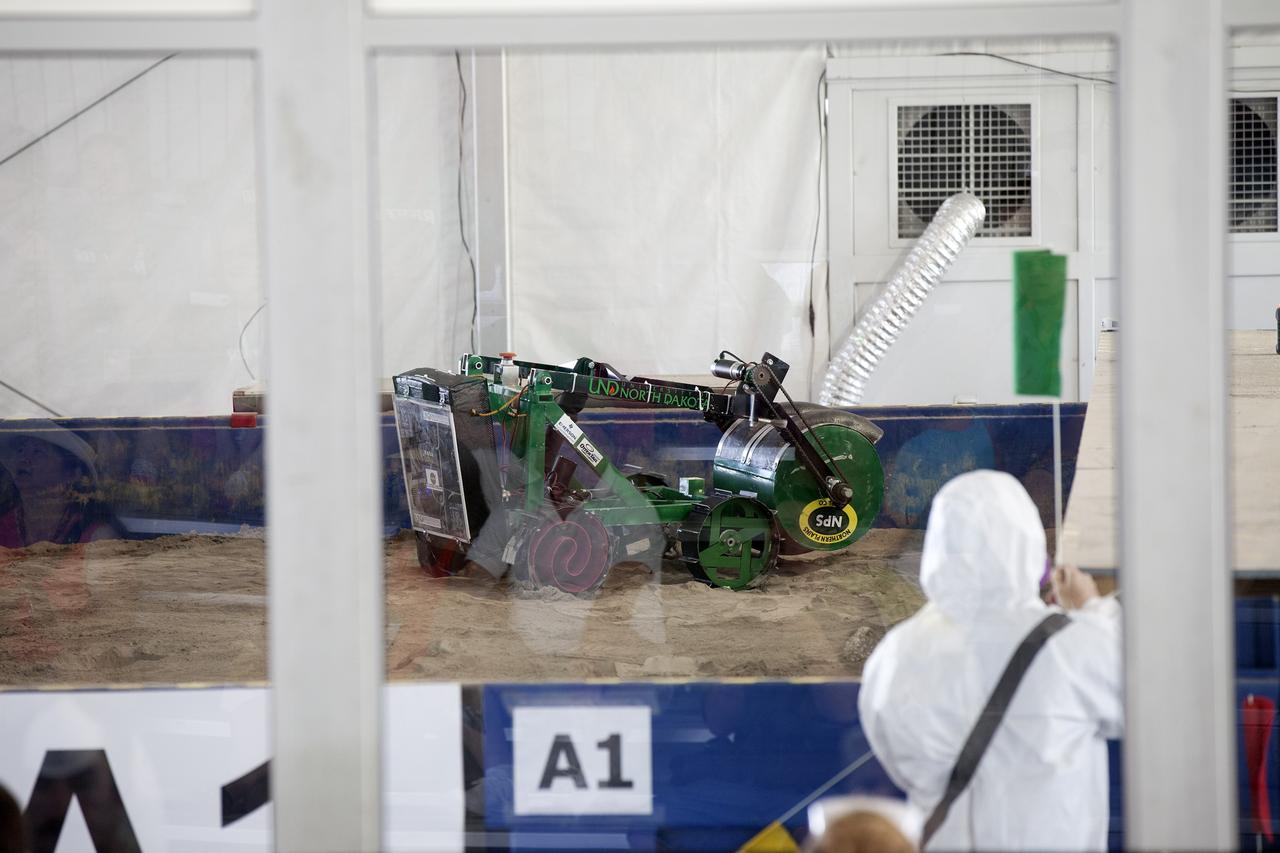

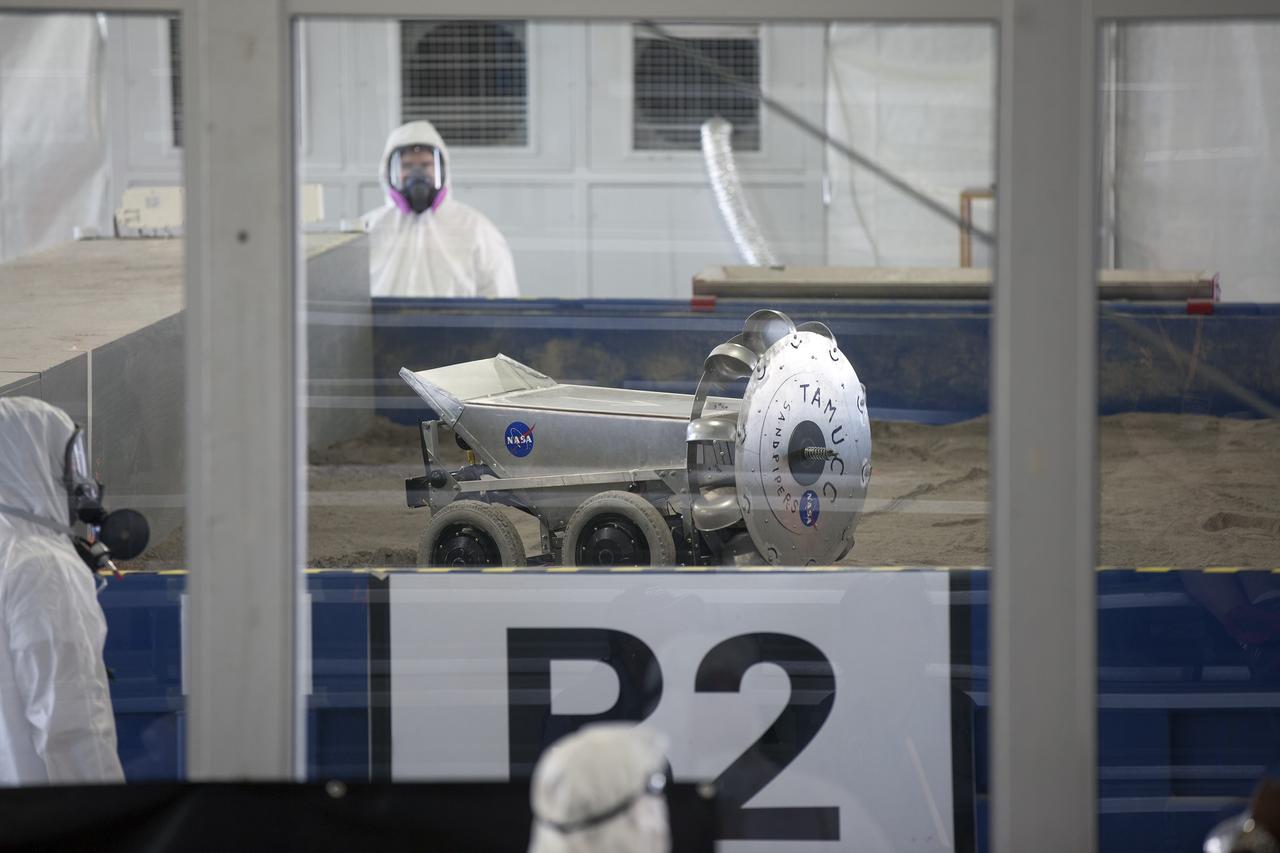
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The University of North Dakota's robotic miner digs in the simulated Martian soil in the Caterpillar Mining Arena on the final day of NASA's 2014 Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. The competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields by expanding opportunities for student research and design. Teams use their remote-controlled robotics to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material that has characteristics similar to Martian soil. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and move the most regolith within a specified amount of time. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/nasarmc. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
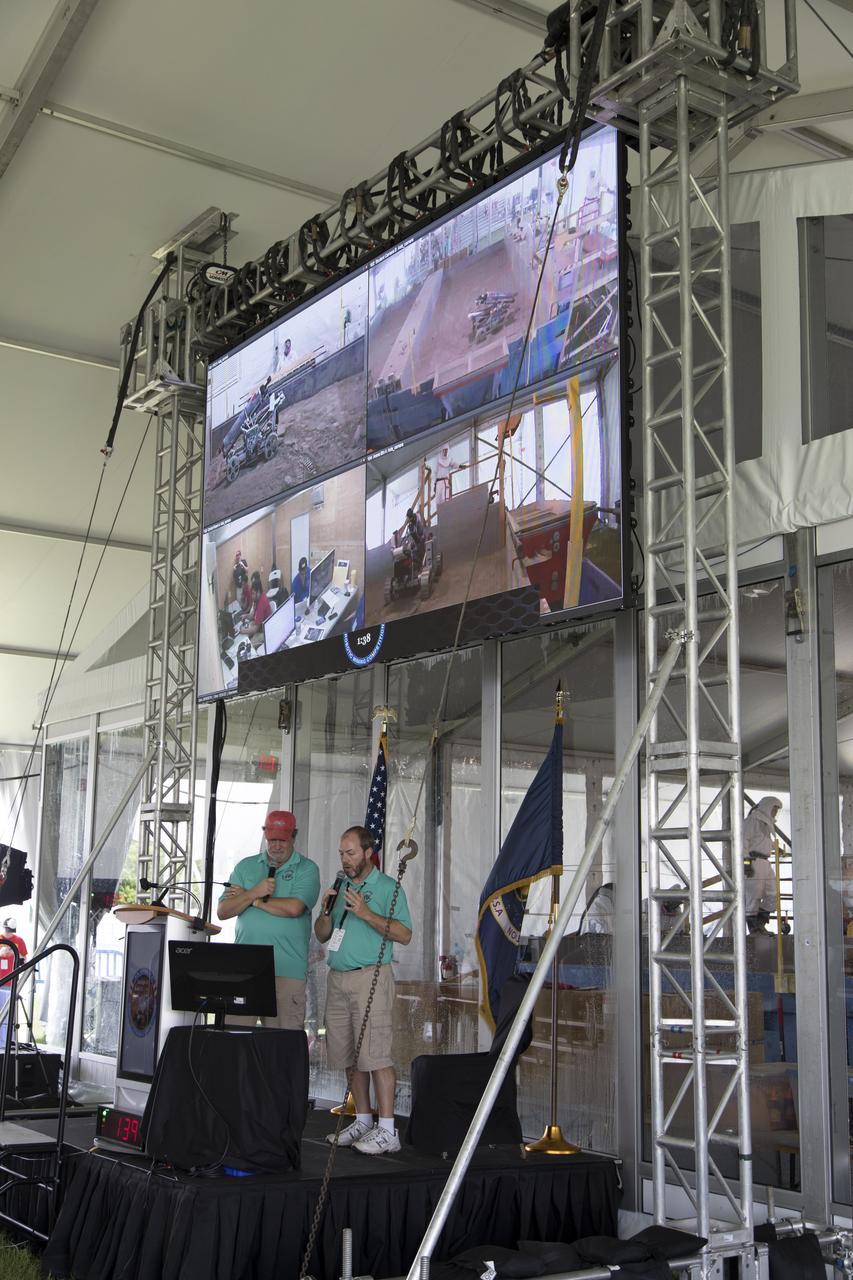

During the third day of NASA's 9th Robotic Mining Competition, May 16, Al Feinberg, left, with Kennedy Space Center's Communication and Public Engagement, and Kurt Leucht, with Kennedy's Engineering Directorate, provide commentary as robot miners dig in the dirt in the mining arena at NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. will use their mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Lunar soil, gravel and rocks, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's deep space missions.
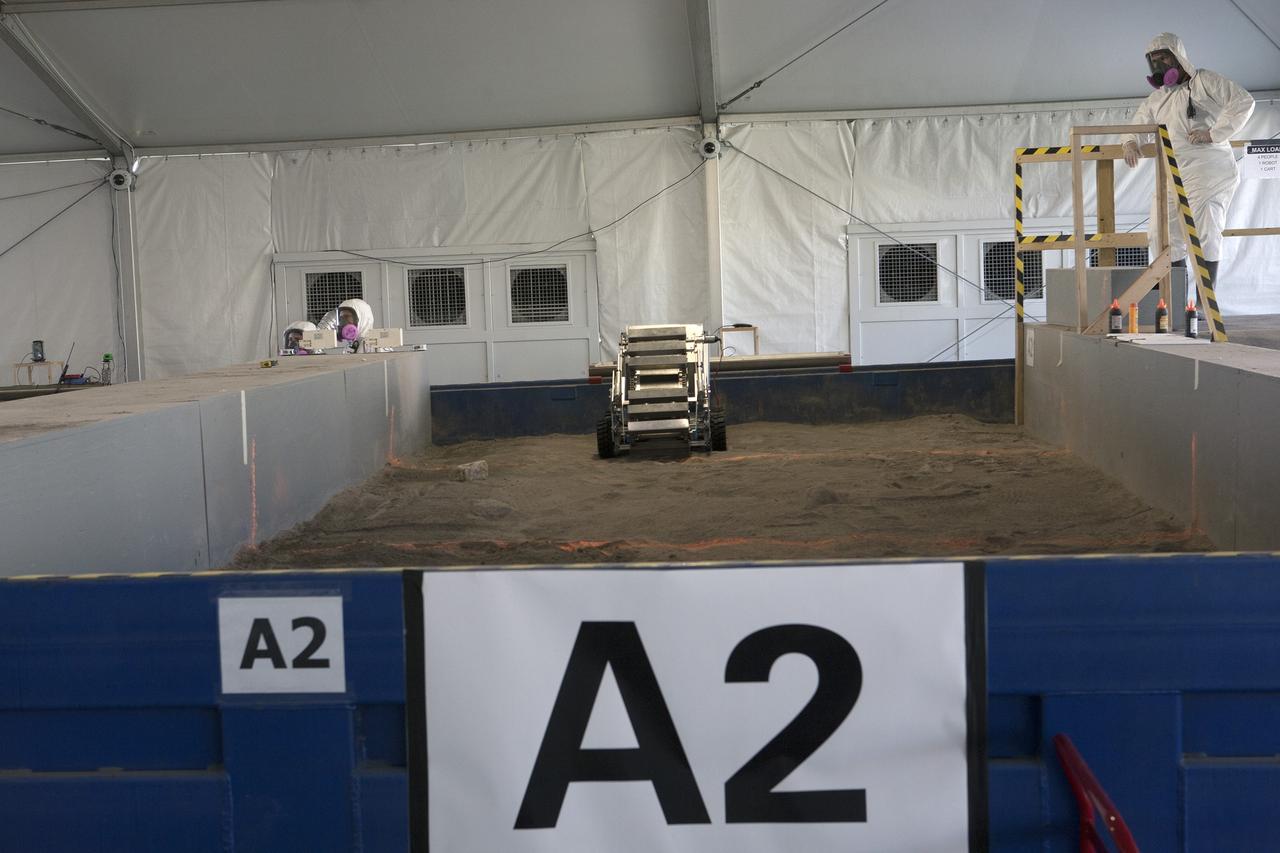

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Competition judges monitor the progress of a robot digging in the simulated Martian soil in the Caterpillar Mining Arena during NASA’s 2014 Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. The competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields by expanding opportunities for student research and design. Teams use their remote-controlled robotics to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material that has characteristics similar to Martian soil. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and move the most regolith within a specified amount of time. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/nasarmc. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro, second from right, watches onscreen as robotic miners dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Second from left is Thad Altman, president and CEO of The Astronauts Memorial Foundation. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
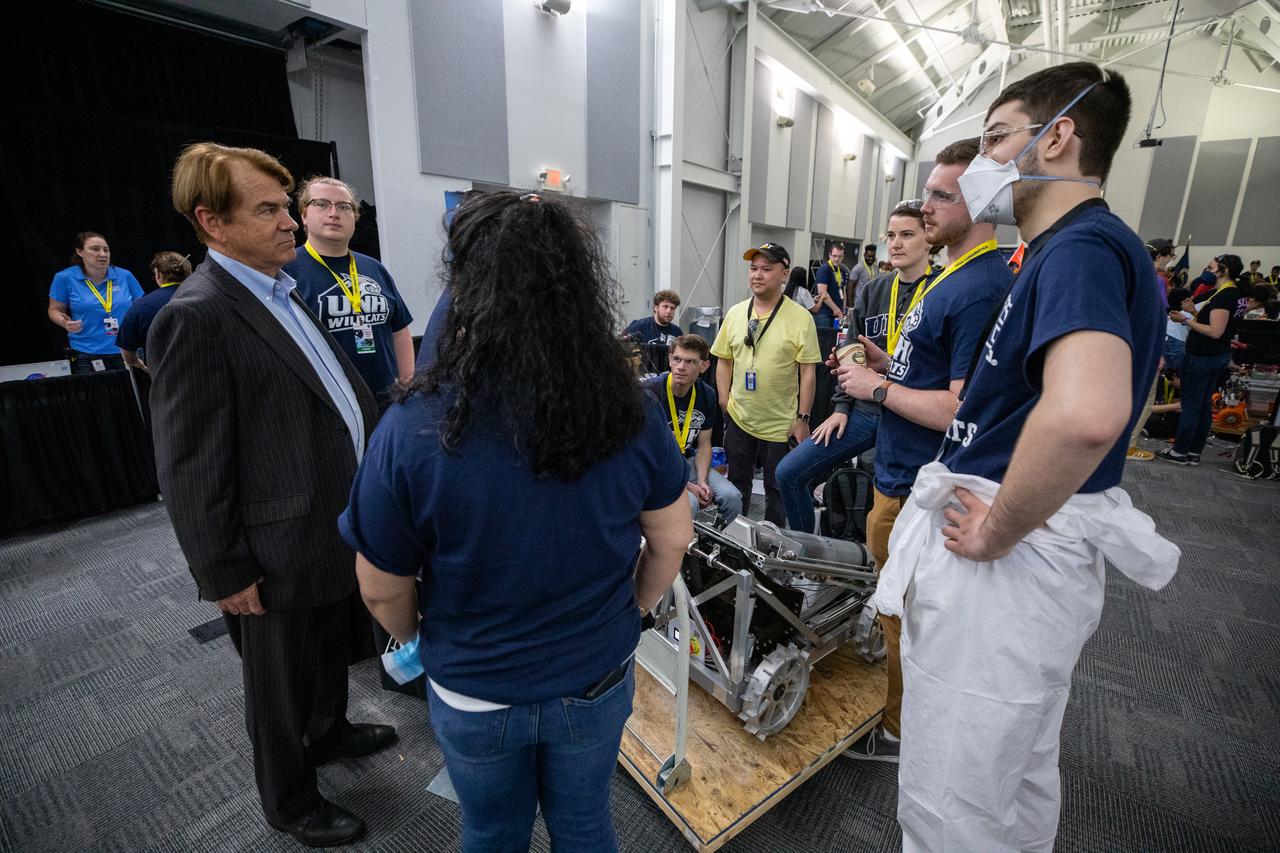

Thad Altman, far left, chairman and CEO of the Astronaut Memorial Foundation, talks to students from the University of New Hampshire as they prepare to take their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 26, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their semi-autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Competition judges monitor the progress of a robot digging in the simulated Martian soil in the Caterpillar Mining Arena during NASA’s 2014 Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. The competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields by expanding opportunities for student research and design. Teams use their remote-controlled robotics to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material that has characteristics similar to Martian soil. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and move the most regolith within a specified amount of time. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/nasarmc. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
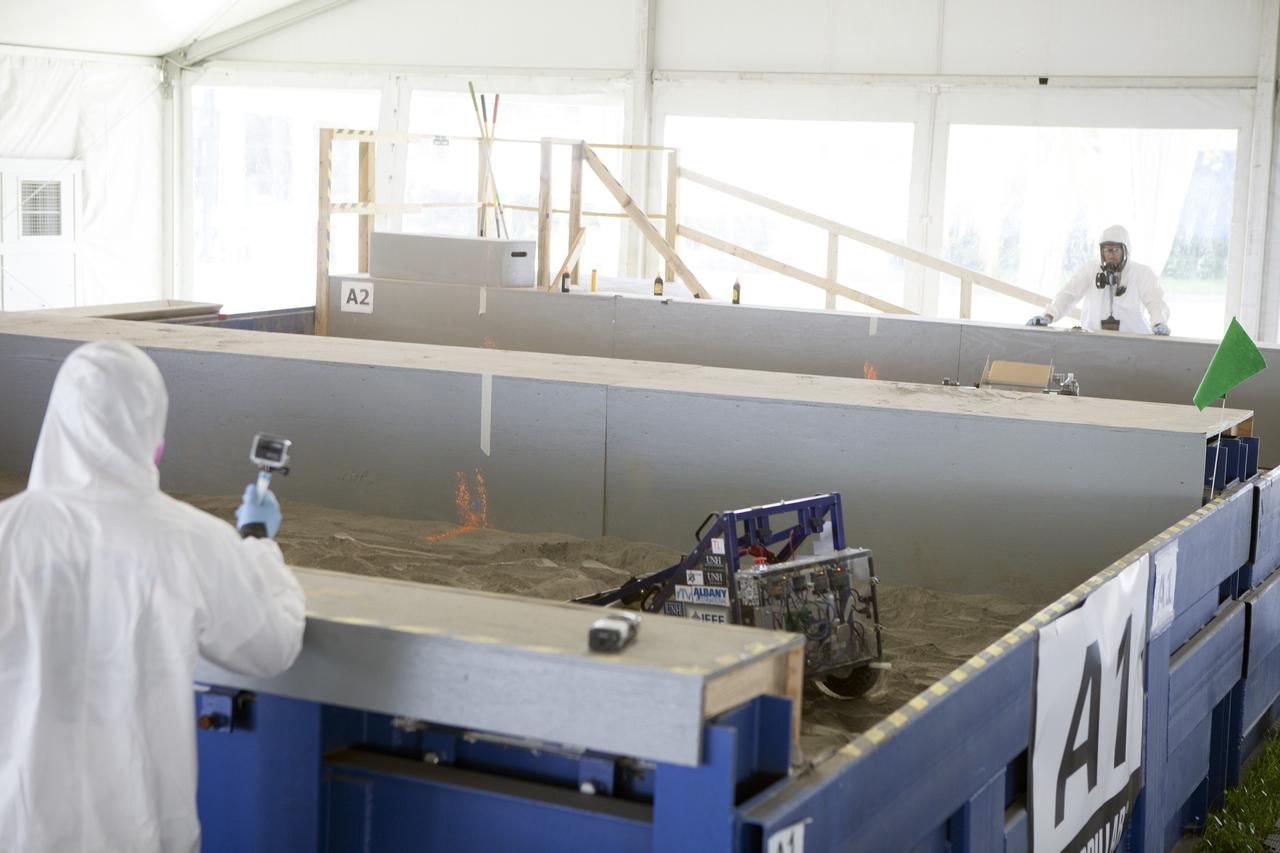

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Competition judges monitor two team's robots digging in the simulated Martian soil in the Caterpillar Mining Arena during NASA’s 2014 Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. The competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields by expanding opportunities for student research and design. Teams use their remote-controlled robotics to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material that has characteristics similar to Martian soil. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and move the most regolith within a specified amount of time. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/nasarmc. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
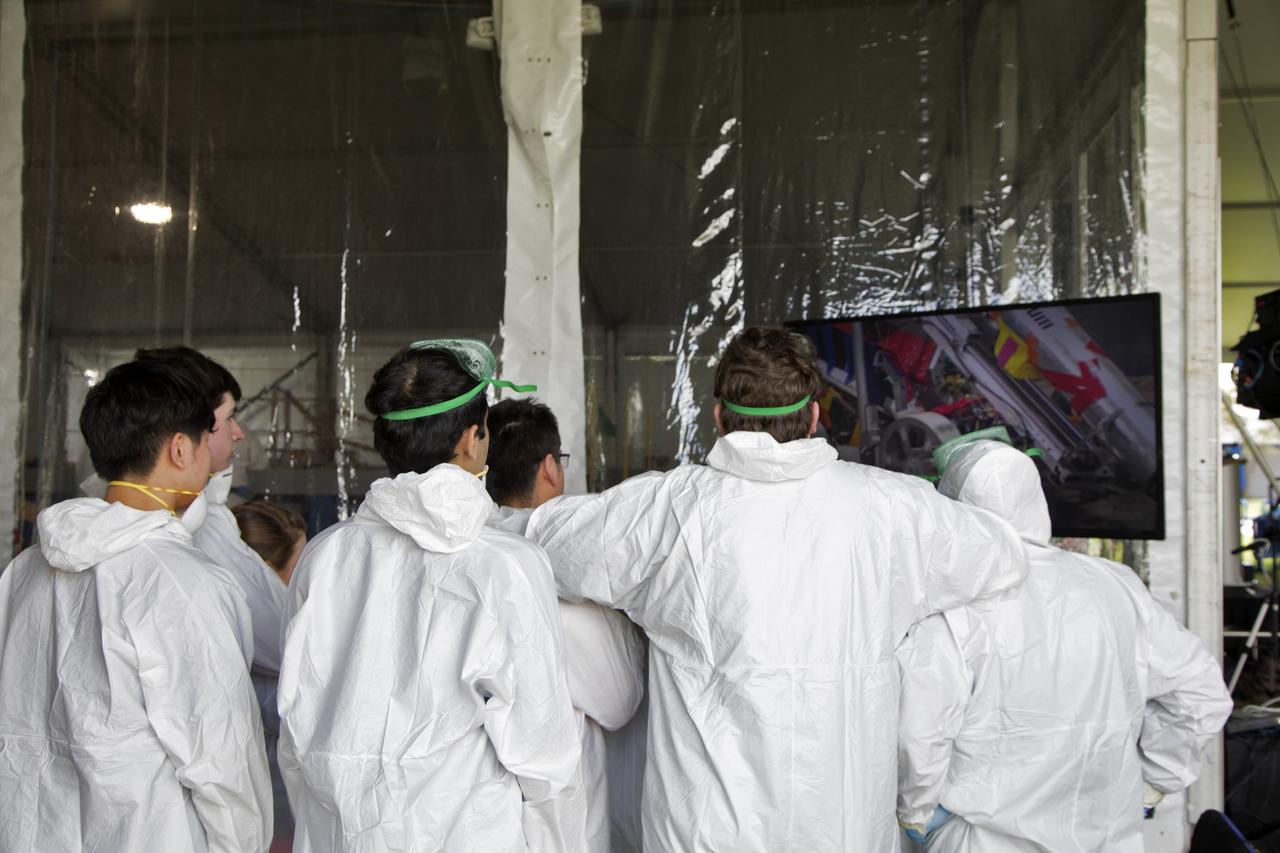

Members of a college team watch on the monitor as their robot miner digs in the mining arena on the third day of NASA's 9th Robotic Mining Competition, May 16, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. will use their mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Lunar soil, gravel and rocks, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's deep space missions.
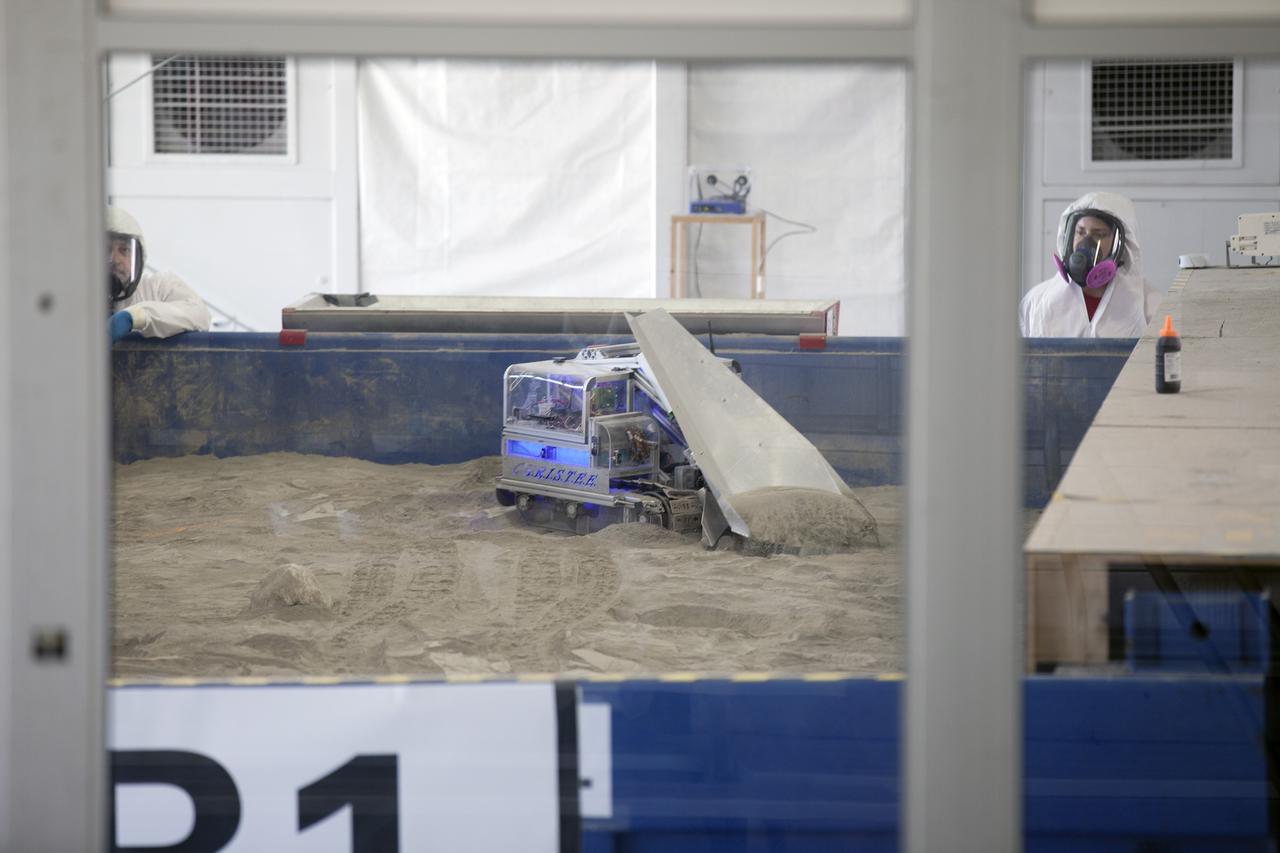

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A robot digs in the simulated Martian soil in the Caterpillar Mining Arena during NASA’s 2014 Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. The competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields by expanding opportunities for student research and design. Teams use their remote-controlled robotics to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material that has characteristics similar to Martian soil. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and move the most regolith within a specified amount of time. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/nasarmc. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
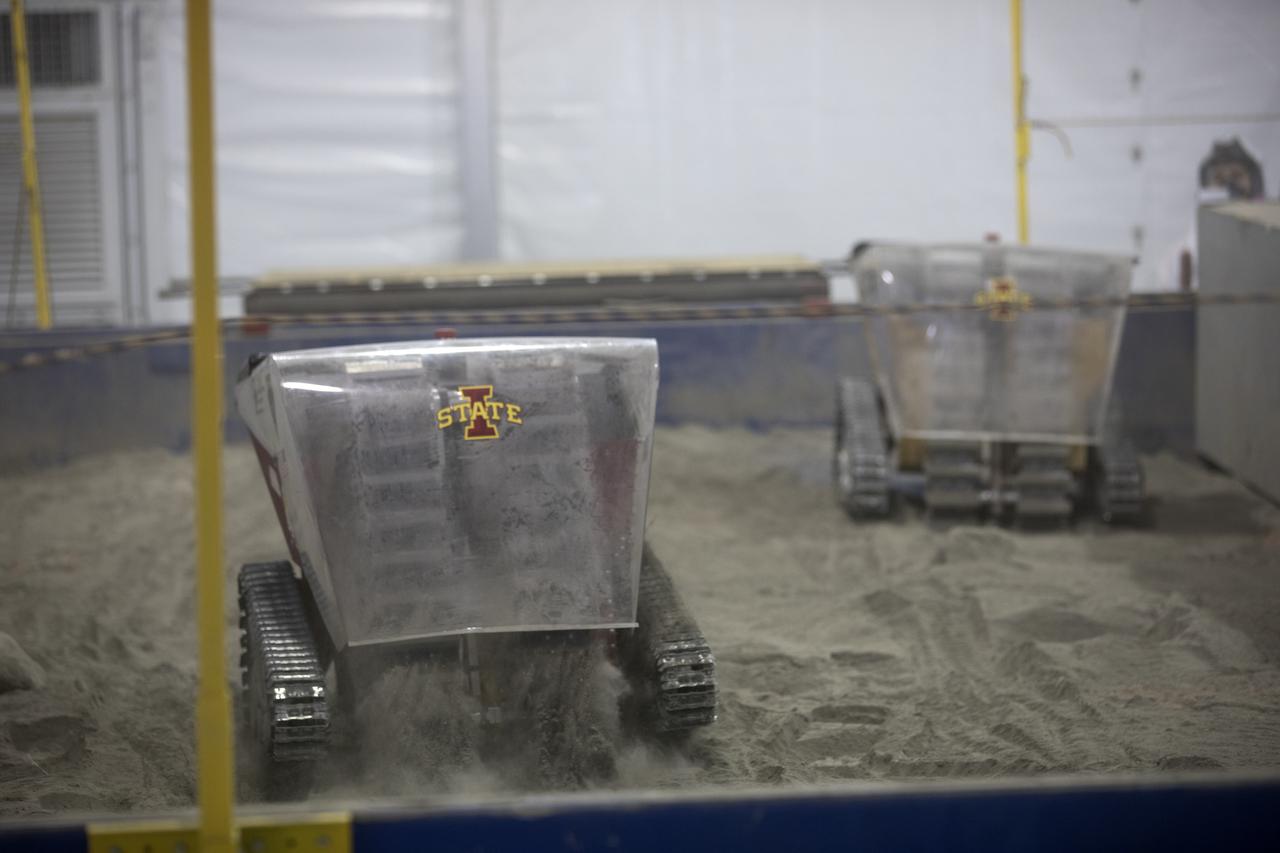

Twin mining robots from the University of Iowa dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Martian soil, during NASA's 8th Annual Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. are using their uniquely-designed mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Martian soil, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's Journey to Mars.
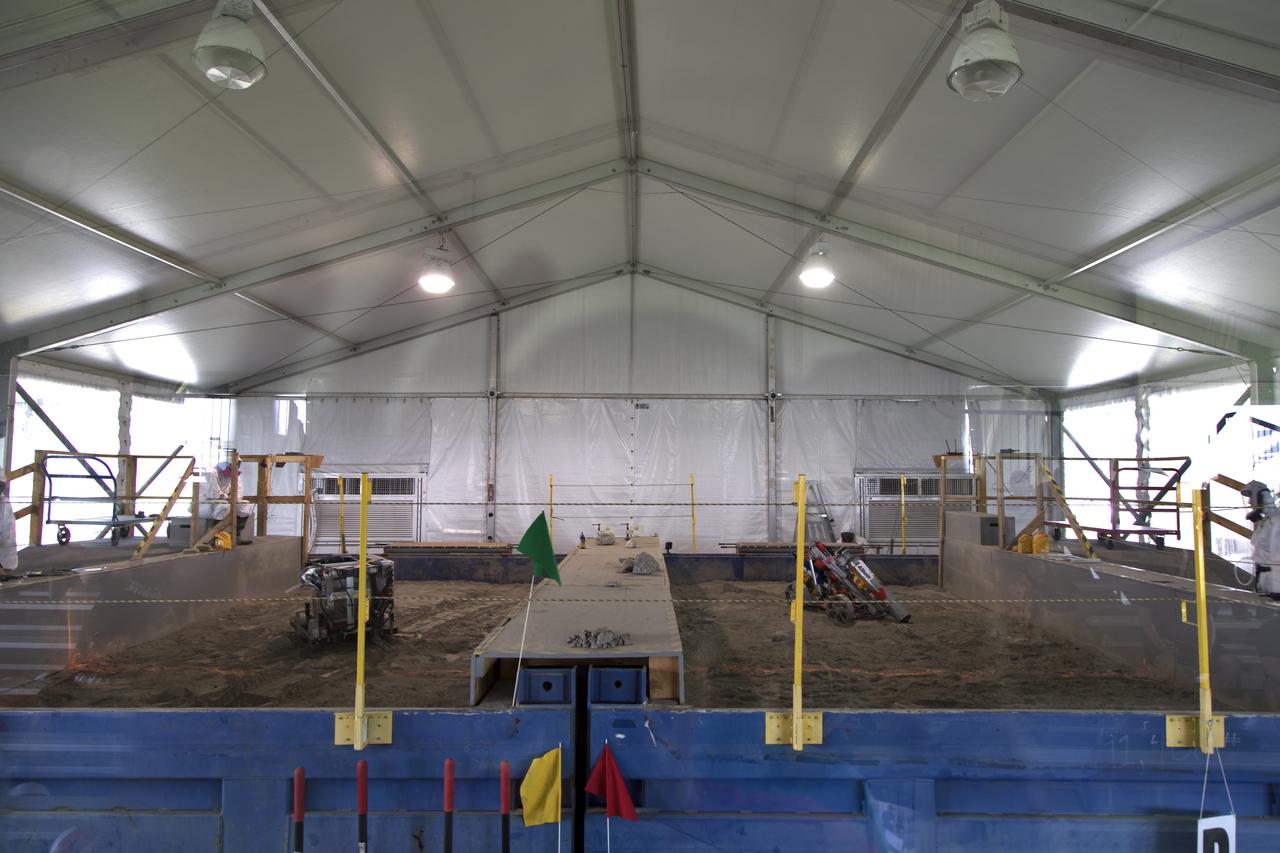

On the third day of NASA's 9th Robotic Mining Competition, May 16, two robot miners dig in the dirt in the mining arena at NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. will use their mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Lunar soil, gravel and rocks, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's deep space missions.
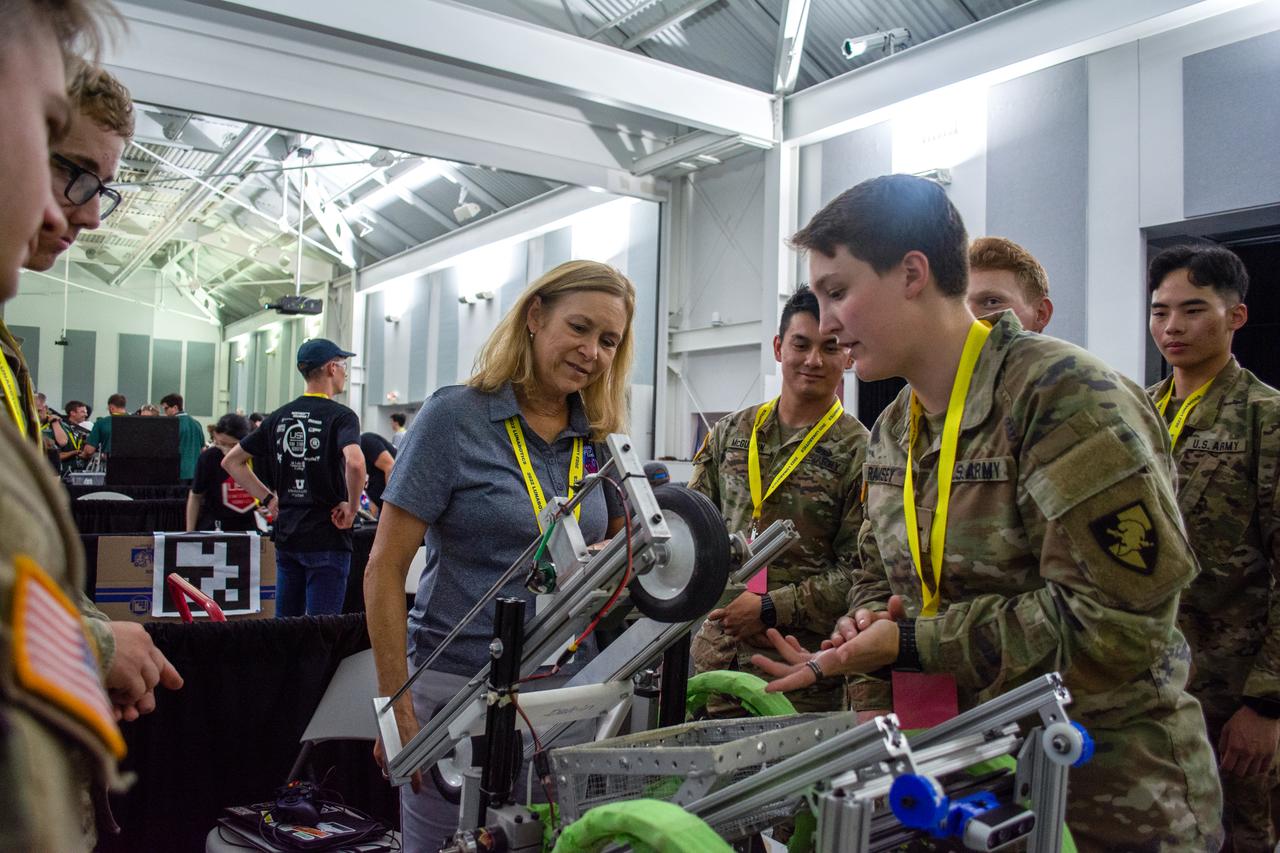

Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro, in the center, visits with students from the United States Military Academy (West Point), during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 23, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, on May 23, 2022. The students are preparing their robotic miner for its turn to dig in the mining arena. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
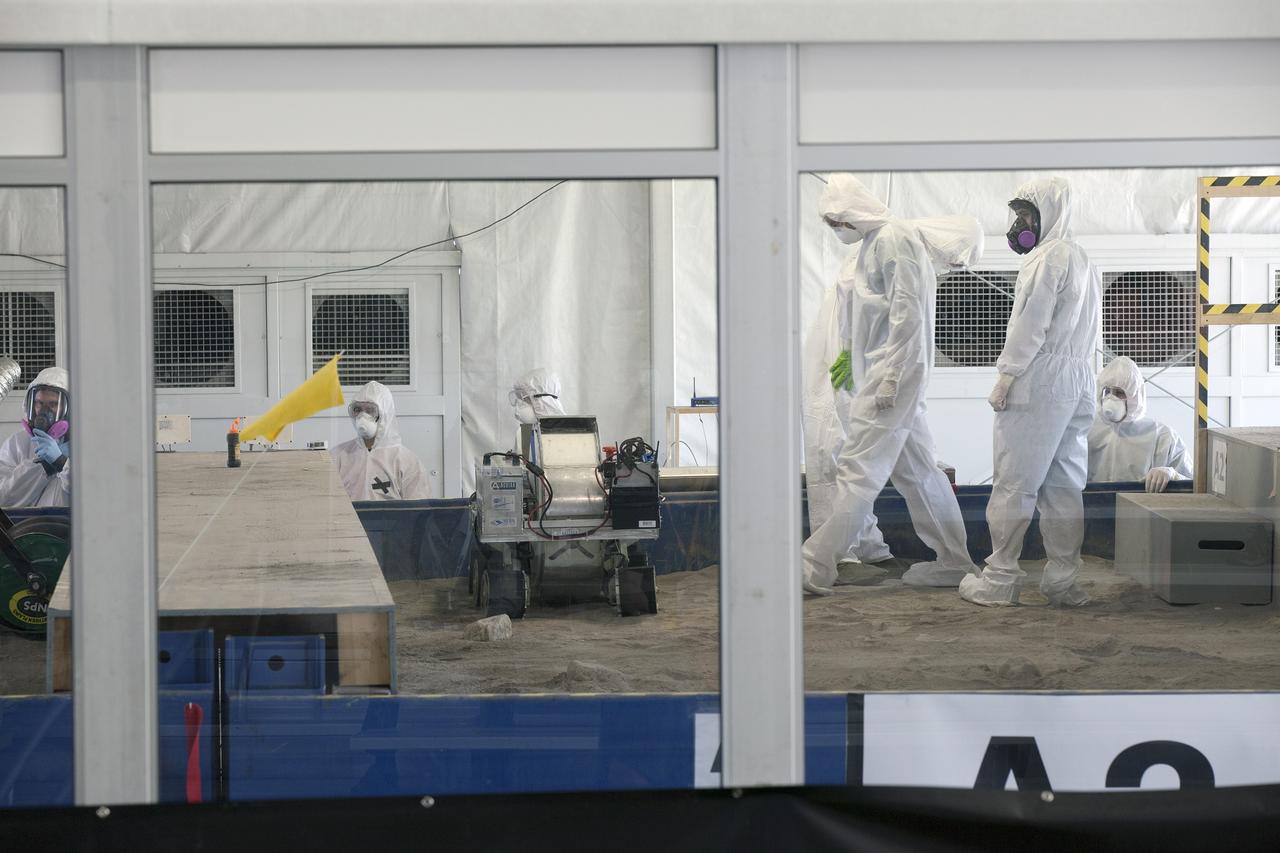

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Team members prepare their robot to dig in simulated Martian soil in the Caterpillar Mining Arena on the final day of NASA's 2014 Robotic Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. The competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields by expanding opportunities for student research and design. Teams use their remote-controlled robotics to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with a crushed material that has characteristics similar to Martian soil. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and move the most regolith within a specified amount of time. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/nasarmc. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
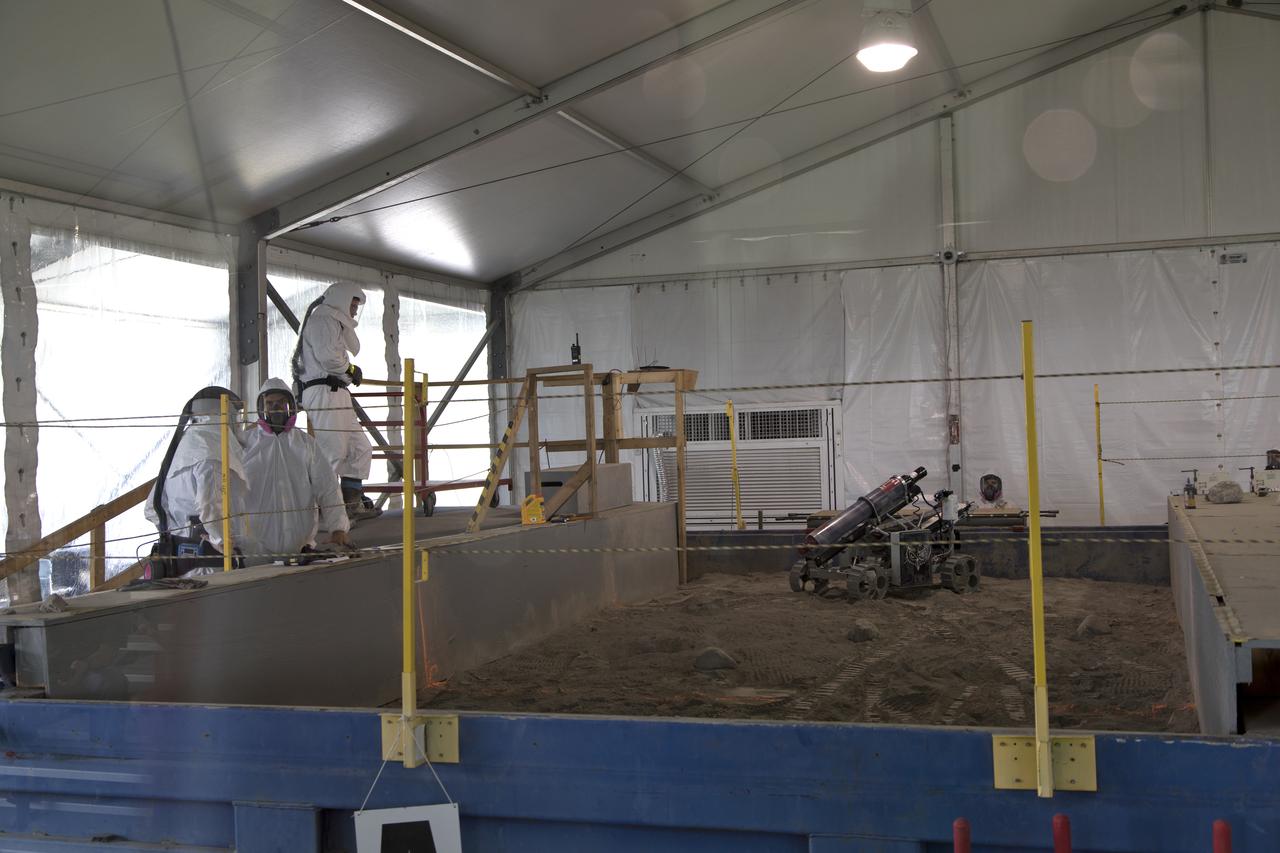

On the third day of NASA's 9th Robotic Mining Competition, May 16, judges watch as a robot miner digs in the dirt in the mining arena at NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 40 student teams from colleges and universities around the U.S. will use their mining robots to dig in a supersized sandbox filled with BP-1, or simulated Lunar soil, gravel and rocks, and participate in other competition requirements. The Robotic Mining Competition is a NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate project designed to encourage students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM fields. The project provides a competitive environment to foster innovative ideas and solutions that could be used on NASA's deep space missions.