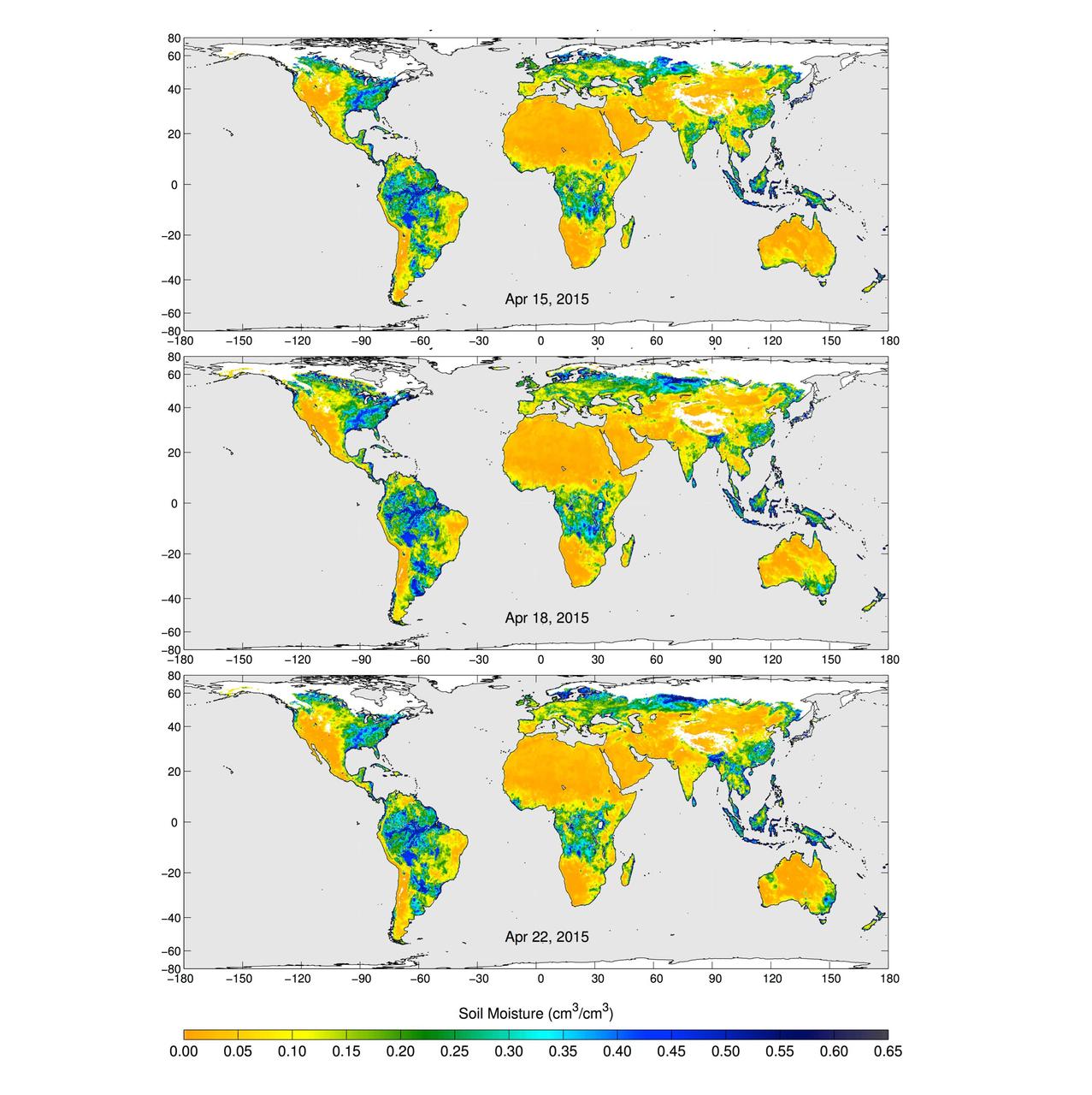
These maps of global soil moisture were created using data from the radiometer instrument on NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP observatory. Evident are regions of increased soil moisture and flooding during April, 2015.
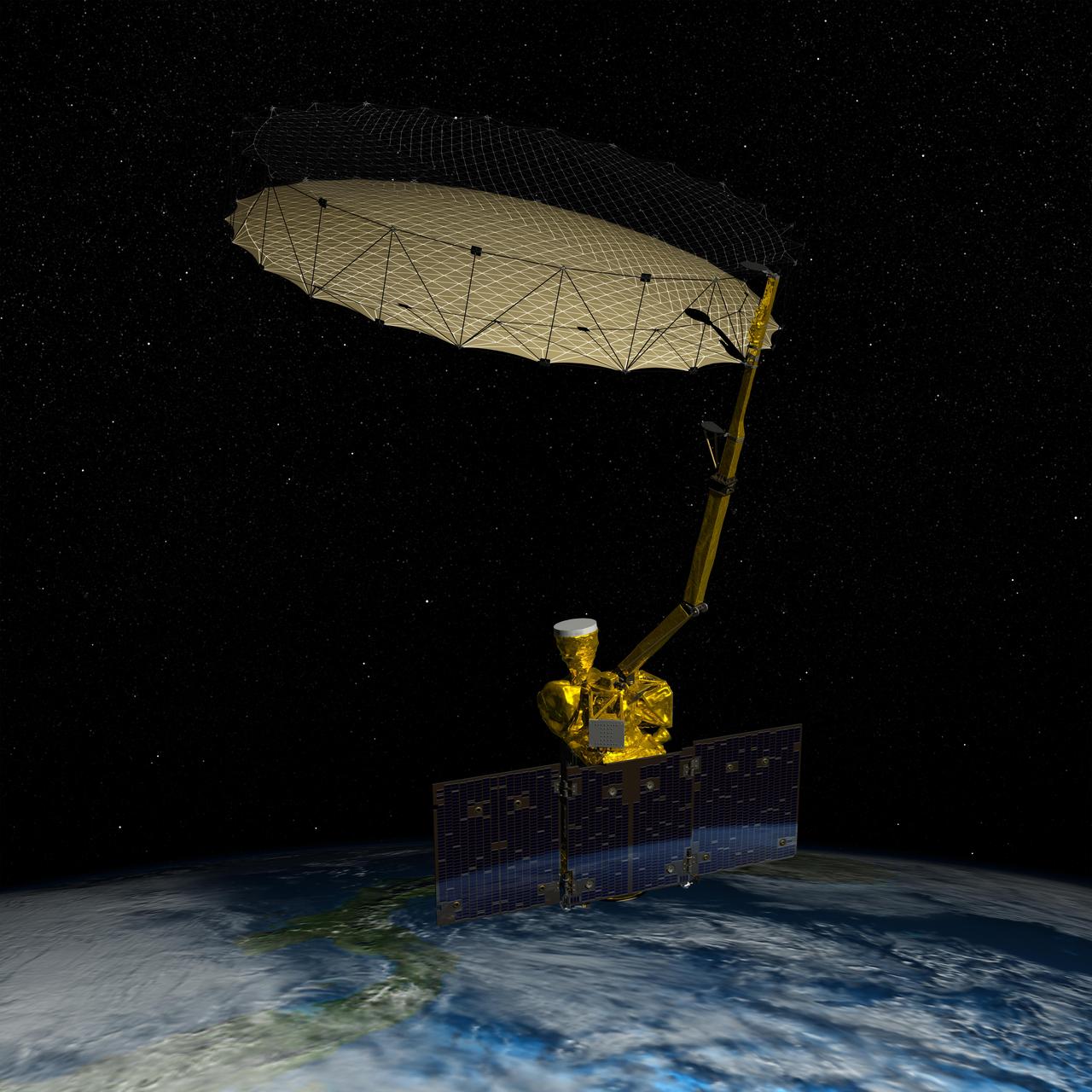
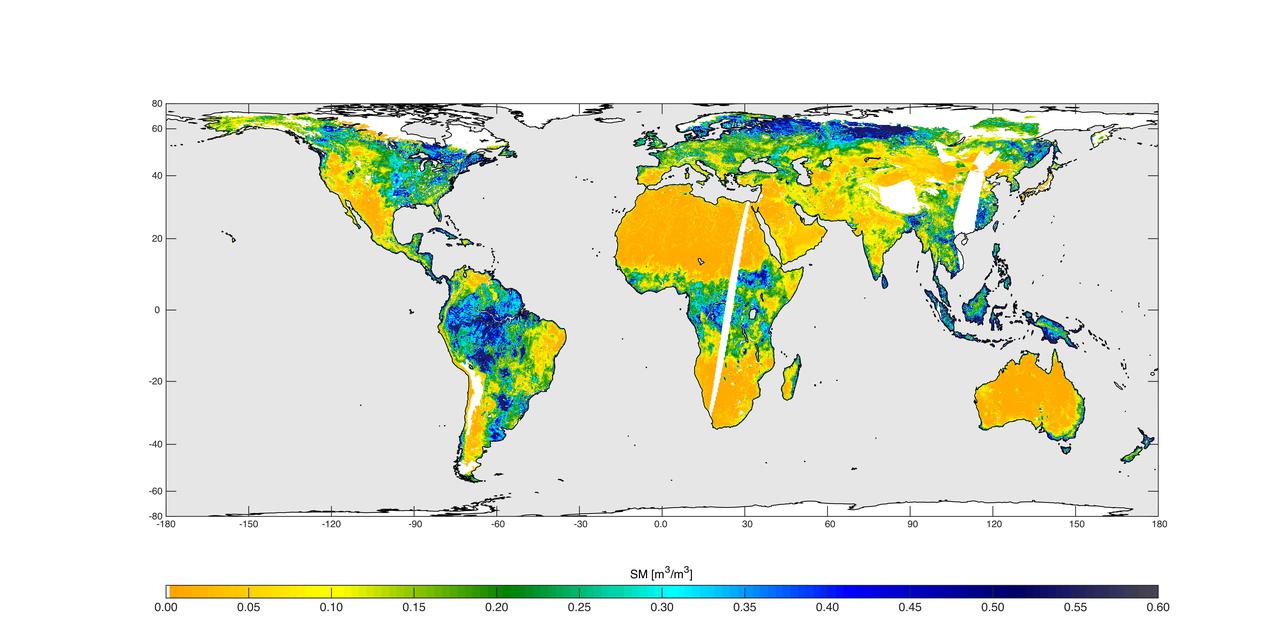
NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP mission will produce high-resolution global maps of soil moisture to track water availability around our planet and guide policy decisions.
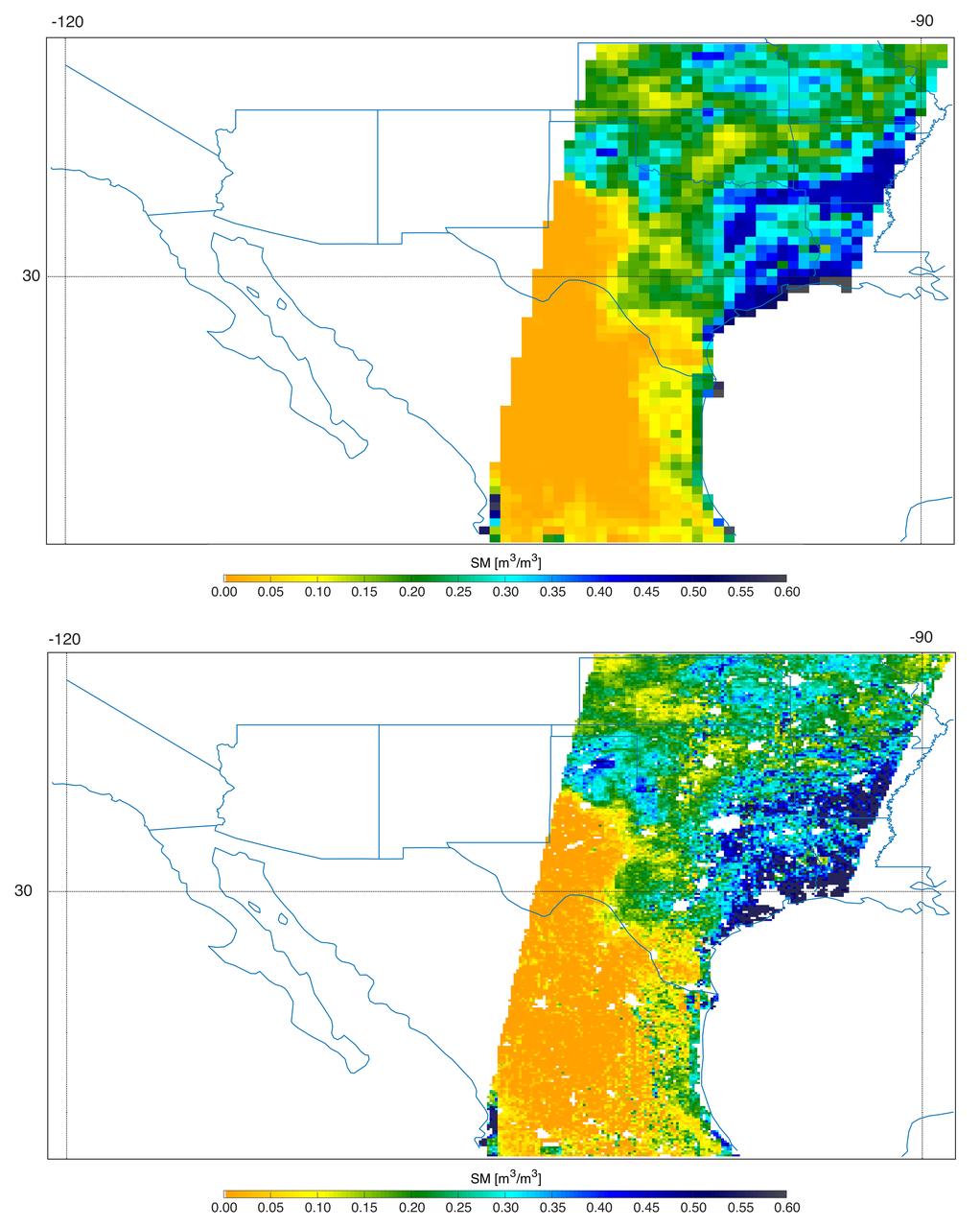
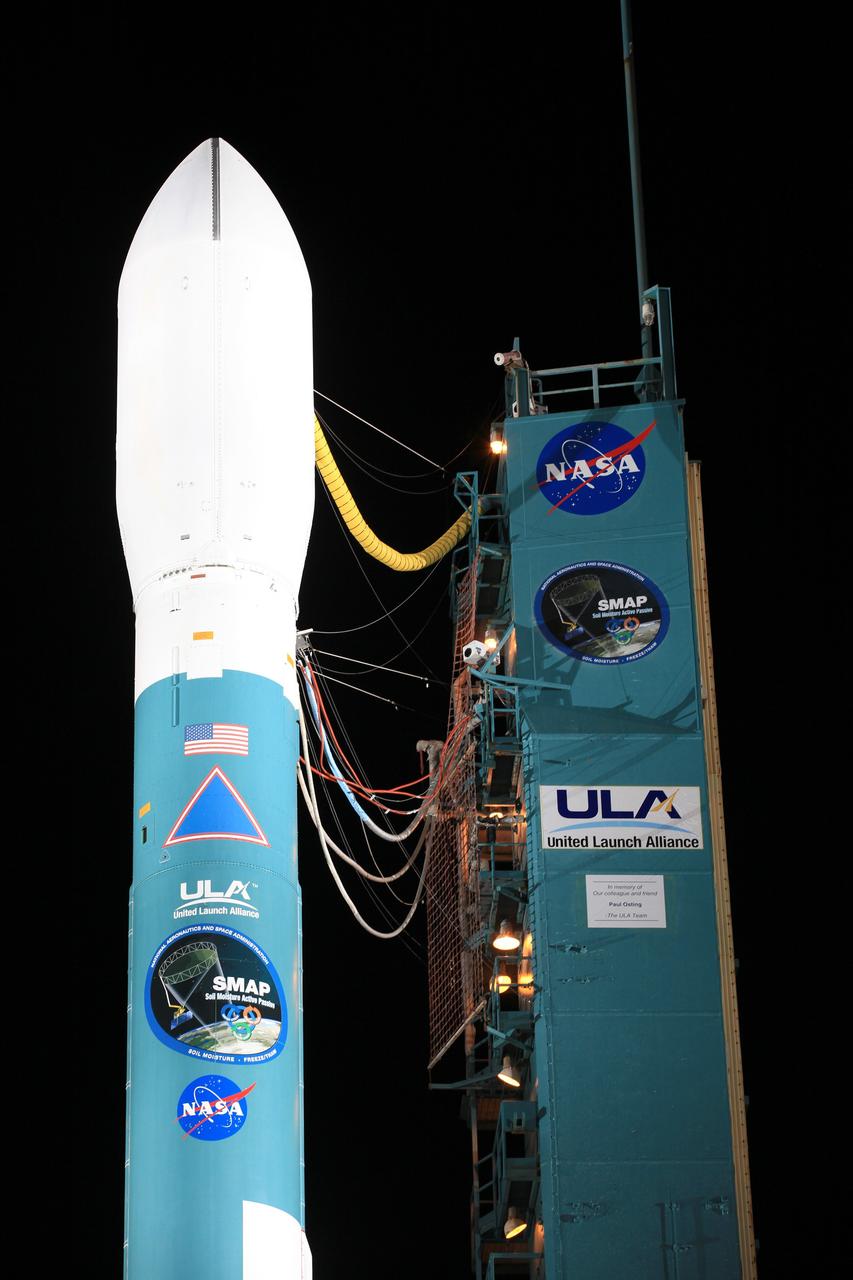
Southern U.S. NASA's SMAP soil moisture retrievals from April 27, 2015, when severe storms were affecting Texas. Top: radiometer data alone. Bottom: combined radar and radiometer data with a resolution of 5.6 miles (9 kilometers). The combined product reveals more detailed surface soil moisture features. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19338
This animation shows a time lapse of sea surface salinity and soil moisture from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite from April 2015 through February 2019. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23146
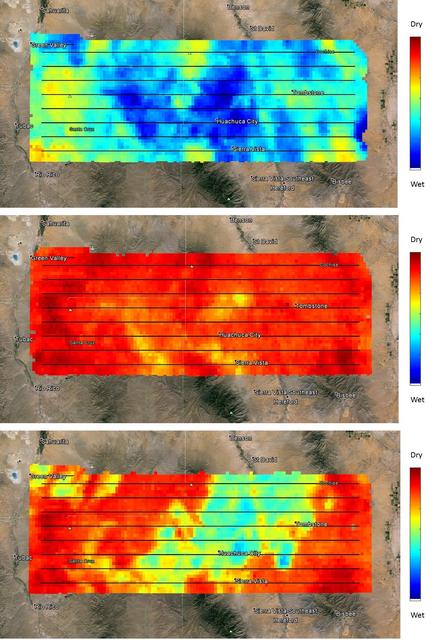
NASA's SMAP (Soil Moisture Active Passive) satellite observatory conducted a field experiment as part of its soil moisture data product validation program in southern Arizona on Aug. 2-18, 2015. The images here represent the distribution of soil moisture over the SMAPVEX15 (SMAP Validation Experiment 2015) experiment domain, as measured by the Passive Active L-band System (PALS) developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, which was installed onboard a DC-3 aircraft operated by Airborne Imaging, Inc. Blue and green colors denote wet conditions and dry conditions are marked by red and orange. The black lines show the nominal flight path of PALS. The measurements show that on the first day, the domain surface was wet overall, but had mostly dried down by the second measurement day. On the third day, there was a mix of soil wetness. The heterogeneous soil moisture distribution over the domain is typical for the area during the North American Monsoon season and provides excellent conditions for SMAP soil moisture product validation and algorithm enhancement. The images are based on brightness temperature measured by the PALS instrument gridded on a grid with 0.6-mile (1-kilometer) pixel size. They do not yet compensate for surface characteristics, such as vegetation and topography. That work is currently in progress. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19879
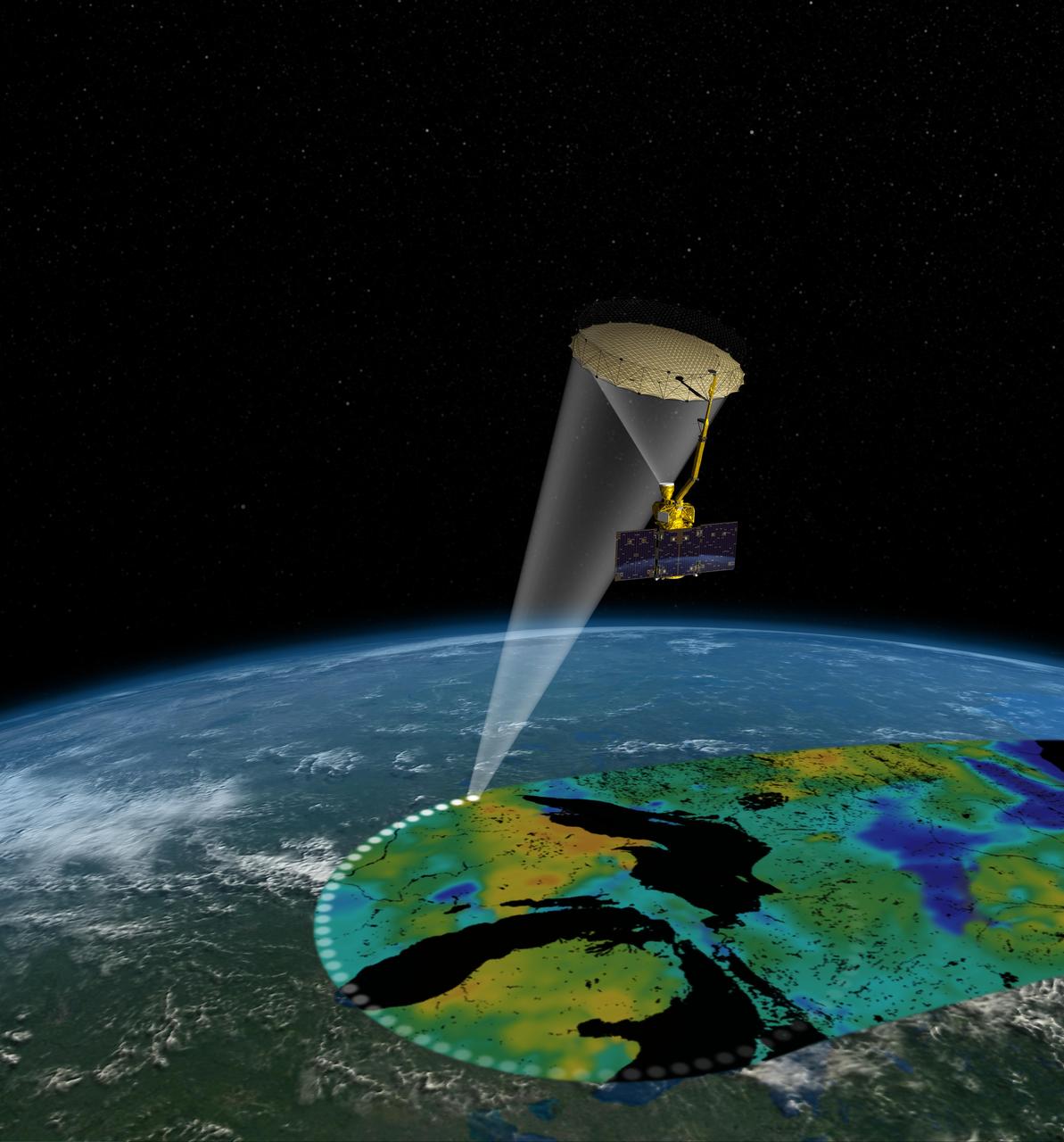
Artist rendering of the Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP satellite. The width of the region scanned on Earth surface during each orbit is about 620 miles 1,000 kilometers.
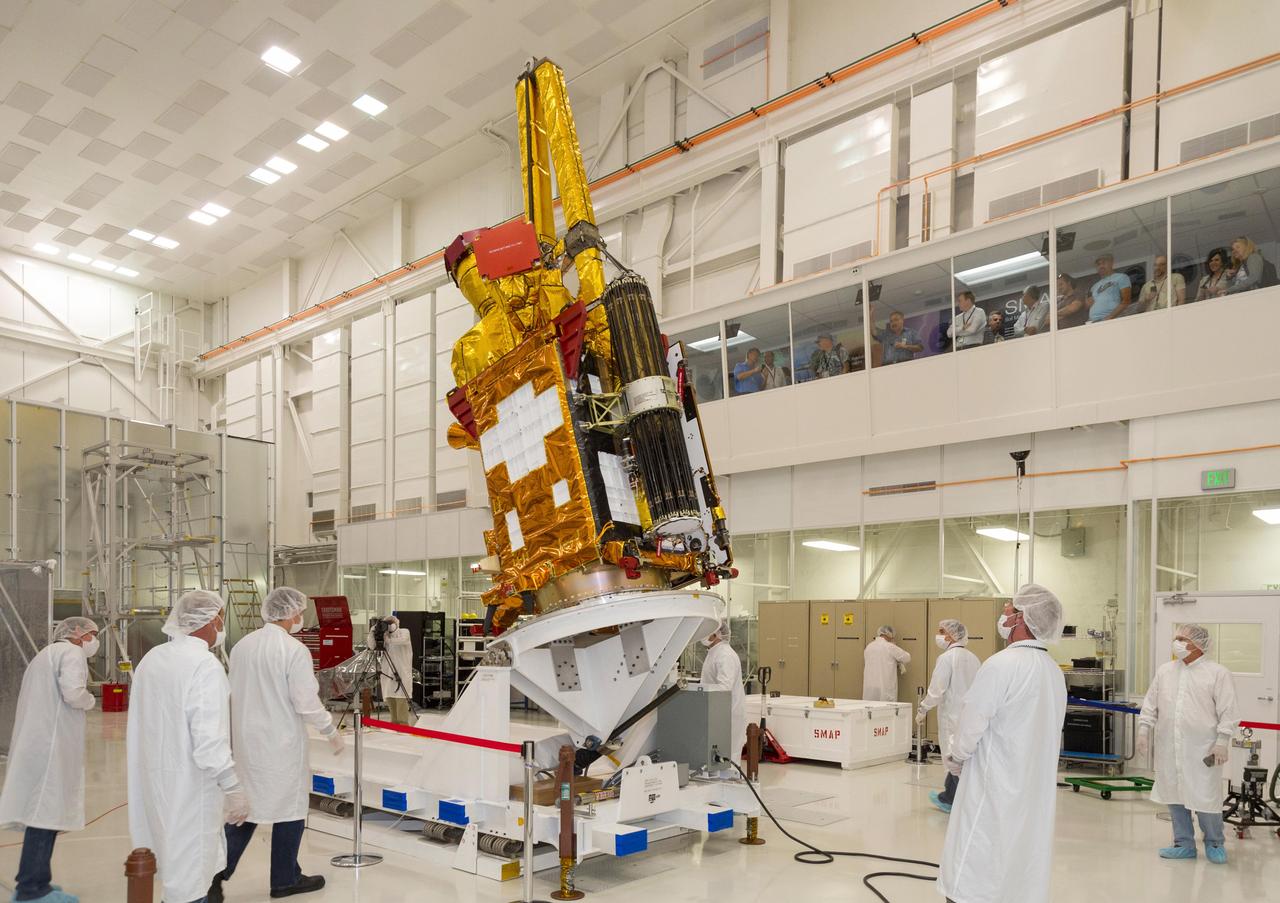

NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP spacecraft is slowly lowered into place in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California.
High-resolution global soil moisture map from NASA SMAP combined radar and radiometer instruments, acquired between May 4 and May 11, 2015 during SMAP commissioning phase. The map has a resolution of 5.6 miles (9 kilometers). The data gap is due to turning the instruments on and off during testing. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19337
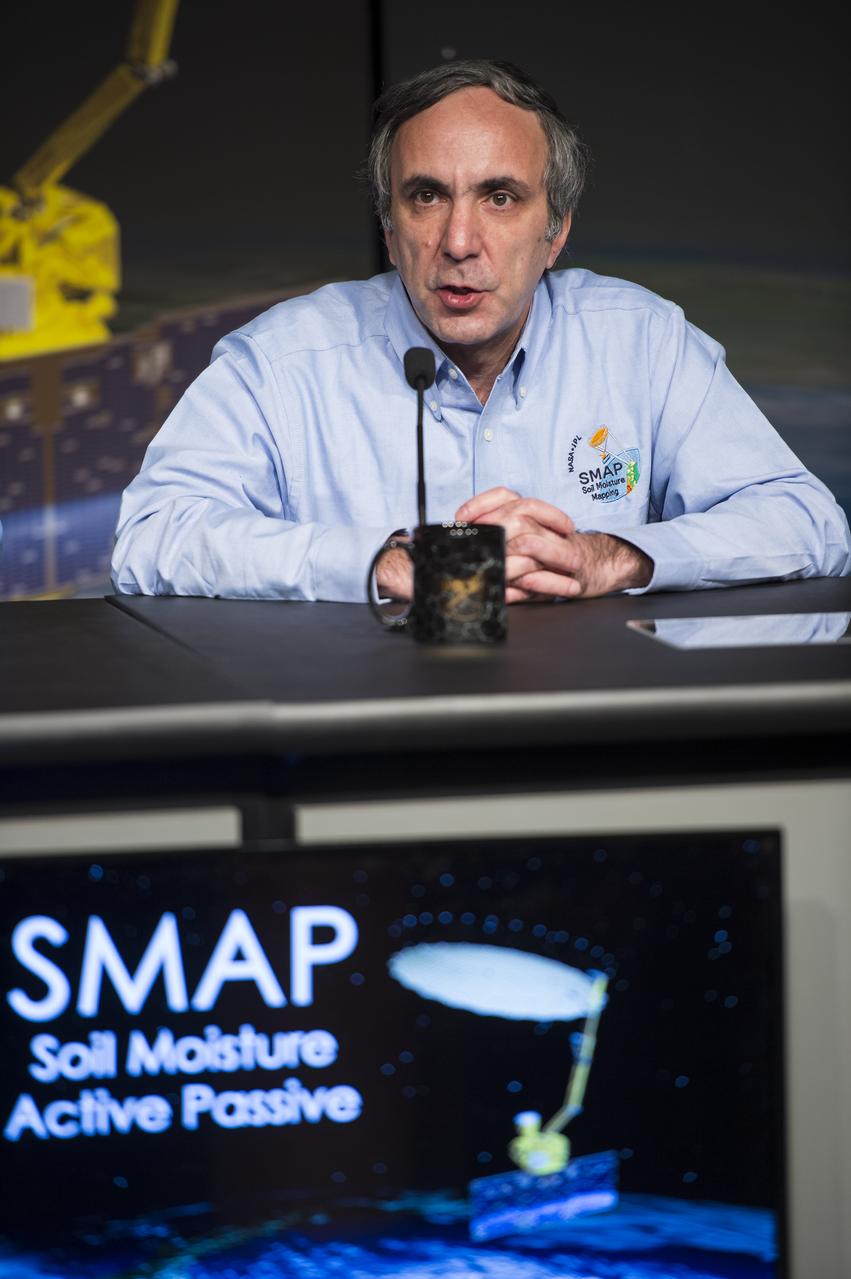

Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, speaks during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
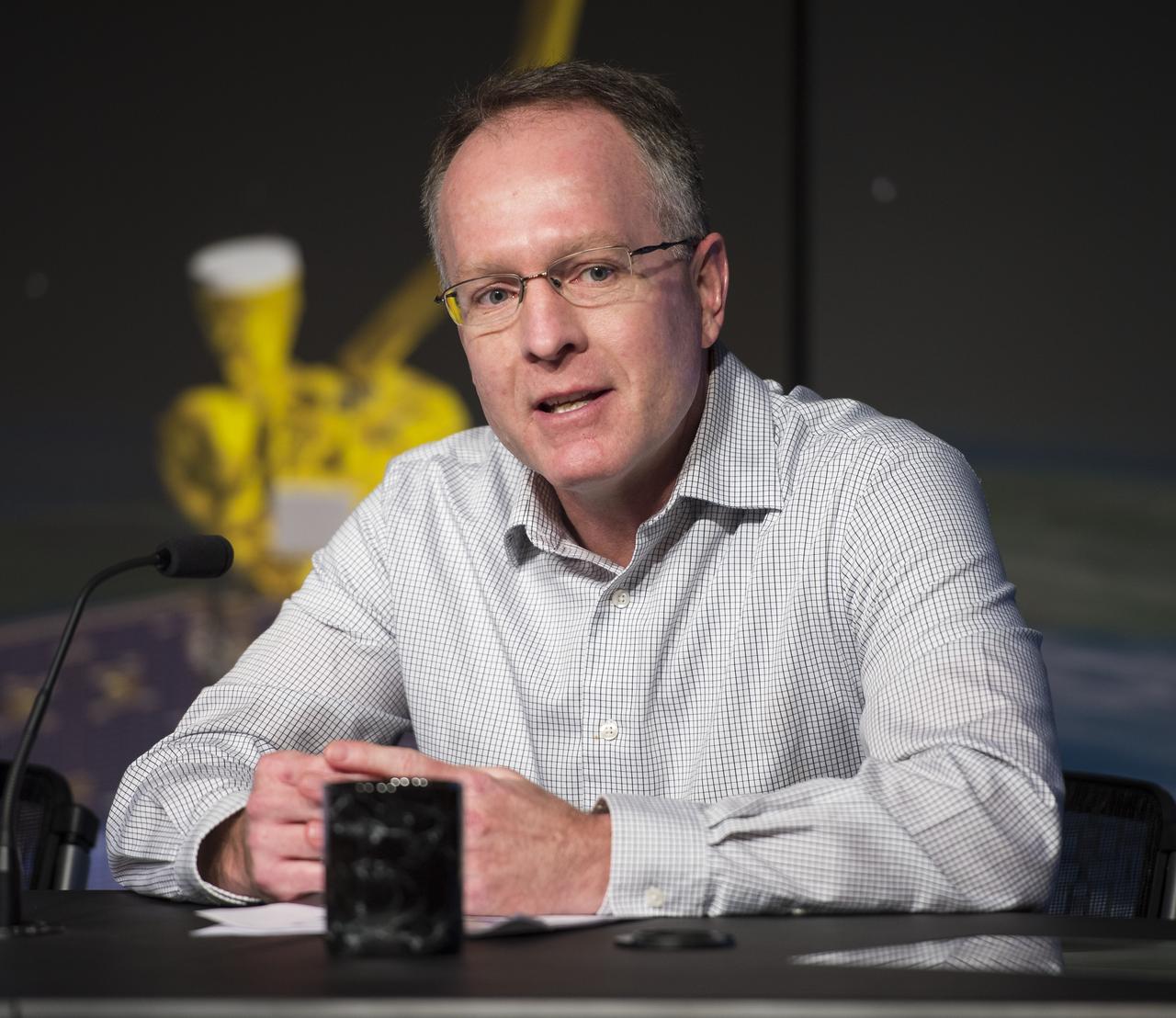

Brad Doorn, SMAP applications lead, Science Mission Directorate’s Applied Sciences Program at NASA Headquarters speaks during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
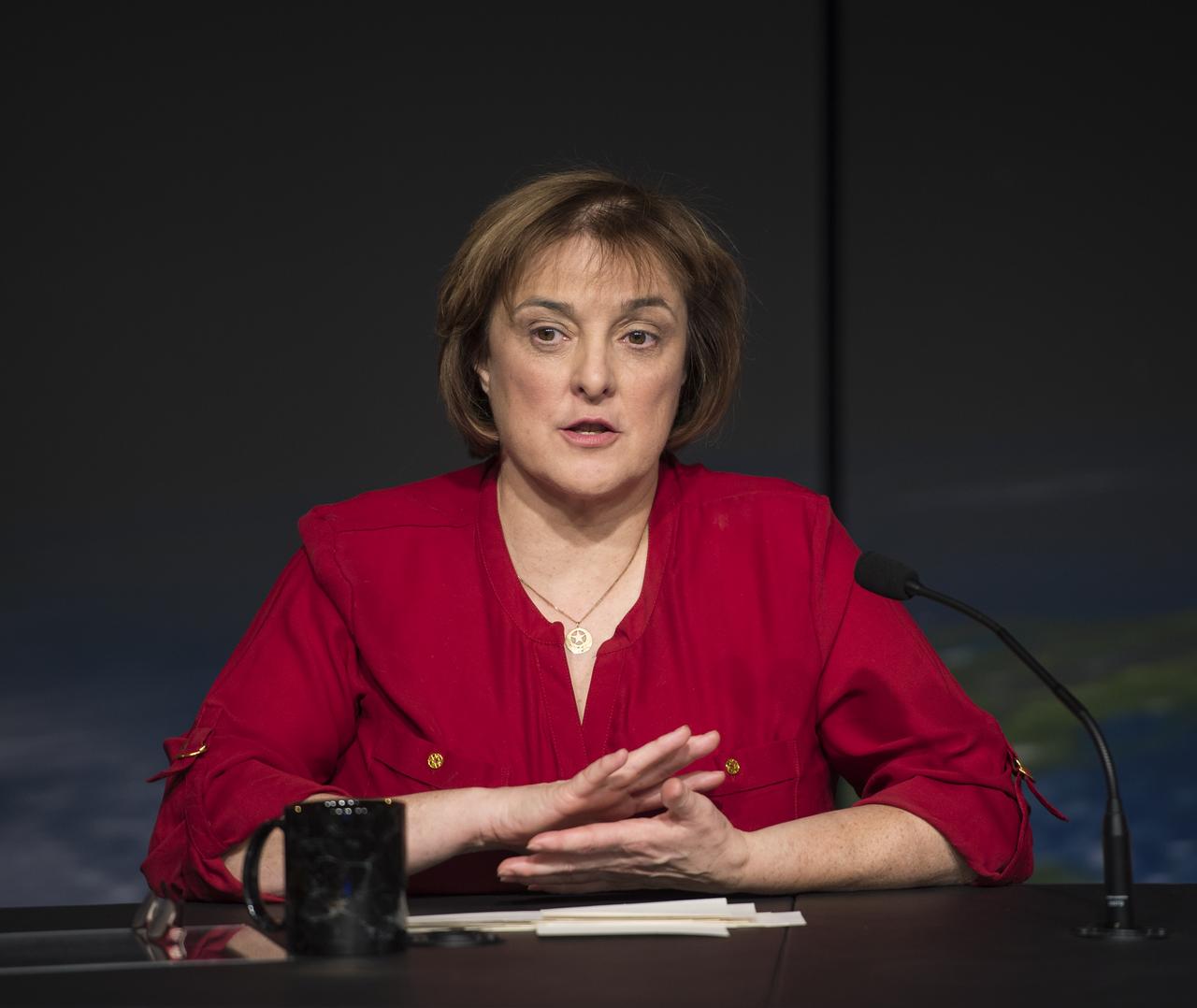

Christine Bonniksen, SMAP program executive with the Science Mission Directorate’s Earth Science Division at NASA Headquarters speaks during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Kent Kellogg, SMAP project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, CA, speaks during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
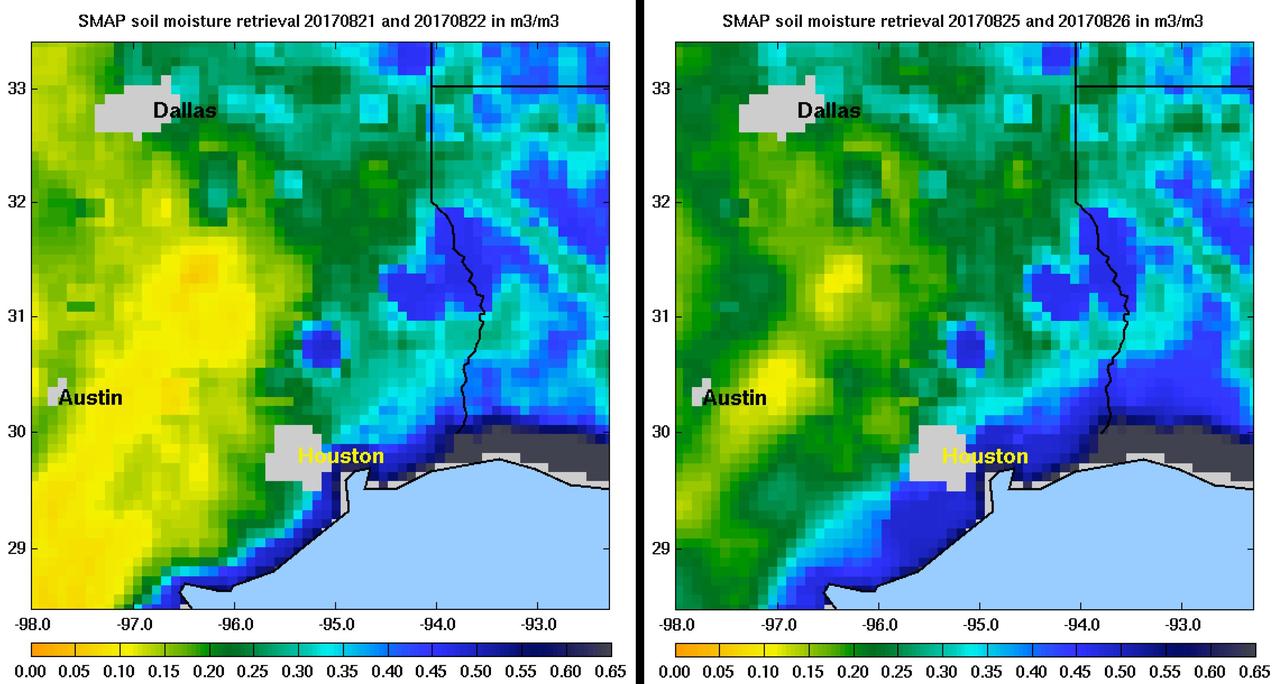
Images of soil moisture conditions in Texas near Houston, generated by NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite before and after the landfall of Hurricane Harvey can be used to monitor changing ground conditions due to Harvey's rainfall. As seen in the left panel, SMAP observations show that soil surface conditions were already very wet a few days before the hurricane made landfall (August 21/22), with moisture levels in the 20 to 40 percent range. Such saturated soil surfaces contributed to the inability of water to infiltrate more deeply into soils, thereby increasing the likelihood of flooding. After Harvey made landfall, the southwest portion of Houston became exceptionally wet, as seen in the right panel image from August 25/26, signaling the arrival of heavy rains and widespread flooding. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21926
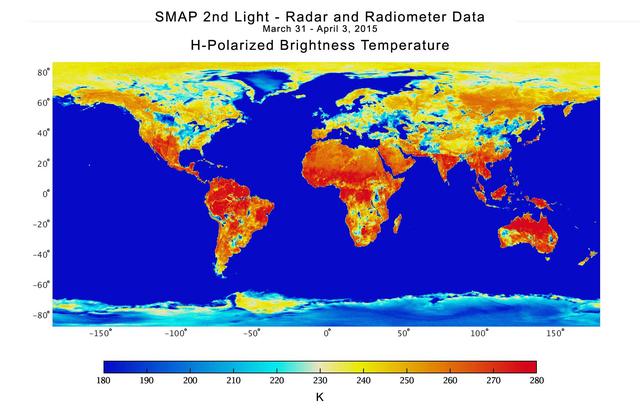
With its antenna now spinning at full speed, NASA new Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP observatory has successfully re-tested its science instruments and generated its first global maps, a key step to beginning routine science operations in May, 2015
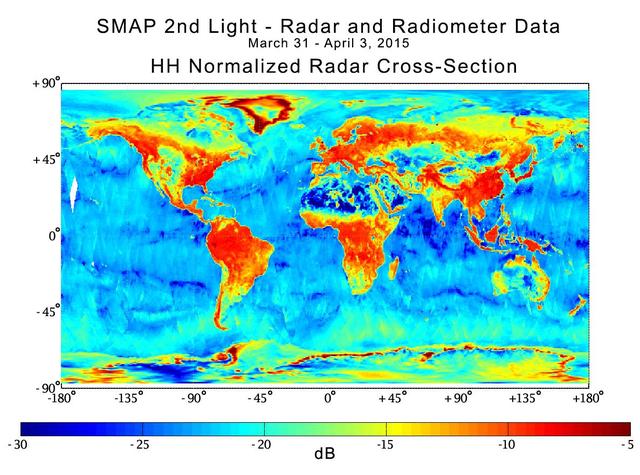
With its antenna now spinning at full speed, NASA new Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP observatory has successfully re-tested its science instruments and generated its first global maps, a key step to beginning routine science operations in May, 2015

Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, center, speaks during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
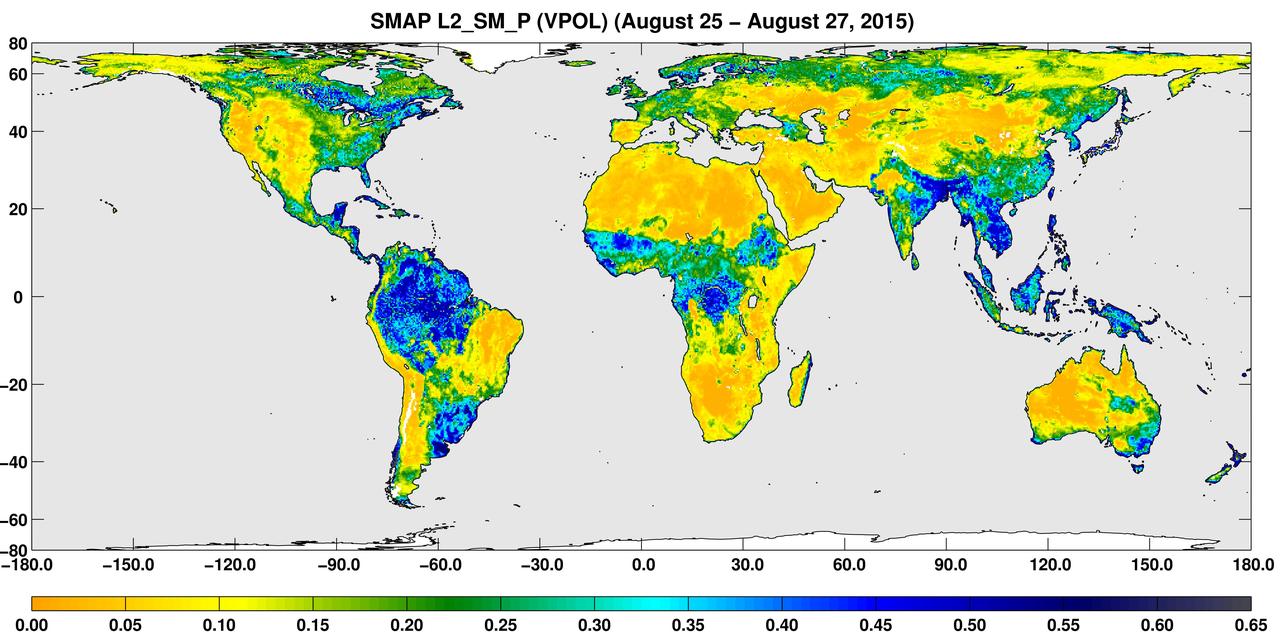
A three-day composite global map of surface soil moisture as retrieved from NASA SMAP radiometer instrument between Aug. 25-27, 2015. Dry areas appear yellow/orange, such as the Sahara Desert, western Australia and the western U.S. Wet areas appear blue, representing the impacts of localized storms. White areas indicate snow, ice or frozen ground. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19877
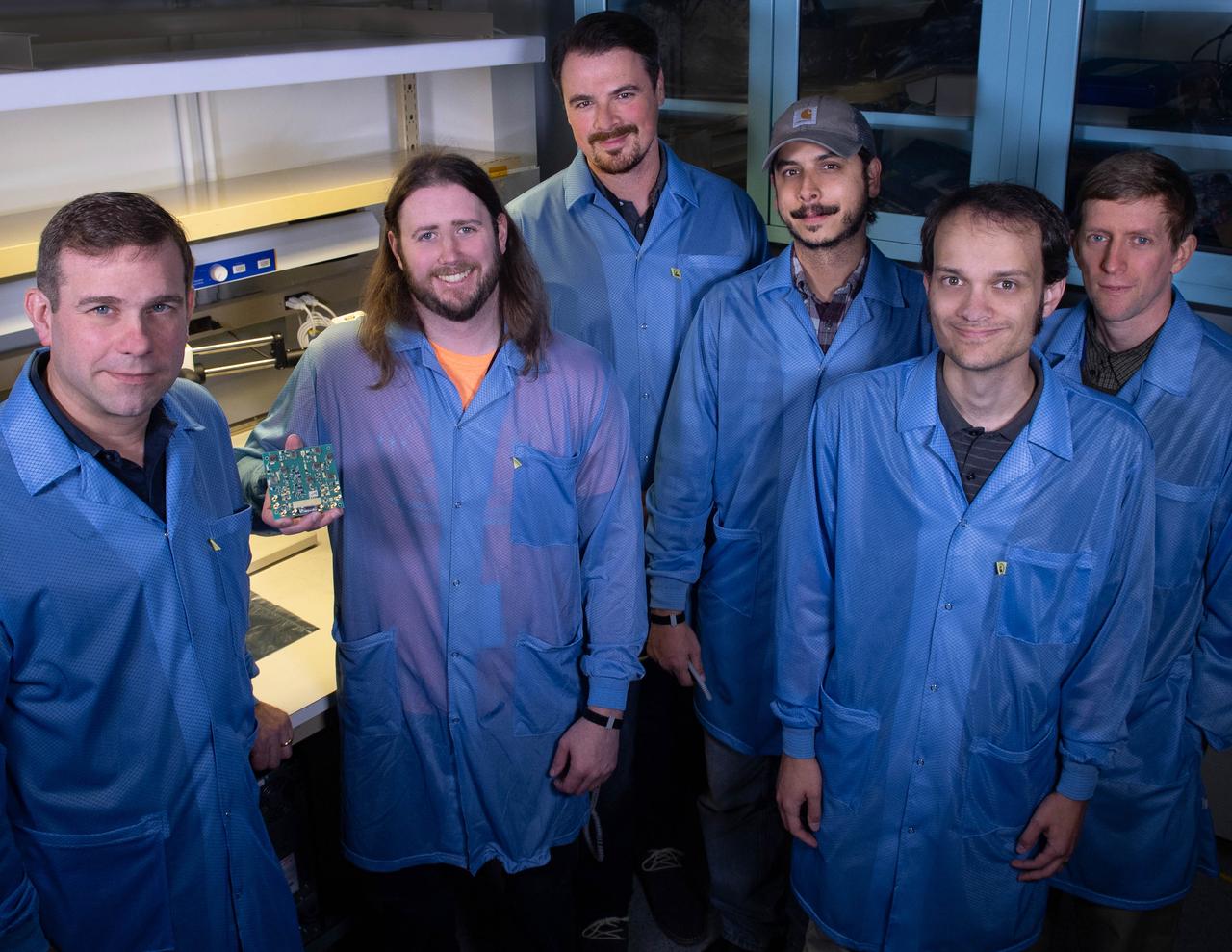

Several Goddard technologists are involved in a new CubeSat technology-demonstration mission called SNoOPI, which employs a novel remote-sensing technique for measuring soil-moisture levels. From left to right: Jeffrey Piepmeier, Chase Kielbasa, who is holding a first-generation prototype circuit board for the SNoOPI instrument, Joseph Knuble, Manuel Vega, Michael Coon, and Derek Hudson.
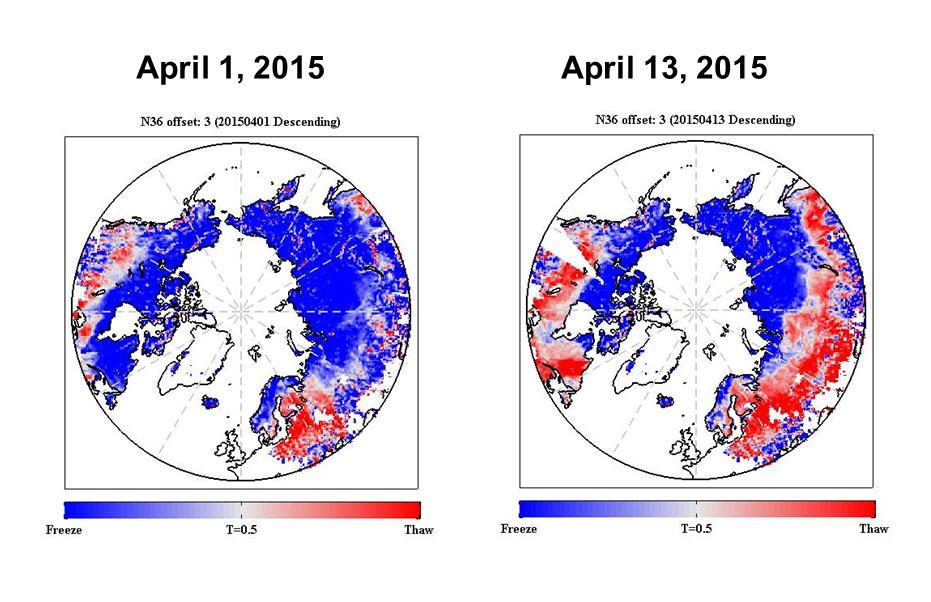
The radar measurements made by NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP observatory are sensitive to whether land surfaces are frozen or thawed.

Christine Bonniksen, SMAP program executive with the Science Mission Directorate’s Earth Science Division, NASA Headquarters, left, Kent Kellogg, SMAP project manager, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), second from left, Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, second from right, and Brad Doorn, SMAP applications lead, Science Mission Directorate’s Applied Sciences Program, NASA Headquarters, right, are seen during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Christine Bonniksen, SMAP program executive with the Science Mission Directorate’s Earth Science Division, NASA Headquarters, left, Kent Kellogg, SMAP project manager, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), second from left, Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, second from right, and Brad Doorn, SMAP applications lead, Science Mission Directorate’s Applied Sciences Program, NASA Headquarters, right, are seen during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

This image, created at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory JPL, shows the Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP mission, specifically depicting how the scanning antenna will fly in space and the swath coverage over the Earth.
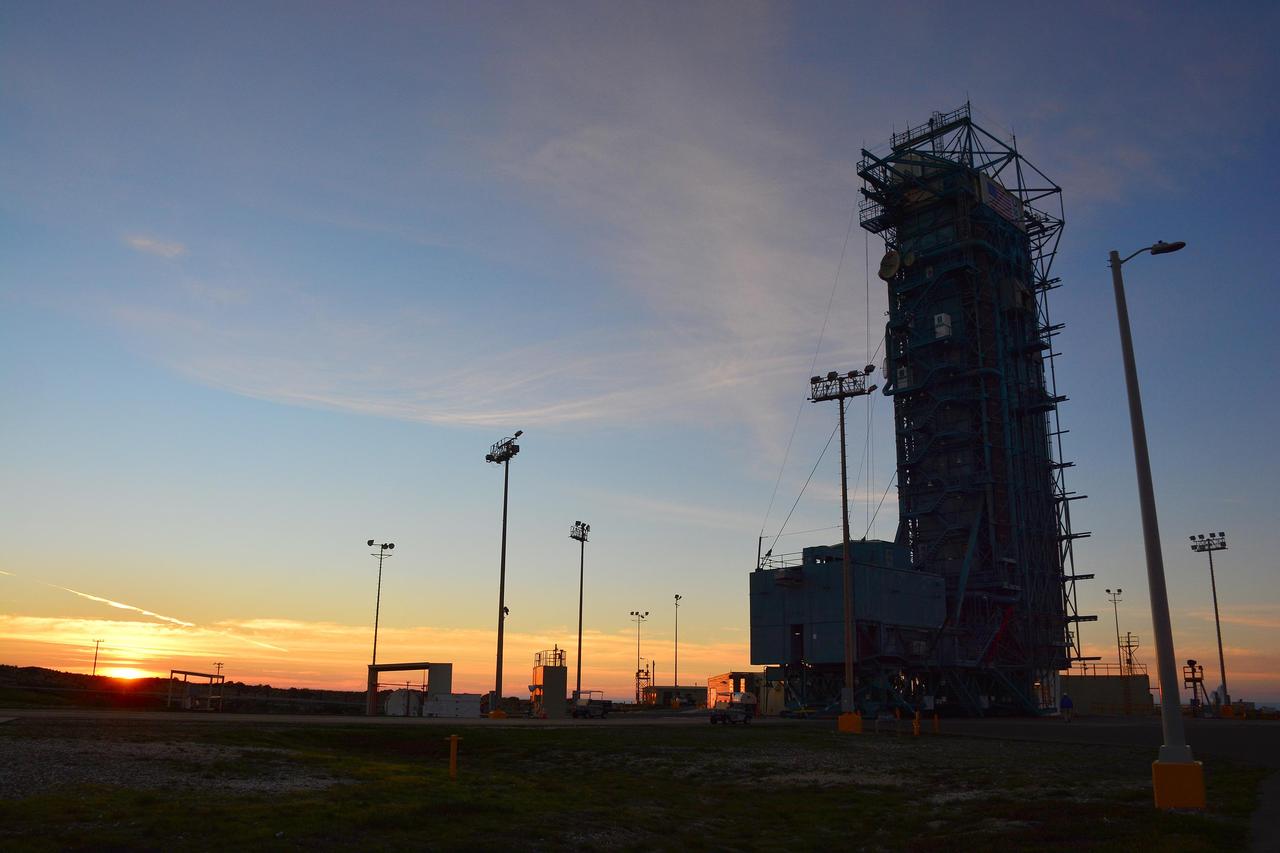

The sun sets behind Space Launch Complex 2, Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, where NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP mission satellite is being prepared for liftoff. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29.
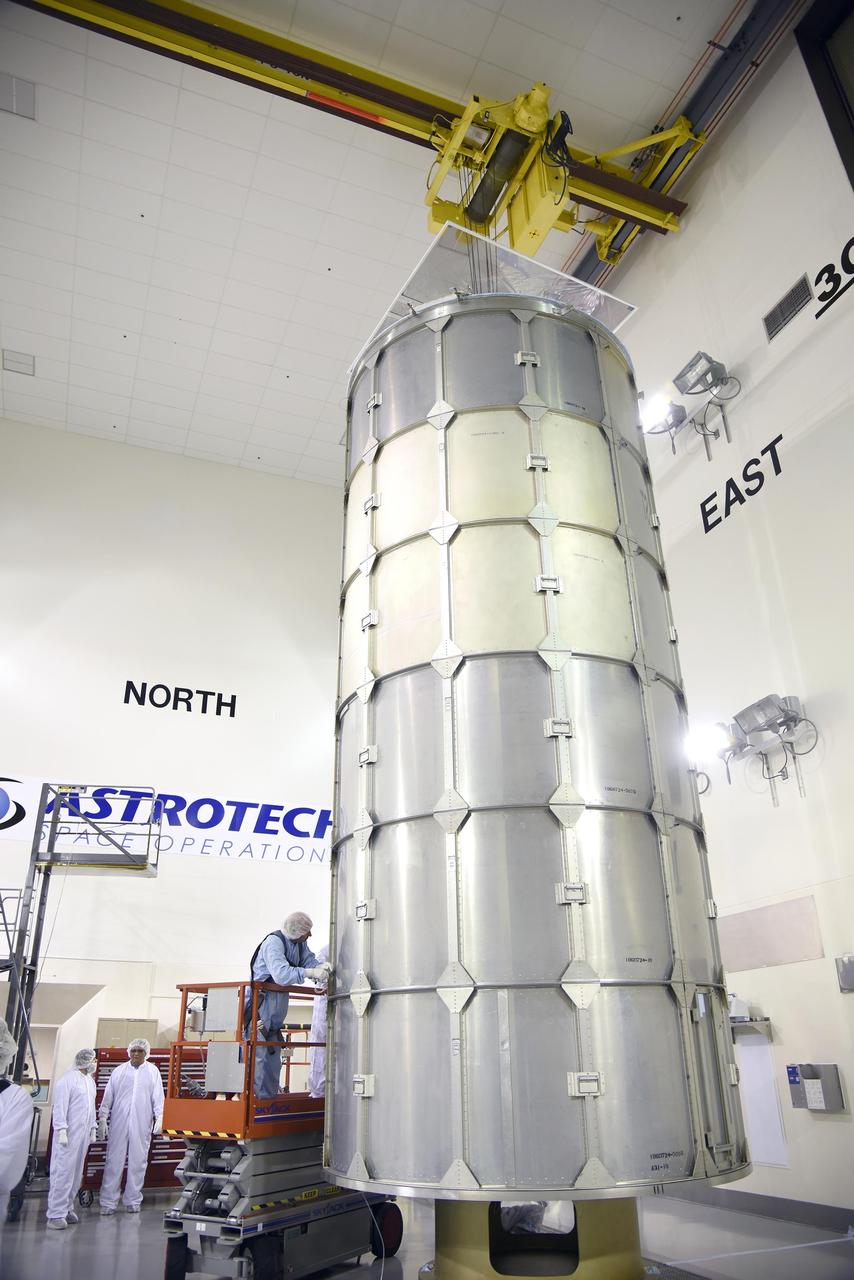

In the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians secure a transportation canister around NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP spacecraft for its move to the launch pad.
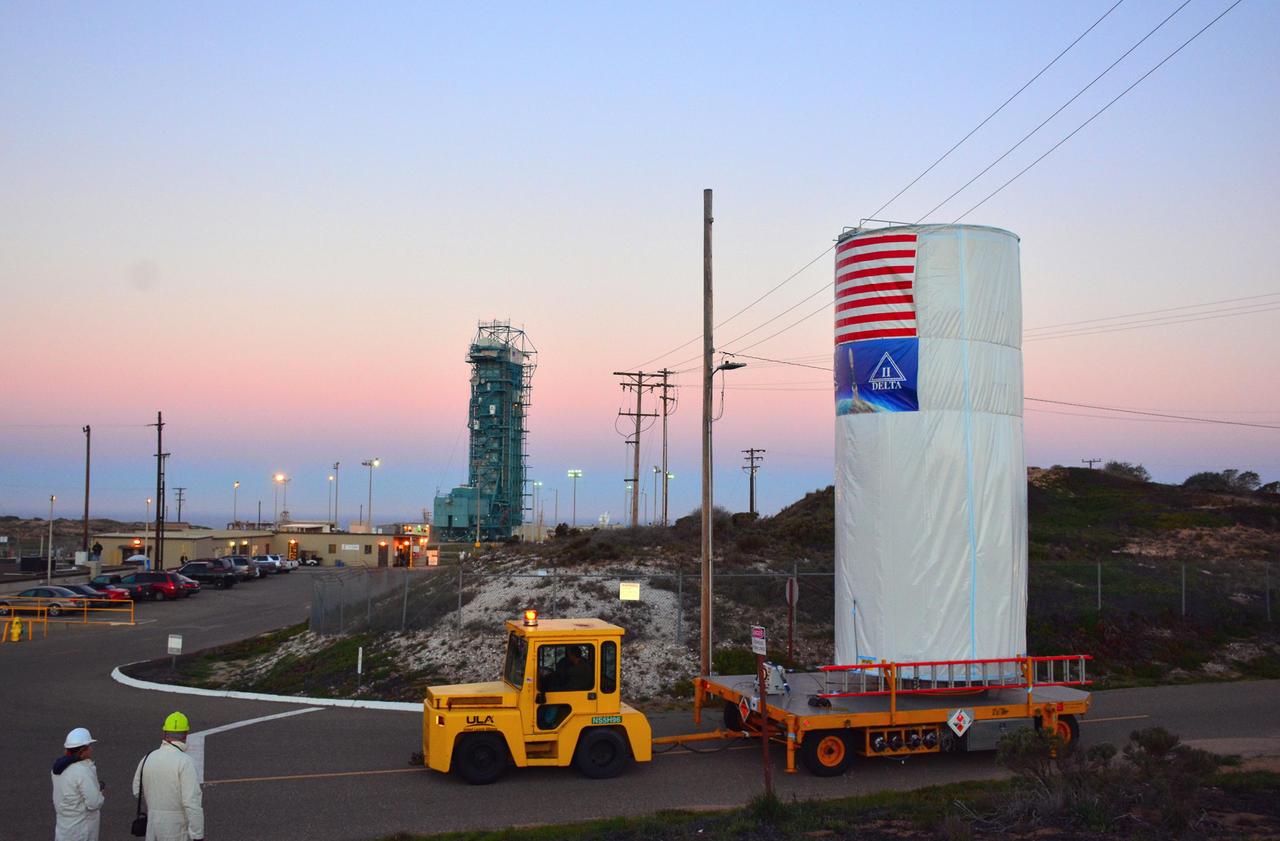

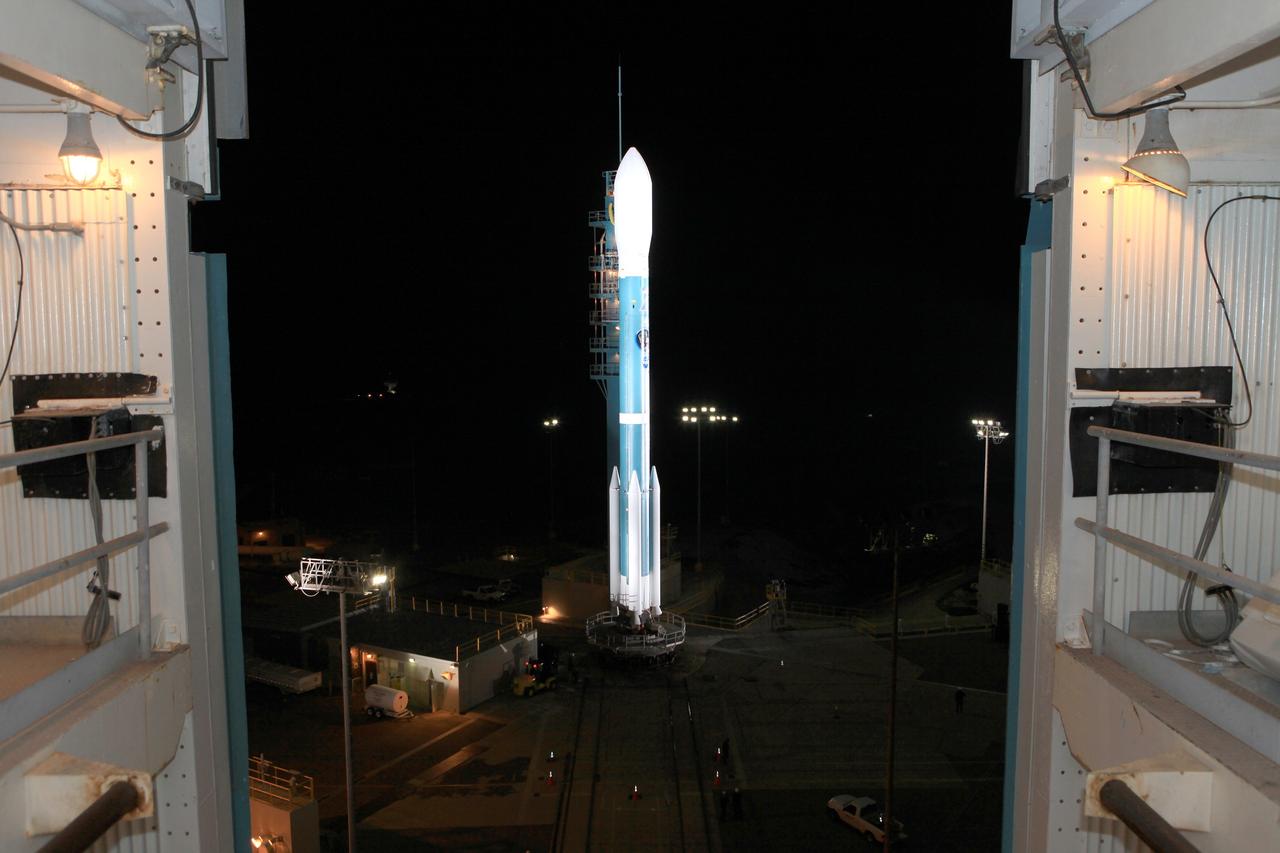
NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP satellite is transported across Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to Space Launch Complex 2, where it will be mated to a Delta II rocket for launch, targeted for Jan. 29.
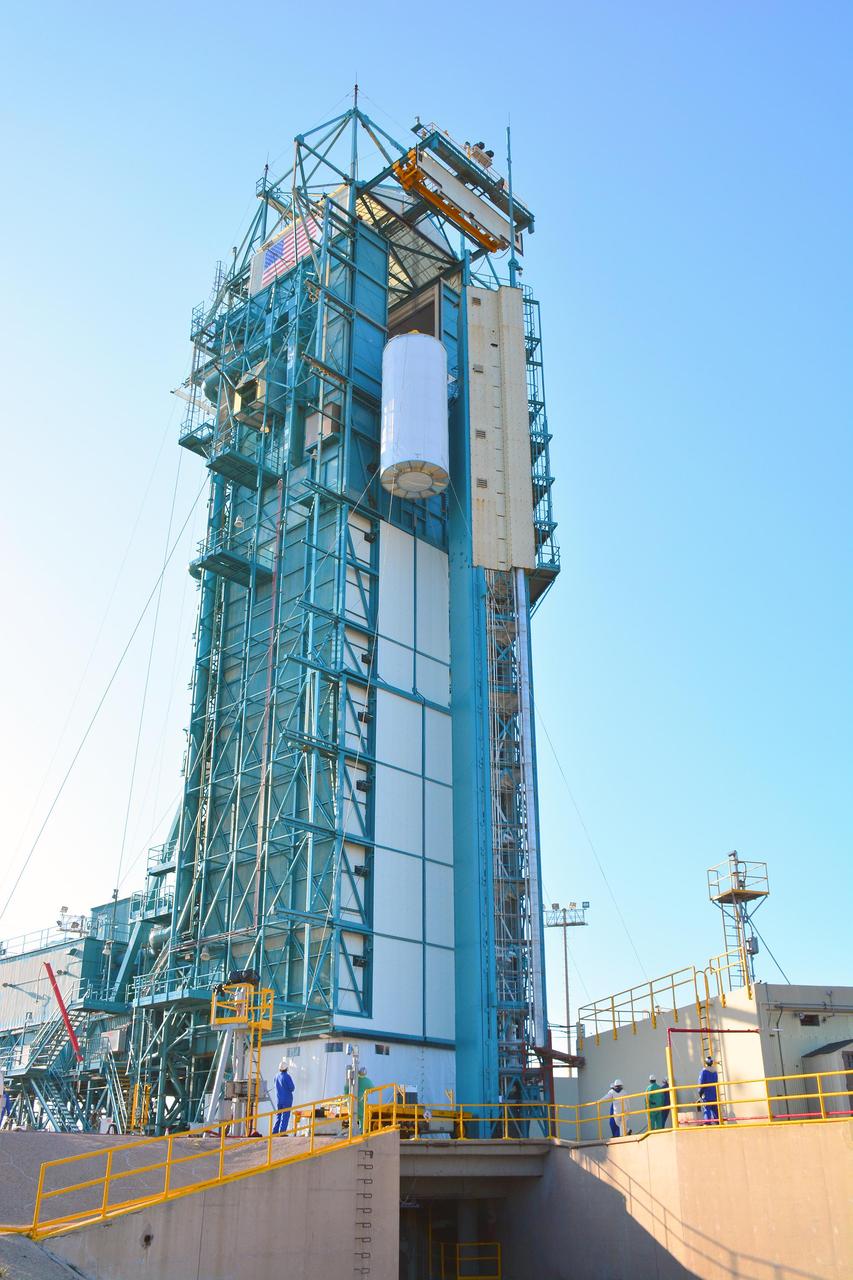

At Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP mission satellite is lifted up the side of a mobile service tower for mating to its Delta II rocket.
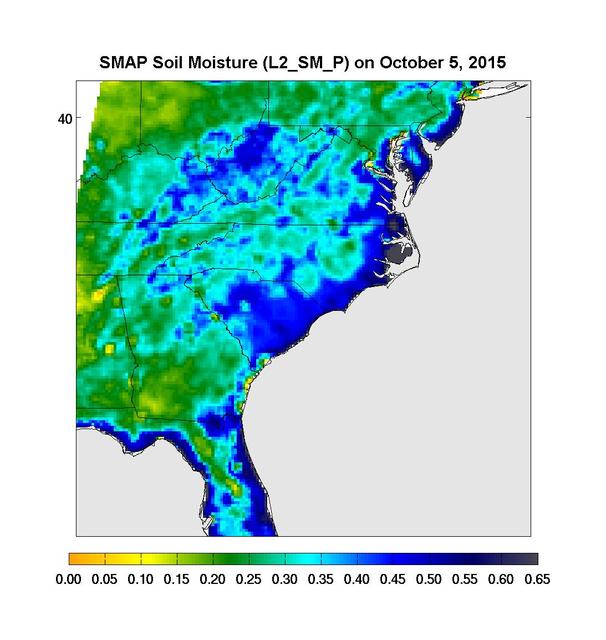
Surface soil moisture in the Southeastern United States as retrieved from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite observatory at around 6 a.m. on Oct. 5, 2015. Large parts of South Carolina appear blue, representing the impact of heavy localized rains and flooding. Regions in blue indicate areas with saturated soil conditions and possible standing water. Large-scale flooding was experienced all over South Carolina on Oct. 5-6, 2015. As of Oct. 7, 17 deaths had been attributed to these floods, with heavy economic losses. In some regions, the intensity of these floods was described as a 1,000-year storm (1-in-1,000 chance of happening in any given year). At least 14 dams have already failed as a result of these floods. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20001

NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive spacecraft is lowered onto the Delta II payload attach structure in the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, in preparation for launch, to take place no sooner than Jan. 29.
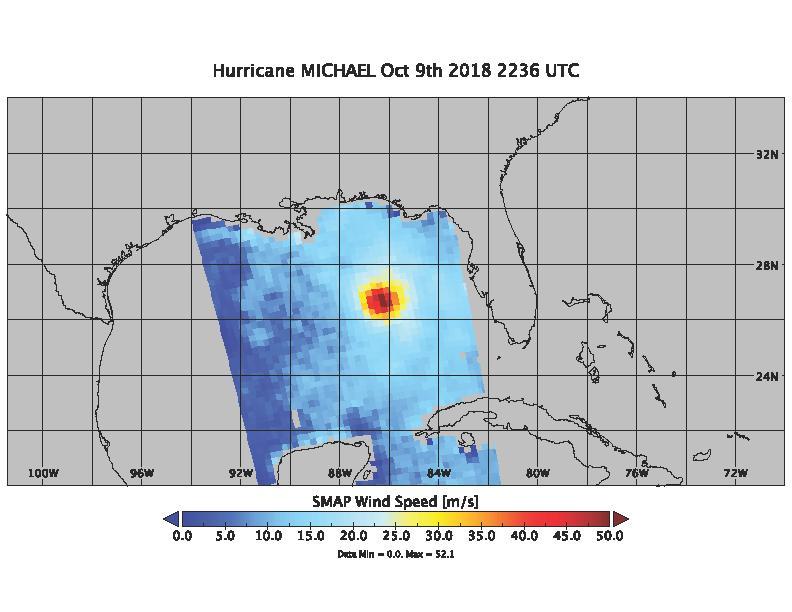
On Oct. 9, 2018 at about 4:30pm EDT, the NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Radiometer got one more snap shot of Hurricane Michael. The radiance acquired by the SMAP L-band Microwave Radiometer can see through clouds and rain, and is sensitive to the extreme ocean surface winds under a tropical storm or hurricane. Hurricane Michael made landfall in the Florida panhandle Wednesday as a major Category 4 storm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22751
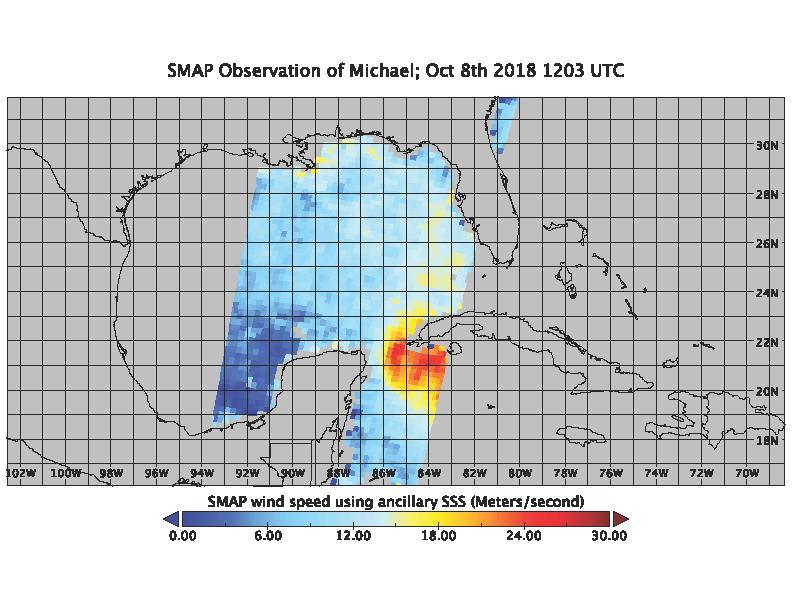
On the morning of Oct. 8, 2018, the NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Radiometer got a snapshot of Hurricane Michael, which has intensified to a Category 2 hurricane over the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico. The radiance acquired by the SMAP L-band Microwave Radiometer can see through clouds and rains, and is sensitive to the extreme ocean surface winds under a tropical storm or hurricane. Areas in red represent higher wind speeds; areas in blue have lower wind speeds. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22747
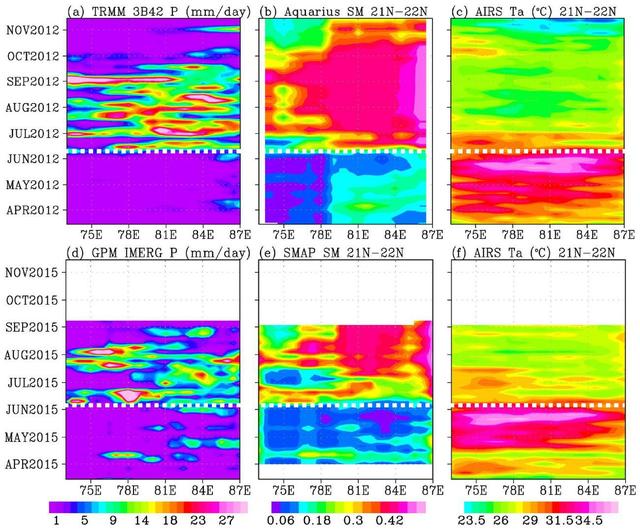
In June 2015, news organizations around the world reported on a deadly heat wave in India that killed more than 2,300 people. Prior to the arrival of the summer monsoon in India, weather conditions had been extremely hot and dry. Such conditions can lead to economic and agricultural disaster, human suffering and loss of life. NASA satellite sensors are allowing scientists to characterize pre-monsoon droughts and heat waves and postulate their scientific cause. This figure shows the longitude-time variations, averaged between 21 and 22 degrees North, across the middle of the India subcontinent from mid-April to mid-June. Longitude from the Arabian Sea to the Bay of Bengal is represented on the horizontal axis; while the vertical axis shows the timeframe. Rainfall is shown on the left, soil moisture is in the center, and surface air temperature is on the right. For both years (2012 and 2015), the summer monsoon begins in June, with sharp rises in rainfall and soil moisture, and a sharp drop in air temperature. The hottest and driest weeks occurred just before the summer monsoon onsets. Similar dry and hot periods, varying from one to a few weeks, were observed in 2013 and 2014. Soil moisture as an indication of drought as measured by NASA's Aquarius mission was first available in 2012. Rainfall data are from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), and surface air temperature is from NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite. The TRMM and Aquarius missions ended in April 2015, before the drought and heat waves. Their data were replaced by those presently available from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive Mission (SMAP) and Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) to show the drought and heatwave in 2015. Scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, have shown that during the summer monsoon season, moisture is transported into the India Subcontinent from the Arabian Sea and out to the Bay of Bengal. The difference between moisture input from the west and output to the east is deposited as rain over land. The pre-monsoon drought and heat waves coincide with the short period when moisture is advected out to the Bay of Bengal ahead of input from the Arabian Sea. The onset of southwest monsoon winds begins in the Bay of Bengal and sucks moisture out from the subcontinent earlier than the onset in the Arabian Sea. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19939
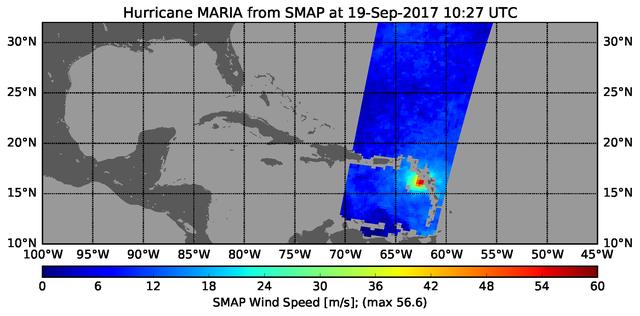
The radiometer instrument on NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) spacecraft captured this image of Hurricane Maria at 6:27 a.m. EDT on Sept. 19, 2017 (10:27 UTC), showing an estimated maximum surface wind speed of 126.6 miles per hour (56.6 meters per second). While Maria was already a Category 5 hurricane at the time of this observation, it is an extremely tightly organized hurricane and SMAP cannot fully resolve its highest winds due to the 25-mile (40-kilometer) resolution of SMAP. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21960
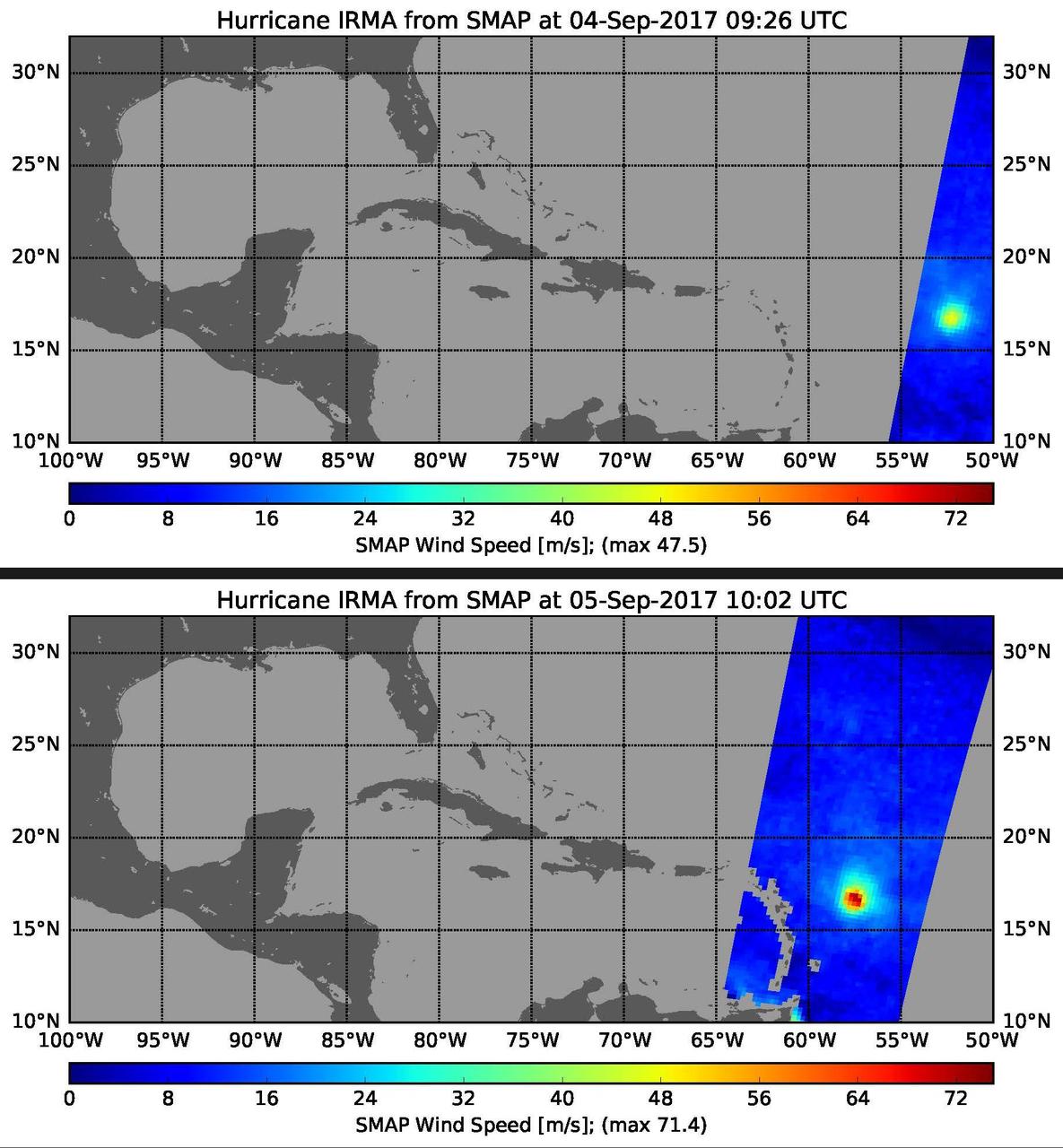
This pair of images shows ocean surface wind speeds for Hurricane Irma as observed at 5:26 a.m. EDT on Sept. 4, 2017 (top) and 24.5 hours later at 6:02 a.m. EDT on September 5th (bottom) by the radiometer instrument on NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite. Color indicates wind speed, with red being highest and blue lowest. Irma intensified from a Category 2 hurricane on Sept. 4 with observed wind speed of 106 miles per hour (47.5 meters per second) to a Category 5 hurricane on Sept. 5 with a maximum observed wind speed of 160 miles per hour (71.4 meters per second). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21939
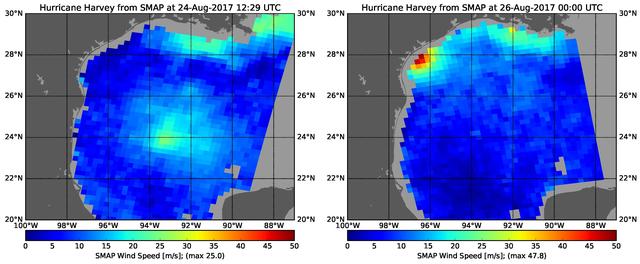
The rapid intensification of Hurricane Harvey is seen in this pair of images of ocean surface wind speeds as observed by the radiometer instrument aboard NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite at 7:29 a.m. CDT Aug. 24th, 2017 (left) and at 7 p.m. CDT Aug. 26th (right). Color indicates wind speed, with red being highest and blue lowest. The images show Harvey's maximum wind speeds increased from approximately 56 miles per hour (25 meters per second) to about 107 miles per hour (47.8 meters per second) in the 36 hours just before landfall. The higher wind speeds estimated near the mouth of the Mississippi River are erroneous and are due to errors in the ancillary sea-surface-salinity data product used by SMAP to estimate extreme wind speeds. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21884
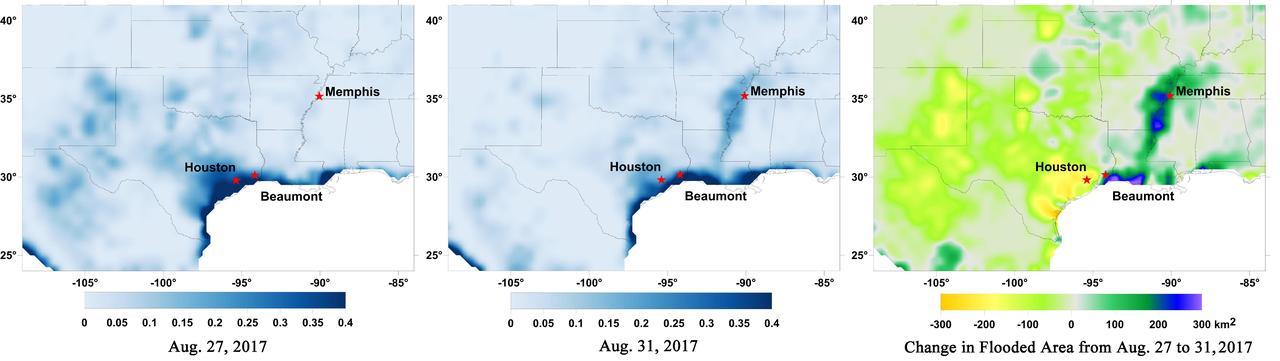
Data from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite have been used to create new surface flooding maps of Southeast Texas and the Tennessee Valley following Hurricane Harvey. The SMAP observations detect the proportional cover of surface water within the satellite sensor's field of view. This sequence of images shows changes in the extent of surface flooding from successive five-day SMAP observation composite images. Widespread flooding can be seen in the Houston metropolitan area on Aug. 27 following record rainfall from the Category 4 hurricane, which made landfall on Aug. 25th, 2017 (left image). Flood waters around Houston had substantially receded by Aug. 31 (middle image), while flooding had increased across Louisiana, eastern Arkansas, and western Tennessee as then Tropical Storm Harvey passed over the area. The far right image shows the change in flooded area between Aug. 27 and Aug. 31, with regions showing the most flooding recession depicted in yellow and orange shades and those where flooding had increased depicted in blue shades. The SMAP satellite has a low-frequency (L-band) microwave radiometer with enhanced capabilities for detecting surface water changes in nearly all weather conditions and under low-to-moderate vegetation cover. SMAP provides global coverage with one-to-three-day repeat sampling that is well suited for global monitoring of inland surface water cover dynamics. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21951
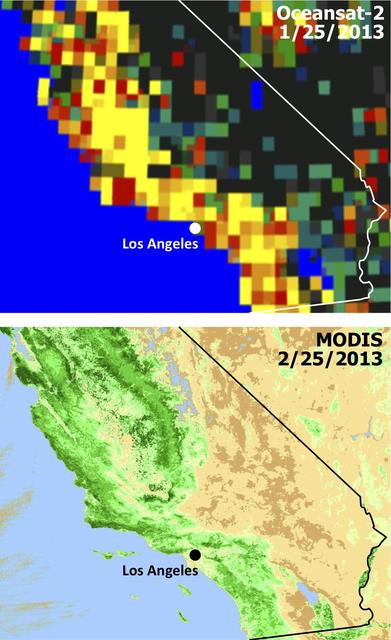
Extensive and persistent rains between Jan. 24 and Jan. 27, 2013, significantly increased soil moisture and enhanced vegetation growth in Southern California based on data from NASA Aqua spacecraft and ISRO Oceansat-2 satellite.
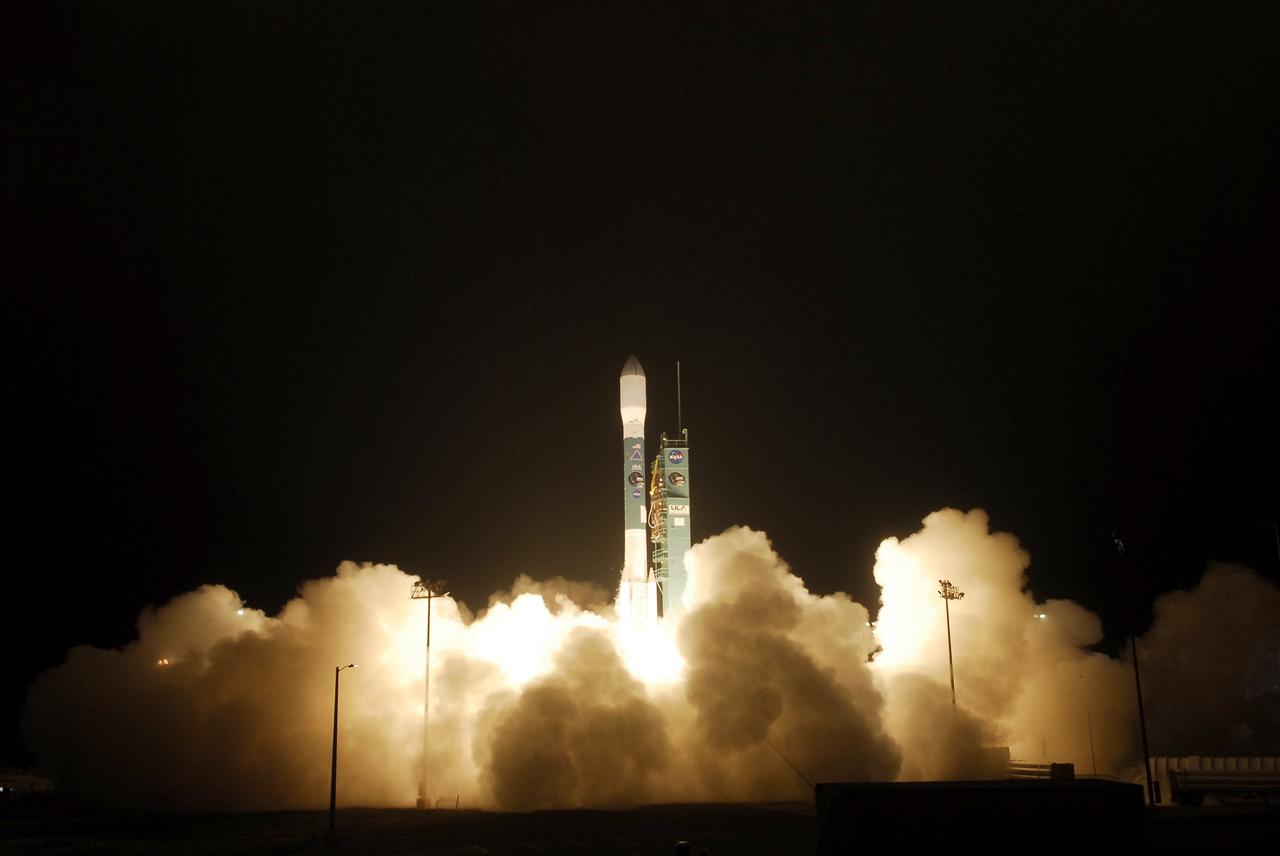

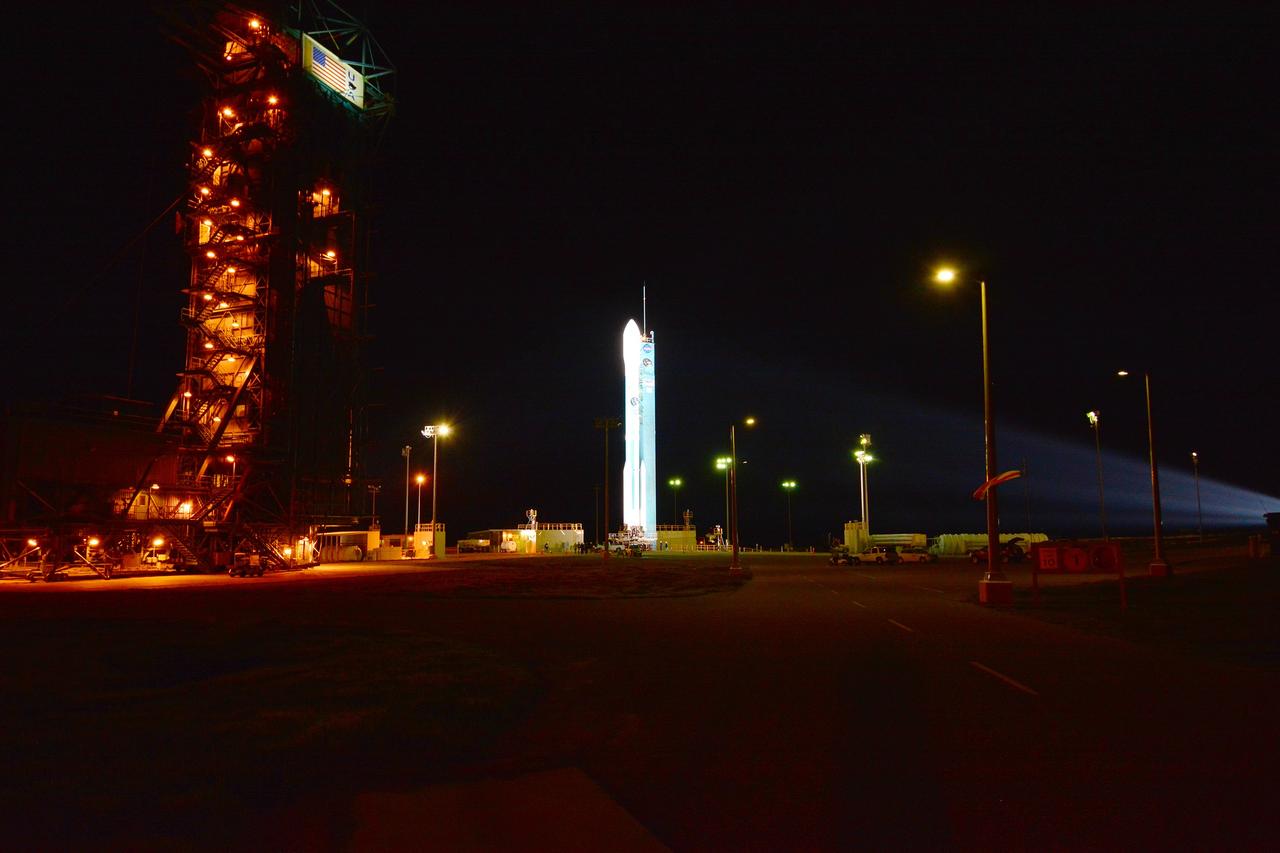
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An exhaust cloud builds around the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket as it lifts off Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, carrying NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, on a mission to study global coverage of soil moisture and freeze/thaw measurements. Launch was at 9:22 a.m. EST. SMAP is designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
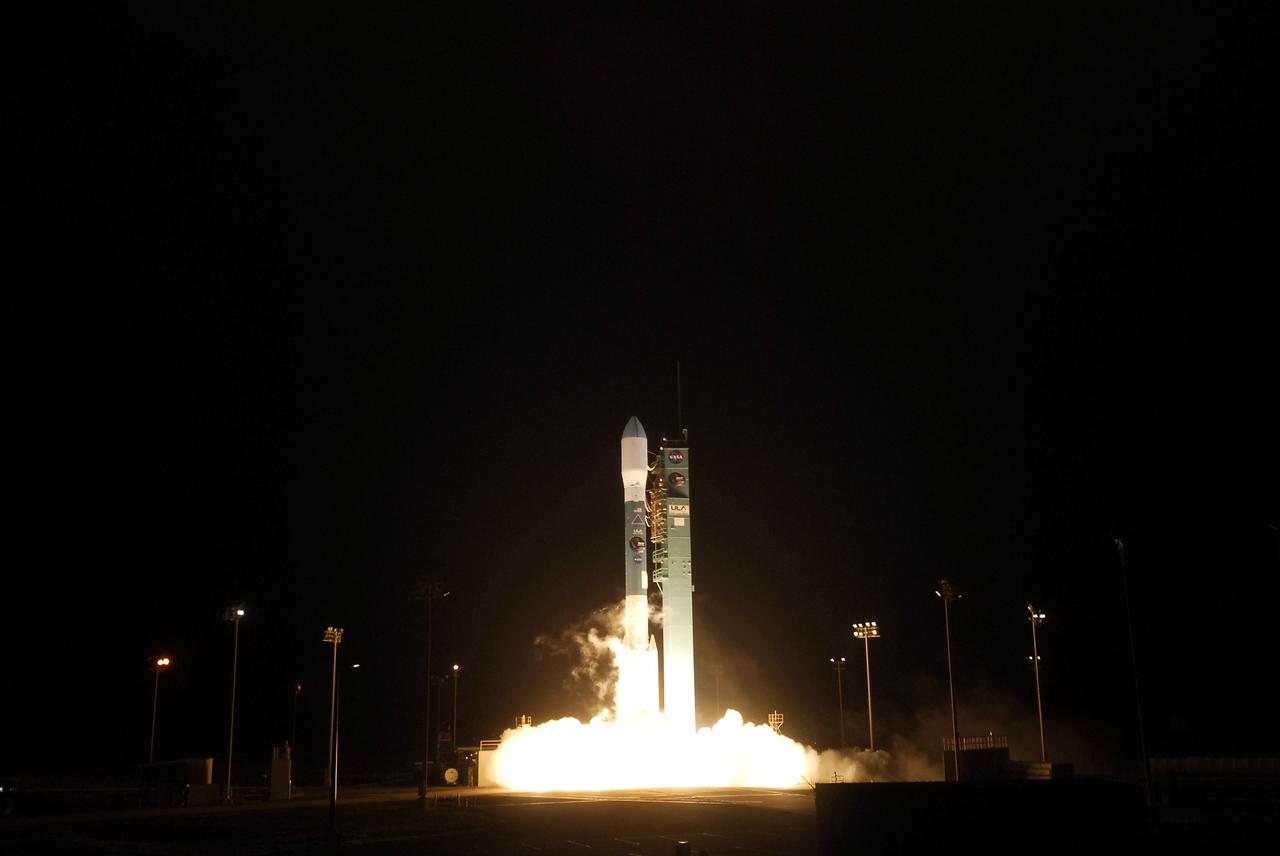

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The two-stage Delta II launch vehicle lifts off Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, carrying NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, on a mission to study global coverage of soil moisture and freeze/thaw measurements. Launch was at 9:22 a.m. EST. SMAP is designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
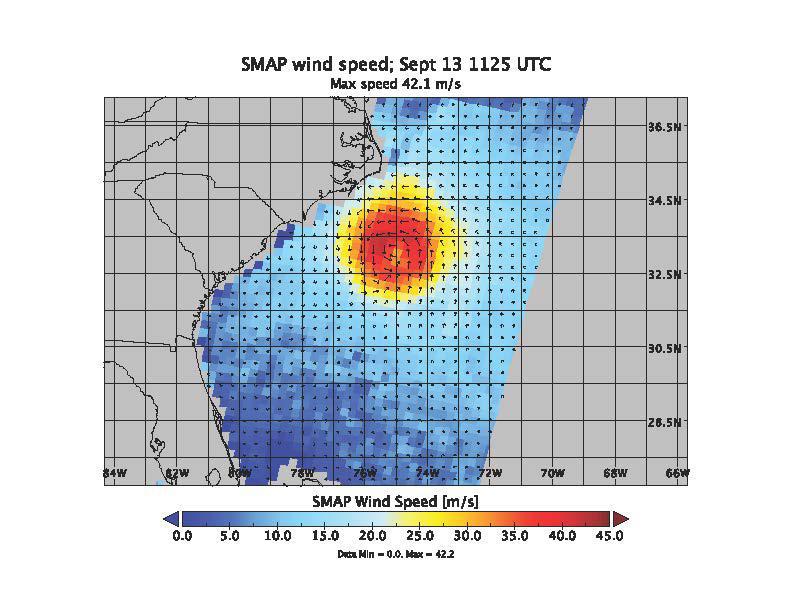
SMAP wind estimates over Hurricane Florence on Sept. 12, 2018 at 10:49 UTC and on Sept. 13, 2018 at 11:25 UTC. We see weakening of the hurricane from the 12th to the 13th; however, the overall size and energy of the storm has increased. The brightness temperatures have been shown to yield unprecedented sensitivity to extreme wind speeds as compared to conventional Ku and C-band scatterometers. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22699
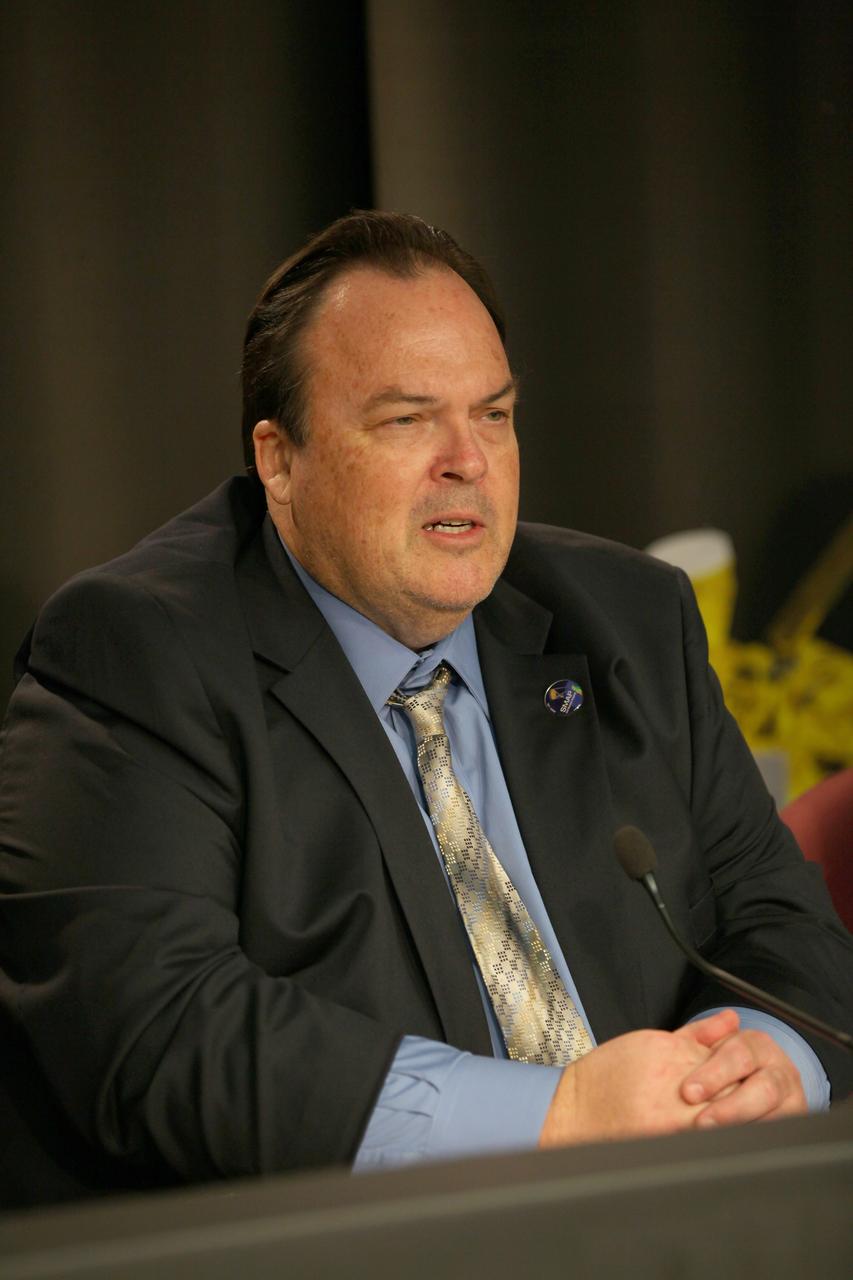

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Kent Kellogg, SMAP project manager at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, participates in a news conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California following NASA's successful launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, on its mission to study the Earth's soil moisture. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
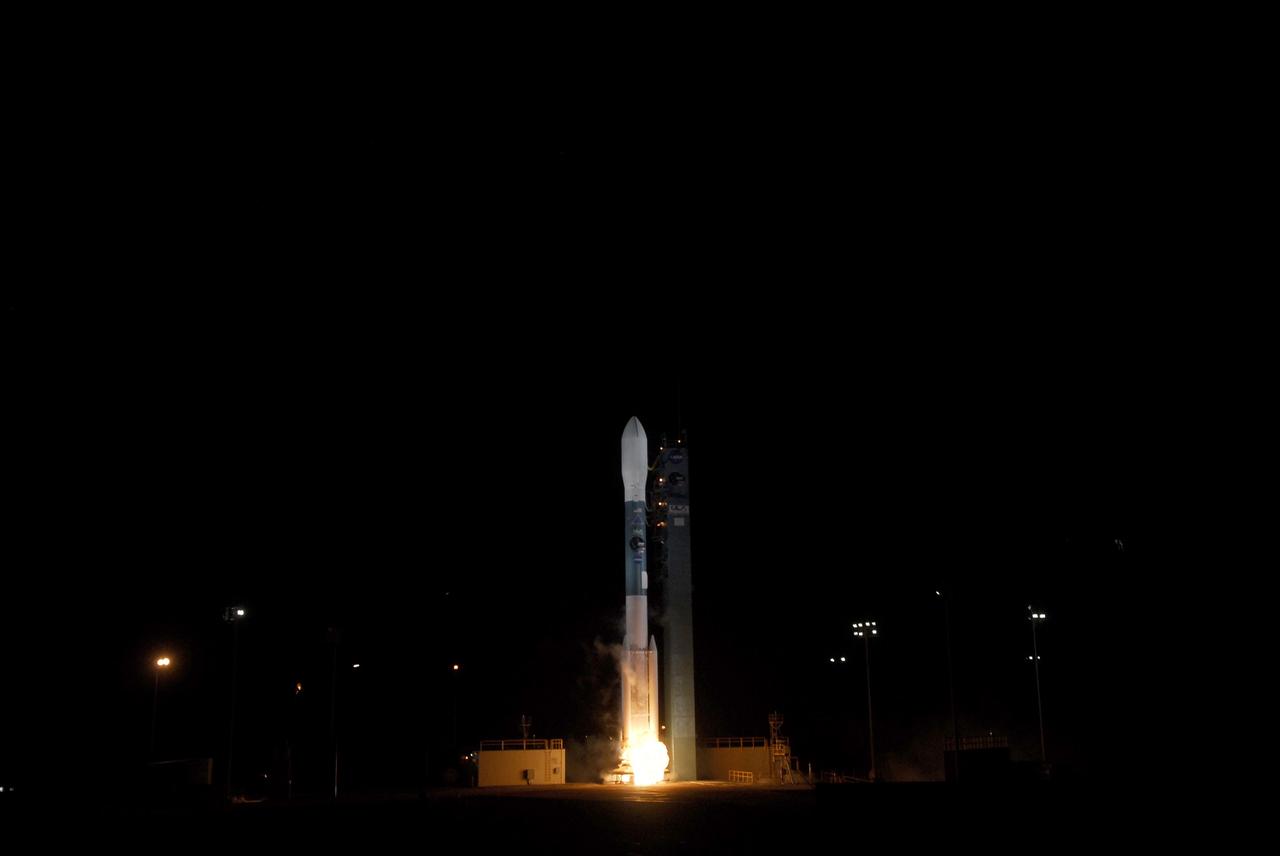

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket springs to life. The liftoff will boost NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, to orbit. Liftoff was at 9:22 a.m. EST. SMAP is designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
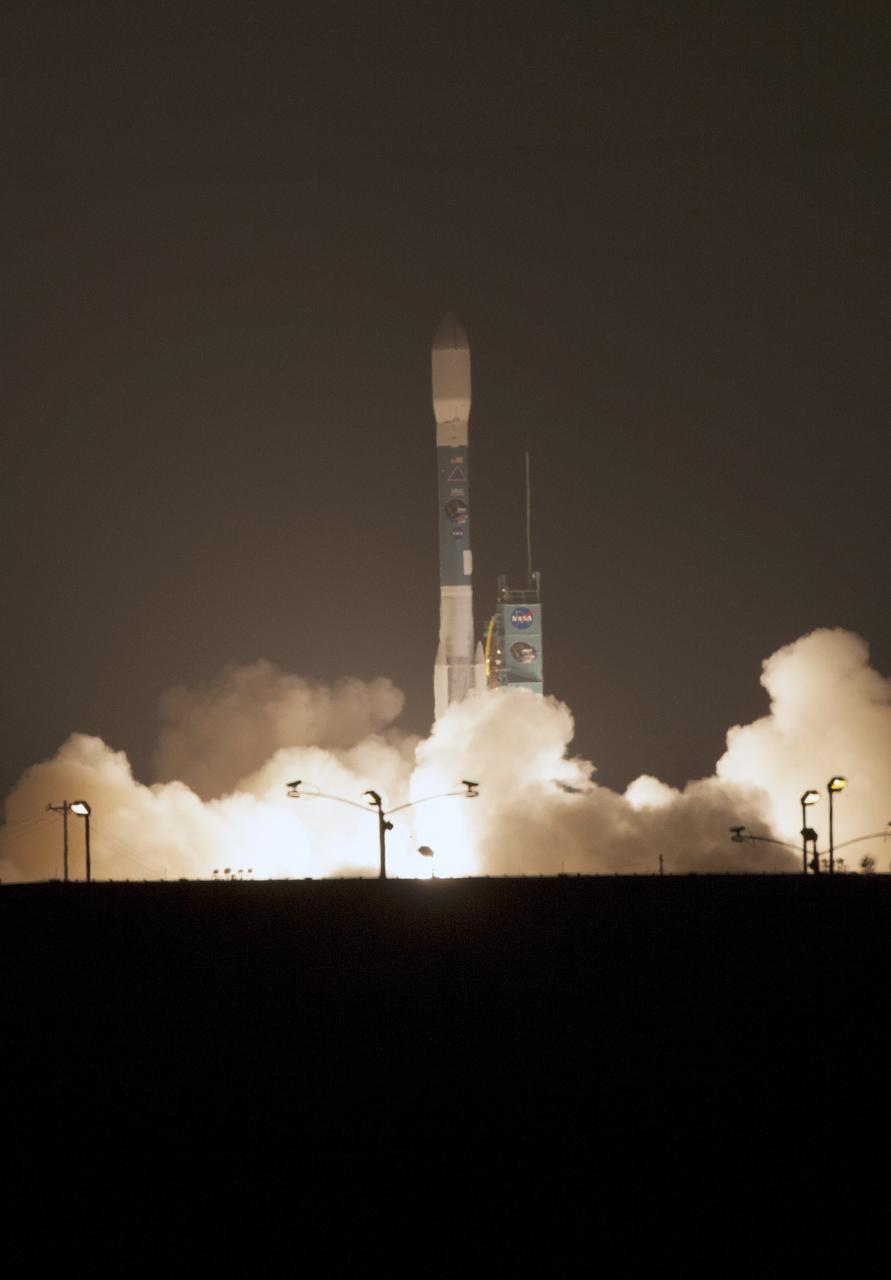

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket roars to life. The liftoff will boost NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, to orbit. Liftoff was at 9:22 a.m. EST. SMAP is designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
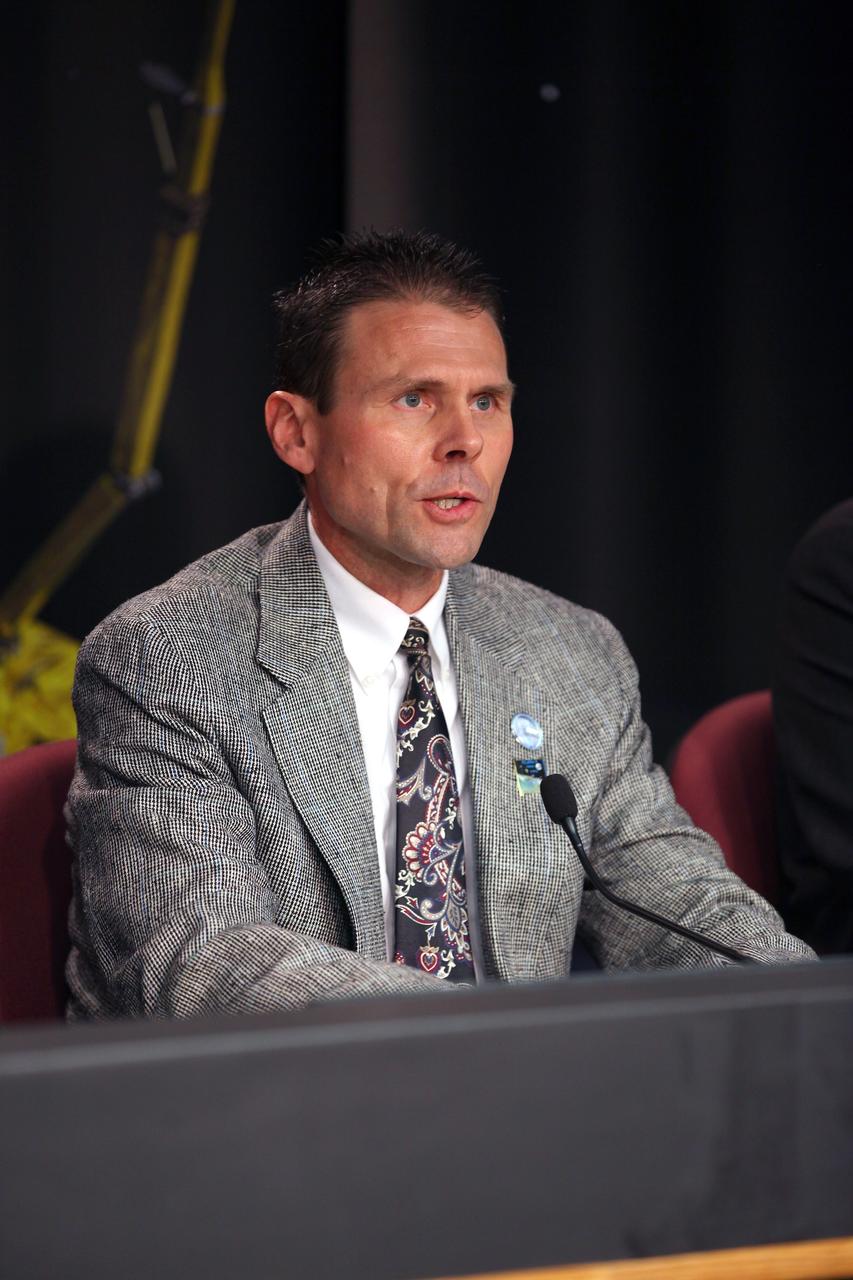

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Scott Higginbotham, NASA mission manager for Educational Launch of Nanosatellites, or ELaNa-X, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in a news conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, following NASA's successful launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, on its mission to study the Earth's soil moisture. To learn more about ELaNa, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
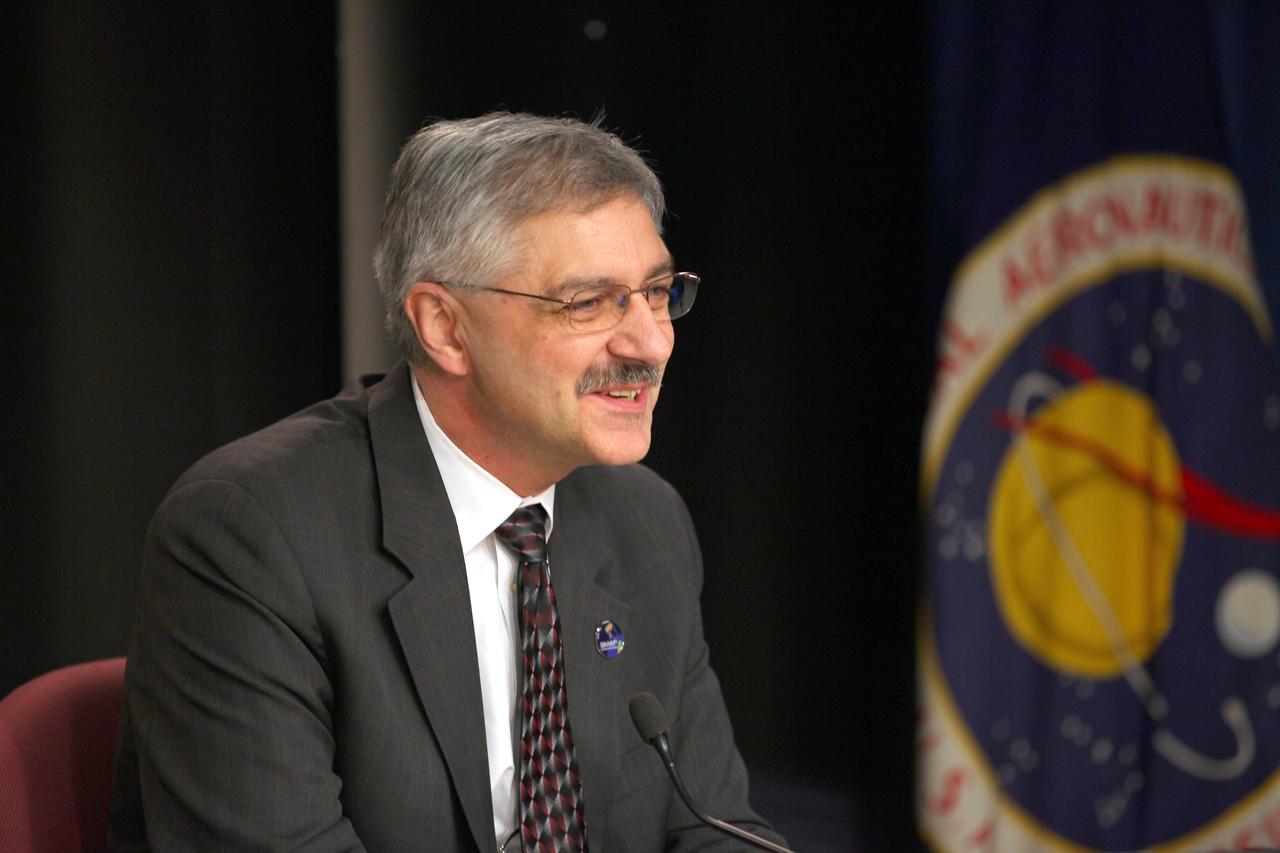

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Geoff Yoder, deputy associate administrator of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., participates in a news conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, following NASA's successful launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, on its mission to study the Earth's soil moisture. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
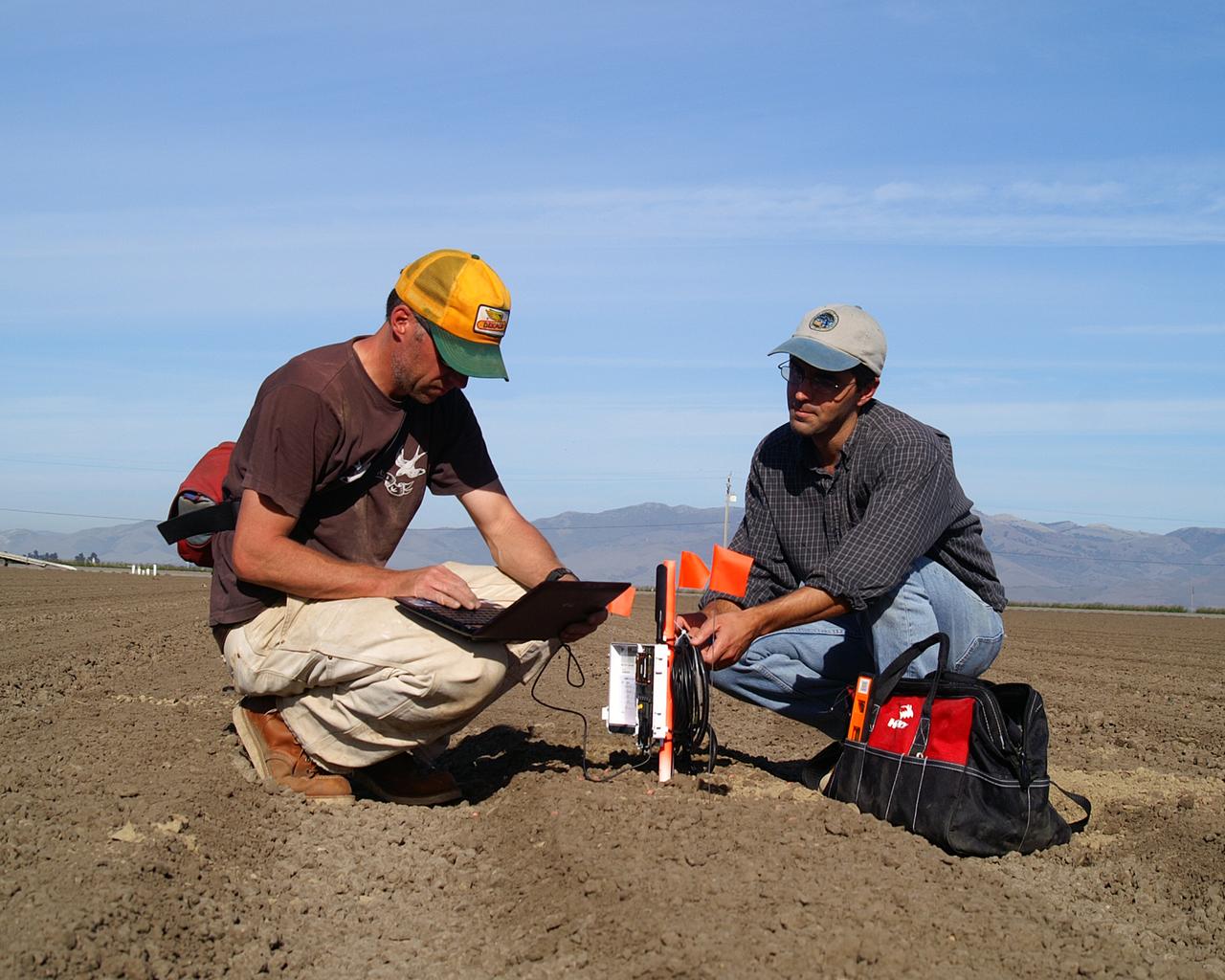

Wireless crop water monitoring project: Dr. Chris Lund and Forrest Melton, California State University Monterey Bay research scientists who work at NASA Ames Research Center, check data being returned from a wireless soil moisture monitoring network, installed in an agricultural field. Data from the soil moisture sensor network will be used to assist in interpretation of the satellite estimates of crop water demand. Image of courtesy of Forrest S. Melton

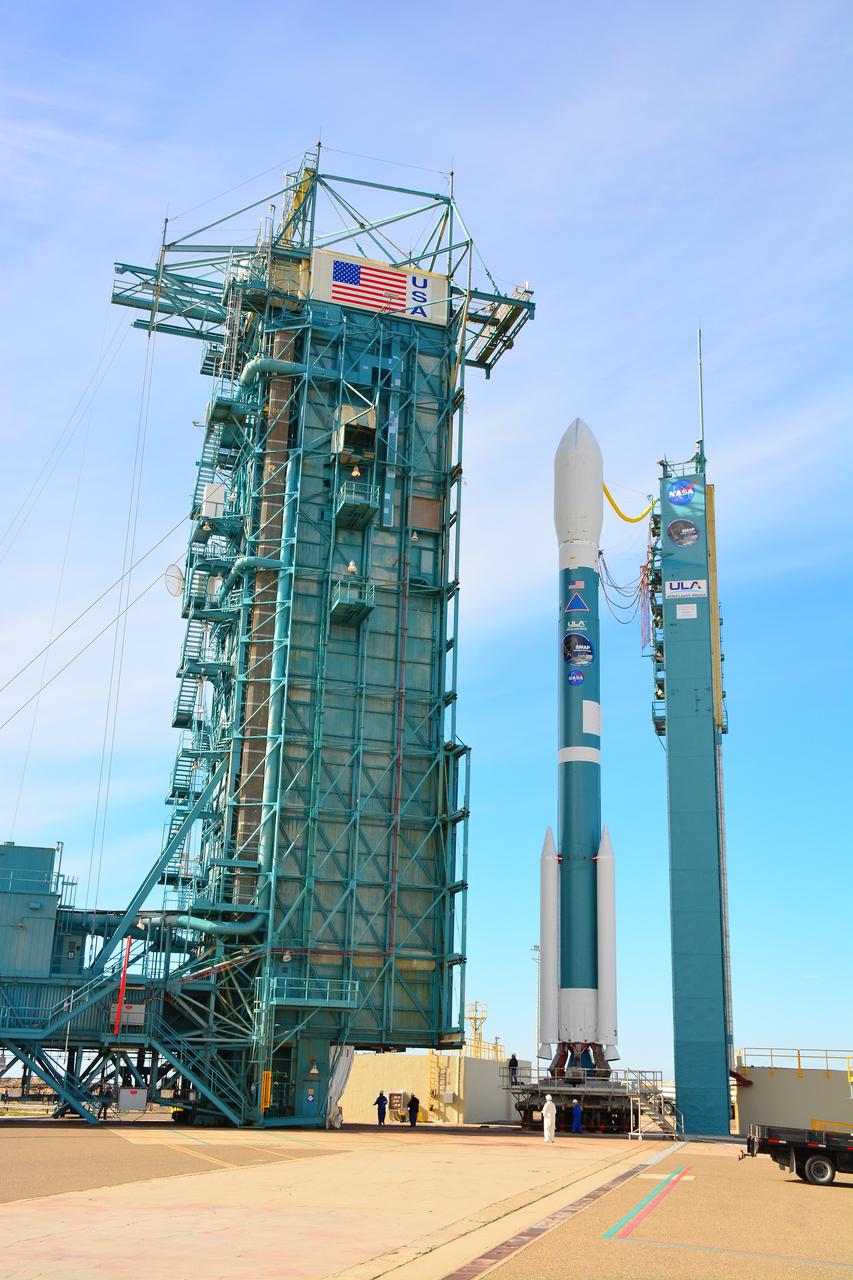
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
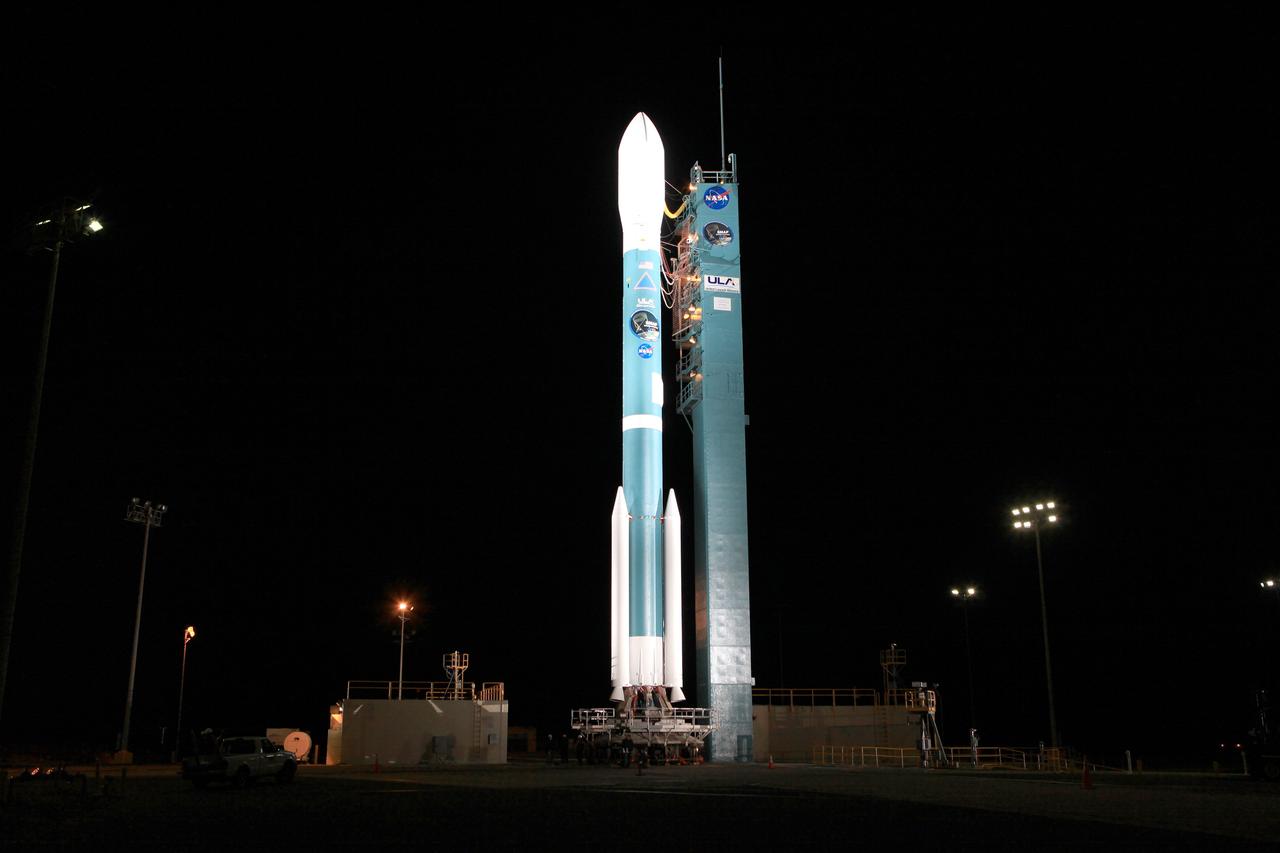

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
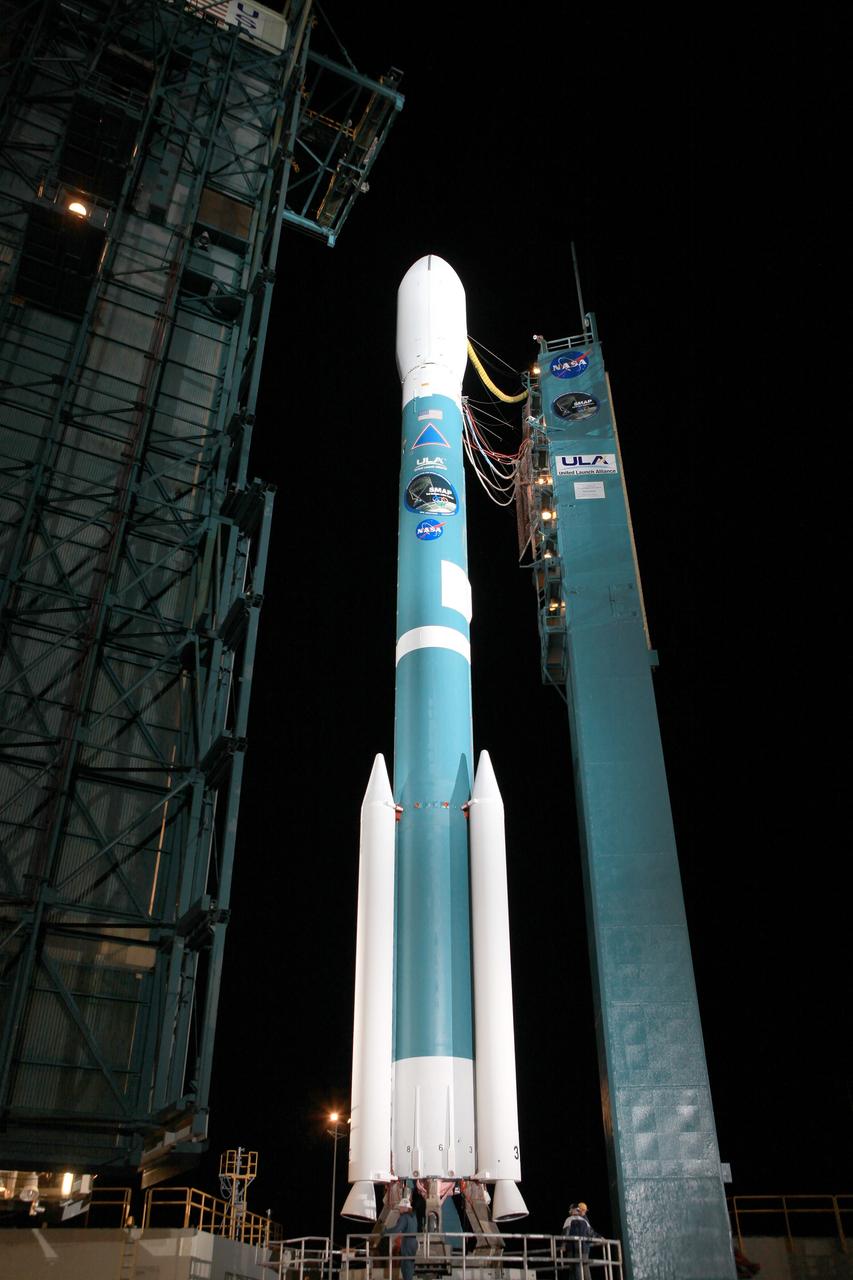

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
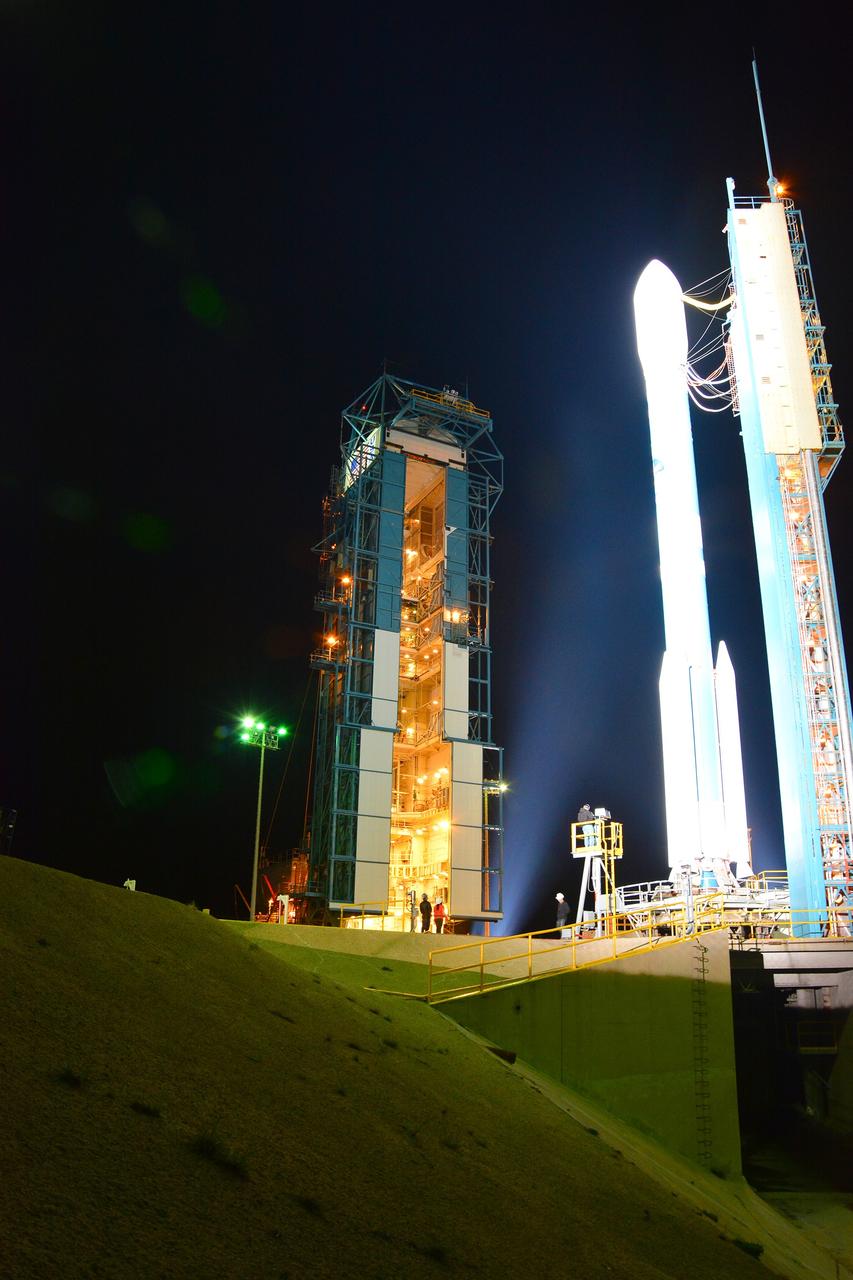

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
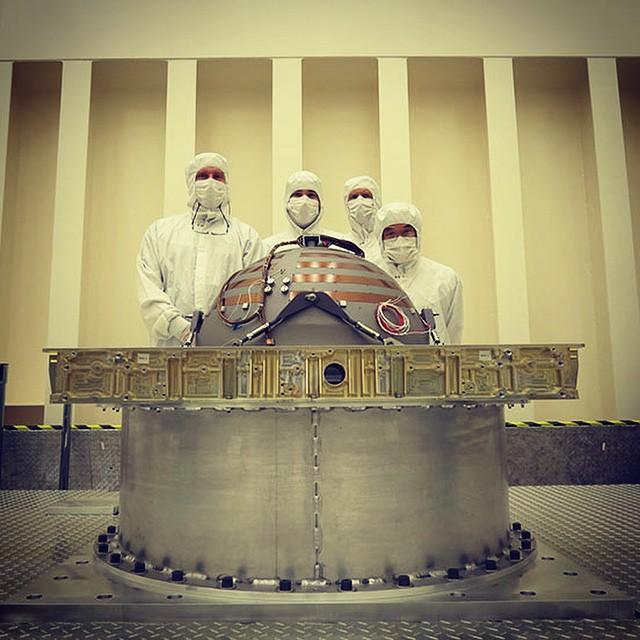

The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, scheduled for launch on Jan. 29, will measure the moisture in Earth's soil with greater accuracy and higher resolution than any preceding mission, producing a global map of soil moisture every three days. Here are five quick facts about the spacecraft and what it studies. 1. Soil moisture is a tiny fraction of water with a big punch. Only 0.001 percent of Earth's total water is lodged in the top few feet of soil. That tiny percentage, however, affects all living things on land and plays an important role in moving water, carbon and heat between land and atmosphere. 2. Soil moisture can compound water risks. A flood follows a heavy rainfall -- but only if the ground cannot soak up the rain. Waterlogged soil makes a region more flood-prone. Going to the opposite extreme, a drought can parch soil to such an extent that plants are unable to grow even after a few rains have fallen. Knowing soil moisture allows hydrologists to make better decisions related to the risk of flooding and drought, such as how much water to retain in reservoirs. 3. Soil moisture controls the on-off switch for carbon dioxide cleanup. The world's vast northern forests remove carbon dioxide from the air as they grow, helping to clean up our emissions from burning fossil fuels. But when the ground freezes, that process switches off. Carbon dioxide builds up in the atmosphere until the ground thaws in the spring and plants begin growing again. Knowing where and for how long the ground is frozen or thawed is an important part of understanding the role of the northern forests in reducing greenhouse warming. SMAP will map frozen and thawed soils north of 45 degrees north latitude (about the latitude of Minneapolis), around the globe. 4. SMAP is a twofer. The spacecraft's radiometer produces an accurate reading of how much moisture is in the top two inches (five centimeters) of soil, but it has low spatial resolution, that is, one measurement covers a large area. A radar instrument produces an image with higher spatial resolution, but it can't measure soil moisture as accurately as a radiometer. Through sophisticated data processing, SMAP combines observations from the two instruments into a very accurate measurement with high spatial resolution. 5. SMAP has a huge, folding, spinning antenna. At 19 feet 8 inches (6 meters) in diameter, SMAP's rotating mesh antenna dwarfs the size of the instruments and spacecraft and is the largest rotating antenna of its kind that NASA has yet deployed. But the entire dish furls into a cylinder one foot (diameter) by four feet (30 by 120 centimeters) to fit inside the rocket’s fairing for launch, and it weighs only 128 pounds (about 58 kilograms). For more information about SMAP, see: <a href="http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">smap.jpl.nasa.gov/</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/smap/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/smap/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
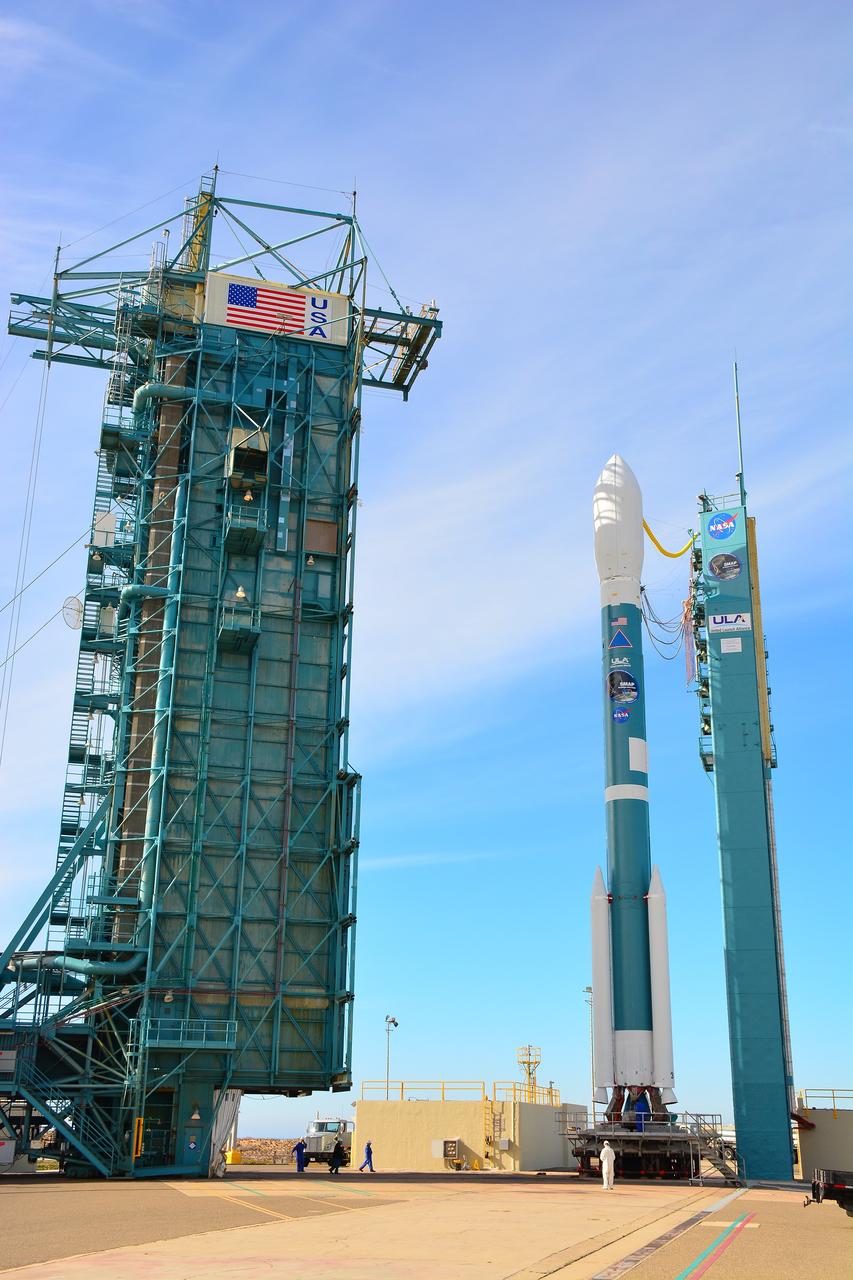

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Operations are underway at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to enclose the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in the launch gantry. Aboard the rocket is NOAA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. Launch was postponed today due to violation of upper-level wind shear constraints. Launch now is targeted for Jan. 31. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
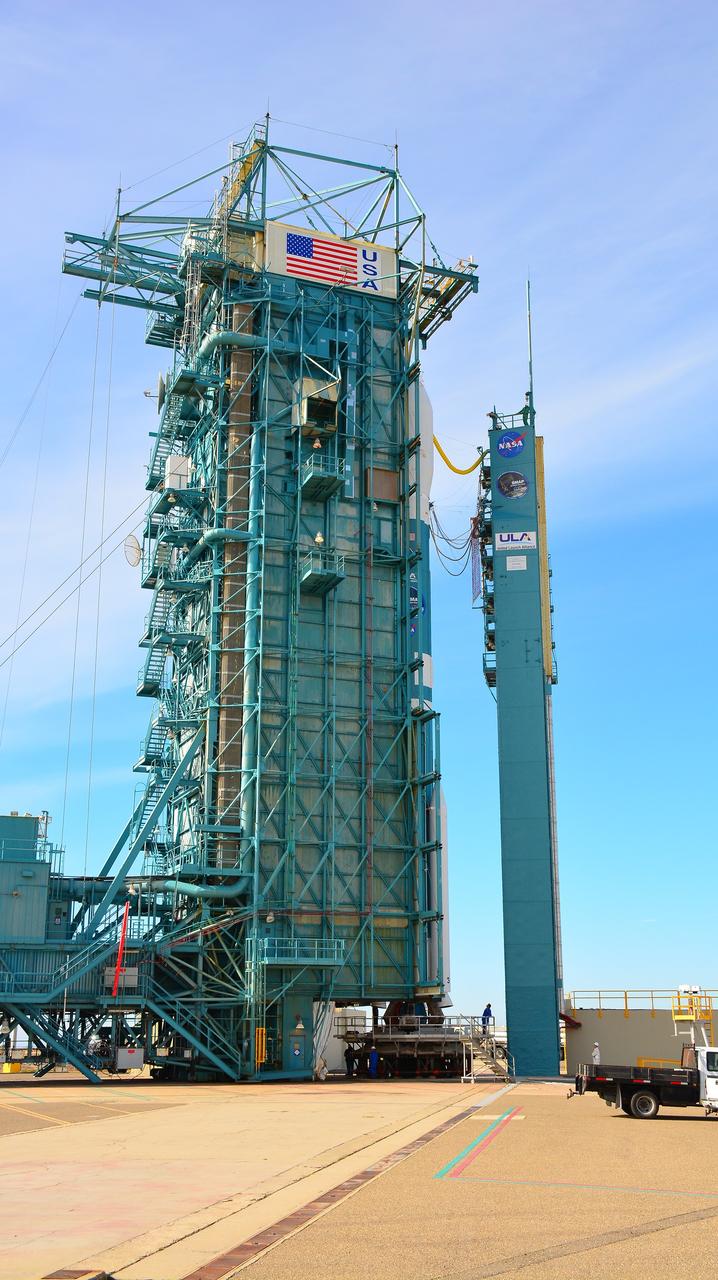

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The mobile service tower rolls toward the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Aboard the rocket is NOAA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. Launch was postponed today due to violation of upper-level wind shear constraints. Launch now is targeted for Jan. 31. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
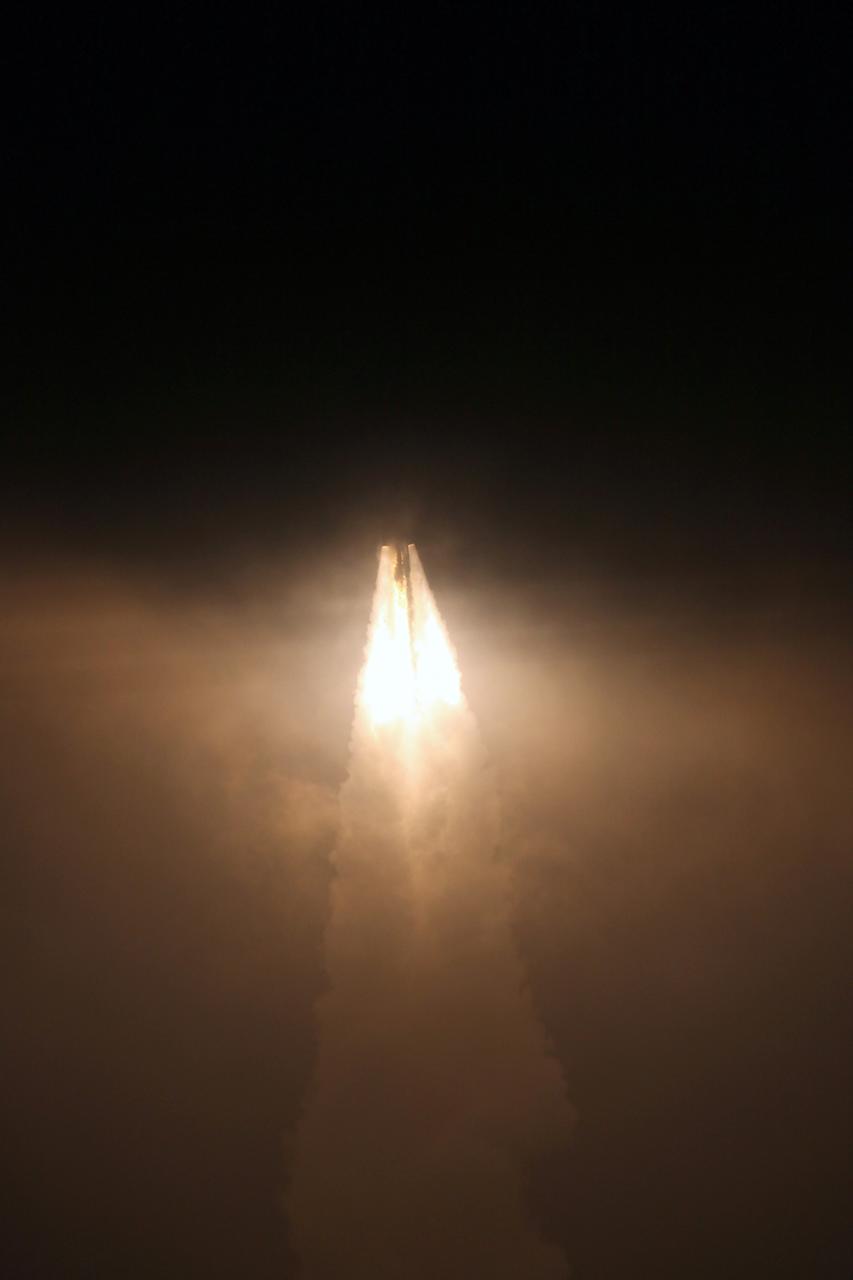

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A Delta II rocket lifts off Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, carrying NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, to Earth orbit. Liftoff was at 9:22 a.m. EST. SMAP's measurements will be invaluable across many science and applications disciplines including hydrology, climate, carbon cycle, and the meteorological, environmental and ecology applications communities. SMAP is designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The mobile service tower rolls toward the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Aboard the rocket is NOAA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. Launch was postponed today due to violation of upper-level wind shear constraints. Launch now is targeted for Jan. 31. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
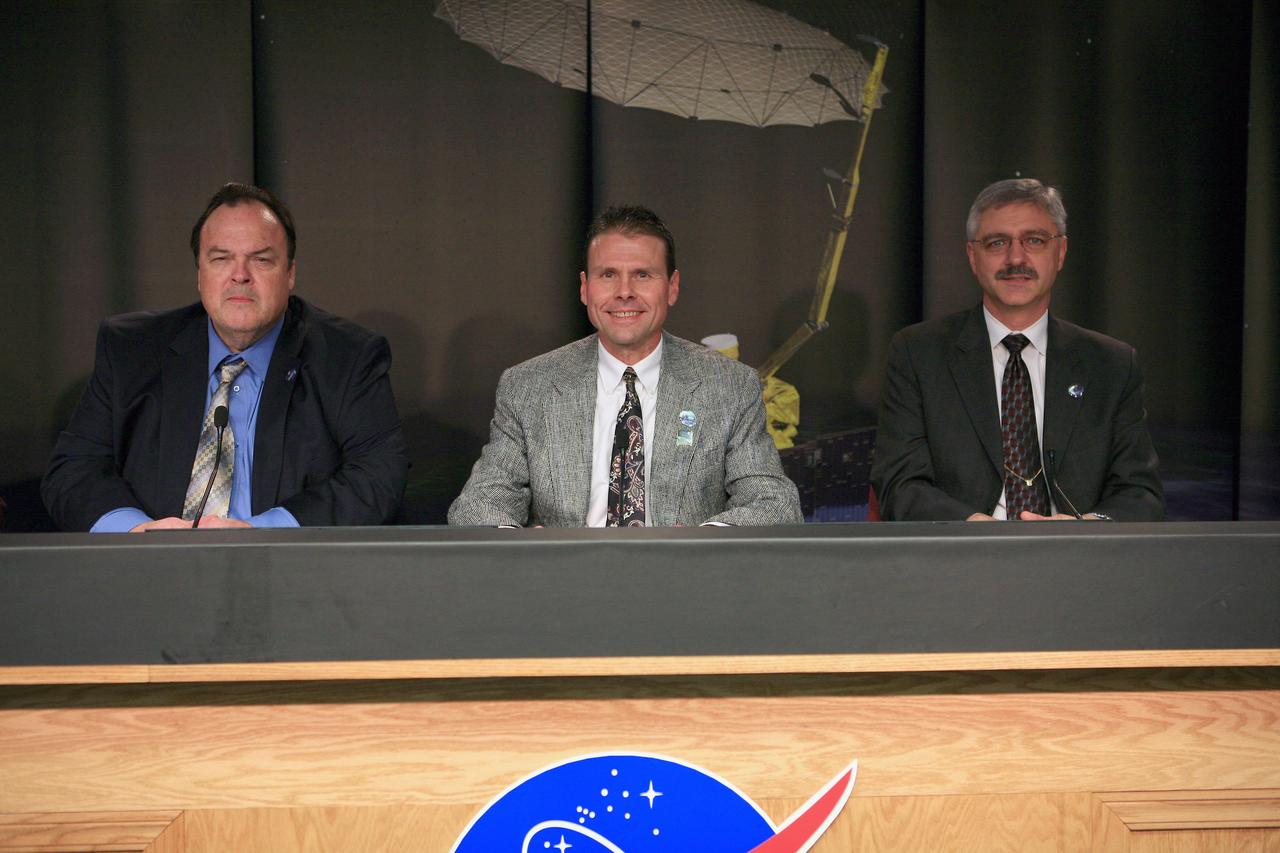

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – During a news conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA officials discuss the launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, and its mission to study the Earth's soil moisture. Participating in the briefing, from left, are Kent Kellogg, SMAP project manager at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, Scott Higginbotham, NASA mission manager for Educational Launch of Nanosatellites, or ELaNa-X, at the Kennedy Space Center, and Geoff Yoder, deputy associate administrator of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
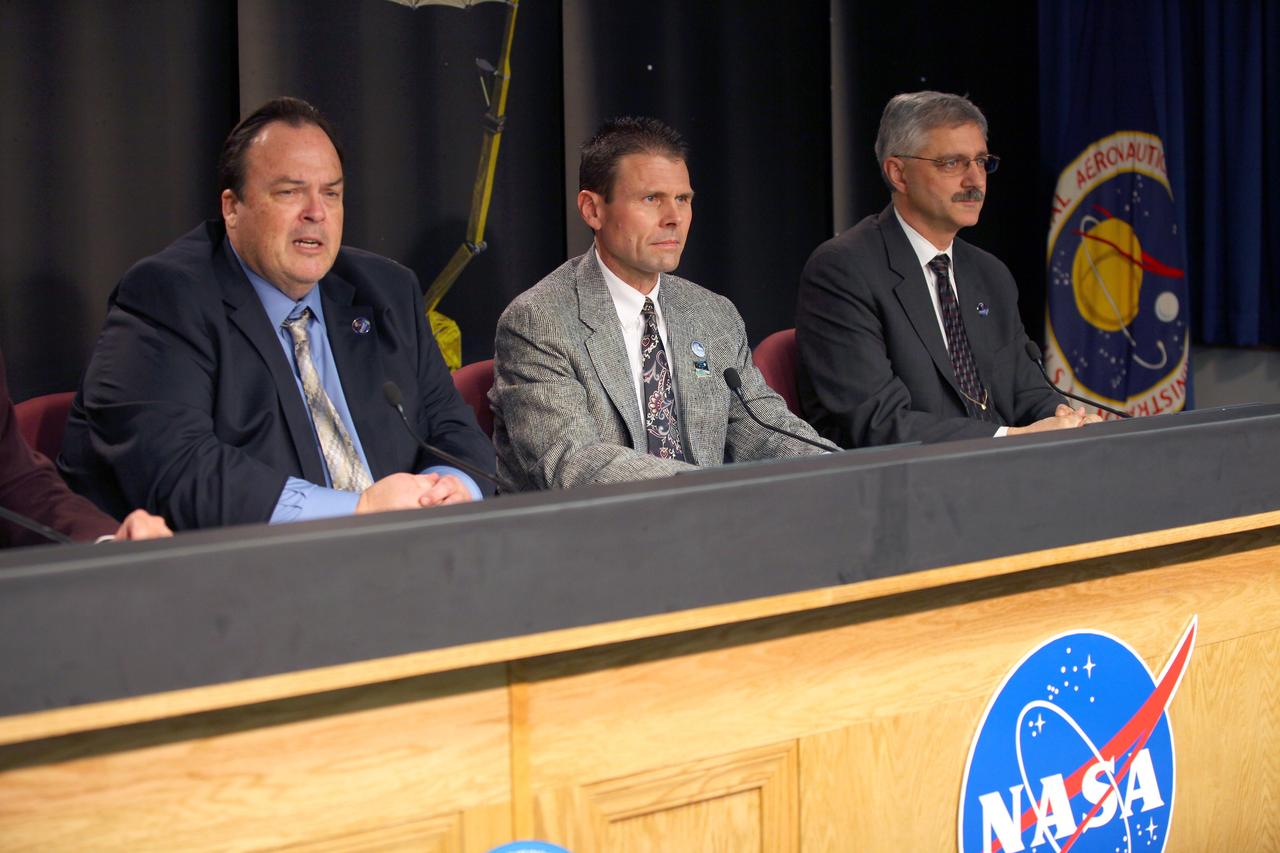

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – During a news conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA officials discuss the launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, and its mission to study the Earth's soil moisture. Participating in the briefing, from left, are Kent Kellogg, SMAP project manager at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, Scott Higginbotham, NASA mission manager for Educational Launch of Nanosatellites, or ELaNa-X, at the Kennedy Space Center, and Geoff Yoder, deputy associate administrator of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
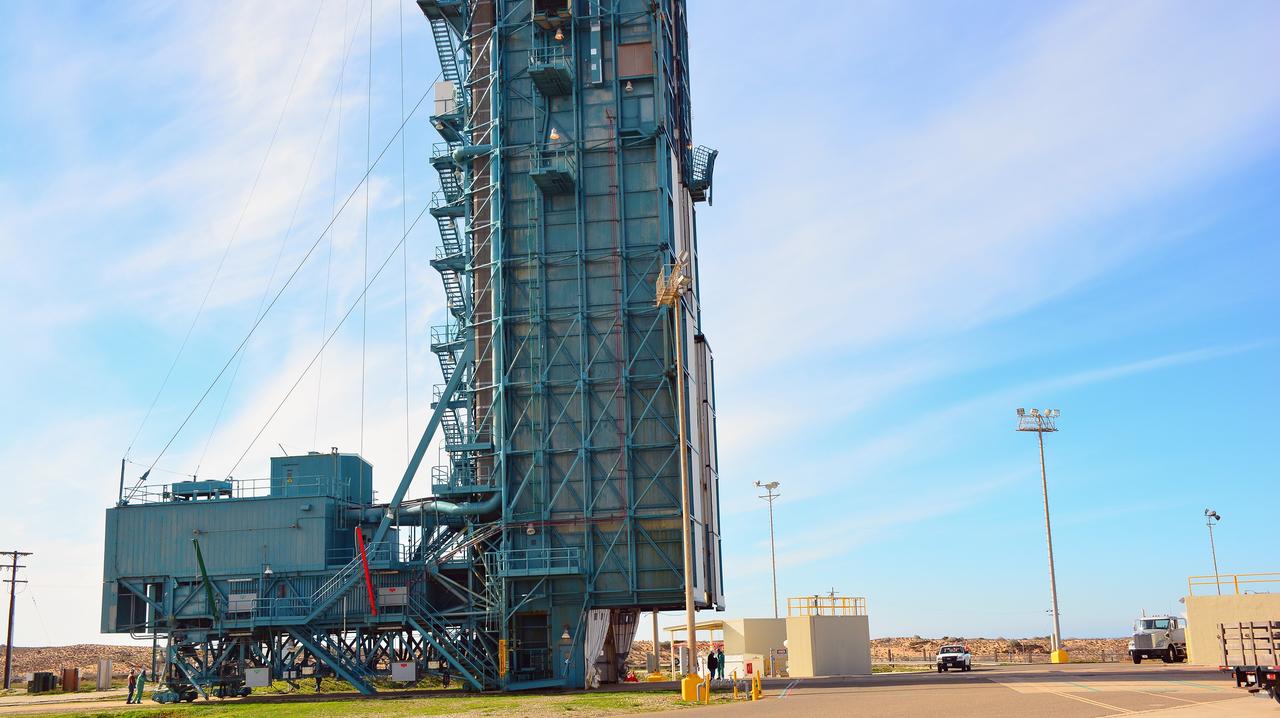

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Operations are underway at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to enclose the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in the launch gantry. Aboard the rocket is NOAA's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, designed to produce the highest-resolution maps of soil moisture ever obtained from space. Launch was postponed today due to violation of upper-level wind shear constraints. Launch now is targeted for Jan. 31. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
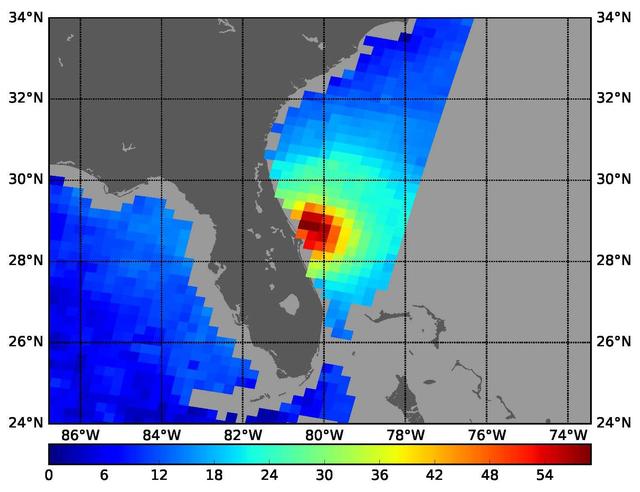
NASA's SMAP radiometer instrument measured Hurricane Matthew's wind speeds at 4:52 a.m. PDT (7:52 a.m. EDT) at up to 132 miles per hour (59 meters per second). SMAP has excellent sensitivity to extreme winds, far beyond that of typical scatterometer instruments now in orbit. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21096
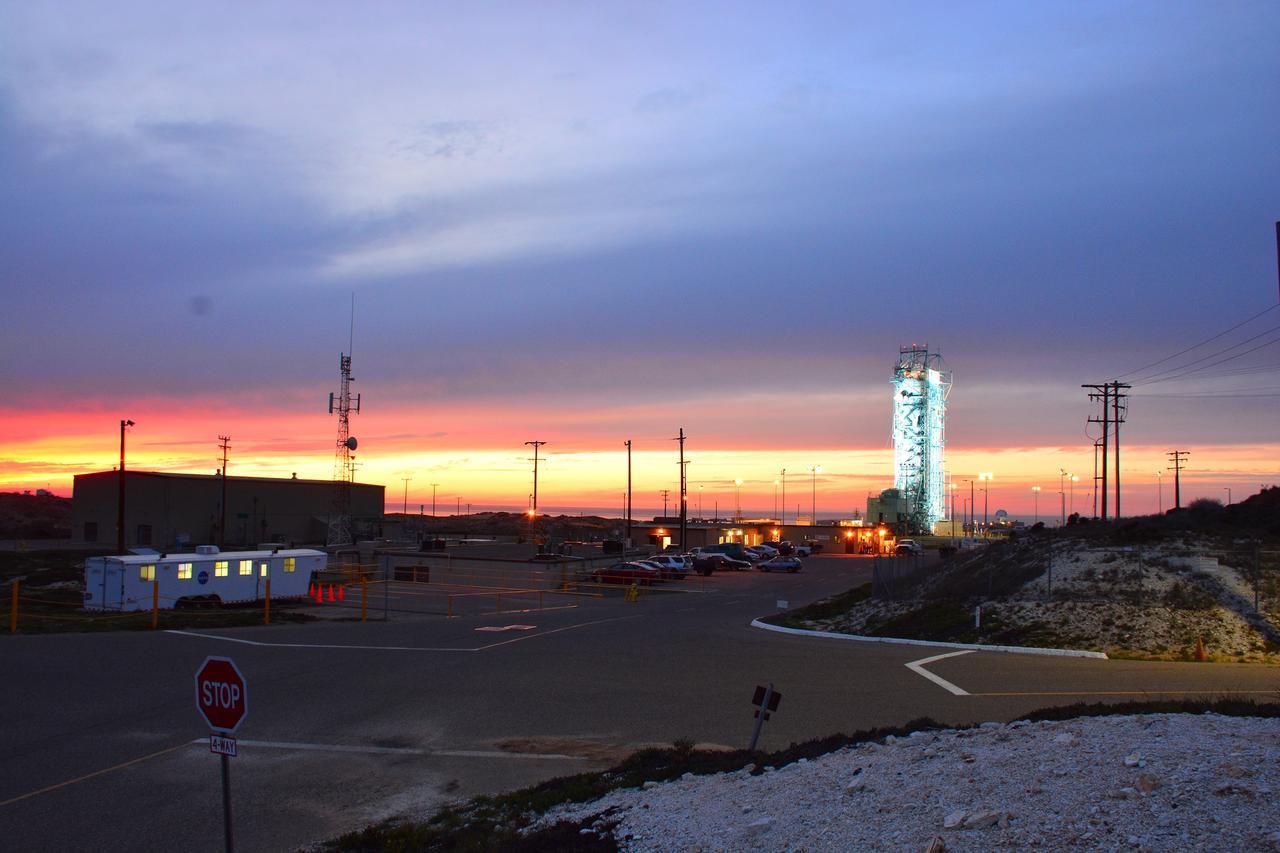

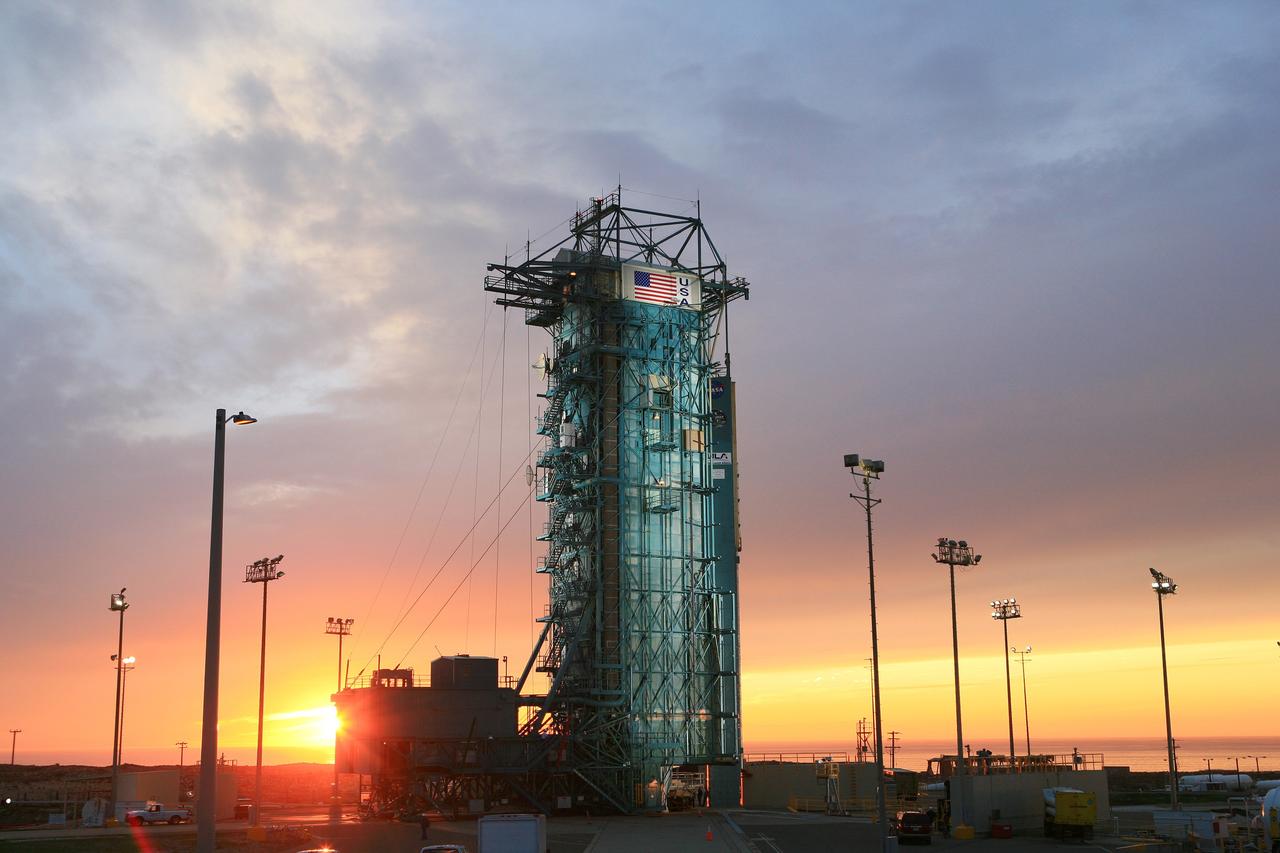
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The sun sets over the West Cost prior to the launch gantry being rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
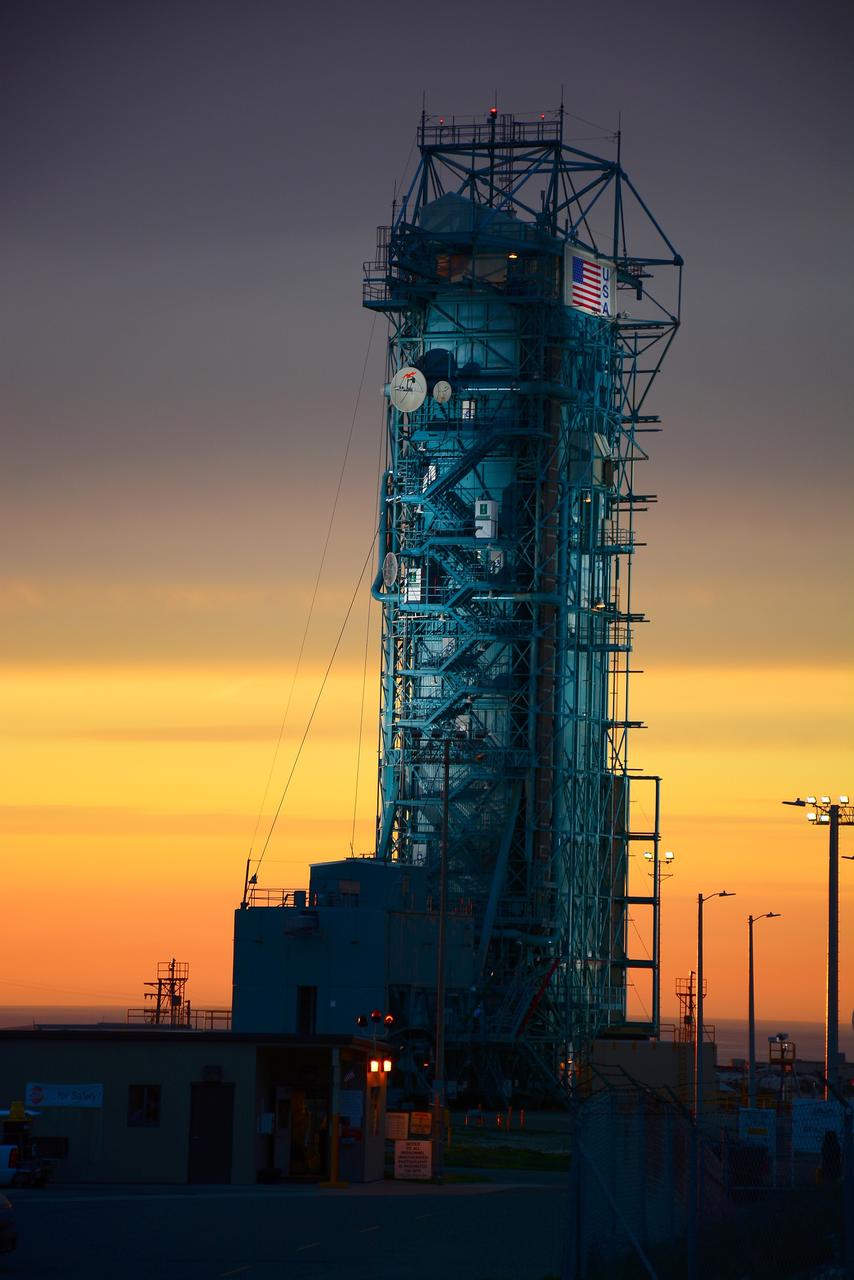

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The sun sets over the West Cost prior to the launch gantry being rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
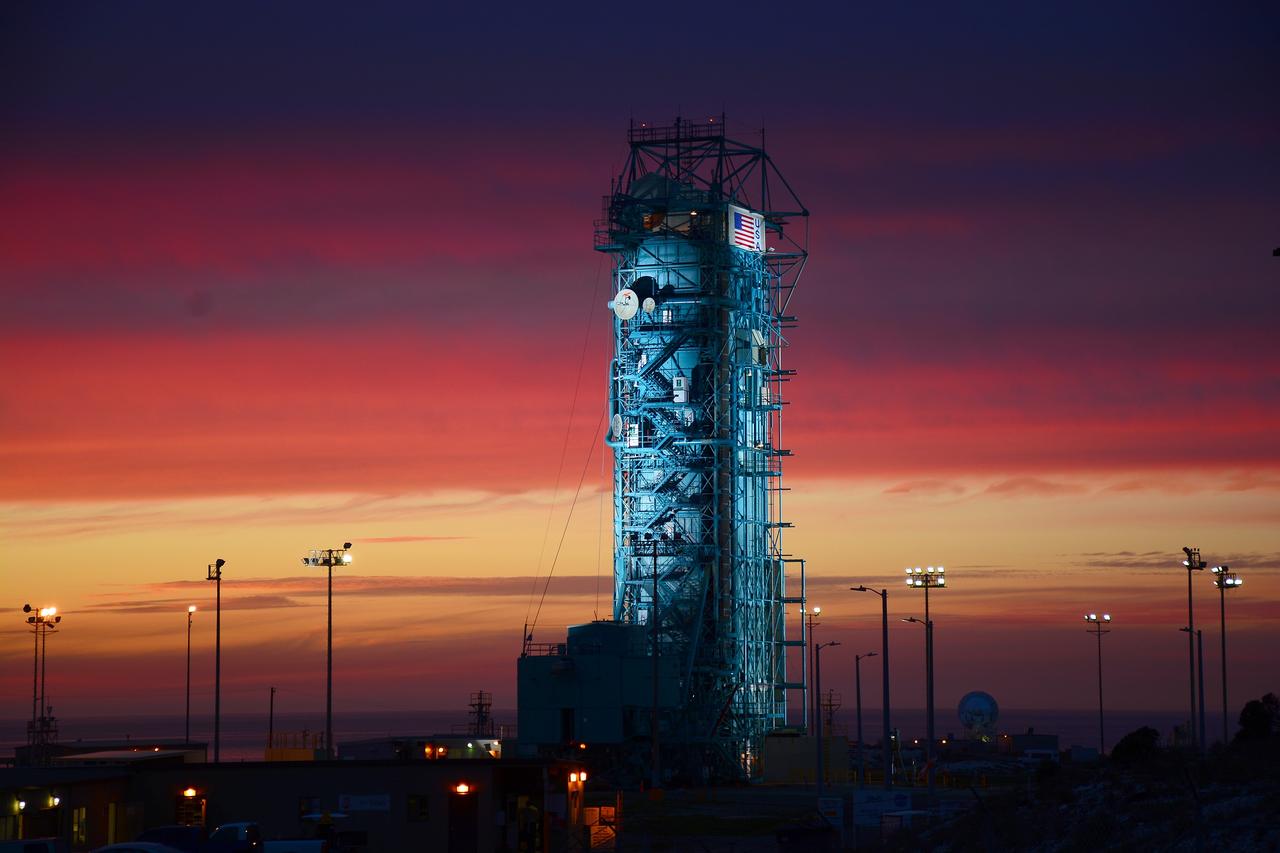

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The sun sets over the West Cost prior to the launch gantry being rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite aboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. SMAP is a remote sensing mission designed to measure and map the Earth's soil moisture distribution and freeze/thaw stat with unprecedented accuracy, resolution and coverage. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
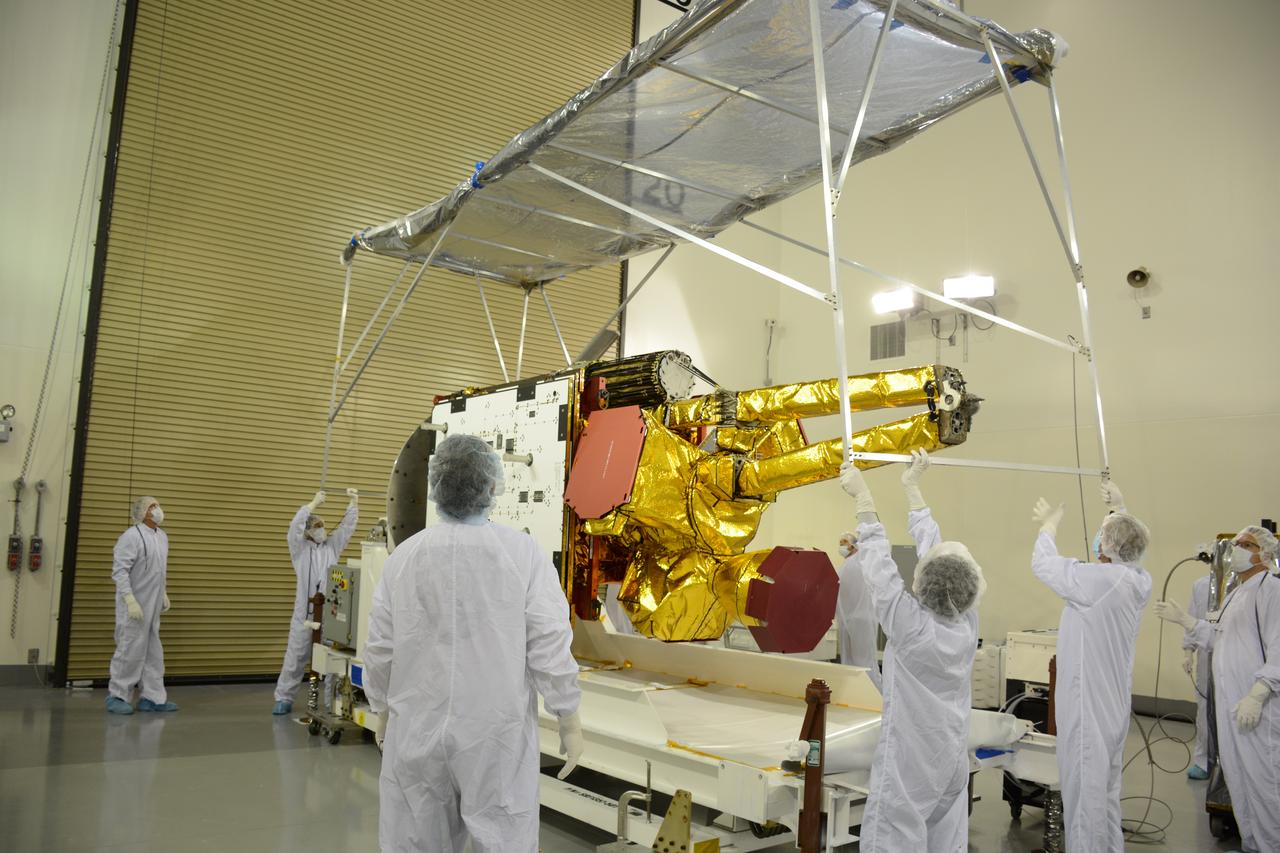

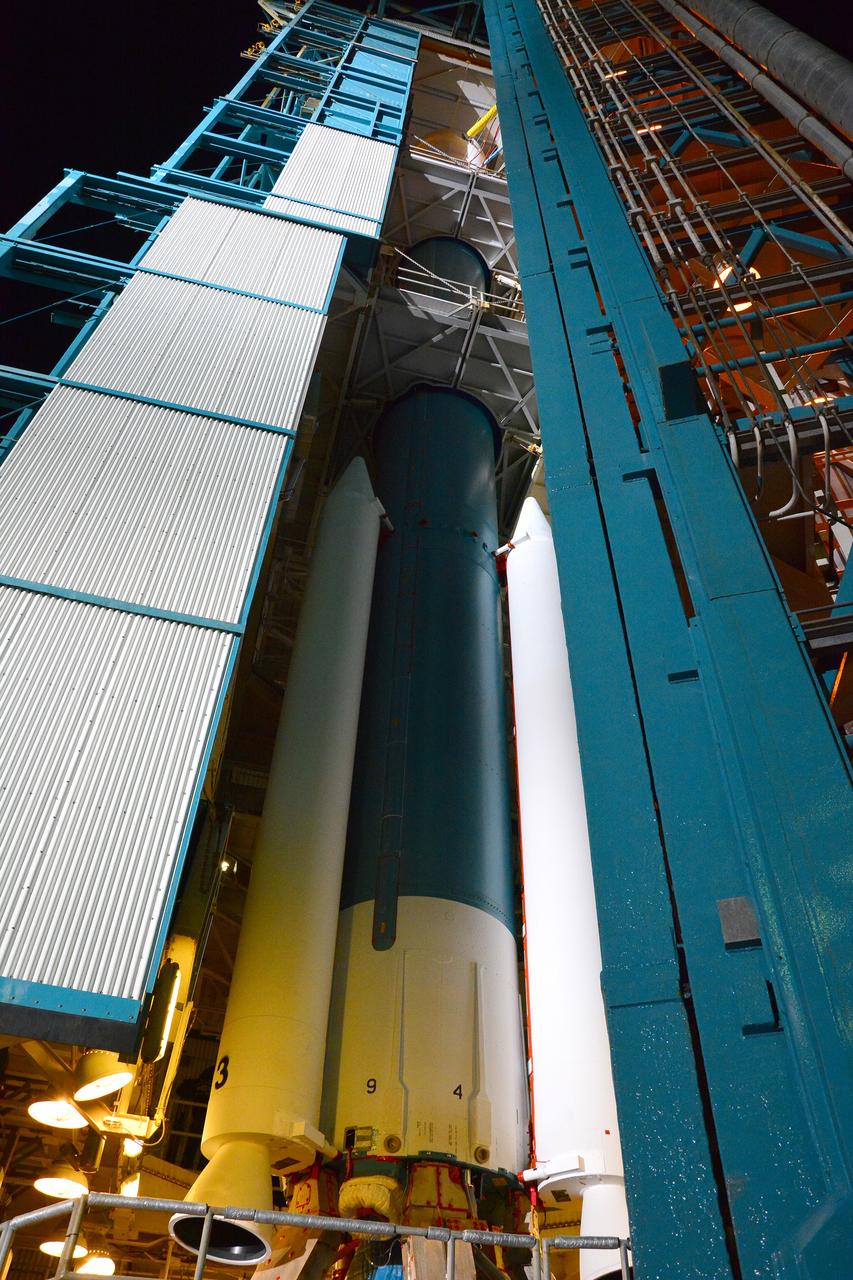
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians remove a protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
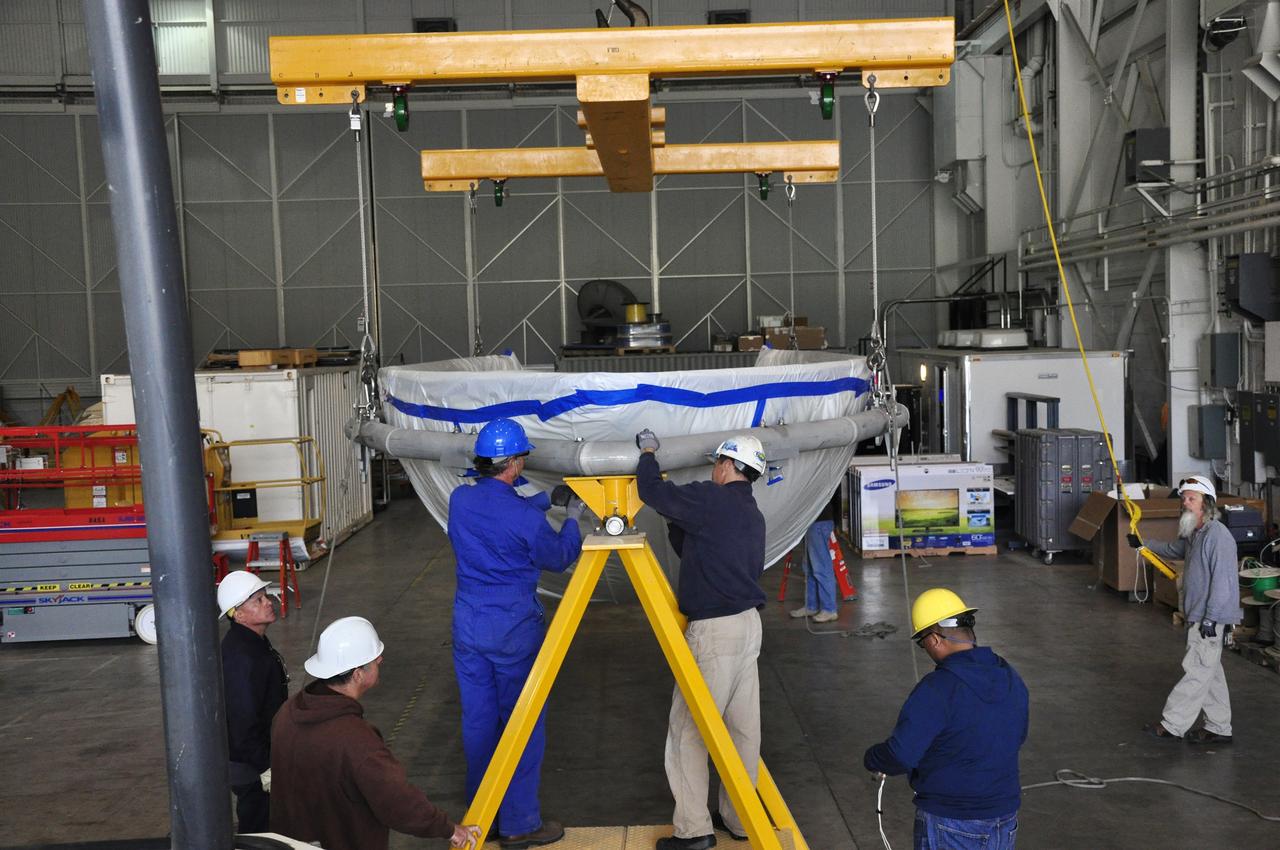

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers prepare to rotate a section of the fairing for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, in a lifting device in the Building 836 high bay on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect the SMAP spacecraft from the heat and aerodynamic pressure generated during its ascent to orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data will also be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
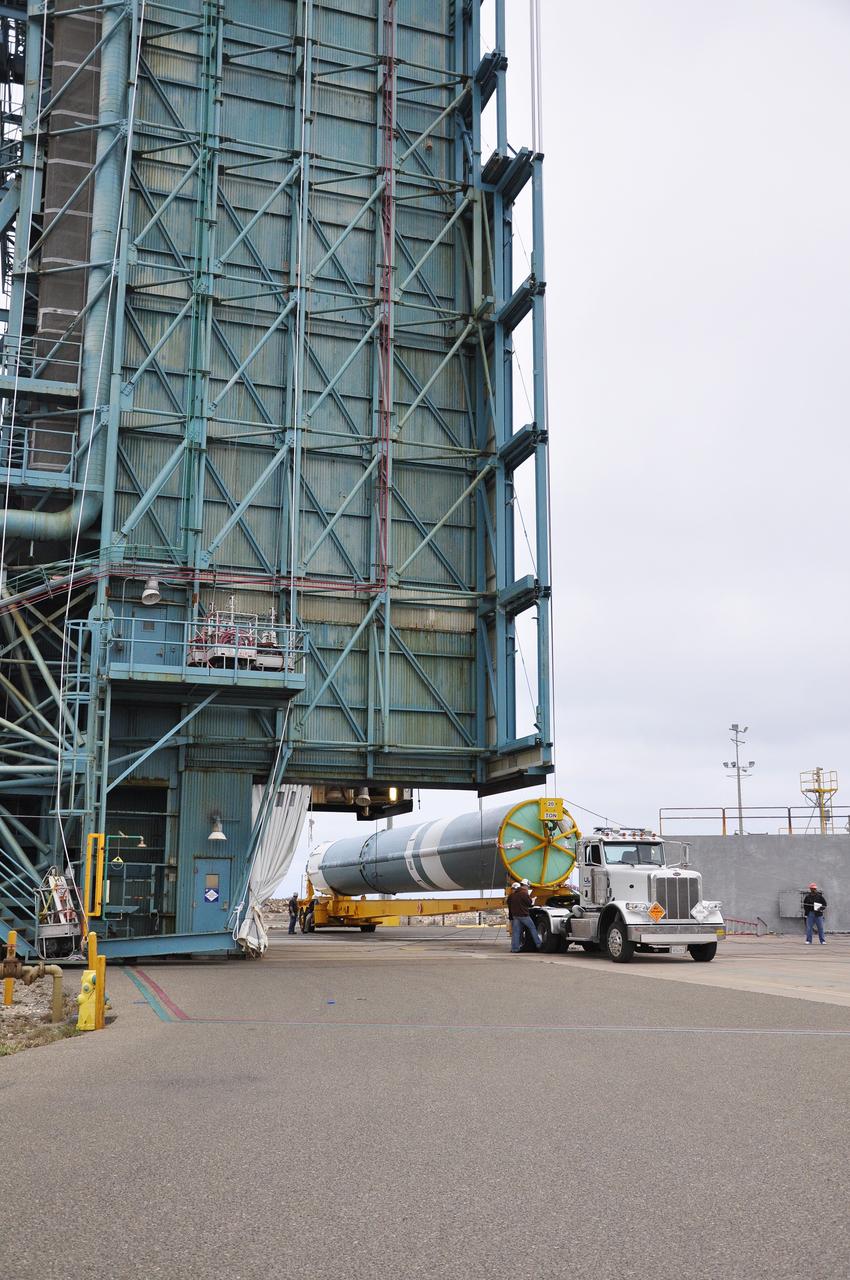

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is delivered to the base of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
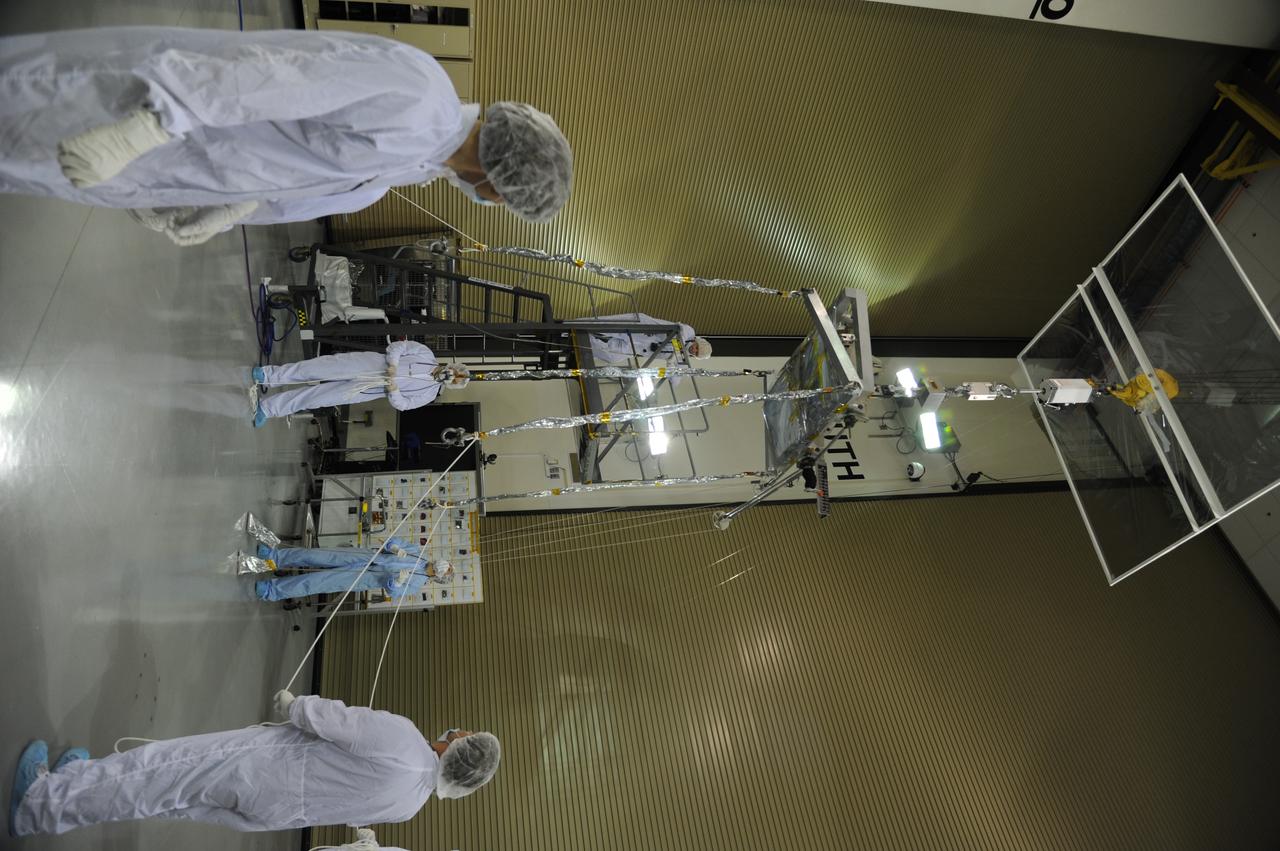

Operations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
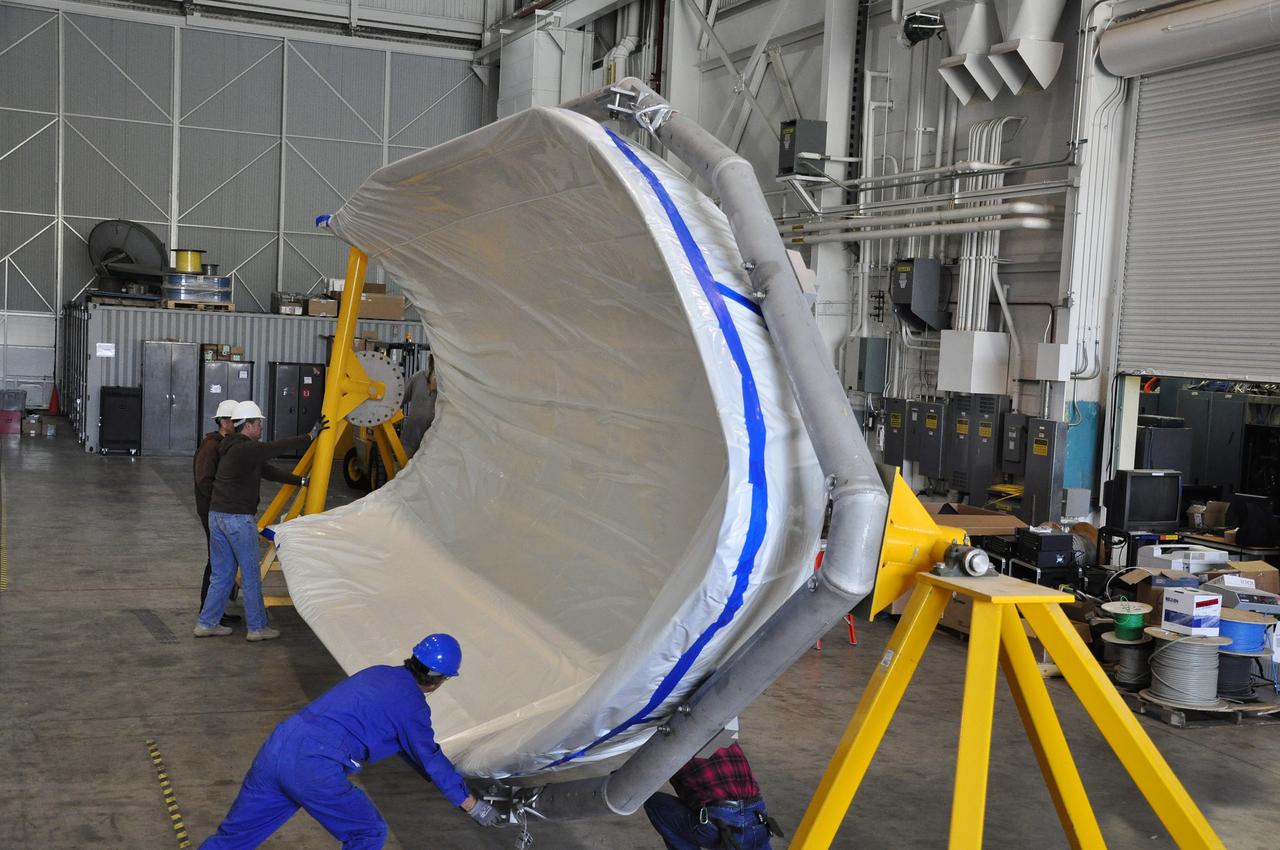

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers rotate a section of the fairing for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, in a lifting device in the Building 836 high bay on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect the SMAP spacecraft from the heat and aerodynamic pressure generated during its ascent to orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data will also be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
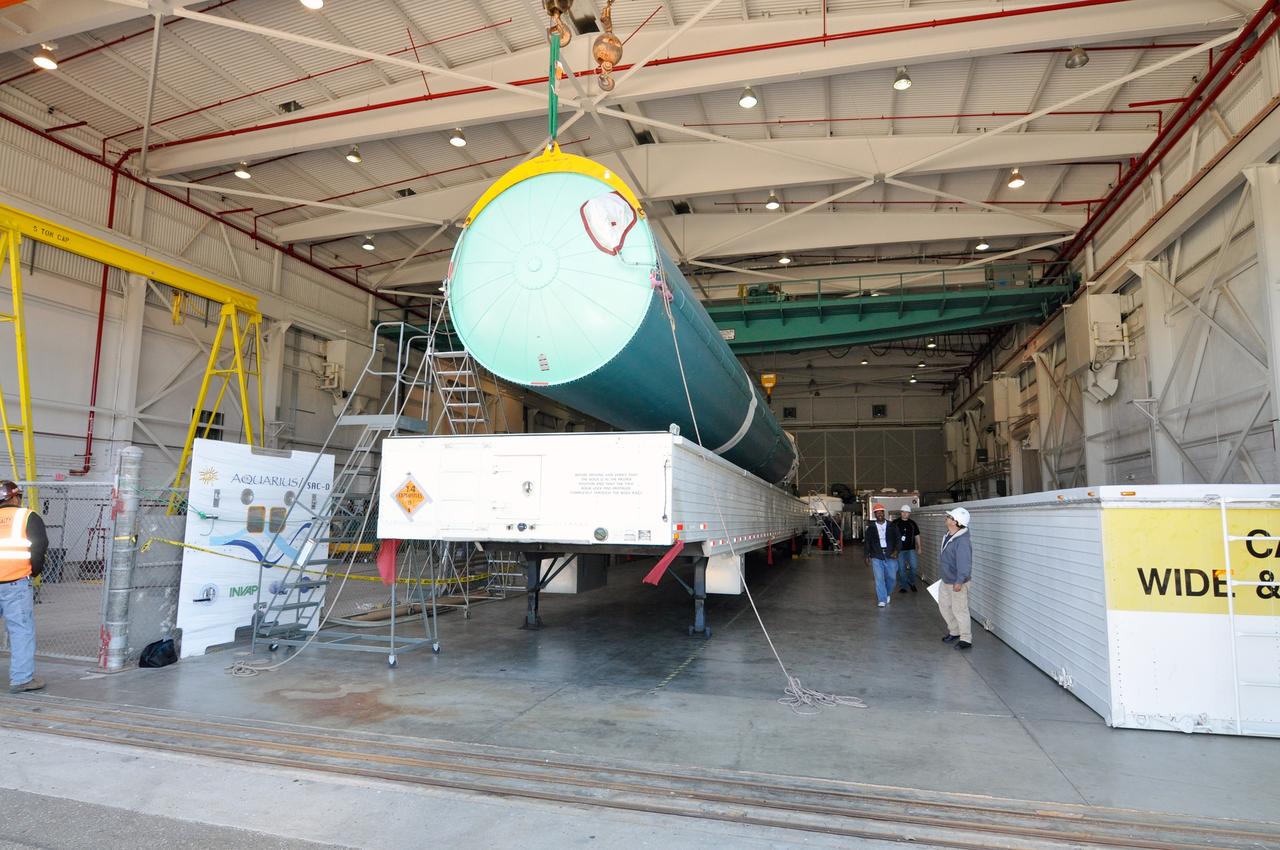

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane is used to offload the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket following its arrival at NASA hangar 836 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The launch vehicle will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
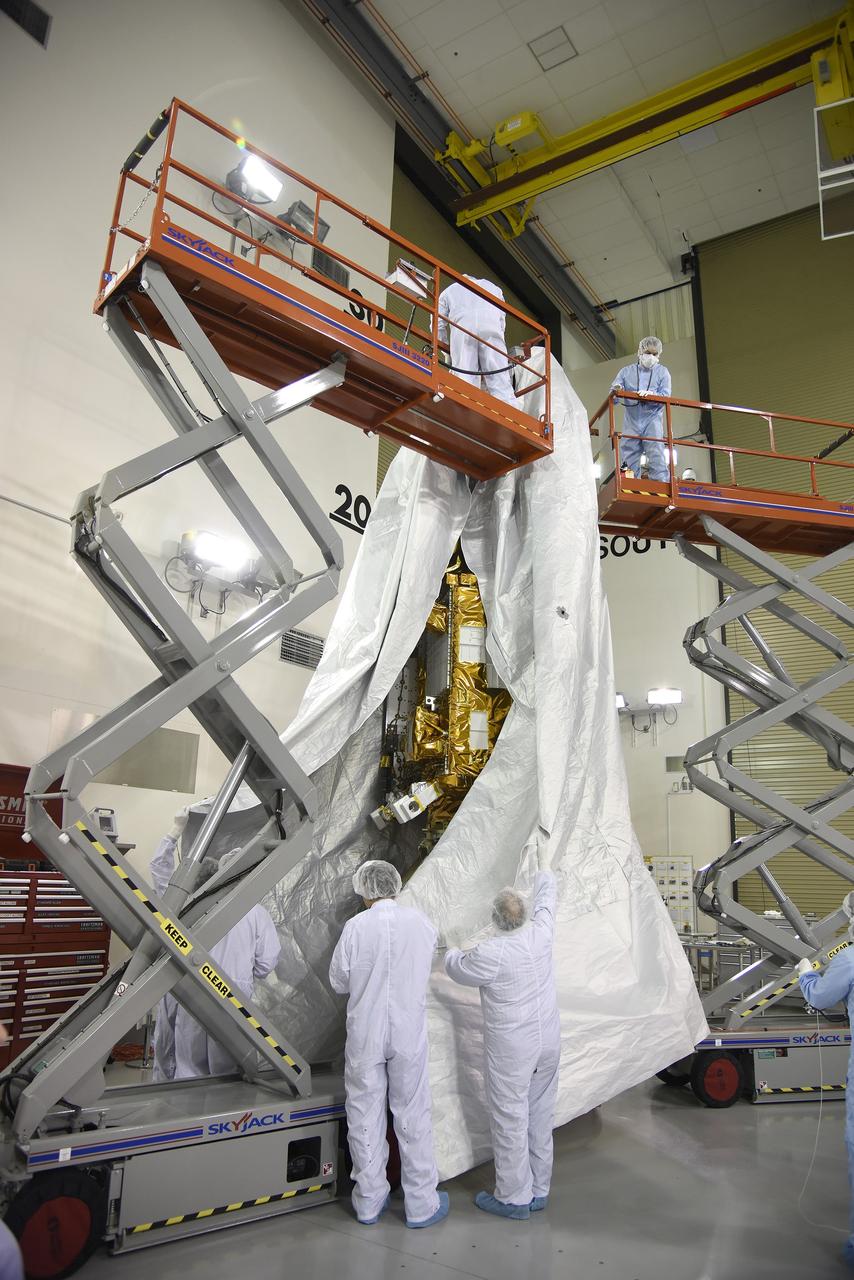

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians place a protective cover over NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, satellite prior the spacecraft being transported to the launch pad. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: Jeremy Moore, USAF Photo Squadron
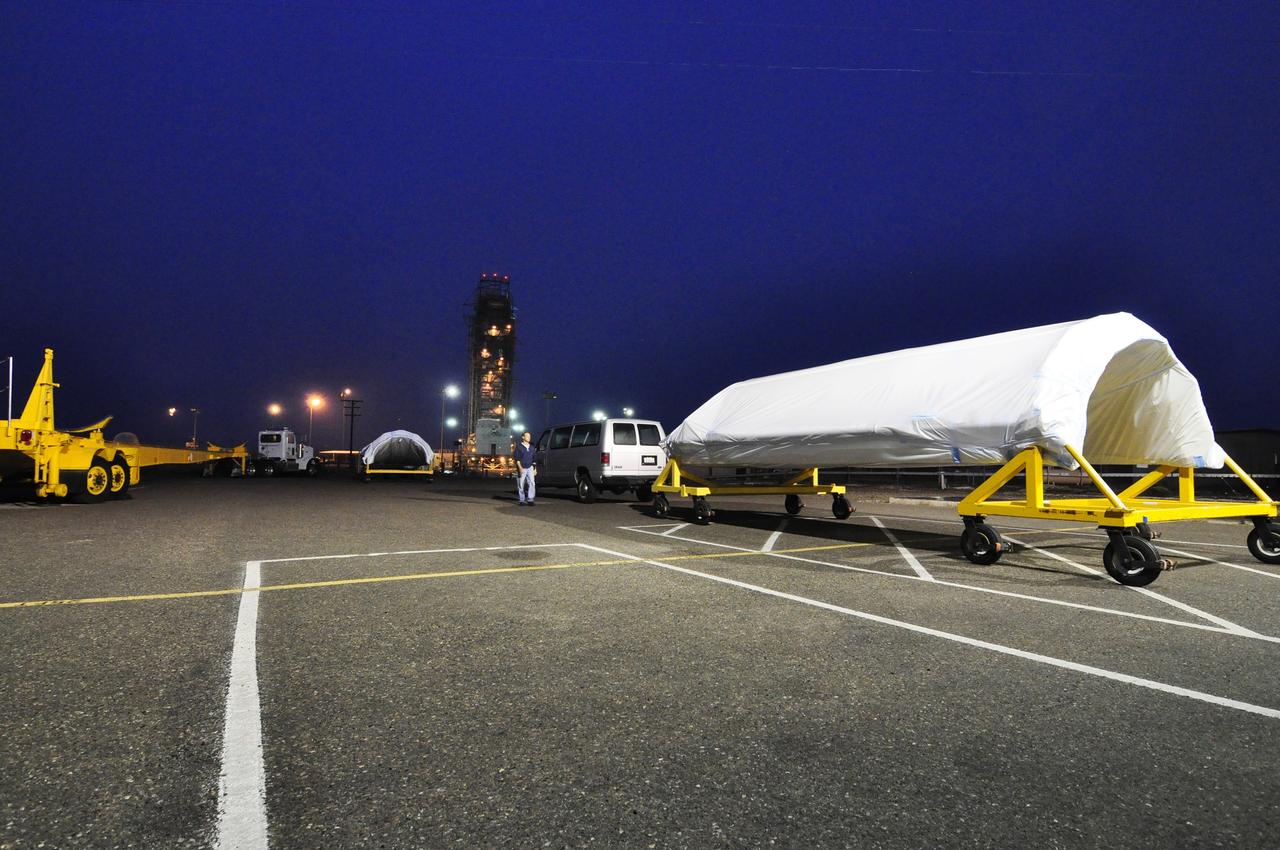

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The half sections of the 10-foot-diameter fairing for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, are delivered to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect the SMAP spacecraft from the heat and aerodynamic pressure generated during its ascent to orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data will also be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
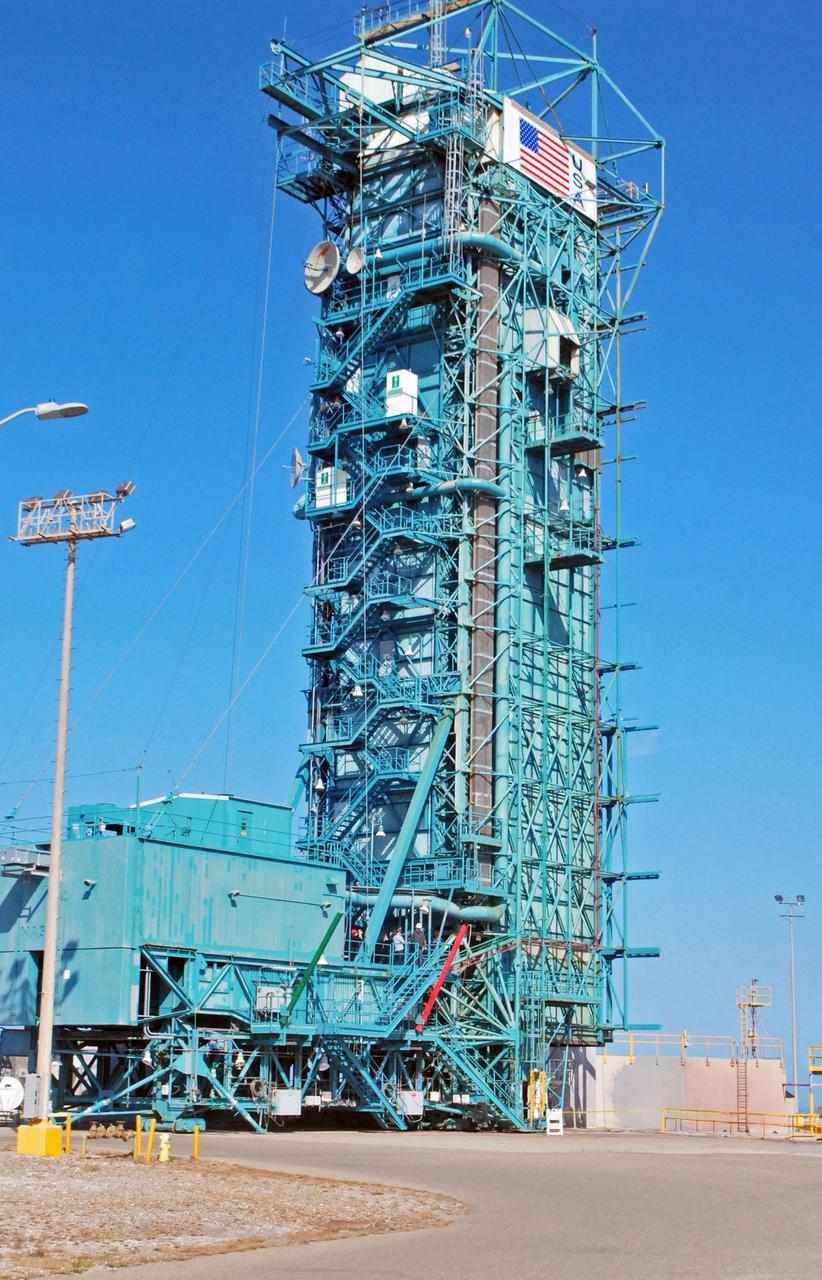

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is scheduled to launch in November 2014 from Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, seen here on a temperate, fog-free summer's day. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will be used to deliver SMAP into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket arrives at NASA hangar 836 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Delta II rocket will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

Preparations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
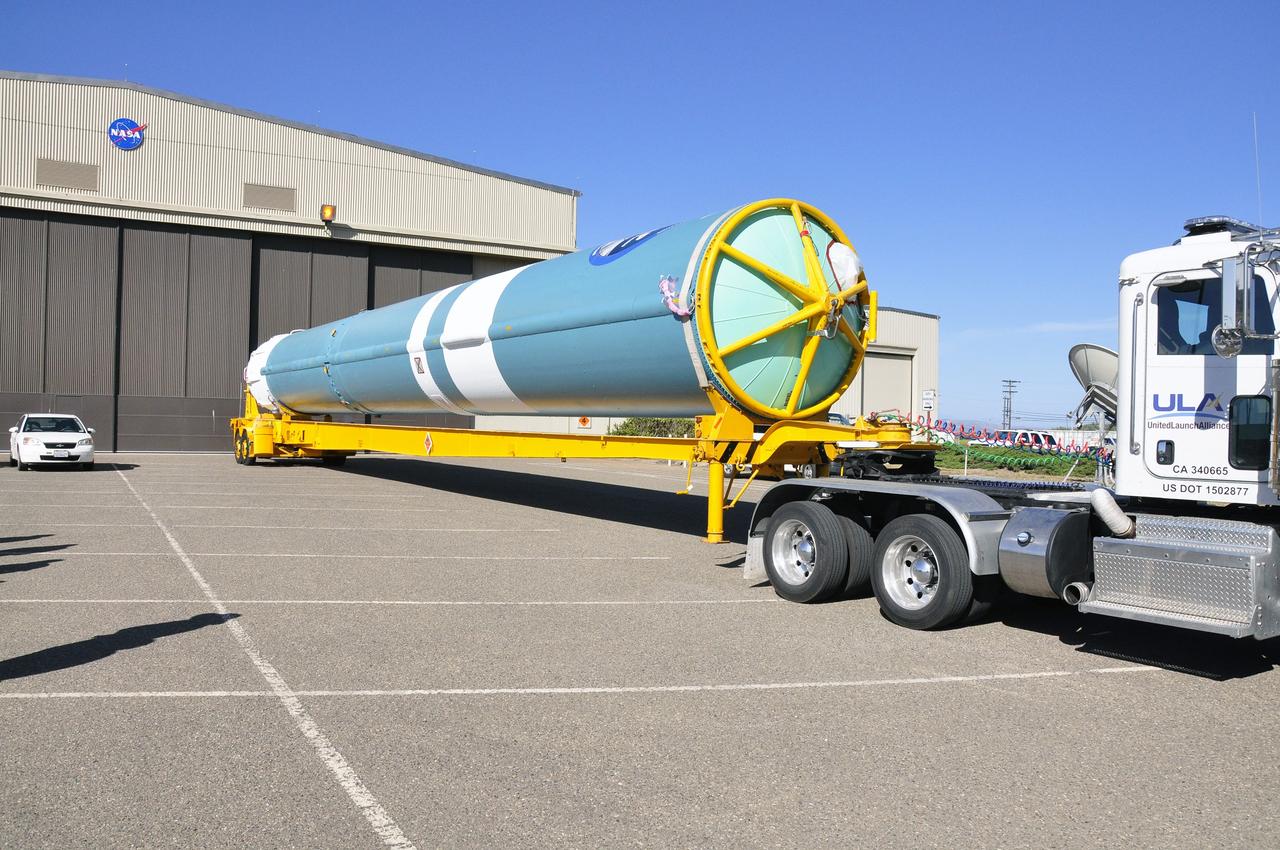

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, begins its journey from the Building 836 hangar to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
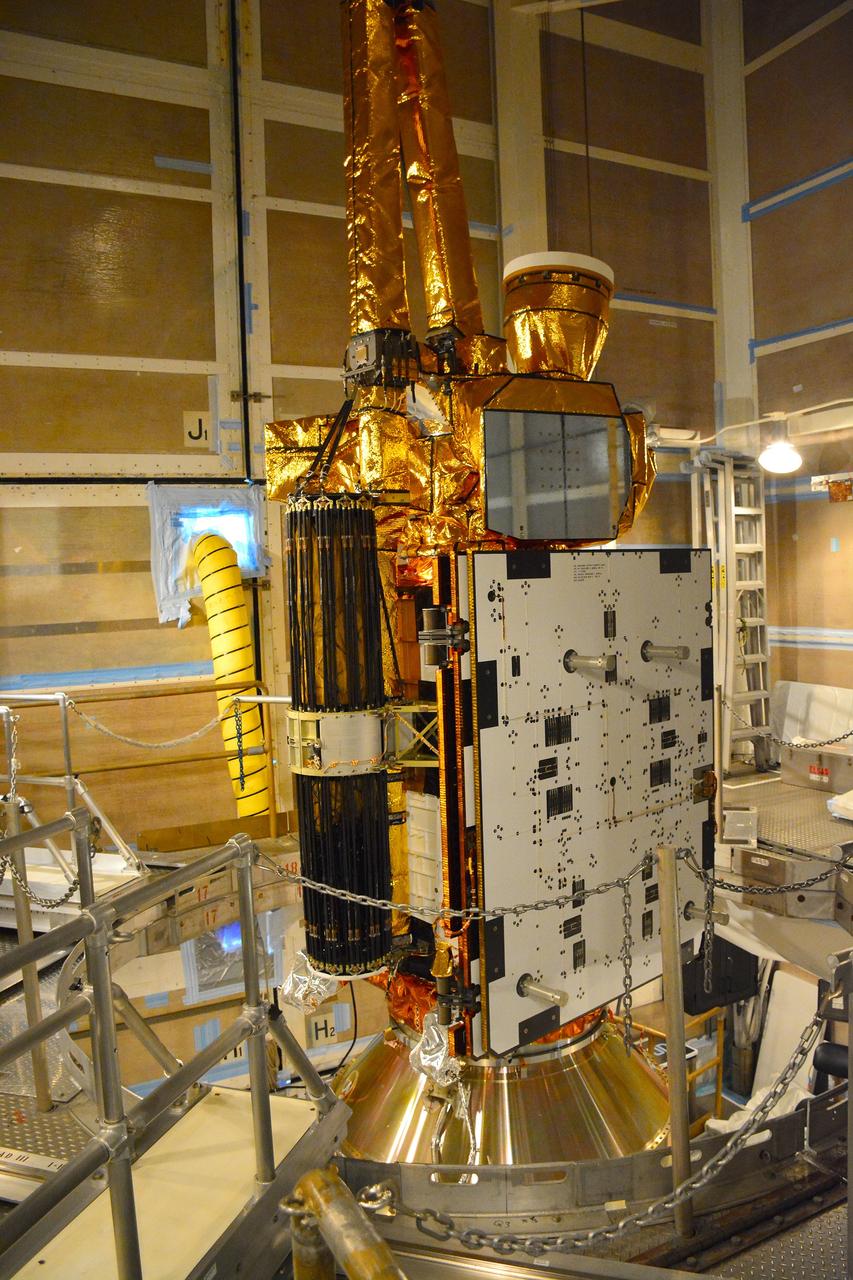

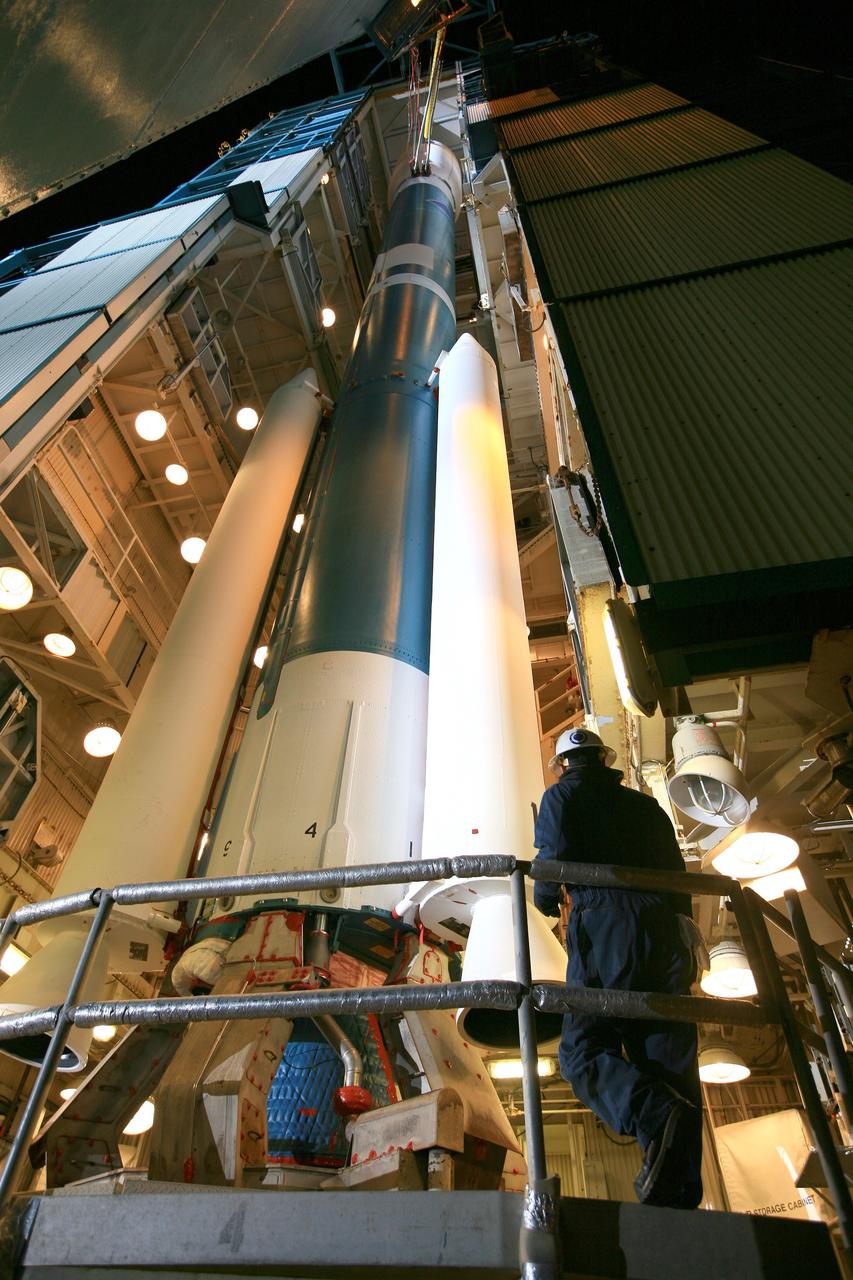
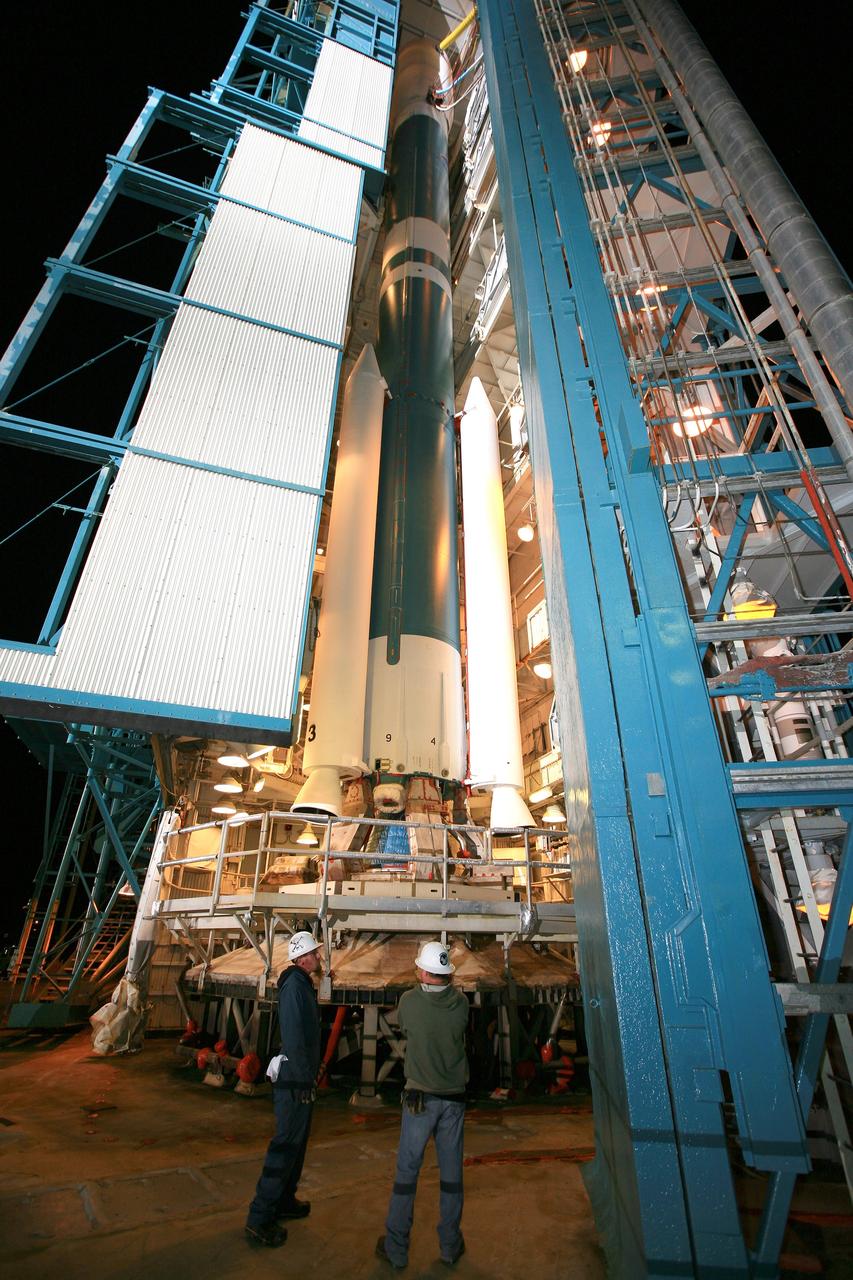
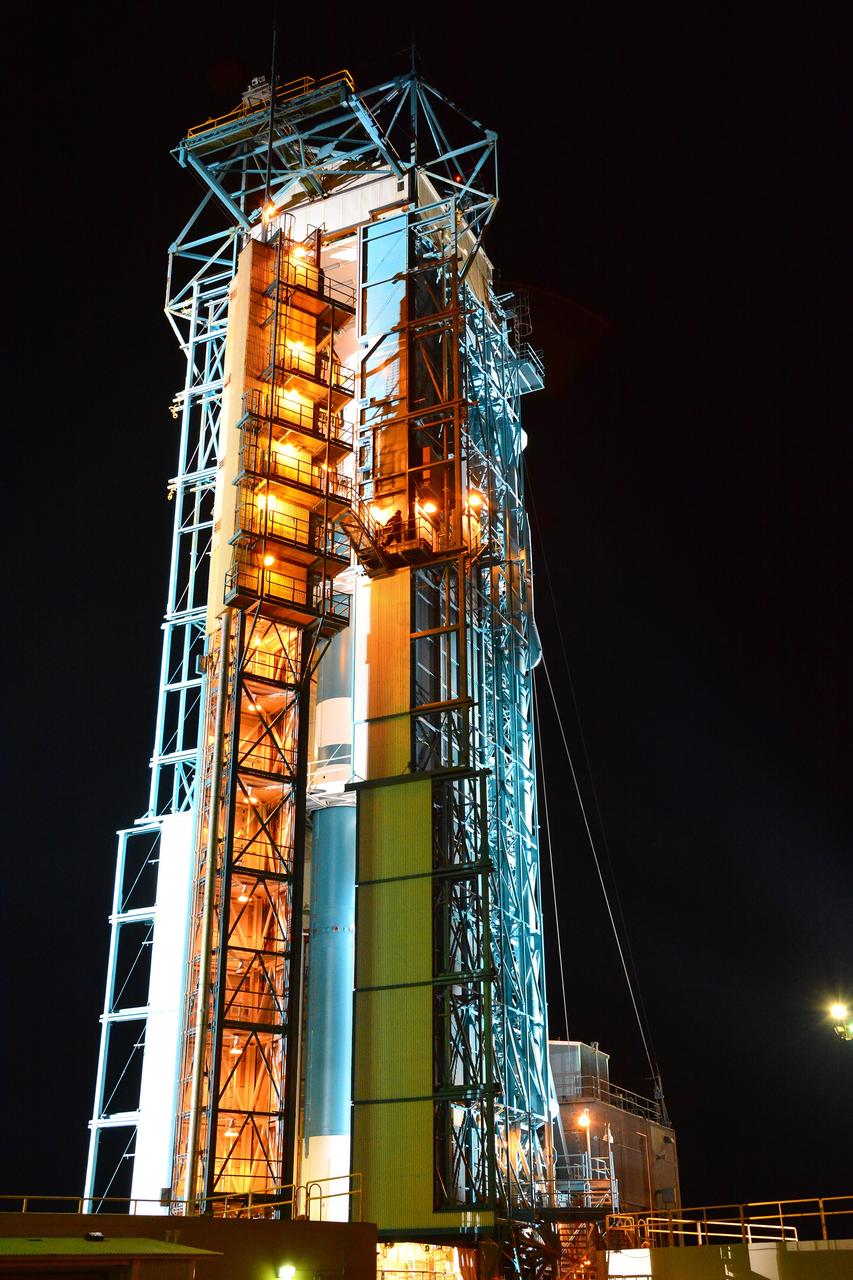
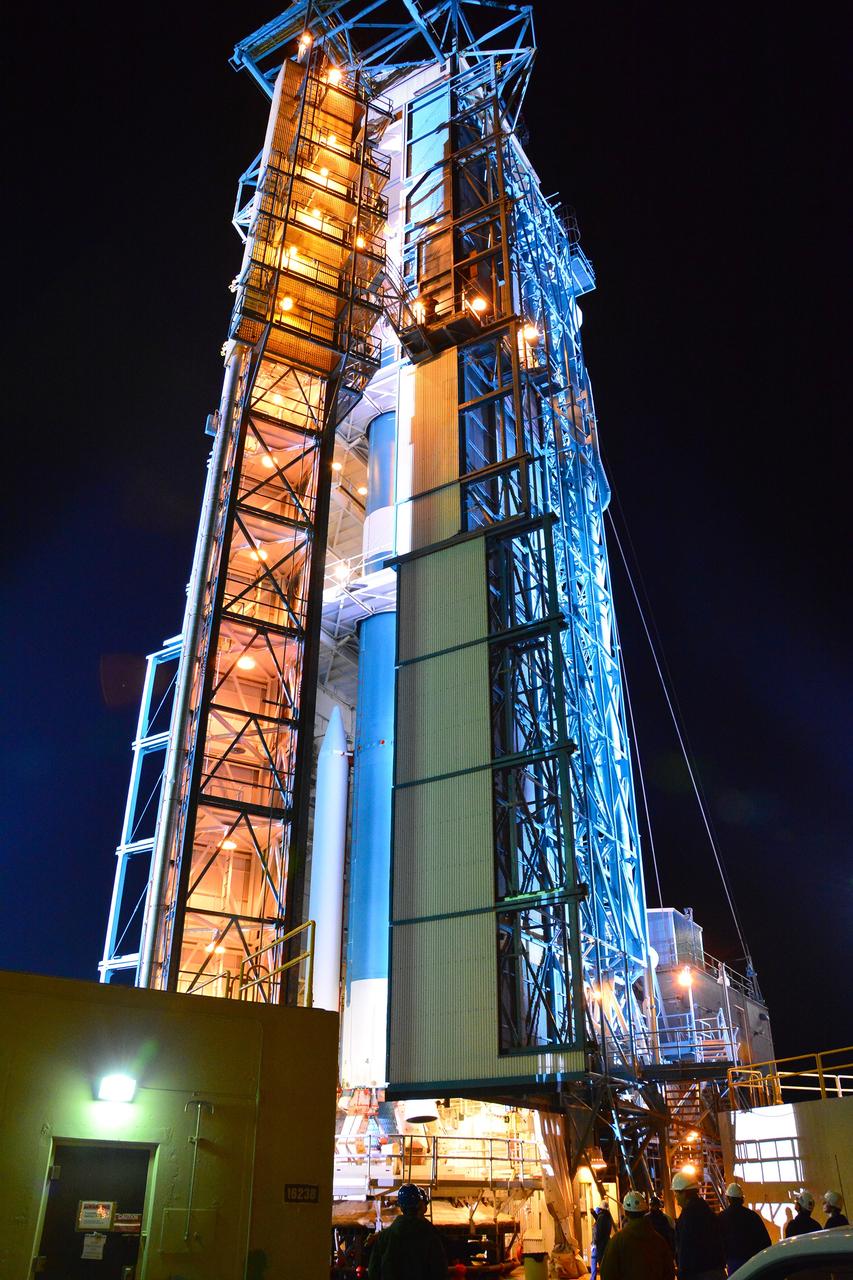
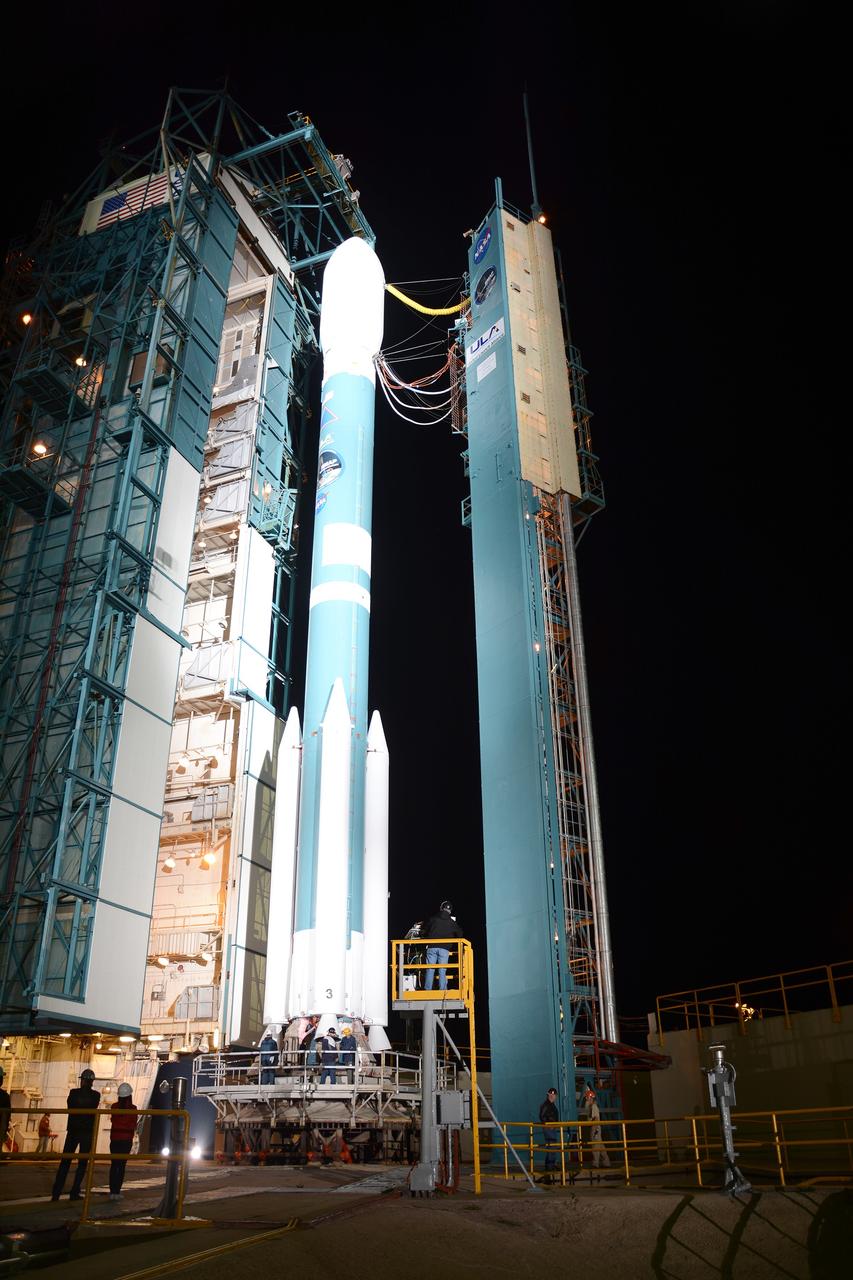
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, satellite is mated to its Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
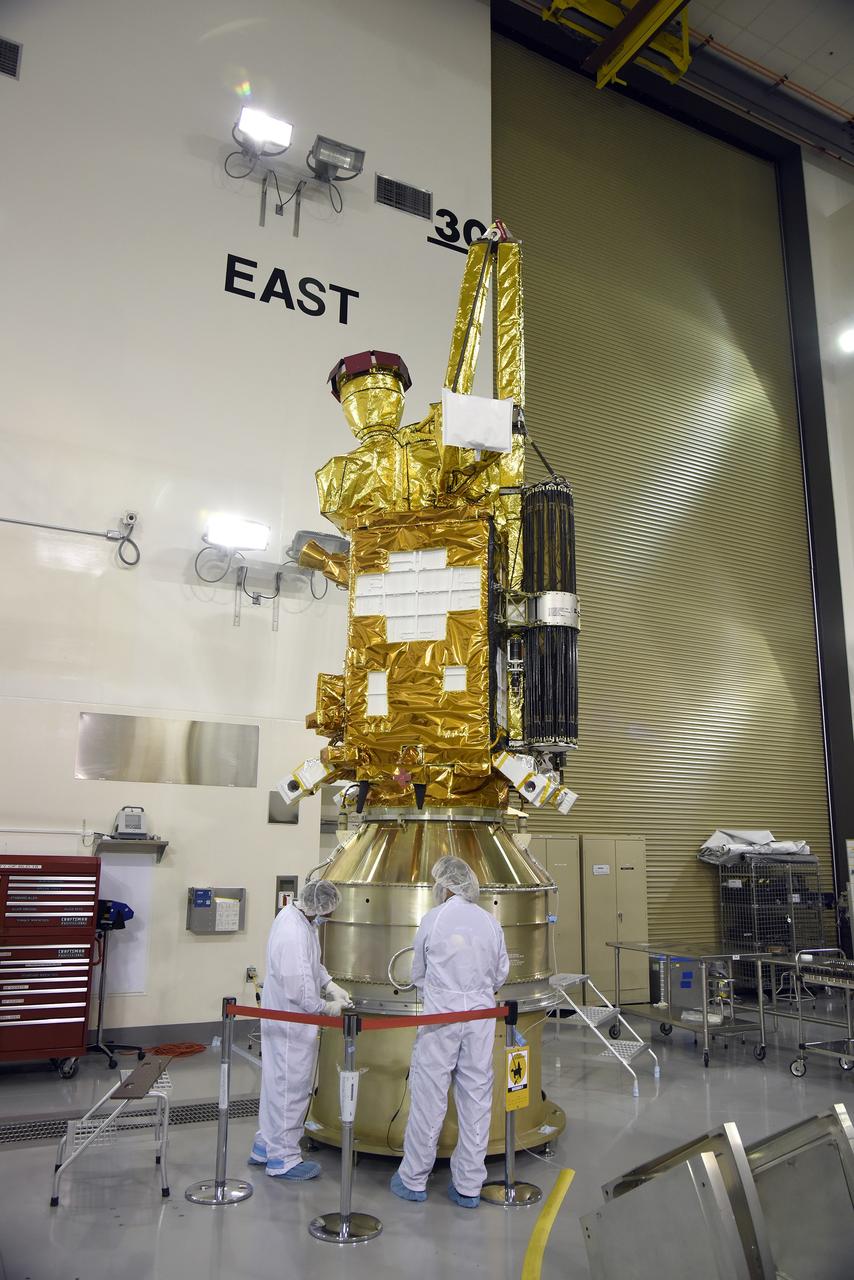

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians inspect NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, satellite. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: Jeremy Moore, USAF Photo Squadron
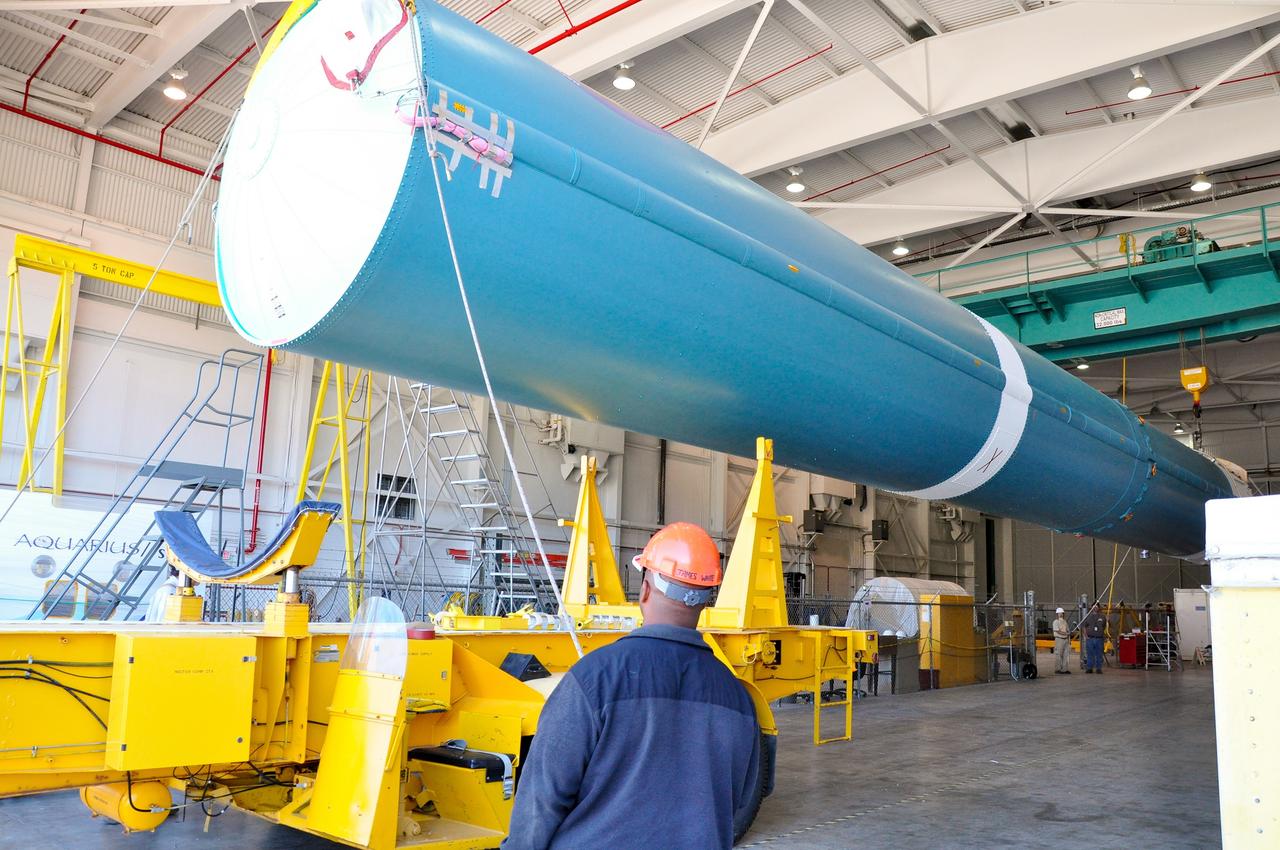

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Under the watchful eye of technicians, crane is used to offload the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket following its arrival at NASA hangar 836 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The launch vehicle will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

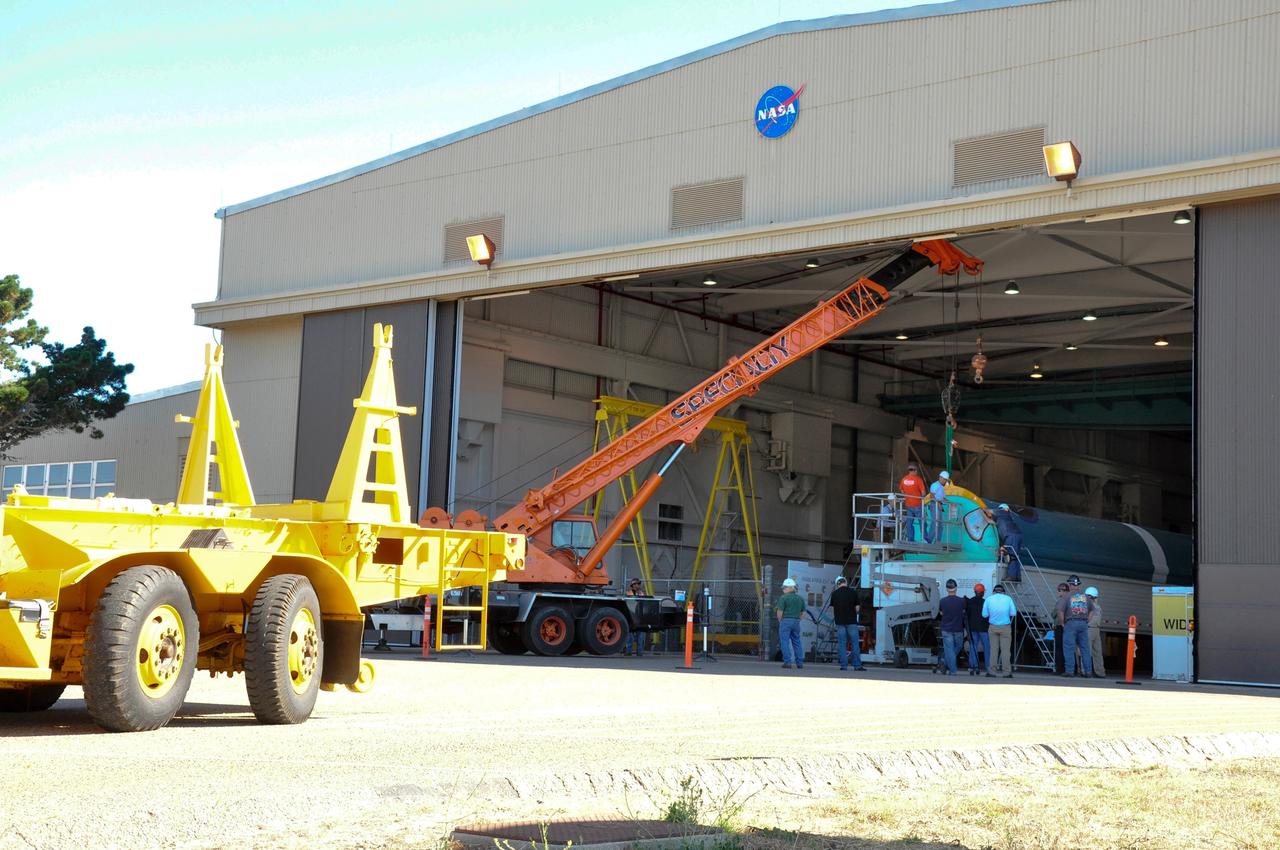
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second stage, or upper stage, of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket begins its journey from Building 836 on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2. The Delta II rocket will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane is positioned to offload the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket following its arrival at NASA hangar 836 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The launch vehicle will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
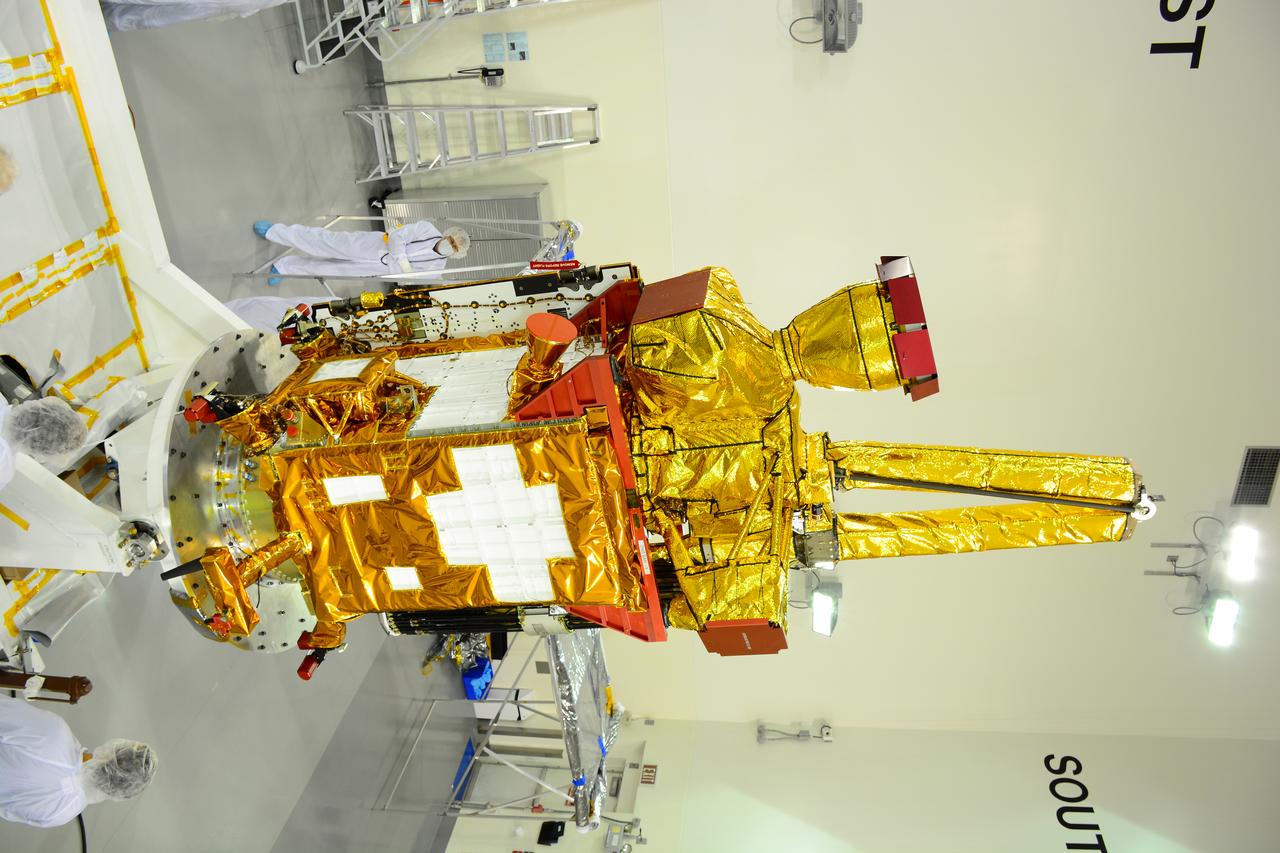

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians rotate NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft to begin processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
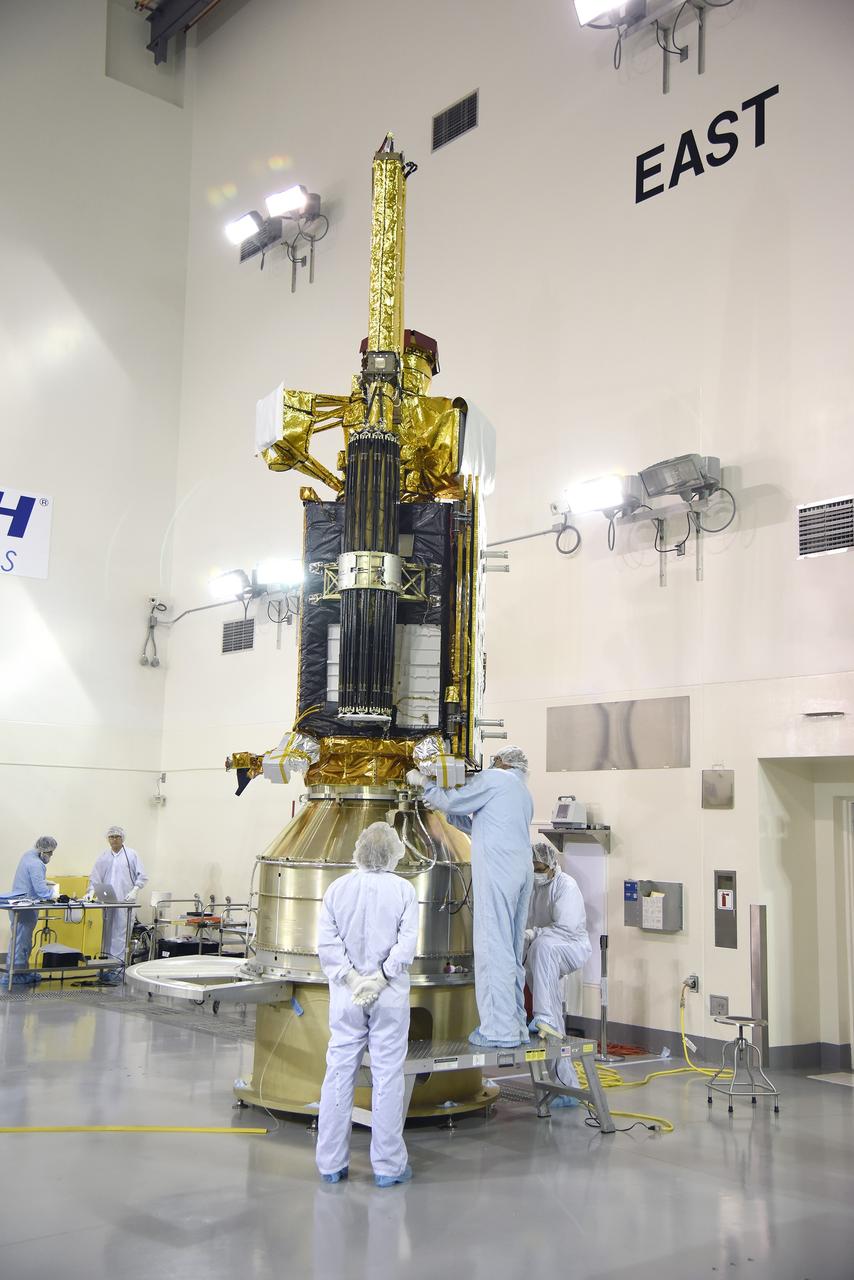

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians inspect NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, satellite. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: Jeremy Moore, USAF Photo Squadron
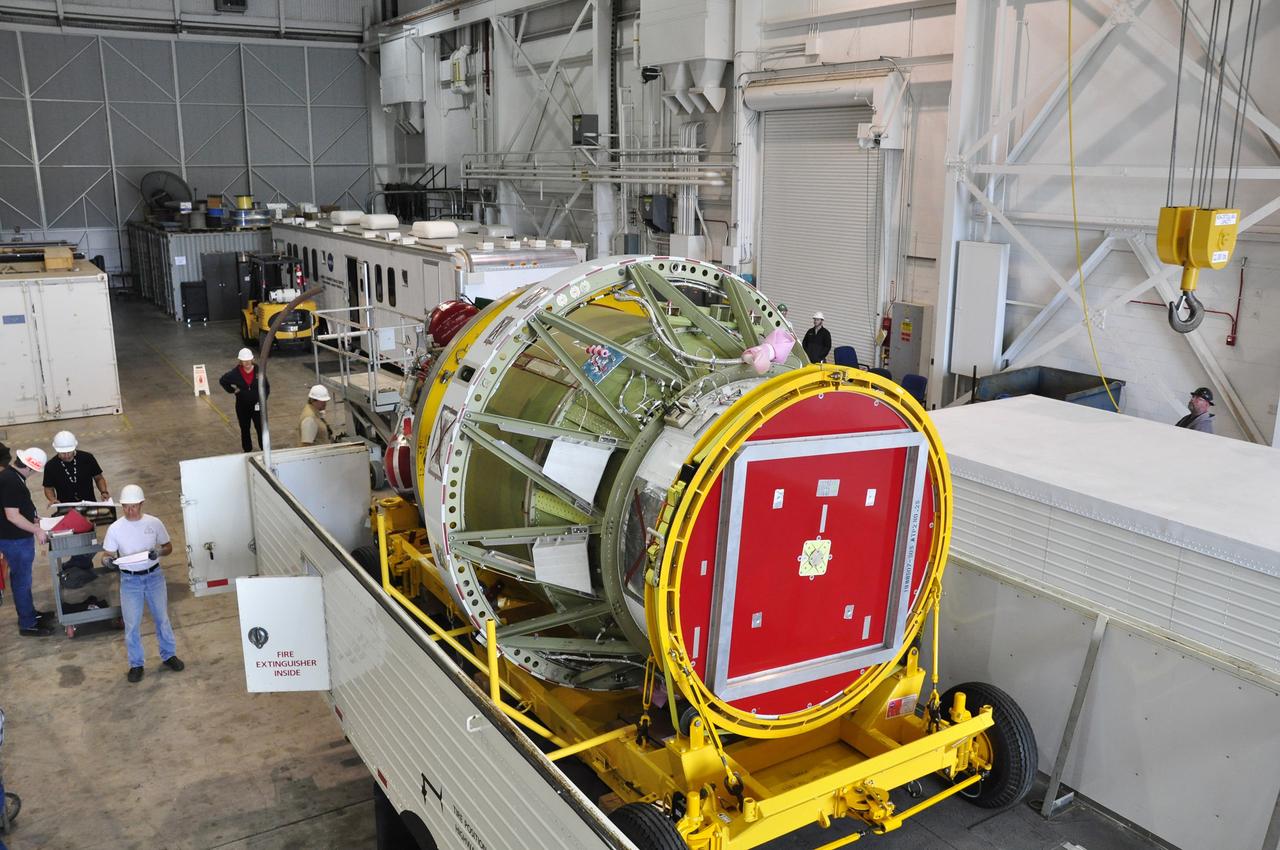

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to lift the second stage, or upper stage, of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from its transportation trailer in the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Delta II rocket will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
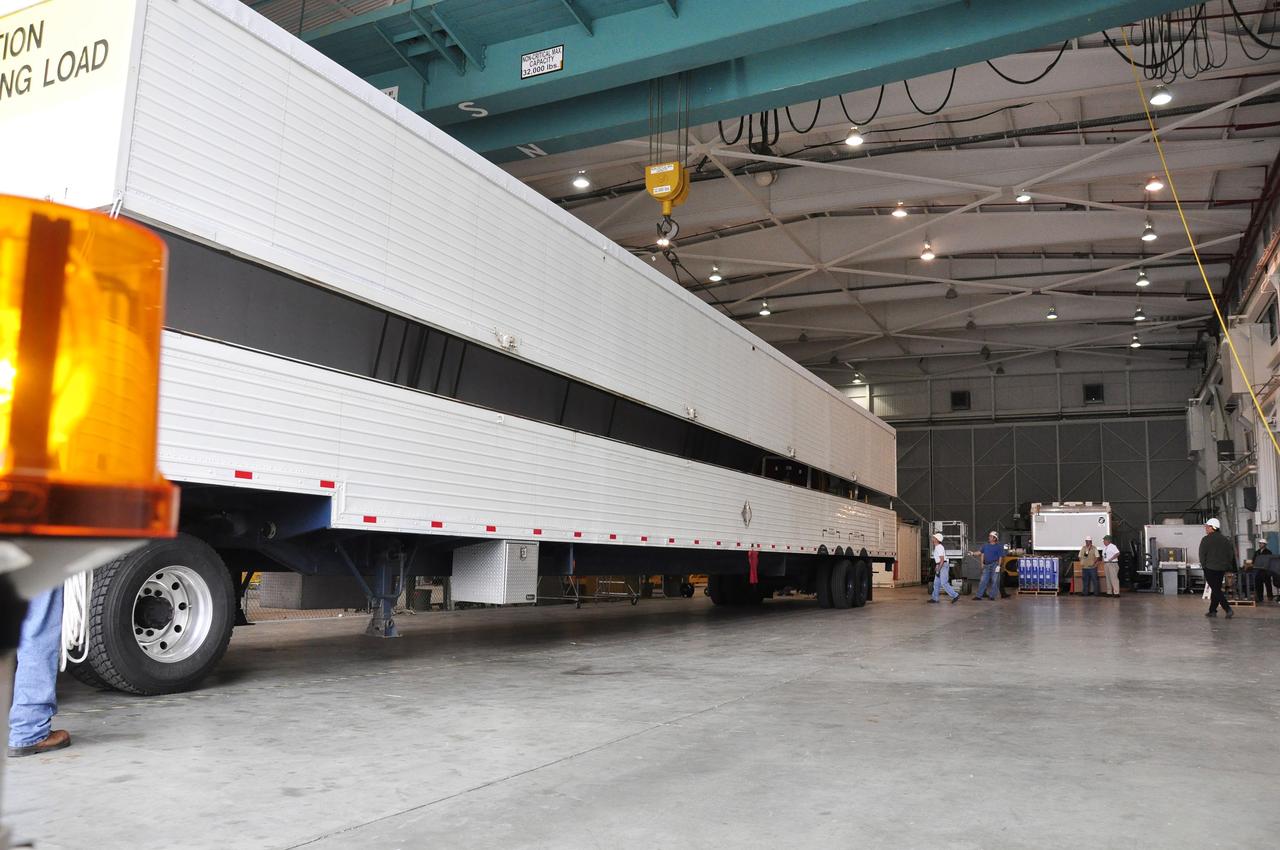

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The transportation trailer carrying the second stage, or upper stage, of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket backs into the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Delta II rocket will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
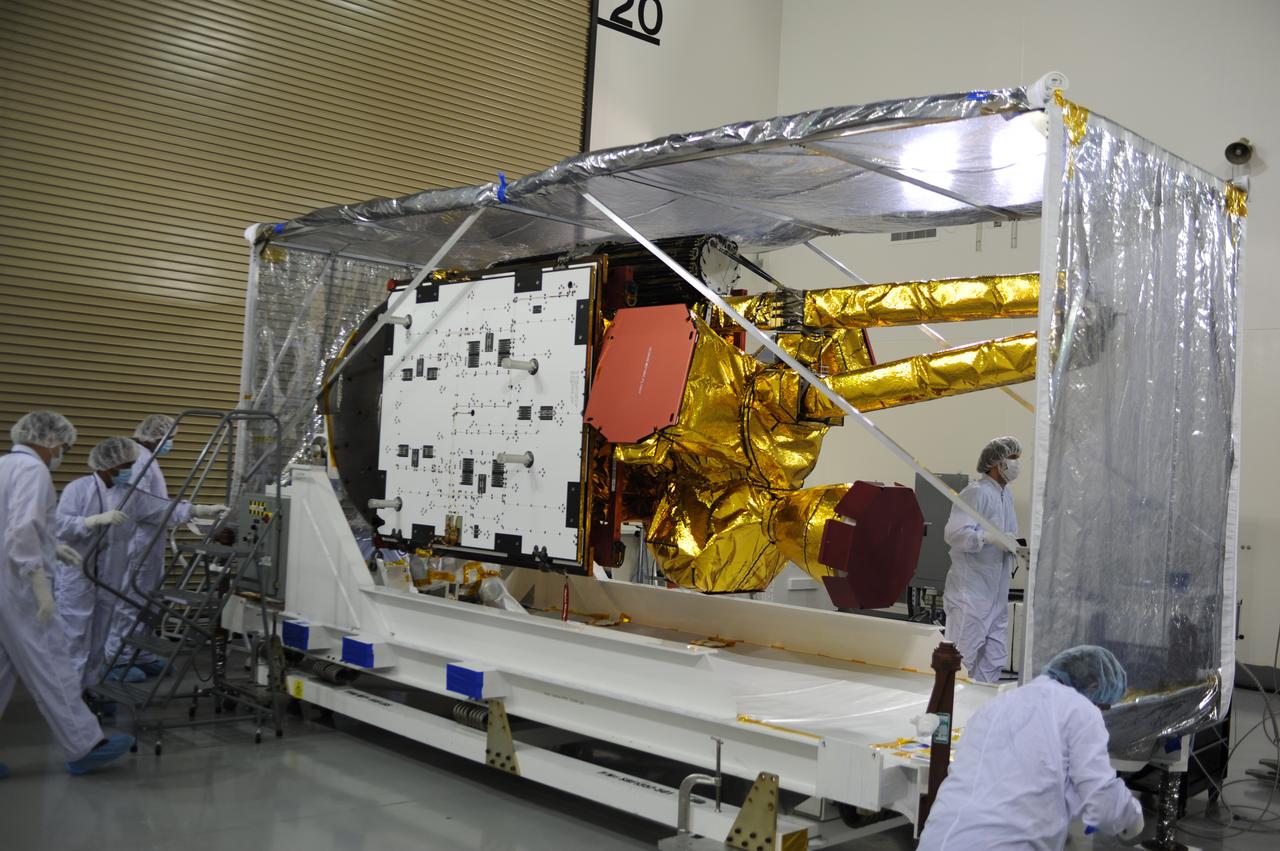

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians remove a protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
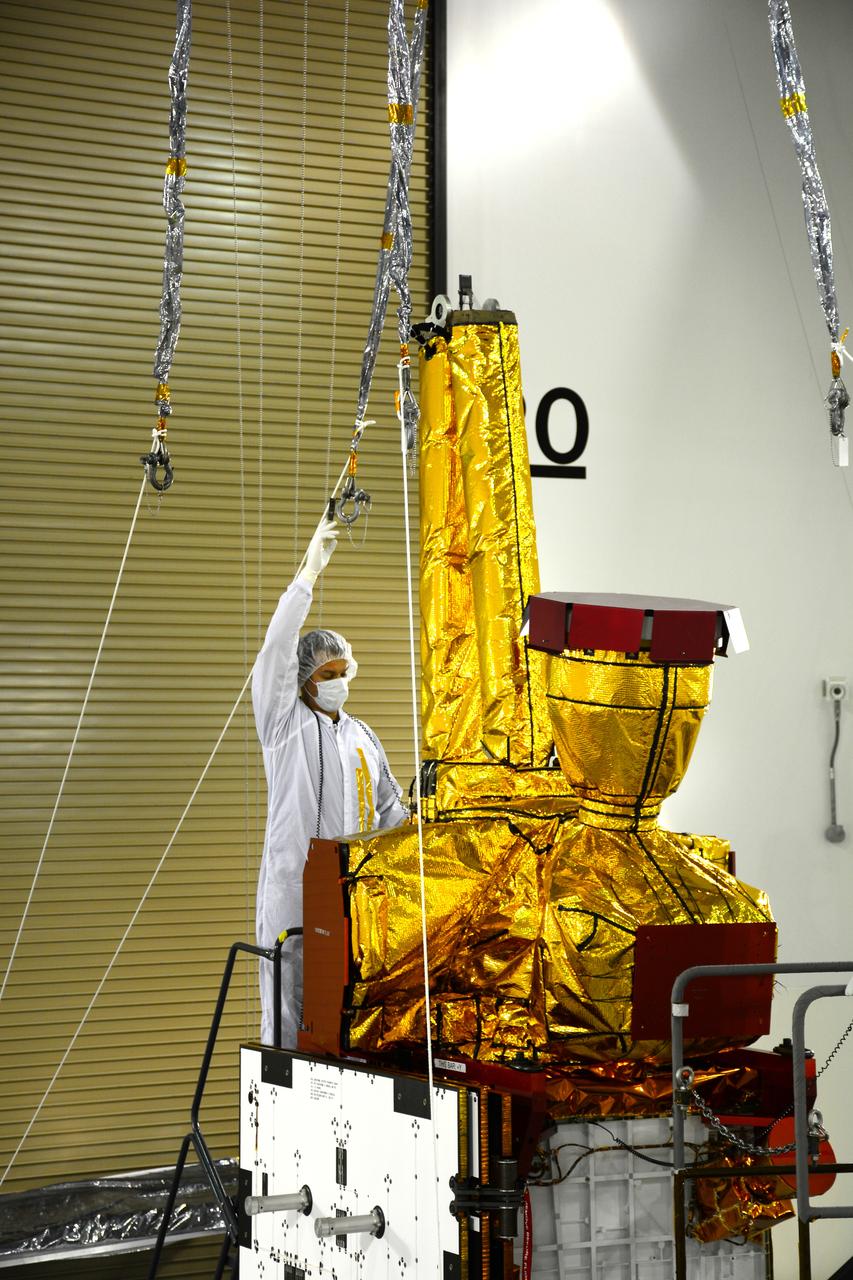

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, an engineer inspects NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
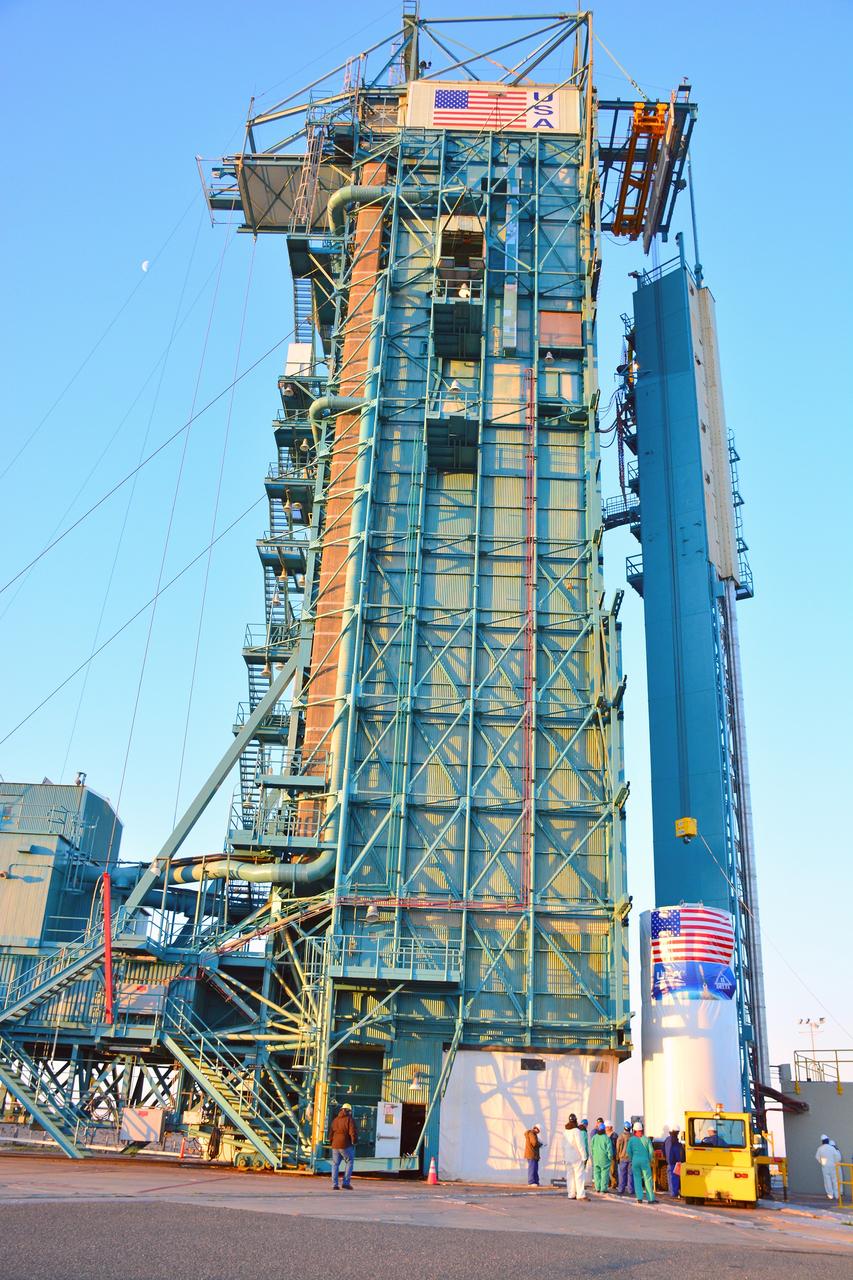

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, satellite is prepared for lifting at Space Launch Complex 2 for mating to its Delta II rocket. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians rotate NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft to begin processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
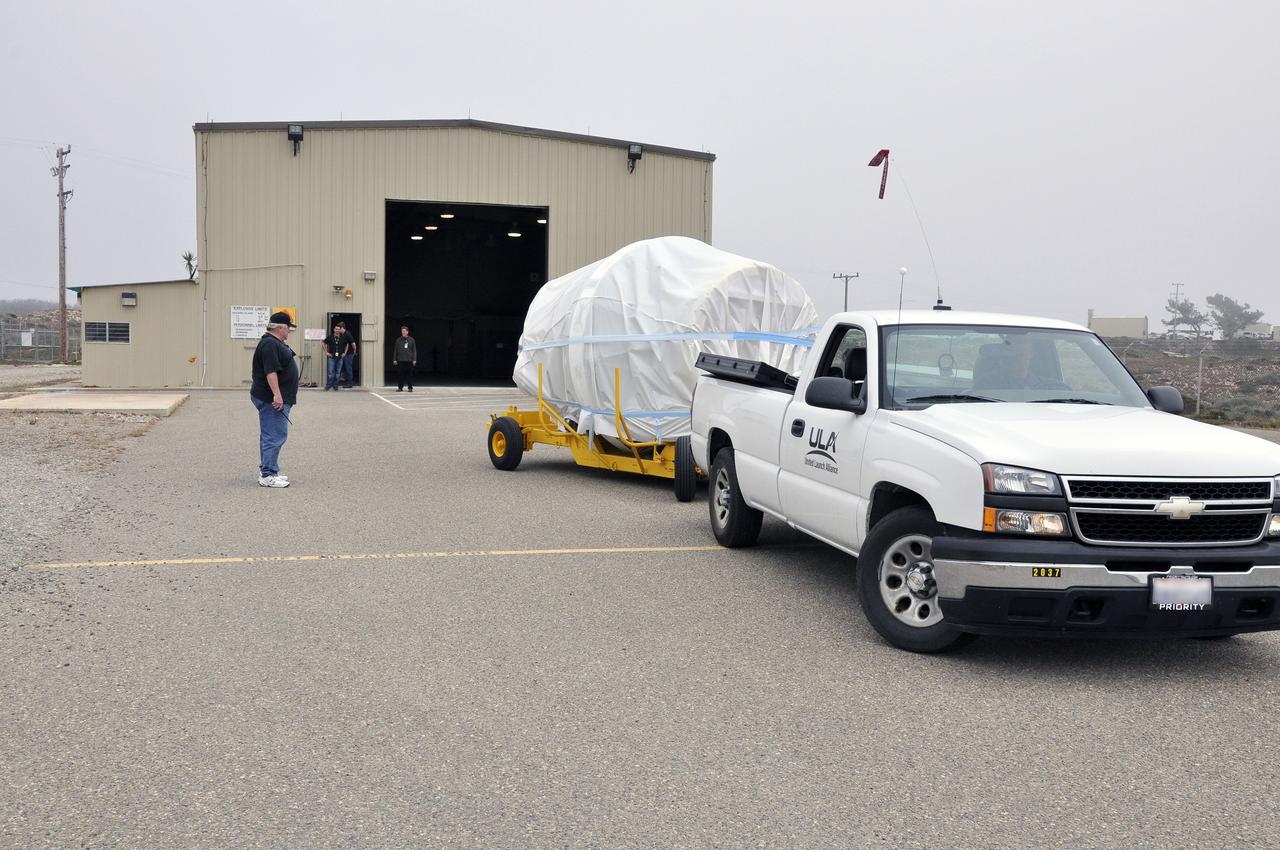

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second stage, or upper stage, of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket arrives at the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Delta II rocket will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
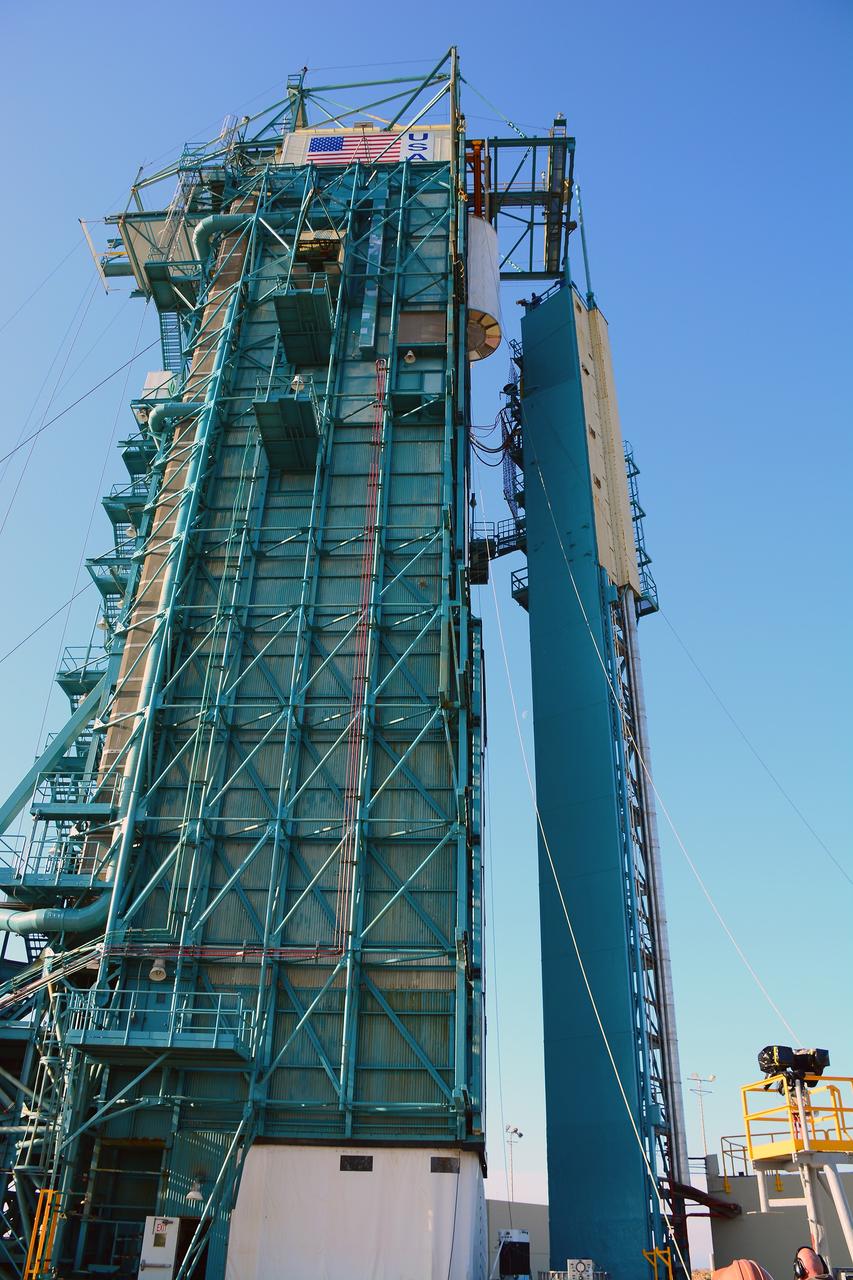

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, satellite is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 for mating to its Delta II rocket. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for Jan. 29, 2015. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
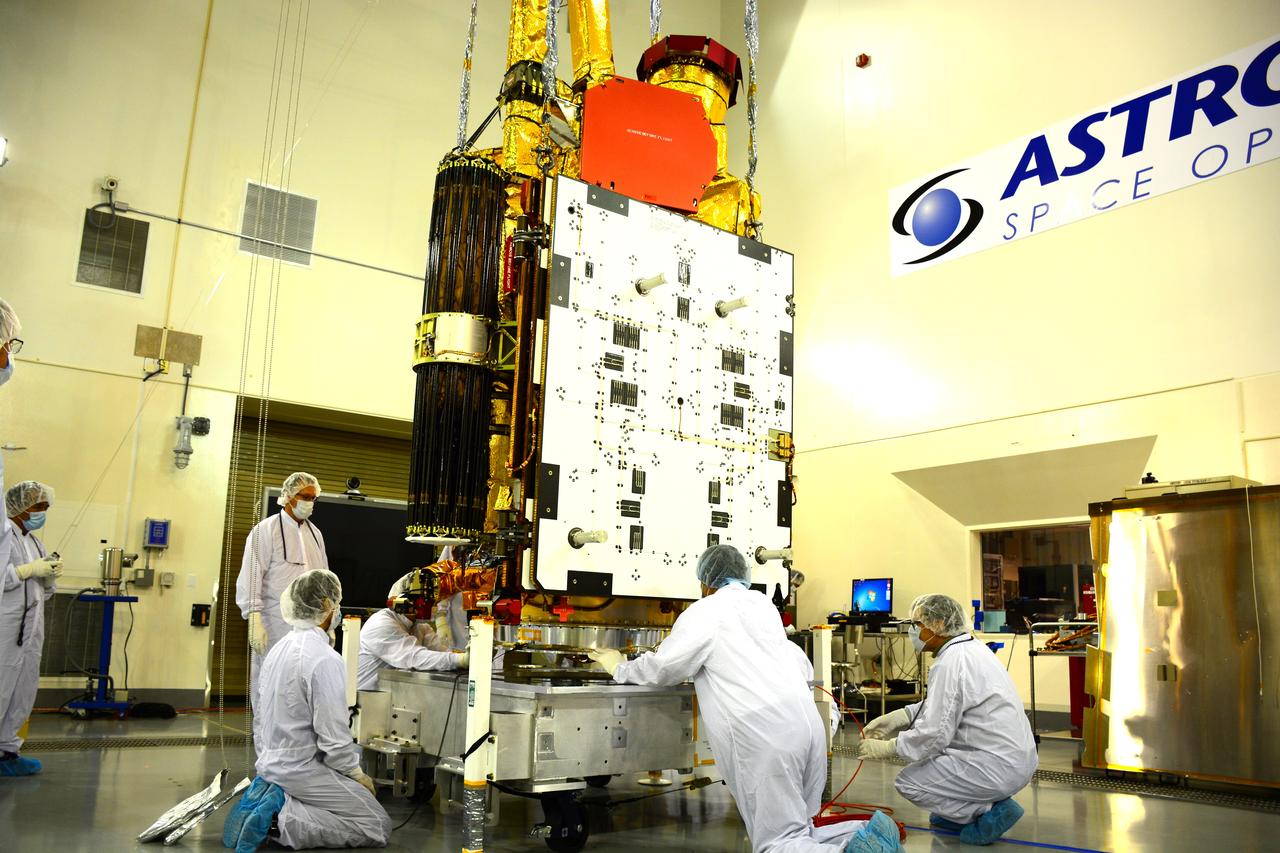

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians mount NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft on a work platform. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
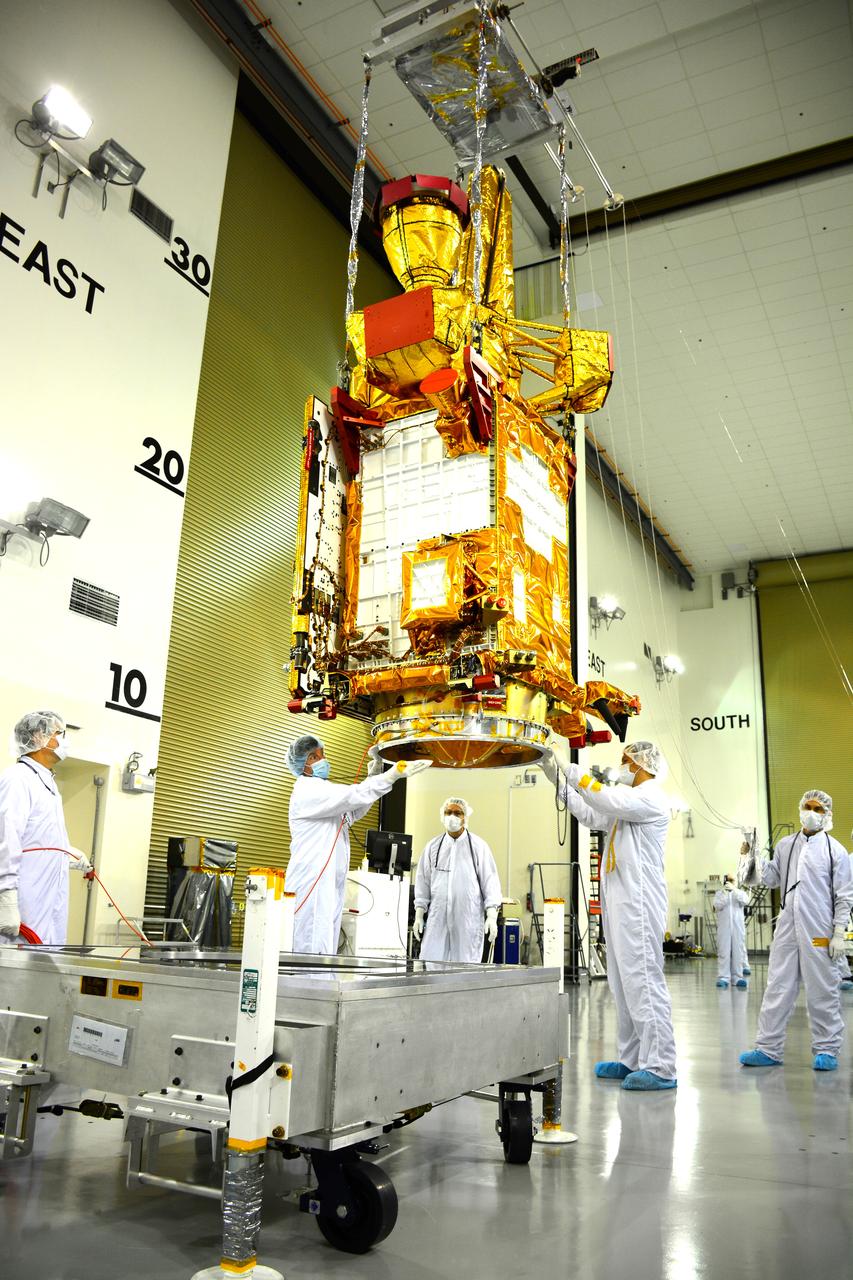

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians use a crane to move NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
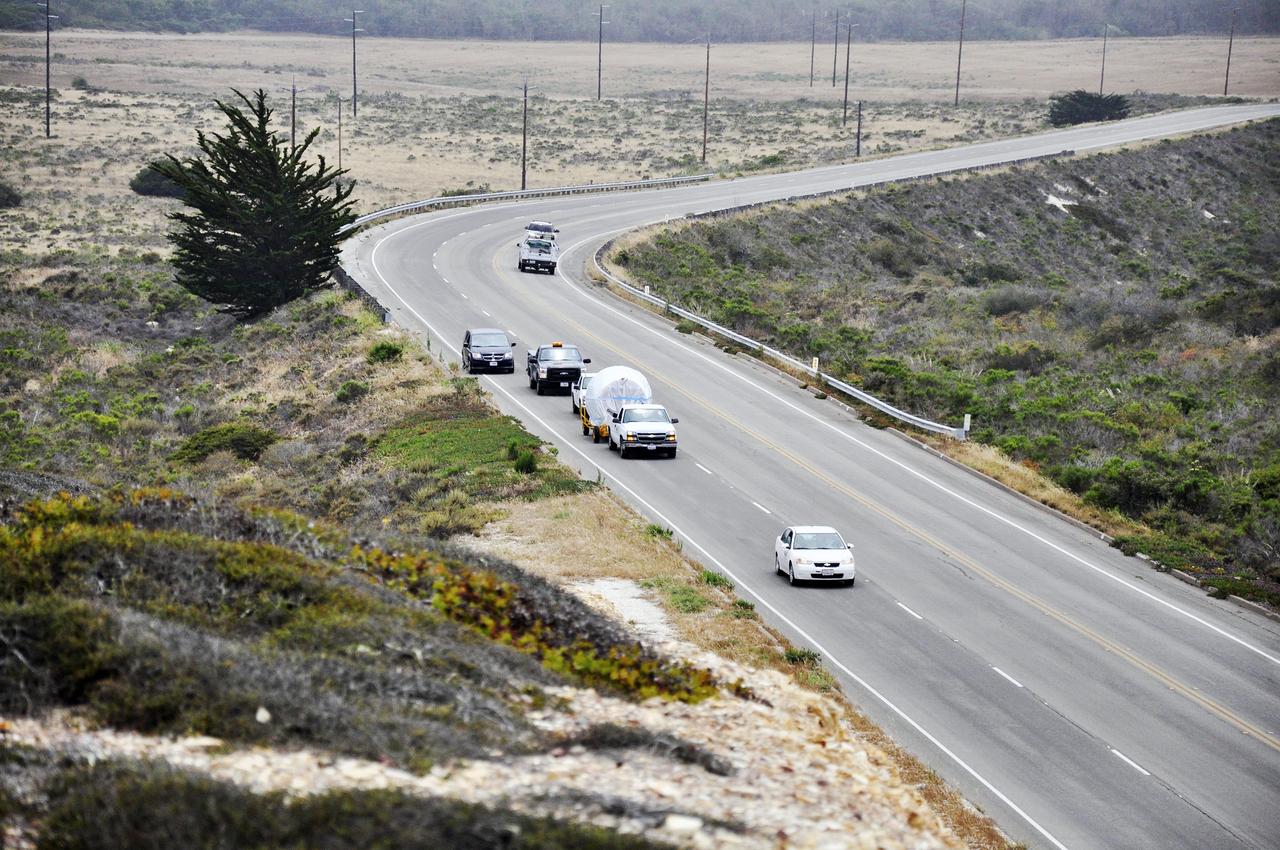

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second stage, or upper stage, of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket winds its way along the roads from Building 836 to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Delta II rocket will be used to deliver NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into orbit. SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin