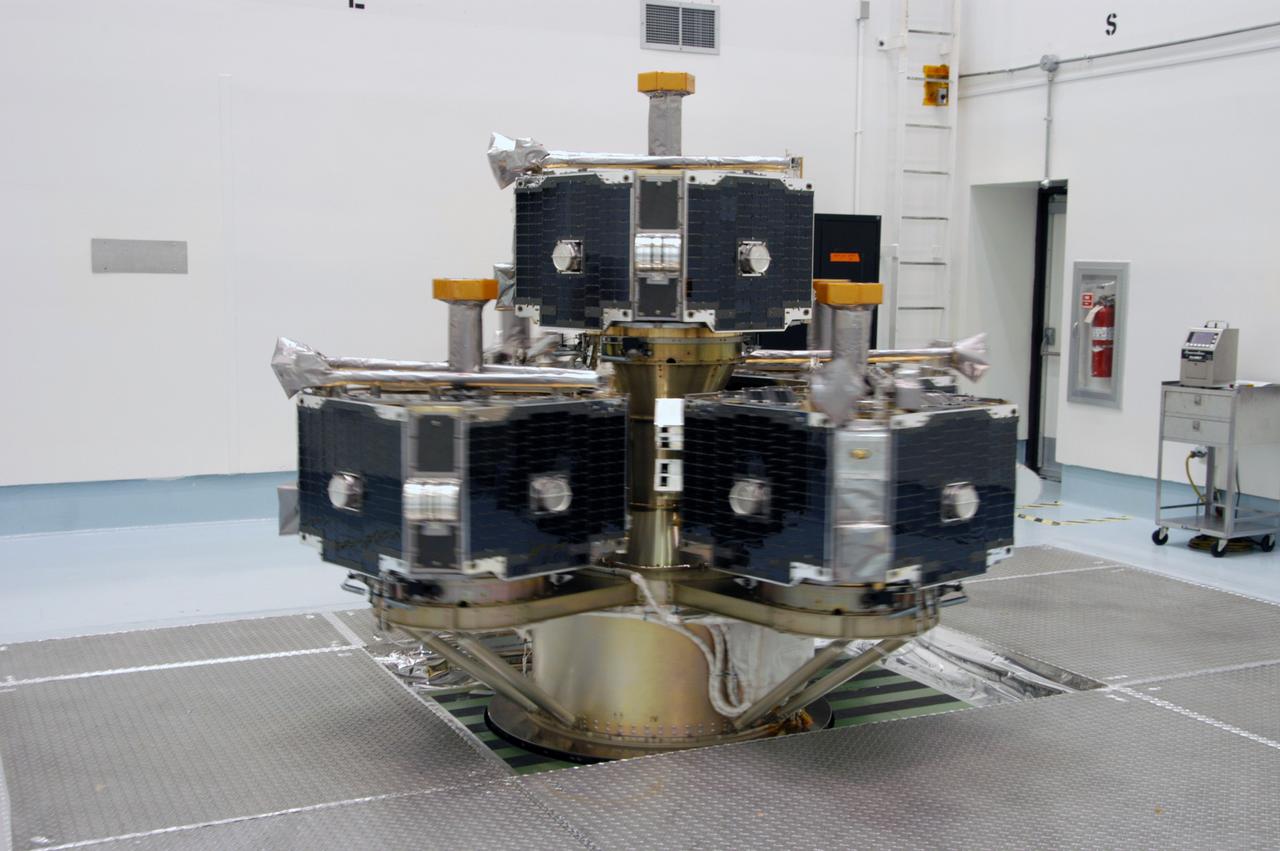
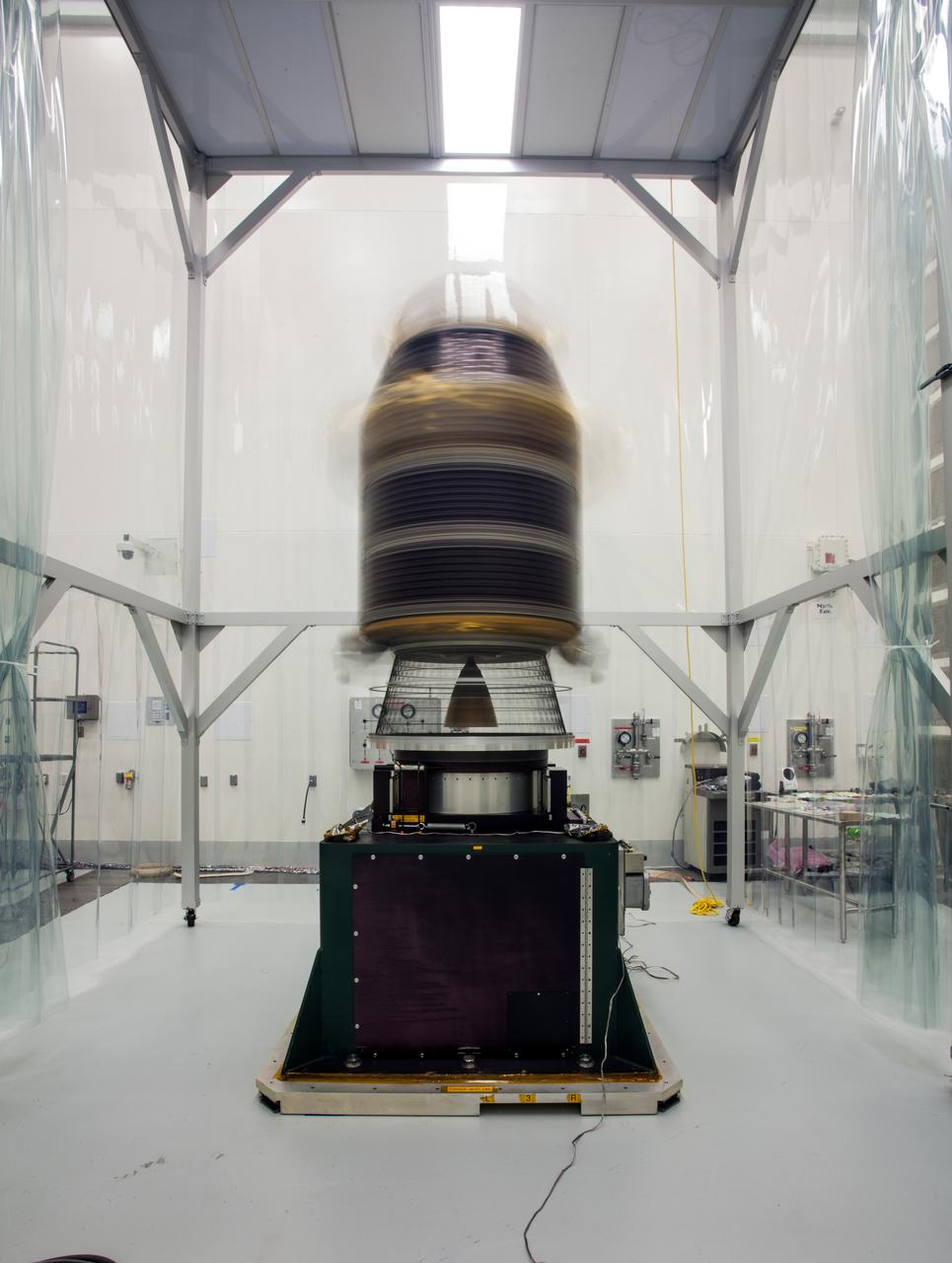
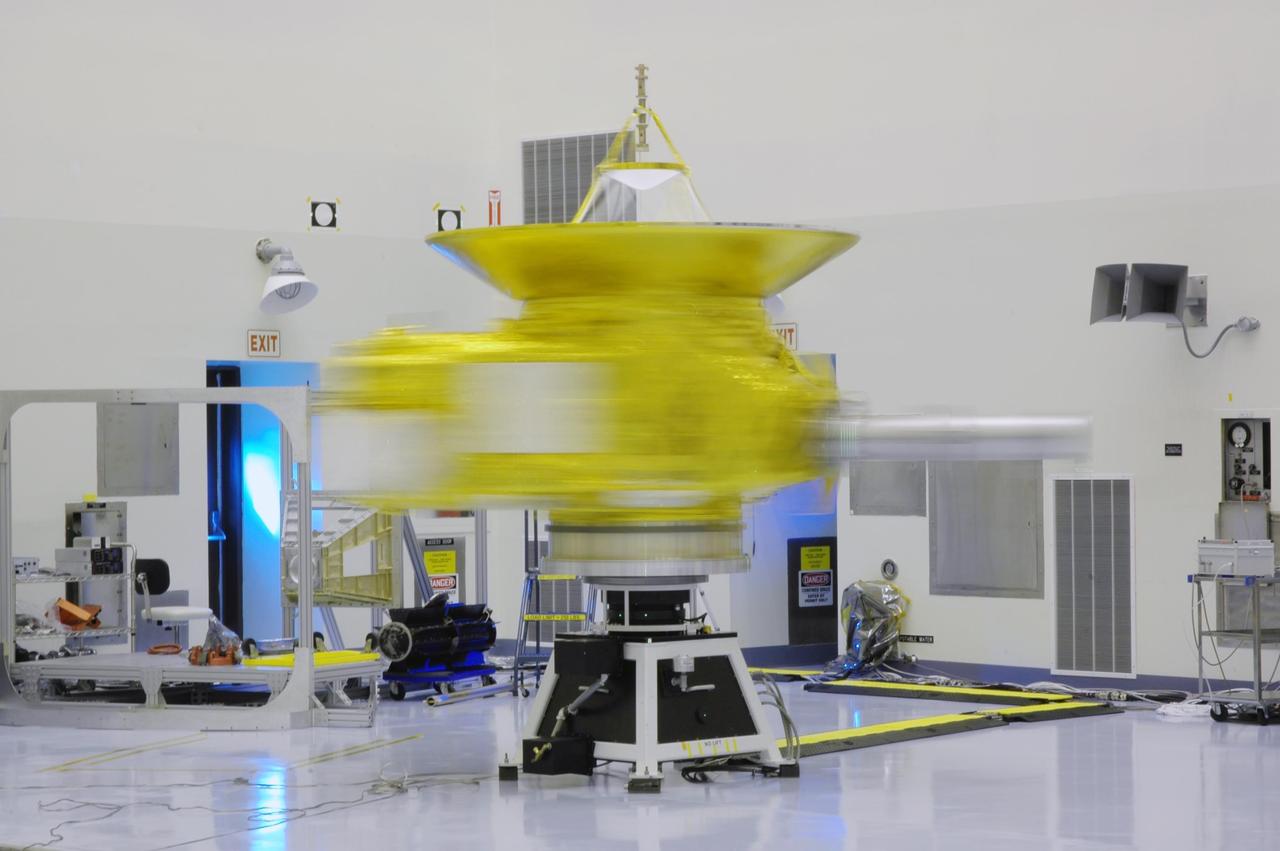
At Astrotech Space Operations, the integrated THEMIS spacecraft is spinning on the spin table, part of spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
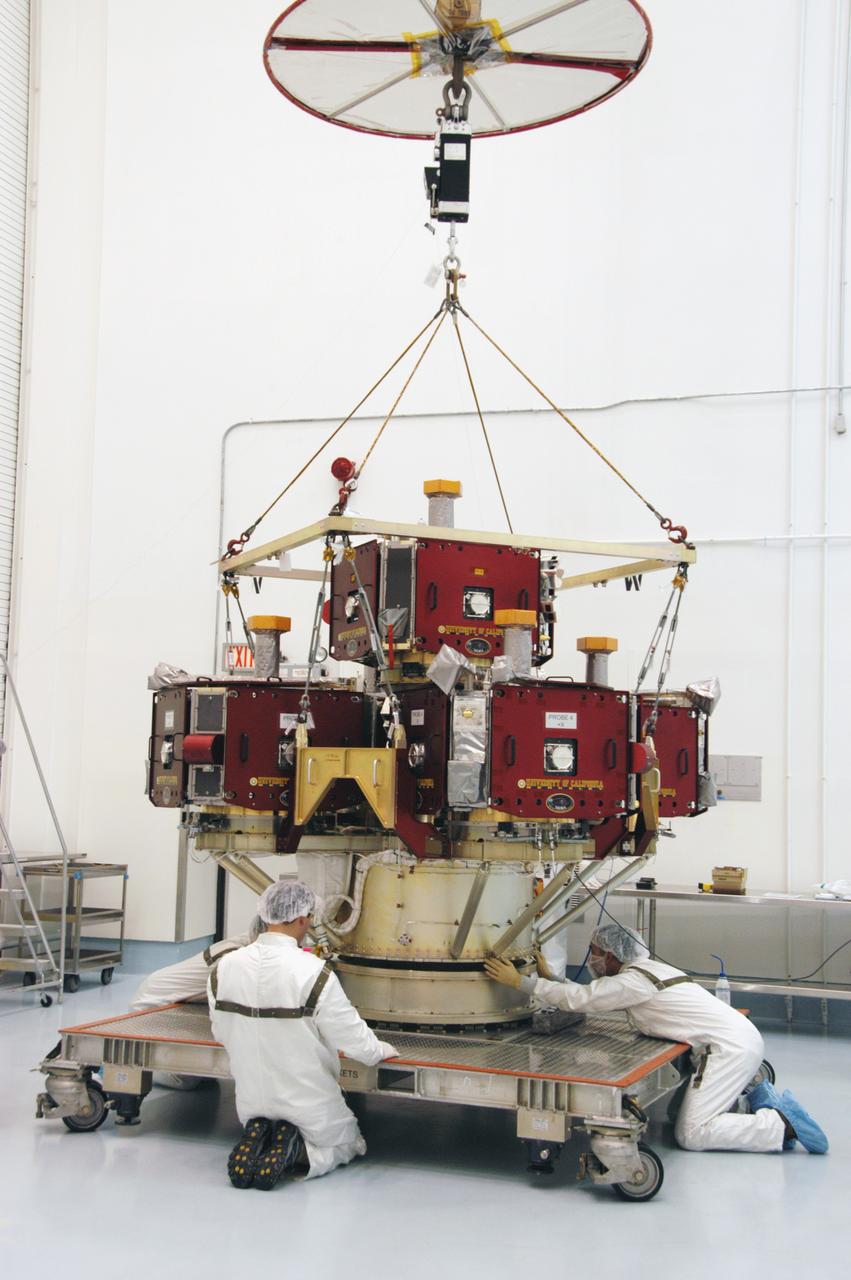

In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers attach an overhead crane to the integrated THEMIS spacecraft. The carrier is being moved to a spin table for spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

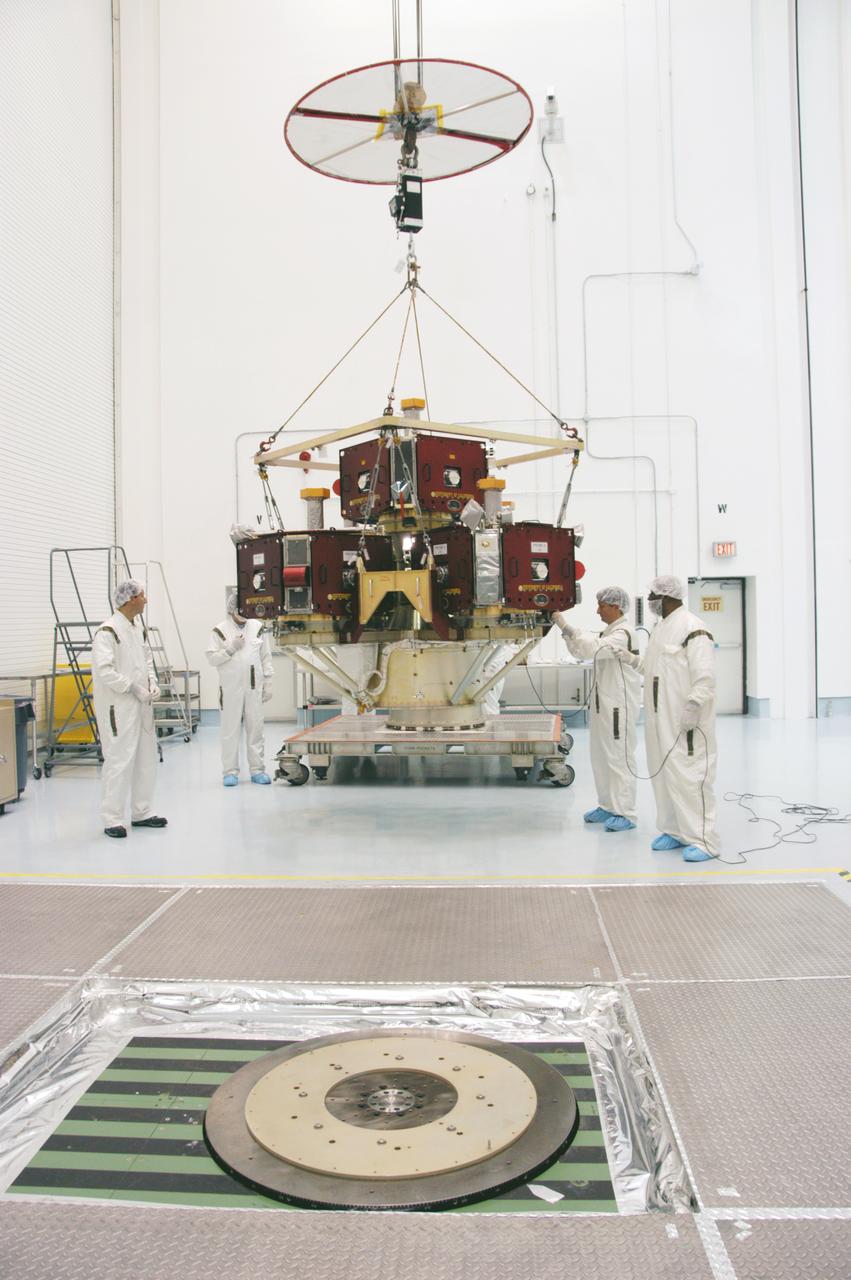
In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers guide the integrated THEMIS spacecraft onto the spin table in the foreground. There it will undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

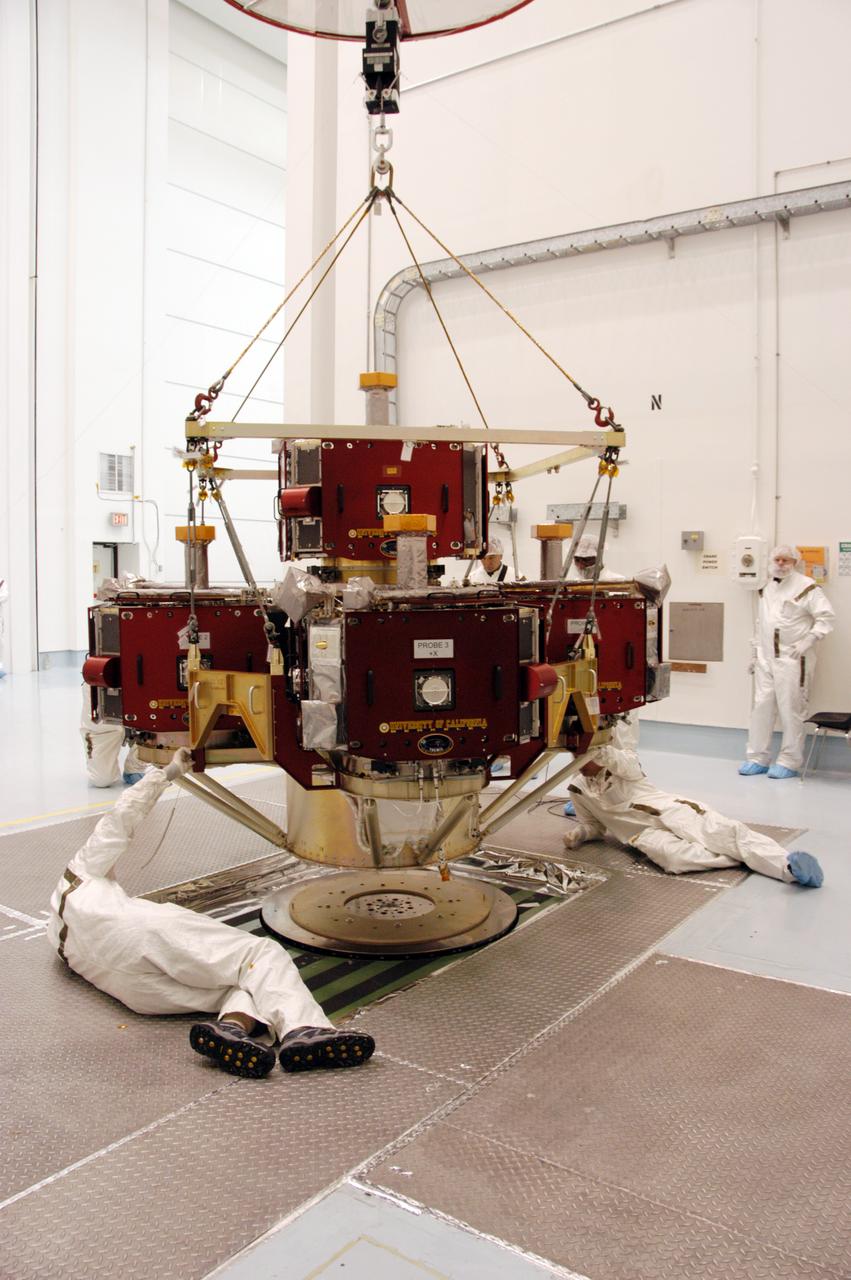
In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers get ready to move the integrated THEMIS spacecraft to the spin table in the foreground. There it will undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

At Astrotech Space Operations, workers look over the integrated THEMIS spacecraft before spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
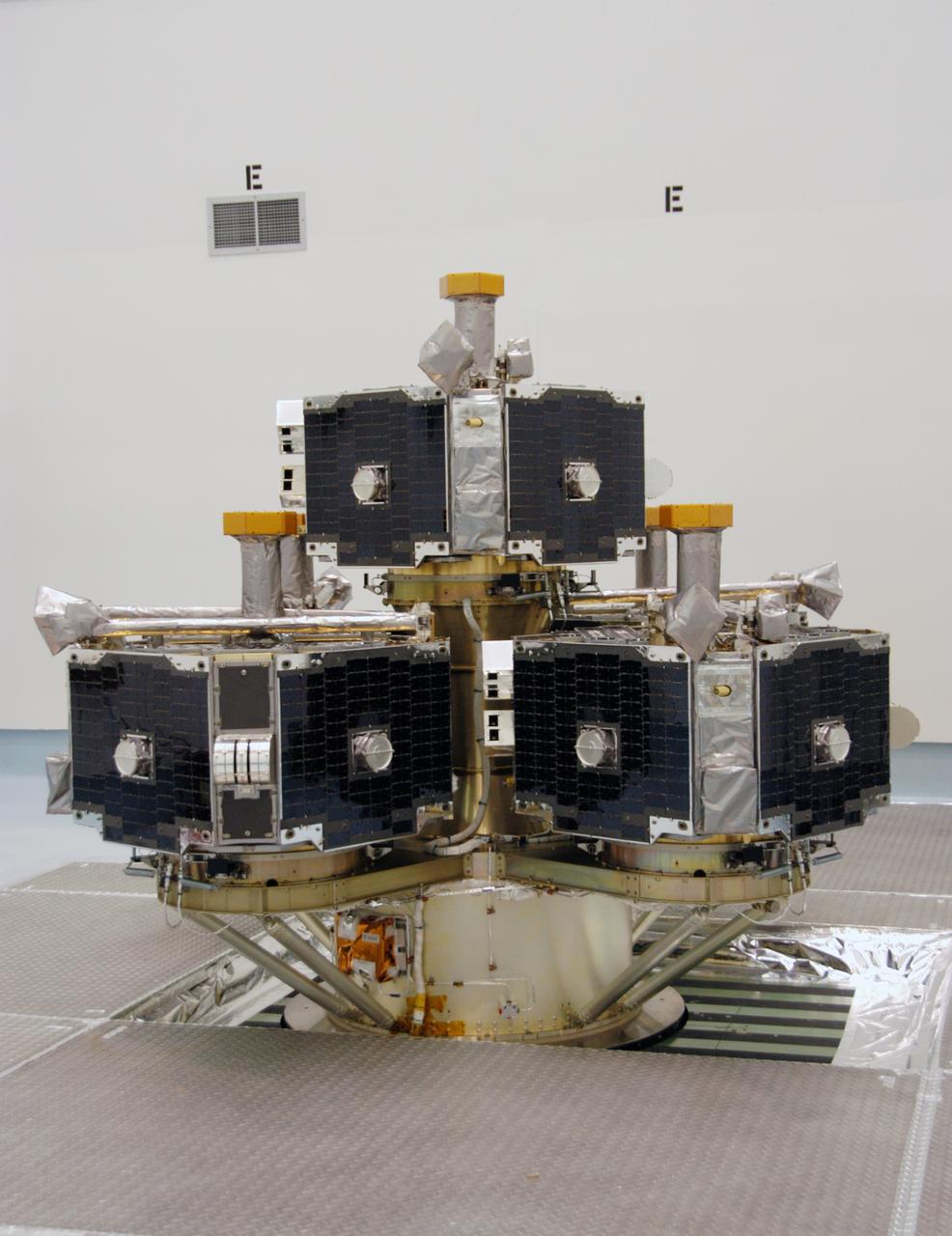
At Astrotech Space Operations, the integrated THEMIS spacecraft is ready for spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
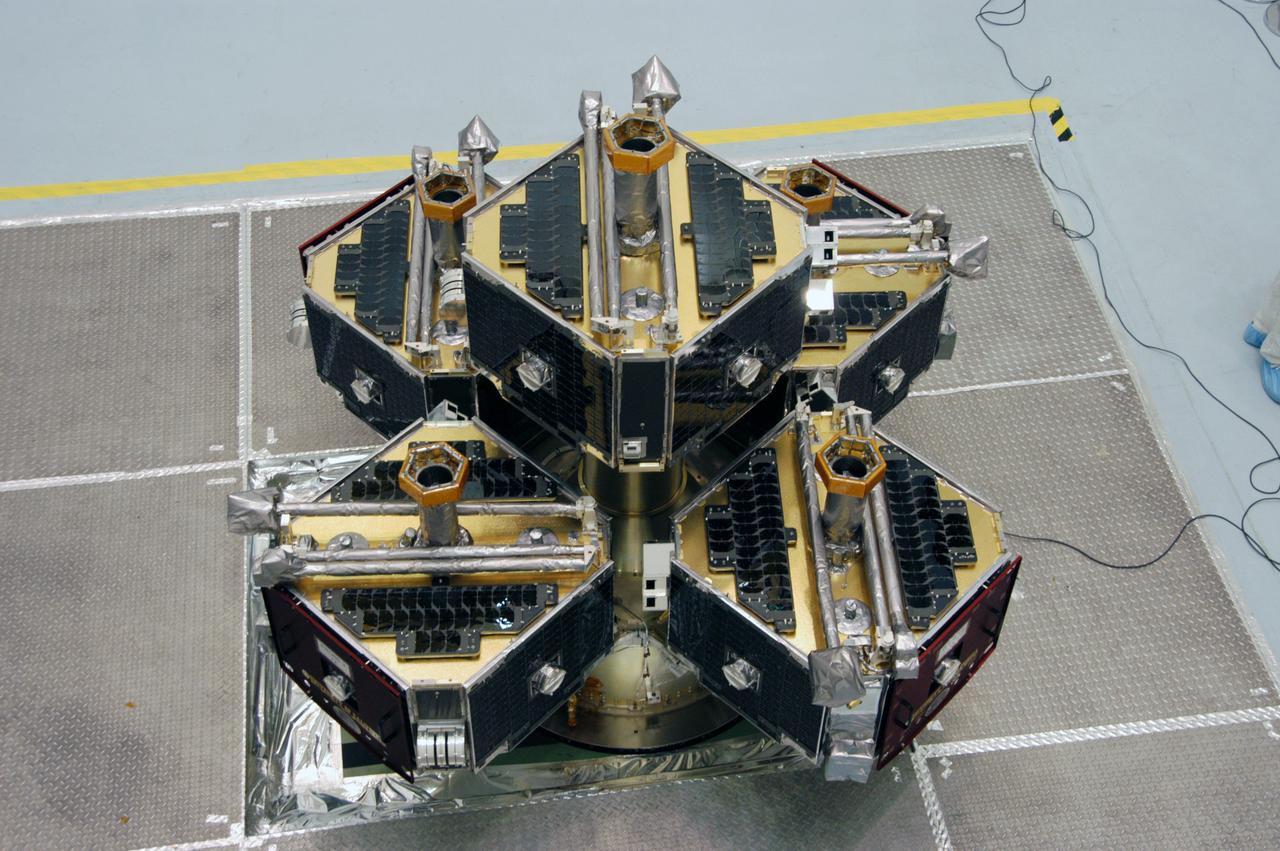
At Astrotech Space Operations, workers prepare the integrated THEMIS spacecraft for spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

At Astrotech Space Operations, the integrated THEMIS spacecraft is on ready for spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

During preparations for NASA's Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) observatory launch on Sept. 6, 2013, the spacecraft went through final preparations and close-outs, which included checking alignment after its cross-country shipment, checking the propulsion system for leaks, inspecting and repairing solar panels, and final electrical tests. After these activities were completed, more challenging portions of the launch preparations began: spin testing and fueling. To make sure that the spacecraft is perfectly balanced for flight, engineers mounted it onto a spin table and rotate it at high speeds, approximately one revolution per second. The team measured any offsets during the spinning, and then added small weights to the spacecraft to balance it. Once the spacecraft was balanced dry, the team loaded the propulsion tanks with fuel, oxidizer, and pressurant. The spin testing was performed again "wet," or with fuel, in order to see if the balance changed with the full fuel tanks. Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif., have now successfully completed launch preparation activities for LADEE, which has been encapsulated into the nose-cone of the Minotaur V rocket at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. LADEE is ready to launch when the window opens on Friday. Image Credit: NASA ----- What is LADEE? The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) is designed to study the Moon's thin exosphere and the lunar dust environment. An "exosphere" is an atmosphere that is so thin and tenuous that molecules don't collide with each other. Studying the Moon's exosphere will help scientists understand other planetary bodies with exospheres too, like Mercury and some of Jupiter's bigger moons. The orbiter will determine the density, composition and temporal and spatial variability of the Moon's exosphere to help us understand where the species in the exosphere come from and the role of the solar wind, lunar surface and interior, and meteoric infall as sources. The mission will also examine the density and temporal and spatial variability of dust particles that may get lofted into the atmosphere. The mission also will test several new technologies, including a modular spacecraft bus that may reduce the cost of future deep space missions and demonstrate two-way high rate laser communication for the first time from the Moon. LADEE now is ready to launch when the window opens on Sept. 6, 2013. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ladee" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ladee</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
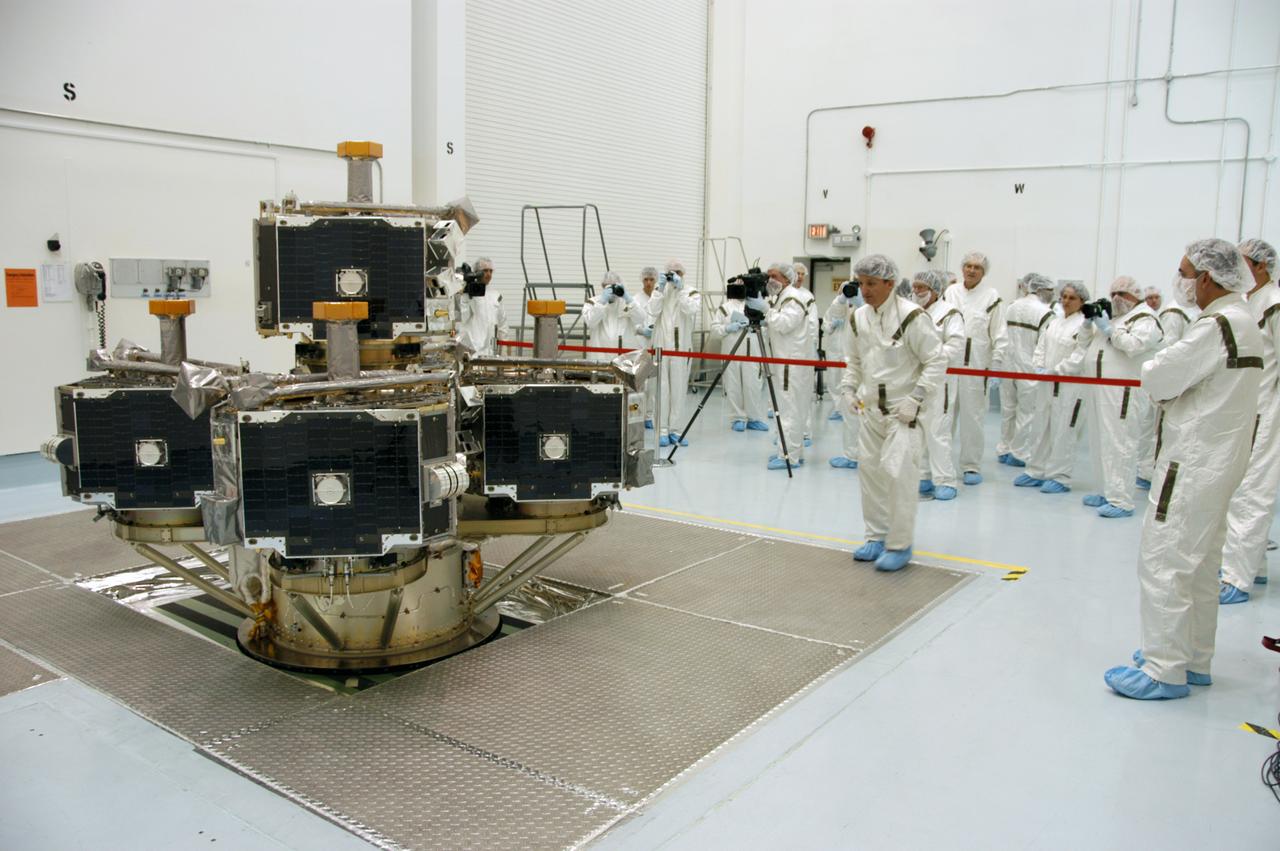

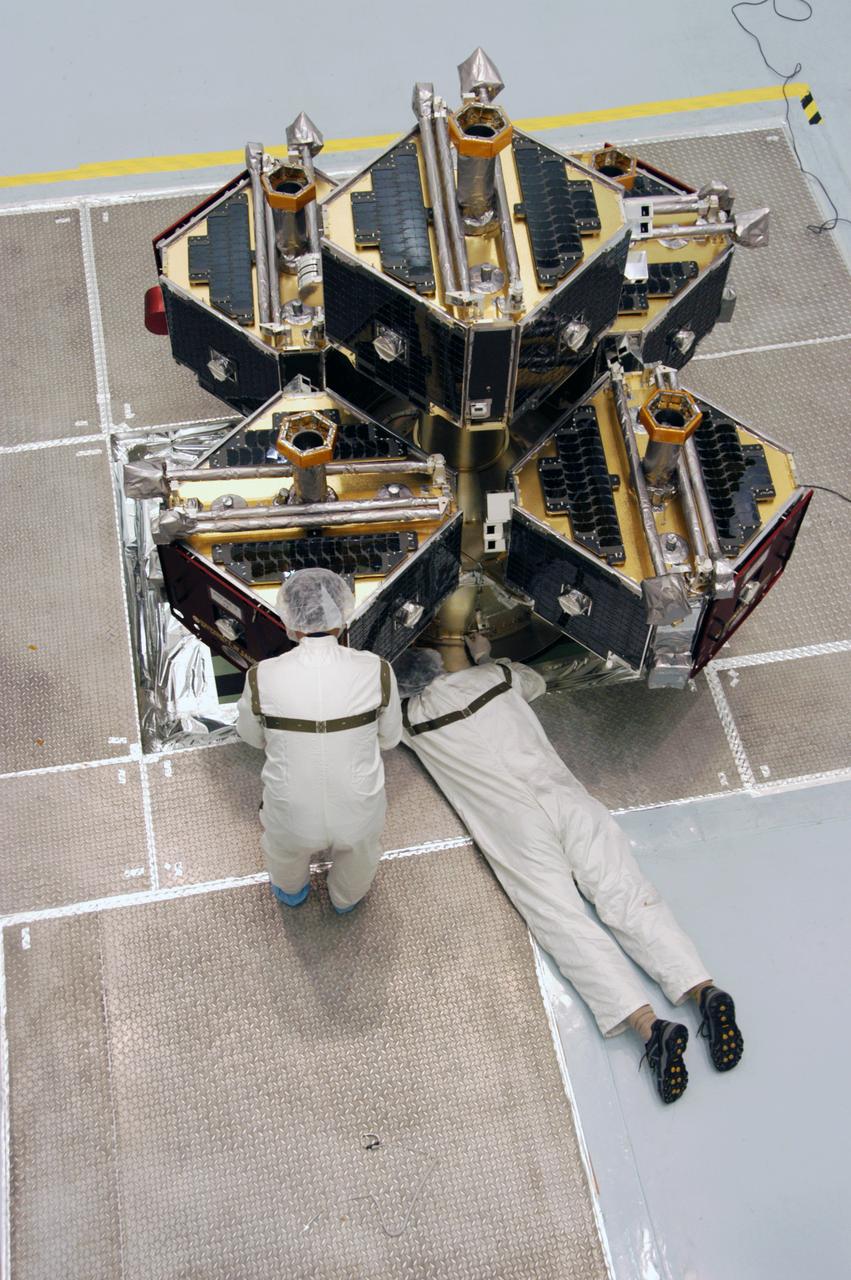
At Astrotech Space Operations, the media are dressed in clean room, or bunny, suits to photograph the integrated THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
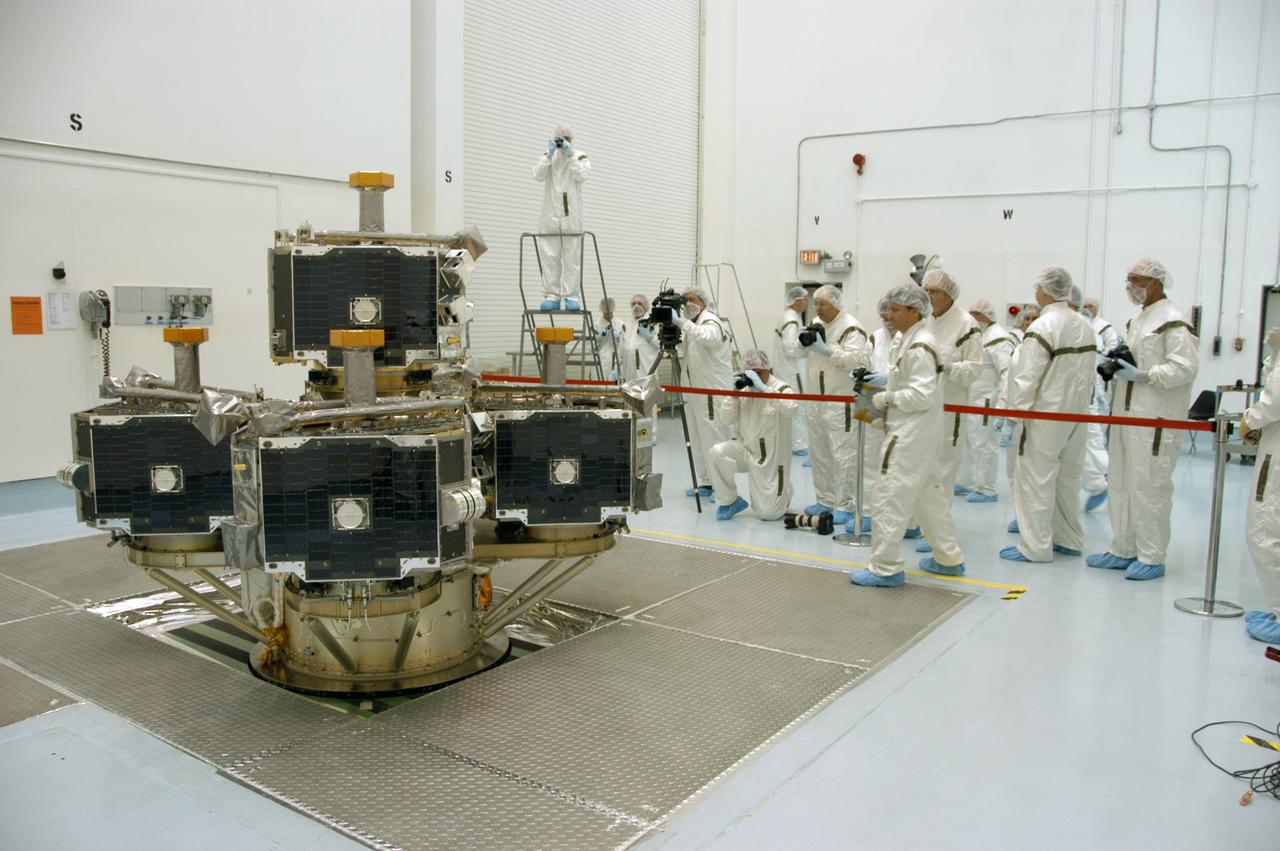

At Astrotech Space Operations, the media are dressed in clean room, or bunny, suits to photograph the integrated THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
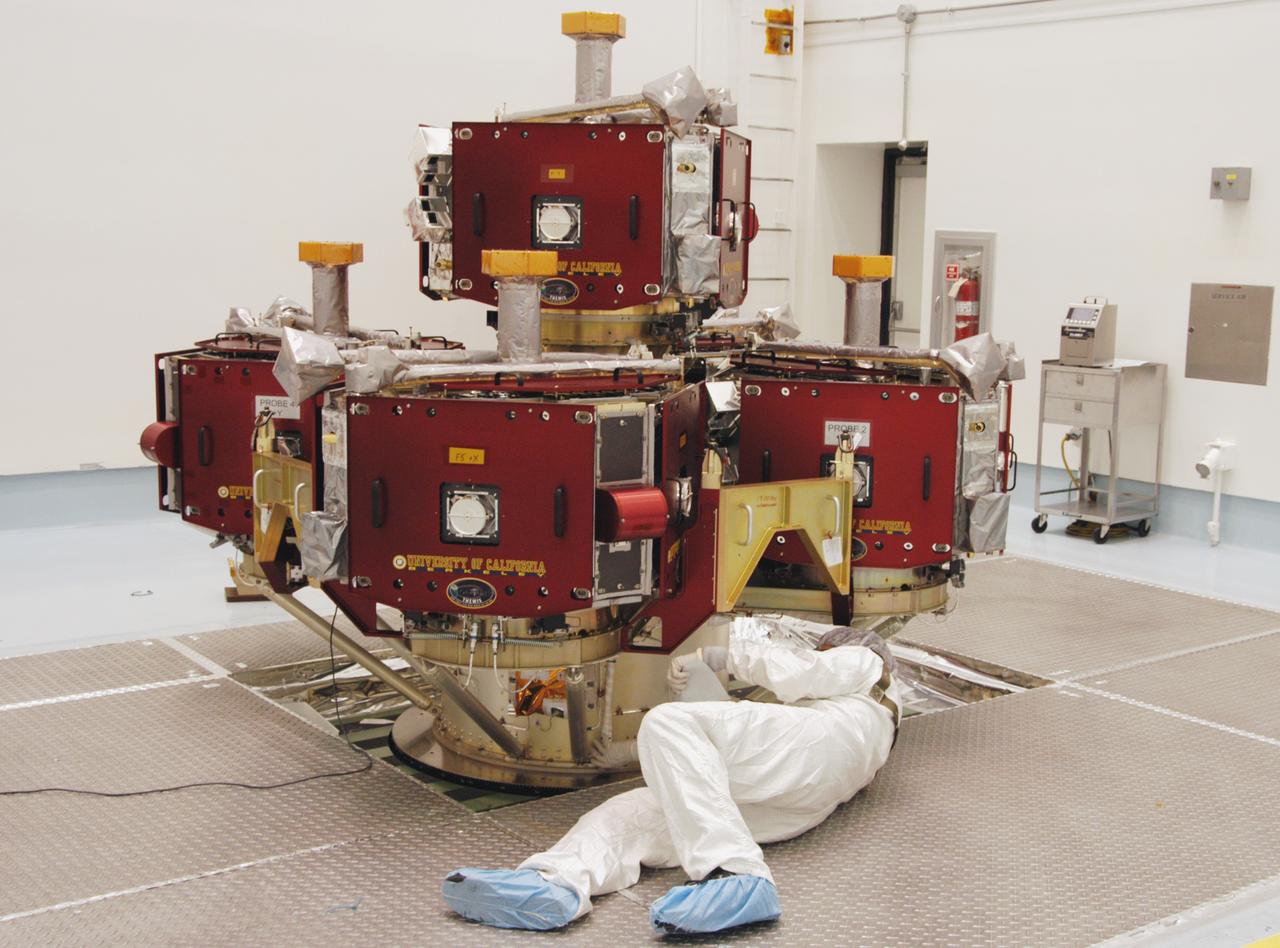

In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, a worker checks data on the integrated THEMIS spacecraft sitting on the spin table. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
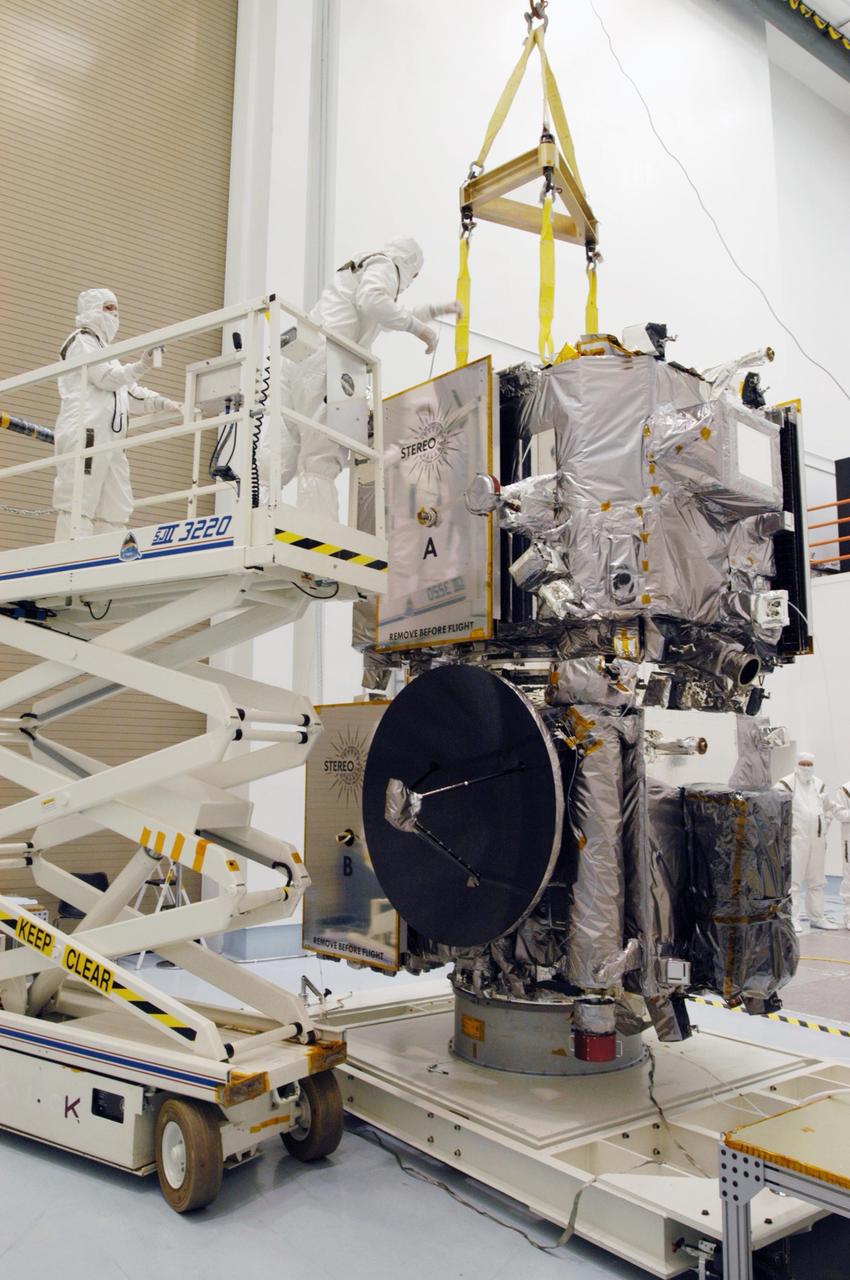

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians inside the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Florida, prepare to move the STEREO spacecraft to the spin table. The twin observatories will undergo a spin test to check balance and alignment in preparation for flight. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31, from Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton.
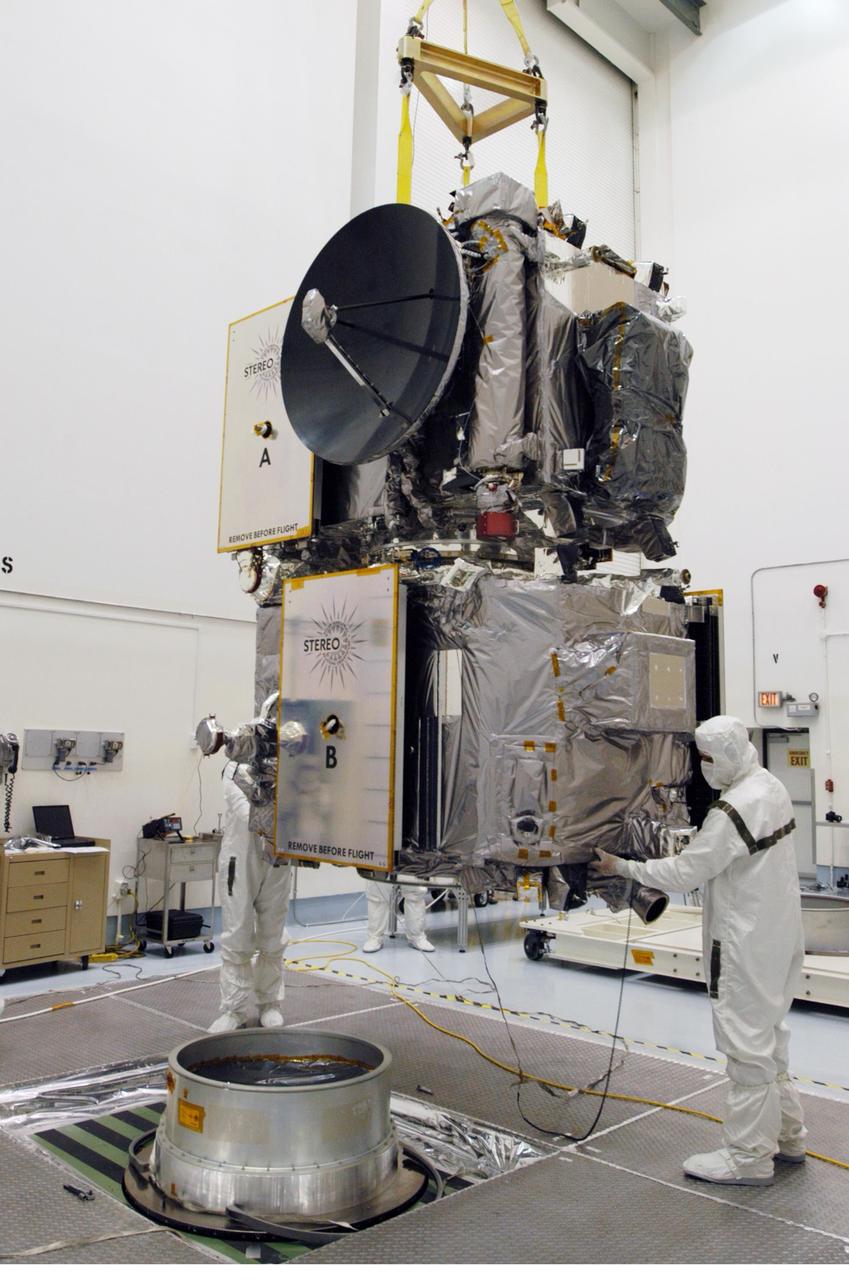

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians inside the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Florida, move the STEREO spacecraft to the spin table. The twin observatories will undergo a spin test to check balance and alignment in preparation for flight. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31, from Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton.
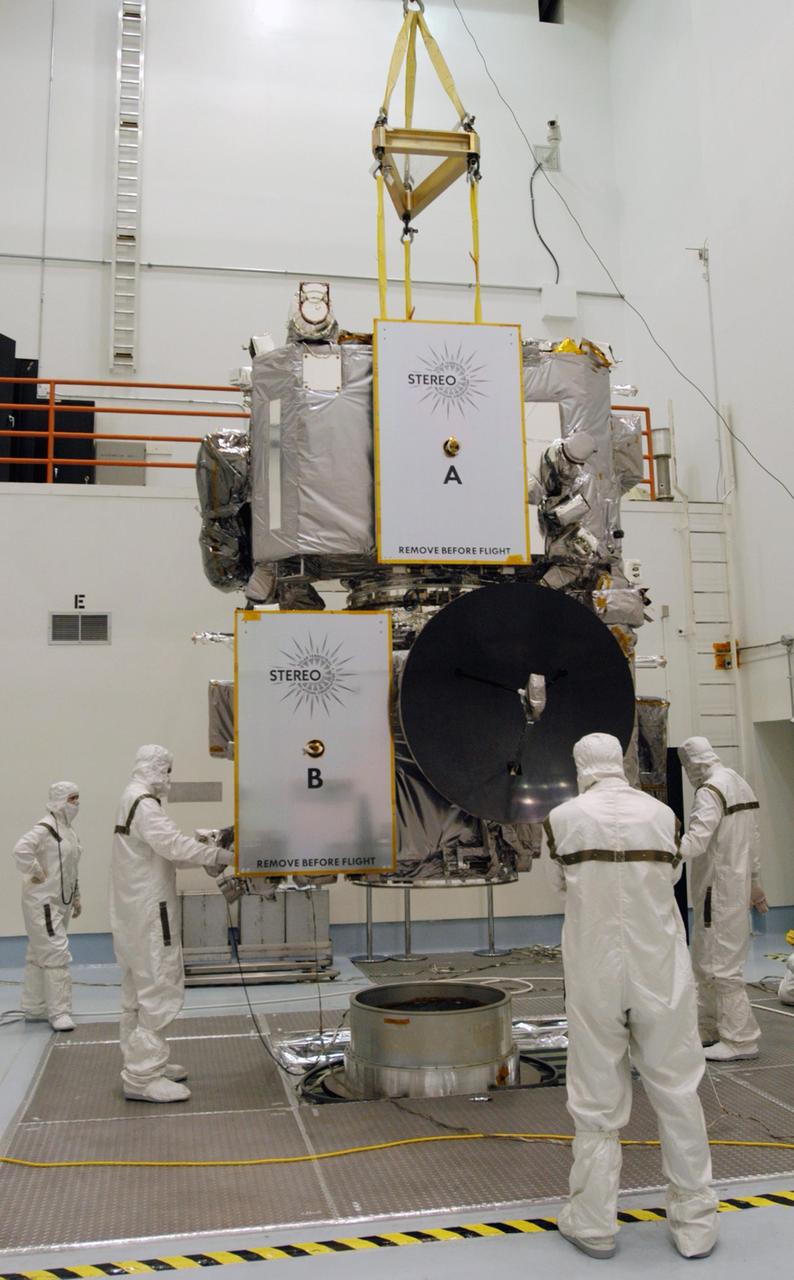

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians inside the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Florida, move the STEREO spacecraft to the spin table. The twin observatories will undergo a spin test to check balance and alignment in preparation for flight. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31, from Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton.
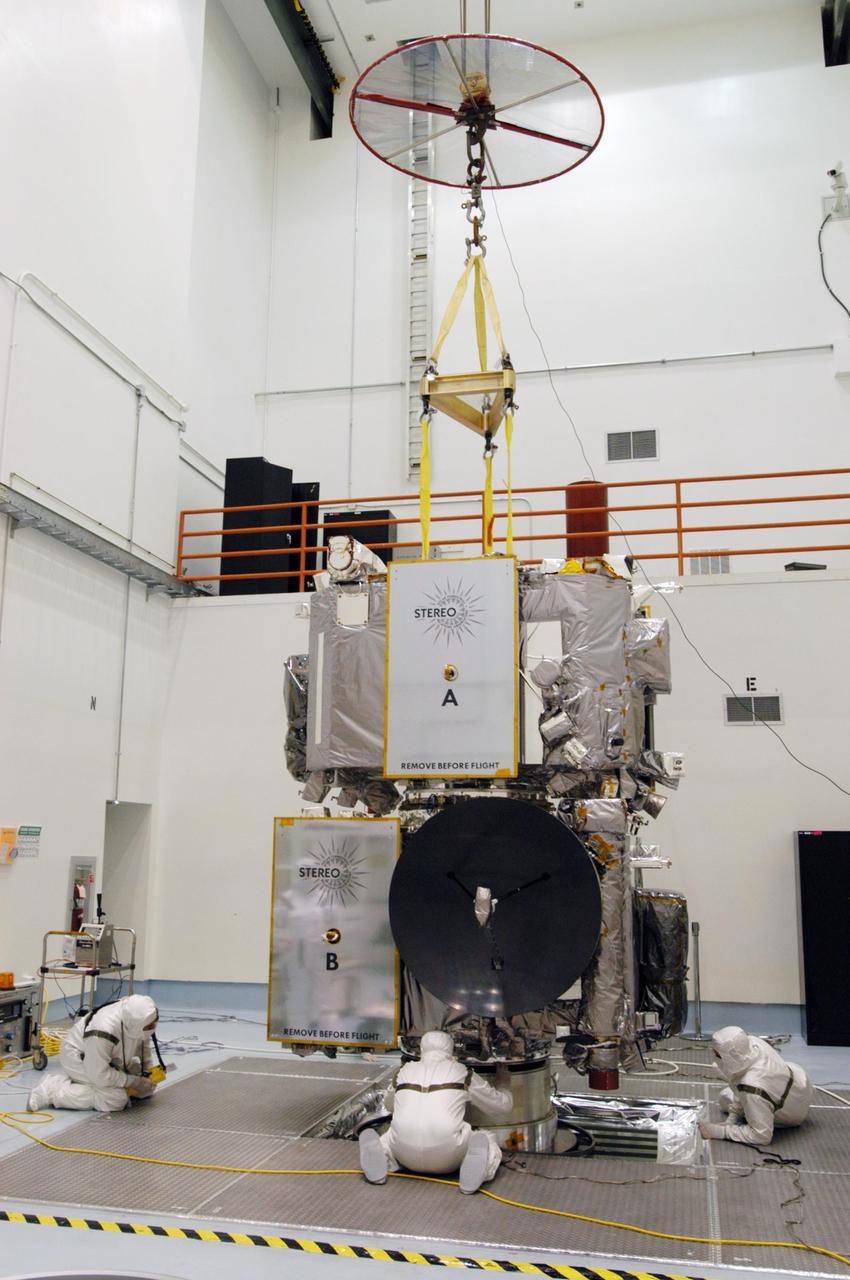

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians inside the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Florida, move the STEREO spacecraft to the spin table. The twin observatories will undergo a spin test to check balance and alignment in preparation for flight. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31, from Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton.
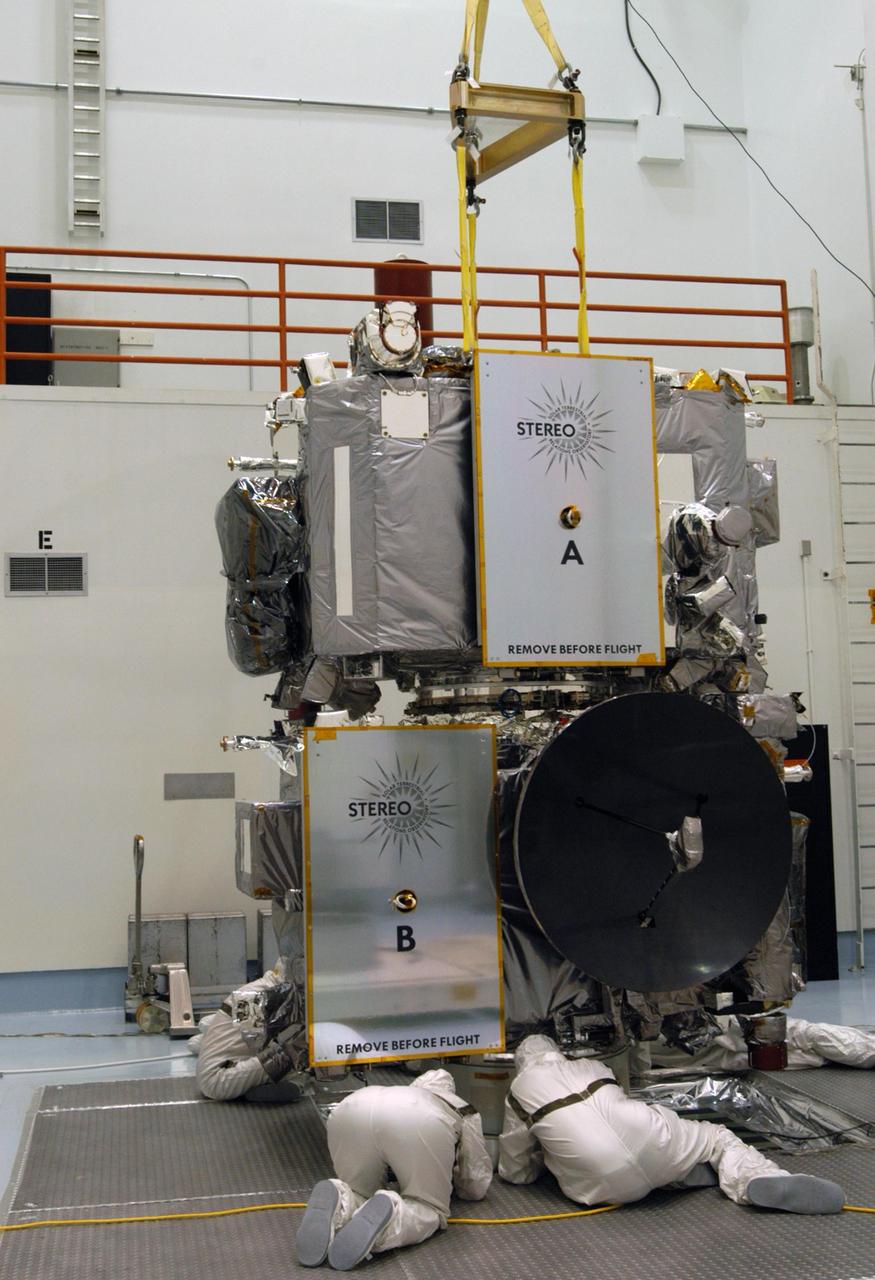

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians inside the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Florida, move the STEREO spacecraft to the spin table. The twin observatories will undergo a spin test to check balance and alignment in preparation for flight. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31, from Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton.
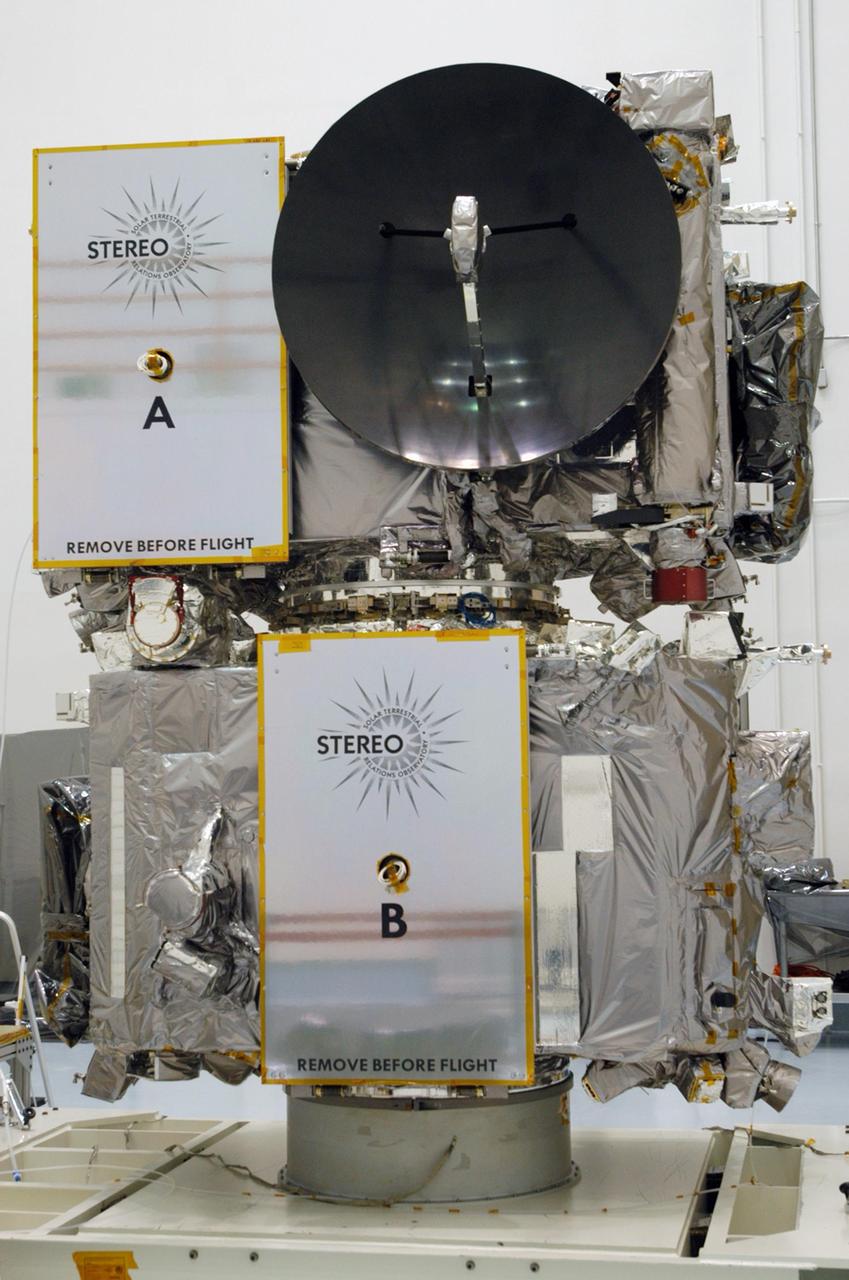

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STEREO spacecraft sits on a test stand inside the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Florida. The twin observatories will undergo a spin test to check balance and alignment in preparation for flight. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31, from Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton.
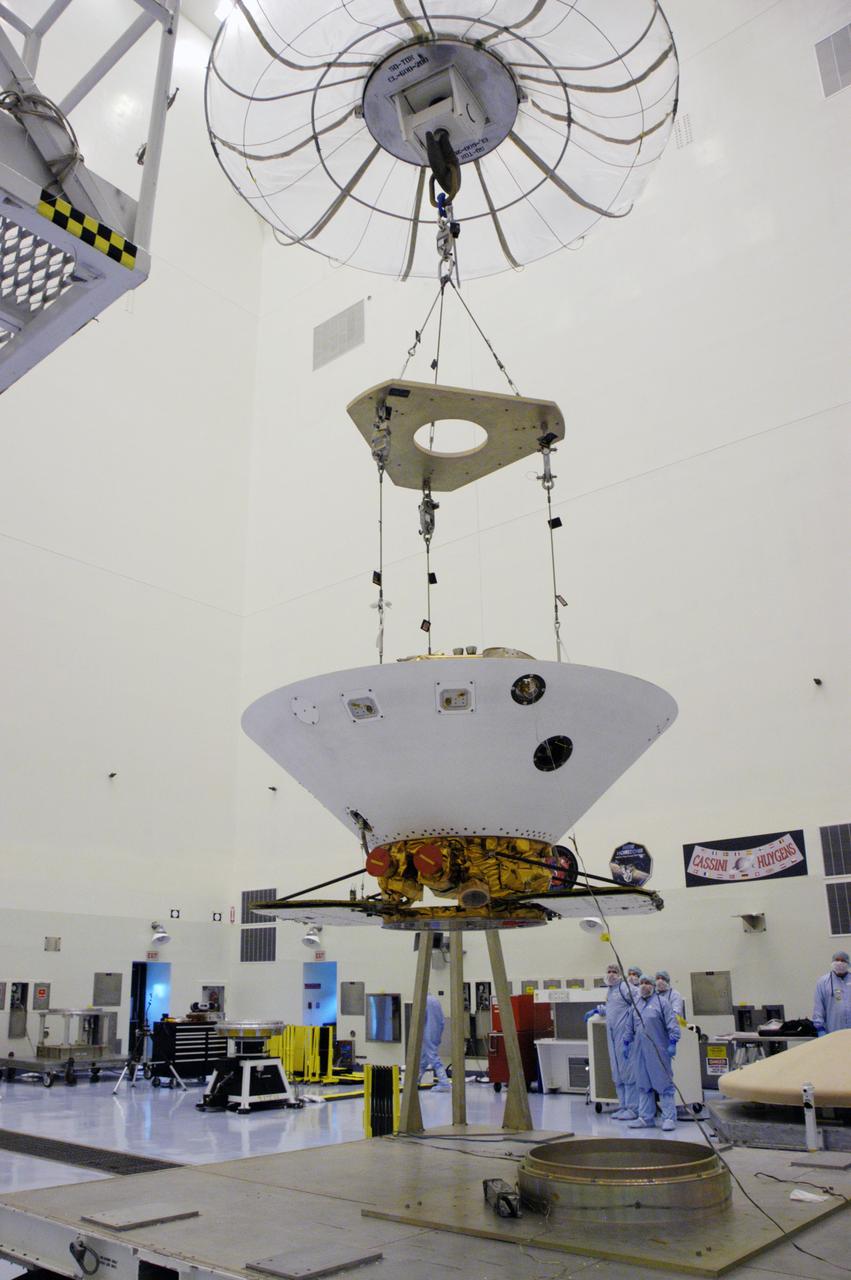

An overhead crane lifts the backshell with the Phoenix Mars Lander inside off its work stand in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The spacecraft is being moved to a spin table (back left) for spin testing. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
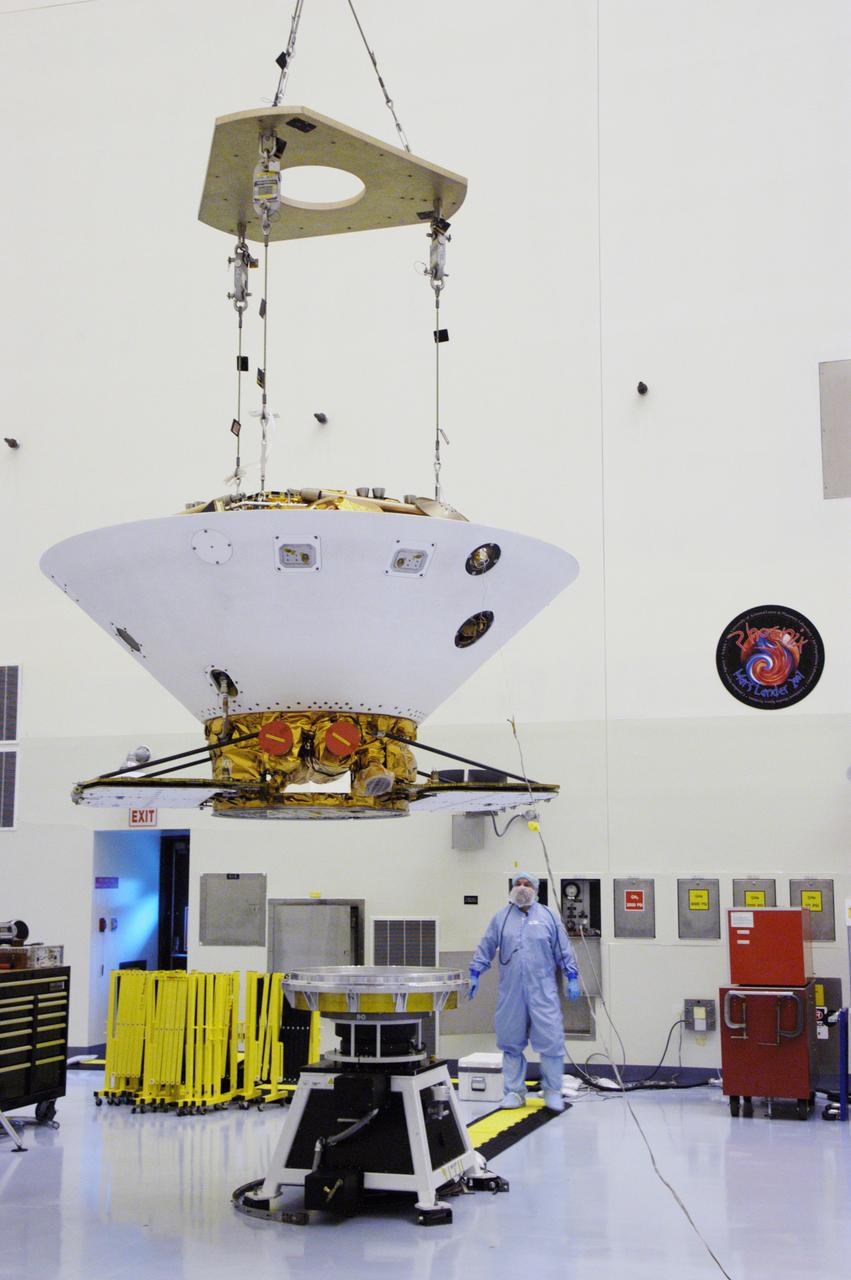

An overhead crane lowers the backshell with the Phoenix Mars Lander inside toward a spin table for spin testing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
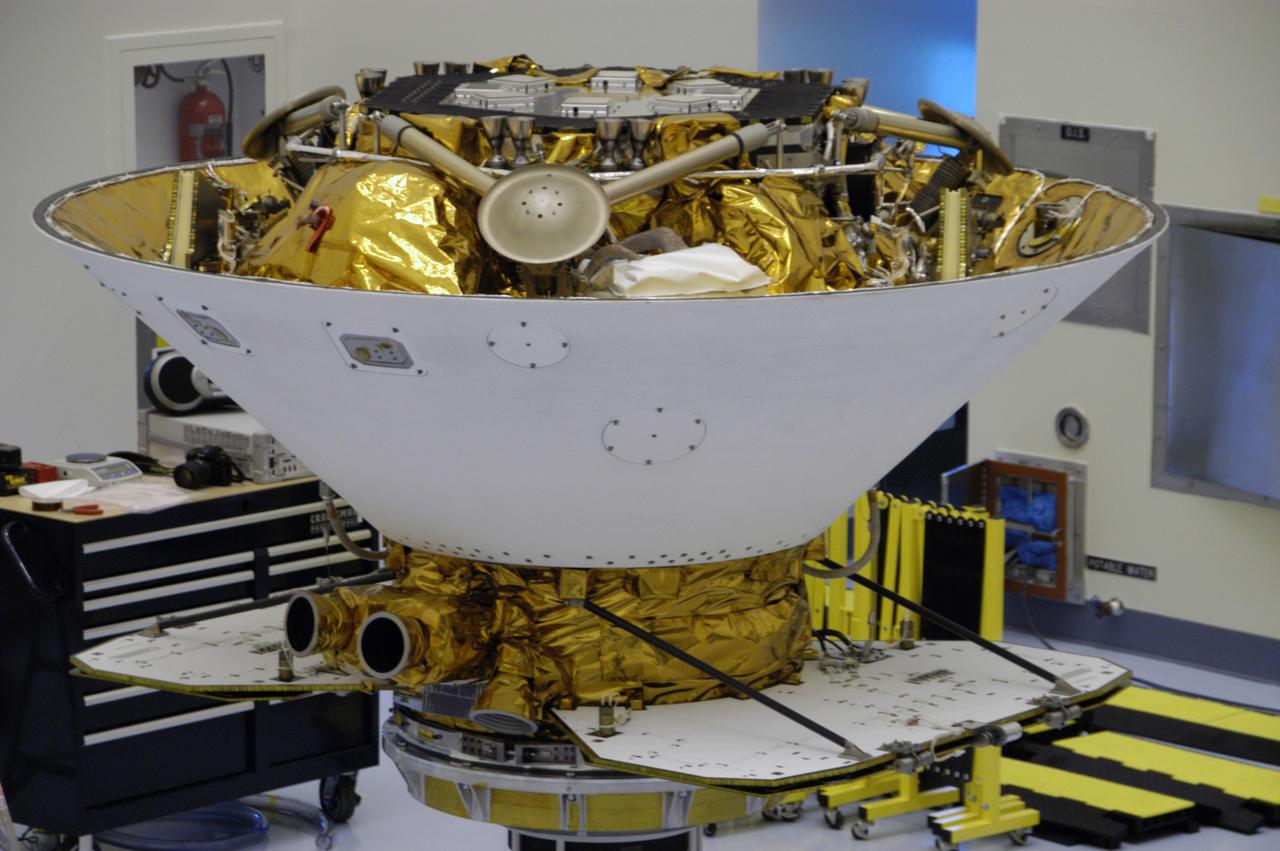

This closeup shows the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft nestled inside the backshell. The spacecraft is ready for spin testing on the spin table to which it is attached in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
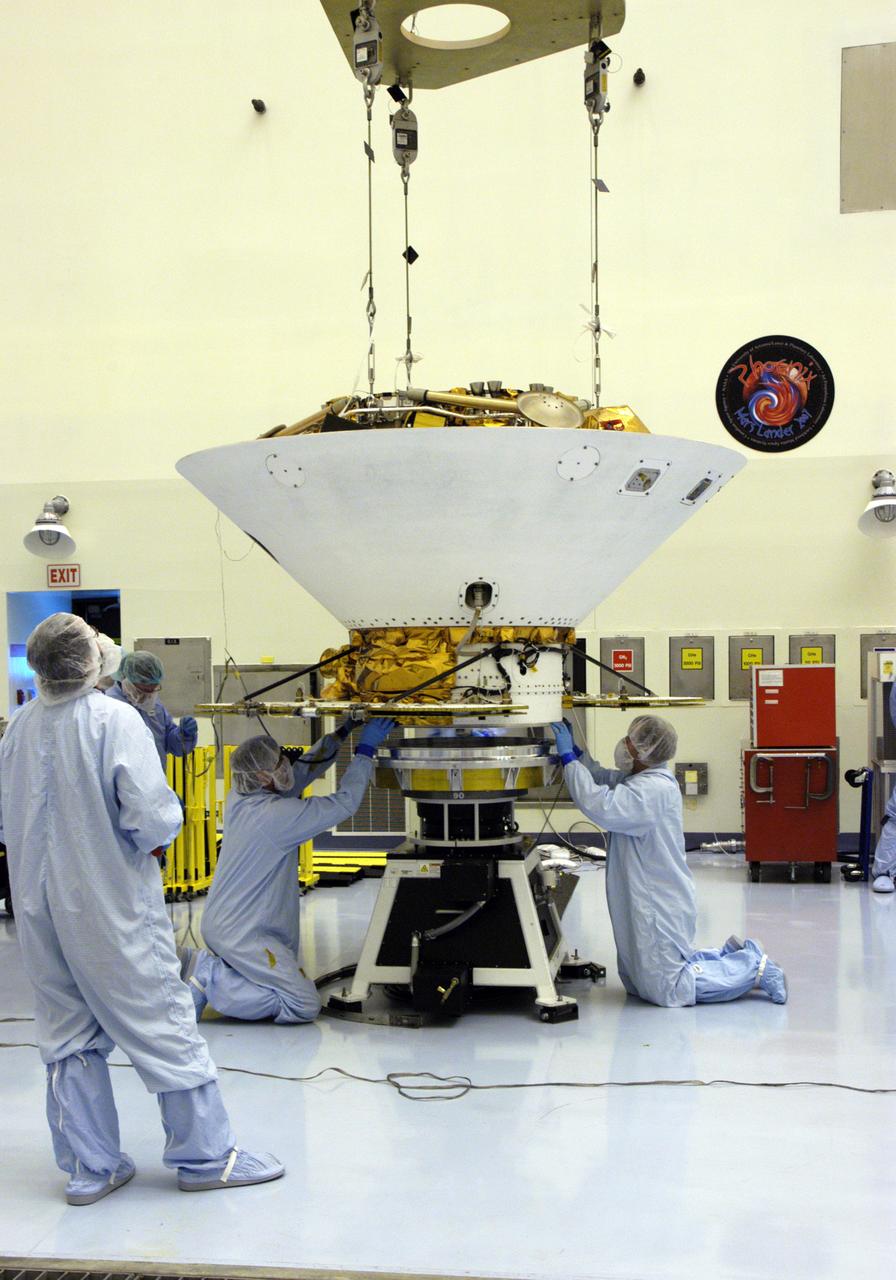

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians secure the backshell with the Phoenix Mars Lander inside onto a spin table for spin testing. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
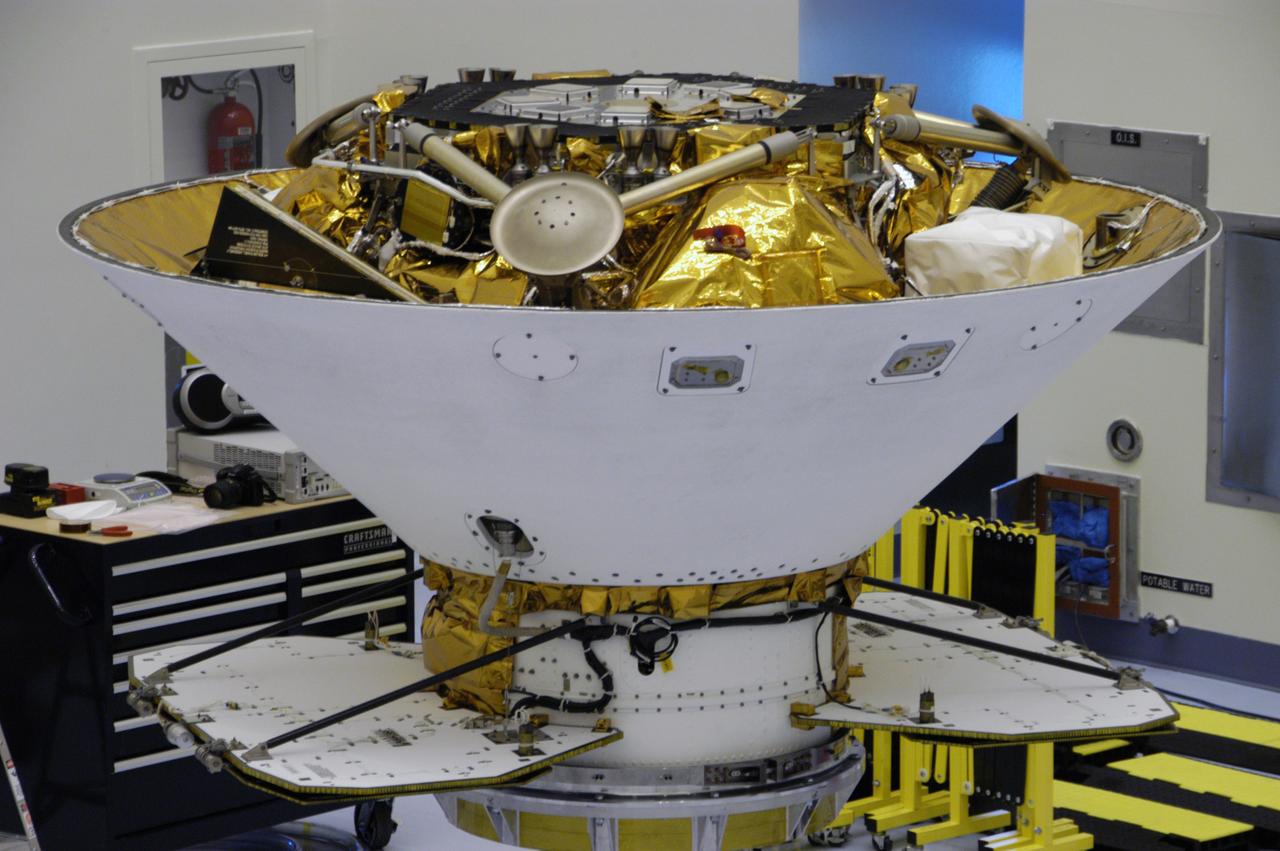

This closeup shows the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft nestled inside the backshell. The spacecraft will undergo spin testing on the spin table to which it is attached in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
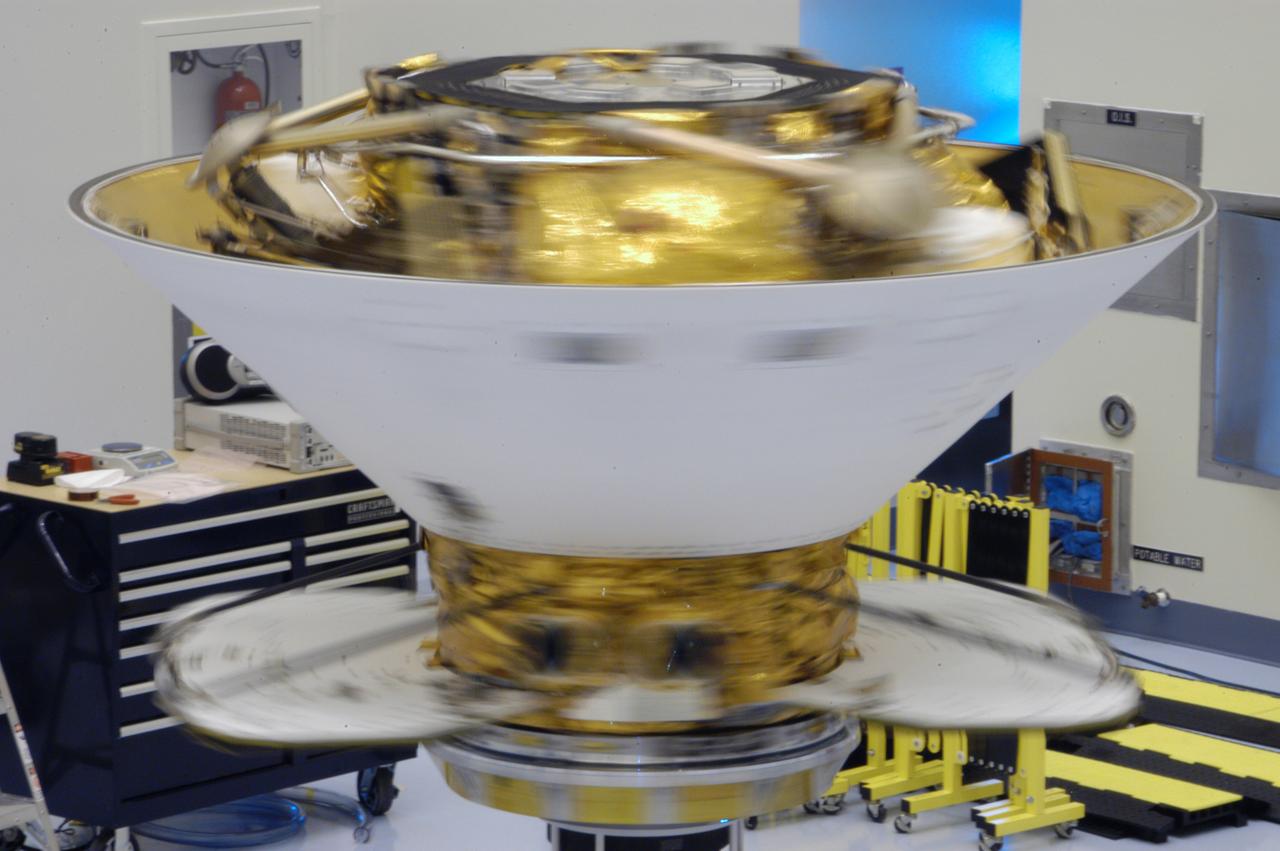

This closeup shows the spin test of the Phoenix Mars Lander in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
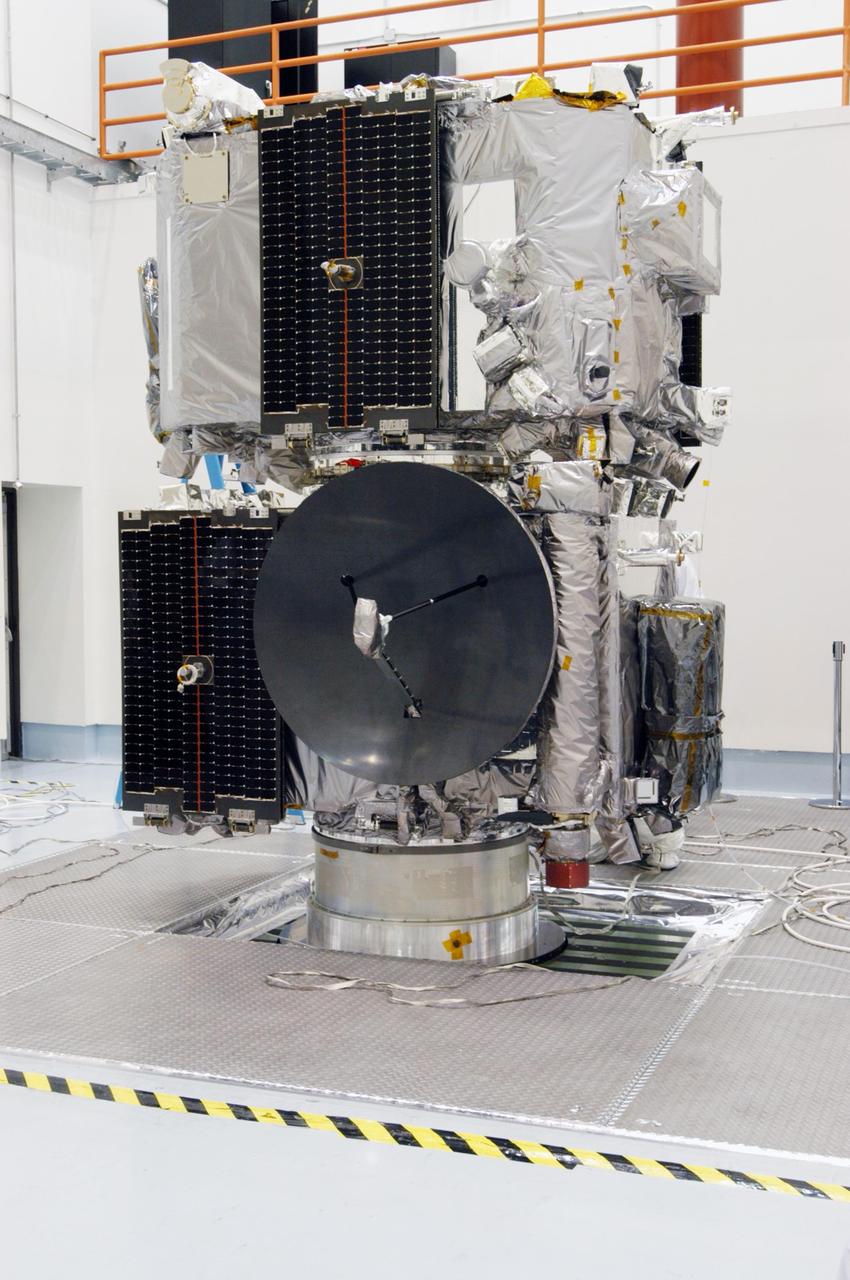

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STEREO observatories are the focus of attention at a media viewing held at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla. The two observatories were mated for launch but will separate into different orbits for their mission. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31, from Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton.
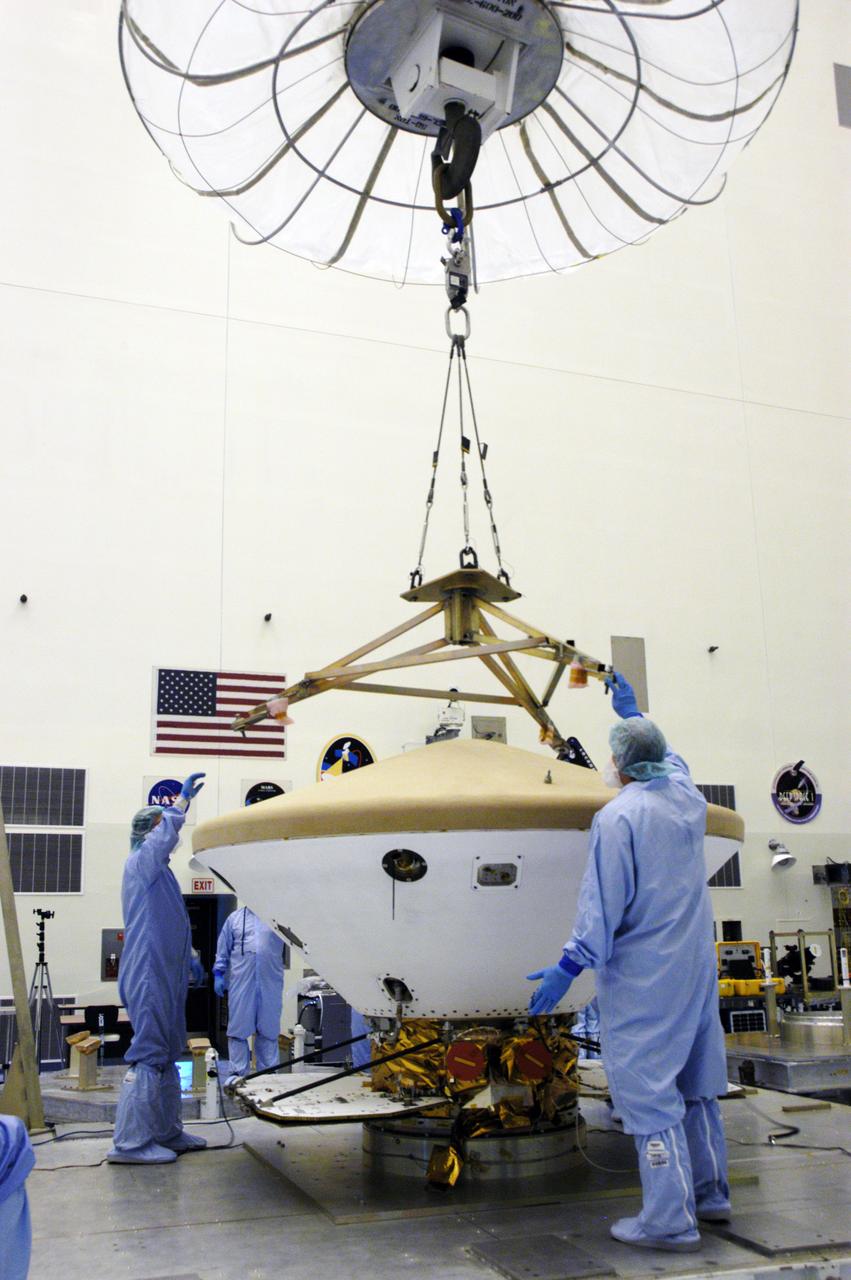

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians lower a crane over the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The crane will be used to remove the heat shield from around the Phoenix. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
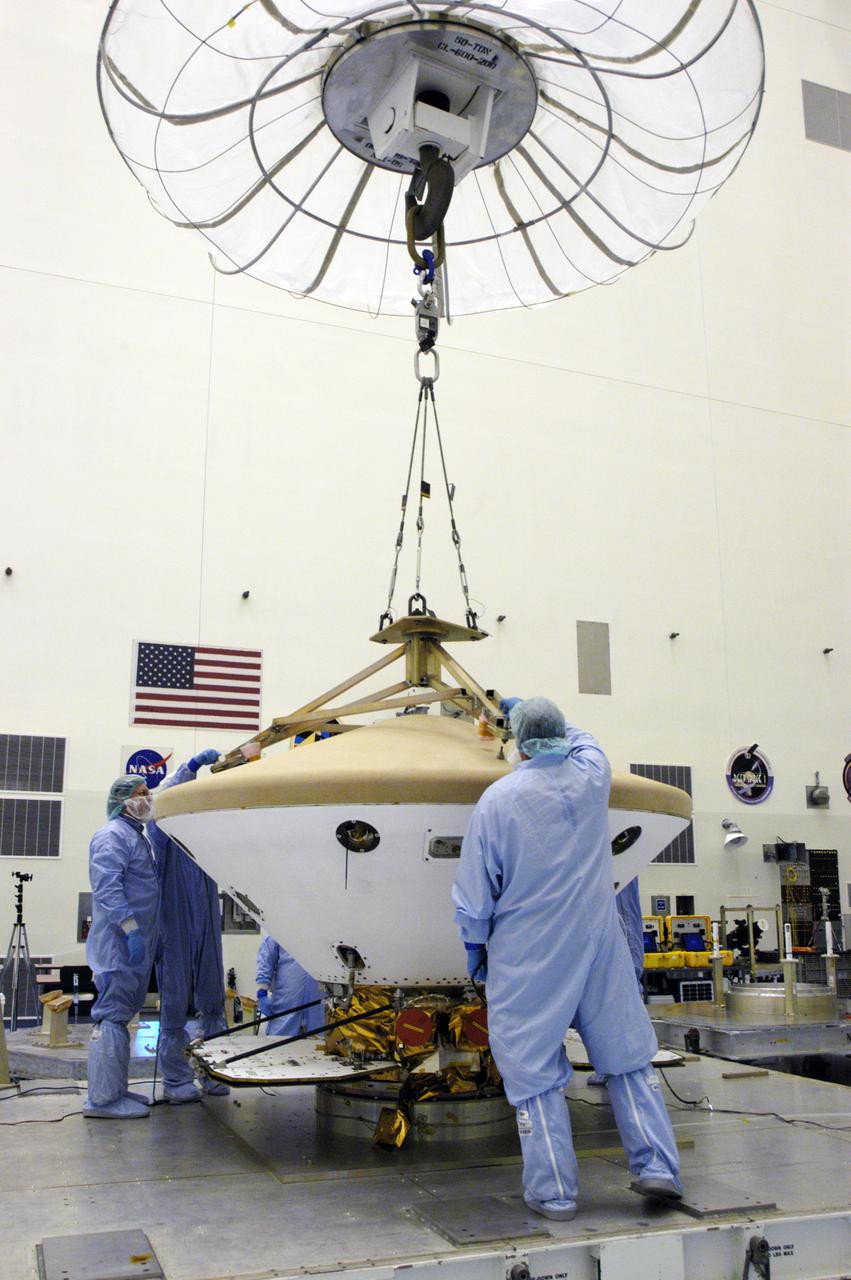

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians attach a crane to the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The crane will be used to remove the heat shield from around the Phoenix. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
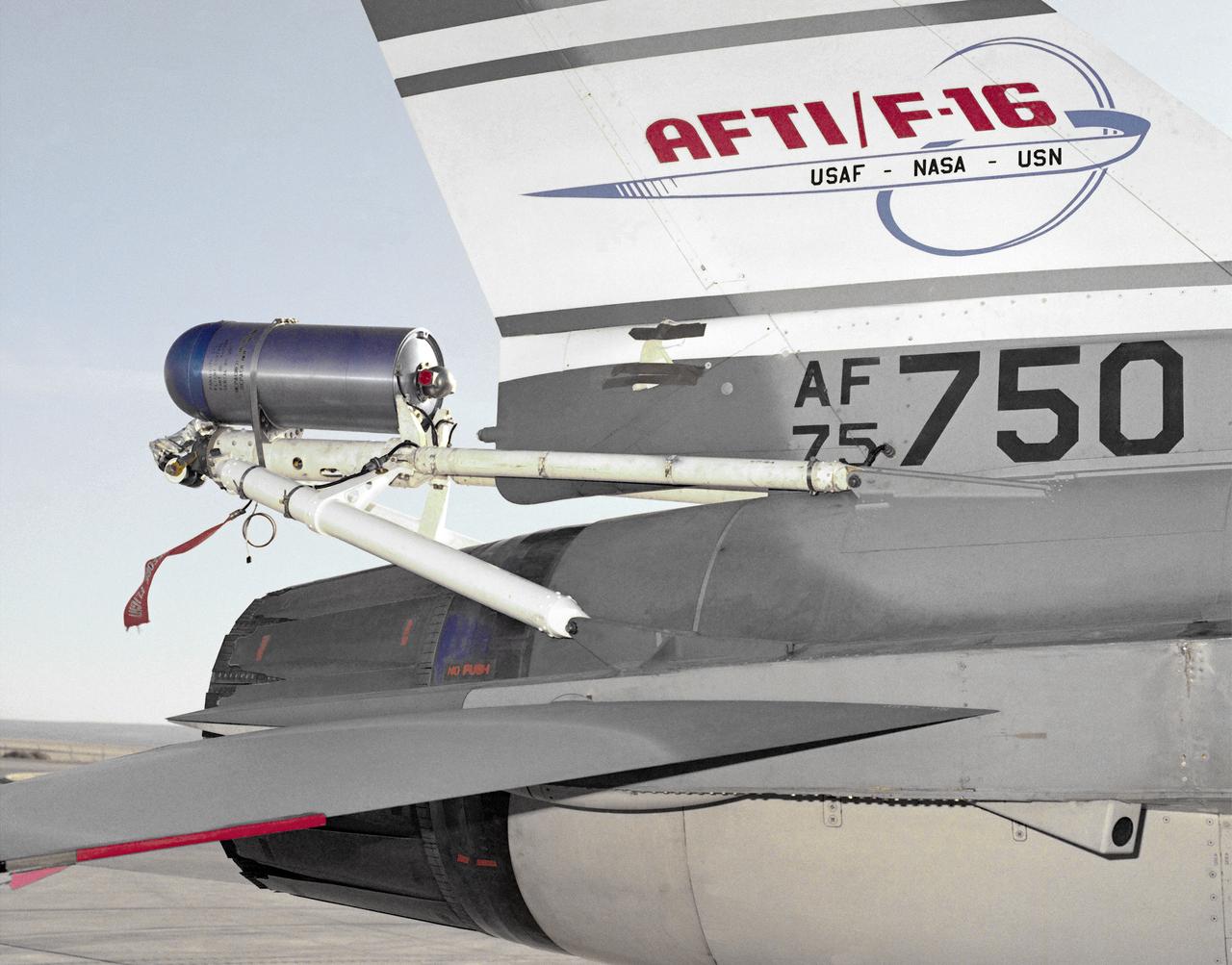

A close-up photo of the spin chute mounted on the rear fuselage of the AFTI F-16, a safety device designed to prevent the loss of aircraft in spin conditions. Under some circumstances, pilots cannot recover from spins using normal controls. It these instances, the spin chute is deployed, thus "breaking" the spin and enabling the pilot to recover. The spin chute is held in a metal cylinder attached to the AFTI F-16 by four tubes, a structure strong enough to withstand the shock of the spin chute opening. Unlike the air probe in the last photo, spin chutes are not standard equipment on research or prototype aircraft but are commonly attached expressly for actual spin tests.
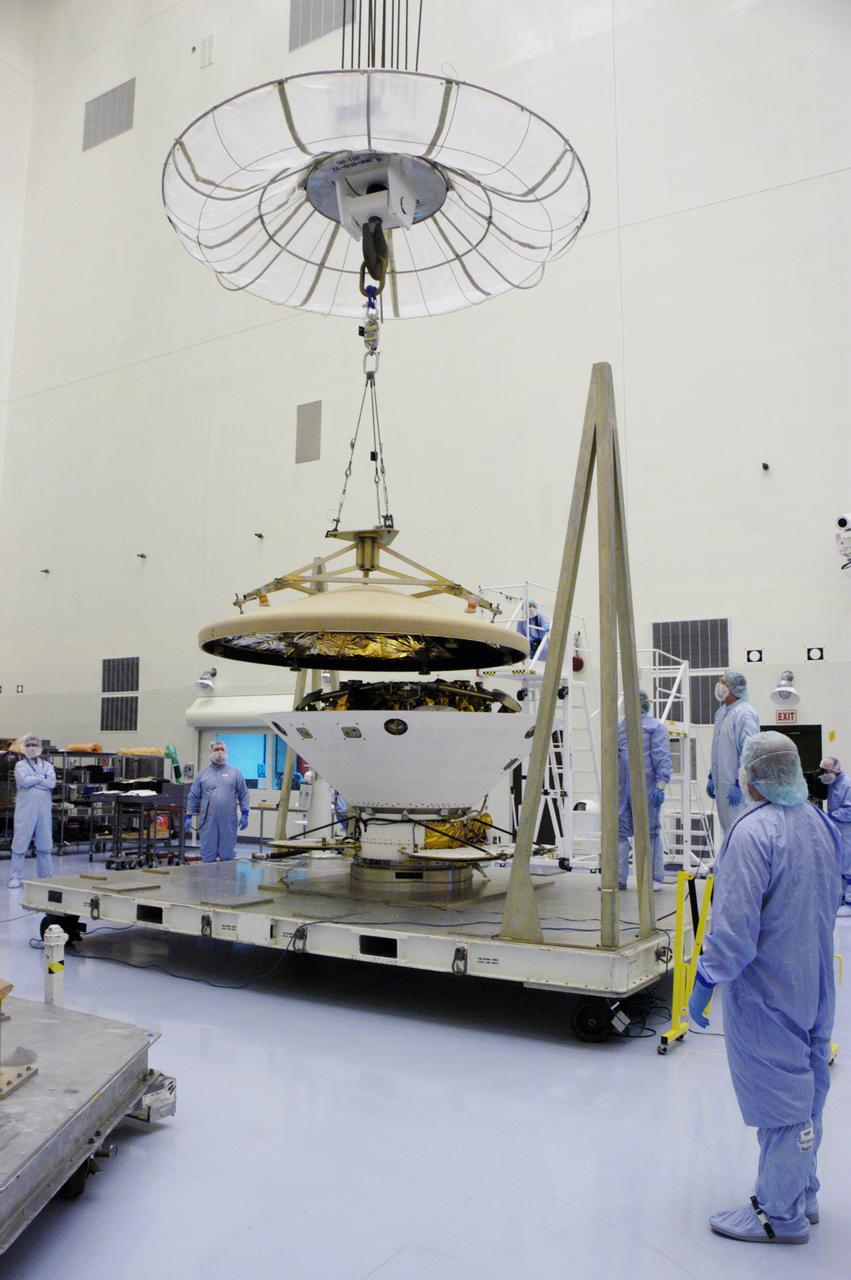

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the heat shield from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
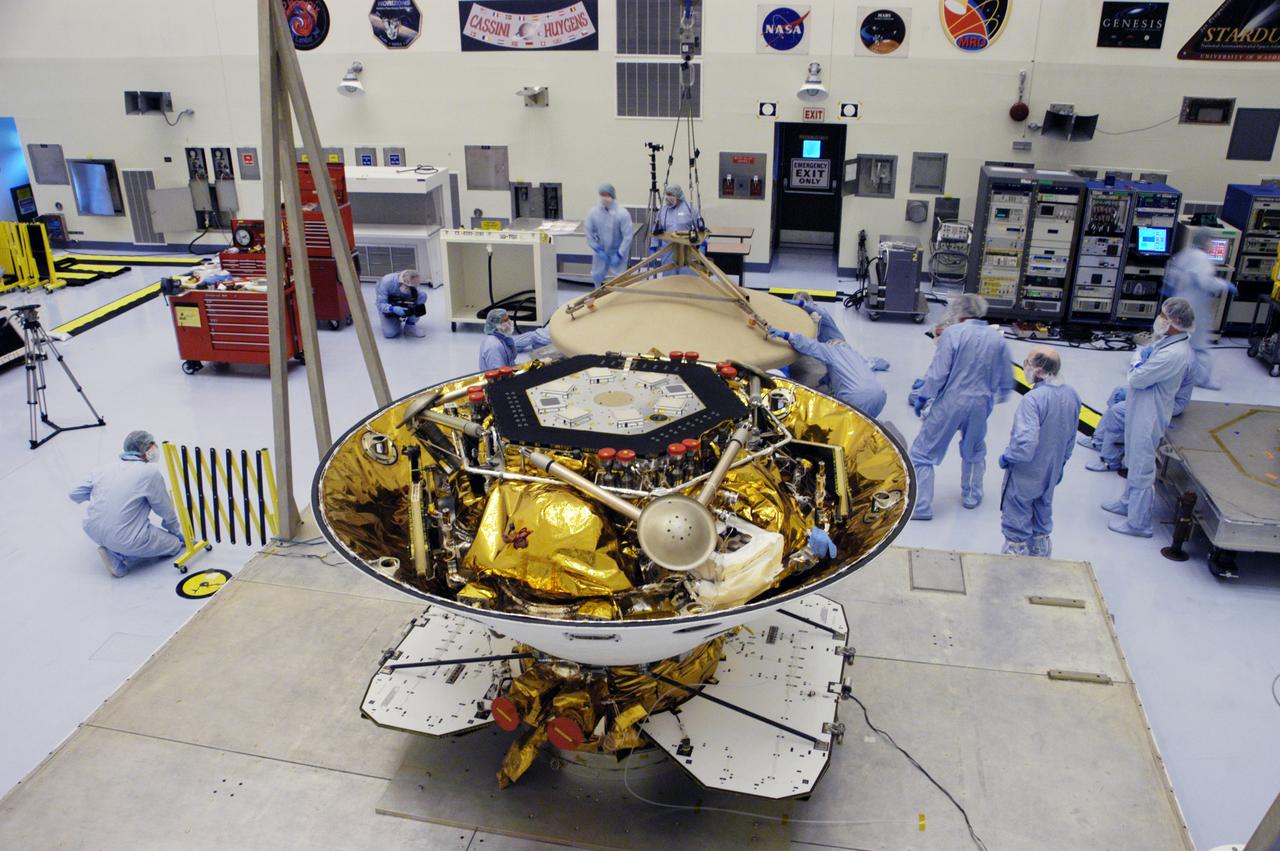

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the Phoenix Mars Lander (foreground) can be seen inside the backshell. In the background, workers are helping place the heat shield, just removed from the Phoenix, onto a platform. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
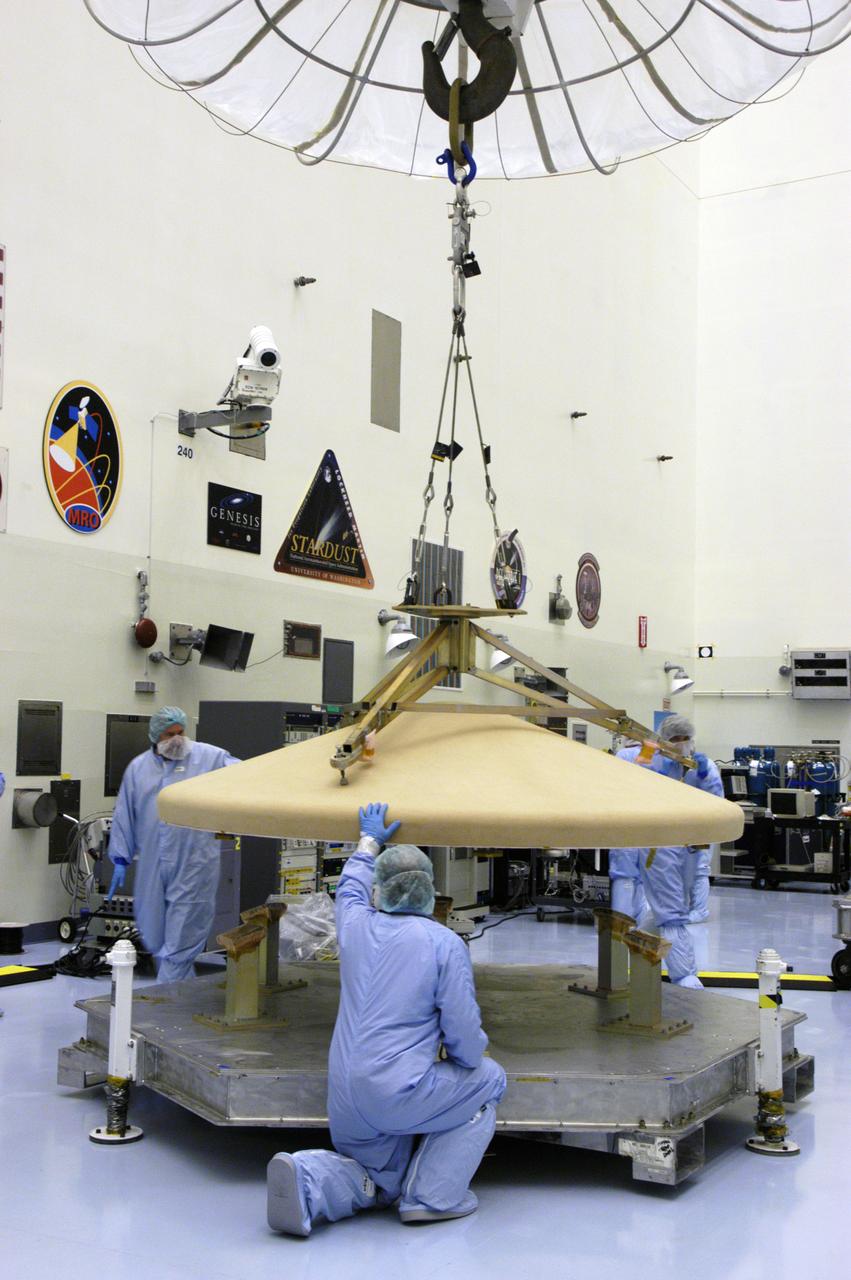

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, workers help guide the heat shield onto a platform. The heat shield was removed from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft.. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
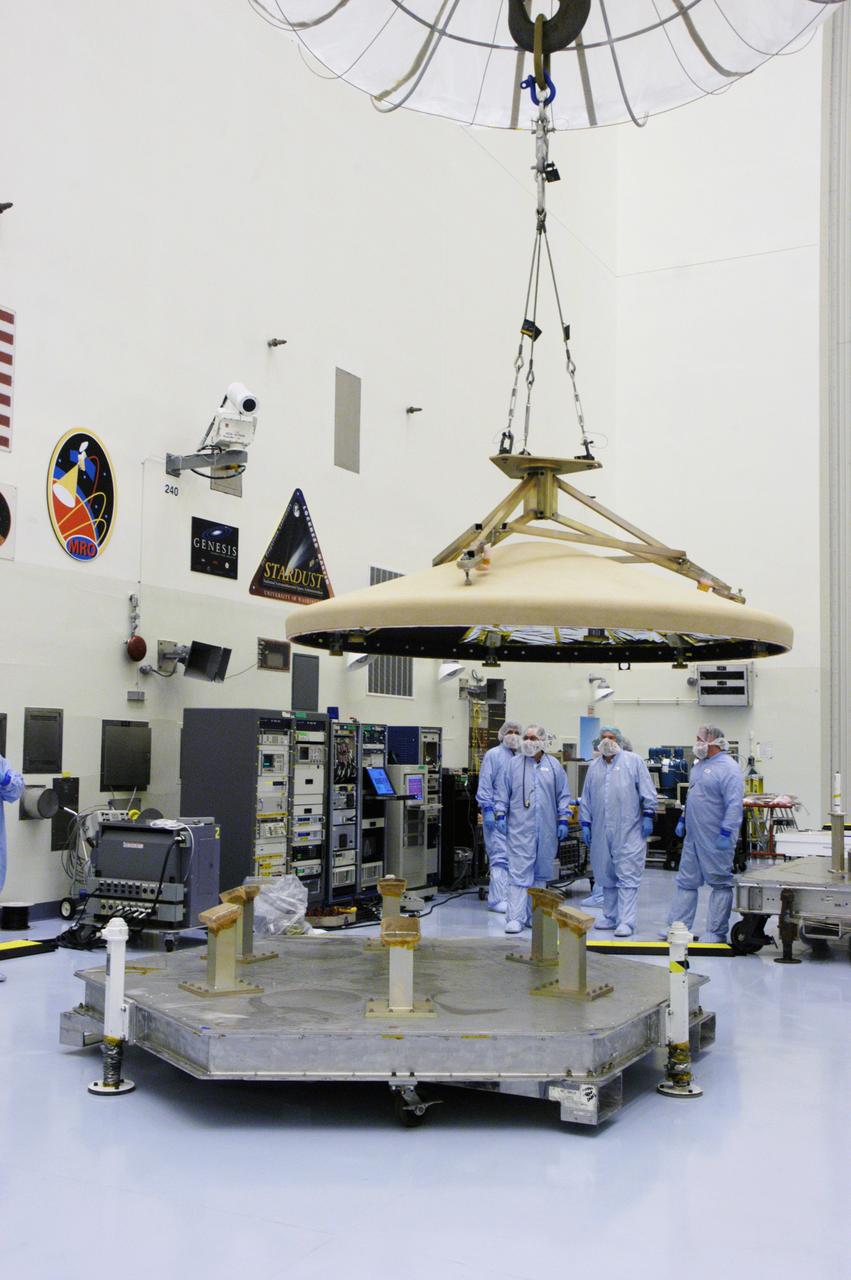

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, workers watch as an overhead crane lowers the heat shield toward a platform. The heat shield was removed from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

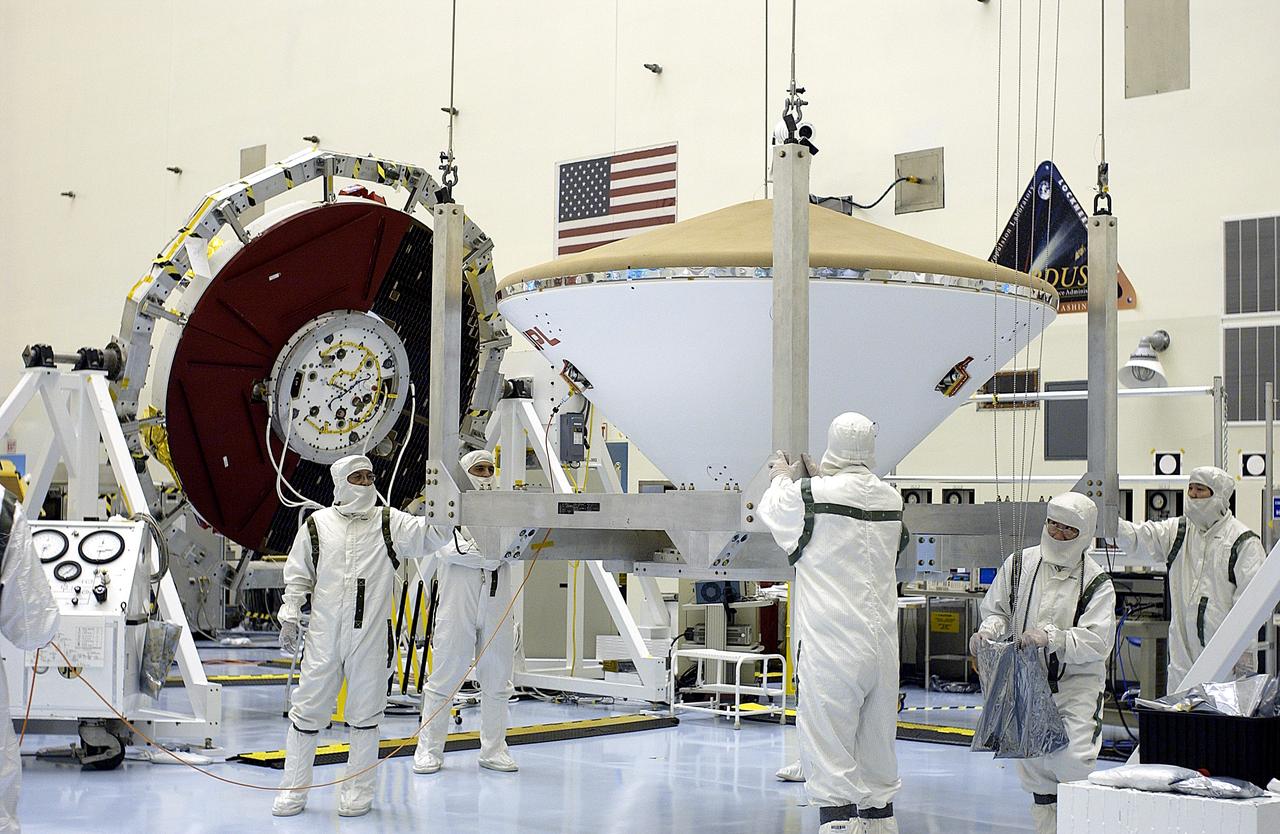
In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, an overhead crane moves the heat shield toward a platform at left. The heat shield was removed from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft at right. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
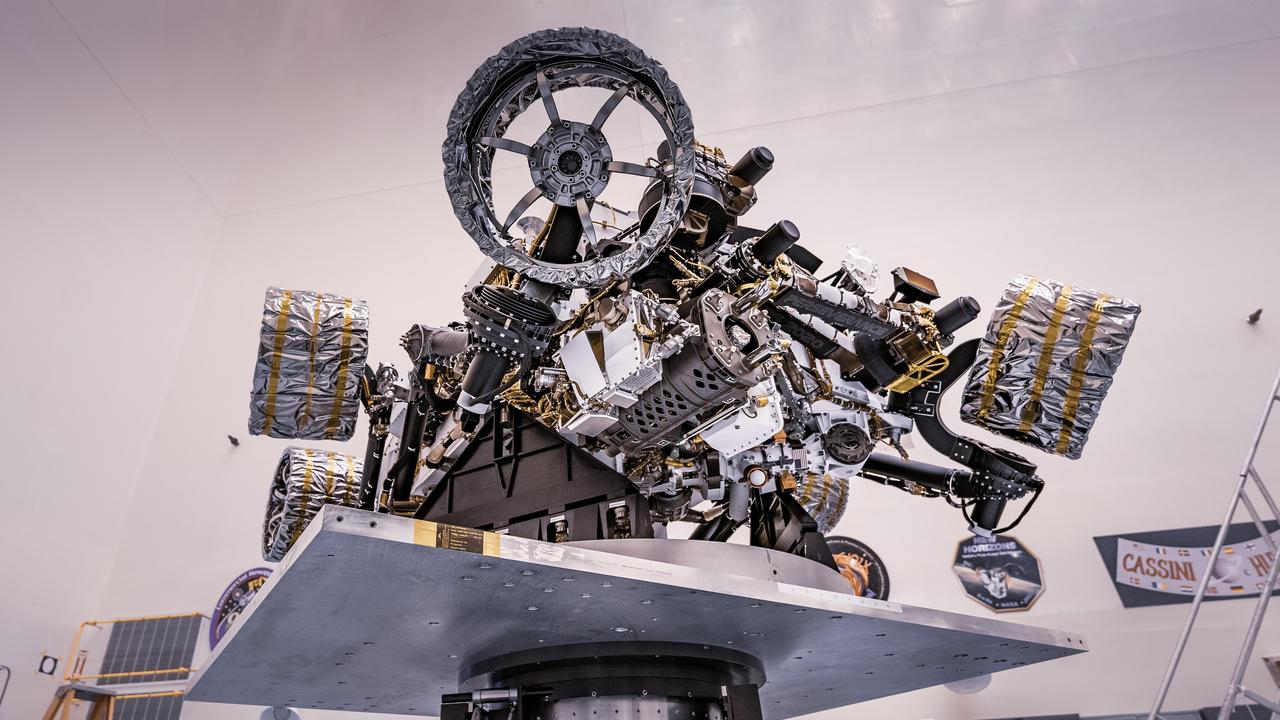
NASA's Perseverance rover can be seen attached to a spin table during a test of its mass properties at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. During the test, the rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise to determine its center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. The image was taken on April 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23826

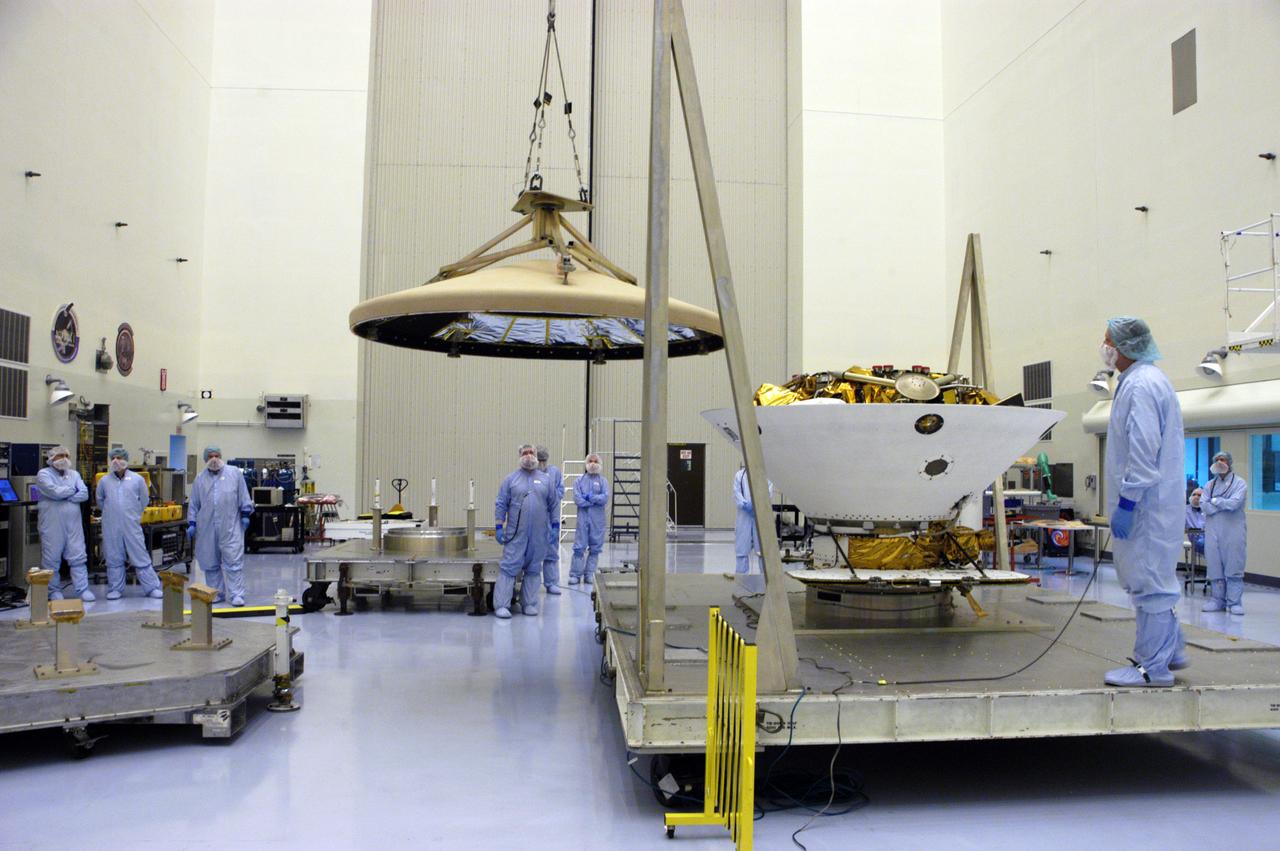
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An overhead crane is in place to lift the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) entry vehicle to move it to a spin table for a dry-spin test. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers designed to cover roughly 110 yards each Martian day over various terrain. Each rover will carry five scientific instruments that will allow it to search for evidence of liquid water that may have been present in the planet's past. Identical to each other, the rovers will land at different regions of Mars. Launch for MER-2 (MER-A) is scheduled for June 5.

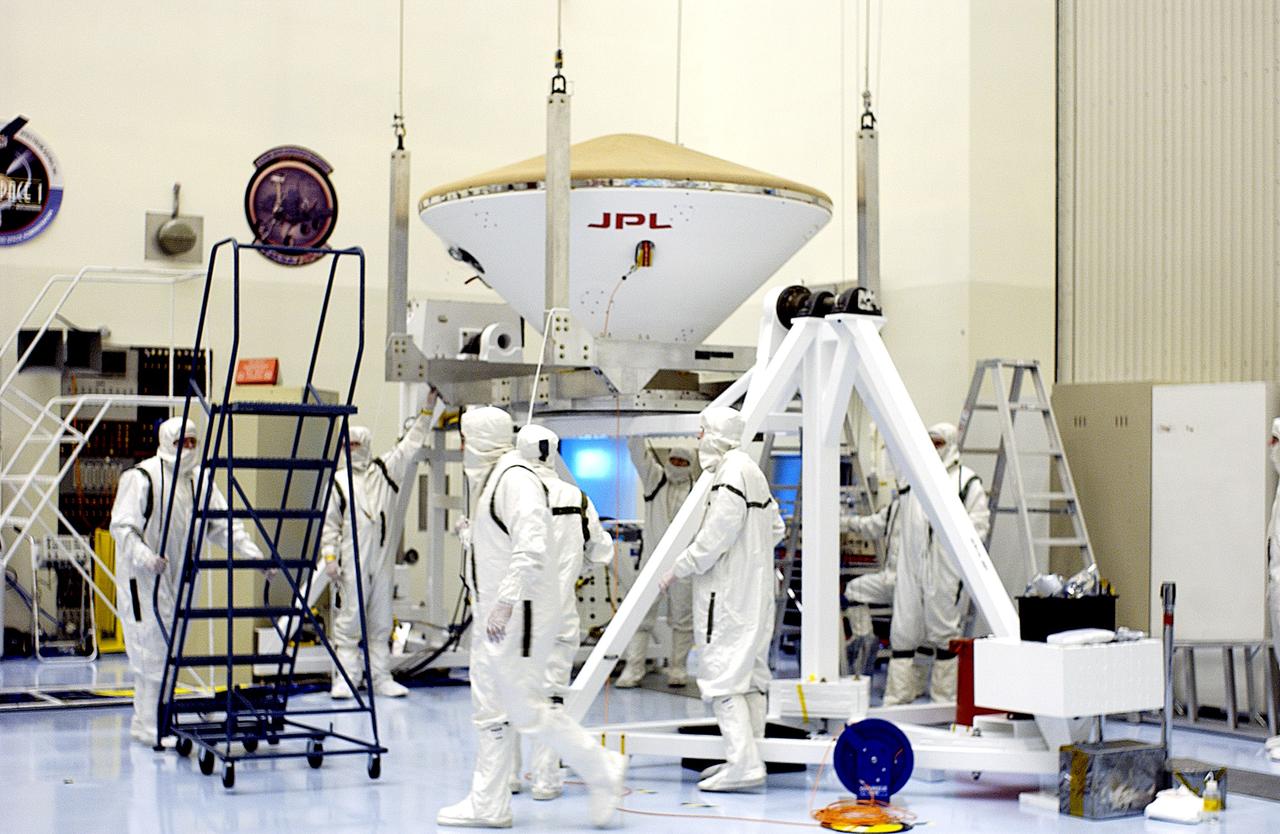
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The overhead crane settles the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) entry vehicle onto a spin table for a dry-spin test. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers designed to cover roughly 110 yards each Martian day over various terrain. Each rover will carry five scientific instruments that will allow it to search for evidence of liquid water that may have been present in the planet's past. Identical to each other, the rovers will land at different regions of Mars. Launch for MER-2 (MER-A) is scheduled for June 5.

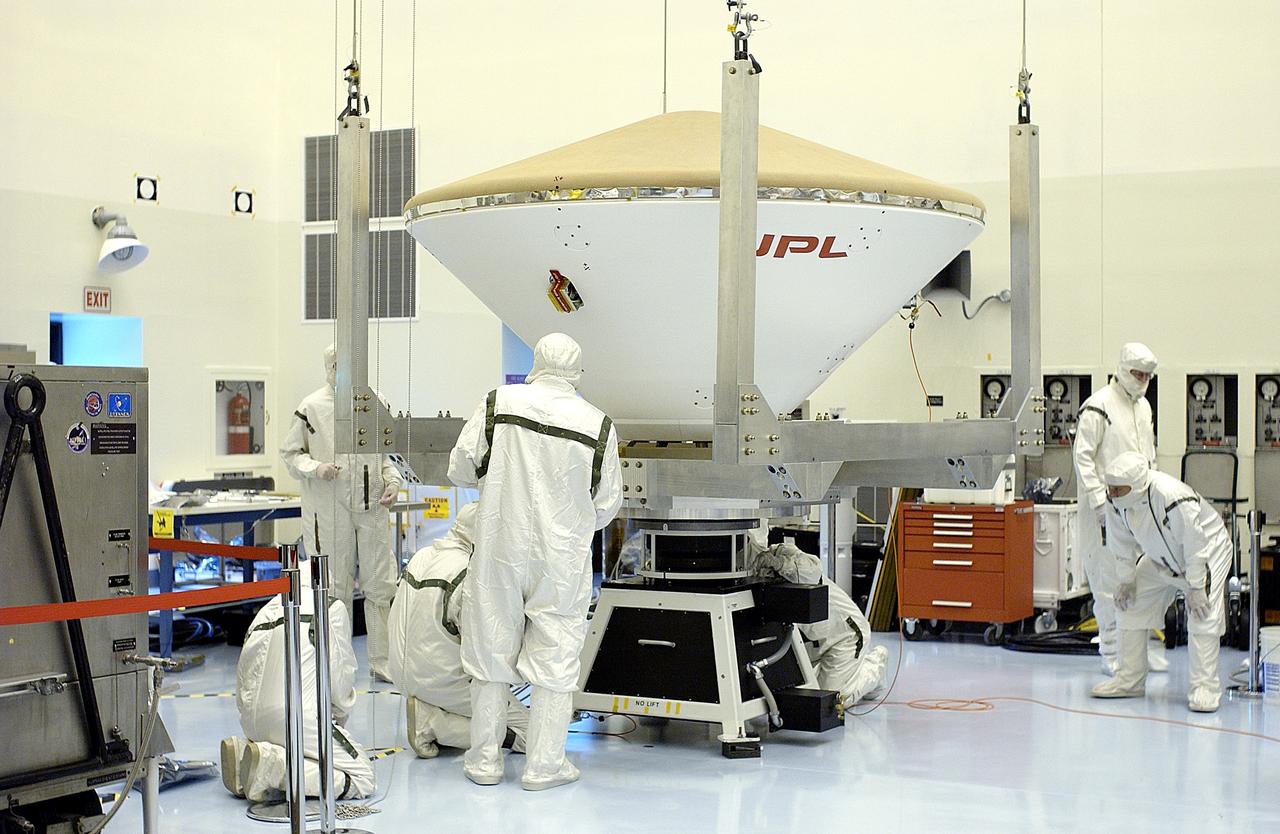
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An overhead crane moves the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) entry vehicle across the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility toward a spin table for a dry-spin test. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers designed to cover roughly 110 yards each Martian day over various terrain. Each rover will carry five scientific instruments that will allow it to search for evidence of liquid water that may have been present in the planet's past. Identical to each other, the rovers will land at different regions of Mars. Launch for MER-2 (MER-A) is scheduled for June 5.
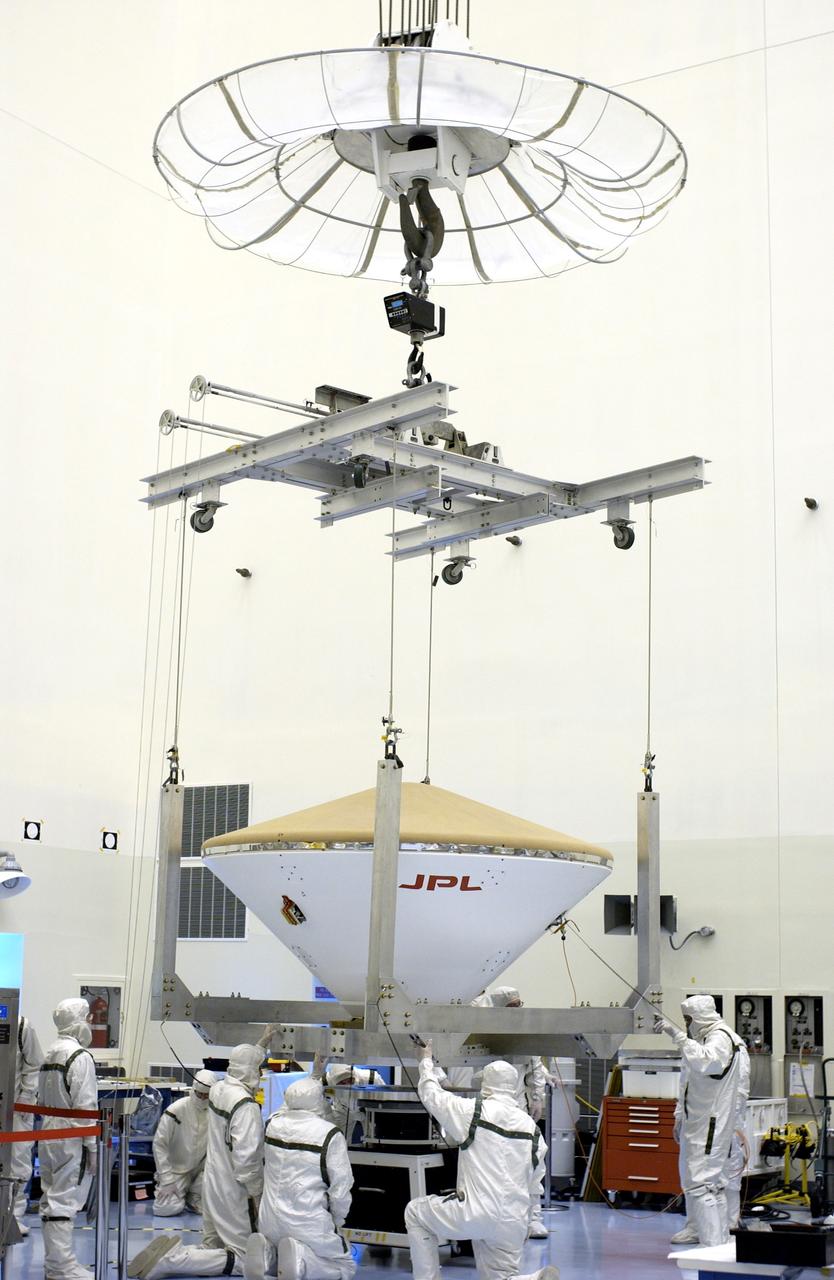

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - With help from workers, the overhead crane lowers the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) entry vehicle onto a spin table for a dry-spin test. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers designed to cover roughly 110 yards each Martian day over various terrain. Each rover will carry five scientific instruments that will allow it to search for evidence of liquid water that may have been present in the planet's past. Identical to each other, the rovers will land at different regions of Mars. Launch for MER-2 (MER-A) is scheduled for June 5.
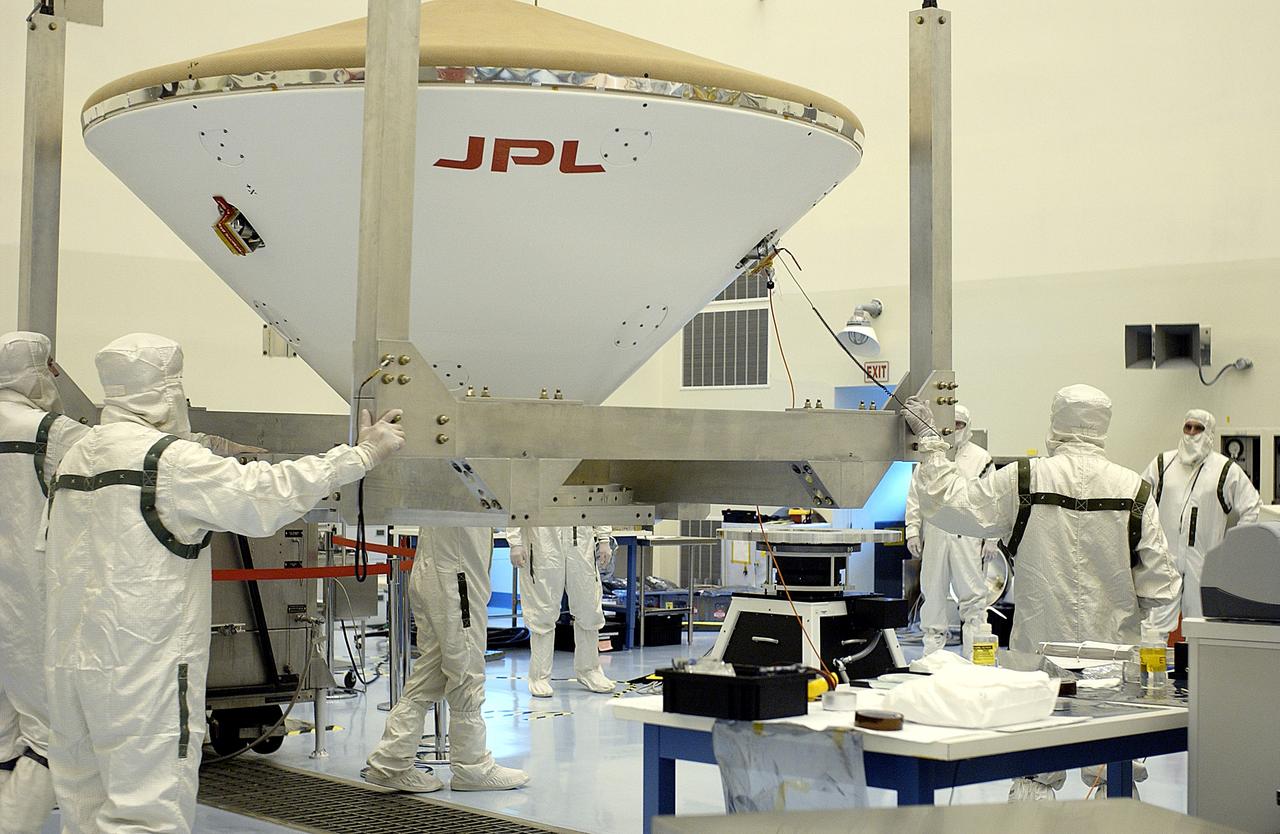

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility help guide the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) entry vehicle toward a spin table for a dry-spin test. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers designed to cover roughly 110 yards each Martian day over various terrain. Each rover will carry five scientific instruments that will allow it to search for evidence of liquid water that may have been present in the planet's past. Identical to each other, the rovers will land at different regions of Mars. Launch for MER-2 (MER-A) is scheduled for June 5.
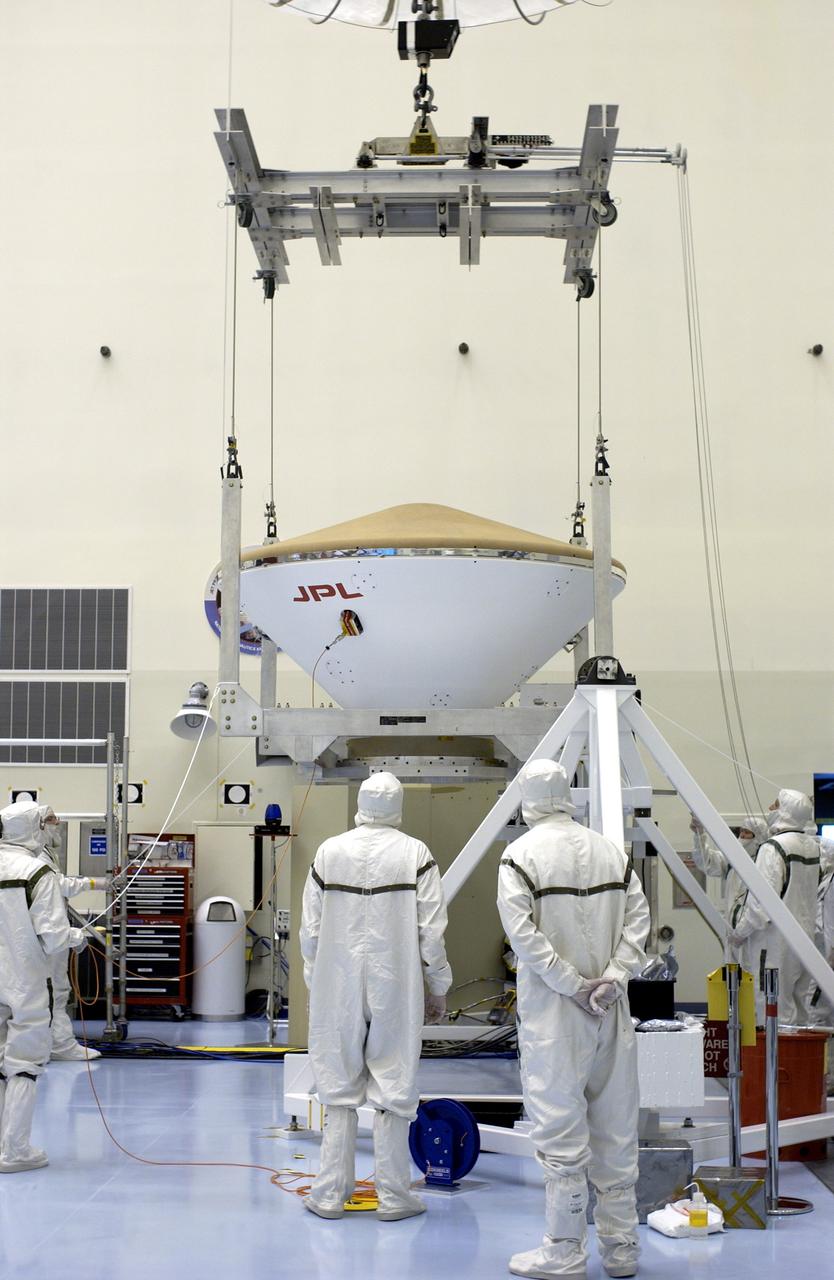

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An overhead crane lifts the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) entry vehicle from its stand to move it to a spin table for a dry-spin test. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers designed to cover roughly 110 yards each Martian day over various terrain. Each rover will carry five scientific instruments that will allow it to search for evidence of liquid water that may have been present in the planet's past. Identical to each other, the rovers will land at different regions of Mars. Launch for MER-2 (MER-A) is scheduled for June 5.
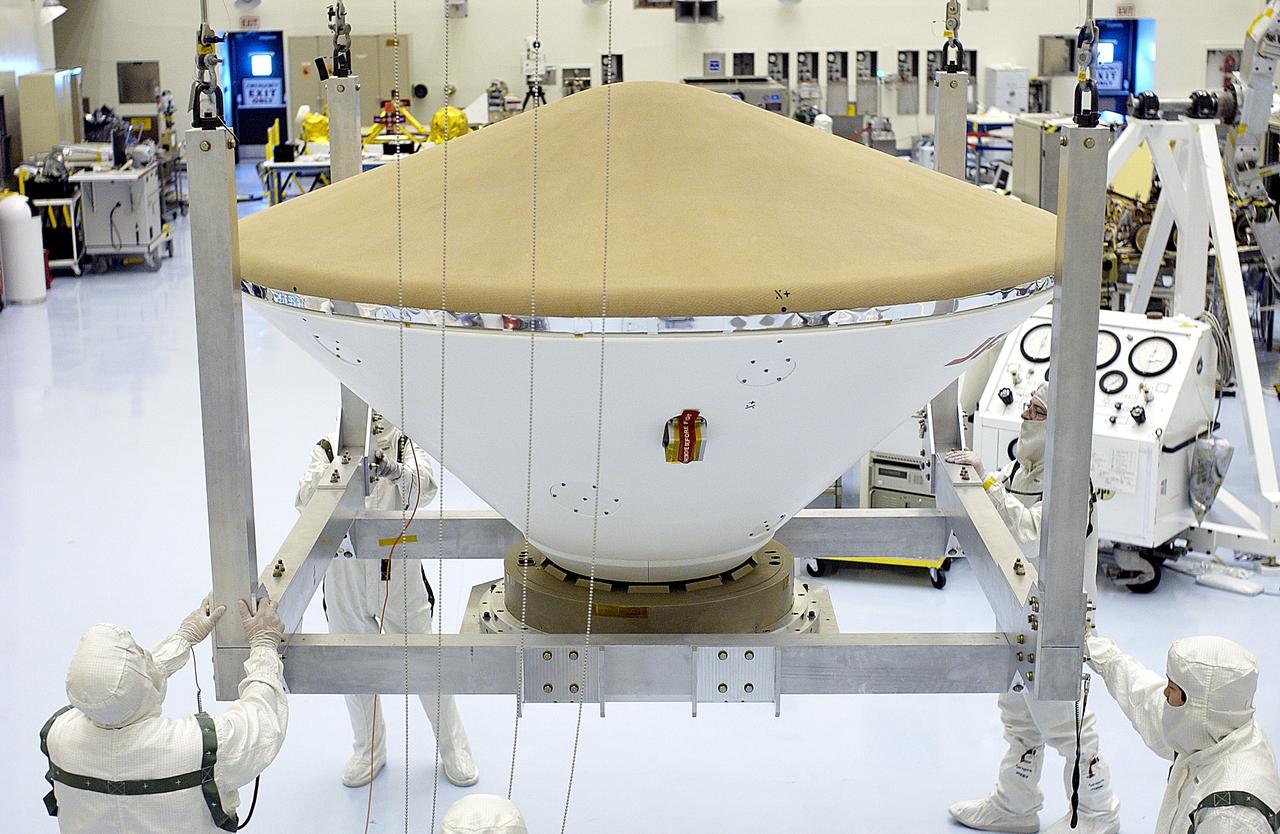

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An overhead crane moves the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) entry vehicle across the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility toward a spin table for a dry-spin test. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers designed to cover roughly 110 yards each Martian day over various terrain. Each rover will carry five scientific instruments that will allow it to search for evidence of liquid water that may have been present in the planet's past. Identical to each other, the rovers will land at different regions of Mars. Launch for MER-2 (MER-A) is scheduled for June 5.
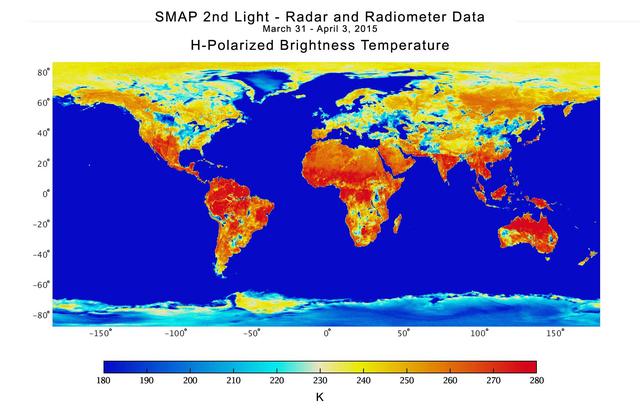
With its antenna now spinning at full speed, NASA new Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP observatory has successfully re-tested its science instruments and generated its first global maps, a key step to beginning routine science operations in May, 2015
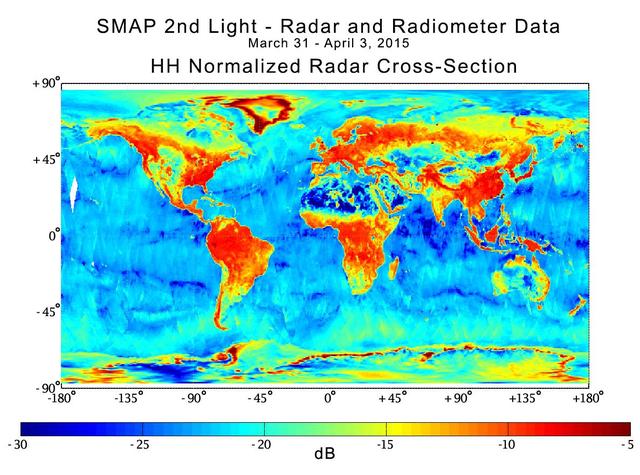
With its antenna now spinning at full speed, NASA new Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP observatory has successfully re-tested its science instruments and generated its first global maps, a key step to beginning routine science operations in May, 2015

XA-39 model mounted for testing in the 7x120ft w.t. at Ames Research Center, California, props spinning.
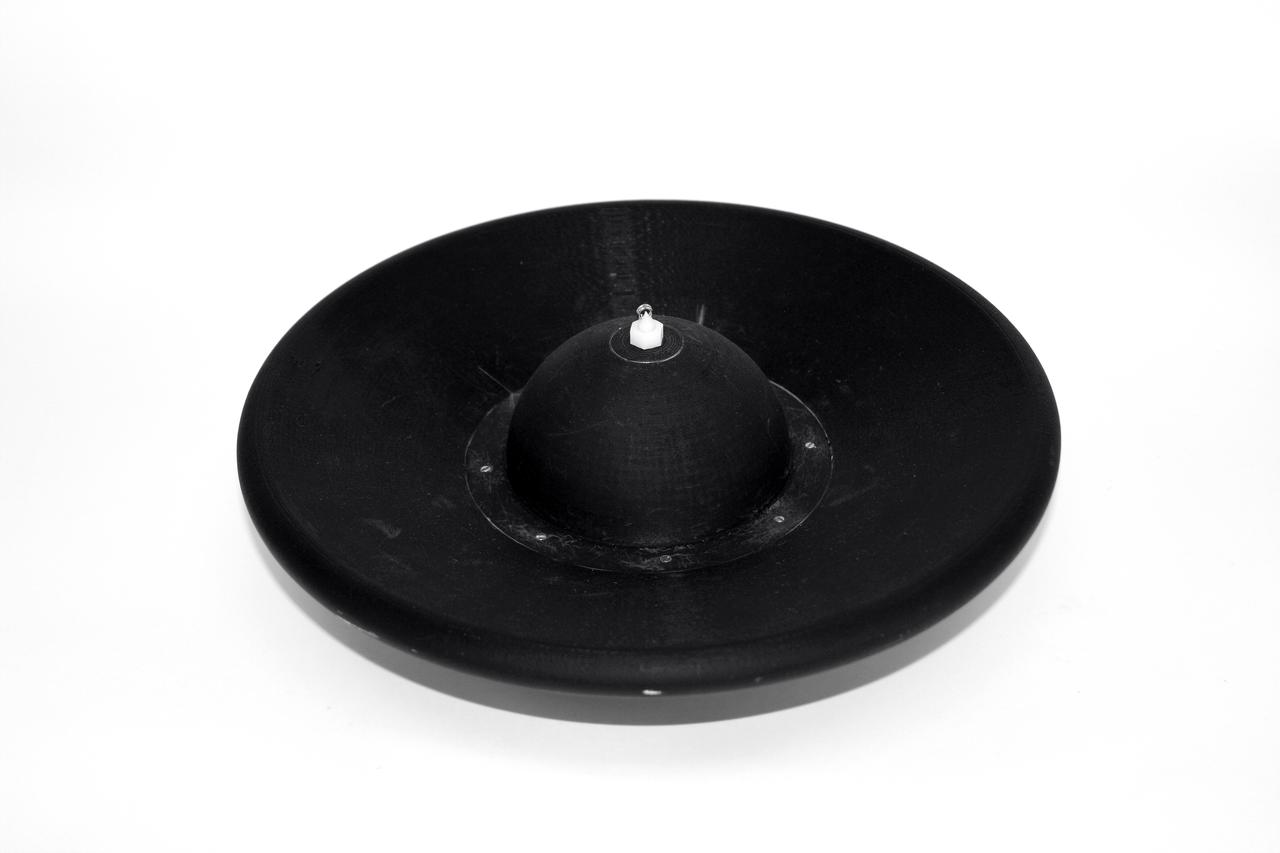

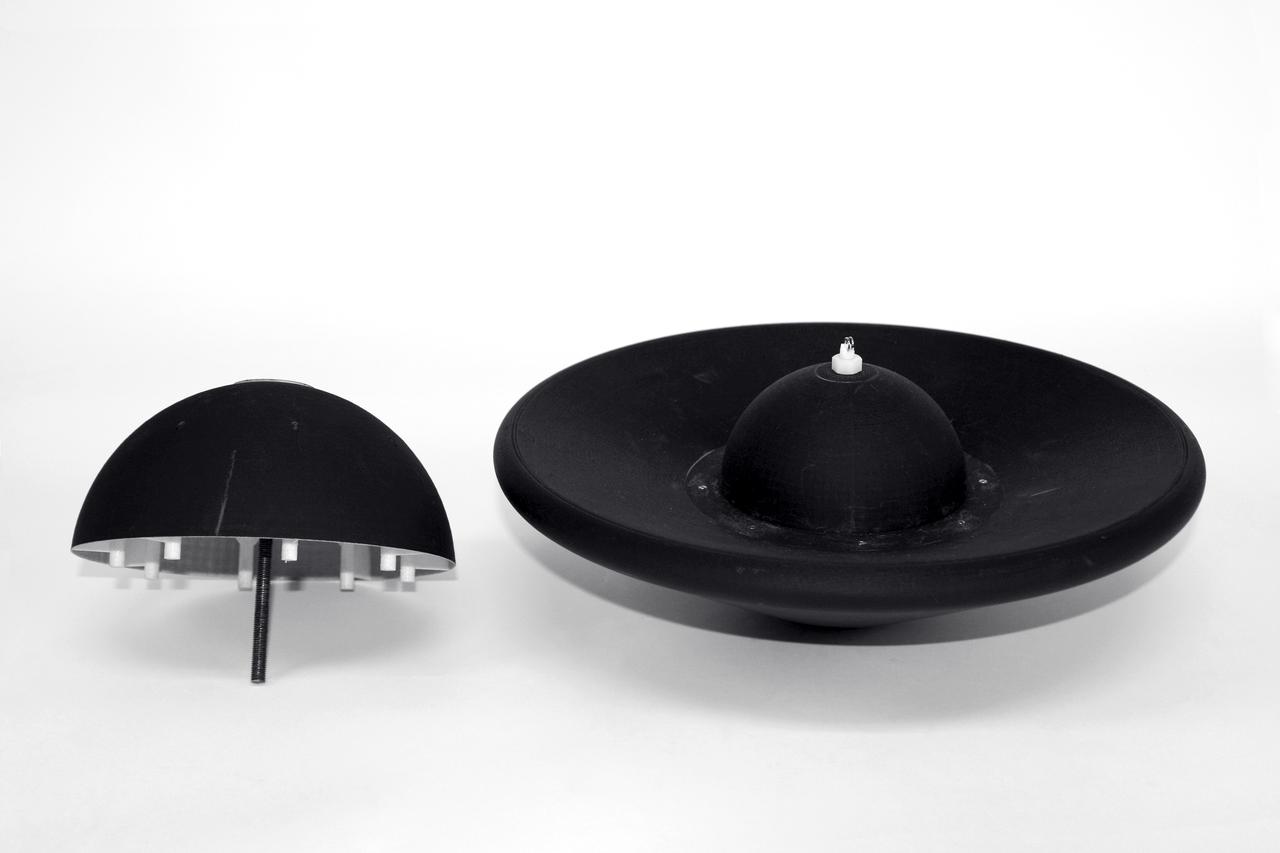
1.2 meter Multi-Mission Earth Entry Vehicle (MMEEV): Tethered and free flying test in 20 foot Vertical Spin Tunnel
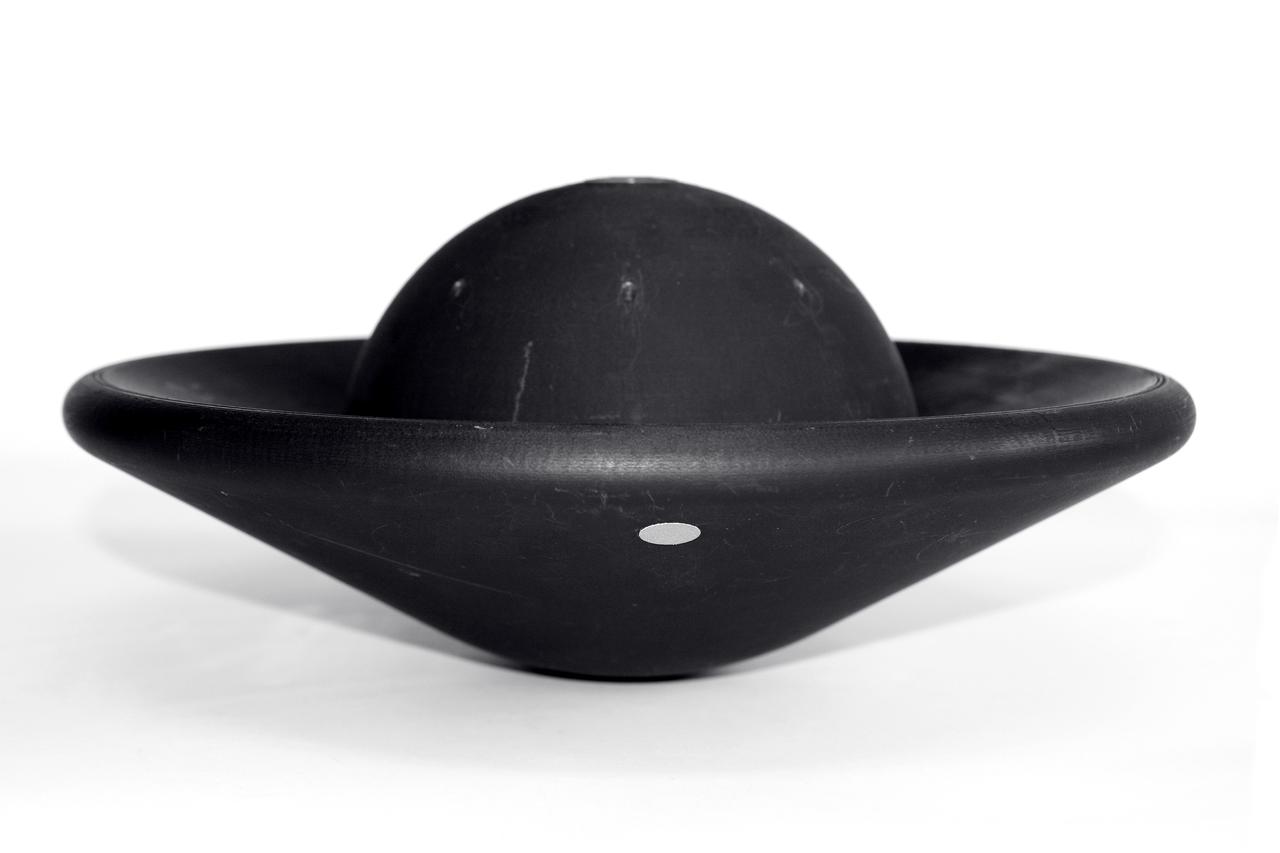

1.2 meter Multi-Mission Earth Entry Vehicle (MMEEV): Tethered and free flying test in 20 foot Vertical Spin Tunnel
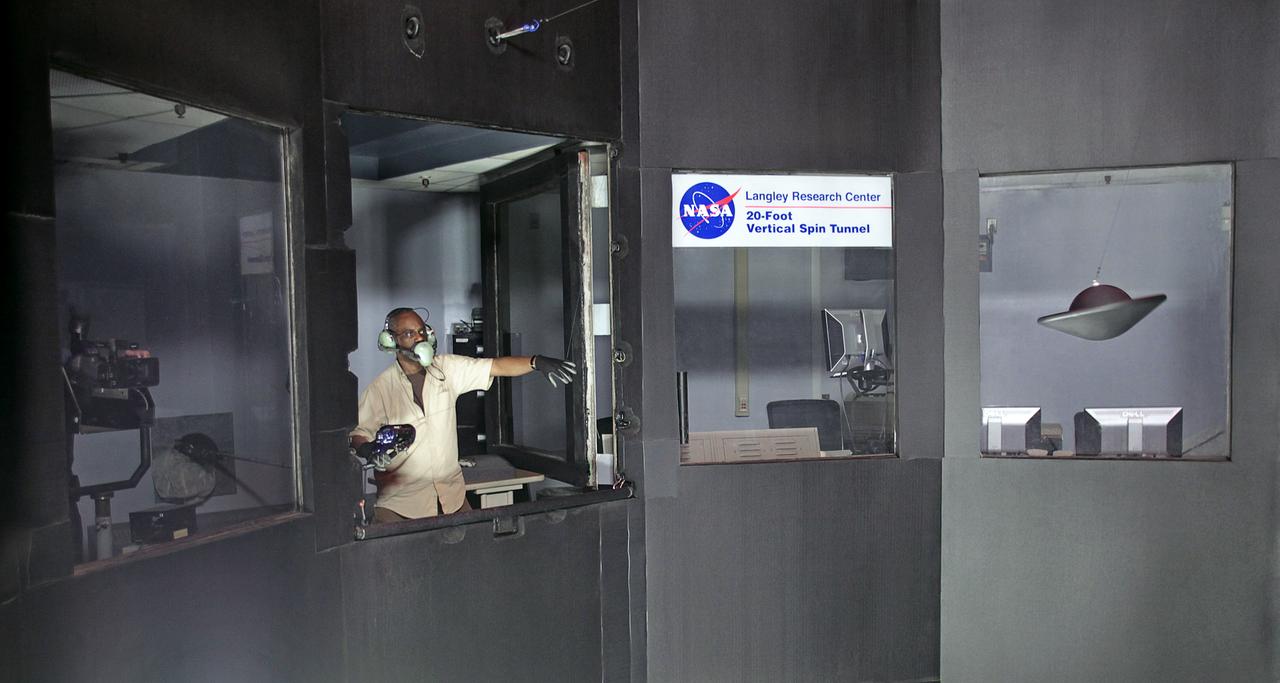

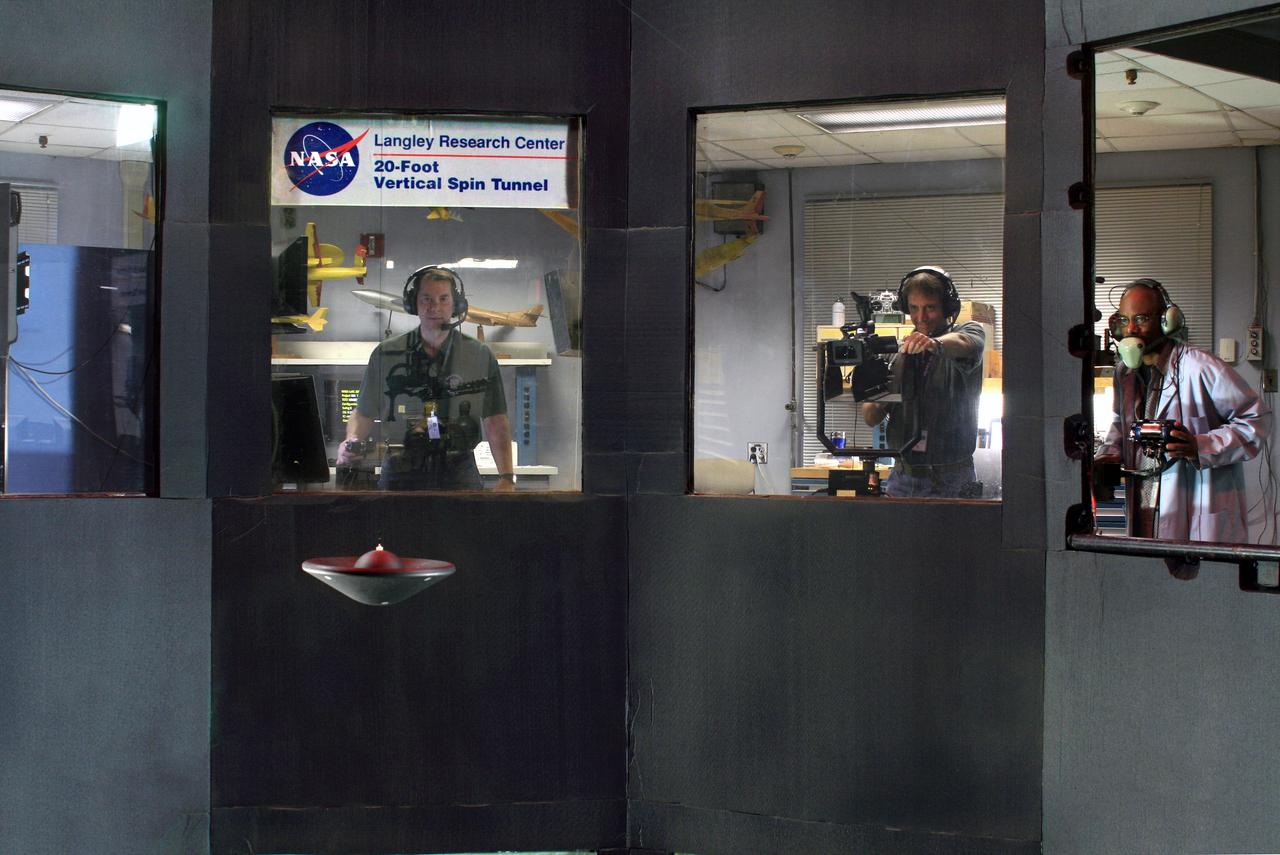
NASA Langley engineer, Clinton Duncan maintains controls of the tethered Multi Mission Earth Entry Vehicle model while being tested in the Vertical Spin Tunnel.
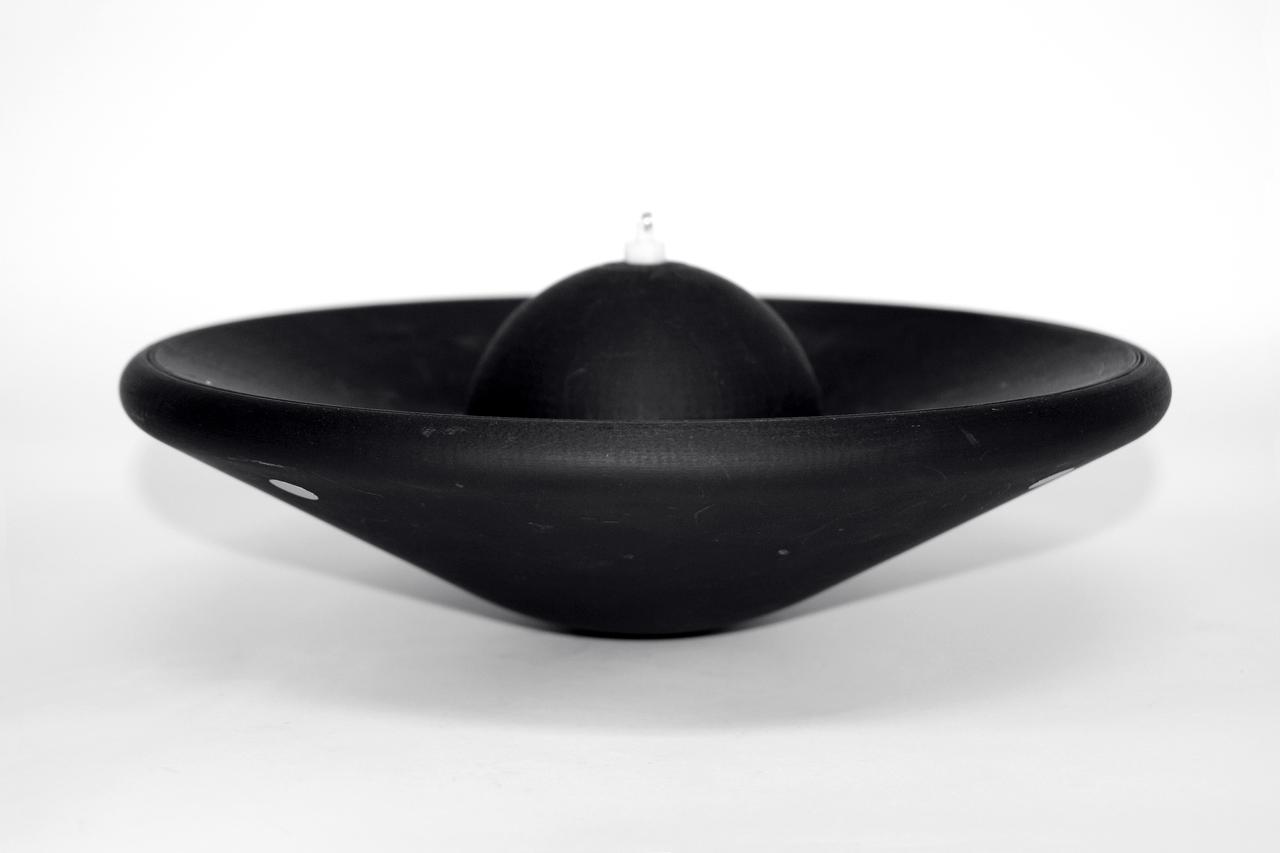

1.2 meter Multi-Mission Earth Entry Vehicle (MMEEV): Tethered and free flying test in 20 foot Vertical Spin Tunnel
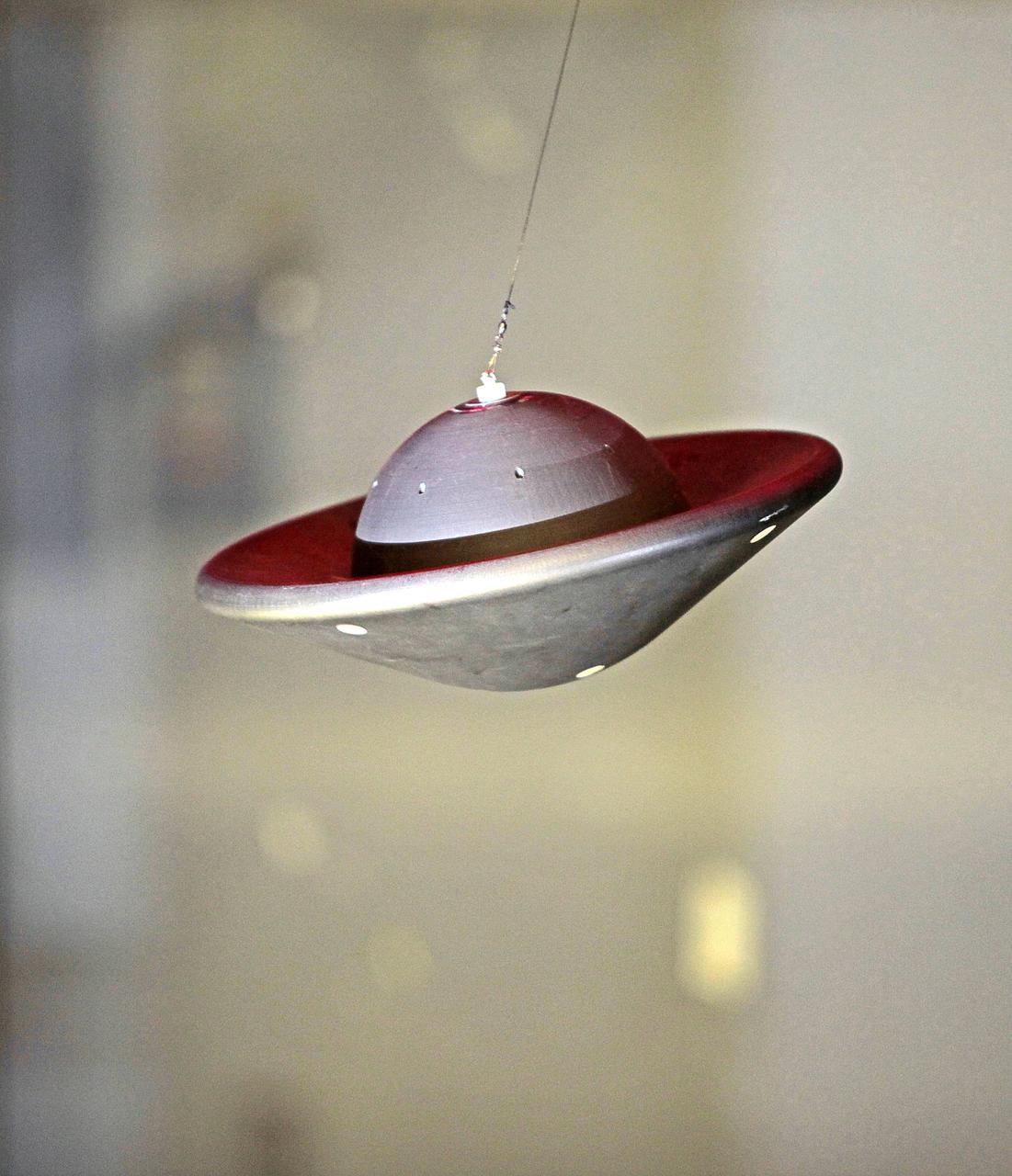

The tethered Multi Mission Earth Entry Vehicle model while being tested in the Vertical Spin Tunnel at NASA Langely Research Center, Hampton VA.

1.2 meter Multi-Mission Earth Entry Vehicle (MMEEV): Tethered and free flying test in 20 foot Vertical Spin Tunnel
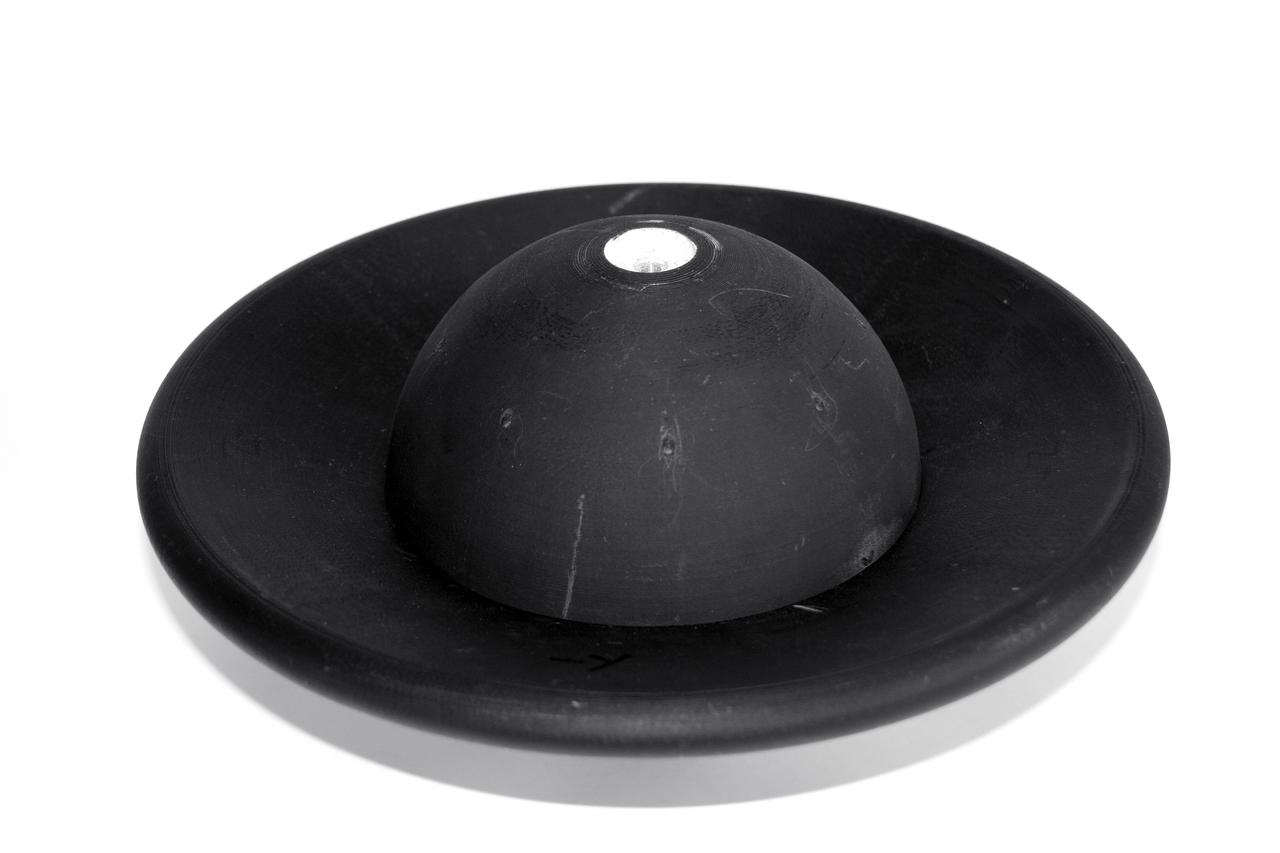

1.2 meter Multi-Mission Earth Entry Vehicle (MMEEV): Tethered and free flying test in 20 foot Vertical Spin Tunnel

1.2 meter Multi-Mission Earth Entry Vehicle (MMEEV): Tethered and free flying test in 20 foot Vertical Spin Tunnel

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft is spin-tested during testing on the spin table at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla. MESSENGER is scheduled to lift off Aug. 2 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It is expected to reach orbit around Mercury in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.

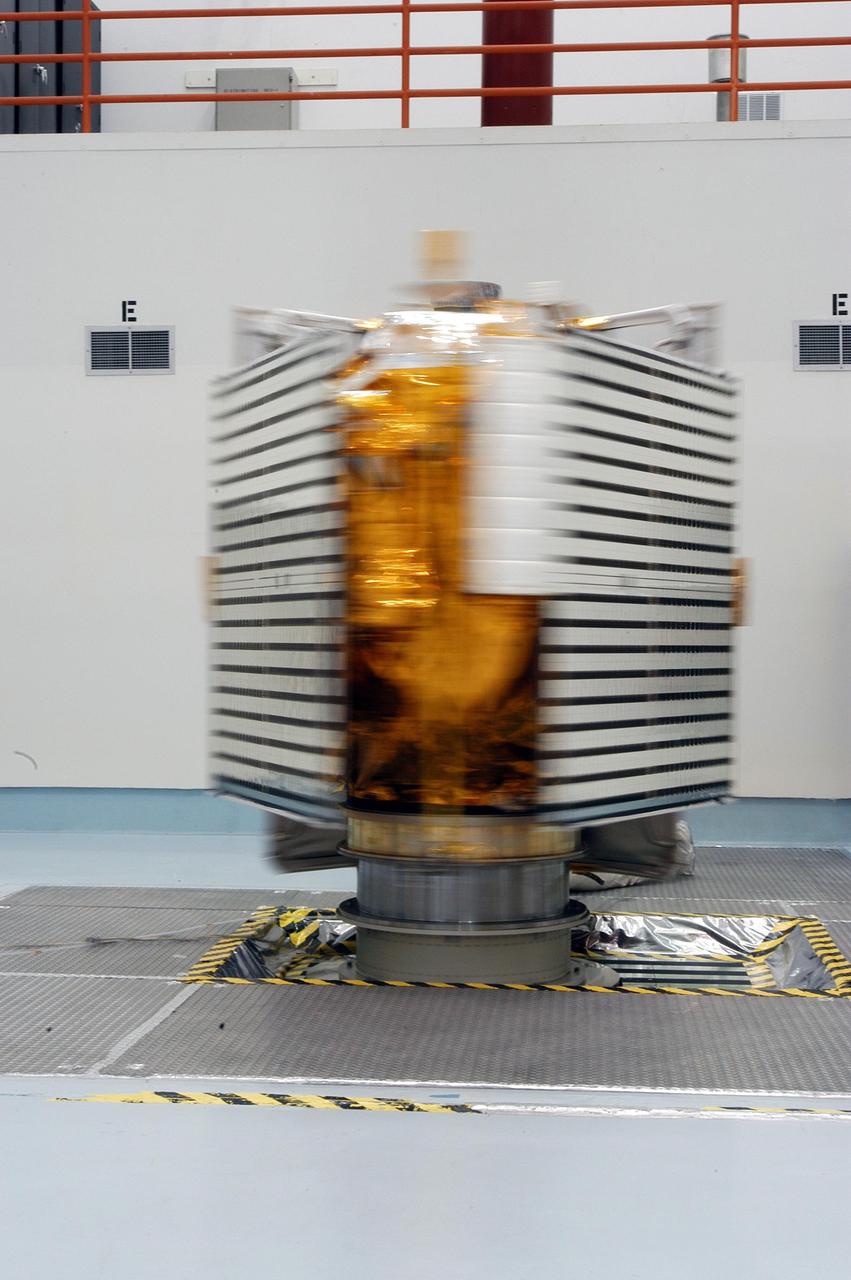
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The blurred image of the New Horizons spacecraft is the result of a spin test being conducted in NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The spacecraft is undergoing the spin test as part of prelaunch processing. New Horizons is expected to be launched in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon. It is expected to reach Pluto in July 2015.
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations, the integrated THEMIS spacecraft is spinning on the spin table, part of spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
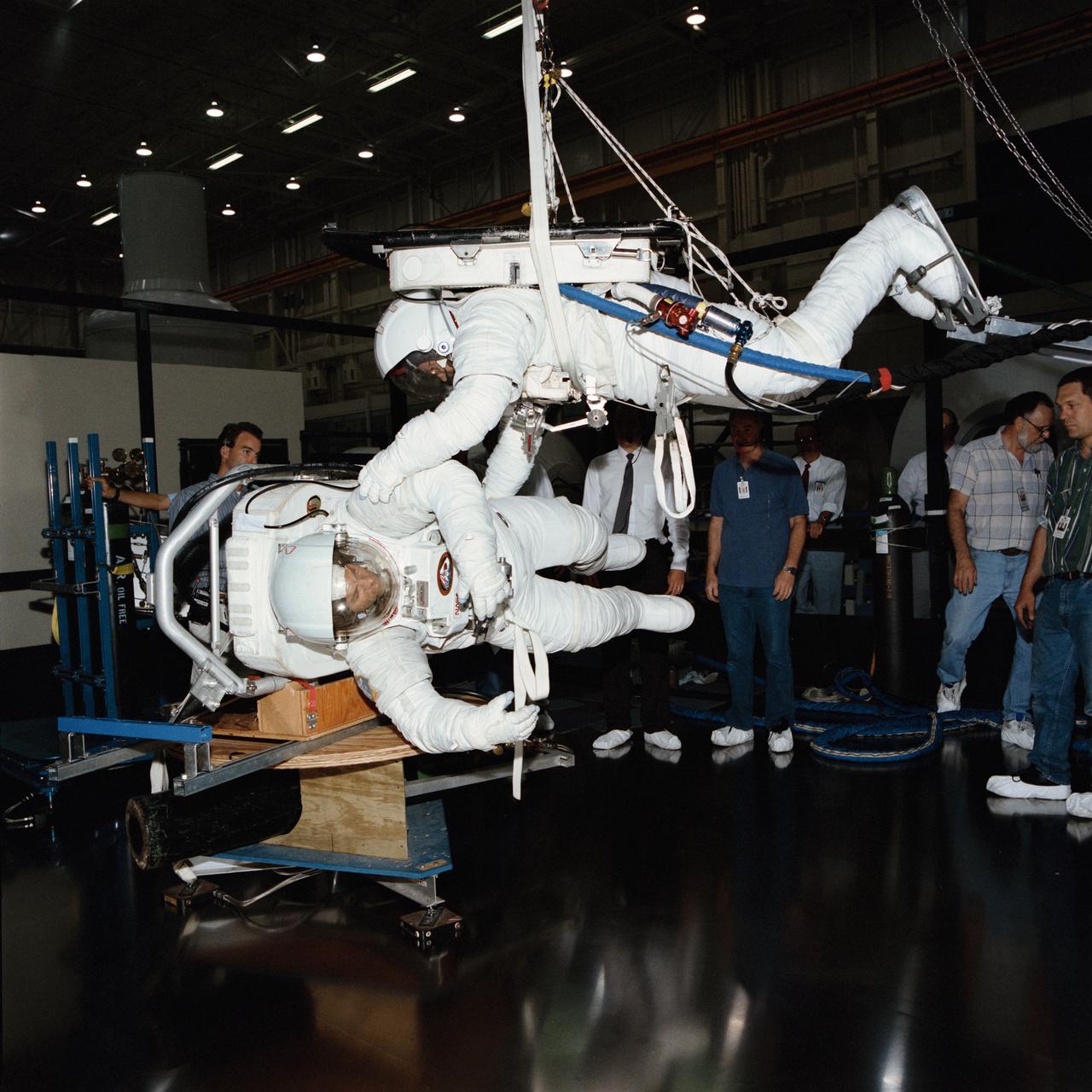

S94-33357 (1994) --- Scott Bleiseth, top, prepares to spin Mike Hess, a fellow EVA engineer, during a test on the air-bearing floor in the Shuttle Mock-up and Integration Laboratory at NASA's Johnson Space Center. The hardware being tested is part of the Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER). The pair was developing techniques by which the non-SAFER equipped spacewalker will impart a rotation to the SAFER-using spacewalker during the STS-64 mission. Once the SAFER astronaut is spinning, the device will be activated and its automatic attitude hold capability will be tested. SAFER is to fly on STS-76 as well. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
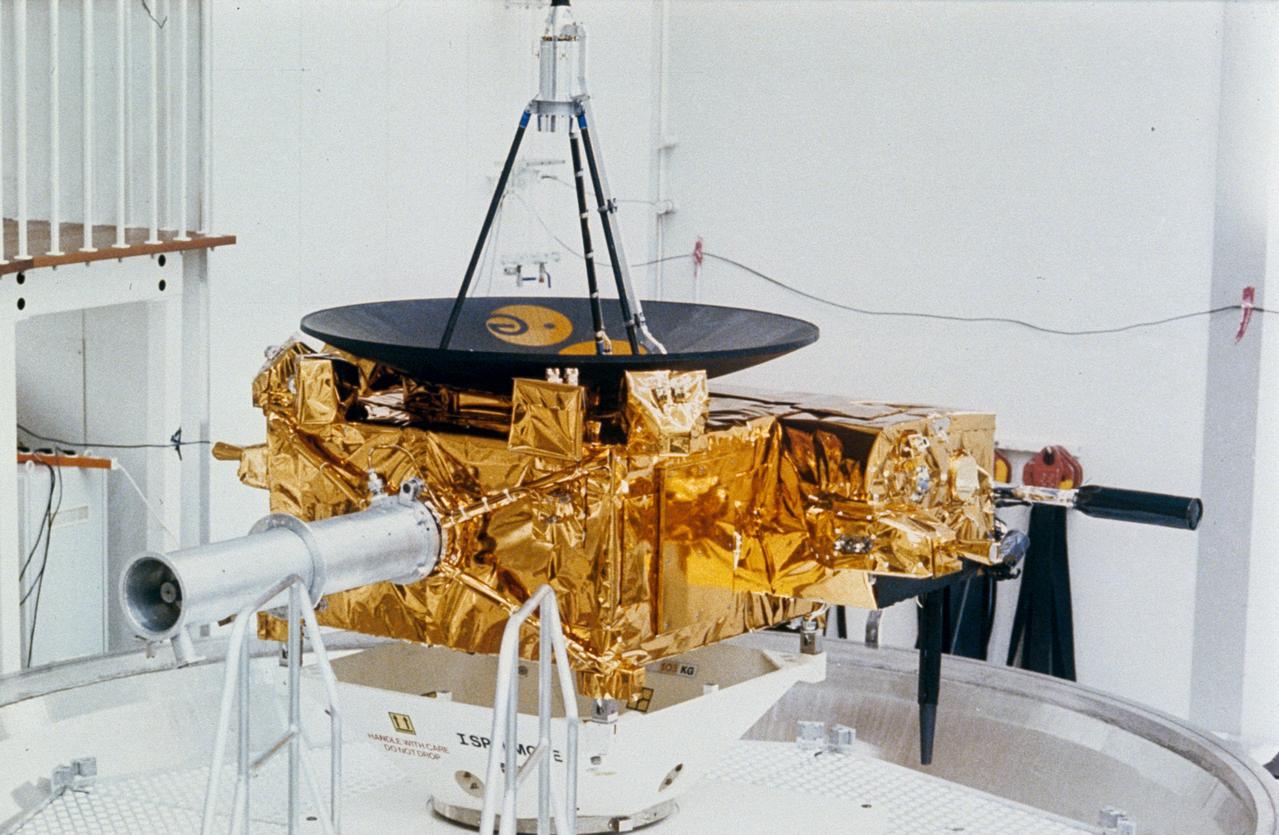
S90-45985 (May 1990) --- The Ulysses spacecraft undergoes testing at the vacuum spin-balancing facility in ESTEC. Careful balancing is required in order to ensure that the high gain antenna, which is aligned with the spacecraft spin axis, can be accurately pointed toward Earth throughout the mission. It will be flown to Kennedy Space Center (KSC) for further processing before being on loaded to Discovery's cargo bay. The Space Shuttle crew of STS-41 will send it off to its long-awaited mission.
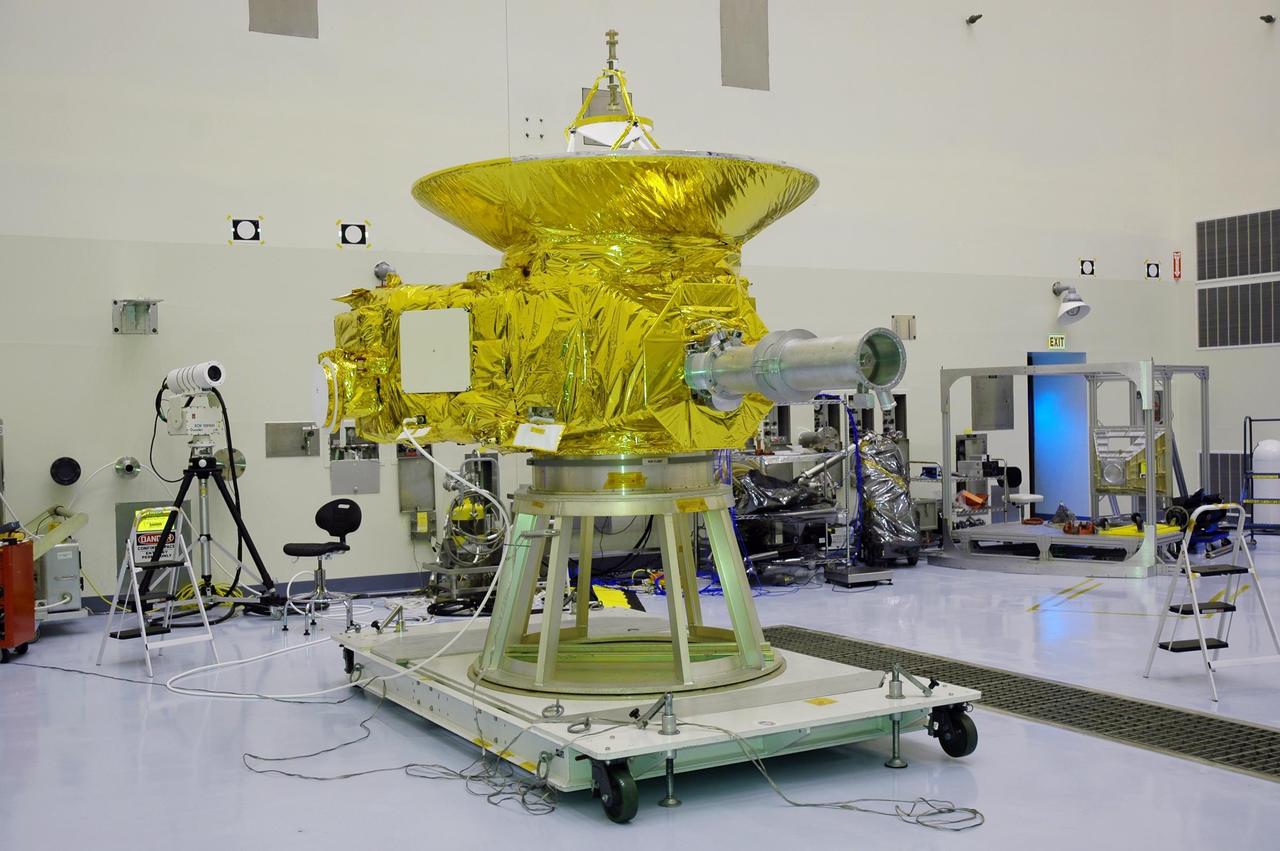

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the New Horizons spacecraft sits on a work stand prior to being moved to a spin table. The spacecraft will undergo a spin test as part of prelaunch processing. New Horizons is expected to be launched in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon. It is expected to reach Pluto in July 2015.
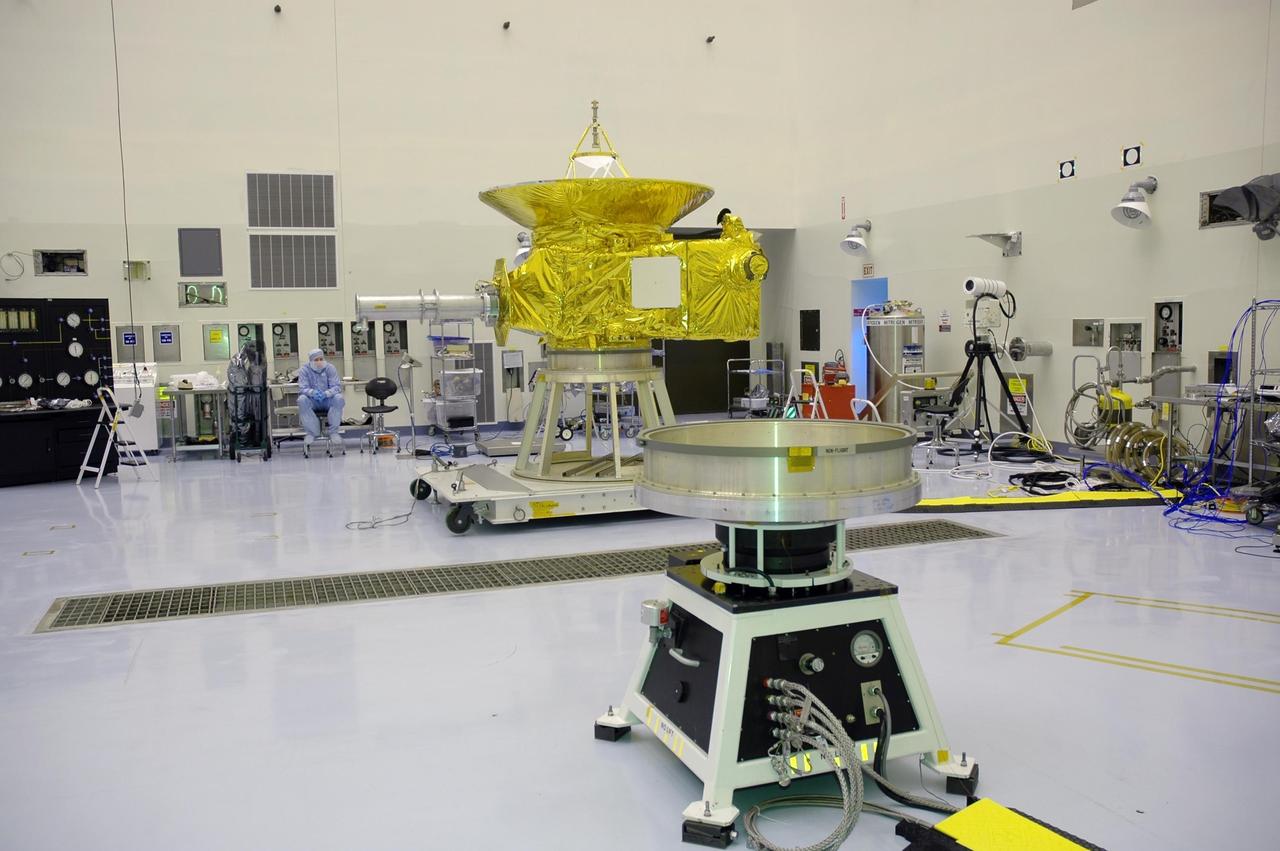

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the New Horizons spacecraft, in the background, sits on a work stand prior to being moved to a spin table, seen in the foreground. The spacecraft will undergo a spin test as part of prelaunch processing. New Horizons is expected to be launched in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon. It is expected to reach Pluto in July 2015.
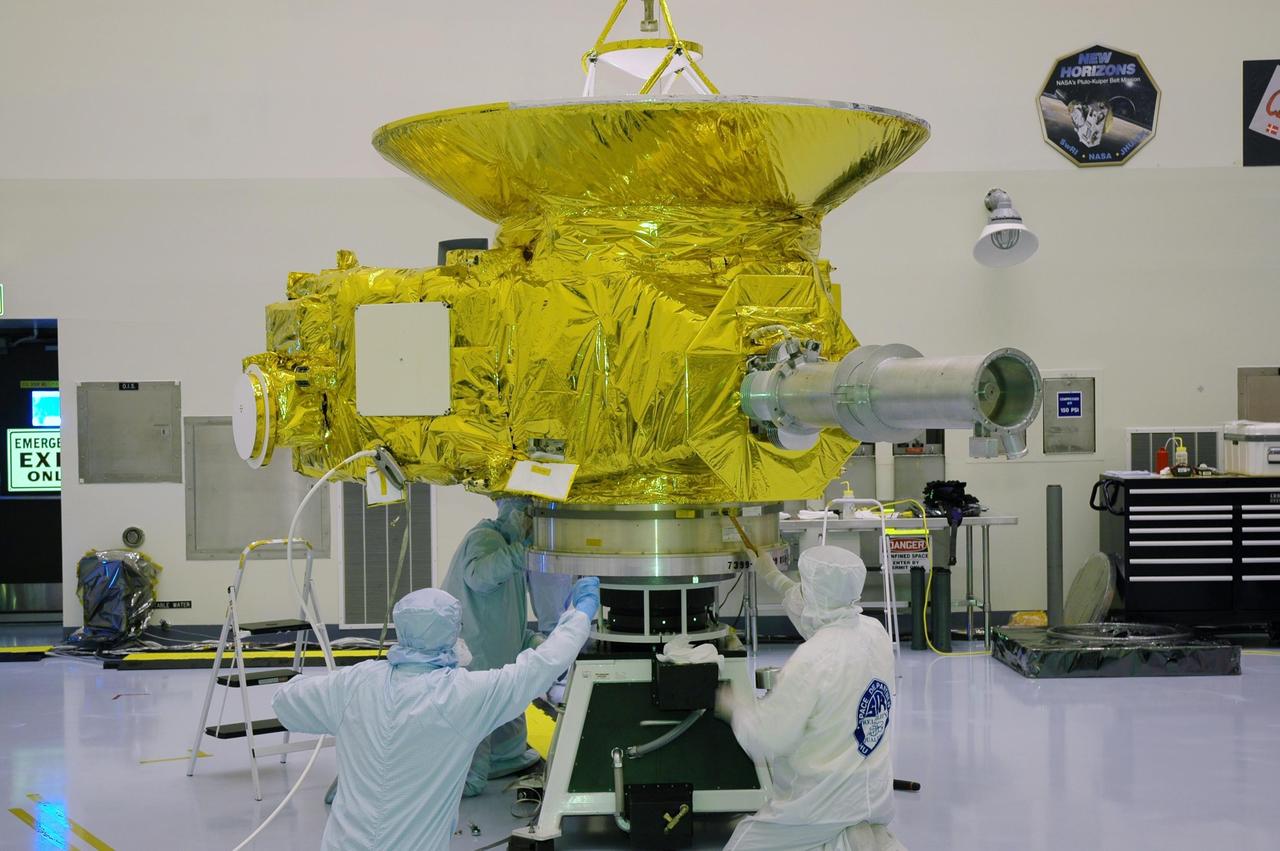

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, workers secure the New Horizons spacecraft onto a spin table. The spacecraft will undergo a spin test as part of prelaunch processing. New Horizons is expected to be launched in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon. It is expected to reach Pluto in July 2015.
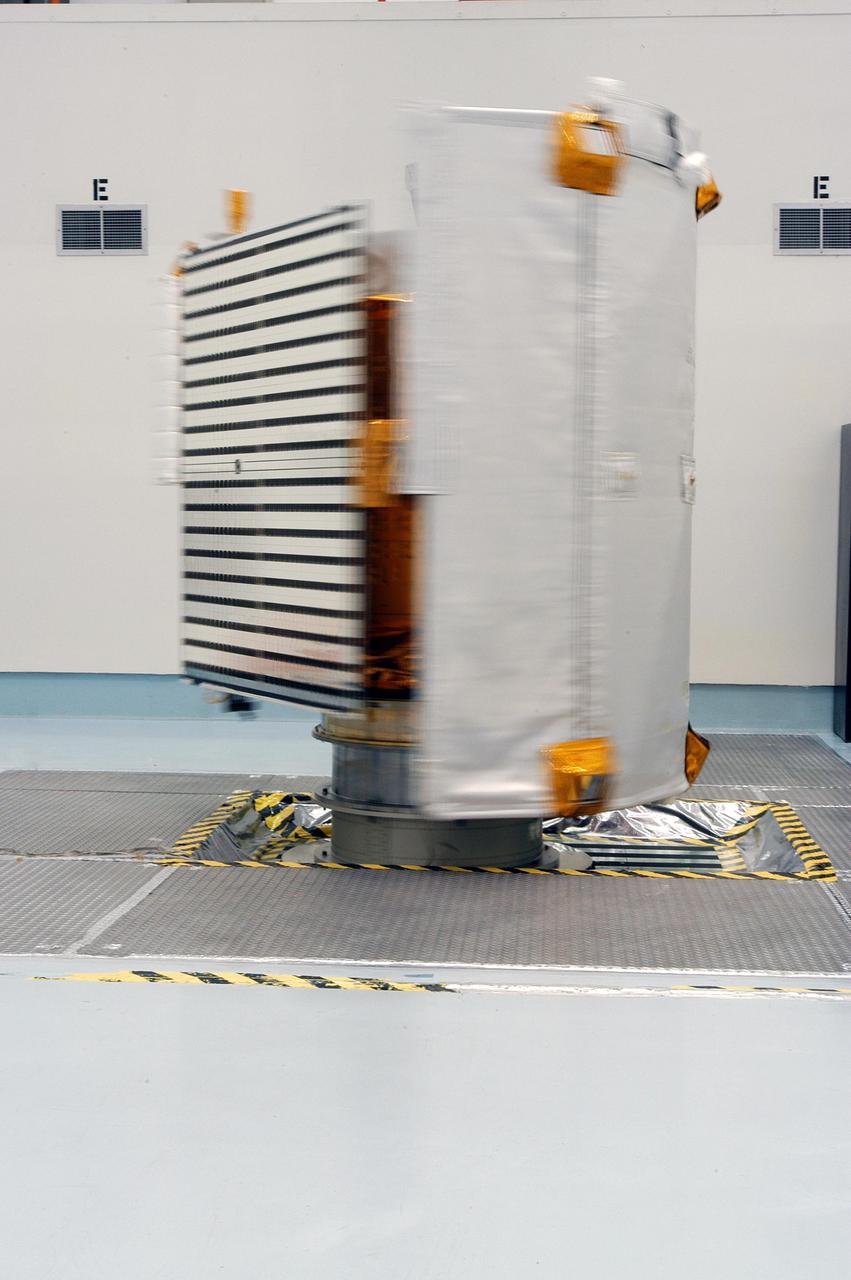
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft spins during testing on the spin table at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla. MESSENGER is scheduled to lift off Aug. 2 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It is expected to reach orbit around Mercury in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
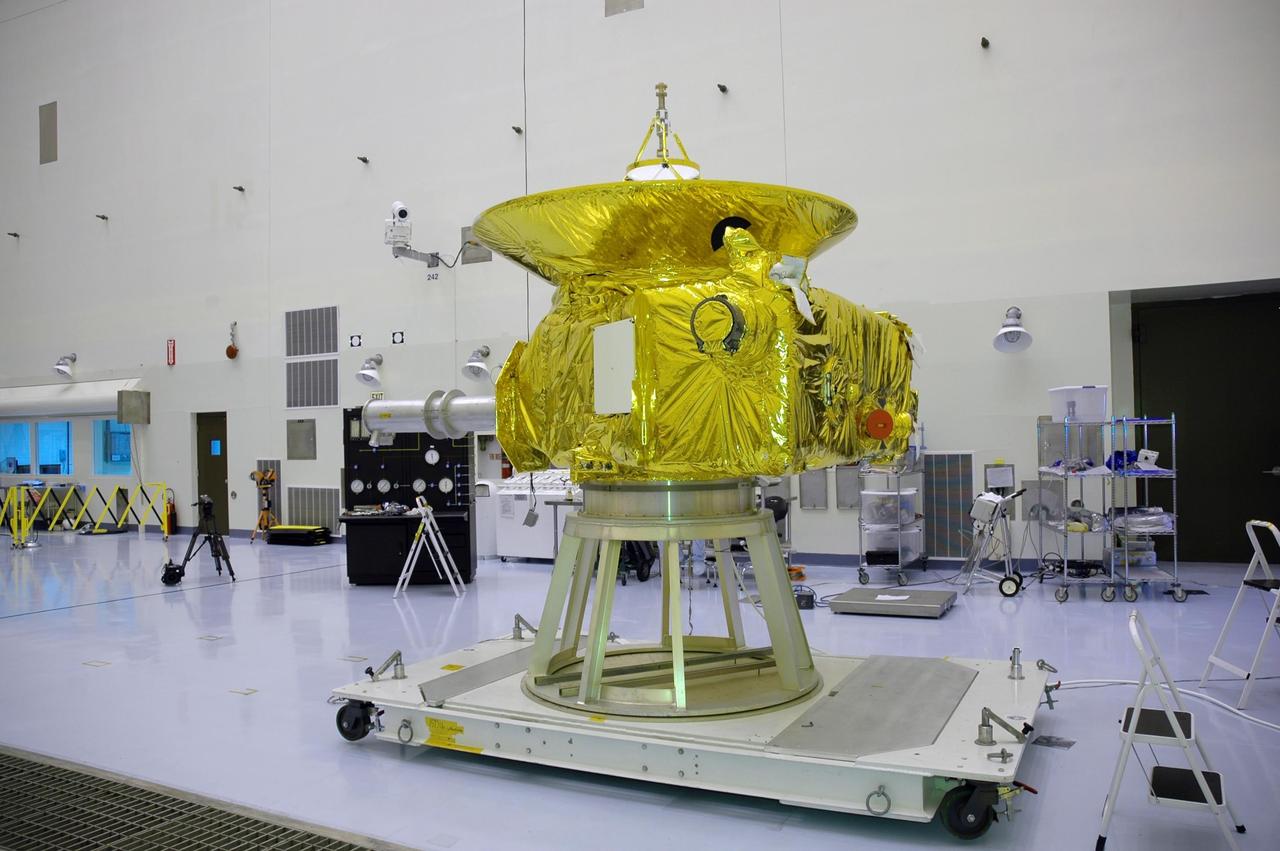

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the New Horizons spacecraft sits on a work stand prior to being moved to a spin table. The spacecraft will undergo a spin test as part of prelaunch processing. New Horizons is expected to be launched in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon. It is expected to reach Pluto in July 2015.
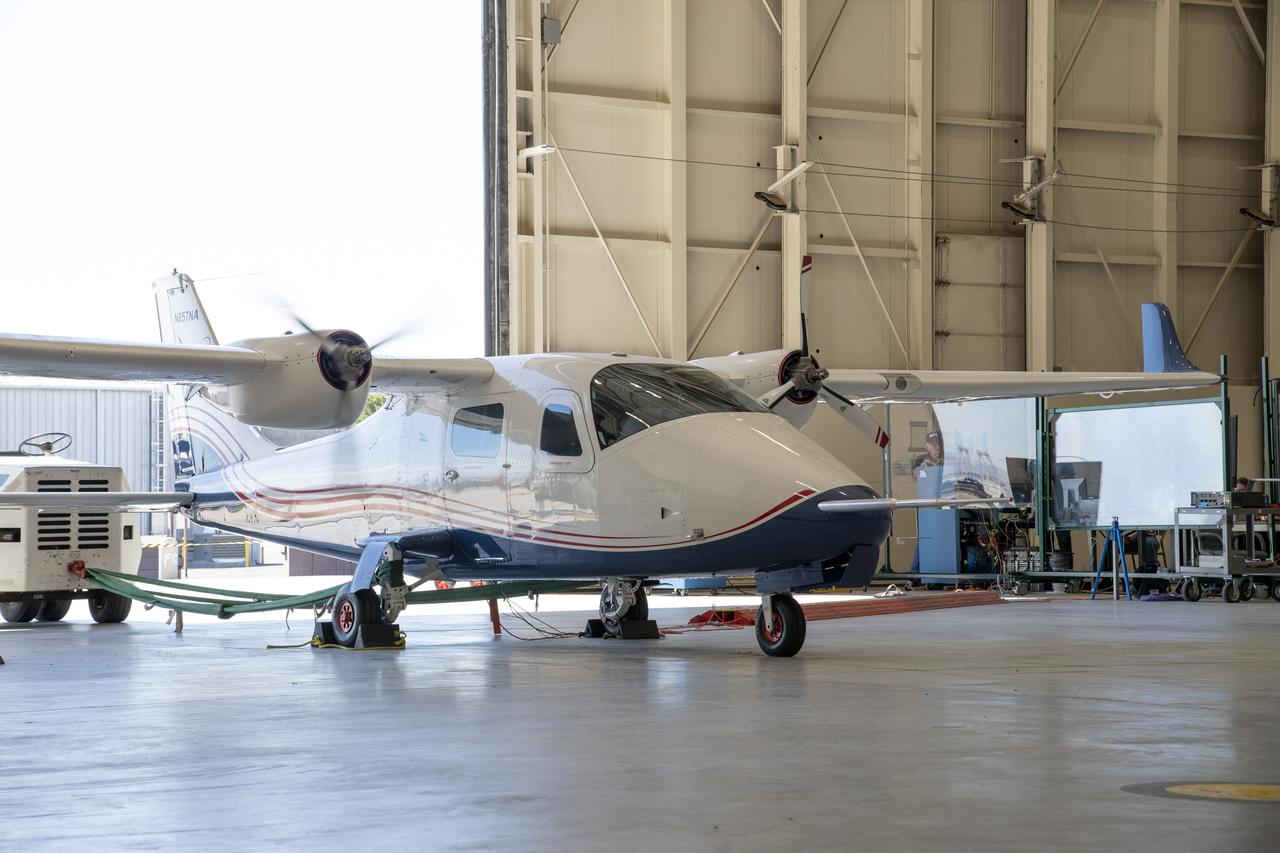

NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell aircraft tests the motors with the battery packs installed on the aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. A goal of the X-57 project is to help the Federal Aviation Administration set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.
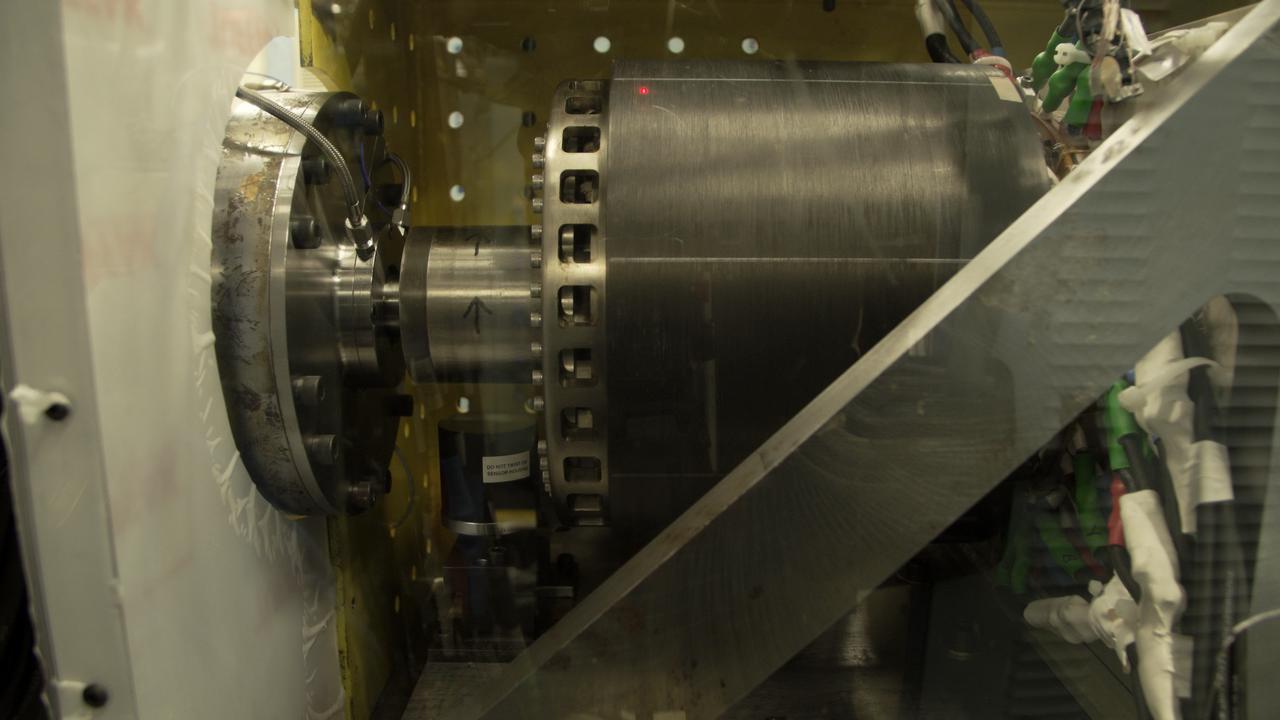
UIUC’s megawatt machine (right) was connected to a dynamometer (left) to test its effectiveness as an electric generator in a safety enclosure at a Collins Aerospace test facility in Rockford, Illinois. This unusual design has its rotating parts on the outside, so that both the cylinder on the right and the cylinder with arrows spin during operation.
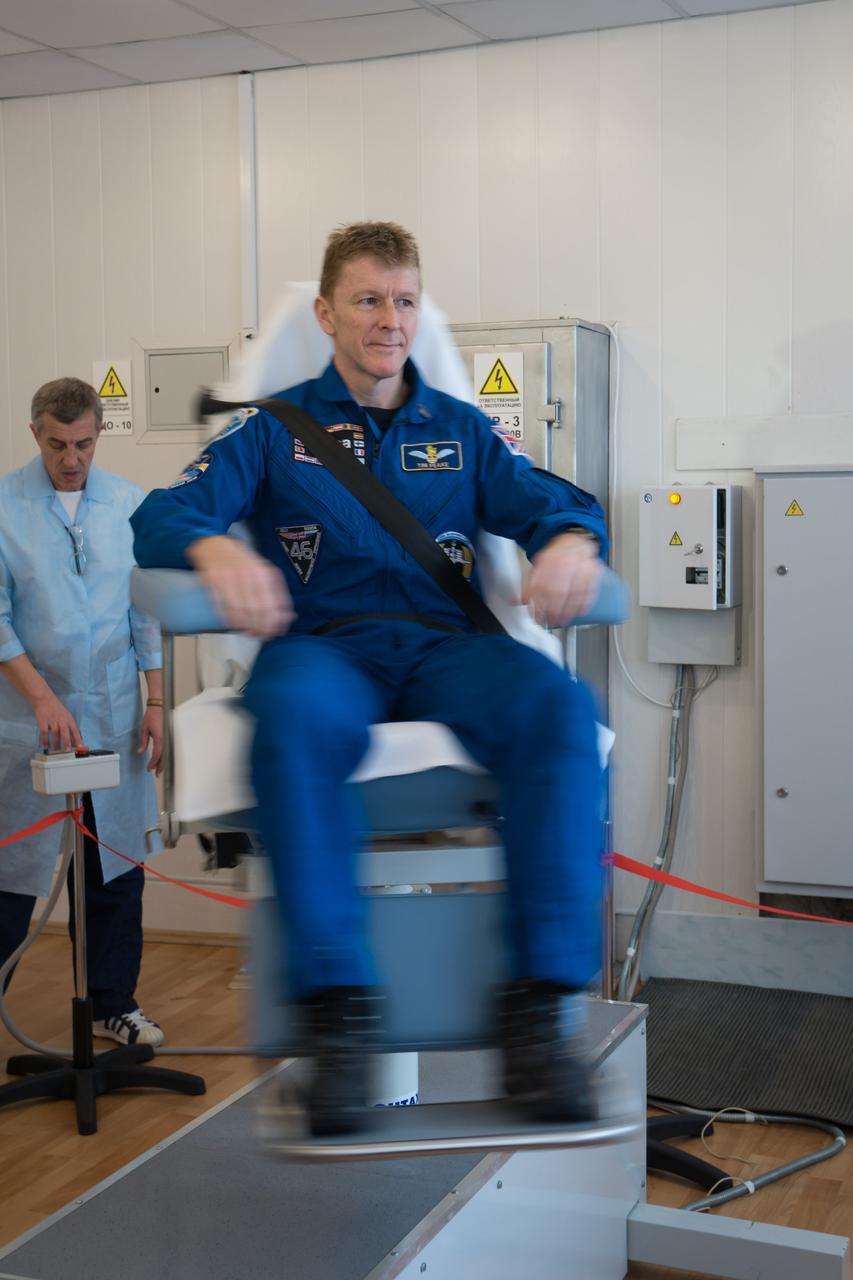

At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 46-47 crewmember Tim Peake of the European Space Agency took a turn in a spinning chair to test his vestibular system Dec. 9 as part of his pre-launch training. Peake, Yuri Malenchenko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Tim Kopra of NASA will launch Dec. 15 on their Soyuz TMA-19M spacecraft for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Victor Zelentsov

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This logo for the Gravity Probe B mission portrays the theory of curved spacetime and "frame-dragging," developed by Einstein and other scientists, that the mission will test. The Gravity Probe B will launch a payload of four gyroscopes into low-Earth polar orbit. Once in orbit, for 18 months each gyroscope’s spin axis will be monitored as it travels through local spacetime, observing and measuring the effects. The experiment was developed by Stanford University, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center and Lockheed Martin.
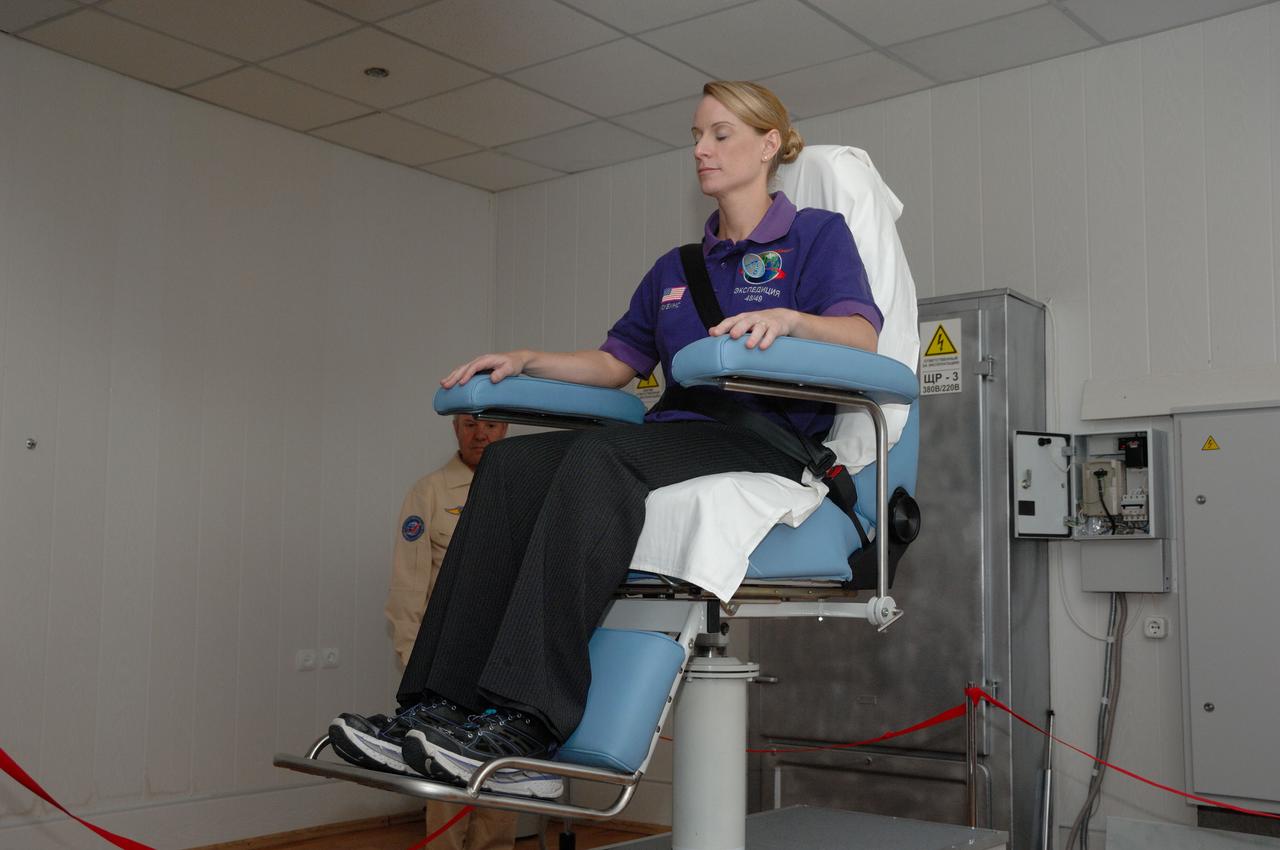
At the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 48-49 crewmember Kate Rubins of NASA takes a spin in a rotating chair to test her vestibular system June 30 as part of pre-launch activities. Rubins, Anatoly Ivanishin of Roscosmos and Takuya Onishi of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency will launch July 7, Baikonur time, on the Soyuz MS-01 spacecraft for a planned four-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Alexander Vysotsky
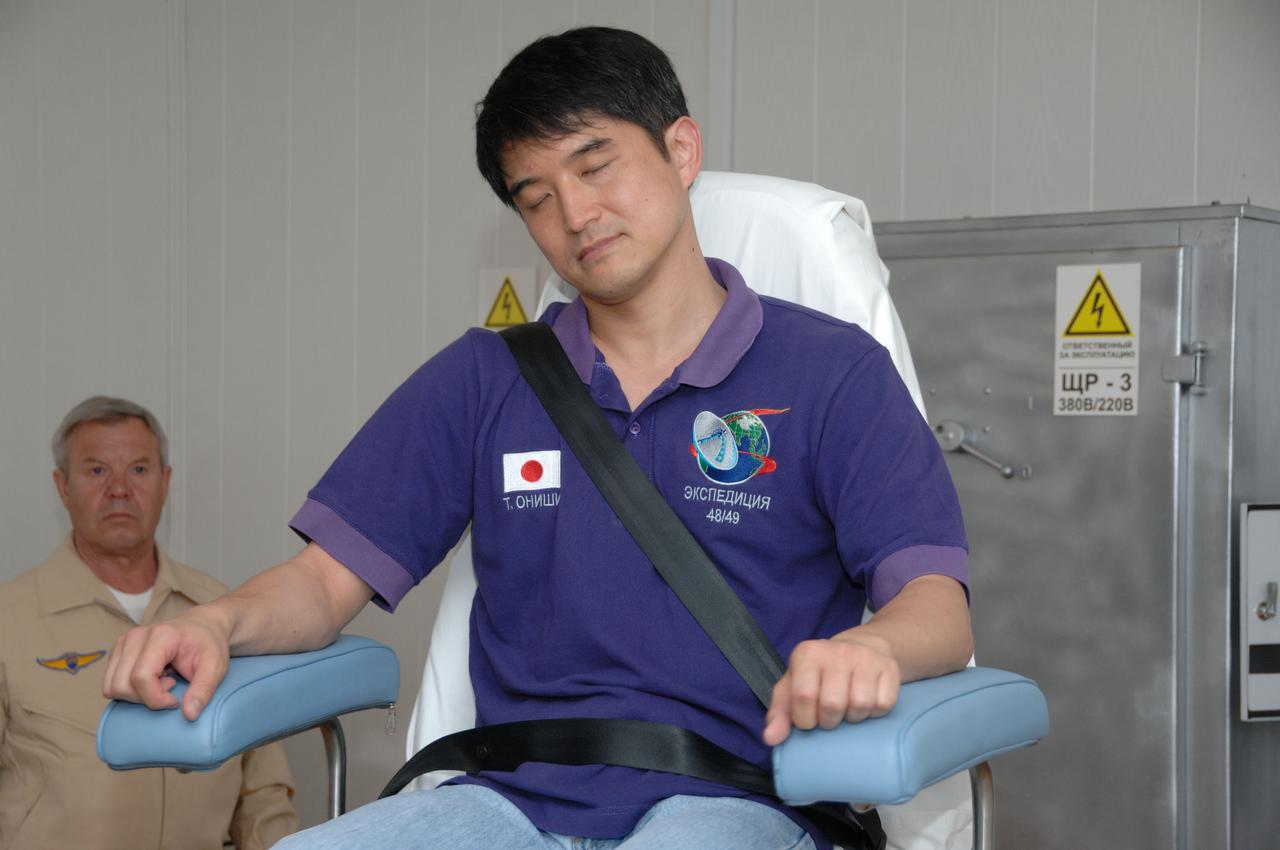
At the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 48-49 crewmember Takuya Onishi of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency takes a spin in a rotating chair to test his vestibular system June 30 as part of pre-launch activities. Onishi, Kate Rubins of NASA and Anatoly Ivanishin of Roscosmos will launch July 7, Baikonur time, on the Soyuz MS-01 spacecraft for a planned four-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Alexander Vysotsky
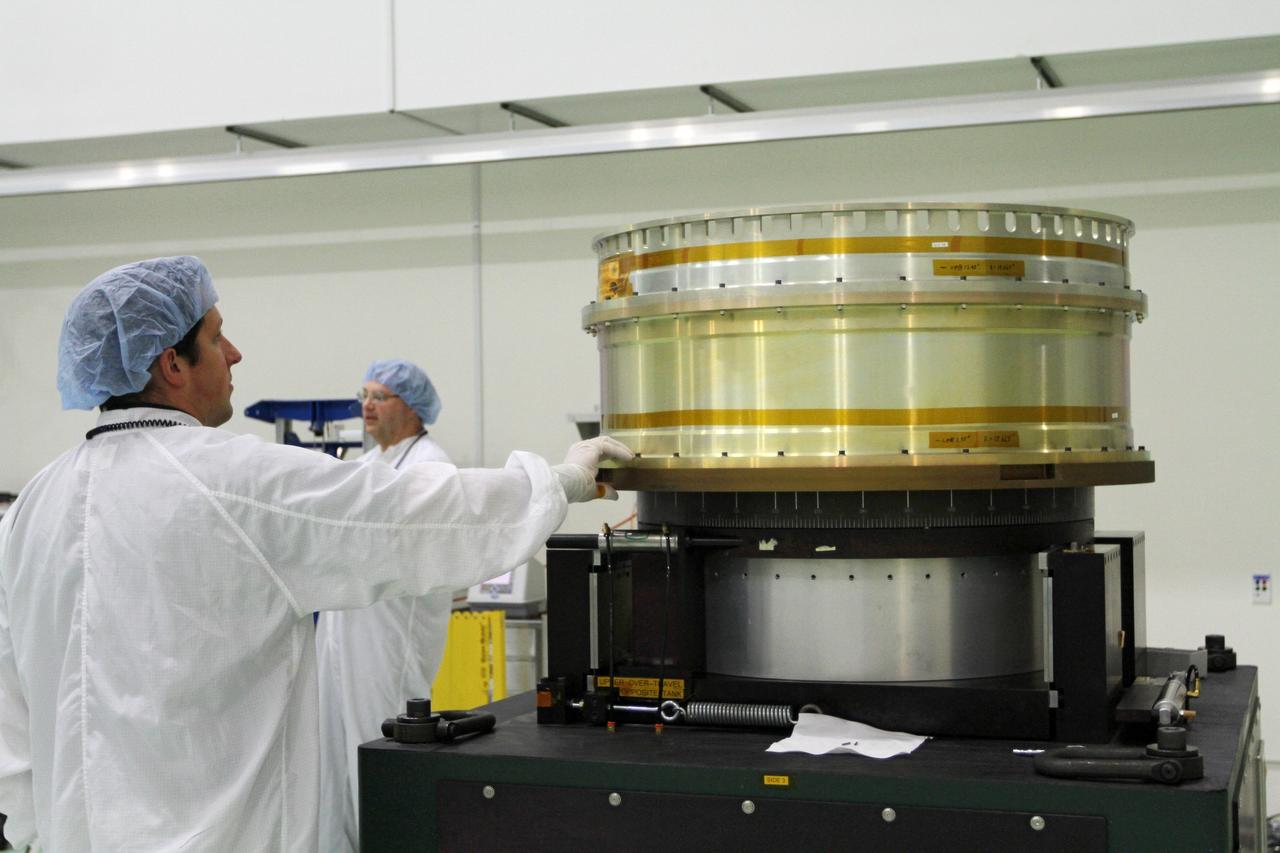

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare the test stand for Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
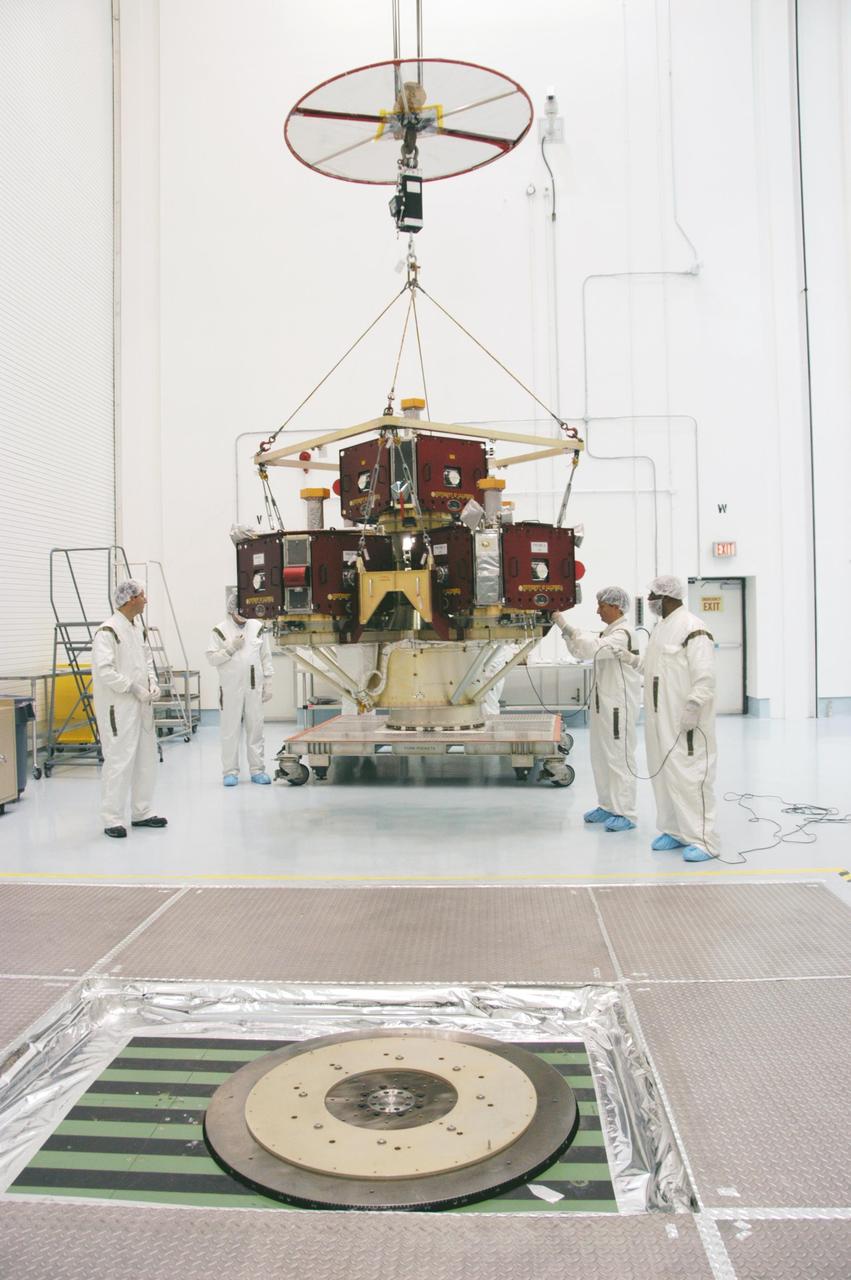

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers get ready to move the integrated THEMIS spacecraft to the spin table in the foreground. There it will undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
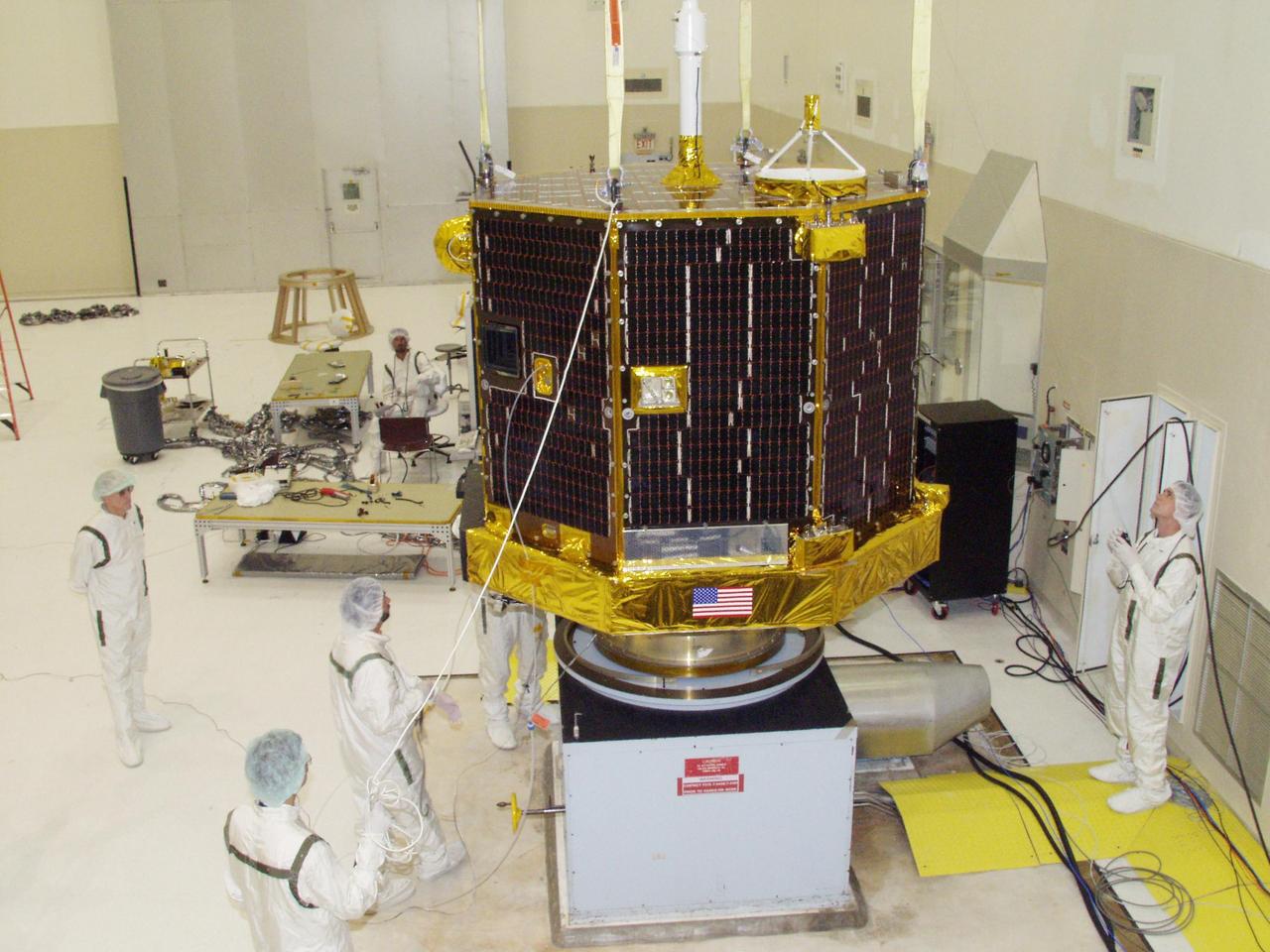

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Comet Nucleus Tour (CONTOUR) spacecraft settles on the spin table in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 for its spin test. CONTOUR will provide the first detailed look into the heart of a comet -- the nucleus. Flying as close as 60 miles (100 kilometers) to at least two comets, the spacecraft will take the sharpest pictures yet of a nucleus while analyzing the gas and dust that surround these rocky, icy building blocks of the solar system. Launch of CONTOUR aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for July 1 from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
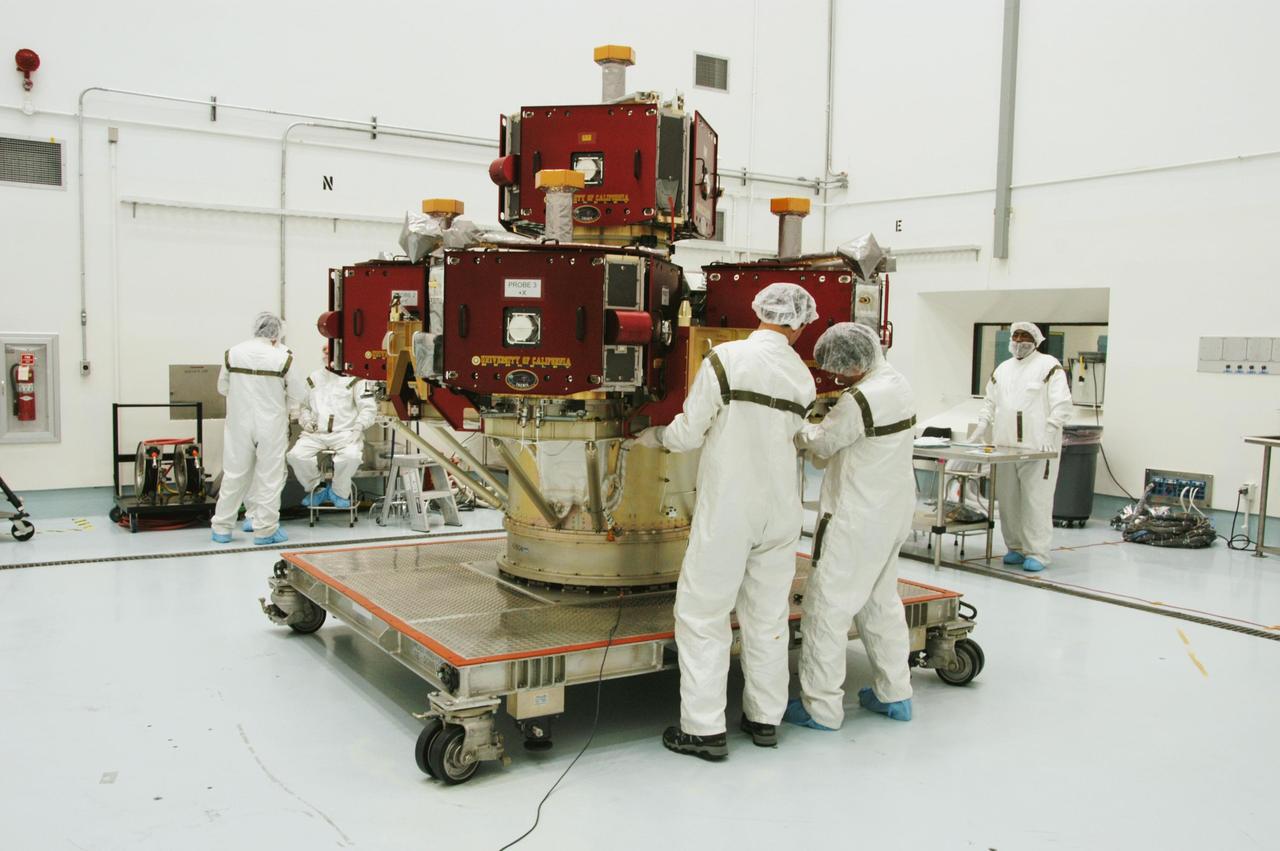

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers prepare the integrated THEMIS spacecraft to be moved to a spin table for spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
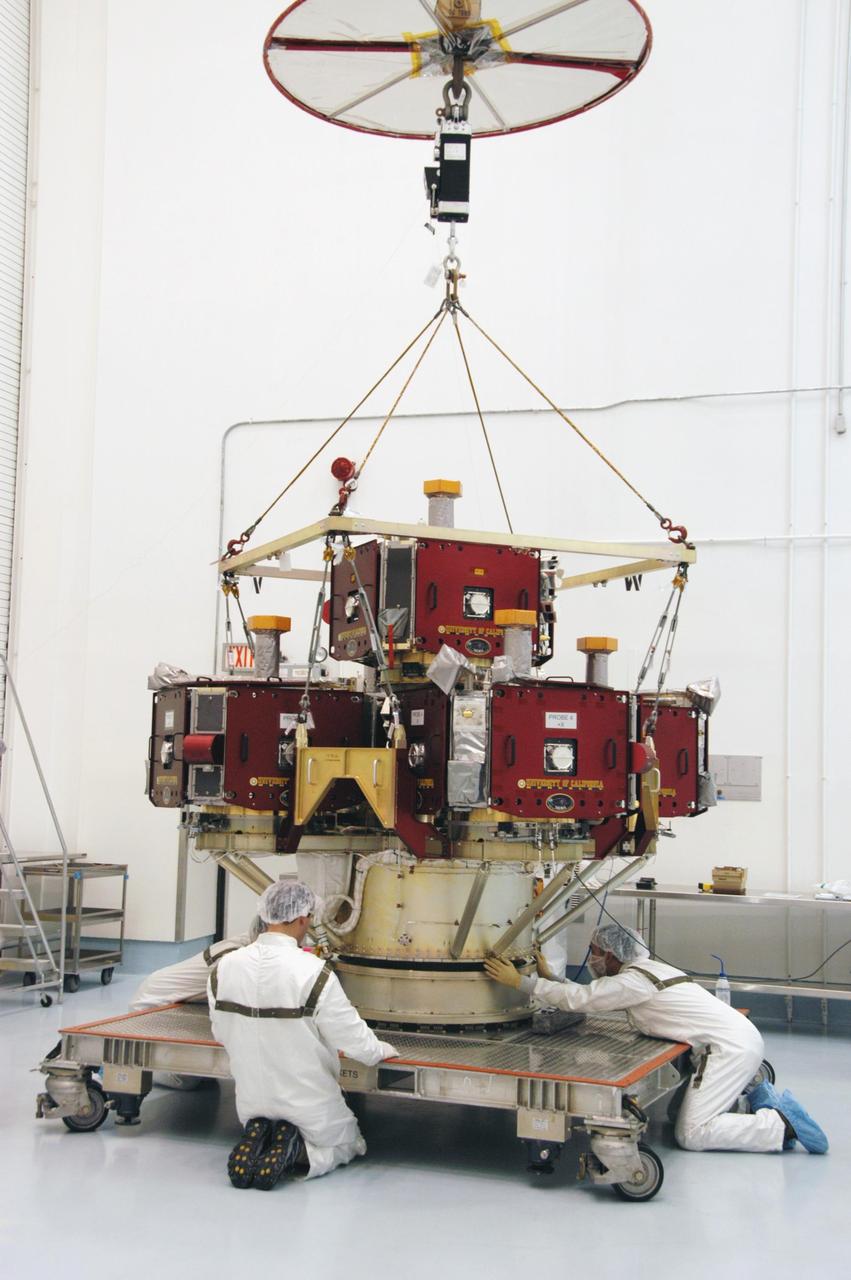

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers attach an overhead crane to the integrated THEMIS spacecraft. The carrier is being moved to a spin table for spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
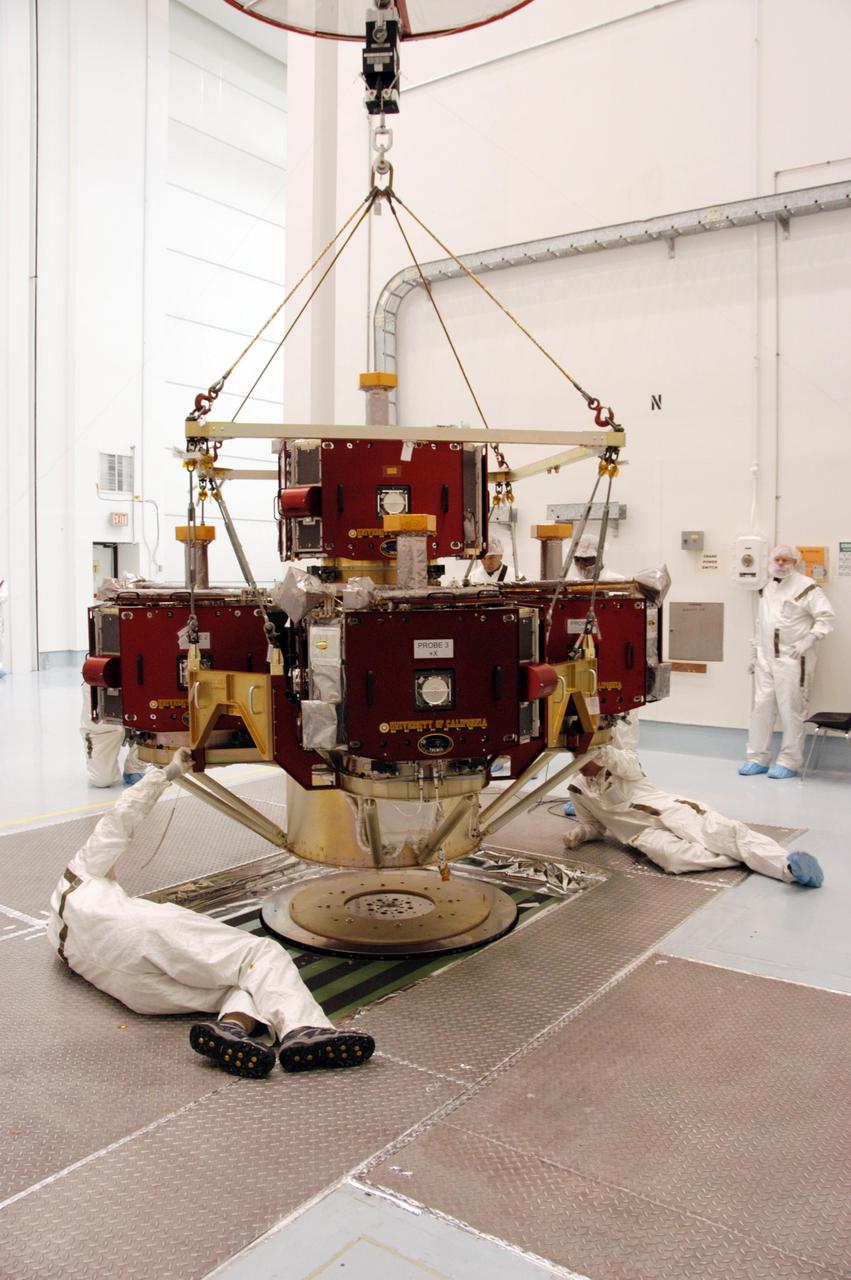

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers guide the integrated THEMIS spacecraft onto the spin table in the foreground. There it will undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
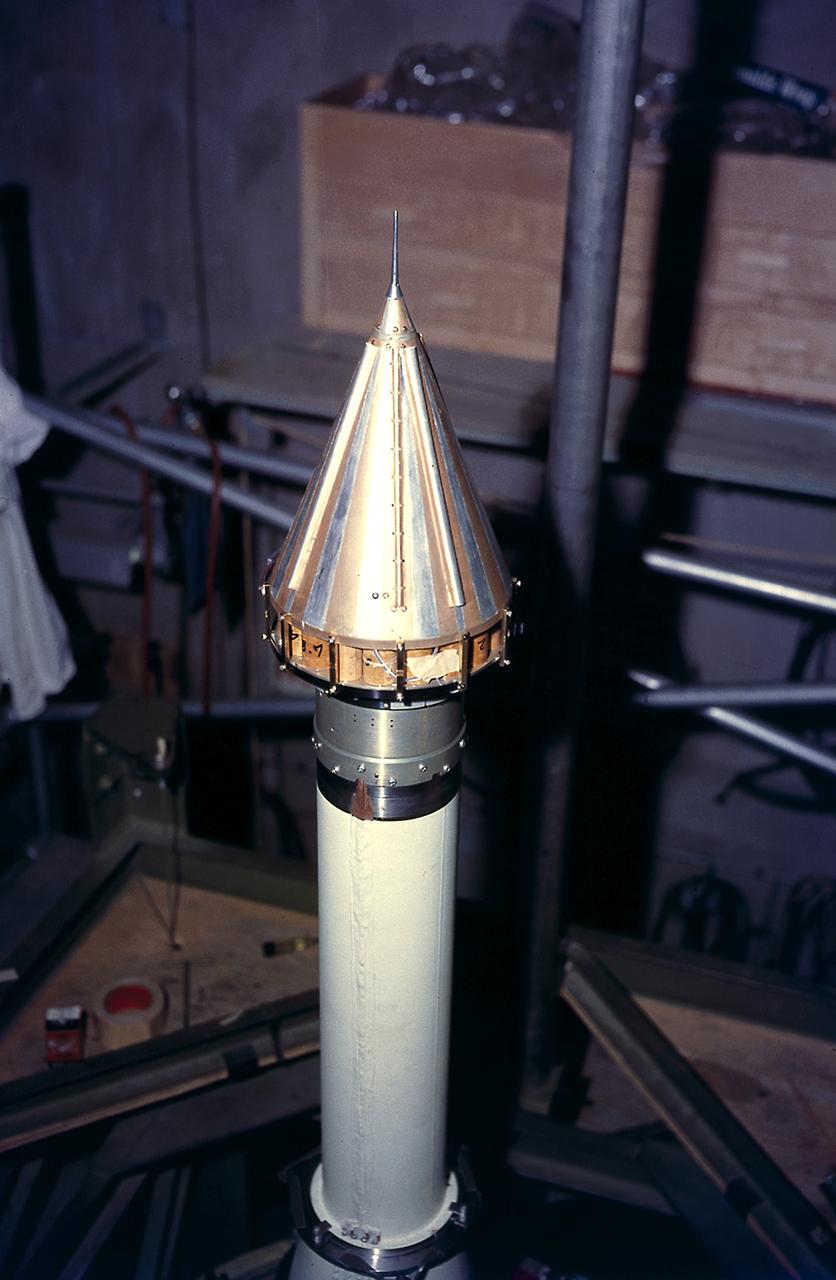
Installing Pioneer IV, payload for AM-14 (Juno II) onto the fourth stage on the cluster before a spin test, February 16, 1959. The Pioneer IV, lunar and planetary exploration satellite, was the first U.S. satellite to orbit the Sun.

jsc2021e007964 (9/30/2020) --- Post-integration solar array characterization testing. The Ionosphere Thermosphere Scanning Photometer for Ion-Neutral Studies (IT-SPINS) produces two-dimensional (2D) tomographic imaging of Earth’s ionosphere in order to increase fundamental understanding of its structure. Image courtesy of Montana State University.

NASA's Ingenuity helicopter does a slow spin test of its blades on April 8, 2021, the 48th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This image was captured by the Mastcam-Z on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie avaiable at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24582
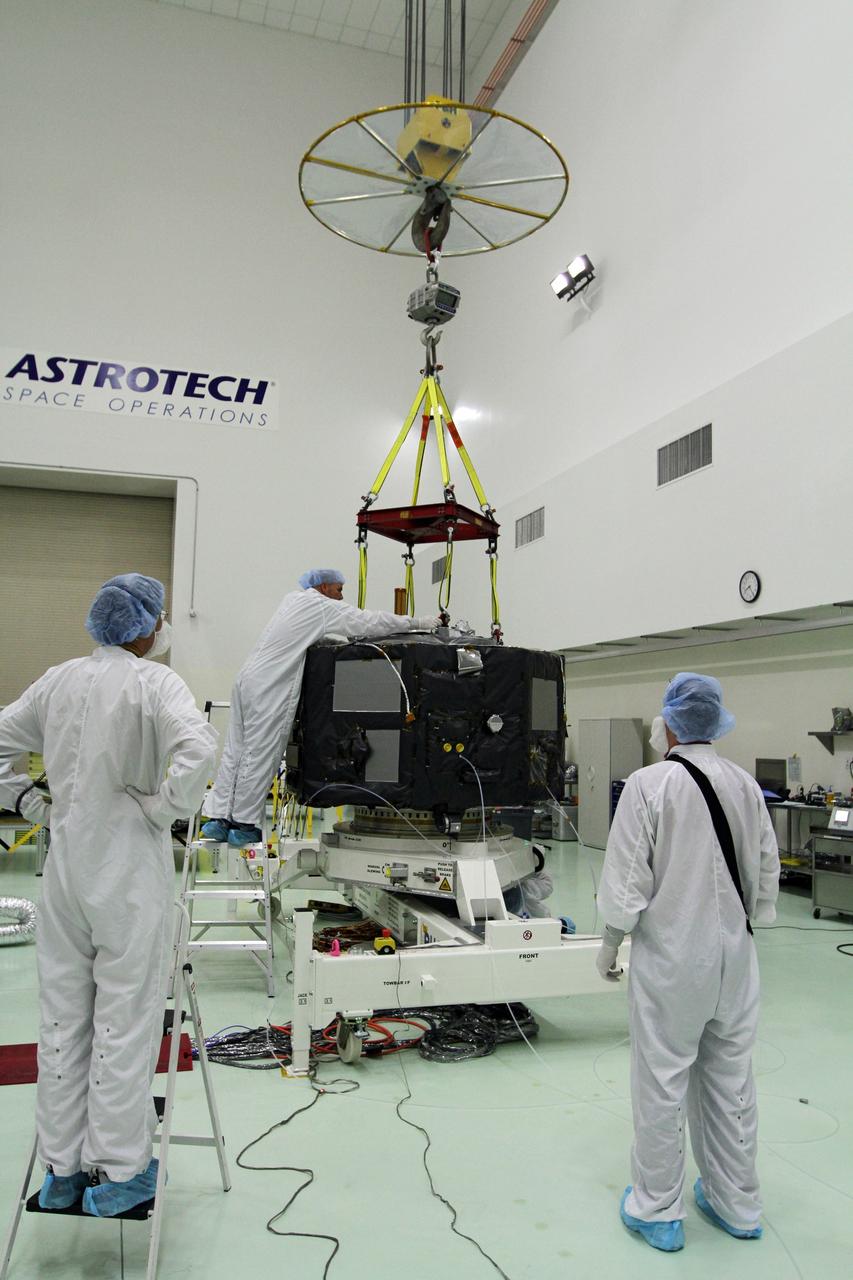

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
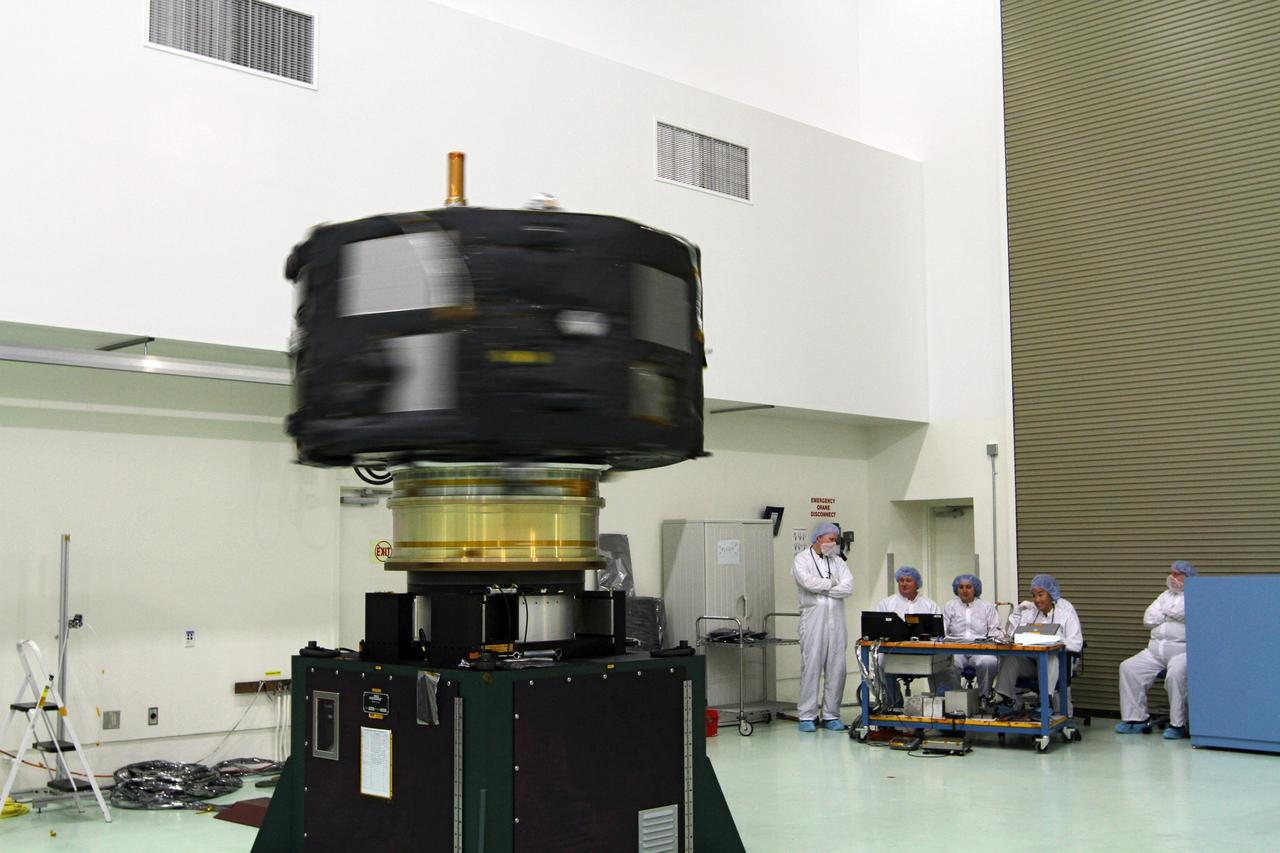

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A undergoes a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
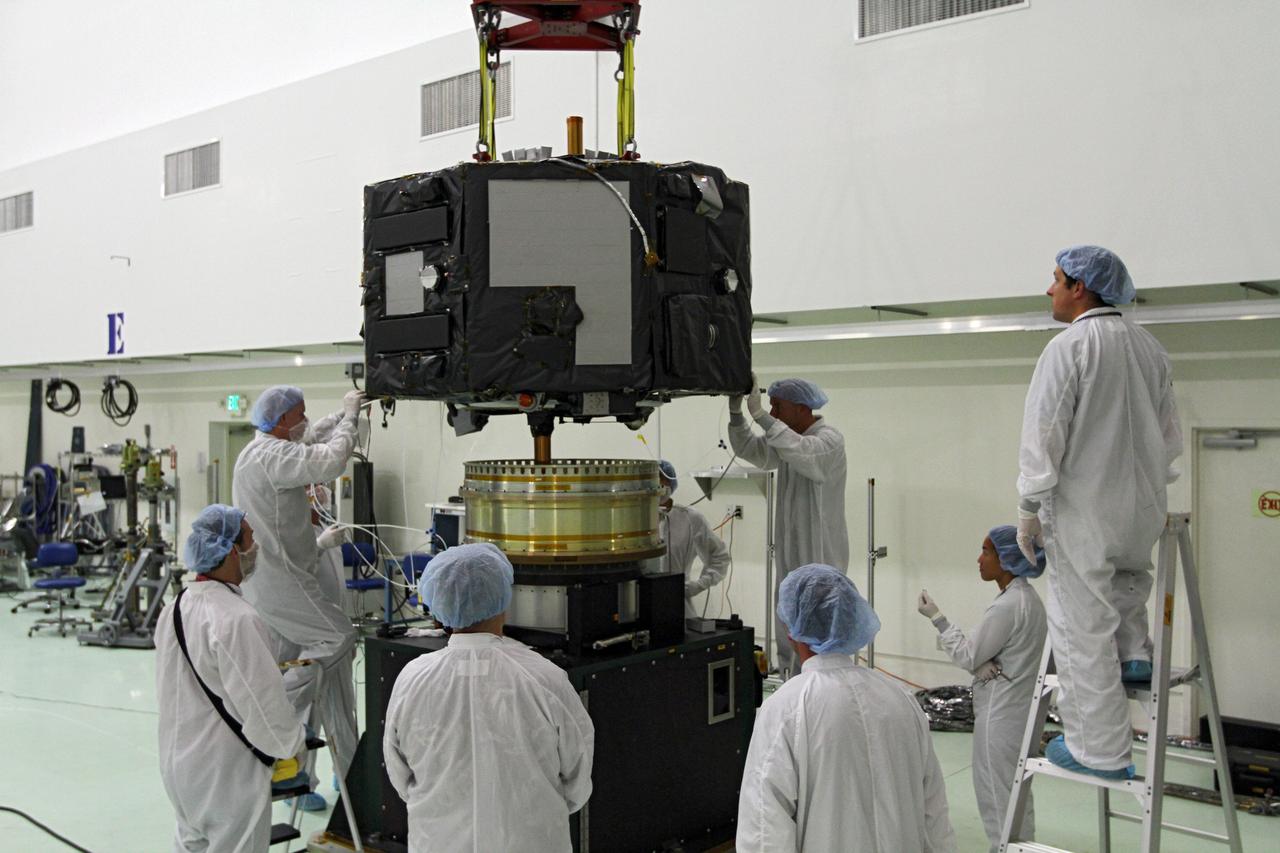

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to place Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A on a spin test stand. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
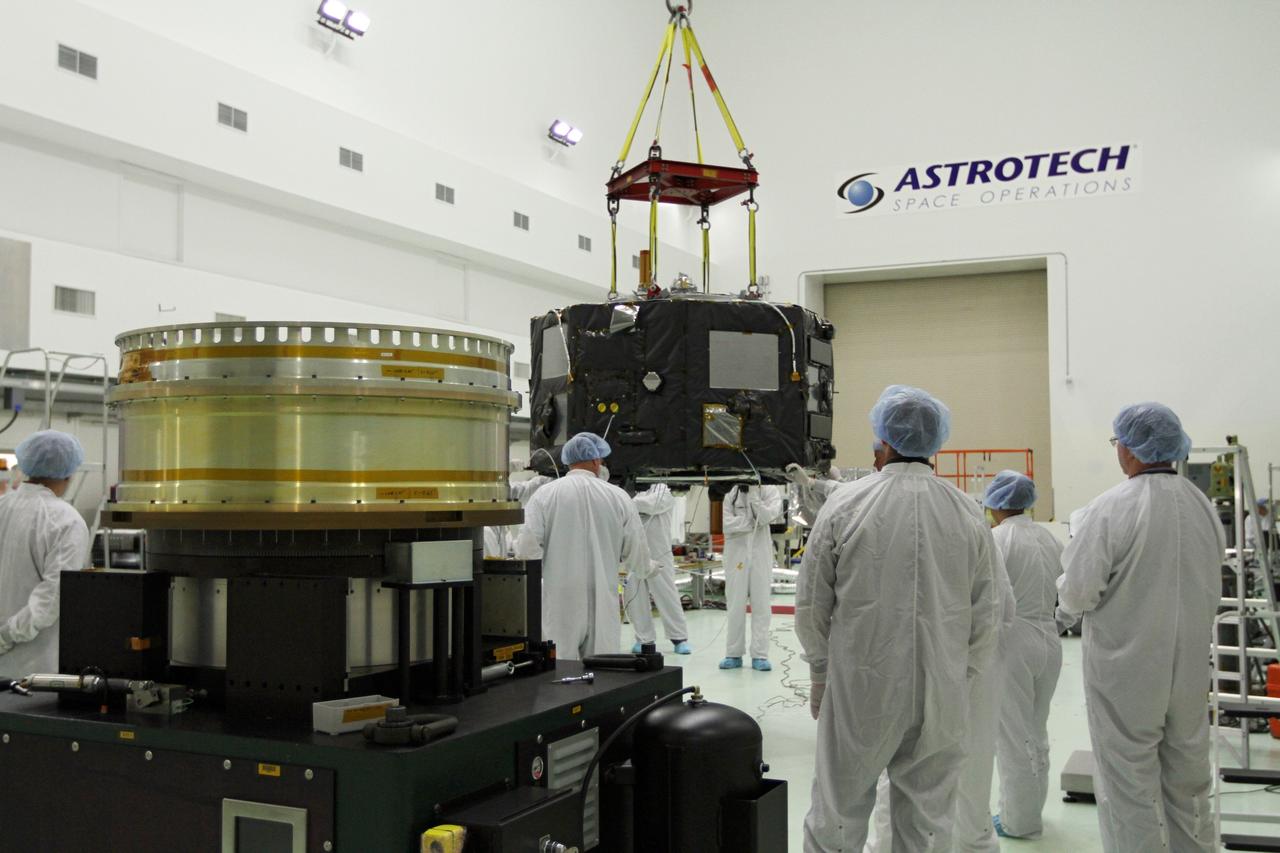

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
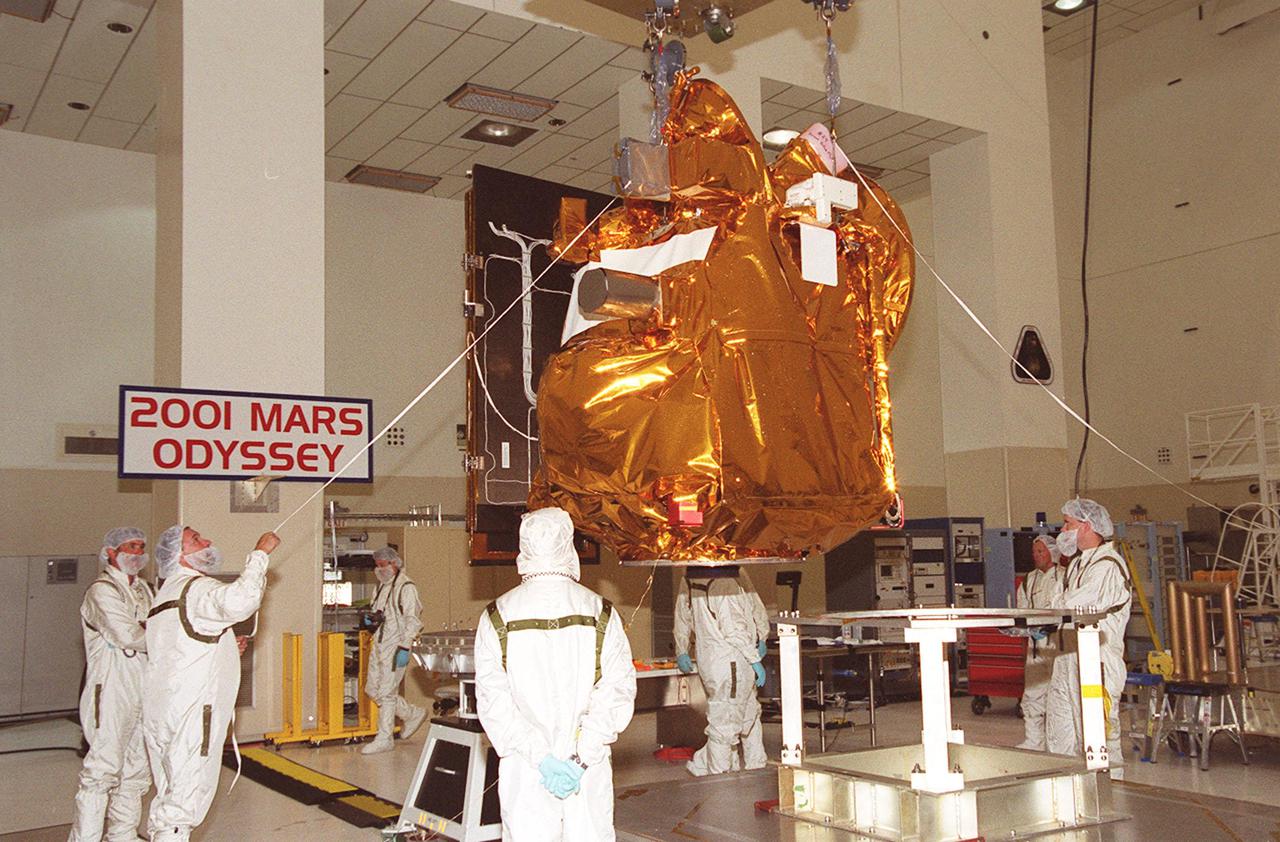

With workers keeping watch, the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, suspended by an overhead crane in the Space Assembly and Encapsulation Building 2, moves toward the spin table at left where it will be tested. The orbiter is being transferred to a spin table for testing. The orbiter carries three science instruments THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE) that will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface, the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface, and characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
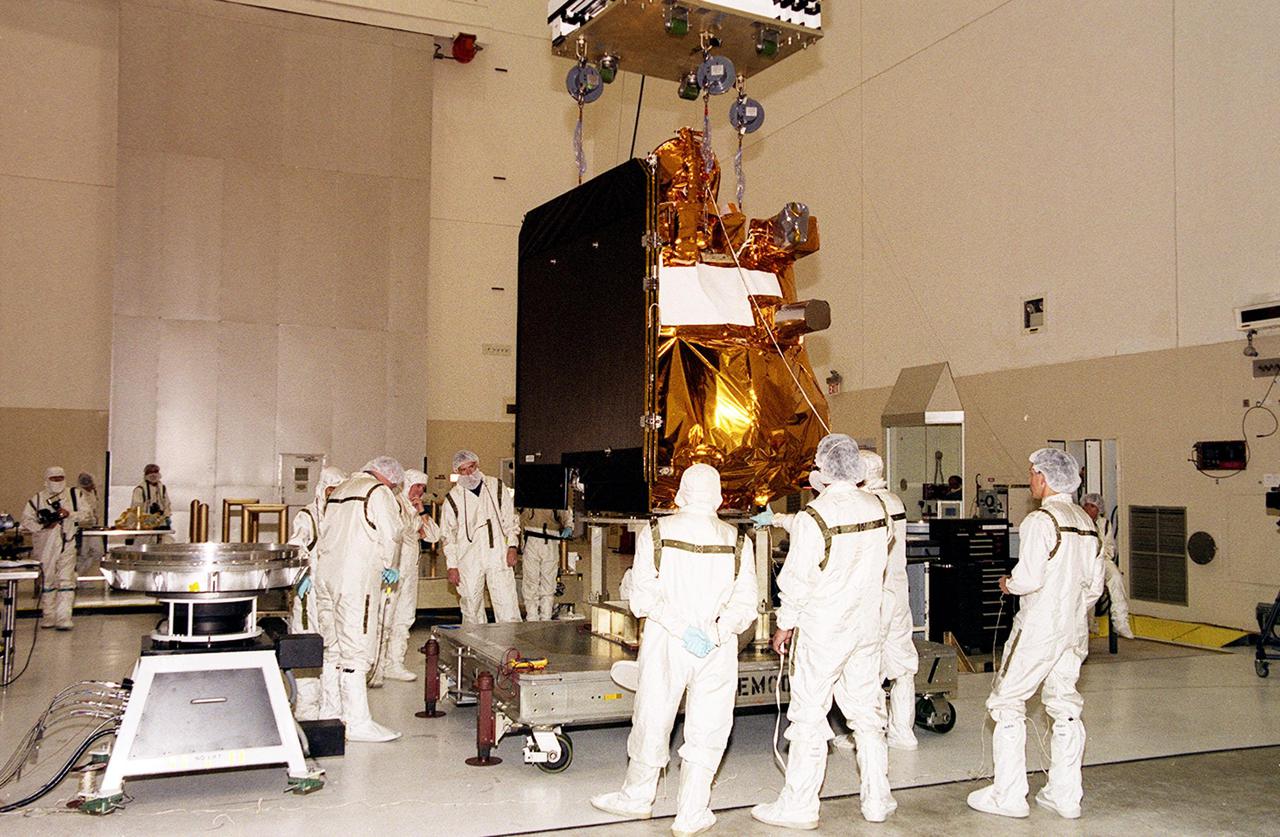

The 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, suspended by an overhead crane in the Space Assembly and Encapsulation Building 2, moves toward the spin table at left where it will be tested. The orbiter is being transferred to a spin table for testing. The orbiter carries three science instruments THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE) that will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface, the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface, and characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
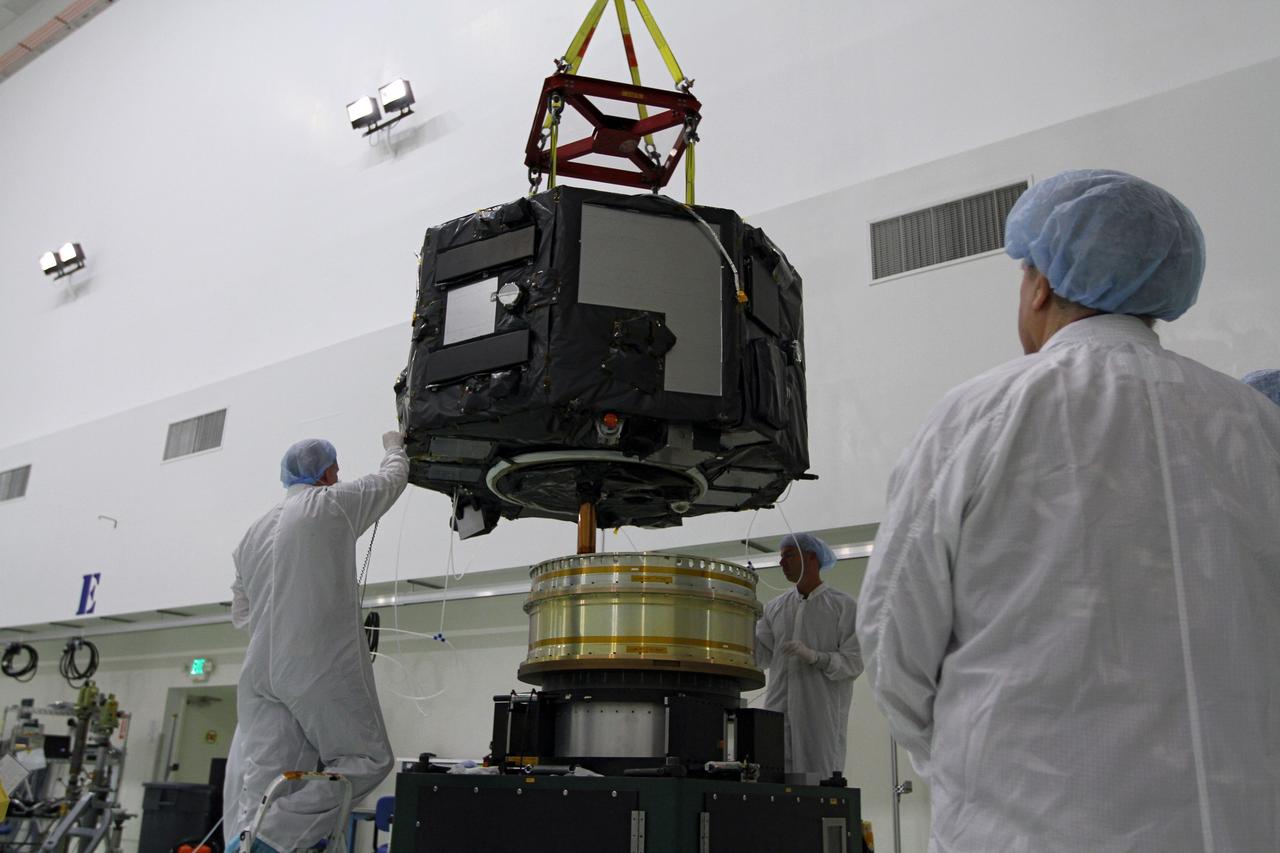

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to place Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A on a spin test stand. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
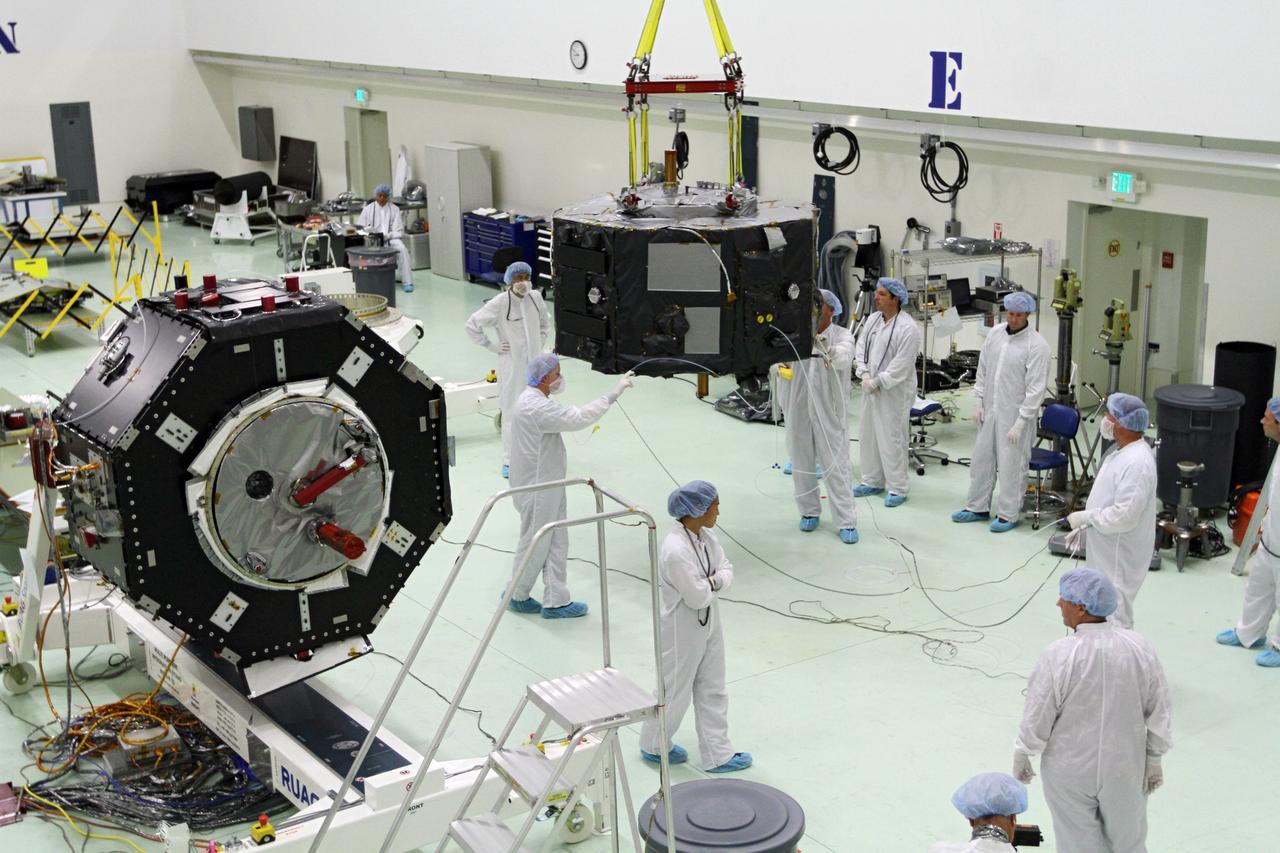

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to place Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A on a spin test stand. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
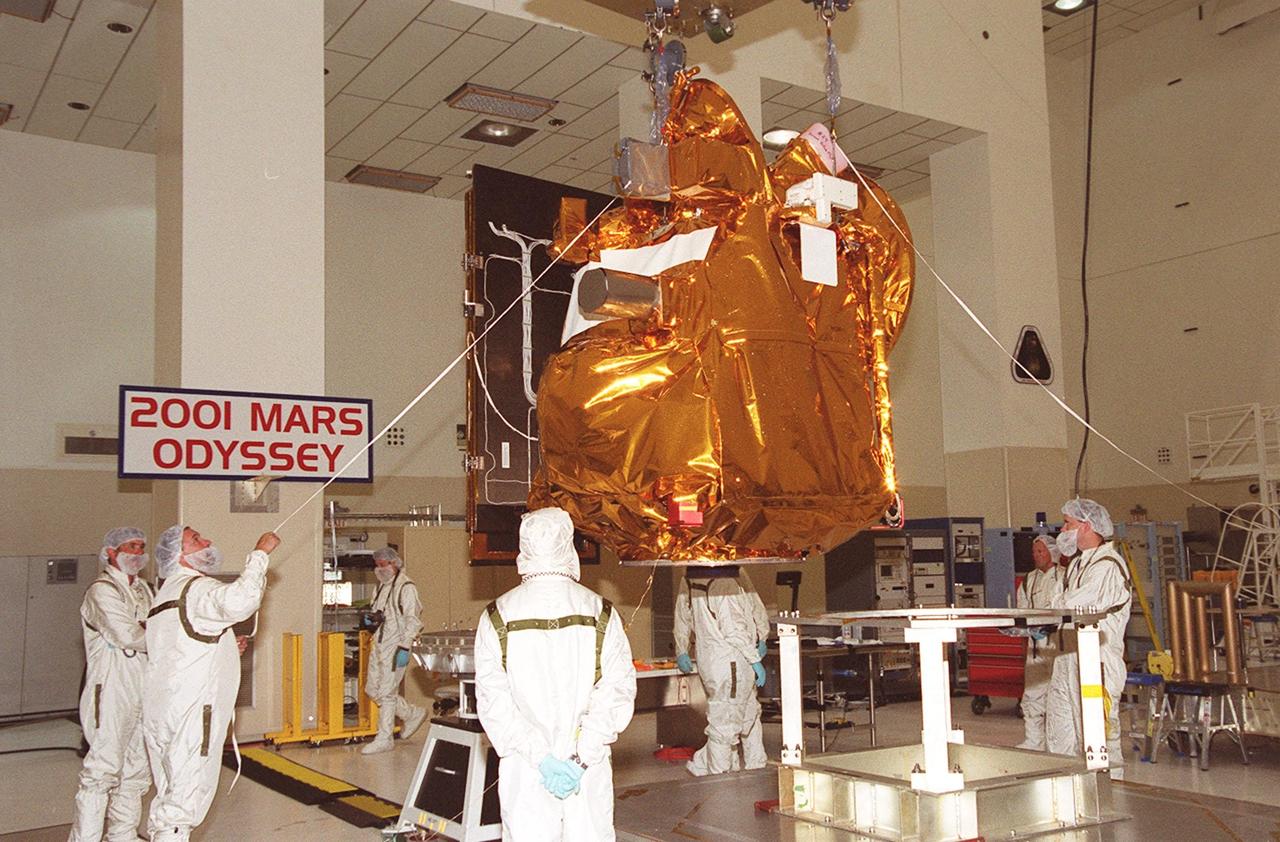

With workers keeping watch, the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, suspended by an overhead crane in the Space Assembly and Encapsulation Building 2, moves toward the spin table at left where it will be tested. The orbiter is being transferred to a spin table for testing. The orbiter carries three science instruments THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE) that will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface, the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface, and characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
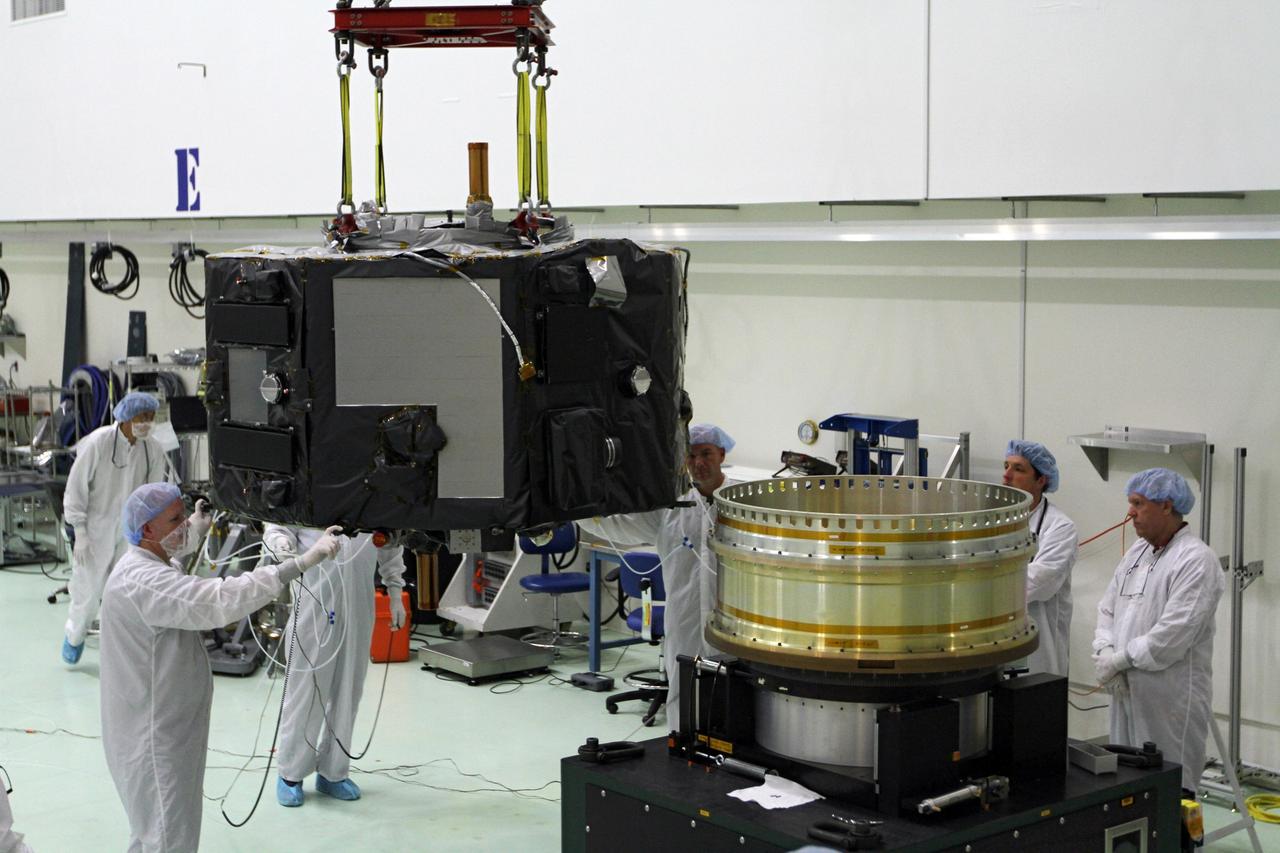

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
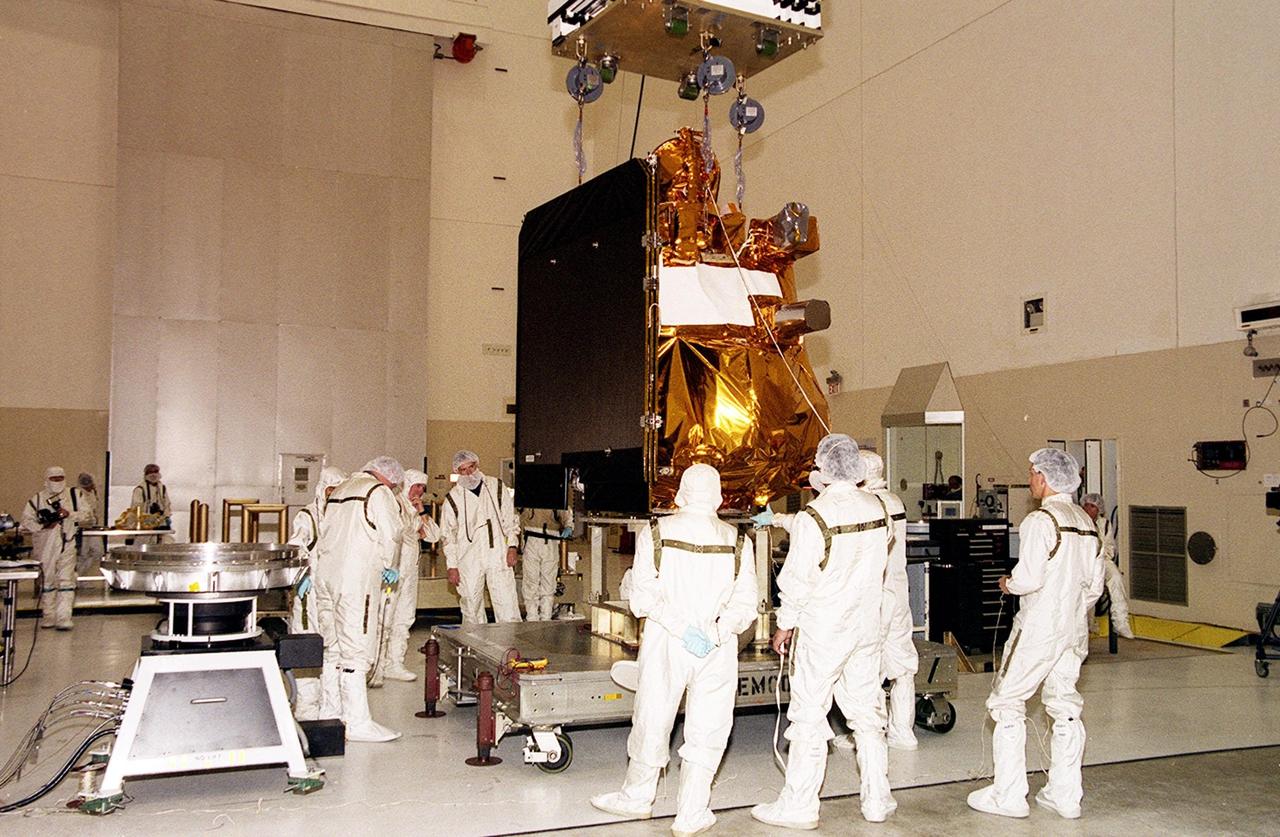

The 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, suspended by an overhead crane in the Space Assembly and Encapsulation Building 2, moves toward the spin table at left where it will be tested. The orbiter is being transferred to a spin table for testing. The orbiter carries three science instruments THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE) that will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface, the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface, and characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
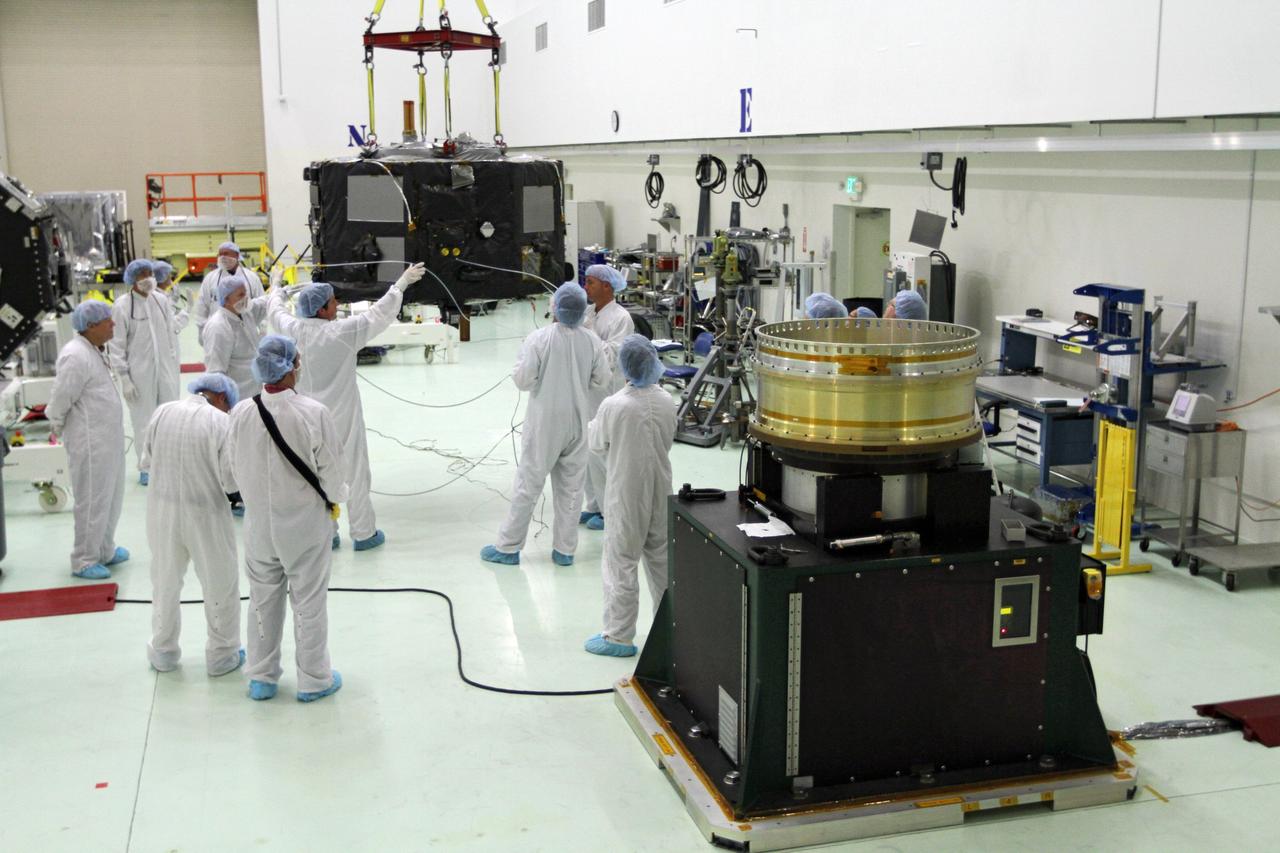

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
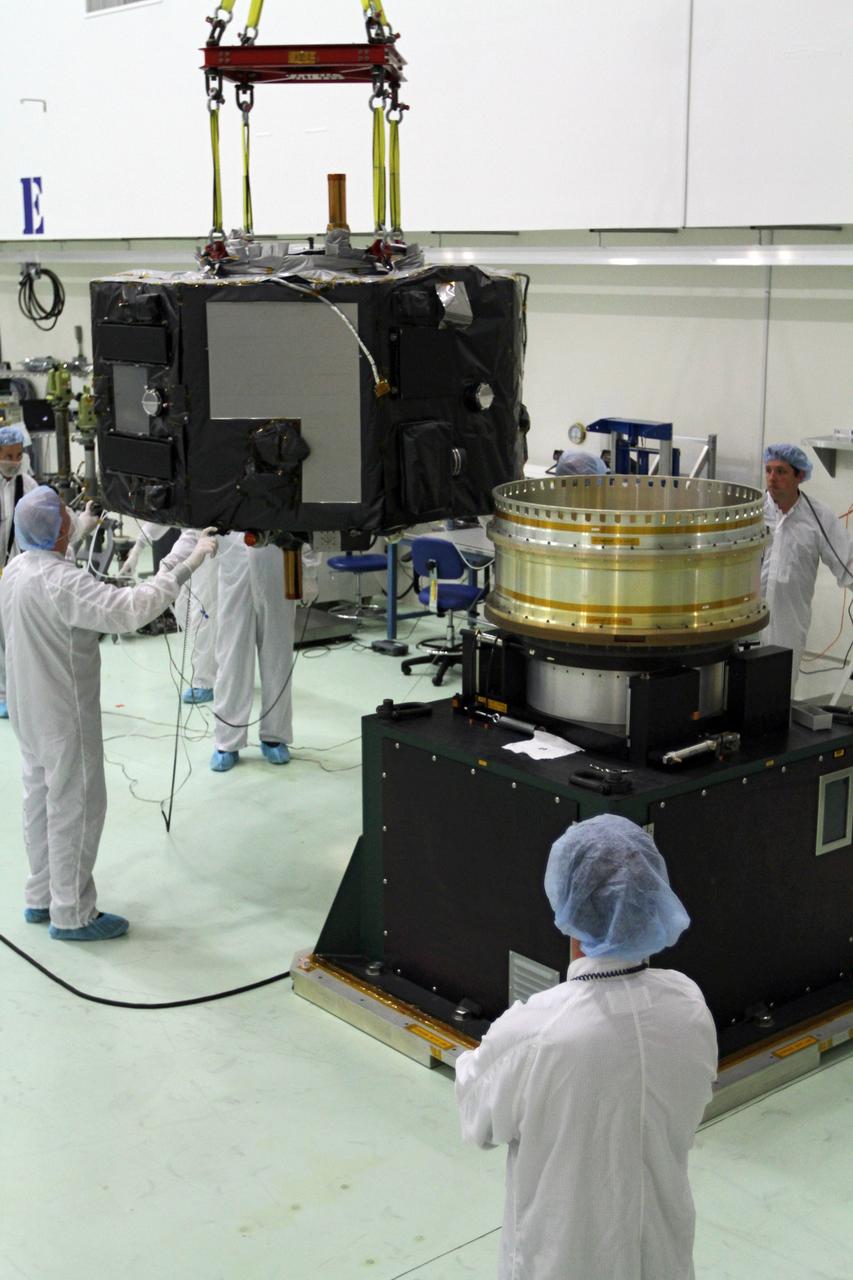

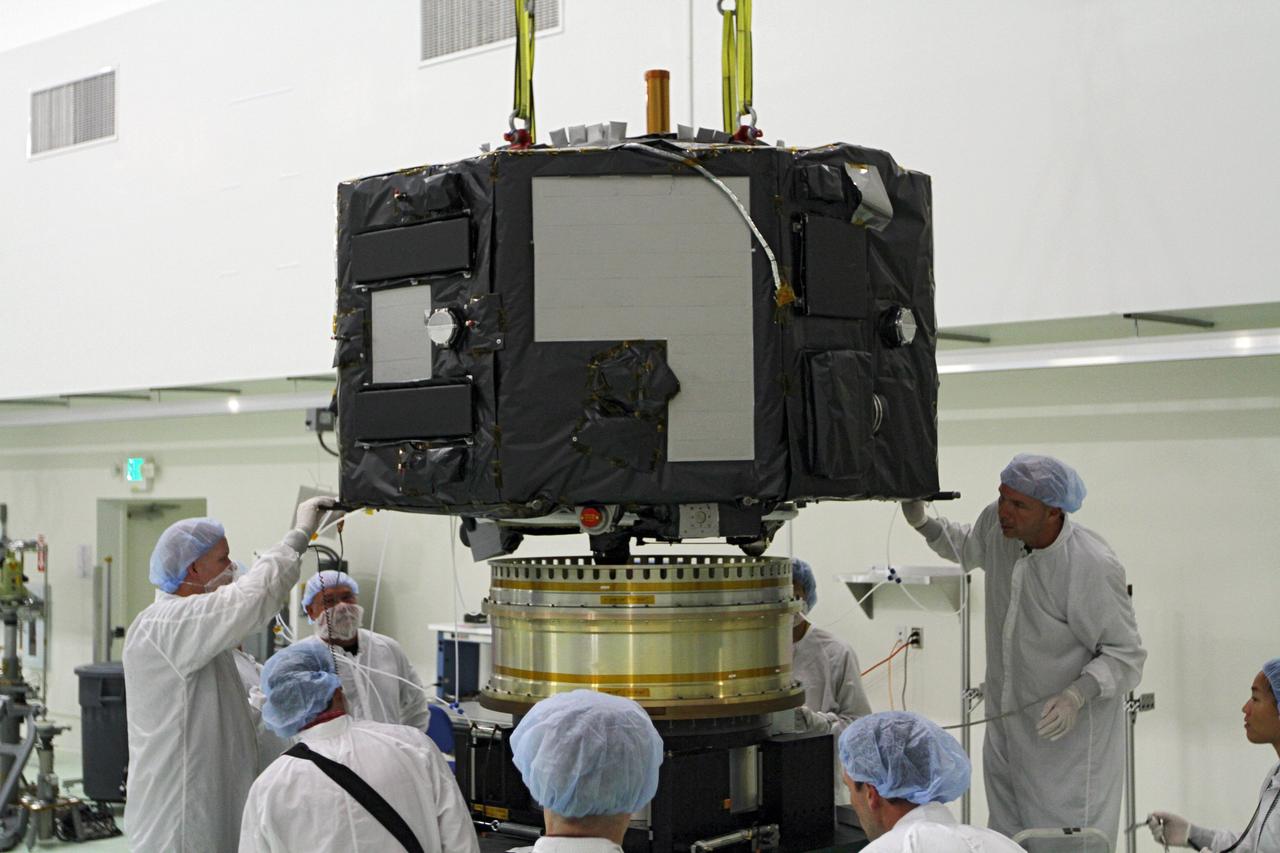
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
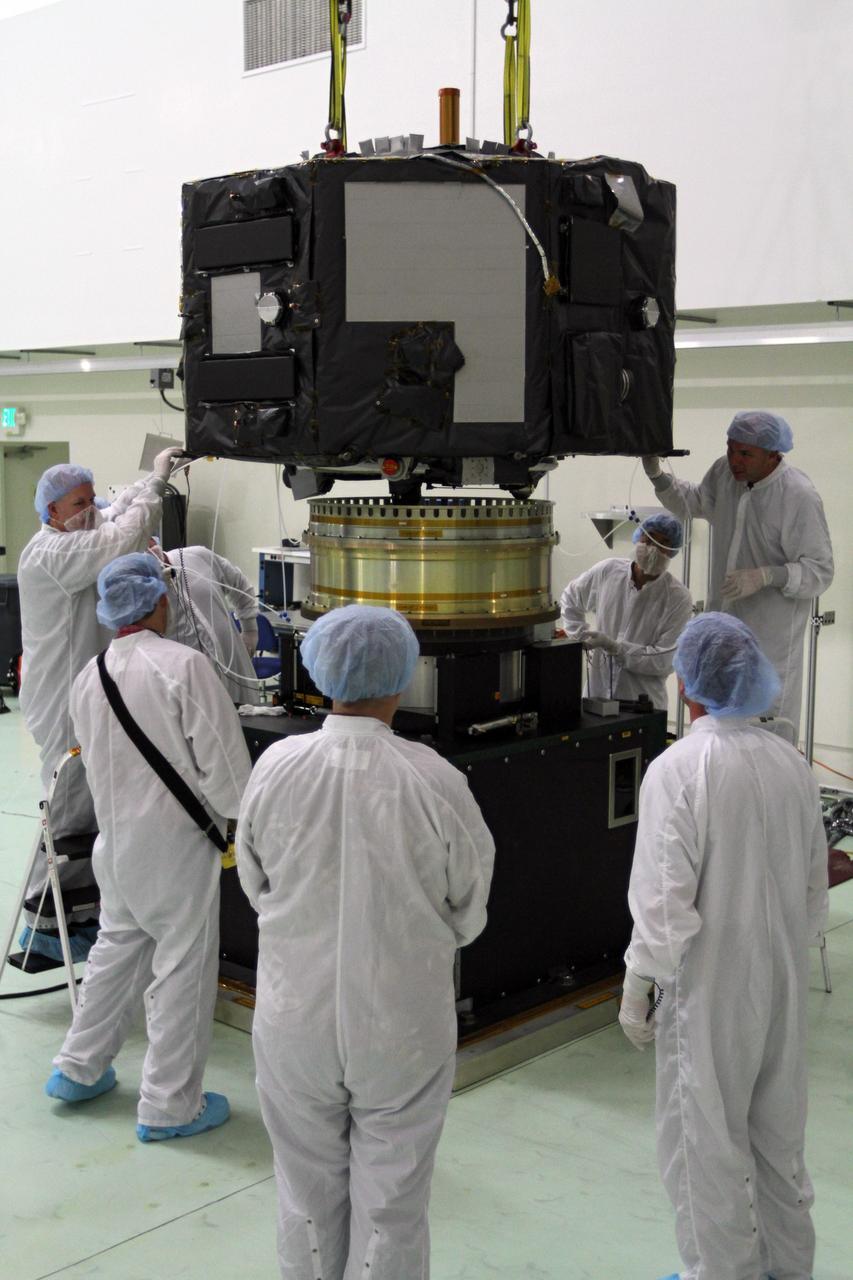

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians lower Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A onto a spin test stand. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
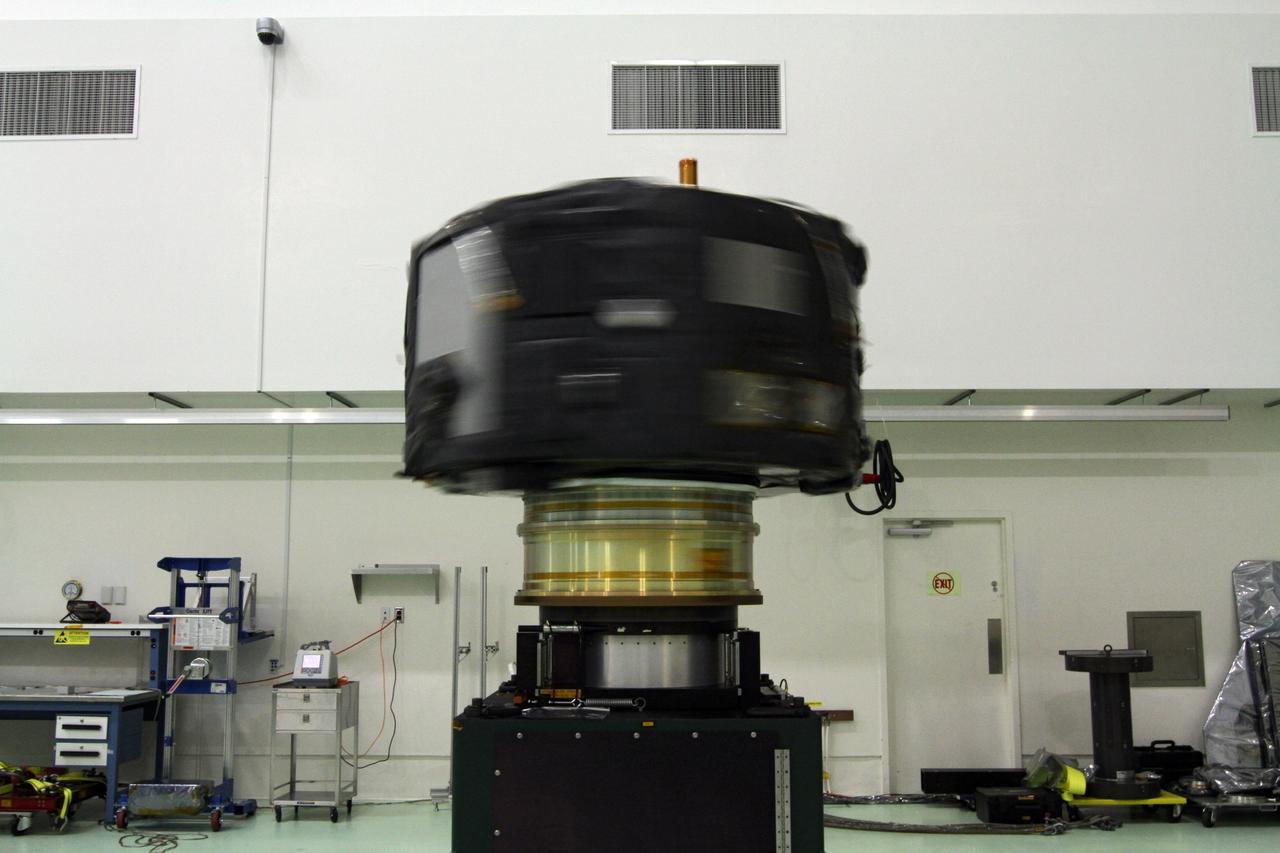
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A is undergoing a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
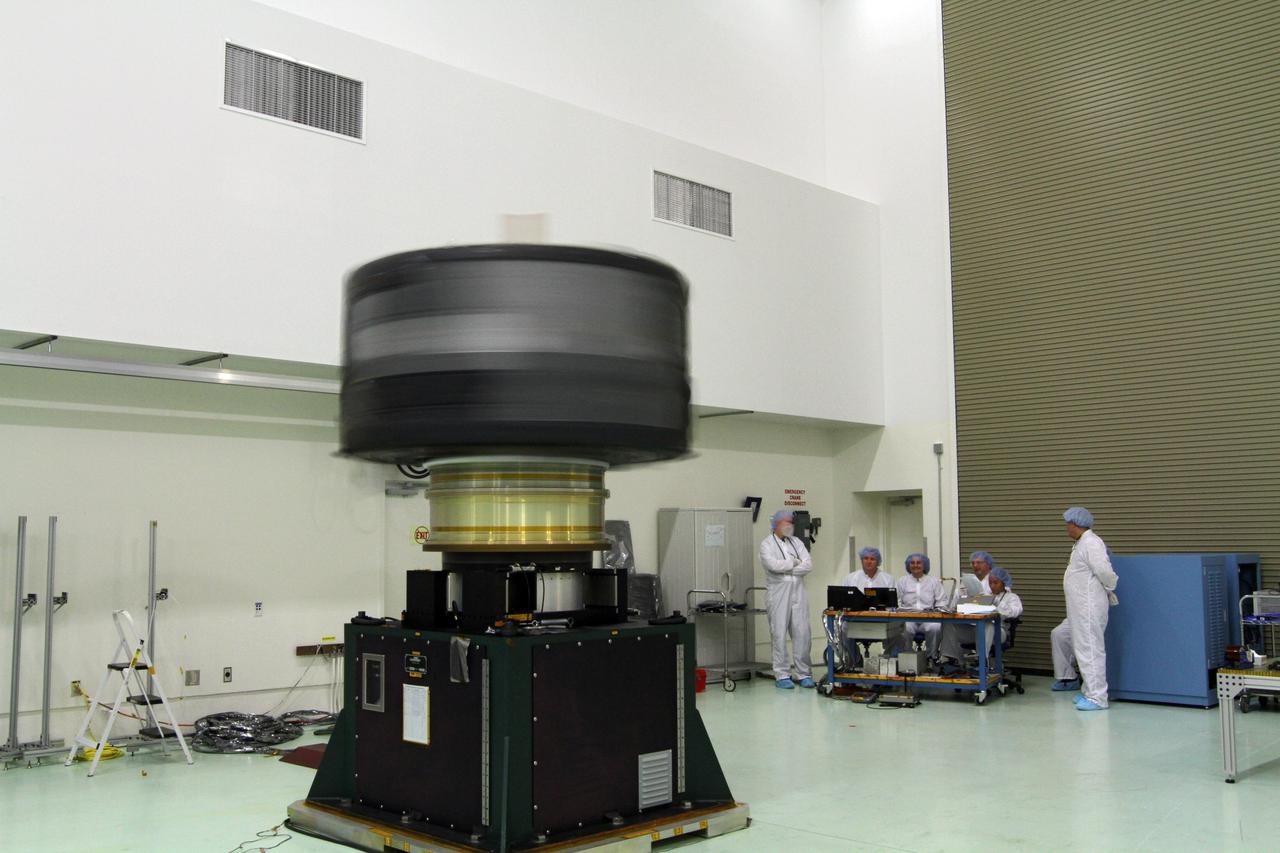

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A undergoes a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
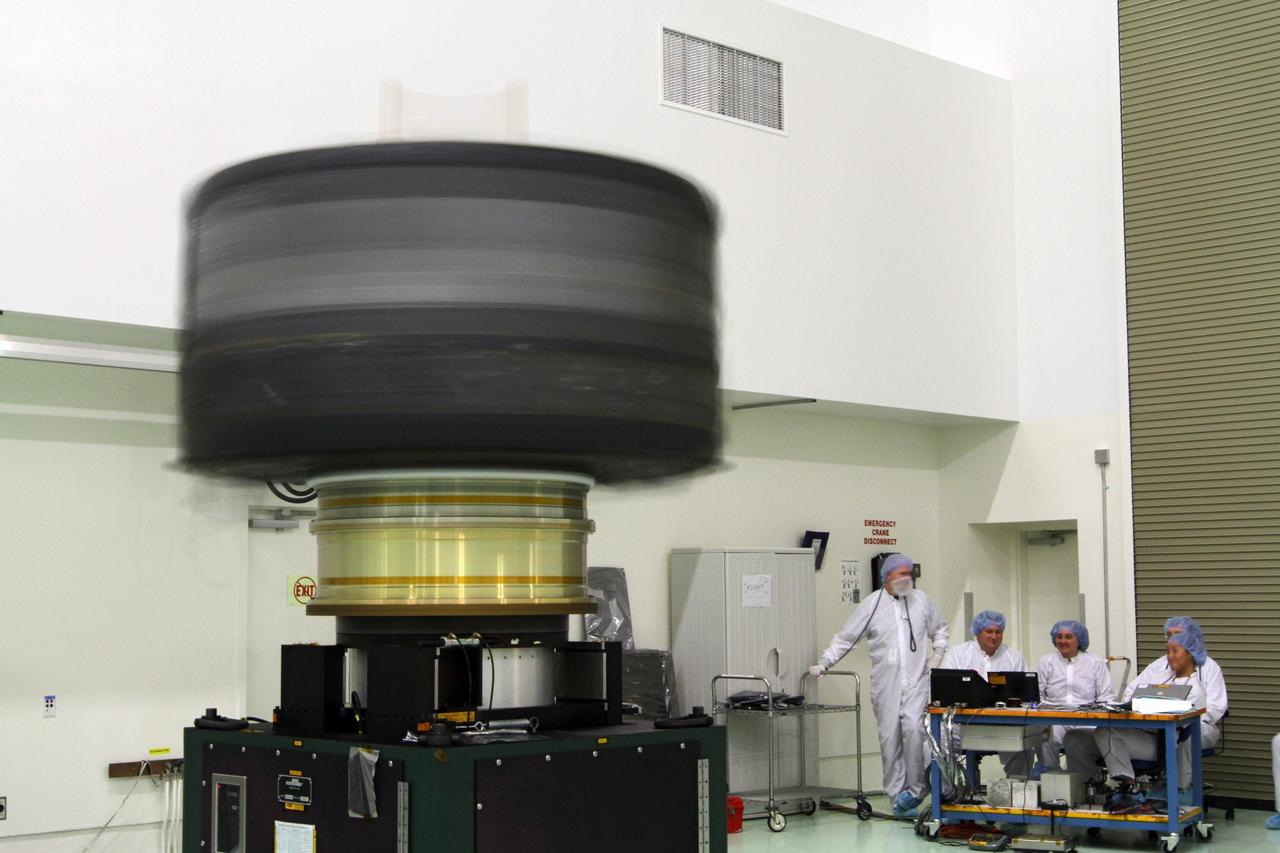

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A undergoes a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
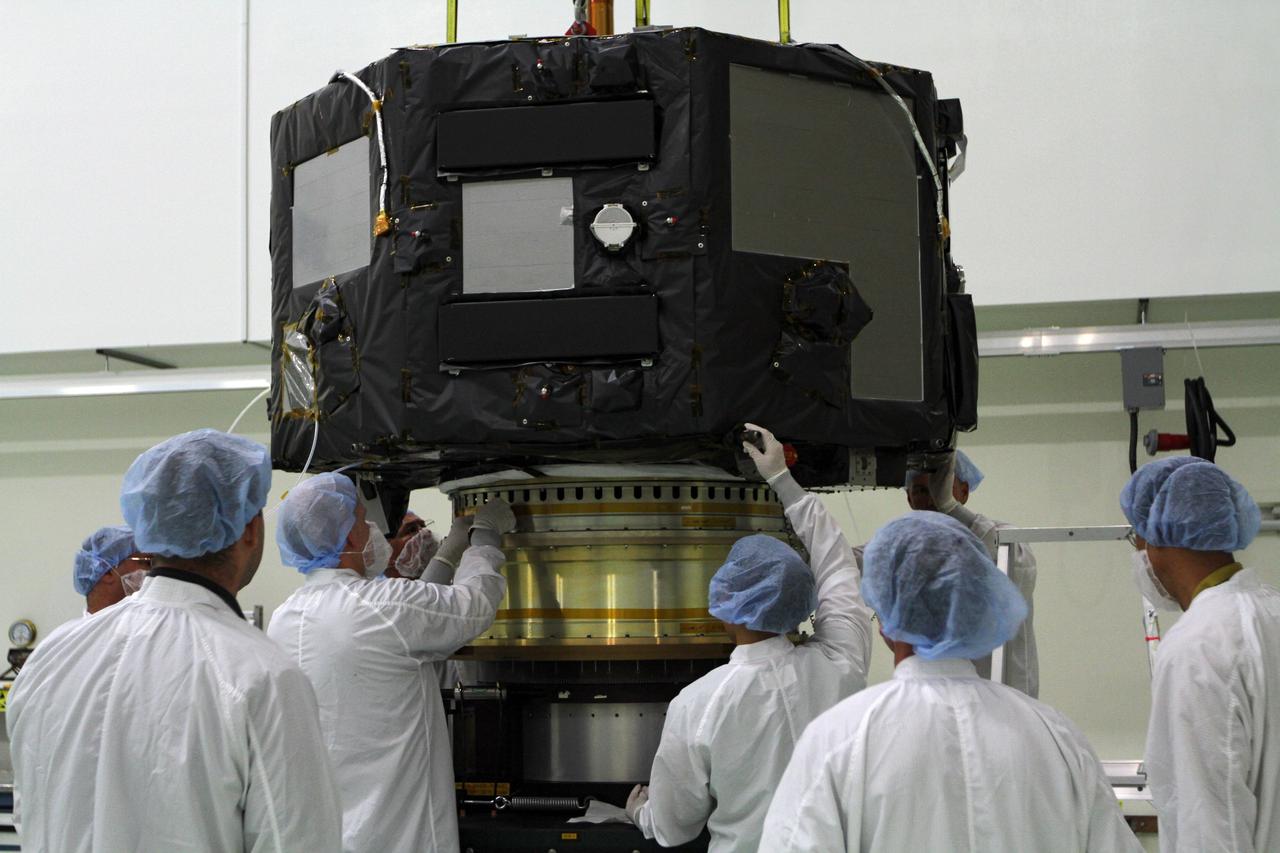

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians have lowered Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A onto a spin test stand. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
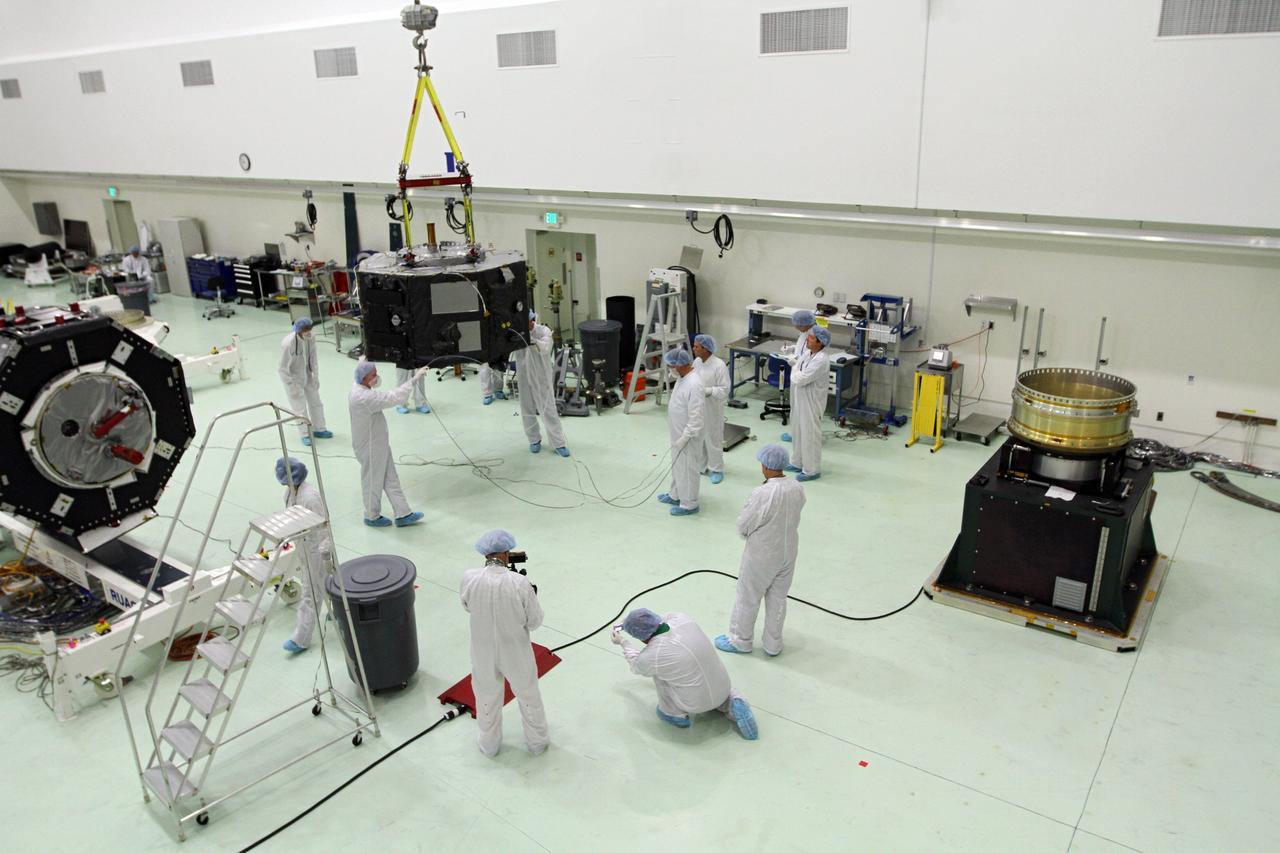

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
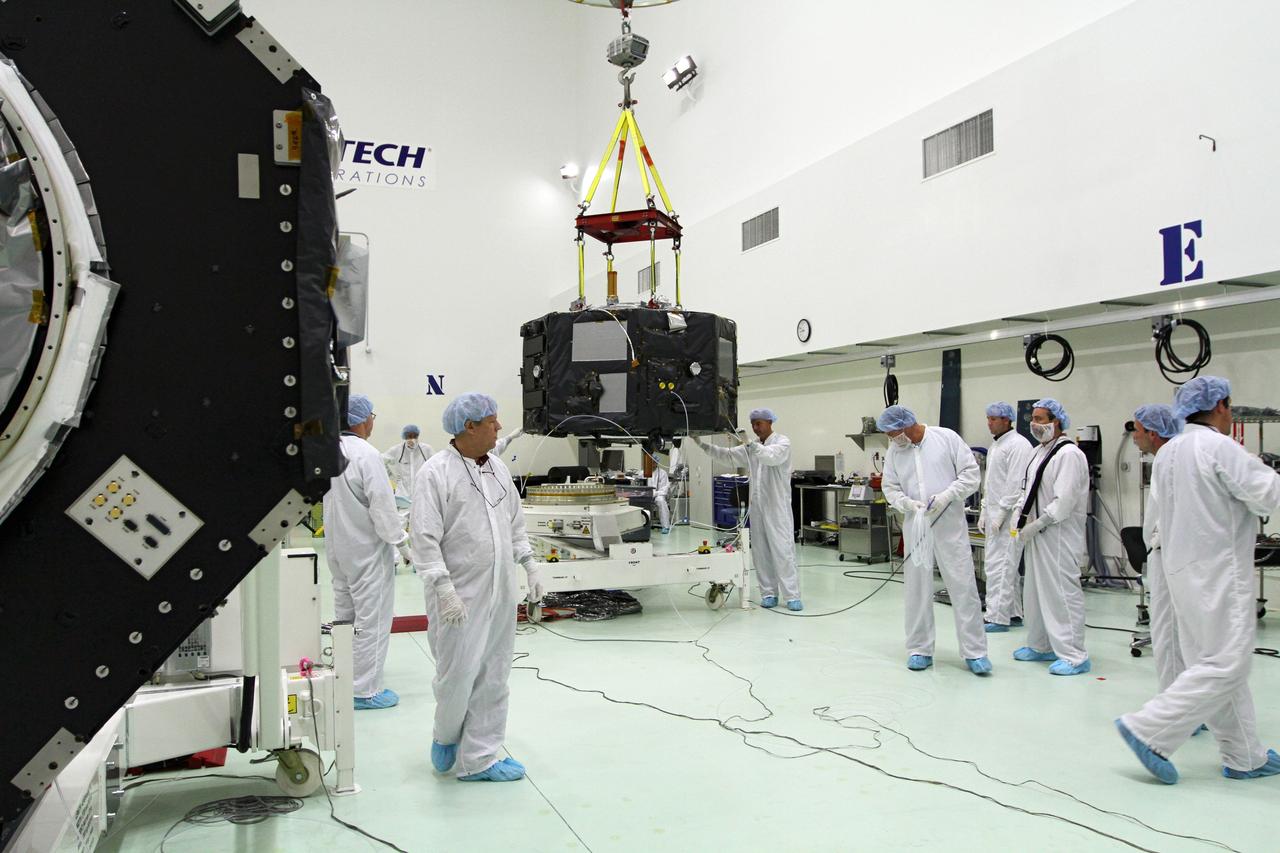

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
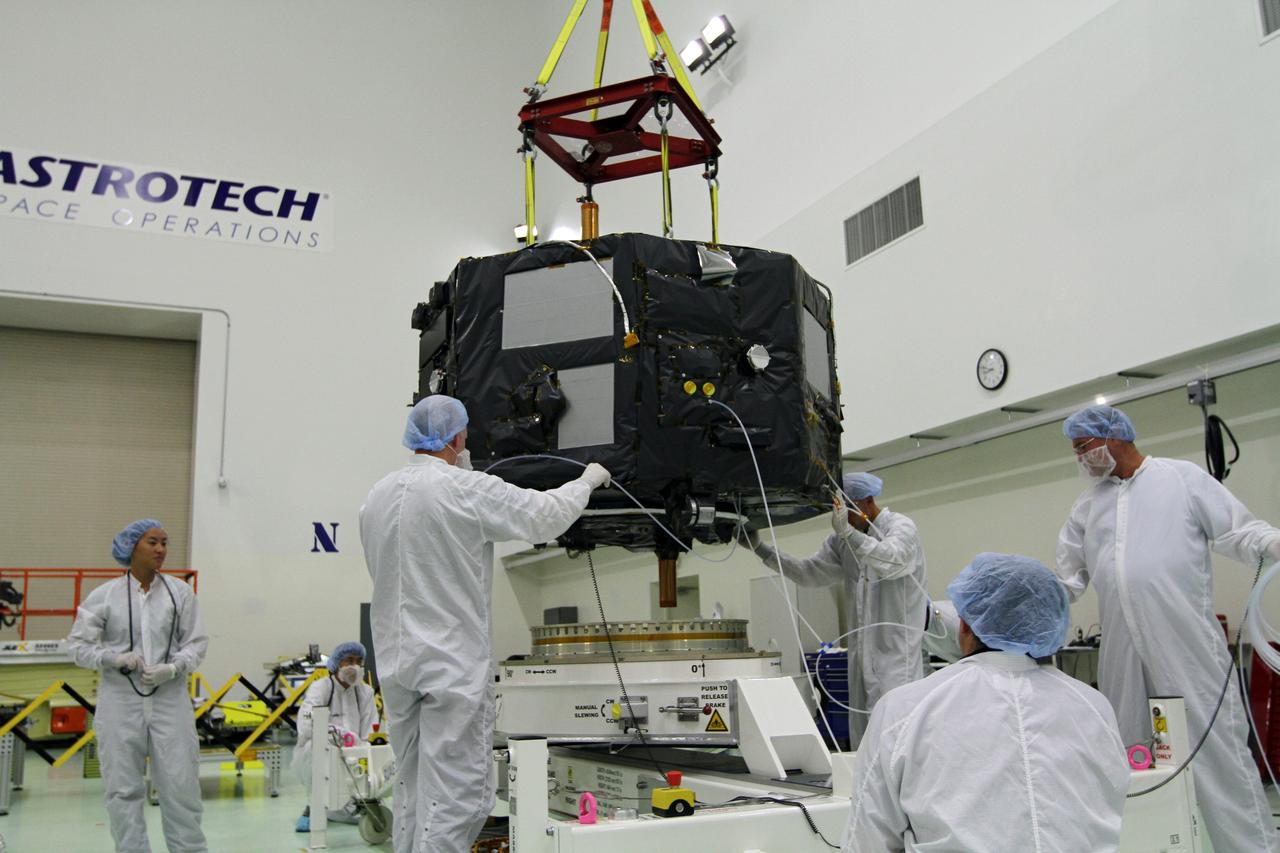

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A for a spin test. During the spin test, the spacecraft is turned at a rate of 55 rpm to ensure that it is properly balanced. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser