
Happy Thanksgiving from the MESSENGER Team!
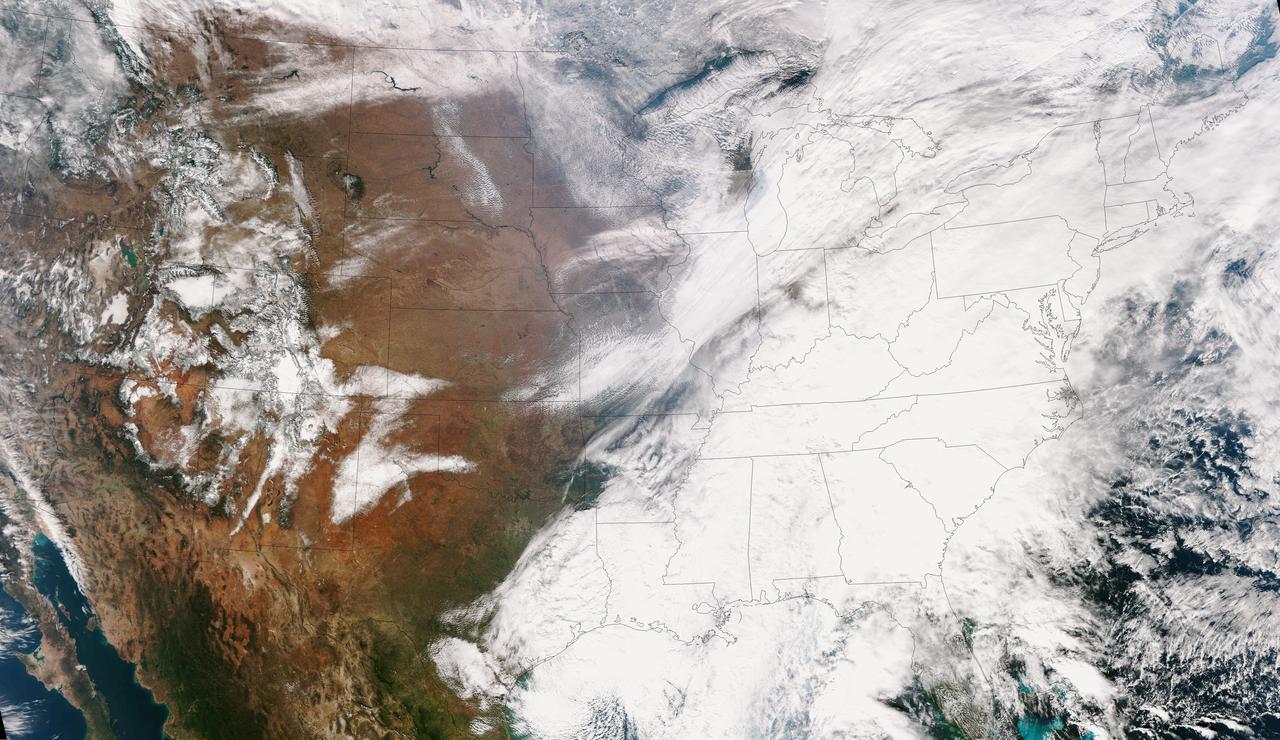
This true color image of the Continental United States was taken on Nov. 25, 2013 by the Suomi NPP satellite and shows the system as it moves through the South and Midwest. The National Weather Service noted that a complex and powerful storm system continues to generate widespread moderate to heavy rainfall and snows in various parts of the eastern United States as travelers make their way to destinations to celebrate Thanksgiving and Hanukkah on Nov. 28. There are two low-pressure areas working together. One was centered near New Jersey while the other was located over the Carolinas. From the Southeast to New England widespread moderate to heavy rainfall is expected. The rains will also affect the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States, although those regions are not expected to get as much of a soaking. The Appalachians and interior New England are expected to receive snowfall. Areas of heavy snow are forecast for northwestern Indiana and northwestern Pennsylvania on Nov. 27. Snows will blanket the north central United States from the Dakotas to Minnesota, Iowa, Wisconsin, Michigan, the Ohio and Tennessee Valleys, upstate New York and parts of northern New England. The National Weather Service noted that cold air is moving in behind the storm and drop temperatures along the eastern U.S. making for a chilly Thanksgiving. Credit: NASA/NOAA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
ISS038-E-009304 (28 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins (mostly out of frame), Expedition 38 flight engineer, offers a close-up view of his Thanksgiving meal in the Unity node of the International Space Station.

On November 23, 2013 at at 2045 UTC/3:45 p.m. EST, Arctic air pours over North America during the week before Thanksgiving, bringing several days of unseasonal freezing temperatures and difficult weather to the United States. Credit: NASA GOES Project/Dennis Chesters <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
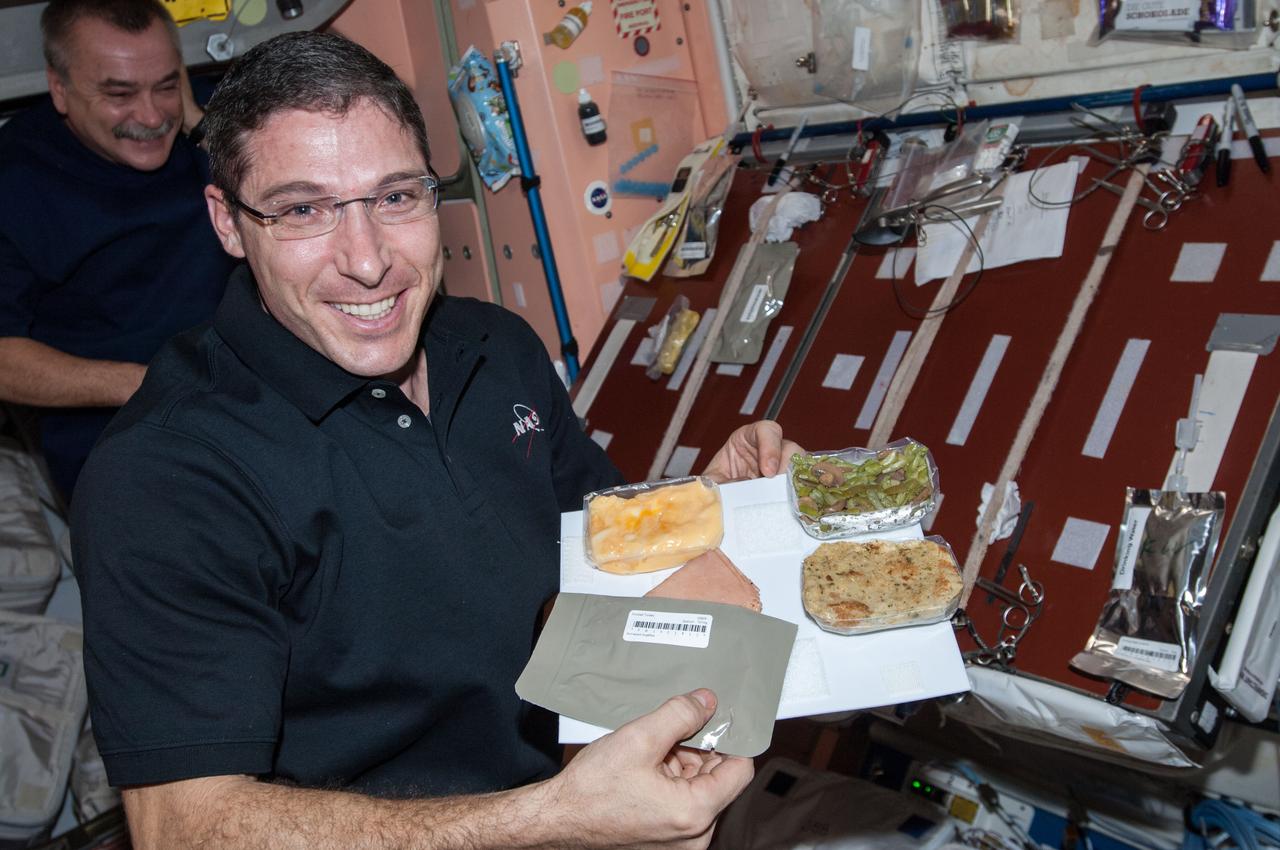

ISS038-E-009300 (28 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, poses for a photo with his Thanksgiving meal in the Unity node of the International Space Station.

NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit used its panoramic camera Pancam to record a 360-degree vista, dubbed the Thanksgiving panorama, from the northwestern side of Husband Hill in late 2004. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
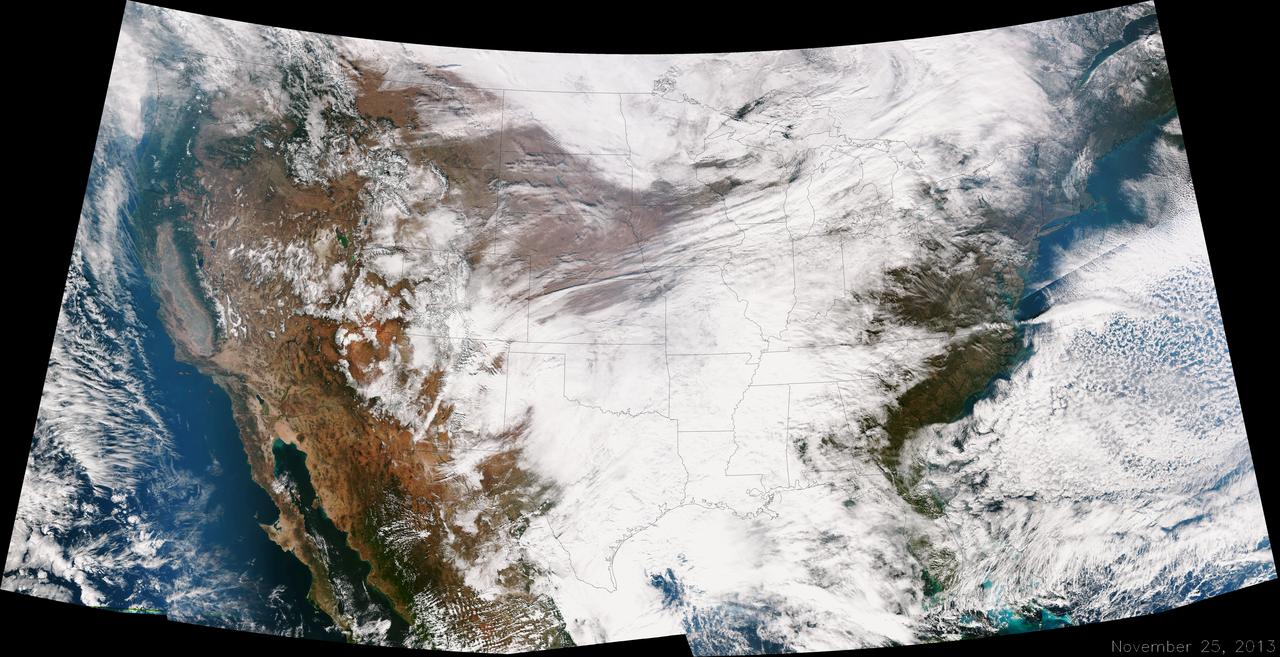

A large winter system is moving across the United States and is combining with cold air moving down from Canada, bringing snow to some areas. Major travel impacts are expected along the main highways throughout the eastern U.S. This true color image of the Continental U.S. was taken on November 25, 2013 by the Suomi NPP satellite and shows the system as it moves through the South and Midwest. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
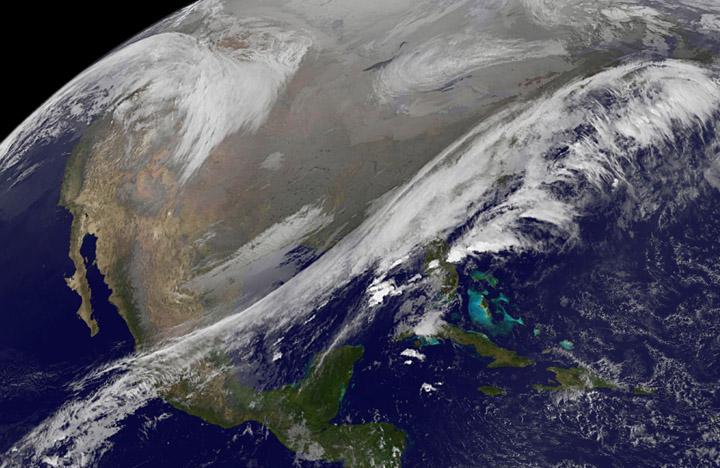

This NOAA's GOES satellite infrared image taken on Nov. 25 at 11:45 UTC (6:45 a.m. EST) shows two main weather systems over the U.S. Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project As the U.S. Thanksgiving holiday approaches this Thursday, November 27, NOAA's GOES-East and GOES-West satellites are keeping a weather eye out for storms that may affect early travelers. In an image from Nov. 25, the satellites show an active weather pattern is in place for travelers across the central and eastern U.S. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provides visible and infrared images over the eastern U.S. and the Atlantic Ocean, while NOAA's GOES-West satellite covers the western U.S. and Pacific Ocean from its fixed orbit in space. Data from both satellites were combined at NASA's GOES Project to create a full view of the U.S. on Nov. 25 at 11:45 UTC (6:45 a.m. EST). The image shows clouds associated with cold front stretching from the Gulf of Mexico over northern Florida and along the U.S. East coast to eastern Canada. Clouds associated with another area of low pressure are in the northern Rockies and northwestern U.S. To create the image, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project takes the cloud data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite and overlays it on a true-color image of land and ocean created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. Together, those data created the entire picture of the storm and show its movement. After the storm system passes, the snow on the ground becomes visible. NOAA's National Weather Service Weather Prediction Center said "a storm system will develop off the coast of the Carolinas early Wednesday (Nov. 25) and strengthen as it moves rapidly up the East Coast Wednesday into early Thursday (Nov. 26). Heavy snow is likely to begin in the central Appalachians early Wednesday morning, spreading northeast through the interior Mid-Atlantic into New England by Wednesday night. Winter Storm Watches are in effect for these areas." For travelers in the western U.S., the Northern Rocky Mountains are expected to receive more snow from the north side of a stationary frontal boundary. South of the boundary rain showers will affect the lower valley. The National Weather Service calls for cold weather to continue in the northern Plains and Upper Midwest as a Canadian surface high pressure rules the weather. The U.S. Southwest will experience nice weather for mid-week. In the Pacific Northwest, the National Weather Service noted that a warm front will bring rain, heavy at times, to the Cascades today and tonight. There will be a break in the heavier rains on Wednesday, then another period of heavy rain for the Cascades Wednesday night through Friday morning as a cold front slowly drags through the area. NOAA's GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric triggers for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes.
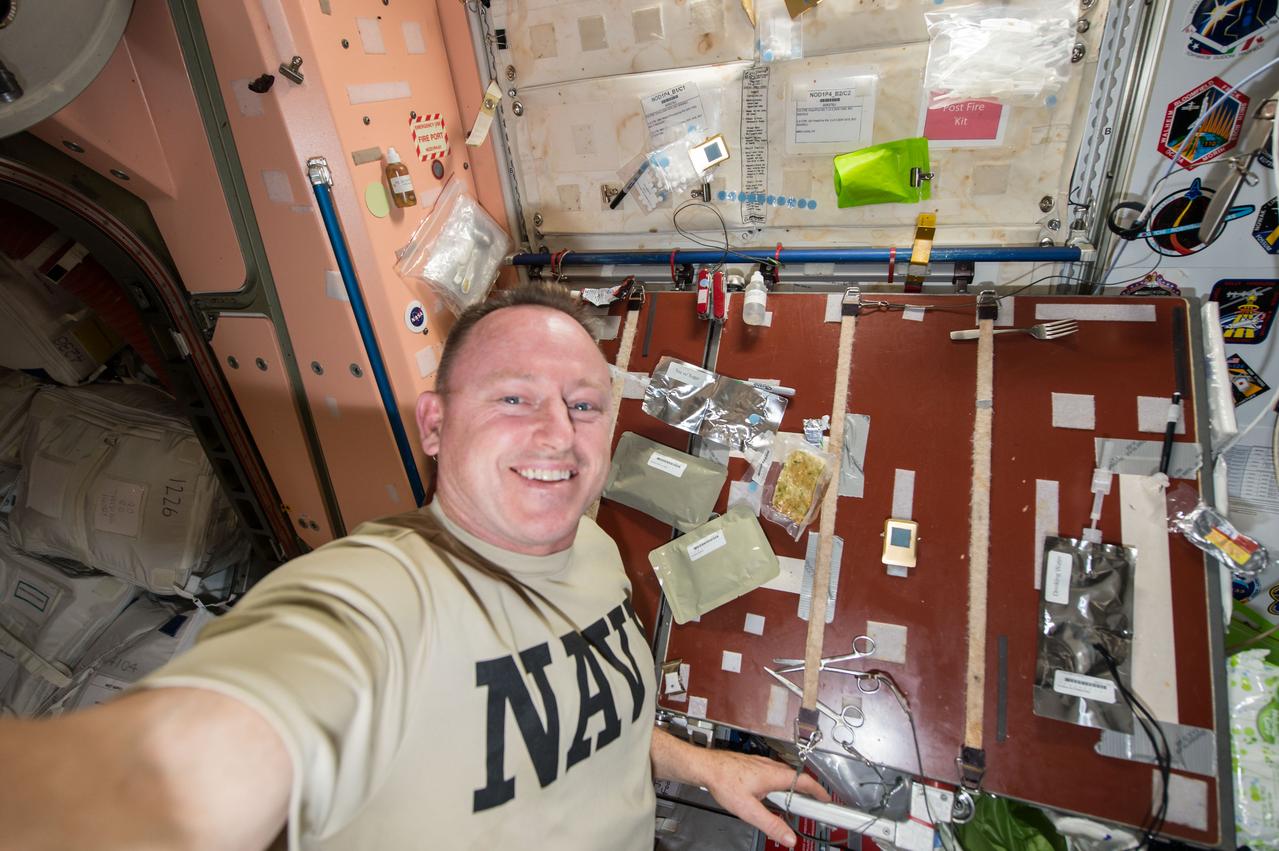

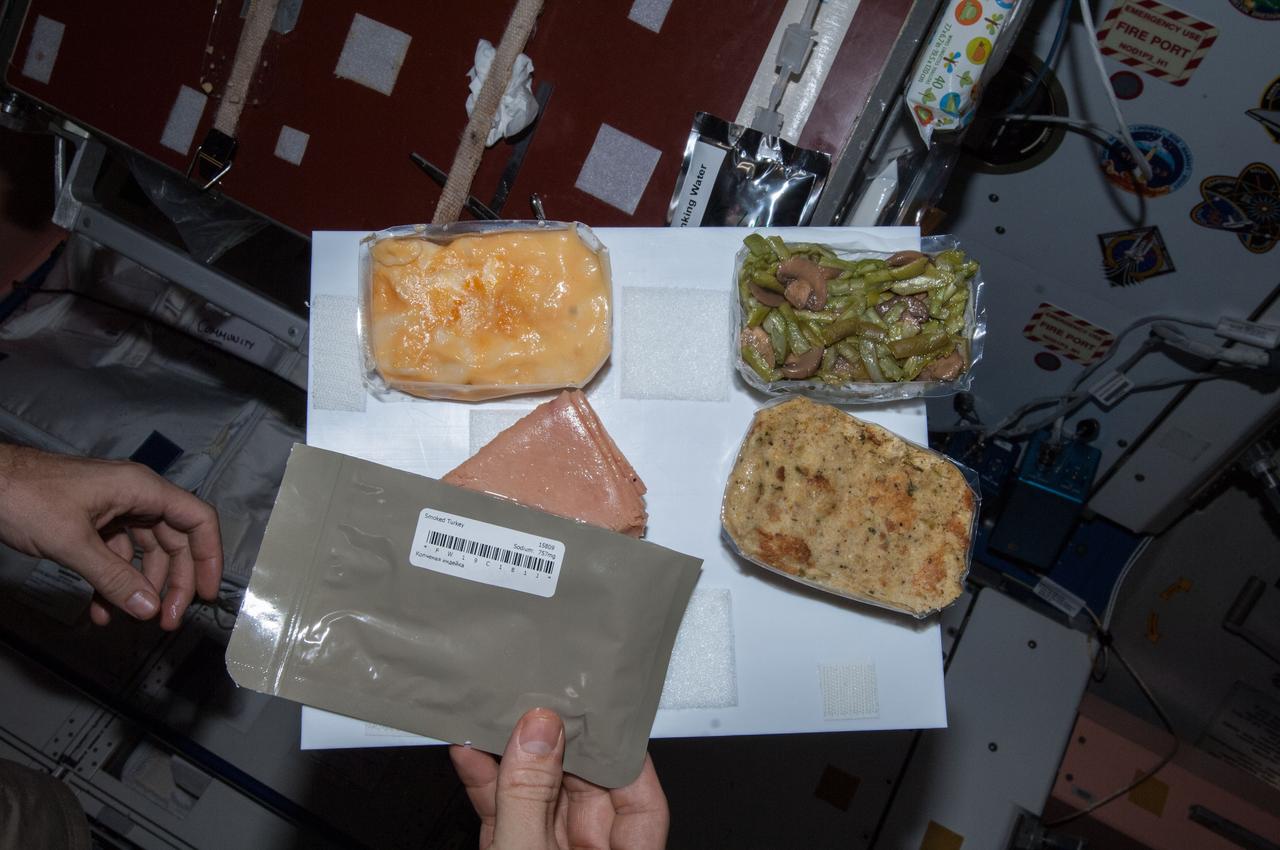
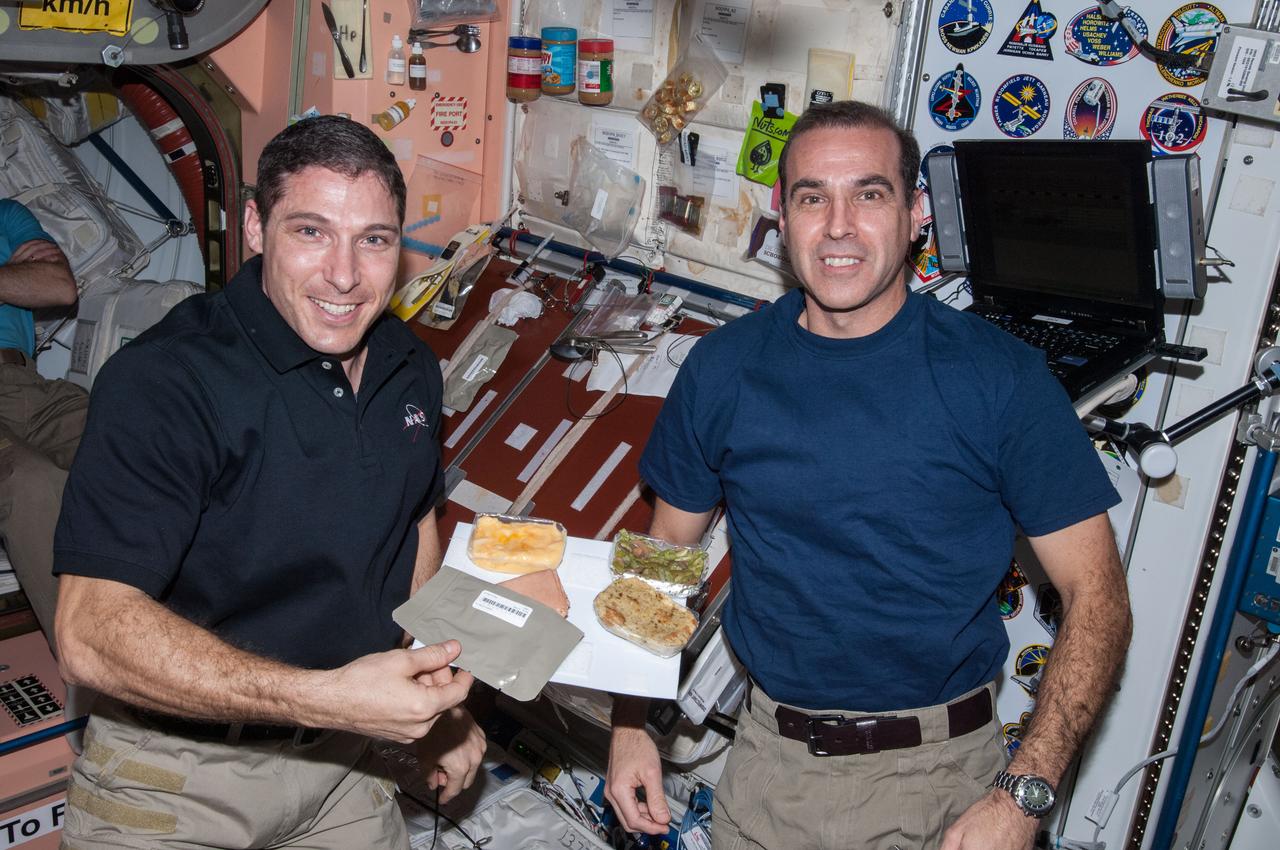
Commander Barry Wilmore takes a self-portrait with food packages (smoked turkey, cranapple dessert, cornbread dressing, and tea with sugar) planned for his Thanksgiving meal. Image was taken near the galley table in the Unity Node 1, and released by Wilmore on Instagram.
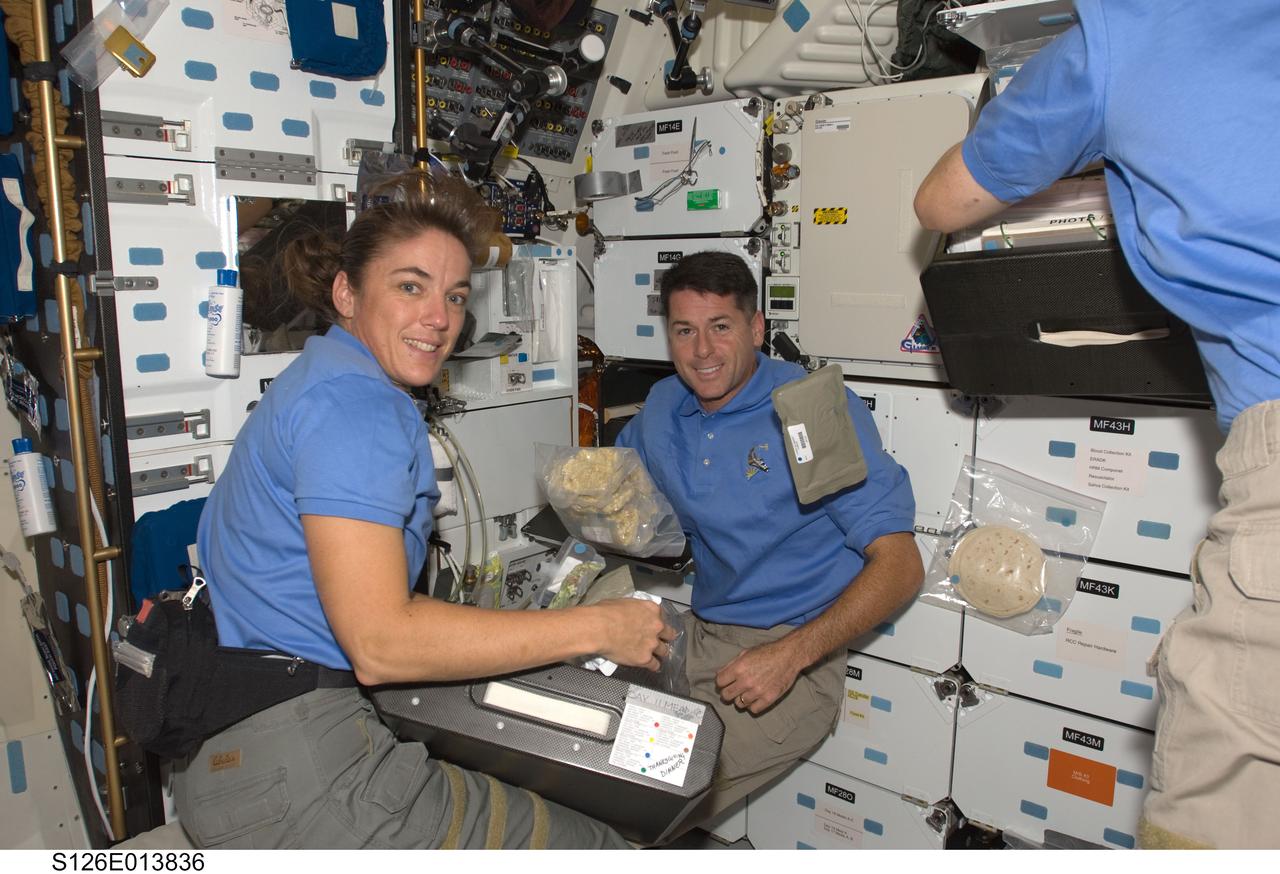

S126-E-013836 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Stationed near the shuttle's galley and stowage lockers, astronauts Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper and Shane Kimbrough, STS-126 mission specialists, assemble the elements of Thanksgiving dinner on the middeck of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, while the orbiter is docked with the International Space Station. A Russian cosmonaut and seven other astronauts are not far away from the scene and all ten shared the meal and observance at a common place and time, on the eve of the scheduled Nov. 28 undocking of the shuttle and station.
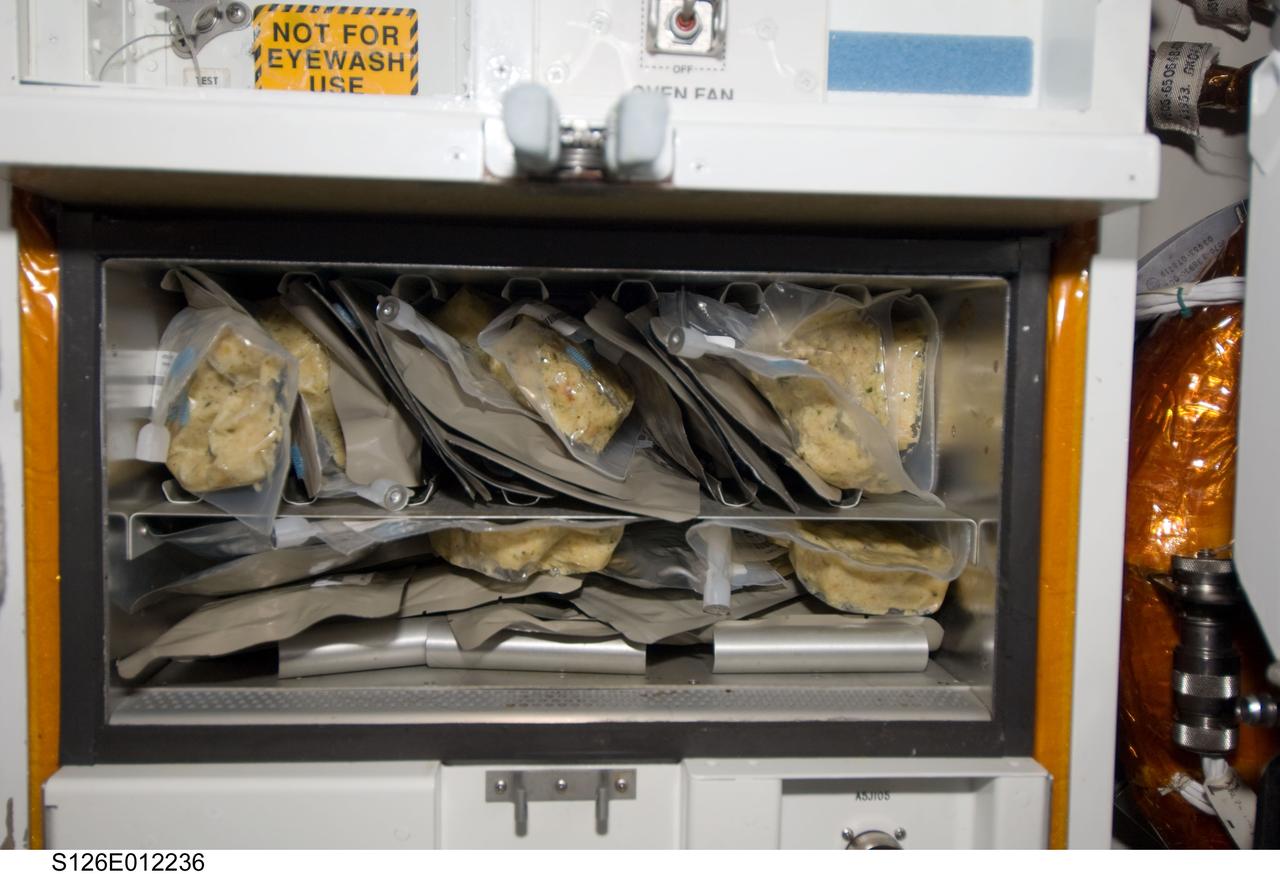

S126-E-12236 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Not far away from this close-up scene of the galley on the Space Shuttle Endeavour were nine astronauts and a cosmonaut eager to share a Thanksgiving meal to top off almost two weeks of joint activities, including an involved home improvement project on the International Space Station. Unlike most of their families and friends on Earth, who probably went through pains to prepare elaborate meals for this festive occasion, the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crewmembers merely needed add water to these prepared packets
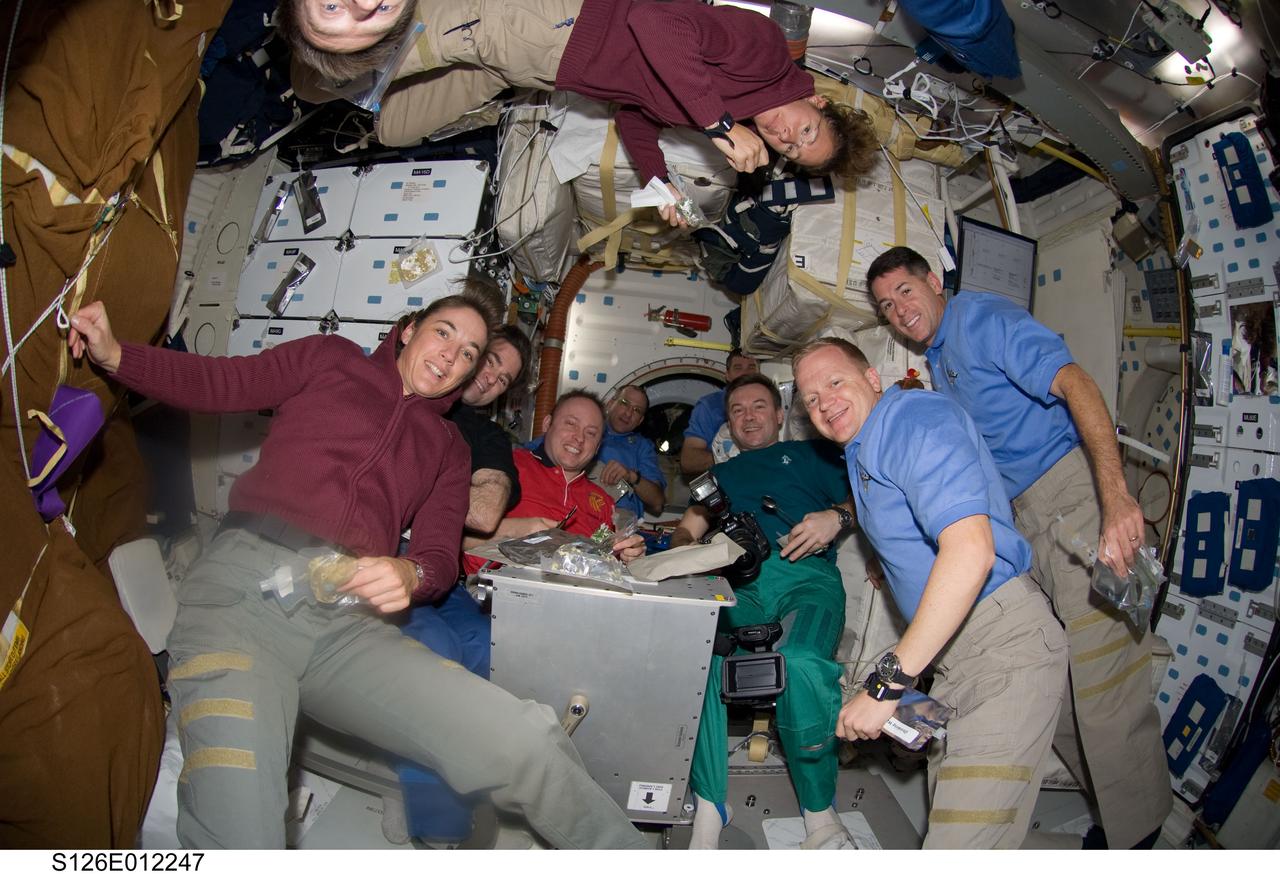

S126-E-012247 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Getting all ten members of an aggregation consisting of seven Endeavour astronauts and three Expedition 18 crewmembers into a single photo wasn't easy as the two crews shared a Thanksgiving meal on the middeck of the orbiter. Astronaut Sandra Magnus, Expedition 18 flight engineer, appears at top center. Clockwise from her position are astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Eric Boe, along with cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, and astronauts Steve Bowen (partially visible behind Lonchakov), Donald Pettit, Michael Fincke, Gregory Chamitoff, Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper and Chris Ferguson (partially visible at top right). Ferguson is STS-126 commander, and Fincke is commander for the station crew.
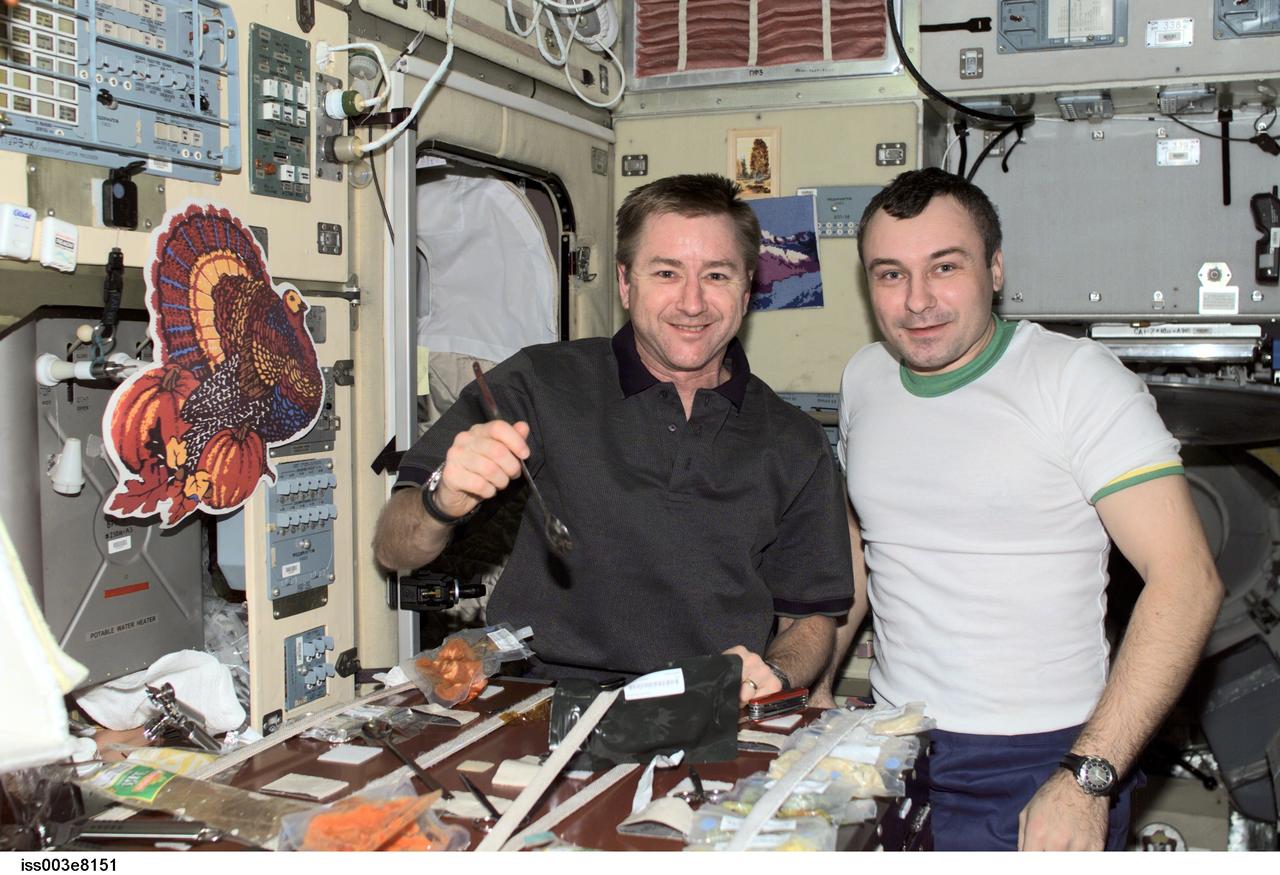

ISS003-E-08151 (22 November 2001) --- Astronaut Frank L. Culbertson (left), Expedition 3 mission commander, and cosmonaut Vladimir N. Dezhurov, flight engineer representing Rosaviakosmos, eat a Thanksgiving meal in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
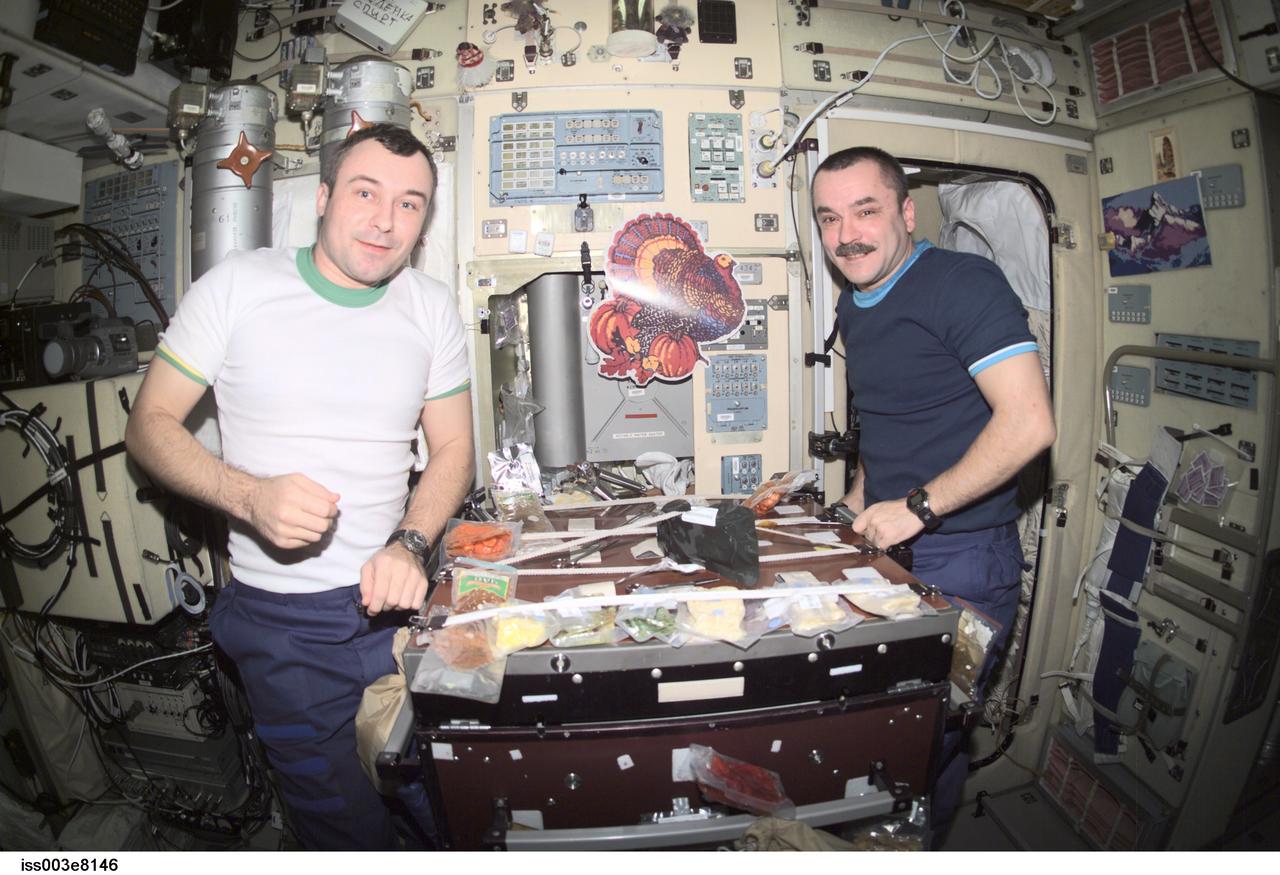

ISS003-E-08146 (22 November 2001) --- Cosmonauts Vladimir N. Dezhurov (left) and Mikhail Tyurin, both Expedition 3 flight engineers representing Rosaviakosmos, eat a Thanksgiving meal in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
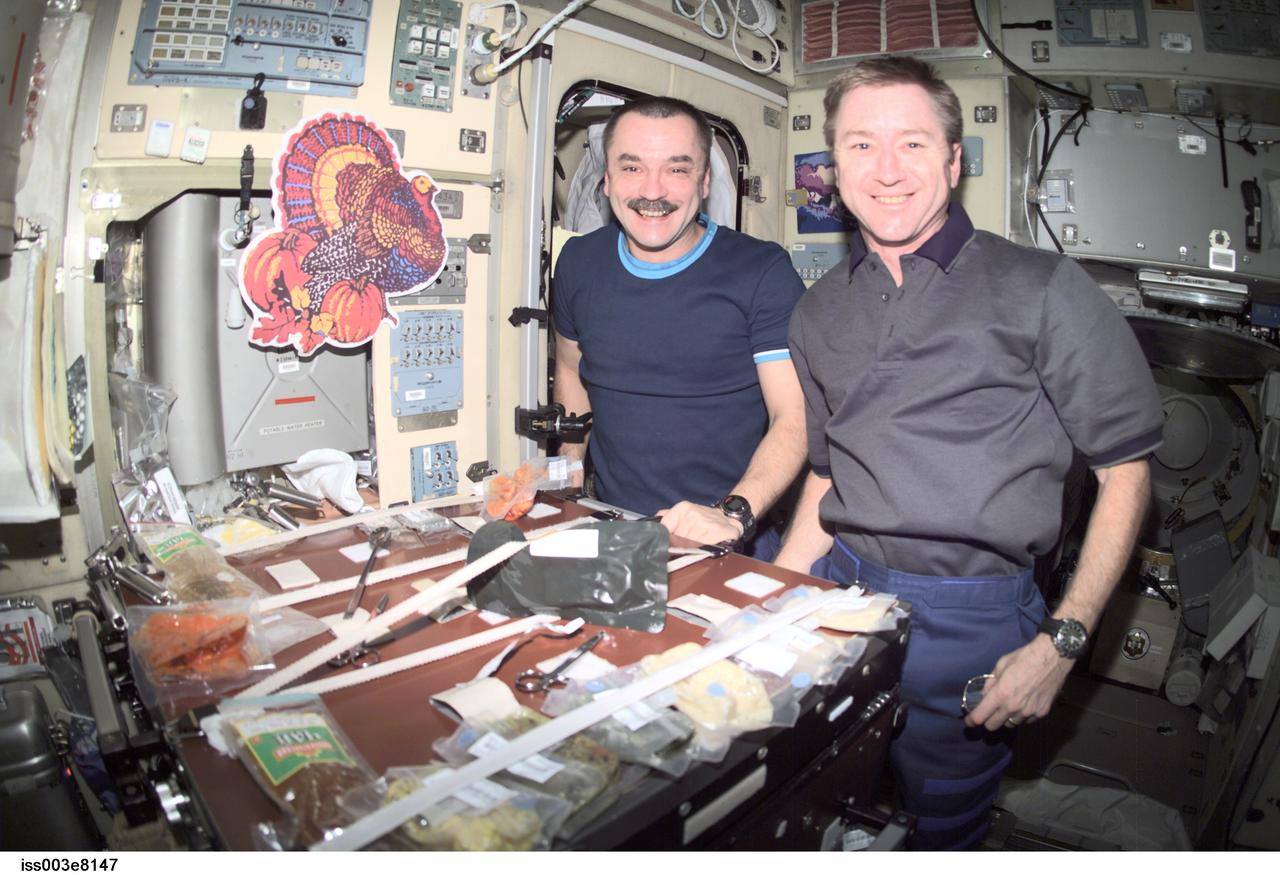

ISS003-E-08147 (22 November 2001) --- Cosmonaut Mikhail Tyurin (left), Expedition 3 flight engineer, and astronaut Frank L. Culbertson, mission commander, eat a Thanksgiving meal in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). Tyurin represents Rosaviakosmos.

ISS038-E-009306 (28 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronauts Michael Hopkins (left) and Rick Mastracchio, both Expedition 38 flight engineers, pose for a photo with a Thanksgiving meal in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
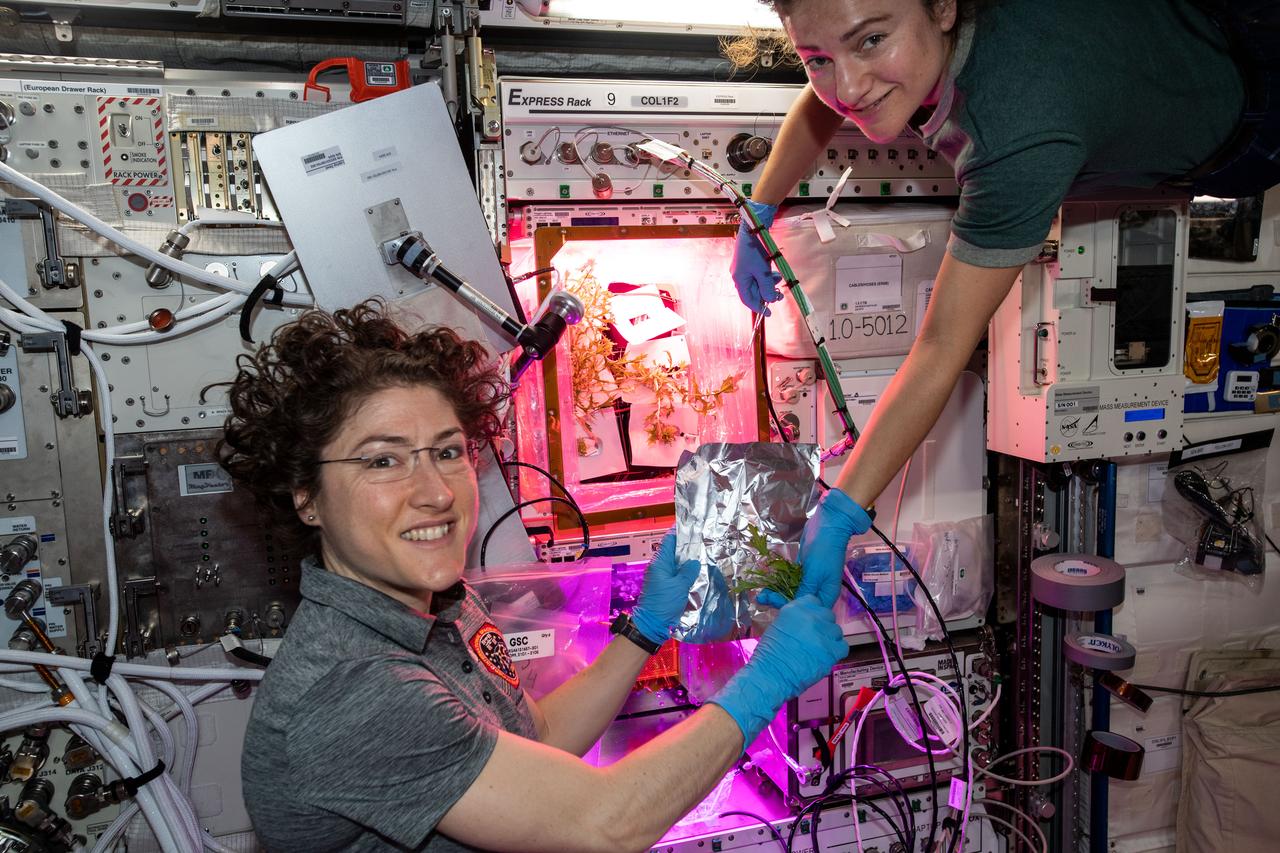

iss061e061596 (Nov. 28, 2019) --- NASA astronauts (left to right) Christina Koch and Jessica Meir harvested Mizuna mustard greens on Thanksgiving day inside the ESA (European Space Agency) laboratory module's VEGGIE facility.
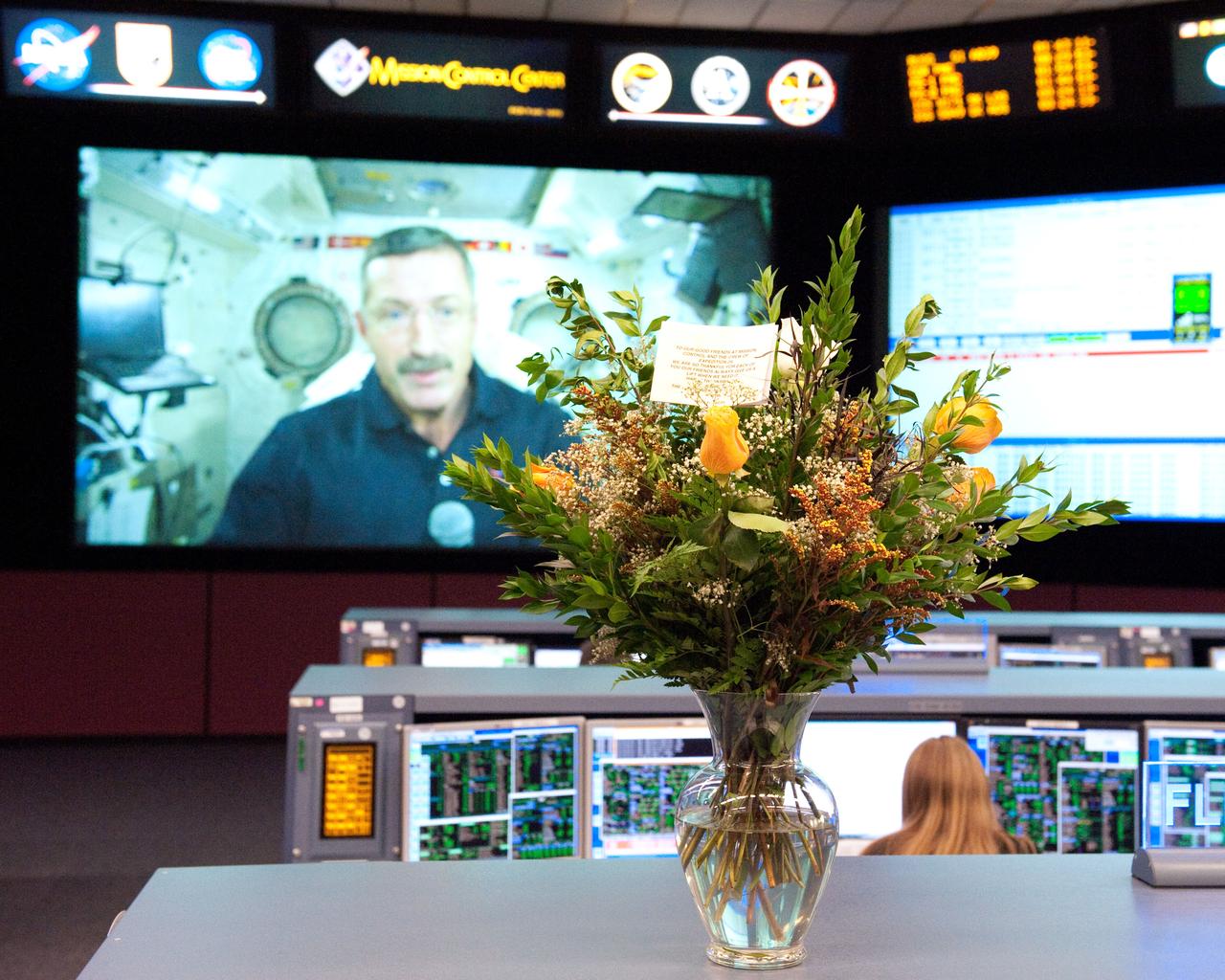

Date: 11-23-11 Location: Bldg 30, FCR-1 Subject: Photograph flowers sent by Shelton/Murphy family in honor of the Expedition 29 flight control team for Thanksgiving Photographer: James Blair

Date: 11-24-11 Location: Bldg 30, FCR-1 Subject: Expedition 29 flight controllers during Thanksgiving Day with Flight Director Ginger Gibson Photographer: James Blair

Date: 11-24-11 Location: Bldg 30, FCR-1 Subject: Expedition 29 flight controllers during Thanksgiving Day with Flight Director Ginger Gibson Photographer: James Blair
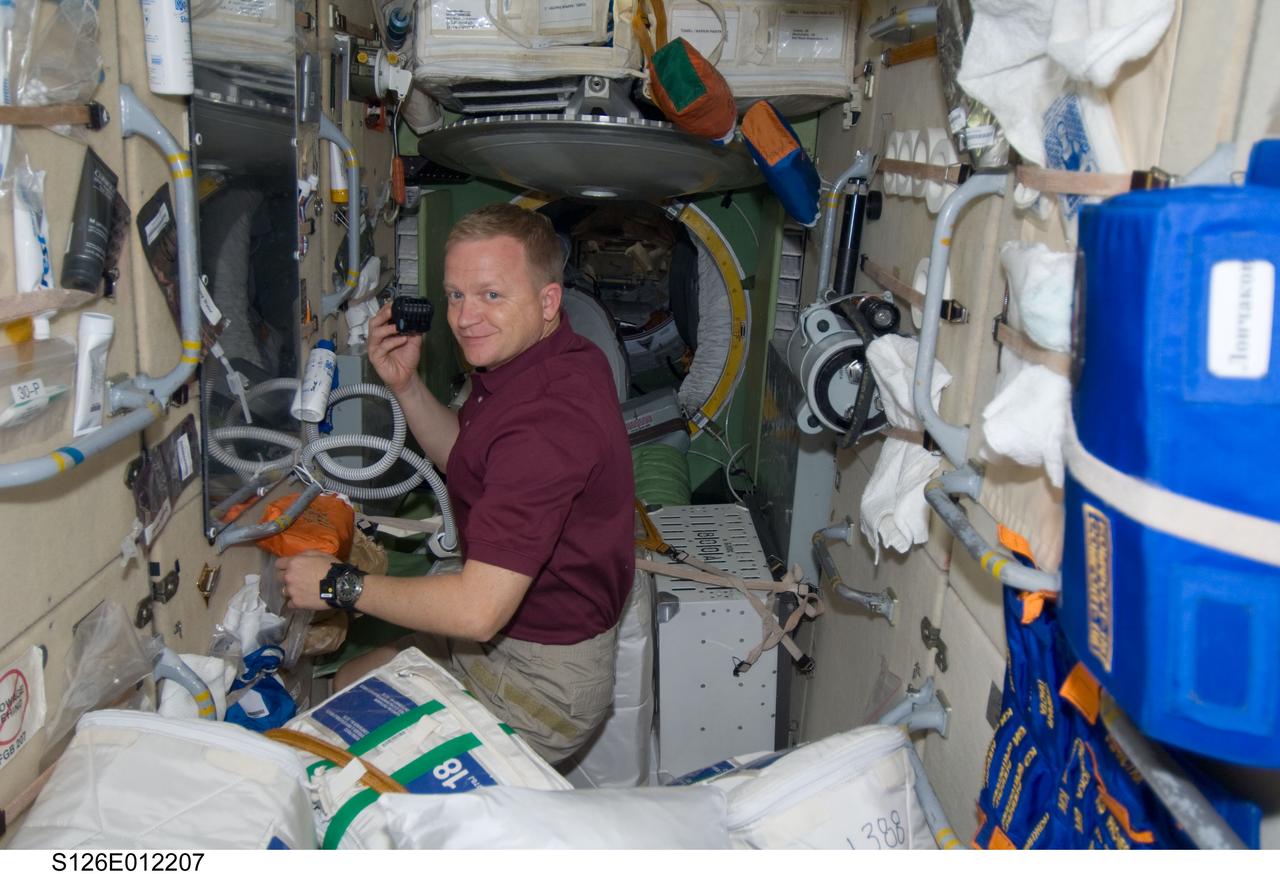

S126-E-012207 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Eric Boe, STS-126 pilot, shaves his face on the aft side of the Zarya functional cargo block aboard the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day.
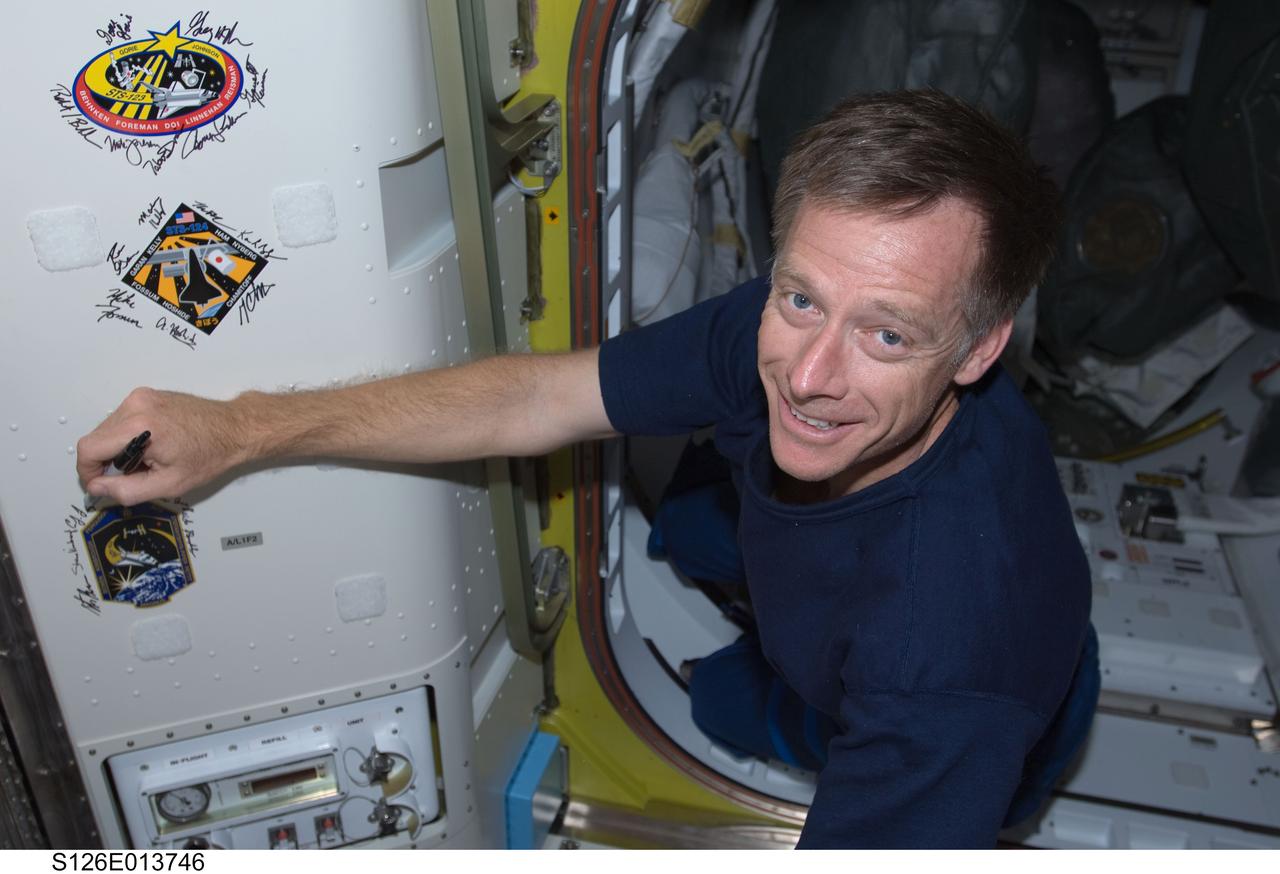

S126-E-013746 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-126 commander, signs Endeavour's crew patch in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.

iss066e083038 (Nov. 25, 2021) --- Expedition 66 crew members gather for a Thanksgiving meal inside the International Space Station's Unity module. From left, are Roscosmos cosmonaut Pyotr Dubrov; ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer; and NASA astronauts Raja Chari.
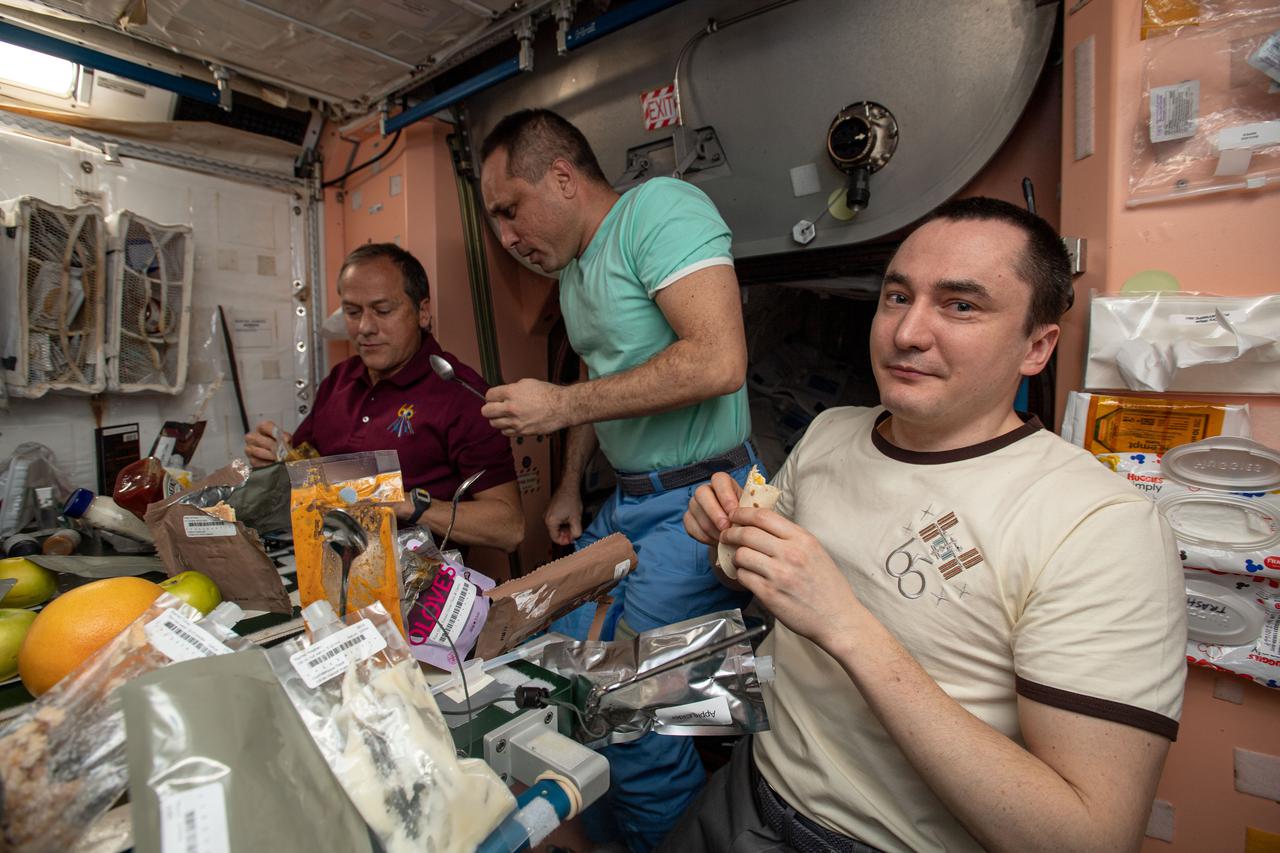

iss066e083008 (Nov. 25, 2021) --- Expedition 66 crew members gather for a Thanksgiving meal inside the International Space Station's Unity module. From left, are NASA astronaut Thomas Marshburn with Roscosmos cosmonauts Anton Shkaplerov and Pyotr Dubrov.
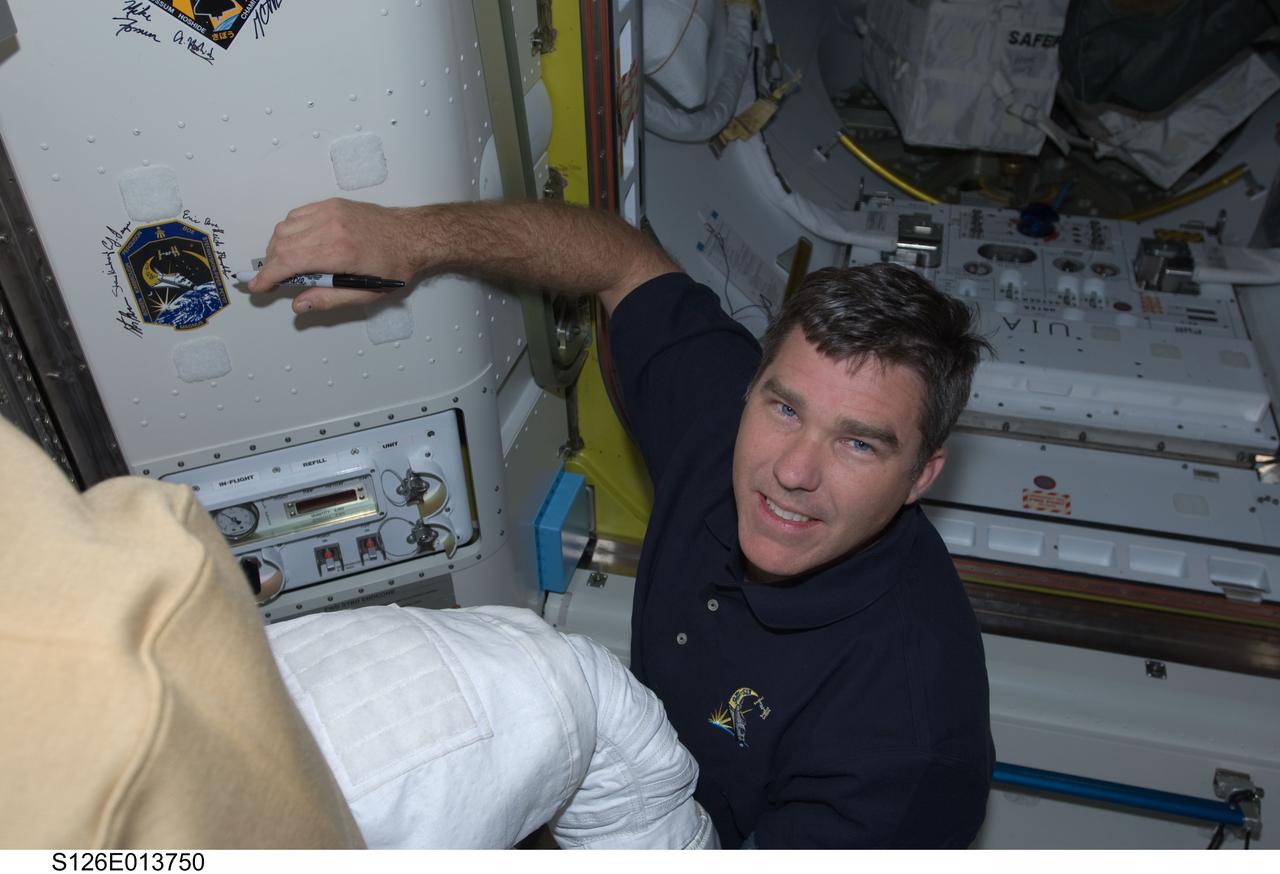

S126-E-013750 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, STS-126 mission specialist, signs Endeavour's crew patch in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.
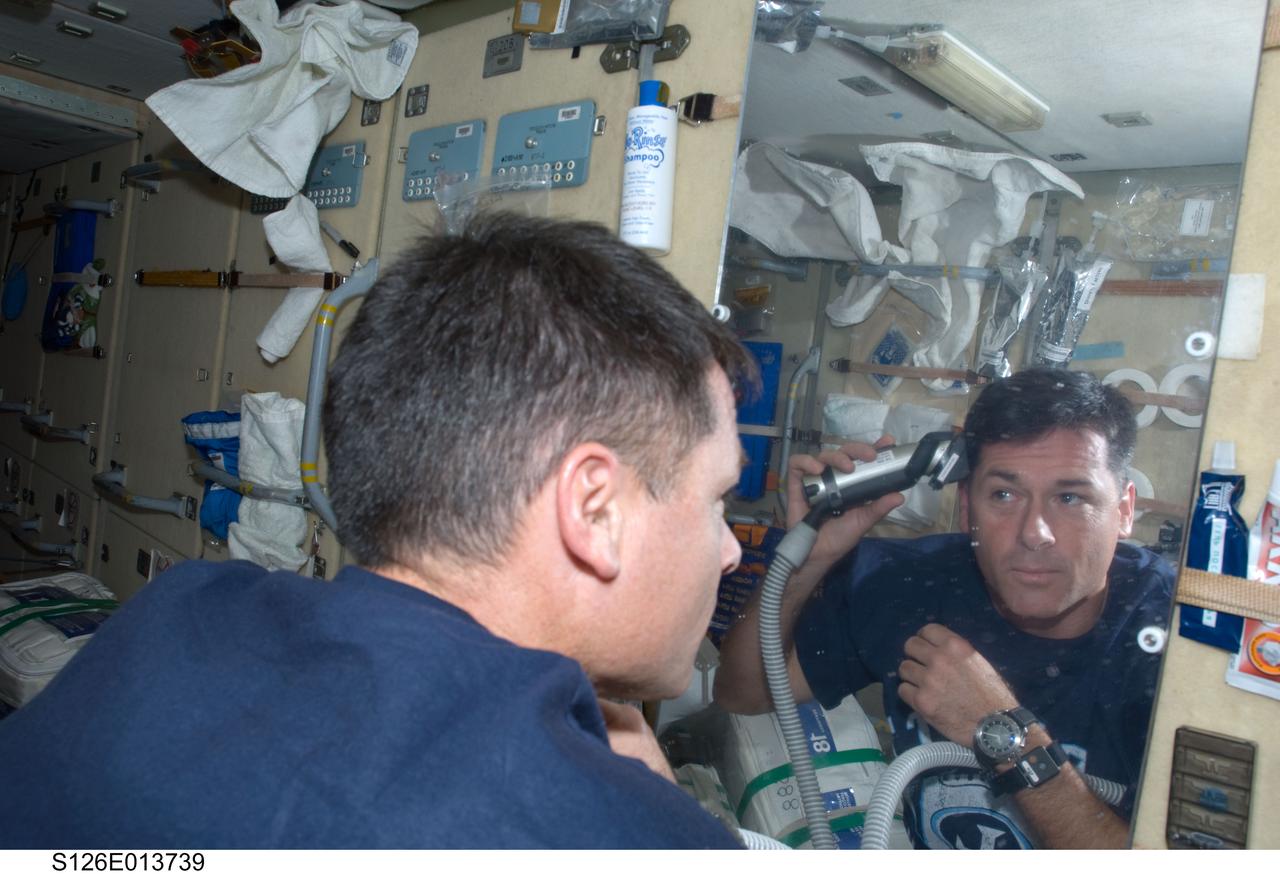

S126-E-013739 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Shane Kimbrough, STS-126 mission specialist, gives himself a hair trim on the aft side of the Zarya functional cargo block aboard the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.

iss066e083027 (Nov. 25, 2021) --- Expedition 66 crew members gather for a Thanksgiving meal inside the International Space Station's Unity module. From left, are Roscosmos cosmonauts Anton Shkaplerov and Pyotr Dubrov with ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer.
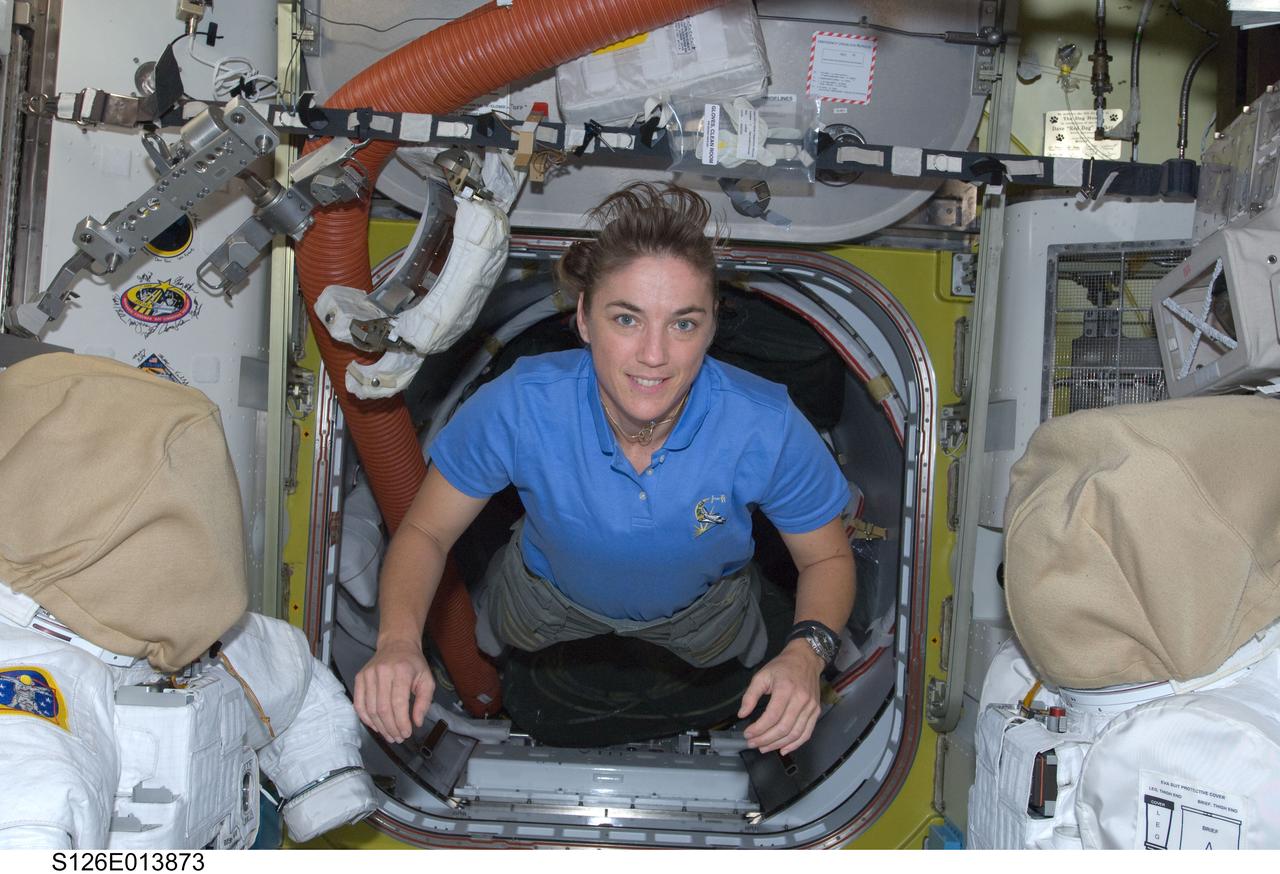

S126-E-013873 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper, mission specialist, floats into the equipment area of the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.
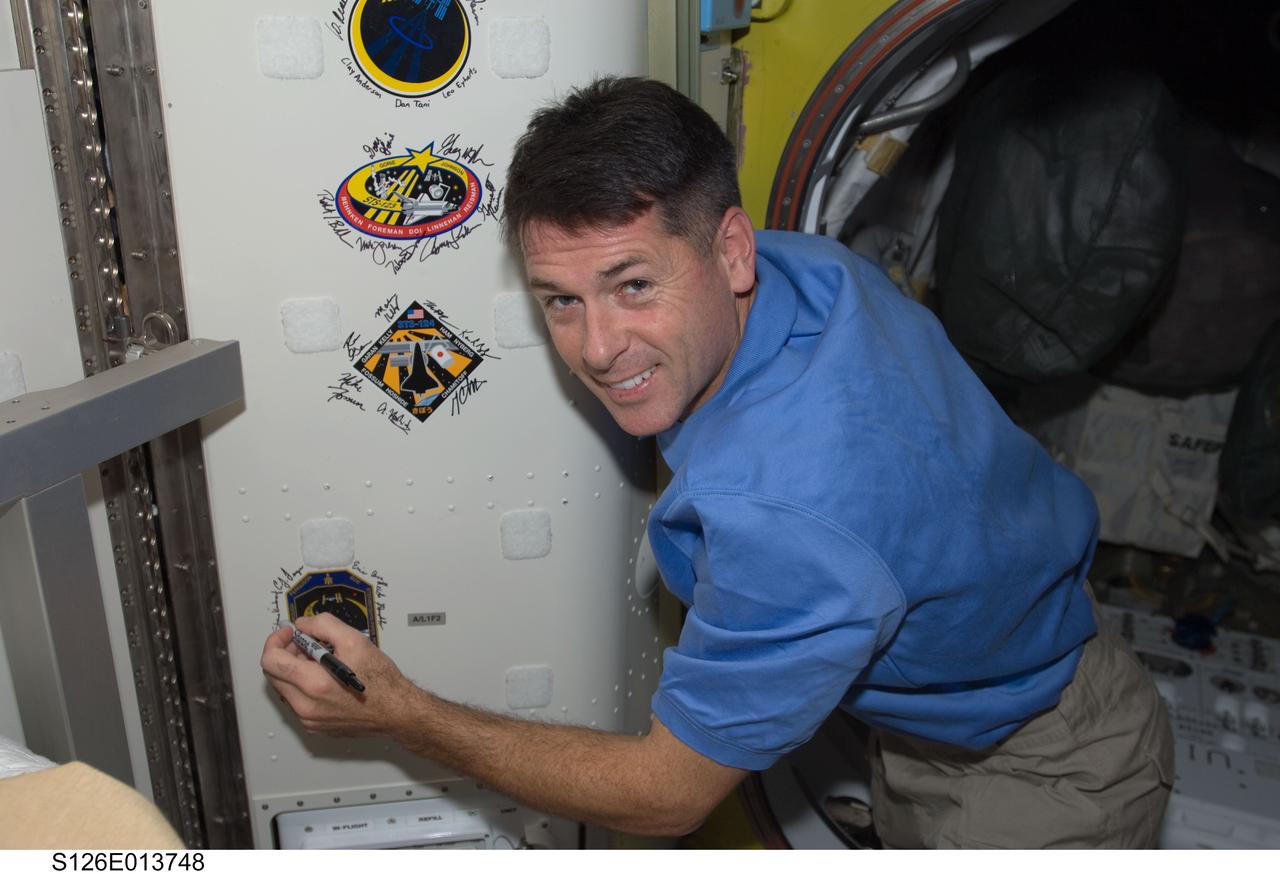

S126-E-013748 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Shane Kimbrough, STS-126 mission specialist, signs Endeavour's crew patch in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.

S126-E-013876 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, mission specialist, floats into the equipment area of the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.
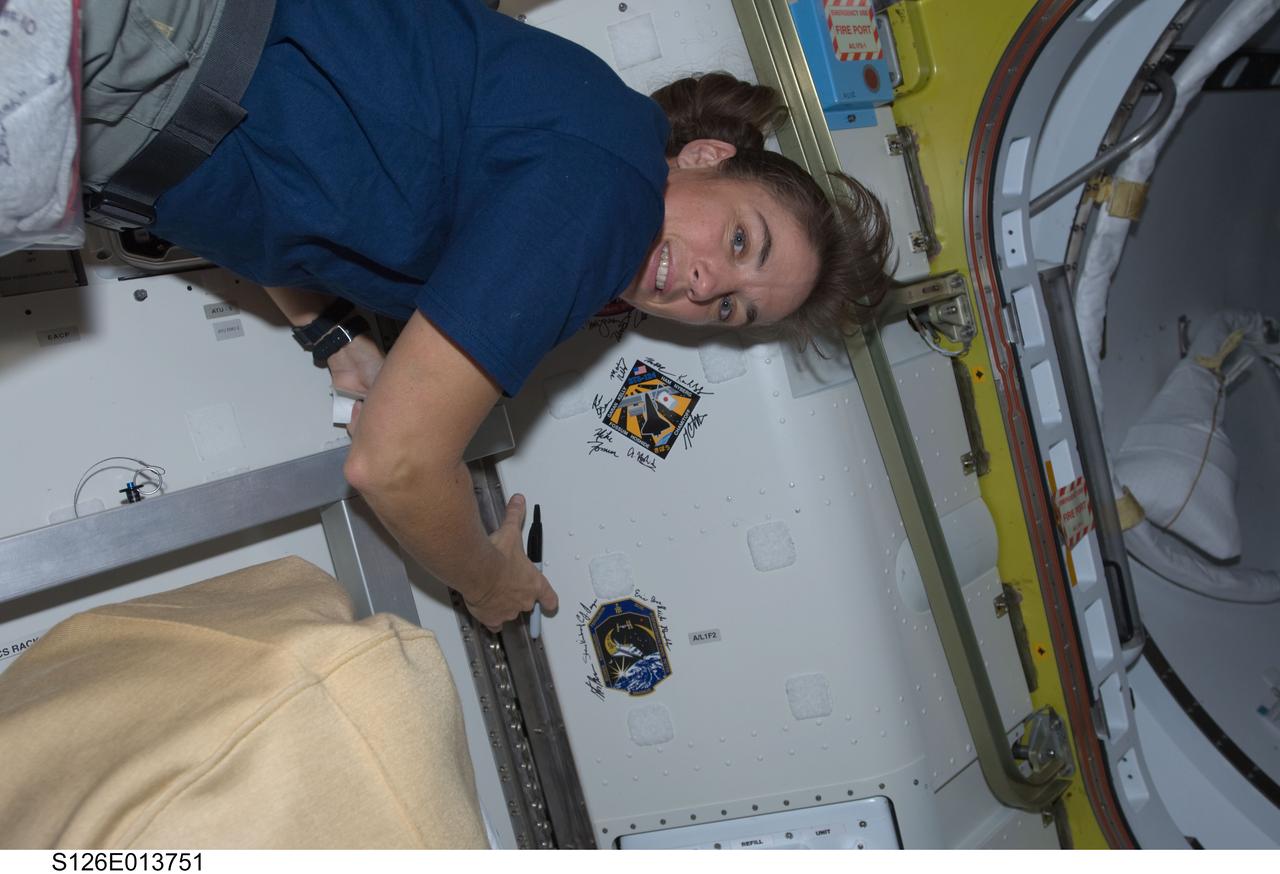

S126-E-013751 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper, STS-126 mission specialist, signs Endeavour's crew patch in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.
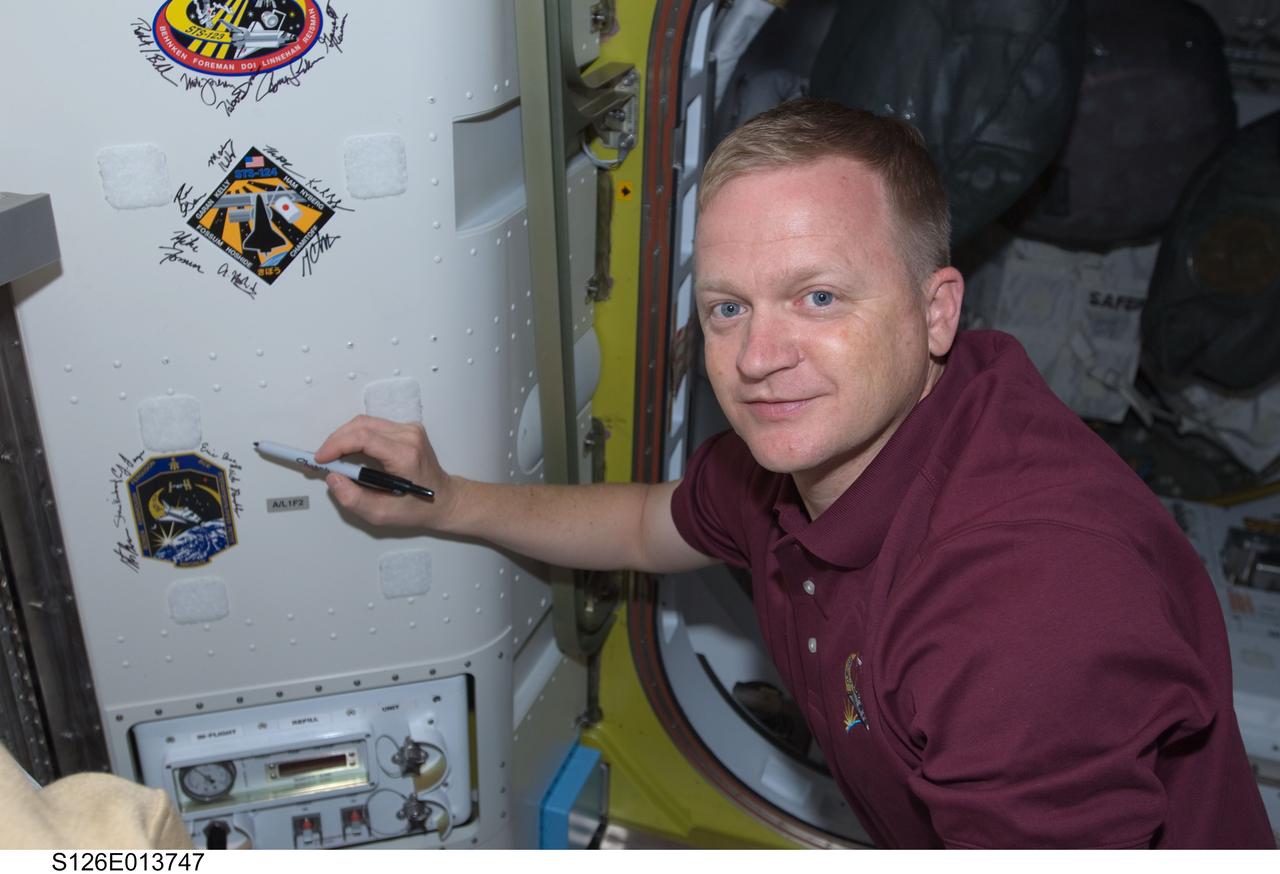

S126-E-013747 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Eric Boe, STS-126 pilot, signs Endeavour's crew patch in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station on Thanksgiving Day. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.
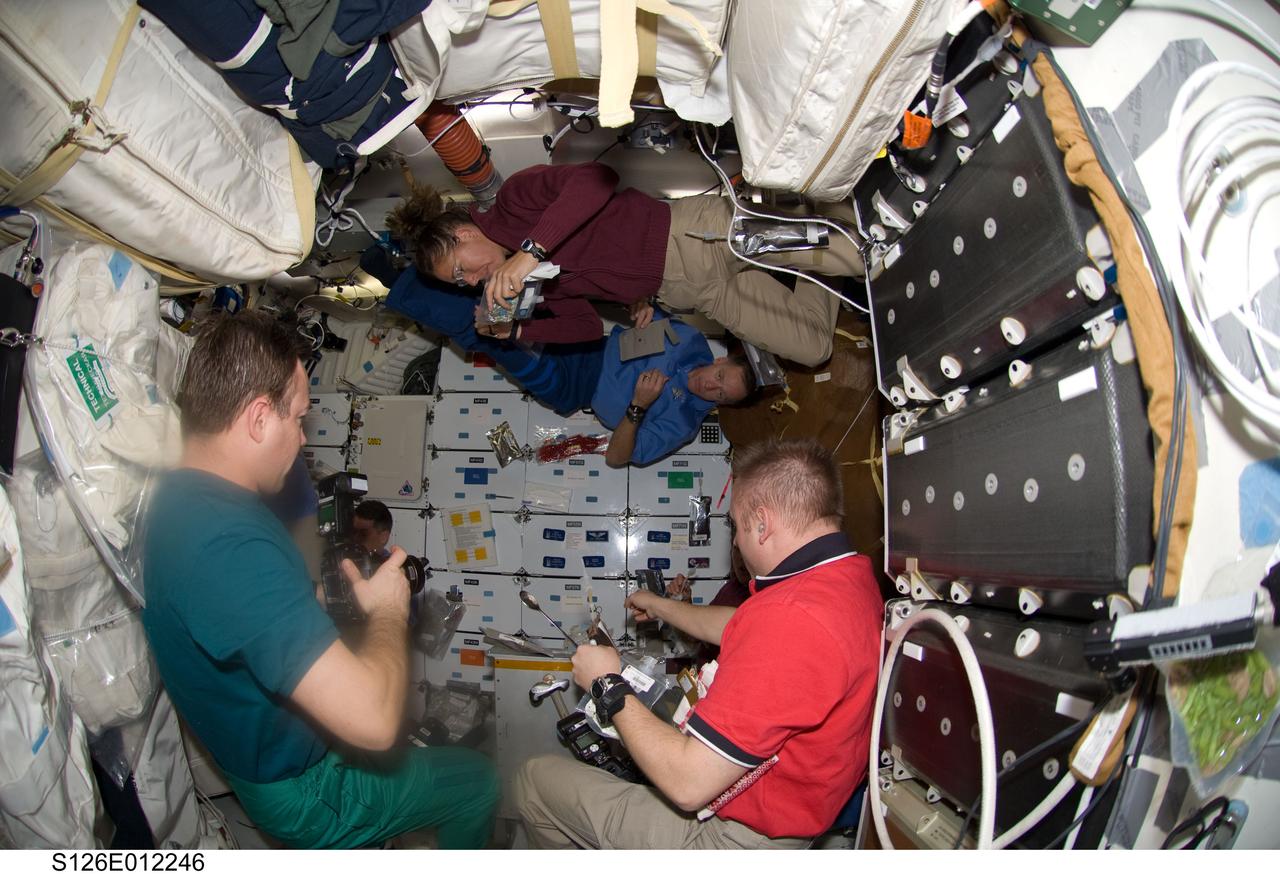

S126-E-012246 (27 Nov. 2008) --- As time winds down to an end of almost two weeks of joint activities between the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crewmembers, the station crew and the shuttle commander busy themselves with final chores on the middeck of the Space Shuttle Endeavour. From left to right are cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov and astronaut Sandra Magnus, both Expedition 18 flight engineers, along with astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-126 commander, and Michael Fincke, station commander.

S126-E-013902 (27 Nov. 2008) --- One of Endeavour's crew members recorded this image of one of the trusses on the International Space Station as crewmembers of both the shuttle and orbital outpost prepared to go separate ways on the following day. The nine astronauts and one cosmonaut did find time to work in a Thanksgiving meal and some brief traditional ceremonies.

S126-E-012093 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped against a massive cloud cover, the aft portion of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, with the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo in stow mode, was captured in a series of photographs by one of the STS-126 crewmembers on Nov. 27, Thanksgiving day, also the eve of departure from the International Space Station on Nov. 28.

S126-E-013825 (27 Nov. 2008) --- The STS-126 Endeavour astronauts and the Expedition 18 crewmembers during their shared activities aboard the International Space Station honored the 50th Anniversary of NASA in several ways, one of which was to display this special version of the event's poster. The image, showing clouds on Earth and part of the orbital outpost through an ISS window, was taken on Thanksgiving Day.
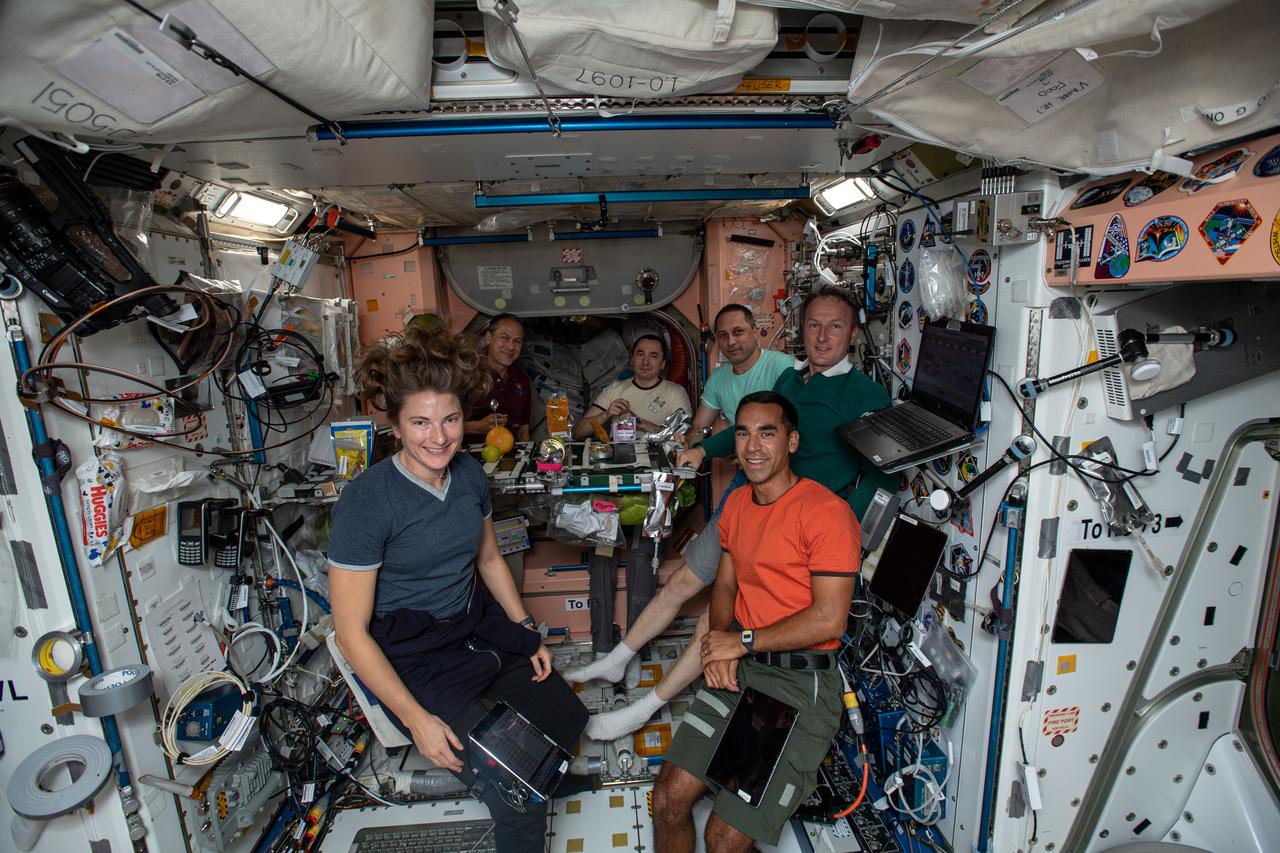

iss066e083000 (Nov. 25, 2021) --- Expedition 66 crew members gather for a Thanksgiving meal inside the International Space Station's Unity module. Clockwise from left, are NASA astronauts Kayla Barron and Thomas Marshburn; Roscosmos cosmonauts Pyotr Dubrov and Anton Shkaplerov; ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer; and NASA astronaut Raja Chari. Not pictured is NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei who was photographing his crewmates.
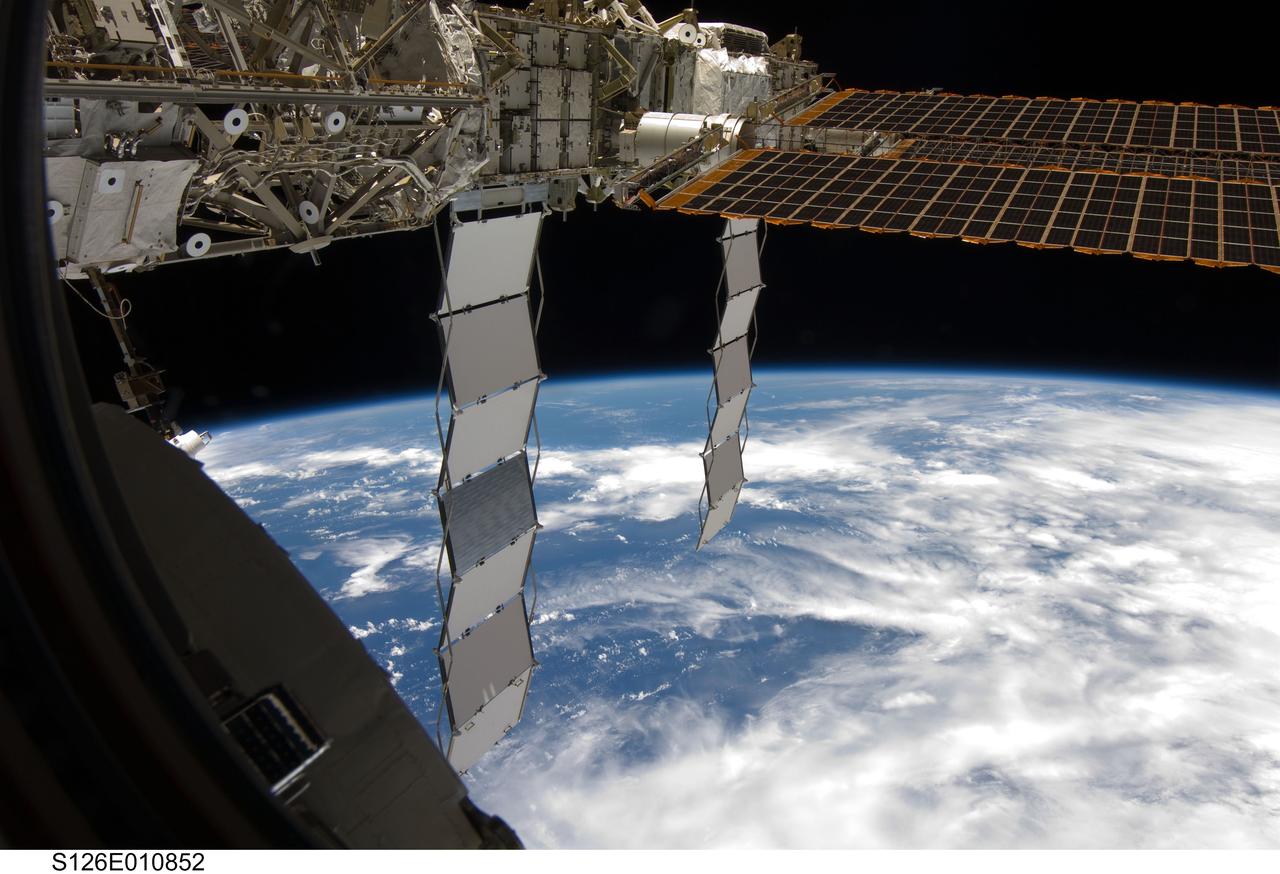

S126-E-010852 (26 Nov. 2008) --- From inside Endeavour, one of the STS-126 astronauts recorded this view of part of one of the International Space Station trusses and part of a solar panel, backdropped against a blue and white Earth on the eve of Thanksgiving. The ISS and Endeavour crewmembers, after spending almost two weeks together in space, will go separate ways in a couple of days when the two spacecraft undock.
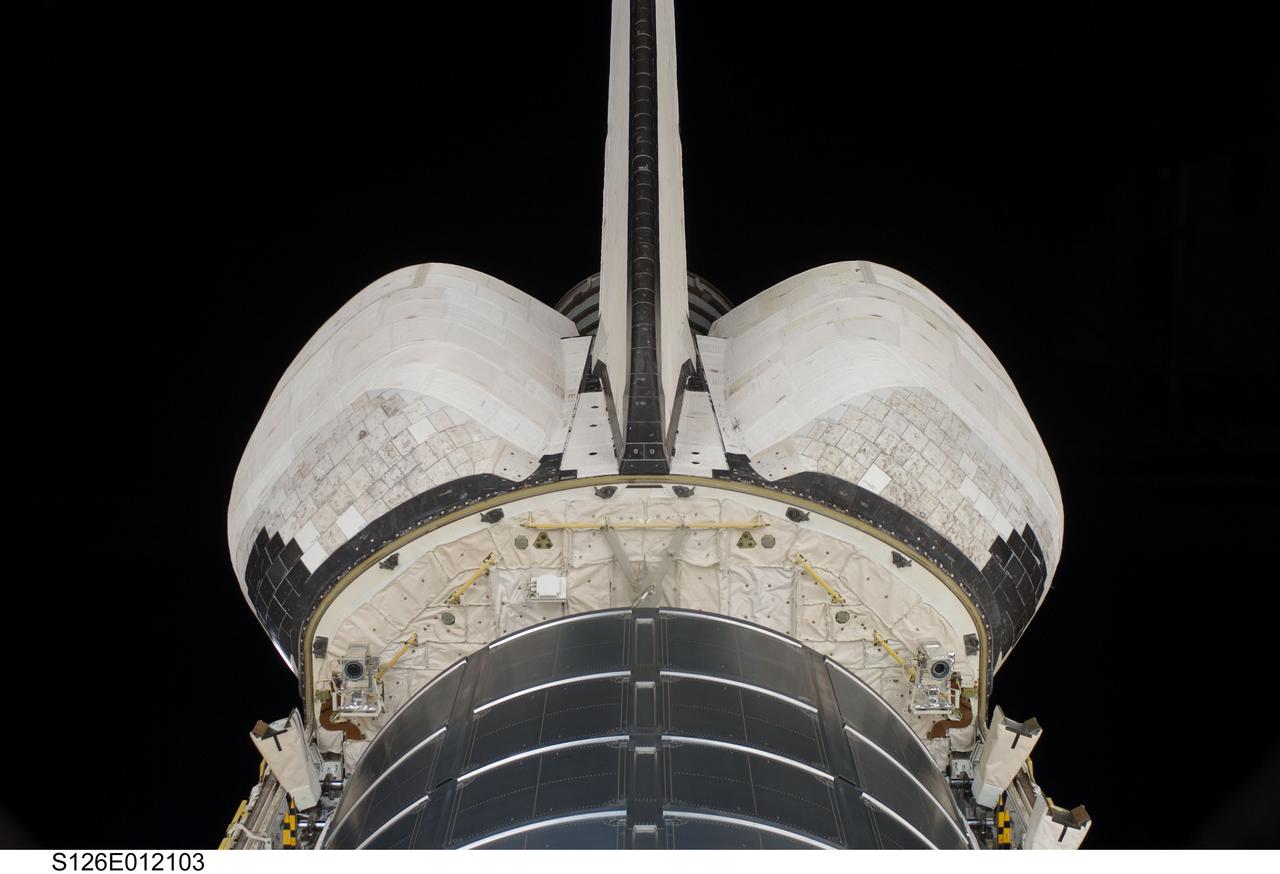

S126-E-012103 (27 Nov. 2008) --- --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the aft portion of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, with the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo in stow mode, was captured in a series of photographs by one of the STS-126 crewmembers on Nov. 27, Thanksgiving day, also the eve of departure from the International Space Station on Nov. 28.
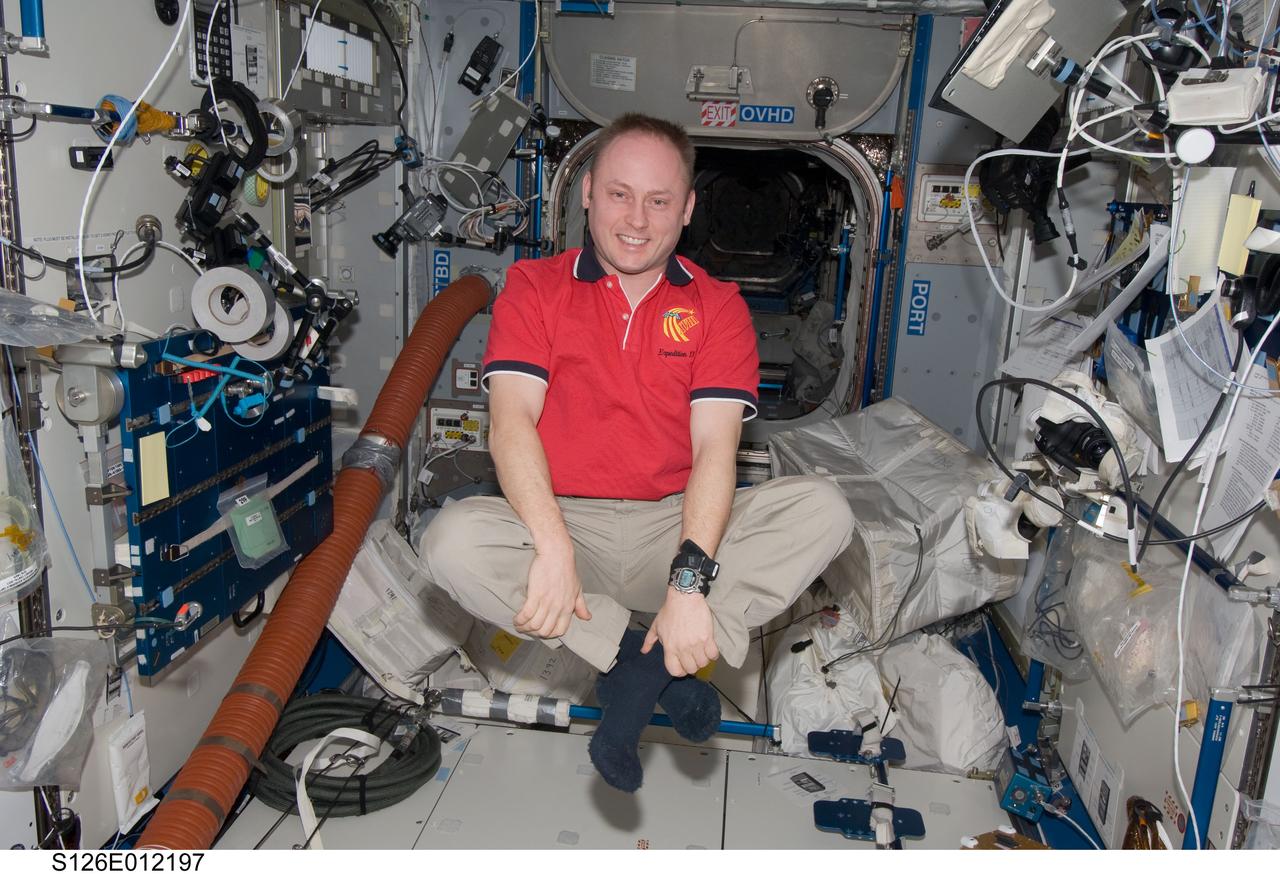

S126-E-012197 (27 Nov. 2008) --- It appears astronaut Michael Fincke, Expedition 18 commander, may be practicing his seating for an upcoming Thanksgiving meal. He had to leave this position in the Harmony or Node 2 of the International Space Station and traverse over to the Space Shuttle Endeavour for the meal, which he shared with two other station crew members and seven Endeavour astronauts.
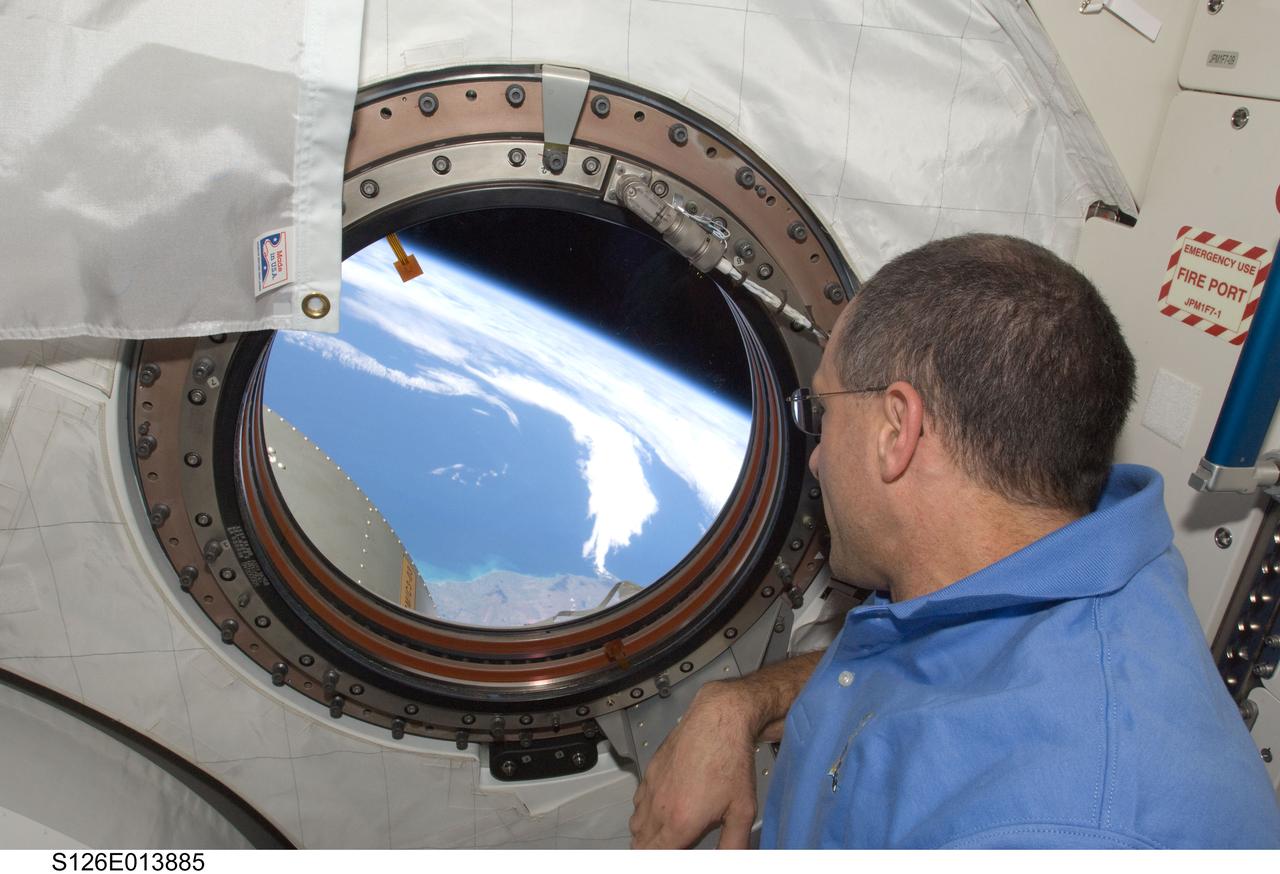

S126-E-013885 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Donald Pettit, STS-126 mission specialist, looks at the home planet from a window inside the Kibo laboratory on Thanksgiving Day. The brownish land in the foreground that Pettit is looking at is the southwest portion of the South Island of New Zealand and covers the coastal area between the cities of Timaru (north or left side of the image) and Dunedin on Sawyers Bay (south or right hand side of the photo). The white is cloud cover over the ocean. One more day remains for the Space Shuttle Endeavour to be docked with the station.
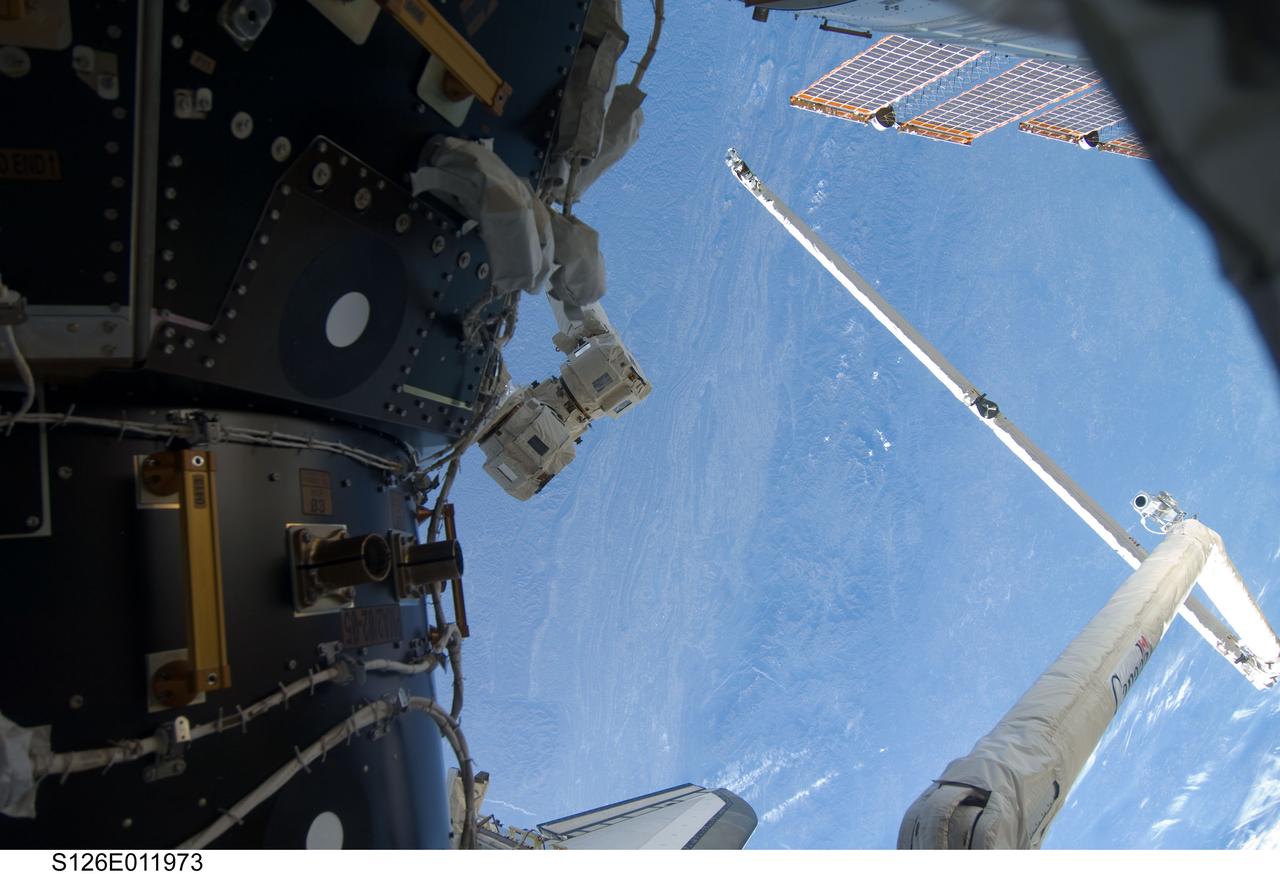

S126-E-011973 (26 Nov. 2008) --- The Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), in its parked position, and part of the International Space Station are featured in this image, photographed over the Blue Ridge Mountains of West Virginia and Tennessee by one of the Endeavour crew members on the eve of Thanksgiving. The OBSS, on the end of the Canadarm, awaits the final part of its STS-126 role when it will inspect the shuttle one more time, following separation of the orbiter from the space station in a couple of days. When that task is complete, it will be stowed across the payload bay from the robot arm.
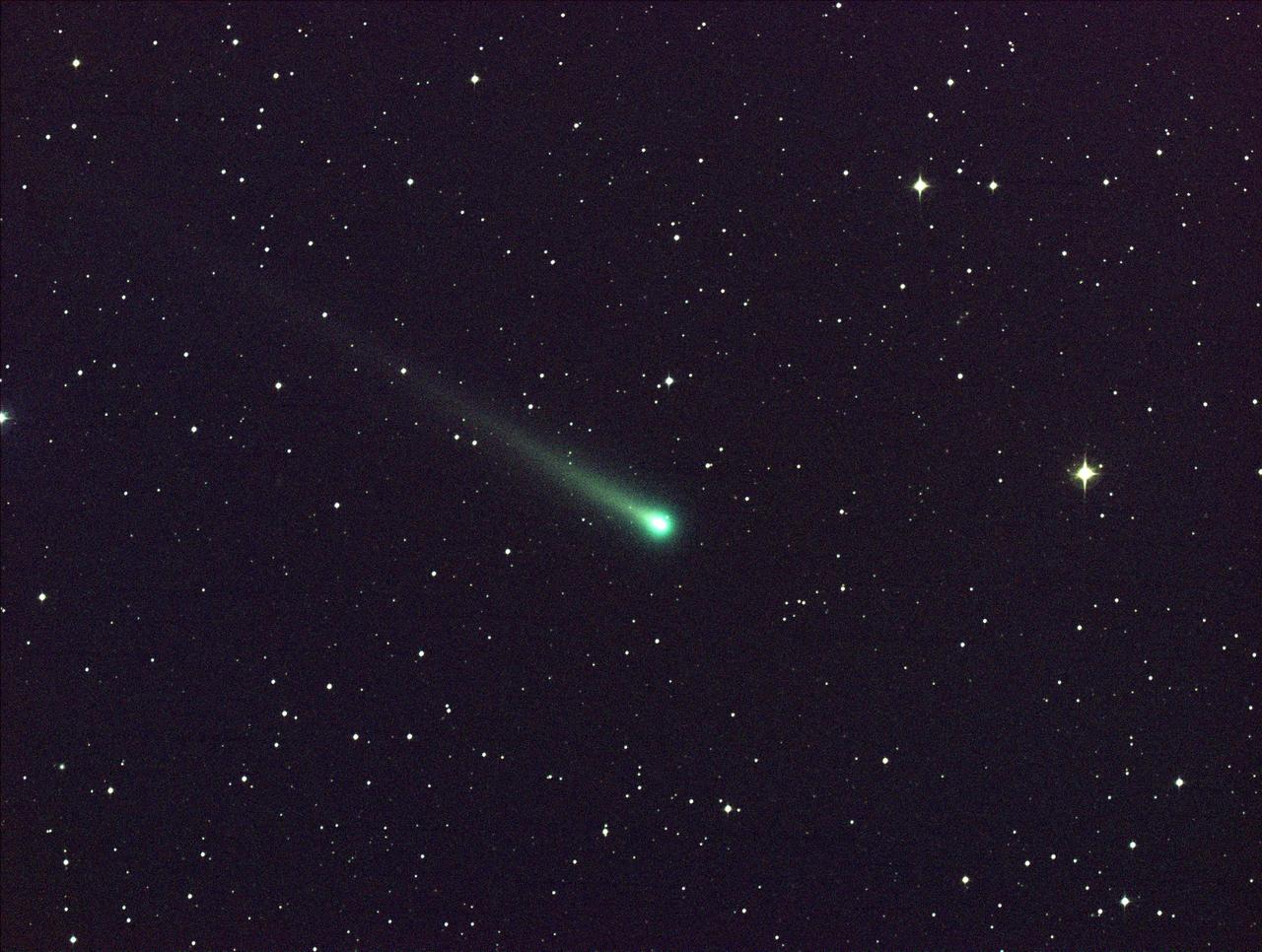

Date: 8 Nov 2013 - Comet ISON shines in this five-minute exposure taken at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center on Nov. 8, 2013.. The image was captured using a color CCD camera attached to a 14" telescope located at Marshall. At the time of this picture, comet ISON was 97 million miles from Earth, moving ever closer toward the sun. Credit: NASA/MSFC/Aaron Kingery -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
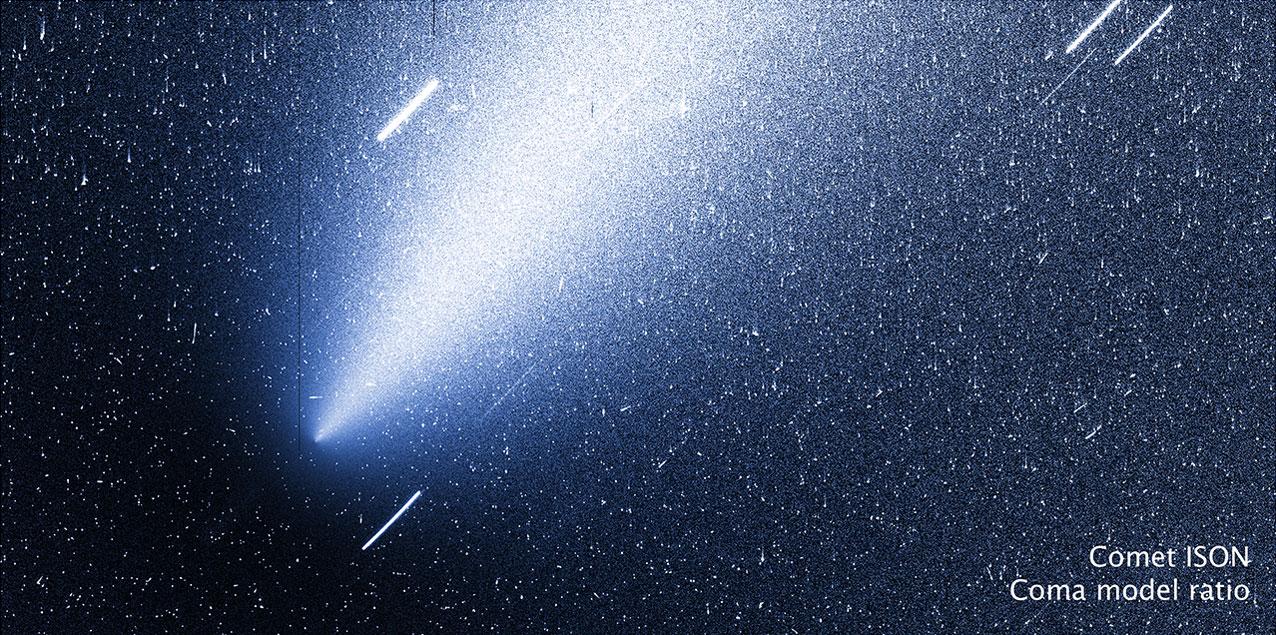

In this modeled image of ISON, the coma has been subtracted, leaving behind the nucleus. Credit: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (AURA/STScI) and Jian-Yang Li (Planetary Science Institute) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Taken on 19 Nov. 2013, this image shows a composite "stacked" image of comet ISON. These five stacked images of 10 seconds each were taken with the 20" Marshall Space Flight Center telescope in New Mexico. This technique allows the comet's sweeping tail to emerge with more detail. Credit: NASA/MSFC/MEO/Cameron McCarty -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/39501</b>
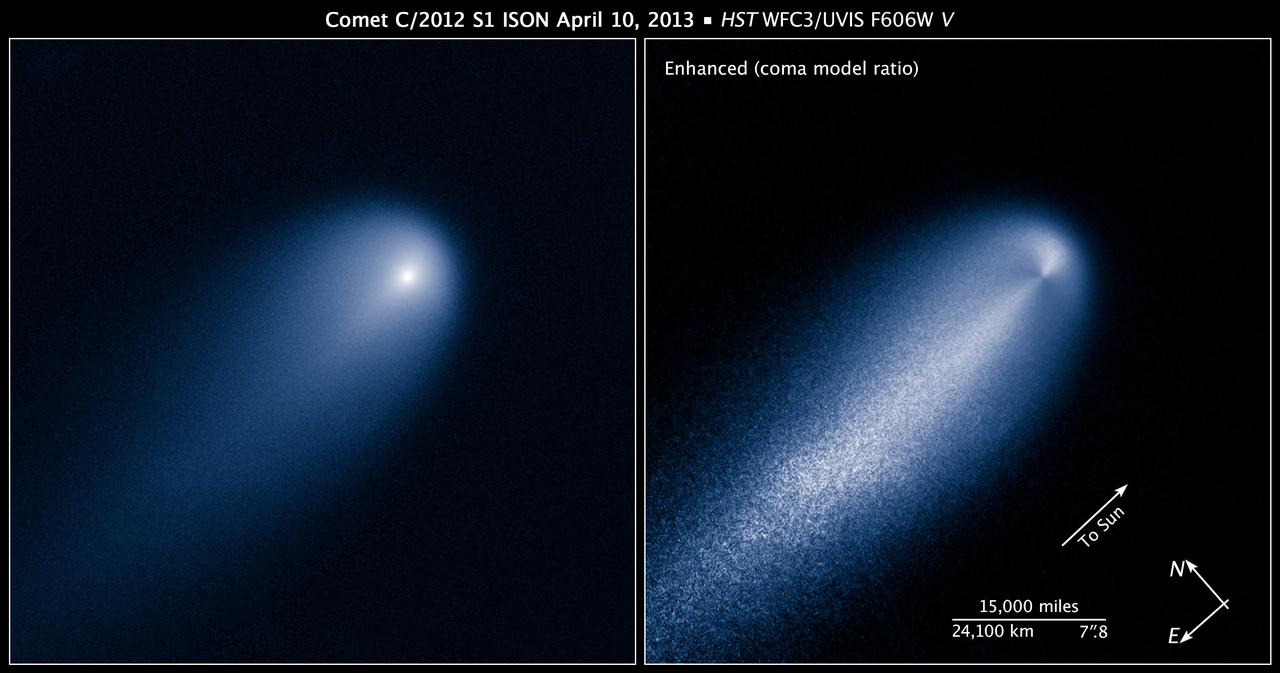

This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of Comet (C/2012 S1) ISON was photographed on April 10, 2013, when the comet was slightly closer than Jupiter's orbit at a distance of 394 million miles from Earth. Even at that great distance the comet is already active as sunlight warms the surface and causes frozen volatiles to boil off. Astronomers used such early images to try to measure the size of the nucleus, in order to predict whether the comet would stay intact when it slingshots around the sun -- at 700,000 miles above the sun's surface -- on Nov. 28, 2013. The comet's dusty coma, or head of the comet, is approximately 3,100 miles across, or 1.2 times the width of Australia. A dust tail extends more than 57,000 miles, far beyond Hubble's field of view. This image was taken in visible light. The blue false color was added to bring out details in the comet structure. Credit: NASA/ ESA/STScI/AURA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Godd</b>
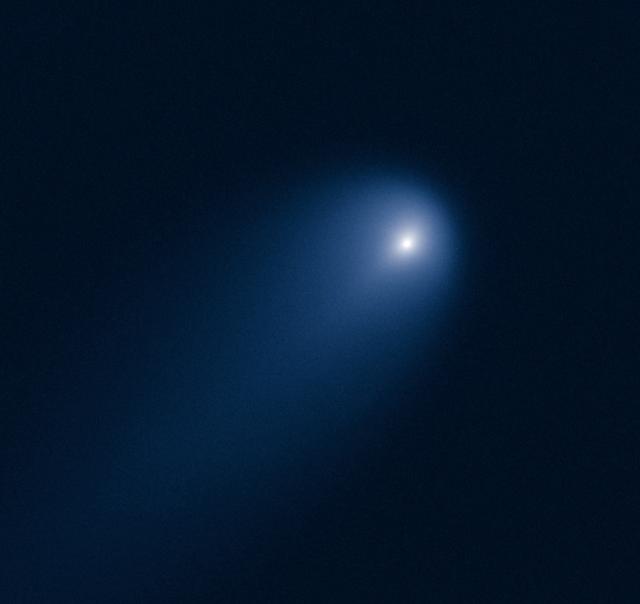

This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of Comet (C/2012 S1) ISON was photographed on April 10, 2013, when the comet was slightly closer than Jupiter's orbit at a distance of 394 million miles from Earth. Even at that great distance the comet is already active as sunlight warms the surface and causes frozen volatiles to boil off. Astronomers used such early images to try to measure the size of the nucleus, in order to predict whether the comet would stay intact when it slingshots around the sun -- at 700,000 miles above the sun's surface -- on Nov. 28, 2013. The comet's dusty coma, or head of the comet, is approximately 3,100 miles across, or 1.2 times the width of Australia. A dust tail extends more than 57,000 miles, far beyond Hubble's field of view. This image was taken in visible light. The blue false color was added to bring out details in the comet structure. Credit: NASA/ ESA/STScI/AURA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Godd</b>
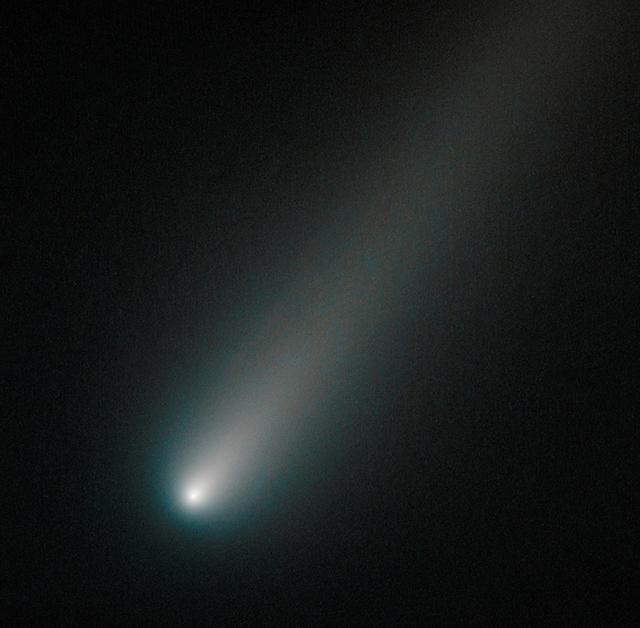

On Oct. 9, 2013, Hubble observed comet ISON once again, when it was inside the orbit of Mars, about 177 million miles from Earth. This image shows that the comet was still intact despite some predictions that the fragile icy nucleus might disintegrate closer to the sun. The comet will pass closest to the sun on Nov. 28, 2013. If the nucleus had broke apart then Hubble would have likely seen evidence of multiple fragments. Moreover, the coma, or head, surrounding the comet's nucleus is symmetric and smooth. This would probably not be the case if clusters of smaller fragments were flying along. This color composite image was assembled using two filters. The comet's coma appears cyan, a greenish-blue color due to gas, while the tail is reddish due to dust streaming off the nucleus. The tail forms as dust particles are pushed away from the nucleus by the pressure of sunlight. Credit: NASA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/39501</b>
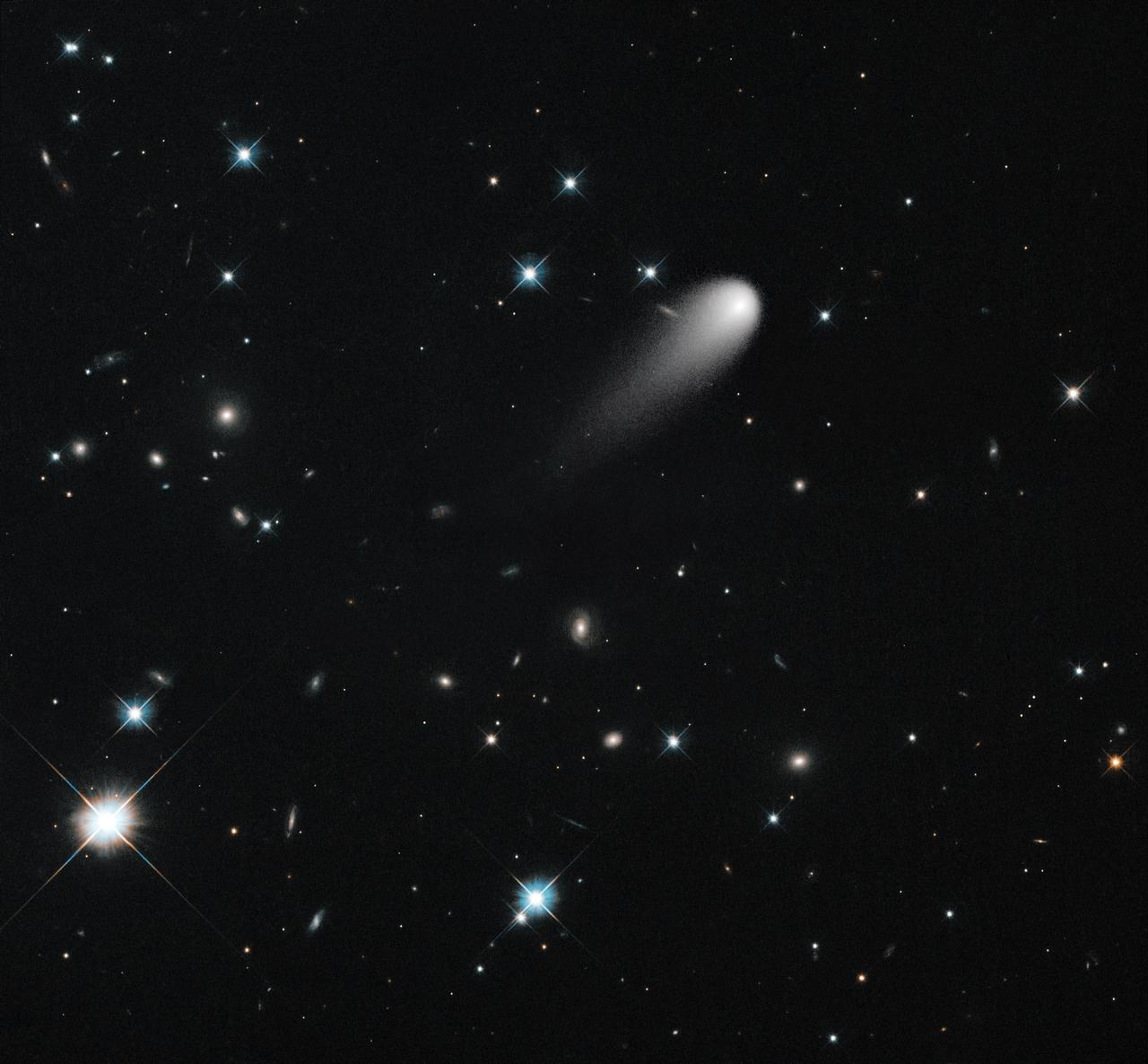

On April 30, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope observed Comet ISON again. The comet is in the upper middle, showing the long tail. Various galaxies and stars appear behind it. In this image, Hubble trained its telescope on the stars instead of following the comet. The result is that the comet appears fuzzier, but the stars and galaxies are more detailed and precise. These dimmer features don't pop out if the camera is moving, following along with ISON. To see them, you really need to dwell in one place until they emerge from the noise. Credit: NASA/ESA/STScI/AURA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
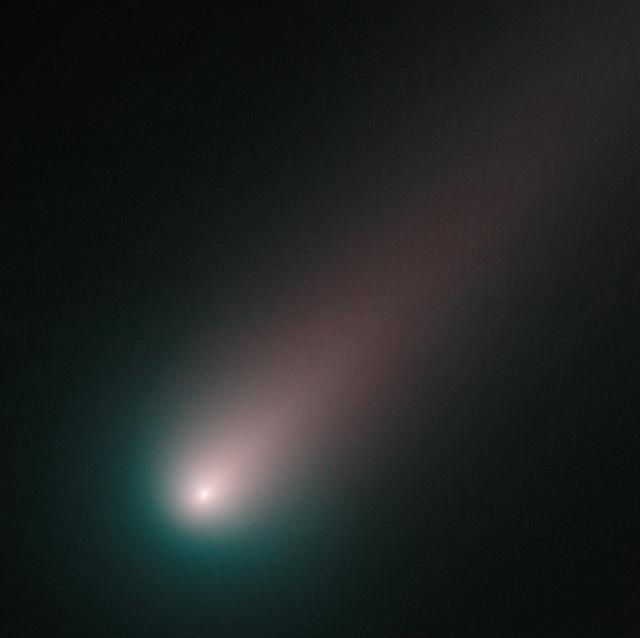

As of mid-November, ISON is officially upon us. Using Hubble, we've taken our closest look yet at the innermost region of the comet, where geysers of sublimating ice are fueling a spectacular tail. Made from observations on November 2nd, the image combines pictures of ISON taken through blue and red filters. As we expect, the round coma around ISON's nucleus is blue and the tail has a redder hue. Ice and gas in the coma reflect blue light from the Sun, while dust grains in the tail reflect more red light than blue light. This is the most color separation we've seen so far in ISON -- that's because the comet, nearer than ever to the Sun, is brighter and more structured than ever before. We've certainly come a long way since Hubble started observing Comet ISON, way back in April. Of course, our eight-month retrospective pales in comparison with ISON's own journey, which started some 10,000 years ago in the Oort cloud. ISON will come closest to the Sun on November 28, a point in its orbit known as perihelion. What's remarkable here is that the entire ISON, this awesome, shimmery space tadpole, is being produced from a dusty ball of ice estimated to be a few kilometers in diameter. Compared to ISON's full extent, Hubble's latest image is tiny. It only shows the very base of the tail. Yet even in this closest closeup we've ever had, a single pixel spans 24 km across the comet. Now that Comet ISON is close, amateur astromers rule the day. But Hubble observations, including this latest image, are still providing key insights into the science and spectacle of a comet we hope will continue to impress. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is
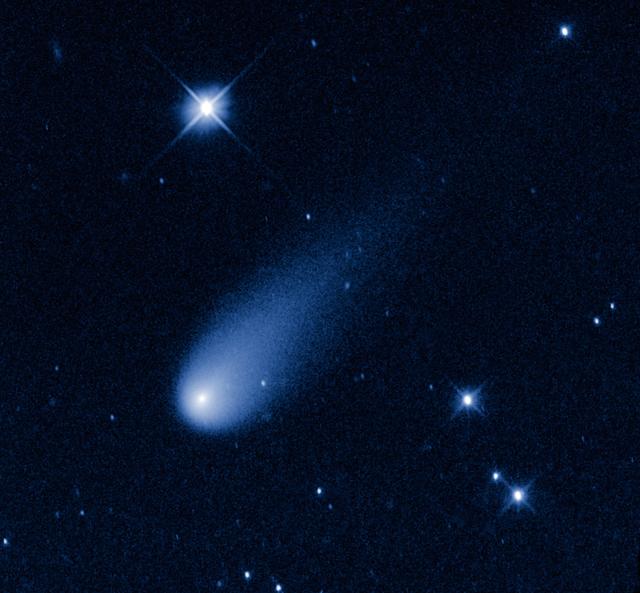

Superficially resembling a skyrocket, Comet ISON is hurtling toward the Sun at a whopping 48,000 miles per hour. Its swift motion is captured in this image taken May 8, 2013, by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. At the time the image was taken, the comet was 403 million miles from Earth, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Unlike a firework, the comet is not combusting, but in fact is pretty cold. Its skyrocket-looking tail is really a streamer of gas and dust bleeding off the icy nucleus, which is surrounded by a bright, star-like-looking coma. The pressure of the solar wind sweeps the material into a tail, like a breeze blowing a windsock. As the comet warms as it moves closer to the Sun, its rate of sublimation will increase. The comet will get brighter and the tail grows longer. The comet is predicted to reach naked-eye visibility in November. The comet is named after the organization that discovered it, the Russia-based International Scientific Optical Network. This false-color, visible-light image was taken with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scienti

Date: 19 Nov 2013 Comet ISON shows off its tail in this three-minute exposure taken on 19 Nov. 2013 at 6:10 a.m. EST, using a 14-inch telescope located at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The comet is just nine days away from its close encounter with the sun; hopefully it will survive to put on a nice show during the first week of December. The star images are trailed because the telescope is tracking on the comet, which is now exhibiting obvious motion with respect to the background stars over a period of minutes. At the time of this image, Comet ISON was some 44 million miles from the sun -- and 80 million miles from Earth -- moving at a speed of 136,700 miles per hour. Credit: NASA/MSFC/Aaron Kingery -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/39501</b>

This collage shows some of the most interesting geological sites that NASA's Dawn spacecraft has revealed at dwarf planet Ceres. Images were acquired with the spacecraft's framing camera during various phases of the mission: Survey orbit at a distance of about 2,700 miles (4,400 kilometers); high-altitude mapping orbit (HAMO) at a distance of 915 miles (1,470 kilometers) from Ceres; and low-altitude mapping orbit (LAMO) at an altitude of 240 miles (385 kilometers). In the first row, from left to right: Ceres in shown in false color, roughly centered on Occator Crater, home of the brightest area on Ceres. This picture combines color images obtained by Dawn in its survey orbit. Red corresponds to a wavelength range around 980 nanometers (near infrared), green to a wavelength range around 750 nanometers (red, visible light) and blue to a wavelength range of around 430 nanometers (blue, visible light). This picture illustrates the diversity of terrains on Ceres where the bluish material points to recently emplaced material and the brownish background material is associated with older terrains. Juling Crater (12 miles, 20 kilometers in diameter) as seen in LAMO. Central coordinates are 36 degrees south latitude, 168 degrees east longitude. It is named after the Sakai/Orang Asli (Malaysia) spirit of the crops. This crater displays evidence for the presence of ice -- for example, in the form of a large flow feature seen at the top of the image. Oxo Crater (6 miles, 10 kilometers in diameter) as seen in LAMO. Center coordinates are 42 degrees north latitude, 0 degrees east longitude. It is named after the god of agriculture in Afro-Brazilian beliefs of Yoruba derivation. Oxo hosts the first site at which Dawn detected ice on Ceres, exposed by a landslide. Ahuna Mons is not only a volcano, but also the tallest mountain on Ceres. It is about 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) high and 11 miles (17 kilometers) wide. Center coordinates are 10 degrees south latitude, 316 degrees east longitude. This view combines images obtained in LAMO in blue (430 nanometers), green (750 nanometers) and infrared (980 nanometers) color filters. Ahuna is named after the Sumi tribe (Nagaland, northeastern India) traditional post-harvest thanksgiving festival. Second Row Occator Crater (57 miles, 92 kilometers across) is seen in LAMO images. Center coordinates are 20 degrees north latitude, 239 degrees east longitude. Named after the Roman agricultural deity of the harrowing. This image shows a "Type I" flow feature with a thick "toe" typical of rock glaciers and icy landslides on Earth as viewed in LAMO. The flow feature, found in Ghanan Crater (77 degrees north latitude, 31 degrees east longitude), is one of the most voluminous on Ceres. Enhanced color view of Haulani Crater (21 miles, 34 kilometers in diameter) in color observed in HAMO. Central coordinates: 6 degrees north latitude, 11 degrees east longitude. Named after the Hawaiian plant goddess. Kokopelli Crater (21 miles, 34 kilometers in diameter) seen in LAMO. Central coordinates: 18 degrees north latitude, 125 degrees east longitude. Named after the Pueblo (SW USA) fertility deity, who presides over agriculture. This crater displays a nice arrangement of scarps that likely formed when the crater partly collapsed during its formation. Third Row Central region of Occator Crater, called Cerealia Facula, seen in color. The facula -- or "bright spot" -- is about 9 miles (14 kilometers) in diameter. Center coordinates: 20 N, 240 E. Cerealia refers to the major festival in Ancient Rome that celebrates the grain goddess Ceres (8 days in mid- to late April). The view was produced by combining the highest resolution images of Occator obtained in LAMO (at image scales of 35 meters, or 115 feet, per pixel) with color images obtained in HAMO (at image scales of 135 meters, or about 440 feet, per pixel). The three images used to produce the color were taken using filters centered at 430, 750 and 980 nanometers (the last being slightly beyond the range of human vision, in the near-infrared). North part of Nar Sulcus seen in LAMO. The full feature is about 39 miles (63 km) in length and is located around 42 degrees south latitude, 280 degrees east longitude. Nar is a Azerbaijani festival of pomegranate harvest held in October-November in Goychay city, center of pomegranate cultivation in Azerbaijan. A sulcus is a set of parallel furrows or ridges. Ikapati Crater (31 miles, 50 kilometers in diameter) seen in LAMO. Central coordinates: 34 degrees north latitude, 46 degrees east longitude. Ikapati is named after the Philippine goddess of the cultivated lands. The crater has a smooth floor, probably because heat from the impact that formed Ikapati caused ice in the ground to melt, and then refreeze. This view of Ceres, taken in LAMO, shows an area located at approximately 86 degrees south longitude, 177 degrees east longitude. This part of Ceres, near the south pole, has such long shadows because, from the perspective of this location, the sun is near the horizon. At the time this image was taken, the sun was 4 degrees north of the equator. If you were standing this close to Ceres' south pole, the sun would never get high in the sky during the course of a nine-hour Cerean day. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22090