When the Going Gets Weird, the Weird Turn Pro
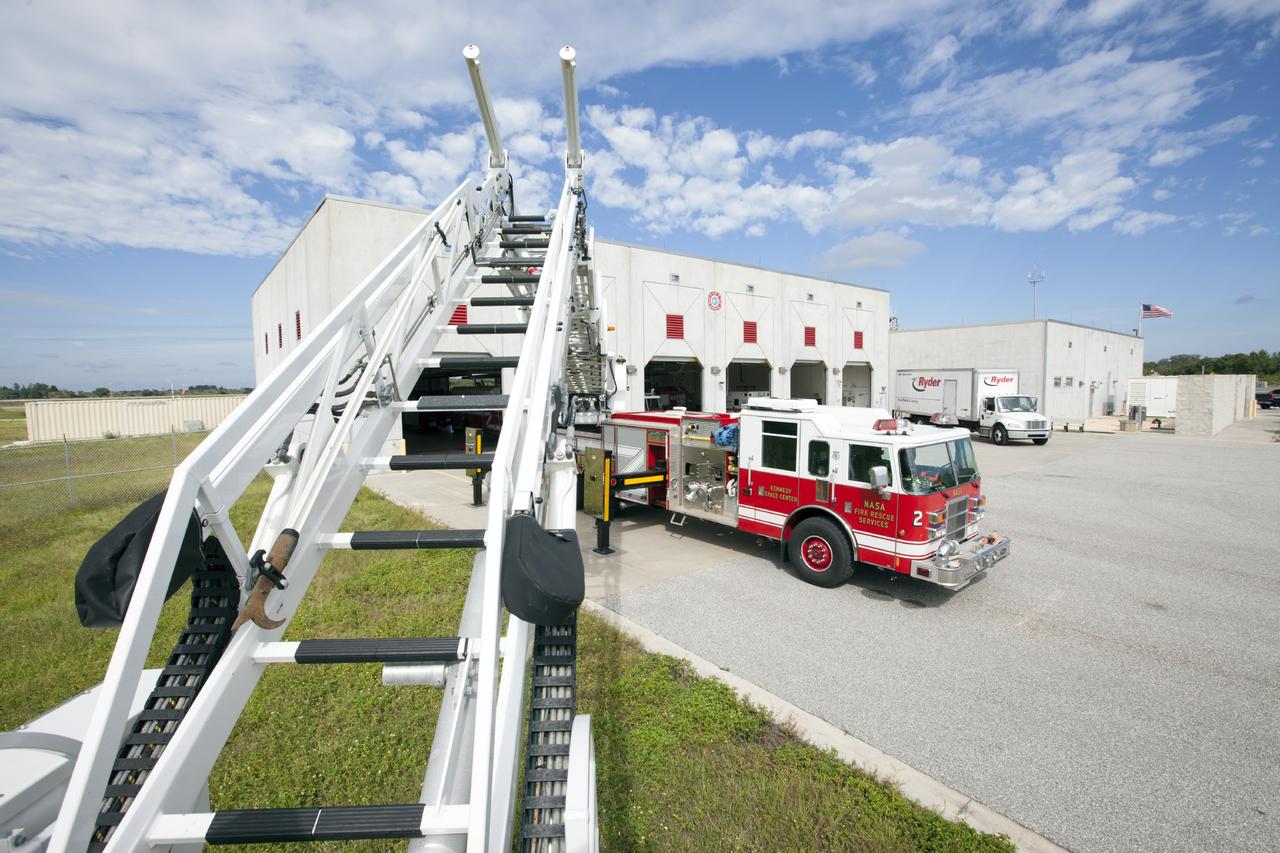

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel have deployed and extended the ladder on the aerial fire truck during training in order to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The stabilizers have been deployed on either side of the fire truck. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
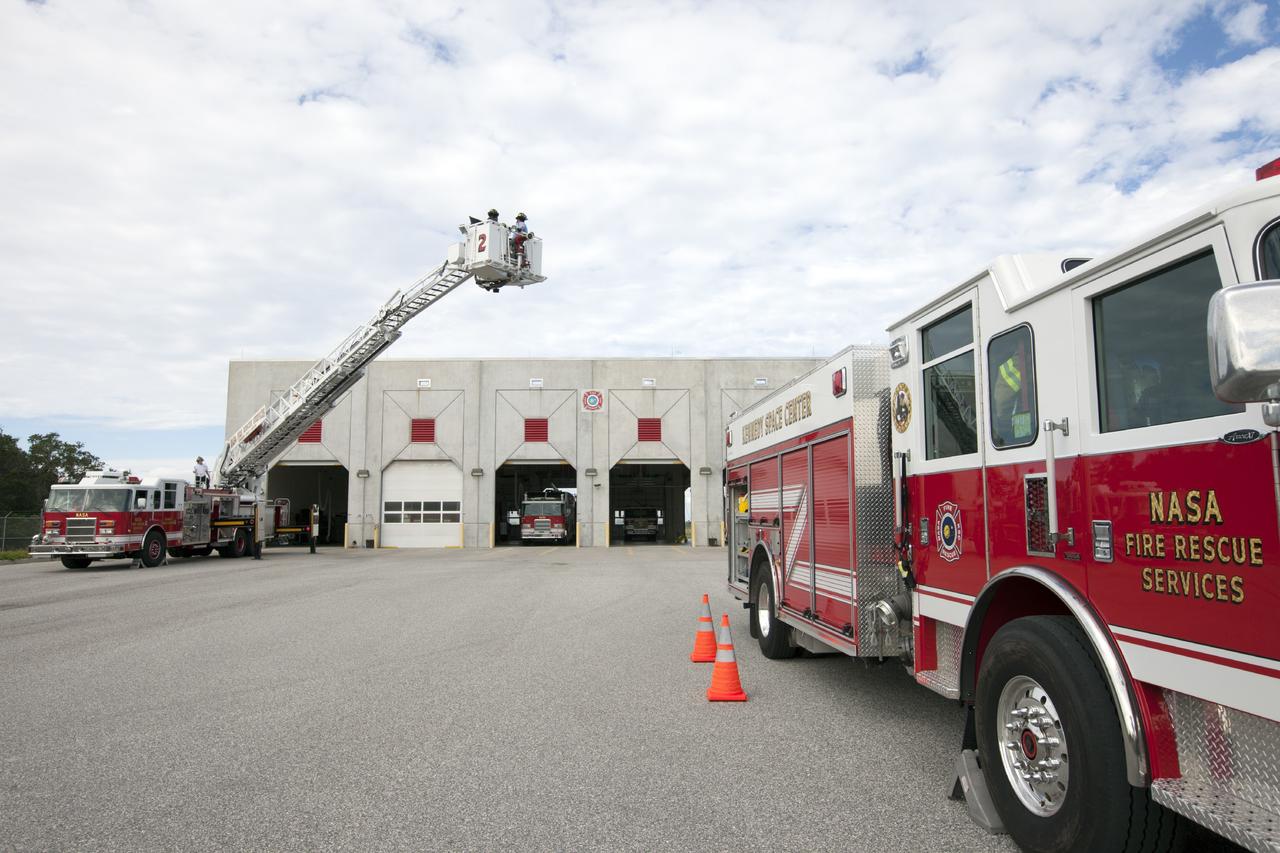

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel have deployed and extended the ladder on the aerial fire truck during training in order to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. Two fire rescue workers are in the bucket practicing harness procedures. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
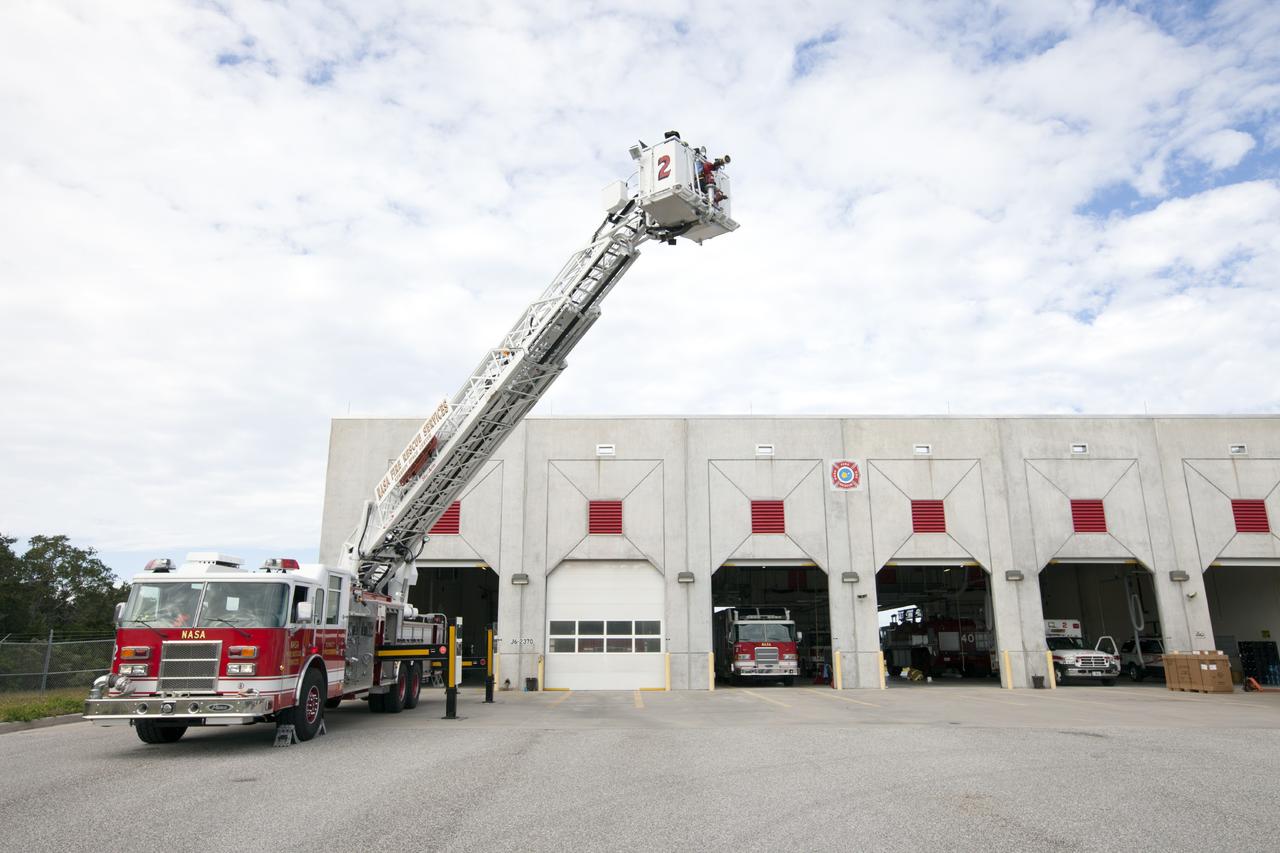

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel have deployed the ladder on the aerial fire truck during training in order to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
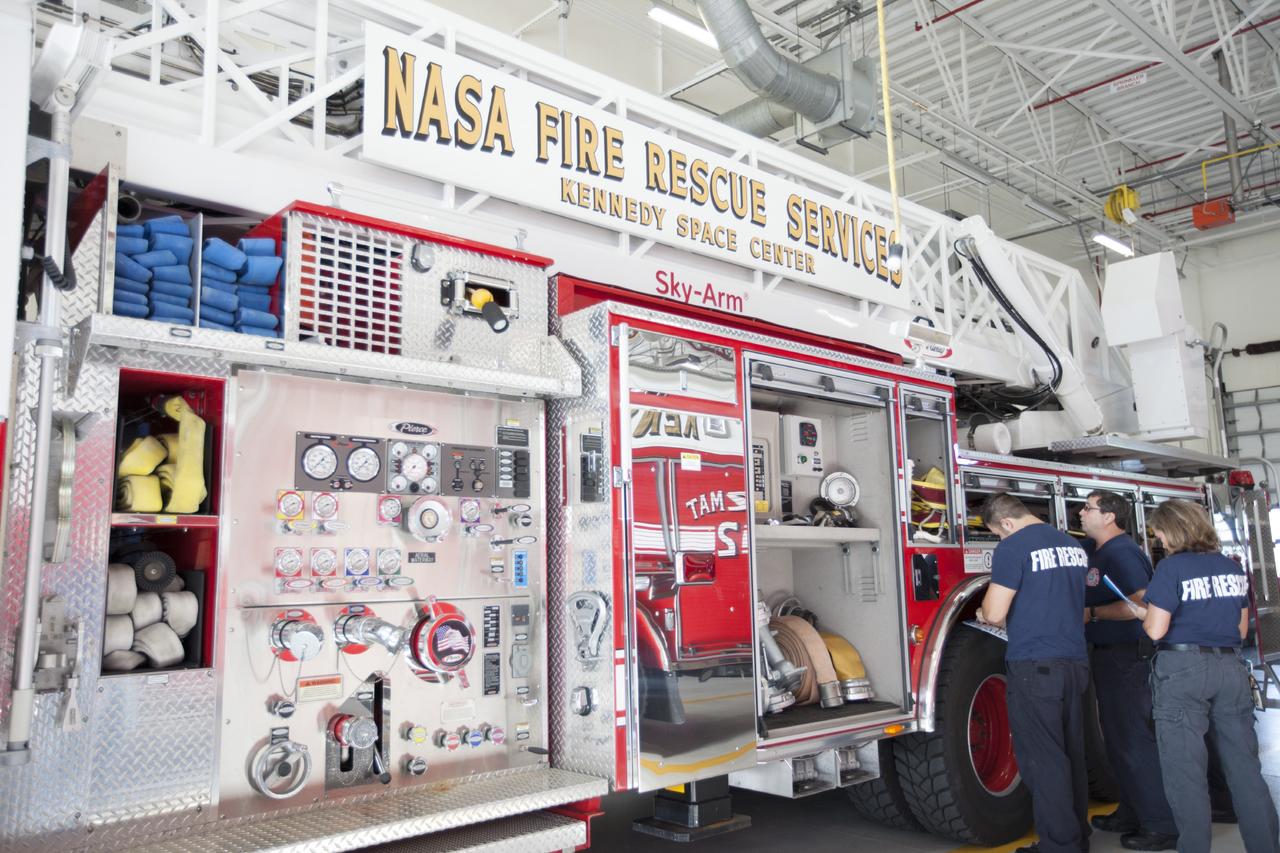

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel review procedures and check equipment on the aerial fire truck as part of the training to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
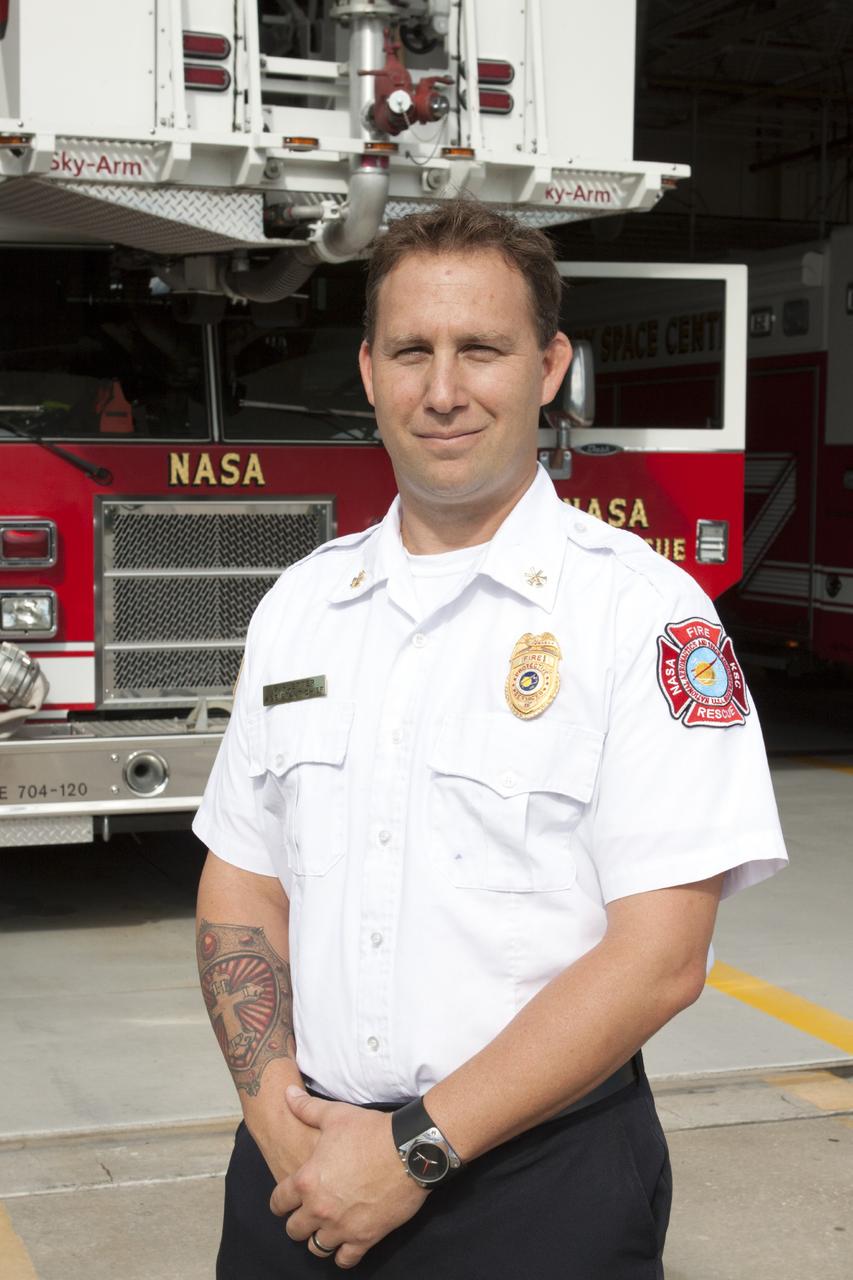

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mark Huetter, assistant chief of training with the center’s Fire Department, prepares to train Fire Rescue Services personnel in the operation and use of the aerial fire truck. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
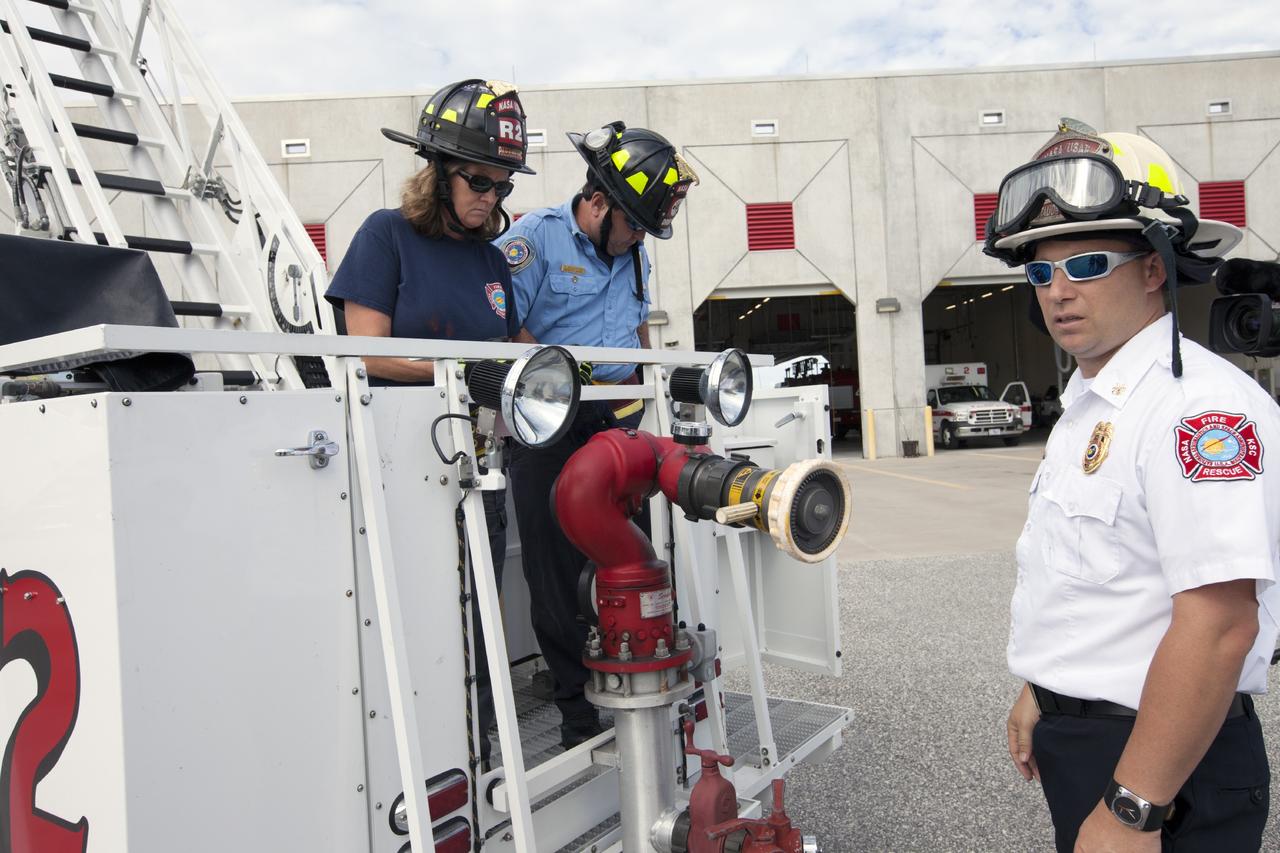

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mark Huetter, assistant chief of training with the center’s Fire Department, monitors training procedures as two Fire Rescue Services personnel prepare to exit the bucket after training on the aerial fire truck. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
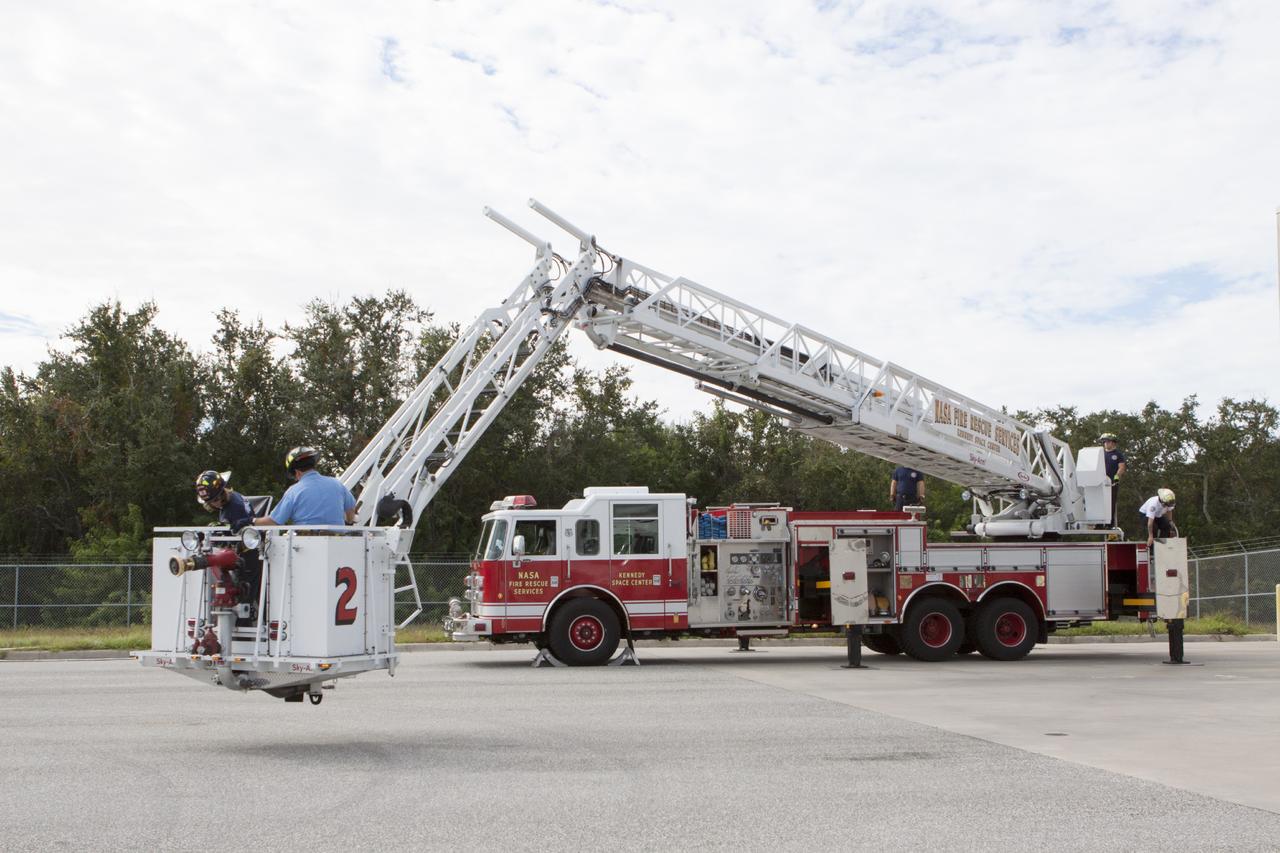

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel lower the extendable ladder so that two fire rescue workers can exit the bucket during training to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
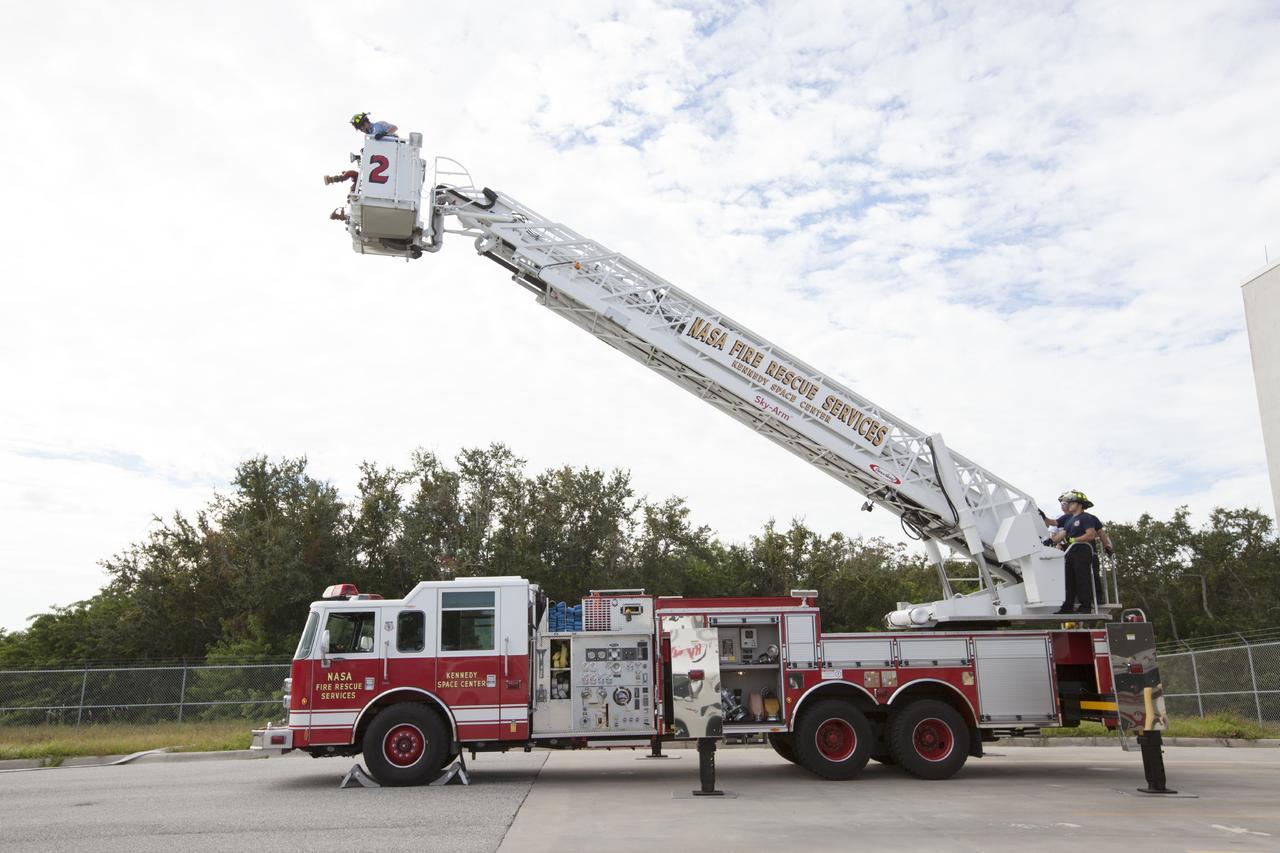

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel have deployed the ladder on the aerial fire truck during training in order to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
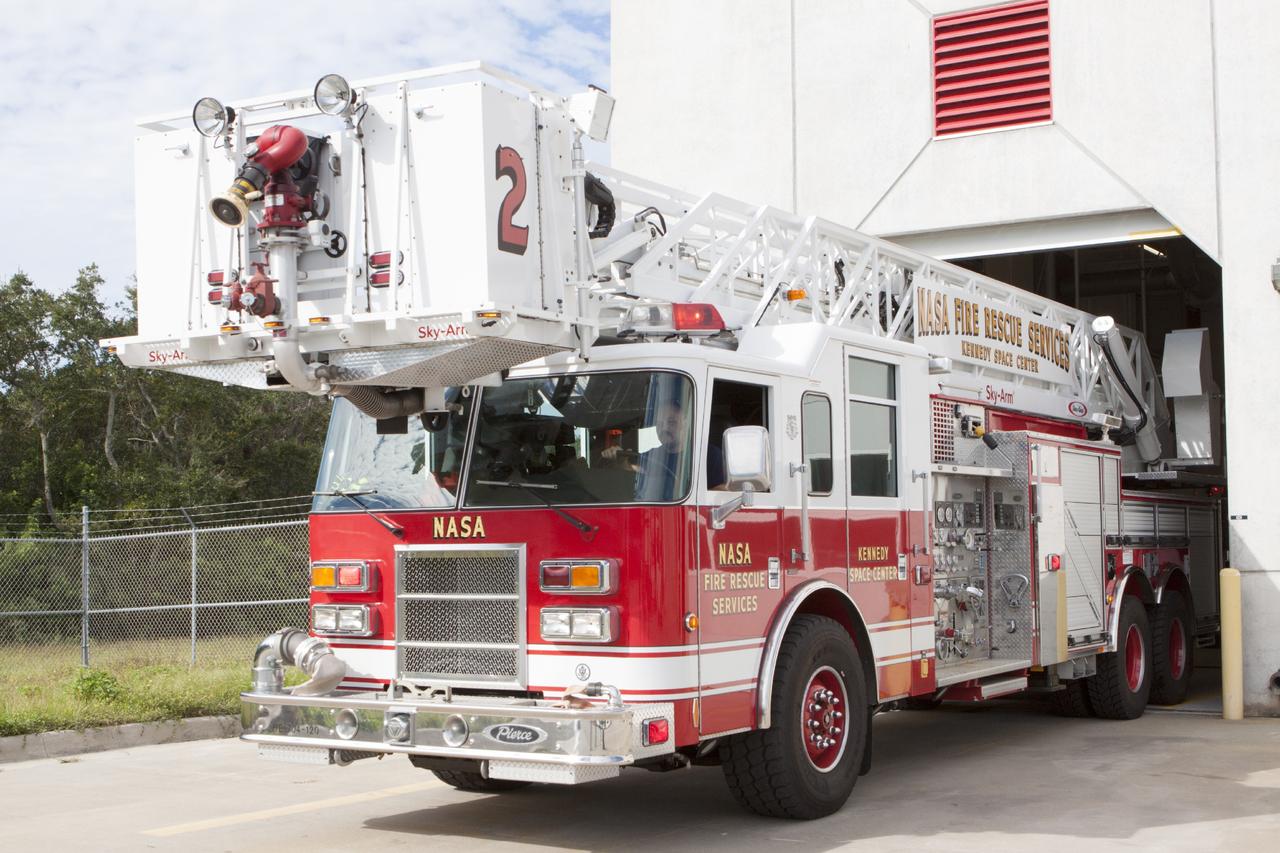

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the aerial fire truck is being driven out of the bay so that Fire Rescue Services personnel can be trained and certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
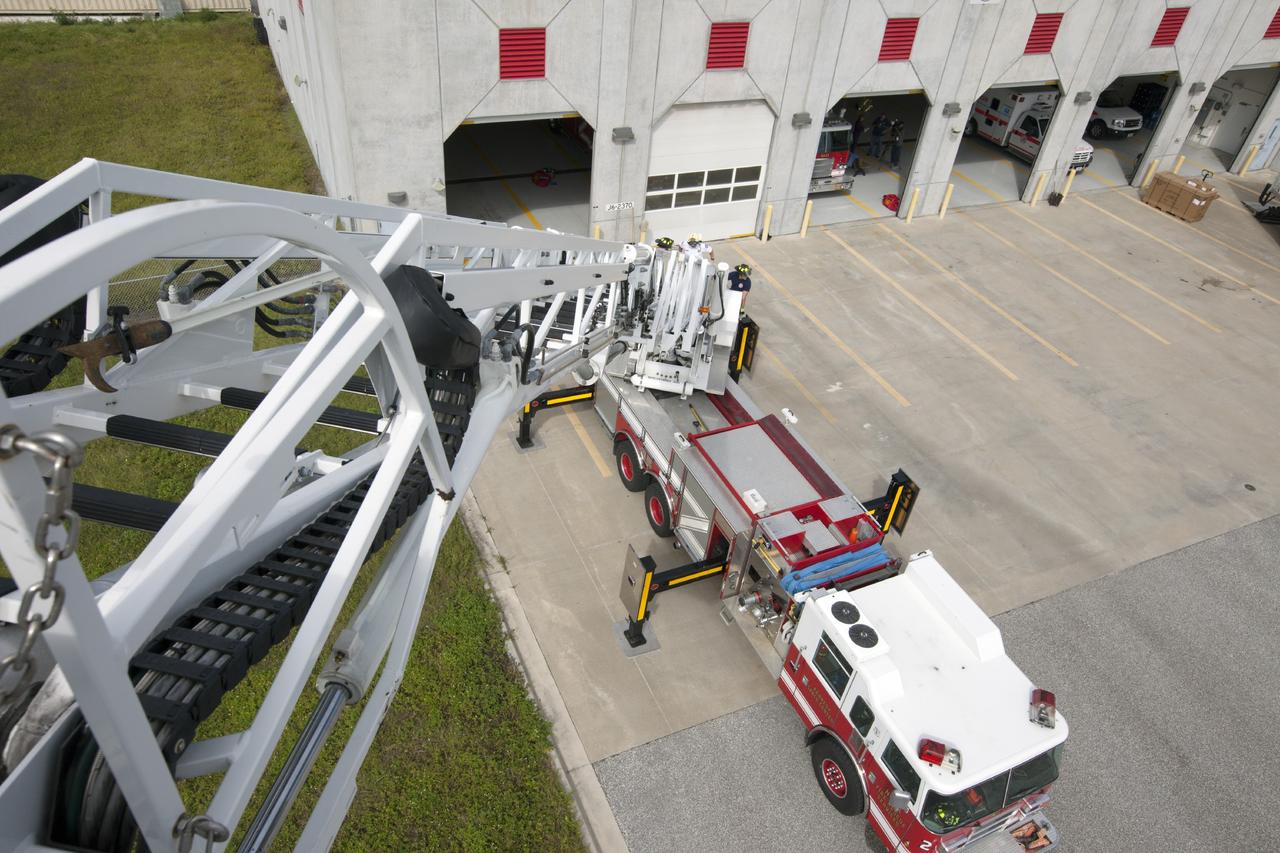

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a bird’s eye view reveals the ladder has been extended on the aerial fire truck during a training exercise. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
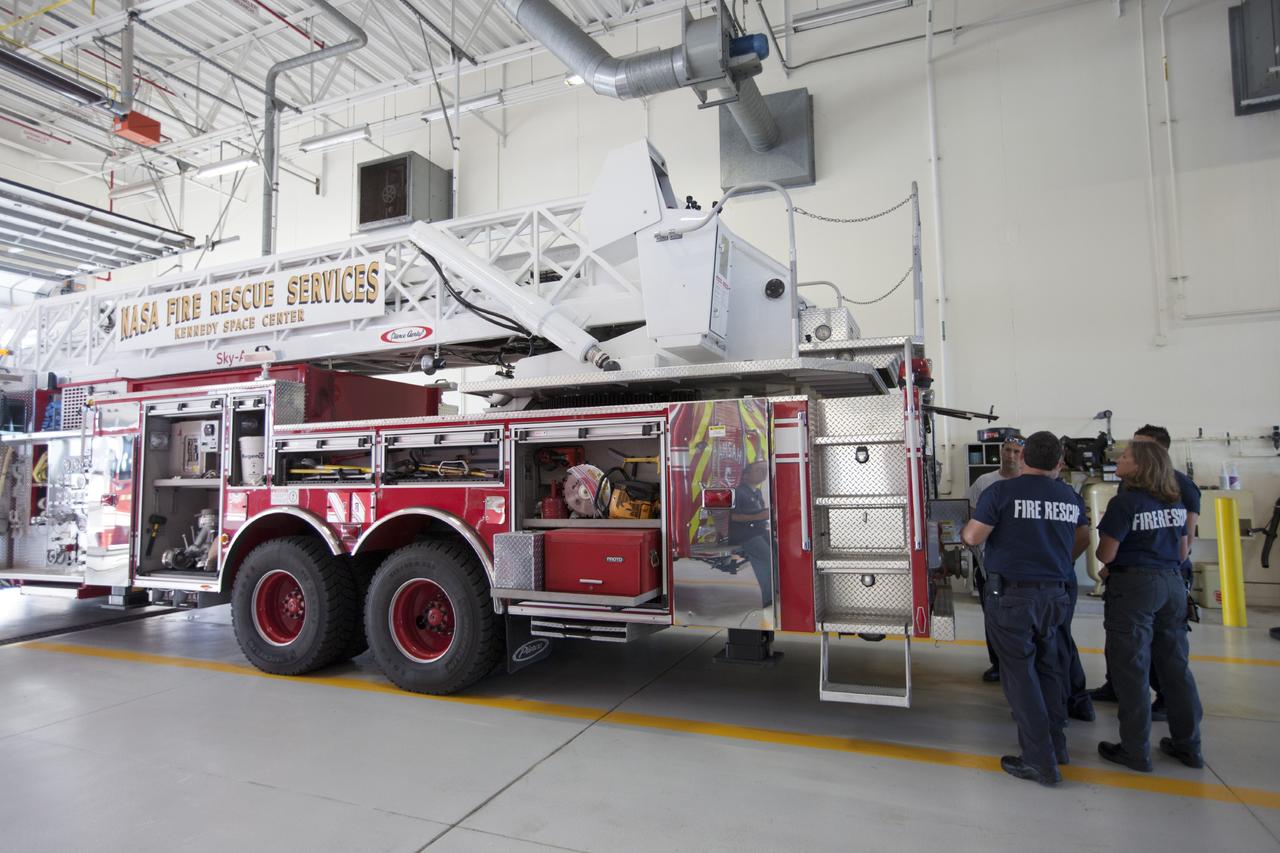

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel review procedures and check equipment on the aerial fire truck as part of the training to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
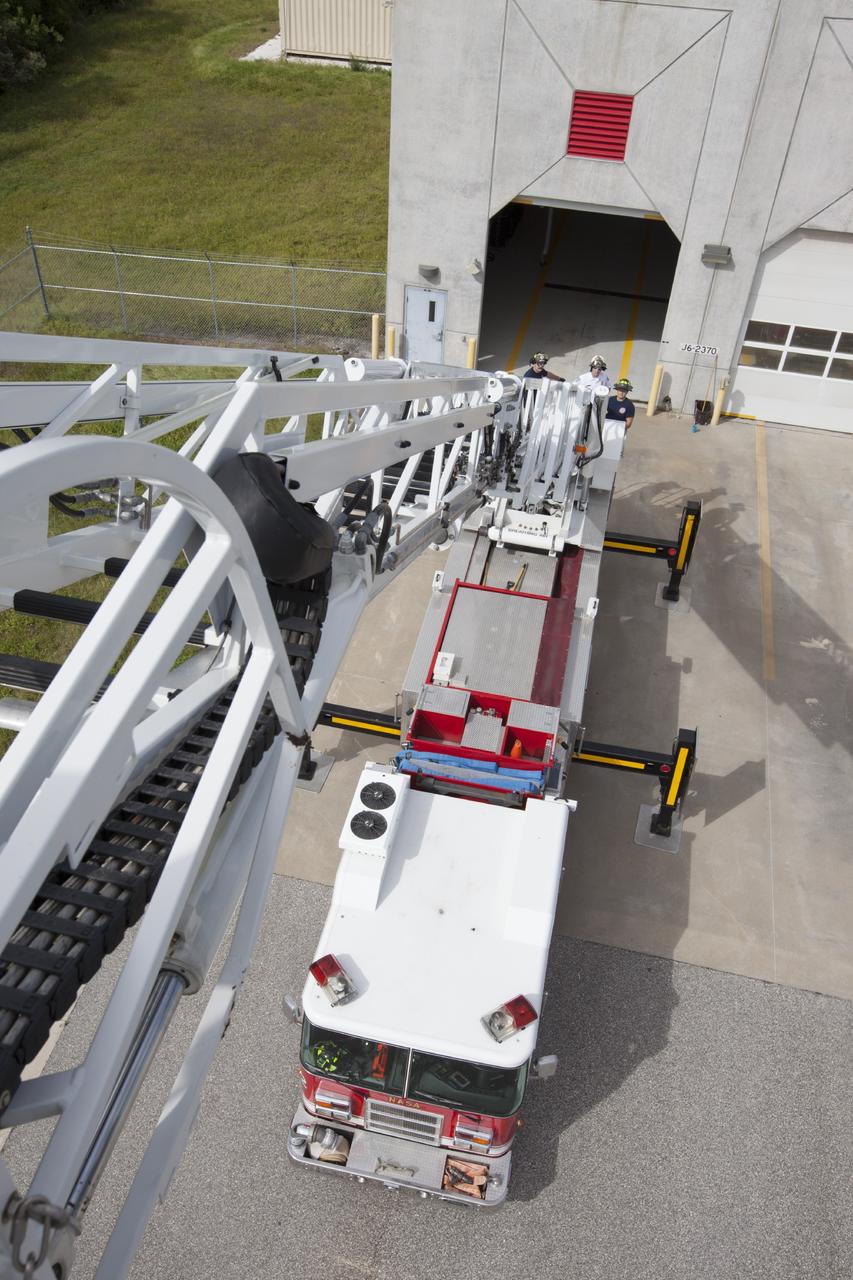

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a bird’s eye view reveals the ladder has been extended on the aerial fire truck during a training exercise. The stabilizers have been deployed on either side of the fire truck. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
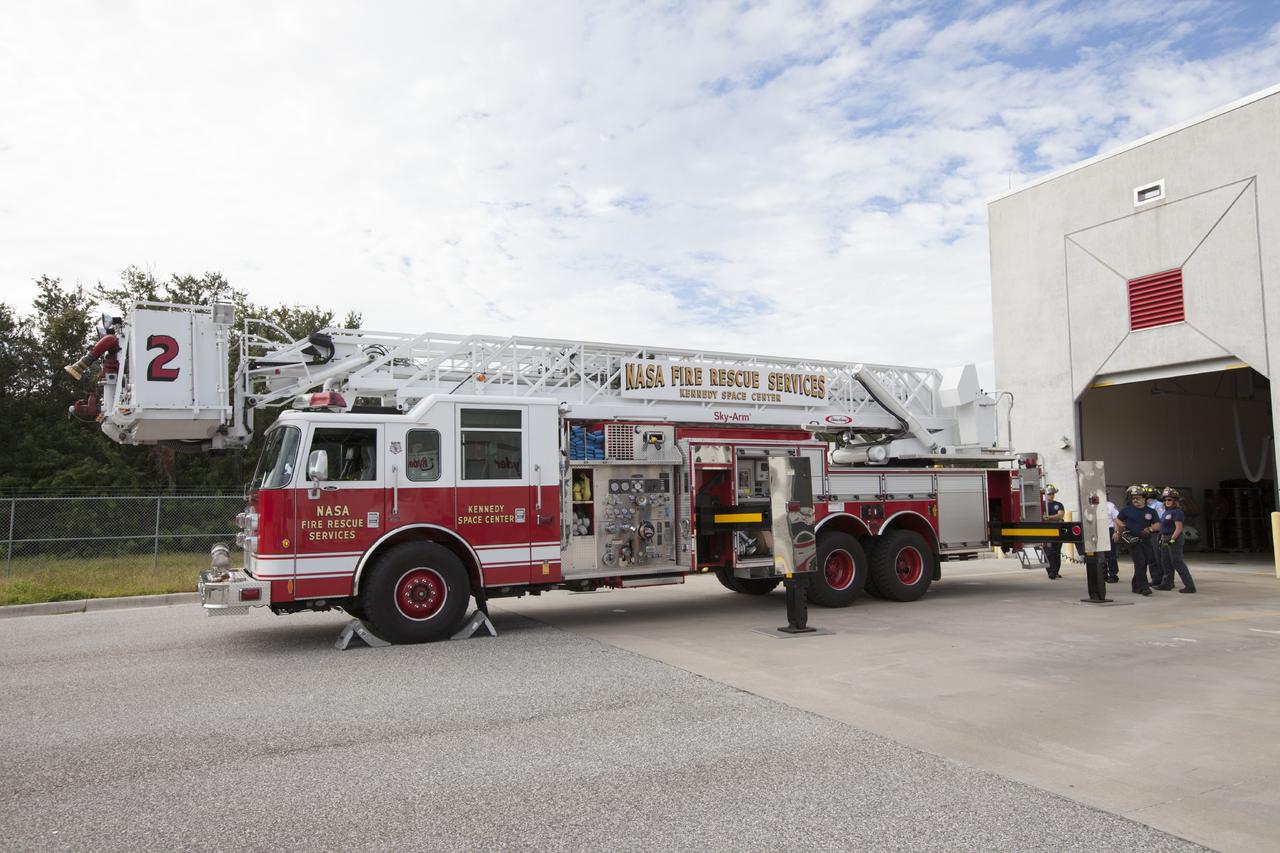

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the aerial fire truck has been moved out of the bay and Fire Rescue Services personnel have deployed the stabilizers on either side of the truck in order to prepare for training to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
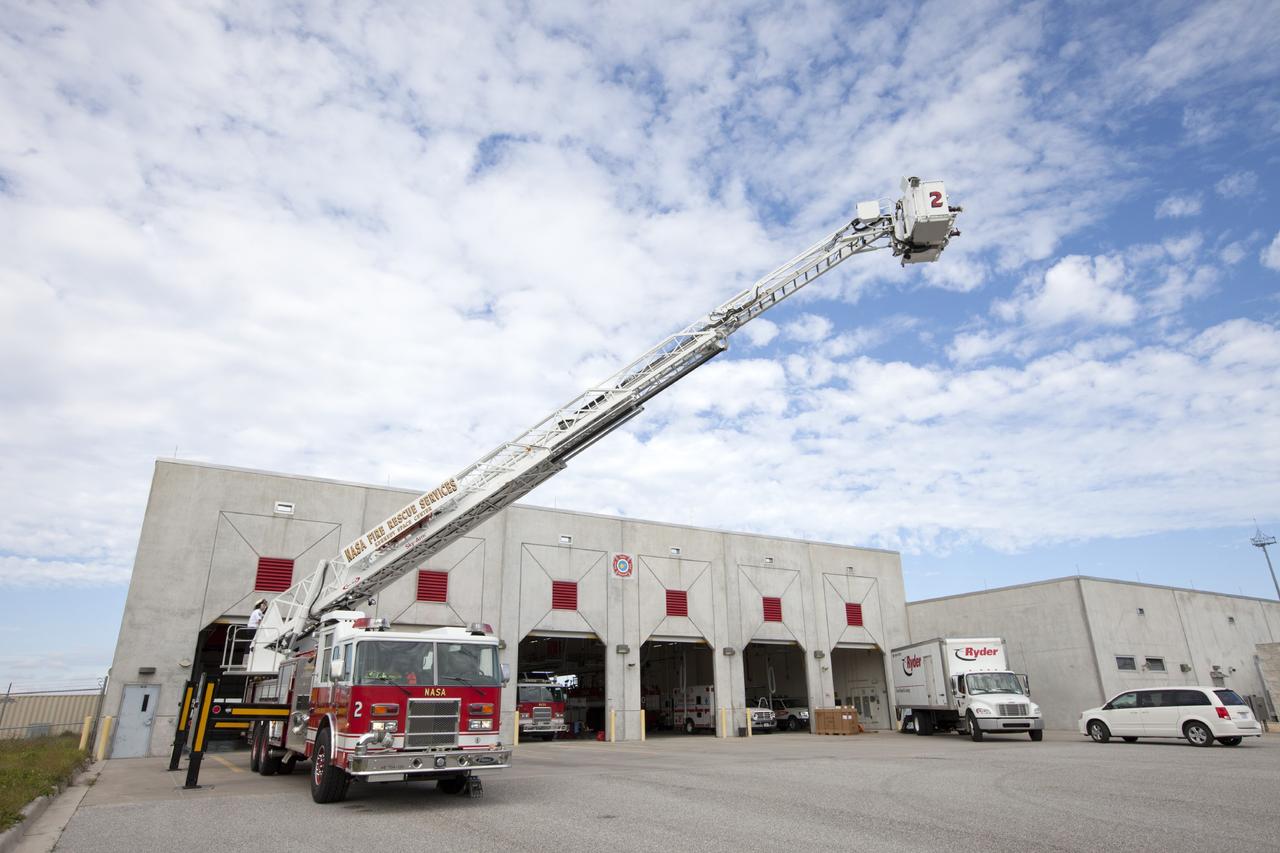

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel have deployed and extended the ladder on the aerial fire truck during training in order to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
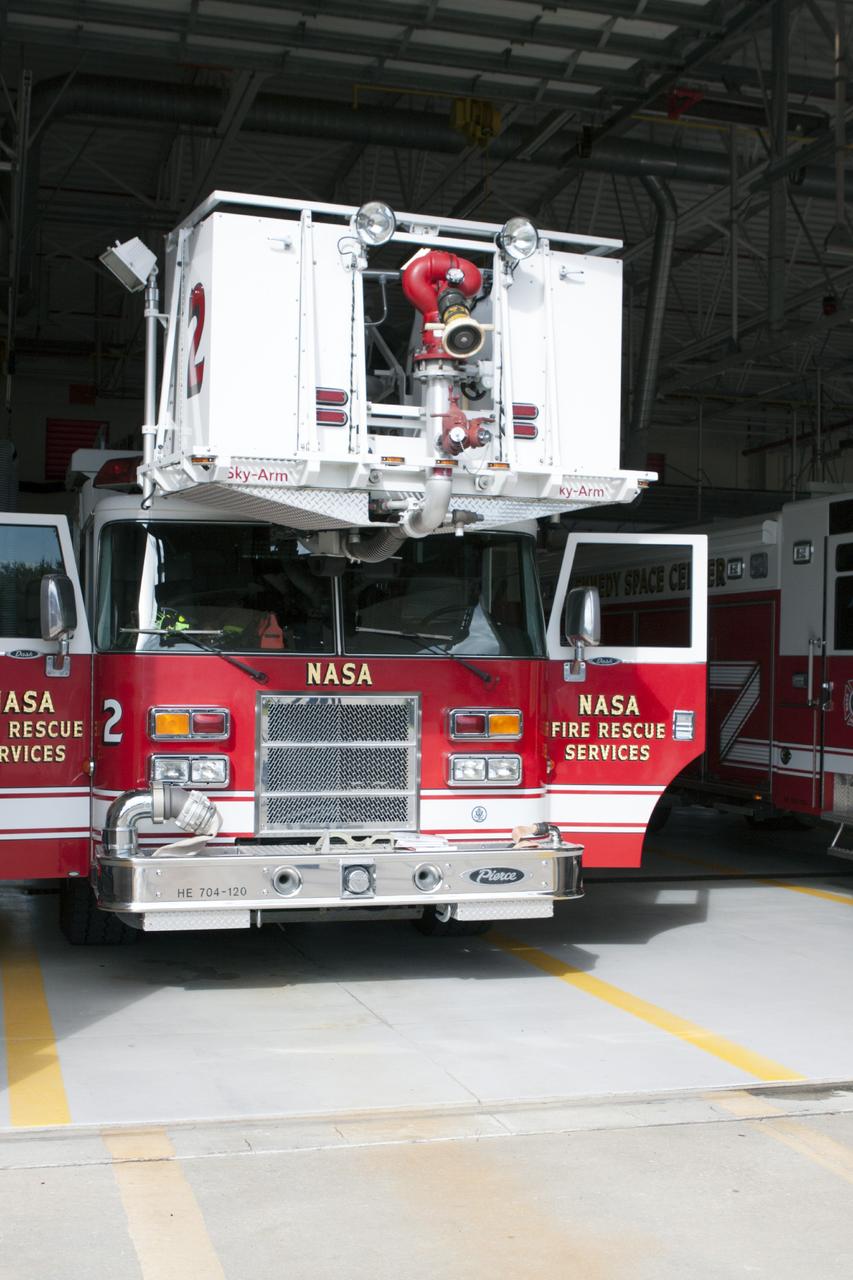

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the aerial fire truck sits in a bay as Fire Rescue Services personnel prepare to drive the fire truck out of the bay and then operate the extendable ladder during training in order to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
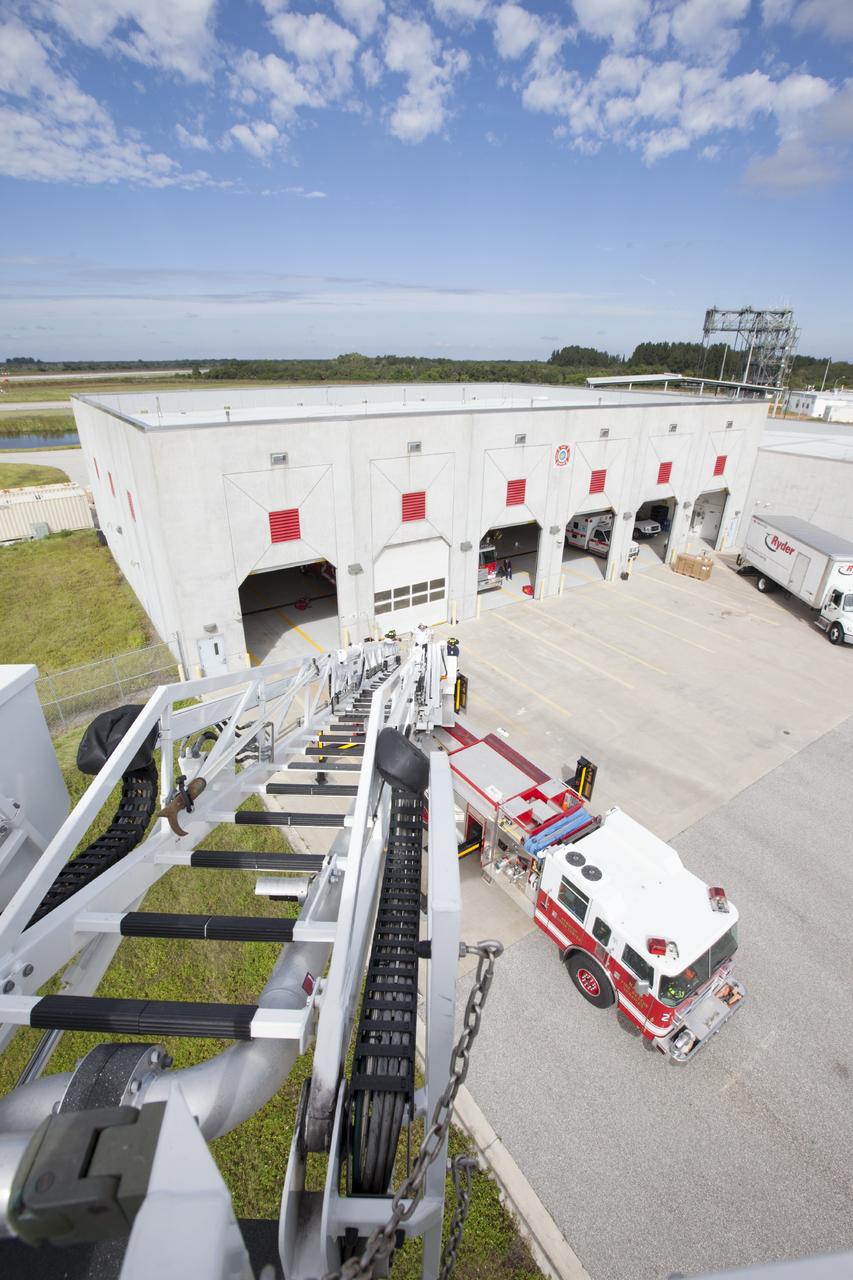

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a bird’s eye view reveals the ladder has been extended on the aerial fire truck during a training exercise. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
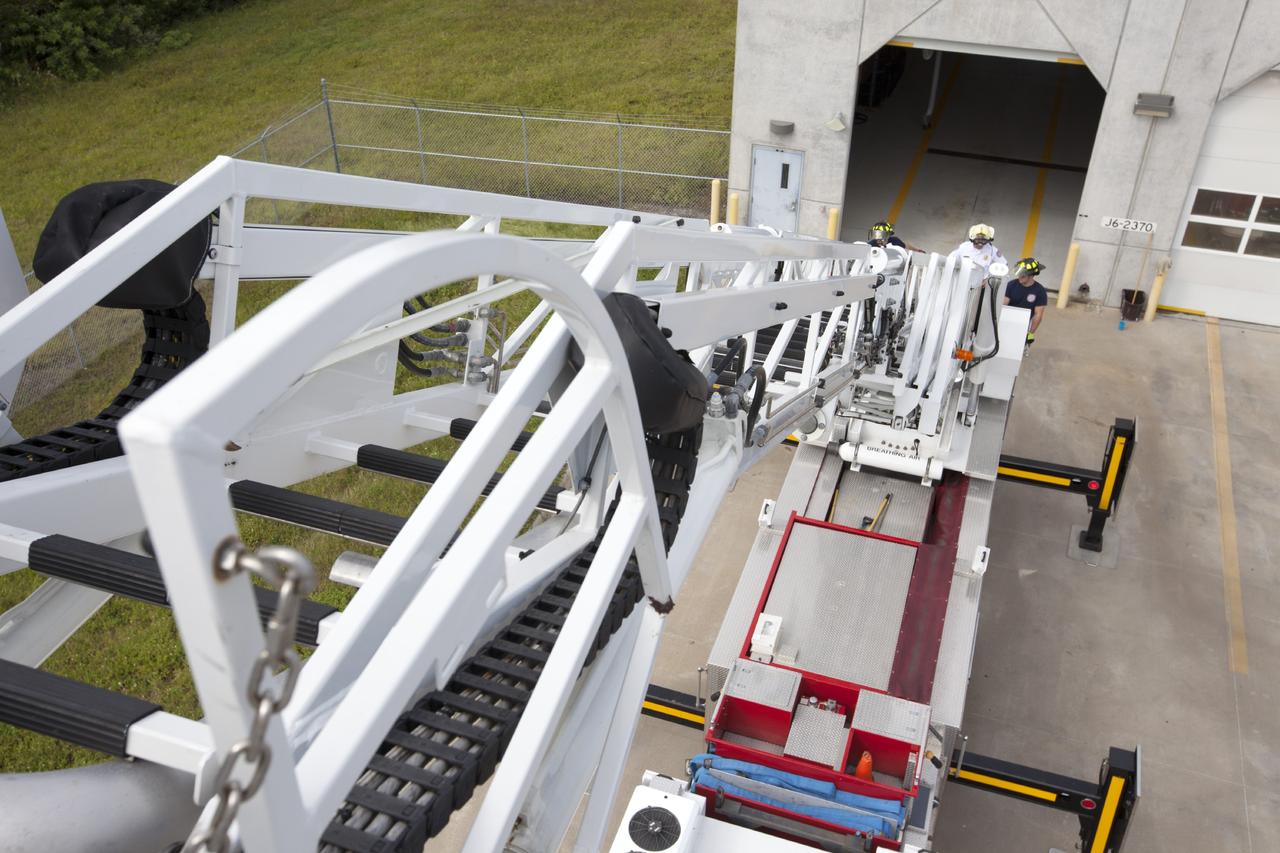

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Fire Station No. 2 near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Fire Rescue Services personnel have deployed and extended the ladder on the aerial fire truck during training in order to be certified in the operation and use of the vehicle. The stabilizers have been deployed on either side of the fire truck. The center’s Fire Rescue Services recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations. Pro Board Certification is a globally recognized certification that puts on multiple courses that all fire departments throughout the world recognize and use to train their personnel. The unique aerial truck contains a 100-foot extendable ladder with a bucket at the end of it that can be used for rescues from taller buildings or aircraft rescue firefighting. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
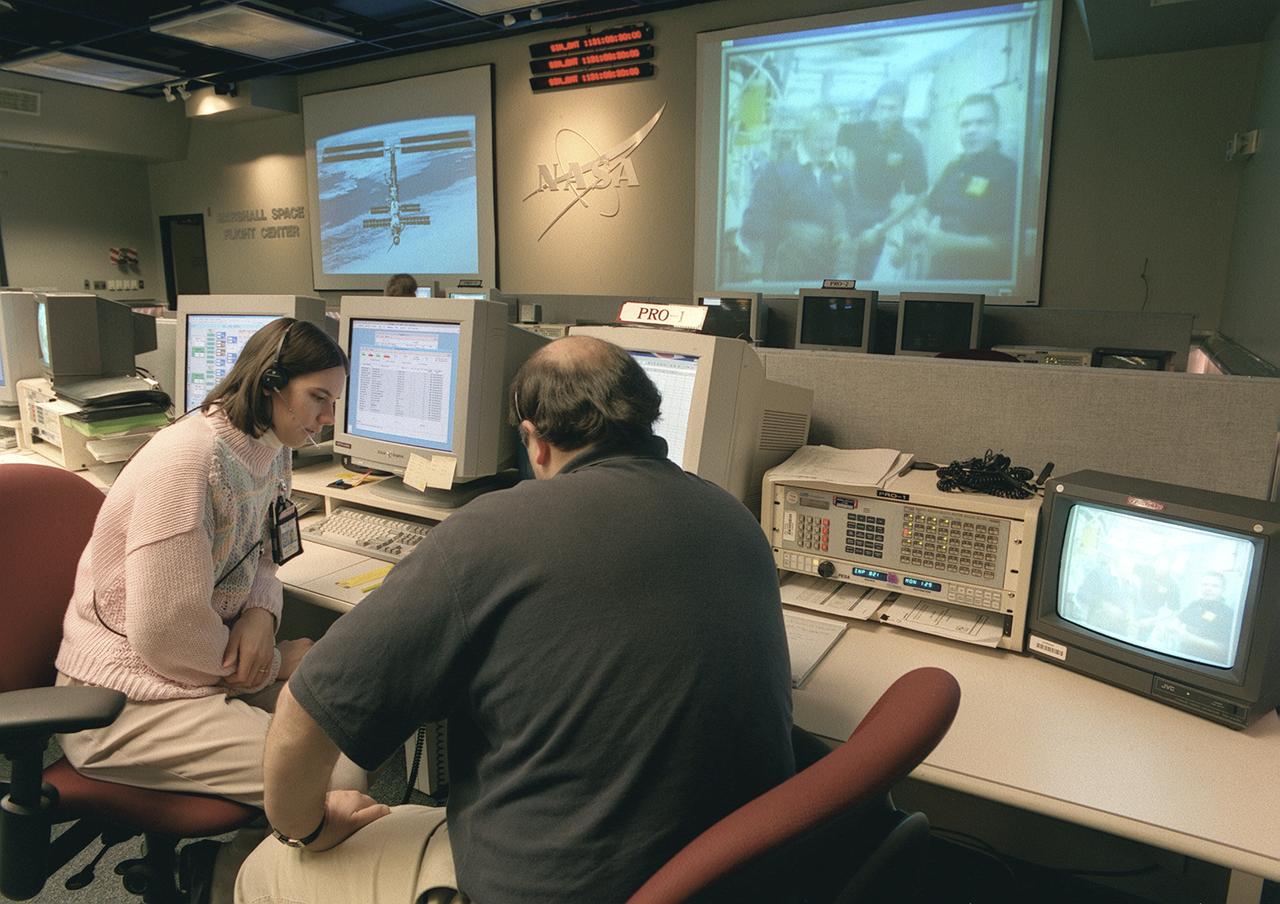

The Payload Operations Center (POC) is the science command post for the International Space Station (ISS). Located at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, it is the focal point for American and international science activities aboard the ISS. The POC's unique capabilities allow science experts and researchers around the world to perform cutting-edge science in the unique microgravity environment of space. The POC is staffed around the clock by shifts of payload flight controllers. At any given time, 8 to 10 flight controllers are on consoles operating, plarning for, and controlling various systems and payloads. This photograph shows a Payload Rack Officer (PRO) at a work station. The PRO is linked by a computer to all payload racks aboard the ISS. The PRO monitors and configures the resources and environment for science experiments including EXPRESS Racks, multiple-payload racks designed for commercial payloads.
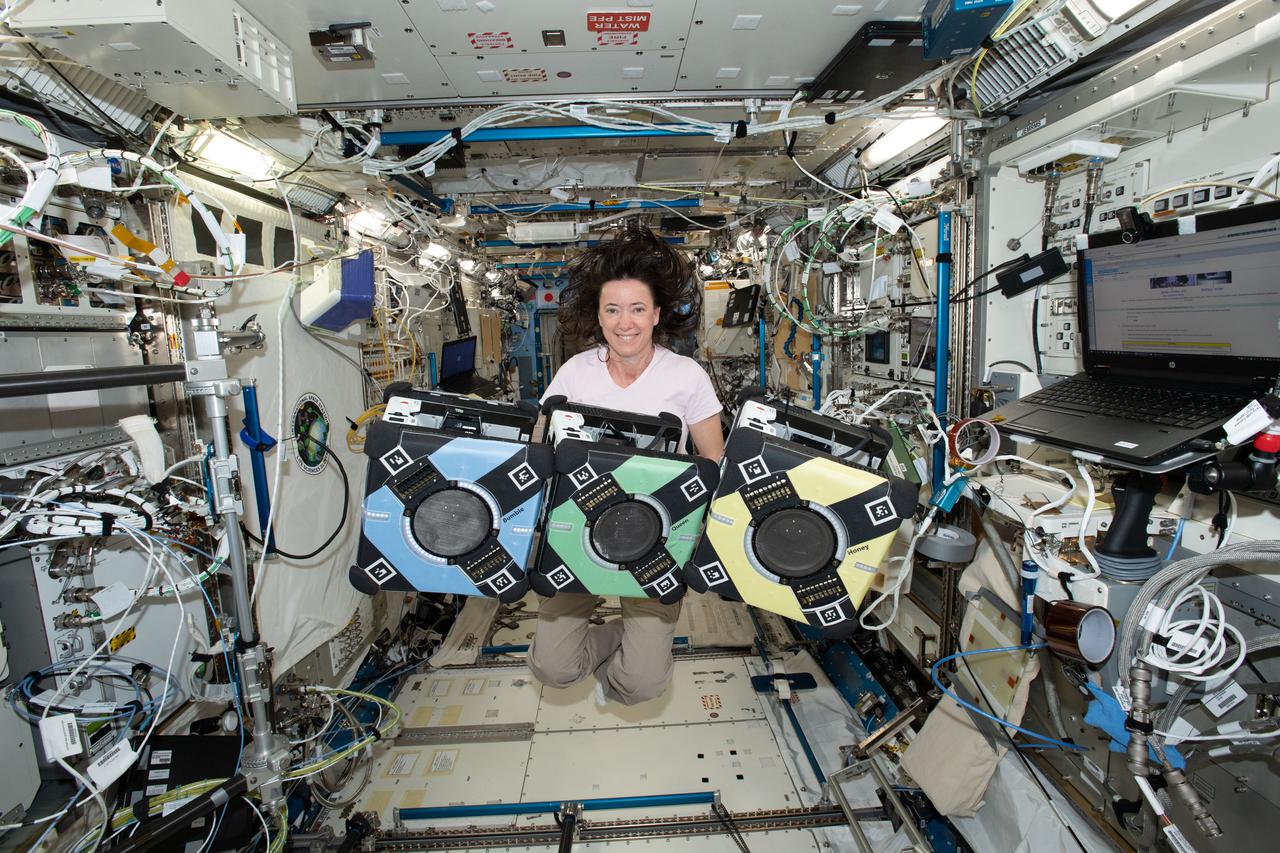

NASA astronaut Megan McArthur poses with the Astrobee robotic free-flyers in support of the Kibo Robot Programming Challenge (Robo-Pro Challenge). The Kibo-RPC, allows students to create programs to control Astrobee, a free-flying robot aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
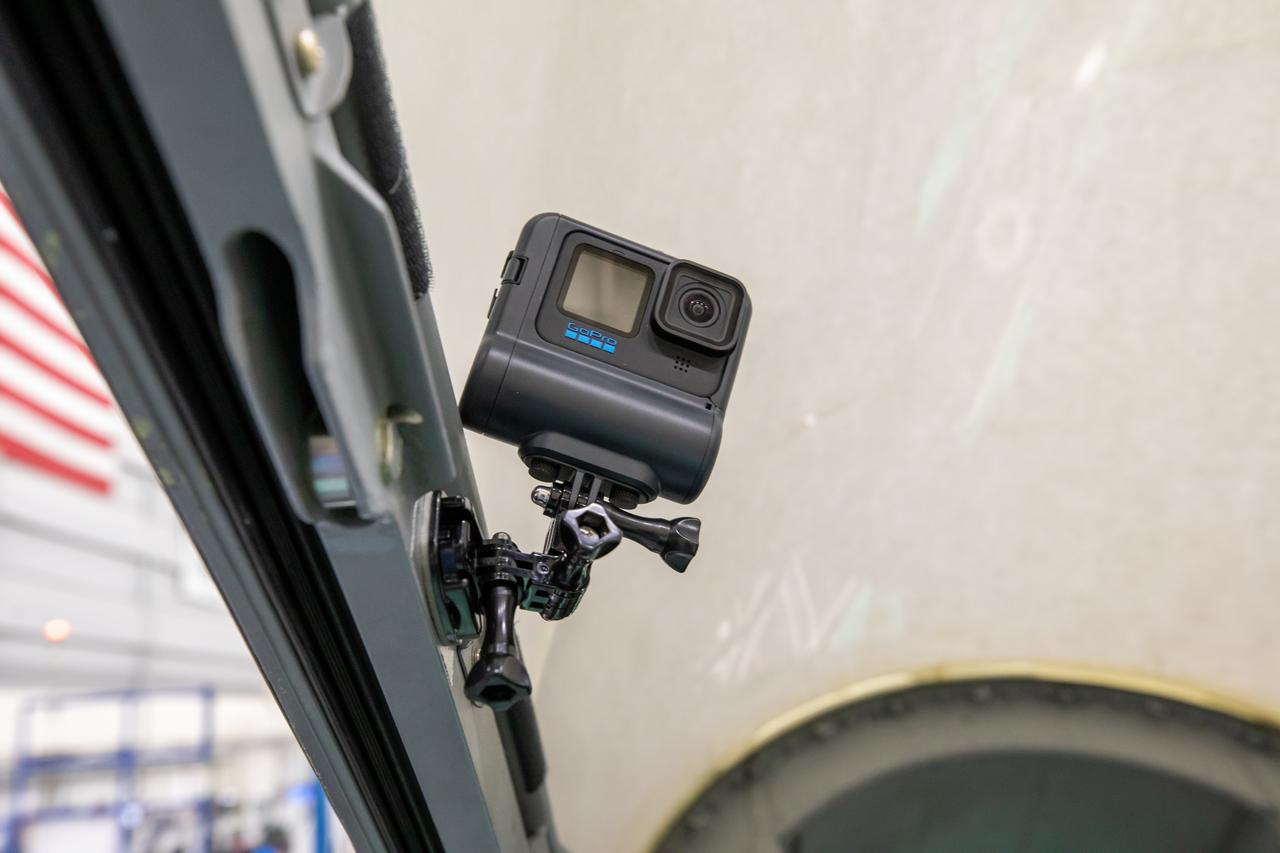

A Go-Pro is mounted on the inside of the X-59’s cockpit to capture the pilots activities during flight.

STS-122 Crew Members visit the Pro Football Hall of Fame in Canton Ohio and present an STS-122 commemorative collage to the Hall of Fame President

STS-122 Crew Members visit the Pro Football Hall of Fame in Canton Ohio. STS-122 Astronaut poses by a Detroit Lions display case. He was drafted by the Lions in 1986
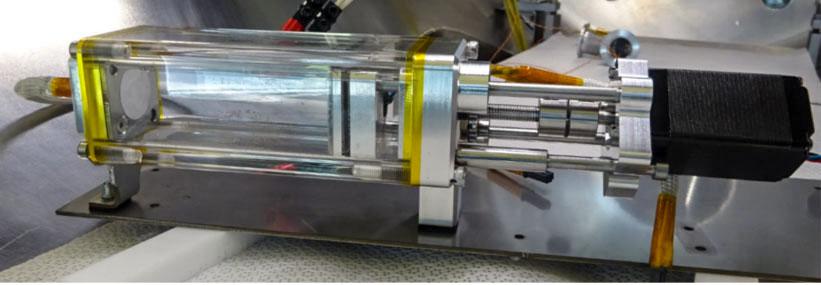
jsc2021e029742 (7/13/2021) --- A preflight photo of the TECHNOLOGY BOX design of the Chladni's Figures experiment. The main objective of Technology Box (Tetr’ISS) is to conduct experiments gathered in support equipment called ‘Platform’, to illustrate science principles based on physics and chemistry. For this mission Tetr’ISS contains the Chladni’s Figures experiment: a physical science experiment to observe the sound waves in 3D thanks to fine particles organized according to nodes and antinodes.
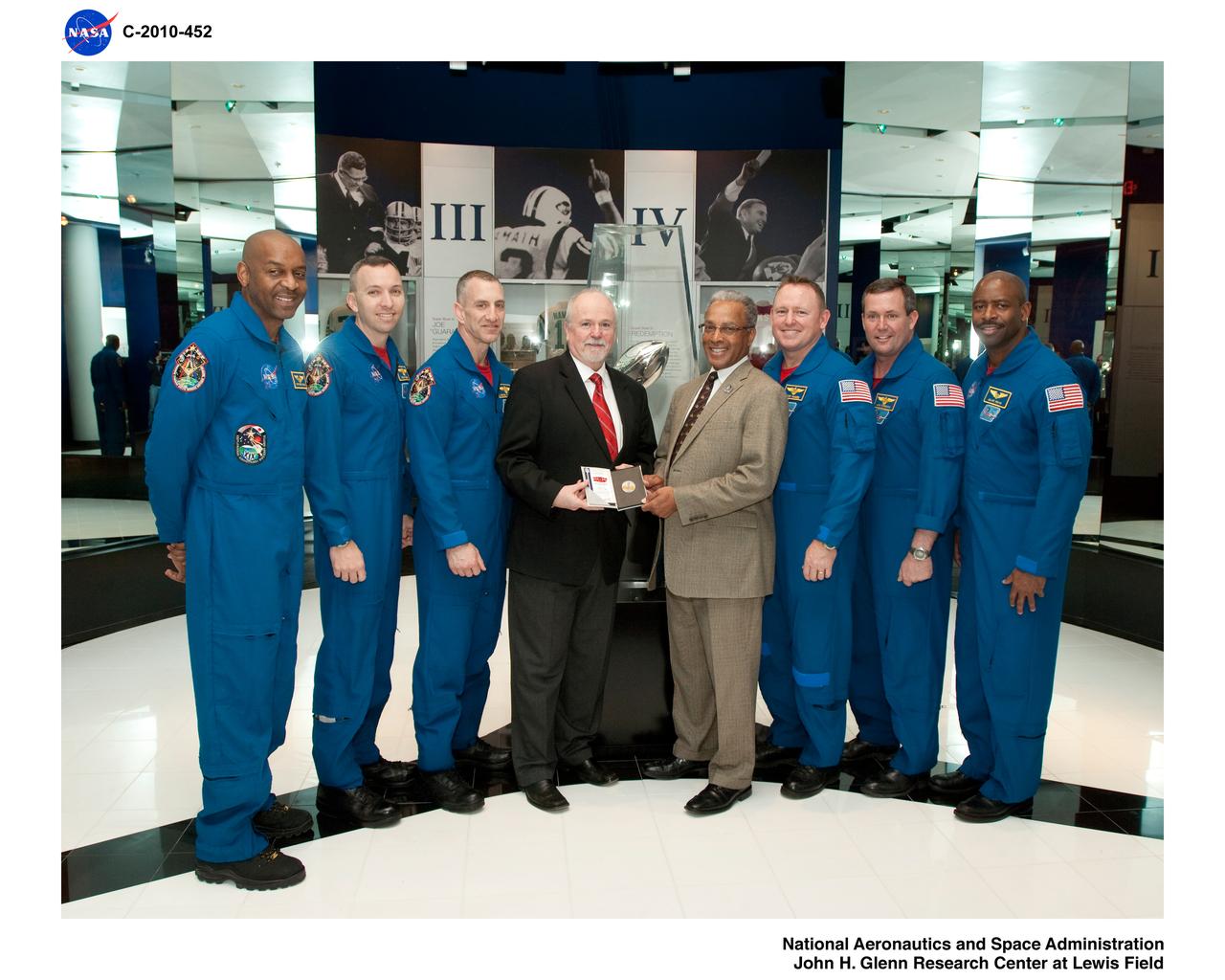

From Space to the Super Bowl Members of the STS-129 shuttle mission present a specially minted silver medallion to National Football League officials on Wednesday, Jan. 27, 2010, at the Pro Football Hall of Fame in Canton, Ohio. The coin, which was flown in space during the November flight of Atlantis, will be used for the official coin toss prior to the kickoff of Super Bowl XLIV on Sunday, Feb. 7, 2010. One member of Atlantis' crew, Leland Melvin, was drafted by the NFL's Detroit Lions in 1986. The crew also flew other NFL-related memorabilia, including jerseys and a football inscribed with the name of every member of the Hall of Fame. From left: Astronauts Bobby Satcher, Randy Bresnik, and Charlie Hobaugh; Joe Horrigan, Vice President of Communications/Exhibits for the Pro Football Hall of Fame, Steve Perry, President/Executive Director of the Pro Football Hall of Fame; astronauts Berry Wilmore, Michael Foreman and Leland Melvin. Photo Credit: NASA/Marv Smith
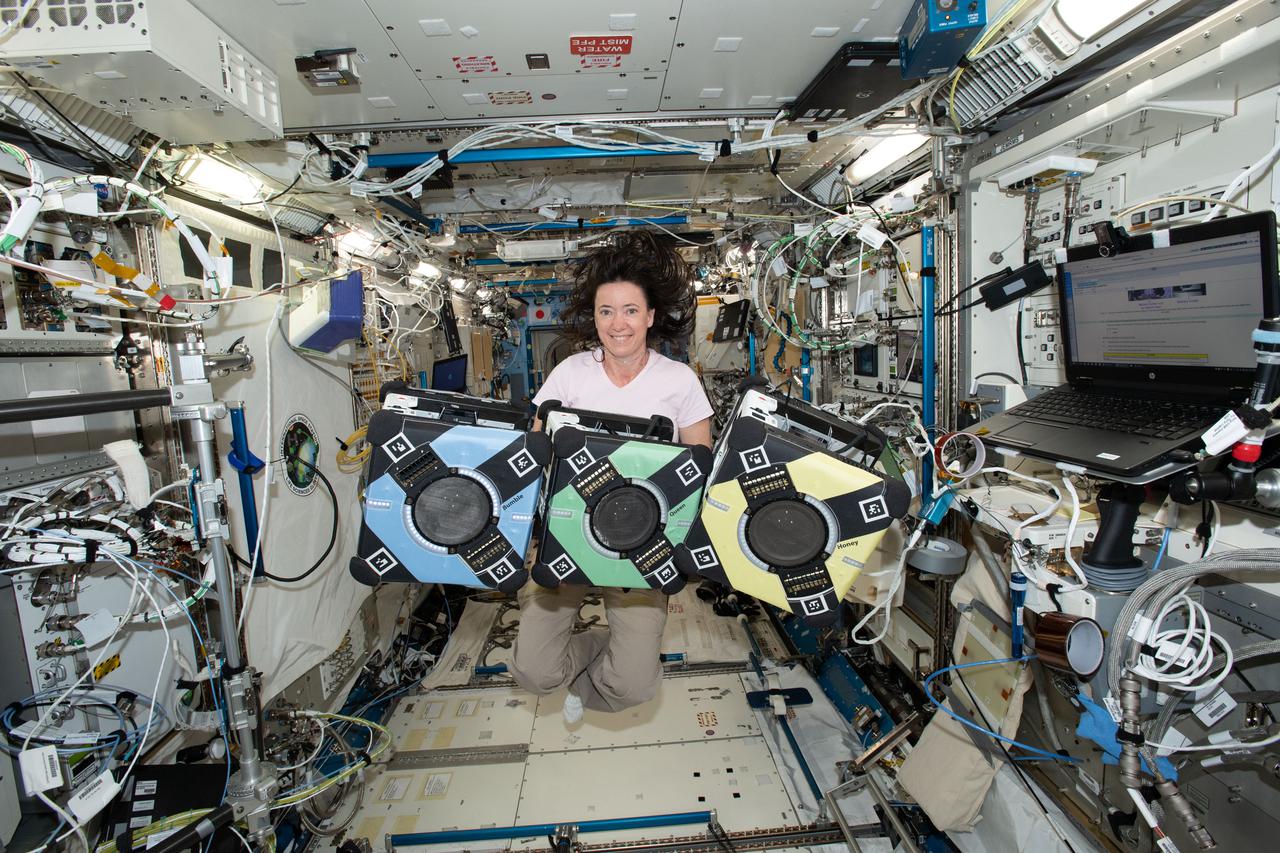

iss065e389383 (9/20/2021) --- NASA astronaut Megan McArthur poses with the Astrobee robotic free-flyers in support of the Kibo Robot Programming Challenge (Robo-Pro Challenge). The Kibo-RPC, allows students to create programs to control Astrobee, a free-flying robot aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
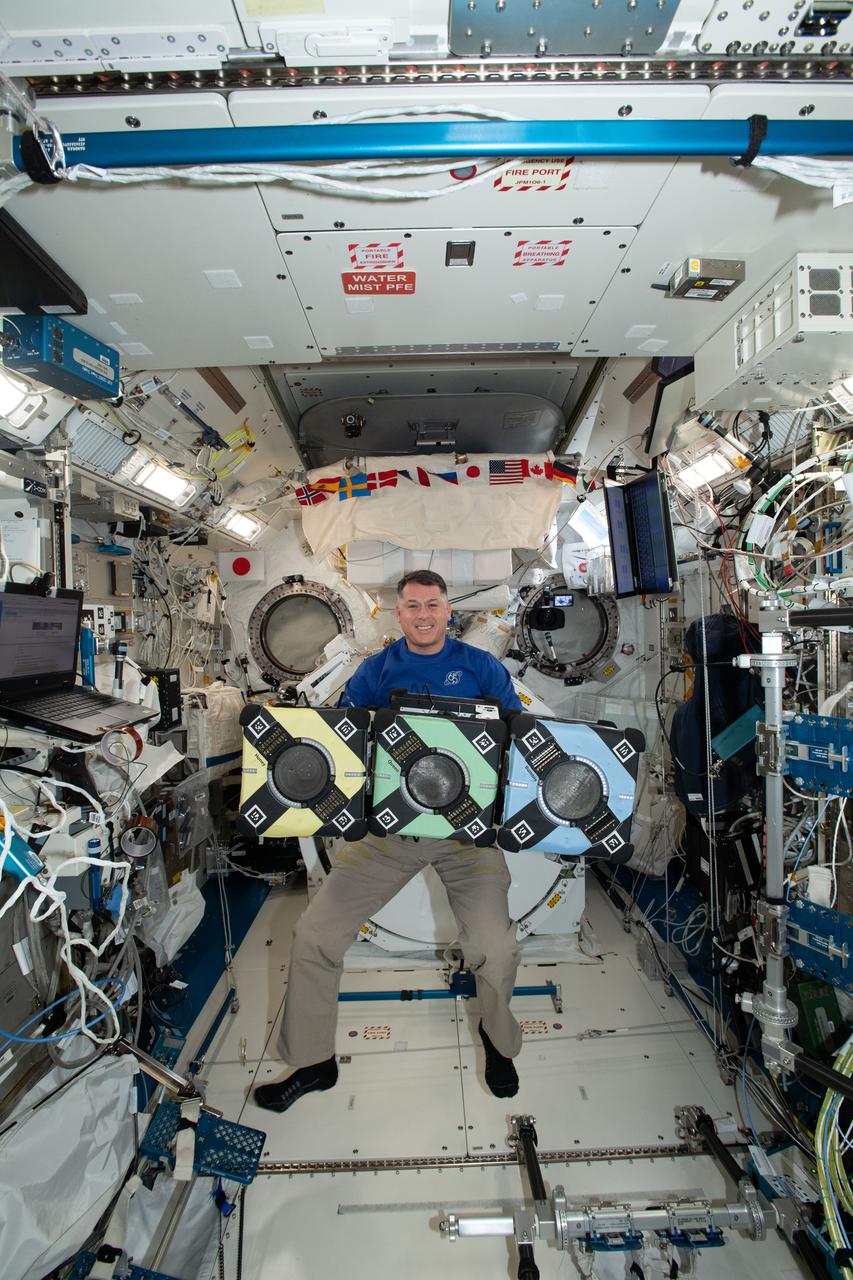

iss065e389375 (9/20/2021) --- NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough poses with the Astrobee robotic free-flyers in support of the Kibo Robot Programming Challenge (Robo-Pro Challenge). The Kibo-RPC, allows students to create programs to control Astrobee, a free-flying robot aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
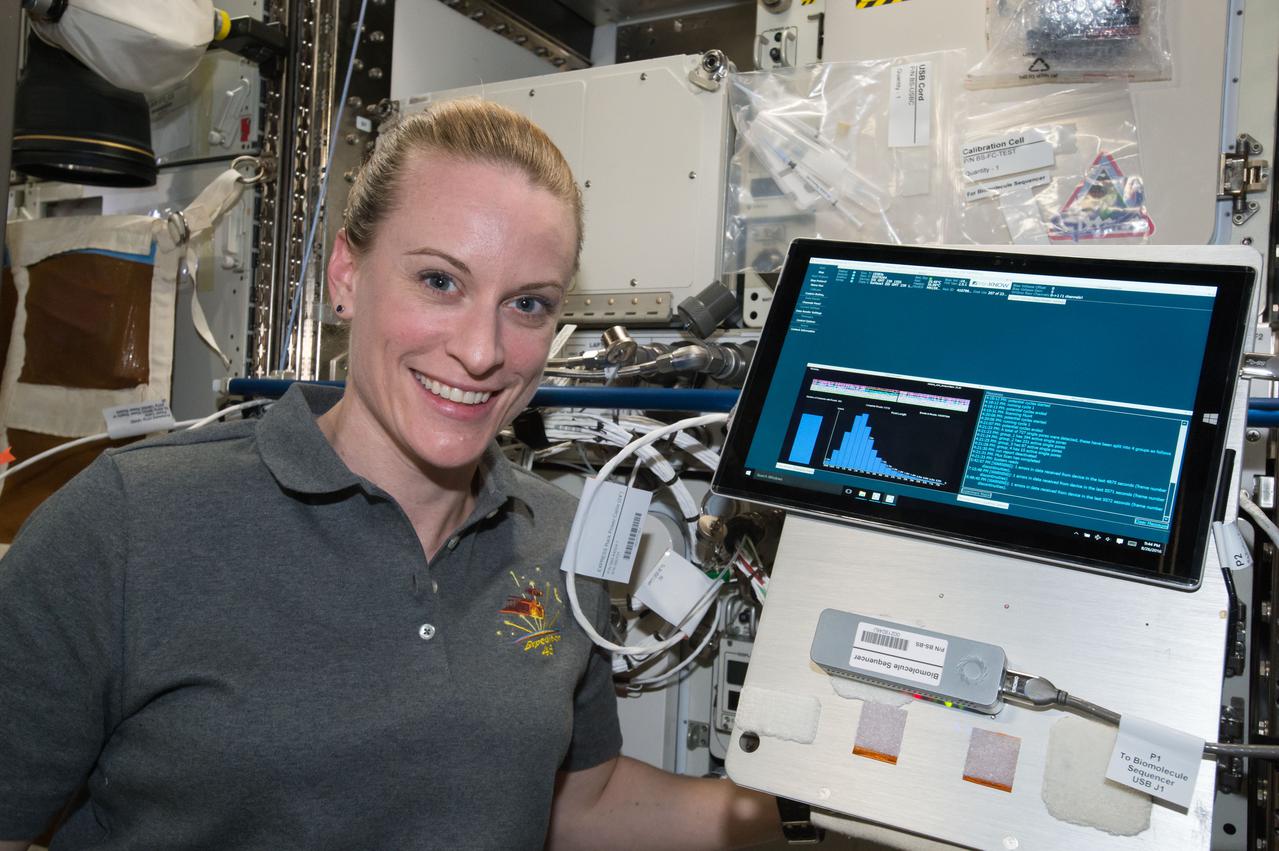

iss048e066523 (8/26/2016) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins poses for a photo with Biomolecule Sequencer experiment hardware (Surface Pro 3 tablet and MinION) during the first sample initialization run. The image was taken in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
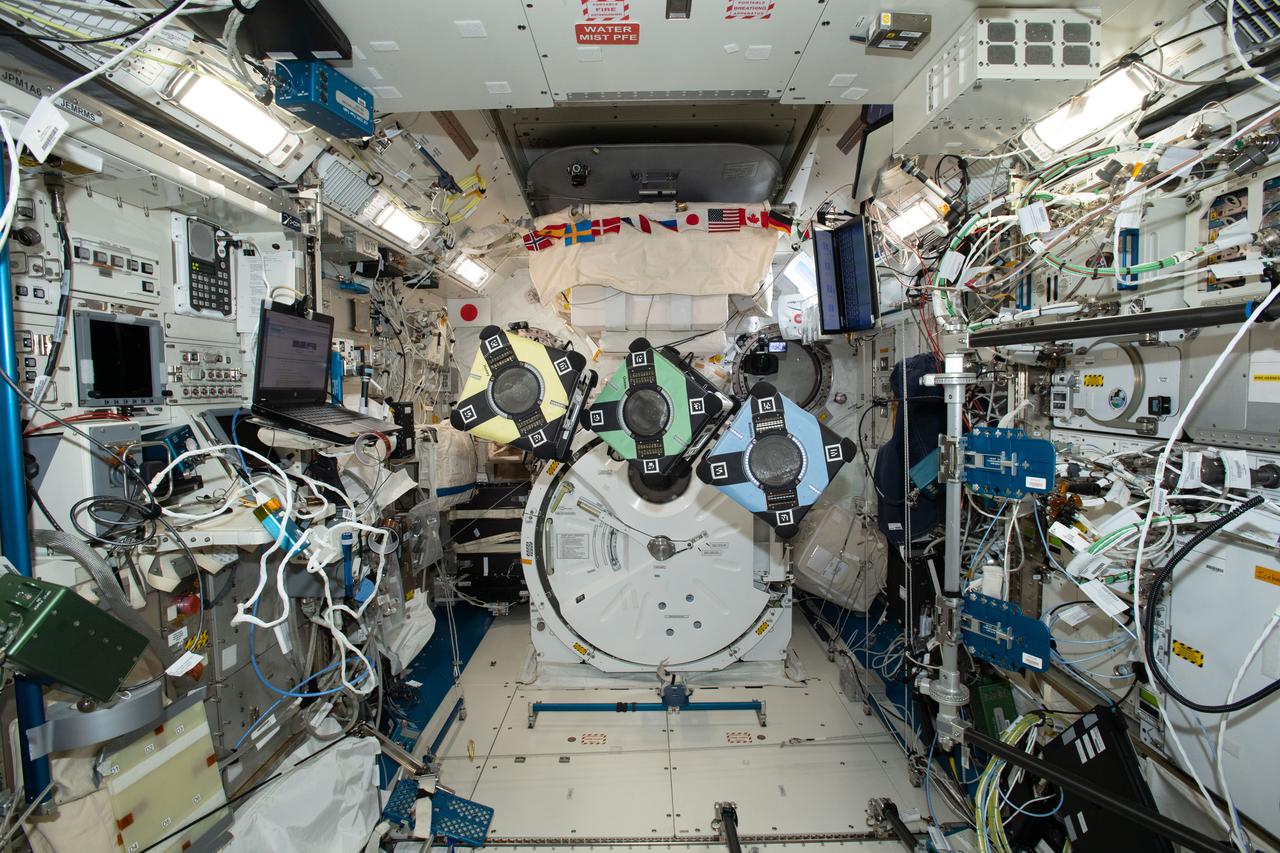

iss065e389379 (9/20/2021) --- A view of the Astrobee robotic free-flyers in support of the Kibo Robot Programming Challenge (Robo-Pro Challenge). The Kibo-RPC, allows students to create programs to control Astrobee, a free-flying robot aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
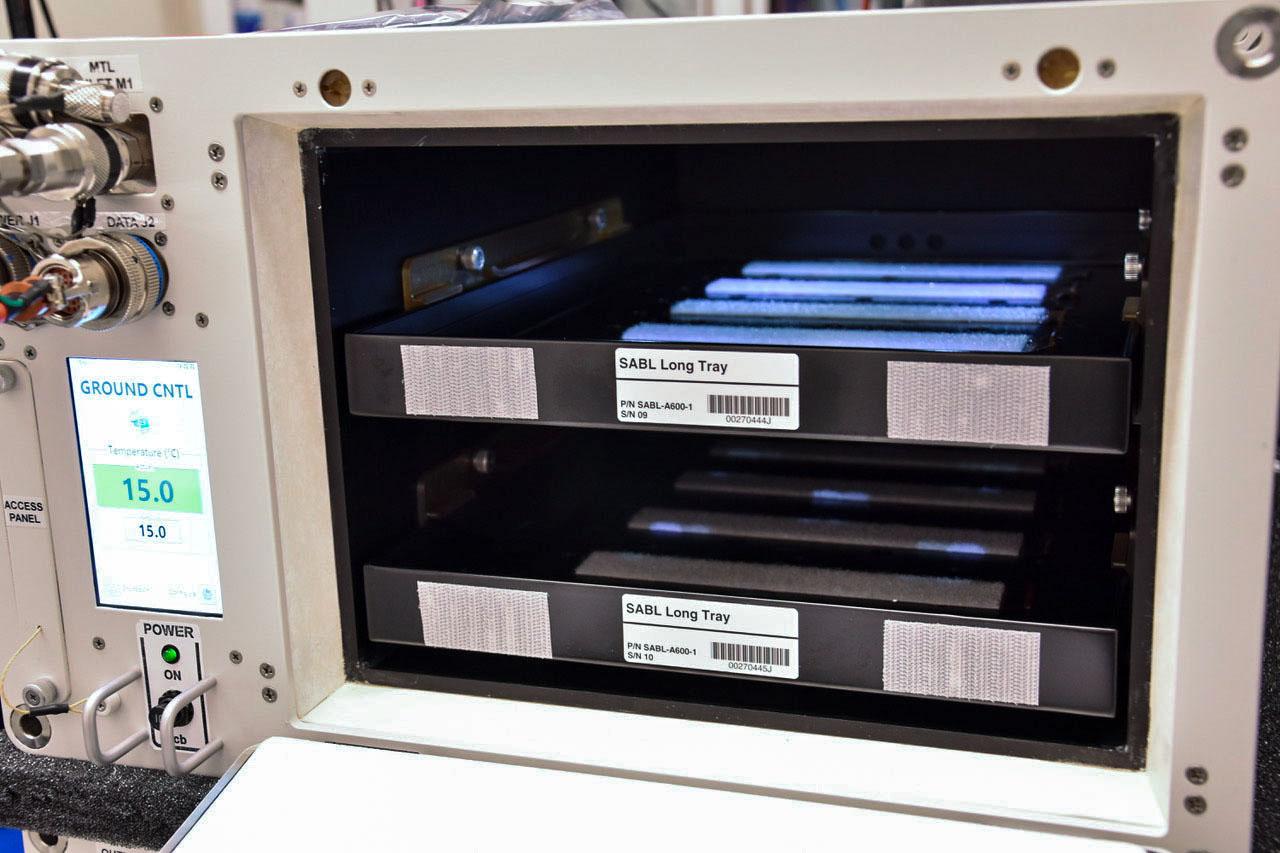

jsc2021e037286 (5/21/2021) --- A preflight view of the SALI incubator. The Space Automated Lab Incubator (SALI) supports a wide variety of investigations in the life, physical, and material sciences, focusing on research on biological systems and processes. SALI accommodates multiple sample packs or habitats and also serves as back-up cold stowage.
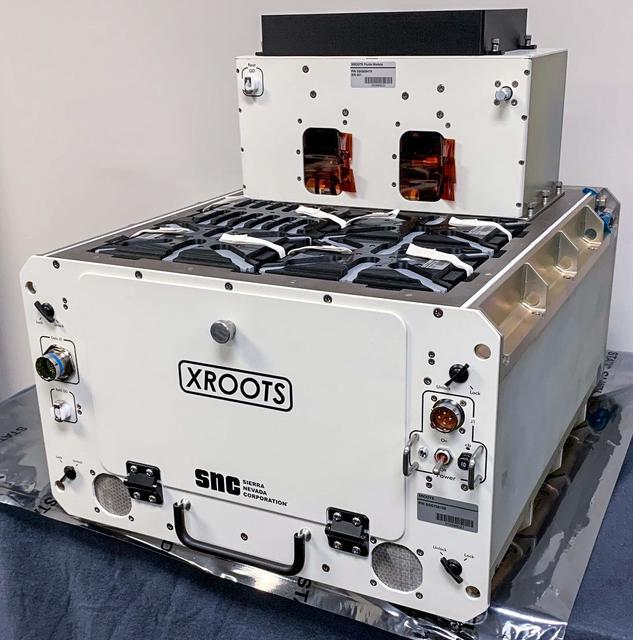

jsc2021e037285 (2/12/2021) --- A preflight view of the XROOTS hardware. The eXposed Root On-Orbit Test System (XROOTS) investigation uses hydroponic and aeroponic techniques to grow plants without soil or other growth media. Video and still images enable evaluation of multiple independent growth chambers for the entire plant life cycle from seed germination through maturity. Results could identify suitable methods to produce crops on a larger scale for future space missions.
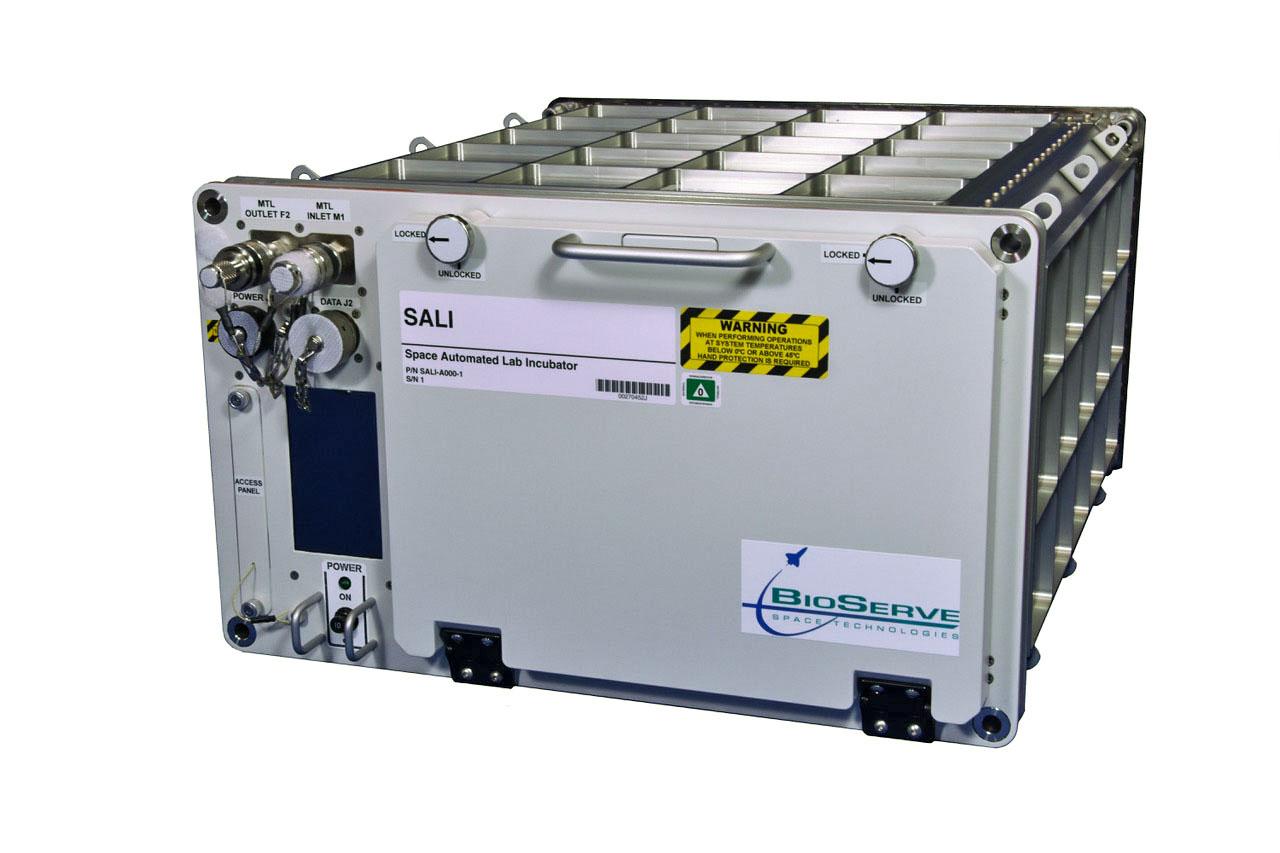

jsc2021e037287 (5/21/2021) --- A preflight view of the SALI incubator. The Space Automated Lab Incubator (SALI) supports a wide variety of investigations in the life, physical, and material sciences, focusing on research on biological systems and processes. SALI accommodates multiple sample packs or habitats and also serves as back-up cold stowage.e.
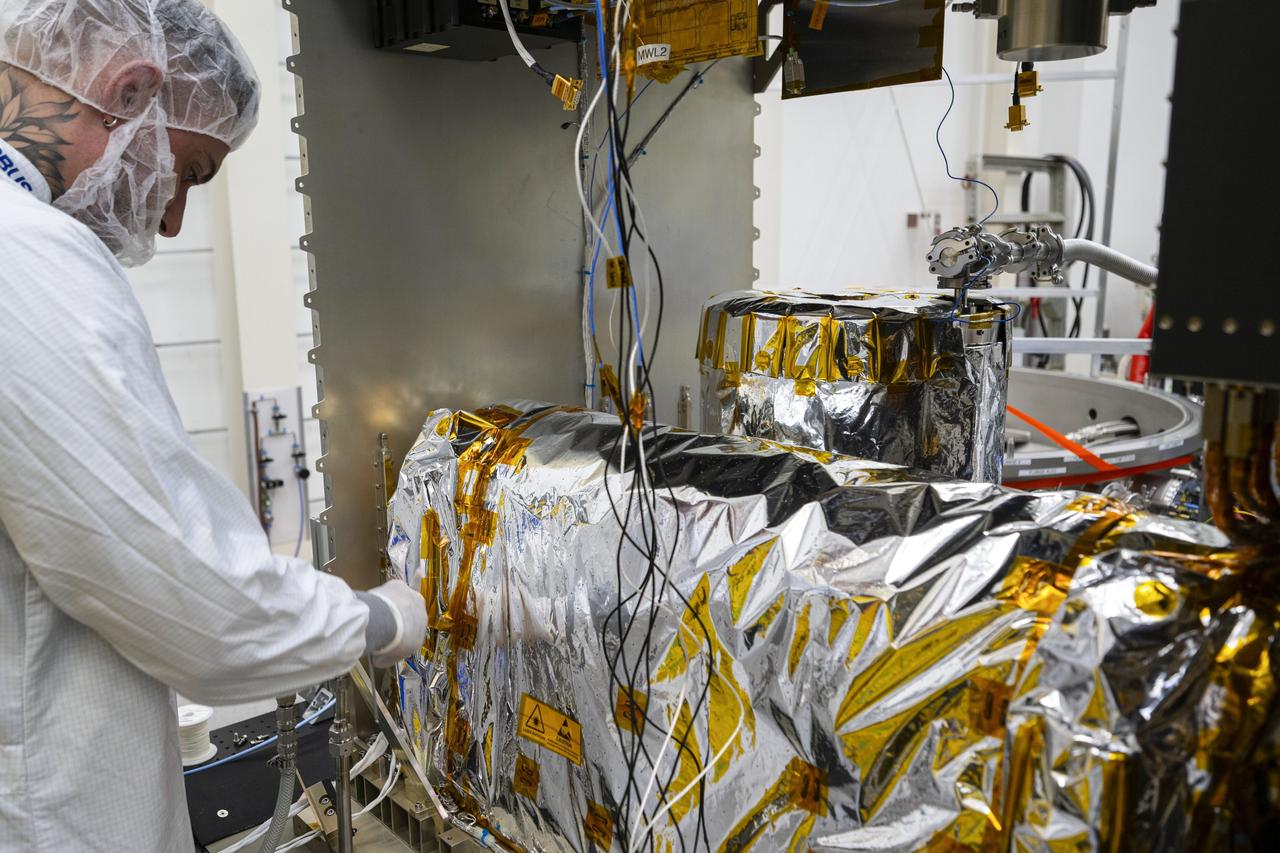

jsc2025e015677 (3/6/2025) --- The closure of the instrument panel of the Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES) has taken place at Airbus Friedrichshafen, Germany. ACES is an ESA instrument that tests fundamental physics, such as Einstein’s theory of general relativity, from the International Space Station. According to this theory, gravity affects the passing of time—time flies faster at the top of Mount Everest than at sea level. This effect has been proven in experiments on Earth, and ACES will make more precise measurements of this phenomenon and other fundamental physics such as the standard model of particle physics, as it flies 400 km high on the space station. ACES contains two clocks: PHARAO, a caesium atomic clock developed by the French Space Agency CNES, and the Space Hydrogen Maser developed by Spectratime, which uses hydrogen atoms as a frequency reference. The payload will be externally mounted to ESA’s Columbus laboratory on the space station. Image courtesy of S. Corvaja (ESA).
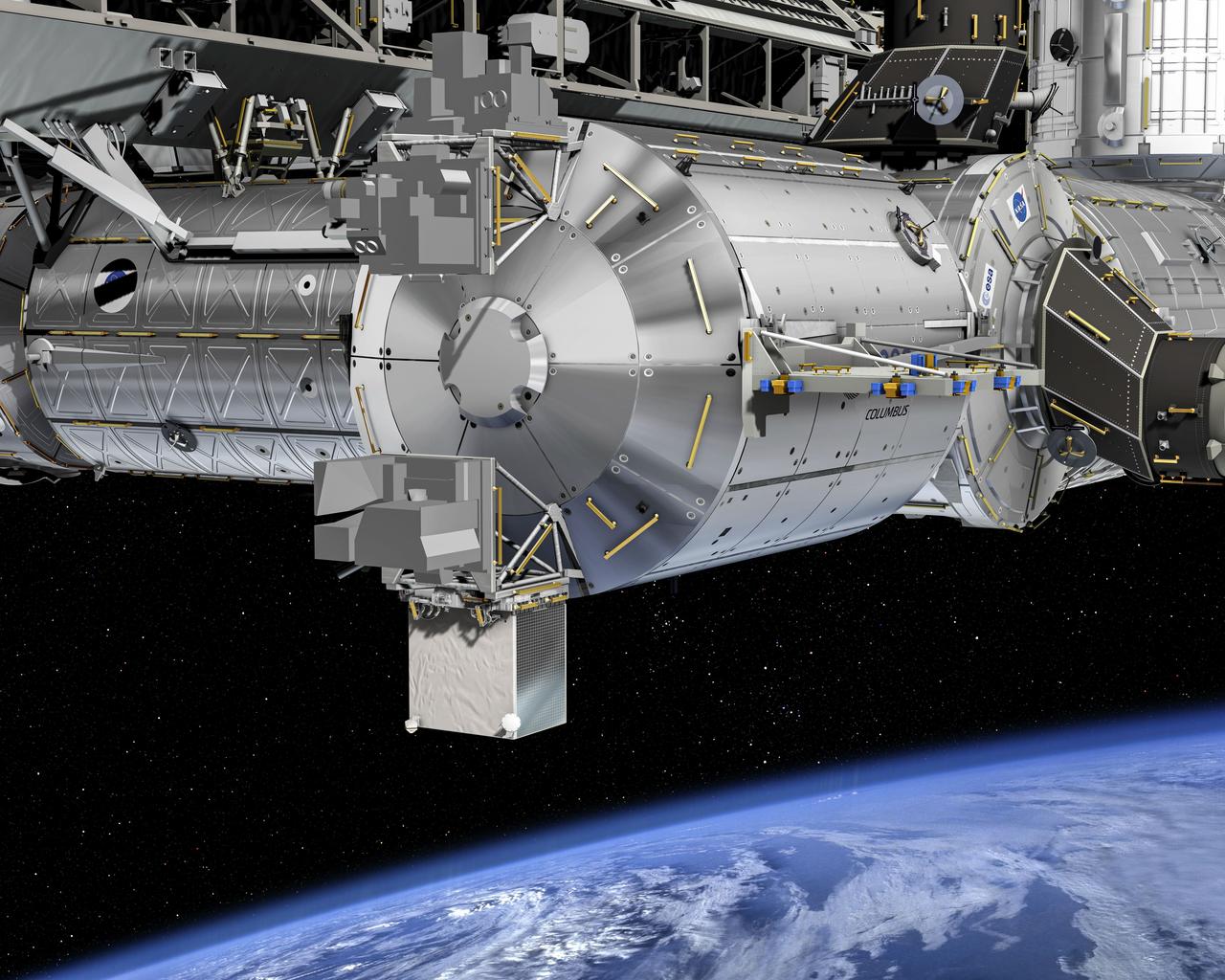
jsc2025e015676 (3/6/2025) --- The Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES) facility attached to the exterior of ESA's Columbus facility on the International Space Station. By creating a "network of clocks", this European facility can link its own highly precise timepieces with the most accurate clocks on Earth and compare them to measure the flow of time. ACES includes two cutting-edge clocks: Project d'Horloge Atomique par Refroidissement d'Atomes en Orbit (PHARAO) and Space Hydrogen Maser (SHM). The excellent stability of SHM over a one hour period, combined with the long-term stability and accuracy of PHARAO, provide timekeeping for ACES with a precision of one second over 300 million years. Once in space, a robotic arm positions ACES onto the Columbus module, where it will remain for 30 months to collect data. ACES aims to record continuous data over at least ten sessions of 25 days each. By comparing clocks in space and on Earth, ACES can provide scientists with precise measurements to test Einstein’s gravitational time dilation effect, search for time variations of fundamental constants of physics, and hunt for dark matter. ACES is fully assembled at Airbus in Friedrichshafen, Germany. Image courtesy of D. Ducros (ESA).

jsc2024e050831 (7/26/2024) --- The Earthshine from ISS investigation involves the thorough analysis of photos taken of the Moon from the International Space Station (ISS) at specific points in the lunar cycle to study changes in the Earth’s reflectance of light, or albedo. This photo was taken by NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick in the station’s Cupola. The intensity scale has been stretched to show off the dark side. This also brings out two reflections of the lunar bright side, caused by the multiple reflections and refractions in the Cupola's thick glass. Pictures of the Moon from space can help determine whether the earthshine method for determining Earth’s albedo can benefit from the absence of an atmosphere. Image courtesy of ESA/NASA.
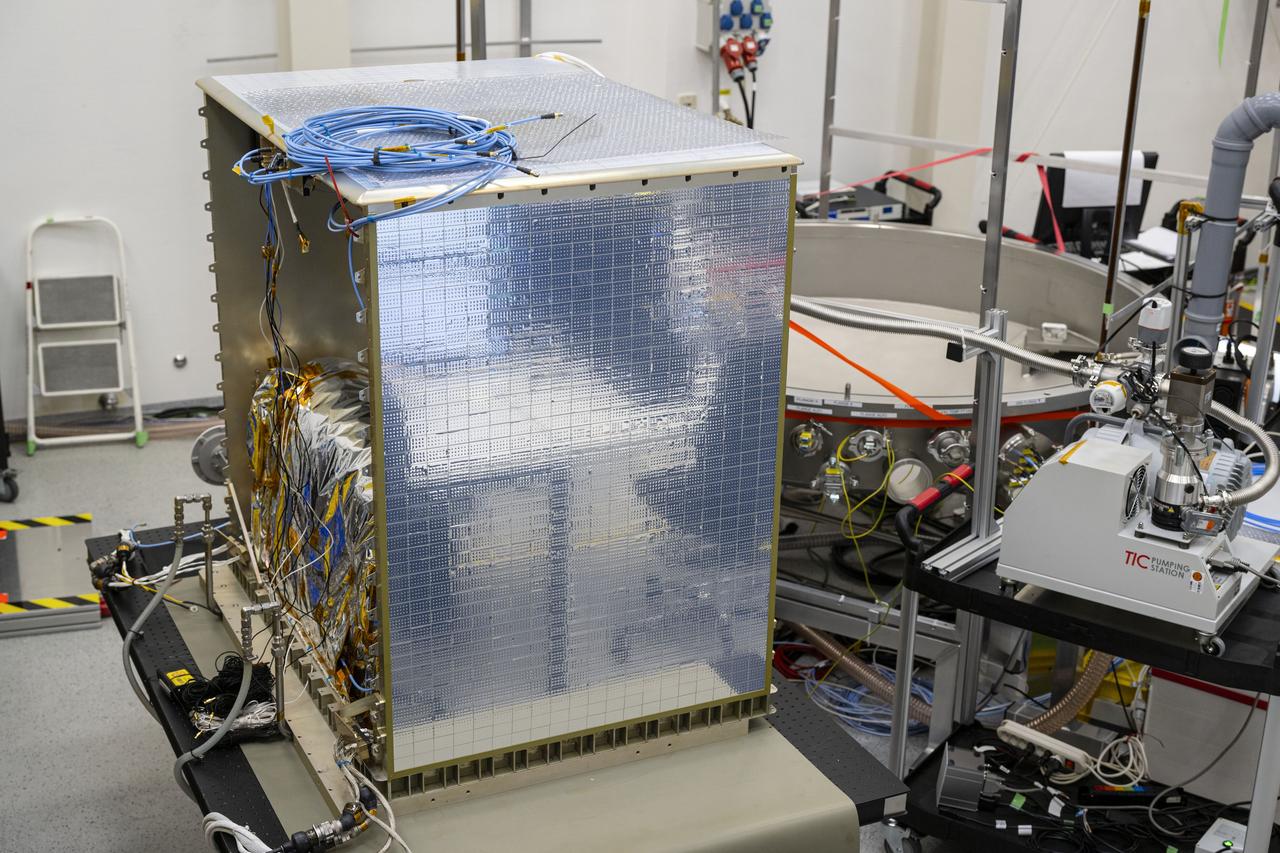
jsc2025e015679 (3/6/2025) --- The closure of the instrument panel of the Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES) has taken place at Airbus Friedrichshafen, Germany. ACES is an ESA instrument that tests fundamental physics, such as Einstein’s theory of general relativity, from the International Space Station. According to this theory, gravity affects the passing of time—time flies faster at the top of Mount Everest than at sea level. This effect has been proven in experiments on Earth, and ACES will make more precise measurements of this phenomenon and other fundamental physics such as the standard model of particle physics, as it flies 400 km high on the space station. ACES contains two clocks: PHARAO, a caesium atomic clock developed by the French Space Agency CNES, and the Space Hydrogen Maser developed by Spectratime, which uses hydrogen atoms as a frequency reference. The payload will be externally mounted to ESA’s Columbus laboratory on the space station. Image courtesy of S. Corvaja (ESA).
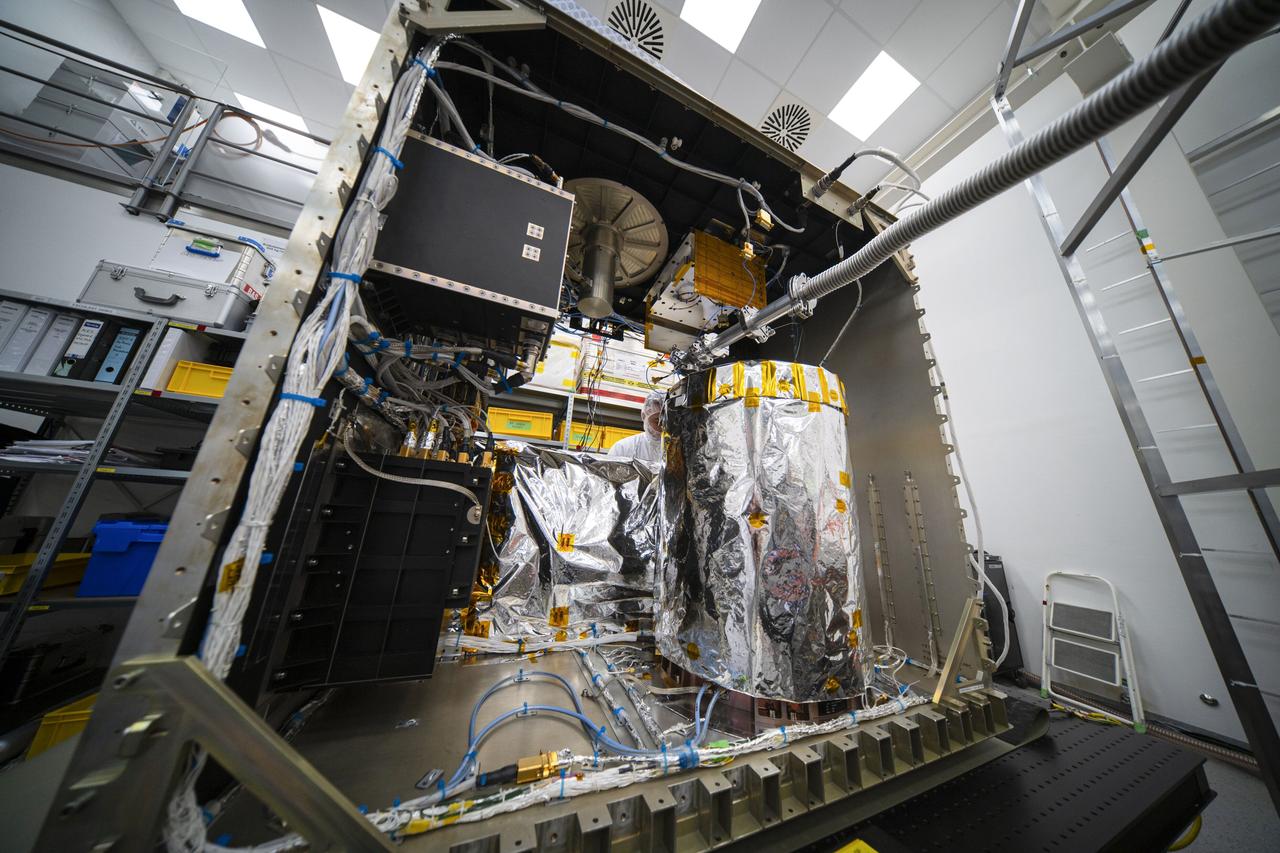

jsc2025e015680 (3/6/2025) --- The closure of the instrument panel of the Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES) has taken place at Airbus Friedrichshafen, Germany. ACES is an ESA instrument that tests fundamental physics, such as Einstein’s theory of general relativity, from the International Space Station. According to this theory, gravity affects the passing of time—time flies faster at the top of Mount Everest than at sea level. This effect has been proven in experiments on Earth, and ACES will make more precise measurements of this phenomenon and other fundamental physics such as the standard model of particle physics, as it flies 400 km high on the space station. ACES contains two clocks: PHARAO, a caesium atomic clock developed by the French Space Agency CNES, and the Space Hydrogen Maser developed by Spectratime, which uses hydrogen atoms as a frequency reference. The payload will be externally mounted to ESA’s Columbus laboratory on the space station. Image courtesy of S. Corvaja (ESA).
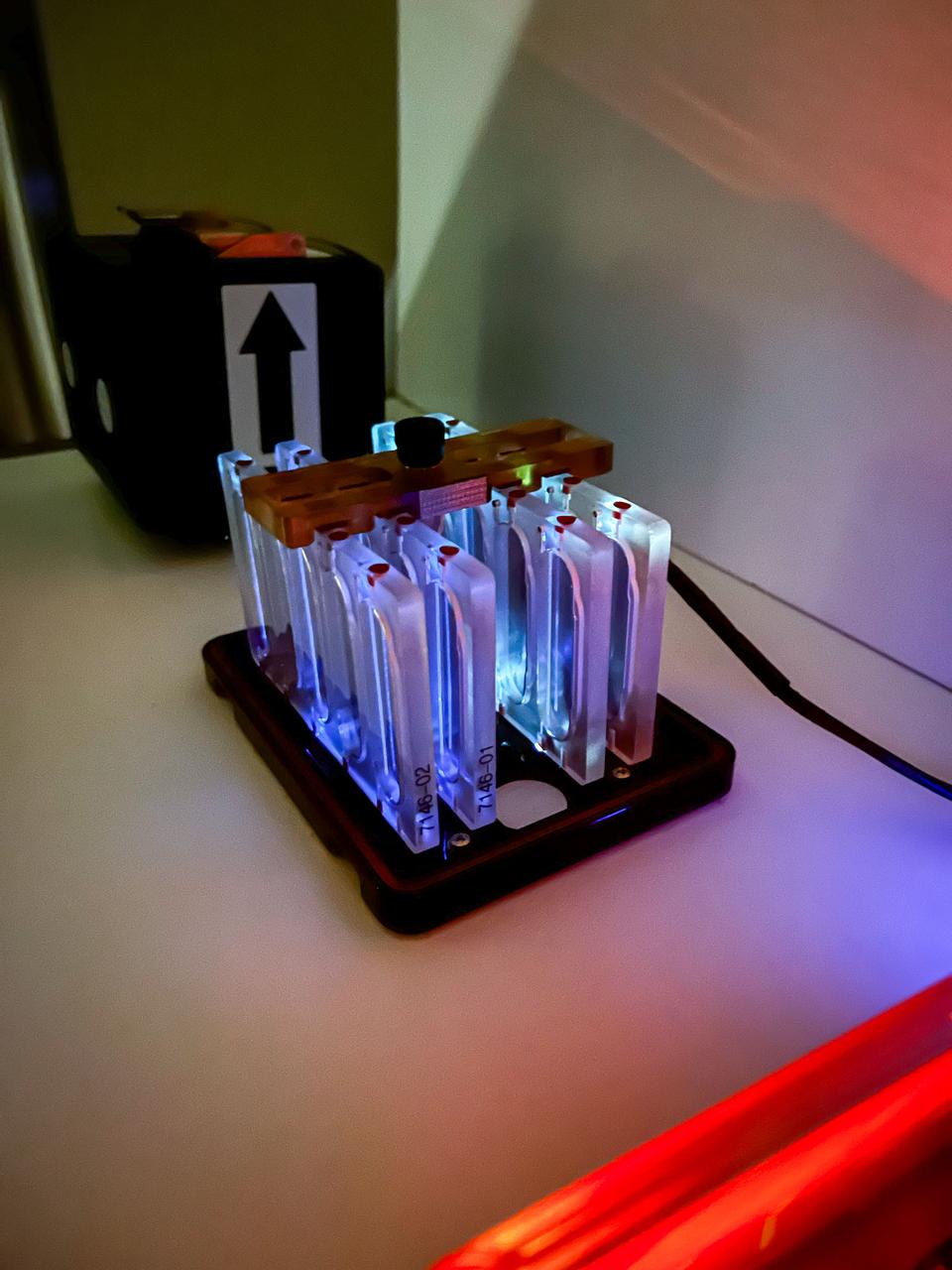

jsc2025e067422 97/9/2025) --- Agar plates for the GULBI investigation. This research uses special optical fibers to deliver ultraviolet (UV) light to inhibit the formation of microbial communities called biofilms and examine how microgravity affects the results. Credit: Arizona State University
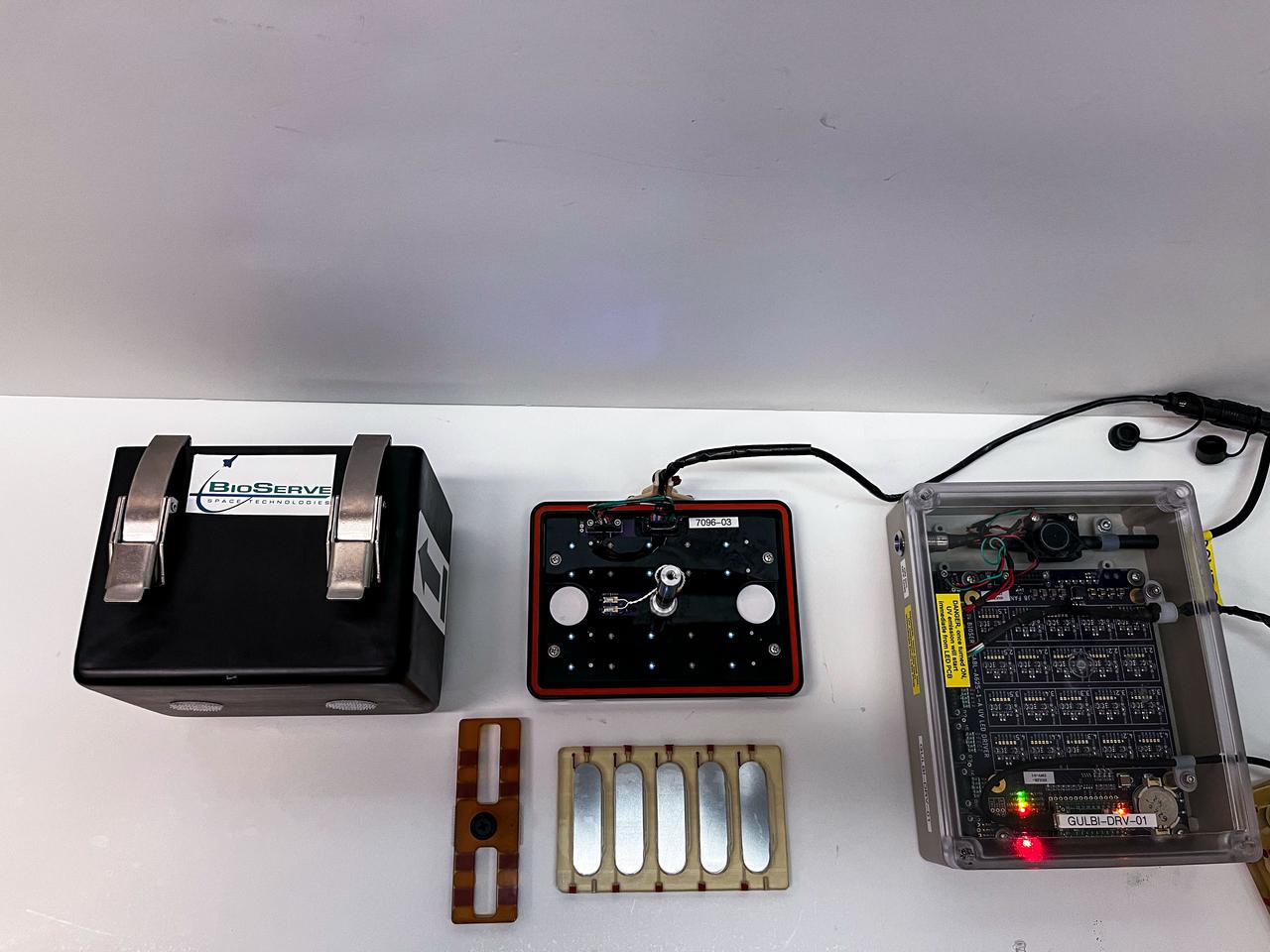

jsc2025e067421 (7/9/2025) --- Individual components of hardware for the GULBI investigation, which examines how microgravity affects the ability of a type of ultraviolet (UV) light to prevent formation of large communities of microbes called biofilms. Credit: Arizona State University
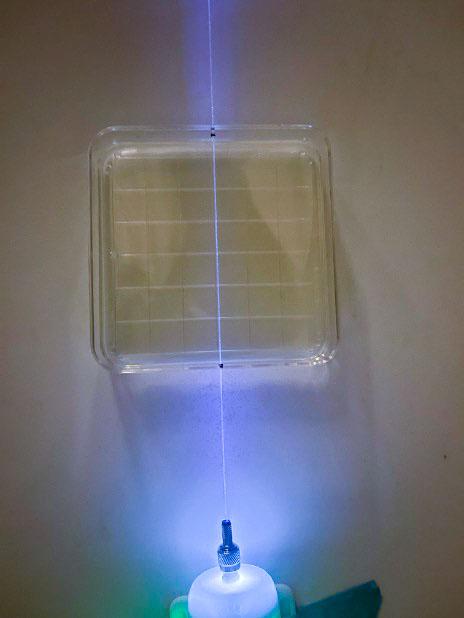
jsc2025e067423 (8/5/20250 --- Germicidal UV light is emitted by an optical fiber running through the center of an agar plate. Researchers are testing whether microgravity changes the ability of the light to prevent growth of microbial communities known as biofilms. Credit: Arizona State University
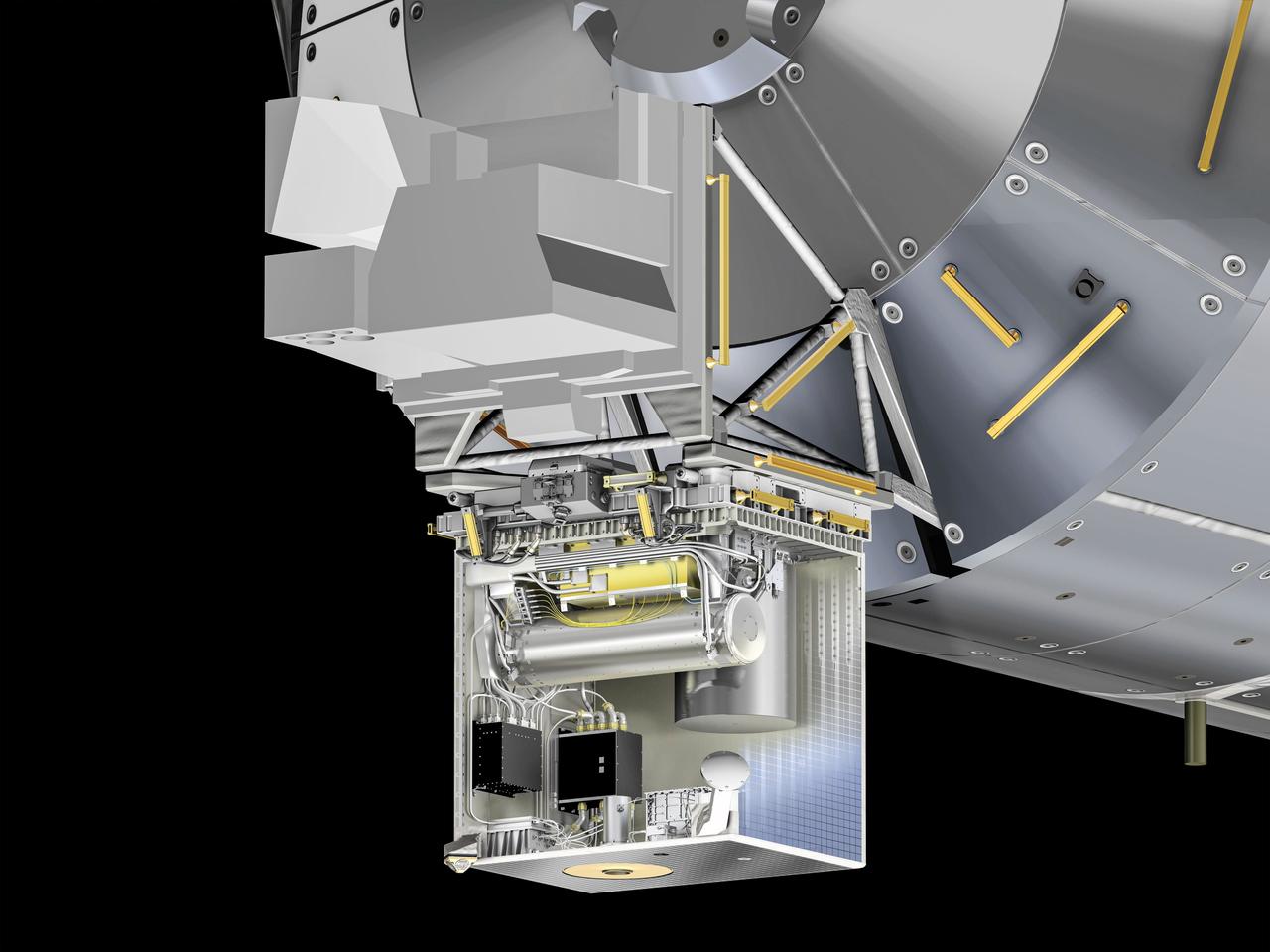
jsc2025e015681 (3/6/2025) --- The Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES) facility attached to the exterior of ESA's Columbus facility on the International Space Station. By creating a "network of clocks", this European facility can link its own highly precise timepieces with the most accurate clocks on Earth and compare them to measure the flow of time. ACES includes two cutting-edge clocks: Project d'Horloge Atomique par Refroidissement d'Atomes en Orbit (PHARAO) and Space Hydrogen Maser (SHM). The excellent stability of SHM over a one hour period, combined with the long-term stability and accuracy of PHARAO, provide timekeeping for ACES with a precision of one second over 300 million years. Once in space, a robotic arm positions ACES onto the Columbus module, where it will remain for 30 months to collect data. ACES aims to record continuous data over at least ten sessions of 25 days each. By comparing clocks in space and on Earth, ACES can provide scientists with precise measurements to test Einstein’s gravitational time dilation effect, search for time variations of fundamental constants of physics, and hunt for dark matter. ACES is fully assembled at Airbus in Friedrichshafen, Germany. Image courtesy of D. Ducros (ESA).
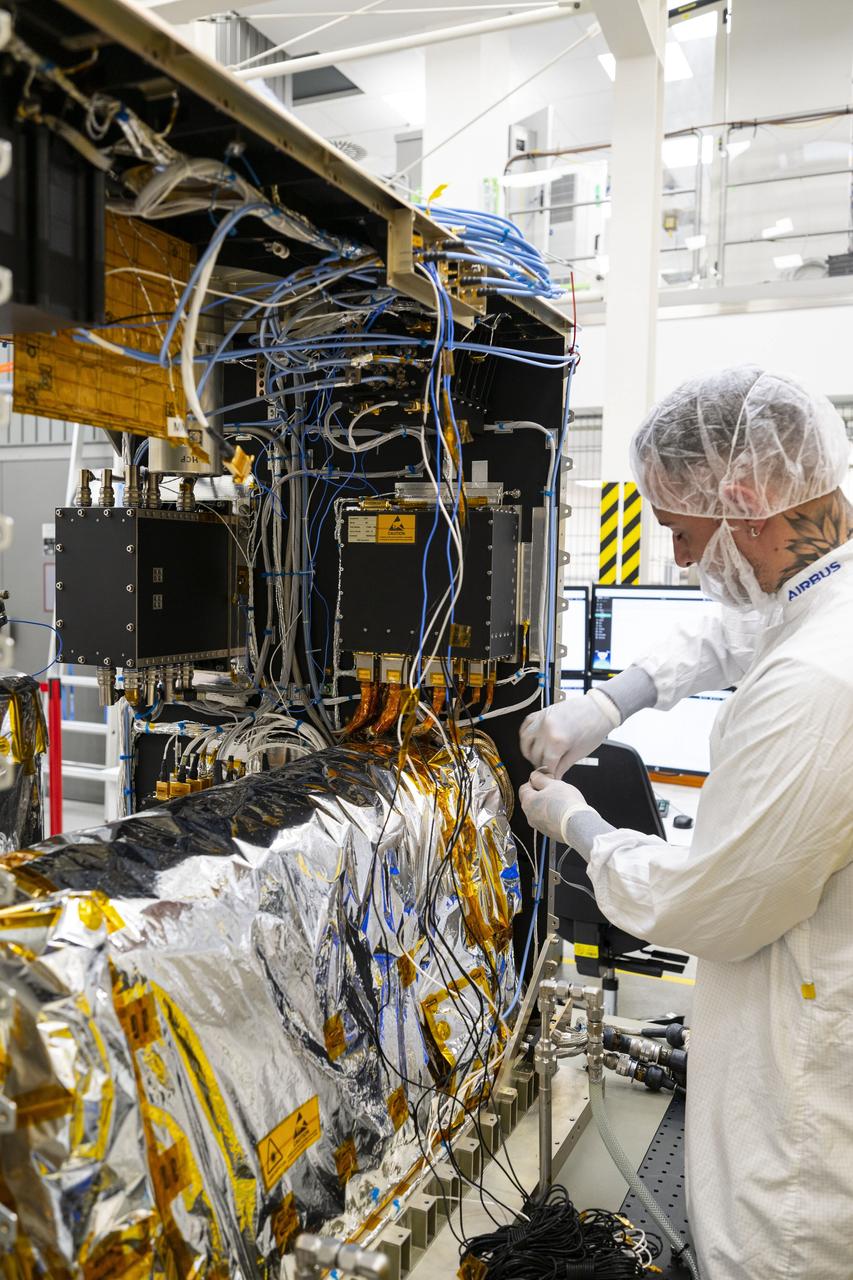

jsc2025e015678 (3/6/2025) --- The closure of the instrument panel of the Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES) has taken place at Airbus Friedrichshafen, Germany. ACES is an ESA instrument that tests fundamental physics, such as Einstein’s theory of general relativity, from the International Space Station. According to this theory, gravity affects the passing of time—time flies faster at the top of Mount Everest than at sea level. This effect has been proven in experiments on Earth, and ACES will make more precise measurements of this phenomenon and other fundamental physics such as the standard model of particle physics, as it flies 400 km high on the space station. ACES contains two clocks: PHARAO, a caesium atomic clock developed by the French Space Agency CNES, and the Space Hydrogen Maser developed by Spectratime, which uses hydrogen atoms as a frequency reference. The payload will be externally mounted to ESA’s Columbus laboratory on the space station. Image courtesy of S. Corvaja (ESA).
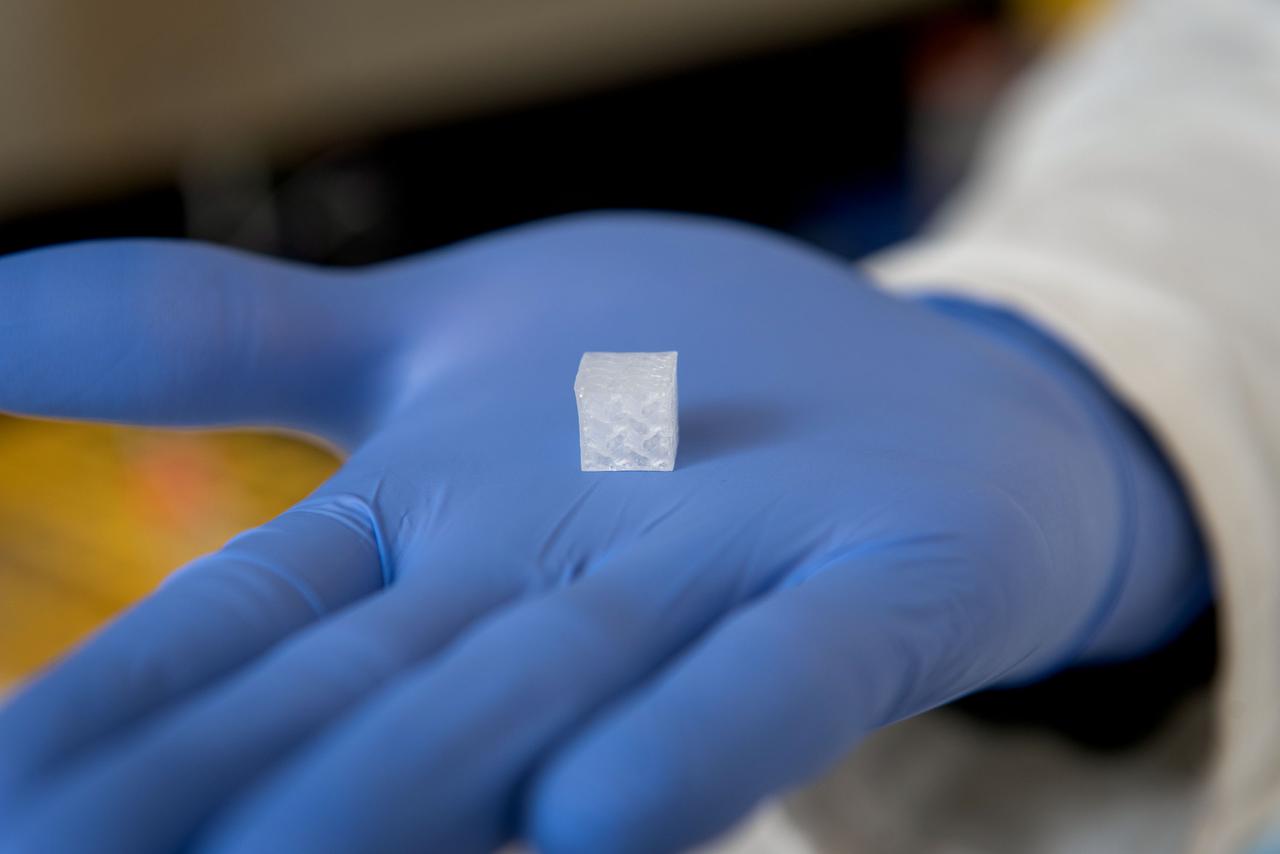

jsc2024e050836 (3/16/2022) --- Maturation of Vascularized Liver Tissue Construct in Zero Gravity (MVP Cell-07) examines the behavior in microgravity of bioprinted or engineered liver tissue constructs that contain blood vessels. The liver tissue constructs with a surface dimension of 1cm x 1cm x 1cm are bioprinted with a gyroid-shaped architecture with interconnected channels, allowing for uniform flow and surface shear stress that adequately covers the entire inner surfaces of cell-laden tissue constructs. The investigation sheds light on the formation of small blood vessels in engineered tissue. Image courtesy of Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
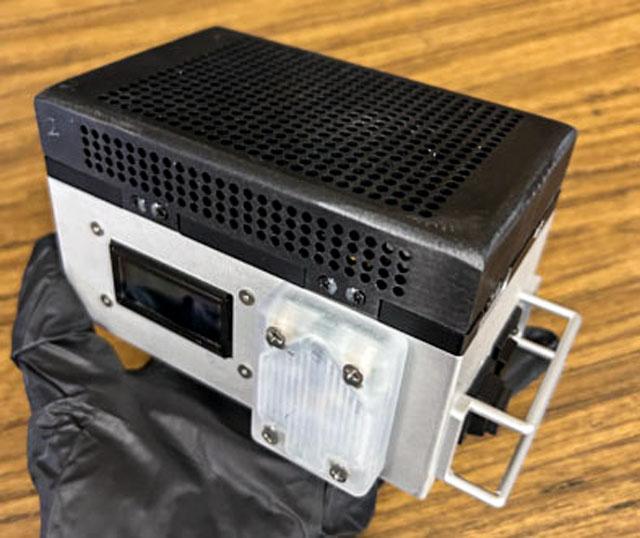

jsc2025e059518 (617/2025) --- A preflight view of the Portable Tunable Laser Spectrometer (PTLS) sensor package. PTLS uses a sensor network to measure the distribution of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and oxygen over time. Image courtesy of JPL.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Leandro James, left to right, Alejandro Azocar, Ron Sterick and Chris Iannello discuss a high-altitude balloon flight for the Rocket University program. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
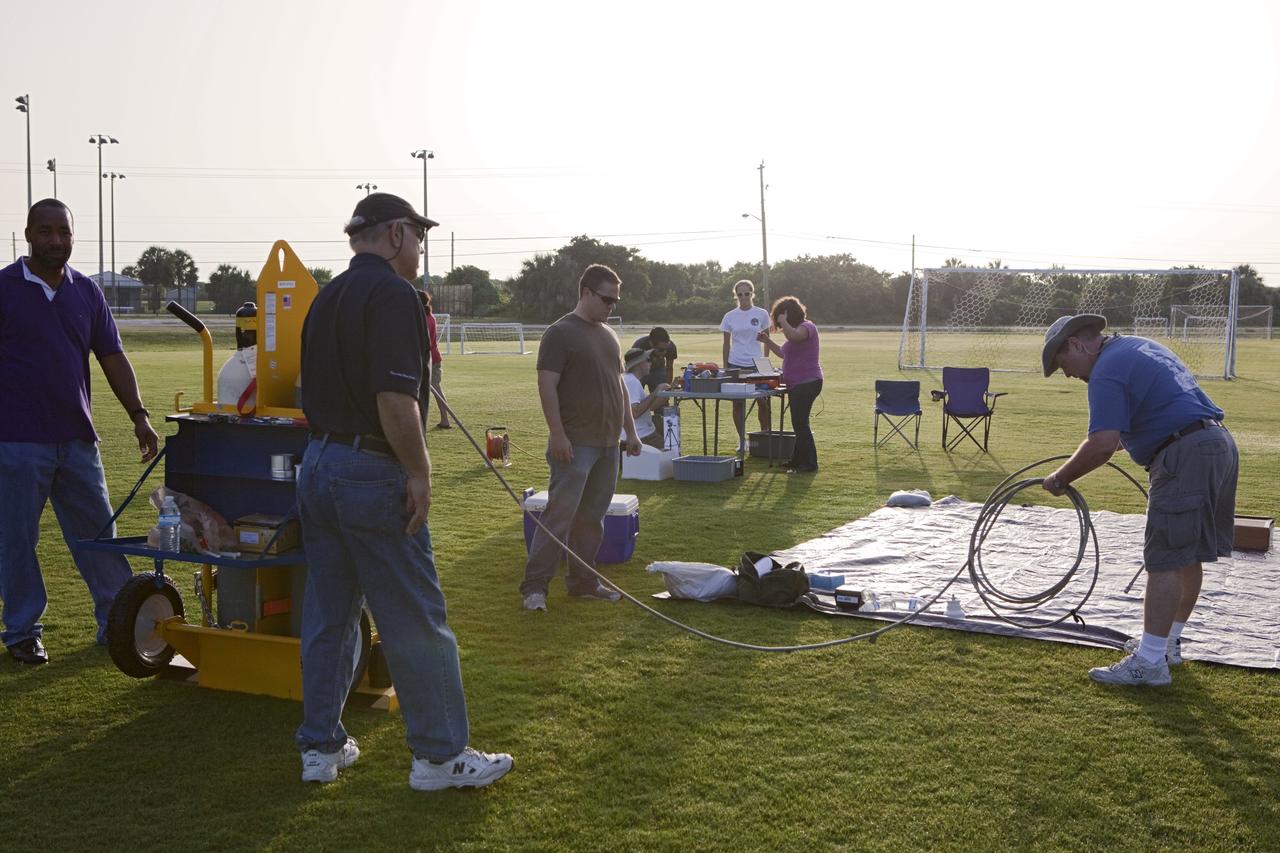

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rocket University participants prepare to launch a high-altitude balloon flight and instrument package. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
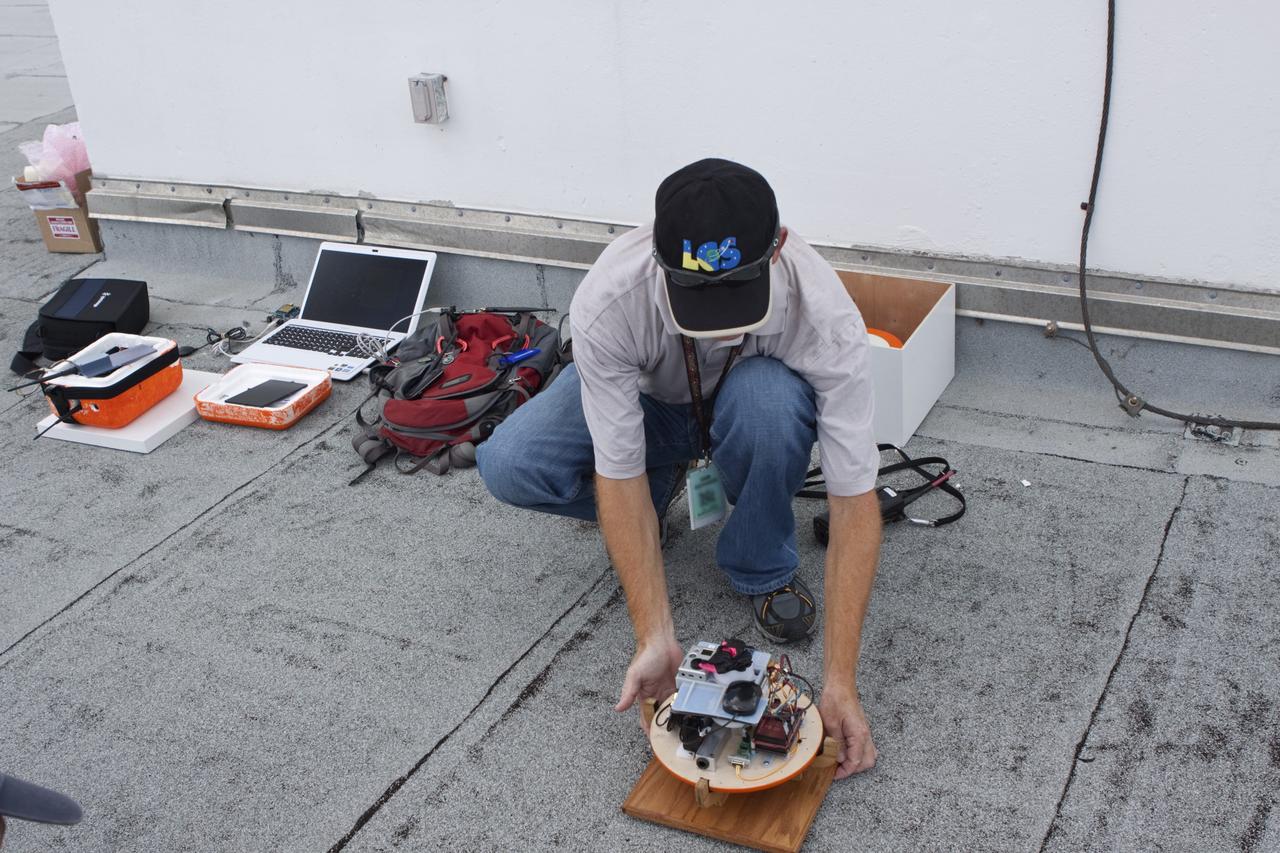

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Karl Stolleis prepares an instrument package for testing as part of a high-altitude balloon flight for the Rocket University program. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
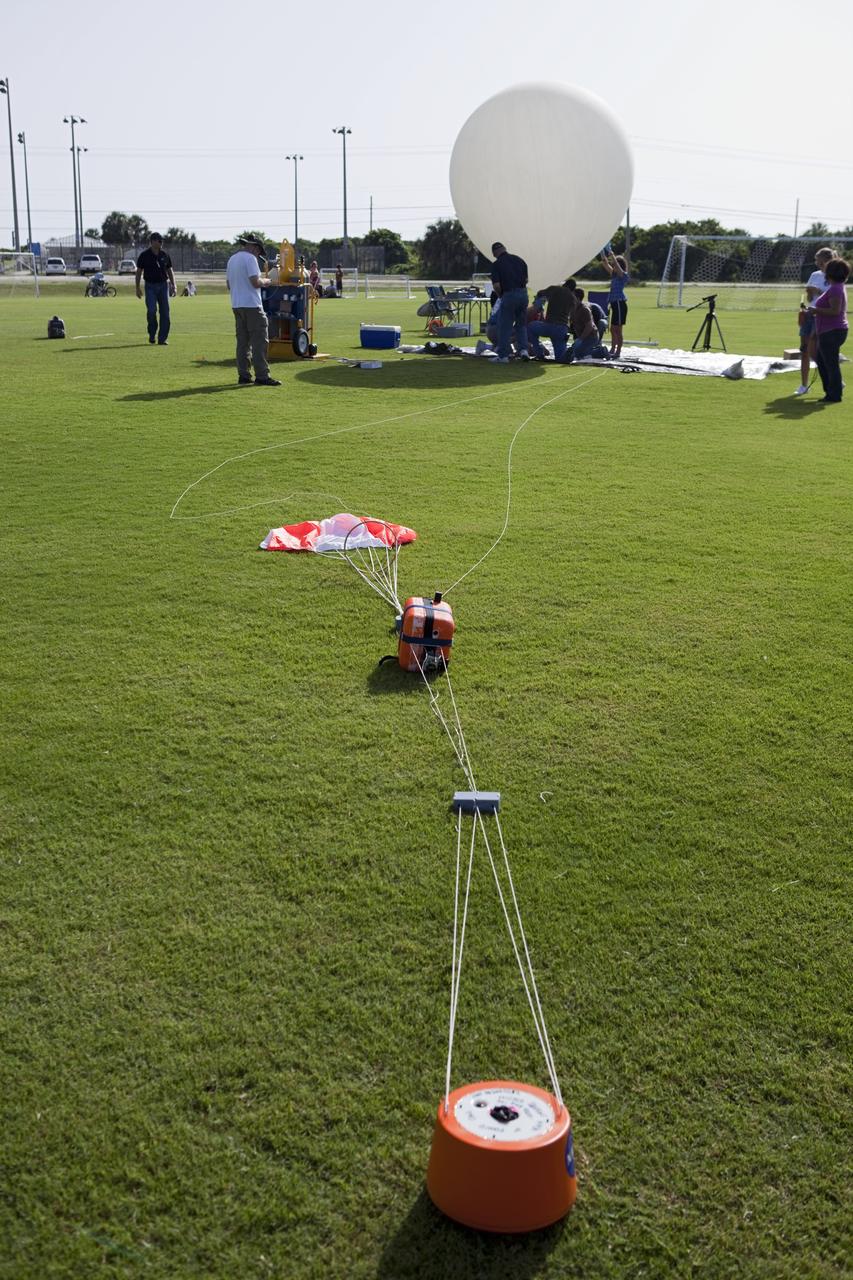

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The instrument package built by Rocket University participants for a high-altitude balloon flight sits on the ground moments before launch. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Karl Stolleis prepares an instrument package for testing as part of a high-altitude balloon flight for the Rocket University program. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
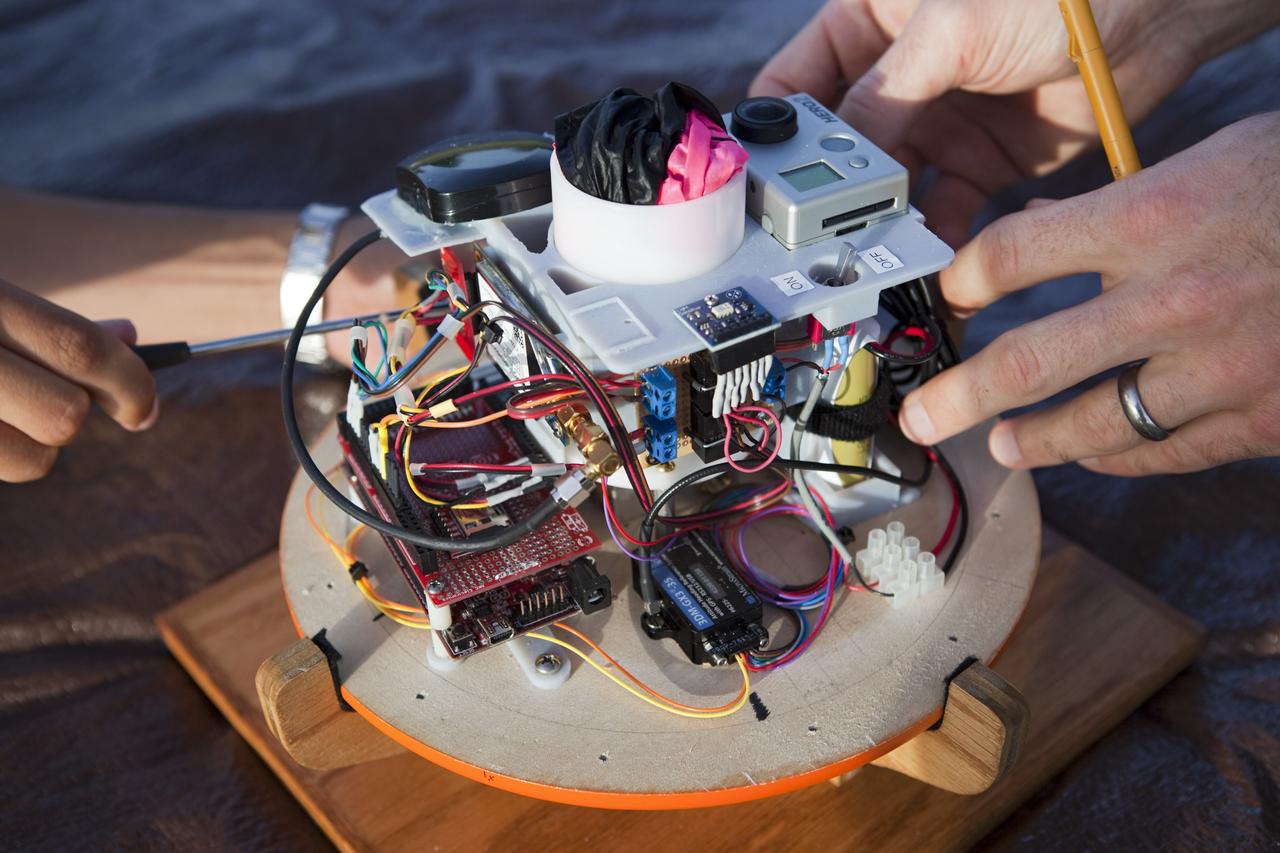
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The instrument package built by Rocket University participants for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
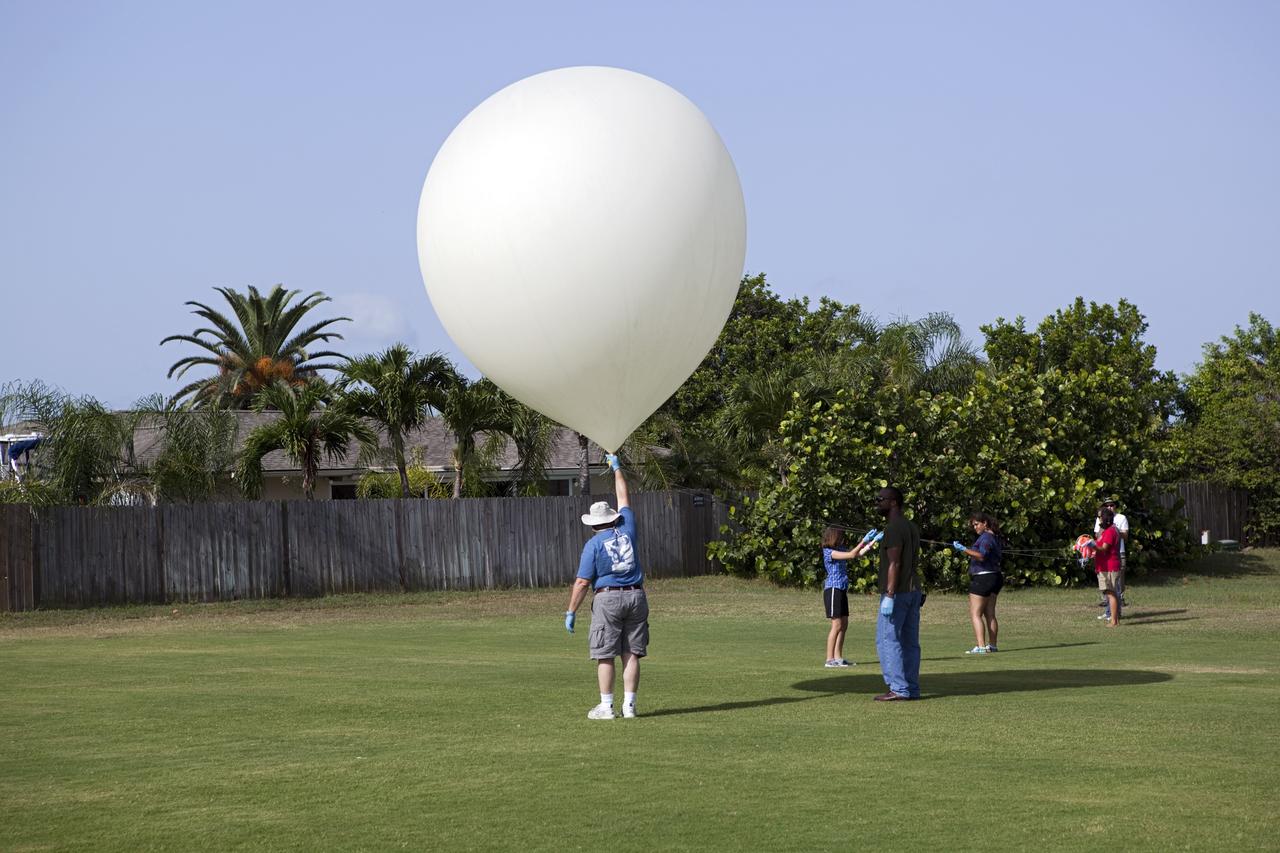

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rocket University participants prepare to launch a high-altitude balloon flight and instrument package. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
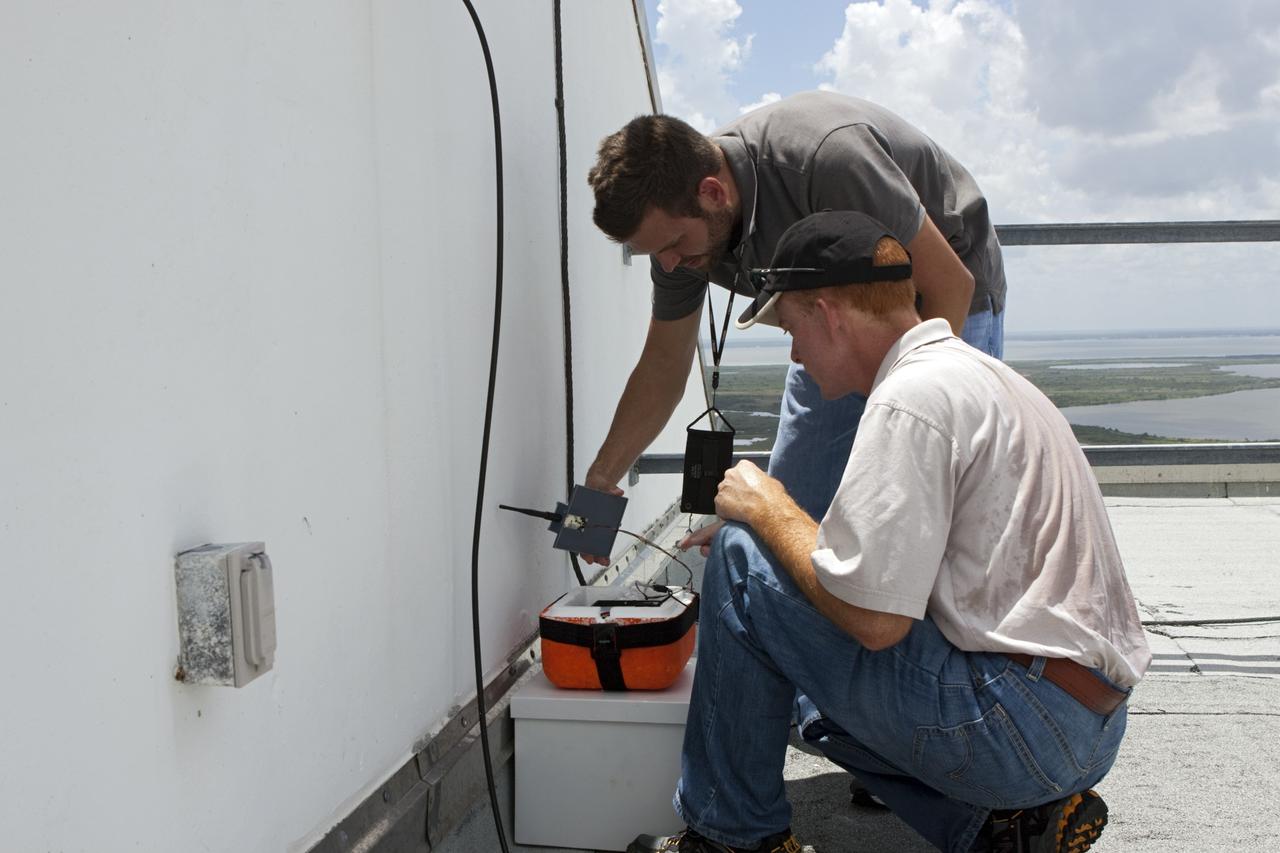

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Karl Stolleis, kneeling, and Nick Pack prepare an instrument package for testing as part of a high-altitude balloon flight for the Rocket University program. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
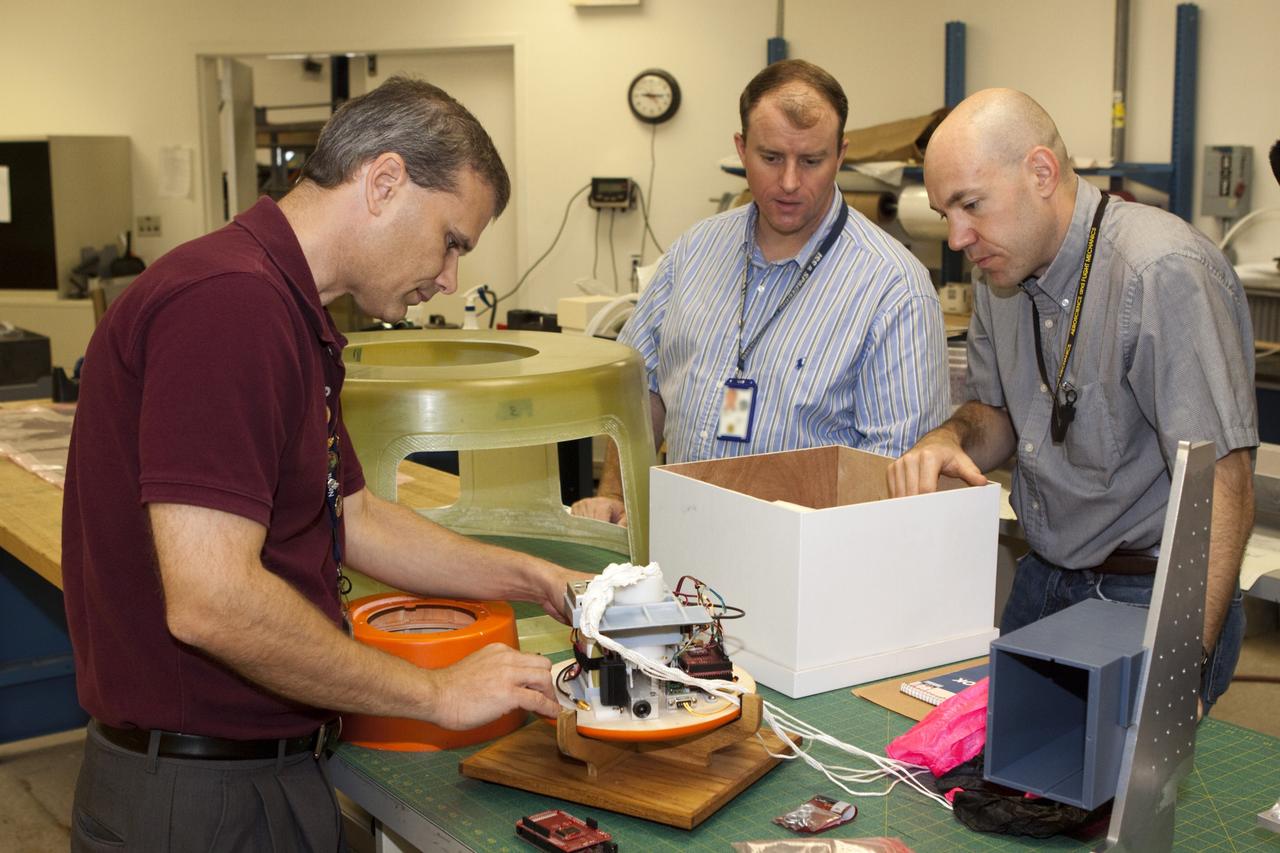

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rocket University participants inspect a capsule that is being prepared for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
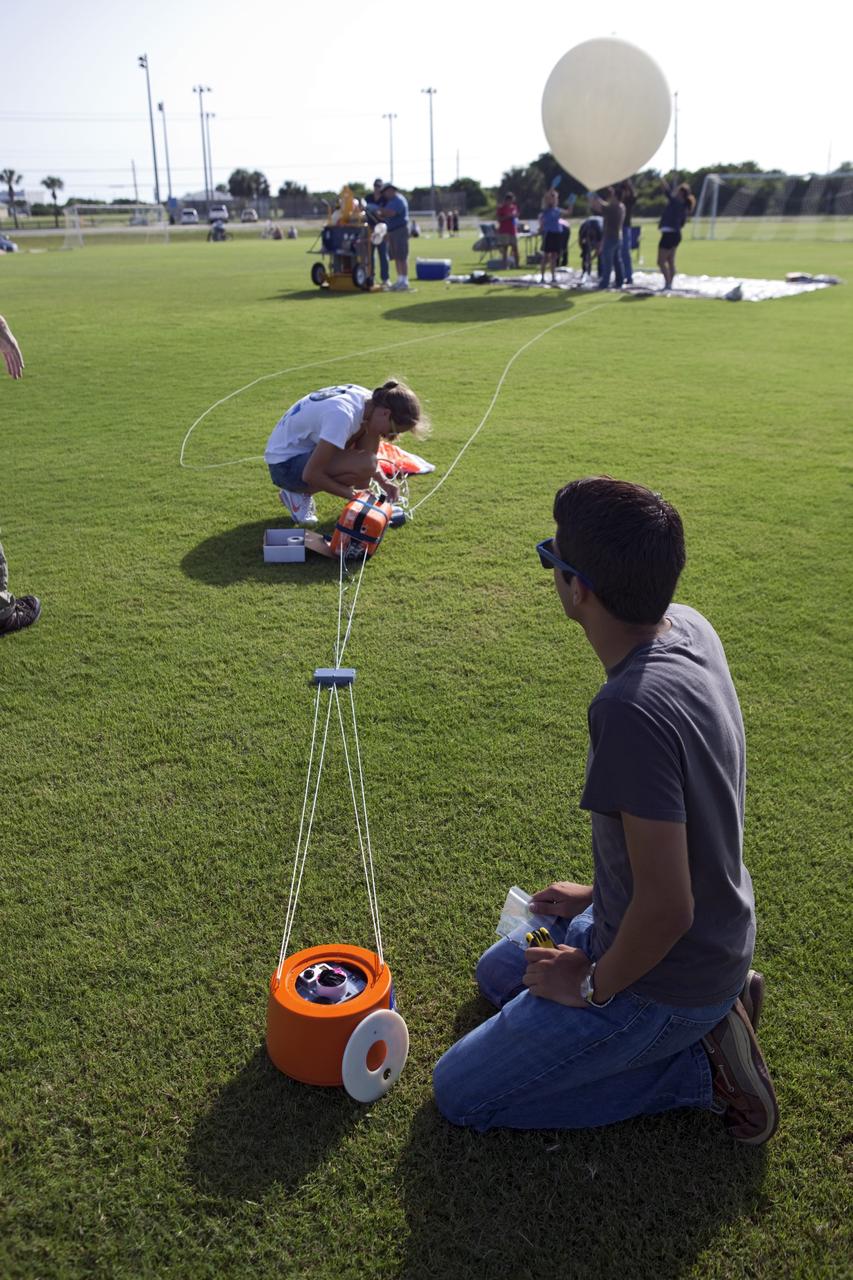

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alejandro Azocar, foreground, and Page Attany, Rocket University participants, prepare an instrument package to launch on a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
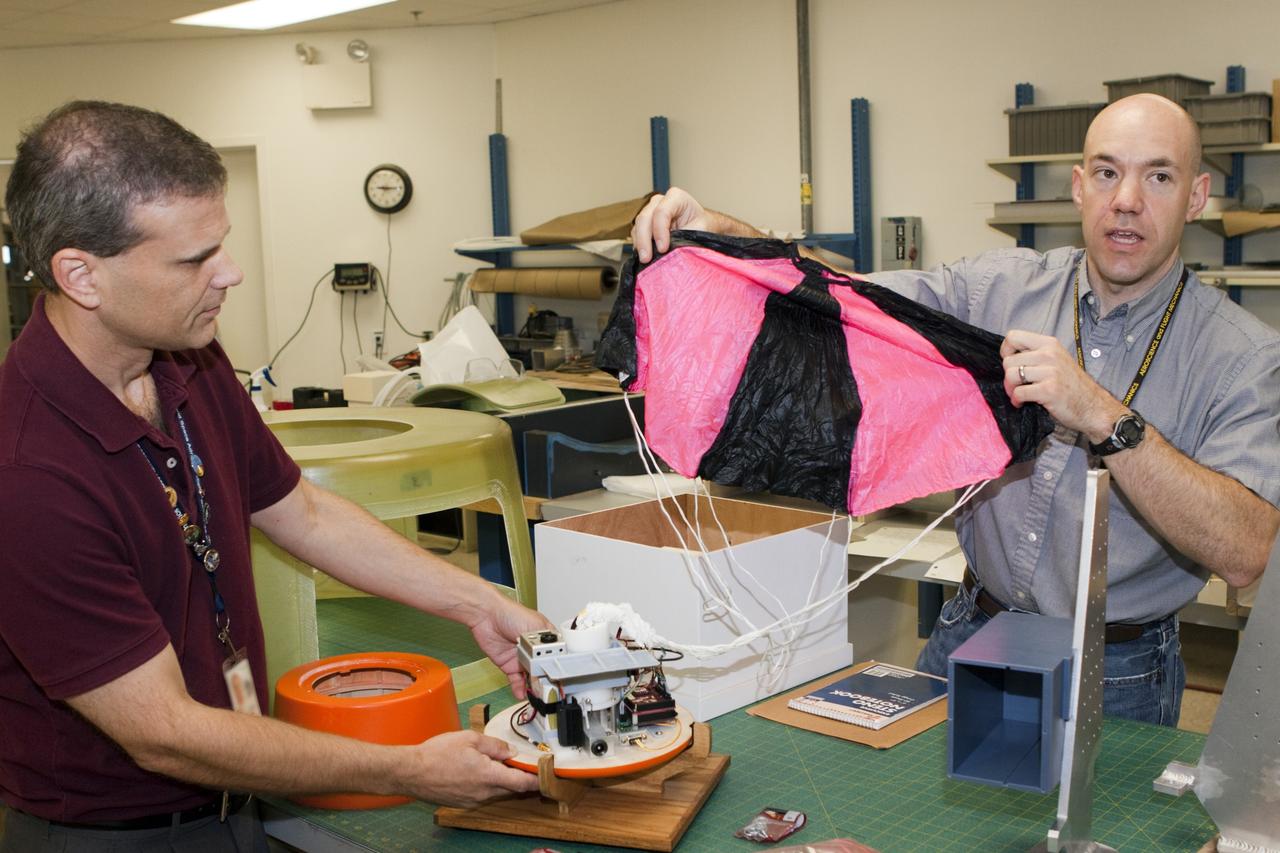

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Paul Paulick, left, and Ron Sterick, both participants in the Rocket University program, inspect a capsule and parachute that are being prepared for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
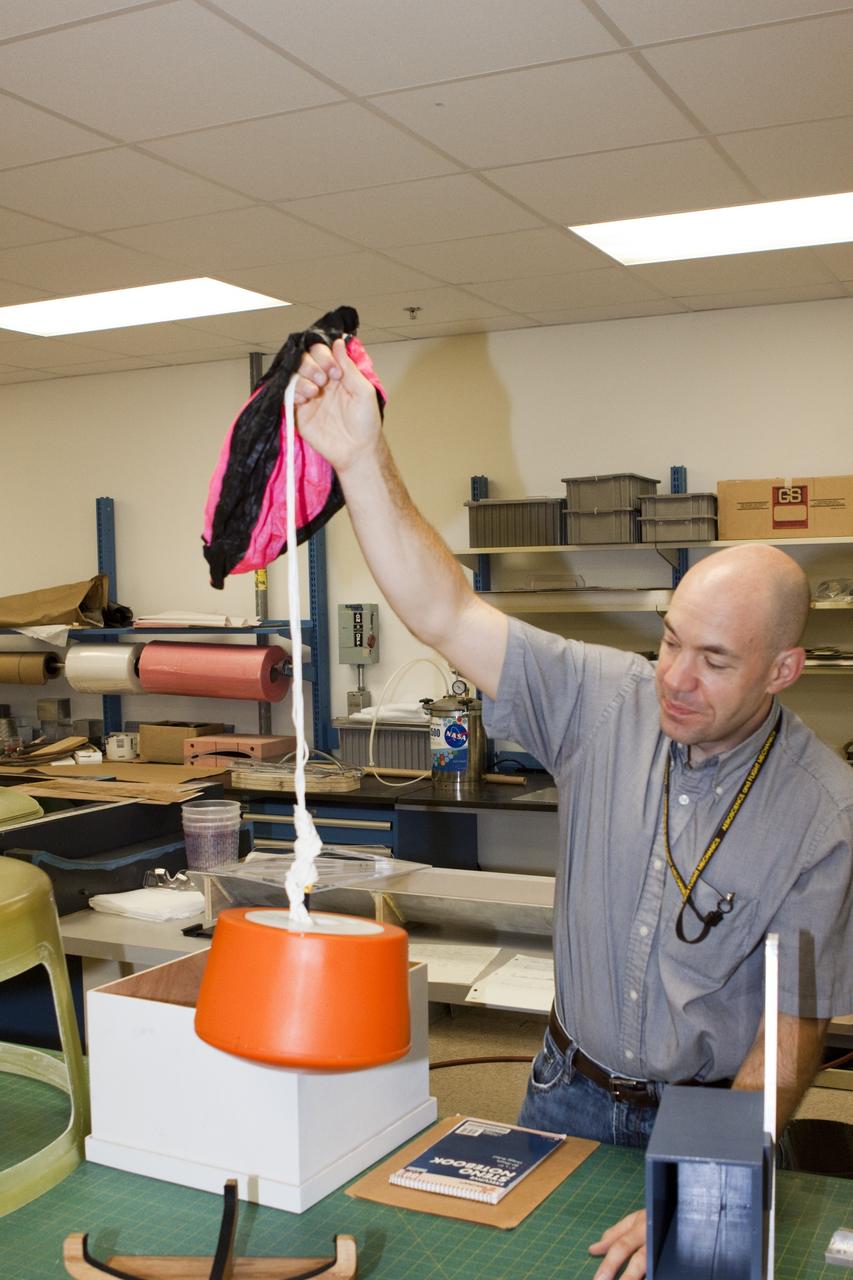

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Ron Sterick, a participant in the Rocket University program, inspects a capsule and parachute that are being prepared for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
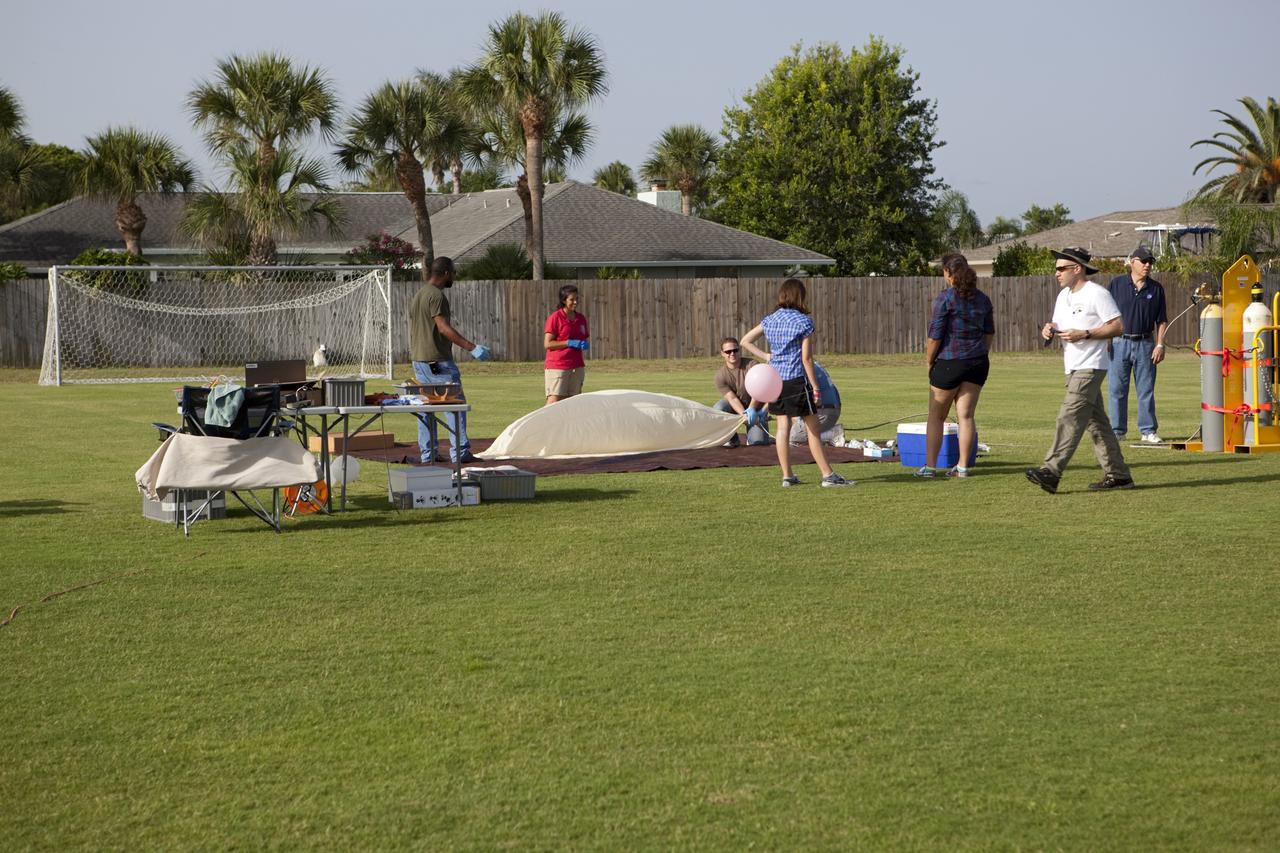

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rocket University participants prepare to launch a high-altitude balloon flight and instrument package. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
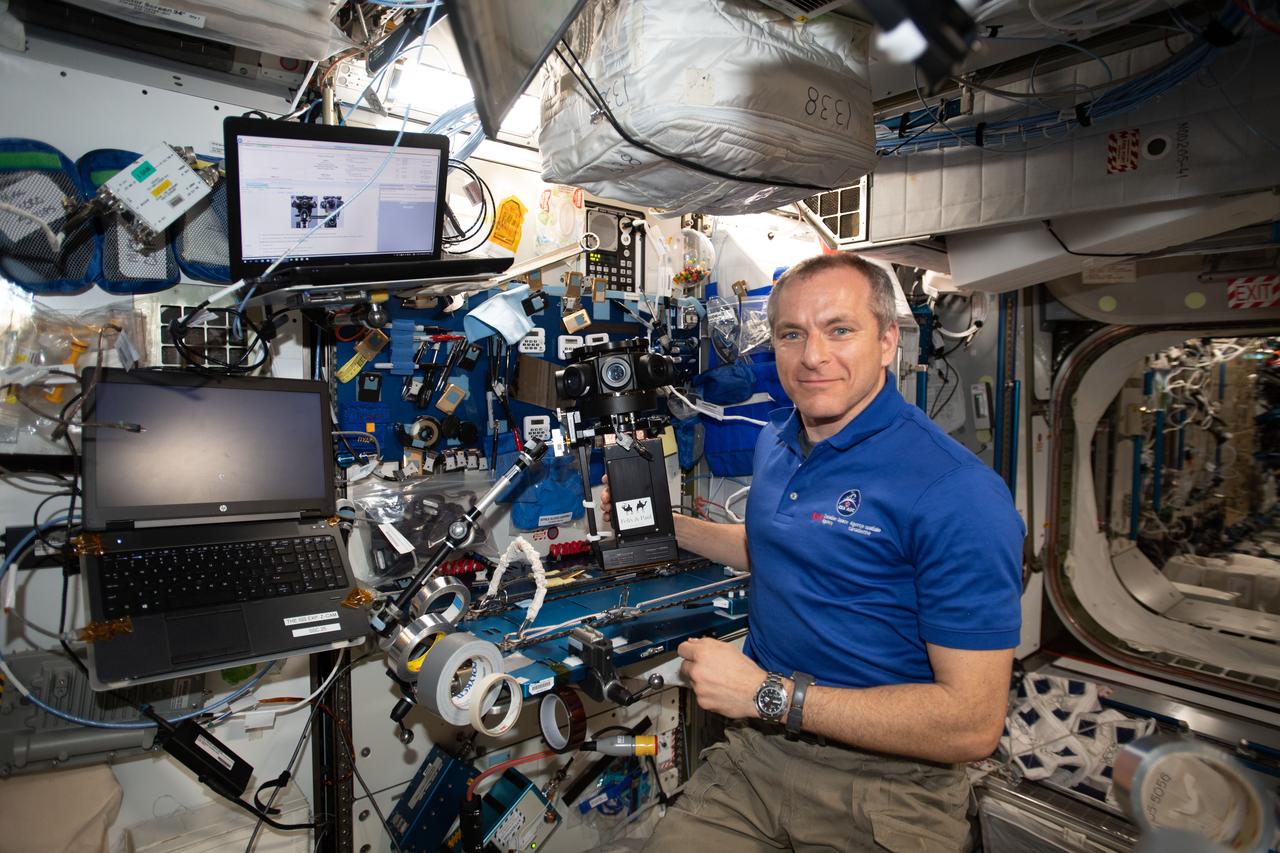

iss058e005160 (1/21/2019) --- A view of Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut David Saint-Jacques setting up the Z-CAM V1 Pro Cinematic camera for the ISS Experience payload. The International Space Station Experience (ISS Experience) creates a virtual reality film documenting daily life aboard the space station. The 8- to 10-minute film created from footage taken during the six-month investigation covers different aspects of crew life, conducting science aboard the station, and the international partnerships involved.
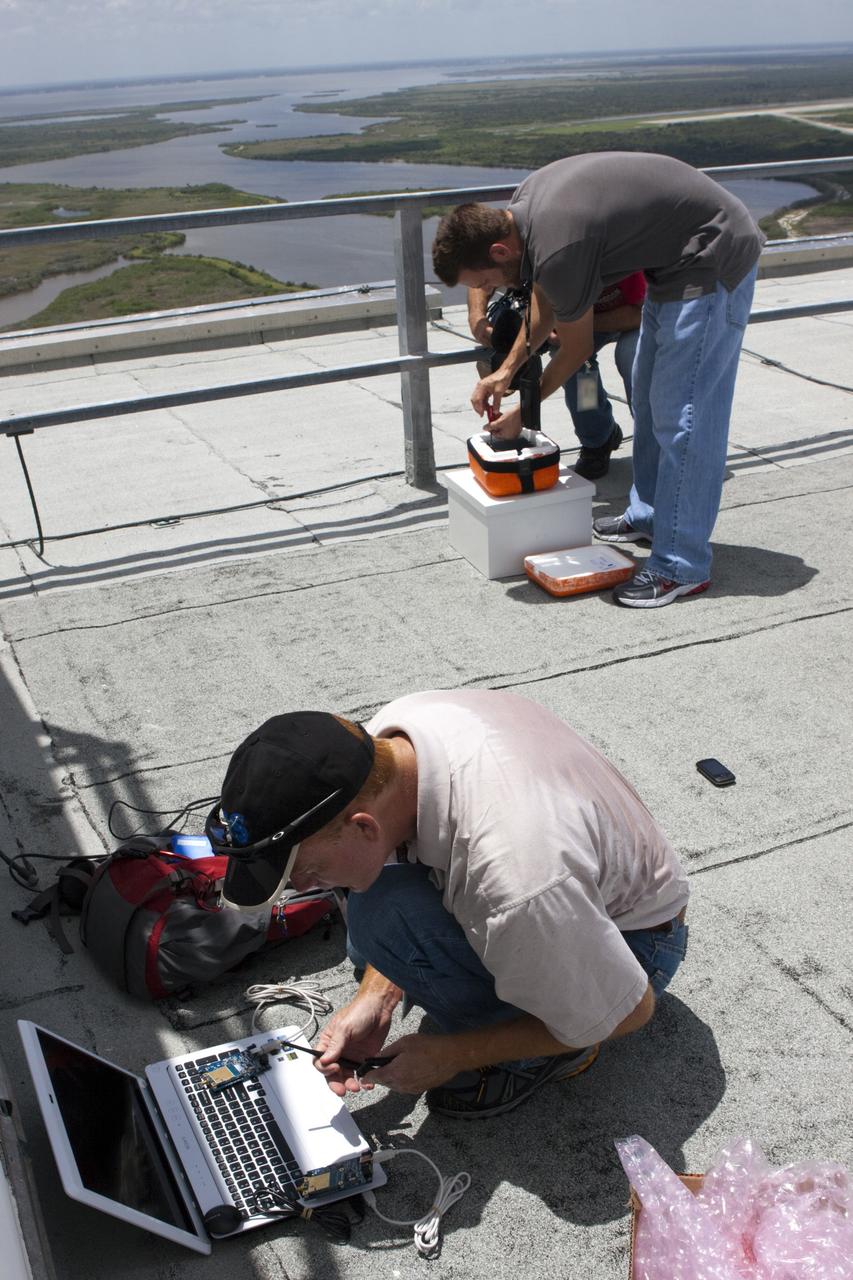

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Karl Stolleis, left and Nick Pack prepare an instrument package for testing as part of a high-altitude balloon flight for the Rocket University program. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
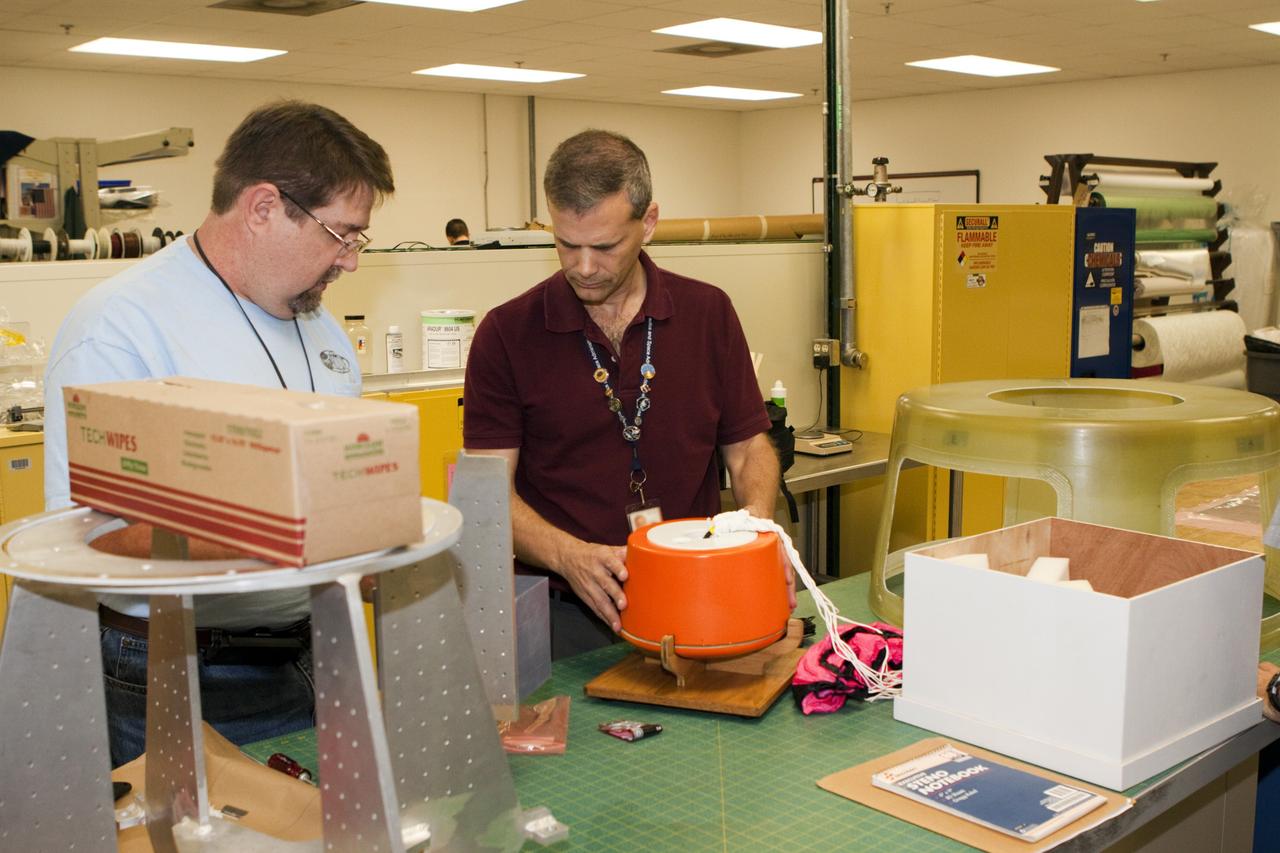

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mike Lane, left, and Paul Paulick, both participants in the Rocket University program, inspect a capsule that is being prepared for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
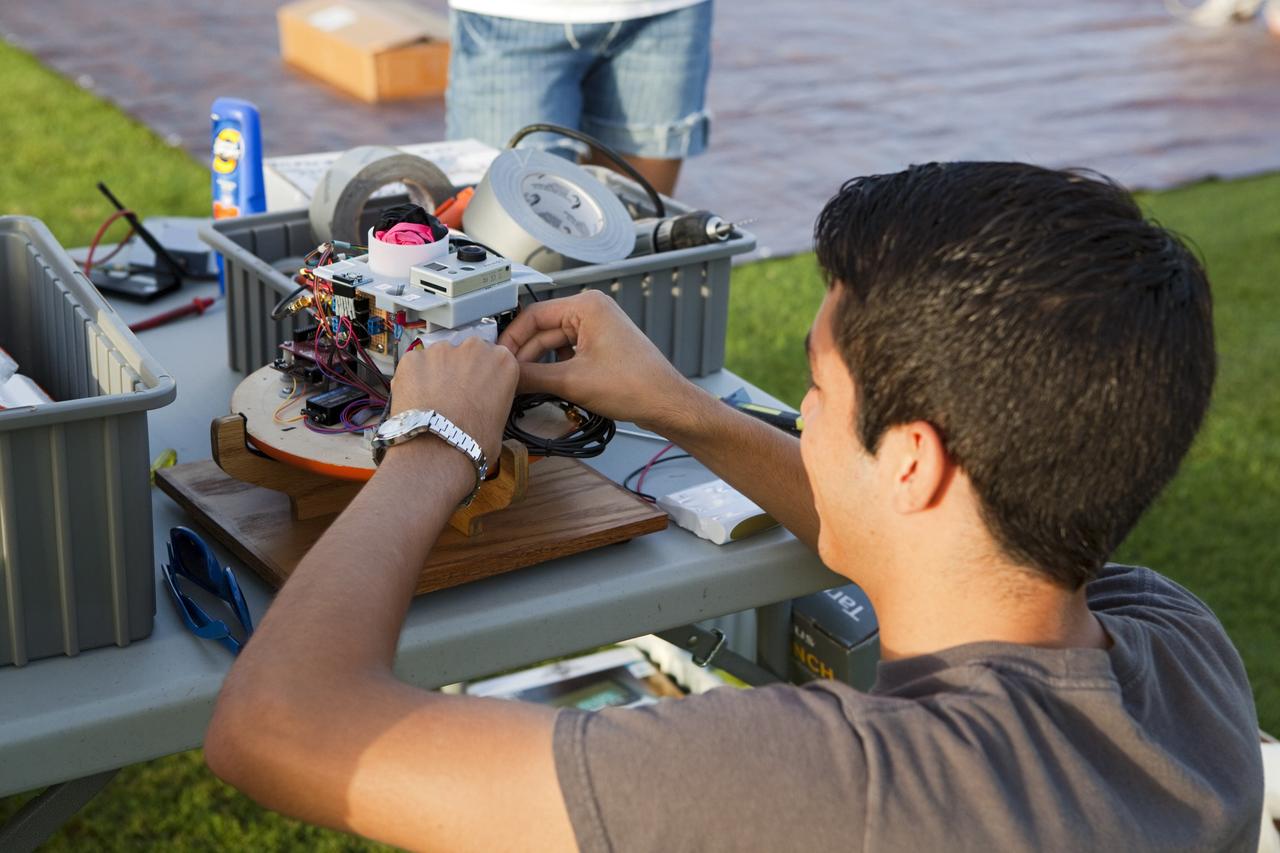

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alejandro Azocar, a Rocket University participant, prepares an instrument package to launch on a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
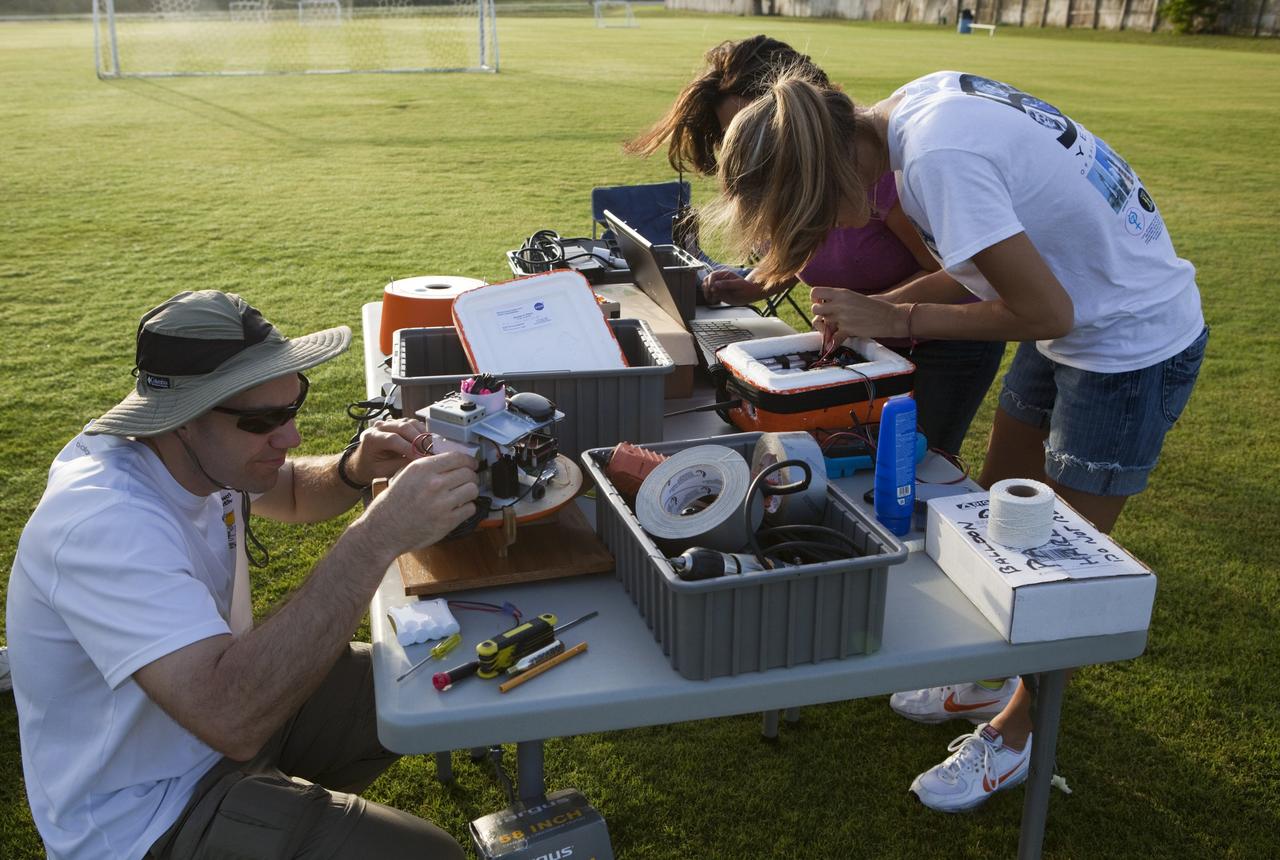

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Ron Sterick, left to right, Nicole Otermat and Page Attany, participants in the Rocket University program, prepare an instrument package to launch on a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
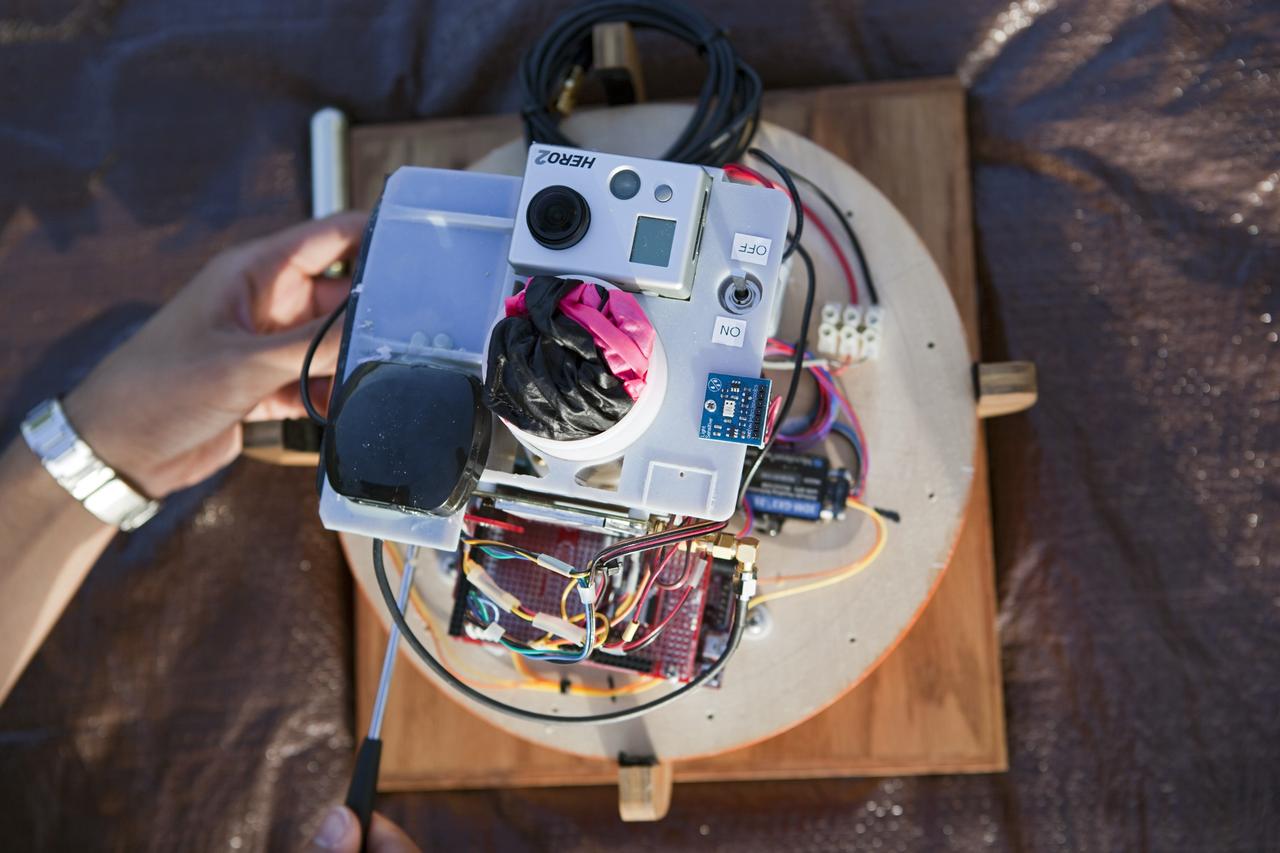
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The instrument package built by Rocket University participants for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The instrument package built by Rocket University participants for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
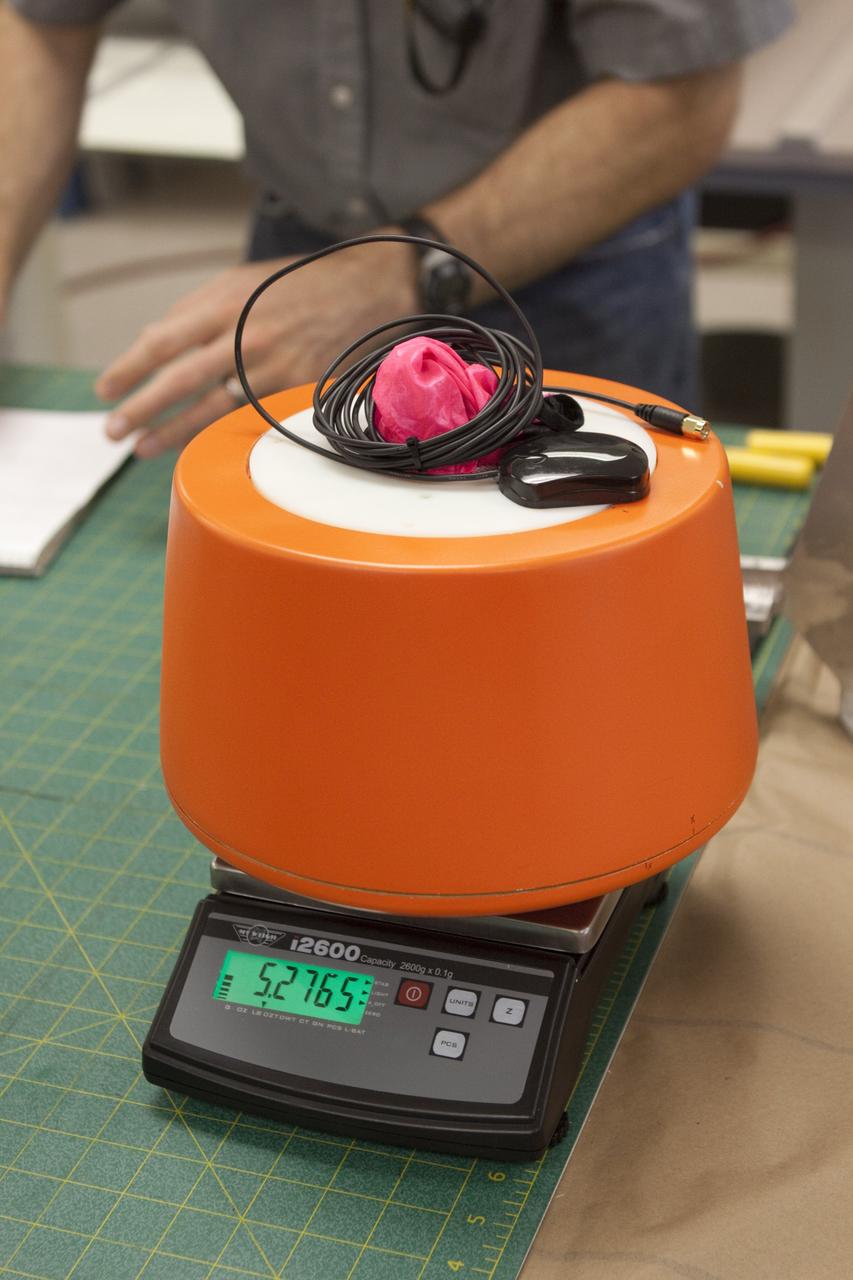

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The instrument package and capsule built by Rocket University participants for a high-altitude balloon flight. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
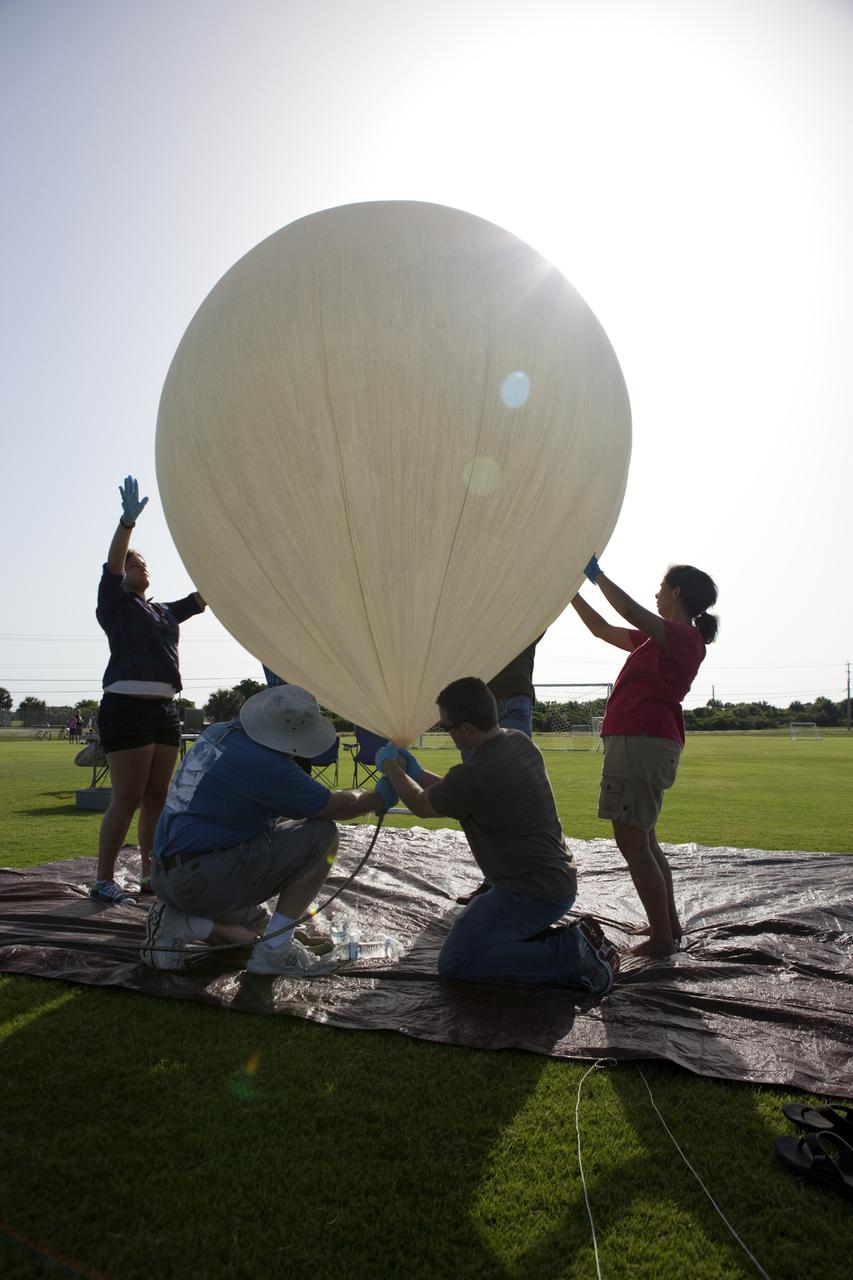

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rocket University participants prepare to launch a high-altitude balloon flight and instrument package. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
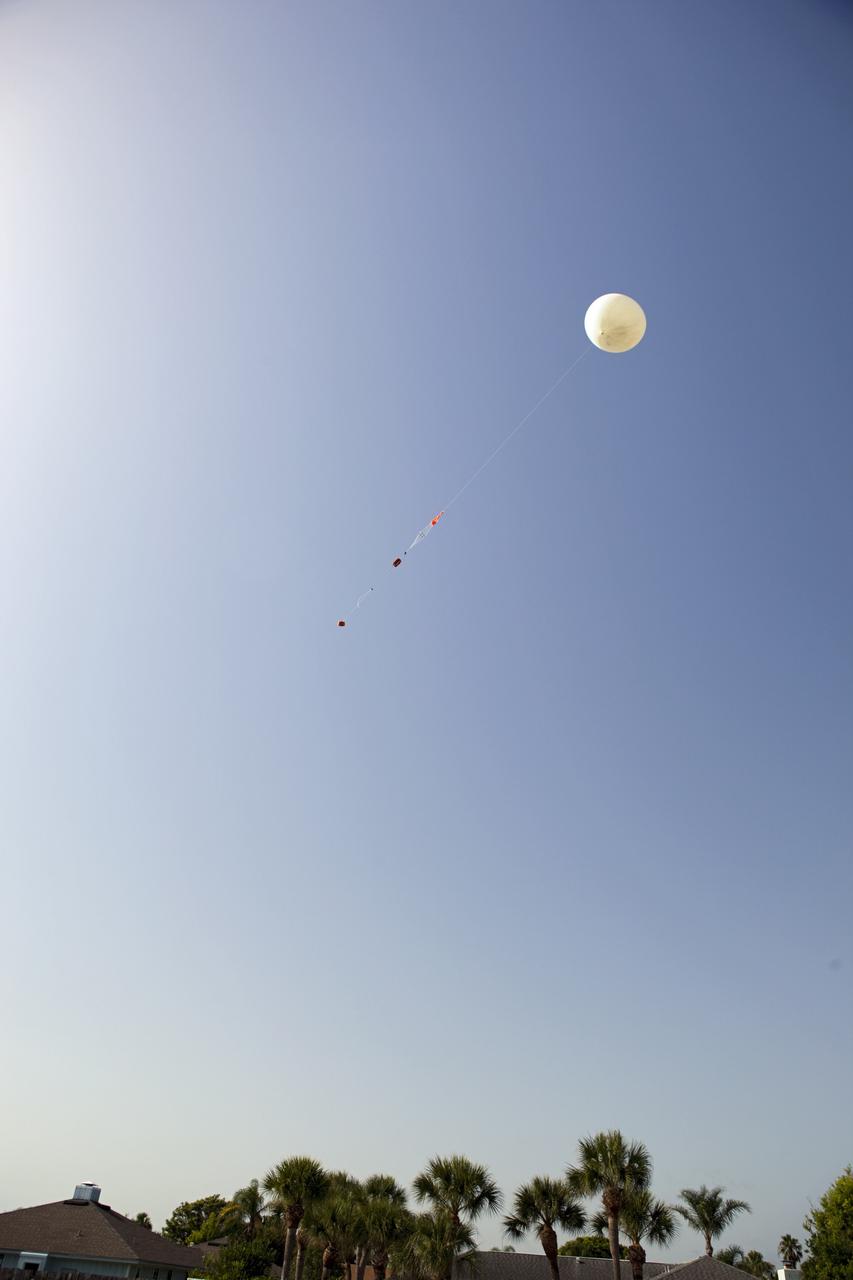

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rocket University participants launch a high-altitude balloon flight and instrument package. The test flight was used to evaluate the stability of an instrumented capsule as it fell to Earth before its parachute opened. Rocket University is a program of courses, workshops, labs and projects offered to engineering and research pros of all stripes to keep their skills fresh and broaden their experiences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
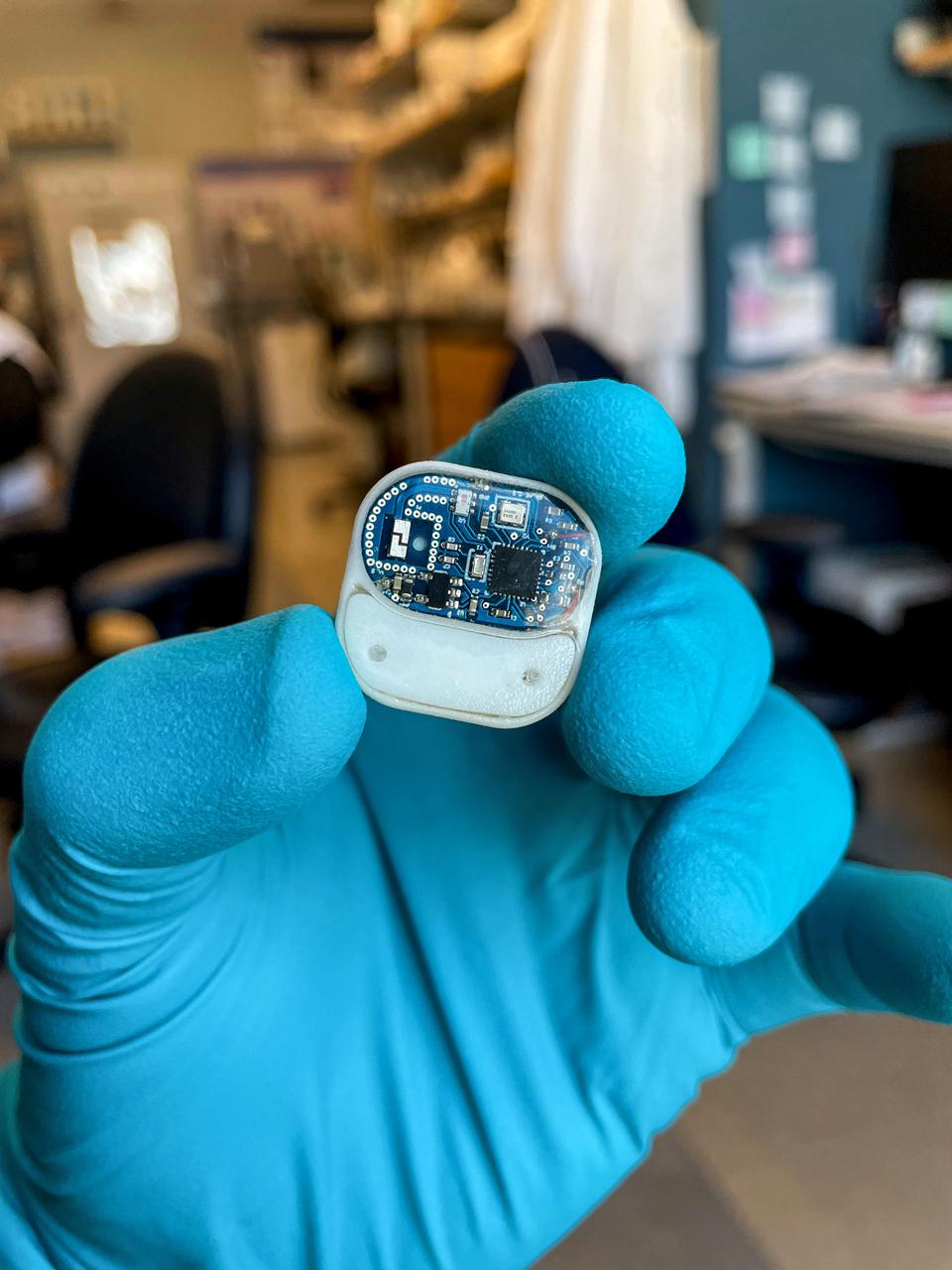

jsc2021e037283 (8/11/2021) --- Nanofluidic Implant Communication Experiment (NICE) (Faraday-NICE) aims to develop an implantable drug delivery system that allows for remote control and modulation of the release of therapeutics over weeks to months. In this investigation, fully assembled implantable devices are tested for remote communication capabilities from Earth to the International Space Station (ISS). This investigation aims to verify that 100% of the communications between controller and implant is achieved and maintained on station. Implants are immersed in saline solution, a surrogate of physiological conditions, then placed and sealed in 15 ml containers. The tubes are mounted within the ProxOpS Faraday experimental box. Image Credit: Houston Methodist Research Institute
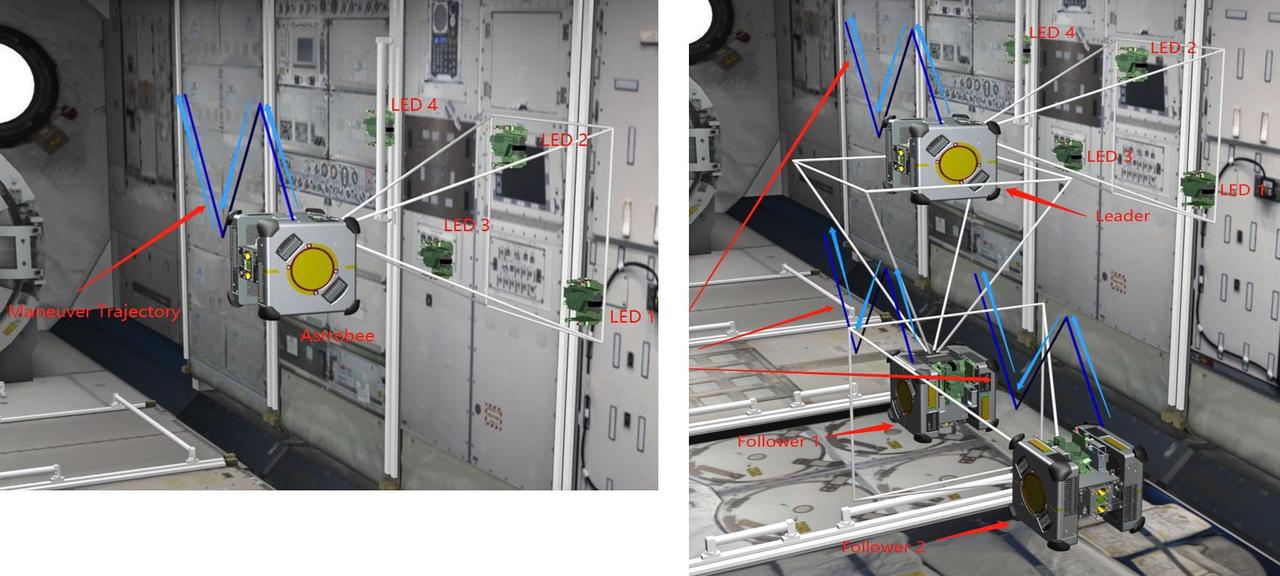
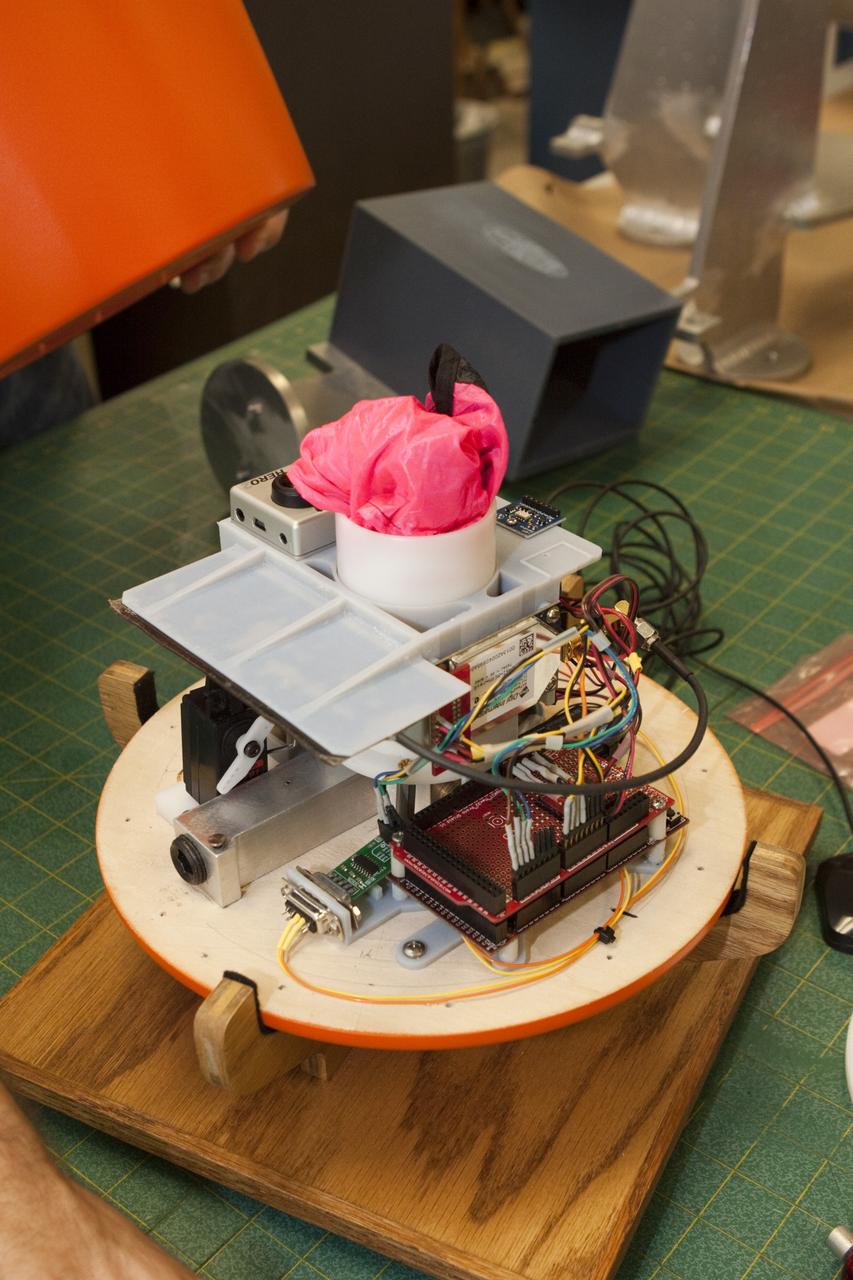
jsc2025e032821 (3/20/2025) --- Smartphone Video Guidance Sensor (SVGS) proximity maneuvers on the International Space Station. Left: navigation based on color-coded targets, Right: formation flight. Image courtesy of Hector Gutierrez.
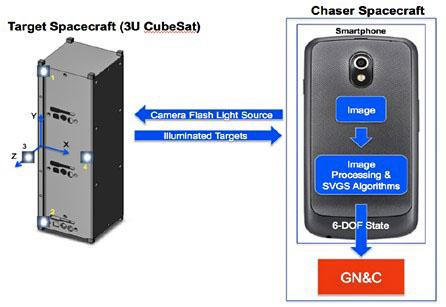
jsc2025e032818 (3/20/2025) --- The operational concept of Smartphone Video Guidance Sensor (SVGS). The target’s six-degrees-of-freedom (6DOF) state can be transmitted from the SVGS device to the spacecraft’s guidance, navigation and control system (GN & C). Image courtesy of Hector Gutierrez.
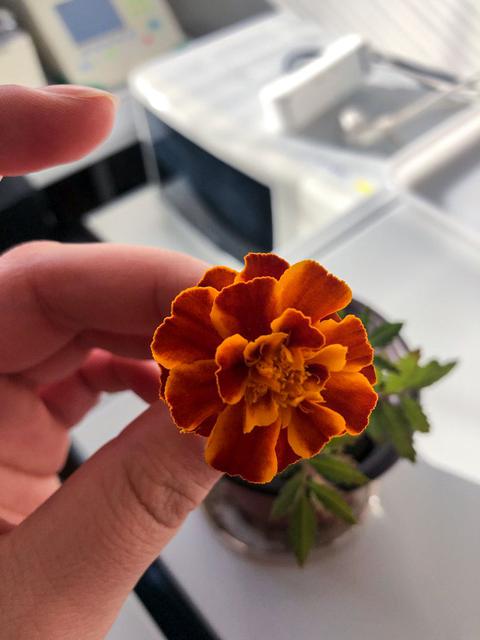

jsc2021e029978 (1/6/2020) --- A Photo of the Marigold flower grown during lab test at Toulouse. The Eklosion investigation consist of a vase that is utilized by a crew member to grow a Marigold flower (Tagetes patula) aboard the ISS. The investigation takes place at the leisure of the crew member and helps to study the process of plant growth in space, as well as using a personally tended house plant in space to help establish a psychological link between the crew member aboard the ISS and Earth. Image courtesy of Eklo association.
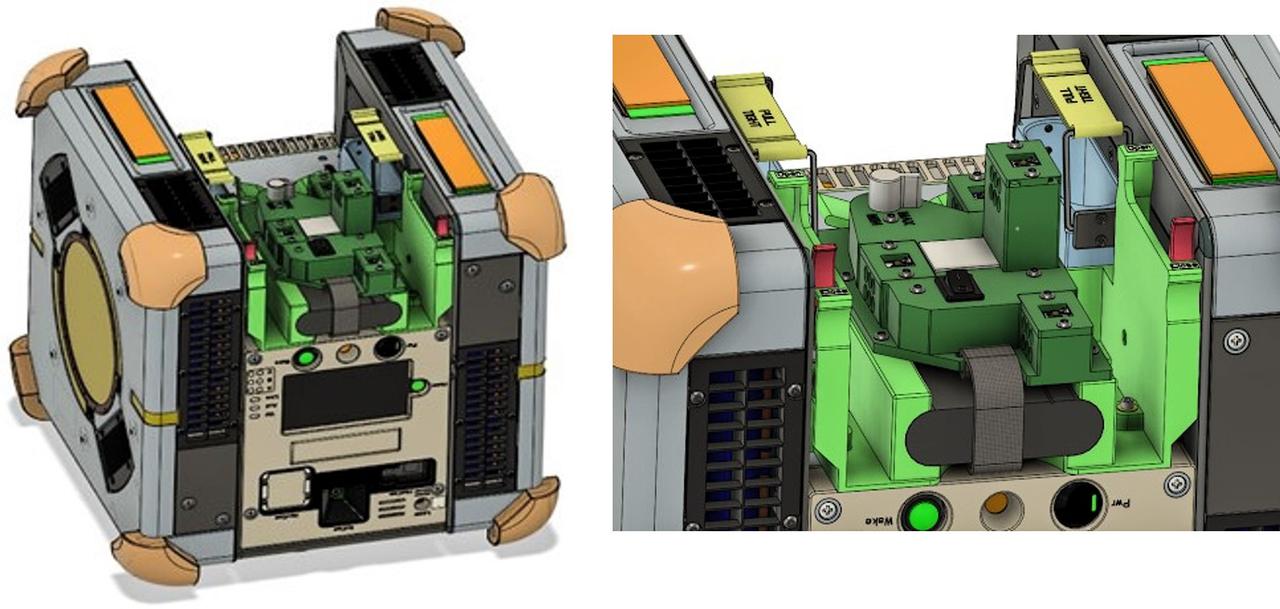
jsc2025e032819 (3/20/2025) --- Integration of Smartphone Video Guidance Sensor (SVGS) beacons and Astrobee using the M561 payload interface. Image courtesy of Hector Gutierrez.

jsc2025e044835 (9/8/2016) --- Contents flown for the NanoRacks-Crystallization Of Silver Nitrate in Microgravity On a Silver Cathode (NanoRacks-COSMOS). This investigation assesses the 3D structure of silver nitrate crystals formed by electrolysis in microgravity. Image courtesy of Dave Schlichting.

jsc2021e036651 (8/4/2021) --- READI FP. Engineer Sara Merola, Test Engineer of ALI Team. REducing Arthritis Dependent Inflammation First Phase (READI FP) evaluates how microgravity and space radiation affect the generation of bone tissue. It also examines the potential protective effects of bio-collagen and bioactive metabolites such as antioxidants during spaceflight. The source of these metabolites are vegetal extracts produced as waste products in wine production.
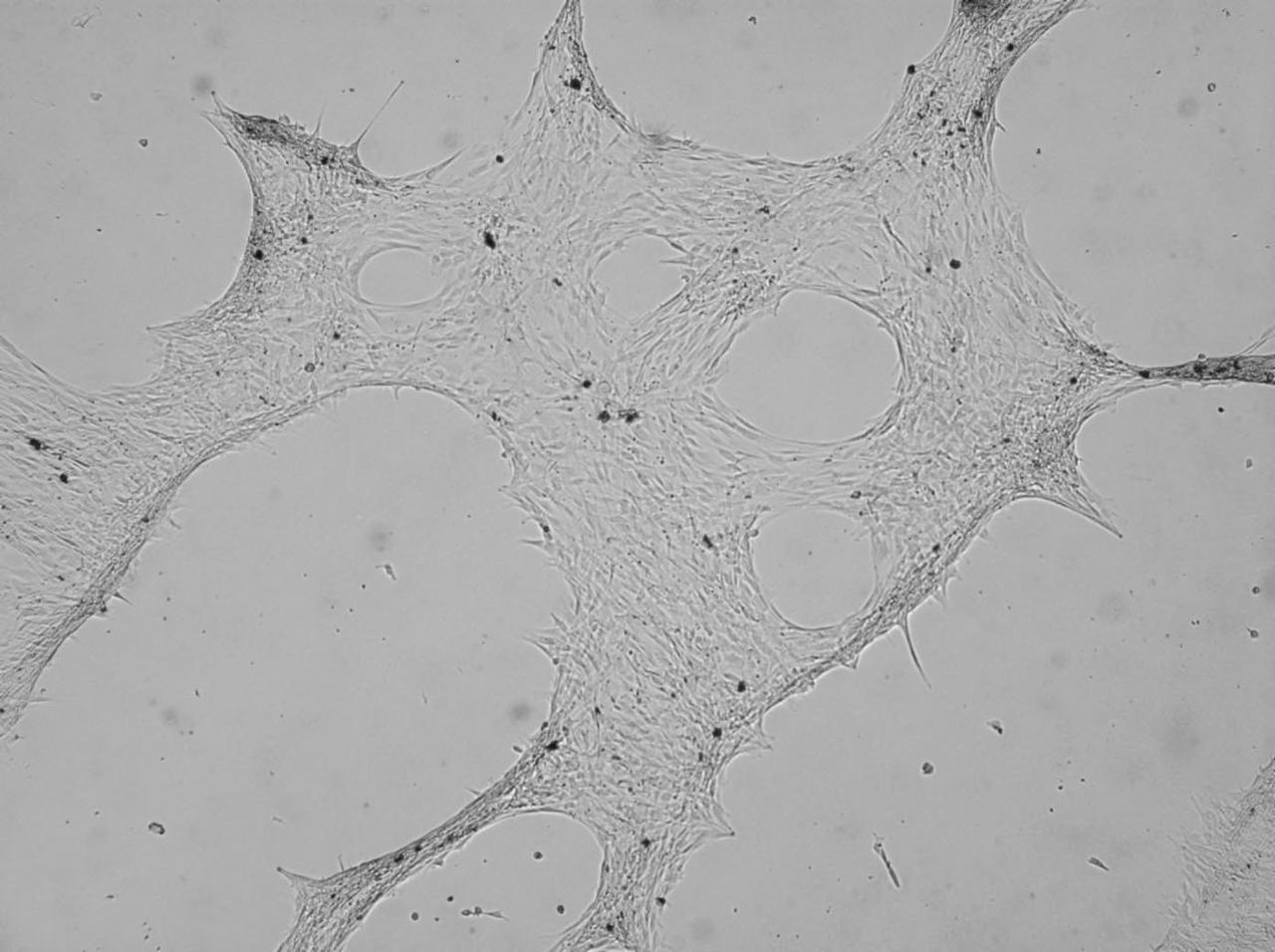
jsc2021e036650 (8/11/2021) --- A view of Osteogenesis-induced differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. REducing Arthritis Dependent Inflammation First Phase (READI FP) evaluates how microgravity and space radiation affect the generation of bone tissue. It also examines the potential protective effects of bio-collagen and bioactive metabolites such as antioxidants during spaceflight. The source of these metabolites are vegetal extracts produced as waste products in wine production.
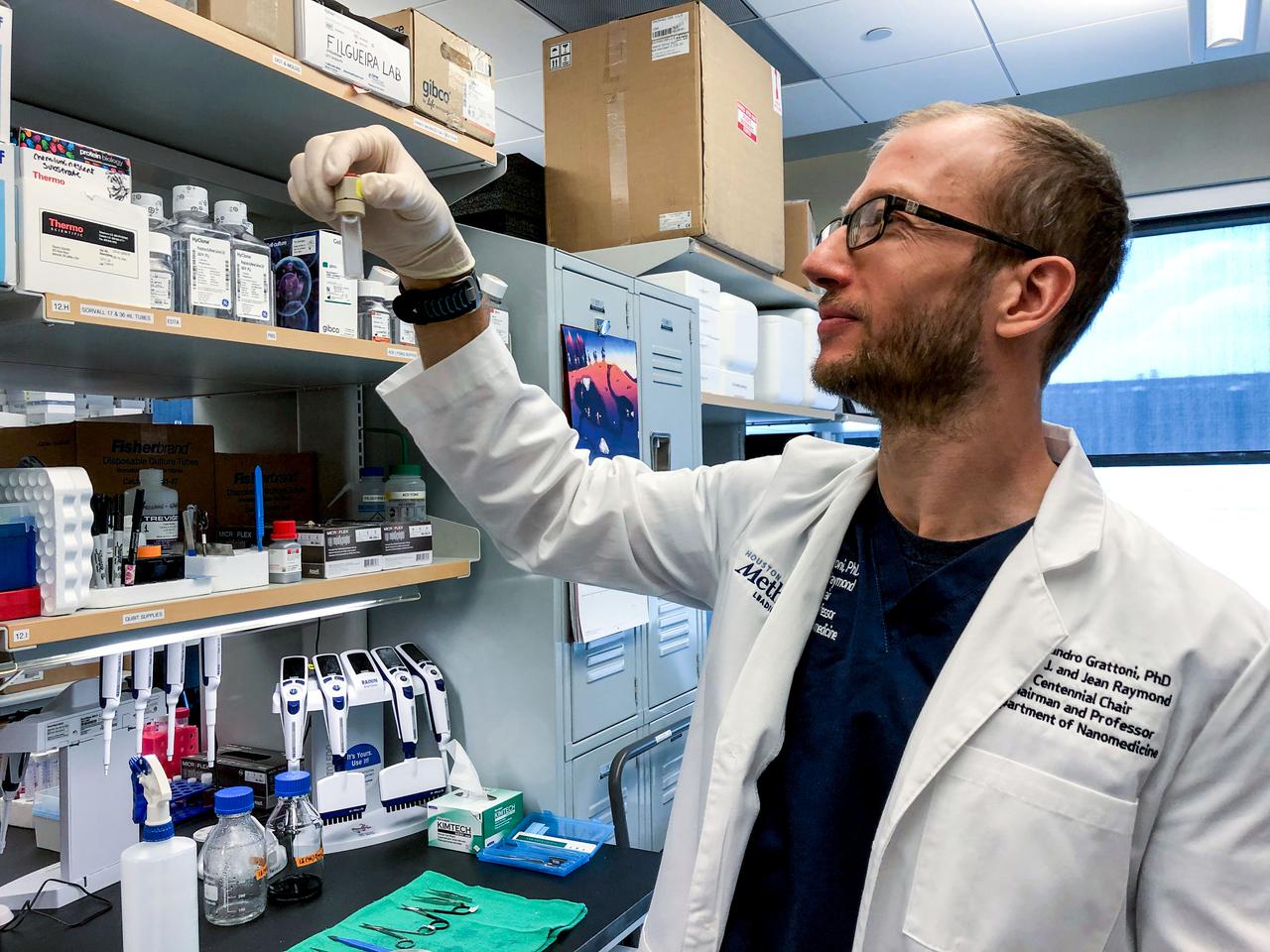

jsc2021e037284 (4/9/2020) --- Nanofluidic Implant Communication Experiment (NICE) (Faraday-NICE) aims to develop an implantable drug delivery system that allows for remote control and modulation of the release of therapeutics over weeks to months. In this investigation, fully assembled implantable devices are tested for remote communication capabilities from Earth to the International Space Station (ISS). This investigation aims to verify that 100% of the communications between controller and implant is achieved and maintained on station. Implants are immersed in saline solution, a surrogate of physiological conditions, then placed and sealed in 15 ml containers. The tubes are mounted within the ProxOpS Faraday experimental box. Image Credit: Houston Methodist Research Institute
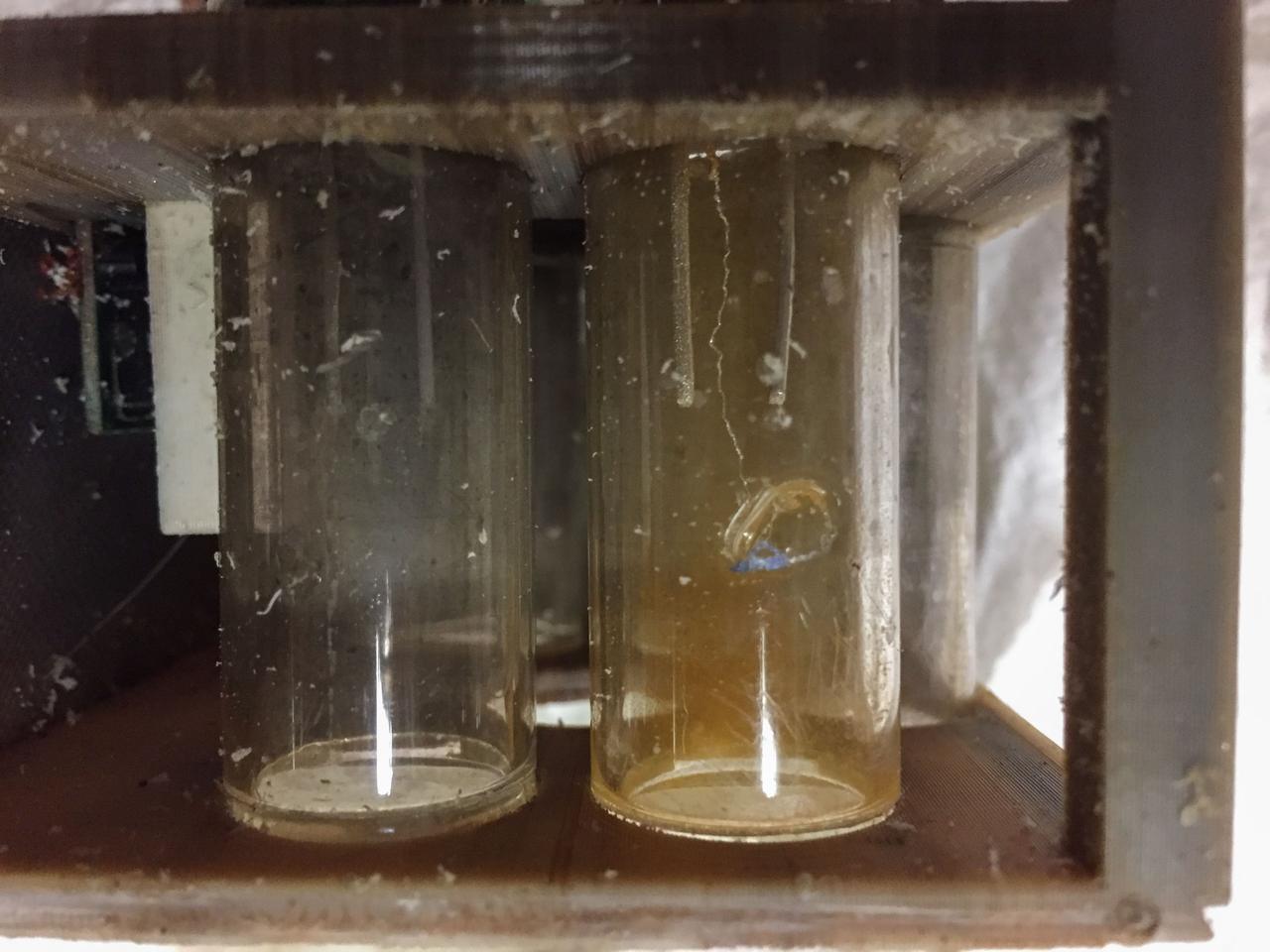

jsc2025e044836 (9/29/2016) --- Silver nitrate crystals grown in microgravity as part of NanoRacks-Crystallization Of Silver Nitrate in Microgravity On a Silver Cathode (NanoRacks-COSMOS). This investigation is designed to assess the 3D structure of silver nitrate crystals formed by electrolysis in microgravity. Results benefit the development of nanoscale electronics, which could be used in spacecraft and instruments on future space missions. Image courtesy of Dave Schlichting.
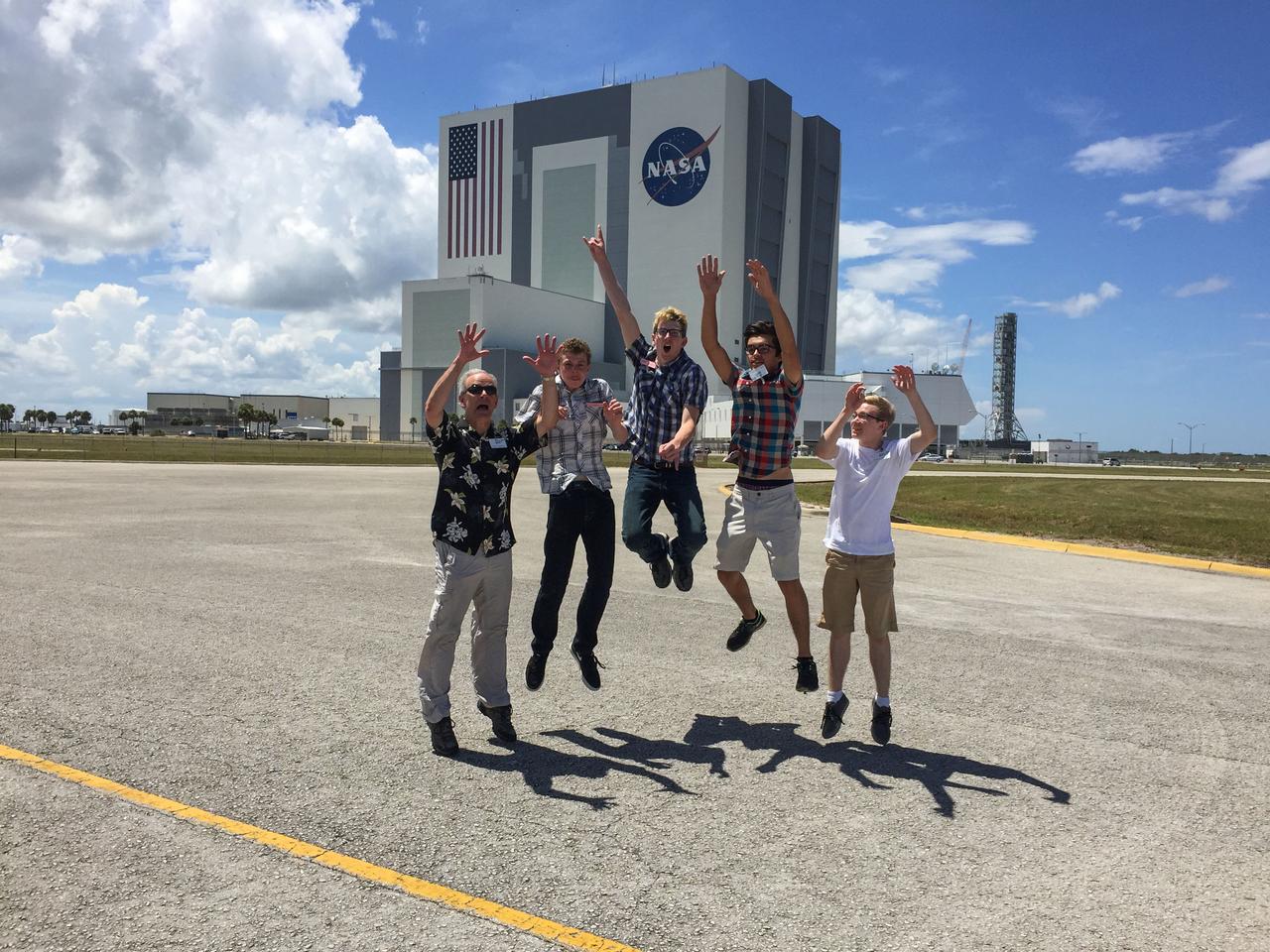

jsc2025e044834 (7/16/2016) --- The NanoRacks-Crystallization Of Silver Nitrate in Microgravity On a Silver Cathode (NanoRacks-COSMOS) research team from Eaglecrest High School in Centennial, Colorado is photographed at Kennedy Space Center on July 18, 2016. This investigation assesses the 3D structure of silver nitrate crystals formed by electrolysis in microgravity. From Left: Dave Schlichting, Gavin Morgenneg, Scott Crowner, Lars Drieth, Ben Sheffer. Image courtesy of Dave Schlichting.
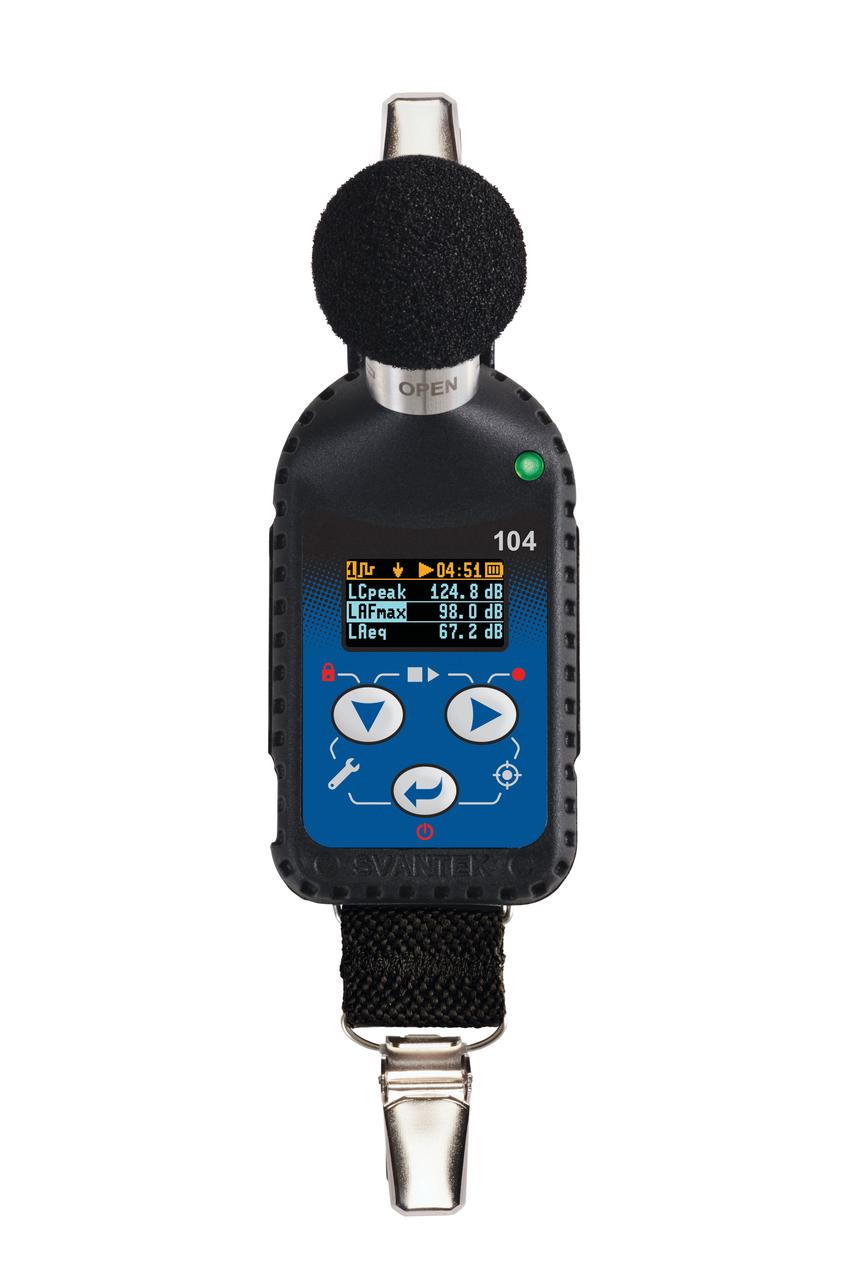

jsc2025e044837 2/19/2019) --- Shown is the SV104A noise dosimeter that measures noise dose and noise levels in the large measurement range of 55 dB to 140 dB aboard the International Space Station. This dosimeter is part of A Next Generation Crew Health & Performance Acoustic Monitoring Capability for Exploration: An International Space Station Technology Demonstration (Wireless Acoustics) investigation. Image courtesy of SVANTEK.

jsc2021e036649 (8/4/2021) --- From left to right: Eng. Michele Cioffi Program Manager, Eng.Marco Fabio Miceli System & Test Engineer, Eng. Pasquale Pellegrino Test Engineer from ALI S.c.a r.l. and Eng.Maurizio Ruggiero Electronic Specialist from Euro.Soft s.r.l.. REducing Arthritis Dependent Inflammation First Phase (READI FP) evaluates how microgravity and space radiation affect the generation of bone tissue. It also examines the potential protective effects of bio-collagen and bioactive metabolites such as antioxidants during spaceflight. The source of these metabolites are vegetal extracts produced as waste products in wine production.
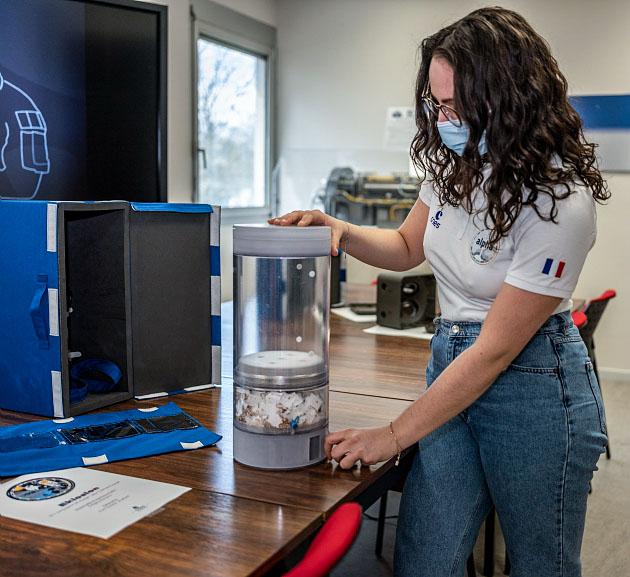

jsc2021e029981 (3/18/2021) --- A Picture of the EKLOSION pot manipulated by Eve Teyssier at CNES Toulouse. The Eklosion investigation consist of a vase that is utilized by a crew member to grow a Marigold flower (Tagetes patula) aboard the ISS. The investigation takes place at the leisure of the crew member and helps to study the process of plant growth in space, as well as using a personally tended house plant in space to help establish a psychological link between the crew member aboard the ISS and Earth. Image courtesy of CNES.
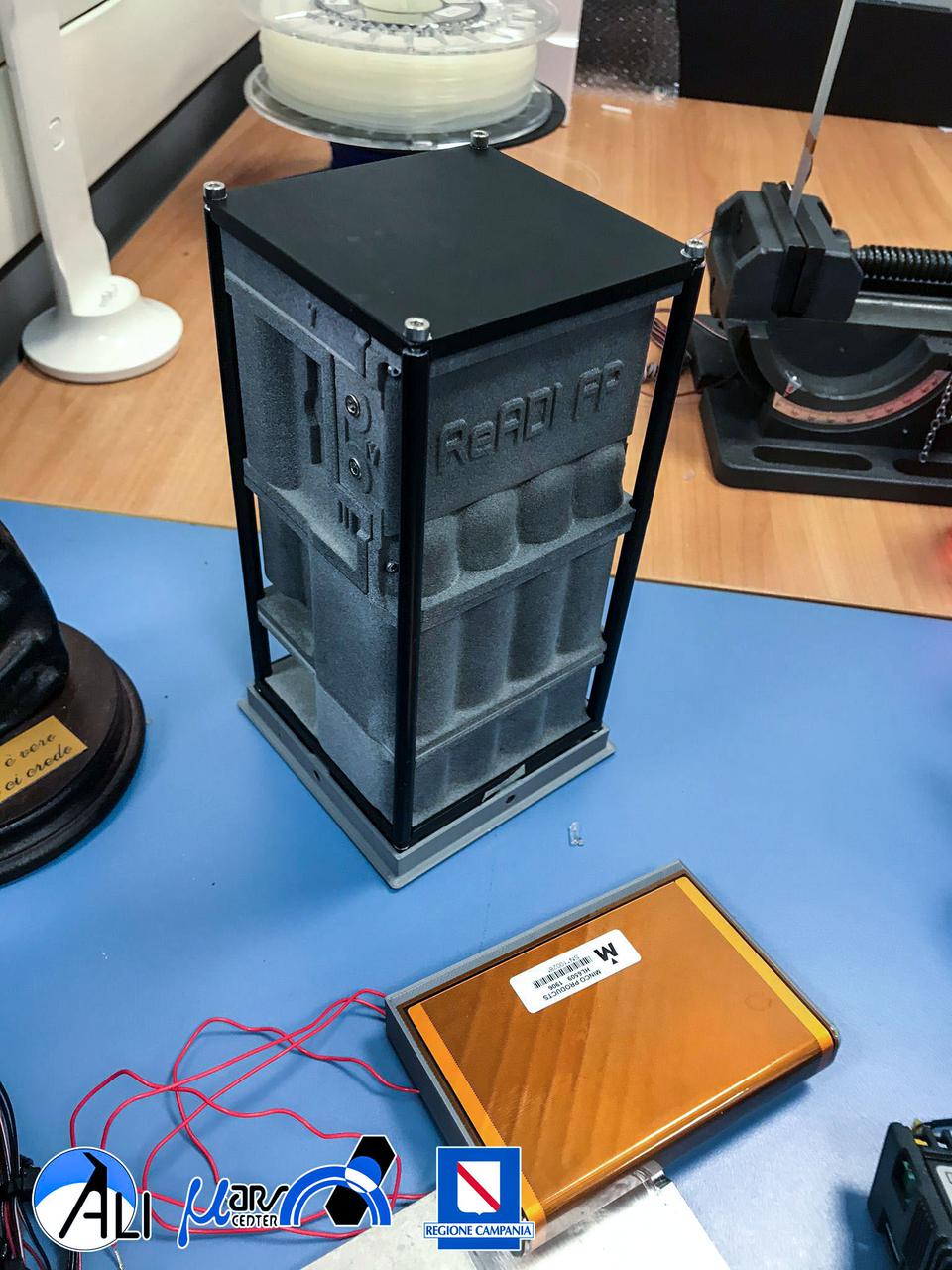

jsc2021e036648 (8/4/2021) --- A preflight image of the READI FP shell assembled before the immersion test. REducing Arthritis Dependent Inflammation First Phase (READI FP) evaluates how microgravity and space radiation affect the generation of bone tissue. It also examines the potential protective effects of bio-collagen and bioactive metabolites such as antioxidants during spaceflight. The source of these metabolites are vegetal extracts produced as waste products in wine production.
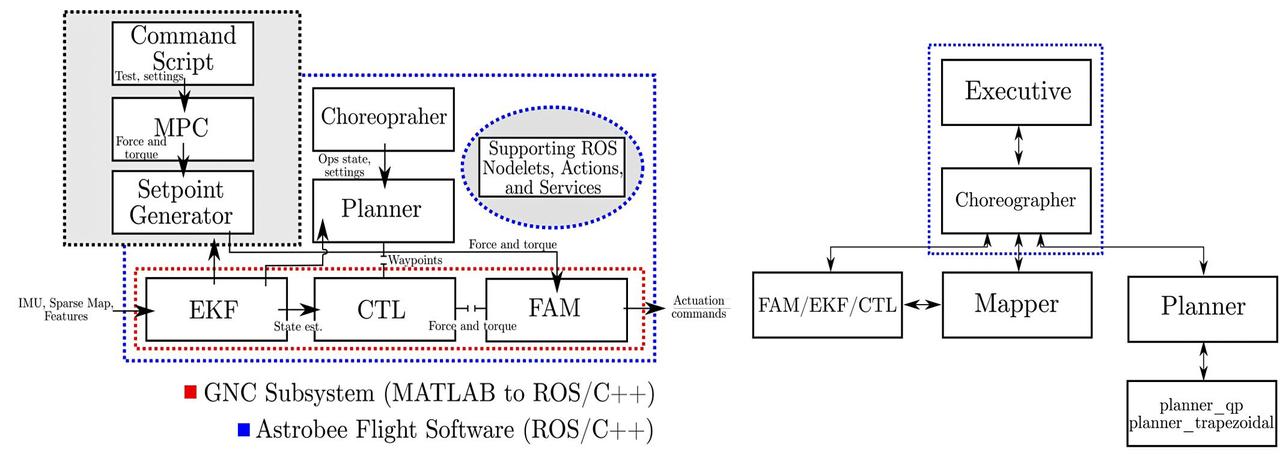
jsc2025e032820 (3/20/2025) --- Left: Astrobee’s guidance, navigation and control (GNC) subsystem. Components shown in black (Matlab/ROS/C++/Python) indicate a replacement pipeline overriding Astrobee’s default GNC subsystem, outlined in red. Right: software interface between GNC components and Astrobee’s finite state machines (FSMs). The FSM-based nodelets are outlined in blue. Image courtesy of Hector Gutierrez.
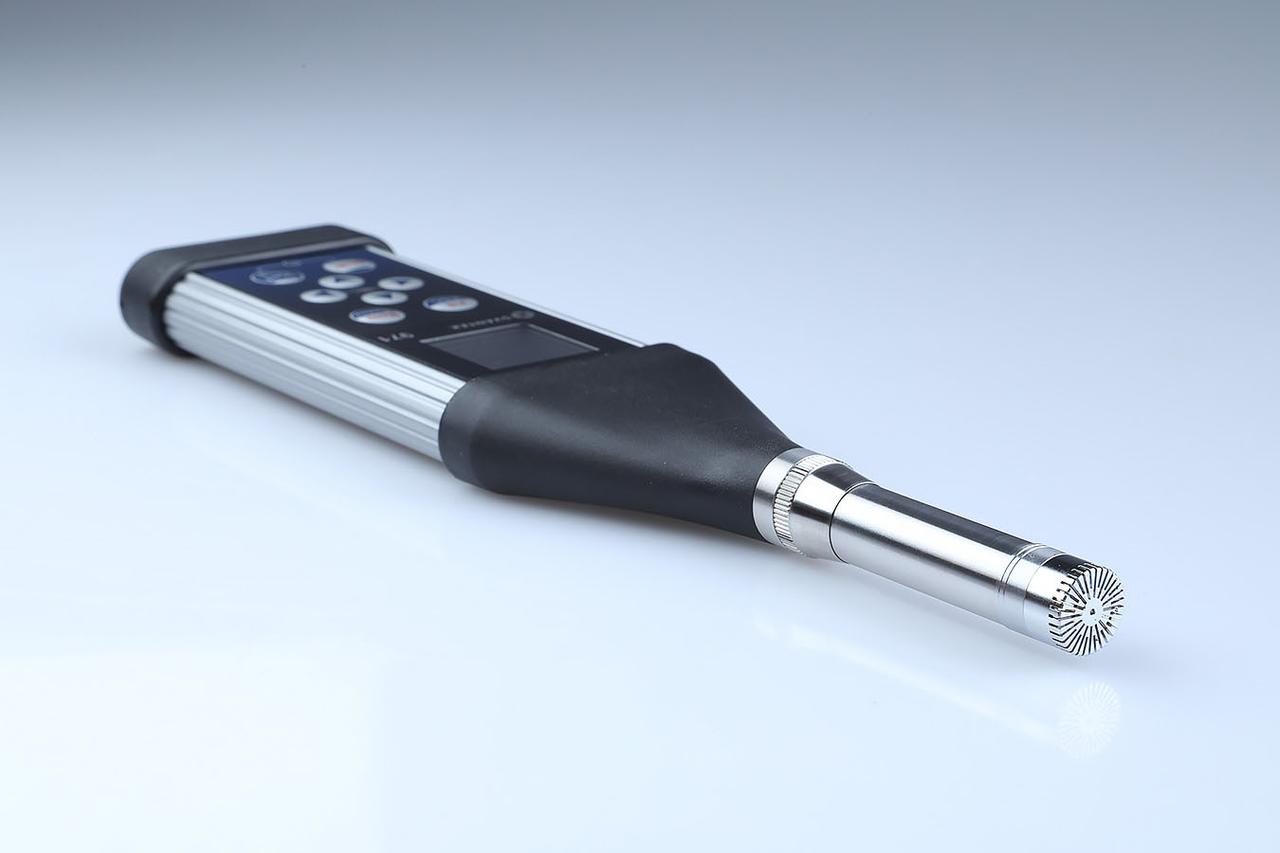

jsc2025e044838 93/25/2021) --- One of the smallest Class 1 sound level meters is shown for A Next Generation Crew Health & Performance Acoustic Monitoring Capability for Exploration: An International Space Station Technology Demonstration (Wireless Acoustics) investigation. Wireless Acoustics aims to showcase a new acoustic monitoring system for crew health and performance to replace an older product using off-the-shelf commercial products Image courtesy of SVANTEK.
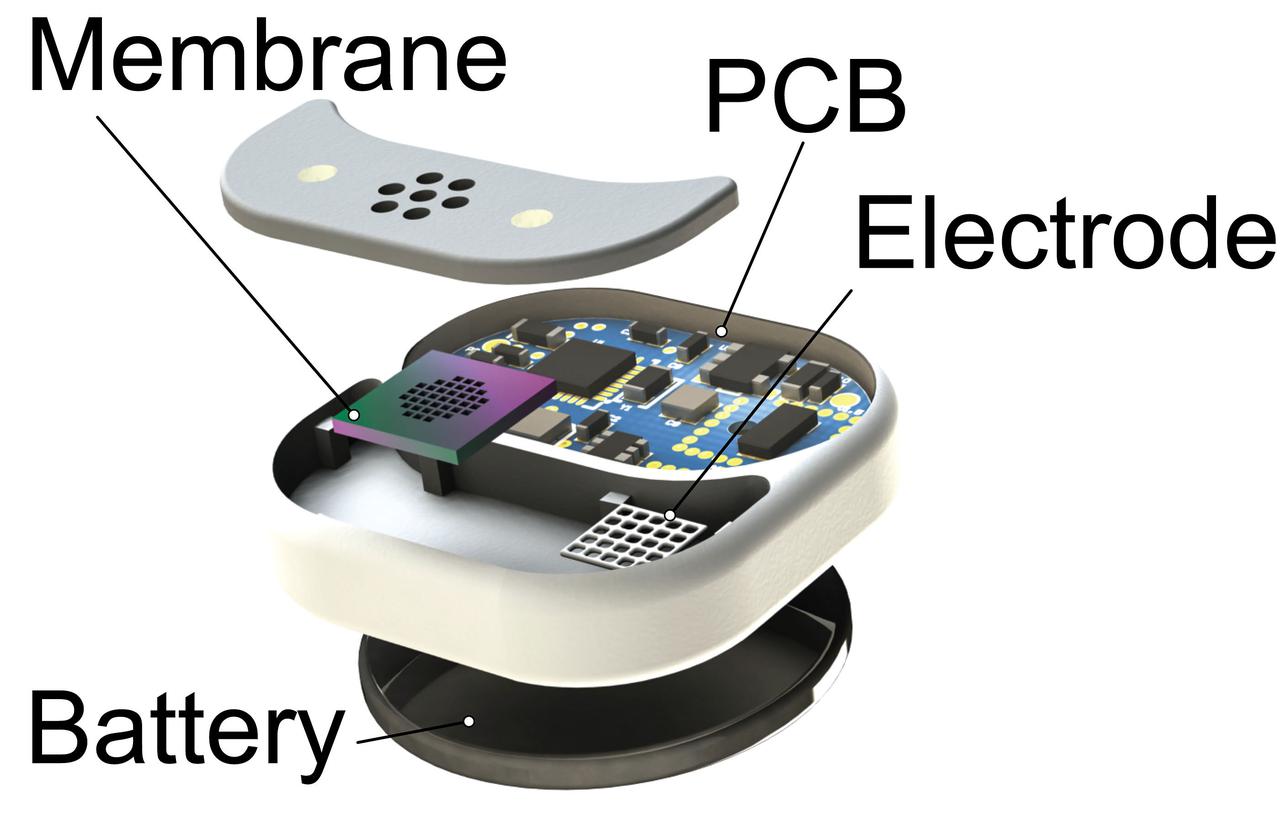
sc2021e037282 (8/20/2021) --- Nanofluidic Implant Communication Experiment (NICE) (Faraday-NICE) aims to develop an implantable drug delivery system that allows for remote control and modulation of the release of therapeutics over weeks to months. In this investigation, fully assembled implantable devices are tested for remote communication capabilities from Earth to the International Space Station (ISS). This investigation aims to verify that 100% of the communications between controller and implant is achieved and maintained on station. Implants are immersed in saline solution, a surrogate of physiological conditions, then placed and sealed in 15 ml containers. The tubes are mounted within the ProxOpS Faraday experimental box. Image Credit: Houston Methodist Research Institute
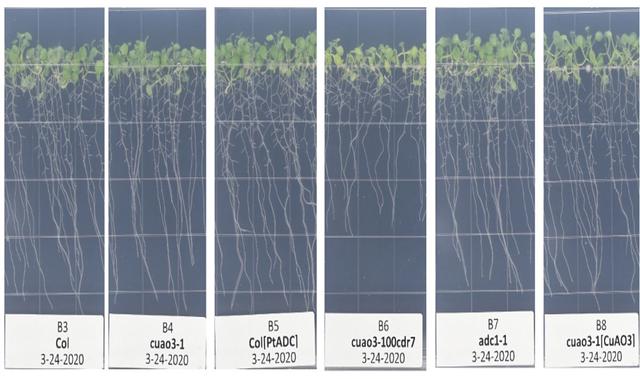
jsc2021e036657 (8/11/2021) --- Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings following 9 days of growth on 1.2% agar-based media in petri dishes in the VEGGIE growth chamber under temperature, humidity and CO2 conditions mimicking those recorded at the International Space Station. The genotypes of these plants are indicated at the bottom of each panel. These images were taken during the Science Verification Test carried out at NASA Kennedy Space Center. All genotypes grew equally well under these conditions except for the cuao3-100cdr7 mutant, which grew more slowly.
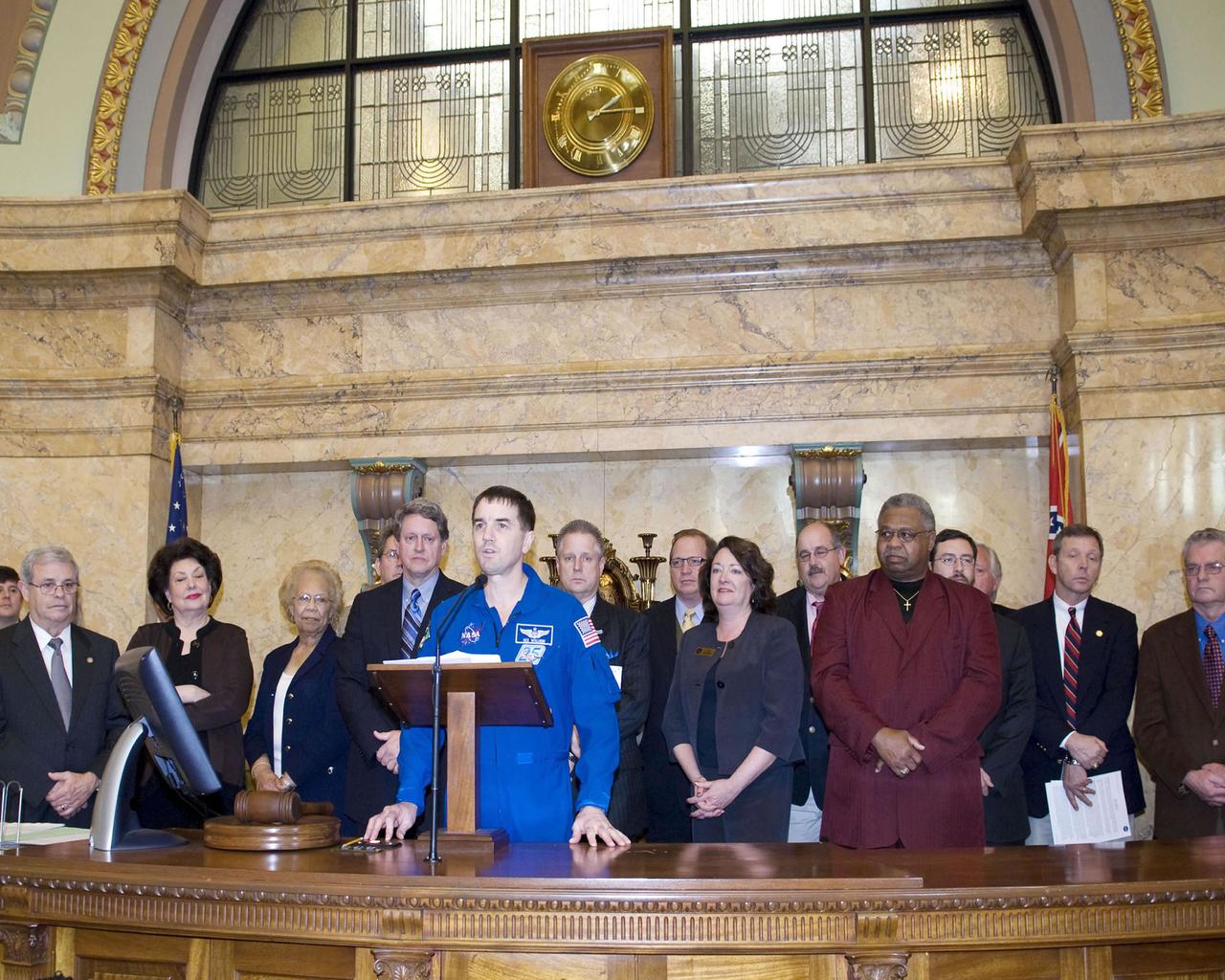

Stennis Space Center leaders and guests visit with Mississippi Senate members in chambers during NASA Day at the Capitol events in Jackson on Feb. 19. Standing at the Senate podium (rear) is Mississippi Lt. Gov. Phil Bryant. Standing at the lectern below are (l to r): Sen. David Baria, D-Bay St. Louis; Partners for Stennis Chair Clay Wagner; NASA Shared Services Center Director Rick Arbuthnot; astronaut Rex Walheim; Stennis Space Center Director Gene Goldman; President Pro Tempore Billy Hewes, R-Gulfport; Sen. Ezell Lee, D-Picayune; and Sen. Tommy Gollott, R-Biloxi.
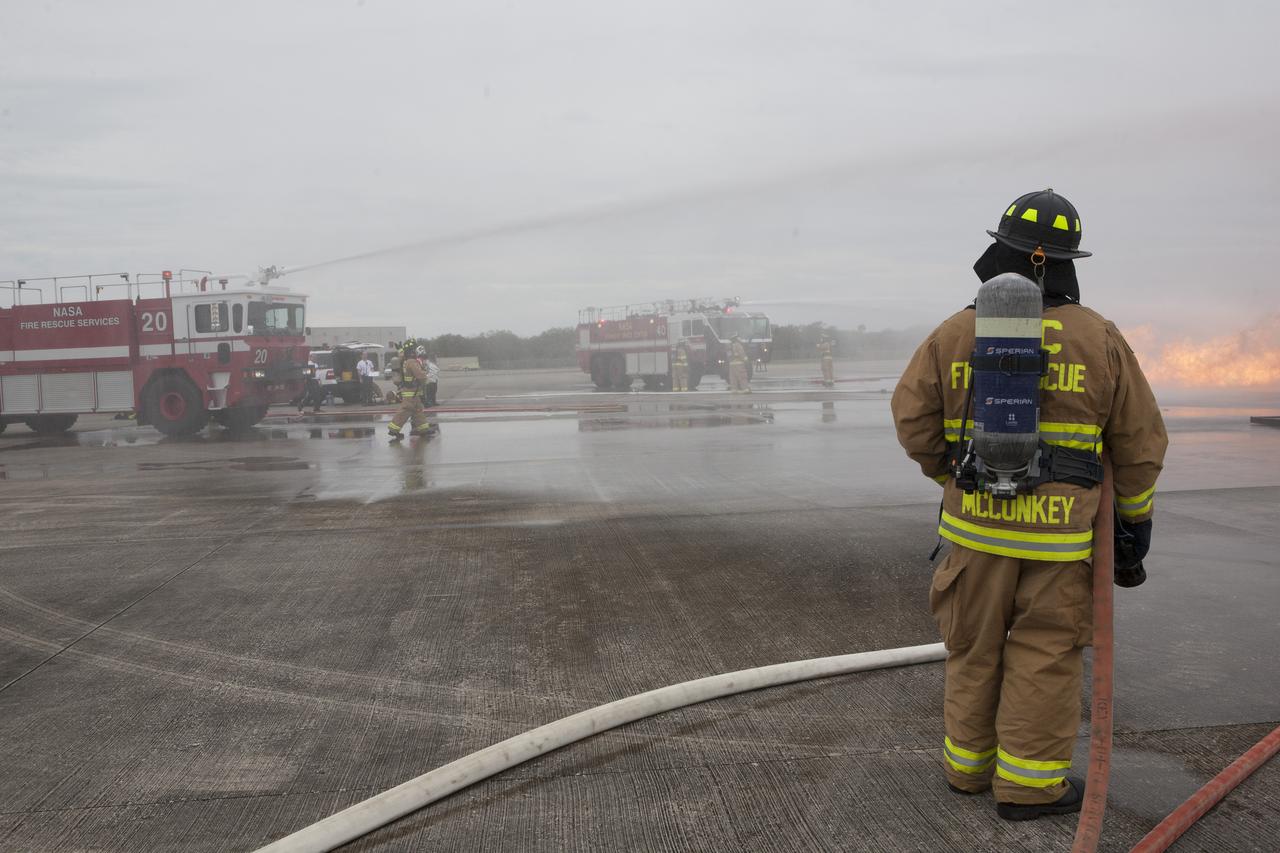

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Special Rescue Operations firefighters with NASA Fire Rescue Services in the Protective Services Office at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to participate in a training exercise at the Shuttle Landing Facility. A small fire is burning near a mock-up of a plane during the training exercise. Kennedy’s firefighters recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations and completed vehicle extrication training using the Jaws of Life. The Protective Services Office is one step closer to achieving certification in vehicle machinery extrication and other rescue skills. Kennedy’s firefighters are with G4S Government Solutions Inc., on the Kennedy Protective Services Contract. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
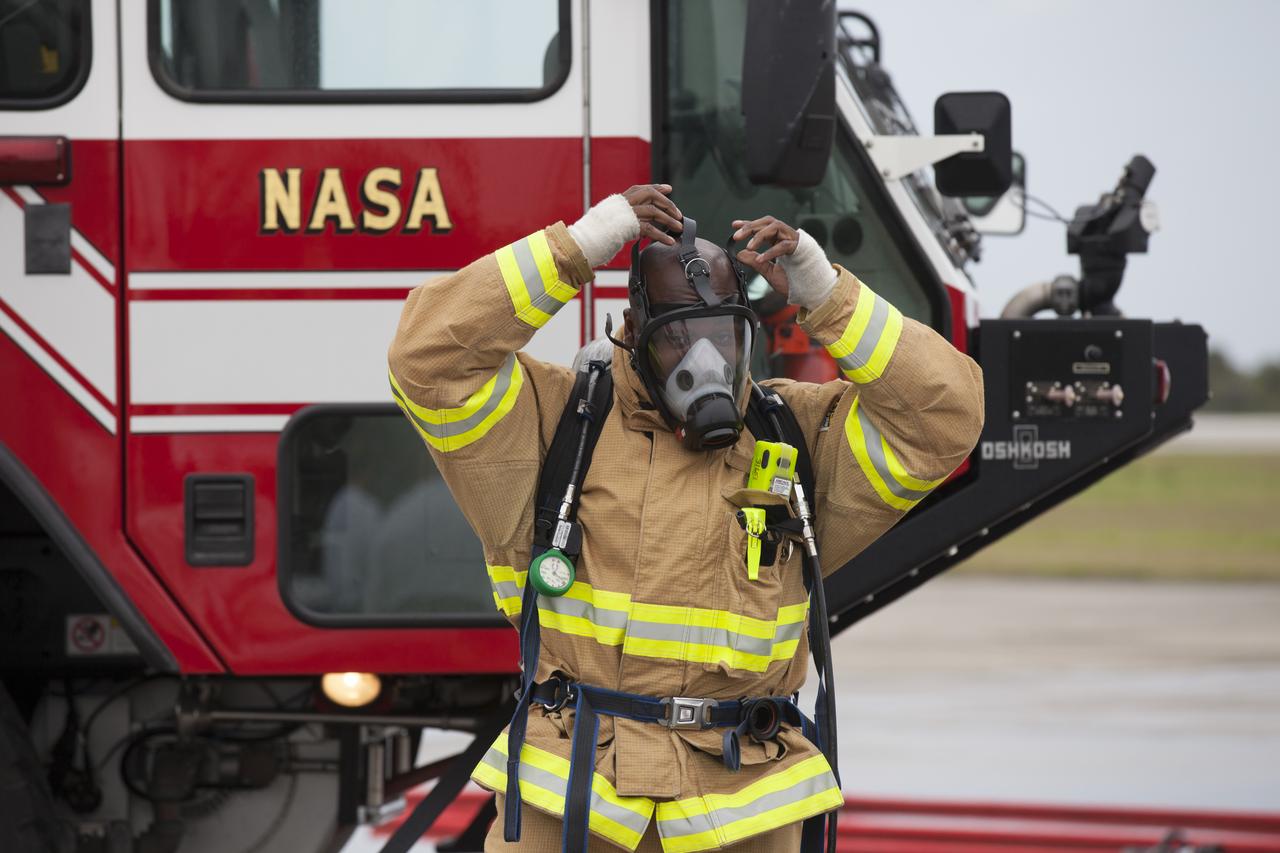

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Special Rescue Operations firefighters with NASA Fire Rescue Services in the Protective Services Office at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice firefighting skills at the Shuttle Landing Facility. A firefighter dons protective gear to prepare for the training simulation. Kennedy’s firefighters recently achieved Pro Board Certification in aerial fire truck operations and completed vehicle extrication training using the Jaws of Life. The Protective Services Office is one step closer to achieving certification in vehicle machinery extrication and other rescue skills. Kennedy’s firefighters are with G4S Government Solutions Inc., on the Kennedy Protective Services Contract. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
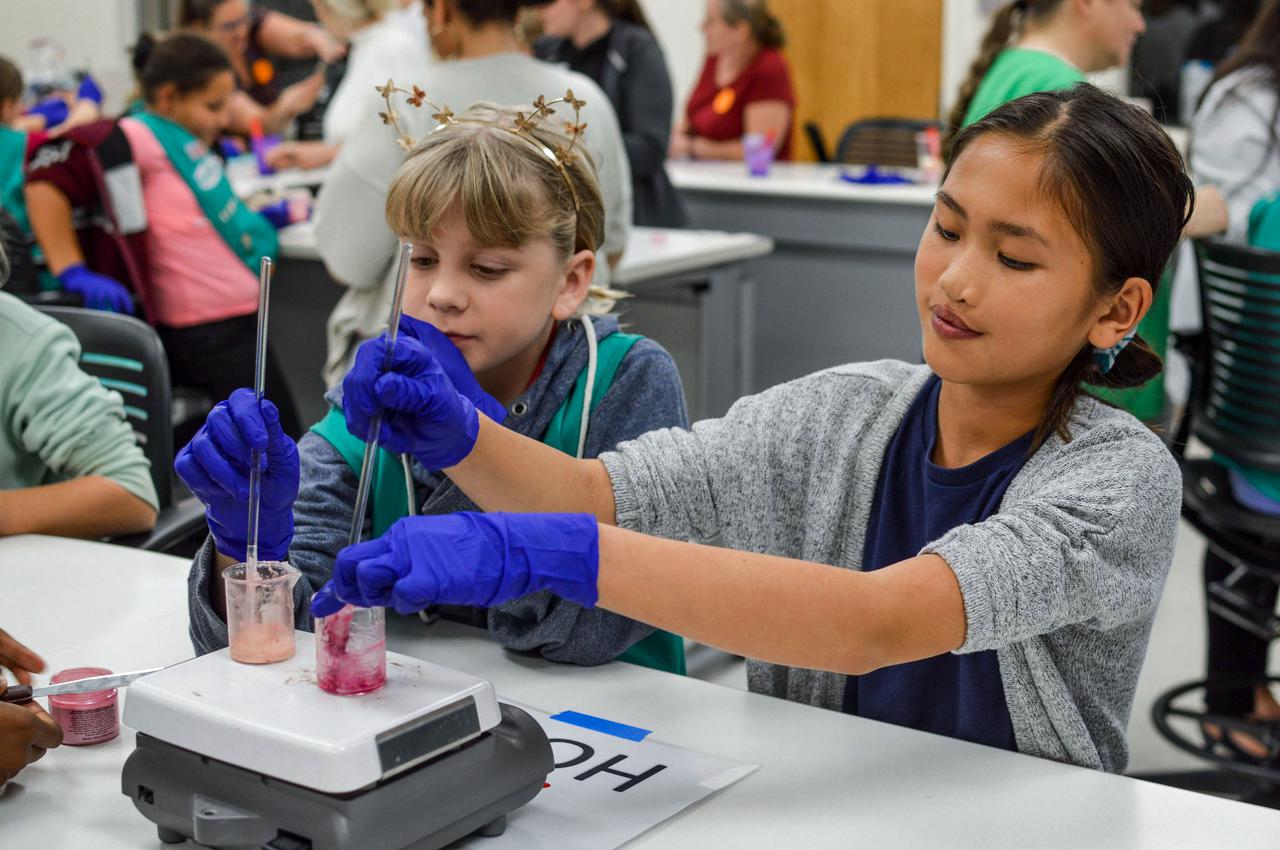

jsc2021e037279 (11/15/2019) --- Girl Scouts prepare experiments as part of a STEM collaboration with the Girl Scouts of Citrus Council. Faraday-Girl Scouts-1 (Faraday-Girls Scouts) offers Girl Scouts the opportunity to conduct a control experiment and observe the actual experiments on plant growth, ant colonization, and brine shrimp lifecycle in Faraday boxes aboard the International Space Station. This is part of a year-long effort by the Girl Scouts of Citrus Council to engage scouts in the study and understanding of space. The program also provides scouts firsthand experience with the concept of an experimental control. Image Credit: Girl Scouts Citrus Council
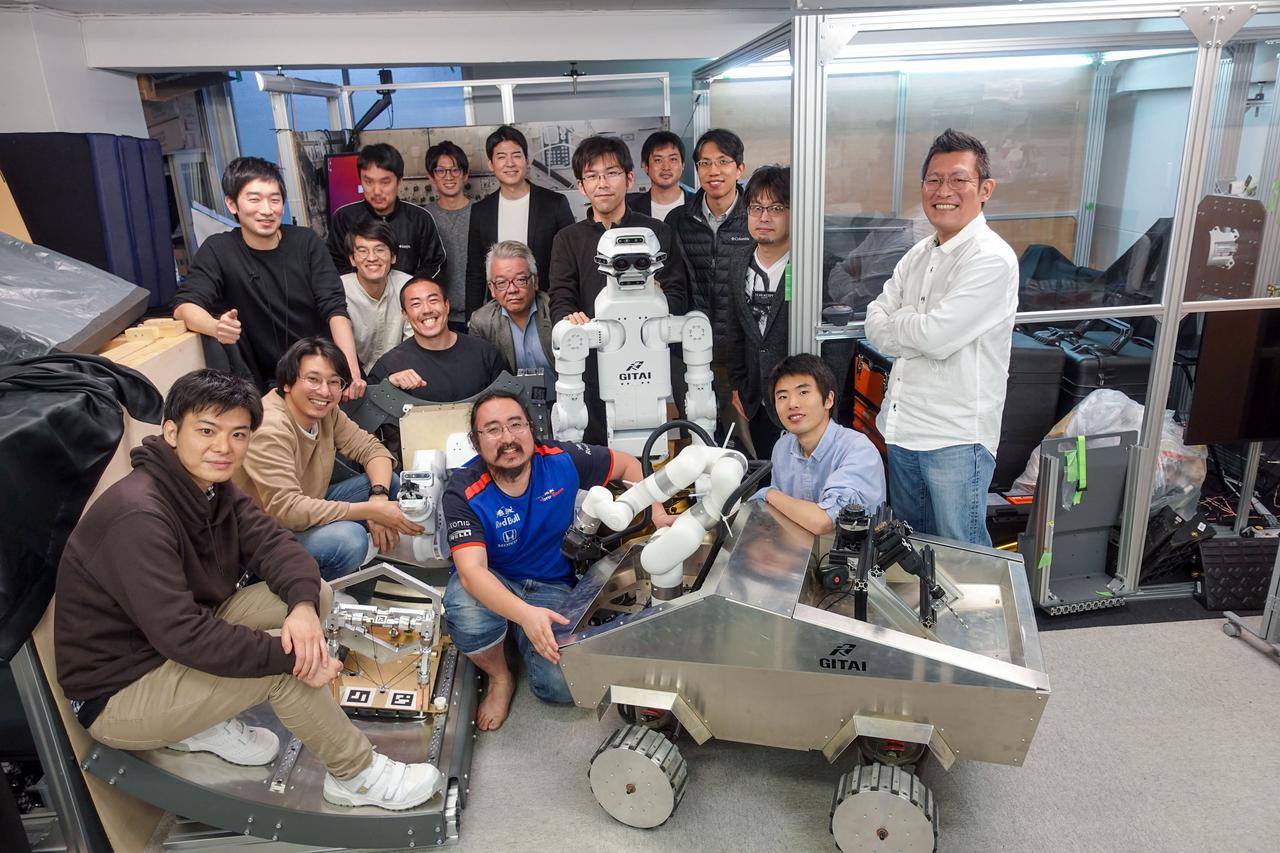
jsc2021e036655 (8/11/2021) --- The GITAI team. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.
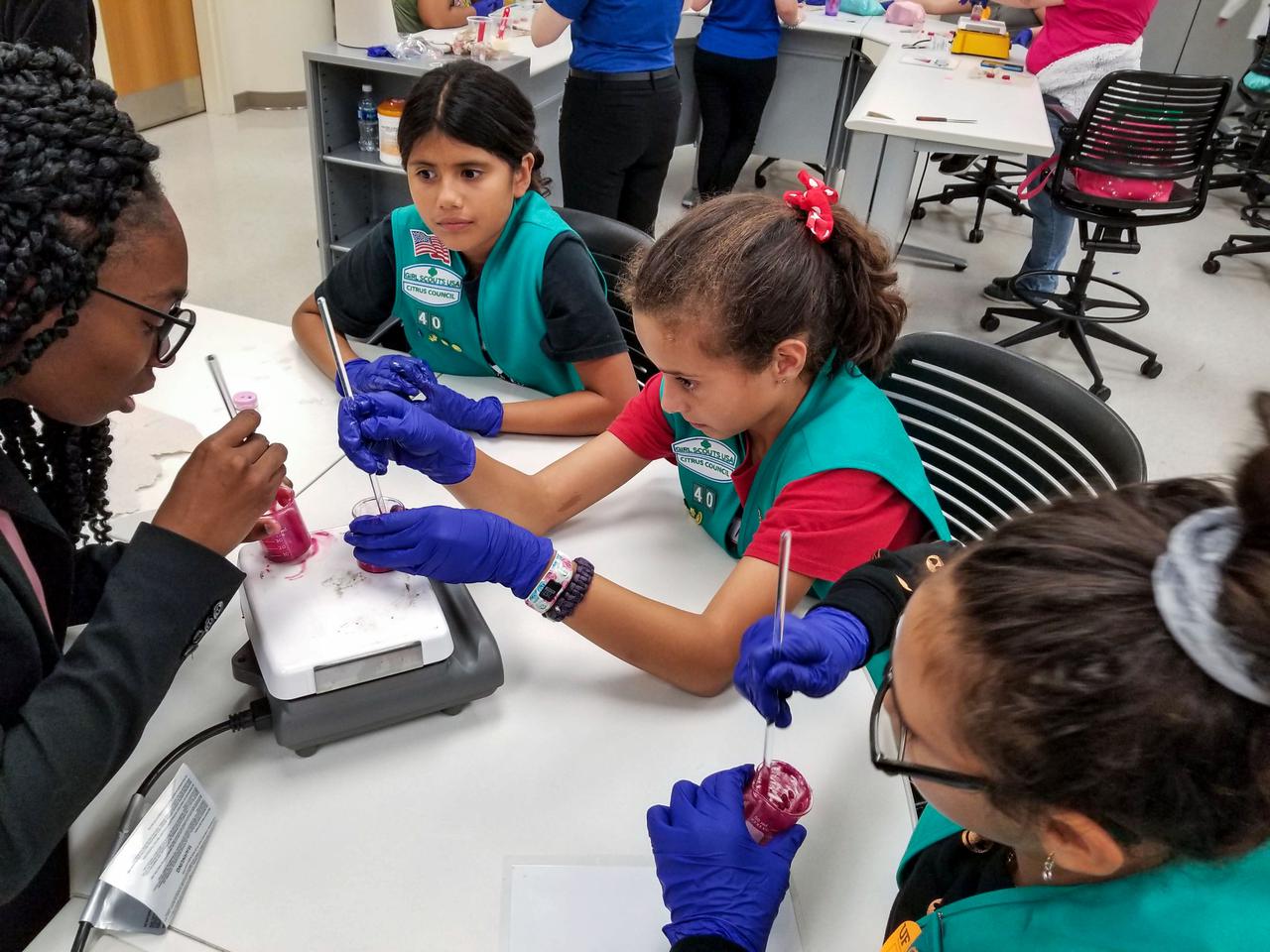

jsc2021e037278 (11/15/2019) --- Girl Scouts prepare experiments as part of a STEM collaboration with the Girl Scouts of Citrus Council. Faraday-Girl Scouts-1 (Faraday-Girls Scouts) offers Girl Scouts the opportunity to conduct a control experiment and observe the actual experiments on plant growth, ant colonization, and brine shrimp lifecycle in Faraday boxes aboard the International Space Station. This is part of a year-long effort by the Girl Scouts of Citrus Council to engage scouts in the study and understanding of space. The program also provides scouts firsthand experience with the concept of an experimental control. Image Credit: Girl Scouts Citrus Council
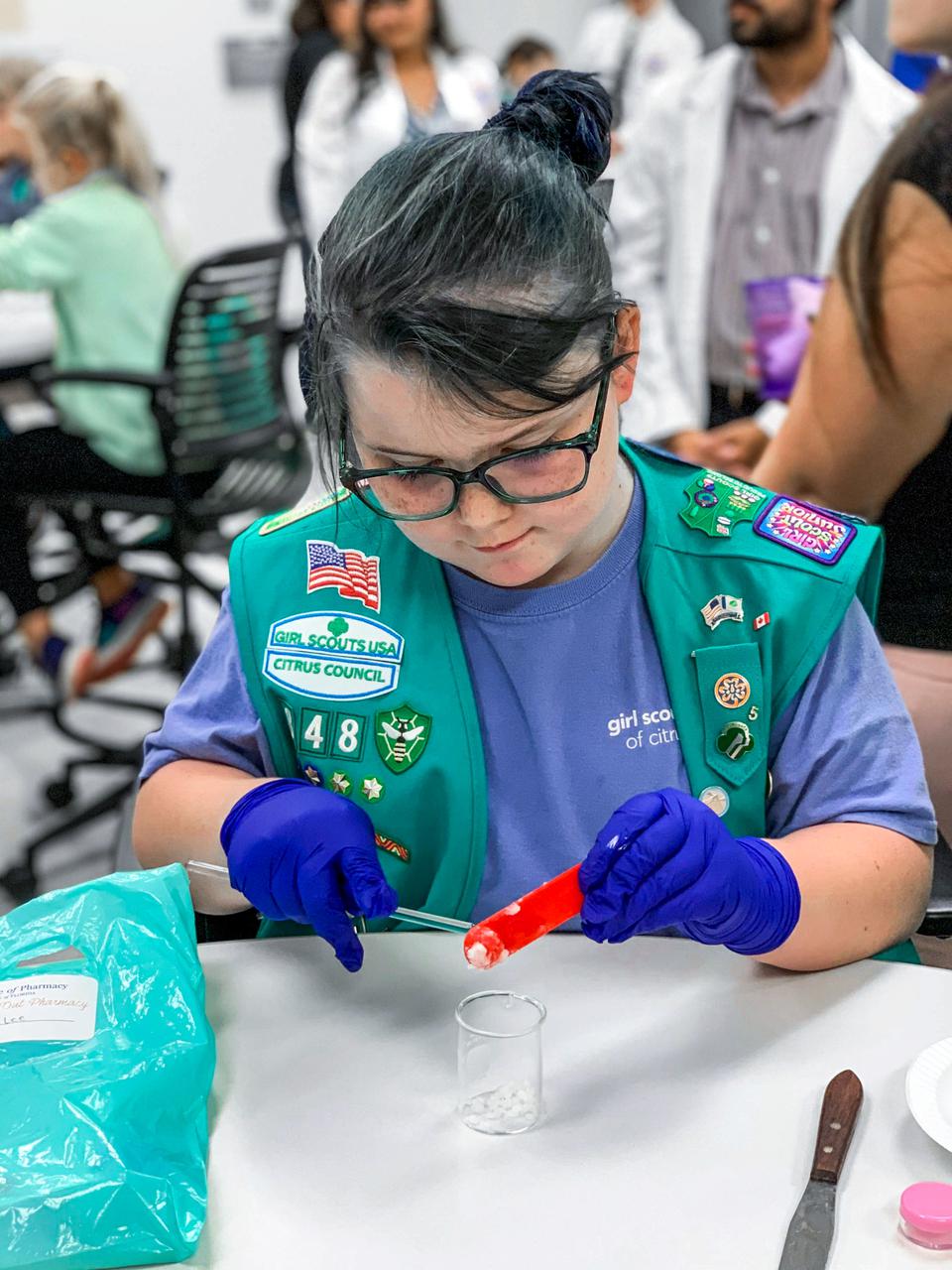
jsc2021e037281 (11/15/2019) --- Girl Scouts prepare experiments as part of a STEM collaboration with the Girl Scouts of Citrus Council. Faraday-Girl Scouts-1 (Faraday-Girls Scouts) offers Girl Scouts the opportunity to conduct a control experiment and observe the actual experiments on plant growth, ant colonization, and brine shrimp lifecycle in Faraday boxes aboard the International Space Station. This is part of a year-long effort by the Girl Scouts of Citrus Council to engage scouts in the study and understanding of space. The program also provides scouts firsthand experience with the concept of an experimental control. Image Credit: Girl Scouts Citrus Council
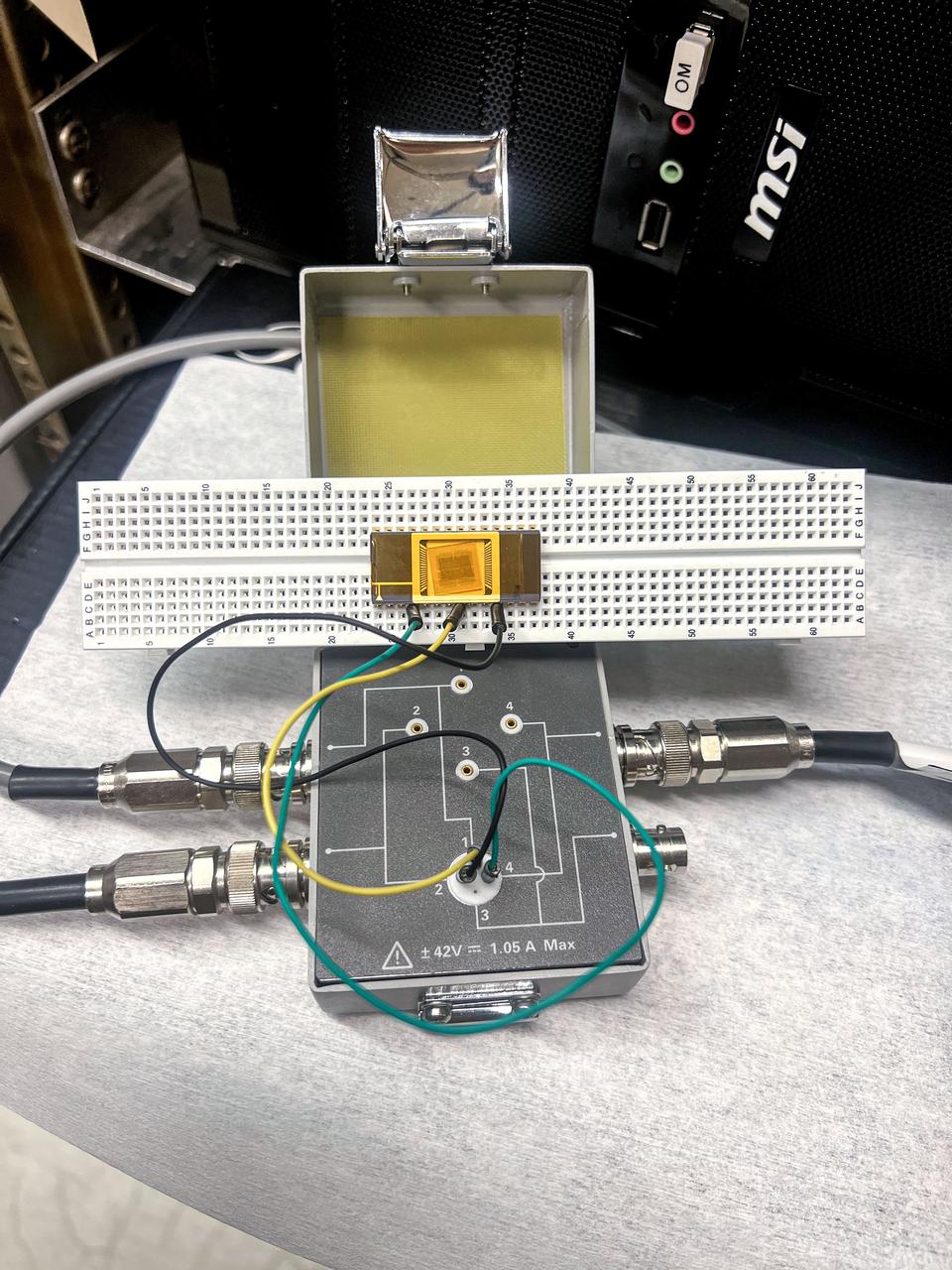
jsc2025e015683 (3/6/2025) --- The chip carrier setup shows the GaN devices are wire bonded to perform electrical measurement as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.

jsc2025e015690 (3/6/2025) --- An overview of the prototype with the various components as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
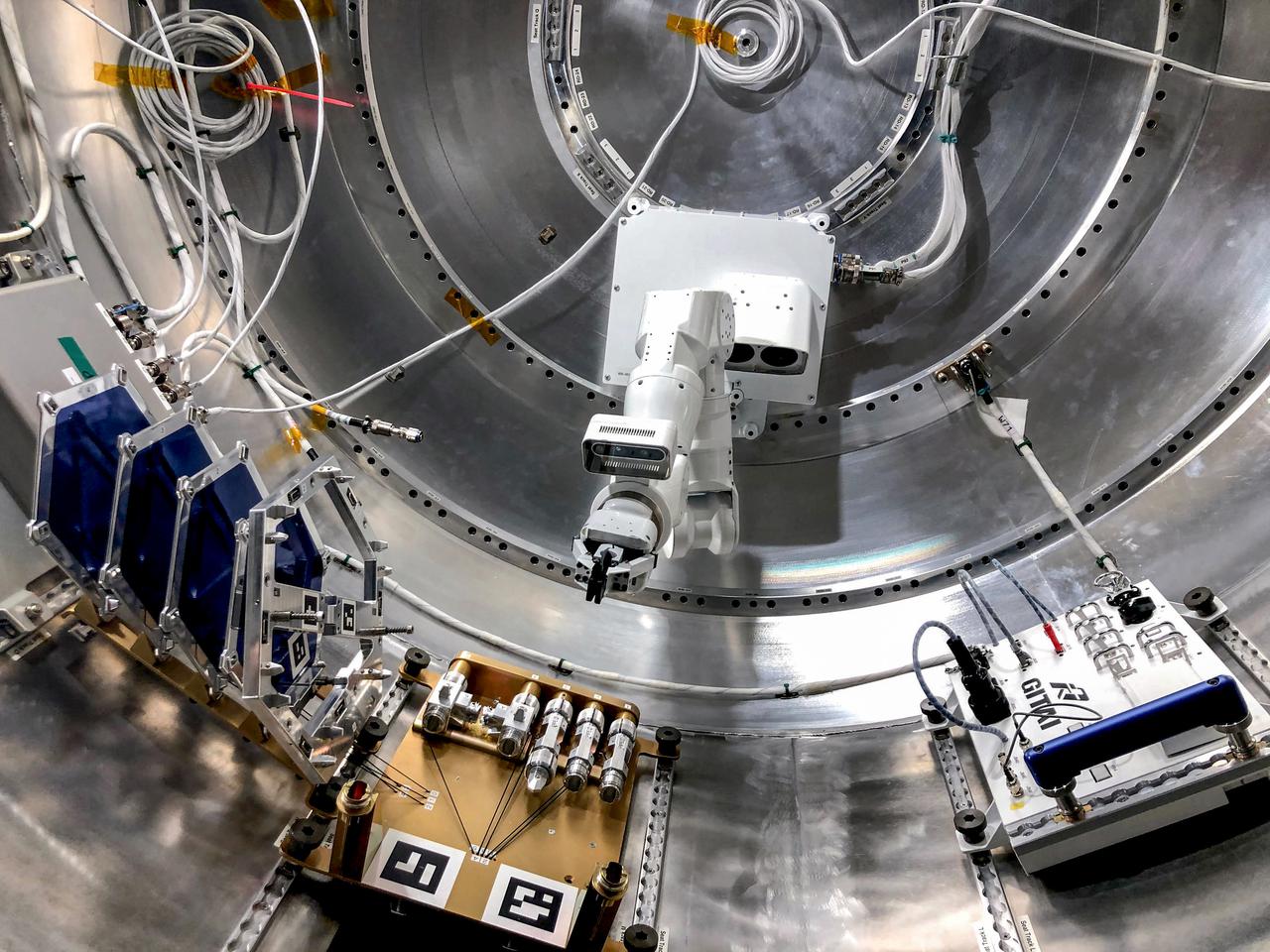
jsc2021e036656 (4/2/2021) --- Complete configuration of the GITAI S1 inside the Bishop airlock mock-up. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.
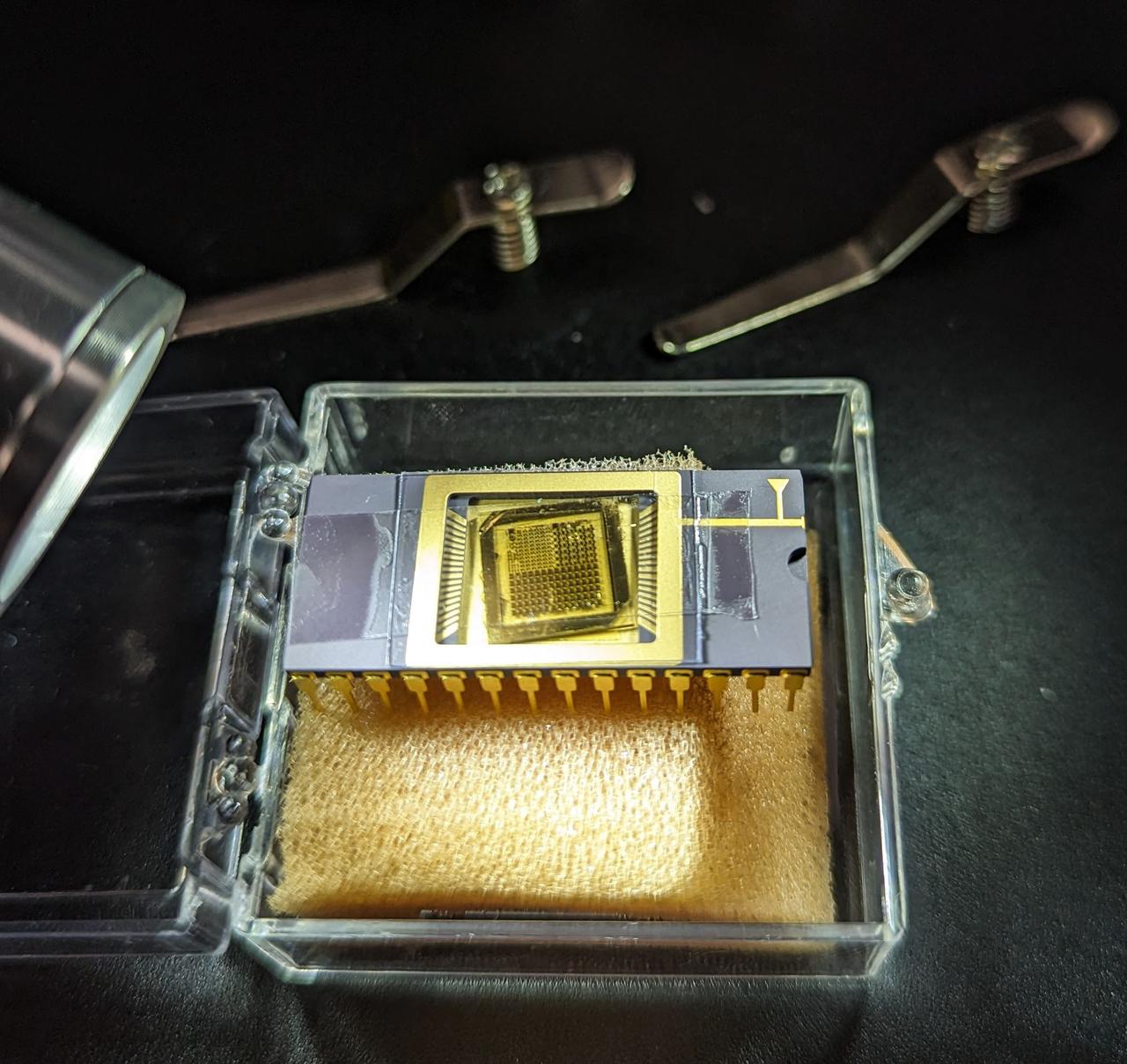
jsc2025e015685c(3/6/2025) --- The GaN devices wire bonded to a chip carrier as part of the High Performance Radiation Hardened GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors for Space Applications (Radiation Harden GaN) investigation which studies how radiation affects a type of transistor used in the semiconductor industry. Researchers measure the performance of the devices before, during, and after flight to determine whether performance degrades. This could help determine how well the transistors can tolerate radiation in space. Image courtesy of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Delaware.
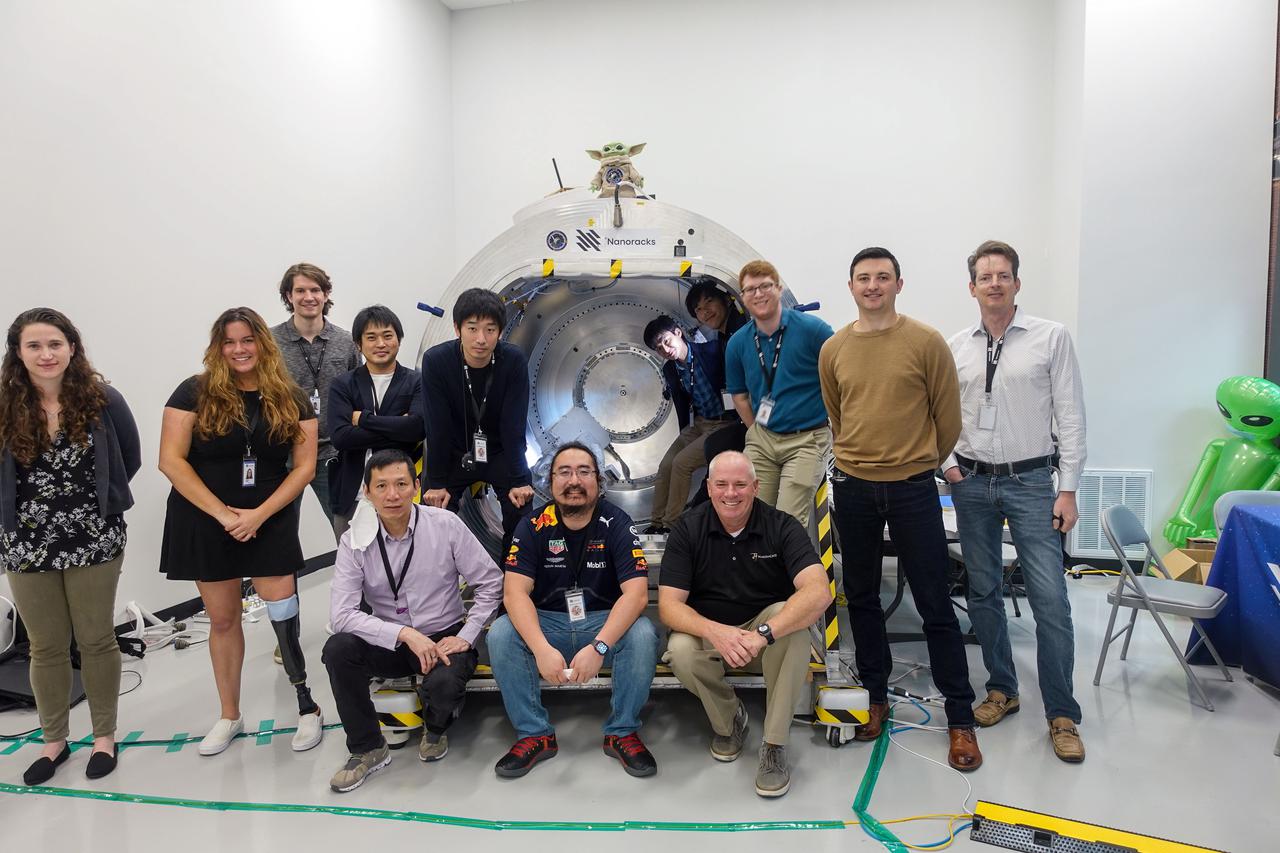
jsc2021e036652 (8/11/2021) --- The GITAI and Nanoracks team group photo. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.

jsc2021e029976 (6/30/2021) --- A preflight view of the TARGIT cubesat. The Tethering And Ranging Mission of the Georgia Institute of Technology (TARGIT) tests a miniaturized Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) imaging camera. The camera tracks and takes images of a tethered inflatable target to verify its performance and demonstrate precision topographic mapping capability and use of an inflatable as a drag device. These capabilities could help support future planetary missions. Image courtesy of Candler Hobbs
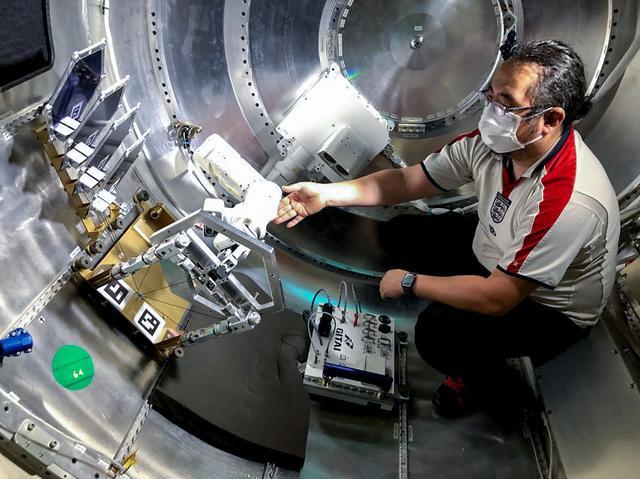

jsc2021e036653 (8/11/2021) --- Final checks of the GITAI S1 Flight Model. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.